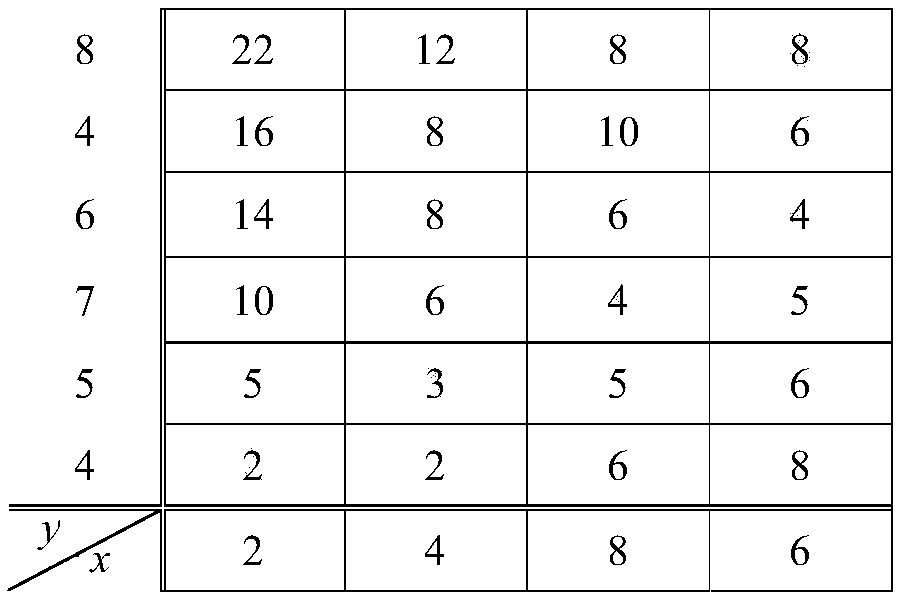
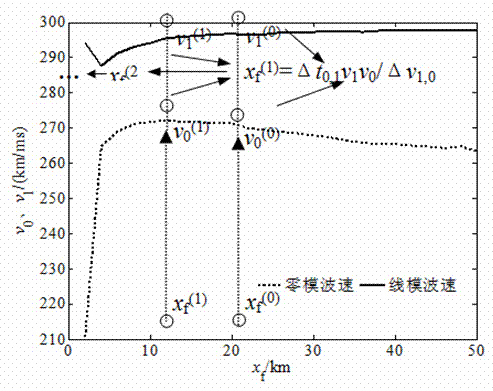
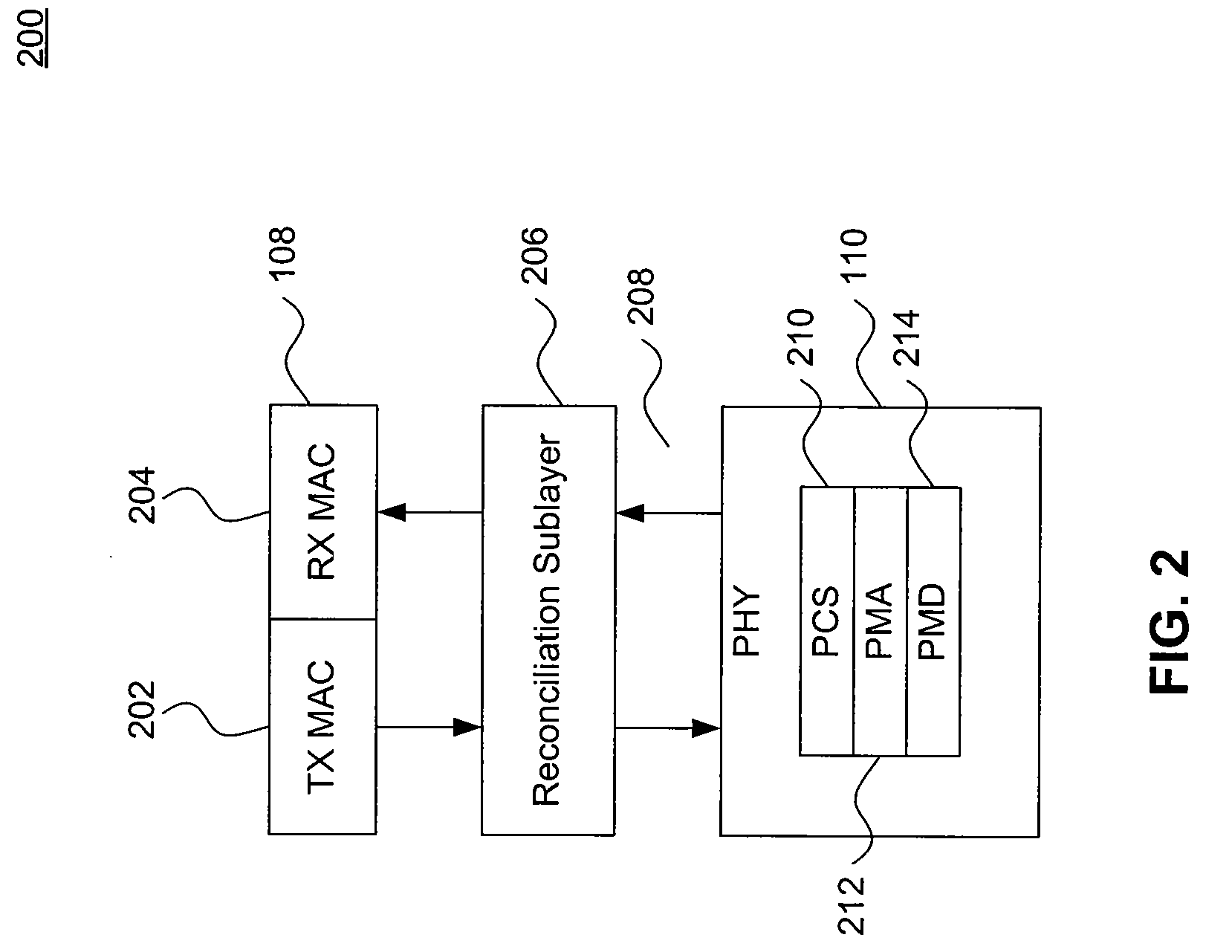
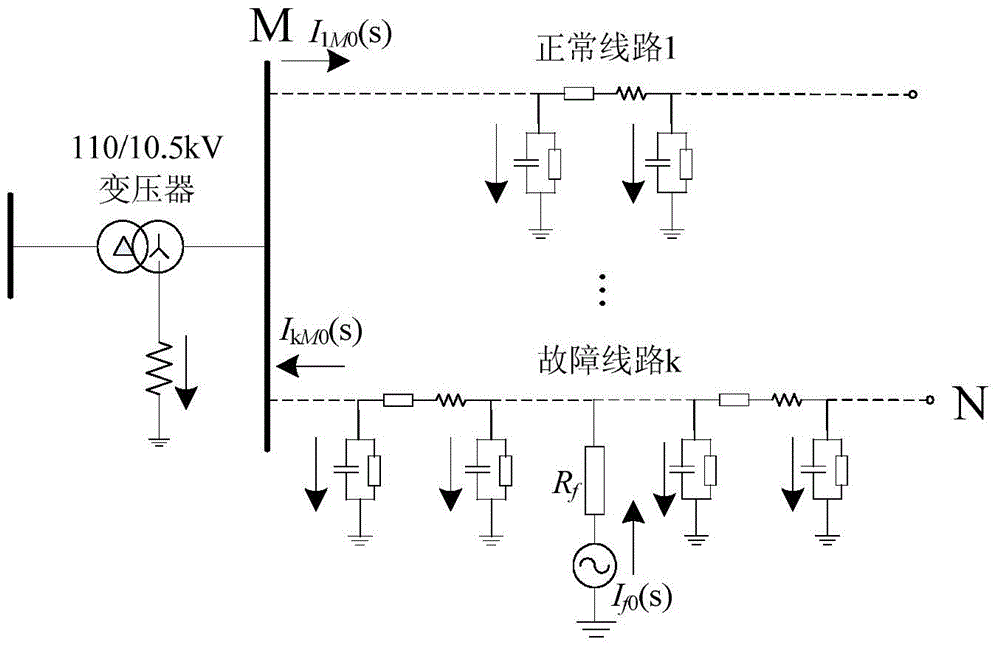
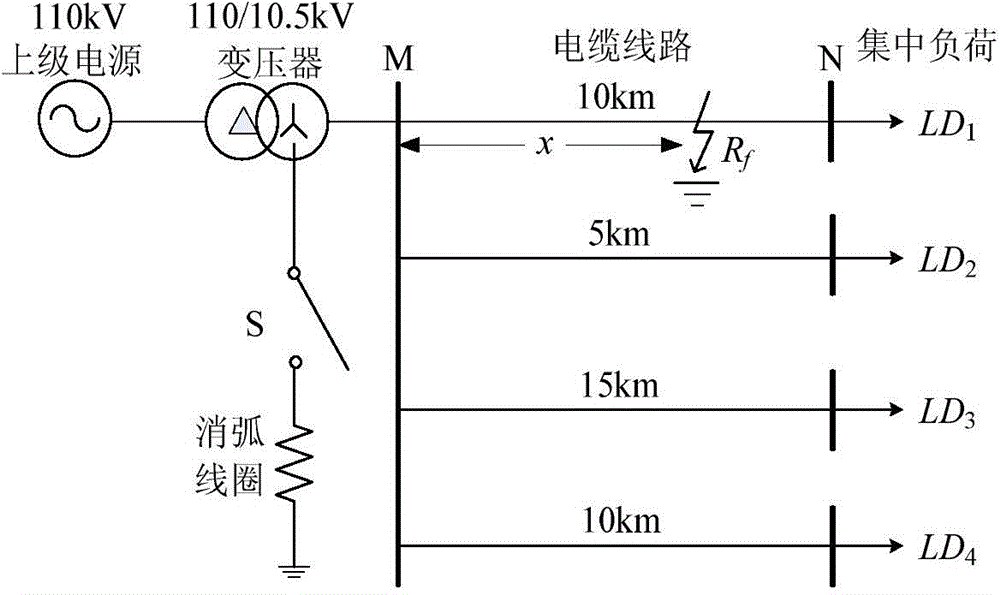
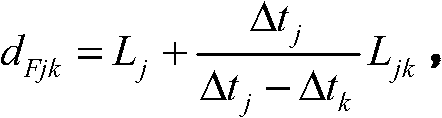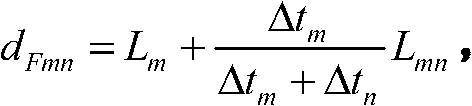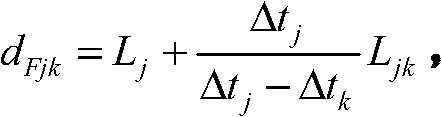Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62 results about "Zero mode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, a zero mode is an eigenvector with a vanishing eigenvalue. In various subfields of physics zero modes appear whenever a physical system possesses a certain symmetry. For example, normal modes of multidimensional harmonic oscillator (e.g. a system of beads arranged around the circle, connected with springs) corresponds to elementary vibrational modes of the system. In such a system zero modes typically occur and are related with a rigid rotation around the circle.
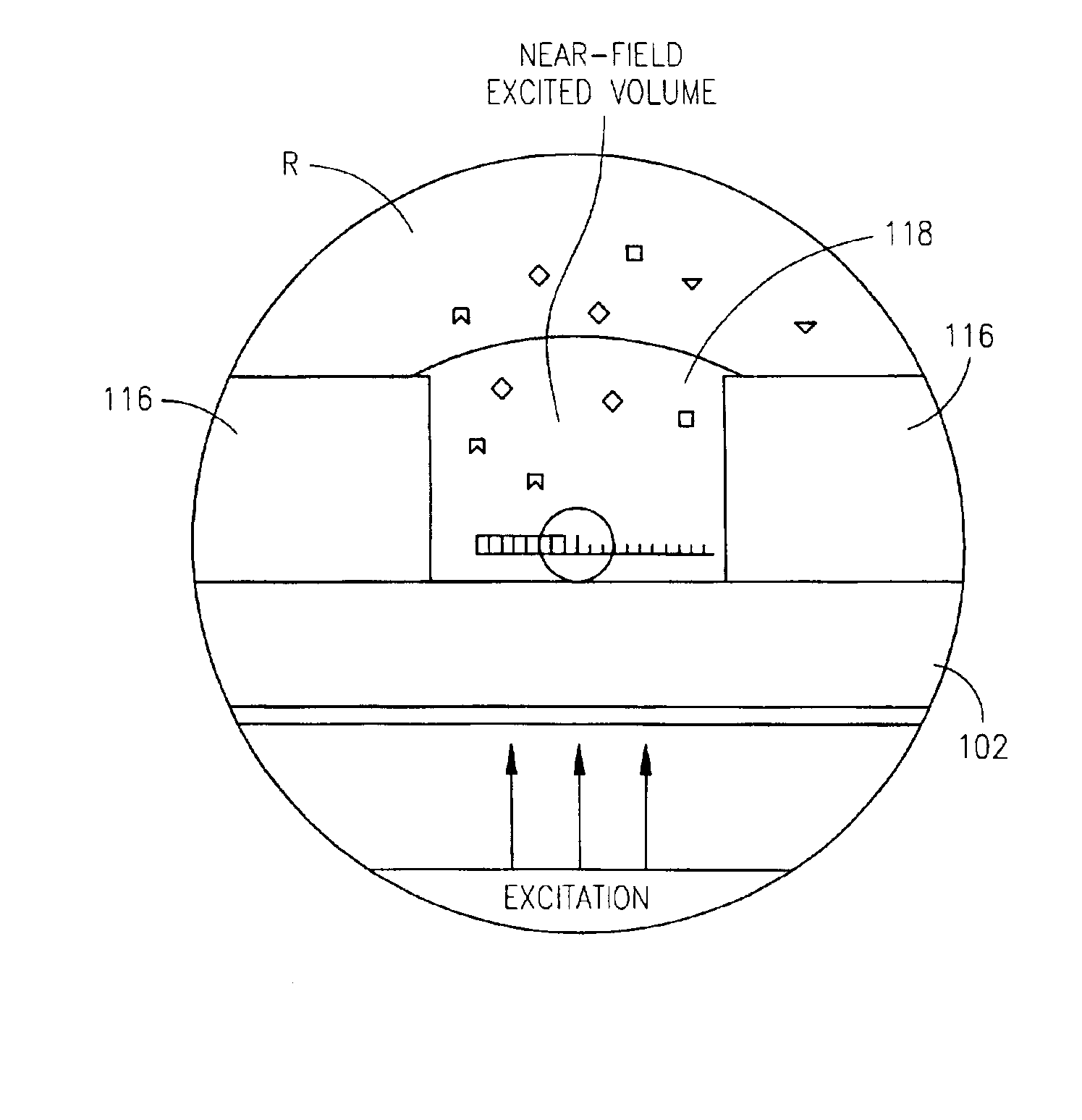
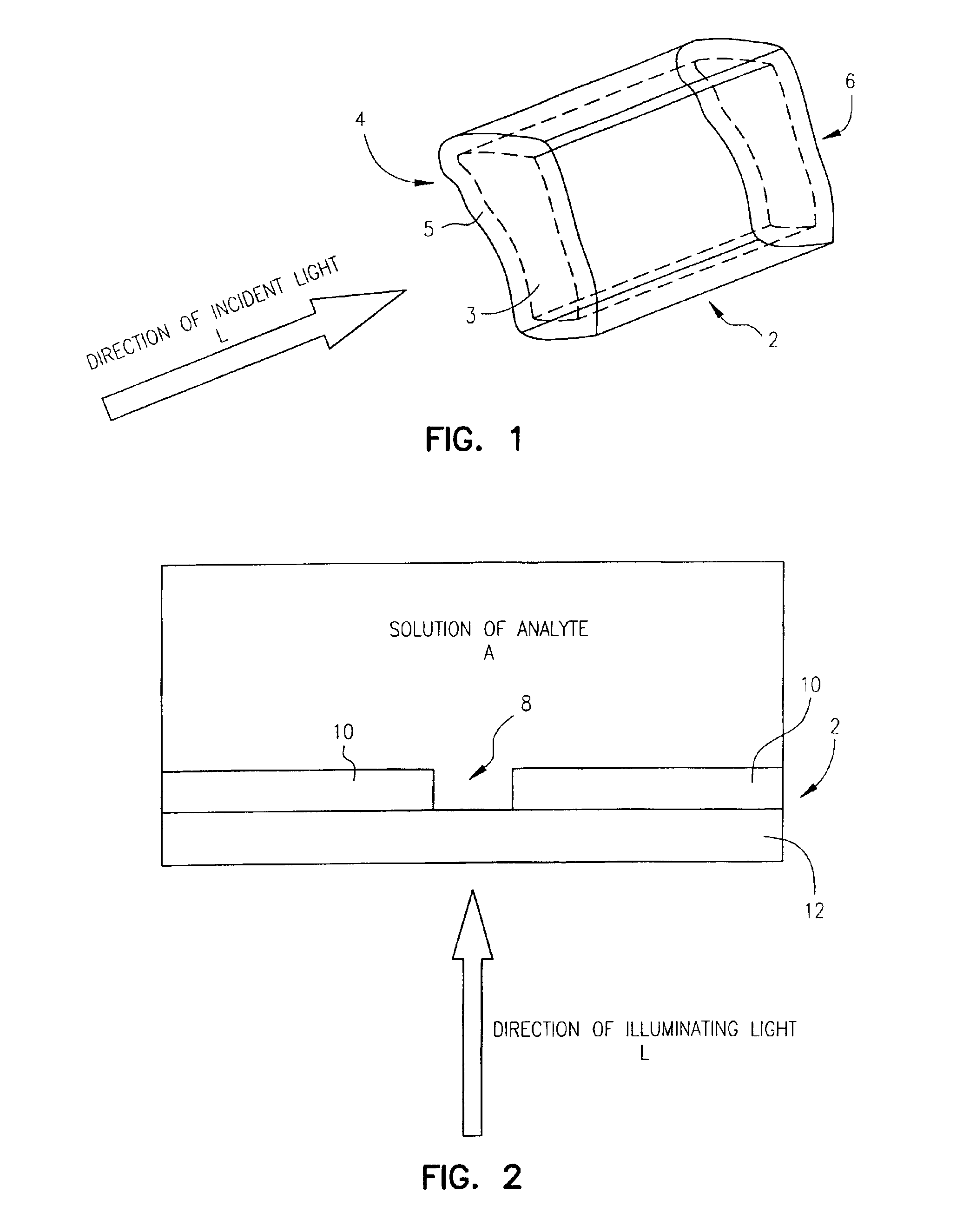
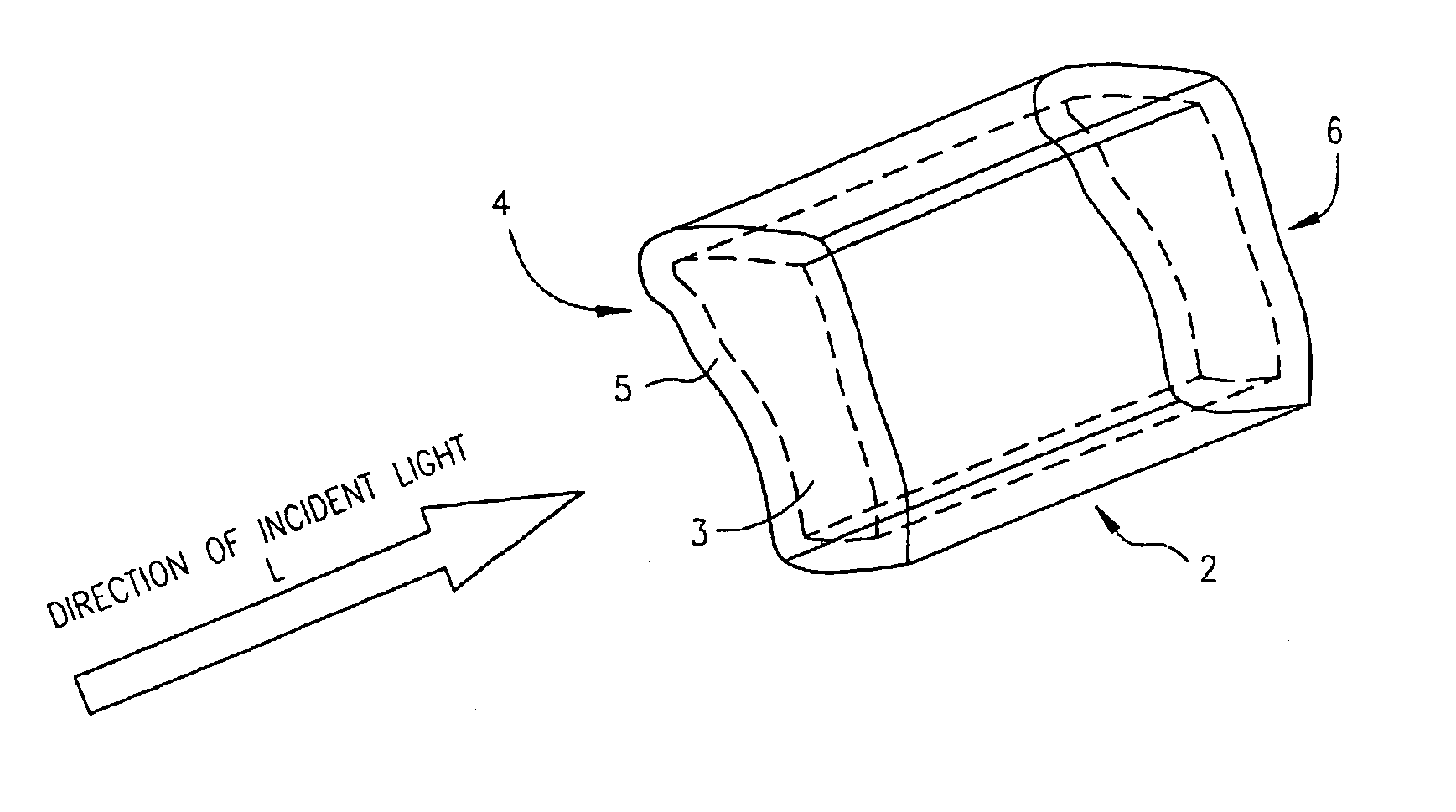
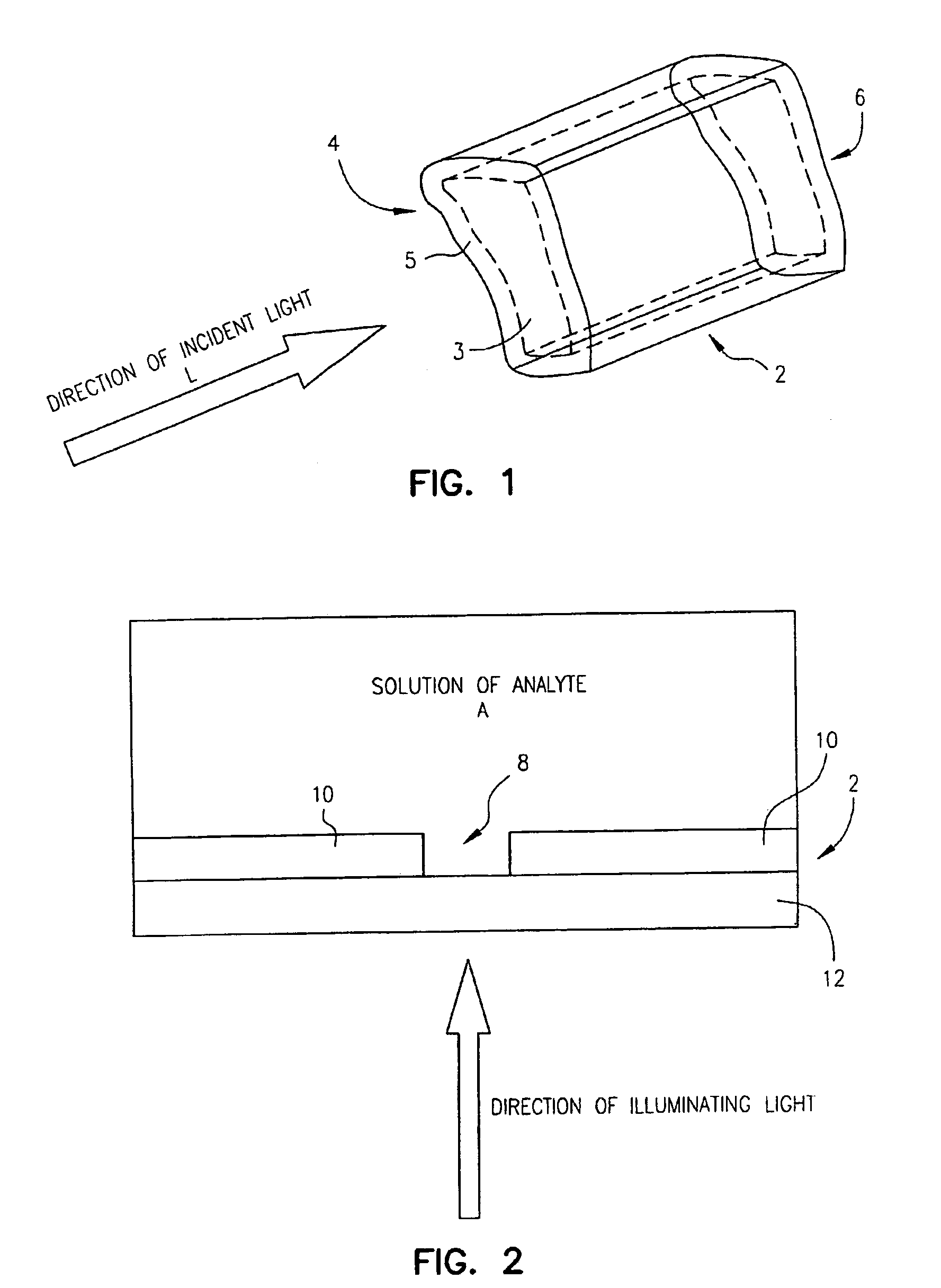
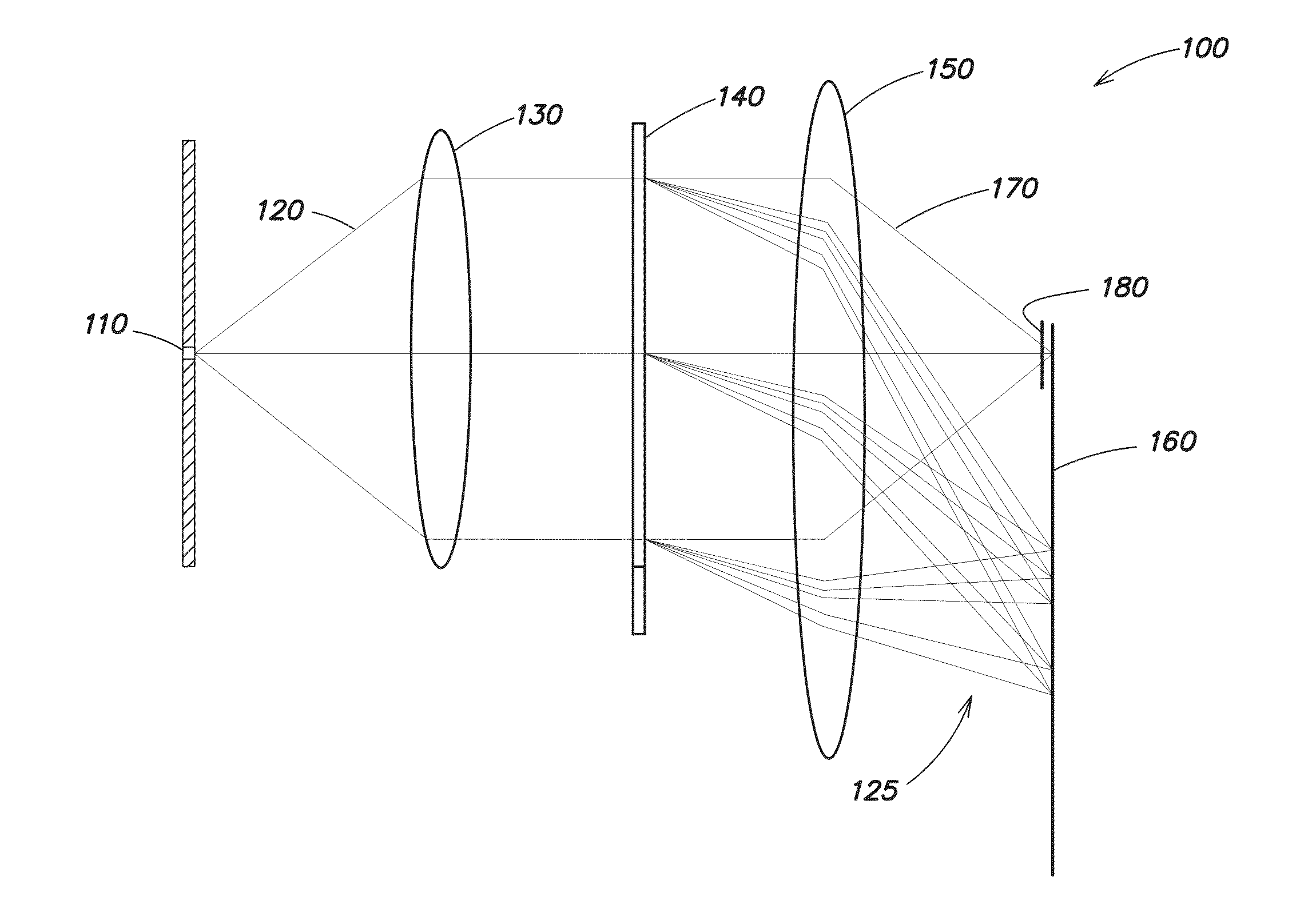
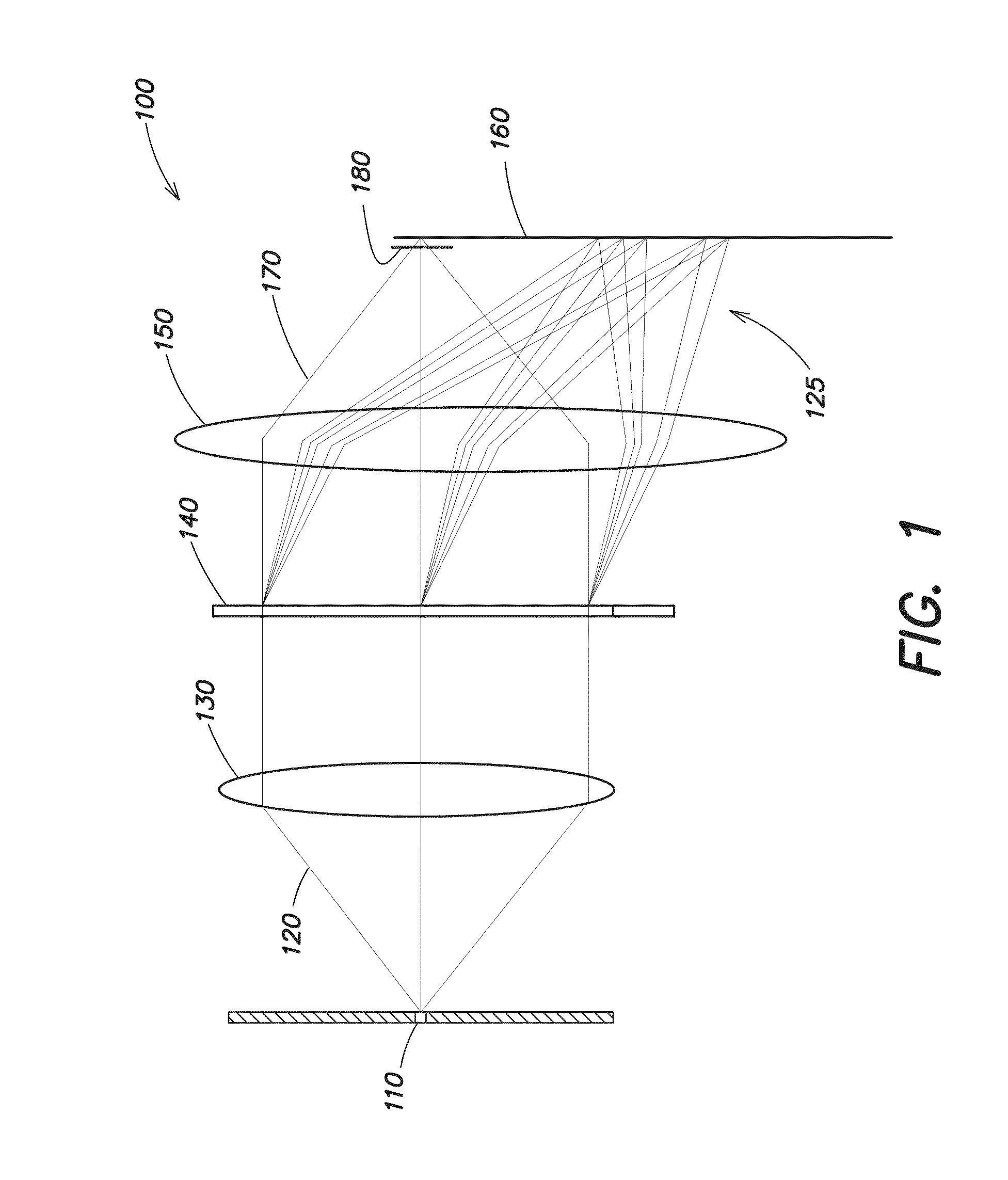
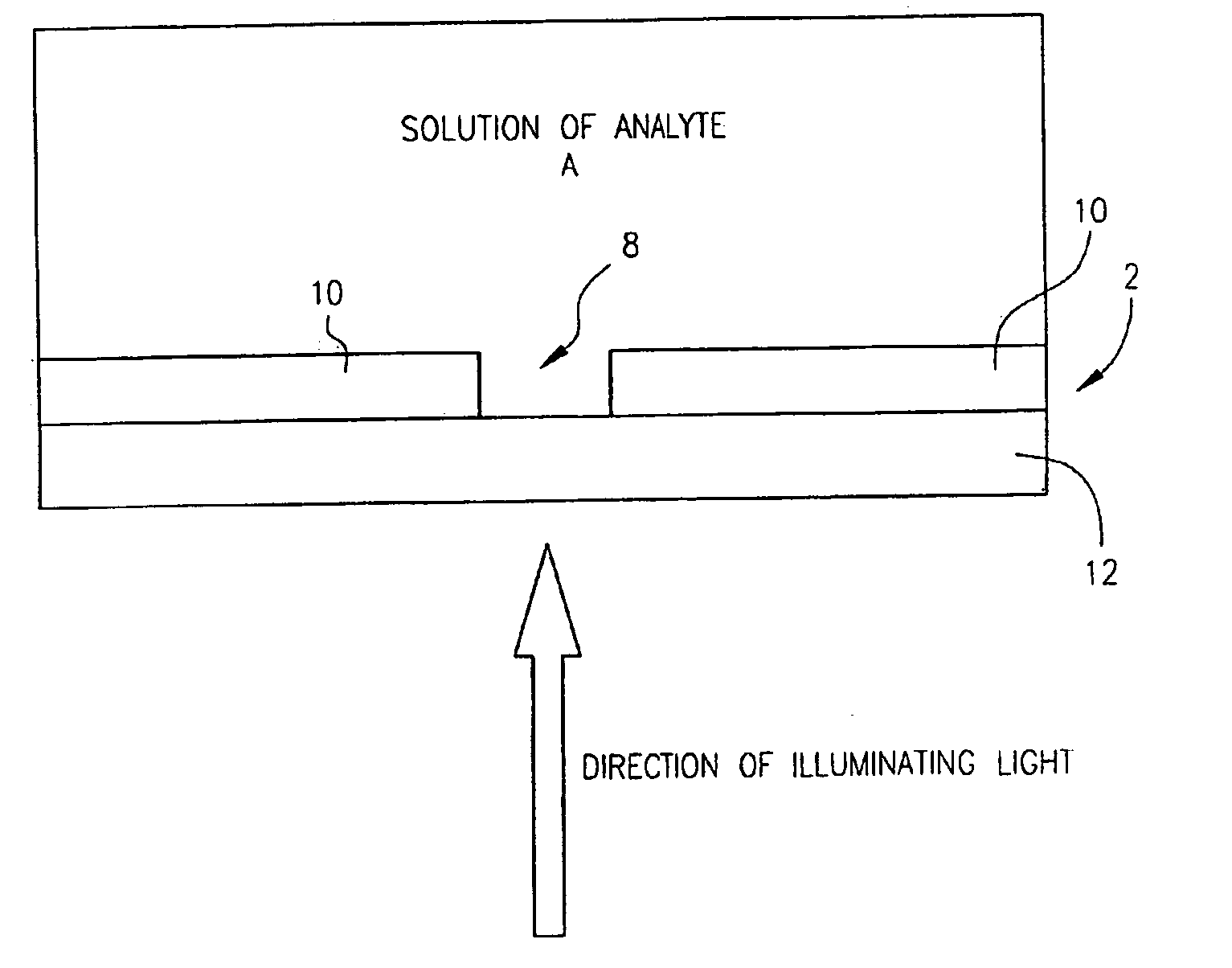
Zero-mode clad waveguides for performing spectroscopy with confined effective observation volumes
InactiveUS6917726B2Effective volumeEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAnalyteSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method and an apparatus for analysis of an analyte. The method involves providing a zero-mode waveguide which includes a cladding surrounding a core where the cladding is configured to preclude propagation of electromagnetic energy of a frequency less than a cutoff frequency longitudinally through the core of the zero-mode waveguide. The analyte is positioned in the core of the zero-mode waveguide and is then subjected, in the core of the zero-mode waveguide, to activating electromagnetic radiation of a frequency less than the cut-off frequency under conditions effective to permit analysis of the analyte in an effective observation volume which is more compact than if the analysis were carried out in the absence of the zero-mode waveguide.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Waveguides for performing spectroscopy with confined effective observation volumes
InactiveUS7013054B2Effective volumeEasy to useCladded optical fibreMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method and an apparatus for analysis of an analyte. The method involves providing a zero-mode waveguide which includes a cladding surrounding a core where the cladding is configured to preclude propagation of electromagnetic energy of a frequency less than a cutoff frequency longitudinally through the core of the zero-mode waveguide. The analyte is positioned in the core of the zero-mode waveguide and is then subjected, in the core of the zero-mode waveguide, to activating electromagnetic radiation of a frequency less than the cut-off frequency under conditions effective to permit analysis of the analyte in an effective observation volume which is more compact than if the analysis were carried out in the absence of the zero-mode waveguide.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Failure line selection method of small current ground system by using simulation after zero mode current measure
InactiveCN101242097AOvercome the influence of small fault transient currentRealize correct line selectionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitanceEngineering
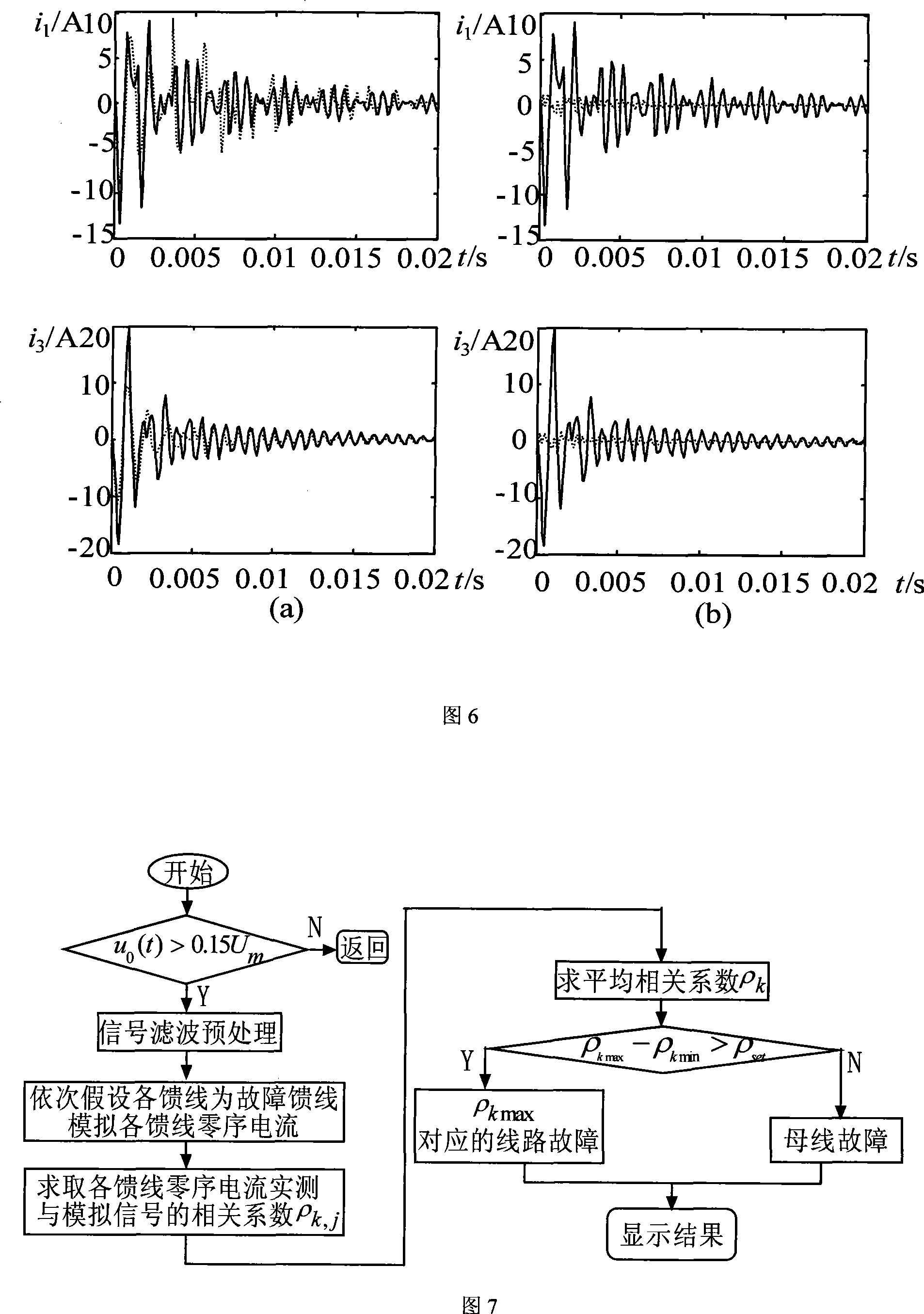
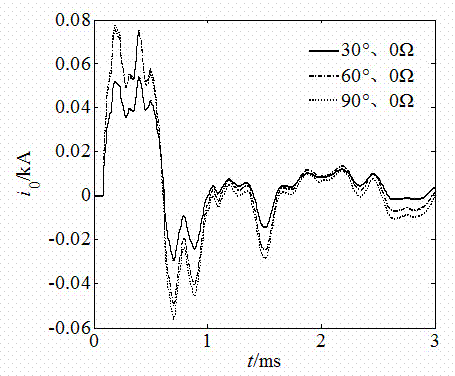
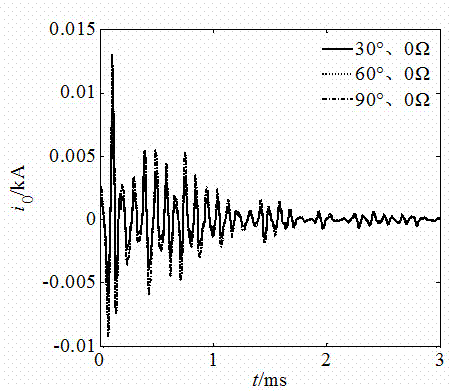
The invention provides a fault route-selecting method by using small current grounding system simulated by measured zero-mode current. The method includes following steps: when a generatrix zero-mode voltage instantaneous value is over the limit, a fault route-selecting is started and recorded immediately; zero-phase shift digital wave filter is used to obtain a high-frequency transient weight of each feed line zero-mode current; orderly the feed line is supposed to be fault feed line, the rest of the high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current is quantificationally solved by using the measured simulative method according to the supposed high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current and each feed line zero-order distributing capacitance parameter; the actual-measured wave shape and simulative wave shape of the high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current are analyzed and a average relative coefficient of the actual-measured wave shape and simulative wave shape of the high-frequency transient weight of the feed line zero-mode current are solved, the route-selecting criterion is formed to achieve the fault route selection. The principle analysis and simulation indicate that route selection of this method is accurate and reliable.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Single-phase earth fault line selection method based on transient state high-frequency component correlation analysis
ActiveCN108663599AOvercome the problem of not being able to select the correct lineImprove reliabilityFault location by conductor typesCapacitanceEngineering
The invention dislcoses a single-phase earth fault line selection method based on transient state high-frequency component correlation analysis. The method comprises the steps that whether or not a single-phase earth fault happens is judged according to the magnitude of a busbar zero-mode voltage instantaneous value, db10 wavelets are adopted for performing five-layer wavelet packet decompositionon zero-mode current of two work frequency periods after each feeder line fault, after the minimum frequency band is removed, node wavelet packet deposition coeffiences are reconstructed and summeredto obtain a fault transient high-frequency capacitance-current component, and a correlation coeefient matrix M between every two feeder lines is obtained; Si is set as a correlation accumulation coefficient for the ith feeder line fault transient high-freuqency capacitance-current component, when rho ij is larger than rho set, Si is equal to 1, 1 is subtracted from Si, and a correlation accumulation coefficient matrix S can be obtained; if Si is larger than 0 constantly, the busbar breaks down; if Si of only one feeder line is smaller than 0, the circuit is a fault circuit; if Si is smaller than 0 constantly, the circuit with the maximum high-frequency-band wavelet packet energy sum is determined as the fault circuit. According to RTDS simulation experimental verification, the method has the good accuracy, adaptability and the like.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
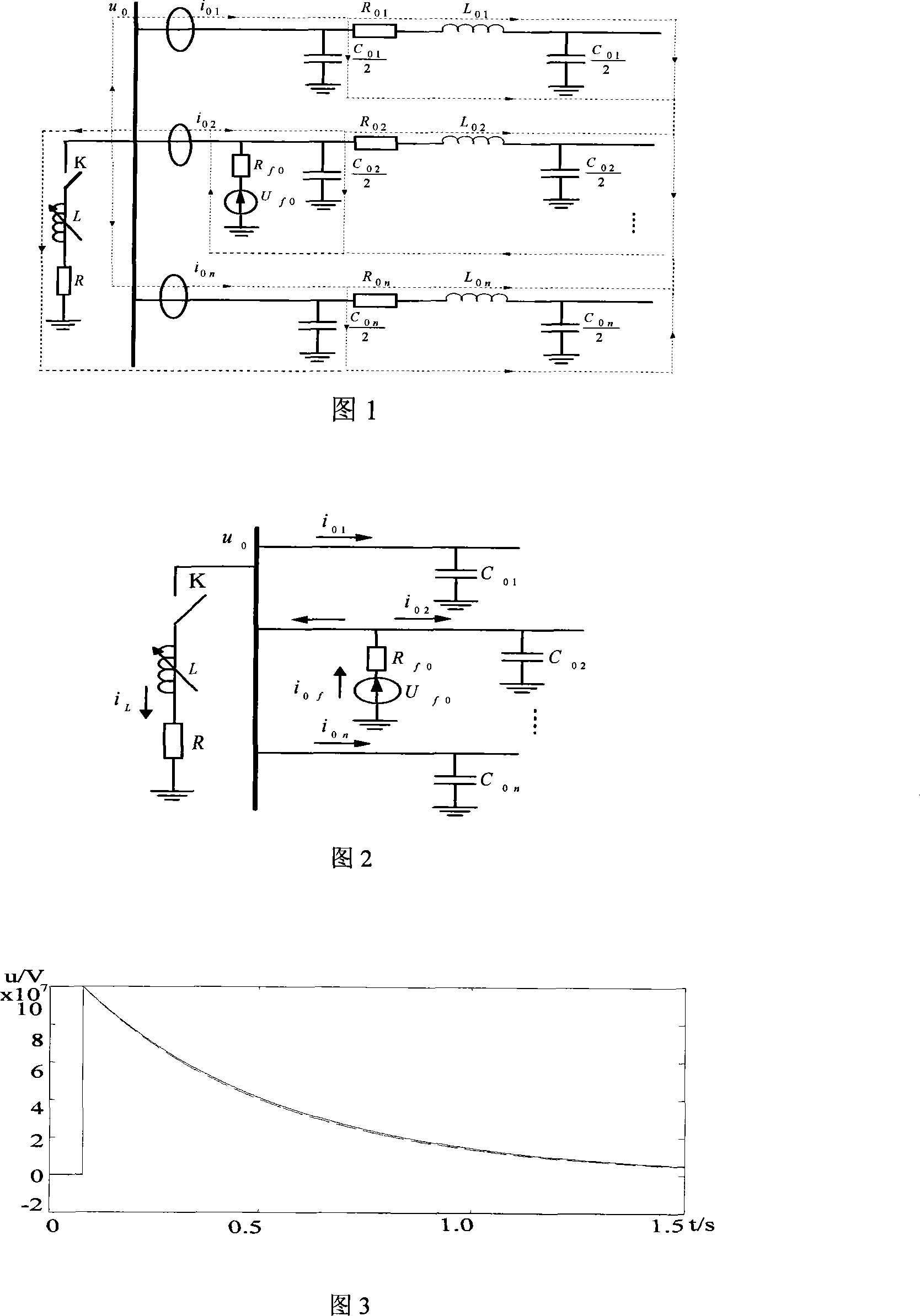
Single phase ground fault section locating method in small current grounding system
InactiveCN102621449AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove detection accuracyFault locationTransient statePrimary station
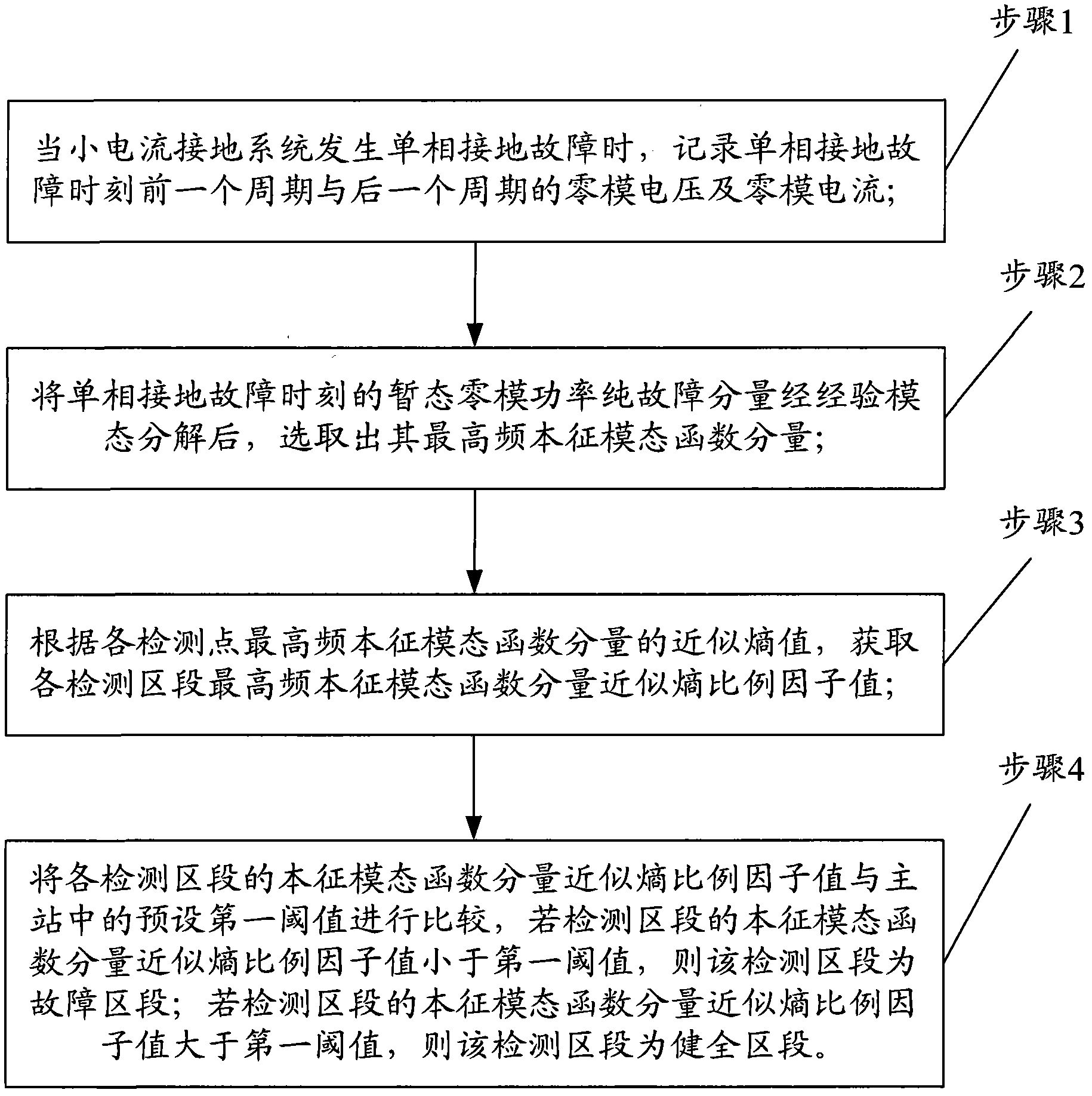
The invention provides a single phase ground fault section locating method in a small current grounding system, which includes the following steps: step 1, recording the zero mode voltage and the zero mode current of the previous period and the next period of the single phase ground fault time when the single phase ground fault occurs to the small current grounding system; step 2, selecting the highest frequency intrinsic mode function component after decomposing the transient zero mode power pure fault component of the single phase ground fault time through empirical mode decomposition; step 3, obtaining the approximate entropy proportionality factor of the highest frequency intrinsic mode function component of each detecting section through the approximate entropy value of the high frequency intrinsic mode function component of each detecting section; and step 4, comparing the approximate entropy proportionality factor of the highest frequency intrinsic mode function component of each detecting section with the preset first threshold in the main station, so as to find out the section with the single phase ground fault. The single phase ground fault section locating method has the characteristics of high detecting precision and universality, and can be widely applied to the power system.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
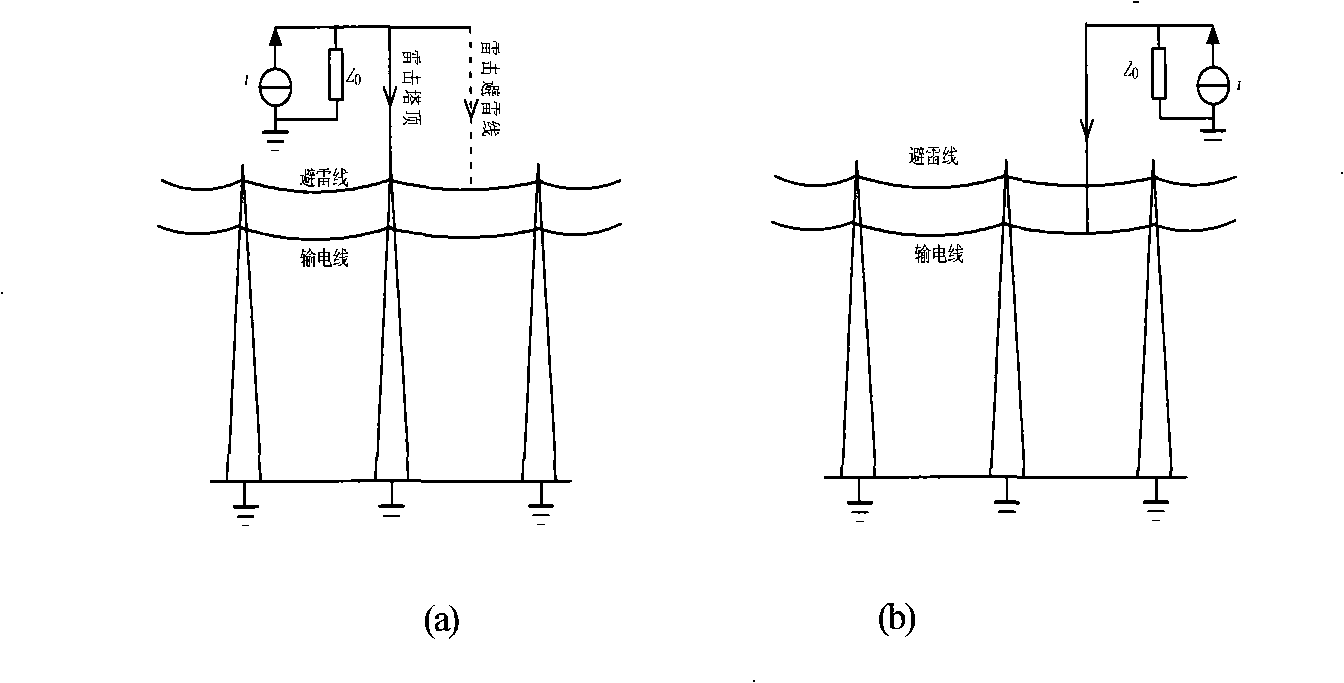
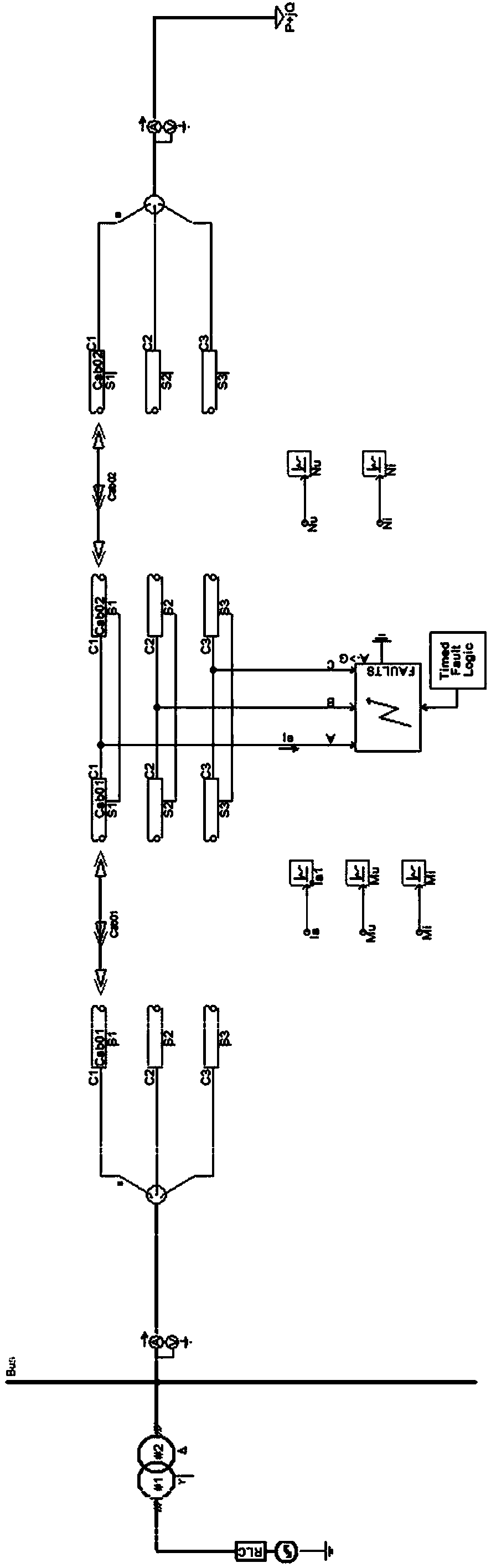
Travelling wave analysis recognition method for thunderbolt shielding failure and counterattack discrimination of direct current transmission line
ActiveCN101345415APhysical concepts are clear and intuitiveEasy to implementEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationElectric power systemEngineering
The invention relates to a traveling wave analysis and recognition method for distinguishing lightning shielding failure from lightning counterattack of direct current transmission line. The lightning shielding failure of line is that lightning avoids the lightning shield line and directly strokes on the transmission line, while lightning counterattack of line is that lightning directly strokes on the lightning shield line or the tower. Because the earth resistance of tower exists, the potential on tower top suddenly increases and causes insulation flashover. The electromagnetic transient component generation mechanism of the high voltage direct current transmission line and the propagation path of lightning electromagnetic transient of the line in the lightning shielding failure are different from those in the lightning counterattack, the size and polarity of the initial surge voltage and the second surge voltage of the voltage transient signal exist significant difference. The traveling wave analysis and recognition method of the invention analyzes zero mode voltage using wavelet and distinguishes the lightning shielding failure and lightning counterattack failure according to the size and polarity of the initial surge voltage and the second surge voltage of the zero mode voltage in the traveling wave analysis and high-speed acquisition system of the protection zone. A lot of simulation results show that the method is reliable and effect. The physical concept of the invention is visible and clear, the method is easy to achieve and wide to use in the direct current system protector, also provides accurate initial data for researching lightning characteristics, analyzing lightning accident, discussing lightning protection countermeasure of transmission line and designing insulation coordination in the power system.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
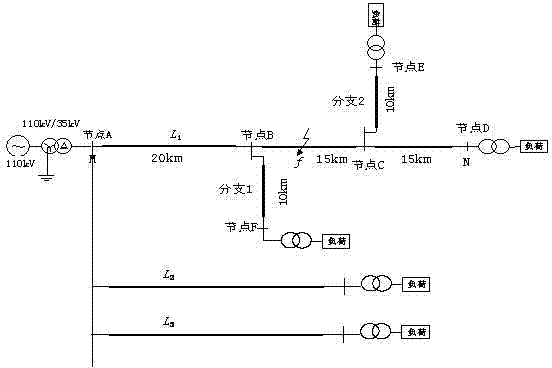
Earth fault distance measurement method based on traveling wave modulus time difference
The invention relates to an earth fault distance measurement method based on traveling wave modulus time difference, belonging to the field of power electronic technology. The invention utilizes traveling wave detection devices installed at detections points along the line to ensures an effective detection point closer to a fault point to accurately distinguish a zero mode and a line mode initial wave head, and uploads the time difference between the zero mode and the line mode initial wave head into a monitor station. The monitor station is used for sequencing all the collected modulus time difference from big to small, firstly judges the detection point which is closed to the fault point for a first step, and then completing accurate fault distance measurement according to the primary locating result. The invention does not need a time synchronous system, has low communication traffic, is not influenced by line tap points, is easy for project implementation, and has higher reliability and distance measurement accuracy.
Owner:STATE GRID BEIJING ELECTRIC POWER +1
Dynamic time bending distance fault section locating method based on time sequence compression
ActiveCN108181547AReduce communication costsImprove robustnessFault location by conductor typesPrimary stationAmplitude response
The technical scheme of the invention is a dynamic time bending distance fault section locating method based on time sequence compression. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the preprocessing of the fault record data collected by a feed line terminal device, wherein the preprocessing operation comprises the extraction of the initial value and extreme values of the record data and the changes of the record data, and obtaining a new time sequence of the record data; transmitting the time sequence to a main station, solving the similarity of zero-mode currents of two adjacent feed lineterminal devices via a dynamic time bending distance algorithm through the main station, and determining a fault section. The beneficial effects of the invention are that the data size, compared withan original time sequence, is reduced by a half or more, thereby greatly reducing the communication cost; for a high-frequency signal, the dynamic time bending distance algorithm is stronger in synchronization error prevention capability and signal amplitude response capability than a correlated coefficient method; the method provided by the invention is higher in robustness, and does not need the strict time synchronization.
Owner:ZHUHAI XJ ELECTRIC +1
Zero-mode and line-mode time difference radiation net fault location method achieved only through voltage without relying on two-terminal synchronization
ActiveCN103941150ANot subject to fault transition resistanceUnaffected by fault initial phase angleFault locationMeasurement deviceElectric power system
The invention provides a zero-mode and line-mode time difference radiation net fault location method achieved only through voltage without relying on two-terminal synchronization, and belongs to the technical field of electric power system relay protection. Traveling wave fault distance measurement devices are arranged on the two sides of a feeder line, and fault distance measurement is conducted through information on the two sides. After grounding faults happen to the feeder line of a power distribution network, line-mode traveling components propagated between wires and zero-mode traveling wave components propagated between the wires and the ground are generated due to the sudden change of the voltage at the fault point. Due to the fact that the line-mode propagation velocity and the zero-mode propagation velocity are different, the arrival moment of the line-mode initial traveling wave and the arrival moment of the zero-mode initial traveling wave detected by a measurement terminal are different. Moment calibration is conduced through the wavelet modulus maximum under the fifth dimension according to the initial line-mode voltage traveling wave data and the initial zero-mode voltage traveling wave data detected by the measurement device, and the fault distance is calculated according to the ground fault single-terminal traveling wave fault location calculation formula for the modulus transmission time difference. Fault location is conducted by integrating single-terminal modulus propagation time difference distance measurement information on the two sides.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Parallel Detection of Remote LPI Request and Send Zero Mode
ActiveUS20100322078A1Robust and quick detectionMinimum delayEnergy efficient ICTError preventionComputer scienceEnergy-Efficient Ethernet
Embodiments of the present invention enable robust and quick parallel detection of the remote LPI request signal (rem_lpi_req) and SEND ZERO mode (SEND_Z) defined in the Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) standard. Embodiments do not rely on energy detection for detecting SEND_Z. Therefore, SEND_Z can be detected reliably and with minimal latency. In addition, since SEND_Z and rem_lpi_req are detected in parallel, embodiments are not concerned with the false detection of rem_lpi_req (before SEND_Z is detected) or the need to disable detection of rem_lpi_req (after SEND_Z is detected).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Distribution network cable single-phase ground fault distance measuring method utilizing transient main frequency component
ActiveCN103941147AThe maximum relative error is smallRelatively small errorFault locationOperation modeZero mode
A conventional line hyperbolic function model is usually used for calculation of phase quantity of power frequency steady state quantity. The model is improved by utilizing Laplace transformation. With combination of a zero mode network after a distribution network cable single-phase ground fault, a single-end distance measuring algorithm utilizing the transient main frequency component is provided, and solving is performed via a frequency domain mode and a time domain mode respectively so that fault distance is obtained. Influence of transition resistance is eliminated by the frequency domain mode, and result optimization is performed by the time domain mode by utilizing redundancy of sampling points. Correctness of the method is verified by a large amount of EMTP simulation experiment results without influence of factors, such as transition resistance, neutral point operation modes, fault initial angles, etc., the maximum relative error of distance measurement is less than 0.231%, an average distance measurement error is less than 20m, and thus practical engineering requirements can be met.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Radiation net fault location method by means of zero mode and aerial mode time difference independent of double-end synchronization and with matching of magnitude of voltages and magnitude of currents
ActiveCN103941151ANot subject to fault transition resistanceUnaffected by fault initial phase angleFault locationElectric power systemCable fault location
The invention provides a radiation net fault location method by means of a zero mode and aerial mode time difference independent of double-end synchronization and with matching of the magnitude of voltages and the magnitude of currents, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. The two sides of a feeder are respectively provided with a traveling wave fault location device, and fault location is carried out according to information on the two sides. After a ground fault of the feeder of a power distribution net occurs, due to sudden changes of the voltage at a fault point, an aerial mode traveling wave component spreading between wires and a zero mode traveling wave component spreading between the wires and the ground are generated. Due to the fact that the spreading speeds of an aerial mode and a zero mode are different, the arrival moment of an aerial mode traveling wave detected by the measurement end and the arrival moment of a zero mode traveling wave detected by the measurement end are different. According to original aerial mode voltage and current traveling wave data and original zero mode voltage and current traveling wave data detected by the measurement end, wave arrival moment calibration is carried out by means of a wavelet modulus maximum value under a fifth dimension, and then the fault position is calculated according to a calculation formula of a ground fault single-end traveling wave fault location method of modulus transmission time differences. Fault location is carried out according to measurement information of the single-end modulus transmission time differences at two sides.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Small current grounding fault location method utilizing circuit equivalent parameter identification principle
ActiveCN103245880AGuaranteed Protection SensitivityGuaranteed protection reliabilityFault locationTransient stateDigital filter
The invention relates to a small current grounding fault location method, particularly to a small current grounding fault location method utilizing the circuit equivalent parameter identification principle. The method is characterized in that changes of a voltage or a current are taken as fault starting conditions; after starting, zero mode voltage or transient state line voltage features detected at detecting points are utilized to determine voltages participating in identifying parameters; then, the scope of selected frequency band is determined; a digital filter is further structured; filtering is performed on the participated voltages and zero mode current signals to obtain components within the selected frequency band; and the participated voltages and zero mode current components in the selected frequency band are then utilized to identify equivalent capacitance of all detecting points so as to further determine the fault section. The small current grounding fault location method simultaneously utilizes transient voltages and current signals, is applicable to fast directional protection of grounding faults of various voltage classes, and can take into consideration of both protection speed and reliability.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +4
Positioning method of single-terminal radiation-type power-distribution-network single phase grounding fault
ActiveCN107219440AAccurate extractionHigh significance in engineering practiceFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemPhase differenceZero mode
The invention discloses a positioning method of a single-terminal radiation-type power-distribution-network single phase grounding fault. A specific frequency amplitude ratio in an initial zero mode voltage traveling wave first wave head signal at a measuring point and a phase difference are used to represent a distortion degree of a zero mode traveling wave high frequency component. A core idea is that a single phase grounding fault is applied to a selected position in a distribution network simulation system; a head and tail end zero mode voltage traveling wave first wave head high frequency component amplitude of a feed line and a phase are extracted to establish a standard amplitude ratio vector and a phase difference vector; through comparing an amplitude ratio and a phase difference acquired via actual fault calculation with a standard amplitude ratio and a phase difference, line selection and line section positioning are performed; and branch positioning is realized through energy of a zero mode current traveling wave first wave head high frequency component. Simulation shows that the method is not influenced by factors of an arc, a synchronous measurement error and the like, and high economical efficiency and a good practical value are possessed.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
High-resistance grounding fault detection method based on flexible DC distribution network
InactiveCN109975656ASensitively judge the running statusAccurate feature extractionFault location by conductor typesTransient stateHigh resistance
The invention discloses a high-resistance grounding fault detection method based on a flexible DC distribution network. The high-resistance grounding fault detection method comprises the steps of: firstly, extracting a feature model IMF1 component of a transient zero-mode current by adopting a complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition algorithm, performing first-order differentiate operation on the IMF1to obtain a sudden change singular point, calculating a cumulative slope sum in the vicinity of the singular point, and distinguishing a faulty state and a normal state through comparing a slope sum value with a starting threshold value; and secondly, adopting a Prony algorithm for carrying out parameter identification on the IMF1 component to obtain a feature frequency component and a direct current component in the IMF1 component, calculating an energy ratio of the feature frequency component to the direct current component, and further distinguishing different states according to the difference of the energy ratio numerical values. Compared with the existing methods, the high-resistance grounding fault detection method can adapt to accurate feature extraction under a strong noise environment, has the advantages of self-adaptability, convenient application and high detection precision in the feature extraction process, can determine the operating state of the distribution network system incisively, and increases the calculation speed.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV +1
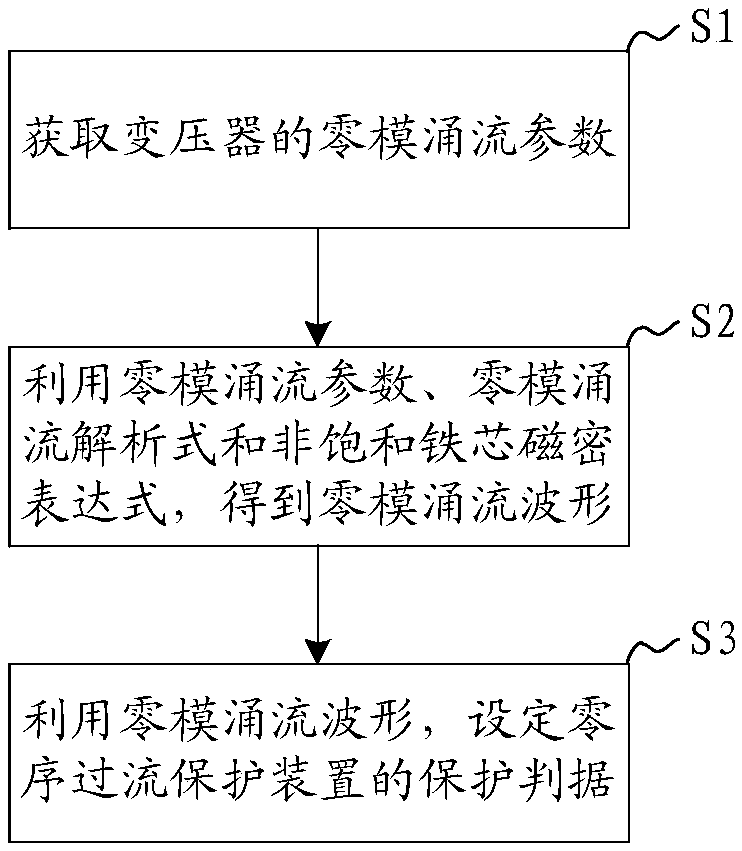
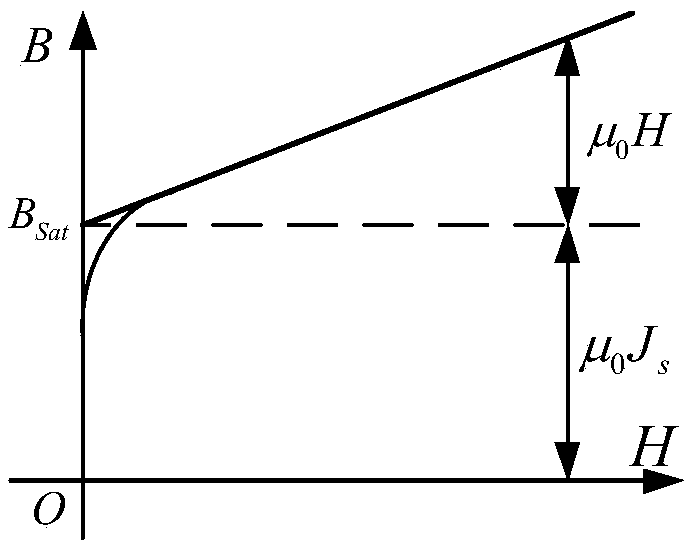
Zero sequence overcurrent protection method, system and device and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN109119971AImplement mathematical analysisPrevent misoperationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsLow voltageEngineering
The invention discloses a zero sequence overcurrent protection method, system and device and a computer readable storage medium. The method can obtain the linear relation between the zero-mode inrushcurrent waveform and the unsaturated core magnetic density and three-phase remanence magnetic density through a zero-mode inrush current analytic equation comprising the saturated mutual inductance ofa transformer, high-voltage side self-leakage resistance, low-voltage side self-leakage resistance, system zero sequence reactance, system voltage, system magnetic density, unsaturated core magneticdensity and remanence magnetic density; can determine the value of the unsaturated core magnetic density in each phase of the three phases through an unsaturated core magnetic density expression. Therefore, after the zero-mode inrush current parameter is substituted into the zero-mode inrush current analytic mode, the zero-mode inrush current waveform can be obtained, thereby achieving the mathematical analysis of the zero-mode inrush current waveform, achieving the analysis of the influence of transformer parameters of different structure types on the magnitude of the zero-mode inrush current. The method can reproduce the waveform when the zero-mode inrush current occurs, and can set the protection criterion of a zero sequence overcurrent protection device, and avoids misoperation of thezero sequence overcurrent protection device.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
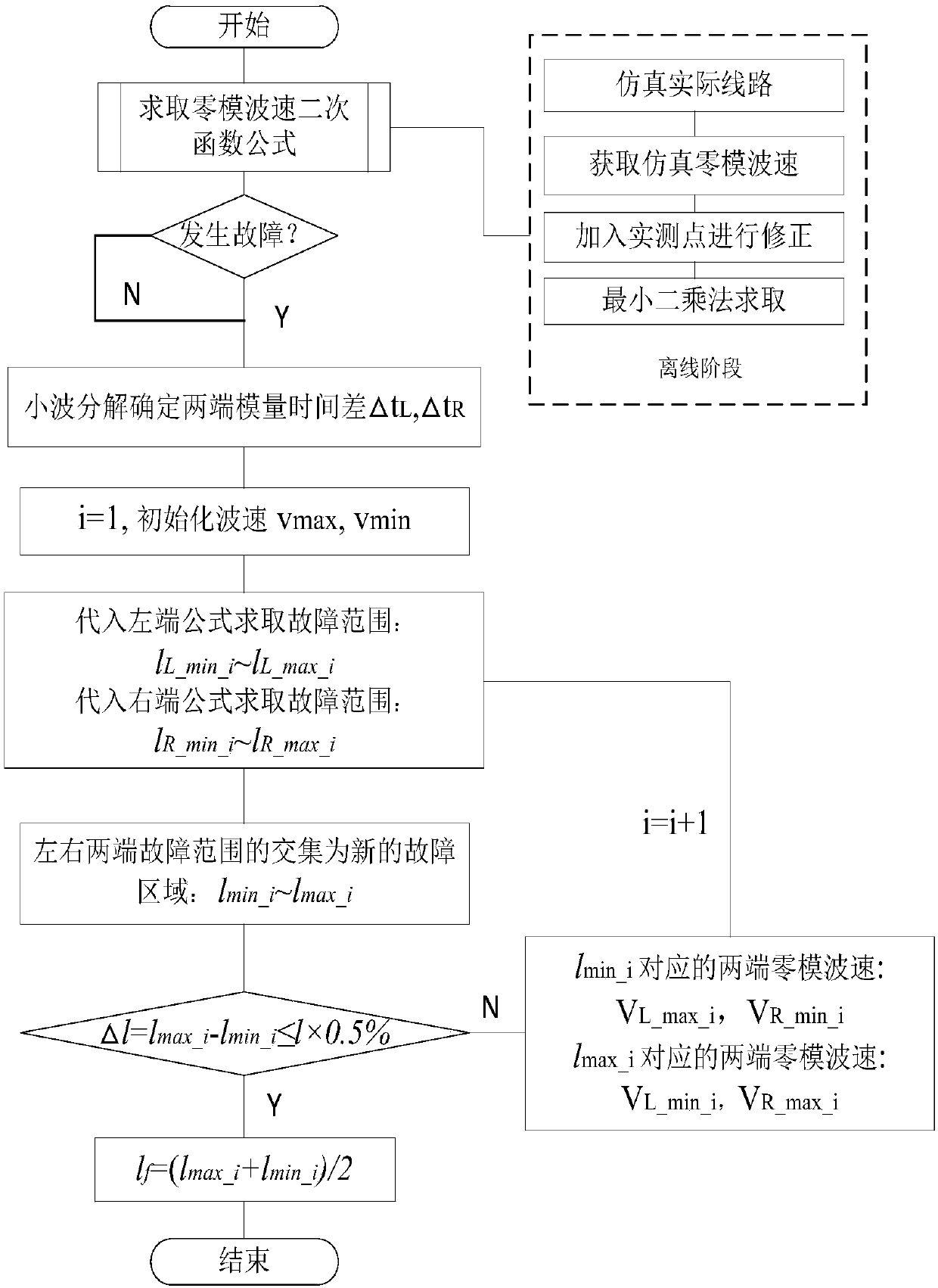
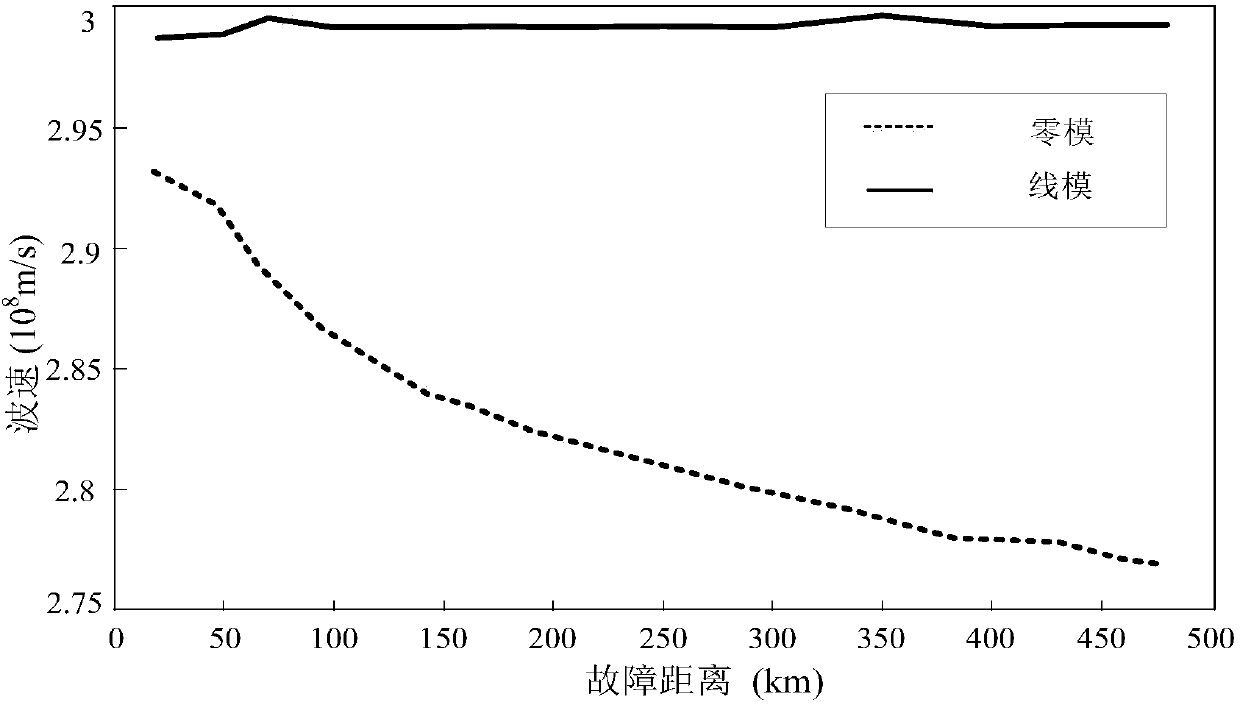
Transmission line iterative distance measuring method based on zero-mode traveling wave velocity variation characteristic
The invention discloses a transmission line iterative distance measuring method based on a zero-mode traveling wave velocity variation characteristic, belonging to a method of grid line fault positioning. After a fault occurs on a transmission line, a transient traveling wave is propagated on the line. According to the method, starting from propagation characteristics of the traveling wave on theline, the relationship between a traveling wave propagation distance and a traveling wave velocity is analyzed, and a function formula between a zero mode and a fault distance is obtained through least square fitting. Combined with a wave speed-distance formula and a time difference of a zero mode and a line mode at two ends of the line, with maximum and minimum zero mode wave velocity on the lineas an initial condition, a modulus time difference formula is substituted, and a precise fault point is positioned through iteration. According to the method, the synchronization of two ends of the line is not needed, the method is not influenced by factors of a system load and fault resistance, traveling wave measuring devices in substations at two ends of the line are used, and the realizationis convenient. The positioning precision is high, and the speed is fast. The positioning method of the invention can be used in trans-regional remote distance high-voltage power transmission line.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Multispectral camera using zero-mode channel
ActiveUS20150156394A1Lack abilityTelevision system detailsPolarisation spectroscopyOptical propertyMultispectral image
A multispectral imaging system and method in which the zero-mode channel is used to provide imaging of any of a variety of optical properties. In one example an imaging method includes spectrally dispersing received electromagnetic radiation into its spectral components with a dispersive element to produce spectrally dispersed electromagnetic radiation, transmitting the electromagnetic radiation through the dispersive element to produce non-dispersed electromagnetic radiation corresponding to a zero order diffraction mode of the dispersive element, imaging the non-dispersed electromagnetic radiation to produce a zero-mode image, and simultaneously imaging the spectrally dispersed electromagnetic radiation to produce a spectral image.
Owner:RAYTHEON CANADA LTD
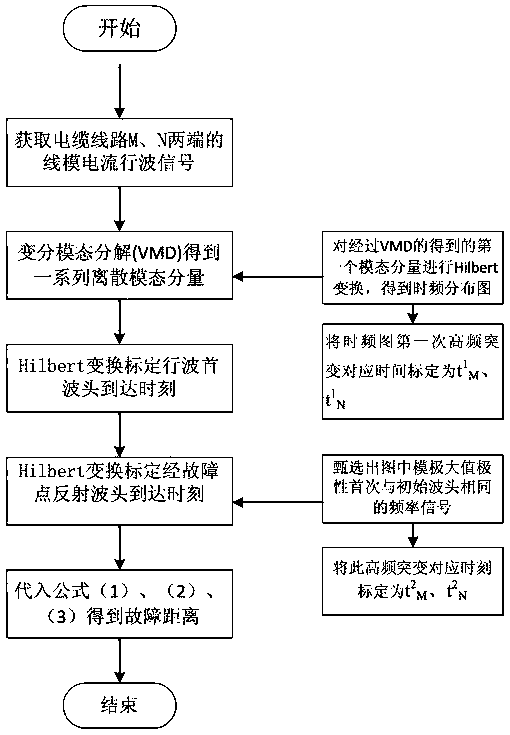
Urban power cable double-end fault ranging method based on VMD-Hilbert transformation
InactiveCN109188210ANot affected by wave speedAvoid Ranging ErrorsFault locationPower cableElectrical polarity
The invention discloses a urban power cable double-end fault ranging method based on VMD-Hilbert transformation. The fault ranging method comprises the following steps: detecting an initial wave headof a fault traveling wave line mode through synchronous measuring devices arranged on both ends of a power cable; demarcating a wave head arrival moment by using a time-frequency diagram obtained by the VMD-Hilbert transformation; performing polarity screening on the wave head reflected by a fault point by using a modular maximum value; and obtaining the distance of the fault point by derivation according to the wave head arrival moment and a known power cable line length. According to the urban power cable double-end fault ranging method disclosed by the invention, a VMD-Hilbert transformation signal analysis method and a double-end traveling wave fault ranging method are combined and applied to power cable lines. Meanwhile, only a linear mode signal that is attenuated and weakened in a propagation process needs to be measured, and the used fault ranging formula used is not affected by the wave velocity. The ranging error caused by the uncertainty of the wave velocity in the power cable and a zero-mode component measurement thereof are avoided. The urban power cable double-end fault ranging method has a good engineering practice value in the power cable lines.
Owner:JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
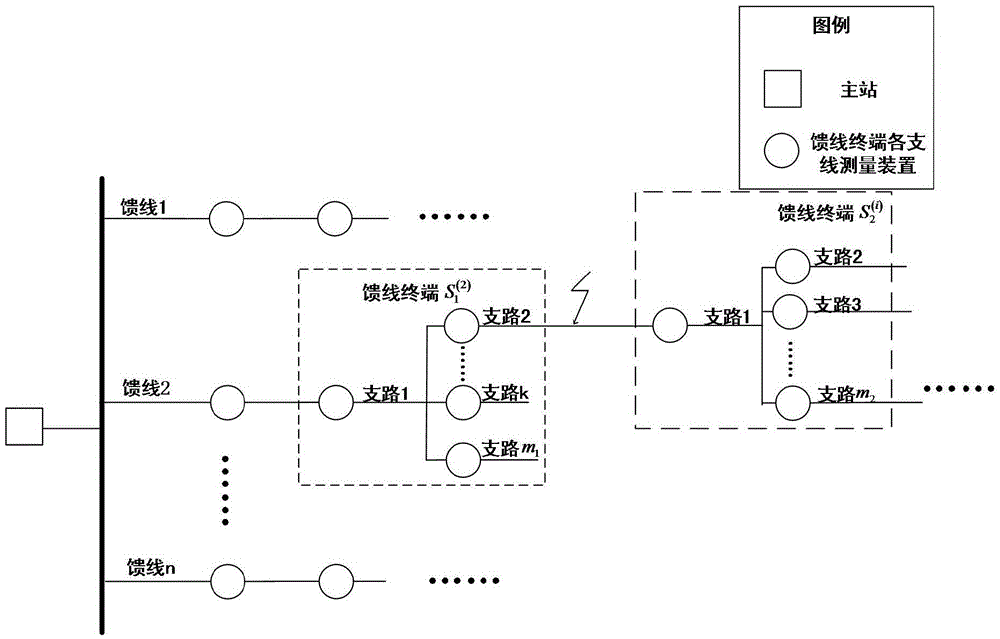
Feeder terminal information interaction-based small-current grounding fault location method
The present invention discloses a feeder terminal information interaction-based small-current grounding fault location method. The method includes the following steps that: 1, a feeder terminal acquires the addresses of adjacent feeder terminals; 2, a main station calculates a fault transient characteristic frequency band and issues the fault transient characteristic frequency band; 3, zero-mode current on each branch is measured; 4, characteristic zero-mode current on each branch is obtained through using an improved empirical mode decomposition algorithm; and 5, the feeder terminal acquires waveform similarities and average phase differences between the branches so as to judge a grounding fault and uploads fault information to the main station. With the feeder terminal information interaction-based small-current grounding fault location method of the invention adopted, a power distribution network can automatically carry out fault location, and therefore, fault location judgment efficiency can be improved, and the reliability of electricity use of users can be increased.
Owner:合肥庐阳科技创新集团有限公司
Multi-outgoing-line radiation network fault distance measuring method for k-NN algorithm based on waveform similarity
The invention relates to a multi-outgoing-line radiation network fault distance measuring method for a k-NN algorithm based on waveform similarity, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. Zero-mode current data of a measuring side at different fault positions and under different fault conditions are acquired through simulation, wavelet decomposition is carried out on the data, and wavelet coefficient organization historical sample data under a sixth scale are obtained. When a single-phase grounding fault occurs, the k-NN algorithm is utilized, similarity matching is carried out on a wavelet coefficient waveform of measured zero-mode current waveforms after wavelet decomposition and wavelet coefficient waveforms in a simulated historical sample under the different fault conditions through correlation analysis, fault distances corresponding to the first three waveform data with the highest similarity are obtained, and the fault distance is obtained through the different application regression methods of weights. A large amount of simulation shows that the method is reliable and high in precision for the single-phase grounding fault.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and device for positioning high-resistance grounding fault section of power distribution network and storage medium
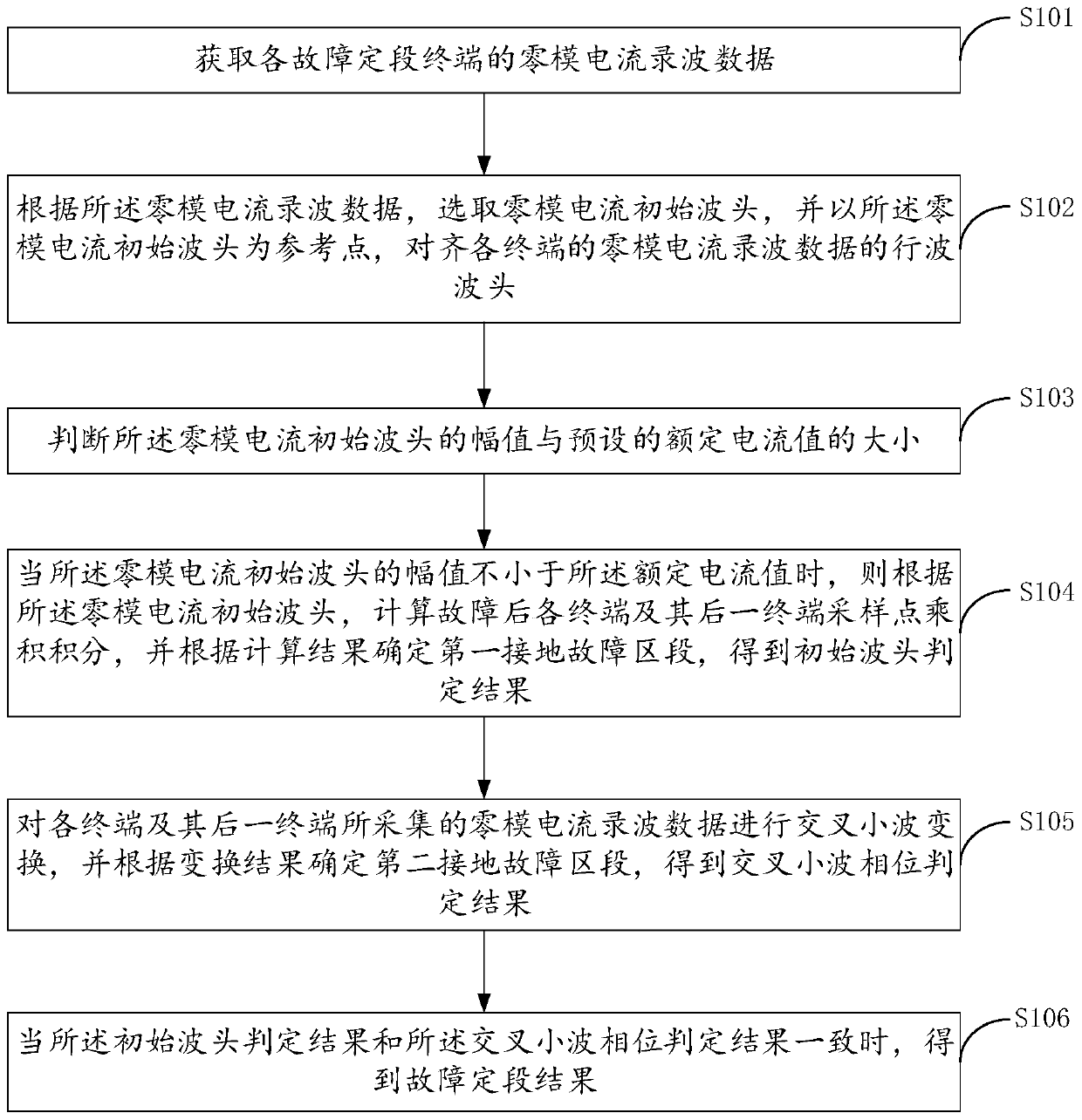
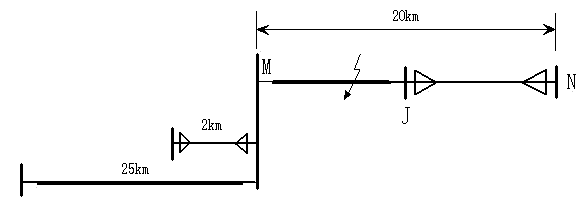
InactiveCN110542833AImprove reliabilityImprove accuracyFault location by conductor typesHigh resistanceComputer science
The invention discloses a method and a device for positioning a high-resistance grounding fault section of a power distribution network and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring zero-mode current recording data of fault fixed-section terminals; selecting zero-mode current initial wave heads according to the zero-mode current recording data, and aligning travelingwave heads of the zero-mode current recording data of the terminals; when the amplitude values of the zero-mode current initial wave heads are not smaller than a rated current value, according to thezero-mode current initial wave heads, calculating a product integral of sampling points of each terminal and the next terminal after breakdown, and determining a first grounding fault section according to a calculation result, thereby obtaining an initial wave head judgment result; performing cross wavelet transformation on the zero-mode current recording data acquired by each terminal and the next terminal, and determining a second grounding fault section according to a transformation result, thereby obtaining a cross wavelet phase judgment result; and when the initial wave head judgment result and the cross wavelet phase judgment result are consistent, obtaining a fault fixed-section result. The fault section can be accurately judged; and the method and the device have relatively high adaptability.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Wavelet analysis-based double-end traveling-wave fault locating method and system
ActiveCN105445614AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionFault location by conductor typesWavelet decompositionSelf correlation
The invention provides a wavelet analysis-based double-end traveling-wave fault locating method. The method comprises the steps of firstly, acquiring a three-phase current during the occurrence of a fault and obtaining parameters in the line mode and in the zero mode after the transformation processing of the three-phase current; secondly, conducting the wavelet decomposition on the three-phase current to reconstruct the three-phase current, and conducting the self-correlation analysis on the current to obtain self-correlation function waveforms formed by a first bus and a second bus respectively; thirdly, screening out a waveform that meets a preset condition and adopting the waveform as a first waveform, and adopting a waveform that does not meet the preset condition as a second waveform; fourthly, acquiring the overall length of a power transmission line, the abscissa time of the first waveform that reaches a maximum value point last time, the abscissa time of the second waveform that reaches a maximum value point last time, and the abscissa time of the second waveform that reaches a third maximum value point last time; fifthly, when the difference between the abscissa time of the first waveform that reaches the maximum value point last time and the abscissa time of the second waveform that reaches the third maximum value point last time is within a preset range, obtaining a distance value between a fault point and the first and / or second bus(es).according to the method, the traveling wave velocity and the line length variation do not need to be considered at all. Meanwhile, the two-terminal accurate synchronism is also not required. Therefore, the distance measurement reliability and the distance measurement accuracy are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU
Cable hybrid line fault distance measuring method for k-NN algorithm based on waveform similarity
ActiveCN103941152AGood ranging effectReduce the impactFault locationElectric power systemWavelet decomposition
The invention discloses a cable hybrid line fault distance measuring method for a k-NN algorithm based on waveform similarity, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. Zero-mode current data of a measuring side at different fault positions and under different fault conditions are acquired through simulation, wavelet decomposition is carried out on the data, and wavelet coefficient organization historical sample data under a sixth scale are obtained. When a single-phase grounding fault occurs, the k-NN algorithm is utilized, similarity matching is carried out on a wavelet coefficient waveform of measured zero-mode current waveforms after wavelet decomposition and wavelet coefficient waveforms in a simulated historical sample under the different fault conditions through correlation analysis, fault distances corresponding to the first three waveform data with the highest similarity are obtained, and the fault distance is obtained through the different application regression methods of weights. A large amount of simulation shows that the method is reliable and high in precision for the single-phase grounding fault.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
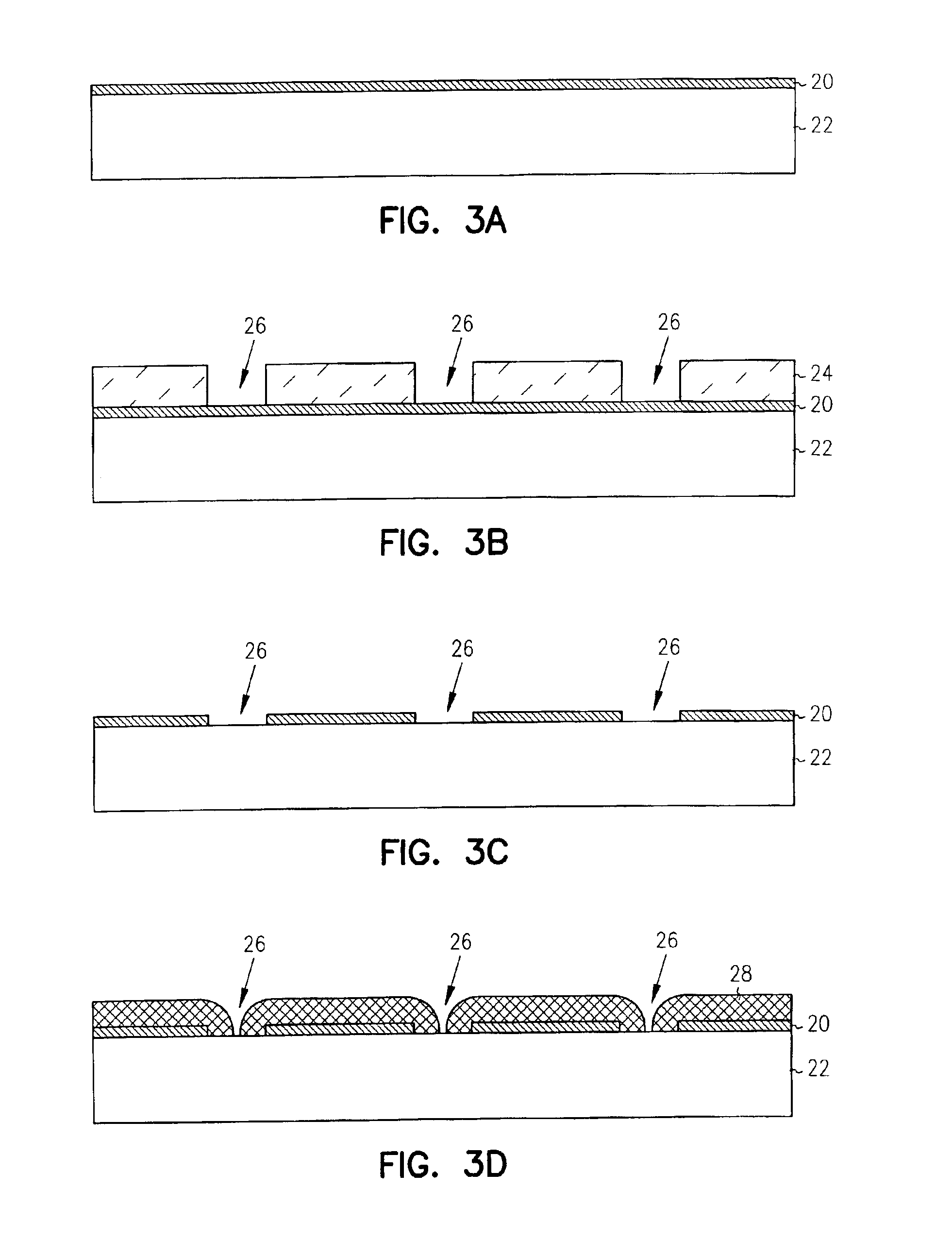
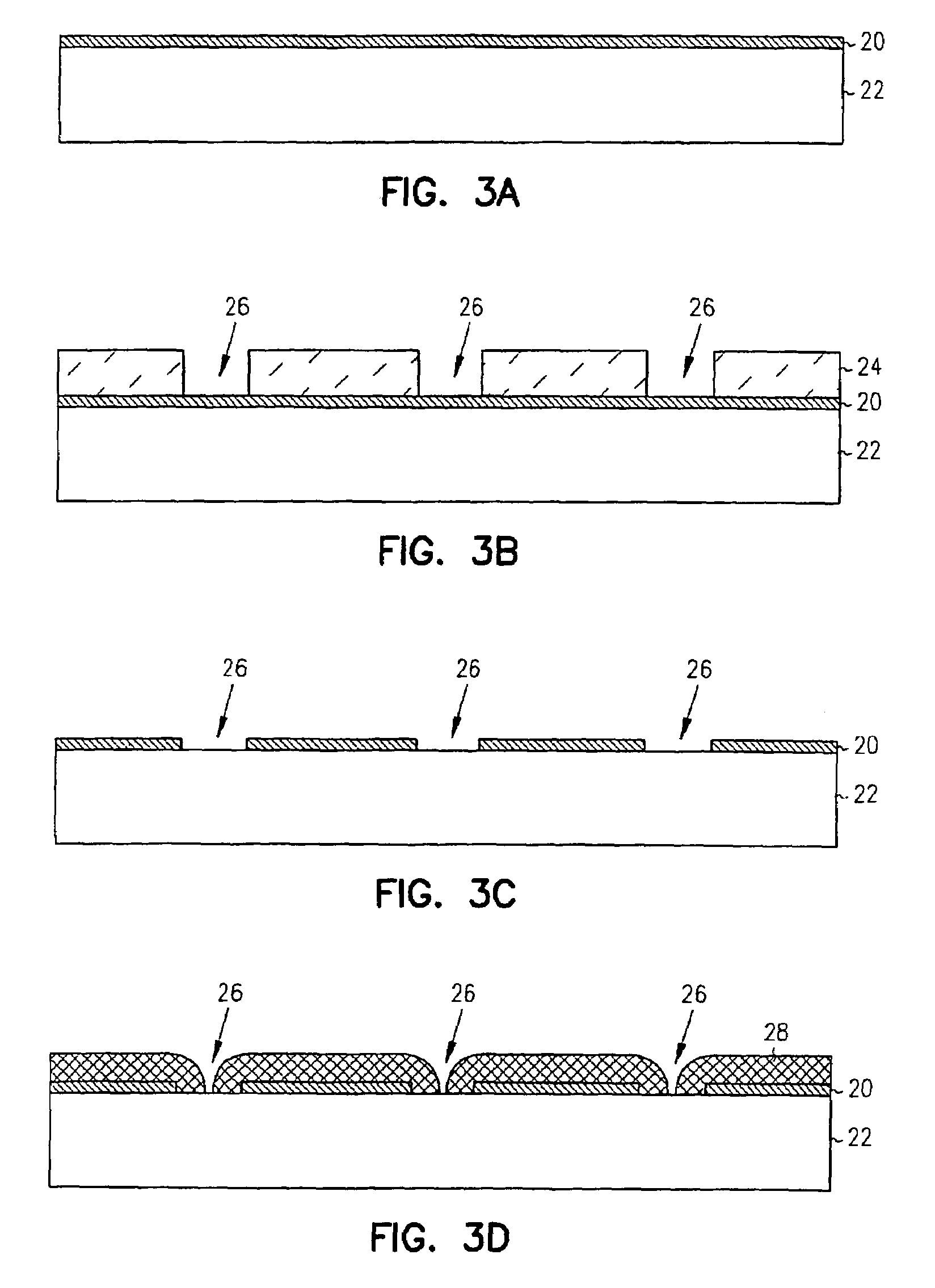
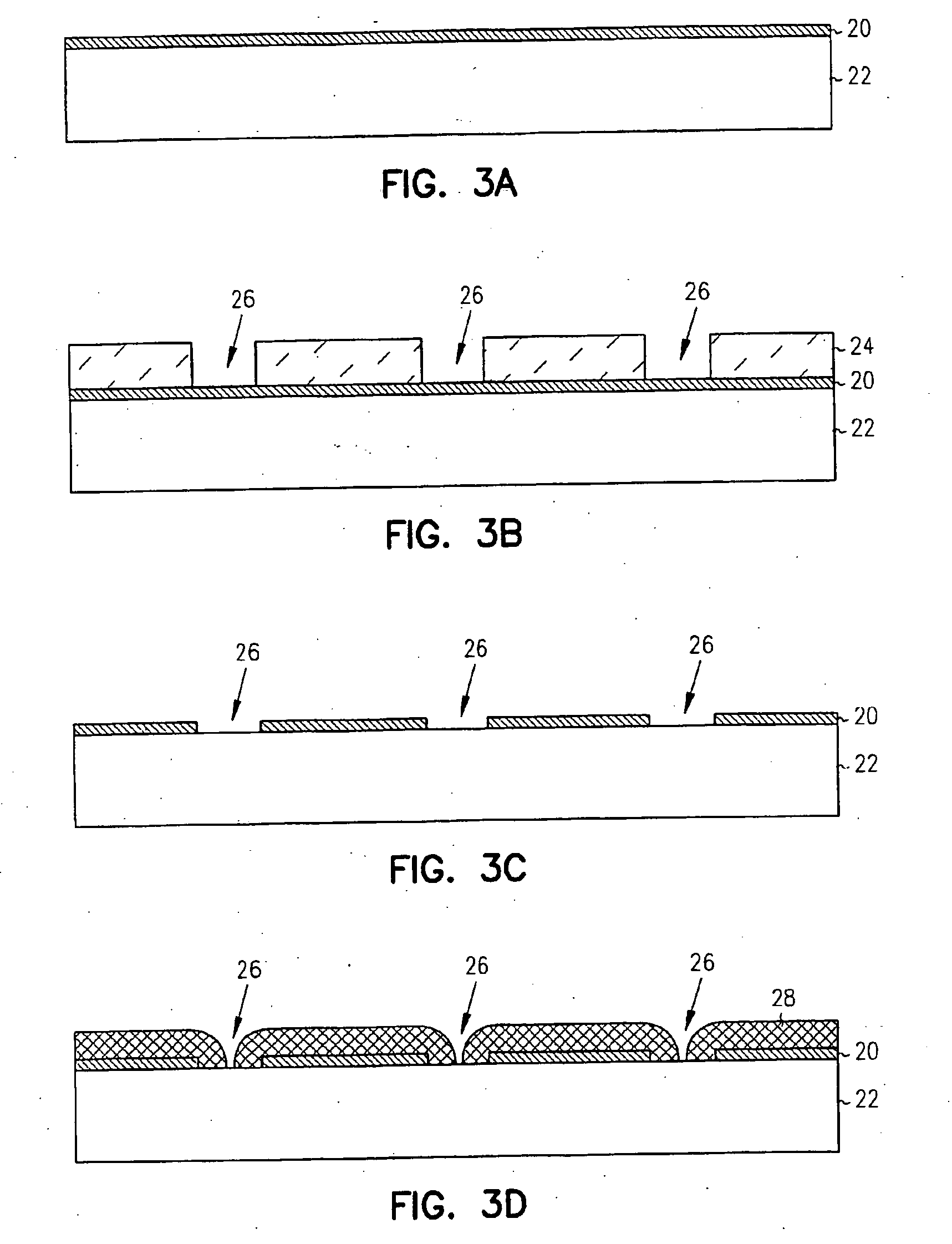
Zero-mode metal clad waveguides for performing spectroscopy with confined effective observation volumes
InactiveUS20050276535A1Effective volumeEasy to useCladded optical fibreMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method and an apparatus for analysis of an analyte. The method involves providing a zero-mode waveguide which includes a cladding surrounding a core where the cladding is configured to preclude propagation of electromagnetic energy of a frequency less than a cutoff frequency longitudinally through the core of the zero-mode waveguide. The analyte is positioned in the core of the zero-mode waveguide and is then subjected, in the core of the zero-mode waveguide, to activating electromagnetic radiation of a frequency less than the cut-off frequency under conditions effective to permit analysis of the analyte in an effective observation volume which is more compact than if the analysis were carried out in the absence of the zero-mode waveguide.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
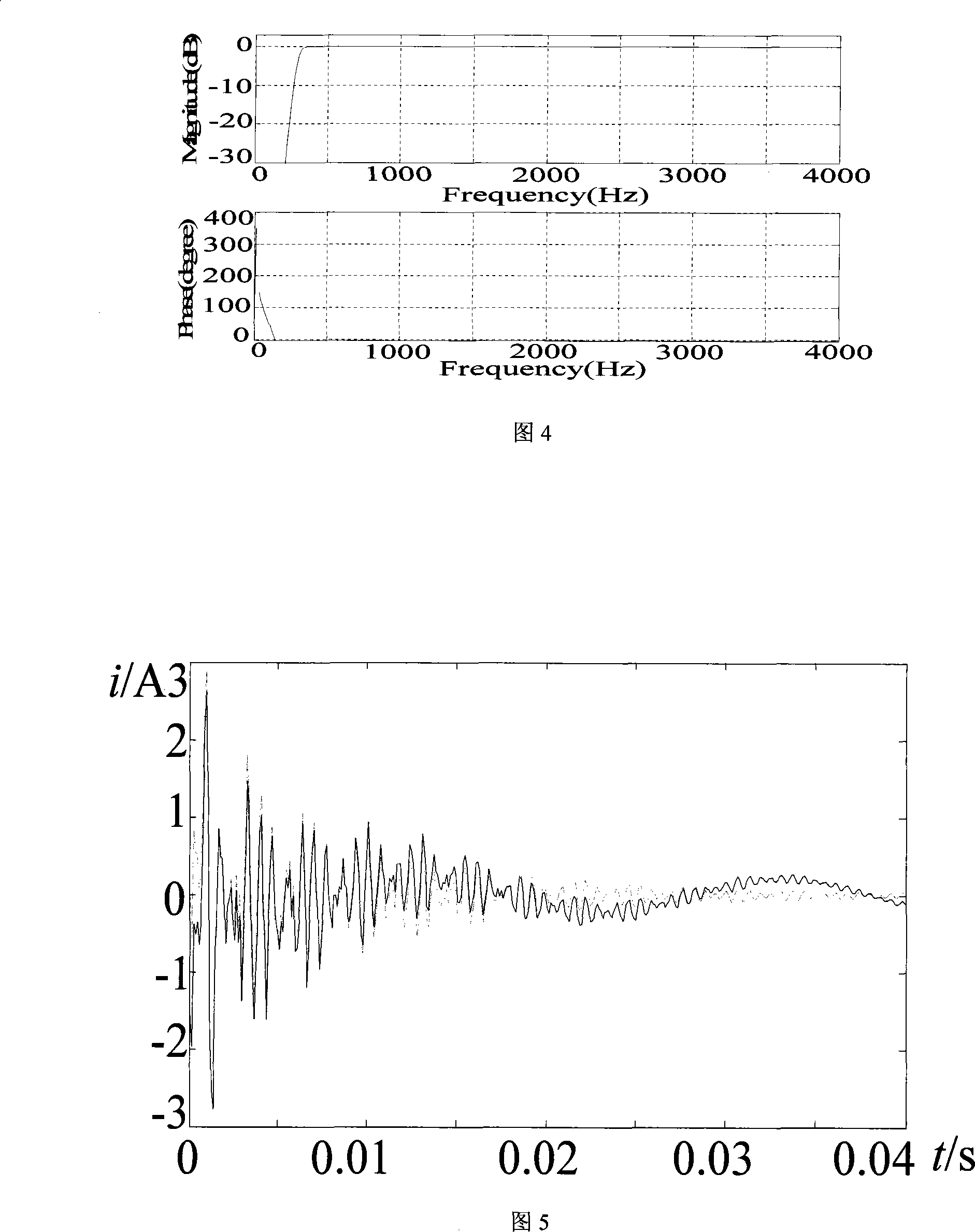
Electric transmission line traveling wave differential protection method
ActiveCN103986132AEasy to set upGuaranteed uptimeEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringZero mode
The invention relates to an electric transmission line traveling wave differential protection method. It is supposed that the total length of a protected both-end electric transmission line is 1, setting valves of traveling wave differential protection are calculated according to the following steps: a zero mode unbalanced coefficient is calculated; the maximum zero mode forward-direction traveling wave current at the m end during an external earth fault in an electric transmission line area is determined, and the maximum zero mode backward-direction traveling wave current at the n end is determined; the setting valves of various phases of the forward-direction traveling wave differential protection and the backward-direction traveling wave differential protection are respectively calculated; the traveling wave differential protection is adjusted according to the setting valves of the various phases of the forward-direction traveling wave differential protection and the backward-direction traveling wave differential protection, failure recognition and judgment and protection movement on the traveling wave differential protection of the various phases are accordingly achieved. By means of the electric transmission line traveling wave differential protection method, protection error movement is not prone to being caused; the electric transmission line traveling wave differential protection method is easy to implement.
Owner:江苏燎源变压器有限公司
High-resistance grounding fault positioning method based on transient current projection coefficient difference comparison
ActiveCN106980069AResolve interferencePractical application value is greatFault location by conductor typesHigh resistanceTransient state
The invention discloses a high-resistance grounding fault positioning method based on transient current projection coefficient difference comparison, which is characterized in that when a system has a high-resistance grounding fault, a substation terminal starts, a fault line is selected, and a line selection result and fault line outlet zero-sequence current acquisition data are reported to a master station; when a sudden change of zero-mode voltage or zero-mode current exceeds a preset threshold, each feed line terminal starts, and fault zero-sequence voltage and current acquisition data is reported to the master station; the master station receives zero-sequence voltage and current acquisition data of each monitoring point of the substation terminal and feed lines, respectively extracts transient components thereof and does not perform processing on sound line terminal data; projecting the transient zero-sequence current of each monitoring point to transient zero-sequence voltage of a bus, and calculating a projection coefficient of the transient zero-sequence current of each monitoring point; calculating the difference of the transient zero-sequence current projection coefficients of upstream and downstream monitoring points of each segment; and selecting a segment with the greatest difference to be a fault segment. The high-resistance grounding fault positioning method solves a problem of positioning a high-resistance grounding fault in a resonant grounding system and has wide practical application values.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
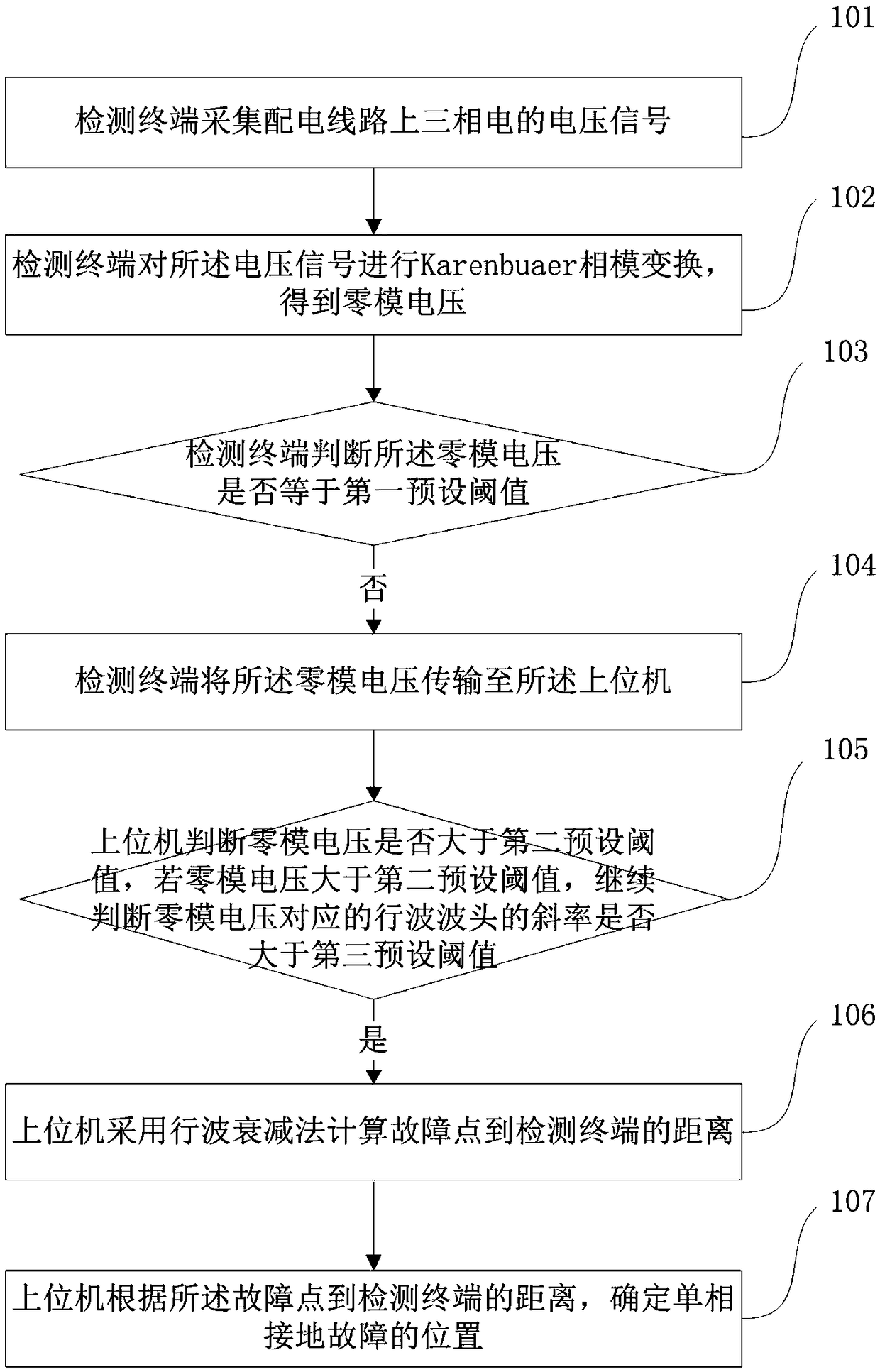
Power transmission line single-phase grounding fault positioning method and system thereof
InactiveCN109387733AEasy to identifyHigh precisionFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemUltrasound attenuationEngineering
The invention provides a power transmission line single-phase grounding fault positioning method and a system thereof, wherein the method comprises the steps of acquiring a voltage signal of three-phase power on the power transmission line by a detecting terminal, performing phase-mode transformation on the voltage signal, and obtaining zero-mode voltage; on the condition that the zero-mode voltage is not equal with a first preset threshold, transmitting the zero-mode voltage to an upper computer; if the zero-mode voltage is higher than a second preset threshold and gradient of a traveling wave front which corresponds with the zero-mode voltage is higher than a third preset threshold, calculating a distance between a fault point and the detecting terminal by the upper computer by means ofa travelling wave attenuation method; and determining the position of the single-phase grounding fault according to the distance between the fault point and the detecting terminal. According to the method of the invention, the position of the single-phase ground fault is fixed by means of a zero-mode voltage traveling wave attenuation characteristic; easy identification and relatively high precision of the zero-mode voltage travelling wave front are realized; the fault position can be quickly found for eliminating a hidden trouble; and a problem of low positioning precision caused by relatively weak to-be-detected amount in a traditional positioning method is settled.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Distribution network fault line selection method based on zero-mode current multi-order difference transformation
InactiveCN104133158AAvoid compensatory effectsImprove reliabilityFault locationElectric power systemCompensation effect
The invention relates to a distribution network fault line selection method based on zero-mode current multi-order difference transformation and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. When feeder lines in a distribution network are in a single-phase earth fault, zero-mode current traveling wave data, recorded into a short time window, of the feeder lines are extracted for multi-order difference transformation; if a first nonzero value achieved after transformation is carried out is greater than zero, it is judged that the feeder lines are in the single-phase earth fault; if the first nonzero value is smaller than zero, it is judged that the feeder lines are not in the single-phase earth fault. By the utilization of the zero-mode current data, in the short time window, of the feeder lines after the fault occurs, at the moment, an arc suppression coil does not compensate for a system, so that the method avoids influence on the compensation effect of the arc suppression coil, and fault feeder lines can be judged out accurately and reliably.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Distributed low-current ground wire selection method and wire selection system thereof
The invention provides a distributed low-current ground wire selection method and a wire selection system thereof. A ground protection device of each circuit is used for respectively obtaining voltageof each phase of a busbar, respectively obtaining three-phase phase or two-phase current of a power supply transformer connected with the busbar and obtaining zero-mode current of a protected circuit. The distributed low-current ground wire selection method is characterized by judging fault circuits by judging whether waveforms of power-frequency-free and high-frequency-free remaining current ofa fault phase of the transformer and zero-mode power-frequency-free and high-frequency-free remaining current of the circuit are in opposite directions. Through the distributed low-current ground wireselection method and the wire selection system thereof, the ground protection devices are few in leading-in wires and are convenient to maintain and manage.
Owner:李晓明 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com