Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about "Network modifications to reduce temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
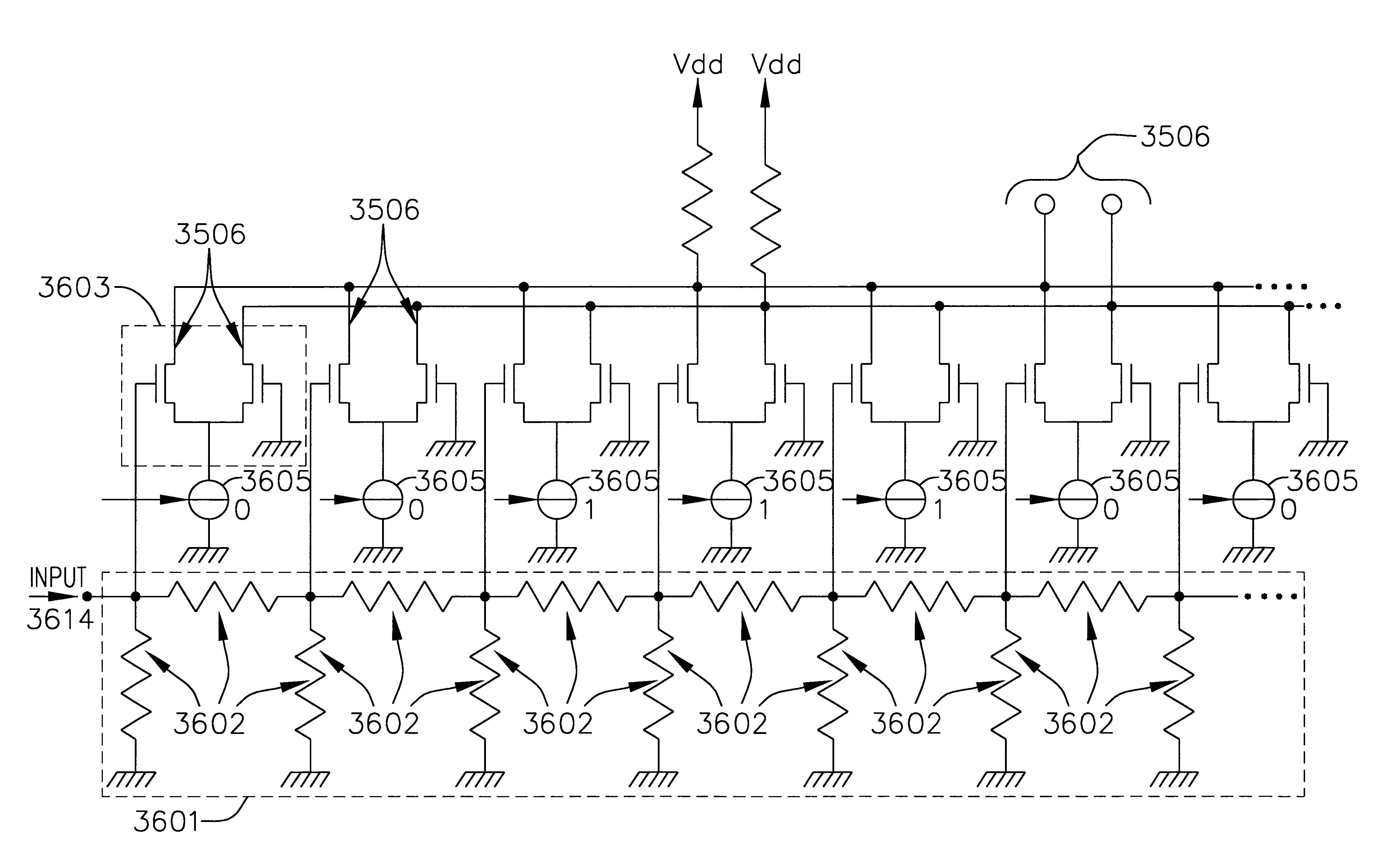
Integrated switchless programmable attenuator and low noise amplifier
InactiveUS6879816B2Multiple-port active networksSwitched capacitor networksCapacitanceLocal oscillator signal
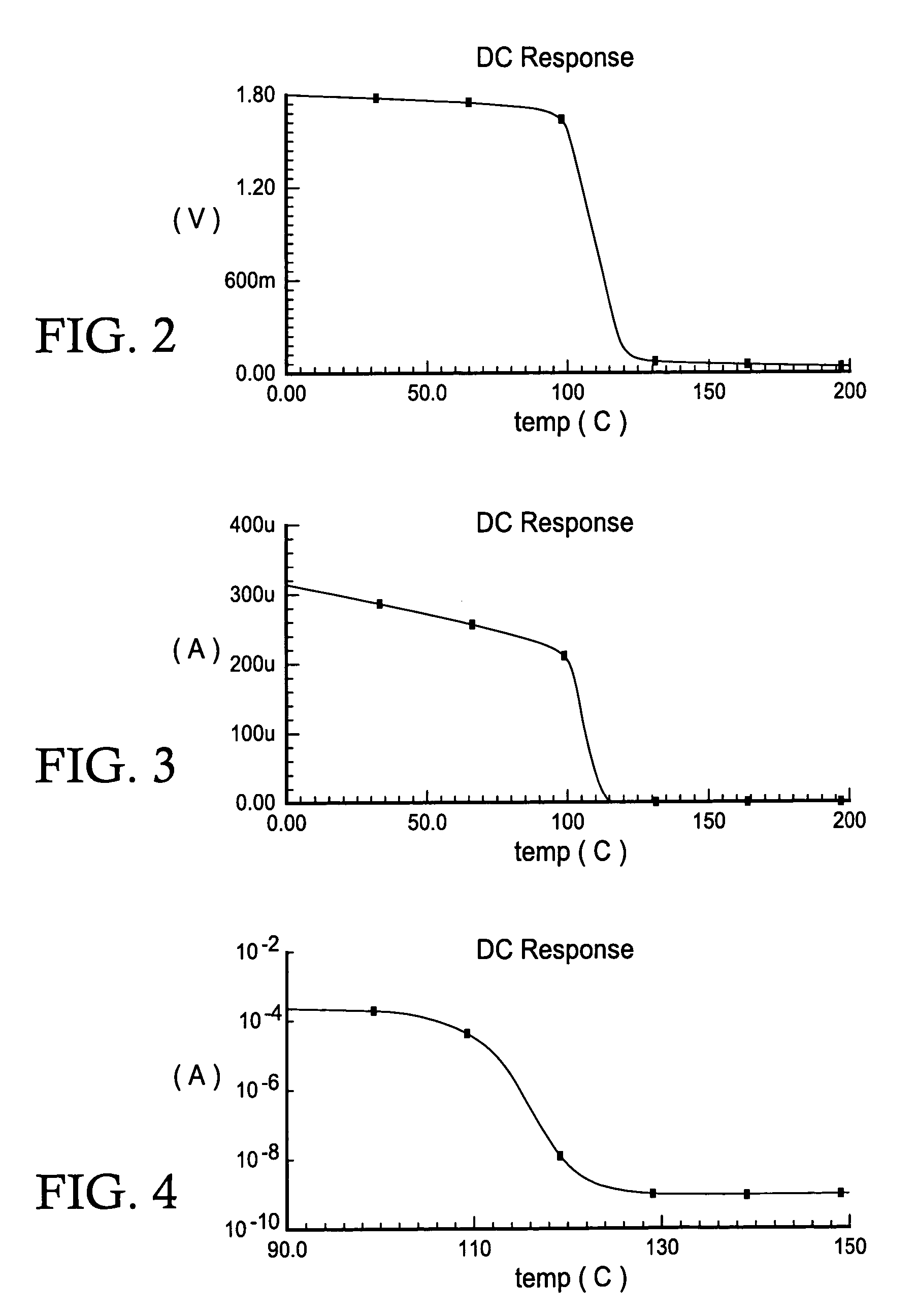
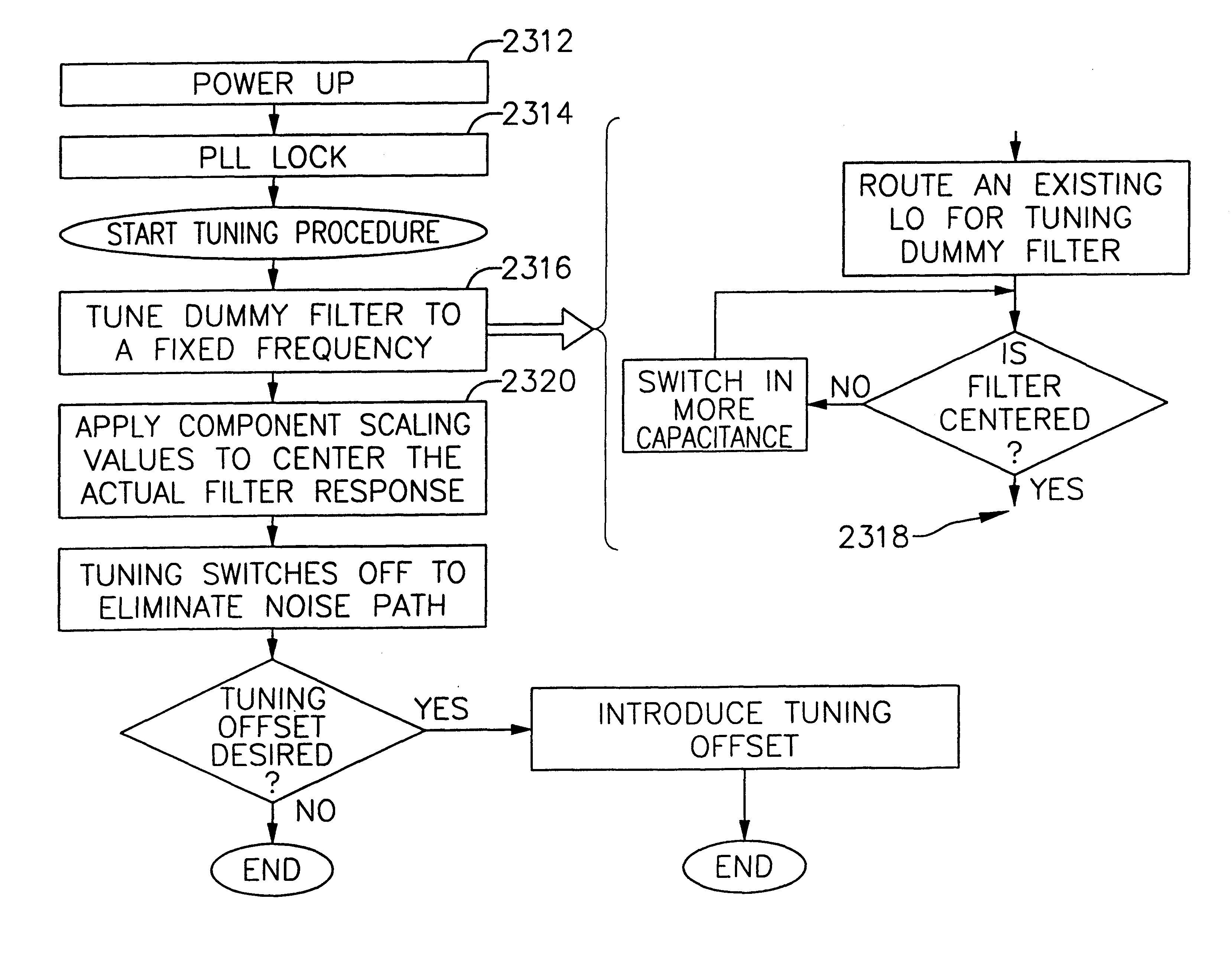
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit is described. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. Frequency conversion circuitry advantageously uses LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers to provide sufficient image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. The filters utilize multi track spiral inductors. The filters are tuned using local oscillators to tune a substitute filter, and frequency scaling during filter component values to those of the filter being tuned. In conjunction with filtering, frequency planning provides additional image rejection. The advantageous choice of local oscillator signal generation methods on chip is by PLL out of band local oscillation and by direct synthesis for in band local oscillator. The VCOs in the PLLs are centered using a control circuit to center the tuning capacitance range. A differential crystal oscillator is advantageously used as a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission is advantageously used throughout the receiver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
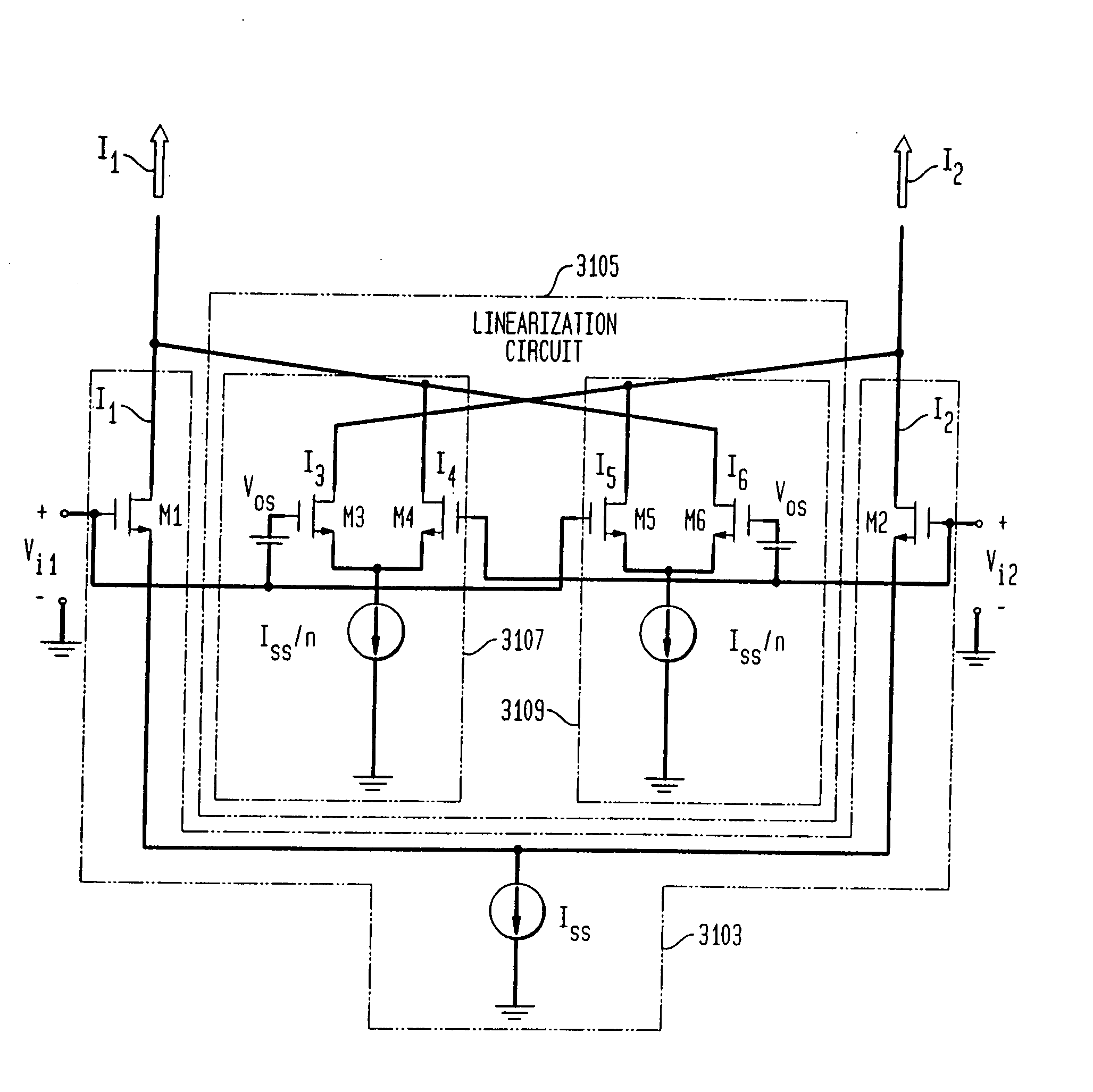
System and method for linearizing a CMOS differential pair
InactiveUS20080036536A1Multiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShunt DeviceFilter tuning
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers provide image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. Active filters utilize multi track spiral inductors with shields to increase circuit Q. The filters incorporate a gain stage that provides improved dynamic range through the use of cross coupled auxiliary differential pair CMOS amplifiers to cancel distortion in a main linearized differential pair amplifier. Frequency planning provides additional image rejection. Local oscillator signal generation methods on chip reduce distortion. A PLL generates needed out of band LO signals. Direct synthesis generates in band LO signals. PLL VCOs are centered automatically. A differential crystal oscillator provides a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission throughout the receiver is used. ESD protection is provided by a pad ring and ESD clamping structure. Shunts utilize a gate boosting at each pin to discharge ESD build up. An IF VGA utilizes distortion cancellation achieved with cross coupled differential pair amplifiers having their Vds dynamically modified in conjunction with current steering of the differential pairs sources.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Transconductance filter control system
InactiveUS6172569B1Increase power consumptionIncrease in sizeContinuous tuning detailsGain controlAudio power amplifierControl system
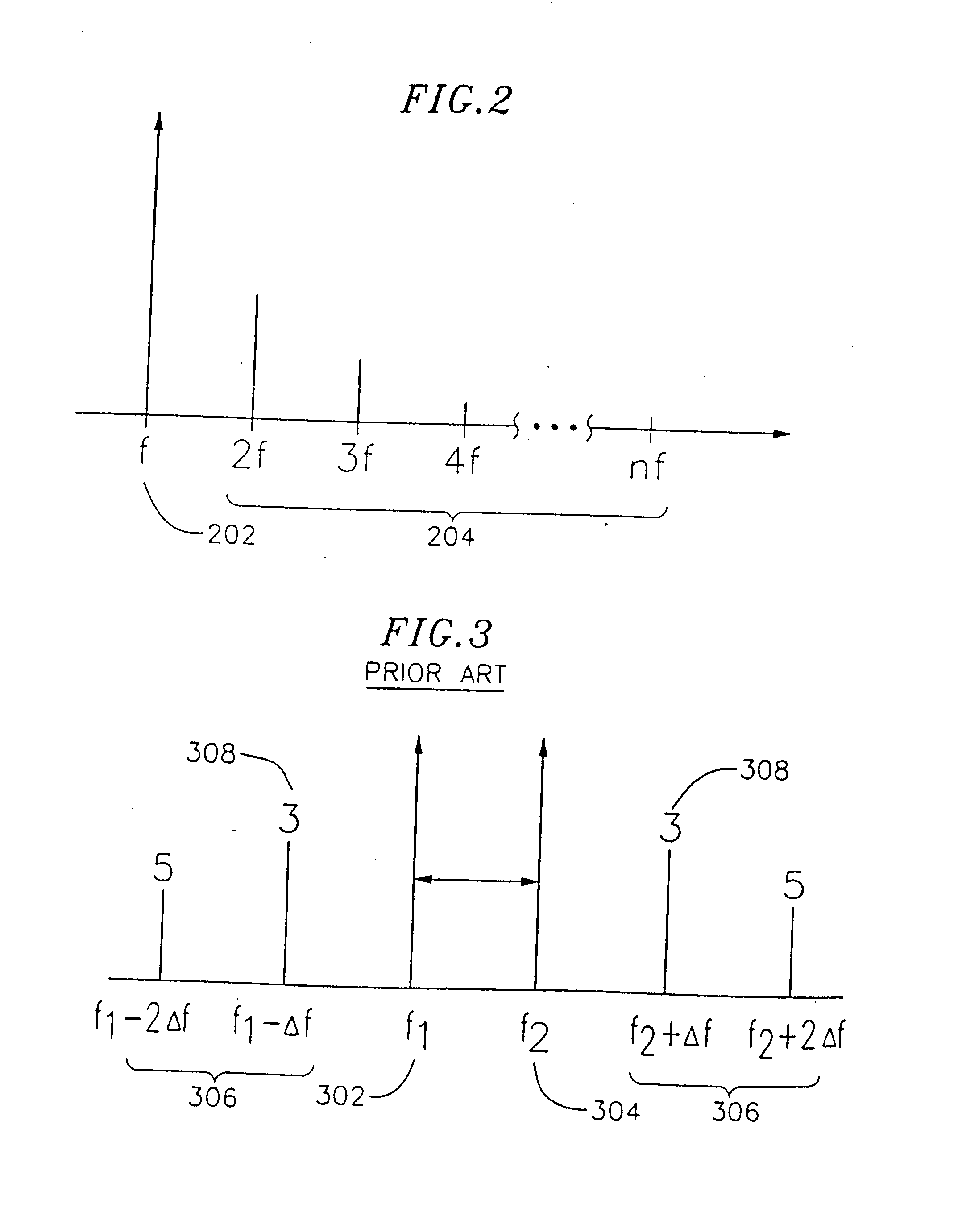
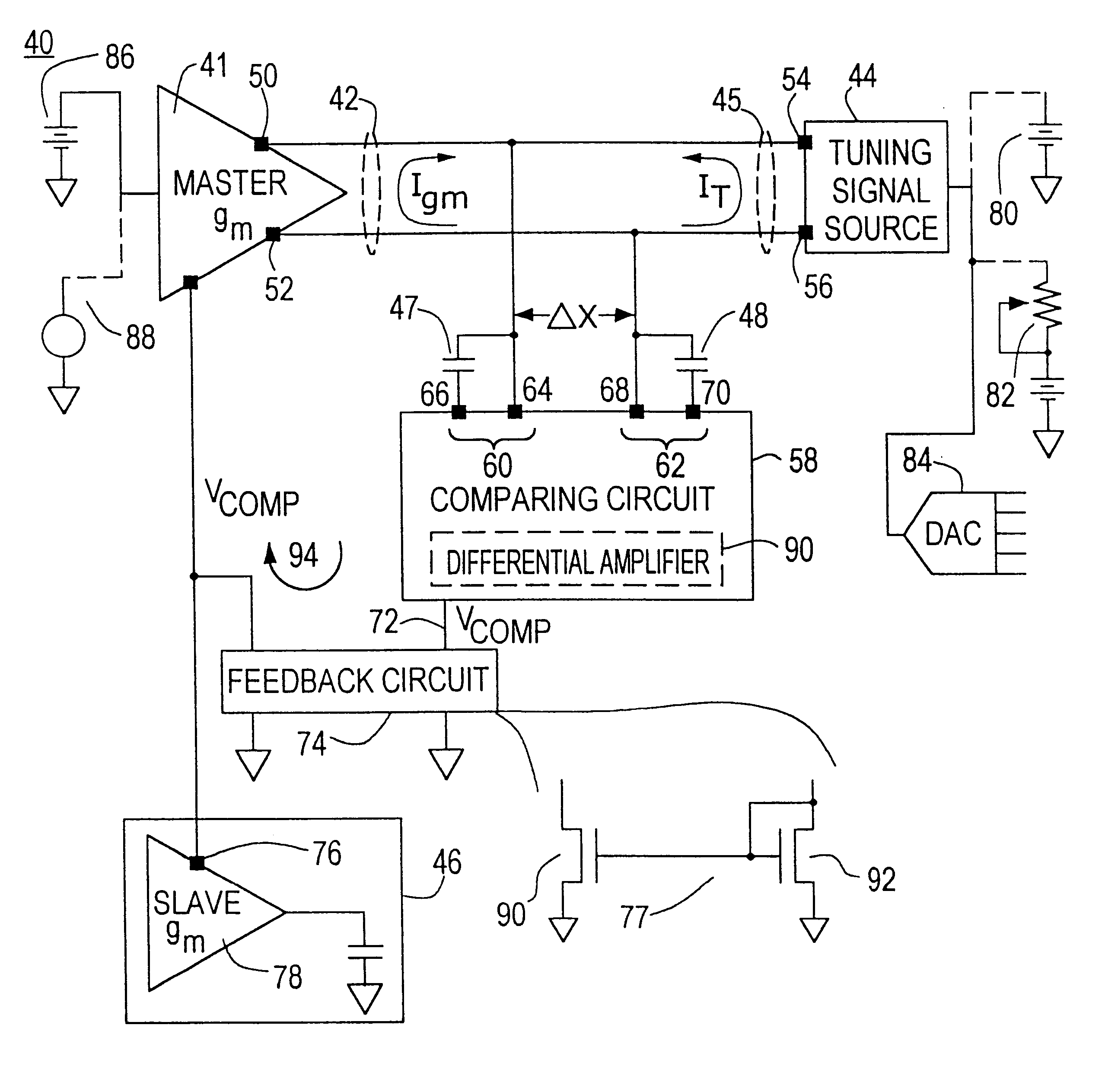
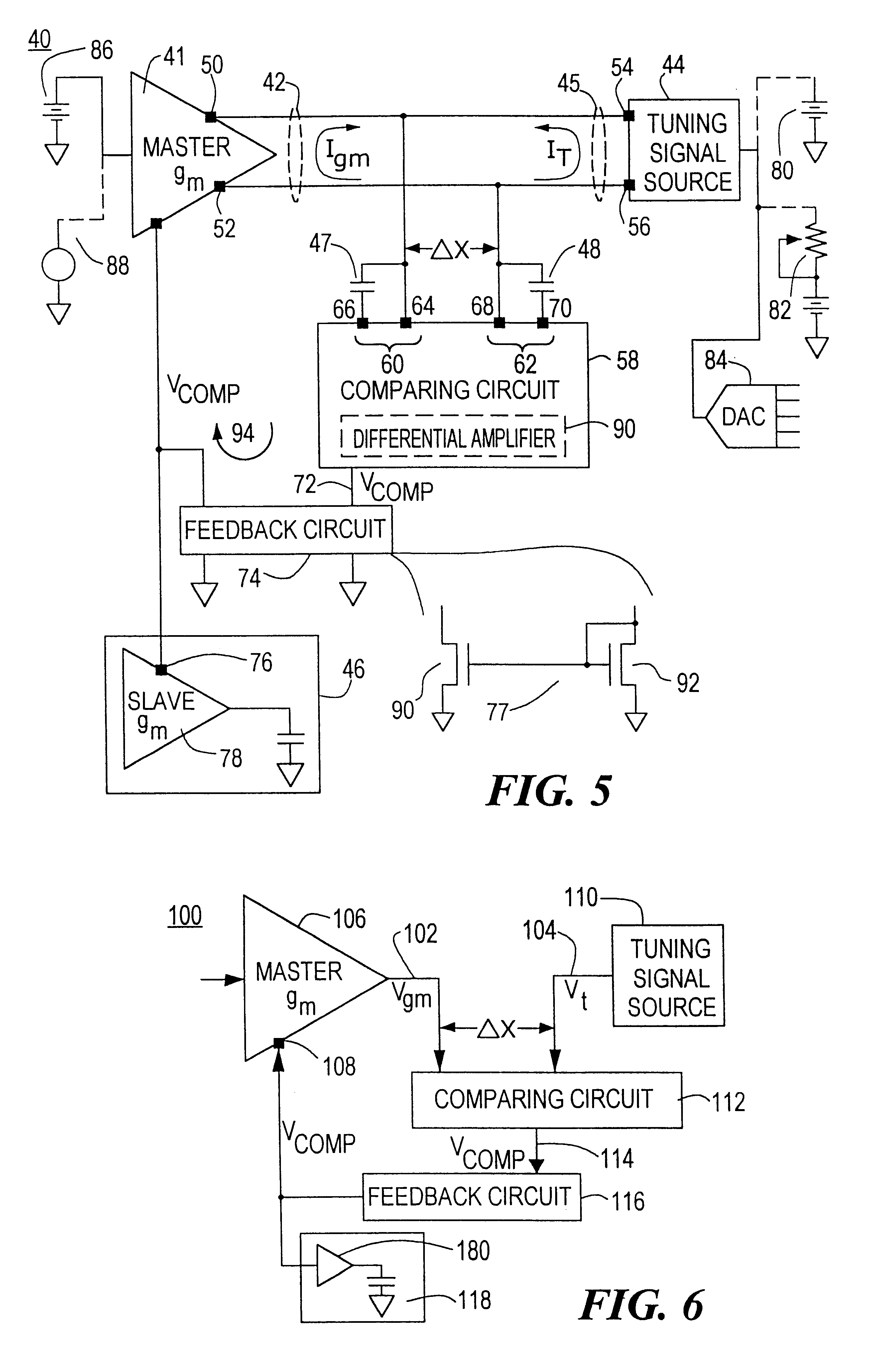
A transconductance filter control system for compensating for drift in transconductance of a slave transconductance amplifier in a continuous time transconductance filter including: a master transconductance amplifier having an output which is a function of its transconductance and a control input for controlling the transconductance of the master transconductance amplifier; a tuning signal source for providing a tuning signal representative of a preselected characteristic of the transconductance filter; a comparing circuit, responsive to any deviation from a predetermined difference between the tuning signal and the output of the master transconductance amplifier, representative of a deviation of the transconductance of the master transconductance amplifier, for providing a compensation signal; and a circuit for applying the compensation signal to the control input of the master transconductance amplifier and to the control input of the slave transconductance amplifier in the transconductance filter to adjust the transconductance of both the master and slave transconductance amplifiers and restore the predetermined difference between the tuning signal and the output of the master transconductance amplifier.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC +1
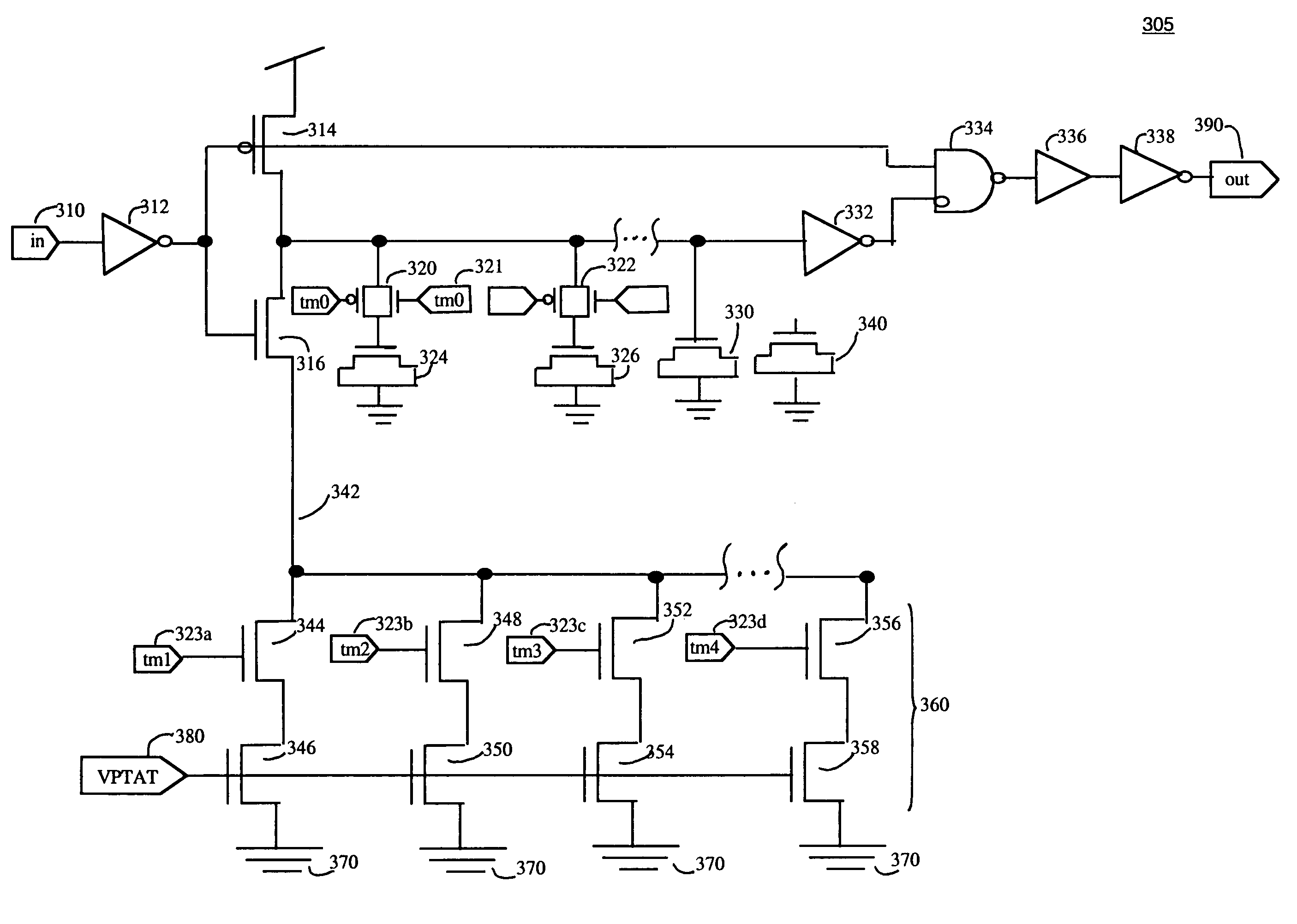
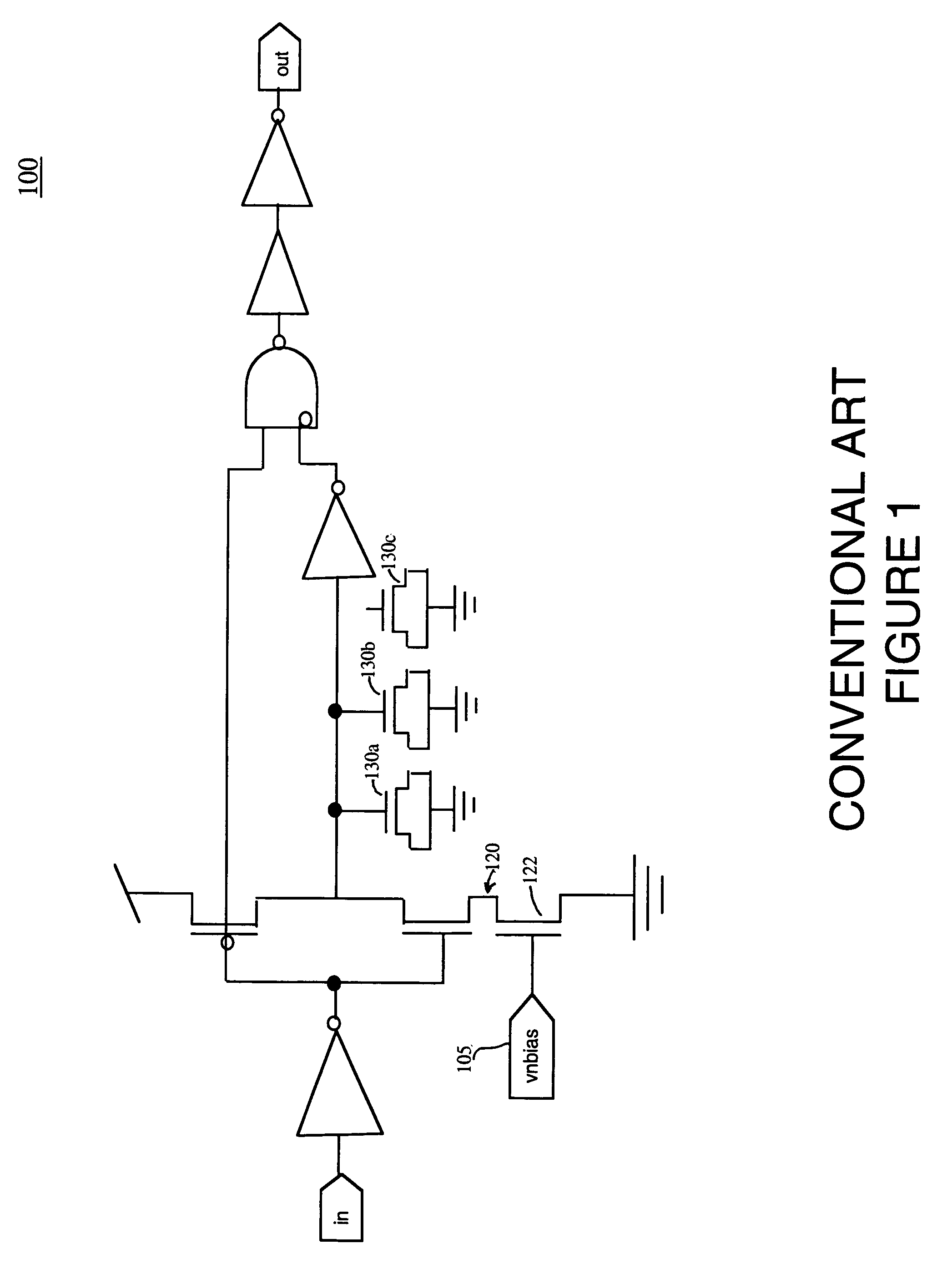
Self-timed thermally-aware circuits and methods of use thereof
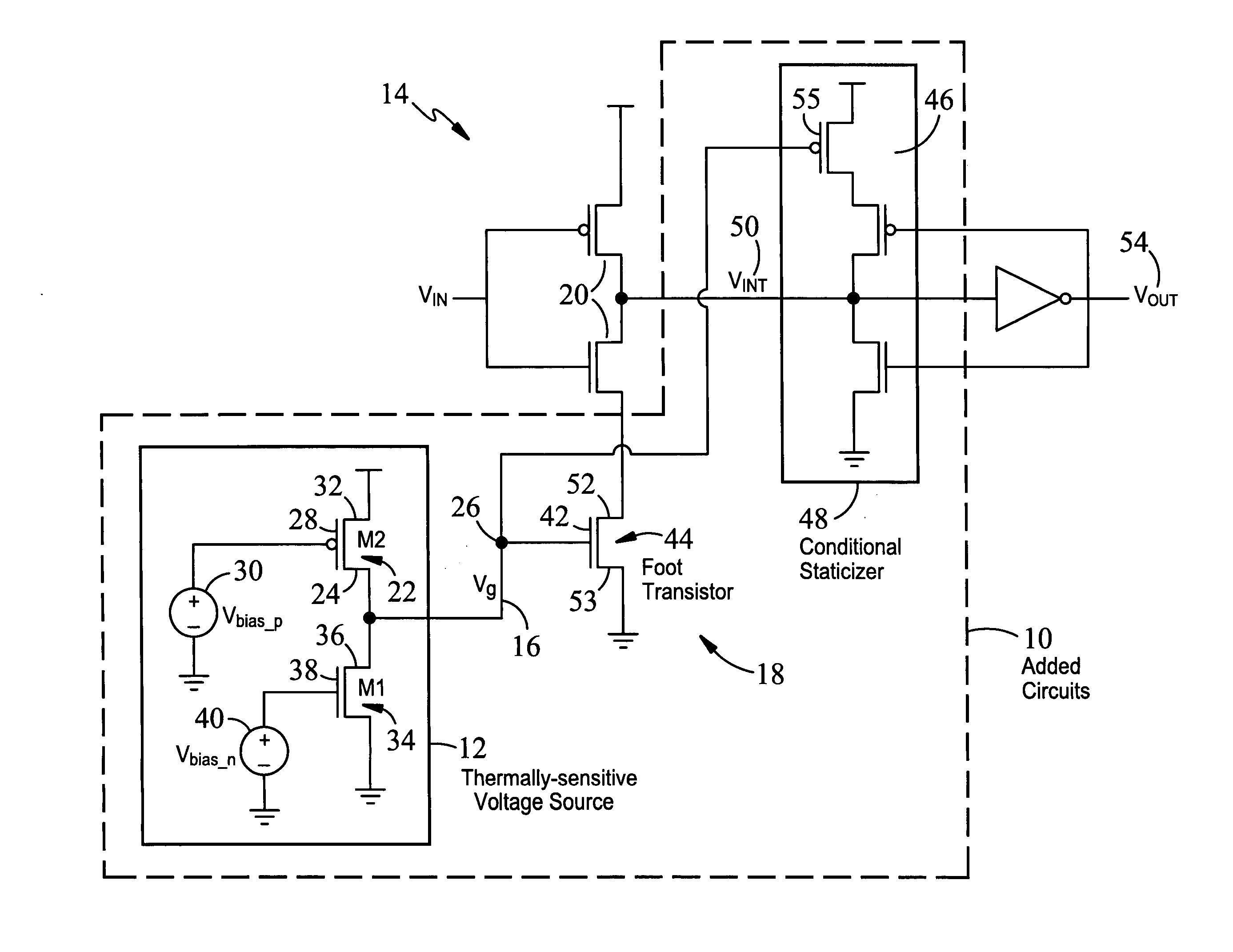
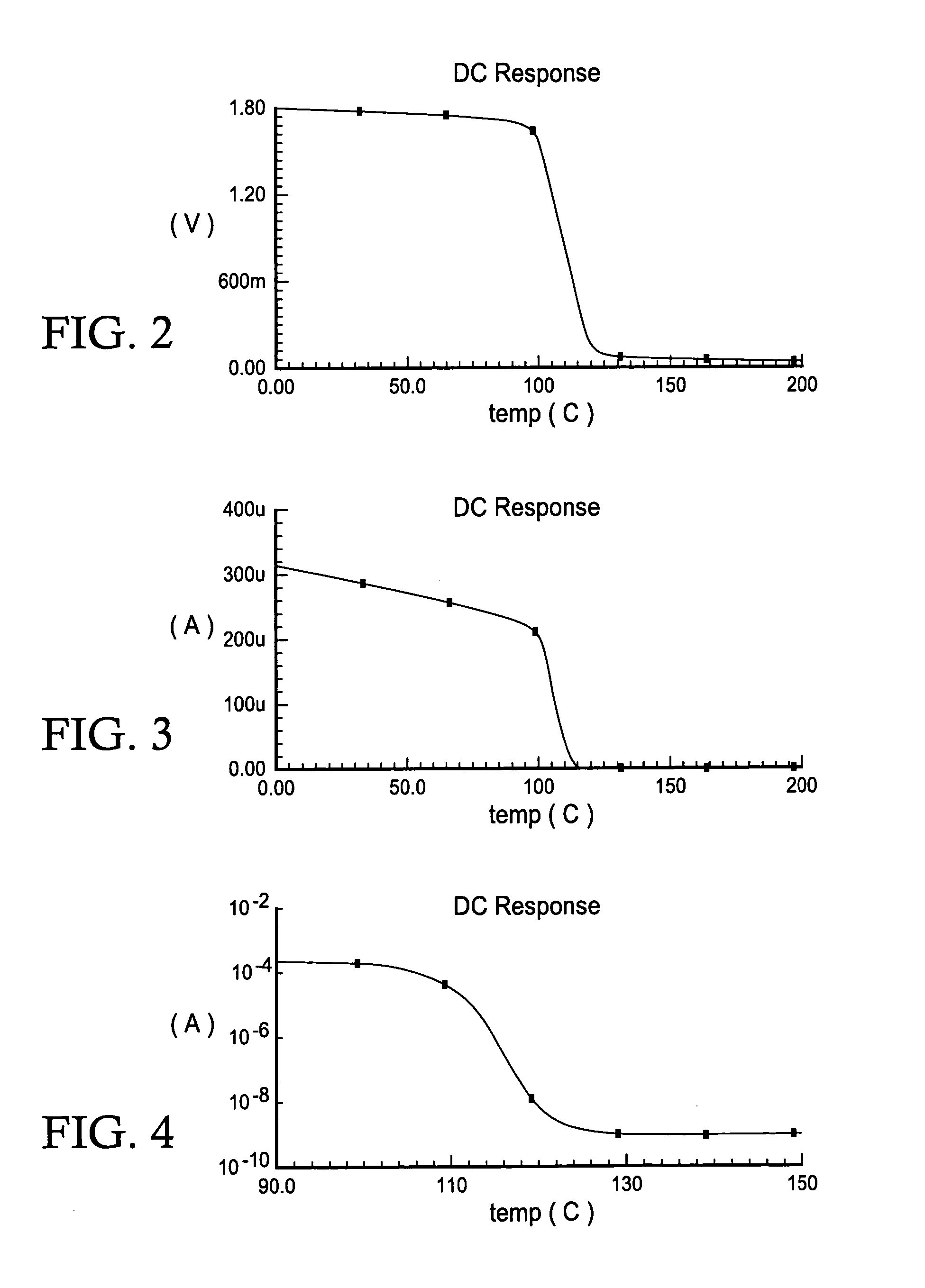
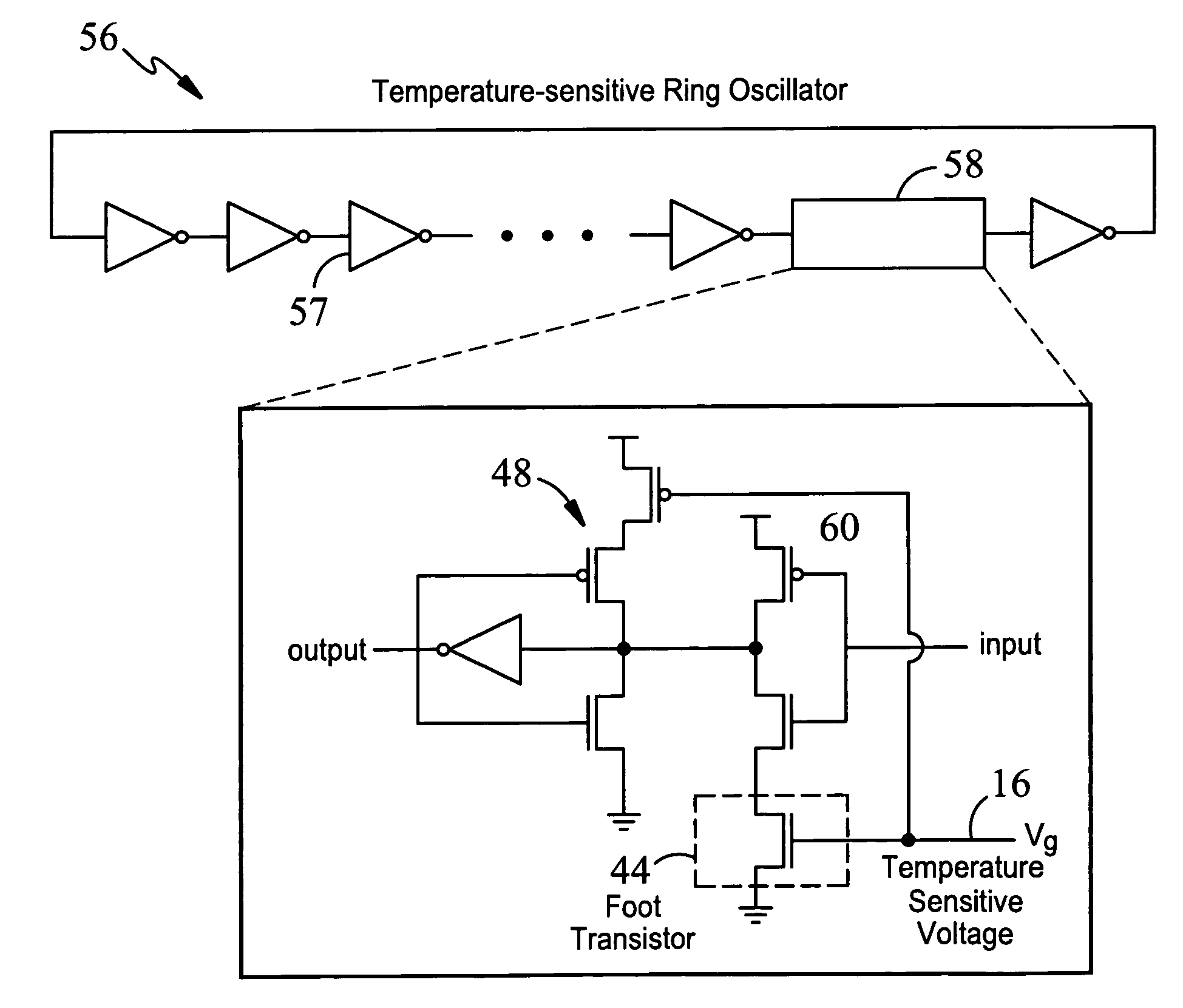
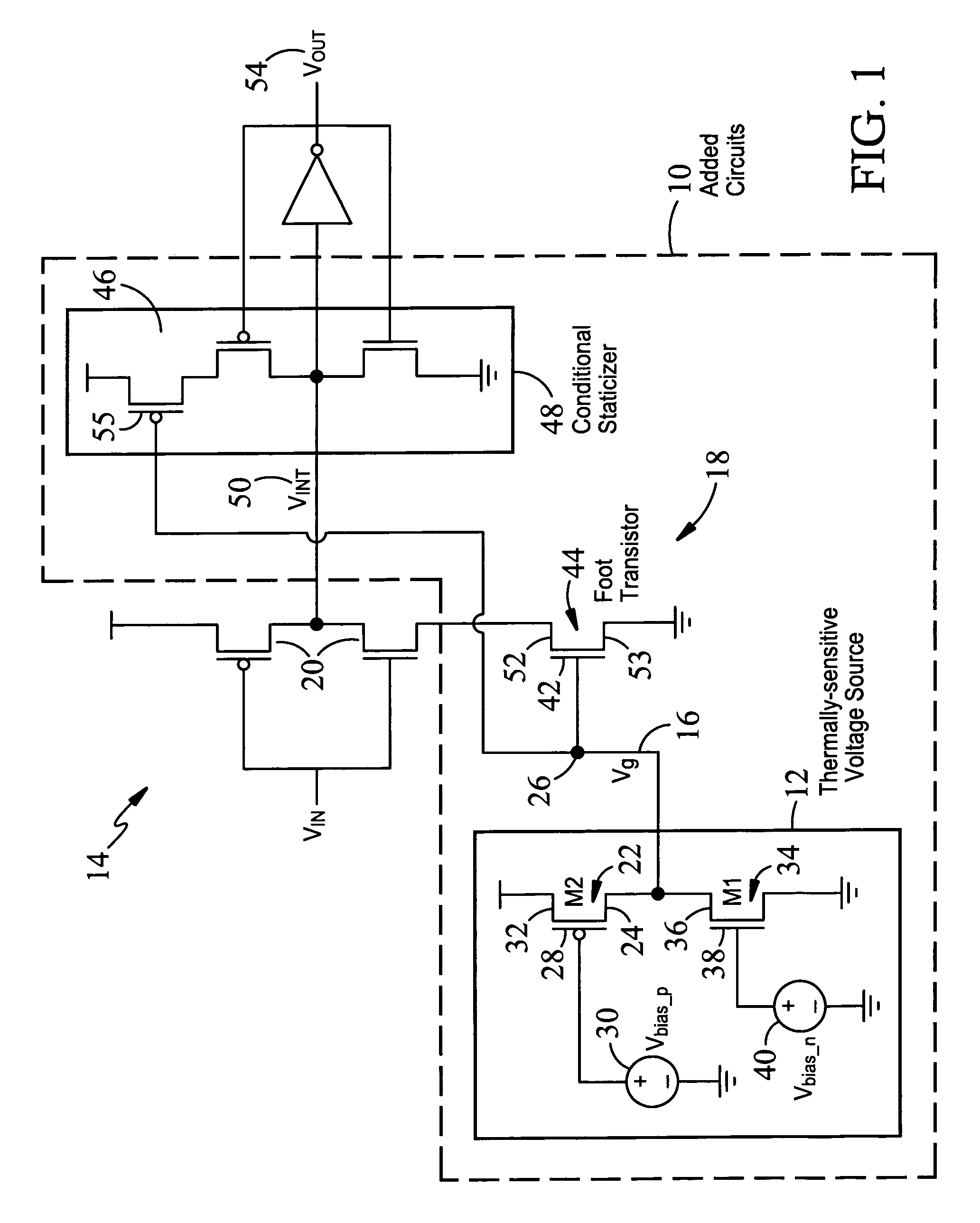
InactiveUS20070200608A1Without imposing significant implementation overheadStall-free performance-throttlingElectronic switchingNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureVoltage sourceThreshold temperature
Apparatus and methods for regulating gate delays of synchronous and asynchronous digital circuits. Thermally-sensitive circuits include, generally, temperature sensitive voltage sources outputting a voltage signal indicative of the temperature of the digital circuit, where the voltage signal reflects non-linear temperature sensitivity above a predetermined threshold temperature, and delay mechanisms receiving said temperature sensitive voltage signal(s) as input and being configured to automatically continuously modulate the speed of signal propagation through the circuit in response to said voltage signal, thereby causing circuit elements within the circuits to switch less frequently and consequently causing the circuit elements to generate less heat with increasing circuit temperature.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Self-timed thermally-aware circuits and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7411436B2Without imposing significant implementation overheadStall-free performance-throttlingElectronic switchingNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureAsynchronous circuitEngineering
Apparatus and methods for regulating gate delays of synchronous and asynchronous digital circuits. Thermally-sensitive circuits include, generally, temperature sensitive voltage sources outputting a voltage signal indicative of the temperature of the digital circuit, where the voltage signal reflects non-linear temperature sensitivity above a predetermined threshold temperature, and delay mechanisms receiving said temperature sensitive voltage signal(s) as input and being configured to automatically continuously modulate the speed of signal propagation through the circuit in response to said voltage signal, thereby causing circuit elements within the circuits to switch less frequently and consequently causing the circuit elements to generate less heat with increasing circuit temperature.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
System and method for on-chip filter tuning
InactiveUS6865381B2Low selectivityMultiple-port active networksSolid-state devicesCapacitanceFilter tuning
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit is described. A receiver front end provides programable attenuation and a programable gain low noise amplifier. Frequency conversion circuitry advantageously uses LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers to provide sufficient image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. The filters utilize multi track spiral inductors. The filters are tuned using local oscillators to tune a substitute filter, and frequency scaling during filter component values to those of the filter being tuned. In conjunction with filtering, frequency planning provides additional image rejection. The advantageous choice of local oscillator signal generation methods on chip is by PLL out of band local oscillation and by direct synthesis for in band local oscillator. The VCOs in the PLLs are centered using a control circuit to center the tuning capacitance range. A differential crystal oscillator is advantageously used as a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission is advantageously used throughout the receiver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
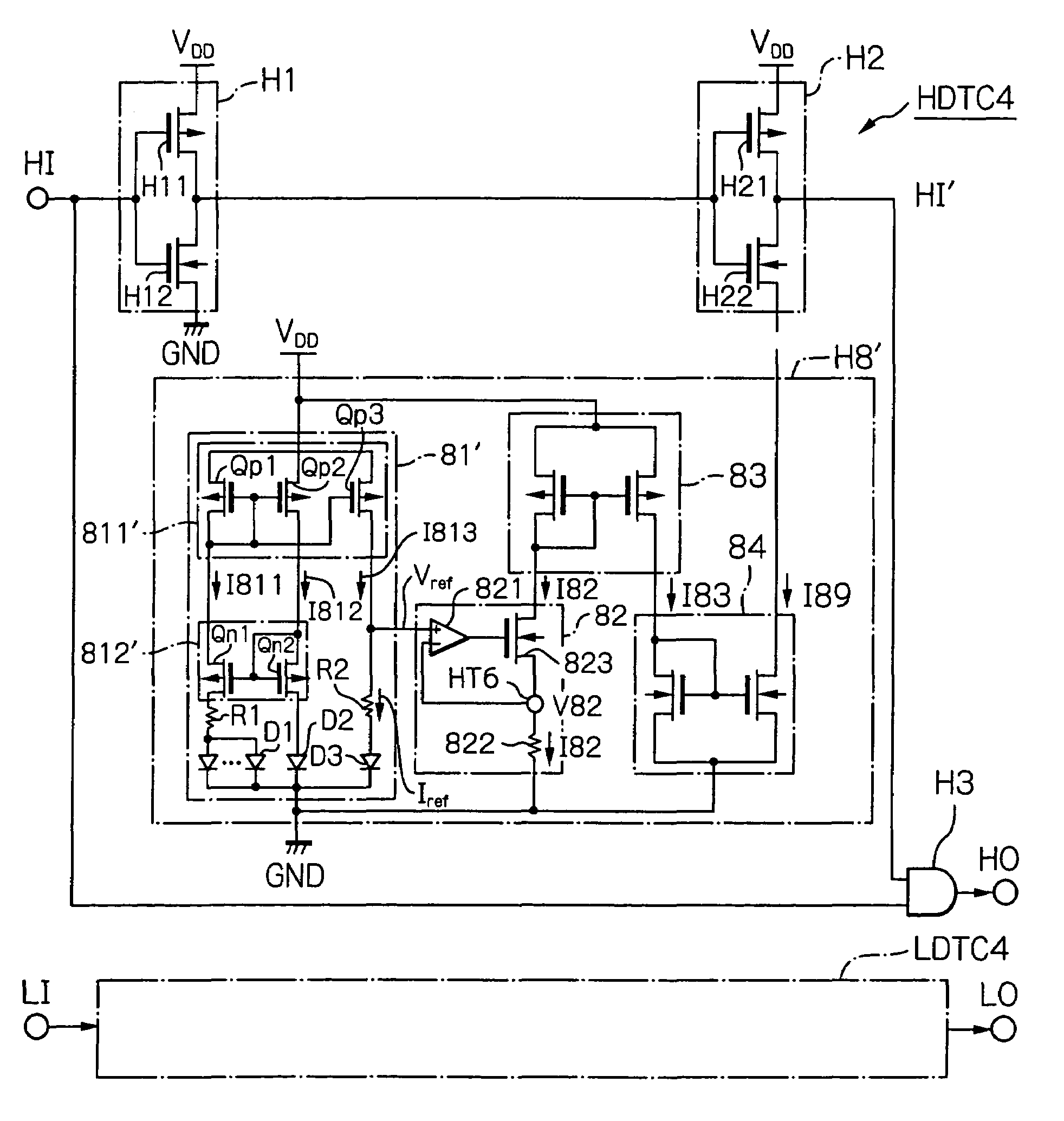
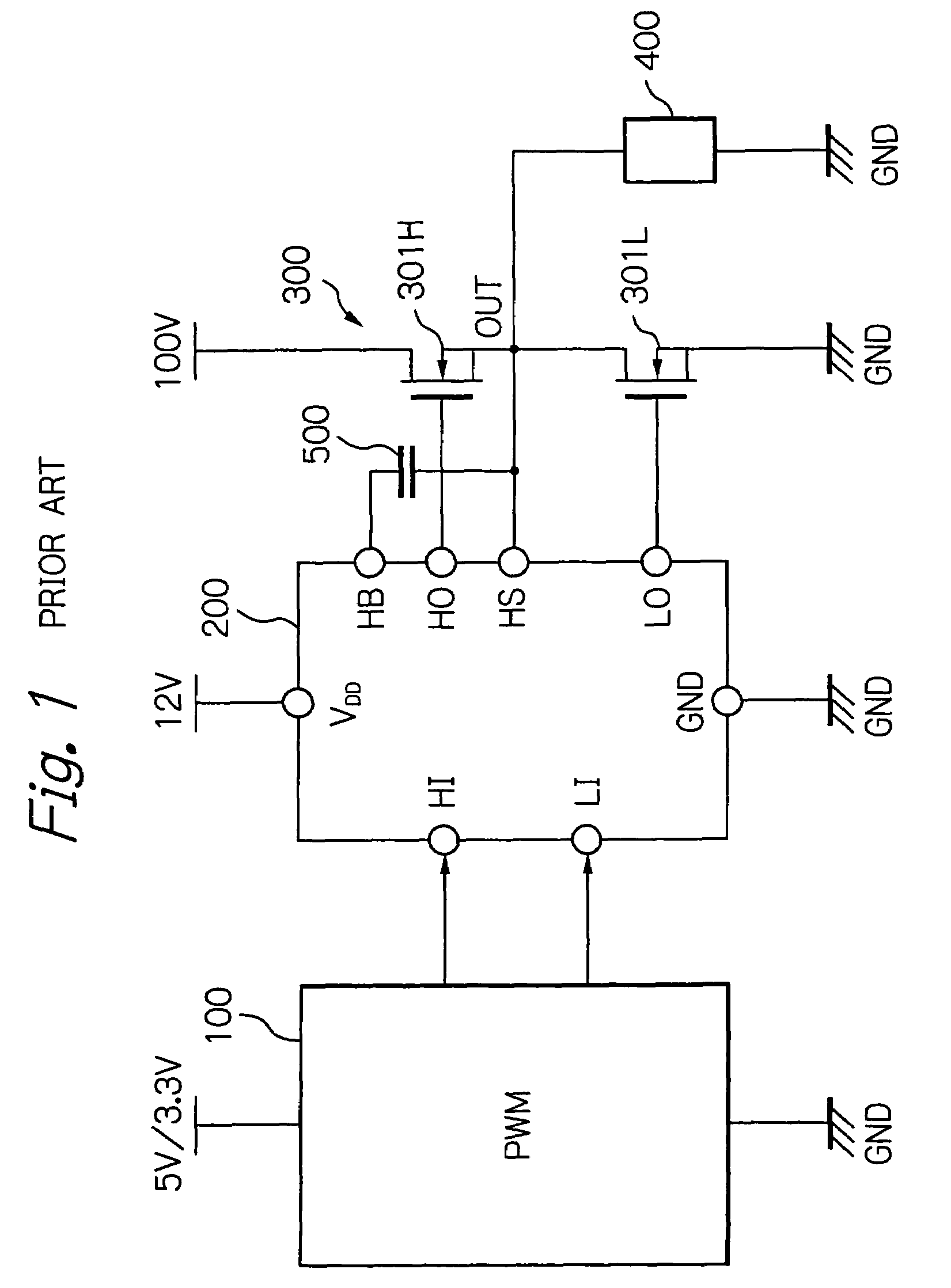
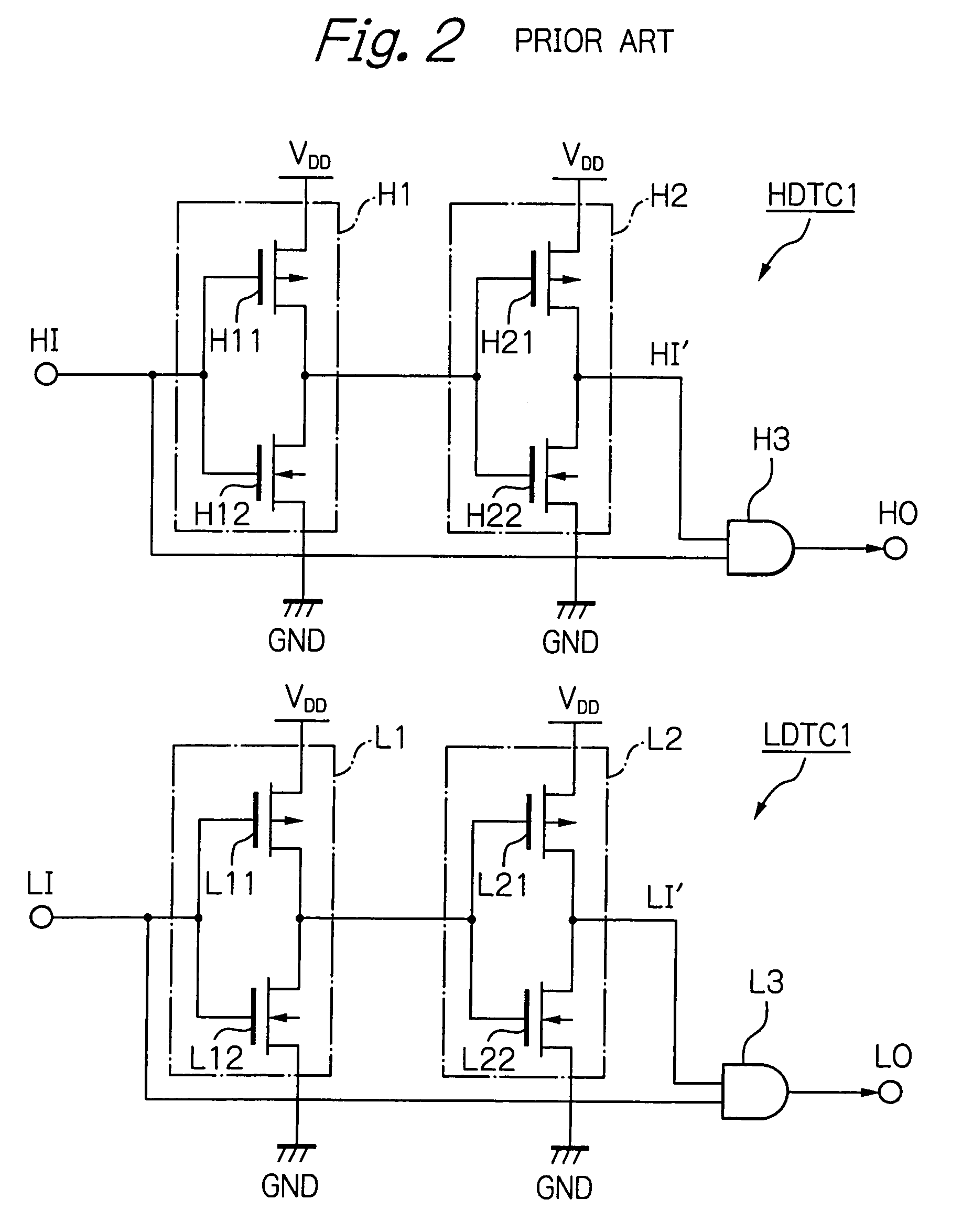
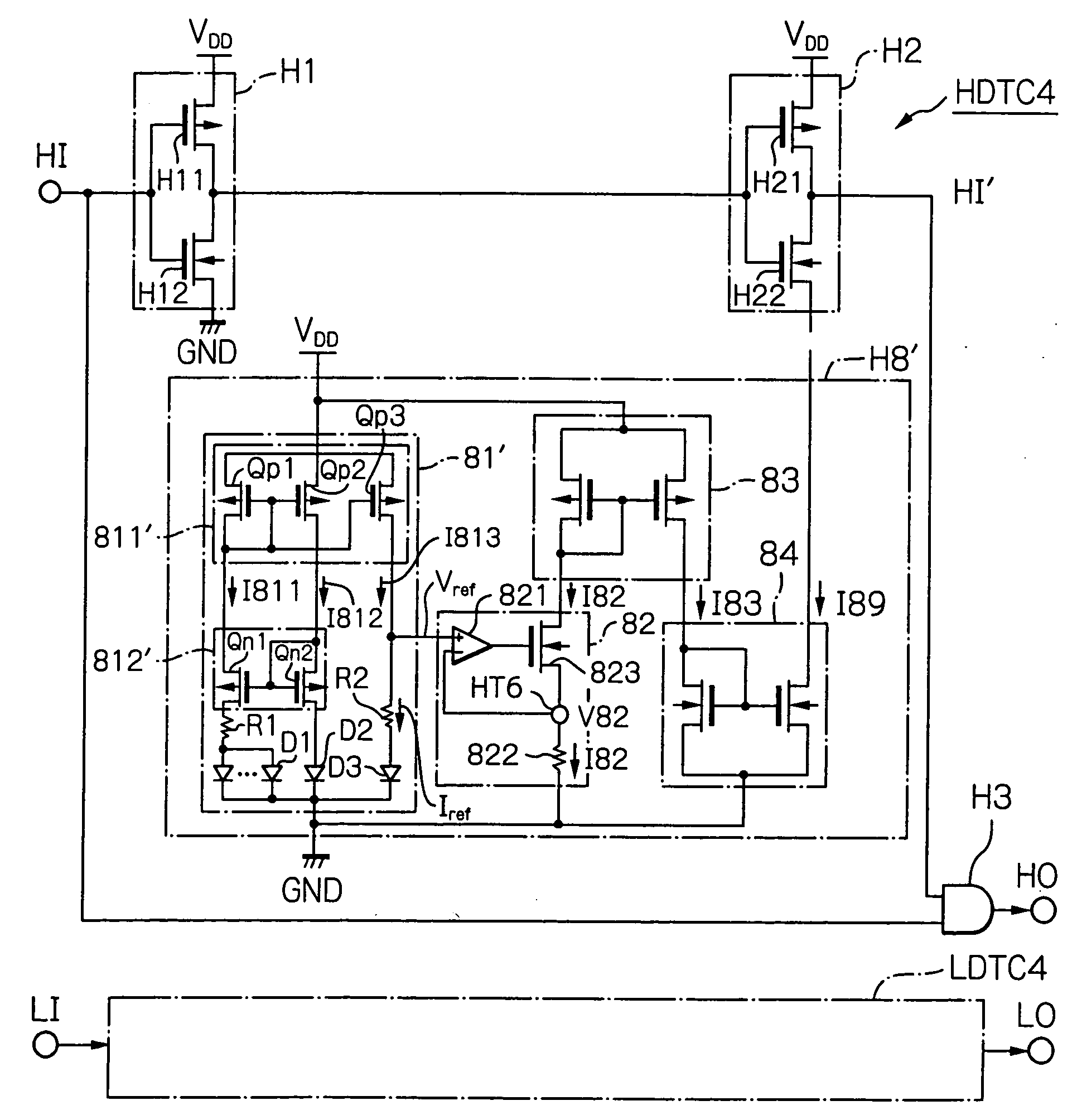
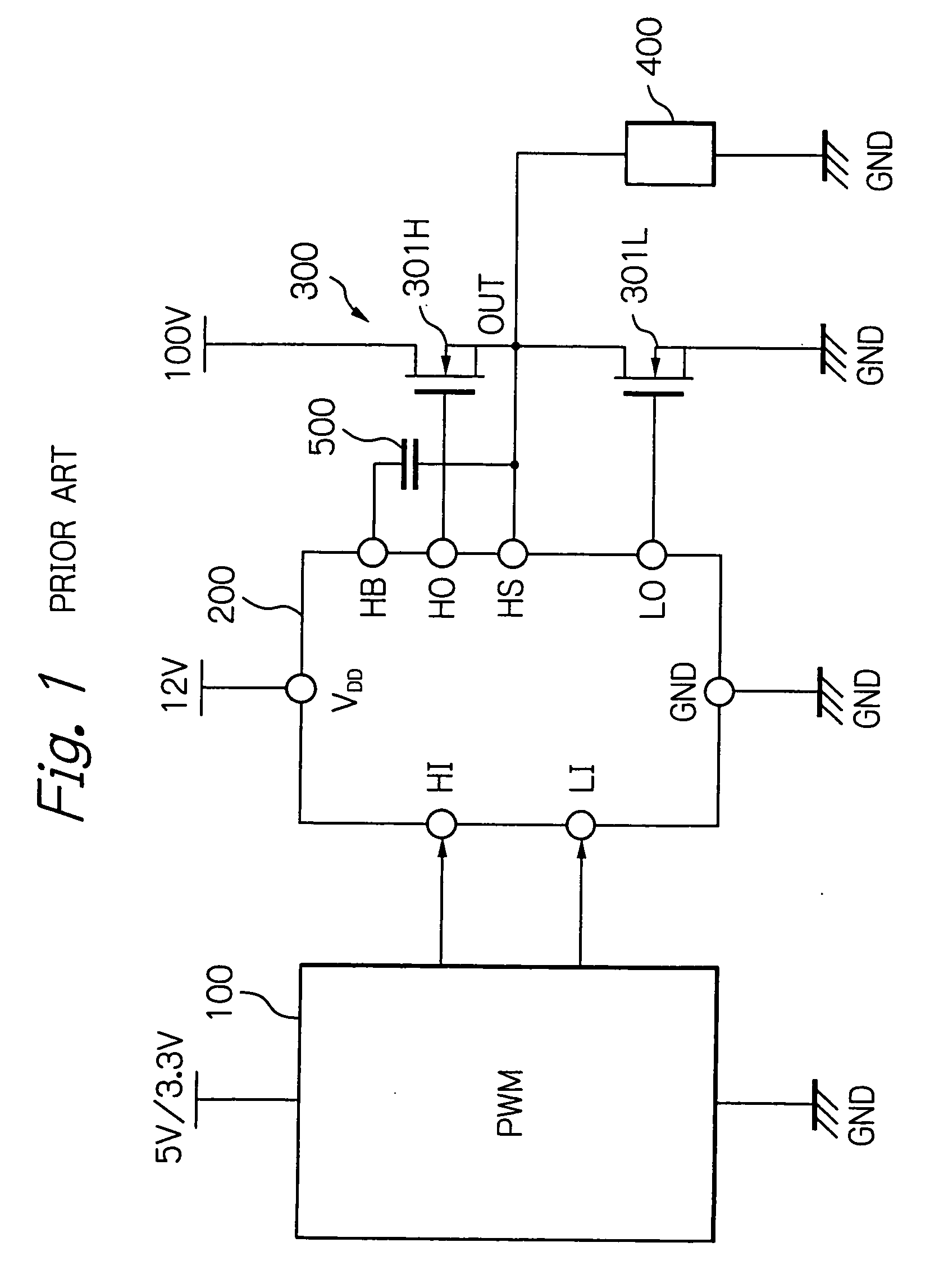
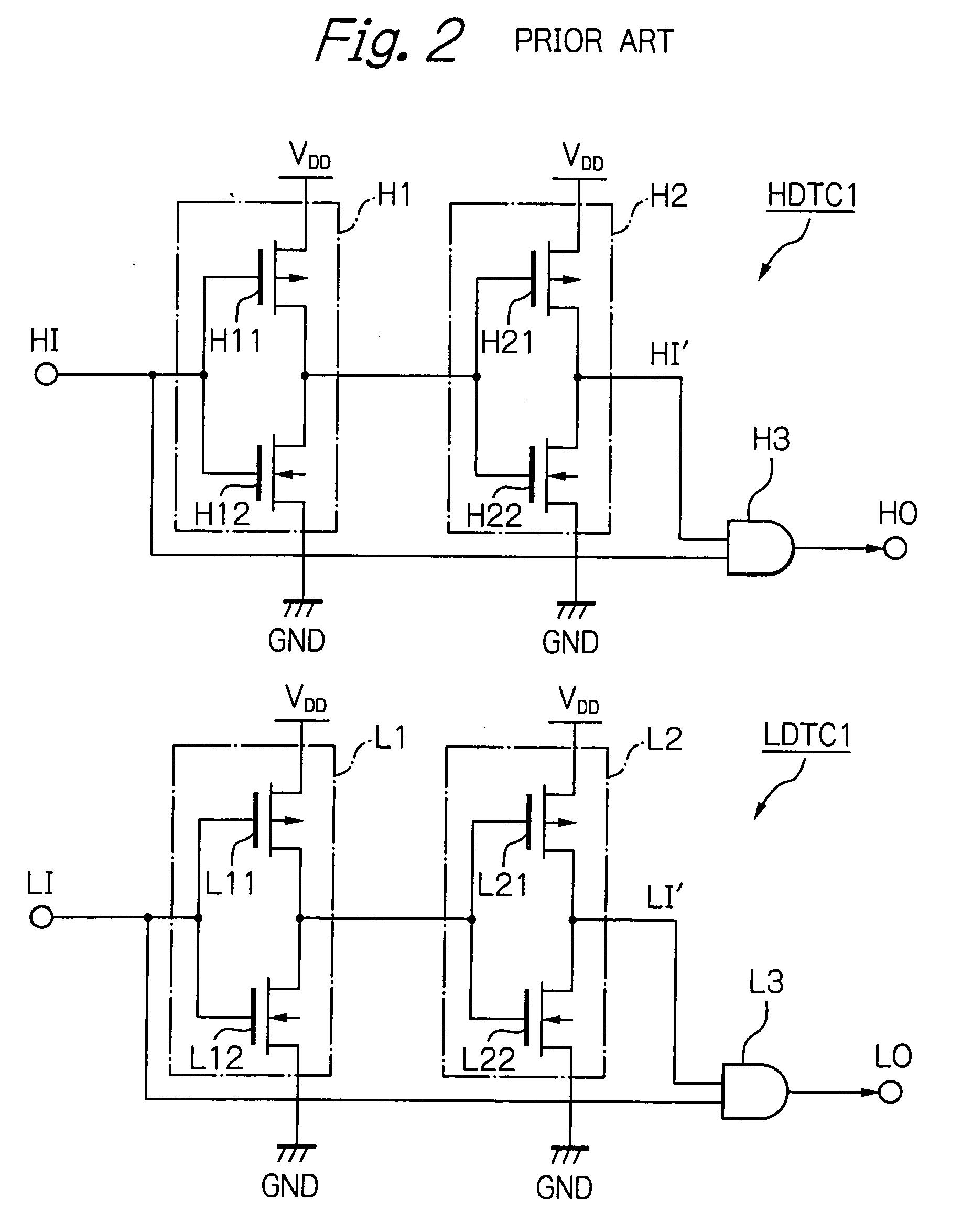
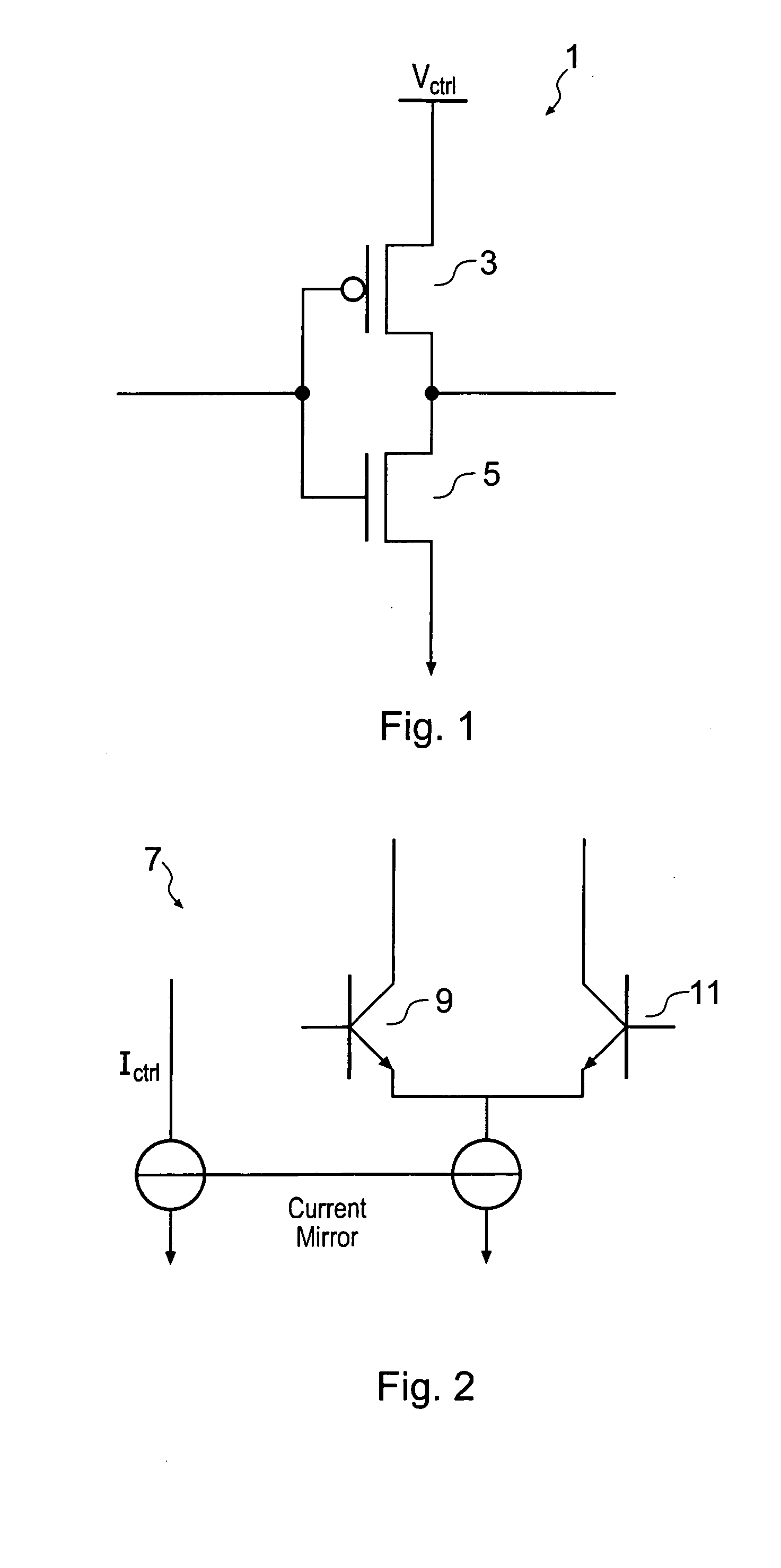
Dead time control circuit capable of adjusting temperature characteristics of dead time
In a dead time control circuit, a delay circuit is connected to an input terminal and adapted to delay signals therethrough by a delay time corresponding to a dead time. A logic circuit has a first input connected via the delay circuit to the input terminal, a second input connected directly to the input terminal, and an output connected to an output terminal. The dead time having adjustable temperature characteristics.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Dead time control circuit capable of adjusting temperature characteristics of dead time
ActiveUS20060290401A1Reliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingDead timeDead time control
In a dead time control circuit, a delay circuit is connected to an input terminal and adapted to delay signals therethrough by a delay time corresponding to a dead time. A logic circuit has a first input connected via the delay circuit to the input terminal, a second input connected directly to the input terminal, and an output connected to an output terminal. The dead time having adjustable temperature characteristics.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Delay inversely proportional to temperature timer circuit
InactiveUS7642833B1Reduce delaysReduce resistanceNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureTime-delay networksEngineeringReference circuit
A timer circuit is disclosed. The timer, having a delay configured to track inversely with temperature of the memory device, includes a reference signal configured to increase in voltage, as the temperature of the memory device increases. The reference signal may be generated from a current that is derived from a bandgap reference circuit. The timer circuit includes a pull-down path made up of a plurality of selectable pull down transistors which are coupled to the reference signal at the gate. Resistance of the pull-down path is reduced as the reference signal is increased and the reduced resistance of the pull-down path decreases the delay of timer. A plurality of selectable delay elements may be preconfigured to adjust the delay and are coupled to the output path of the current starved inverter.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
System and method for linearizing a CMOS differential pair
InactiveUS7696823B2Multiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLocal oscillator signalFilter tuning
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers provide image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. Active filters utilize multi track spiral inductors with shields to increase circuit Q. The filters incorporate a gain stage that provides improved dynamic range through the use of cross coupled auxiliary differential pair CMOS amplifiers to cancel distortion in a main linearized differential pair amplifier. Frequency planning provides additional image rejection. Local oscillator signal generation methods on chip reduce distortion. A PLL generates needed out of band LO signals. Direct synthesis generates in band LO signals. PLL VCOs are centered automatically. A differential crystal oscillator provides a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission throughout the receiver is used. ESD protection is provided by a pad ring and ESD clamping structure. Shunts utilize a gate boosting at each pin to discharge ESD build up. An IF VGA utilizes distortion cancellation achieved with cross coupled differential pair amplifiers having their Vds dynamically modified in conjunction with current steering of the differential pairs sources.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
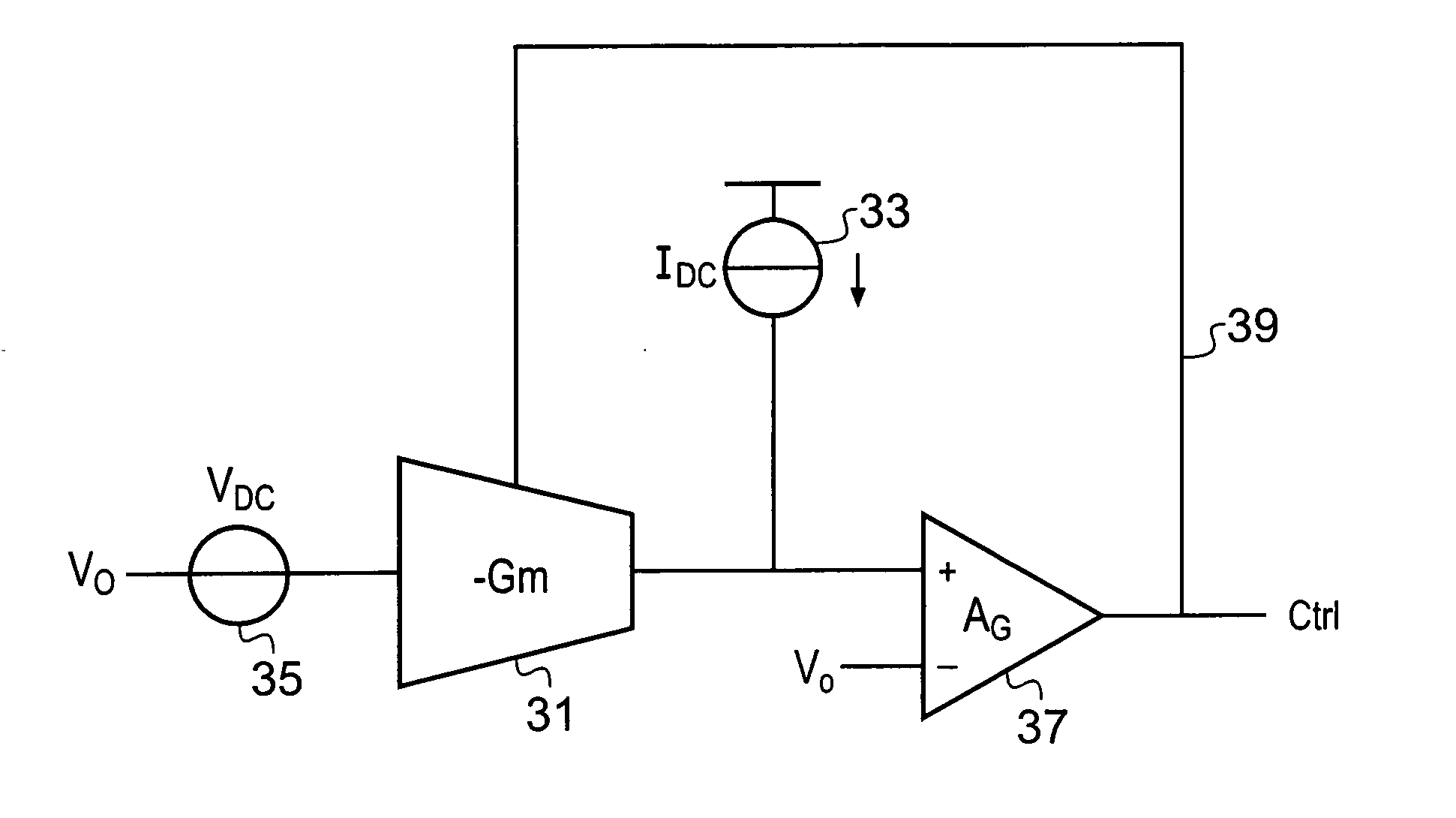
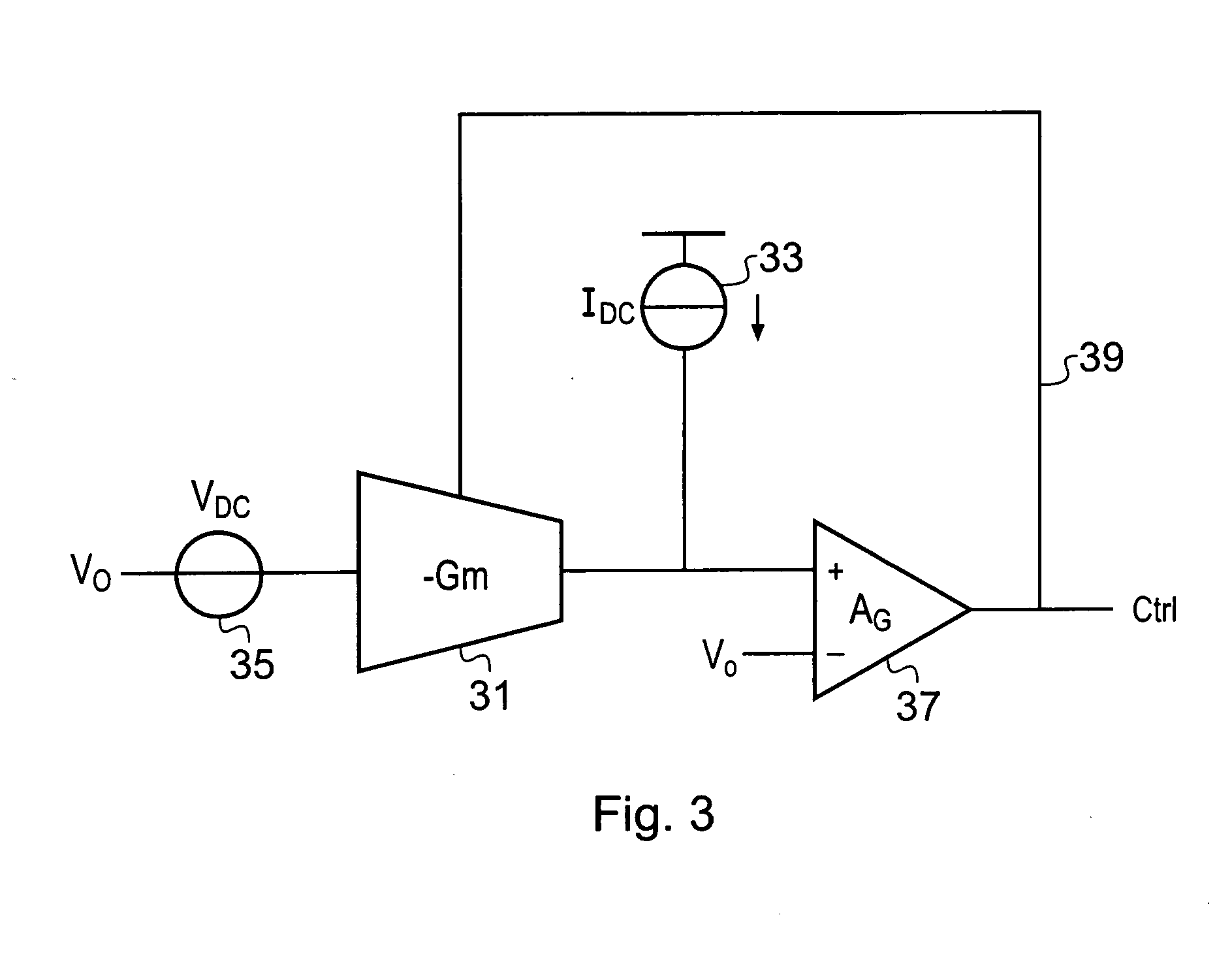
Integrated circuit
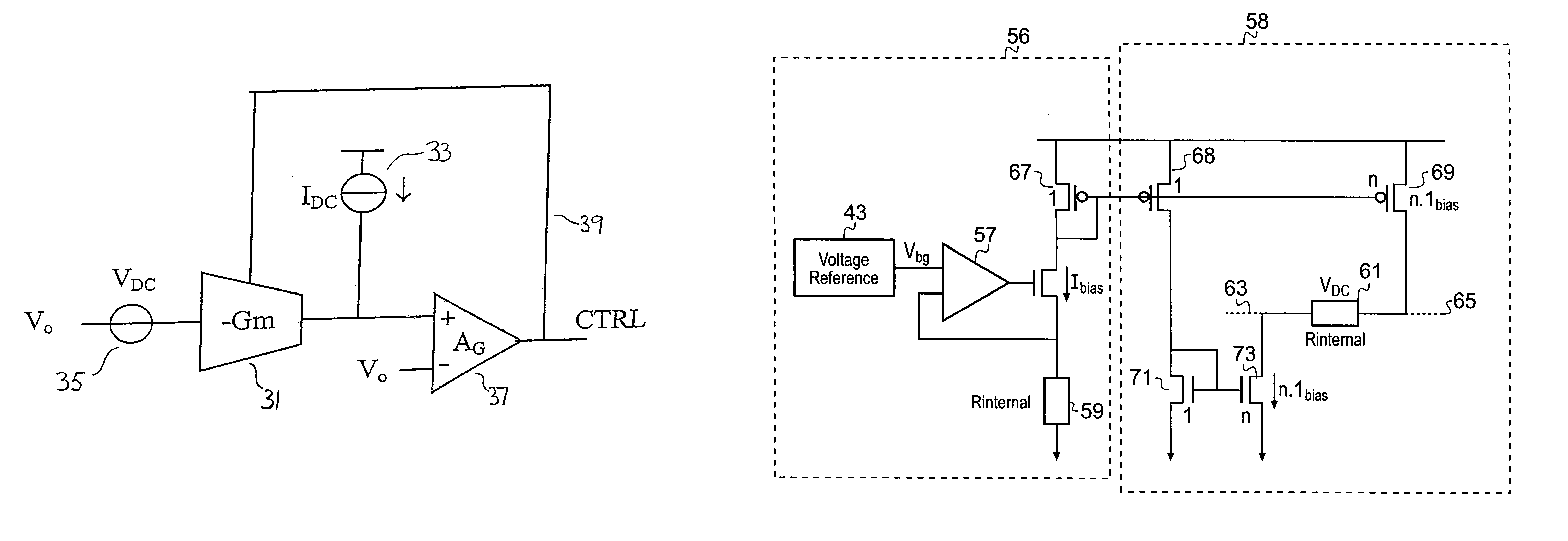
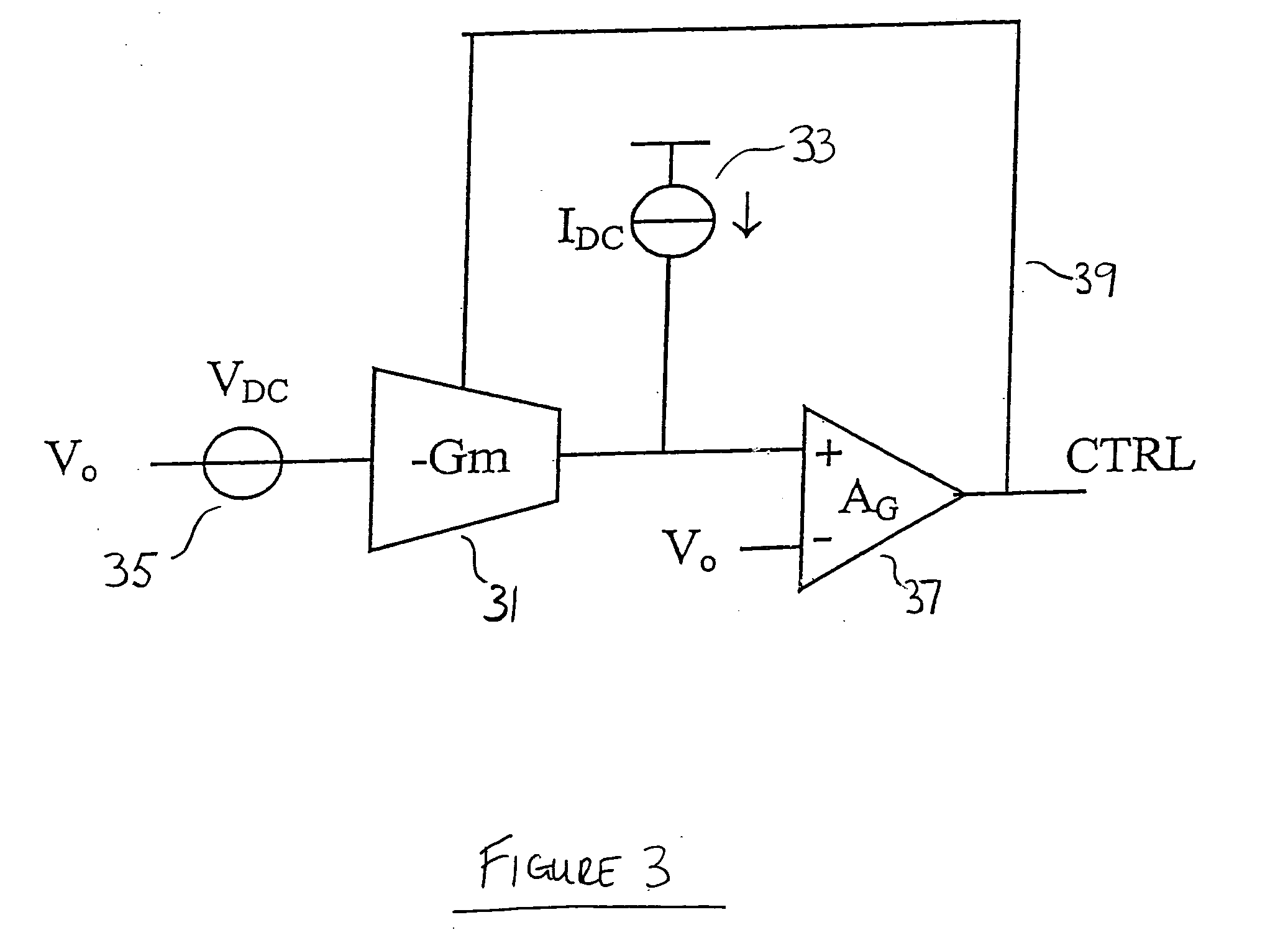
InactiveUS6933773B2Amplifier combinationsNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
An integrated circuit comprises a biasing circuit for maintaining the transconductance of a Gm cell constant. The integrated circuit comprises an on-chip constant voltage source and an on-chip constant current source. The on-chip constant current source has a connection for an external resistance, the value of the external resistance determining the current generated by the constant current source. The biasing circuit comprises means for providing a first fraction (β) of the current generated by the on-chip current source to bias the output of the Gm cell, and means for providing a second fraction (α) of the voltage generated by the on-chip voltage source to bias the input of the Gm cell. The transconductance of the Gm cell is controlled to be equal to the ratio of said fraction of the current generated by the on-chip current source to said fraction of the voltage generated by the on-chip voltage source.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Active load generation circuit and filter using same
ActiveUS20190149146A1High impedanceReduce areaInput/output impedence modificationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringVoltage reference
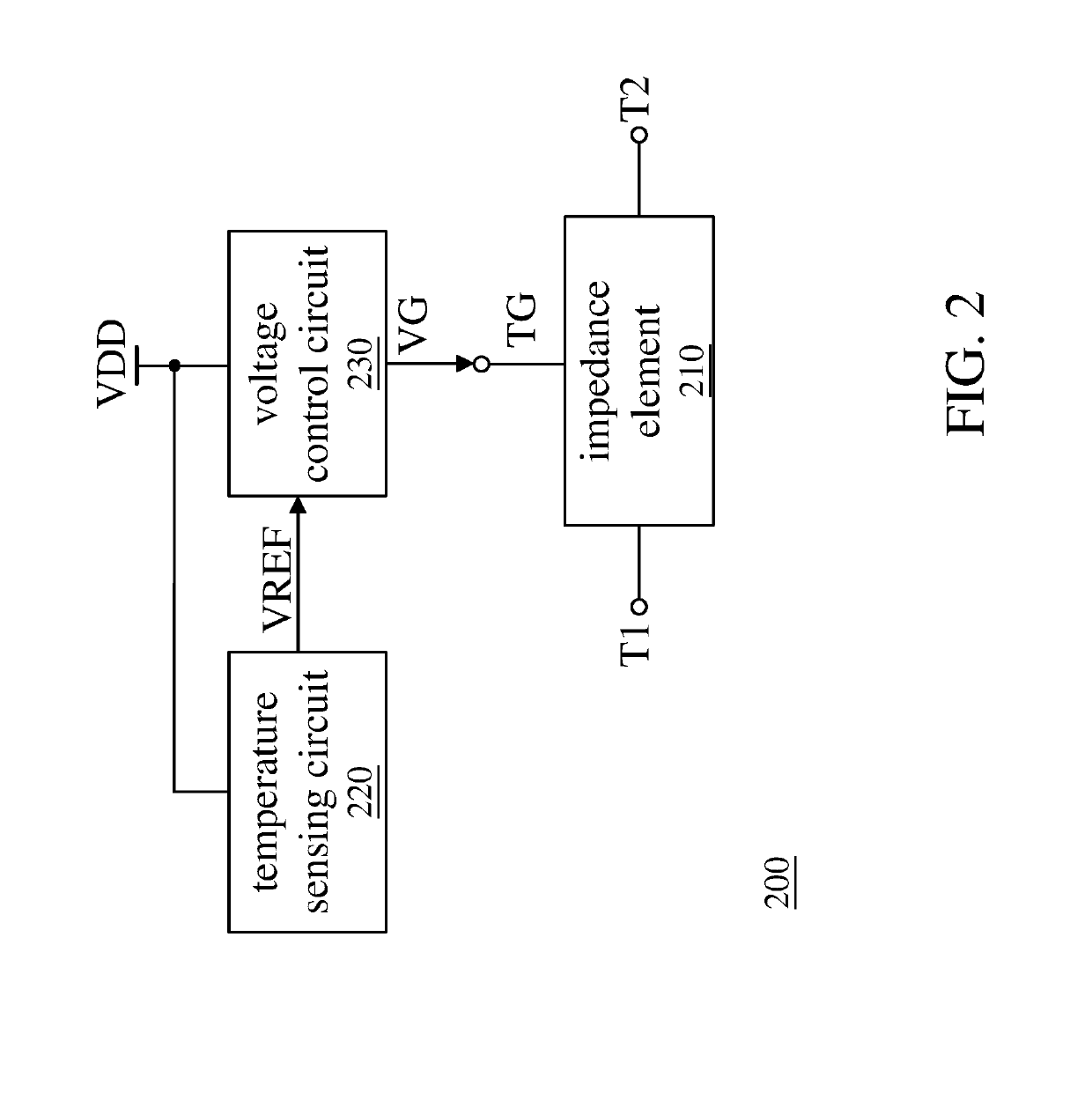
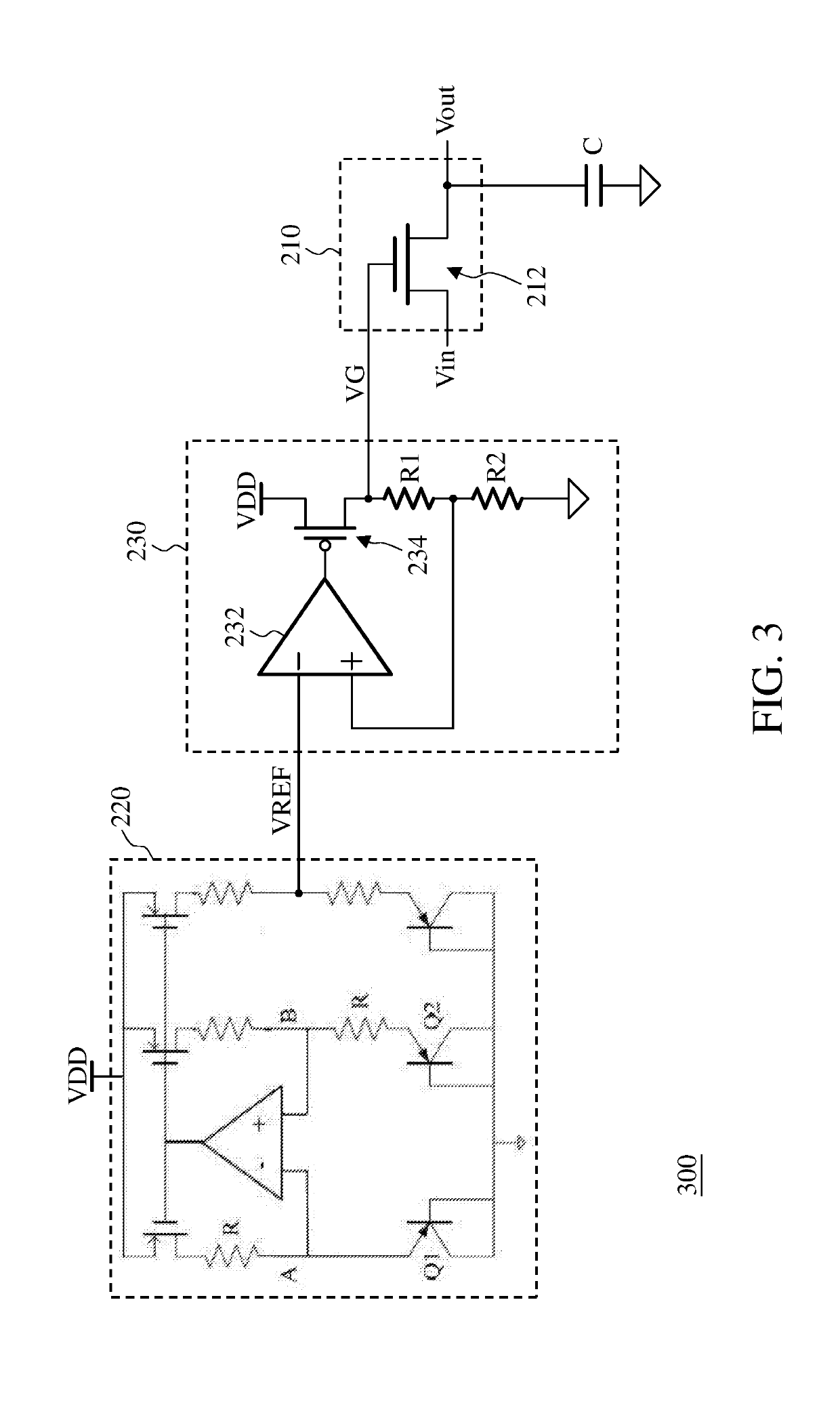
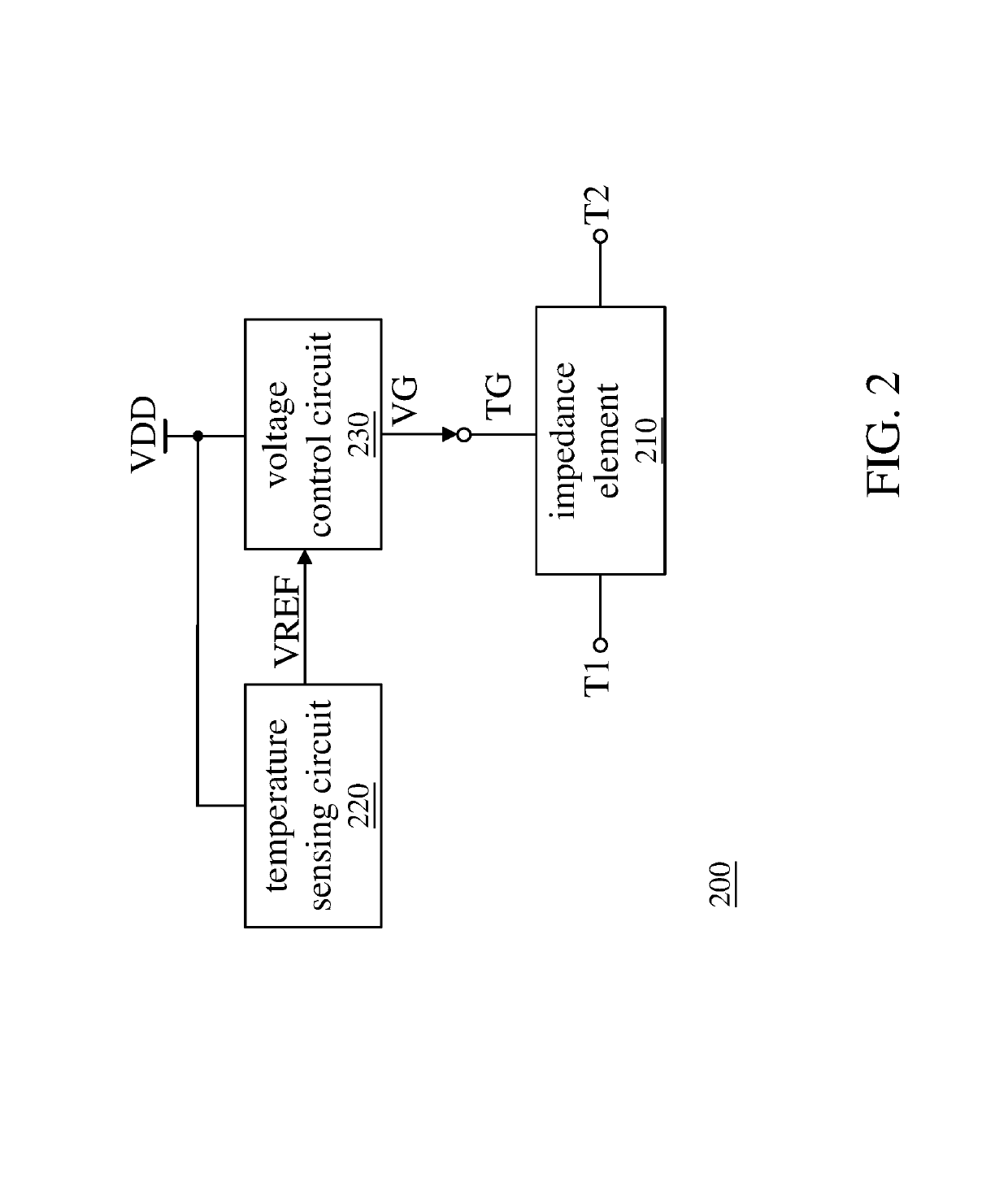
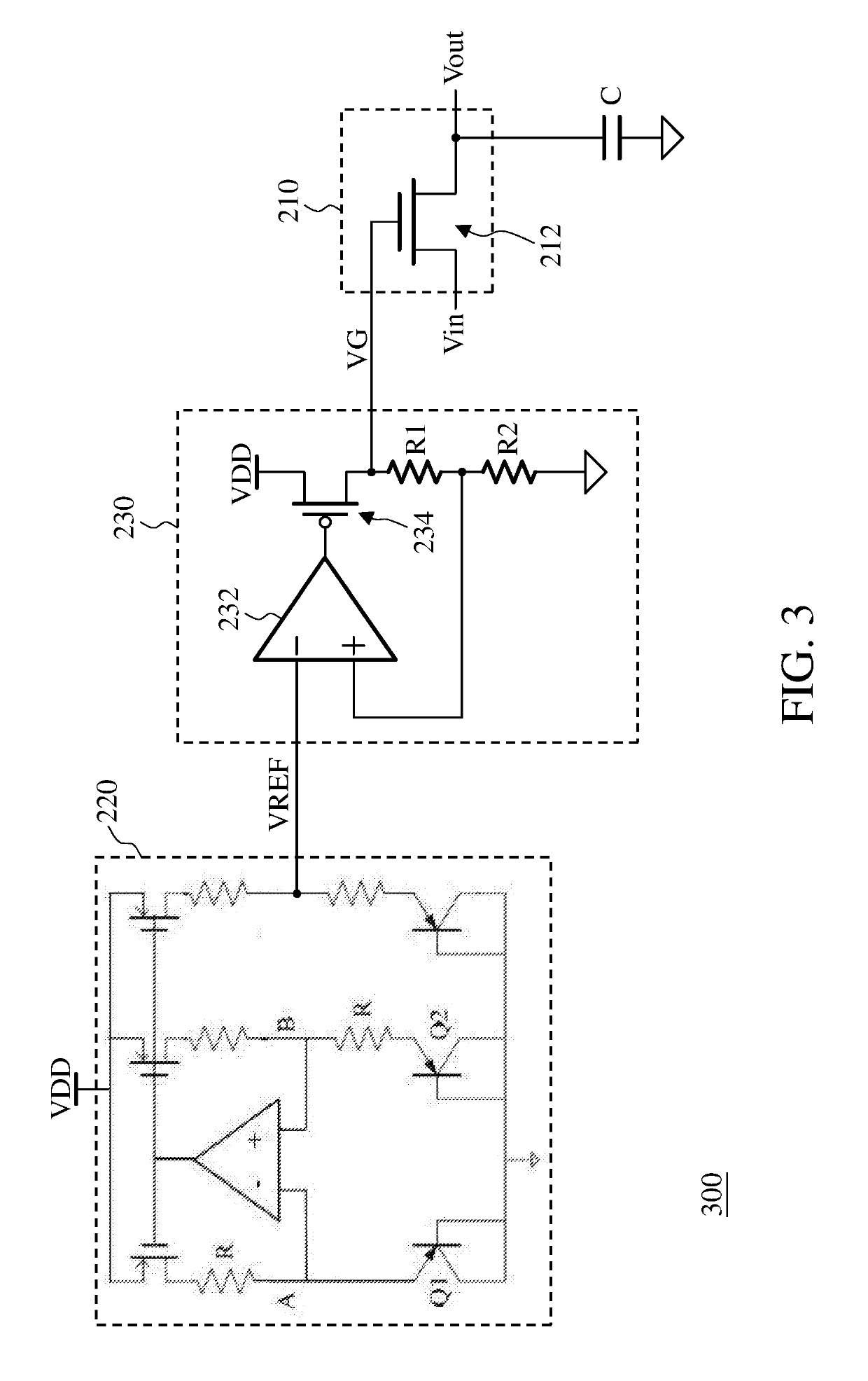
This invention discloses an active load generation circuit and a filter. The active load generation circuit includes a transistor, a voltage control circuit, a voltage offset and tracking circuit, and a temperature sensing circuit. The transistor provides an impedance and includes a control terminal and an input terminal. The control terminal receives a control voltage, the input terminal receives an input signal, and the impedance is associated with the control voltage. The voltage control circuit generates an intermediate voltage according to a power supply voltage and a first reference voltage. The voltage offset and tracking circuit generates the control voltage according to the input signal and the intermediate voltage such that the control voltage varies with the input signal. The temperature sensing circuit senses an ambient temperature of the active load generation circuit and adjusts the first reference voltage according to the ambient temperature.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Active filter RC time constant calibration circuit and method
InactiveCN108134592AAvoid influenceOne-port active networksNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureCapacitanceRC time constant
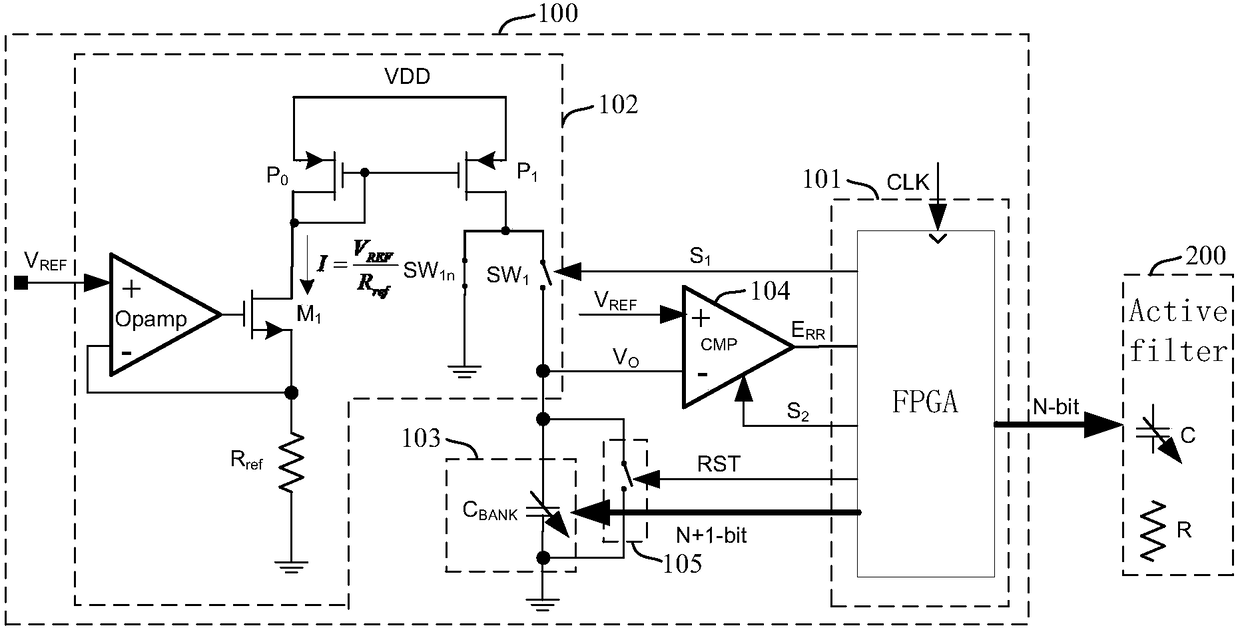
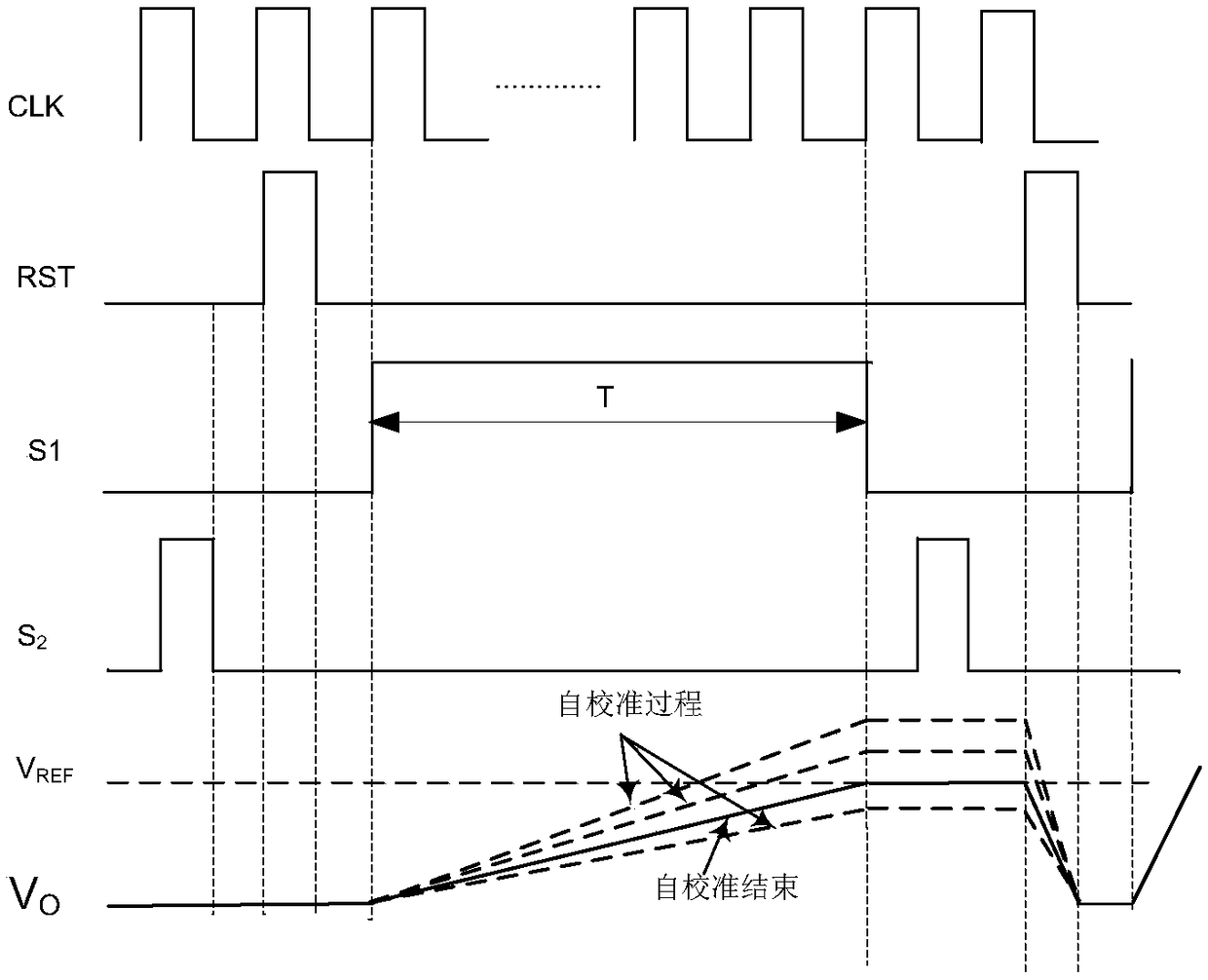
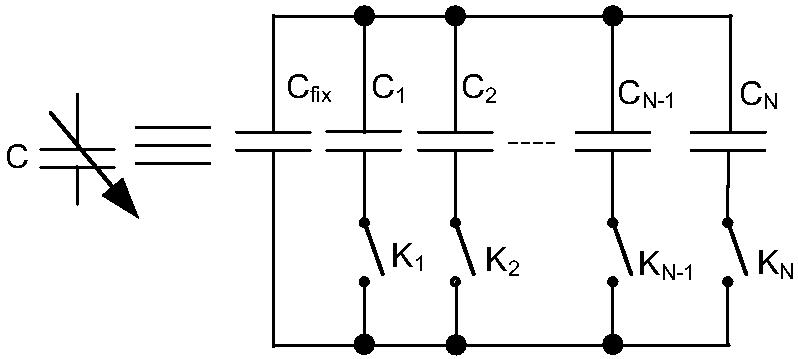
The invention provides an active filter RC time constant calibration circuit and method. The method is characterized by charging a calibration capacitor array CBANK with a constant current, charging time being T; and measuring an actual capacitance value through the voltage VO of the calibration capacitor array CBANK, and correcting the capacitance value of a capacitor array C in an active filter,wherein the calibration capacitor array CBANK and the capacitor array C form a proportional relation, and the charging time T is related to the expected RC time constant of the active filter.
Owner:MIARTECH
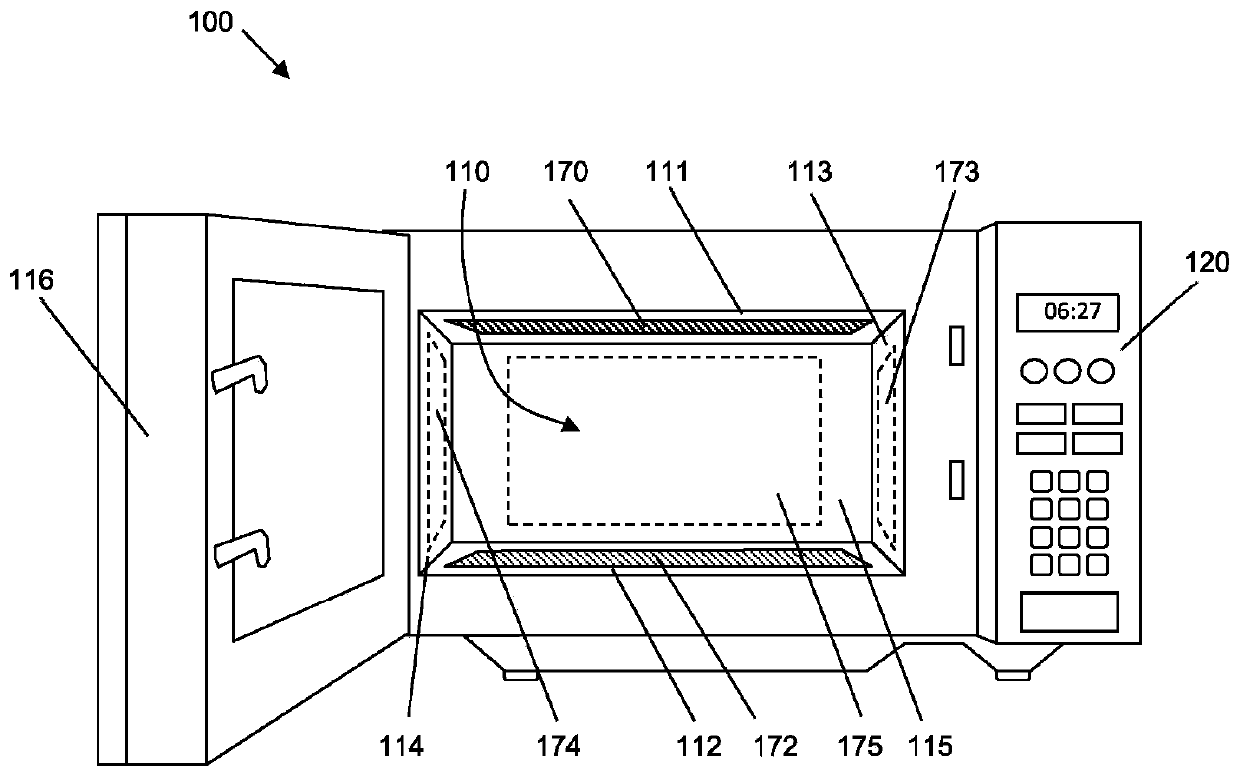
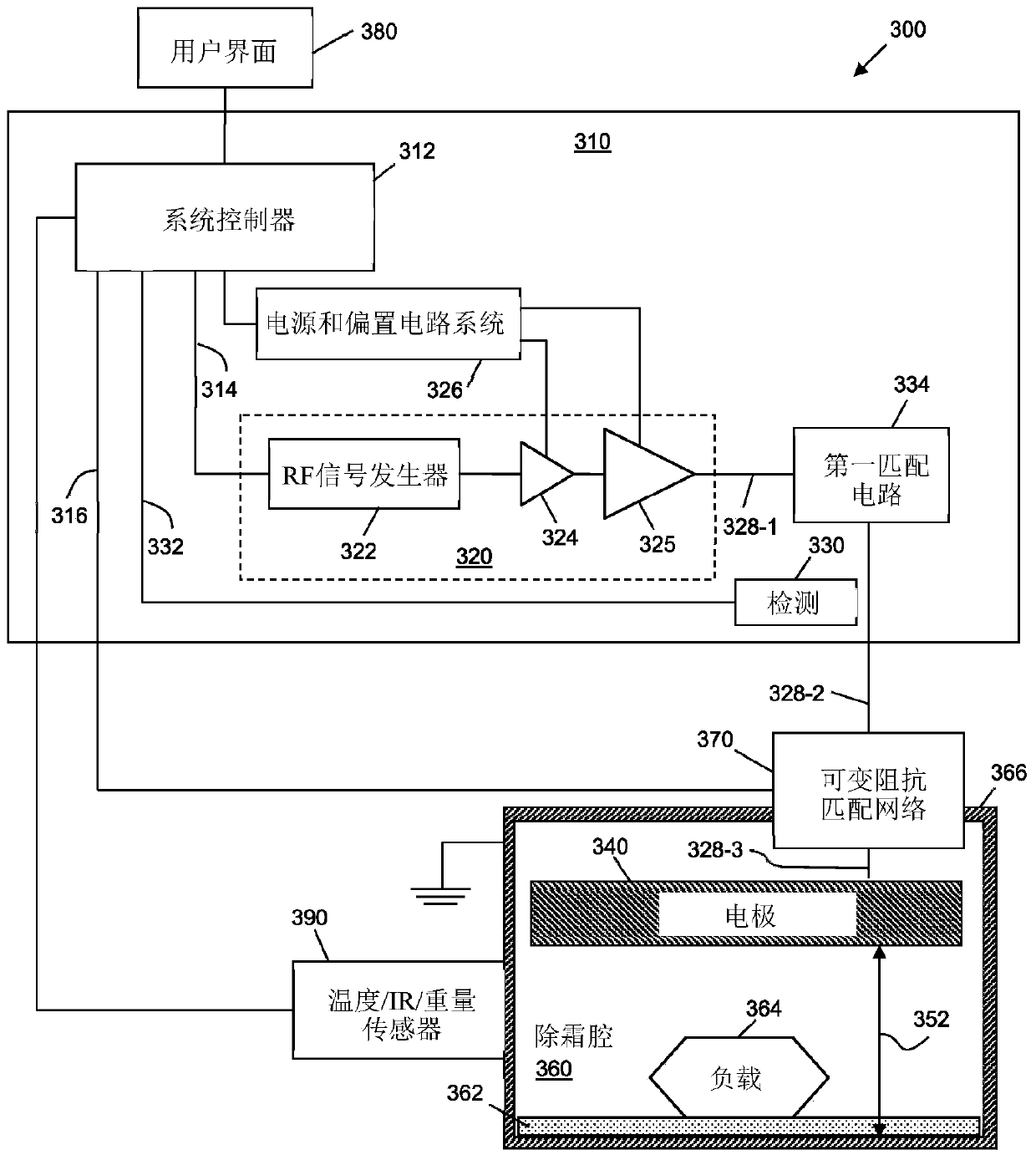
Defrosting apparatus and methods for operation thereof
The invention relates to a defrosting apparatus and methods for operation thereof. The system includes an RF source, two electrodes proximate to a cavity within which a load to be defrosted is positioned, a transmission path between the RF signal source and the electrodes, and an impedance matching network electrically coupled along the transmission path between the output of the RF signal sourceand the electrodes. The system also includes power detection circuitry coupled to the transmission path and configured to detect reflected signal power along the transmission path. A system controlleris configured to modify, based on the reflected signal power, values of variable capacitors of the impedance matching network to reduce the reflected signal power. The impedance matching network maybe a single-ended network or a double-ended network.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Double-port input control circuit with Schmidt property and capable of suppressing temperature drift
ActiveCN102412807AForm Schmidt characteristicsLow temperature driftNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureInput controlNegative feedback
The invention discloses a novel double-port input control circuit with a temperature drift suppressing property and a Schmidt property. The circuit consists of a temperature drift suppressing circuit and a window circuit and can be used in the internal or external part of a transformer isolated or photo-isolated solid relay as a control drive of the preceding stage. With the mutual suppression of a triode, the control circuit realizes the temperature drift resisting function through utilizing a current feedback function and ensures connection of the solid relay and relative stable of the closed threshold voltage; meanwhile, the control circuit realizes overturning of the output voltage through utilizing the reversal function of the triode; and the control circuit realizes the window property, namely the Schmidt property of the connected voltage and turnoff voltage of the solid relay through the negative feedback formed by a resistor. Compared with the traditional temperature suppression circuit, the input function of the Schmidt property is increased, so that the problem that the PN junction voltage input in a control apparatus is changed with the change of the environment temperature is solved, and stable input and reliable application of the solid relay in the total temperature operating scope are ensured.
Owner:BEIJING KEYTONE ELECTRONICS RELAY
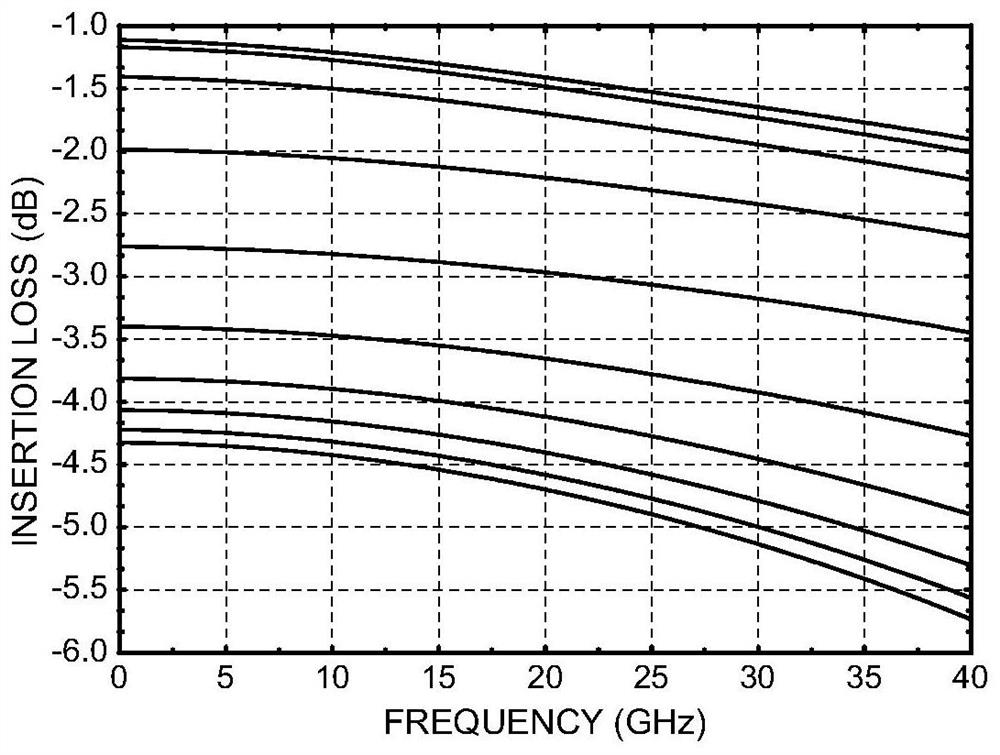
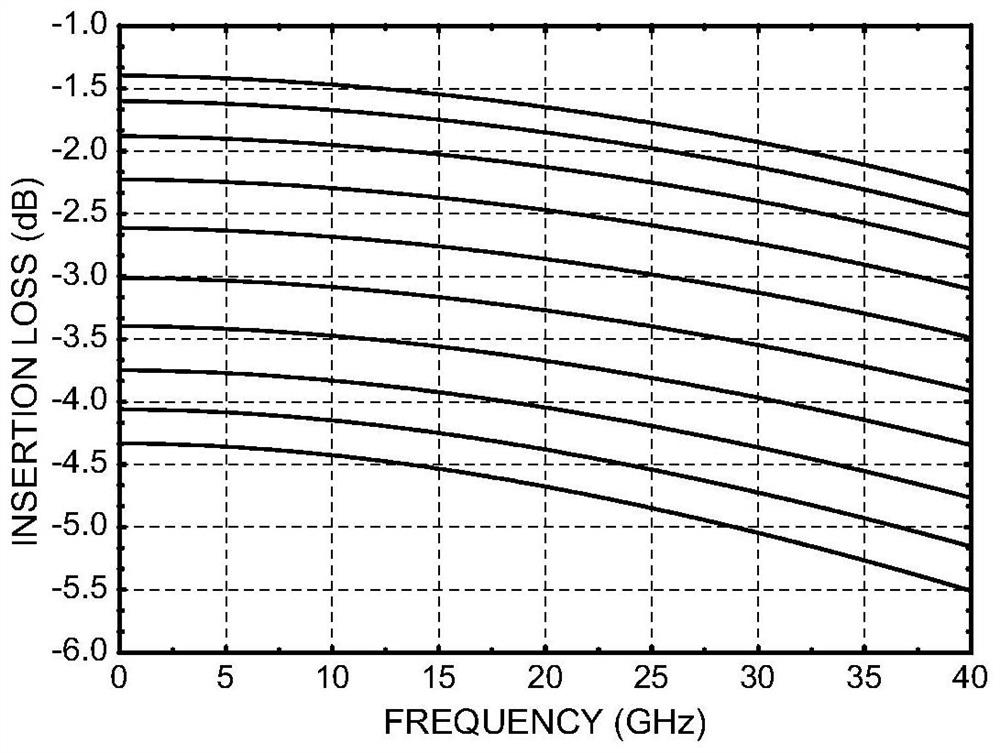
Temperature compensation attenuator
PendingCN111769818AGain flatNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureFrequency selective two-port networksEngineeringRF module
The invention discloses a temperature compensation attenuator, which is applied to a radio frequency system along with temperature rise and attenuation drop under the condition of keeping matching, and can realize the effect of compensating high and low temperature gain changes of other radio frequency modules, so that the high and low temperature gain of a transceiving link is flat, and the design difficulty of high and low temperature application of the radio frequency system is reduced.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP NO 14 RES INST
Adjustable active inductance irrespective to temperature and supply voltage
InactiveCN101174821AReduce areaStable inductance valueImpedence convertorsNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureAudio power amplifierInput control
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuits, in particular to an adjustable active inductance independent of temperature and power supply voltage. It is mainly composed of active inductors and their control circuits. Among them, the active inductor uses a two-stage loop-back amplifier as the equivalent inductance of the active inductor, and the control circuit is composed of a two-stage operational amplifier and a feedback control loop. The control circuit generates a control voltage through comparison and feedback, which is used to bias the active inductance circuit, so that its transconductance stability is only related to the external control voltage, and has nothing to do with the power supply voltage and temperature. The equivalent inductance value of the active inductance proposed by the present invention is only controlled by the external input control voltage, and has a linear relationship with it.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Transduction type active low-pass filter
InactiveCN105048992ASimple structureImprove thermal conductivityNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureThermodynamicsLow-pass filter
The invention relates to a transduction type active low-pass filter. The filter comprises a case, a heat absorbing layer, a filtering main body and four pins. The heat absorbing layer is arranged at the inner side of the case; the filtering main body is arranged at the central position in the case; the four pins are arranged around the filtering main body, and the filtering main body is electrically connected with the four pins via leads. Heat-dissipating graphite flakes fill the gap in the case; the two ends of the case are connected with a thermal energy conversion storage; one end of the thermal energy conversion storage is fixedly connected with an output port. The transduction type active low-pass filter is simple in structure. The heat-dissipating graphite flakes are three-dimensional in structure and not only has excellent heat conductivity in the vertical direction, but also could conduct heat in the longitudinal direction, so that the heat could be fast conducted to the heat absorbing layer via the characteristic of the longitudinal heat conduction when local thermal energy is too high. The thermal energy conversion storage could be used for converting the thermal energy into electric energy, and storing the electric energy to be used as power for the filter. The transduction type active low-pass filter is economical and environmental-friendly, and prolongs the service life of equipment, reduces the production cost, and is easy for popularization.
Owner:南通中意达知识产权服务有限公司
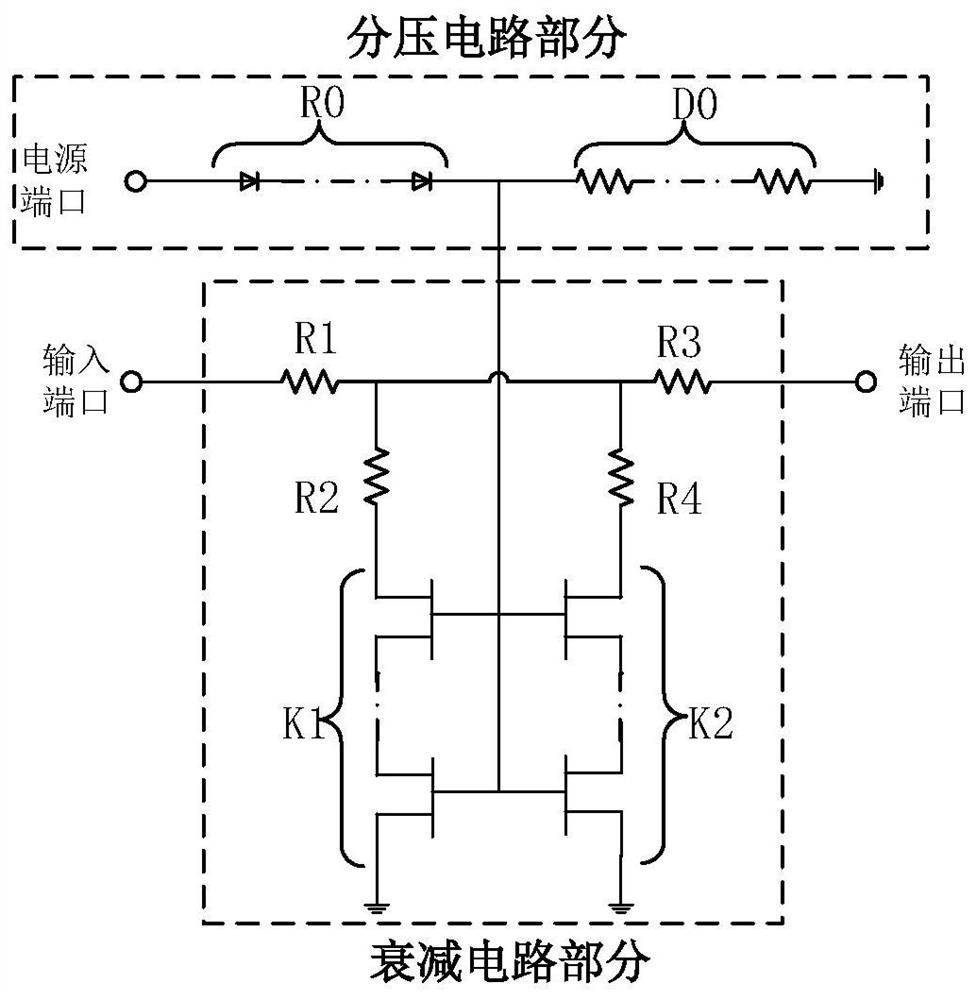
Novel high-linearity temperature compensation attenuator
PendingCN111682861ASame design indexGood standing wave characteristicsNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureFrequency-independant attenuatorsDividing circuitsHemt circuits
The invention relates to the technical field of attenuators, in particular to a novel high-linearity temperature compensation attenuator. The attenuator comprises a voltage division circuit part and an attenuation circuit part, the voltage division circuit part comprises a group of diodes D0 with temperature characteristics and a group of resistors RO, R0 and DO which are connected in series to obtain voltage capable of changing along with temperature, and the voltage is connected to the grid end of a transistor in the attenuation circuit part through a connecting microstrip line; according tothe attenuation circuit part, resistors R1, R2, R3 and R4 and two sets of transistors K1 and K2 form an attenuation circuit of a pi-like structure, one end of the transistor set is connected with theresistor, the other end of the transistor set is grounded, and the grid end of the transistor set is connected with voltage led out by the voltage division circuit part. The attenuator is suitable for the design of various different technologies, the design of the whole circuit can be correspondingly completed for various types of transistors, and the same design index is finally achieved.
Owner:天津中科海高微波技术有限公司
Integrated circuit
InactiveUS20050077956A1Amplifier combinationsNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage source
An integrated circuit comprises a biasing circuit for maintaining the transconductance of a Gm cell constant. The integrated circuit comprises an on-chip constant voltage source and an on-chip constant current source. The on-chip constant current source has a connection for an external resistance, the value of the external resistance determining the current generated by the constant current source. The biasing circuit comprises means for providing a first fraction (β) of the current generated by the on-chip current source to bias the output of the Gm cell, and means for providing a second fraction (α) of the voltage generated by the on-chip voltage source to bias the input of the Gm cell. The transconductance of the Gm cell is controlled to be equal to the ratio of said fraction of the current generated by the on-chip current source to said fraction of the voltage generated by the on-chip voltage source.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Active load generation circuit and filter using same
ActiveUS10461734B2Save areaHigh impedanceInput/output impedence modificationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringVoltage reference
This invention discloses an active load generation circuit and a filter. The active load generation circuit includes a transistor, a voltage control circuit, a voltage offset and tracking circuit, and a temperature sensing circuit. The transistor provides an impedance and includes a control terminal and an input terminal. The control terminal receives a control voltage, the input terminal receives an input signal, and the impedance is associated with the control voltage. The voltage control circuit generates an intermediate voltage according to a power supply voltage and a first reference voltage. The voltage offset and tracking circuit generates the control voltage according to the input signal and the intermediate voltage such that the control voltage varies with the input signal. The temperature sensing circuit senses an ambient temperature of the active load generation circuit and adjusts the first reference voltage according to the ambient temperature.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
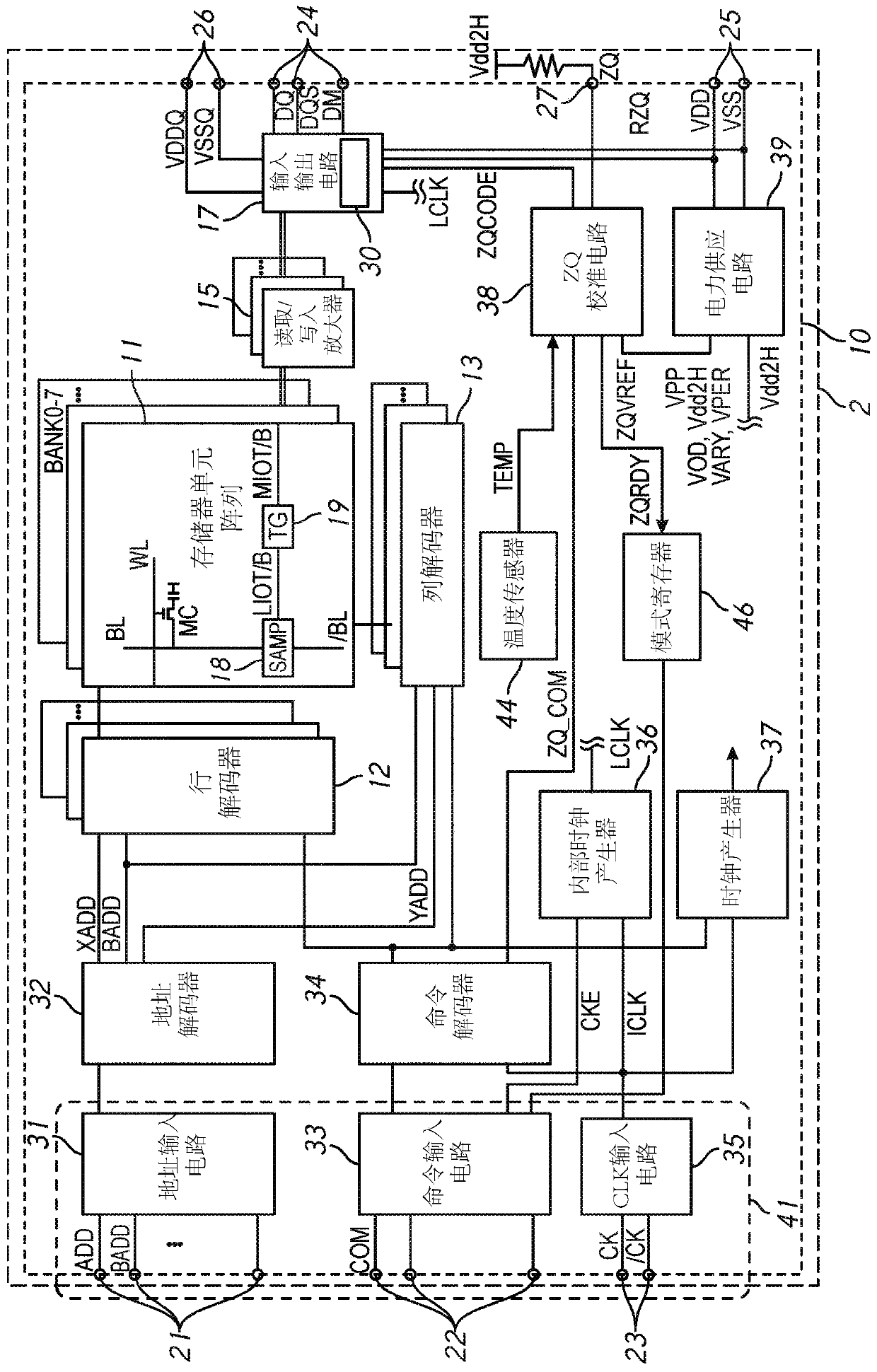
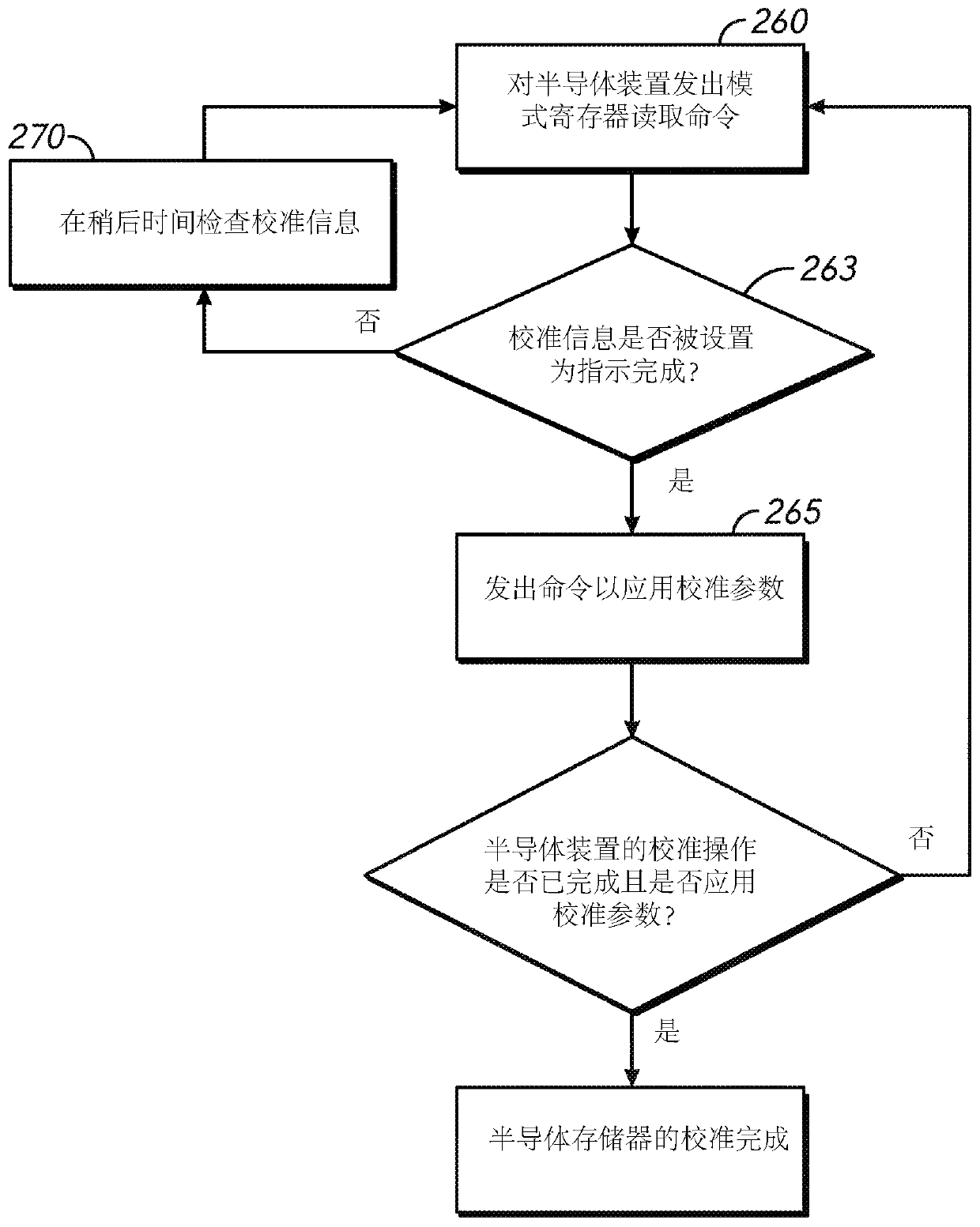
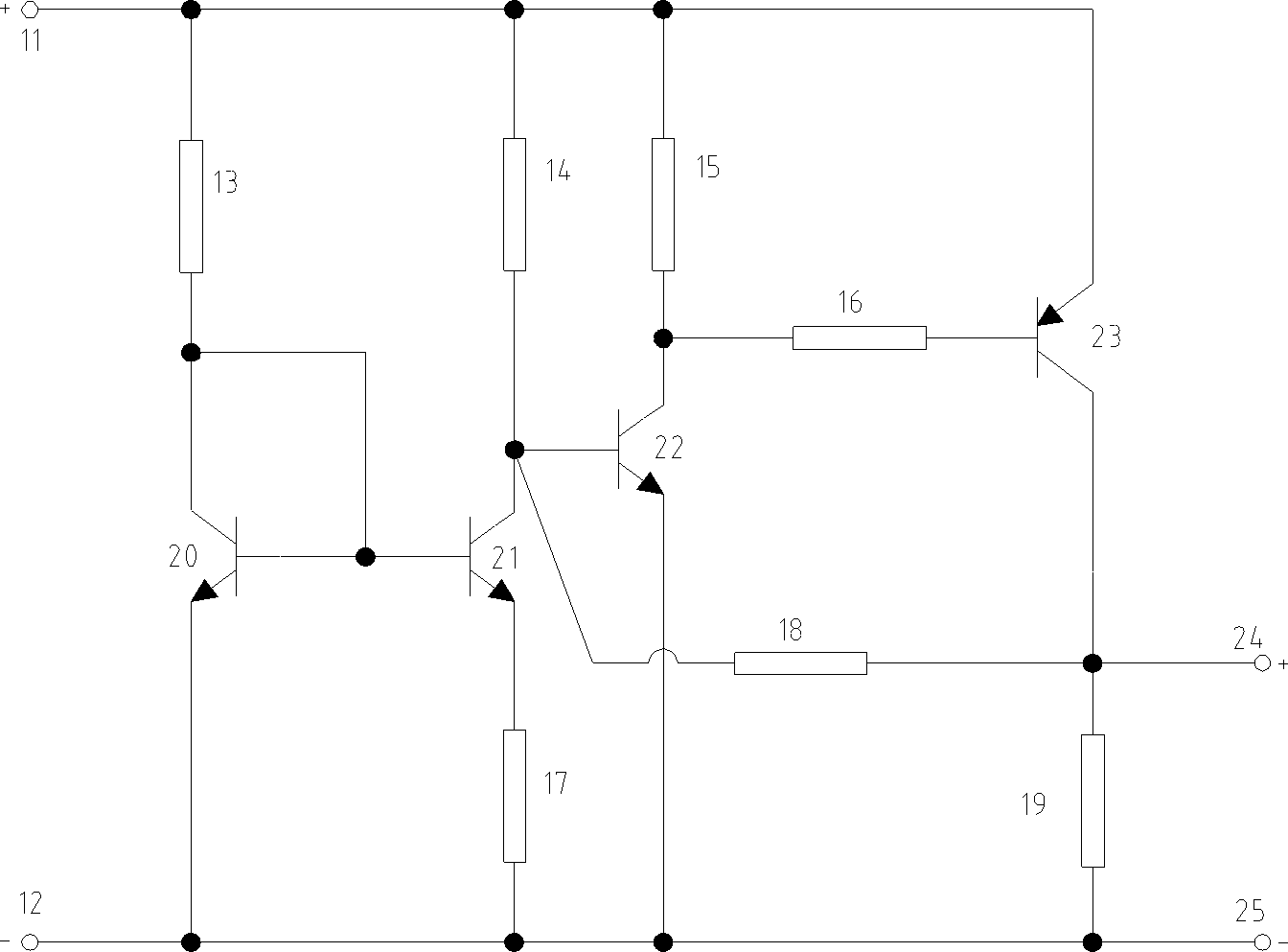
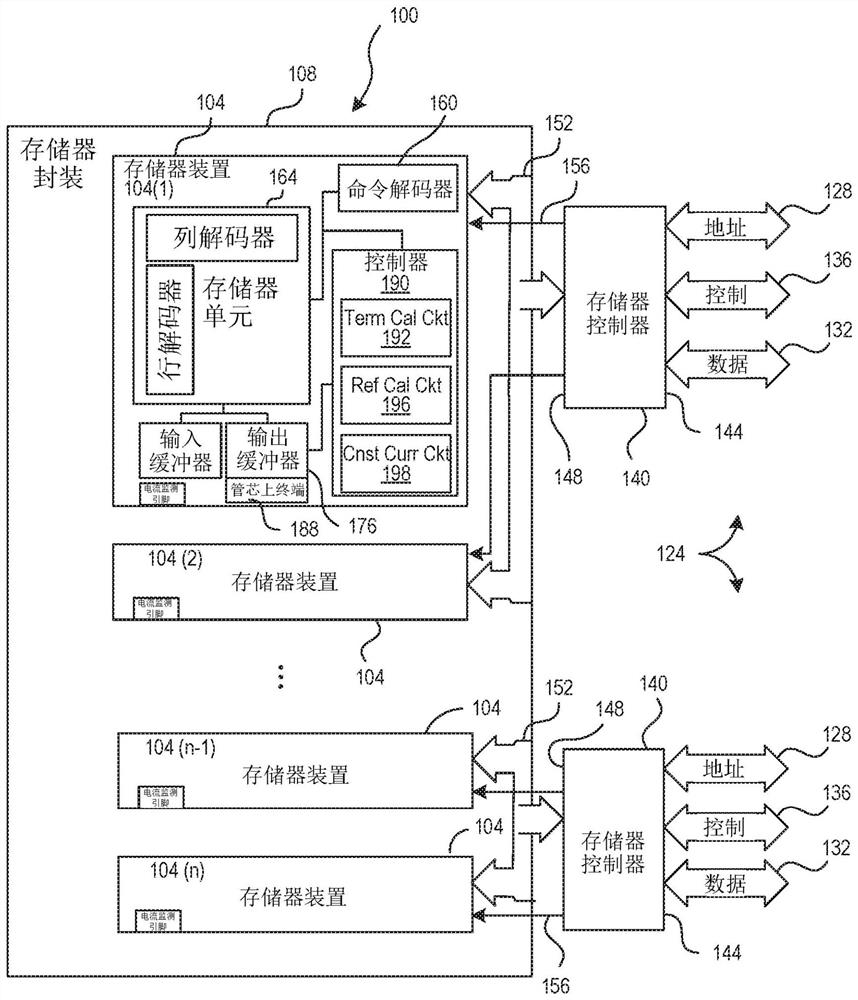
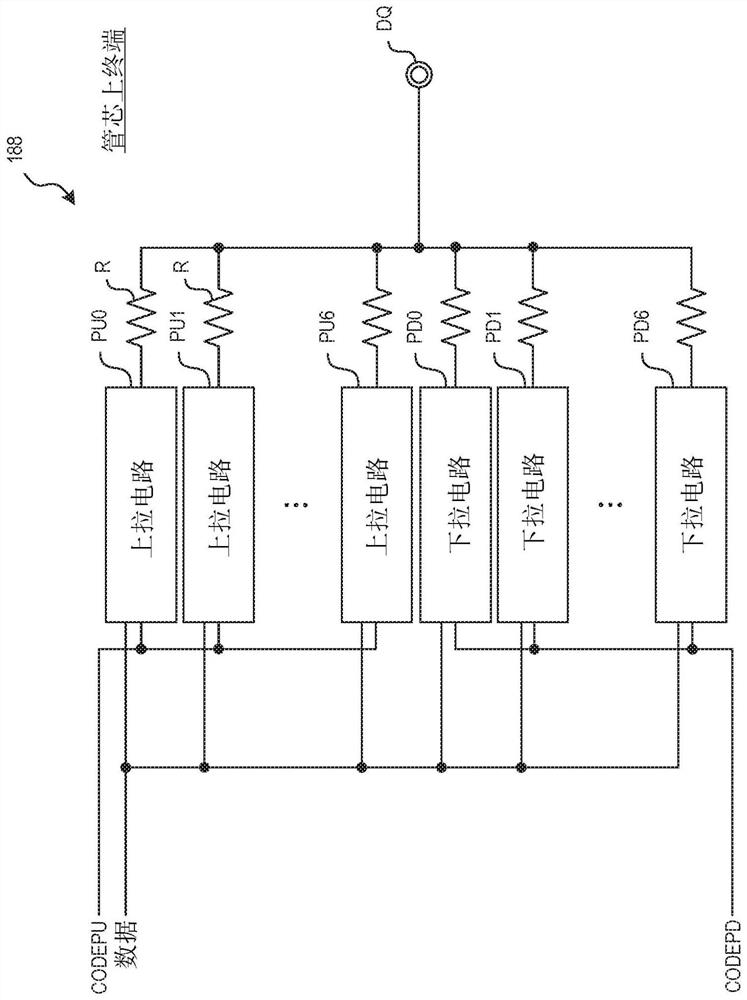
Apparatuses and methods for calibrating adjustable impedances of a semiconductor device
ActiveCN110073439AInput/output impedence modificationImpedence matching networksElectrical resistance and conductanceDevice material
Apparatuses and methods for calibrating adjustable impedances of a semiconductor device are disclosed in the present application. An example apparatus includes a register configured to store impedancecalibration information and further includes programmable termination resistances having a programmable impedance. The example apparatus further includes an impedance calibration circuit configured to perform a calibration operation to determine calibration parameters for setting the programmable impedance of the programmable termination resistances. The impedance calibration circuit is further configured to program the impedance calibration information in the register related to the calibration operation.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
A two-port input control circuit with Schmitt characteristics to suppress temperature drift
ActiveCN102412807BFeatures two-port inputForm Schmidt characteristicsNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureElectrical resistance and conductanceNegative feedback
Owner:BEIJING KEYTONE ELECTRONICS RELAY
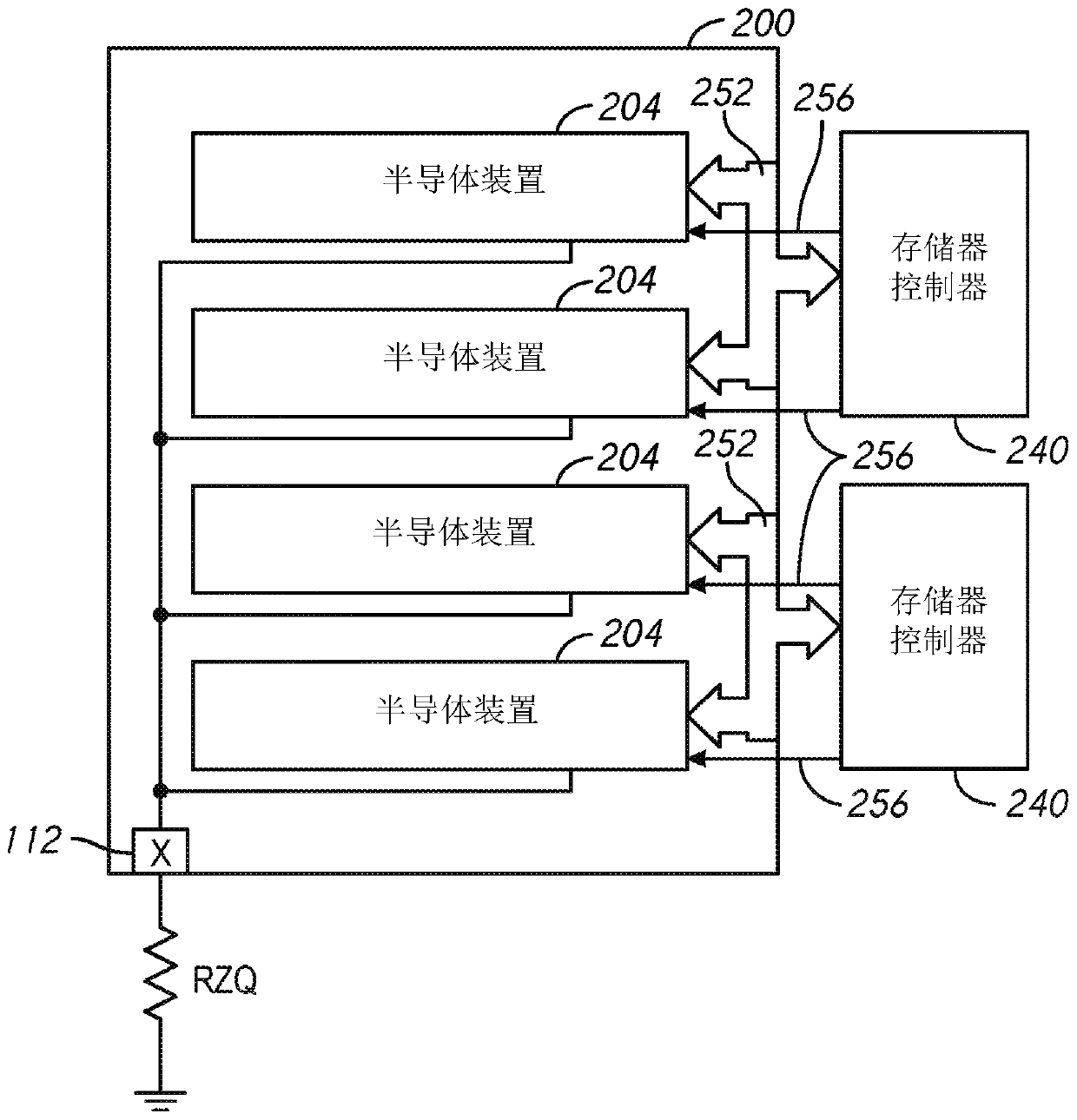
ZQ calibration using current source
ActiveCN112652350AInput/output impedence modificationImpedence matching networksSoftware engineeringHemt circuits
The invention relates to ZQ calibration using a current source. A memory device includes a terminal calibration circuit having at least one of a pull-down circuit or a pull-up circuit used in calibrating an impedance of a data bus termination. The memory device also includes a reference calibration circuit configured to generate a calibration current. The terminal calibration circuit can be configured to program an impedance of the least one of a pull-down circuit or a pull-up circuit based on the calibration current.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
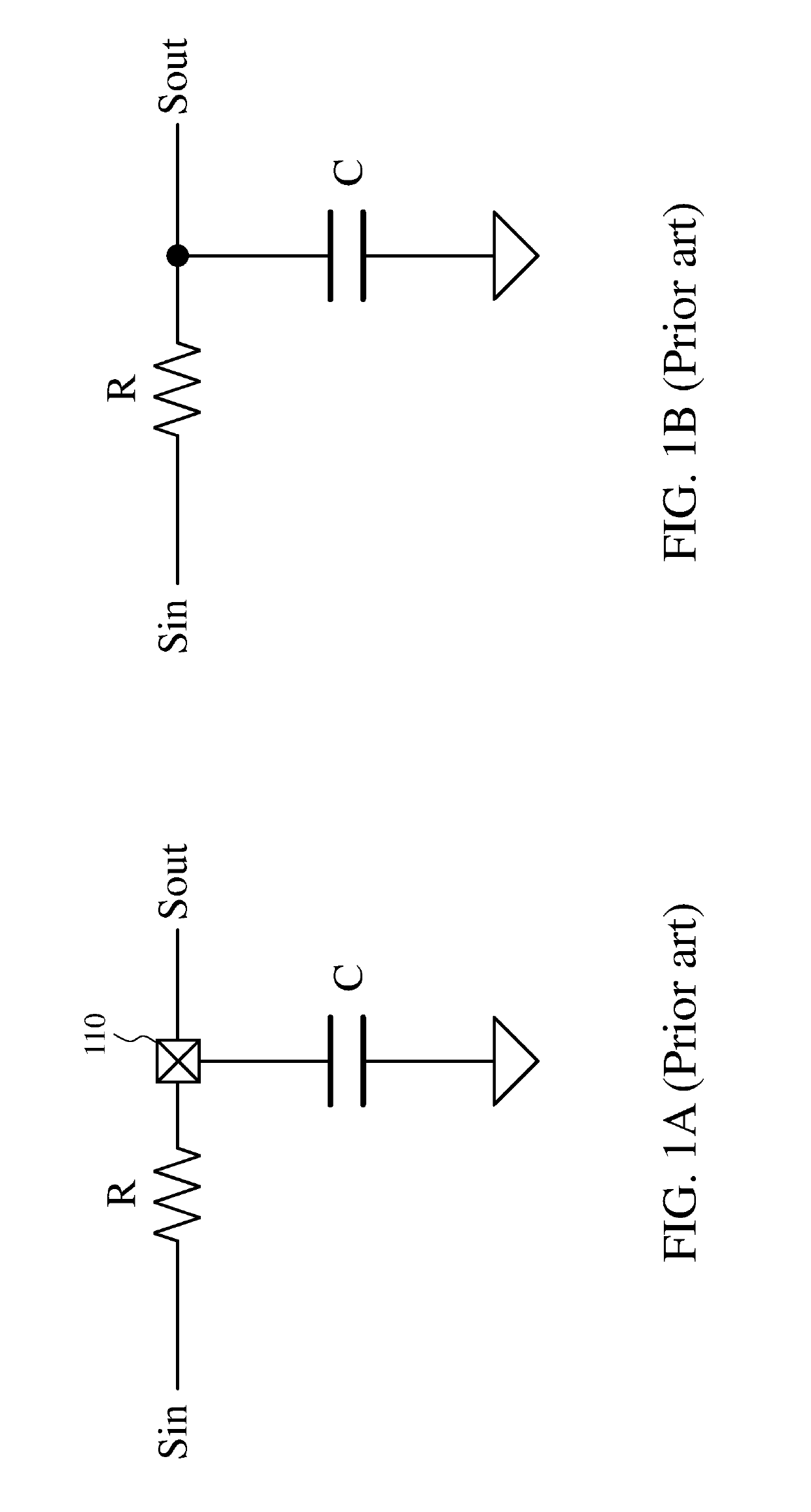
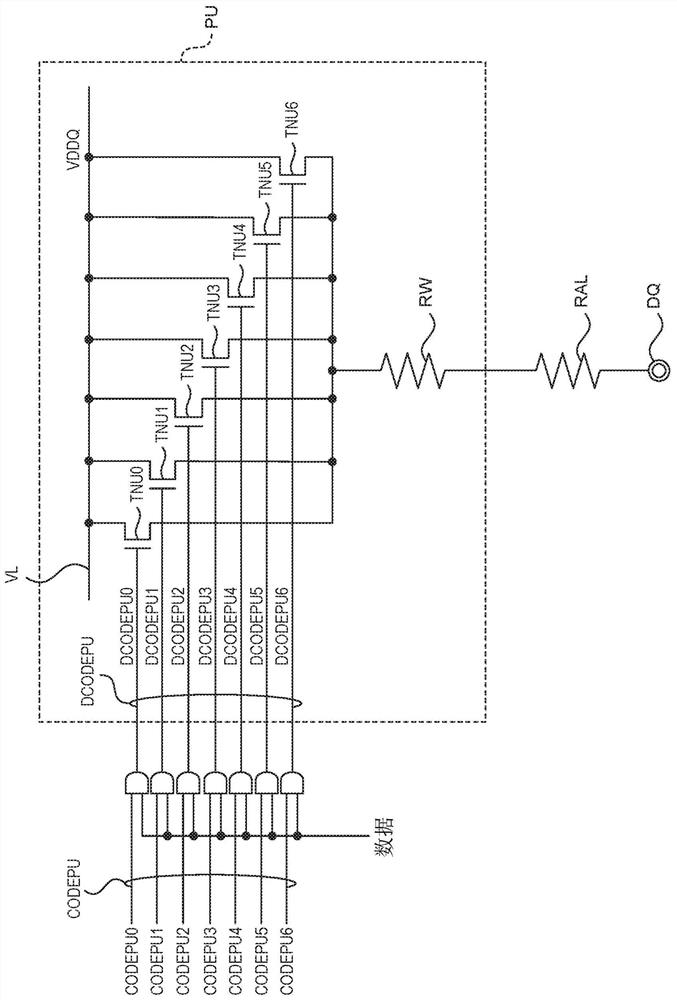
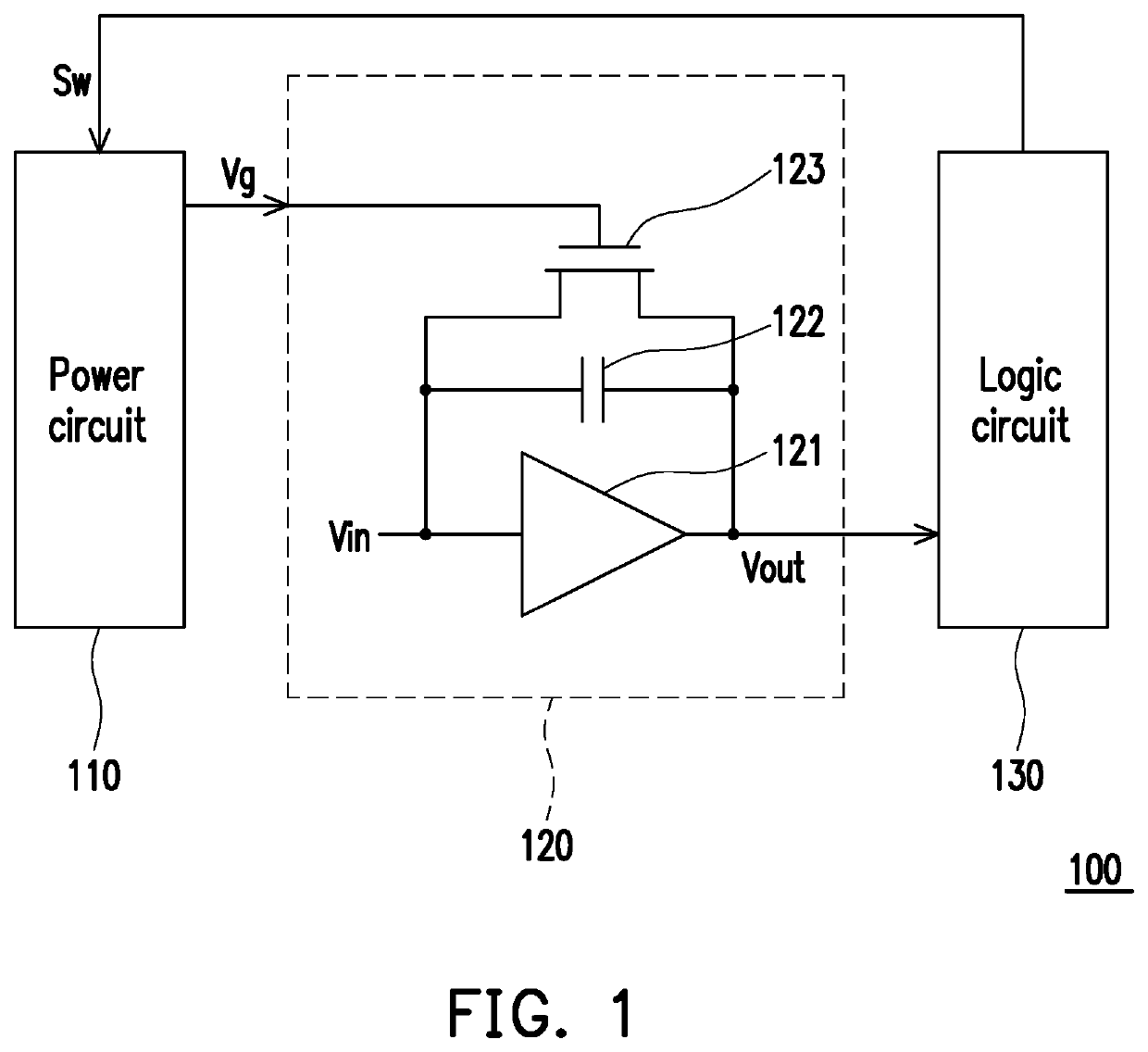
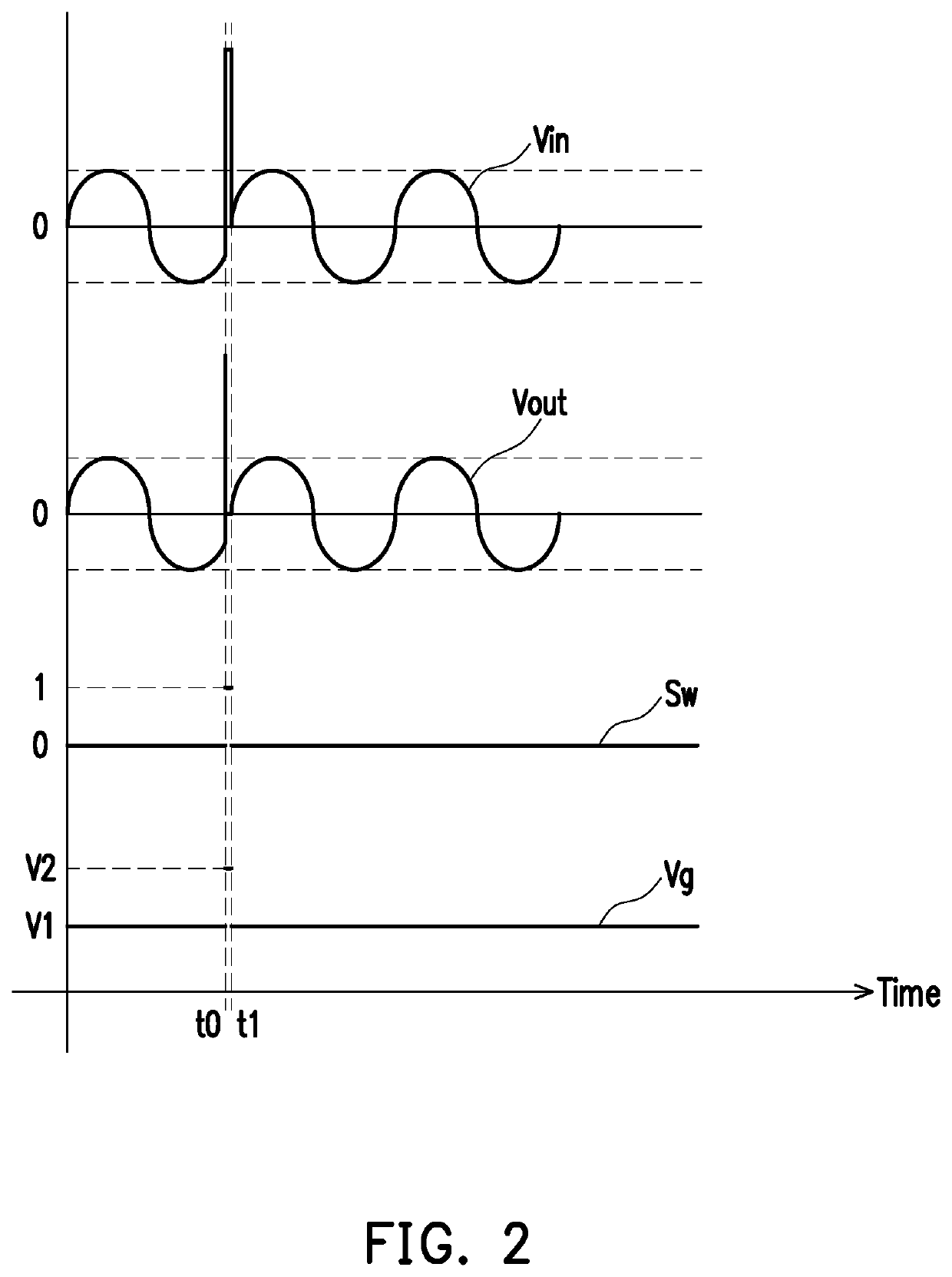
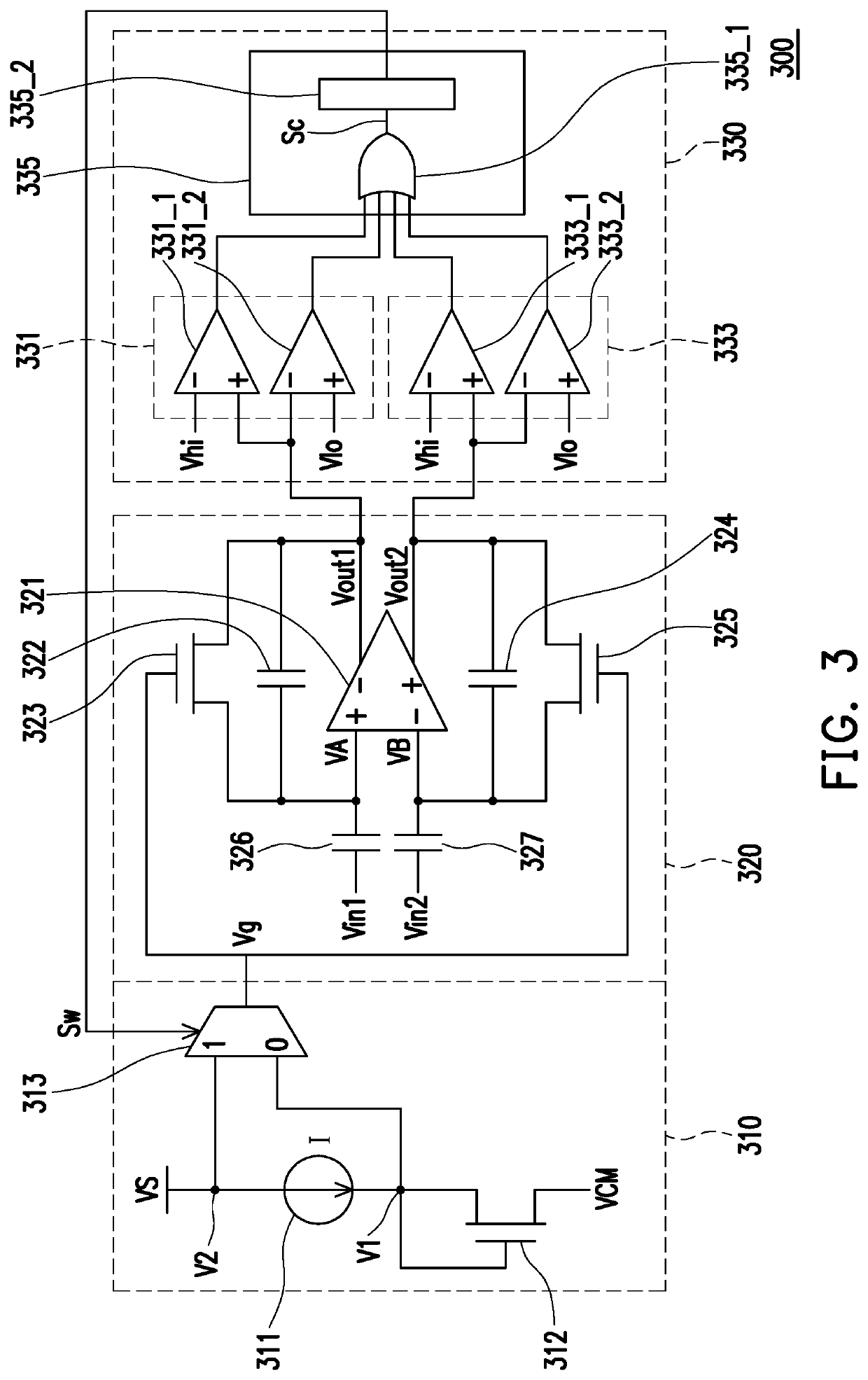
Filter and operating method thereof
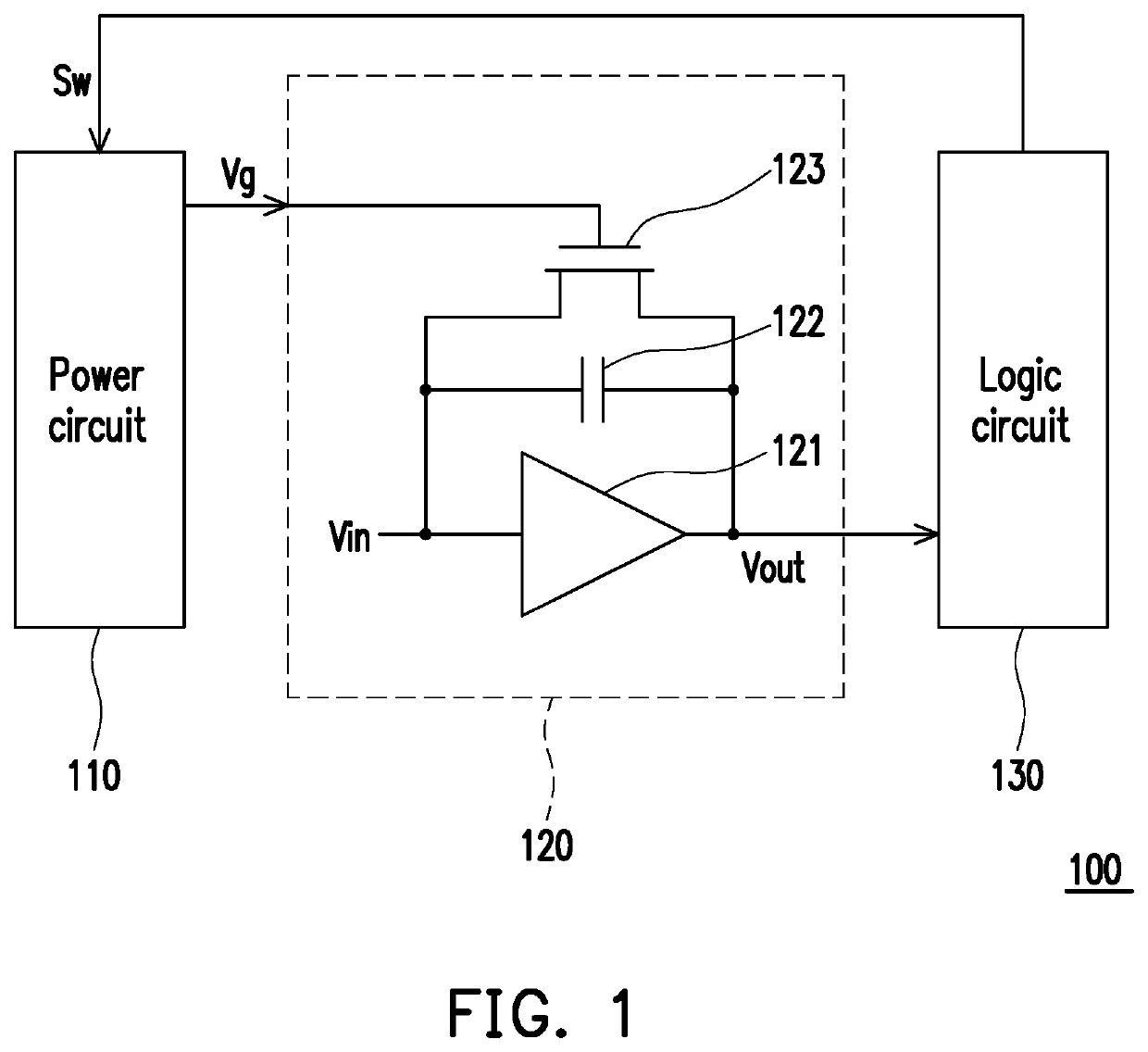
ActiveUS20200204162A1Accurate filter signal output functionSlow changeHigh frequency amplifiersSwitched capacitor networksControl signalSoftware engineering
A filter and an operating method thereof are provided. The filter includes a logic circuit, a power circuit and a filter circuit. The logic circuit provides a switching control signal. The power circuit is coupled to the logic circuit. The filter circuit is coupled to the power circuit and the logic circuit. The filter circuit includes an amplifier, a first capacitor and a first transistor. An output end of the amplifier is coupled to the logic circuit, and provides an output signal. The first capacitor is coupled between an input end and output end of the amplifier. The first transistor is connected in parallel with the first capacitor. A control end of the first transistor is coupled to the power circuit. The logic circuit provides a switching control signal to the power circuit according to the output signal. The power circuit supplies a control voltage to the first transistor according to the switching control signal. Therefore, the filter of the present invention and its method of operation can provide an accurate filtered signal output function.
Owner:UPI SEMICON CORP
Antenna system for radio microphones
ActiveCN104682915BAchieving frequency-independent transmissionDon't make the intercept worseMultiple-port active networksMouthpiece/microphone attachmentsUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
Owner:AKG ACOUSTICS
Filter and operating method thereof
ActiveUS10715114B1Precise functionStable and accurate output functionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersControl signalSoftware engineering
A filter and an operating method thereof are provided. The filter includes a logic circuit, a power circuit and a filter circuit. The logic circuit provides a switching control signal. The power circuit is coupled to the logic circuit. The filter circuit is coupled to the power circuit and the logic circuit. The filter circuit includes an amplifier, a first capacitor and a first transistor. An output end of the amplifier is coupled to the logic circuit, and provides an output signal. The first capacitor is coupled between an input end and output end of the amplifier. The first transistor is connected in parallel with the first capacitor. A control end of the first transistor is coupled to the power circuit. The logic circuit provides a switching control signal to the power circuit according to the output signal. The power circuit supplies a control voltage to the first transistor according to the switching control signal. Therefore, the filter of the present invention and its method of operation can provide an accurate filtered signal output function.
Owner:UPI SEMICON CORP
Pseudo resistance circuit and cascade circuit thereof
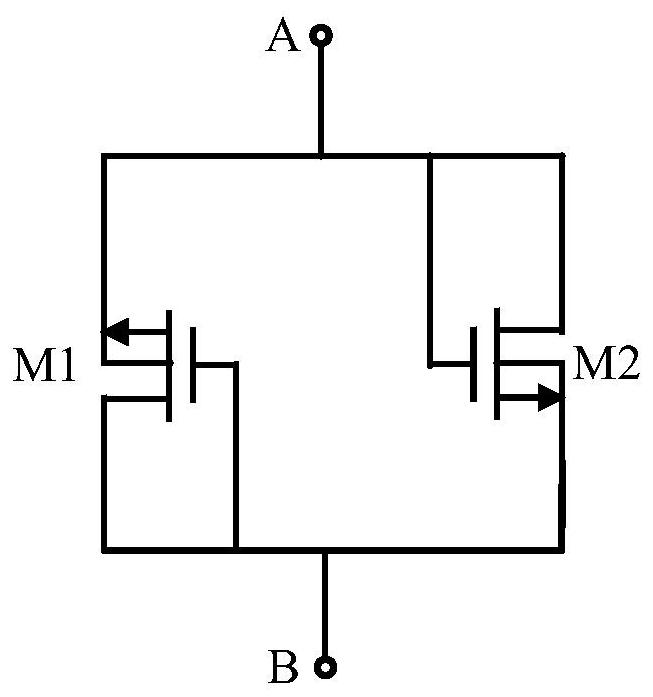
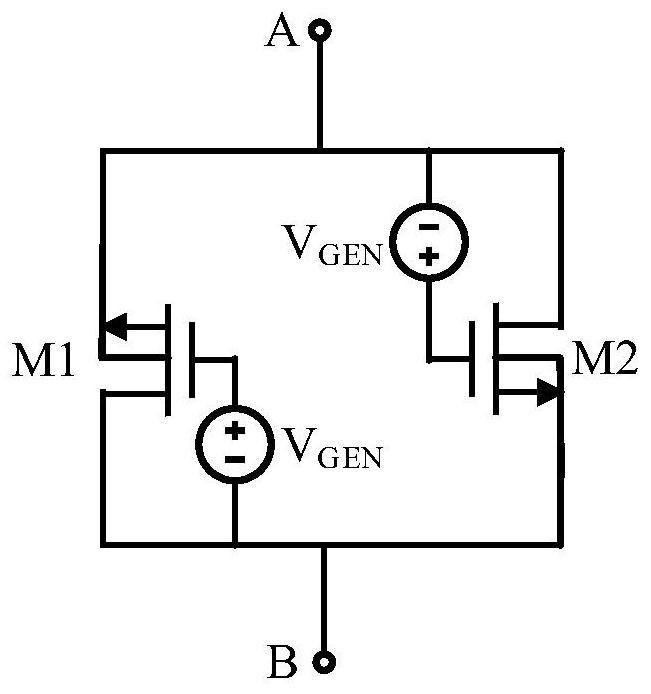
ActiveCN113381728AImprove linearityNetwork simulating resistancesNetwork modifications to reduce temperatureResistive circuitsHemt circuits
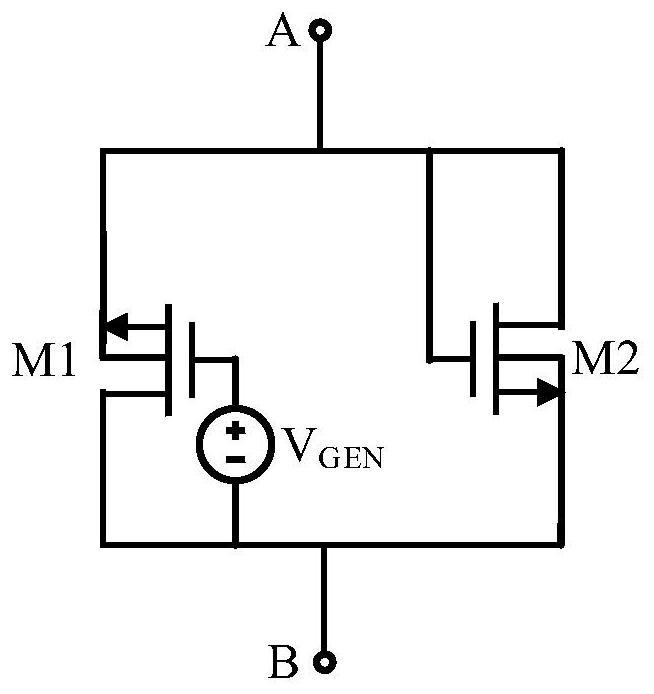
The invention discloses a pseudo resistance circuit and a cascade circuit thereof, and the pseudo resistance circuit comprises: a transistor M1 which is provided with a first electrode, a second electrode and a control electrode, wherein the first electrode and the second electrode of the transistor M1 are respectively connected with the second end and the first end; a bias voltage generating circuit which corresponds to the transistor M1, wherein two ends of the bias voltage generating circuit are respectively connected with the first electrode and the control electrode of the transistor M1, and the bias voltage generating circuit is used for increasing the bias voltage between the first electrode and the control electrode of the transistor M1; and a transistor M2 which is provided with a first electrode, a second electrode and a control electrode, wherein the first electrode and the second electrode of the transistor M2 are connected with the first end and the second end respectively, and the first electrode of the transistor M2 is further connected with the control electrode of the transistor M2. According to the invention, the bias voltage generation circuit VGEN is used to solve some problems of a current pseudo resistor, such as the improvement of the linearity of an equivalent resistance value and the like.
Owner:上海料聚微电子有限公司
Antenna system of a radio microphone
ActiveCN104682915AAchieving frequency-independent transmissionDon't make the intercept worseMultiple-port active networksMouthpiece/microphone attachmentsUltrasound attenuationElectrical resistance and conductance
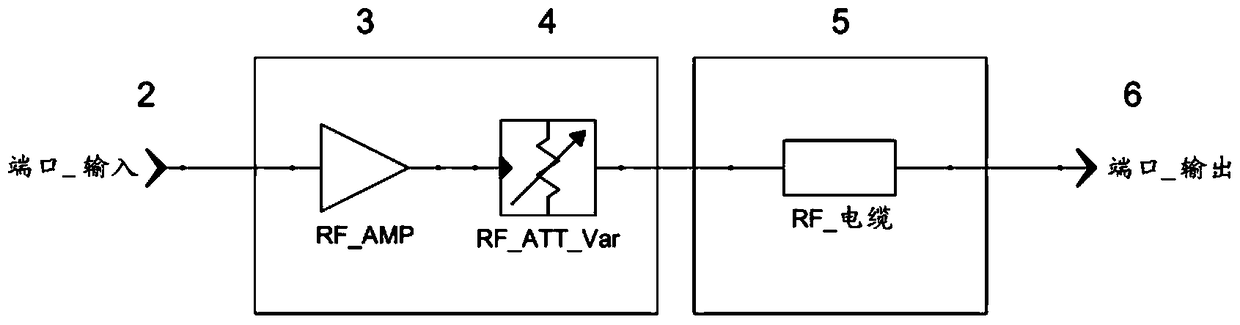
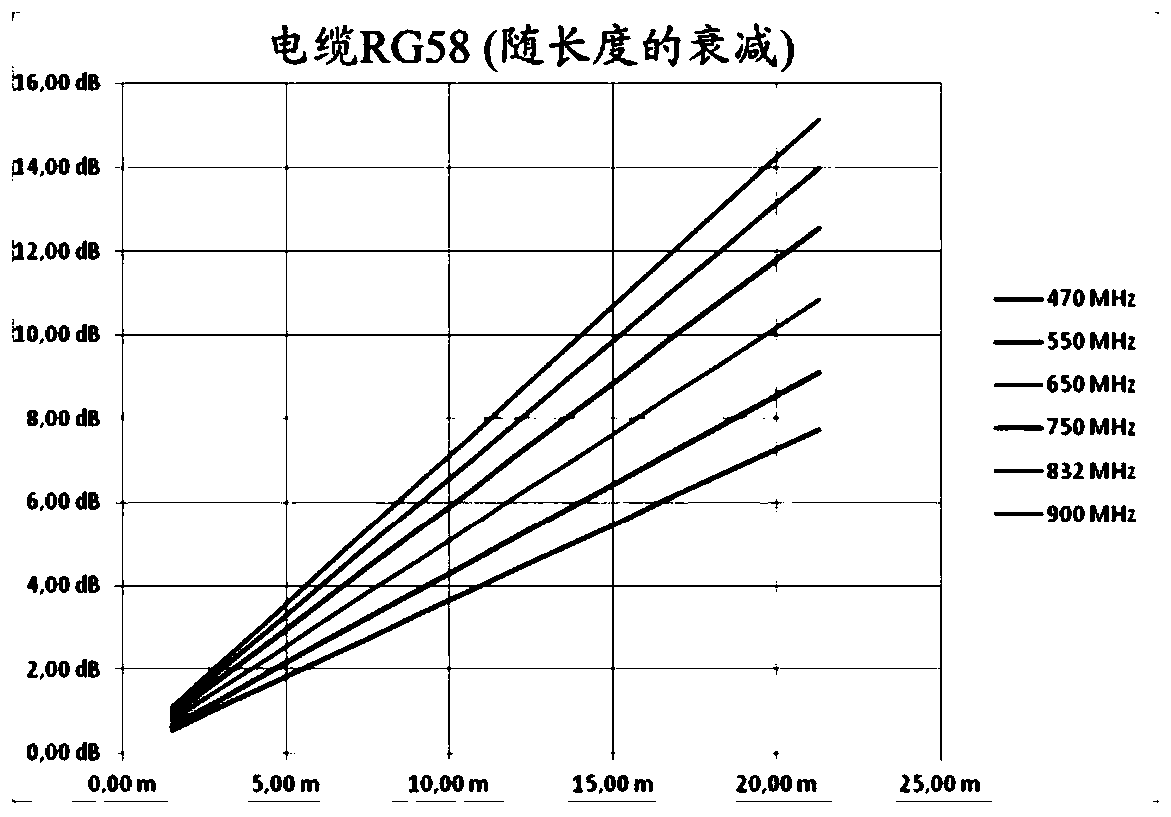
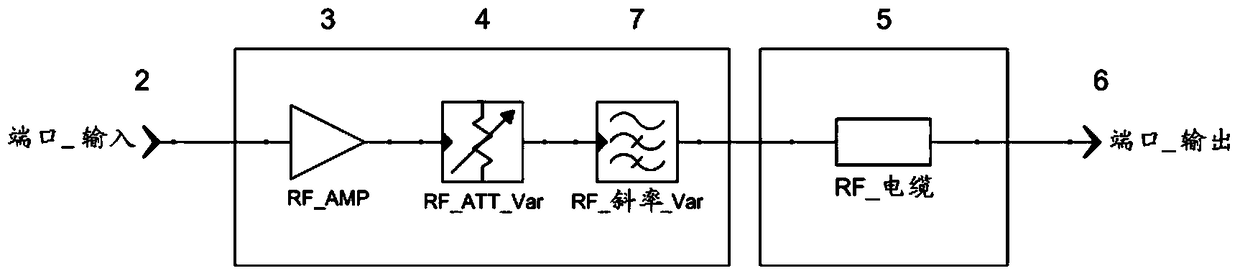
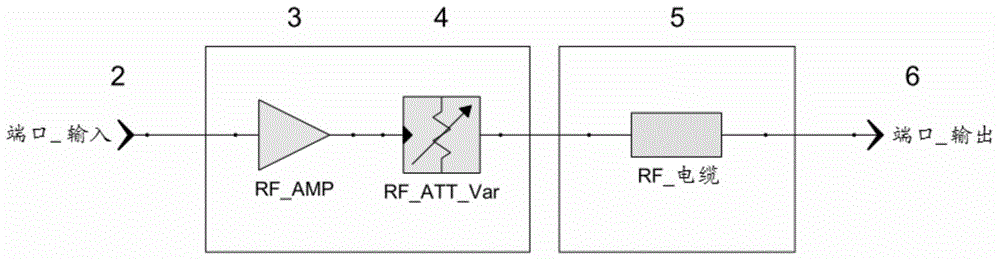
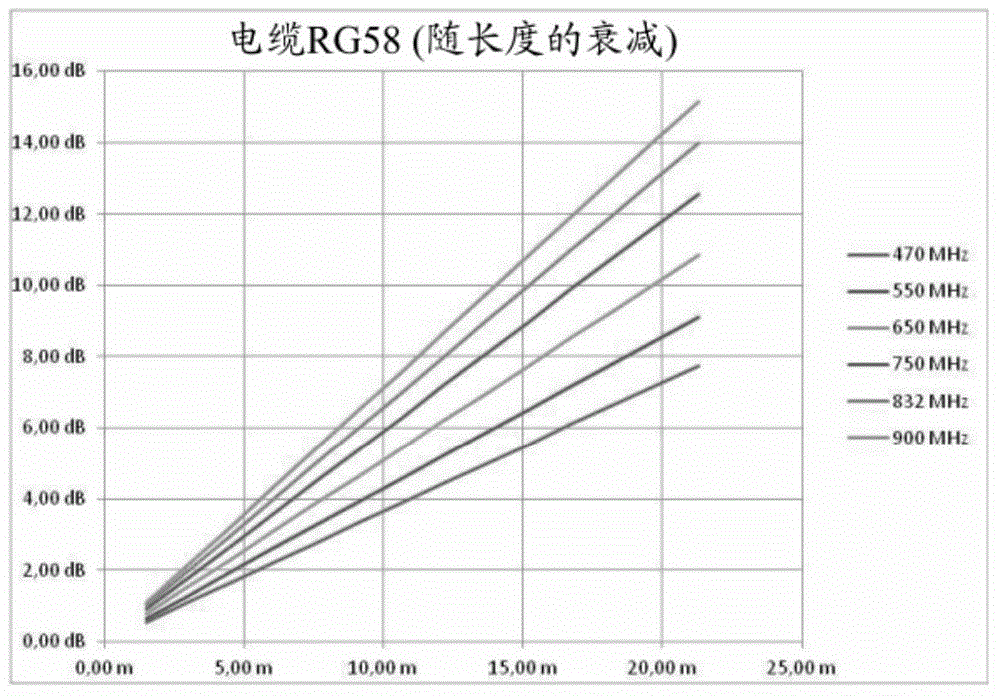
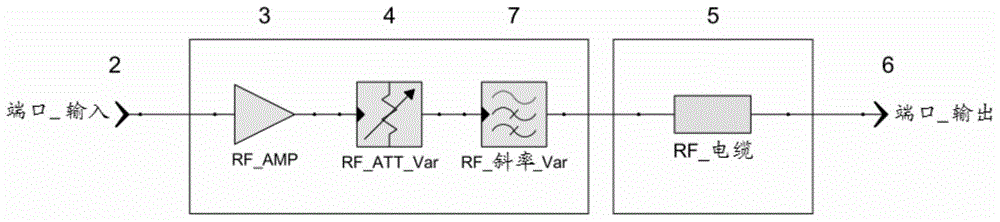
The invention concerns an antenna system of a radio microphone, containing an antenna path starting at an In port (2), and ending at an Out port (6), with an amplifier (3) and a RF cable (5). In order to compensate for various cable attenuations, an attenuator (4) is provided in series with a variable slope compensator (7) between the amplifier (3) and the RF cable (5). In order to avoid the negative effect on large signal behavior of variable slope compensators according to the prior art, FETs or pin diodes or similar "micro-switches" are used for switching of the resistances, but only as pure switches without an effect on the signal, so that an excellent large signal behavior is achieved.
Owner:AKG ACOUSTICS
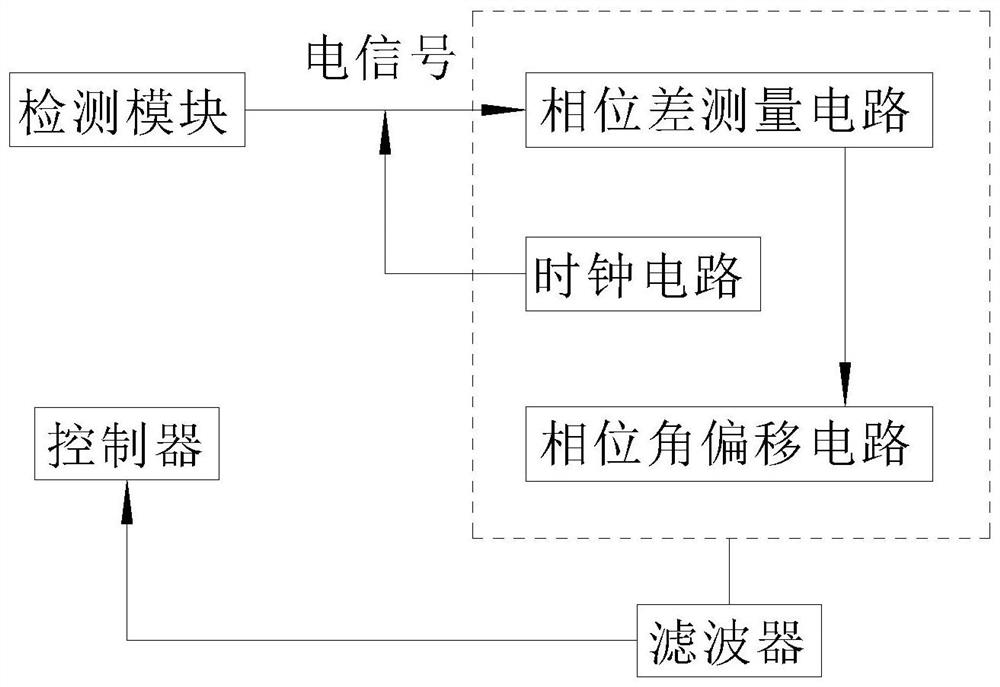
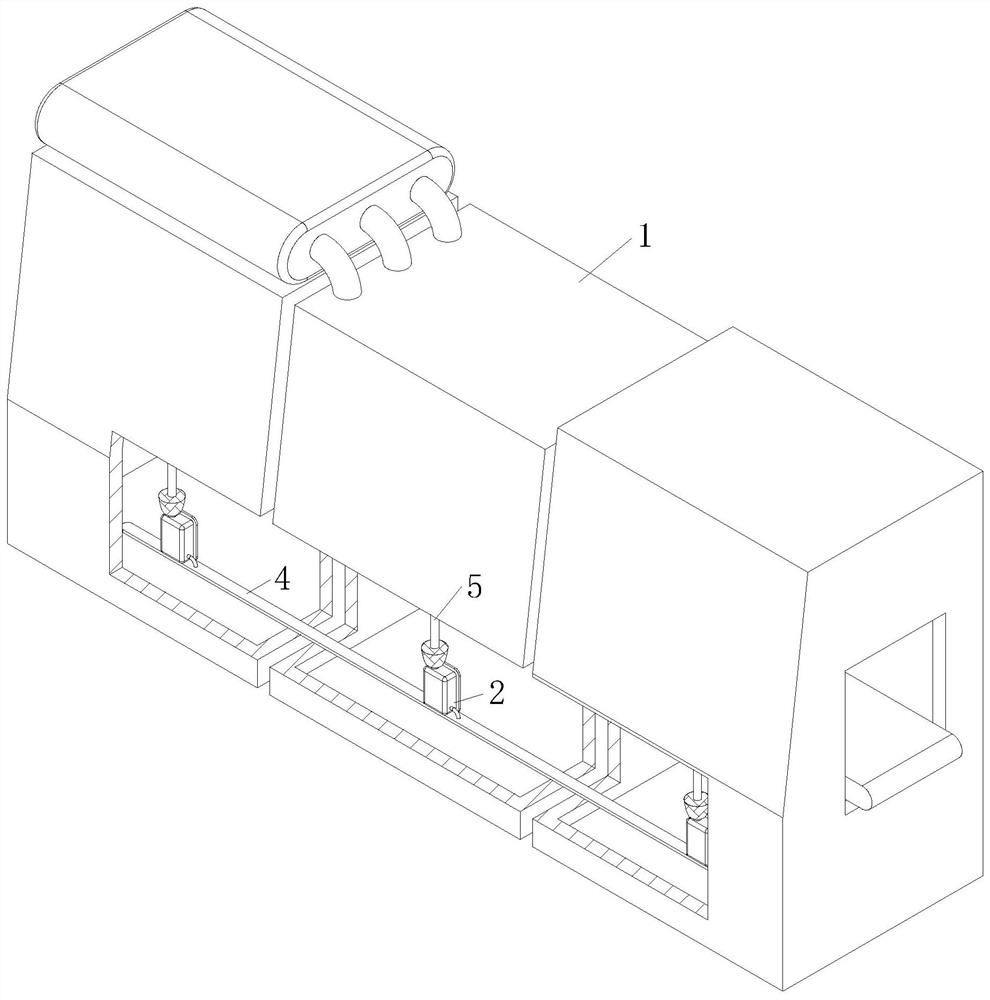
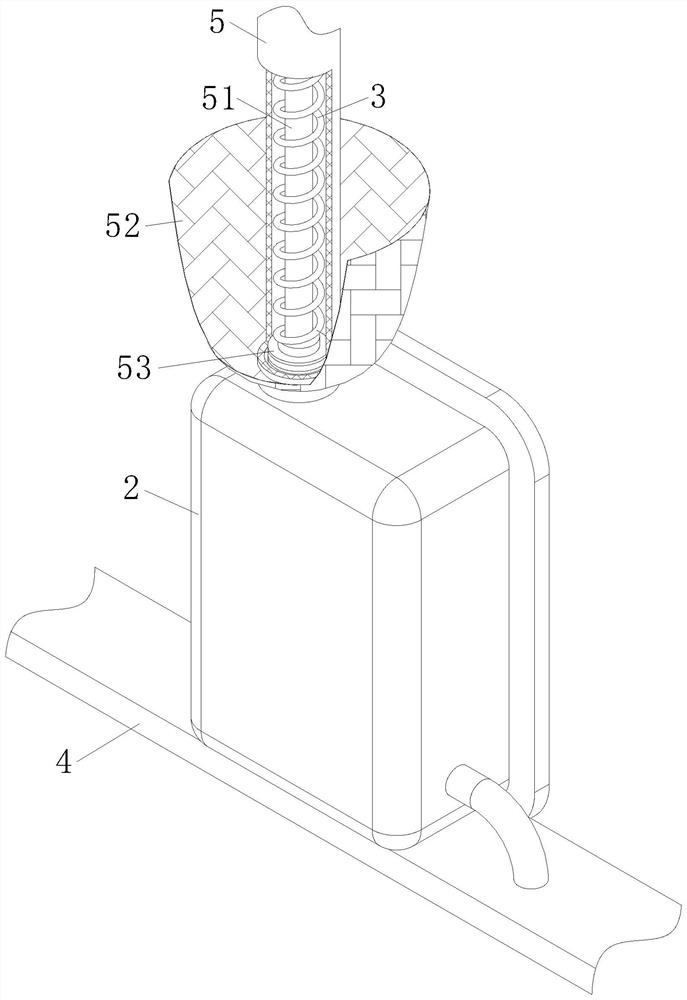
Signal fuzzy control filter for wafer detection device
PendingCN113452347APlay the role of fuzzy screeningReduce processingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingSignal waveWafer
The invention relates to the technical field of filters, in particular to a signal fuzzy control filter for a wafer detection device. The signal fuzzy control filter comprises a wafer machine table, a detection module, a filter terminal and a controller. Due to the conditions of fragments and the like of the wafer in the circulation process, the operation of a machine table needs to be suspended for cleaning, and the application effect of the wafer detection device in production is influenced, so phase angle analysis is carried out on electric signal waveforms of wafer position information of the wafer detection device in different stations of a wafer machine table through the arranged phase circuit and clock circuit, and the position error of each wafer in the wafer machine table is converted into the relative position difference between the circulating wafers in each station; the signal fuzzy control filter for the wafer detection device has a fuzzy screening effect on the electric signal data transmitted by the wafer detection device, and reduces the processing capacity of a controller after the filter terminal processes the peak-valley value of the electric signal waveform through the analysis of the waveform phase angle, thereby improving the application effect of the signal fuzzy control filter for the wafer detection device.
Owner:樊一平
Popular searches
Angle demodulation by phase difference detection Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influence Gated amplifiers Fixed inductances Transformers/inductances circuits Unwanted magnetic/electric effect reduction/prevention Dual/triple band amplifier Electric component structural association Low noise amplifier Multi-frequency-changing modulation transference
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com