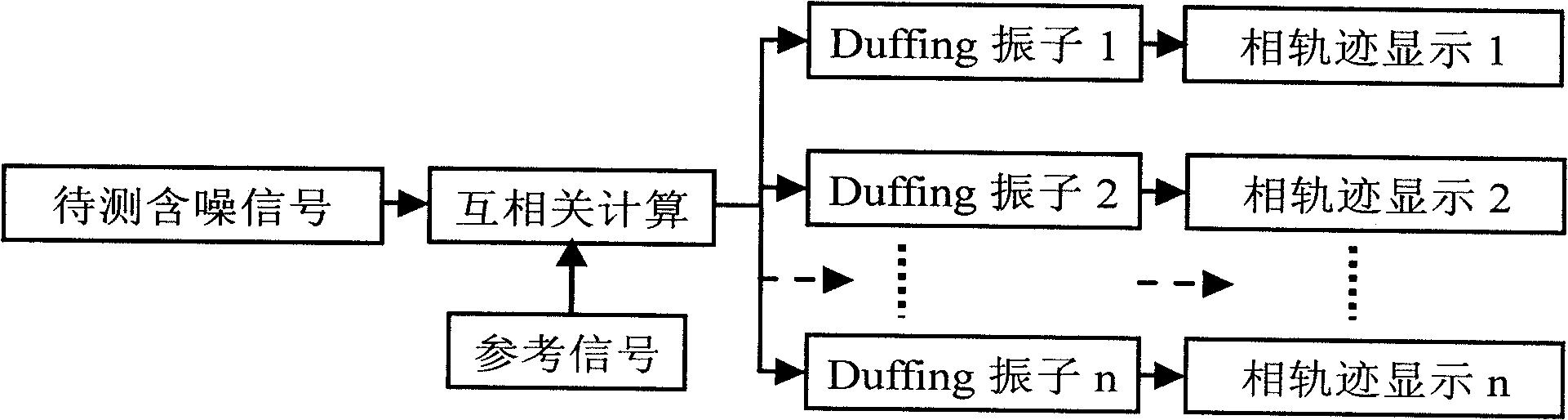
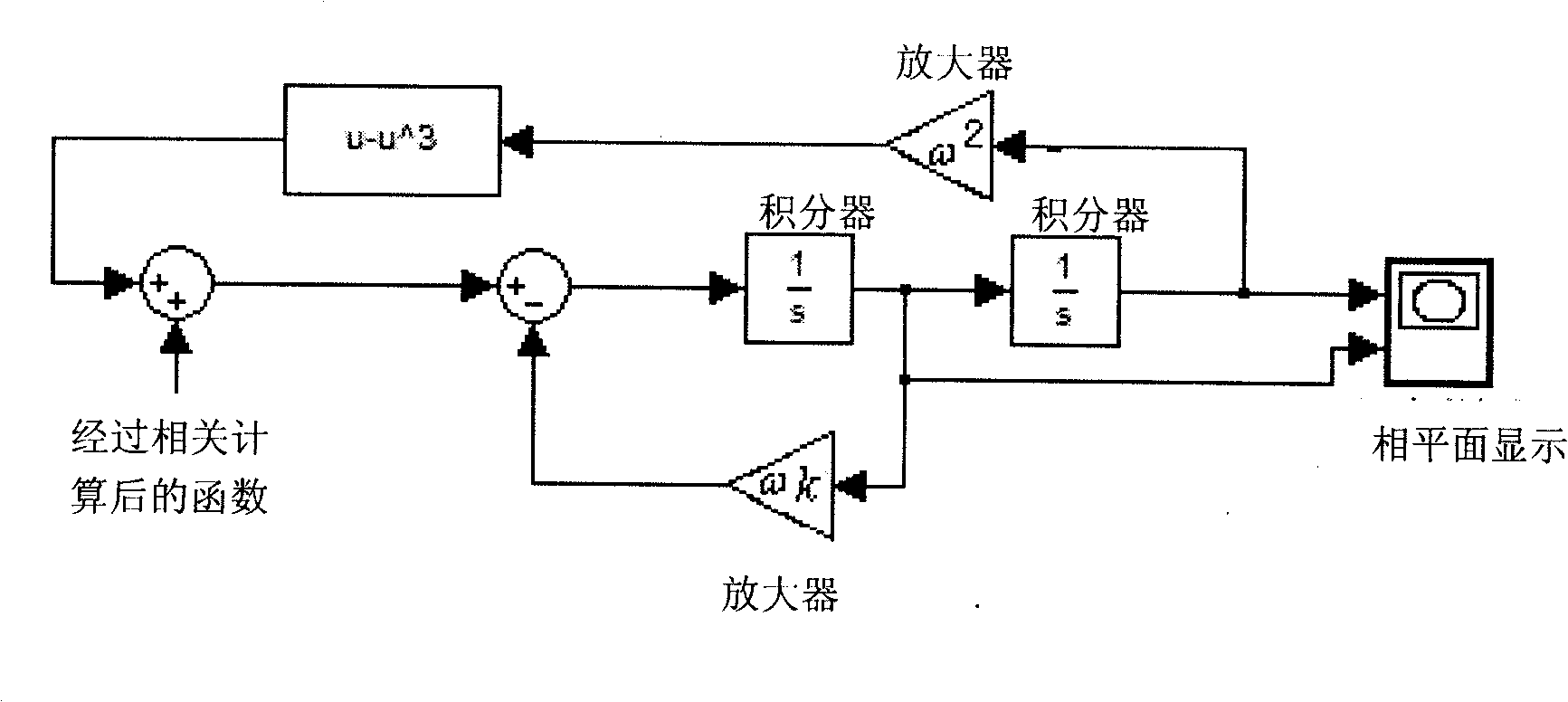
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1249 results about "Noise removal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
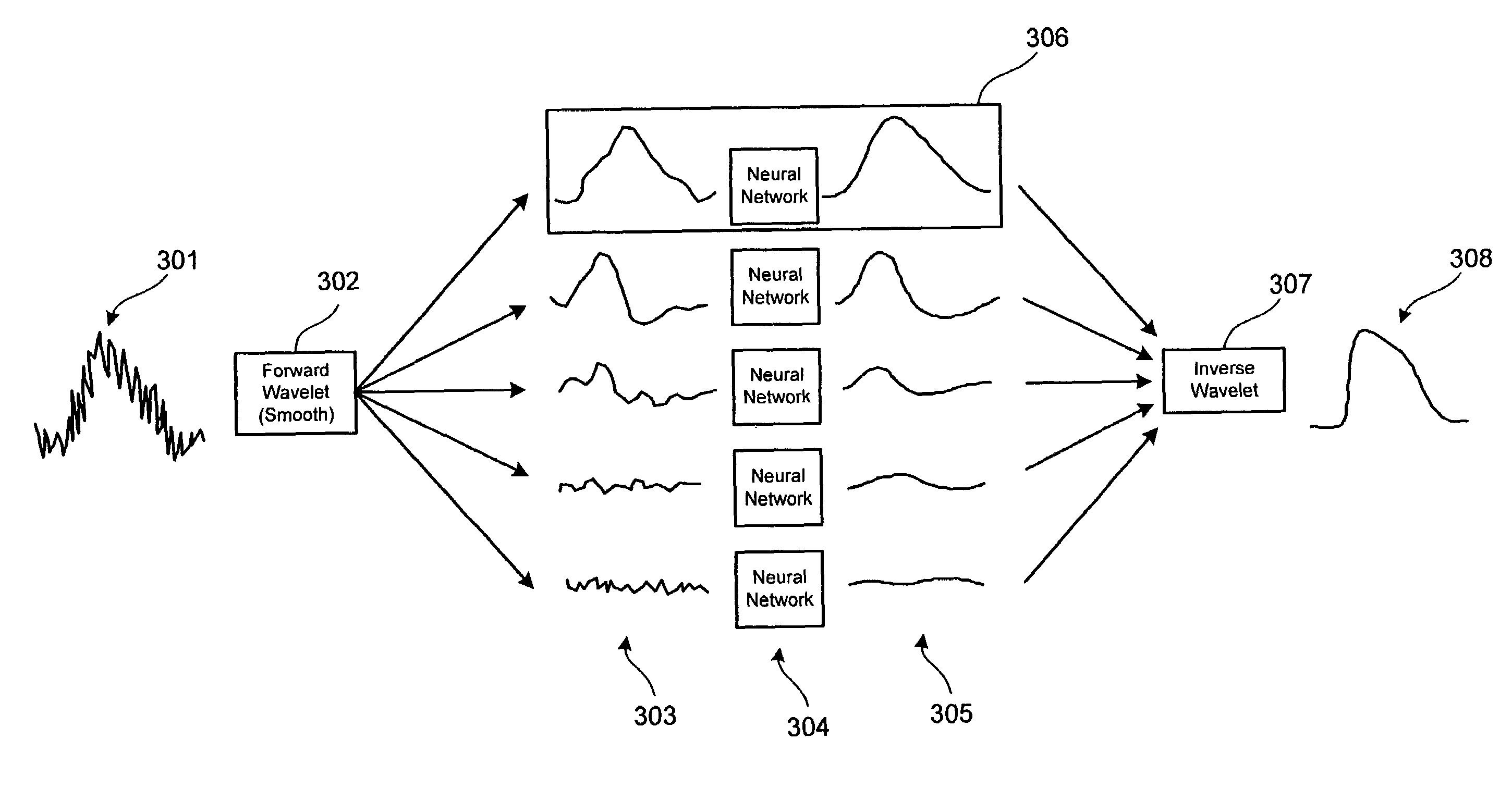
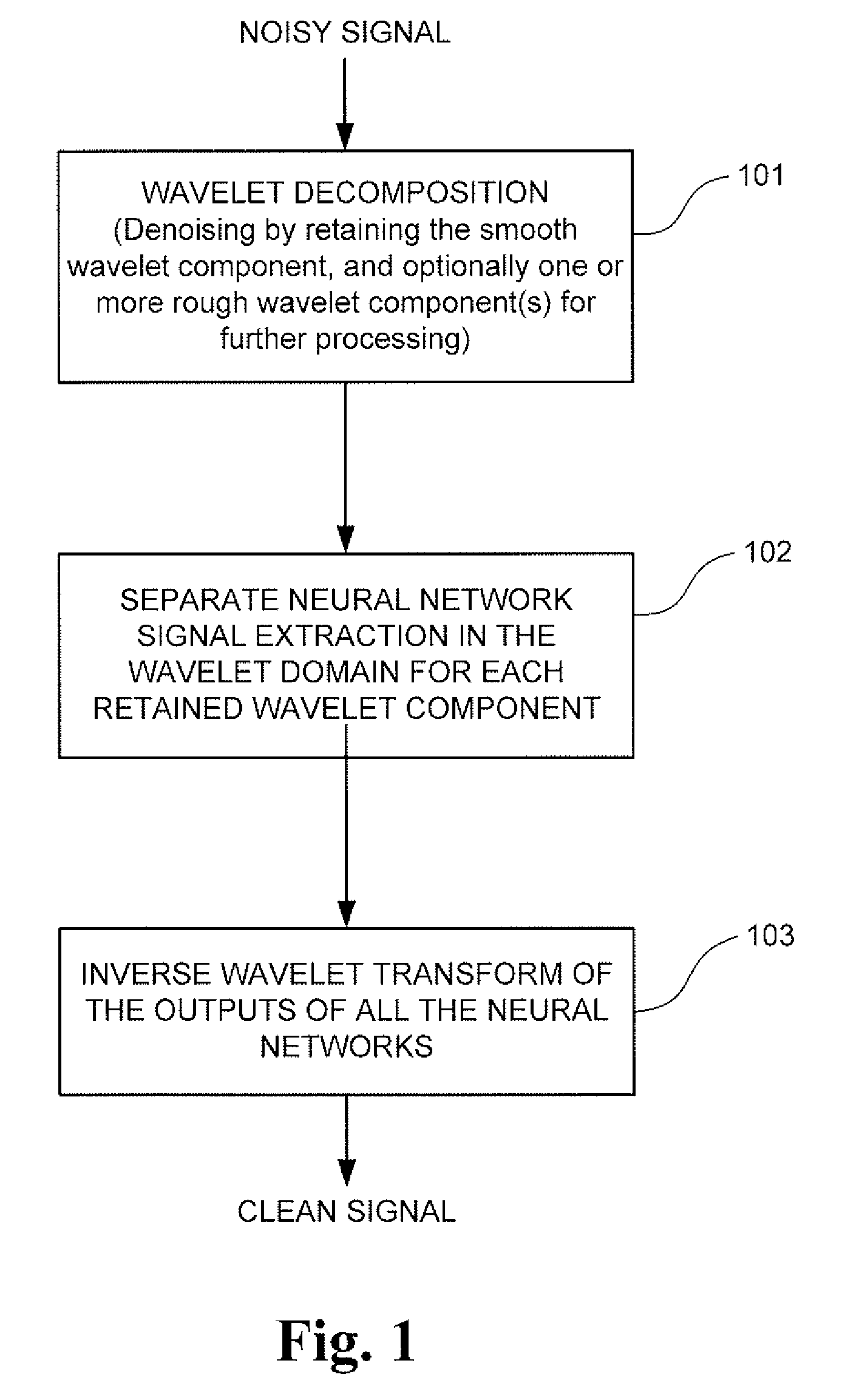
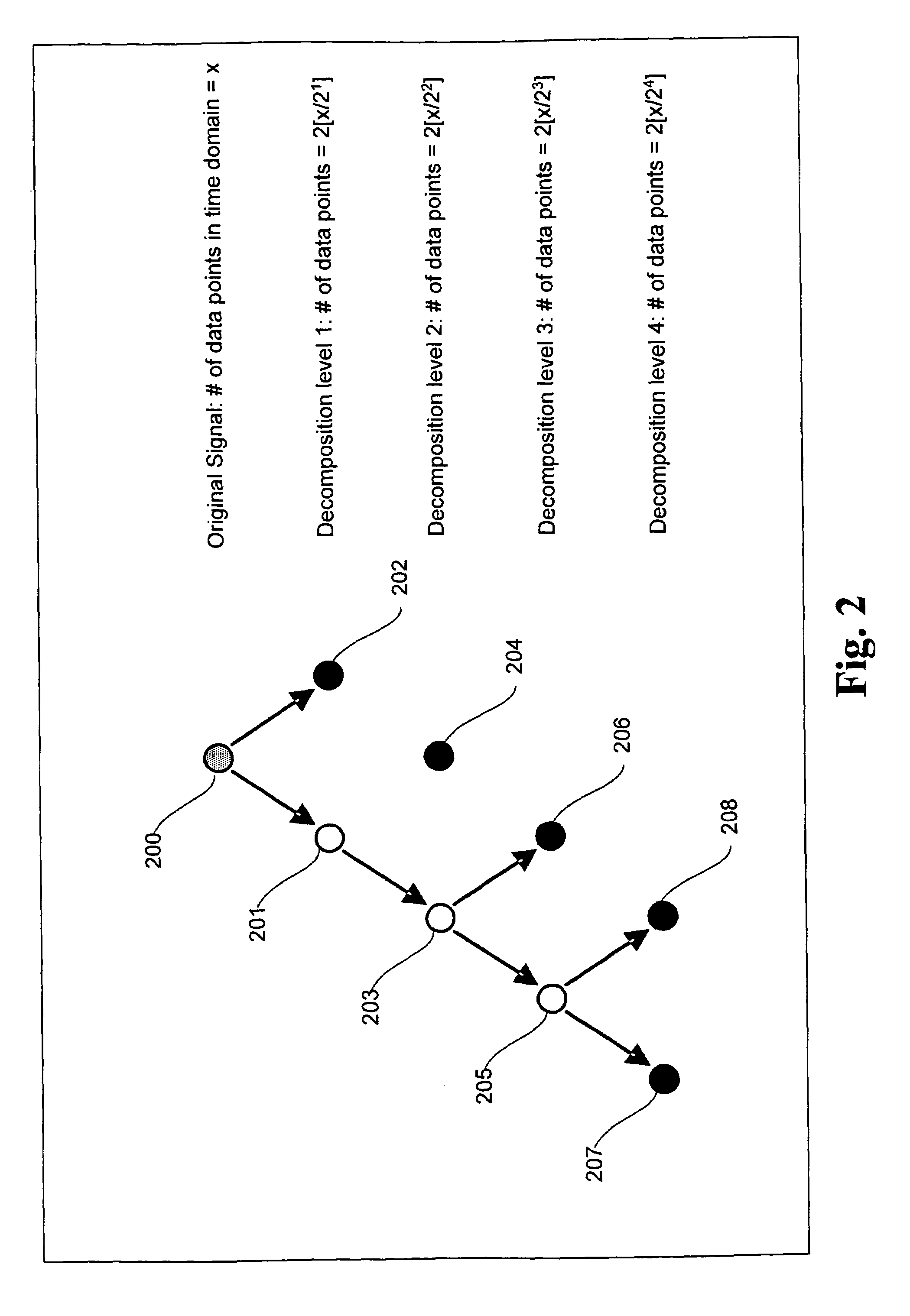
Signal processing method and system for noise removal and signal extraction
InactiveUS7519488B2Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainDecomposition
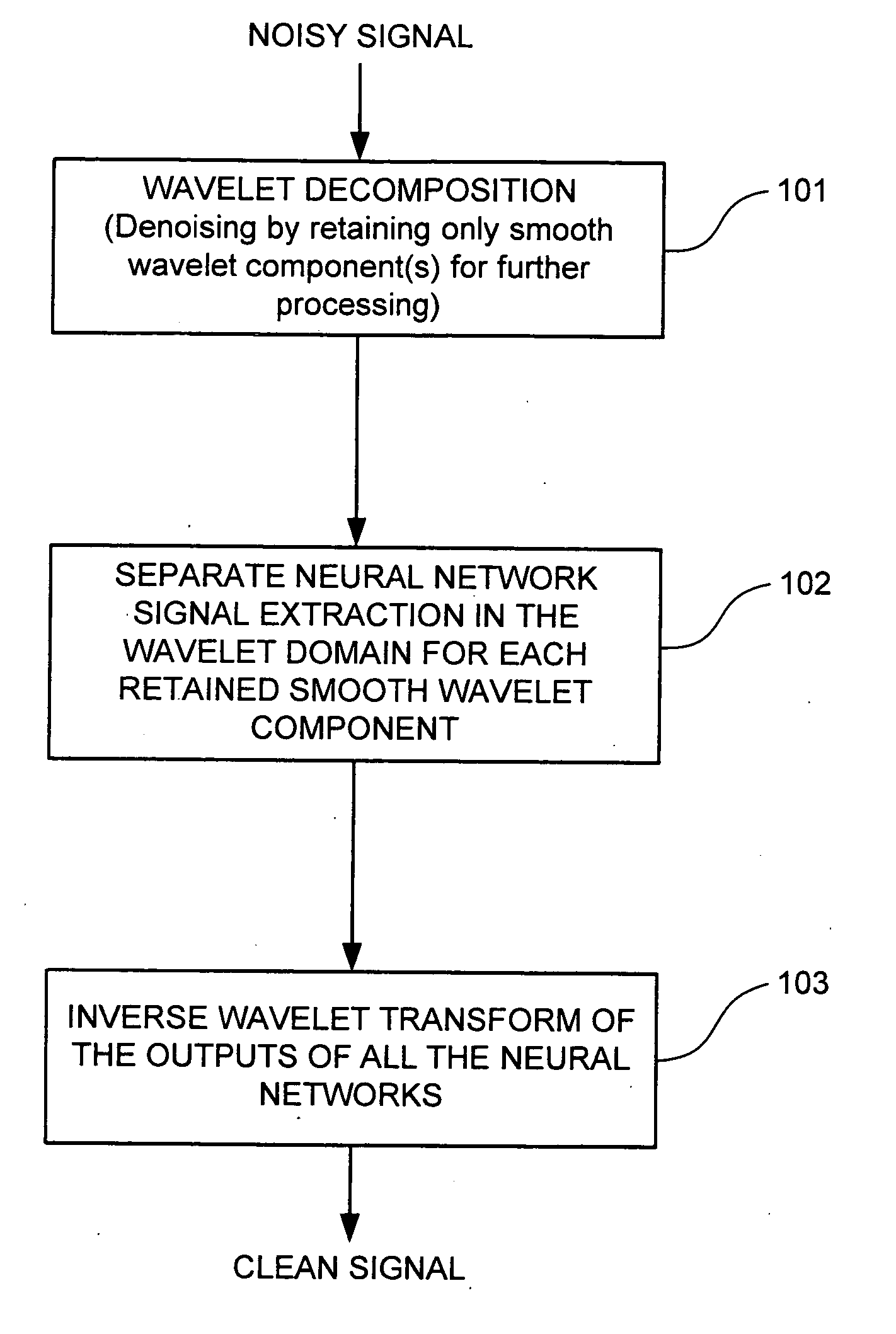
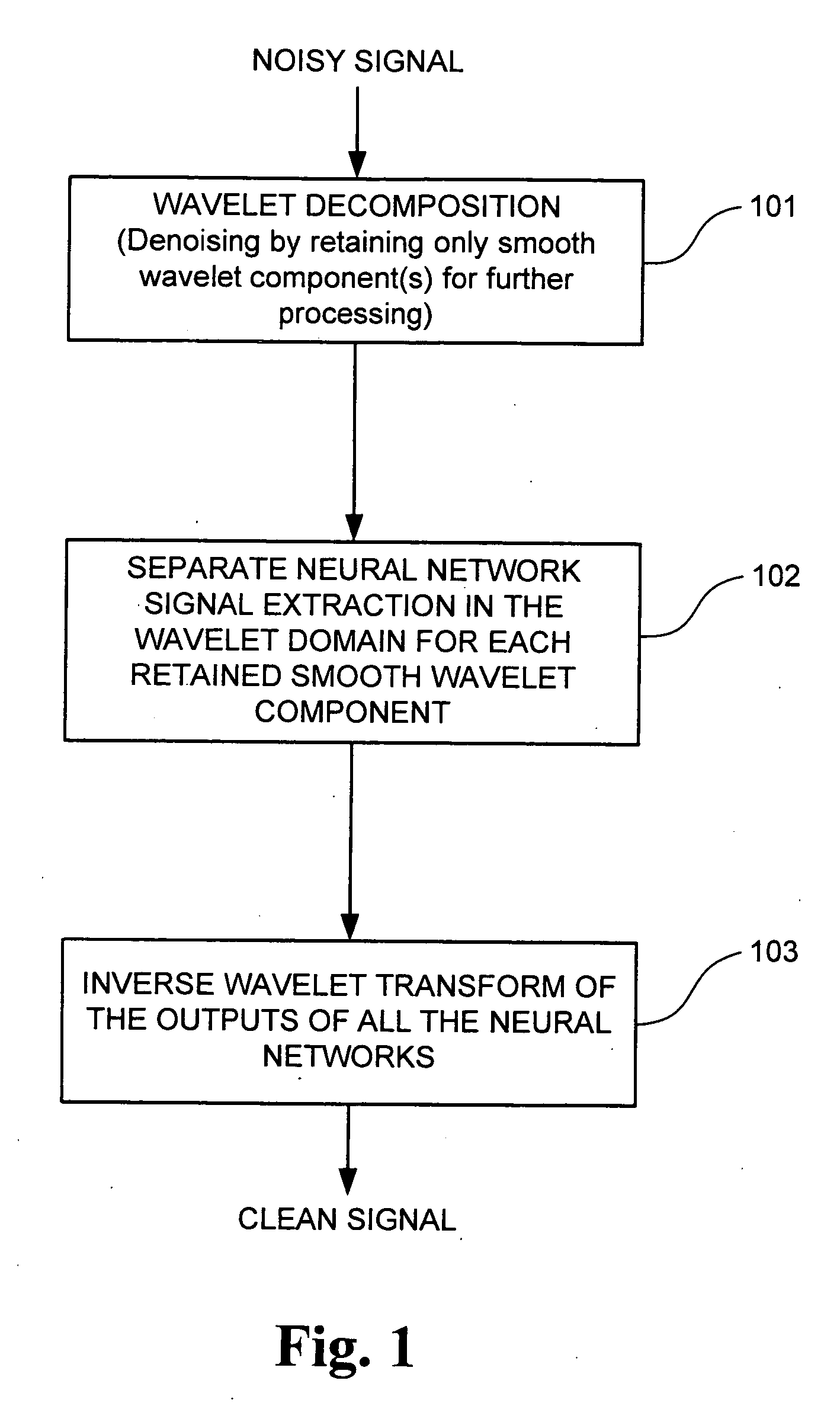
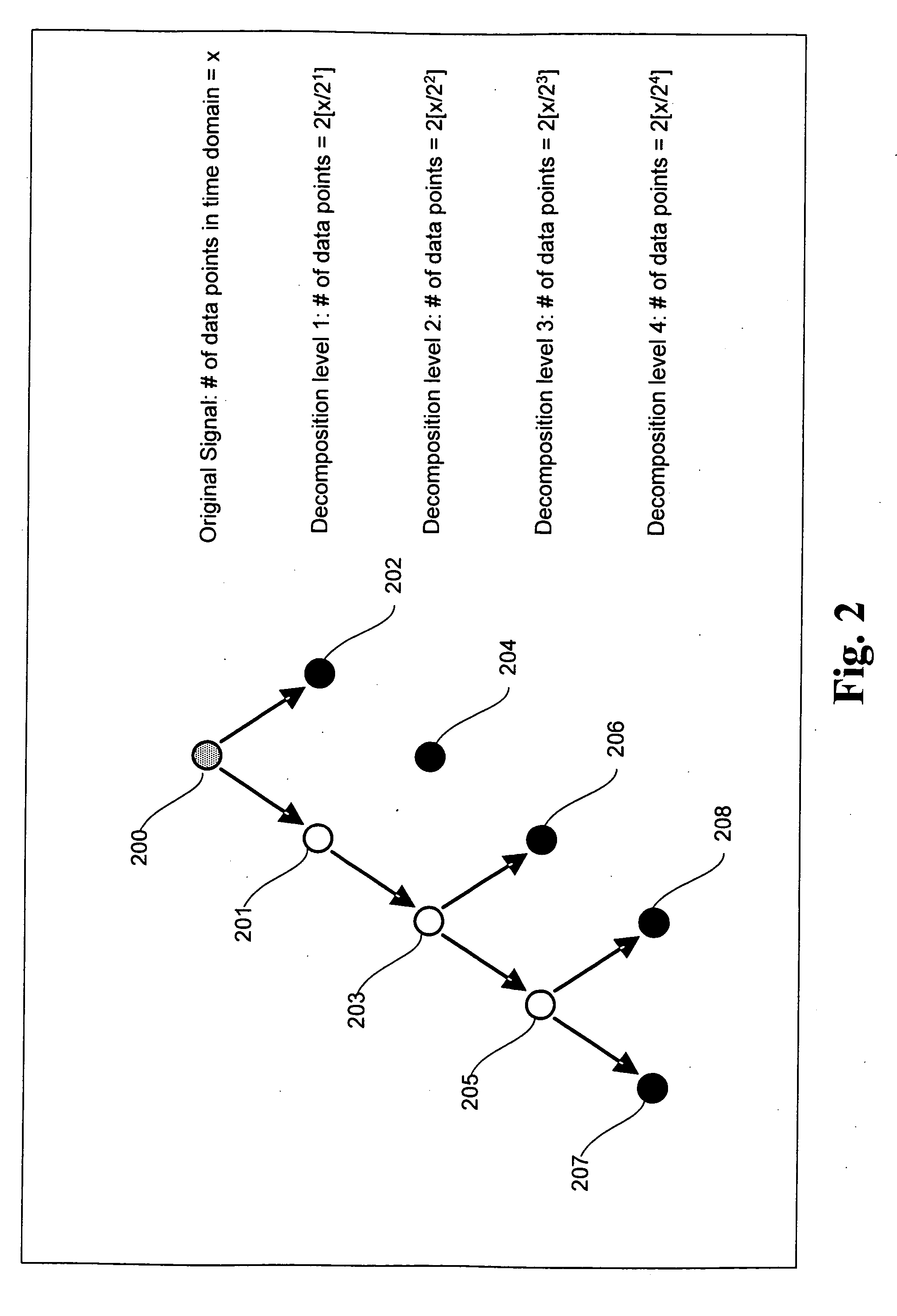
A signal processing method and system combining smooth level wavelet pre-processing together with artificial neural networks all in the wavelet domain for signal denoising and extraction. Upon receiving a signal corrupted with noise, an n-level decomposition of the signal is performed using a discrete wavelet transform to produce a smooth component and a rough component for each decomposition level. The nth level smooth component is then inputted into a corresponding neural network pre-trained to filter out noise in that component by pattern recognition in the wavelet domain. Additional rough components, beginning at the highest level, may also be retained and inputted into corresponding neural networks pre-trained to filter out noise in those components also by pattern recognition in the wavelet domain. In any case, an inverse discrete wavelet transform is performed on the combined output from all the neural networks to recover a clean signal back in the time domain.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
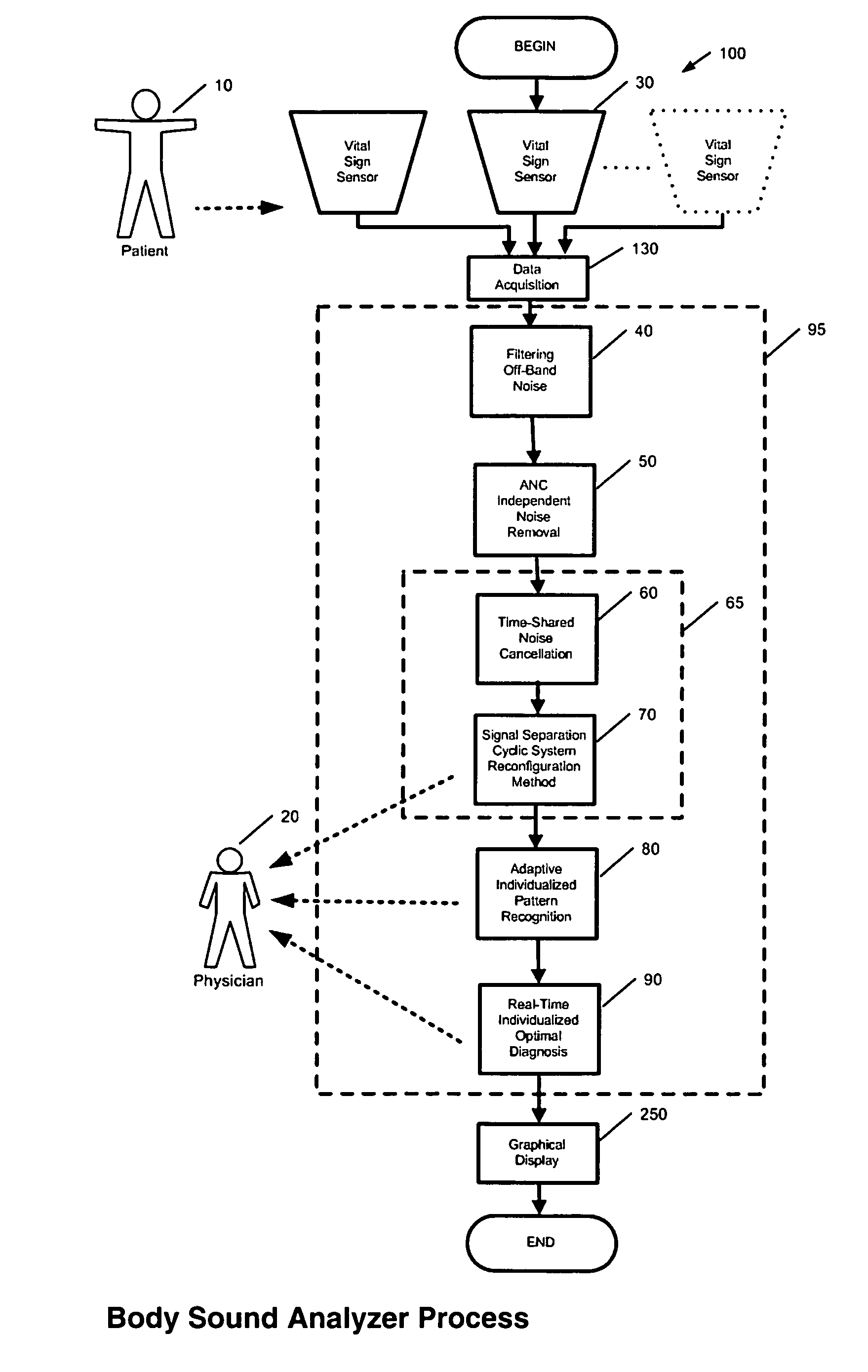
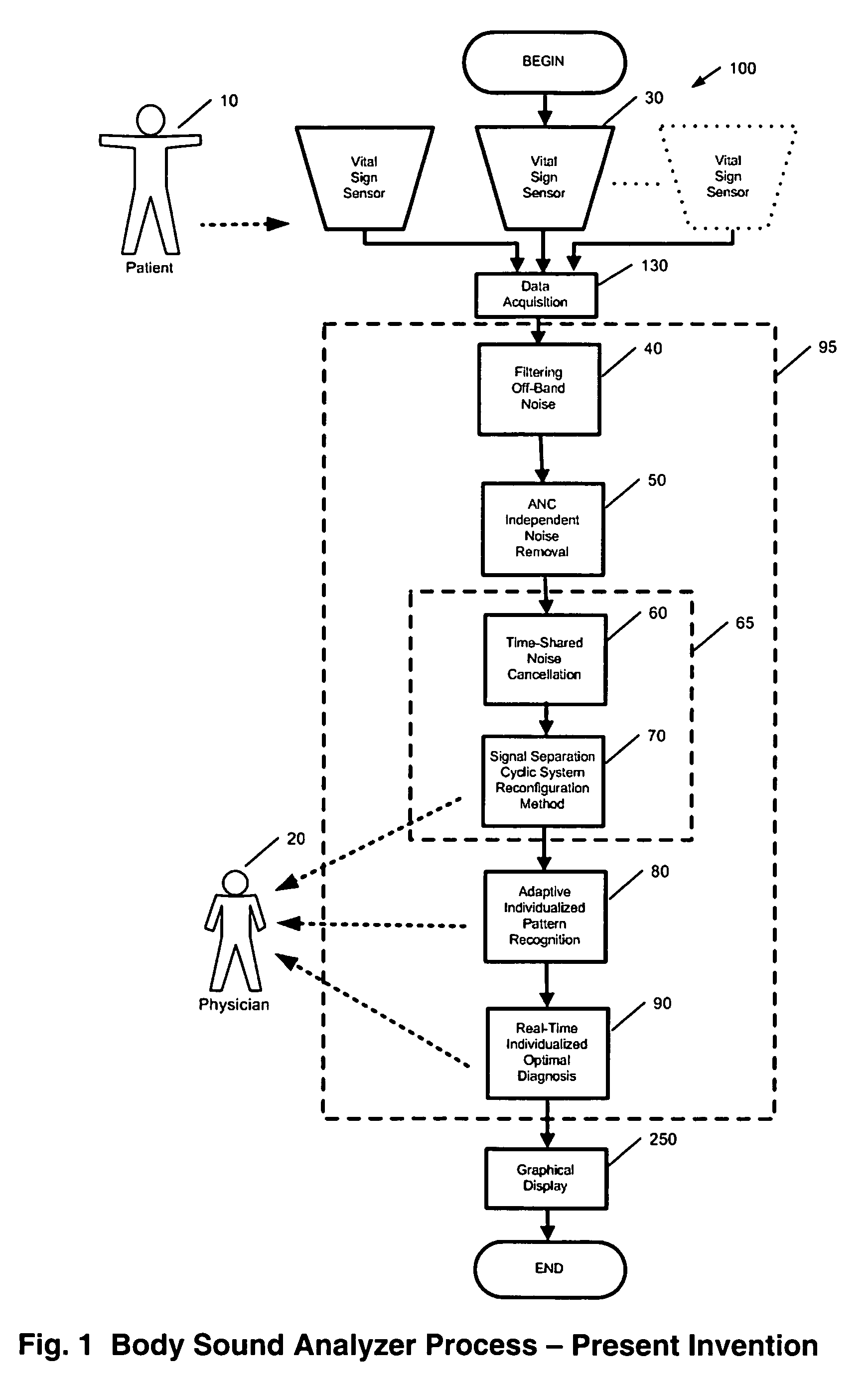
Method and system for continuous monitoring and diagnosis of body sounds
InactiveUS20060198533A1Reduce the impactQuality improvementStethoscopeTransmission noise suppressionContinuous measurementReal time analysis
A method and system is invented for automated continuous monitoring and real-time analysis of body sounds. The system embodies a multi-sensor data acquisition system to measure body sounds continuously. The sound signal processing functions utilize a unique signal separation and noise removal methodology by which authentic body sounds can be extracted from cross-talk signals and in noisy environments, even when signals and noises may have similar frequency components or statistically dependent. This method and system combines traditional noise canceling methods with the unique advantages of rhythmic features in body sounds. By employing a multi-sensor system, the method and system perform cyclic system reconfiguration, time-shared blind identification and adaptive noise cancellation with recursion from cycle to cycle. Since no frequency separation or signal / noise independence is required, this invention can provide a robust and reliable capability of noise reduction, complementing the traditional methods. The invention further includes a novel method by which pattern recognition of groups of key parameters can be used to diagnosis physical conditions associated with body sounds, with confidence intervals on the diagnostic criterion to indicate accuracy of diagnosis.
Owner:WANG LE YI +1
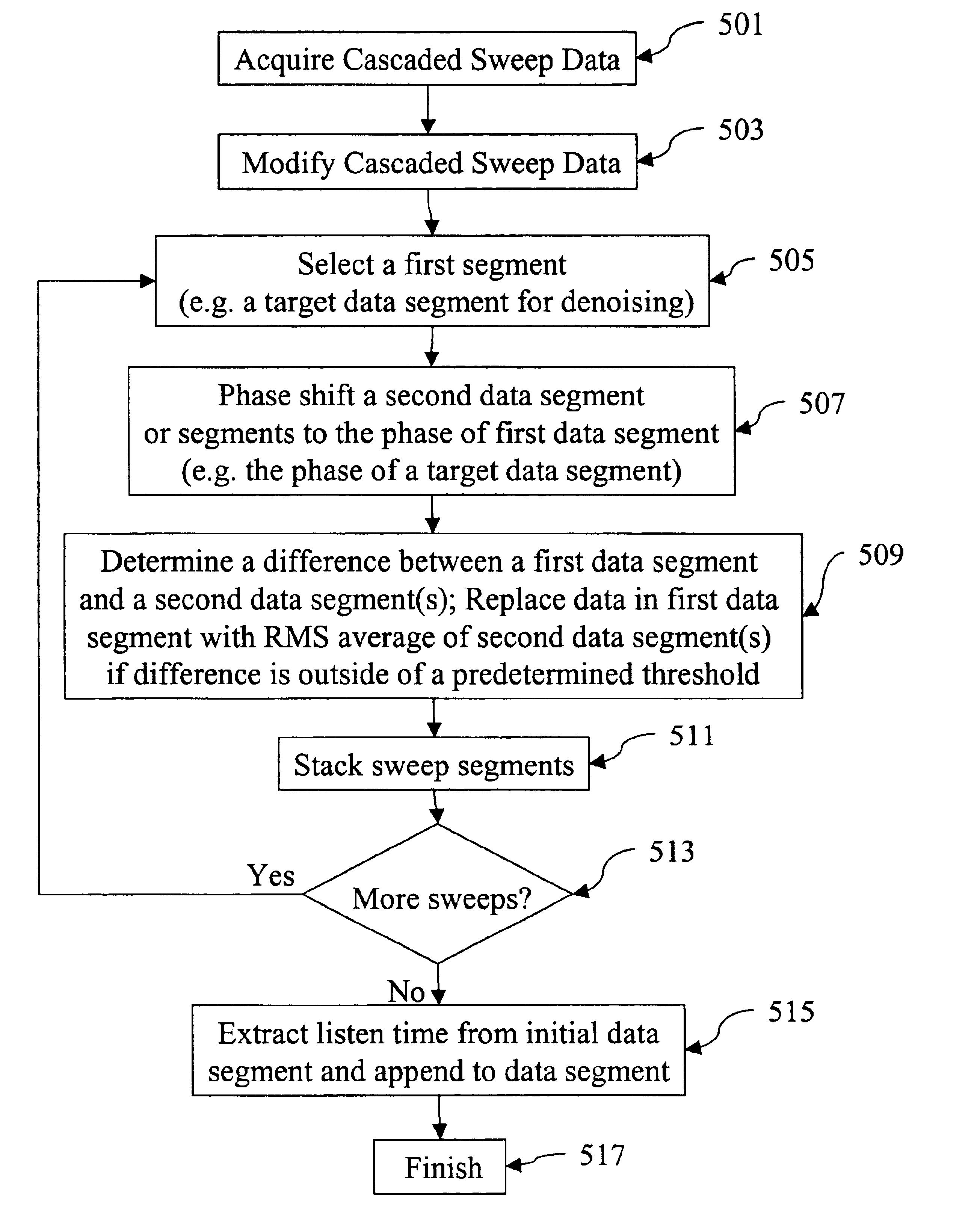
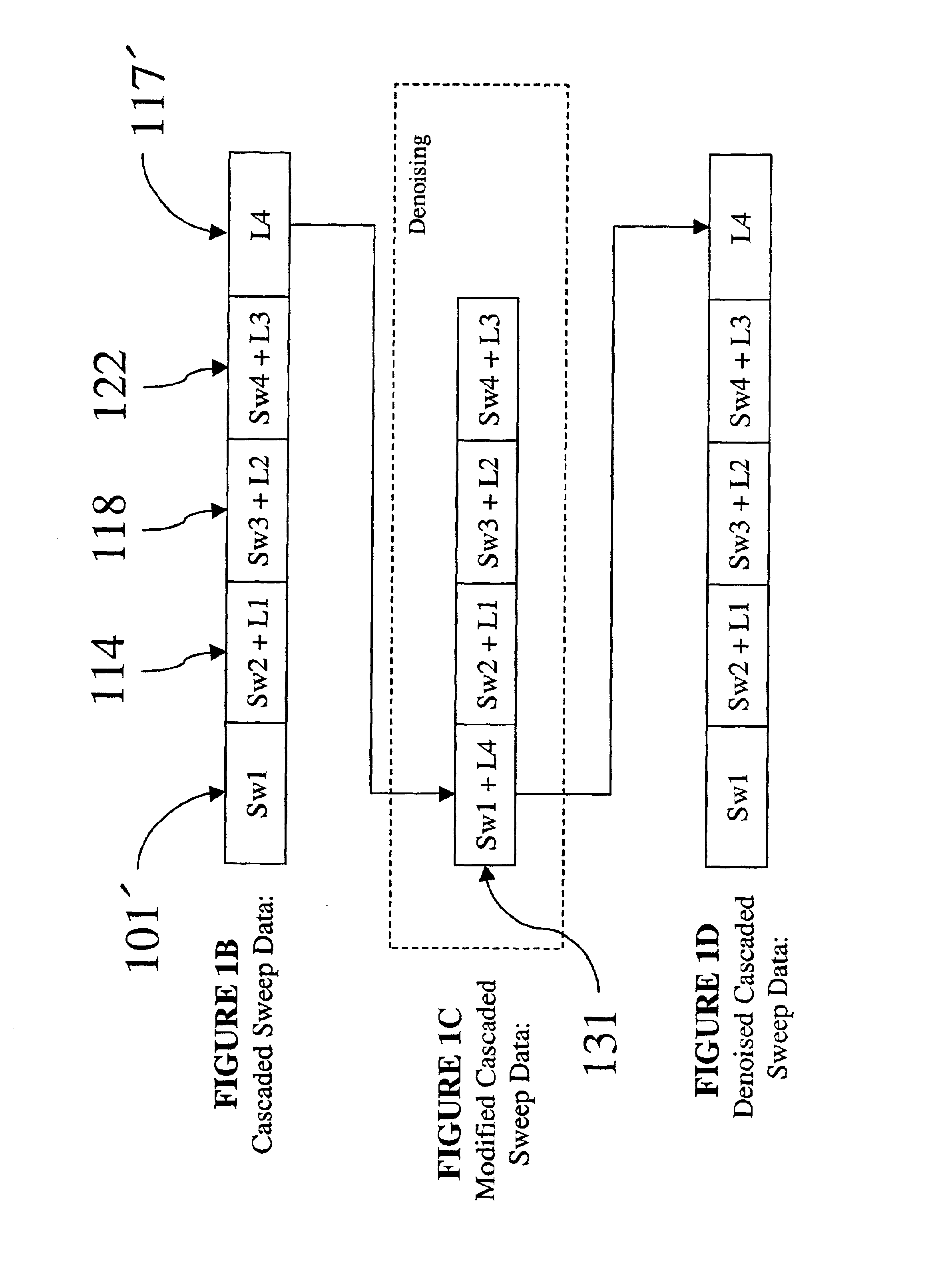
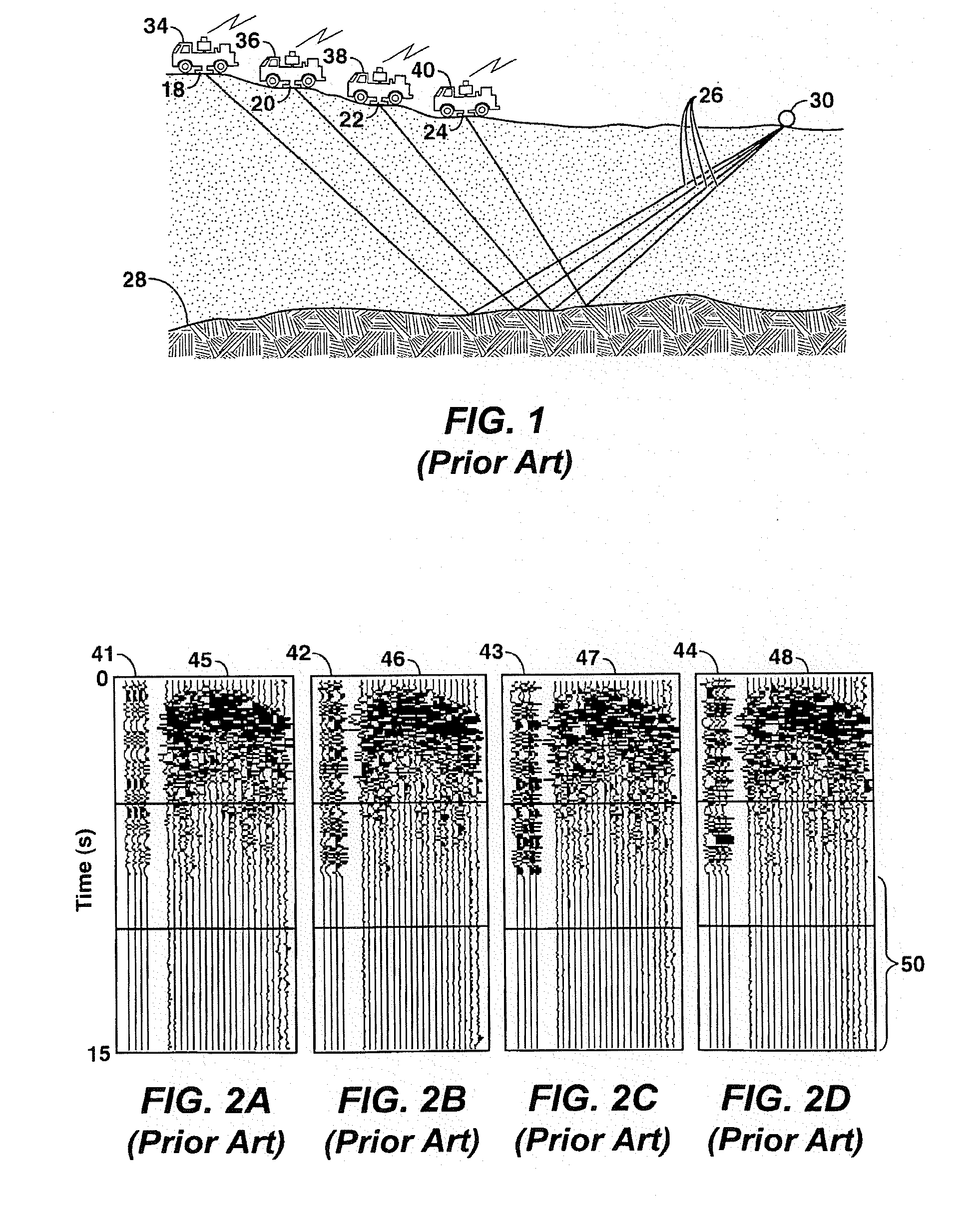
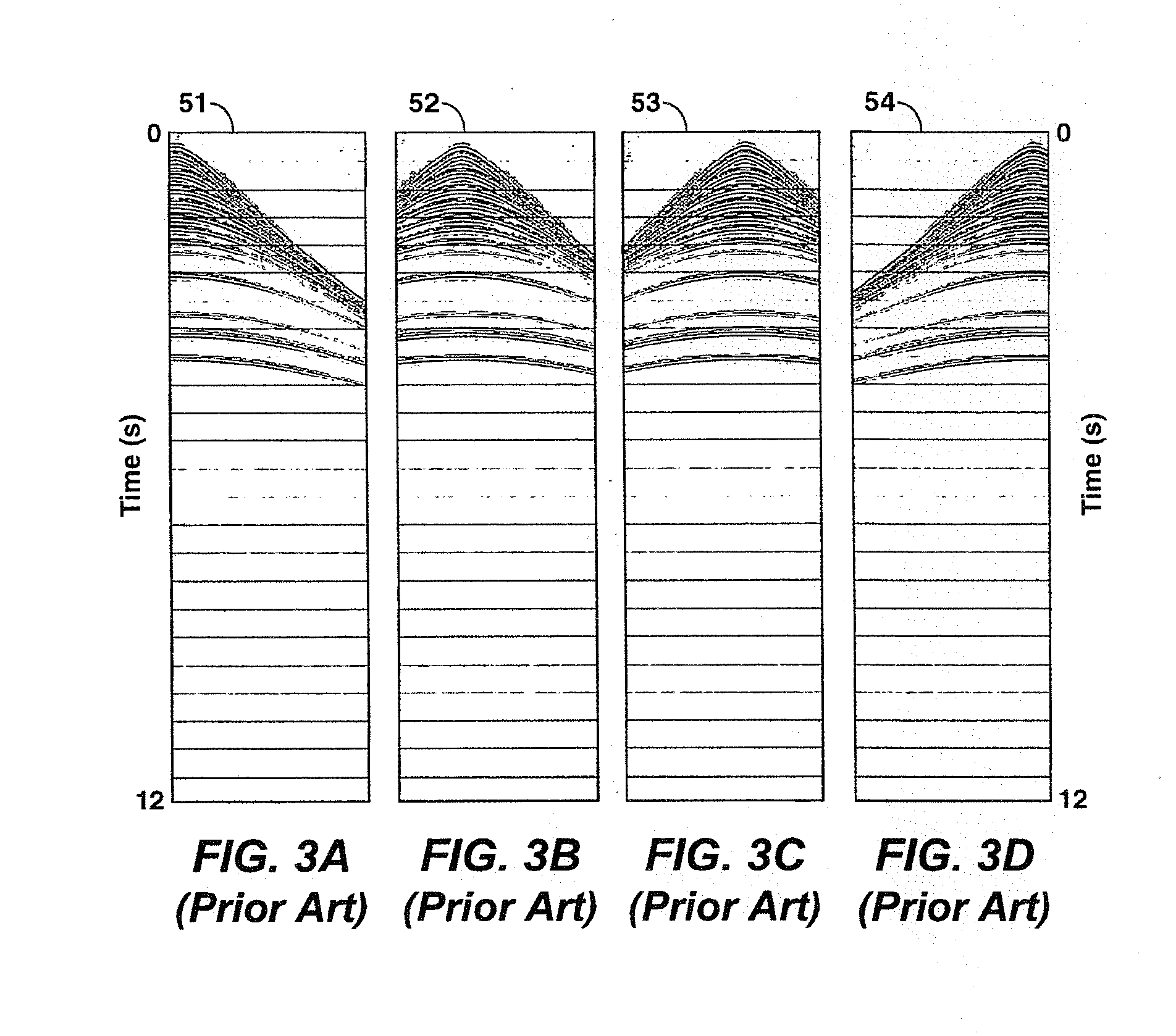
Method of noise removal for cascaded sweep data
InactiveUS6842701B2Seismic signal processingAnalogue computers for heat flowPhase shiftedData segment
The present invention is a method for processing seismic data comprising acquiring seismic data using a sweep sequence including a plurality of cascaded sweep segments. The seismic data include a plurality of data segments and a listen time. The listen is combined with an initial data segment. The seismic data segments are phase shifted to a phase of a target data segment to be denoised (i.e. removal of ambient, harmonic and coherent noise). A difference between the target data segment and the remaining data segments is determined. If the determined difference exceeds a predetermined threshold, data in the target data segment is replaced with data derived from the remaining data segments. The data segments may be stacked to form a new target data segment. The listen time is extracted from the initial data segment.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
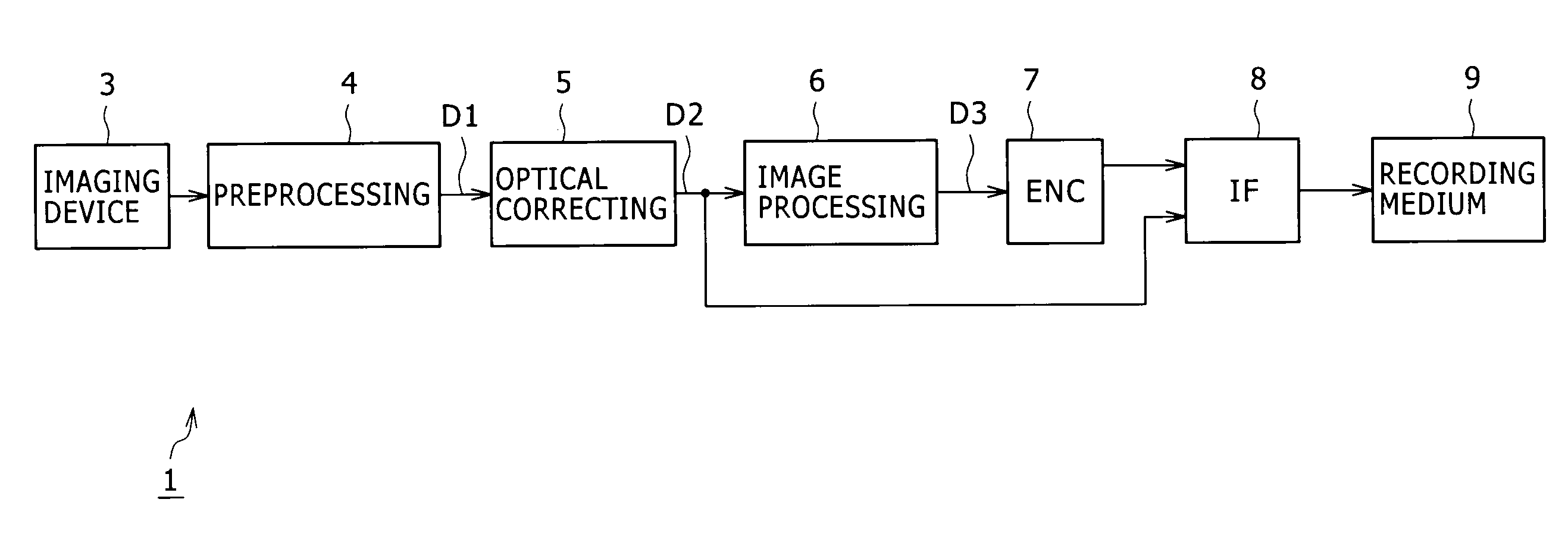
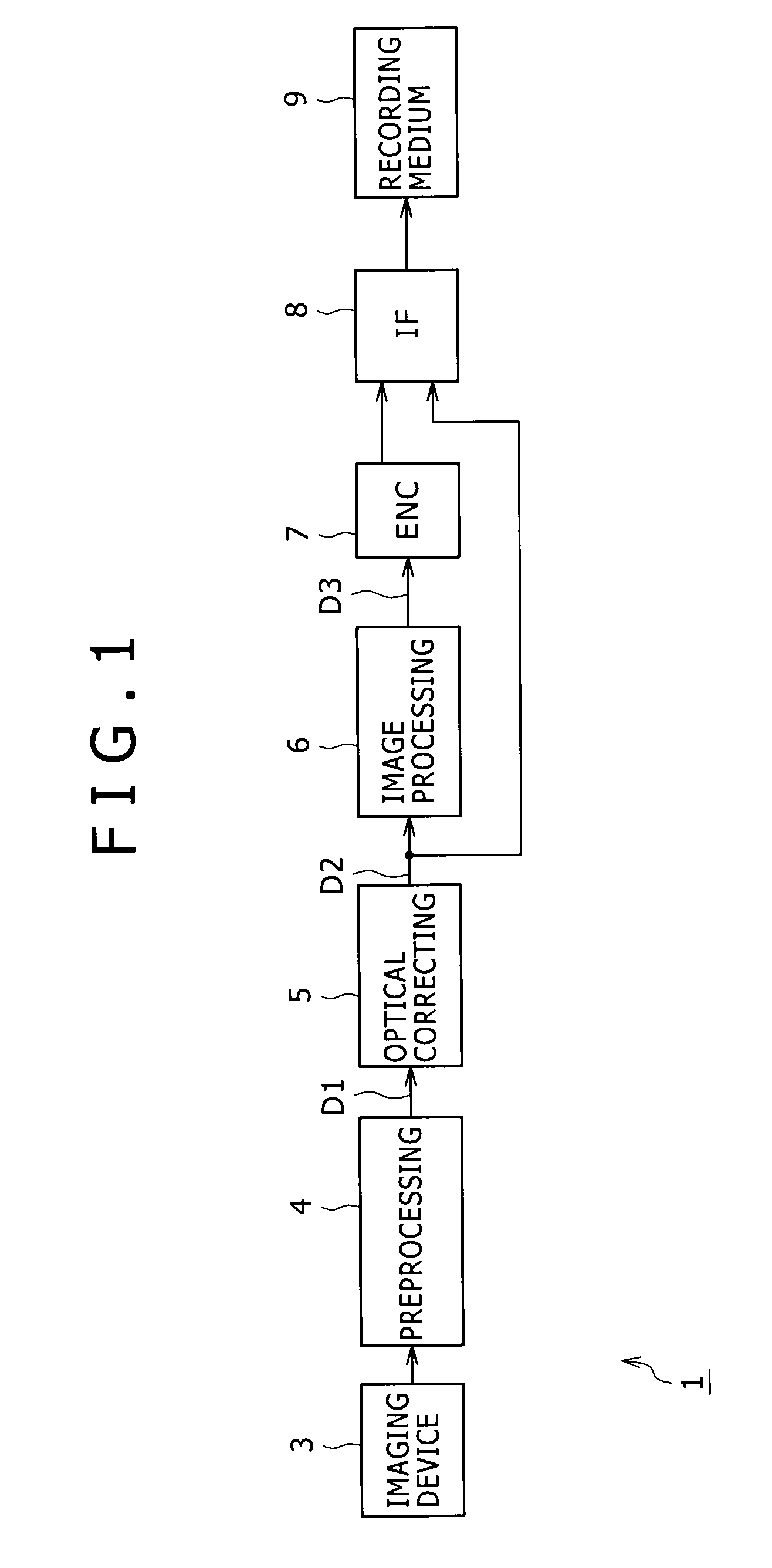
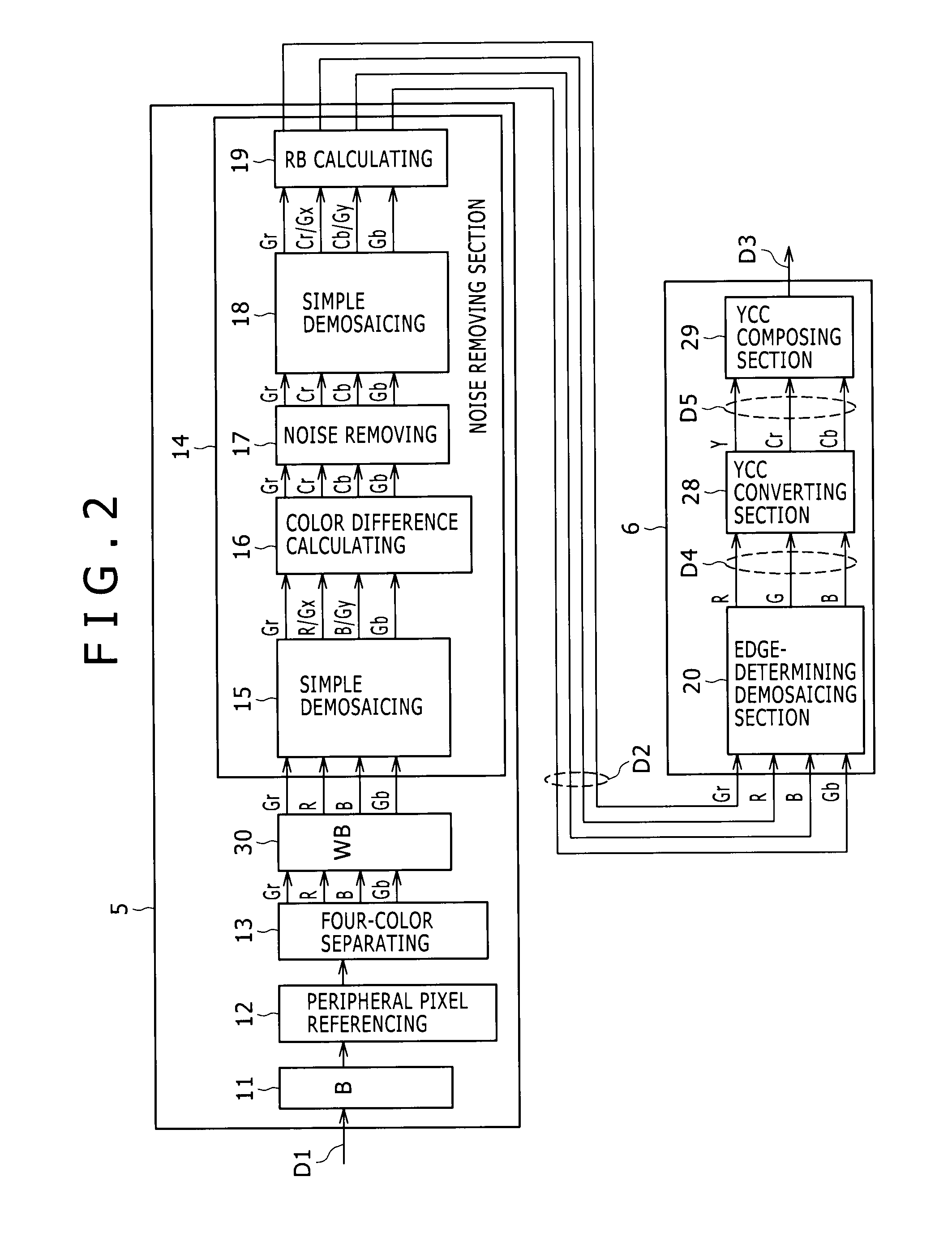
Imaging device, image processing device, image processing method, program for image processing method, and recording medium having program for image processing method recorded thereon
ActiveUS20090052797A1Color noise can be suppressedLuminescence signal can be reducedTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging processingNoise removal
A method and apparatus to remove color noise included in raw data while effectively preventing image quality degradation. For Interest pixels serially set onto a mosaic image formed of raw data, conversion is executed into a pixel value for noise removal based on a processing reference pixel value having a unified color signal component in each interest pixel, noise is removed from the pixel value for noise removal, and the pixel value for noise removal with noise removed is converted into the source pixel value, whereby only color noise can be removed without affecting a luminance signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
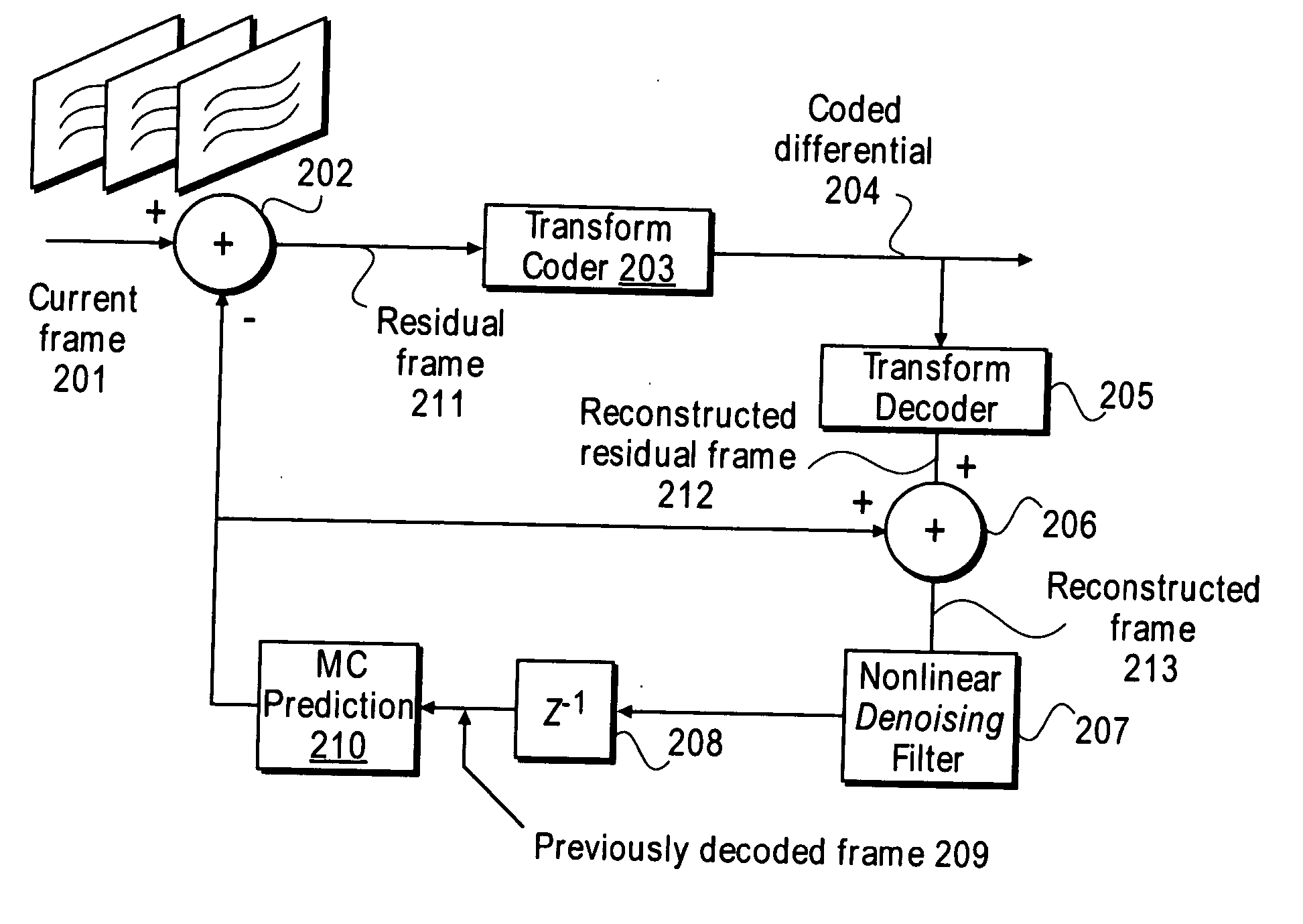
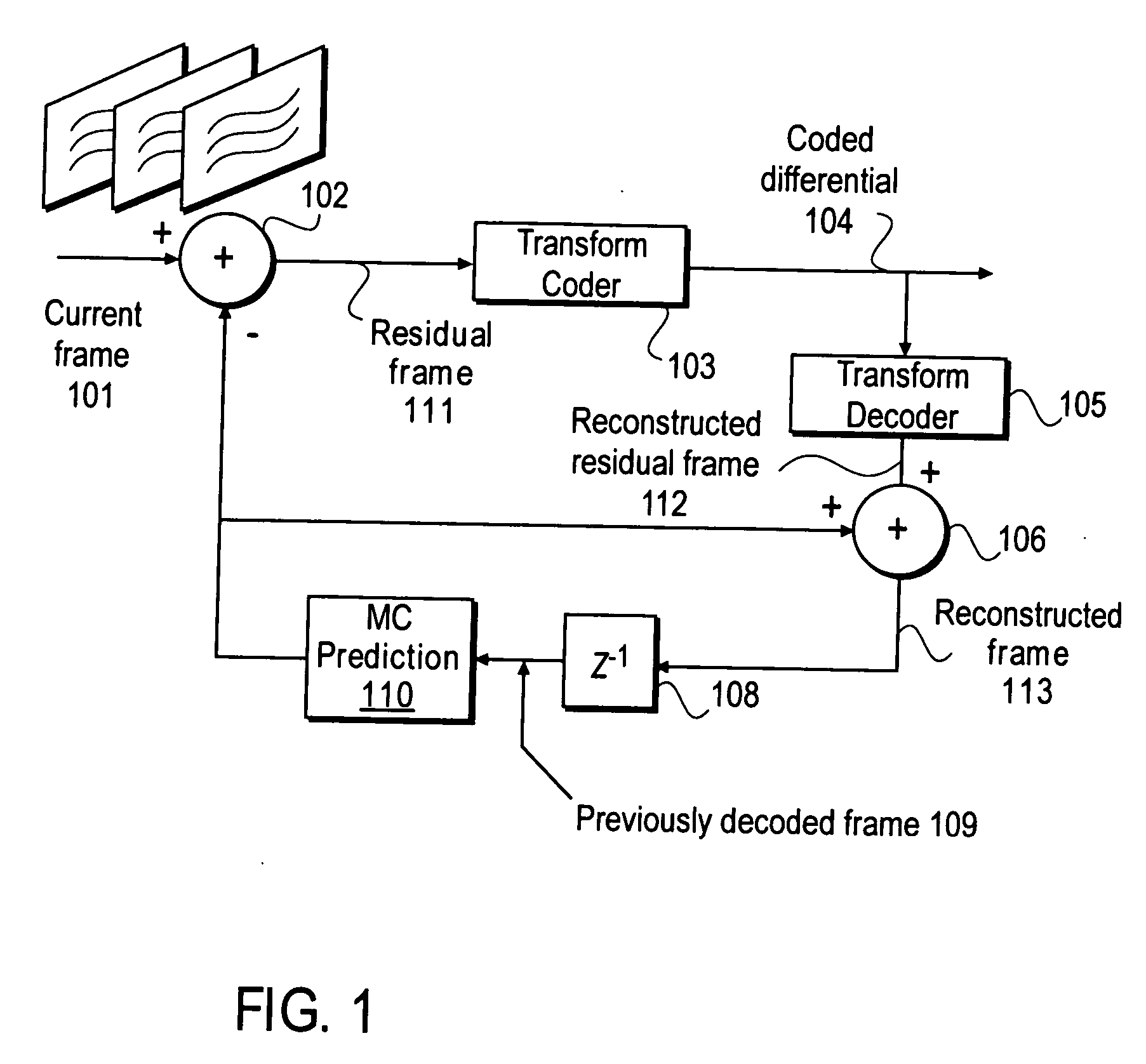
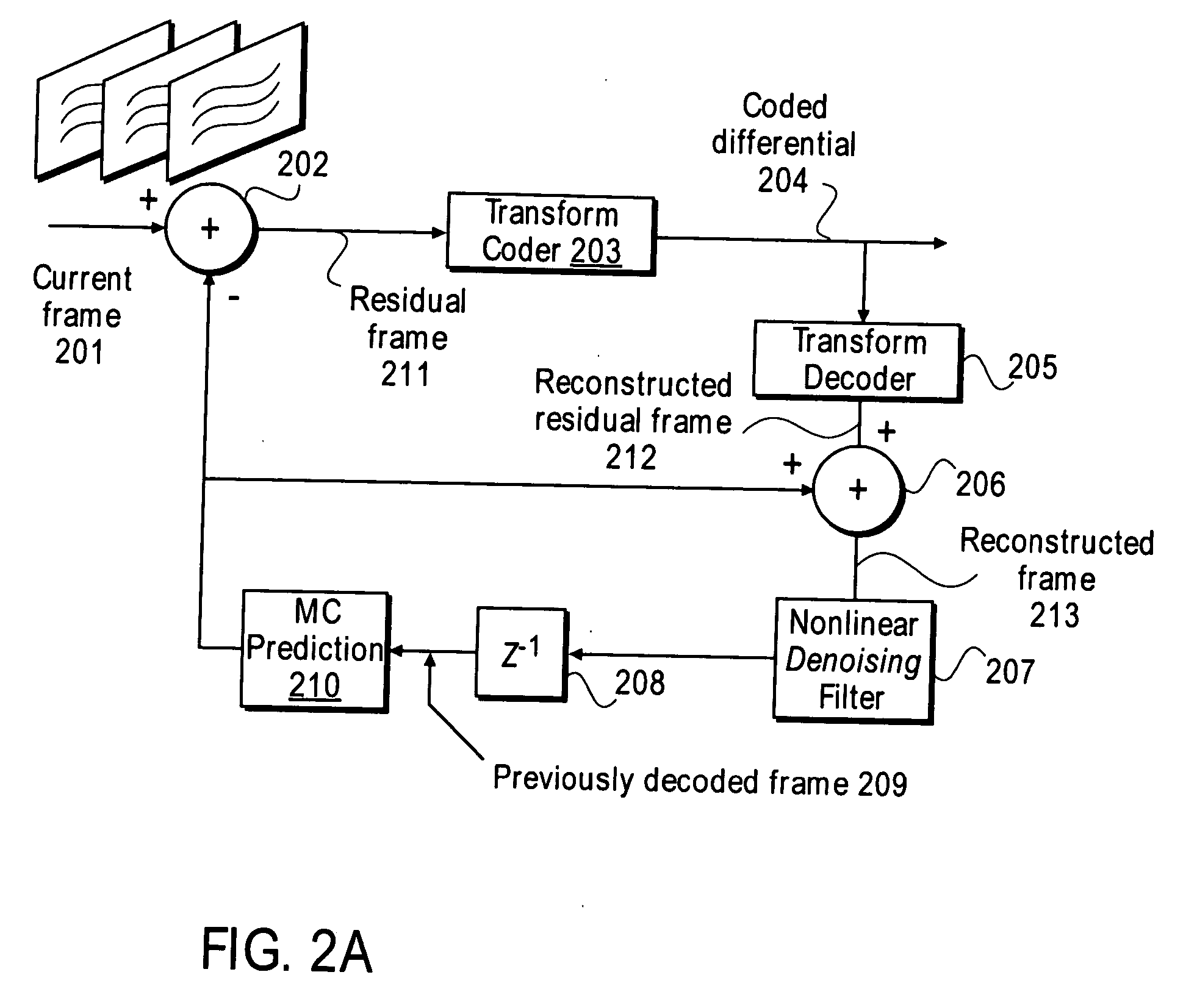
Nonlinear, in-the-loop, denoising filter for quantization noise removal for hybrid video compression
InactiveUS20060153301A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNoise removalComputer science
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for using an in-the-loop denoising filter for quantization noise removal for video compression. In one embodiment, the video encoder comprises a transform coder to apply a transform to a residual frame representing a difference between a current frame and a first prediction, the transform coder outputting a coded differential frame as an output of the video encoder; a transform decoder to generate a reconstructed residual frame in response to the coded differential frame; a first adder to create a reconstructed frame by adding the reconstructed residual frame to the first prediction; a non-linear denoising filter to filter the reconstructed frame by deriving expectations and performing denoising operations based on the expectations; and a prediction module to generate predictions, including the first prediction, based on previously decoded frames.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
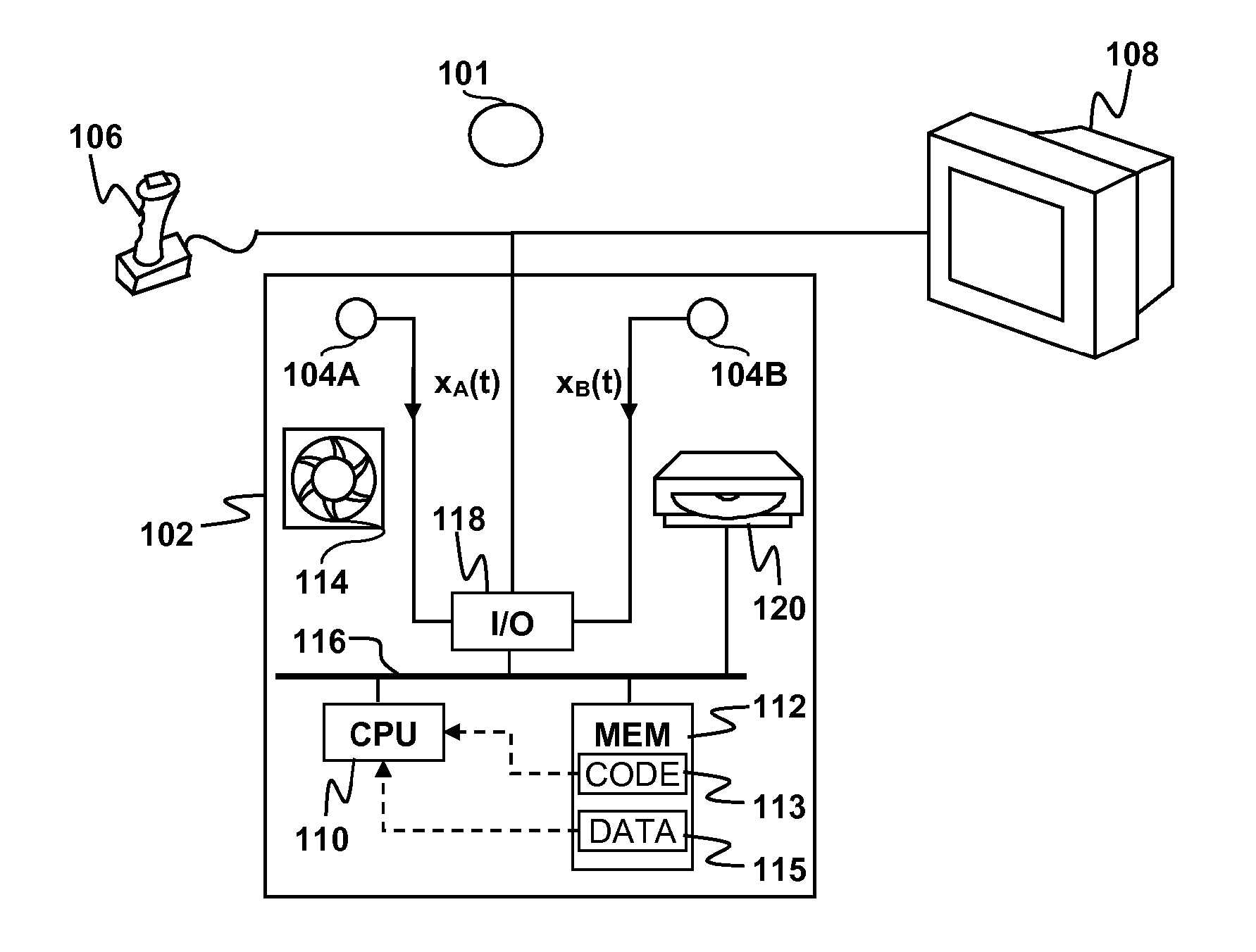
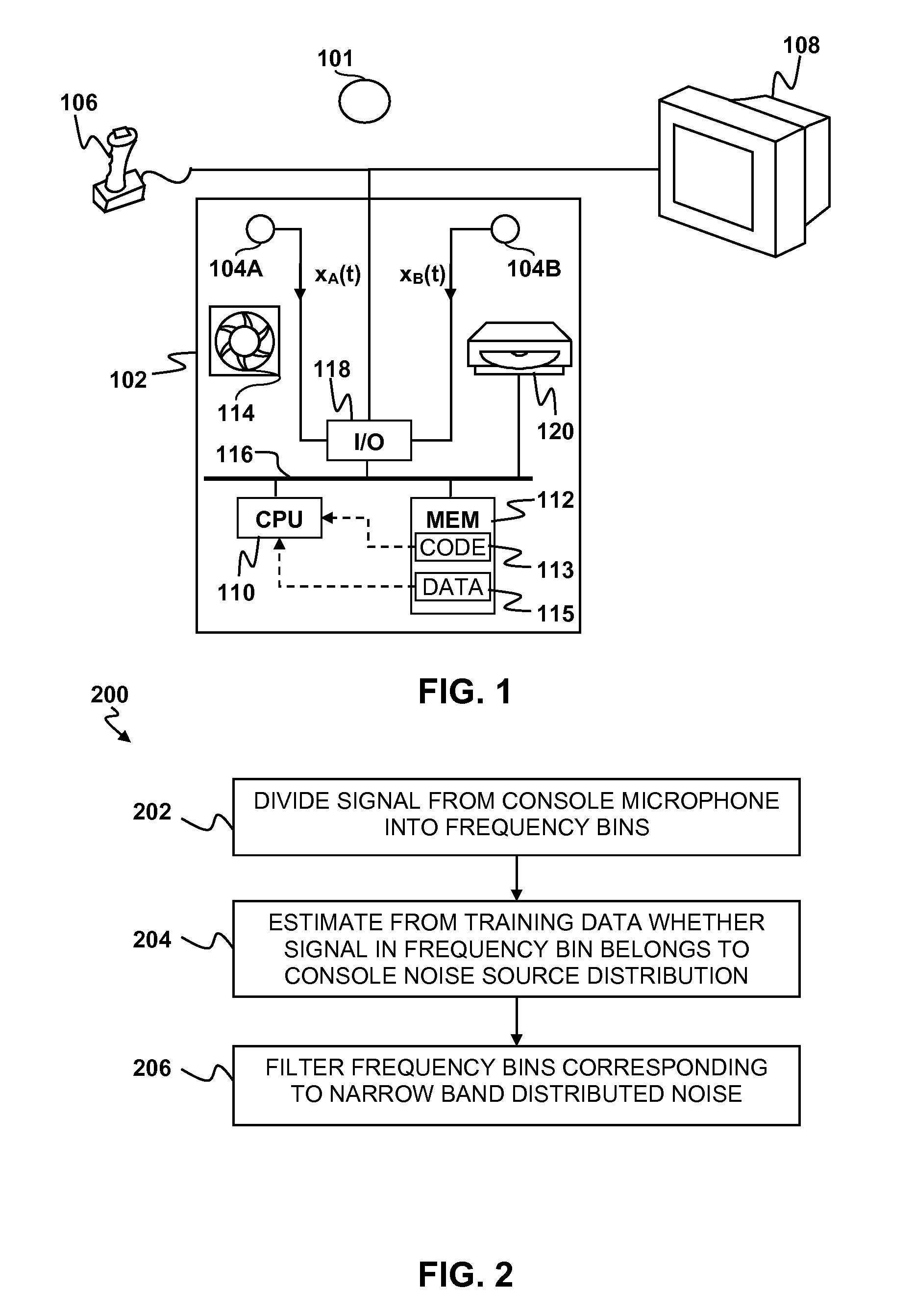
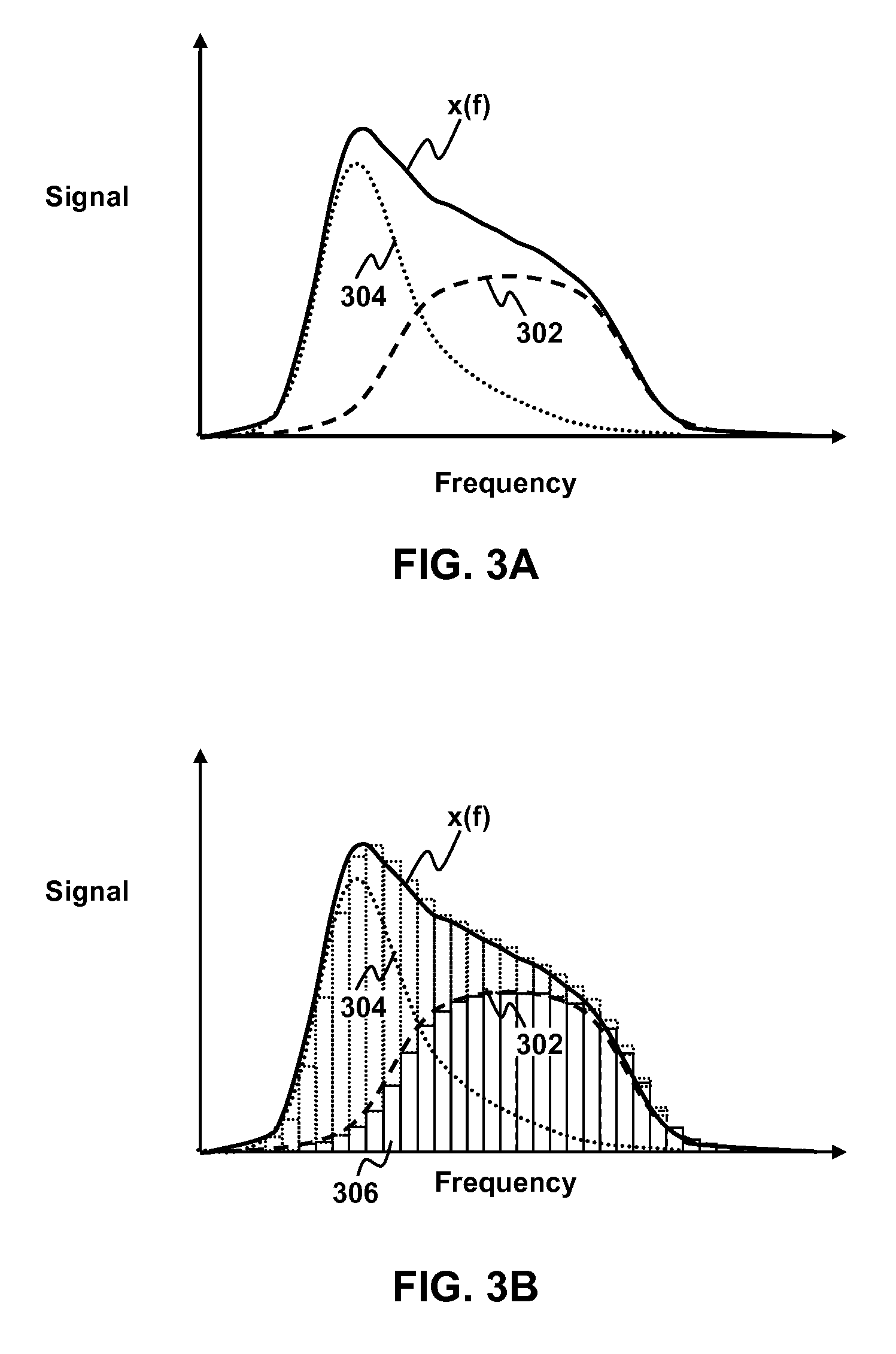
Noise removal for electronic device with far field microphone on console
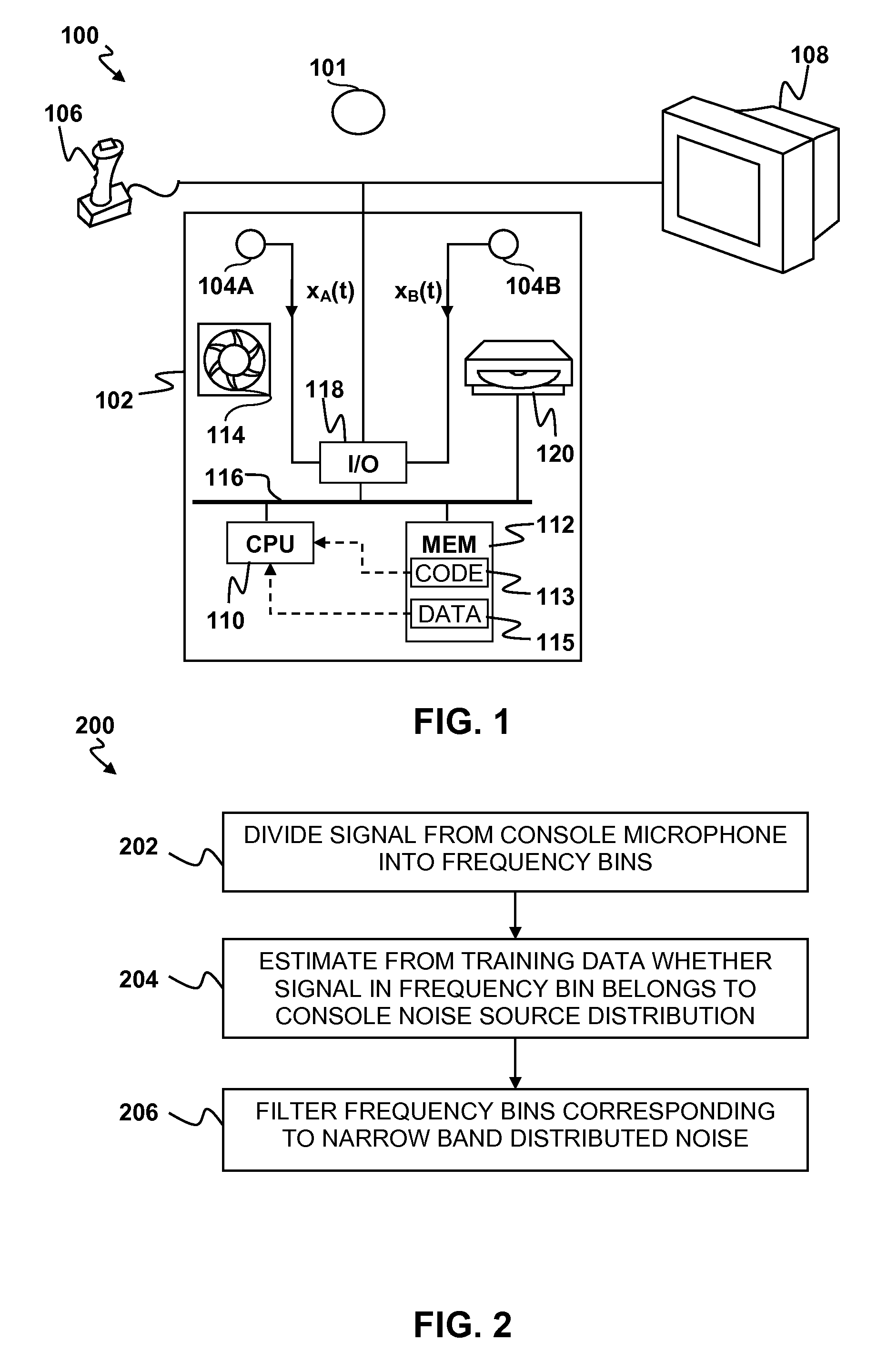
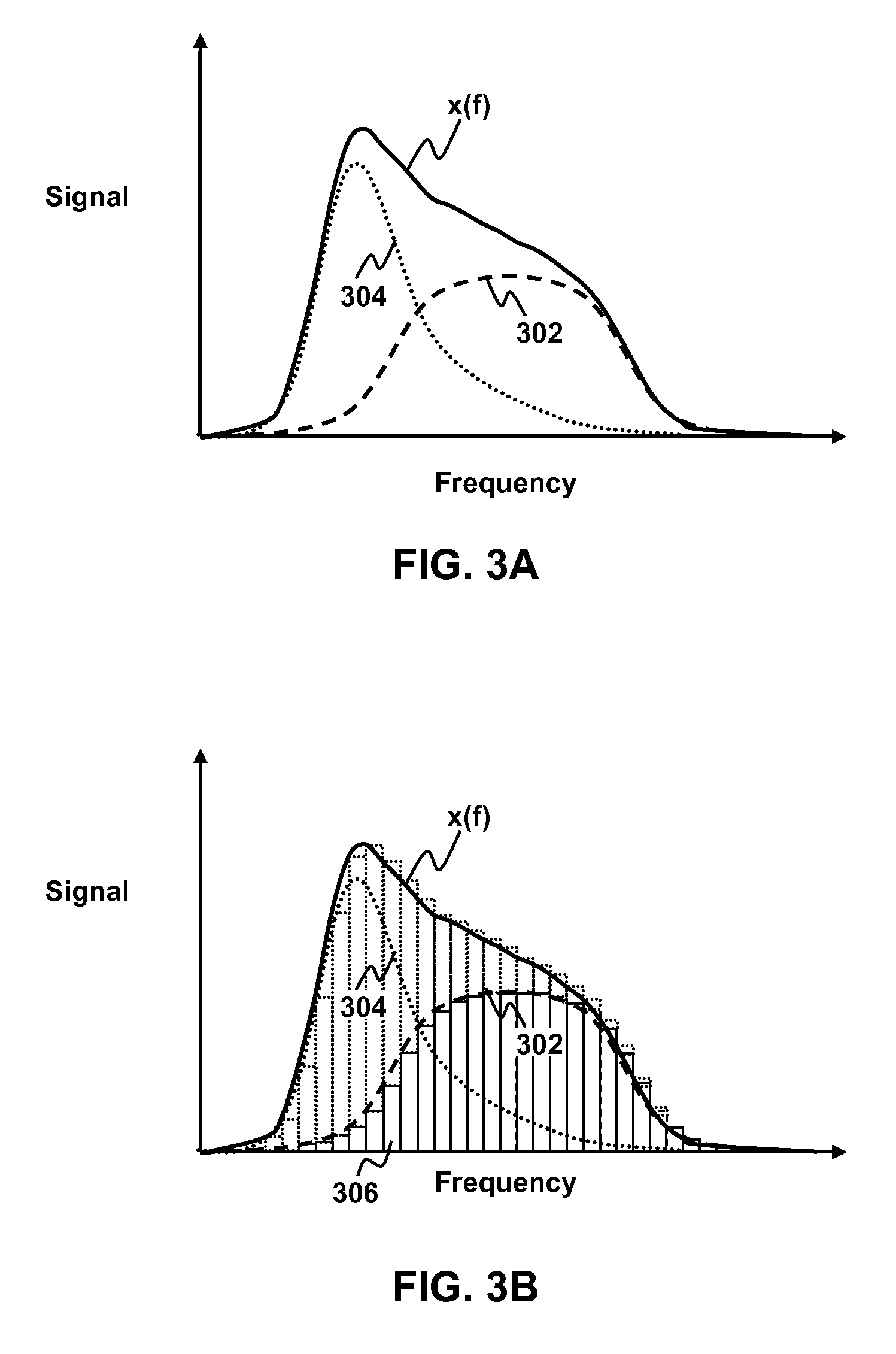
Reduction of noise in a device having a console with one or more microphones and a source of narrow band distributed noise located on the console is disclosed. A microphone signal containing a broad band distributed desired sound and narrow band distributed noise is divided amongst a plurality of frequency bins. For each frequency bin, it is determined whether a portion of the signal within the frequency bin belongs to a narrow band distribution characteristic of the source of narrow band noise located on the console. Any frequency bins containing portions of the signal belonging to the narrow band distribution are filtered to reduce the narrow band noise.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Noise suppression apparatus and recording medium recording processing program for performing noise removal from voice
InactiveUS6044341AIncreasing auditory sound qualityImprove sound qualitySpeech recognitionTransmission noise suppressionDiscriminatorFrequency spectrum
A noise suppression apparatus of the present invention includes a voice / non-voice discriminator for discriminating a frame signal divided into frames having a predetermined length; a Fourier transform unit for converting a frame signal into a spectrum; a noise spectrum estimation unit for estimating a noise spectrum of a frame judged as a non-voice signal; an amplitude spectrum subtractor for subtracting the product of an estimated noise spectrum and a predetermined coefficient from a spectrum obtained by the transform unit; an auditory correction noise adder for adding aa auditory correction noise spectrum to a spectrum outputted from the subtractor; and an inverse Fourier transform unit for performing inverse Fourier transform to an output of the adder. The noise suppression apparatus further includes a negative amplitude value counter for counting the number of frequency components in an output of the subtractor whose amplitude values are negative; a subtraction coefficient setting unit for gradually decreasing a subtraction coefficient unit the counted value becomes not more than a predetermined value; an inverse Fourier transform unit for performing inverse Fourier transform to an output of the counter; and a noise spectrum estimation unit for calculating spectrum information of noise in the frame signal using different spectrum information according to the current type of frame signal.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method and system for removing noise by using change in activity pattern
ActiveUS7620450B2Fast noiseSure easyElectrocardiographyElectromyographyNoise generationNoise removal
A noise removal method and system using a change in activity pattern, in which it is recognized that noise components exist in different frequency bands and different filters for removing noise are stored according to each activity pattern, thereby optimally removing the noise components. A method of removing noise by using a change in an activity pattern includes: recognizing an activity pattern of the subject using an activity sensor; sensing a first bio signal corresponding to the activity pattern from the subject using an electric potential sensor; recognizing a noise generation pattern according to the activity pattern by analyzing a noise component for each section of the first bio signal; selecting filter information for each section according to the noise generation pattern; storing the filter information selected for each section in association with the activity pattern; and removing noise from a second bio signal sensed from the subject by applying the stored filter information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Signature noise removal
ActiveUS20070078649A1Improve processing qualityImprove reception qualitySpeech recognitionNoise removalSpeech sound
A speech enhancement system improves the perceptual quality of a processed voice signal. The system improves the perceptual quality of a voice signal by removing unwanted noise components from a voice signal. The system removes undesirable signals that may result in the loss of information. The system receives and analyzes signals to determine whether an undesired random or persistent signal corresponds to one or more modeled noises. When one or more noise components are detected, the noise components are substantially removed or dampened from the signal to provide a less noisy voice signal.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
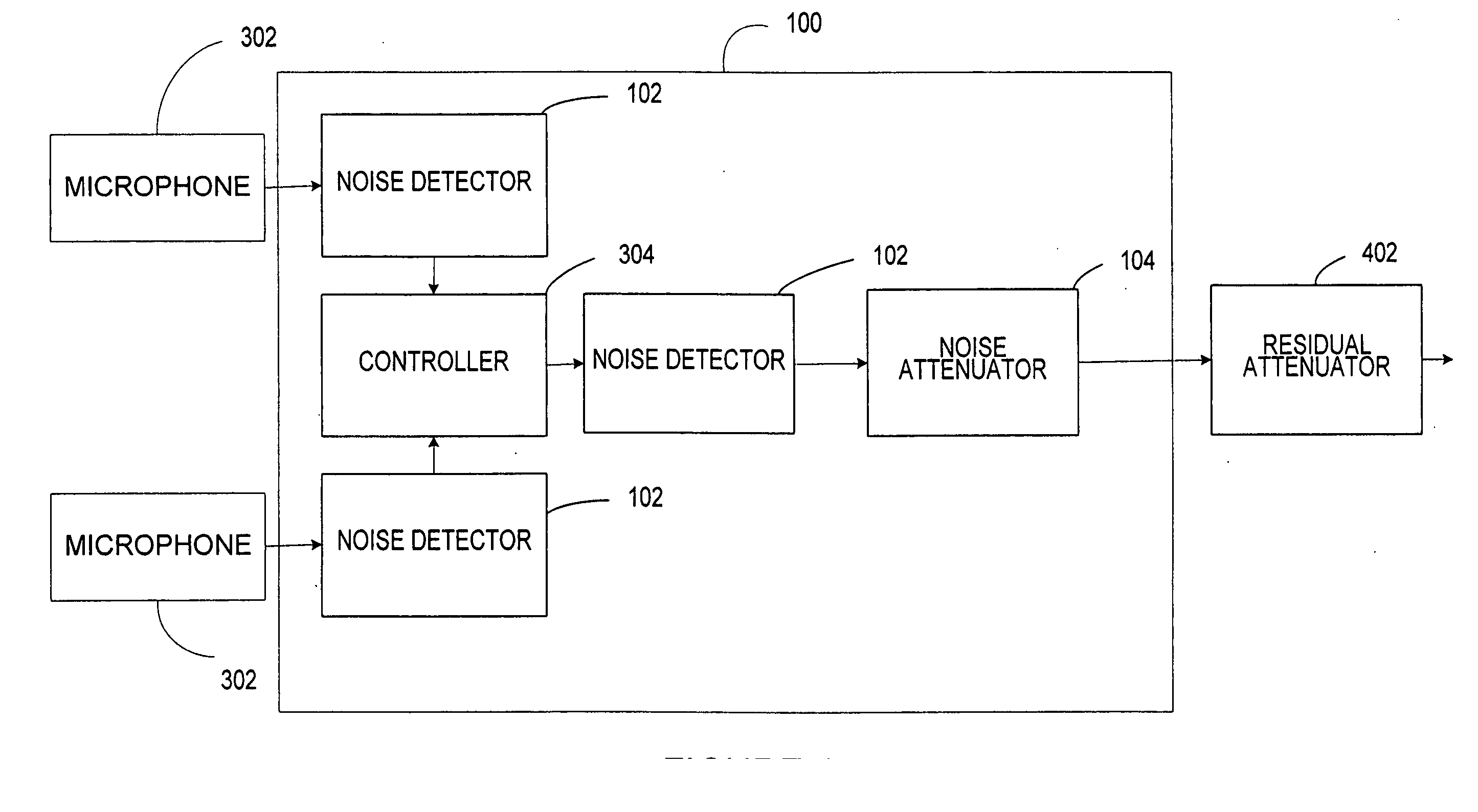
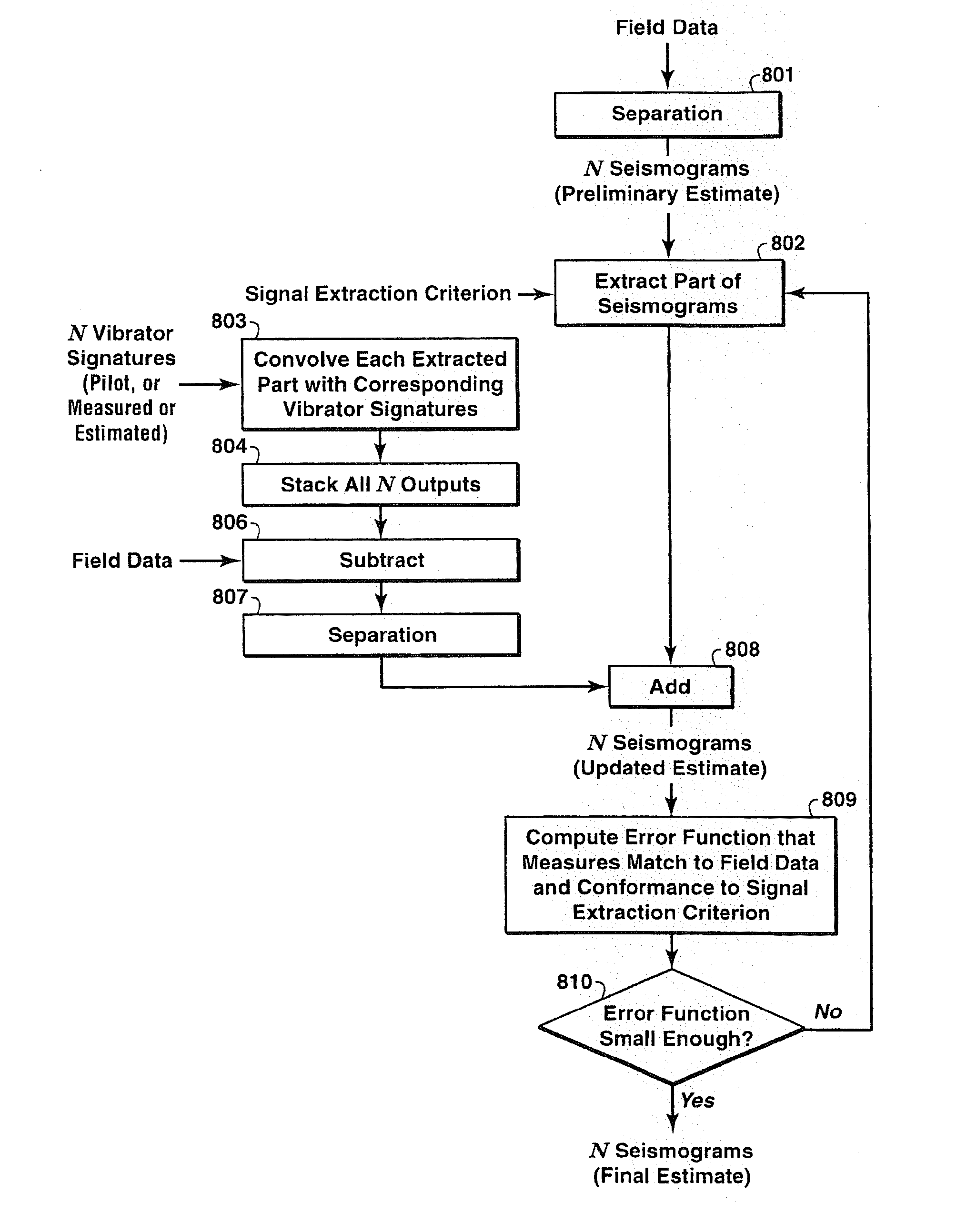
Separation and Noise Removal for Multiple Vibratory Source Seismic Data
The invention discloses a way to recover separated seismograms with reduced interference noise by processing vibroseis data recorded (or computer simulated) with multiple vibrators shaking simultaneously or nearly simultaneously (200). A preliminary estimate of the separated seismograms is used to obtain improved seismograms (201). The preliminary estimate is convolved with the vibrator signature and then used to update the seismogram. Primary criteria for performing the update include fitting the field data and satisfying typical criteria of noise-free seismograms (202). Alternative ways to update are disclosed, including signal extraction, modeled noise extraction, constrained optimization based separation, and penalized least-squares based separation. The method is particularly suited for removing noise caused by separating the combined record into separate records for each vibrator, and is advantageous where the number of sweeps is fewer than the number of vibrators (200).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
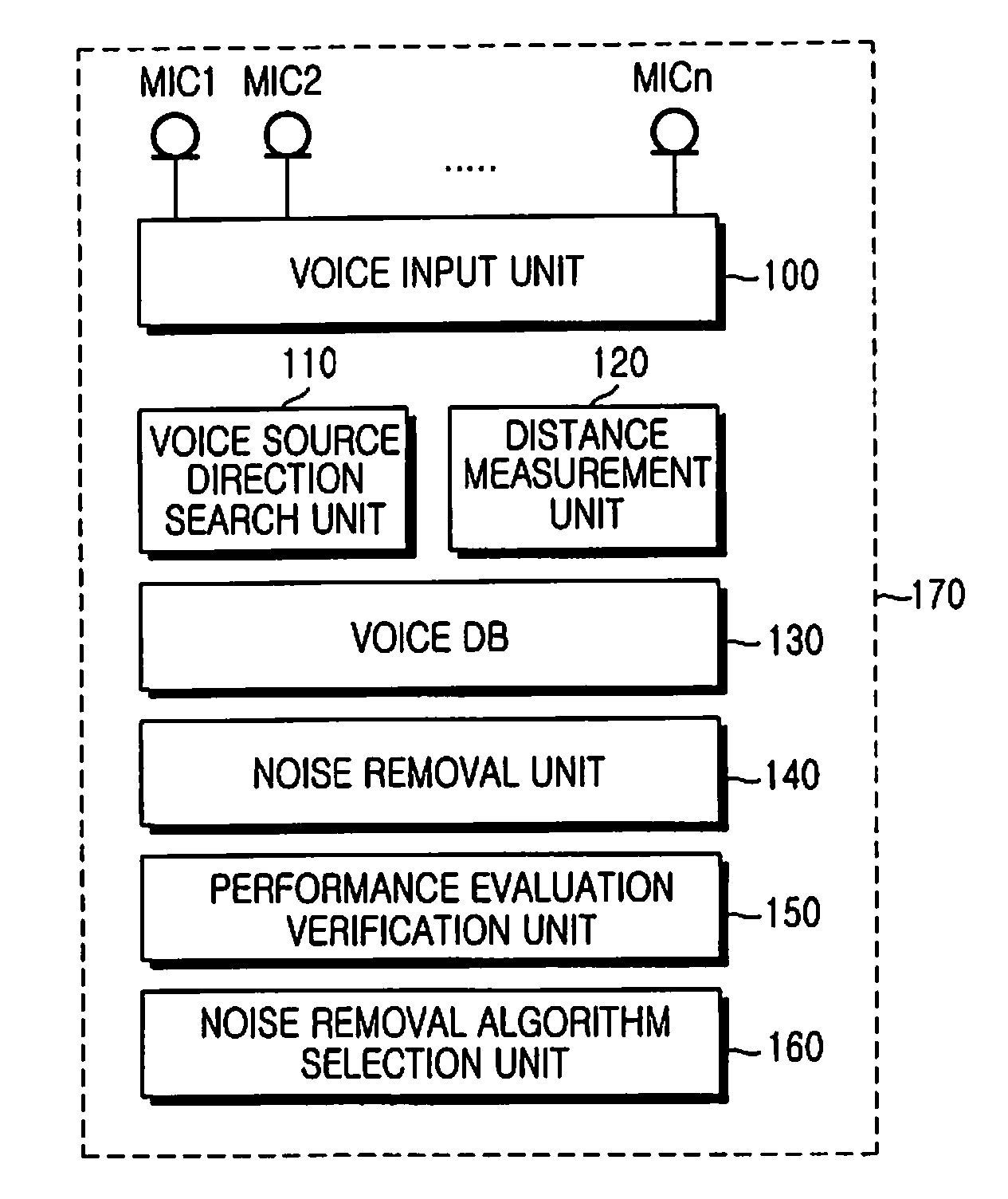
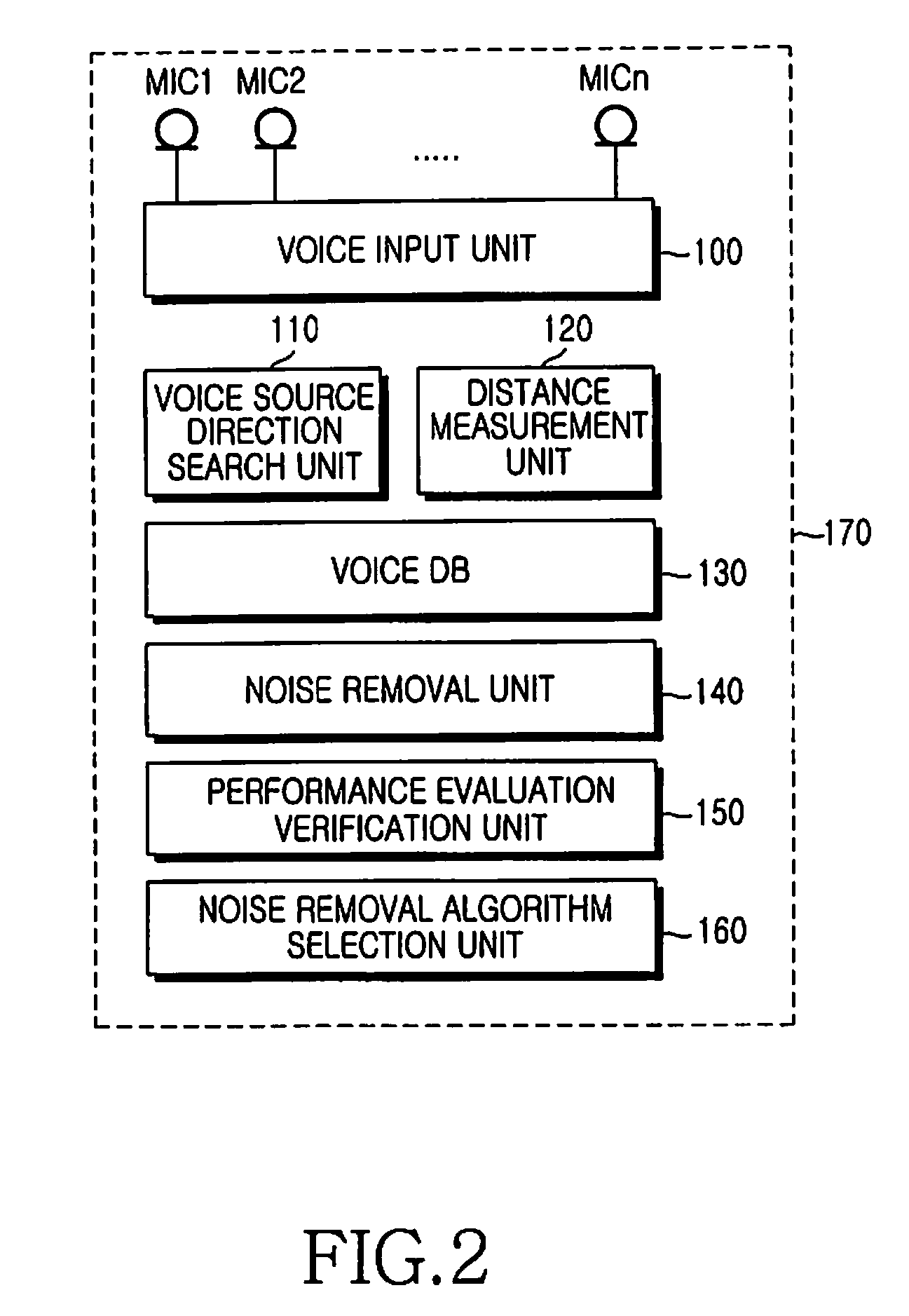
Voice performance evaluation system and method for long-distance voice recognition
A system and a method are provided for evaluating a voice performance in order to recognize a long-distance voice. The system implements a voice performance evaluation function for long-distance voice input in a robot. Particularly, in robots including a network robot, it is required to normally perform voice recognition so that a speaking subject and a surrounding situation can be recognized by a robot. Accordingly, in order to obtain the most optimal voice quality, it is important to find a noise removal algorithm through an optimal hardware configuration and an optimal combination of the optimal hardware configuration and software. Therefore, a method for finding a noise removal algorithm appropriate for each of cases, including one case where a distance from a speaking subject is fixed and another case where a distance from a speaking subject changes. As a result, the most optimal voice quality can be obtained regardless of a noise environment even when the speaking subject is a long distance away from the robot.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Signal processing method and system for noise removal and signal extraction
A signal processing method and system combining smooth level wavelet pre-processing together with artificial neural networks all in the wavelet domain for signal denoising and extraction. Upon receiving a signal corrupted with noise, an n-level decomposition of the signal is performed using a discrete wavelet transform to produce a smooth component and a rough component for each decomposition level. The nth level smooth component is then inputted into a corresponding neural network pre-trained to filter out noise in that component by pattern recognition in the wavelet domain. Additional rough components, beginning at the highest level, may also be retained and inputted into corresponding neural networks pre-trained to filter out noise in those components also by pattern recognition in the wavelet domain. In any case, an inverse discrete wavelet transform is performed on the combined output from all the neural networks to recover a clean signal back in the time domain.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
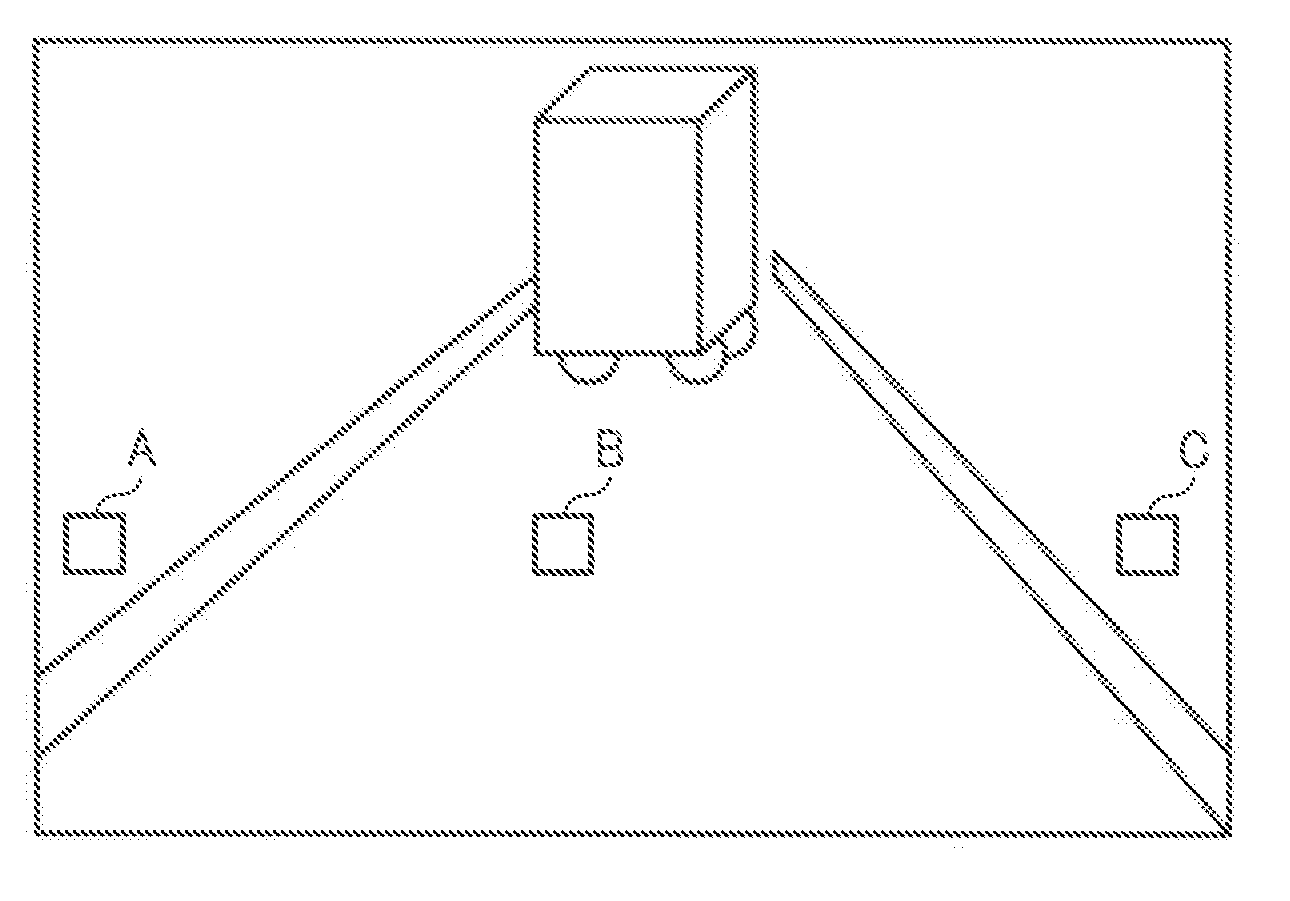
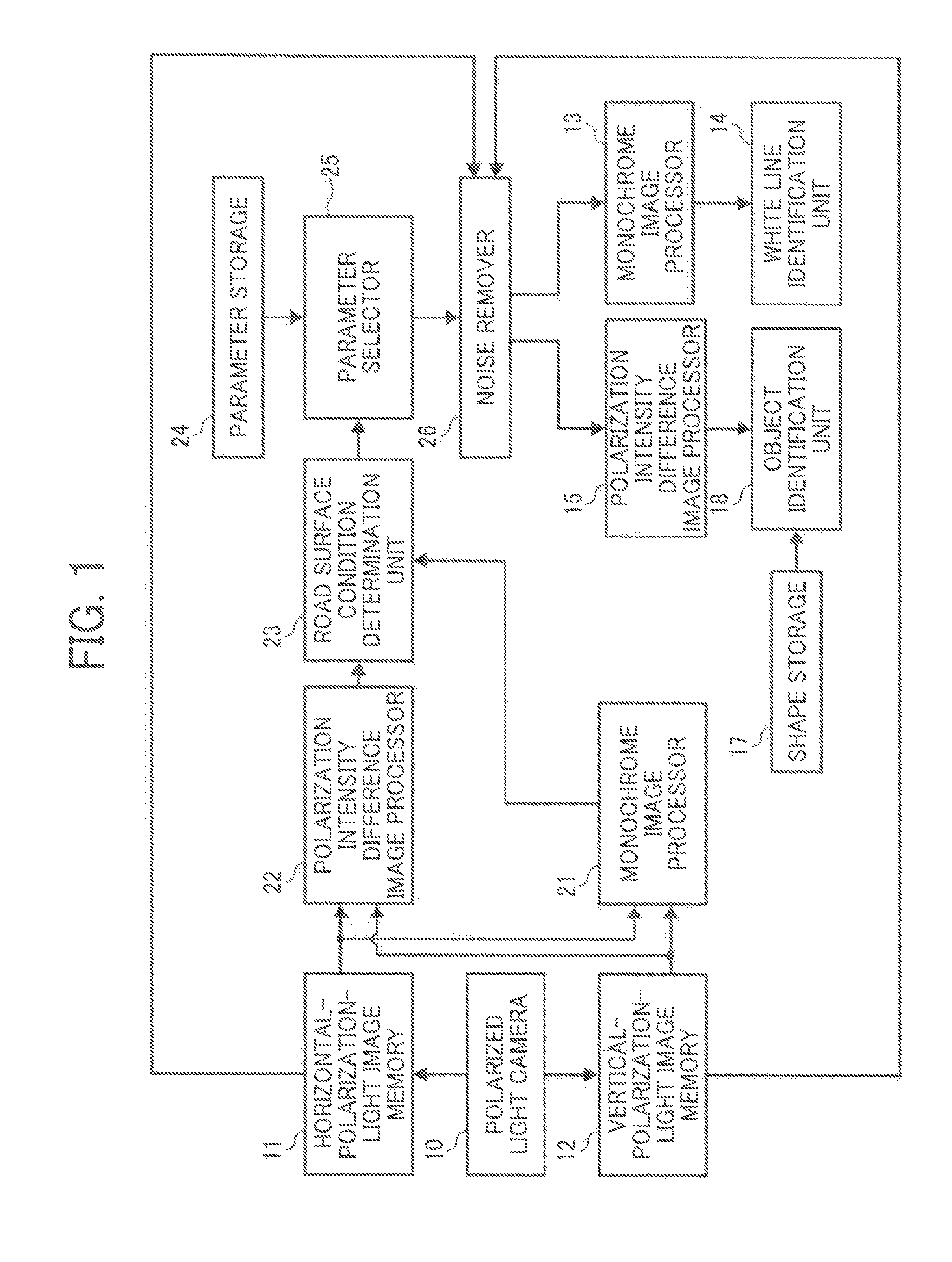
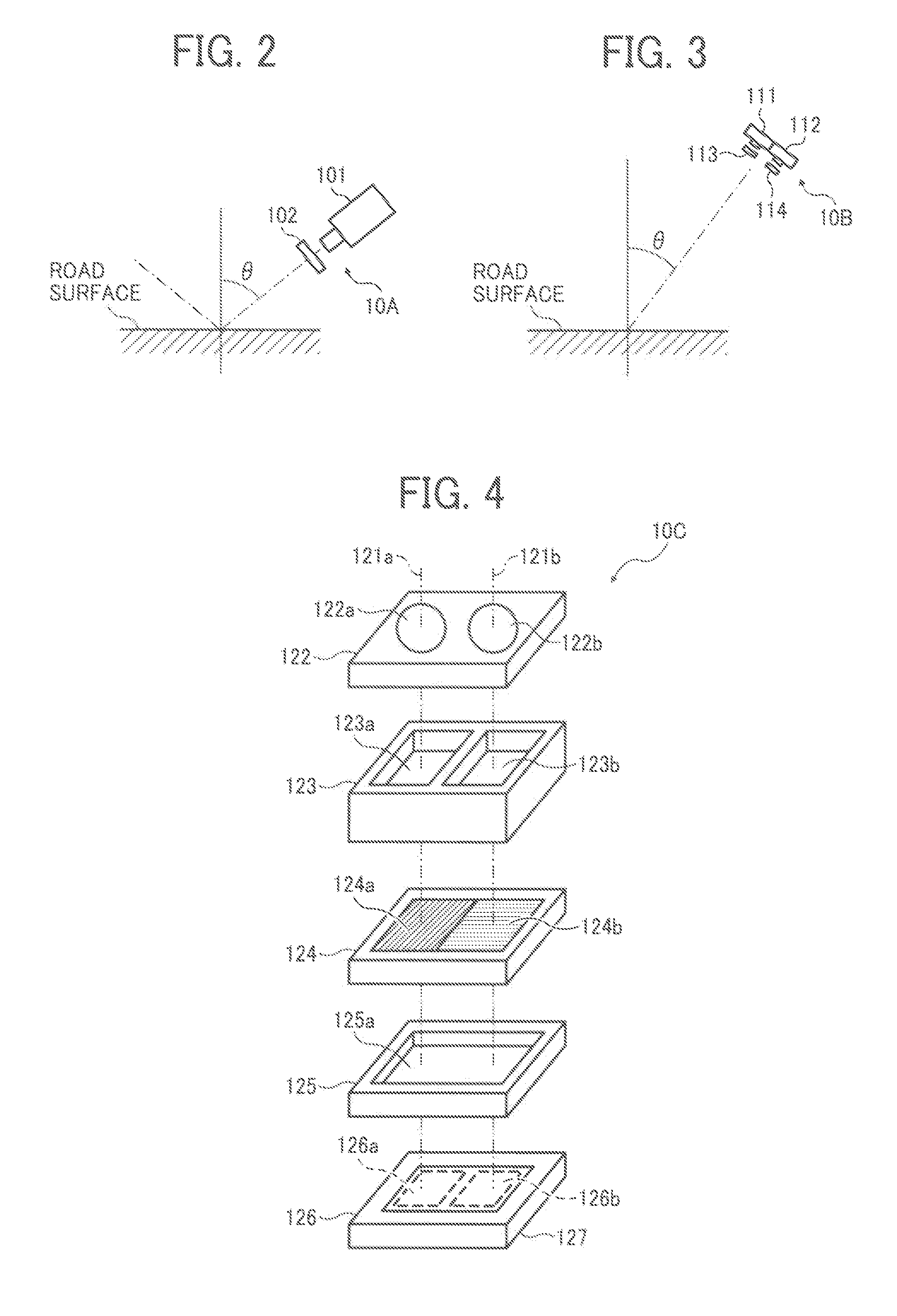
Object identification device, moving object controlling apparatus having object identification device, information presenting apparatus having object identification device, and spectroscopic image capturing apparatus
An object identification device includes an image capturing device to capture images polarized in different directions. A noise removal unit removes noise in the polarized images using a noise removing parameter. An index value computing unit computes an object identification index value for identification-processing areas in the polarized images using data of noise-removed polarized images. An object identification processing unit conducts object identification by determining identification processing areas corresponding to an identification target object based on the object identification index value. An environment information obtaining unit obtains environment information. An environmental condition determination unit determines an environmental condition based on the environment information. A parameter storage unit stores noise removing parameters prepared for mutually exclusive environmental conditions. The noise removal unit reads a noise removing parameter from the parameter storage unit to conduct noise removal. A method of identifying an object and a spectroscopic image capturing apparatus are also provided.
Owner:RICOH KK
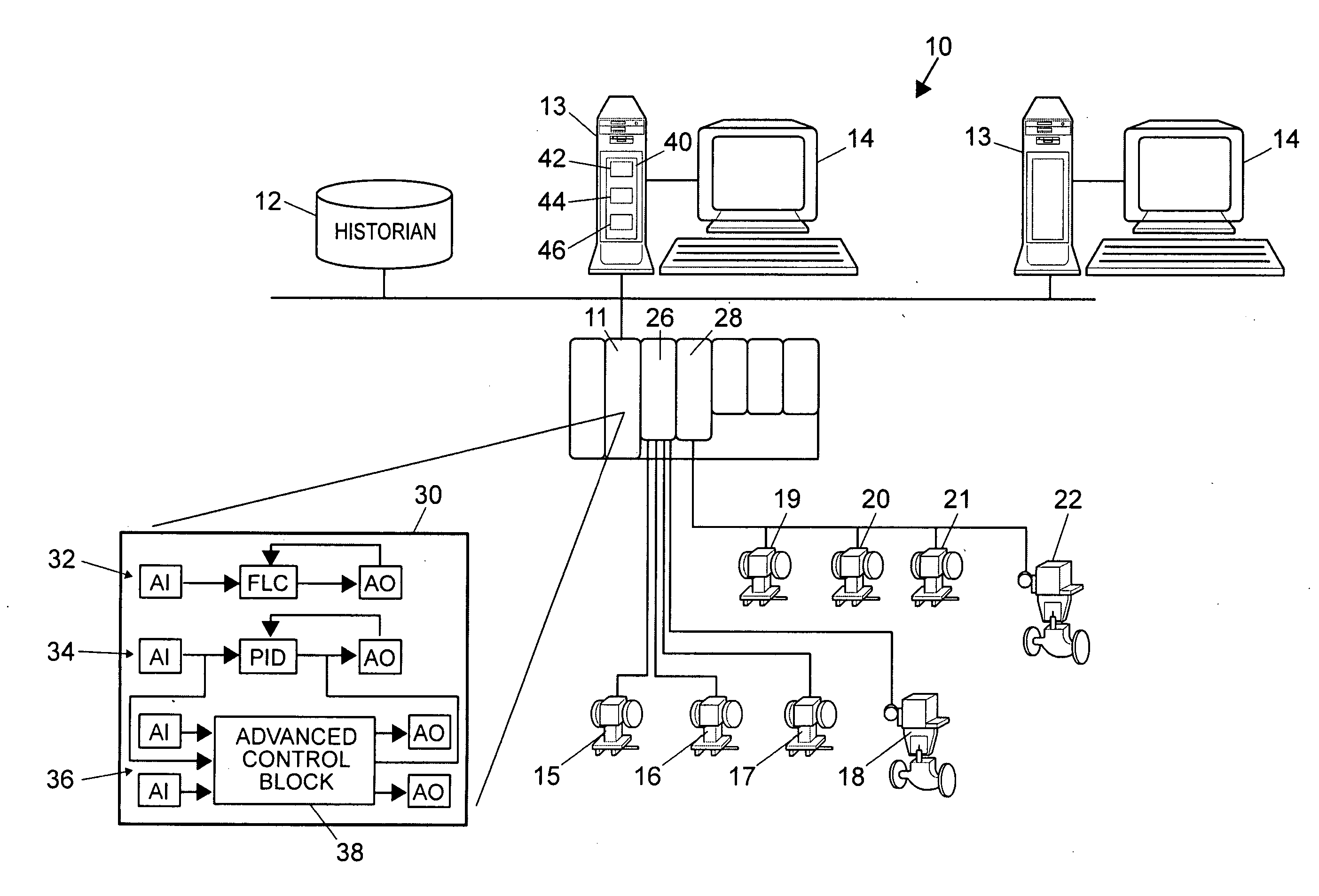
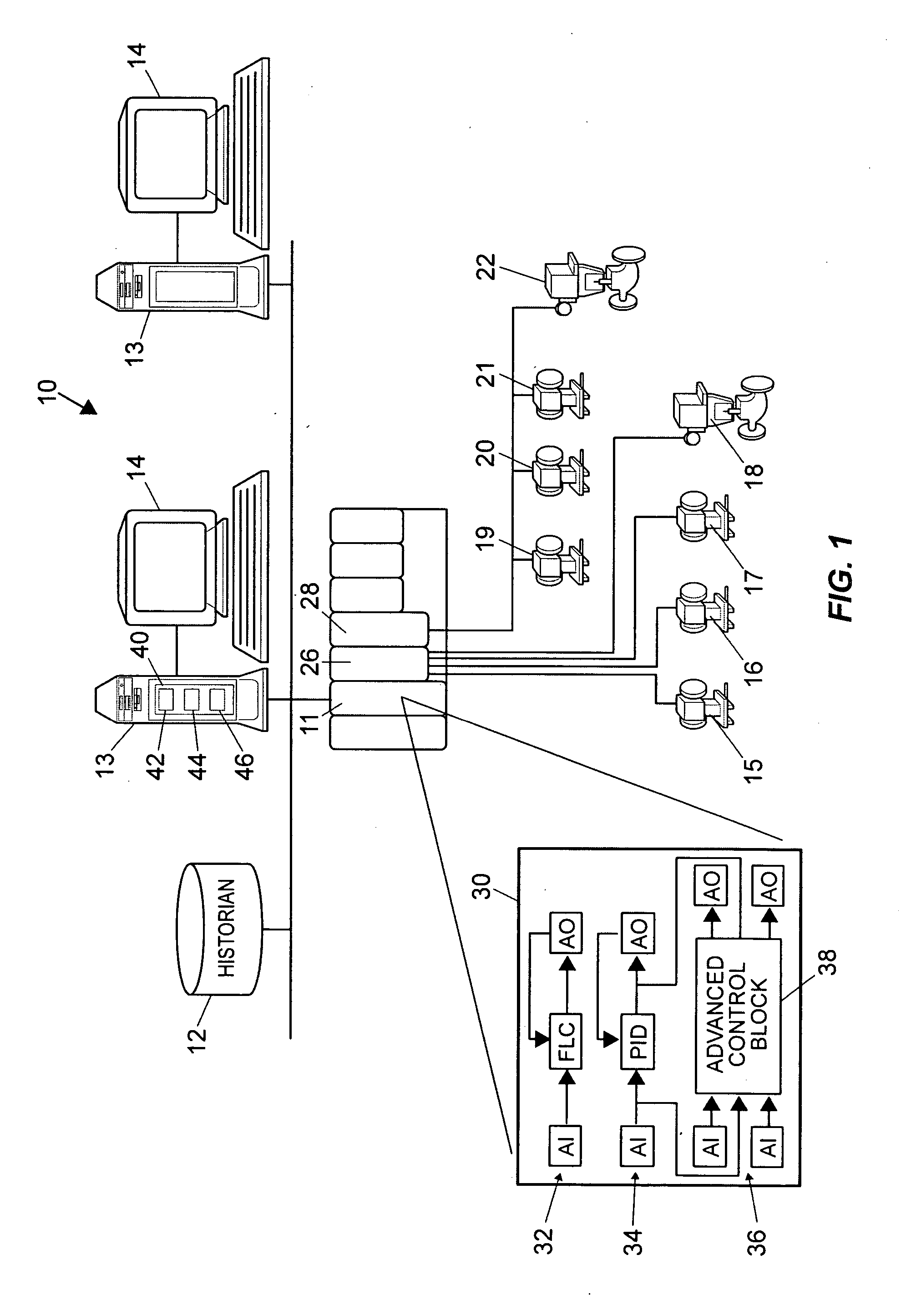
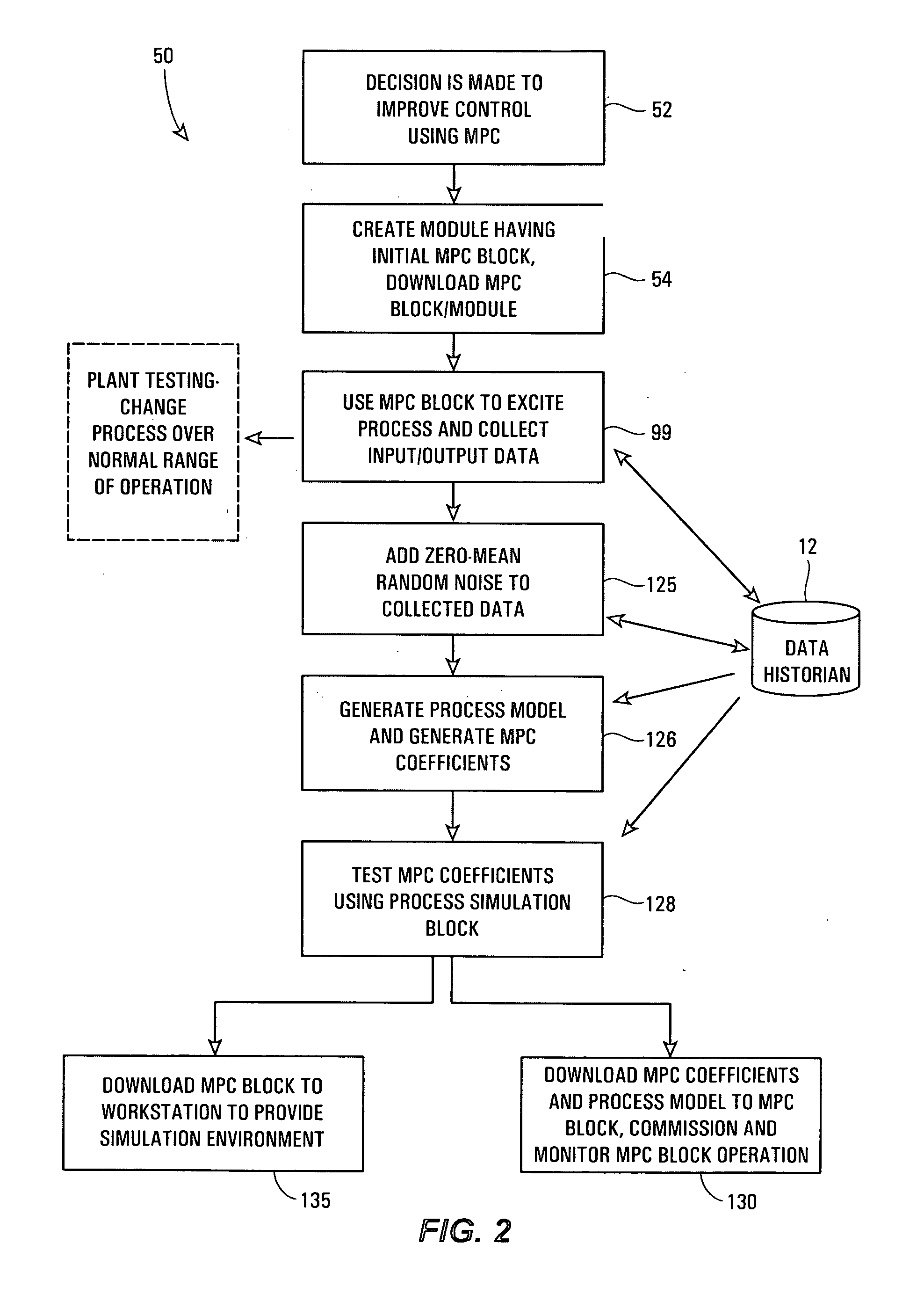
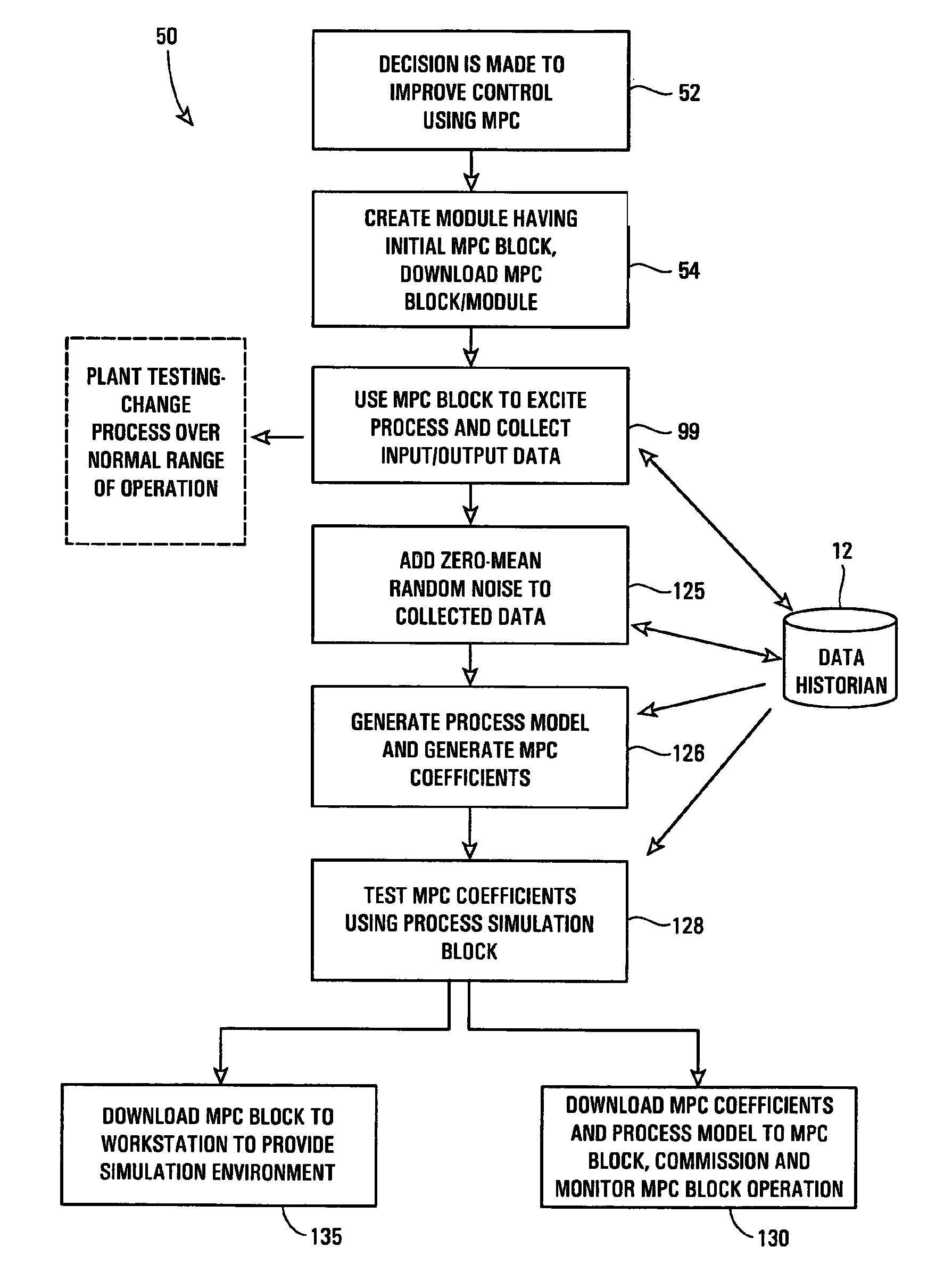
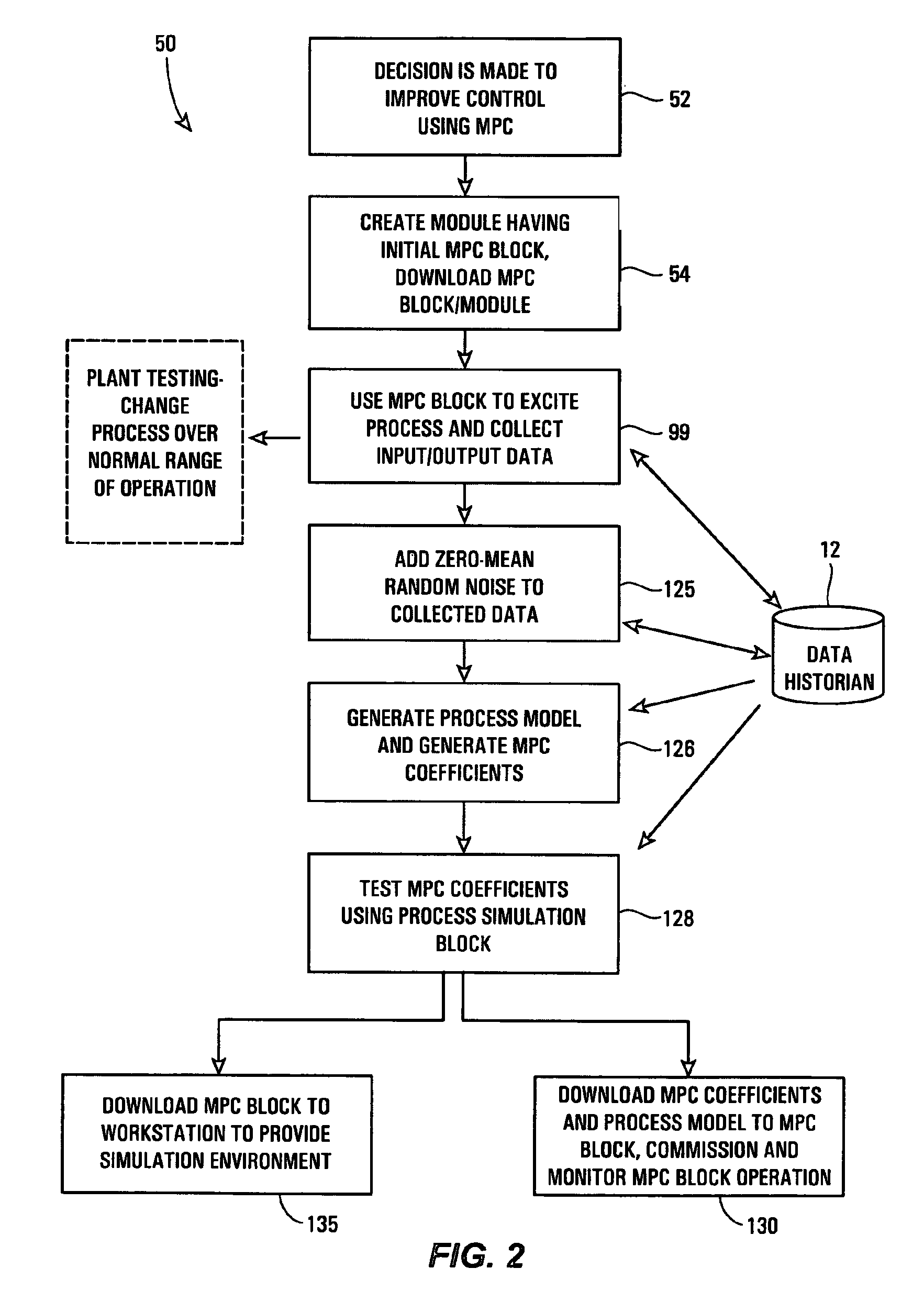
Robust process model identification in model based control techniques
ActiveUS20070244575A1Robust methodAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSimulator controlGeneration processTest input
A robust method of creating process models for use in controller generation, such as in MPC controller generation, adds noise to the process data collected and used in the model generation process. In particular, a robust method of creating a parametric process model first collects process outputs based on known test input signals or sequences, adds random noise to the collected process data and then uses a standard or known technique to determine a process model from the collected process data. Unlike existing techniques for noise removal that focus on clean up of non-random noise prior to generating a process model, the addition of random, zero-mean noise to the process data enables, in many cases, the generation of an acceptable parametric process model in situations where no process model parameter convergence was otherwise obtained. Additionally, process models created using this technique generally have wider confidence intervals, therefore providing a model that works adequately in many process situations without needing to manually or graphically change the model.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
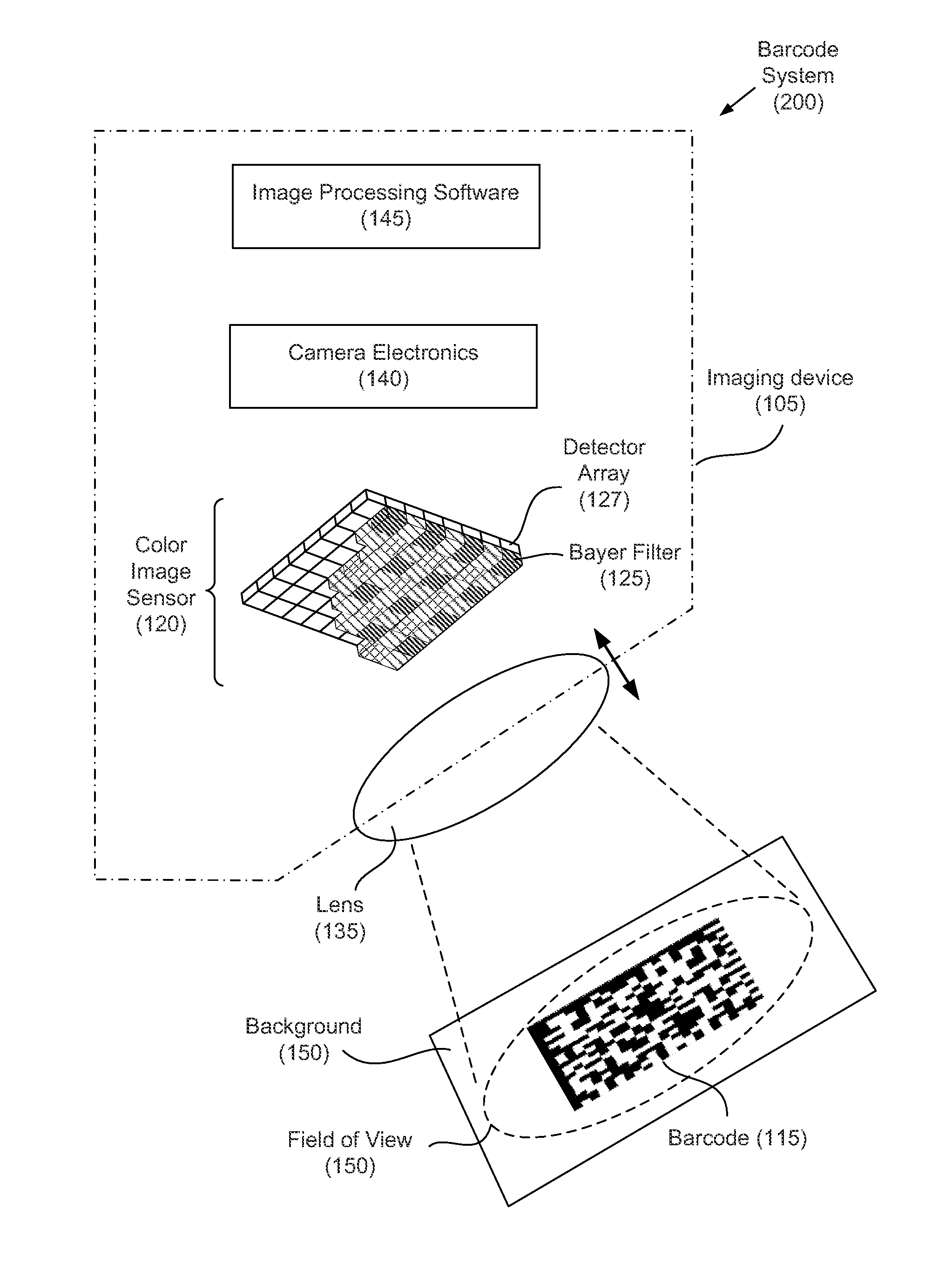
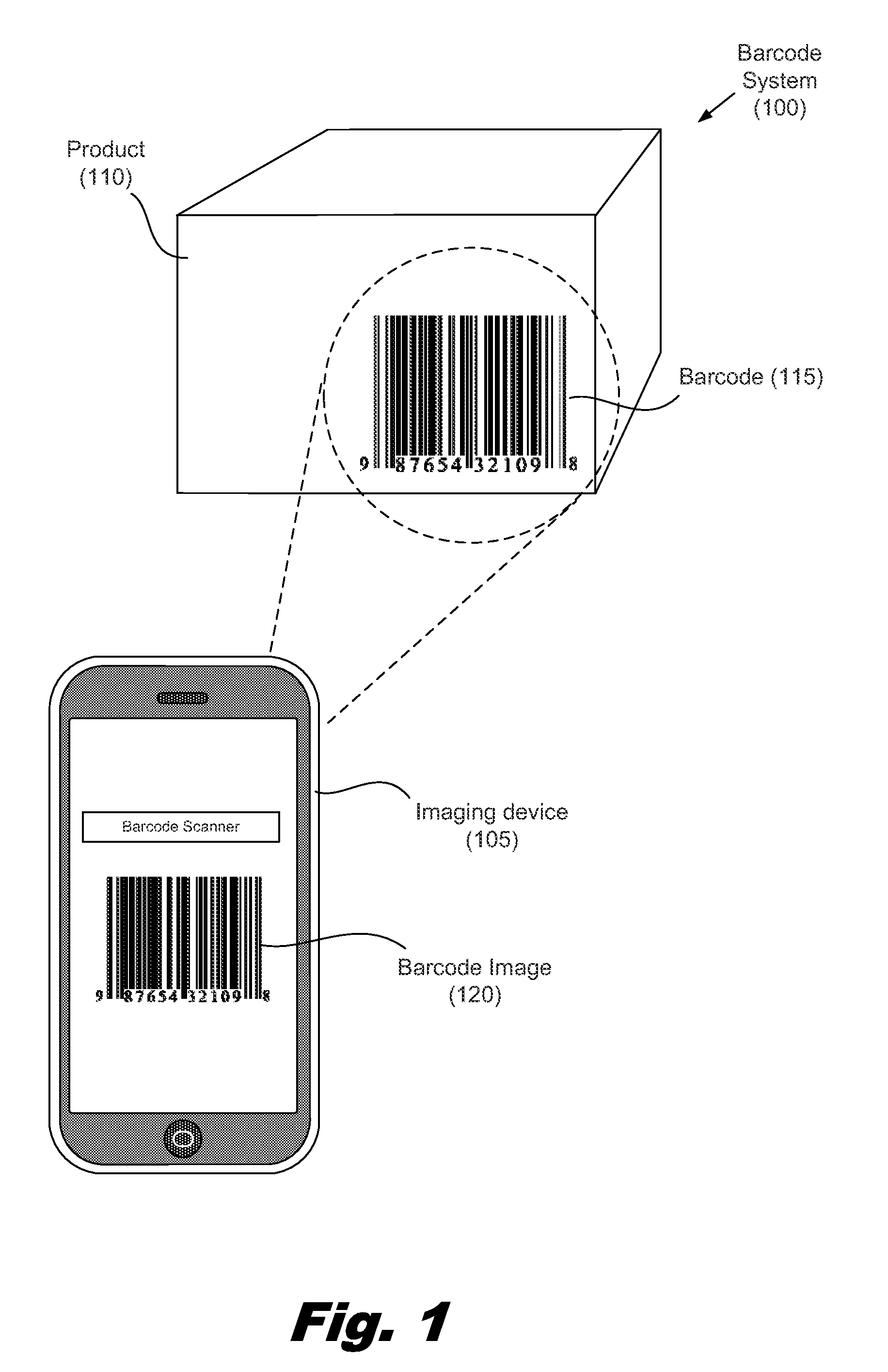
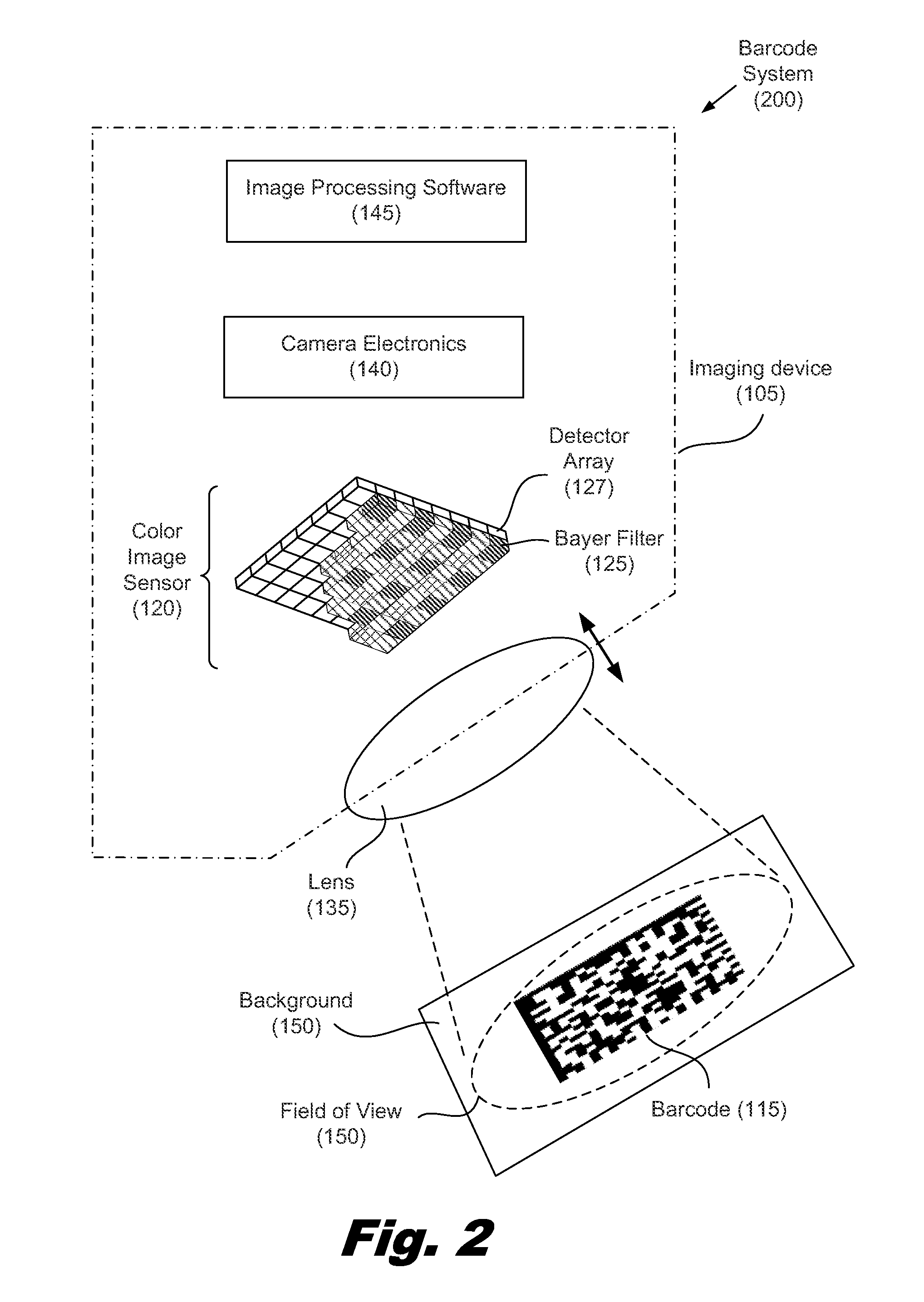
Noise removal from color barcode images
ActiveUS20120000983A1Reduce contrastReduce contributionGain controlRecord carriers used with machinesColor imageNoise removal
A method for noise removal from color barcode images includes acquiring a barcode image using a color imaging array and separating the barcode image into color channels. Weighting factors are associated with the color channels and at least one weighting factor is reduced. The weighting factors are applied to the color channels to produce a first transformed image. A portion of the first transformed image is analyzed to produce a first set of decoded data from the barcode.
Owner:IBM CORP
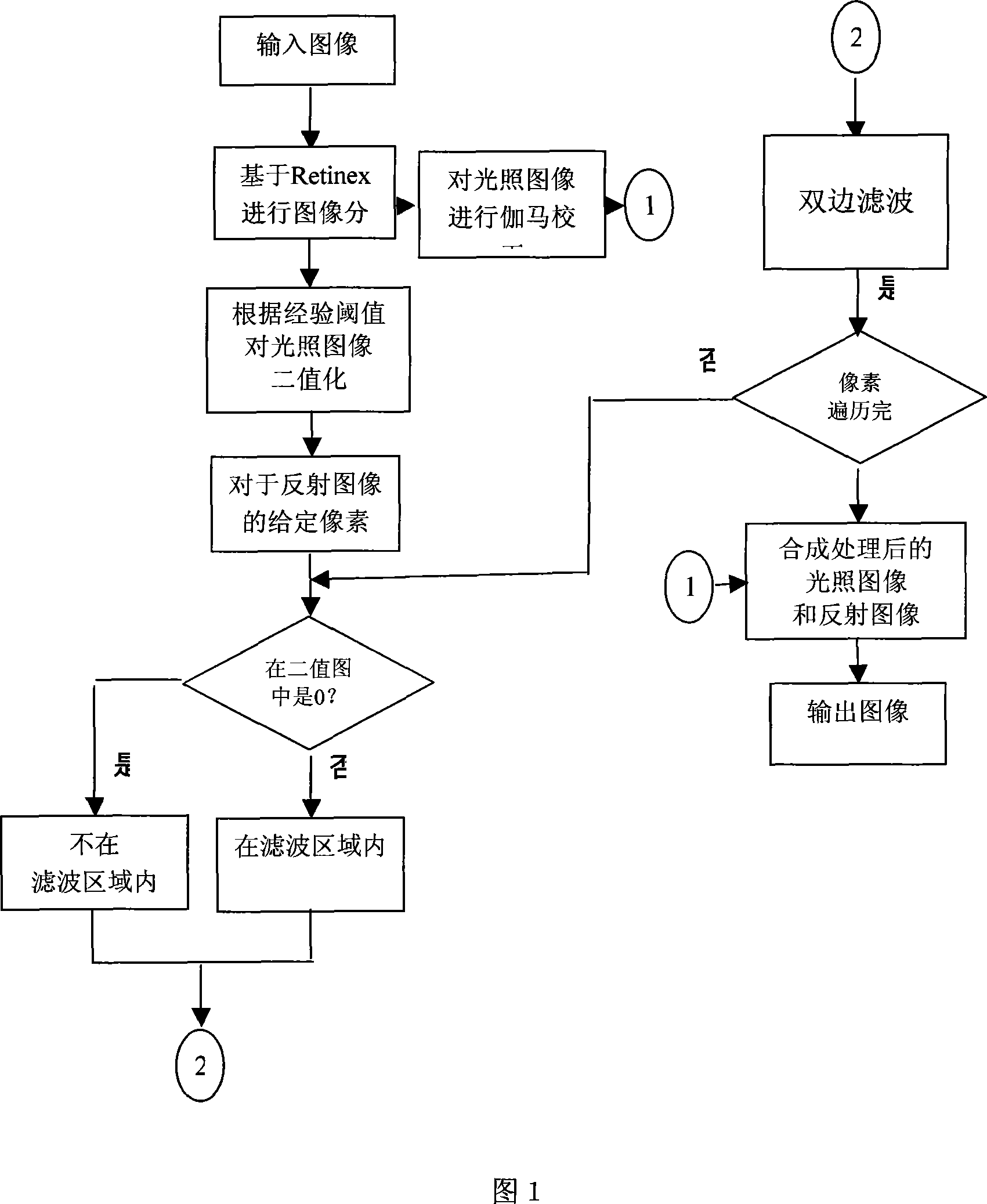
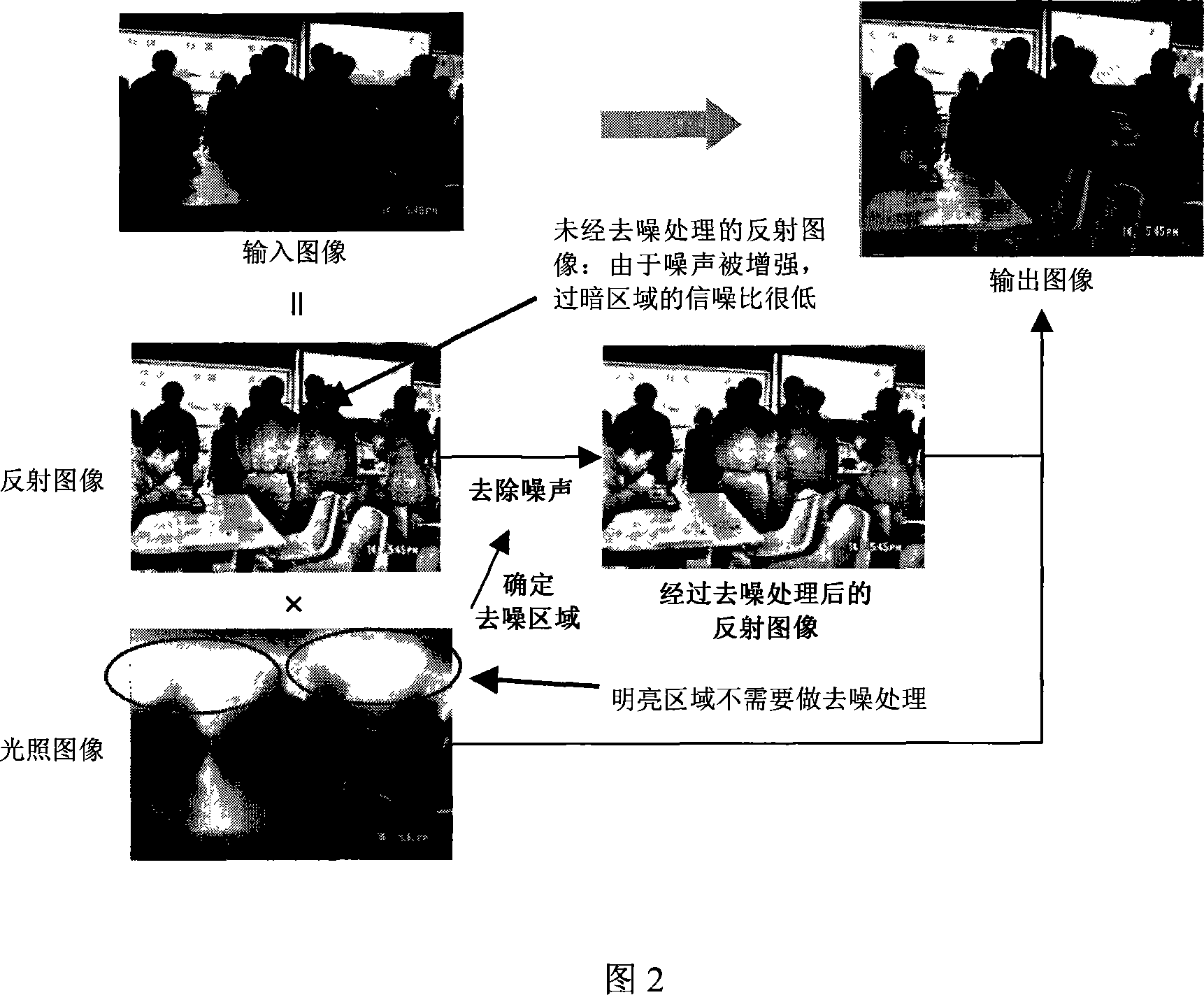
Real time digital image processing and enhancing method with noise removal function
InactiveCN101102399AQuality improvementImprove the problem of increased noise volumeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsAfter treatmentNoise removal
The method comprises: reading out a digital image; saving the color and gray values of each pixel into an allocated memory; dividing the inputted image into a light illumination image and a reflection image; respectively making the treatment for both images; after treatment, said two images are combined into one image that is outputted to the output device. By the invention, the digital photos can get a high dynamical range (from the most brightness to the most darkness) according to the partial image information obtained at different light condition.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
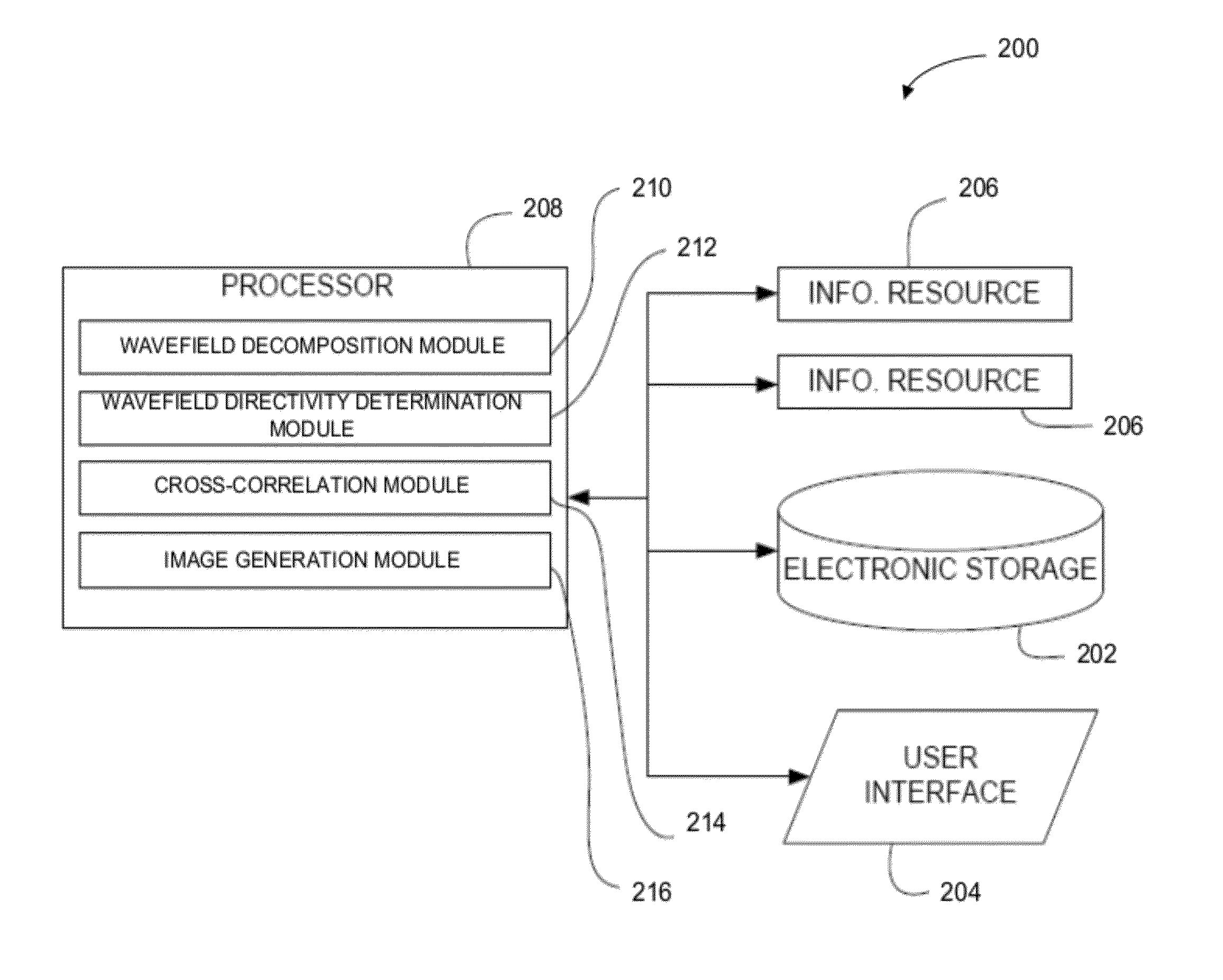
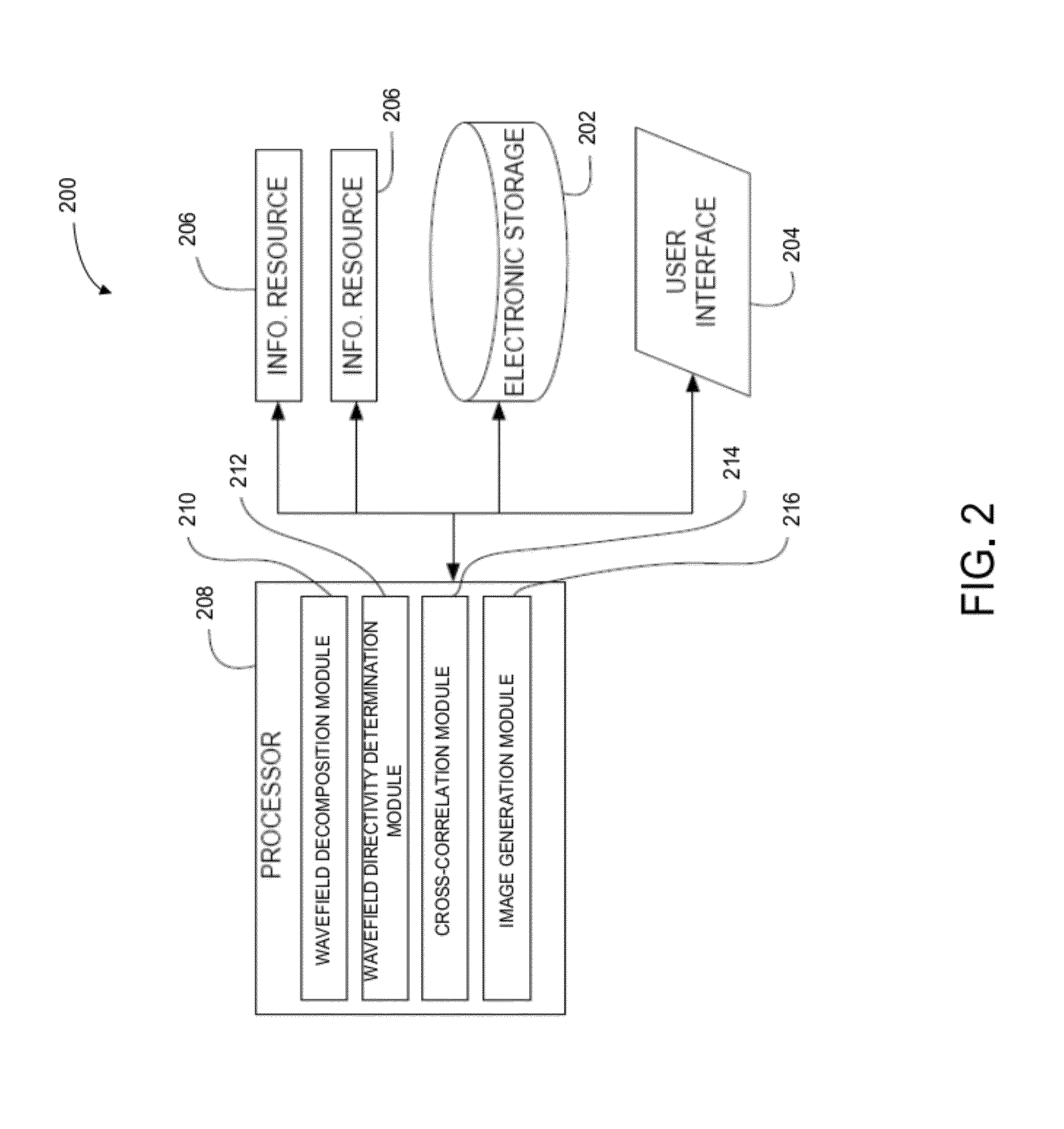
Reverse time migration back-scattering noise removal using decomposed wavefield directivity
Images of a subsurface region may be generated in conjunction with reverse time migration with reduced or no backscattering noise. Two or more wavefields may be decomposed to produce two or more corresponding decomposed wavefields. The two or more decomposed wavefields may include a source wavefield and a receiver wavefield. Directivity of the two or more decomposed wavefields may be determined to produce corresponding direction-dependent components of the two or more decomposed wavefields. One or more of the direction-dependent components of one or more decomposed source wavefields may be cross-correlated with one or more of the direction-dependent components of one or more corresponding decomposed receiver wavefields. An image of the subsurface region may be generated based on the cross-correlation.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
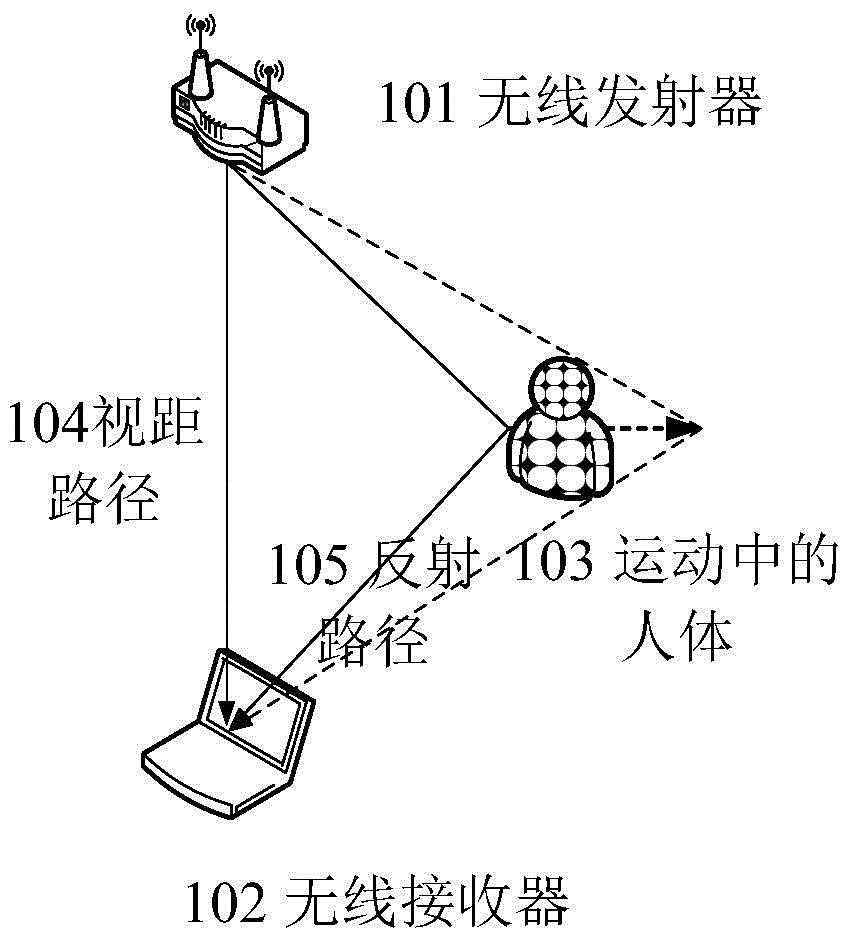
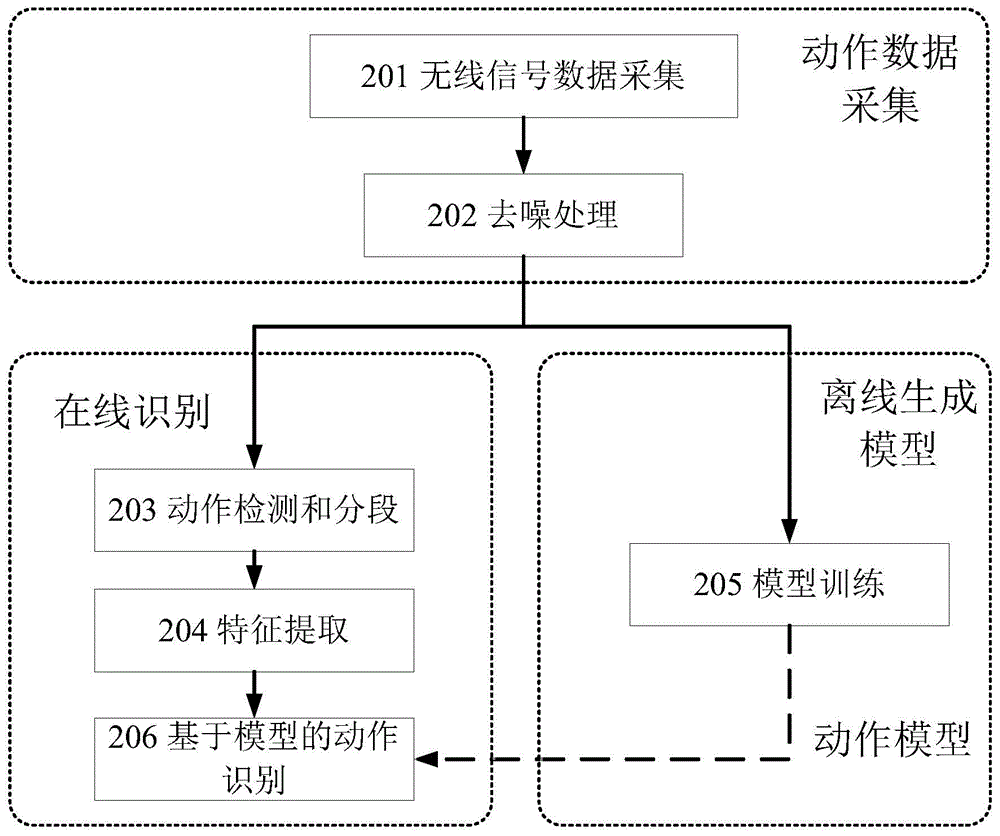
Action detecting and identifying method based on radio signals
ActiveCN104951757AEasy to identifyImprove anti-interference abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionRadio networksFeature extraction
The invention discloses an action detecting and identifying method based on radio signals and relates to the field of radio network and pervasive computing, in particular to an action detecting and identifying method based on radio signals. Radio signals are interfered by means of human actions, a universal radio device acquires radio signal data, and data is subjected to noise removal and characteristic extraction correlated with action speed to identify action. The radio signal data is acquired via one or more universal radio devices, radio data is subjected to noise removal by means of multichannel radio signal data, and characteristics correlated to human action speed can be extracted from the radio data so as to detect and identify the actions. The action detecting and identifying method includes steps of data acquisition, data denoising, data segmenting, characteristic extraction, model training and action identifying.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and computer program
InactiveUS20090092337A1Reduce image qualityHigh-quality high-resolution imageImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingNoise removal
An image processing apparatus includes an image correction processing unit configured to correct an input image so as to generate a corrected image and a super-resolution processing unit configured to receive the corrected image generated by the image correction processing unit and increase a resolution of the corrected image through super-resolution processing so as to generate a high-resolution image. The image correction processing unit performs at least one of a time-direction noise removal process, a space-direction noise removal process, a compression noise removal process, and an aperture control correction process.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Noise removal for electronic device with far field microphone on console
ActiveUS20070258599A1Reduce noiseReduce narrow band noiseSignal processingEar treatmentNoise removalDistribution characteristic
Reduction of noise in a device having a console with one or more microphones and a source of narrow band distributed noise located on the console is disclosed. A microphone signal containing a broad band distributed desired sound and narrow band distributed noise is divided amongst a plurality of frequency bins. For each frequency bin, it is determined whether a portion of the signal within the frequency bin belongs to a narrow band distribution characteristic of the source of narrow band noise located on the console. Any frequency bins containing portions of the signal belonging to the narrow band distribution are filtered to reduce the narrow band noise.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
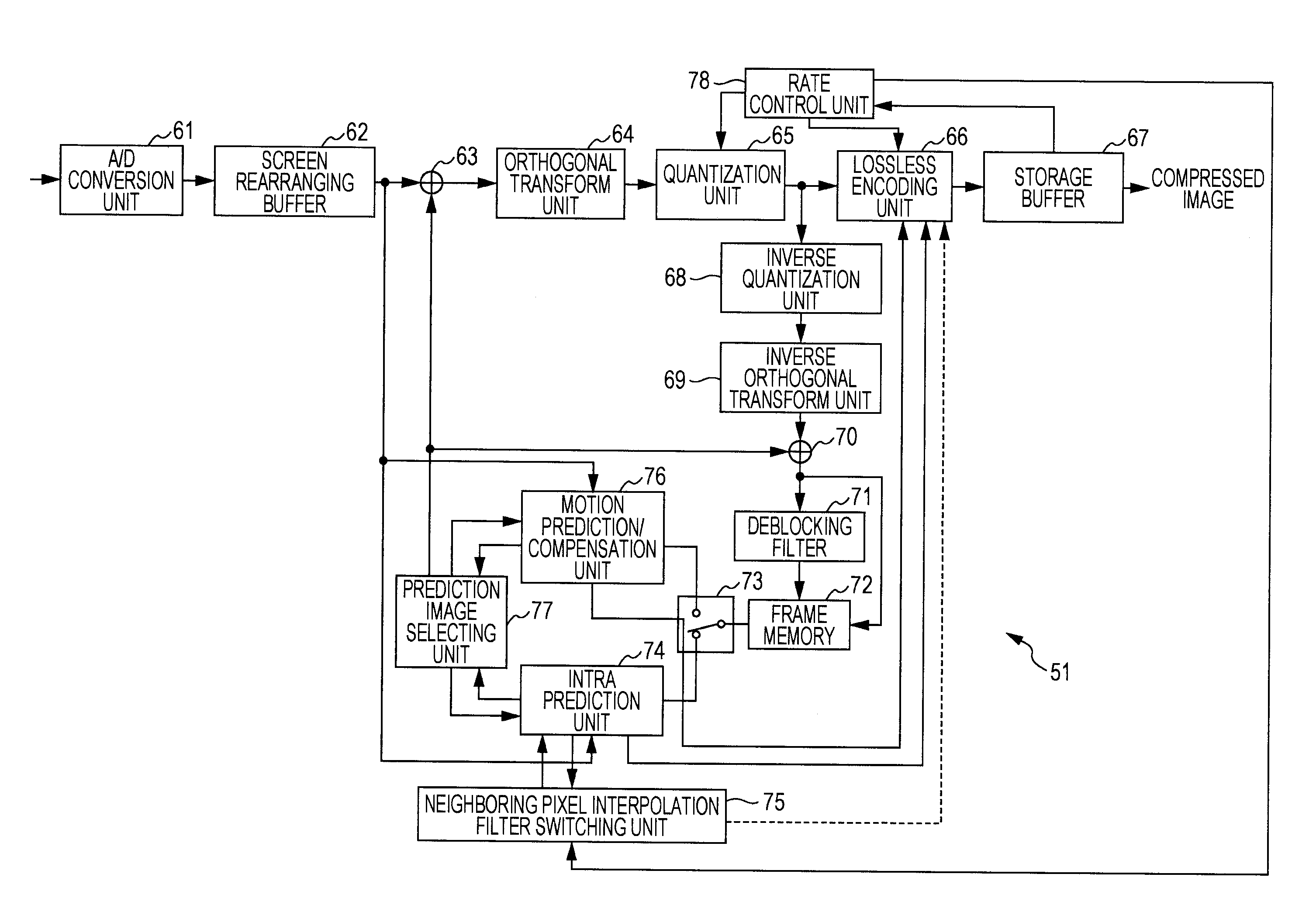
Image processing device and method
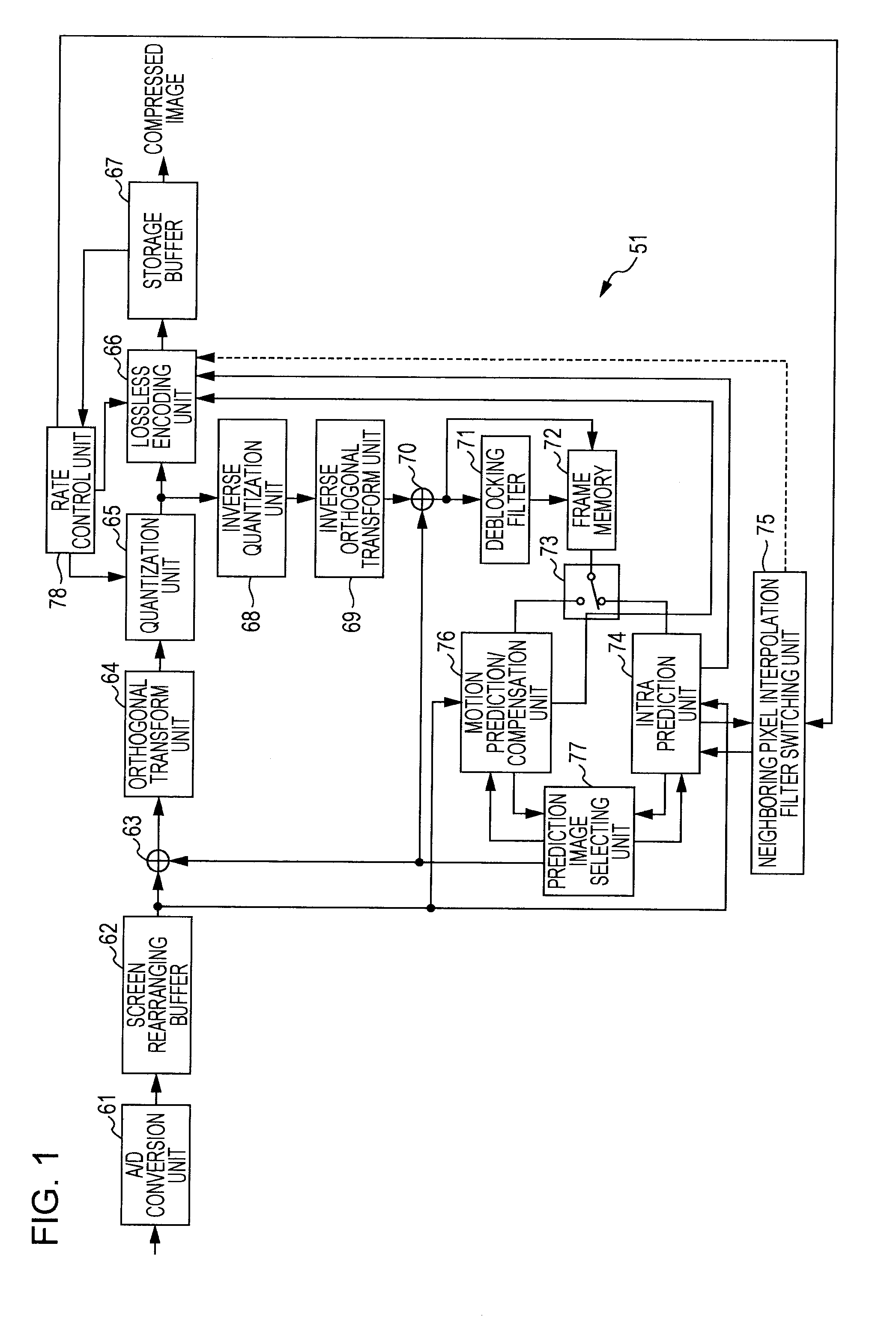
The present invention relates to an image processing device and method enabling noise removal to be performed according to images and bit rates.A low-pass filter setting unit 93 sets, from filter coefficients stored in a built-in filter coefficient memory 94, a filter coefficient corresponding to intra prediction mode information and a quantization parameter. A neighboring image setting unit 81 uses the filter coefficient set by the low-pass filter setting unit 93 to subject neighboring pixel values of a current block from frame memory 72 to filtering processing. A prediction image generating unit 82 performs intra prediction using the neighboring pixel values subjected to filtering processing, from the neighboring image setting unit 81, and generates a prediction image. The present invention can be applied to an image encoding device which encodes with the H.264 / AVC format, for example.
Owner:SONY CORP
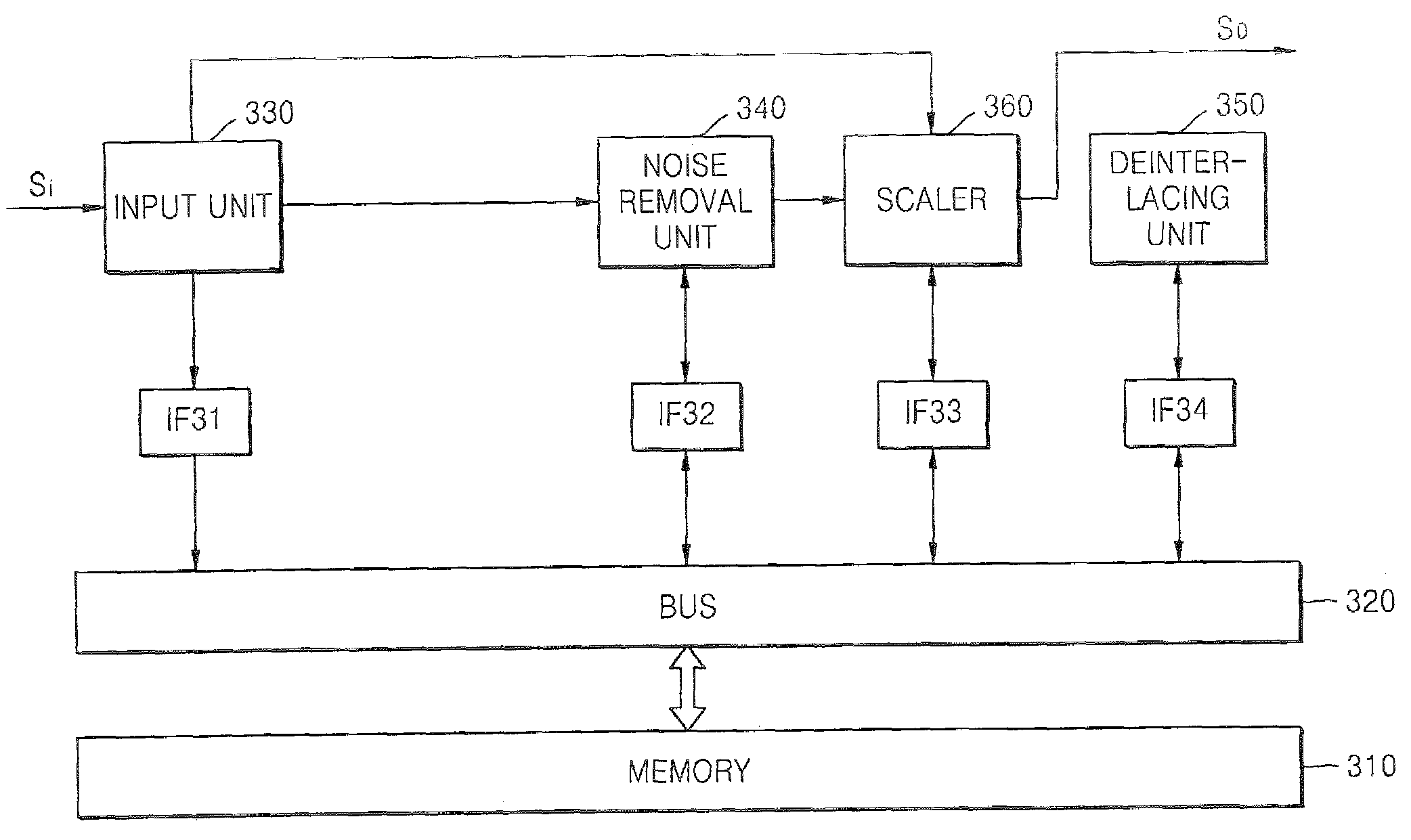
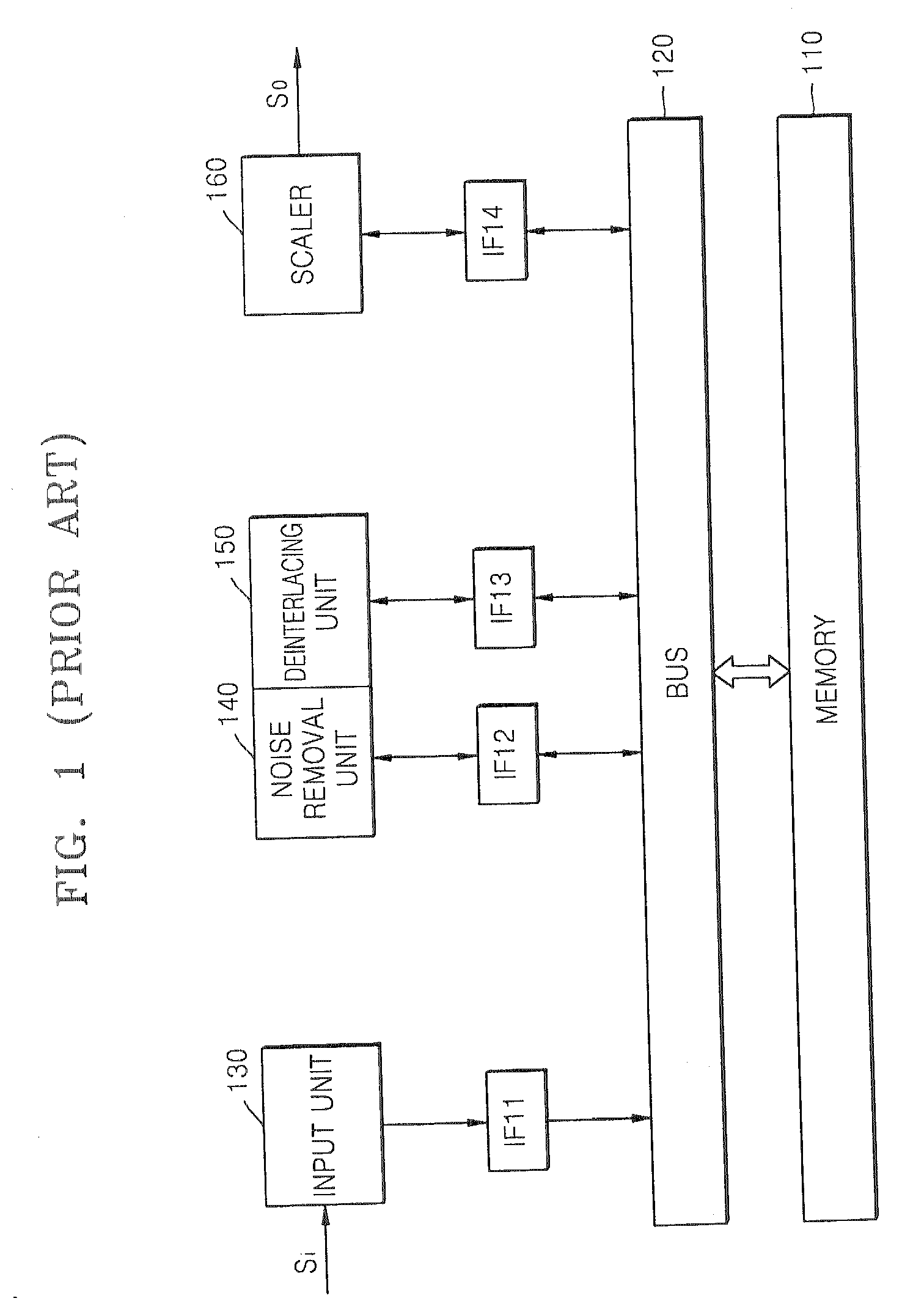
Apparatus and method for processing image signal without requiring high memory bandwidth
ActiveUS20070159642A1Reduce image sizeTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersControl signalNoise removal
An image signal processor for processing an input image signal to output an output image signal includes an input unit receiving the input image signal, a noise removal unit removing noise from the input image signal, and a scaler reducing, maintaining or magnifying the image size of the input image signal. The scaler directly receives the input image signal from the input unit or the noise removal unit in response to a route control signal, reduces the image size of the input image signal when the image size of the input image signal is larger than the image size of the output image signal and stores the image signal with a reduced image size in a memory. The scaler maintains or magnifies the image size of the image signal stored in the memory and outputs the image signal with a maintained or magnified image size as the output image signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Noise suppression apparatus
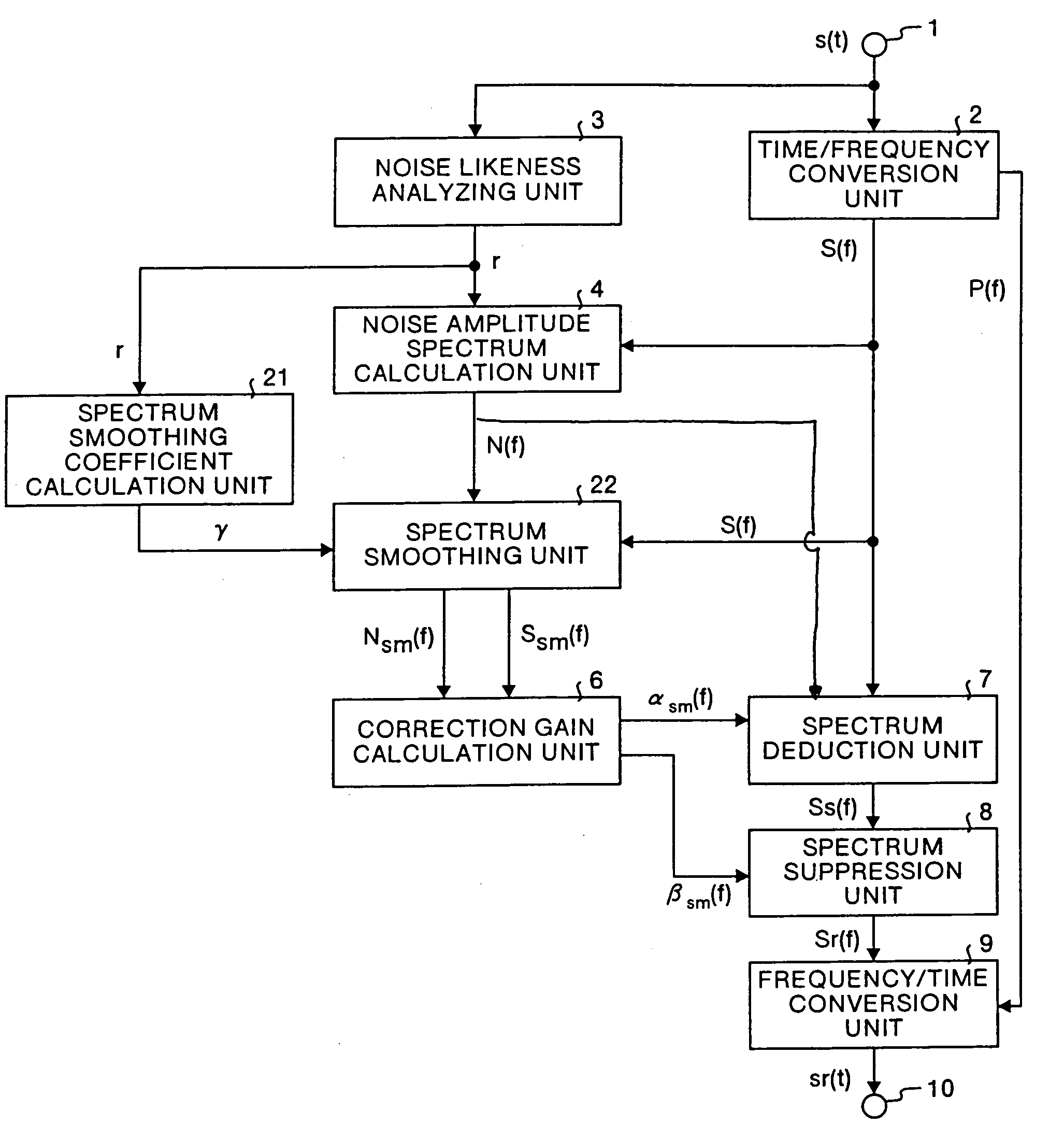
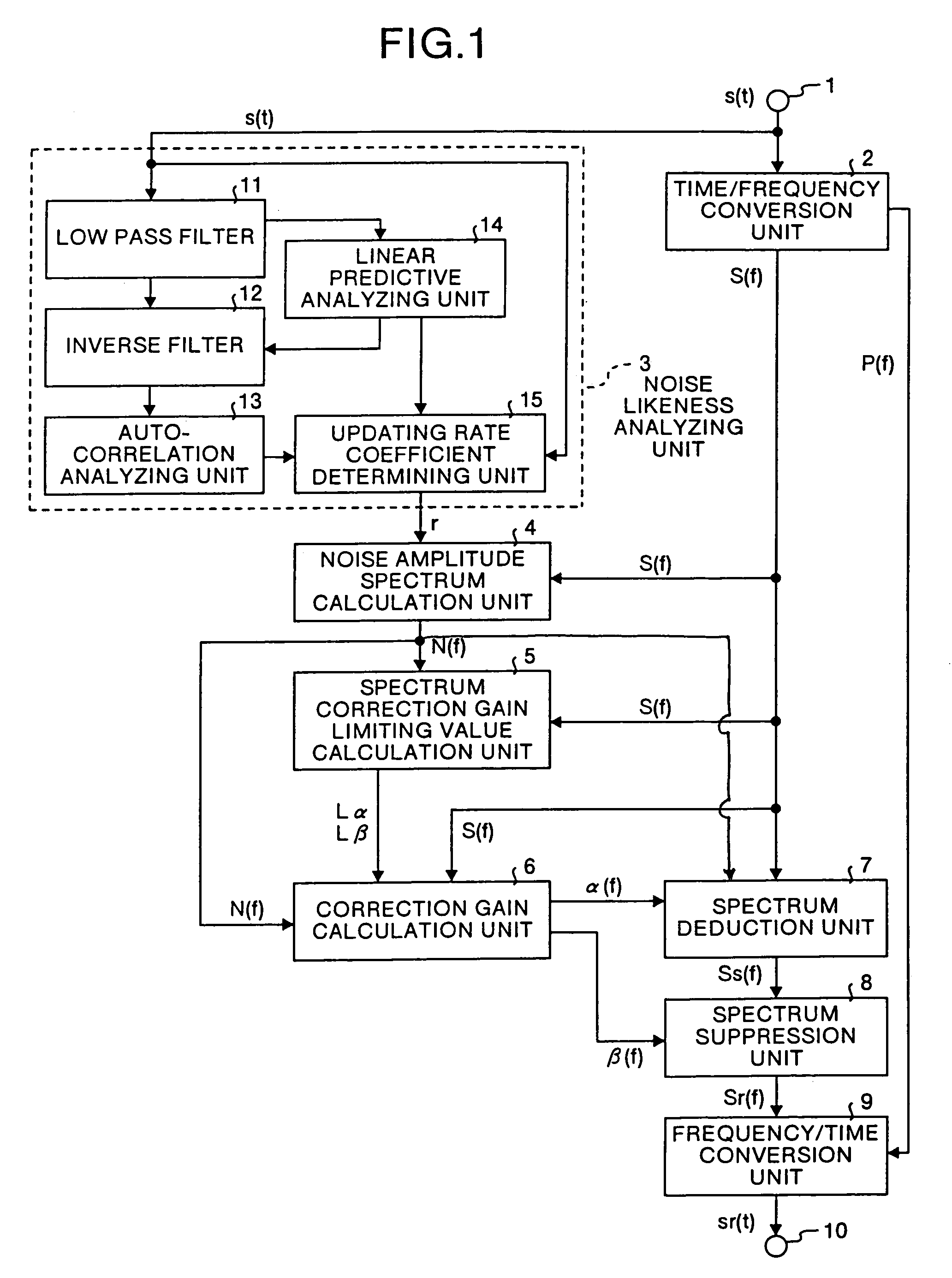
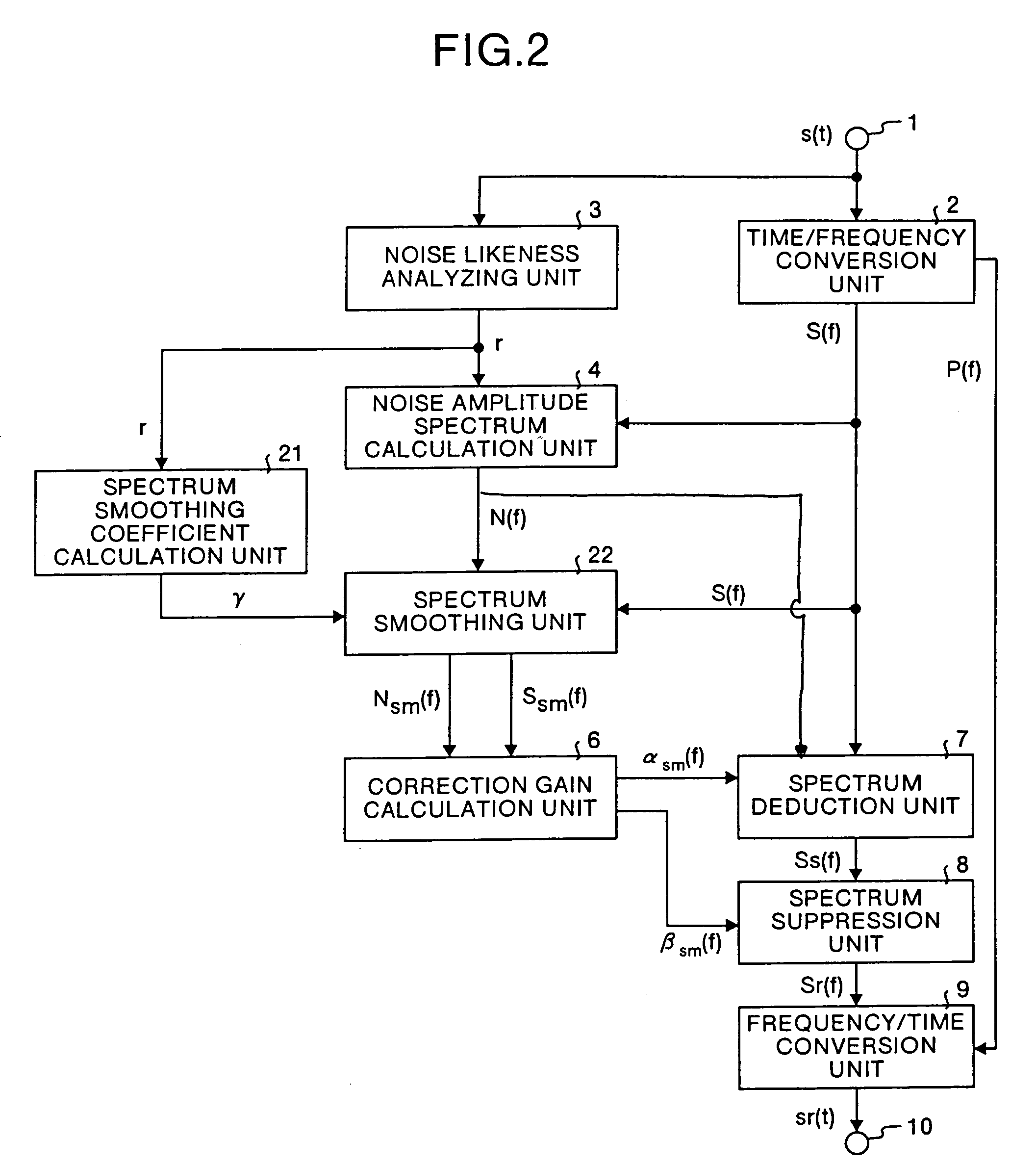
InactiveUS7158932B1Suppress noiseQuality improvementCode conversionSpeech recognitionTime domainFrequency spectrum
In the noise suppression apparatus, a spectrum correction gain calculation unit calculates the noise amplitude spectrum correction gain and the noise removal spectrum correction gain using the input amplitude spectrum, noise amplitude spectrum and respective coefficients; a spectrum deduction unit deducts the product of the noise amplitude spectrum and the noise amplitude spectrum correction gain from the input amplitude spectrum and outputs the result as a first noise removal spectrum; a spectrum suppression unit multiplies the first noise removal spectrum by the noise removal spectrum correction gain and outputs the result as a second noise removal spectrum; finally a frequency / time conversion unit converts the second noise removal spectrum into a time domain signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Multi-frequency weak signal detecting method for early failure of rotor
InactiveCN101294845AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove detection signal-to-noise ratioSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Noise removal
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
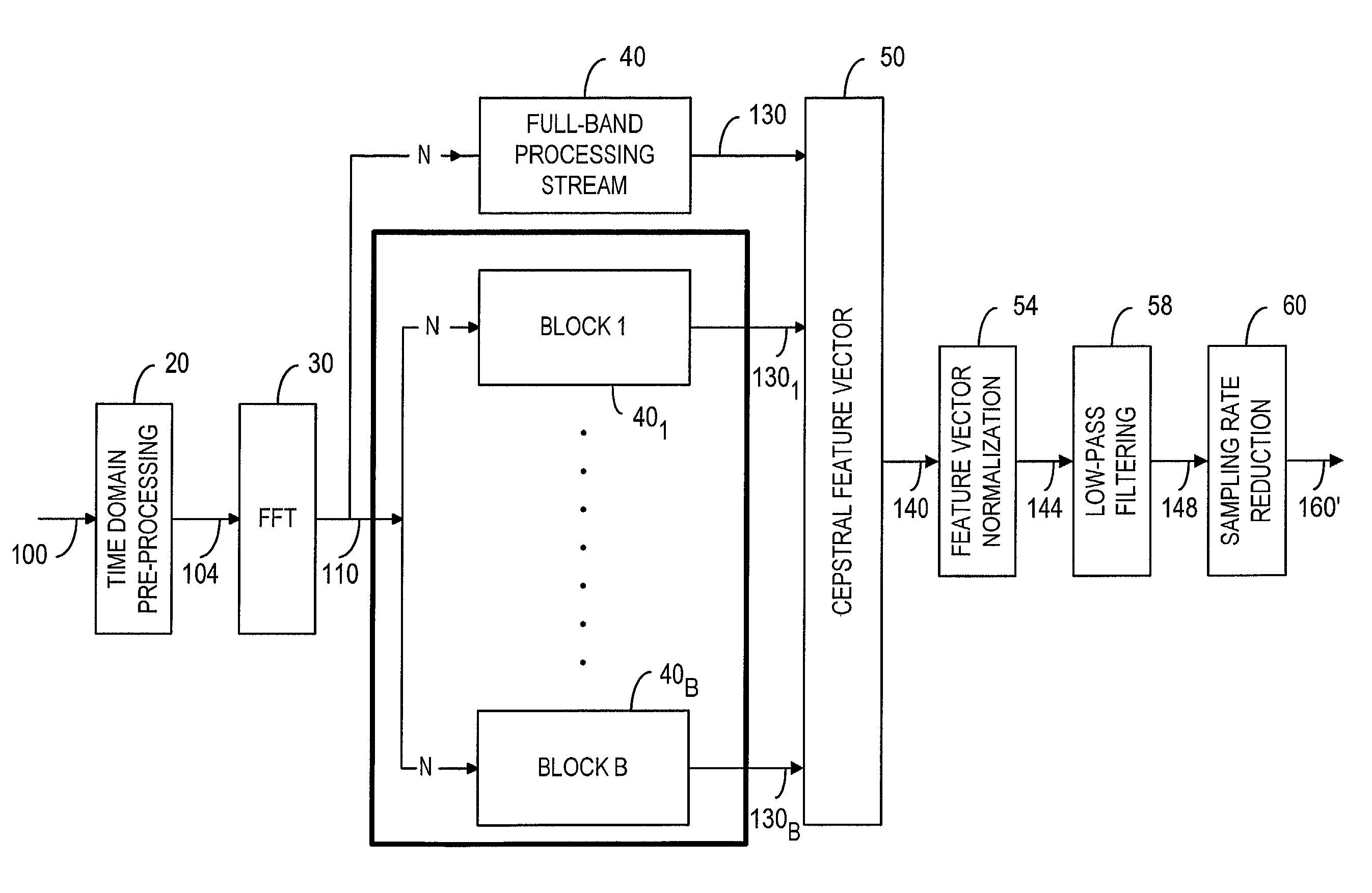
Data-driven filtering of cepstral time trajectories for robust speech recognition
InactiveUS7035797B2Improve Speech Recognition EfficiencyEfficiently filter out the noise component in the speech parametersSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumSpeech identification
A method and apparatus for speech processing in a distributed speech recognition system having a front-end and a back-end. The speech processing steps in the front-end are as follows: extracting speech features from a speech signal and normalizing the speech features in order to alter the power of the noise component in the modulation spectrum in relation to the power of the signal component, especially with frequencies above 10 Hz. A low-pass filter is then used to filter the normalized modulation spectrum in order to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in the speech signal. The combination of feature vector normalization and low-pass filtering is effective in noise removal, especially in a low SNR environment.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Robust process model identification in model based control techniques
ActiveUS7840287B2Robust methodAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSimulator controlGeneration processTest input
A robust method of creating process models for use in controller generation, such as in MPC controller generation, adds noise to the process data collected and used in the model generation process. In particular, a robust method of creating a parametric process model first collects process outputs based on known test input signals or sequences, adds random noise to the collected process data and then uses a standard or known technique to determine a process model from the collected process data. Unlike existing techniques for noise removal that focus on clean up of non-random noise prior to generating a process model, the addition of random, zero-mean noise to the process data enables, in many cases, the generation of an acceptable parametric process model in situations where no process model parameter convergence was otherwise obtained. Additionally, process models created using this technique generally have wider confidence intervals, therefore providing a model that works adequately in many process situations without needing to manually or graphically change the model.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
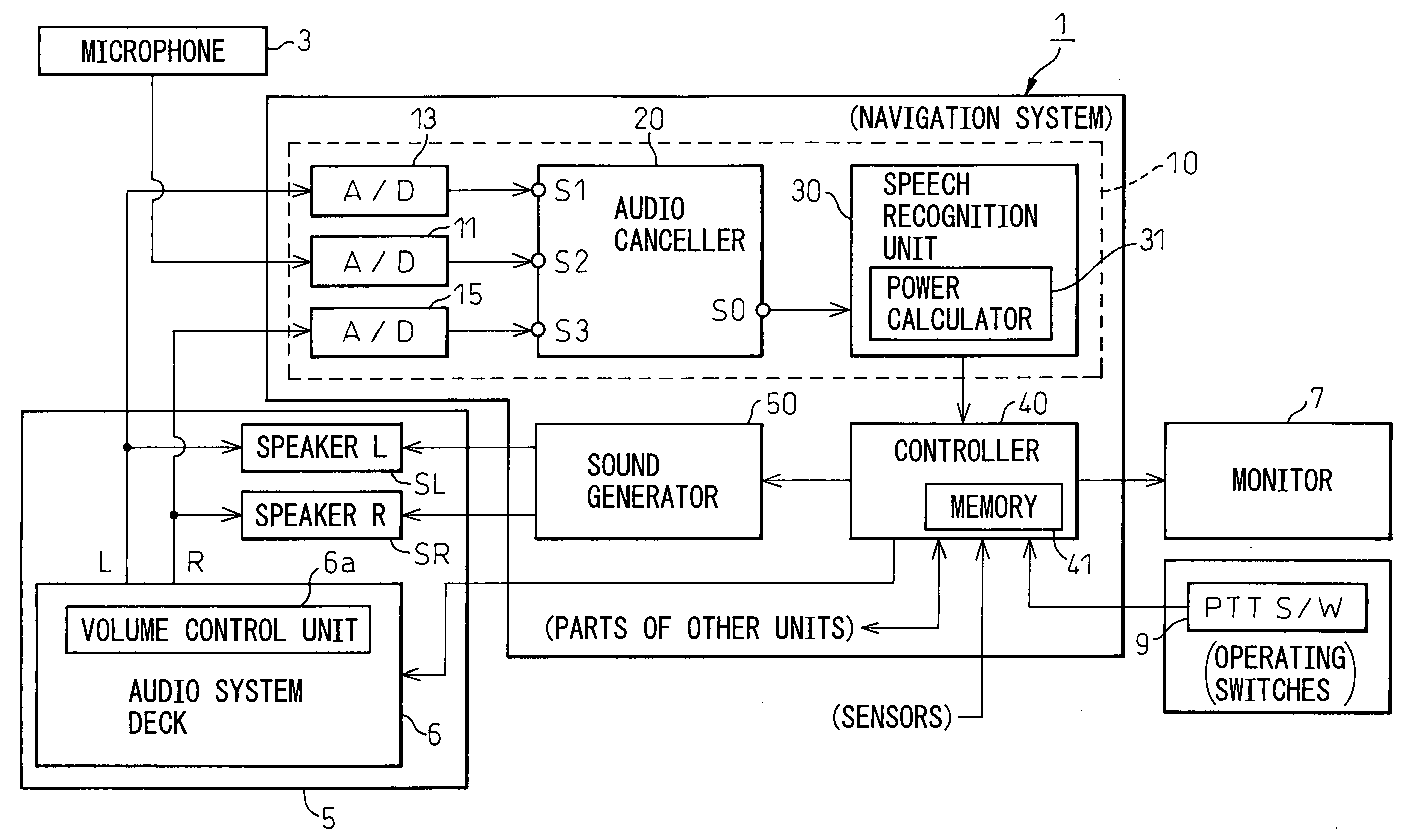
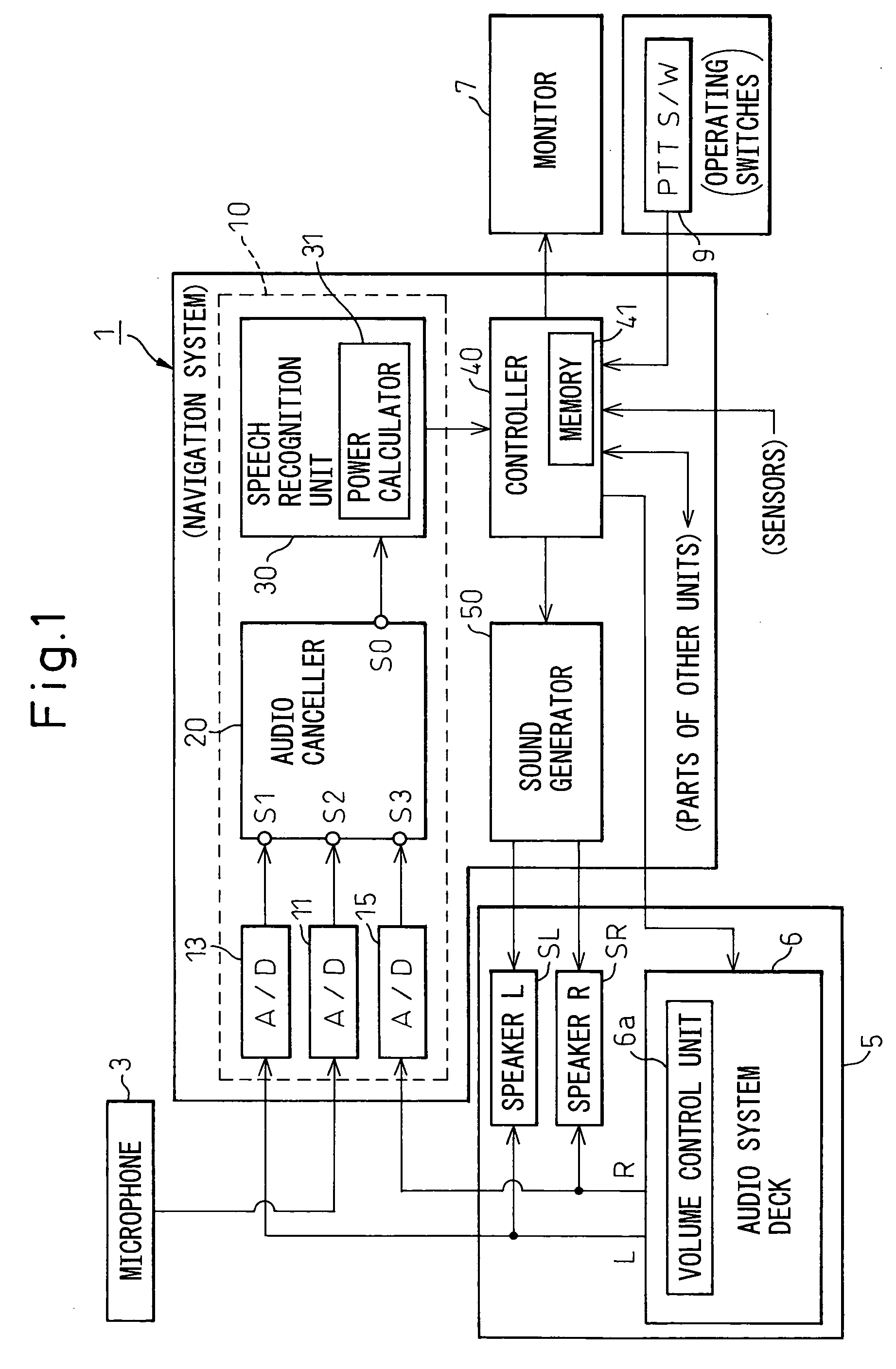
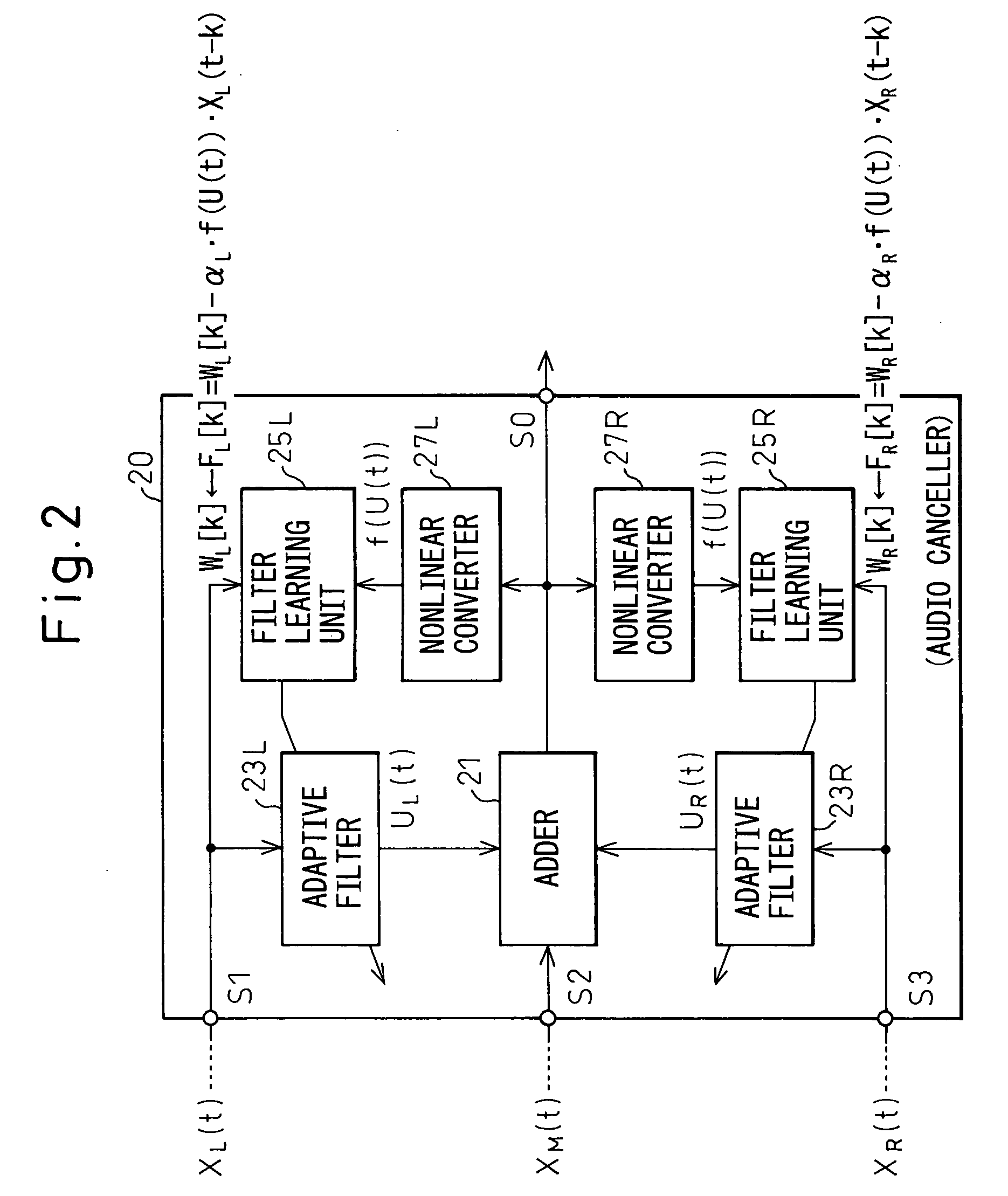
Noise cancellation system, speech recognition system, and car navigation system
InactiveUS20050159945A1Improve performanceSuperior in noise cancellation abilityInstruments for road network navigationEar treatmentAdaptive filterEngineering
A noise cancellation system with improved performance for canceling from an input signal of a microphone a noise component relating to reproduced sound of an audio system reproducing multiple channels of sound, provided with an audio canceller for acquiring audio signals of two channels and processing them by filter coefficients by convolutional processing so as to produce noise cancellation signals at adaptive filters, an adder for adding the input signal of the microphone and the noise cancellation signals, canceling the noise component from the input signal, and outputting the signal after noise cancellation, nonlinear converters for nonlinear conversion of the signal after noise cancellation, and filter learning units for calculating the filter coefficients to be set next based on the nonlinear converted signal.
Owner:DENSO CORP
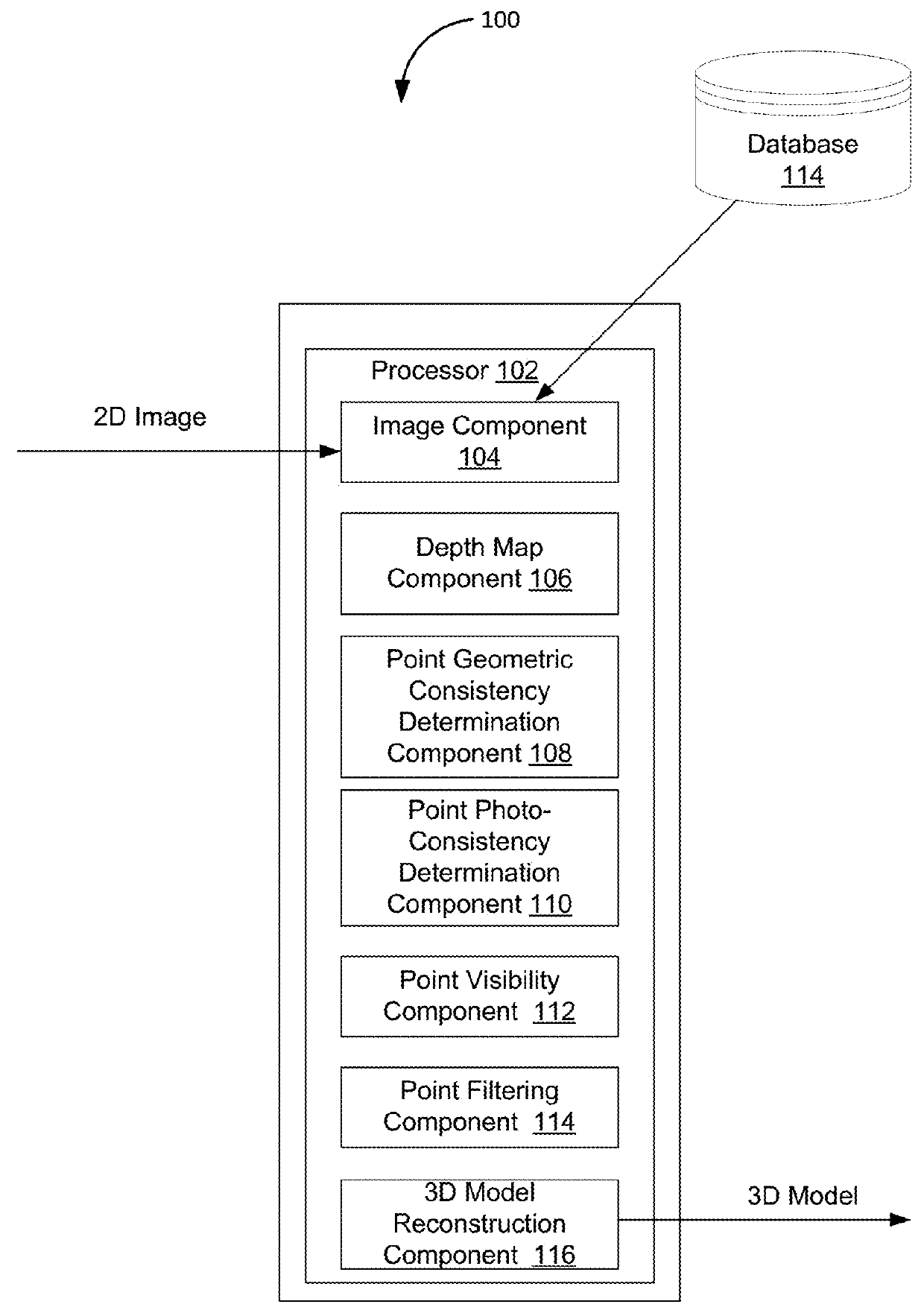
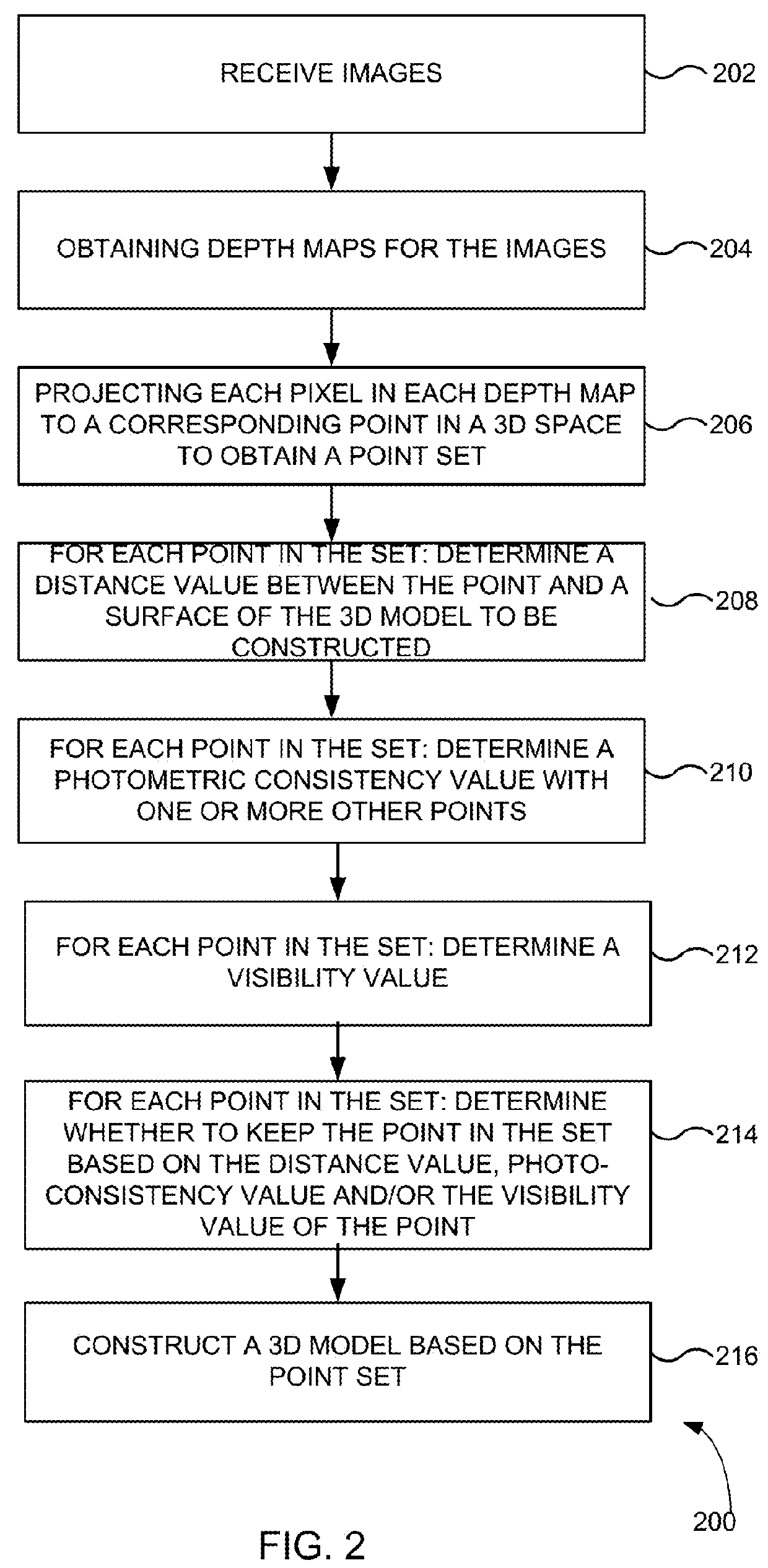
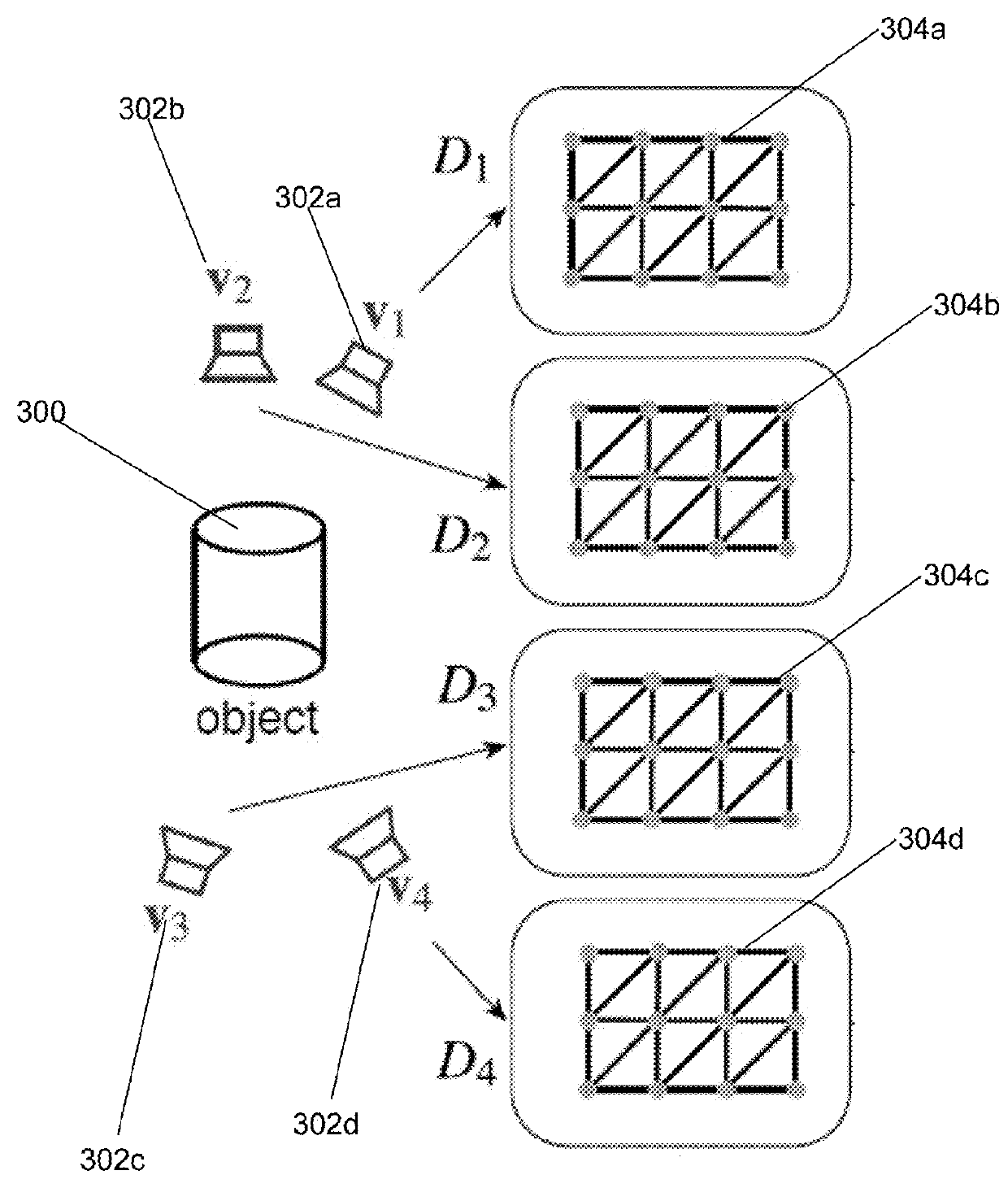
Point cloud noise and outlier removal for image-based 3D reconstruction
ActiveUS20180096463A1Good removal effectLess smoothingImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudNoise removal
Enhanced removing of noise and outliers from one or more point sets generated by image-based 3D reconstruction techniques is provided. In accordance with the disclosure, input images and corresponding depth maps can be used to remove pixels that are geometrically and / or photometrically inconsistent with the colored surface implied by the input images. This allows standard surface reconstruction methods (such as Poisson surface reconstruction) to perform less smoothing and thus achieve higher quality surfaces with more features. In some implementations, the enhanced point-cloud noise removal in accordance with the disclosure can include computing per-view depth maps, and detecting and removing noisy points and outliers from each per-view point cloud by checking if points are consistent with the surface implied by the other input views.
Owner:ETH ZURICH EIDGENOSSISCHE TECHN HOCHSCHULE ZURICH +1
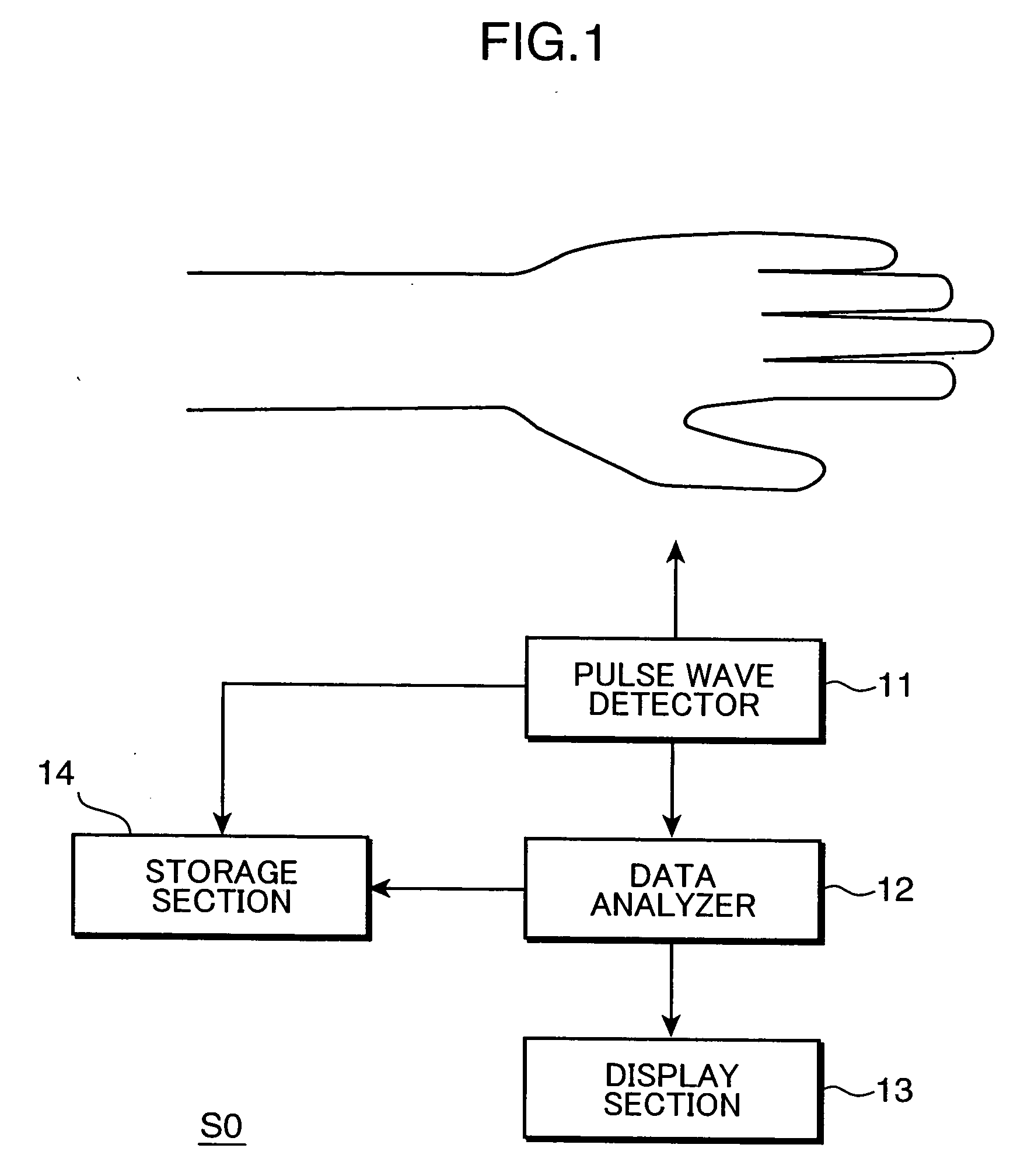
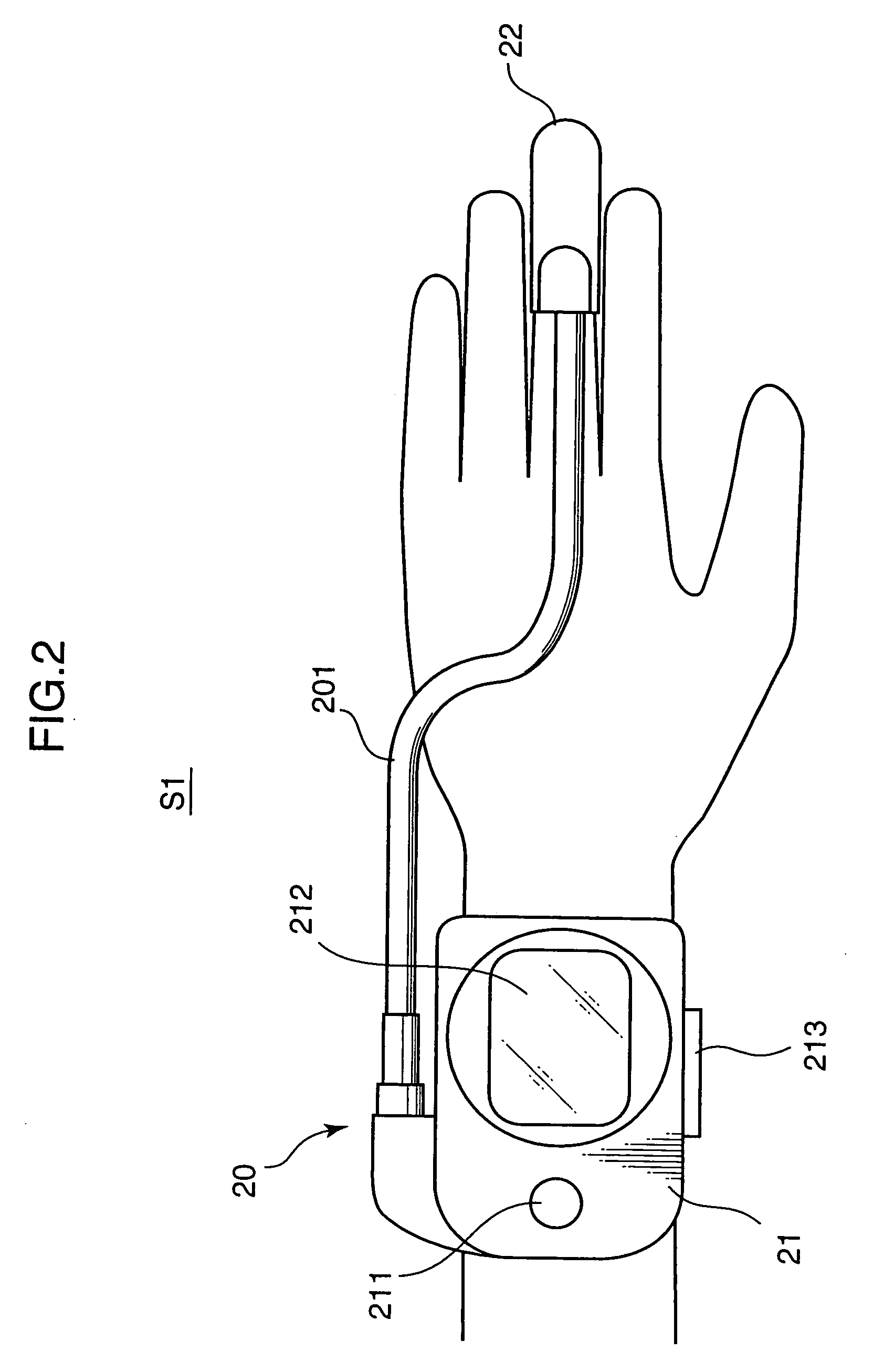
Pulse wave data analyzing method, system, and program product
ActiveUS20070123787A1Accurate detectionIncrease heightElectrocardiographyCatheterNoise removalPeak value
There is provided a pulse wave data analyzing method for extracting vital information out of pulse wave data concerning a living body. The method comprises a noise removal step of: detecting bottom values and peak values along a time axis in a time-series manner out of pulse wave data obtained by sequentially measuring a pulse wave of a subject for a predetermined period; making pairs with respect to the bottom values and the peak values adjacent to each other on the time axis to obtain bottom-to-peak amplitude values along the time axis, the bottom-to-peak amplitude value being a difference between the bottom value and the peak value in each of the pairs; and comparing each set of the two bottom-to-peak amplitude values adjacent to each other along the time axis to remove the bottom value and the peak value relating to the smaller bottom-to-peak amplitude value in the each set as a noise, if a ratio of the one of the two bottom-to-peak amplitude values to the other one of the two bottom-to-peak amplitude values is larger than a predetermined value.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA SENSING INC
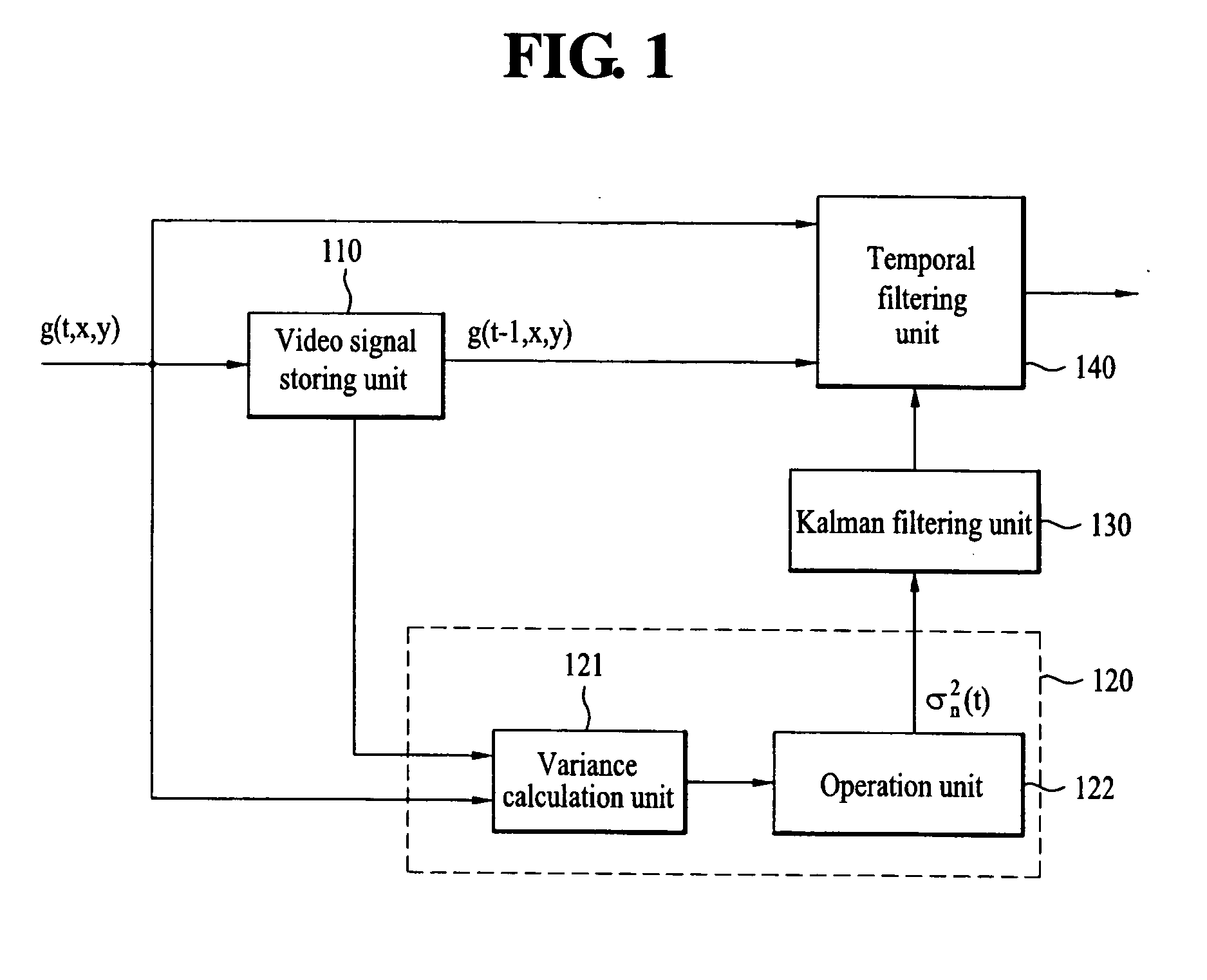
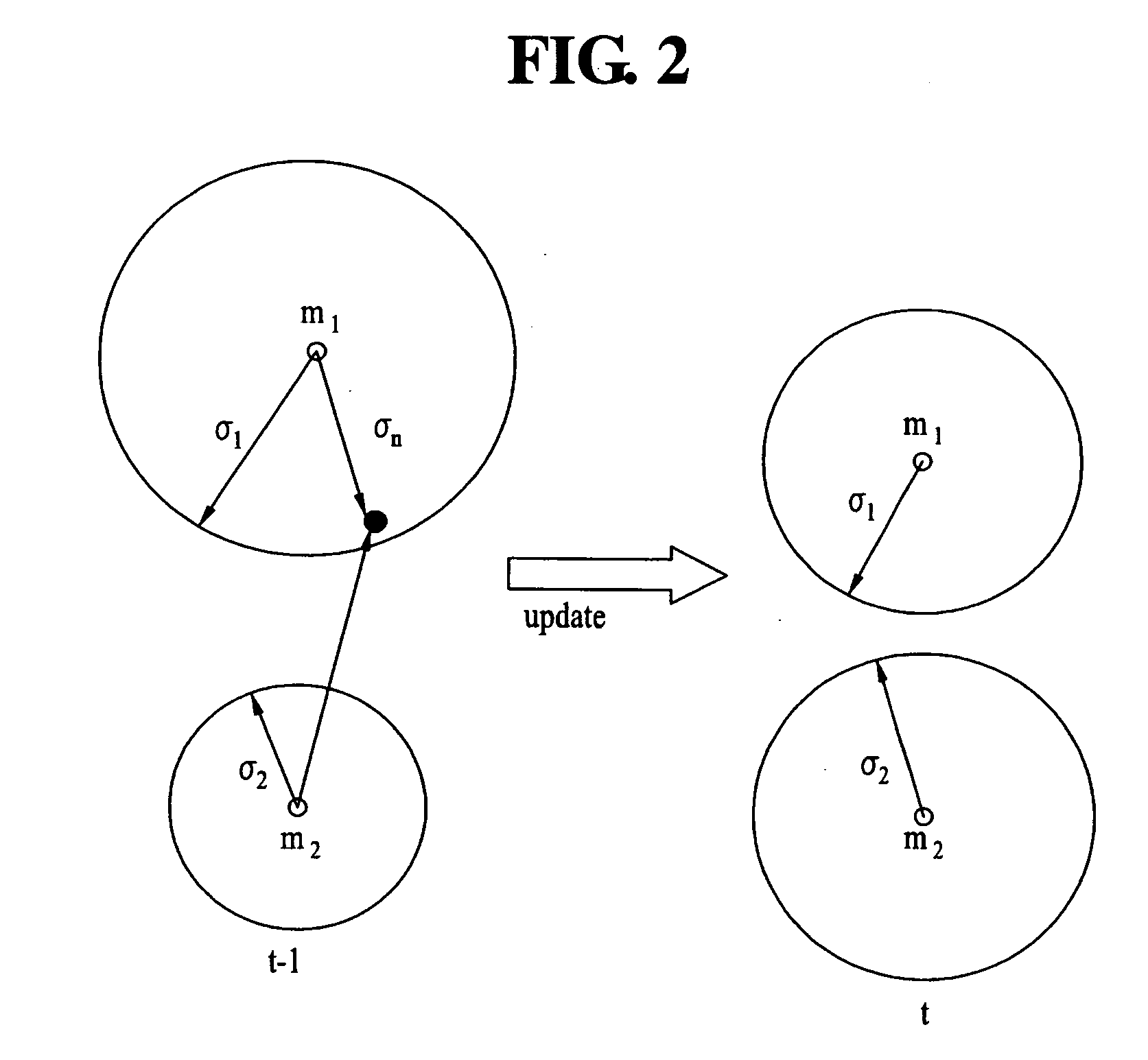
Apparatus for removing noise of video signal
InactiveUS20060158562A1Improve image qualityNoise levelTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsNoise removalNoise level
An apparatus for removing a noise of a video signal is disclosed, by which a noise level can be effectively estimated to enhance an image quality of the video signal, by which the noise can be removed in a manner of effectively estimating a noise level though motion adaptive filtering, and by which blurring is prevented in the process of removing the noises. The present invention includes a temporal noise level estimation unit estimating a level of a temporal noise included in the video signal using a difference between two temporally consecutive videos, a noise correction unit correcting a noise estimated by the temporal noise level estimation unit, and a noise removal unit removing the noise included in the video signal using a level of the corrected noise.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com