Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
361results about "Frequency-independant attenuators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
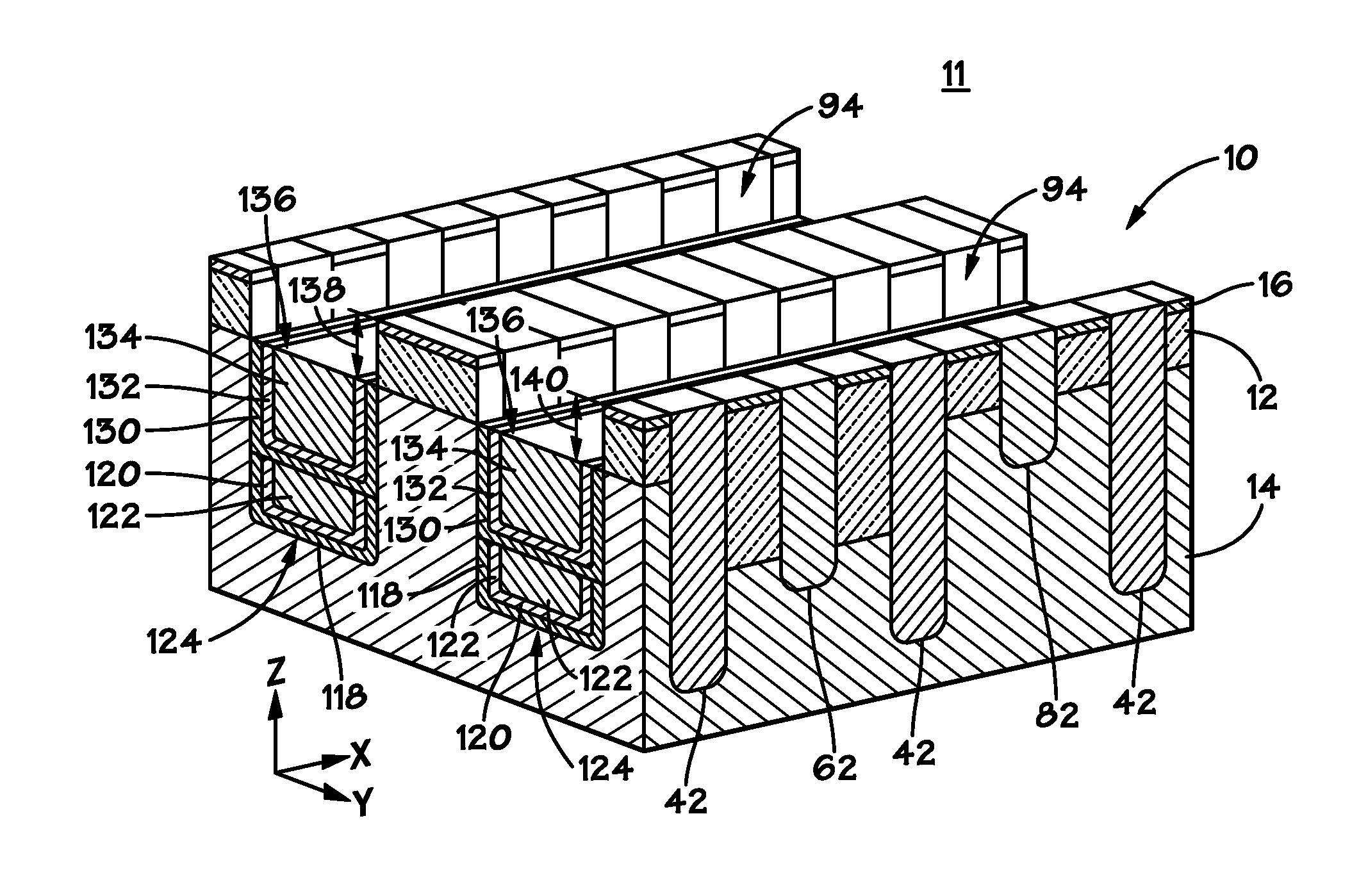
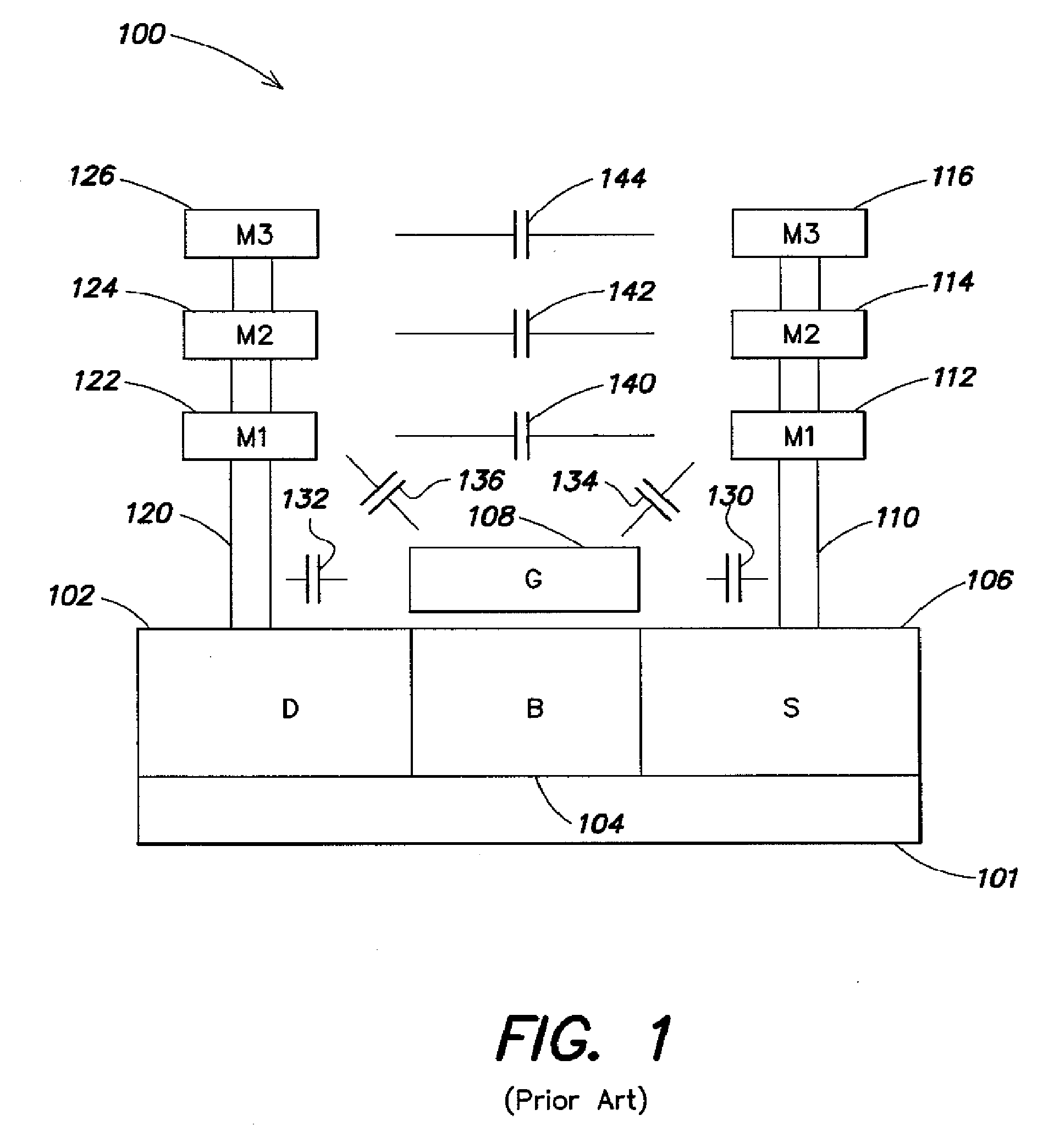
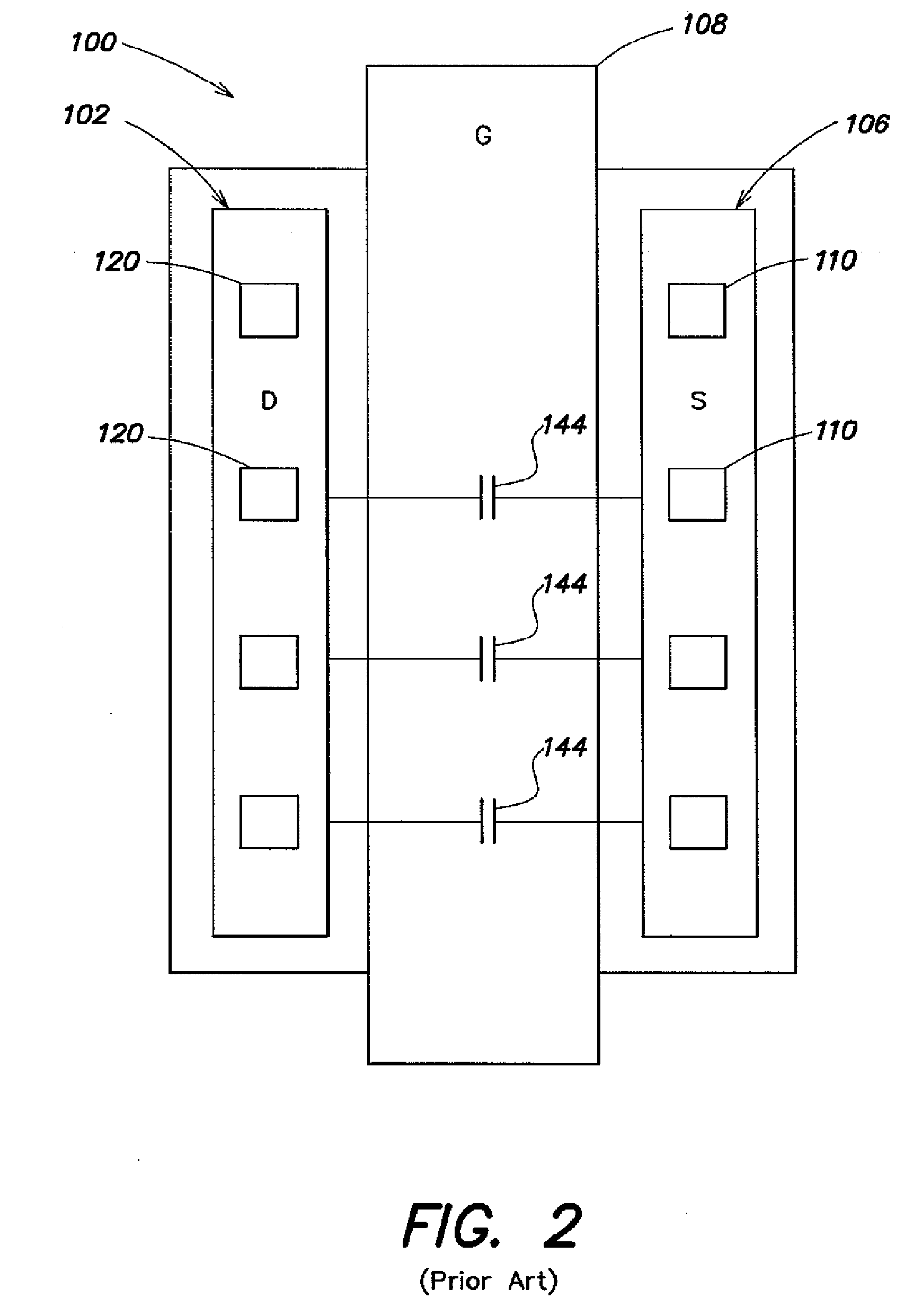
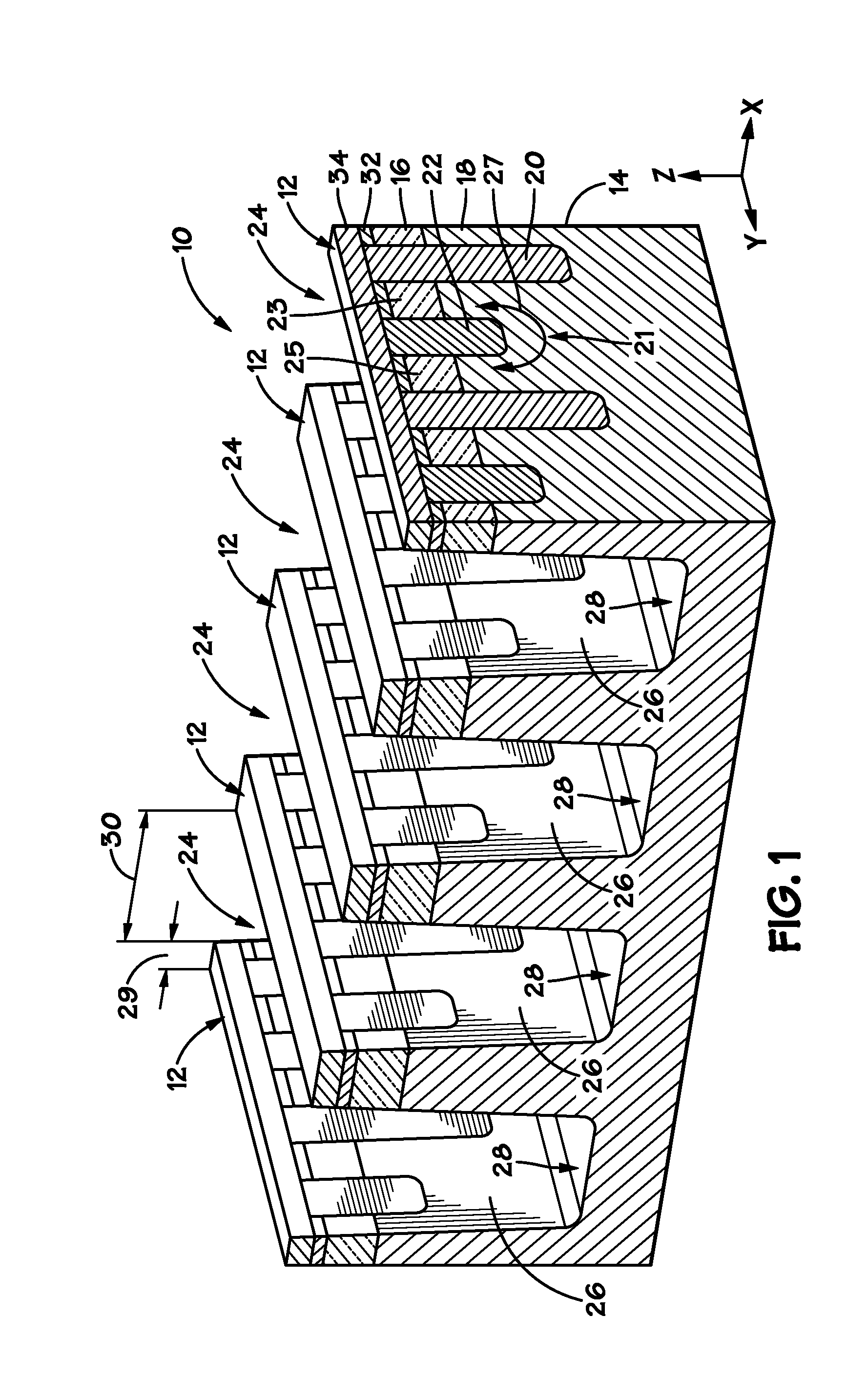
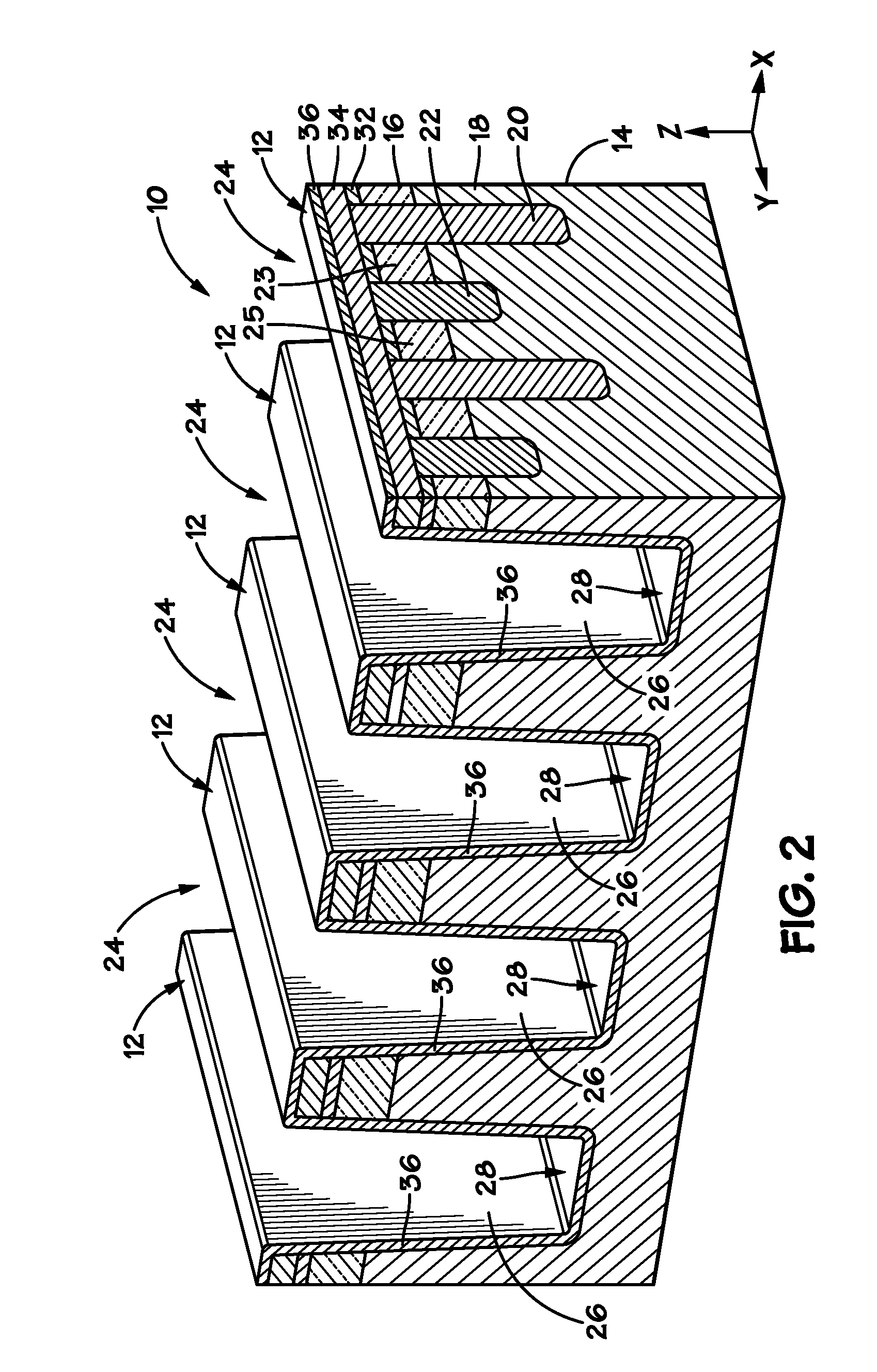
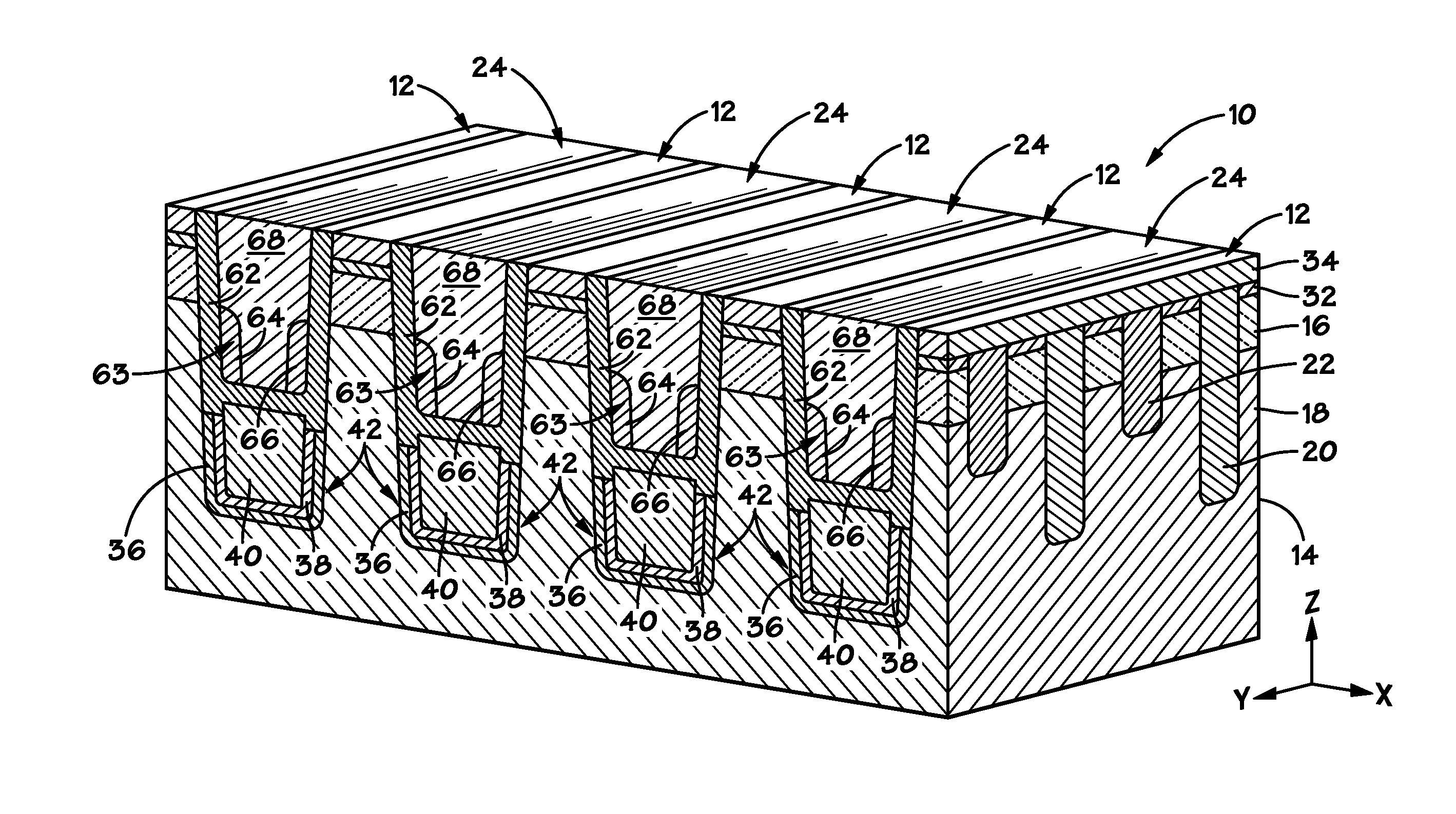
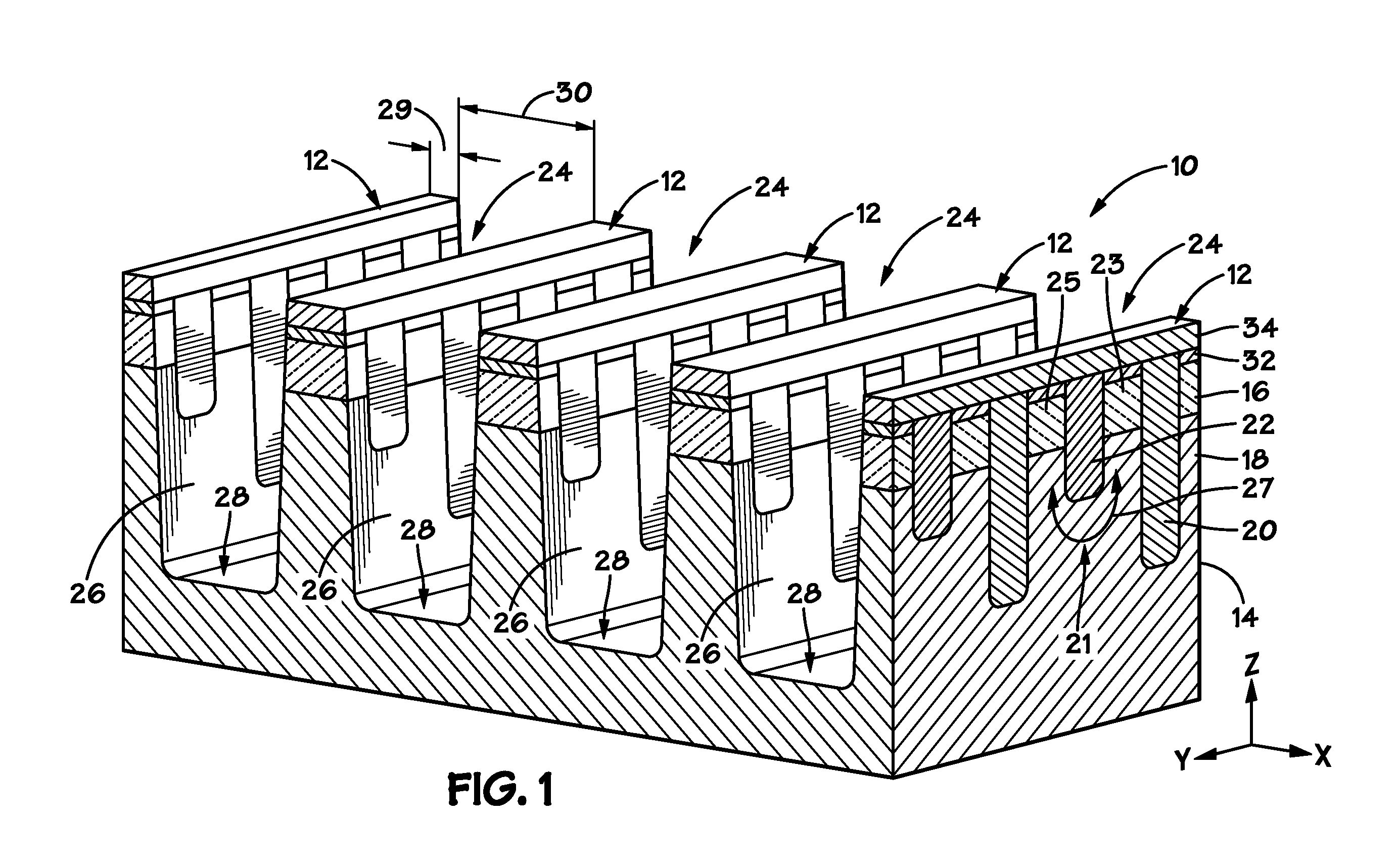
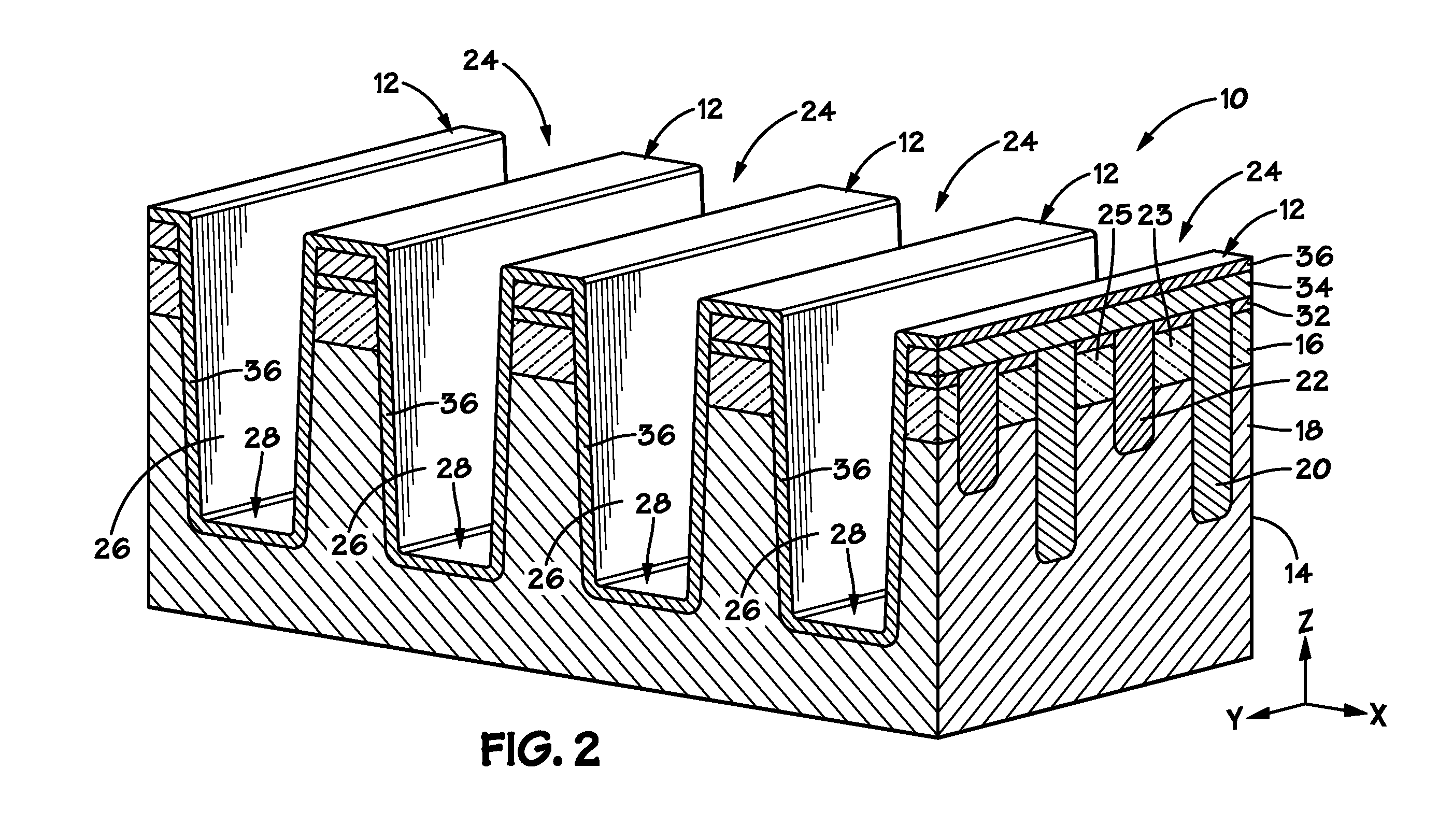
Vertically stacked fin transistors and methods of fabricating and operating the same
A semiconductor device is disclosed having vertically stacked (also referred to as vertically offset) transistors in a semiconductor fin. The semiconductor fin may include lower transistors separated by a first trench and having a source and drain in a first doped region of the fin. The semiconductor fin also includes upper transistors vertically offset from the first transistors and separated by a second trench and having a source and drain in a second doped region of the fin. Upper and lower stacked gates may be disposed on the sidewalls of the fin, such that the lower transistors are activated by biasing the lower gates and upper transistors are activated by biasing the upper gates. Methods of manufacturing and operating the device are also disclosed.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
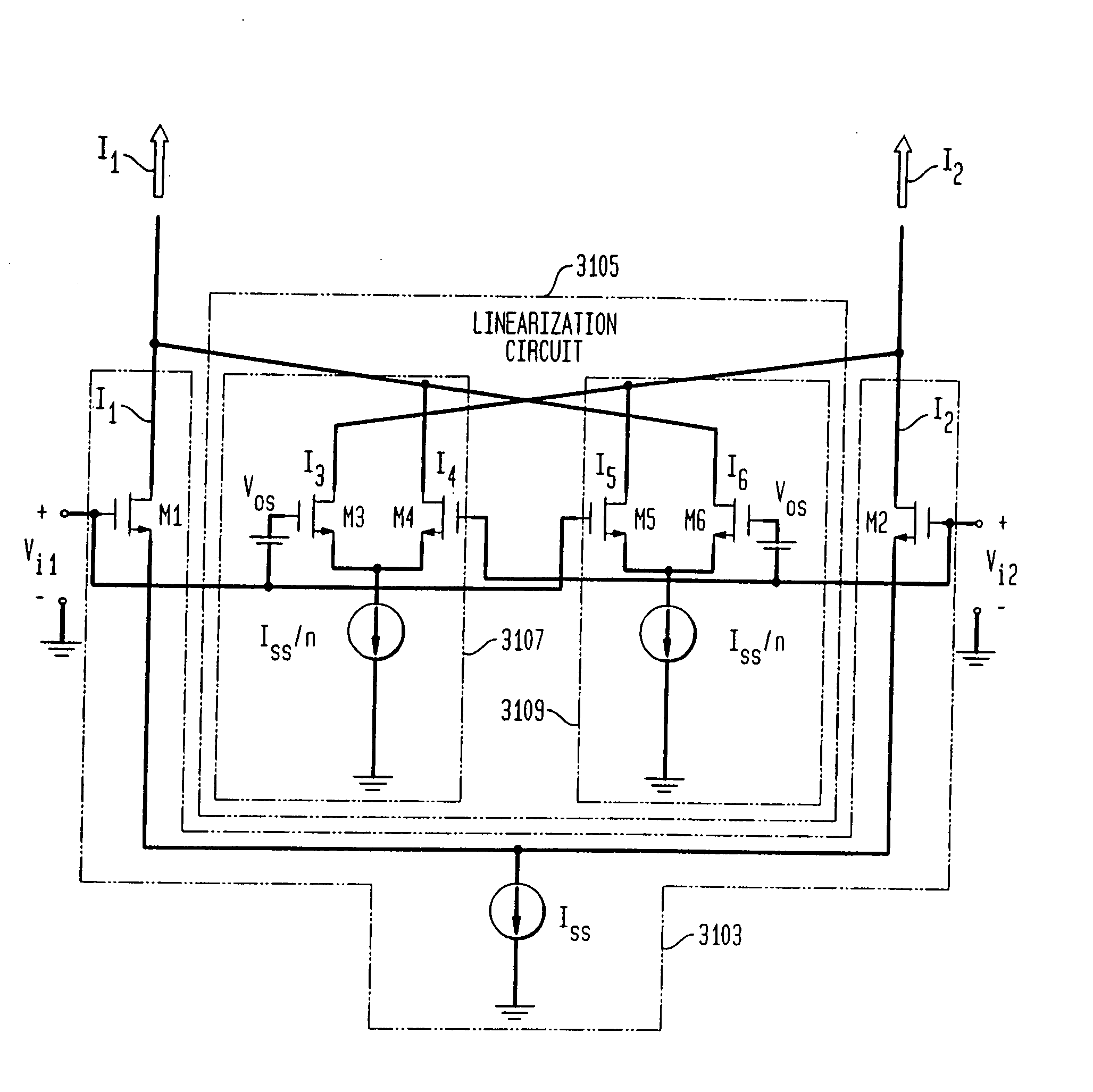
System and method for linearizing a CMOS differential pair
InactiveUS20080036536A1Multiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShunt DeviceFilter tuning
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers provide image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. Active filters utilize multi track spiral inductors with shields to increase circuit Q. The filters incorporate a gain stage that provides improved dynamic range through the use of cross coupled auxiliary differential pair CMOS amplifiers to cancel distortion in a main linearized differential pair amplifier. Frequency planning provides additional image rejection. Local oscillator signal generation methods on chip reduce distortion. A PLL generates needed out of band LO signals. Direct synthesis generates in band LO signals. PLL VCOs are centered automatically. A differential crystal oscillator provides a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission throughout the receiver is used. ESD protection is provided by a pad ring and ESD clamping structure. Shunts utilize a gate boosting at each pin to discharge ESD build up. An IF VGA utilizes distortion cancellation achieved with cross coupled differential pair amplifiers having their Vds dynamically modified in conjunction with current steering of the differential pairs sources.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
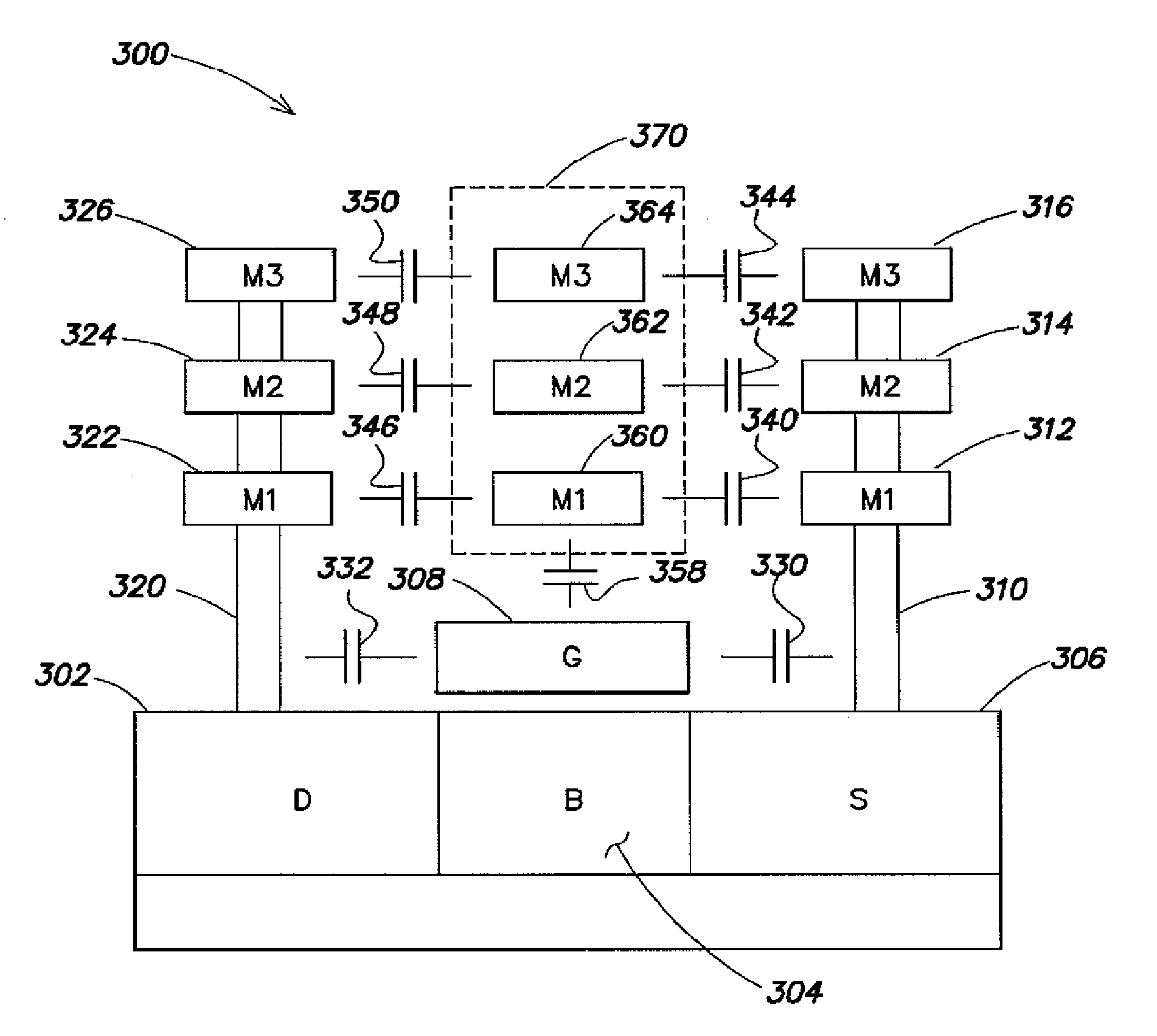
Multi-cascode transistors
InactiveUS6888396B2Boards/switchyards circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceMOSFETCascode
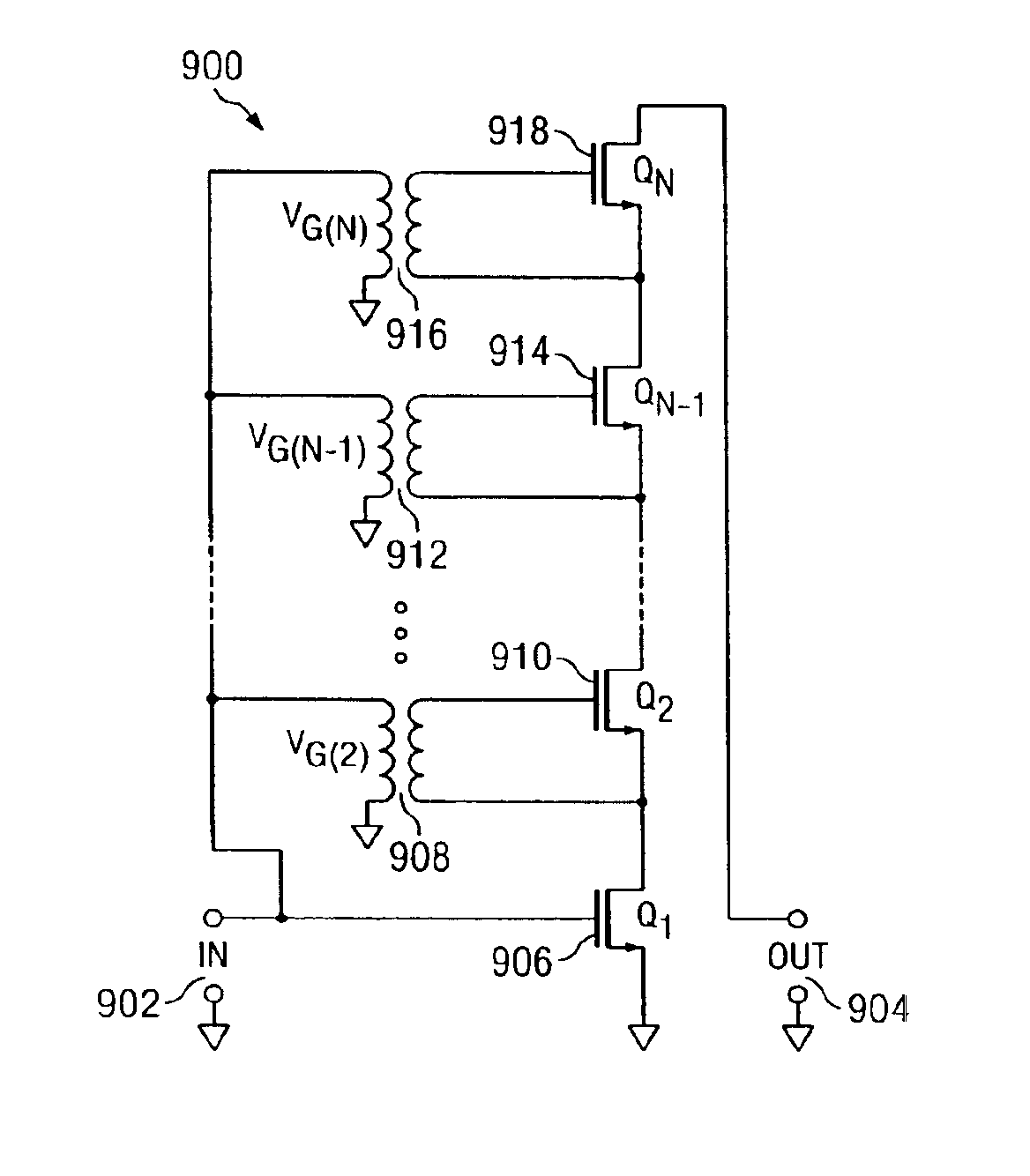
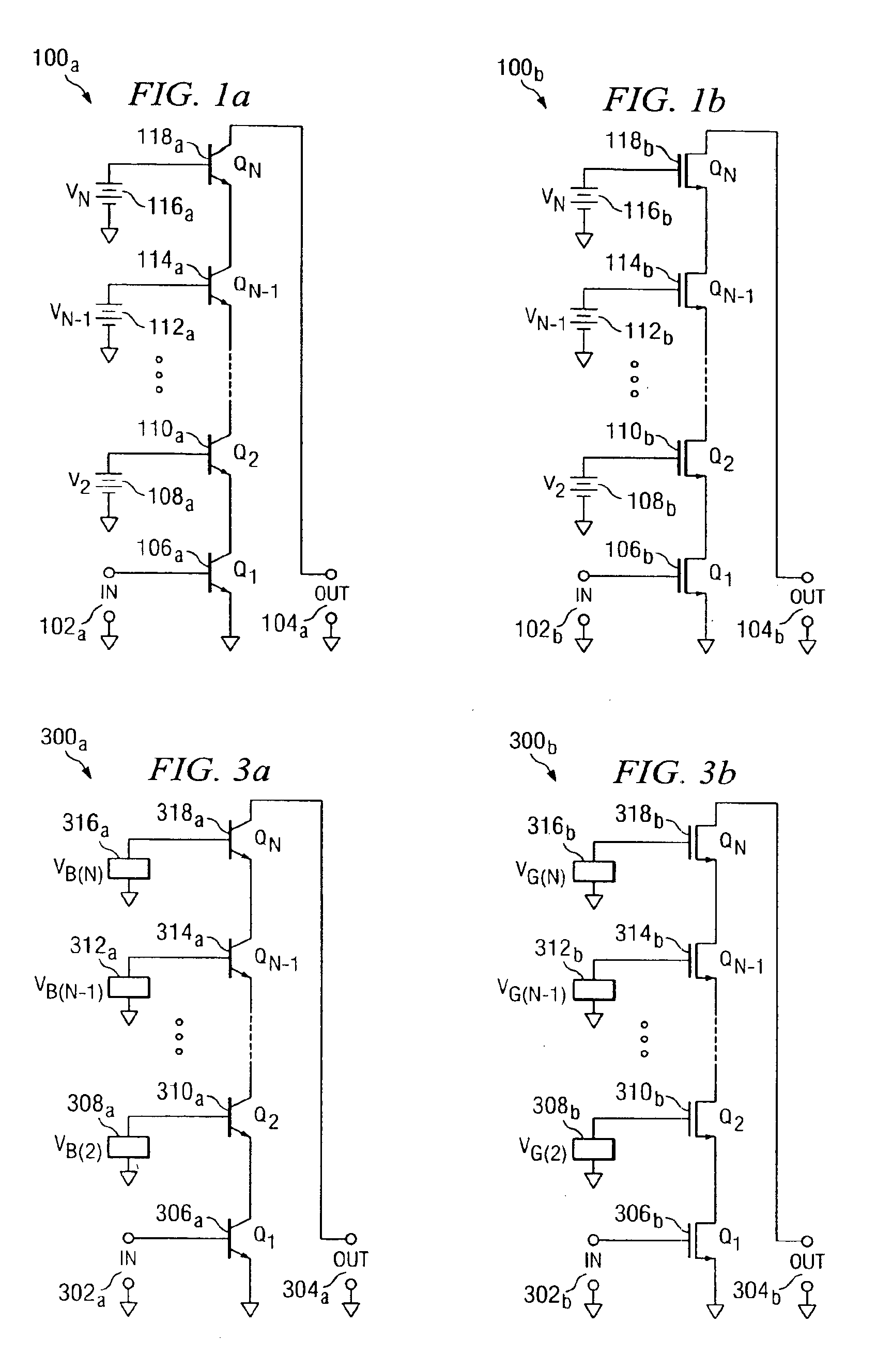
A cascode circuit with improved withstand voltage is provided. The cascode circuit includes three or more transistors, such as MOSFET transistors. Each transistor has a control terminal, such as a gate, and two conduction terminals, such as a drain and a source. The conduction terminals are coupled in series between two output terminals, such as where the drain of each transistor is coupled to the source of another transistor. A signal input is provided to the gate for the first transistor. Two or more control voltage sources, such as DC bias voltages, are provided to the gate of the remaining transistors. The DC bias voltages are selected so as to maintain the voltage across each transistor to a level below a breakdown voltage level.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
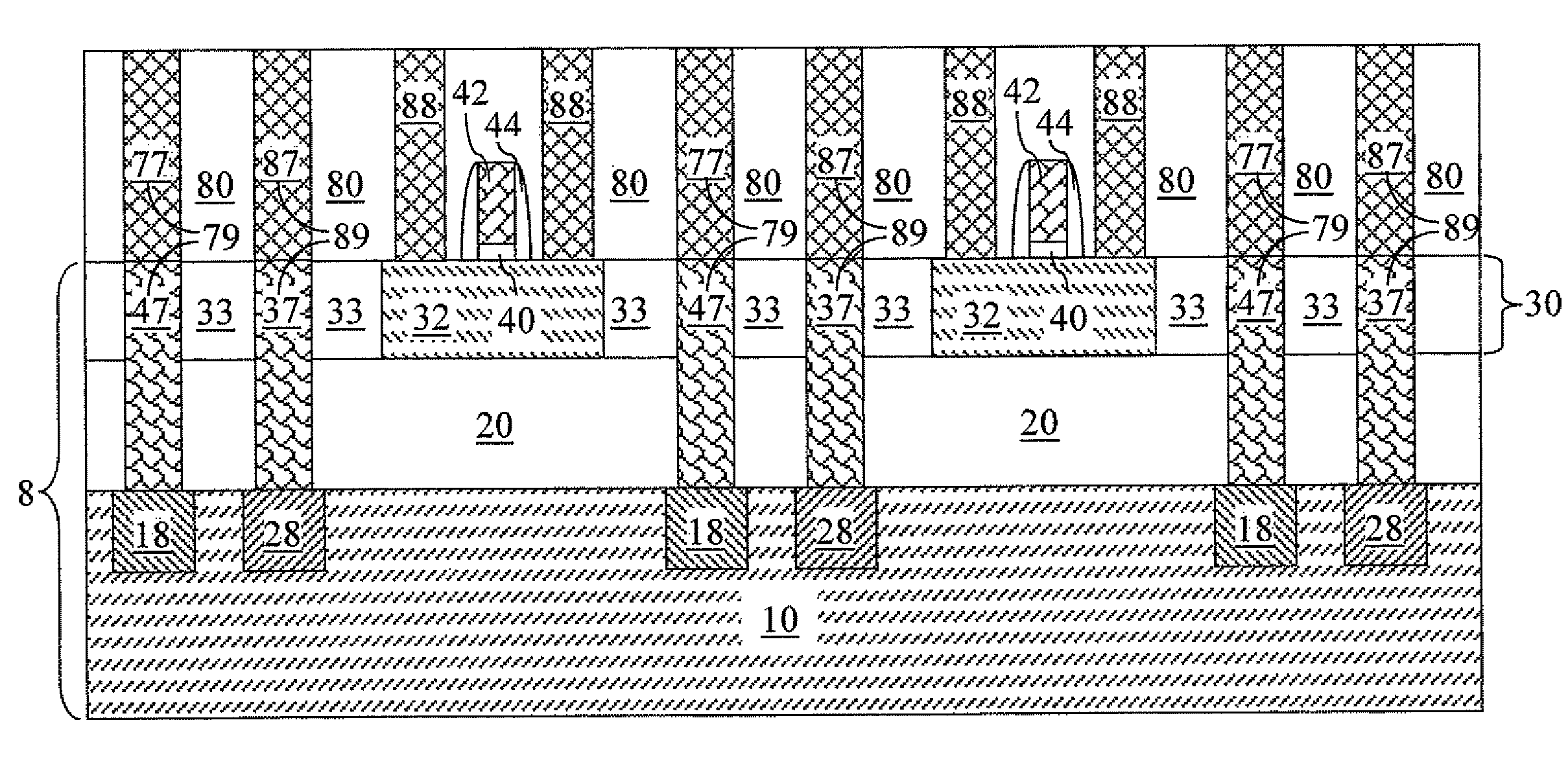
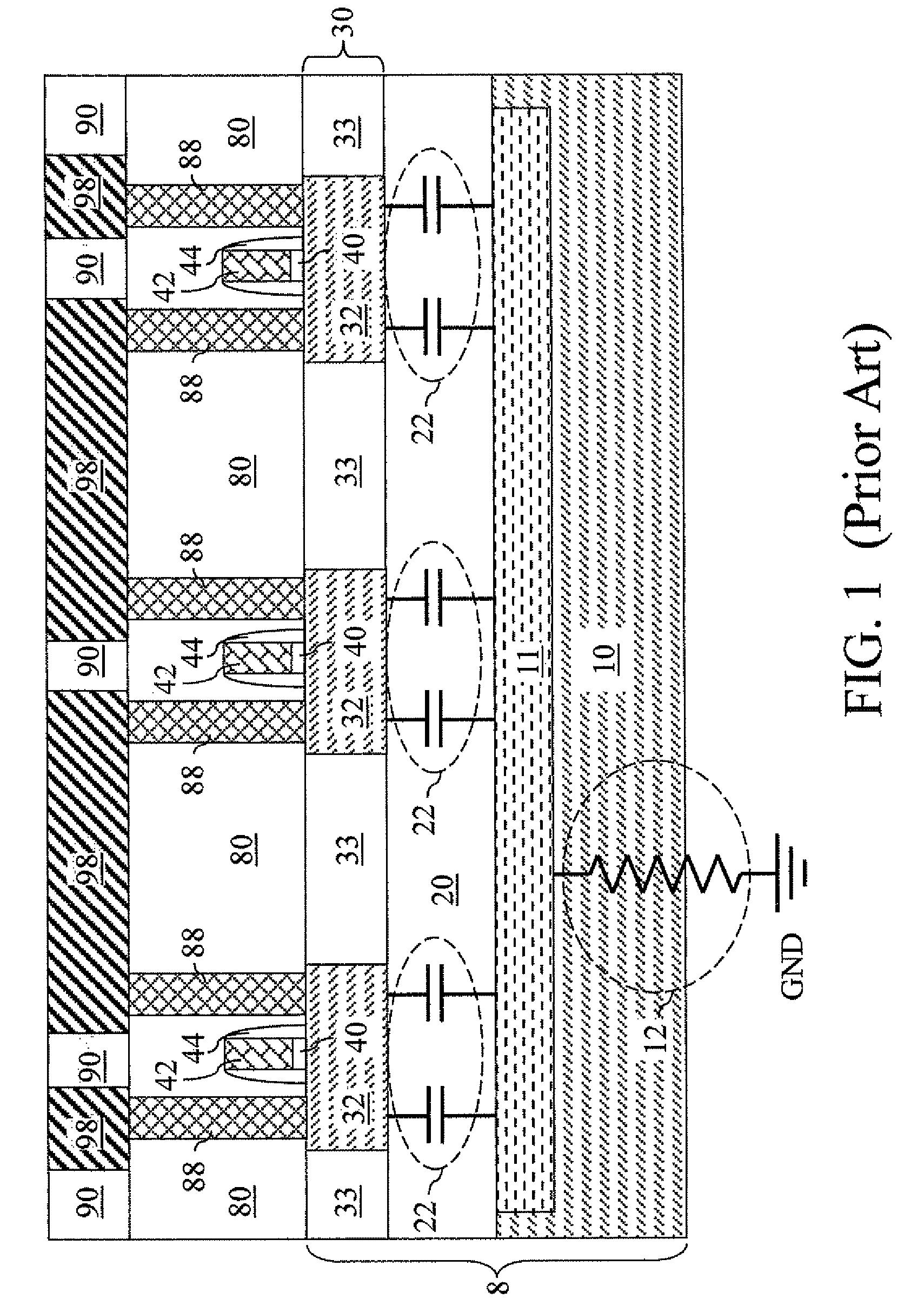
Transistor device and method
ActiveUS20090134939A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrequency-independant attenuatorsSemiconductor heterostructuresEngineering
A field-effect transistor device, including: a semiconductor heterostructure comprising, in a vertically stacked configuration, a semiconductor gate layer between semiconductor source and drain layers, the layers being separated by heterosteps; the gate layer having a thickness of less than about 100 Angstroms; and source, gate, and drain electrodes respectively coupled with said source, gate, and drain layers. Separation of the gate by heterosteps, rather than an oxide layer, has very substantial advantages.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
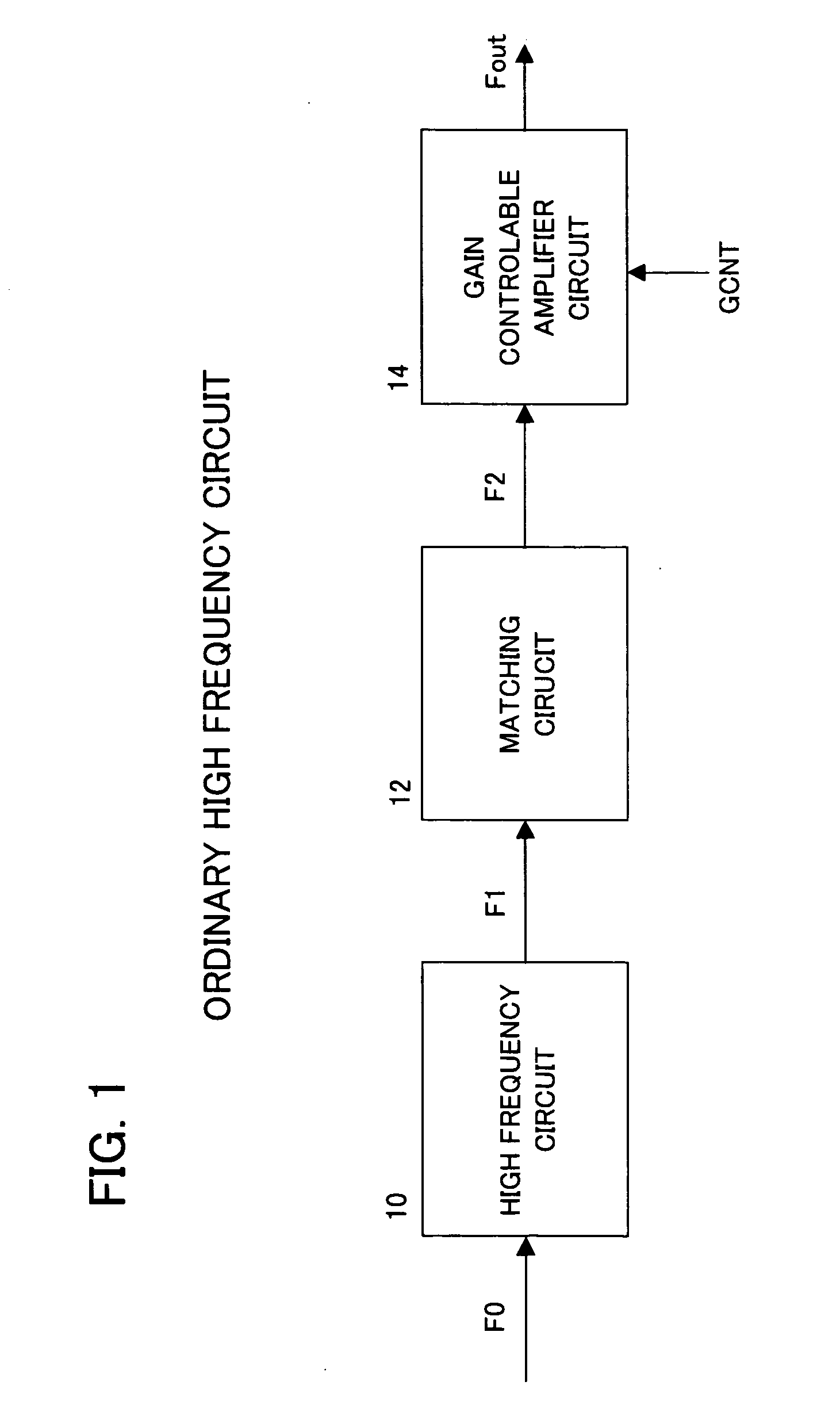
High frequency amplifier circuit permitting variable gain control
InactiveUS20050118971A1Reduce noise figureAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower managementCapacitanceUltrasound attenuation
The present invention is an amplifier circuit that permits variable gain control, comprising an input terminal to which a high frequency input signal is supplied; an amplifier transistor to the gate of which the high frequency input signal supplied to the input terminal is supplied and which generates an amplified signal at the drain side; and a variable attenuator provided in a signal transmission line between the input terminal and the gate of the amplifier transistor, in which a plurality of attenuation units in which an attenuation capacitor and a switch transistor are serially connected are provided in parallel between the signal transmission line and a power supply, and the attenuation ratio of which is variably controlled by controlling the conduction of the switch transistor.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
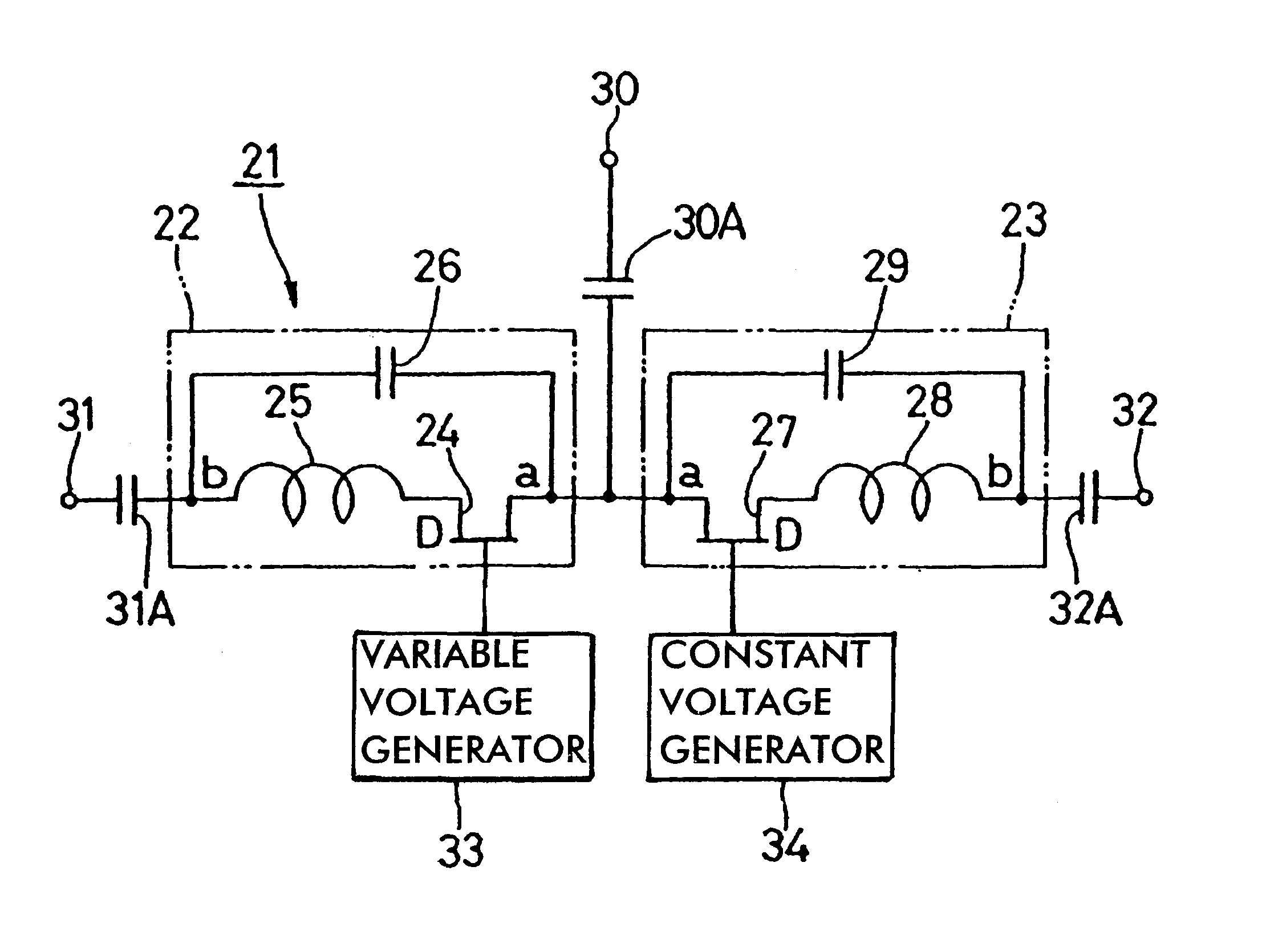
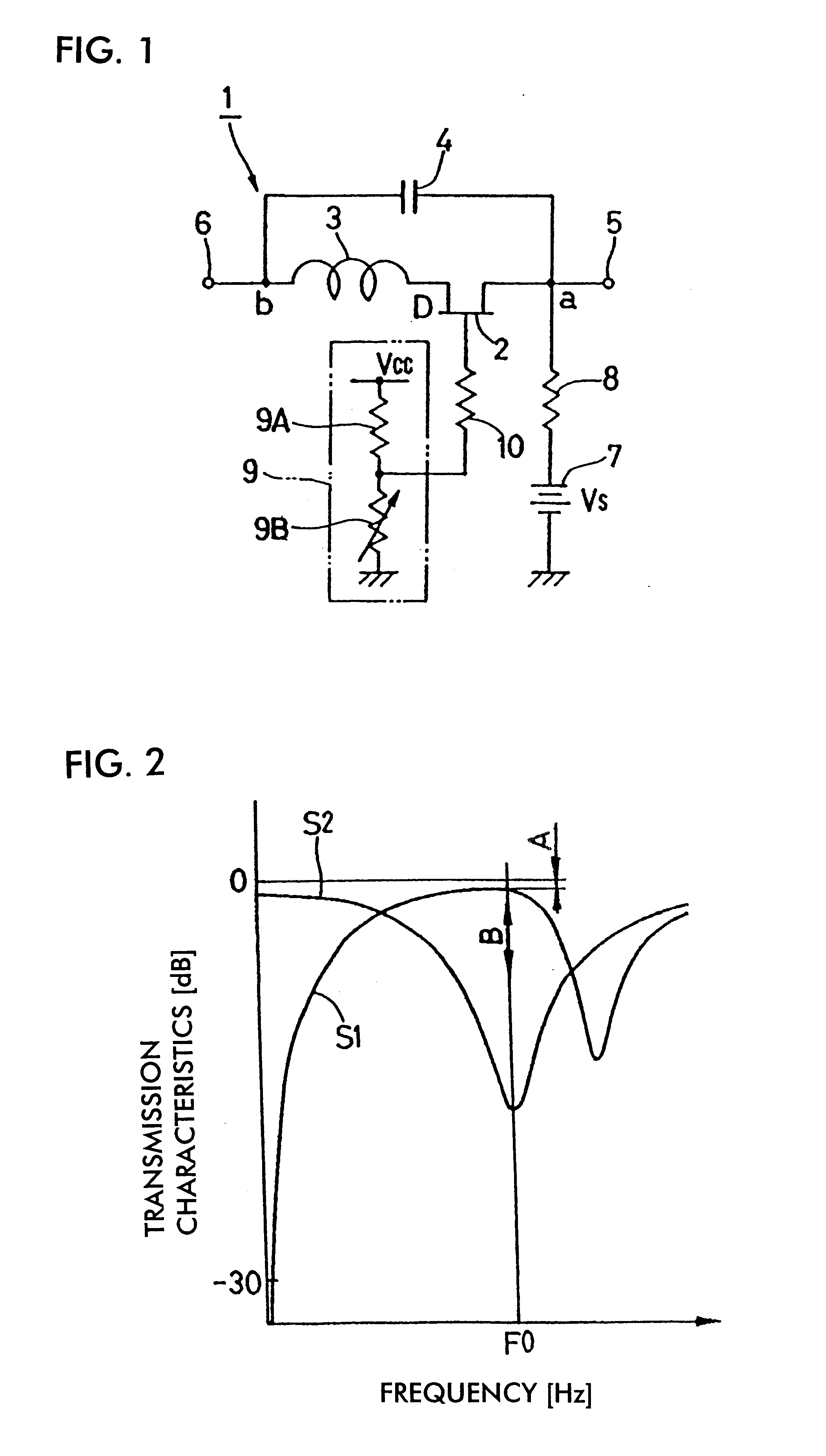
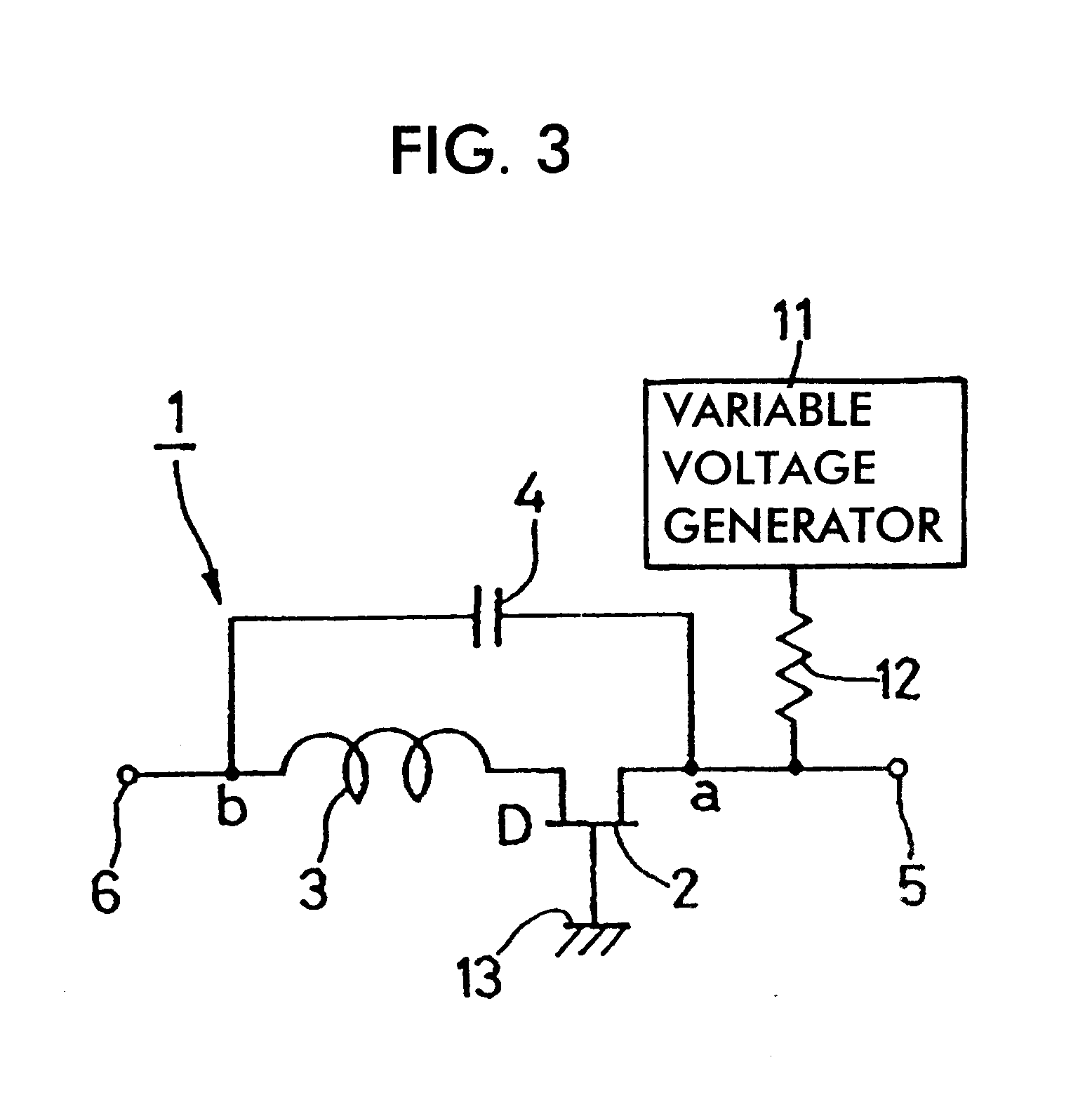
Variable attenuator
InactiveUS6720850B2Improve isolationIncrease rangeMultiple-port networksPulse automatic controlCapacitanceUltrasound attenuation
A resonance type SPST switch is formed by connecting an inductive element in series with the drain of an FET, and then by connecting a capacitive element in parallel with the series connection of the FET and the inductive element. A constant-voltage source for feeding a voltage Vs is connected to the source of the FET, and a variable-voltage generator for switching the FET between an on state and a state in the vicinity of pinchoff is connected to the gate of the FET. When the variable-voltage generator feeds a voltage Valpha in the vicinity of a pinchoff voltage to the gate of the FET, the SPST switch is closed while the amount of attenuation between first and second terminals is variably set. The resulting variable attenuator is thus compact in size, allows a large amount of attenuation to be set, and involves low manufacturing costs.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
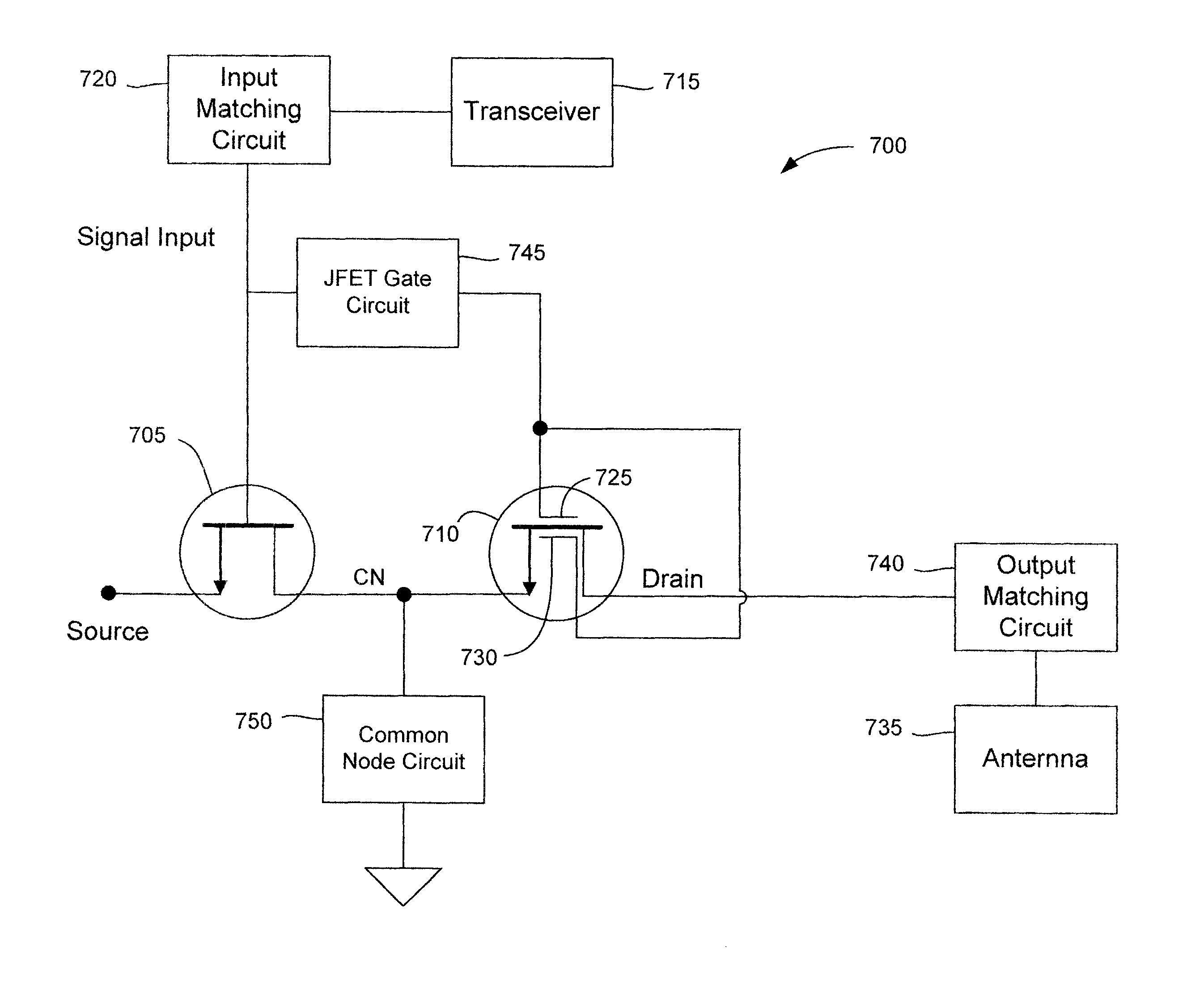
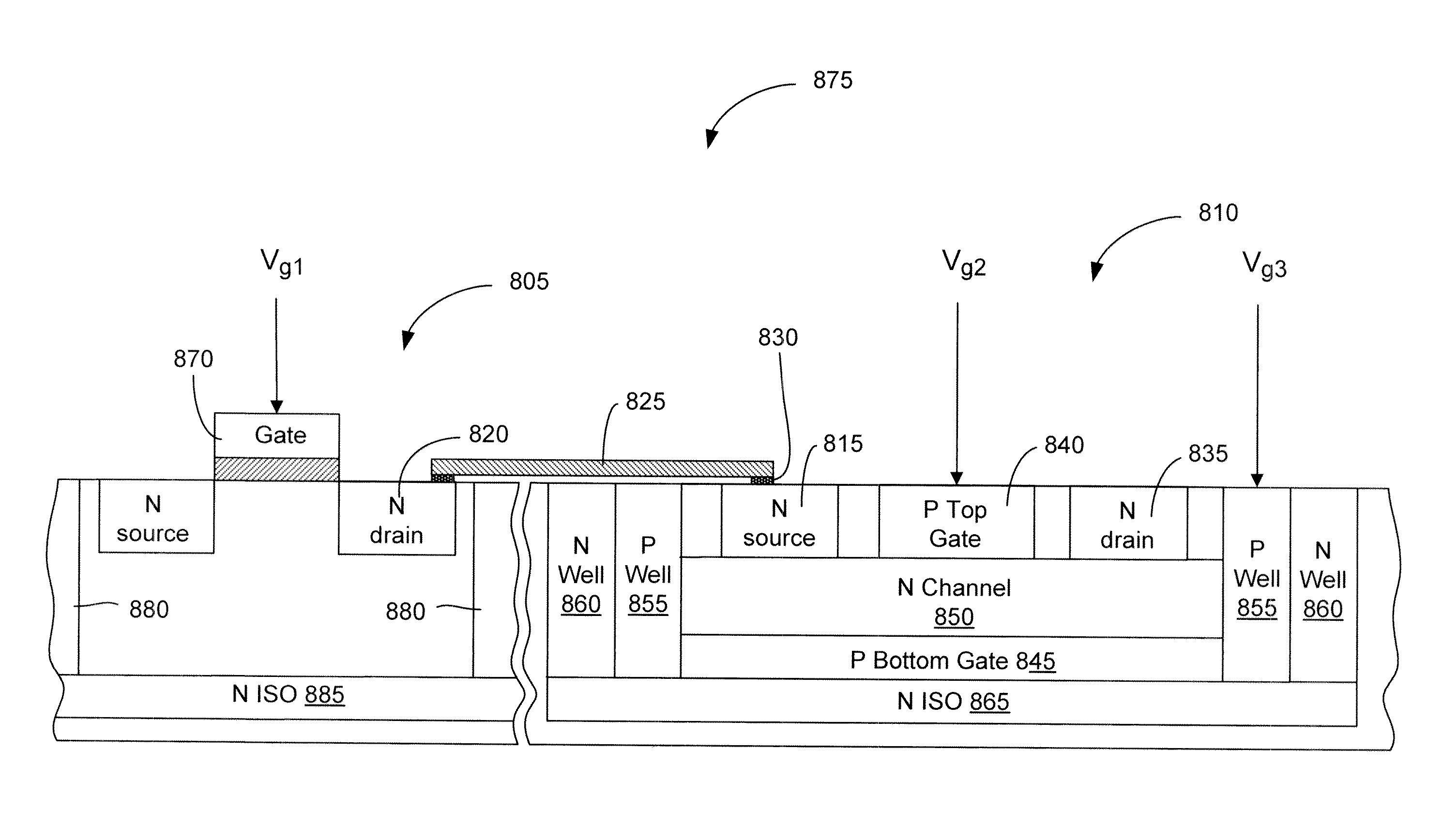
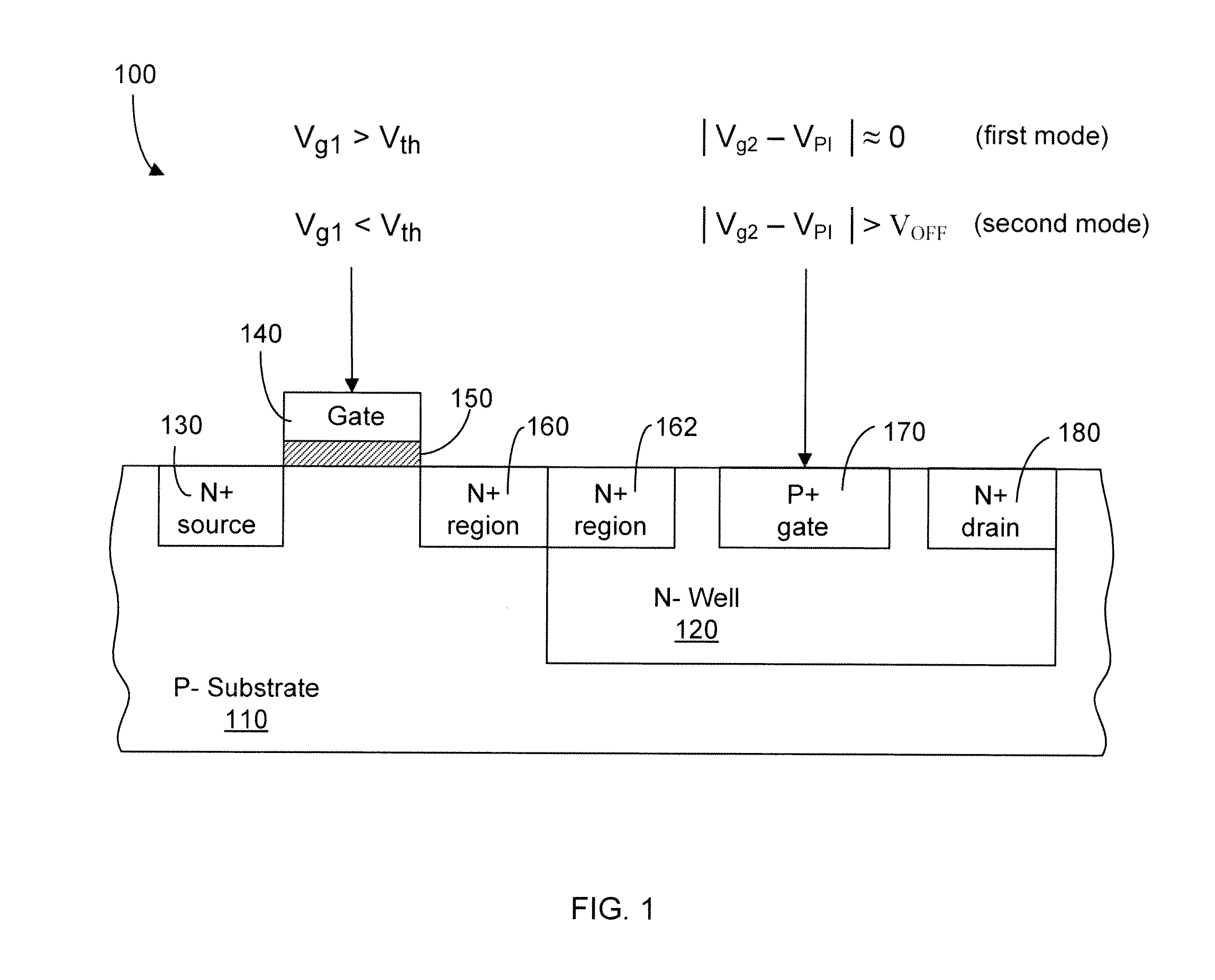
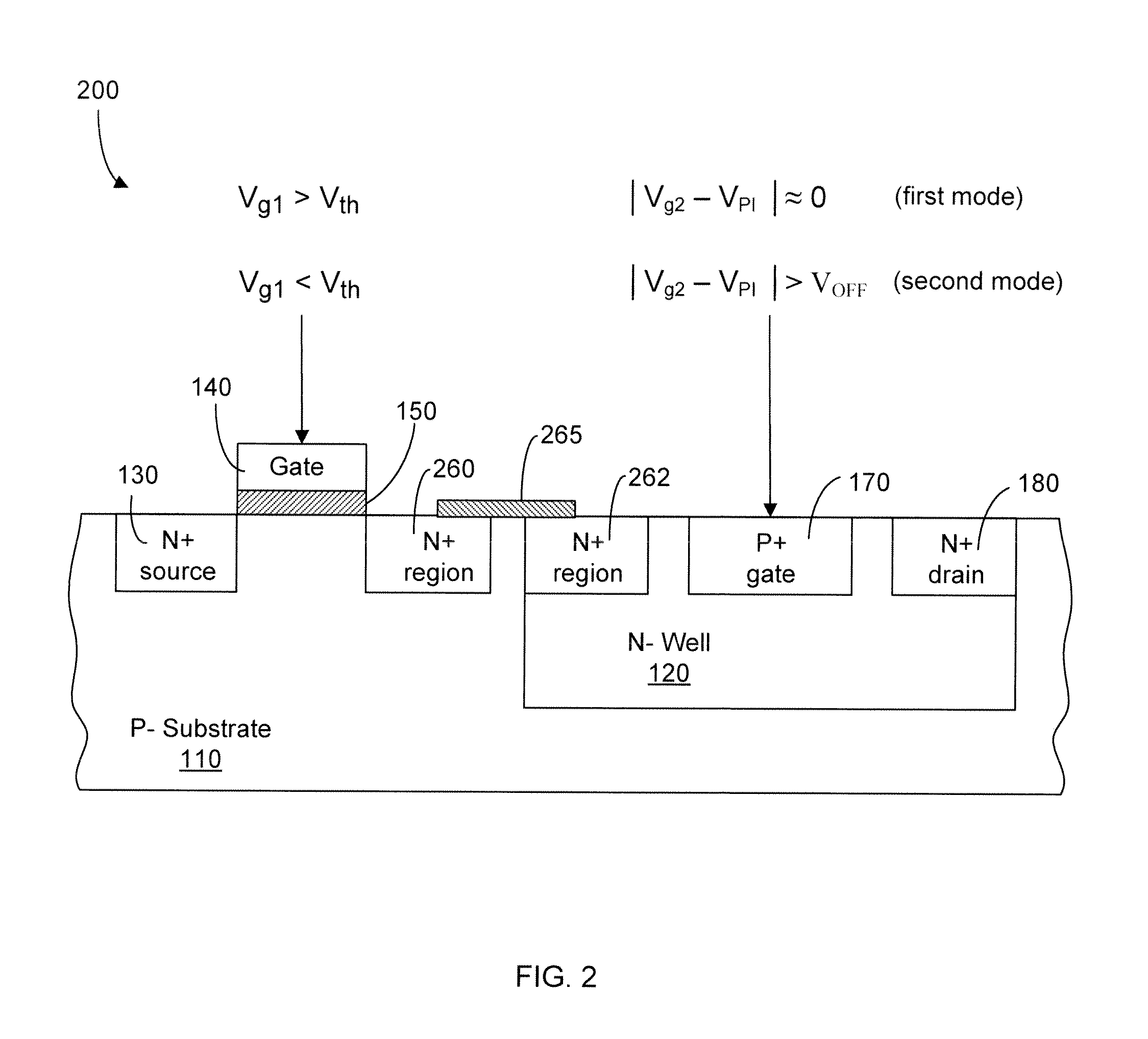
Electronic circuits including a MOSFET and a dual-gate JFET
Electronic circuits and methods are provided for various applications including signal amplification. An exemplary electronic circuit comprises a MOSFET and a dual-gate JFET in a cascode configuration. The dual-gate JFET includes top and bottom gates disposed above and below the channel. The top gate of the JFET is controlled by a signal that is dependent upon the signal controlling the gate of the MOSFET. The control of the bottom gate of the JFET can be dependent or independent of the control of the top gate. The MOSFET and JFET can be implemented as separate components on the same substrate with different dimensions such as gate widths.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
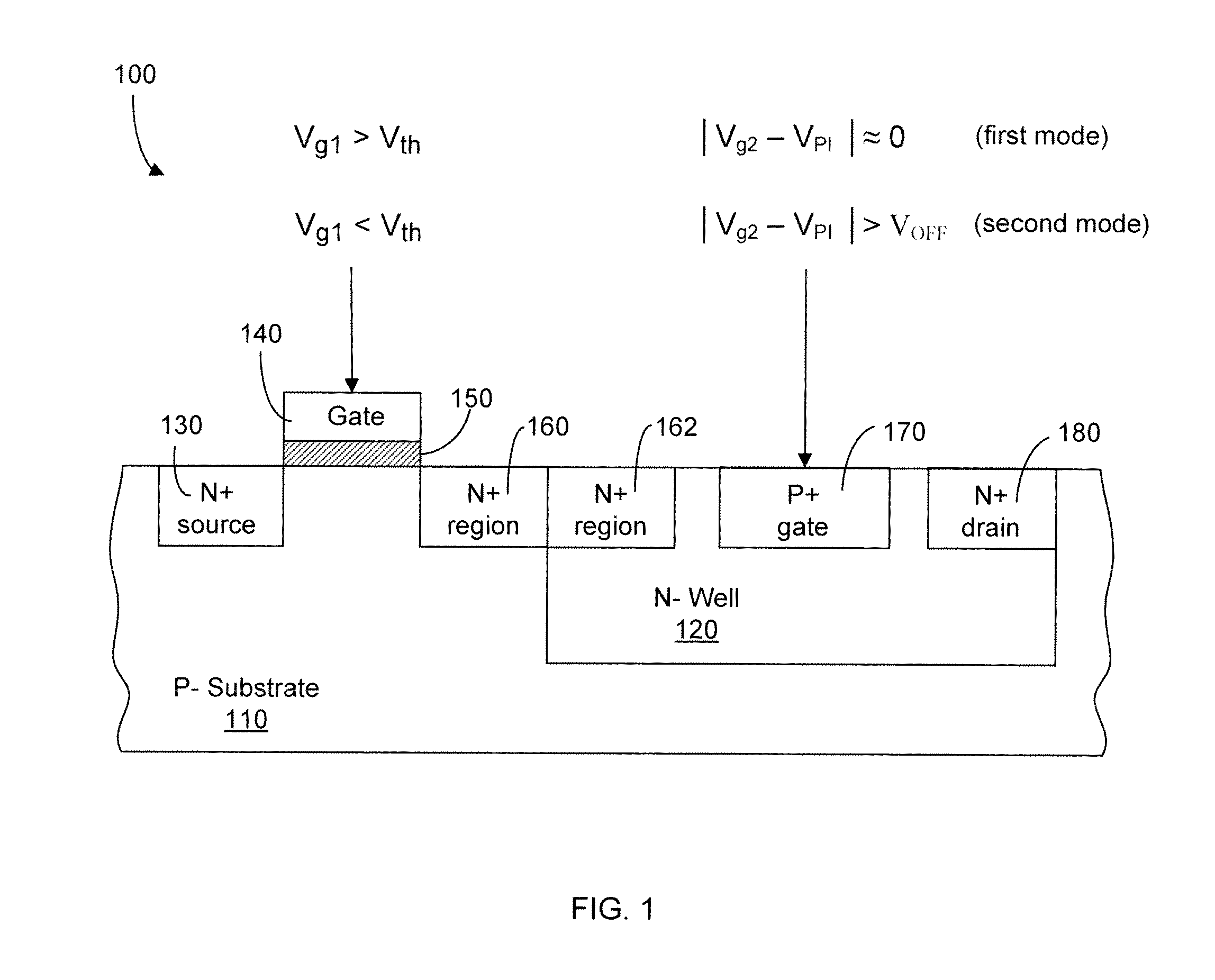
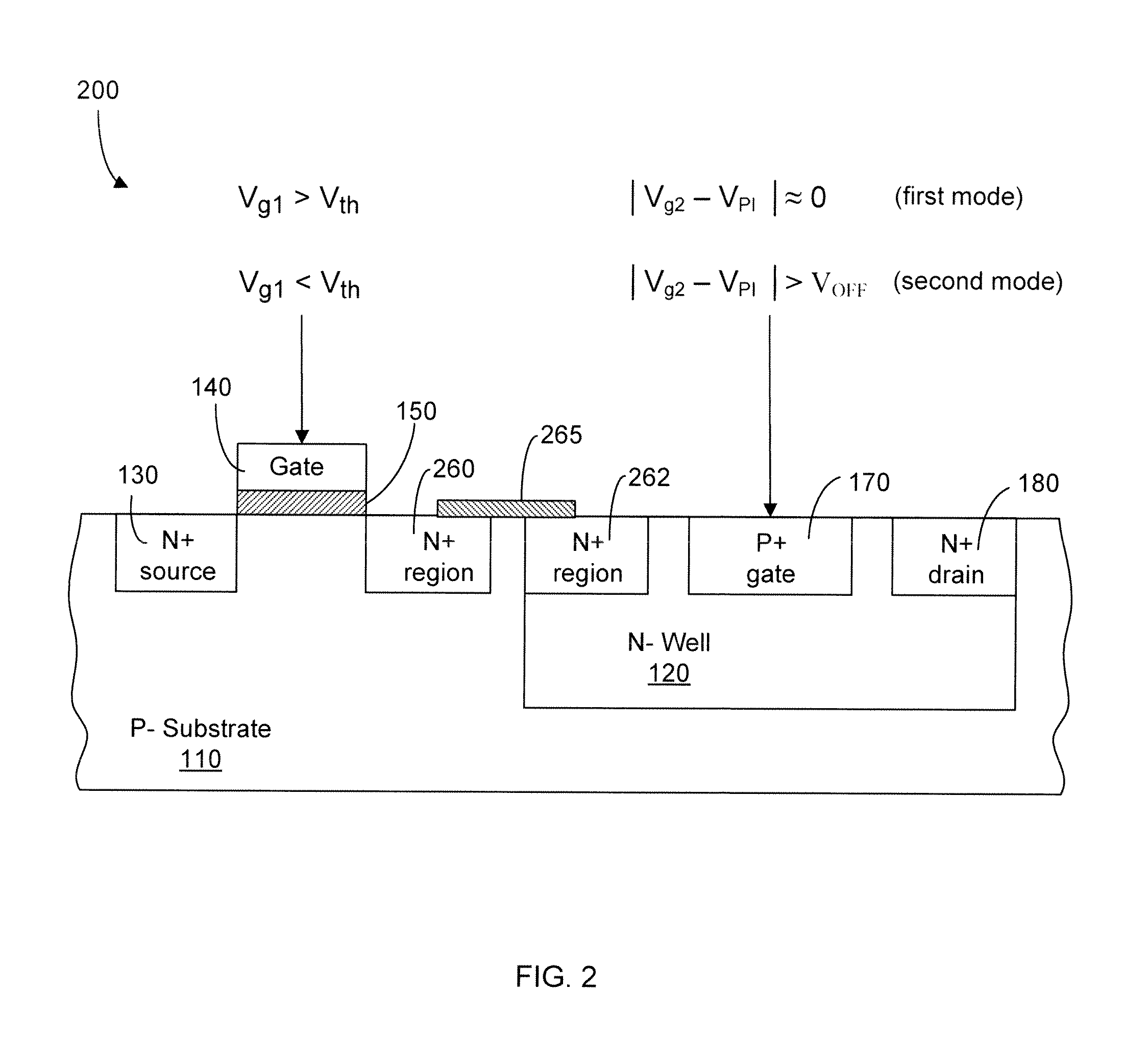
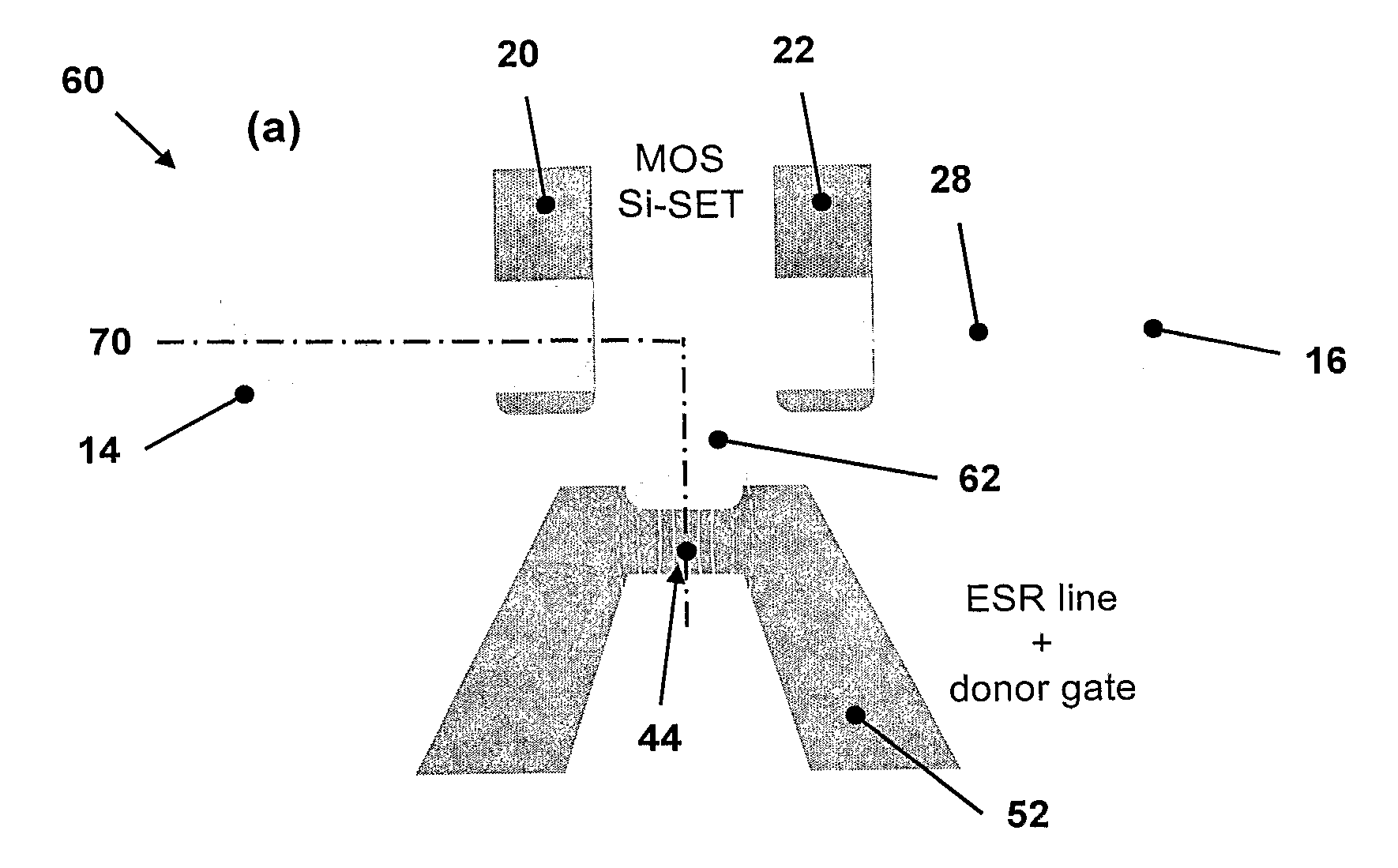
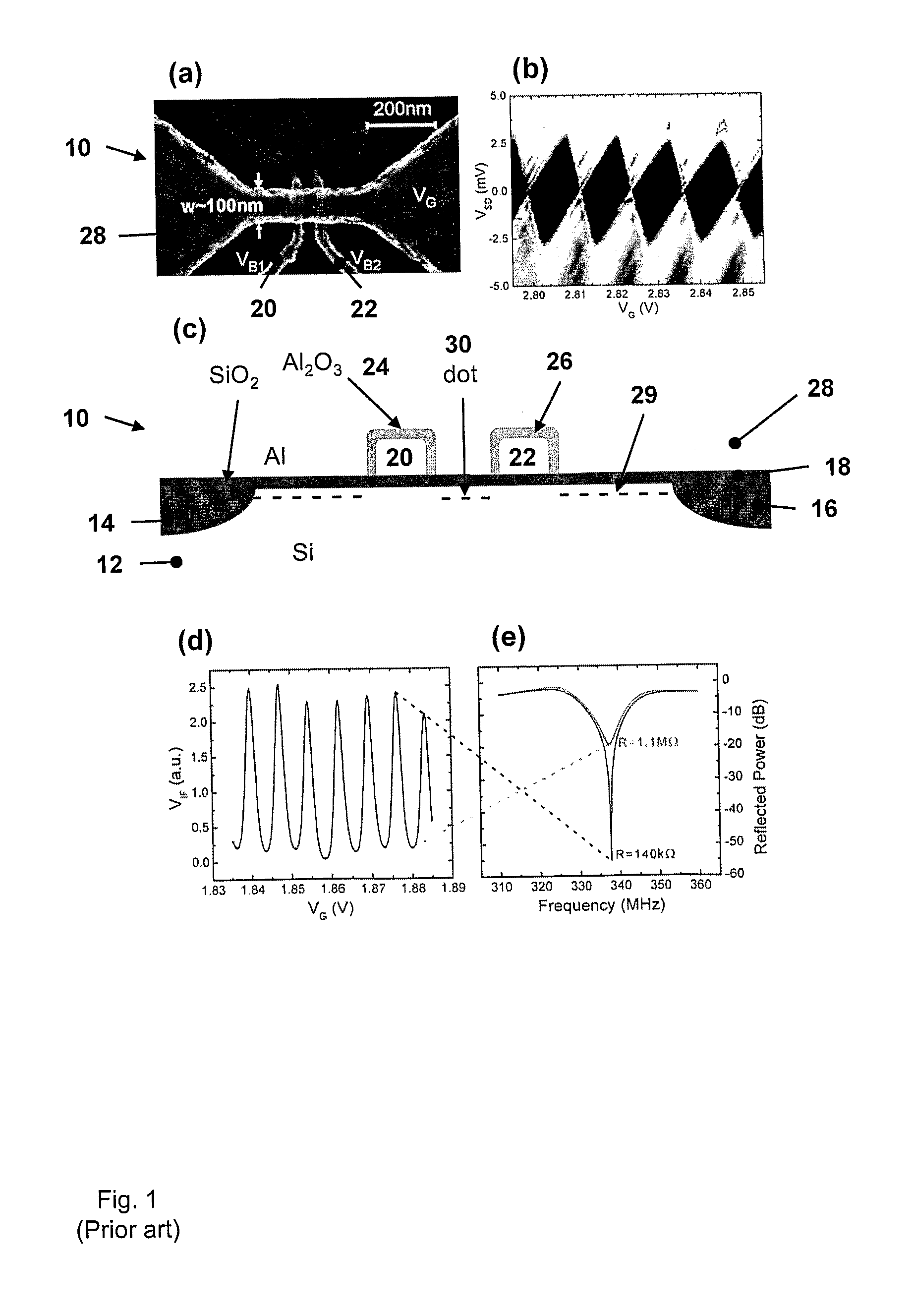
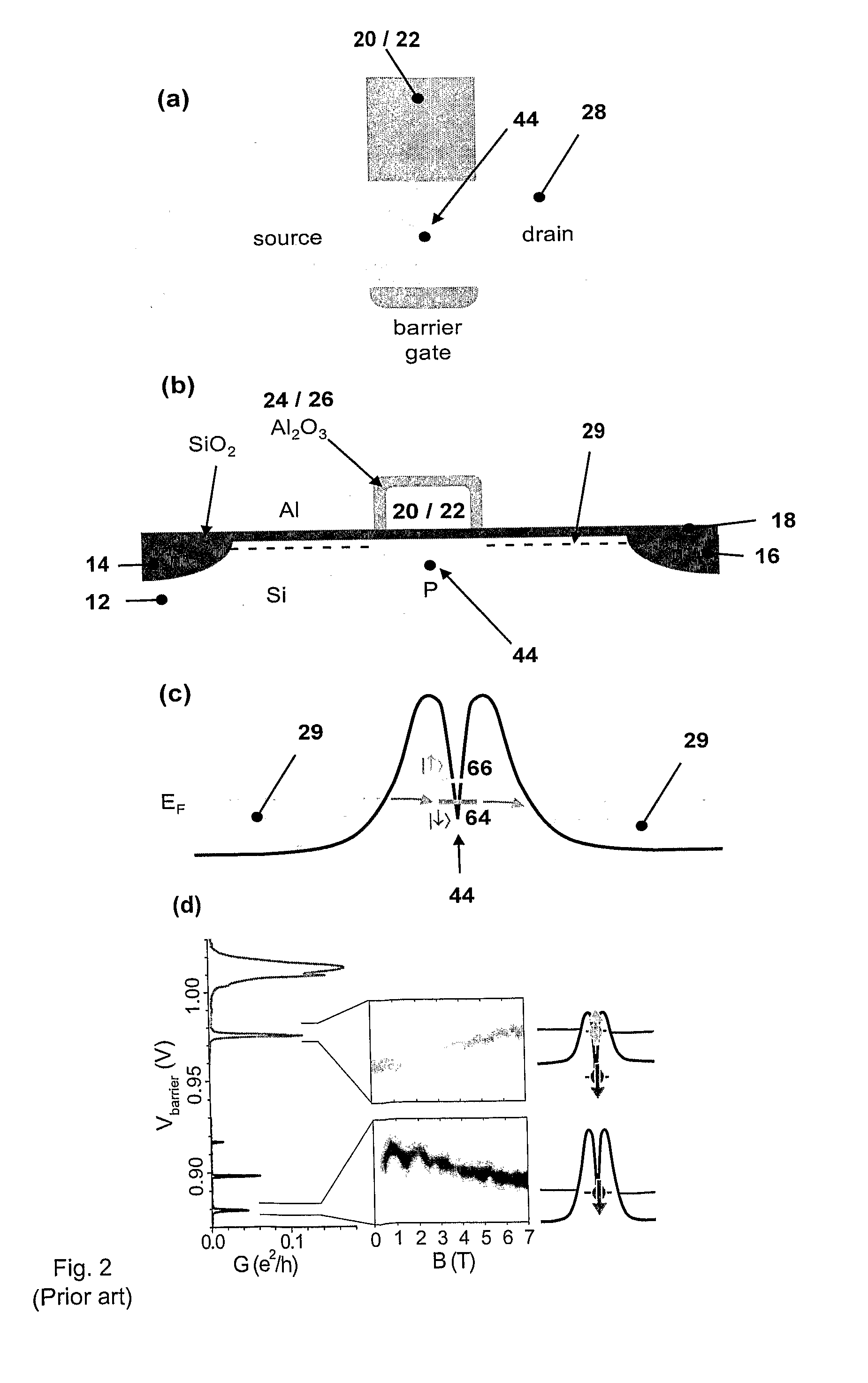
Control and readout of electron or hole spin
This invention concerns an electronic device for the control and readout of the electron or hole spin of a single dopant in silicon. The device comprises a silicon substrate in which there are one or more ohmic contact regions. An insulating region on top of the substrate. First and second barrier gates spaced apart to isolate a small region of charges to form an island of a Single Electron Transistor (SET). A third gate over-lying both the first and second barrier gates, but insulated from them, the third gate being able to generate a gate-induced charge layer (GICL) in the ESR line substrate beneath it. A fourth gate in close proximity to a single dopant donor gate atom, the dopant atom being encapsulated in the substrate outside the region of the GICL but close enough to allow spin-dependent charge tunnelling between the dopant atom and the SET island under the control of gate potentials, mainly the fourth gate. In use either the third or fourth gate also serve as an Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) line to control the spin of the single electron or hole of the dopant atom. In a further aspect it concerns a method for using the device.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
Quantum interference transistors and methods of manufacturing and operating the same
A quantum interference transistor may include a source; a drain; N channels (N≧2), between the source and the drain, and having N−1 path differences between the source and the drain; and at least one gate disposed at one or more of the N channels. One or more of the N channels may be formed in a graphene sheet. A method of manufacturing the quantum interference transistor may include forming one or more of the N channels using a graphene sheet. A method of operating the quantum interference transistor may include applying a voltage to the at least one gate. The voltage may shift a phase of a wave of electrons passing through a channel at which the at least one gate is disposed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Analog circuit and semiconductor device
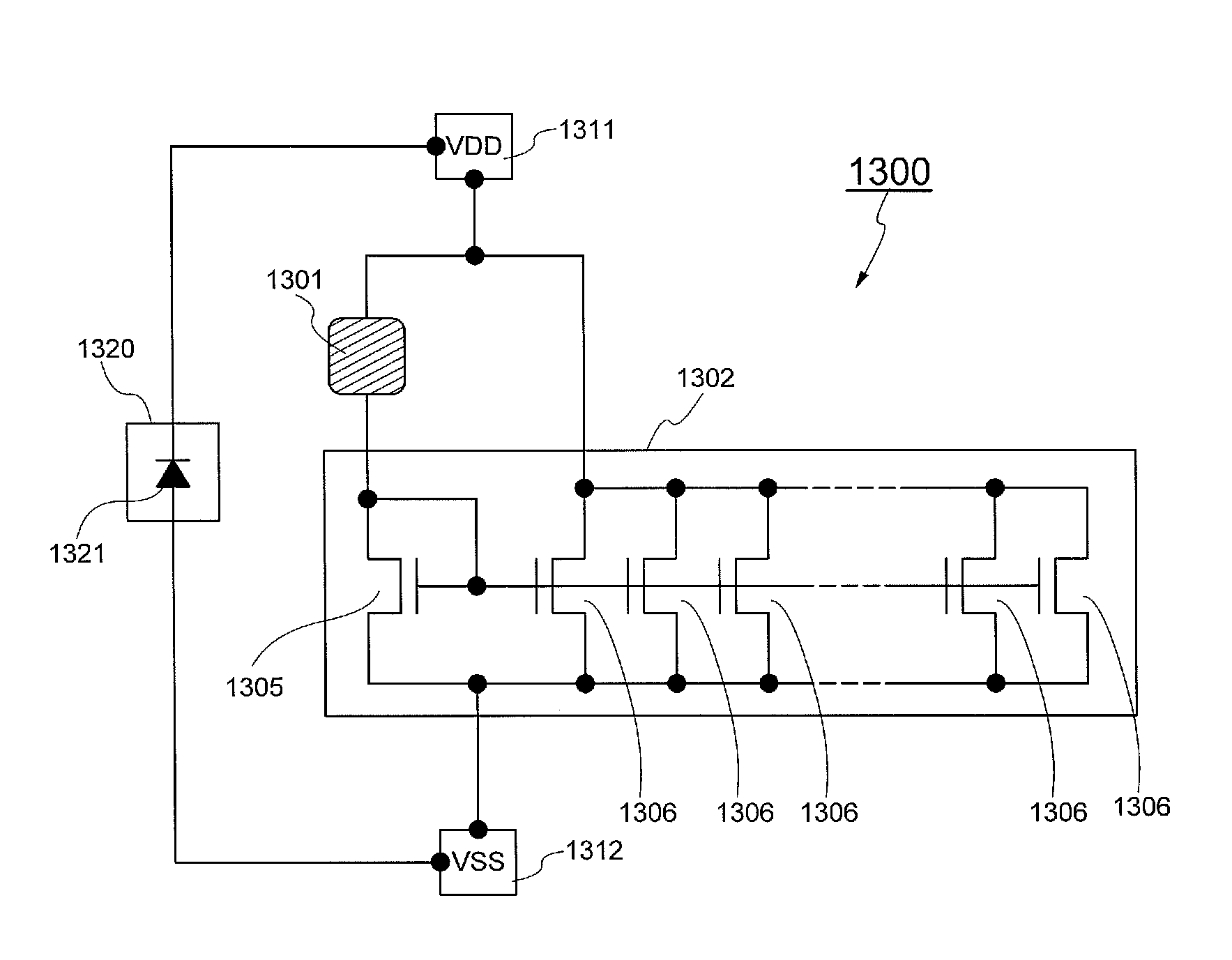
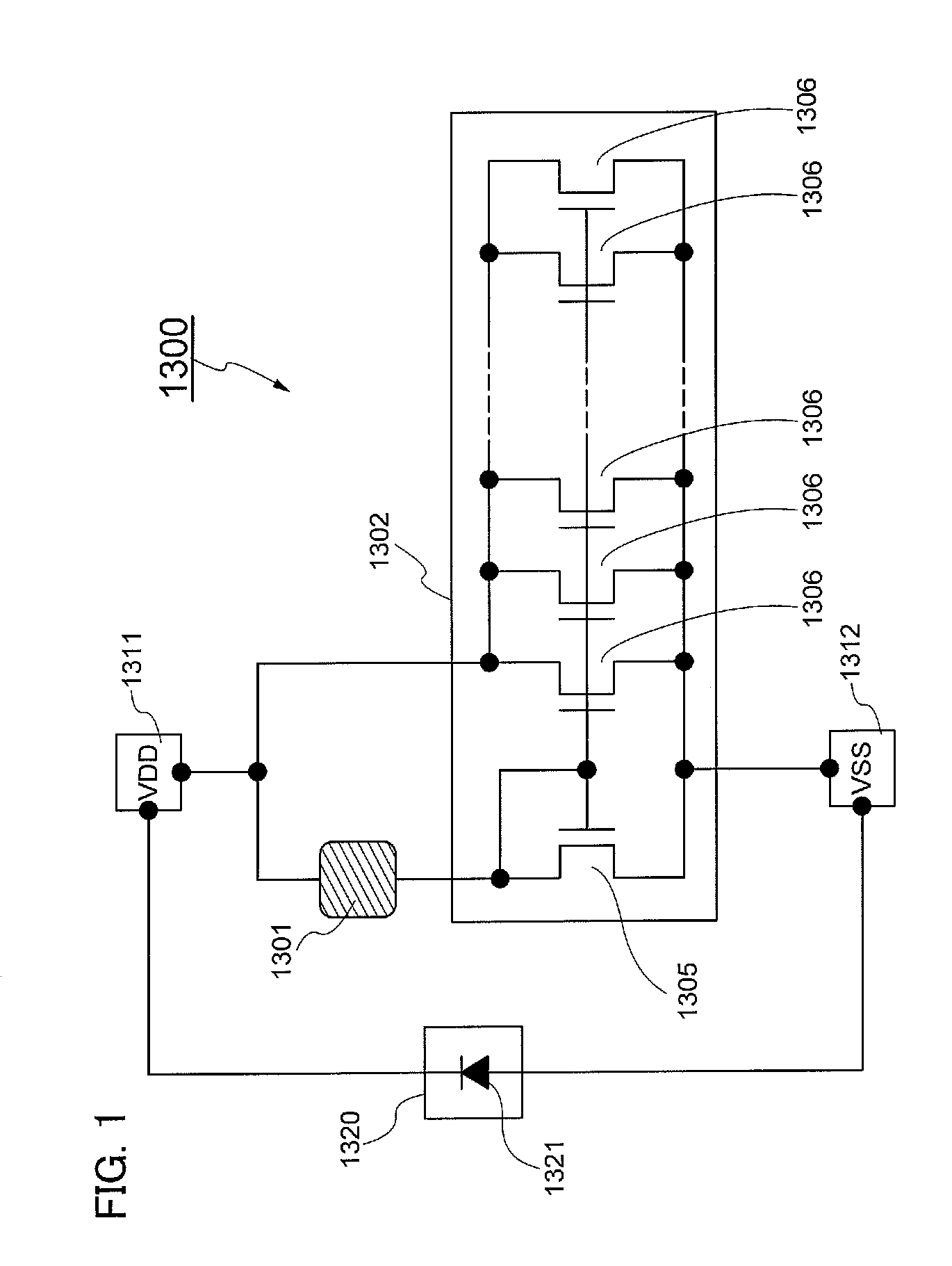
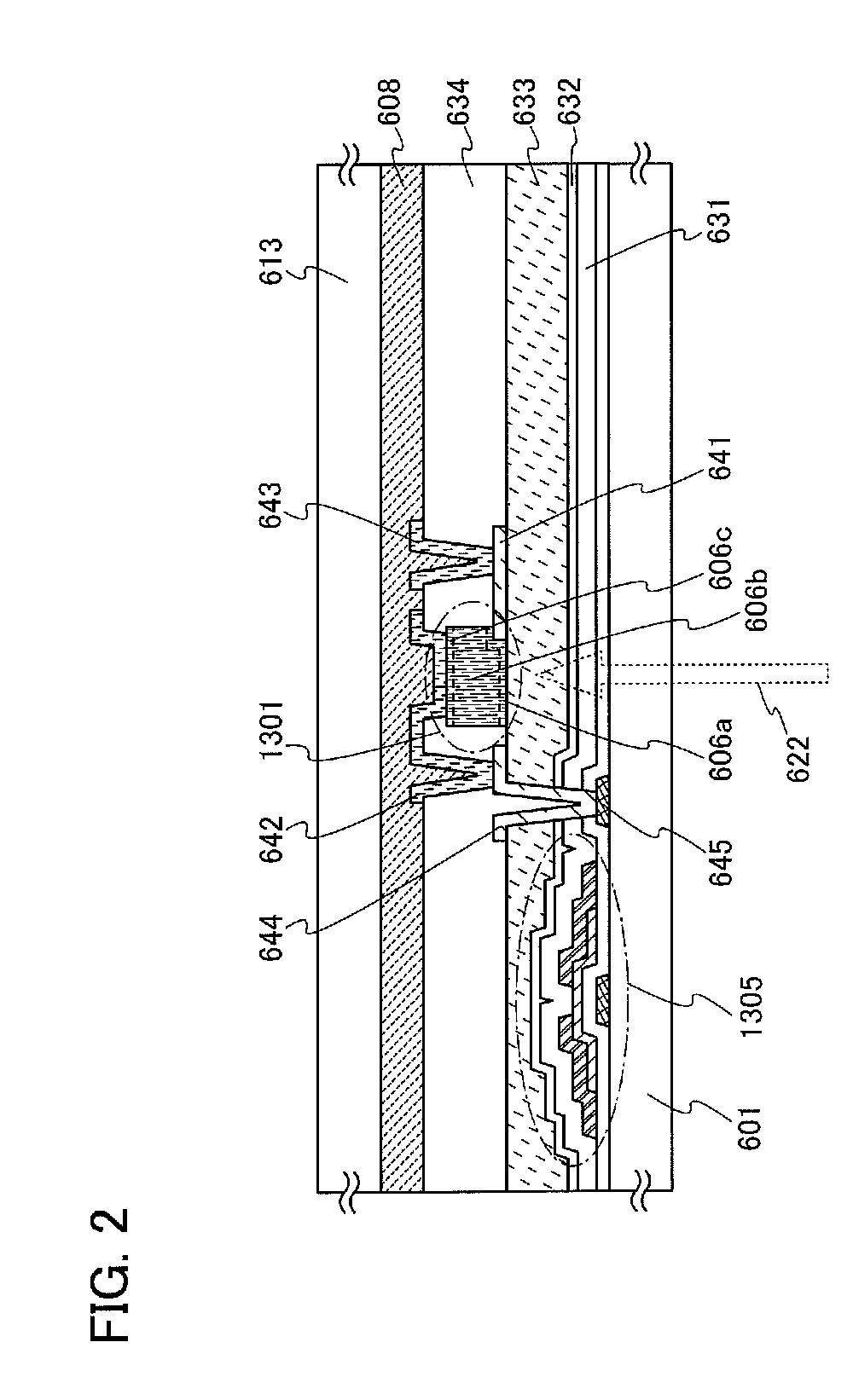
ActiveUS20110090006A1Reduce failureImprove dynamic rangeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen concentrationWide dynamic range
An object is to obtain a semiconductor device having a high sensitivity in detecting signals and a wide dynamic range, using a thin film transistor in which an oxide semiconductor layer is used. An analog circuit is formed with the use of a thin film transistor including an oxide semiconductor which has a function as a channel formation layer, has a hydrogen concentration of 5×1019 atoms / cm3 or lower, and substantially functions as an insulator in the state where no electric field is generated. Thus, a semiconductor device having a high sensitivity in detecting signals and a wide dynamic range can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electronic Circuits including a MOSFET and a Dual-Gate JFET
Electronic circuits and methods are provided for various applications including signal amplification. An exemplary electronic circuit comprises a MOSFET and a dual-gate JFET in a cascode configuration. The dual-gate JFET includes top and bottom gates disposed above and below the channel. The top gate of the JFET is controlled by a signal that is dependent upon the signal controlling the gate of the MOSFET. The control of the bottom gate of the JFET can be dependent or independent of the control of the top gate. The MOSFET and JFET can be implemented as separate components on the same substrate with different dimensions such as gate widths.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
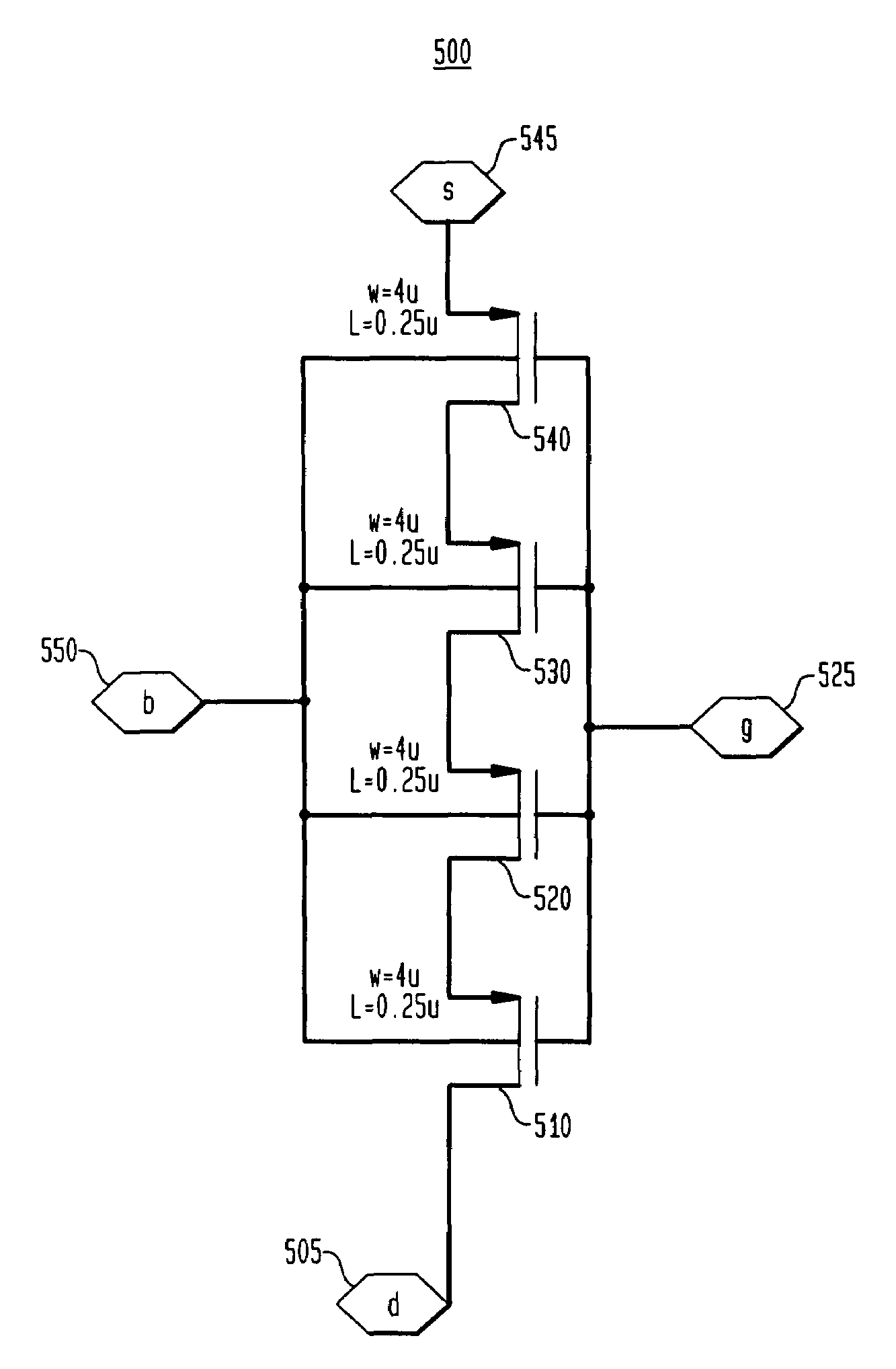
High voltage gain topology for analog circuits in short channel technologies
InactiveUS7652520B2Reduce leakageImprove noise immunityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringHigh pressure
A stacked MOS configuration for use in short channel length analog circuit technologies is provided. The stacked MOS configuration comprises a plurality of short-channel MOS transistors coupled in series and sharing a common gate terminal. In an embodiment, a first peripheral transistor provides a drain terminal for the stacked MOS configuration. A second peripheral transistor provides a source terminal for the stacked MOS configuration. Adjacent transistors in the stacked MOS configuration are connected in a drain-to-source configuration.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
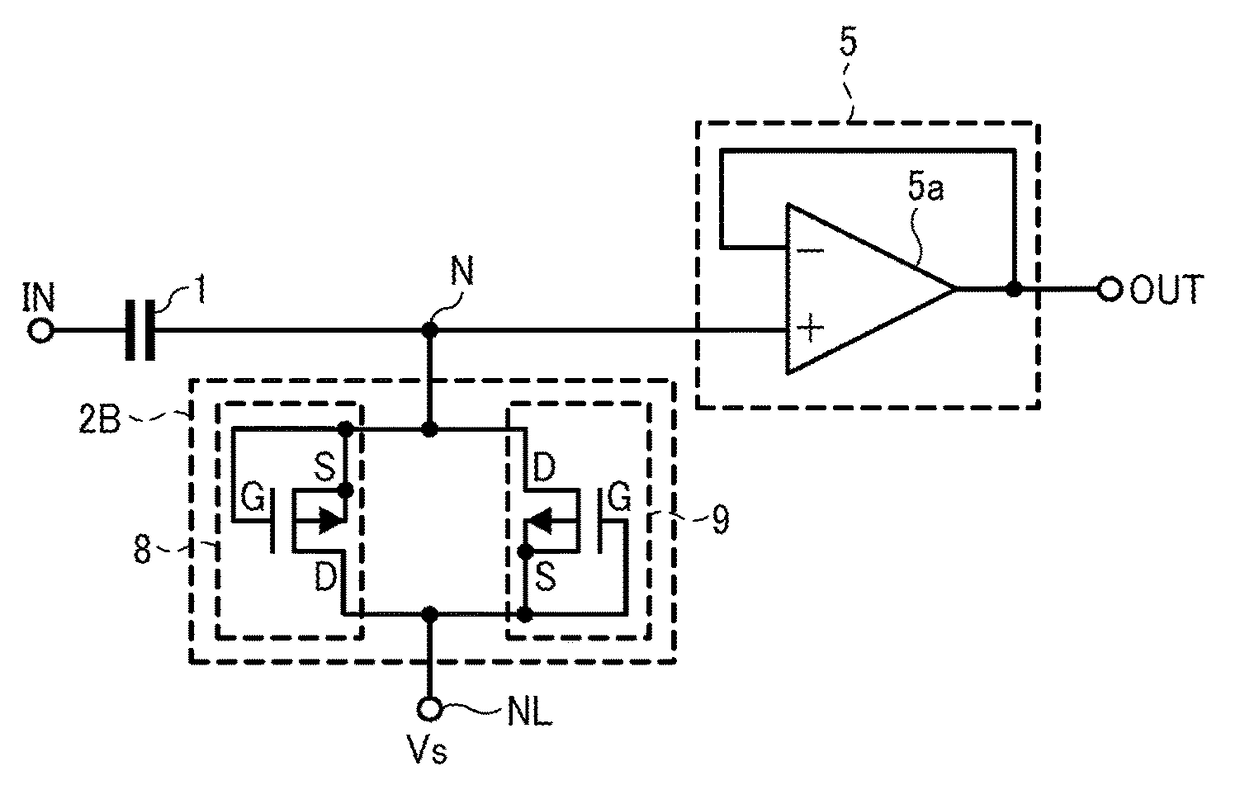
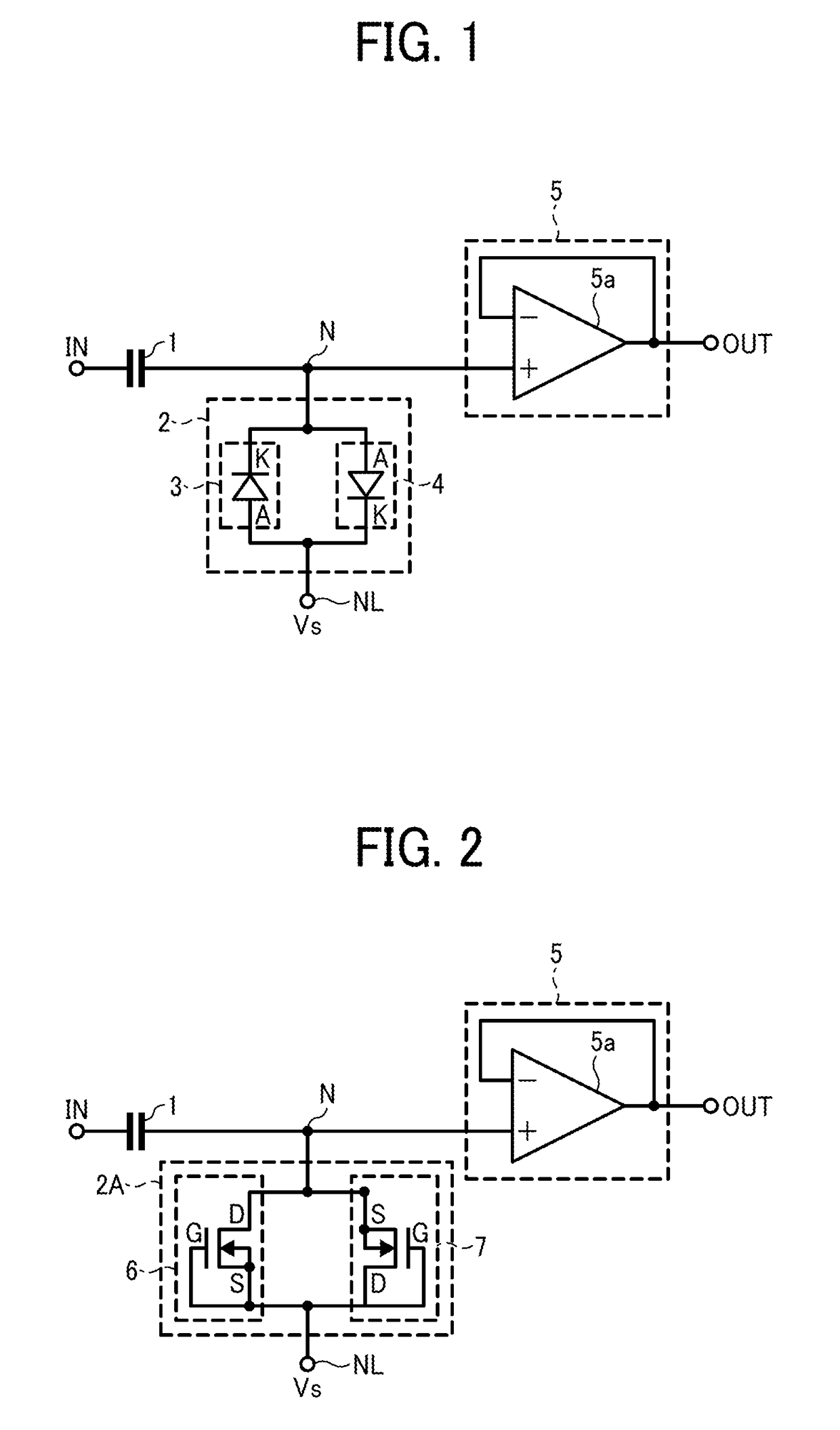
High-pass filter circuit and band-pass filter circuit
ActiveUS9923546B2Multiple-port networksFrequency selective two-port networksBandpass filteringHemt circuits
Two types of high-pass filter circuit and a band-pass filter circuit are provided. Both types of high-pass filter circuit include a capacitor configured to input an input signal, a resistor connected between an output terminal of the capacitor and a prescribed bias voltage, and a signal output circuit connected to the output terminal of the capacitor and configured to buffer-amplify the input signal for output. In one of the two types of high-pass filter circuits, the resistor is formed on an SOI semiconductor substrate and includes two PN junction diodes that are inversely connected to each other in parallel. In the other one of the high-pass filter circuits, the resistor is formed on an SOI semiconductor substrate and includes two MOS transistors that are inversely connected to each other in parallel.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method and Apparatus for Preventing Digital Step Attenuator Output Power Peaking During Attenuation State Transitions
ActiveUS20150171828A1Reducing positive switching transients (glitches)Reduce the required powerMultiple-port networksWaveguide type devicesUltrasound attenuationPeak value
A method and circuit for significantly reducing positive switching transients (glitches) of digital step attenuators (DSA's) by controlling the timing of state transitions for individual attenuator stages within a DSA. Such control prevents the DSA output power from peaking during attenuation state transitions and ensures that any transient glitch during the transition results in reduced power at the DSA output. Attenuation stage timing delay can be implemented on an integrated circuit die or “chip” for monolithic implementations of a DSA by adding circuitry which ensures that any attenuation state changes result in increased attenuation rather than decreased attenuation, thereby reducing or eliminating positive transient glitches at the DSA output.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Analog circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS8242837B2Reduce failureImprove dynamic rangeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen concentrationWide dynamic range
An object is to obtain a semiconductor device having a high sensitivity in detecting signals and a wide dynamic range, using a thin film transistor in which an oxide semiconductor layer is used. An analog circuit is formed with the use of a thin film transistor including an oxide semiconductor which has a function as a channel formation layer, has a hydrogen concentration of 5×1019 atoms / cm3 or lower, and substantially functions as an insulator in the state where no electric field is generated. Thus, a semiconductor device having a high sensitivity in detecting signals and a wide dynamic range can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for reducing coupling in a mos device
Mutual capacitances between regions of a MOS device become substantial factors that limit the speed and performance of the device as the device dimensions are reduced in size. A MOS transistor with a shielding structure formed above the gate is described. The shielding structure is connected to ground and is configured to reduce at least some of these mutual capacitances.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
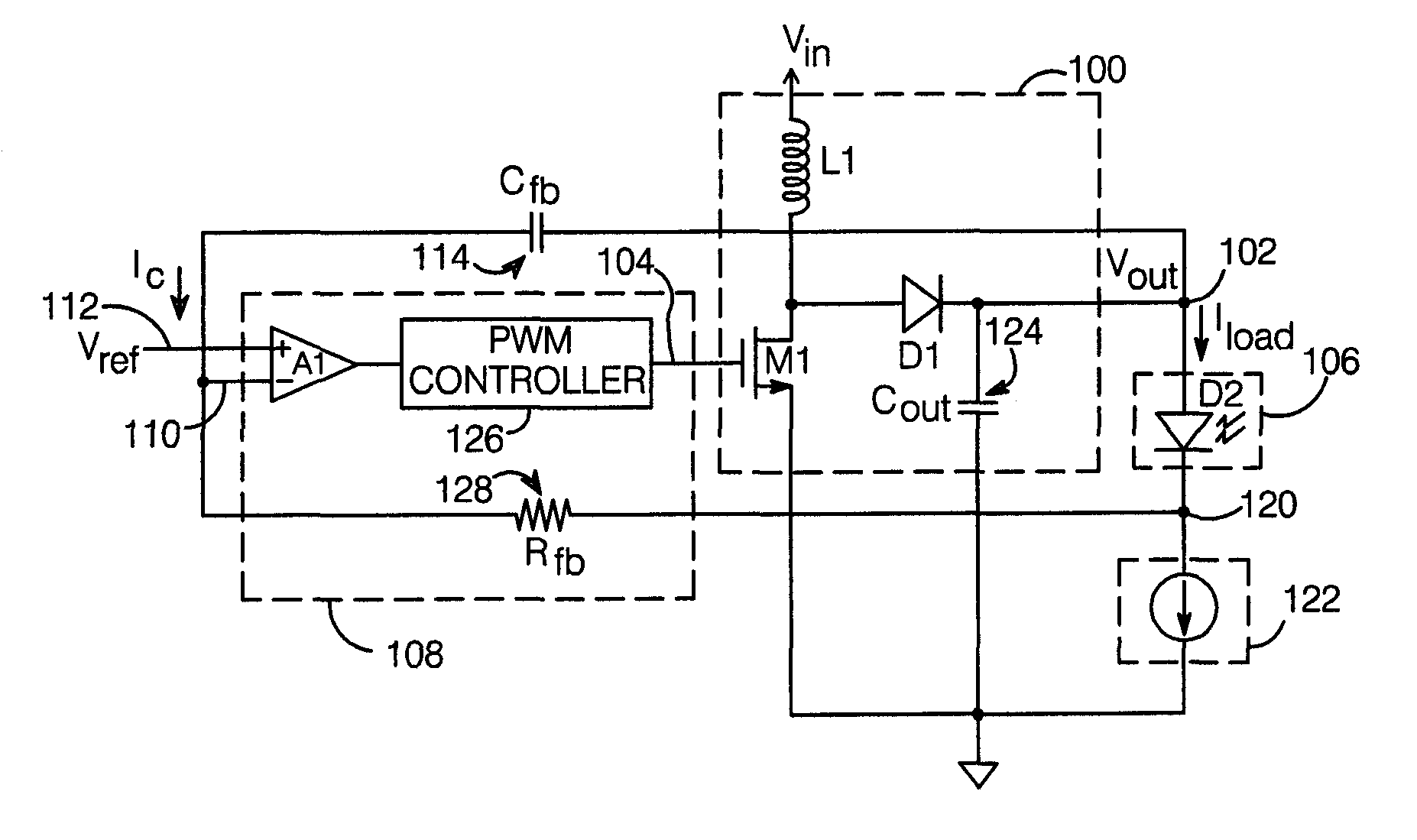
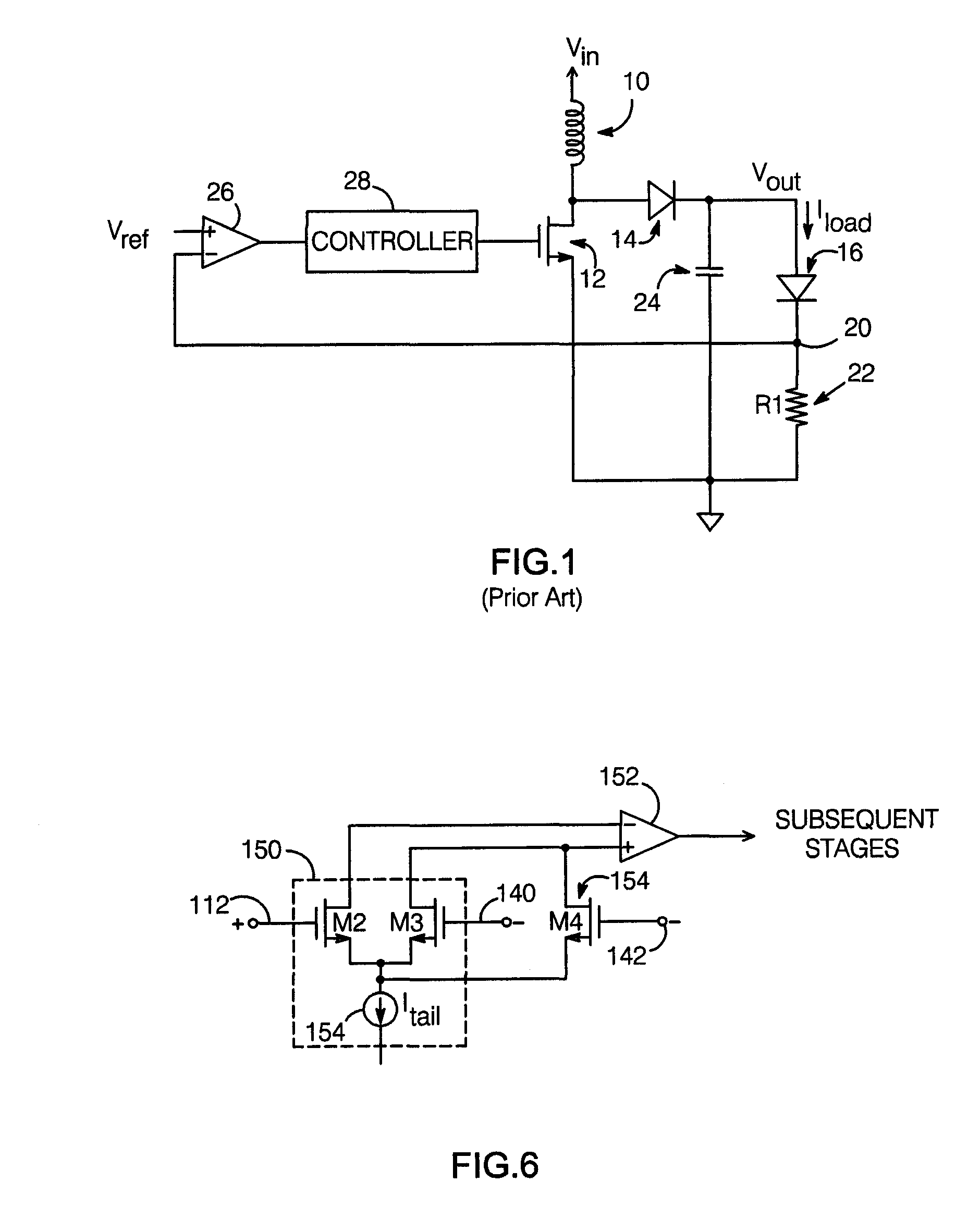
Switching power converter with controlled startup mechanism
ActiveUS20090167200A1Large currentLarge be damagedElectroluminescent light sourcesDc-dc conversionControl signalEngineering
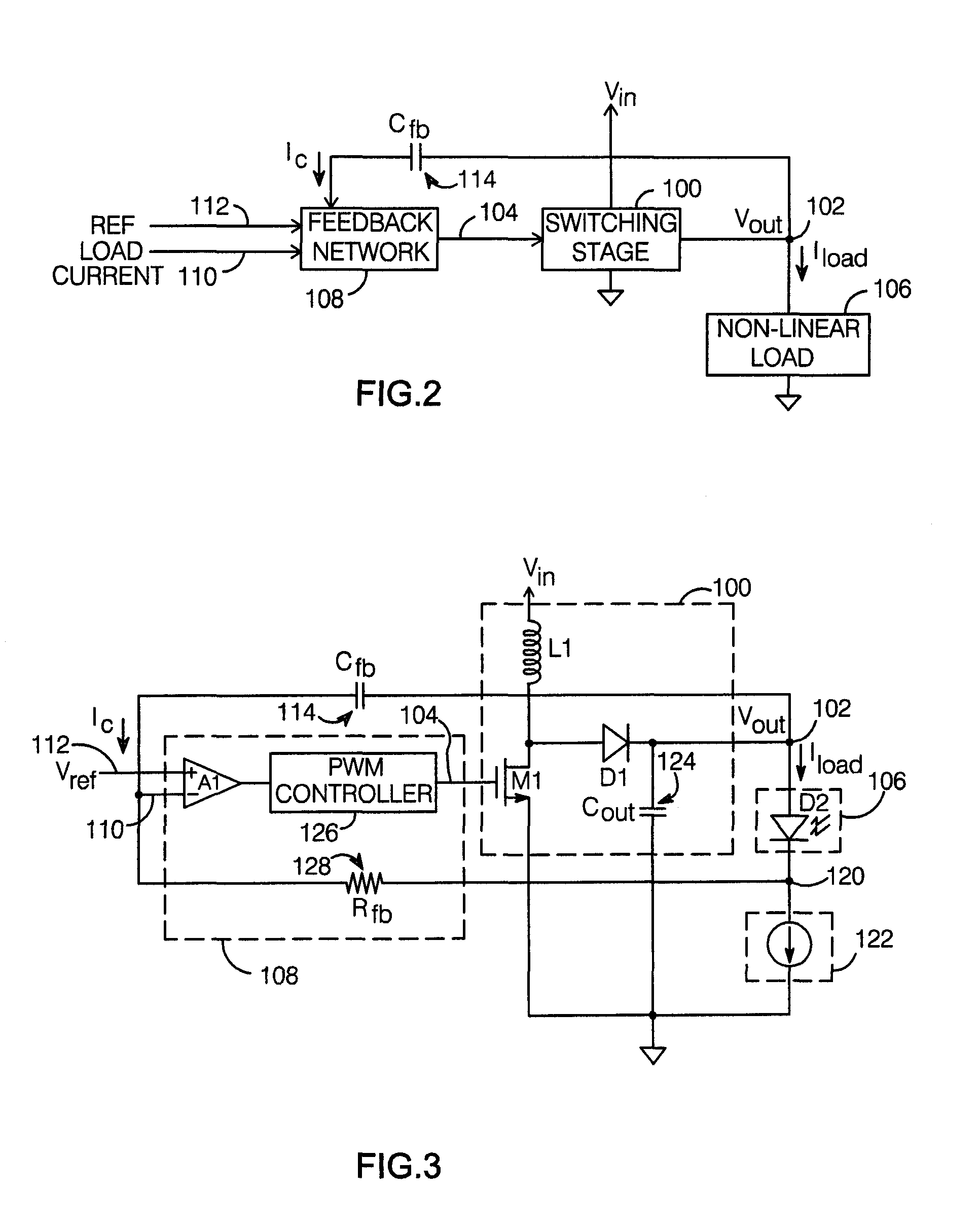
A switching power converter with a controlled startup mechanism includes a switching stage which provides a voltage Vout at an output node in response to a switching control signal, with the output node adapted for connection to a non-linear load. A feedback network compares a signal which varies with the current conducted by the load (Iload) with a reference signal, and provides the switching control signal so as to maintain Iload at a desired value. A capacitor connected to the output node provides a current Ic to the feedback network which varies with dVout / dt. The feedback network is arranged to limit dVout / dt in response to current Ic when Iload is substantially zero. In this way, large inrush currents or damage that might otherwise occur during startup are avoided.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
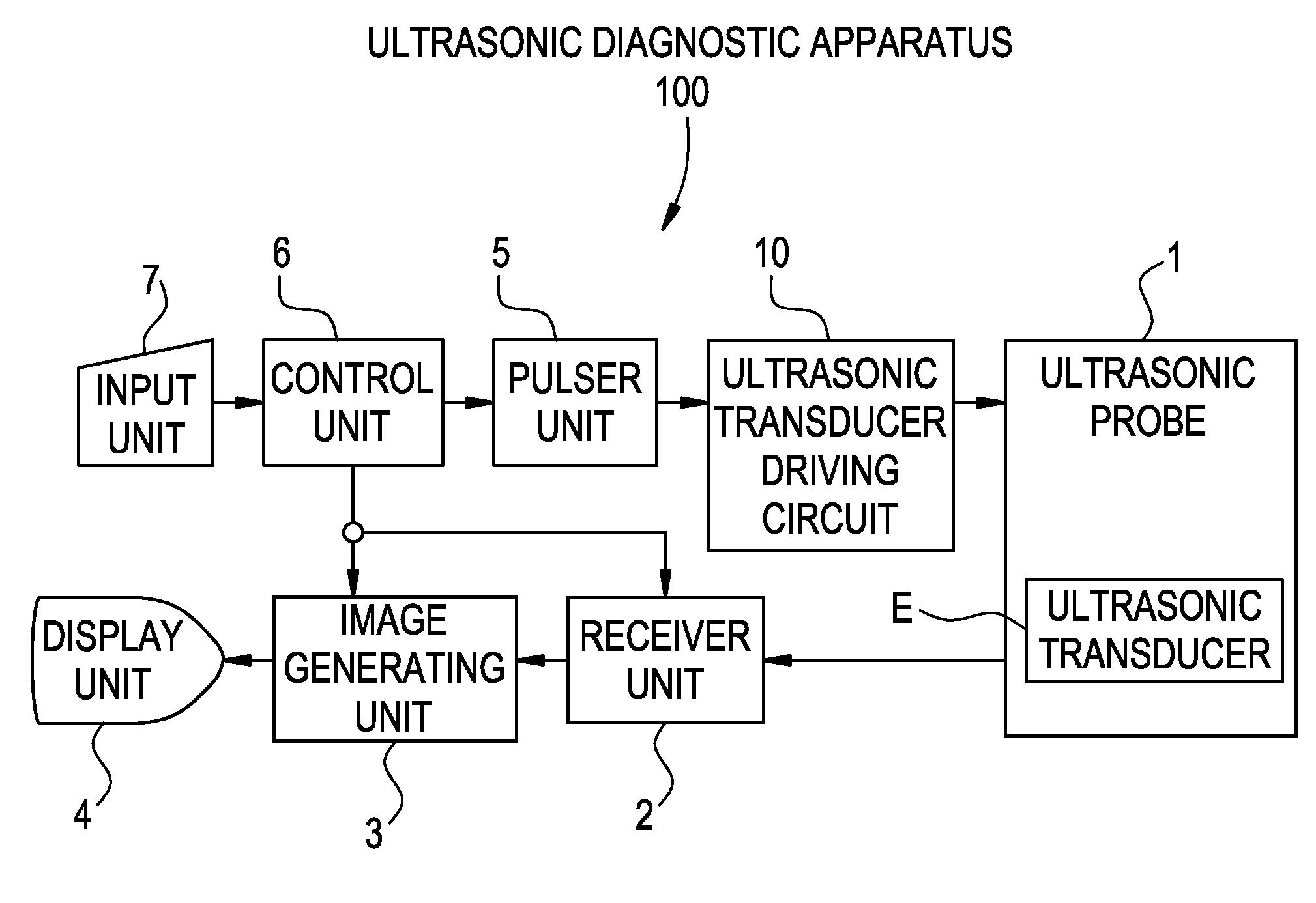
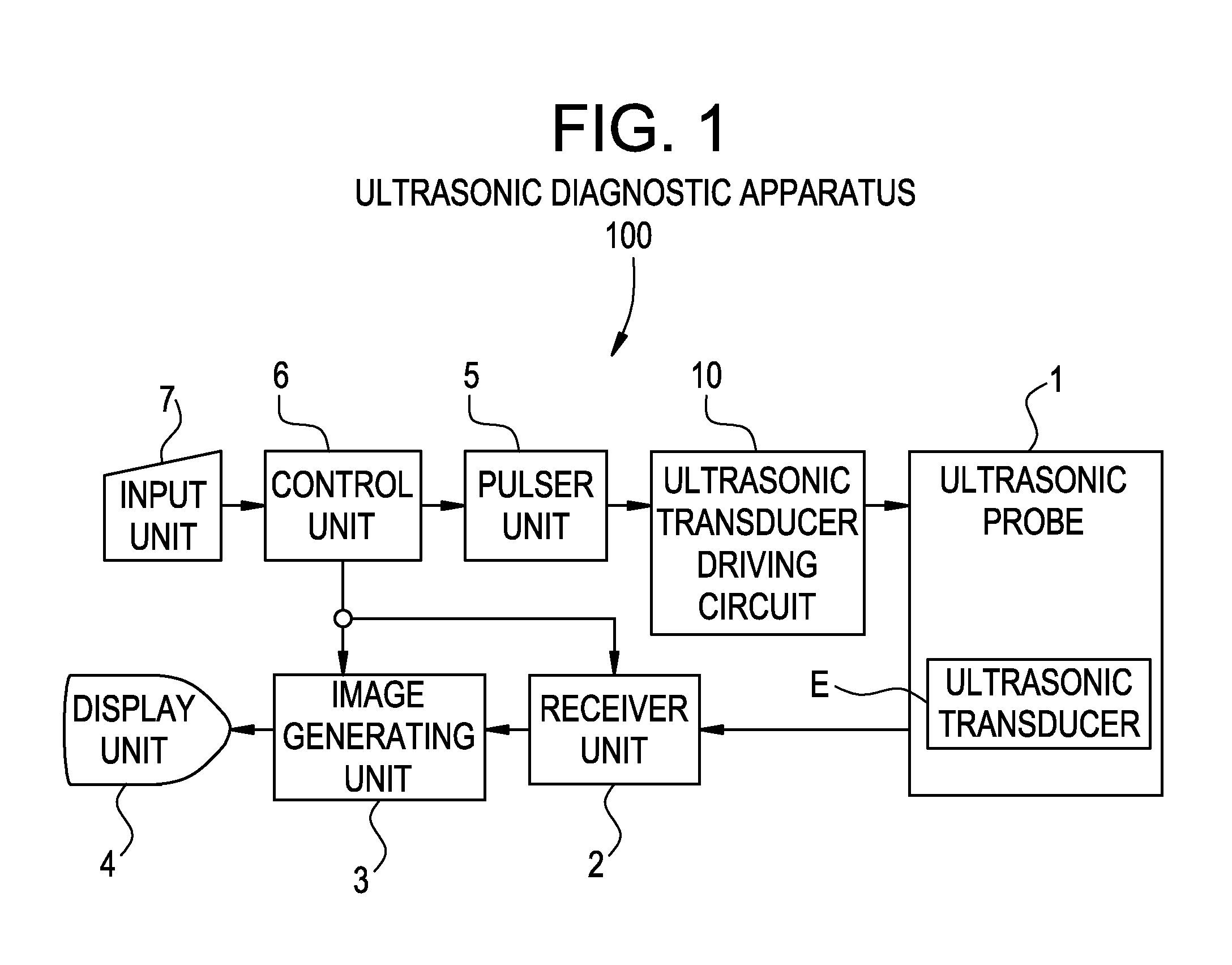
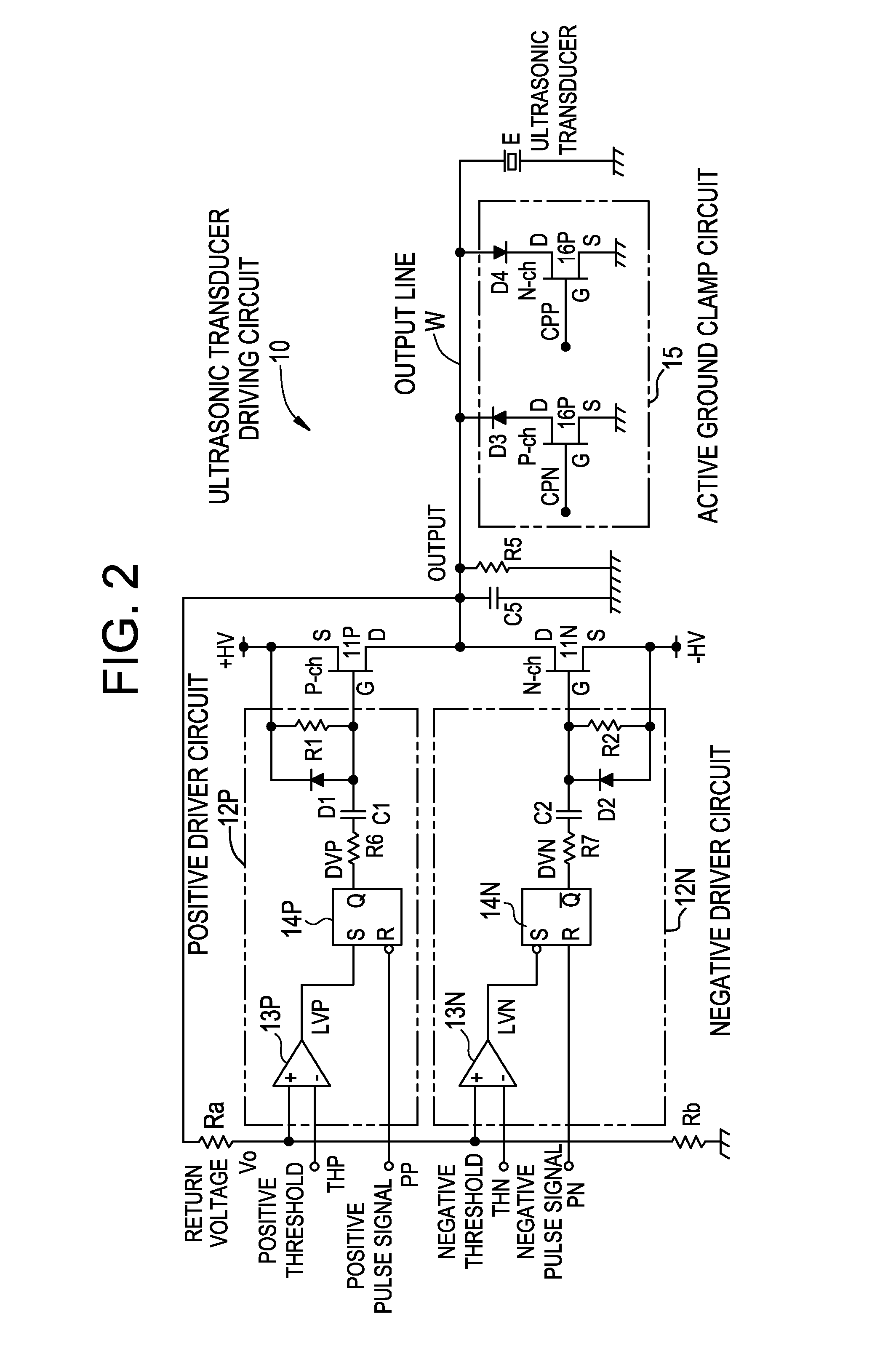
Ultrasonic transducer driving circuit and ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
InactiveUS20080066552A1Suppress power consumptionReduce circuit sizeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic sensorDriving circuit
With the aim of suppressing power consumption and reducing circuit size, a positive FET is turned on in accordance with a positive pulse signal and turned off when a return voltage rises up to a positive threshold. An active ground clamp circuit causes the output line to return to the ground voltage after the elapse of a predetermined period of time. A negative FET is turned on in accordance with a negative pulse signal and turned off when the return voltage falls down to a negative threshold. The active ground clamp circuit causes the output line to return to the ground voltage after the elapse of a predetermined period of time.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
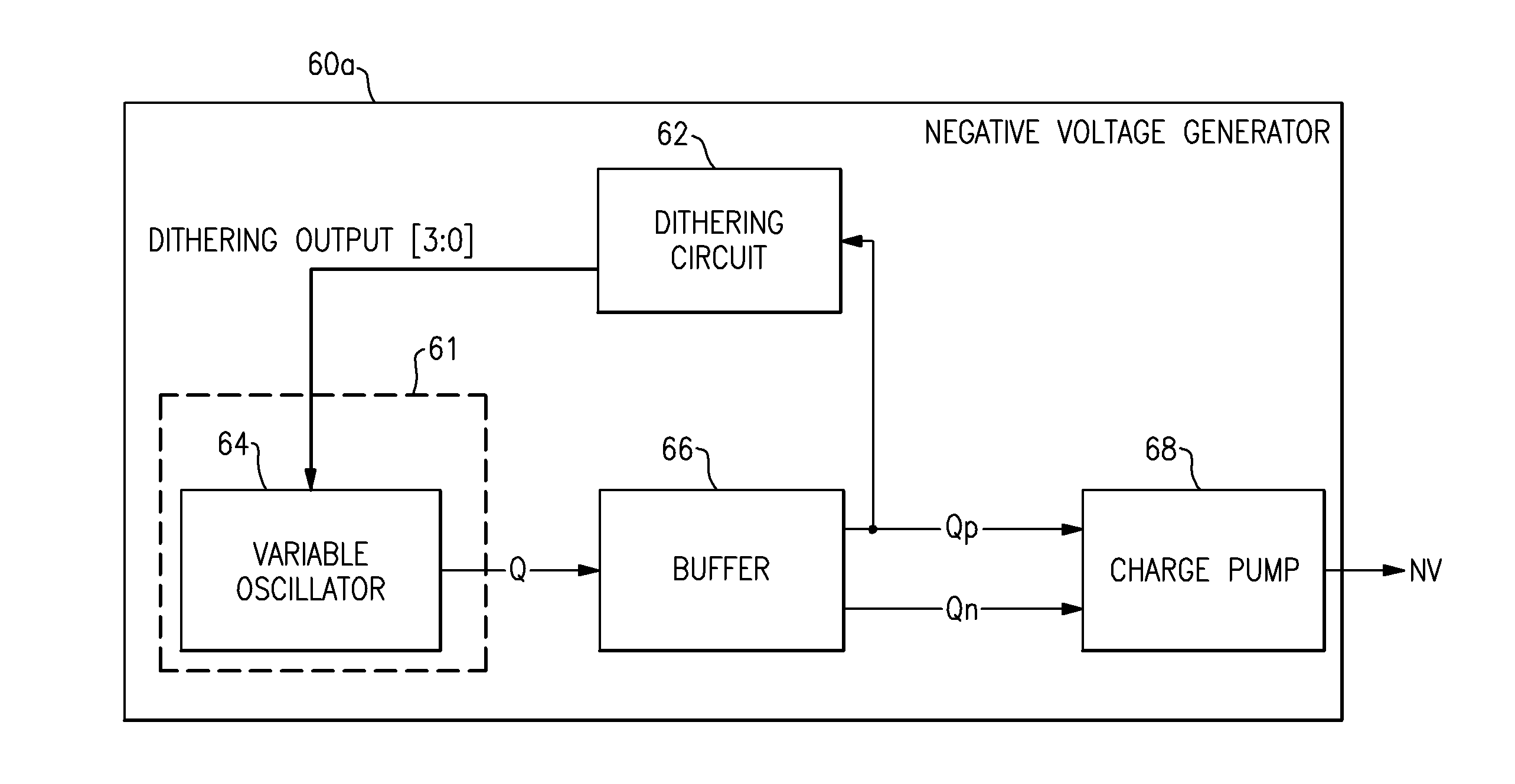
Variable frequency circuit controller
ActiveUS20120242379A1Network traffic/resource managementPulse automatic controlEngineeringRadio frequency
Apparatus and methods for distributing spurious tones through the frequency domain are disclosed. One such apparatus can include a dithering circuit configured to generate a sequence of numbers that exhibit statistical randomness and a variable frequency circuit configured to adjust a frequency of an output based on the sequence of numbers so as to spread energy of spurious tones in a frequency response of the output to lower a noise floor. In one example, spurious tones can be reduced in a negative voltage generator of a radio frequency (RF) attenuator.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Double gated 4f2 dram chc cell and methods of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20120126885A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering physics
A semiconductor device is provided that includes a fin having a first gate and a second gate formed on a first sidewall of the fin in a first trench, wherein the first gate is formed above the second gate. The device includes a third gate and a fourth gate formed on a second sidewall of the fin in a second trench, wherein the third gate is formed above the fourth gate. Methods of manufacturing and operating the device are also included. A method of operation may include biasing the first gate and the fourth gate to create a current path across the fin.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
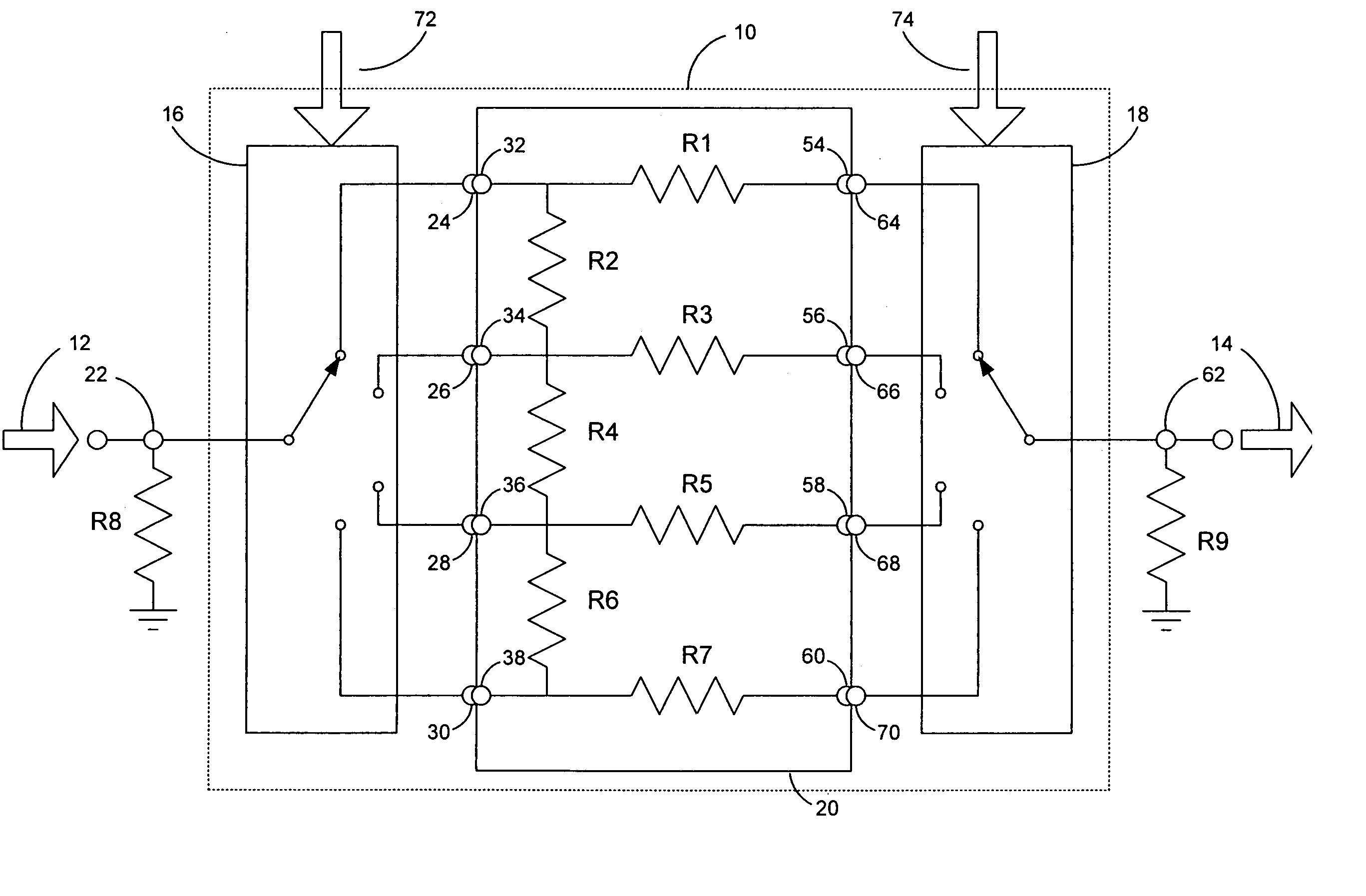
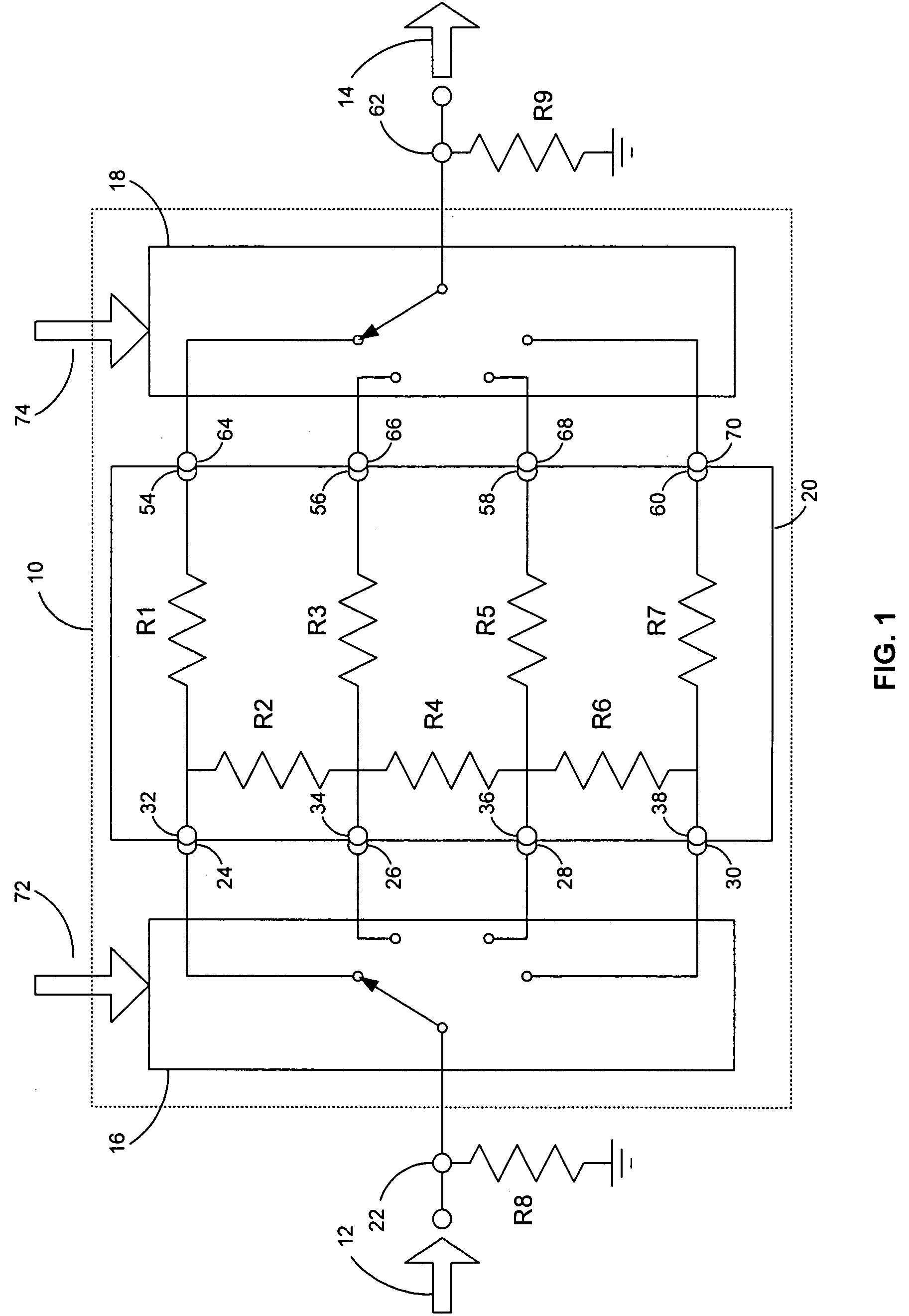
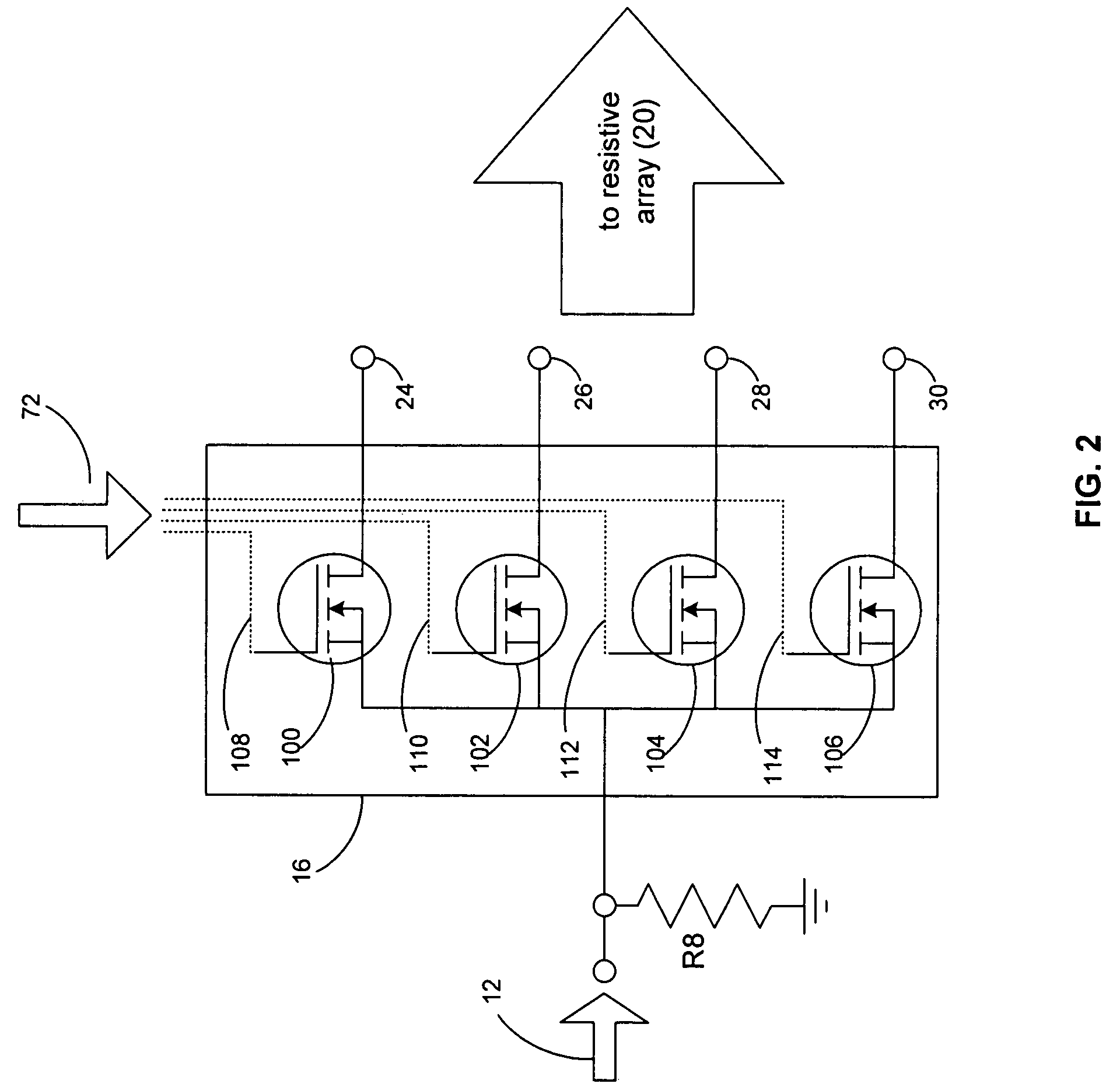
High-resolution variable attenuation device
InactiveUS7196566B2Uniform attenuation stepMultiple-port networksPulse automatic controlUltrasound attenuationEngineering
A variable attenuation device includes a resistive array having two or more input nodes, two or more output nodes, and two or more resistive devices for coupling the input nodes and the output nodes. A first switch has an input terminal and two or more selectable output terminals, such that the input terminal is configured to receive an input signal and the two or more selectable output terminals are coupled to the two or more input nodes of the resistive array. A second switch has two or more selectable input terminals and an output terminal, such that the output terminal is configured to provide an attenuated output signal and the two or more selectable input terminals are coupled to the two or more output nodes of the resistive array. The output terminal selected on the first switch and the input terminal selected on the second switch varies the resistance seen by the input signal, and the values of the two or more resistive devices are configured to allow for substantially-uniform attenuation steps of the input signal.
Owner:LTX CORP
Microwave switching with illuminated field effect transistors
ActiveUS6876271B2Reduce resistanceShorten the switching timeTransistorMultiple-port networksMicrowaveSemiconductor chip
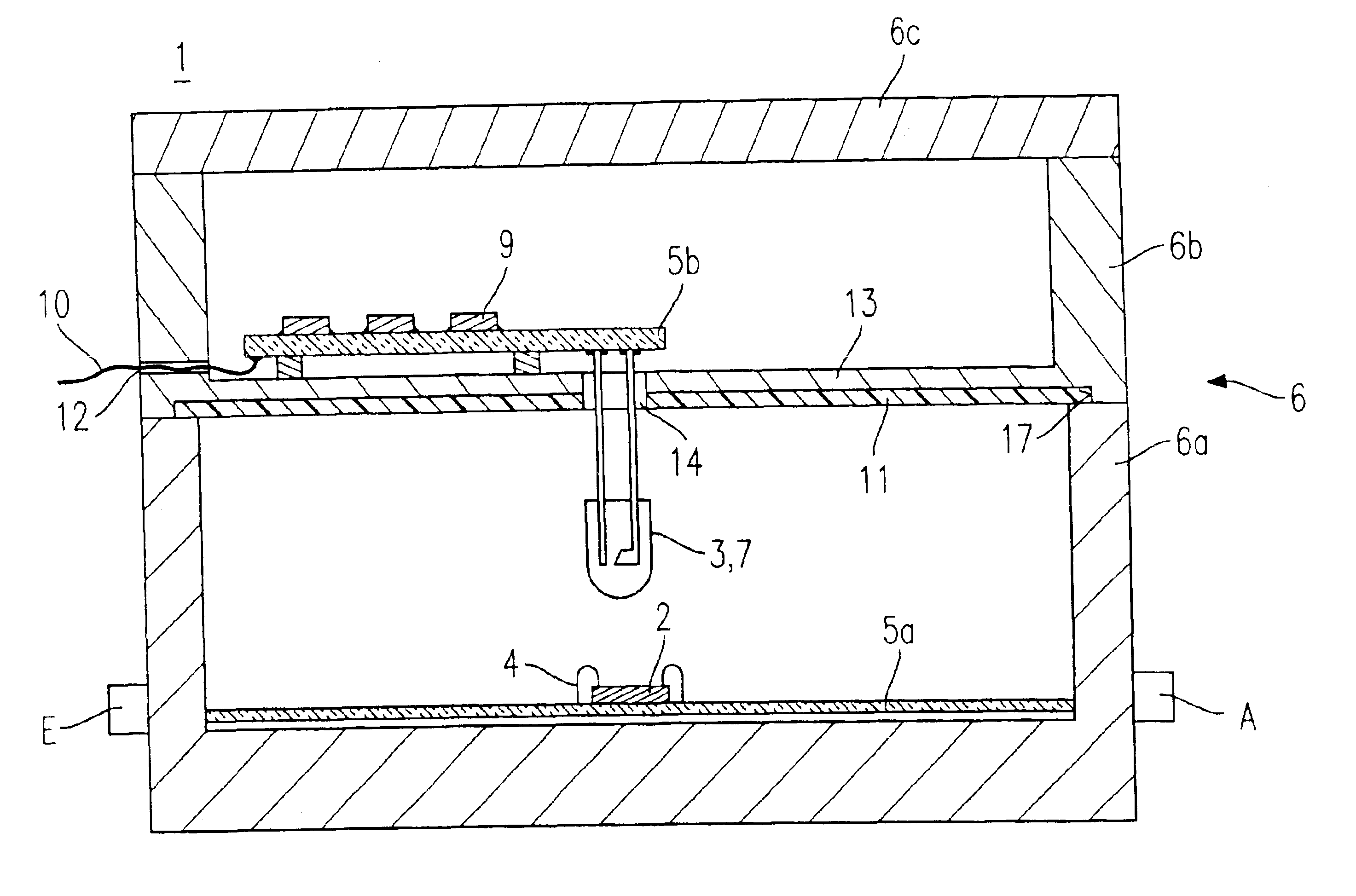
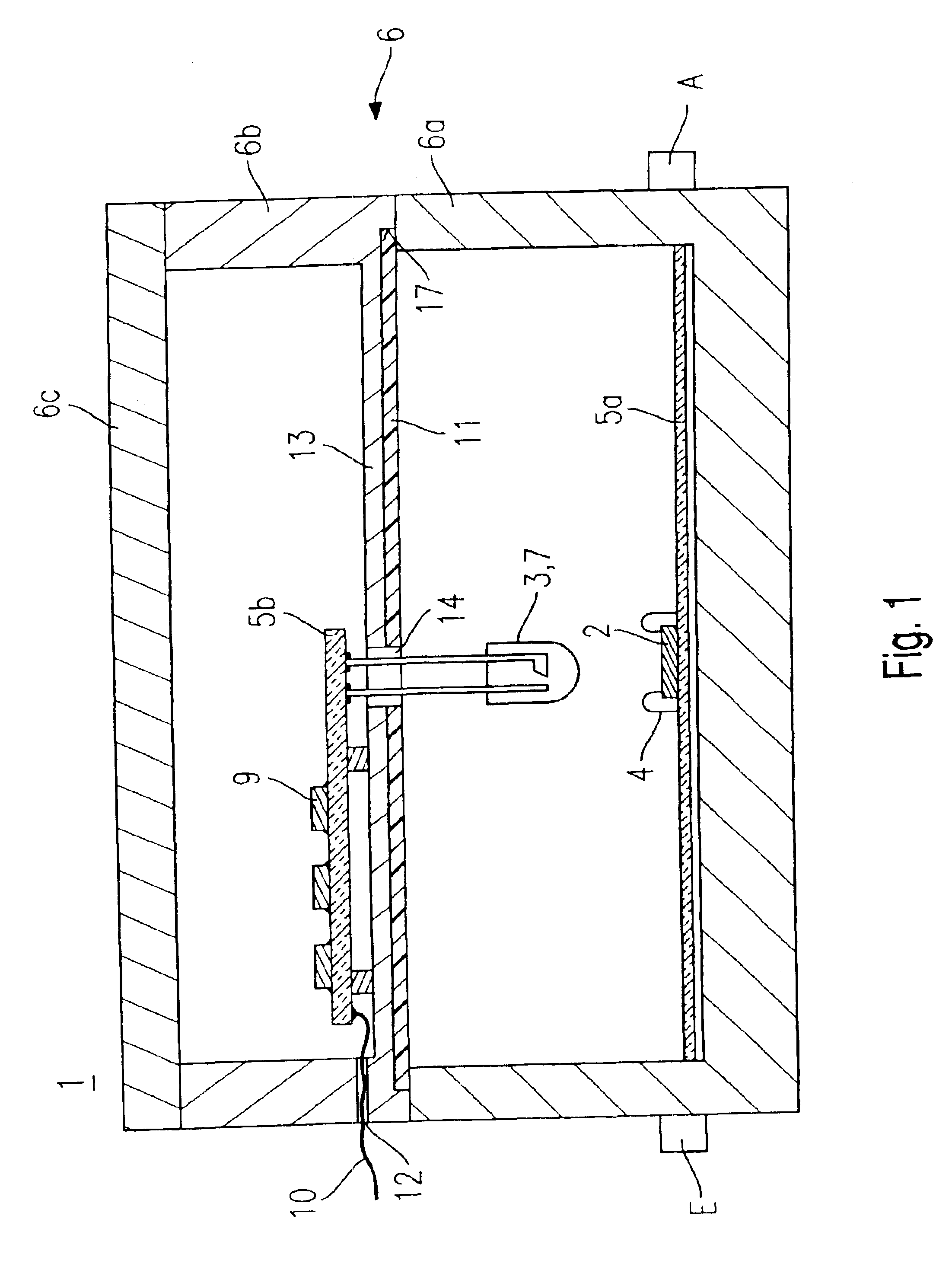
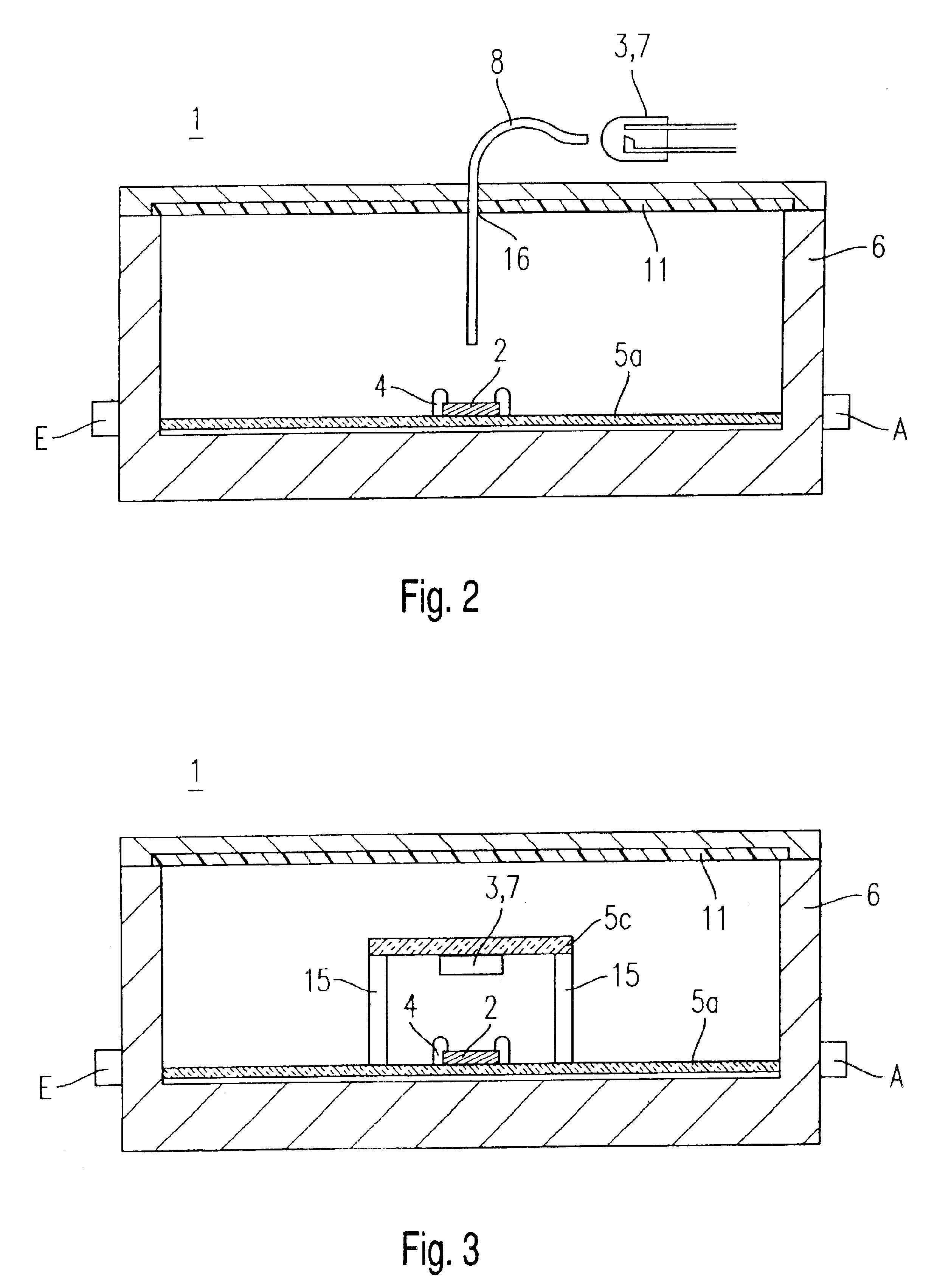
An electronic microwave circuit (1) with field effect transistors which are integrated on at least one semiconductor chip (2), has a light source (3), which radiates the field effect transistors with light and possesses a housing (6) which encloses in a microwave excluding manner the semiconductor chip (2) and the light source (3) or a light conducting means (8) connected with the light source (3).
Owner:ROHDE & SCHWARZ GMBH & CO KG
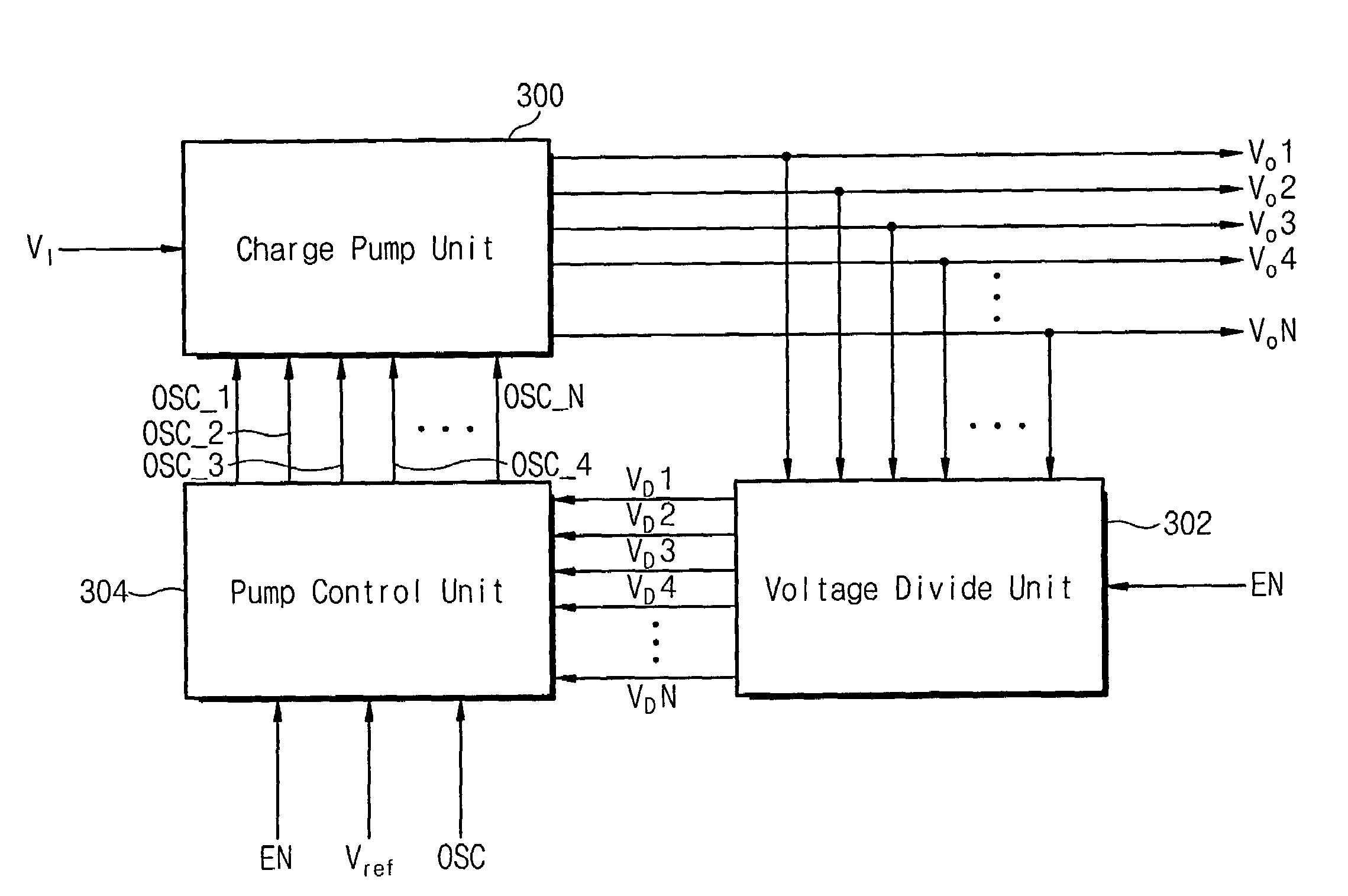
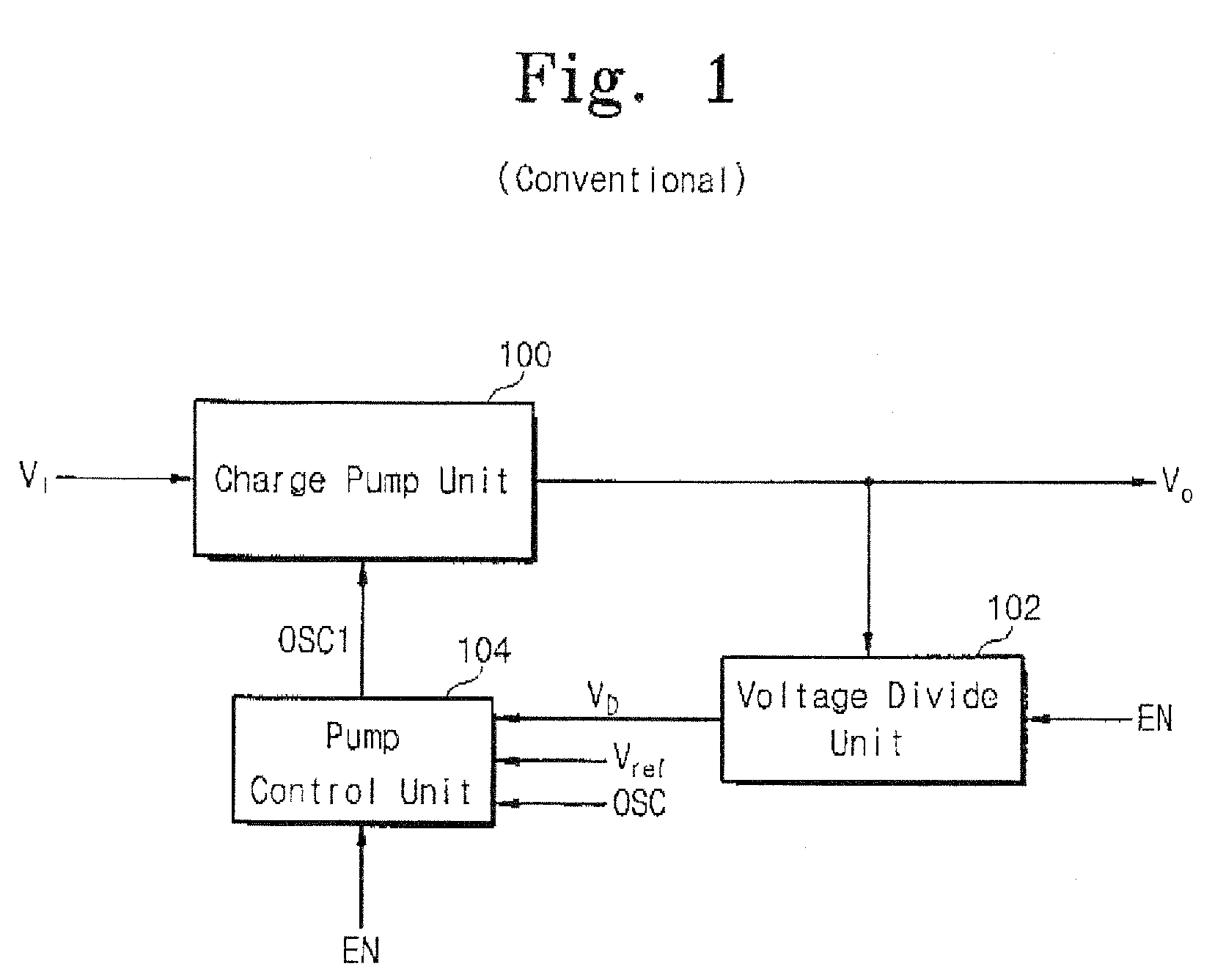
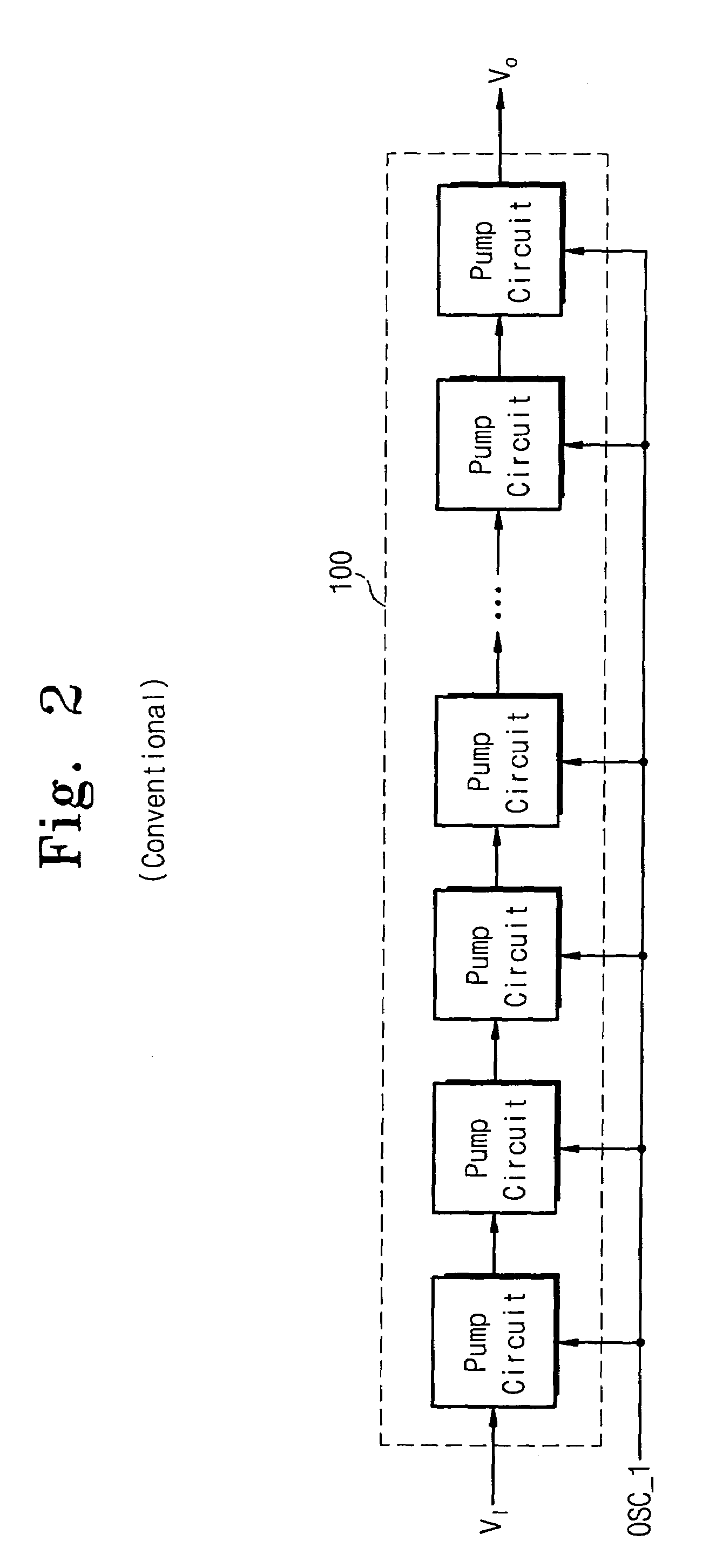
Multi-level high voltage generator
A multi-level high voltage generator according to embodiments of the invention is capable of simultaneously generating high voltages of various levels by using one charge pump. The multi-level high voltage generator includes a charge pump unit, a voltage divider unit, and a pump control unit. The charge pump unit raises an input voltage applied at an input terminal to simultaneously output a number of high voltages having different levels. The voltage divider unit divides the voltages from the charge pump unit. The pump control unit operates according to an enable signal and generates pump control signals in response to a reference voltage, a control clock signal, and a divided voltage from the voltage divider unit. The charge pump unit generates the high voltages and is controlled by the pump control signals from the pump control unit.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
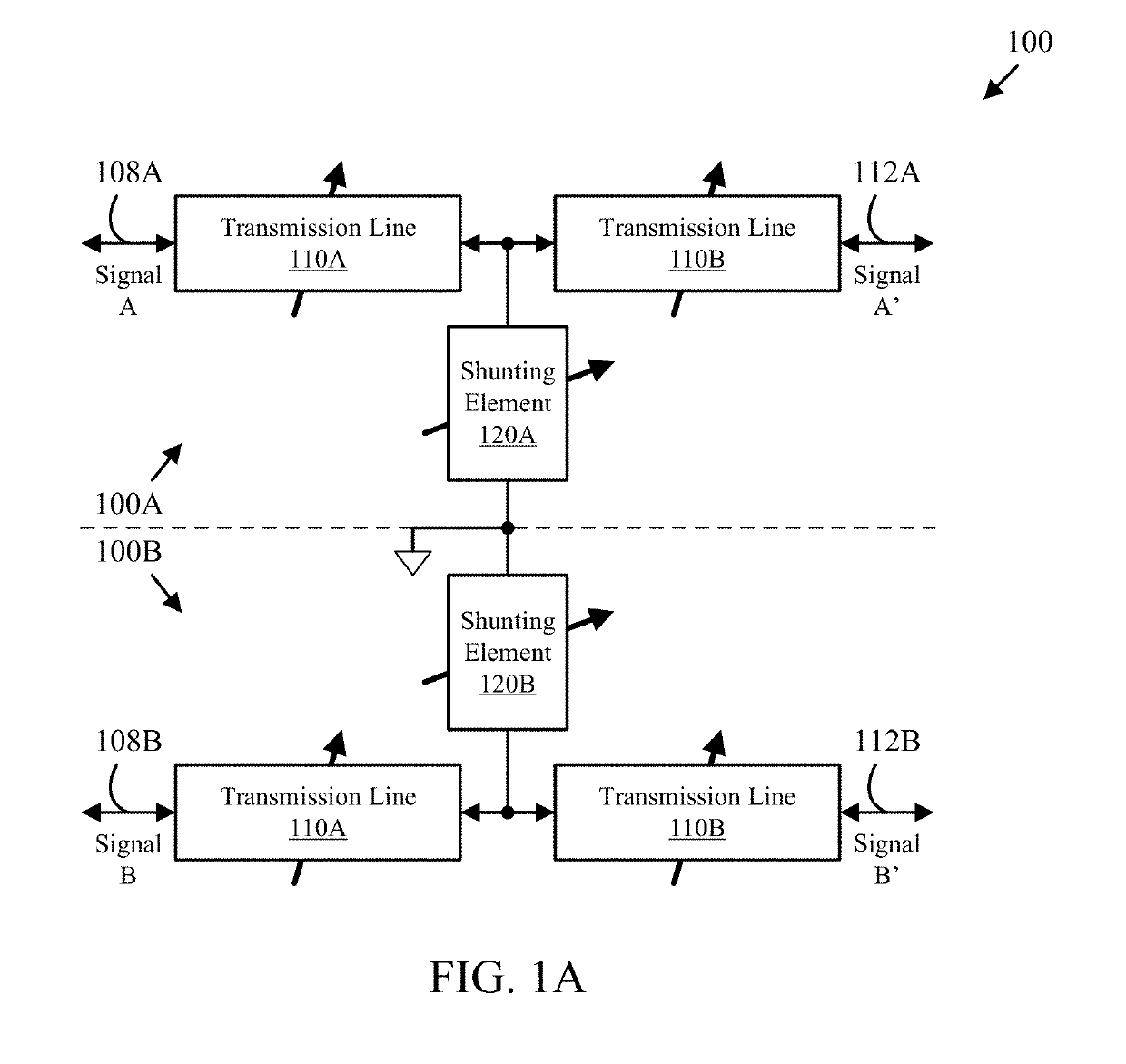
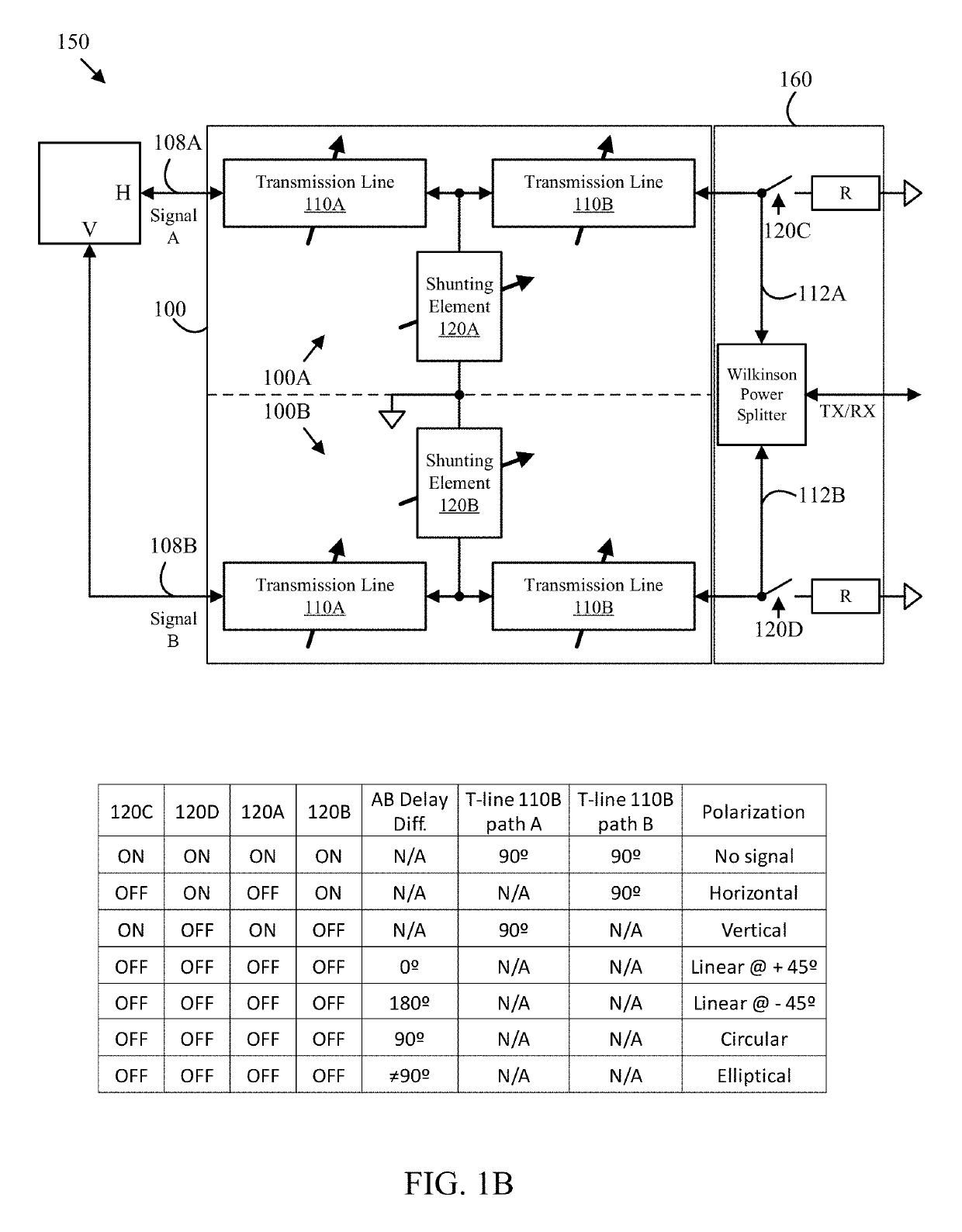
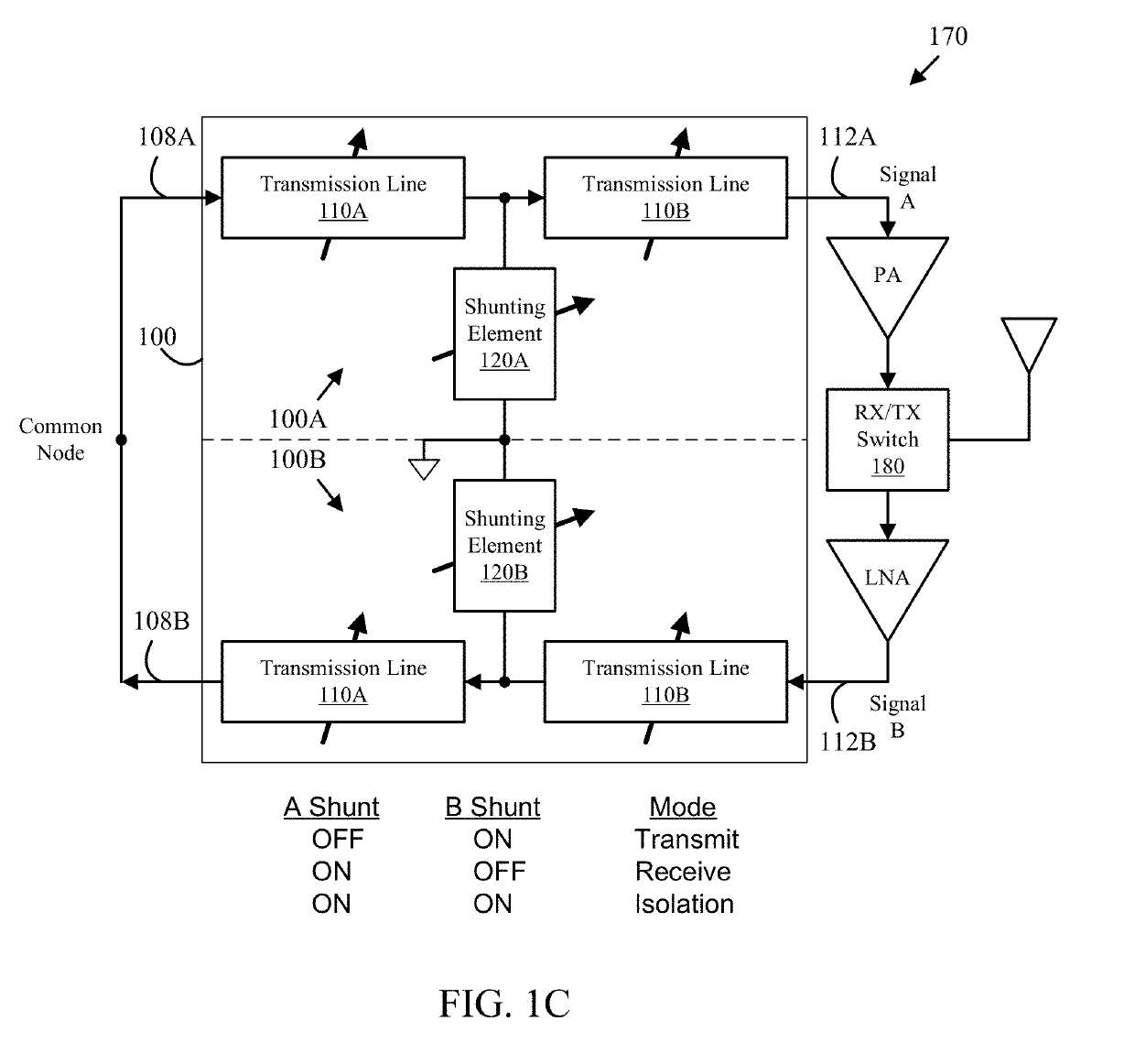
RF signal switching, phase shifting and polarization control
An apparatus includes first and second electronically tunable transmission lines configured to transmit or receive a signal pair and provide a selected phase delay difference to the signal pair corresponding to a selected polarization, a first attenuation element connected to the first electronically tunable transmission line and a second attenuation element connected to the second electronically tunable transmission line. The first and second attenuation elements may each be configured to selectively attenuate signals carried on the electronically tunable transmission line to which they are connected according to a selected attenuation setting of a plurality of selectable attenuation settings provided by one or more attenuation control signals and thereby provide a selected attenuation to the signal pair that corresponds to the selected polarization. A corresponding method is also disclosed herein.
Owner:IBM CORP
Double gated fin transistors and methods of fabricating and operating the same
ActiveUS20120126884A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering physics
A semiconductor device is provided that includes a fin having a first upper gate on a sidewall of the fin in a first trench and a second upper gate formed on the opposite sidewall of the fin. The device also includes a first lower gate on the sidewall and a second lower gate on the opposite sidewall, wherein the first upper gate is formed above the first lower gate and the second upper gate is formed above the second lower gate. Methods of manufacturing and operating the device are also included. A method of operation may include biasing the first upper gate and second upper gate to preselect the transistors of a fin and then biasing the first lower gate and second lower gate to operate the transistors of the fin.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
SOI radio frequency switch with enhanced signal fidelity and electrical isolation
ActiveUS7999320B2Reduce distortionReduce generationTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureCharge layer
A doped contact region having an opposite conductivity type as a bottom semiconductor layer is provided underneath a buried insulator layer in a bottom semiconductor layer. At least one conductive via structure extends from an interconnect-level metal line through a middle-of-line (MOL) dielectric layer, a shallow trench isolation structure in a top semiconductor layer, and a buried insulator layer and to the doped contact region. The doped contact region is biased at a voltage that is at or close to a peak voltage in the RF switch that removes minority charge carriers within the induced charge layer. The minority charge carriers are drained through the doped contact region and the at least one conductive via structure. Rapid discharge of mobile electrical charges in the induce charge layer reduces harmonic generation and signal distortion in the RF switch. A design structure for the semiconductor structure is also provided.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
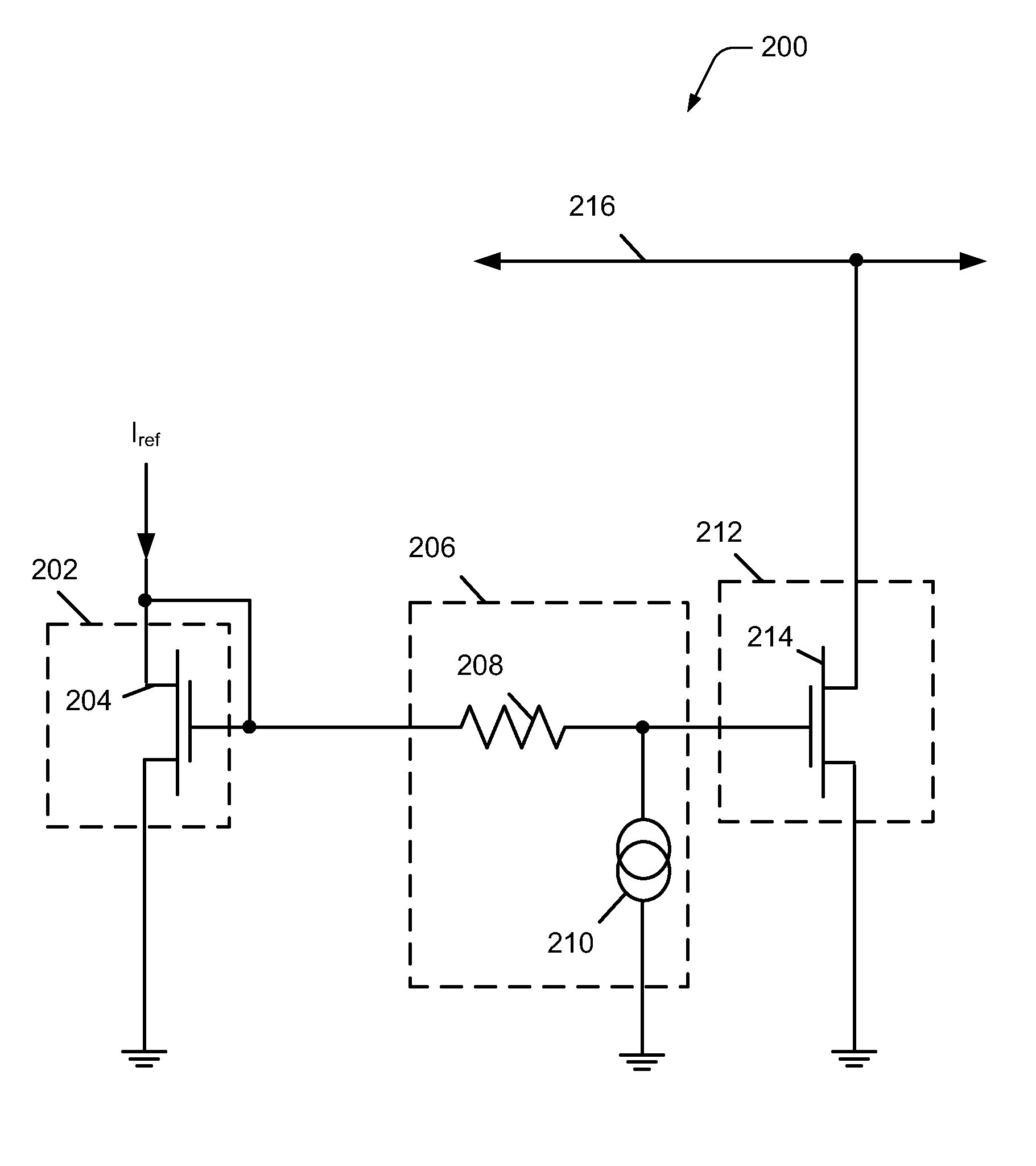
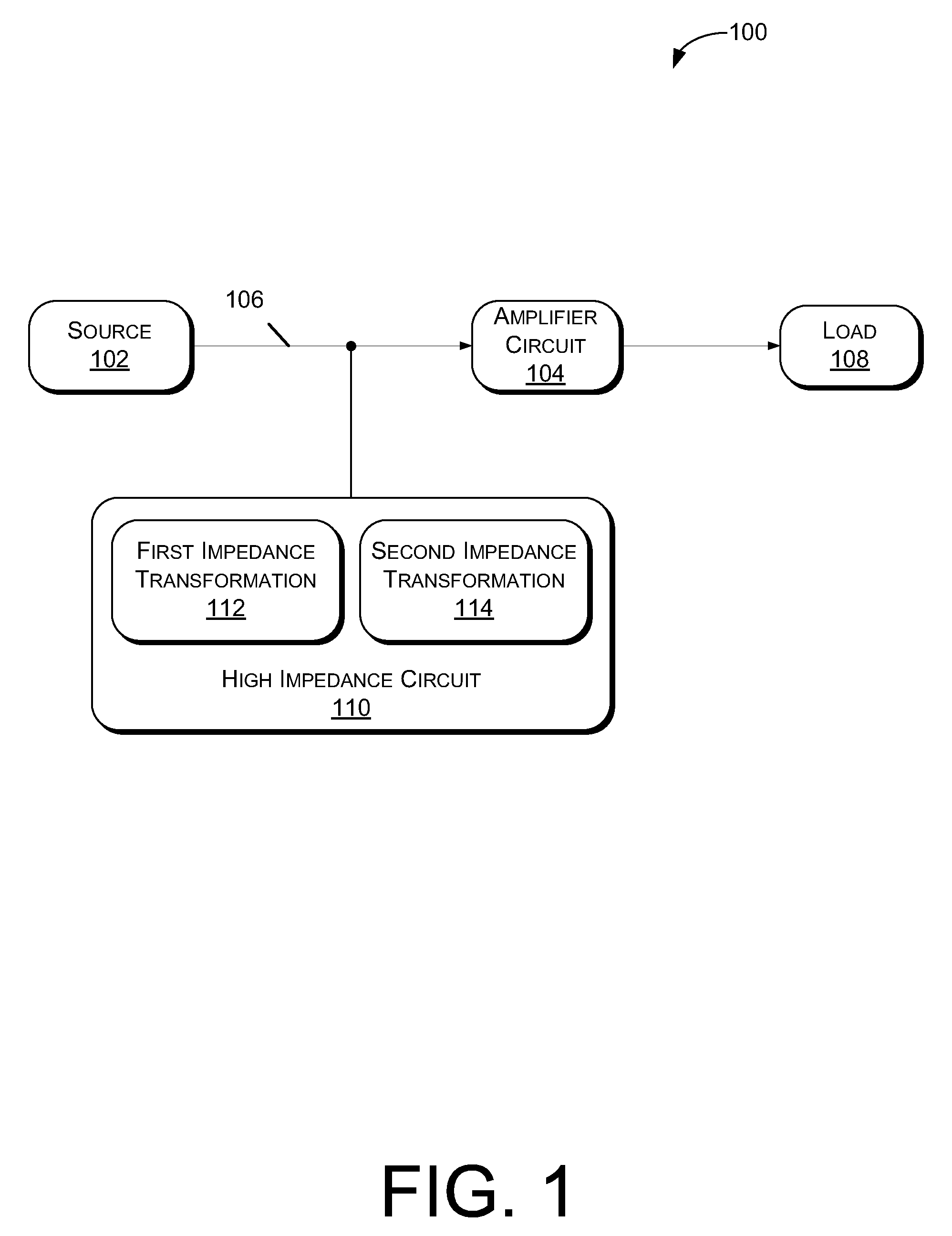
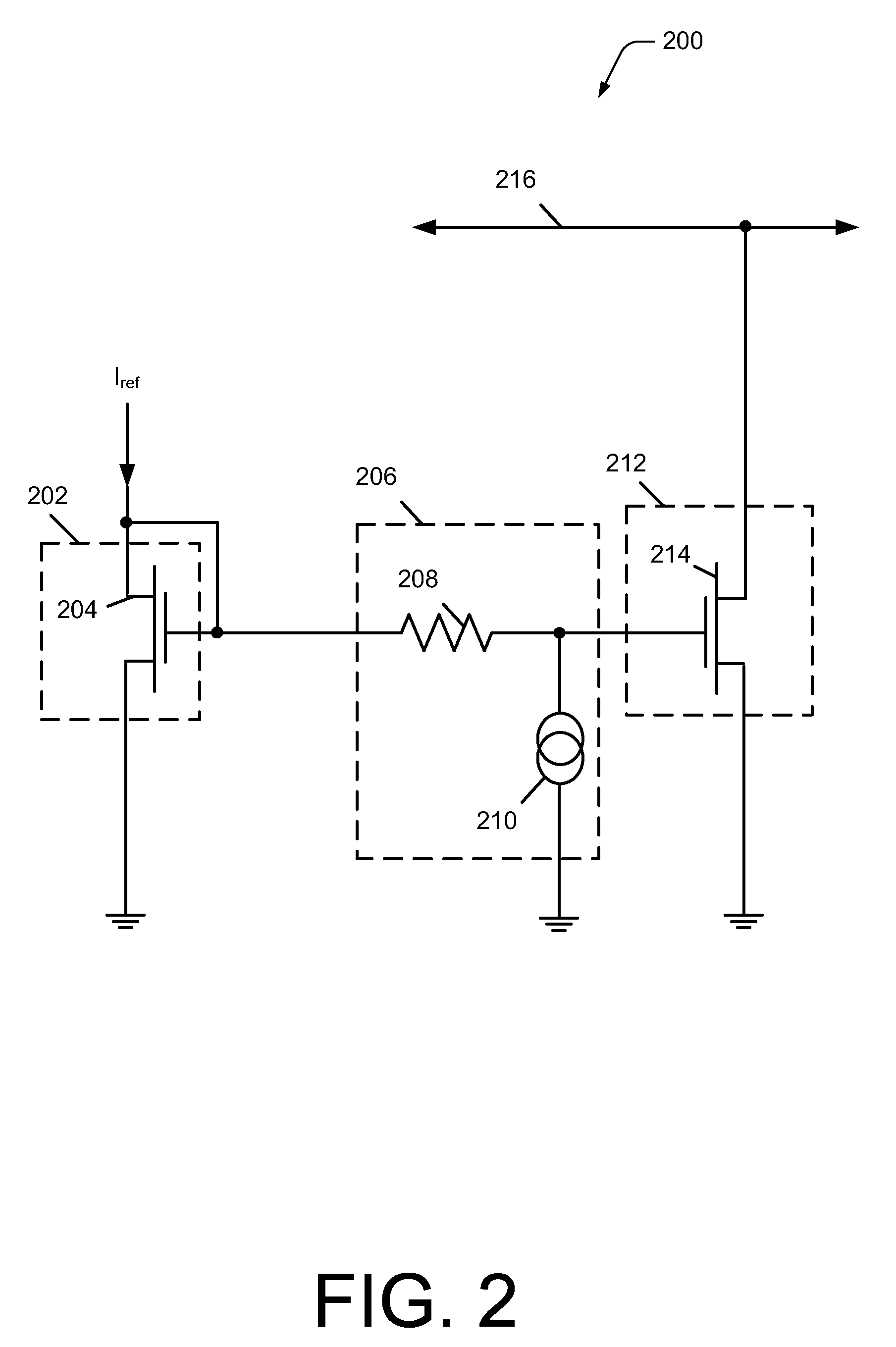
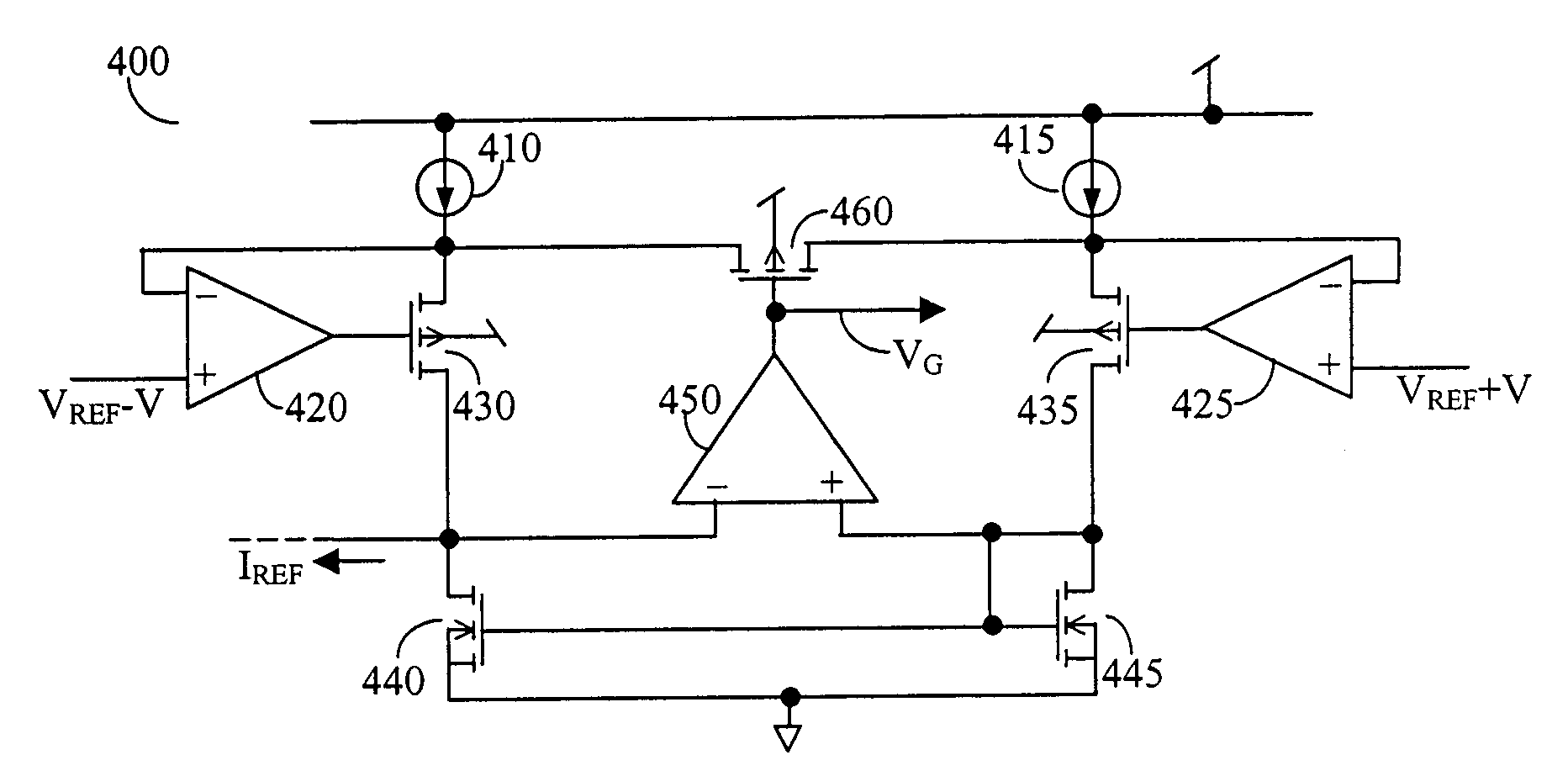
Impedance transformation with transistor circuits
ActiveUS8004350B2Amplifier input/output impedence modificationFrequency-independant attenuatorsTransistor circuitsElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
One-pin automatic tuning of MOSFET resistors
Methods and apparatus for automatic tuning of MOSFET resistors providing accuracy and linearity throughout process and temperature variations. In accordance with the methods, the source and drain of a MOSFET device are biased in a balanced manner around a common mode voltage using a circuit controlling the gate voltage of the MOSFET to set the current through the MOSFET responsive to the value of a resistor. Operating MOSFETs, such as in MOSFET-C filters, with the same device conductivity type, gate bias, substrate voltage and signal common mode voltage provides linear MOSFET resistors, accurately set by a single resistance value. Use of an external resistor provides a single pin setting of MOSFET resistances, that may be independent of temperature and process variations. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:THETA IP
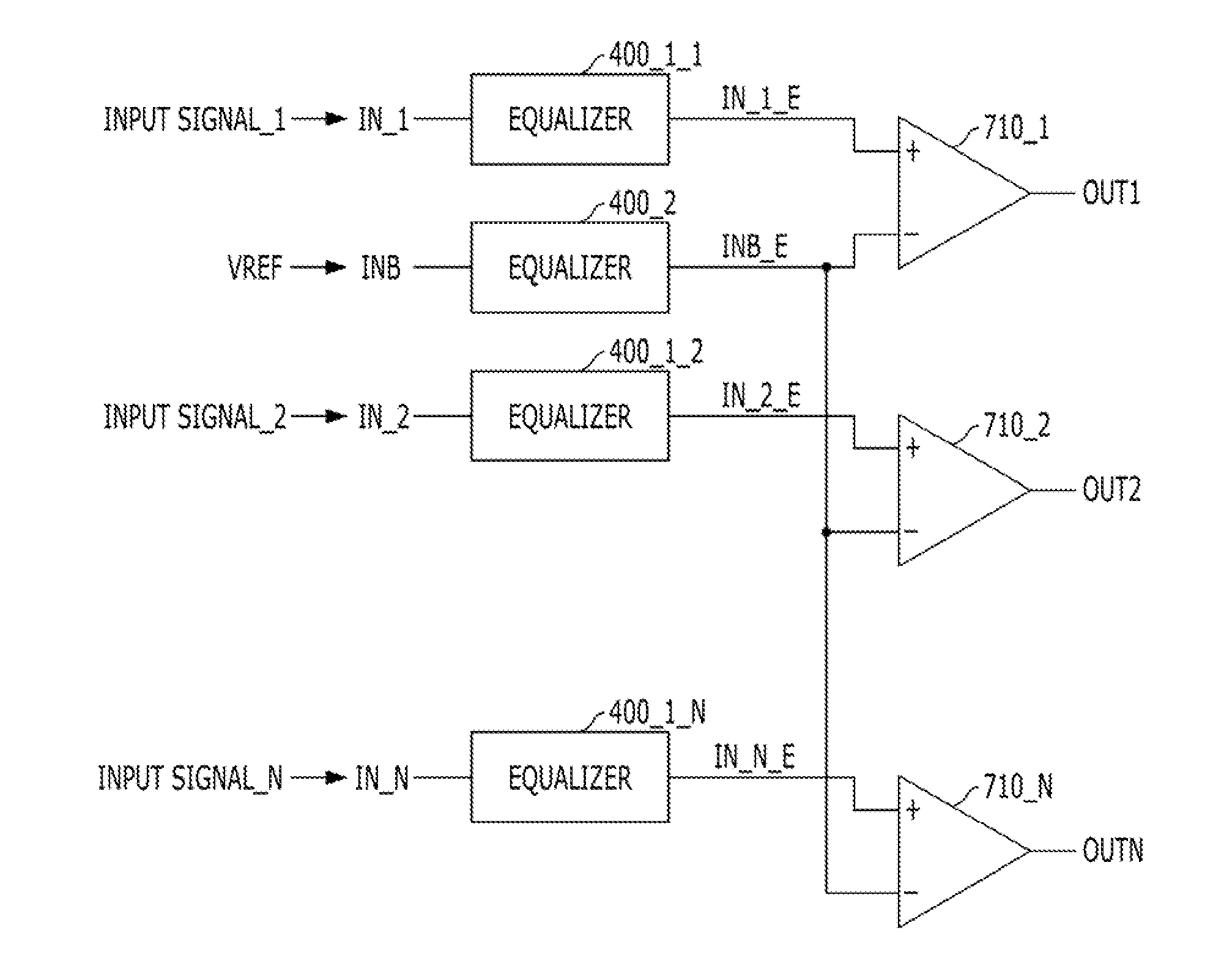
Equalizer circuit and receiver circuit including the same
An equalizer circuit includes an input terminal, a pull-up driving unit suitable for pull-up driving an output terminal based on a signal of the input terminal, a pull-down driving unit suitable for pull-down driving the output terminal, and a capacitor connected between the input terminal and the output terminal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
High-resolution variable attenuation device
InactiveUS20050093606A1Uniform attenuation stepMultiple-port networksPulse automatic controlUltrasound attenuationHigh resolution
A variable attenuation device includes a resistive array having two or more input nodes, two or more output nodes, and two or more resistive devices for coupling the input nodes and the output nodes. A first switch has an input terminal and two or more selectable output terminals, such that the input terminal is configured to receive an input signal and the two or more selectable output terminals are coupled to the two or more input nodes of the resistive array. A second switch has two or more selectable input terminals and an output terminal, such that the output terminal is configured to provide an attenuated output signal and the two or more selectable input terminals are coupled to the two or more output nodes of the resistive array. The output terminal selected on the first switch and the input terminal selected on the second switch varies the resistance seen by the input signal, and the values of the two or more resistive devices are configured to allow for substantially-uniform attenuation steps of the input signal.
Owner:LTX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com