Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42results about How to "Reduce rise and fall times" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
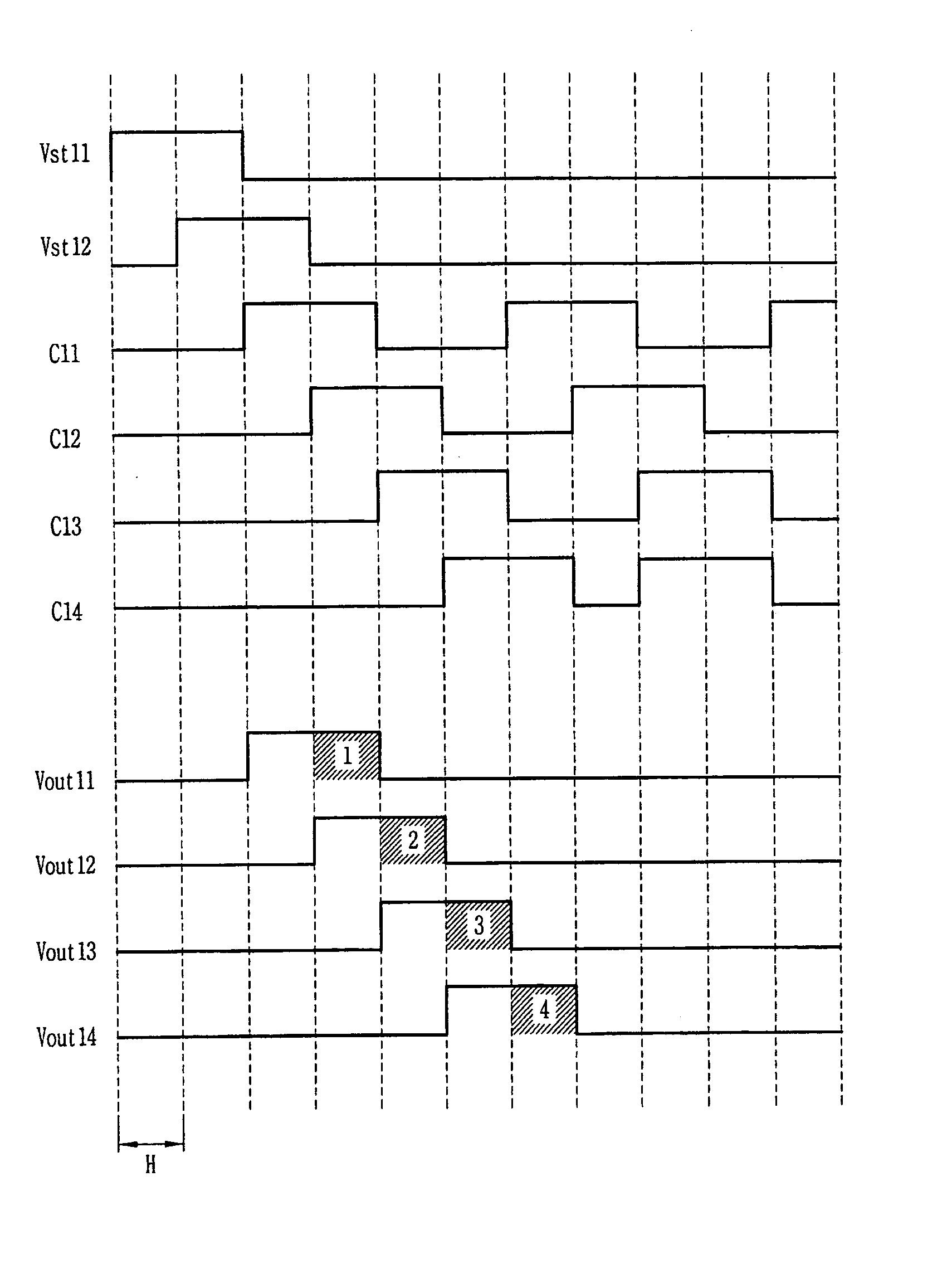
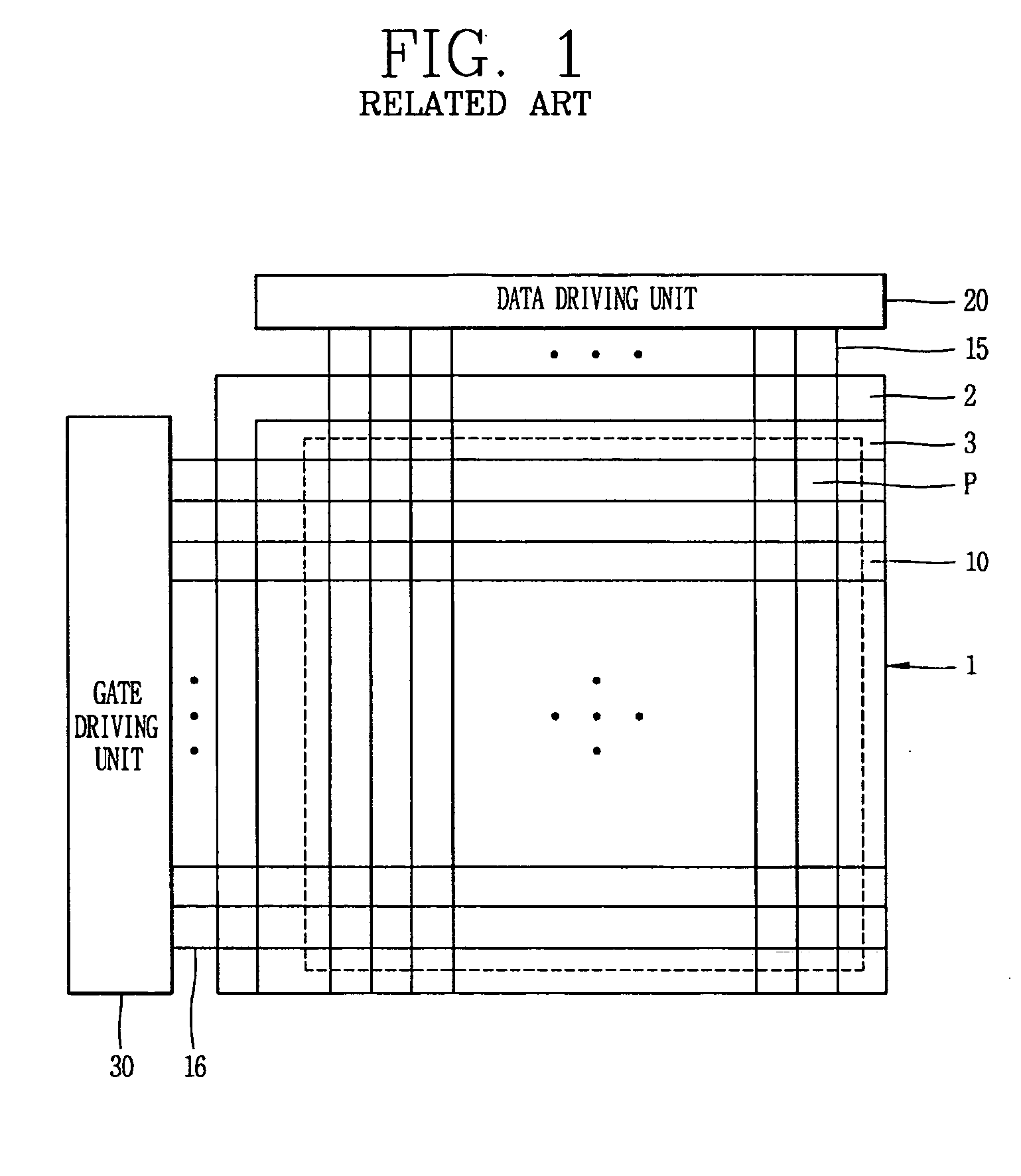
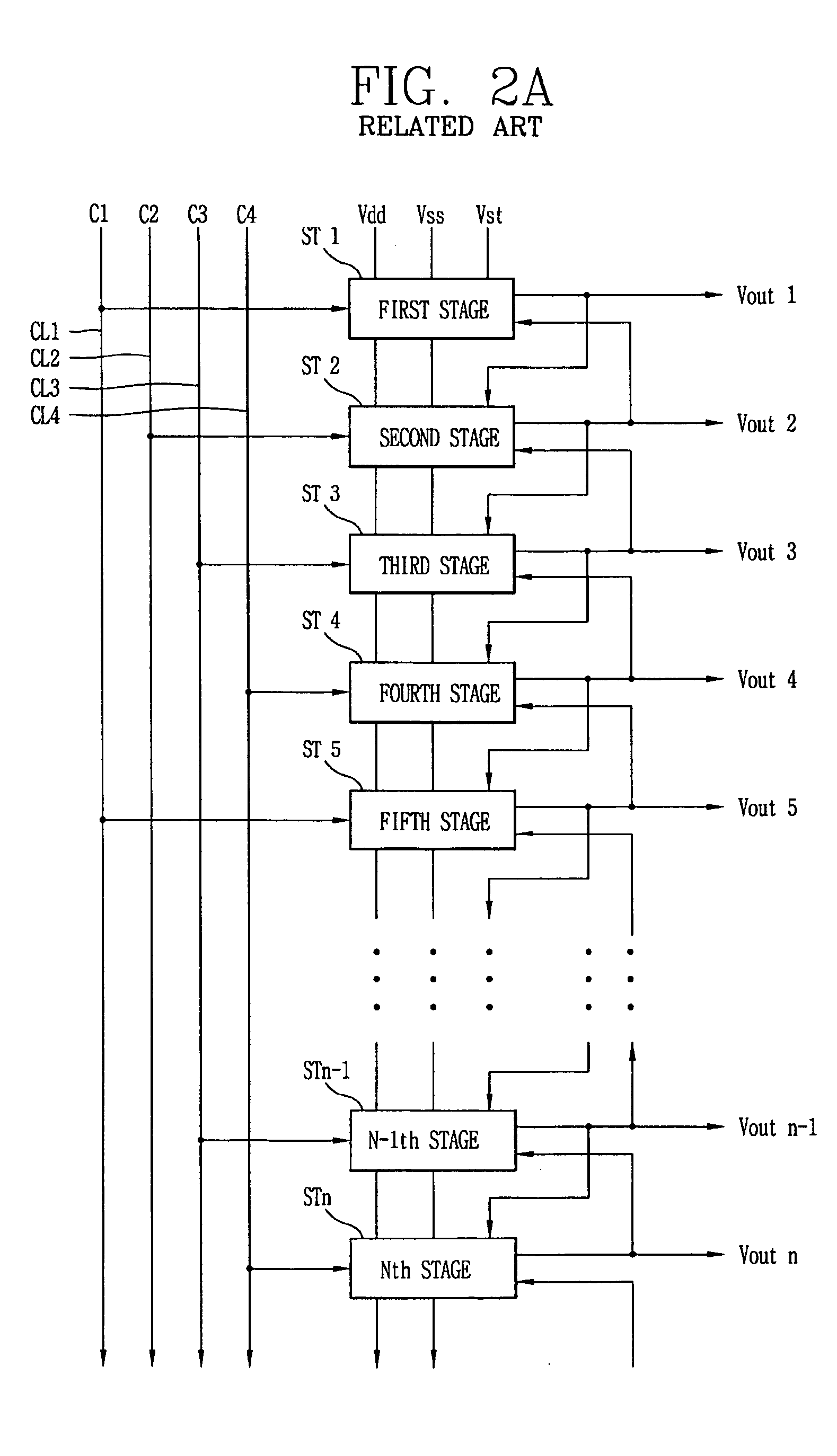
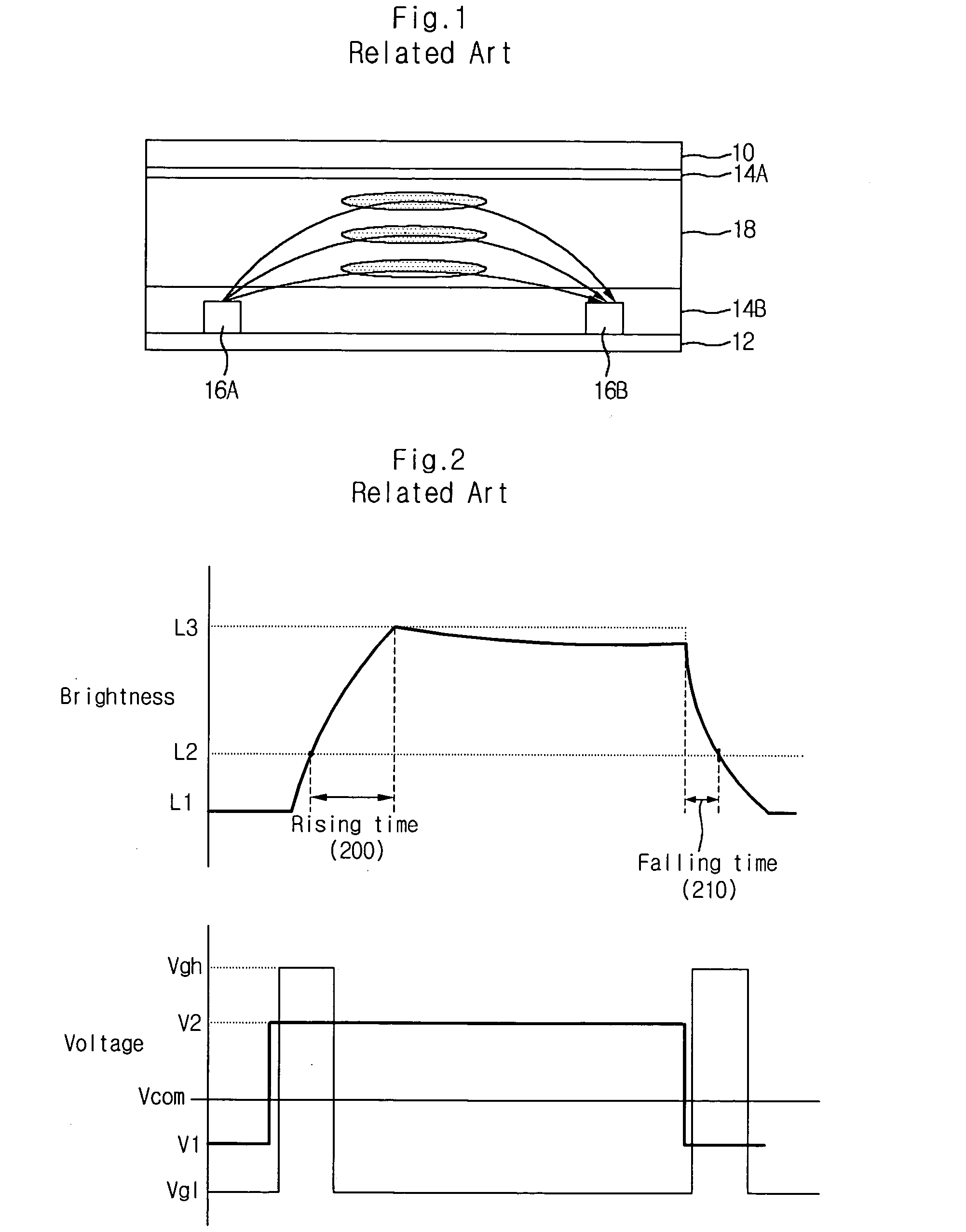
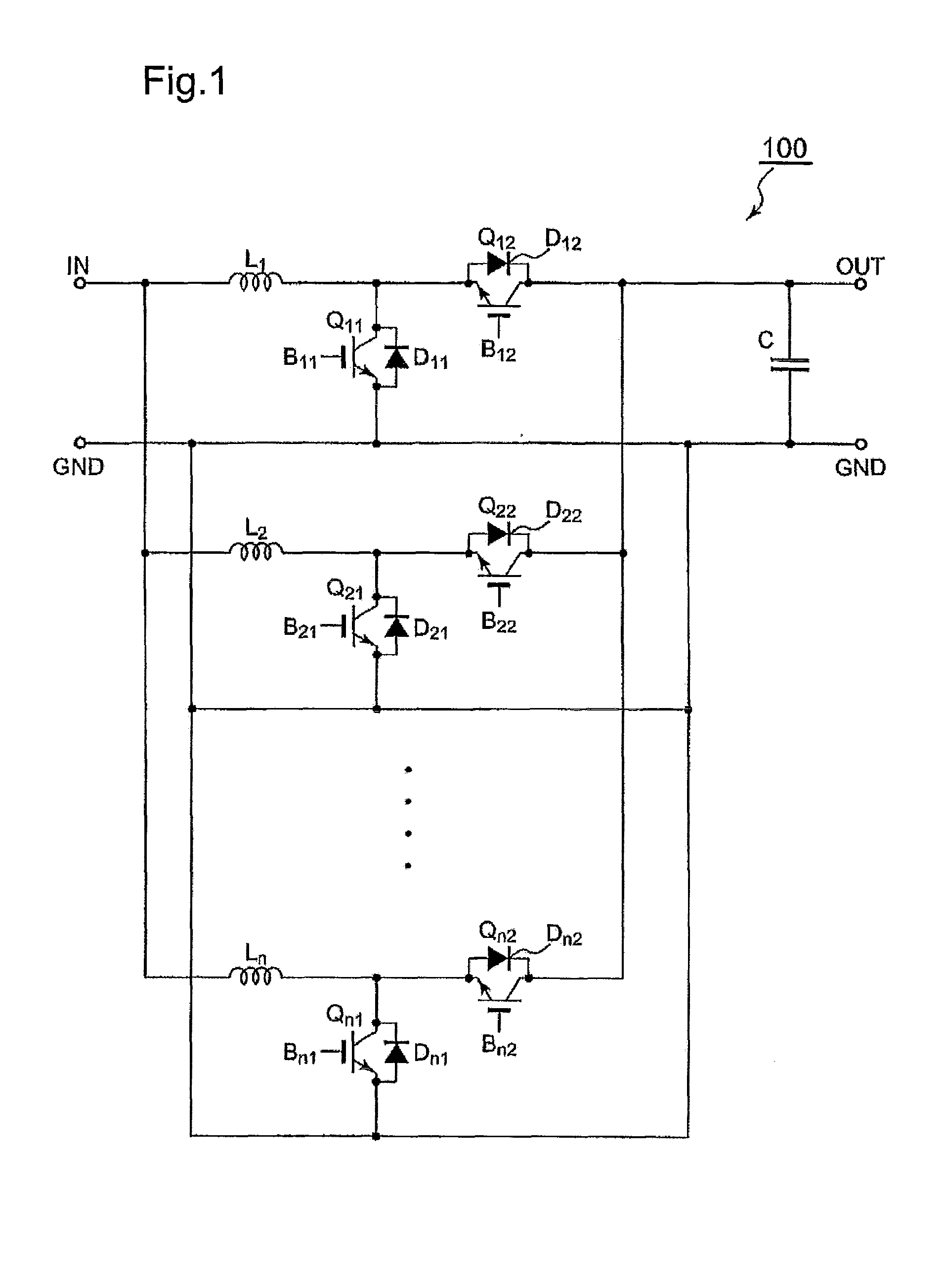
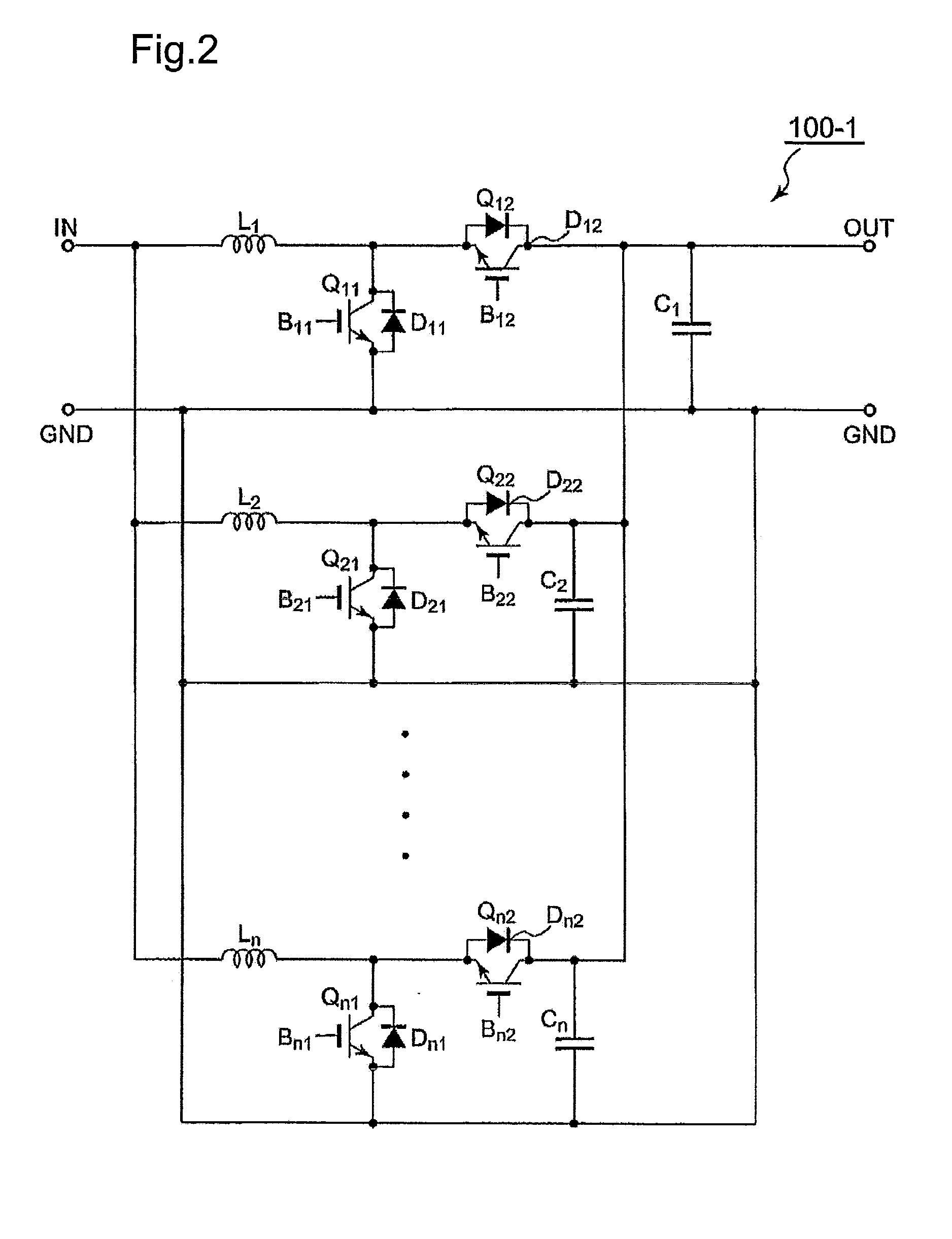
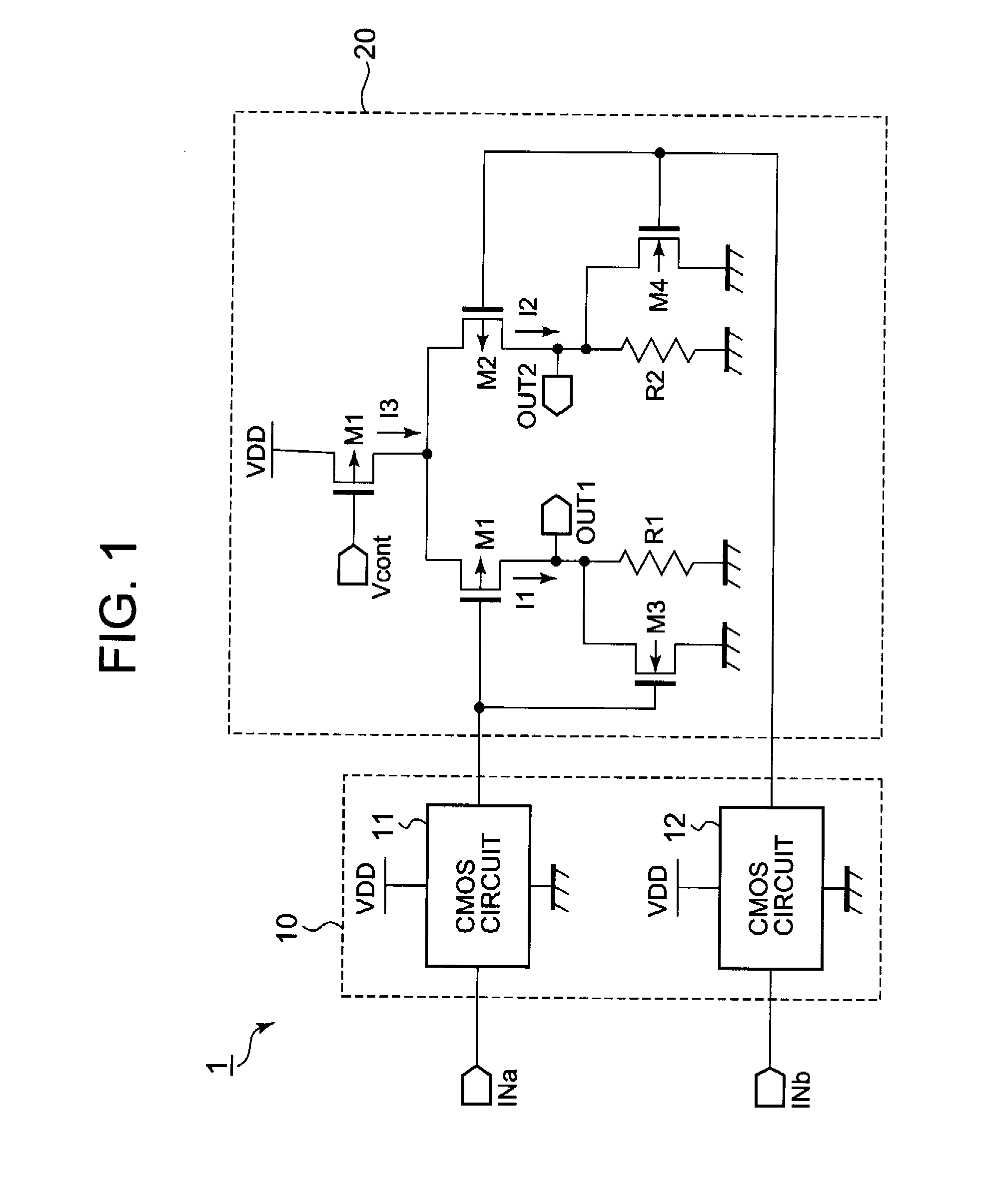
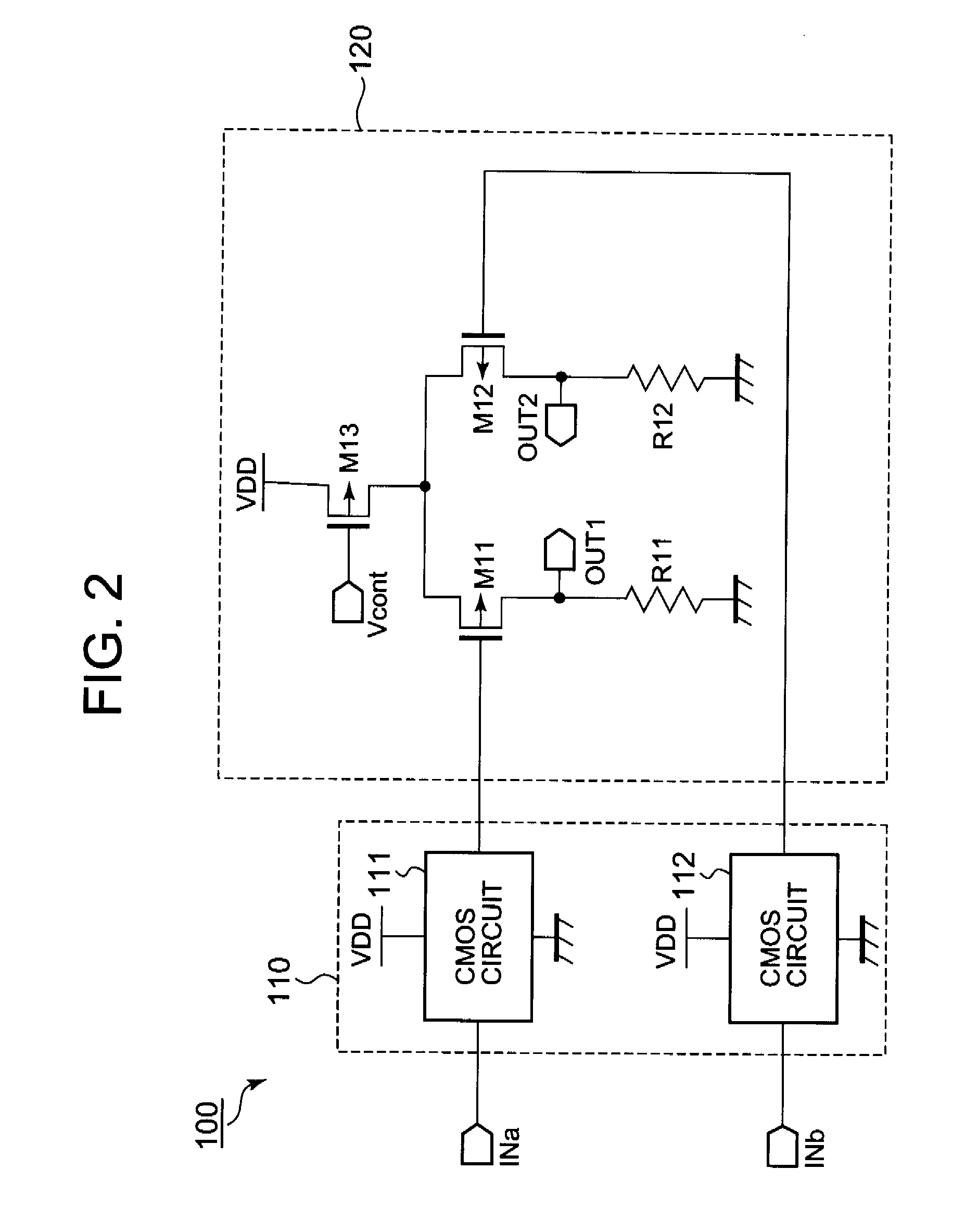
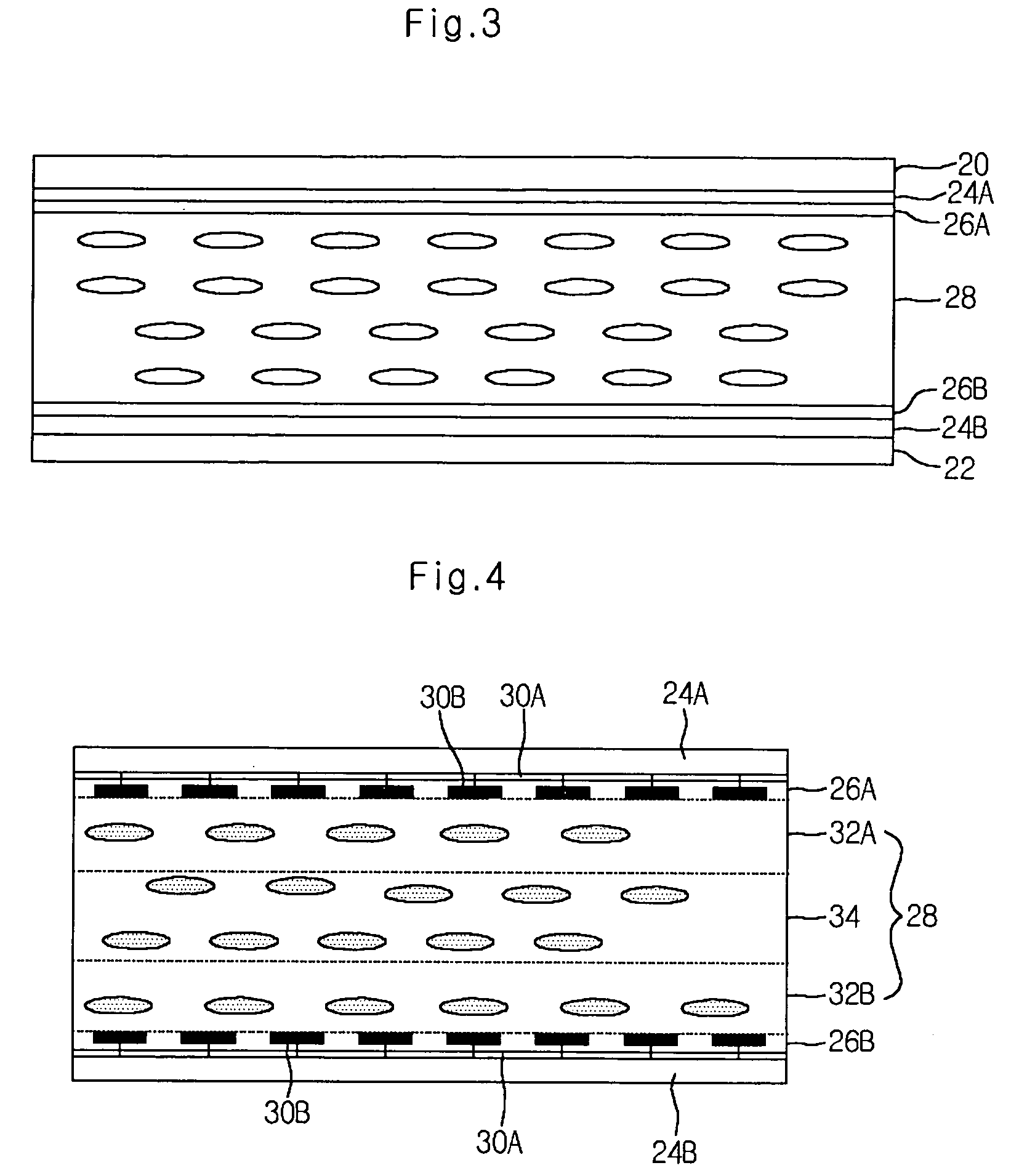
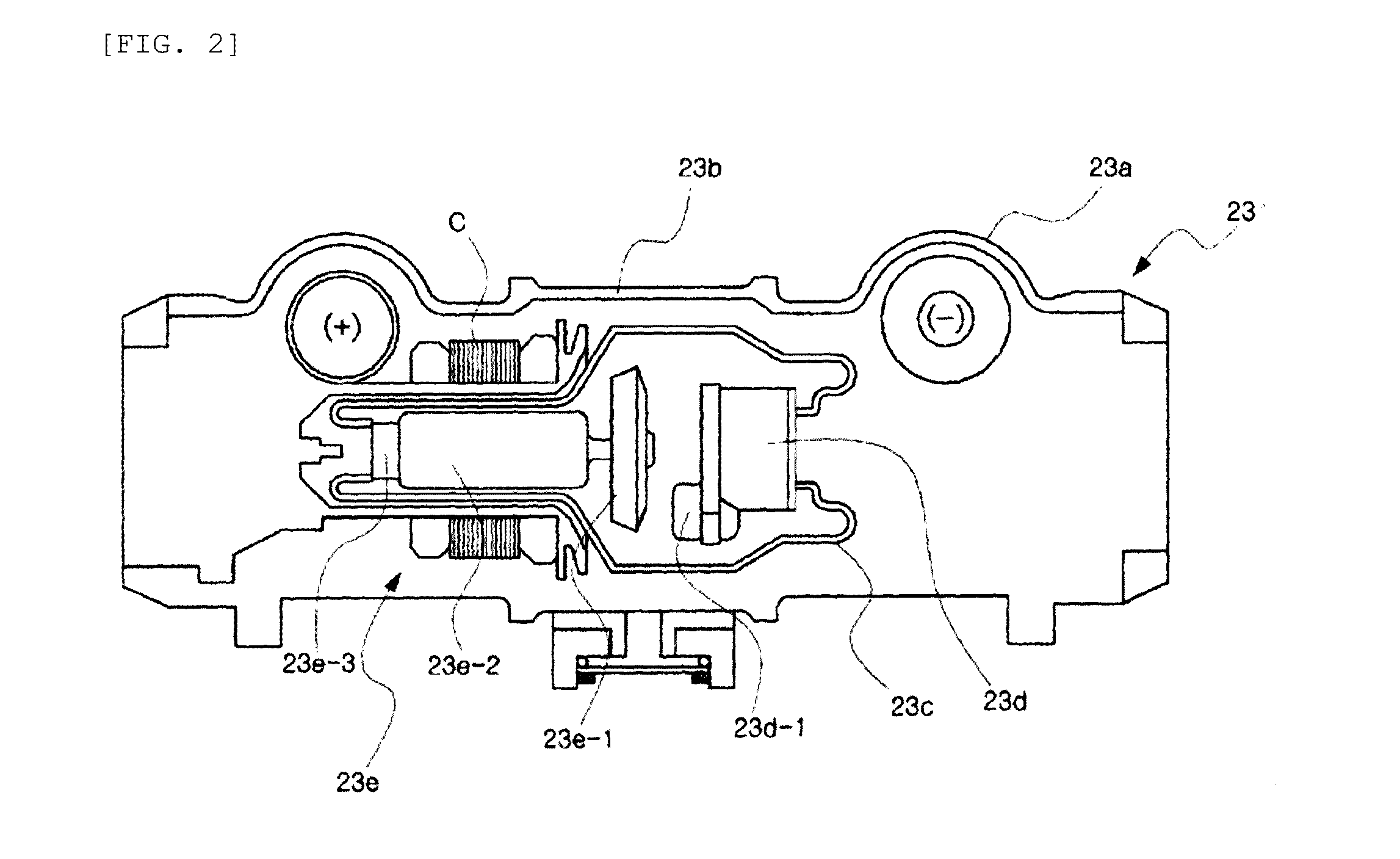
Driving unit for liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20060145998A1Solve the insufficient charging timeShortened fall timeStatic indicating devicesDigital storageLiquid-crystal displayVoltage
A driving unit for a liquid crystal display device is provided. The driving unit includes a first group of driving stages and a second group of driving stages. A first driving stage of the first group receives a first gate start voltage. The first group of driving stages sequentially outputs scan signals according to a first clock signal. The scan signal outputted by one driving stage of the first group is sent to a next subsequent driving stage of the first group. A first driving stage of the second group receives a second start voltage. The second group of driving stages sequentially outputs the scan signals according to a second clock signal. The scan signal outputted by one driving stage of the second group is sent to a next subsequent driving stage of the second group. The driving stages of the first group and the second group alternately output the scan signals.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
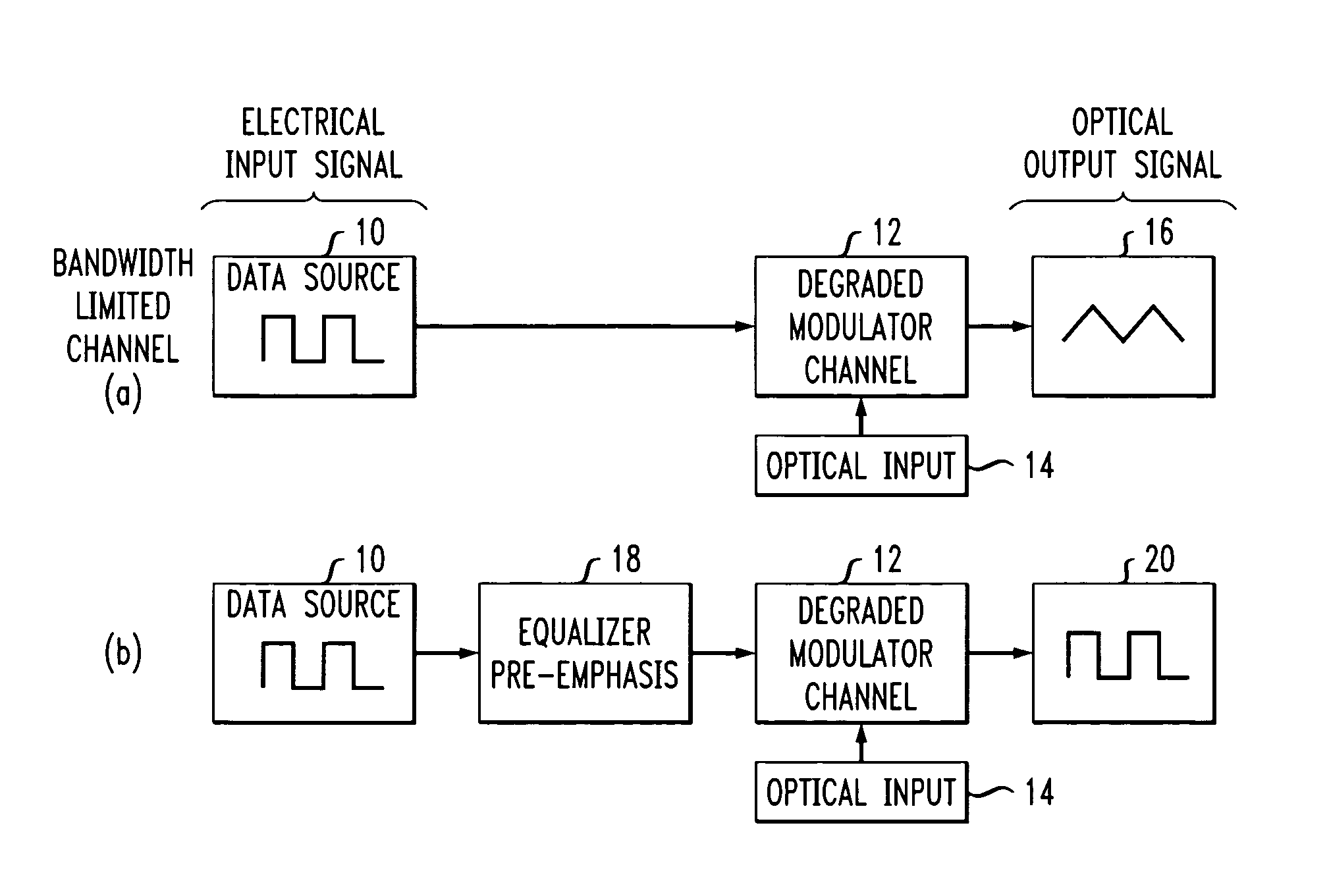
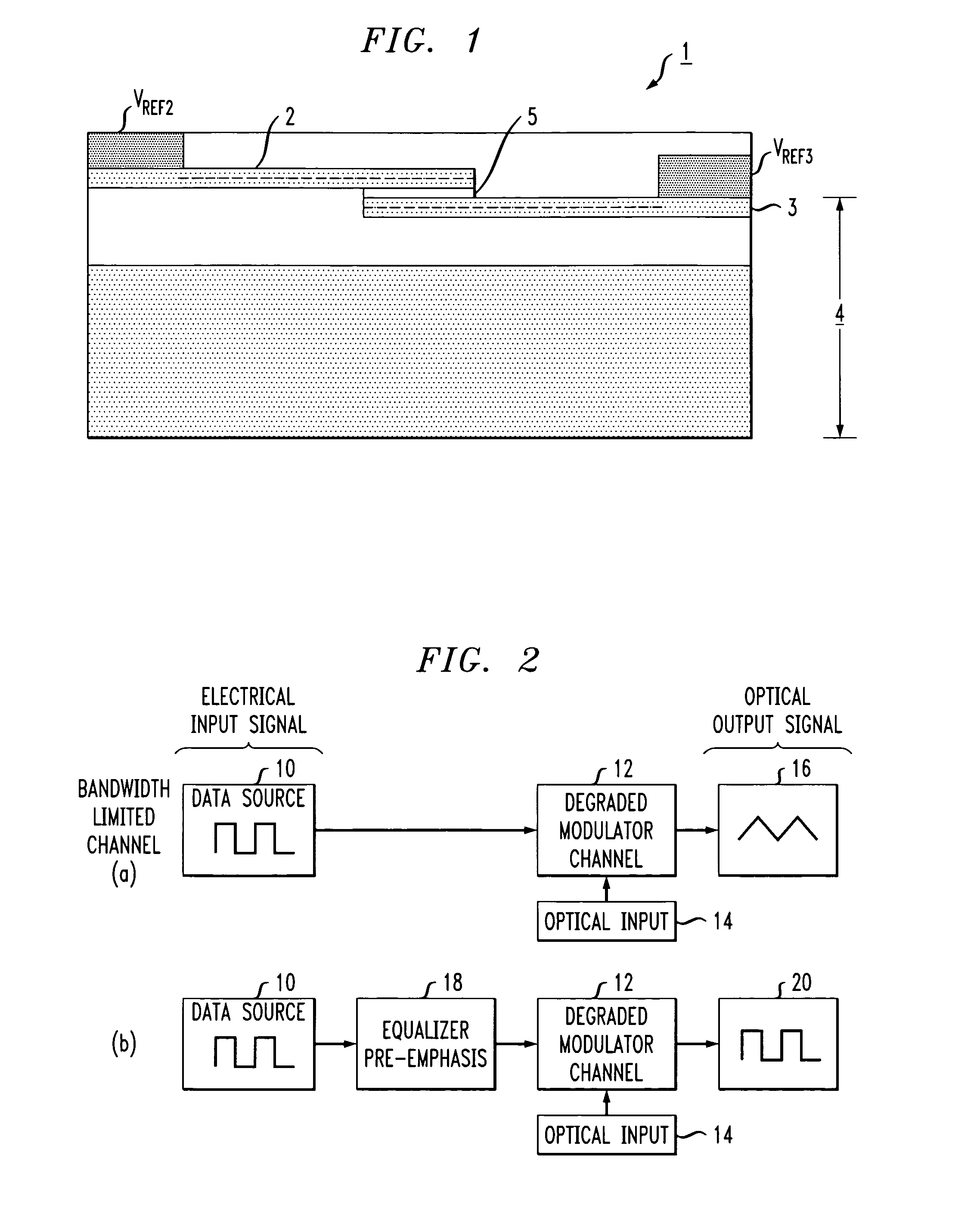
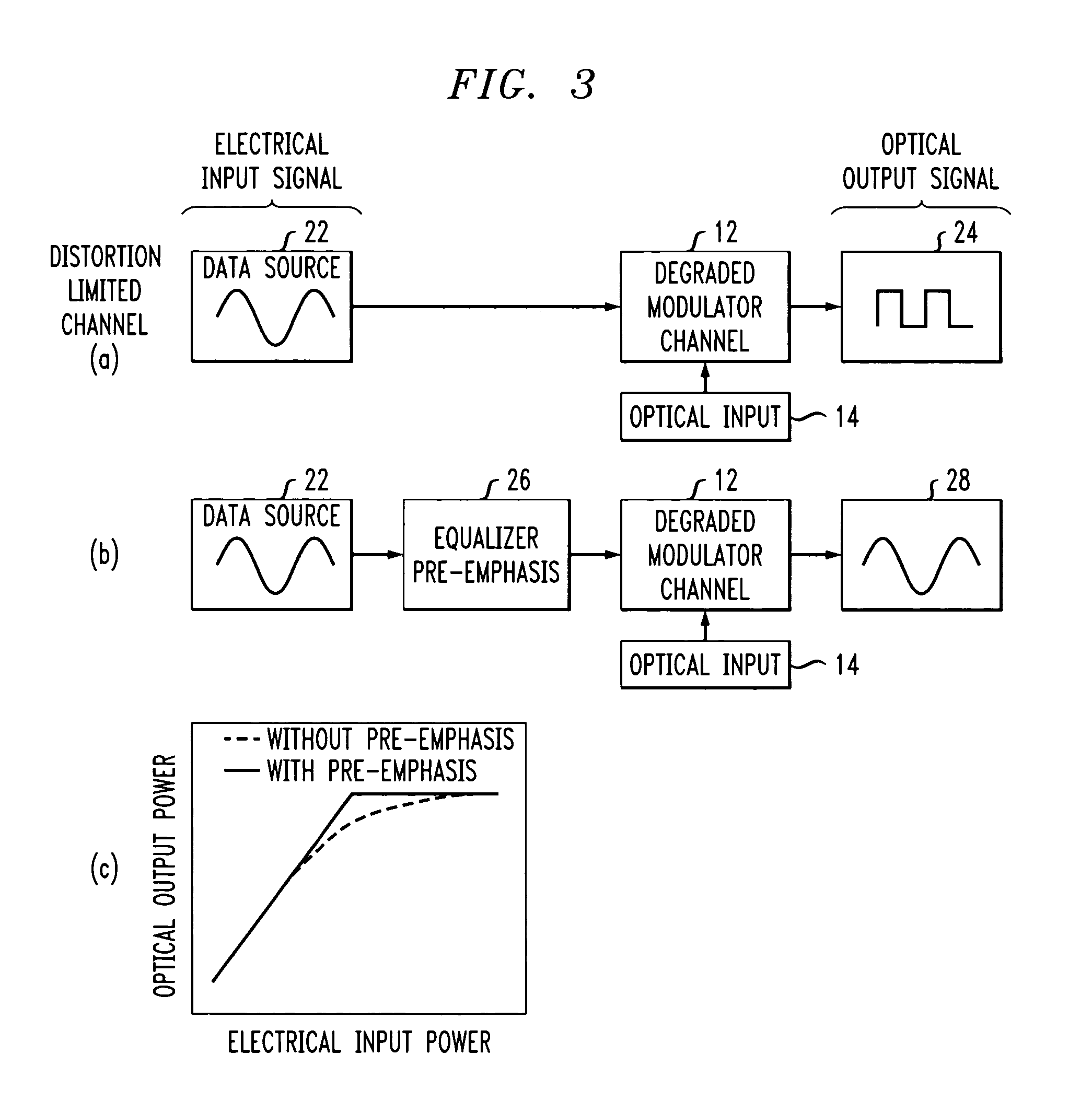
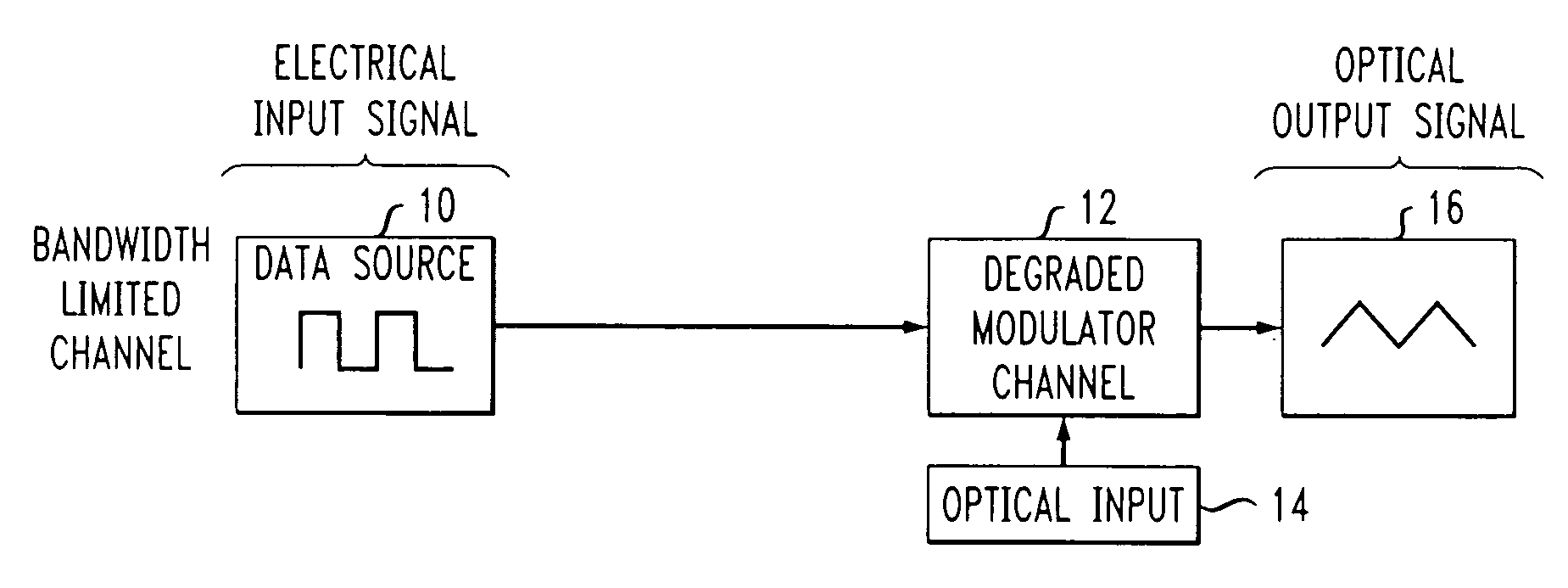
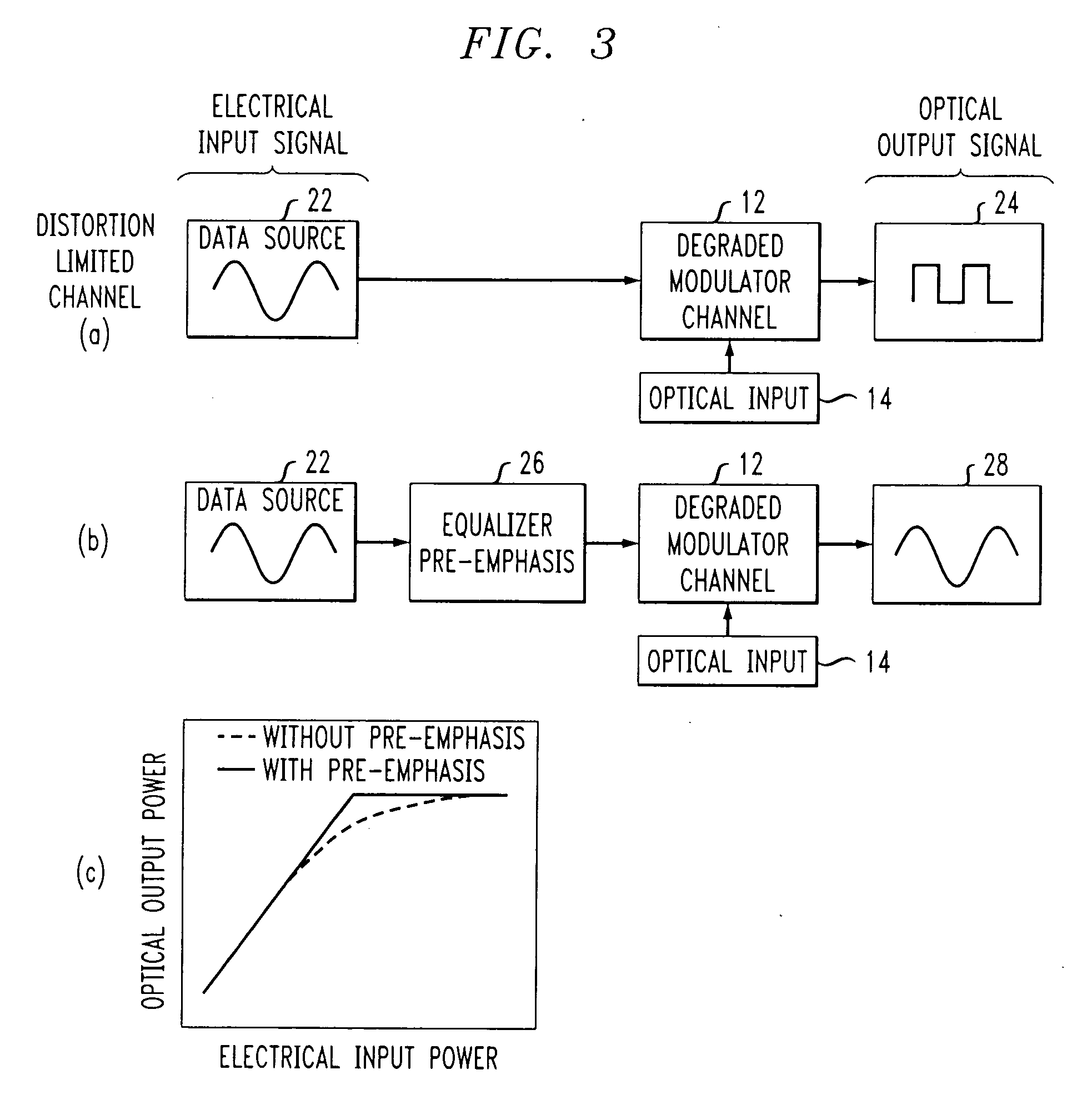
High speed, silicon-based electro-optic modulator
ActiveUS7065301B2Fast switching speedReduce fallsElectromagnetic transmittersOptical light guidesCarrier signalRefractive index
An electro-optic modulator arrangement for achieving switching speeds greater than 1 Gb / s utilizes pre-emphasis pulses to accelerate the change in refractive index of the optical waveguide used to form the electro-optic modulator. In one embodiment, a feedback loop may be added to use a portion of the modulated optical output signal to adjust the magnitude and duration of the pre-emphasis pulses, as well as the various reference levels used for modulated. For free carrier-based electro-optic modulators, including silicon-based electro-optic modulators, the pre-emphasis pulses are used to accelerate the movement of free carriers at the transitions between input signal data values.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20110018915A1Suppress signal distortionShortened fall timeElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDevice materialHemt circuits
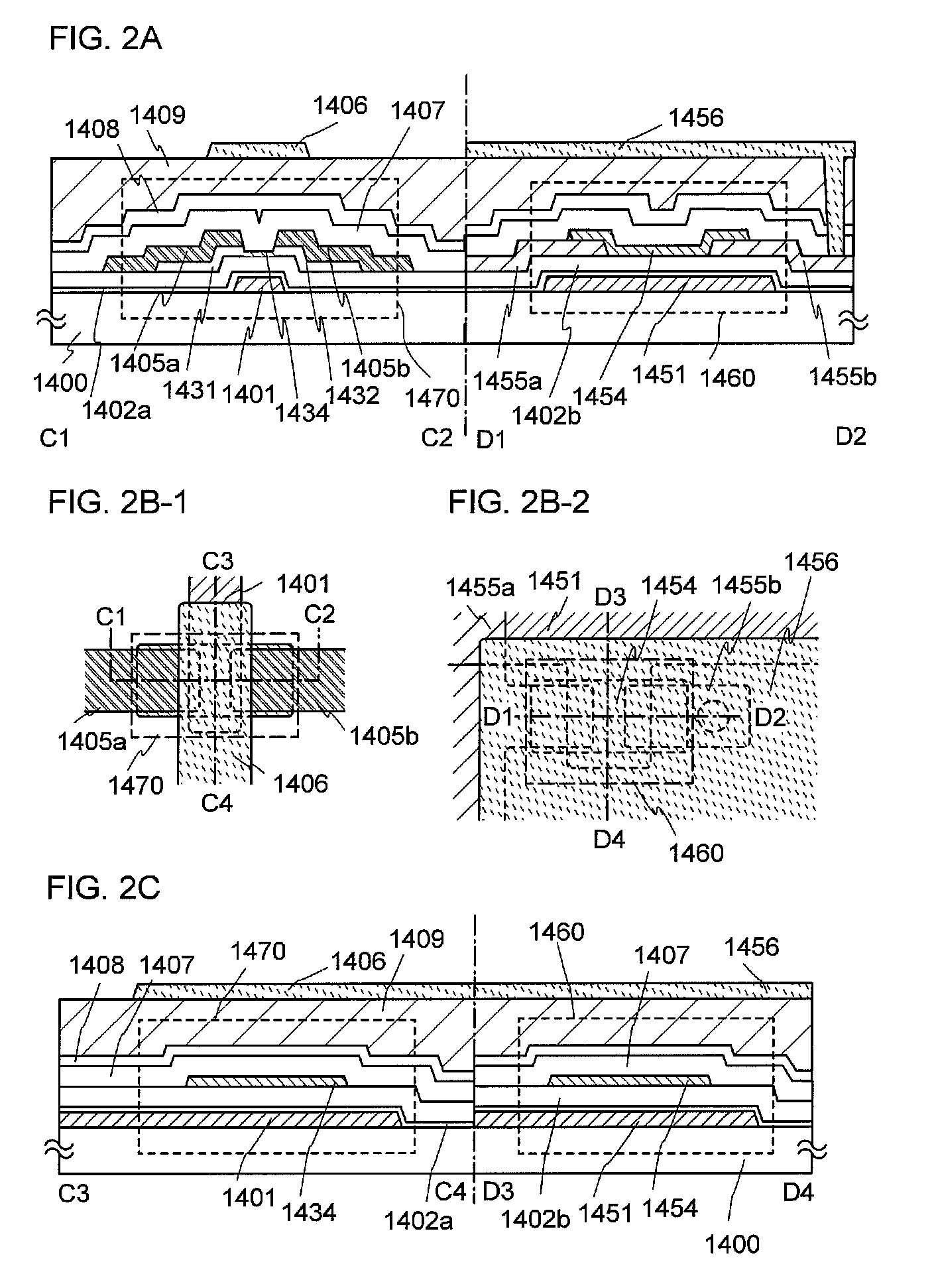
It is an object to provide a semiconductor device which can supply a signal with sufficient amplitude to a scan line while power consumption is kept small. Further, it is an object to provide a semiconductor device which can suppress distortion of a signal supplied to the scan line and shorten a rising time and a falling time while power consumption is kept small. A semiconductor device which includes a plurality of pixels each including a display element and at least one first transistor and a scan line driver circuit supplying a signal for selecting the plurality of pixels to a scan line. A light-transmitting conductive layer is used for a pixel electrode layer of the display element, a gate electrode layer of the first transistor, source and drain electrode layers of the first transistor, and the scan line. The scan line driver circuit includes a second transistor and a capacitor for holding a voltage between a gate electrode layer of the second transistor and a source electrode layer of the second transistor. The source electrode of the second transistor is connected to the scan line.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Driving method of in-plane-switching mode LCD
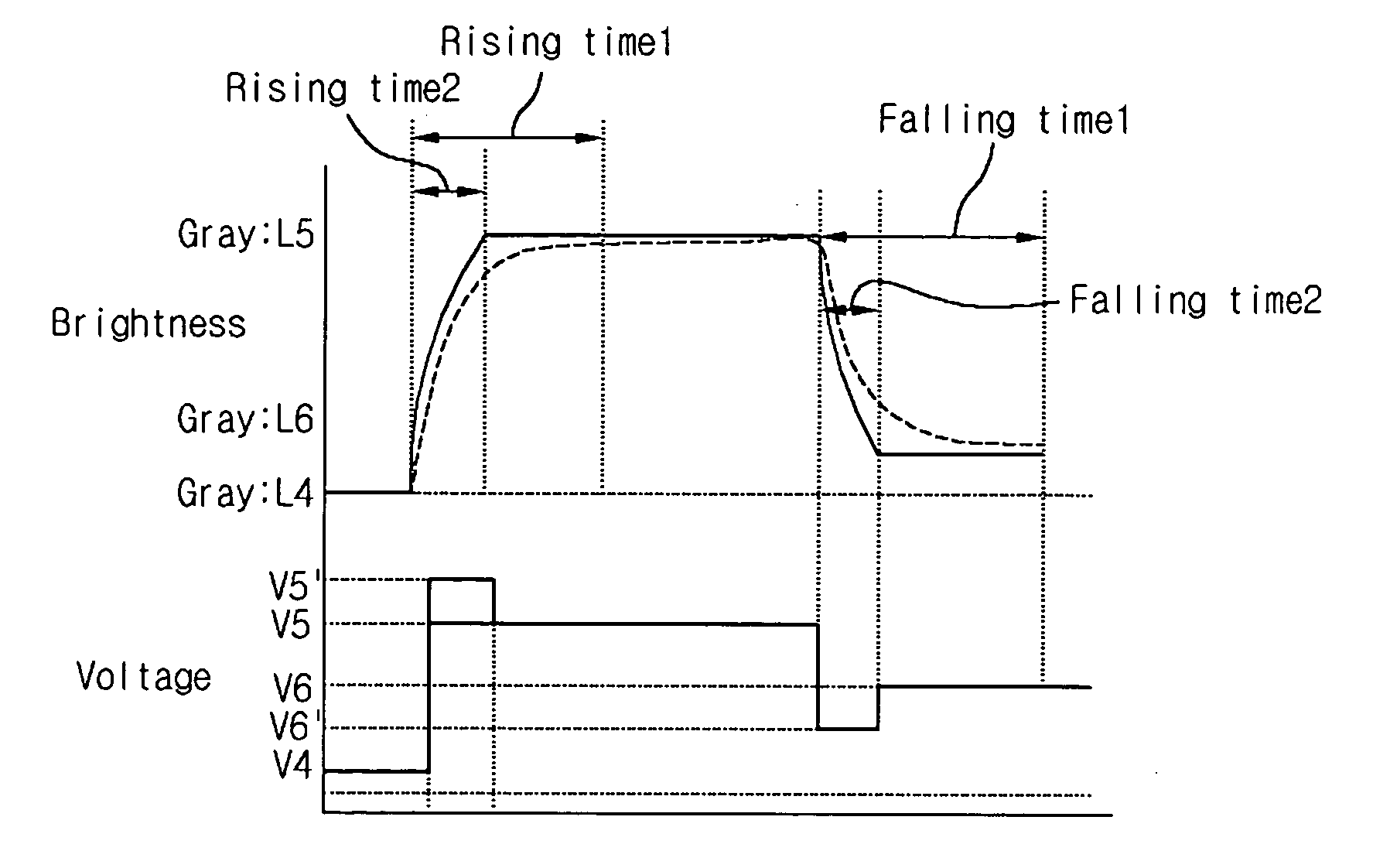
ActiveUS20050140617A1Shortened fall timeShorten rise timeStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsIn planeData signal
A method of driving an IPS mode LCD includes applying a common voltage to a common electrode of the LCD panel, the LCD panel including a liquid crystal (LC) cell and driving the LC cell to express light at a predetermined brightness level associated with a predetermined data signal voltage applied to a pixel electrode, the driving including applying a compensation voltage to the LC cell prior to applying the predetermined data signal voltage, wherein a voltage difference between a previously applied data signal voltage and the compensation voltage is greater than a voltage difference between a previously applied data signal voltage and the predetermined data signal voltage.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Boosted converter for pulsed electric machine control
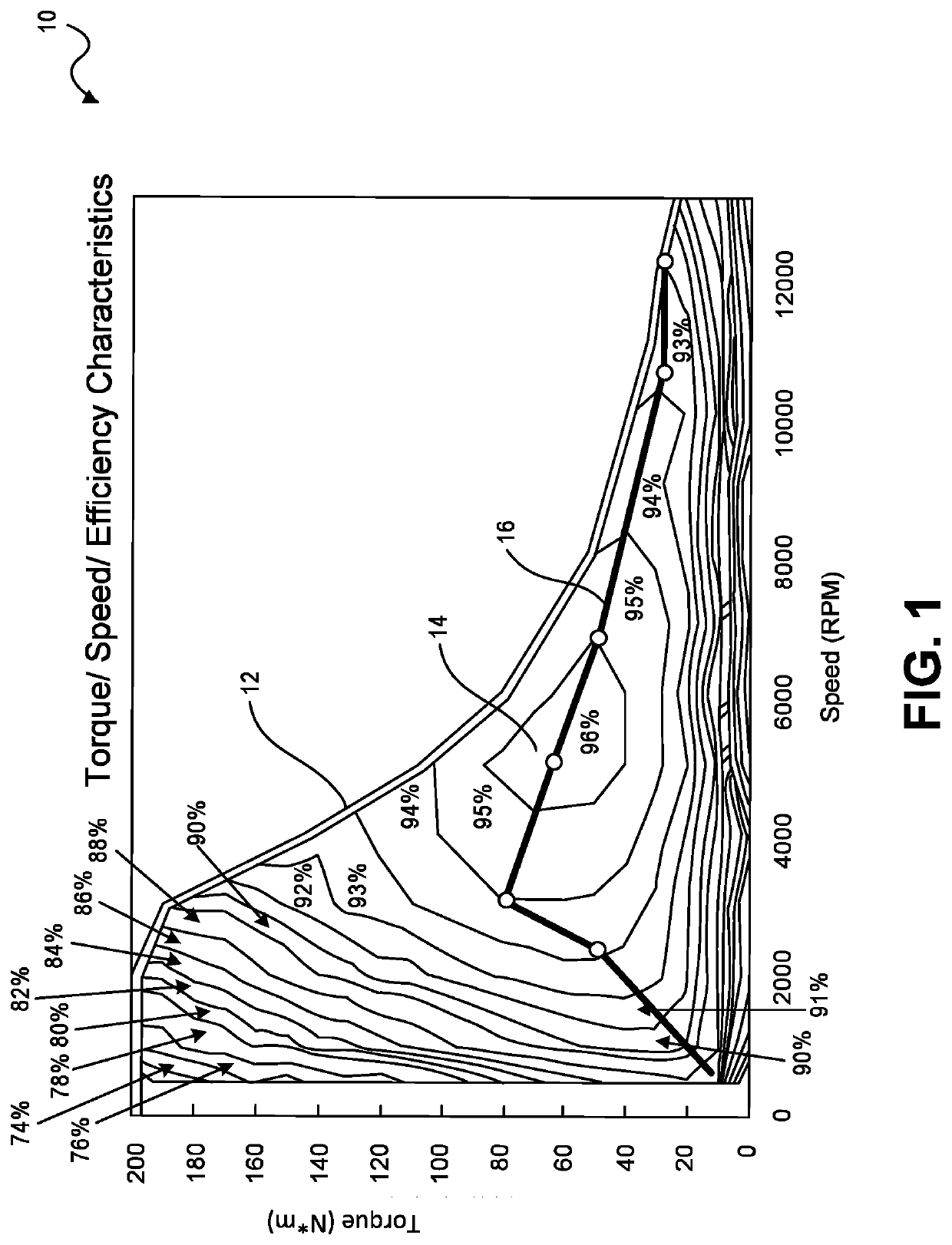
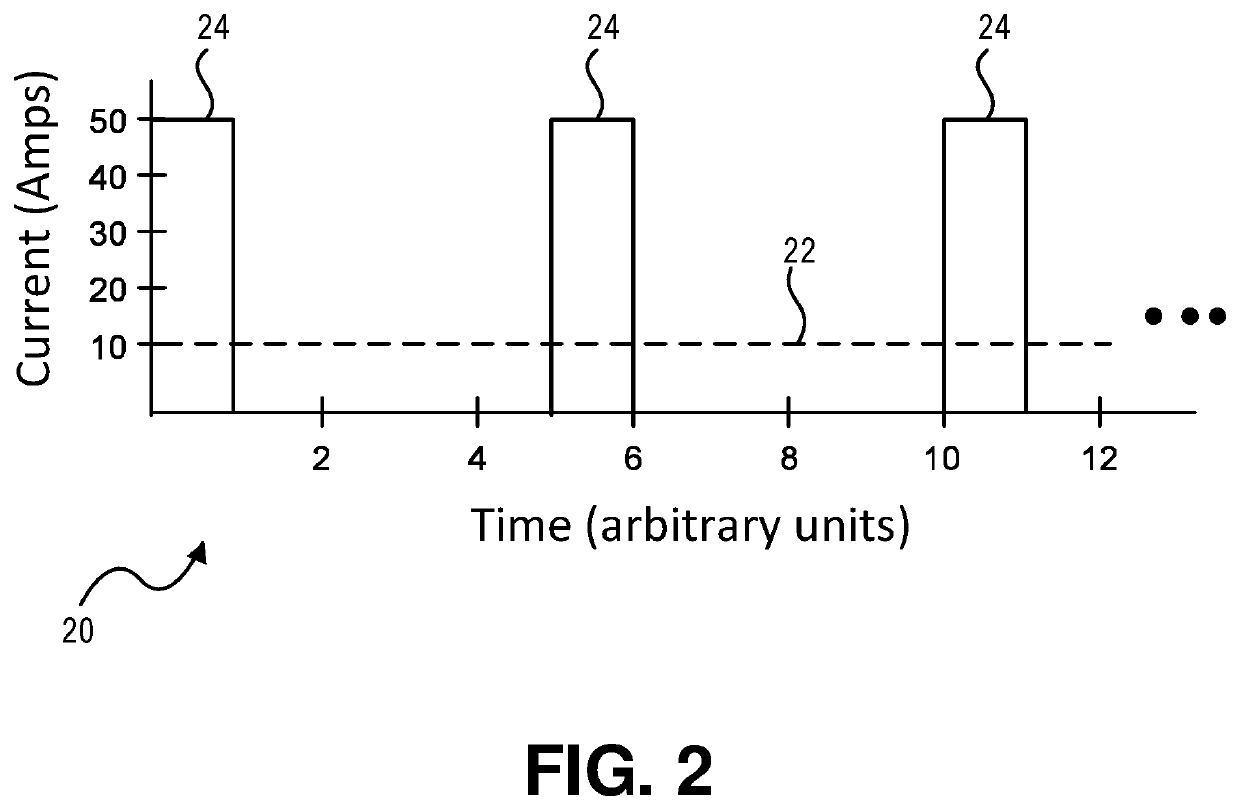
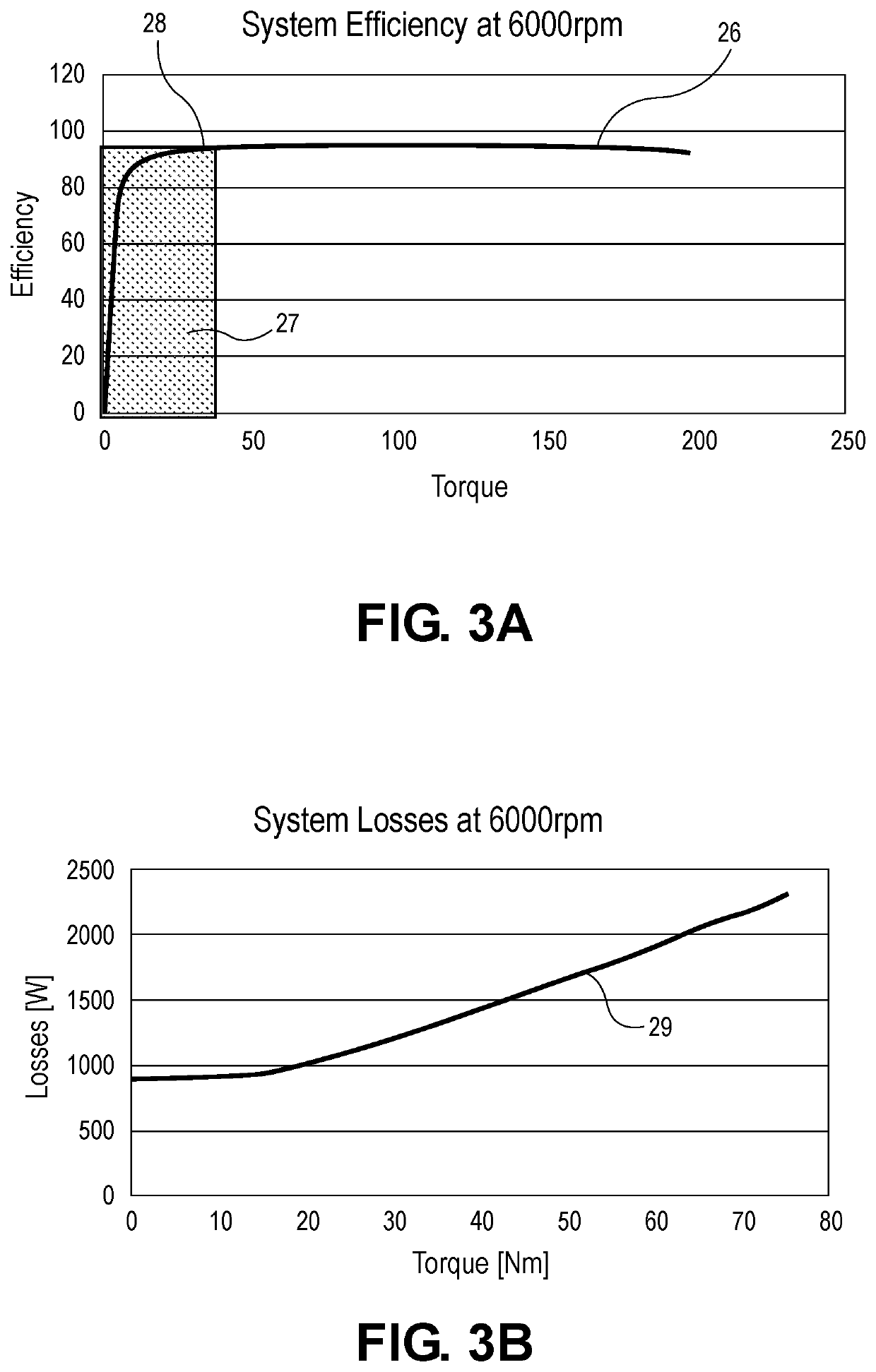
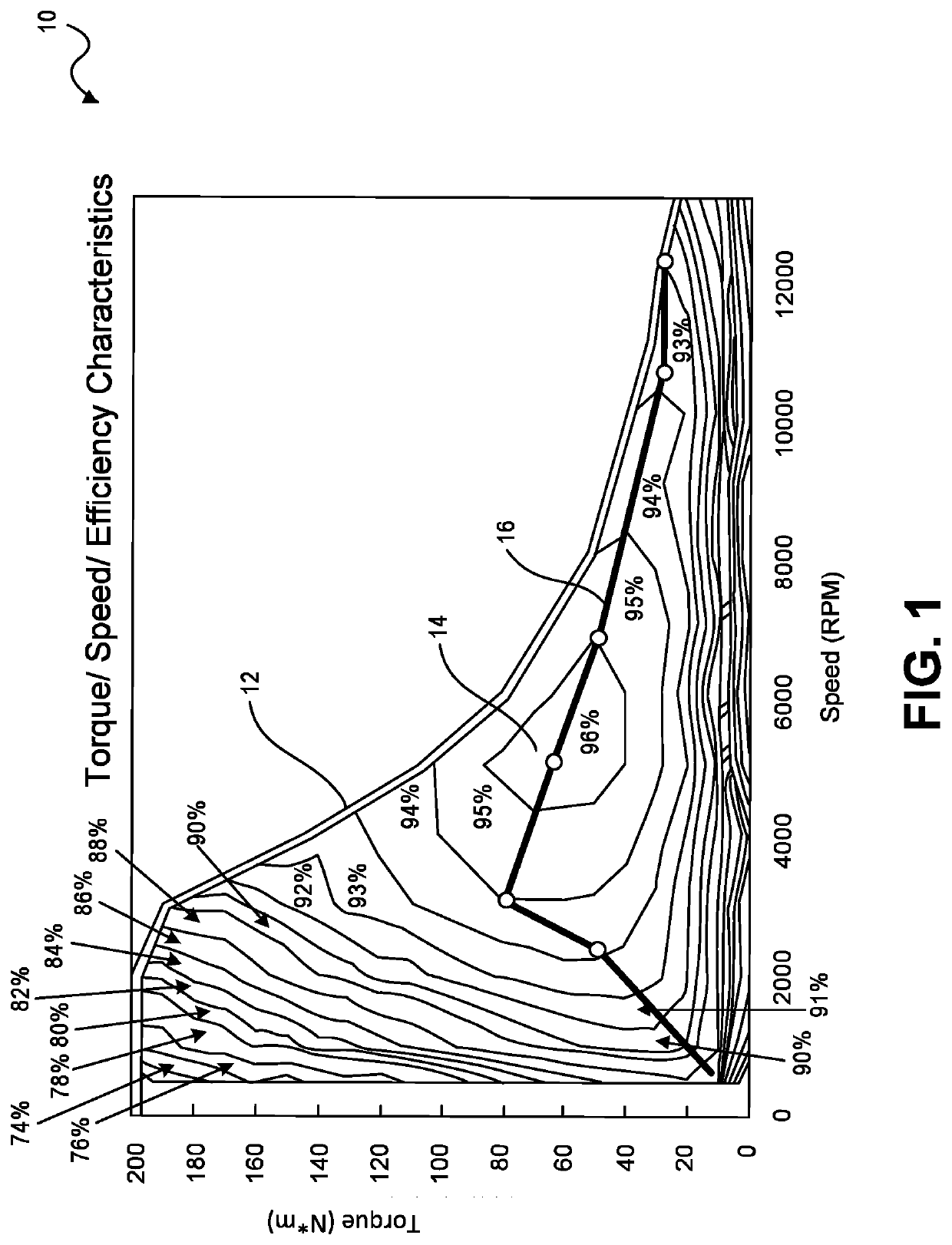
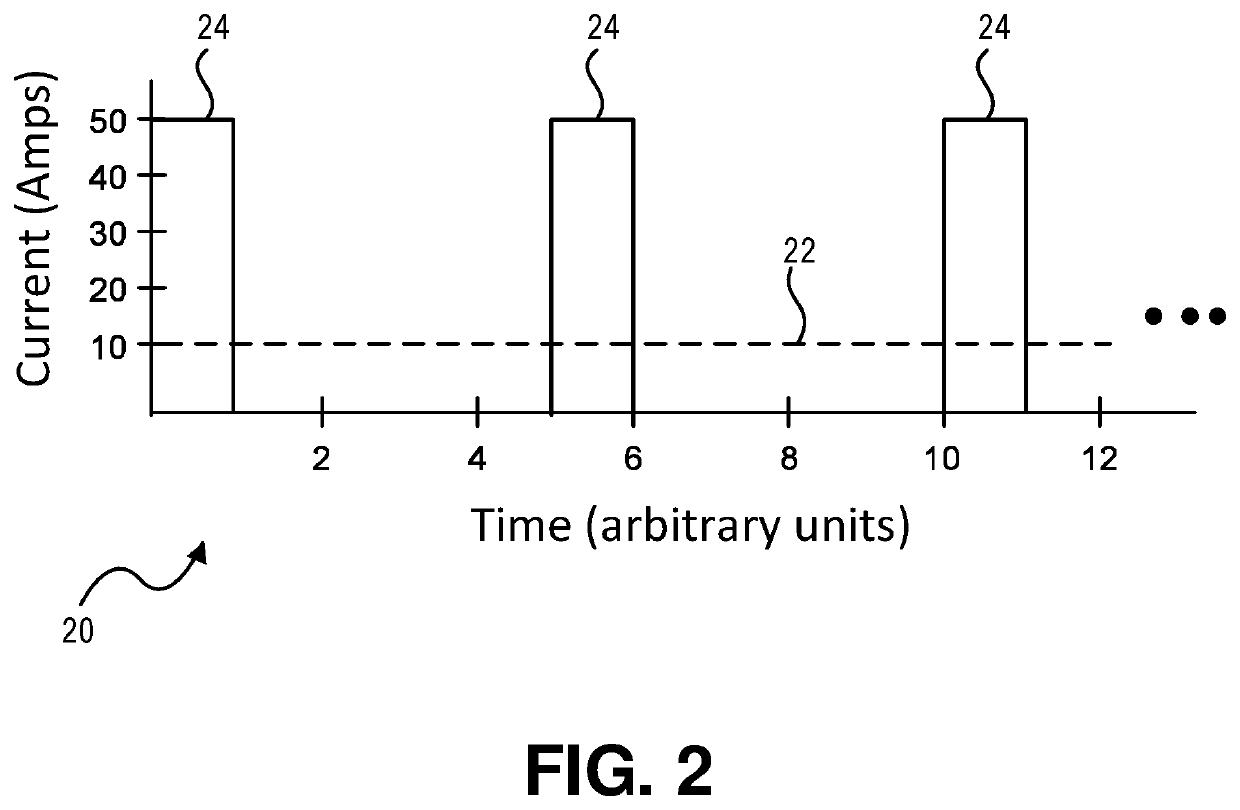
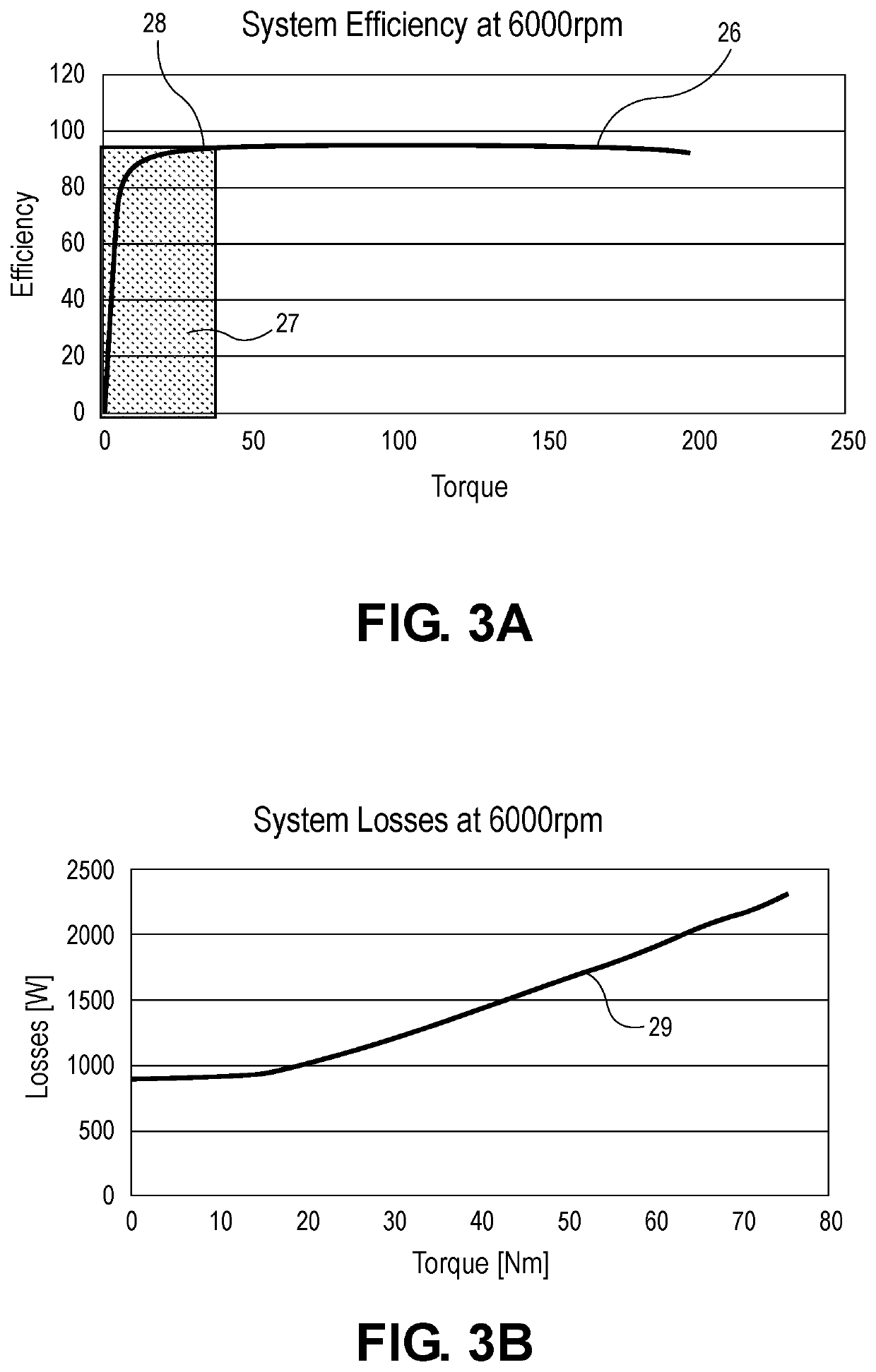
ActiveUS10944352B2Reduce rise and fall timesEasy to operateSpeed controllerMotor control for low load efficiencyConvertersPulse control
A boost circuit is arranged to reduce rise and fall times of pulsed power used for pulsed control operation of electric machines. Magnetic energy present in the electric machine at the end of a pulse is extracted by the boost circuit to reduce the pulse fall time. The energy is stored by the boost circuit and then applied at the beginning of a subsequent pulse to reduce the rise time. By reducing rise and fall times compared to not using such a boost circuit, machine efficiency is improved.
Owner:TULA ETECH INC
Boosted converter for pulsed electric machine control
ActiveUS20200212834A1Operation efficiency can be improvedShortened fall timeSpeed controllerMotor control for low load efficiencyConvertersPulse control
A boost circuit is arranged to reduce rise and fall times of pulsed power used for pulsed control operation of electric machines. Magnetic energy present in the electric machine at the end of a pulse is extracted by the boost circuit to reduce the pulse fall time. The energy is stored by the boost circuit and then applied at the beginning of a subsequent pulse to reduce the rise time. By reducing rise and fall times compared to not using such a boost circuit, machine efficiency is improved.
Owner:TULA ETECH INC
Semiconductor device, light emission control circuit, and electronic appliance
ActiveUS20180267395A1Increasing consumptionIncreasing noiseElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesControl signalEngineering
A semiconductor device of the invention is a semiconductor device that controls a transistor that controls an electric current that flows through a light emitting element, the transistor including a gate that is connected to one end of a capacitor. The semiconductor device includes: a first terminal that is connected to the gate of the transistor and the one end of the capacitor; a second terminal that is connected to the other end of the capacitor; a first driving circuit that outputs a first control signal to the first terminal; and a second driving circuit that, in order to control the transistor in an on-state or an off-state, activates or deactivates a second control signal, and outputs the second control signal to the second terminal, the second control signal having a potential lower than a potential of the first control signal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
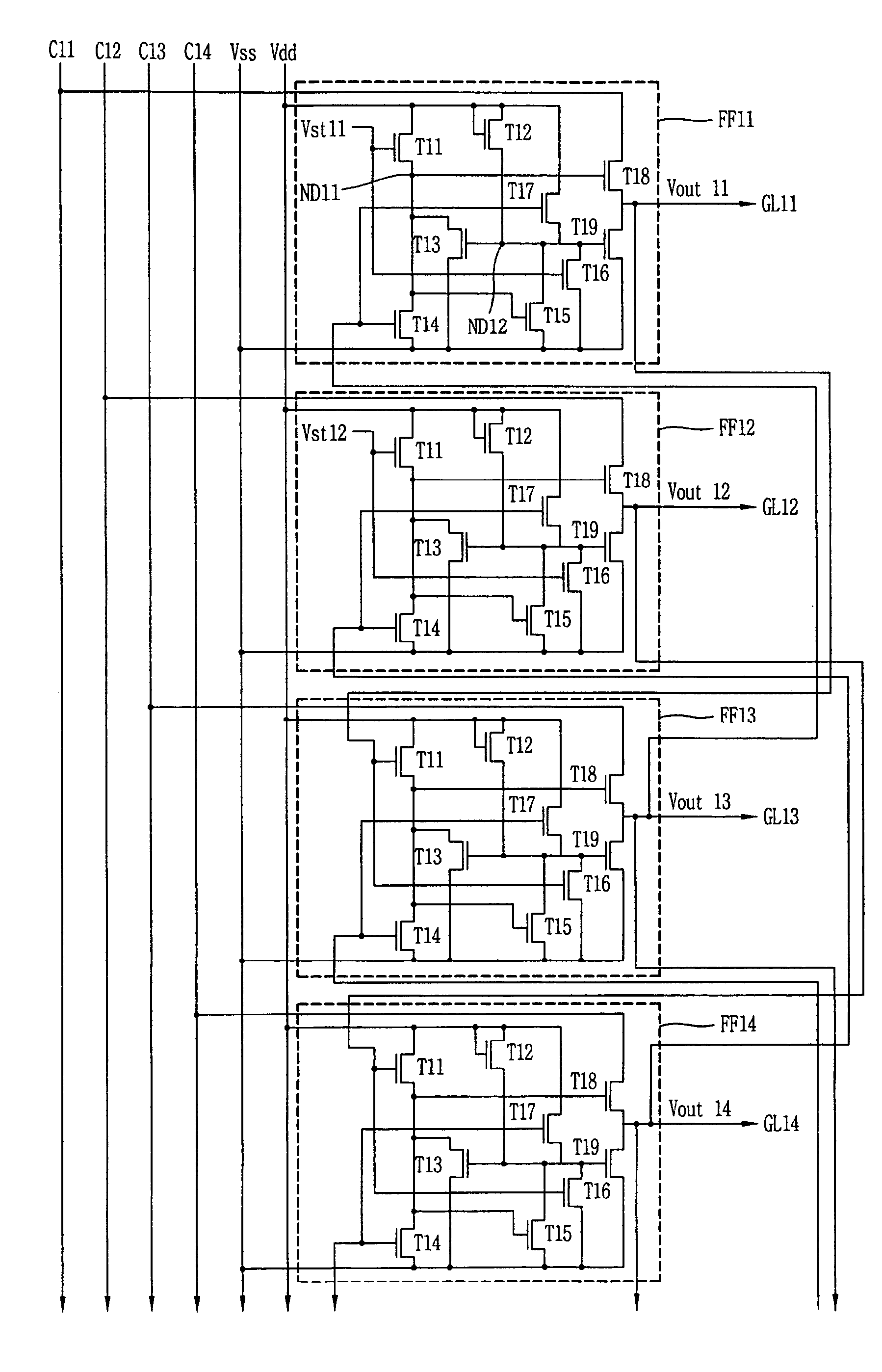
Gate driving circuit unit and gate driving circuit
The invention discloses a gate driving circuit unit and a gate driving circuit. The gate driving circuit unit comprises a driving control module, a driving module, a low-level maintaining module, a scanning signal output end and a transmission signal output end. The driving control module further comprises bootstrap series units. The gate driving circuit comprises the gate driving circuit units in N-grade cascade connection. The driving control module of the gate driving circuit unit controls the driving module to be in a charging or discharging state according to an input signal; the driving module charges the scanning signal output end and the transmission signal output end in a charging state and discharges the scanning signal output end and the transmission signal output end in a discharging state. According to the design of bootstrap series units, when the threshold voltage of a transistor is negative, electric leakage at a driving control end can be inhibited; when the threshold voltage of the transistor is positive, charging of the driving control end can be accelerated, so that rising / dropping time of an output signal is shortened, and the threshold voltage application range of the circuit is expanded.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
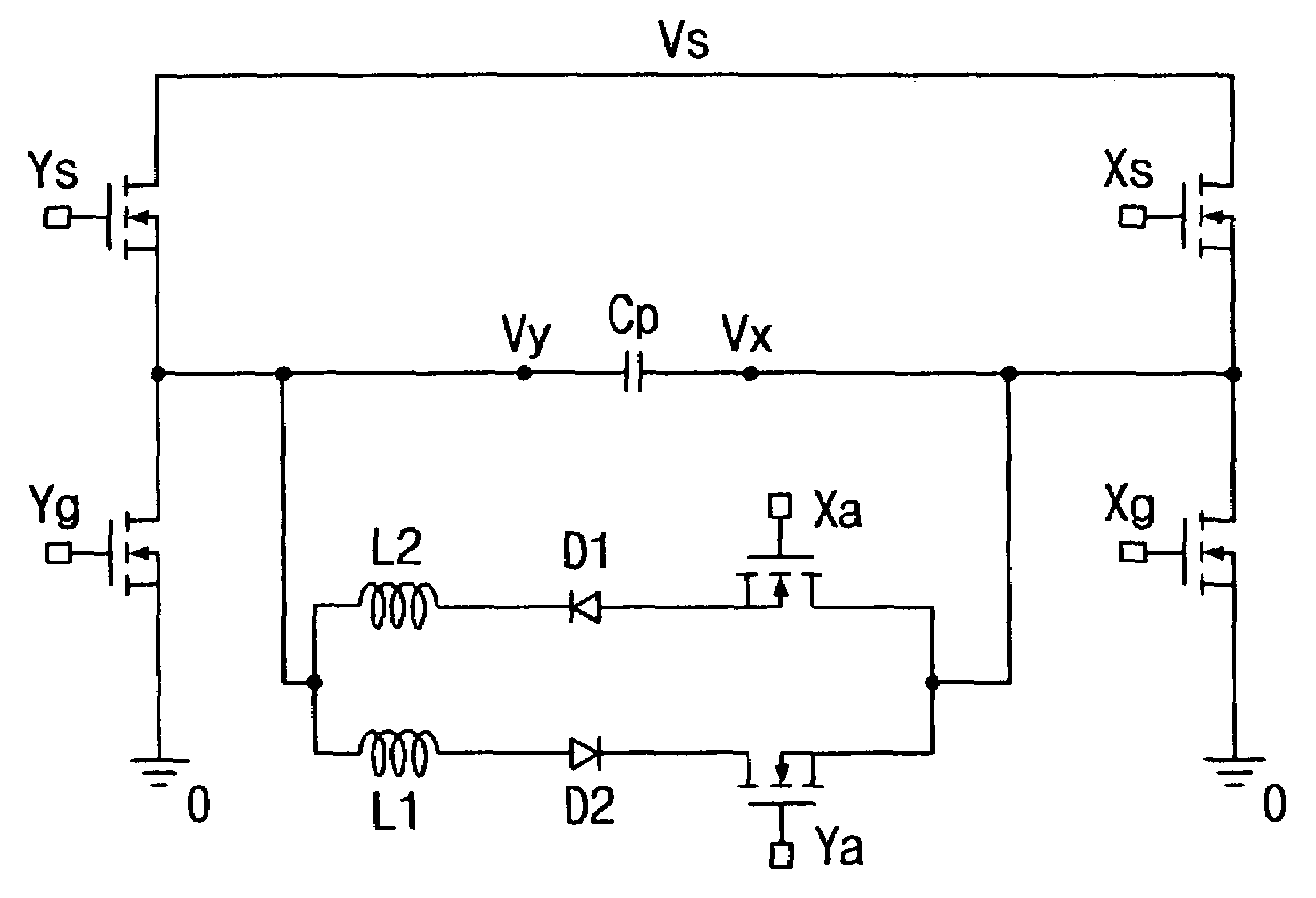
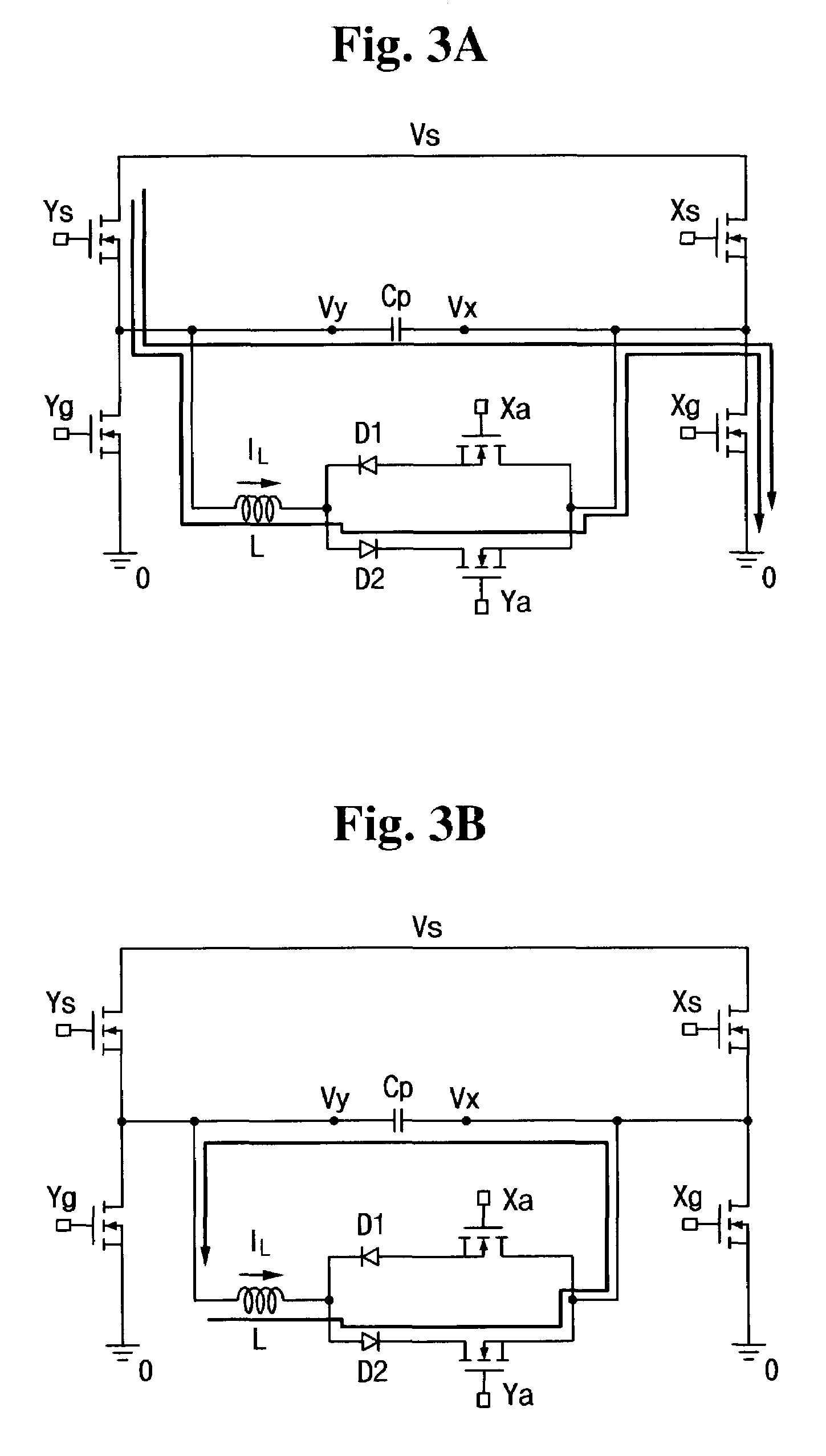
Electric vehicle drive dc-dc converter and electric vehicle
InactiveUS20100033011A1Reduce the amplitudeHigh frequencySpeed controllerElectric devicesDc dc converterElectric vehicle
An electric vehicle drive DC-DC converter and an electric vehicle are provided in which the electric vehicle drive DC-DC converter is constructed by connecting a plurality of DC-DC converter units in parallel, and in which a smoothing capacitor is allowed to be reduced in size thereof so that the DC-DC converter unit can be constructed in a small size, and electric power required by the electric vehicle can be coped with by only increasing the number of DC-DC converter units. Each of the DC-DC converter units includes: a coil having both ends thereof being connected to a DC power source and an electric vehicle drive source (motor); and a drive element which is connected in parallel to the electric vehicle drive source and driven in response to a signal supplied from a control circuit, the drive element having combined therewith a load current commutation diode. A single smoothing capacitor is connected in parallel to the electric vehicle drive source so that the respective drive elements of the plurality of DC-DC converter units are driven by the control circuit at different timings.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
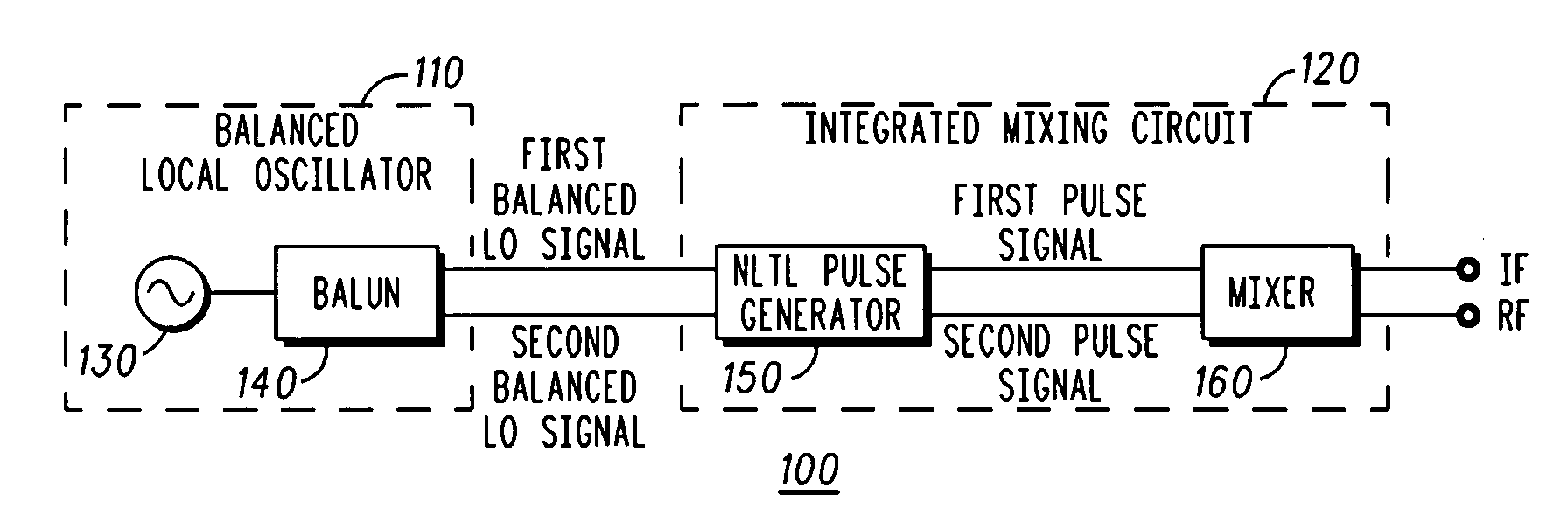
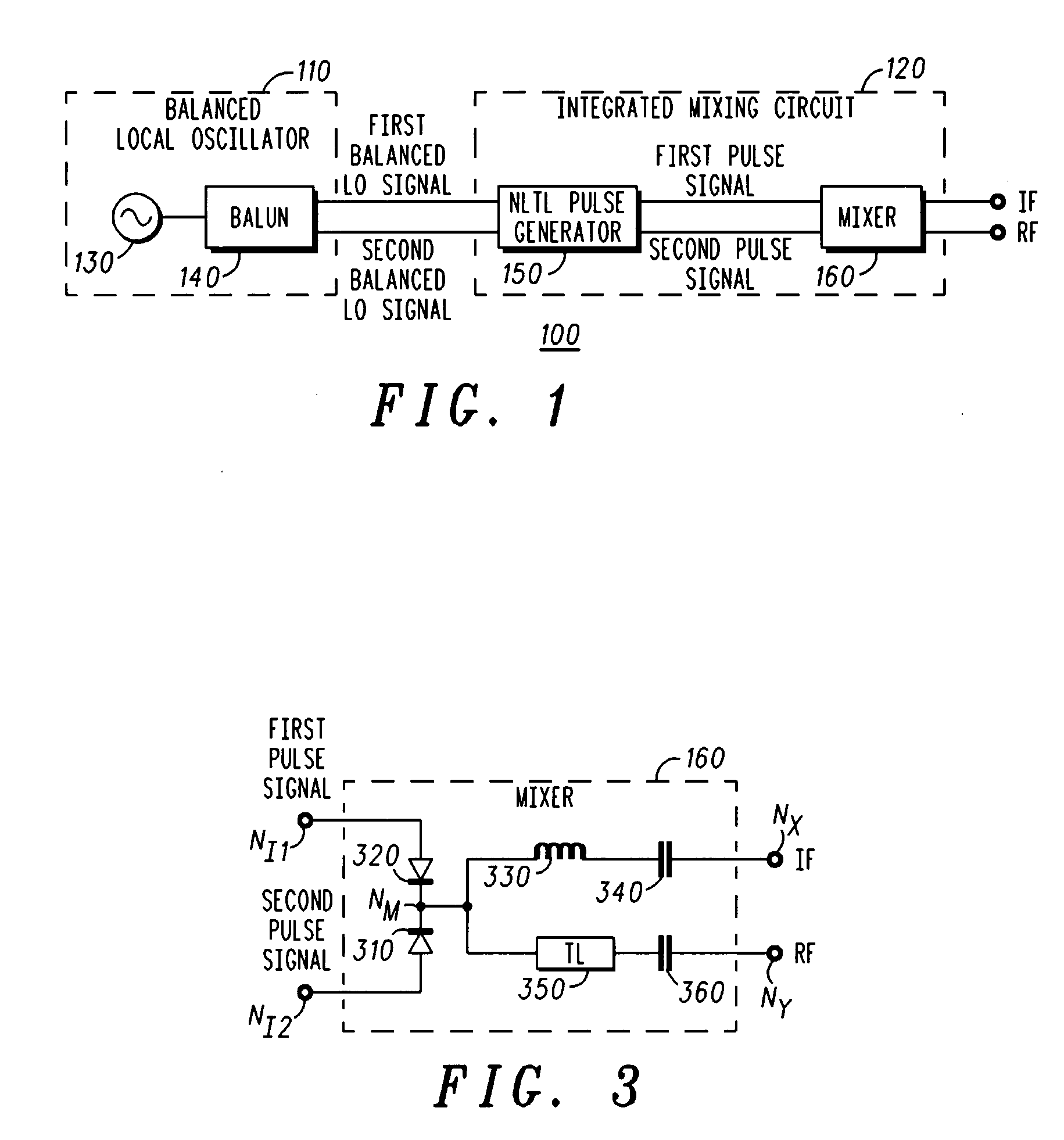
High linearity frequency conversion system and method
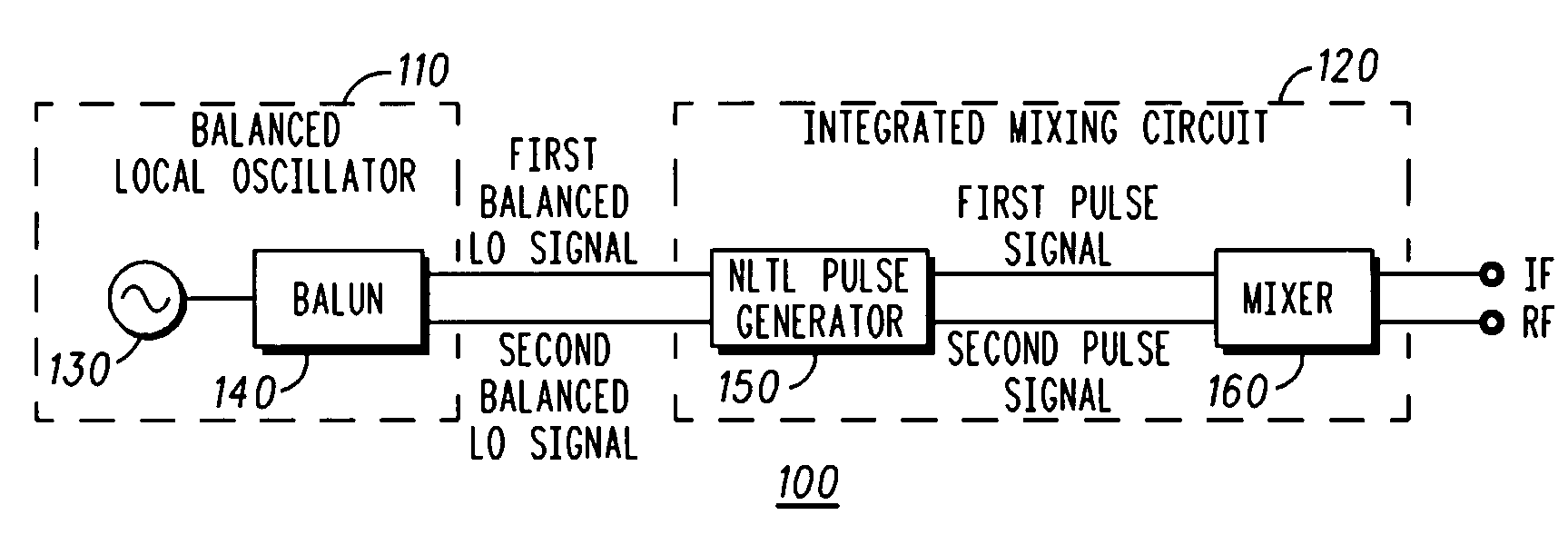
ActiveUS20080254759A1Shorten rise timeShortened fall timeModulation transferenceTransmission noise suppressionLocal oscillator signalFrequency conversion
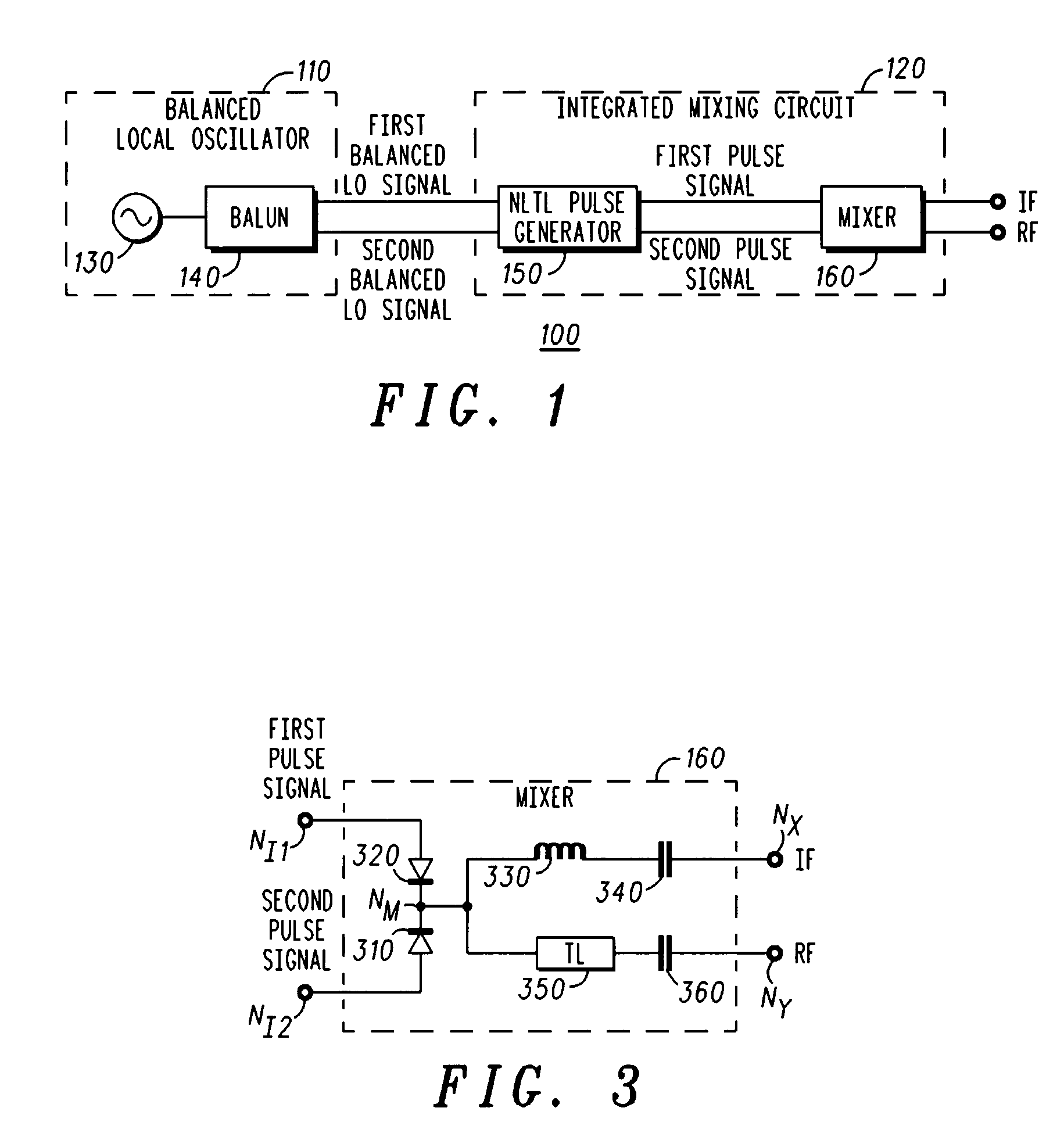
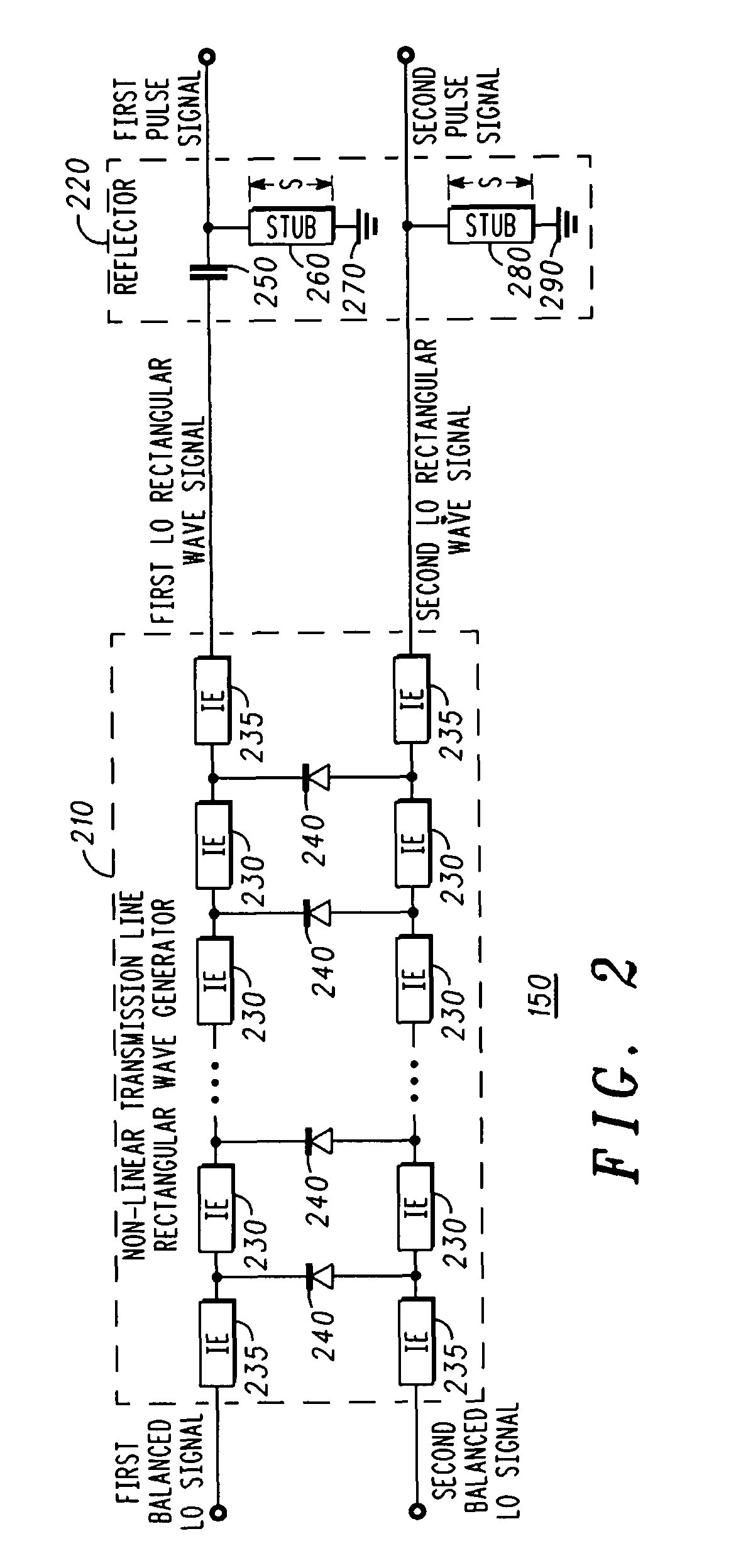
A frequency converter (100) is provided, comprising: a pulse generator (150) configured to receive a balanced local oscillator signal pair and to generate a balanced rectangular pulse signal pair having the reference frequency; and a mixer (160) configured to mix an input signal having an input frequency with the balanced rectangular pulse signal pair to generate an output signal having an output frequency. The input frequency is different from the output frequency, and the pulse generator and the mixer are formed on a single integrated circuit (120). The frequency converter may comprise a balanced local oscillator (110) configured to generate the balanced local oscillator signal pair. The balanced local oscillator may comprise: an unbalanced local oscillator (130) configured to provide an unbalanced local oscillator signal having the reference frequency; and a balun (140) configured to generate the balanced local oscillator signal pair based on the unbalanced local oscillator signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
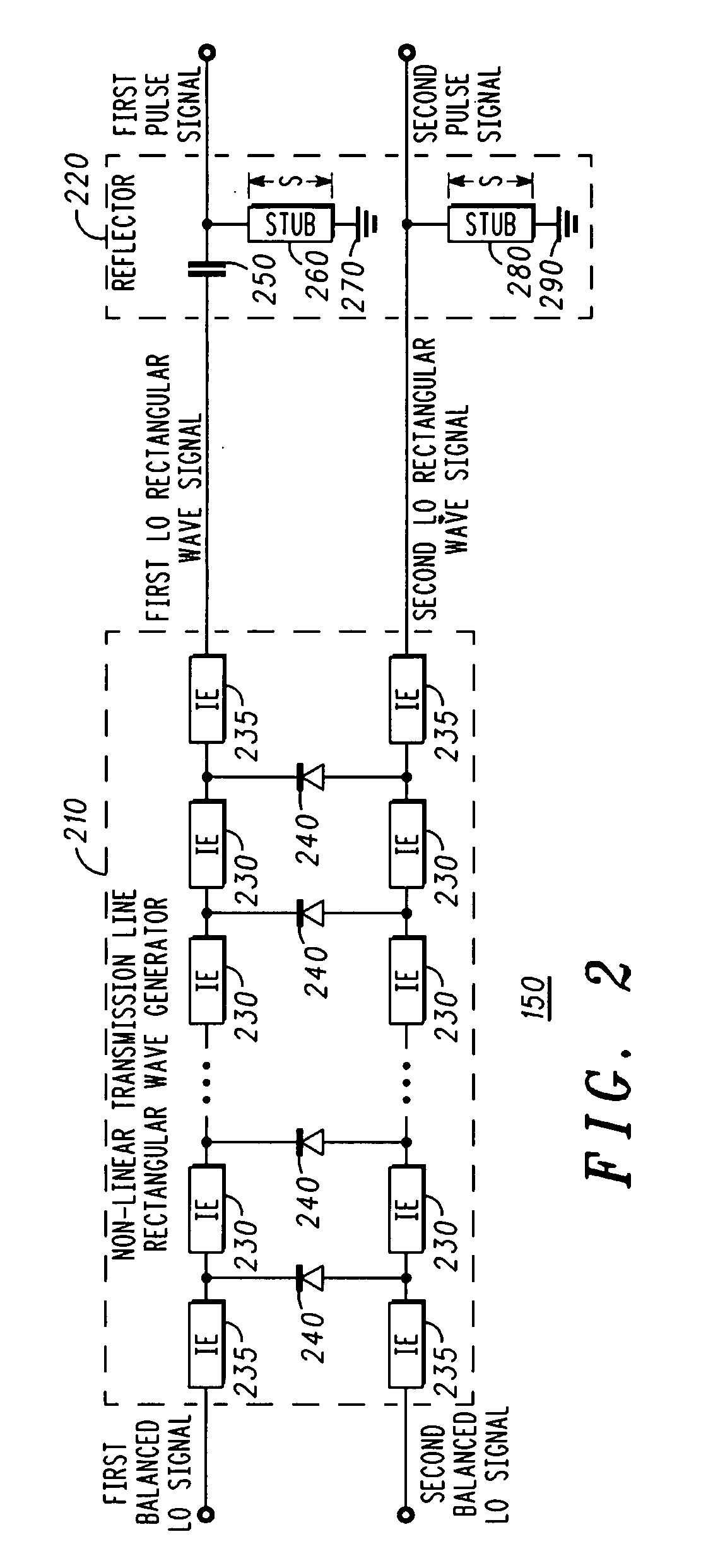
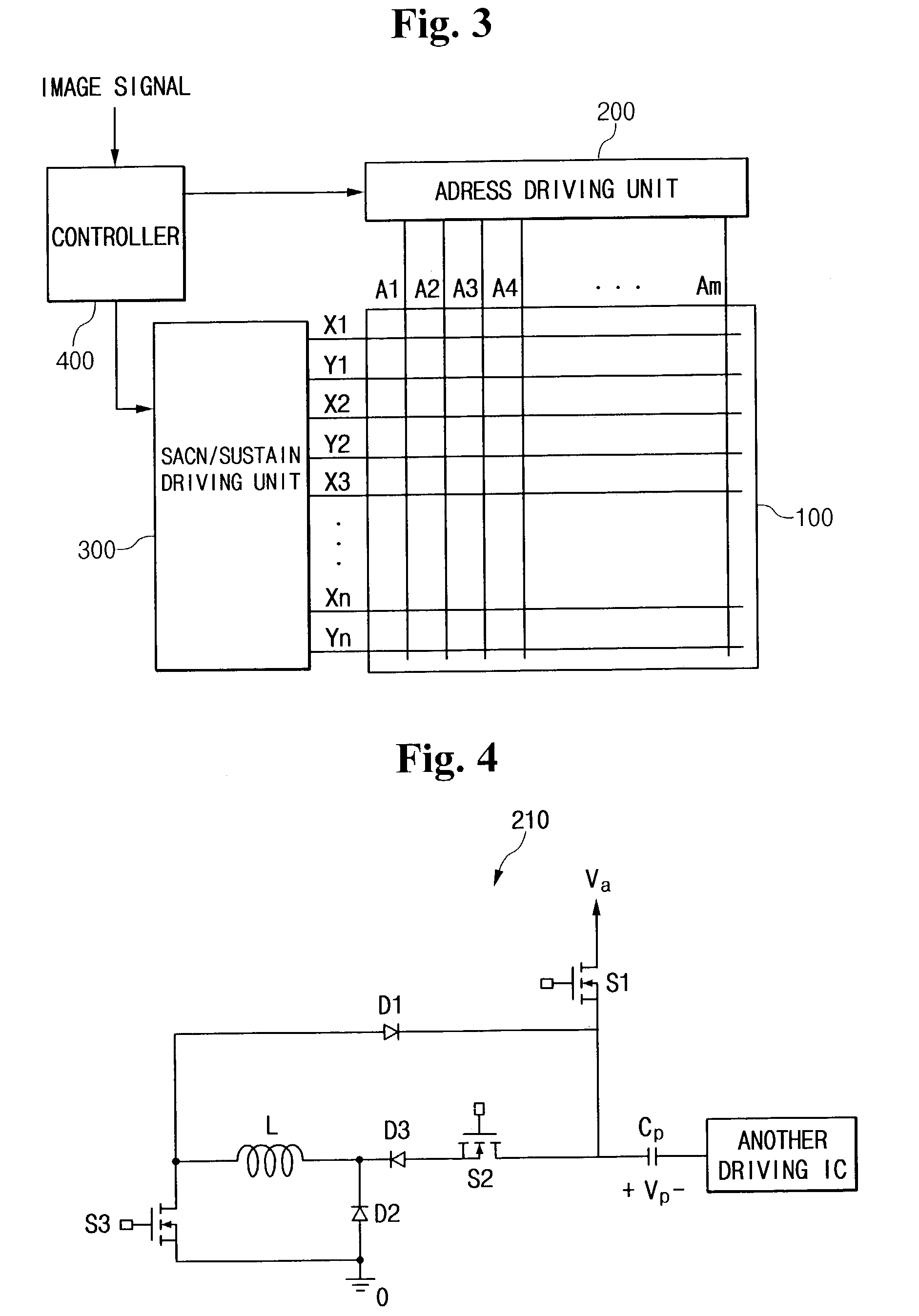
Device and method for driving plasma display panel
In a PDP driver, first and second signal lines for a voltage of Vs and third and fourth signal lines for a voltage of 0V are formed. While maintaining Y and X electrodes of the panel capacitor at Vs and 0V, a first current path is formed from the first signal line to the fourth signal line through an inductor to supply a first-directional current to the inductor. A second current path is formed from the Y electrode to the X electrode through the inductor to change the Y and X electrode voltages using the resonance. When the electrode voltages become 0V and Vs, a third current path is formed from the third signal line to the second signal line through the inductor to reduce the first-directional current.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
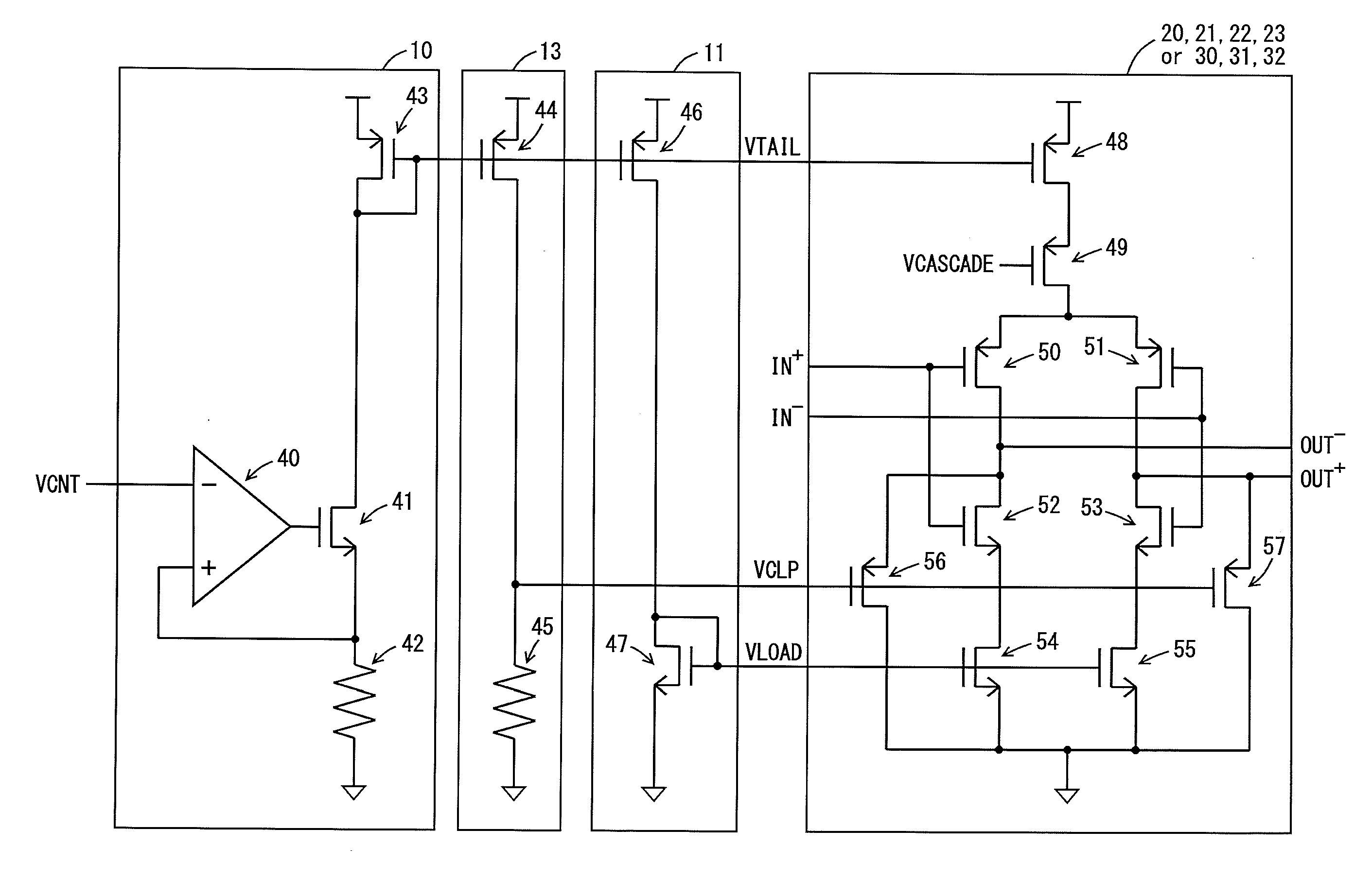
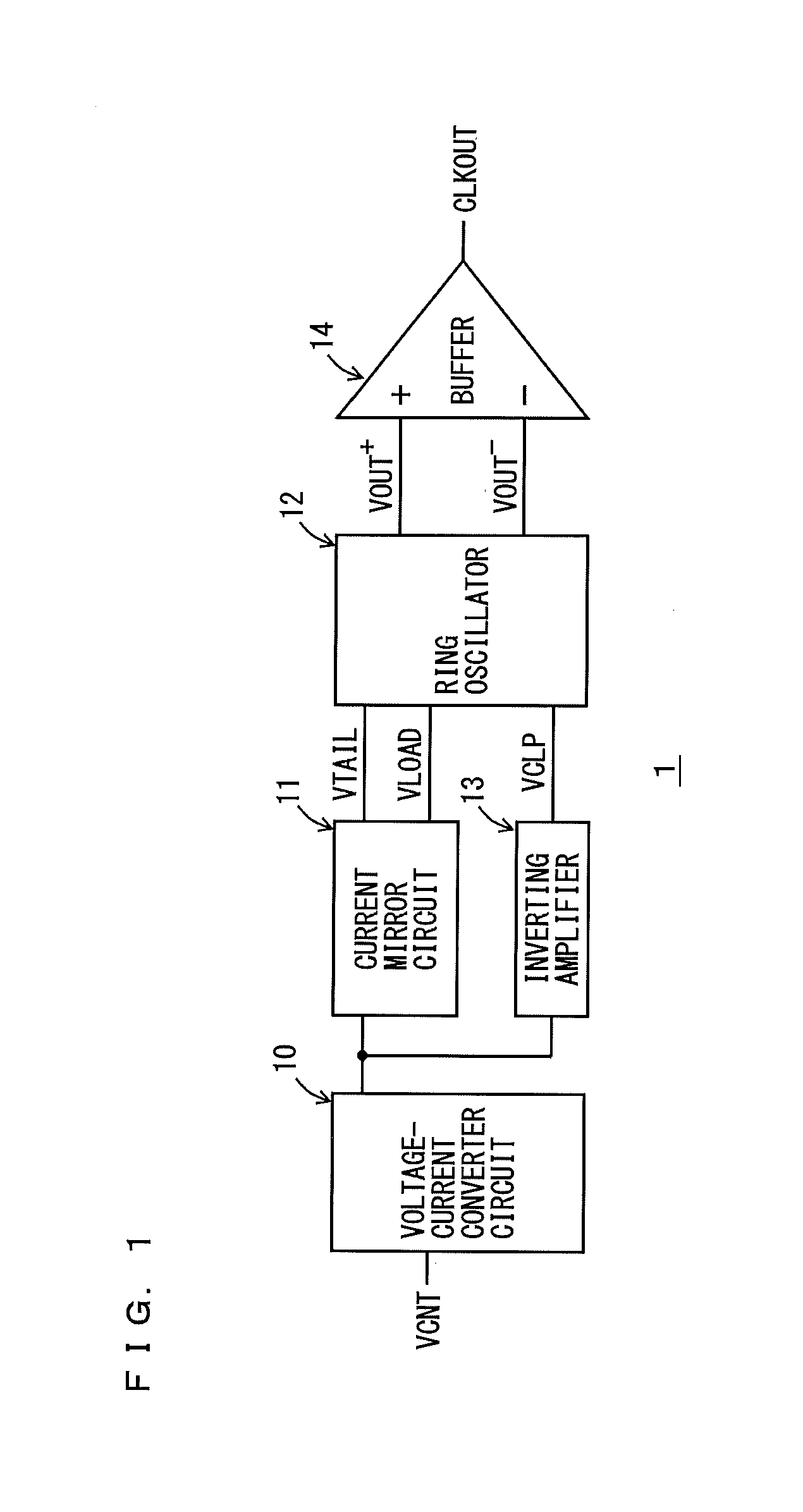
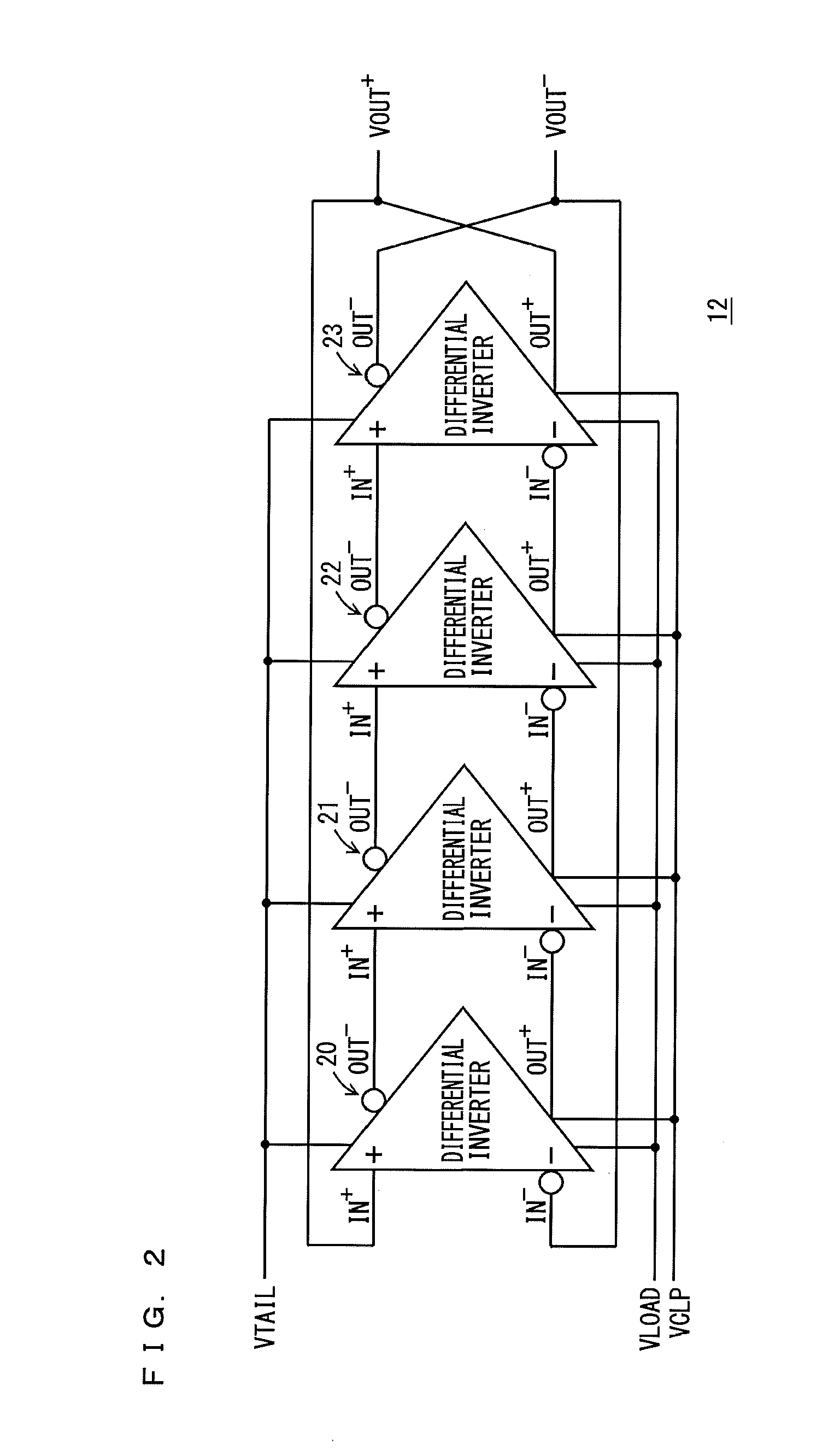
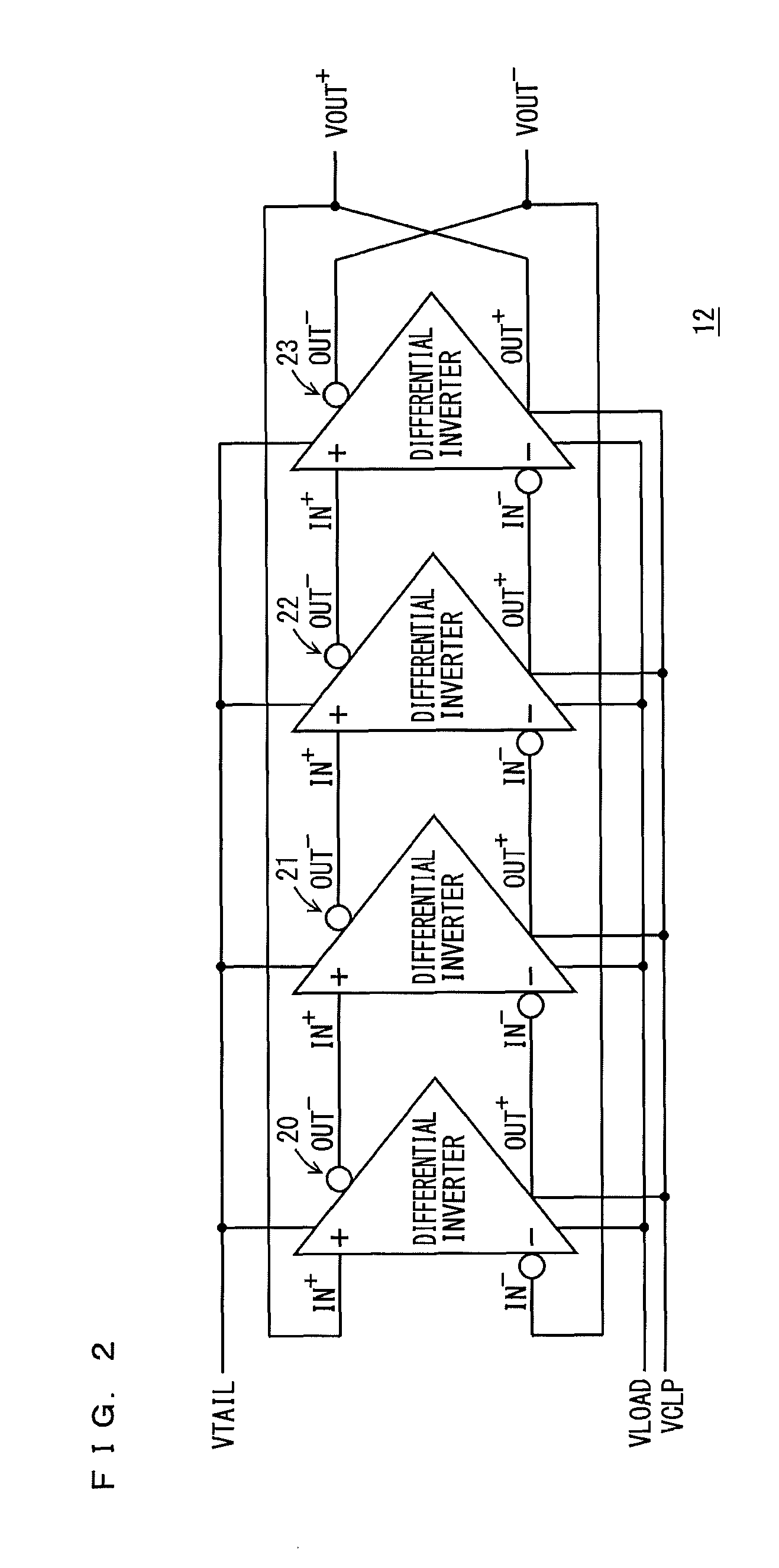
Differential ring oscillator-type voltage control oscillator
InactiveUS20130015894A1Shortened fall timeShorten rise timePulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsRC oscillatorAmplifier
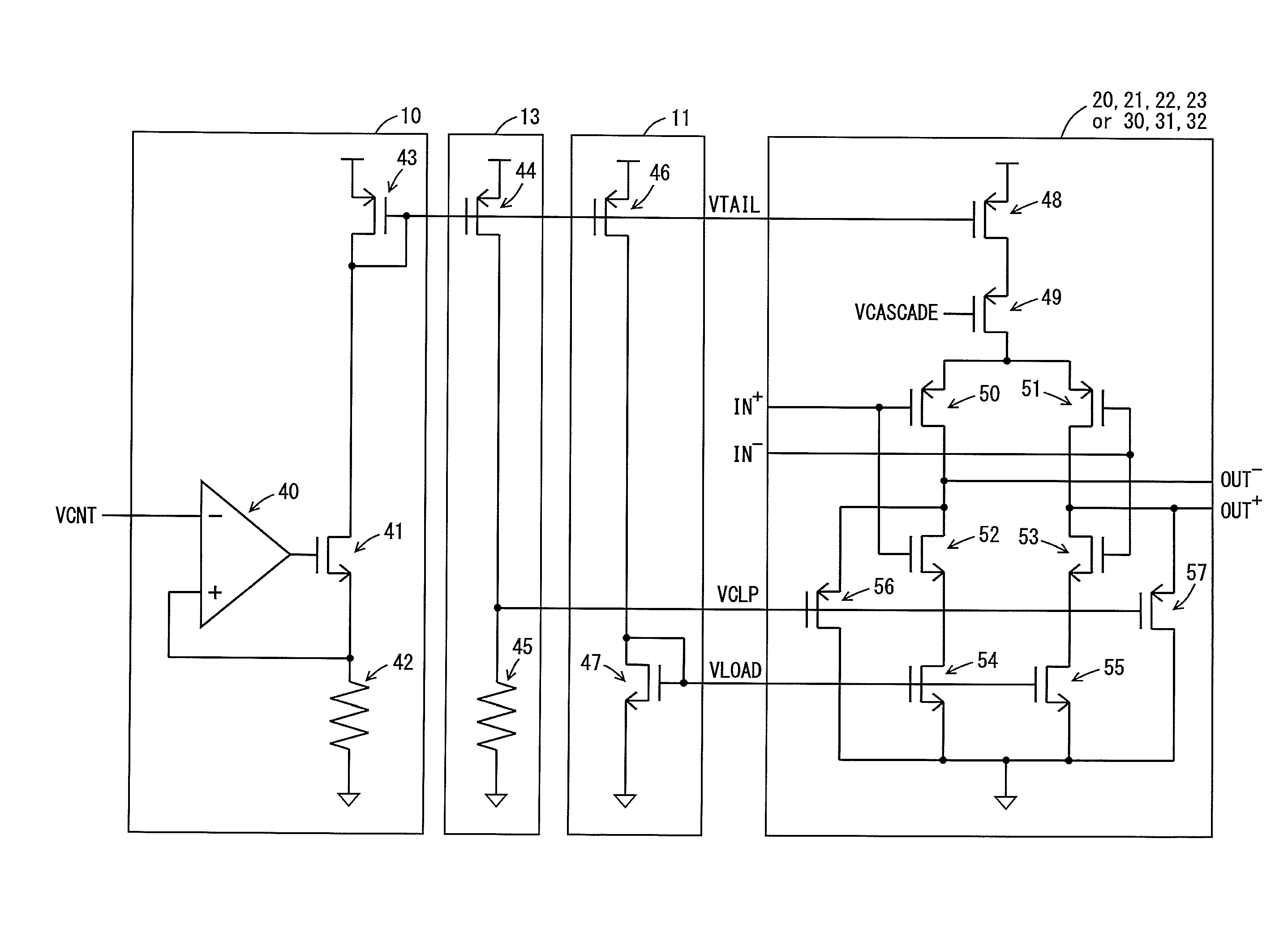
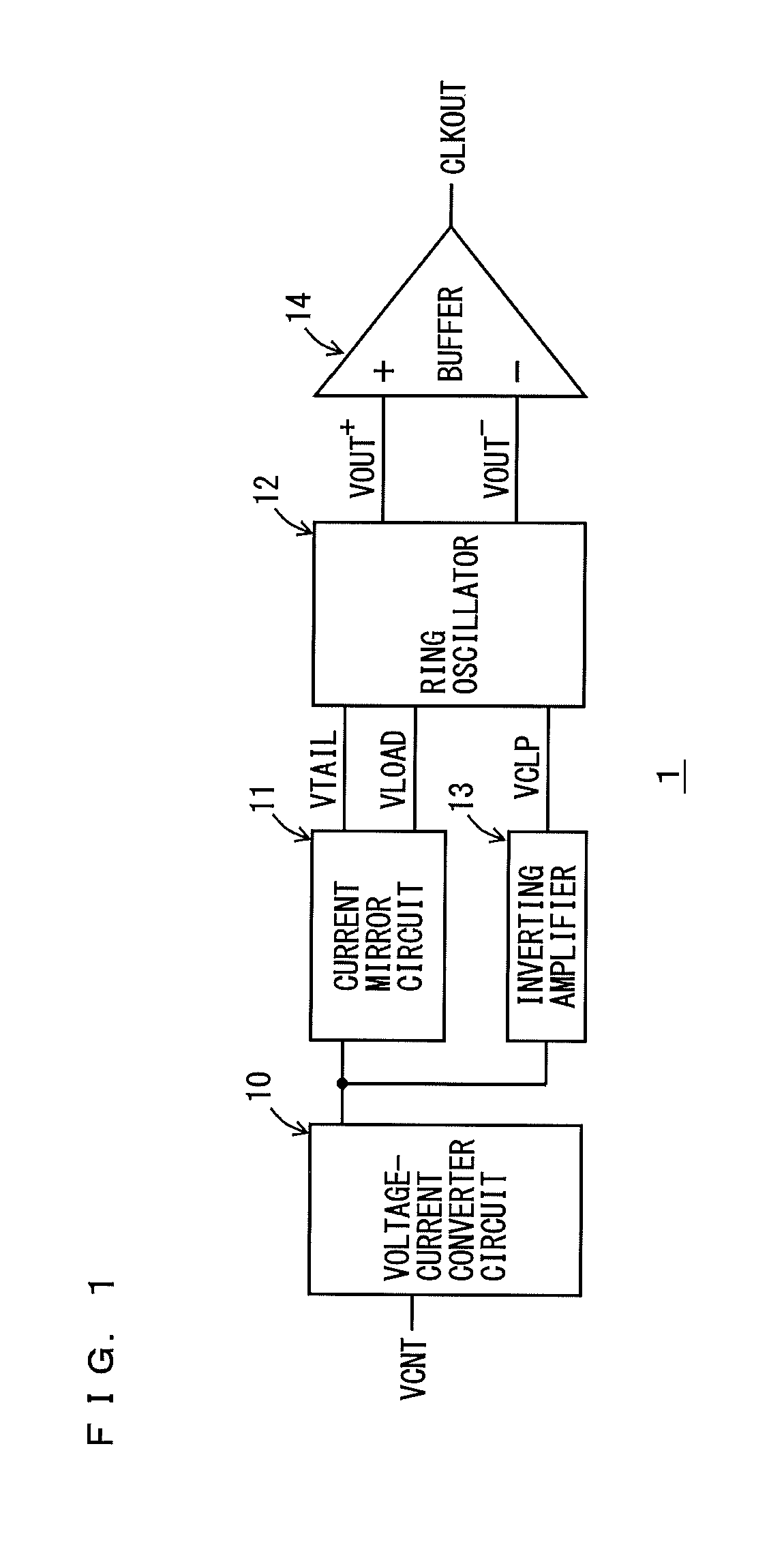
A voltage control oscillator according to the present invention includes: a voltage-current converter circuit that converts an inputted voltage to a current according to the value of the voltage; a current mirror circuit; a ring oscillator including differential inverters connected in multiple stages; an inverting amplifier; and a buffer. The ring oscillator outputs, from each of the differential inverters, a signal amplitude-limited by a “current converted by the voltage-current converter circuit and the current mirror circuit” and a “voltage applied from the inverting amplifier” and the ring oscillator outputs an oscillatory frequency in response to the output signal.
Owner:KOUYAMA KUNIHIKO
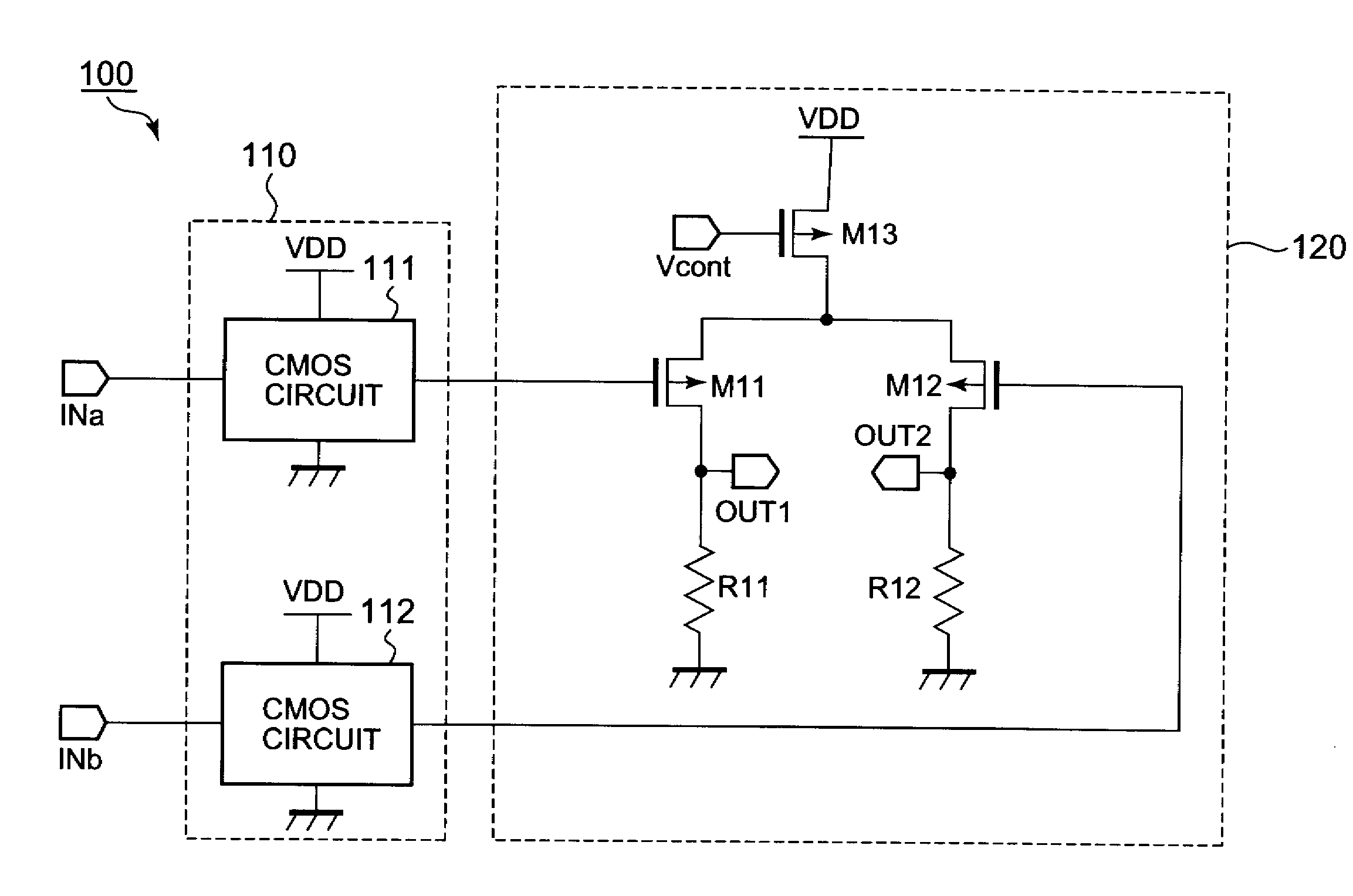
Cml circuit
InactiveUS20080150584A1Shortened fall timeShorten rise timeLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsTransistorResistive element
Disclosed herein is a CML circuit that can solve a conventional problem that it has been impossible to input a large amplitude signal to a differential pair. The CML circuit of the present invention includes an internal signal generation circuit for generating an input differential signal having an amplitude to be ranged approximately from a ground potential to a power supply potential, a first MOS transistor having a gate for inputting a differential signal having one of the two amplitudes, a second MOS transistor having a gate for inputting a differential signal having the other of the two amplitudes and having a common source shared with the first MOS transistor, a first resistance element connected between the drain of the first MOS transistor and a first power supply terminal, a second resistance element connected between the drain of the second MOS transistor and the first power supply terminal, a third MOS transistor connected to the first resistance element in parallel, and a fourth MOS transistor connected to the second resistance element in parallel.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
High-speed, silicon-based electro-optic modulator with feedback control
InactiveUS20060140645A1Fast switching speedReduce rise and fall timesCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersRefractive indexEngineering
An electro-optic modulator arrangement for achieving switching speeds greater than 1 Gb / s utilizes pre-emphasis pulses to accelerate the change in refractive index of the optical waveguide used to form the electro-optic modulator. In one embodiment, a feedback loop may be added to use a portion of the modulated optical output signal to adjust the magnitude and duration of the pre-emphasis pulses, as well as the various reference levels used for modulated. For free carrier-based electro-optic modulators, including silicon-based electro-optic modulators, the pre-emphasis pulses are used to accelerate the movement of free carriers at the transitions between input signal data values.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
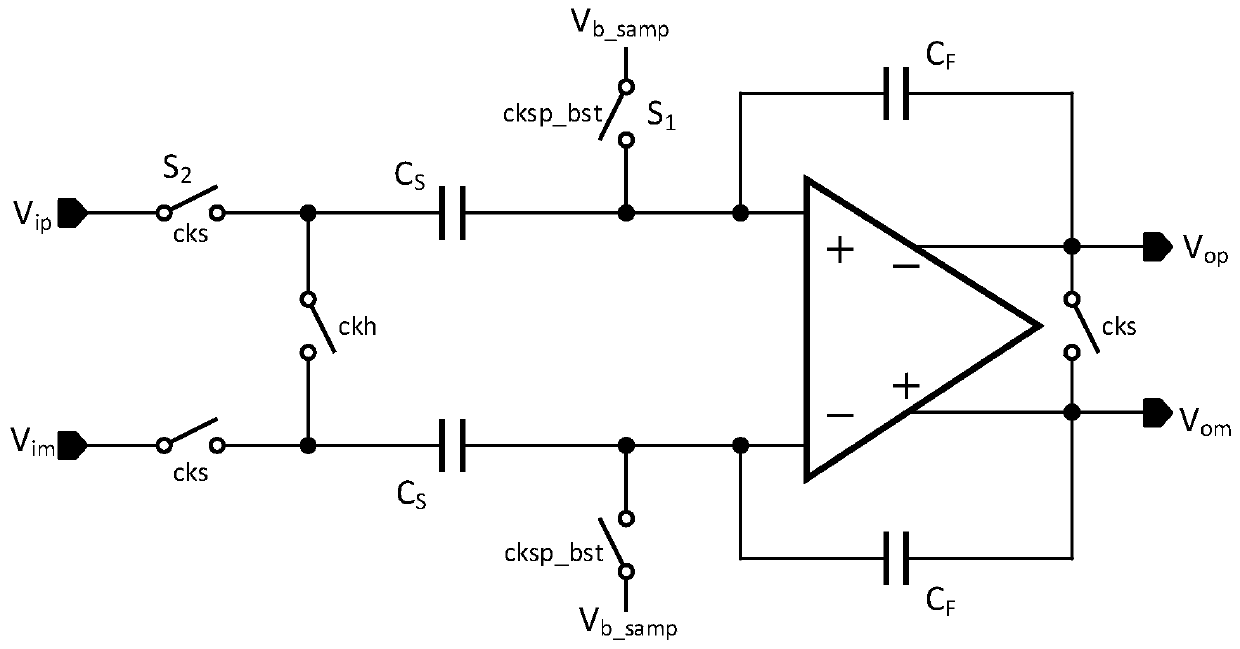
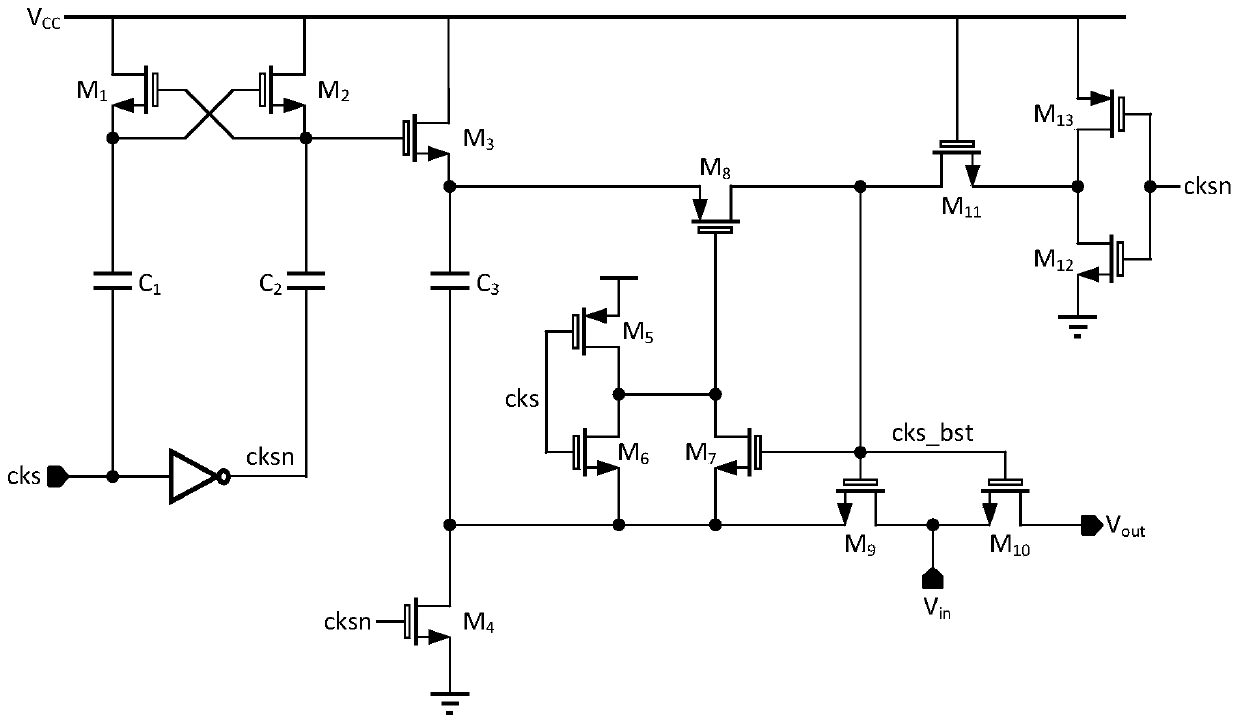
Bootstrap sampling switch circuit, sample hold circuit and analog-to-digital converter
PendingCN111384951ARandom combinationReduce rise and fall timesElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersA d converterVoltage regulation
The invention discloses a bootstrap sampling switch circuit, a sampling hold circuit and an analog-to-digital converter. The bootstrap switching circuit comprises: a voltage regulator used for generating a first voltage and a second voltage, wherein the first voltage is equal to the sum of a common-mode voltage and a third voltage, and the second voltage is equal to the sum of the common-mode voltage and the third voltage; a level shift circuit, wherein the level shift circuit takes a first voltage as a power supply voltage and is used for generating a clock, the high level of the clock is equal to the first voltage, and the low level of the clock is equal to the second voltage; and a bootstrap main circuit, wherein the bootstrap main circuit takes a first voltage as a power supply voltageand takes a second voltage as ground, and the bootstrap main circuit is controlled by the clock and is used for generating a constant voltage at a gate-source end of the switching tube. The MOS tubesin the circuit are low-voltage thin gate tubes. The bootstrap sampling switching circuit is realized by adopting the low-voltage thin gate tube, so that the ascending and descending time of an outputclock is greatly shortened on the premise of not sacrificing the swing amplitude of an input signal, and the ADC sampling rate is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI BEILING
Gate driver on array (GOA) unit, goa circuit, and liquid crystal display (LCD) panel
InactiveUS20190285930A1Shortened fall timeShorten rise timeStatic indicating devicesDigital storageLiquid-crystal displayComputer module
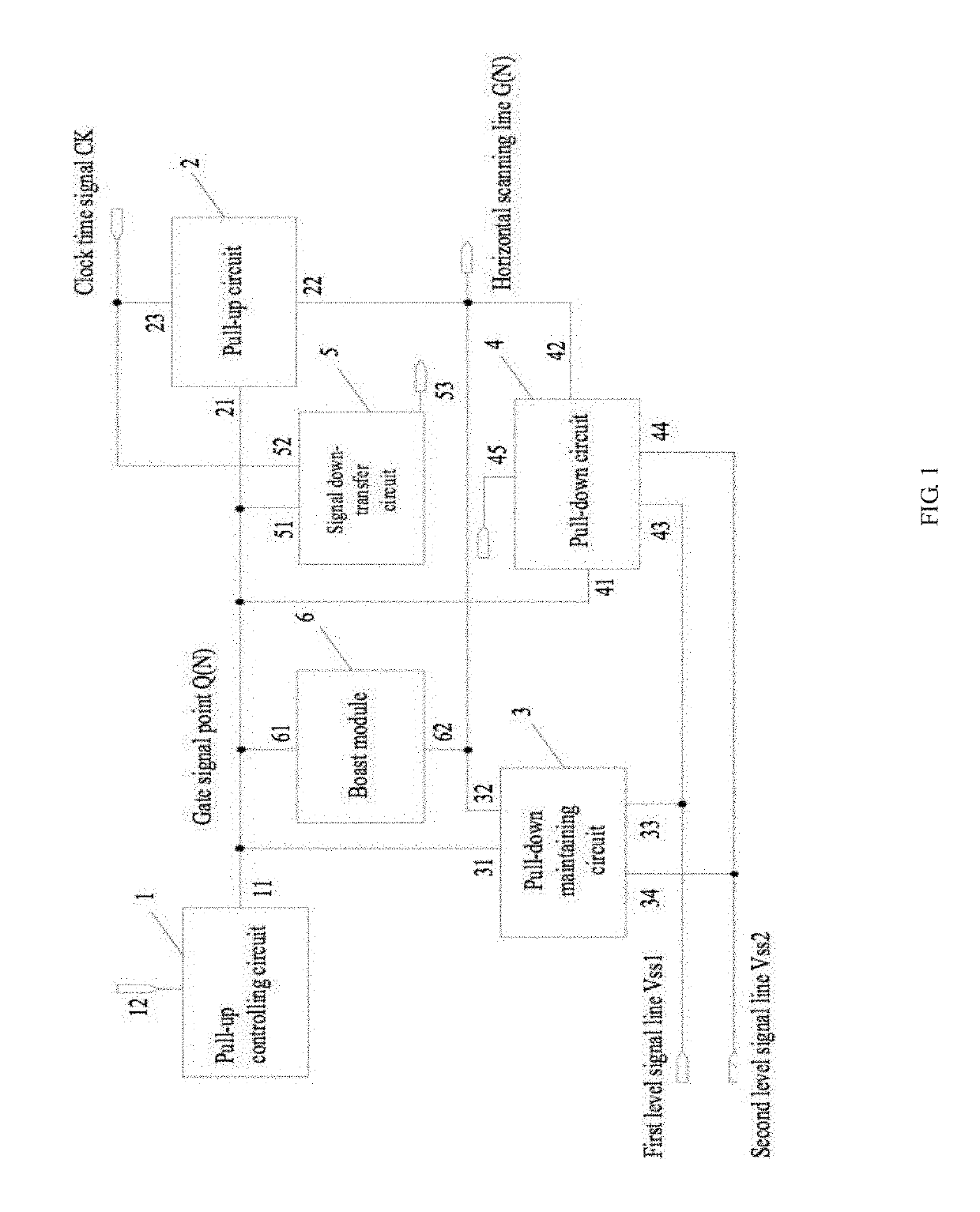
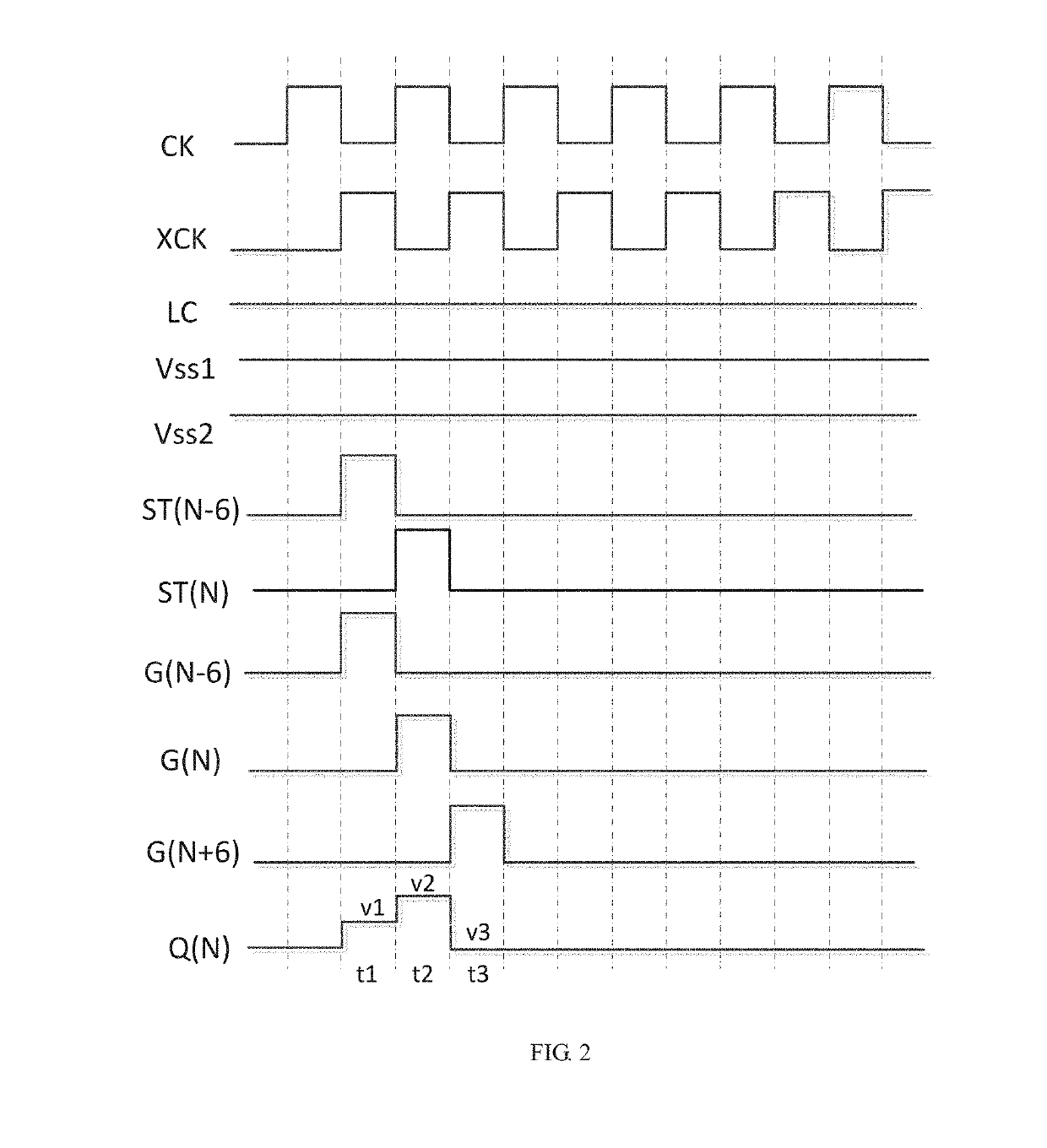
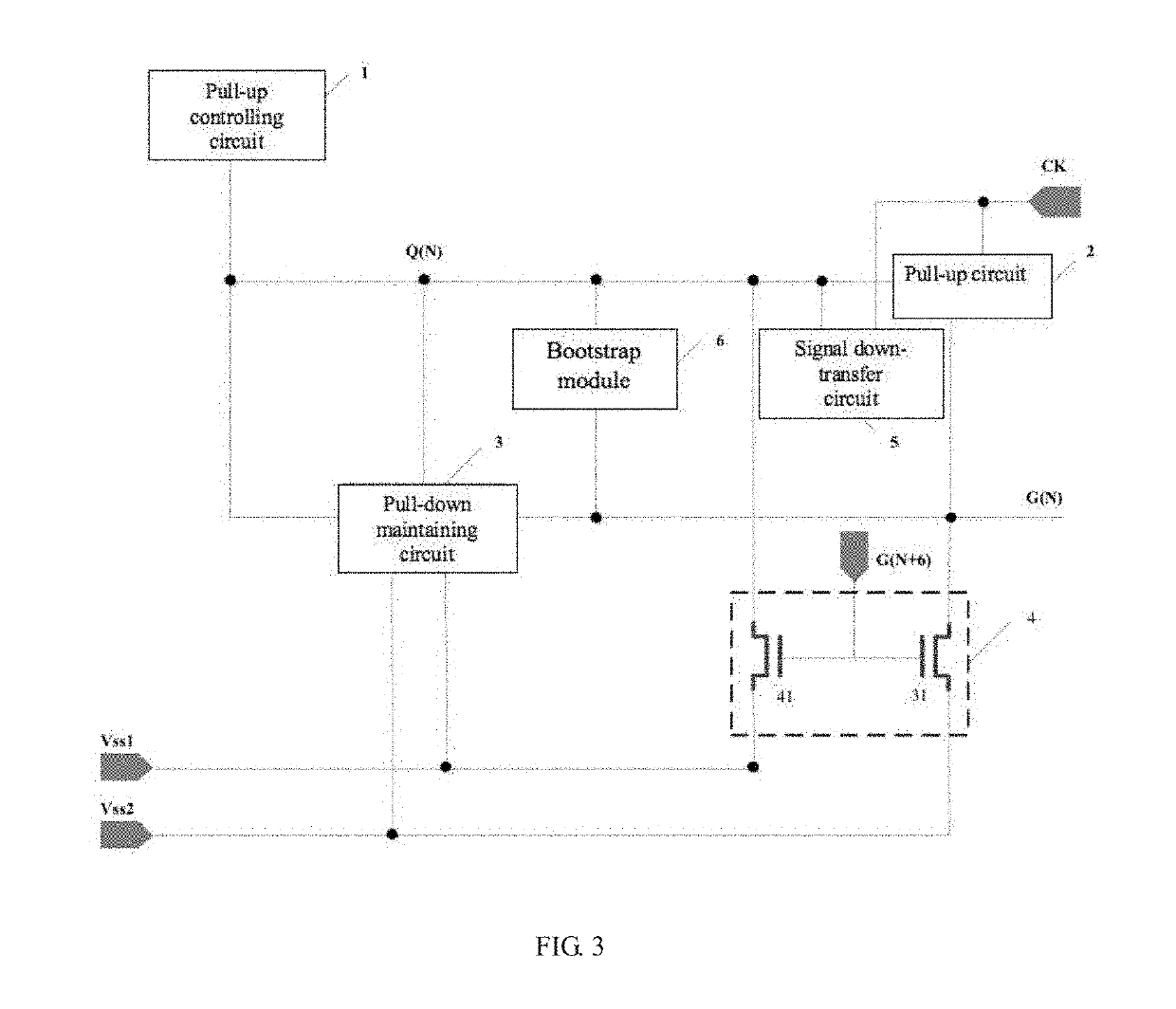
The present disclosure relates to a gate driver on array (GOA) unit. An output end of the pull-up controlling module, a control end of the pull-up circuit, a first end of the pull-down maintaining circuit, a first end of the pull-down circuit, a control end of the signal down-transfer circuit, and a first end of the bootstrap module connect to a gate signal point. A second end of the pull-down maintaining circuit, a second end of the pull-down circuit, a second end of the bootstrap module, and an output end of the pull-up circuit connect to a horizontal scanning line. A third end of the pull-down maintaining circuit and a third end of the pull-down circuit connect to a first level signal line. A fourth end of the pull-down maintaining circuit and a fourth end of the pull-down circuit connect to a second level signal line.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
High linearity frequency conversion system and method
ActiveUS7844241B2Reduce rise and fall timesModulation transferenceTransmission noise suppressionLocal oscillator signalFrequency conversion
A frequency converter (100) is provided, comprising: a pulse generator (150) configured to receive a balanced local oscillator signal pair and to generate a balanced rectangular pulse signal pair having the reference frequency; and a mixer (160) configured to mix an input signal having an input frequency with the balanced rectangular pulse signal pair to generate an output signal having an output frequency. The input frequency is different from the output frequency, and the pulse generator and the mixer are formed on a single integrated circuit (120). The frequency converter may comprise a balanced local oscillator (110) configured to generate the balanced local oscillator signal pair. The balanced local oscillator may comprise: an unbalanced local oscillator (130) configured to provide an unbalanced local oscillator signal having the reference frequency; and a balun (140) configured to generate the balanced local oscillator signal pair based on the unbalanced local oscillator signal.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Differential ring oscillator-type voltage control oscillator
InactiveUS8604885B2Reduce rise and fall timesReduce jitterPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsPower flowCurrent limiting
A voltage control oscillator includes: a voltage-current converter circuit that converts an inputted voltage to a current according to the value of the voltage; a current mirror circuit; a ring oscillator including differential inverters connected in multiple stages; an inverting amplifier; and a buffer. The ring oscillator outputs, from each of the differential inverters, a signal amplitude-limited by a current converted by the voltage-current converter circuit and the current mirror circuit and a voltage applied from the inverting amplifier and the ring oscillator outputs an oscillatory frequency in response to the output signal.
Owner:KOUYAMA KUNIHIKO
Semiconductor Device, Display Module, and Electronic Appliance
InactiveUS20160027810A1Shorten time fall timeShorten rise time timeStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesPotential differenceComputer module
The circuit includes a first transistor; a second transistor whose first terminal is connected to a gate of the first transistor for setting the potential of the gate of the first transistor to a level at which the first transistor is turned on; a third transistor for setting the potential of a gate of the second transistor to a level at which the second transistor is turned on and bringing the gate of the second transistor into a floating state; and a fourth transistor for setting the potential of the gate of the second transistor to a level at which the second transistor is turned off. With such a configuration, a potential difference between the gate and a source of the second transistor can be kept at a level higher than the threshold voltage of the second transistor, so that operation speed can be improved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for controlling the mode of an electronic application
InactiveUS20050229015A1Shortened fall timeShorten rise timeEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementControl systemNormal mode
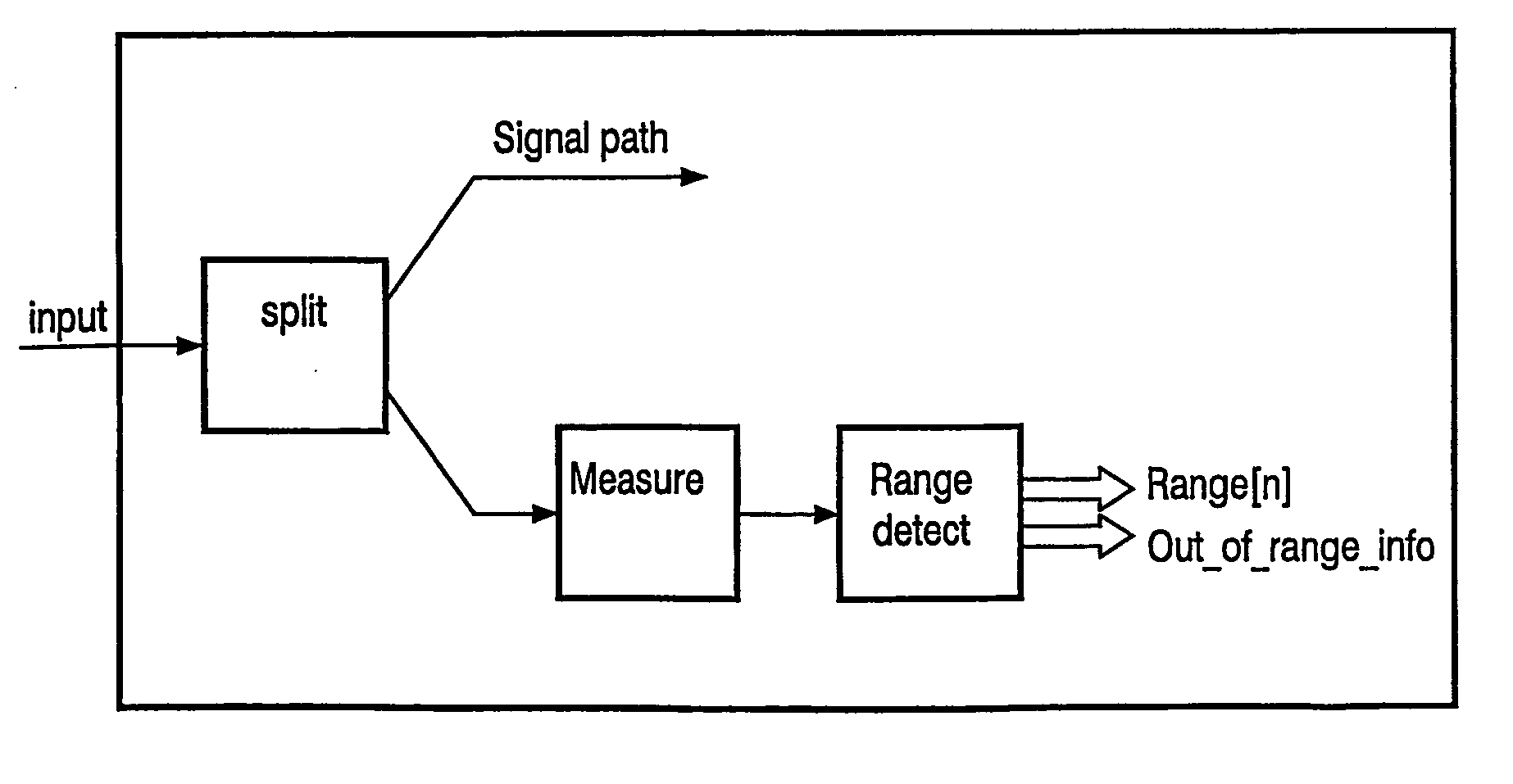
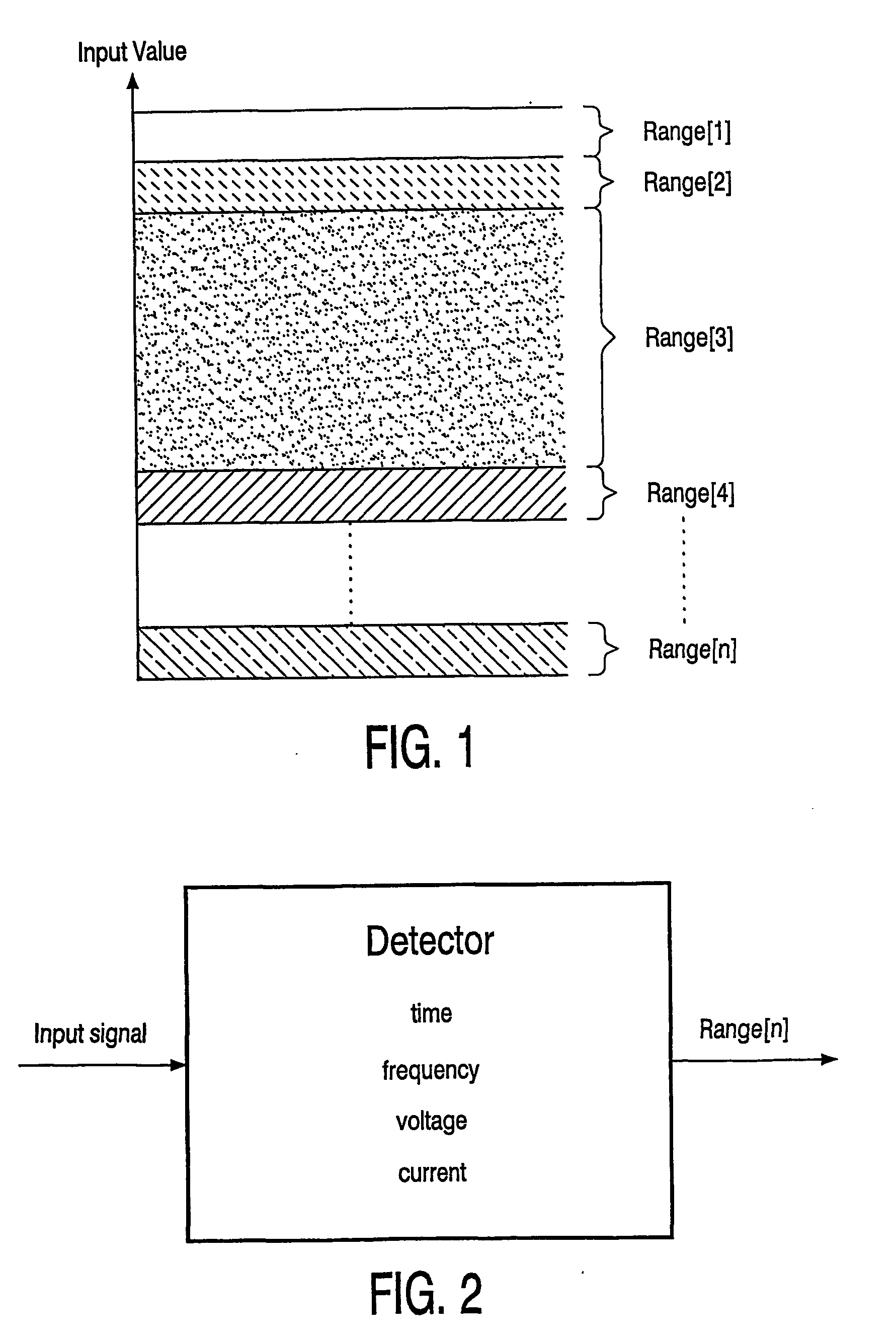
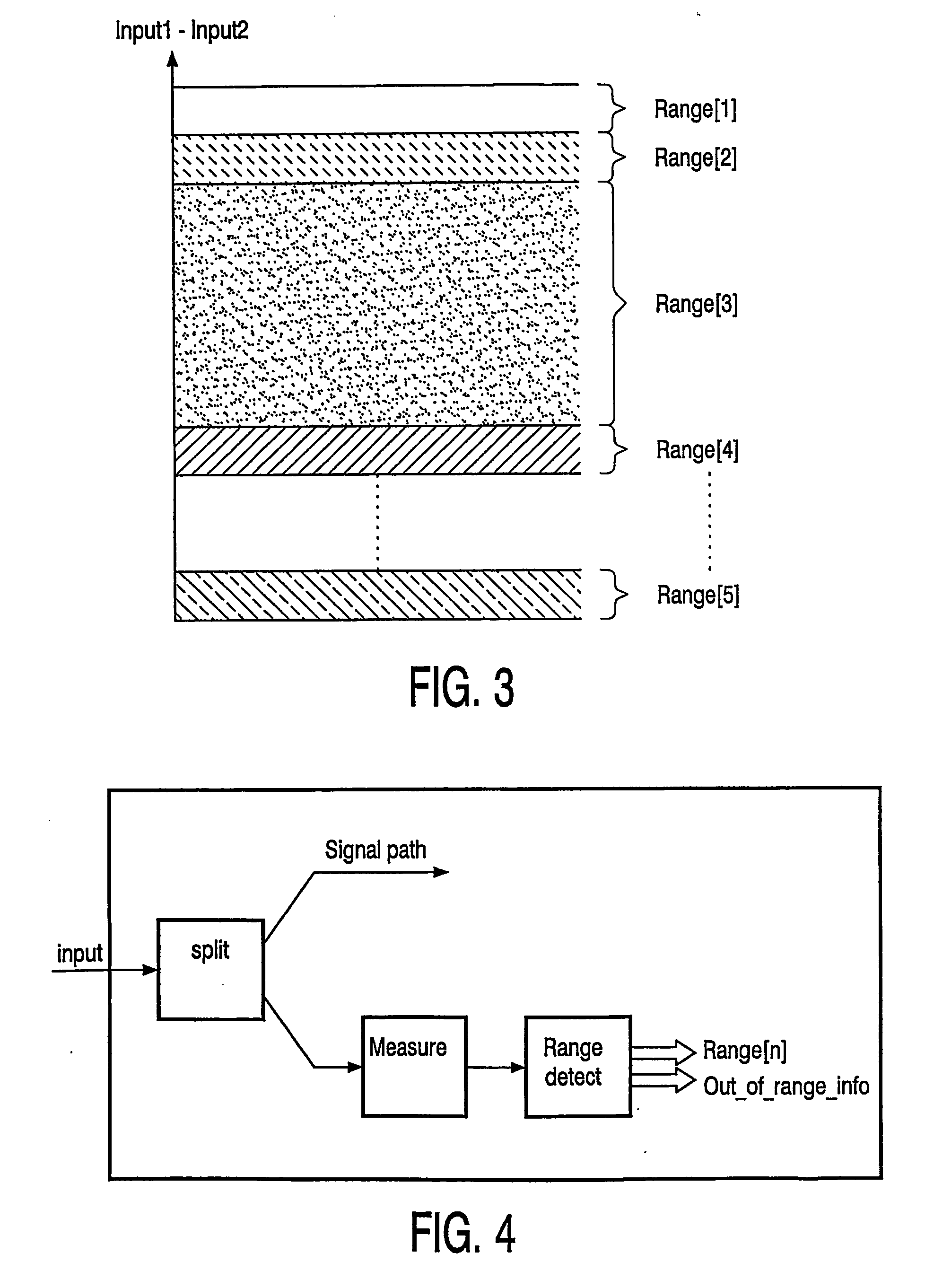
Method for controlling the mode of an electronic application like audio systems, display systems or portable equipment. The output stage of the electronic application controls the modes of the system, for example a normal mode, a standby mode or a sleep mode. The inventive method uses the existing connections for the input signals of the output stage. The allover level of the input signal or signals is divided into several ranges. One of the ranges is the normal operation range and the others who lay above or under the normal range are the extended ranges. The different ranges can be of different levels. The input signal can be a time, frequency, current or voltage. The inventive electronic application can be configured as a single-ended input as a differential input or as a multiple input.
Owner:NXP BV
Dental raidography device
ActiveUS9788805B2Reduce rippleReduce rise and fall timesRadiation diagnosis data transmissionX-ray apparatusEngineeringDental radiography
The present invention relates to a dental radiography device capable of: reducing the amount of radiation exposure and the amount of battery consumption by reducing radiation exposure time by using a high switching frequency of 100 kHz or greater; preventing occurrence of operation errors caused by a momentary high voltage, etc. while using the high switching frequency; and easily setting X-ray irradiation time according to the type of teeth. Thus, the dental radiography device is safe, accurate and easy to use, and can have a small size and light weight.
Owner:HUNET INC
Driving method of in-plane-switching mode LCD
ActiveUS7817122B2Reduce rise and fall timesStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsIn planeData signal
A method of driving an IPS mode LCD includes applying a common voltage to a common electrode of the LCD panel, the LCD panel including a liquid crystal (LC) cell and driving the LC cell to express light at a predetermined brightness level associated with a predetermined data signal voltage applied to a pixel electrode, the driving including applying a compensation voltage to the LC cell prior to applying the predetermined data signal voltage, wherein a voltage difference between a previously applied data signal voltage and the compensation voltage is greater than a voltage difference between a previously applied data signal voltage and the predetermined data signal voltage.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
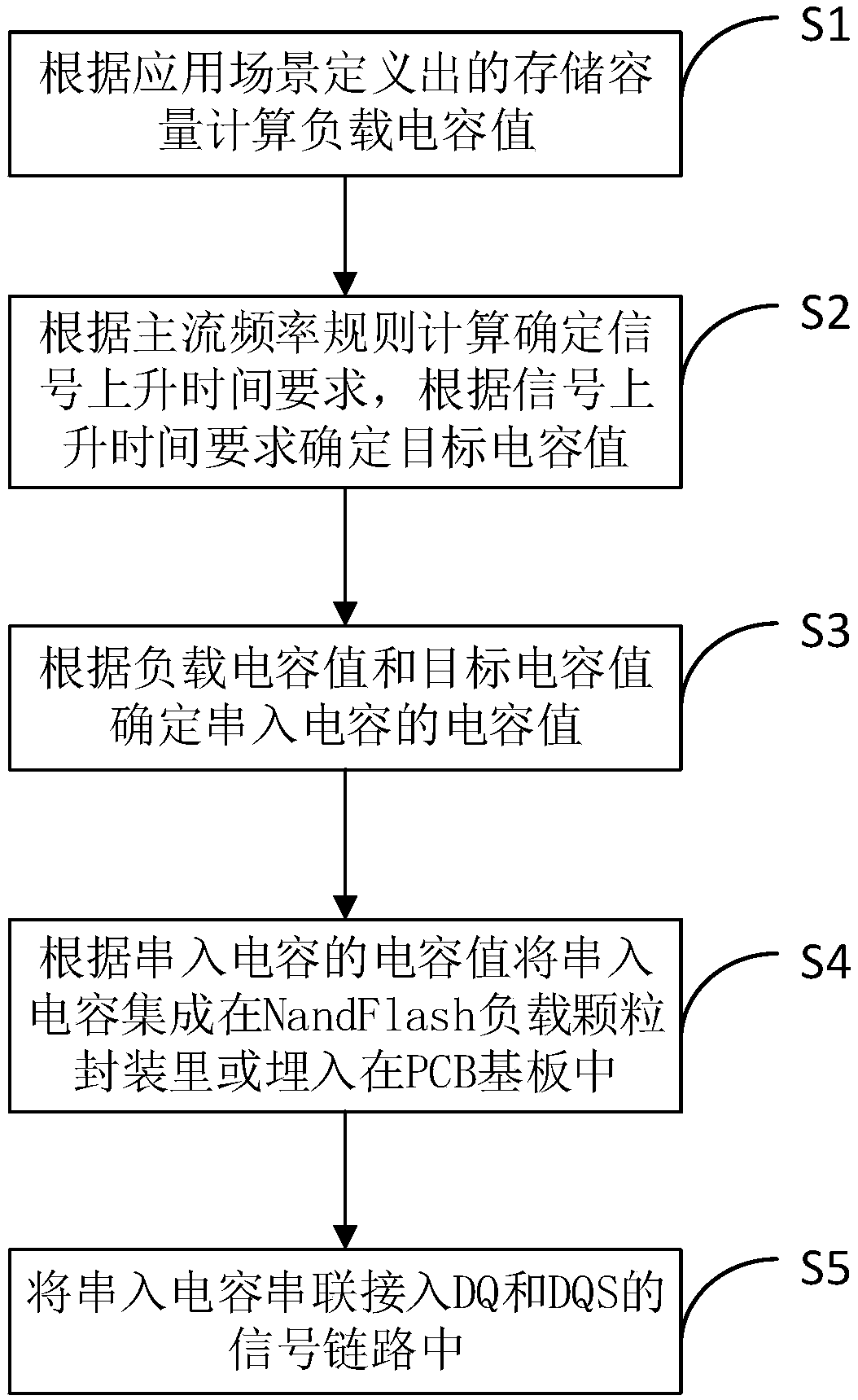
Method for improving timing margin of NandFlash bus
InactiveCN108763115AImprove Timing MarginImprove IOPS performanceElectric digital data processingTiming marginCapacitance
The present invention discloses a method for improving the timing margin of a NandFlash bus. The method comprises the following steps: calculating a load capacitance value according to a storage capacity; determining a target capacitance value according to a signal rise time requirement; and serially connecting a series capacitor to the DQ and DQS signals, and determining a capacitance value of aseries capacitor according to the load capacitance value and the target capacitance value. According to the method for improving the timing margin of a NandFlash bus disclosed by the present invention, by using the principle that after two capacitors are connected in series, the equivalent capacitance is smaller than the capacitance of any one of the series capacitors, and by serially connecting the series capacitors in the IO signal link, the timing margin of the bus is improved, the contradiction between the large capacity and the high speed is solved, and consideration of both of the largecapacity and the high speed can be achieved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Dental raidography device
ActiveUS20170049409A1Reduce rippleShortened fall timeRadiation diagnosis data transmissionX-ray apparatusX-raySwitching frequency
The present invention relates to a dental radiography device capable of: reducing the amount of radiation exposure and the amount of battery consumption by reducing radiation exposure time by using a high switching frequency of 100 kHz or greater; preventing occurrence of operation errors caused by a momentary high voltage, etc. while using the high switching frequency; and easily setting X-ray irradiation time according to the type of teeth. Thus, the dental radiography device is safe, accurate and easy to use, and can have a small size and light weight.
Owner:HUNET INC
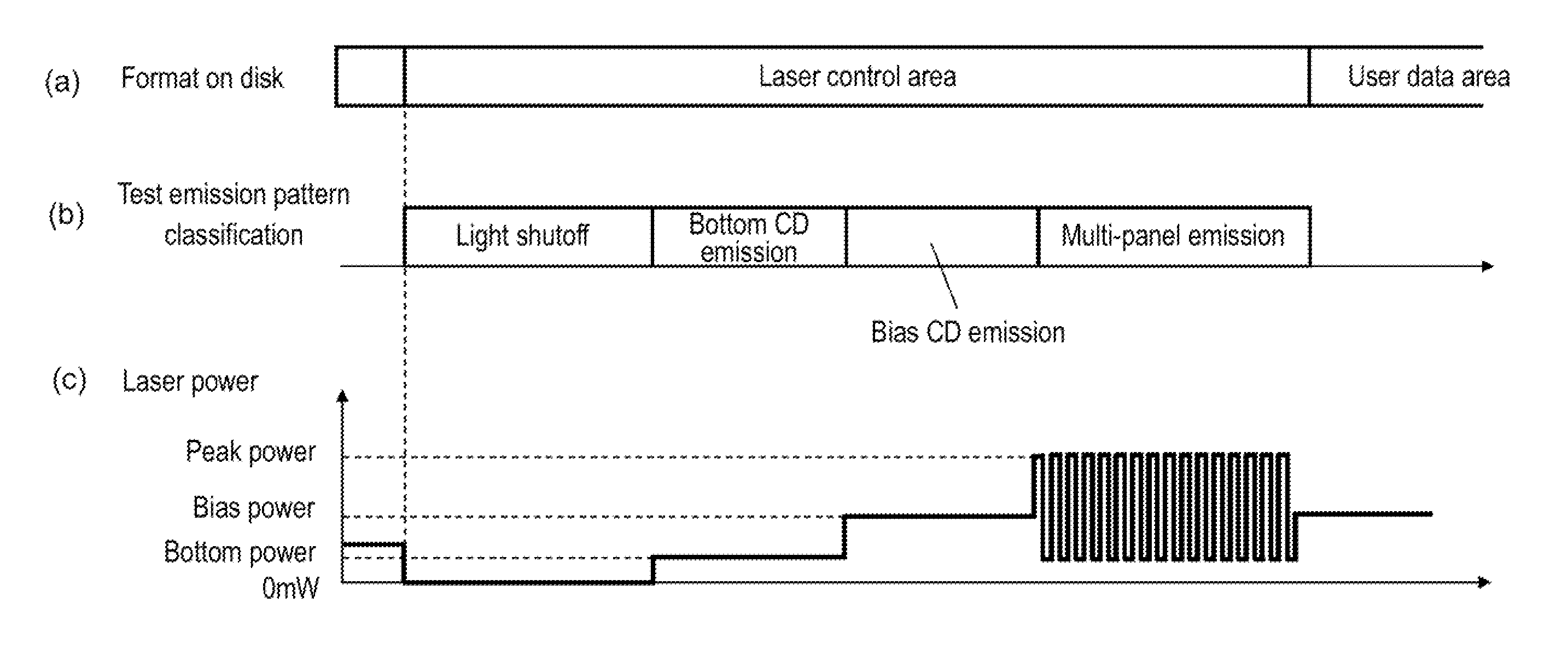
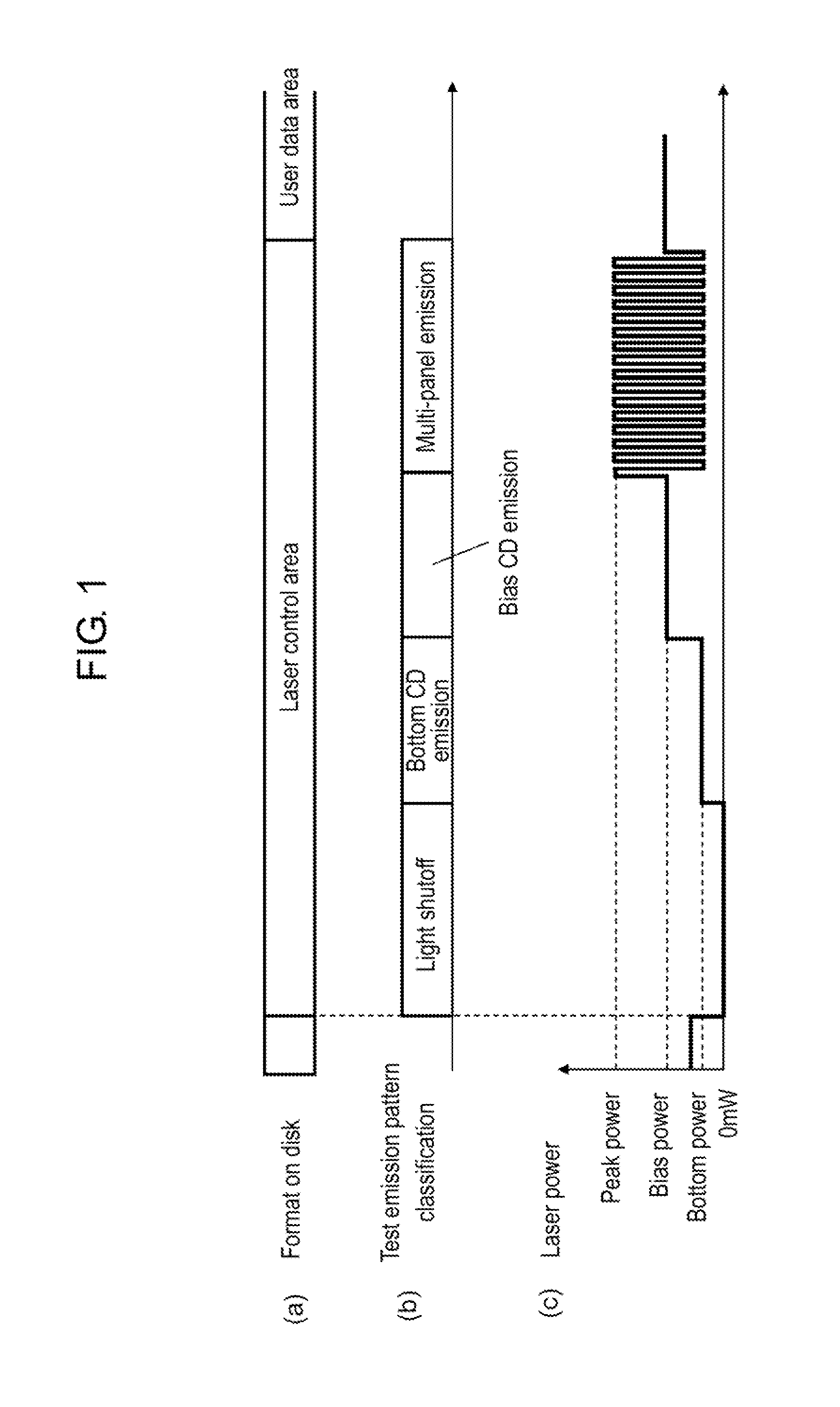
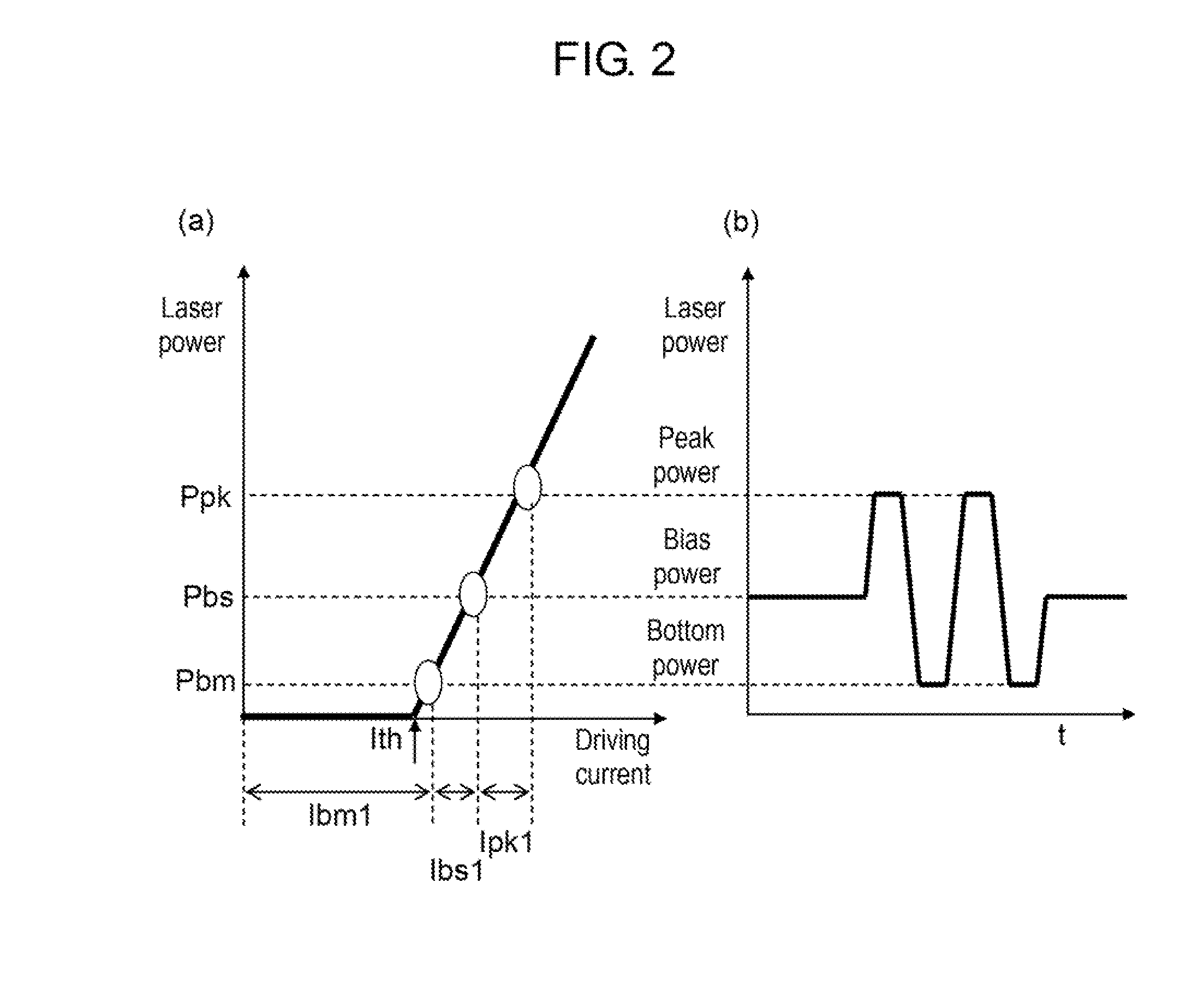
Laser power control method and laser power control apparatus
InactiveUS20120170436A1Shortened fall timeShorten rise timeTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersDriving currentFall time
With a large capacity of an optical disk and high-speed recording, a frequency of a recording signal is increased and a pulse width is narrowed. In the case that a laser is driven by a signal having the short pulse width, unfortunately the high-speed recording is hardly performed to an optical disk when a rise time and a fall time of the optical pulse are lengthened.During user data recording, a bottom driving current is set to a second bottom driving current value that is a current value of a threshold or less, so that the rise time and the fall time of the optical pulse can be shortened to perform the high-speed recording of the optical disk.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Voltage level switching circuit
InactiveCN104348472AReduce rise and fall timesReduce areaLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsHigh resistanceFall time
The invention provides a voltage level switching circuit. The voltage level switching circuit comprises a first transistor, a second transistor, a third transistor, a fourth transistor, a fifth transistor, a sixth transistor, a seventh transistor and an eighth transistor. The sixth transistor and the seventh transistor are arranged to provide equivalent high resistance, and the latch capacity of the third transistor and the fourth transistor is reduced. When the voltage difference of the input voltage is in a low level, the state of the circuit can be switched smoothly. The fifth transistor and the eighth transistor are arranged to provide a breakover path, the rising time or the falling time of output signals can be shortened. Under the demand of the same switching time, compared with the prior art, the voltage level switching circuit is advantaged in that the layout area and dynamic current consumption can be reduced.
Owner:ILI TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Low voltage sub-nanosecond pulsed current driver IC for high-resolution lidar applications
PendingUS20200400785A1Decrease riseShortened fall timeLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersLow voltageCurrent driver
A low voltage sub-nanosecond pulsed current driver for driving current to a load, which comprises a regulated current source connected to the load, for driving controlled current to the load (which may be a laser diode for LIDAR applications); a current routing network, being connected in parallel to the load following the regulated current source and consisting of a plurality of controlled power switches; and a controller for individually timing the operation of the plurality of controlled power switches, to generate a current pulse having desired narrow pulse width and reduced rise and fall times that will be delivered to the load.
Owner:B G NEGEV TECH & APPL LTD
Plasma display panel with energy recovery circuit and driving method thereof
InactiveUS7324100B2Reduce rise and fall timesReduce in quantityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectricityTerminal voltage
A plasma display panel with a driving apparatus including an inductor of which one end is electrically connected to one end of a panel capacitor. The driving apparatus of the plasma display panel alters a terminal voltage of the panel capacitors into a second voltage by storing energy in the inductor using energy of the panel capacitor charged with a first voltage. The terminal voltage of the panel capacitor is changed into the second voltage, and thereafter, it is maintained at the second voltage by freewheeling current flowing through the inductor. In addition, the terminal voltage of the panel capacitor is changed into the first voltage using the energy stored in the inductor. The terminal voltage of the panel capacitor is maintained at the first voltage by connecting one end of the panel capacitor to a first voltage source after it is changed into the first voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Liquid crystal display device and driving unit thereof
ActiveUS8384648B2Solve the insufficient charging timeReduce rise and fall timesStatic indicating devicesDigital storageLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A driving unit for a liquid crystal display device is provided. The driving unit includes a first group of driving stages and a second group of driving stages. A first driving stage of the first group receives a first gate start voltage. The first group of driving stages sequentially outputs scan signals according to a first clock signal. The scan signal outputted by one driving stage of the first group is sent to a next subsequent driving stage of the first group. A first driving stage of the second group receives a second start voltage. The second group of driving stages sequentially outputs the scan signals according to a second clock signal. The scan signal outputted by one driving stage of the second group is sent to a next subsequent driving stage of the second group. The driving stages of the first group and the second group alternately output the scan signals.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Semiconductor device, light emission control circuit, and electronic appliance
ActiveUS10101646B2Increasing consumptionIncreasing noiseElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesControl signalEngineering
A semiconductor device of the invention is a semiconductor device that controls a transistor that controls an electric current that flows through a light emitting element, the transistor including a gate that is connected to one end of a capacitor. The semiconductor device includes: a first terminal that is connected to the gate of the transistor and the one end of the capacitor; a second terminal that is connected to the other end of the capacitor; a first driving circuit that outputs a first control signal to the first terminal; and a second driving circuit that, in order to control the transistor in an on-state or an off-state, activates or deactivates a second control signal, and outputs the second control signal to the second terminal, the second control signal having a potential lower than a potential of the first control signal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com