Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37results about How to "Enhance productivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
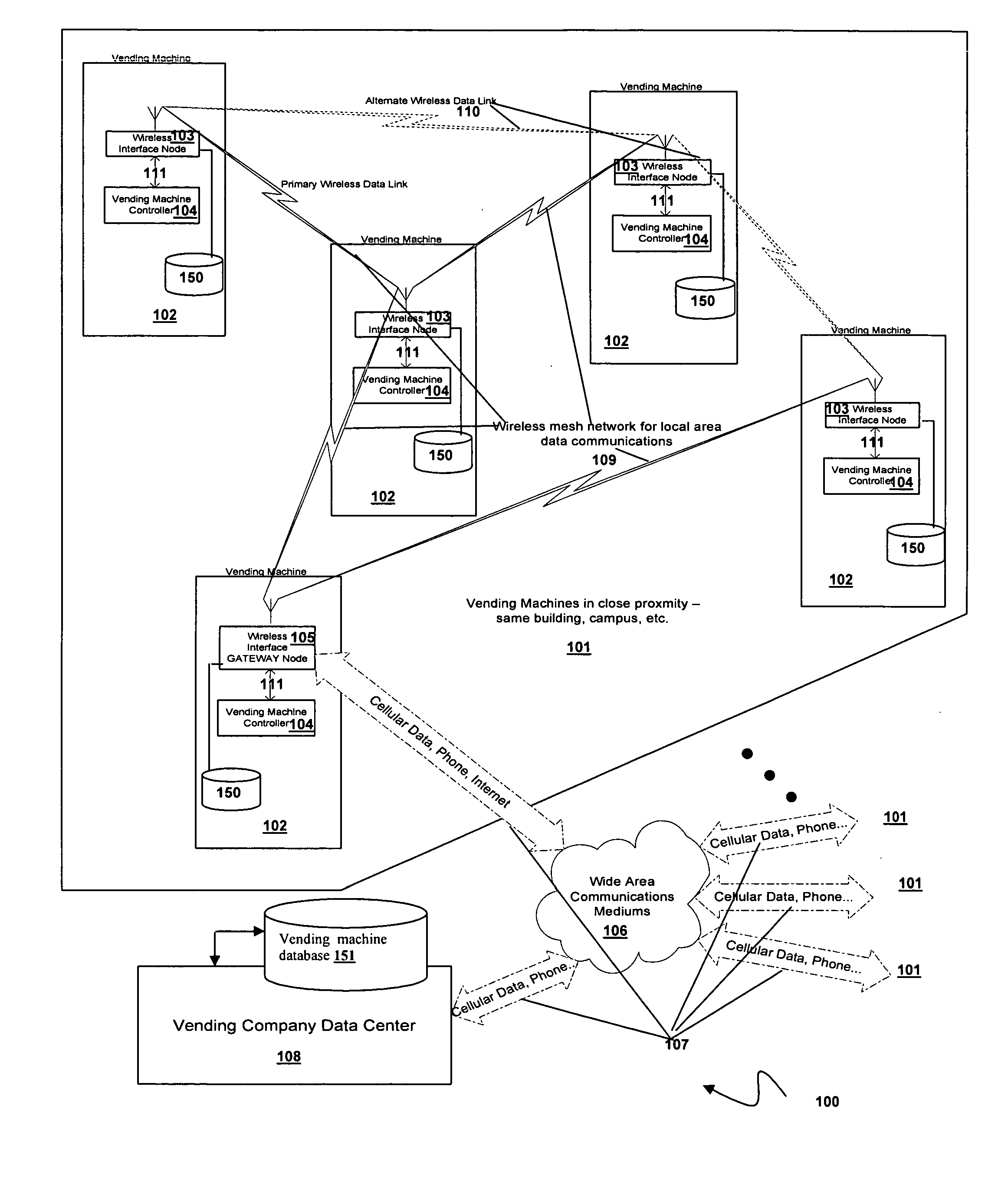
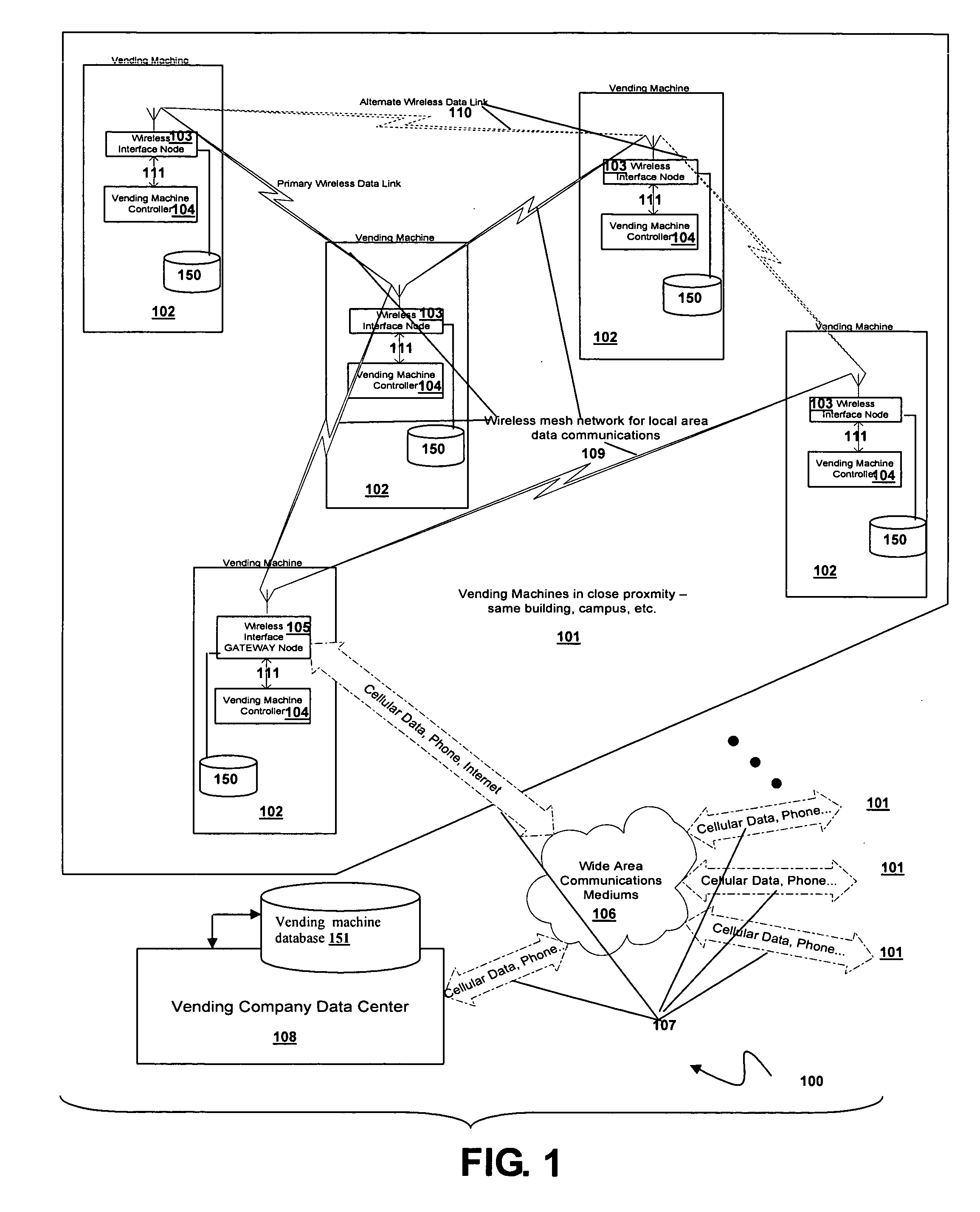
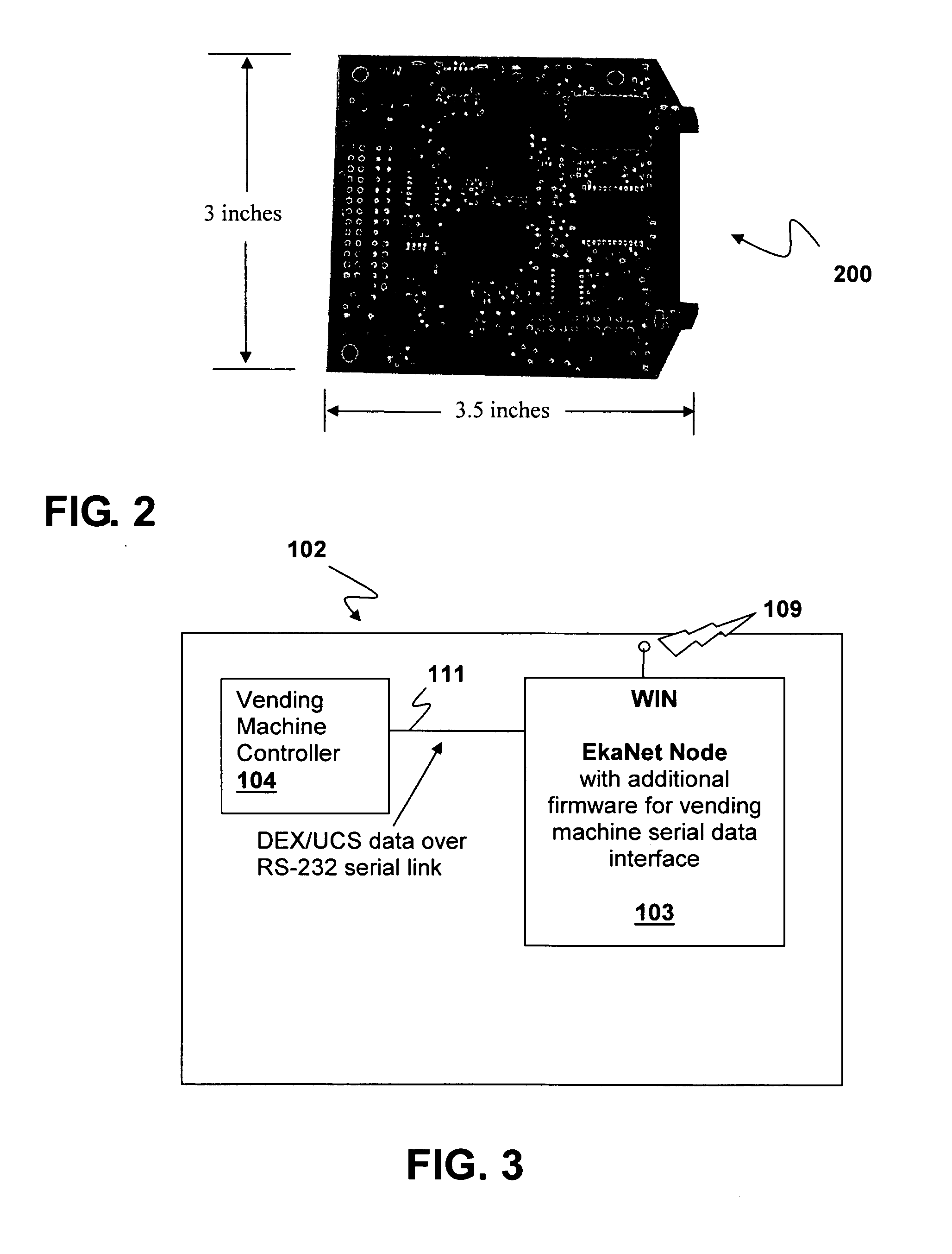
Vending machine monitoring system
InactiveUS20060106490A1Enhance productivityCost-effectiveCoin-freed apparatus detailsSpecial data processing applicationsOff the shelfProcess engineering
A system and method for using mesh technology to remotely monitor a plurality of vending machines is provided. Each vending machine includes a node that supports the DEX / UCS standard using customized off-the-shelf mesh networking and metering components to reach a gateway node included in a vending machine to provide access to and by a vending machine data center.
Owner:ADMMICRO PROPERTIES
LED backlight unit
ActiveUS20070195551A1Enhance productivityImprove productivityPlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsProduction rateAdhesive
An LED backlight unit which can be assembled without a thermosetting adhesive, improved in heat radiation effects to maintain high brightness, and also significantly improved in productivity. A light source has a substrate and a plurality of light emitting diodes disposed on the substrate. A light guide plate is placed adjacent to the light source. A chassis fixes the light source and the light guide plate therein. Fixing means engagingly fit a side of the light guide plate into the light source plate and chassis. Here, the substrate of the light source is fixed in surface contact with the chassis. The light guide plate assemblable without a thermosetting adhesive facilitates assembling and ensures effective radiation of heat generated from the LED, thereby maintaining high brightness and achieving superb light emitting capability.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for high performance data analysis
InactiveUS20160180240A1Enhance productivityImprove productivityArtificial lifeProbabilistic networksTheoretical computer scienceHypothesis
A system that learns by synthesizing completely new data patterns by an economic trading model of hypotheses or evidence as goods to be traded. The system comprises a society of processing modules that collectively interact with one another until steady state equilibrium is reached, in order to solve a given problem.
Owner:KYNDI
High Carbon steel wire material having excellent wire drawability and manufacturing process thereof
InactiveUS20060130946A1Excellent wire drawabilityEnhance productivityFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCarbon steelCrystallite
A high carbon steel wire material which is made of high carbon steel as a raw material for wire products such as steel cords, bead wires, PC steel wires and spring steel, allows for these wire products to be manufactured efficiently at a high wire drawing rate and has excellent wire drawability and a manufacturing process thereof. This high carbon steel wire material is made of a steel material having specific contents of C, Si, Mn, P, S, N, Al and O, and the Bcc-Fe crystal grains of its metal structure have an average crystal grain diameter (Dave) of 20 μm or less and a maximum crystal grain diameter (Dmax) of 120 μm or less, preferably an area ratio of crystal grains having a diameter of 80 μm or more of 40% or less, an average sub grain diameter (dave) of 10 μm or less, a maximum sub grain diameter (dmax) of 50 μm or less and a (Dave / dave) ratio of the average crystal grain diameter (Dave) to the average sub grain diameter (dave) of 4.5 or less.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Film pattern, device, electro-optic device, electronic apparatus, method of forming the film pattern, and method of manufacturing active matrix substrate
InactiveUS20060256247A1Enhance productivitySimplify processSolid-state devicesPrinted circuit manufactureSolventSide chain
A method of forming a film pattern by disposing a functional liquid on a substrate includes a step of forming a bank on the substrate, the bank corresponding to an area on which the film pattern is to be formed, a step of disposing the functional liquid to the area partitioned by the bank, and a step of curing the functional liquid to form the film pattern, one of a polysilazane liquid and a polysiloxane liquid is applied, exposed, developed, patterned, and burnt, thereby forming the bank made of a material having a hydrophobic group in the side chain and a siloxane bond as a framework in the step of forming the bank, and a liquid containing one of a water type dispersion medium and a water type solvent is used as the functional liquid.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
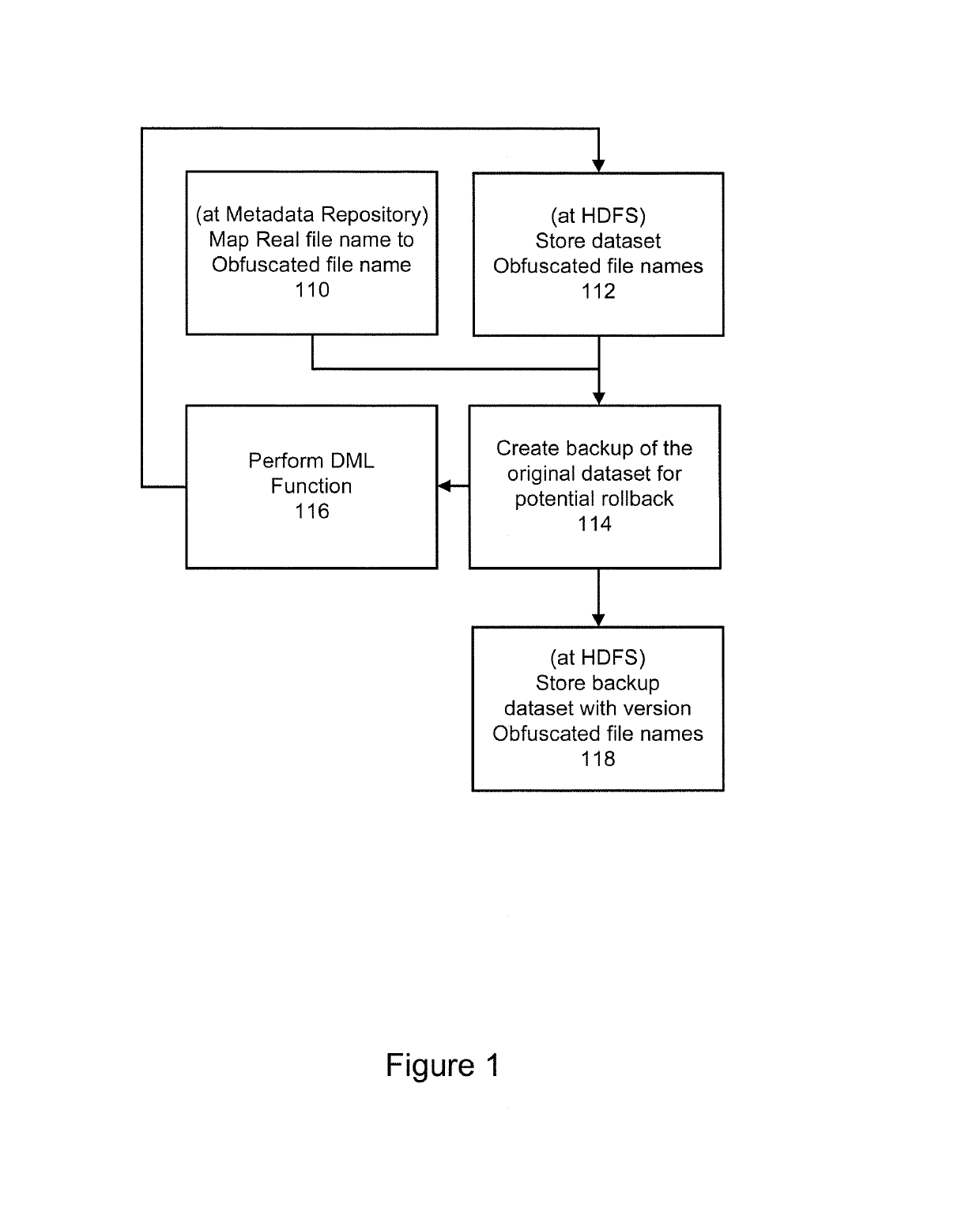
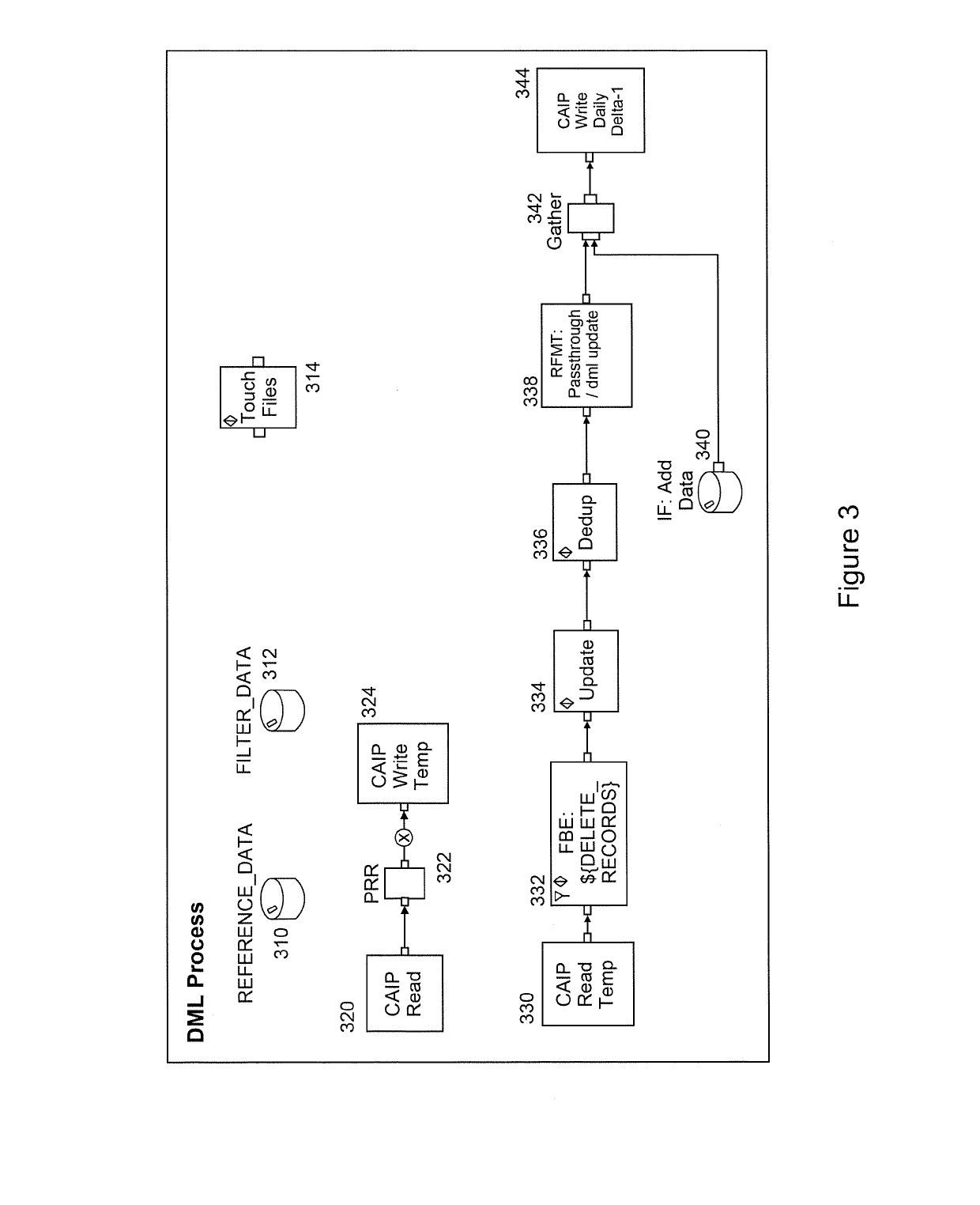
System and method for implementing data manipulation language (DML) on hadoop
ActiveUS20190102263A1Enhance productivityImprove productivityFile access structuresRedundant operation error correctionFrequent useData transformation
An embodiment of the present invention is directed to creating a re-usable code component that may be used with the data manipulation and transformation tool to natively support DML functionality. In addition to Insert, Update, and Delete, an addition function directed to “DeDup” may be implemented as it is used frequently in data transformation processes. An embodiment of the present invention is directed to capability to roll-back to a prior version of the original dataset. Any number of versions as required may be maintained.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
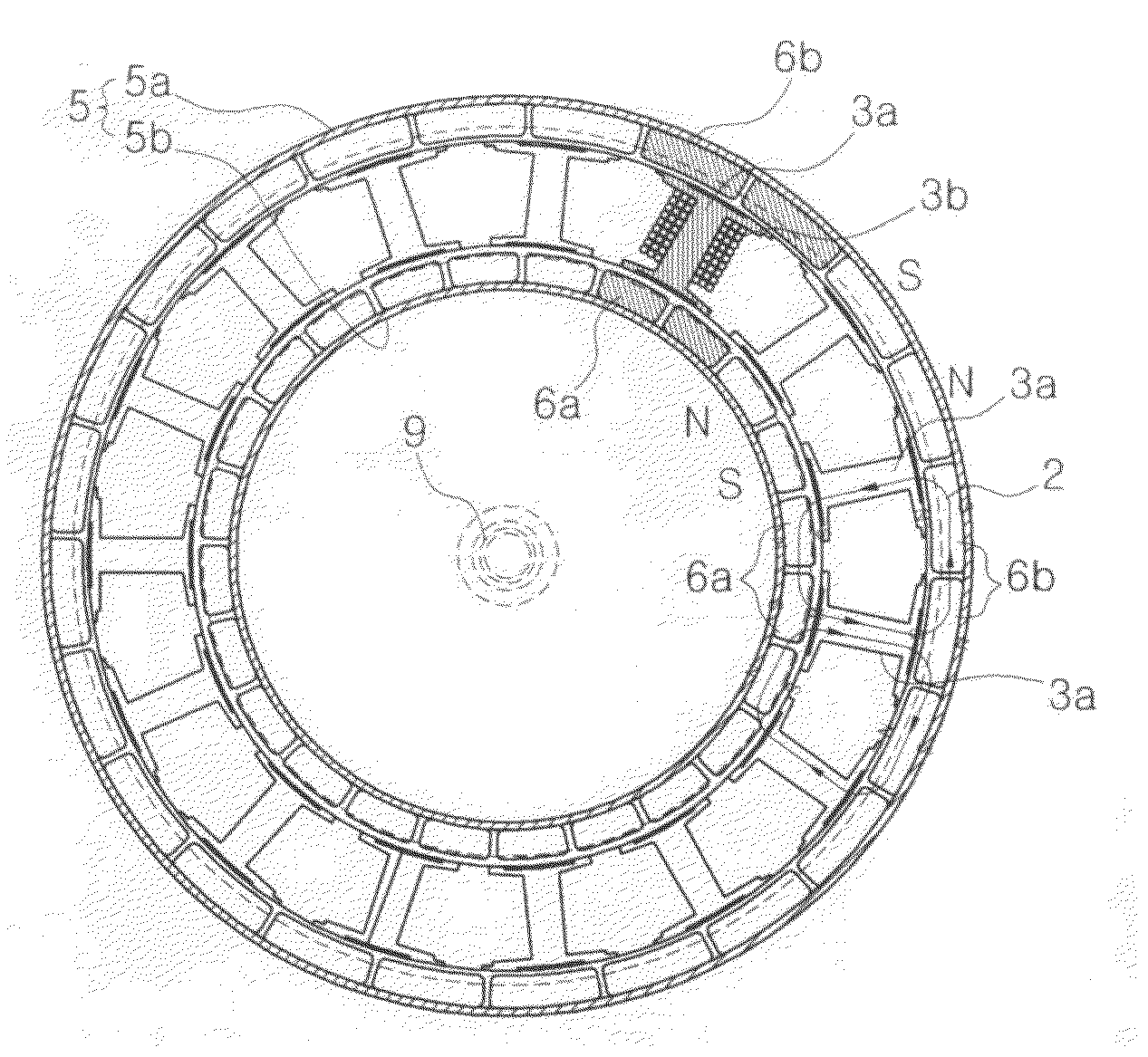
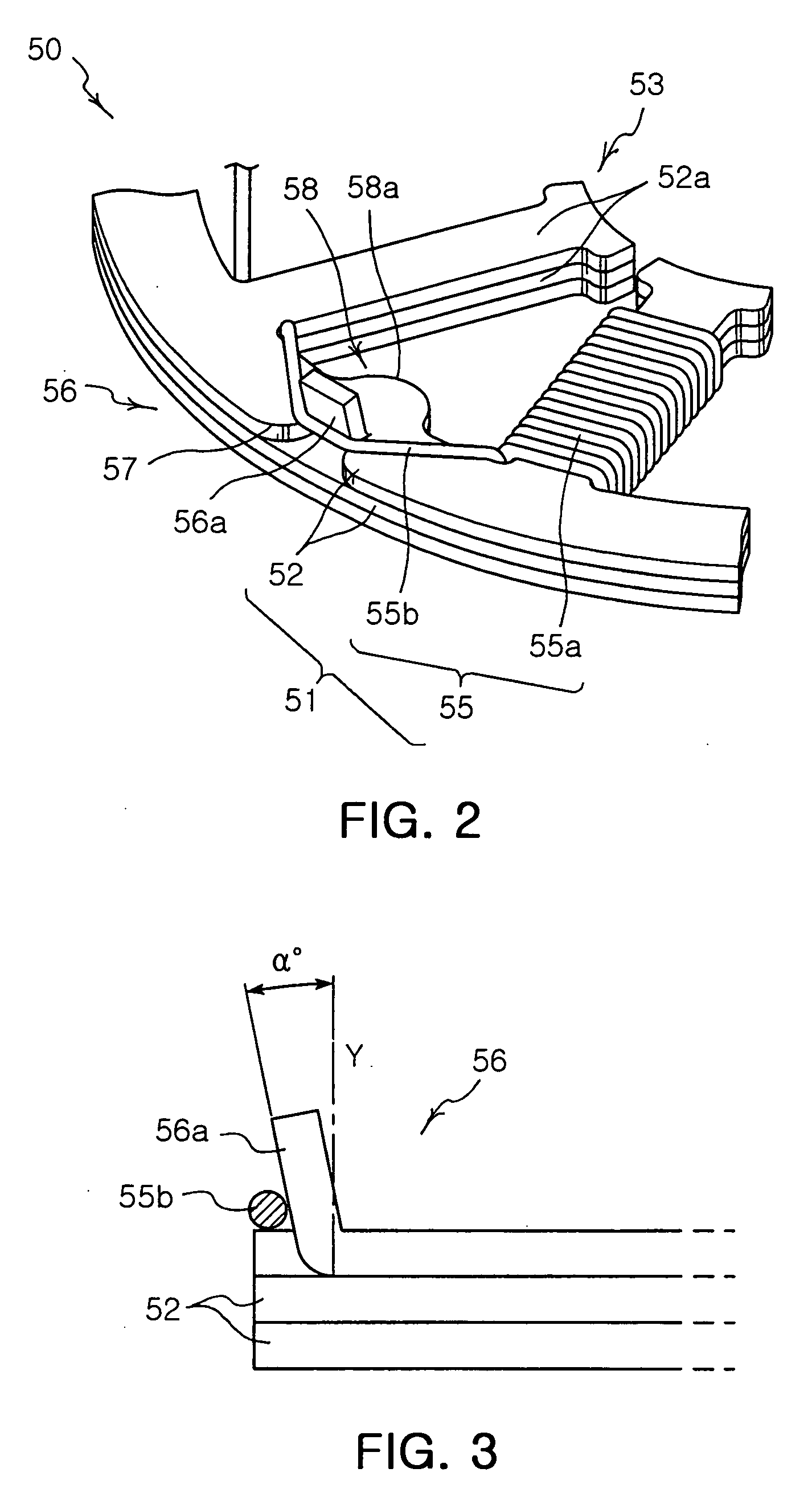
Stator for bldg motor BLDC motor having double rotors/ single stator and vehicle cooler using the same
ActiveUS20100186687A1Enhance productivityReinforce for durabilitySynchronous generatorsWindingsRotational axisPrinted circuit board
Provided are a stator for a brushless direct-current (BLDC) motor, a BLDC motor having a double-rotor / single-stator structure, and a vehicle cooler using the same, which uses a printed circuit board for an assembly that automatically sets an assembly position of stator core assemblies, to thereby secure waterproof, light-weight, and high power features. The stator includes a holder, a boss which has built-in bearings in order to support a rotational axis, and which enables the rotational axis to be rotated, a number of stator core assemblies which respectively enclose bobbins having inner and outer flanges at the inner and outer sides of a number of division type stator cores and in which coils are wound around the bobbins, and a printed circuit board for an assembly in which each stator core assembly is automatically position-set and then assembled and both end portions of the coil are mutually connected by each phase of U, V and W. After each stator core assembly has been temporarily assembled on the assembly PCB, the stator core assembly is insert molded using thermosetting resin to thereby integrally form the holder and the boss in the stator.
Owner:AMOTECH
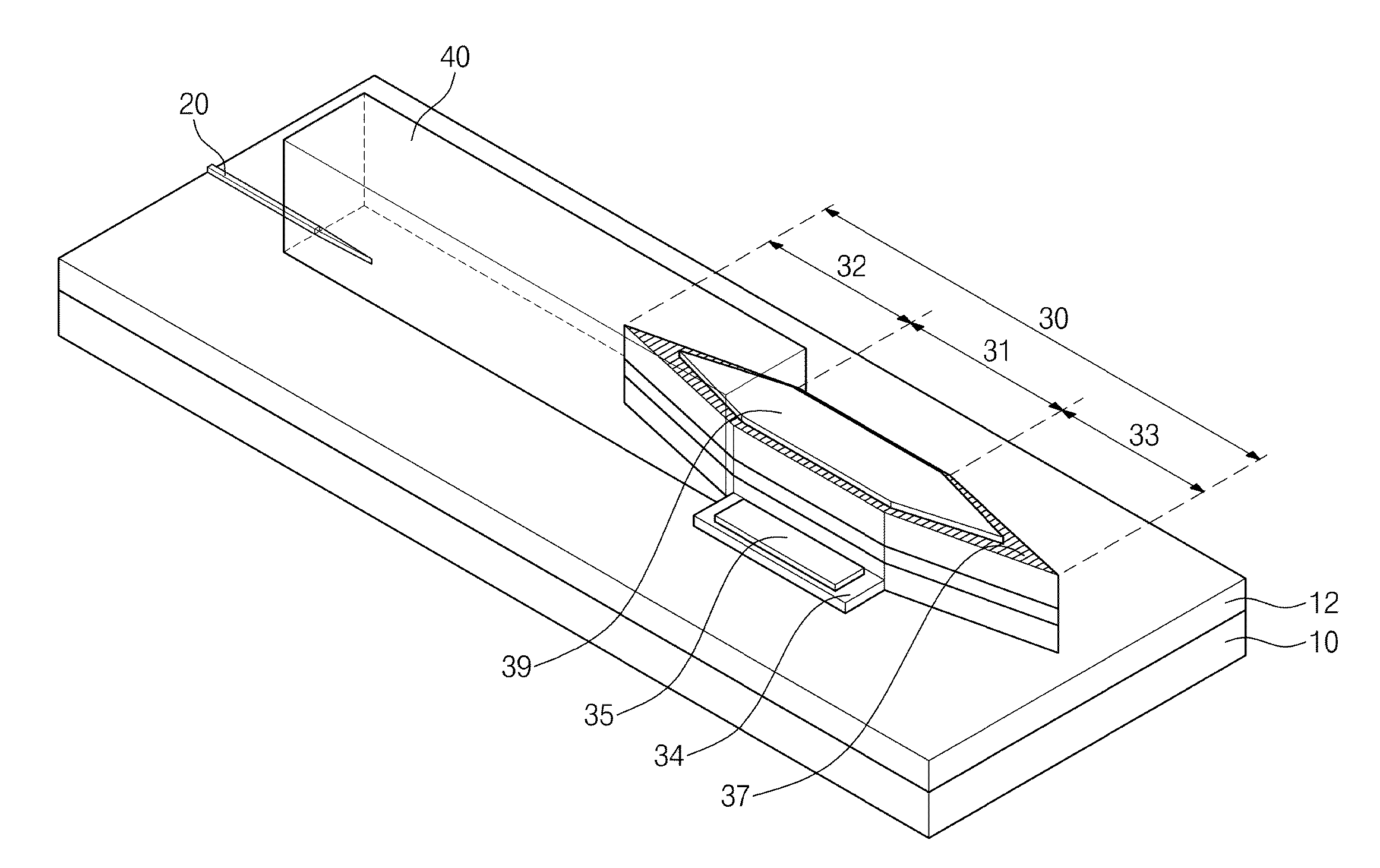
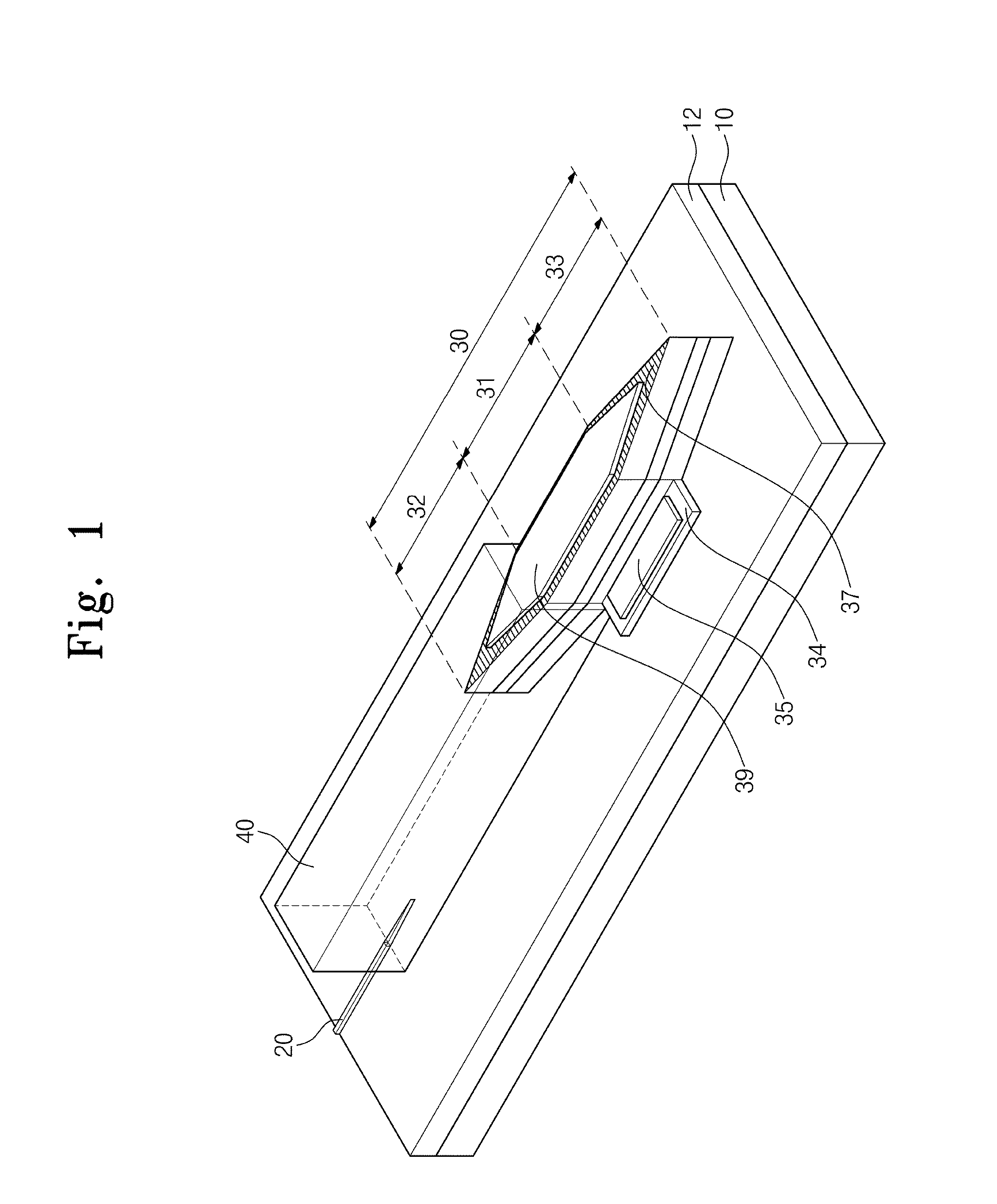
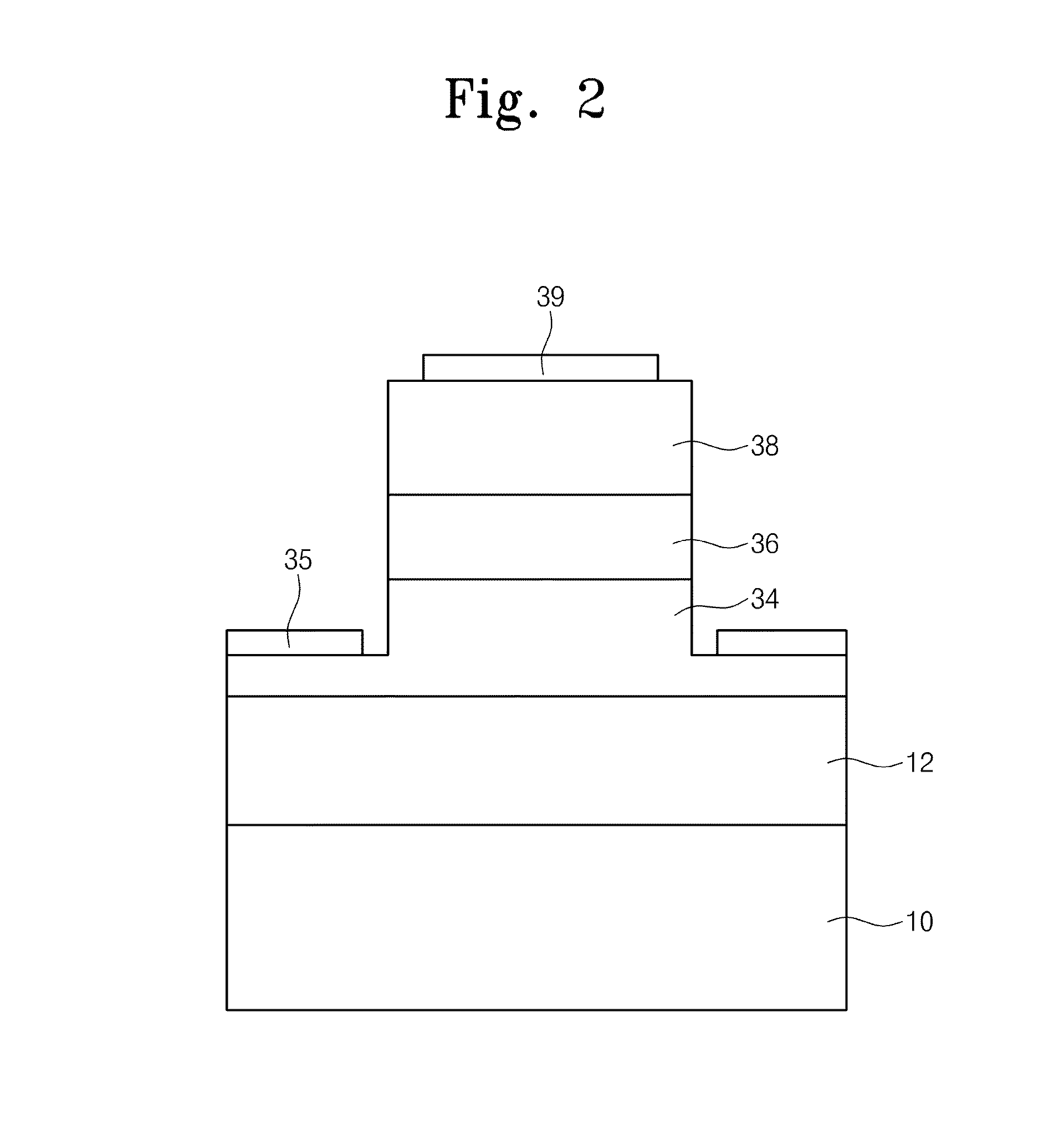
Optical device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20150030282A1Enhance productivityImprove productivityLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaveguideLaser
Provided is an optical device including a first optical waveguide on one side of a substrate; a laser separated from the first optical waveguide and disposed on the other side of the substrate; and a first coupled waveguide between the laser and the first optical waveguide. The laser may be monolithically integrated on the substrate.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Recording device and control method for recording device
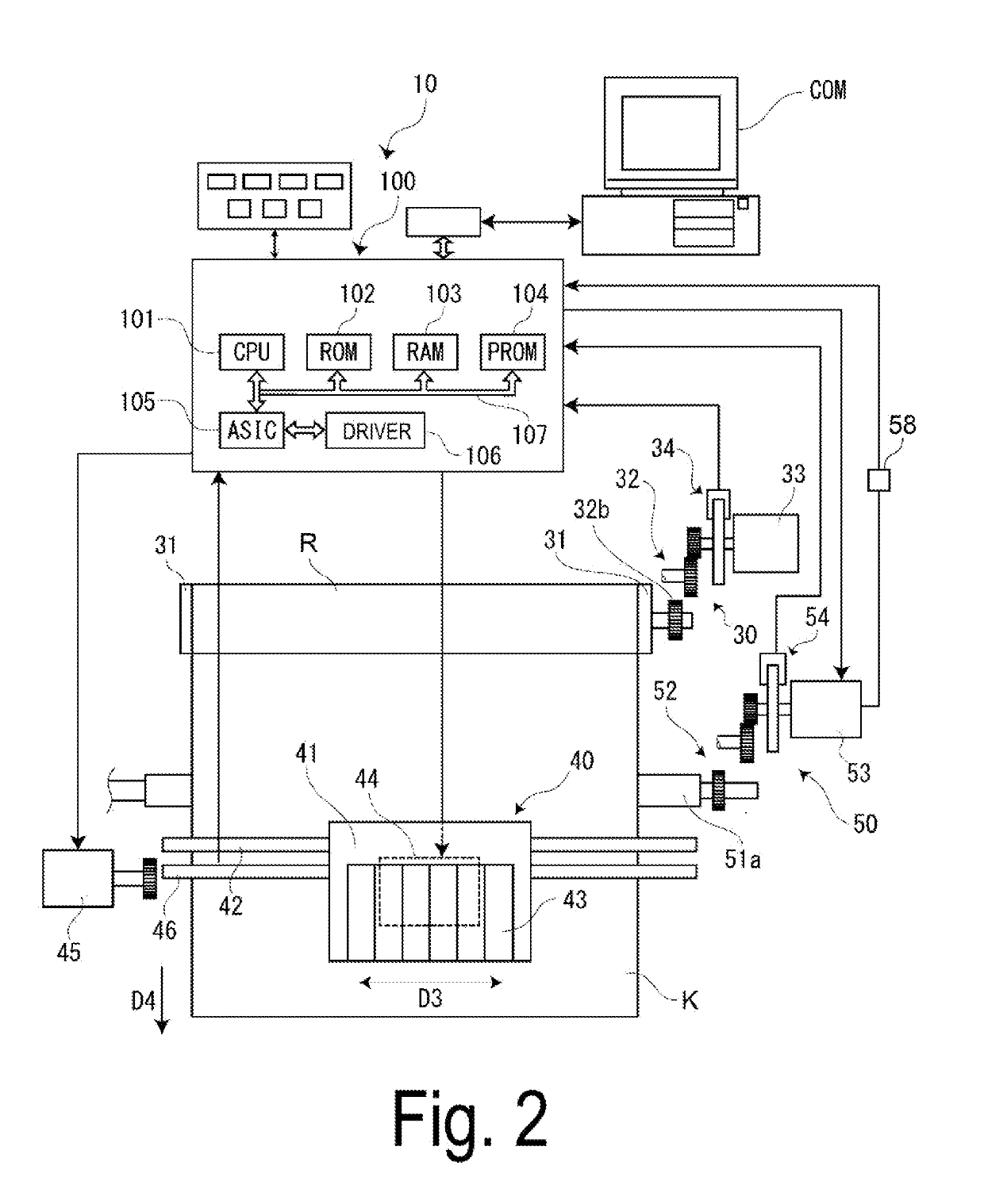
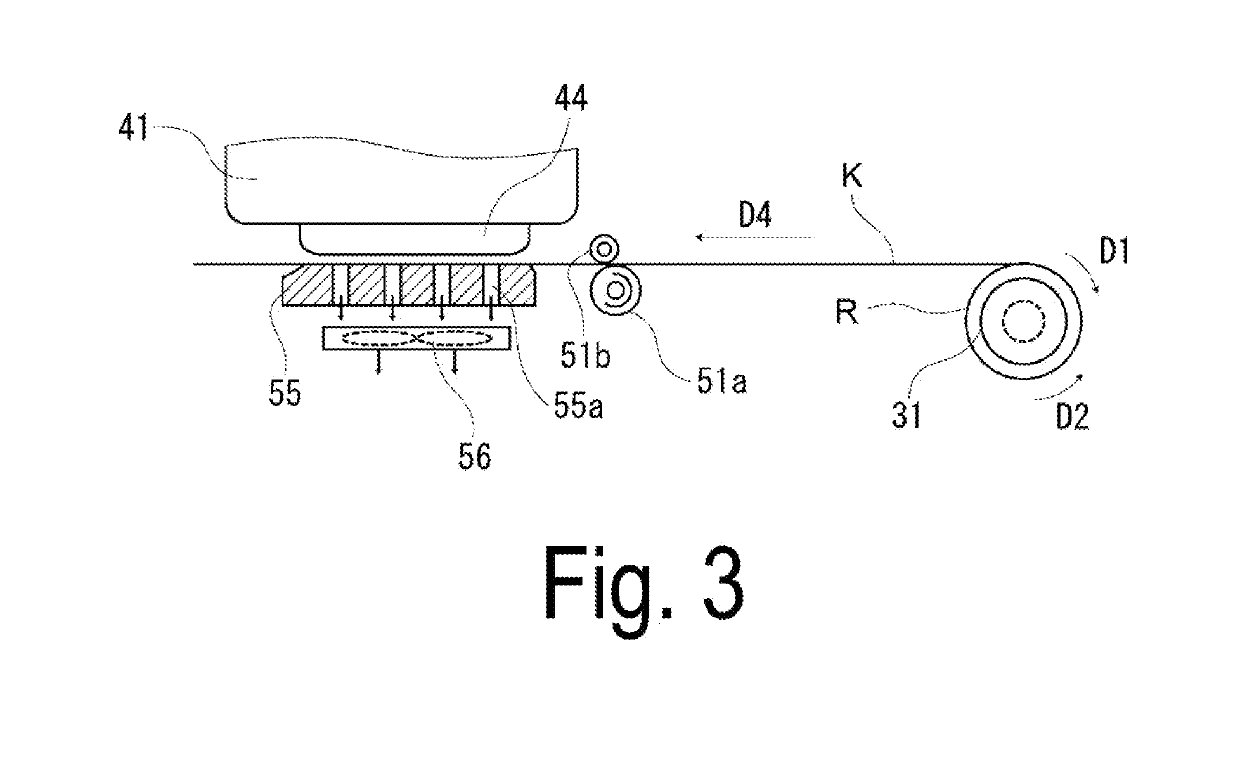
ActiveUS20190193975A1Reduce waiting timeEnhance productivityFunction indicatorsCurrent measurements onlyTransmission mediumCurrent sensor
A recording device includes: a transport unit configured to transport a medium in a plurality of transport speed modes; a driving unit configured to drive the transport unit with a plurality of speed profiles, each corresponding to one of the plurality of transport speed modes; a current sensor configured to measure a reference current the driving unit, the reference current being a current flowing in the driving unit when the medium is transported in a loosened state; and a control configured to acquire a plurality of current profiles, each corresponding to one of the speed profiles, based on the reference current. The control unit is configured to acquire a first current profile based on the reference current when the medium is transported in a first transport speed mode, and to generate a second current profile based on the first current profile.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
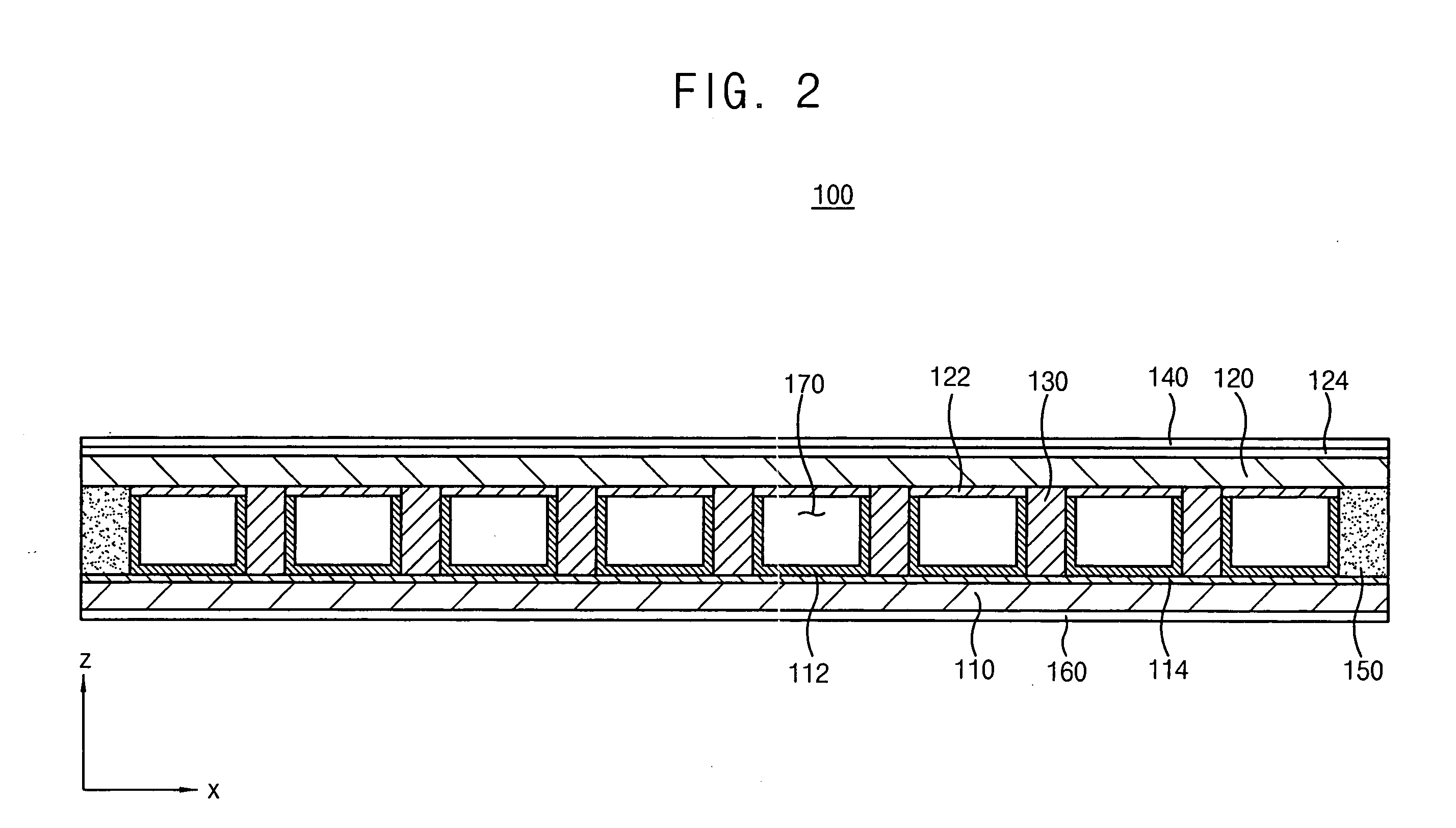
Optical film, method of manufacturing the same, and flat fluorescent lamp and display device having the same
InactiveUS20060131522A1Enhance luminance uniformityEnhance productivityGas discharge lampsInvestigating moving sheetsLiquid crystalDisplay device
An optical film includes liquid crystal layers and adhesive layers. The liquid crystal layers are disposed at a base substrate. Each of the liquid crystal layers reflects light having a first wavelength and transmits light having a wavelength different from the first wavelength. Each of the adhesive layers is disposed between adjacent ones of the liquid crystal layers to combine the liquid crystal layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
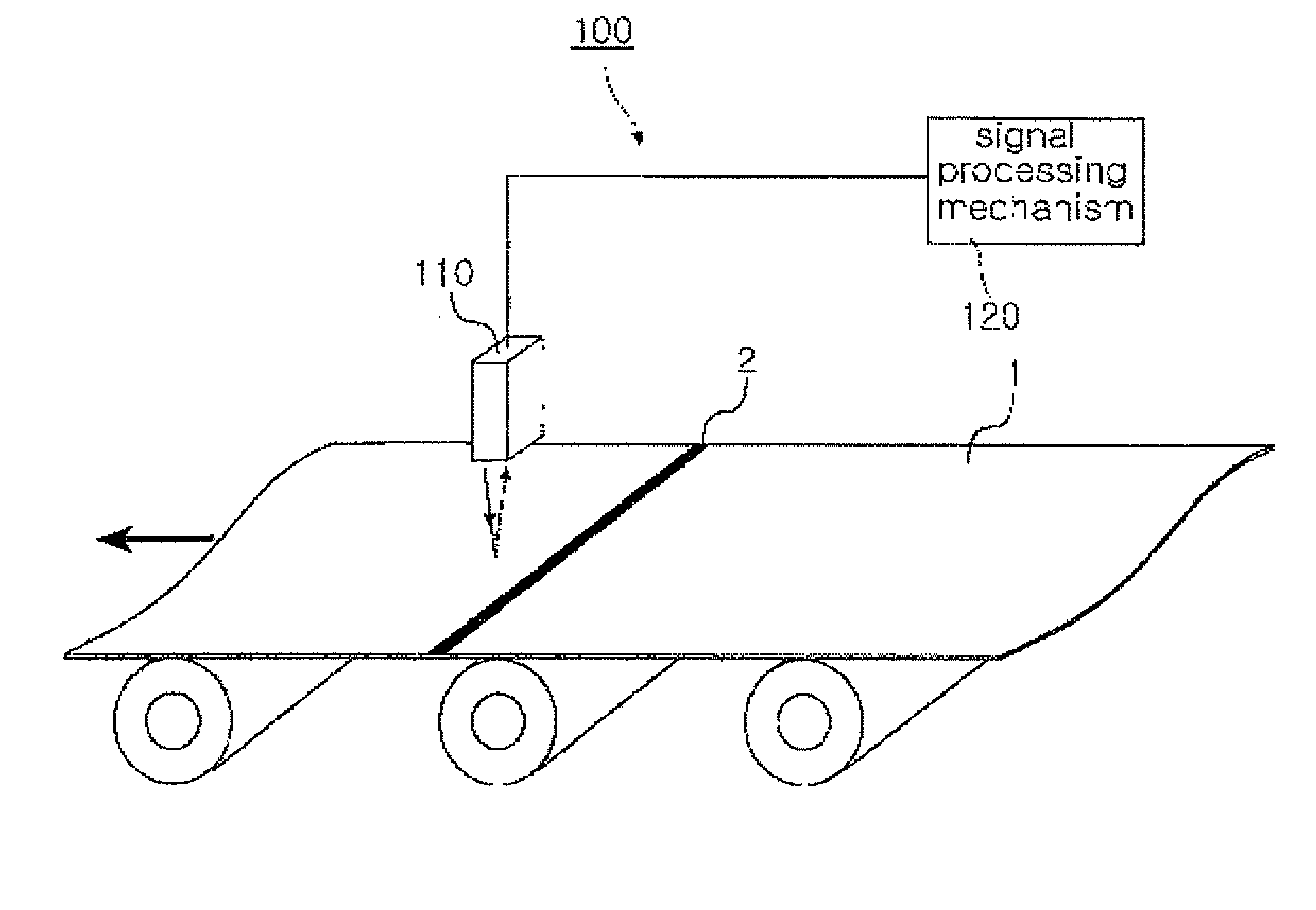
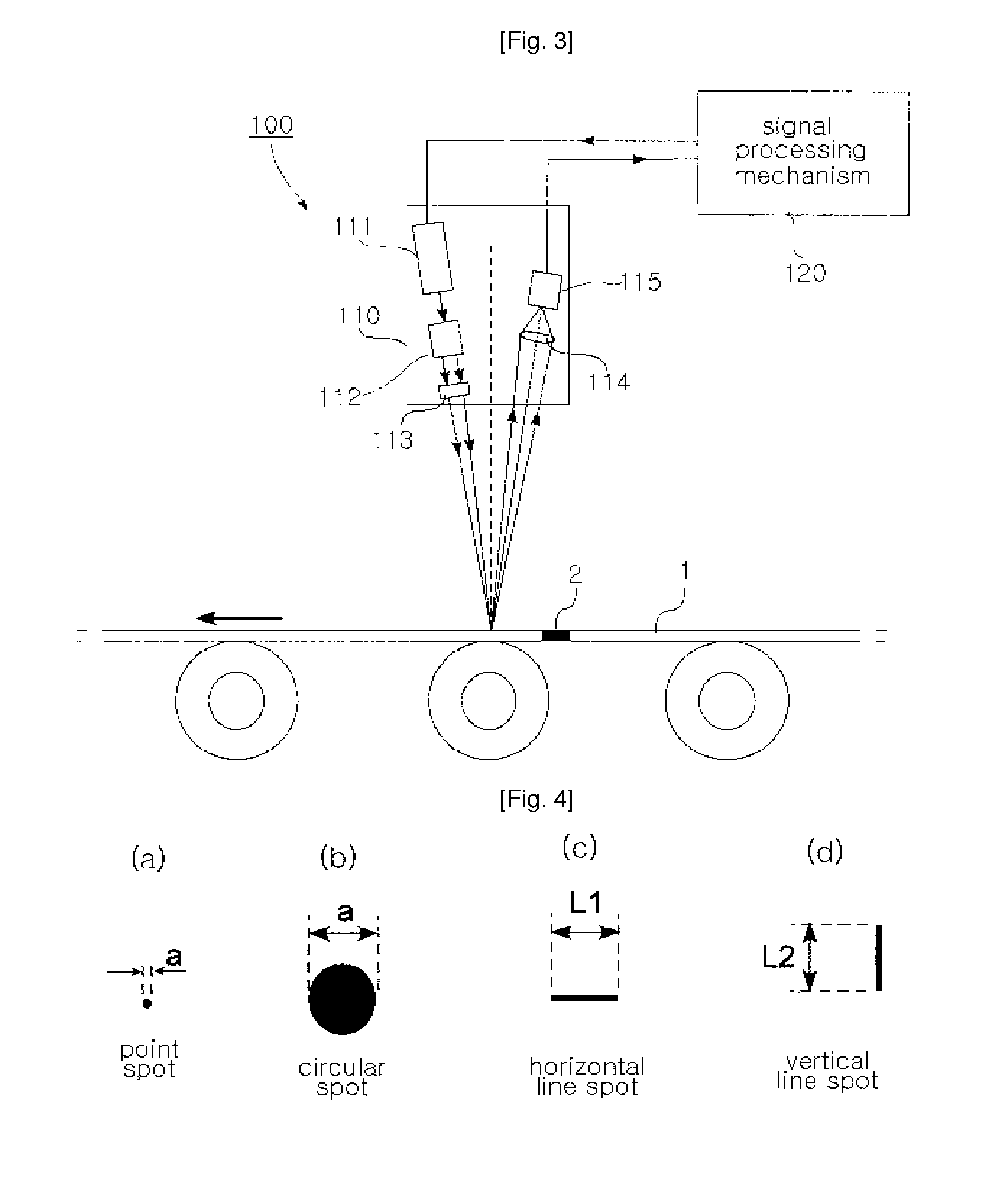
Apparatus and method for on-line detecting welding part of strip
ActiveUS20090279096A1Easily detectEnhance productivityScattering properties measurementsInvestigating moving sheetsPhysicsLaser beams
There is provided an on-line detection system and method for a weld of a steel strip, which can emit a laser beam onto the surface of a steel strip moving at a high speed and measure the reflectivity of the laser beam reflecting from the same, thereby detecting the weld of the steel strip easily on-line. In the on-line detection system, reflectivity measuring means emits a laser beam onto a moving steel strip and continuously measuring the reflectivity of the laser beam returning from the surface of the steel strip, and signal processing means detects a weld of the steel strip based on change in the reflectivity measured on the weld.
Owner:POSCO
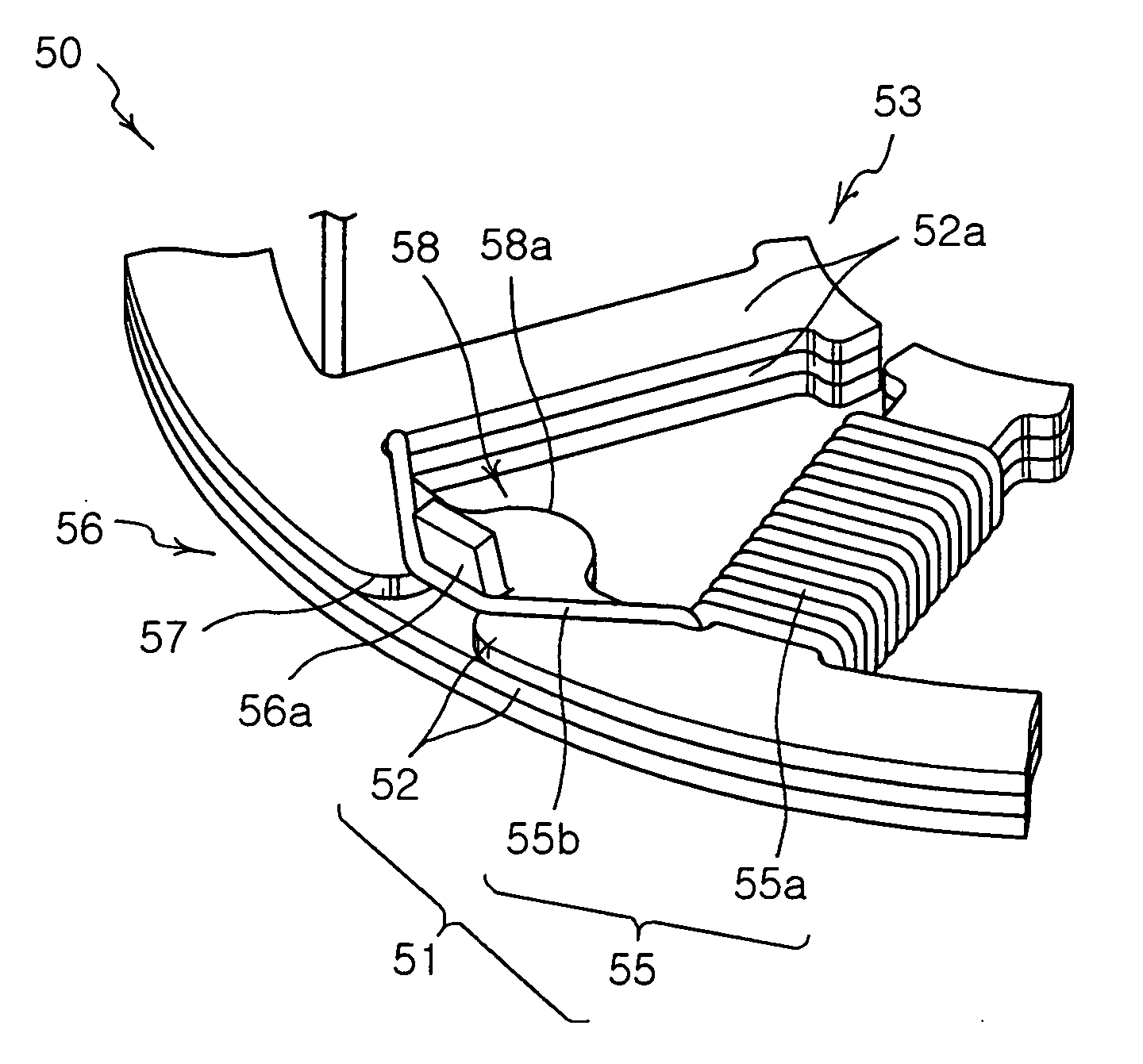
Stator and electric motor having the same
InactiveUS20060186753A1Simple bending processEnhance productivityWindingsMagnetic circuit stationary partsProduction rateStator
The present invention provides a stator including a core having a plurality of core plates piled on one another, and a plurality of teeth formed in a regular interval on the circumference of the core. The stator also has a plurality of protuberant parts bent upward from outside to inside on one of the plurality of core plates. The stator further has at least one coil having winding parts wound on the teeth of the core and connecting parts hitched on the protuberant parts. The present invention allows simpler bending process of the core, with fewer molds, thus reducing the manufacture cost and the manufacture time to enhance productivity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Backlight assembly and liquid crystal display apparatus having the same
InactiveUS20060044793A1Lower costEnhance productivityWith electric batteriesElectric lighting with batteriesLiquid-crystal displayVoltage
A backlight assembly includes a receiving container, a first mold, a voltage applying part and lamps. The receiving container includes a bottom portion and a side portion to provide a receiving space. The first mold is disposed at an end portion of the receiving container. The voltage applying part slides into the first mold to become fixably attached to the first mold. The voltage applying part includes conductive material. The lamps are combined with the voltage applying part parallel to each other. The lamps generate light when a driving voltage is applied to the lamps through the voltage applying part. A liquid crystal display apparatus includes the backlight assembly, a liquid crystal display panel displaying images using light generated from the backlight assembly, and a top chassis fixing the liquid crystal display panel to the backlight assembly.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
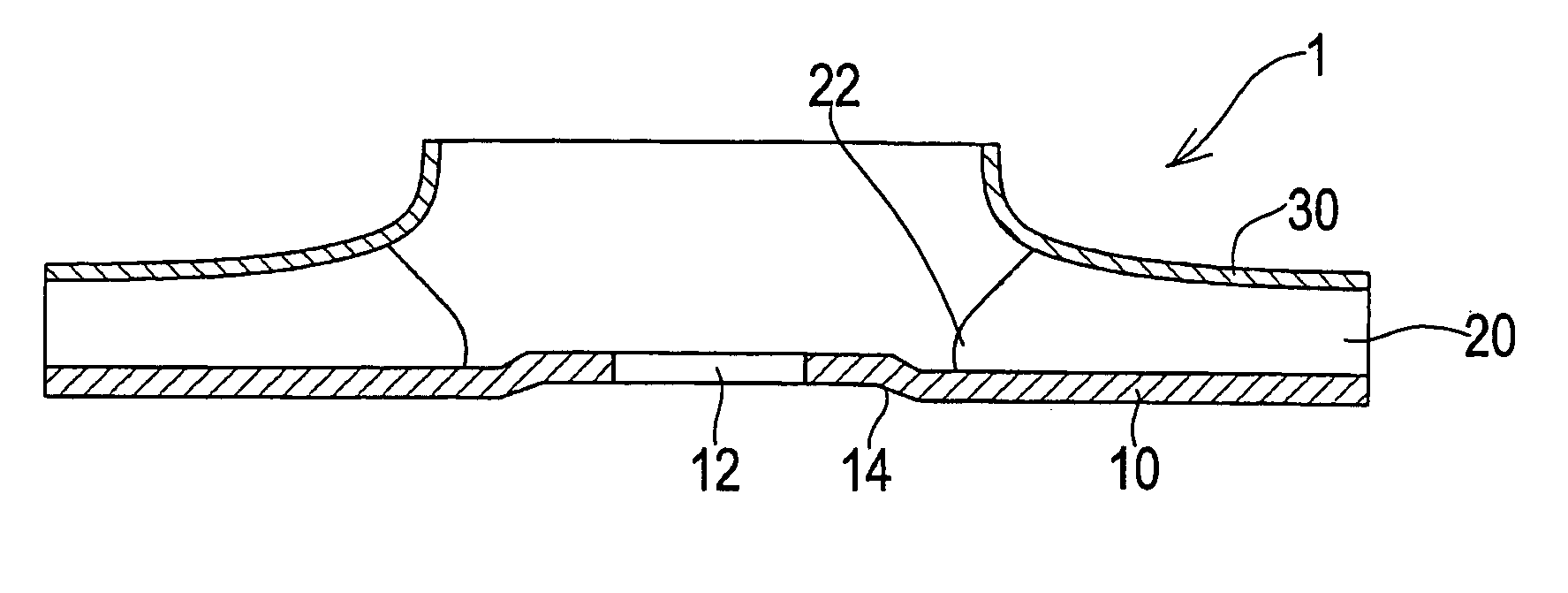
Impeller
ActiveUS20050002789A1Prolonged life timeEnhance productivityPropellersPump componentsImpellerEngineering
An impeller (1) according to the present invention has a disk-like main plate (10), a blade (20) joined to the main plate, and a side plate (30) having a suction port. A boss hole (12) is formed in a central portion of the main plate for attaching a boss which engages with a pump shaft to the boss hole. A step portion (14) is formed around the boss hole, which is formed in the main plate, by drawing.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Electric storage device, electrode, method for fabricating electrode, and management method
InactiveUS20090214955A1Enhance productivityImprove productivityHybrid capacitor electrodesElectrolytic capacitorsCurrent collectorLithium
A mixture layer for an electrode is formed on a punched current collector. For example, the mixture layer is made of an active material, conductive assistant, binder, and the like. The mixture layer having the structure described above is formed into a slurry, for example, and applied onto the current collector. The applied mixture layer is dried to fabricate an electrode. The thus formed electrode is used to assemble an electric storage device. Upon the assembly, lithium ions are pre-doped into a negative electrode. The pre-doping time is determined according to air permeability of the electrodes.
Owner:FUJI JUKOGYO KK
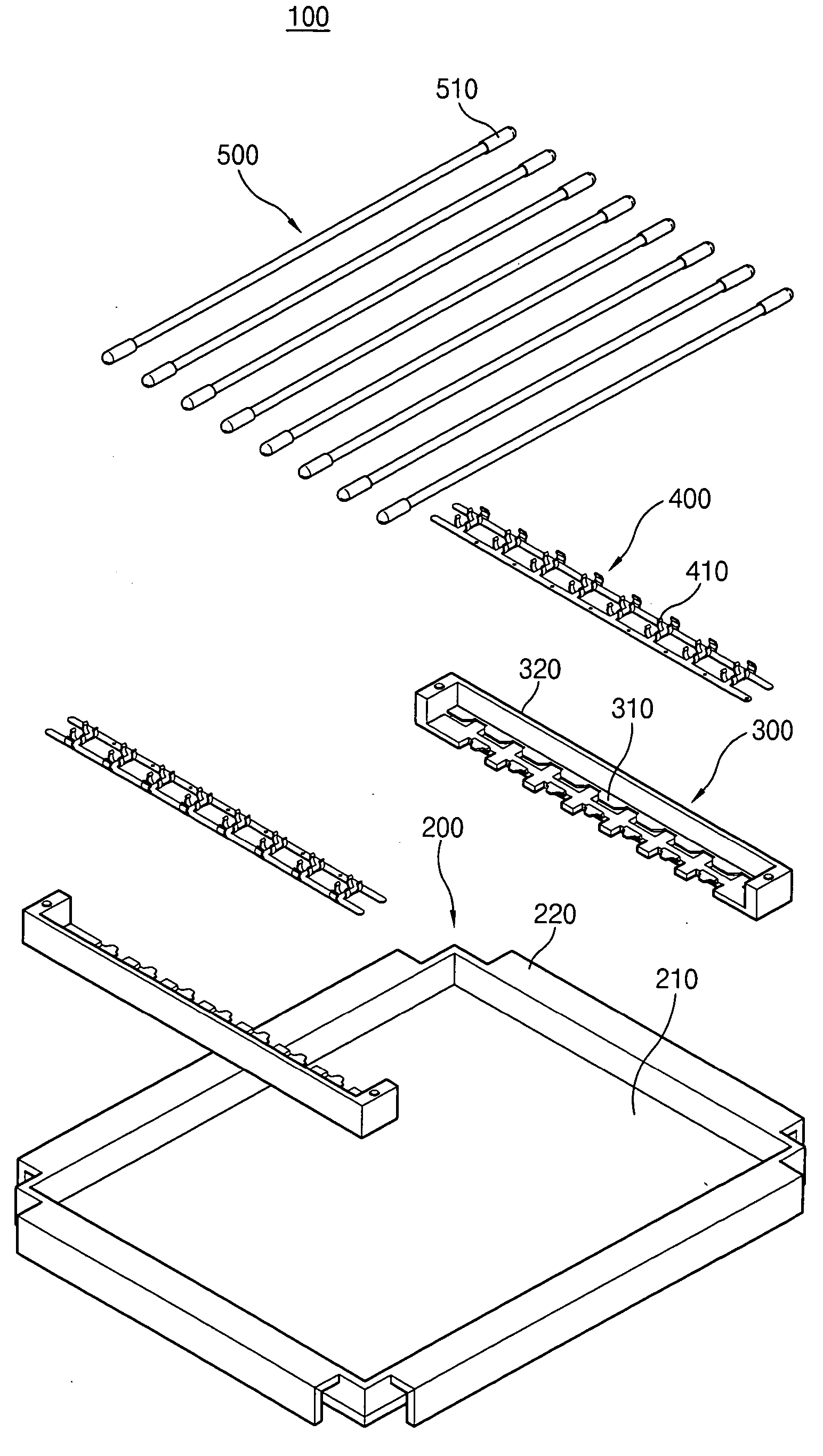
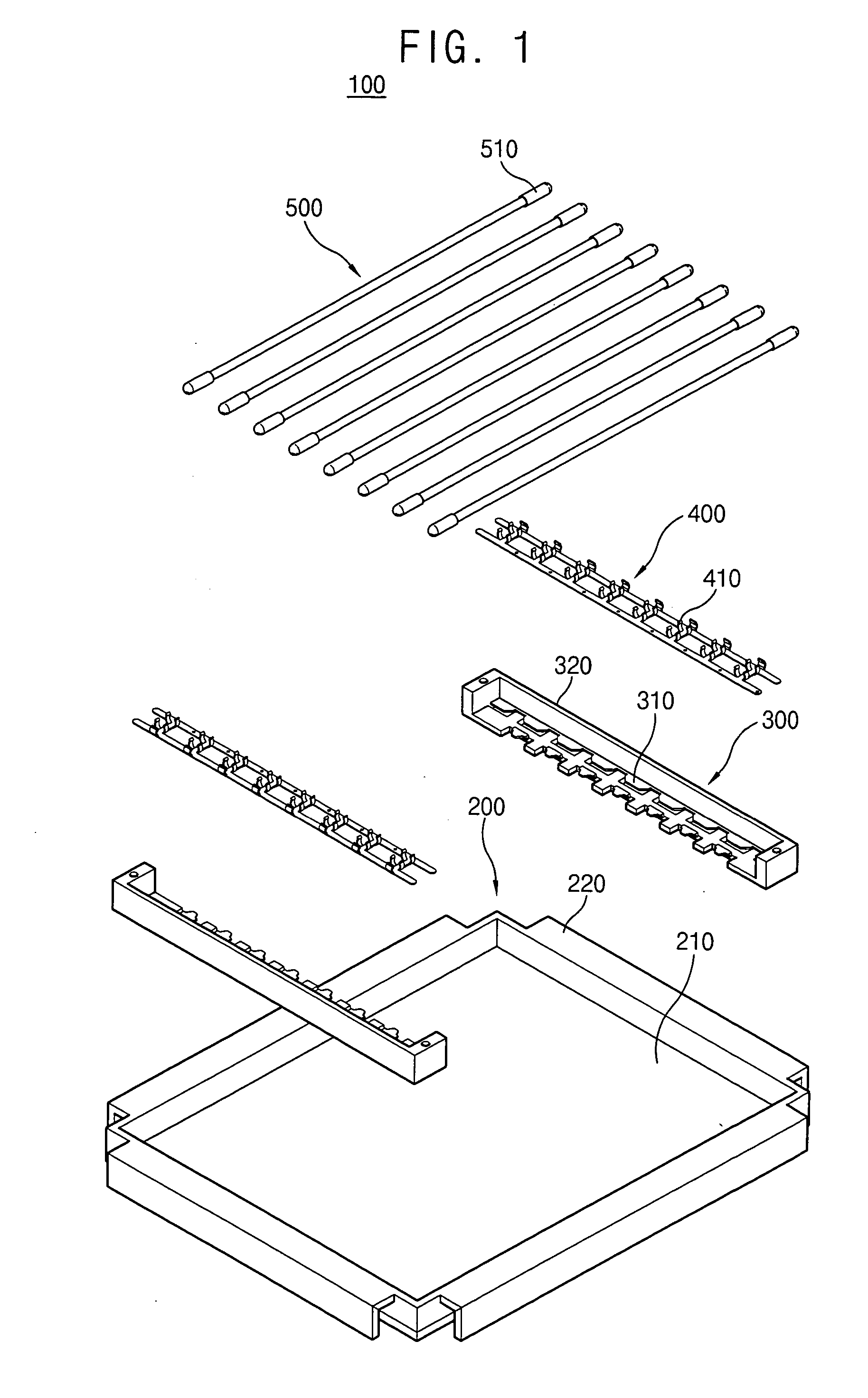
Ballast socket for compact fluorescent lamp
InactiveUS6864635B2Enhance productivityImprove compatibilityElectric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesProduction ratePrinted circuit board
A ballast socket for compact fluorescent lamp is disclosed. The ballast socket includes: a case having an upper case, which has a receiving space for receiving a lamp and a connection terminal connected with the lamp at a side of the receiving space, and a lower case, which has a through hole at a lower center of the upper case; a controller mounted inside the case for controlling lighting of the lamp; pins for connecting PCB and the connection terminal; and a printed circuit board on which various circuit components are mounted. The ballast socket looks similar to an incandescent lamp socket in outward form, but the compact fluorescent lamp, which does not have ballast, is used in the ballast socket. Therefore, the ballast socket prevents waste of resources and environmental pollution by saving electricity, and improves productivity of the lamp by manufacturing the lamp not adhering ballast thereon.
Owner:MOON DAI SUNG
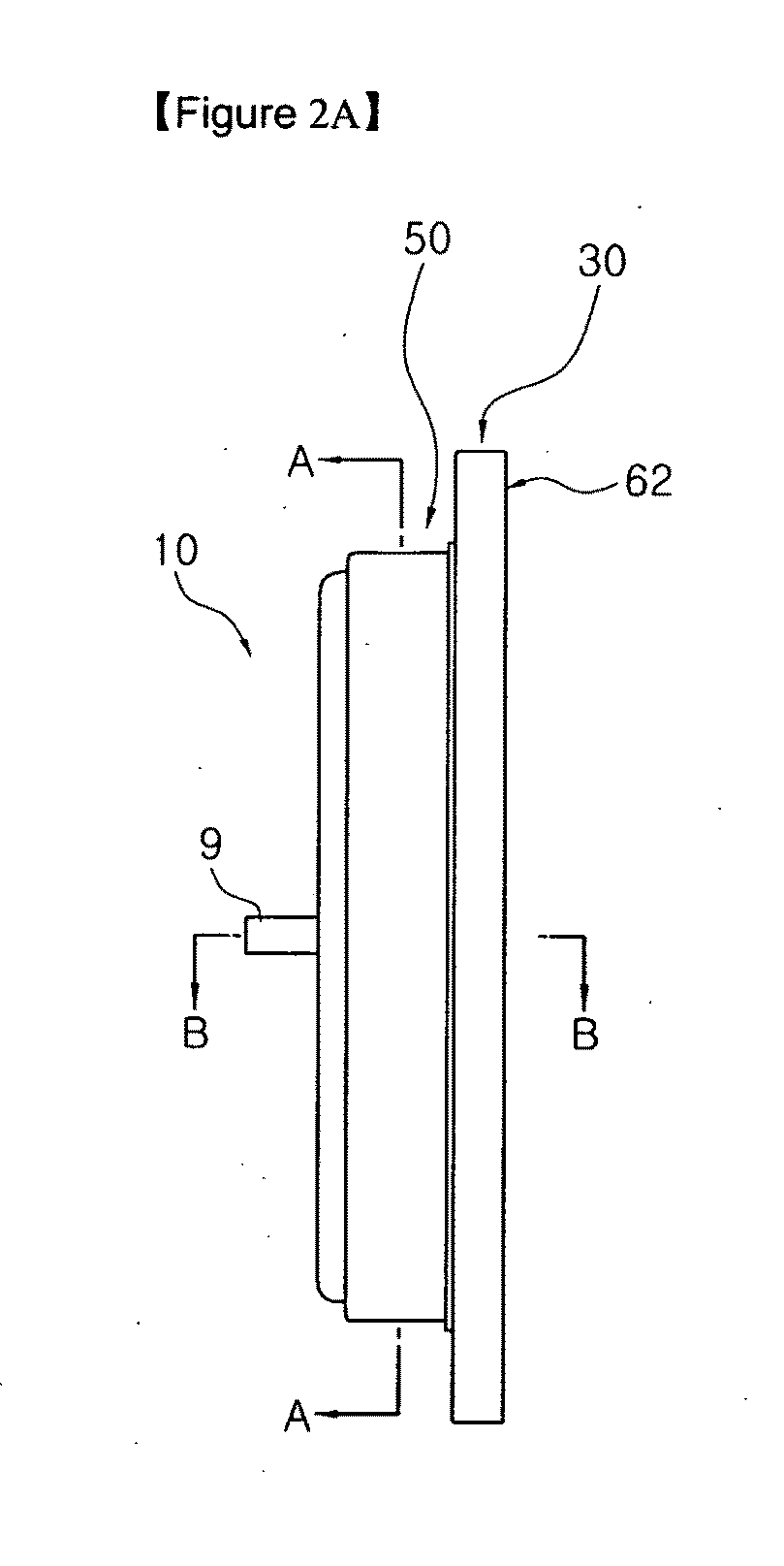
Stator foar aspiration motor, aspiration motor and in-car sensor using the same
ActiveUS20100141058A1Enhance productivityMinimize inferiorityWindings insulation shape/form/constructionAsynchronous induction motorsMiddle lineProduction rate
Provided are a stator for an aspiration motor, an aspiration motor and an in-car sensor using the same, in which a bobbin is integrally formed with a stator, to thus use an inexpensive insulation wire and enhance a productivity and lower an inferiority using an insert-molding technology. The stator for the aspiration motor includes a stator support plate, a support boss which is vertically extended from the central portion of the stator support plate, a bobbin which is bent and formed on the lateral surface of the support boss, and which is separated from the upper side surface of the stator support plate, to thereby provide a space, and a stator coil which is formed by making a wire wound in the space provided by the bobbin.
Owner:AMOTECH
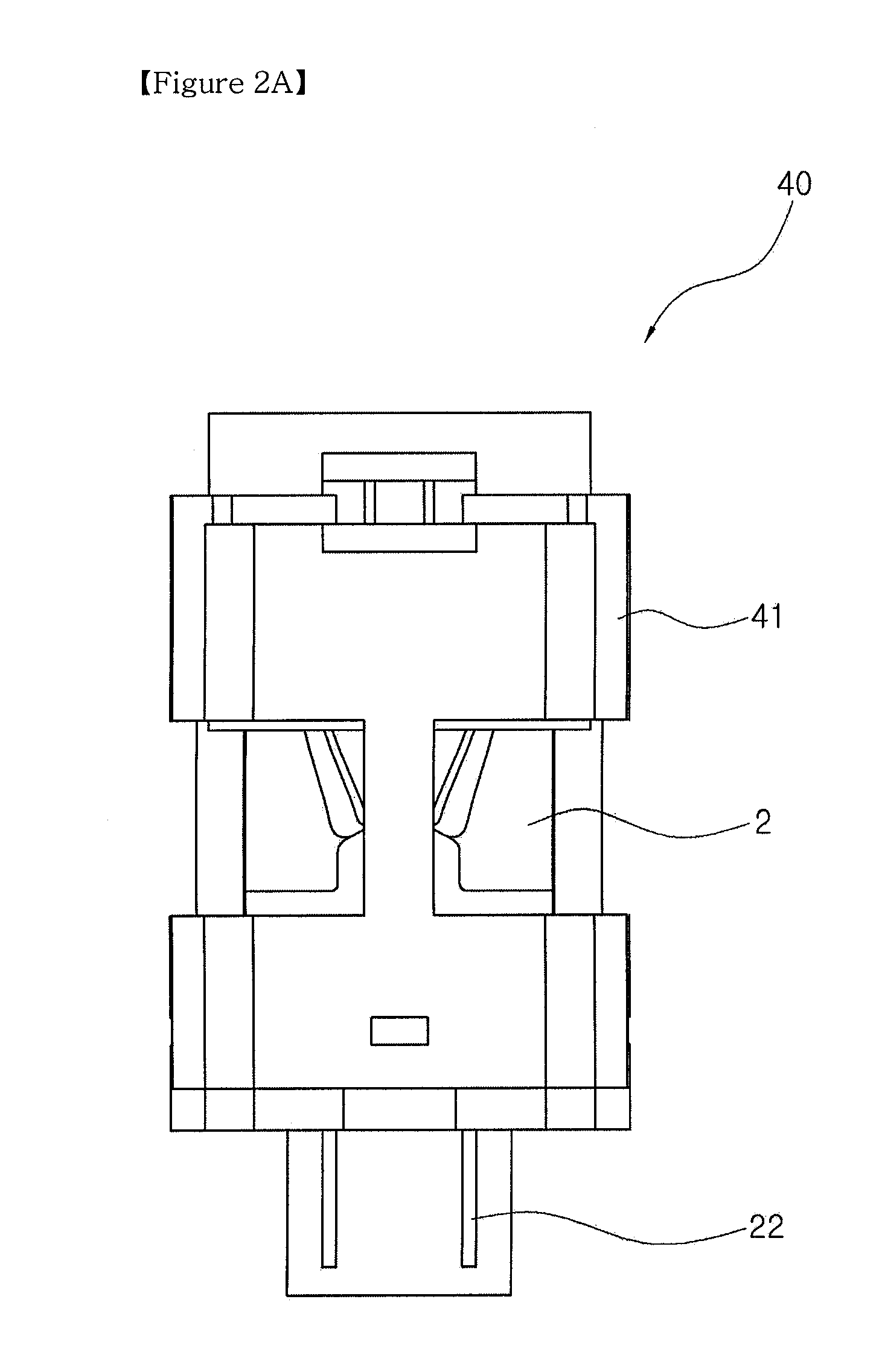
Image Forming Device, Image Forming Device Terminal, and Program
ActiveUS20090153895A1Enhance operabilityEnhance productivityVisual presentation using printersComputer security arrangementsProduction rateGenerating unit
The present invention provides an image forming device terminal for enhancing the productivity of the image forming process such as printing. An image forming device terminal for instructing execution of a printout process on an image forming device capable of executing an authentication print printing, includes a selection accepting unit which accepts a selection of an image forming device for executing the printout process from a plurality of image forming devices; a determination unit which classifies the selected image forming device to a first type image forming device or a second type image forming device based on whether or not the selected image forming device is a default set image forming device; and a generating unit which generates job data as a printout process of not the authentication print printing in a case where the selected image forming device is the first type image forming device, and generates job data as a printout process of the authentication print printing in a case where the image forming device is the second type image forming device.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
Fabrication of alloy variant structures using direct metal deposition
InactiveUS20050224209A1Improve longevityEnhance productivityMolten spray coatingRadiation applicationsLoop controlHardness
Direct-metal deposition (DMD), preferably under closed-loop control, is used to fabricate alloy-variant material structures which provide a combination of desirable physical and mechanical properties. Use of the invention facilitates the production of high-strength, high-wear, and impact-resistant structures which decrease the likelihood of erosion, heat checking and brittle failure in injection molds, die casting, thixomolding and other, more exotic tooling. The invention uses DMD to deposit a first material or alloy in an area exposed to high wear, such as the tooling gate area, with a second material or alloy being used elsewhere in the tool for greater impact resistance. Advantageously, the areas may be of a user-defined thickness to further improve longevity. The resulting composite material structure has mechanical properties (i.e., yield strength, hardness and abrasion resistance) which exceed that of the homogeneous compositions currently used for mold materials, thereby enhancing productivity while improving part quality in these and other applications.
Owner:DM3D TECH
Method and apparatus for chemical plasma processing of plastic container
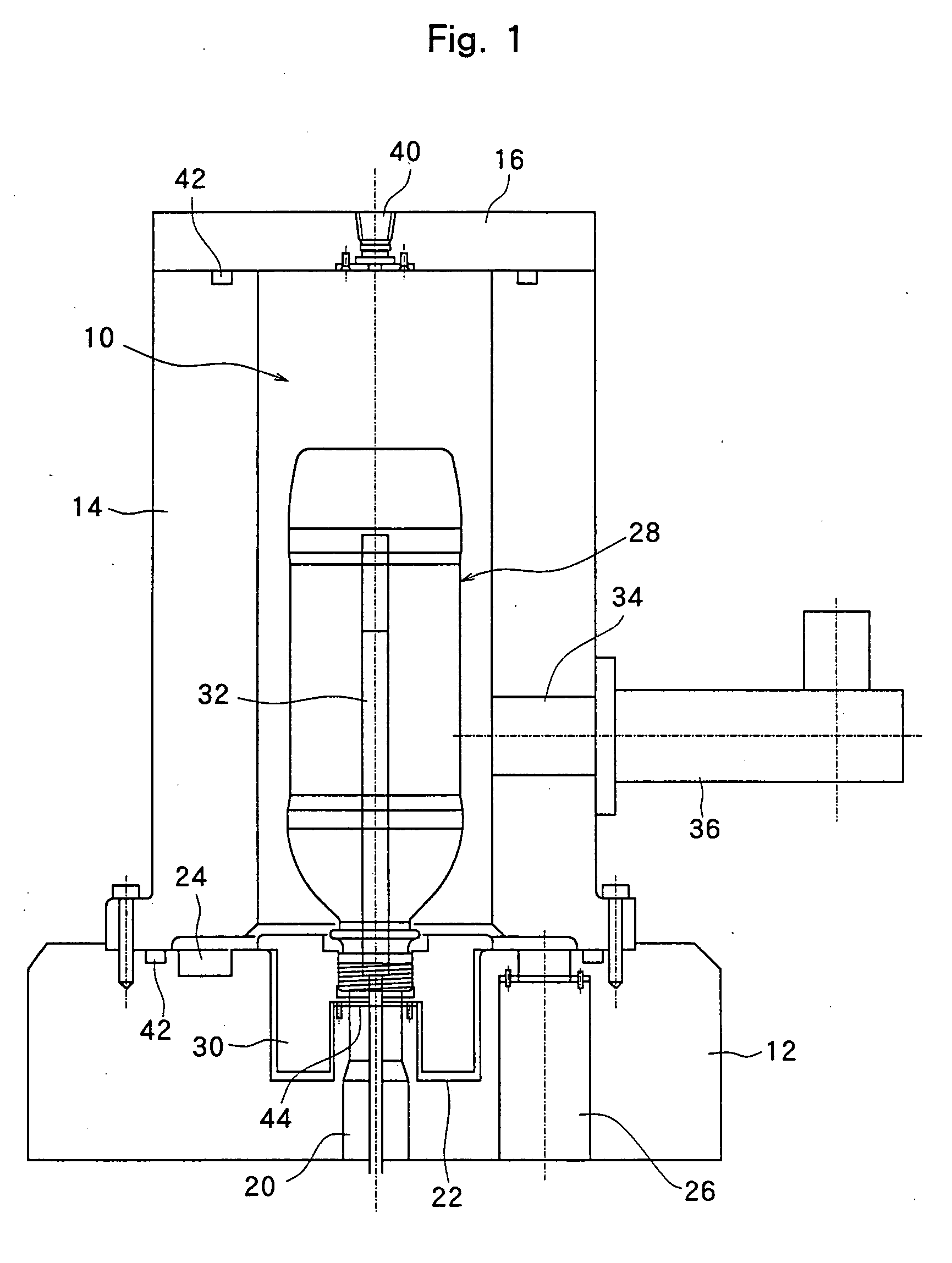
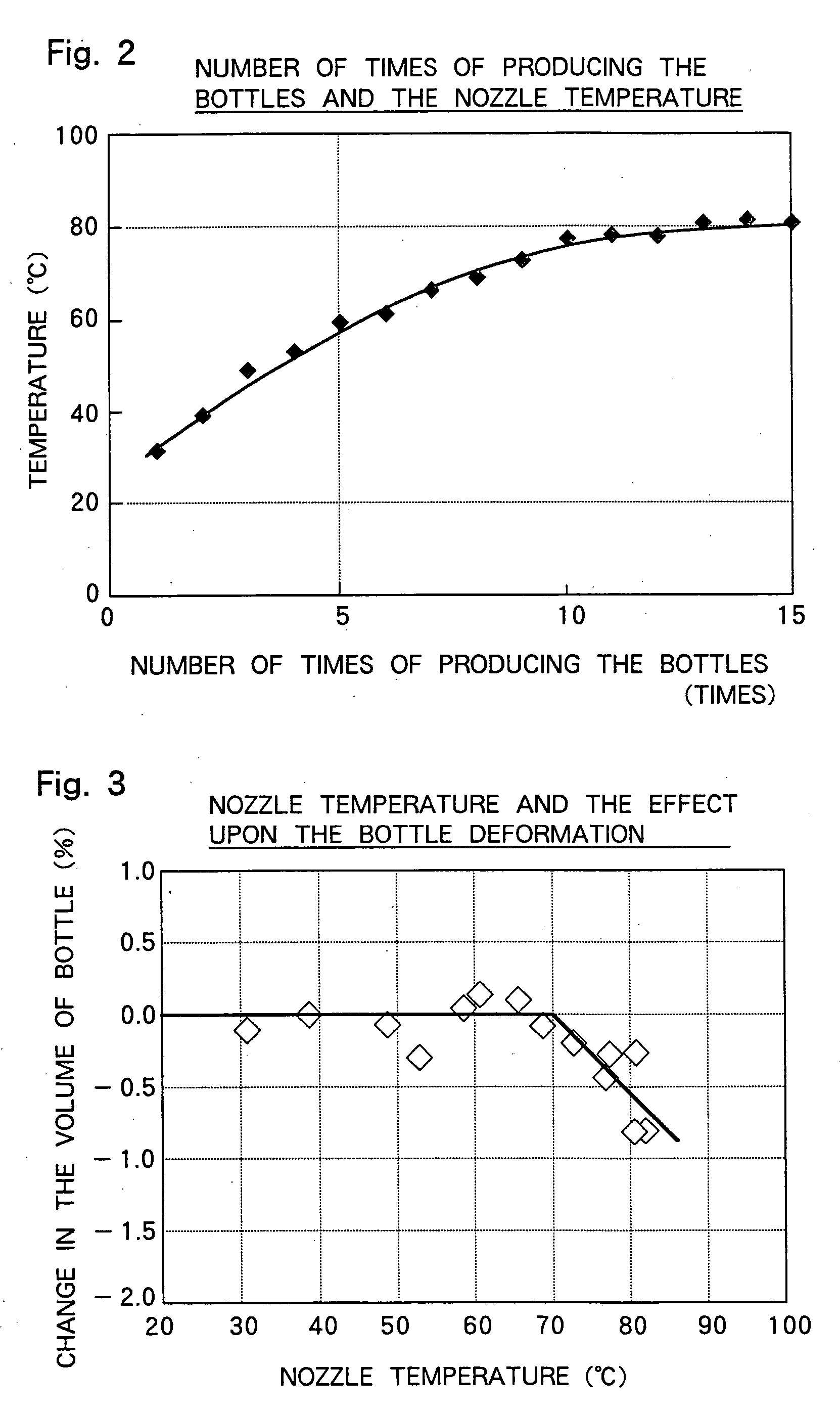
InactiveUS20060172085A1Enhance productivitySuppression of deformationLaser detailsElectric discharge tubesGlow dischargePlasma treatment
A method of treating plastic containers with a chemical plasma by forming a film by CVD on the plastic containers by generating a glow discharge by feeding a gas for plasma treatment and energy such as microwaves for plasmatization into a plasma-treating chamber, wherein the plastic containers are cooled. This method effectively suppresses the plastic containers from being deformed, is capable of forming the film by CVD on the inner surfaces of the plastic containers consecutively for extended periods of time, and greatly enhances the productivity.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN KAISHA LTD
Method for Producing Aromatic L-Amino Acid Using Bacterium Belonging to the Genus Methylophilus
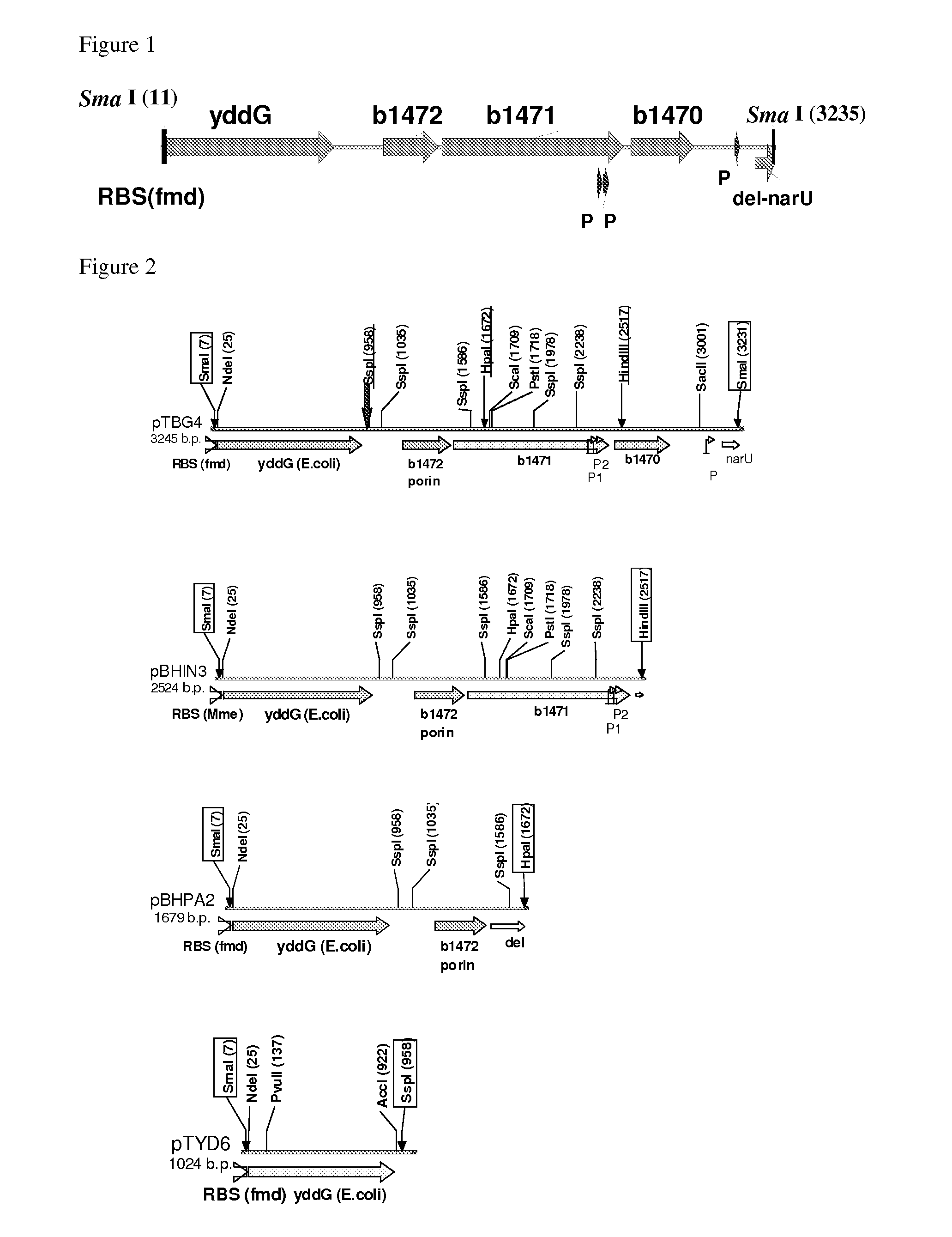
InactiveUS20070166807A1Enhance productivityImprove productivityBacteriaBacteria peptidesGenus MethylophilusGenus
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium belonging to the genus Methylophilus which has been modified to enhance expression of genes involved in the efflux of aromatic L-amino acids, particularly the yddG, yddL, yddK, and yddJ genes from Escherichia coli.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Herbal cattle feed supplement compositions for enhancing productivity and quality of milk
The present invention relates to multi purpose herbal cattle feed supplement compositions for enhancing the productivity and quality of milk by improved bioavailability / bioenhancing of nutrients. The herbal composition comprises an effective amount of an extract and / or at least one bioactive fraction or powder from herbs such as Asparagus, Withania, Lepidium, Bacopa, Nardostachys, Vetiveria, Pueraria, Emblica, Tinospora etc.; one or more additive selected from Probiotics, decorticated cotton seed extract (DCC), chelated mineral mixture, mineral nutrients, dicalcium phosphate (DCP), dolomite, calcite, vitamins and amino acids to obtain the herbal feed supplement compositions.
Owner:PATIL PRASHANT NEMINATH
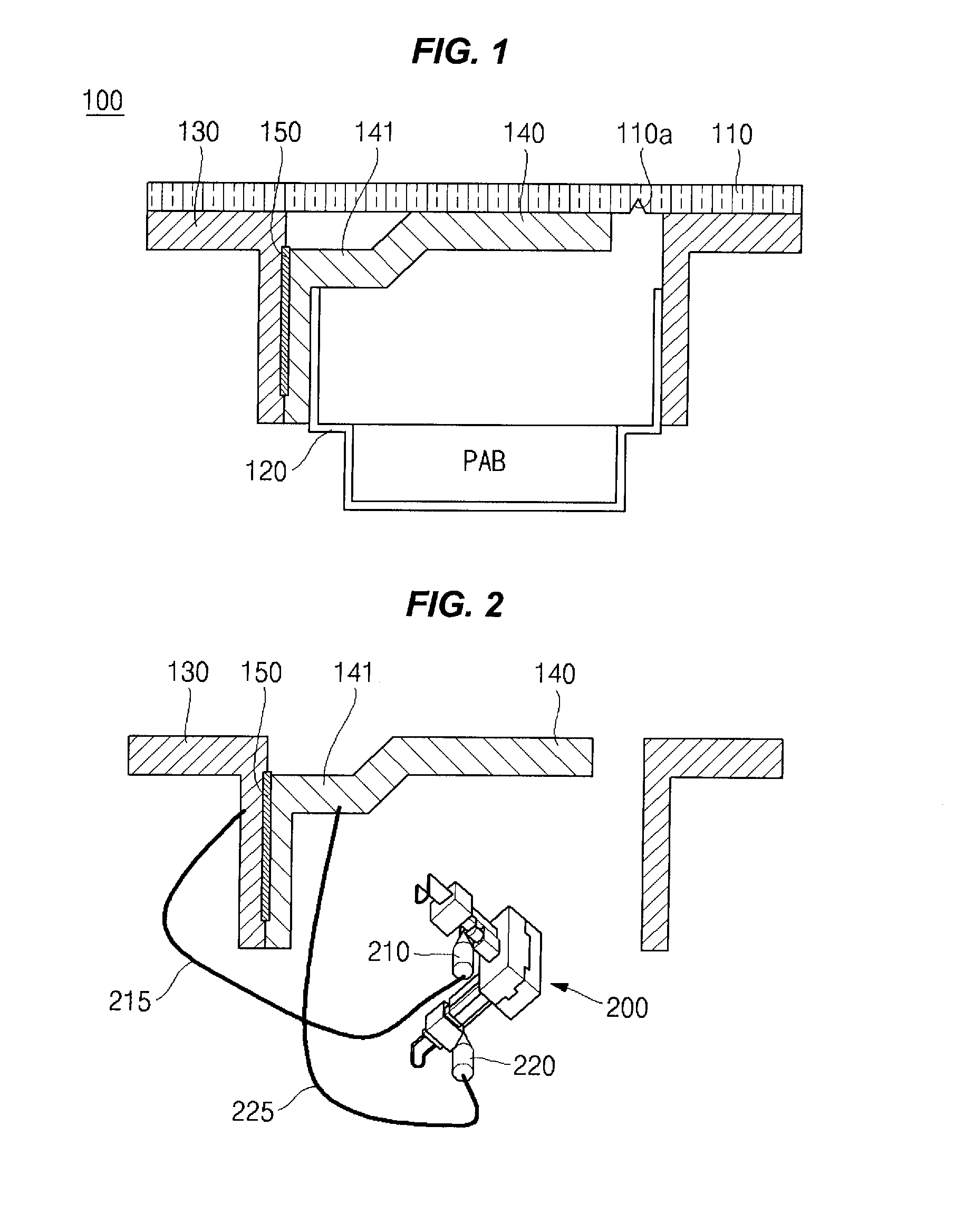
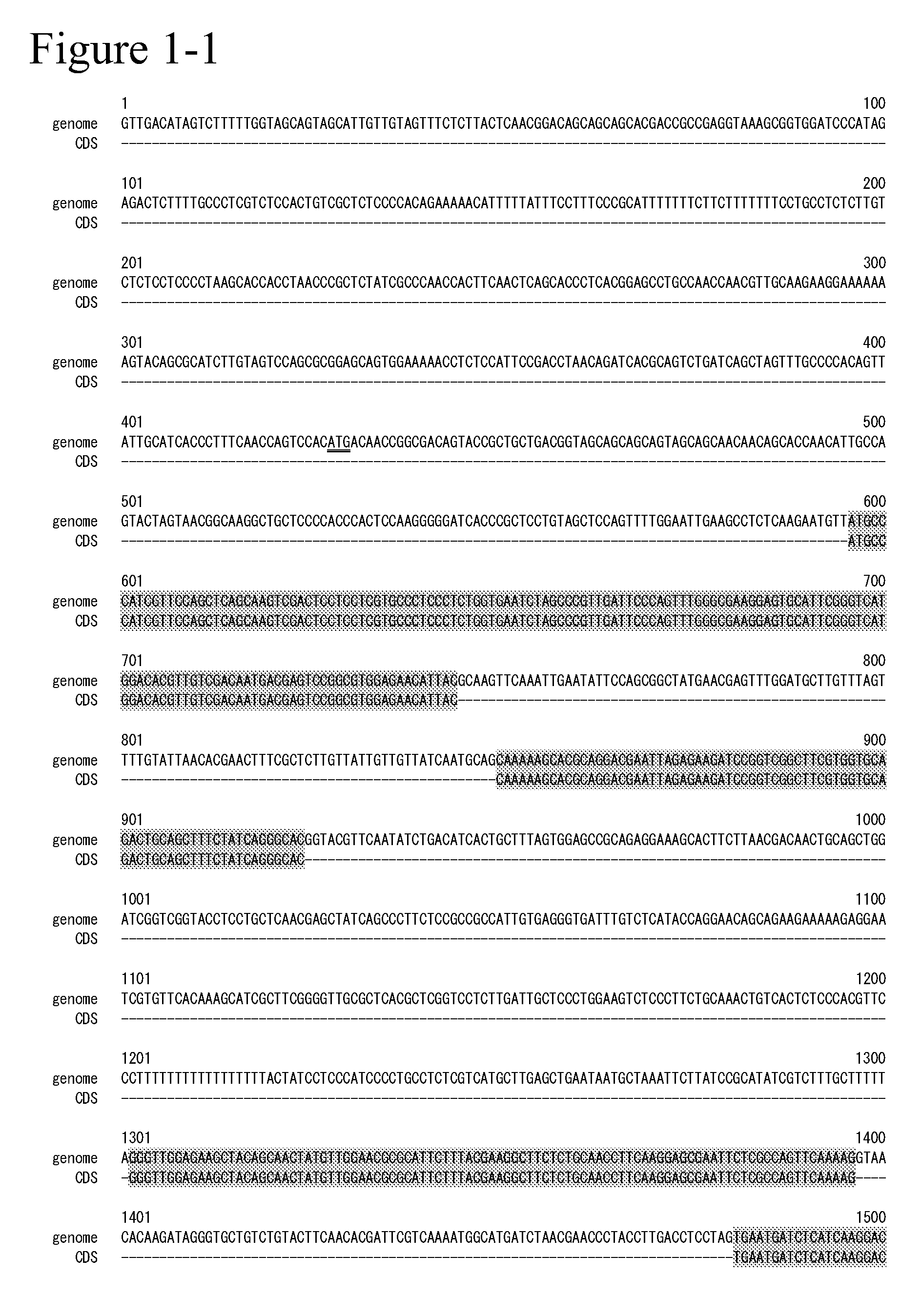
Airbag Door Connecting Structure of Passenger Seat in Vehicle
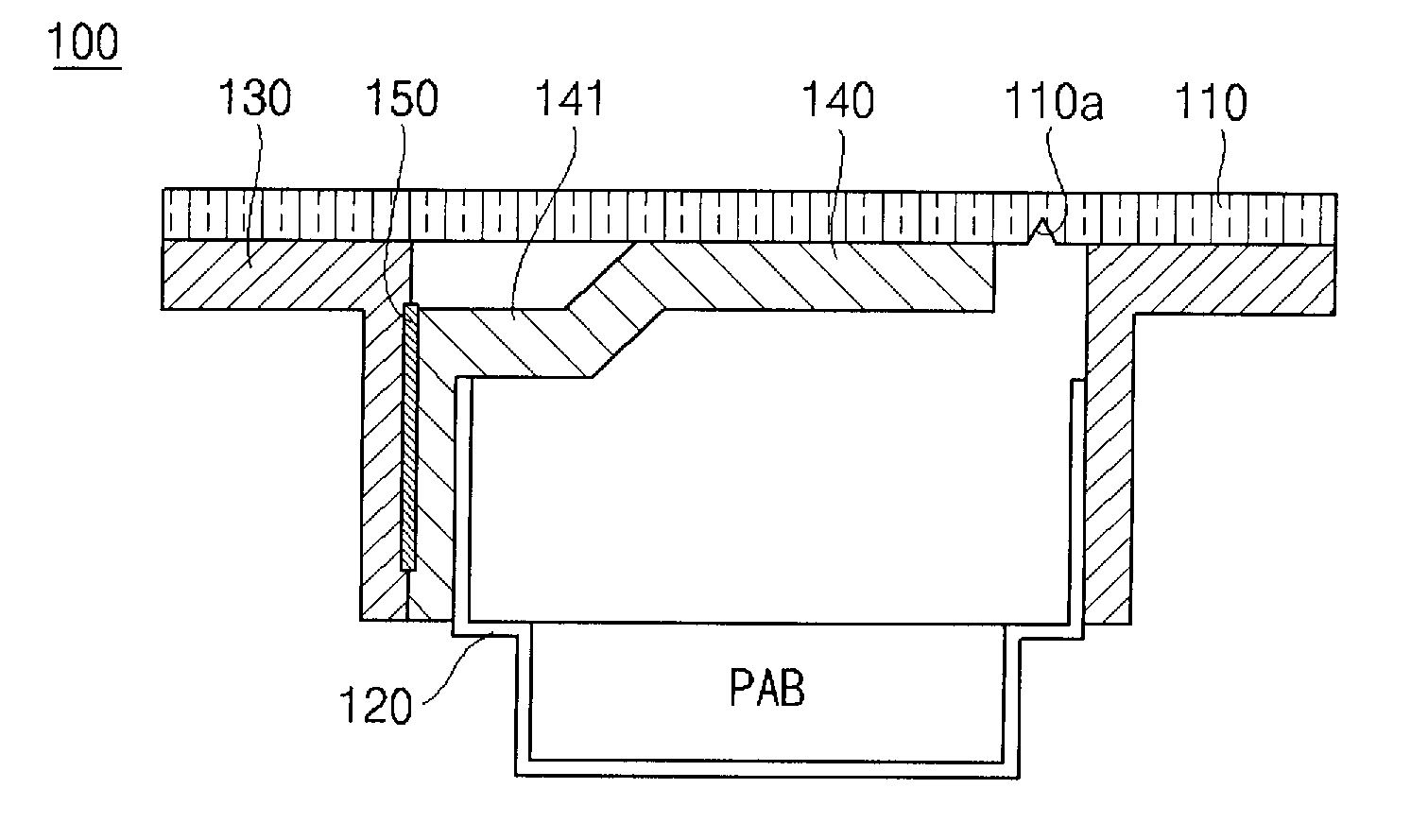
ActiveUS20100295275A1Reduce weightEnhance productivityPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementDomestic articlesIn vehicleEngineering
An airbag door connecting structure of a passenger seat of a vehicle may include a crash pad formed with interior finishing material of a dash board extending over a front surface of a passenger seat; a housing disposed to a lower portion of the crash pad, wherein a space is defined between the housing and the crash pad in which a passenger airbag (PAB) is installed; a chute coupled to the crash pad by vibration welding outside the housing and couples the housing to the crash pad; and an airbag door disposed in the chute and covering the space of the housing, the airbag door having a hinge portion which is bent inwards so as to elastically rotate about a coupling portion of the hinge portion outwards by the passenger airbag in a crash accident of the vehicle, wherein the coupling portion is coupled to the housing and to the chute.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD +1
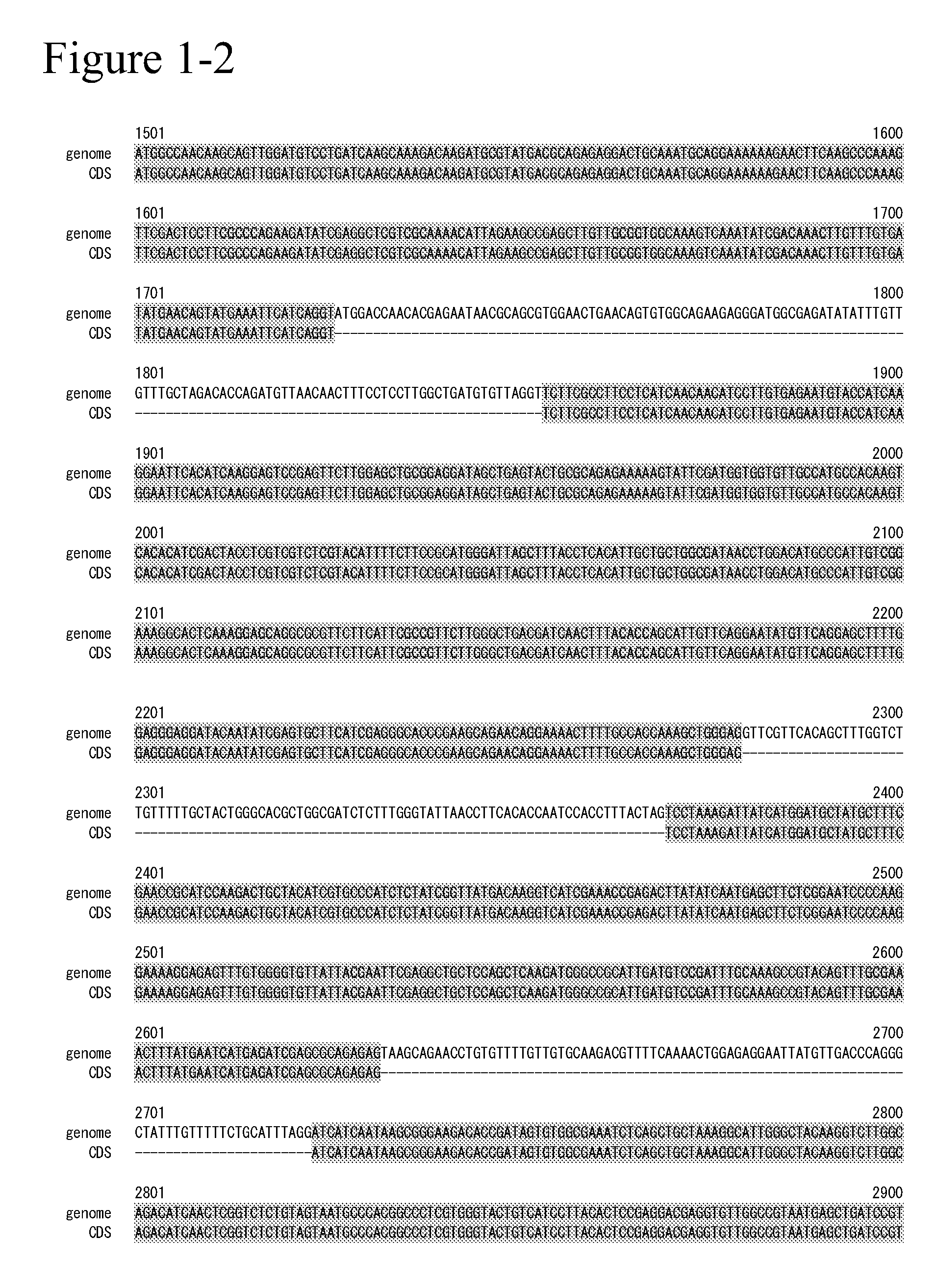
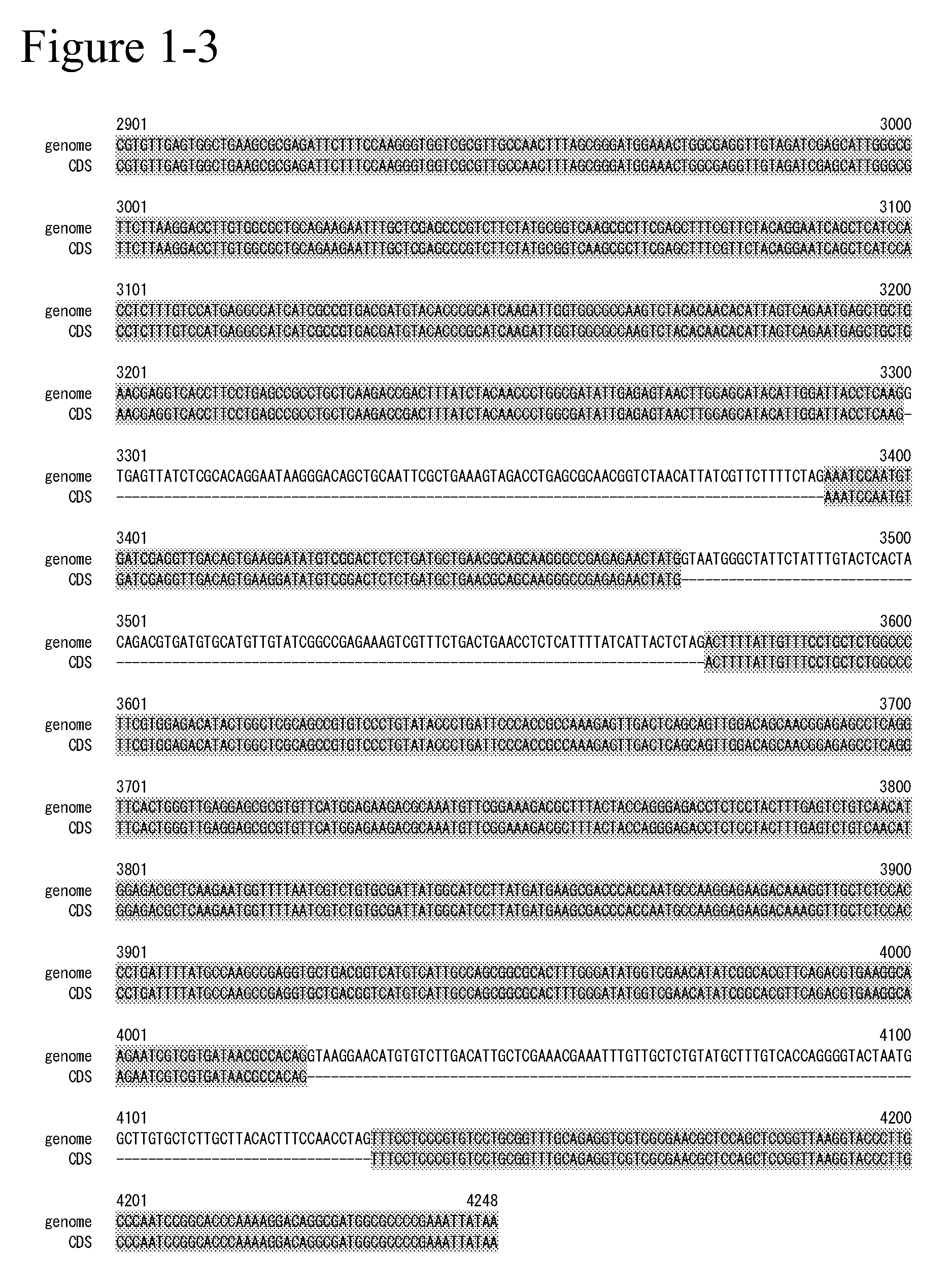
Glycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferase homologue and use thereof
The present invention provides a novel glycerol 3-phosphateacyltransferase gene and use thereof. The object of the present invention can be solved by providing a nucleic acid having a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, 4, or 8, SEQ ID NO: 3, 6, or 11, or SEQ ID NO: 7 or 12 and a mutant thereof. The present invention also provides a protein having an amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 2, 5, or 9 and a mutant thereof.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Swivel snap hook of synthetic resin
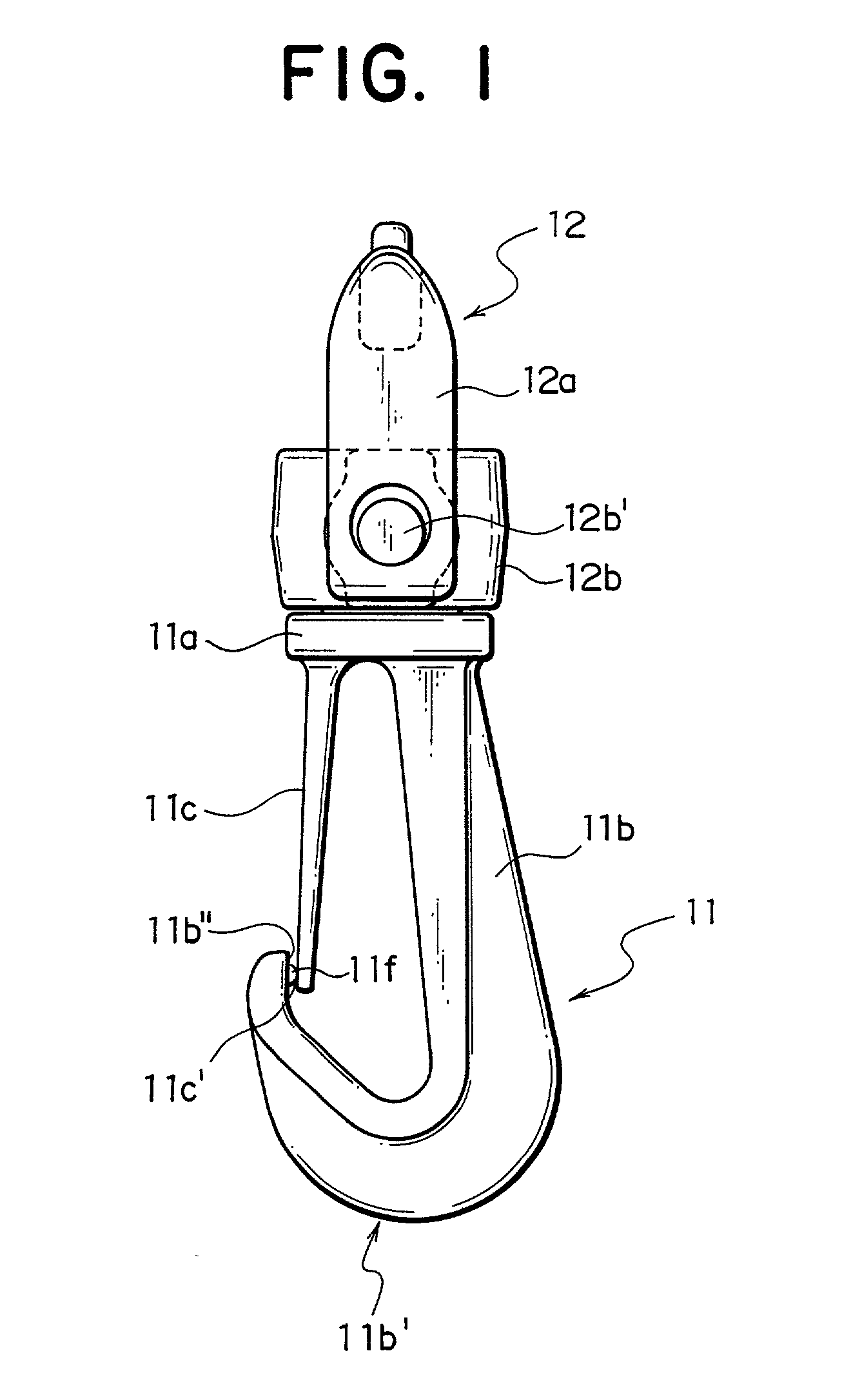
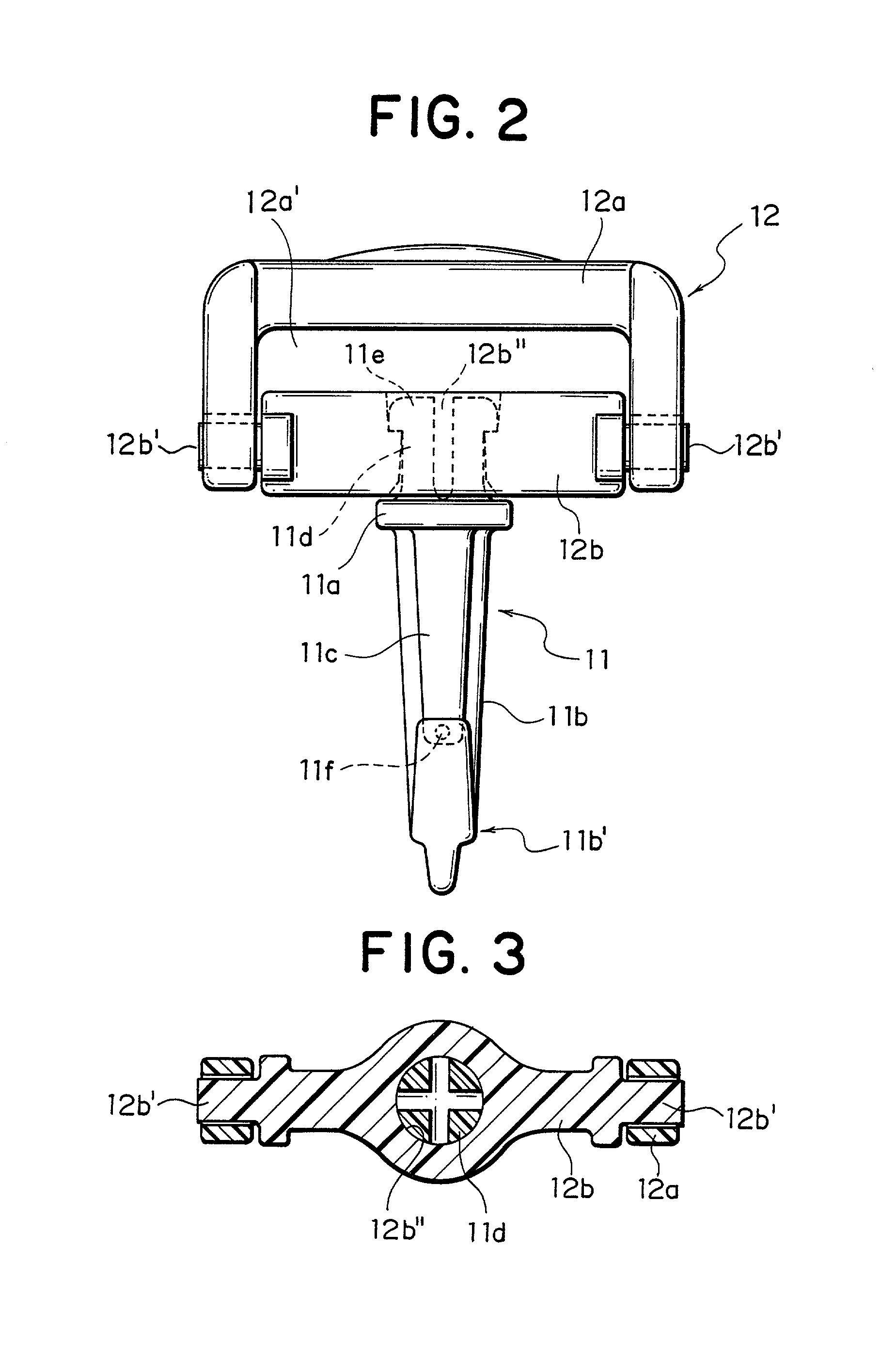
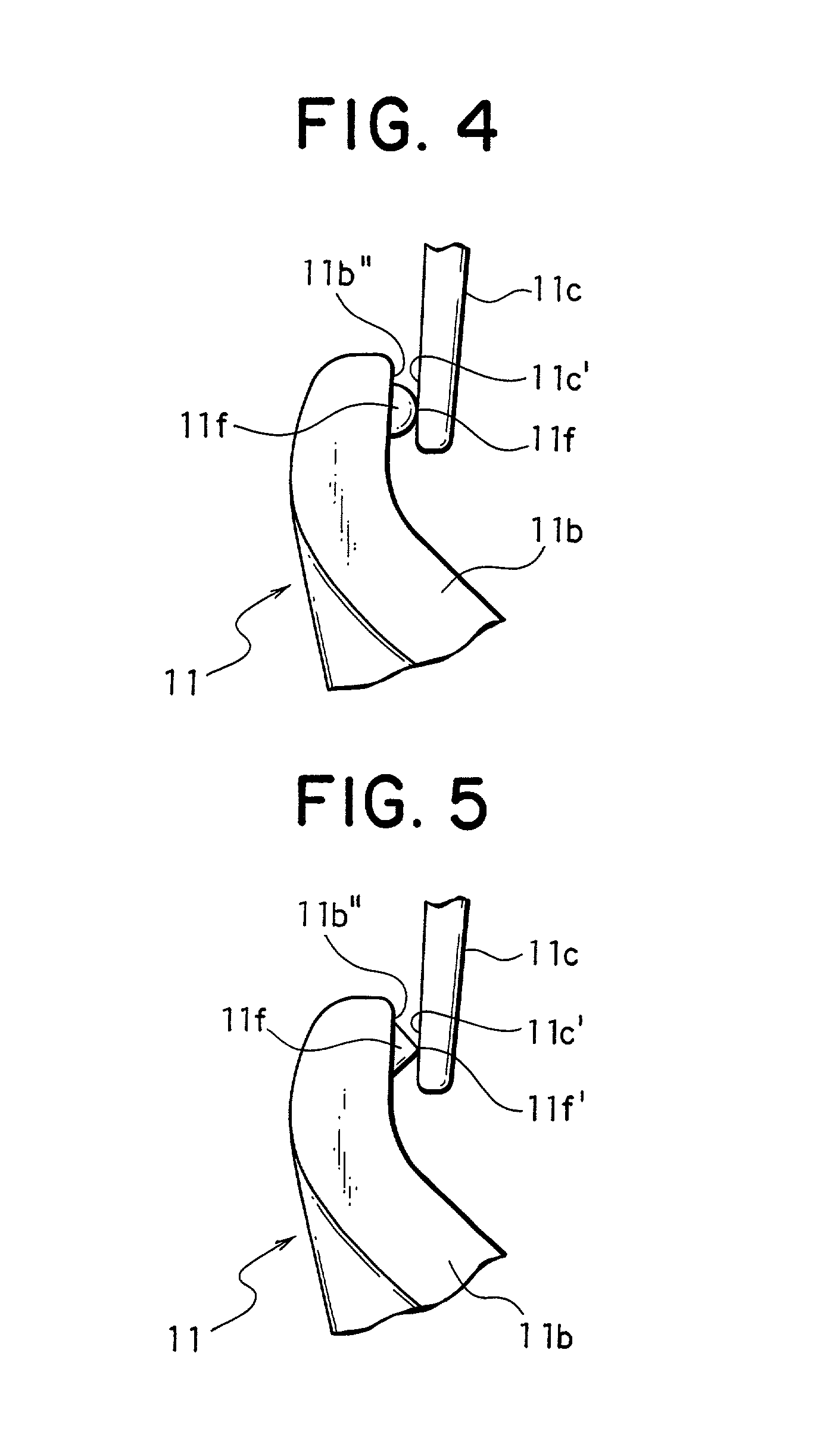
InactiveUS20010037543A1Structure , operation and effectEnhance productivityOther accessoriesHook fastenersEngineeringMechanical engineering
In a swivel snap hook having a hook body and a stopper piece, a protrusion, which is molded integrally with a front-end inside engaging face or a front-end outside engaging face of the hook body or the stopper piece, is provided so as to have a minute protruding height and be protruded toward a mating engaging face. Further, a minute portion at a tip end of the protrusion is molded integrally with the mating engaging face. Consequently, the swivel snap hook can be molded such that the front-end outside engaging face of the stopper piece is closed to the front-end inside engaging face of the hook body. Therefore, in the swivel snap hook, a length and a depth of the hook body thereof can be set as the conventional ones, while it can be molded in a state that the front-end outside engaging face of the stopper piece is kept in contact with the front-end inside engaging face of the hook body.
Owner:YKK CORP
Coupling structure of electromagnetic valve for controlling water supply
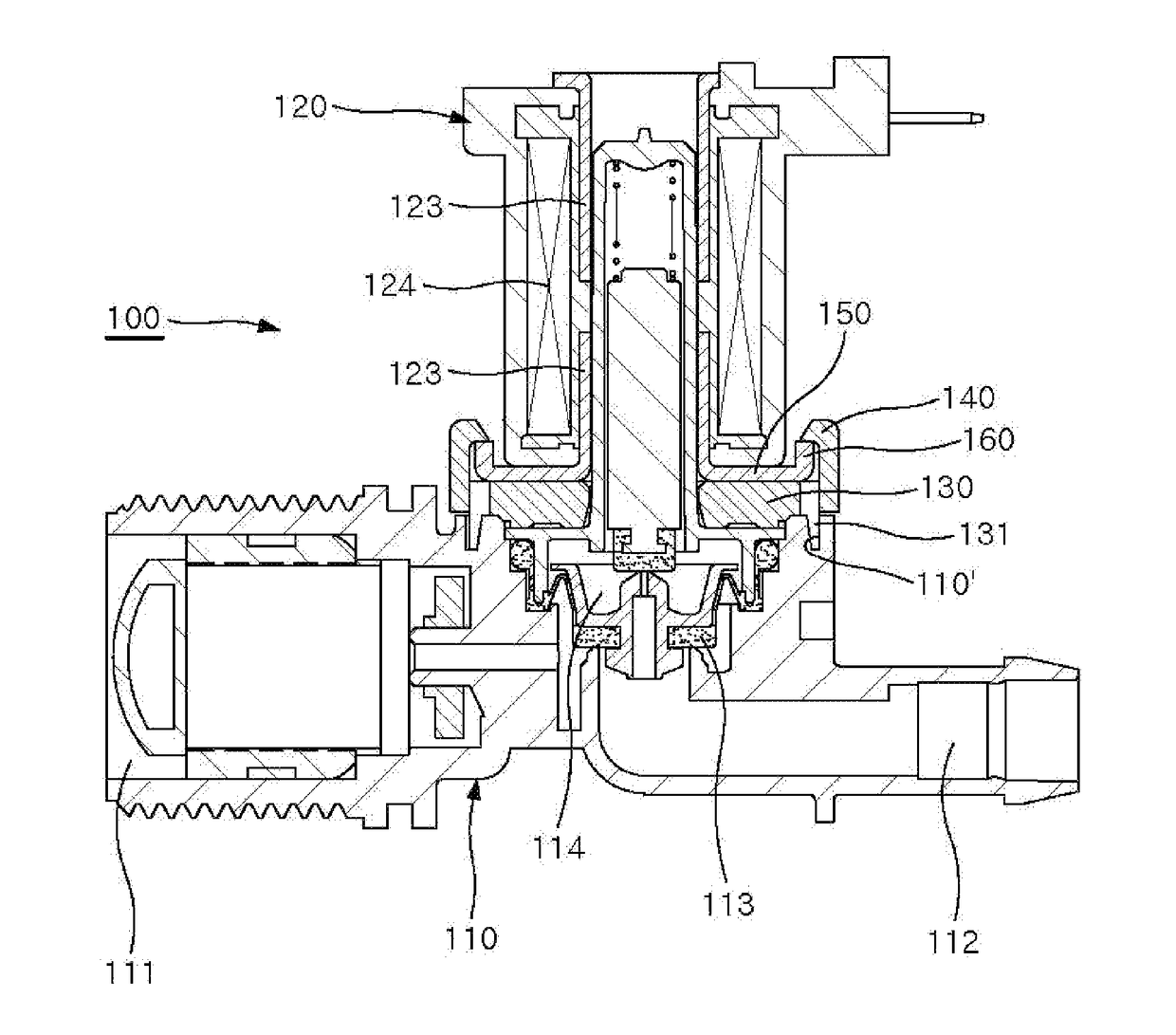
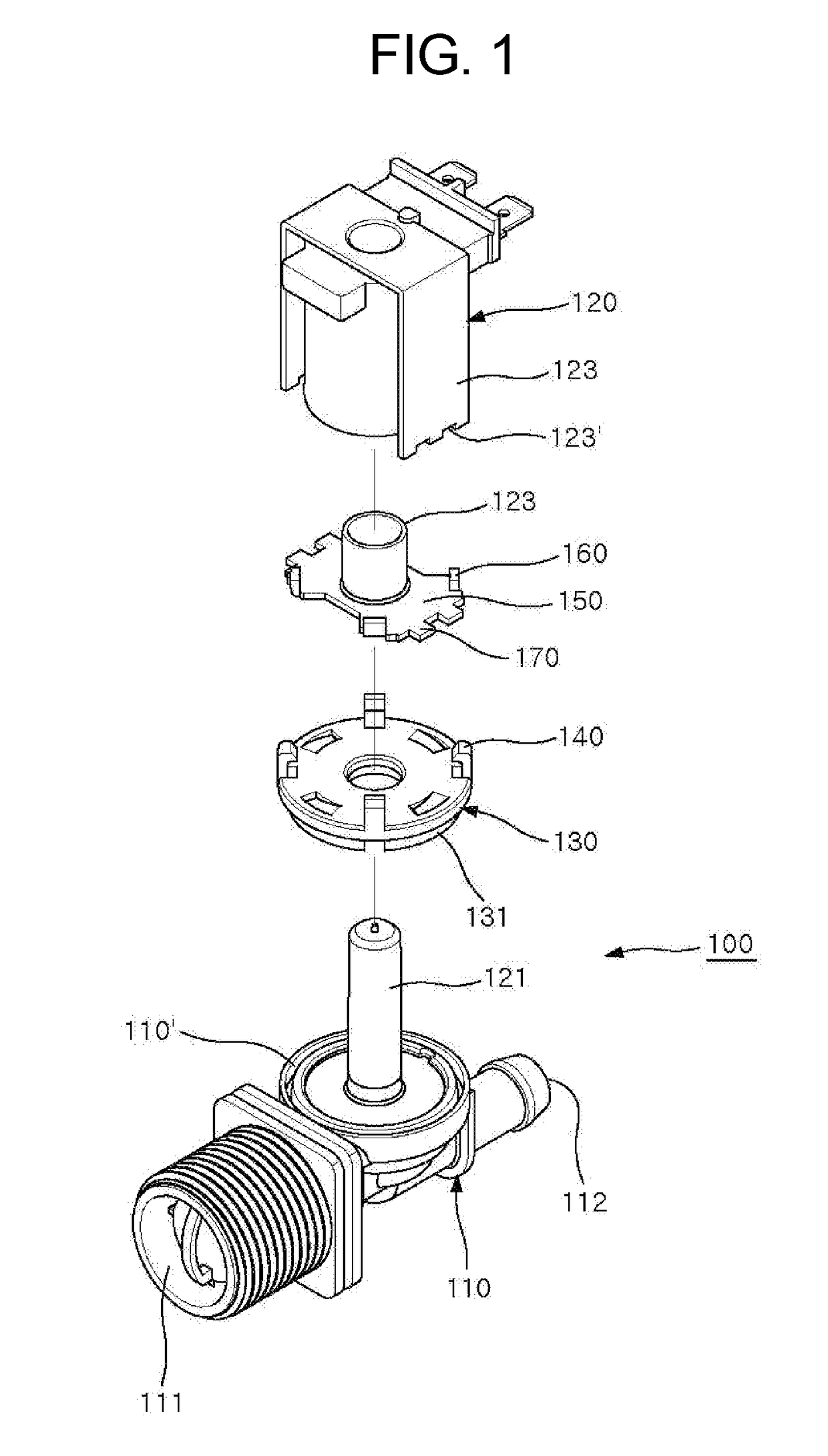
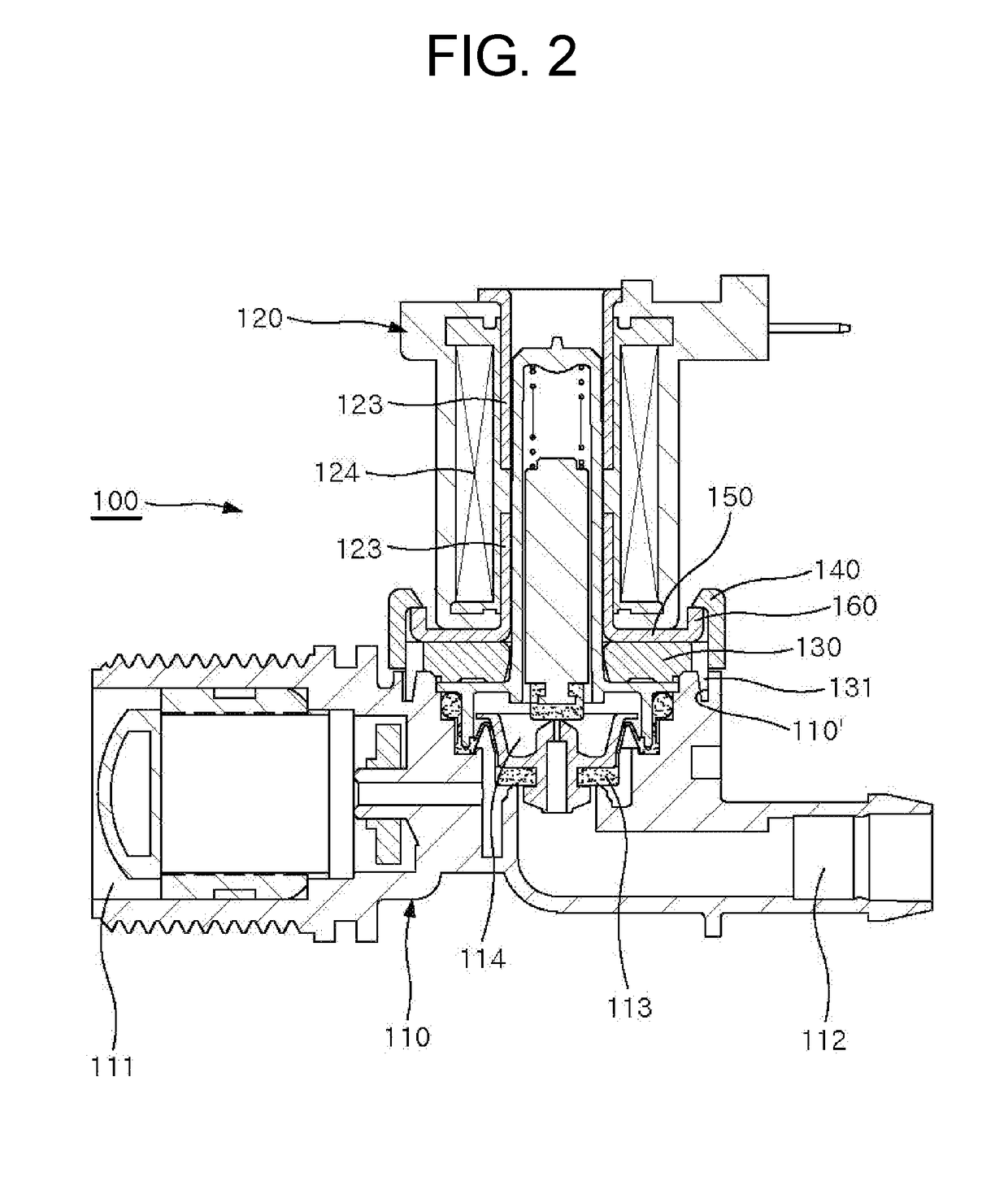
ActiveUS20170067567A1Enhance productivitySimple assemblyDiaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringWater supply
Provided is a coupling structure of an electromagnetic valve for controlling water supply. The coupling structure comprises: a coupling member provided with a coupling protrusion to be coupled to an upper portion of the valve body; at least one hook provided on the coupling member to be hooked to a locking piece; a supporting plate outwardly extending from a lower end of a sleeve to support the electromagnetic part, the sleeve being divided into upper and lower parts provided at upper and lower portions of the electromagnetic part; the locking piece provided at an end of the supporting plate by being bent upwardly to be hooked to the hook; and engaging pieces protruding from opposite sides of the supporting plate to engage with engaging grooves of the sleeve, thereby preventing the electromagnetic part from rotating.
Owner:USEONG ELECTRO MECHANICS
Downtime monitoring apparatus and method
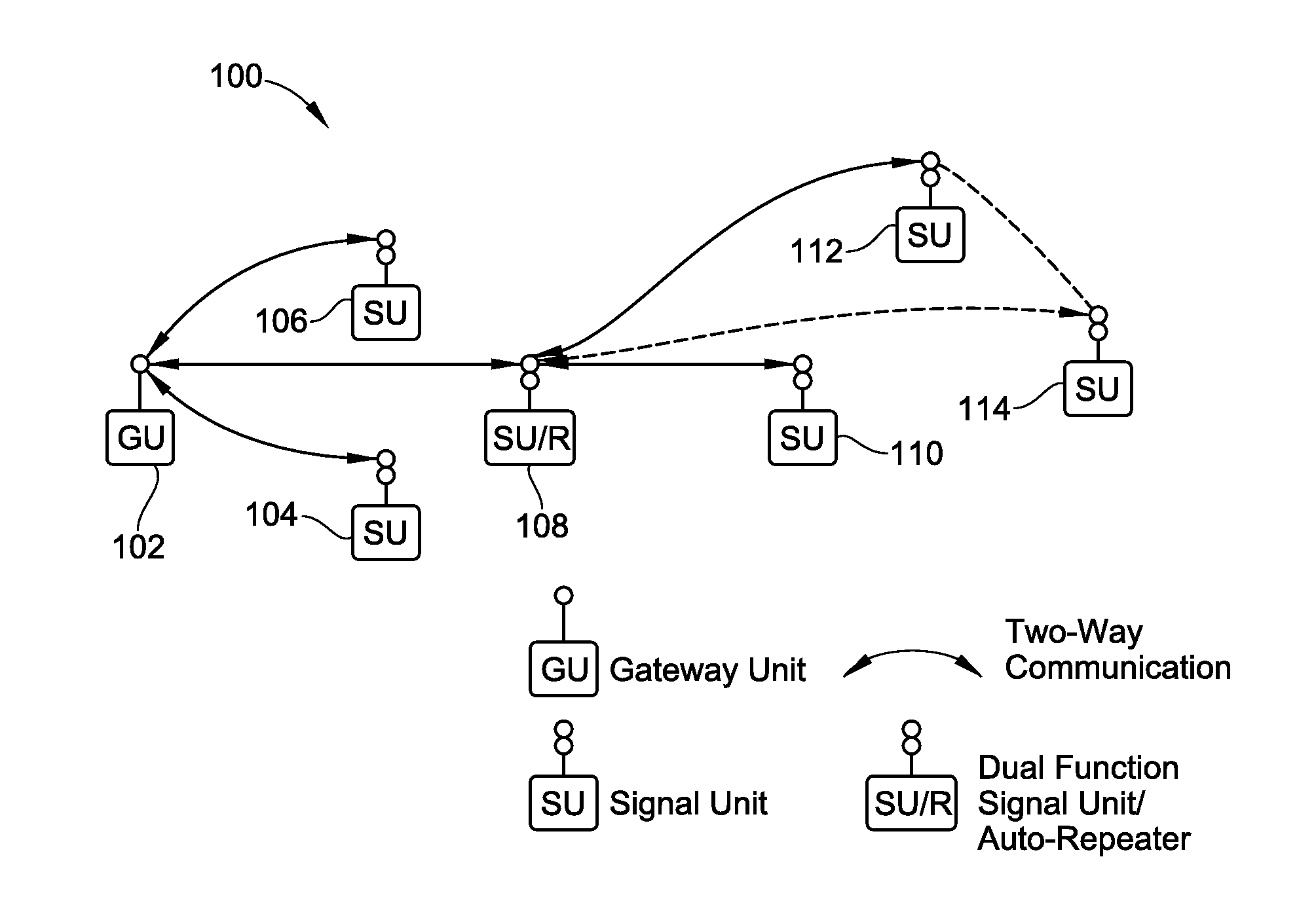
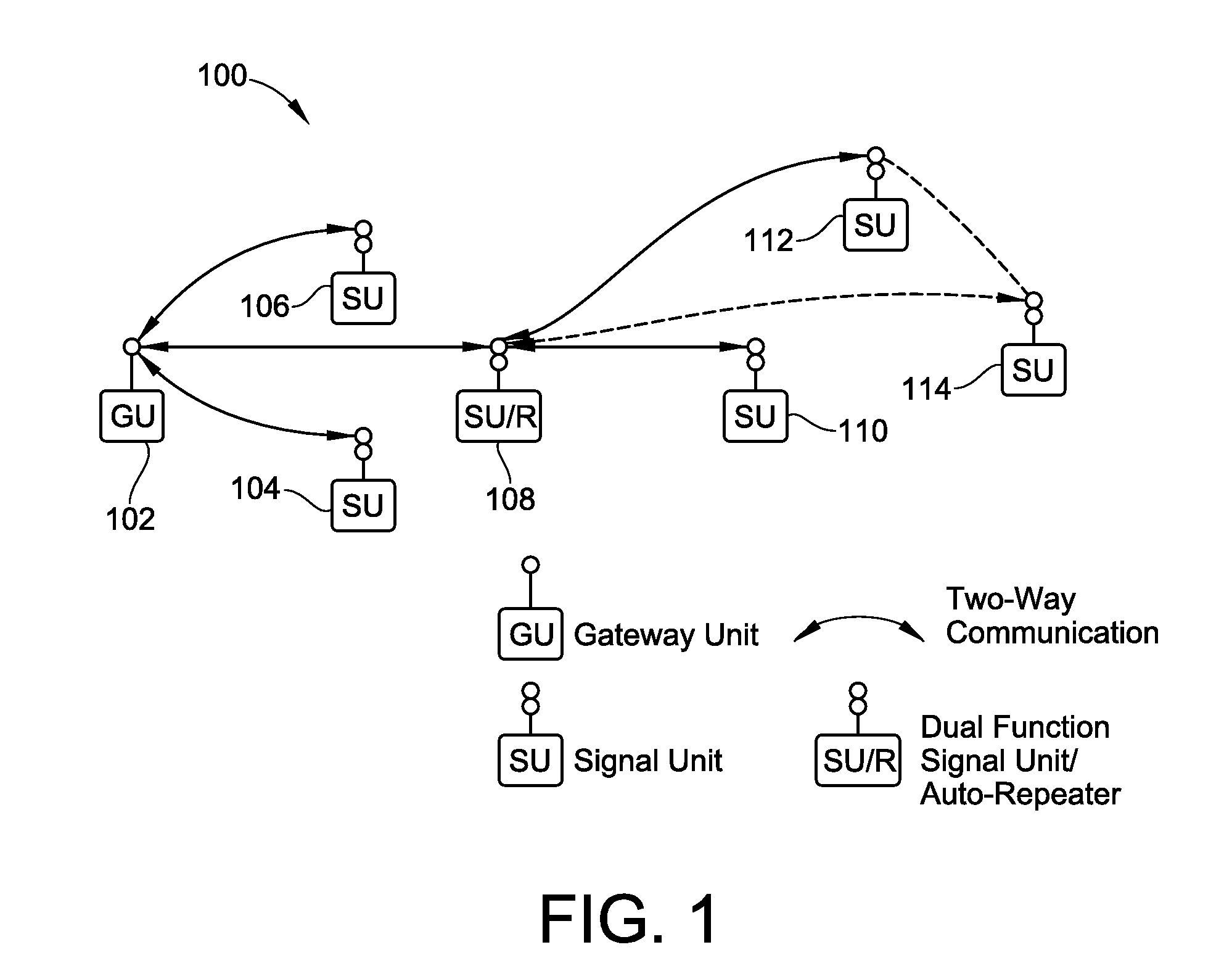
InactiveUS20100194548A1Enhance productivityEnhance qualityPower distribution line transmissionRepeater circuitsFacilitated communicationVisibility
An apparatus and method are provided for monitoring and facilitating a process, through the use of wirelessly-linked, portable signal units. The signal units have one or more signal lights, and can be placed adjacent to process stations. When a signal light is actuated by operator input at one or more of the process stations, the lights at all of the other process stations also are illuminated in a recognizable pattern to enhance visibility and identification at a glance as to which process station needs attention. Signal units also can function as repeaters to facilitate communication and operation. Designation of certain signal units as repeaters and optimization of communication between signal units is automatically carried out in accordance with one or more optimization approaches. In an embodiment, a time-based record of operation of the signal lights is provided for process monitoring and improvement.
Owner:TM IND
Method for mass culturing photosynthetic microalgae by additionally supplying environmental water
ActiveUS20170044484A1Economically and efficiently mass cultureEnhance productivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhotobioreactorEcology
The present invention relates to a method for culturing microalgae, including: (a) immersing a photobioreactor including a culture container through which a culture solution but not microalgae passes into environmental water; and (b) supplying additional environmental water into the culture container. Through the present invention, it is expected that microalgae can be economically and efficiently mass cultured.
Owner:INHA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION
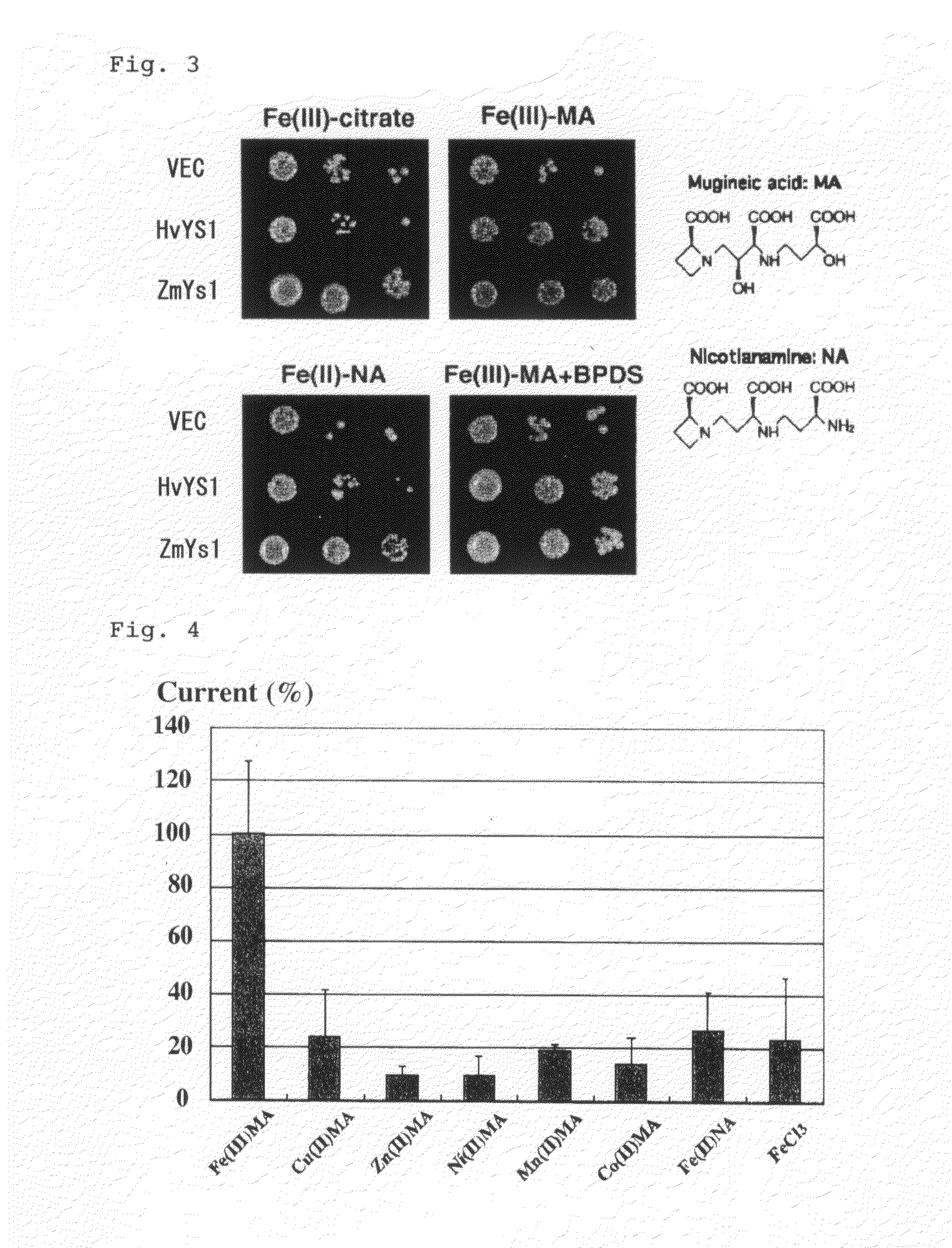
Gene of transporter selective to mugineic acid-iron complex
InactiveUS20110016579A1Small riskEnhance productivityImmunoglobulinsFermentationGMO PlantsTranslocator protein
The invention provides a method for creating a transgenic plant comprising a gene containing a DNA to encode a transporter protein which selectively absorbs mugineic acid-iron complex. The transgenic plant is useful as a plant capable of growing in alkaline soil containing no bivalent iron but containing, for example, trivalent iron.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
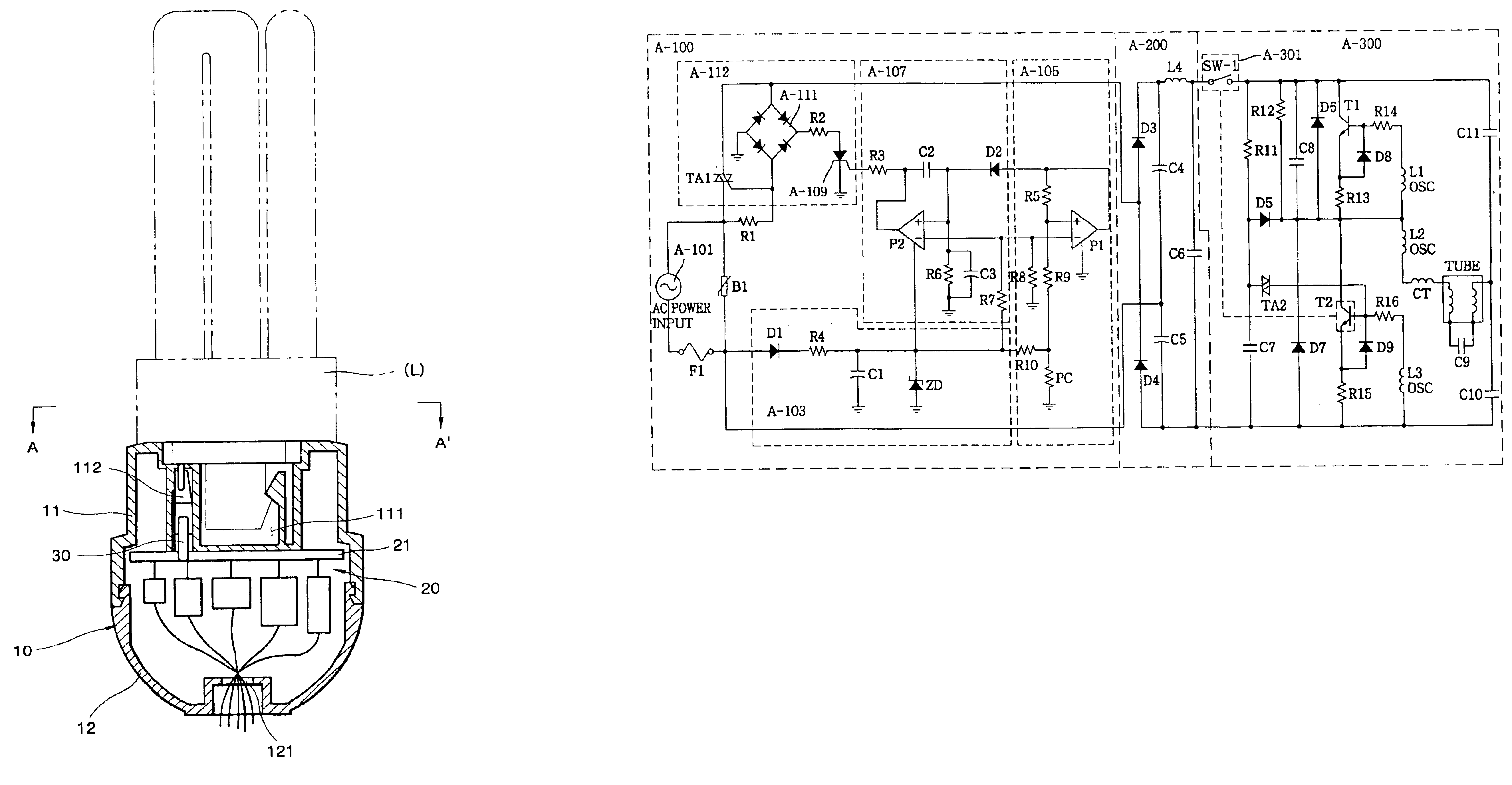
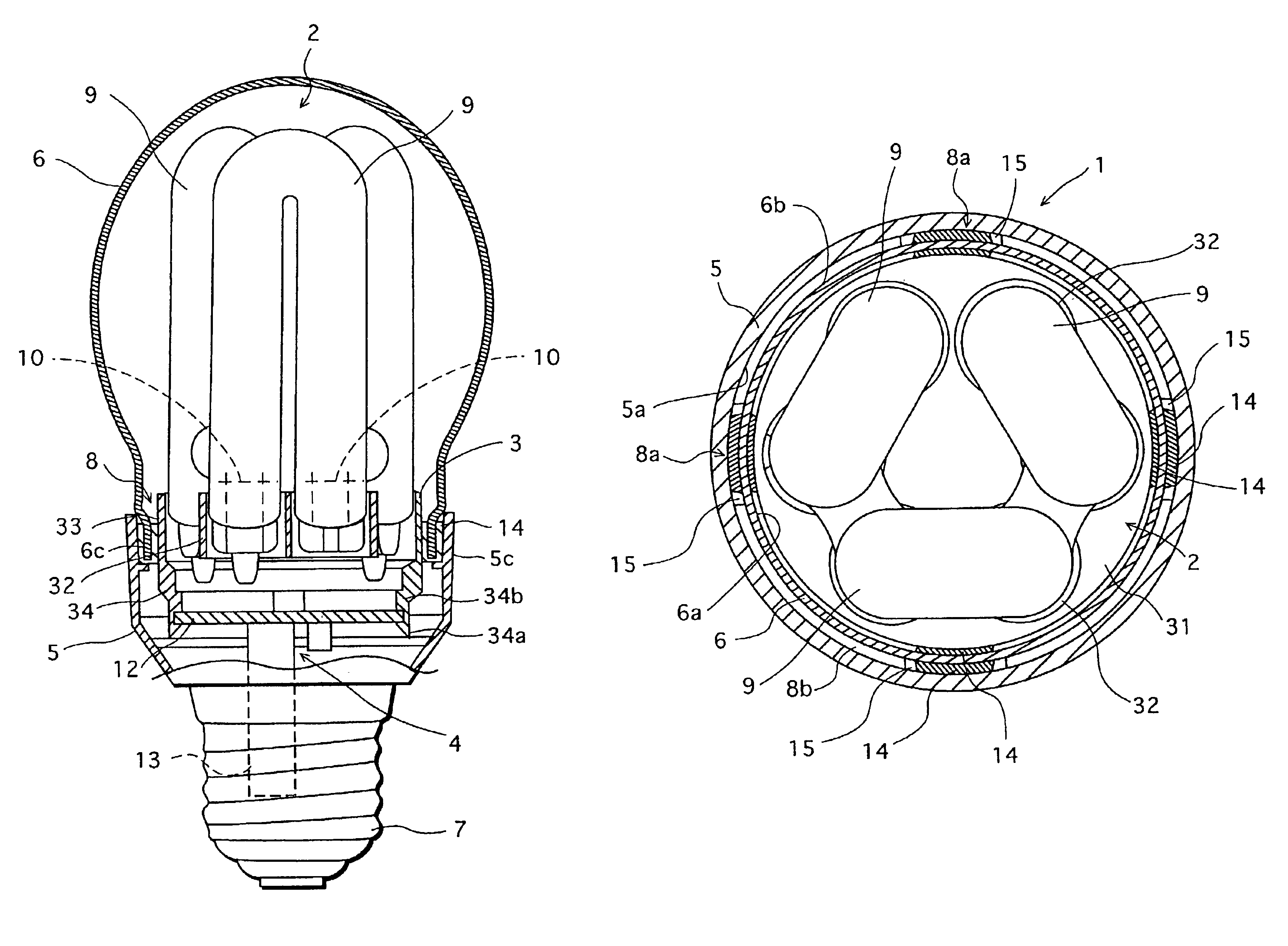
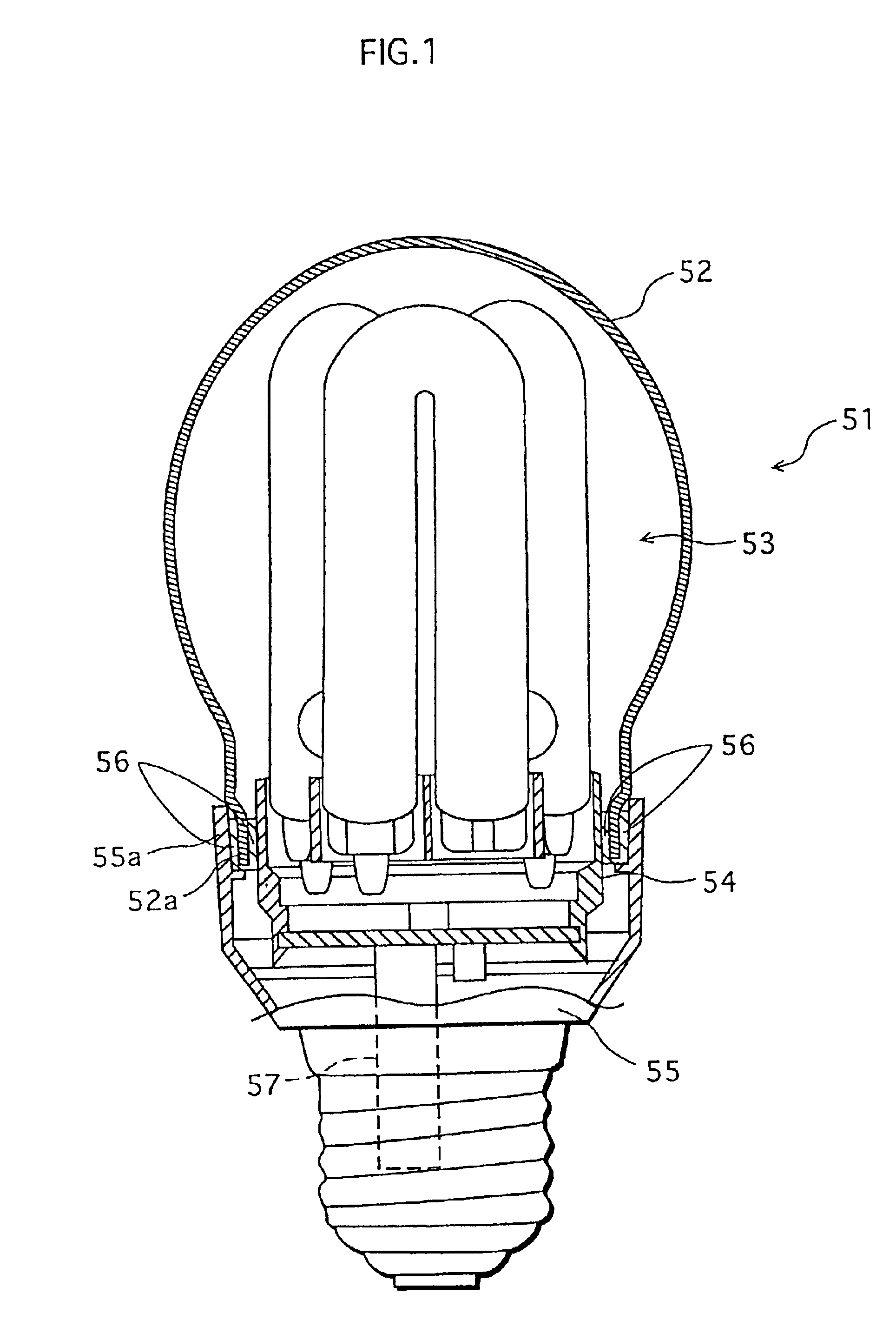
Low-pressure mercury vapor discharge lamp with improved heat dissipation, and manufacturing method therefore
InactiveUS6972514B2Prevent temperature riseEnhance productivityCoupling device connectionsElectric discharge tubesAdhesiveMercury vapors
A bulb-type fluorescent lamp has a case having an open end portion for housing a lighting circuit therein, an arc tube extending outside through the open end portion of the case, and a globe having an open end portion for housing the arc tube therein. An adhesive is supplied to the inner surface of the open end portion of the case at four circumferentially spaced areas, and the open end portion of the globe is inserted into the open end portion of the case. As a result, the globe is fixed to the case with the adhesive.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com