Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53results about How to "Minimal handling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
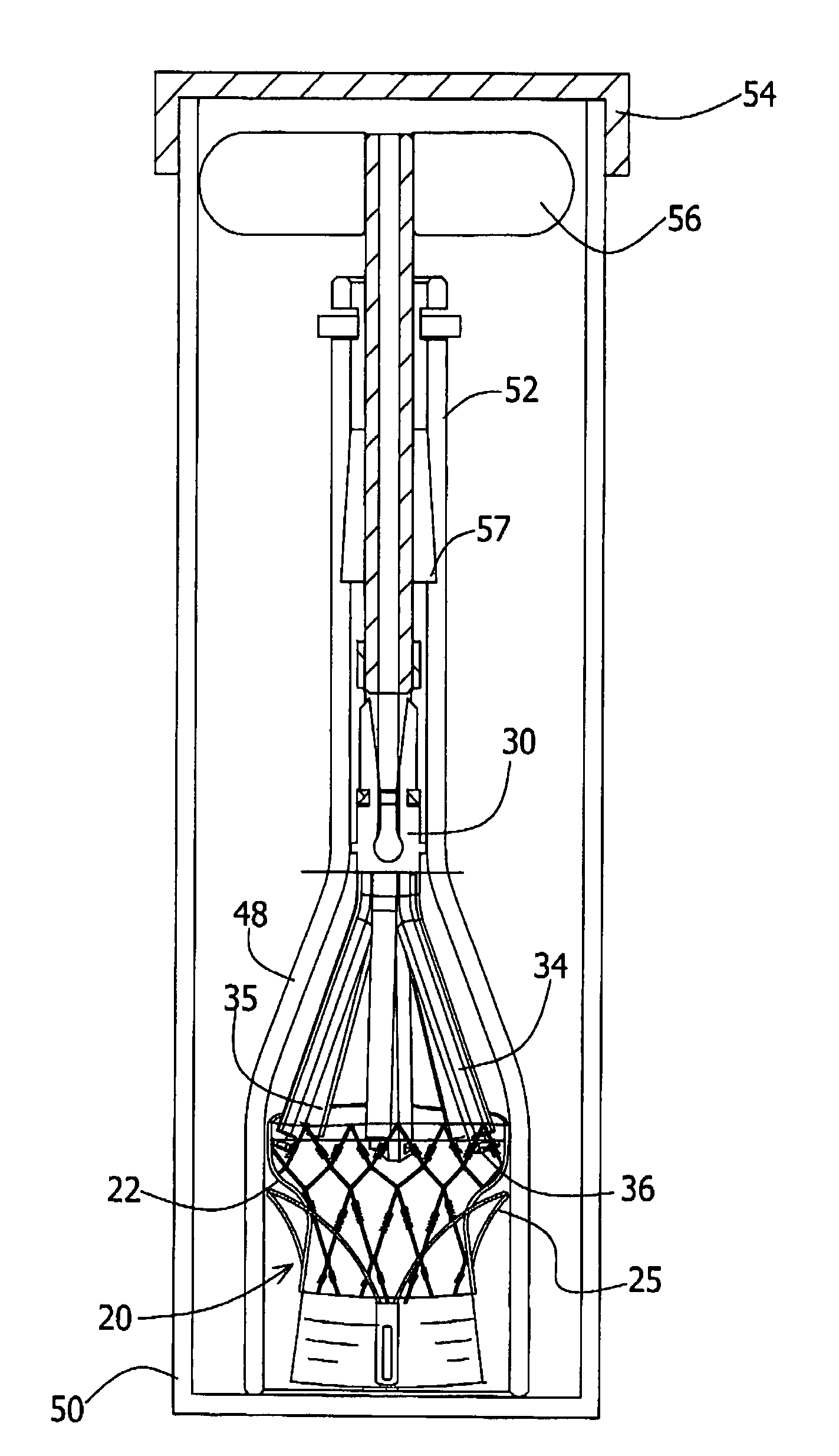
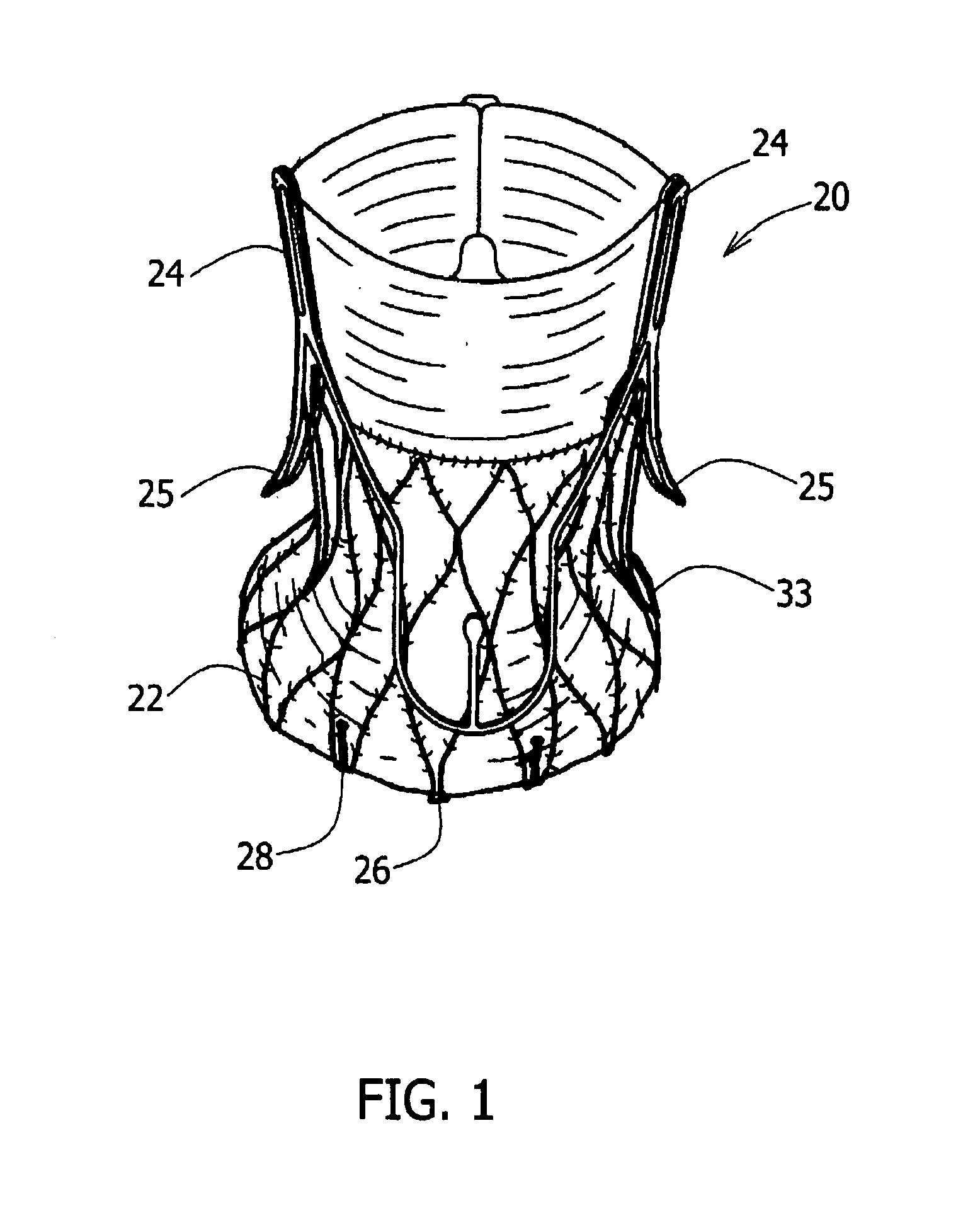
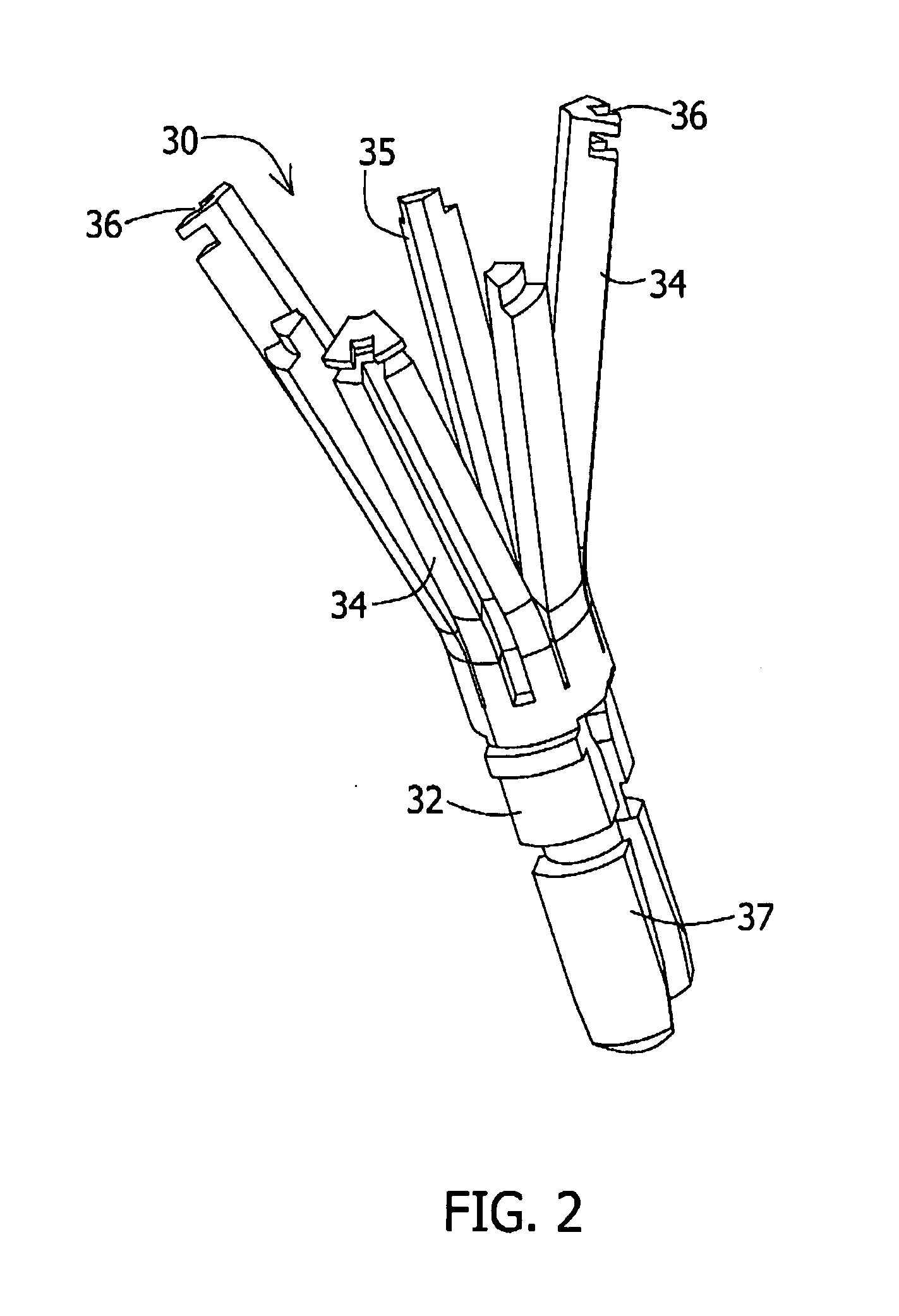
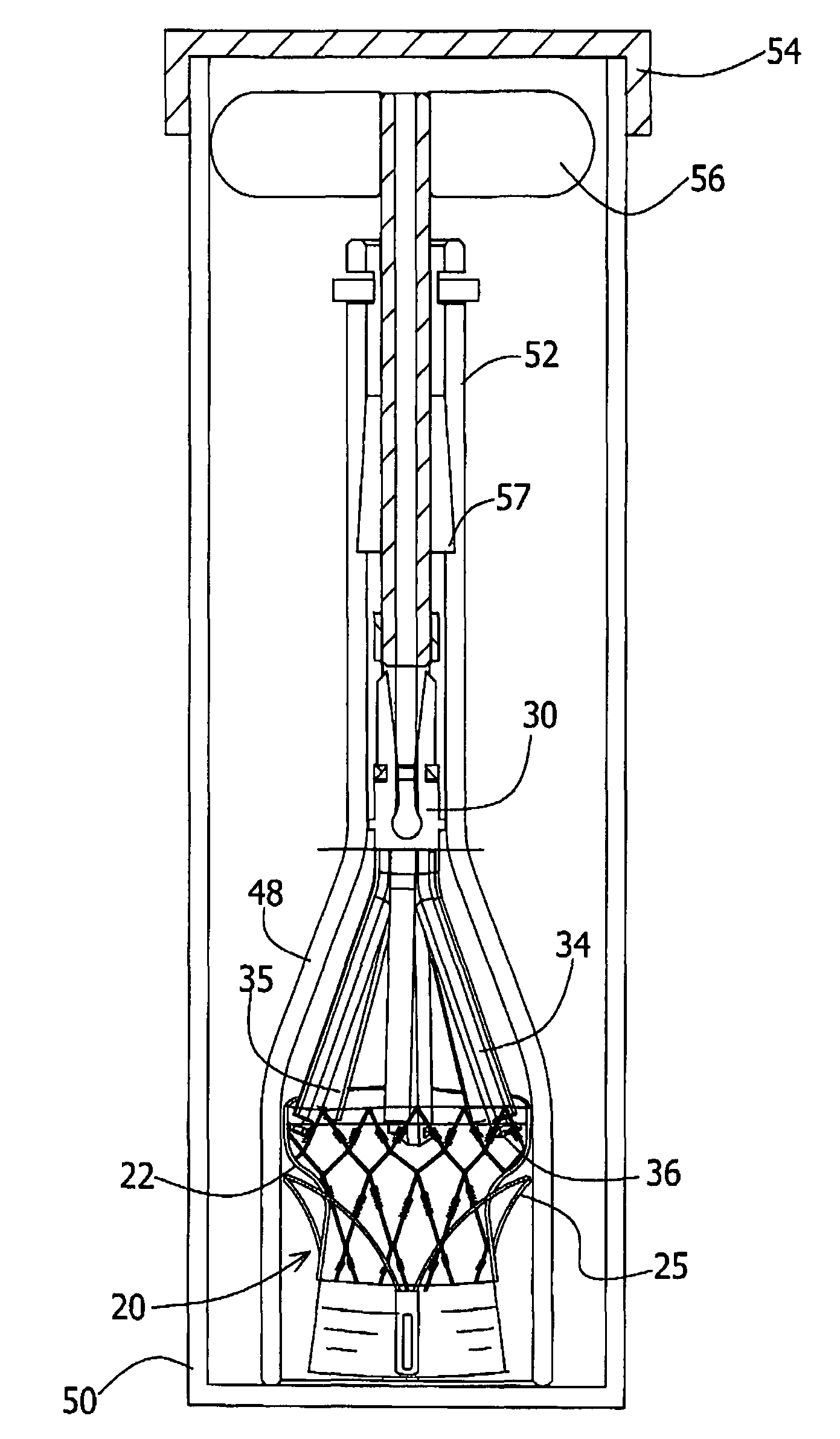
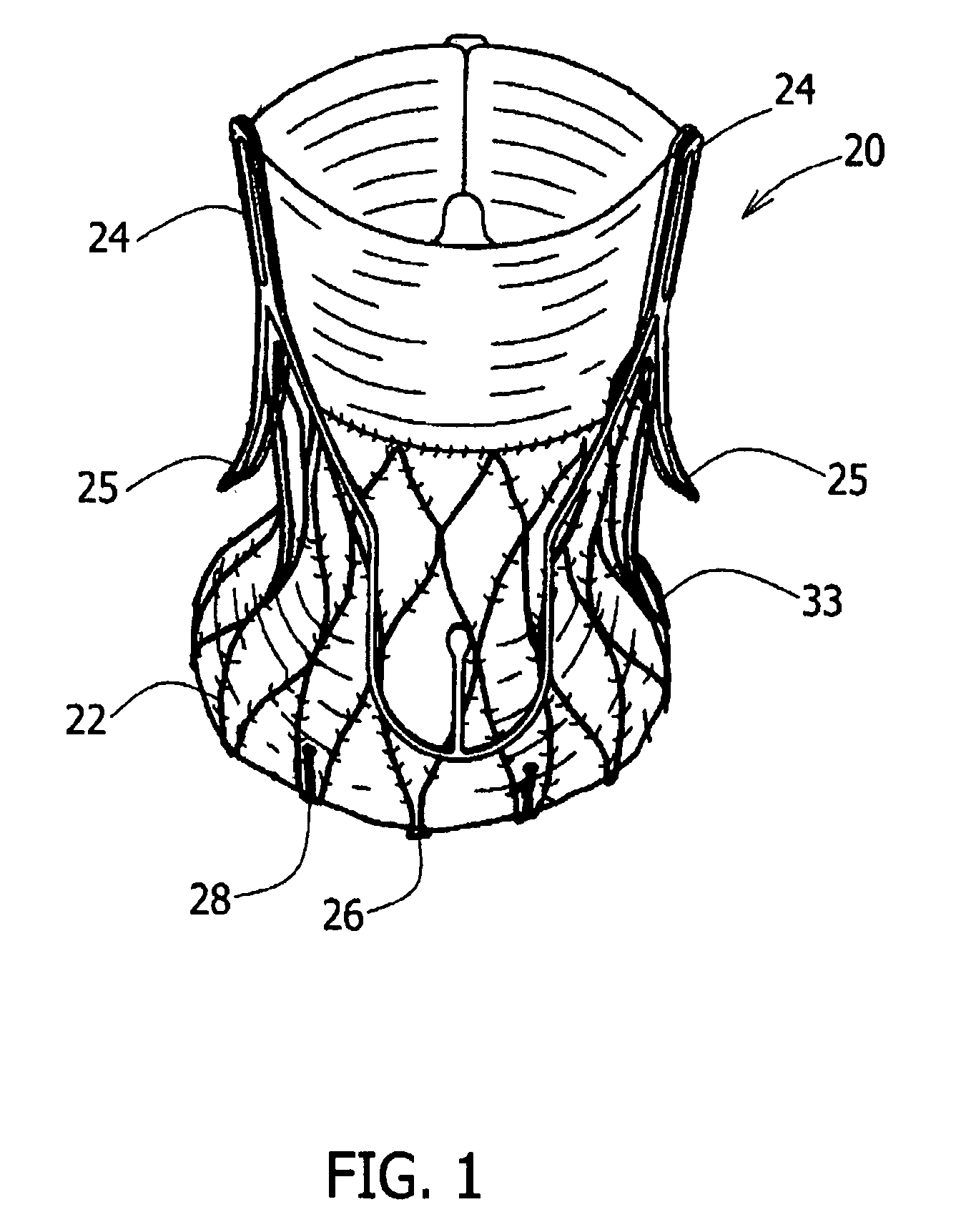
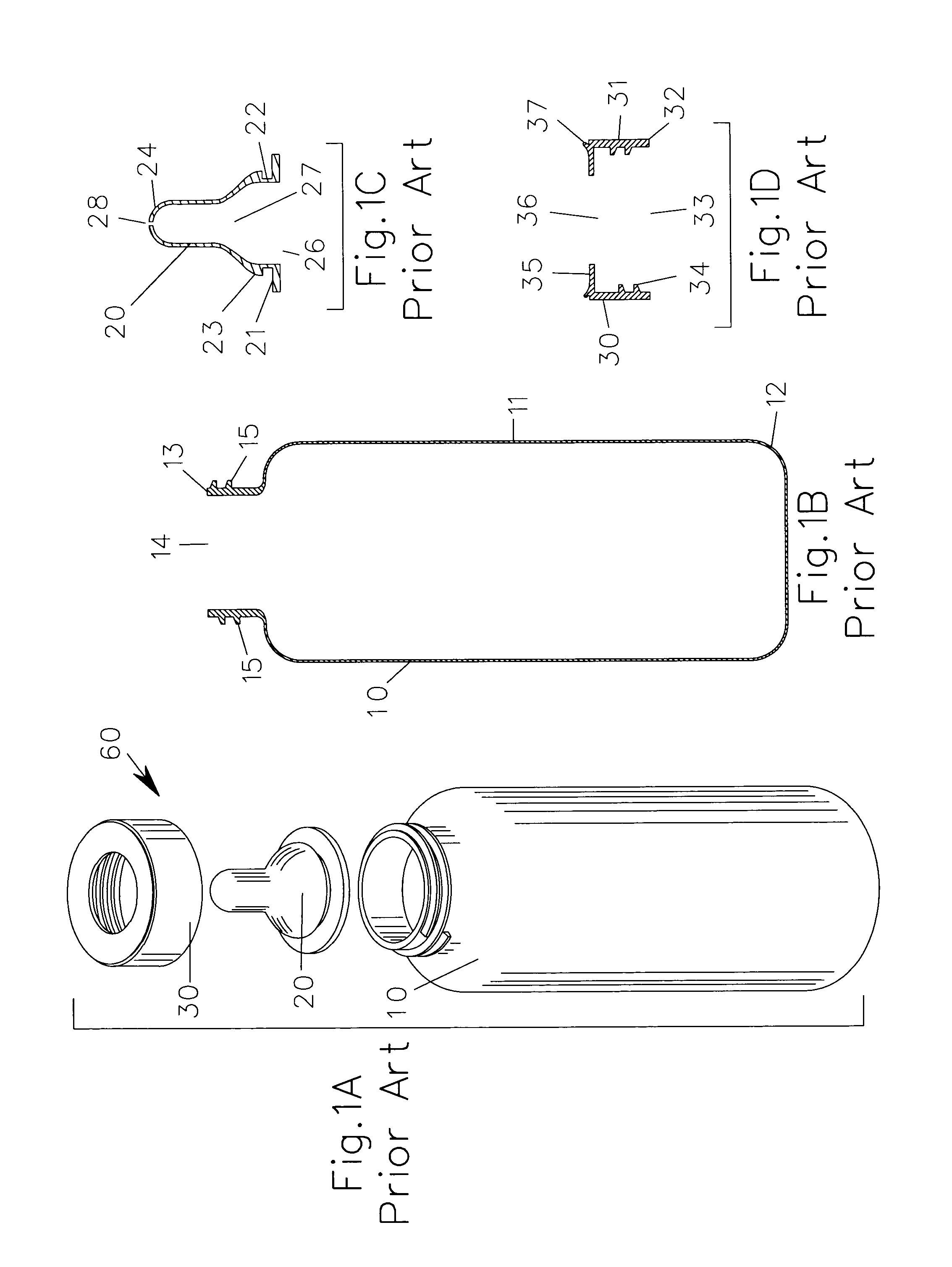
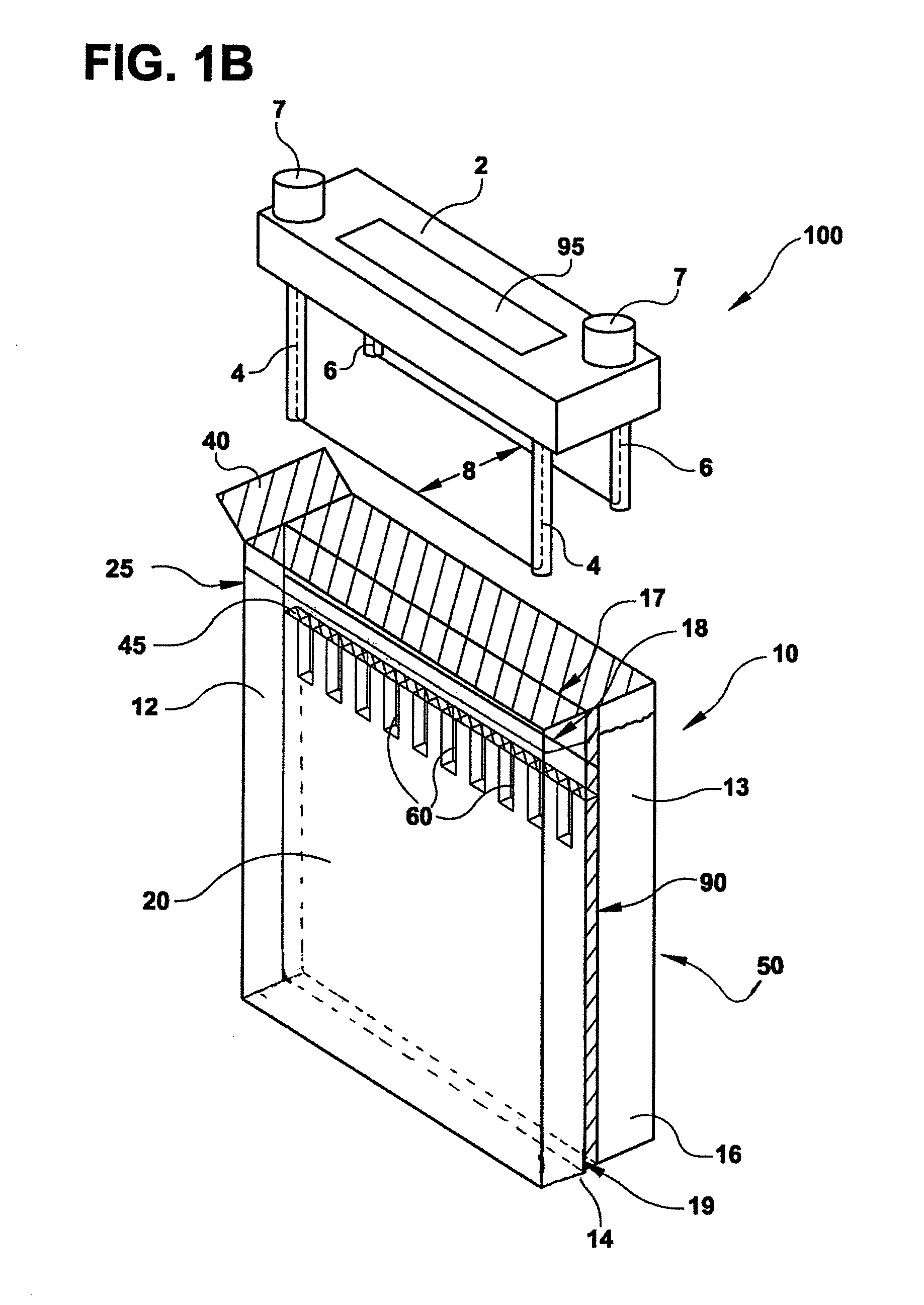
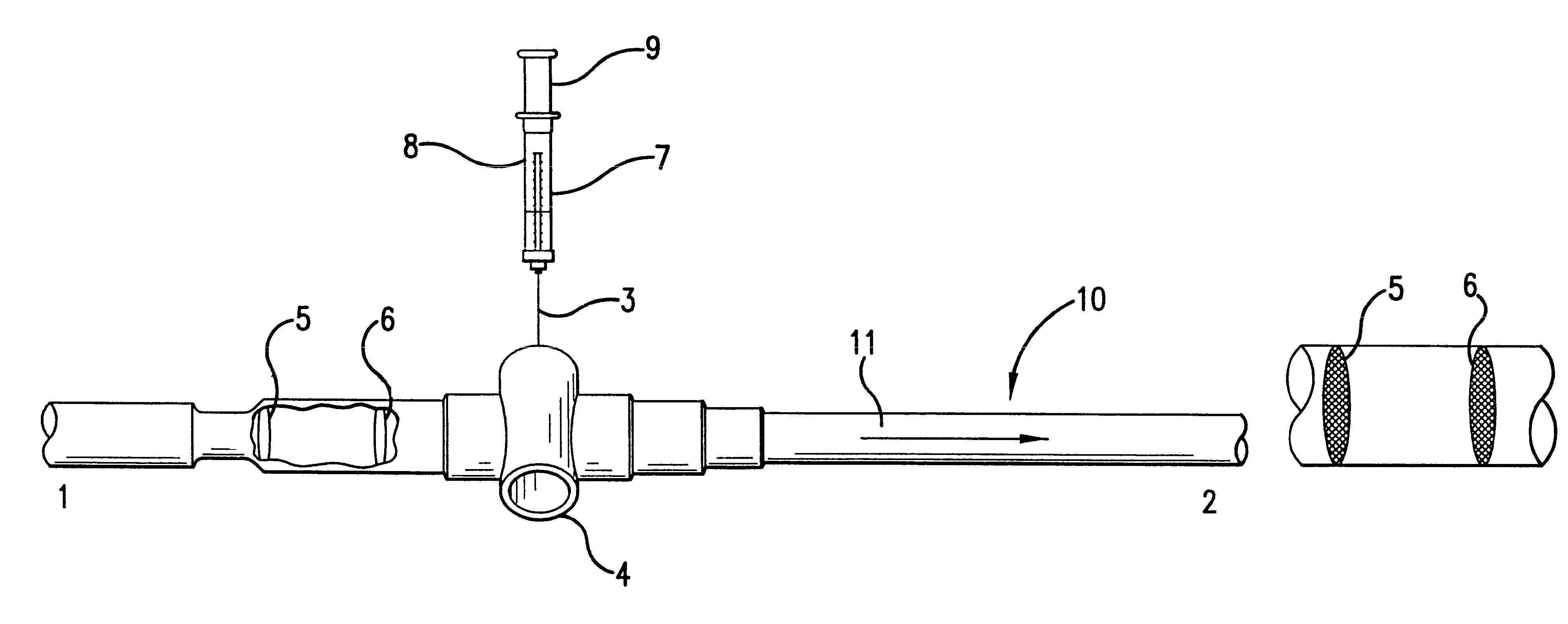
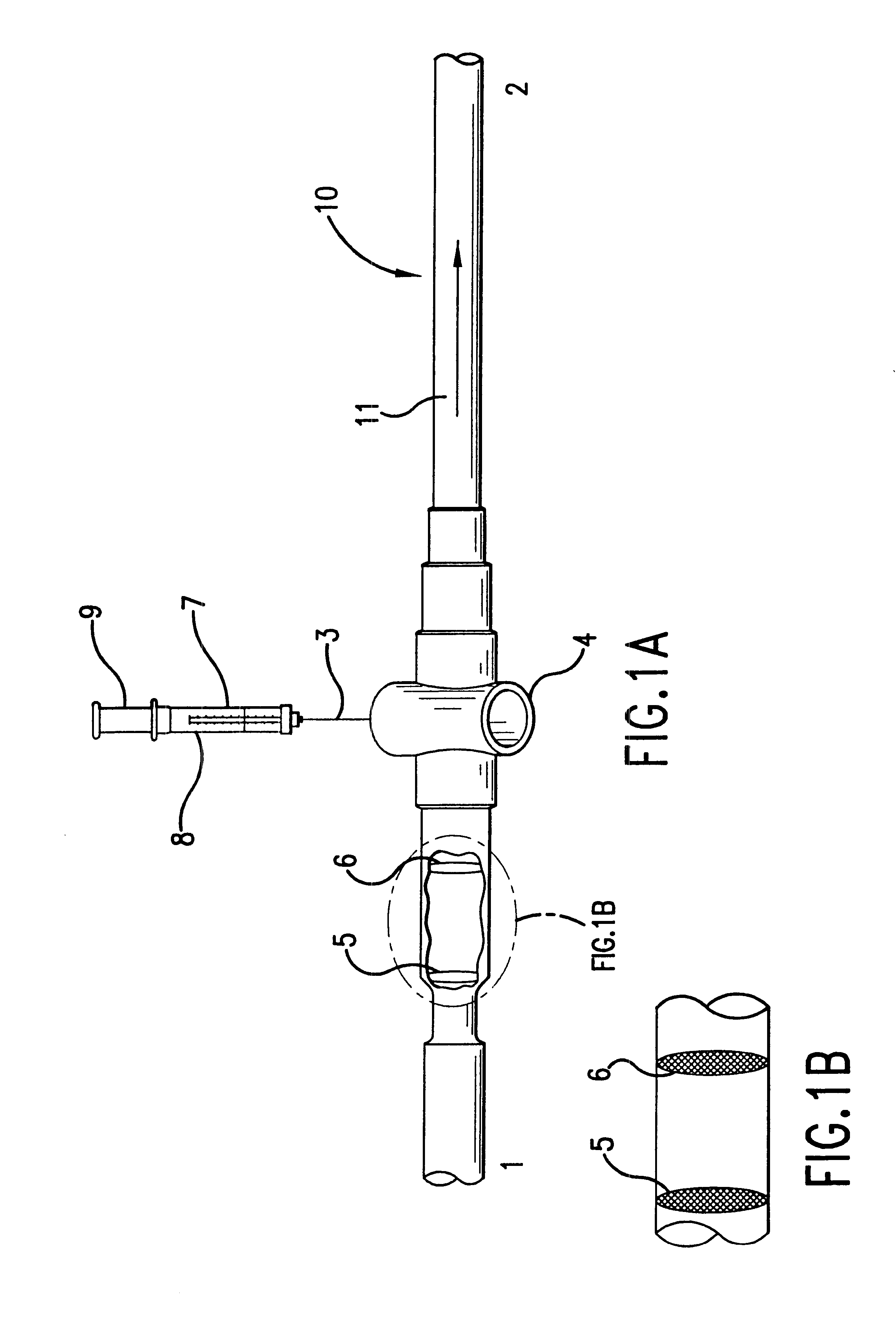
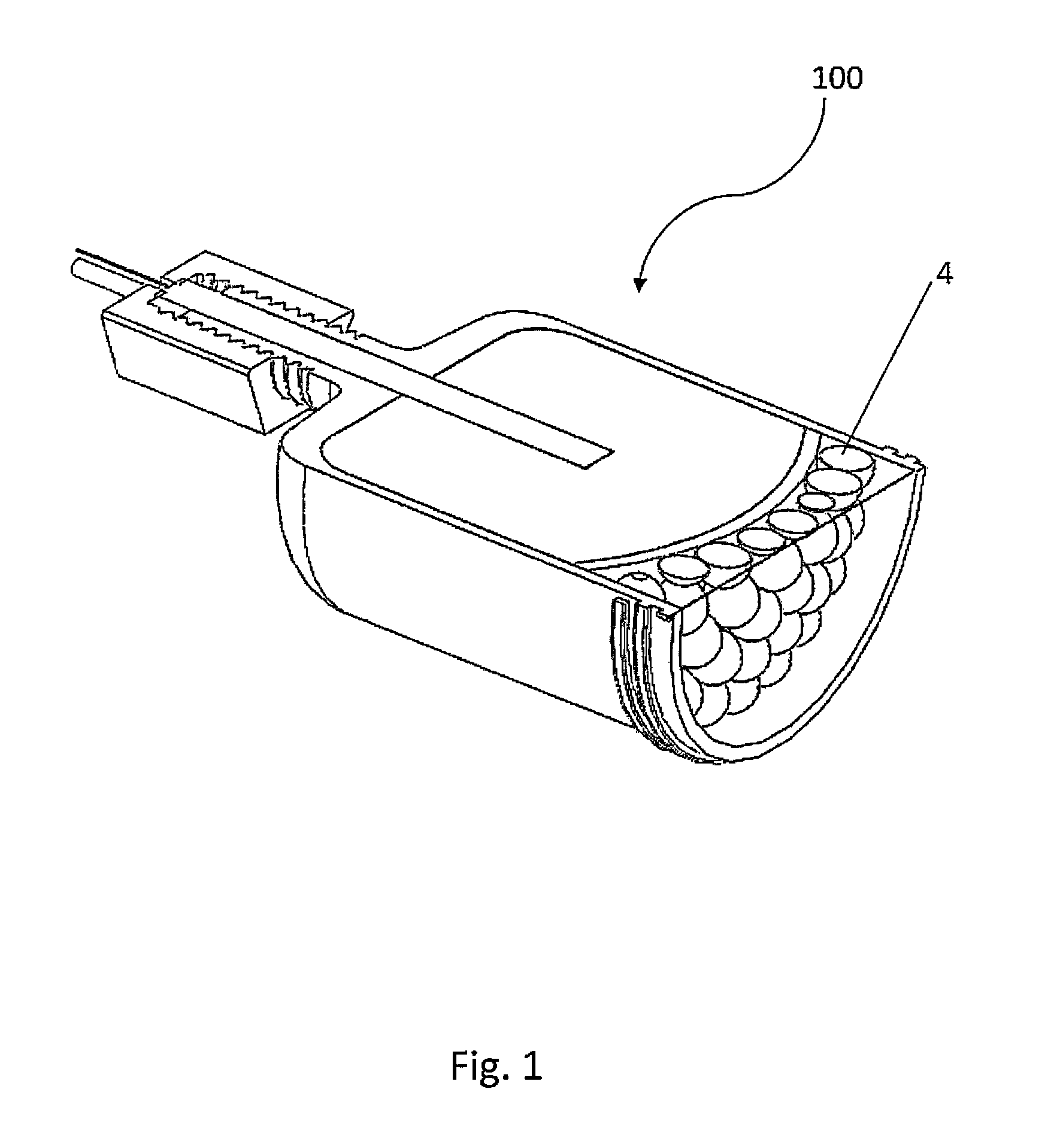
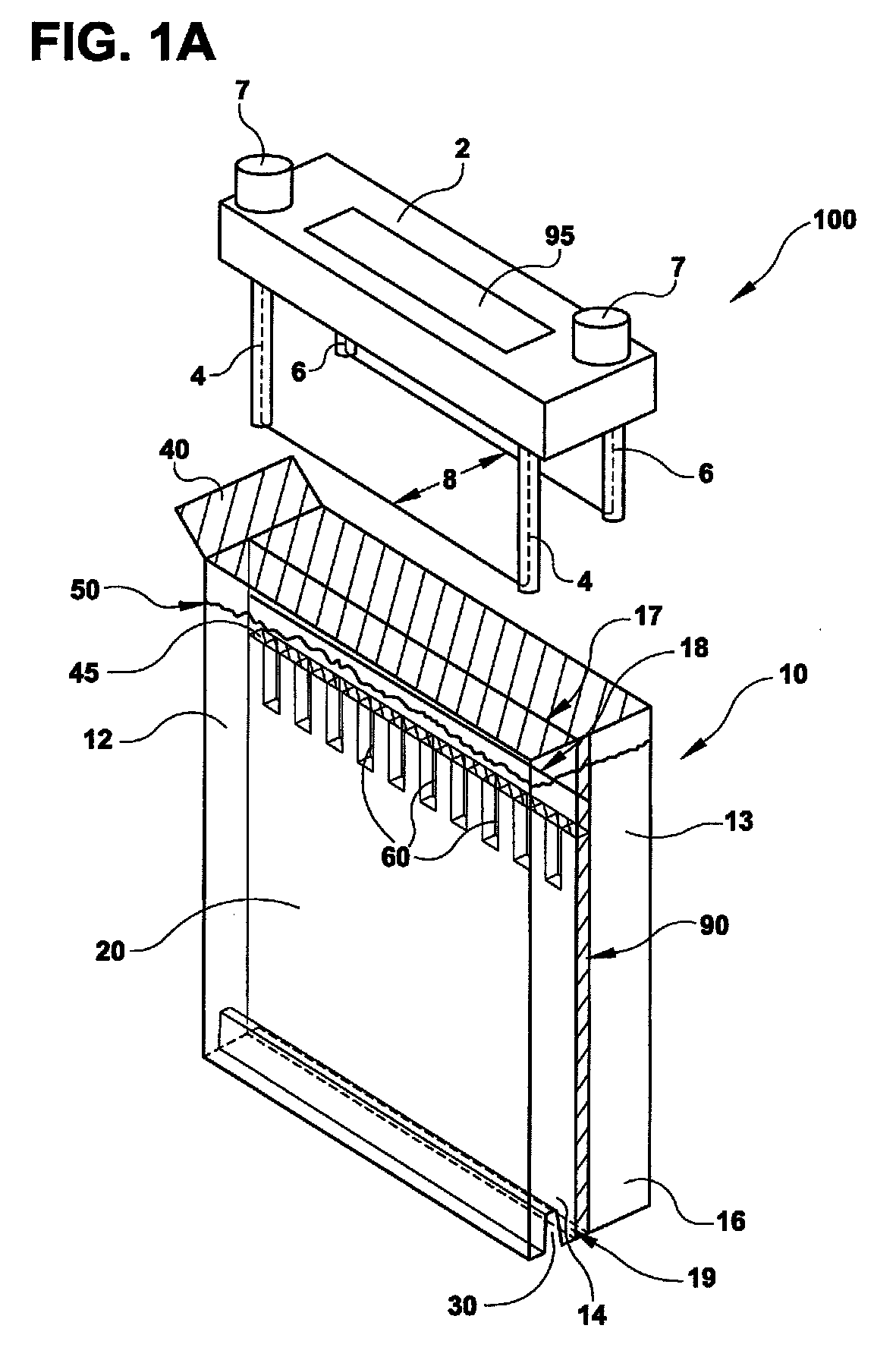
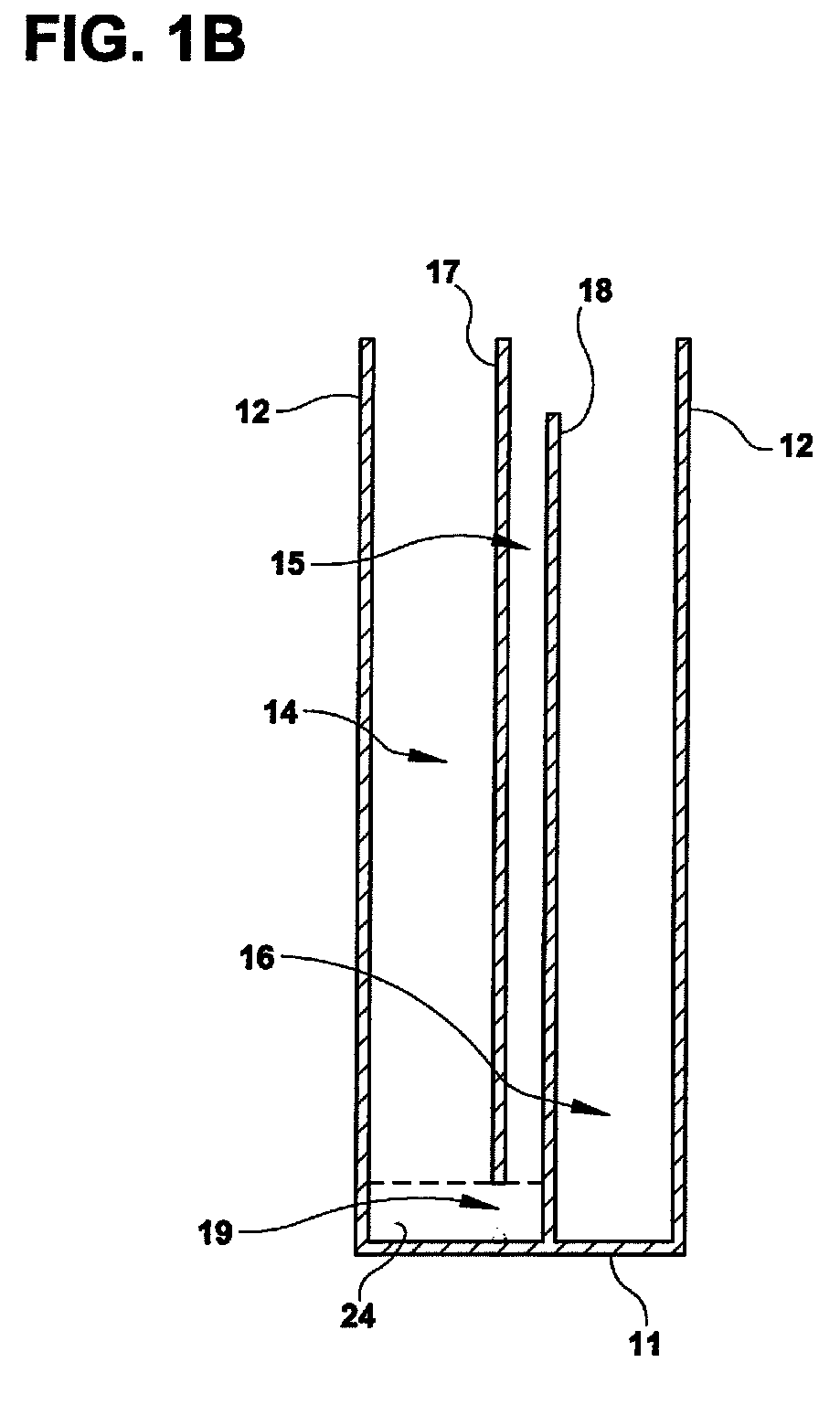
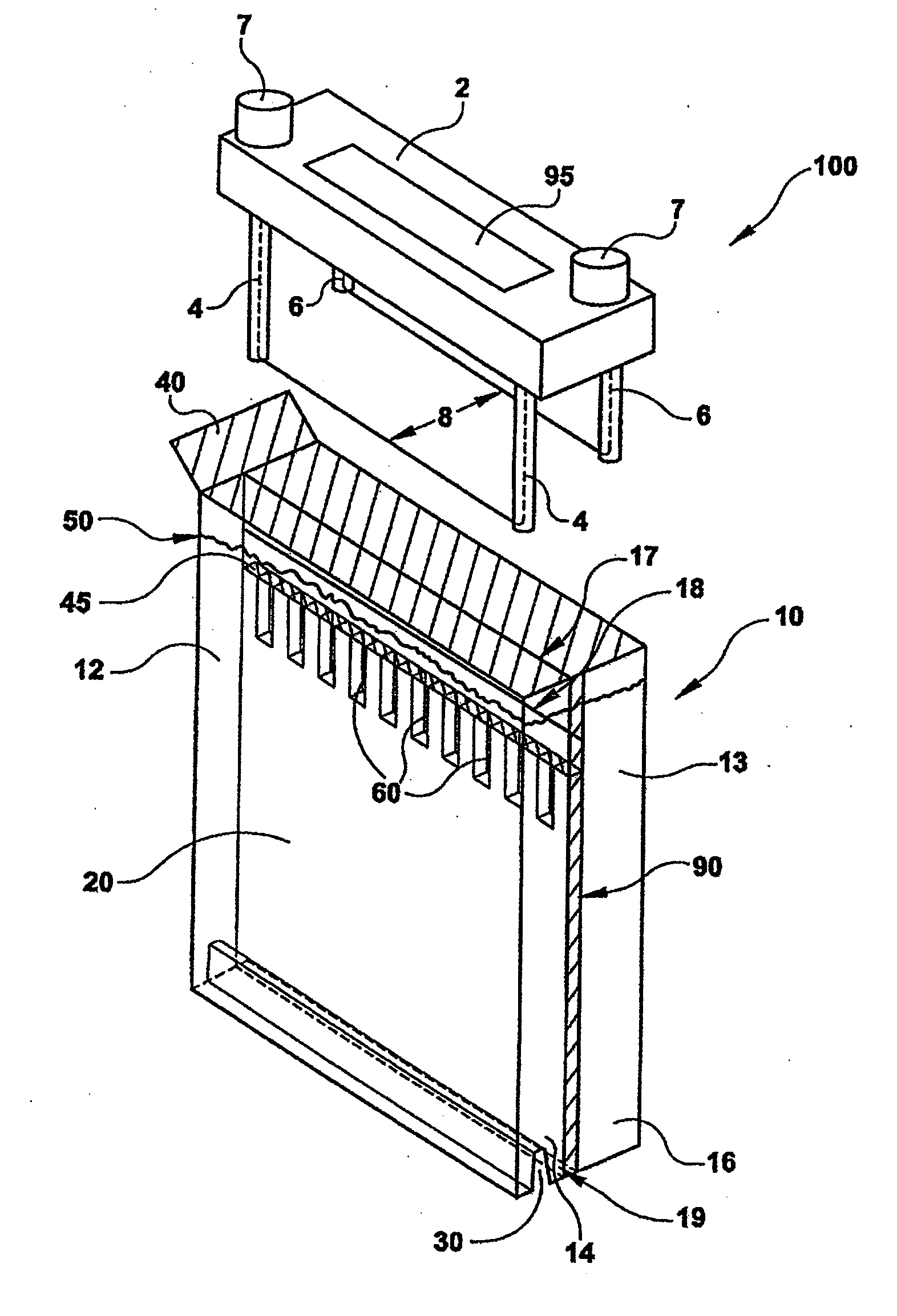
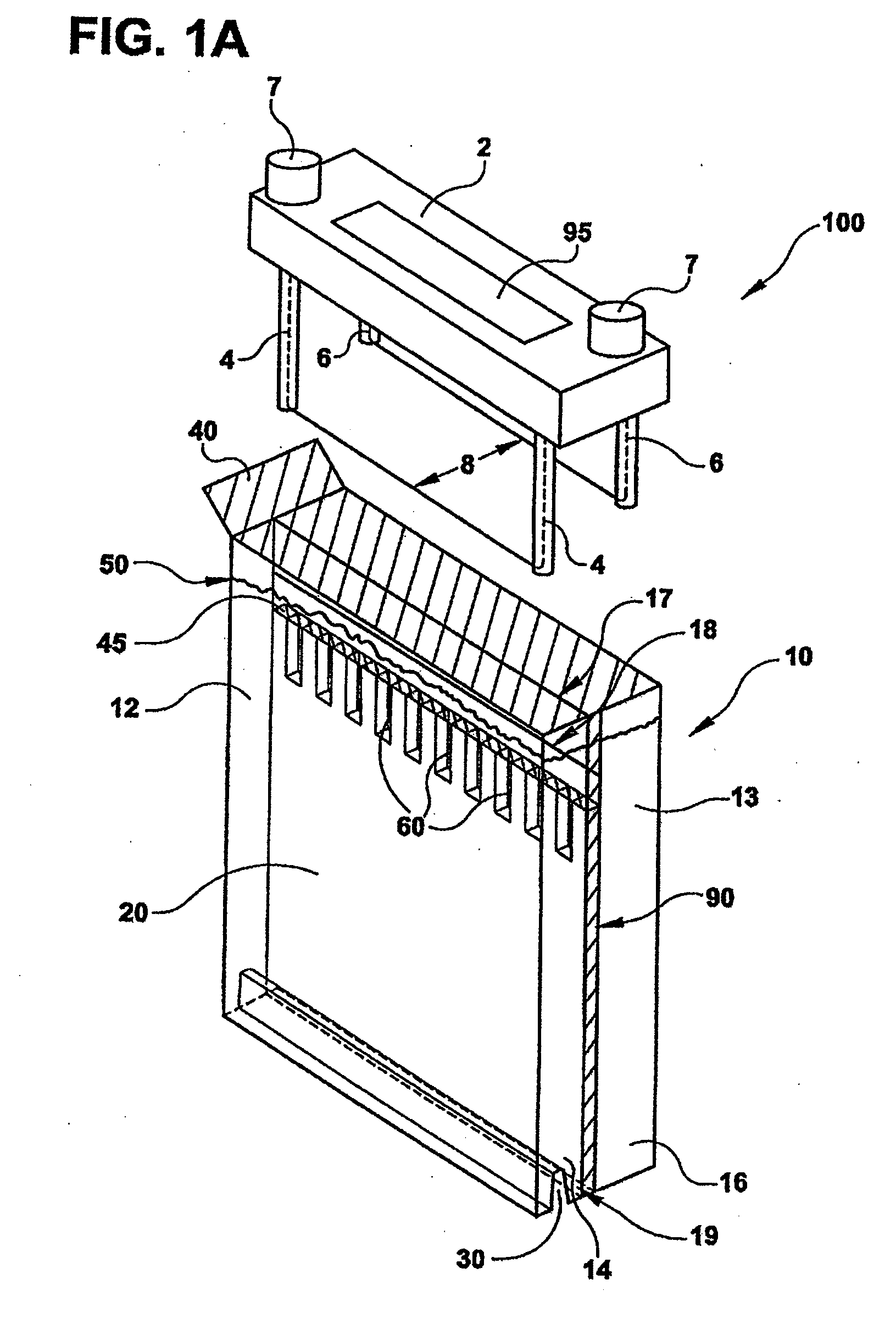
Stent loading tool and method for use thereof
ActiveUS20090054976A1The method is simple and reliableEasy to pushStentsHeart valvesVALVE PORTCatheter device
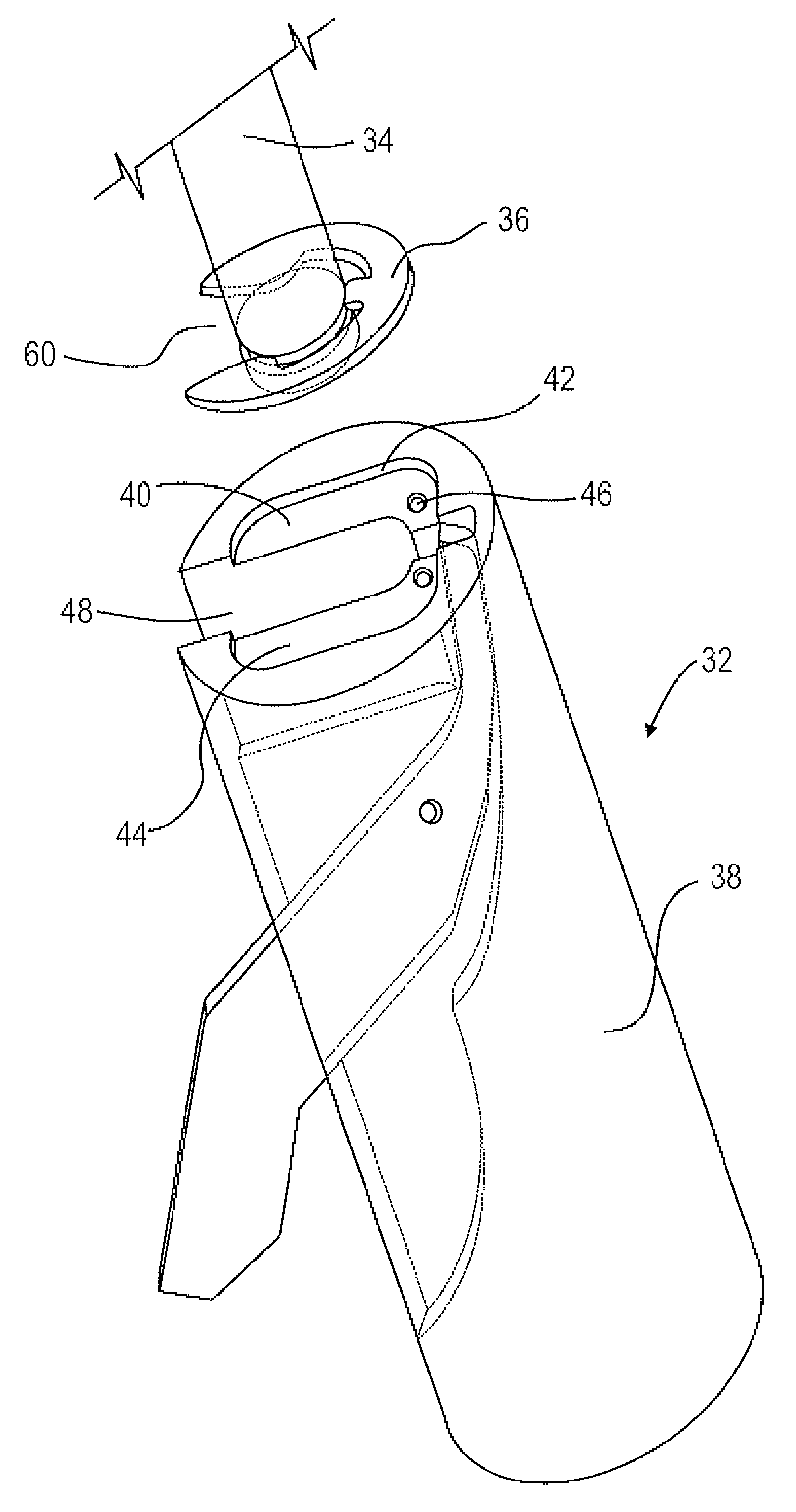
A loading tool for withdrawing, crimping, and loading a stent-mounted valve into a delivery catheter, and for pushing the stent-mounted valve from the delivery catheter into a native heart valve orifice. The loading tool comprises at least one connector adapted for being removably connected to the stent of the stent-mounted valve. A crimping tool having a generally converging shape is adapted for use with the loading tool. Following connection of the loading tool to the stent-mounted valve, the loading tool operates to allow the stent-mounted valve to be drawn through the crimping tool, and loaded, in a crimped state, into a delivery catheter. Also disclosed is a kit of the of the various components for effecting the delivery of the stent-mounted valve and a method for withdrawing, crimping, and loading a stent-mounted valve from a storage container into a delivery catheter for the performance of a transcatheter valve implantation procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VENTOR TECH
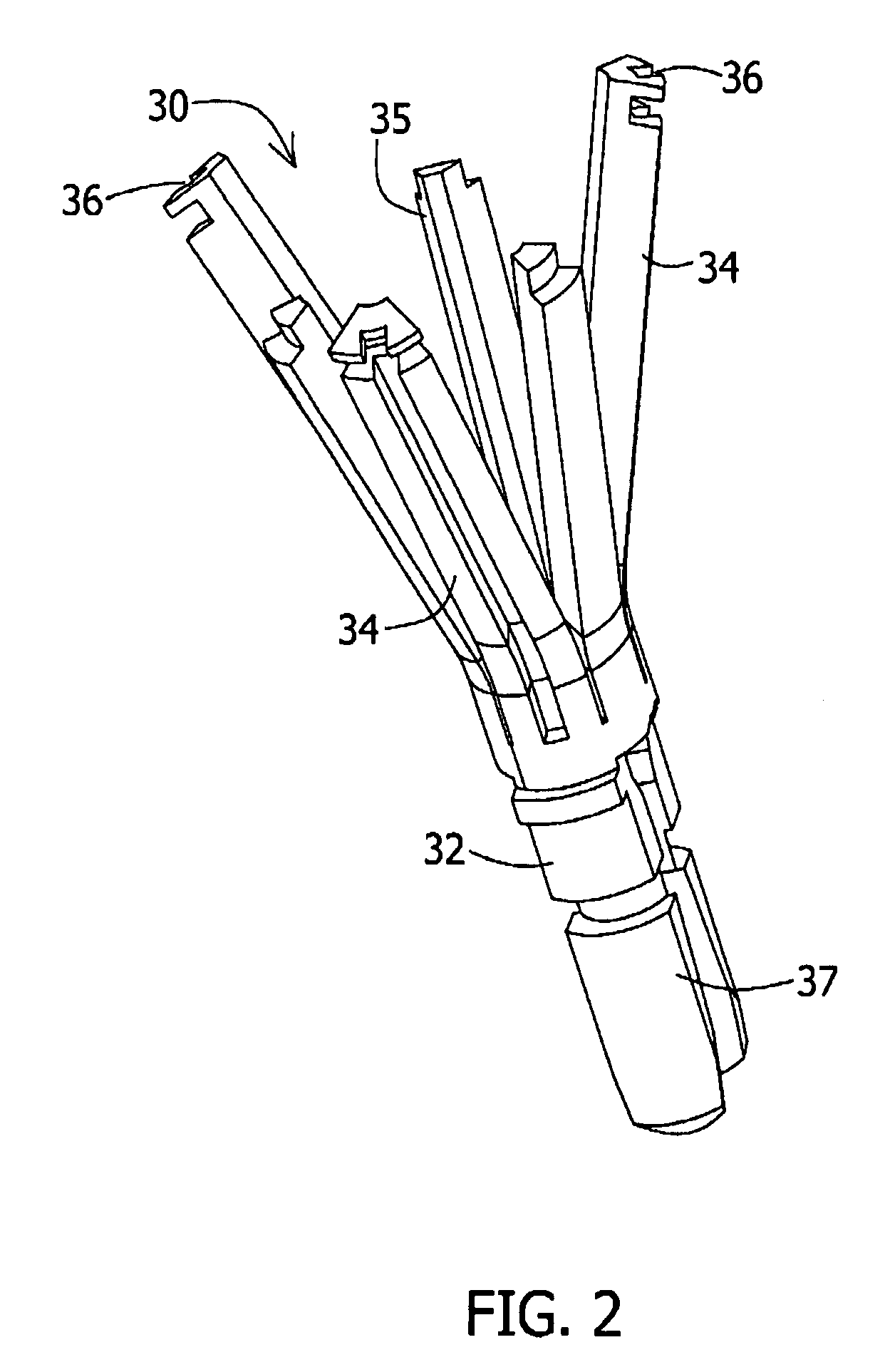
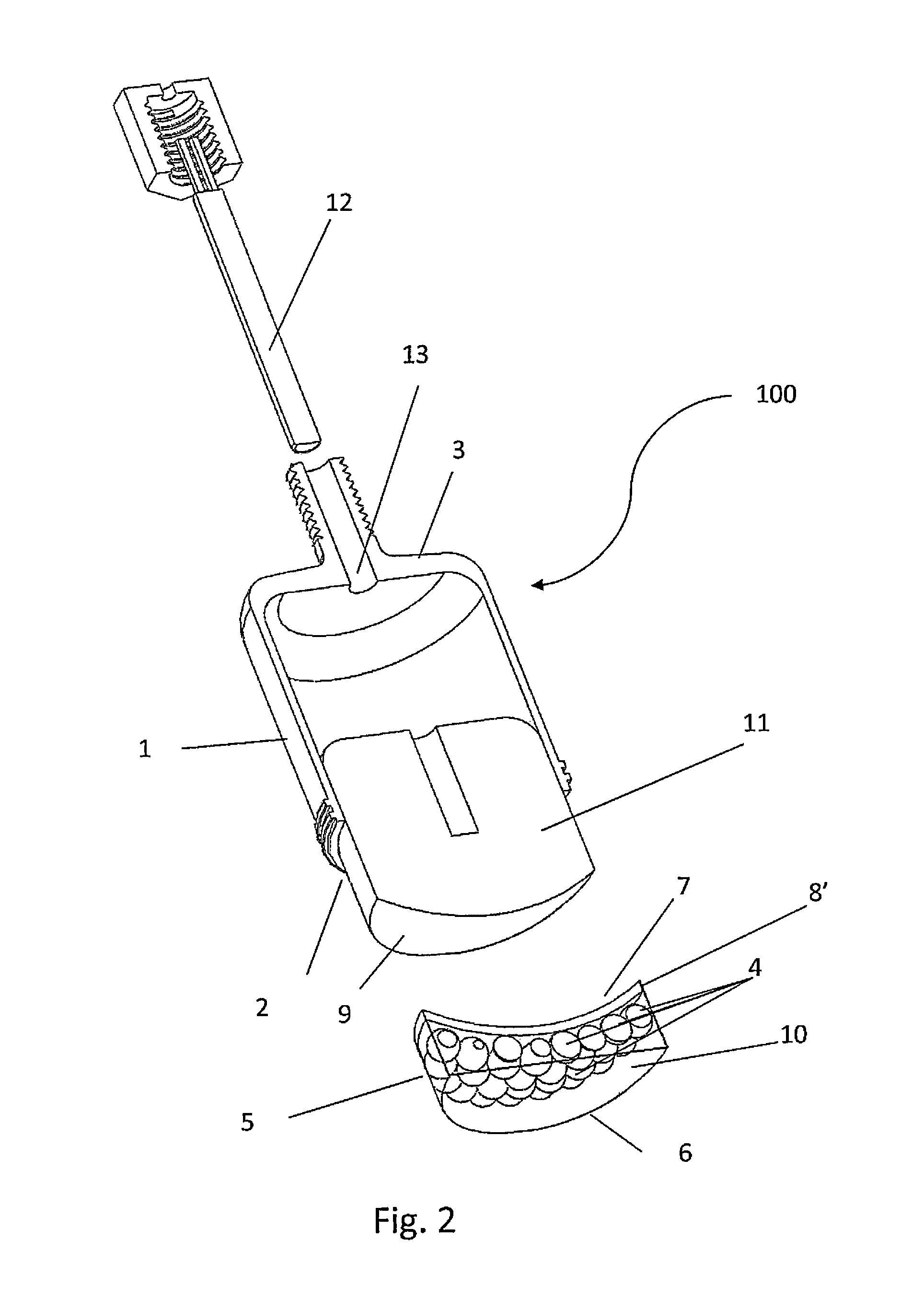
Stent loading tool and method for use thereof
ActiveUS8747458B2The method is simple and reliableEasy to pushStentsHeart valvesInsertion stentEngineering
Owner:MEDTRONIC VENTOR TECH
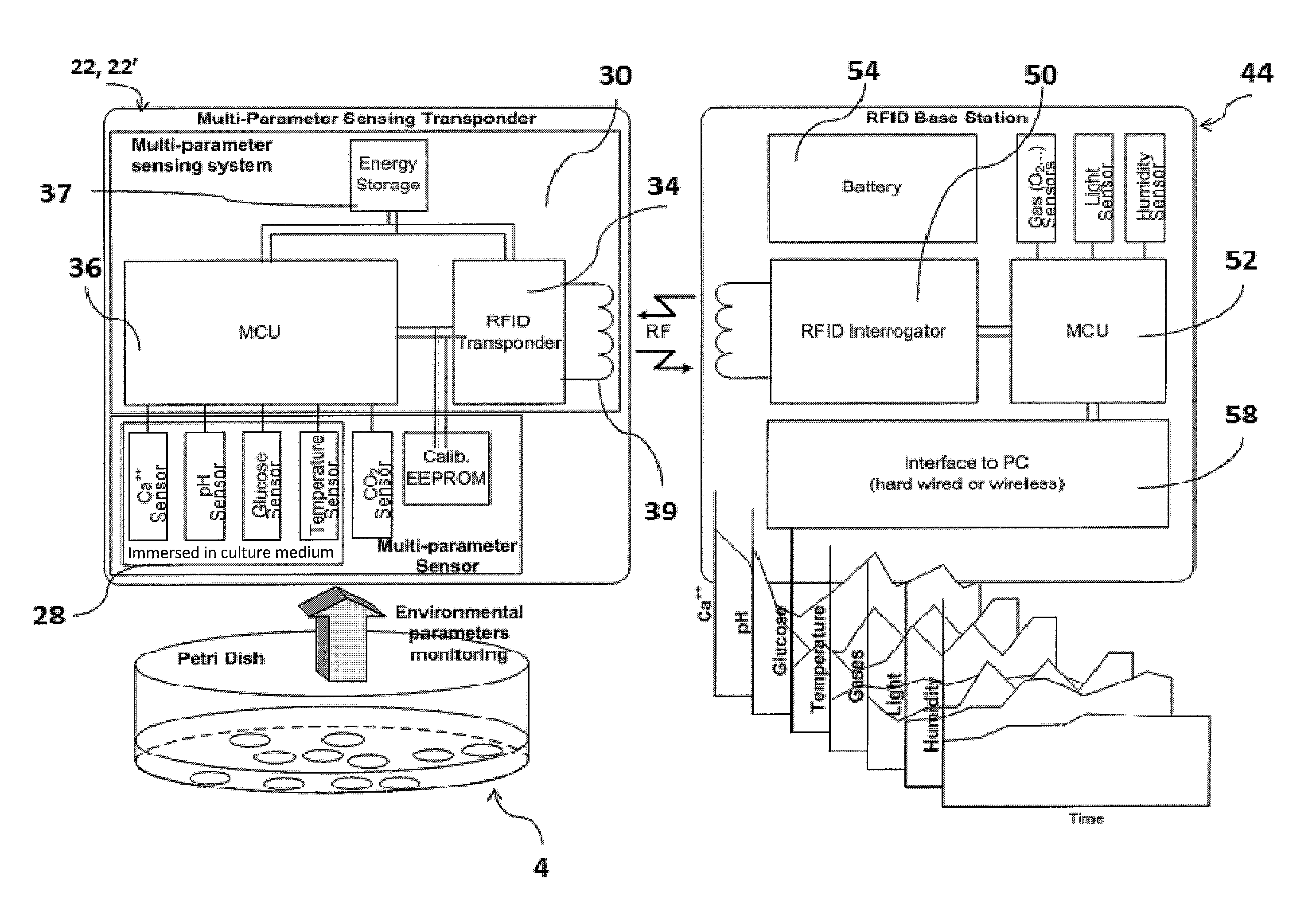
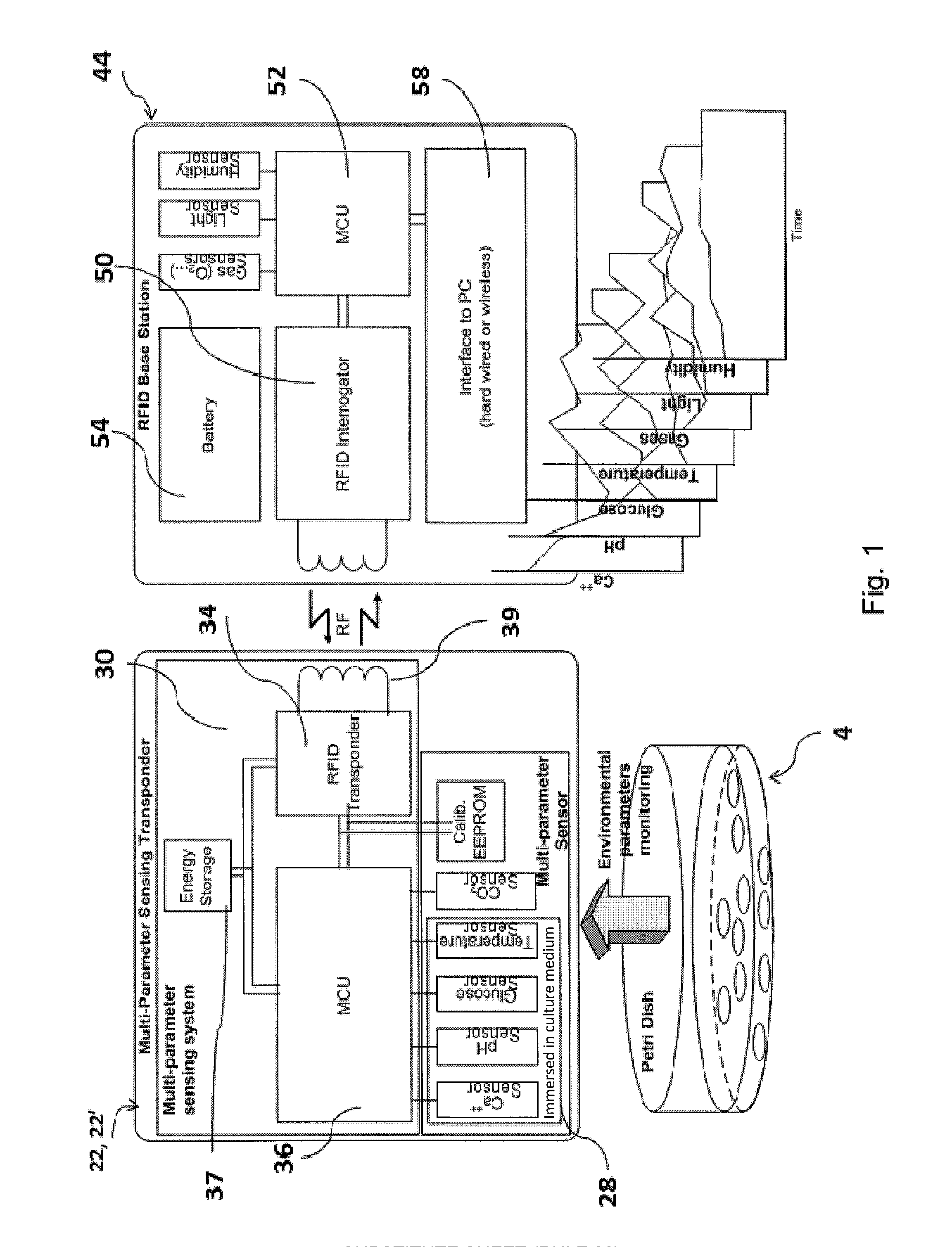
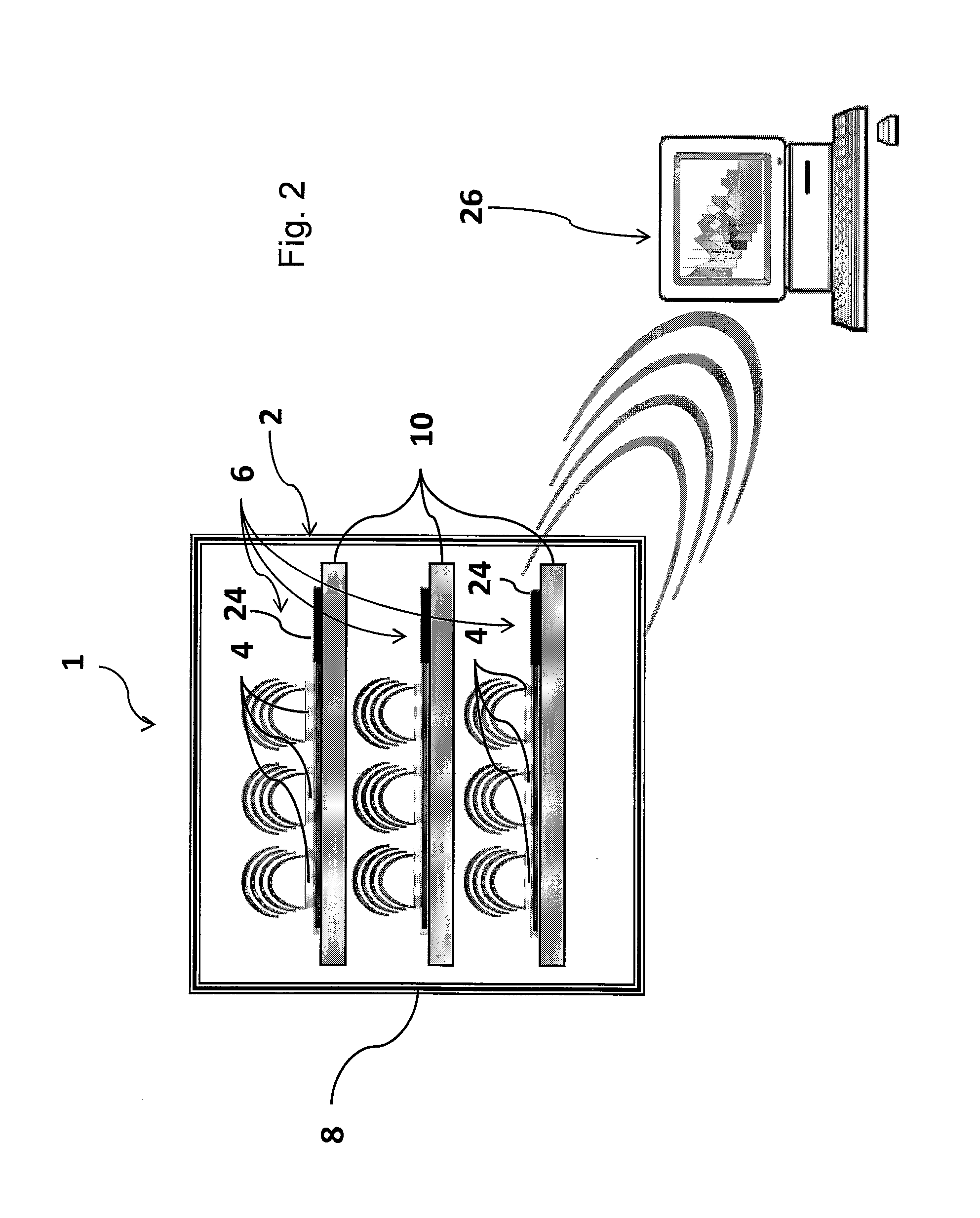
Monitoring system for cell culture
InactiveUS20130316442A1Minimal handlingSafe and reliableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMixed cell cultureGrowth cell
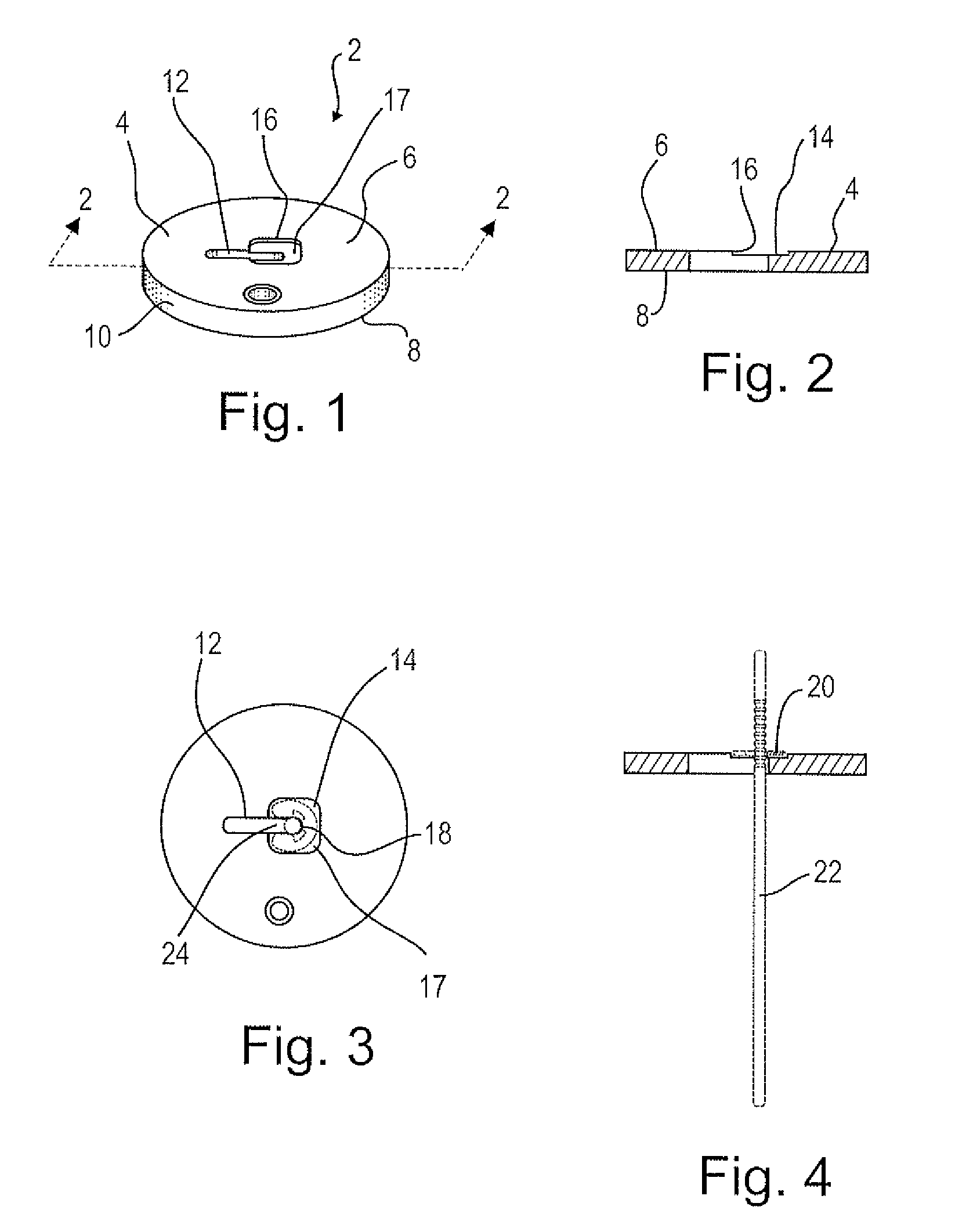
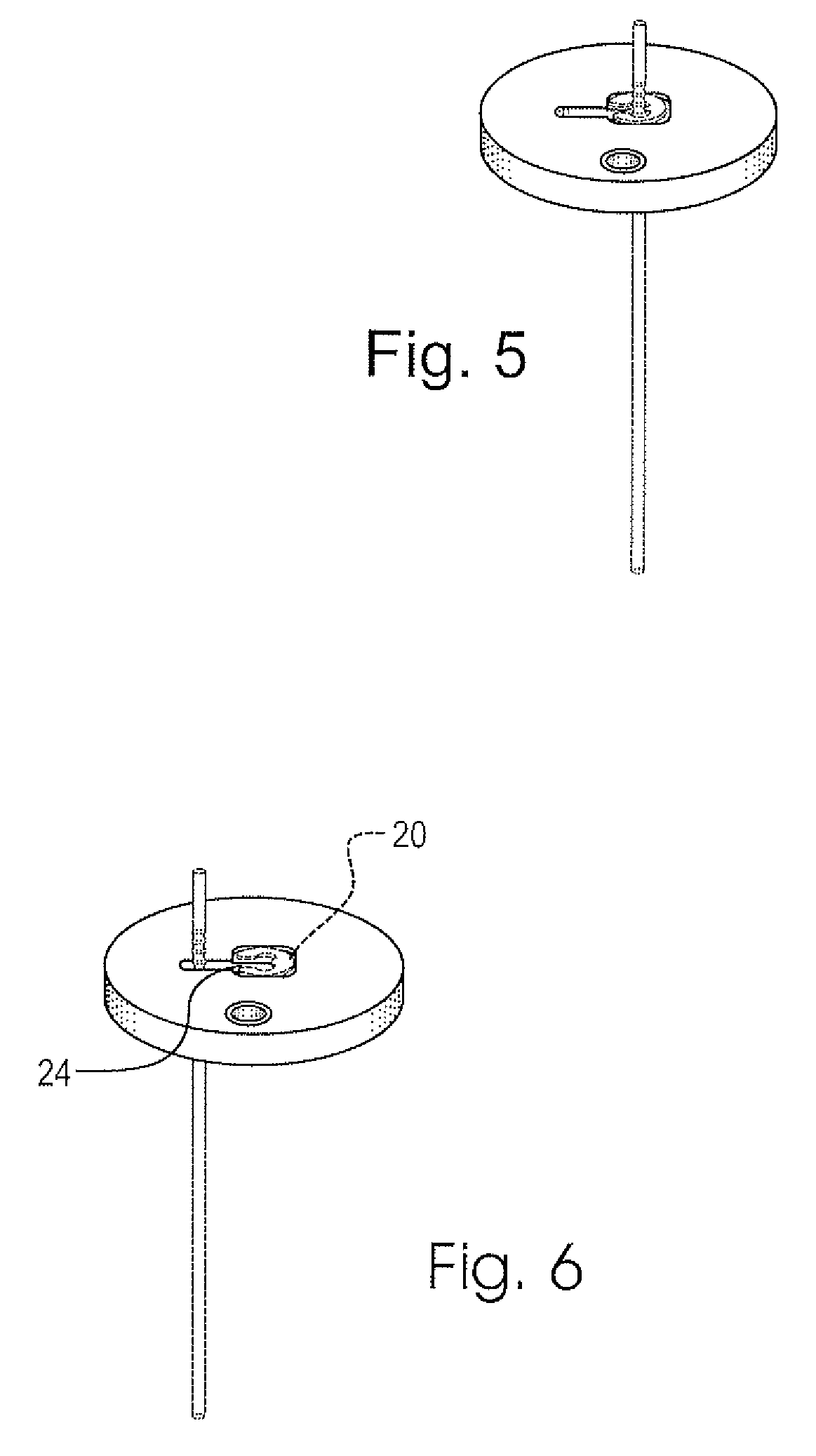
Cell culture environment monitoring system (6) for monitoring parameters relevant to cell growth in at least one culture dish (4) containing a cell growth medium (14), including at least one sensing device (22, 22′) configured to measure environmental parameters relevant to cell growth, and a tray (24) supporting said at least one culture dish. The sensing device is configured for mounting inside said culture dish at least partially within said cell growth medium, and comprises an RFID transponder (34). The tray (24) comprises an RFID base station (44) configured to interrogate the RFID transponder to obtain measurements of said parameters relevant to cell growth.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Collapsible container
A collapsible container has a base having a lower hinge portion which includes a first lower hinge portion and a second lower hinge portion. The container also includes a plurality of upstanding side walls attached to the base having an upper hinge portion extending downwardly. The upper hinge portion includes a first elongate upper hinge portion and a second elongate upper hinge portion. The first lower hinge portion includes a first opening for receiving the first elongate upper hinge portion therein and also includes a flange for securing the first upper hinge portion thereunder. The second lower hinge portion includes a second opening correspondingly sized to receive the second elongate upper hinge member therein for limiting lateral movement between the side walls and the base.
Owner:REHRIG PACIFIC CO INC
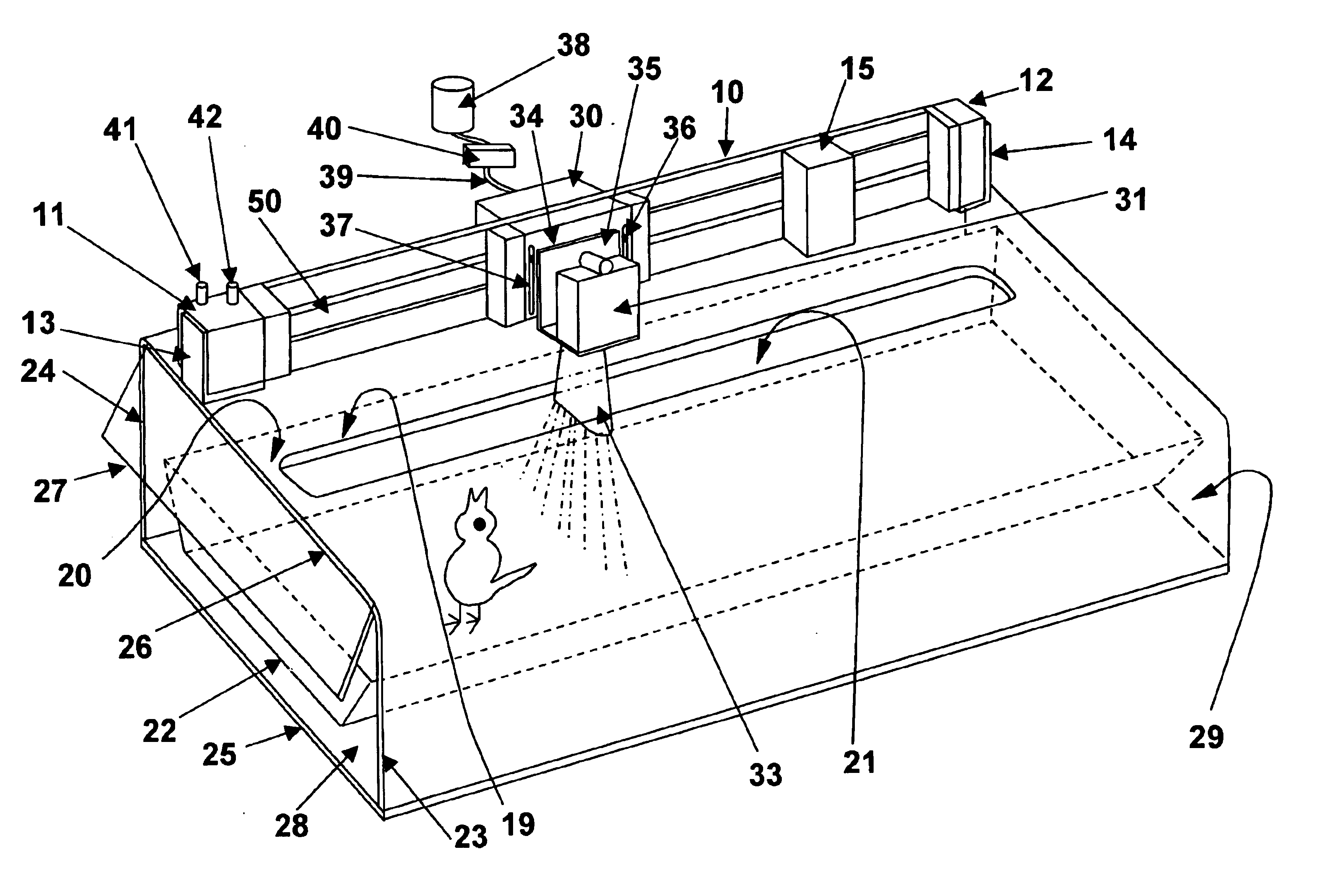
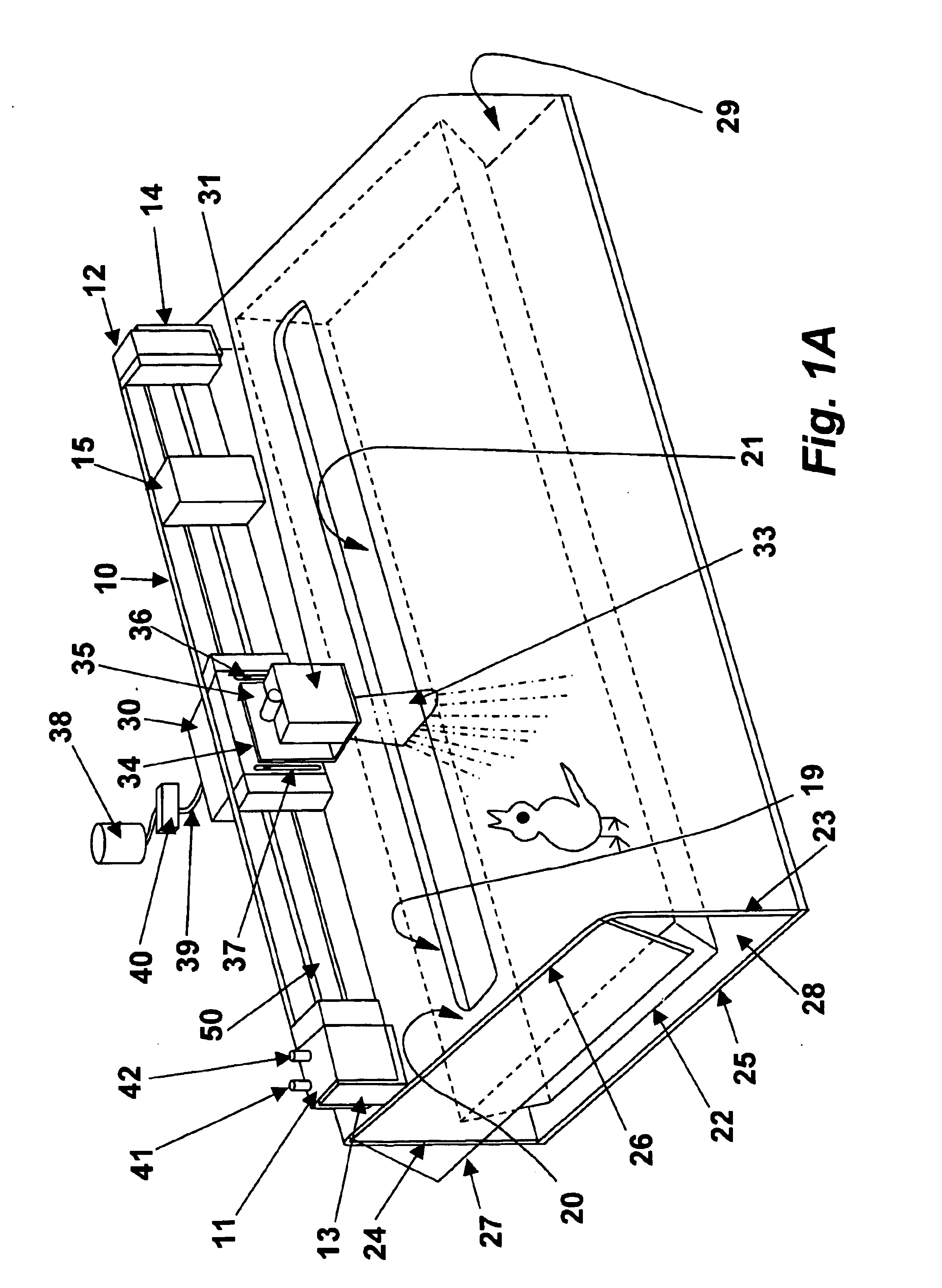
Vaccine spray system
InactiveUS6910446B2Minimal oversprayReduce wasteCannulasMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzleMechanical engineering
A spray delivery system and methods of use thereof, suitable for delivering a fan-shaped vaccine spray to birds or chicks held within an open-topped container, comprising a cover, an elongated guide rail mounted thereon, and a spray head may move reversibly on the guide rail. The spray head comprises a spray nozzle assembly having a spray port and optionally a fan-shaped nozzle for delivering a fan-shaped fluid spray. The cover has an elongated slot that permits the spray nozzle assembly to extend below the plane of the cover while allowing the spray nozzle assembly to freely traverse the length of an open-topped container placed beneath the cover. By reversibly moving the spray head along the guide rail, the spray delivery system can deliver a substantially uniform fluid spray to an open-topped container with minimal overspray and reduced fluid wastage.
Owner:MERIAL INC
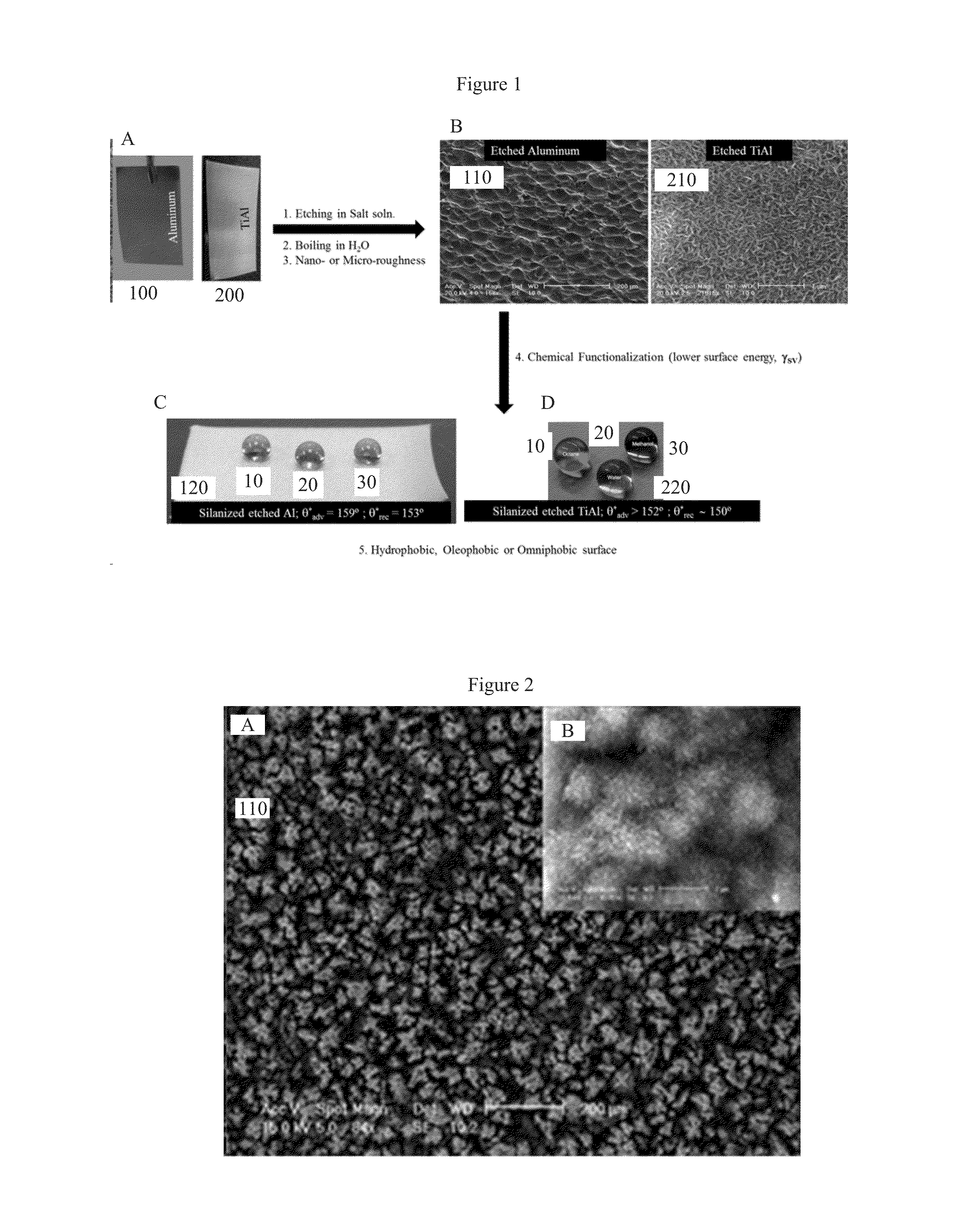
Salt Based Etching of Metals and Alloys for Fabricating Superhydrophobic and Superoleophobic Surfaces
InactiveUS20160153094A1Reduce etchingEasy disposalDecorative surface effectsMetallic material coating processesEtchingRe entrant
A process to etch hierarchical, re-entrant texture into the surface of metals and their alloys using salt-based etching solutions. The process imbues superhydrophobic, oleophobic or superoleophobic, omniphobic or superomniphobic properties by further imparting a low surface energy coating onto the etched surfaces by chemical functionalization by low surface energy hydrophobilizing compounds.
Owner:TUTEJA ANISH +2
Bottle insert for storing and dispensing baby formula
InactiveUS20050056608A1Facilitating cleanlinessEasy to measure accuratelyBottlesPharmaceutical containersBottleBiomedical engineering
Owner:NESIN MILTON SCOTT
Methods of saponifying xanthophyll esters and isolating xanthophylls
ActiveUS20120107380A1High yieldAvoid insufficient purityOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsWaxSaponification
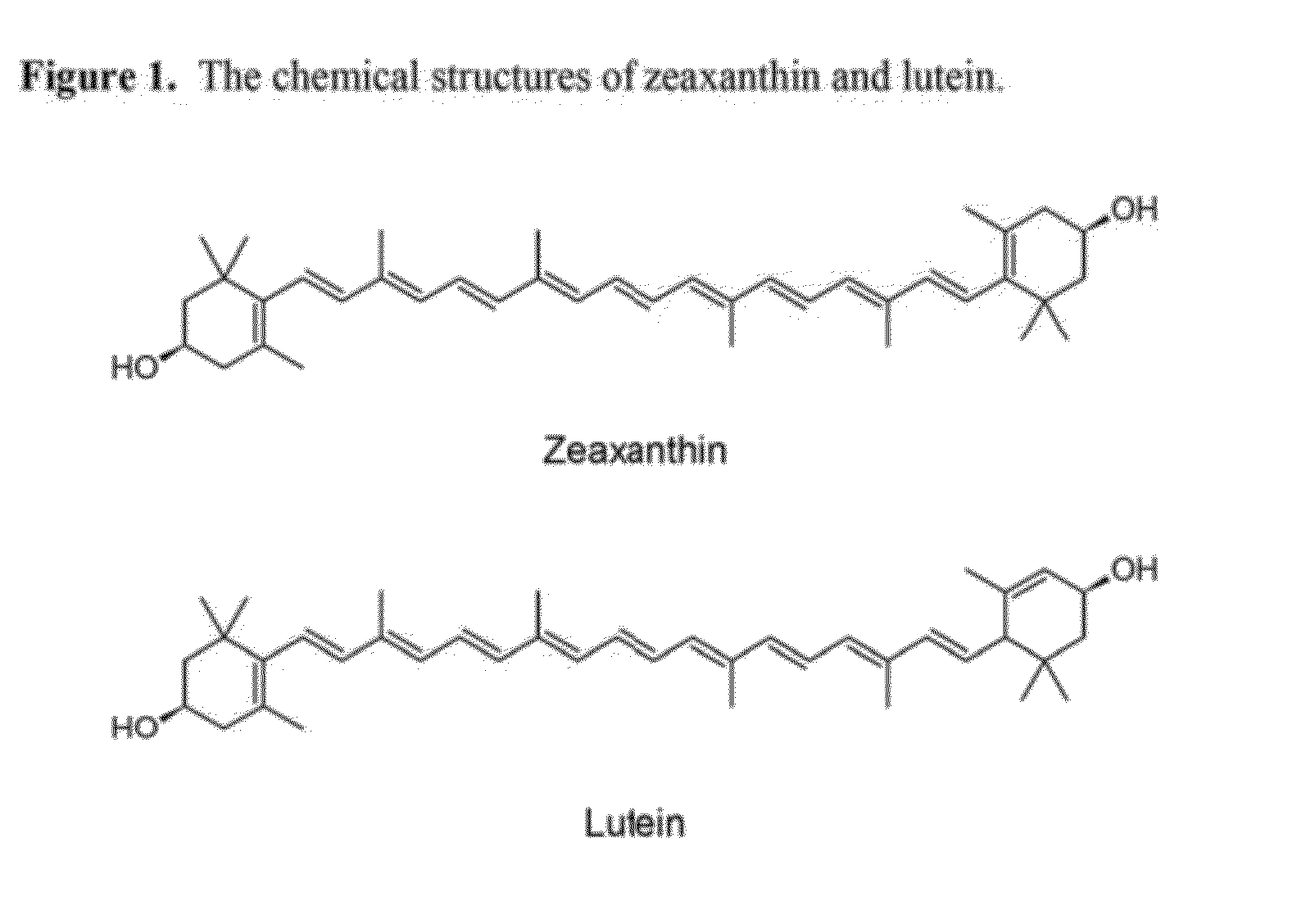
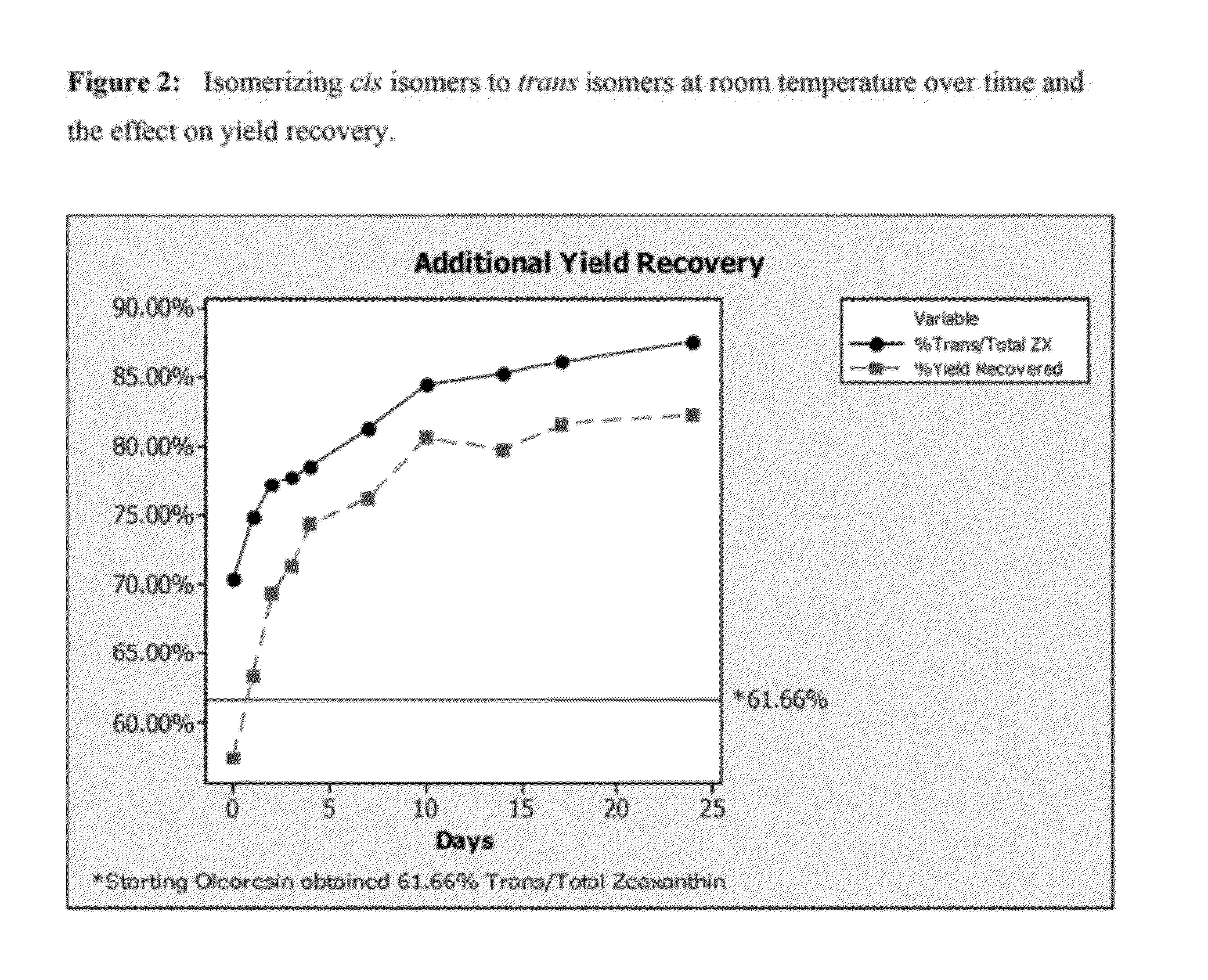
This invention relates to a practical and effective process for converting esterified xanthophylls, including zeaxanthin, to non-esterified xanthophylls through saponification. In addition, the invention provides a process for obtaining esterified zeaxanthin in high yields and purities, isolating the xanthophylls from interfering substances such as waxes, oils, and fats. A product of this process is a zeaxanthin rich substrate that is suitable for use in foods, nutritional supplements, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and related products.
Owner:KALAMAZOO HLDG INC
Methods for simultaneous isolation of biologically active transcription factors and DNA
InactiveUS6921817B1Fast wayEfficient analysisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug biological activityBiology
A rapid isolation method permits the isolation of DNAs, RNAs and transcription factors simultaneously from a wide range of lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells, either from patients or in culture, without the loss of biological activity. A significant advantage of this method is that it entails minimal handling of samples from the patients with various disease states and pathogenic conditions such as AIDS, hepatitis, and other infectious diseases, which require substantial precautions during isolation of DNAs and proteins.
Owner:BANERJEE RANJIT
Centrifugal device and method for ova detection
InactiveUS20090258411A1Simple and rapid and highly accurateEasy to separateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideCentrifugation
A centrifugal device and method are provided for the separation of buoyant material such as parasitic ova from fecal matter. A rotor assembly, rotatable about its central axis in a centrifuge, includes a housing with a centrally located top opening leading to a centrally located mixing chamber. An annular sediment chamber is provided, also coaxial about the central axis, connected by a passage with the mixing chamber. A coring assembly is used to retrieve and insert a fecal sample into the mixing chamber for mixing with a flotation fluid. During centrifugation, heavier fecal components pass radially outwardly to the sediment chamber while the ova collect on the inward surface of the flotation fluid. After centrifugation, more flotation fluid is added, if needed, until a meniscus forms at the top opening. A coverslip is placed over the top opening and the ova float to the surface of the fluid and adhere to the coverslip. The coverslip is removed and the ova detected using standard microscopy procedures. In another aspect, a centrifugal device is provided in which the ova are delivered through centrifugation to a pipette tip for dispensing onto a microscope slide or coverslip.
Owner:STATSPIN
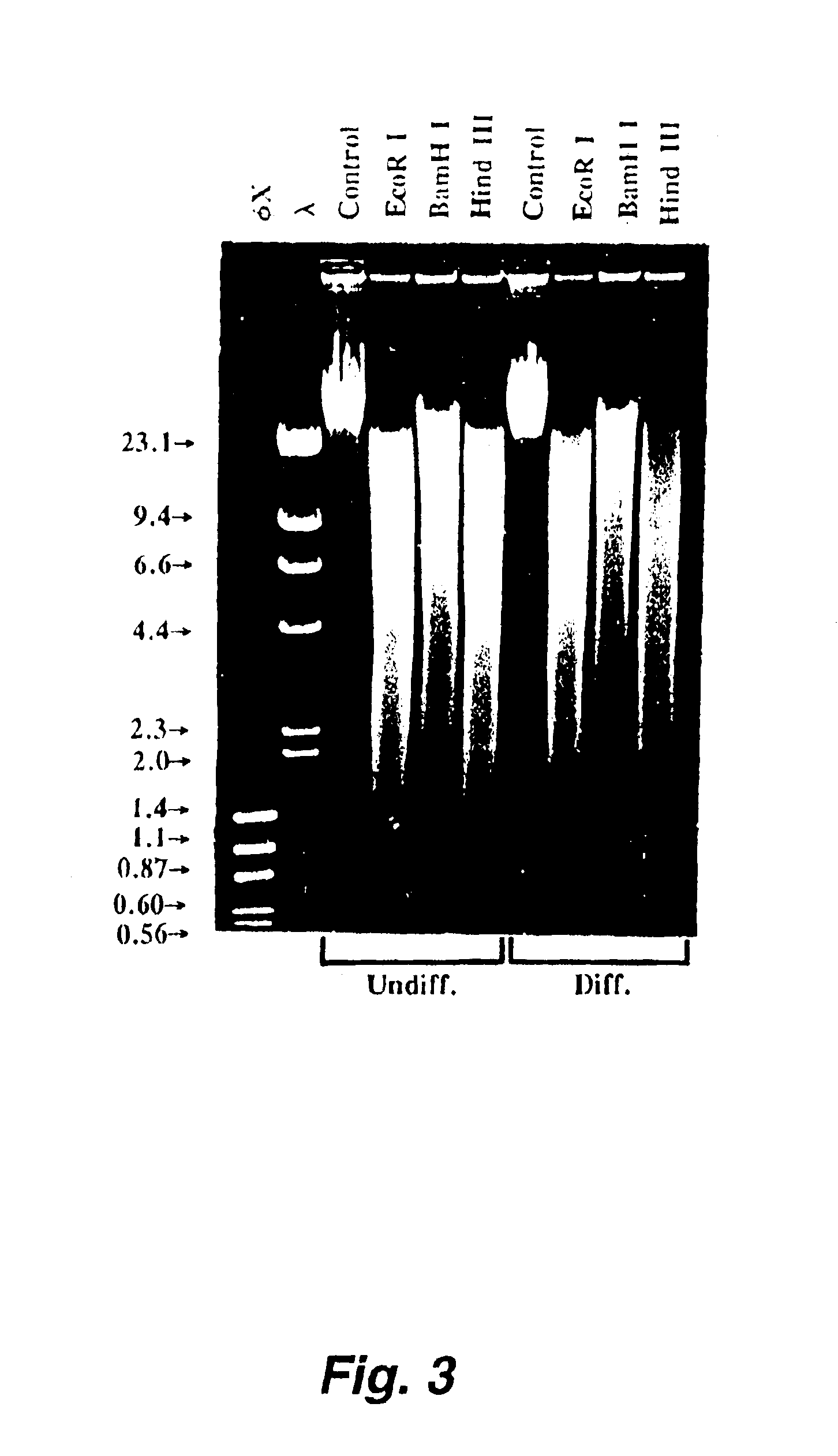
Monolithic electrophoresis flat gel system
InactiveUS8449745B2Minimal handlingMinimal preparationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisElectrical connection
Apparatus, systems and methods for performing gel electrophoresis using a horizontal monolithic electrophoresis unit that at least includes first and second buffer chambers containing buffer solution and a gel chamber containing a pre-cast flat gel, whereby all of these chambers are integrated into a pre-fabricated single unit that is ready for use. In performing gel electrophoresis, a top seal of this monolithic electrophoresis unit is removed, target samples are loaded into the pre-cast gel, interior walls of the unit are broken to allow buffer from anode and cathode chambers to combine within the gel chamber and cover the loaded gel matrix, a reusable lid is attached to the top surface of the unit, and an electrical connection is provided through the reusable lid into the horizontal monolithic electrophoresis unit for performing electrophoresis on the flat pre-cast gel.
Owner:WANG YI
Apparatus and method for the treatment of waste
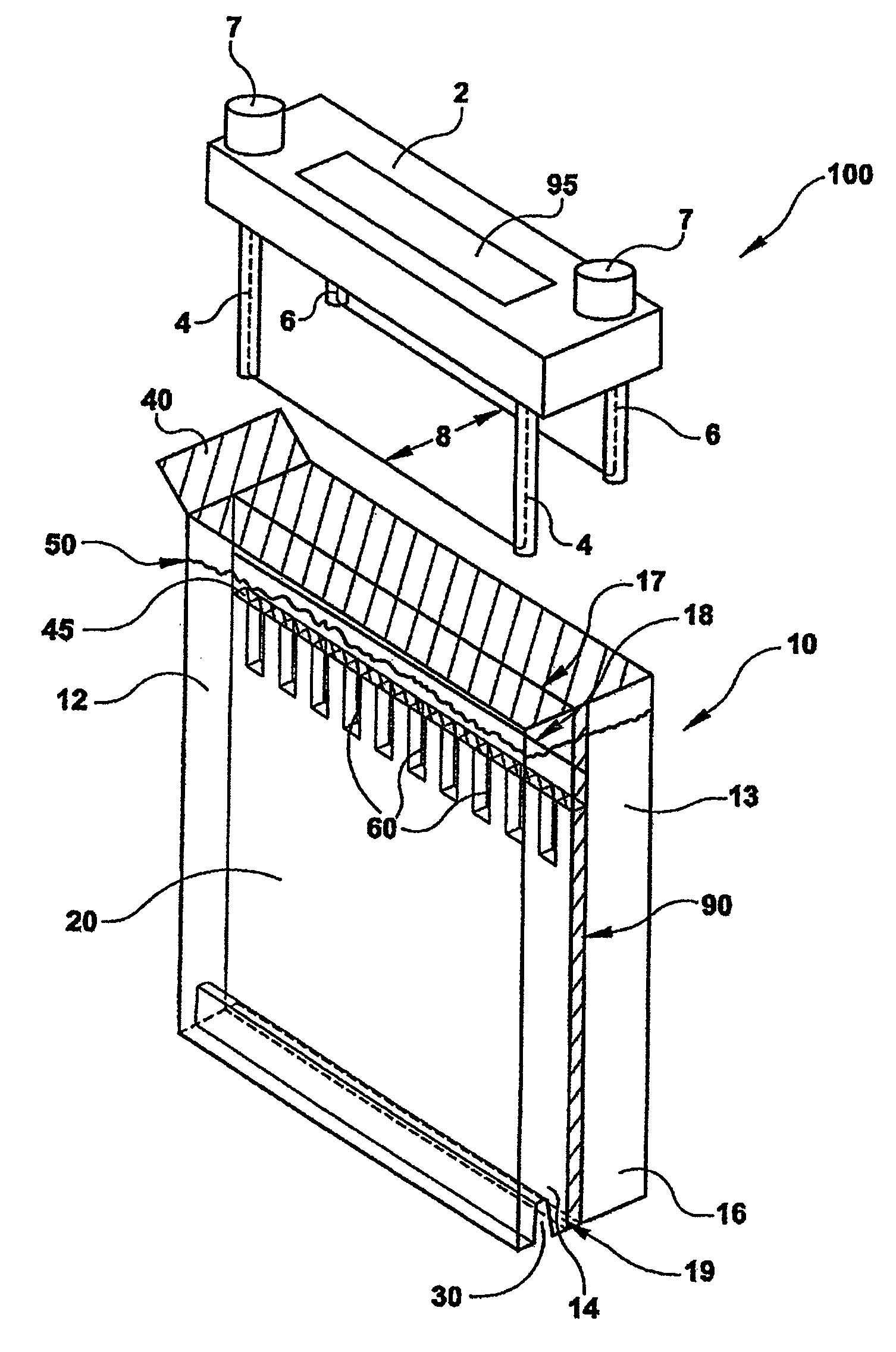
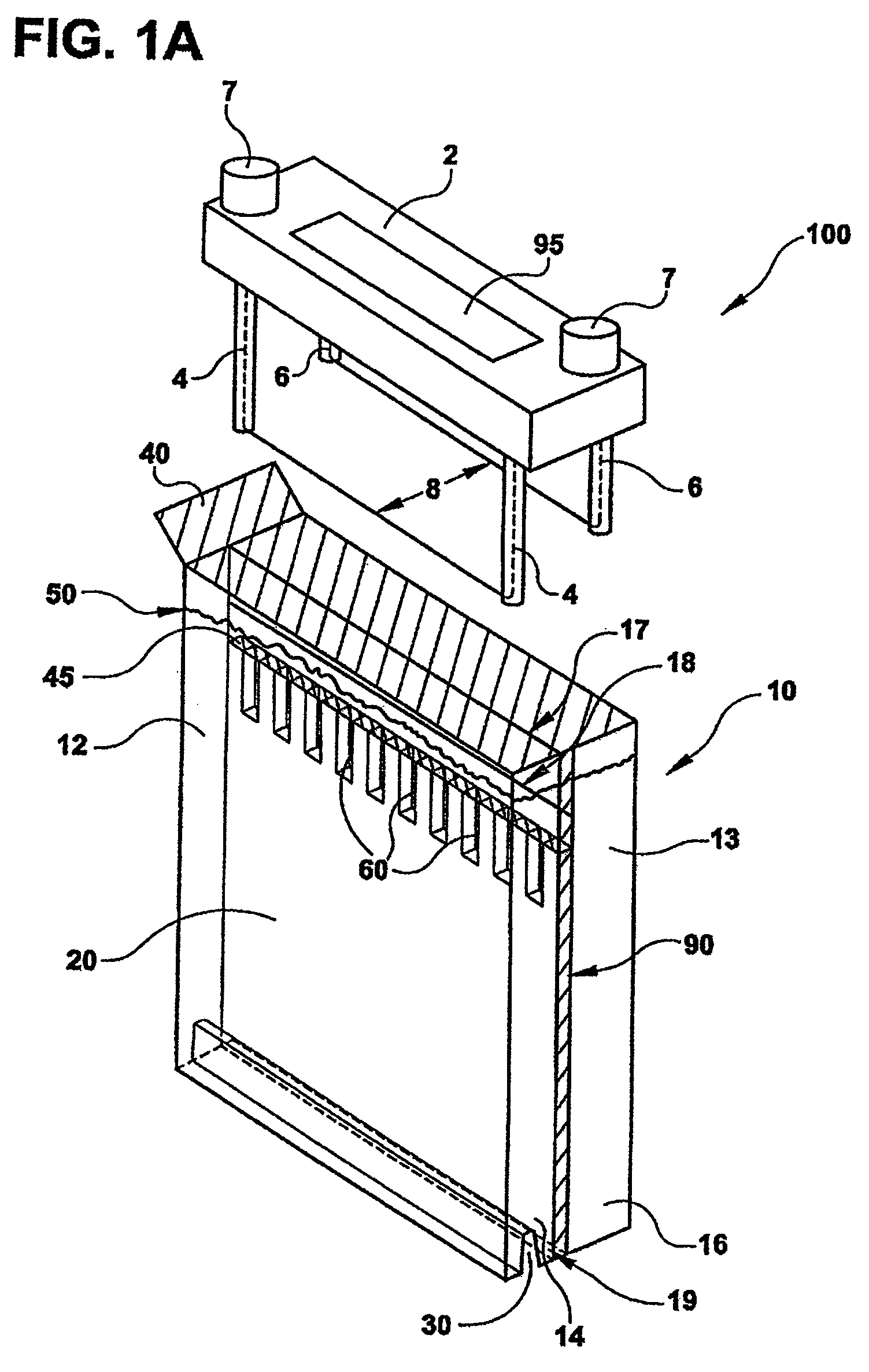
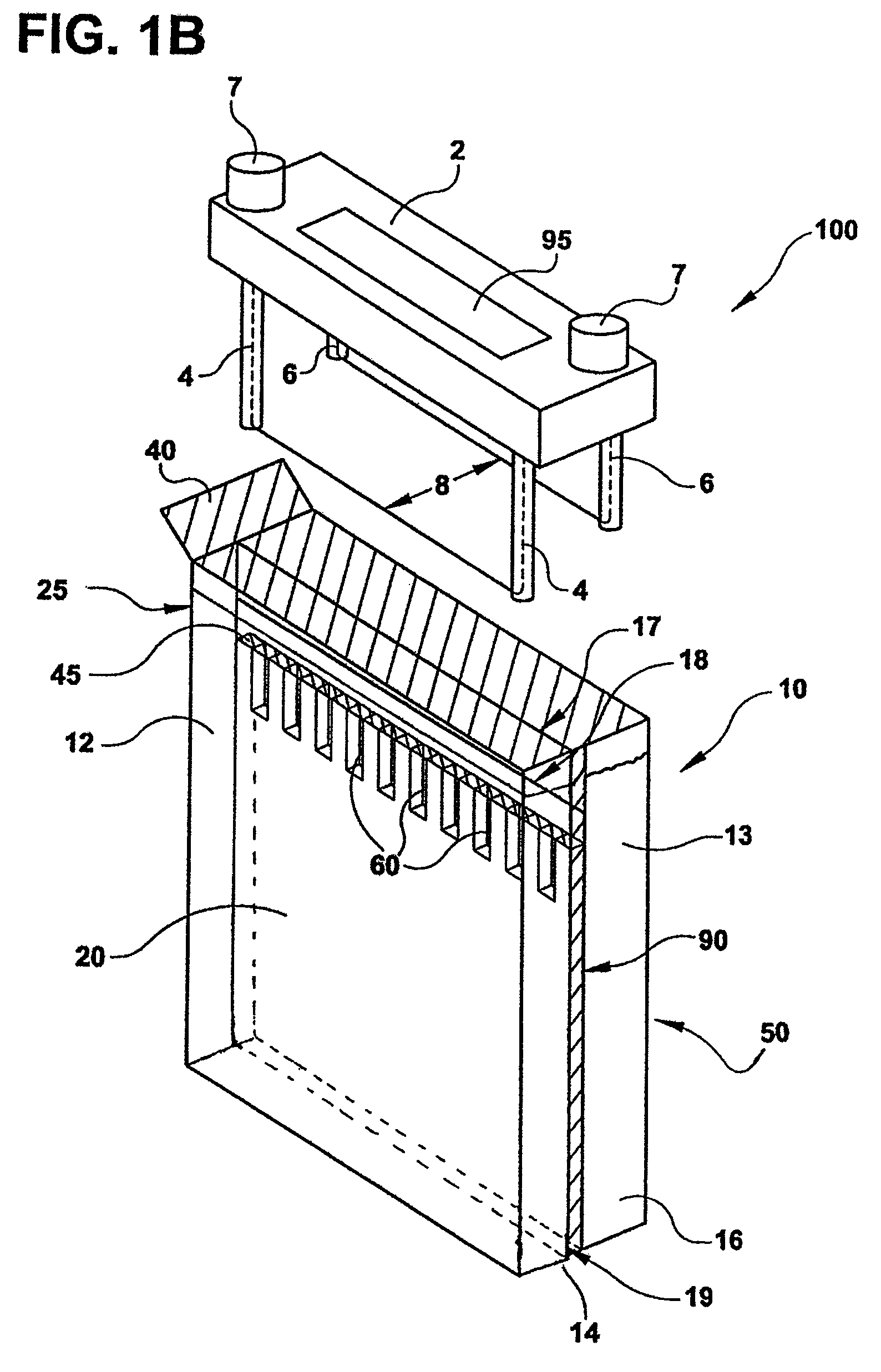
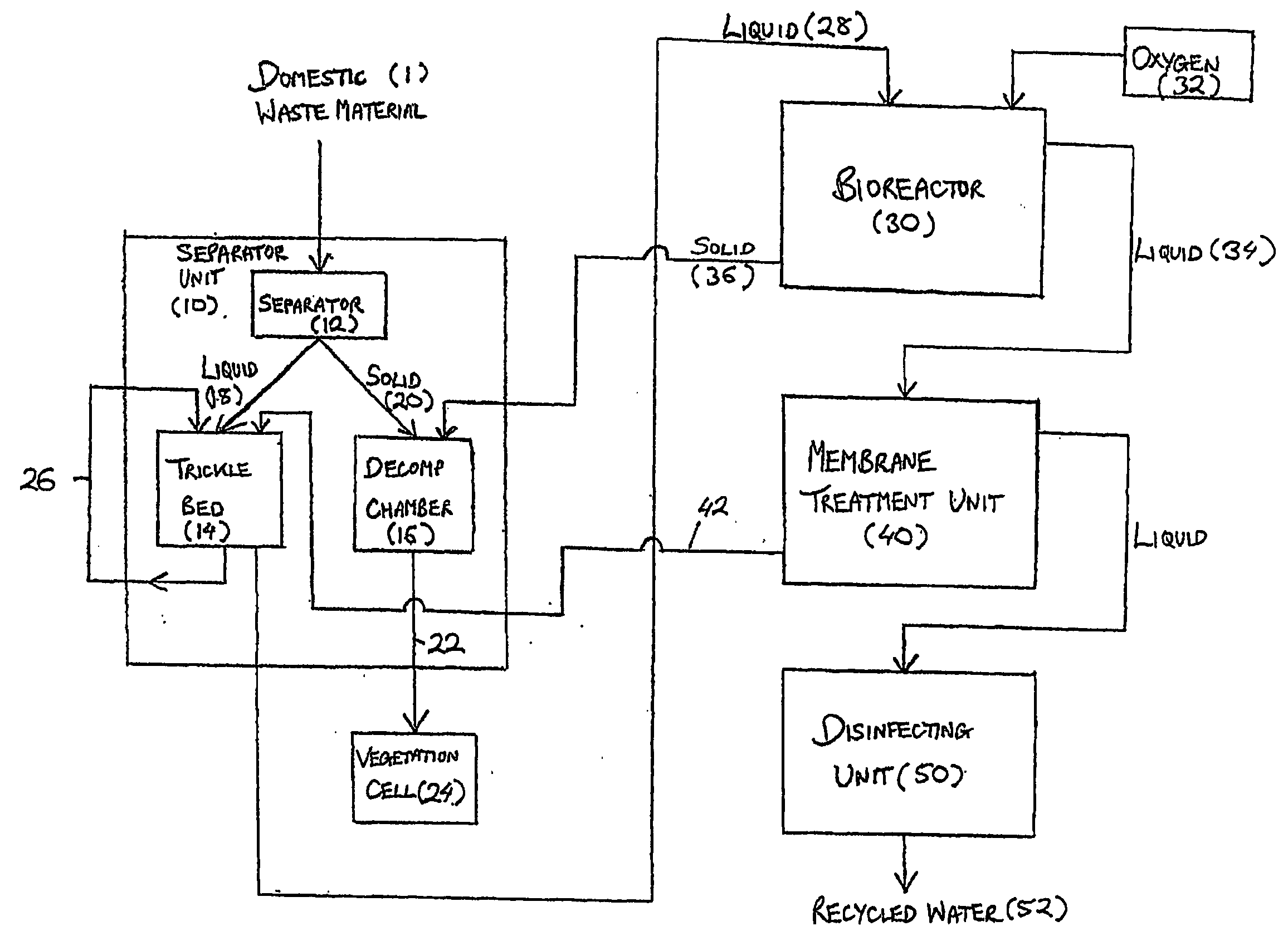
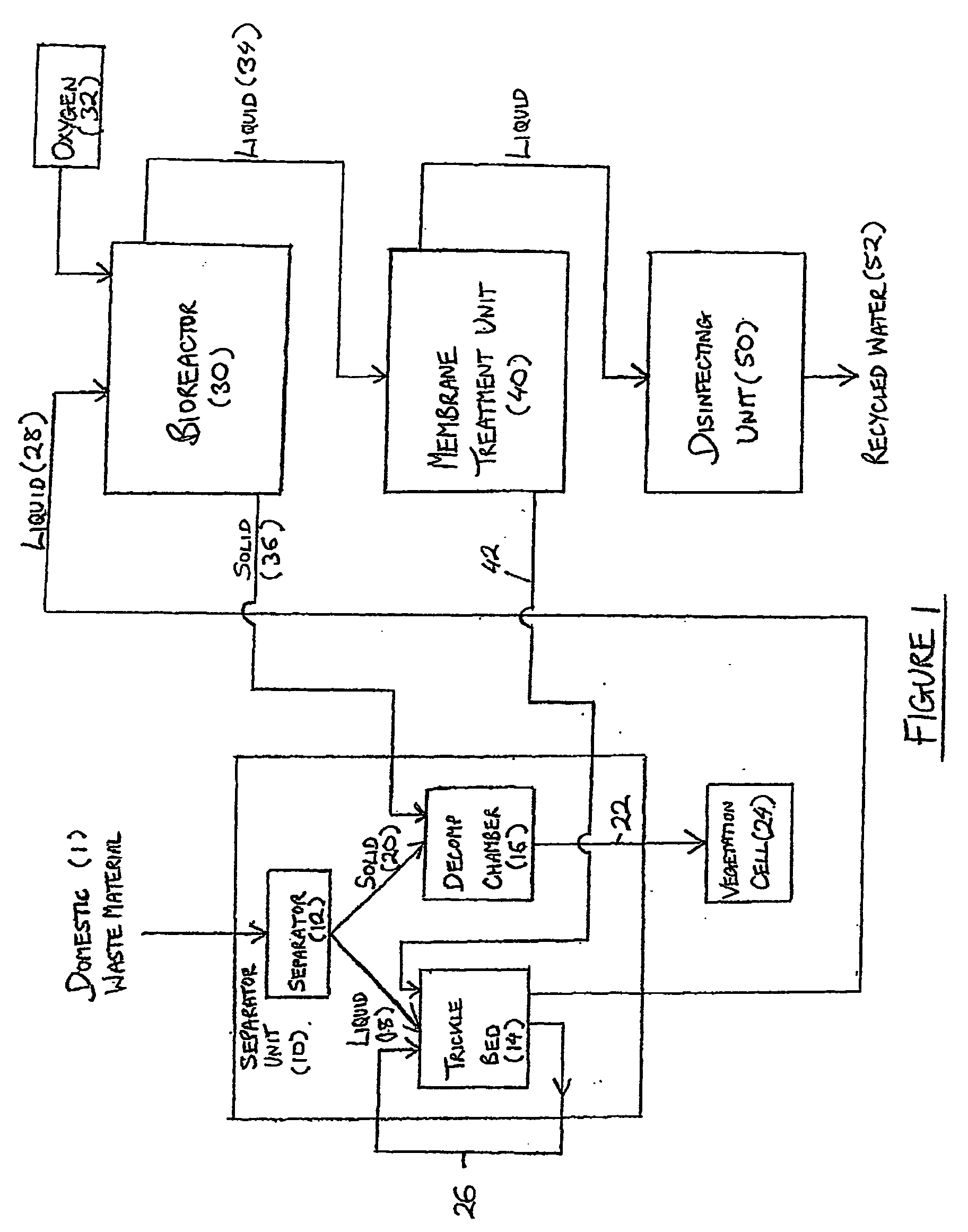
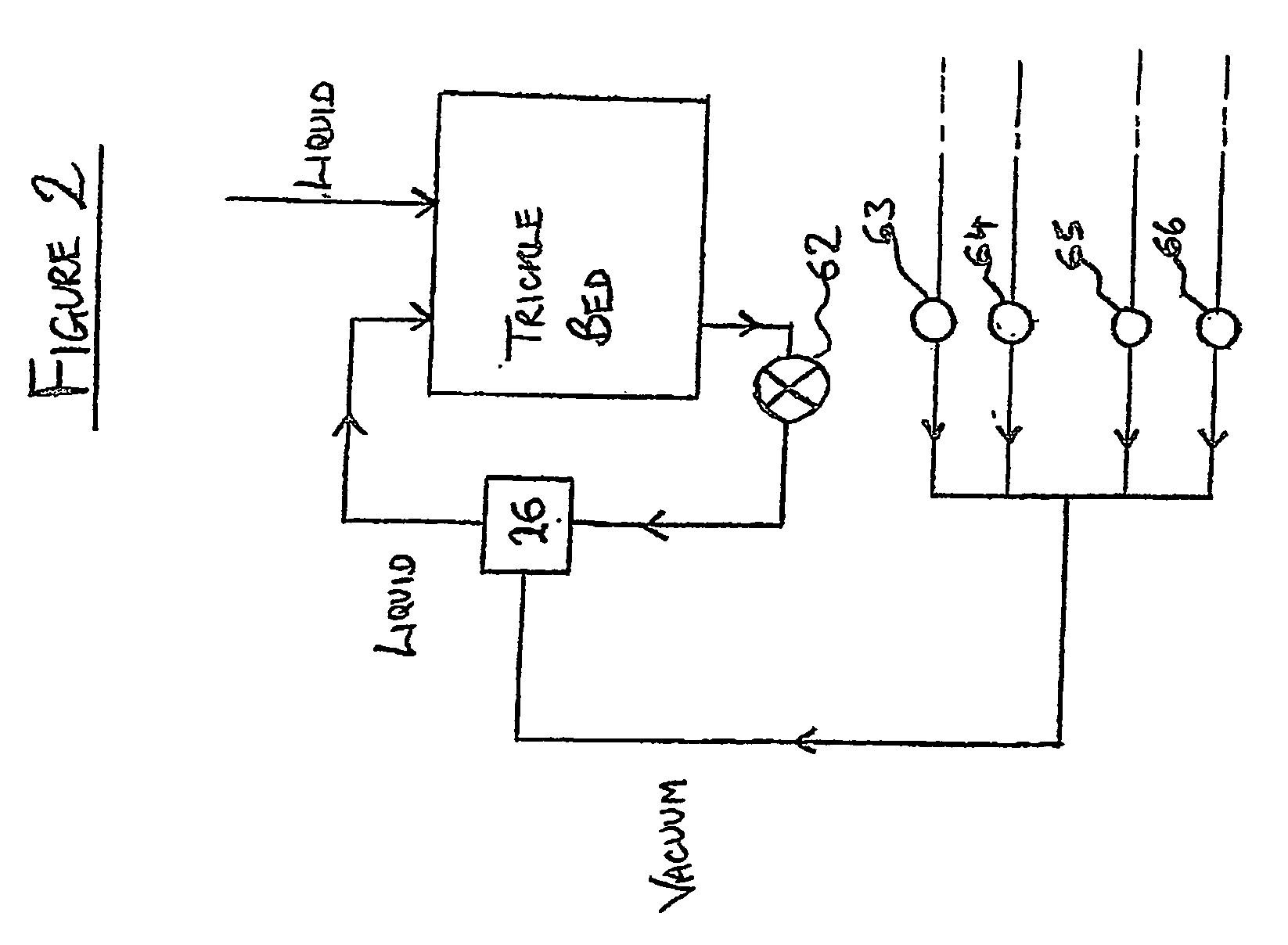
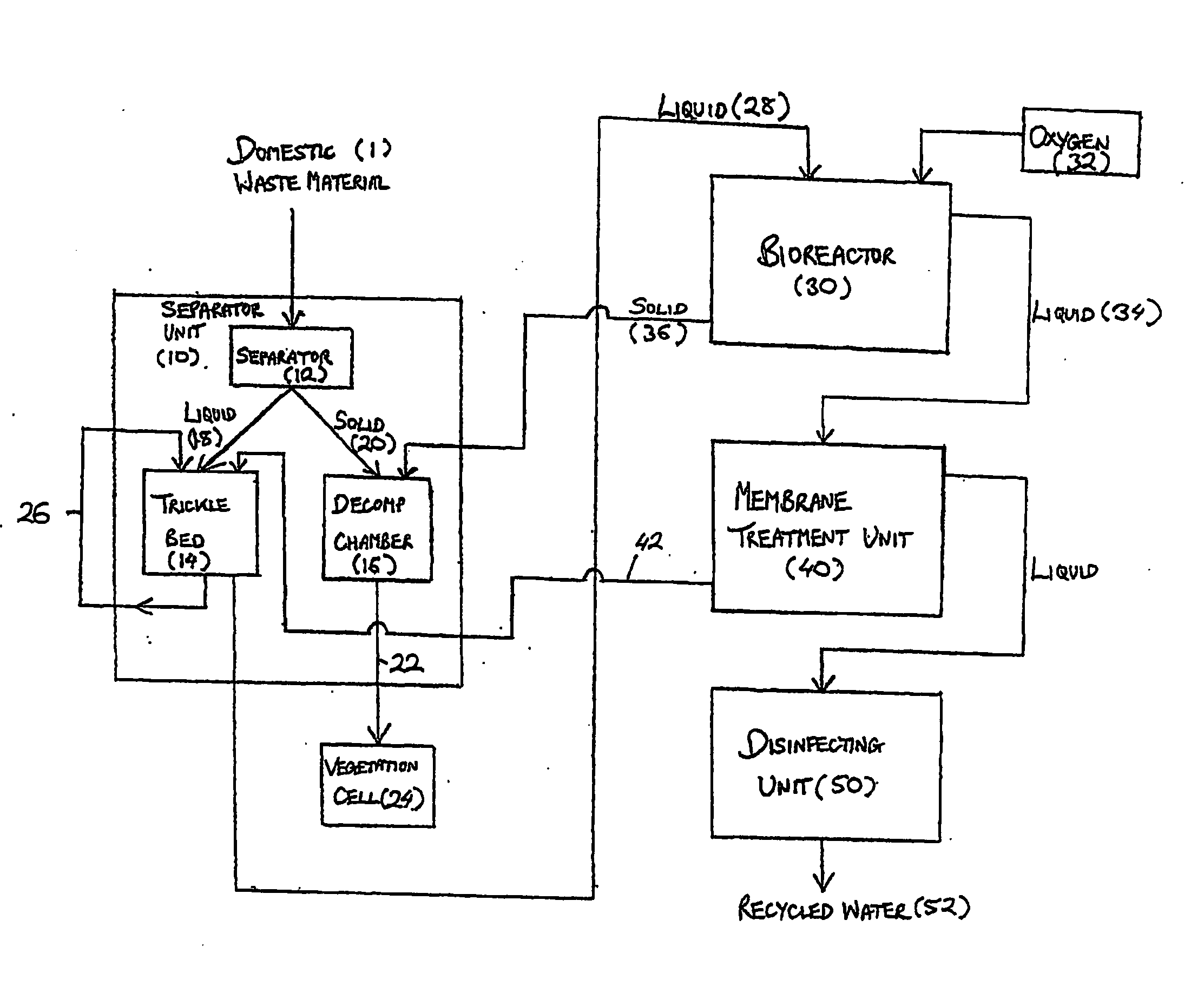
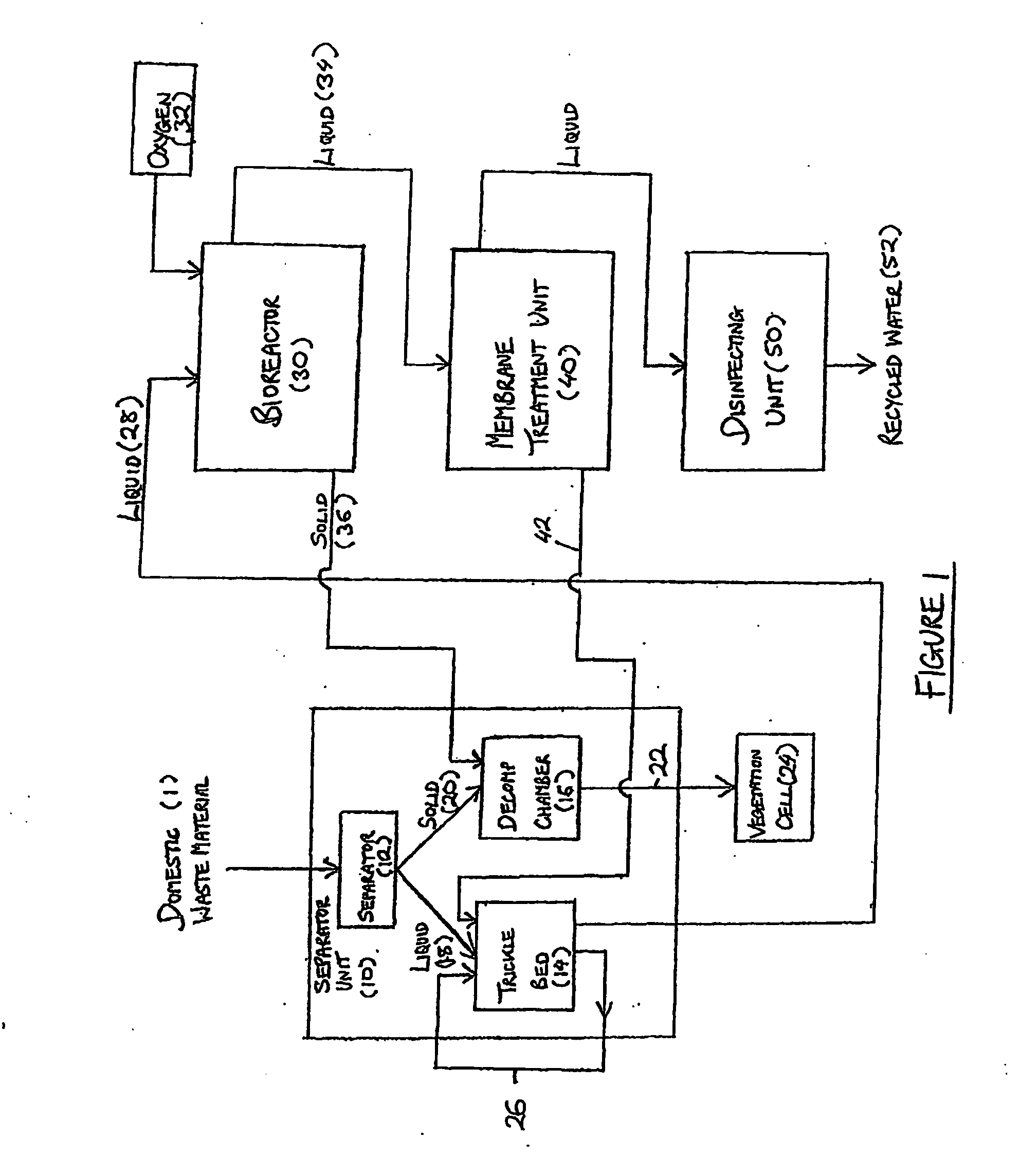
InactiveUS20060108282A1Maximises degree of digestionInhibit transferTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsVegetationDecomposition
A waste treatment system suitable for domestic use and capable of producing water suitable for recycling within the household. The system includes a bioreactor (30) and a decomposition chamber (16). The bioreactor (30) is adapted to digest liquid-base waste material using bacteria and is operable under anaerobic, anoxic and / or aerobic conditions. The decomposition chamber (16) decomposes substantially solid waste generated in the bioreactor. The bioreactor and decomposition chamber are in fluid communication such that substantially solid waste material generated in the bioreactor can be transferred to the decomposition chamber for further treatment. Resulting solids may optionally be forwarded to a vegetation cell (24) and the liquid (34) leaving the bioreactor may be optionally passed to a membrane treatment unit (40) and a disinfection unit (50).
Owner:AQUA CLARUS HLDG
Monolithic electrophoresis gel system
InactiveUS8361294B2Minimal handlingMinimal preparationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisElectrical connection
Apparatus, systems and methods for performing gel electrophoresis using a monolithic electrophoresis unit that at least includes first and second chambers containing one or more buffer solutions and a gel chamber containing a pre-cast gel, whereby all of these chambers are integrated into a pre-fabricated single unit that is ready for use. In performing gel electrophoresis, a top seal of this monolithic electrophoresis unit is removed, followed by optionally removing a gel chamber seal from over the gel chamber, such that, buffer solution contacts the pre-cast gel within the gel chamber. Target samples are loaded into the gel chamber for contact with the pre-cast gel, a reusable lid is attached to the top surface of the monolithic electrophoresis unit, and an electrical connection is provided through the reusable lid into the monolithic electrophoresis unit for performing electrophoresis on the pre-cast gel.
Owner:WANG YI
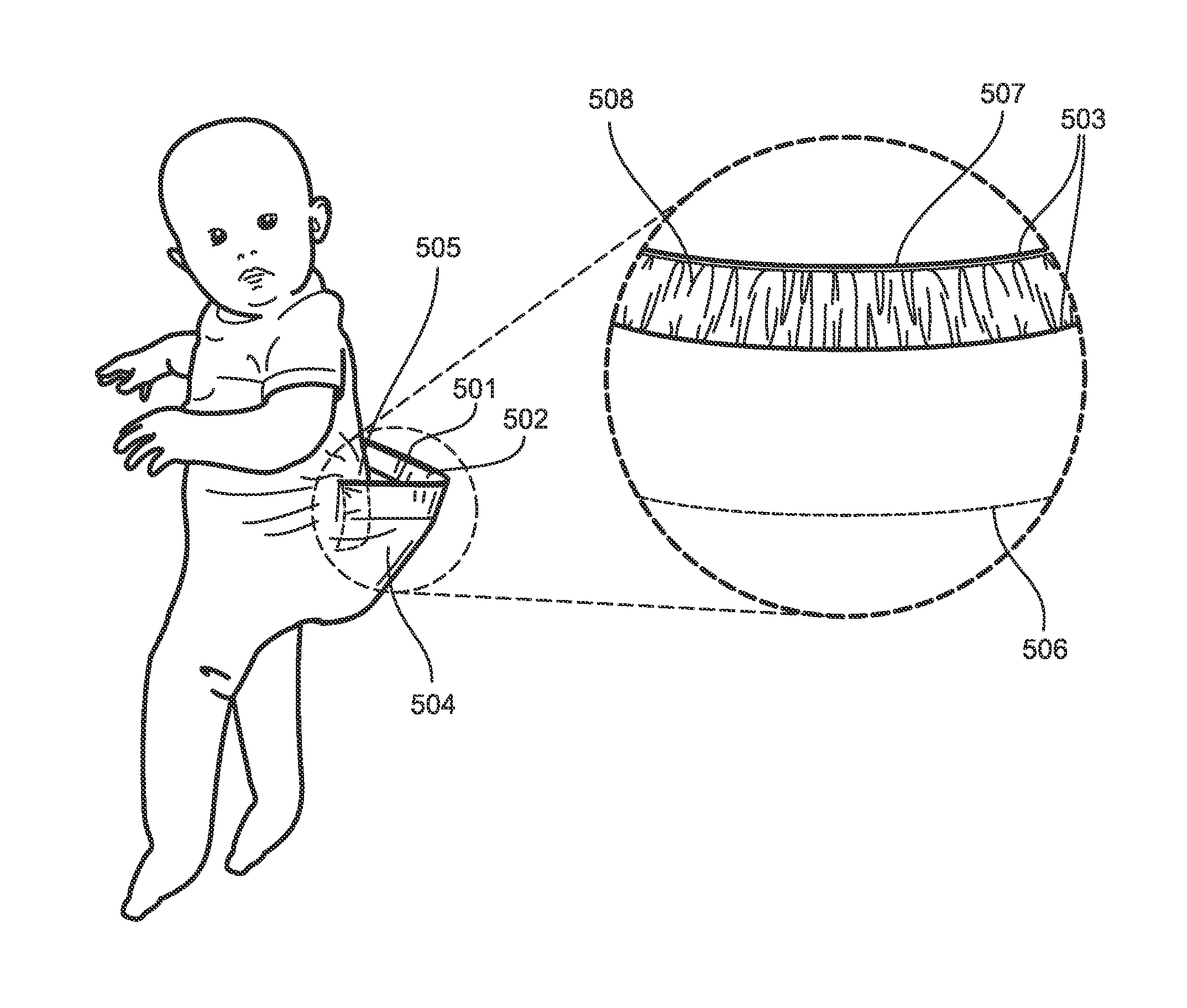
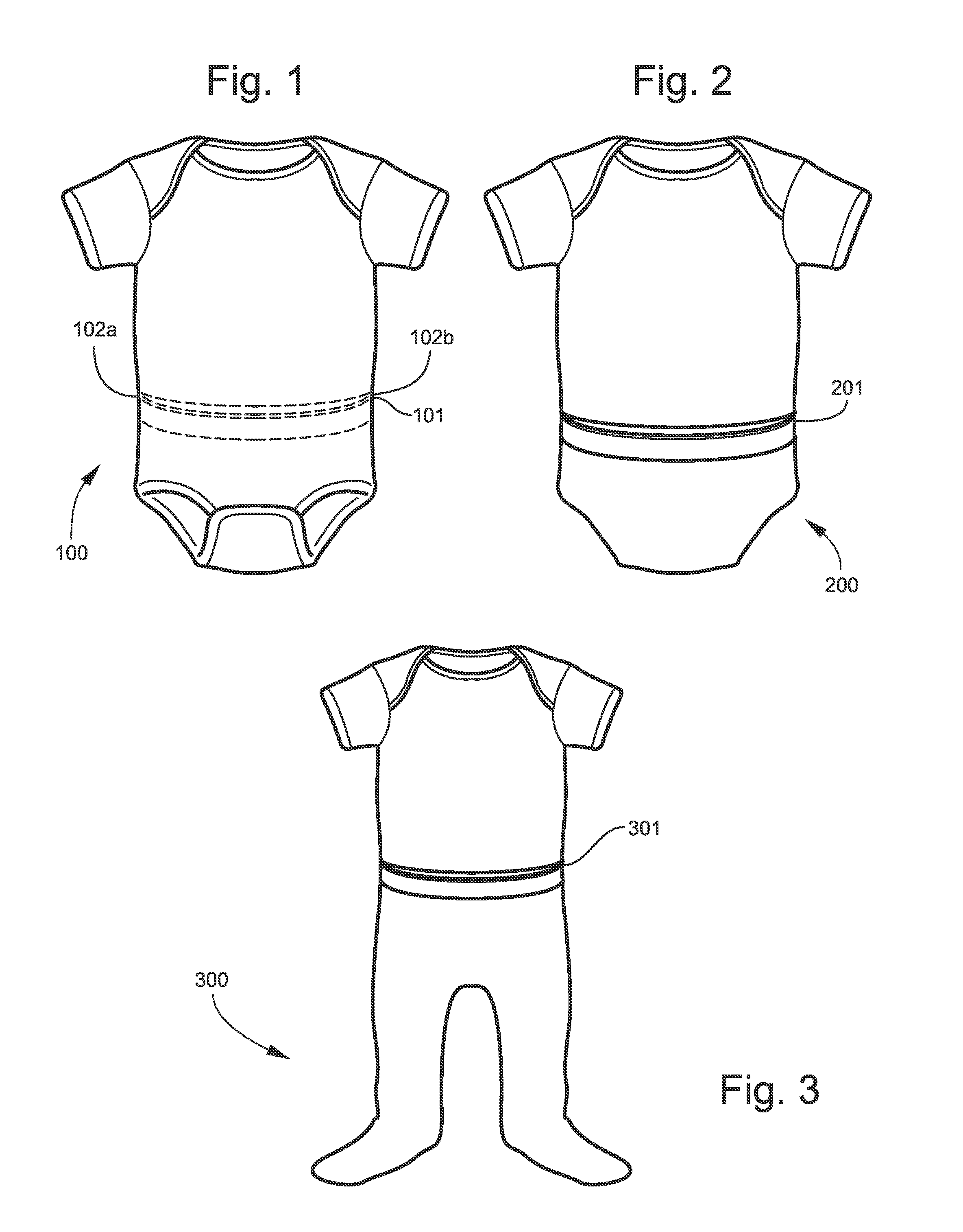
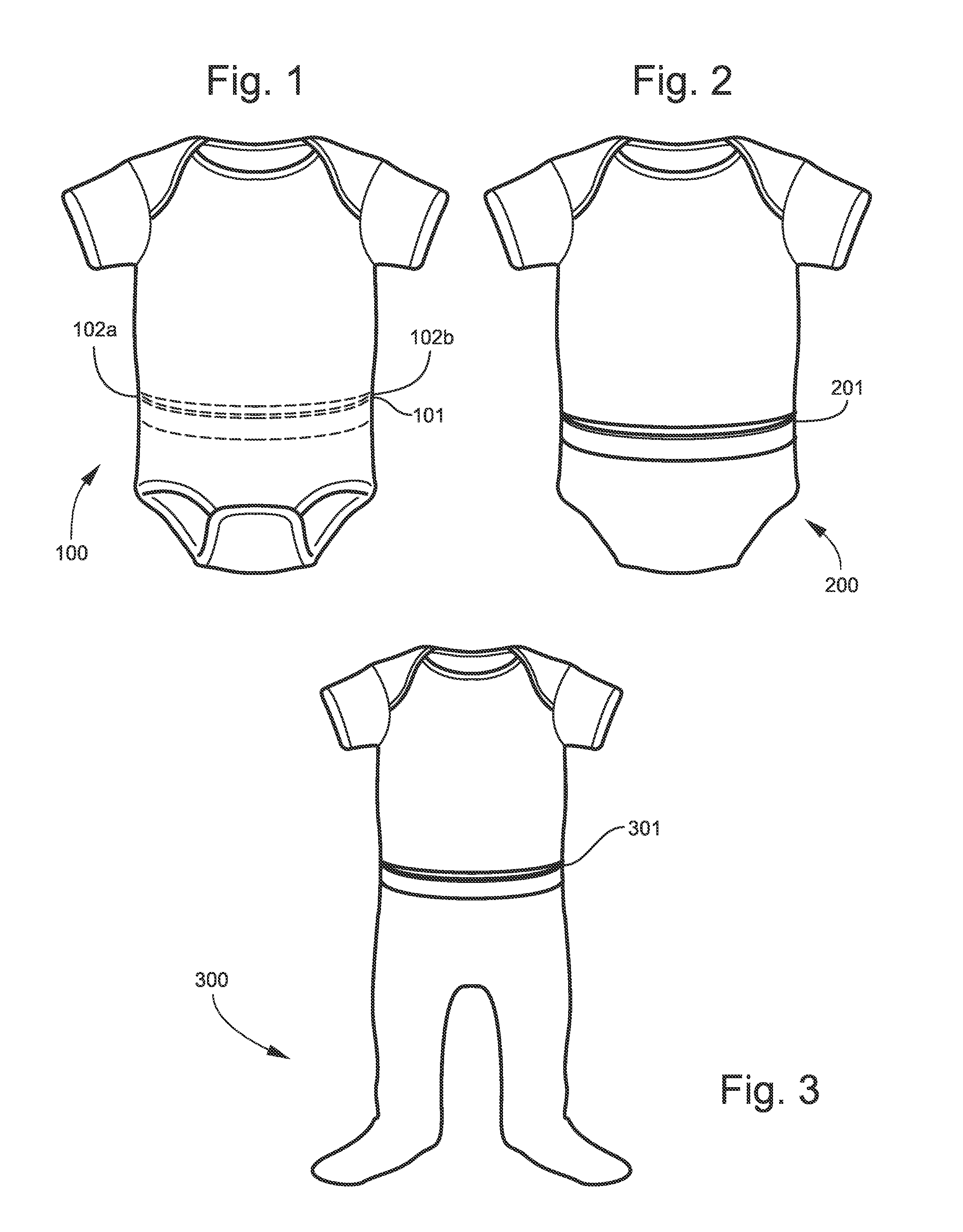
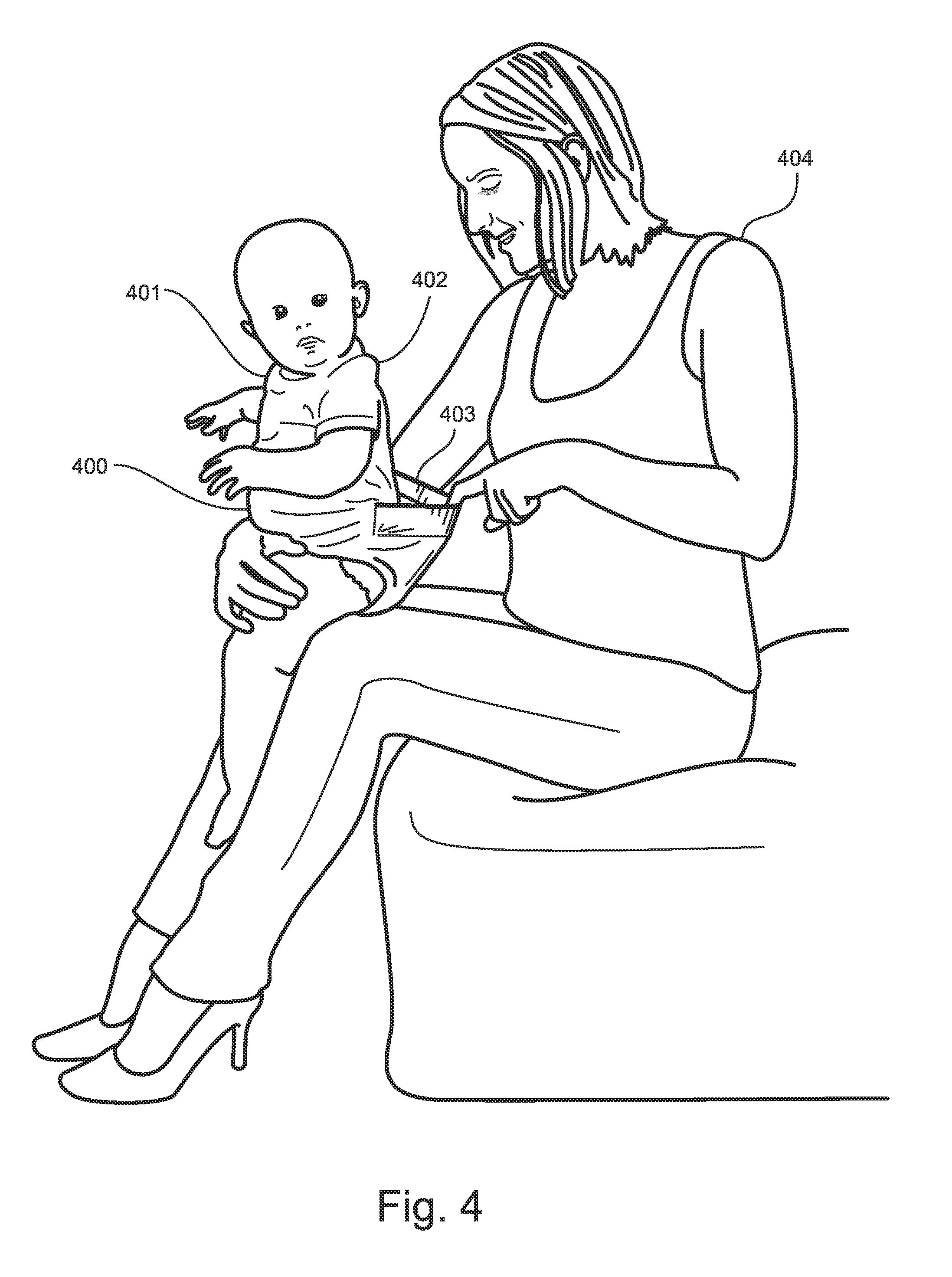
Inspection pocket for baby garment
ActiveUS20140053314A1Quickly and efficiently and cleanly checkA large amountGarmentsBaby linensCare giverComputer science
Owner:MOM MADE PEEKS LLC
Apparatus and method for magnetizing casing string tubulars
InactiveUS7538650B2Accurate distance measurementAccurate placementElectromagnets without armaturesAutomatic controlMagnetization
An apparatus for magnetizing a wellbore tubular includes a plurality of co-axial magnetizing coils deployed on a frame. The coils are typically deployed about a track on which the tubular may be traversed. Exemplary embodiments may further include a magnetic field sensor disposed to measure the imparted magnetic field along the length of the tubular as it is removed from the track after magnetization. Exemplary embodiments of this invention provide for semi-automated control of tubular magnetization and thereby enable a repeatable magnetic pattern to be imparted to each of a large number of wellbore tubulars.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Apparatus and method for the treatment of waste
InactiveUS20060254978A1Reduce usageMinimize handlingTreatment using aerobic processesSpecific water treatment objectivesVegetationDecomposition
A waste treatment system suitable for domestic use and capable of producing water suitable for recycling within the household. The system includes a bioreactor (30) and a decomposition chamber (16). The bioreactor (30) is adapted to digest liquid-base waste material using bacteria and is operable under anaerobic, anoxic and / or aerobic conditions. The decomposition chamber (16) decomposes substantially solid waste generated in the bioreactor. The bioreactor and decomposition chamber are in fluid communication such that substantially solid waste material generated in the bioreactor can be transferred to the decomposition chamber for further treatment. Resulting solids may optionally be forwarded to a vegetation cell (24) and the liquid (34) leaving the bioreactor may be optionally passed to a membrane treatment unit (40) and a disinfection unit (50).
Owner:AQUA CLARUS HLDG
Apparatus and method for generating moisture standards in gases
An apparatus and method for generating moisture standards in gases are disclosed. In particular, the invention relates to an apparatus for introducing a preselected amount of water vapor or other vaporized liquid into a flowing gas stream at a constant rate, which comprises a suitable syringe having a needle attached thereto; an evaporator attached to said needle, wherein the evaporator is located in the flowing gas stream; and a means for applying pressure to the syringe, such that water or other liquid may be delivered at a constant rate from the syringe through the needle into the evaporator. The invention also relates to a method for introducing a preselected amount of water vapor or other vaporized liquid into a flowing gas stream at a constant rate, which comprises providing a syringe having a needle attached thereto, wherein the syringe contains the water or other liquid to be vaporized; applying pressure to the syringe, such that water or other liquid is transferred at a constant rate from the syringe through the needle into an evaporator, said evaporator being attached to one end of the needle, and situated in the flowing gas stream; and allowing the water or other liquid to evaporate from the evaporator into the flowing gas stream. The apparatus and method of the invention are useful for the generation of low levels of moisture, and are especially useful where quick and reliable changes of moisture level in the gas is desired. Thus, the apparatus and method are useful in the generation of primary moisture standards for use in the calibration of moisture analyzing instruments, such as FTIR spectrometers.
Owner:MATHESON TRI GAS
Suspension device and seasoning
InactiveUS20140120215A1High strengthEasy to useMilk preservationConfectioneryBiomedical engineeringFood products
The present invention relates to a food and a suspension device (10), the food product being covered with a seasoning, the suspension device (10) configured be attached to a location in an oven.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Apparatus and method for magnetizing casing string tubulars
InactiveUS20080012672A1Accurate well placementImprove quality controlElectromagnets without armaturesAutomatic controlMagnetization
An apparatus for magnetizing a wellbore tubular includes a plurality of co-axial magnetizing coils deployed on a frame. The coils are typically deployed about a track on which the tubular may be traversed. Exemplary embodiments may further include a magnetic field sensor disposed to measure the imparted magnetic field along the length of the tubular as it is removed from the track after magnetization. Exemplary embodiments of this invention provide for semi-automated control of tubular magnetization and thereby enable a repeatable magnetic pattern to be imparted to each of a large number of wellbore tubulars.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
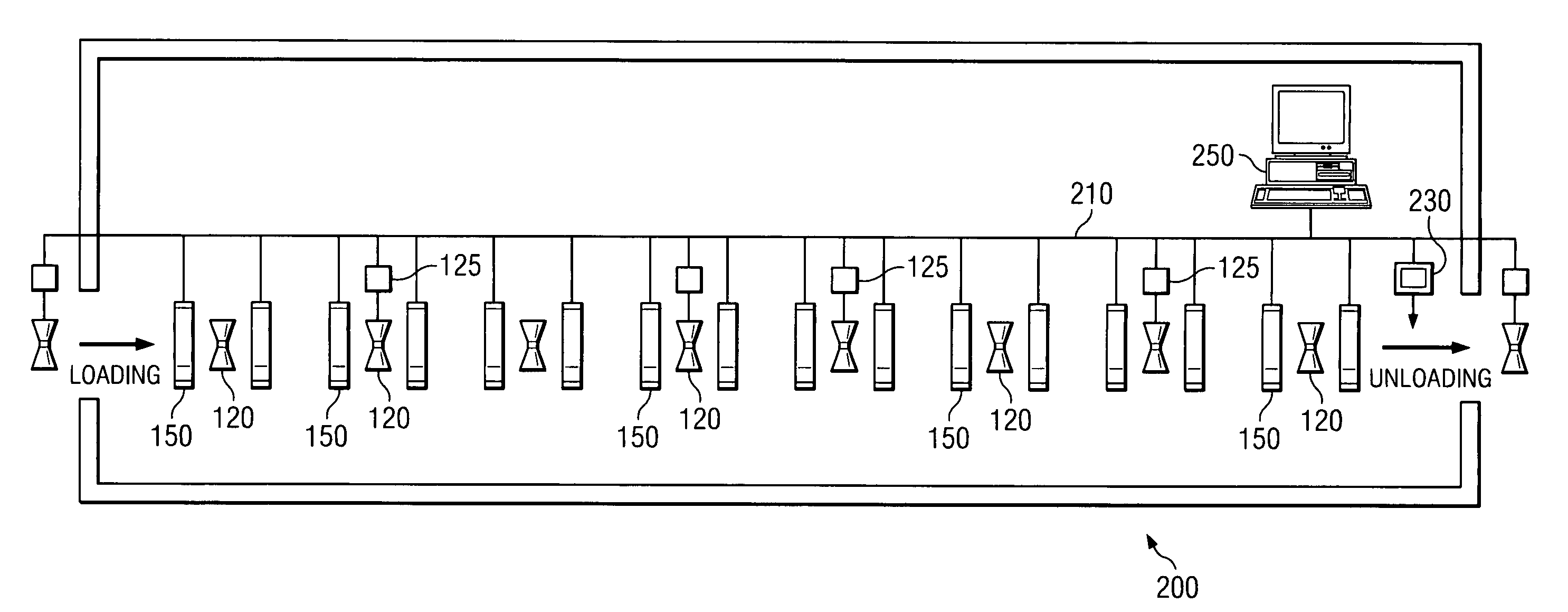
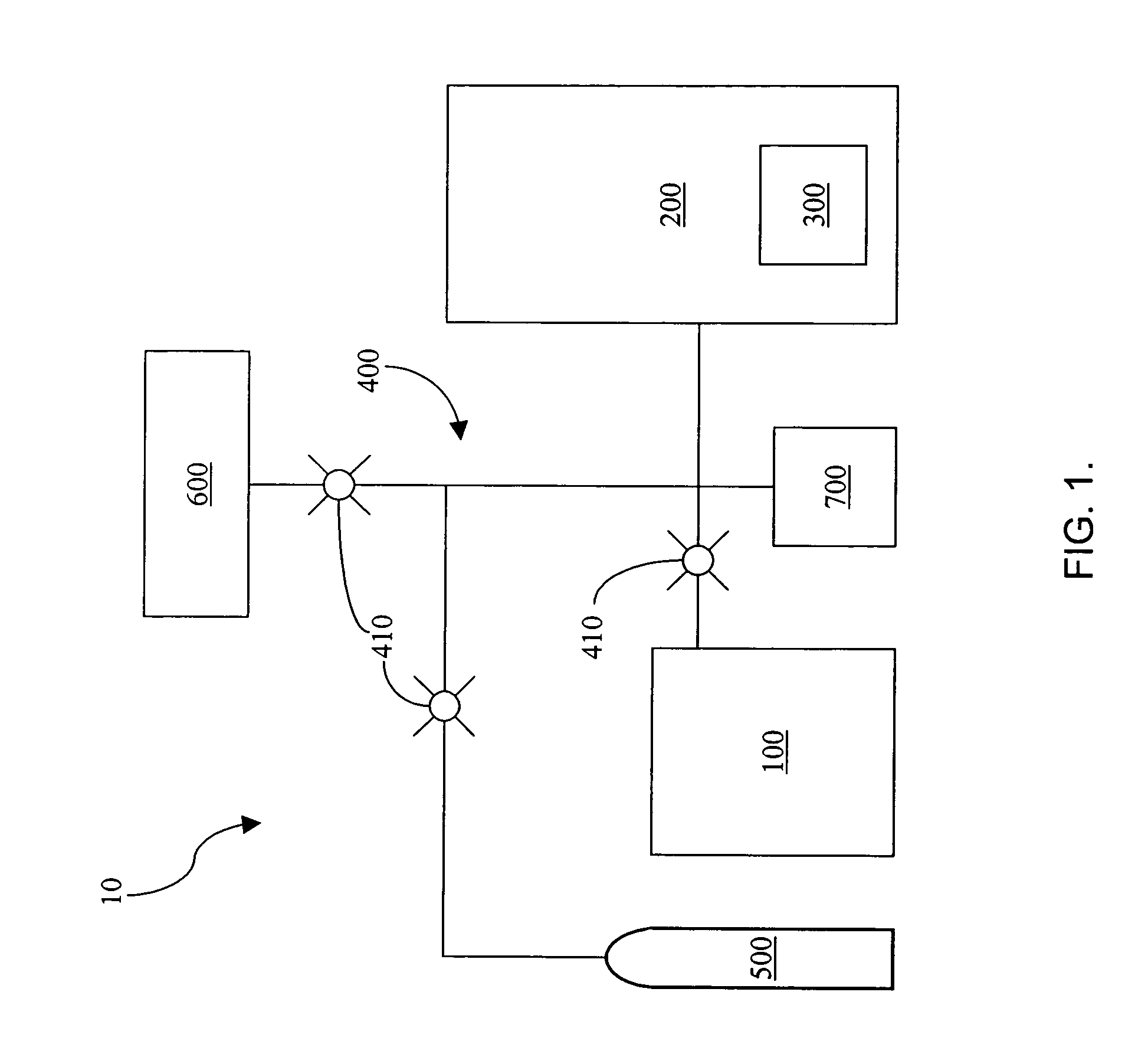
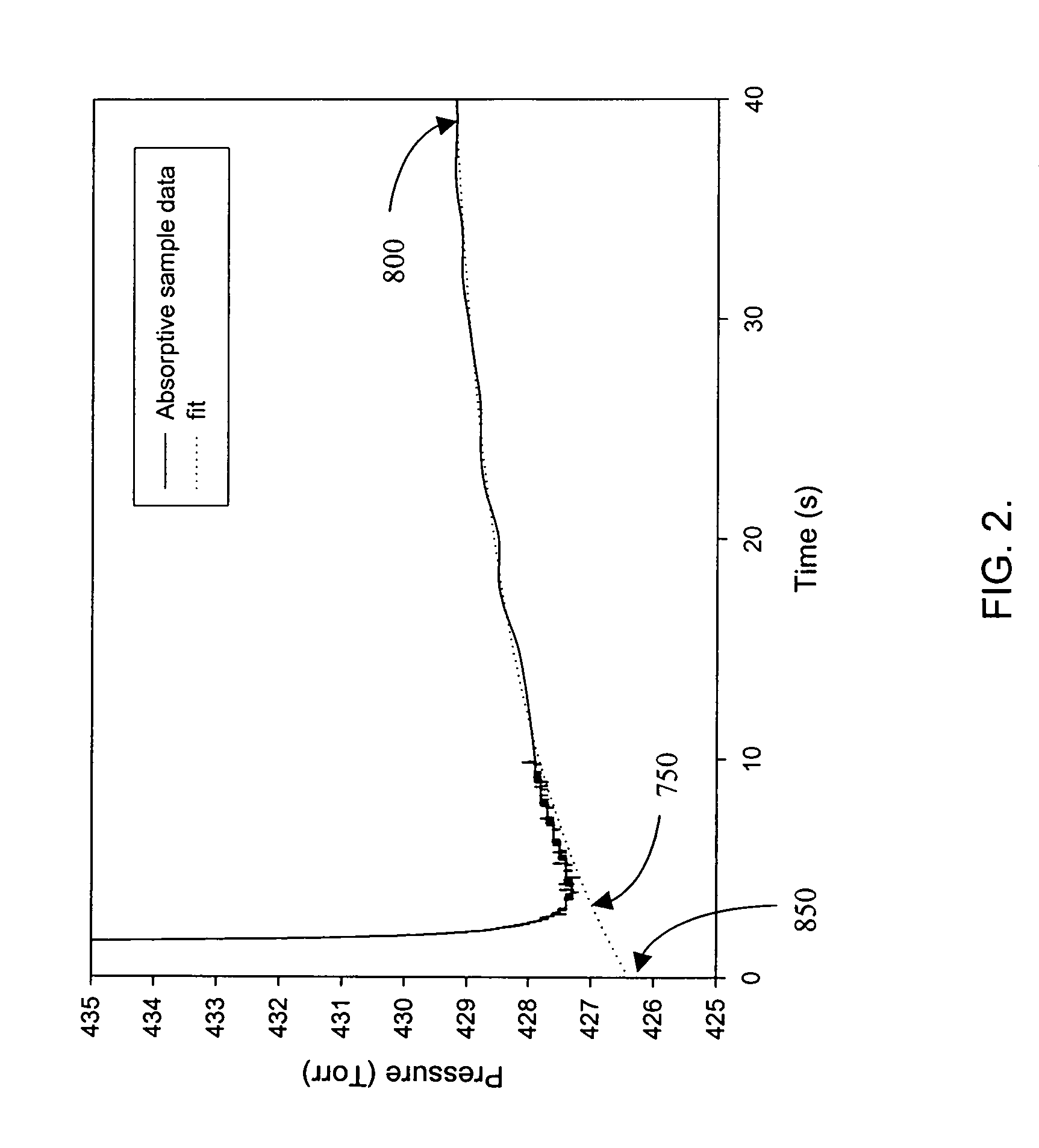
System and method for determining material properties of samples
ActiveUS6990848B2High precisionShorten the timeInflated body pressure measurementSpecific gravity by measuring pressure differencesNon destructiveAbsolute density
A method is provided for nondestructively determining a material property of a porous sample. A first vessel is evacuated to a sub-atmospheric pressure, while a test pressure, greater than the sub-atmospheric pressure, is established in a second vessel containing the sample. The pressures of the first and second vessels are equalized by opening a valve mechanism therebetween. The resulting pressure change in the second vessel exhibits an initial pressure drop followed by a transition to an equalization pressure. The envelope volume of the sample is determined from a minimum pressure attained by the second vessel upon initial opening of the valve mechanism, wherein the minimum pressure is related to the initial pressure drop. The envelope density of the sample is thus a quotient of the mass and the envelope volume of the sample. The absolute density and relative absorption of the sample may also be determined and an associated system is provided.
Owner:TROXLER ELECTRONICS LAB INC
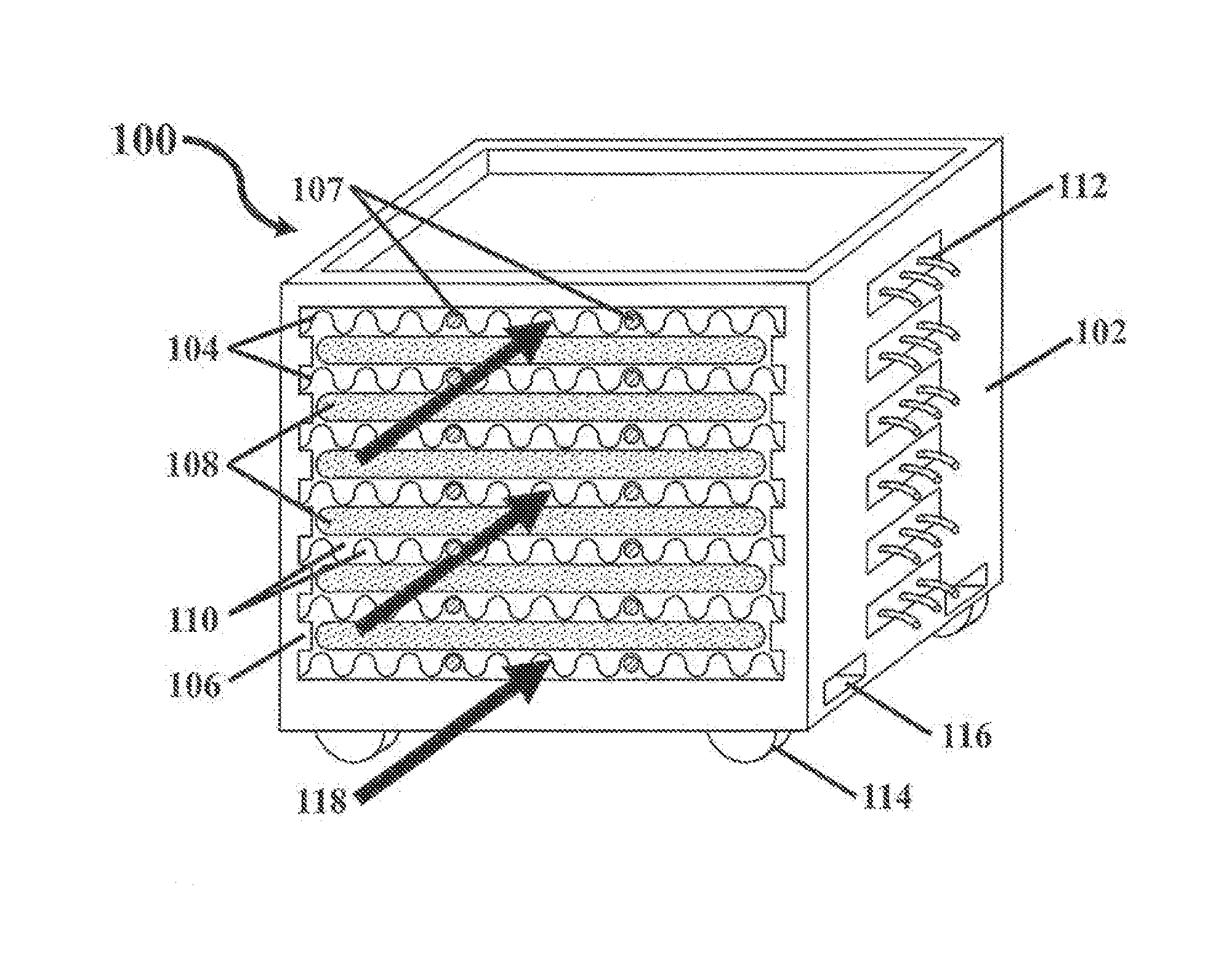
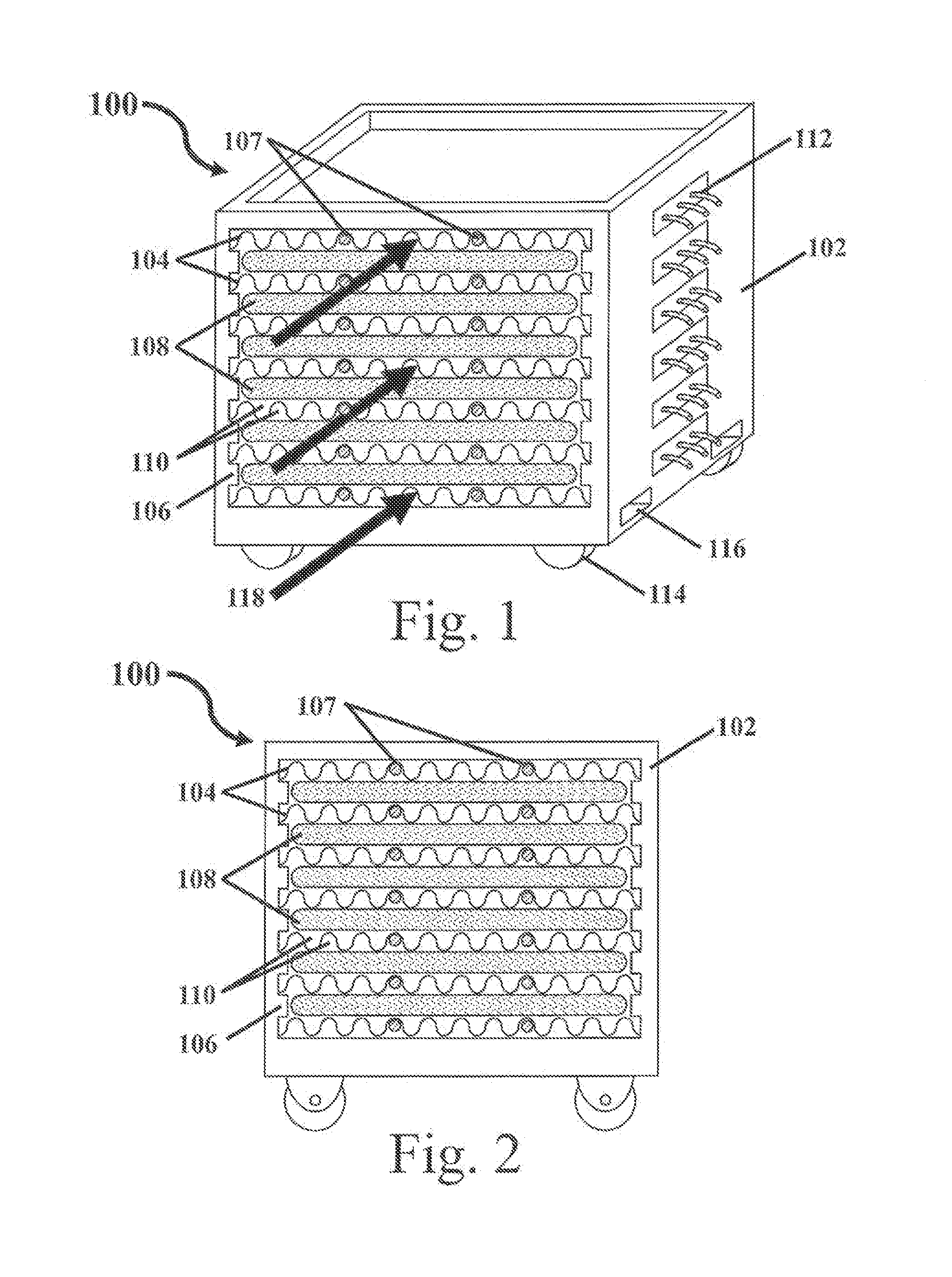
Bulk freezing of biopharmaceuticals
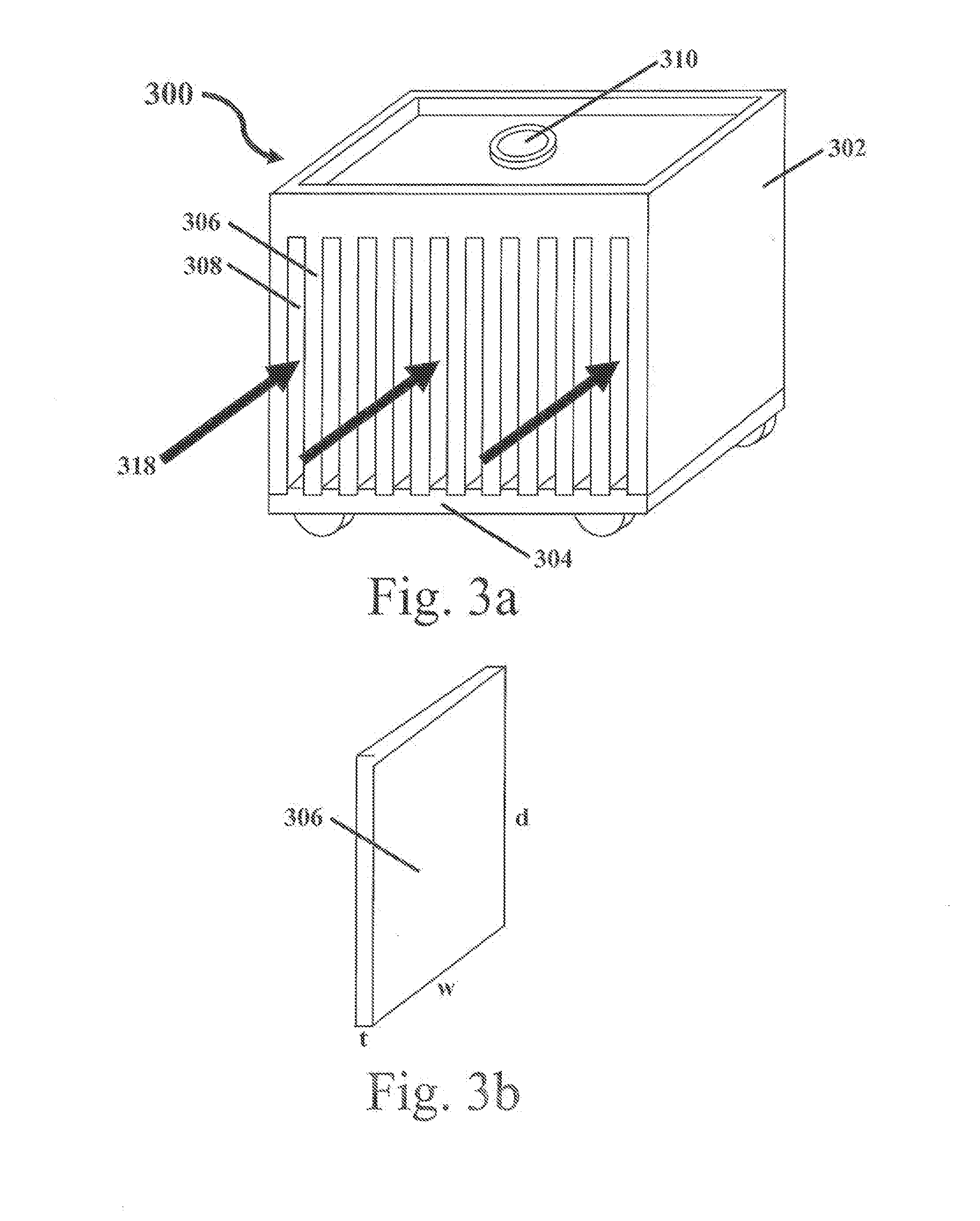
InactiveUS20140047851A1Improve uniformityEasy to controlIce productionFood preservationBiopharmaceuticalEngineering
A system and method for bulk freezing is provided. In one embodiment, the system and method for bulk freezing includes a bulk freezing container adapted to hold at least one and preferably a plurality of bags holding a biopharmaceutical liquid. The bulk freezing container includes at least a first and second shelf having corrugations wherein the second shelf is vertically arranged above the first shelf with the bags disposed between the shelves. The bags and the corrugations of the first and second shelves define a plurality of substantially parallel flow channels through which a cryogenic cold fluid or a warming fluid is passed to freeze and / or thaw the biopharmaceutical fluid. In another embodiment, the bulk freezing system and method includes a bulk freezing container with a plurality of adjacent elongated chambers adapted for holding the biopharmaceutical fluid. The adjacent elongated chambers have side walls defining a plurality of substantially parallel flow channels between the plurality of adjacent elongated chambers through which a heat transfer medium is passed for heat exchange through the side walls of the elongated chambers to the fluid within the elongated chambers.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Retaining ring removal tool
InactiveUS20090000096A1Minimal handlingSimple but effectiveMetal-working hand toolsEngineeringRetaining ring
A tool for removal of a rod from an opening in a ring clip or for insertion of the rod through the opening into the ring clip. The tool comprises a body having an upper surface, a ring clip receiving depression in that surface and an aperture in that surface extending below the depression and to one side thereof. The aperture is of a size to receive at least a portion of the rod to which is, or is to be, attached while the ring clip is seated within the depression. The depression has a base and walls which are configured so as to seat a ring clip therein to restrain it against relative movement in a direction towards the opening of the ring clip when the rod is moved in that direction for removal from the ring clip through the opening, and to restrain it against relative movement in an opposite direction when the rod is moved in that opposite direction to be inserted into the ring clip through the opening.
Owner:BLOK STEPHEN
Projector for defeating buried mines
An relatively small anti-personnel mine device having a housing about 2 to about 3 inches in diameter, by about 2 to about 4 inches in length, which device projects a dispersion pattern of ⅛ to ⅜ inch diameter hard fragments over at least a 3 to 4 inch radius circle to neutralize a typical, buried, anti-personnel mine. The device contains about 125 to 190 grams of plastic explosive, which when detonated impacts a gas push plate against which an array of the fragments are lodged—the gas push plate and the fragments being encased in a puck shaped matrix of plastic or resin. The effect of the device is such that in addition to neutralizing the mine, the overburden atop the buried mine is expelled exposing the mine, providing enhanced safety in removal and a warning if the mine is daisy-chained to other mines.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Device For the Growth of Macromolecular Crystals and Drug Screening
InactiveUS20090129983A1Improve efficiencyMinimal handlingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsInterior spaceCapillary Tubing
The invention is a device for counter-diffusion applications comprising a removable cartridge having a plurality of capillary tubes that may be disposed between first and second members. The first member may be moveable into at least a first and second position. The second member may be moveable into a sealing position wherein the distal ends of the capillary tubes contact a sealant material. In the first position, the proximal ends of the capillary tubes may contact a macromolecular solution, which may cause the macromolecular solution to diffuse into the interior space of the capillary tube. In the second position, the proximal ends of the capillary tubes may be inserted into a corresponding reservoir well having a precipitating solution. The macromolecular solution and the precipitating solution may then counter diffuse against each other in each capillary tube. The removable cartridge may then be removed and replaced with a new removable cartridge.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Mineral extraction system and process
InactiveUS20090183599A1Lower cost of capitalMinimal handlingFurnace typesProcess efficiency improvementCycloneLower grade
A trench leaching system including a tank containing a charge of ore flooded with a liquid solvent up to the level of a gutter. A pump recirculates the solvent upwardly through the charge of ore via a sparging array for dissolving minerals which are reclaimed through a series of cyclones and stripped out of the pregnant solvent by a carbon column. The rate and pressure of the solvent flowing through the sparging array upwardly though the of ore are kept below the amount that would fluidise the ore and at an amount that produces channels which follow random paths that vary with time through the ore, wherein particles of ore in the channels are agitated by the solvent and wherein particles of ore outside the channels are maintained substantially static and in contact with the liquid solvent. Such a system can process low grade ore at low operating and capital costs.
Owner:DEVERE MINING TECH
Monolithic electrophoresis gel system
InactiveUS20100326830A1Minimal handlingMinimal preparationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical connectionBiomedical engineering
Apparatus, systems and methods for performing gel electrophoresis using a monolithic electrophoresis unit that at least includes first and second buffer chambers containing buffer solution and a gel chamber containing a pre-cast gel, whereby all of these chambers are integrated into a pre-fabricated single unit that is ready for use. In performing gel electrophoresis, a top seal of this monolithic electrophoresis unit is removed, followed by removing a gel chamber seal from over the gel chamber, such that, buffer solution contacts the pre-cast gel within such gel chamber. Target samples are loaded into the gel chamber for contact with the pre-cast gel, a reusable lid is attached to the top surface of the monolithic electrophoresis unit, and an electrical connection is provided through the reusable lid into the monolithic electrophoresis unit for performing electrophoresis on the pre-cast gel.
Owner:WANG YI
Monolithic electrophoresis flat gel system
InactiveUS20120055794A1Minimal handlingMinimal preparationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisElectrical connection
Apparatus, systems and methods for performing gel electrophoresis using a horizontal monolithic electrophoresis unit that at least includes first and second buffer chambers containing buffer solution and a gel chamber containing a pre-cast flat gel, whereby all of these chambers are integrated into a pre-fabricated single unit that is ready for use. In performing gel electrophoresis, a top seal of this monolithic electrophoresis unit is removed, target samples are loaded into the pre-cast gel, interior walls of the unit are broken to allow buffer from anode and cathode chambers to combine within the gel chamber and cover the loaded gel matrix, a reusable lid is attached to the top surface of the unit, and an electrical connection is provided through the reusable lid into the horizontal monolithic electrophoresis unit for performing electrophoresis on the flat pre-cast gel.
Owner:WANG YI
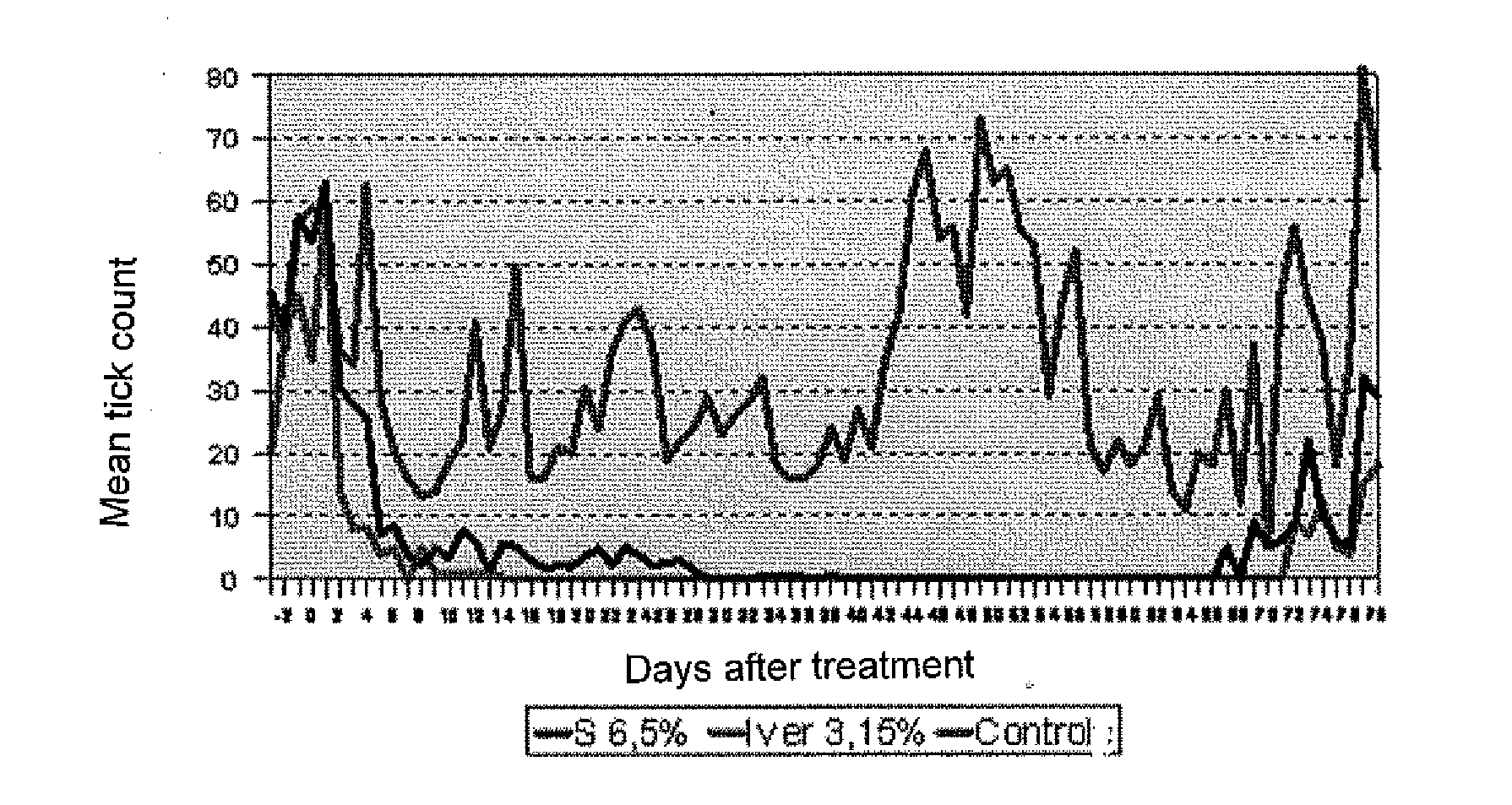
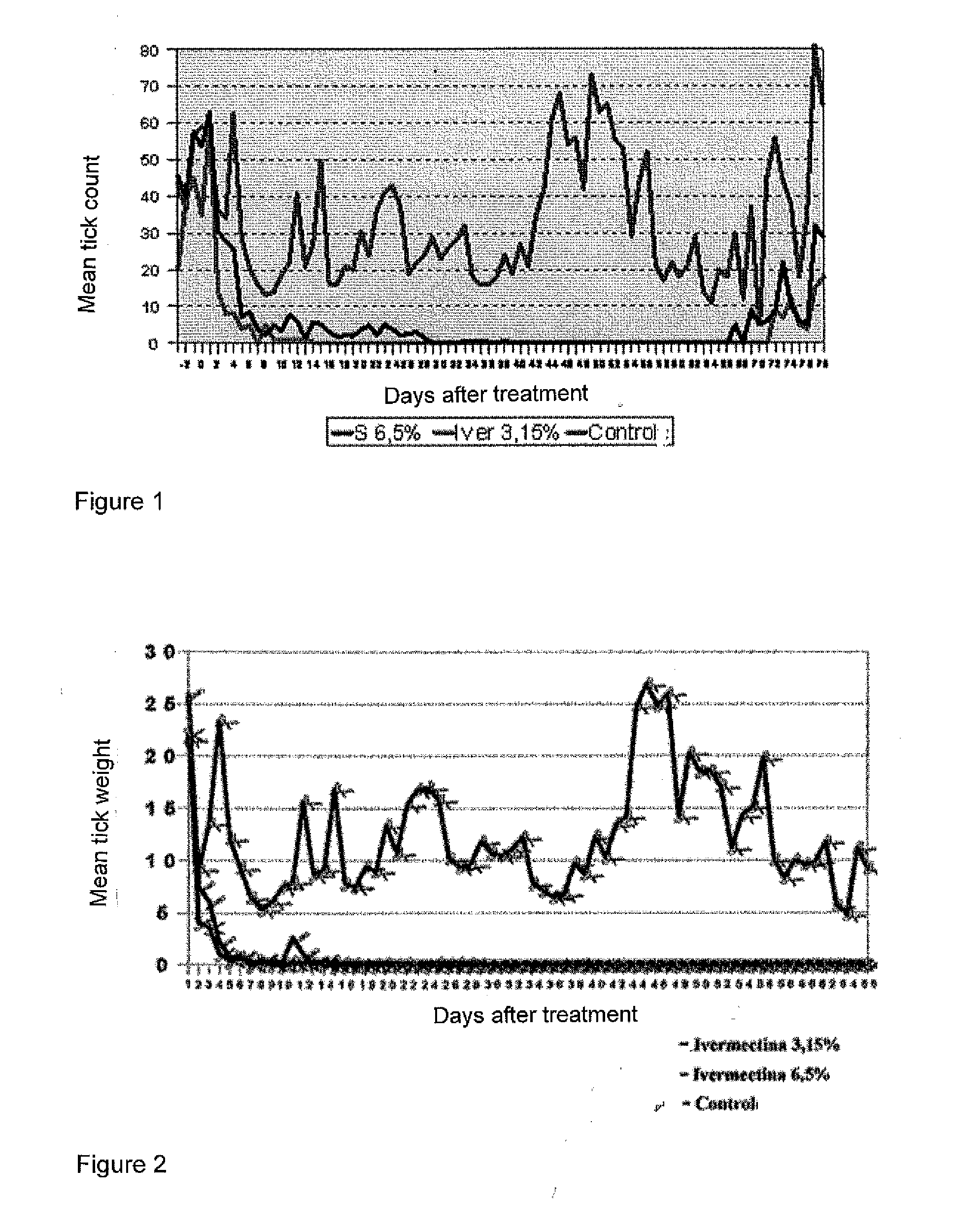
Long Acting Injectable Formulations
InactiveUS20110039794A1Minimal administrationEfficient use ofBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismMacrocyclic lactoneBiodegradable polyester
Long acting injectable formulations of macrocyclic lactones comprising a biologically acceptable and biodegradable polyester polymer in a solvent system for use in the field of veterinary medicine, especially for use in combating ecto- and endoparasites in animals.
Owner:CORGOZINHO CAROLINA NUNES COSTA +3
Inspection pocket for baby garment
ActiveUS9456636B2Quickly and efficiently and cleanly checkA large amountBaby linensComputer scienceEngineering
Owner:MOM MADE PEEKS LLC
Process For Cleaning, Drying and Hydrophilizing A Semiconductor Wafer
ActiveUS20080308122A1Improve concentrationOvercome disadvantagesPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsHydrogen fluorideEngineering
Semiconductor wafers are cleaned, dried, and hydrophilized the following steps in the order stated:a) treating the semiconductor wafer with a liquid aqueous solution containing hydrogen fluoride, the semiconductor wafer rotating about its center axis at least occasionally, andb) drying the semiconductor wafer by rotation of the semiconductor wafer about its center axis at a rotational speed of 1000 to 5000 revolutions per minute in an ozone-containing atmosphere, the liquid aqueous solution containing hydrogen fluoride flowing away from the semiconductor wafer on account of the centrifugal force generated by the rotation, and the surface of the semiconductor wafer being hydrophilized by ozone.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com