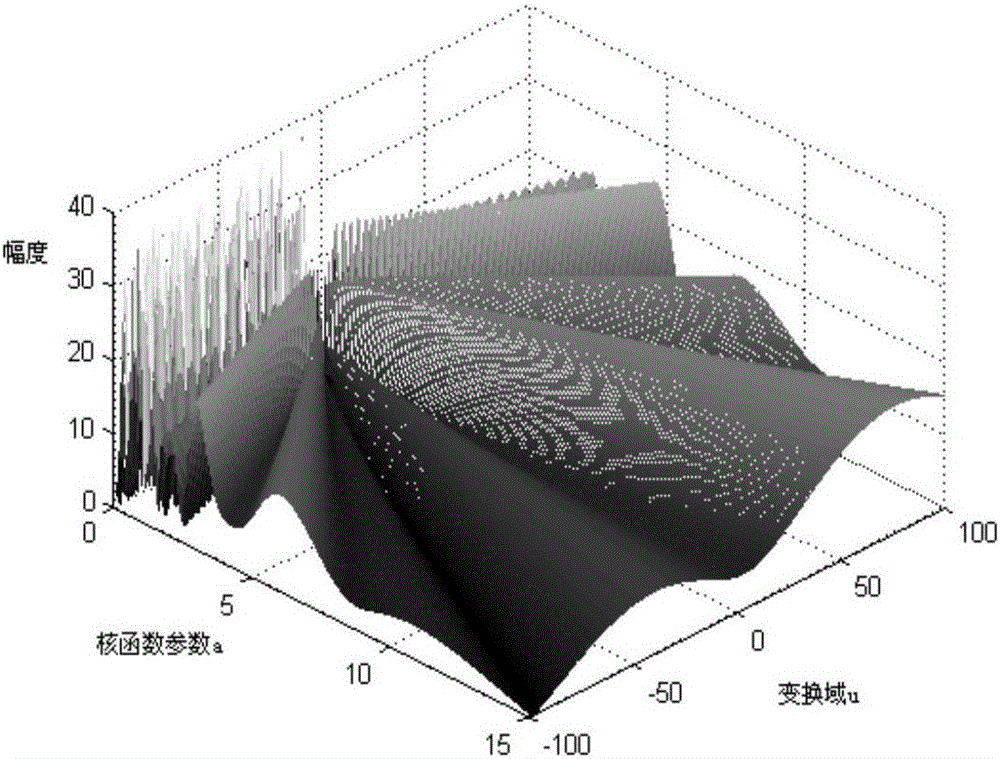
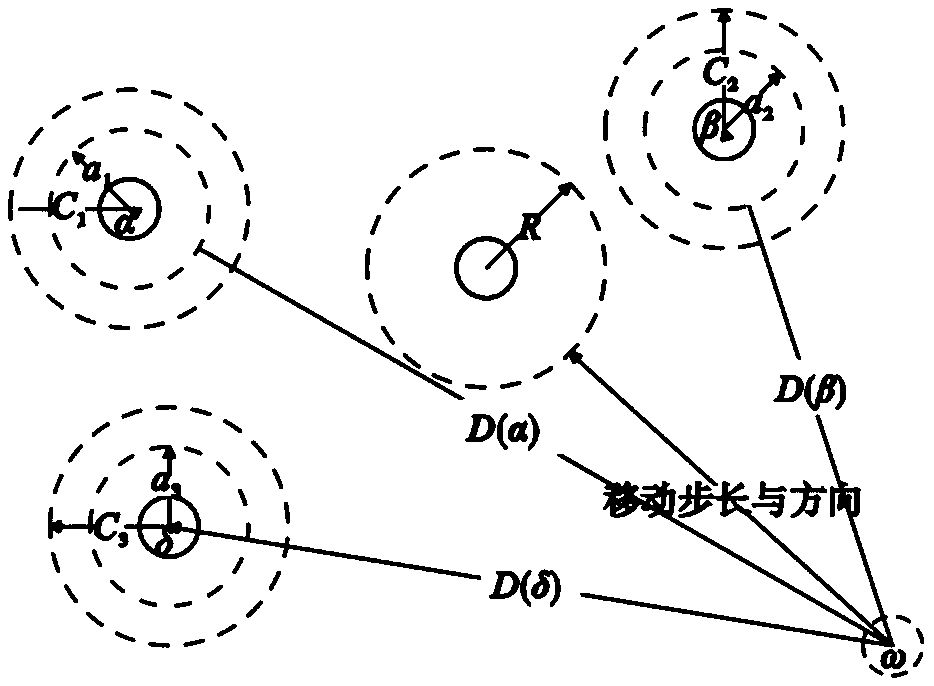
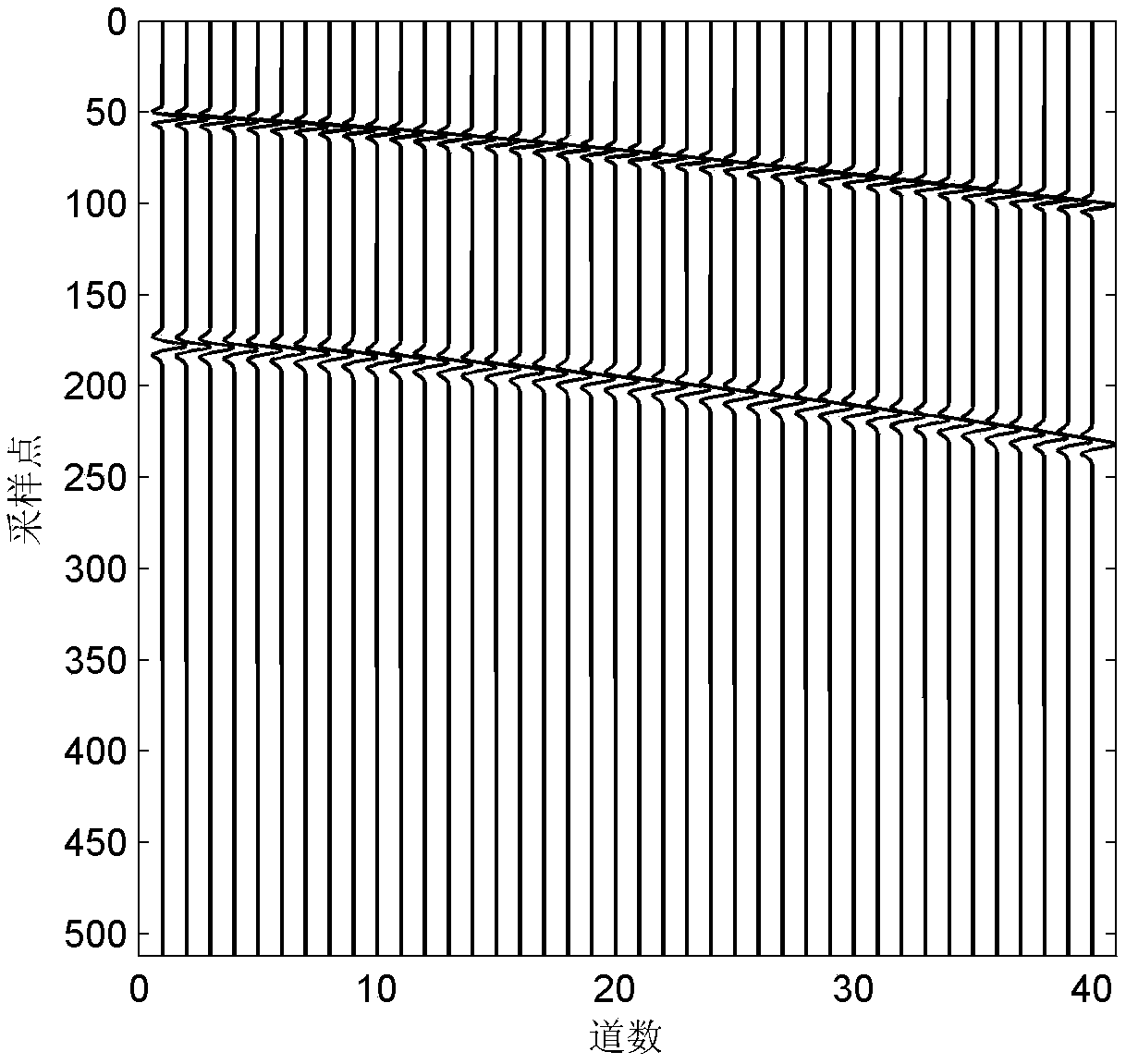
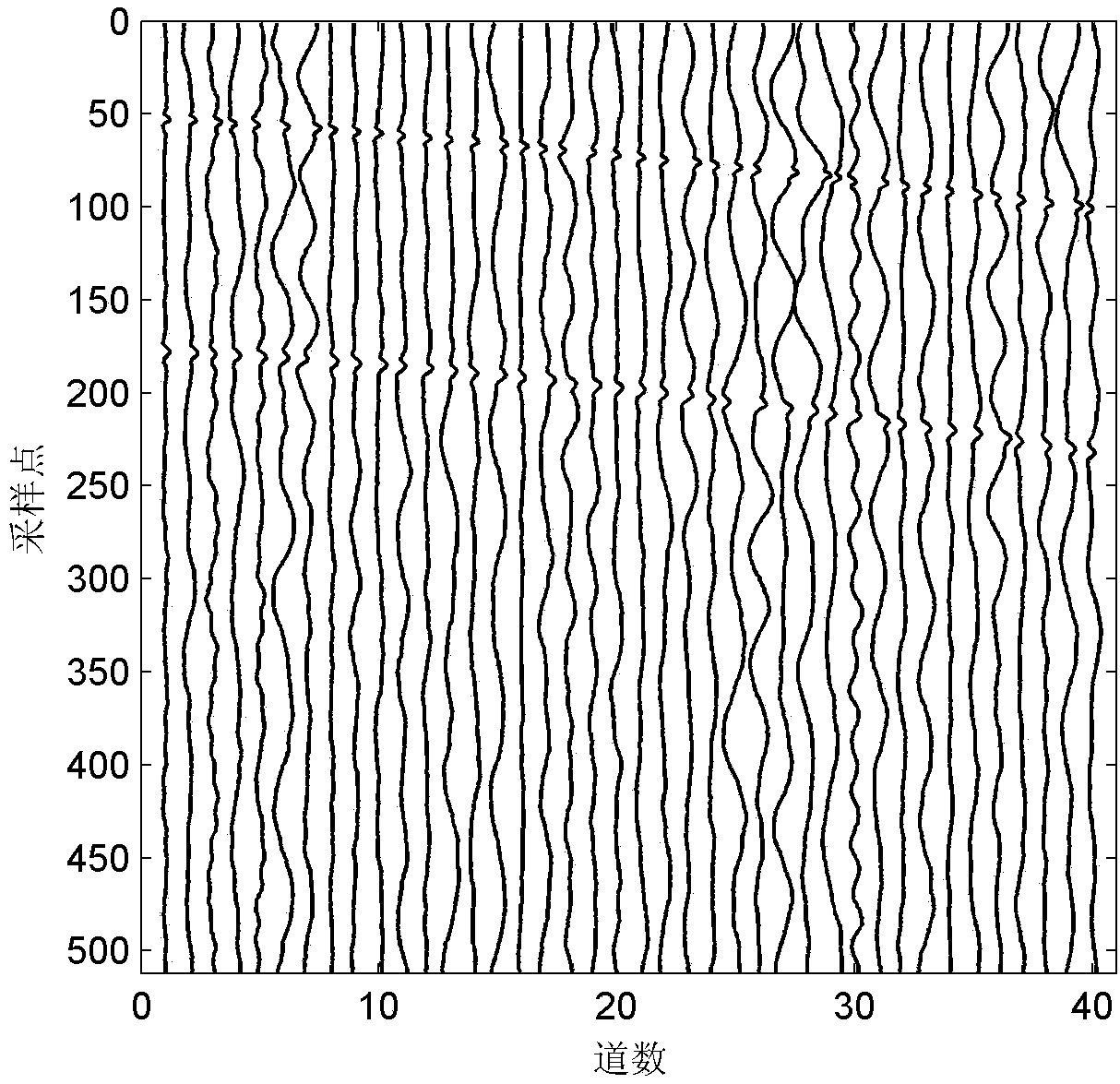
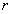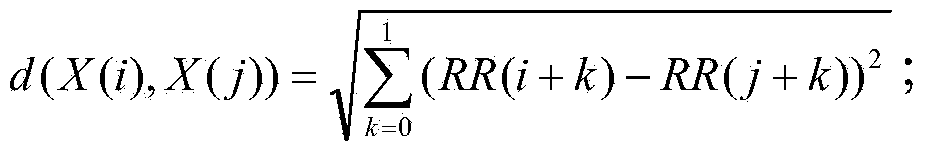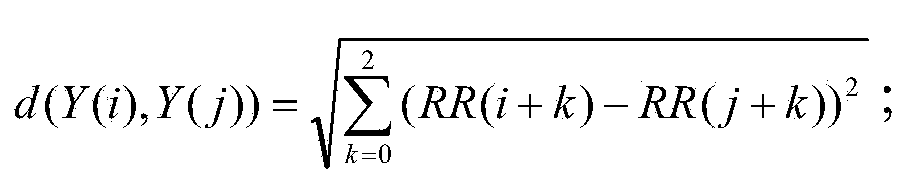Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
151 results about "Approximate entropy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In statistics, an approximate entropy (ApEn) is a technique used to quantify the amount of regularity and the unpredictability of fluctuations over time-series data.
Short-term load prediction method of variational mode decomposition and deep belief network
InactiveCN107392364AImprove forecast accuracyEasy to handleForecastingResourcesDeep belief networkAlgorithm
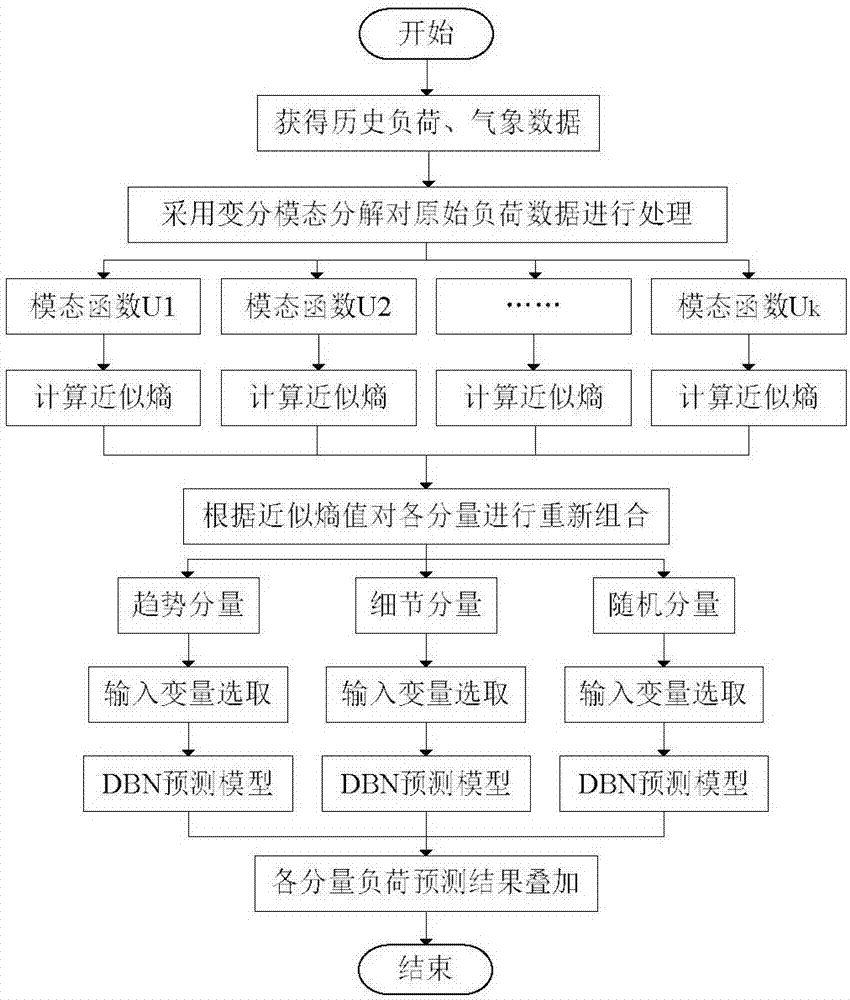
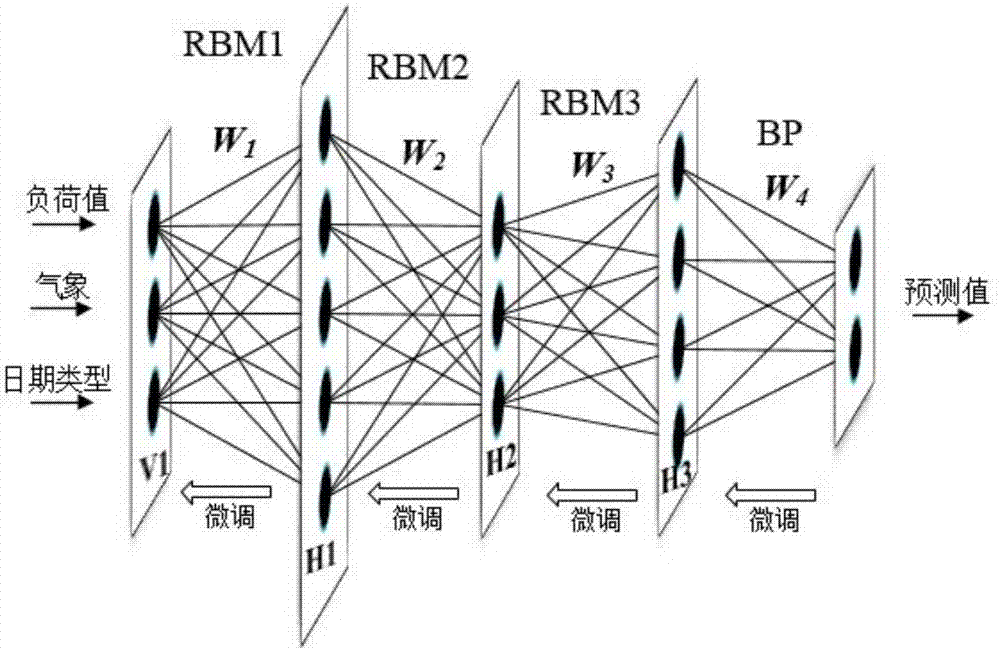
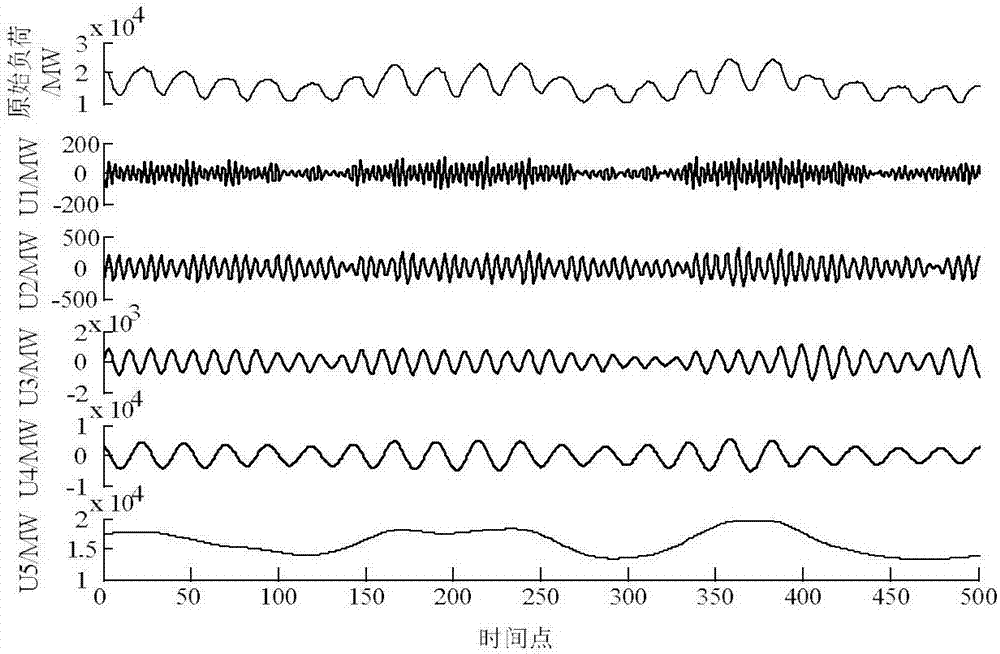
The invention discloses a short-term load prediction method of a variational mode decomposition and deep belief network. The method comprises the following steps of 1) using a variational mode decomposition method to decompose original historical load data into a series of mode functions with different characteristics; 2) using an approximate entropy to calculate each modal function complexity, merging the modal functions whose approximate entropy values are similar into a new component, and carrying out characteristic analysis on each component; 3) in order to calculating correlation of an influence factor and an output variable, carrying out normalization processing on data; 4) combining a period characteristic of a load, and using a mutual information theory to select an input variable set from aspects of a historical load, a meteorology factor, a date type and the like; and 5) constructing the short-term load prediction method based on the deep belief network (DBN), and verifying method validity through a load prediction scene before 24h. By using the method, short-term load prediction precision is effectively increased and an electric power system load prediction problem can be well solved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for extracting and fusing time, frequency and space domain multi-parameter electroencephalogram characters
ActiveCN104586387AEfficient extractionAll-round extractionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSingular value decompositionFunctional disturbance
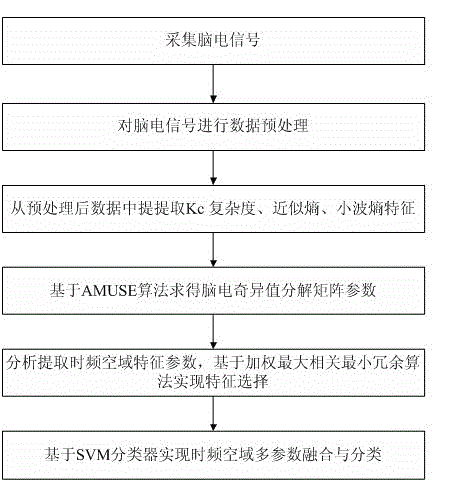
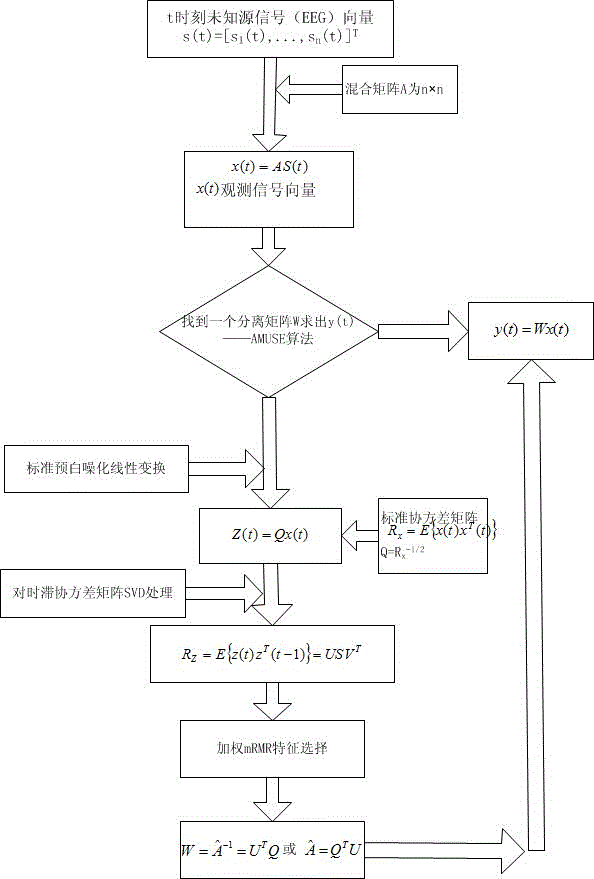
The invention relates to a method for extracting and fusing time, frequency and space domain multi-parameter electroencephalogram characters, which comprises the following steps: 1) collecting an electroencephalogram signal; 2) performing data pre-processing on the electroencephalogram signal; 3) extracting Kc complexity, approximate entropy and wavelet entropy from the pre-processed data; 4) on the basis of AMUSE algorithm, acquiring an electroencephalogram singular value decomposition matrix parameter; 5) performing character selection on the time, frequency and space domain character parameters for the extracted Kc complexity, approximate entropy, wavelet entropy and electroencephalogram singular value decomposition matrix parameters; 6) utilizing a SVM classifier to fuse and classify the four parameters of the time, frequency and space domains after the character selection. According to the method provided by the invention, the Kc complexity, the approximate entropy, the wavelet entropy and the electroencephalogram singular value decomposition matrix parameter can be selected for comprehensively presenting electroencephalogram character information, and then subsequent effective fusion is performed, so that effective support and help can be supplied to early diagnosis assessment for the brain functional disordered diseases, such as, Alzheimer disease, mild cognitive impairment, and the like.
Owner:秦皇岛市惠斯安普医学系统股份有限公司 +1
Single phase ground fault section locating method in small current grounding system
InactiveCN102621449AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove detection accuracyFault locationTransient statePrimary station
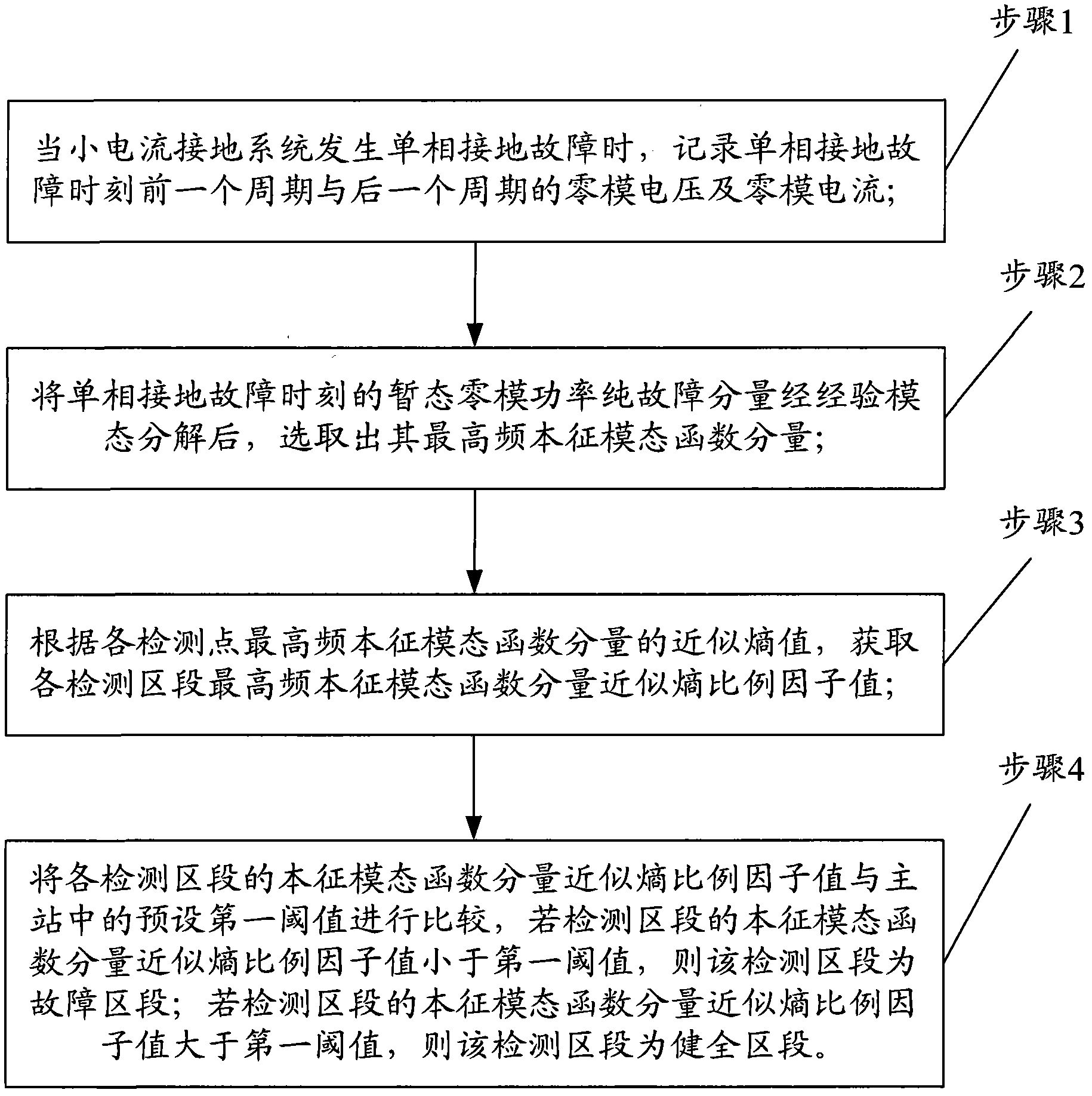
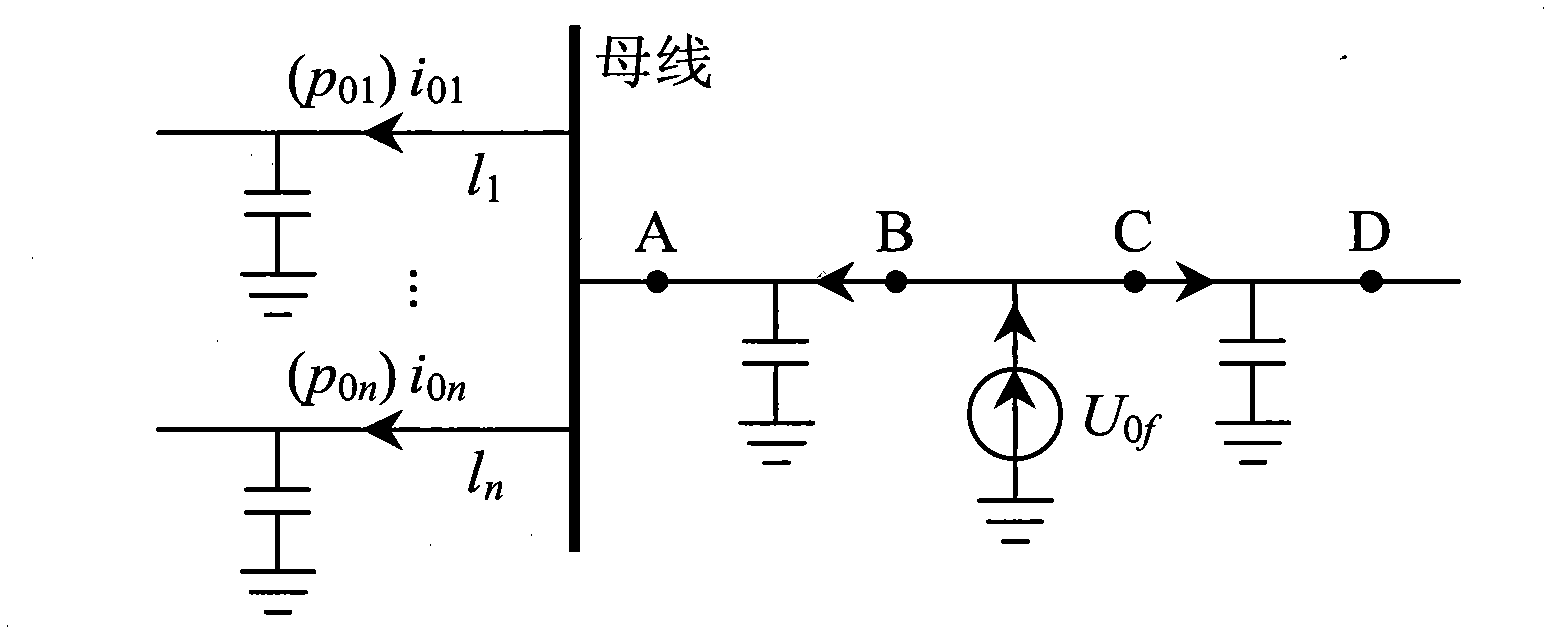
The invention provides a single phase ground fault section locating method in a small current grounding system, which includes the following steps: step 1, recording the zero mode voltage and the zero mode current of the previous period and the next period of the single phase ground fault time when the single phase ground fault occurs to the small current grounding system; step 2, selecting the highest frequency intrinsic mode function component after decomposing the transient zero mode power pure fault component of the single phase ground fault time through empirical mode decomposition; step 3, obtaining the approximate entropy proportionality factor of the highest frequency intrinsic mode function component of each detecting section through the approximate entropy value of the high frequency intrinsic mode function component of each detecting section; and step 4, comparing the approximate entropy proportionality factor of the highest frequency intrinsic mode function component of each detecting section with the preset first threshold in the main station, so as to find out the section with the single phase ground fault. The single phase ground fault section locating method has the characteristics of high detecting precision and universality, and can be widely applied to the power system.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
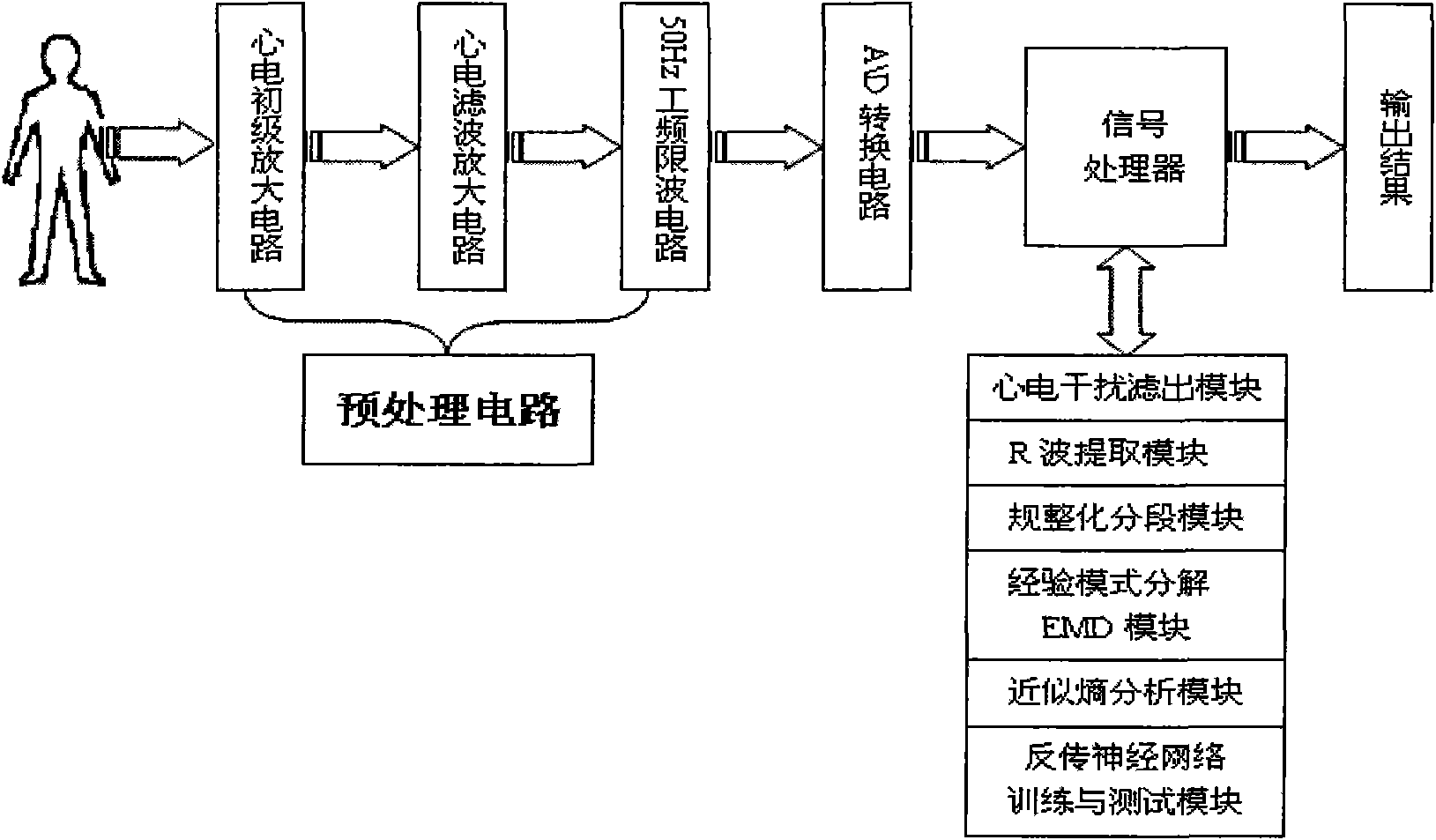
Device and method for detecting attention focusing degree based on analysis of heart rate variability
InactiveCN101658425AReduce distractionsEasy to collectSensorsPsychotechnic devicesRR intervalDecomposition
The invention discloses a device and a method for detecting attention focusing degree based on the analysis of heart rate variability, mainly solving the problems of large interference and inconvenient testing of reference signals for attention judgment in the prior art. The method comprises the following testing steps: acquiring original electrocardiographic digital signals according to a MV5 lead mode; filtering the interference in the original electrocardiographic digital signals, extracting the position of a R wave and calculating heart rate variability signals; integrating and segmentingthe heart rate variability signals; performing empirical mode decomposition on each segment of the heart rate variability signals; calculating the approximate entropy of the heart rate variability signals and intrinsic mode function component signals; training a neutral network by using the calculated approximate entropy as an input vector of a reverse transmit neural network algorithm, and determining the parameters of codes of a neutral network; and detecting the attention focusing degree of a subject by utilizing the trained neutral network and outputting the test result. The invention hasthe advantages of large reference signal strength, convenient test and high accuracy, and is used for testing the attention focusing degree of a human body.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
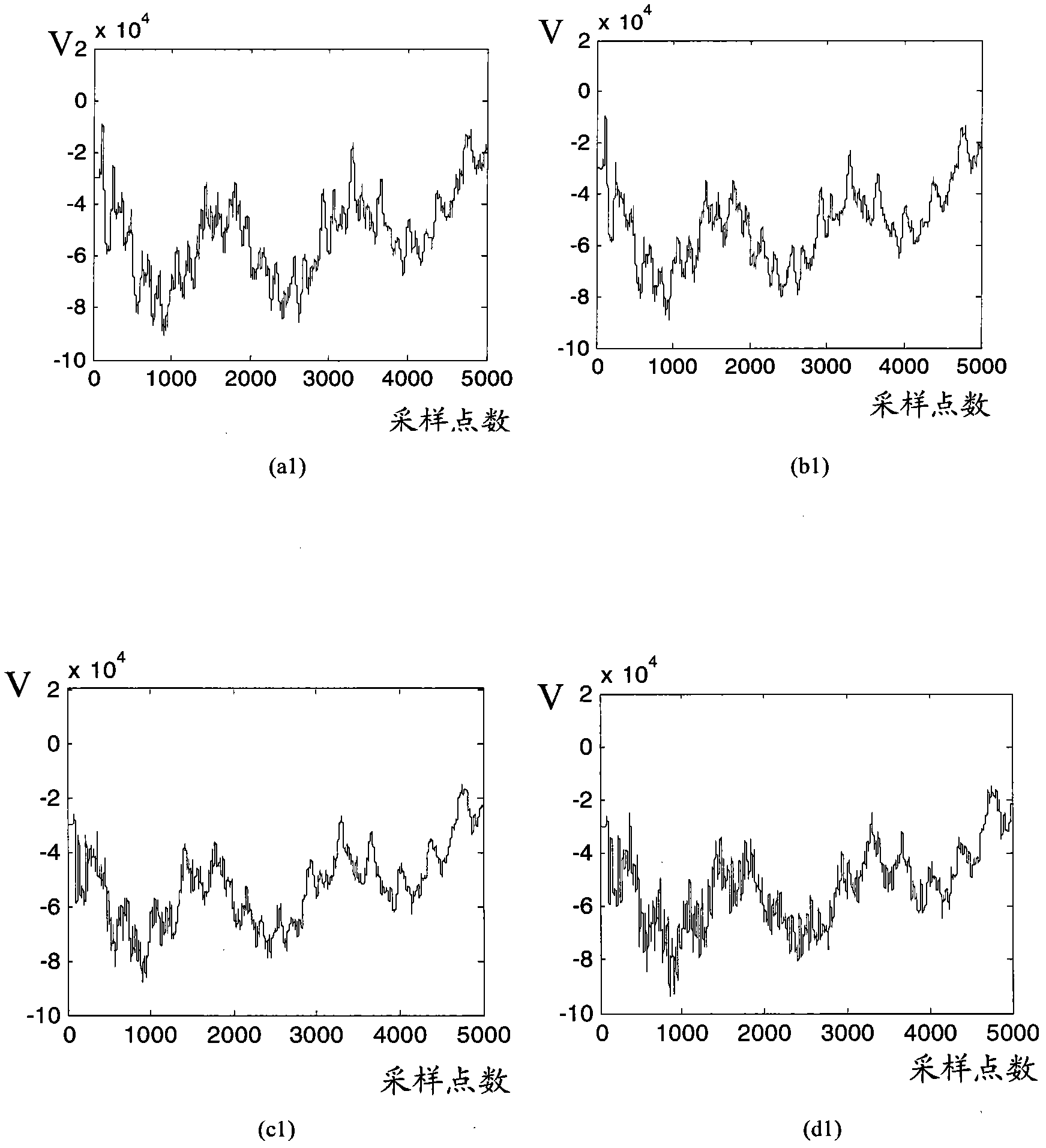
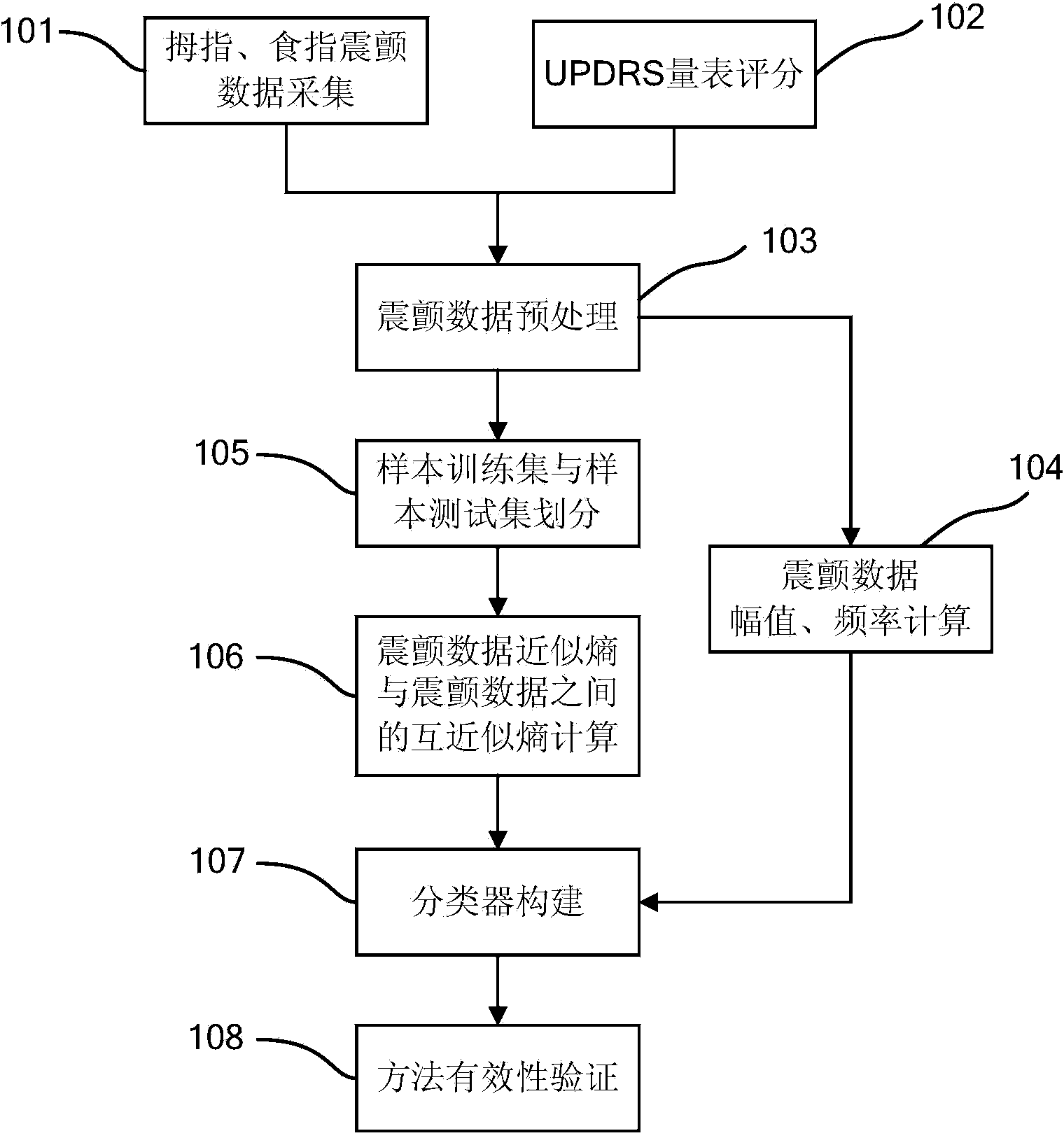
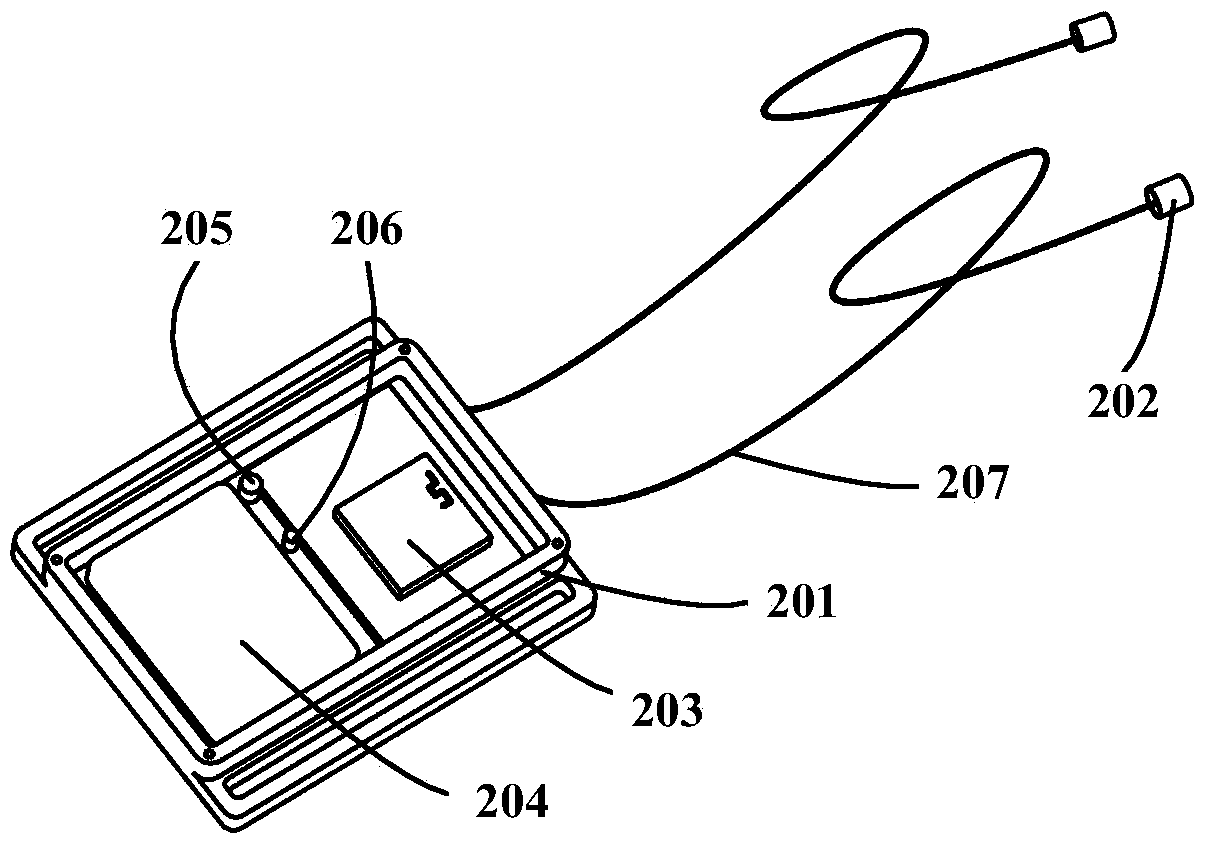
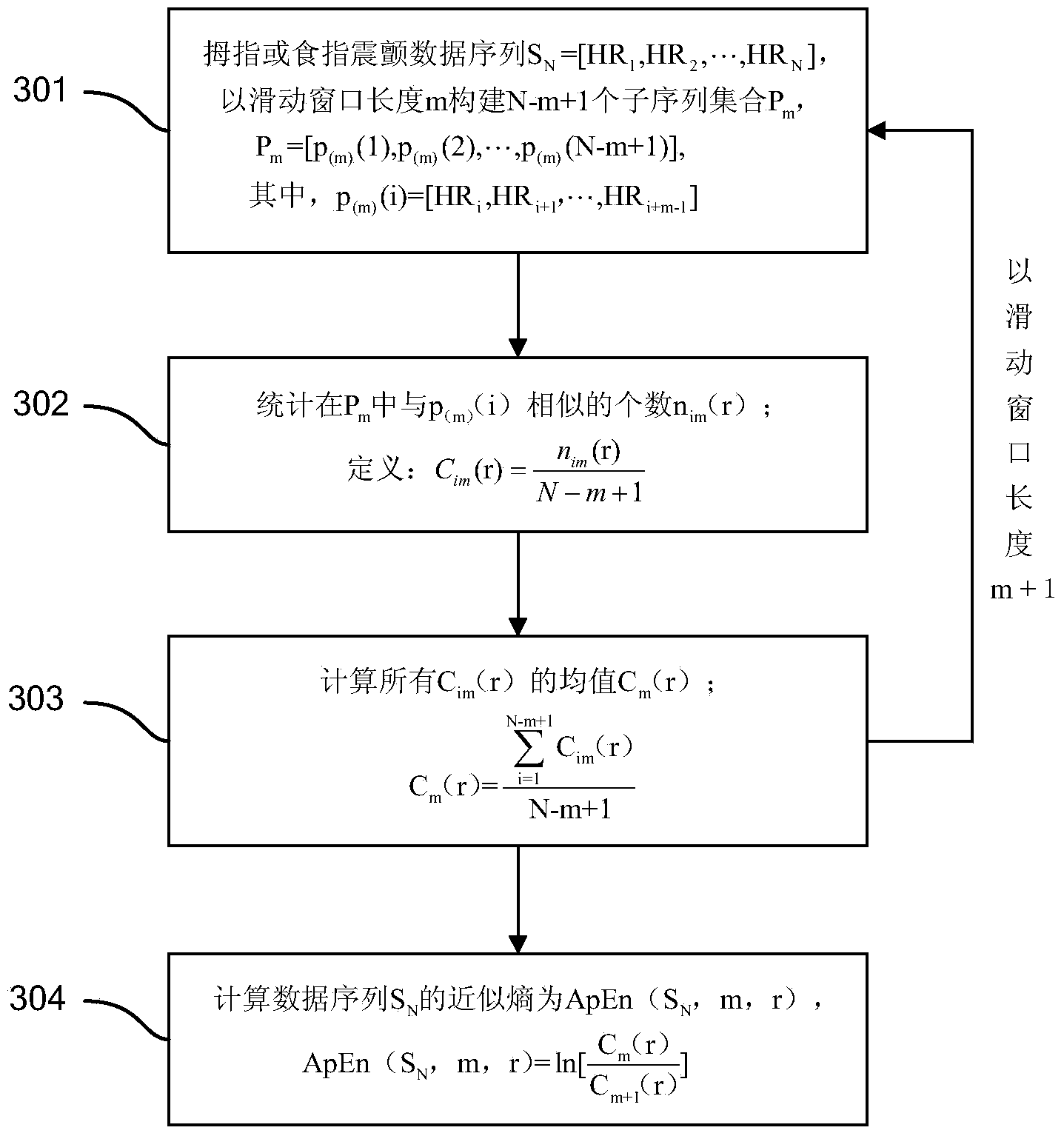
Method for quantitatively evaluating symptoms of tremor of patient with Parkinson's disease according to approximate entropy and cross approximate entropy
ActiveCN104398263ANo damageUnpredictableDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTremor amplitudeMedicine
The invention provides a method for quantitatively evaluating the symptoms of tremor of a patient with Parkinson's disease according to the approximate entropy and the cross approximate entropy, belonging to the fields of health care and pattern recognition. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: collecting the data of specified tremor of the thumb, collecting the data of specified tremor of the index finger, and grading the specified tremor of the thumb and the specified tremor of the index finger according to a UPDRS (unified Parkinson's disease rating scale); preprocessing the data of tremor; separating a sample training set from a sample testing sample; calculating the approximate entropy and the cross approximate entropy of the data of tremor; constructing the model of a classifier, and verifying the effectiveness of a method. The regularity and the synchronization of the tremor of the patient with Parkinson's disease are disclosed effectively according to the approximate entropy and the cross approximate entropy, and the symptoms of tremor can be accurately and quantitatively classified according to the tremor amplitude, the tremor frequency and other characteristics of the patient. The method is used for objectively evaluating the symptoms of tremor of the patient with Parkinson's disease, and can be applied to the fields of treatment and rehabilitation assessment of the patient with Parkinson's disease and the like.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Coma degree evaluating method based on multiple indexes of non-linearity and complexity
InactiveCN102178514AReal-time monitoring of comaReduce the influence of subjective factorsCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringAlgorithmBrain state
The invention discloses a coma degree evaluating method based on multiple indexes of non-linearity and complexity, which is used for monitoring the brain state of a patient in a coma, and can realize continuous coma depth monitoring, and coma phase grading and early warning. Multiple complexity indexes such as complexity, Lyapunov exponent, approximate entropy, related dimensions, and the like are extracted from coma electroencephalographic signals by adopting a nonlinear dynamics analytical method, and a comprehensive coma state exponent is obtained by combining a traditional GOS (Glasgow Outcome Scale) evaluation system and a traditional GCS (Glasgow Coma Scale) evaluation system; the coefficients of the correlation between the parameters are obtained by clinical experiments; a coma state grading database is founded and a parameter fusion coefficient is determined on the basis of clinical effects; and finally, complete conscious state grading evaluation exponents are founded to guide the treatment of a patient and make prognosis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Epilepsia electroencephalogram signal classified detection device and method
InactiveCN102429657AImprove detection rateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDecompositionComputer science
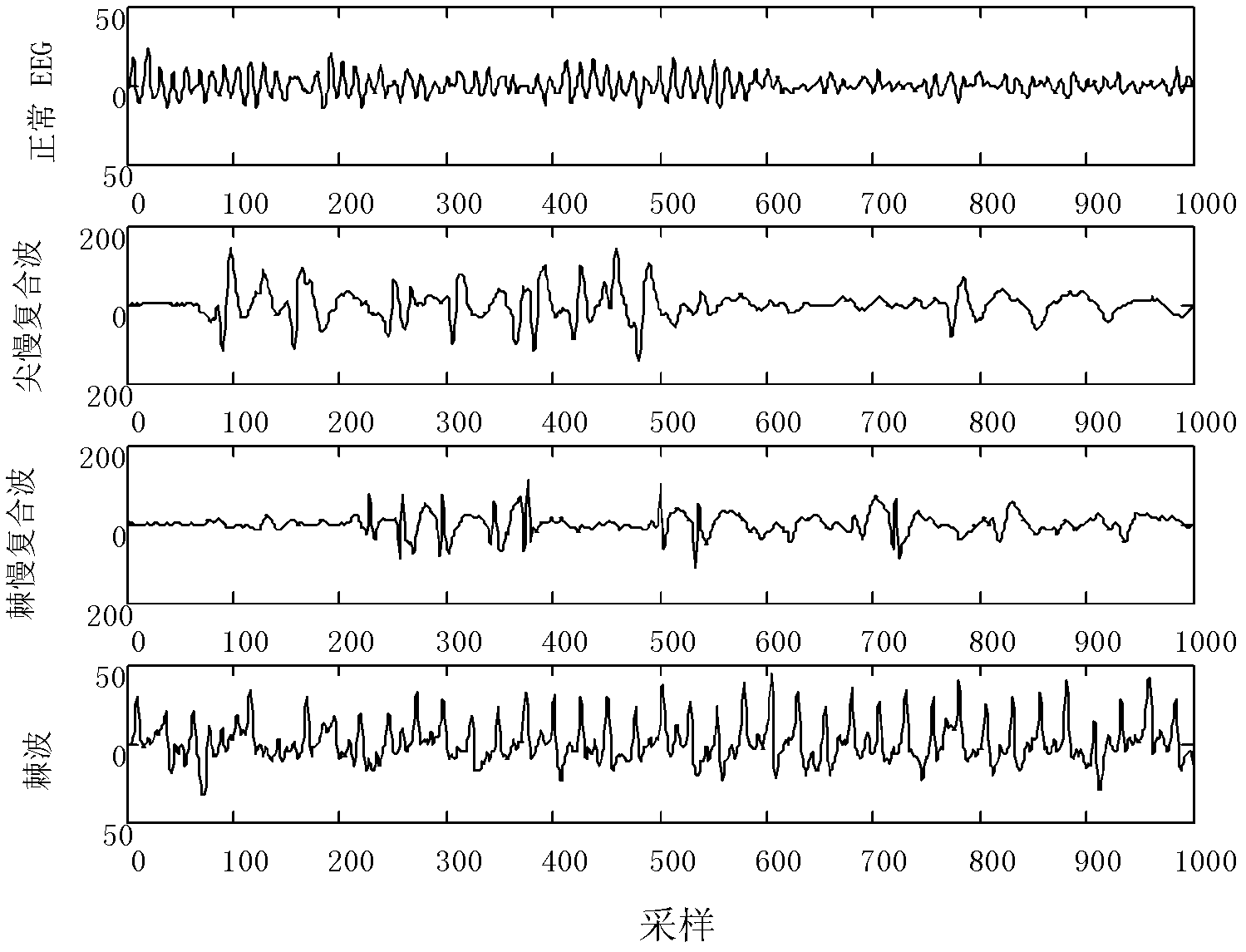
The invention discloses an epilepsia electroencephalogram signal classified detection device which comprises a module for carrying out small wave analysis on a normal electroencephalogram signal and an epilepsia electroencephalogram signal, a module for calculating approximate entropy of each layer of detailed signal obtained after small wave decomposition of the small wave analysis device, and a module for further carrying out classified detection utilizing a Neyman-Pearson criteria. According to the invention, various different types of epilepsia activities are distinguished from the obtained epilepsia signal by clinical data, electroencephalogram signal characteristics are extracted by a small wave analysis and approximate entropy combined mode, judgment and detection are carried out by the NEYMAN-PEARSON criteria, and as compared with the obtained result with unclassified detection result, the detection rate of the epilepsia electrical activity of brain is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
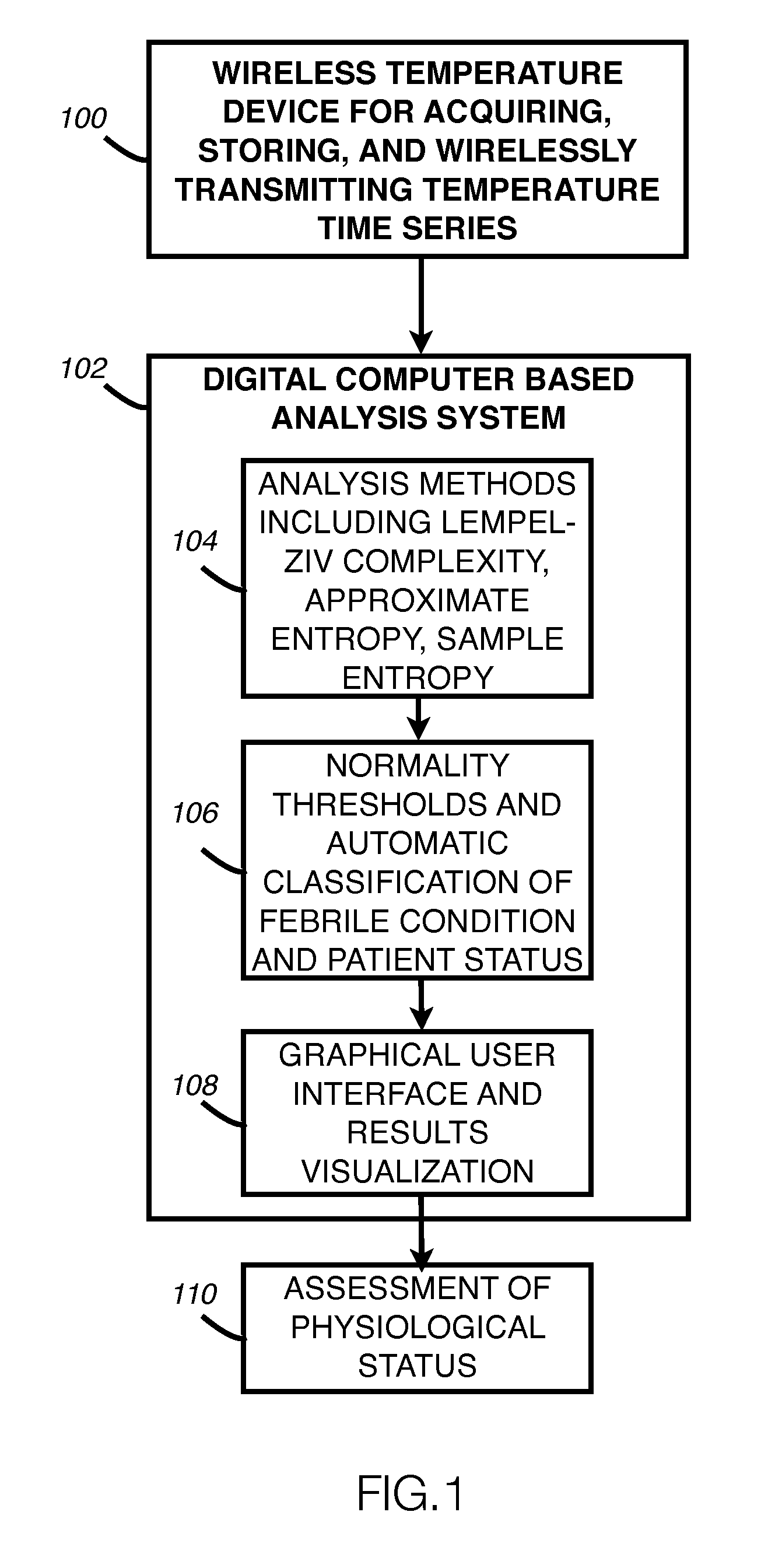
System and apparatus for wireless high-frequency temperature acquisition and analysis
InactiveUS20100042013A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionMulti methodSample entropy
We disclose a system, an apparatus, and a method for high frequency temperature monitoring and analysis. According to a disclosed embodiment the system comprises: (a) a wireless temperature acquisition and logging device especially designed for multi-day, high-frequency, and high-resolution temperature sampling; and (b) an analysis system implemented in a digital computer with one or more processors in order to analyze and characterize said temperature using a plurality of methods including complexity analysis techniques such as Lempel-Ziv complexity, Approximate Entropy, Sample Entropy, Multiscale Entropy, and Detrended Fluctuation Analysis; and other statistical time-series analysis techniques. According to one embodiment the temperature monitoring system is designed to capture the dynamic aspects of temperature in order to enable researchers and clinicians to study temperature regulation, thermal physiology, and clinical thermometry.
Owner:INNOVATEC
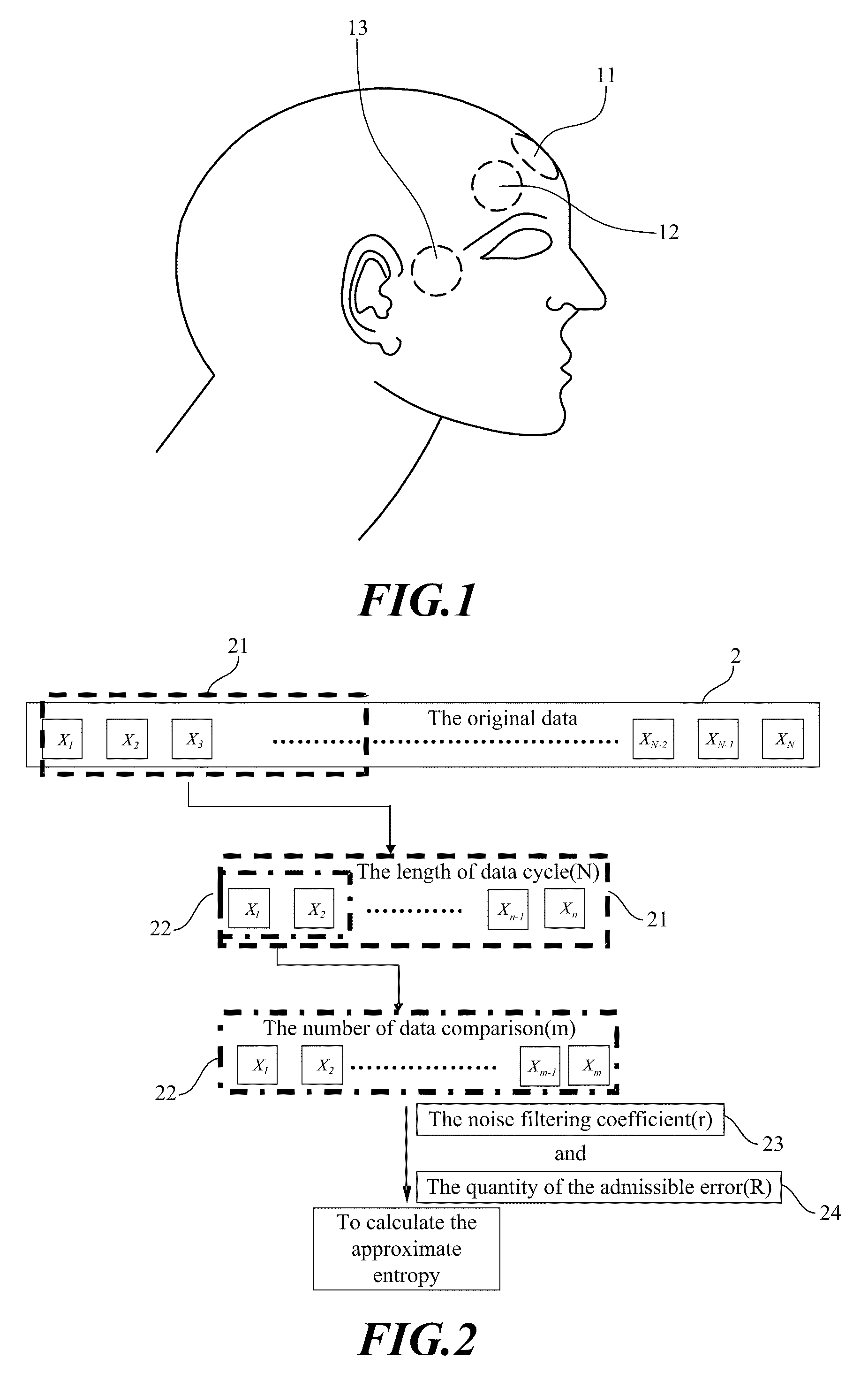
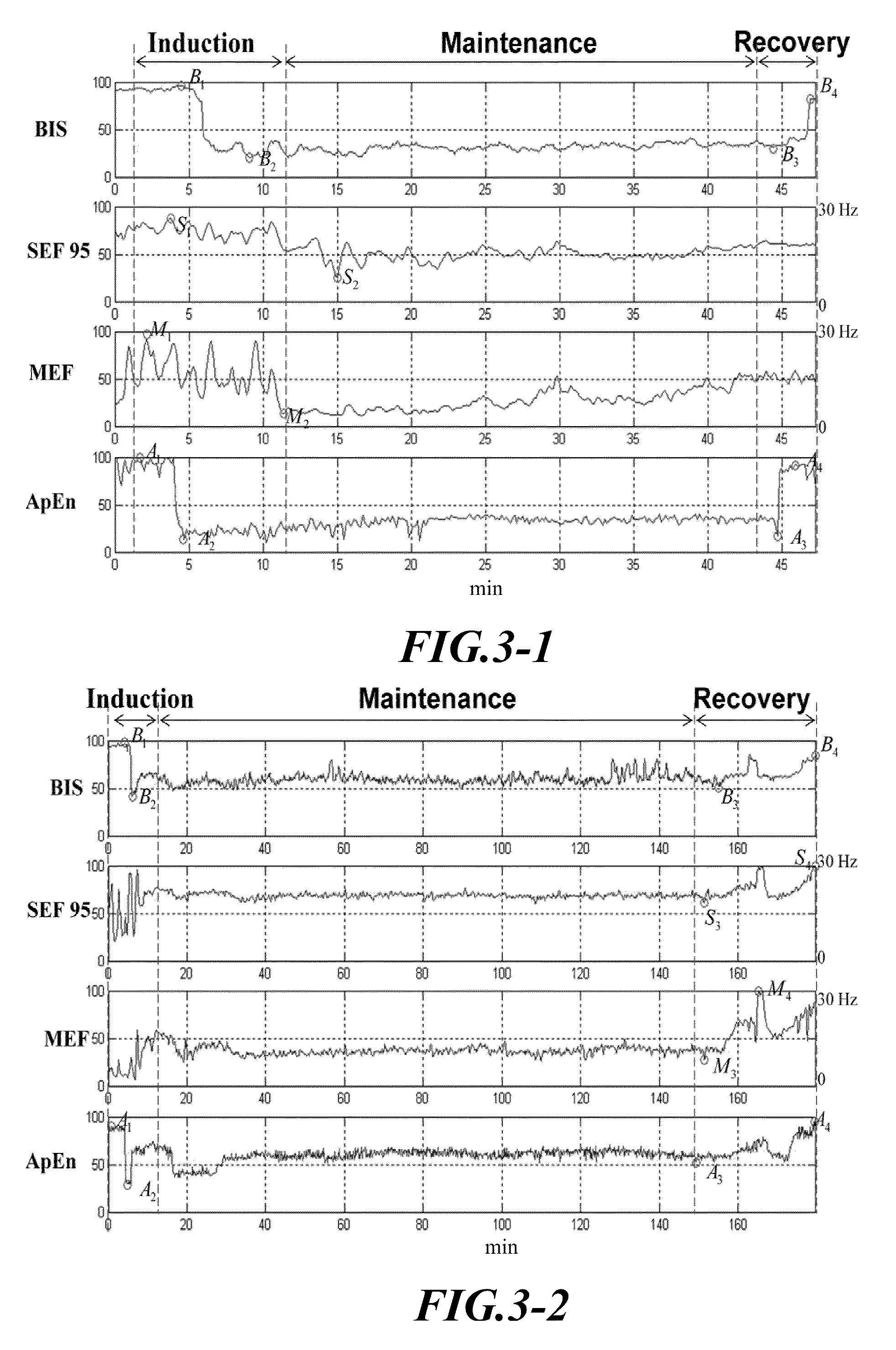
Method for Monitoring the Depth of Anesthesia
InactiveUS20080255469A1Conveniently comparedElectroencephalographySensorsEeg electroencephalographyDepth of anesthesia
A method for monitoring the depth of anesthesia is provided for detecting the conscious state of one being anesthetized in order to facilitate an anesthesiologist to predict exactly the dosage of an anesthetic required. At first, an original electroencephalogram (EEG) is taken from one being tested. Then, the original electroencephalogram is analyzed by approximate entropy to obtain its approximate entropy value. Next, the approximate entropy value is multiplied by 1000 / 17, and the corrected value is assumed as the predicted value of depth of anesthesia. The predicted value of depth of anesthesia represents degree of the conscious state or the depth of anesthesia for the one being tested. The higher the predicted depth of anesthesia value, the more conscious the one being tested is, i.e., in a shallower depth of anesthesia. On the other hand, the lower the predicted depth of anesthesia value, the less conscious the one being tested is, i.e., in a deeper depth of anesthesia.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
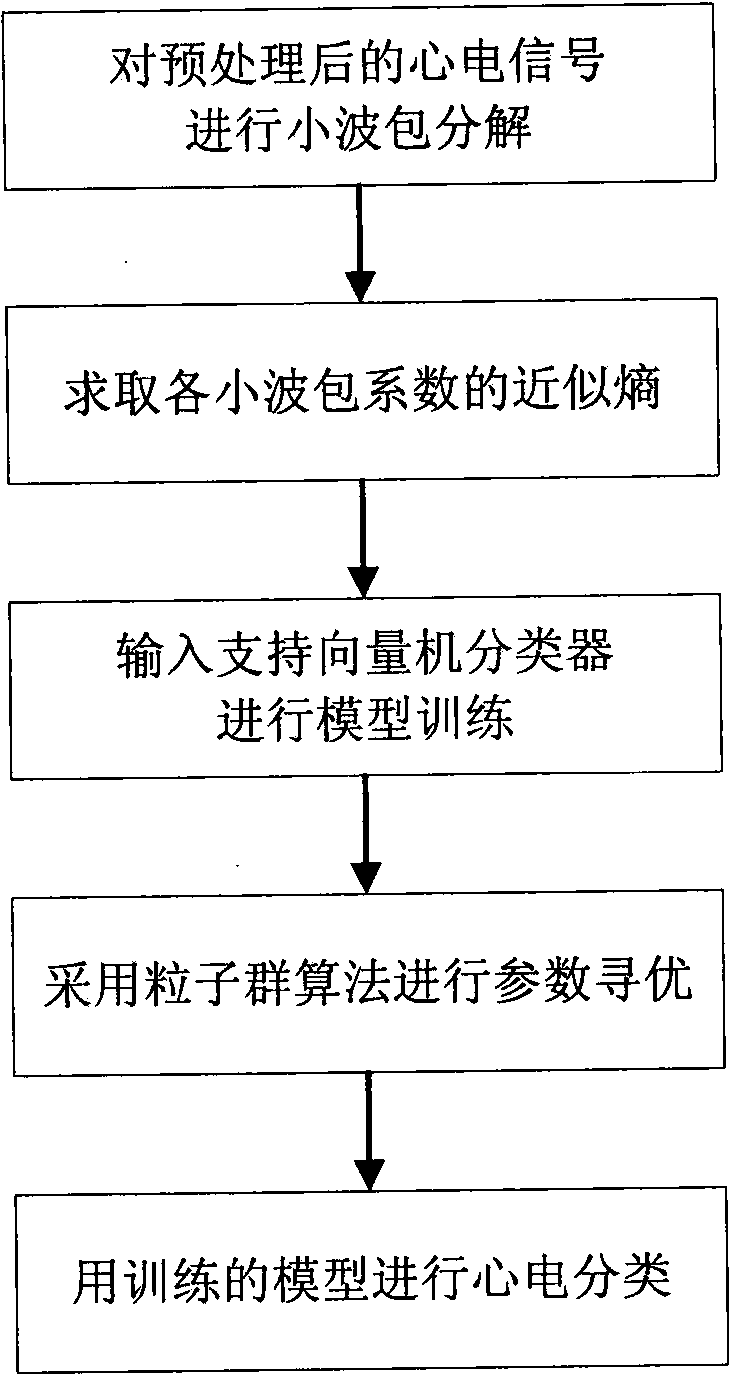
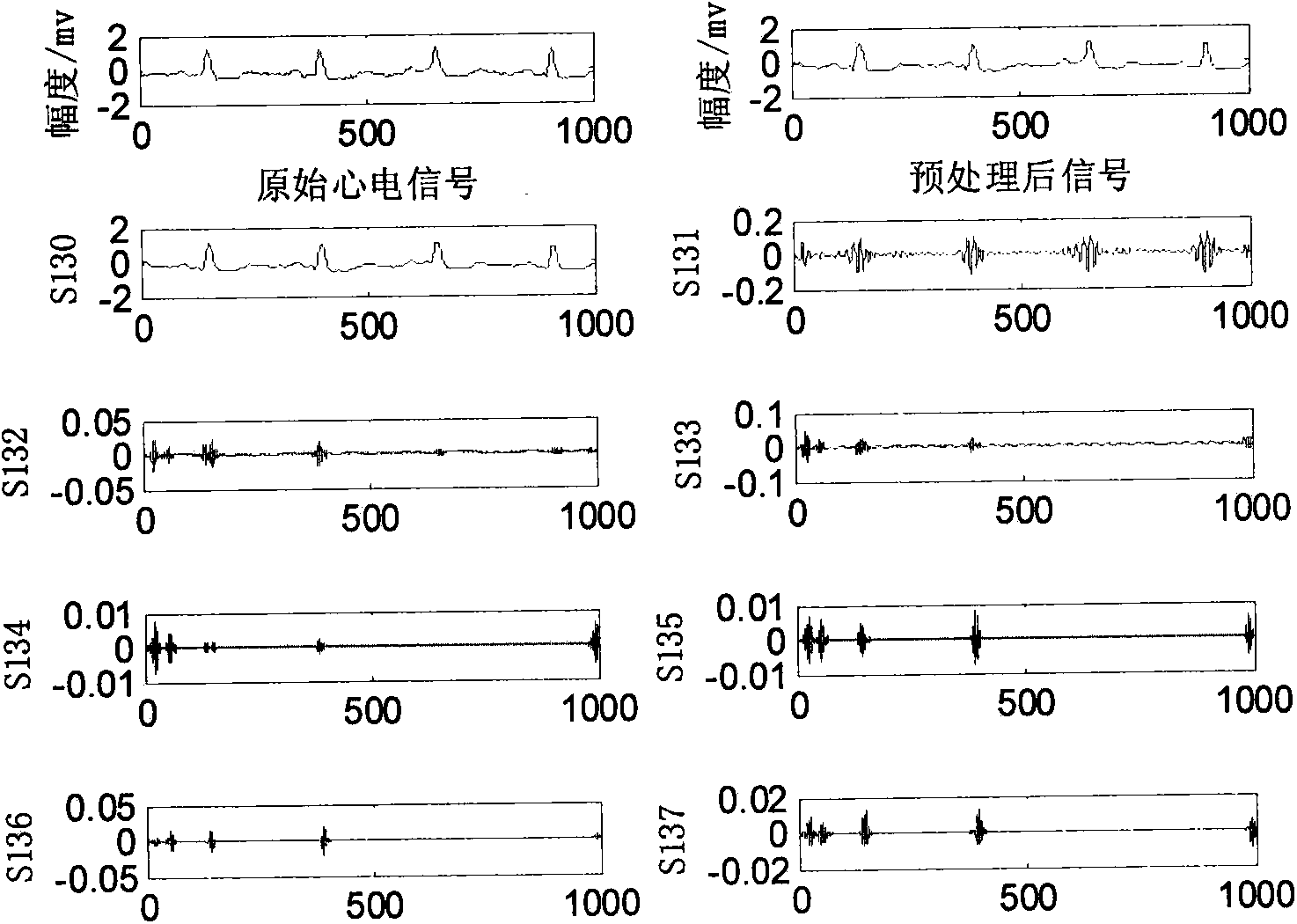
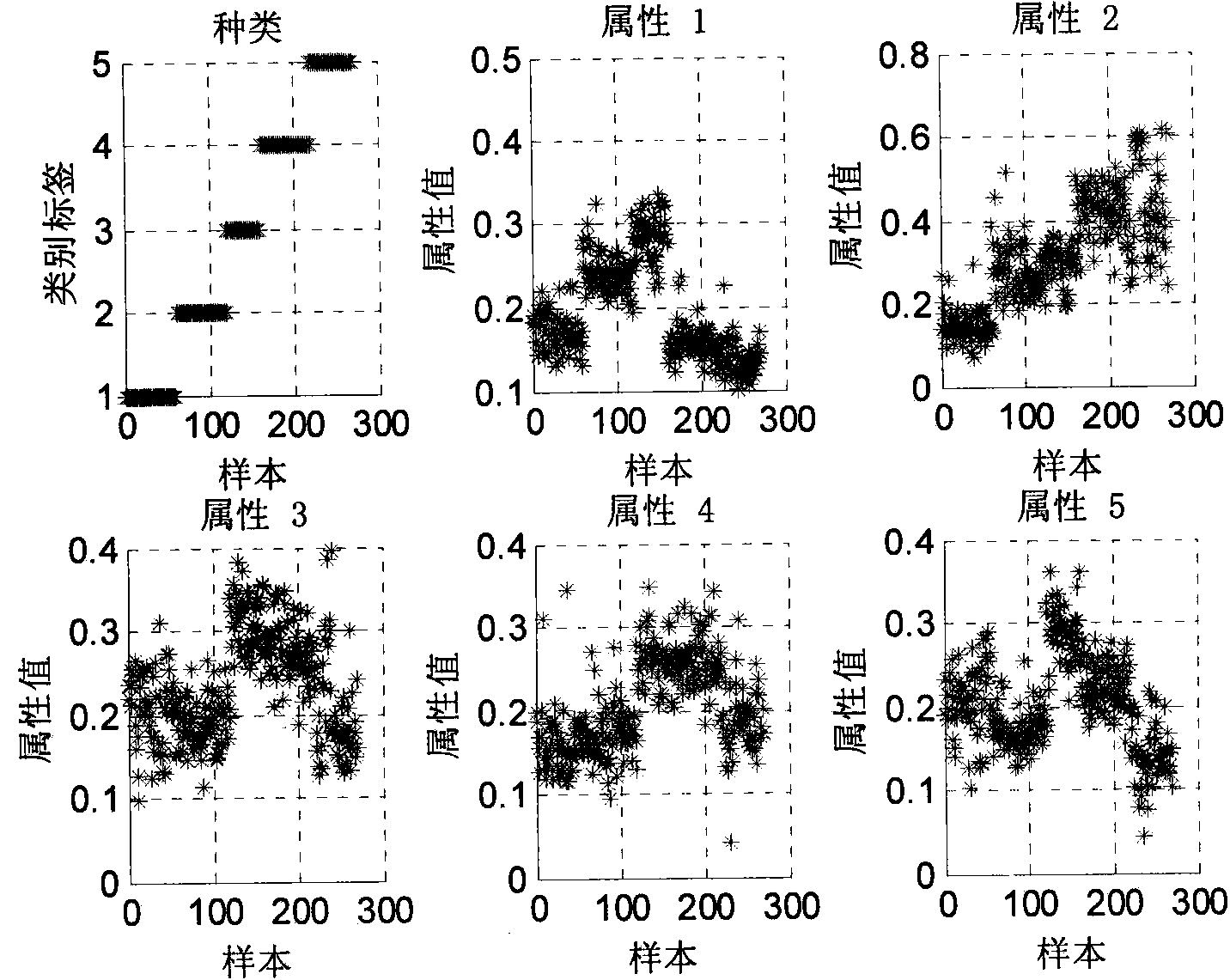
ECG signal classifying method based on wavelet packet and approximate entropy
InactiveCN103927556AImprove efficiencyImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionEcg signalFeature vector
The invention discloses an ECG signal classifying method based on a wavelet packet and approximate entropy. The method comprises the steps that wavelet packet decomposition is conducted on preprocessed ECG signals, the wavelet packet coefficients of all nodes are extracted, and then the approximate entropy of all the wavelet packet coefficients is calculated; the obtained approximate entropy is used as a feature vector to be input into a support vector machine classifier, a particle swarm algorithm is used for seeking the optimal parameter of the support vector machine classifier, and various ECG signals are classified. Wavelet packet decomposition is an effective method for analyzing non-stationary signals. The approximate entropy can be used for obtaining stable estimation values only by a small amount of data, good noise-proof and anti-interference capacity is achieved, and the approximate entropy can both be used no mater what the signals are, stochastic or deterministic. According to the ECG signal classifying method, an algorithm for extracting feature vectors is simple, dimensionality reduction in a traditional method is of no need, the speed is high, consumed time is small, the classifying accuracy is high, and the ECG signal classifying method is suitable for an ECG automatic analysis auxiliary diagnosis system.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
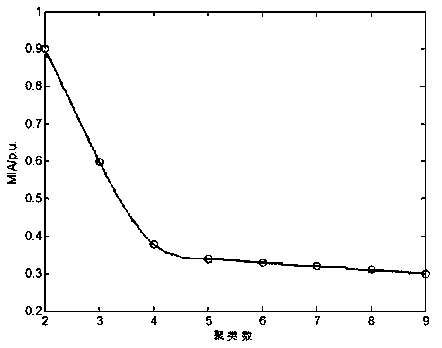
Dynamic weighted hybrid clustering algorithm based circuit breaker fault diagnosis method
InactiveCN109444728AImprove robustnessImprove accuracyMachine part testingSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementAlgorithmDecision taking
The invention discloses a dynamic weighted hybrid clustering algorithm based circuit breaker fault diagnosis method. The method includes the following steps: (1) capturing the energy changes of mechanical drive during the operation of a circuit breaker by utilizing three-axis vibration and two-way sound signals, decomposing the signals through local mean, and extracting the approximate entropy ofeach PF component as the characteristic quantity of a circuit breaker vibration signal; (2) optimizing the initialized clustering center of fuzzy kernel clustering by utilizing the maximum density peak decision of a density peak clustering algorithm, and considering different influences of different characteristics and different samples on clustering results; (3) performing checking on a clustering number K through a cluster validity index MIA; (4) inputting correctly classified characteristics into a multi-level classifier of a support vector machine to perform training; and (5) finding the optimal parameter of the support vector machine through mesh generation, and inputting test data samples to perform final fault classification prediction so that classification accuracy rates can be obtained;. The method has advantaged of being fast in fault diagnosis speed and high in accuracy rate.
Owner:JIYUAN POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID HENAN ELECTRIC POWER
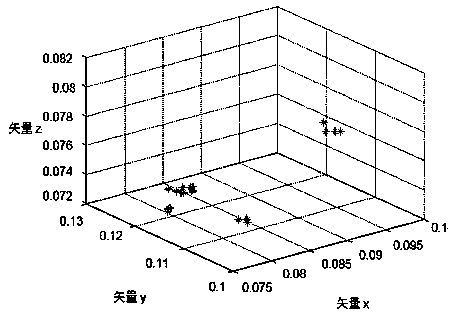
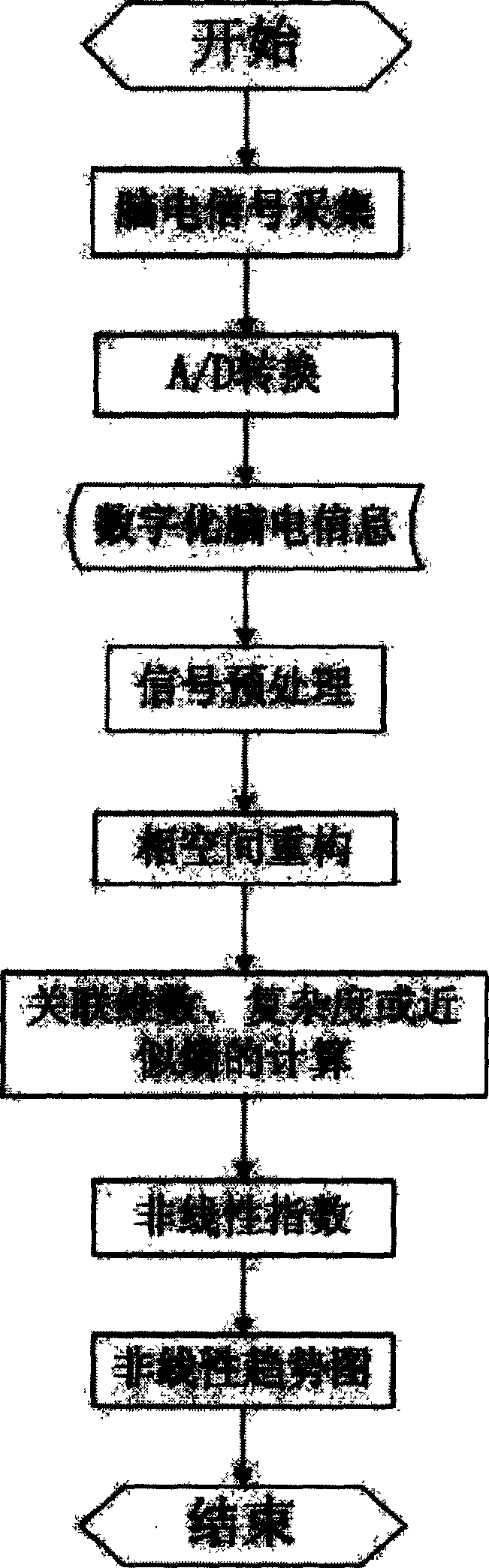
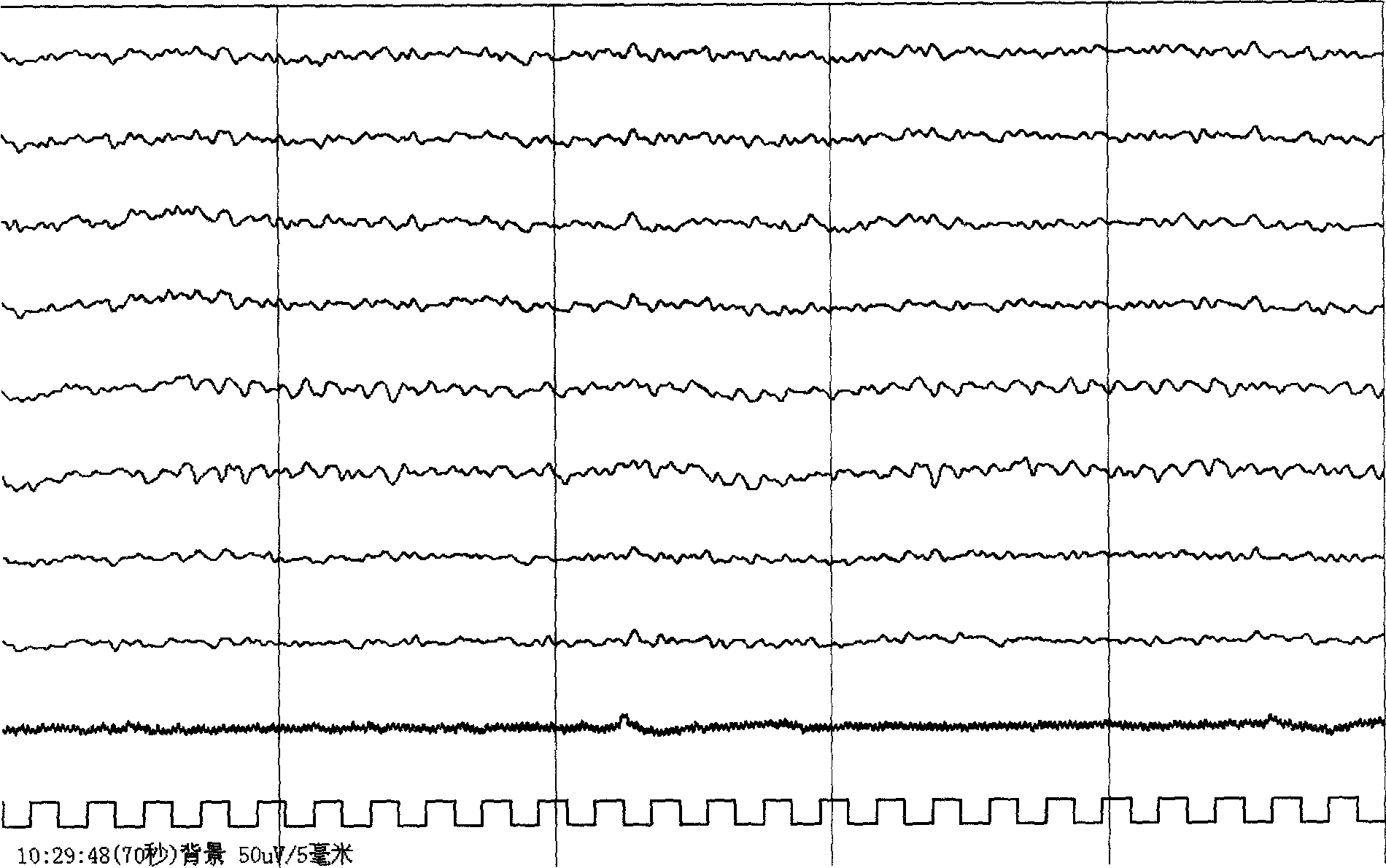
Method for generating electrocortical potential nonlinear trend diagram used in real-time monitoring
InactiveCN1567331AEnable real-time analysisEasy to understandSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmNon linear dynamic
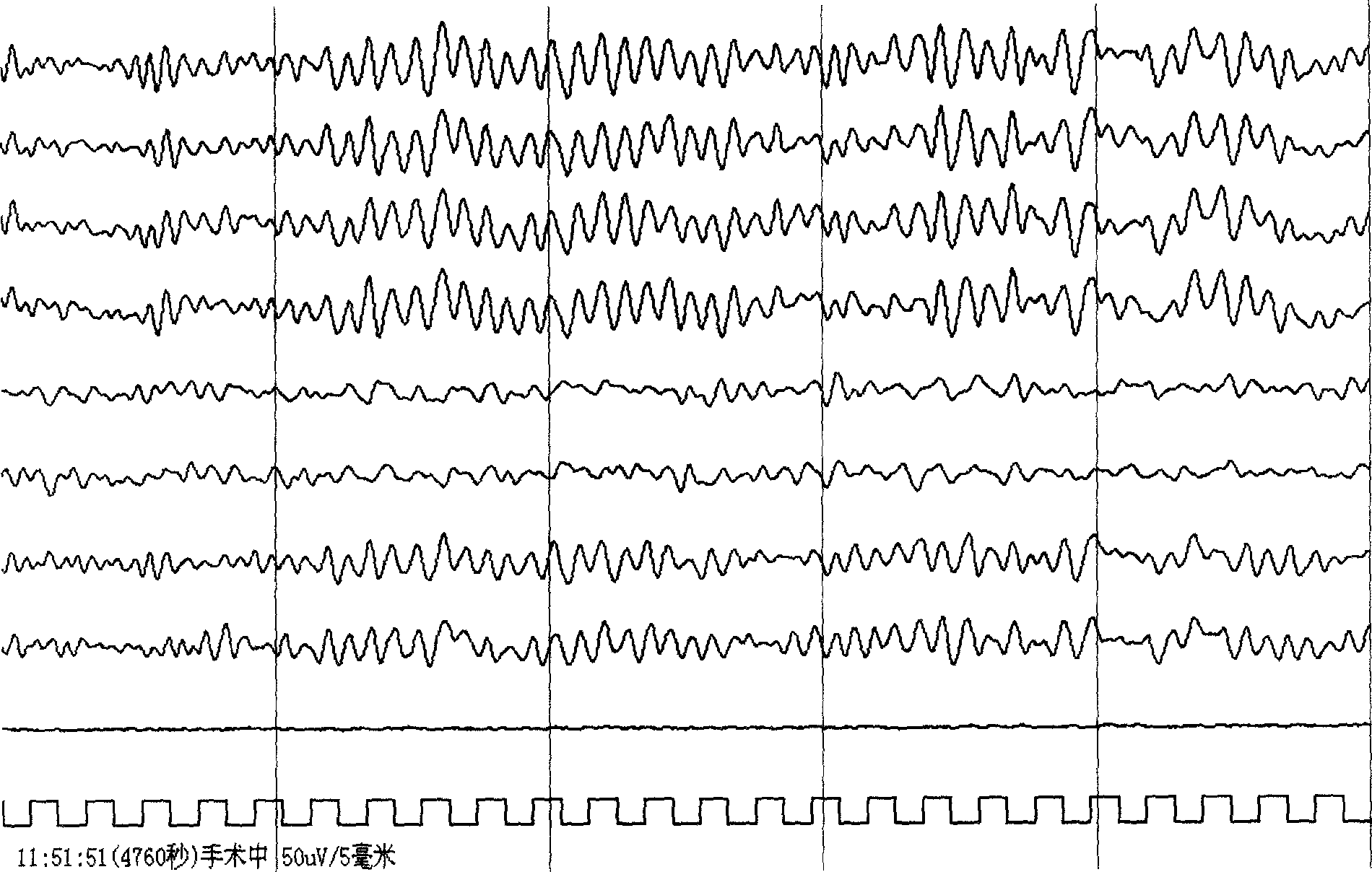
This invention discloses a kind of generating method of real-time monitored brain potential trend chart by adopting computer technique and non-linear dynamics analysis method. It relates to a kind of generating method of brain potential non-linear trend chart. It comprises the following steps: first, collecting original EEG information from different position of scalp; A / D converting to digital EEG information; according to the non-linear dynamics theory and by adopting the trail of state space in time sequence reconstruction system, within one second, converting the conductive digital EEG information to non-linear index that relating to dimension, complexity and approximate entropy, which reflected the current non-linear dynamics characteristic; drawing the non-linear trend chart by using the non-linear index of time sequence, to reflect the non-linear dynamics characteristic variation condition of entire course. This invention can real-time monitor the anaesthesia effect, reflect the variation of anaesthesia effect accurately and promptly.
Owner:XUANWU HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL UNIV OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for Monitoring the Depth of Anesthesia
A method for monitoring the depth of anesthesia is provided for detecting the conscious state of one being anesthetized in the recovery phase or induction phase of anesthesia course in order to facilitate an anesthesiologist to predict exactly the dosage of an anesthetic required. At first, an original electroencephalogram (EEG) is taken from one being tested. Then, the original electroencephalogram is analyzed by approximate entropy to obtain its approximate entropy value. Next, the approximate entropy value is multiplied by 1000 / 17, and the corrected value is assumed as the predicted value of depth of anesthesia. The predicted value of depth of anesthesia represents degree of the conscious state or the depth of anesthesia for the one being tested. The higher the predicted depth of anesthesia value, the more conscious the one being tested is, i.e., in a shallower depth of anesthesia. On the other hand, the lower the predicted depth of anesthesia value, the less conscious the one being tested is, i.e., in a deeper depth of anesthesia.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
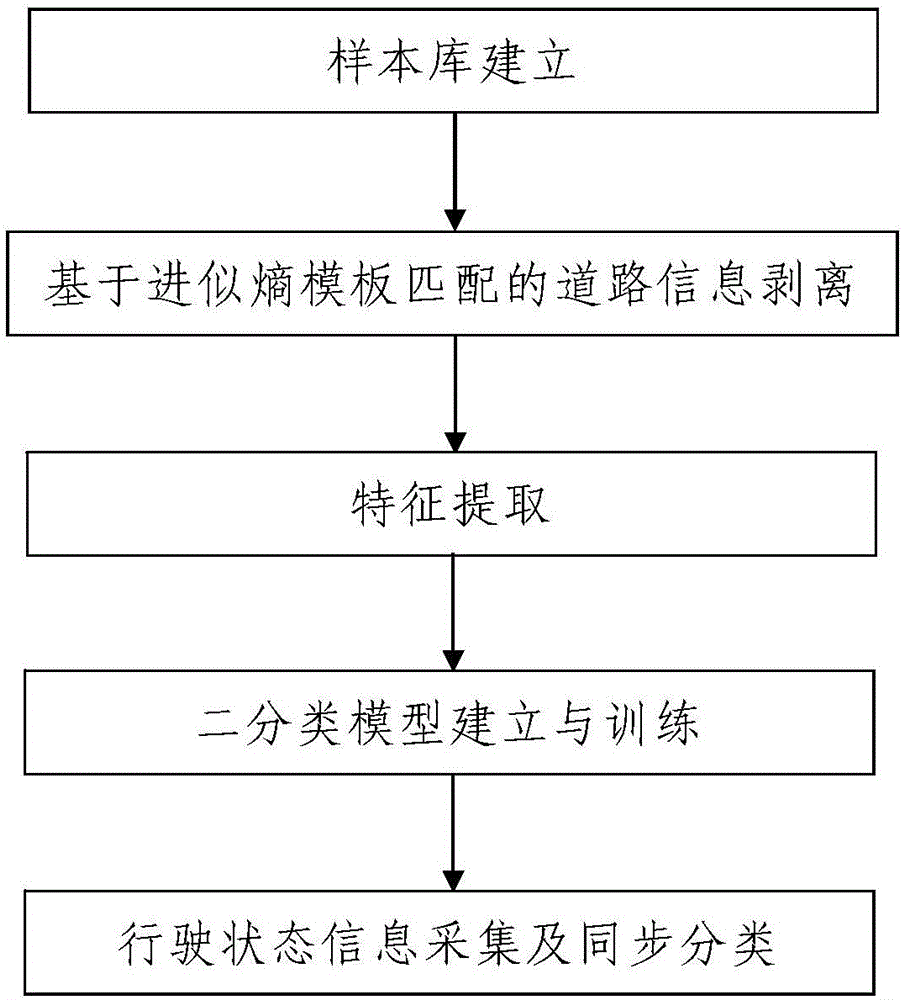
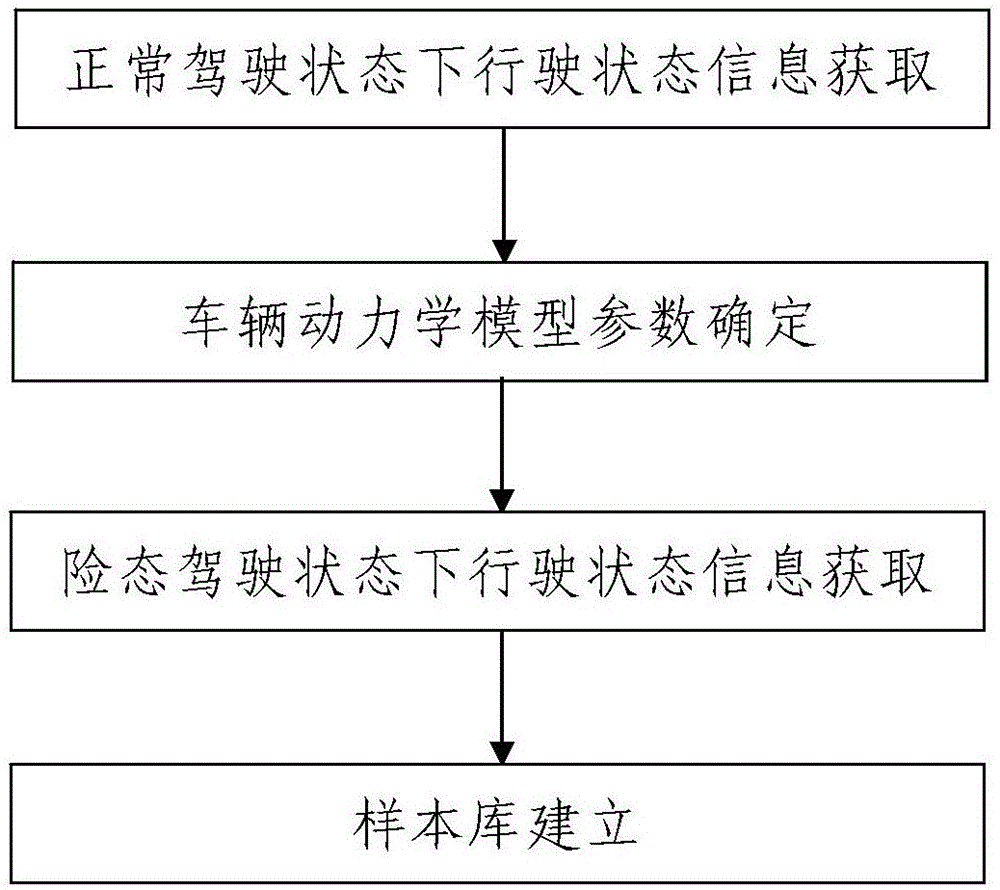
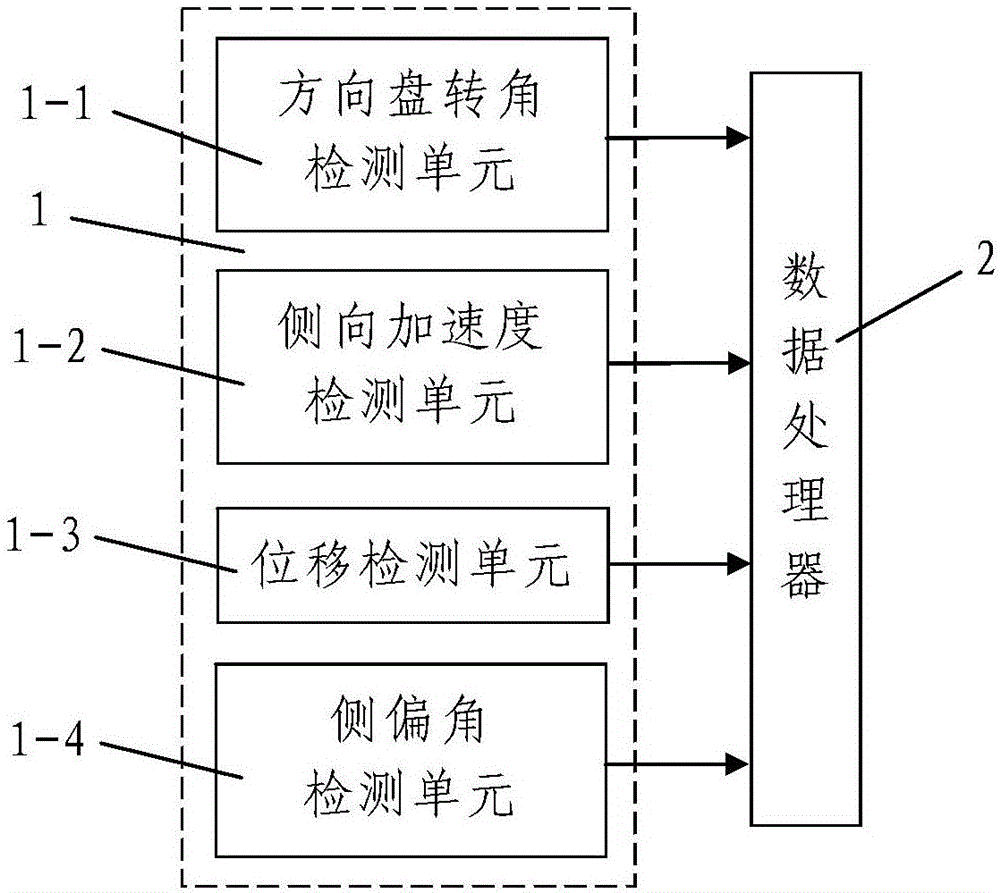
Driving state recognition method based on approximate entropy template matching
ActiveCN106446812AThe method steps are simpleReasonable designCharacter and pattern recognitionTemplate matchingTurn angle
The invention discloses a driving state recognition method based on approximate entropy template matching, and the method comprises the steps: 1, sample library building, wherein samples of one type in the sample library are a plurality of steering wheel turning angle signals in a normal driving state, and samples of the other type in the sample library are a plurality of steering wheel turning angle signals in a dangerous driving state; 2, road information segmentation based on the approximate entropy template matching: carrying out the call of a signal correction module based on the approximate entropy template matching to correct the steering wheel turning angle signals in the library sample, wherein the correction process of any one steering wheel turning angle signal is as follows: carrying out the EMD (Empirical Mode Decomposition), the effectiveness recognition of an intrinsic mode function component, and signal reconstruction; 3, feature extraction; 4, two-class model building and training; 4, driving state information collection and synchronous classification. The method is simple in steps, is reasonable in design, is easy and convenient to implement, is good in use effect, can accurately recognize the driving state of a driver simply and conveniently, and is high in recognition precision.
Owner:陕西智慧路衡电子科技有限公司
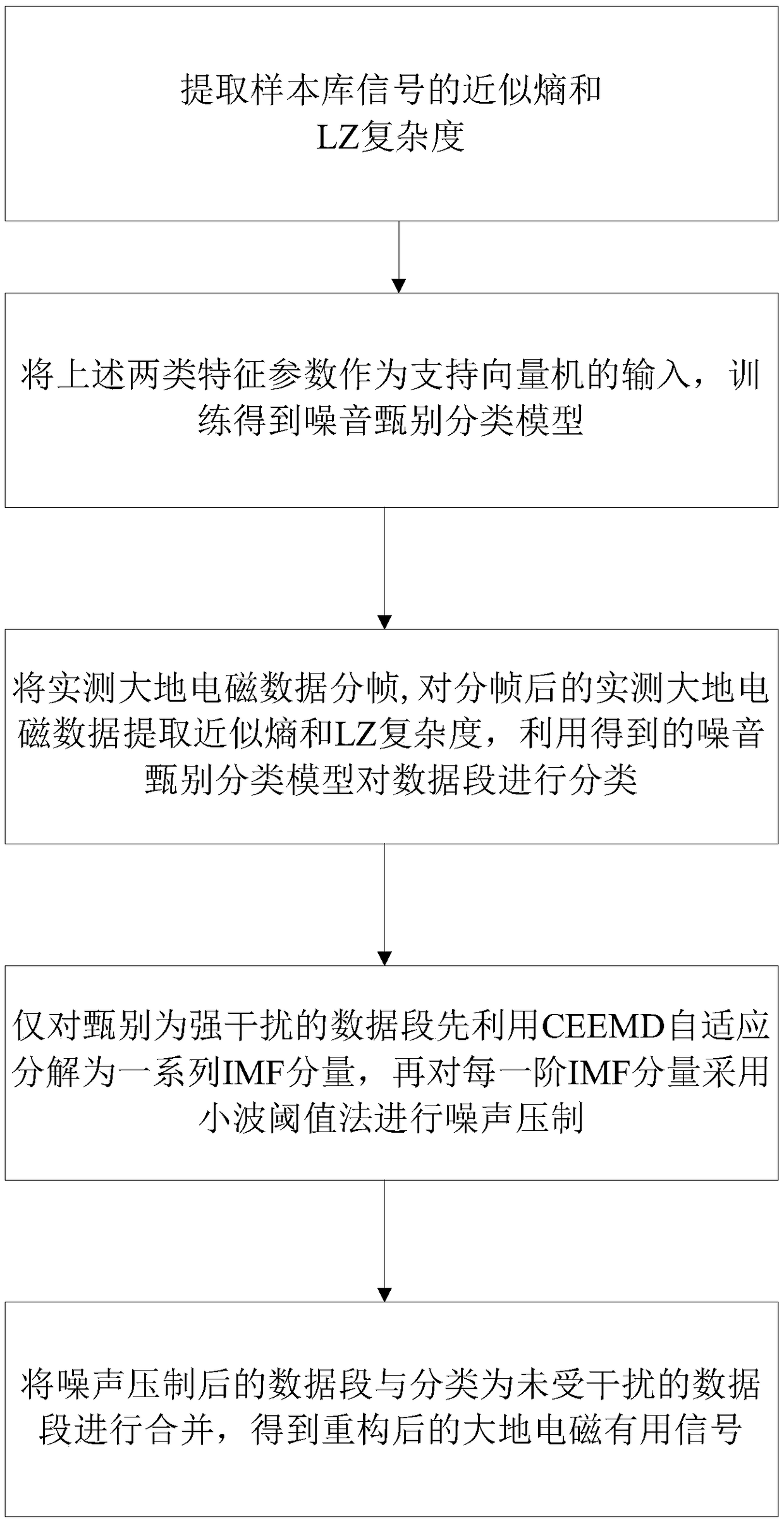
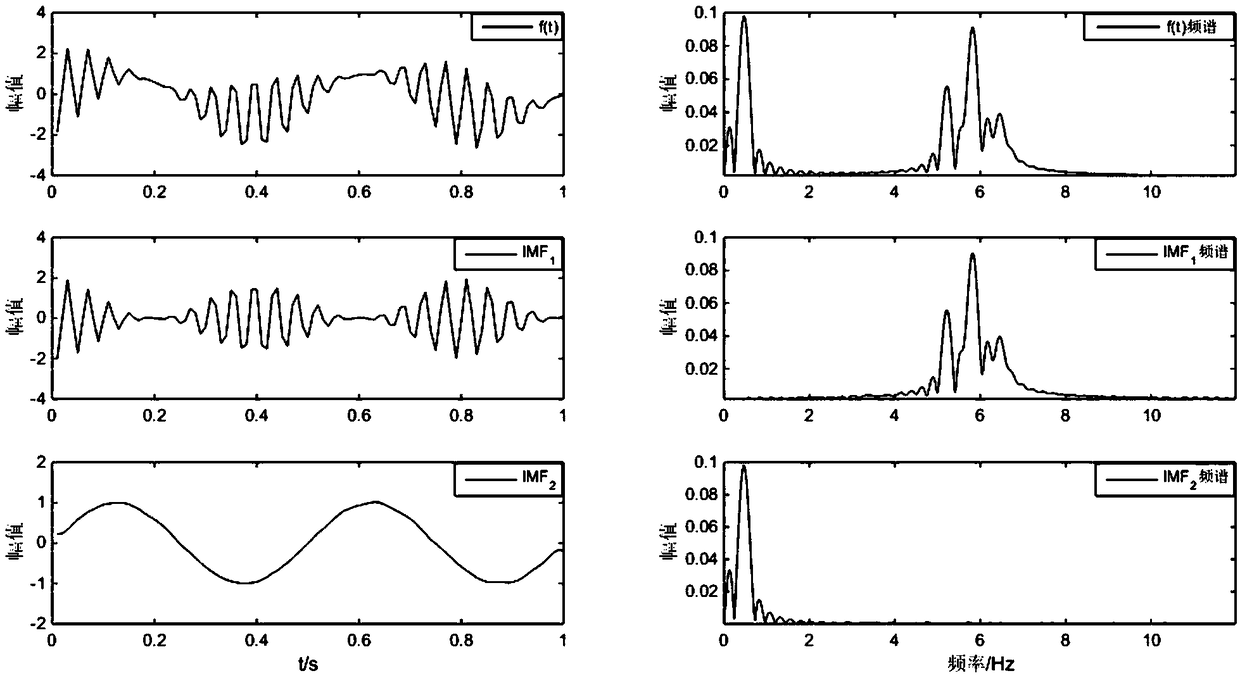
A denoising method of magnetotelluric signal based on noise discrimination
ActiveCN109101910AAvoid filteringImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionData segmentDecomposition
The invention discloses a magnetotelluric signal denoising method based on noise discrimination, which comprises the following steps: calculating approximate entropy and LZ complexity of each electromagnetic signal sample; using the approximate entropy, LZ complexity and class value of each electromagnetic signal sample to train the preset classification model to get the noise discrimination classification model; acquiring magnetotelluric signals to be processed, and performing noise screening on the magnetotelluric signals to be processed according to the noise screening classification modelto obtain electromagnetic signal segments with non-strong interference and electromagnetic signal segments with strong interference; combining the empirical mode decomposition of complementary set andwavelet threshold method, the strong disturbance electromagnetic signal being suppressed; the reconstructed magnetotelluric signal being obtained by combining the de-noising suppressed electromagnetic signal with the non-strong disturbance electromagnetic signal. The method of the invention can more accurately discriminate the data segments with strong interference and non-strong noise interference, retain the real magnetotelluric signal, and improve the denoising effect of the magnetotelluric signal.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
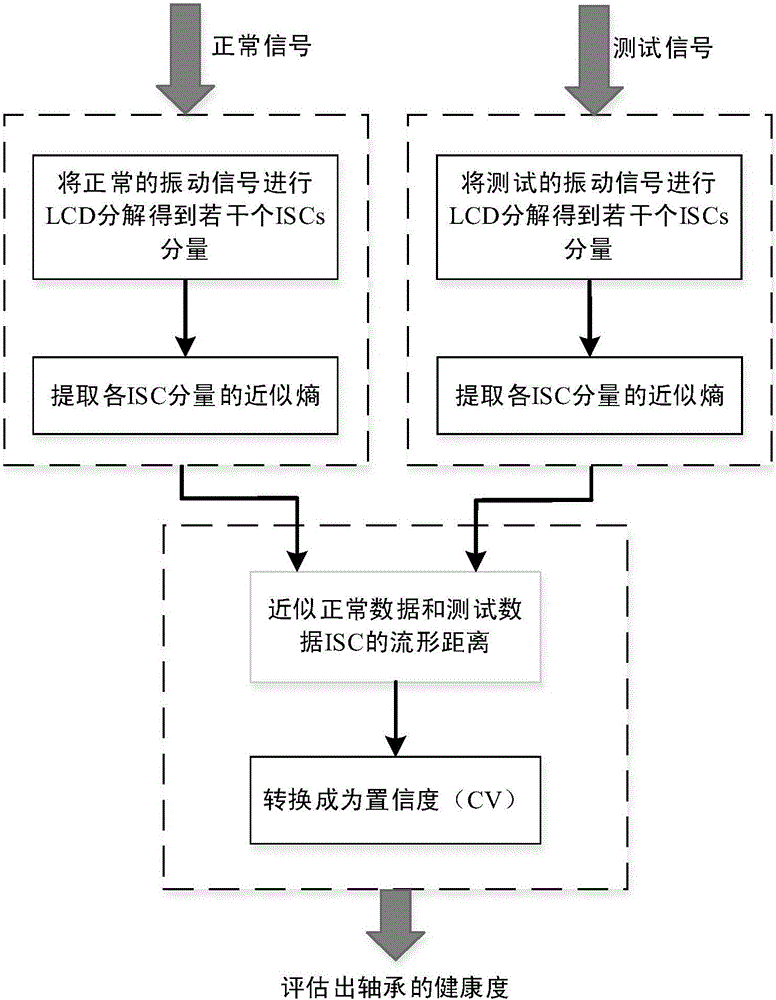
Rolling bearing health evaluation method based on local characteristic scale decomposition-approximate entropy and manifold distance
InactiveCN105973593AAvoid the disadvantage of large amount of calculationReduce endpoint effectsMachine bearings testingCharacter and pattern recognitionRolling-element bearingBearing vibration
The invention proposes a rolling bearing health evaluation method based on local characteristic scale decomposition-approximate entropy (APEn) and manifold distance. First, an original vibration signal is decomposed by LCD into a plurality of intrinsic scale components (ISCs); then, the approximate entropy of each ISC is calculated; and finally, the manifold distance between the approximate entropy of the ISCs and the approximate entropy of normal data is calculated, and the calculated manifold distance is normalized into confidence (CV) to express the health degree of a rolling bearing. The normal operation of rolling bearings is particularly important in the modern industrial complex mechanical system, so that rolling bearing performance evaluation is of great significance in prediction and health assessment of the mechanical system. However, as bearing vibration signals are nonlinear and unsteady, it is particularly difficult to accurately extract the characteristics of bearing vibration signals. Local characteristics of signals can be extracted accurately using the method proposed by the invention. Results show that the method proposed by the invention can be used to evaluate the health degree of rolling bearings effectively.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Systems, methods, and computer medium to provide entropy based characterization of multiphase flow
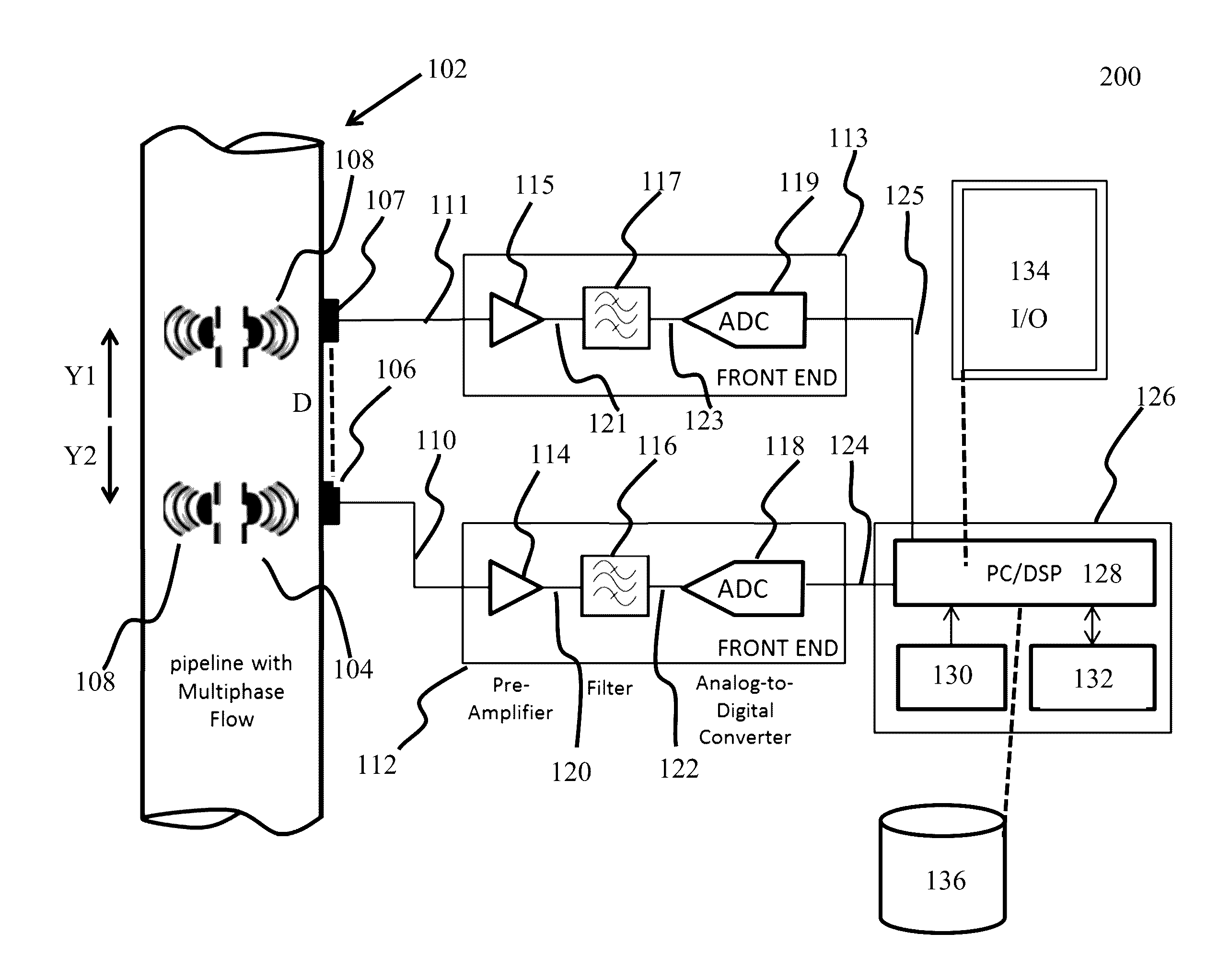
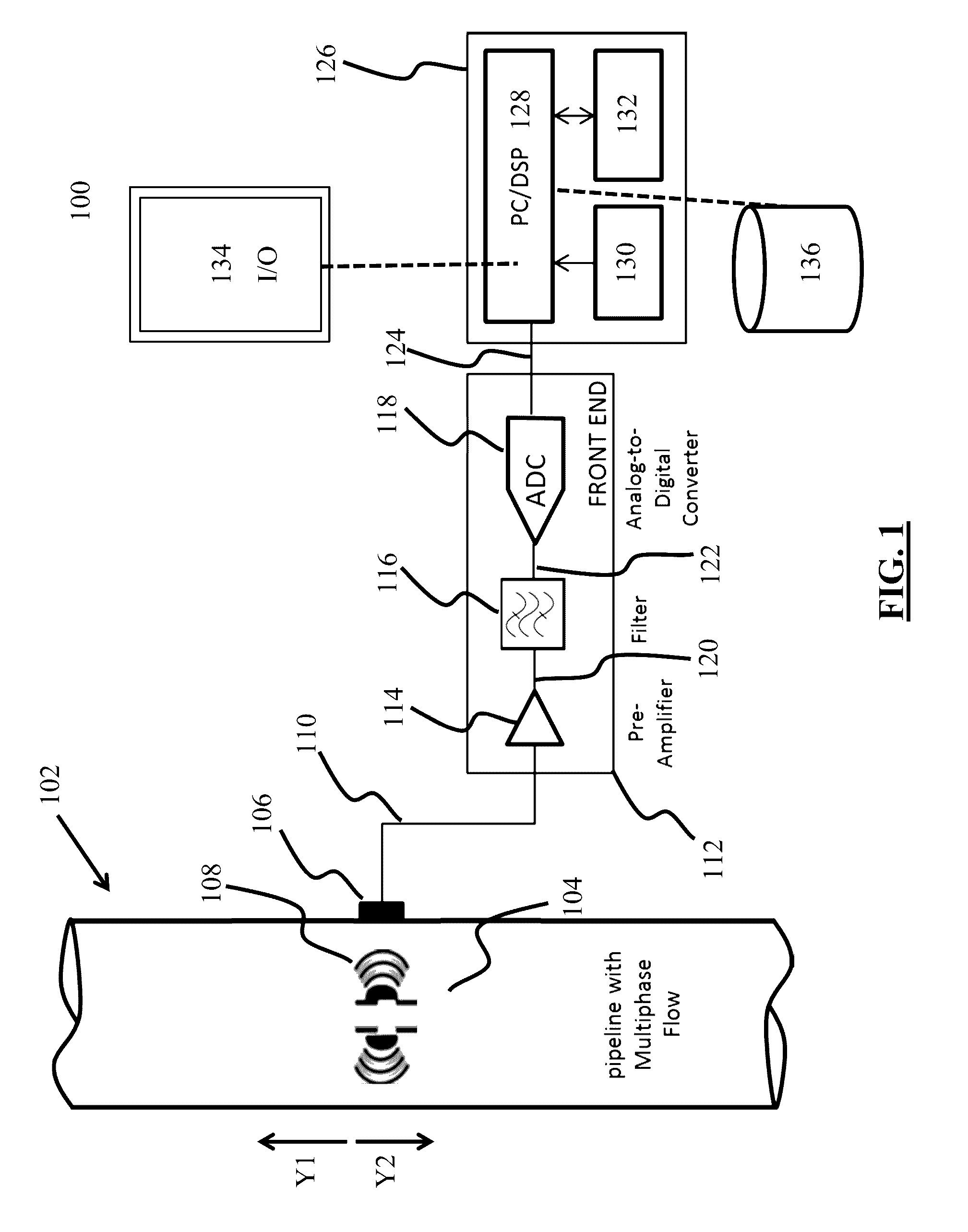
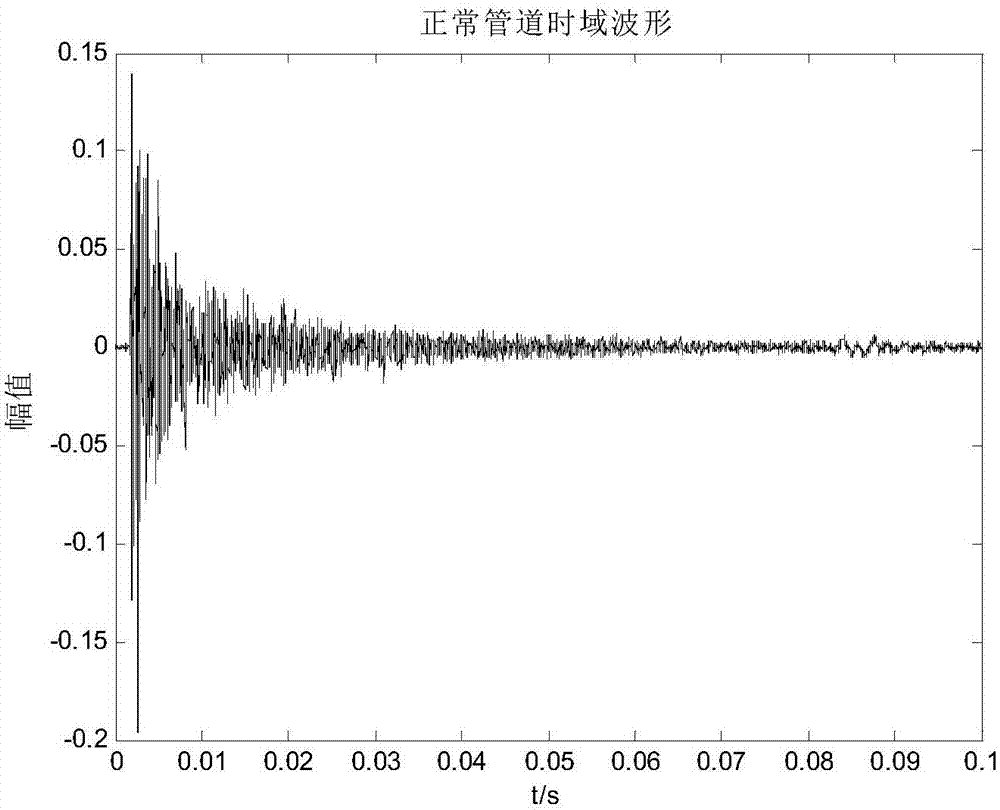
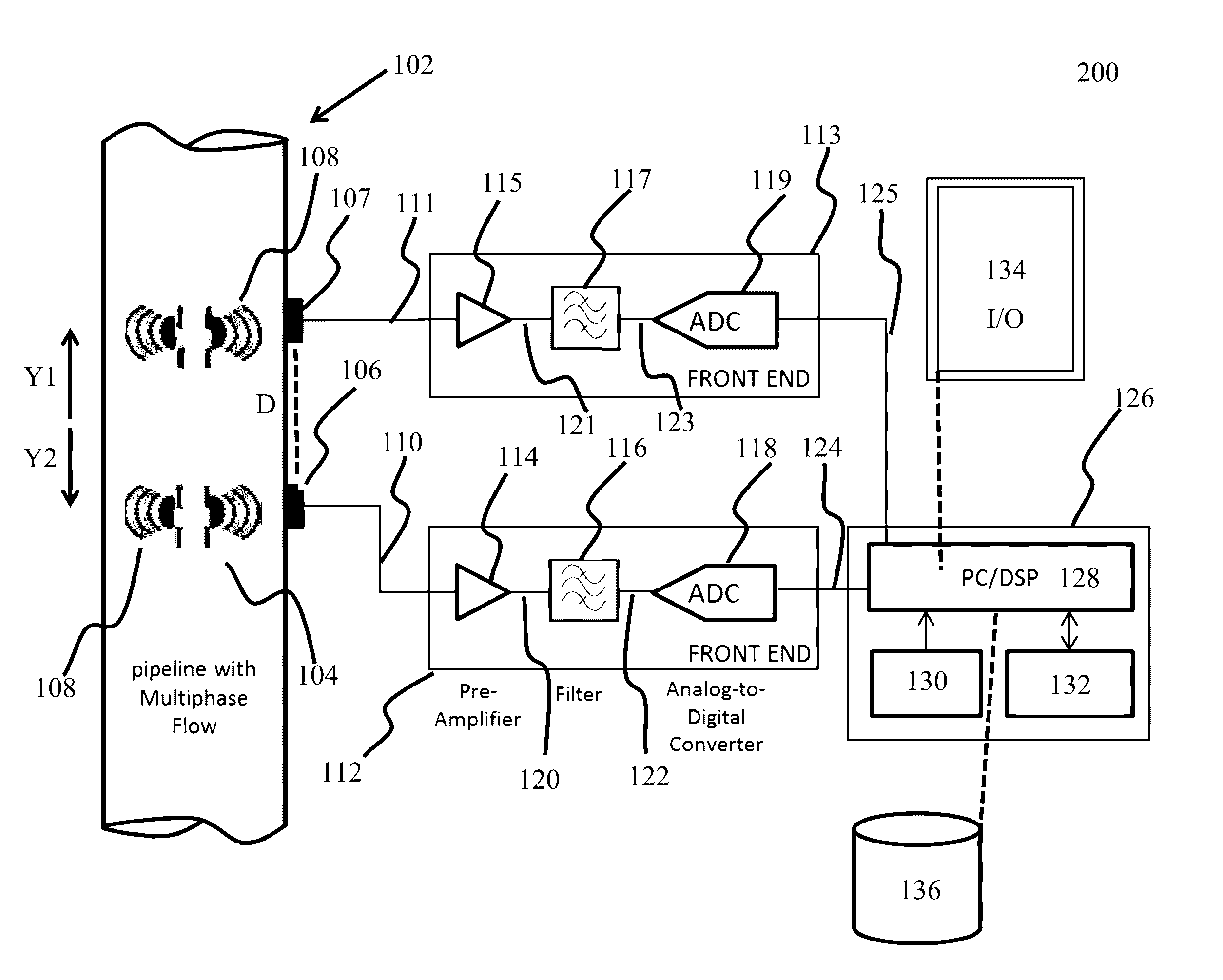
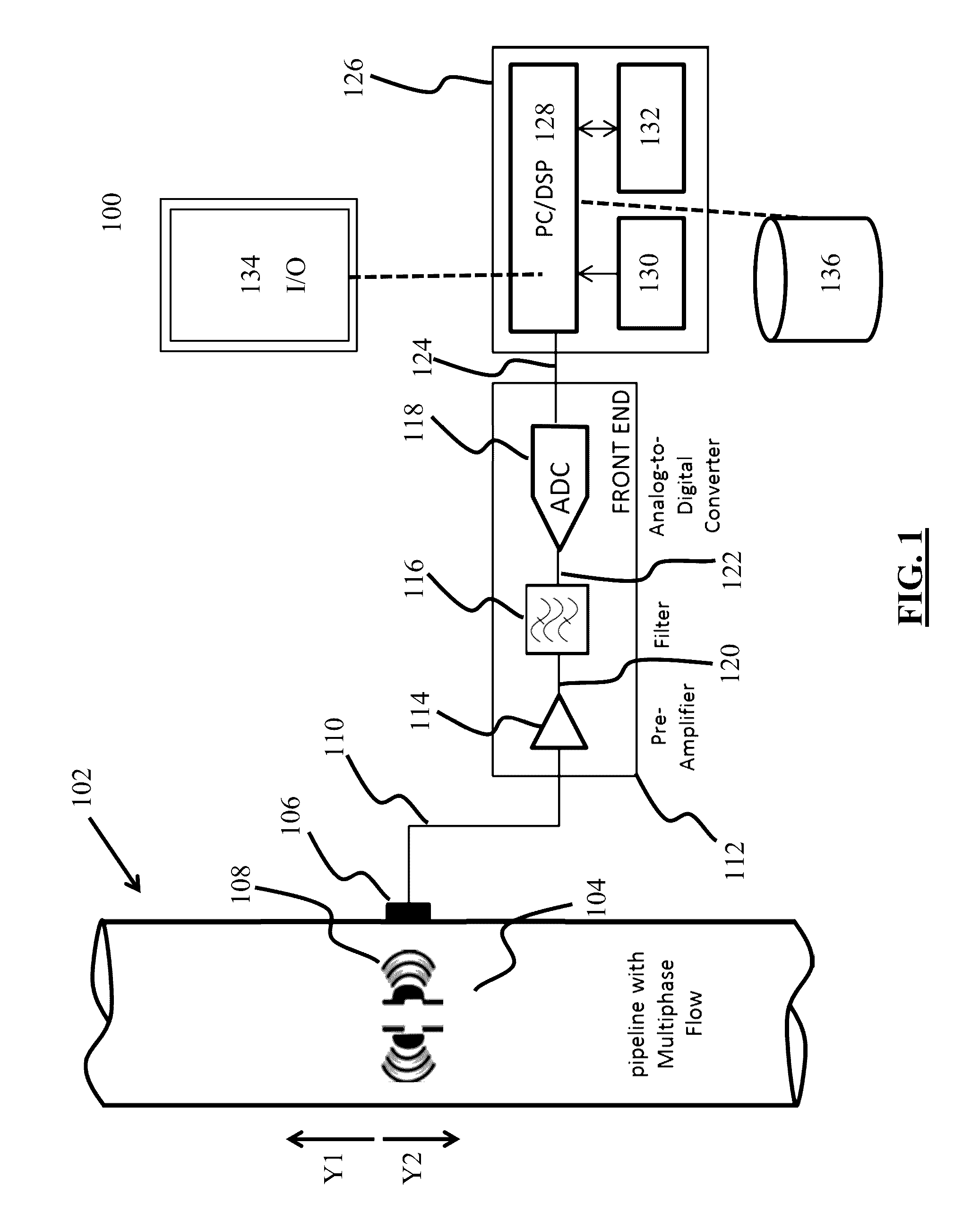
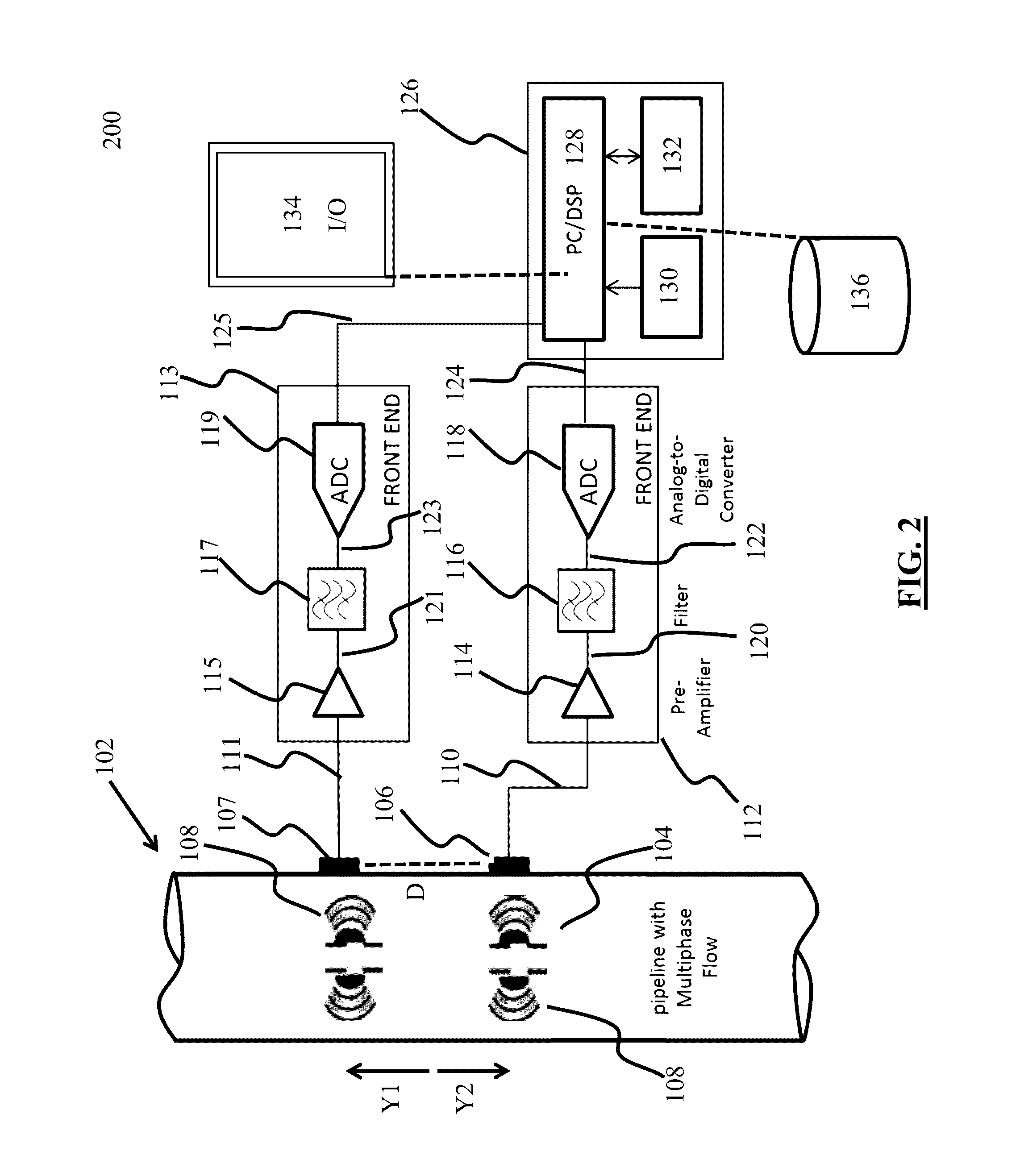
ActiveUS20160369624A1Easy to monitorIncrease productionAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurveyPrincipal component analysisComputer science
Systems, computer-implemented methods, and non-transitory computer-readable medium having a stored computer program provide characterization of multiphase fluid flow (MPF) using approximate entropy calculation techniques to enhance measuring and monitoring of a flow regime in a segment of pipe for hydrocarbon-production operations. The systems and methods can be optimized using principal component analysis.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Weak target detection method and weak target detection system under background of sea clutter
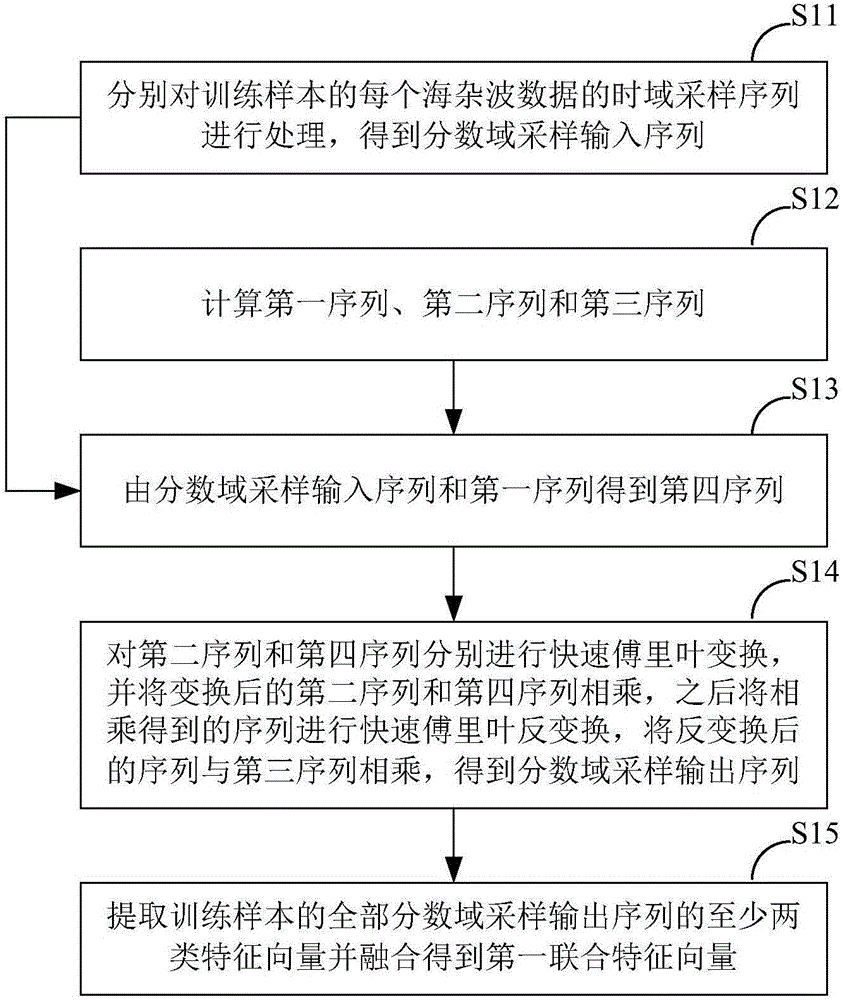
ActiveCN105894033AAchieve distinctionImprove detection accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorRadar detection
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar detection, and provides a weak target detection method and a weak target detection system under the background of sea clutter. The method comprises the following steps: using a sea clutter signal in a known state as data of a training sample, extracting at least two feature vectors of the training sample, and fusing the at least two feature vectors into a first joint feature vector; training a detection system to make the training sample detection accuracy of the detection system reach an ideal value; and solidifying the parameter values of the detection system for training, and transferring the parameters to a test detector to judge the state of unknown sea clutter data, wherein only one training process is needed. According to the invention, approximate entropy is used as a feature vector for describing the characteristics of sea clutter, and the detection accuracy for sub target units is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Modulation signal classification method for cuckoo search-improved gray wolf optimizer-least square support vector machine
ActiveCN108694390AImprove impactImprove the inability to adapt to changesCharacter and pattern recognitionArtificial lifeLearning machineSignal classification
The invention discloses a modulation signal classification method for cuckoo search-improved gray wolf optimizer-least square support vector machine. The method selects a high-order cumulant and a local mean decomposition amount approximate entropy for the characteristic parameter of a modulation signal, and utilizes cuckoo search for the second update of the wolf position to optimize the two keyparameters of a least squares support vector machine model, namely, the penalty coefficient Gamma and the kernel parameter Sigma, so as to obtain the optimal kernel limit learning machine parameter value. The method reduces the influence of noise factor on the signal recognition result, makes up for the defects of under-envelope, over-envelope and boundary effects in the traditional modal empirical decomposition, and effectively improves the defect that the gray wolf optimization global searching ability is poor and is easy to fall into the local optimal solution in processing of high-dimensional data, compared with the original gray wolf optimization result by MATLAB simulation, is it proved that the method can intelligently classify the modulated signal more efficiently and accurately, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Desert seismic signal denoising method based on VMD approximate entropy and multi-layer perceptron
ActiveCN108845352AAvoid settingSolve the defect that signal-to-noise separation cannot be achievedSeismic signal processingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Noise removal
The invention relates to a desert seismic signal denoising method based on the VMD approximate entropy and a multi-layer perceptron and belongs to the field of geophysical technology. The two-dimensional desert seismic record is subjected to variational mode decomposition to obtain a series of eigenmode components, the approximate entropy of each eigenmode component is calculated, all the eigenmode components are respectively divided into an effective signal dominant component and a noise dominant component, a characteristic quantity is constructed through effective signal correlation, the characteristic quantity is inputted into the multi-layer perceptron for classification, the valid signal portion determined by the multi-layer perceptron classifier is reserved, the noise portion determined by the multi-layer perceptron classifier is removed, the noise dominant component is denoised through combining an autocorrelation coefficient with tzhe multi-layer perceptron, and lastly, desertseismic signal denoising is realized through reconstruction. The desert seismic signal denoising method is advantaged in that noise removal under strong noise and low signal to noise ratio conditionsis achieved, the desert seismic signal denoising method has fast speed, high accuracy and strong anti-interference ability, and denoising of desert seismic signals under low frequency and low SNR canbe realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
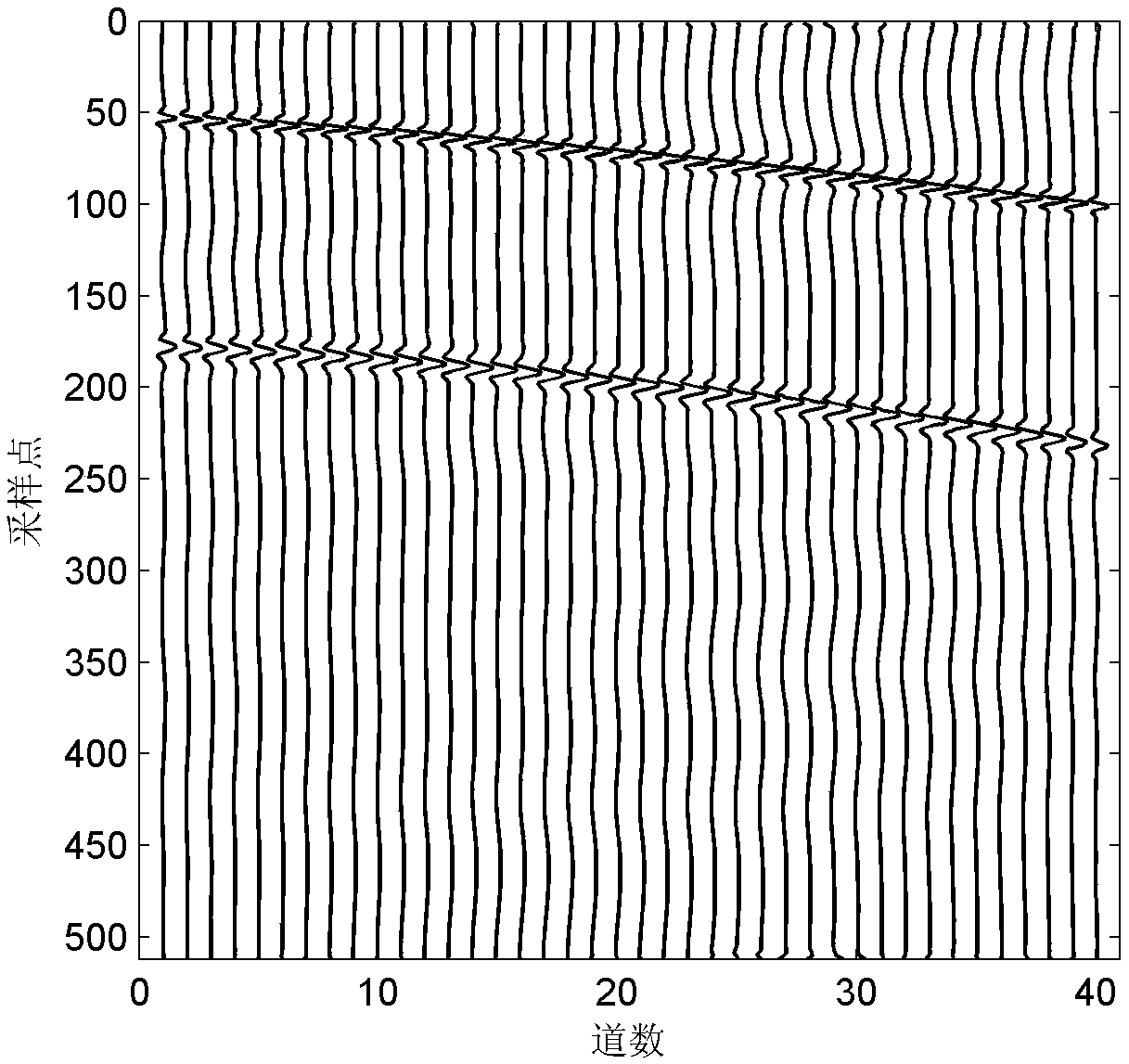
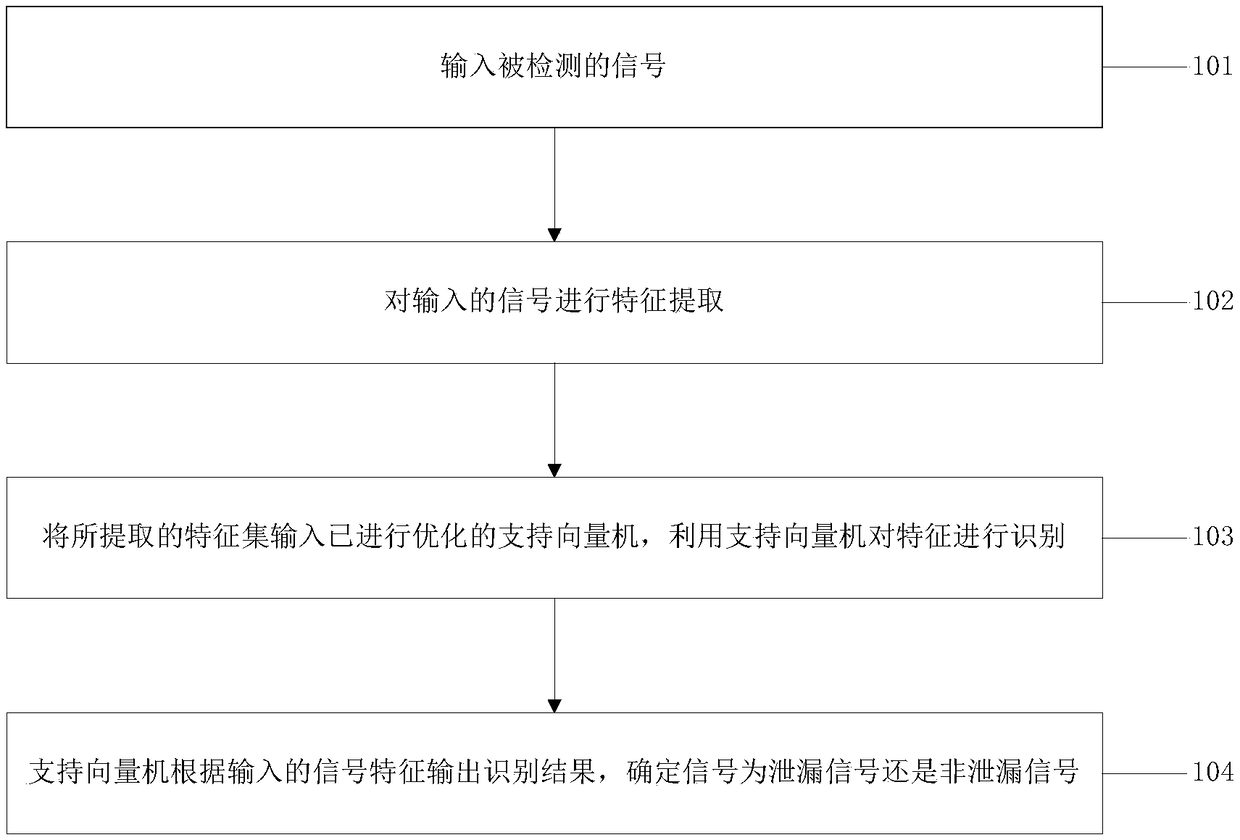
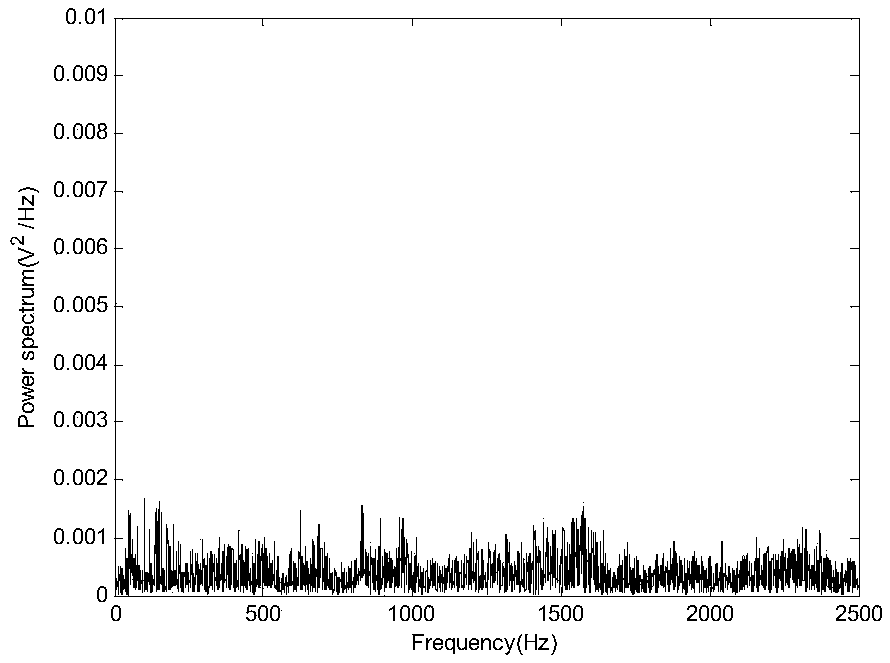
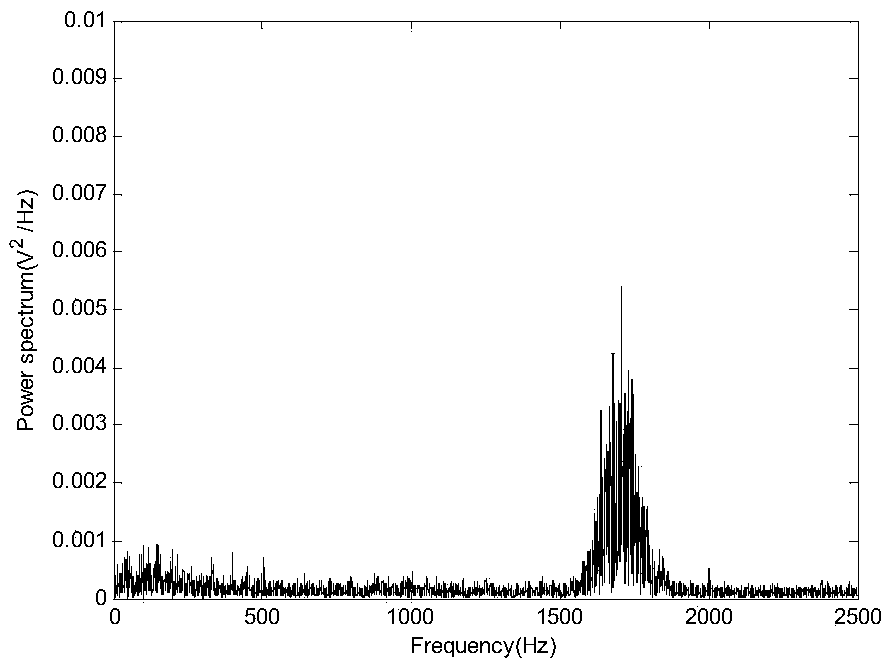
Water supply pipeline leakage identification method based on signal time-frequency characteristics and support vector machine
ActiveCN109284777AComprehensive detection effectAvoid problems with a high probability of misjudgmentCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineFeature set
The invention discloses a water supply pipeline leakage identification method based on signal time-frequency characteristics and support vector machine, belonging to the technical field of water leakage detection and positioning. The method includes: inputting a detected signal; performing feature extraction of the input signal; the extracted feature set is input to the optimized support vector machine, and the feature is recognized by the support vector machine. The support vector machine outputs a recognition result according to the input signal characteristics, and determines whether the signal is a leakage signal or a non-leakage signal. Based on the intrinsic mode function, approximate entropy and principal component analysis, three time-frequency characteristics of leakage signal areproposed by using its randomness and centralized frequency spectrum. Using these features to construct feature matrix as input of support vector machine, support vector machine is used as classifierto recognize the signal and output recognition results, thus solving the existing pipeline leak detection technology problems such as modeling difficulty coefficient is large, high misjudgment rate ishigh.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
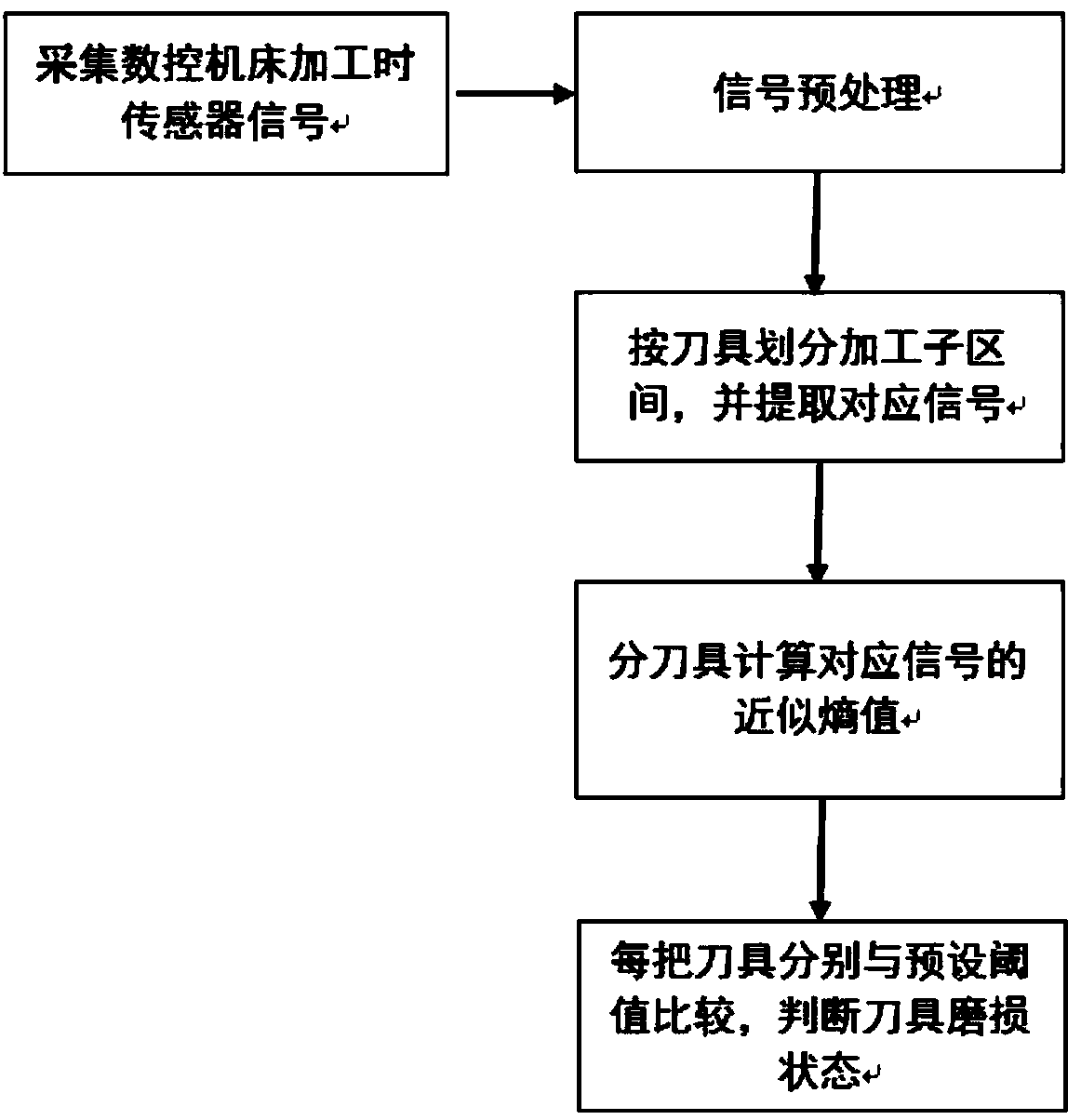
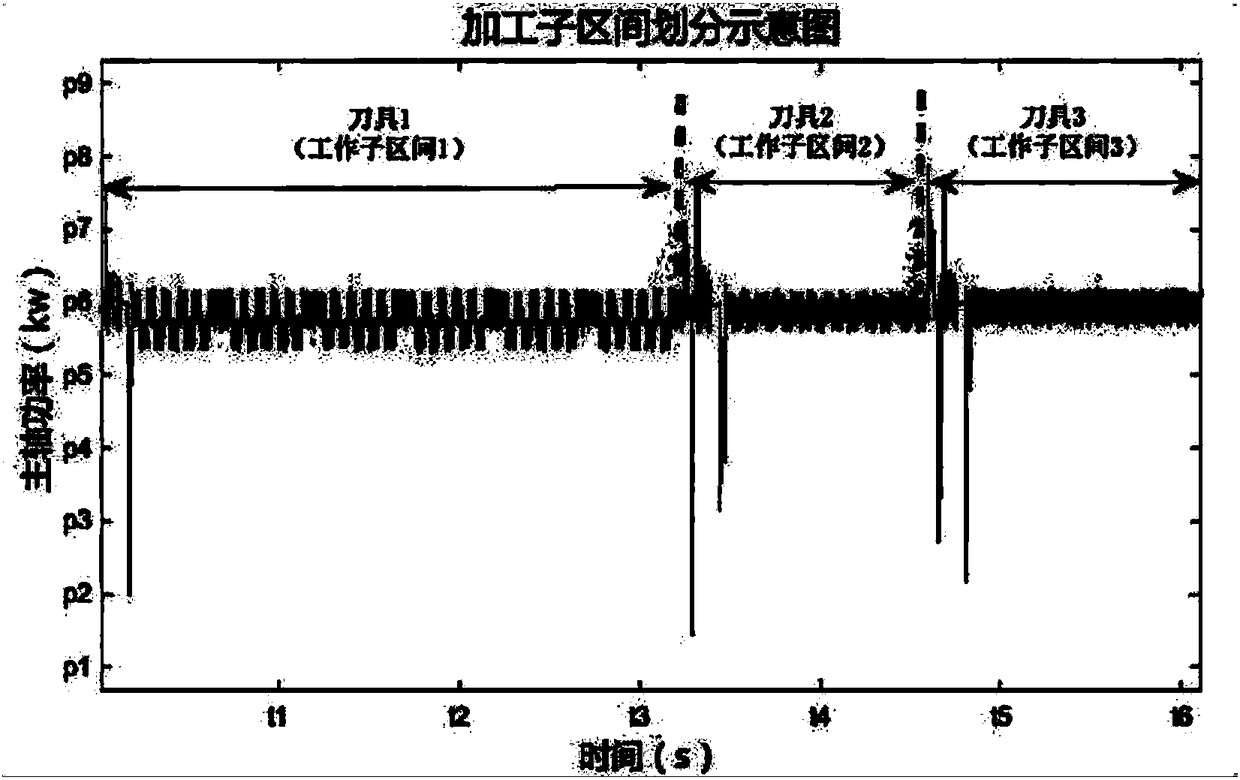
Numerical control machine tool cutting tool wear state real-time monitoring method
ActiveCN108490880ANo change in structureDoes not affect dynamic characteristicsProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlMeasurement device
The invention discloses a numerical control machine tool cutting tool wear state real-time monitoring method, which comprises the following steps: collecting sensor signals during machining of a numerical control machine tool in real time, and carrying out signal preprocessing; dividing the machining process into a plurality of working subintervals according to different machining tools, and extracting signal data during machining of each tool of the numerical control machine tool; calculating approximate entropy of the signal obtained during machining of each tool of the numerical control machine tool; and comparing the calculated approximate entropy of each tool and a preset threshold, and judging the tool wear state. The method has the advantages of needing no measuring equipment and needing no construction of an experiment platform, and is fast in prediction speed and high in accuracy; and meanwhile, the tool does not need to be assembled or disassembled, normal machining of the numerical control machine tool is not affected, and real-time monitoring of the wear state of the numerical control machine tool cutting tool can be realized.
Owner:谷城万利铸造有限公司
Short-term wind power prediction method of CEEMD and random forest
InactiveCN107392363AReduce reconstruction errorImprove forecast accuracyForecastingDecompositionElectric power system
The invention discloses a short-term wind power prediction method based on complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition (CEEMD) and a random forest. The method comprises the following steps of 1) using a CEEMD technology to decompose an original wind power sequence into a series of intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) with different characteristics; 2) using an approximate entropy to calculate each intrinsic modal function complexity, merging modal functions with similar approximate entropy values into new components which are a random component, a detail component and a trend component; 3) carrying out zero equalization processing on different component data; 4) using a partial autocorrelation function (PACF) to determine an input variable set for the different components; and 5) constructing a random forest (RF) prediction model for each new component, superposing each component prediction result to acquire a final short-term wind power prediction value, and through an example, verifying validity of the method of the invention. By using the method of the invention, short-term wind power prediction precision is effectively increased and a short-term wind power prediction problem of an electric power system can be well solved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
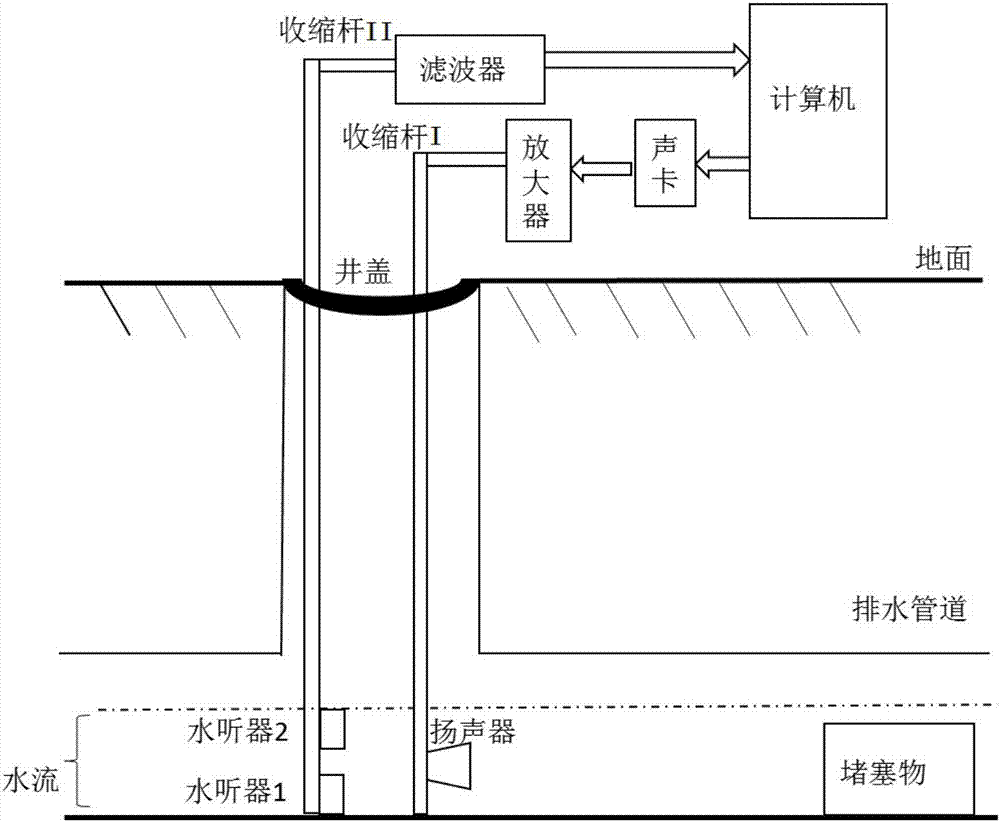
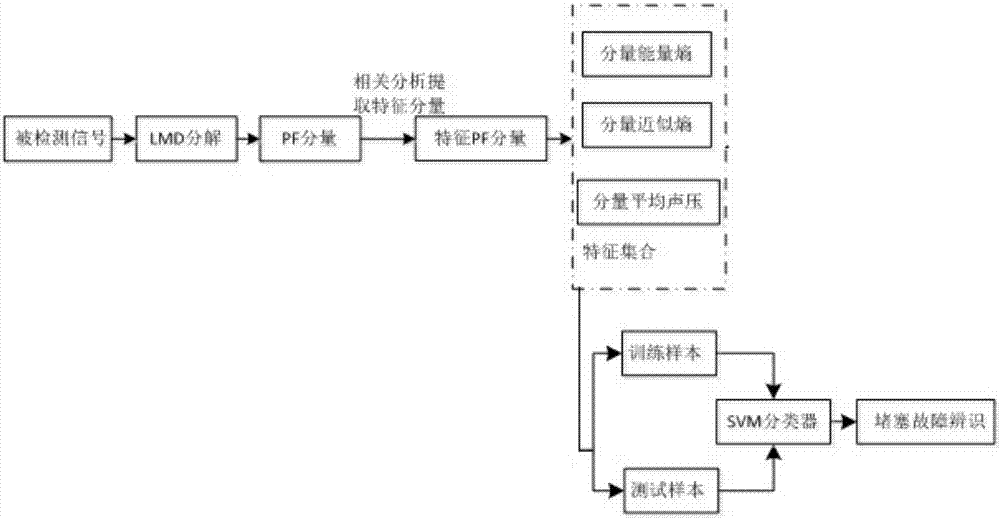
Detection method of detection device for drainage pipeline blockage faults
ActiveCN107218518AOvercoming Disadvantages of Fault DetectionHighlight failure conditionsPipeline systemsCorrelation coefficientDecomposition
The invention discloses a detection method of a detection device for drainage pipeline blockage faults. The method comprises the steps that the detection device for the drainage pipeline blockage faults is arranged; a computer obtains a signal of a normal / blocked pipeline from the receiving end; acoustic response signals in two working conditions of a drainage pipeline are acquired; LMD decomposition is conducted on the acoustic response signals of the normal pipeline and the blocked pipeline; correlation coefficients of all PF components of the normal pipeline and an original signal and correlation coefficients of all PF components of the blocked pipeline and the original signal are calculated by adopting a Pearson correlation coefficient method, and each component of which the correlation coefficient exceeds 15% is taken as an effective PF component signal; energy entropy indexes, approximate entropy indexes and average acoustic pressure indexes of the effective PF components of the normal pipeline and the blocked pipeline are calculated to serve as a characteristic set; an optimal parameter of the characteristic set is sought through a K-CV method; the steps are repeated, and fault identification is conducted on other sections of the pipeline by adopting an SVM classifier with the trained parameter. According to the detection method, the detection procedure is conveniently conducted, and the accuracy and reliability of a detection result are improved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for monitoring the depth of anesthesia
A method for monitoring the depth of anesthesia is provided for detecting the conscious state of one being anesthetized in the recovery phase or induction phase of anesthesia course in order to facilitate an anesthesiologist to predict exactly the dosage of an anesthetic required. At first, an original electroencephalogram (EEG) is taken from one being tested. Then, the original electroencephalogram is analyzed by approximate entropy to obtain its approximate entropy value. Next, the approximate entropy value is multiplied by 1000 / 17, and the corrected value is assumed as the predicted value of depth of anesthesia. The predicted value of depth of anesthesia represents degree of the conscious state or the depth of anesthesia for the one being tested. The higher the predicted depth of anesthesia value, the more conscious the one being tested is, i.e., in a shallower depth of anesthesia. On the other hand, the lower the predicted depth of anesthesia value, the less conscious the one being tested is, i.e., in a deeper depth of anesthesia.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
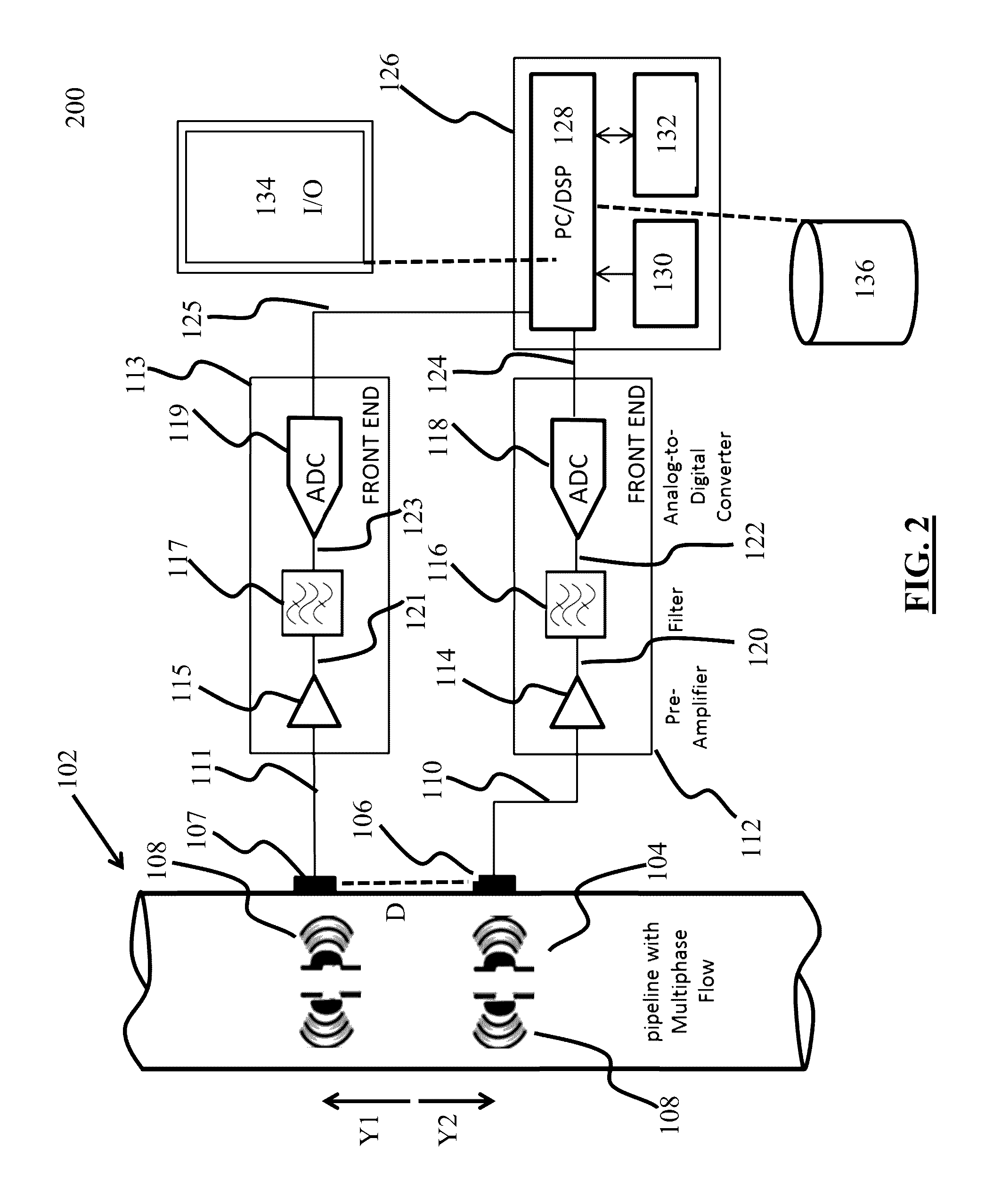
Systems, methods, and computer medium to provide entropy based characterization of multiphase flow
ActiveUS20160369623A1Easy to monitorIncrease productionAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurveyPrincipal component analysisComputer science
Systems, computer-implemented methods, and non-transitory computer-readable medium having a stored computer program provide characterization of multiphase fluid flow (MPF) using approximate entropy calculation techniques to enhance measuring and monitoring of a flow regime in a segment of pipe for hydrocarbon-production operations. The systems and methods can be optimized using principal component analysis.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Water turbine tail water pipe dynamic characteristic extraction method
InactiveCN103955601AImprove accuracyImprove decomposition efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsWater turbineField tests
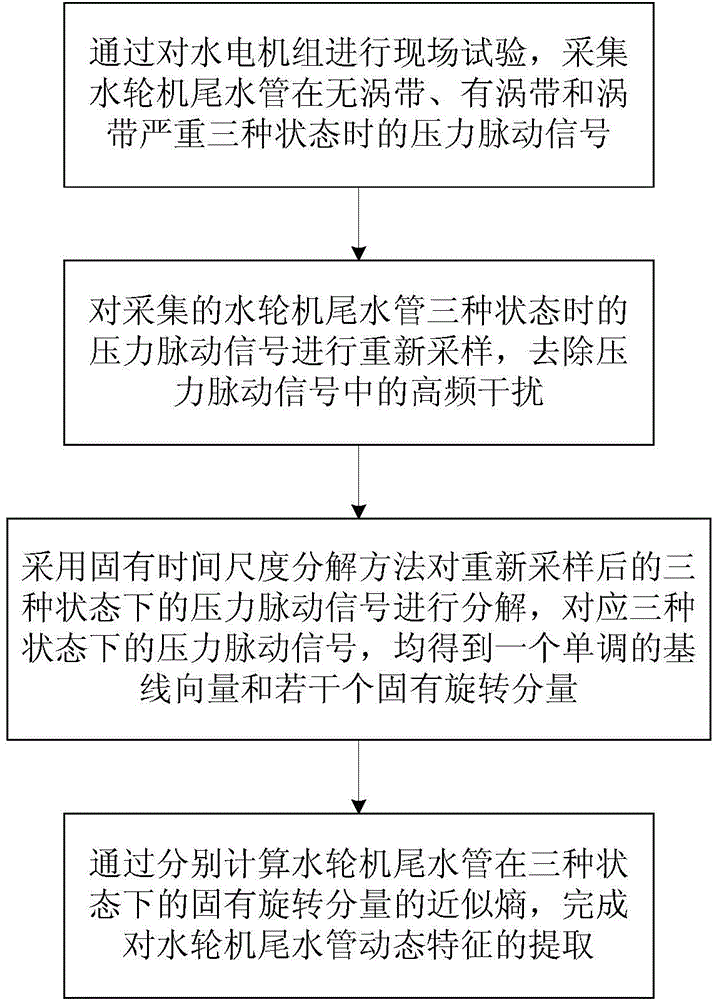
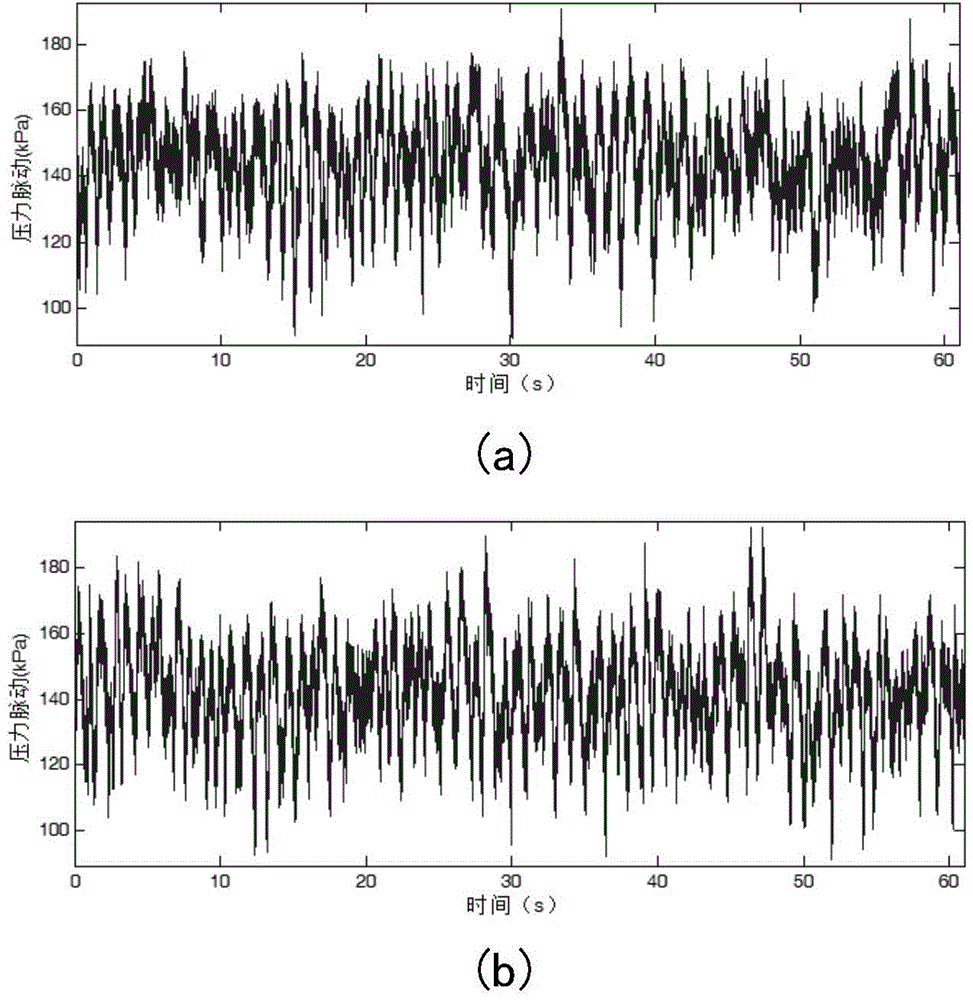
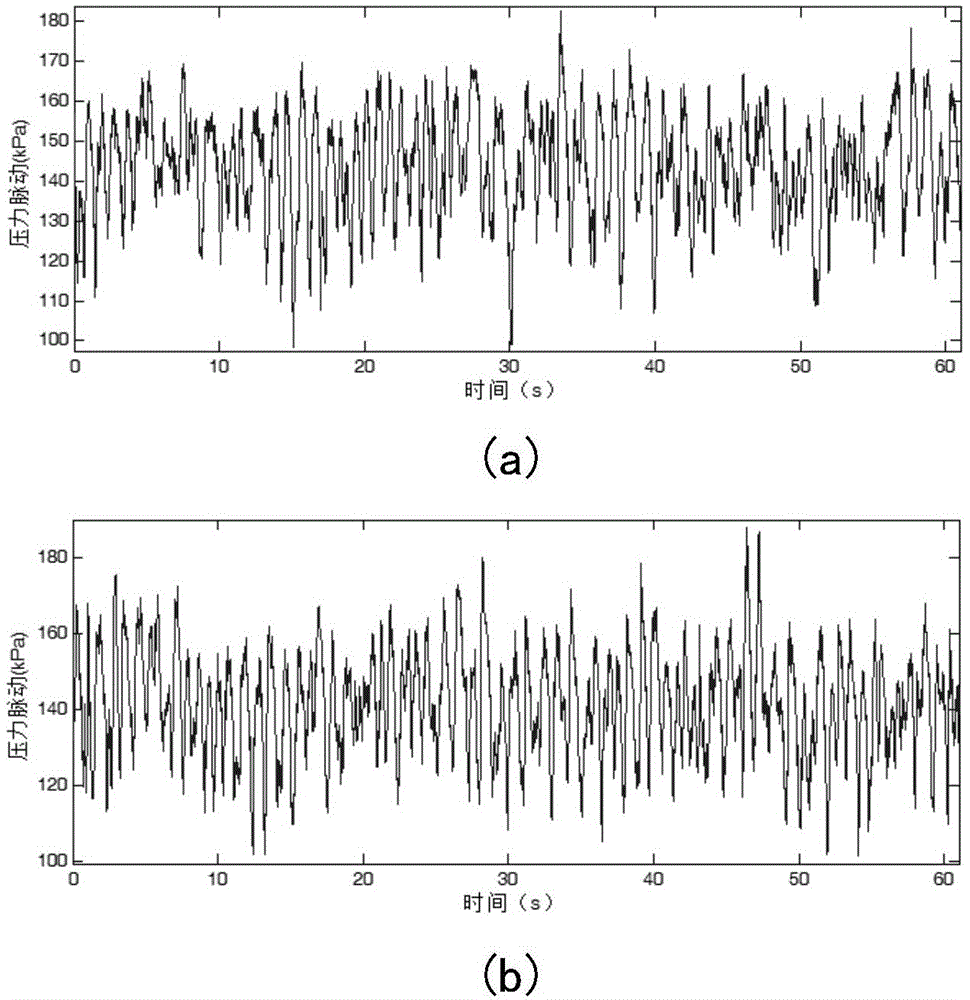
The invention relates to a water turbine tail water pipe dynamic characteristic extraction method. The method comprises the following steps that pressure fluctuation signals of a water turbine tail water pipe under three states of no vortex strip, vortex strips and serious vortex strips are collected by a field test which is carried out by a hydroelectric generating set; the collected pressure fluctuation signals are subjected to resample under the three states of the water turbine tail water pipe, and high-frequency interference in the pressure fluctuation signals is removed; the pressure fluctuation signals subjected to resample under the three states are resolved by adopting an intrinsic time-scale decomposition method, and a monotonous baseline vector and a plurality of intrinsic rotational components are obtained corresponding to the pressure fluctuation signals under the three states; the dynamic characteristics of the water turbine tail water pipe are extracted by the approximate entropy of the intrinsic rotational components, which is respectively obtained by calculation, of the water turbine tail water pipe under the three states. The water turbine tail water pipe dynamic characteristic extraction method has the advantages of efficiency, strong instantaneity and the like, and can be widely applied to the fields of running guarantee of the hydroelectric generating set.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Urination sensing detection method and device
InactiveCN103445770AExtract maximizationHigh detection sensitivitySensorsUrological function evaluationEcg signalSide effect
The invention discloses an urination sensing detection method and an urination sensing detection device. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring original bladder impedance information and an original electrocardiosignal; extracting urination sensing characteristic parameters comprising an electrocardio approximate entropy, an electrocardio high and low frequency energy ratio, an impedance approximate entropy and an impedance high and low frequency energy ratio; establishing a neural network urination sensing detection model, using the urination sensing characteristic parameters as input vectors of a neural network, training the neural network and determining neural network parameters; and detecting the urination sensing degree of tested personnel by utilizing the trained neural network and outputting a detection result. The urination sensing detection method and the urination sensing detection device utilize the electronic technology to implement urination sensing detection and urination awakening on an enuresis patient, are safe and effective and have no any side effects.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
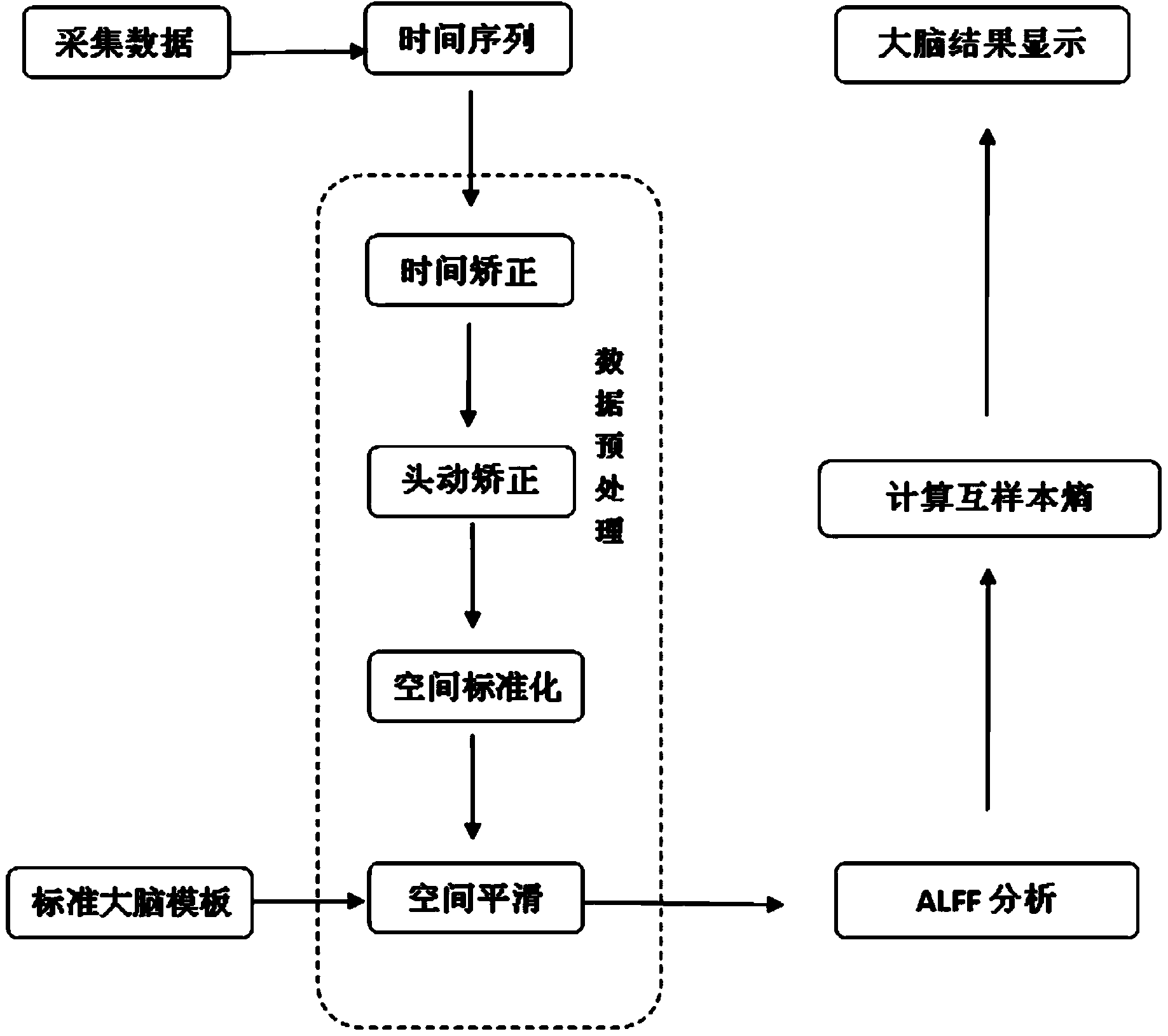
Obese patient functional image analysis method based on mutual sample entropy
InactiveCN104207775AOvercoming the problem of insufficient time resolutionImprove spatial resolution2D-image generationDiagnostic recording/measuringVoxelSample entropy
The invention discloses an obese patient functional image analysis method based on mutual sample entropy. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of collecting resting-state functional magnetic resonance data of a brain; selecting interest areas; extracting a time sequence of voxels in each interest area, up-sampling the time sequence of each voxel, and calculating the mutual sample entropy value of any two interest areas; comparing the mutual sample entropy value of any two interested area of the obese patient with the mutual sample entropy value of corresponding two interested areas of a normal testee, and determining the reason for obesity or worsening of the obesity. The method has the beneficial effects that starting with the physiological line of the obese patient through the resting-state imaging way, the changing of physiological activity of the brain of the patient can be accurately reflected; the EEG signal brain network establishing method is applied to fMRI, and the problem that the fMRI time resolution is not high can be overcome by utilizing the up-sampling method; the mutual sample entropy overcomes the matching problem of the mutual approximate entropy.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
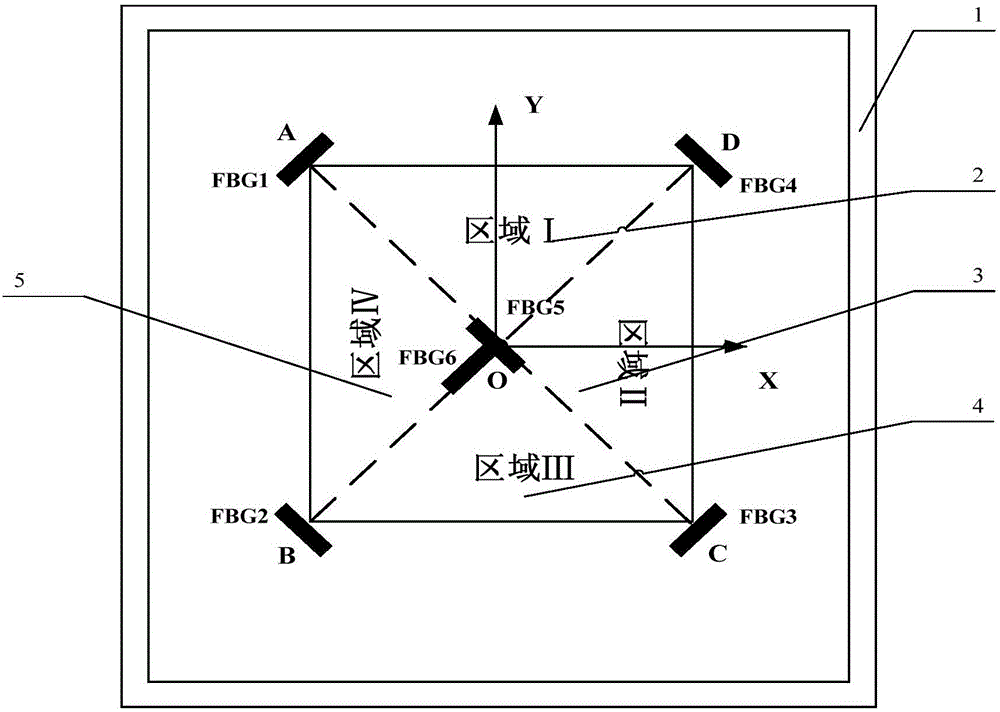
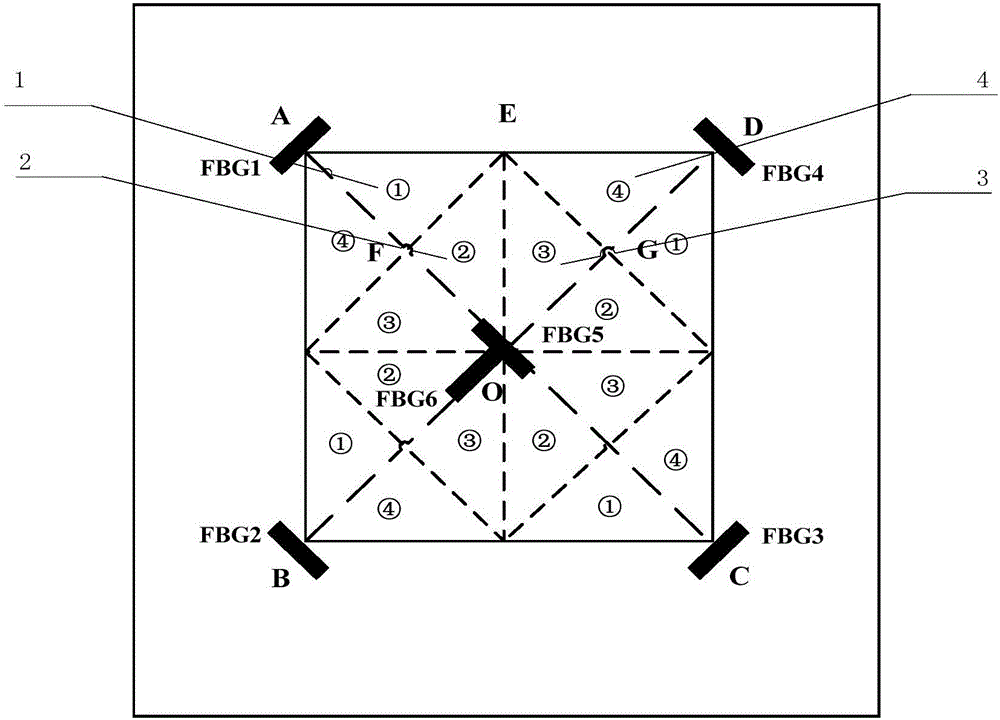
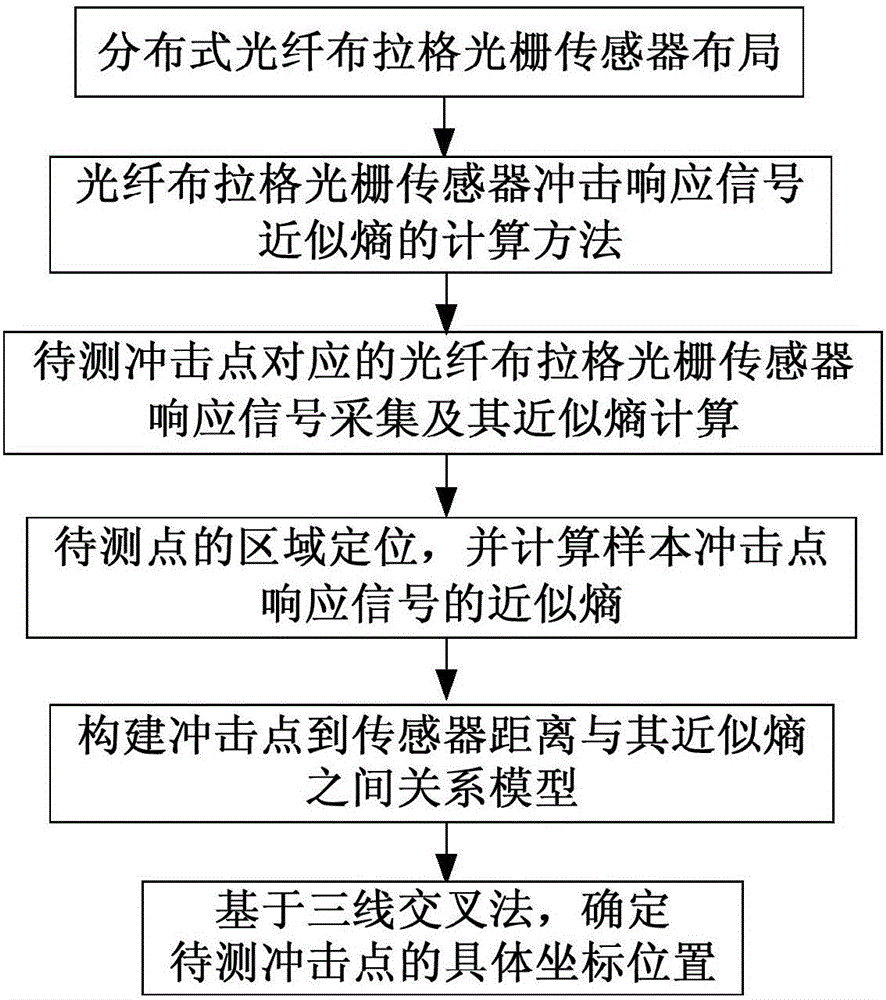
Low speed impact position identification method based on approximate entropy calculation
ActiveCN106482639AImprove anti-interference abilityThe method is simple and reliableUsing optical meansShock testingGratingRelational model
The invention discloses a low speed impact position identification method based on approximate entropy calculation and belongs to the impact monitoring technology field of structure health monitoring. The method comprises the following steps of step1, carrying out distributed optical fiber bragg grating sensor layout; step2, adopting a calculating method of optical fiber bragg grating sensor impulse response signal approximate entropy; step3, collecting an optical fiber bragg grating sensor response signal corresponding to an impulse point to be measured and carrying out approximate entropy calculation; step4, determining an area where the point to be measured is located and calculating an approximation entropy of a sample impulse point response signal in the area; step5, constructing a relation model of a distance of the impulse point to a sensor and a corresponding approximation entropy difference value; and step6, based on a three-line crossing method, determining a position of the impulse point to be measured. A positioning algorithm in the invention possesses characteristics that a lot of prior knowledge is not needed; and practicality is high and so on.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com