Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
219results about How to "Appropriate distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Photographing optical lens assembly
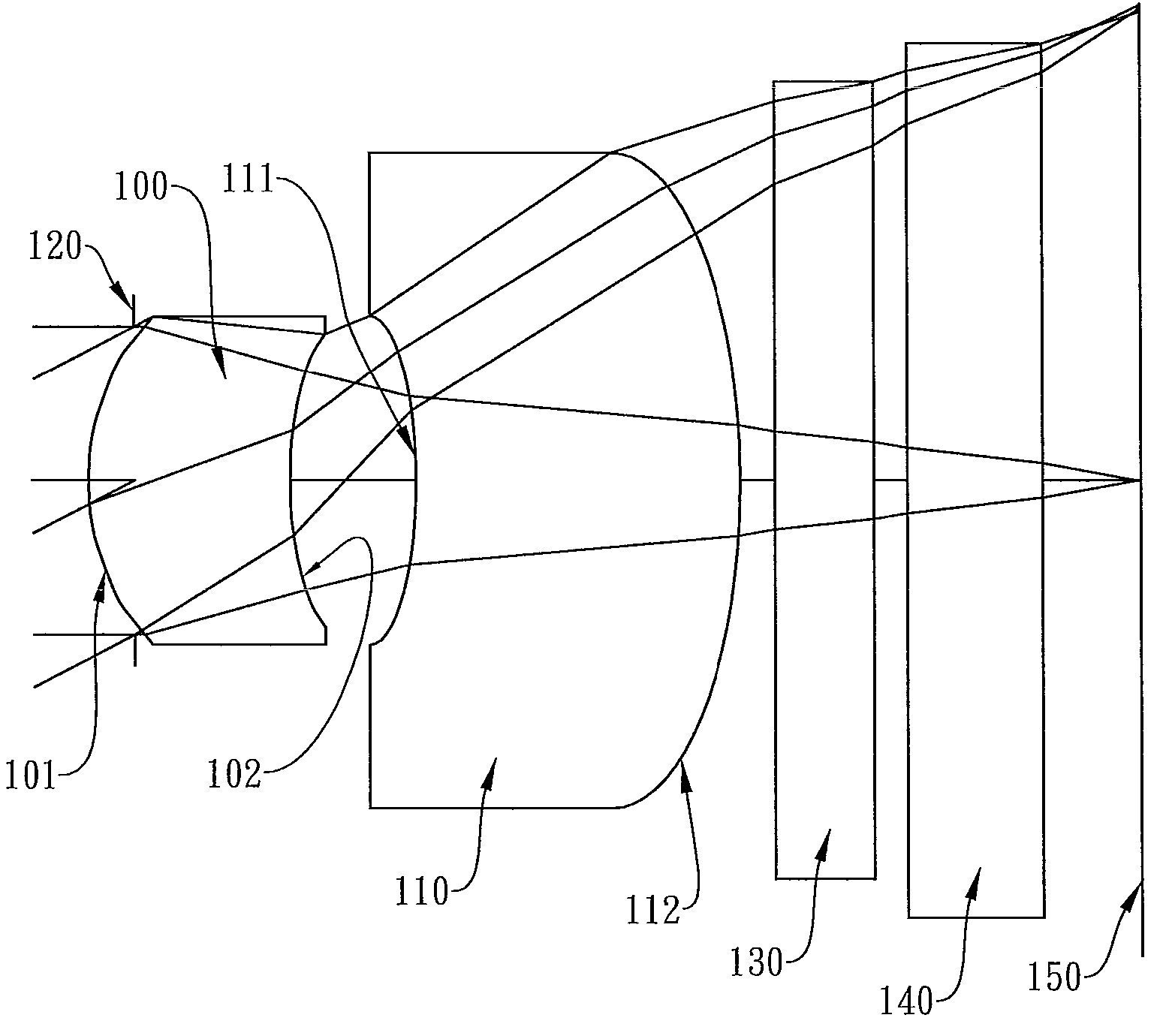
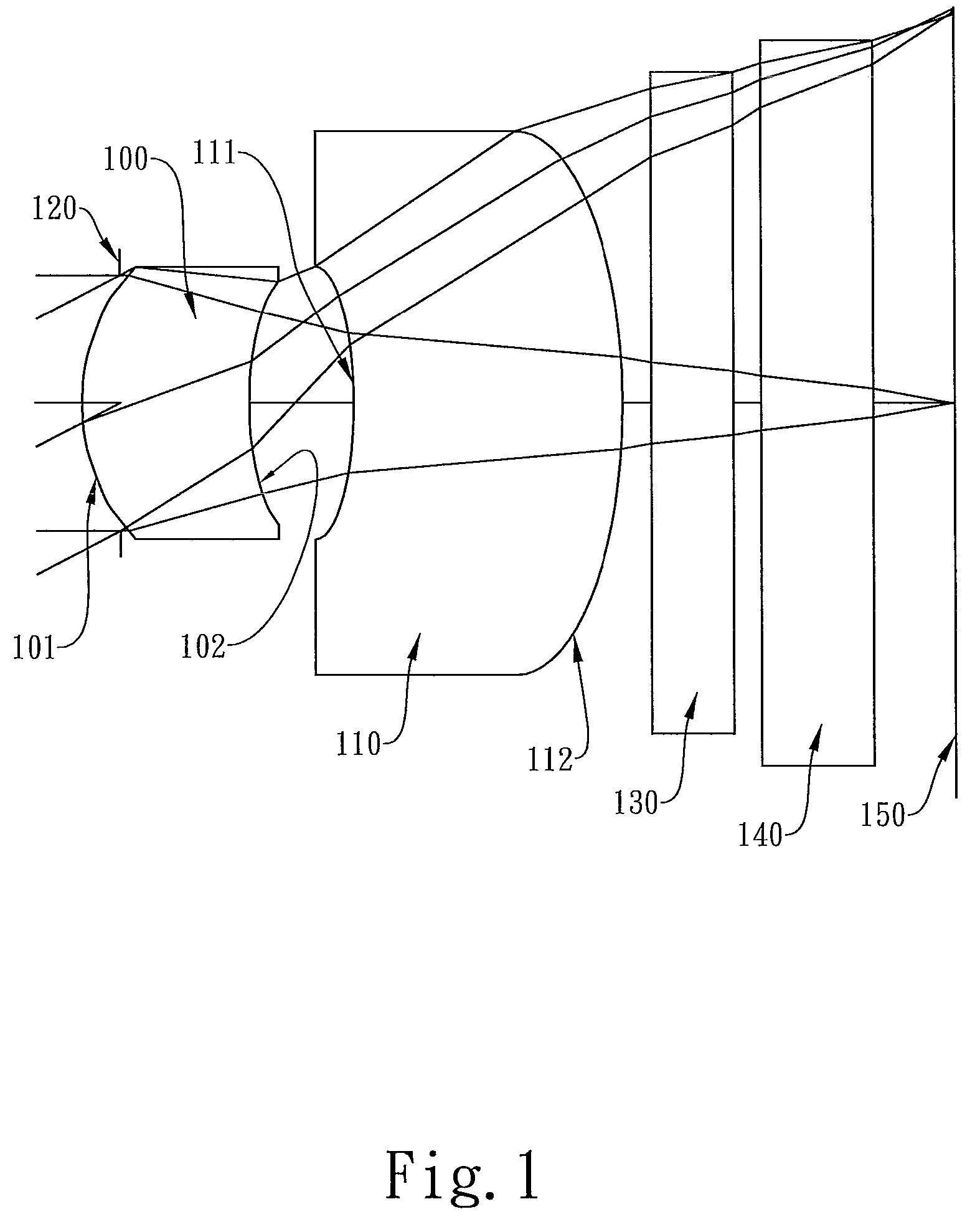
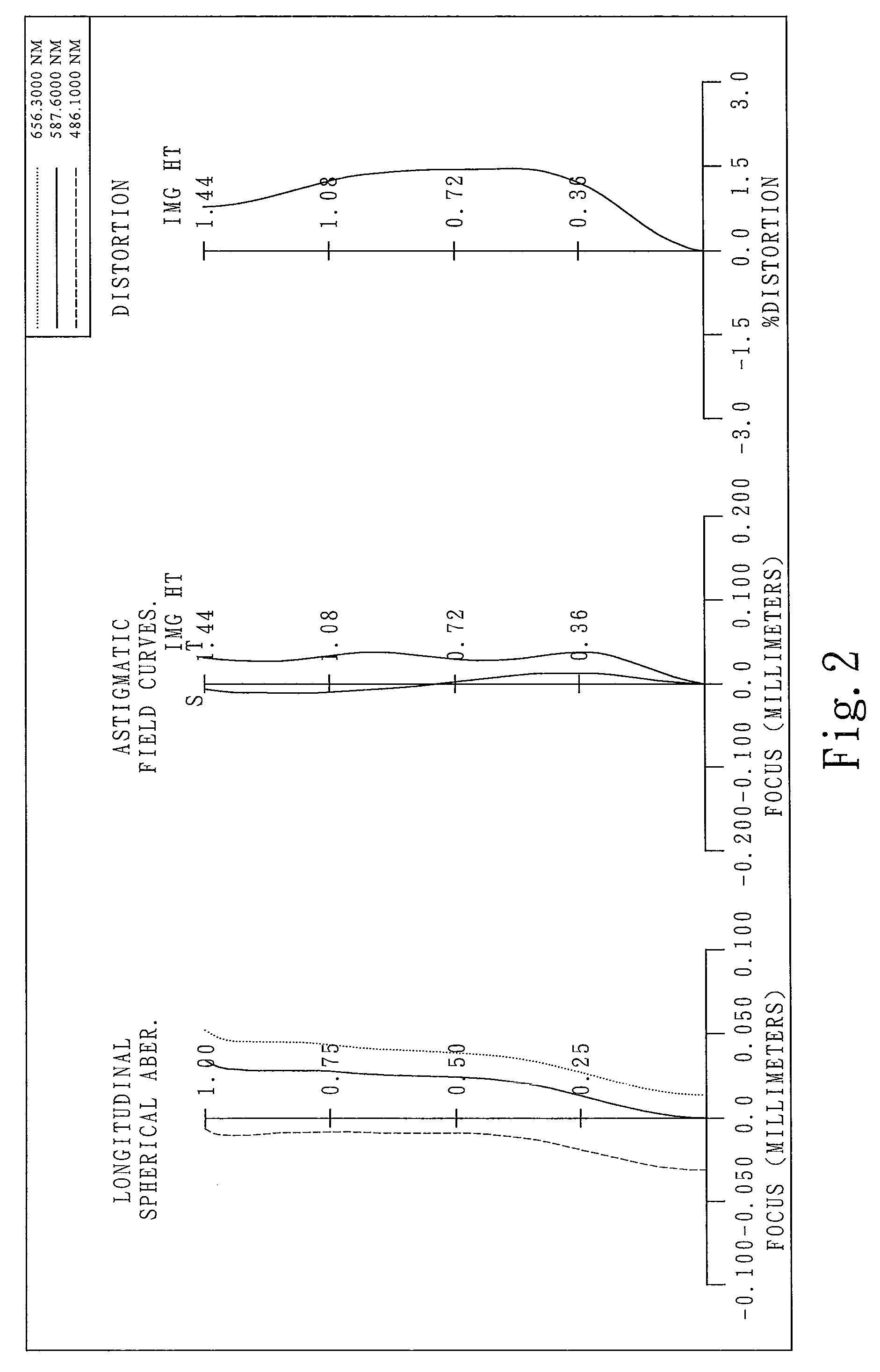
The present invention provides a photographing optical lens assembly comprising, in order from the object side to the image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; a second lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; and an aperture stop located in front of the first lens element; wherein an Abbe number of the first lens element is V1, an Abbe number of the second lens element is V2, and they satisfy the relation: |V1−V2|<15; and wherein the number of the lens elements of the photographing optical lens assembly is limited to two. Such an arrangement of optical elements can effectively reduce the volume of the lens assembly and the sensitivity of the optical system and enable the lens assembly to obtain a higher resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
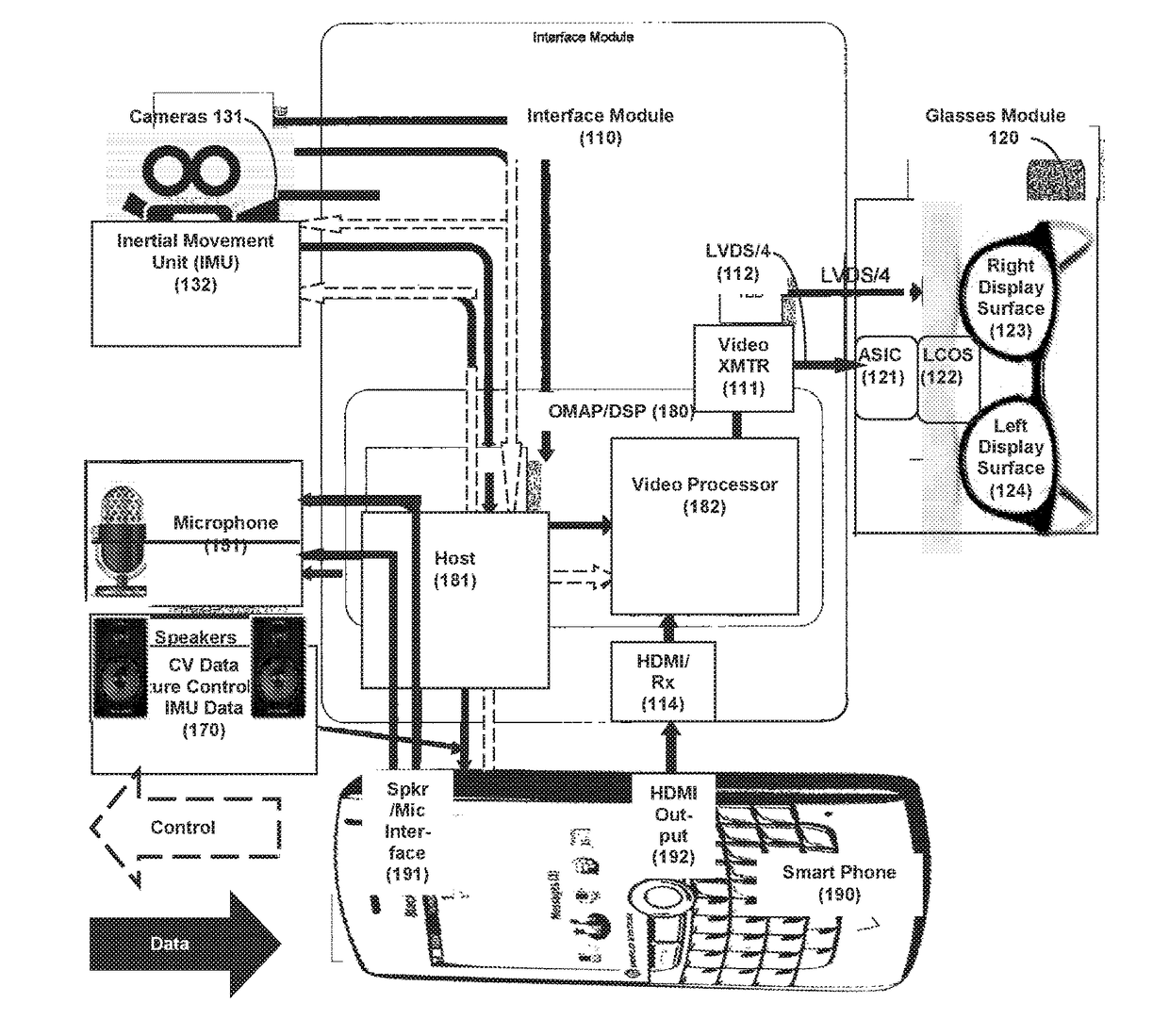
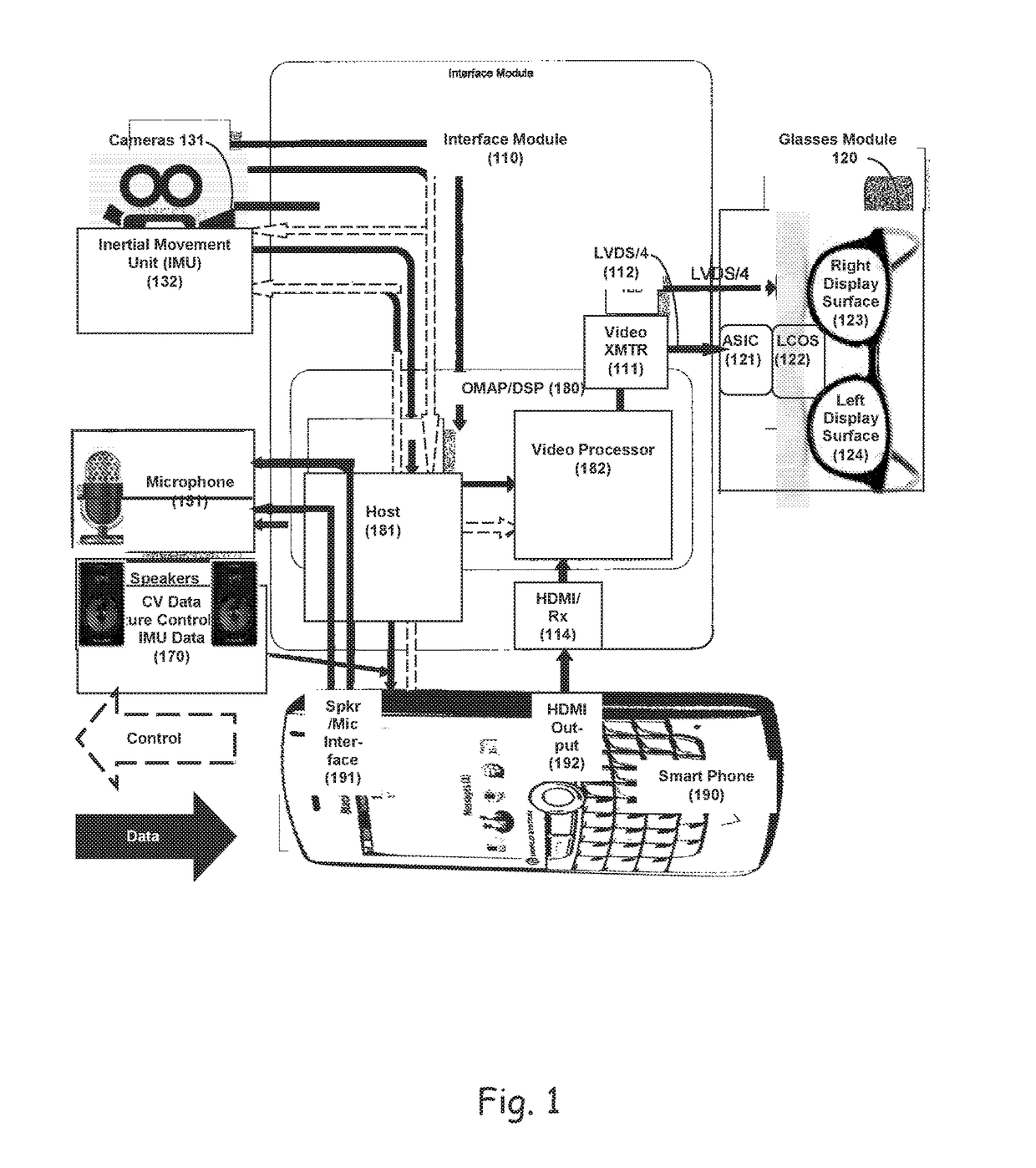
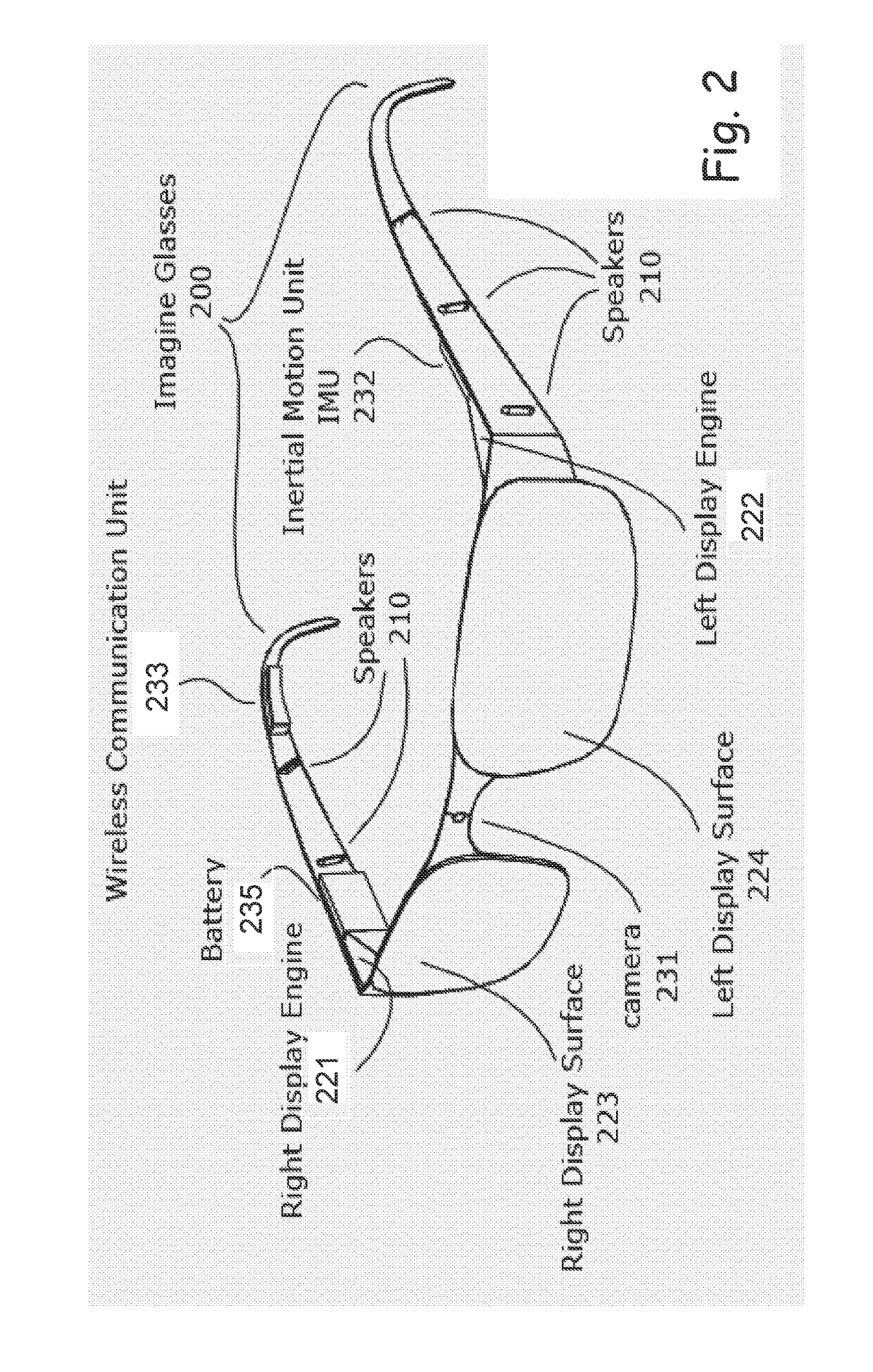
Audiovisual Surround Augmented Reality (ASAR)
InactiveUS20170153866A1More integratedAppropriate distributionInput/output for user-computer interactionMicrophone structural associationEmbedded softwareLoudspeaker
A system and method to enable realistic augmented reality 2D or 3D audiovisual imagery, integrating virtual object(s) and audio source data in the vicinity of a user / wearer of a head-mounted device (HMD), the HMD integrated with a mobile communication device. The system includes a HMD to facilitate enhancement of the user / wearer's audiovisual capabilities, a mobile communication device integrated with the HMD. The system also includes a dedicated system mounted on the HMD and comprising at least an embedded software solution, at least four (4) miniature speakers mounted on the HMD and configured to optimize the audio provided to the user / wearer and an inertial measurement unit (IMU) mounted on the HMD for processing the data on and through the speakers according to the data imputed to the software instructions, thereby providing realistic sound in the HMD and anchoring of sounds deriving from virtual objects in the real world.
Owner:REALITY PLUS LTD
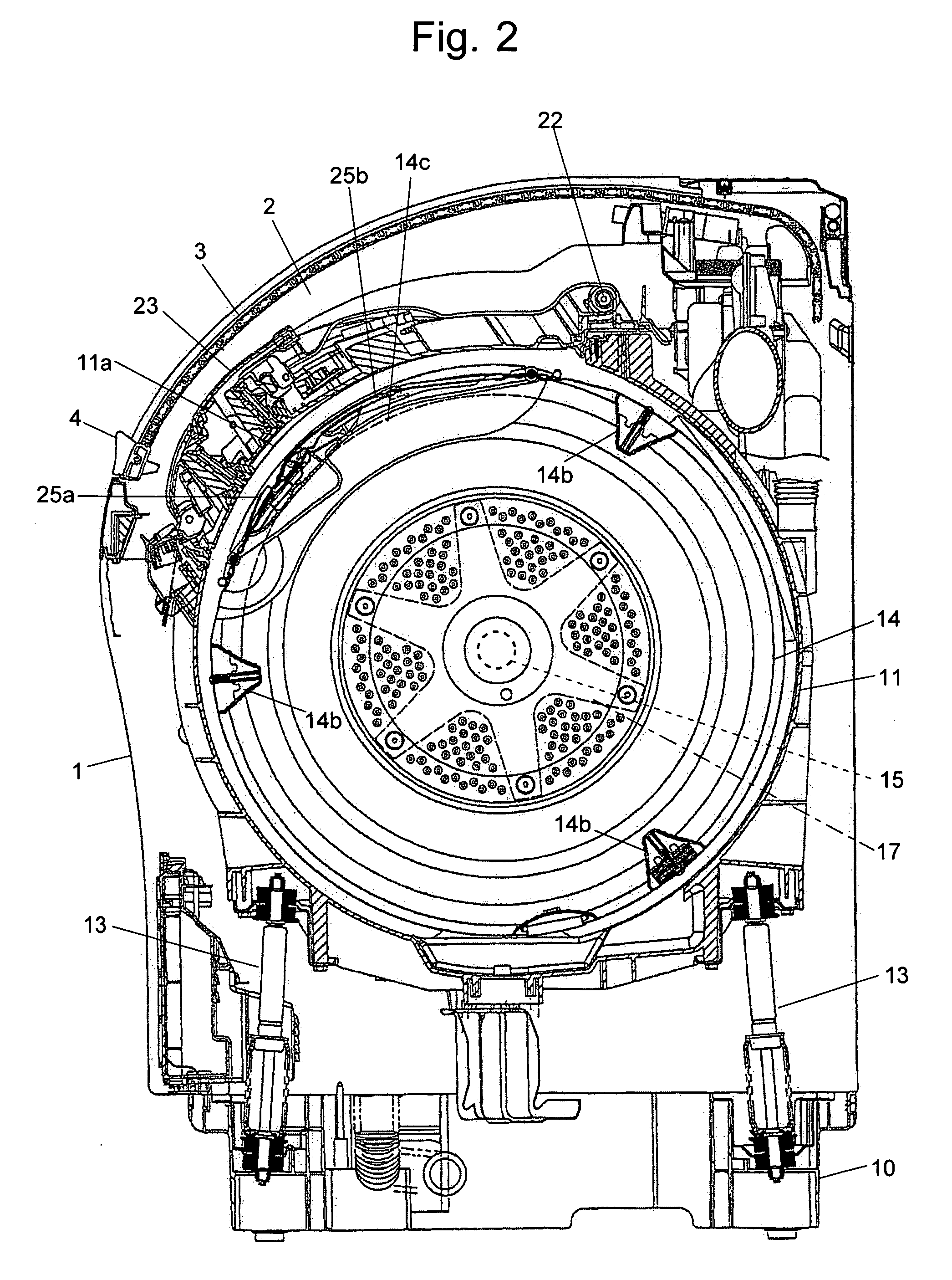
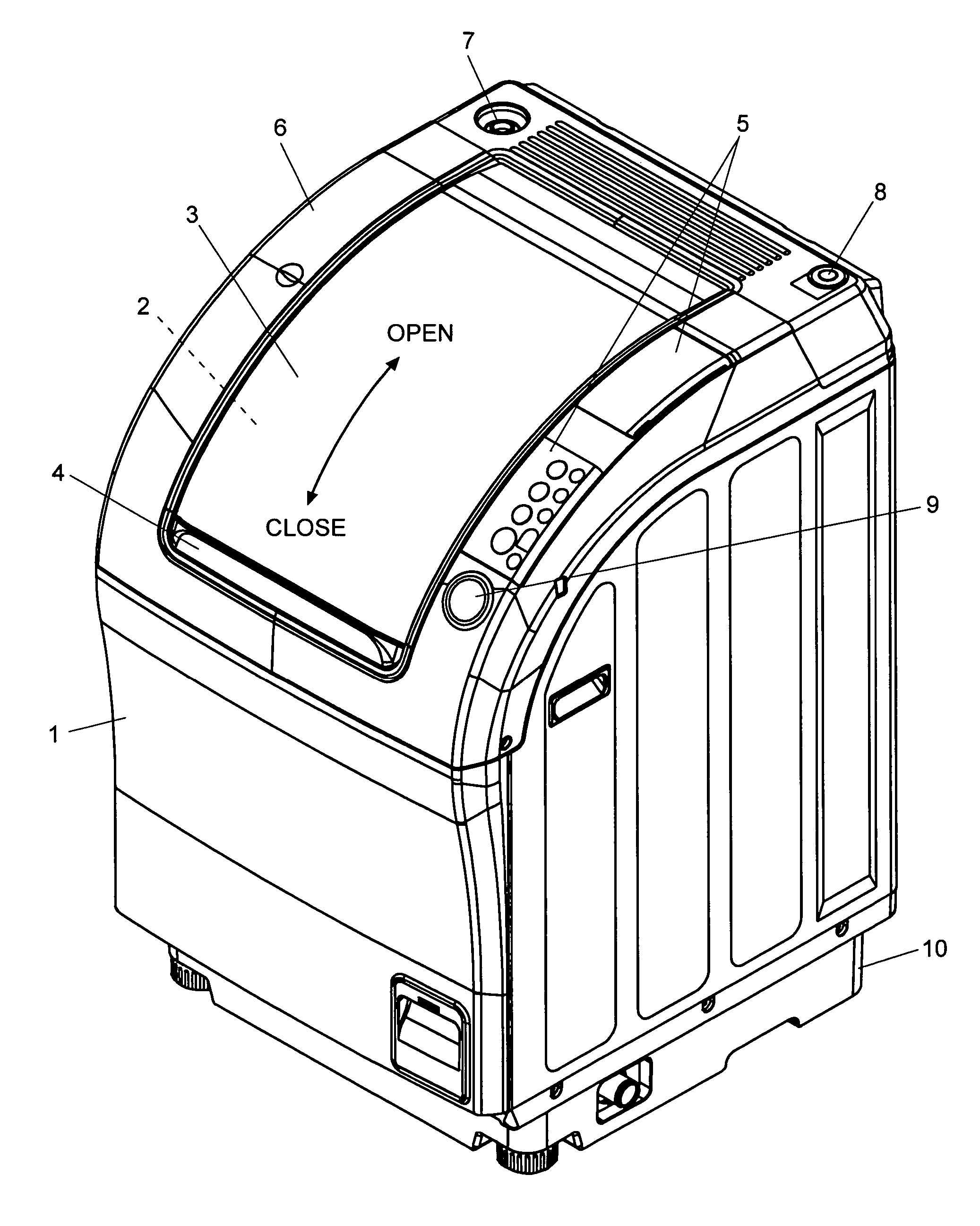
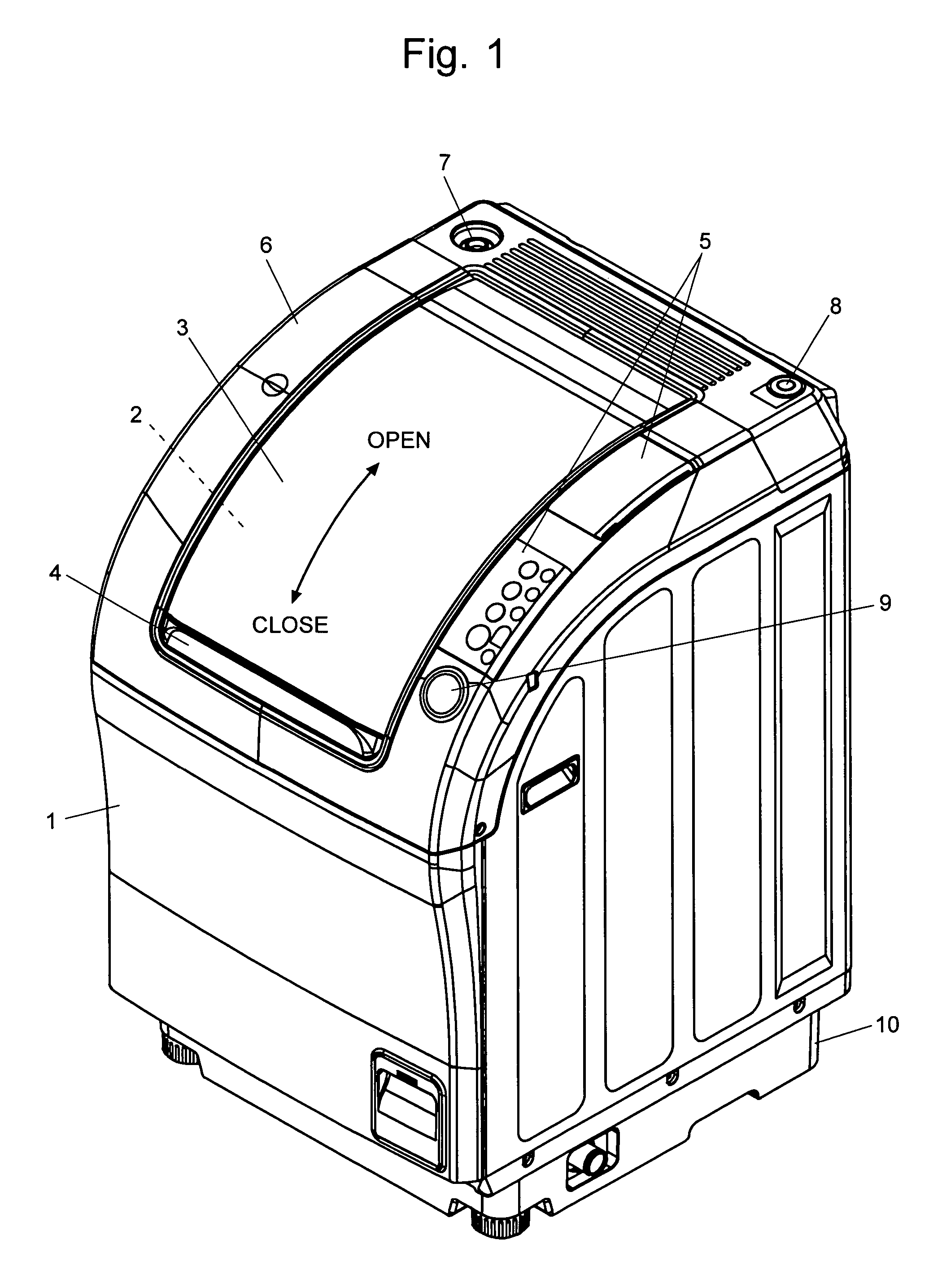
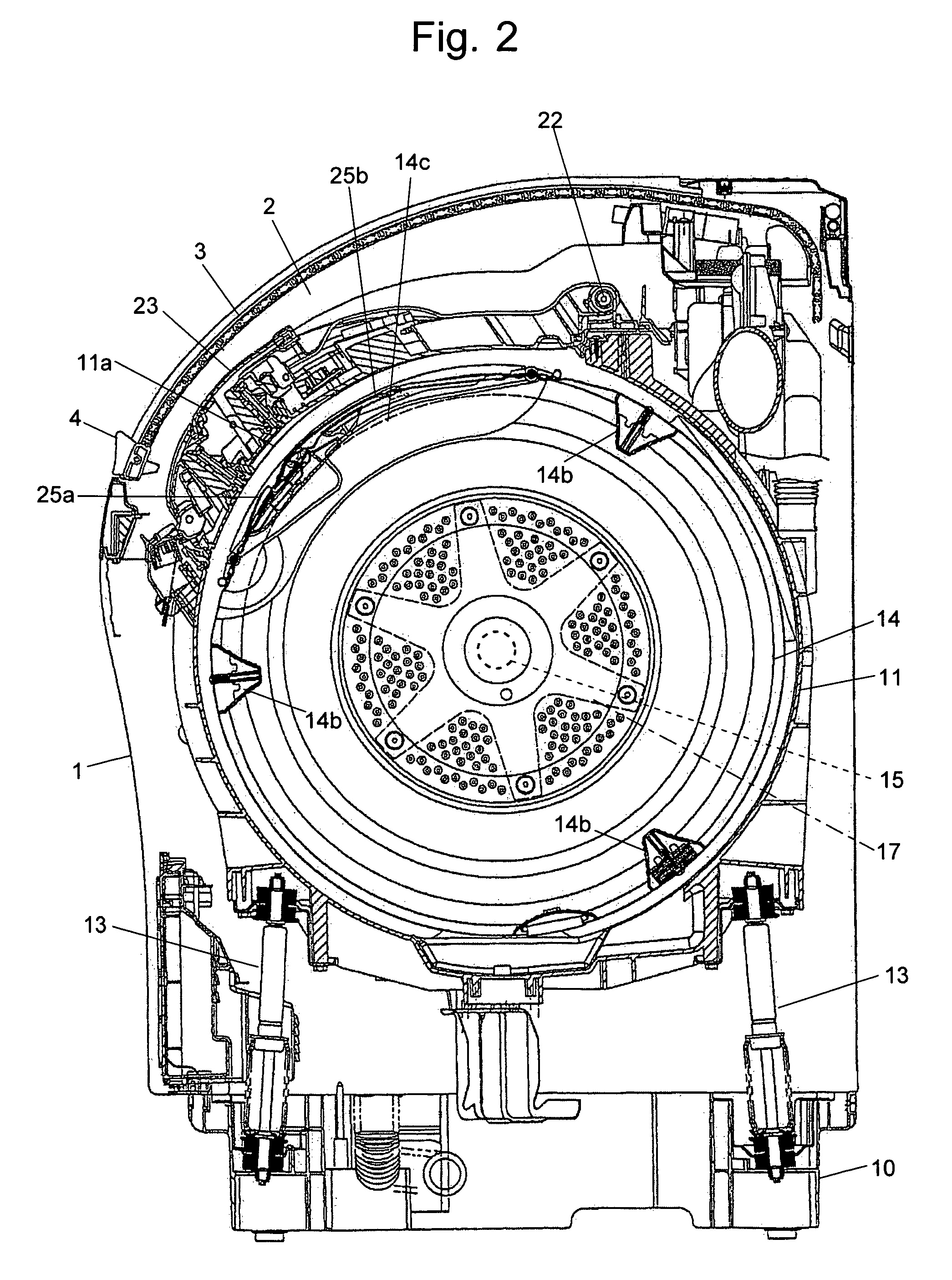
Drum type washing machine
ActiveUS20050268670A1Increase speedShort timeOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusHigh probabilityStart up time
The present invention provides a drum type washing machine capable of adequately distributing the laundry articles along the inner circumferential wall of the drum at the start-up of the dehydrating operation with high probability, thereby reducing the start-up time of the dehydration. In an embodiment of the present invention, the drum is controlled to rotate at a constant speed 50 r.p.m. to agitate the laundry articles (Step S12), and the drum speed is almost continuously monitored. If the change in the speed does not exceed 1.5 r.p.m. for 0.5 second (Steps S13 through S16), the laundry articles are loosened and easy to distribute. Therefore, the drum speed is raised to 80 r.p.m. (Steps S17 and S18). If the eccentric load detected at this speed does not exceed a predetermined value (Steps S19 and S20), the laundry articles are adequately distributed along and pressed onto the inner circumferential wall of the drum. If a sudden change in the speed has been detected within a short period of time that is less than 36 milliseconds (Step S22), the laundry articles are tangled in a mass form. Therefore, the rotating direction of the drum is reversed, and the agitating direction is restarted in the opposite direction (Step S21).
Owner:QINGDAO HAIER WASHING MASCH CO LTD +1
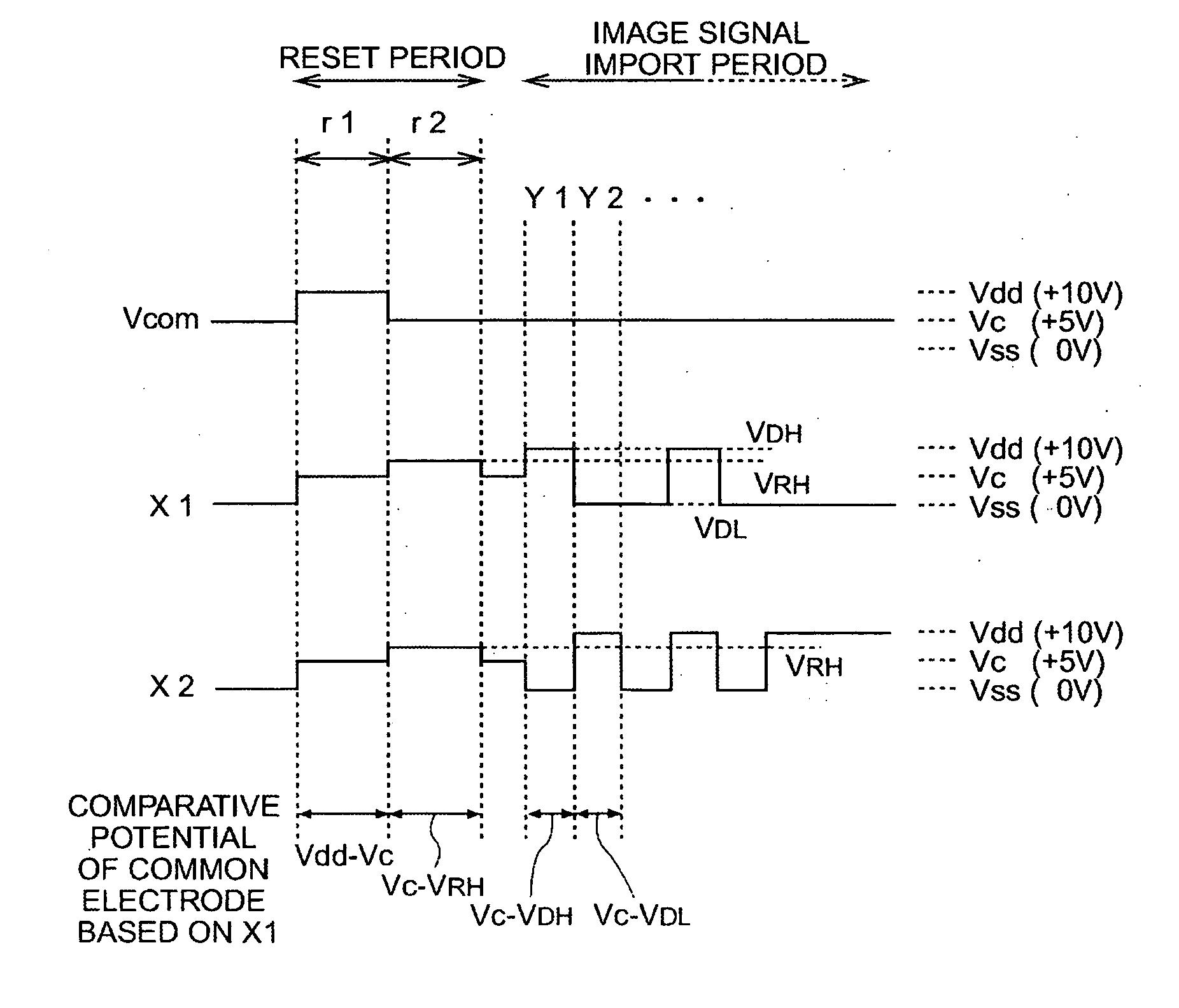
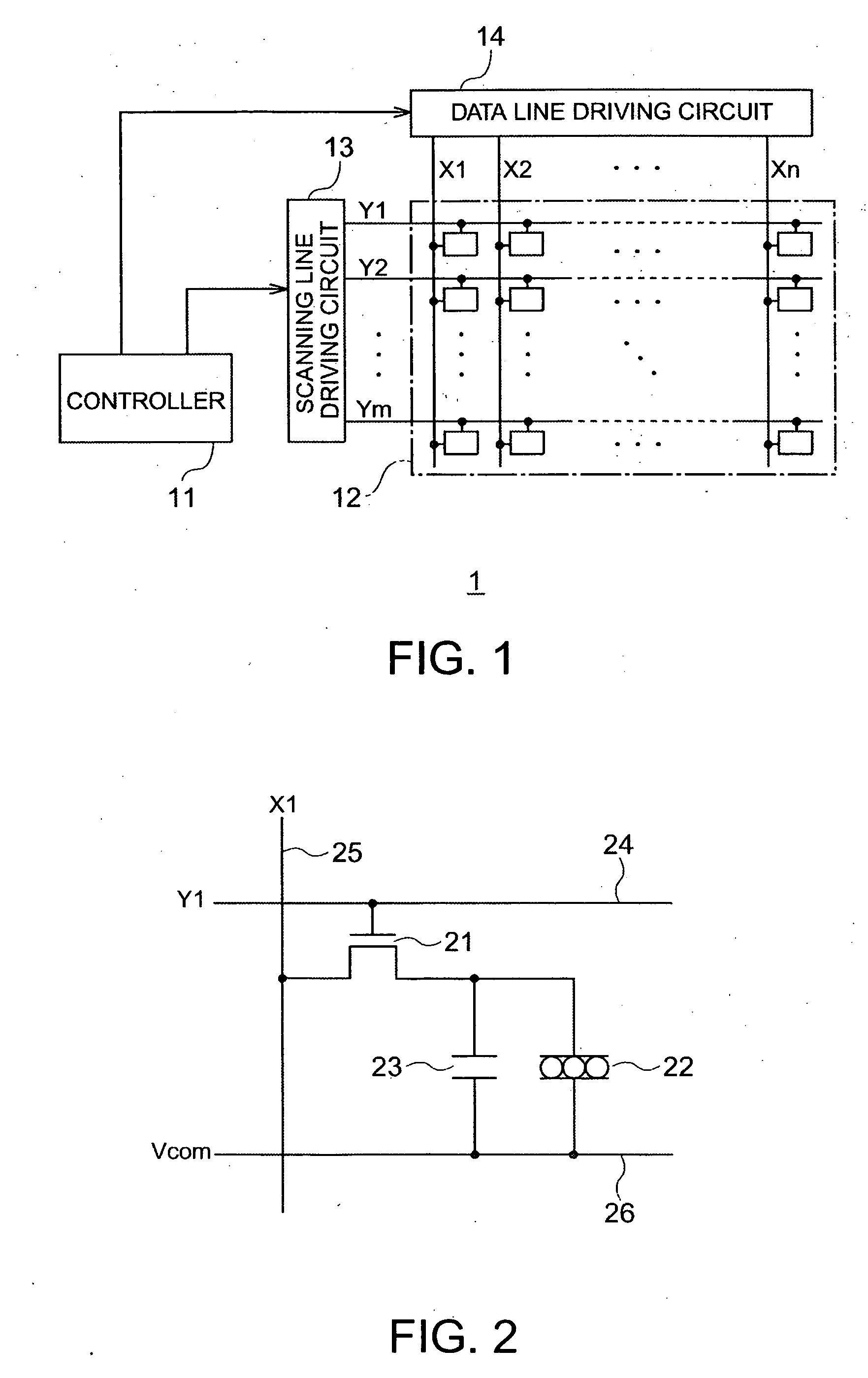
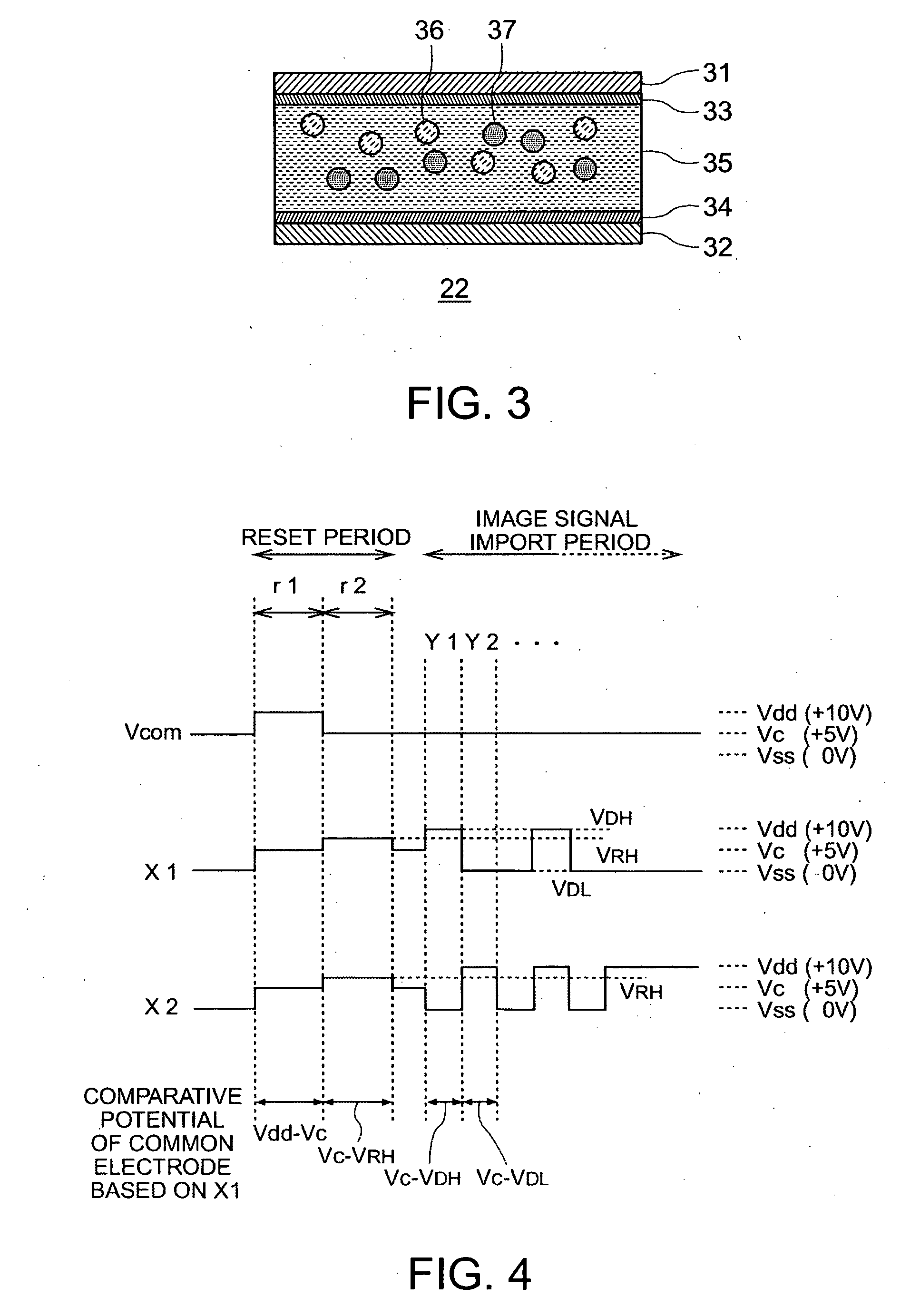
Electrophoretic device, electronic apparatus, and method for driving the electrophoretic device
ActiveUS20060139309A1Improve image qualityIncrease brightnessStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisEngineering
A method for driving an electrophoretic device, having: an electrophoretic element, in which a dispersal system that includes electrophoretic particles is laid between a common electrode and a pixel electrode; a driving circuit for driving the electrophoretic element by applying a voltage between the common electrode and the pixel electrode; and a controller for controlling the driving circuit; the method including: an image rewrite period process for controlling the driving circuit by the controller, and applying a voltage on the common electrode and the pixel electrode, thereby conducting an image rewrite, the image rewrite period process including a reset period and an image signal import period that follows the reset period; wherein the reset period includes: a first reset period process, during which a voltage-equivalent of a first gradation, which has a higher level of brightness than an intermediate gradation, is applied between the common electrode and the pixel electrode, thereby causing the electrophoretic particles to migrate; and a second reset period process, during which a voltage-equivalent of a third gradation which is between a second gradation and the first gradation is applied between the common electrode and the pixel electrode, the second gradation being at a lower level of brightness than the intermediate gradation, thereby causing the electrophoretic particles to migrate.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Drum type washing machine
ActiveUS7490490B2Increase probabilityReduce partial loadOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusHigh probabilityStart up time
The present invention provides a drum type washing machine capable of adequately distributing the laundry articles along the inner circumferential wall of the drum at the start-up of the dehydrating operation with high probability, thereby reducing the start-up time of the dehydration. In an embodiment of the present invention, the drum is controlled to rotate at a constant speed 50 r.p.m. to agitate the laundry articles (Step S12), and the drum speed is almost continuously monitored. If the change in the speed does not exceed 1.5 r.p.m. for 0.5 second (Steps S13 through S16), the laundry articles are loosened and easy to distribute. Therefore, the drum speed is raised to 80 r.p.m. (Steps S17 and S18). If the eccentric load detected at this speed does not exceed a predetermined value (Steps S19 and S20), the laundry articles are adequately distributed along and pressed onto the inner circumferential wall of the drum. If a sudden change in the speed has been detected within a short period of time that is less than 36 milliseconds (Step S22), the laundry articles are tangled in a mass form. Therefore, the rotating direction of the drum is reversed, and the agitating direction is restarted in the opposite direction (Step S21).
Owner:QINGDAO HAIER WASHING MASCH CO LTD +1
Porous membrane of vinylidene fluoride resin and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20060178480A1Improve heat distortion resistanceFacilitate stretchingSemi-permeable membranesMembranesSolventPorous membrane
There is provided a porous membrane of vinylidene fluoride resin which has pores of appropriate size and distribution and also excellent mechanical strength represented by tensile strength and elongation at break and is useful as a microfiltration membrane or a separator for batteries. The porous membrane of vinylidene fluoride resin is characterized by the presence in mixture of a crystalline oriented portion and a crystalline non-oriented portion as confirmed by X-ray diffraction, and is produced by subjecting a melt-extruded composition obtained by mixing a vinylidene fluoride resin having a molecular weight distribution which is appropriately broad and high as a whole with a plasticizer and a good solvent for vinylidene fluoride resin, to cooling for solidification from one surface, extraction of the plasticizer and stretching.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
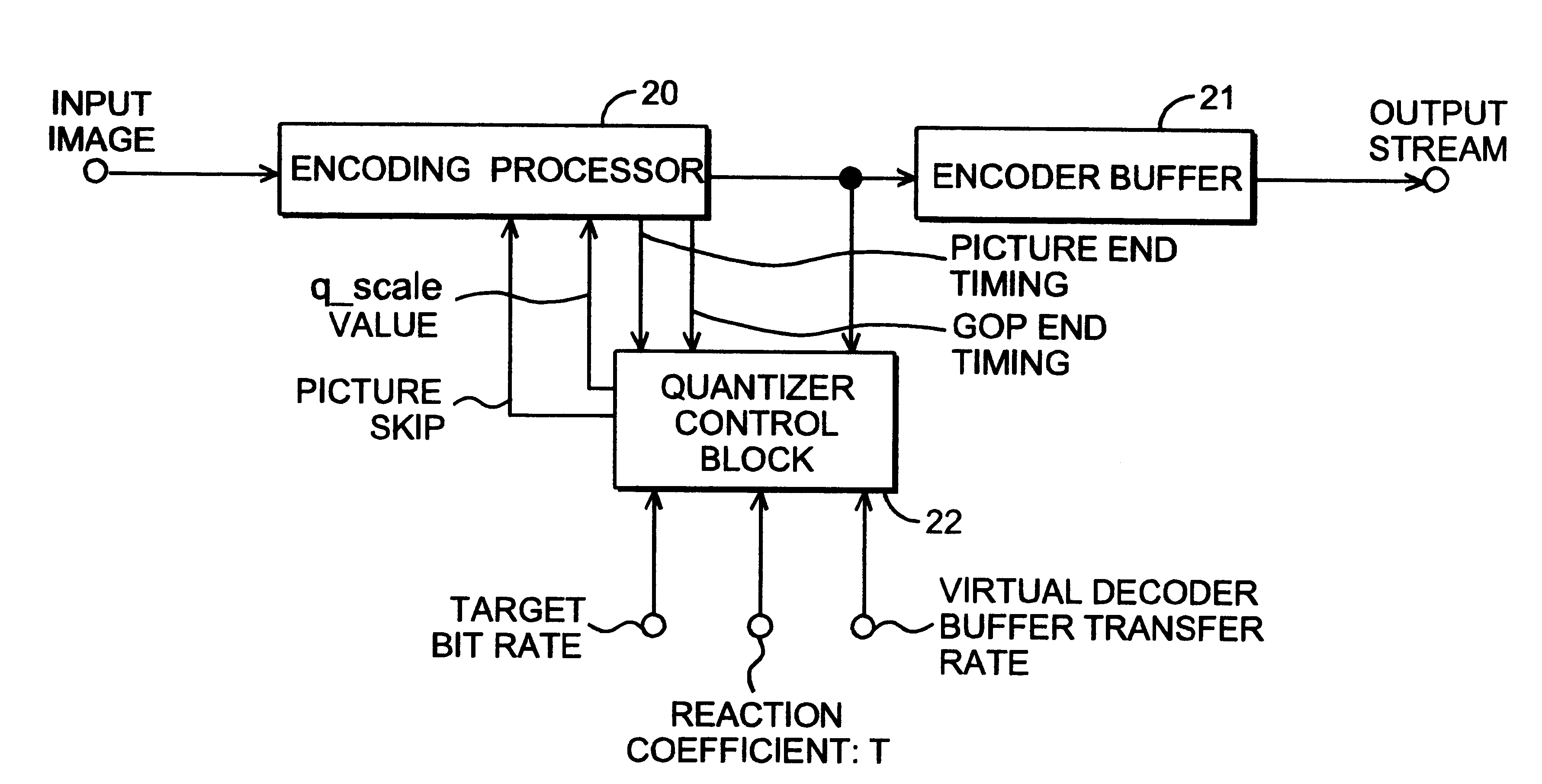
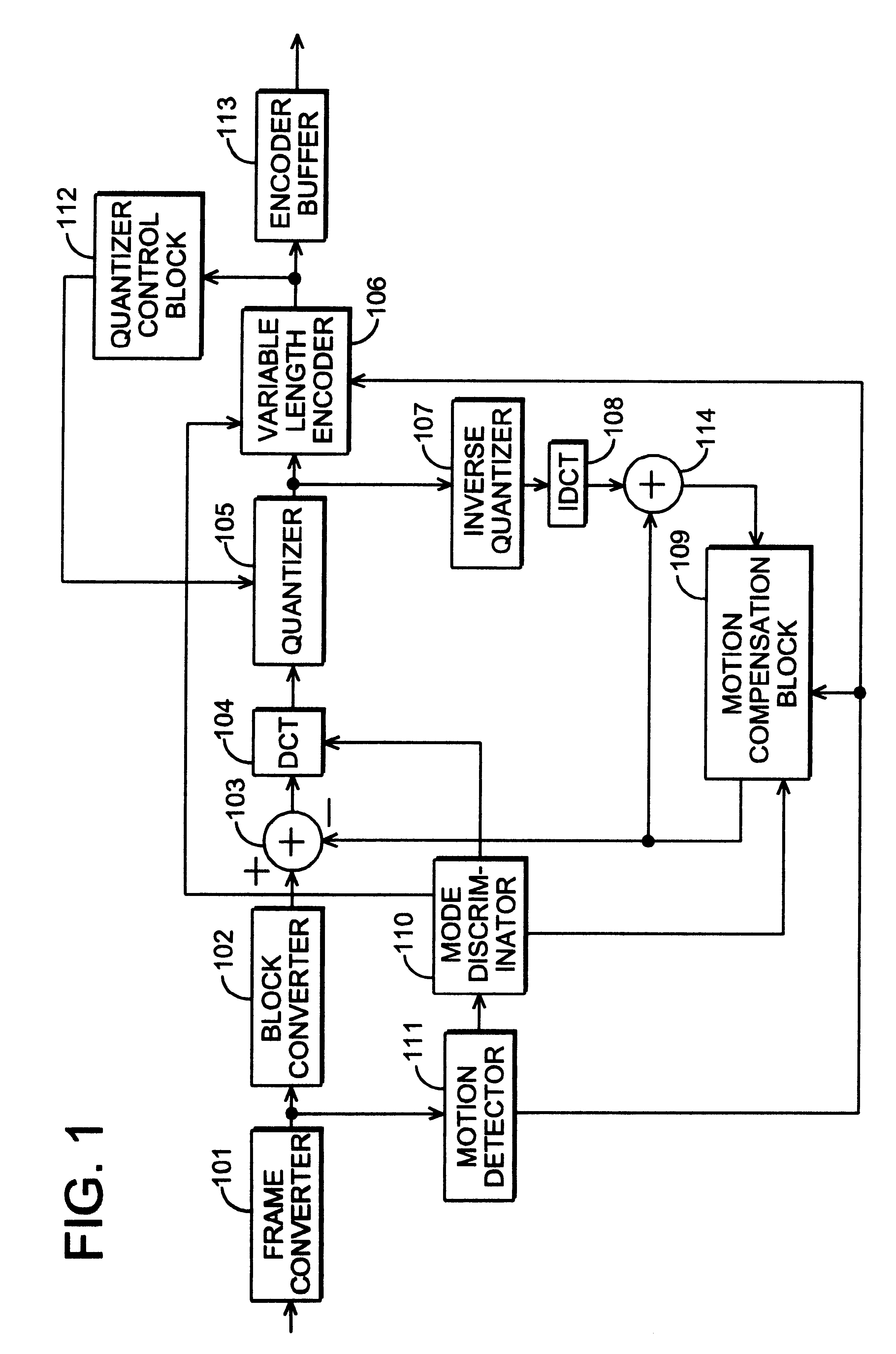
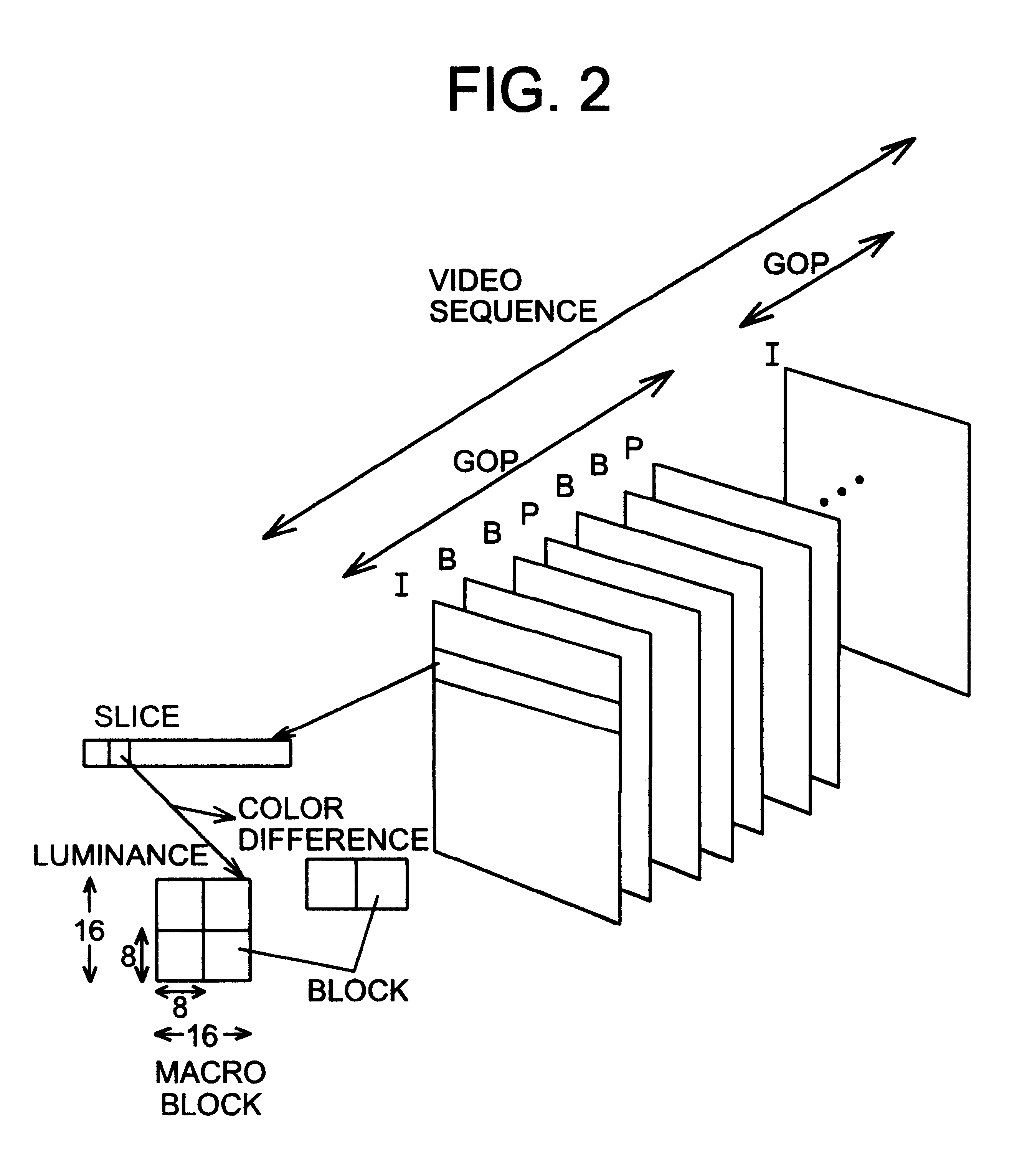
Moving picture encoding apparatus and method
InactiveUS6173012B1Appropriate distributionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer scienceBit rate
An MPEG2 conforming encoding apparatus and method wherein a control unit adjusts a target number of bits depending on the result of dividing by at least 2 the error between a target number of bits corresponding to the target bit rate and the number of generated bits required for encoding an immediately preceding image segment group, and controls a quantizing parameter for encoding the image segment group in accordance with the adjusted target number of bits.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
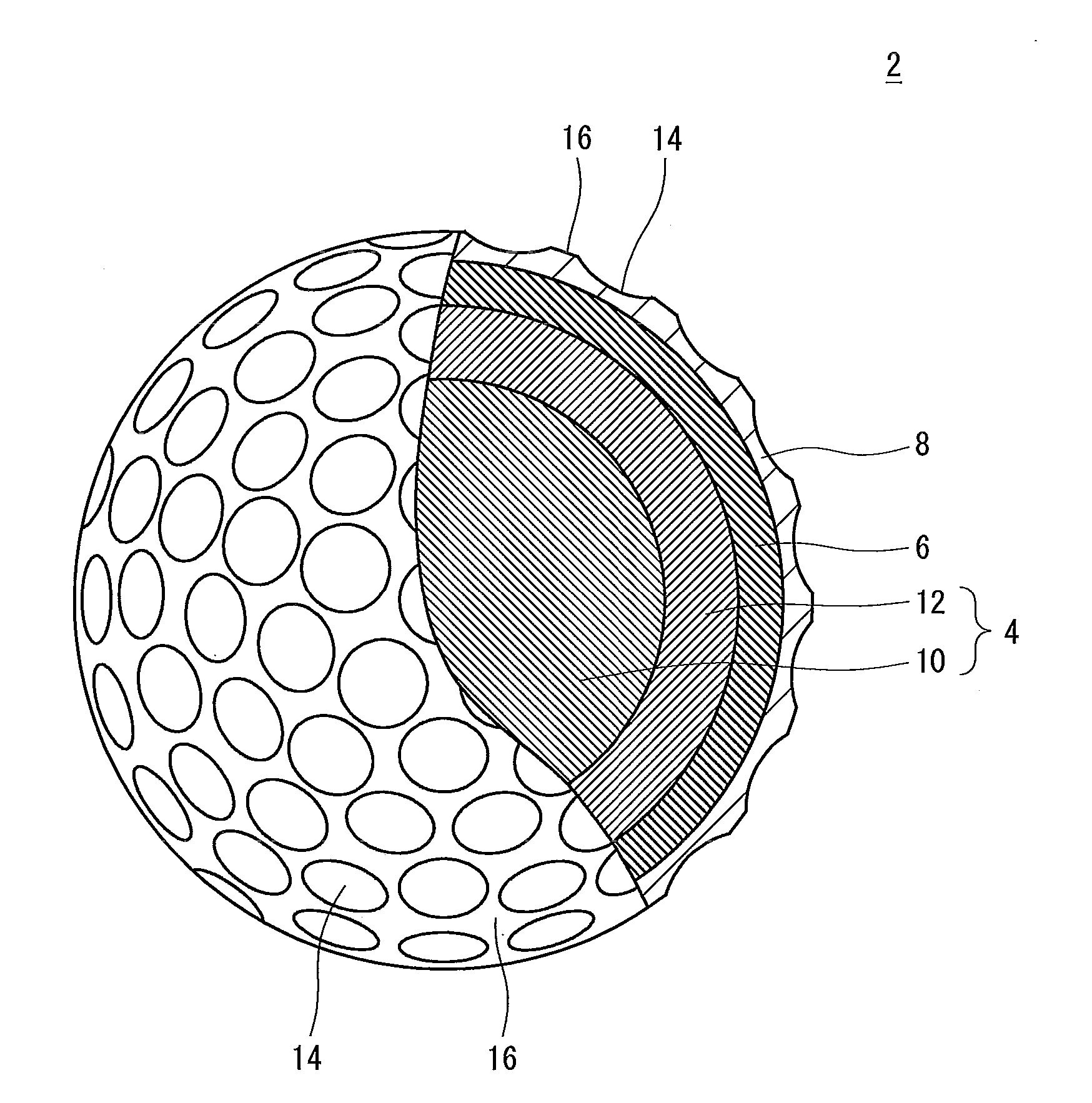
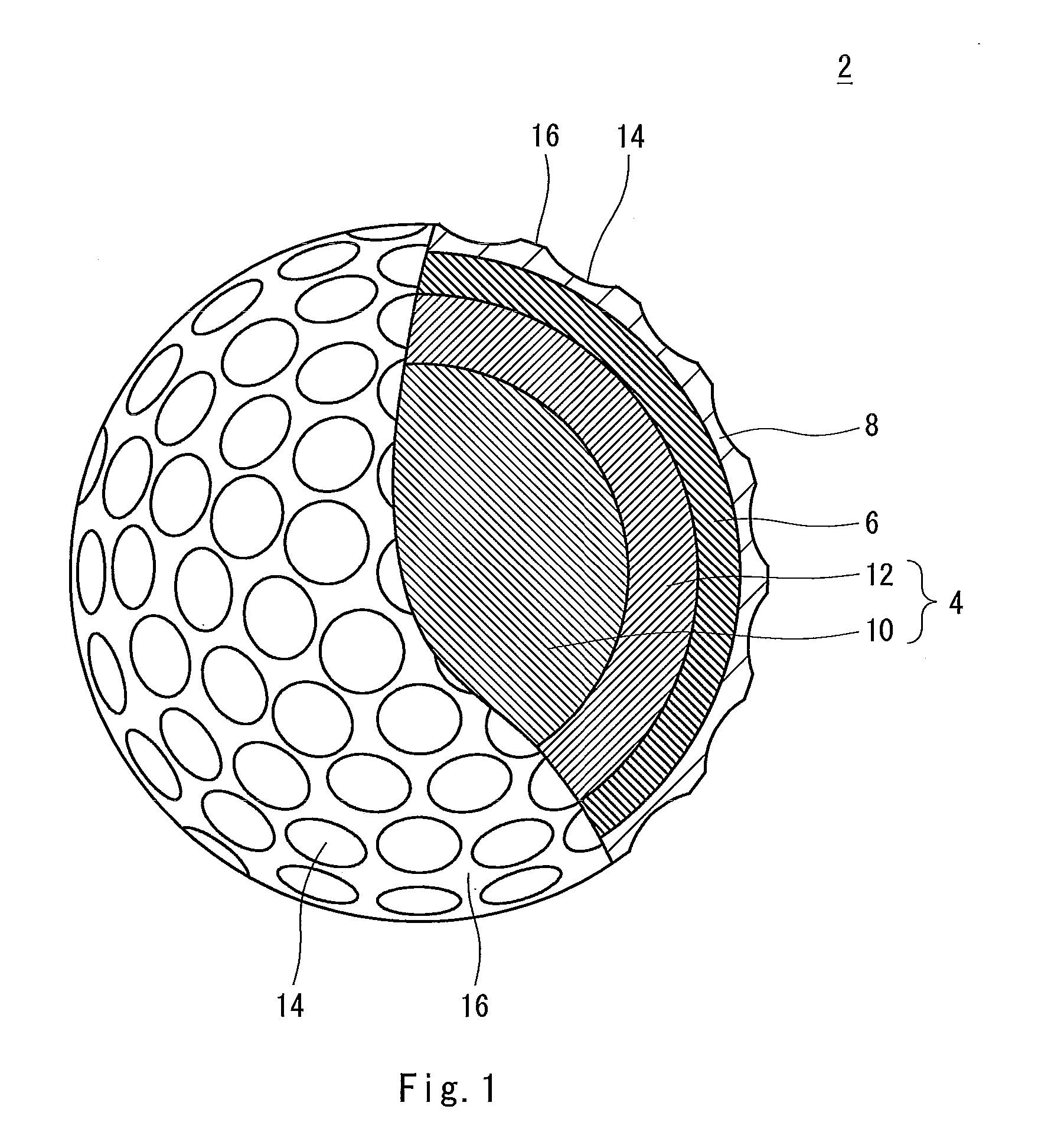
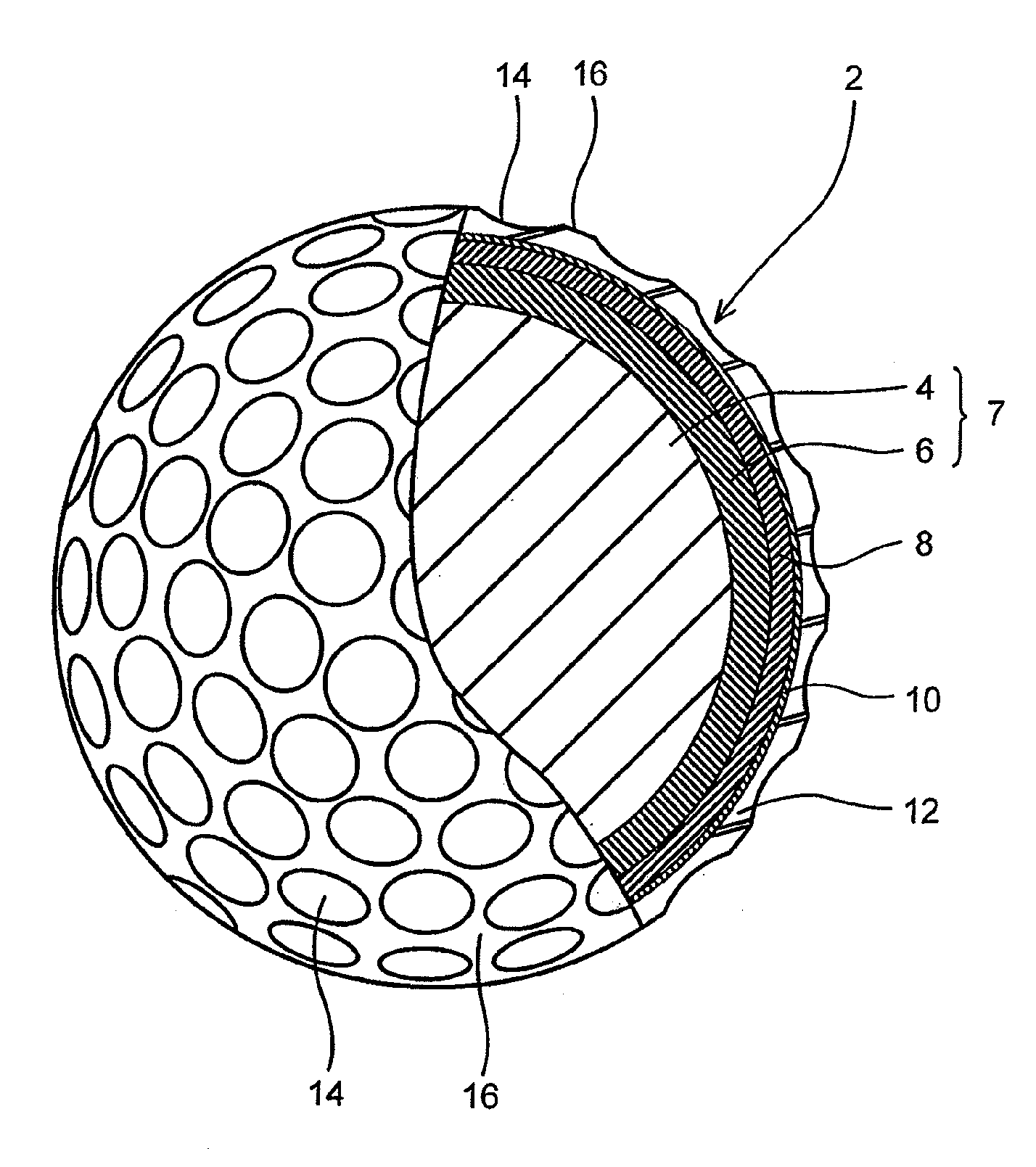
Golf ball
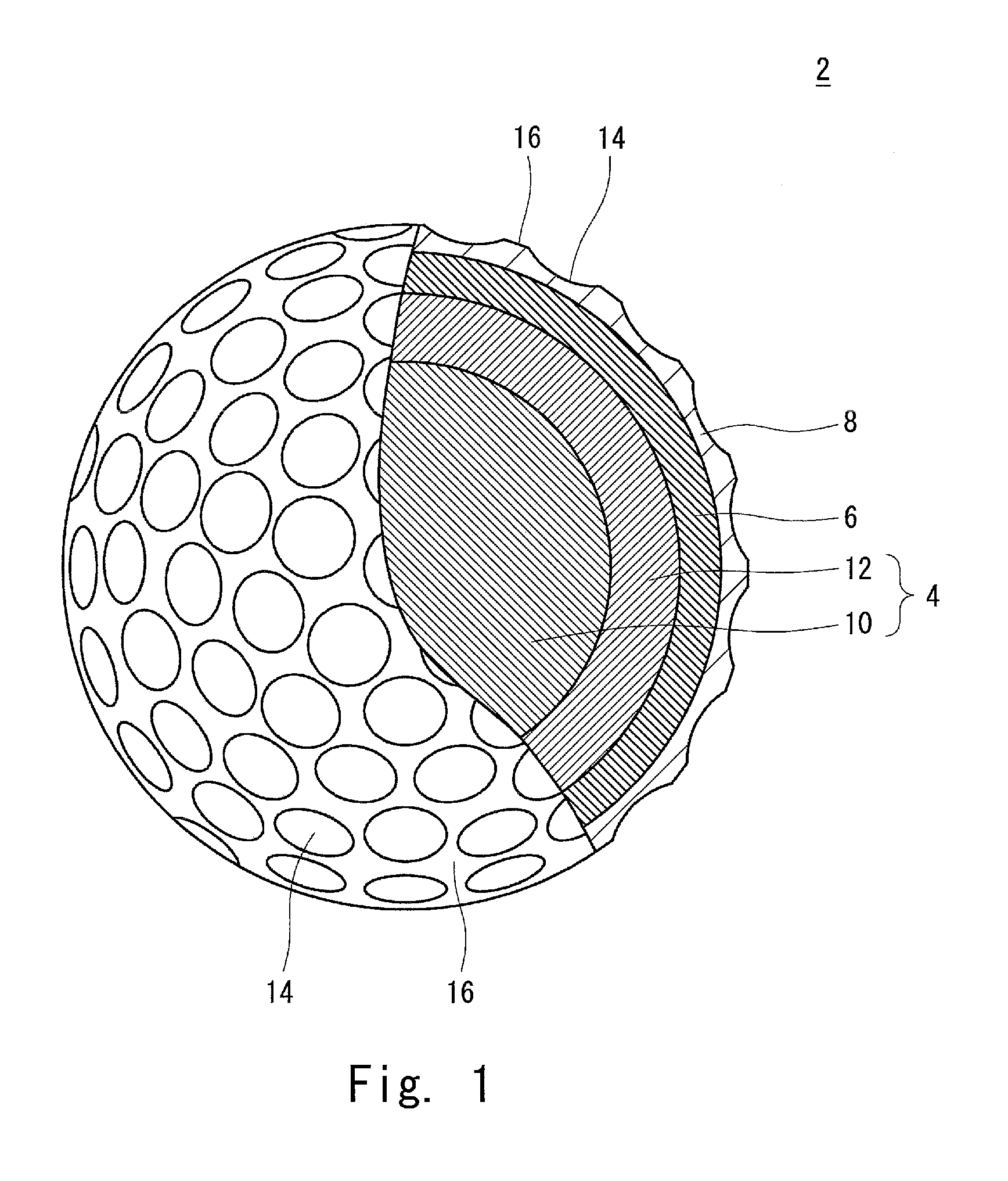
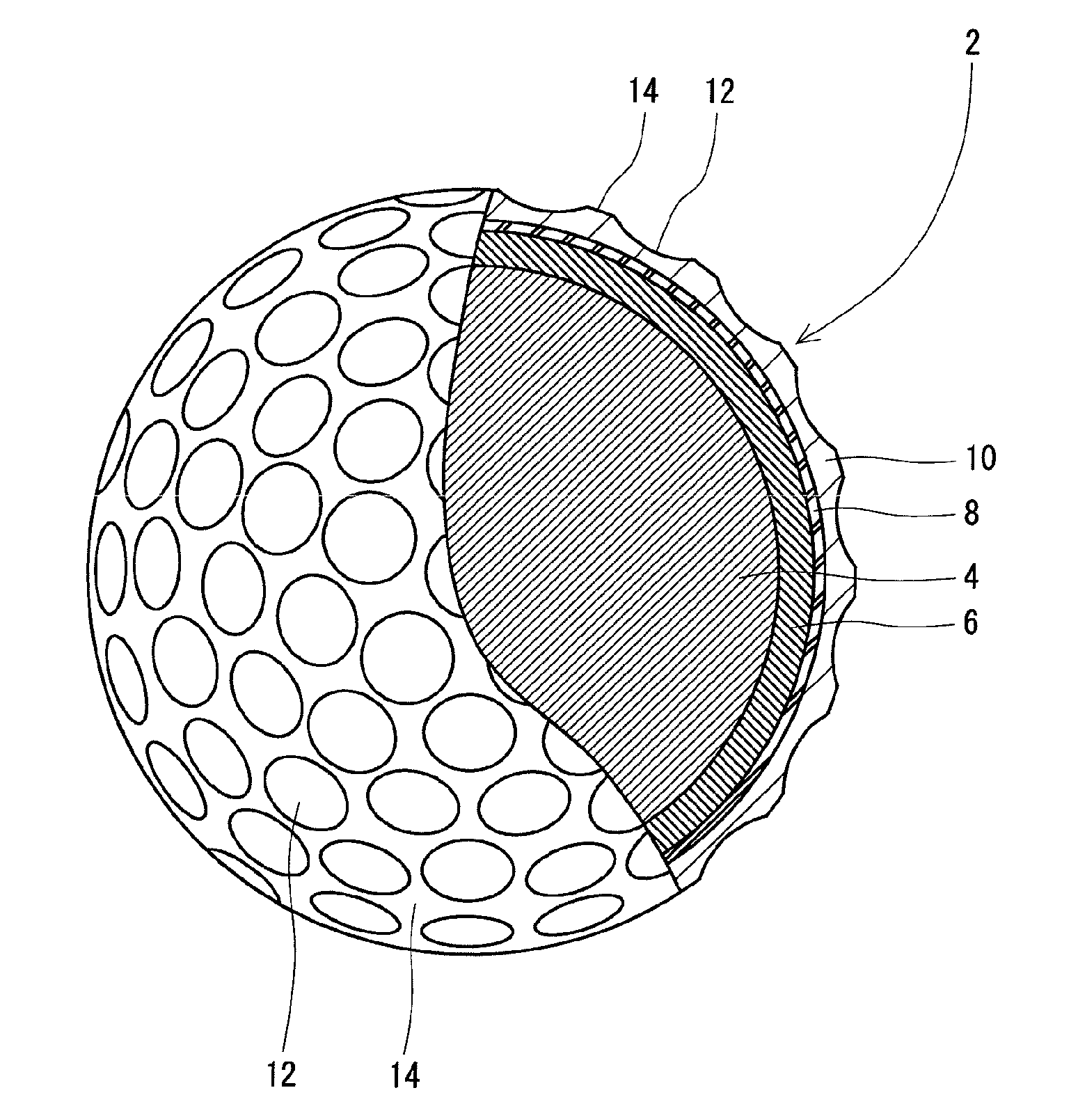
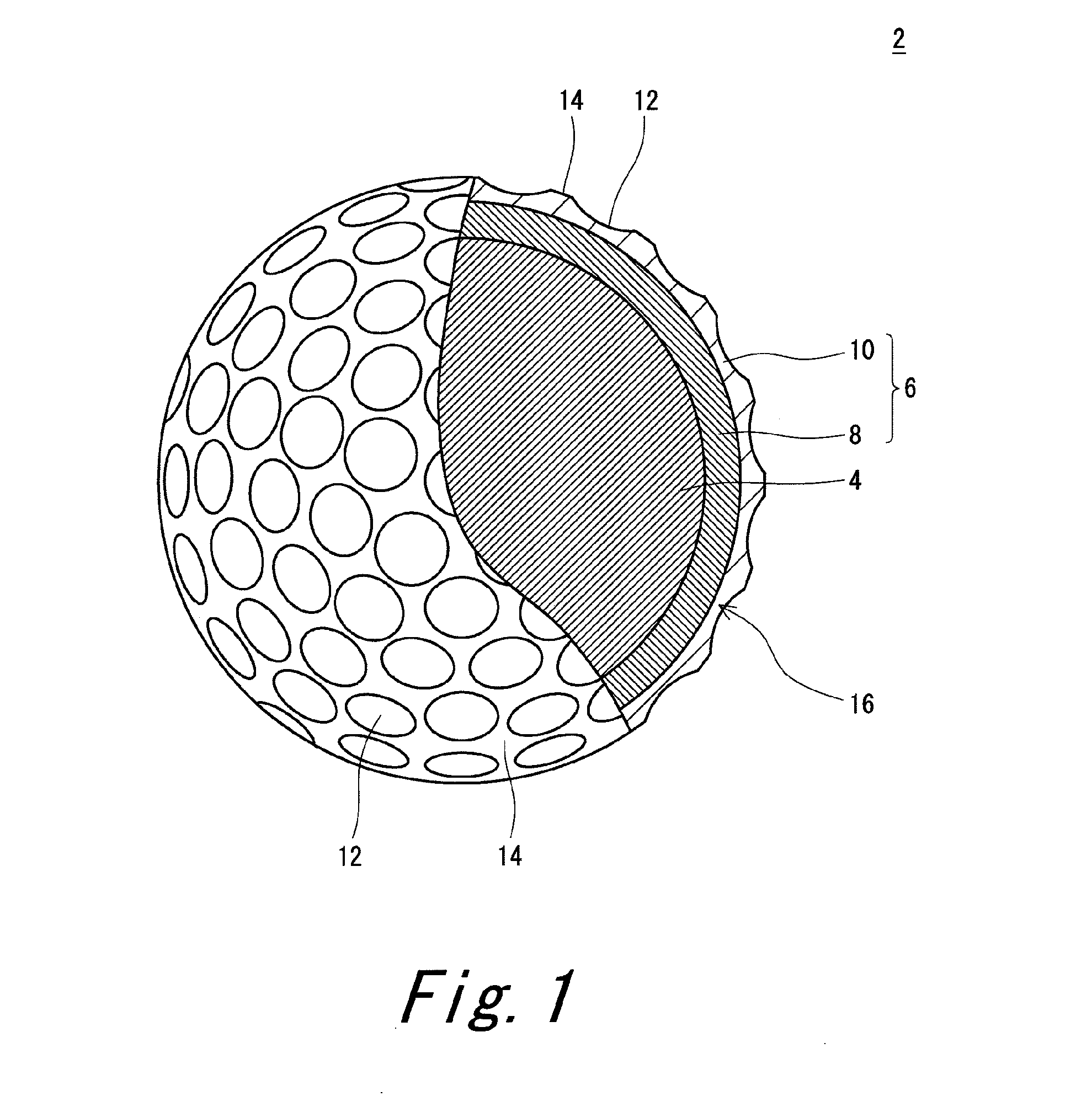
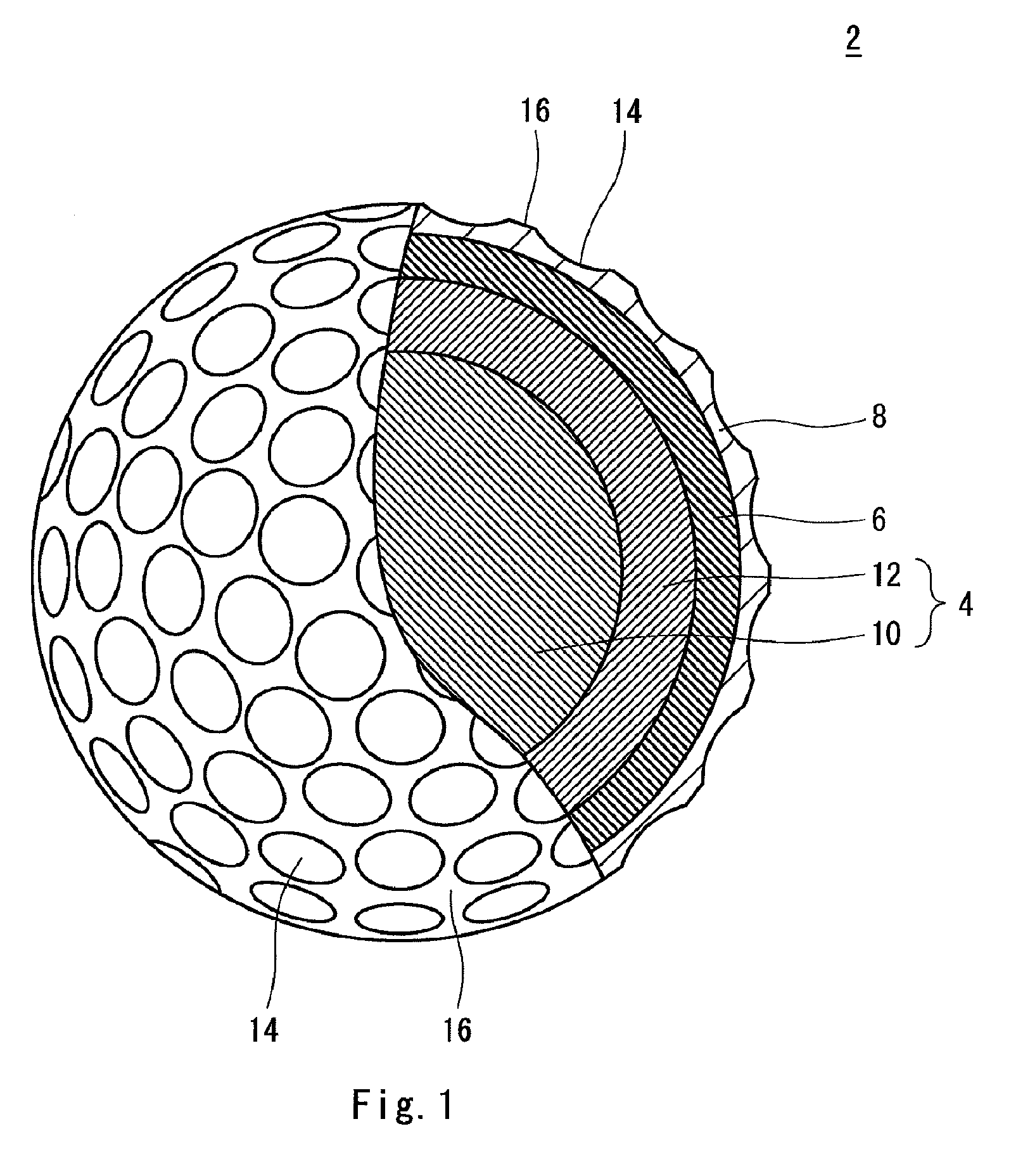
InactiveUS20110159998A1Improve control effectLess energy lossGolf ballsSolid ballsEngineeringGolf Ball
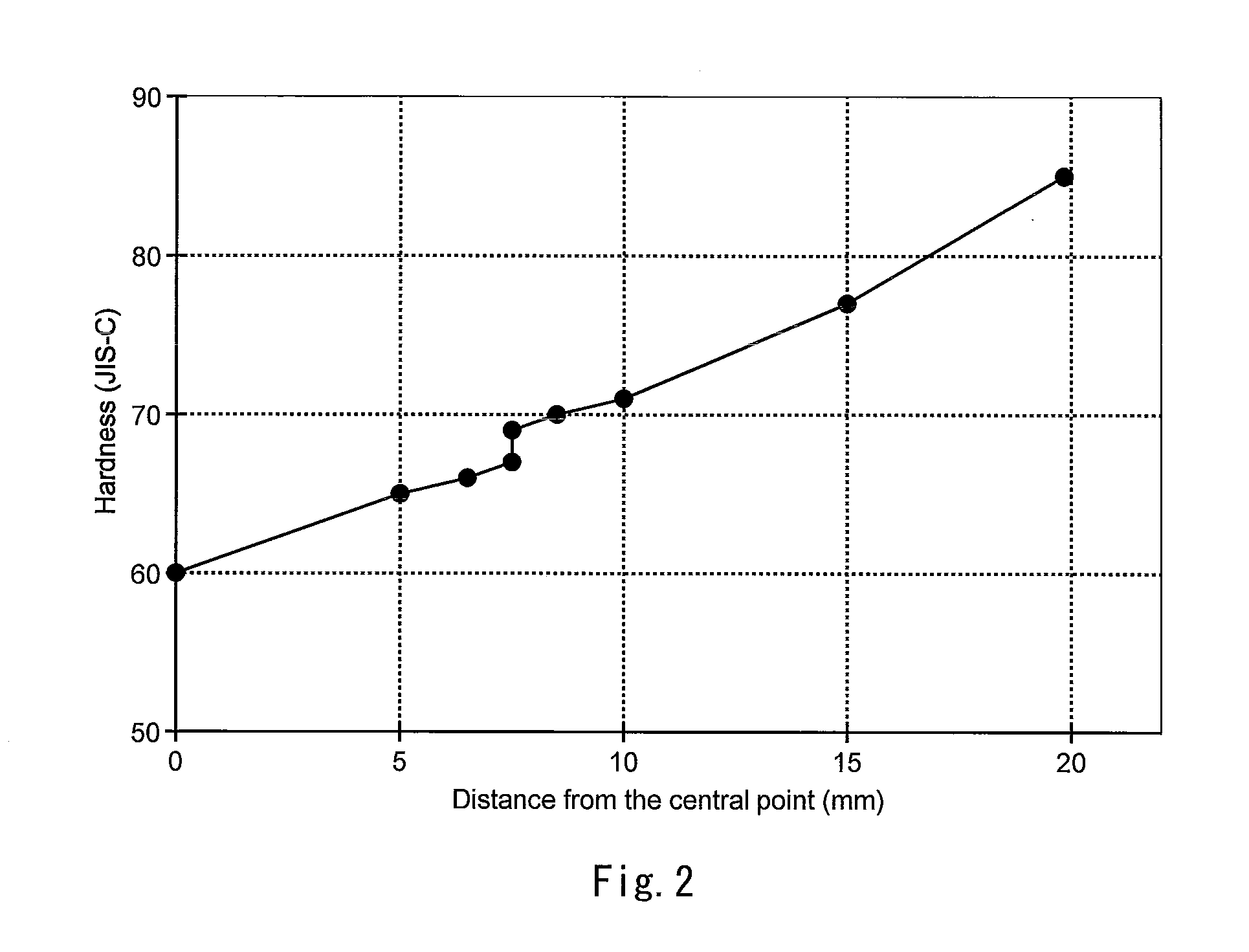
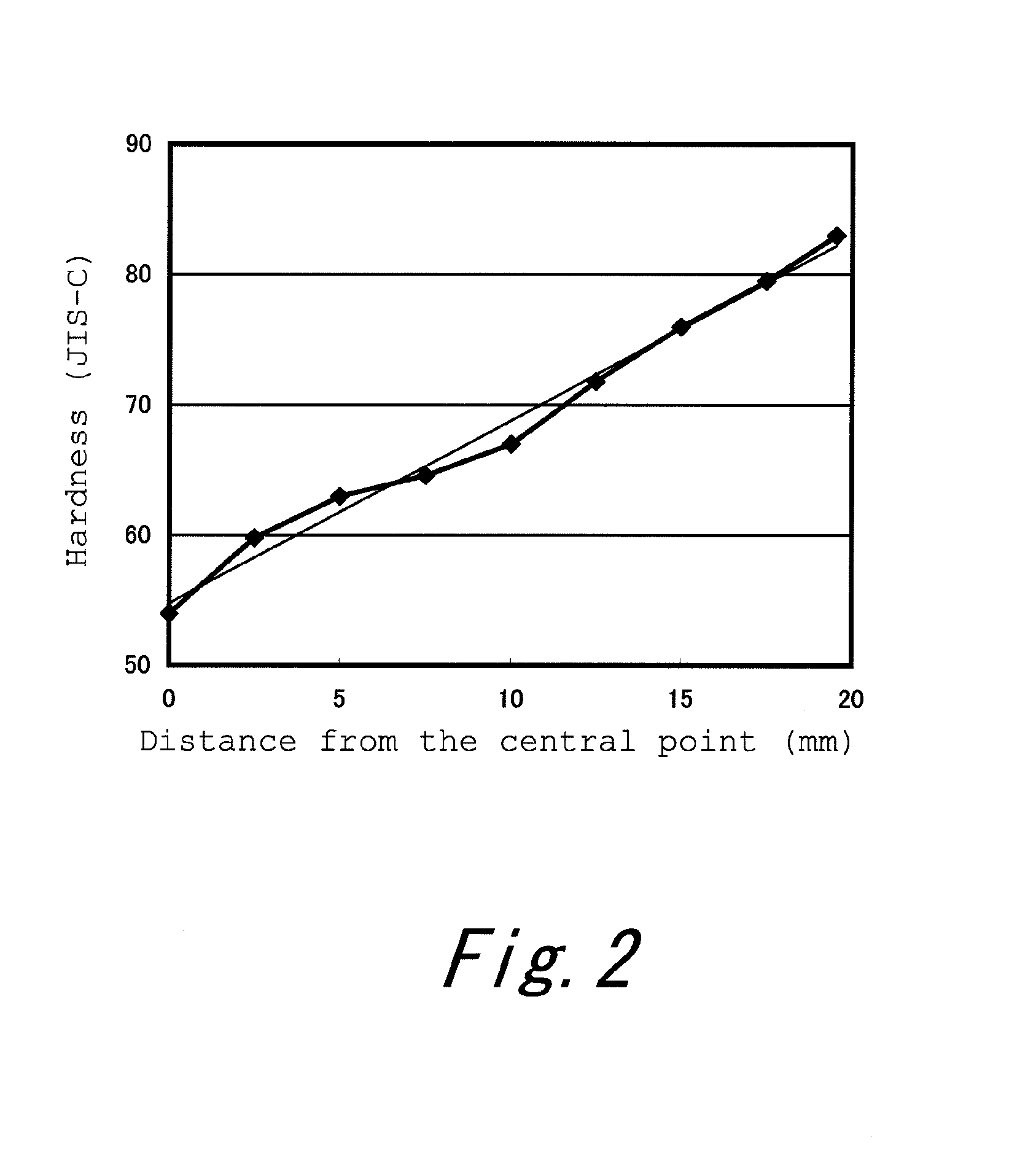
A golf ball 2 has a spherical core 4, a mid layer 6 situated on the external side of the core 4, and a cover 8 situated on the external side of the mid layer 6. The core 4 has a spherical center 10 and an envelope layer 12 situated on the external side of the center 10. At all points P included in a zone away from the central point of the core 4 at a distance of 1 mm or greater and 15 mm or less, the following mathematical expression is satisfied.H2−H1≦5In the above mathematical expression, H1 represents the JIS-C hardness at a point P1 that is located inside the point P along the radial direction and away from the point P at a distance of 1 mm, and H2 represents the JIS-C hardness at a point P2 that is located outside the point P along the radial direction and away from the point P at a distance of 1 mm.
Owner:DUNLOP SPORTS CO LTD
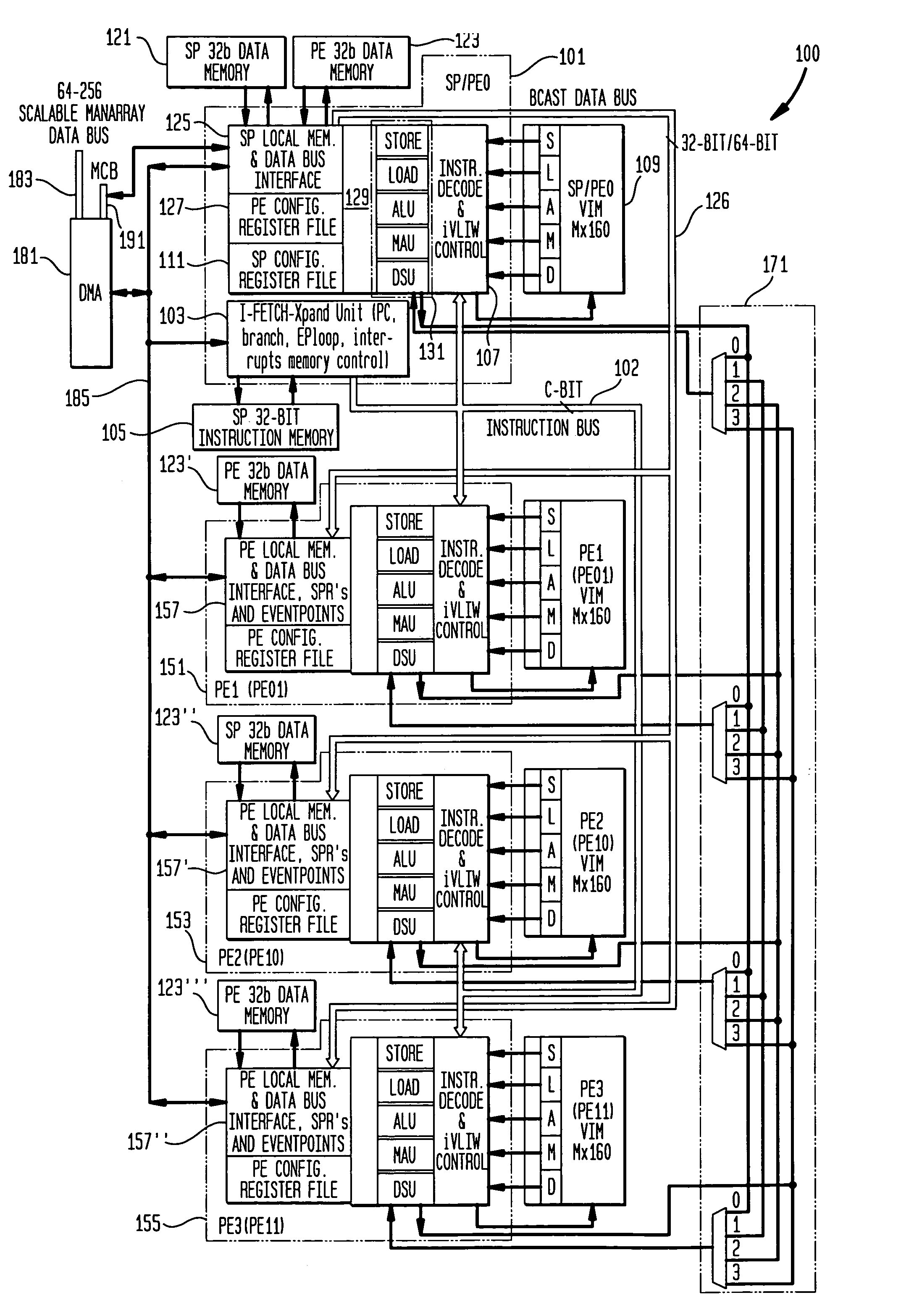
Methods and apparatus for indirect VLIW memory allocation
InactiveUS7181730B2Small sizeAppropriate distributionSoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsInstruction memoryMulti processor
Techniques and a set of heuristics are described to perform allocation of the special instruction memory where indirect very long instruction words (VLIW's) are stored for the ManArray family of multiprocessor digital signal processors (DSP). This approach substantially reduces the cost of pre-initializing the contents of VLIWs.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
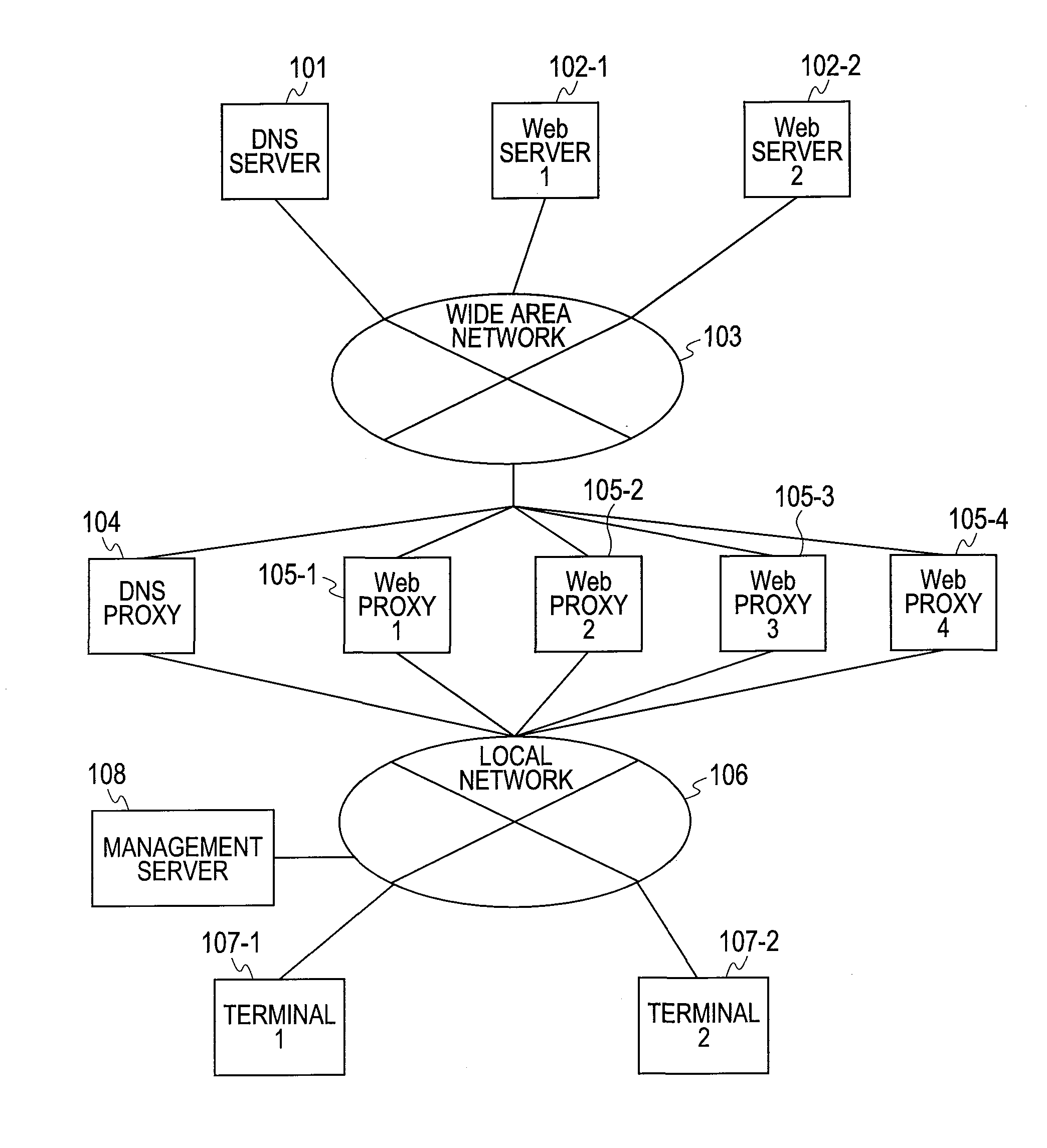
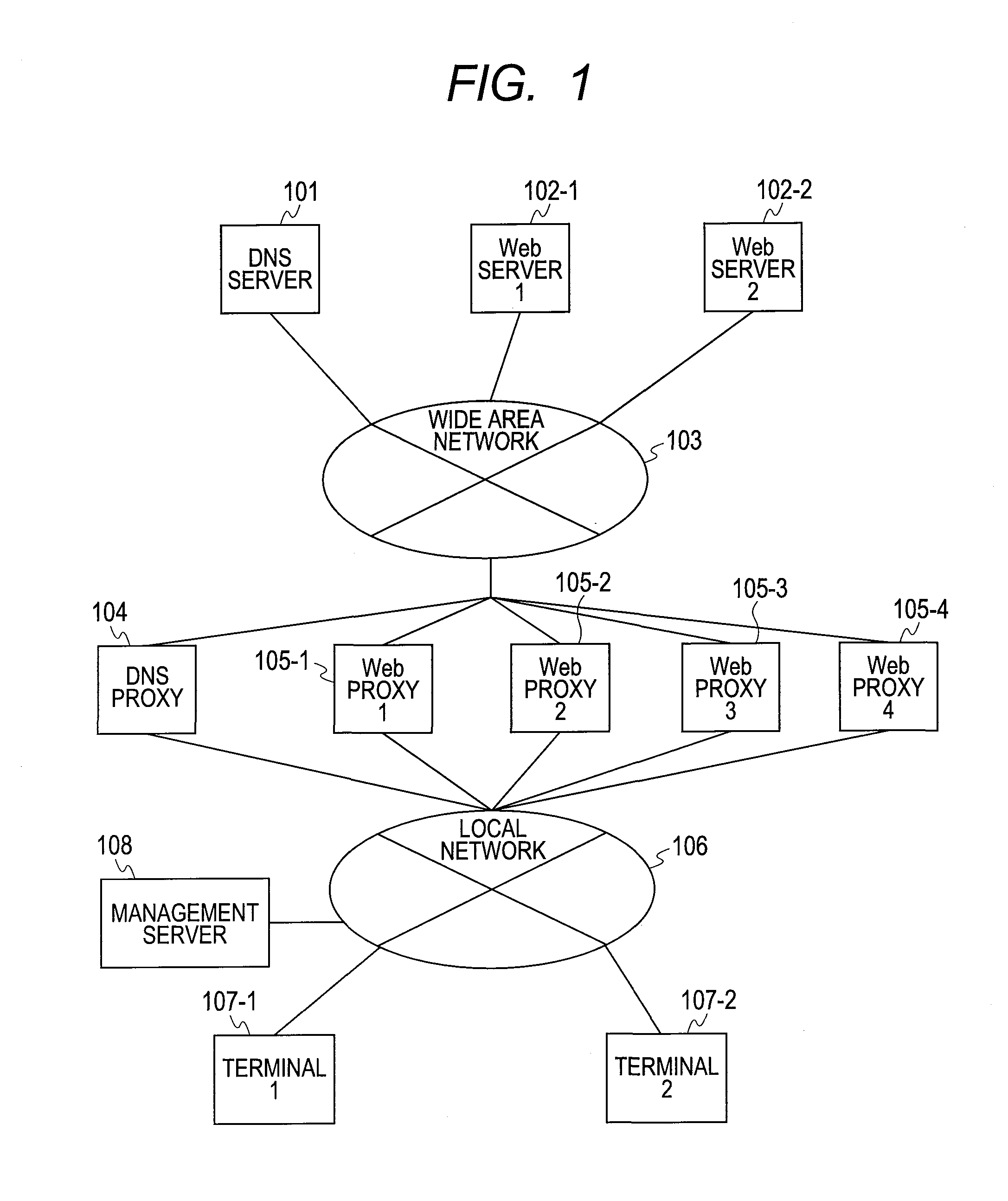
Gateway System and Control Method
InactiveUS20110035437A1Evenly distributedAppropriate distributionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionIp addressUniform resource locator
A gateway system for distributing requests from multiple terminals to multiple first servers includes a second server device and a name resolution device wherein: an address generating function for generating an IP address from a character string is distributed to the name resolution device, and multiple specified IP addresses are registered in the second server devices; when the name resolution device receives a first request for resolving a name, the name resolution device extracts the access destination URL from the first request, generates an IP address from the character string of the host name of the extracted URL by utilizing the address generating function, and sends the generated IP address to the terminal; and when the terminal sends a second request setting the access destination of the URL for the first server device, to the second server device where the IP address is registered, the second server device transfers that transmitted second request to the first server device based on the URL of the access destination.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
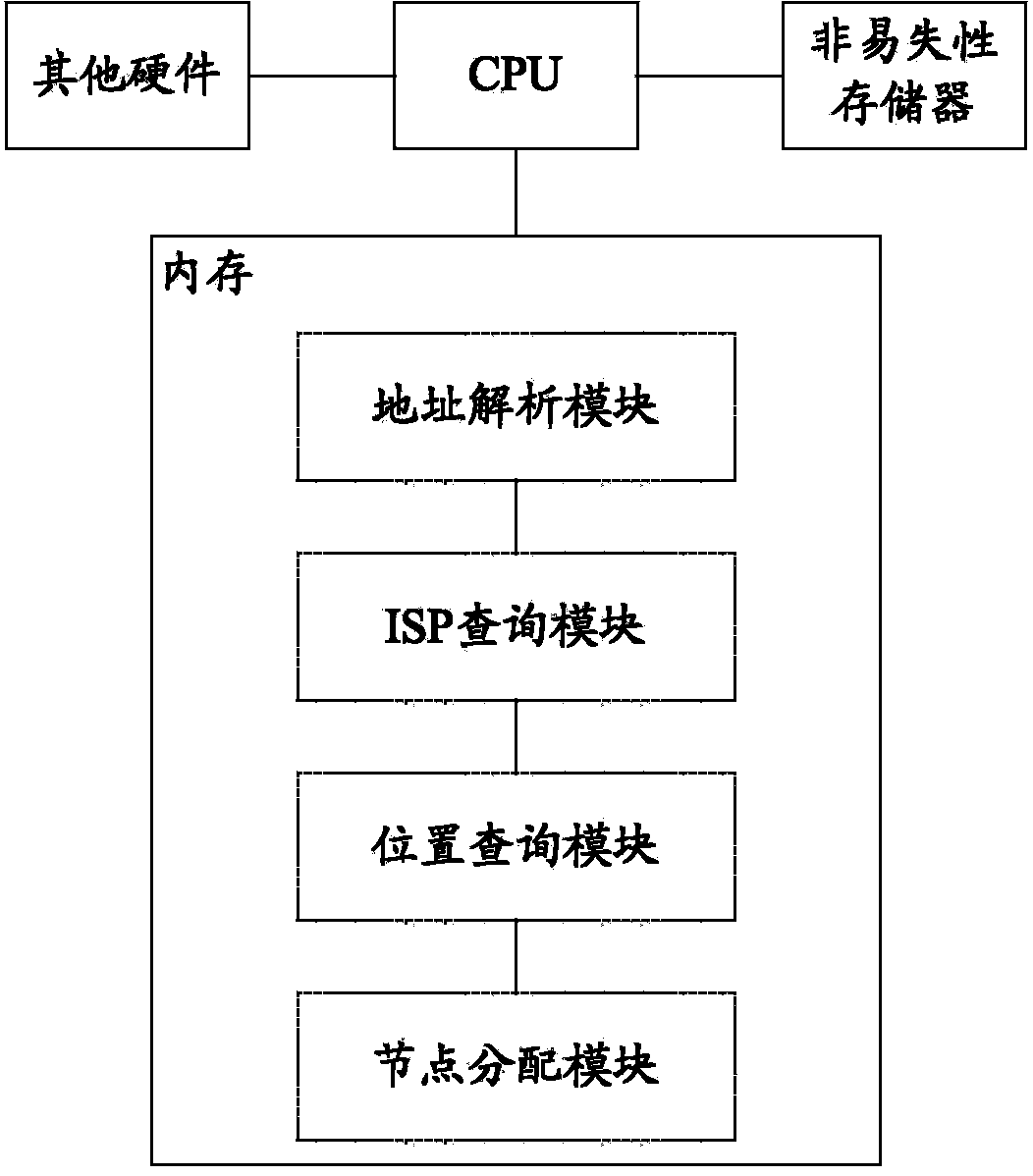
CDN node distribution server and system
The invention provides a CDN node distribution server and system. The CDN node distribution server comprises a request analyzing module, an ISP inquiry module, a positioning inquiry module and a node distribution module, wherein the request analyzing module is used for receiving service requests of a client side and analyzing source IP addresses from the service requests, the ISP inquiry module is used for inquiring ISPs where the source IP addresses belong, the positioning inquiry module is used for inquiring regions where the source IP addresses belong, and the node distribution module is used for selecting CDN nodes matched with the client side according to the required ISPs where the source IP addresses belong and the regions where the source IP addresses belong and according to the preset rule, and issuing the IP addresses of the selected CDN nodes to the client side. Thus, compared with the prior art, by means of the CDN node distribution server and system, more suitable CDN nodes can be distributed for users.
Owner:北京花房科技有限公司
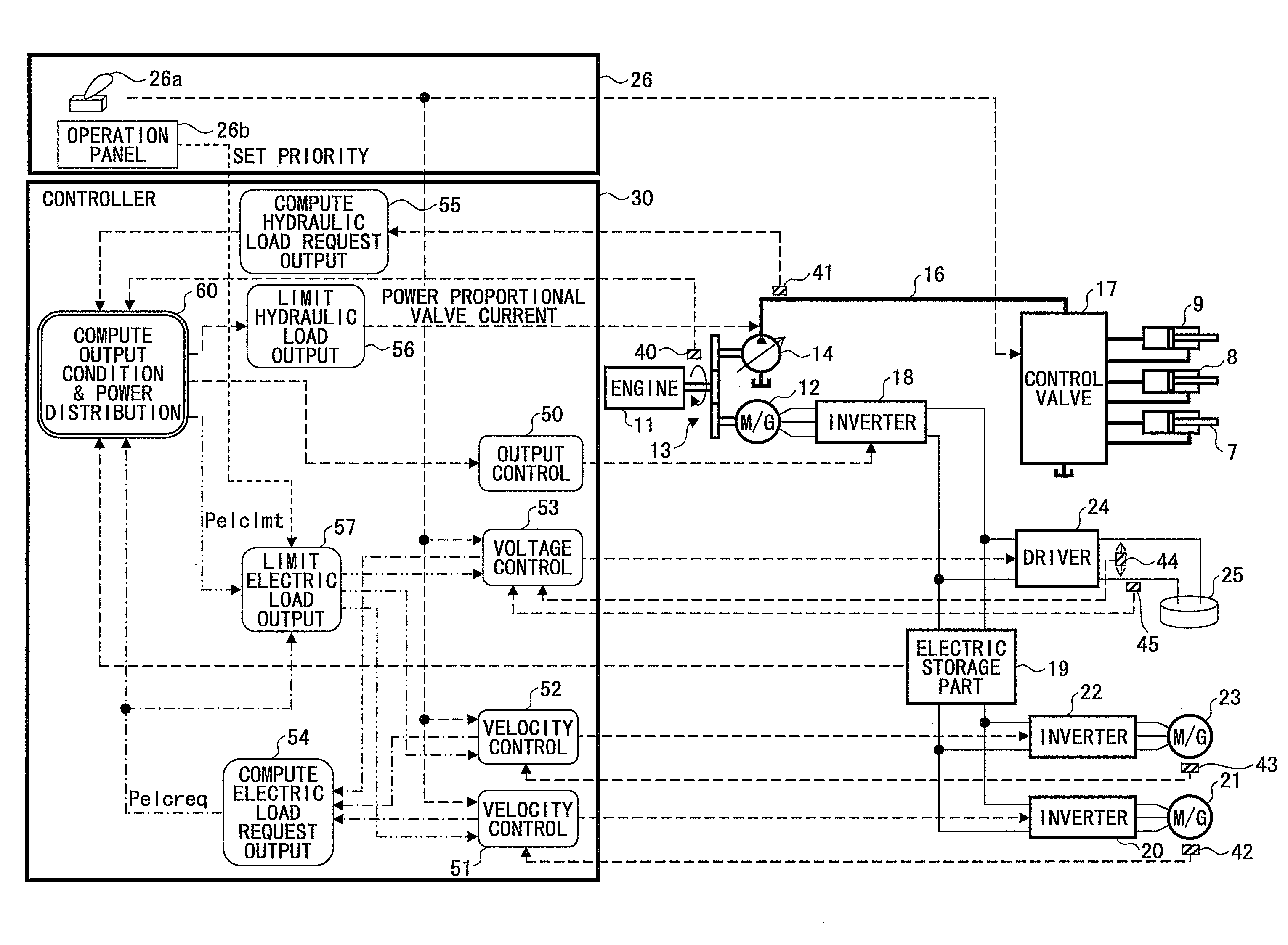
Hybrid-type working machine
InactiveUS20100268407A1Appropriate distributionDc network circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsHybrid typeElectricity
A hybrid-type working machine includes a plurality of electric loads and an electric storage part supplying an electric power to a motor generator and the electric loads. A priority setting part sets a priority to each electric load. A supply power computing part computes an available electric power, which can be supplied from the motor generator and the electric storage part to the electric loads. A total power computing part computes a total electric power amount by summing electric power amounts requested by the electric loads. A power distributing part compares the available electric power with the total electric power amount, and, when the available electric power is larger than the total electric power amount, determines a distribution ratio of electric power amounts to be supplied to the respective electric loads based on the priority to limit the electric power amounts supplied to the electric loads.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
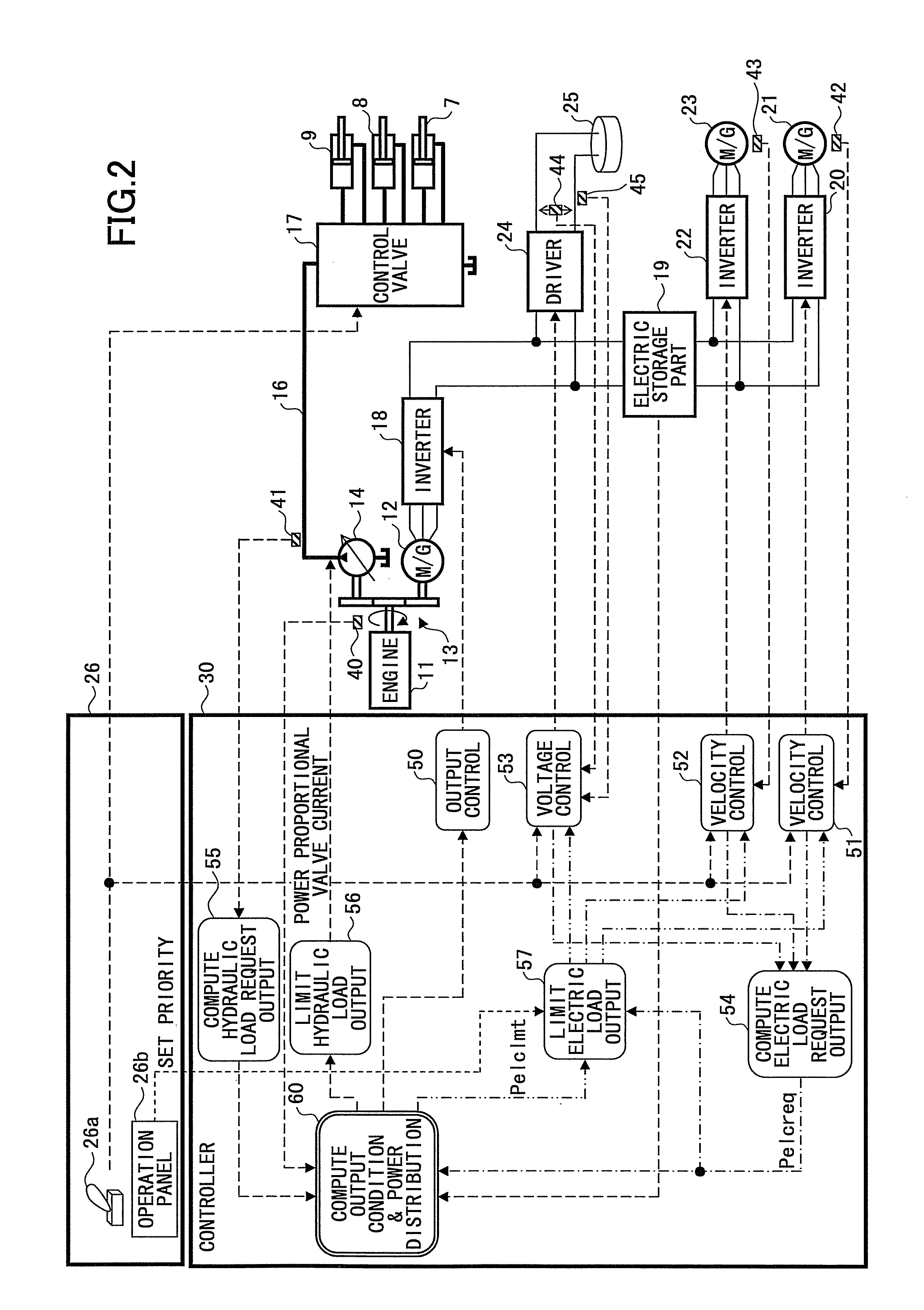
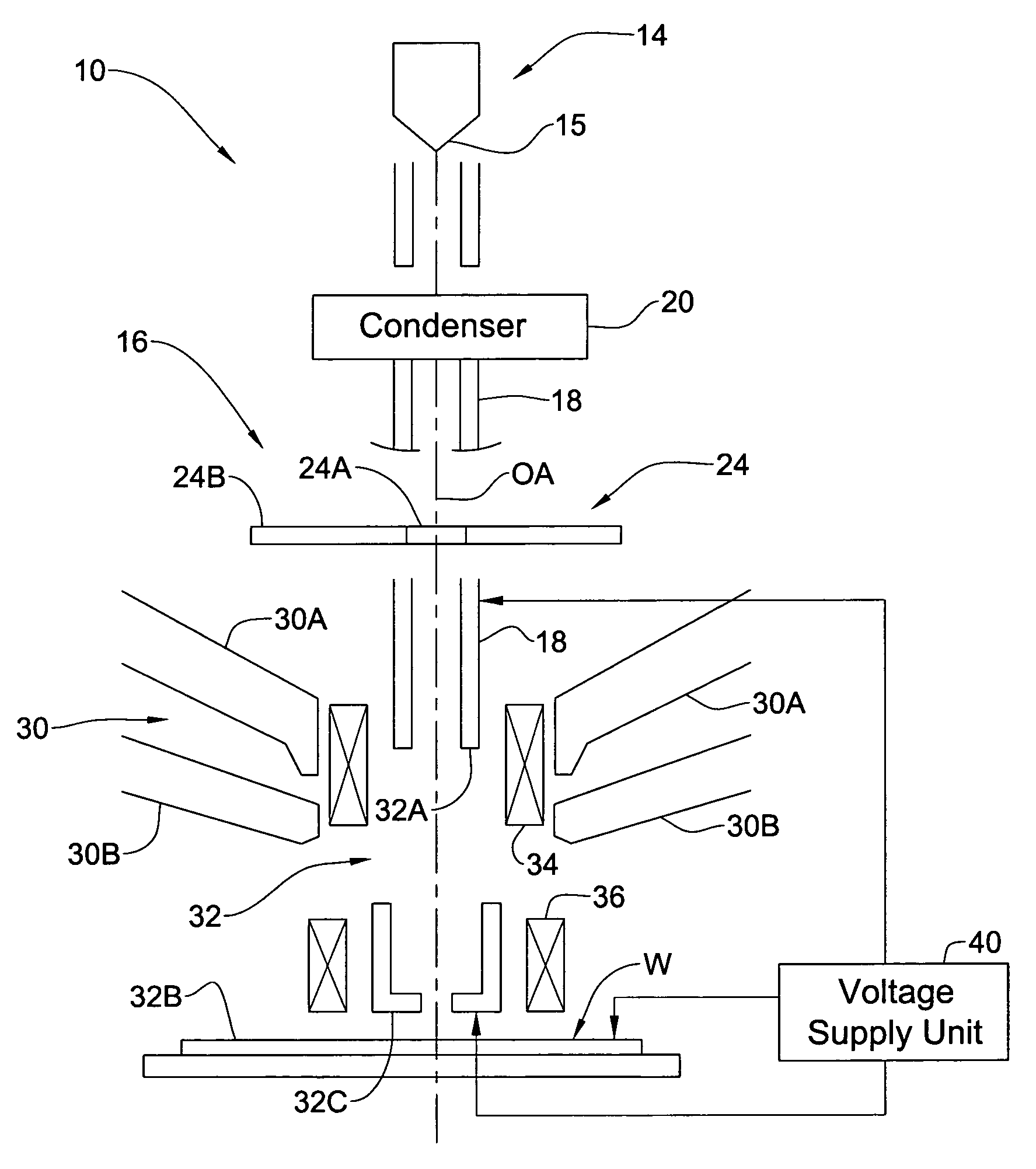
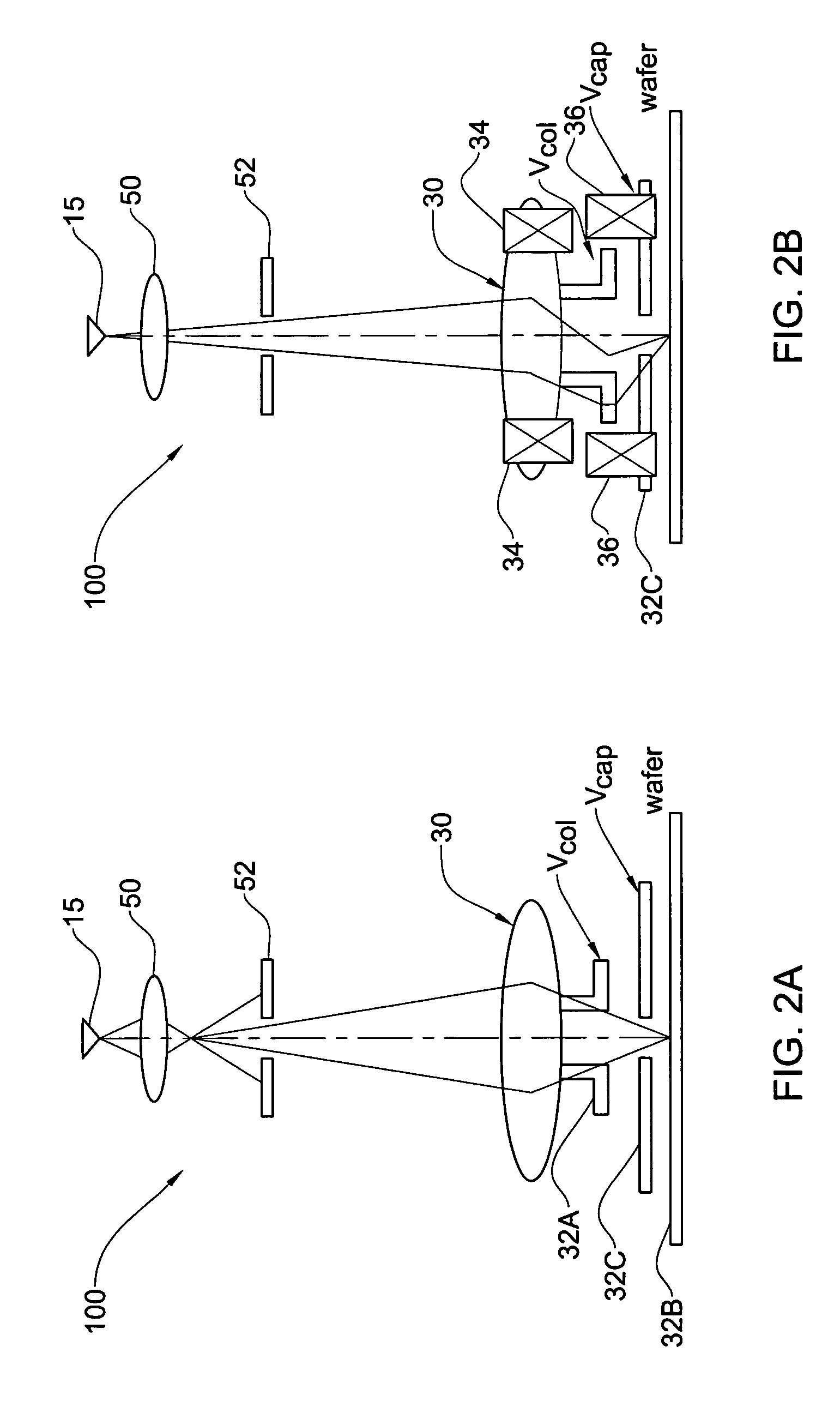
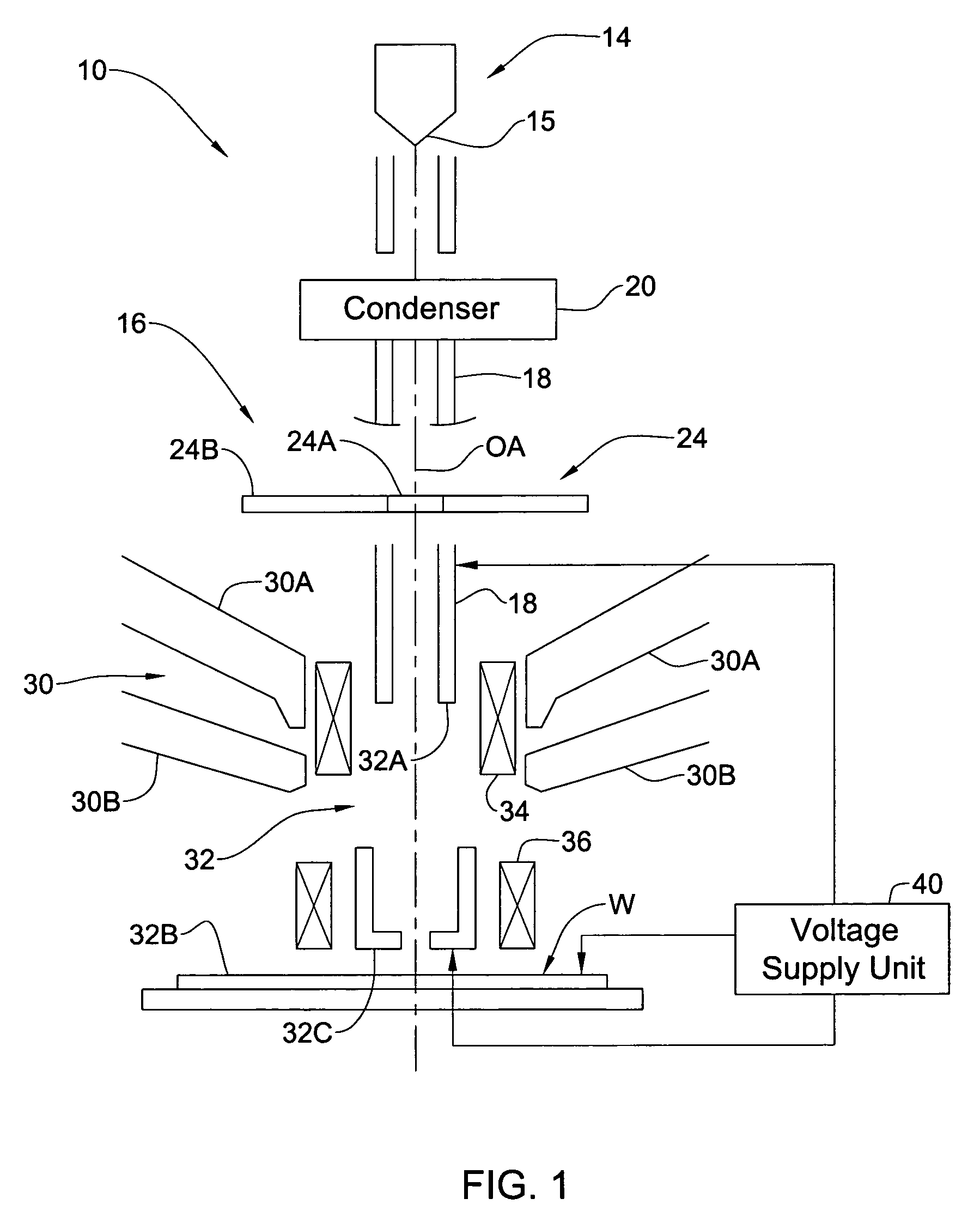
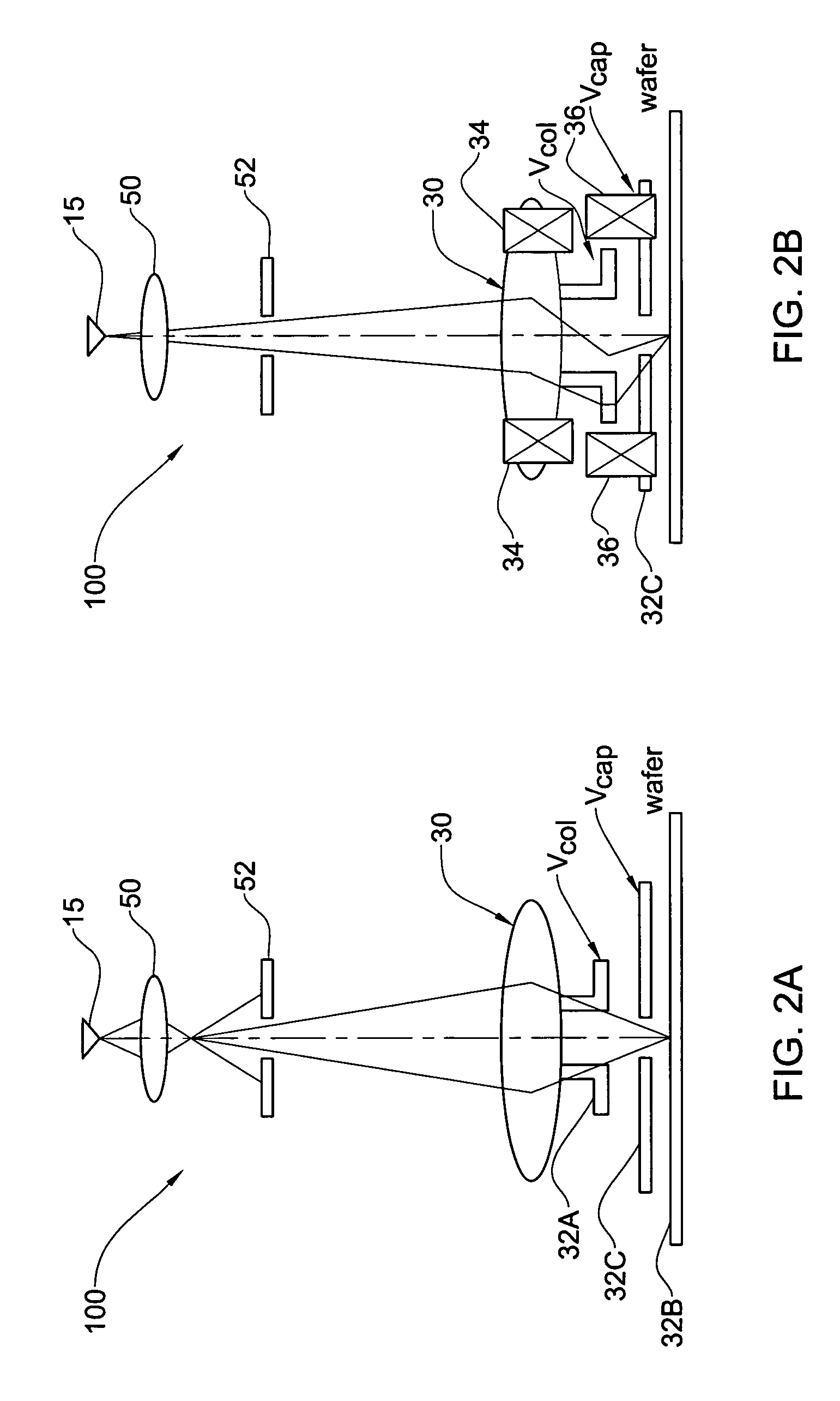
Charged particle beam column and method of its operation
ActiveUS7067807B2Improve imaging resolutionReduce stepsThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAcceleration voltageCharged particle beam
A method and system are presented for controlling inspection of a sample with a charged particle beam. A certain given voltage is supplied to an anode of the column to provide a required accelerating voltage for a charged particle beam. A certain negative voltage is supplied to the sample selected so as to provide a desirably high effective voltage of the column at said given voltage of the anode. A certain voltage is supplied an electrode of a lens arrangement located closer to the sample, this voltage being selected to satisfy one of the following conditions: the electrode voltage is either equal to or slightly lower than that of the sample; and the electrode voltage is significantly higher than that of the sample.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Charged particle beam column and method of its operation
ActiveUS20060049348A1Increase effective voltageImprove imaging resolutionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAcceleration voltageCharged particle beam
A method and system are presented for controlling inspection of a sample with a charged particle beam. A certain given voltage is supplied to an anode of the column to provide a required accelerating voltage for a charged particle beam. A certain negative voltage is supplied to the sample selected so as to provide a desirably high effective voltage of the column at said given voltage of the anode. A certain voltage is supplied an electrode of a lens arrangement located closer to the sample, this voltage being selected to satisfy one of the following conditions: the electrode voltage is either equal to or slightly lower than that of the sample; and the electrode voltage is significantly higher than that of the sample.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Golf ball
An object of the present invention is to provide a golf ball having an improved controllability and shot feeling while maintaining a flight distance on driver shots. The present invention provides a golf ball having a core, an intermediate layer disposed around the core, and a cover disposed around the intermediate layer, wherein the core has a center and an envelope layer disposed around the center, and has a specific hardness distribution, and the intermediate layer is formed from an intermediate layer composition comprising, as a resin component, (A) a modified polyester elastomer and (B) a binary ionomer resin, and having a flexural modulus ranging from 150 MPa to 450 MPa, a maximum loss factor (tan δ) between −20° C. and 0° C. of 0.08 or less, a repulsive modulus of 55% or more, and a slab hardness ranging from 60 to 90 in JIS-hardness.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Distributed medicine supplying device and medicine packaging device
ActiveUS7861495B2Appropriate distributionImprove work efficiencyDigital data processing detailsDrug and medicationsPrescription dataBiomedical engineering
There is provided a distributed medicine supplying device, which allows medicines to be distributed at a time relative to a plurality of prescription data and to be distributed appropriately in response to various types of requests. The distributed medicine supplying device includes: a receiving unit 7 for receiving prescription data; a storing unit 8 for storing an assignment condition to medicine to be accommodated in measures 4 of a tray 5; a central processing unit 10 for determining a position of the medicine to be distributed to each of the measures 4 of the tray 5 in accordance with the assignment condition stored in the storing unit 8 based on the prescription data 12 sequentially received by the receiving unit 7; and a displaying unit 9 for displaying the distribution position determined by the central processing unit 10.
Owner:YUYAMA MFG CO LTD
Golf ball
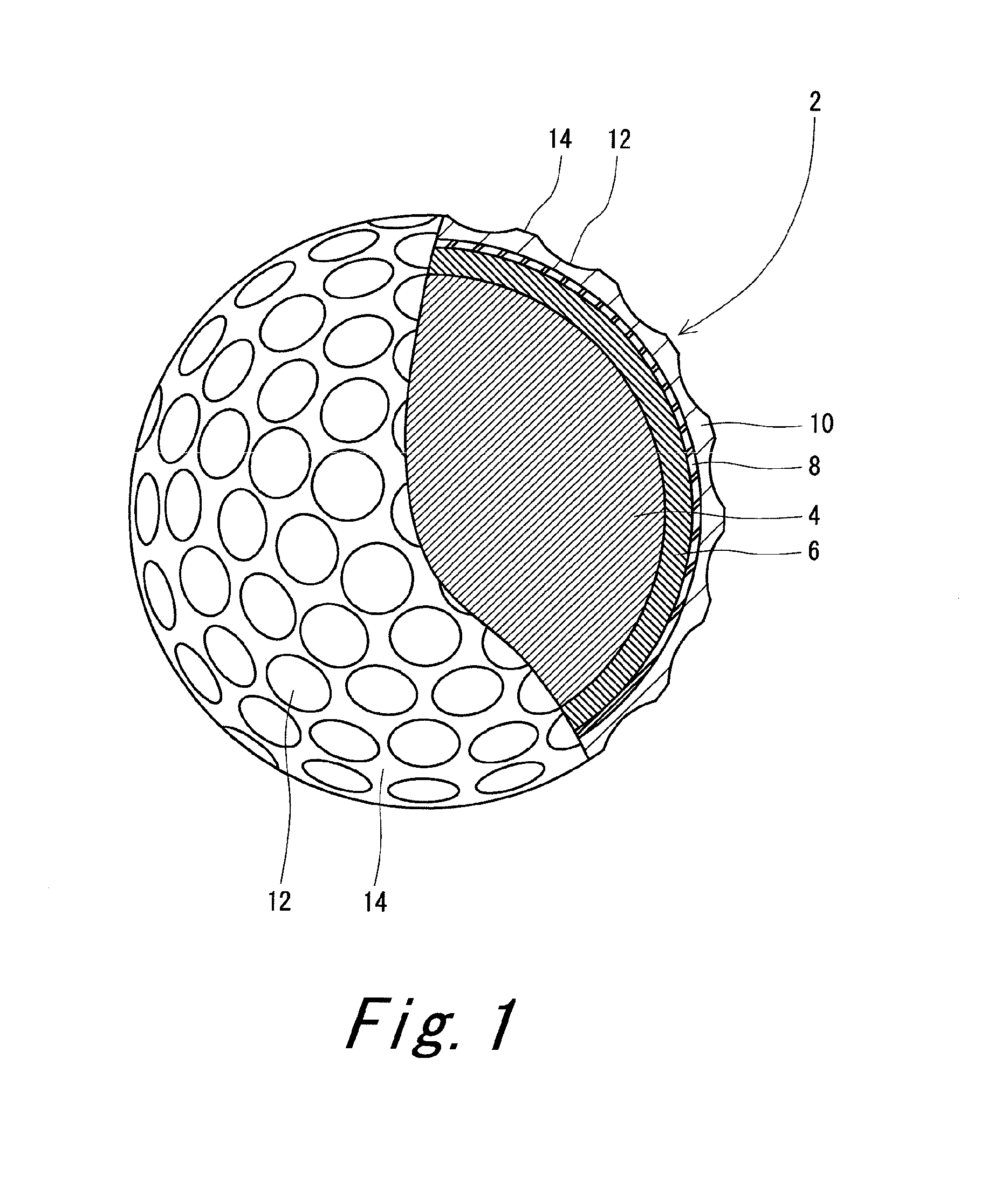
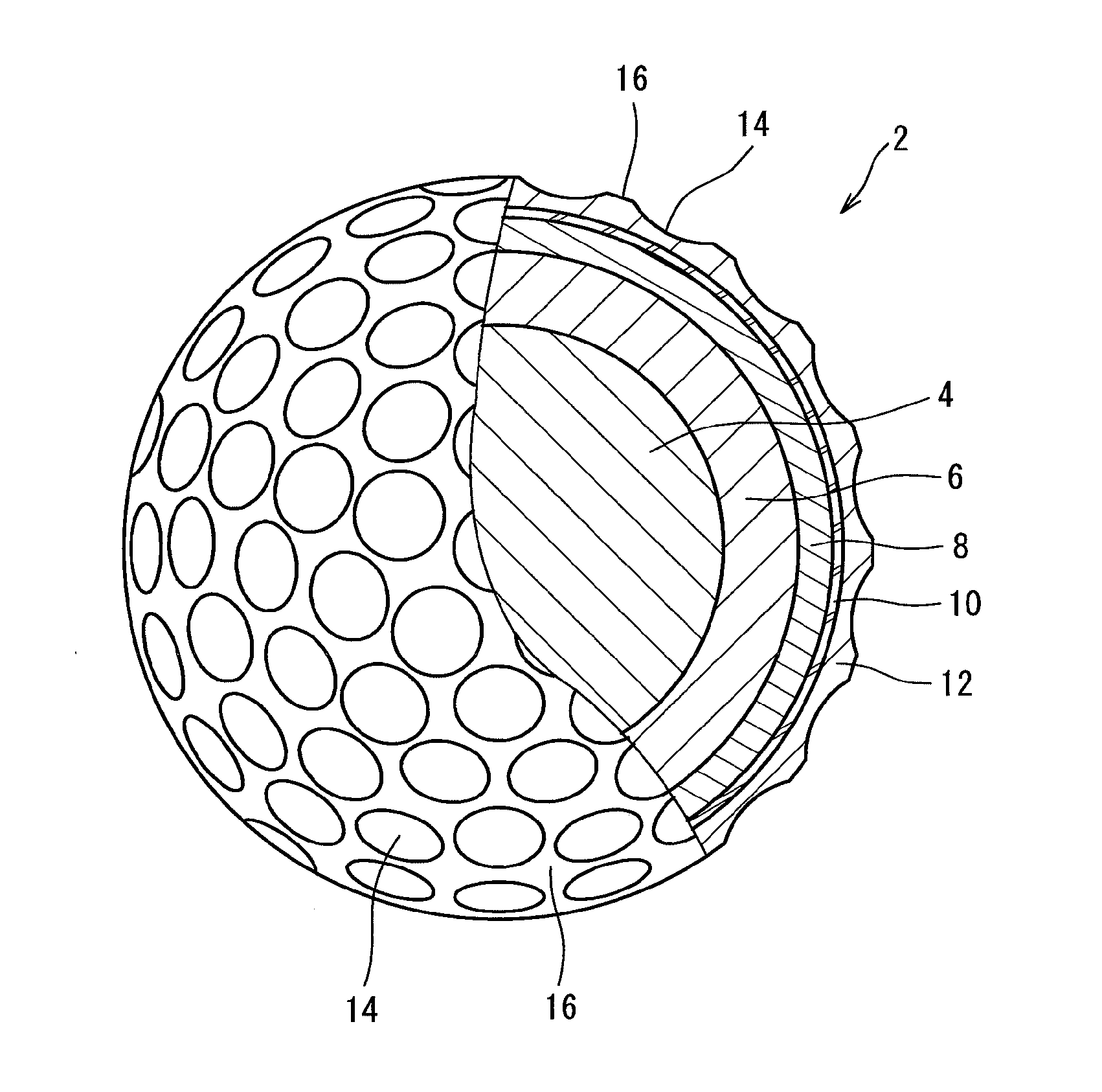
ActiveUS20120088604A1Reduce energy lossImprove controllabilityGolf ballsSolid ballsEngineeringGolf Ball
A golf ball 2 includes a spherical core 4, a mid layer 6 outside the core 4, and a cover 8 outside the mid layer 6. The core 4 includes a spherical center 10 and an envelope layer 12 outside the center 10. At all points P included in a zone that extends over a distance range from equal to or greater than 1 mm to equal to or less than 15 mm from the central point of the core 4, the following mathematical formula is satisfied.−5<H2−H1<5In the mathematical formula, H1 indicates the JIS-C hardness at a point P1 located radially inward of each point P at a distance of 1 mm from the point P, and H2 indicates the JIS-C hardness at a point P2 located radially outward of each point P at a distance of 1 mm from the point P.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Rotational method and apparatus for welding beam-mount structure to the side(s) of a column
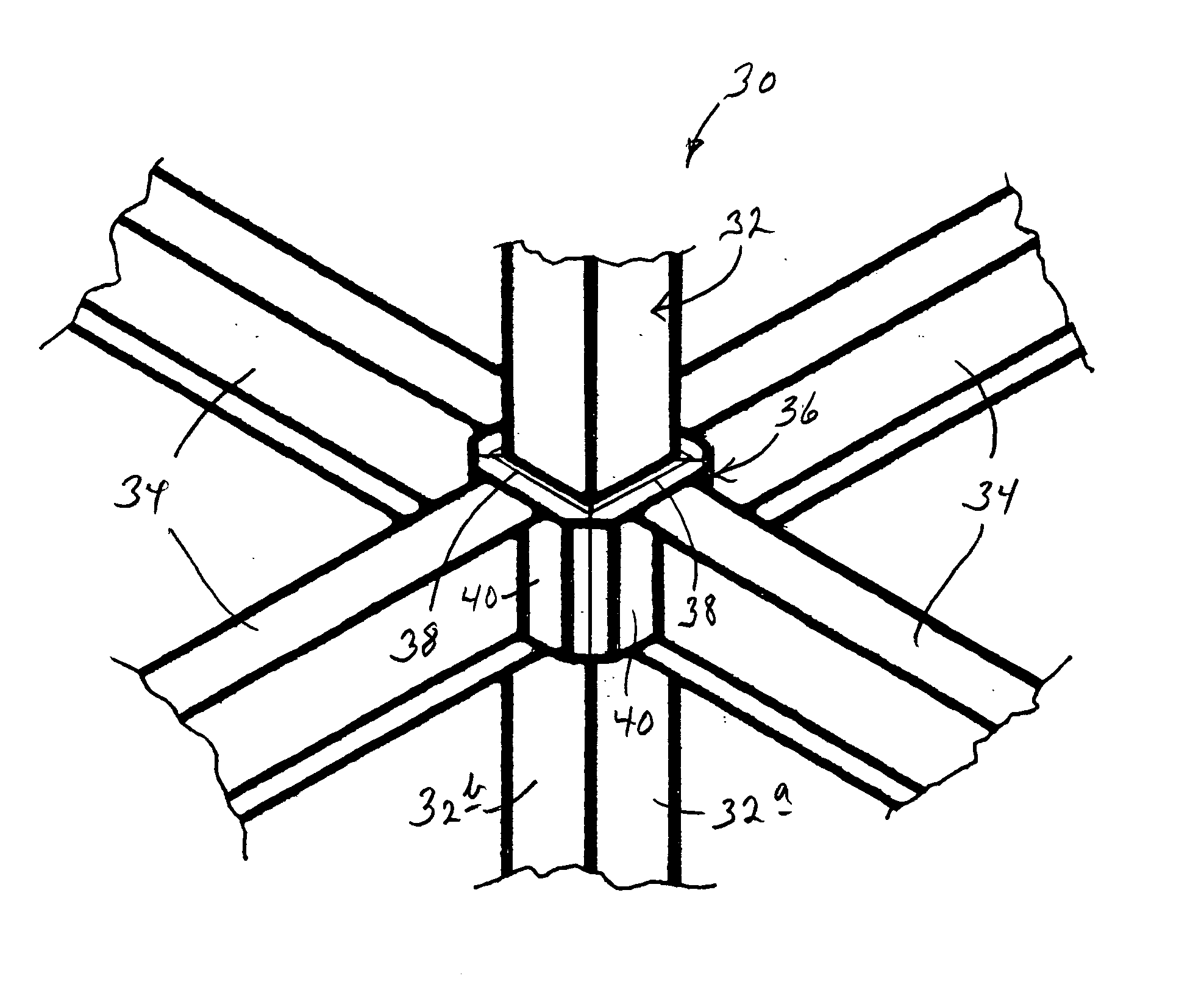
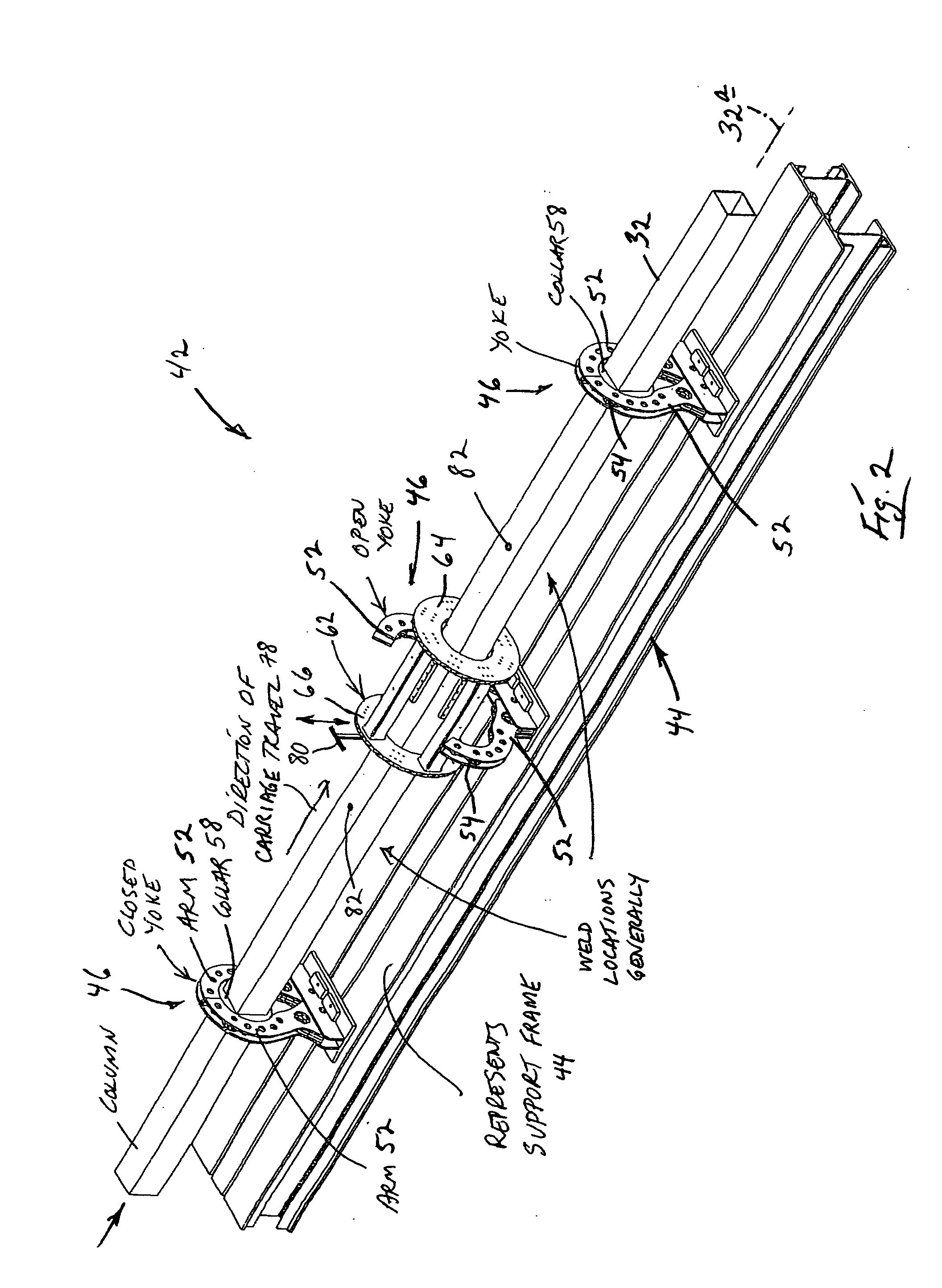
ActiveUS20050055954A1Big ratioShorten assembly timeFloorsLoad-supporting pillarsRotation methodEngineering
A method and related apparatus for precision deploy-attaching beam-mount structure to the outside of an elongate column at plural, defined attachment sites that are distributed and spaced along the length of the column. The method involves (a) preparing an elongate column to act as a travel way for a carriage which is designed to transport and deploy beam-mount structure, shifting such a carriage progressively along the column from defined attachment site to defined attachment site, and at each such site, deploy-attaching from the carriage to the column the carriage-carried beam-mount structure.
Owner:CONXTECH INC
Porous membrane of vinylidene fluoride resin and process for producing the same
There is provided a porous membrane of vinylidene fluoride resin which has pores of appropriate size and distribution and also excellent mechanical strength represented by tensile strength and elongation at break and is useful as a microfiltration membrane or a separator for batteries. The porous membrane of vinylidene fluoride resin is characterized by the presence in mixture of a crystalline oriented portion and a crystalline non-oriented portion as confirmed by X-ray diffraction, and is produced by subjecting a melt-extruded composition obtained by mixing a vinylidene fluoride resin having a molecular weight distribution which is appropriately broad and high as a whole with a plasticizer and a good solvent for vinylidene fluoride resin, to cooling for solidification from one surface, extraction of the plasticizer and stretching.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Exhaust gas post treatment system
ActiveUS20080041040A1MinimizeCounter pressure is increasedInternal combustion piston enginesSilencing apparatusInternal combustion engineReducing agent
An exhaust gas post treatment system for nitrogen oxide and particle reduction of internal combustion engines operated with excess air, comprising a particle filter disposed in the exhaust gas stream of the internal combustion engine. The particle filter is a surface-type particle filter or a deep bed filter, and is charged on an outlet side with an SCR-active catalyst material for reducing nitrogen oxides. Ammonia or an ammonia-releasing reduction agent is supplied to the exhaust gas stream upstream of the particle filter.
Owner:MAN NUTZFAHRZEUGE AG
Preparation of chlorinated polythylene
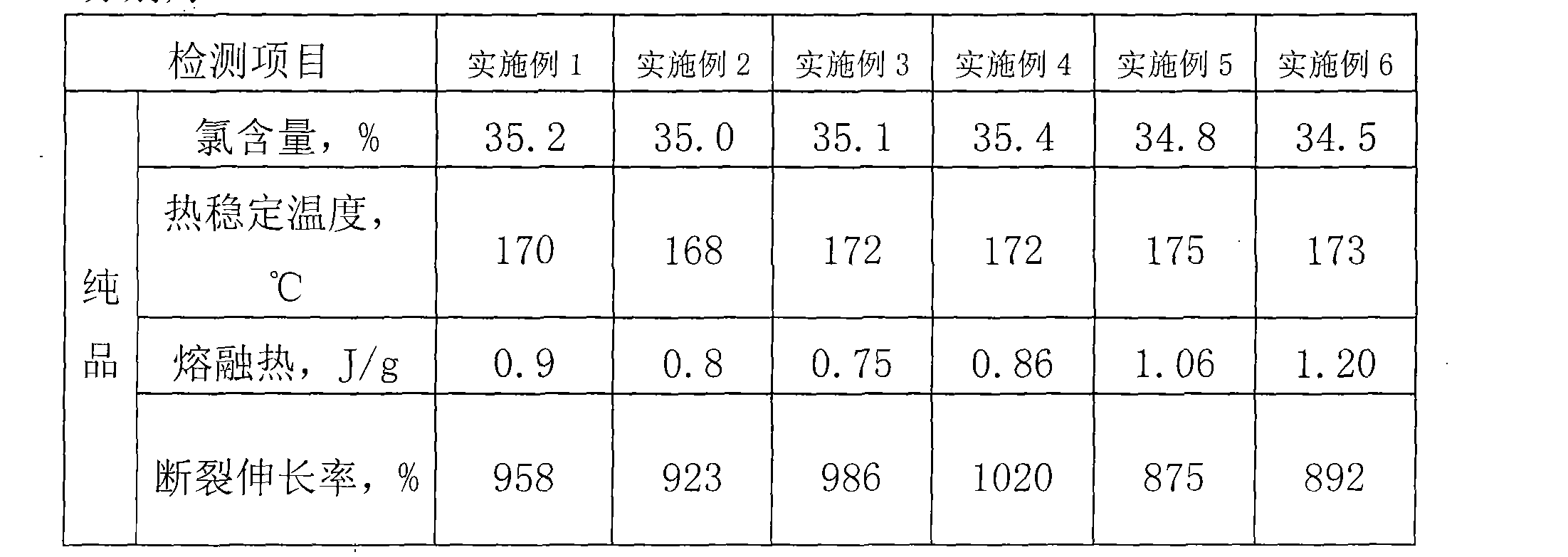
InactiveCN101280030AReduce chlorination timeThe degree of chlorination in depthPolymer scienceChlorinated polyethylene
The invention belongs to plastic profile product modifier technical field and discloses a preparation method for a PVC anti-impact modifier chlorinated polyethylene. The invention is mainly technically characterized in that after dispersant, emulsifier, initiator and powdery high-density polyethylene resin are added into a chlorinating reactor with water inside in a stirring state, then the mixture is heated and processed through three chlorine reactions at different temperature ranges; after the reaction, the enwrapped HCl formed in the reactor is discharged; after repeated hot water washing, centrifugal dehydration and drying, calcium stearate, calcium carbonate and lanthanum carbonate are added to obtain the finished product through stirring, mixing and screening. As the high-density polyethylene resin in the preparation technology is high-mesh powdery material and three chlorine reactions are needed in the process, the chlorinated polyethylene prepared by the technology has higher thermal stable temperature and lower melting heat; if the chlorinated polyethylene serves as the anti-impact modifier of PVC products, the PVC product produced thereby has strong impact strength and tensile strength.
Owner:HEBEI JINGXIN CHEM GRP CO LTD
Golf ball
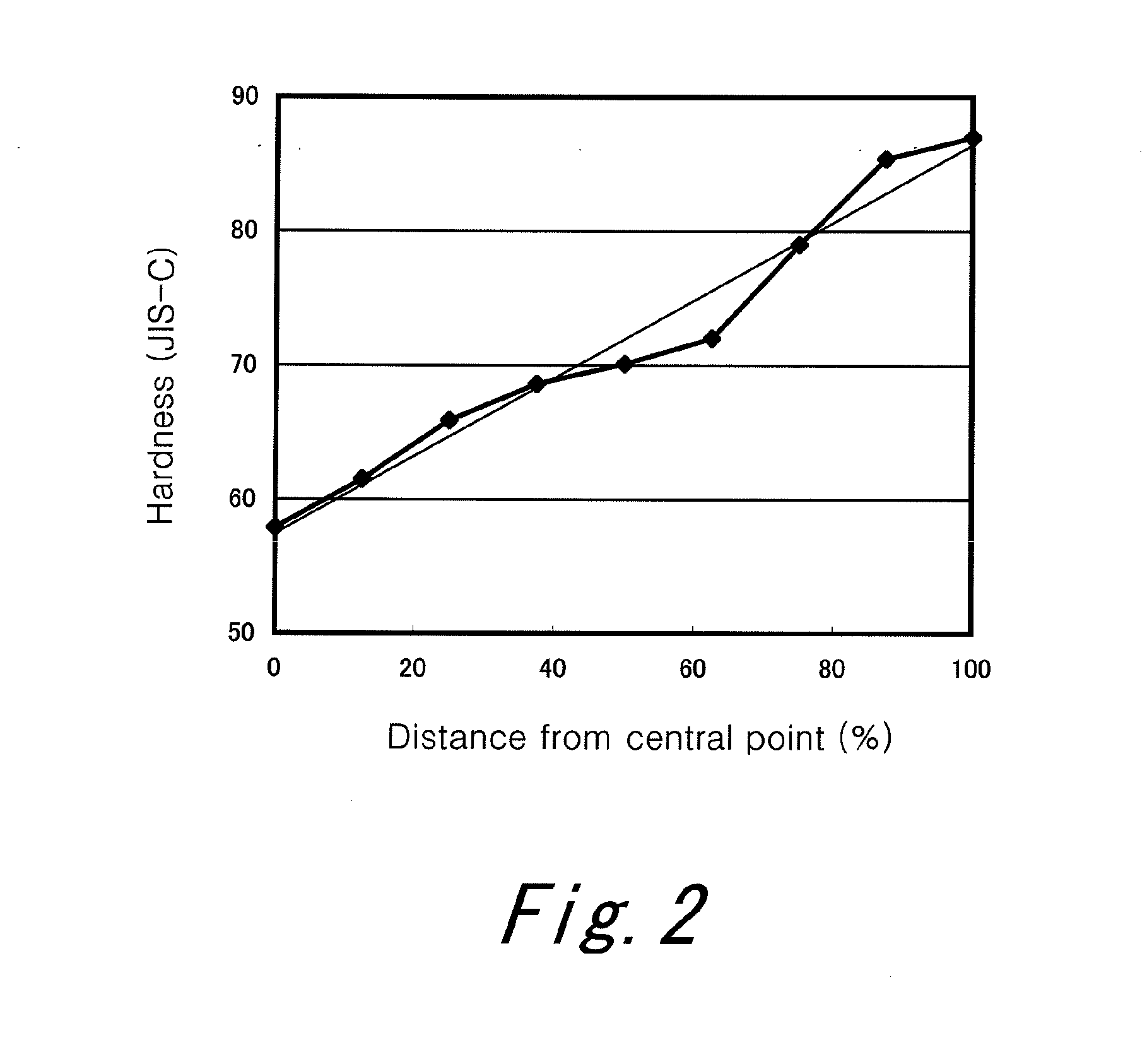
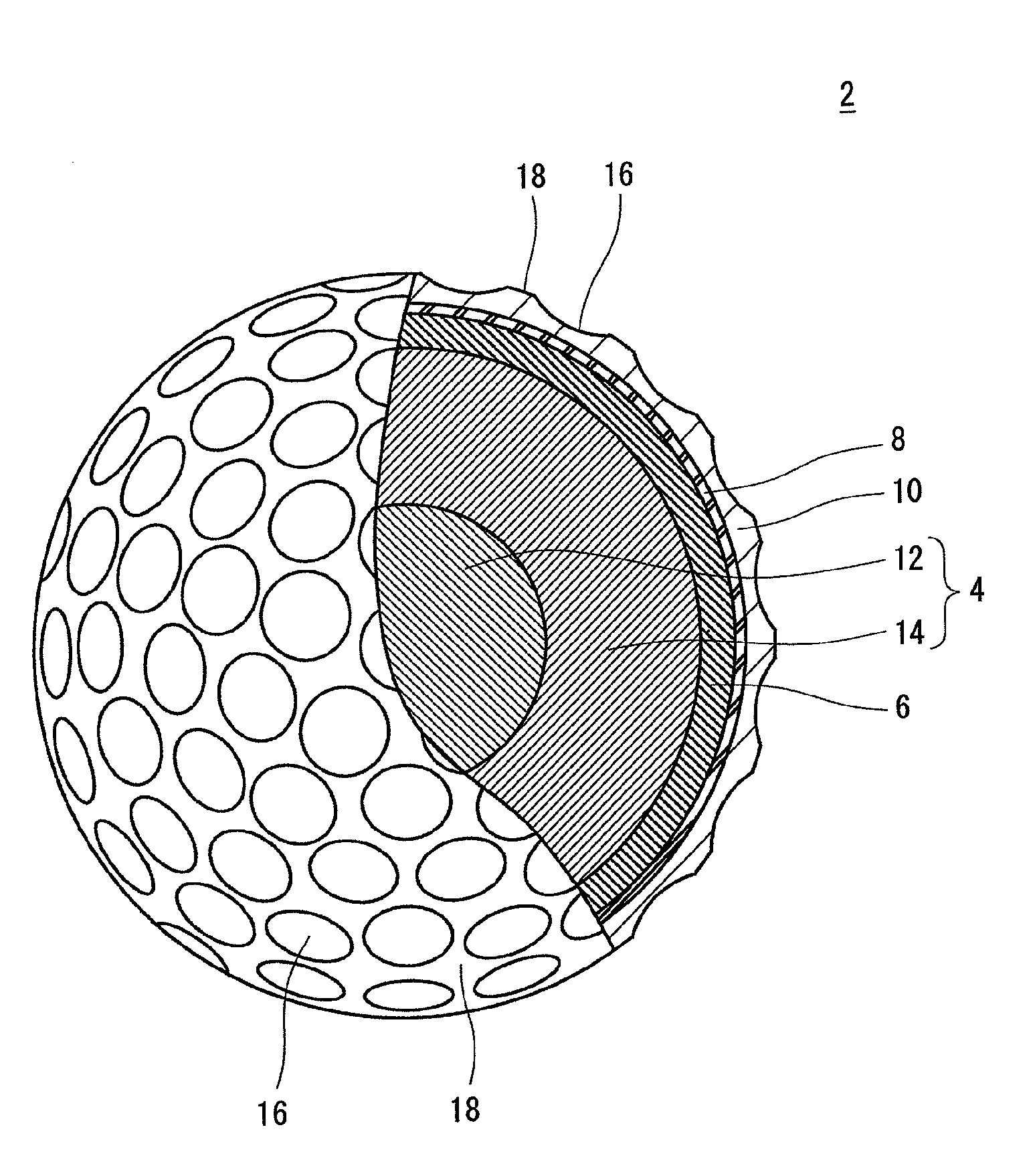
InactiveUS20130005508A1Increase elasticityLarge flight distanceGolf ballsSolid ballsEngineeringGolf Ball
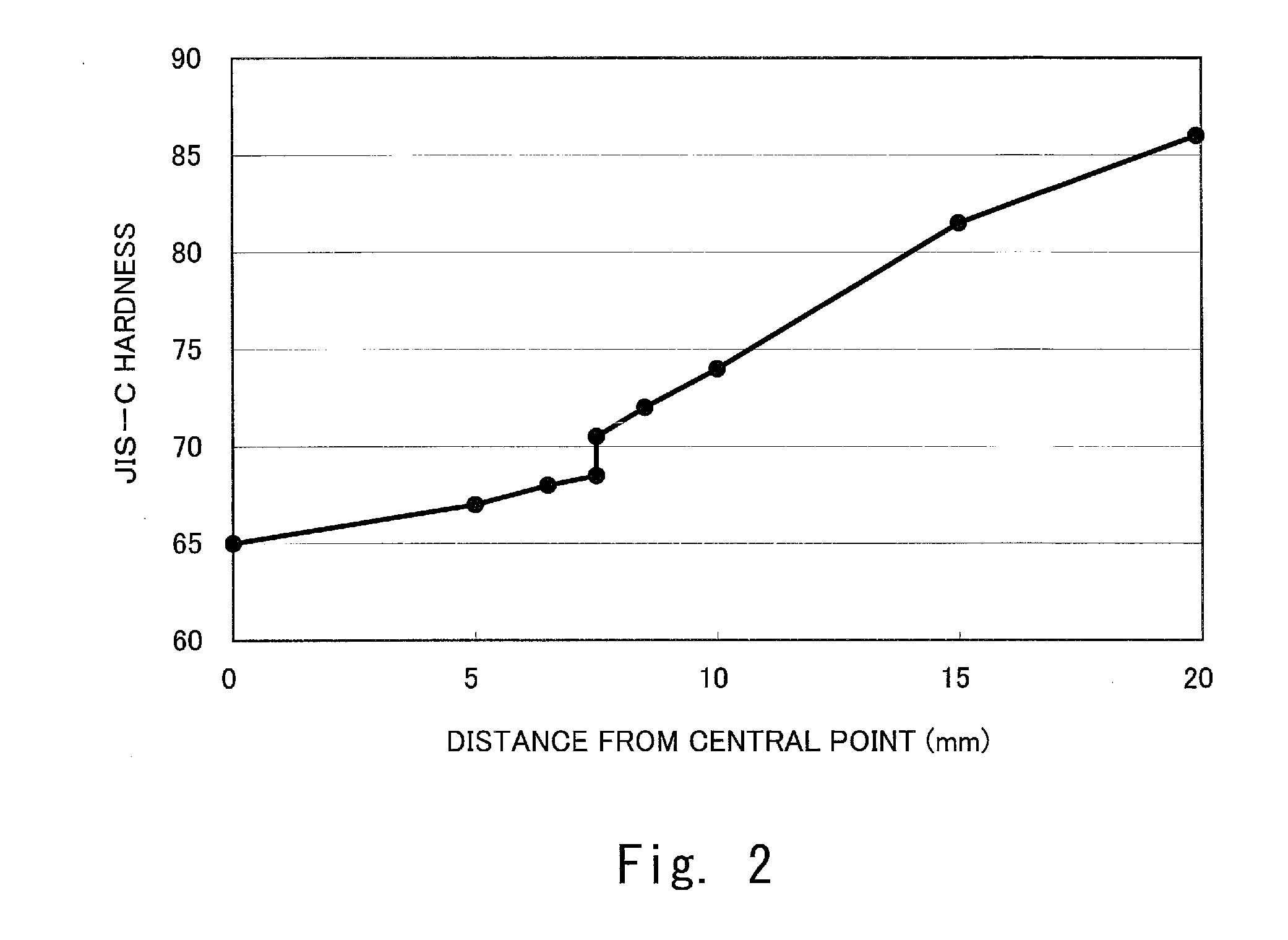
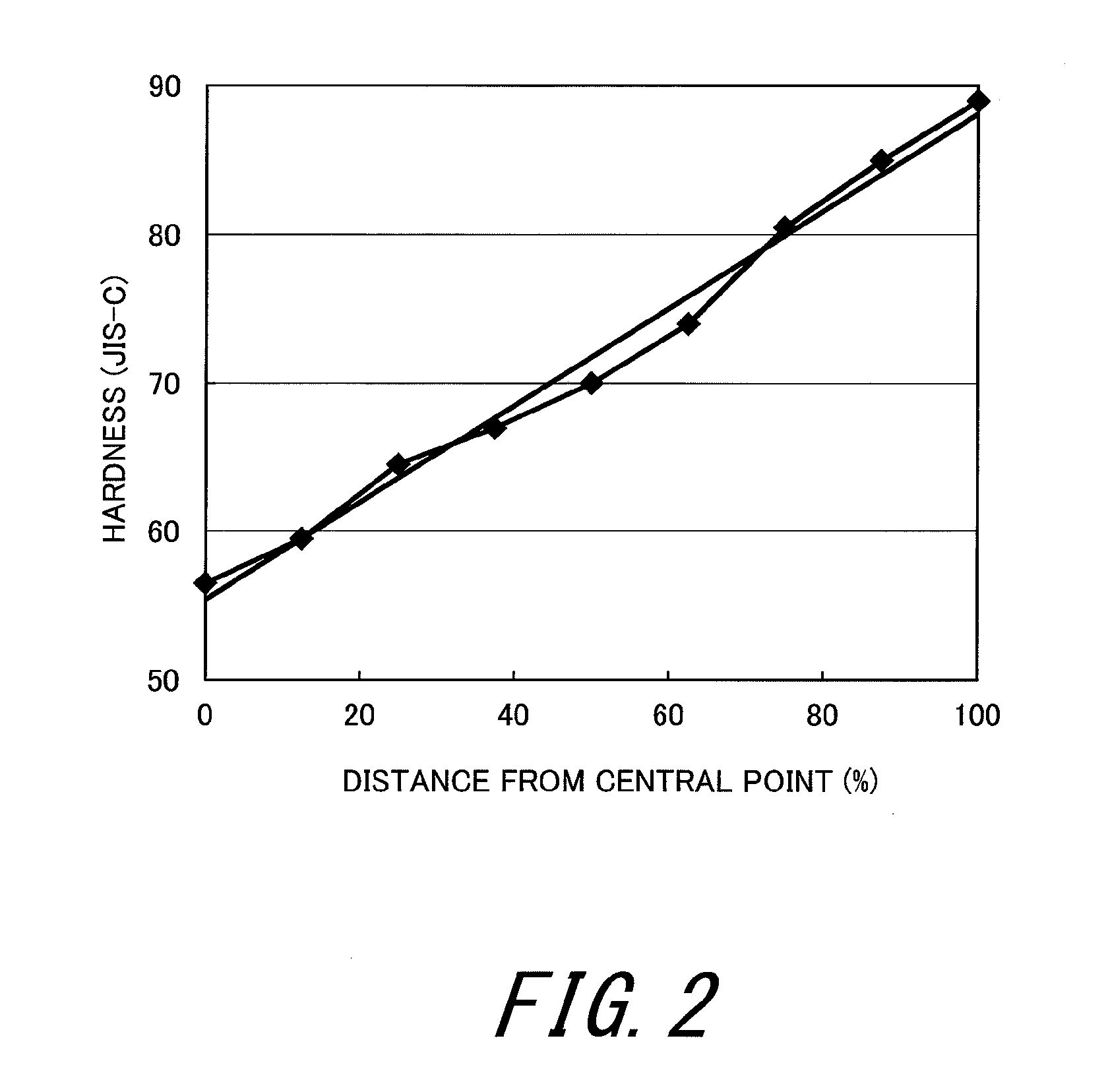
A golf ball 2 includes a core 4, a mid layer 6, a reinforcing layer 8, and a cover 10. When distances (%) from the central point of the core 4 to nine points and JIS-C hardnesses at the nine points, which are obtained by dividing a region from the central point of the core 4 to the surface of the core 4 at intervals of 12.5% of the radius of the core 4, are plotted in a graph, R2 of a linear approximation curve obtained by a least-square method is equal to or greater than 0.95. The difference (H(100)−H(0)) between a JIS-C hardness H(100) at the surface of the core 4 and a JIS-C hardness H(0) at the central point of the core 4 is equal to or greater than 15.
Owner:DUNLOP SPORTS CO LTD
Facility communications infrastructure
ActiveUS20160241988A1Minimal changeMinimal costWireless architecture usageWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemComputer science
A system and method for improving upon limitations of conventional infrastructure communications systems. A sensor architecture may include a multiple protocol communications paradigm to enhance whole building sensor management. A system may have one or more innovations that include anticipatory alarms, nuisance alarm reduction, and big data building profiling.
Owner:THE DETECTION GRP
Optical-fiber-characteristic measuring device and optical-fiber-characteristic measuring method
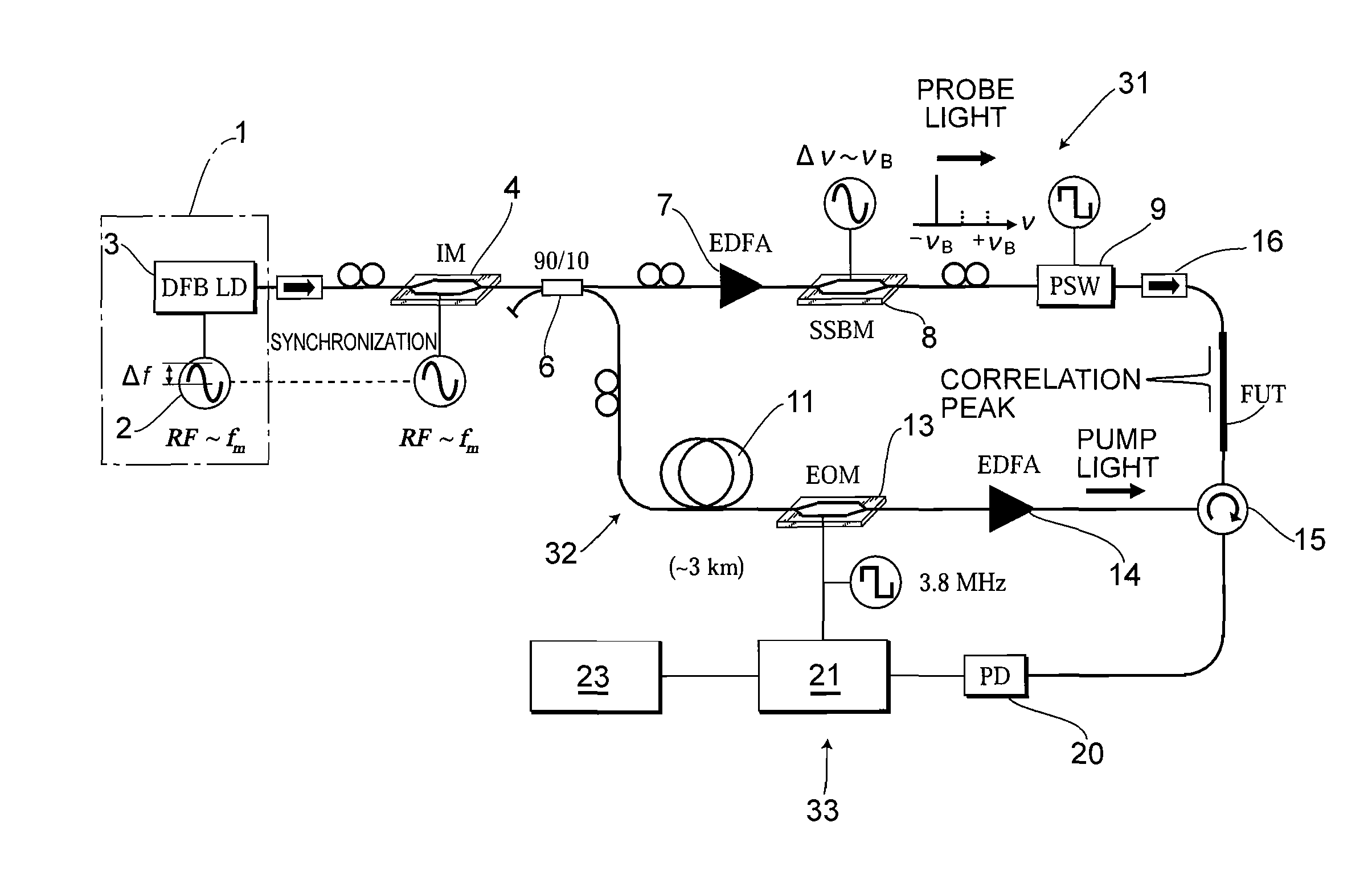
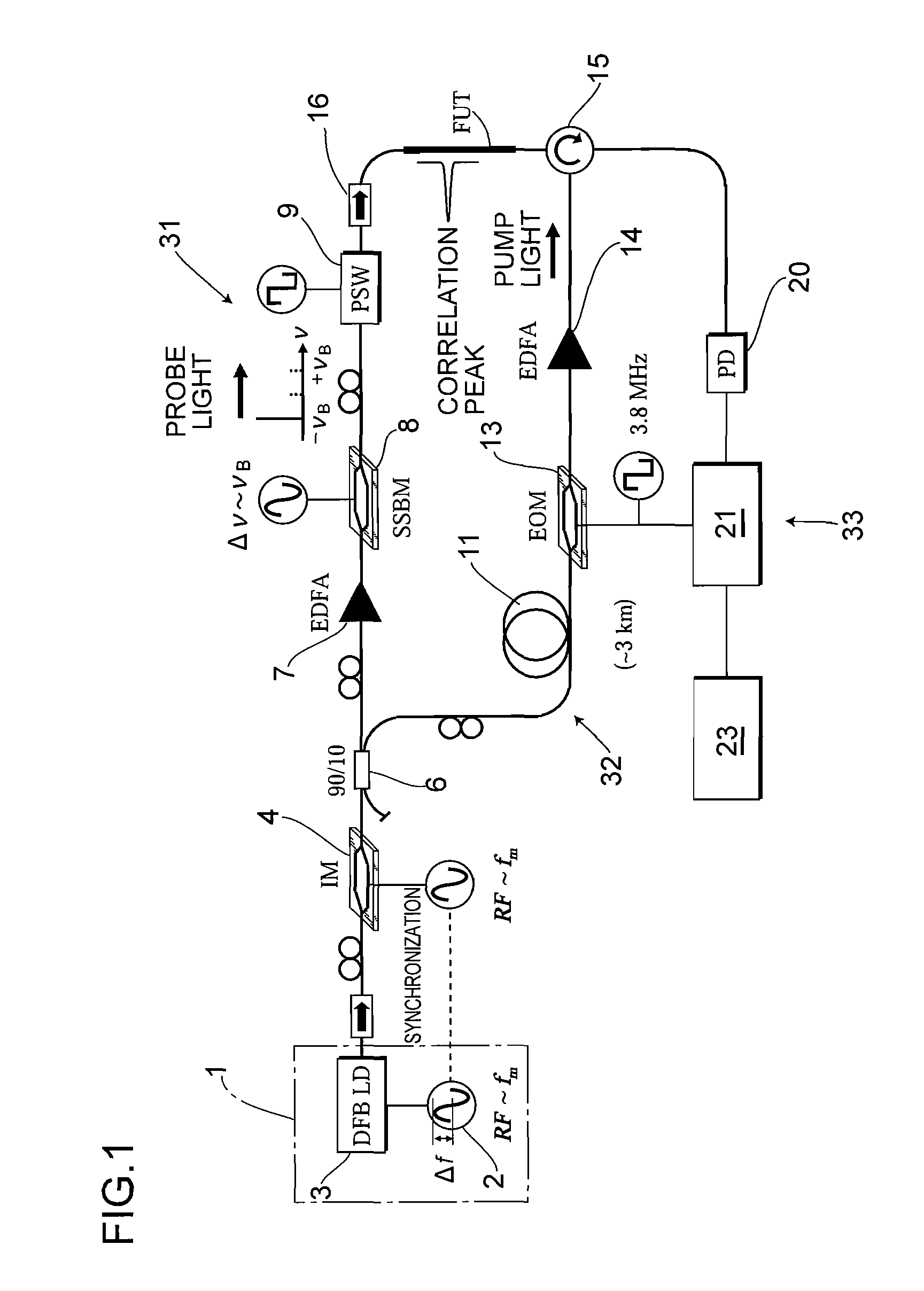
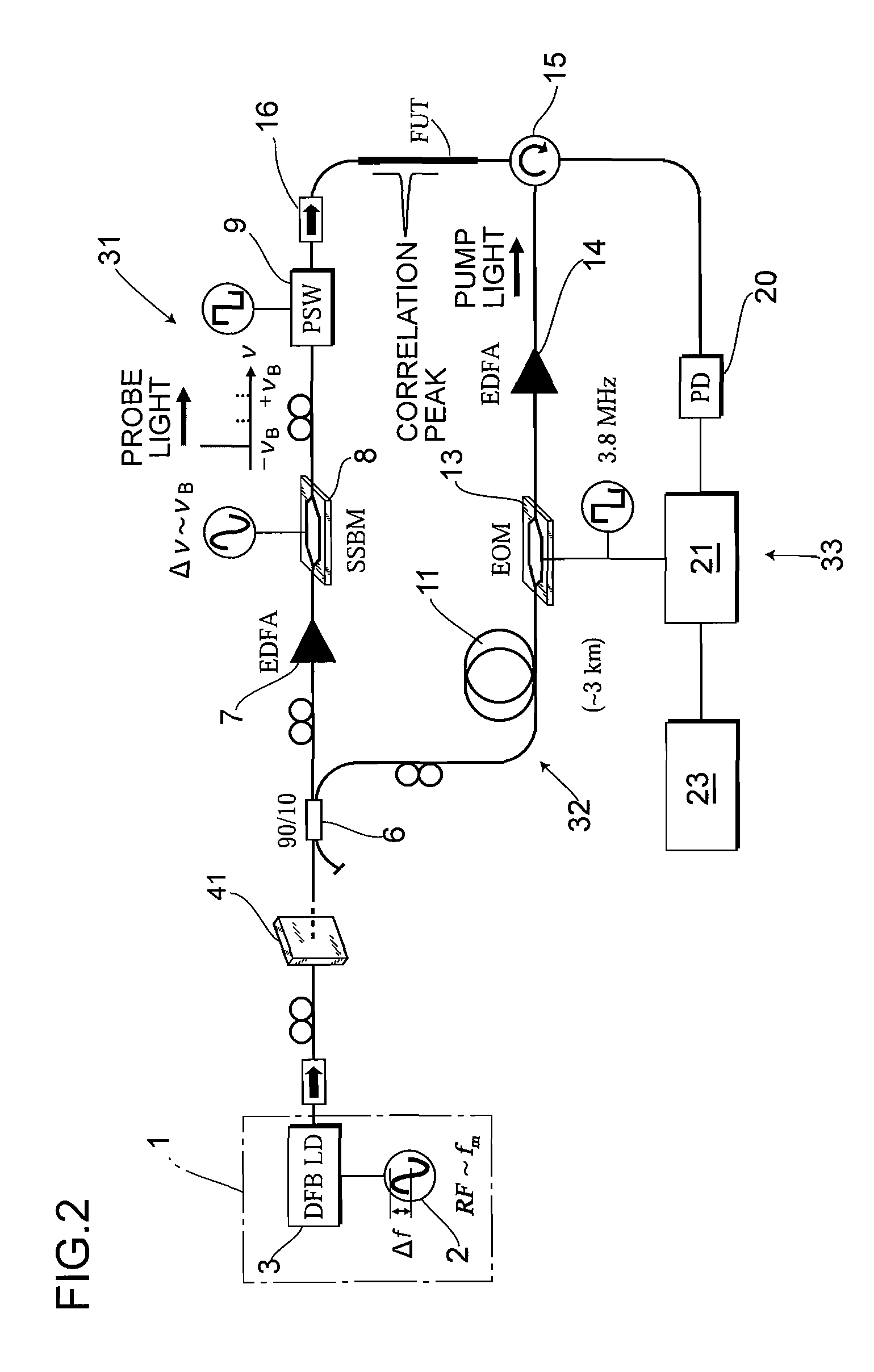
ActiveUS20100225900A1Intensity of output light can be increased and reducedExpand the measurement rangeReflectometers dealing with polarizationForce measurementMeasurement deviceFrequency spectrum
A measurement precision is improved and a measurement range is extended by efficiently suppressing a noise level of integrated unnecessary components from non-correlation positions. Measuring means 33 detects the Brillouin gain of a probe light output from a measurement-target optical fiber FUT while sweeping a frequency difference between the pump light and the probe light, and measures the distribution of strains of the measurement-target optical fiber FUT. An optical intensity modulator 4 performs intensity modulation on output light in synchronization with frequency modulation performed on a light source 1. Accordingly, the spectrum distribution with respect to the frequency of light from the light source 1 can be adjusted arbitrarily, and a noise spectrum shape generated at a position other than a correlation peak position and spreading over a frequency axis can be adjusted, and the peak frequency of a Lorentz spectrum generated at the correlation peak position can be measured precisely. Moreover, a measurement range dm can be extended.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
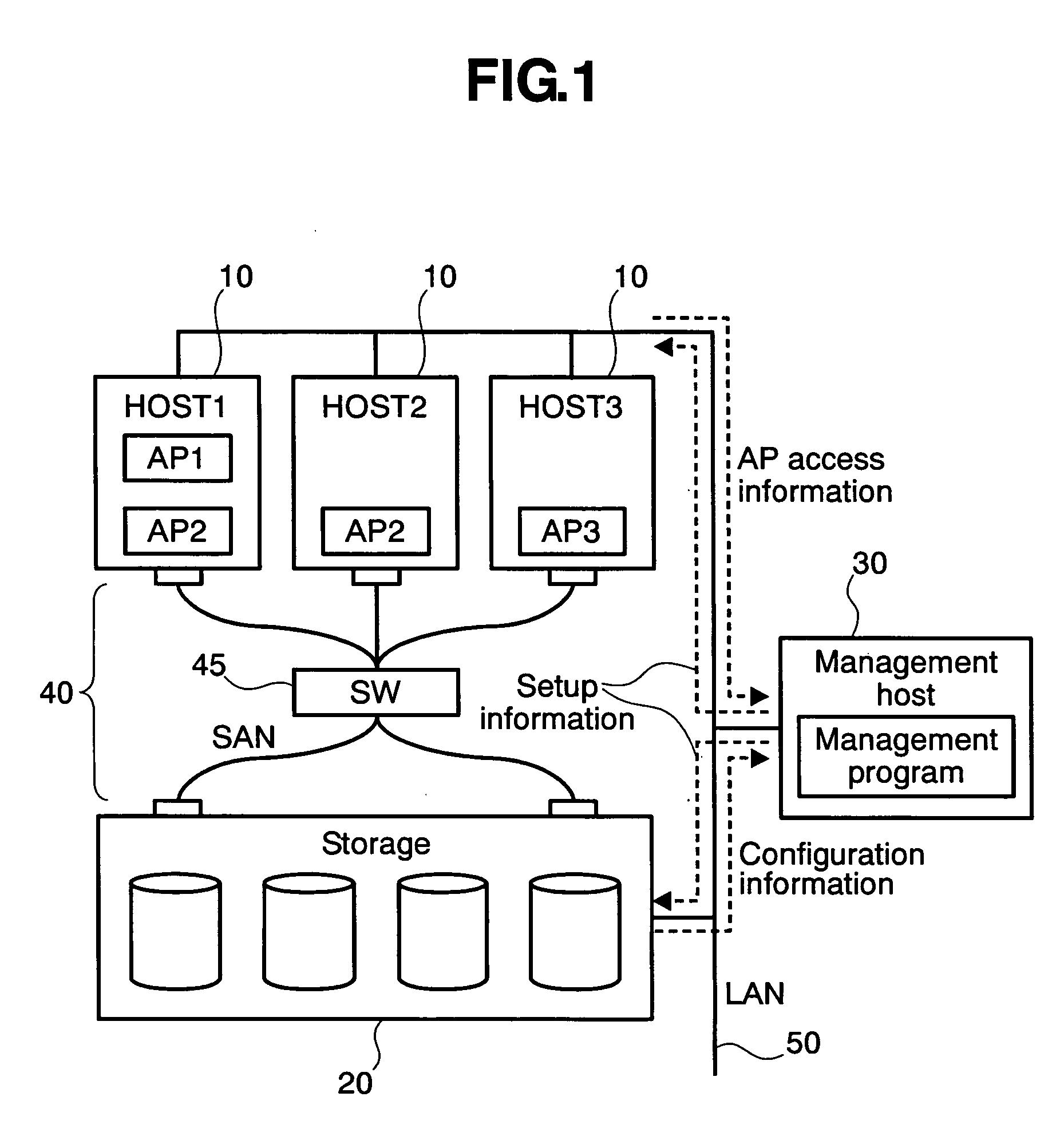
Information processing system and method
InactiveUS20050108235A1Appropriate distributionInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsInformation processingHandling system
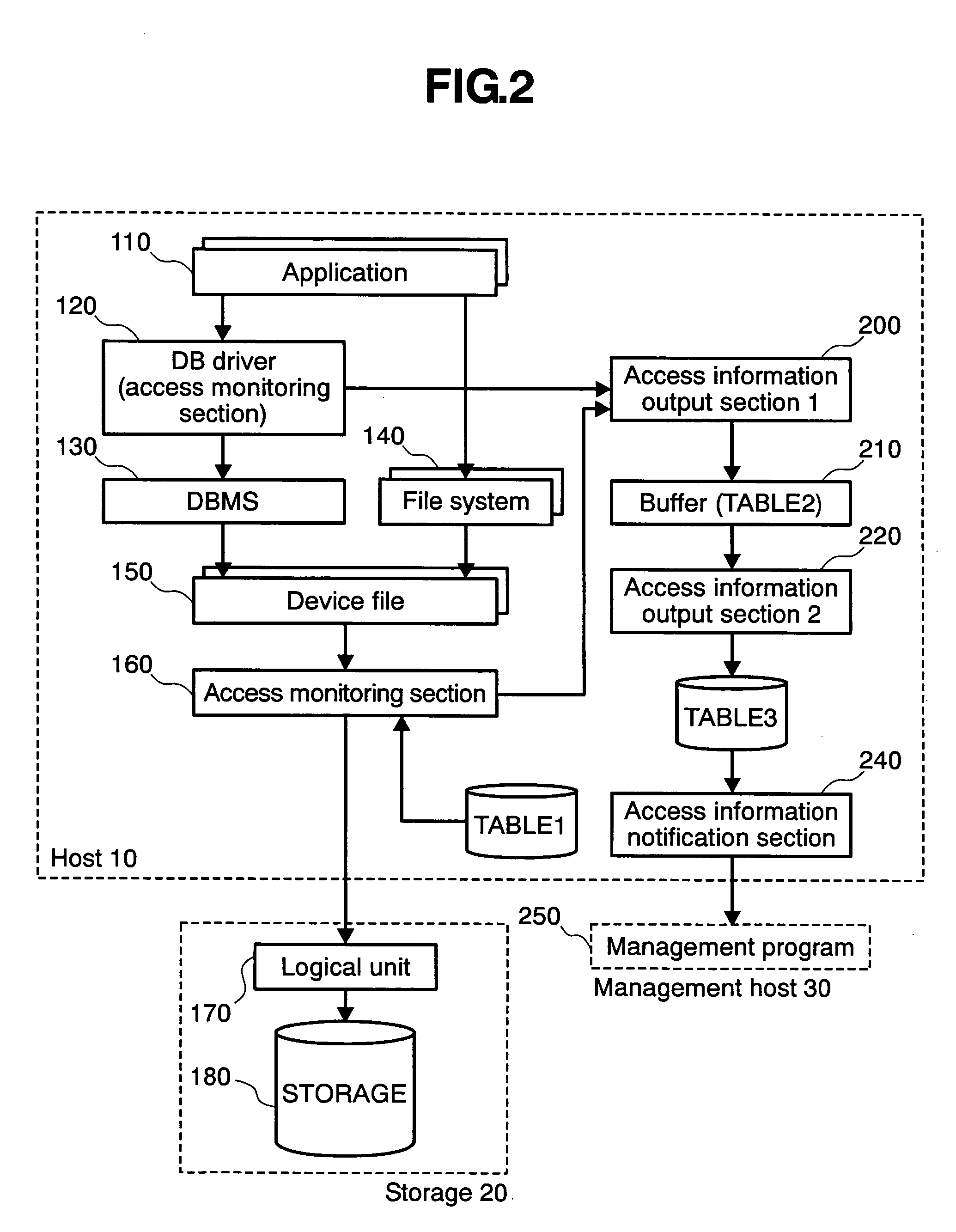
An information processing system comprises an information processing apparatus and a management host. The information processing apparatus is used to operate a plurality of applications to request data input / output from a storage. The management host manages the storage. The information processing apparatus comprises an access monitoring section. The access monitoring section monitors an access request from the application and obtains information about the access request for each of the applications. The management host comprises an acceptance section, an estimated load calculation section and a load data output section. The acceptance section accepts specification of a new application. The estimated load calculation section calculates estimated load data in case of addition of the application based on information obtained by the access monitoring section. The load data output section outputs estimated load data calculated by the estimated load calculation section.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Golf ball
ActiveUS20130005505A1Increase elasticityLarge flight distanceGolf ballsSolid ballsCarboxylic saltEngineering
A golf ball 2 includes a spherical core 4 and a cover 6 covering the core 4 and including an inner cover 8 and an outer cover 10 positioned outside the inner cover 8. The core 4 is obtained by crosslinking a rubber composition. The rubber composition includes a base rubber (a), a co-crosslinking agent (b), a crosslinking initiator (c), and a carboxylate (d). The co-crosslinking agent (b) is:(b1) an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid having 3 to 8 carbon atoms; or(b2) a metal salt of an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid having 3 to 8 carbon atoms.The amount of the carboxylate (d) is equal to or greater than 1 parts by weight but less than 40 parts by weight per 100 parts by weight of the base rubber (a). A hardness of an innermost layer of the cover is equal to or less than a surface hardness of the core.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Golf ball
A golf ball 2 includes a core 4, amid layer 6, a reinforcing layer 8, and a cover 10. The core 4 includes a center 12 and an envelope layer 14. The envelope layer 14 is formed by a rubber composition being crosslinked. The rubber composition includes a base rubber (a), a co-crosslinking agent (b), a crosslinking initiator (c), and an acid and / or a salt (d). The co-crosslinking agent (b) is:(b1) an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid having 3 to 8 carbon atoms; or(b2) a metal salt of an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid having 3 to 8 carbon atoms.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Golf ball
ActiveUS20110159999A1Appropriate hardness distributionLess energy lossGolf ballsSolid ballsMedicineGolf Ball
At all points Pa included in zone “A” away from the central point of the core 4 at a distance of 1 mm or greater and less than 5 mm, the following mathematical expression (I) is satisfied, and at any point Pb included in zone “B” away from the central point of the core 4 at a distance of 5 mm or greater and 10 mm or less, the following mathematical expression (II) is satisfied.Ha2−Ha1<5 (I)Hb2−Hb1≧5 (II)Ha1 represents the hardness at a point Pa1 that is located inside the point Pa along the radial direction and away from the point Pa at a distance of 1 mm, and Ha2 represents the hardness at a point Pa2 that is located outside the point Pa along the radial direction and away from the point Pa at a distance of 1 mm. Hb1 represents the hardness at a point Pb1 that is located inside the point Pb along the radial direction and away from the point Pb at a distance of 1 mm, and Hb2 represents the hardness at a point Pb2 that is located outside the point Pb along the radial direction and away from the point Pb at a distance of 1 mm.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Golf ball
A golf ball 2 includes a spherical core 4, an inner mid layer 6, an outer mid layer 8, a reinforcing layer 10, and a cover 12. When distances (%) from a central point of the core 4 to nine points and JIS-C hardnesses at the nine points, which nine points are obtained by dividing a region from the central point of the core 4 to a surface of the core 4 at intervals of 12.5% of a radius of the core 4, are plotted in a graph, R2 of a linear approximation curve obtained by a least-square method is equal to or greater than 0.95. Hm1 is greater than Hm2. Hc is less than Hm1. T2 is equal to or greater than 0.5 mm but equal to or less than 1.6 mm.
Owner:DUNLOP SPORTS CO LTD
Residual oil hydrogenation catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103861595AHigh activityAvoid inactivationCatalyst carriersMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsComponent LoadActive component
The invention discloses a residual oil hydrogenation catalyst, comprising a carrier and an active metal component loaded on the carrier, wherein the carrier is a graphited reaming coal material; the specific surface area of the graphited reaming coal material is 200-960m<2> / g, the mean pore size is 10-100nm, the pore volume is 0.3-1.0cm<3> / g, the active metal component comprises one or more of VIII metallic oxides and VIB metal oxides, and the graphited reaming coal material is graphited reaming activated coal or graphited reaming semicoke. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the residual oil hydrogenation catalyst. Firstly, a carbon raw material is graphited and chambered to obtain the required carrier, and then the active component is soaked into the vector to obtain the residual oil hydrogenation catalyst.
Owner:BEIJING HUASHI UNITED ENERGY TECH & DEV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com