Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1146results about How to "Reduce cleaning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
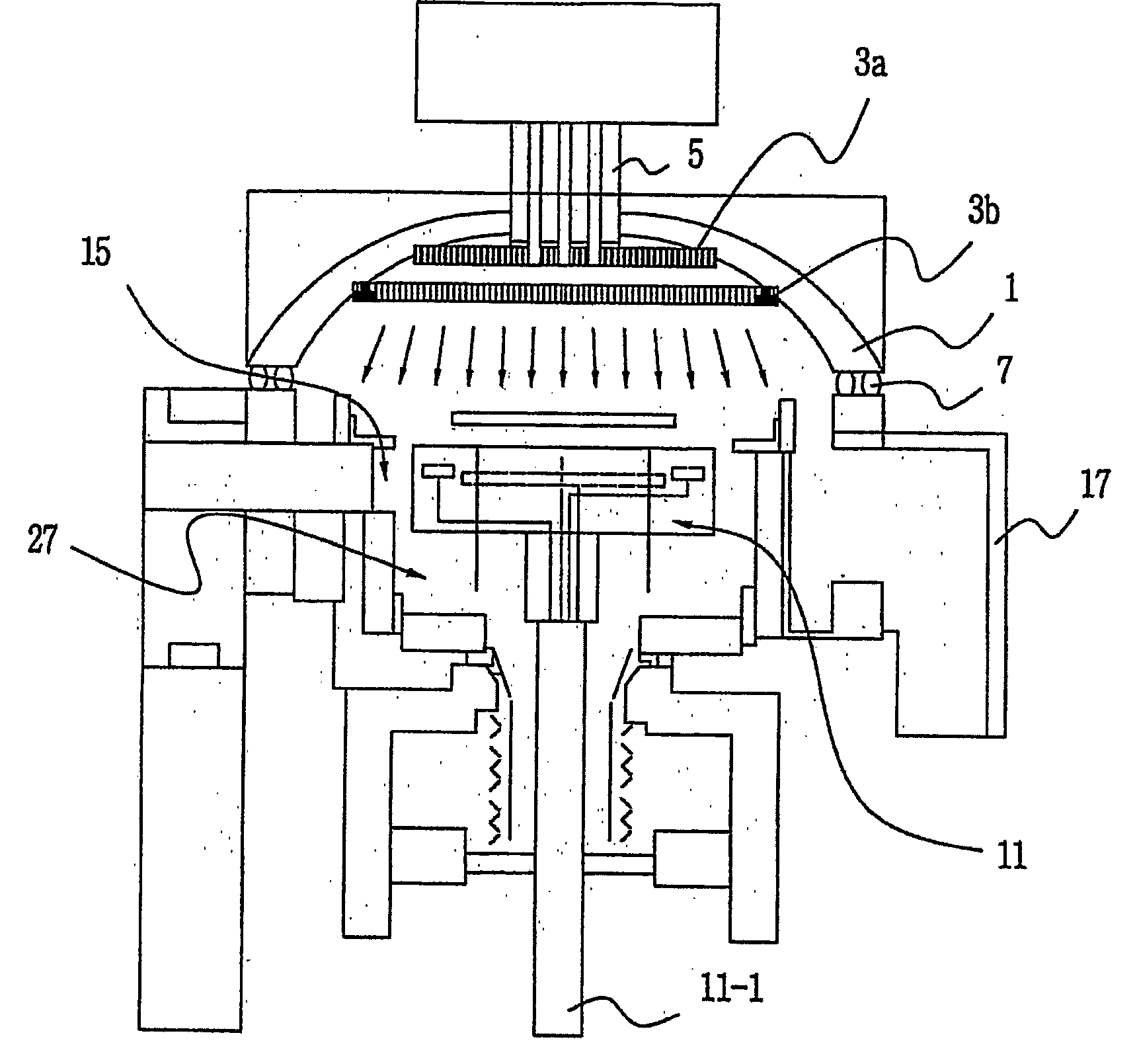
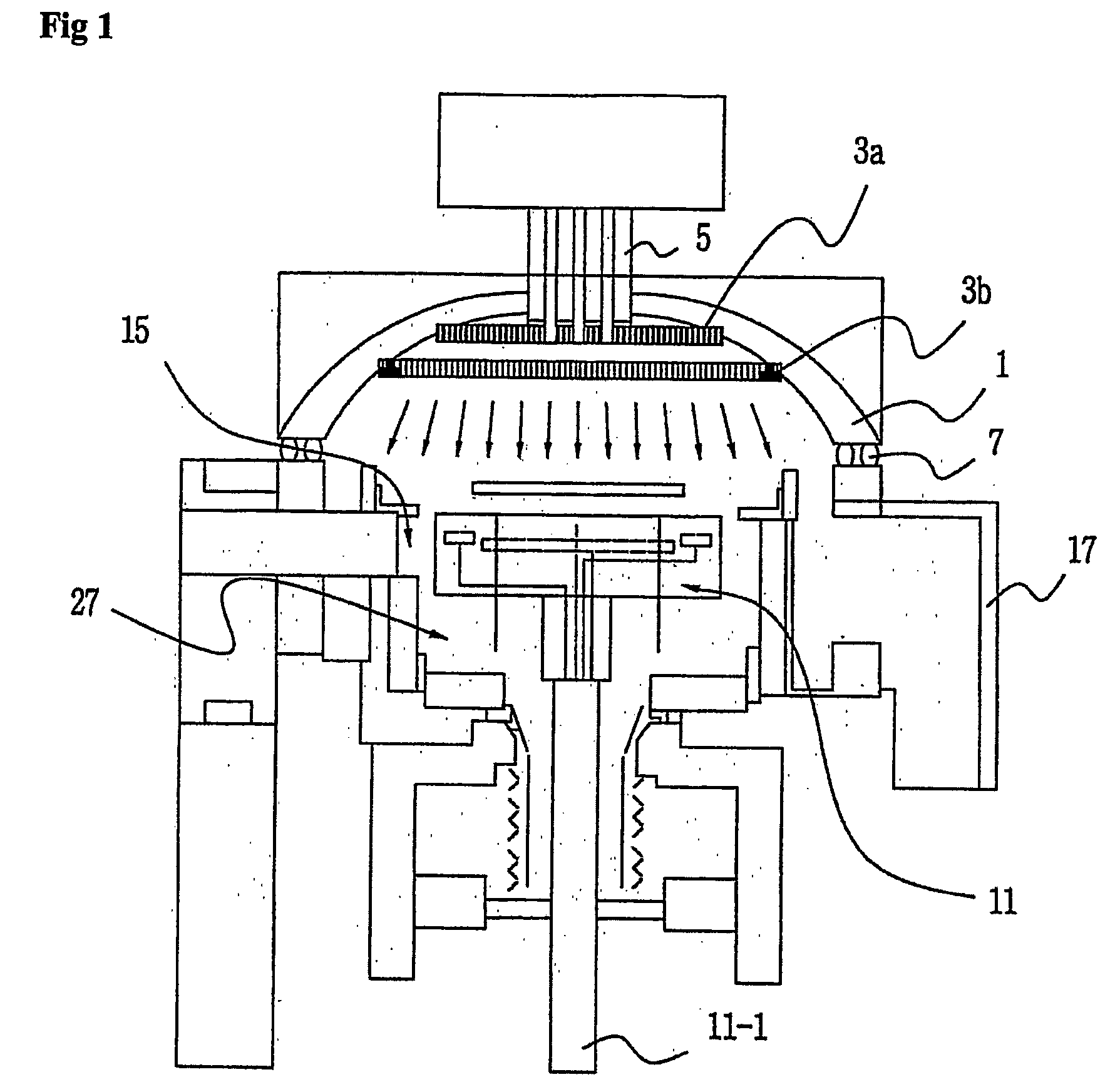
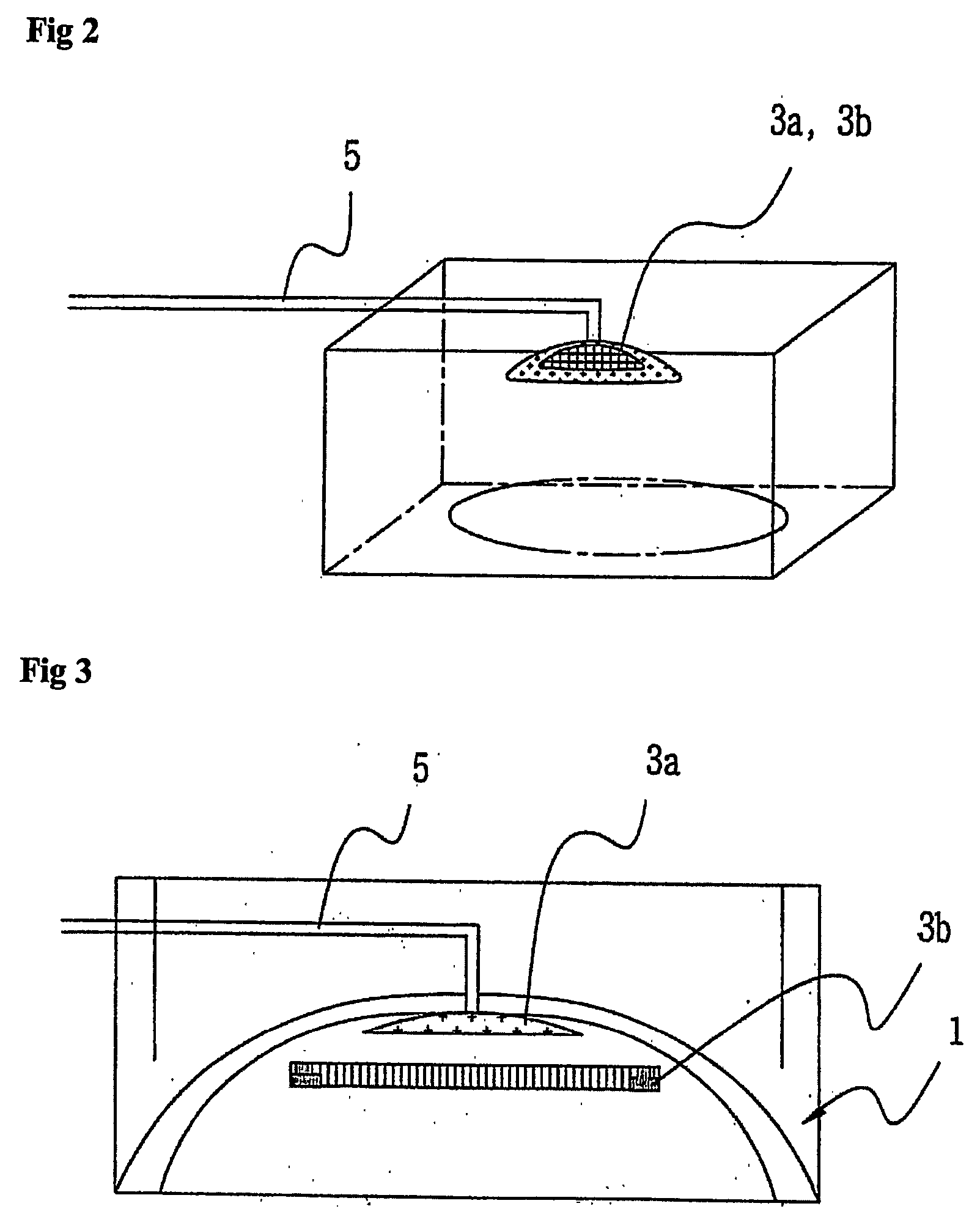
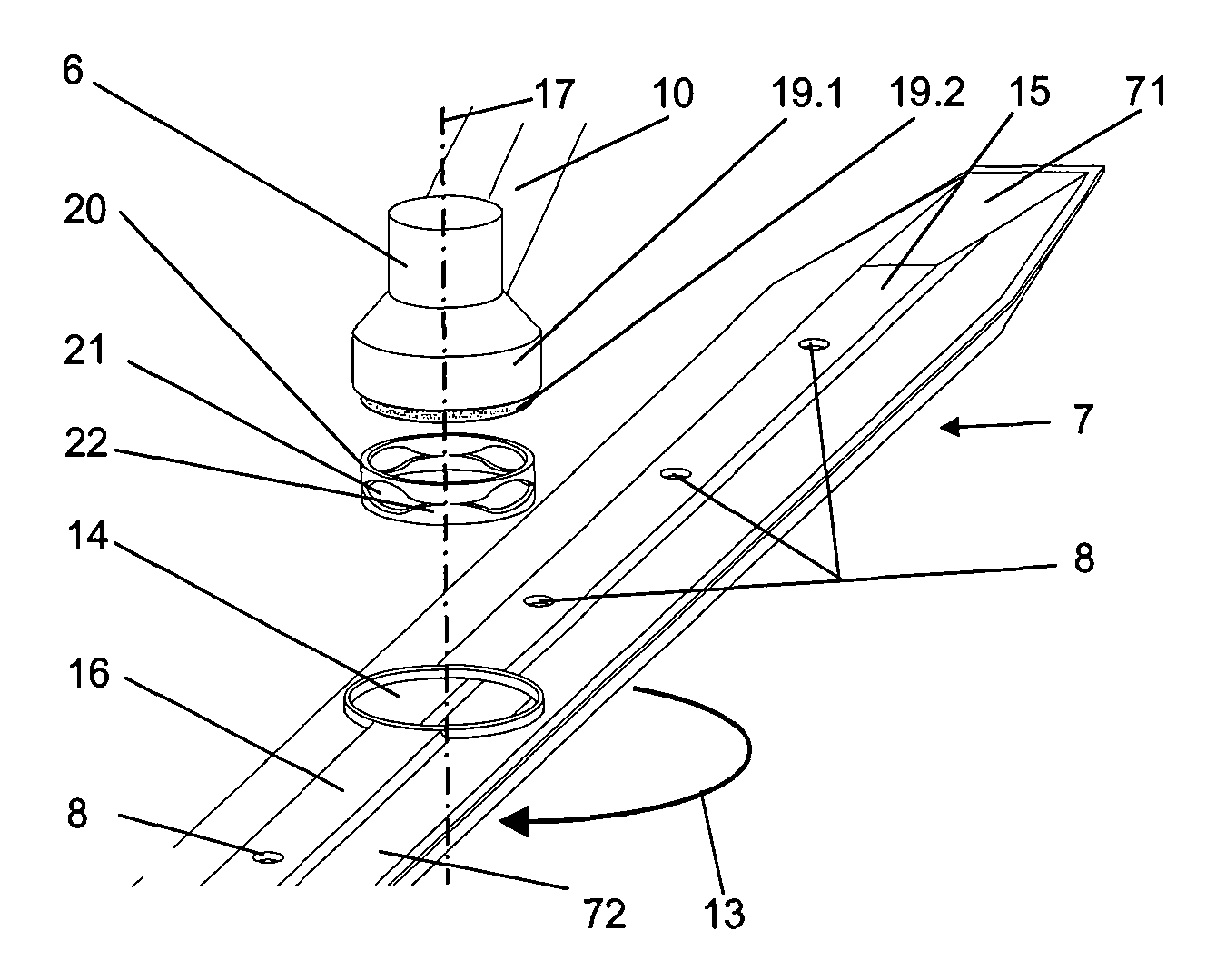
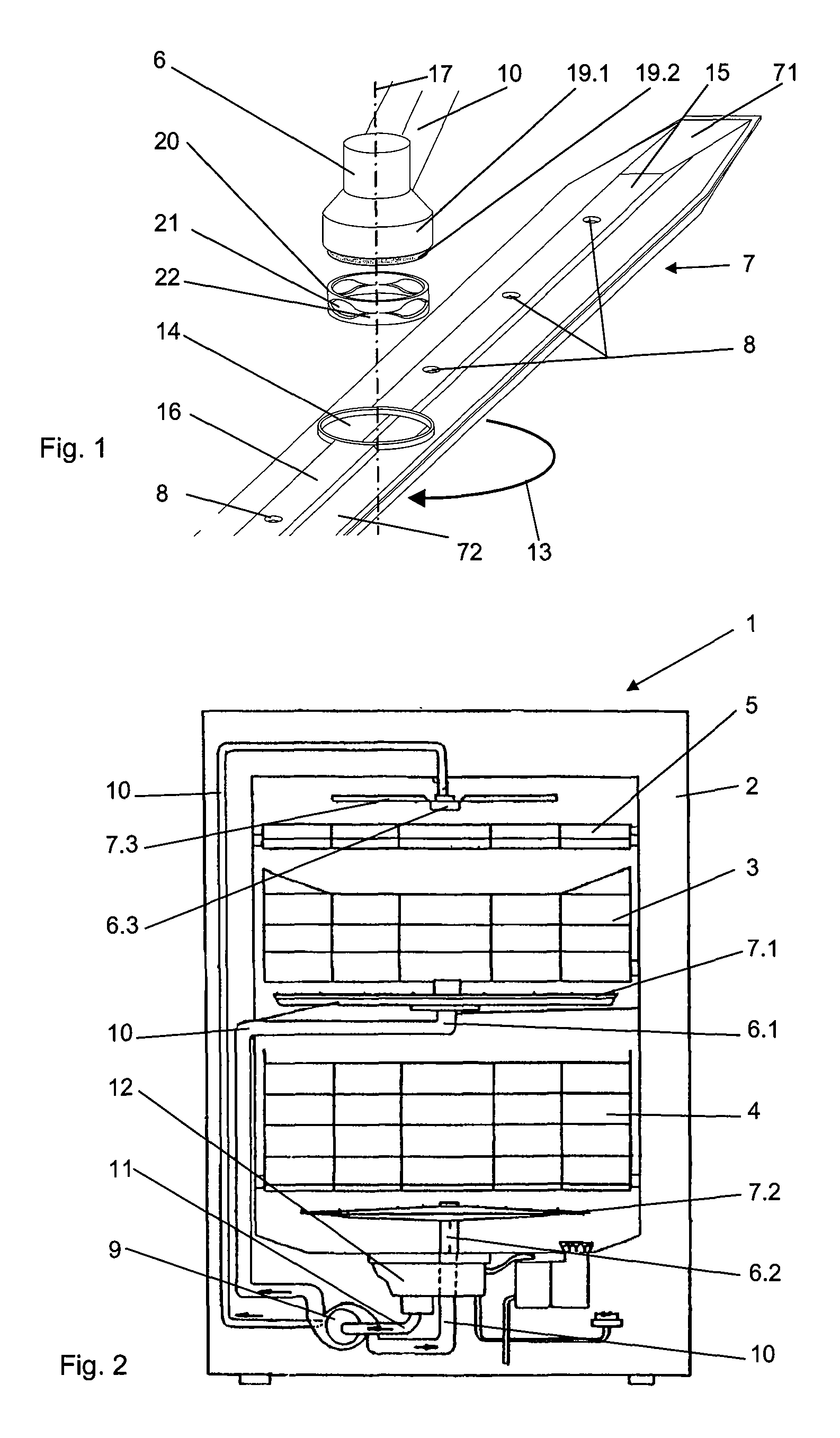
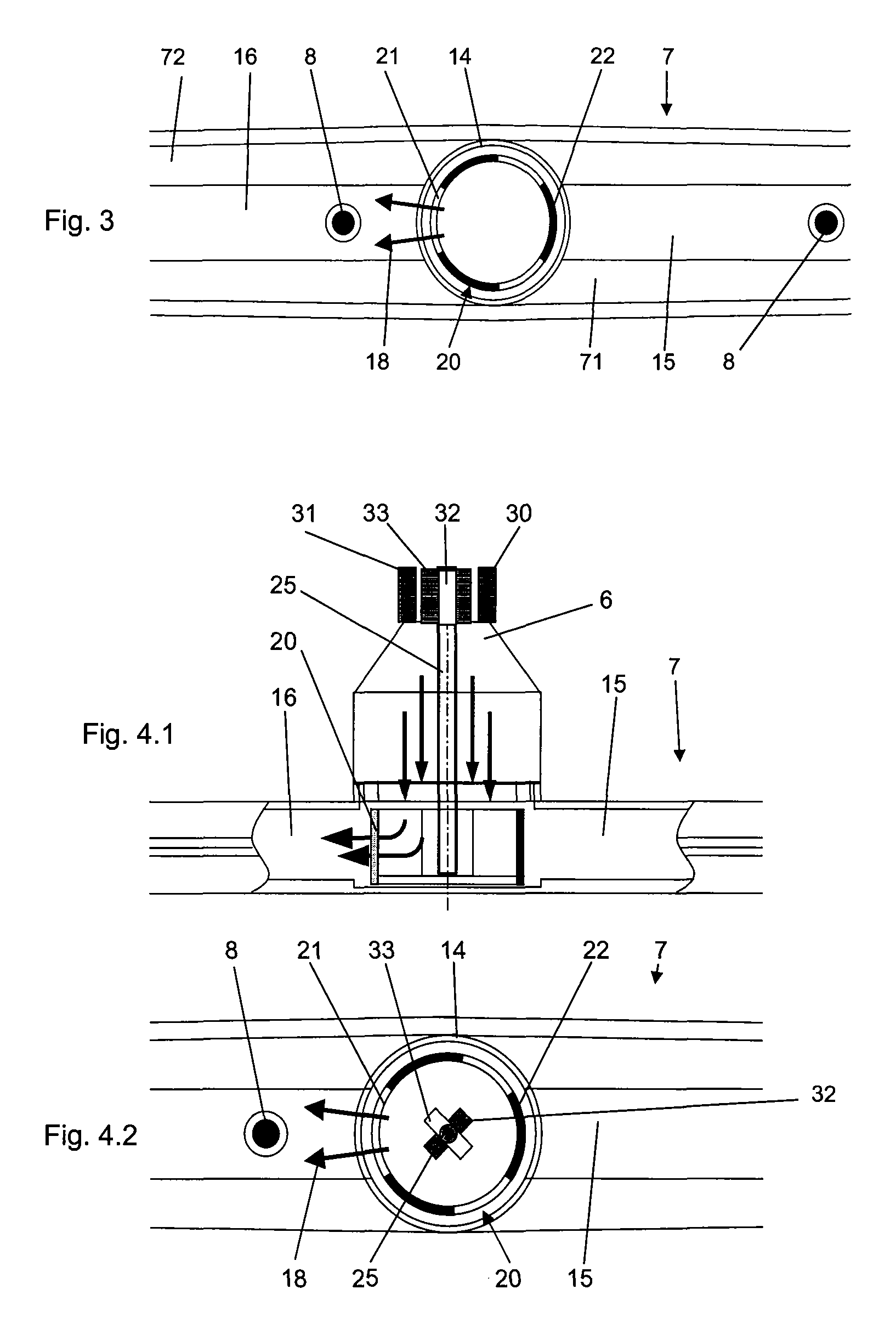
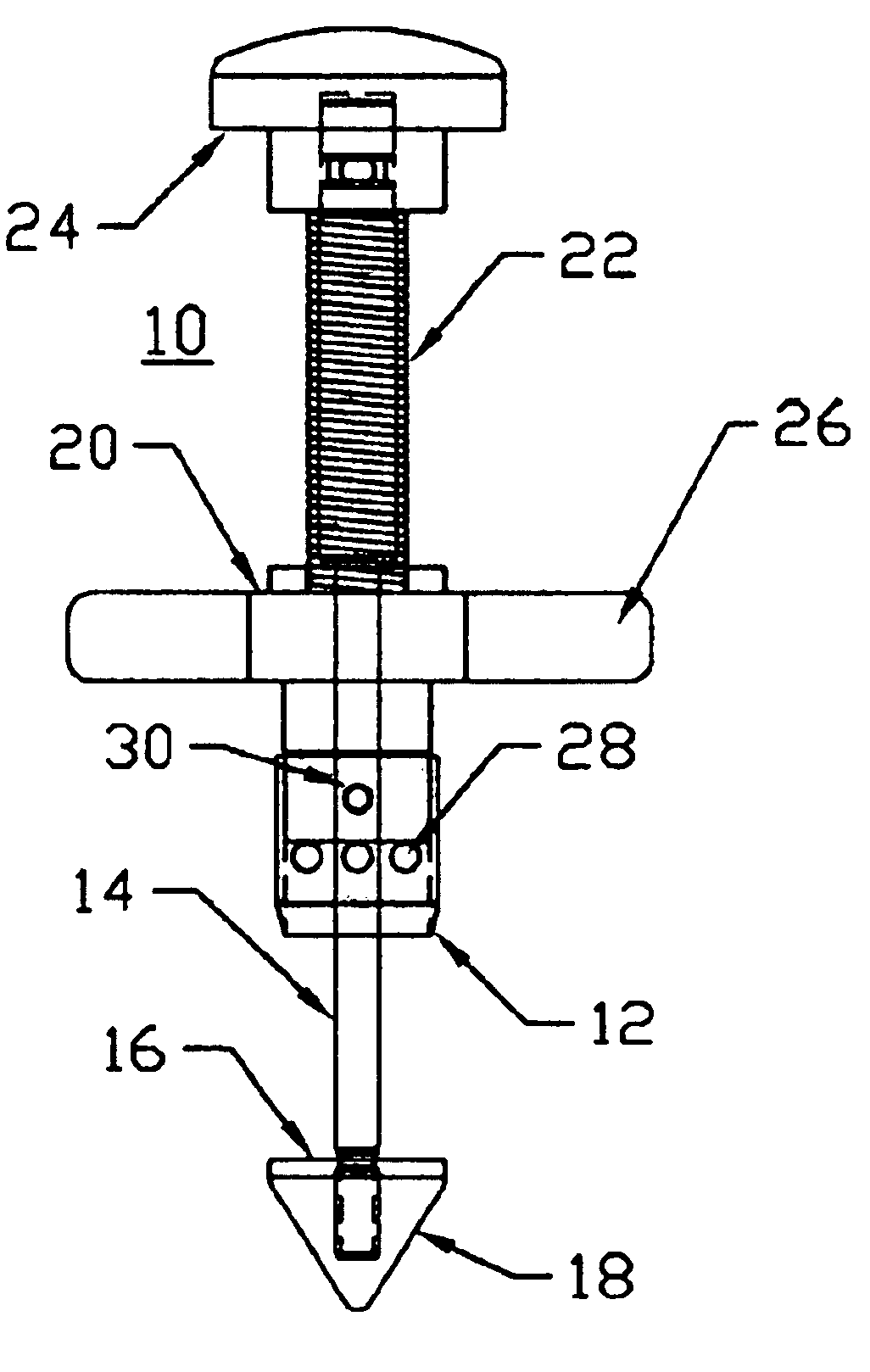
Apparatus of chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS20050054198A1Improving deposit uniformityMinimize formationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseEngineering
Disclosed is an apparatus for chemical vapor deposition including: a dome-shaped upper chamber having a half-round surface or a curved surface of a predetermined angle; a shower head disposed in the upper chamber, for ejecting a reaction gas for film deposition straight or radially according to the shape of the upper chamber; a lower chamber sealed off from the upper chamber by way of an O-ring; a heater disposed at the center of the bottom surface of the lower chamber as a heat energy source for forming the films; and a nozzle for ejecting the reaction gas and preventing entrance of the reaction gas from the bottom of the heater. The apparatus ejects the reaction gas for film deposition straight or radially onto the surface of the wafer to secure films excellent in deposition uniformity and remarkably reduce the formation of products in the chamber.
Owner:EUGENE TECH CO LTD
Air flow passage for a vacuum cleaner
InactiveUS6902596B2Reduce back pressureImprove performanceCleaning filter meansSuction filtersCycloneCyclonic separation
A vacuum cleaner is provided having improved pressure loss characteristics. A fluid supply conduit in flow communication with an inlet to a cyclone is integrally formed as part of a cyclone bin. The present invention may be adapted for use with cyclonic separation devices of all types, including single- and multi-stage cyclonic separators.
Owner:OMACHRON INTPROP
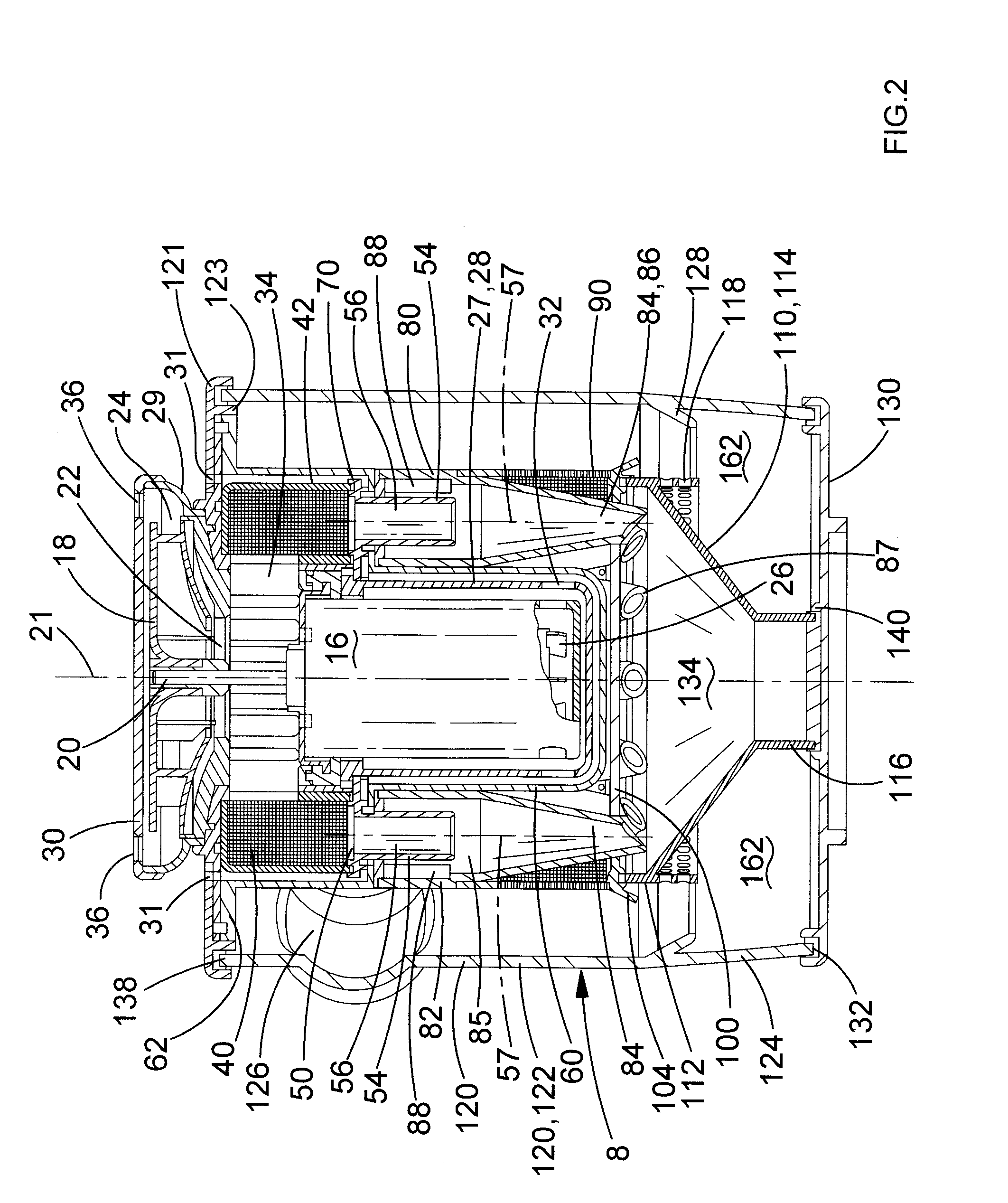
Motor, fan and cyclonic separation apparatus arrangement
ActiveUS20130091812A1Less spaceEasy to useMotor fan assembly mountingDispersed particle separationCycloneBrushless motors
A motor, fan and cyclonic separation apparatus arrangement for a vacuum cleaner comprising: a motor coupled to a fan for generating air flow; and a cyclonic separation apparatus located in a path of the air flow generated by the fan. The cyclonic separation apparatus comprises: a plurality of cyclones each with an air inlet port and an air outlet port; and a cooling air flow path. The motor comprises a permanent magnet brushless motor, a switched reluctance motor or a flux switching motor. The fan has an outer diameter the same or less than the diameter of the motor. The plurality of cyclones, the motor and the fan are arranged in a circular array about a central axis of the cyclonic separation apparatus. The arrangement comprises a baffle for directing air flow from the fan out of the circular array. The motor is located in the cooling air flow path.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
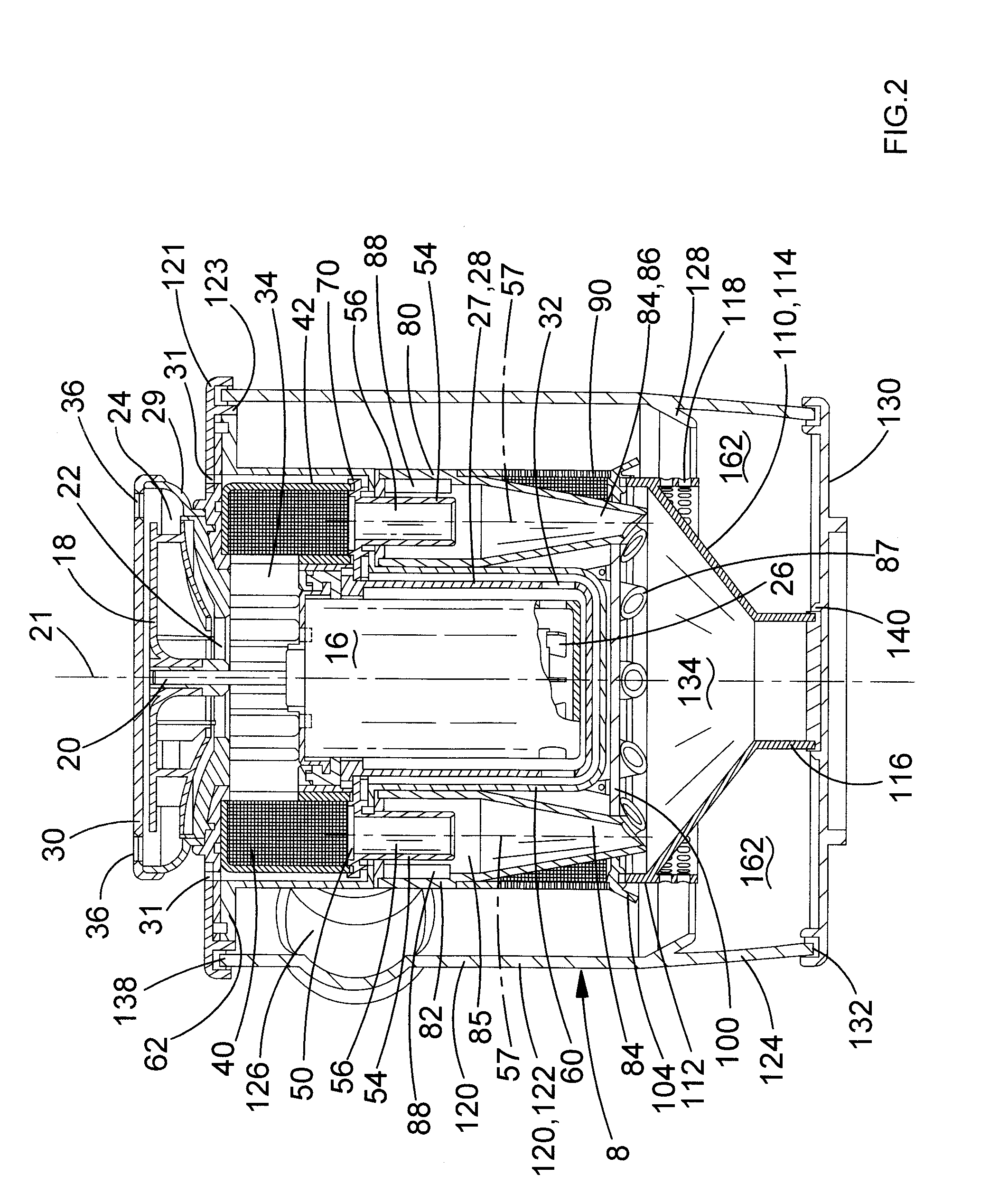
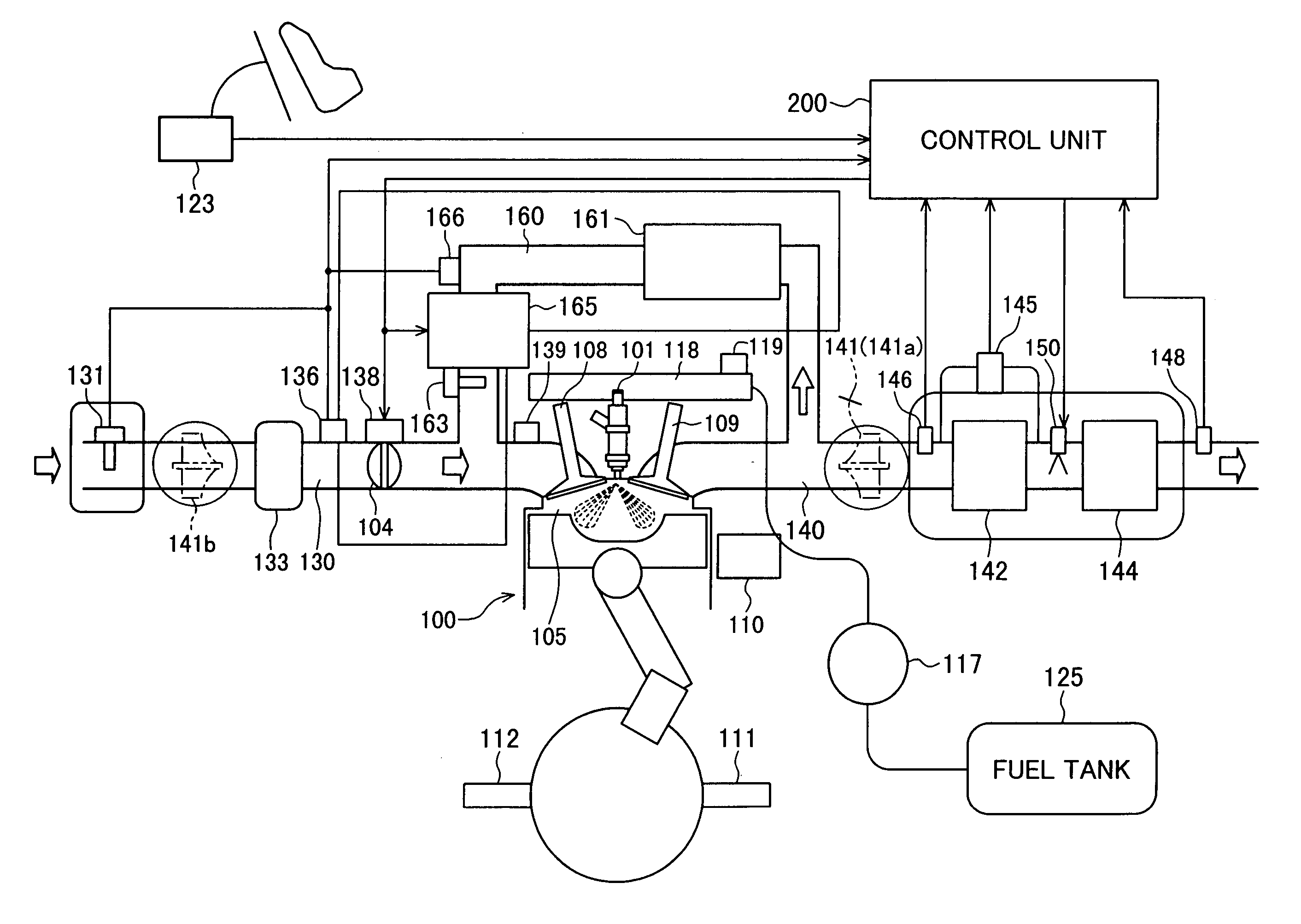
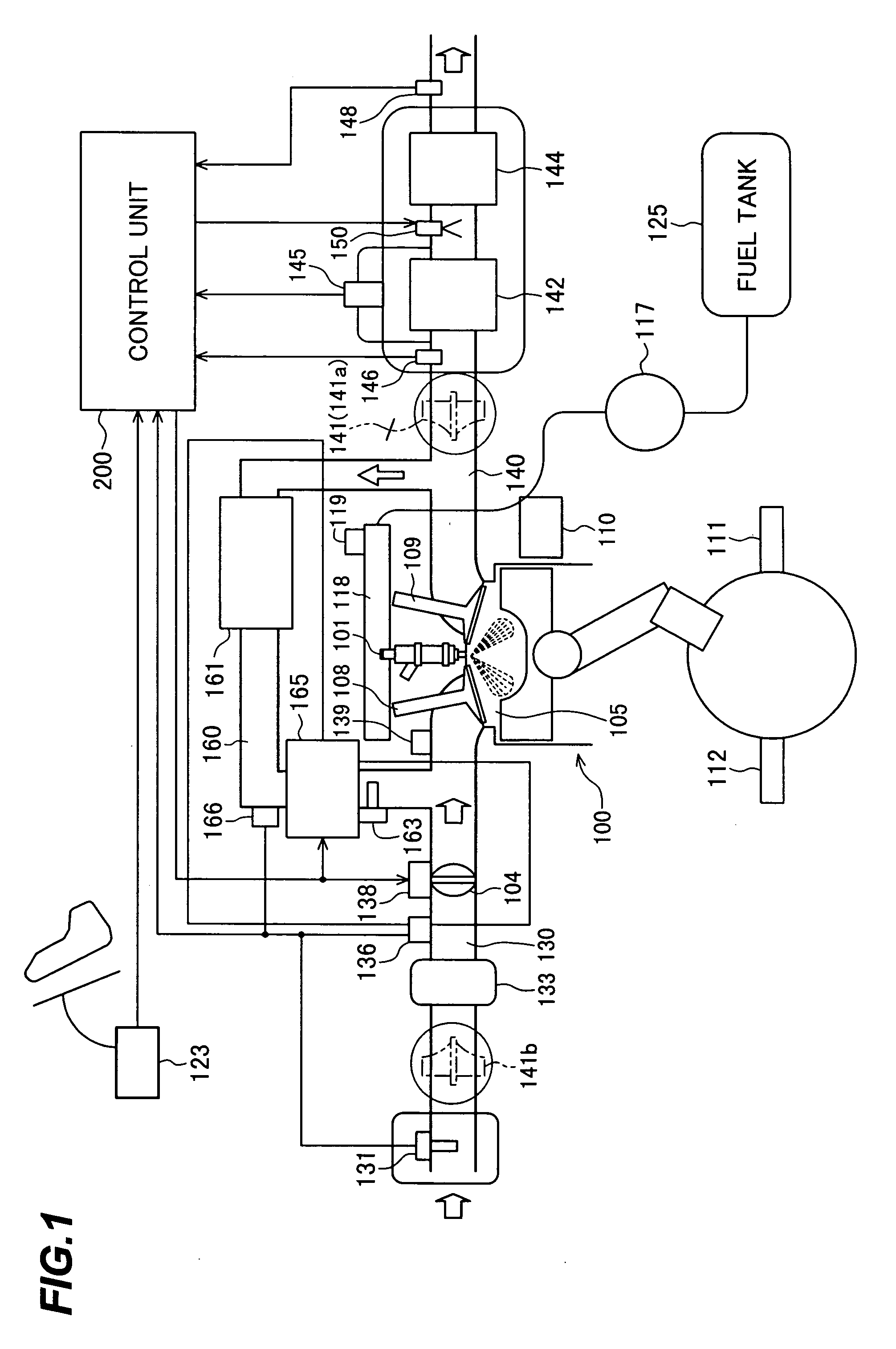
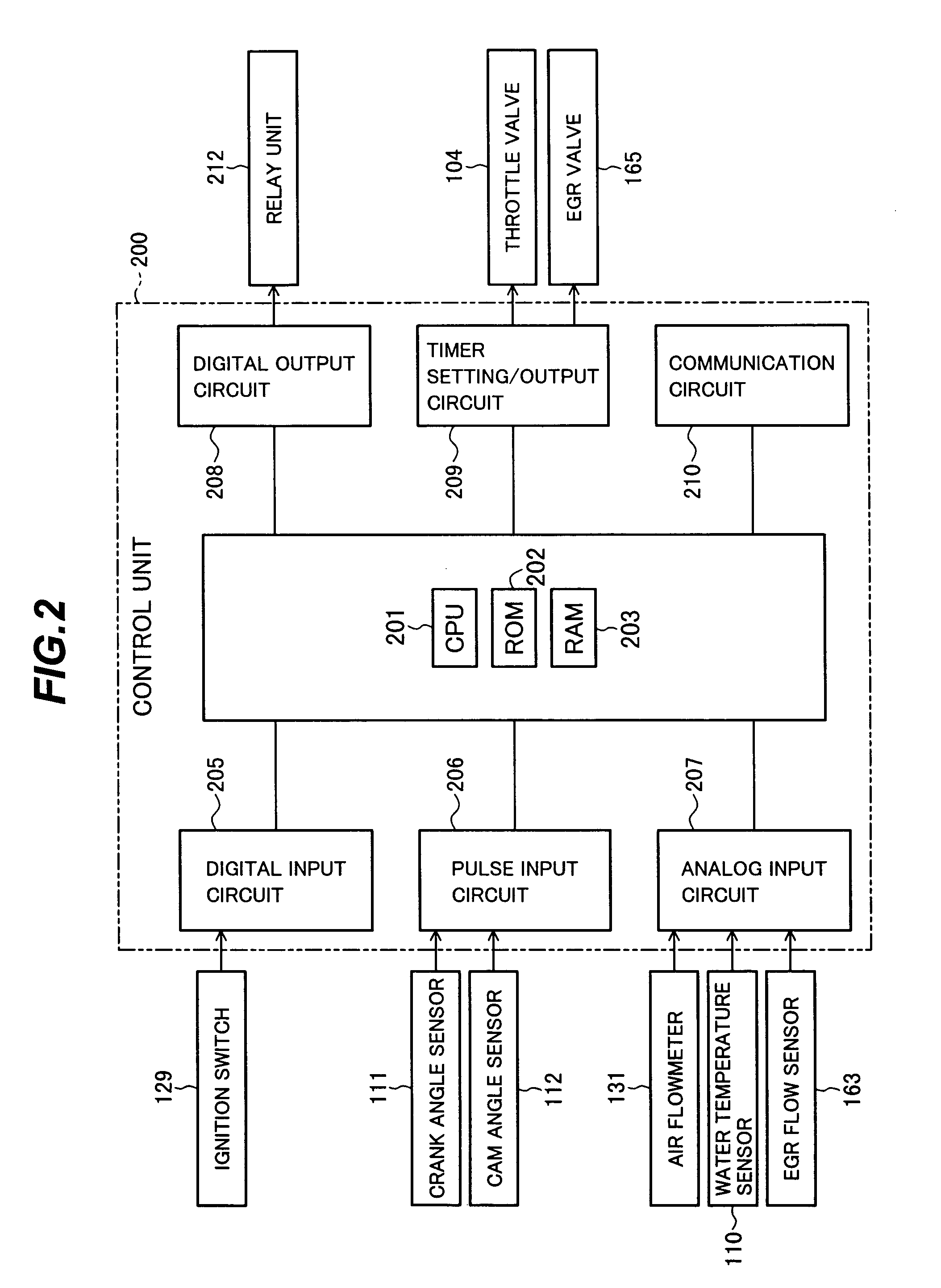
Engine exhaust gas cleaning method and system
InactiveUS20060086080A1Emission reductionReduce cleaning rateElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust fumesEnvironmental engineering
An engine exhaust gas cleaning method and system, which can effectively reduce emission amounts of particular components, such as NOx, contained in exhaust gas by adding an additive, such as urea water or light oil, into an exhaust passage, which is adaptable for a reduction of the cleaning rate caused by deterioration of a catalyst, which can always maintain a high cleaning rate during acceleration and deceleration as well, and which can minimize environmental pollution with use of the additive in the least necessary amount. The engine exhaust gas cleaning system comprises a catalyst for removing a particular component, represented by NOx, contained in exhaust gas of an engine, an additive adding unit for adding, to the exhaust gas, an additive for reducing the particular component represented by NOx, and an EGR amount adjusting unit for adjusting an EGR amount. An addition amount of the additive and the EGR amount are set depending on an operating state and deterioration of the catalyst with time. The catalyst is regenerated when a cleaning capability of the catalyst has reduced to a predetermined value or below.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Dishwasher
InactiveUS20060278258A1Reduce complexitySmall space requirementElectrostatic cleaningTableware washing/rinsing machinesSpray nozzleEngineering
Owner:MIELE & CO KG
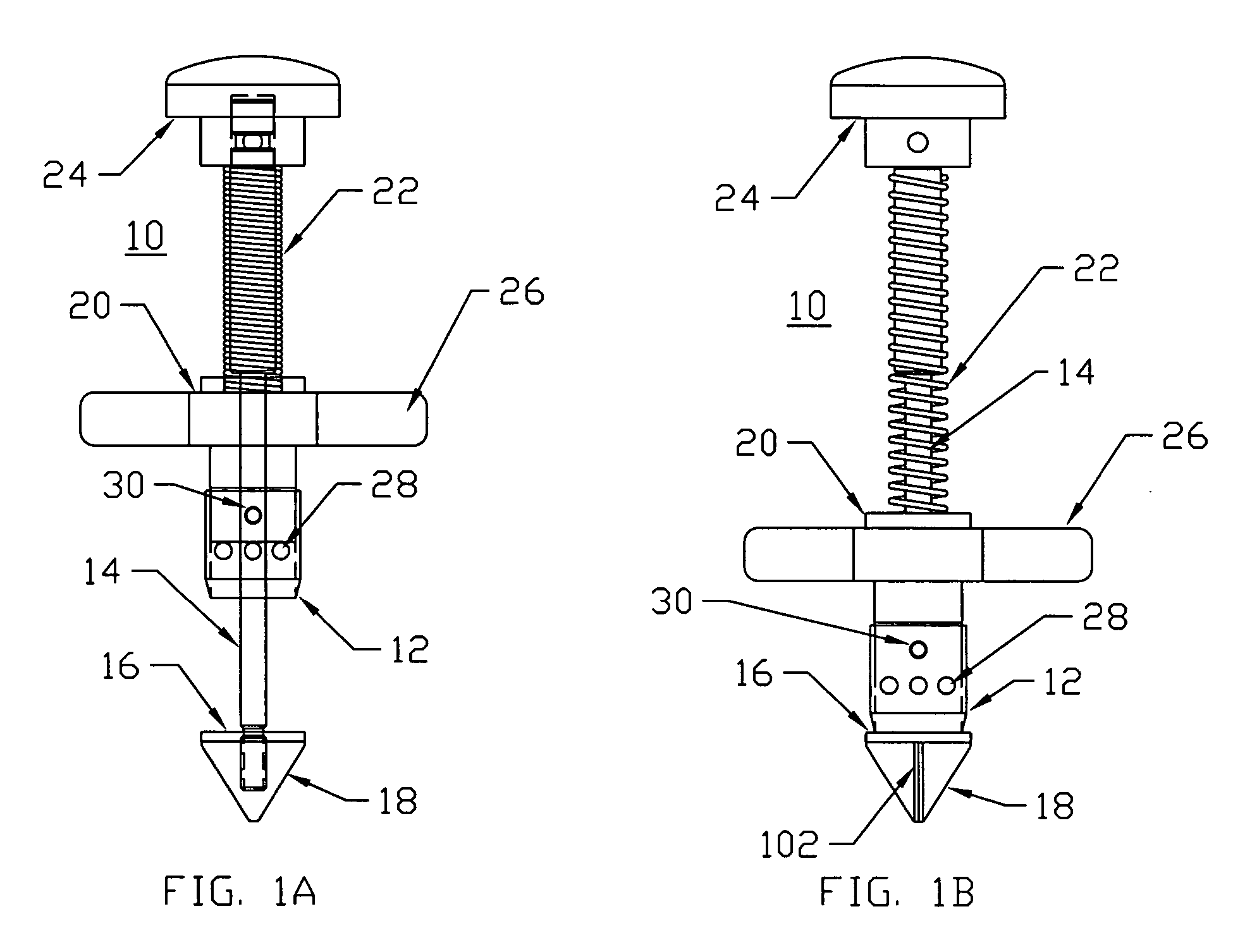
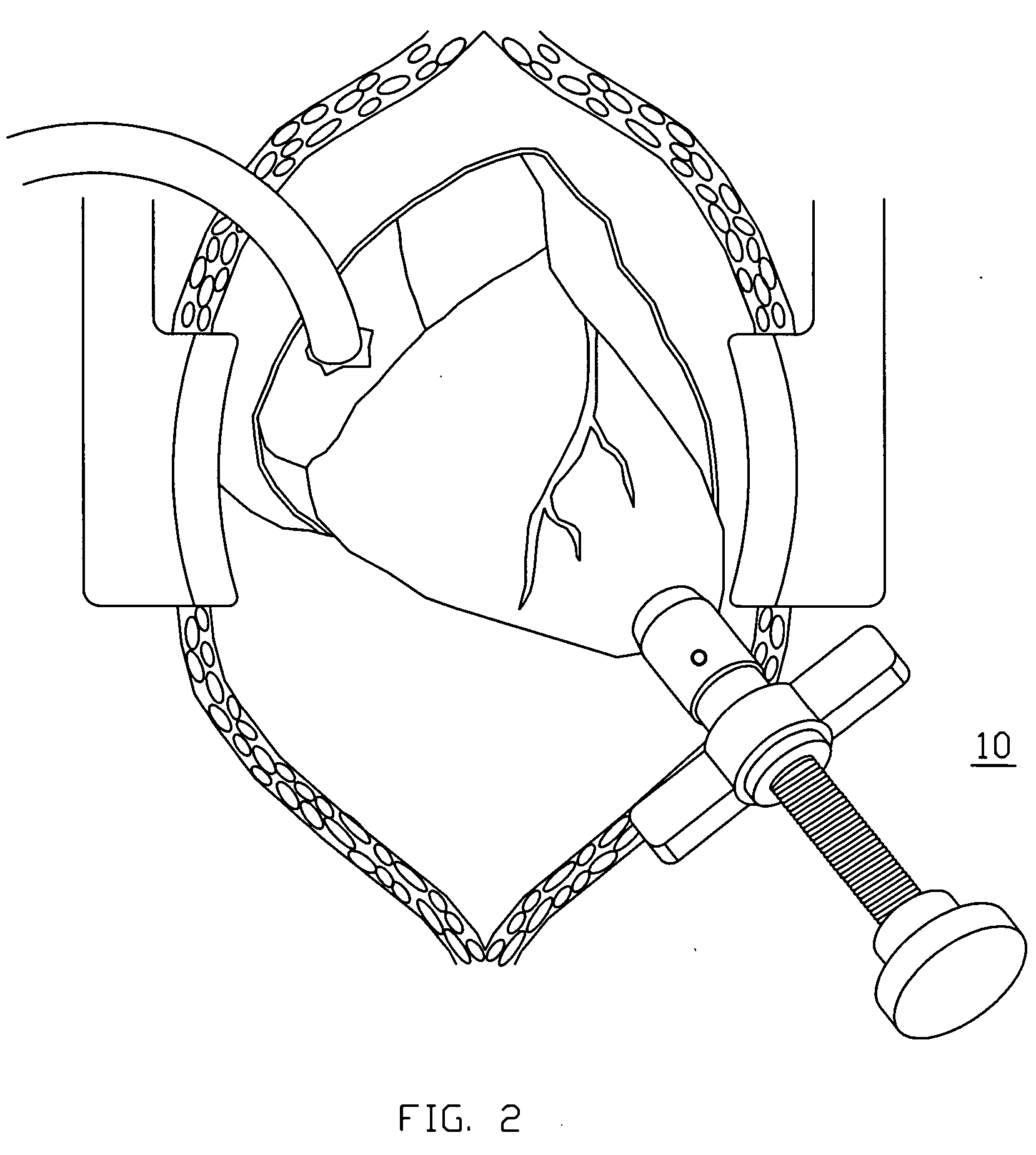
Method and apparatus for trephinating body vessels and hollow organ walls
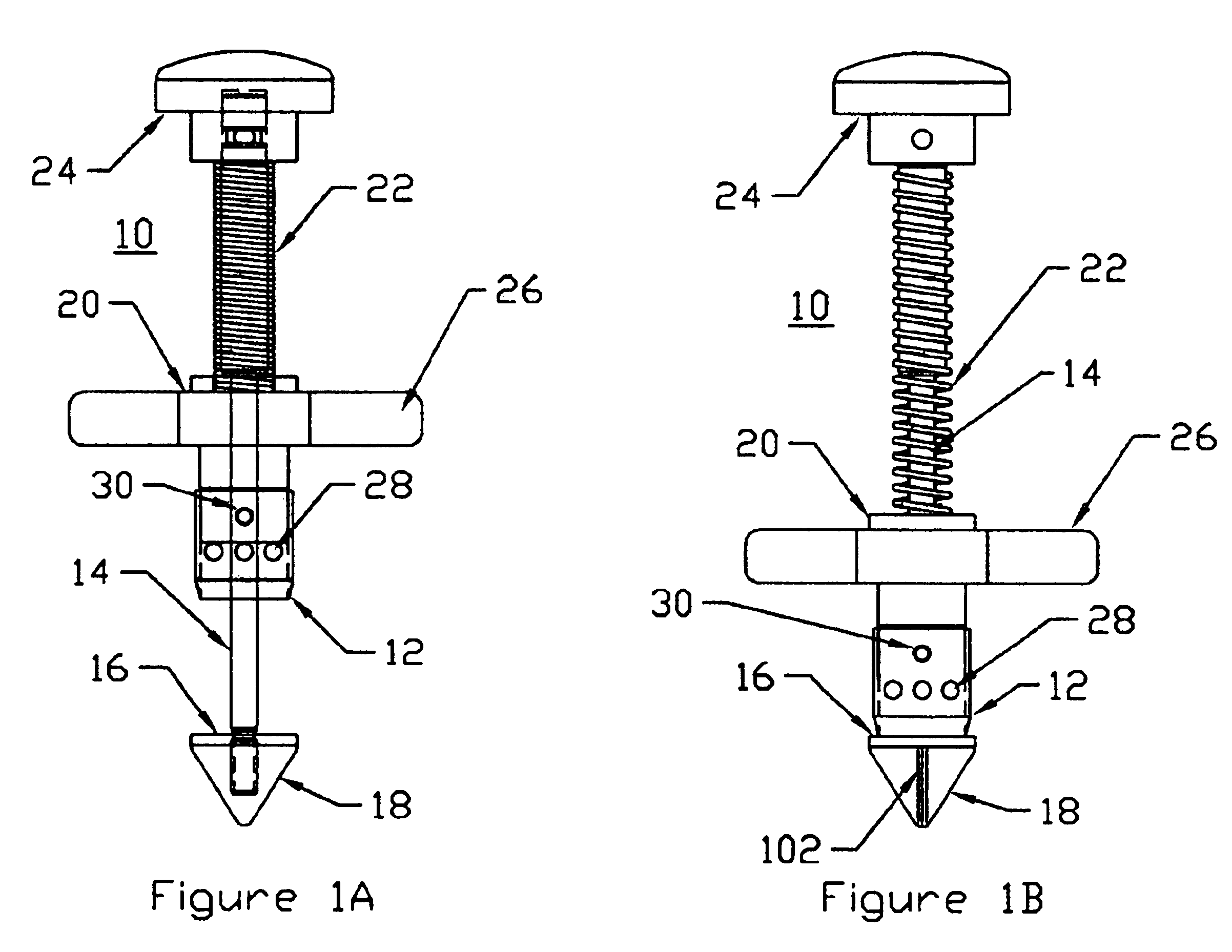
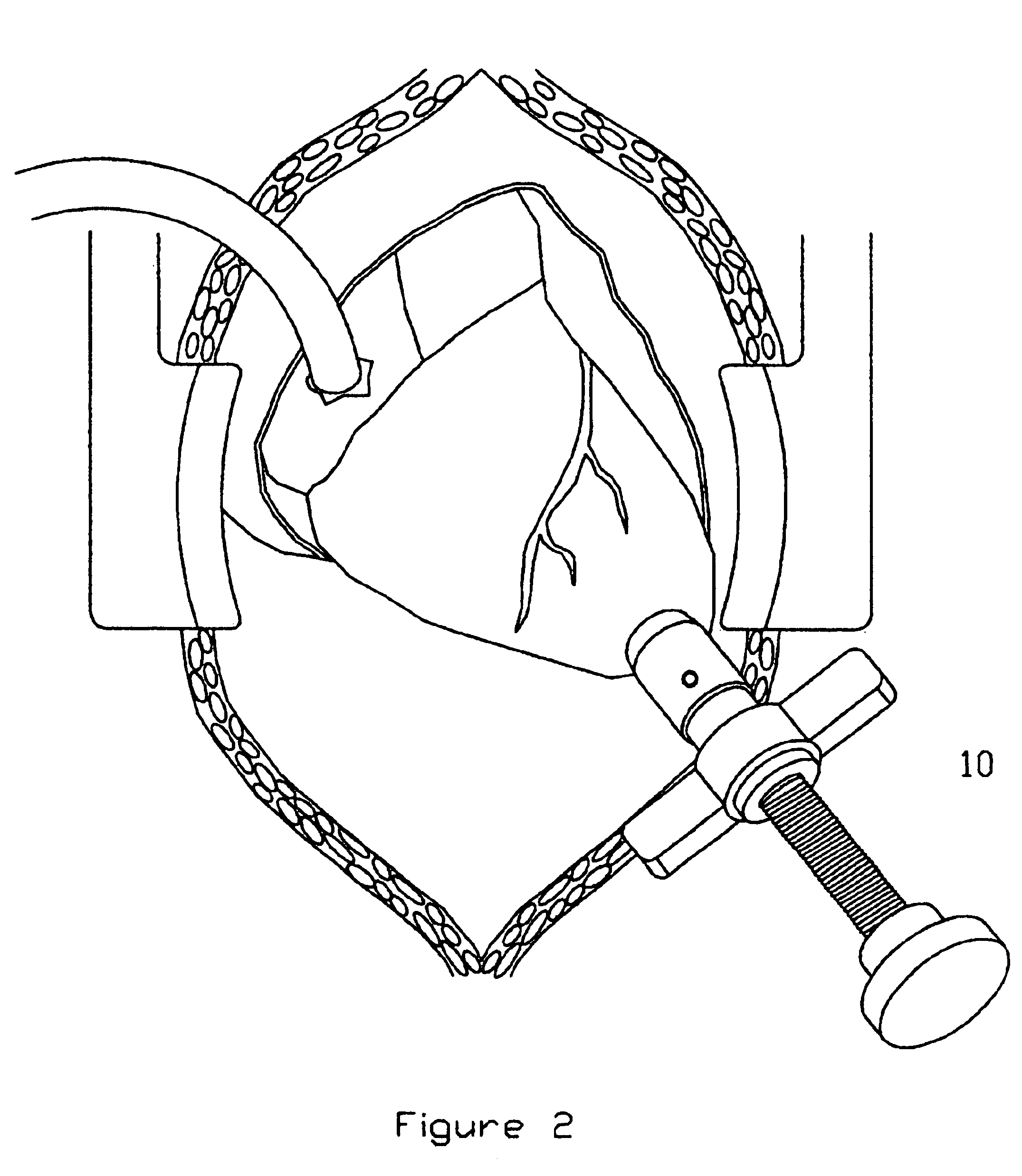
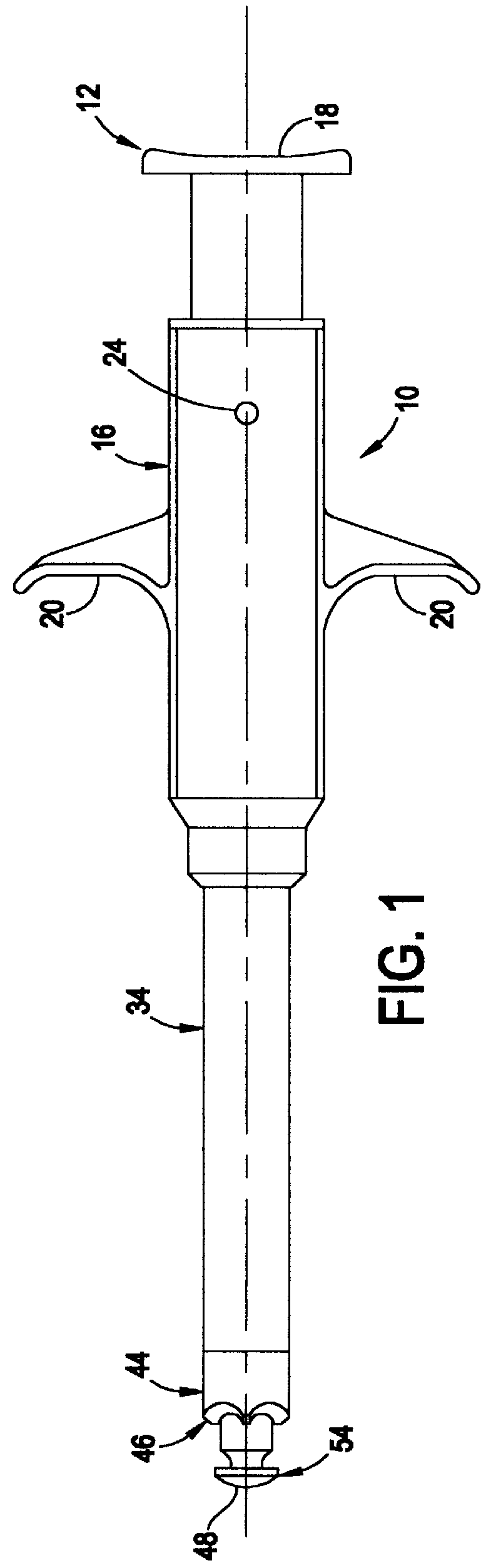
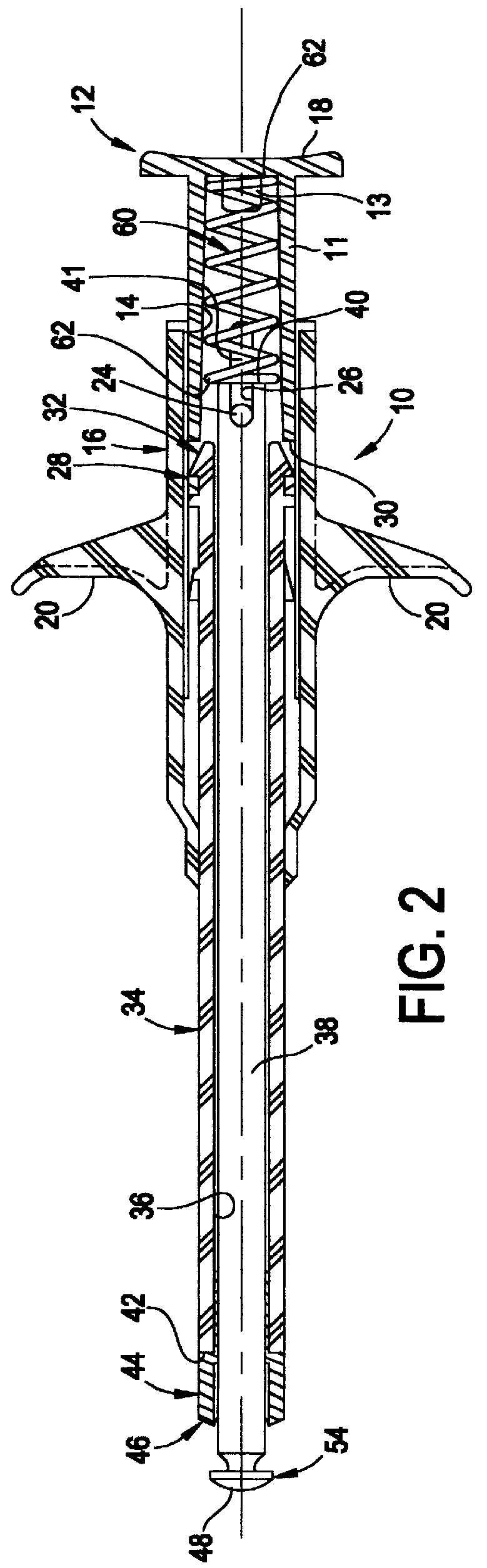
InactiveUS6863677B2Improve permeabilityReduce cleaningSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsPapillary muscleBone trephine
A system is disclosed for creating a hole in a body vessel or hollow organ. Such holes are useful in surgically preparing the hollow organ or body vessel for connection with another hollow organ, body vessel or prosthetic conduit. For example, an assist device is generally connected to the left ventricle through a ventriculotomy created at the apex of the left ventricle. This ventriculotomy is most easily created with a punch or trephine. Control over such a procedure must be precise so as not to damage the ventricular wall or intracardiac structures such as papillary muscles, chordae tendinae, etc. The punch of the current invention allows for precise location and alignment of the cutting segment. The punch of the current invention also allows for precise advance of the cutting blade and a very clean cut of the tissue. Such clean cuts improve the healing when the hole in the body vessel or hollow organ is closed or attached to a connection, either prosthetic or natural.
Owner:INDIAN WELLS MEDICAL
Medical punch with high shear angle cutting edges
InactiveUS6080176AClean and accurate cutReduce wearSurgical needlesExcision instrumentsEngineeringHand pressure
A medical punch having a plurality of cutting edges. The fact that the medical punch has a plurality of cutting edges provides, for example, that the medical punch can be used to achieve a clean and accurate cut, and provides that an excessive amount of hand pressure need not be employed to effect the cut.
Owner:ATRION MEDICAL PRODS
Remover compositions for dual damascene system
InactiveUS20050266683A1Avoid corrosionAvoid inhibitionNon-surface-active detergent compositionsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricAnti-reflective coating
A new remover chemistry based on a choline compound, such as choline hydroxide, is provided in order to address problems related to removal of residues, modified photoresists, photoresists, and polymers such as organic anti-reflective coatings and gap-fill and sacrificial polymers from surfaces involved in dual damascene structures without damaging the dielectrics and substrates involved therein. An etch stop inorganic layer at the bottom of a dual damascene structure may or may not be used to cover the underlying interconnect of copper. If not used, a process step of removing that protective layer can be avoided through a timed etch of the via in trench-first dual damascene processes.
Owner:EKC TECH
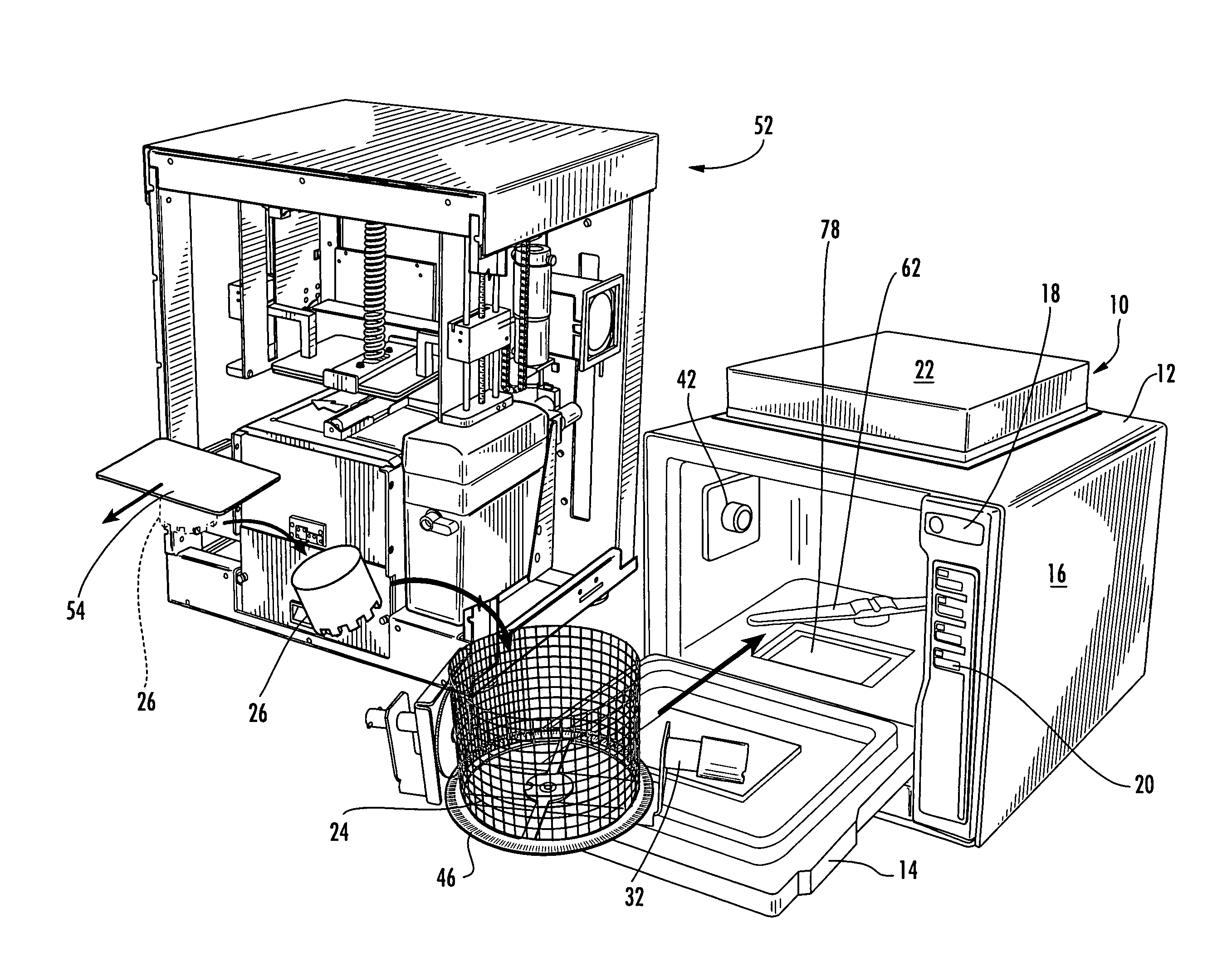
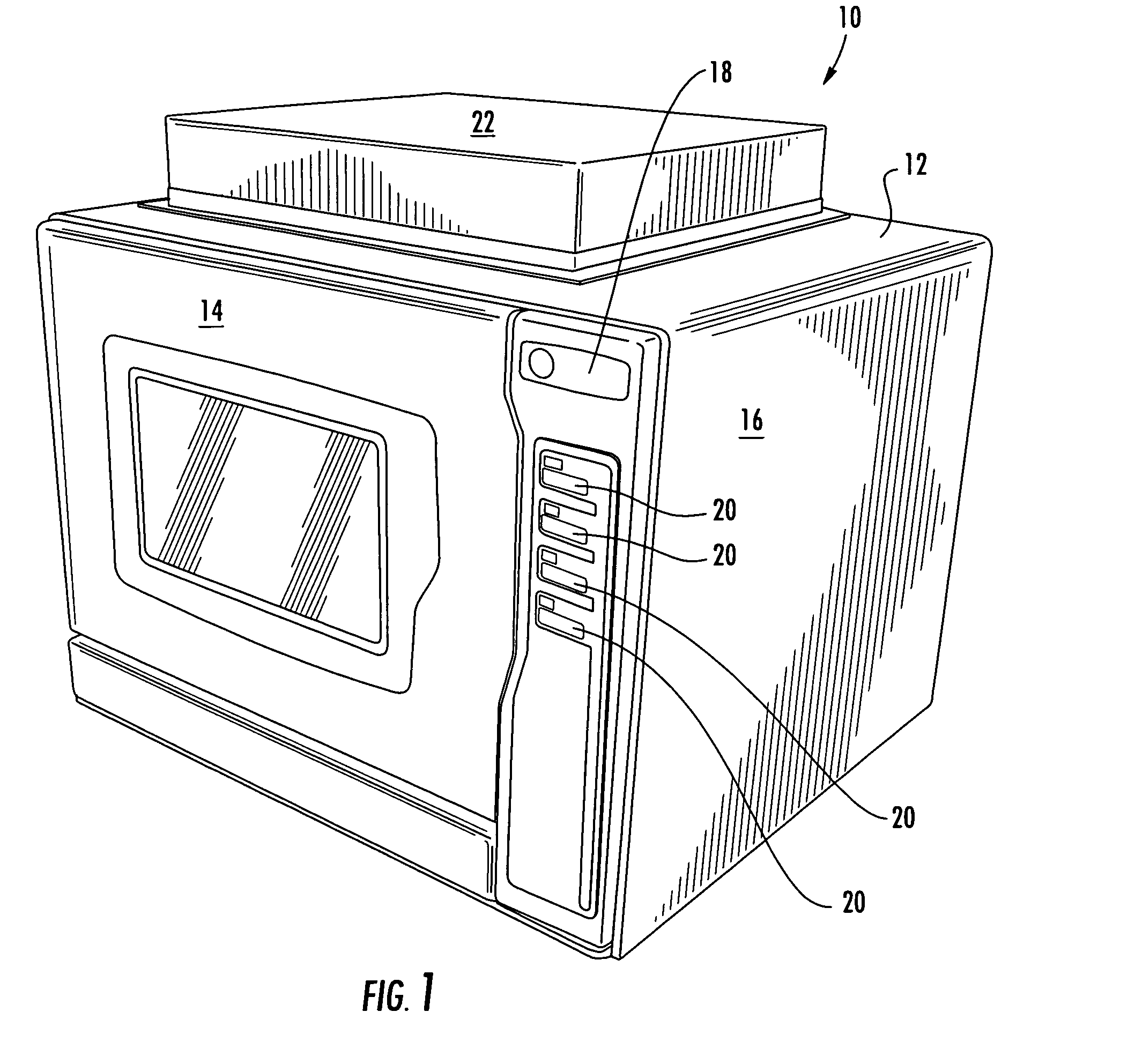
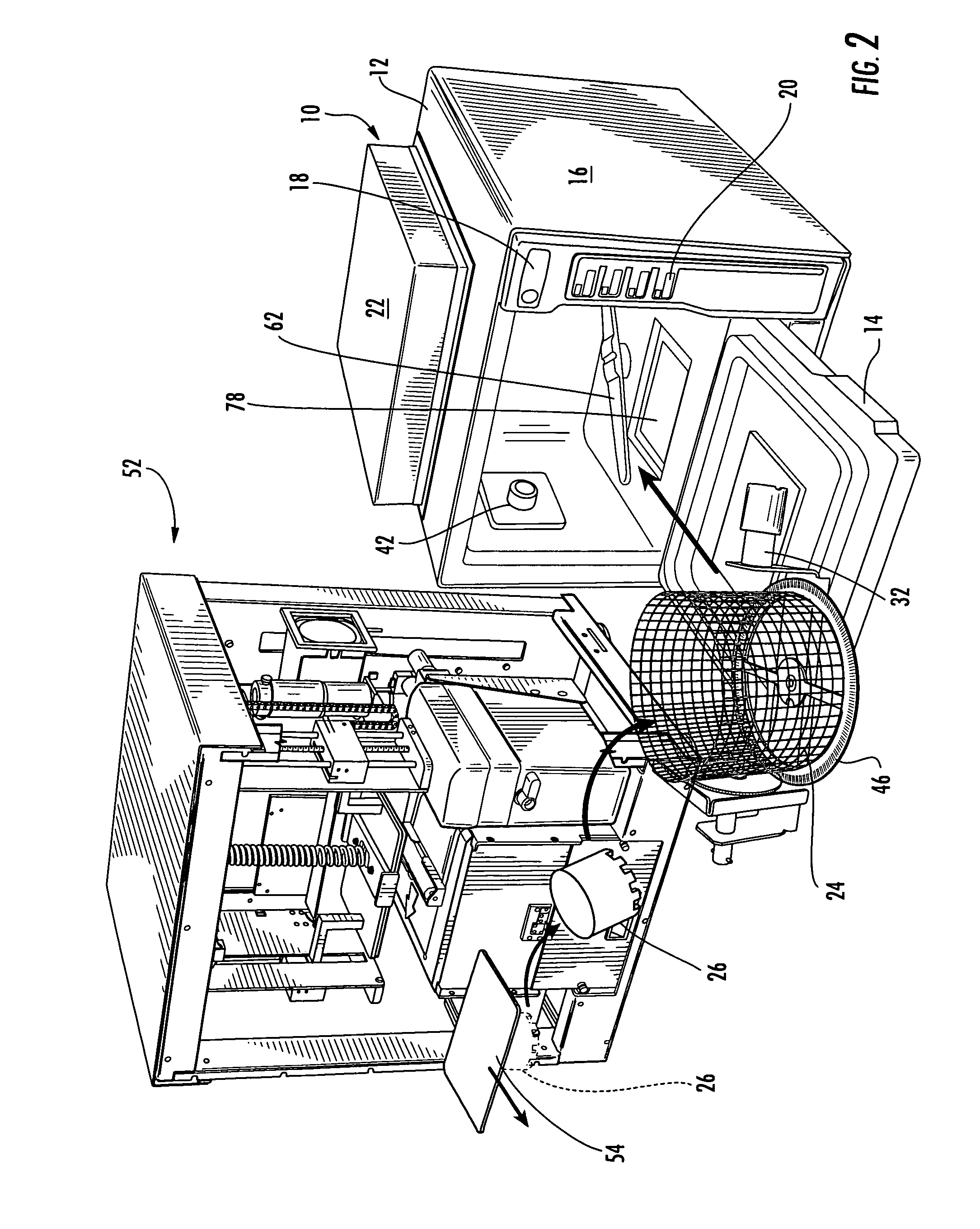
Post-Processing System For Solid Freeform Fabrication Parts
InactiveUS20090283119A1Improve post-processing qualityReduced post-processing timeElectrostatic cleaning3D object support structuresFiltrationBiomedical engineering
A post-processing system is provided for cleaning and / or curing a part produced by solid freeform fabrication (SFF). The post-processing systems include a housing, a part retaining device to retain the part within the housing, and an actinic radiation source to cure the part with actinic radiation. The systems also include a fluid circulation device adapted to expose the part to cleaning fluid and / or to allow the cleaning fluid to absorb actinic radiation to permit filtration of removed build material to allow extended use of the cleaning fluid. Certain systems include a first rotating portion that can rotate the retained part about a first axis, and further systems include a second rotating portion that can rotate the retained part about a second axis. The systems also include additional features to provide safe and efficient cleaning and / or curing of parts produced by SFF.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Method and apparatus for trephinating body vessels and hollow organ walls
InactiveUS20050154411A1Improve permeabilityReduce cleaningSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsPapillary muscleBone trephine
A system is disclosed for creating a hole in a body vessel or hollow organ. Such holes are useful in surgically preparing the hollow organ or body vessel for connection with another hollow organ, body vessel or prosthetic conduit. For example, an assist device is generally connected to the left ventricle through a ventriculotomy created at the apex of the left ventricle. This ventriculotomy is most easily created with a punch or trephine. Control over such a procedure must be precise so as not to damage the ventricular wall or intracardiac structures such as papillary muscles, chordae tendinae, etc. The punch of the current invention allows for precise location and alignment of the cutting segment. The punch of the current invention also allows for precise advance of the cutting blade and a very clean cut of the tissue. Such clean cuts improve the healing when the hole in the body vessel or hollow organ is closed or attached to a connection, either prosthetic or natural.
Owner:BREZNOCK EUGENE M +1
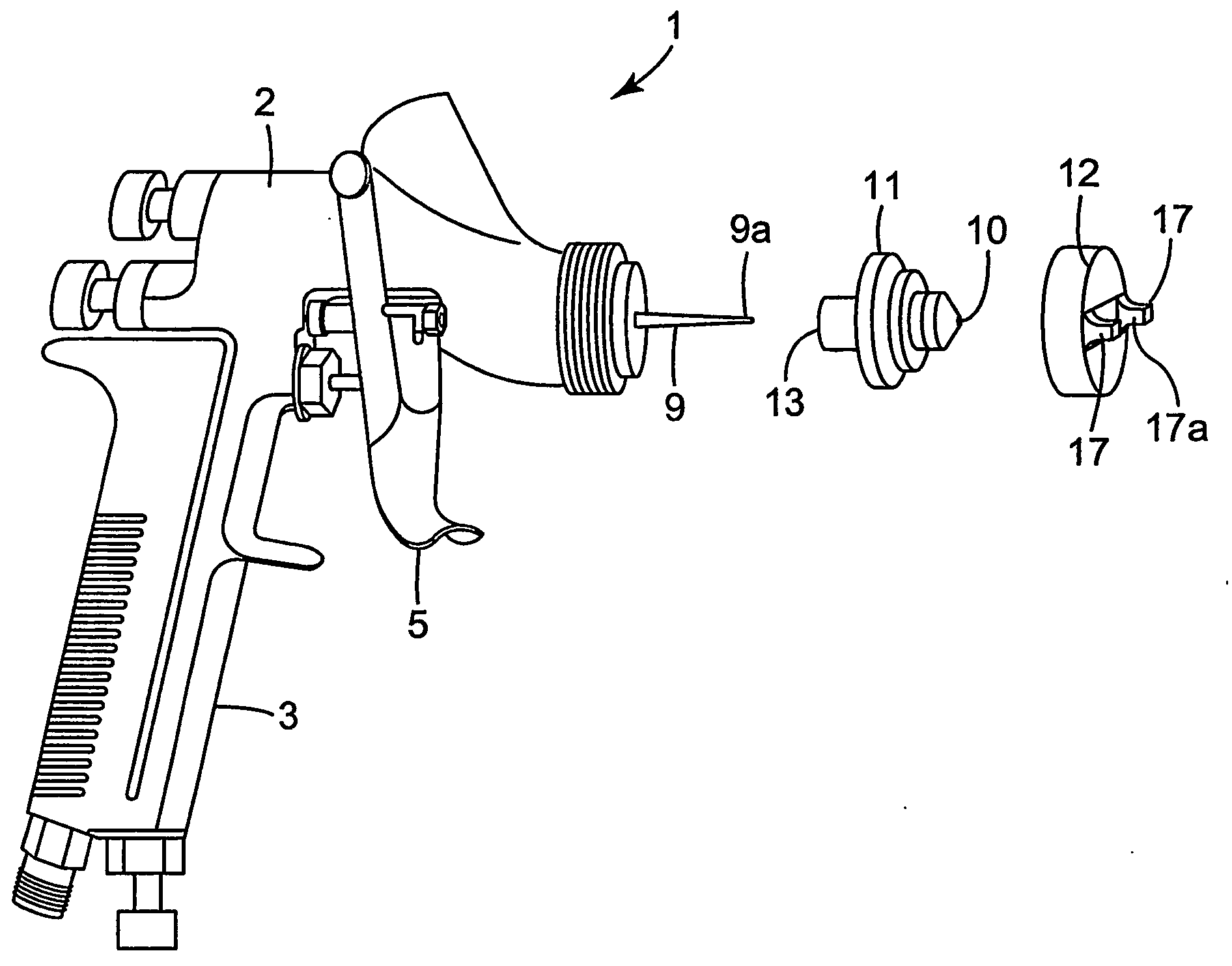
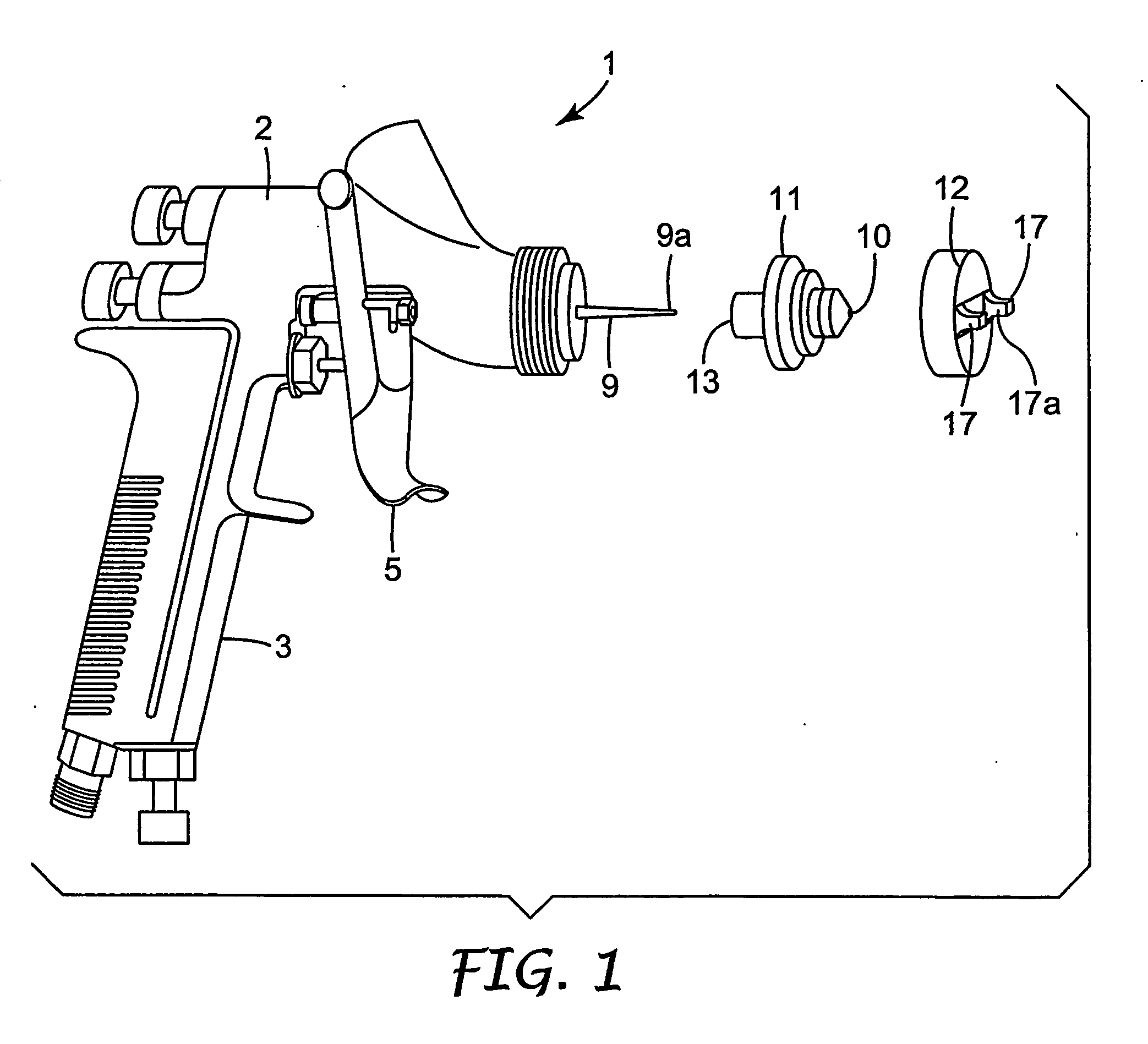
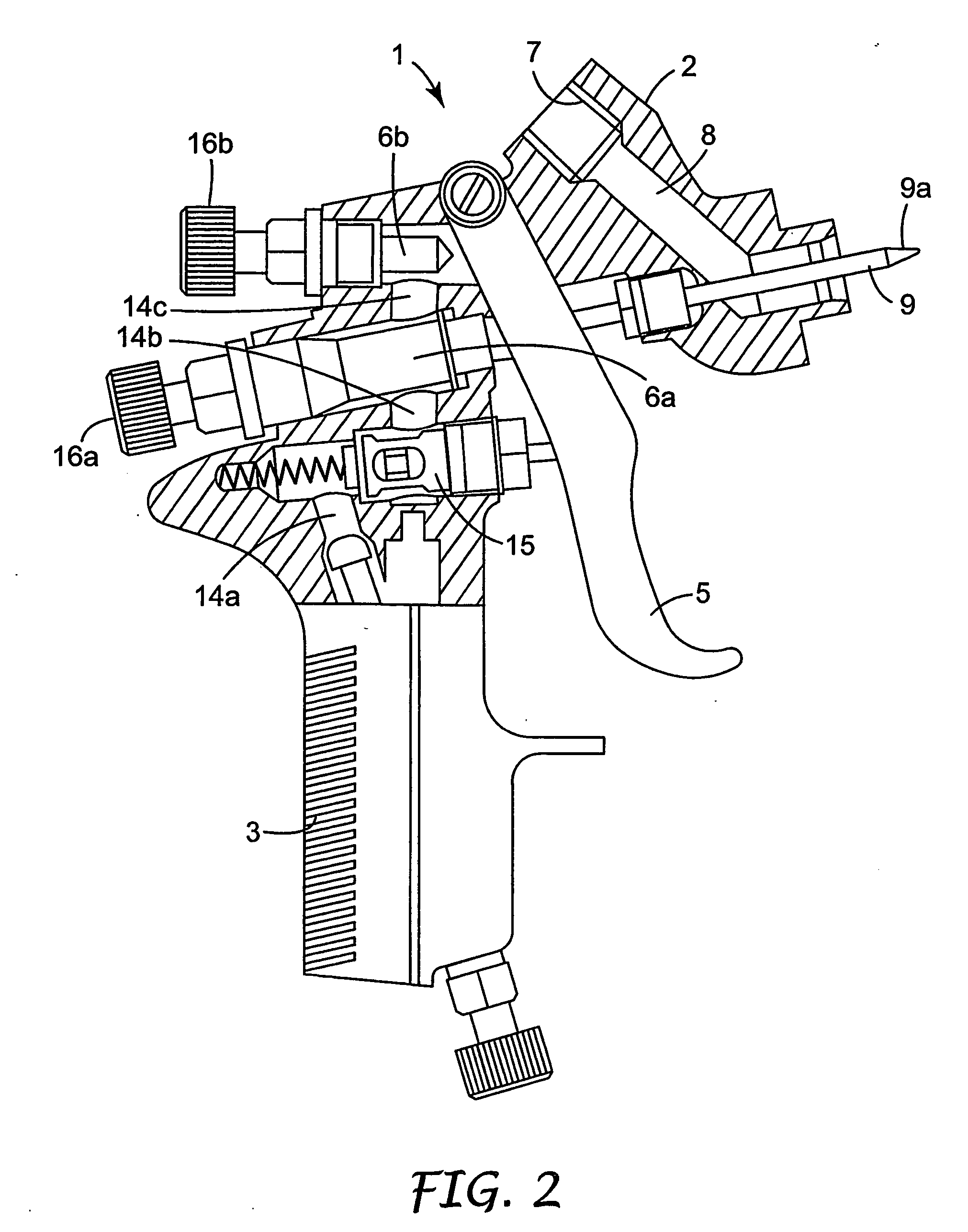
Easy clean spray gun
ActiveUS20060065761A1Reduce the amount requiredEasy to cleanSpray nozzlesLiquid spraying apparatusSpray nozzleEngineering
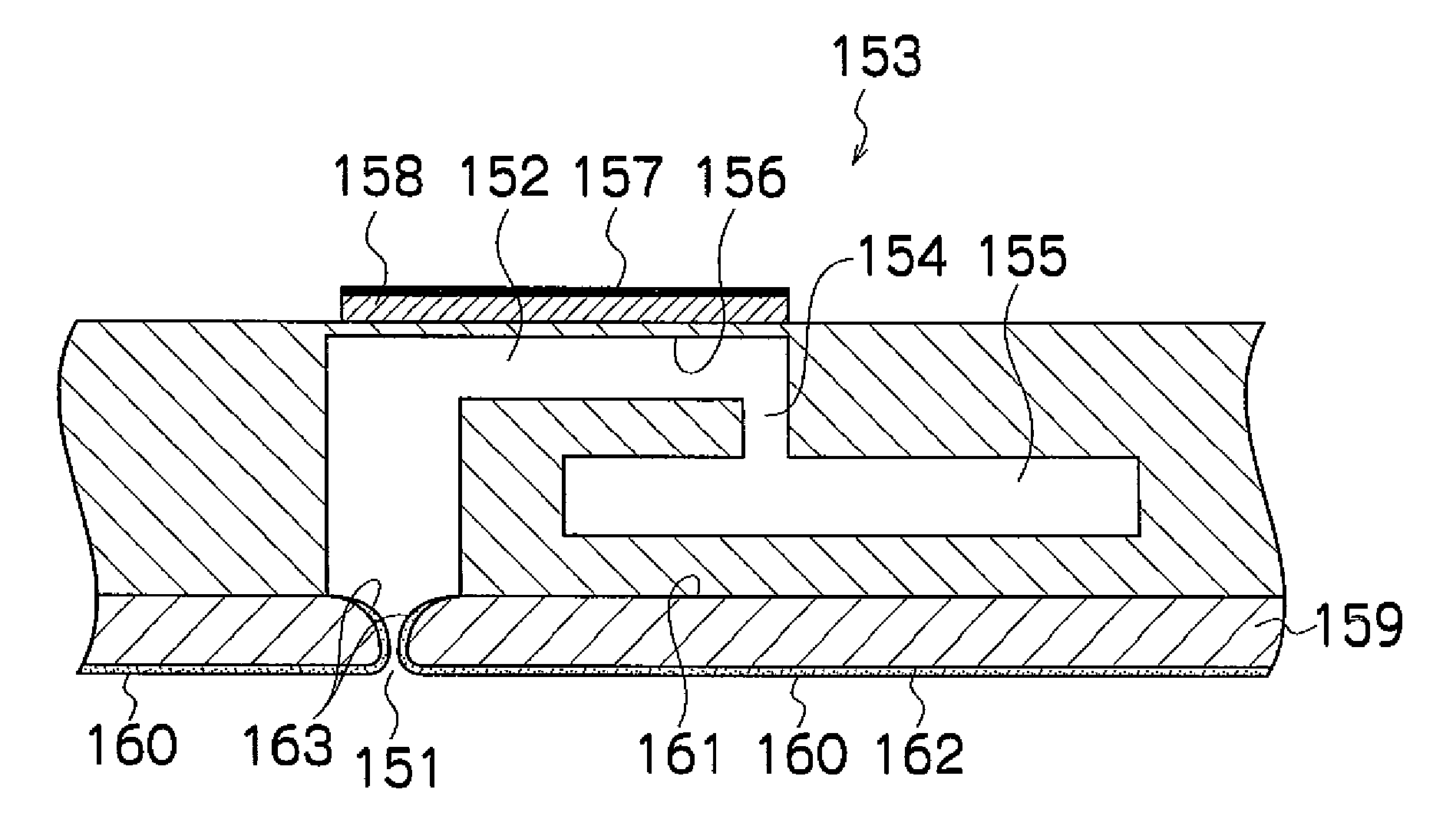
A spray gun 101 has a spray head 150 connected to a body 102 of the spray gun 101 and a reservoir 156 connected to the spray head 150 for supplying liquid to a spray nozzle 153 of the spray head 150. The spray head 150 is arranged so that liquid from the reservoir 156 is delivered to the spray nozzle 153 without passing through the spray gun body 102 in response to actuation of the spray gun 101 via a trigger 105. The spray head 150 is releasably secured and can be detached from the spray gun body 102 and thrown away after use. The reservoir 156 is mounted on the spray head 150 and can be removed and thrown away with the spray head 150 after use.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
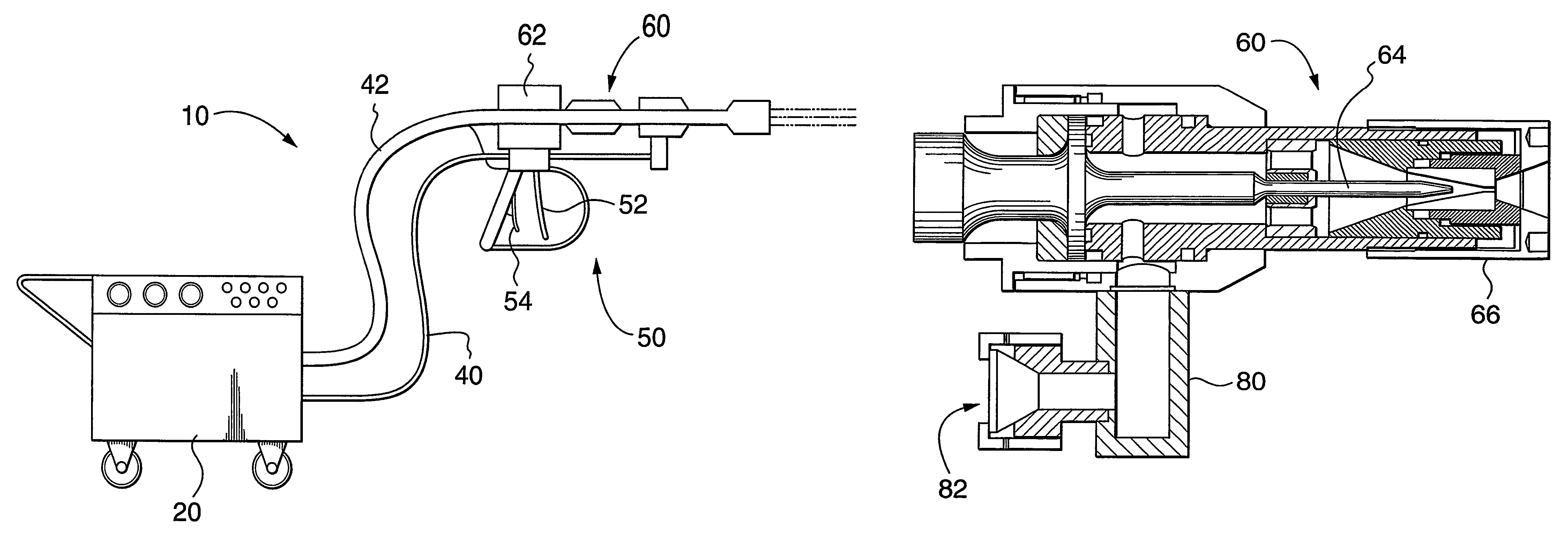
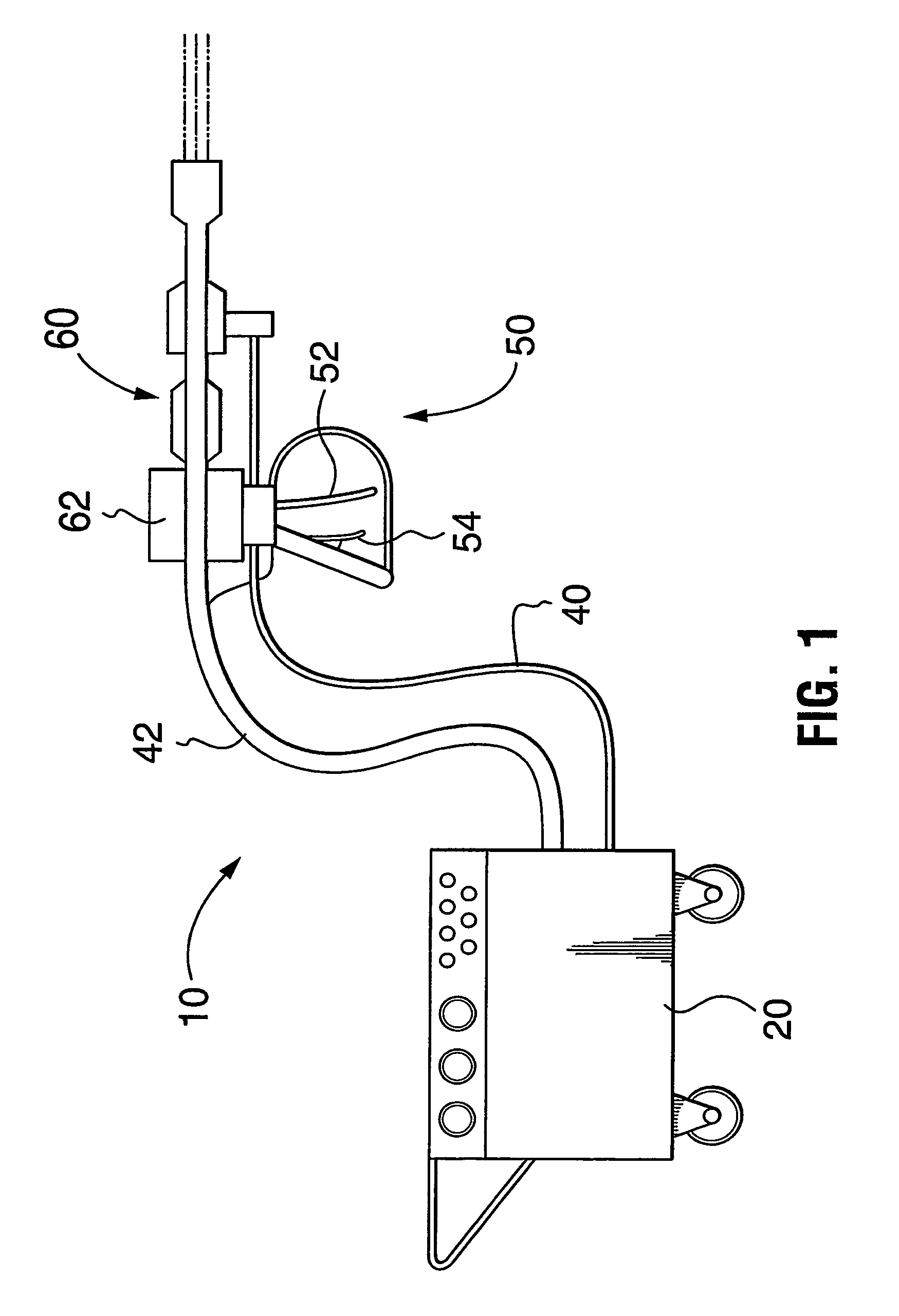
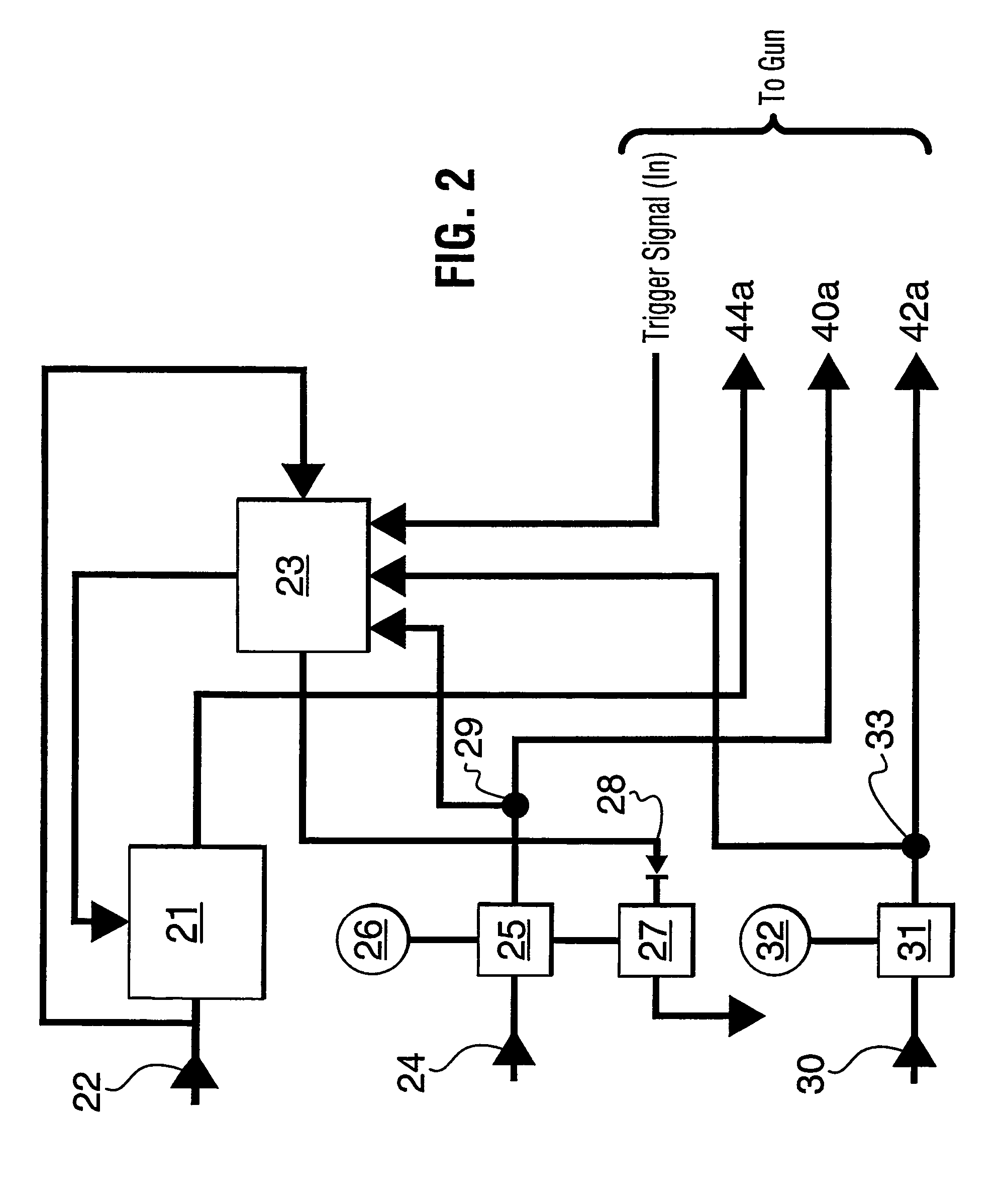
Ultrasonic waterjet apparatus
ActiveUS7594614B2Reduce cleaningReduce pressureLiquid surface applicatorsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonic nozzleUltrasonic nozzle
An ultrasonic waterjet apparatus (10) has a mobile generator module (20) and a high-pressure water hose (40) for delivering high-pressure water from the mobile generator module (20) to a hand-held gun (50) with a trigger and an ultrasonic nozzle (60). An ultrasonic generator in the mobile generator module (20) transmits high-frequency electrical pulses to a piezoelectric or magnetostrictive transducer (62) which vibrates to modulate a high-pressure waterjet flowing through the nozzle (60). The waterjet exiting the ultrasonic nozzle (60) is pulsed into mini slugs of water, each of which imparts a waterhammer pressure on a target surface. The ultrasonic waterjet apparatus (10) may be used to cut and de-burr materials, to clean and de-coat surfaces, and to break rocks. The ultrasonic waterjet apparatus (10) performs these tasks with much greater efficiency than conventional continuous-flow waterjet systems because of the repetitive waterhammer effect. A nozzle with multiple exit orifices or a rotating nozzle (76) may be provided in lieu of a nozzle with a single exit orifice to render cleaning and de-coating large surfaces more efficient. A water dump valve (27) and controlling solenoid are located in the mobile generator module (20) rather than the gun (50) to make the gun lighter and more ergonomic.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY MILLTARY AFTERMARKET SERVICES
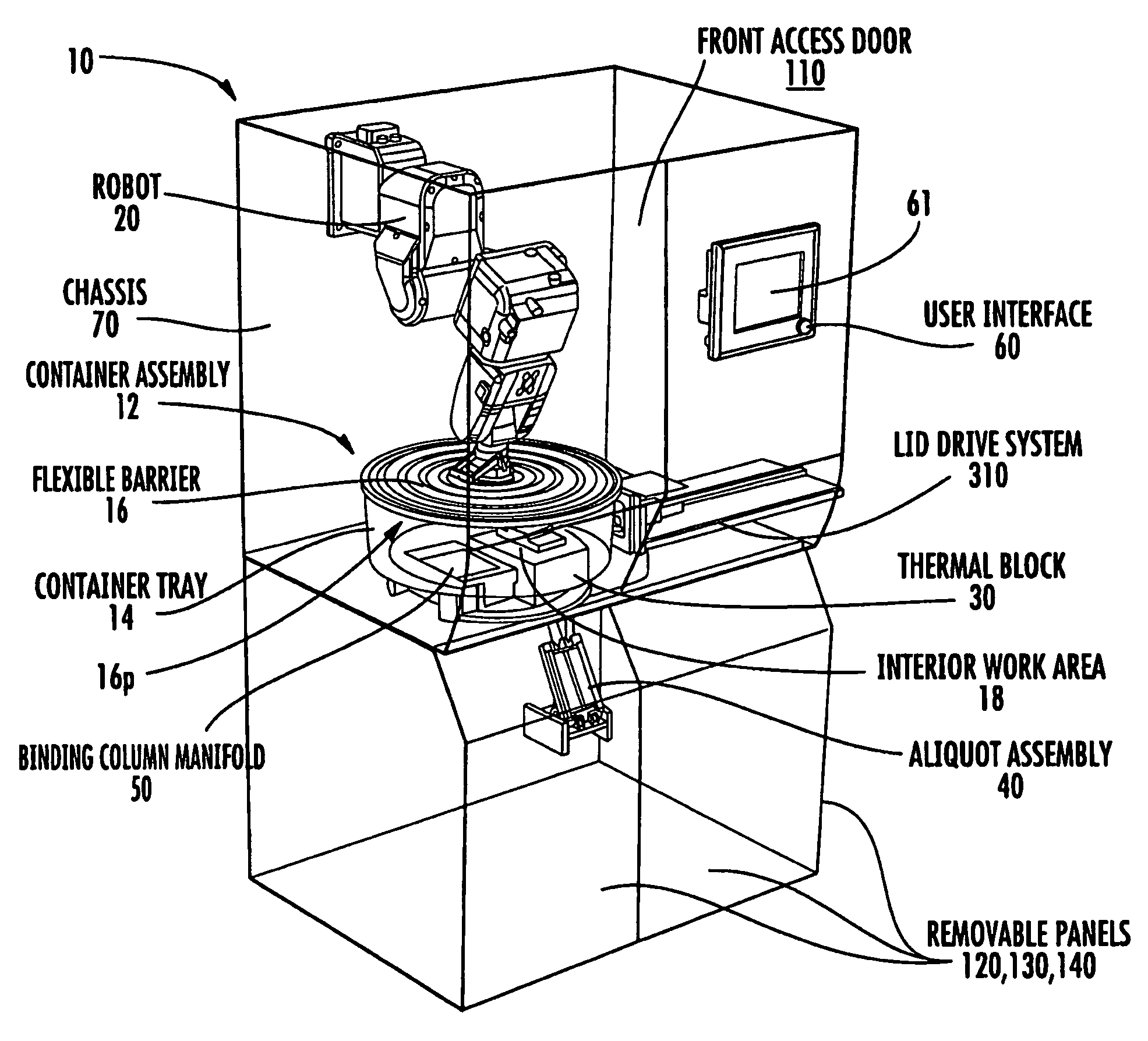
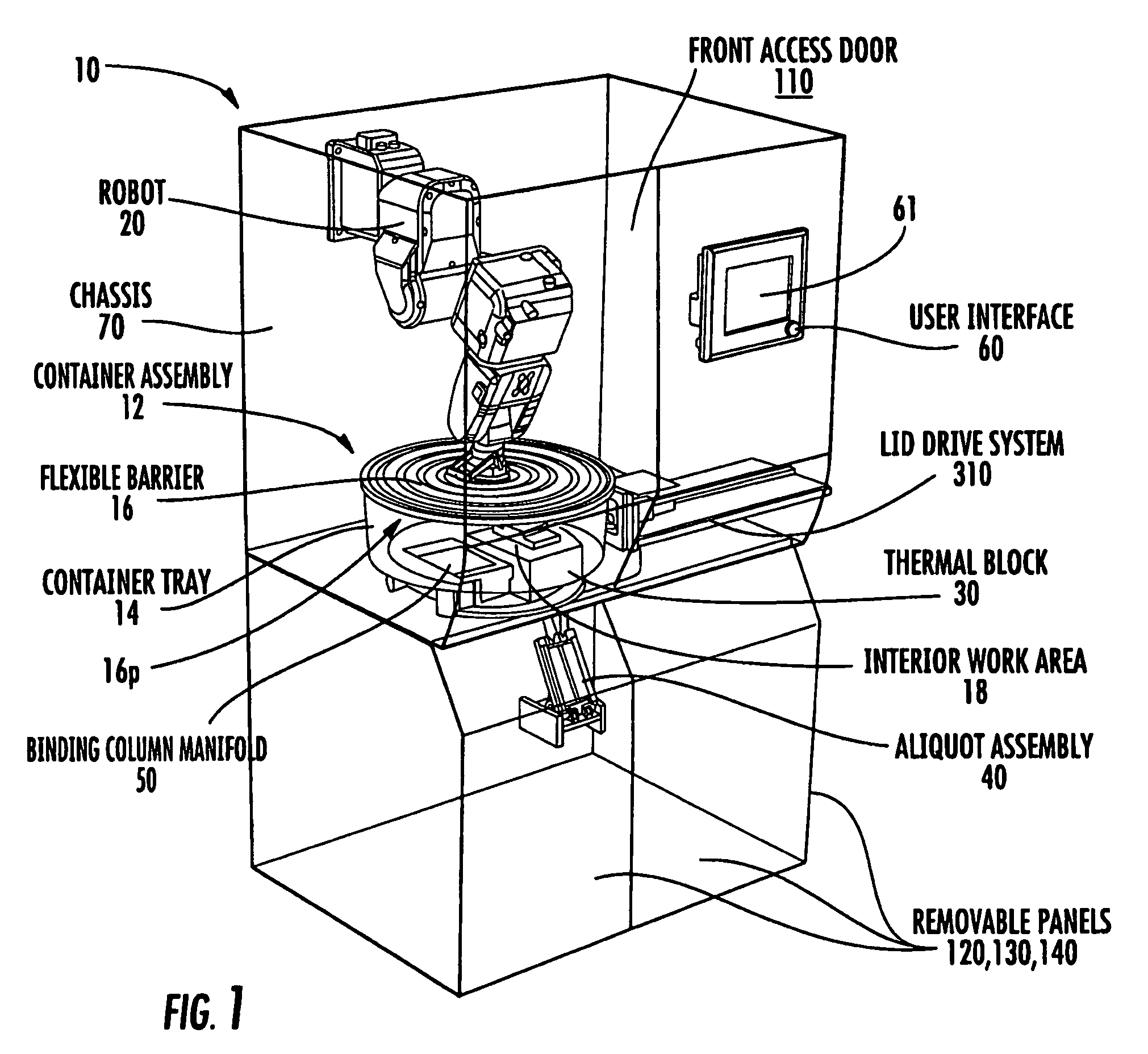
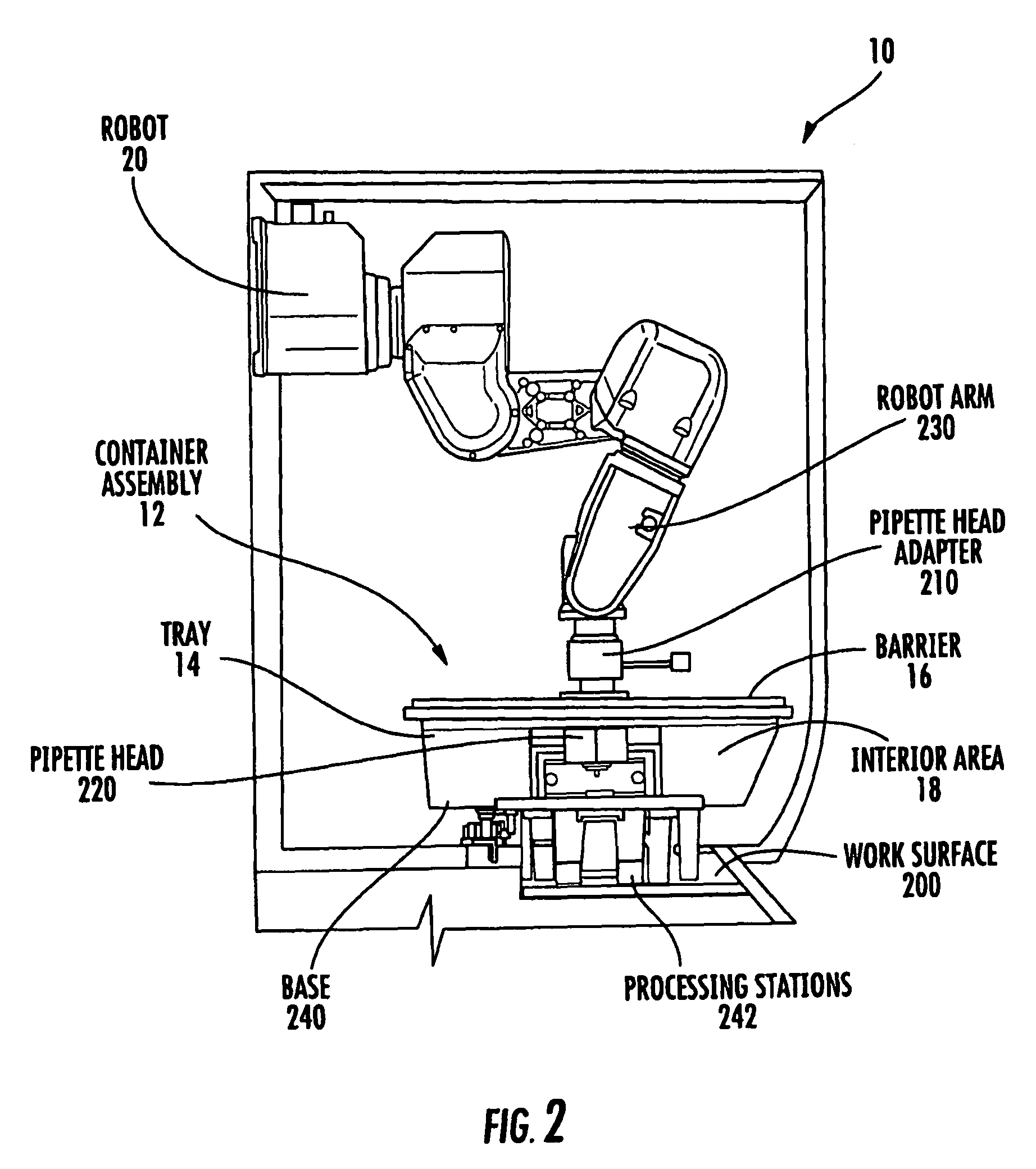
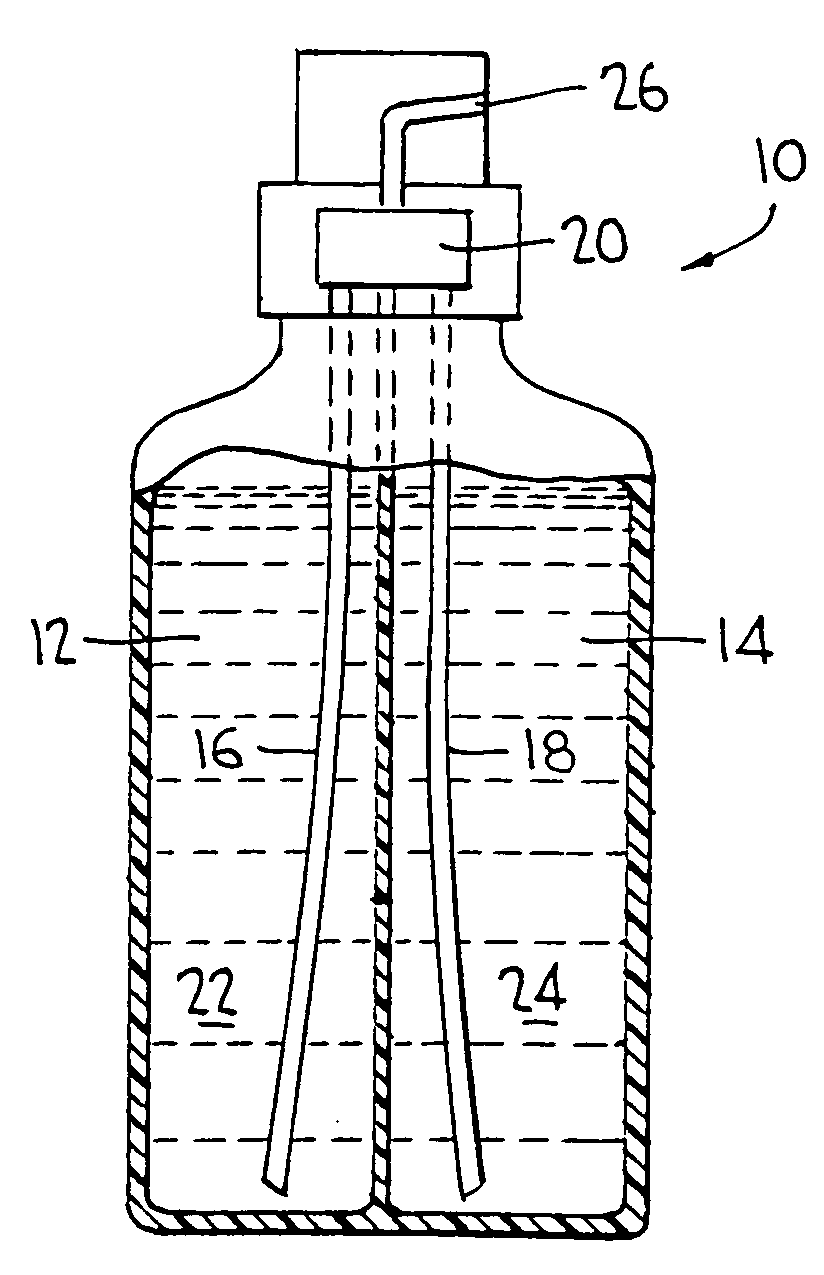
Systems and methods for processing samples in a closed container, and related devices
ActiveUS8030080B2Reduce riskPreventing possible contamination of processing systemBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRobotic armPipette
Owner:COIMMUNE INC
Two part cleaning composition
InactiveUS20050282722A1Maximize clean efficiencyQuantity minimizationInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsChemistryOxidizing agent
A two part cleaning composition, apparatus and method of use is described. One part of the cleaning composition contains an oxidizing agent. The two part cleaning composition provides for shelf stability during storage by controlling the pH solution at a different level in each of the first part and the second part of the composition. At a point of use of the cleaning composition, the first part and the second part are combined resulting in an automatic adjustment of the pH level through admixture of the first part and the second part to provide a pH level for the combined composition to achieve optimum cleaning of a surface with the composition. One part of the cleaning composition is maintained at a pH of from about 4 to about 5 and a second part of the composition is maintained at a pH of greater than 10. The pH of the combined composition at the point of use is from 7 to 12, preferably from about 8 to about 11. Surfaces suitable for treatment by the cleaning composition include hard surfaces, e.g. bathroom and kitchen surfaces, and soft surfaces, e.g. carpet.
Owner:MCREYNOLDS KENT B +1
Motor, fan and cyclonic separation apparatus arrangement for a vacuum cleaner
ActiveUS9005324B2Shorten the lengthReduce energy lossCombination devicesSuction filtersCycloneCyclonic separation
A motor, fan and cyclonic separation apparatus arrangement for a vacuum cleaner, the arrangement comprising: a motor coupled to a fan for generating air flow; and a cyclonic separation apparatus located in a path of the air flow generated by the fan, wherein the cyclonic separation apparatus comprises: a plurality of cyclones each with an air inlet port and an air outlet port wherein the cyclones are arranged in a generally circular array about a central axis of the cyclonic separation apparatus; and a cooling air flow path, wherein the motor is nested within the generally circular array of cyclones and wherein the motor is located in the cooling air flow path. A vacuum cleaner comprising the motor, fan and cyclonic separation apparatus arrangement.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
System and method for cleaning semicondutor fabrication equipment parts
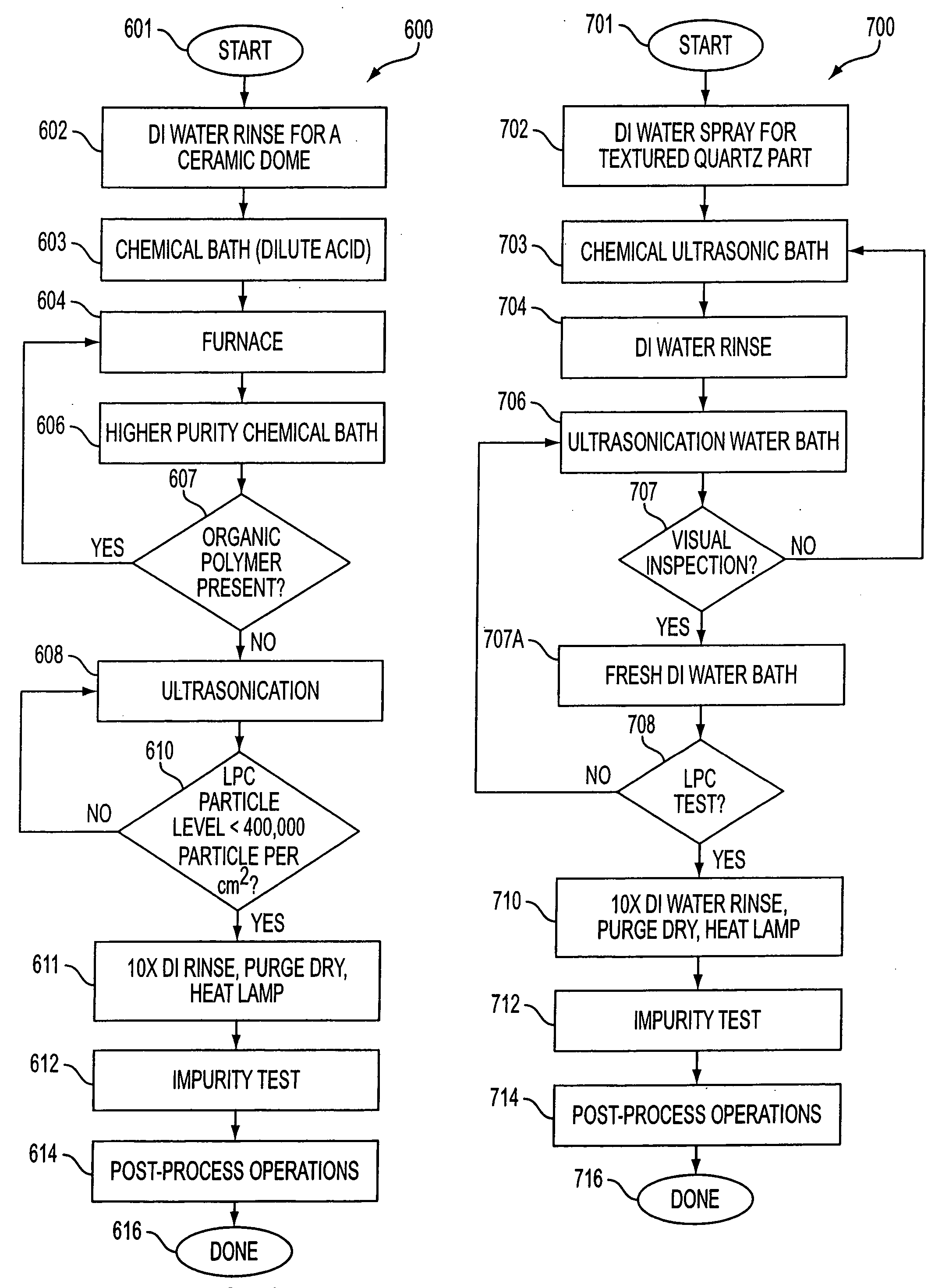
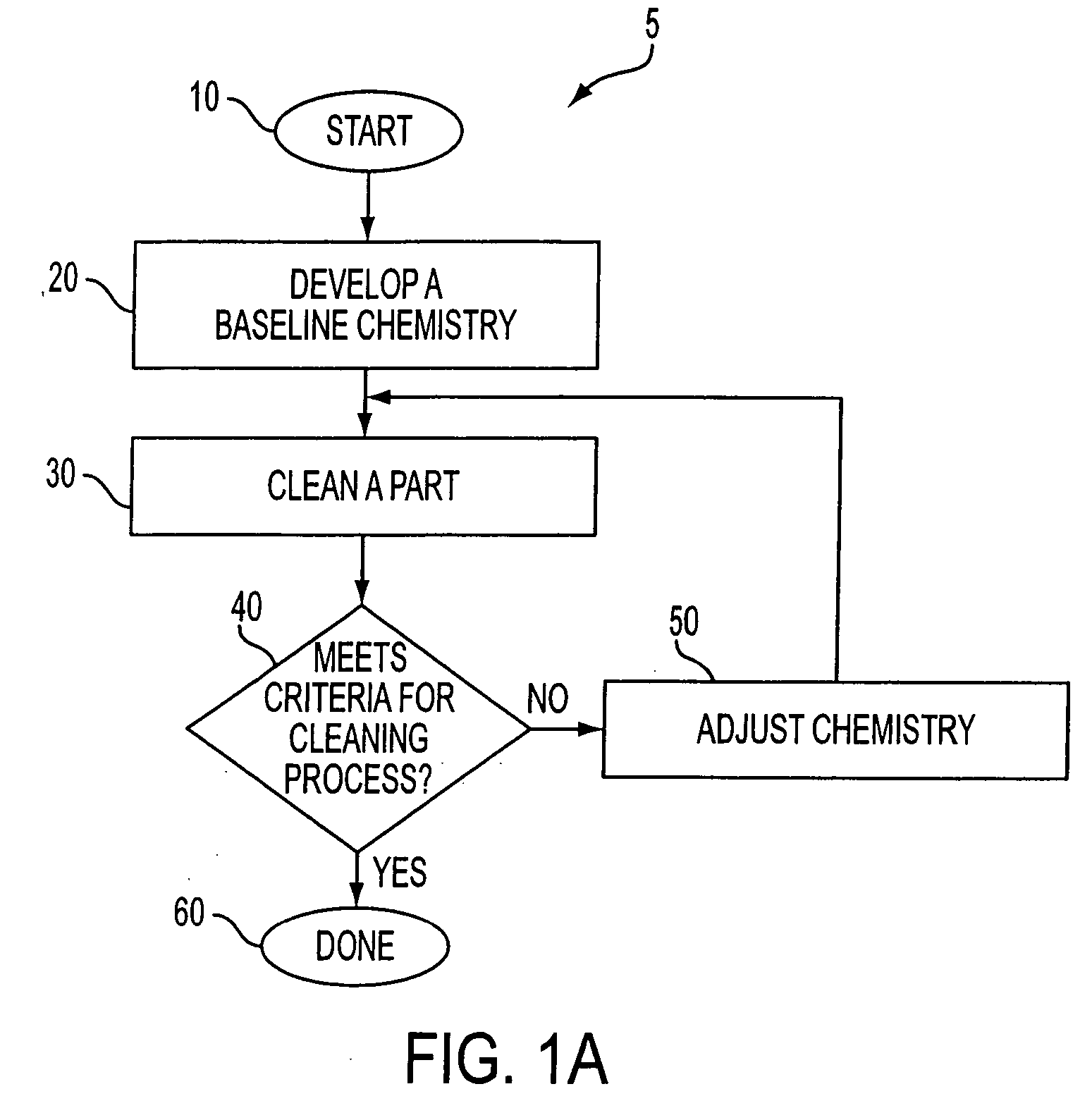
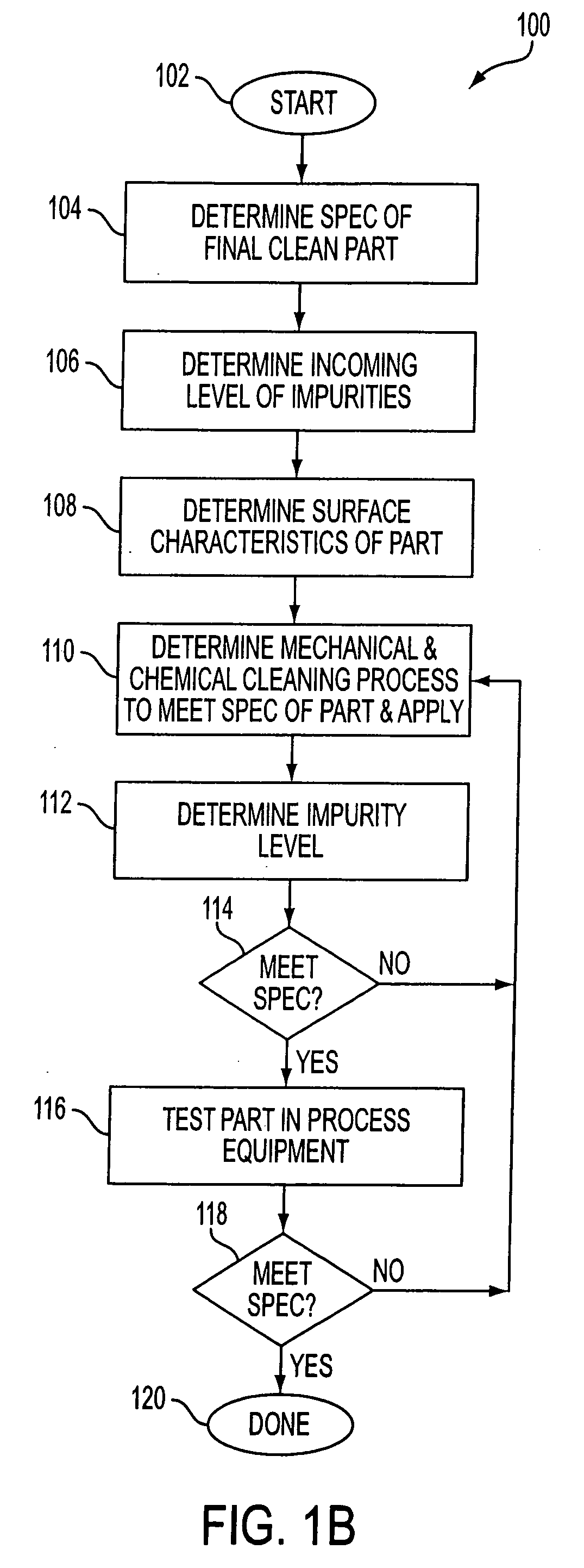
InactiveUS20050045209A1Reduce cleaningImprove accuracyLighting and heating apparatusFlow propertiesEtchingCompound (substance)
A process for cleaning semiconductor fabrication equipment parts includes determining a definition for a clean part including multiple maximum acceptable impurity levels; determining an initial multiple impurity levels of a part prior to its cleaning; determining a cleaning process to apply to the part; applying the cleaning process to the part, wherein the cleaning process creates reduced multiple impurity levels for the part below that of the initial multiple impurity levels; determining the reduced multiple impurity levels; comparing the reduced multiple impurity levels against the multiple maximum acceptable impurities levels of the definition; and repeating the application of the cleaning process to the part if the reduced multiple impurity levels do not meet the definition of a clean part. A dilute aqueous cleaning solution for cleaning parts includes 0.5-1.5% wt. HF; 0.1-0.5% wt. HNO3; and 1-10% wt H2O2. A method for reducing sub-surface damage to a part includes determining how deep is the sub-surface damage beneath a surface of a part; chemically etching said surface of said part; and stopping said chemical etching of said surface at about said depth of said sub-surface damage.
Owner:TAN SAMANTHA
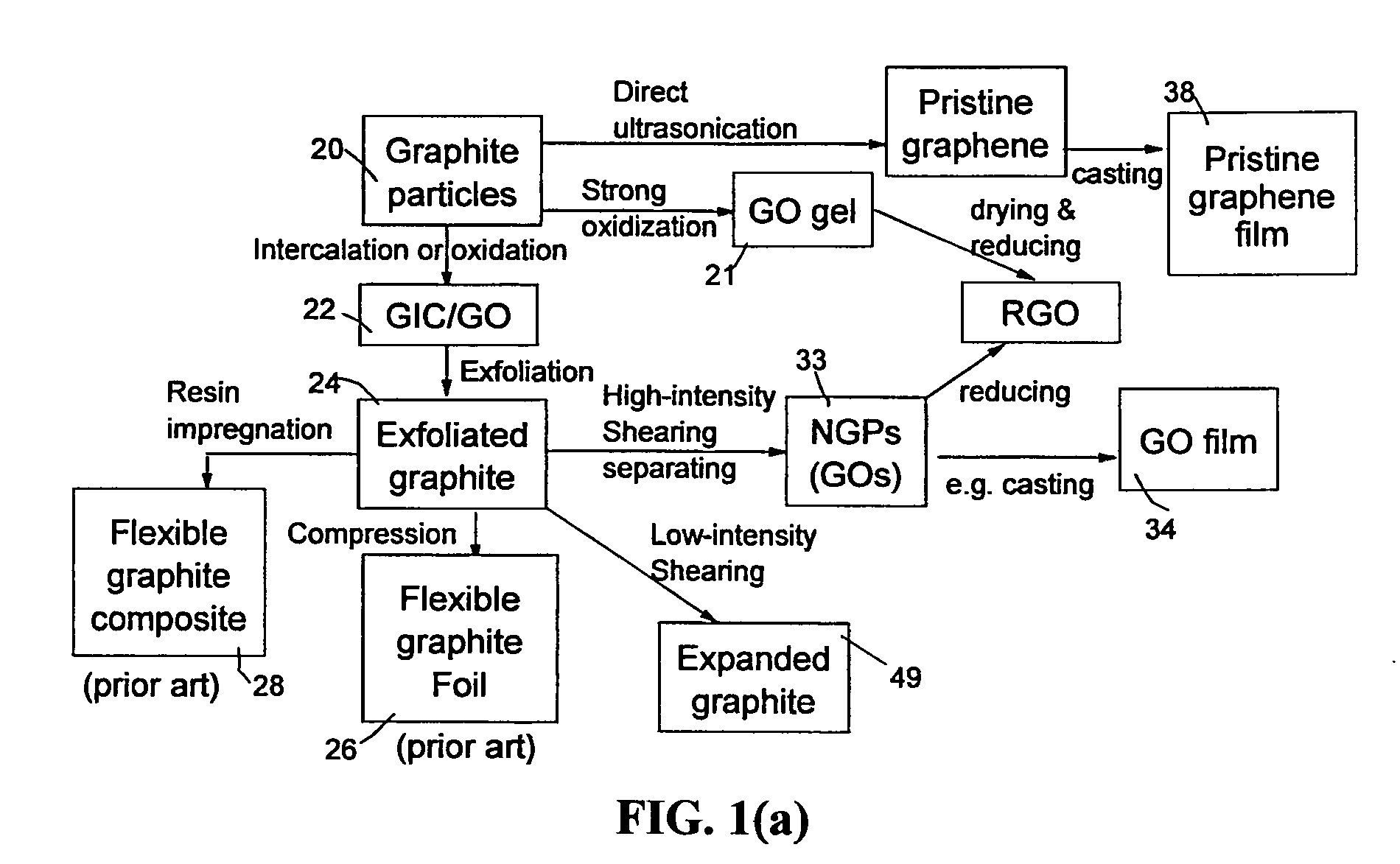
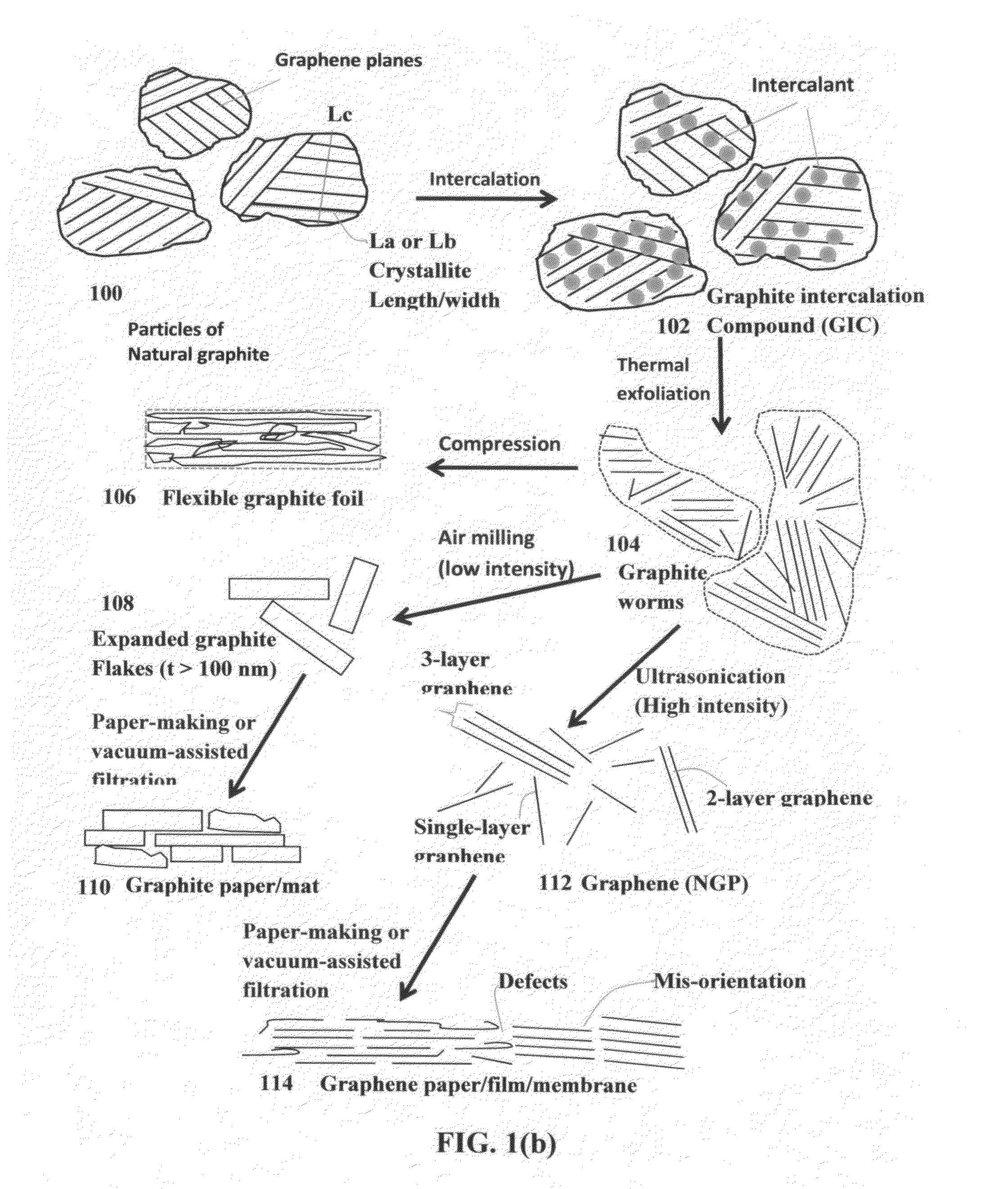
Process for Producing Highly conducting and Transparent Films From Graphene Oxide-Metal Nanowire Hybrid Materials
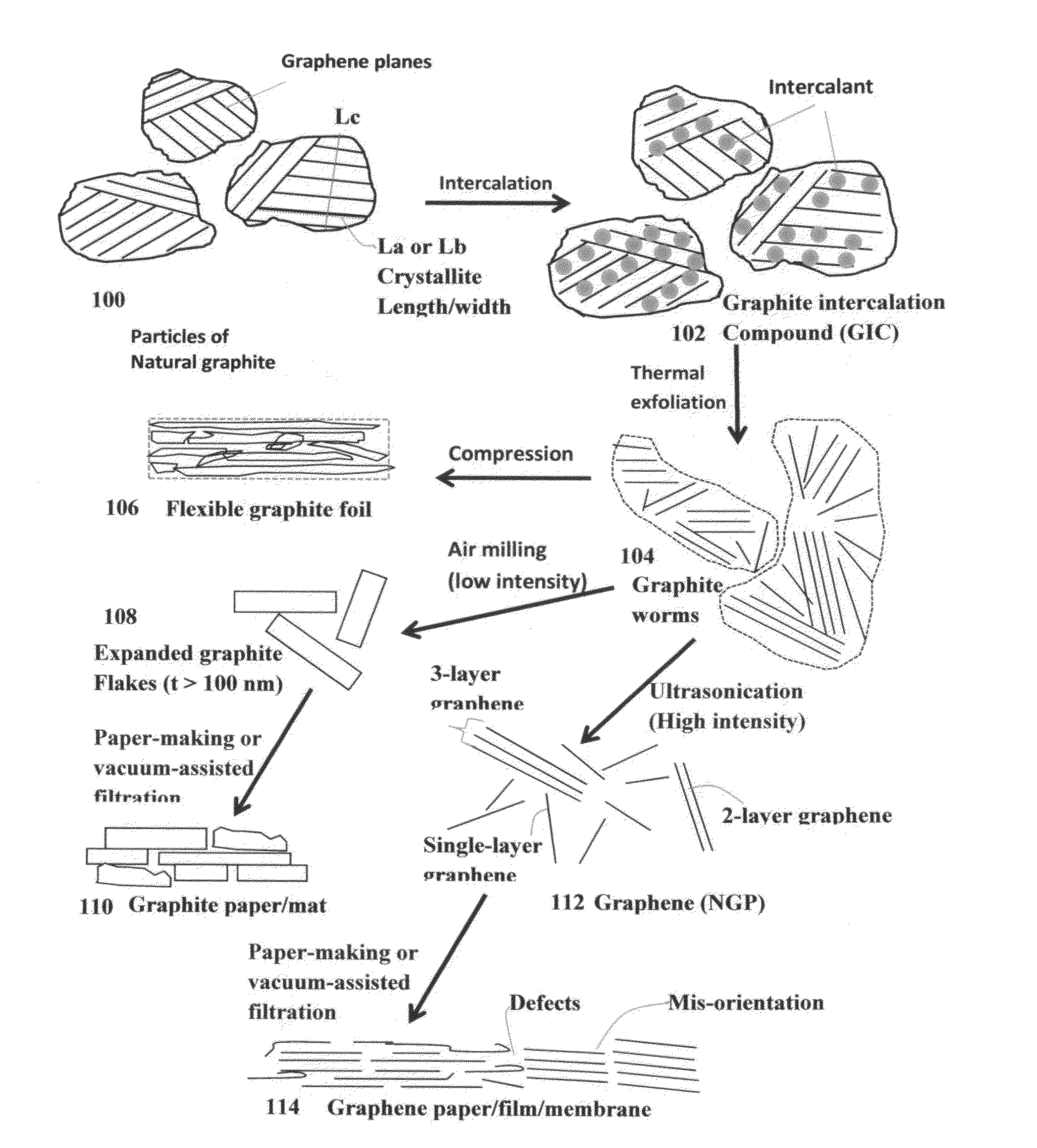
ActiveUS20140231718A1Low sheet resistanceReduce cleaningMaterial nanotechnologyElectric shock equipmentsSheet resistanceMetal nanowires
A process for producing a transparent conductive film, comprising (a) providing a graphene oxide gel; (b) dispersing metal nanowires in the graphene oxide gel to form a suspension; (c) dispensing and depositing the suspension onto a substrate; and (d) removing the liquid medium to form the film. The film is composed of metal nanowires and graphene oxide with a metal nanowire-to-graphene oxide weight ratio from 1 / 99 to 99 / 1, wherein the metal nanowires contain no surface-borne metal oxide or metal compound and the film exhibits an optical transparence no less than 80% and sheet resistance no higher than 300 ohm / square. This film can be used as a transparent conductive electrode in an electro-optic device, such as a photovoltaic or solar cell, light-emitting diode, photo-detector, touch screen, electro-wetting display, liquid crystal display, plasma display, LED display, a TV screen, a computer screen, or a mobile phone screen.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Motor, fan and cyclonic separation apparatus arrangement
A motor, fan and cyclonic separation apparatus arrangement for a vacuum cleaner comprising: a motor coupled to a fan for generating air flow; and a cyclonic separation apparatus located in a path of the air flow generated by the fan. The cyclonic separation apparatus comprises: a plurality of cyclones each with an air inlet port and an air outlet port; and a cooling air flow path. The motor comprises a permanent magnet brushless motor, a switched reluctance motor or a flux switching motor. The fan has an outer diameter the same or less than the diameter of the motor. The plurality of cyclones, the motor and the fan are arranged in a circular array about a central axis of the cyclonic separation apparatus. The arrangement comprises a baffle for directing air flow from the fan out of the circular array. The motor is located in the cooling air flow path.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
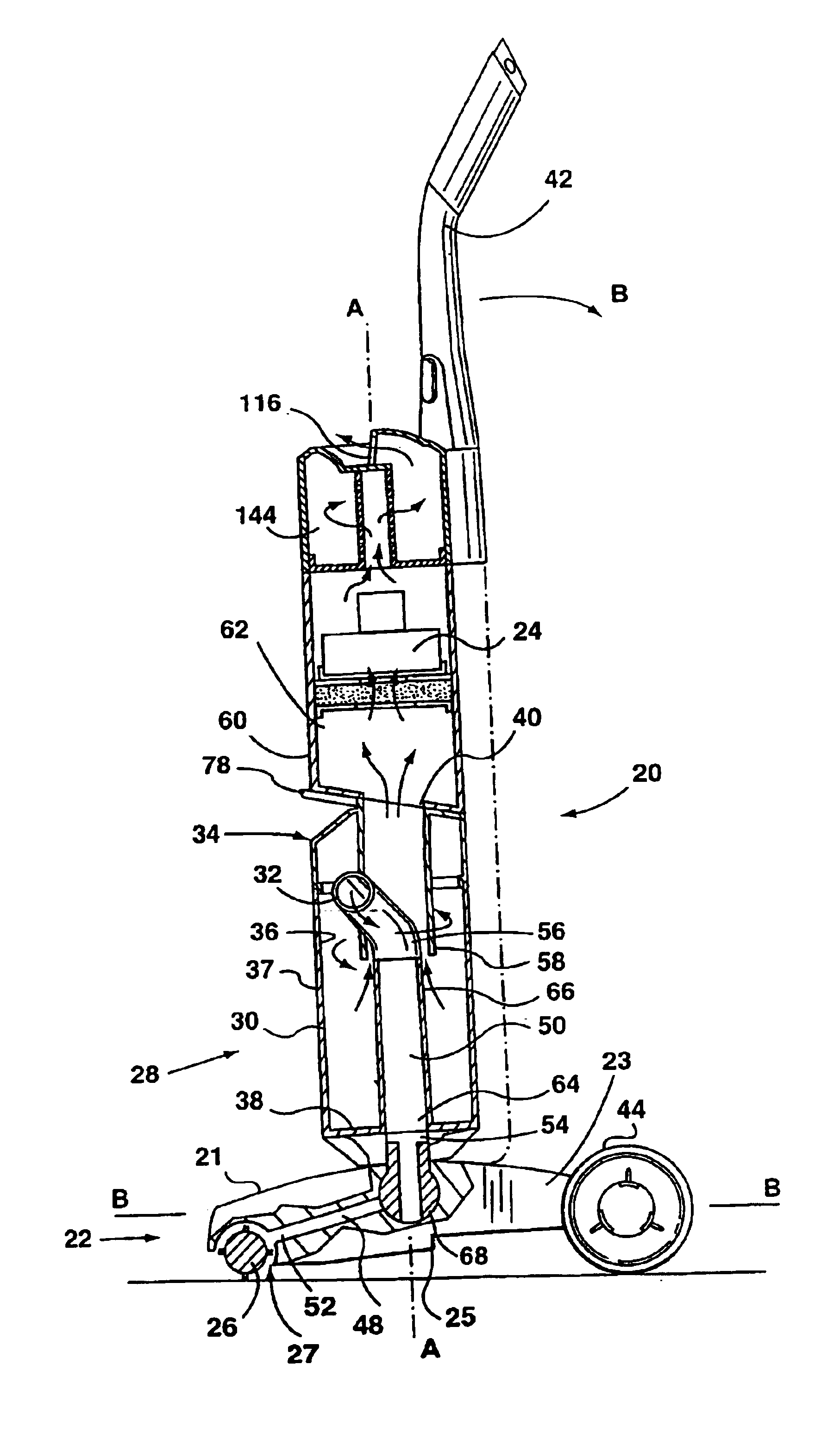
Vacuum cleaner having wet cleaning function
InactiveUS20060288517A1Simple structureReduce cleaningCarpet cleanersFloor cleanersEngineeringFriction force
A vacuum cleaner with a wet cleaning function comprises a main body, a brush assembly having a contaminant suction port facing a cleaning surface, a brush of the contaminant suction port to rotate in contact with the cleaning surface, and a water exhaust nozzle, the contaminants suction port is fluidly communicated with the main body, and a front and a rear block parts formed at a front and a rear of the brush on a bottom surface of the brush assembly to selectively open or block a contaminant suction path by a friction force against the cleaning surface.
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of treating air on board on a vehicle, and a device for use when performing the method
InactiveUS7022163B2Compact structureReduce manufacturing costHuman health protectionCombination devicesOn boardSolid particle
In a vehicle air is compressed for being used in the brake system of the vehicle, for instance. In the compressor, used for the compression, the air is contaminated with oil and solid particles. In order to be relieved from these particles, before the air is conveyed through a drying filter, the compressed is brought to rotation by means of a rotating member in a centrifugal separator. The rotating member may advantageously include a pile of conical separation discs forming flow passages between each other for the compressed air to be cleaned. By means of an efficient cleaning of the compressed air from particles the life time of the drying filter may be increased.
Owner:ALFA LAVAL CORP AB +1
Dust repellant compositions
InactiveUS6949271B2Maintain appearanceApplication securityOther chemical processesConductive materialEngineeringPolymer
Sprayable, liquid polymeric film-forming compositions containing an amount of an anti-static polymer that is effective to provide films formed from the composition with resistance to the deposition of dust, soil or grime on the surface thereof, wherein the surface tension of the liquid composition is less than about 25 milli-newtons per meter. Methods for preventing the accumulation of dust, soil or grime on surfaces such as a vehicle tire, wheel or wheel cover are also disclosed.
Owner:PETROFERM INC
Dust repellant compositions
InactiveUS20060035030A1Appearance hasMaintenanceOther chemical processesFibre treatmentEngineeringPolymer
Sprayable, liquid polymeric film-forming compositions containing an amount of an anti-static polymer that is effective to provide films formed from the composition with resistance to the deposition of dust, soil or grime on the surface thereof, wherein the surface tension of the liquid composition is less than about 25 milli-newtons per meter. Methods for preventing the accumulation of dust, soil, or grime on surfaces such as a vehicle tire, wheel or wheel cover are also disclosed.
Owner:PETROFERM INC
Personal Care Compositions Containing Cationically Modified Starch and an Anionic Surfactant System
InactiveUS20090176675A1Increase depositionReduce cleaningCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsPersonal careSodium Pyrithione
Personal care compositions comprise (a) from about 0.01 wt. % to about 10 wt. % of a water-soluble cationically modified starch polymer, wherein said water-soluble cationically modified starch polymer has a molecular weight from about 850,000 to about 15,000,000 and a charge density from about 0.2 meq / g to about 5 meq / g; (b) from about 5 wt. % to about 50 wt. % of an anionic surfactant system, said anionic surfactant system comprising at least one anionic surfactant and having an ethoxylate level and an anion level, (i) wherein said ethoxylate level is from about 1 to about 6, and (ii) wherein said anion level is from about 1 to about 6; c) an effective amount of a pyrithione or a polyvalent metal salt of a pyrithione; d) an effective amount of a zinc-containing layered material; and (e) a cosmetically acceptable medium. Personal care compositions as described above further comprise from about 0.01 wt. % to about 10 wt. % of one or more oily conditioning agents. Methods of treating hair or skin comprise applying the personal care compositions as described above to the hair or skin and rinsing the hair or skin.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Lighting module for a vehicle headlight
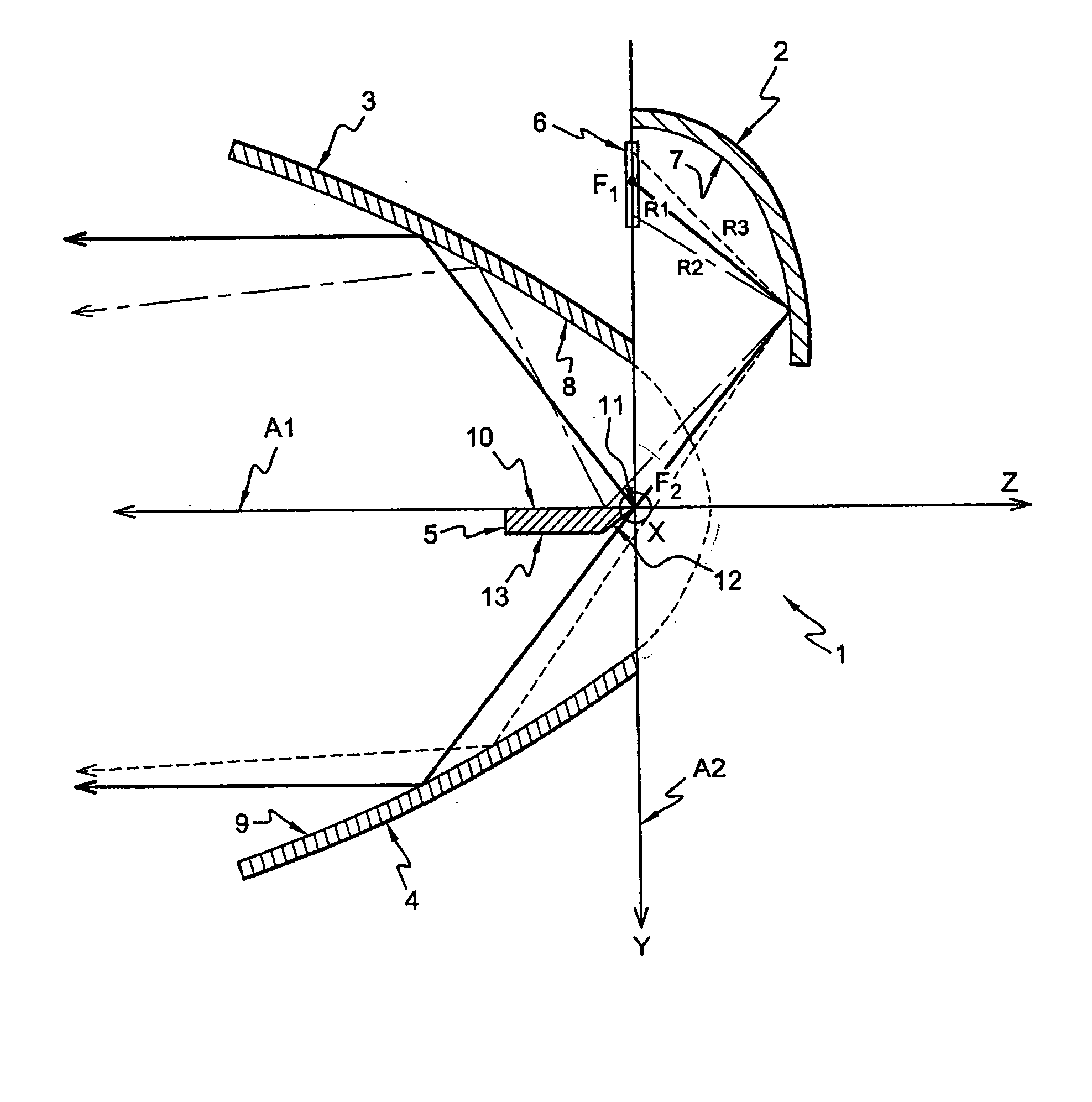
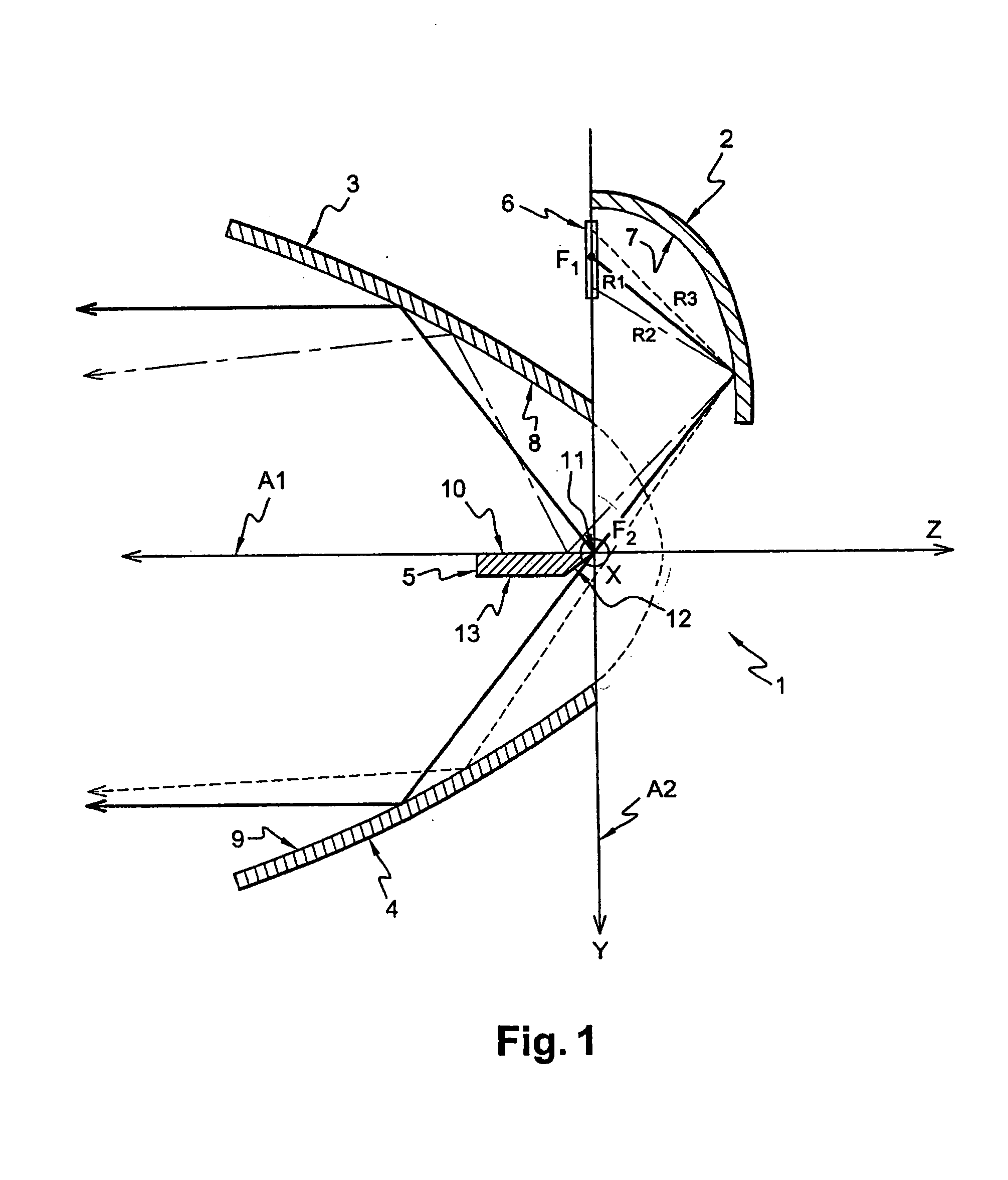
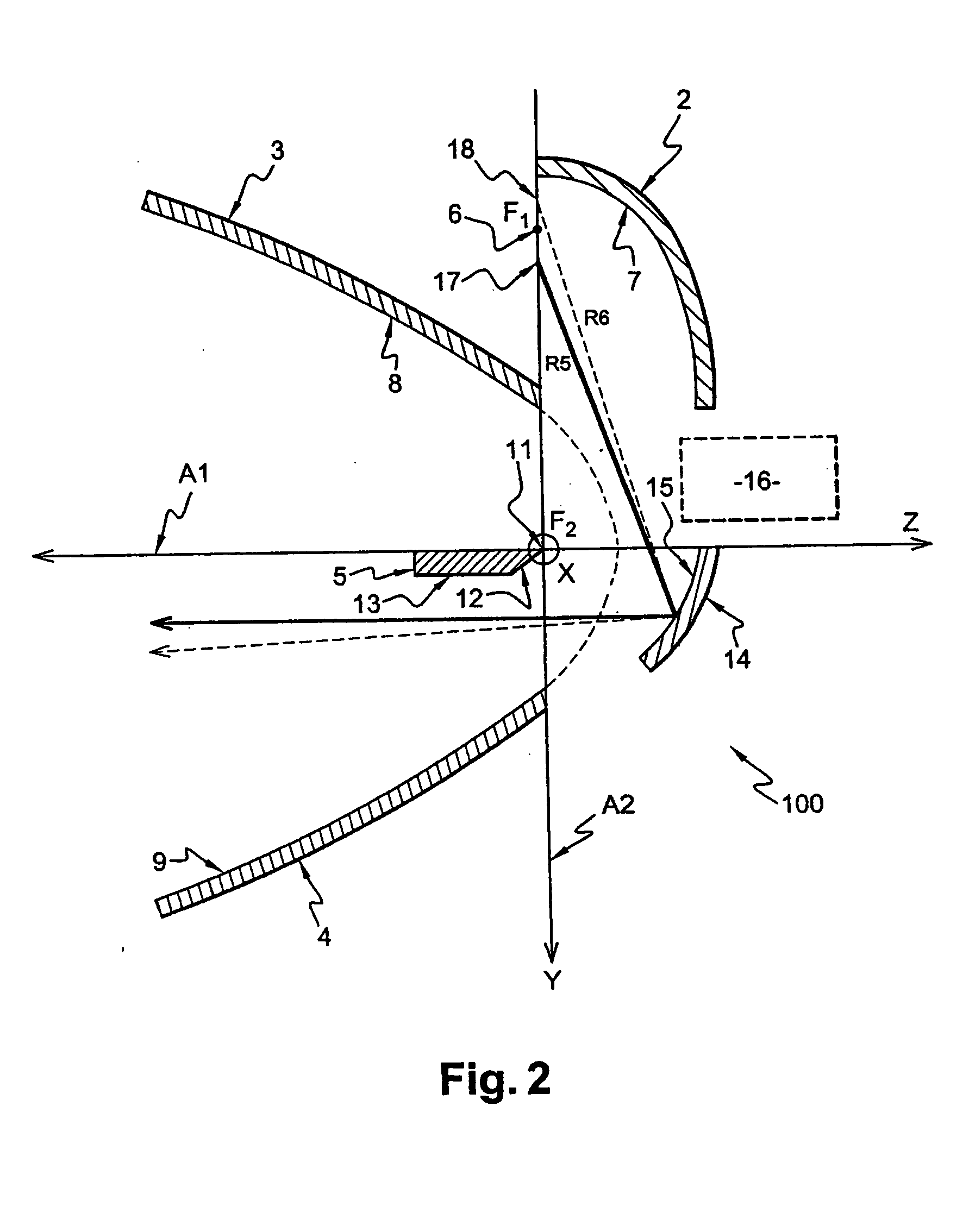
InactiveUS20050094402A1Reduce the amount of lightEliminate useVehicle headlampsLighting support devicesOptical axisLight beam
The present invention relates to a lighting module for a vehicle headlight which produces a lighting beam of the type having a cut-off, and which is particularly well adapted for use with light emitting diodes. The module has a first reflector which includes an elliptical surface for reflecting light rays and having an elliptical generatrix, together with at least one first light source which is arranged in the vicinity of the first focus of the said first reflector. The module also includes: a second reflector, for producing a first portion of the cut-off beam and having an optical axis, which passes through the second focus of the first reflector and at right angles to the optical axis of the said first reflector; a third reflector producing a second portion of the cut-off beam and having an optical axis passing through the second focus of the said first reflector and at right angles to the optical axis of the said first reflector; and a fourth reflector or bender, which is arranged between the said second reflector and the said third reflector. The bender has an edge referred to as a cut-off edge, which is arranged close to the said focus of the said first reflector, in such a way as to form the cut-off in the lighting beam, together with a reflective top face which contains the said optical axes of the second and third reflectors respectively.
Owner:VALEO VISION SA
Robot cleaner and control method thereof
ActiveUS20140100736A1Easy to cleanImprove efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutomatic obstacle detectionControl engineeringStraight path
A control method of a robot cleaner for traveling to clean includes checking information about a predetermined traveling pattern; determining a traveling trajectory based on a traveling speed; generating a traveling pattern based on the determined traveling trajectory and the information about the predetermined traveling pattern, wherein the traveling pattern includes a first straight path, a first rotation path connected to the first straight path and for rotation in a first direction, a second straight path connected to the first rotation path, and a second rotation path connected to the second straight path and for rotation in a second direction; and repeatedly traveling along the generated traveling pattern at regular intervals. Therefore, since the robot cleaner performs cleaning without scattering dust, the efficiency of cleaning may be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Inkjet image forming method and apparatus, and ink composition therefor
InactiveUS20080143785A1Improve fixing characteristicReduce cleaningMaterial nanotechnologyInking apparatusEngineeringNozzle
An inkjet image forming method of forming an image on a recording medium includes the step of ejecting an ink composition through a nozzle hole onto the recording medium so that the image is formed on the recording medium. The ink composition contains coloring material particles and polymer particles, the polymer particles including an anionic hydrophilic functional group, and having a minimum film forming temperature of not higher than 25° C. and a ratio Mv / Mn of a volume-average particle size Mv to a number-average particle size Mn of not less than 1 and not greater than 1.5; and the nozzle hole is provided in a nozzle plate which is uniformly coated with an ink repelling film on a front surface of the nozzle plate, an inner surface of the nozzle hole and a part of a rear surface of the nozzle plate surrounding the nozzle hole, the ink repelling film having properties to repel the ink composition.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Pet bed cover
InactiveUS20060060147A1Promote absorptionReduce cleaningAnimal housingOther apparatusInter layerAbsorbent material
A disposable cover for a pet bed or resting surface comprises an outer layer having a perimeter; an elastic member located about the perimeter for fixing the cover with respect to the pet bed / resting surface; an inner layer for contact with the resting surface; and an intermediate layer which includes odor-absorbent material. A method of eliminating pet odor comprises providing a resting surface for a pet; covering the resting surface with a disposable odor-absorbent cover; and fixing the disposable cover to the resting surface with the attachment member.
Owner:APPELHANS JACQUELINE M
Friction stir welding tool cleaning method and apparatus
ActiveUS20070284419A1Easy to useReduce inspectionWelding/cutting auxillary devicesElectrostatic cleaningEngineeringCleaning methods
The invention is directed to a friction stir welding tool cleaning method and apparatus for fixed and retractable pin tools. The method and apparatus use a heating component, a temperature indicator component, a controller component, and a rotatable tool cleaner component for cleaning fixed pin tools. An additional bore cleaner component is used for cleaning retractable pin tools. Heat is applied to a friction stir welding tool having a surface with weld process residue material until the process residue material is sufficiently plasticized, and then the tool cleaner component is applied to the heated tool to remove the plasticized residue on the pin and shoulder surfaces of the tool, and for retractable pin tools, the bore cleaner component is applied to the heated tool to remove the plasticized residue in the tool bore.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Plastic sheet cutter
ActiveUS7743512B1Reduce problemsReduce the possibilityHand equipmentsMetal working apparatusEngineeringPlastic film
A cutter operative to pierce and cut a sheet of material includes a handle and a body portion coupled to the handle. The body portion includes two puncture fingers having tips for piercing the sheet of material and two blades for cutting two parallel cuts in the sheet of material. in a method of installing a zipper on a sheet of material, left and right portions of a zipper are applied to a sheet of material. A swath portion of the sheet of material is cut having two parallel, spaced-apart cuts between the left and right portions of the zipper. In this manner, zipper installation is established in a manner that avoids formation of flap of material that would otherwise remain between the left and right flanges of the zipper.
Owner:ZIPWALL
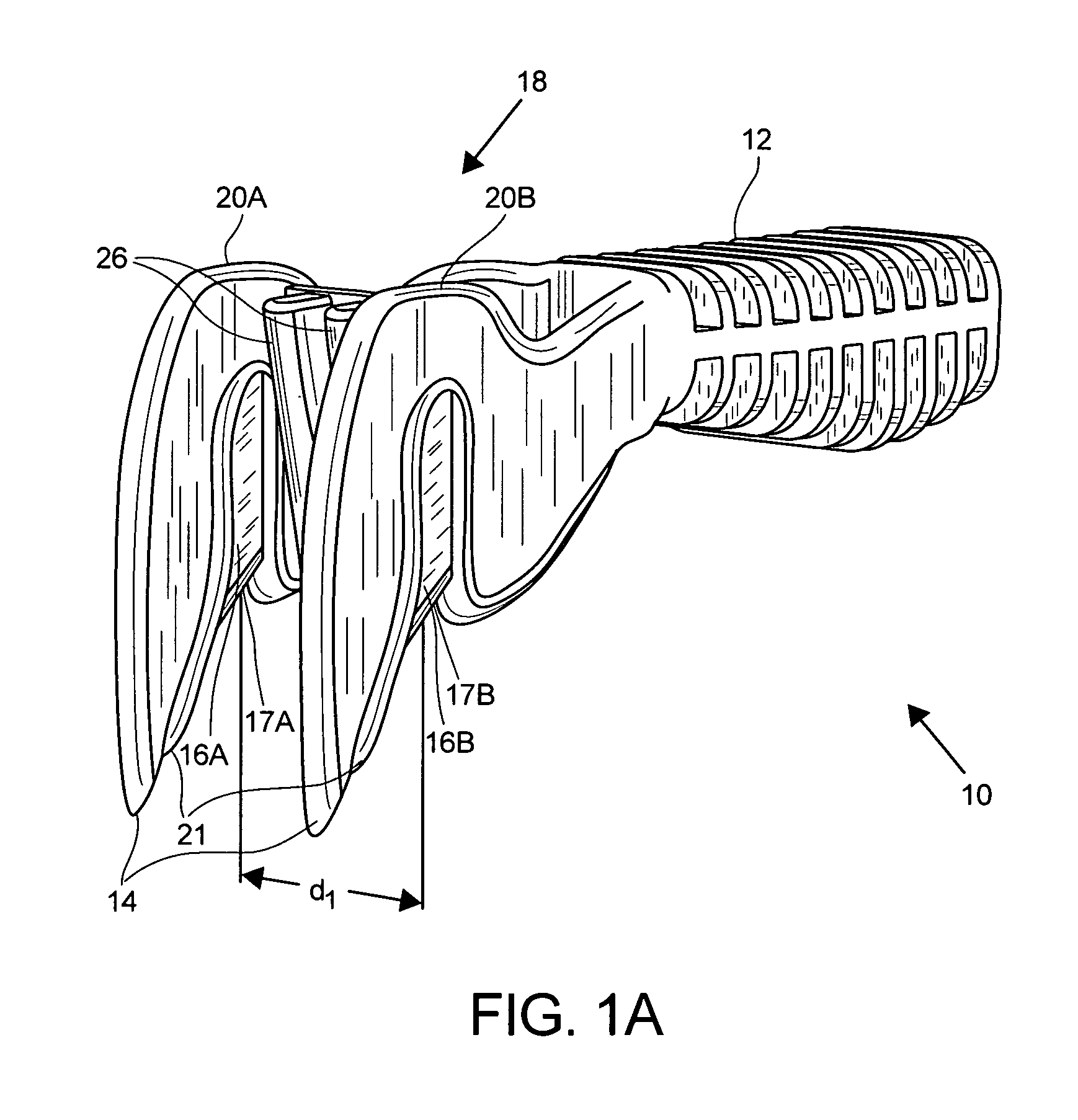
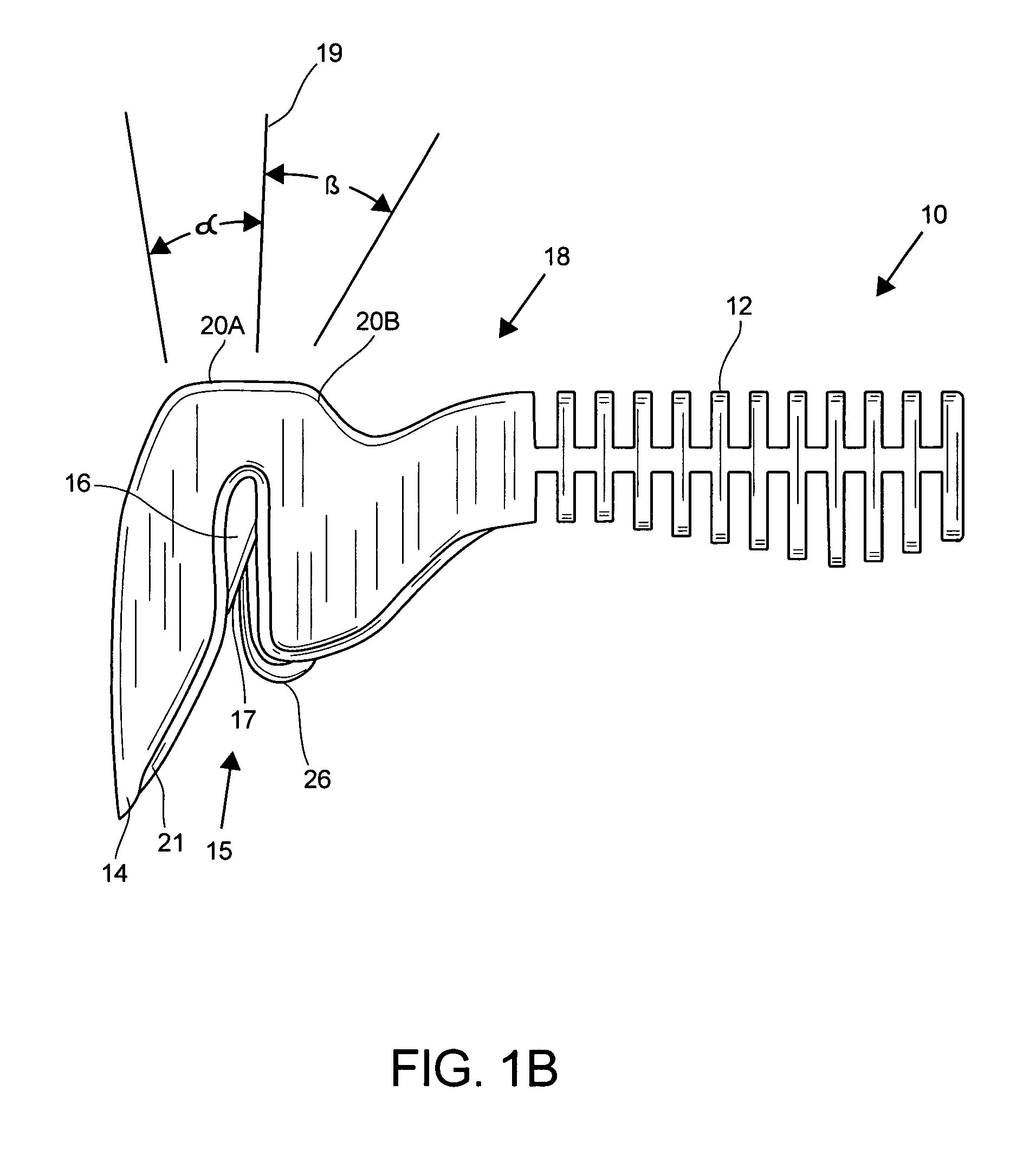
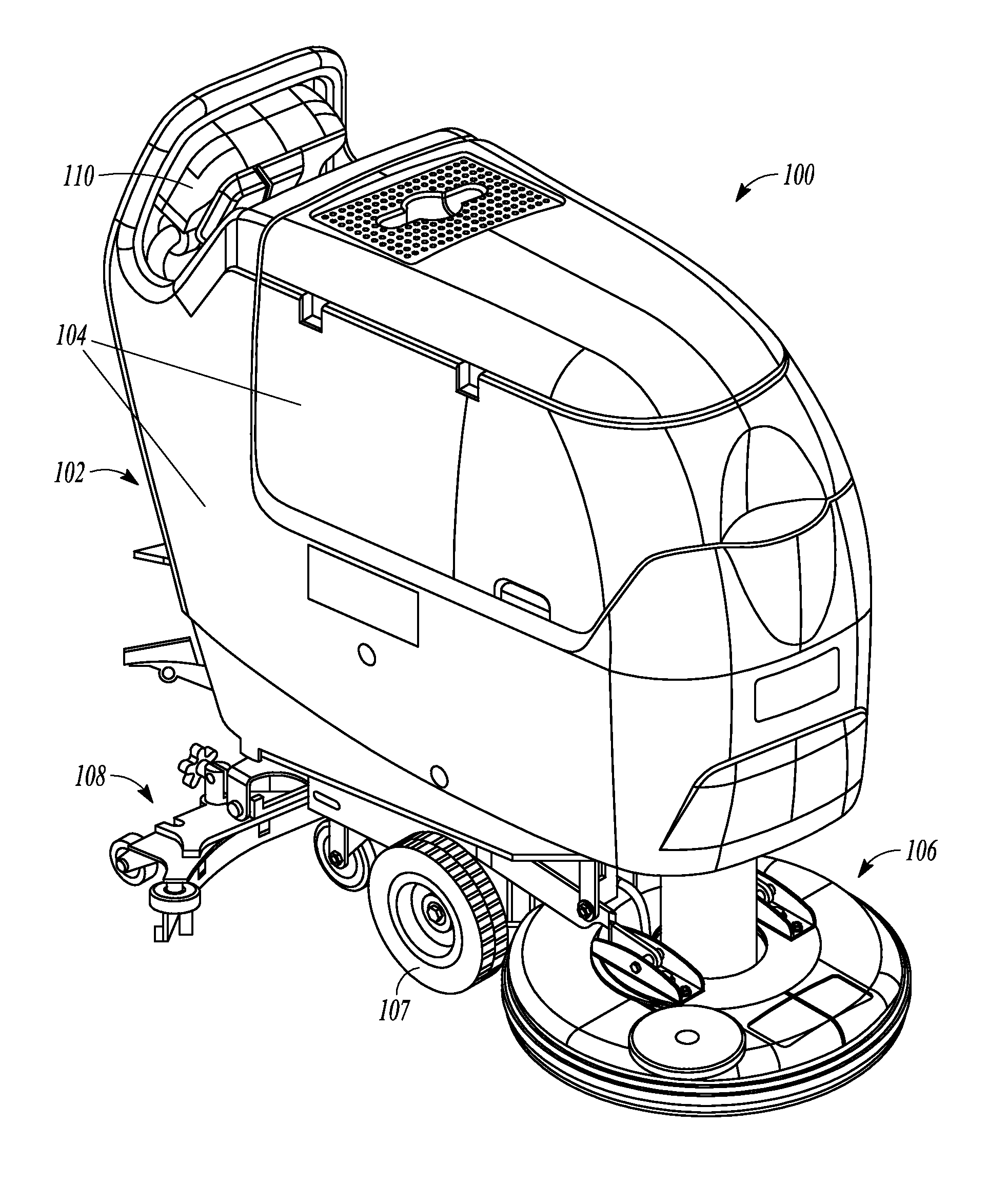
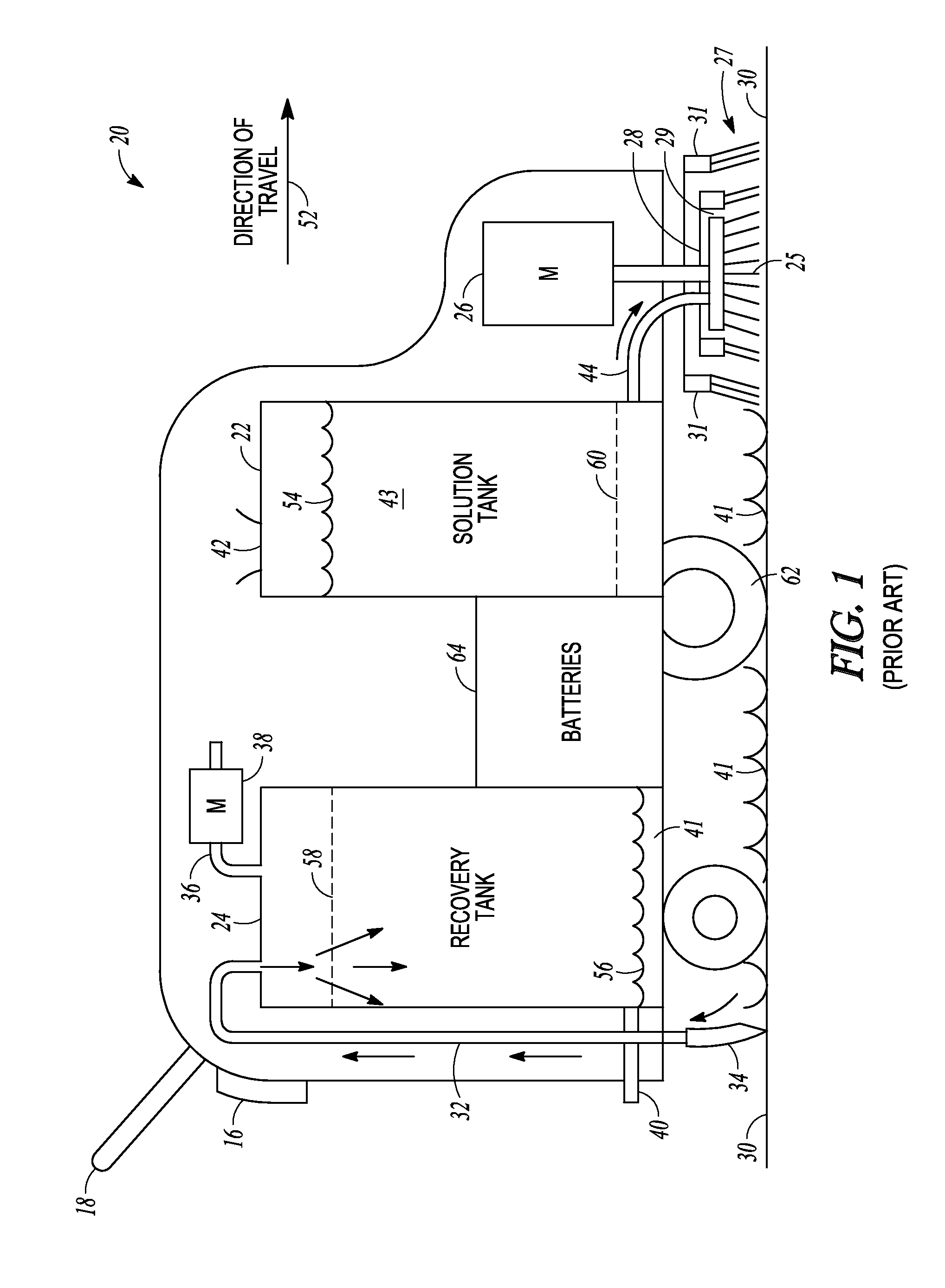
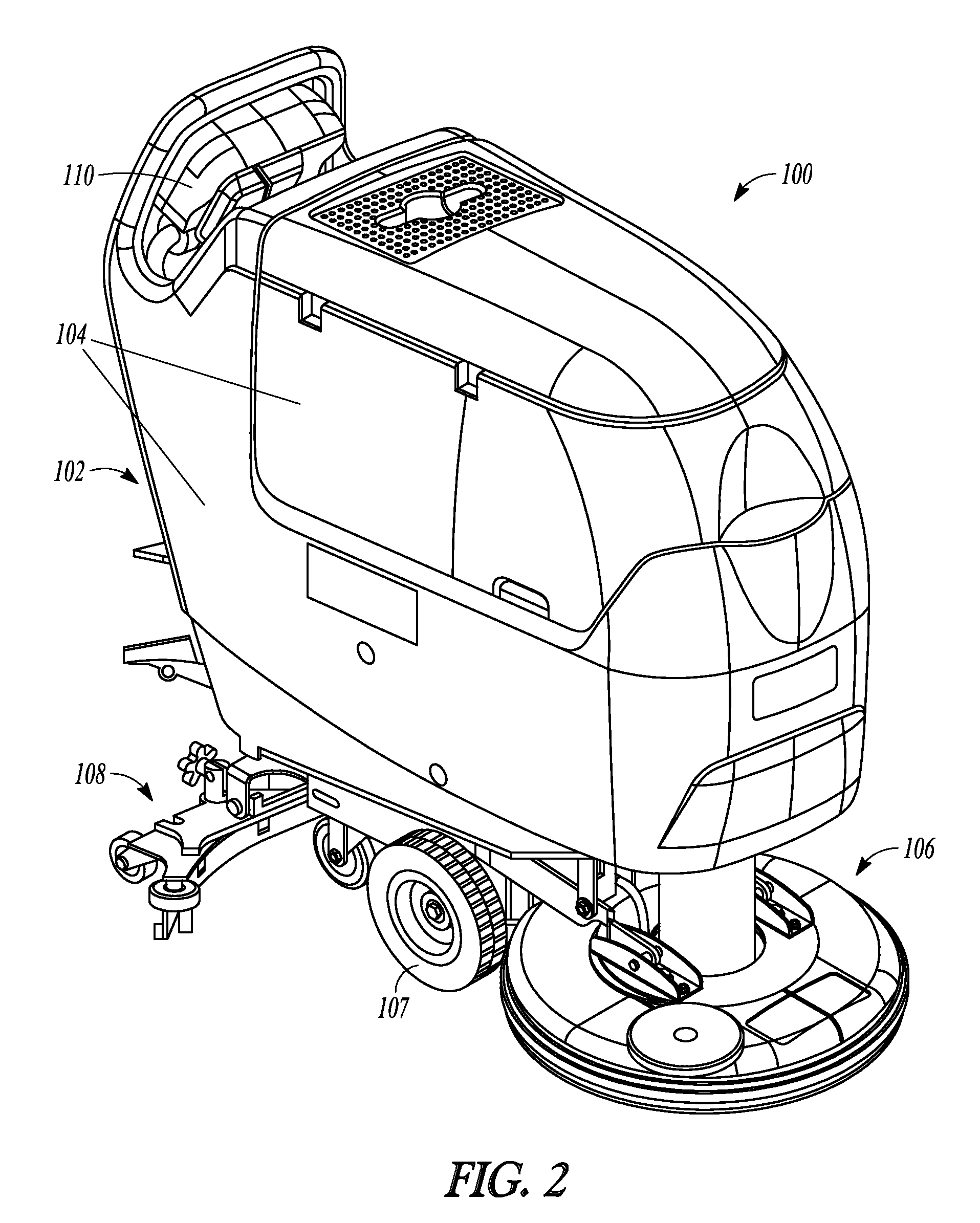
Random orbit disc scrubber
ActiveUS20120118319A1Equally distributedImprove cleanlinessBowling gamesCarpet cleanersOrbitFront and back ends
A random orbit scrubber comprises a main body having a front end and a rear end, a squeegee assembly coupled to the rear end of the main body, and a cleaning head assembly coupled to the front end of the main body. The cleaning head assembly can include a cleaning element structured for contact with a floor surface. The cleaning head assembly can further include a motor that is operable to impart rotational and orbital movement on the cleaning element.
Owner:NILFISK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com