Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Implementation complexity can be reduced" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
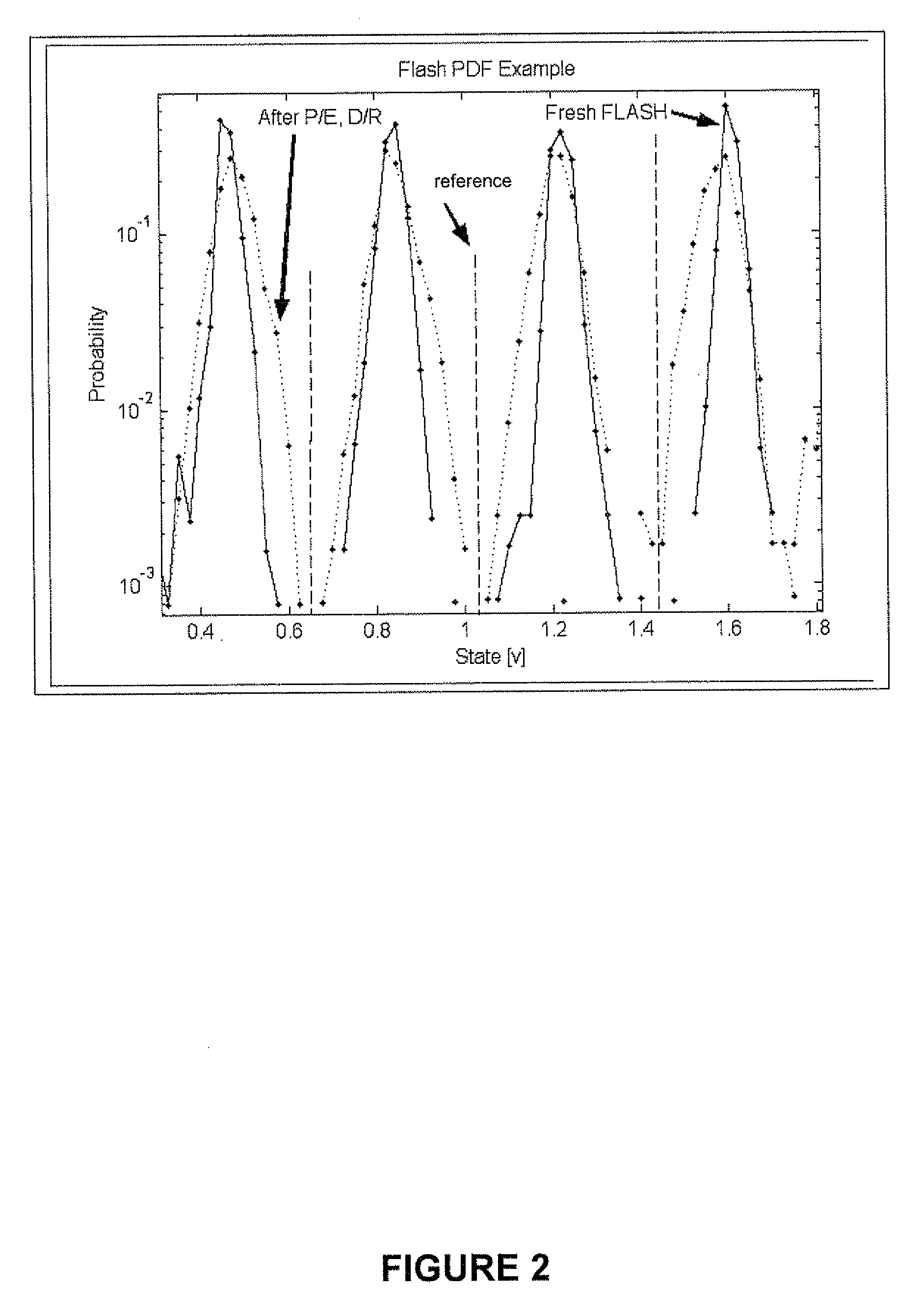
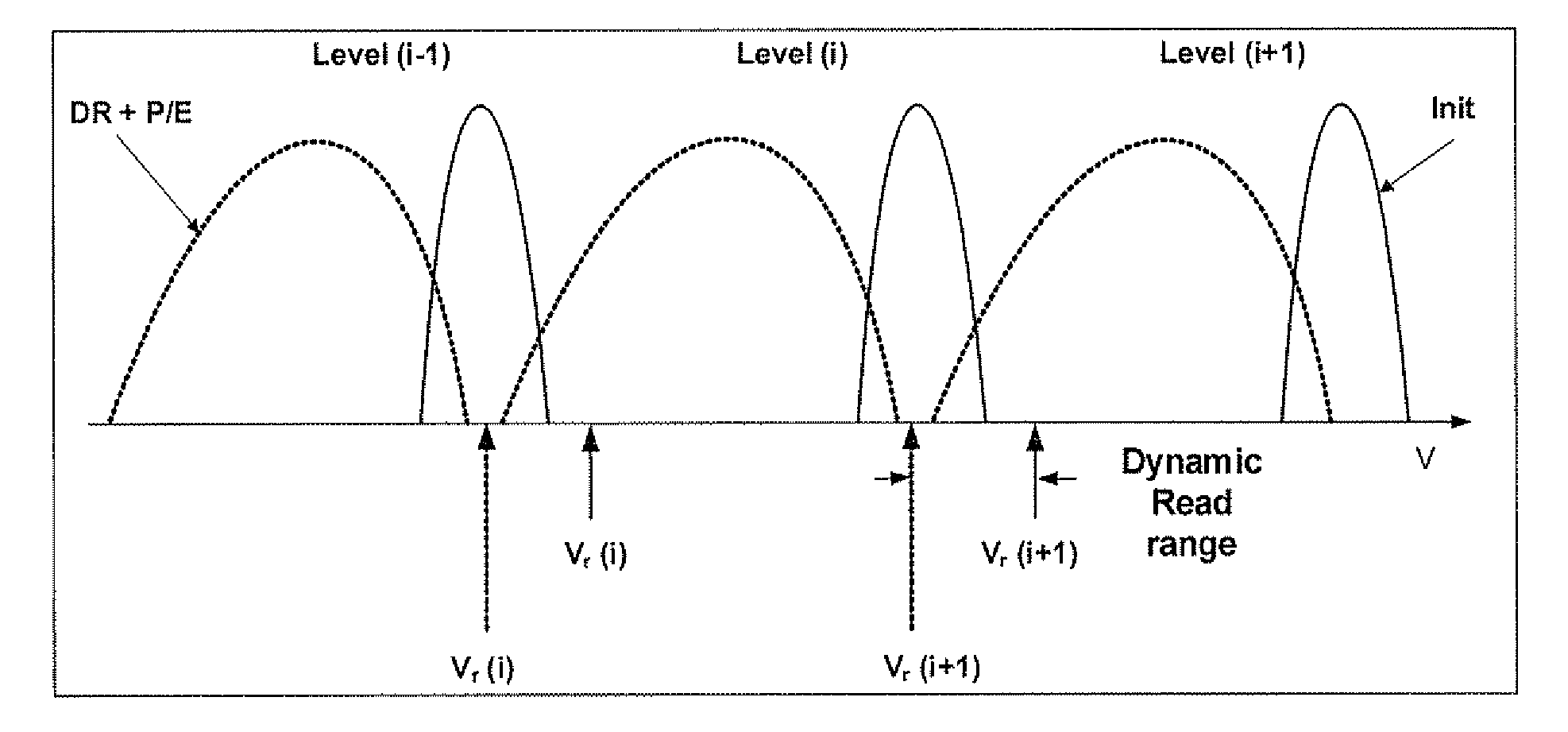
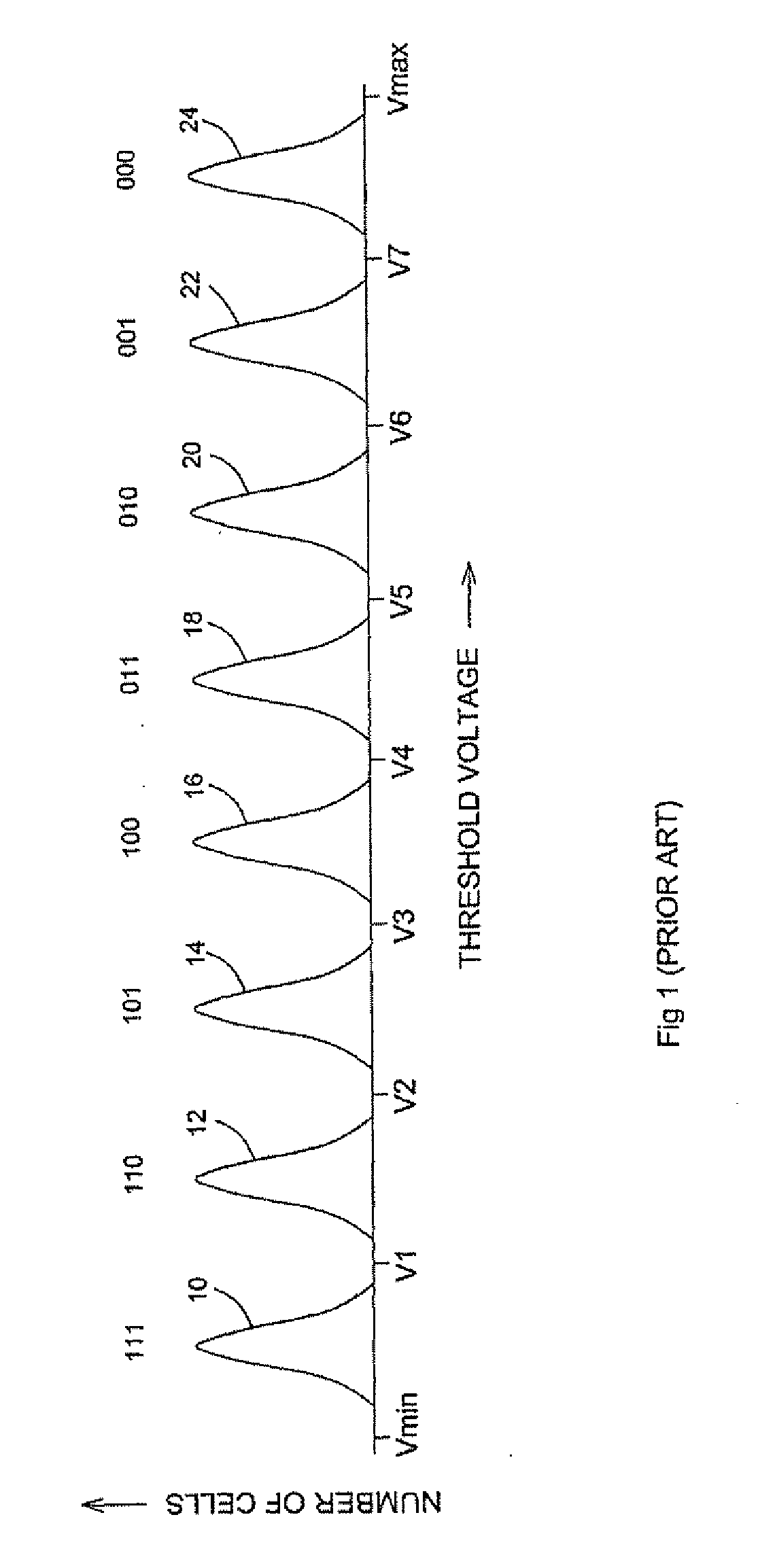
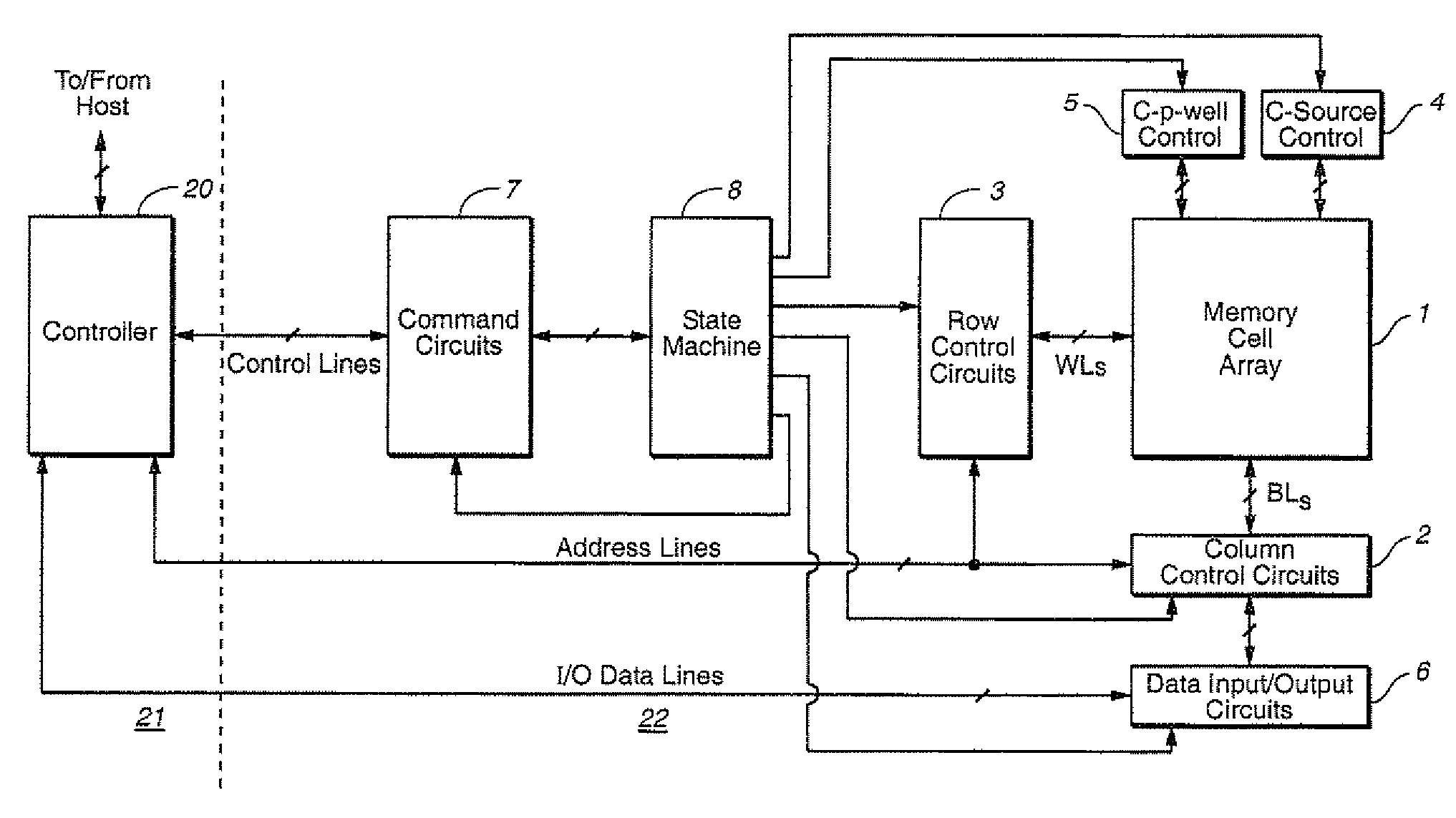
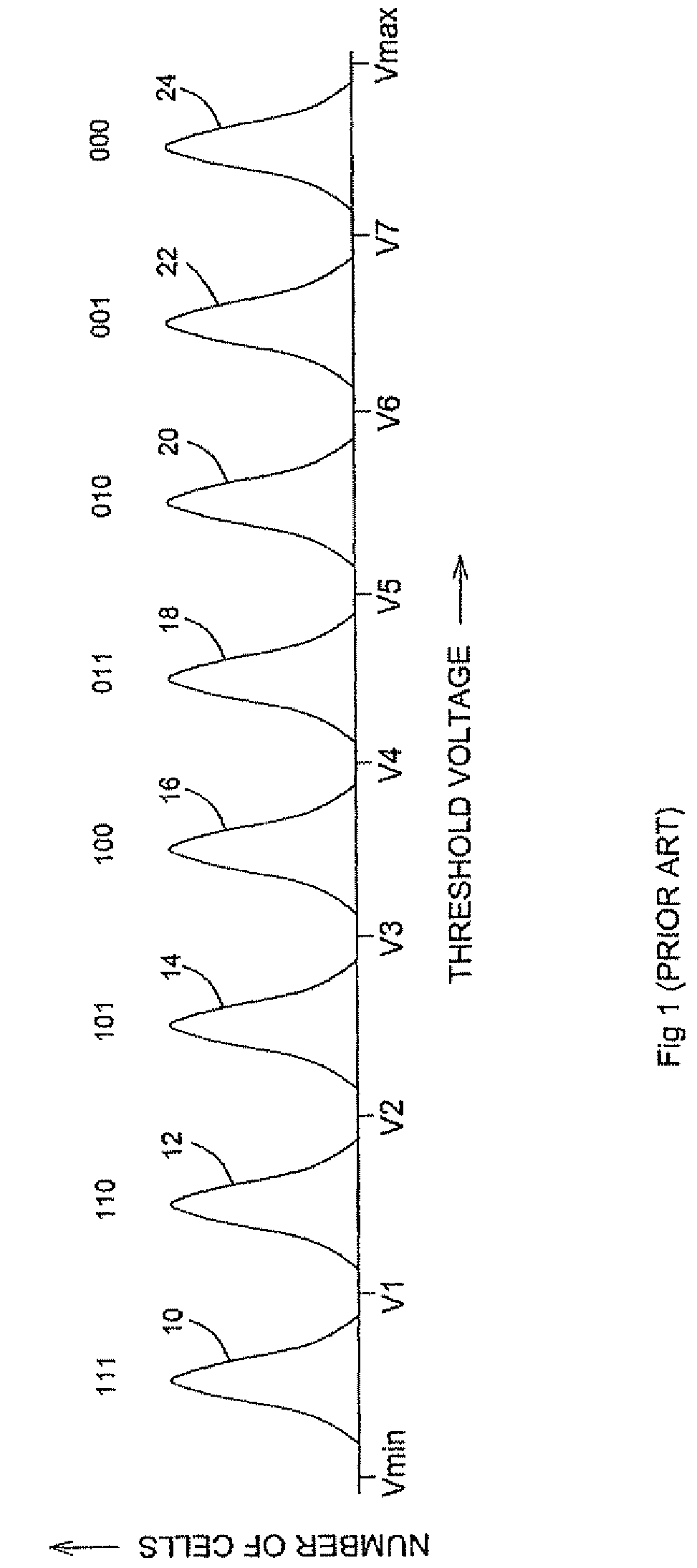
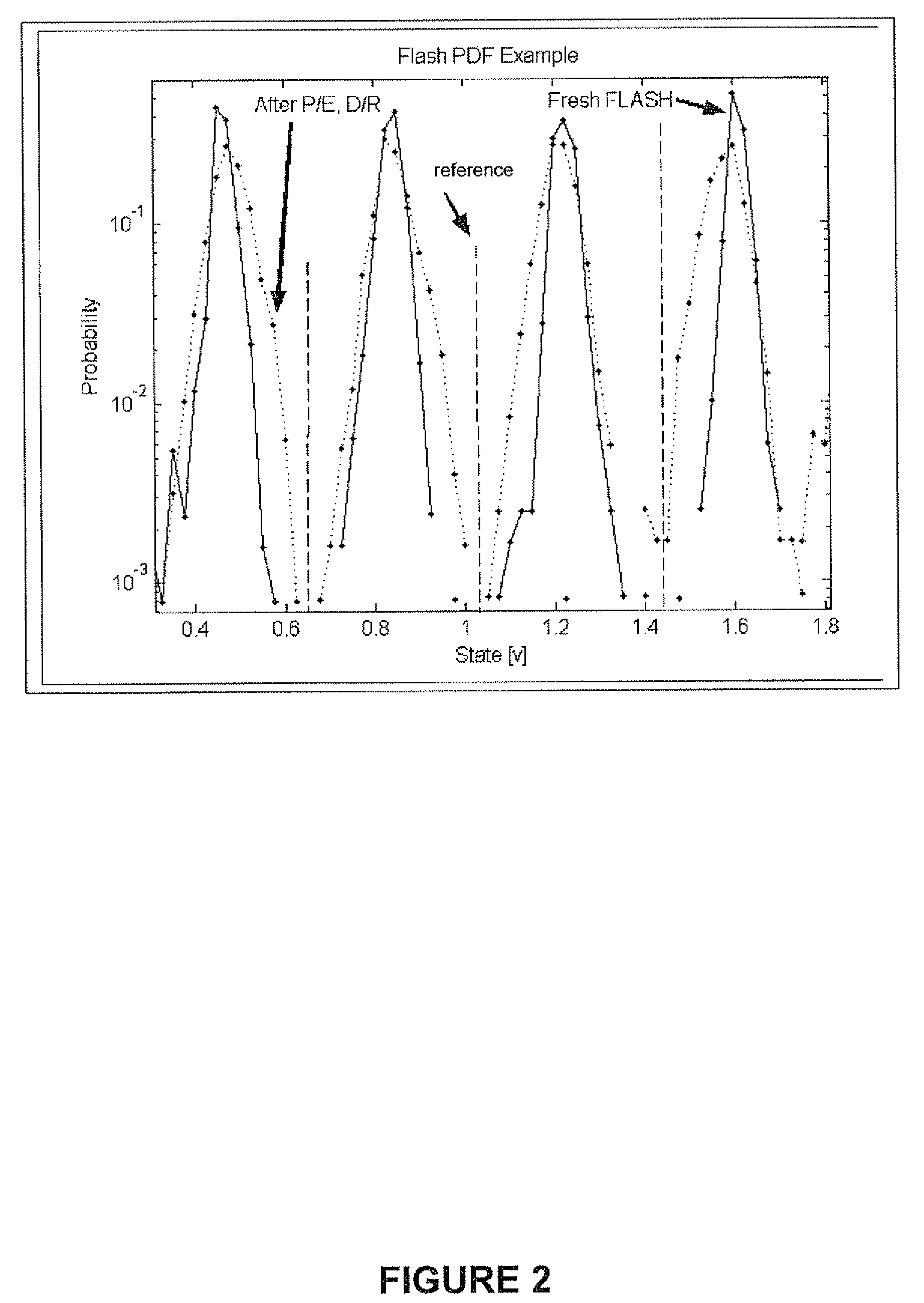
Adaptive dynamic reading of flash memories
InactiveUS20080263265A1Implementation complexity can be reducedImprove accuracyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesVoltage referenceSelf adaptive
Each of a plurality of flash memory cells is programmed to a respective one of L≧2 threshold voltage states within a threshold voltage window. Values of parameters of threshold voltage functions are adjusted in accordance with comparisons of the threshold voltages of some or all of the cells to two or more of m≧2 threshold voltage intervals within the threshold voltage window. Reference voltages for reading the cells are selected based on the values. Alternatively, the m threshold voltage intervals span the threshold voltage window, and respective threshold voltage states are assigned to the cells based on numbers of cells whose threshold voltages are in the intervals, without re-reading the cells.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
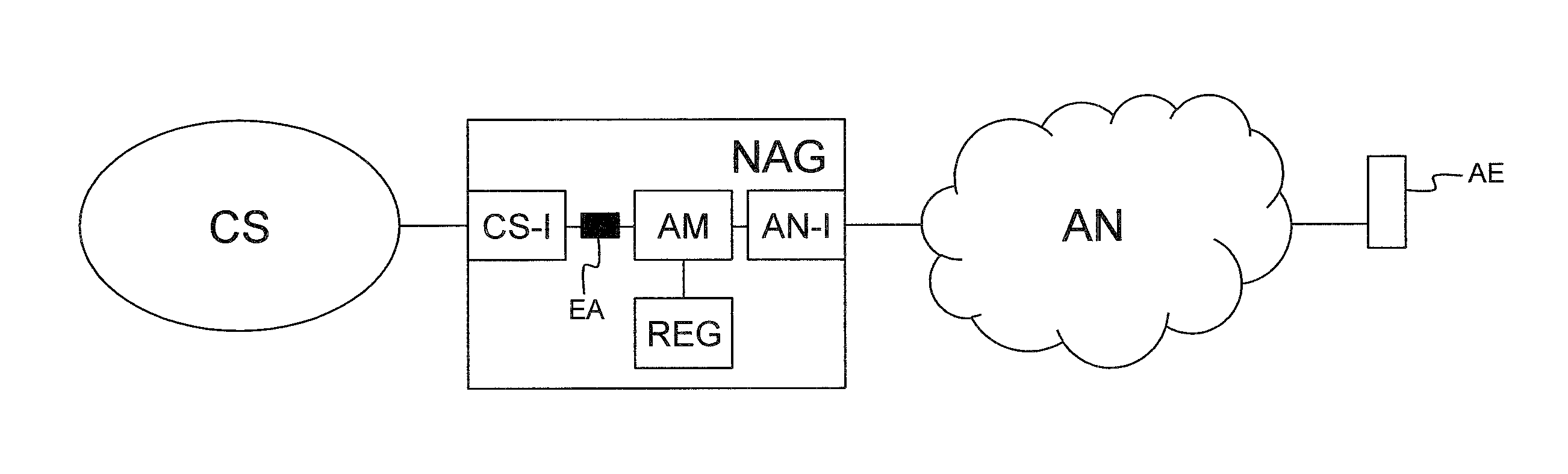
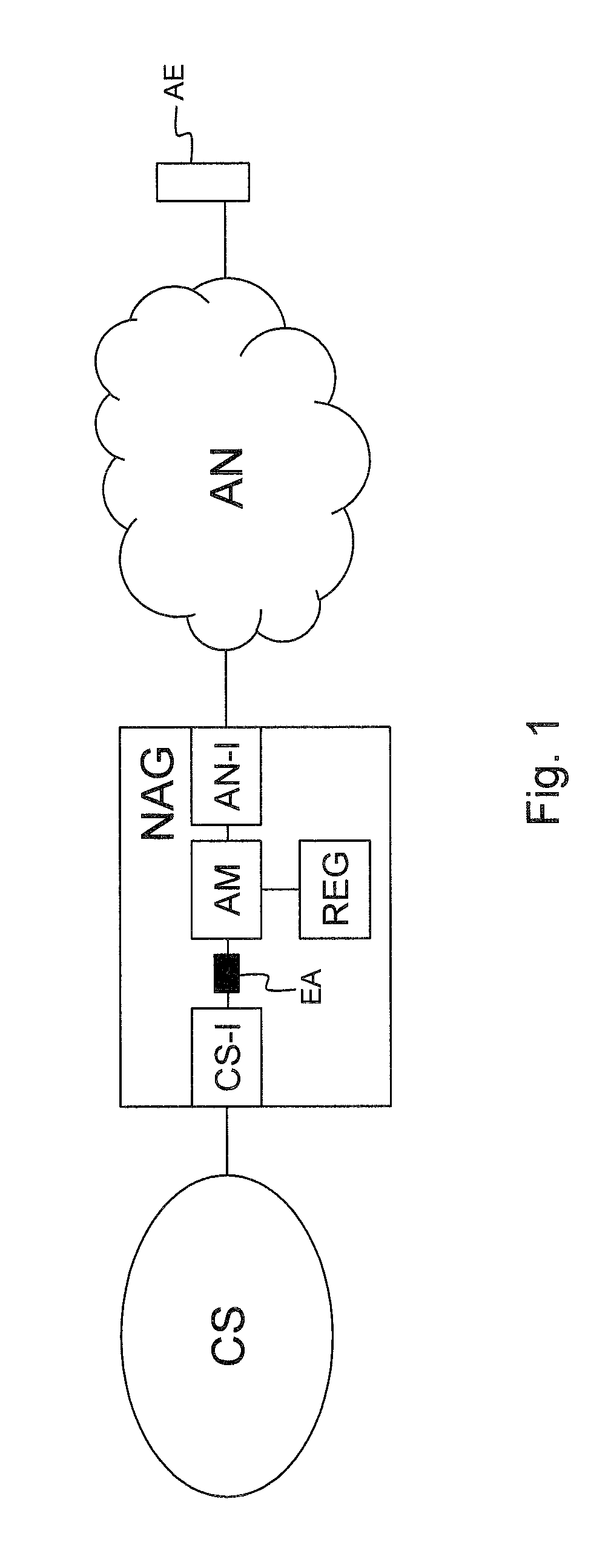
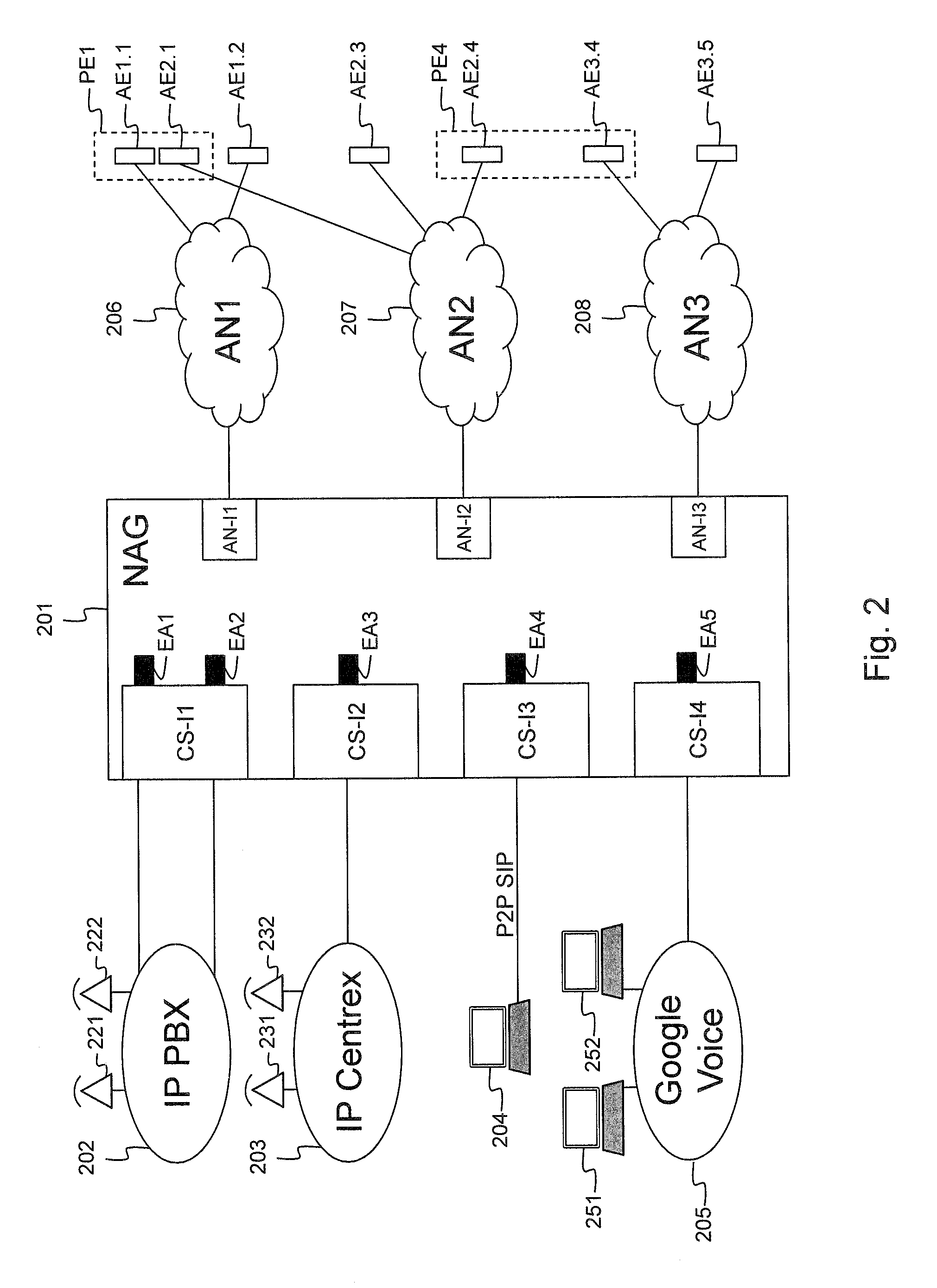
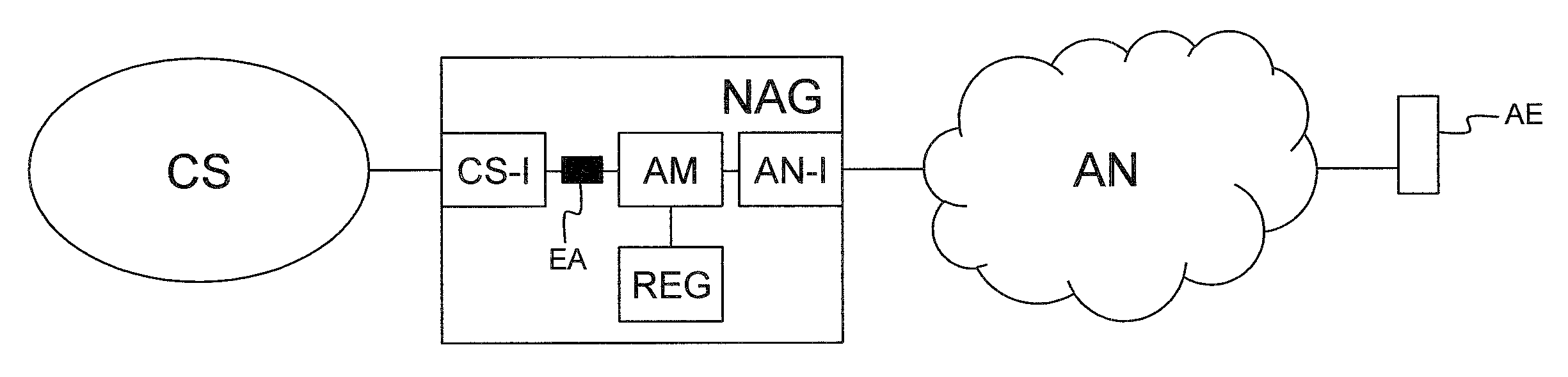
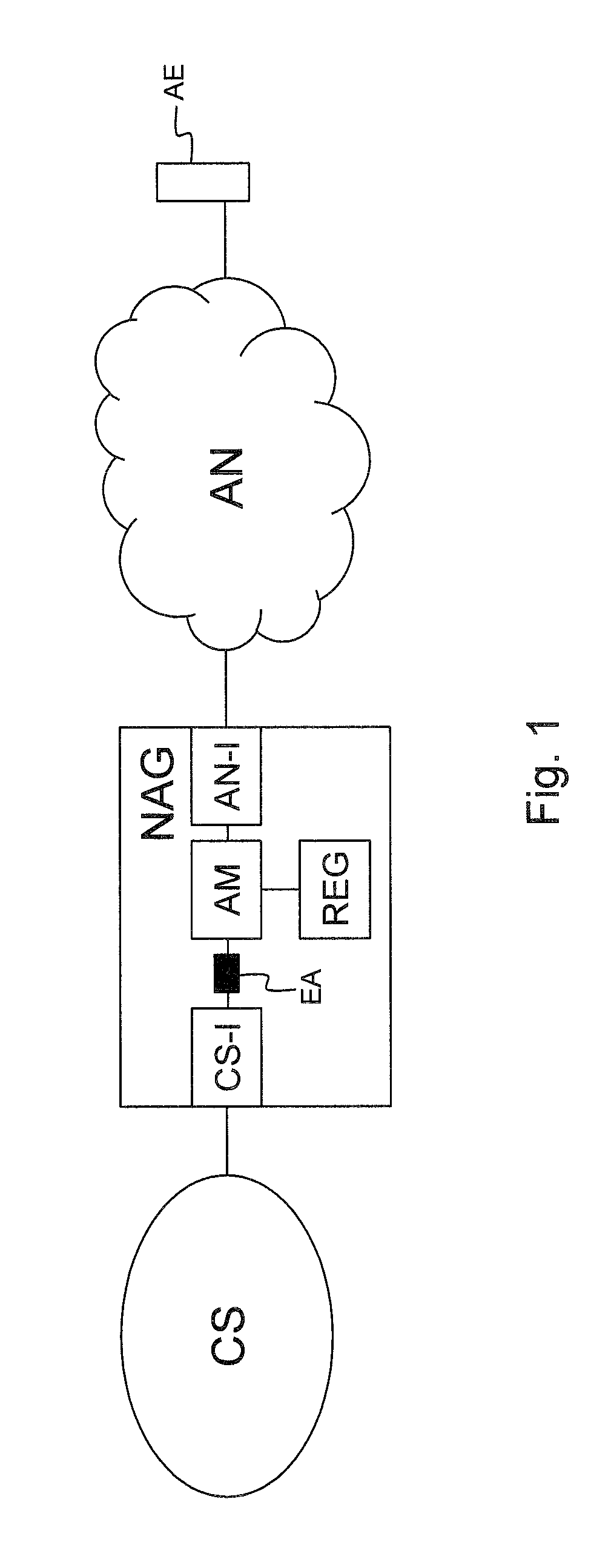
Network abstraction gateway and corresponding method to abstract an endpoint
ActiveUS20120188892A1Implementation complexity can be reducedInterconnection arrangementsError preventionCommunications systemDistributed computing
A network abstraction gateway includes at least one abstracted network interface for connectivity with an abstracted network wherein a user has an abstracted endpoint having a first identity in the abstracted network; a communication system interface for connectivity with at least one user's communication system and exposing abstracted endpoint behavior via a second identity in the user's communication system; means adapted to register a one-to-one relationship between the first identity and the second identity; means for extracting behavior of the abstracted endpoint; and endpoint abstraction means adapted to abstract the abstracted endpoint in the user's communication system via an endpoint abstraction using the second identity. The endpoint abstraction is responsive to behavior of the abstracted endpoint and is adapted to implement at least one feature and / or state of the user's communication system and to bi-directionally map the behavior of the abstracted endpoint.
Owner:ESCAUX
Adaptive dynamic reading of flash memories
ActiveUS7876621B2Implementation complexity can be reducedImprove accuracyRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage referenceEngineering
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
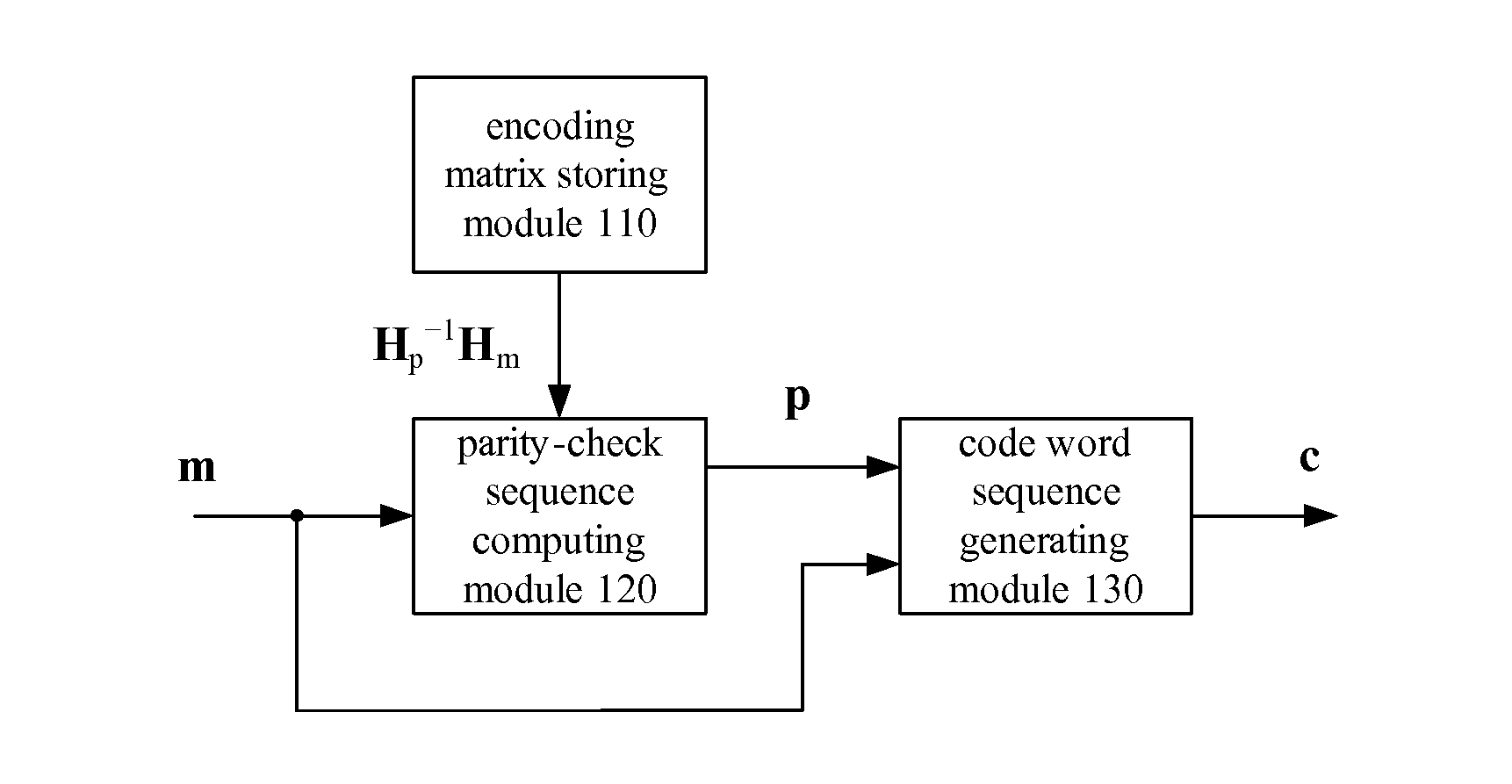
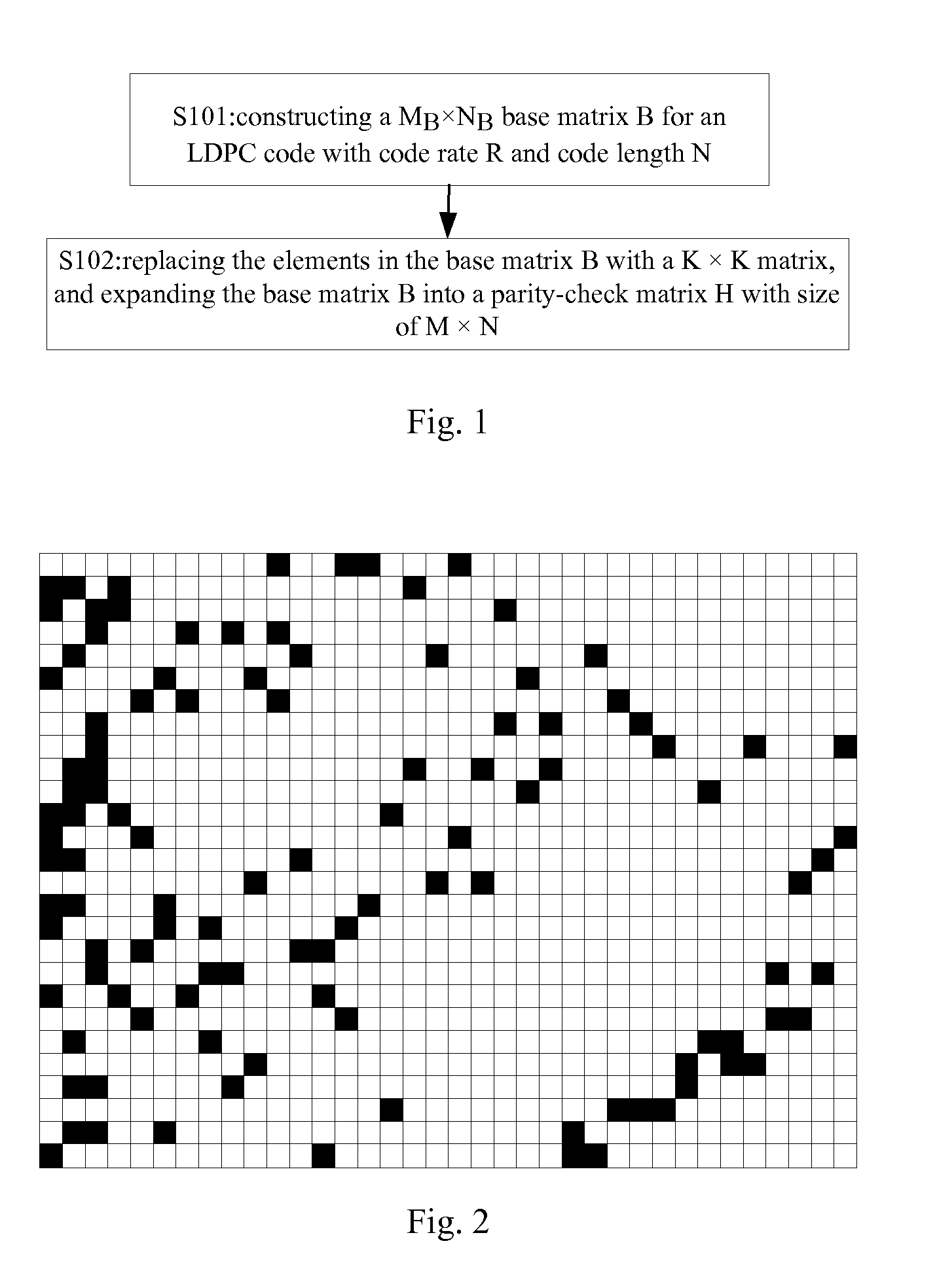
Method of constructing parity-check matrix of LDPC code and encoding method and encoding apparatus based on the method
InactiveUS20120173949A1Improve performanceImplementation complexity can be reducedError preventionCode conversionExpansion factorParity-check matrix
The embodiments of the present invention provide a method of constructing parity-check matrix of LDPC code. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a MB×NB base matrix B for an LDPC code with code rate R and code length N, wherein MB=M / K, NB=N / K, M=N (1−R), K is the expansion factor of the base matrix, Kεφ, and φ is the set of the common factors of M and N; and replacing the elements of the base matrix B with a K×K matrix, and expanding the base matrix B into a parity-check matrix H with size of M×N for the encoding or decoding of the LDPC code. An encoding method and apparatus of LDPC code are also provided by the embodiments of the present invention. The technical solutions provided by the embodiments of the present invention can construct LDPC codes with good performance, solve the storage problem of the parity-check matrix, and effectively reduce the implementation complexity of the encoding apparatus.
Owner:TIMI TECH
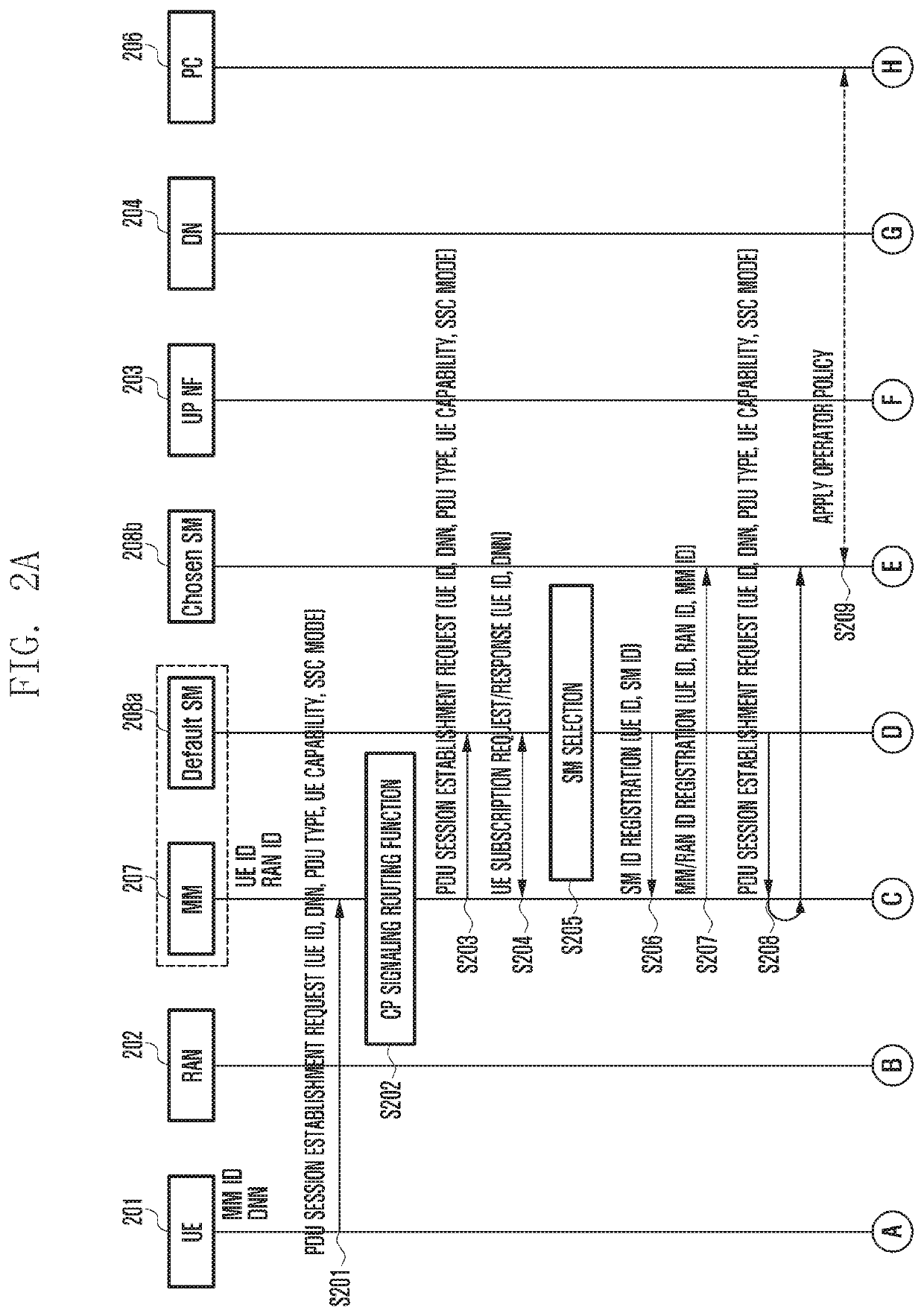
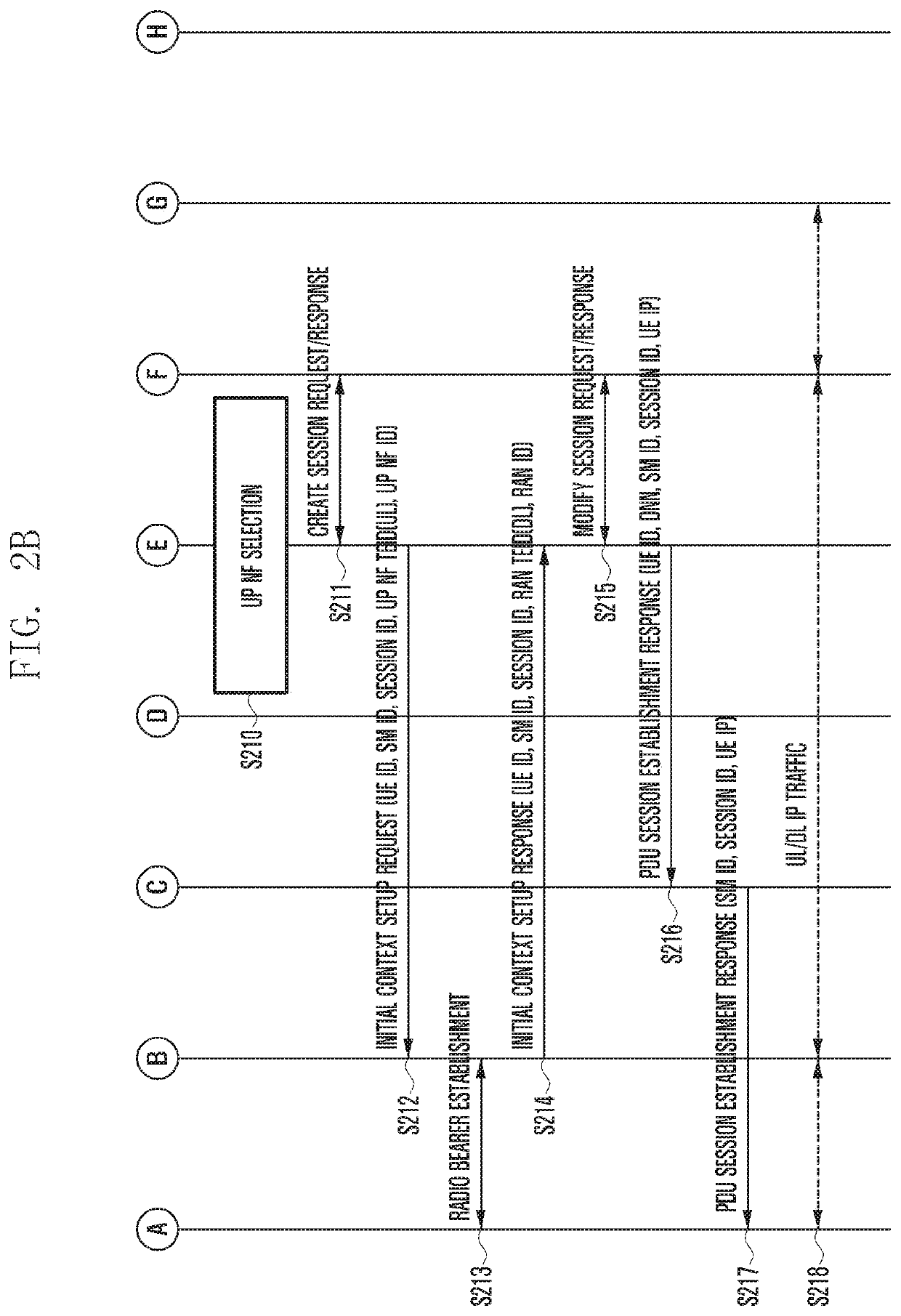
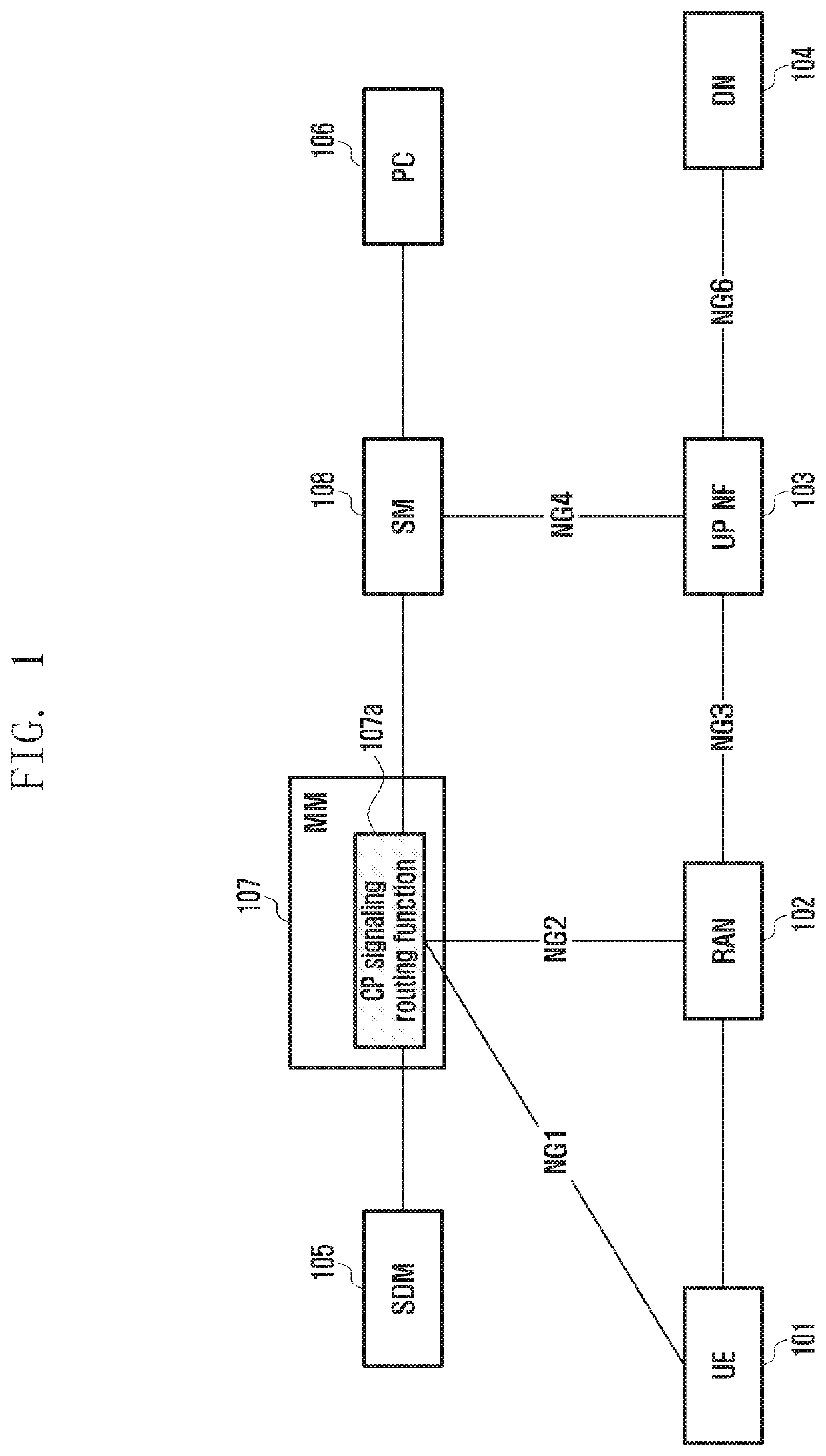
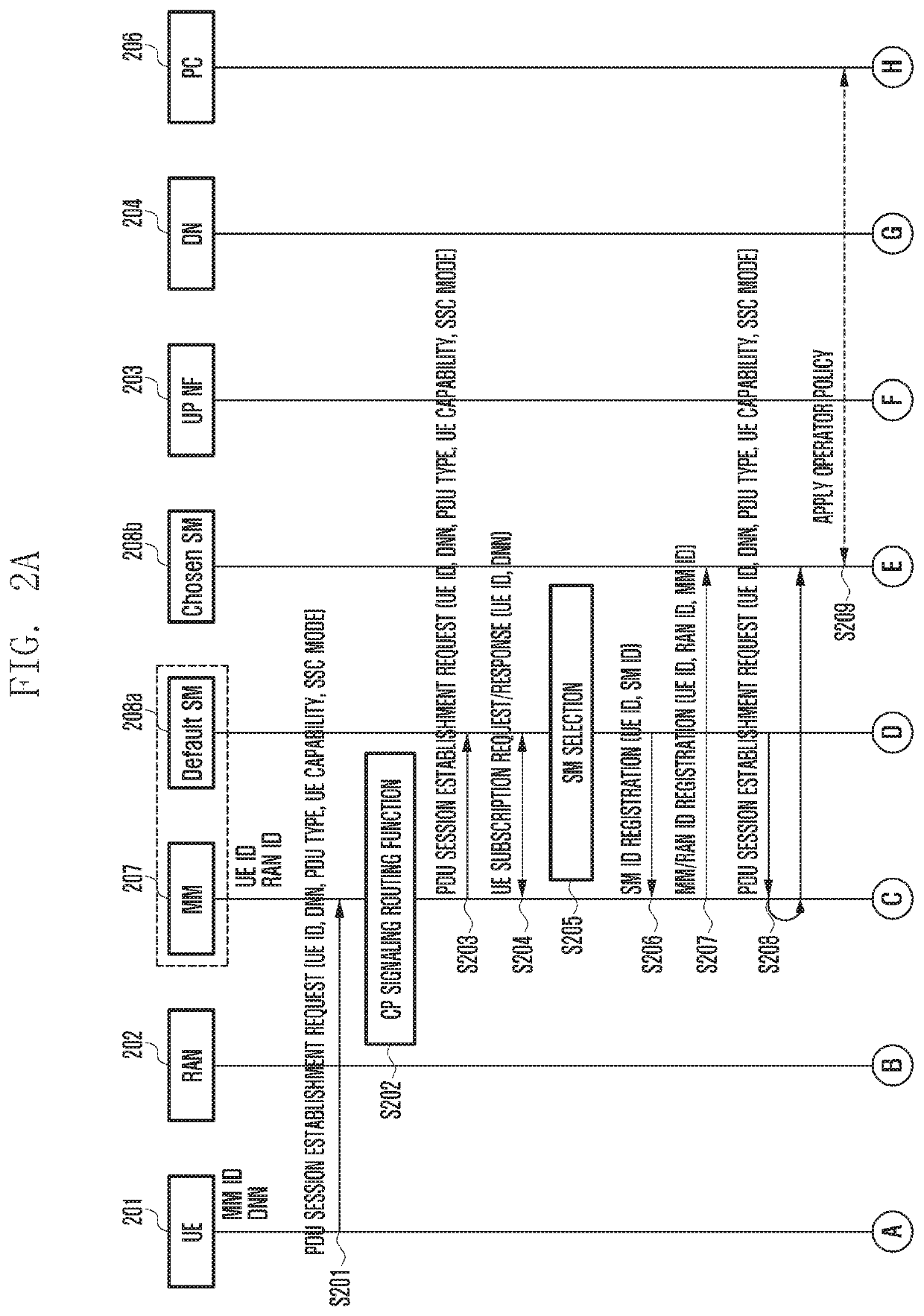
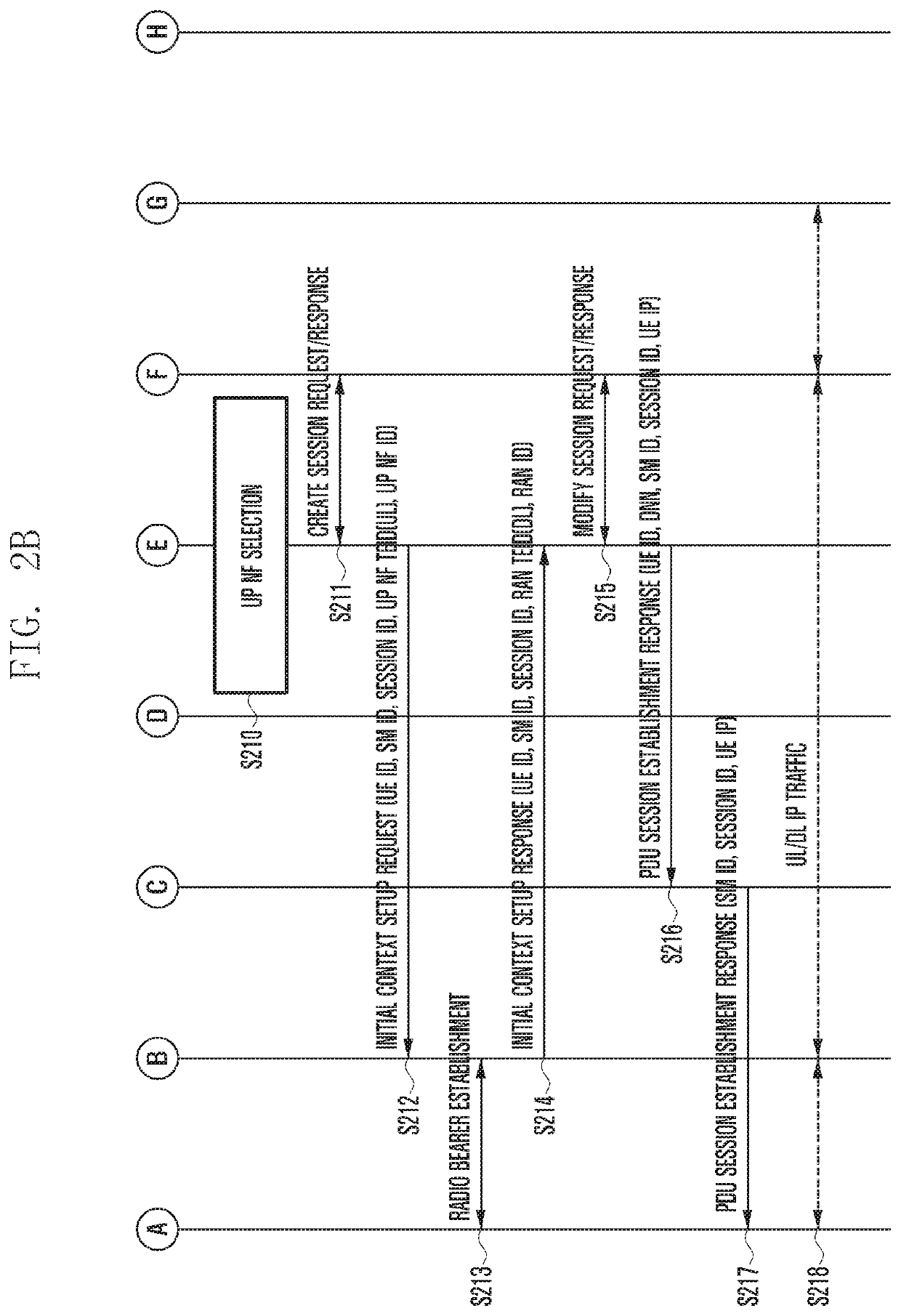
Method and apparatus for operating wireless communication system having separated mobility management and session management
ActiveUS20200187277A1Reduce implementation complexityMinimizing signaling loadNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementAccess networkSession management
The present invention defines signaling required for separating a network entity (NE) responsible for mobility management (MM) and session management (SM), which are main function of a control plane (CP) in a next generation (NextGen) mobile communication system, and presents a basic procedure for providing mobile communication services including the signaling. Therefore, complexity of core equipment responsible for the CP is reduced in order to implement a network slice function and provide various levels of mobility, and an effect of minimizing a signaling load therebetween can be obtain. In addition, it is possible to efficiently manage the resources of a base station (radio access network (RAN)) and a user plane network entity (UP NF).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for performing access control in next generation wireless network
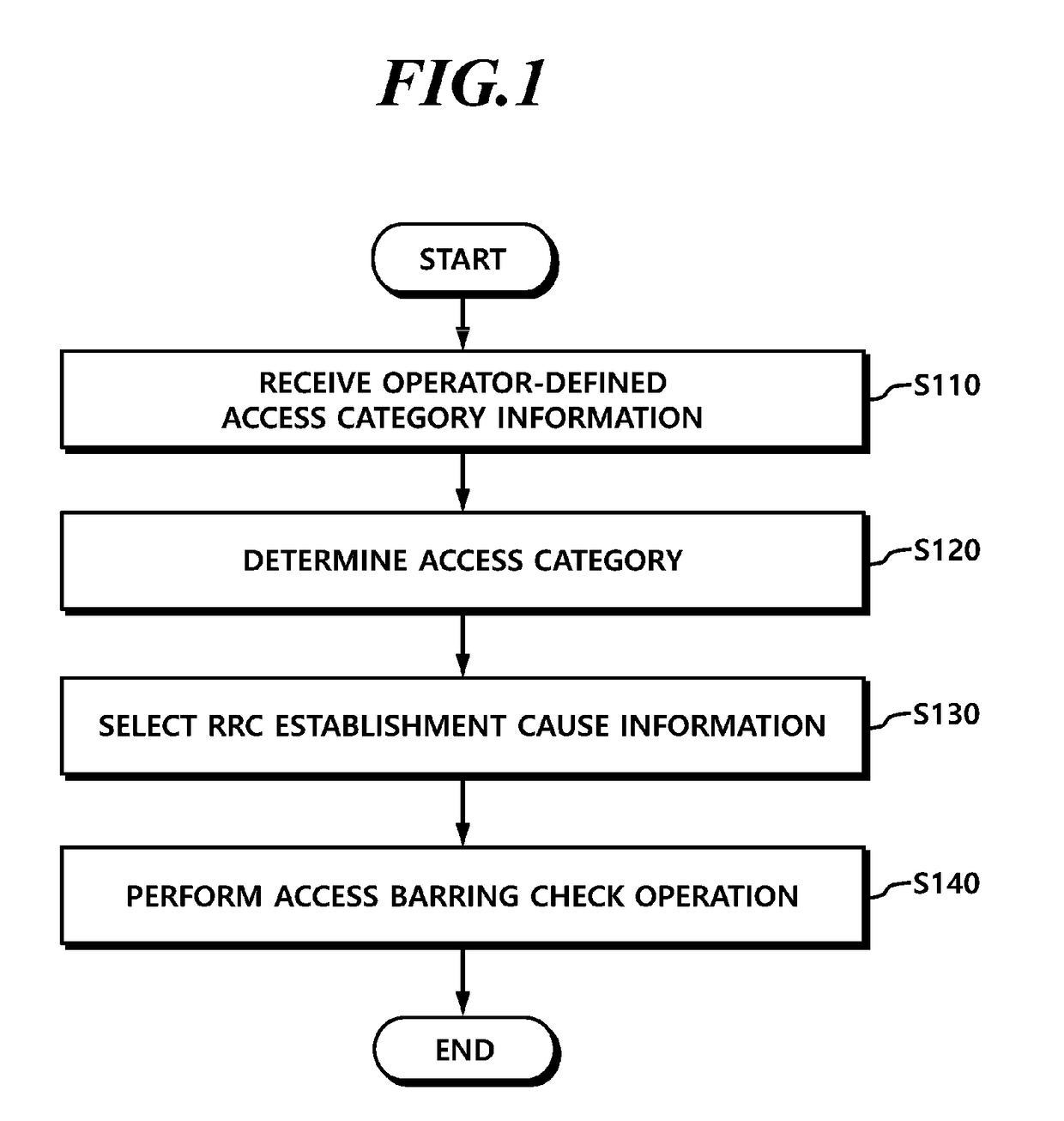
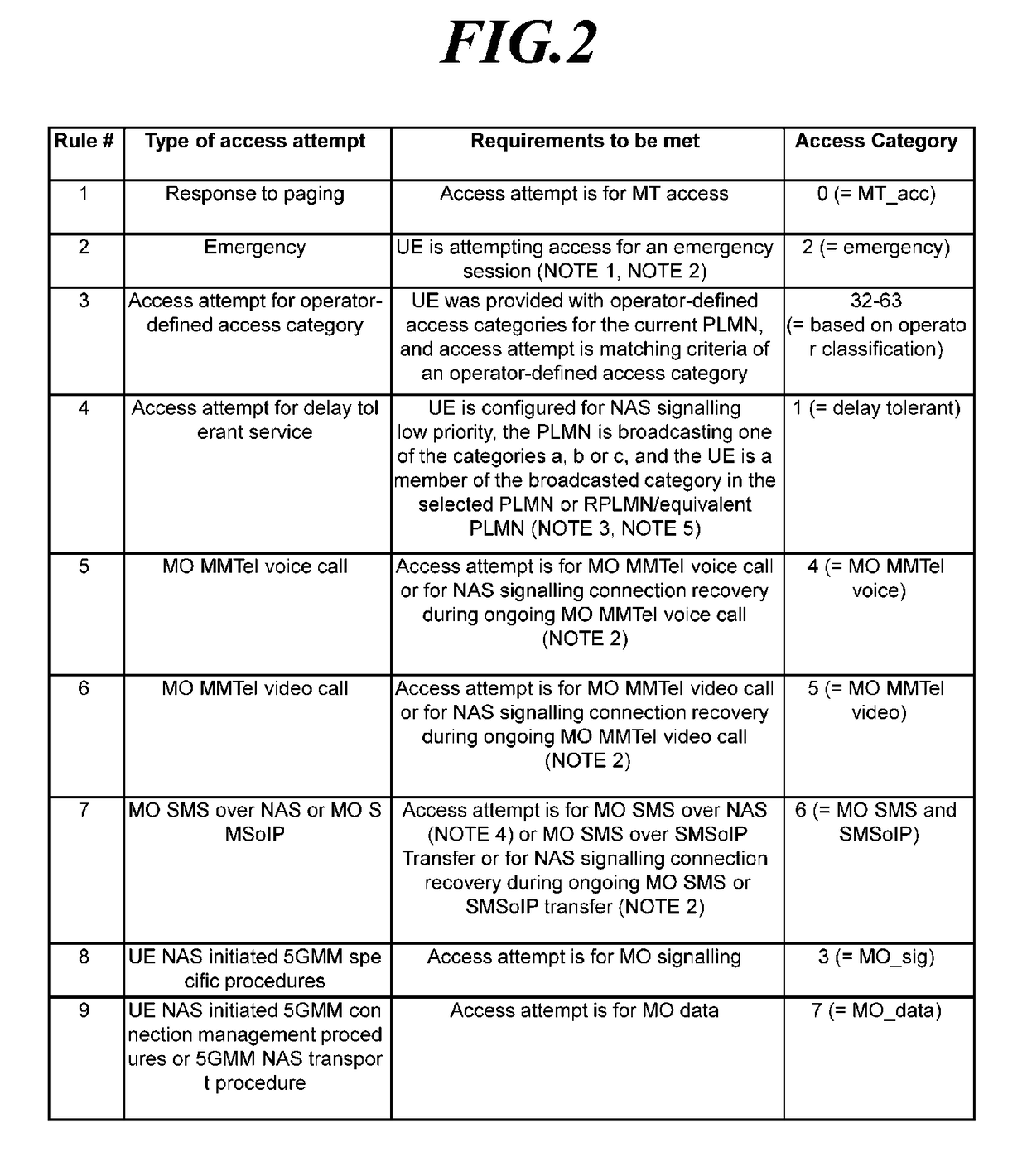
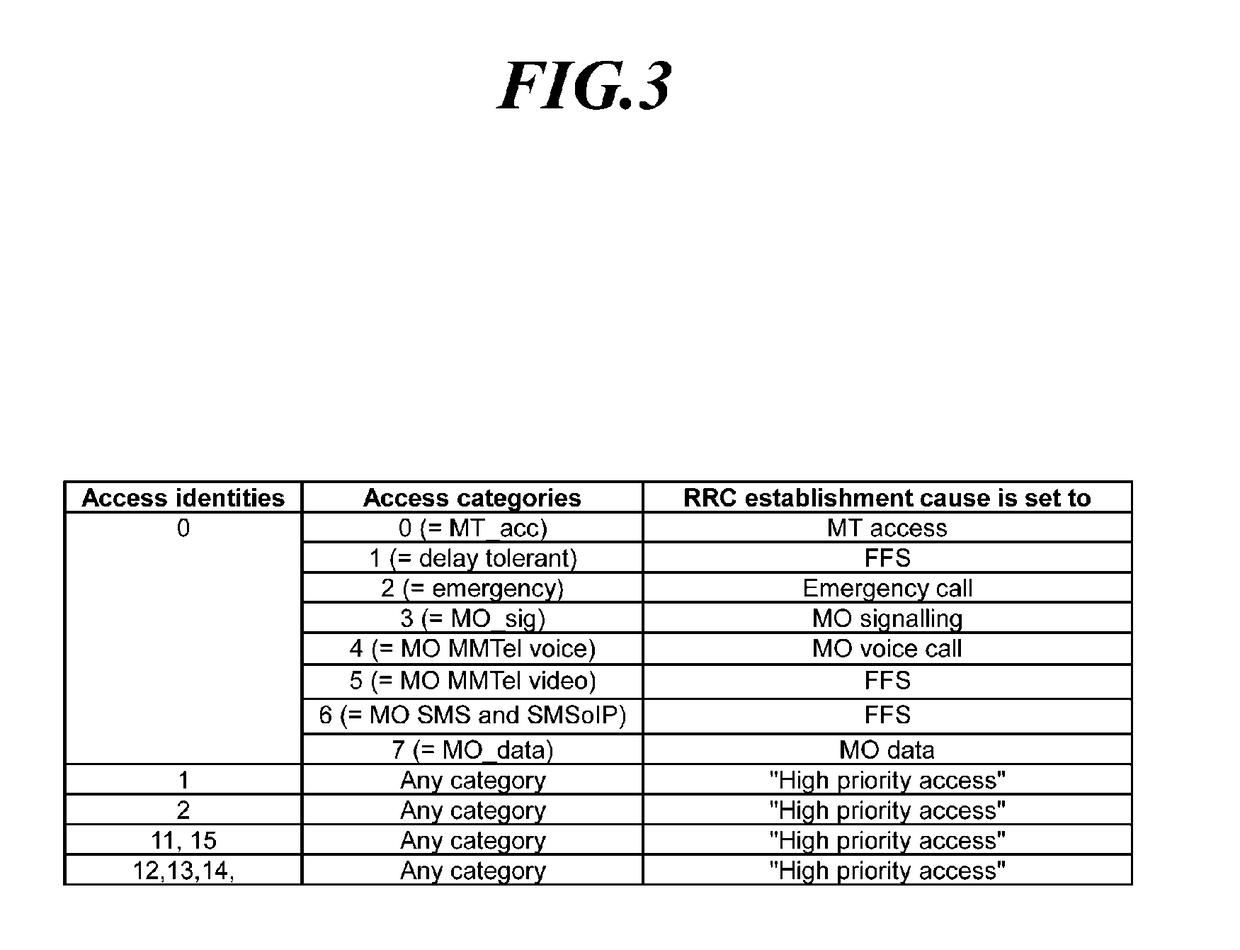
ActiveUS20190082376A1Reduce implementation complexityImplementation complexity can be reducedAssess restrictionConnection managementTelecommunicationsMedia access control
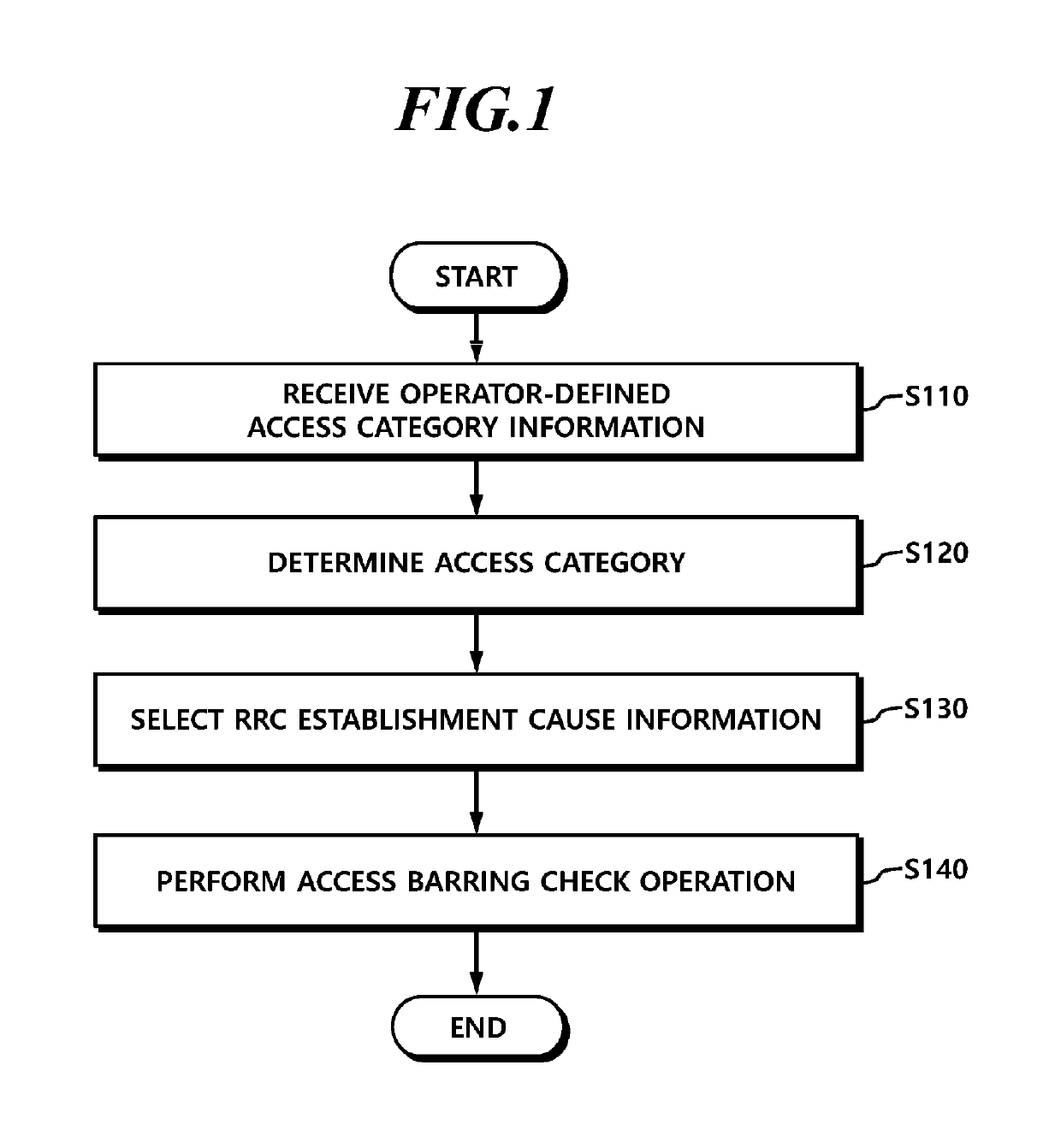
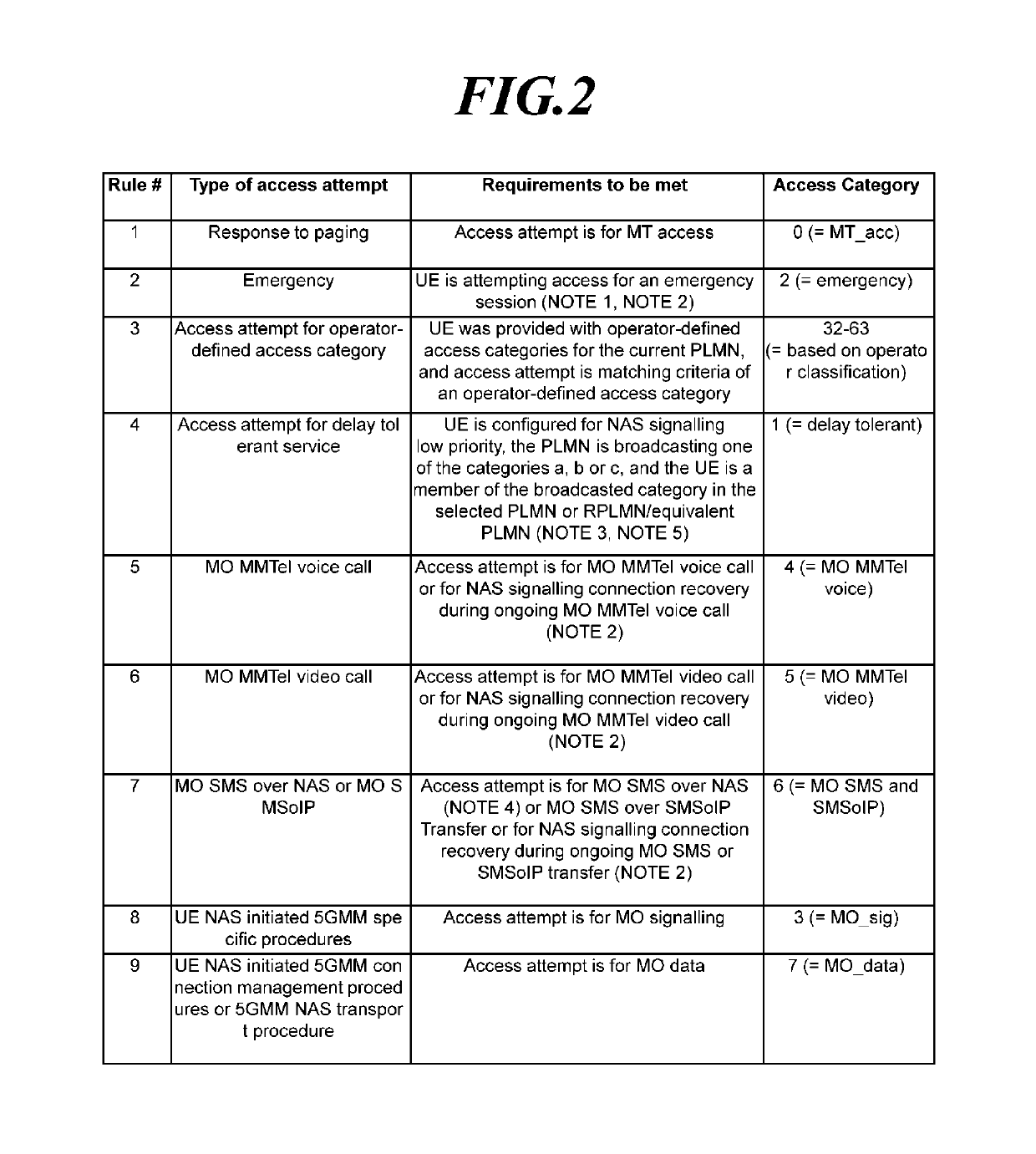
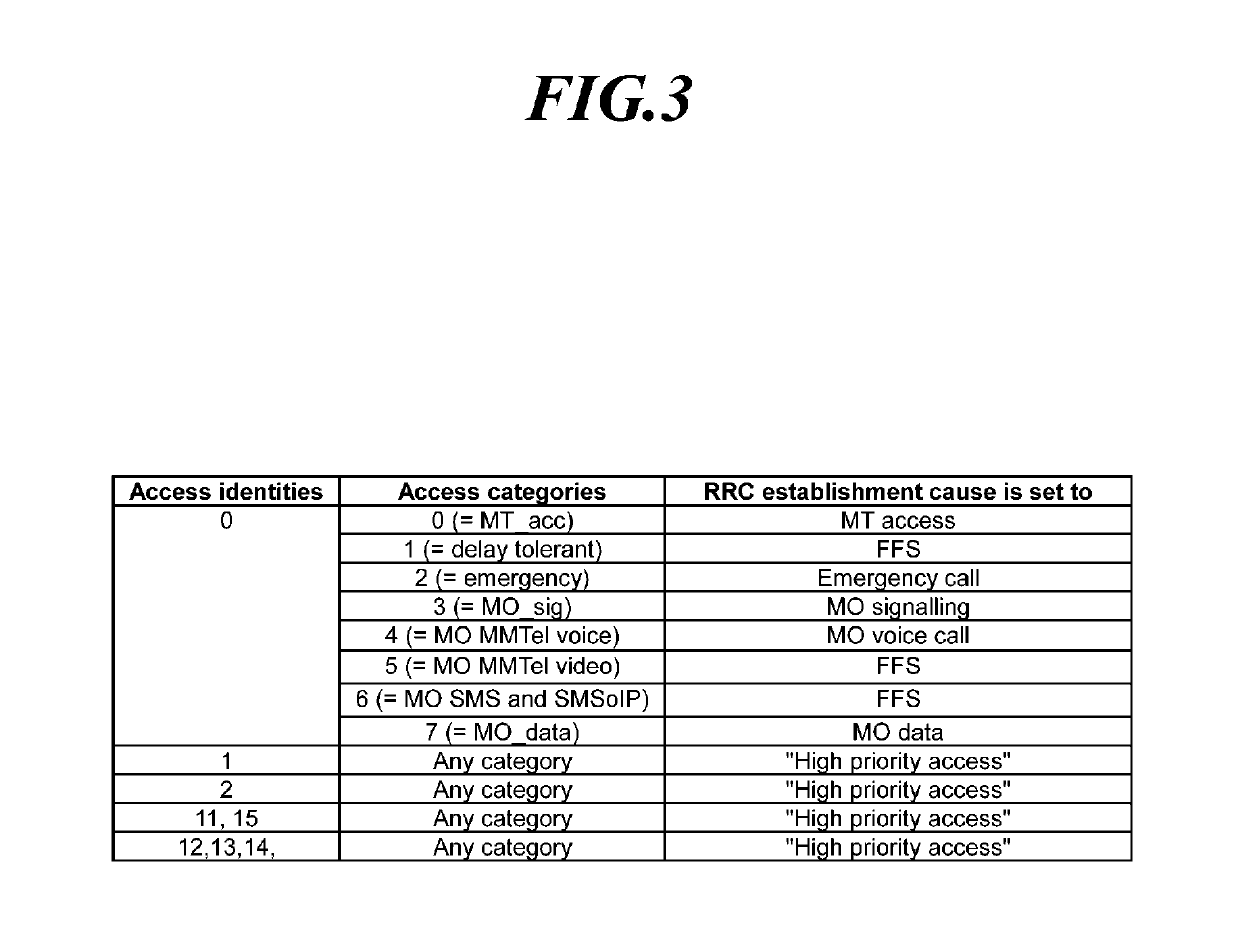
Disclosed is a technique for an access control operation of a user equipment (UE) in a next-generation mobile communication network, and more specifically, a unified access control method for a UE and a specific access control method for a service with low sensitivity. Further, a method of a UE is provided for performing an access control operation. The method may include receiving operator-defined access category information through non-access stratum (NAS) signaling when an access attempt of the UE is triggered, determining one access category for the access attempt in an NAS layer or an access stratum (AS) layer; selecting RRC establishment cause information associated with the access category; and performing an access barring check operation in the AS layer using access barring parameters associated with the access category.
Owner:KT CORP
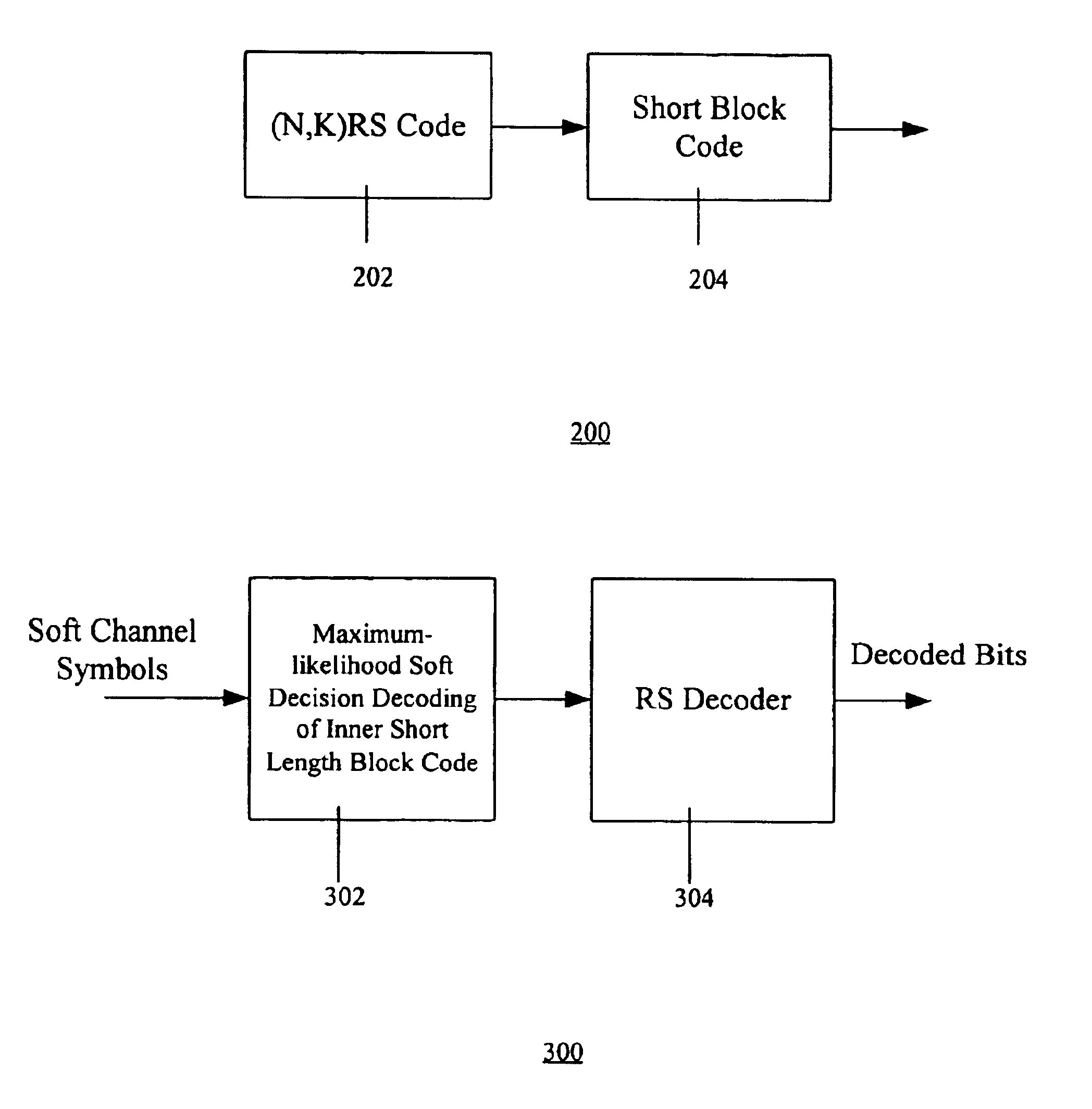
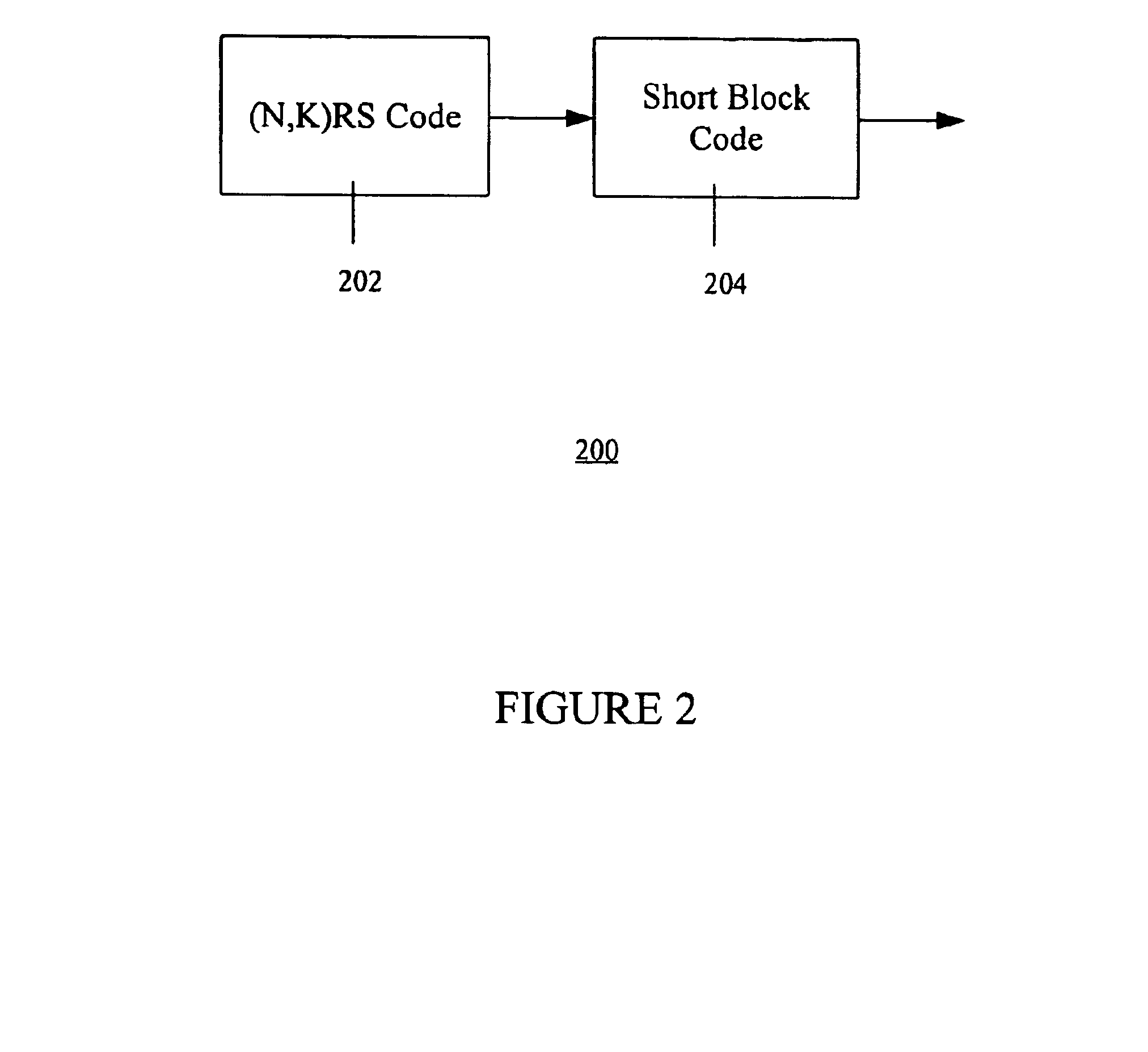
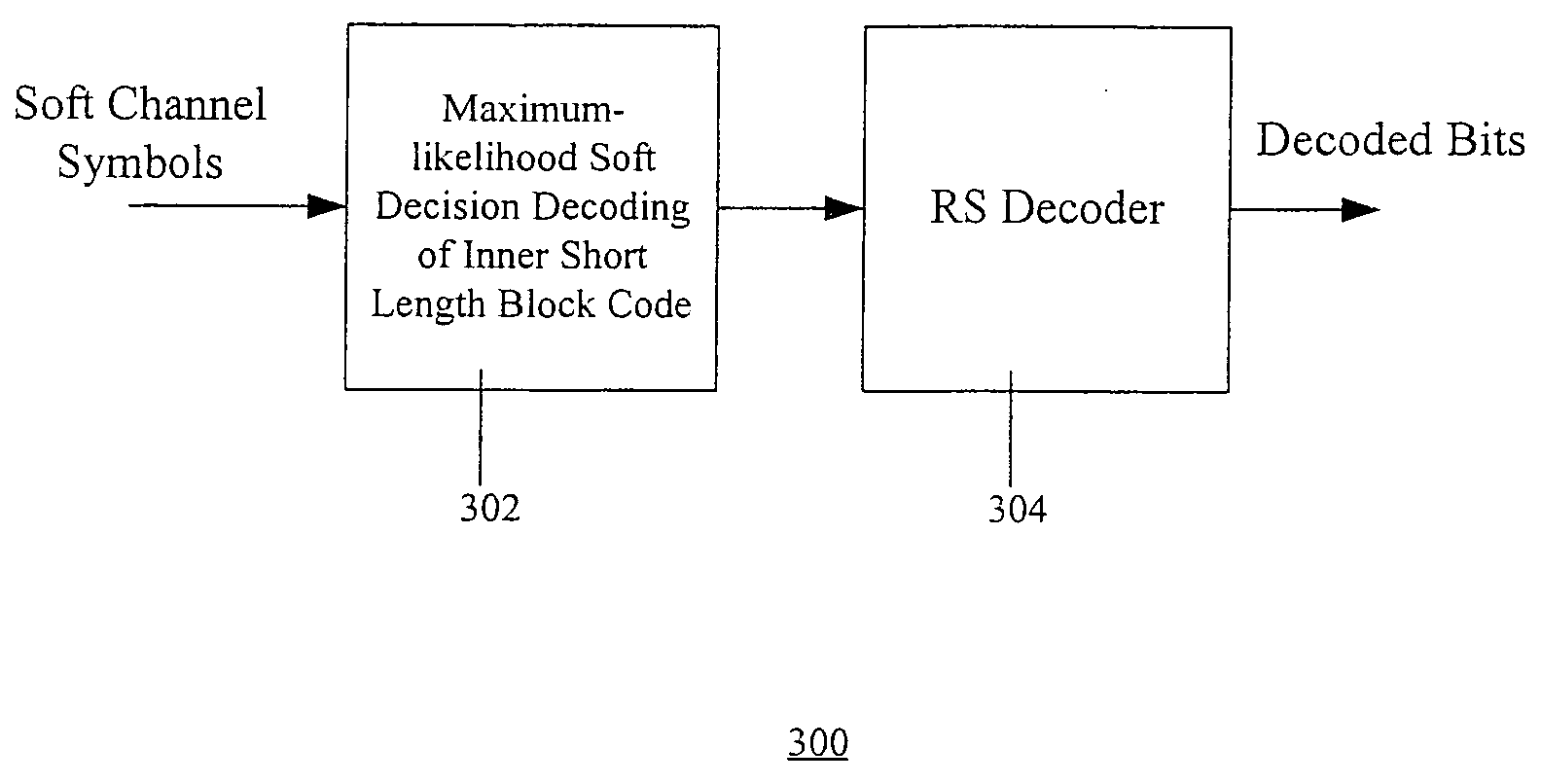
Method and apparatus for concatenated channel coding with variable code rate and coding gain in a data transmission system
InactiveUS20050102605A1Valid encodingReduce complexityError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionComputer hardwareBlock code
A novel method and apparatus for efficiently coding and decoding data in a data transmission system is described. A concatenated coding scheme is presented that is easily implemented, and that provides acceptable coding performance characteristics for use in data transmission systems. The inventive concatenated channel coding technique is well suited for small or variable size packet data transmission systems. The technique may also be adapted for use in a continuous mode data transmission system. The method and apparatus reduces the complexity, cost, size and power consumption typically associated with the prior art channel coding methods and apparatuses, while still achieving acceptable coding performance. The present invention advantageously performs concatenated channel coding without the necessity of a symbol interleaver. In addition, the present invention is simple to implement and thereby consumes much less space and power that do the prior art approaches. The present invention not only eliminates the need for a symbol interleaver between the outer and inner codes, but it also enjoys a drastically reduced implementation complexity of the inner code Viterbi decoder. The preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises an inner code having short length block codes derived from short constraint length convolutional codes utilizing trellis tailbiting and a decoder comprising four four-state Viterbi decoders having a short corresponding maximum length. The inner code preferably comprises short block codes derived from four-state (i.e., constraint length 3), nonsystematic, punctured and unpunctured convolutional code. One significant advantage of the preferred embodiment of the present concatenated coding technique is that packet data transmission systems can be designed to have variable coding gains and coding rates.
Owner:TUMBLEWEED HLDG LLC +1
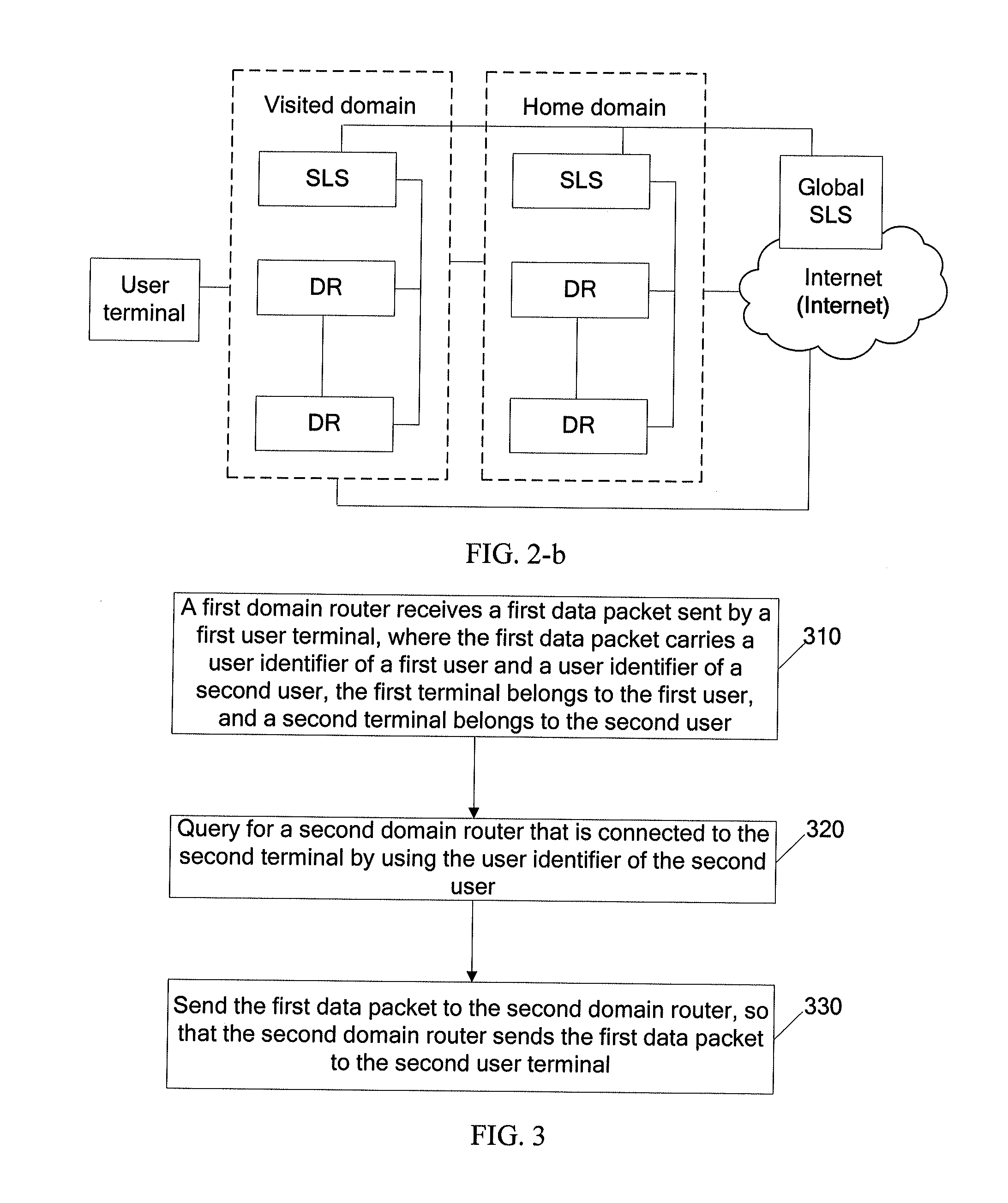
User-oriented communication method, route registration method and device, and communication system
InactiveUS20120177052A1Add supportReduce implementation complexityData switching by path configurationSecuring communicationCommunications systemNetwork packet
Embodiments of the present disclosure disclose a user-oriented communication method, a route registration method and device, and a communication system. In the method, a first domain router receives a first data packet sent by a first terminal. The first data packet includes a user identifier of a first user and a user identifier of a second user, the first terminal belongs to the first user, and a second terminal belongs to the second user. The first domain router queries for a second domain router connected to the second terminal according to the user identifier of the second user and sends the first data packet to the second domain router, so that the second domain router sends the first data packet to the second terminal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
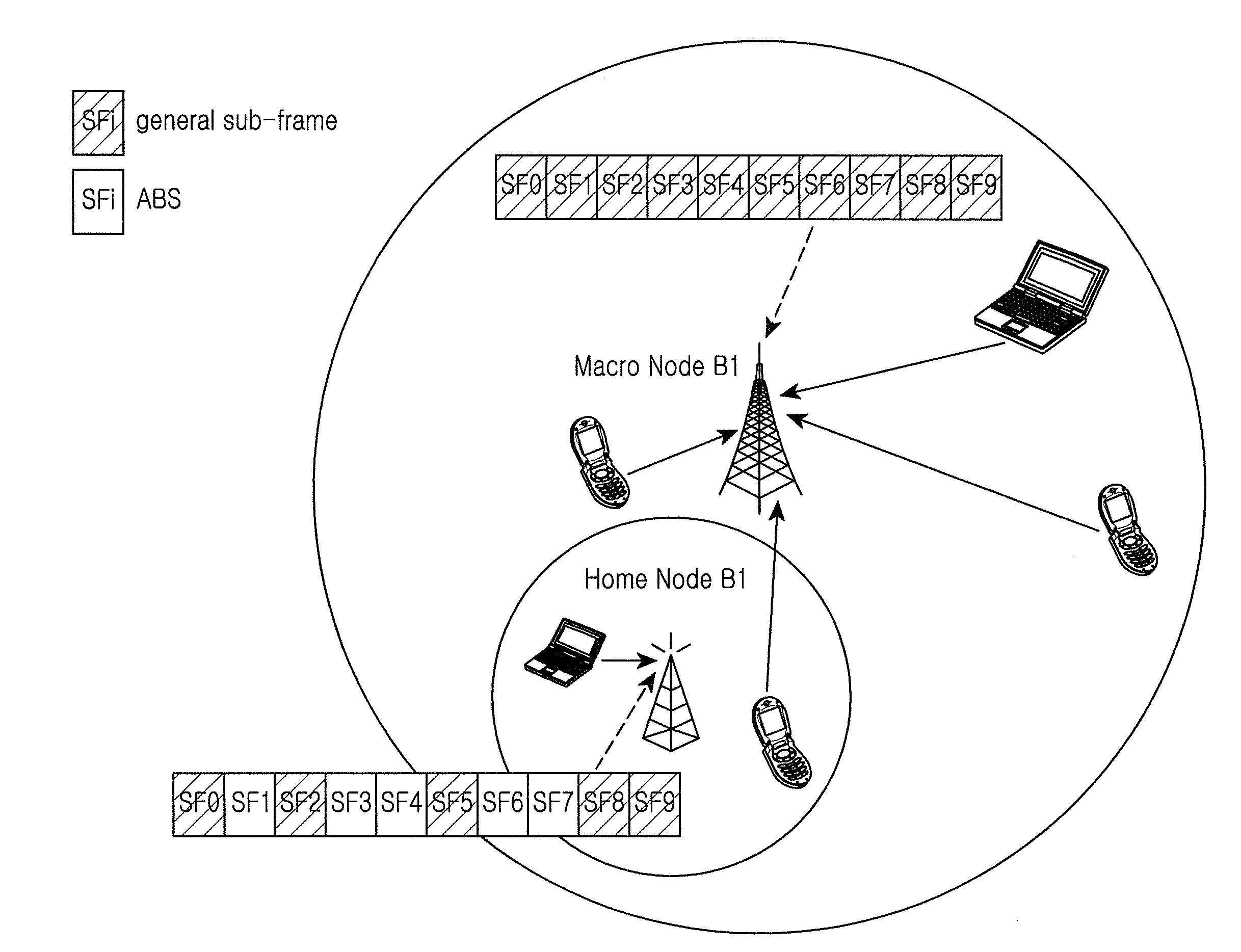
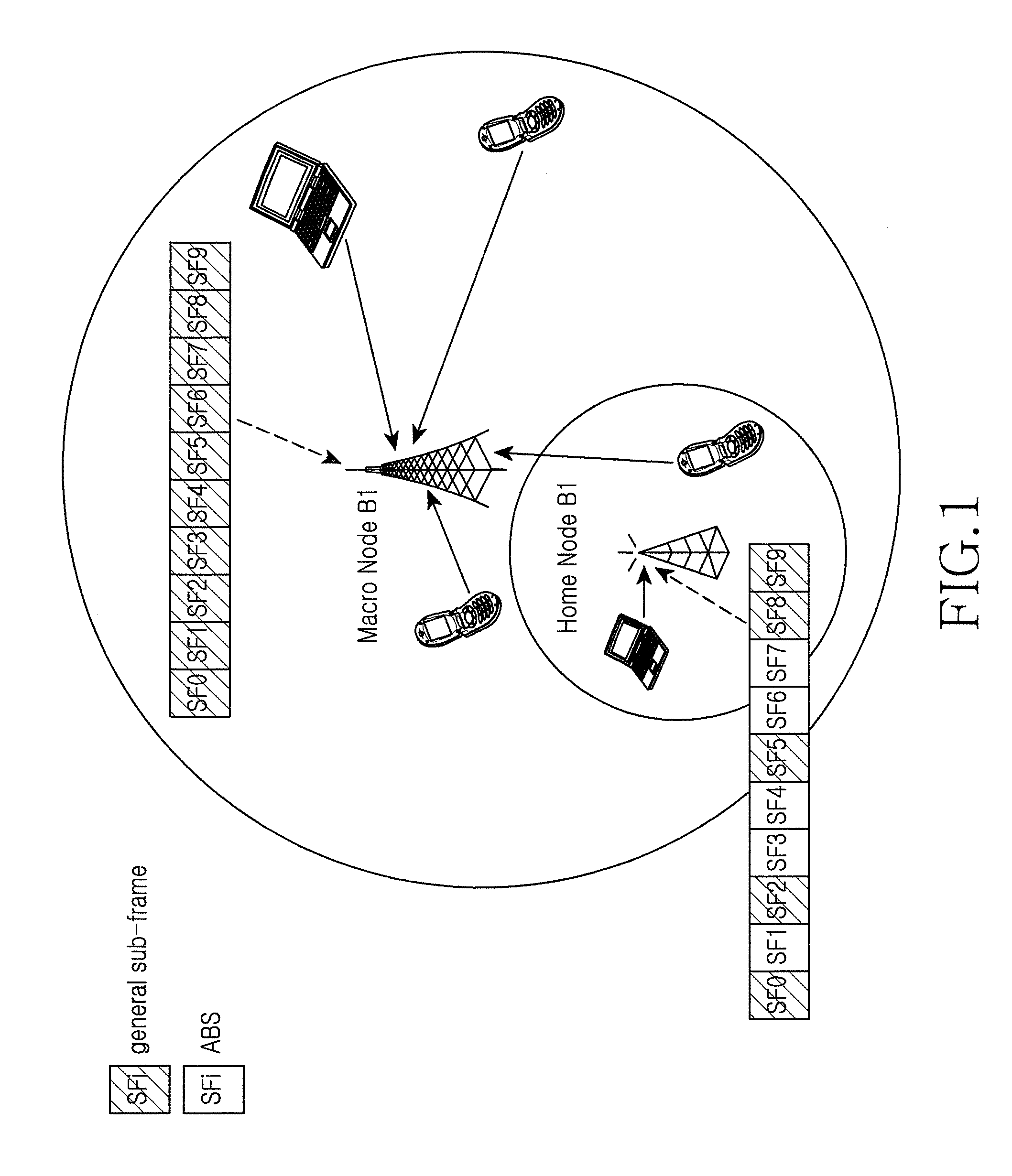
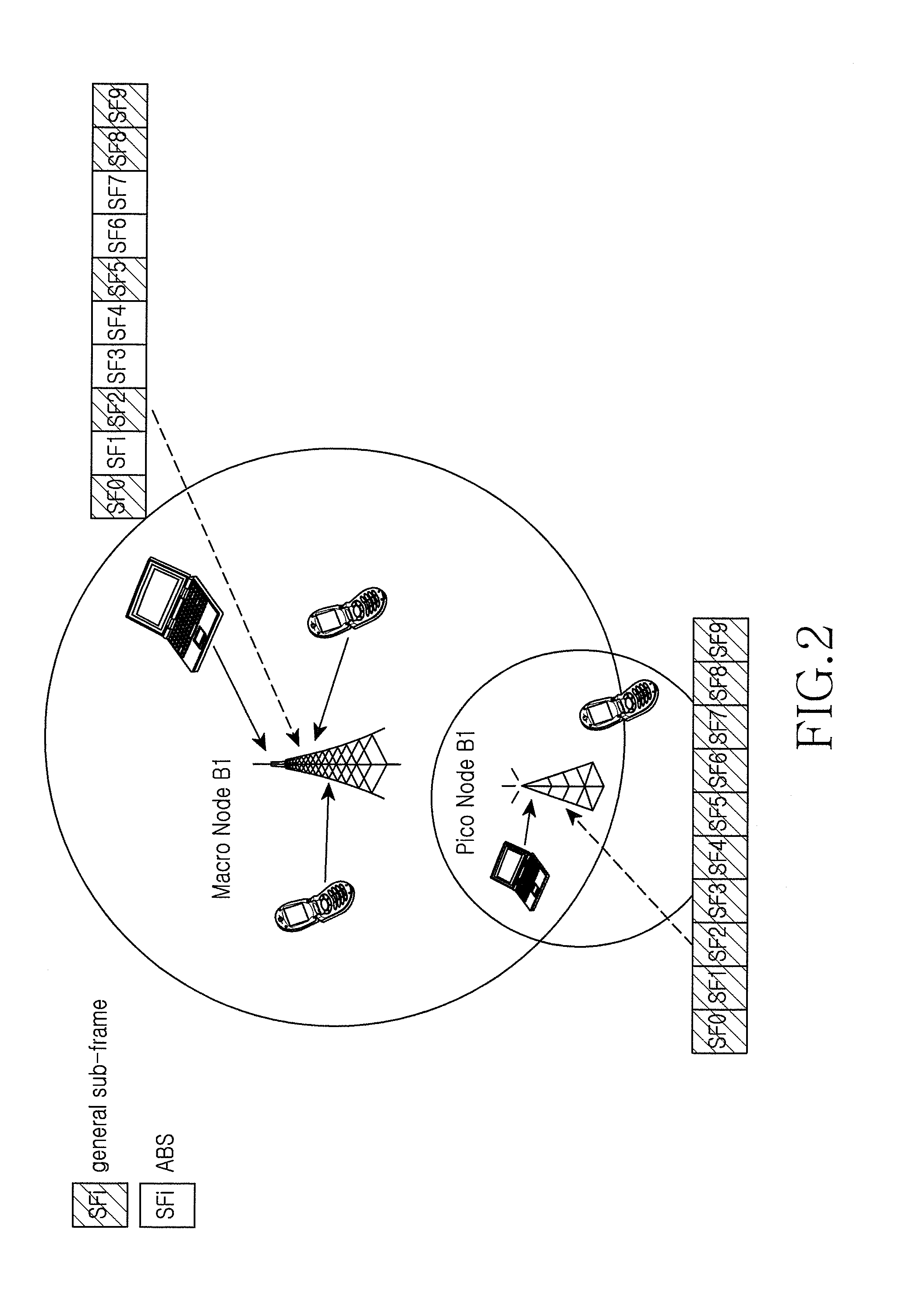
Method and apparatus for radio resource measurement in heterogeneous network
ActiveUS20120115529A1Avoid unnecessary complex measurement processMeasurement complexity is greatly reducedAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsRound complexity
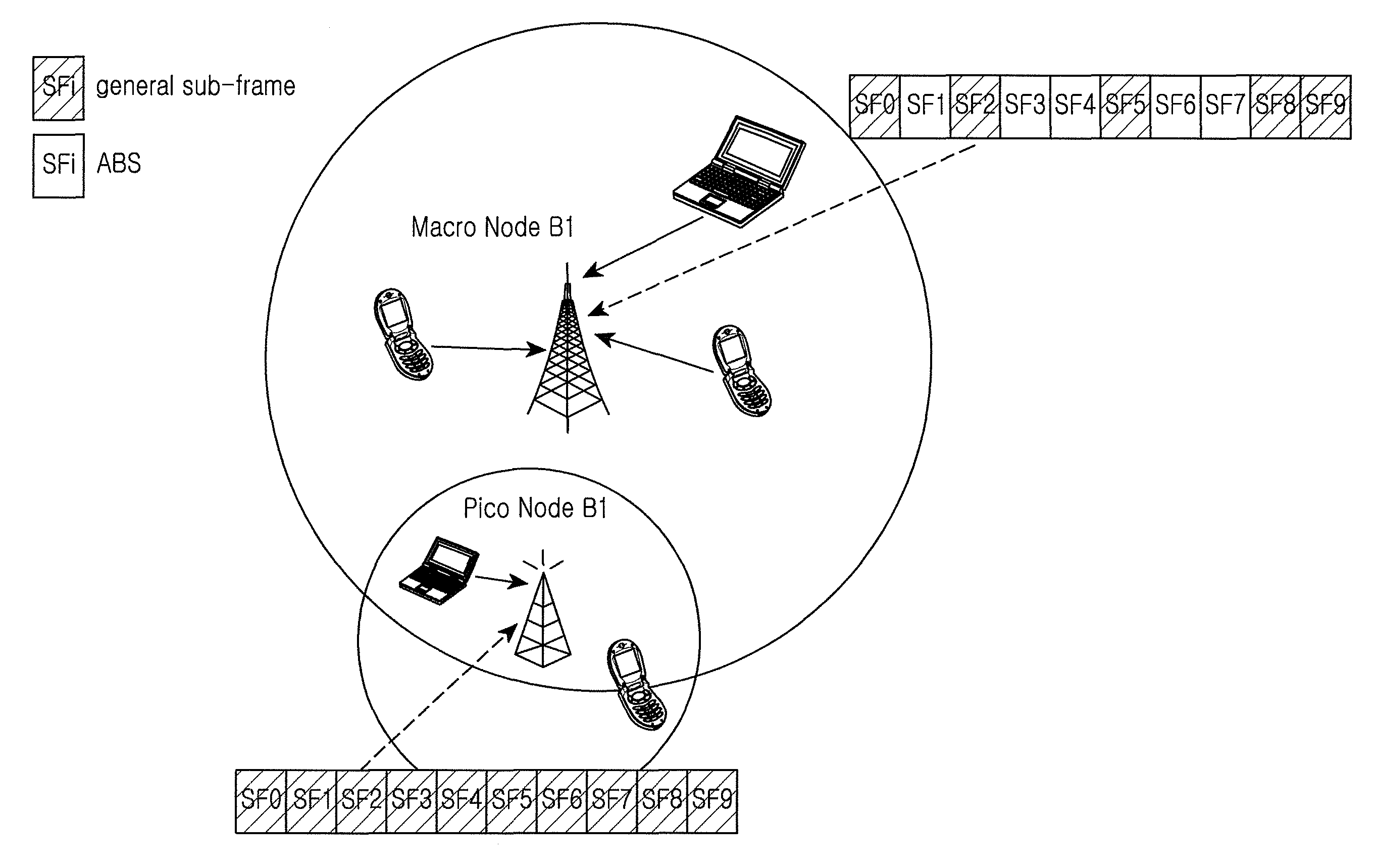
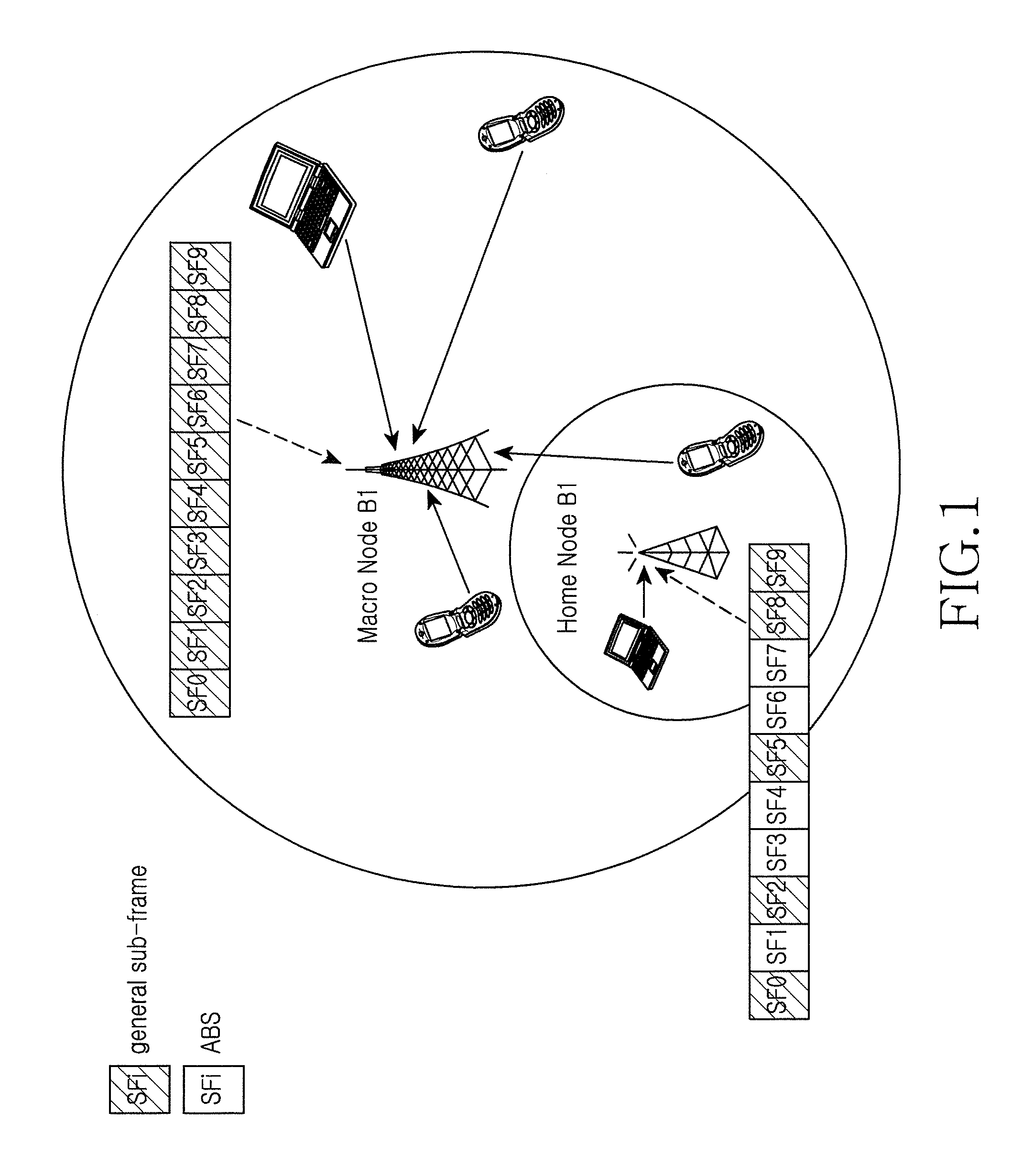
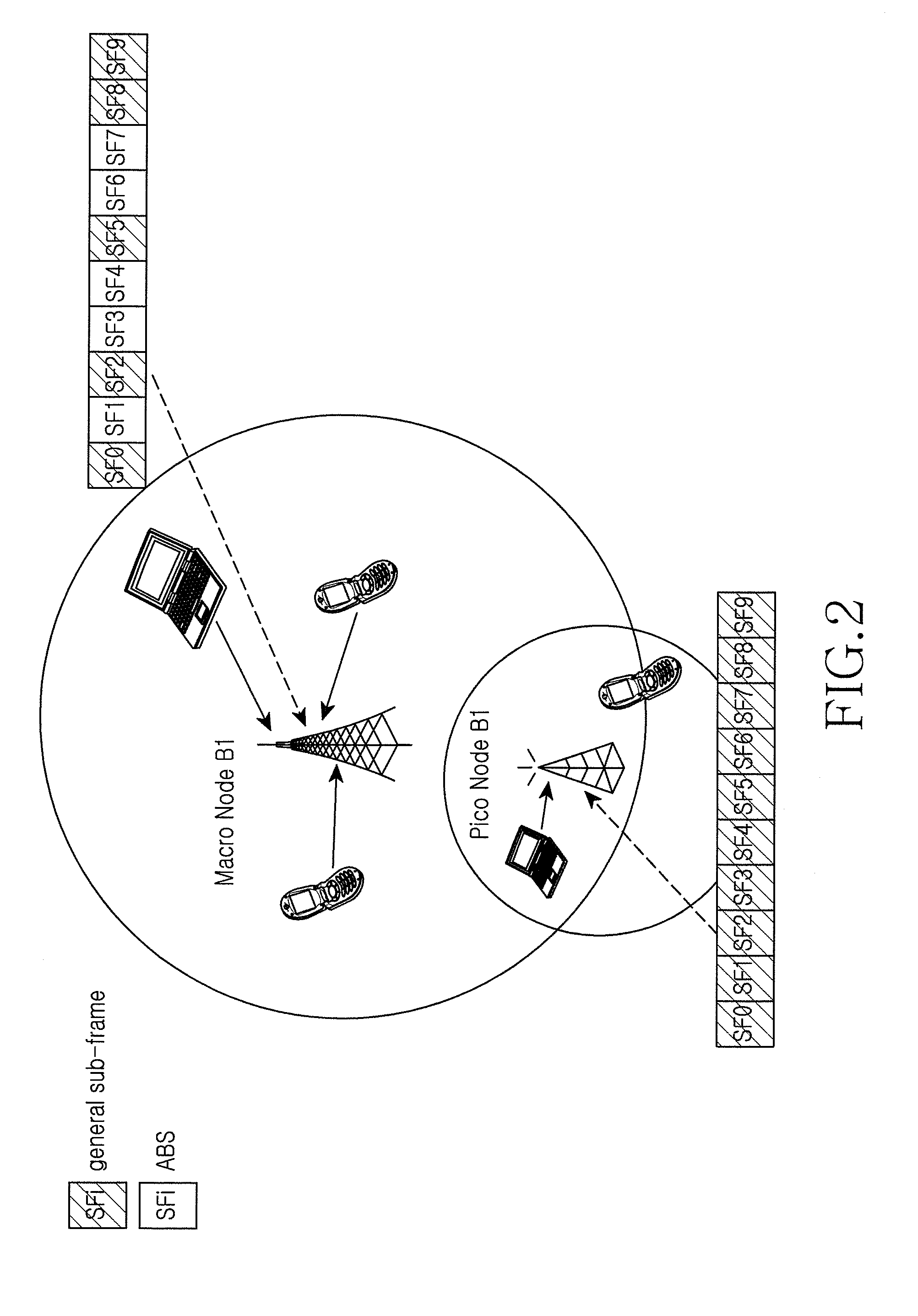
A radio resource measurement method in a heterogeneous network includes a user equipment (UE) that performs radio resource measurement; when a measurement result meets a predefined condition, the UE performs radio resource measurement on restricted resources according to configuration information of the restricted resources, wherein the restricted resources are a set of all sub-frame resources corresponding to Almost Blank Sub-frames (ABSes) or are a subset of the set. Therefore, the precision of RLM measurement or RRM measurement of a mobility system can be improved, and the implementation complexity of the UE can be decreased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
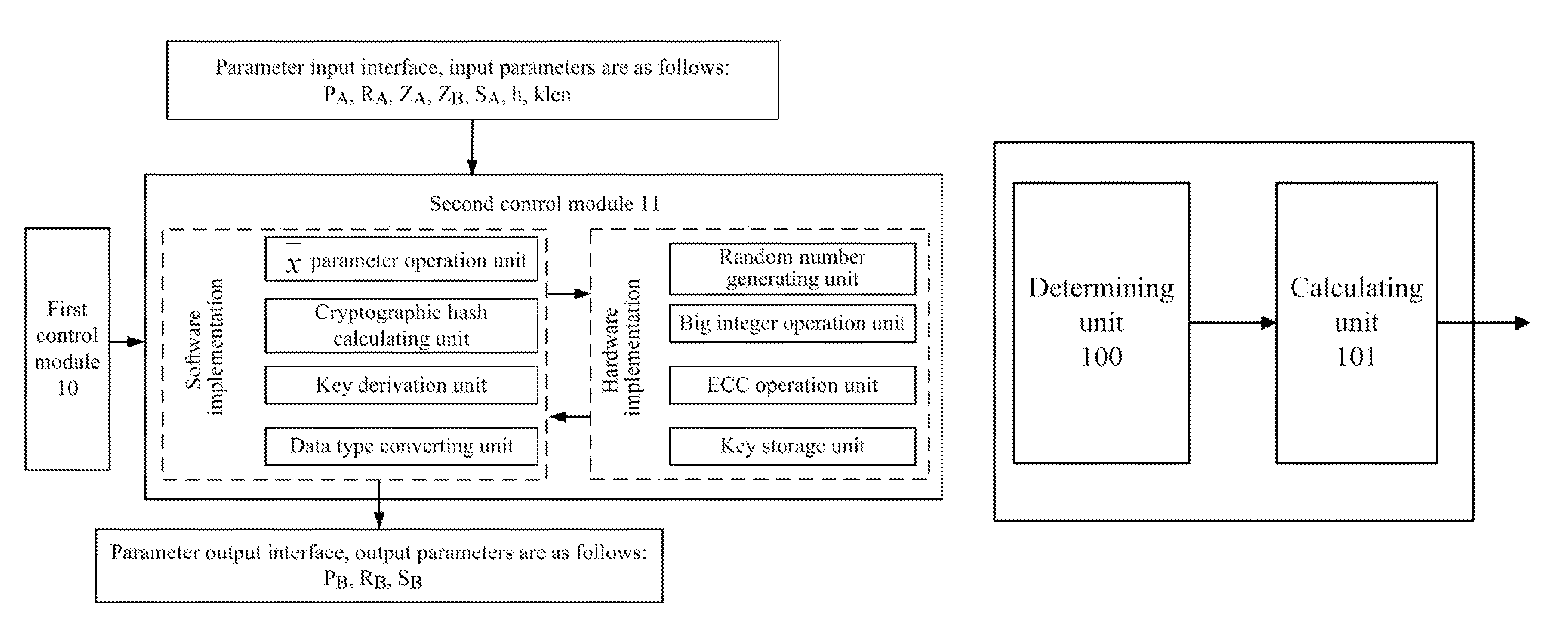
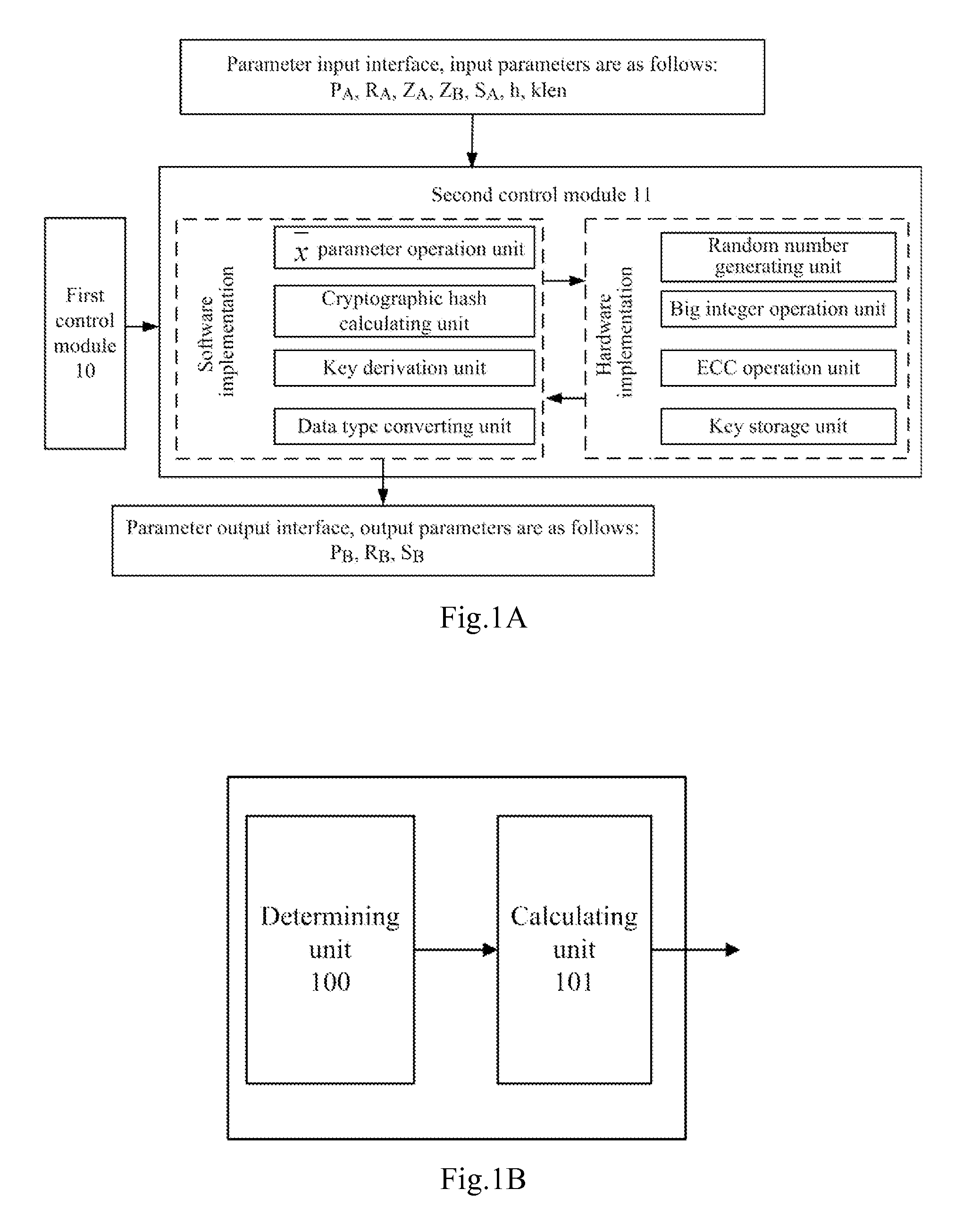
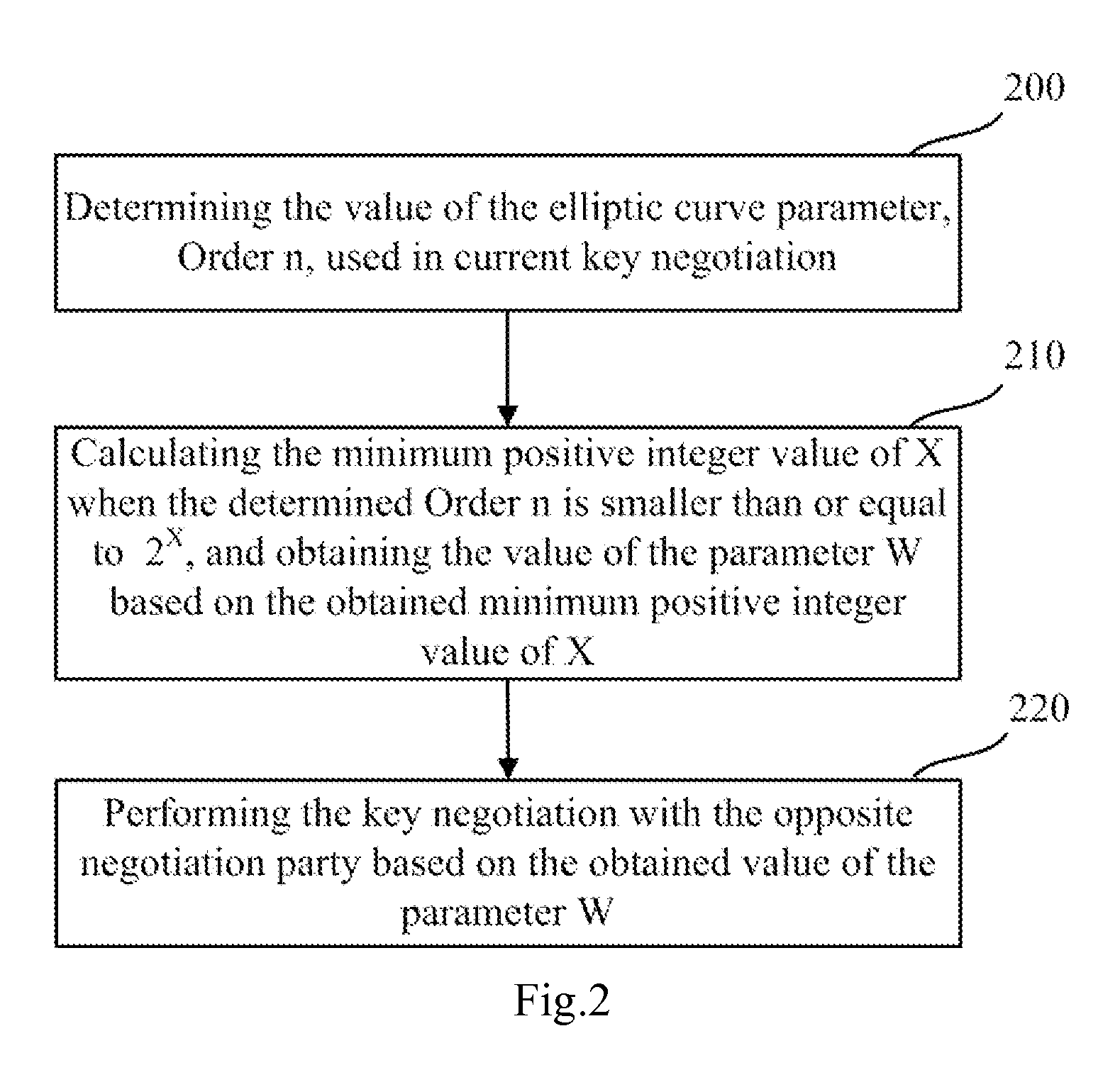
Key negotiation method and apparatus according to sm2 key exchange protocol
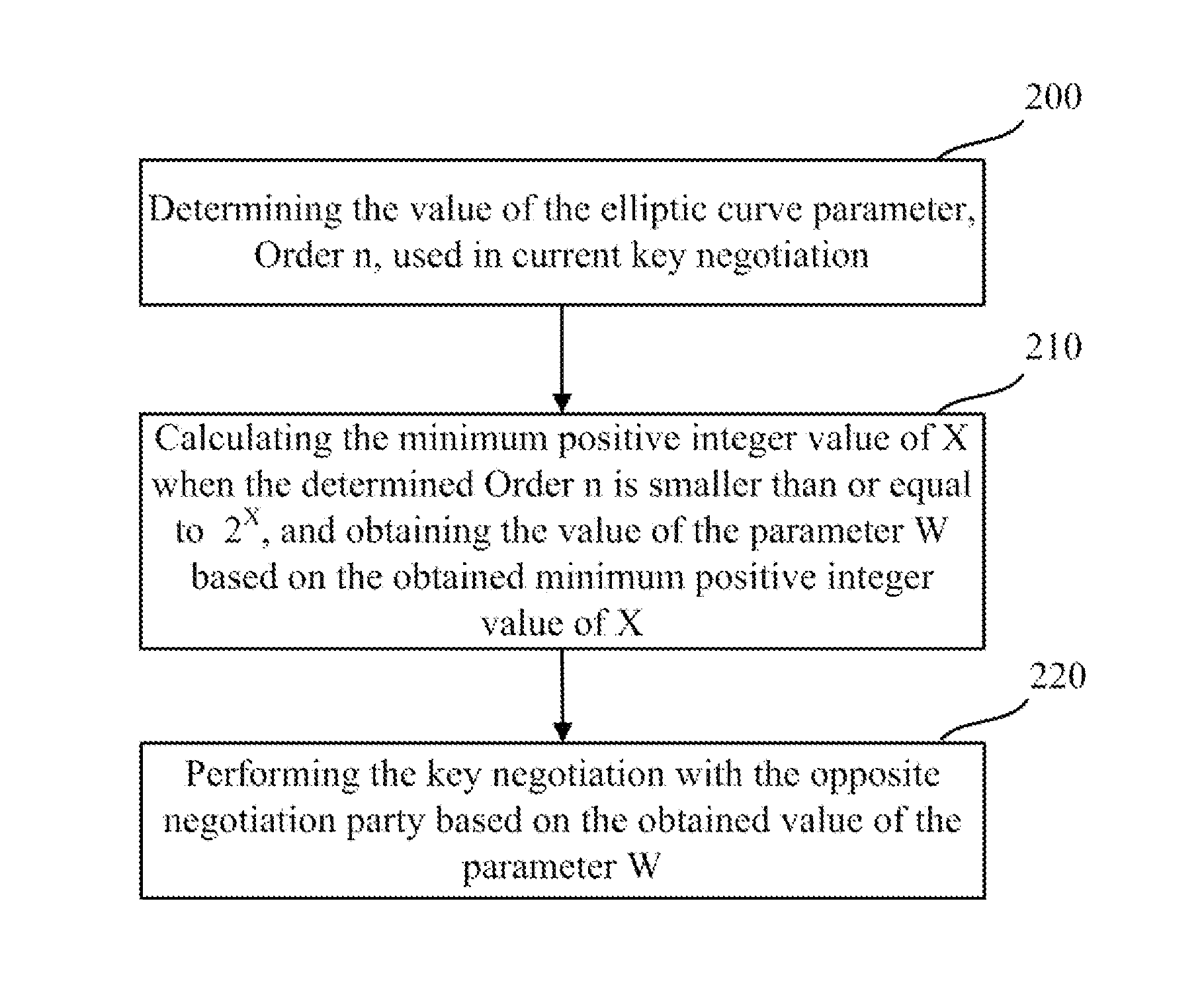
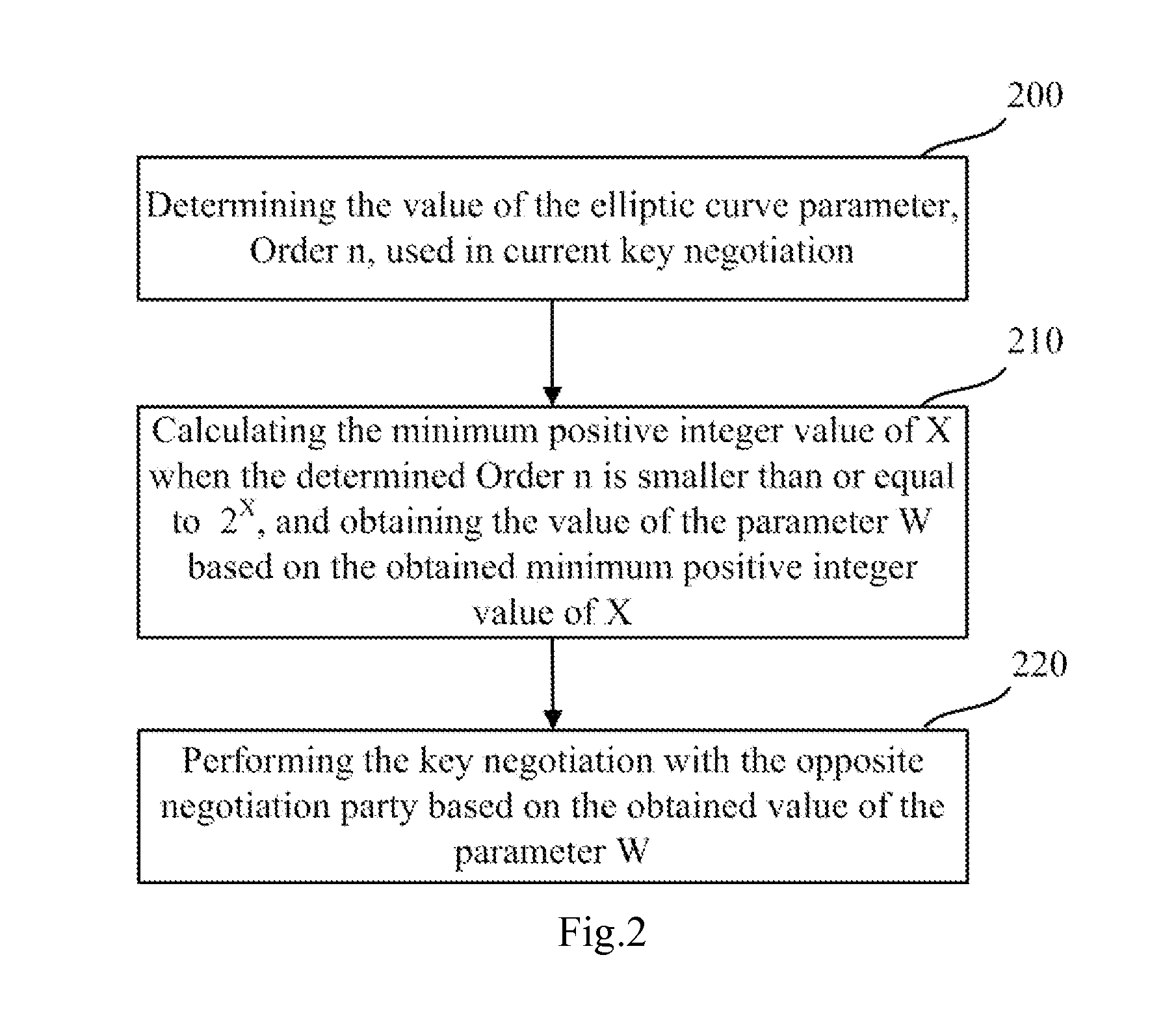
ActiveUS20150124970A1Implementation complexity can be reducedImprove execution efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageKey exchangeComputer hardware
The invention relates to the technical field of information, and disclosed in the present invention are a key negotiation method and apparatus according to the SM2 key exchange protocol. The method is implemented as follows: two negotiation parties both calculate a parameter W according to the minimum positive integer value in the permissible values of X which enable an inequality n≦2X to hold, and perform key negotiation with the opposite negotiation party according to the parameter W. Compared with a method for calculating the parameter W through calculating log2 (n) logarithmic value firstly and then rounding up the logarithmic value, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the calculated amount is effectively reduced, and the implementation complexity of an algorithm is reduced, thereby greatly improving the implementation efficiency of the key negotiation process based on the SM2 key exchange protocol, and then optimizing the engineering implementation of the SM2 key exchange protocol.
Owner:CHINA IWNCOMM
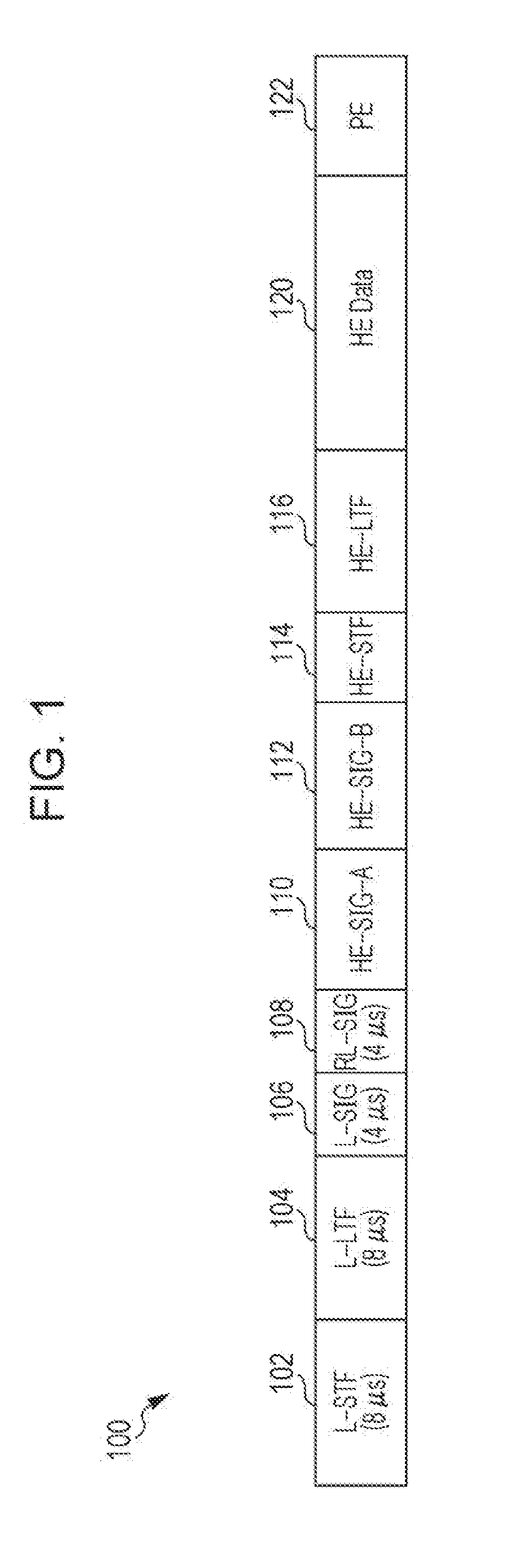
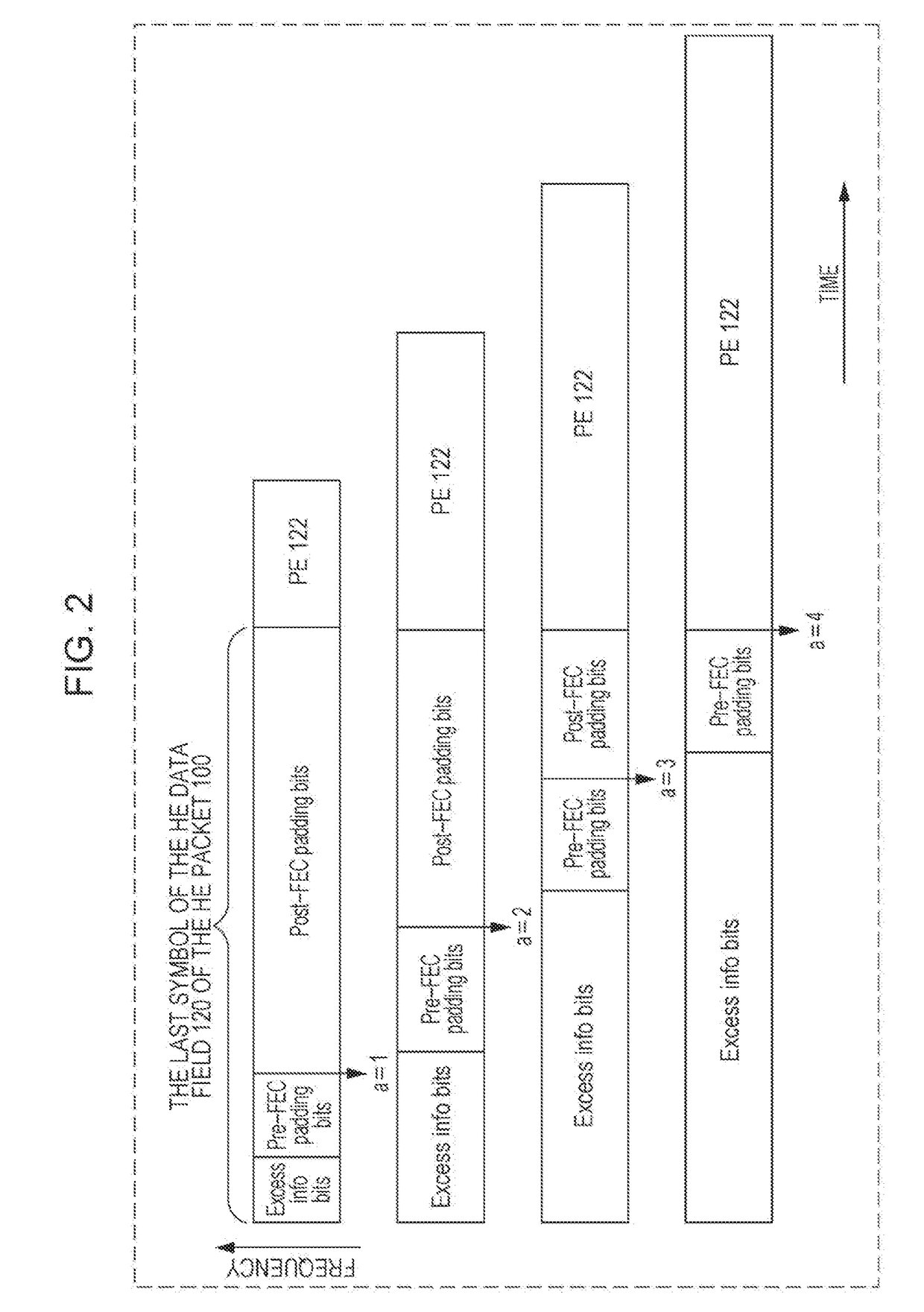
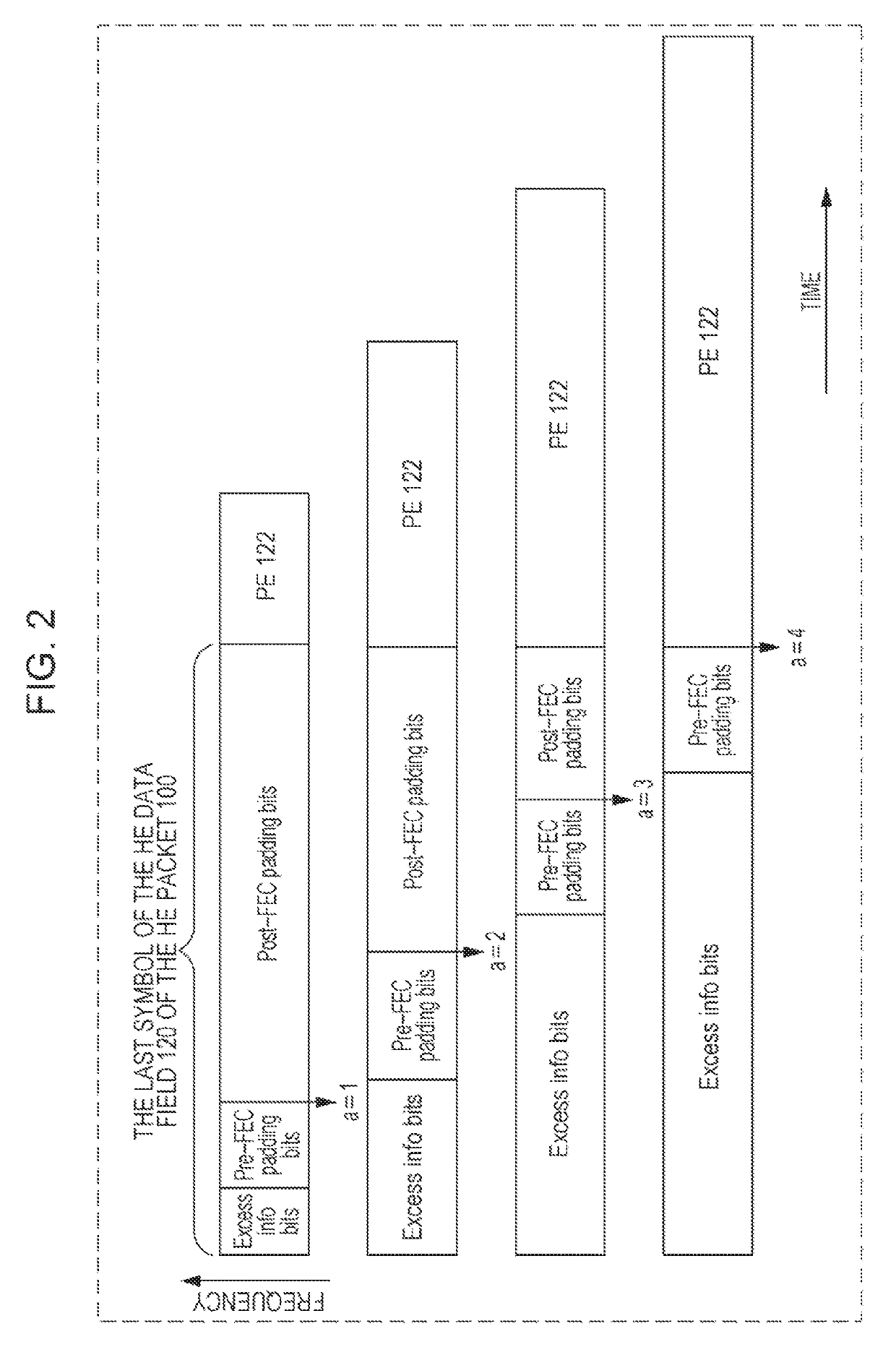
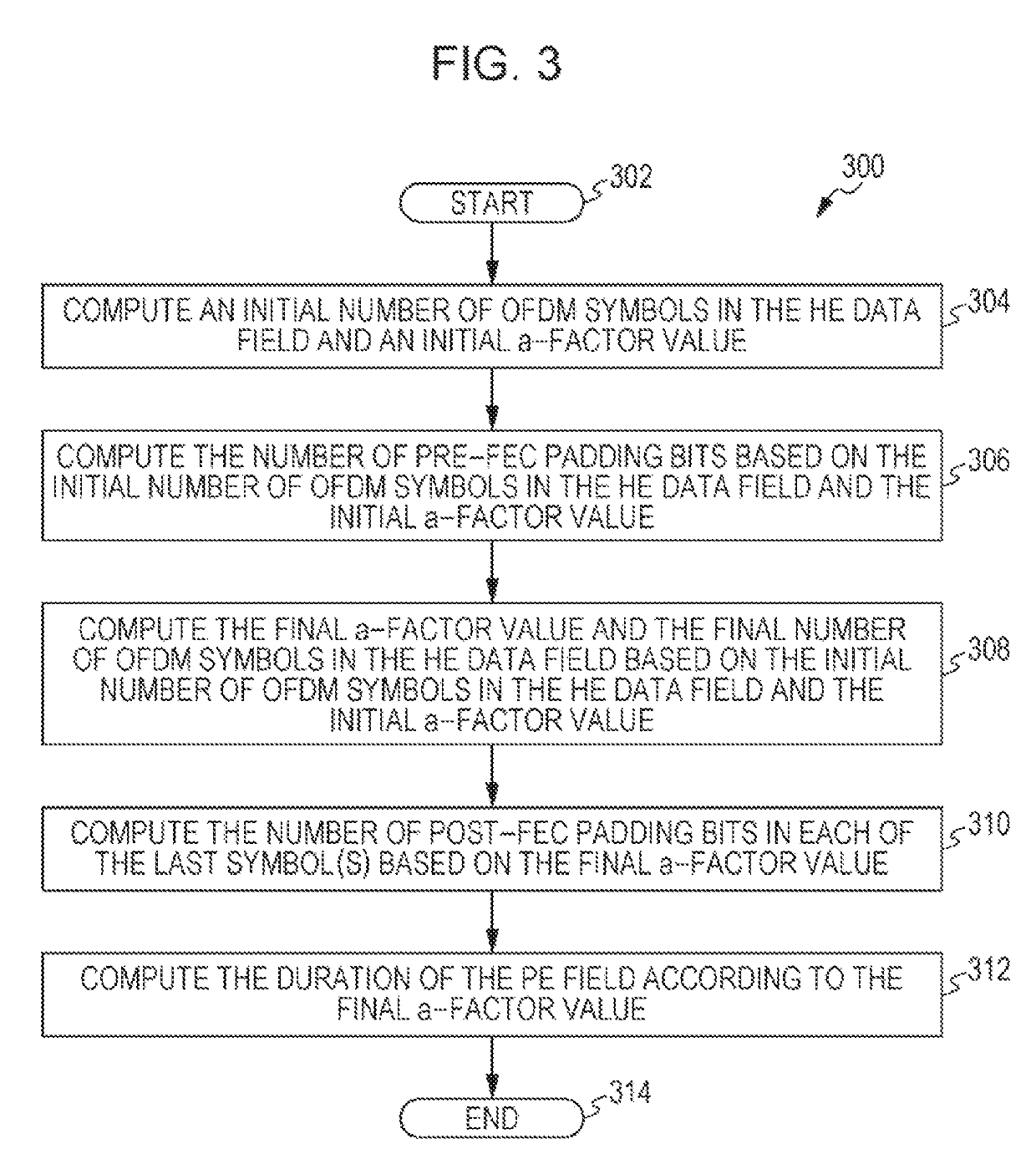
Transmission apparatus and transmission method for padding and packet extension for downlink multiuser transmission
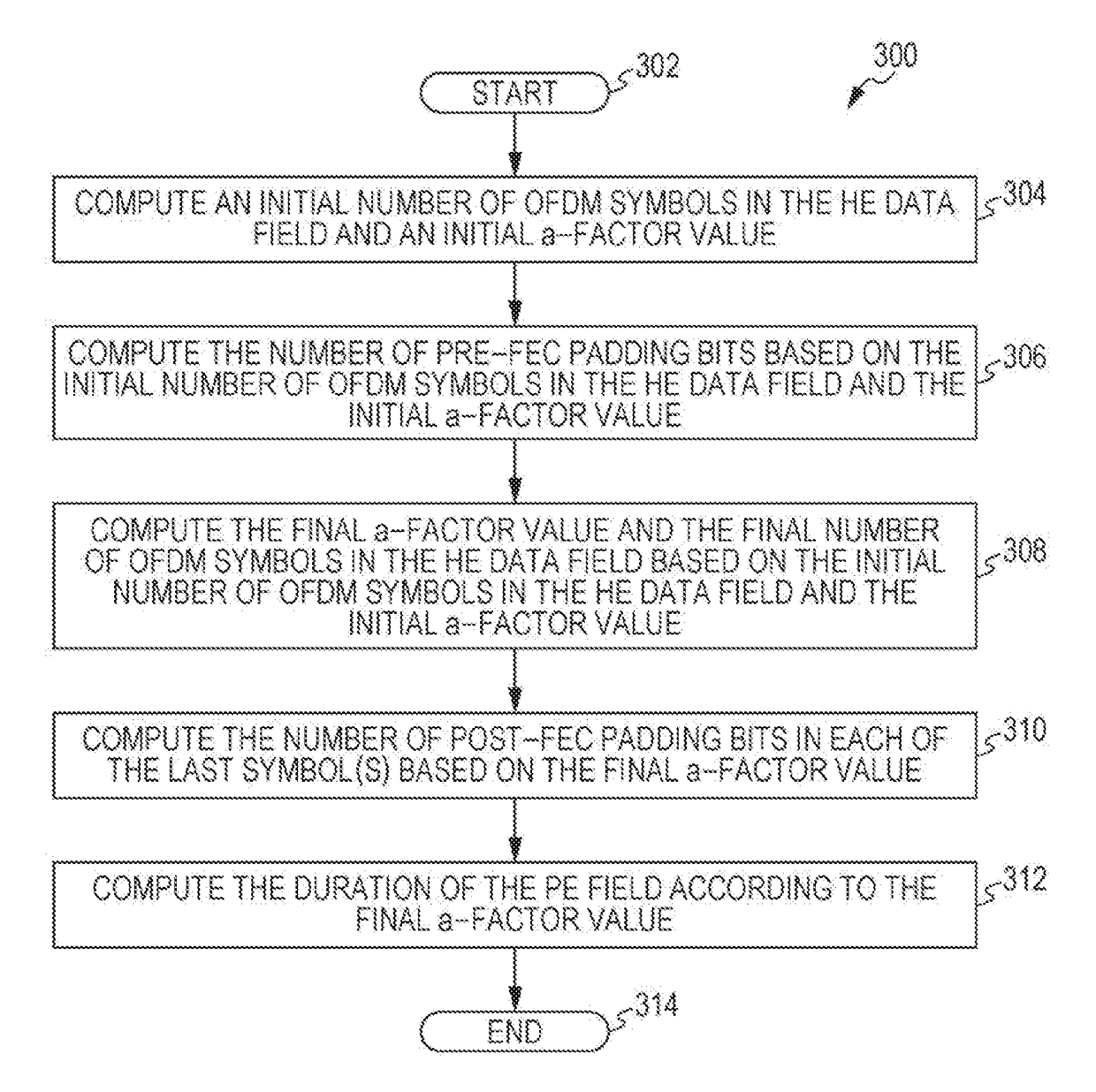
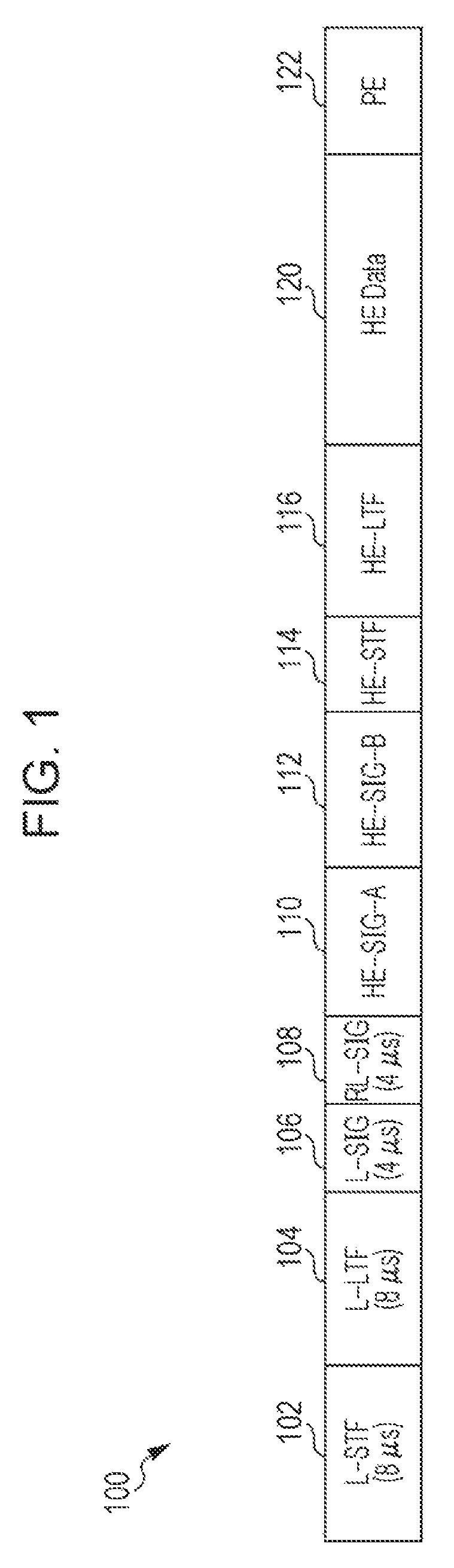
ActiveUS20180302256A1Increase system overheadReduce implementation complexityError preventionTransmission path divisionComputer scienceDuration time
A transmission method comprises: generating a transmission signal including OFDM symbols, wherein the last OFDM symbol of the OFDM symbols can be partitioned into four segments, and wherein the generating includes: computing an initial padding factor value associated with one of the four segments and computing an initial number of OFDM symbols; determining a user with a longest packet duration among plural users; determining a common padding factor value being the initial padding factor value and a common number of OFDM symbols being the initial number of OFDM symbols of the determined user with the longest packet duration; adding pre-FEC padding bits toward one of four possible boundaries of the last OFDM symbol, the one of four possible boundaries being represented by the determined common padding factor value; and adding post-FEC padding bits in remaining segment(s) of the last OFDM symbol; and transmitting the generated transmission signal.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Method and apparatus for concatenated channel coding with variable code rate and coding gain in a data transmission system
InactiveUS6883133B1Valid encodingReduce complexityError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesComputer hardwareBlock code
A novel method and apparatus for efficiently coding and decoding data in a data transmission system is described. A concatenated coding scheme is presented that is easily implemented, and that provides acceptable coding performance characteristics for use in data transmission systems. The inventive concatenated channel coding technique is well suited for small or variable size packet data transmission systems. The technique may also be adapted for use in a continuous mode data transmission system. The method and apparatus reduces the complexity, cost, size and power consumption typically associated with the prior art channel coding methods and apparatuses, while still achieving acceptable coding performance. The present invention advantageously performs concatenated channel coding without the necessity of a symbol interleaver. In addition, the present invention is simple to implement and thereby consumes much less space and power that do the prior art approaches. The present invention not only eliminates the need for a symbol interleaver between the outer and inner codes, but it also enjoys a drastically reduced implementation complexity of the inner code Viterbi decoder. The preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises an inner code having short length block codes derived from short constraint length convolutional codes utilizing trellis tailbiting and a decoder comprising four four-state Viterbi decoders having a short corresponding maximum length. The inner code preferably comprises short block codes derived from four-state (i.e., constraint length 3), nonsystematic, punctured and unpunctured convolutional code. One significant advantage of the preferred embodiment of the present concatenated coding technique is that packet data transmission systems can be designed to have variable coding gains and coding rates.
Owner:TUMBLEWEED HLDG LLC +1
Method and apparatus for concatenated channel coding with variable code rate and coding gain in a data transmission system
InactiveUS20070033509A1Valid encodingReduce complexityError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionComputer hardwareTransport system
A novel method and apparatus for efficiently coding and decoding data in a data transmission system is described. A concatenated coding scheme is presented that is easily implemented, and that provides acceptable coding performance characteristics for use in data transmission systems. The inventive concatenated channel coding technique is well suited for small or variable size packet data transmission systems. The technique may also be adapted for use in a continuous mode data transmission system. The method and apparatus reduces the complexity, cost, size and power consumption typically associated with the prior art channel coding methods and apparatuses, while still achieving acceptable coding performance. The present invention advantageously performs concatenated channel coding without the necessity of a symbol interleaver. In addition, the present invention is simple to implement and thereby consumes much less space and power that do the prior art approaches. The present invention not only eliminates the need for a symbol interleaver between the outer and inner codes, but it also enjoys a drastically reduced implementation complexity of the inner code Viterbi decoder. The preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises an inner code having short length block codes derived from short constraint length convolutional codes utilizing trellis tailbiting and a decoder comprising four four-state Viterbi decoders having a short corresponding maximum length. The inner code preferably comprises short block codes derived from four-state (i.e., constraint length 3), nonsystematic, punctured and unpunctured convolutional code. One significant advantage of the preferred embodiment of the present concatenated coding technique is that packet data transmission systems can be designed to have variable coding gains and coding rates.
Owner:TUMBLEWEED HLDG LLC +1
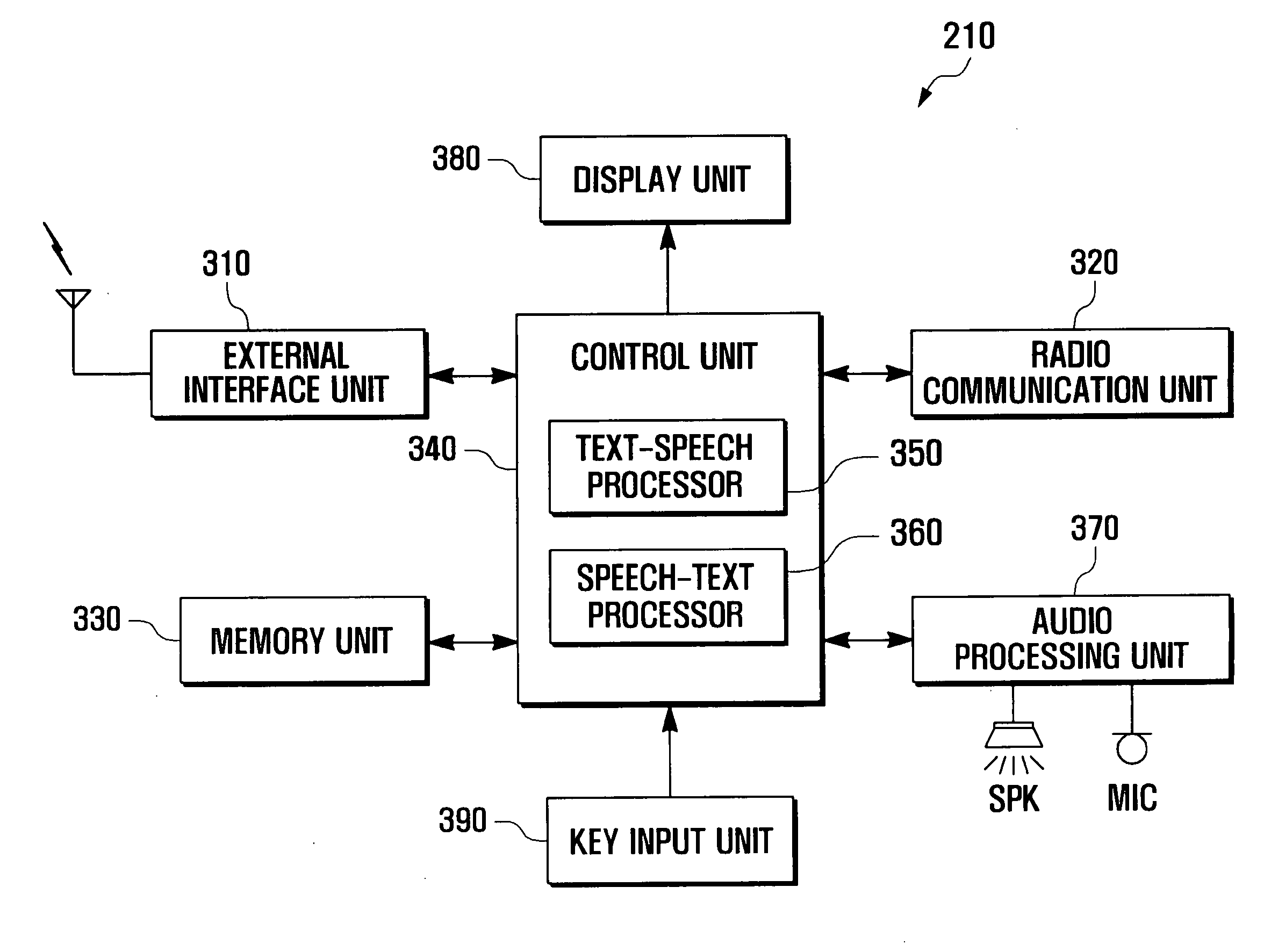
Communication method and terminal
InactiveUS20110112834A1Reduce implementation complexityImprove user convenienceInformation formatContent conversionUser inputTransformation of text
A communication method and terminal assist hearing and speech impaired persons. The communication method includes generating a text by combining at least one character input in a text call mode. The text is converted to a speech, and the converted speech is transmitted to a counterparty terminal. The communication terminal of the present invention is capable of converting the text input by the user to a speech signal for the counterparty terminal and converting the speech signal received from the counterparty terminal to a text such that it is possible for the user to conduct a communication with the counterparty regardless of whether the counterparty is a hearing or speech impaired or whether the counterparty's terminal supports the text call service, resulting in reduction of the text call service implementation complexity and improvement of user convenience.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
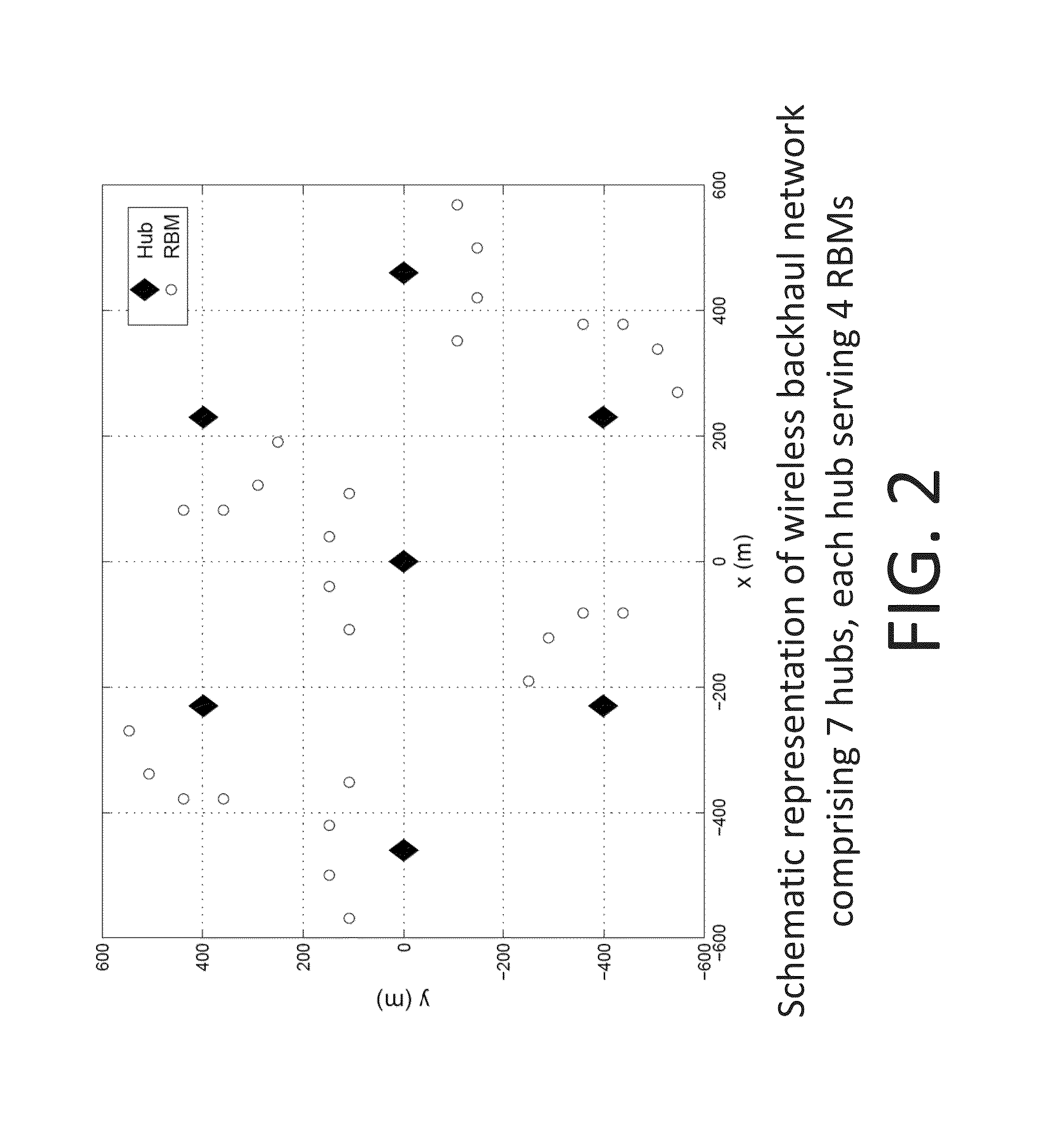
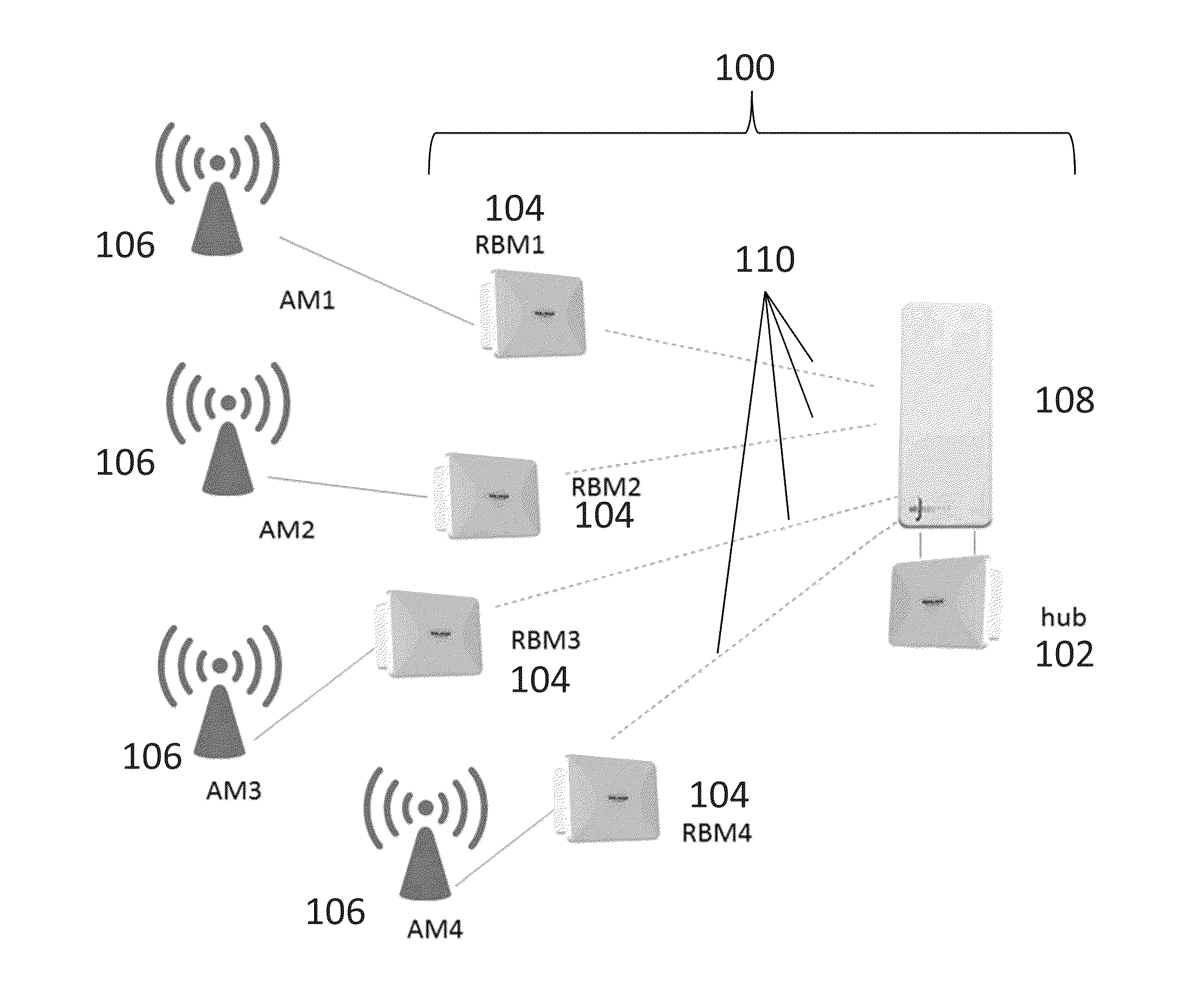
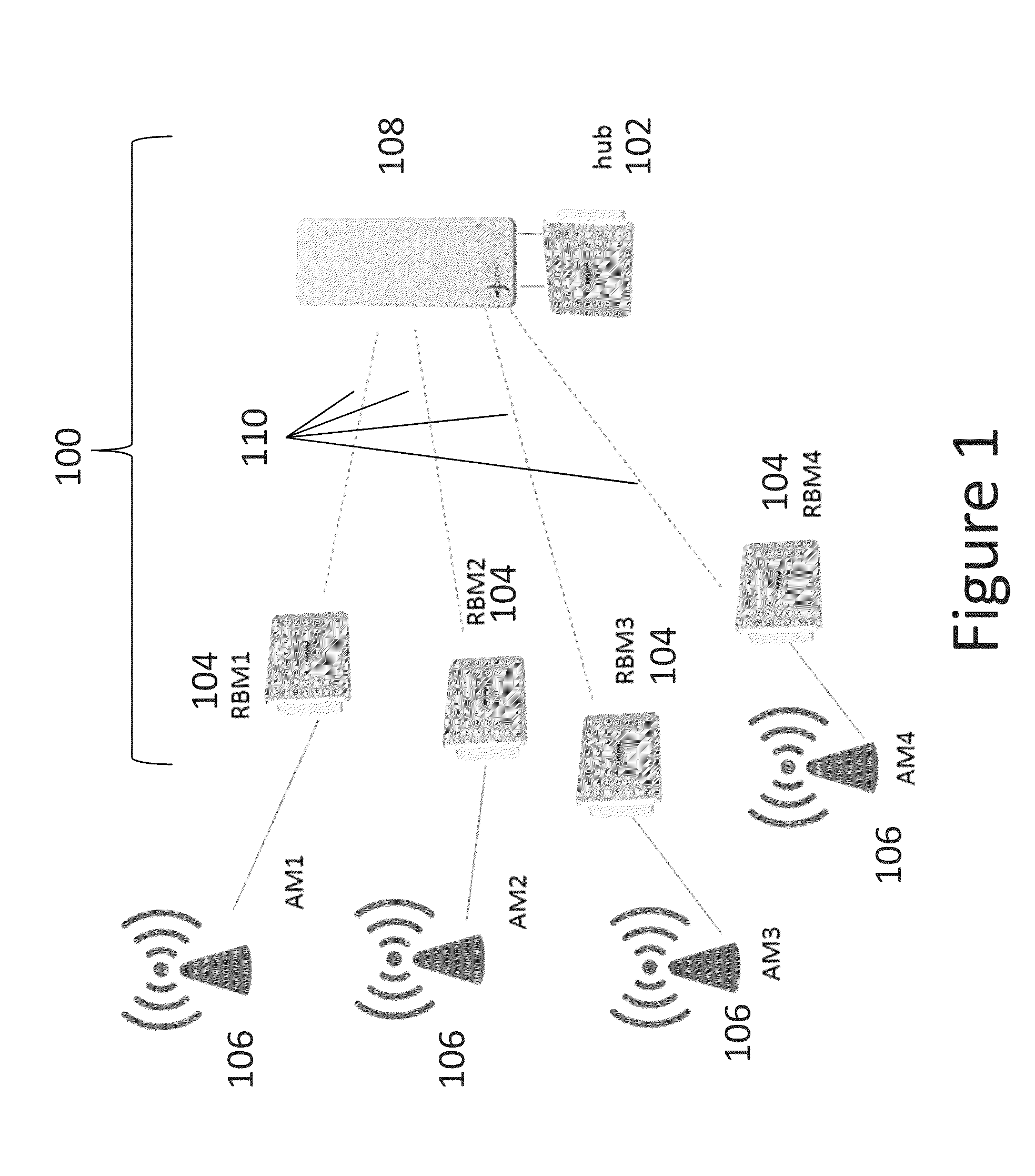
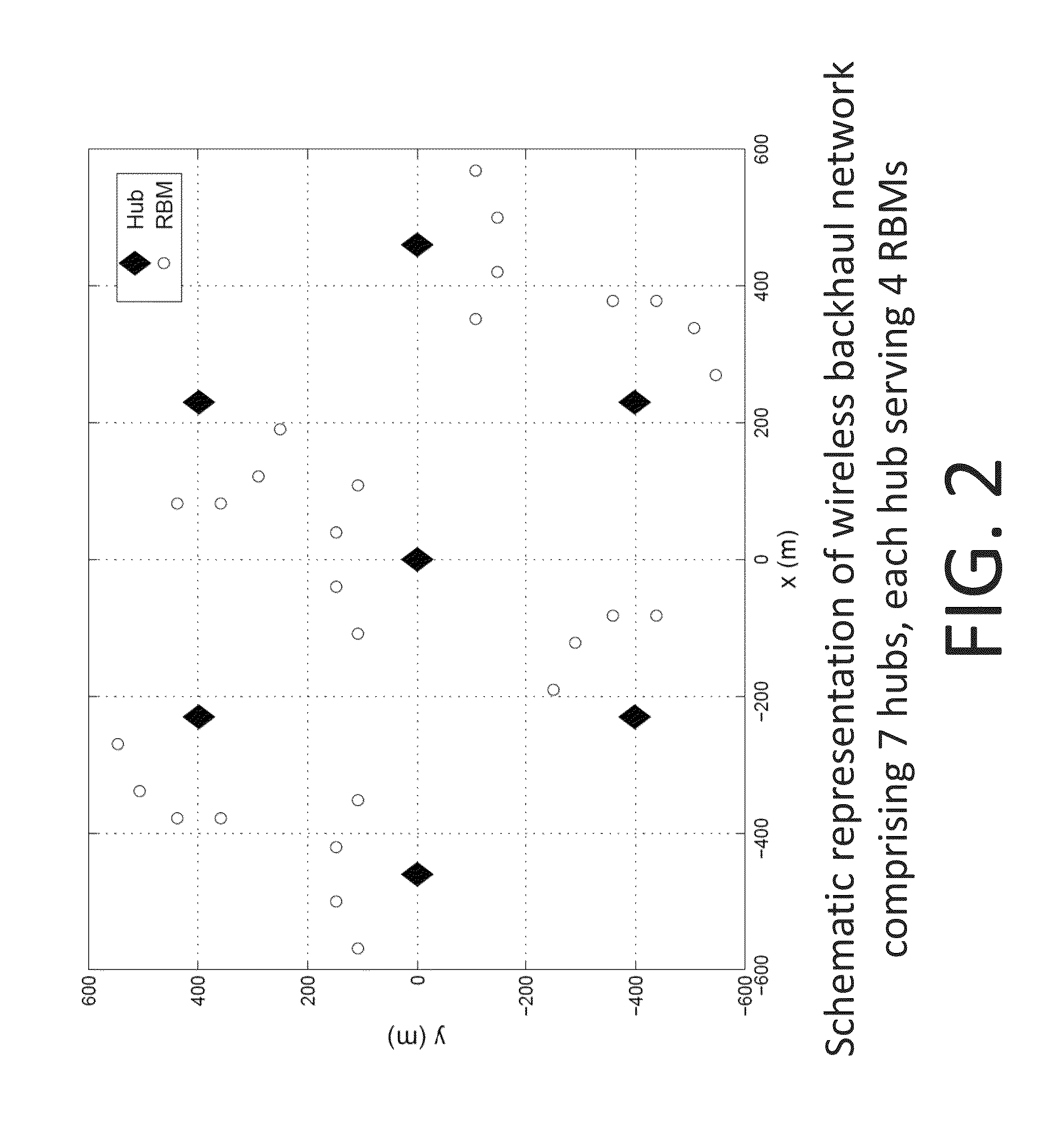
Method and apparatus for managing interference in wireless backhaul networks through power control with a one-power-zone constraint
ActiveUS20130260817A1Eliminate, orReduce disadvantagesPower managementRadio transmissionComputation complexityNewton's method
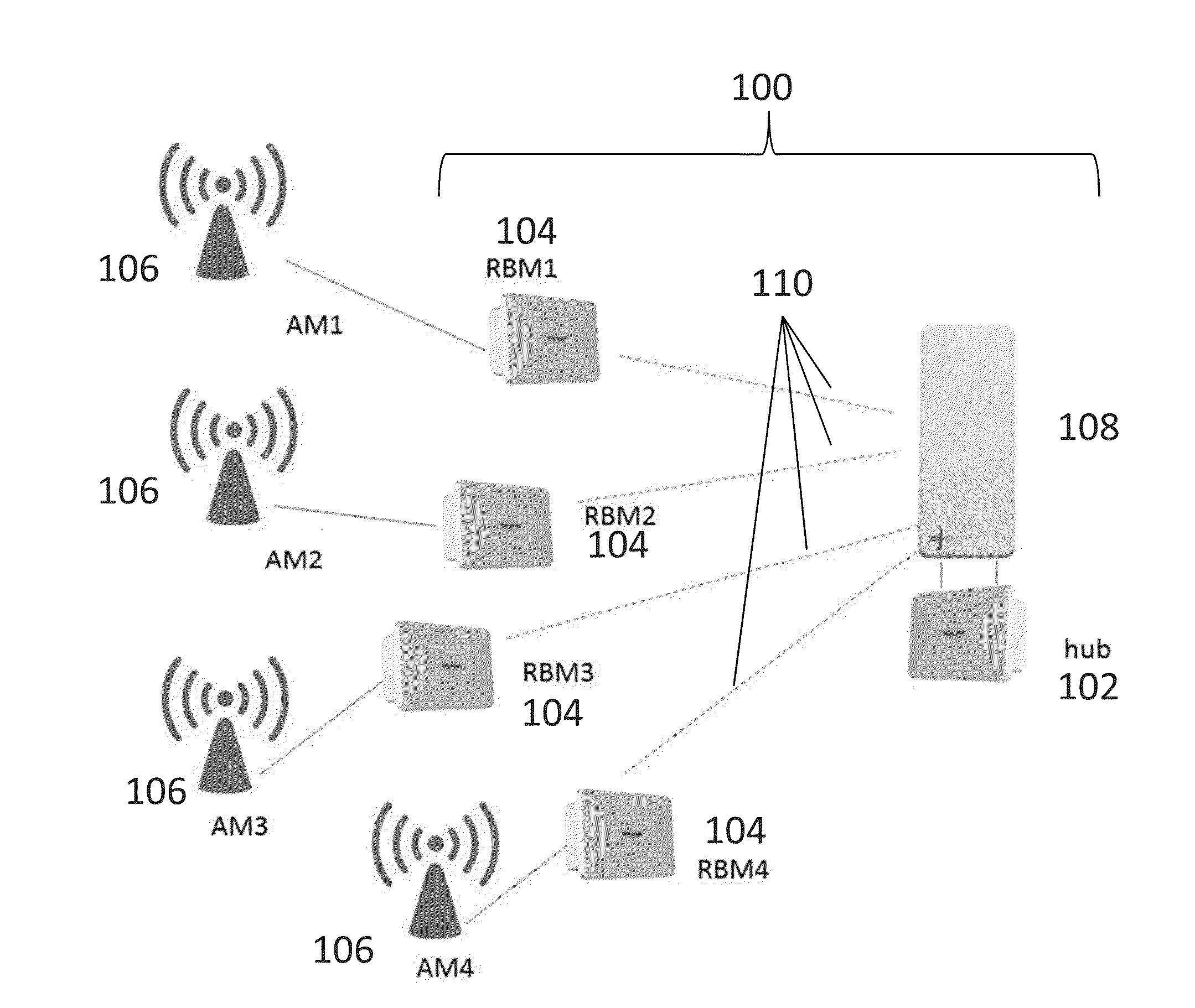
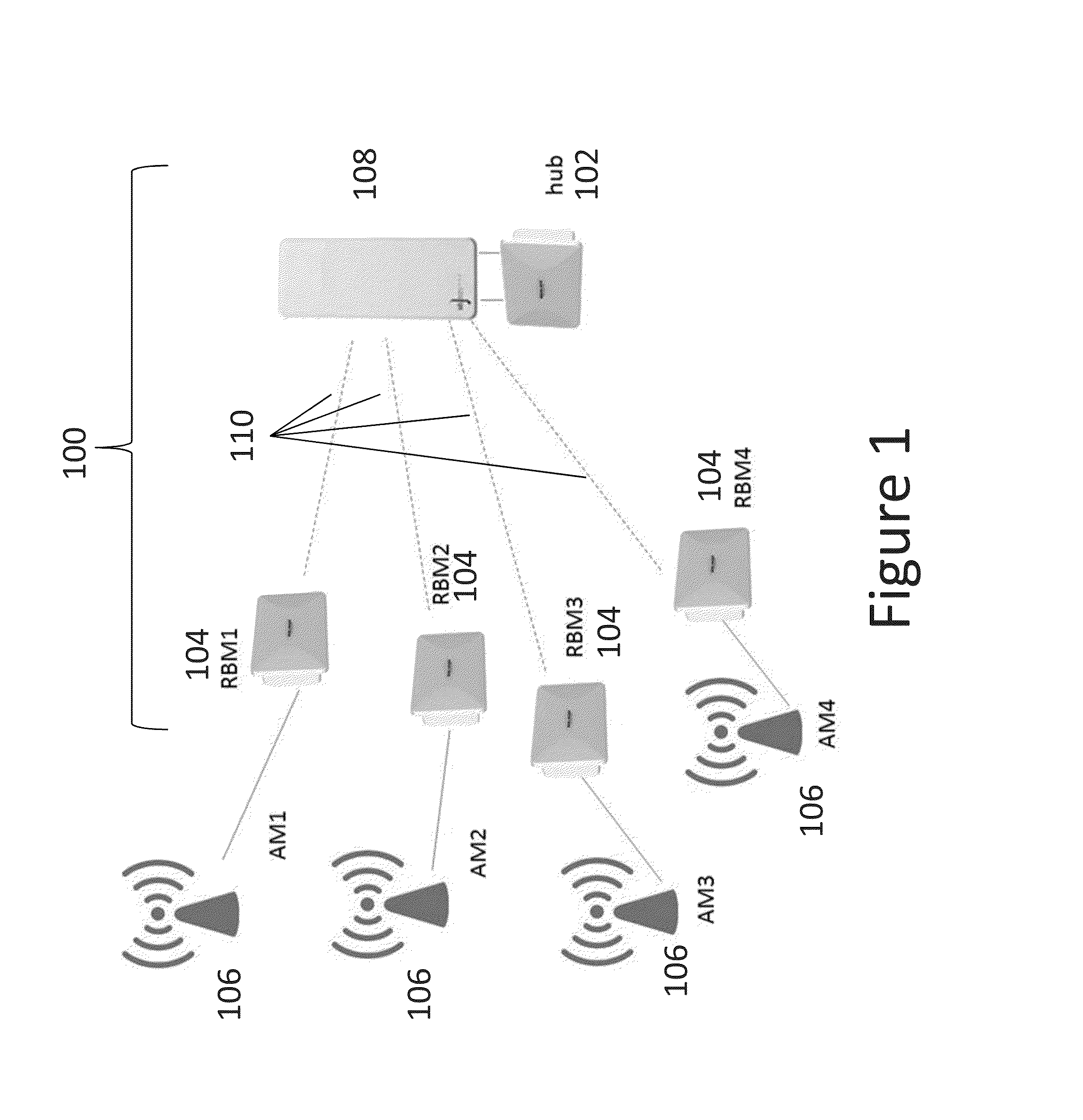
Methods and apparatus are provided for managing interference in a wireless backhaul network comprising a plurality of hubs, each hub serving a plurality of remote backhaul modules (RBM), using power control with a one-power-zone (OPZ) constraint. Each hub uses a transmit frame structure comprising a plurality of zones, each RBM is scheduled on a different zone, and the same power level is maintained across all zones within a transmit frame. Under the OPZ constraint, and for scheduling policies under which the number of zones assigned to each RBM is fixed, the power and scheduling sub-problems are decoupled. This enables power control independent of scheduling, using methods having lower computational complexity. Methods are disclosed comprising iterative function evaluation or Newton's method approaches based on a weighted sum-rate maximization across the network, which can be implemented in a distributed fashion. Some of the methods can be implemented asynchronously at each hub.
Owner:BLINQ NETWORKS
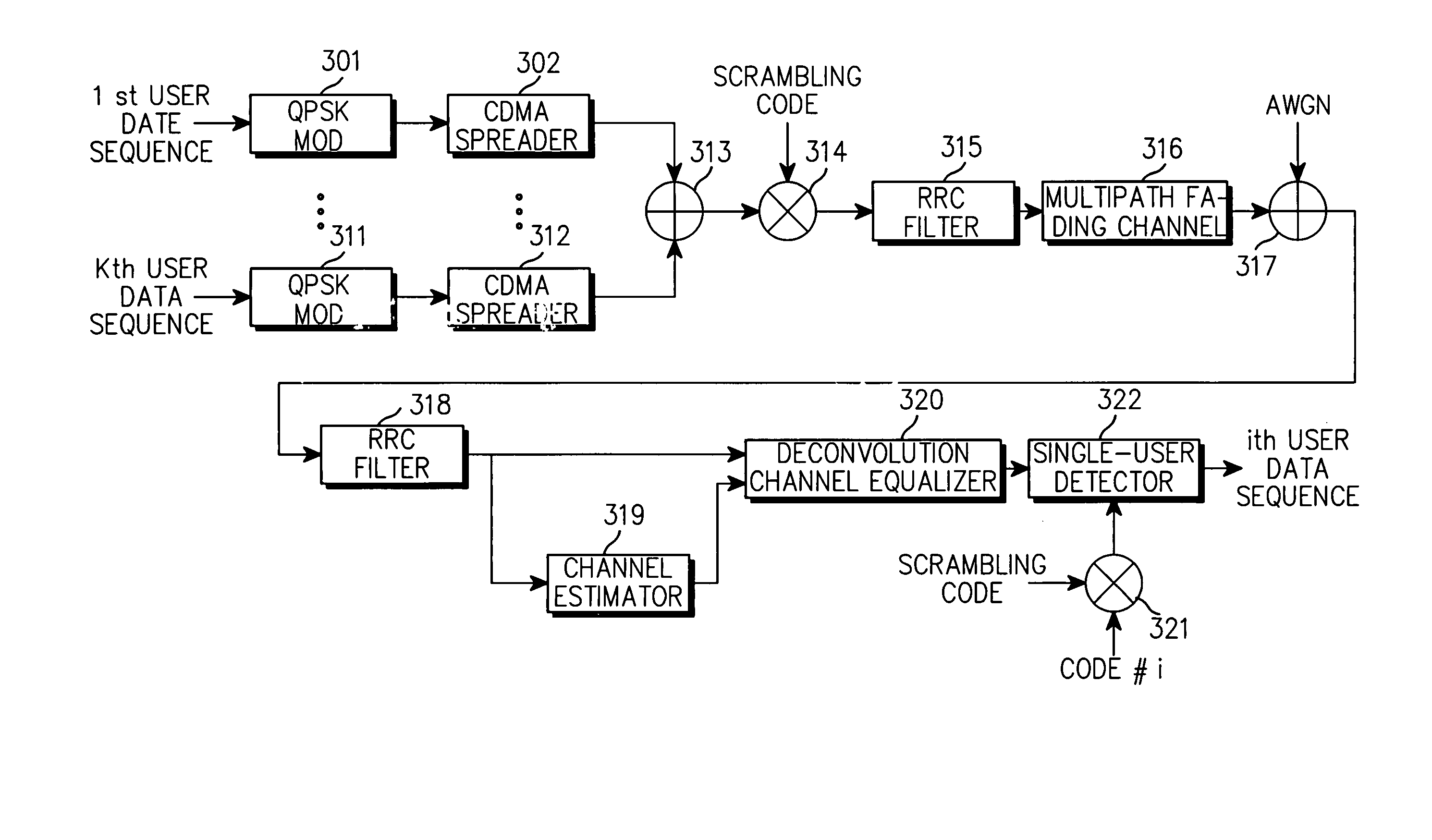
Method and apparatus for downlink joint detection in a communication system
InactiveUS7161972B2Reduce complexityImplementation complexity can be reducedTransmitter/receiver shaping networksChannel impulse responseCommunications system
A ZF joint detection apparatus for a downlink receiver, the apparatus comprising: a channel estimator for estimating a channel impulse response of a multipath fading channel of a received signal; a channel equalizer for estimating a transmission signal by performing channel compensation and removing multipath interference by a deconvolution technique based on the estimated channel impulse response; and a user detector for detecting a symbol-level data sequence transmitted by a specific user by despreading the transmission signal estimated by the channel equalizer with a spreading code for the specific user and a scrambling code.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP +1
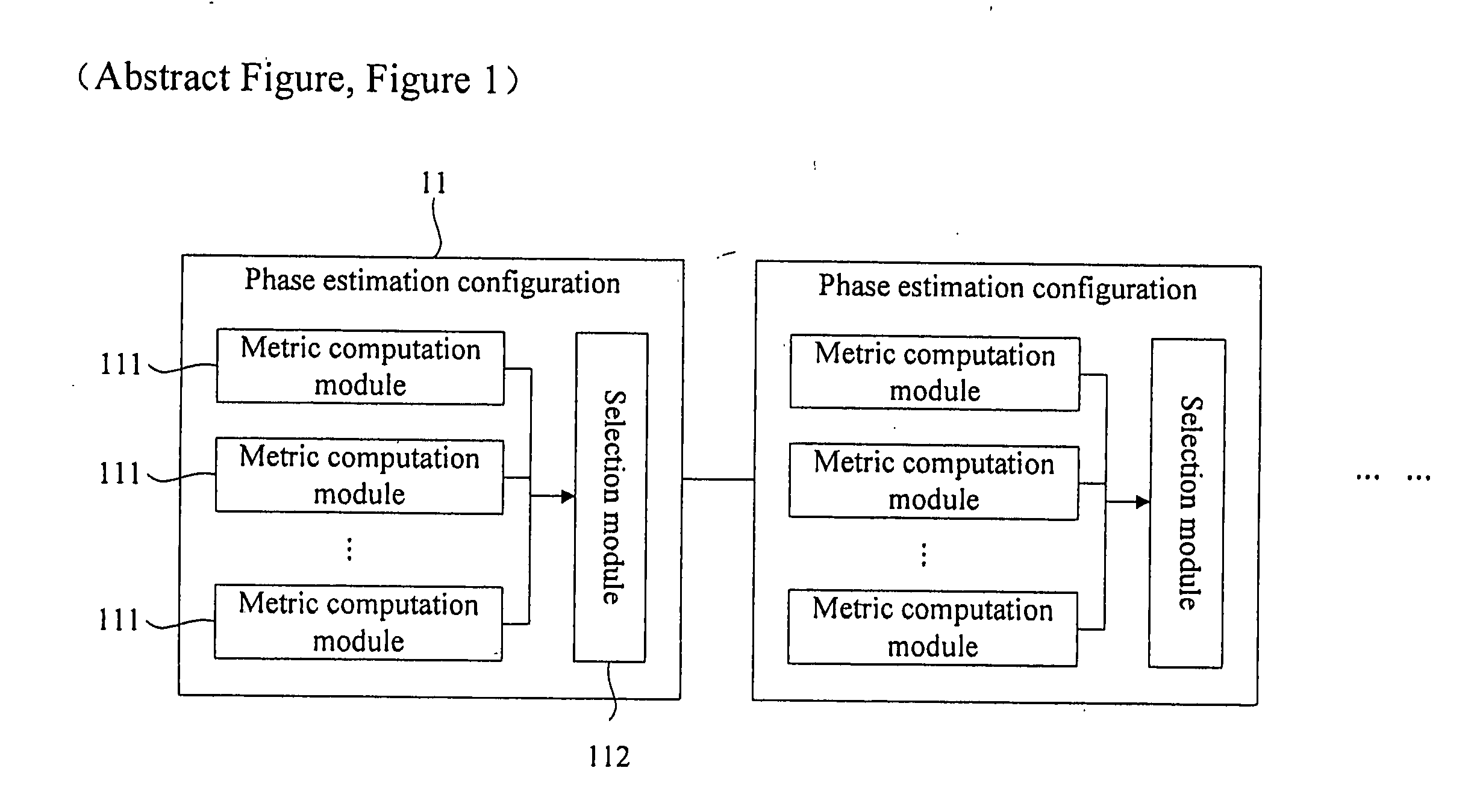
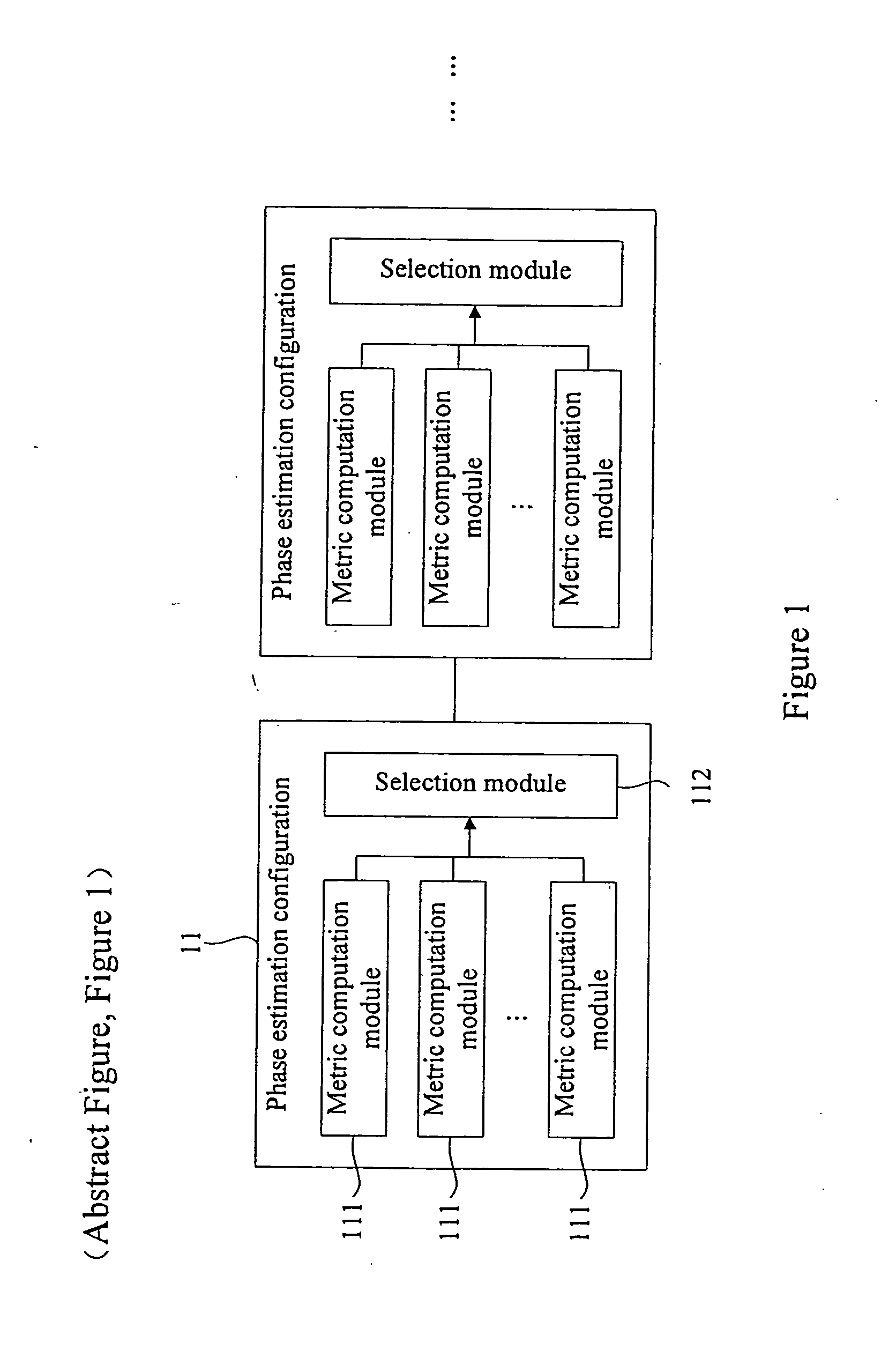
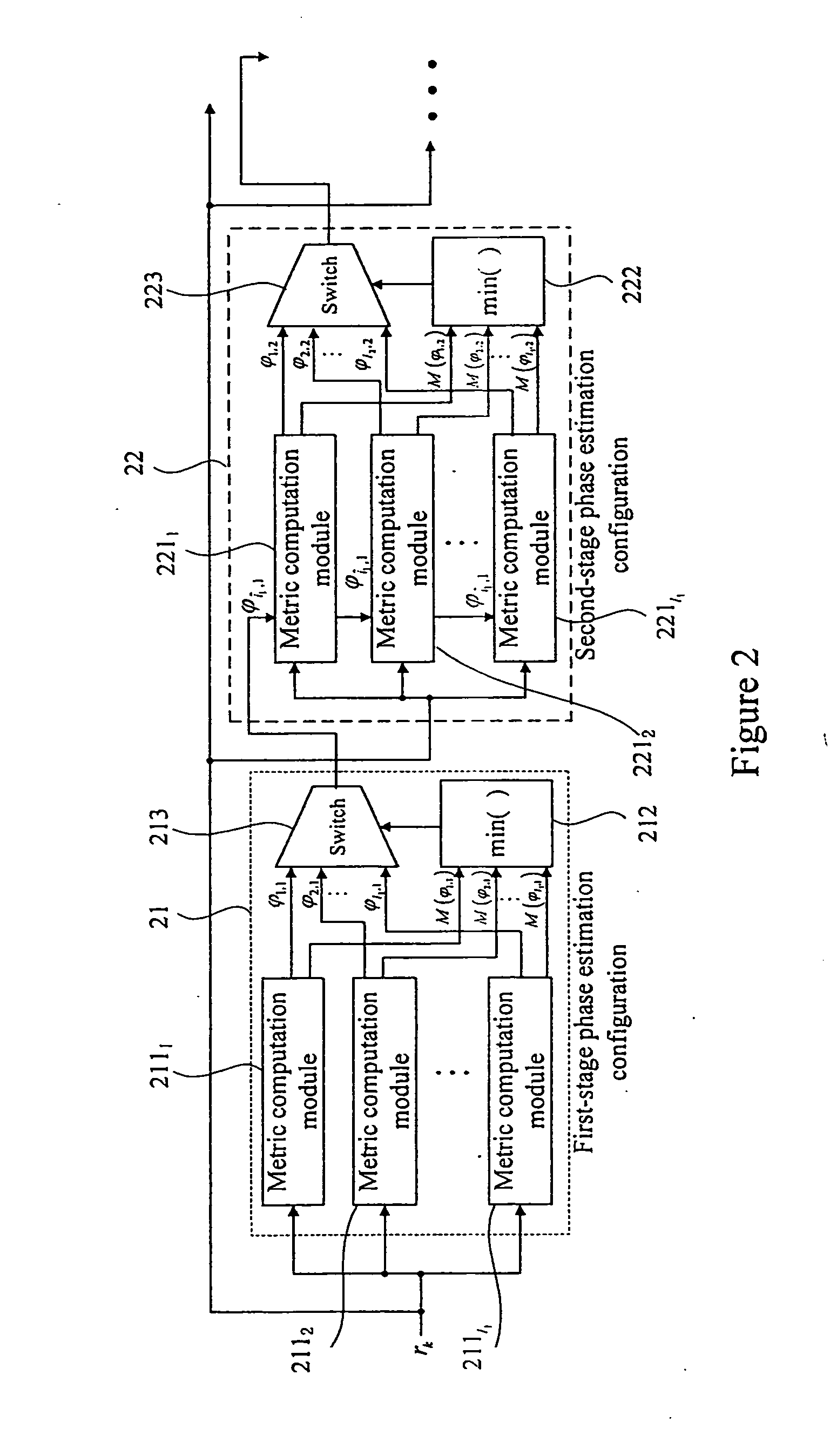
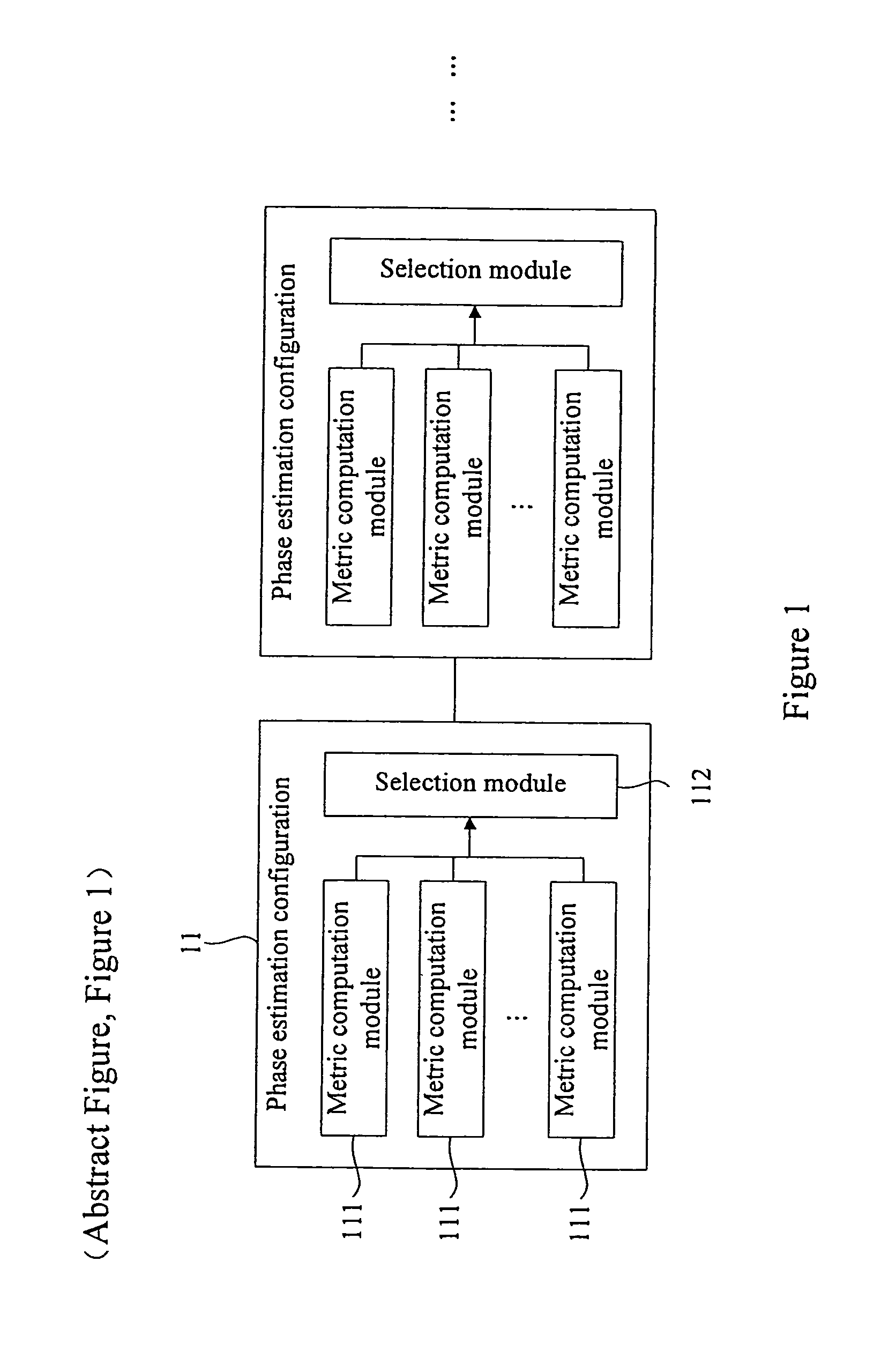
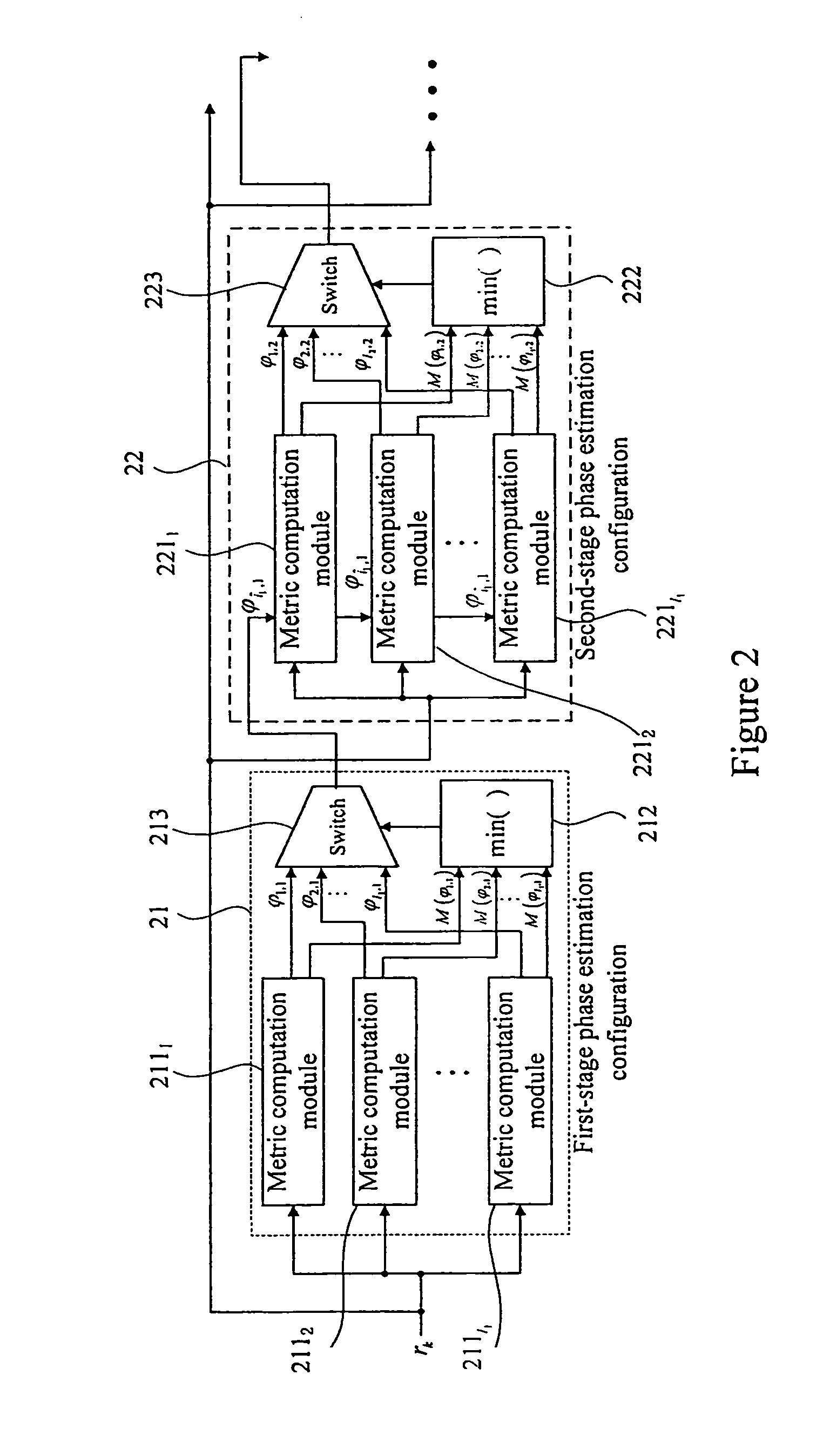
Multi-stage phase estimation method and apparatus
ActiveUS20120269247A1Reduce complexityRemove restrictionsCarrier regulationTransmission monitoringAlgorithmEstimation methods
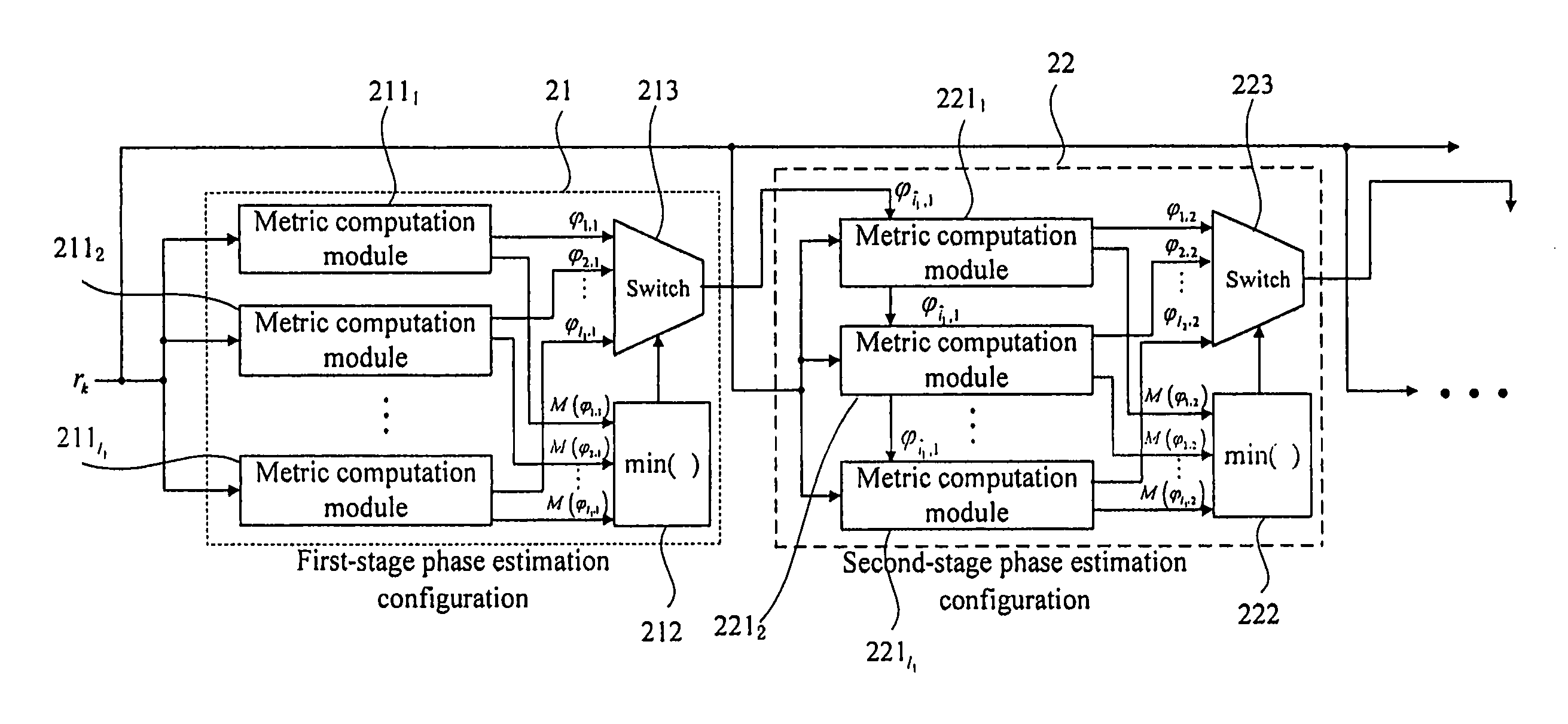
The embodiments provide a multi-stage phase estimation method and apparatus. The apparatus i a multi-stage phase estimation configuration. Each stage of the phase estimation configuration includes metric computation modules. Each of the metric computation modules computing a distance metric and search phase angles according to an input signal and an initial search phase angle or a search phase angle of the former stage phase estimation configuration. The number of the metric computation modules is equal to that of the search phase angles of this stage. A selection module selects the search phase angle corresponding to the minimal distance metric as the phase estimation result output of this stage according to the computation results of all metric computation modules. The average time window length of the former stage phase estimation configuration is larger than that of the subsequent stage phase estimation configuration.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
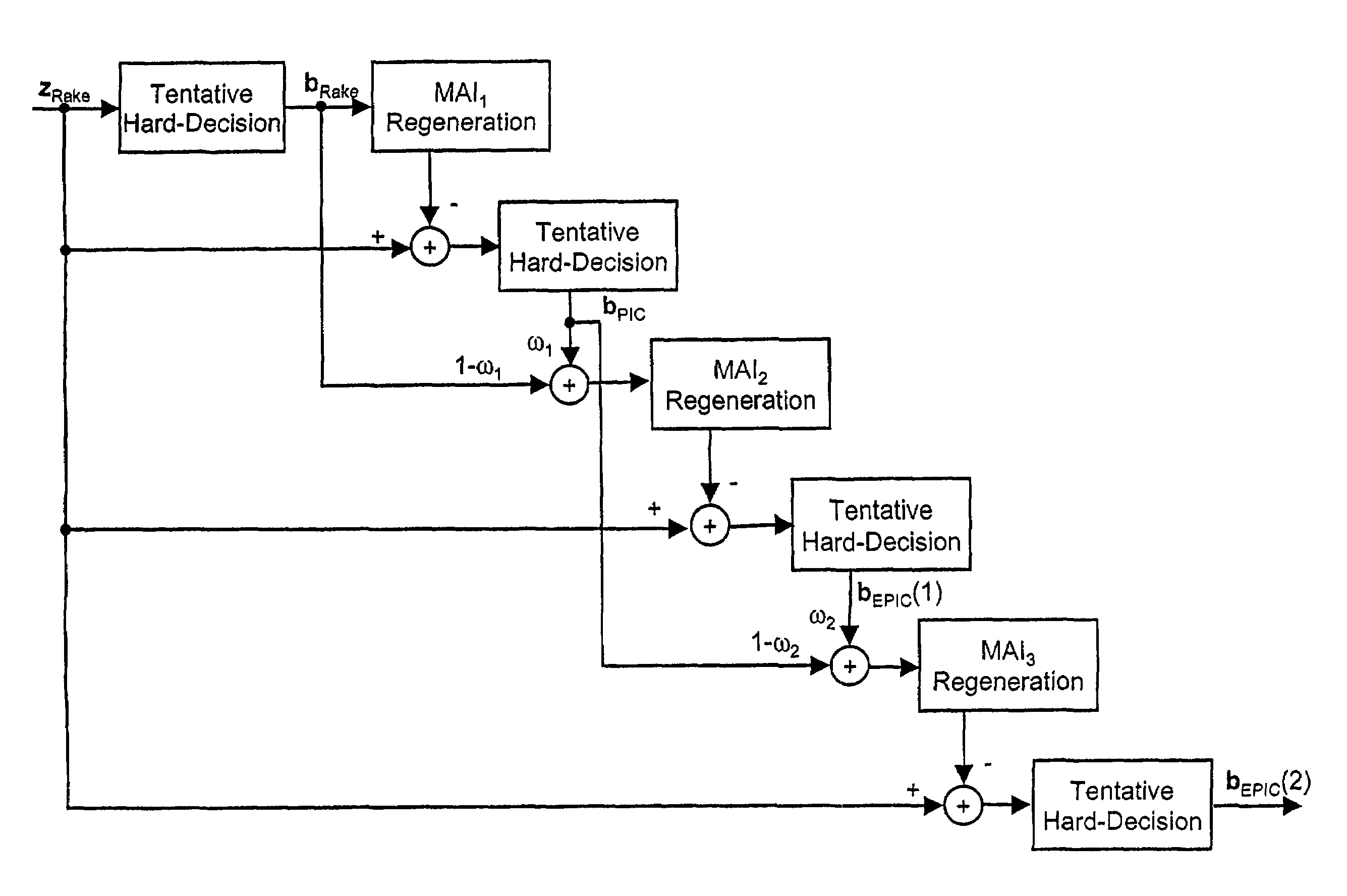
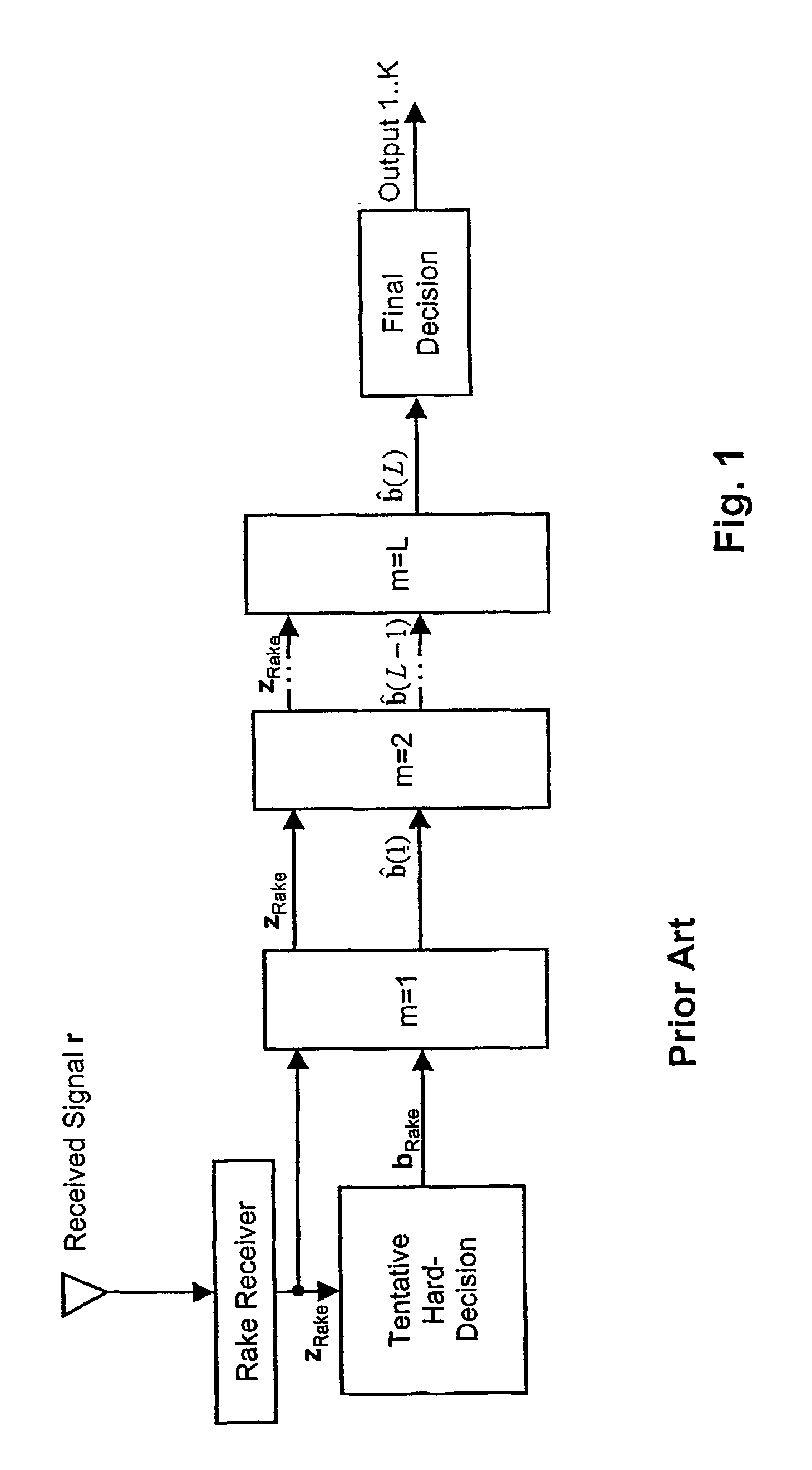
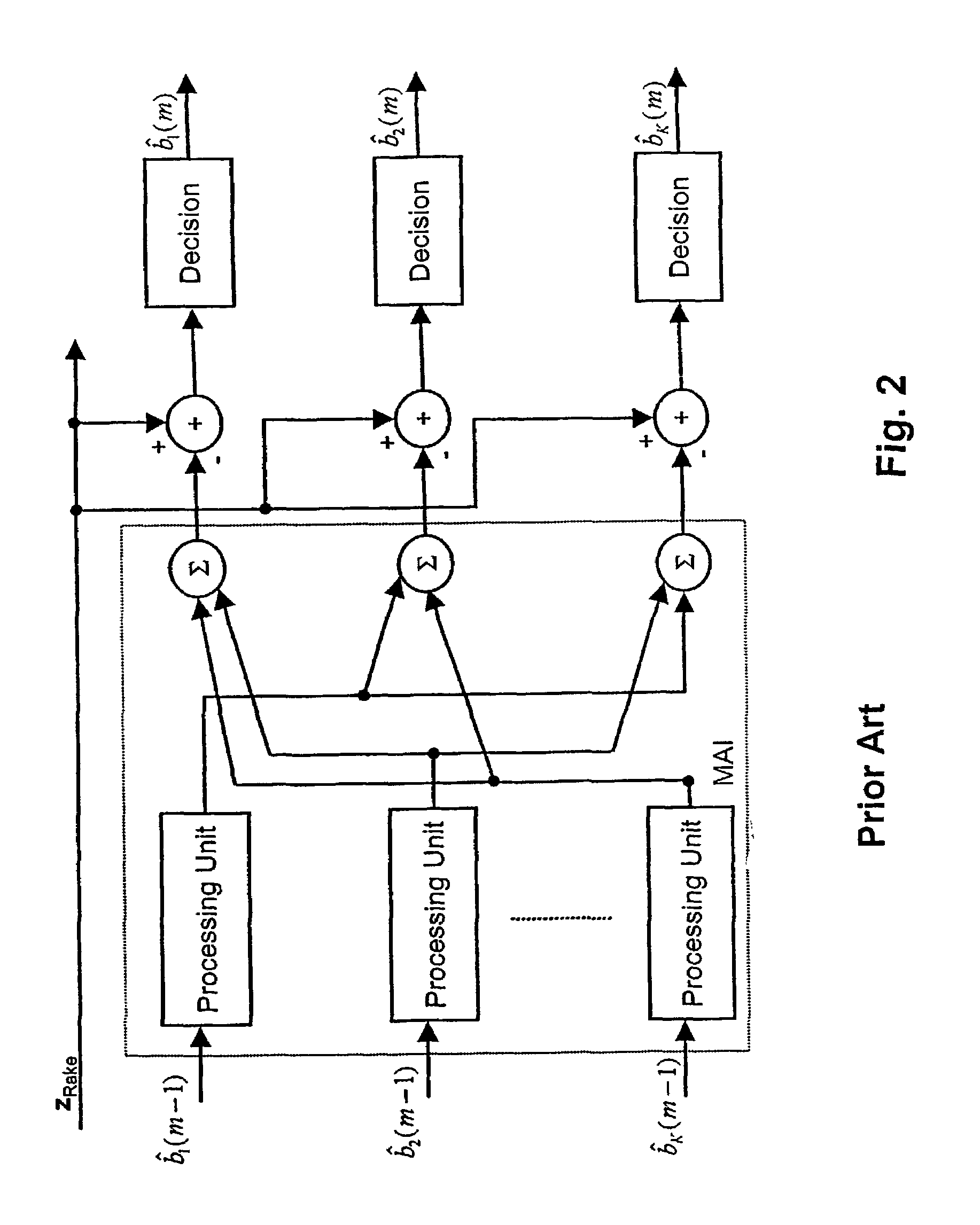
Equalized parallel interference cancellation EPIC for CDMA systems
InactiveUS7242708B1Improve system performanceIncrease complexityError preventionModulated-carrier systemsCdma systemsMultiuser detection
A new multiuser detection scheme EPIC (Equalized Parallel Interference Cancellation) is disclosed. A rake receiver signal zRake output by a rake receiver is detected, which receives a spread spectrum composite signal r comprising plural user signals b1,b2, . . . ,bK that have been spread with spreading codes. At first, first hard-decision values bRake are produced on the basis of the rake receiver outputs. Then, first parallel interference cancellation values are produced on the basis of the first hard-decision values, and second hard-decision values bPIC are produced on the basis of the first parallel interference cancellation values. After that, the first and second hard-decision values are combined for producing first combination values, and second parallel interference cancellation values are on the basis of the first combination values. Finally, third hard-decision values are produced on the basis of the second parallel interference cancellation values and the third hard-decision values are output as first stage equalized parallel interference cancellation values bEPIC(1).
Owner:NOKIA CORP
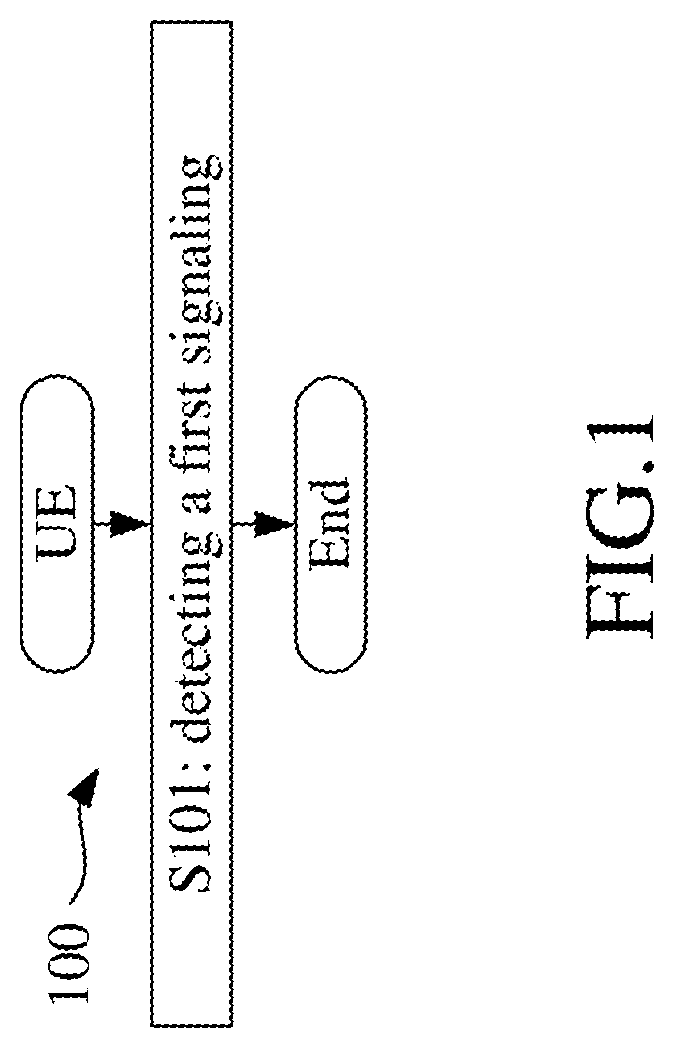
Method and device for dynamic scheduling in ue and base station
ActiveUS20190380136A1Reduce control overheadImprove transmission efficiencyError prevention/detection by using return channelSignalling characterisationComputer hardwareSpectral efficiency
The disclosure provides a method and a device for dynamic scheduling in a User Equipment (UE) and a base station. The UE detects a first signaling. The first signaling is a physical layer signaling. The first signaling includes a first bit block, and a number of bits in the first bit block is related to a transmission mode of the first signaling. The transmission mode of the first signaling is one of multiple candidate modes. For the first candidate mode, the first bit block is transmitted multiple times; and for the second candidate mode, the first bit block is transmitted once. The disclosure establishes a relationship between a payload size of the first signaling and a transmission mode of the first signaling, thus reducing the payload size of the first signaling, simplifying the complexity of blind decoding of control signalings, and improving transmission efficiency and spectrum efficiency of the system.
Owner:SHANGHAI LANGBO COMM TECH CO LTD
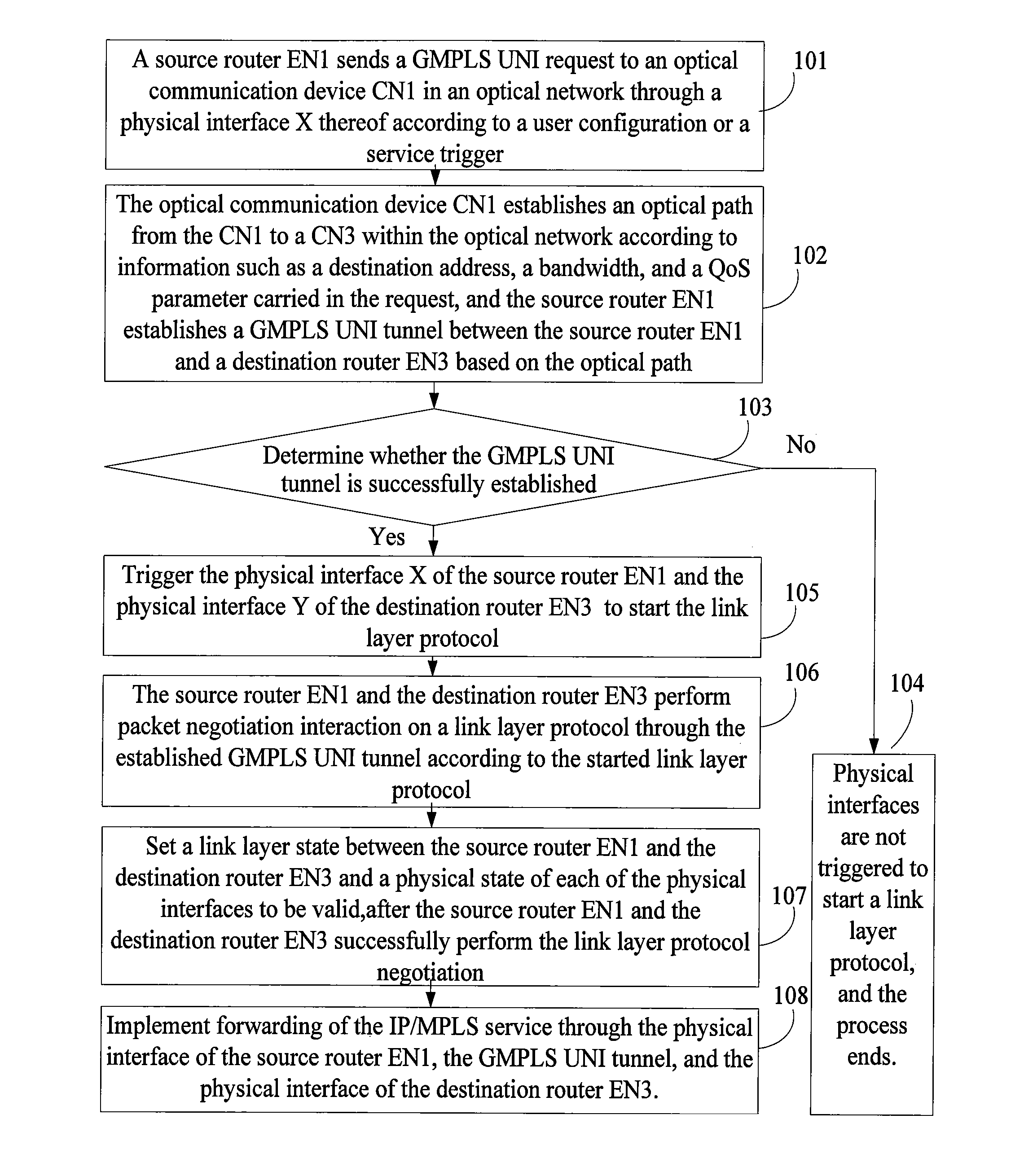
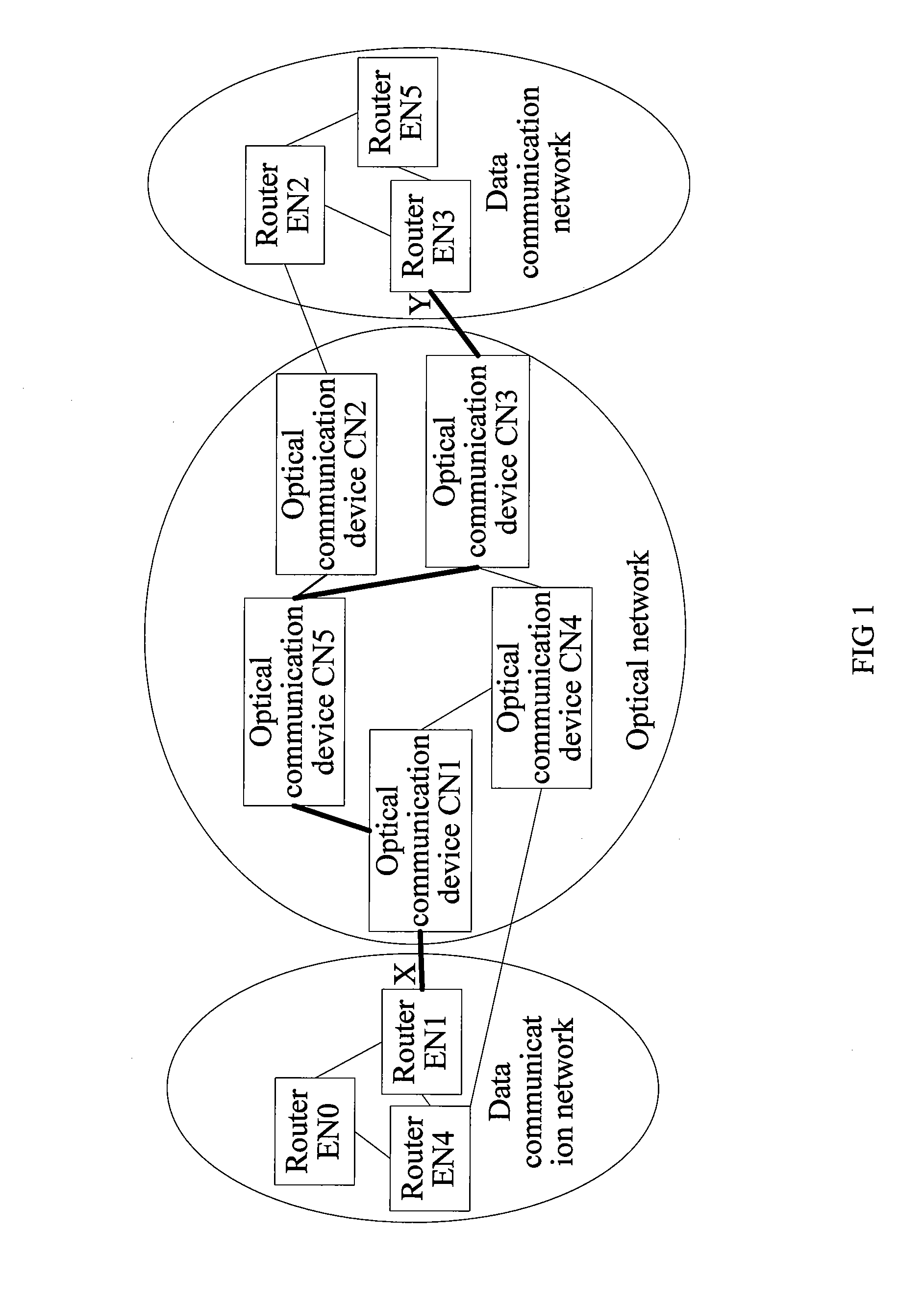
Method, system, and device for implementing service forwarding
InactiveUS8902909B2Implementation complexity can be reducedDegrade reconstructionMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationMulti protocolForwarding plane
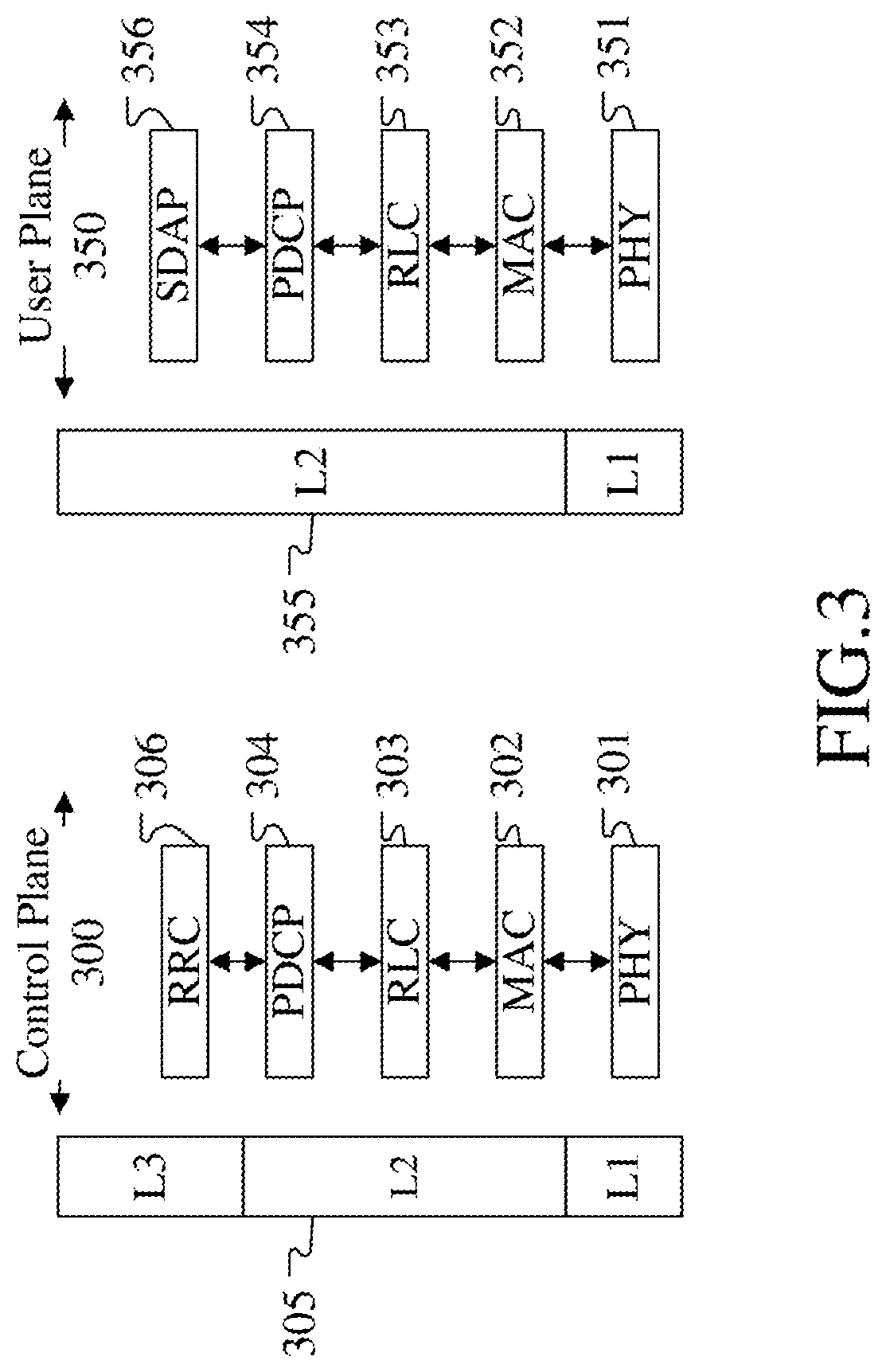
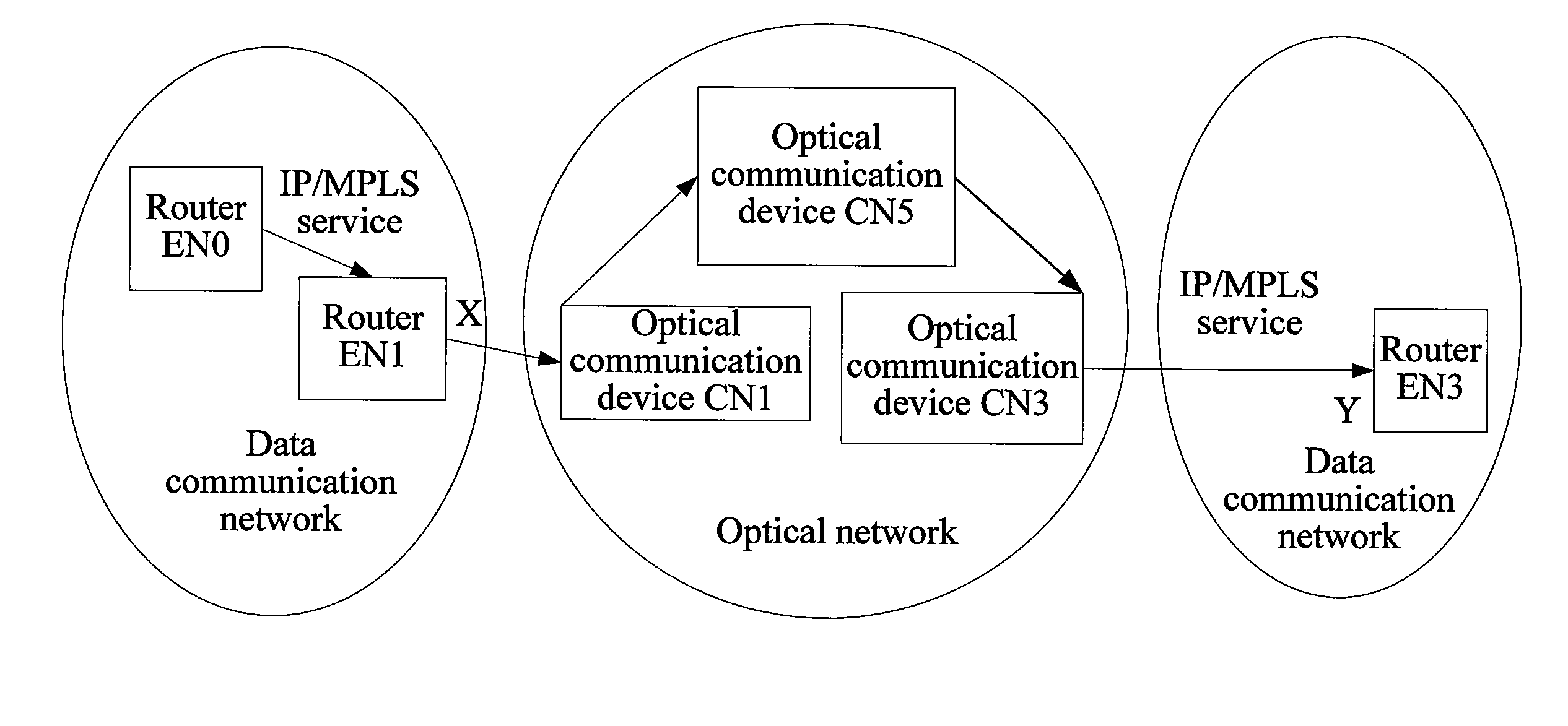
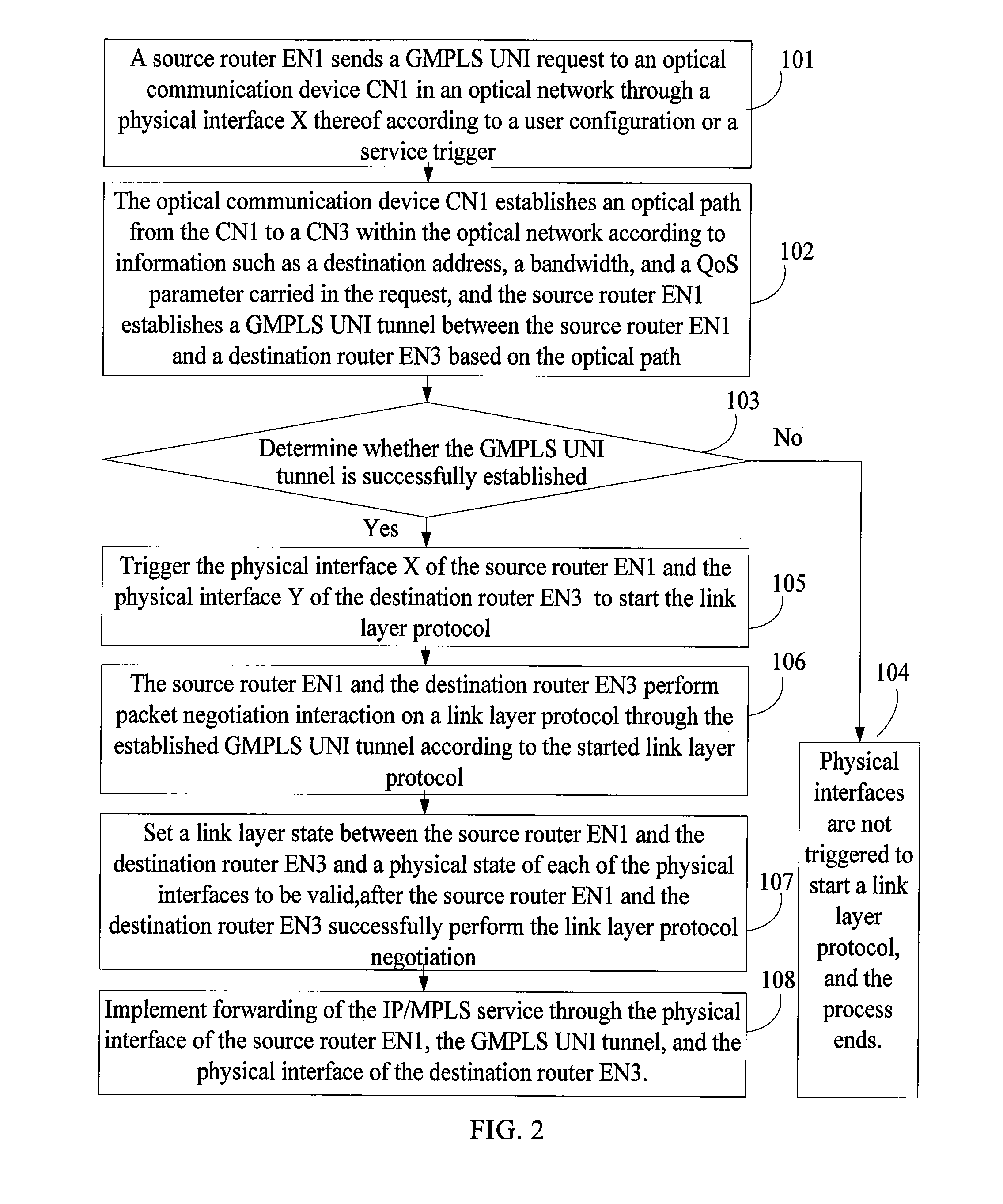
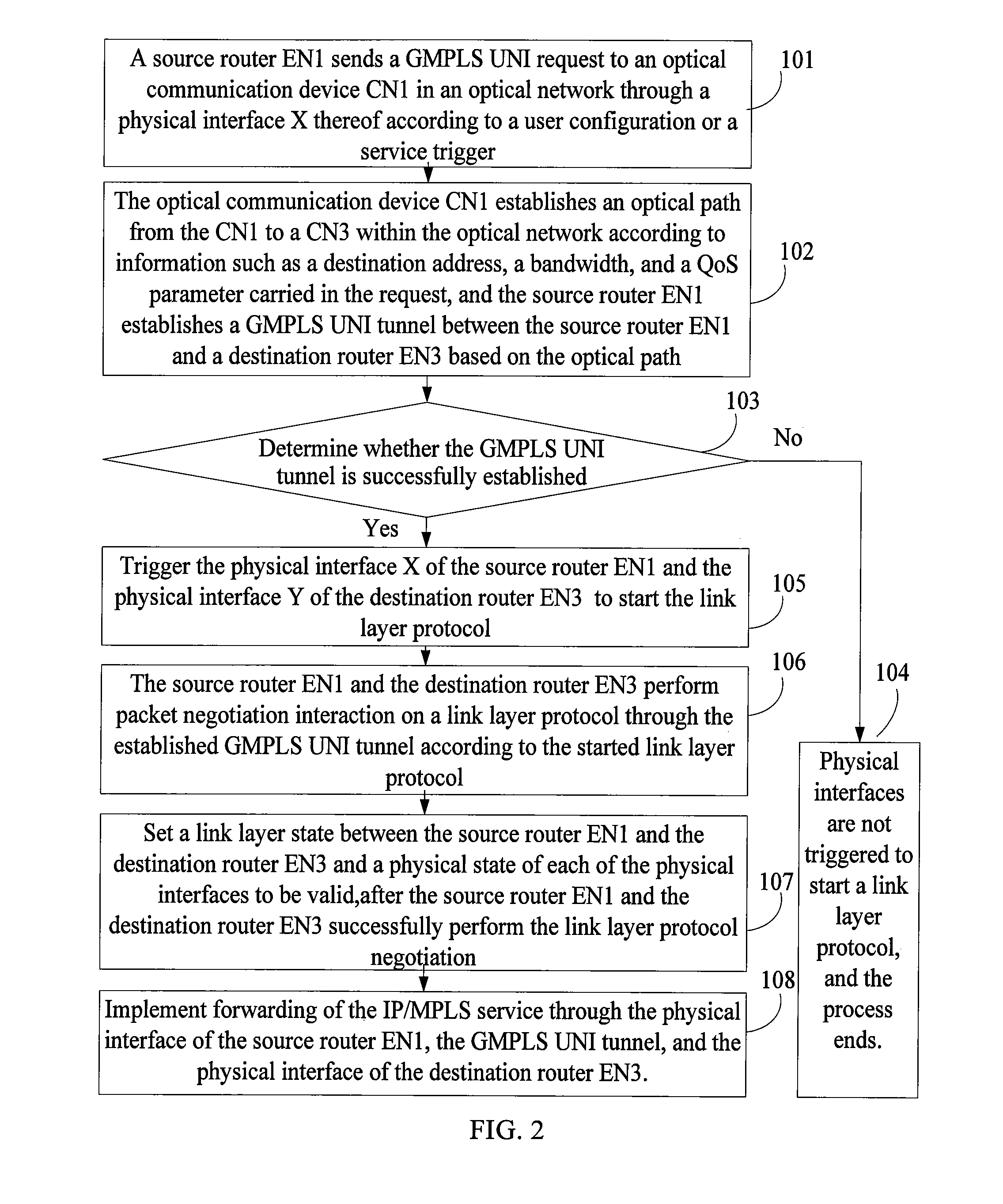
In the field of communications, a method, a system, and a device for implementing service forwarding are disclosed. The method includes: establishing an optical network tunnel between data communication devices; triggering physical interfaces of the data communication devices directly connected to an optical network to start a link layer protocol after the optical network tunnel is successfully established; performing, by the data communication devices, link layer negotiation through the optical network tunnel according to the link layer protocol; setting a link layer state between the data communication devices and a physical state of the physical interfaces to be valid after the link layer negotiation is performed successfully; and implementing, service forwarding, by the data communication devices through the optical network tunnel after the link layer state and the physical state of the physical interfaces are set to be valid. In this way, Internet Protocol (IP) / Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) service forwarding of the data communication devices is implemented, implementation complexity of bearing the IP / MPLS service over a Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching User-Network Interface (GMPLS UNI) tunnel is reduced, reconstruction on an IP / MPLS control plane and a forwarding plane is decreased, and forwarding performance is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Transmission apparatus and transmission method for padding and packet extension for downlink multiuser transmission
ActiveUS10447519B2Implementation complexity can be reducedIncrease overheadError preventionTransmission path divisionComputer scienceReal-time computing
A transmission method comprises: generating a transmission signal including OFDM symbols, wherein the last OFDM symbol of the OFDM symbols can be partitioned into four segments, and wherein the generating includes: computing an initial padding factor value associated with one of the four segments and computing an initial number of OFDM symbols; determining a user with a longest packet duration among plural users; determining a common padding factor value being the initial padding factor value and a common number of OFDM symbols being the initial number of OFDM symbols of the determined user with the longest packet duration; adding pre-FEC padding bits toward one of four possible boundaries of the last OFDM symbol, the one of four possible boundaries being represented by the determined common padding factor value; and adding post-FEC padding bits in remaining segment(s) of the last OFDM symbol; and transmitting the generated transmission signal.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Key negotiation method and apparatus according to SM2 key exchange protocol
ActiveUS9313026B2Implementation complexity can be reducedImprove execution efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareKey exchange
The invention relates to the technical field of information, and disclosed in the present invention are a key negotiation method and apparatus according to the SM2 key exchange protocol. The method is implemented as follows: two negotiation parties both calculate a parameter W according to the minimum positive integer value in the permissible values of X which enable an inequality n≦2X to hold, and perform key negotiation with the opposite negotiation party according to the parameter W. Compared with a method for calculating the parameter W through calculating log 2 (n) logarithmic value firstly and then rounding up the logarithmic value, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the calculated amount is effectively reduced, and the implementation complexity of an algorithm is reduced, thereby greatly improving the implementation efficiency of the key negotiation process based on the SM2 key exchange protocol, and then optimizing the engineering implementation of the SM2 key exchange protocol.
Owner:CHINA IWNCOMM
Network abstraction gateway and corresponding method to abstract an endpoint
ActiveUS8457140B2Implementation complexity can be reducedInterconnection arrangementsError preventionCommunications systemDistributed computing
Owner:ESCAUX
Method and apparatus for radio resource measurement in heterogeneous network
ActiveUS8755829B2Implementation complexity can be reducedHigh precisionAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsHeterogeneous network
A radio resource measurement method in a heterogeneous network includes a user equipment (UE) that performs radio resource measurement; when a measurement result meets a predefined condition, the UE performs radio resource measurement on restricted resources according to configuration information of the restricted resources, wherein the restricted resources are a set of all sub-frame resources corresponding to Almost Blank Sub-frames (ABSes) or are a subset of the set. Therefore, the precision of RLM measurement or RRM measurement of a mobility system can be improved, and the implementation complexity of the UE can be decreased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-stage phase estimation method and apparatus
ActiveUS8654826B2Reduce complexityReduce needAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsPolarisation multiplex systemsEstimation methodsComputer science
The embodiments provide a multi-stage phase estimation method and apparatus. The apparatus is a multi-stage phase estimation configuration. Each stage of the phase estimation configuration includes metric computation modules. Each of the metric computation modules computing a distance metric and search phase angles according to an input signal and an initial search phase angle or a search phase angle of the former stage phase estimation configuration. The number of the metric computation modules is equal to that of the search phase angles of this stage. A selection module selects the search phase angle corresponding to the minimal distance metric as the phase estimation result output of this stage according to the computation results of all metric computation modules. The average time window length of the former stage phase estimation configuration is larger than that of the subsequent stage phase estimation configuration.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method, system, and device for implementing service forwarding
InactiveUS20110222847A1Service degradationImprove forwarding performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringMulti protocolComputer science
In the field of communications, a method, a system, and a device for implementing service forwarding are disclosed. The method includes: establishing an optical network tunnel between data communication devices; triggering physical interfaces of the data communication devices directly connected to an optical network to start a link layer protocol after the optical network tunnel is successfully established; performing, by the data communication devices, link layer negotiation through the optical network tunnel according to the link layer protocol; setting a link layer state between the data communication devices and a physical state of the physical interfaces to be valid after the link layer negotiation is performed successfully; and implementing, service forwarding, by the data communication devices through the optical network tunnel after the link layer state and the physical state of the physical interfaces are set to be valid. In this way, Internet Protocol (IP) / Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) service forwarding of the data communication devices is implemented, implementation complexity of bearing the IP / MPLS service over a Generalized Multi-Protocol Label Switching User-Network Interface (GMPLS UNI) tunnel is reduced, reconstruction on an IP / MPLS control plane and a forwarding plane is decreased, and forwarding performance is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for performing access control in next generation wireless network
ActiveUS10524189B2Implementation complexity can be reducedAssess restrictionConnection managementTelecommunicationsMedia access control
Disclosed is a technique for an access control operation of a user equipment (UE) in a next-generation mobile communication network, and more specifically, a unified access control method for a UE and a specific access control method for a service with low sensitivity. Further, a method of a UE is provided for performing an access control operation. The method may include receiving operator-defined access category information through non-access stratum (NAS) signaling when an access attempt of the UE is triggered, determining one access category for the access attempt in an NAS layer or an access stratum (AS) layer; selecting RRC establishment cause information associated with the access category; and performing an access barring check operation in the AS layer using access barring parameters associated with the access category.
Owner:KT CORP
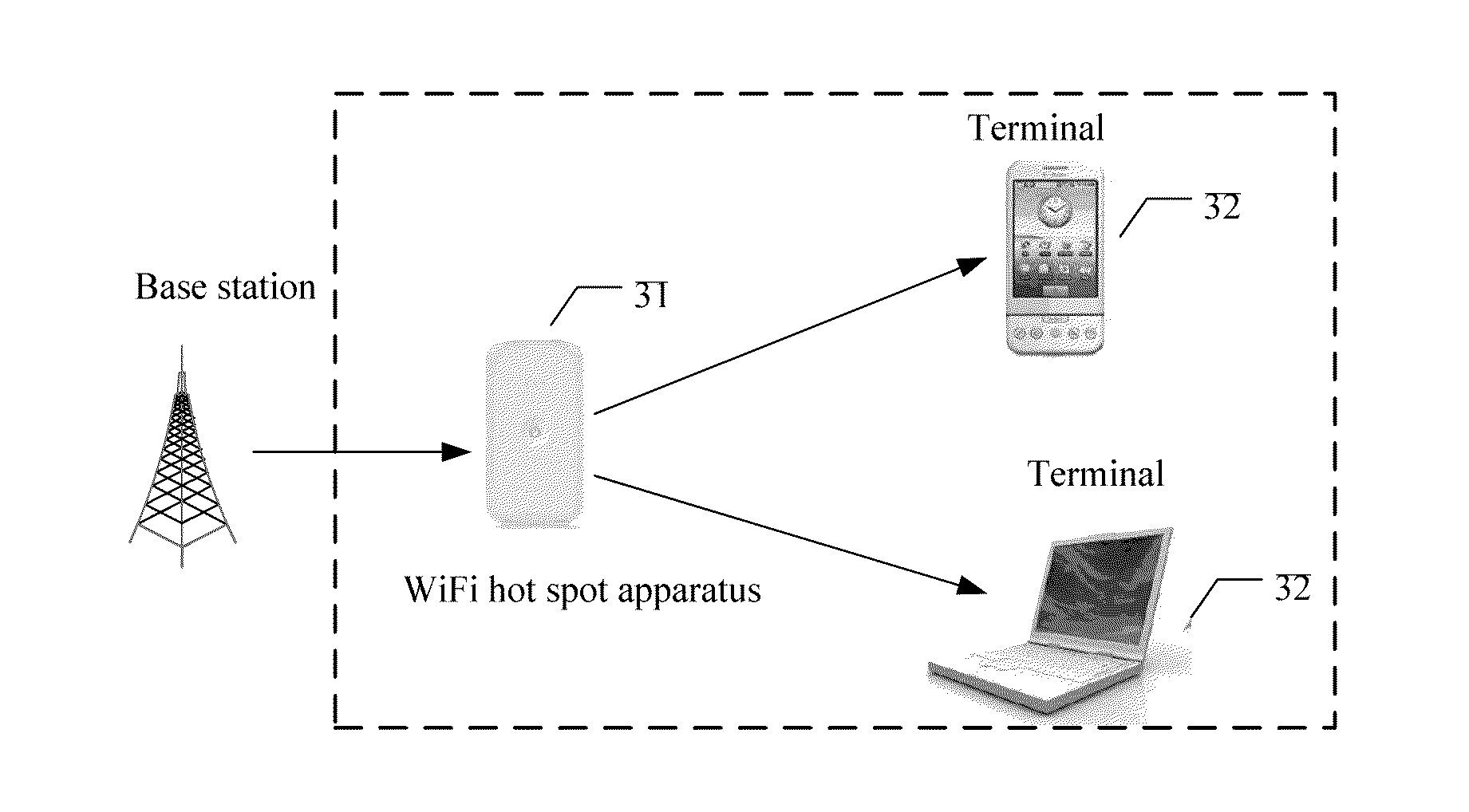
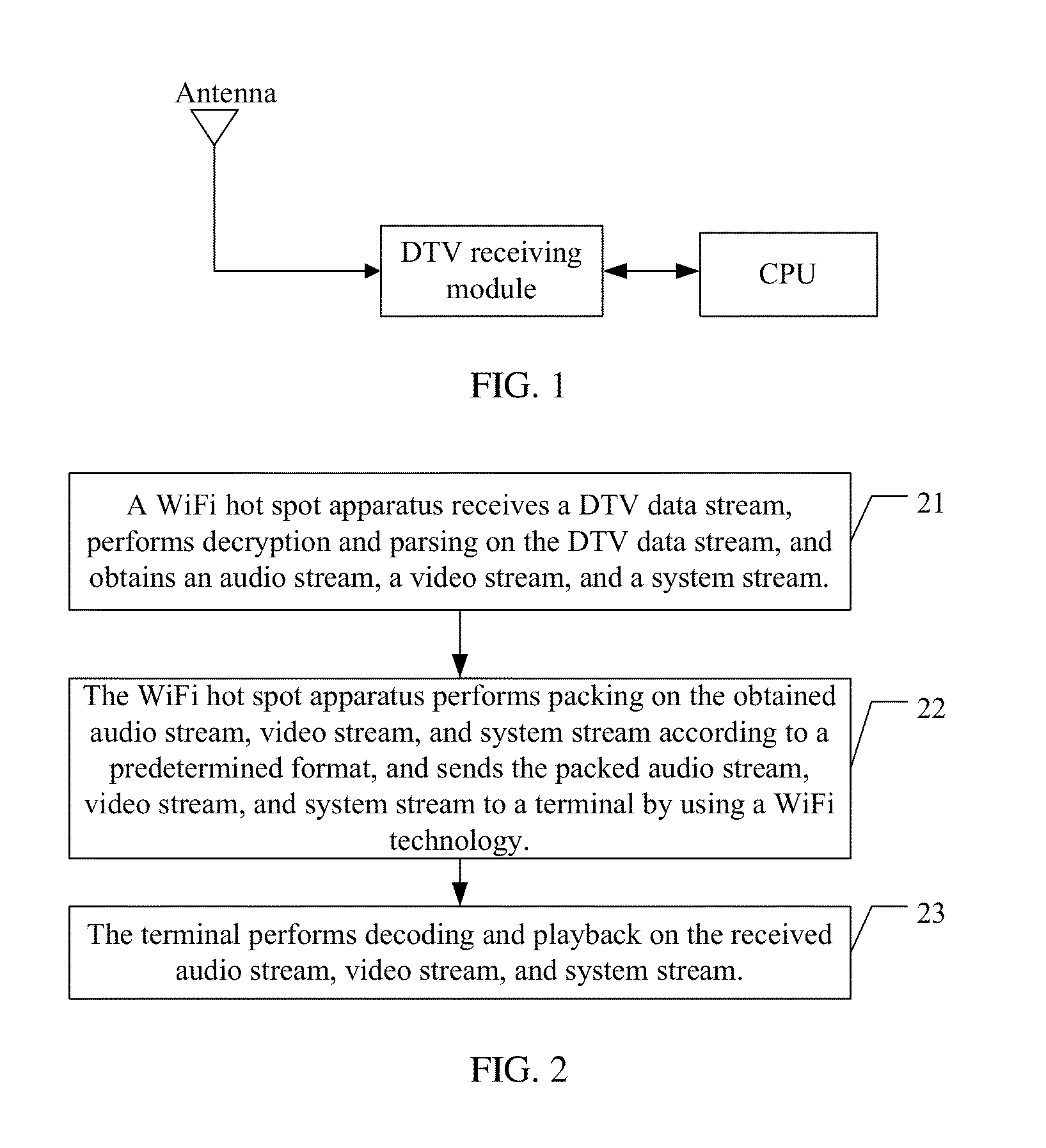
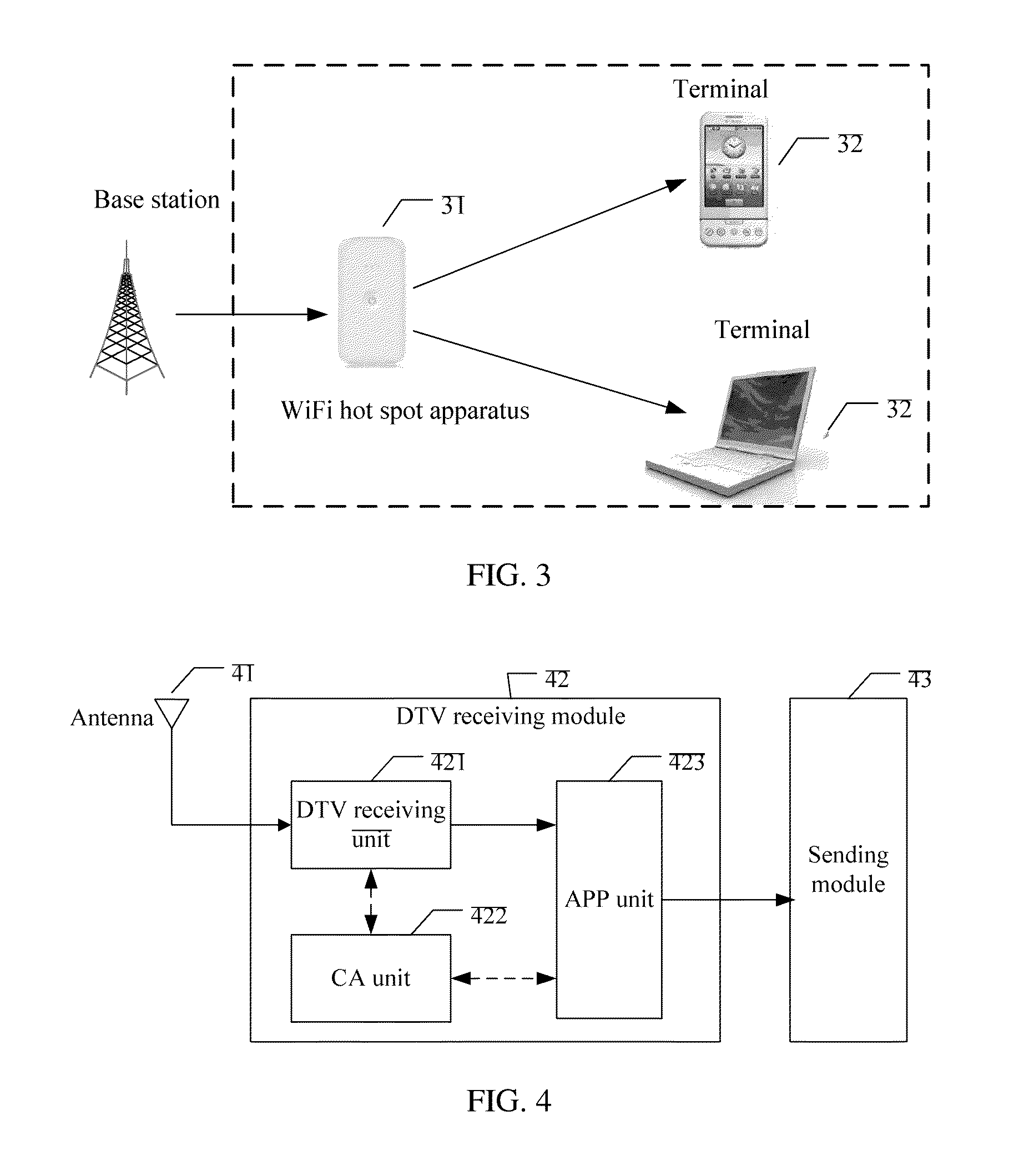
Method for implementing digital television technology and wireless fidelity hot spot apparatus
InactiveUS20140013362A1Reduce technology requirementsReduce complexityAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSelective content distributionTechnology of televisionDigital television
The present invention discloses a method for implementing a digital television technology, including performing, by a wireless fidelity hot spot apparatus, decryption and parsing on a received digital television data stream, obtaining an audio stream, a video stream, and a system stream, performing packing on the obtained audio stream, video stream, and system stream according to a predetermined format, sending the packed audio stream, video stream, and system stream to a terminal by using a wireless fidelity technology, and performing, by the terminal, decoding and playback on the packed audio stream, video stream, and system stream received from the wireless fidelity hot spot apparatus. The present invention also discloses a wireless fidelity hot spot apparatus. By applying the method and the apparatus according to the present invention, implementation complexity of a digital television technology is decreased.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
Method and apparatus for managing interference in wireless backhaul networks through power control with a one-power-zone constraint
ActiveUS9237529B2Eliminate, orReduce disadvantagesPower managementRadio transmissionComputation complexityStructure of Management Information
Methods and apparatus are provided for managing interference in a wireless backhaul network comprising a plurality of hubs, each hub serving a plurality of remote backhaul modules (RBM), using power control with a one-power-zone (OPZ) constraint. Each hub uses a transmit frame structure comprising a plurality of zones, each RBM is scheduled on a different zone, and the same power level is maintained across all zones within a transmit frame. Under the OPZ constraint, and for scheduling policies under which the number of zones assigned to each RBM is fixed, the power and scheduling sub-problems are decoupled. This enables power control independent of scheduling, using methods having lower computational complexity. Methods are disclosed comprising iterative function evaluation or Newton's method approaches based on a weighted sum-rate maximization across the network, which can be implemented in a distributed fashion. Some of the methods can be implemented asynchronously at each hub.
Owner:BLINQ NETWORKS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com