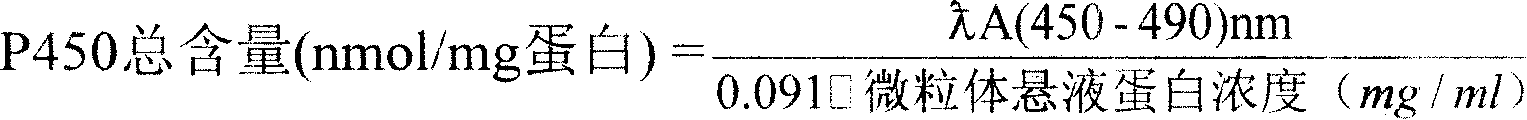Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44results about How to "Avoid Measuring Inaccuracies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
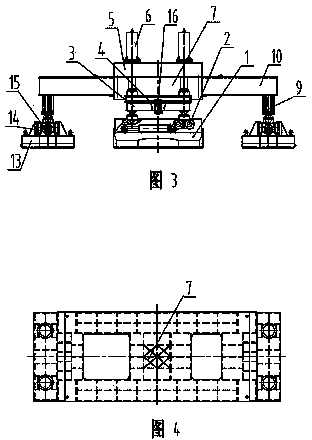
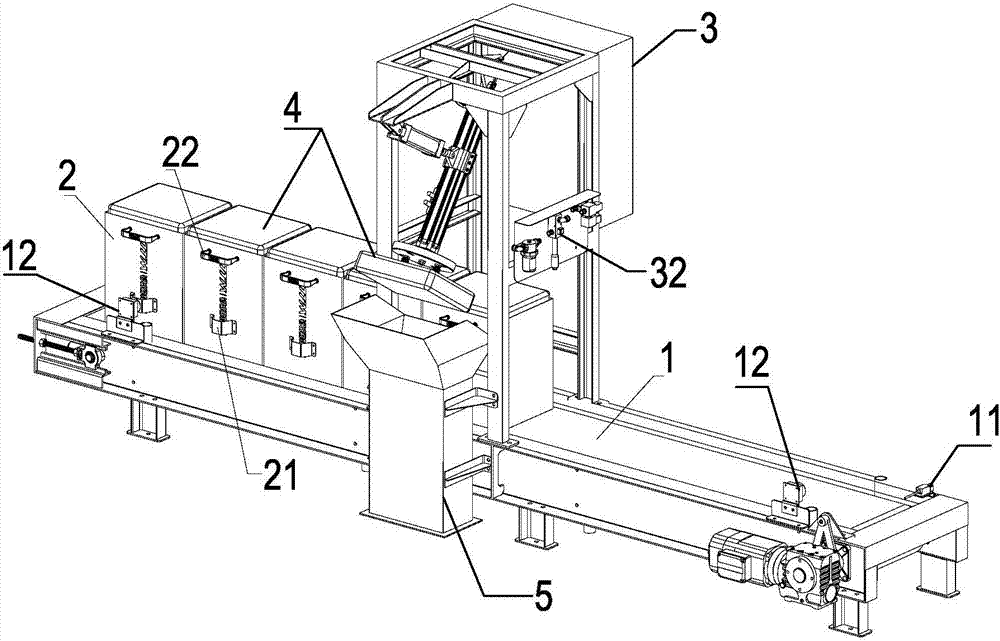
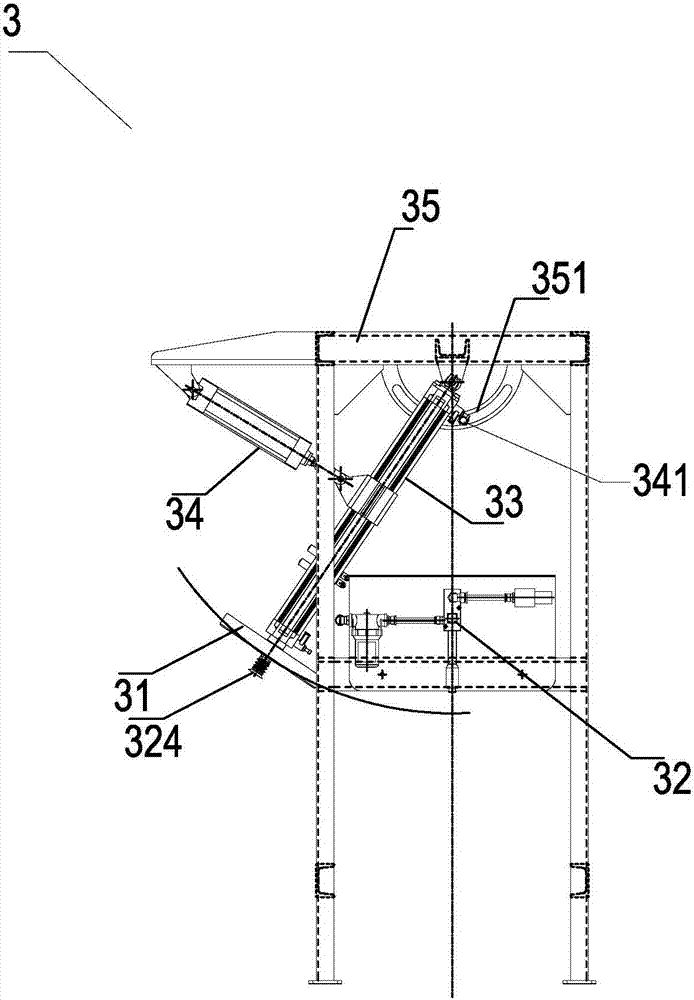
Walking type detection platform for static load of engineering foundation piles
InactiveCN103362150ARealize rotary motionFlexible and convenient to moveFoundation testingHydraulic cylinderControl engineering
The invention discloses a walking type detection platform for the static load of engineering foundation piles, which comprises a supporting platform movably supported on two long boats and two short boats, wherein the two short boats are respectively arranged at two ends of the supporting platform, and a short-boat walking vehicle is arranged on each short boat and is fixedly connected with a short-boat slewing platform; vertical lifting hydraulic cylinders mounted on the supporting platform is hinged to the short-boat supporting platforms; the short-boat slewing platforms are hinged to the short-boat supporting platforms through swing pin shafts; two long-boats are respectively arranged on two sides of the supporting platform; each long boat is provided with two movable long-boat walking vehicles which are hinged to the lower ends of the corresponding legs of the long boats; the legs of the long boats are mounted on the supporting platform through beams of legs of the long boats; long-boat walking hydraulic cylinders are arranged between the long-boat walking vehicles and the long boats; a crane is mounted on the supporting platform. The detection platform can perform self-propelled move as a whole, requires no repetitive construction and hoisting, and has the features of safety in use, reasonable structure, high operating efficiency and the like.
Owner:江苏久工重型机械股份有限公司
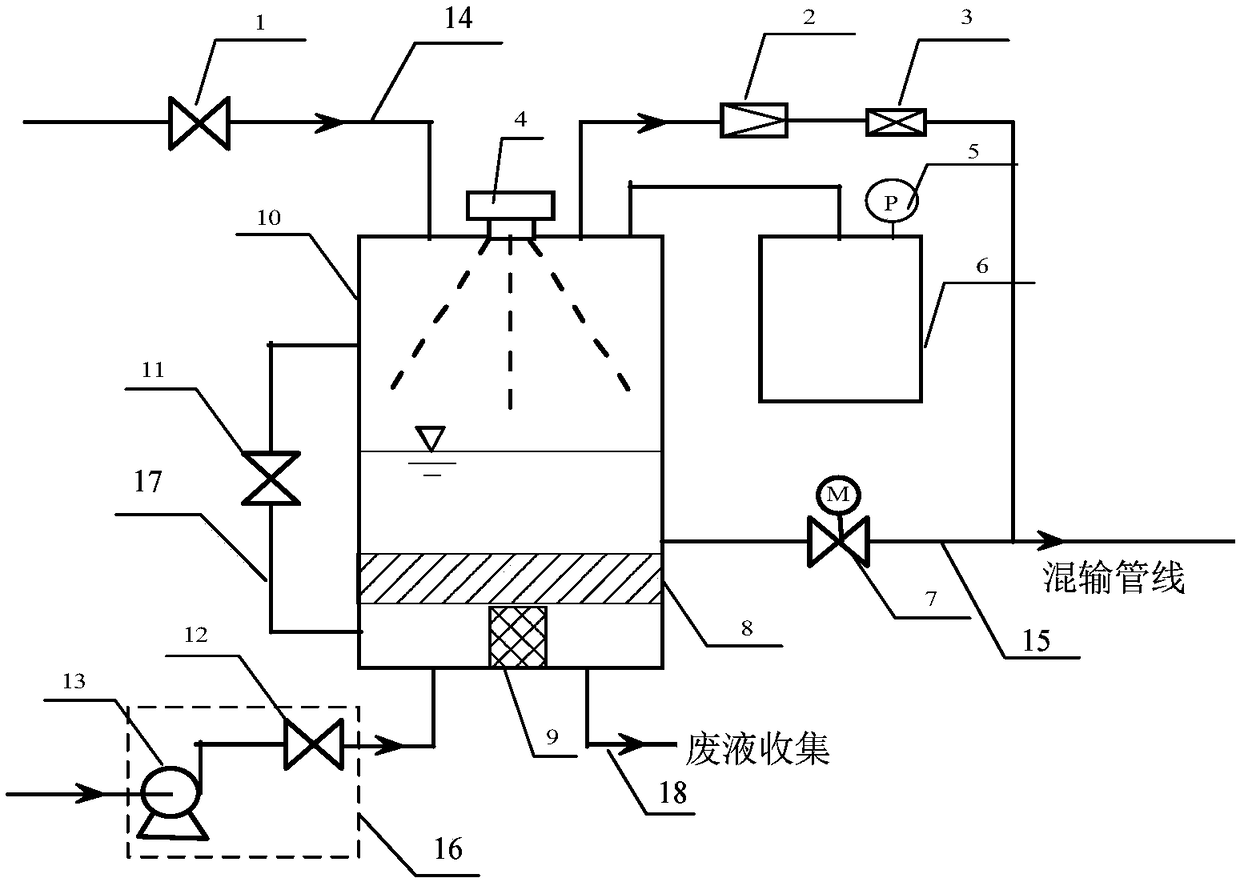
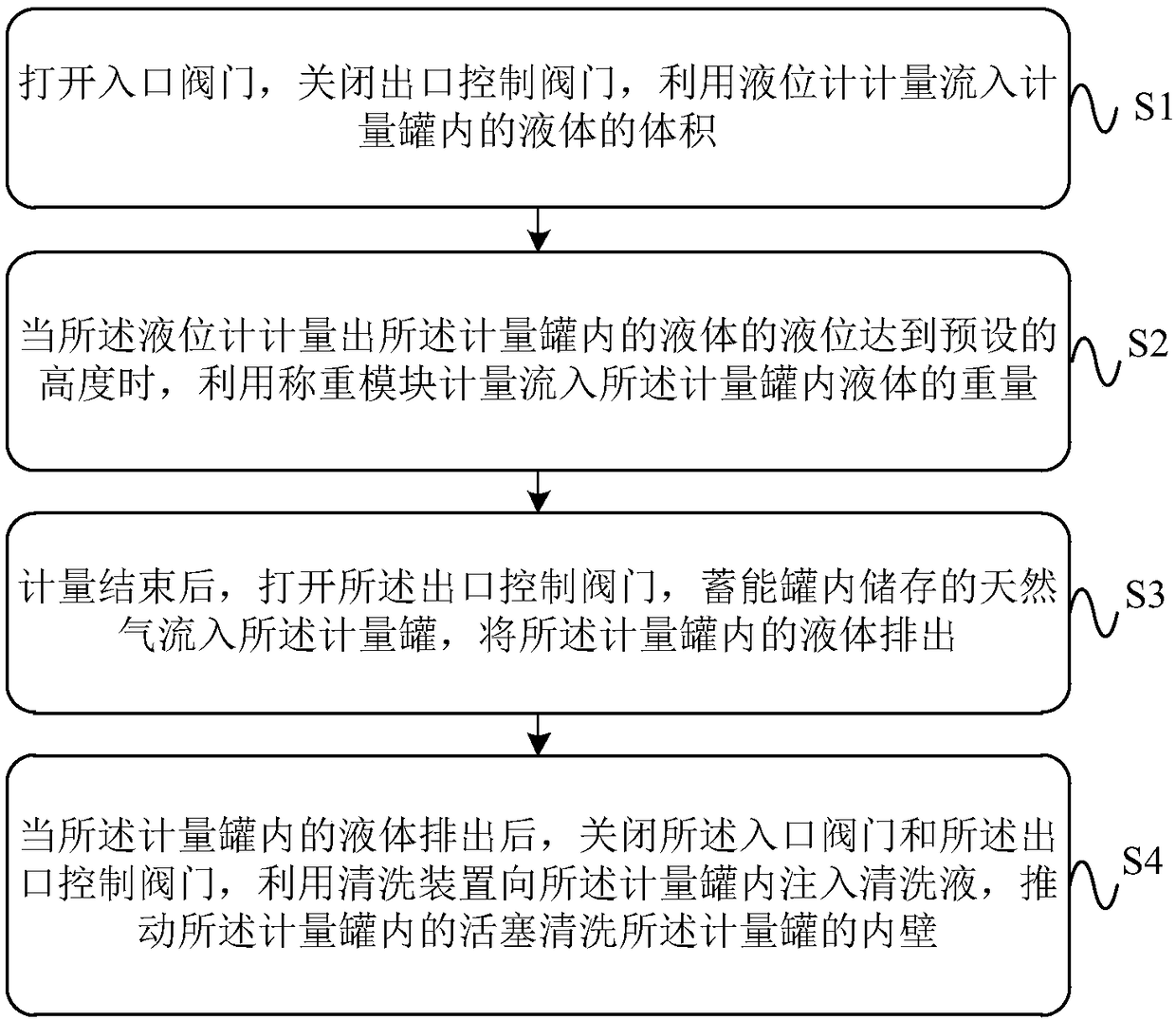
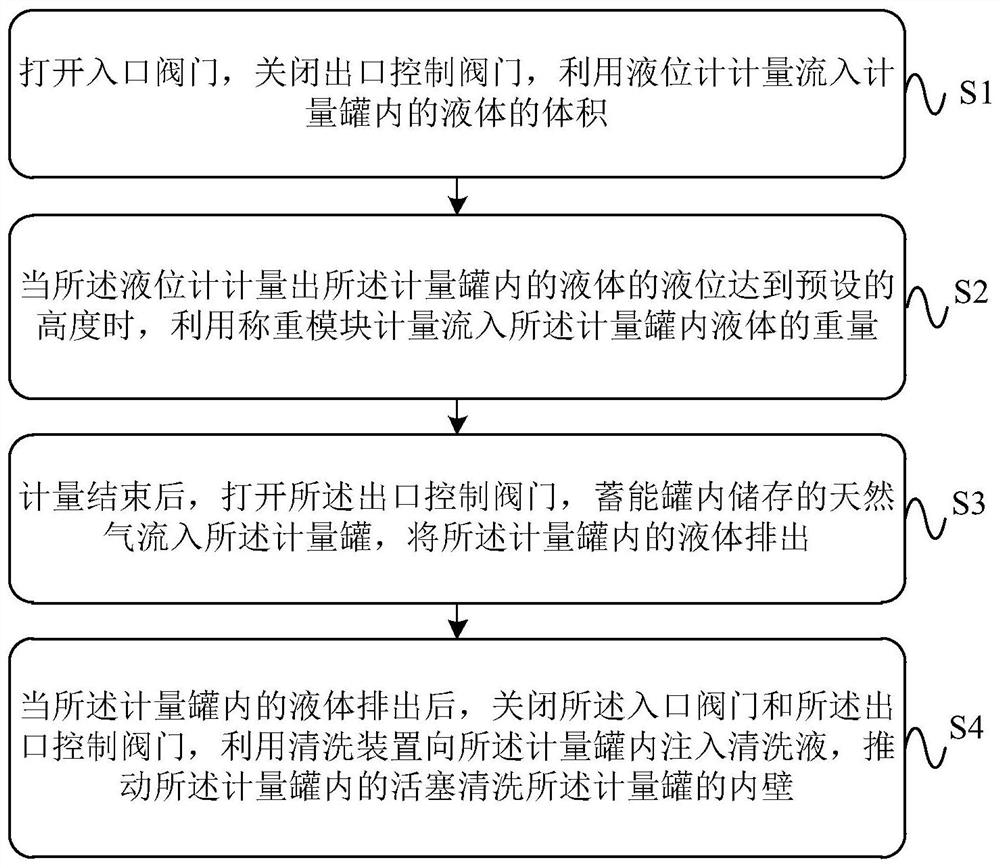
Oil field single-well metering device and method
The invention provides an oil field single-well metering device and method. The oil field single-well metering device comprises a metering tank and an energy-storage tank which mutually communicate. Gas with the preset pressure is stored in the energy-storage tank, and a liquid inlet pipeline, a liquid level meter, a liquid outlet pipeline and a weighing module are arranged on the metering tank. An inlet valve is arranged on the liquid inlet pipeline, and an outlet control valve is arranged on the liquid outlet pipeline. A piston for cleaning the metering tank is further arranged in the metering tank, and the bottom of the metering tank is connected with a cleaning device which is used for injecting cleaning liquid in the metering tank. Through all embodiments of the oil field single-wellmetering device and method, the structure is simple, operation is convenient, oil field single-well metering is achieved under the situation that additional power is not needed, and the accuracy of the single-well metering result is improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Biological marker-earthworm internal organ p450 content measuring method
InactiveCN101210918AGuaranteed accurate quantificationAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsCytochrome P450Glycerol
The invention relates to cytochrome P450, specifically to a method for measuring the content of a biomarker-cytochrome P450 in earthworm viscera, which comprises the following steps of: (1) soaking a live earthworm in glycerol solution, and immediately dissecting and taking out the viscera thereof; (2) cleaning the viscera with cold saline water, transferring to a homogenization buffer, breaking cells with a glass tissue grinder, centrifuging with a ultra-speed centrifuge at low temperature (3DEG C) and 10,000g for 20min, centrifuging the supernatant at 150,000g for 90min, removing the supernatant, and collecting microsome sediment; and (3) dissolving the microsome sediment in a storage buffer, mixing, and measuring the total amount of cytochrome P450 and the protein content in the microsome suspension. The total amount of cytochrome P450 is quantified with sodium hydrosulfite-reduced CO difference spectra method. The invention has the advantages of simplicity, rapidness, low consumption, and accurate qualification and quantitation.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
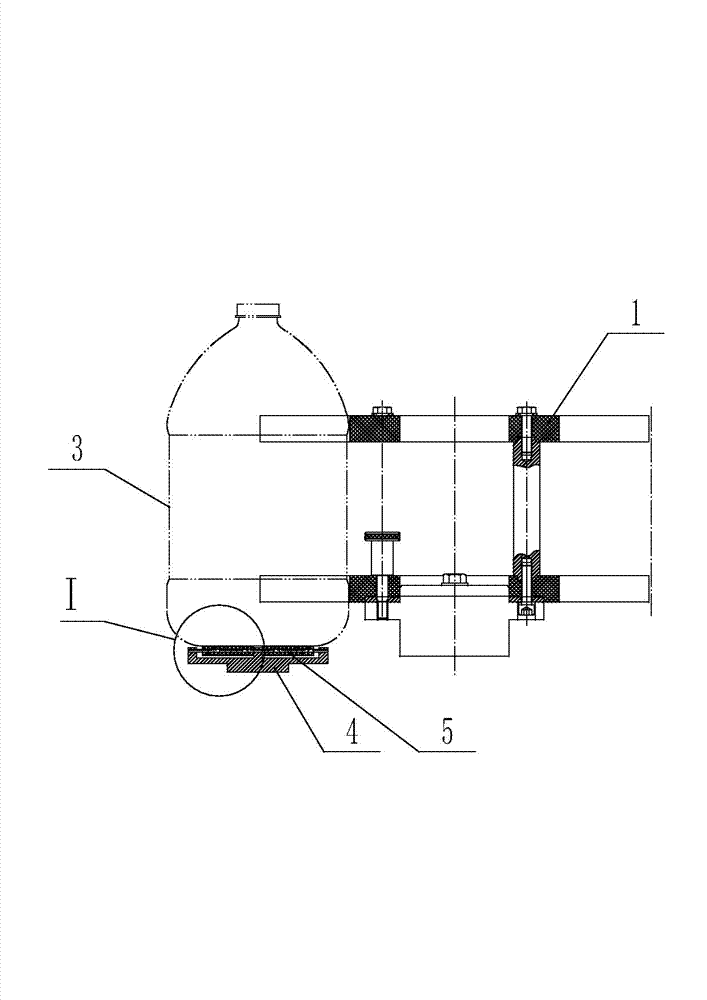
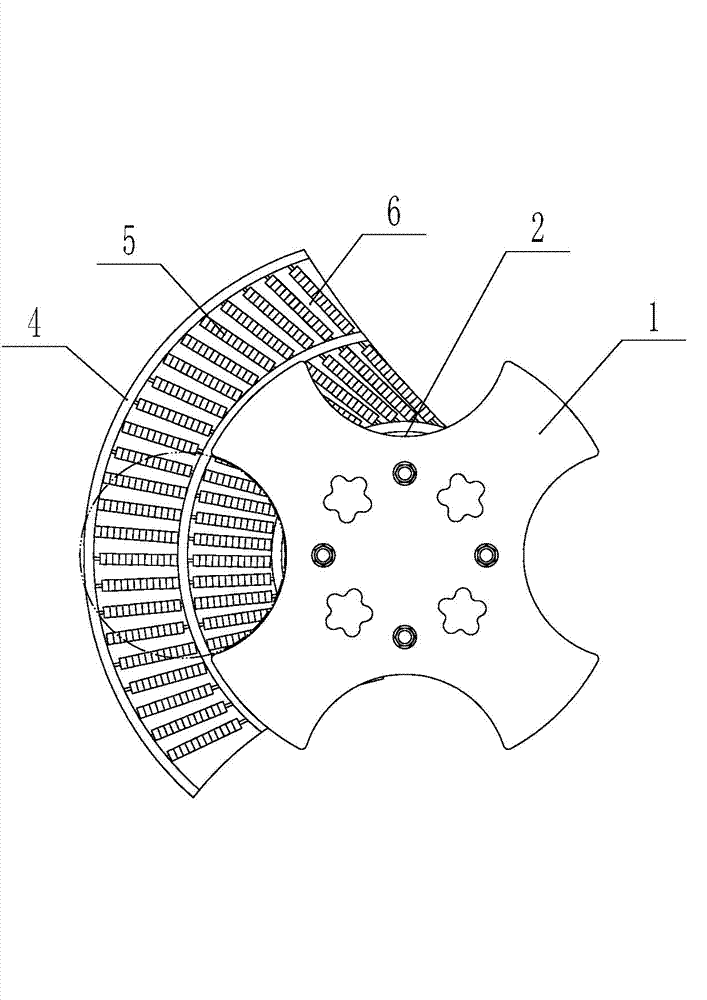
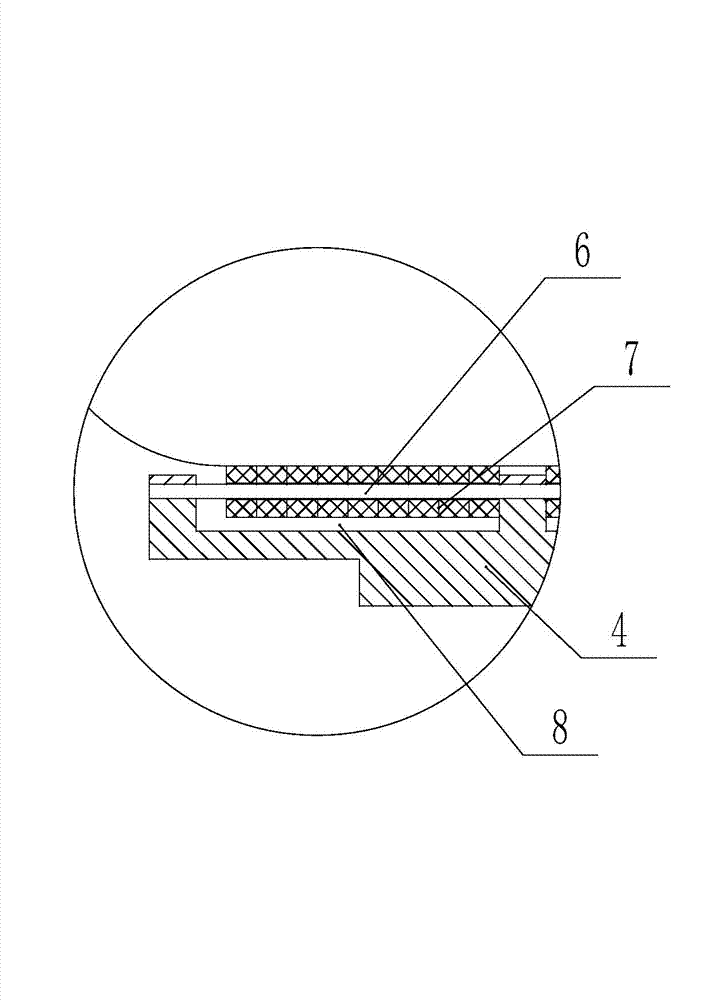
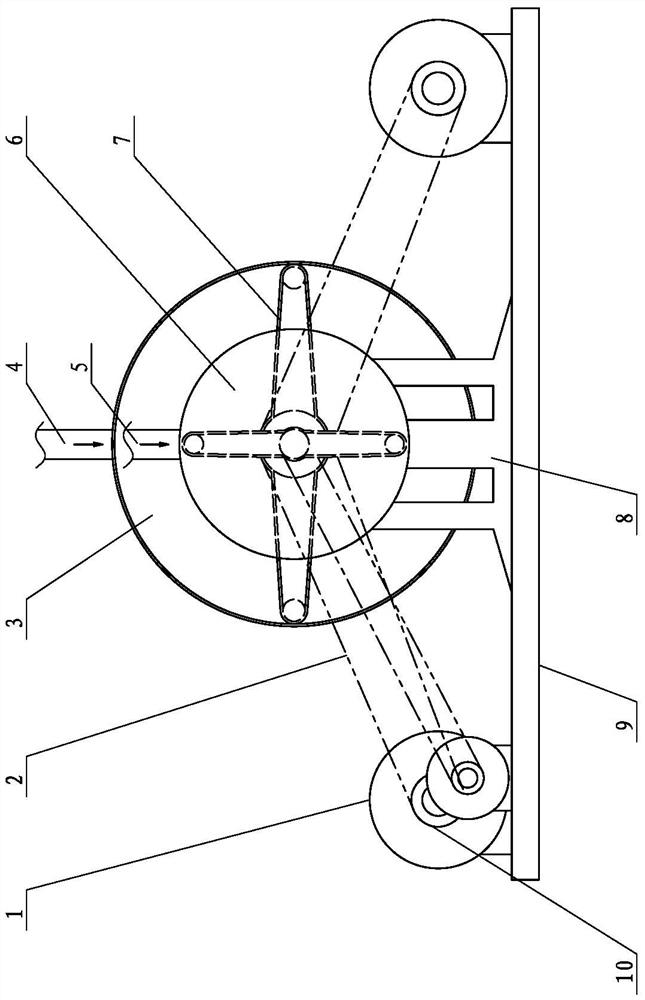
Bottle transport device
InactiveCN103171888AWon't squeezeExtrusion will not causeConveyor partsProduction lineRolling resistance
The invention relates to a bottle transport device which comprises a star wheel which can rotate, wherein a plurality of bottle grooves are formed in the periphery wall of the star wheel, and the sizes of the bottle grooves are matched with the size of the bottle. A bottle supporting plate is arranged below the star wheel, and a plurality of rolling bodies which can freely rotate are arranged in the bottle supporting plate. The bottle transport device is suitable for a filling production line, is slightly improved based on a traditional bottle transport device, enables a bottle bottom and the bottle supporting plate to conduct rolling friction when the bottle is transported, and greatly reduces friction resistance. The star wheel does not produce squeezing on the bottle, so that deformation of the bottle does not occur, liquid is not squeezed out of a bottle opening, the phenomenon of inaccurate metering is avoided, and pollution on the bottle opening does not occur.
Owner:JIANGSU NEWAMSTAR PACKAGING MACHINERY
High-temperature-resistant precipitation antagonist
ActiveCN112481008AImprove thermal stabilityReduced chromaticity variationTransportation and packagingMixer accessoriesCresolUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant precipitation antagonist, which belongs to the technical field of lubricating oil preparation. The high-temperature-resistant precipitation antagonist is characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3-5 parts of 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol, 3-5 parts of zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate, 0.5-1 part of an anticoagulant, 0.5-1.5 parts of a dispersing agent, 5-10 parts of an ultraviolet light absorber, and the balance of base oil. The anticoagulant and the dispersing agent are added into the component A or thecomponent B or the component C in proportion; the component A, the component B and the component C are added into lubricating oil to be updated through online blending and filling equipment; and theaddition amount of the high-temperature-resistant precipitation antagonist is 0.1-0.2% of the lubricating oil to be updated. The quantitative premixing device, the nitrogen adding pulse blending device and the suction type replacement device are sequentially connected from front to back.
Owner:山东恒利热载体工程技术有限公司
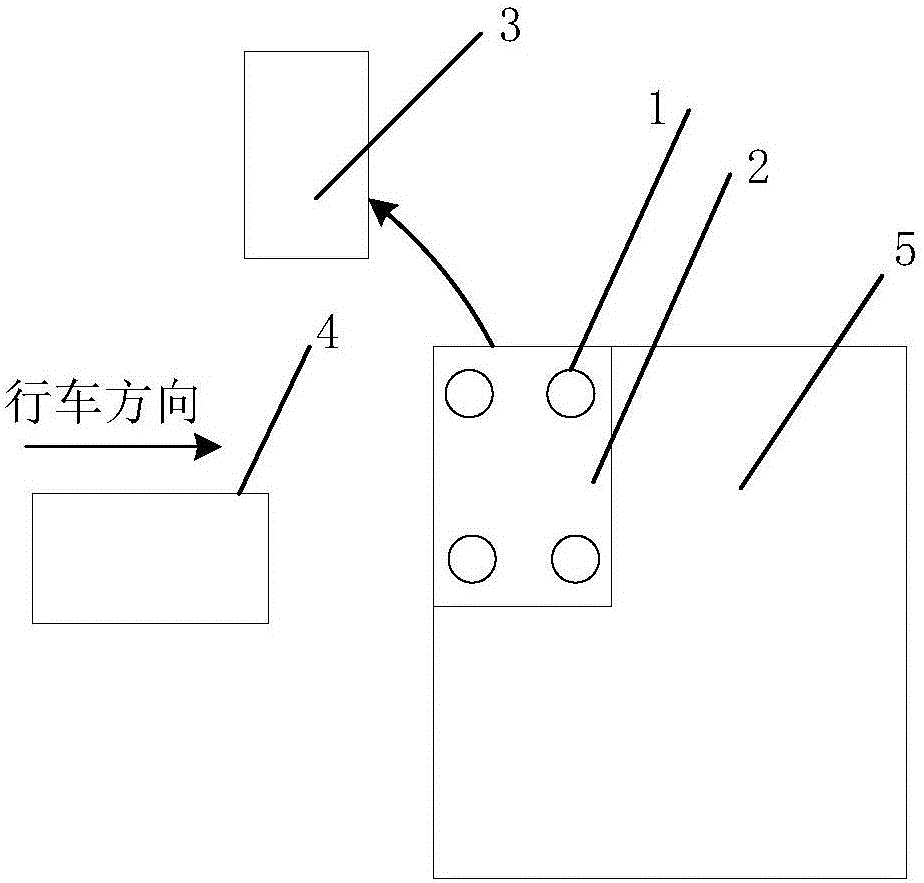
Vehicle dynamic weighing axle identification system and realization method thereof
ActiveCN106404141ASolve the problem of rolling carImprove traffic efficiencySpecial purpose weighing apparatusVehicle dynamicsData information
The invention relates to a vehicle dynamic weighing axle identification system. The system comprises a basic weighing platform, an axle identification loader, axle identification sensors and an axle identification controller, wherein the signal output ends of the axle identification sensors are connected with the signal input end of the axle identification controller, each path of axle identification is composed of four axle identification sensors, two sensors at each side of the axle identification loader vertical to a driving direction are connected in parallel to form one path of signals, and the axle identification controller is used for receiving data information acquired by the axle identification sensors, performing classification processing on these data information and calculating the quantity of axles, vehicle speeds and driving directions of vehicles passing by. According to the invention, the quantity of the axles, the driving directions and the driving speeds can be effectively obtained, the phenomena of too many axles and too few axles in a continuous passing process are solved, and the vehicle pass efficiency of a highway is effectively improved.
Owner:JINAN JINZHONG ELECTRONICS SCALE
Quality data issuing and monitoring method, apparatus and system as well as quality data acquisition instrument
ActiveCN104964896AEasy to judgeAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesData processing applicationsVolume indication and recording devicesReal-time dataQuality data
The invention discloses a quality data issuing and monitoring method, apparatus and system as well as quality data acquisition instrument. The method comprises the following steps: a gas station acquiring, by the quality data acquisition instrument, natural gas quality data provided by a natural gas upstream gas supplier, and sending the natural gas quality data and marking information to a remote server (an issuing platform) by virtue of a wireless way; the remote server displaying the issued natural gas real-time components, standard density, heating amount, average standard density of a preset period and average heating amount on a server and a user terminal by virtue of calculation, the remote server comparing the received real-time data with an average value of a previous preset period, and performing the prompting or alarming if the difference is more than a preset value. By adopting the technical scheme, a portable technical means can be provided for the accurate measurement of natural gas and trade settlement, quality data issuance and monitoring can be realized, the information is convenient to disclose, and the fairness and justness of the natural gas transaction can be promoted.
Owner:北京博思达新世纪测控技术有限公司
Movable concrete mixing plant for road and bridge construction
ActiveCN110435001AEasy transitionAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesMixing operation control apparatusIngredients weighing apparatusScrew conveyorMaterial storage
The invention discloses a movable concrete mixing plant for road and bridge construction and belongs to the technical field of building construction equipment. The movable concrete mixing plant comprises a stirrer, a material weighing device and a water tank and can be arranged on transportation equipment for transferring; a screw conveyor is arranged between a feeding opening of the stirrer and the material weighing device; the water tank is connected with the stirrer through a water pump and a water inlet pipe with a flowmeter; the material weighing device comprises a material storage hopperof which the bottom is provided with a dynamic weighing and measuring module; the material storage hopper is connected with a turning mechanism; the stirrer comprises a tank body, a stirring shaft and stirring blades; the stirring shaft is vertically arranged in the tank body; a motor for driving the stirring shaft is arranged at the bottom of the tank body; and a plurality of stirring blades areradially arranged at the periphery of the stirring shaft from top to bottom. The dynamic weighing and measuring module weighs all powdery or solid materials; the flowmeter meters the water consumption for stirring; and when the materials are weighed, the turning mechanism and the screw conveyor are started for conveying the materials into the tank body for mechanically stirring and mixing. The movable concrete mixing plant disclosed by the invention can accurately meter the materials, so that the quality of concrete is ensured.
Owner:韩保勤
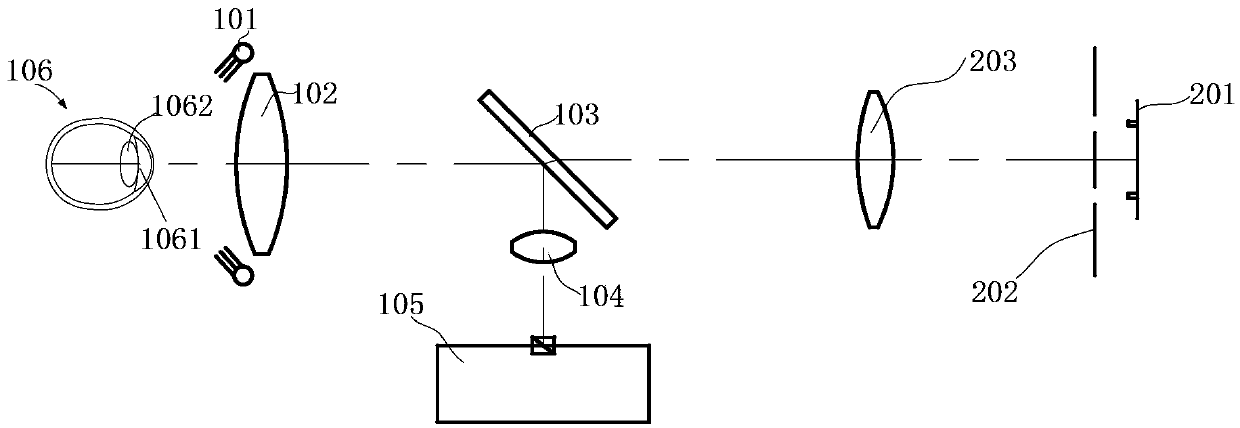
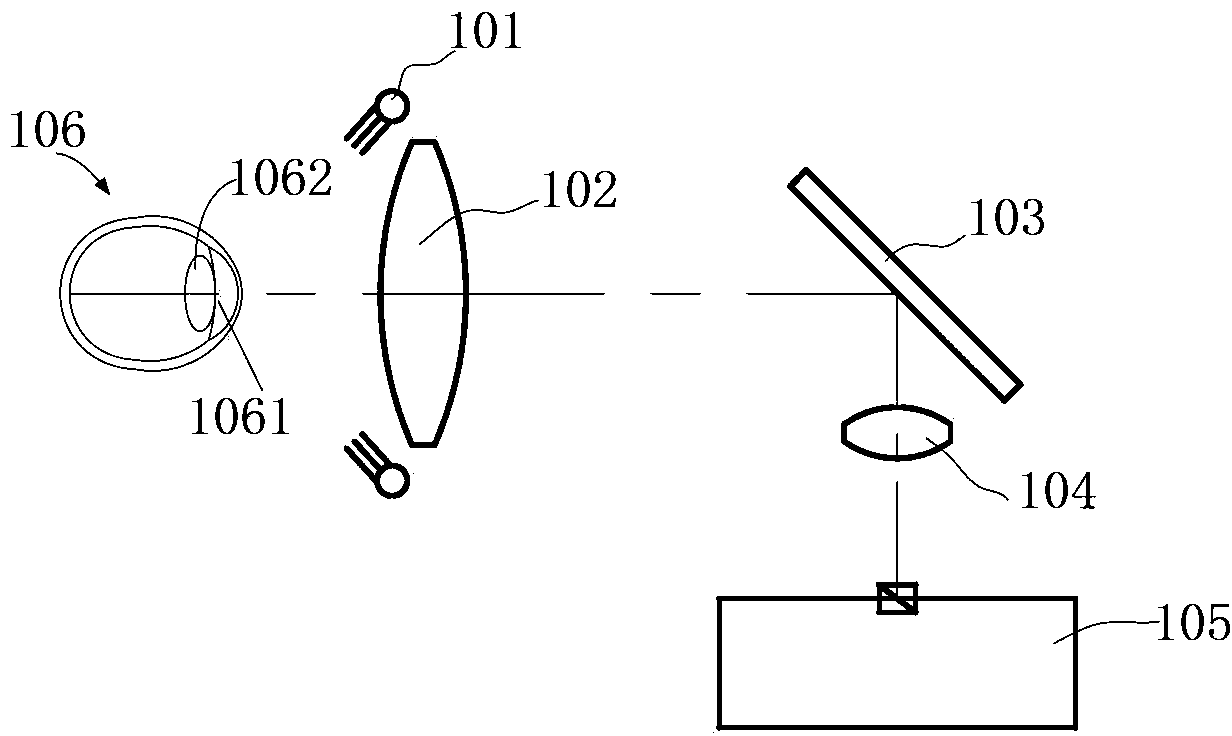
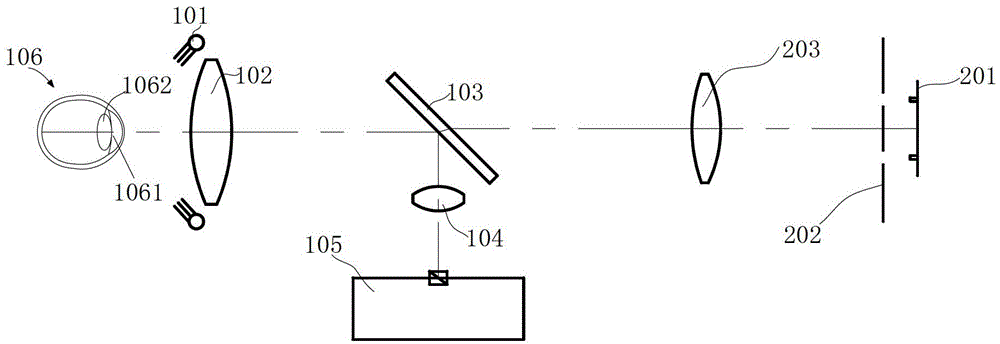
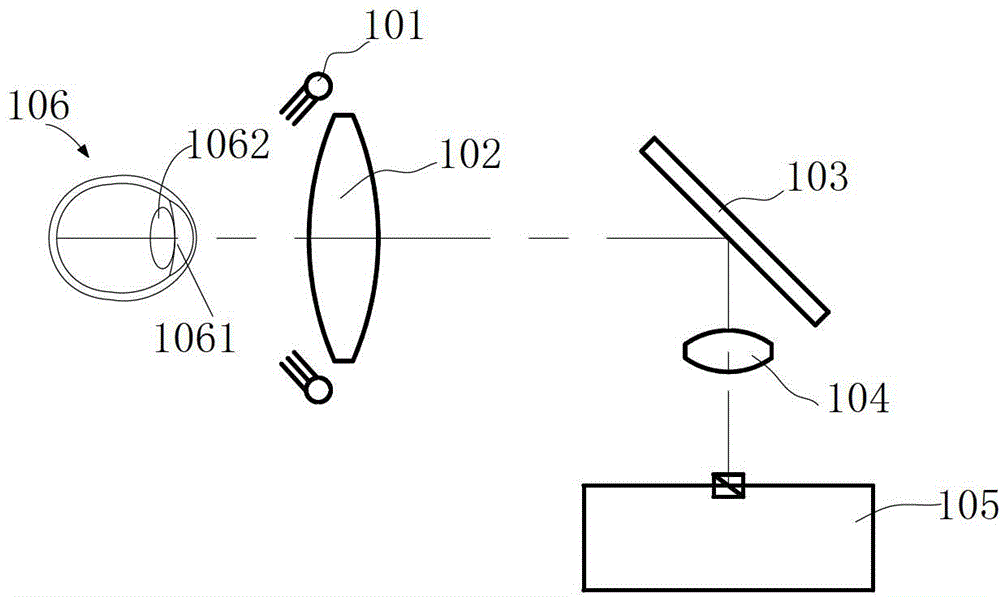
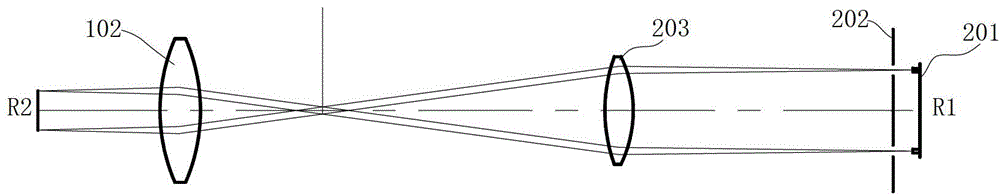
Optical system and optical method for measuring human eye white-to-white distance
ActiveCN103961055AAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesImprove measurement accuracyEye diagnosticsPupil diameterLight beam
An optical system for measuring human eye white-to-white distance comprises a first optical system and a second optical system, wherein the first optical system is composed of a double-light-emitting light source, a double-path diaphragm, a first lens, a dichroscope and an eye lens on a light path in sequence; the second optical system is composed of the dichroscope, a second lens and an iris pickup device on the light path in sequence. The double-light-emitting light source transmits through the first lens after passing the double-path diaphragm, a part of light beams transmit the dichroscope, enter human eyes through the eye lens and focus on the irises of the human eyes. A part of light beams is reflected by the irises, transmits to the eye lens, is reflected by the dichroscope and then transmits to the second lens, and finally images on the iris pickup device. The double-light-emitting light source is arranged on one of focal planes of the first lens, another focal plane of the first lens is superposed on one of focal planes of the eye lens. By the aid of the optical system and the optical method, parameters such as the eye white-to-white distance and the pupil diameter can be accurately measured.
Owner:SHENZHEN CERTAINN TECH CO LTD
Method for accurately measuring organic carbon content of shale
InactiveCN105842417AAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesAccurate and comprehensive measurement resultsChemical analysis using titrationEarth material testingSulfatePotassium dichromate
The invention discloses a method for accurately measuring organic carbon content of shale. The method comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring a complete block of shale in proportion; 2) extracting shale gas in the shale into an enclosed container containing water; 3) carrying out ultraviolet oxidation treatment on the enclosed container having absorbed the shale gas; 4) measuring the organic carbon content of an aqueous solution having undergone oxidation in virtue of a TOC instrument and measuring the organic carbon content of water at the same time, wherein the obtained difference value represents the organic carbon content of the shale gas; 5) crushing the shale in which shale gas is extracted into a powdery sample; 6) dissolving the powdery sample with concentrated sulfuric acid; 7) measuring the organic carbon content of a uniform solution cooled in the step 6) by using a potassium dichromate oxidation-ferrous sulfate titration method; and 8) summing together the organic carbon content of the shale gas measured in the step 4) and the organic carbon content measured in the step 7) so as to obtain the total organic carbon content of the shale. The method provided by the invention can accurately measure the organic carbon content of the shale.
Owner:CHENGDU CHUANGYUAN OIL & GAS TECH DEV
Oil product light stabilizer
ActiveCN112625781AReduced chromaticity variationIncrease the cost of useLubricant compositionUltraviolet lightsUv absorber
The invention relates to an oil product light stabilizer, and belongs to the technical field of lubricating oil preparation. The oil product light stabilizer is characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3-5 parts of an antioxidant 1010, 5-10 parts of an ultraviolet light absorber; 5-10 parts of an antioxidant 168; and balance of base oil. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing the antioxidant 1010 and the base oil according to a weight ratio of 1: 10-15 to obtain a component A; mixing the ultraviolet light absorber and base oil according to a weight ratio of 1: 10-20 to obtain a component B; mixing the antioxidant 168 and the base oil according to a weight ratio of 1: 10-15 to obtain a component C; and blending the component A, the component B and the component C by online blending and filling equipment and adding the blended components into lubricating oil to be renewed, wherein the adding mass of the oil product light stabilizer is 0.1%-0.2% of the lubricating oil to be updated. A quantitative premixing device, a nitrogen adding pulse blending device and a suction type replacement device are sequentially connected from front to back.
Owner:山东恒利热载体工程技术有限公司
Engineering slope measuring instrument and using method
ActiveCN110657780AAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesNo shakingIncline measurementMeasuring instrumentEngineering
The invention relates to the field of engineering slope measurement, and discloses an engineering slope measuring instrument and a using method. The engineering slope measuring instrument comprises ameasuring instrument body, a dial is embedded into the outer surface of the front end of the measuring instrument body, a circular hole is formed in the outer surface of the front end of the measuringinstrument body in a penetrating way, the circle center of the circular hole coincides with that of the dial, and a fixing groove and a fixing mechanism are arranged at the two sides of the inner wall of the dial in the horizontal direction respectively and are symmetrical by taking the circle center of the circular hole as the center, and a pressing mechanism is arranged at the upper end of themeasuring instrument body. According to the engineering slope measuring instrument and the using method thereof, the replacement cost can be reduced, the using stability can be improved, the measuringprecision can be guaranteed, and more labor can be saved in the using process.
Owner:王晓帆
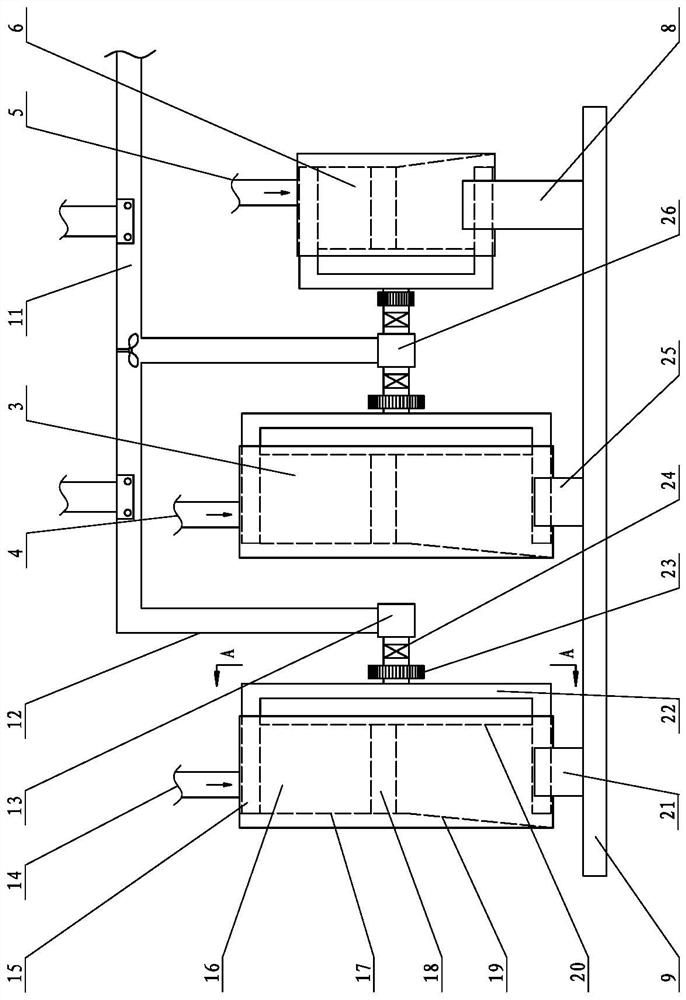
High-pressure orifice plate gas stagnation temperature control device and method
ActiveCN106444889AGuaranteed measurement accuracyImprove accuracyTesting/calibration apparatusTemperature control using electric meansOrifice plateElectric heating
The present invention belongs to the orifice plate gas flow measurement technical field and relates to a high-pressure orifice plate gas stagnation temperature control device and method. The control device is a temperature control gas tank; a temperature control gas tank inlet flange is externally connected with the outlet of a gas source; a front porous rectifying plate is clamped to a temperature control gas tank wall through a temperature control gas tank inlet expanding type clamp plate flange by means of bolts; electric heating rods are fixedly clamped to a rear porous rectifying plate through the front porous rectifying plate; line collection rings are located on the rear porous rectifying plate; electrode springs are clamped between electric heating rod inner electrodes and external electrodes; the external electrodes are embedded in insulating materials; the insulating materials are embedded in metal plugs; the metal plugs are welded to ball head-taper surface sealing structures; the ball head-taper surface sealing structures are welded to the temperature control gas tank wall; and outer periphery flow guiding holes and inner periphery flow guiding holes are located on the rear porous rectifying plate. With the high-pressure orifice plate gas stagnation temperature control device and method of the invention adopted, gas temperature at the inlet of an orifice plate can be effectively compensated in a certain range, the accuracy of key parameter measurement participating in the calculation of the discharge coefficient of the orifice plate can be ensured, and the accuracy of the calibration of the discharge coefficient of the orifice plate can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE INST FOR METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT TECH +1
A high-pressure orifice gas stagnation temperature control device and method
ActiveCN106444889BControllable temperature parametersAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesTesting/calibration apparatusTemperature control using electric meansVena contracta diameterTemperature control
The present invention belongs to the orifice plate gas flow measurement technical field and relates to a high-pressure orifice plate gas stagnation temperature control device and method. The control device is a temperature control gas tank; a temperature control gas tank inlet flange is externally connected with the outlet of a gas source; a front porous rectifying plate is clamped to a temperature control gas tank wall through a temperature control gas tank inlet expanding type clamp plate flange by means of bolts; electric heating rods are fixedly clamped to a rear porous rectifying plate through the front porous rectifying plate; line collection rings are located on the rear porous rectifying plate; electrode springs are clamped between electric heating rod inner electrodes and external electrodes; the external electrodes are embedded in insulating materials; the insulating materials are embedded in metal plugs; the metal plugs are welded to ball head-taper surface sealing structures; the ball head-taper surface sealing structures are welded to the temperature control gas tank wall; and outer periphery flow guiding holes and inner periphery flow guiding holes are located on the rear porous rectifying plate. With the high-pressure orifice plate gas stagnation temperature control device and method of the invention adopted, gas temperature at the inlet of an orifice plate can be effectively compensated in a certain range, the accuracy of key parameter measurement participating in the calculation of the discharge coefficient of the orifice plate can be ensured, and the accuracy of the calibration of the discharge coefficient of the orifice plate can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE INST FOR METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT TECH +1
Method for measuring ferrous oxide content in iron ore
InactiveCN111257500AAvoid being oxidizedAvoid OxidationChemical analysis using titrationSodium bicarbonateIron(II) oxide
The invention discloses a method for determining the content of ferrous oxide in iron ore. The method comprises steps of a, weighing an iron ore sample, putting the sample into a conical flask, sequentially adding potassium fluoride, sodium bicarbonate and hydrochloric acid, covering with a porcelain cover, putting the flask on an electric furnace, and heating to boiling; b, transferring the diluted solution obtained in the step a into a beaker special for a potentiometric titrator; and c, inserting an indicating electrode and a reference electrode of the potentiometric titrator into the beaker special for the potentiometric titrator in the step b, titrating by adopting potassium dichromate standard solution, starting the potentiometric titrator, and starting titration. The method is advantaged in that problems that reliability of the detection result is easily influenced by indicator end point judgment and subjective judgment of different analysts in the existing measurement, ferrousoxide is extremely easy to oxidize in the decomposition and titration processes, and the analysis result is relatively low can be avoided.
Owner:JIUQUAN IRON & STEEL GRP
Suspension type impulse plate flow meter
PendingCN106840280AHigh measurement accuracyExtended service lifeVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectControl theoryForce sensor
The invention discloses a suspension type impulse plate flow meter. The suspension type impulse plate flow meter comprises a body and a flow guide groove arranged at the upper end of the body, wherein the body is internally provided with an impulse plate; four corners of the impulse plate are connected with steel wire ropes with the same length; one side of the impulse plate is suspended at the top of the body through two steel wire ropes and the other side of the impulse plate is suspended on a connecting plate at the top of the body through two steel wire ropes, so that a certain included angle is formed between the impulse plate and the horizontal plane; a push block is arranged at the middle position of the lower surface of the impulse plate; the push block is connected with a force transmission rod and a connector is arranged at the other end of the force transmission rod; the force transmission rod is connected to a force-measuring sensor through the connector. The suspension type impulse plate flow meter has the advantages that the metering precision is greatly improved; zero drift can be effectively avoided; the flow guide groove is arranged so that the problem that the metering is not accurate, caused by the fact that the size of an impact force on the impulse plate by each material is different, can be avoided; the force-measuring sensor is firmly mounted in the body and the problem that the metering is not accurate, caused by equipment vibration, can be avoided.
Owner:HEFEI GOODTIMES AUTOMATION
Ultrasonic gas meter time sampling method aiming at pulsating flow influence
ActiveCN111457977AAccurate and stable outputAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesVolume/mass flow measurementVolume meteringStochastic algorithmsEngineering
The invention provides an ultrasonic gas meter time sampling method aiming at pulsating flow influence. Non-metering time ti in an acquisition period (500ms) is equally divided into four equal parts te; when a data updating period (2s) begins, an array Tval = [0, 1, 2, 3] is declared, which means that metering sampling is started after 0 * te, 1 * te, 2 * te and 3 * te time of waiting respectively; the waiting time of each period is determined through a random algorithm, obtained instantaneous flow values after the sampling of the acquisition period is completed are obtained; the obtained instantaneous flow values are sorted through a bubbling sorting method; the first n maximum values and the first n minimum values are taken, wherein n is smaller than or equal to N; and instantaneous flowoutput by the data updating period is calculated. According to the method, a set of software random algorithm is provided for the time sampling of an ultrasonic gas meter, so that the ultrasonic gasmeter can output accurate and stable flow, and the problem that the ultrasonic gas meter is inaccurate in metering due to the fact that a pulsating flow device is additionally arranged externally andmanually can be solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WEIXING INTELLIGENT METER STOCK
Tipping bucket type rain gauge
PendingCN112198561ASimple bracket structureReduce the use of fastenersRainfall/precipitation gaugesEngineeringAtmospheric sciences
The invention discloses a tipping bucket type rain gauge. The gauge comprises a base, a gantry support fixedly arranged on the base and integrally formed, a support fixedly arranged at the top of thegantry support, a rain bearing funnel having the bottom penetrating through the support and fixedly installed on the support, a plurality of tipping buckets and metering buckets installed on the gantry support in a turnover mode, a rainfall induction mechanism fixedly installed on the gantry support, an output terminal connected and matched with the rainfall induction mechanism and one-point positioning mechanisms. The tipping buckets are installed on the gantry support in a turnover mode from top to bottom from the position below an outlet in the bottom of the rain bearing funnel through a plurality of pairs of tipping bucket supporting points, and longitudinal positioning grooves and the one-point positioning mechanism are further installed at the installation positions of the metering buckets of the gantry support. And the rainfall induction mechanism is located between the metering buckets and the tipping buckets above the metering tipping buckets, measures and counts rainfall andtransmits a result to the output terminal for final output of a rainfall numerical value. The gauge has the advantages of small rainfall metering error, high precision and simple structure.
Owner:孙纯虎 +1
Precise conveying mechanism of high-precision weight reduction type weighing scale
PendingCN111361963AThe output speed can be set arbitrarilyAccurate output speedConveyorsWeighing apparatus for materials with special property/formDrive wheelControl engineering
The invention discloses a precise conveying mechanism of a high-precision weight reduction type weighing scale. The precise conveying mechanism comprises a shell with a feeding bin, a drive wheel assembly, a driven wheel assembly, a conveying belt and a drive assembly, wherein the drive wheel assembly and the driven wheel assembly are oppositely arranged. The feeding bin is provided with a feedingport and a discharging port. The drive wheel assembly and the driven wheel assembly are arranged in the feeding bin. A tooth-shaped synchronous belt is arranged on the inner side of the conveying belt, the two ends of the synchronous belt are engaged to synchronous wheels of the drive wheel assembly and the driven wheel assembly correspondingly, the center of the conveying belt is located below the feeding port, and the discharging port is located in the front end in the conveying belt advancing direction. The drive assembly is used for driving the drive wheel assembly to work. The tooth-shaped synchronous belt is arranged on the inner side of the conveying belt, the purposes of friction force increasing and anti-skid transmission are achieved through meshing of the synchronous belt and the synchronous wheels of the drive wheel assembly and the driven wheel assembly, inaccurate metering caused by conveying belt skidding is avoided, accordingly, the work stability of the conveying mechanism is improved, and the metering precision of a weight reduction type scale is improved.
Owner:XIAMEN BANGZHONG TECH
SMA fiber material automatic delivery device and method
The invention provides an automatic delivery device for SMA fiber materials, comprising: a transmission mechanism, a material storage mechanism, a delivery mechanism, a fiber storage bag, a control mechanism and a material receiving mechanism; the storage mechanism is vertically arranged on the transmission The conveyor belt surface of the mechanism; the storage mechanism has a storage chamber, and the fiber storage bags are stacked in the storage chamber; the delivery mechanism includes a grabbing device, an air control module, a swing cylinder and a grabbing cylinder The air control module is controlled by the control mechanism, so that the swing cylinder controls the grabbing device to swing to a position corresponding to the upper surface of the material storage mechanism, or to a position corresponding to the opening of the material receiving mechanism; The grasping cylinder controls the lengthening or shortening of the grasping device. The invention provides an automatic delivery device and delivery method for SMA fiber materials, which are accurate in measurement, simple in maintenance and simple in equipment structure.
Owner:FUJIAN TIETUO MACHINERY
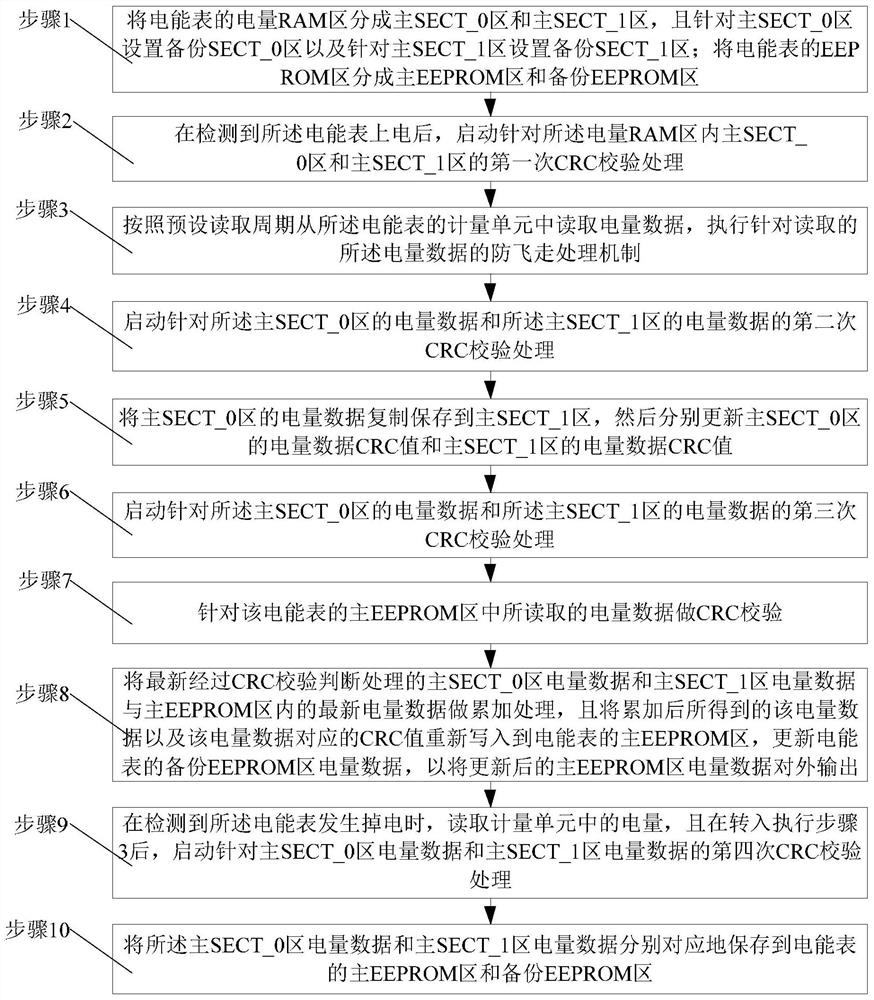
Method for measuring electric quantity of electric energy meter
ActiveCN110333387BAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesRealize data backupElectrical measurementsChecksumEngineering
The invention relates to a power metering method of an electric energy meter. By introducing a CRC check and a data backup mechanism, a backup area is set correspondingly for each main area divided into the power RAM area, and a backup area is also set for the main EEPROM area of the EEPROM area. In the EEPROM area, data backup is realized to avoid the loss of the original energy data stored in the main area; after the energy meter is powered on, after the anti-fly away processing mechanism is executed for the read energy data, and the power failure of the energy meter is detected The CRC verification process is performed every time, so as to ensure that the power data before entering the next step is the normal power data that has passed the CRC verification, so as to ensure that the subsequent measured power is accurate; and for the power that has not passed the CRC verification The data introduces an error correction mechanism, that is, uses the power data in the backup area to update the power data in the corresponding main area to ensure that the power data in the main area is correct.
Owner:NINGBO SANXING MEDICAL & ELECTRIC CO LTD
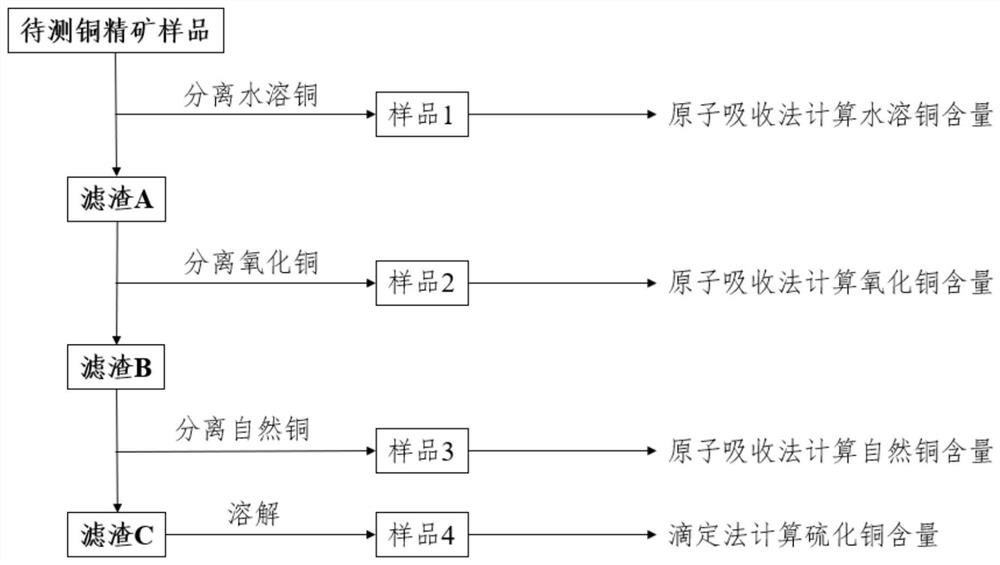
A chemical analysis method of copper phase in copper concentrate
ActiveCN113406266BHighly toxicDetermination process safetyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationChemical analysis using titrationBromineCopper oxide
The invention discloses a chemical analysis method for copper phase in copper concentrate, which belongs to the field of chemical analysis. The method comprises the following steps: S1 separating the water-soluble copper in the copper concentrate to be tested, and determining the content of the water-soluble copper by atomic absorption method; S2 separating the copper oxide in the filter residue A obtained in step S1, and measuring the content of copper oxide by atomic absorption method; S3 separates the natural copper in the filter residue B obtained in the step S2, and adopts atomic absorption method to measure the content of natural copper; S4 separates the copper sulfide in the filter residue C obtained in the step S3, adopts a titration method to measure the content of copper sulfide; wherein, the The step of separating copper sulfide in the step S4 includes: first heating and dissolving filter residue C with dilute nitric acid, then adding dilute sulfuric acid to continue heating and decomposing, then evaporating the solution to dryness, adding dilute sulfuric acid to heat and dissolve to obtain a mixture of copper and iron, and then masking Iron and the titration method was used to determine the content of copper sulfide. Adopting the method of the invention avoids the use of highly toxic liquid bromine, and the determination process is safer.
Owner:南京海关工业产品检测中心
Mobile concrete mixing plant for road and bridge construction
ActiveCN110435001BEasy to measureRealize mechanized feedingMixing operation control apparatusIngredients weighing apparatusArchitectural engineeringElectric machinery
The invention discloses a mobile concrete mixing station for road and bridge construction, which belongs to the technical field of building construction equipment, and includes a mixer, a material weighing device and a water tank, which can be placed on the transportation equipment for transfer, and the material feeding port of the mixer is connected with the material weighing A screw conveyor is arranged between the devices, and the water tank is connected to the mixer through a water pump and an inlet pipe with a flow meter. The material weighing device includes a storage hopper with a dynamic weighing and metering module at the bottom, and the storage hopper is connected to the turning mechanism; the mixer includes Tank body, stirring shaft and stirring blades, the stirring shaft is vertically arranged in the tank body, the motor driving the stirring shaft is arranged at the bottom of the tank body, and a plurality of stirring blades are radially arranged around the stirring shaft from top to bottom. The dynamic weighing and measuring module weighs various powdery or solid materials, and the flow meter measures the water consumption for mixing; when the materials are weighed, the turning mechanism and the screw conveyor are started to transport the materials to the tank for mechanical stirring and mixing. The material measurement of the invention is accurate, and the concrete quality is guaranteed.
Owner:韩保勤
A testing device for flatness and tensile strength of sewing parts
ActiveCN110849249BLarge clamping rangeIncrease flexibilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsCouplingElectric machinery
The invention discloses a device for detecting the flatness and tensile strength of sewing parts, which relates to the technical field of textile cloth production; in order to solve the problem that only the cloth can be detected but the cloth after sewing cannot be tested for pulling resistance and flatness; it specifically includes A fixed seat, the side wall of the fixed seat is welded with a motor table, the top of the motor table is fixed with a motor through a bolt, the output shaft of the motor is connected with a lead screw through a coupling, and one end of the lead screw is fixed with a stopper through a bearing. The block is welded to the inner wall of the fixed seat, the outer wall slider of the lead screw is connected with a movable frame, one side of the top of the fixed seat is welded with a fixed frame, the top of the outer wall of one side of the fixed frame is provided with a fixed clamping frame, and one side of the movable frame is The top of the outer wall is provided with a movable clamping frame. The present invention provides a fixed clamping frame and a movable clamping frame with a rectangular sheet structure, so that the clamping range is large, so that the clamping position can be adjusted according to requirements, and the flexibility of equipment use is improved.
Owner:济宁天久工贸有限公司
Insoluble sulfur and its preparation method and oil-extended insoluble sulfur and its application and ionic liquid as a stabilizer
ActiveCN104724680BImprove stabilityThe production will notSulfur preparation/purificationSulfurThermal stability
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
An oilfield single well metering device and metering method
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
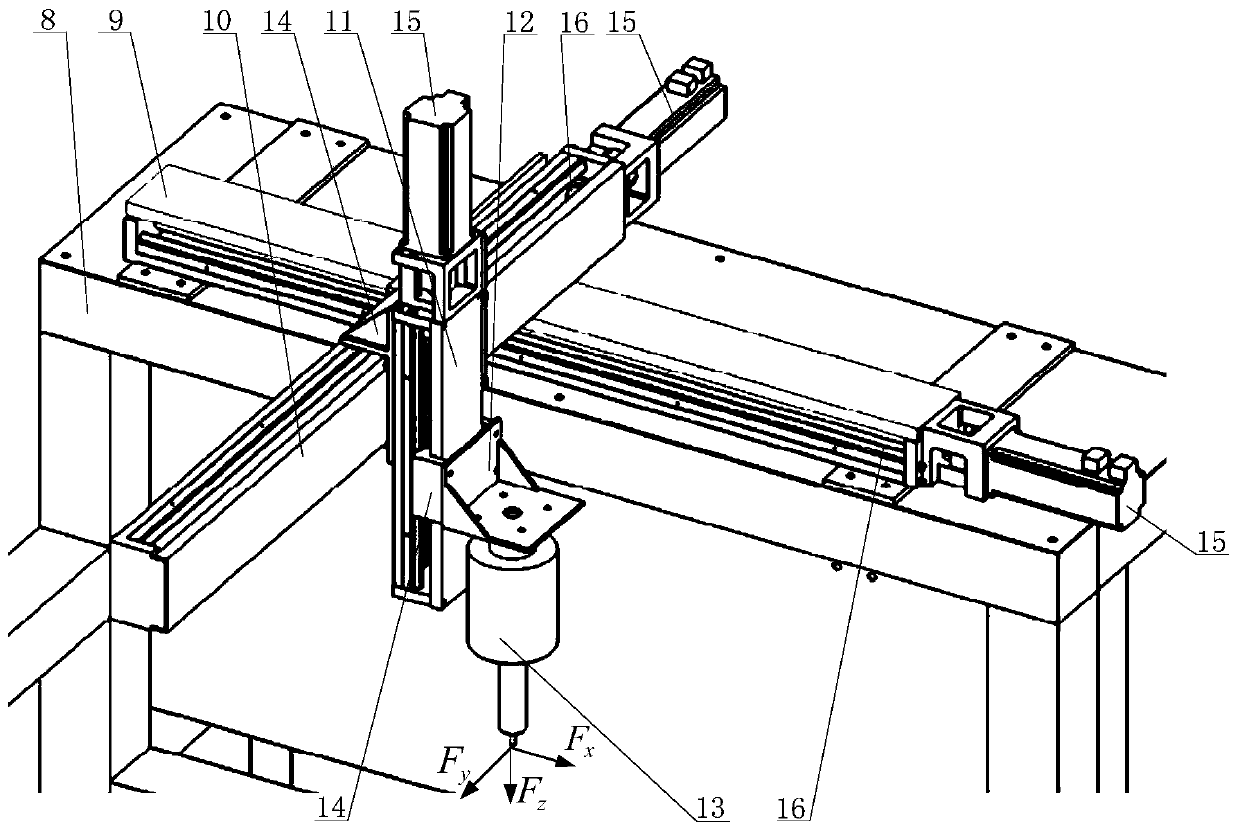
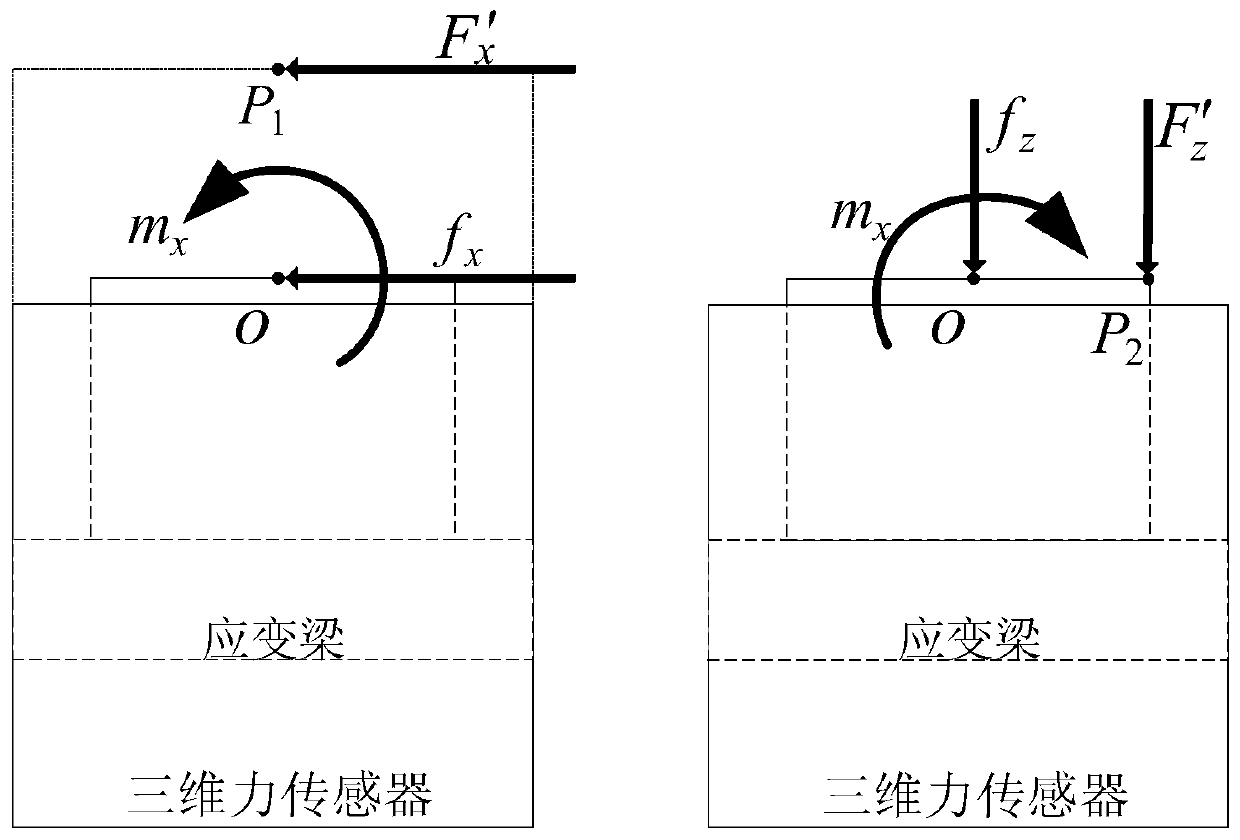
Three-dimensional force sensor decoupling calibration and filtering method and device for constant force grinding
ActiveCN106644253BAccurate measurementAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingMotion controllerContact force
The invention discloses a three-dimensional force sensor decoupling calibration and filtering method for constant-force grinding. The method comprises the steps of loading a constant weight in three directions of a three-dimensional force sensor, respectively measuring and recording output voltage of three channels of the sensor, and obtaining a decoupling matrix equation; calculating an actual bearing force in each direction through the decoupling matrix equation, and performing filtering on an interference signal according to an adaptive inertia filtering method of a force signal, thereby obtaining a real-time effective contact force signal; and then entering a motion controller through conversion of a signal amplifier, thereby finishing decoupling and filtering processing. The invention further discloses a device for realizing the method. The control part of the device comprises a PC host, an embedded controller, a terminal board, a signal amplifier, a three-dimensional force sensor, a servo controller and a three-coordinate driving and transmission mechanism. The mechanical part of the device comprises an x-axis motion mechanism, a y-axis motion mechanism and a z-axis motion mechanism, a sensor clamping frame, and a machining tool, wherein the x-axis motion mechanism, the y-axis motion mechanism and the z-axis motion mechanism are mounted on the three-coordinate driving and transmission mechanism on a workbench.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Optical system and optical method for measuring human eye white-to-white distance
ActiveCN103961055BAvoid Measuring InaccuraciesImprove measurement accuracyEye diagnosticsPupil diameterLight beam
An optical system for measuring human eye white-to-white distance comprises a first optical system and a second optical system, wherein the first optical system is composed of a double-light-emitting light source, a double-path diaphragm, a first lens, a dichroscope and an eye lens on a light path in sequence; the second optical system is composed of the dichroscope, a second lens and an iris pickup device on the light path in sequence. The double-light-emitting light source transmits through the first lens after passing the double-path diaphragm, a part of light beams transmit the dichroscope, enter human eyes through the eye lens and focus on the irises of the human eyes. A part of light beams is reflected by the irises, transmits to the eye lens, is reflected by the dichroscope and then transmits to the second lens, and finally images on the iris pickup device. The double-light-emitting light source is arranged on one of focal planes of the first lens, another focal plane of the first lens is superposed on one of focal planes of the eye lens. By the aid of the optical system and the optical method, parameters such as the eye white-to-white distance and the pupil diameter can be accurately measured.
Owner:SHENZHEN CERTAINN TECH CO LTD
A kind of production process of high temperature resistant precipitation antagonist
ActiveCN112481008BImprove thermal stabilityReduced chromaticity variationTransportation and packagingMixer accessoriesCresolPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a production process of a high-temperature-resistant precipitation antagonist, which belongs to the technical field of lubricating oil preparation. It is characterized in that it is made from the following raw materials, and the parts are all parts by weight: 2,6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol, 3-5 parts; dialkyl zinc dithiophosphate, 3-5 parts; Anticoagulant, 0.5-1 part; Dispersant, 0.5-1.5 part; UV absorber, 5-10 part; The rest is base oil; The anticoagulant and dispersant are added in proportion to component A or component B or In component C; the above-mentioned components A, B and C are added to the lubricating oil to be renewed through online blending and filling equipment; the addition amount of the high temperature resistant precipitation antagonist is 0.1-0.2% of the lubricating oil to be renewed. The quantitative premixing device, the nitrogen-adding pulse blending device and the suction displacement device are sequentially arranged from front to back.
Owner:山东恒利热载体工程技术有限公司
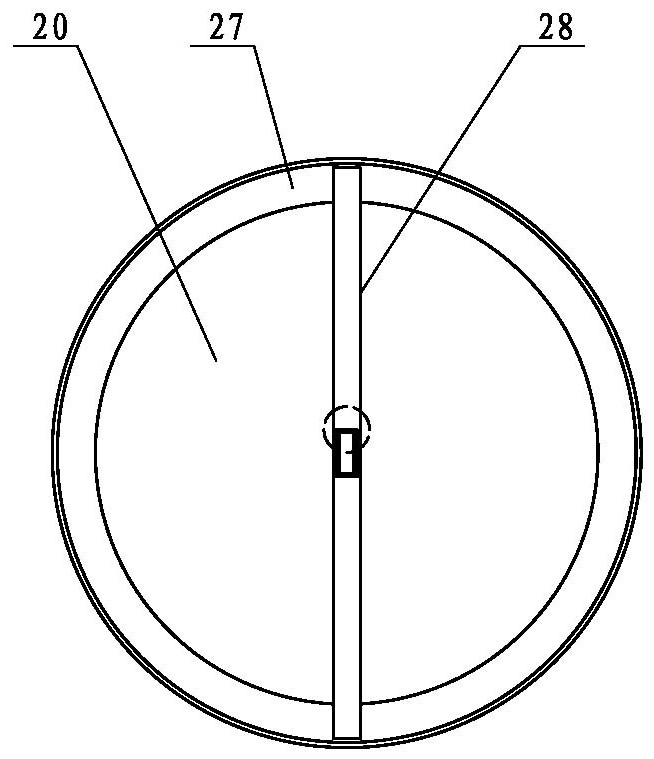
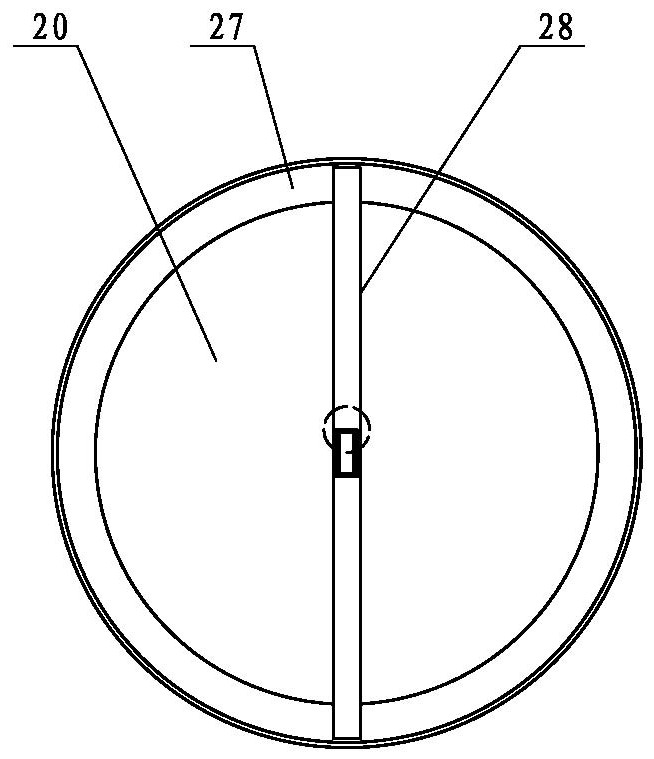
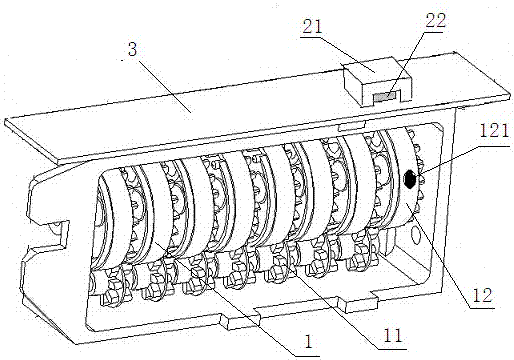
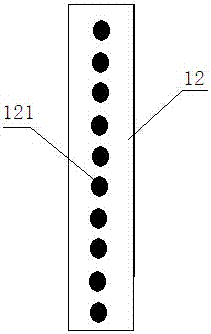
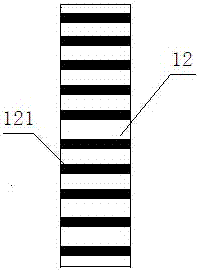
A magnetic induction character wheel counter
ActiveCN104915712BAccurate magnetic field change sensingStable induction of magnetic field changesCounting mechanisms/objectsGear wheelFerromagnetism
The invention relates to the field of data identification in measurement technology, in particular to a magnetic induction word wheel counter. A character wheel group, the character wheel group comprises two or more coaxially arranged character wheels, and adjacent character wheels are connected by a carry gear; The character wheel group comprises at least one character wheel provided with a ferromagnetic substance; The ferromagnetic material is arranged on the character wheel where at least one number is located; the magnetic induction unit corresponds to the character wheel provided with the ferromagnetic material and is arranged on the circuit board, including a U-shaped magnetic block and A magnetic induction chip arranged in the U-shaped notch of the magnetic block; when the ferromagnetic material rotating with the character wheel approaches the corresponding magnetic block, the magnetic field of the magnetic block changes, and the magnetic induction chip is used for sensing the magnetic field of the magnetic block. The magnetic field changes and outputs count pulses to the circuit board. The installation process of the technical solution provided by the present invention can realize a greater degree of automation, and the magnetic induction chip can sense the magnetic field change of the U-shaped magnetic block more stably and accurately, which increases the stability and service life of the counting device.
Owner:CHENGDU QIANJIA TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com