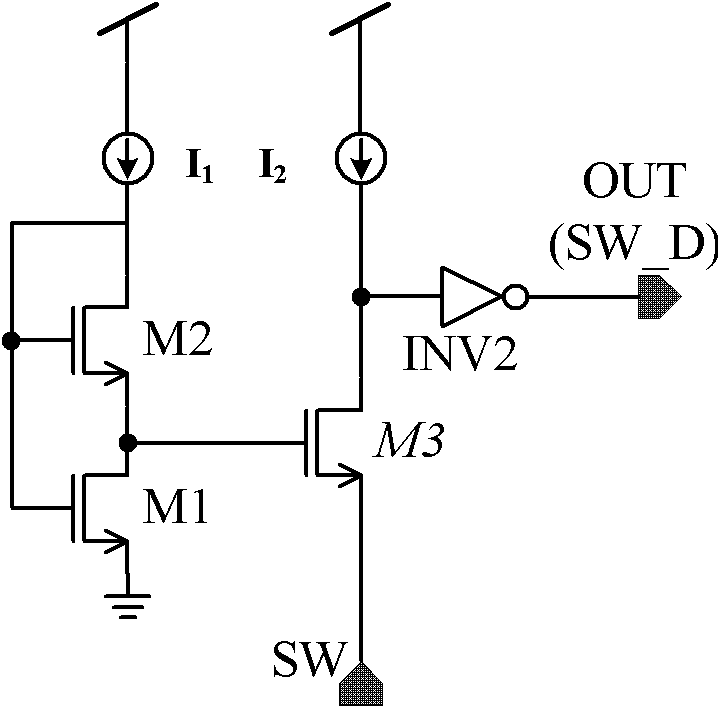
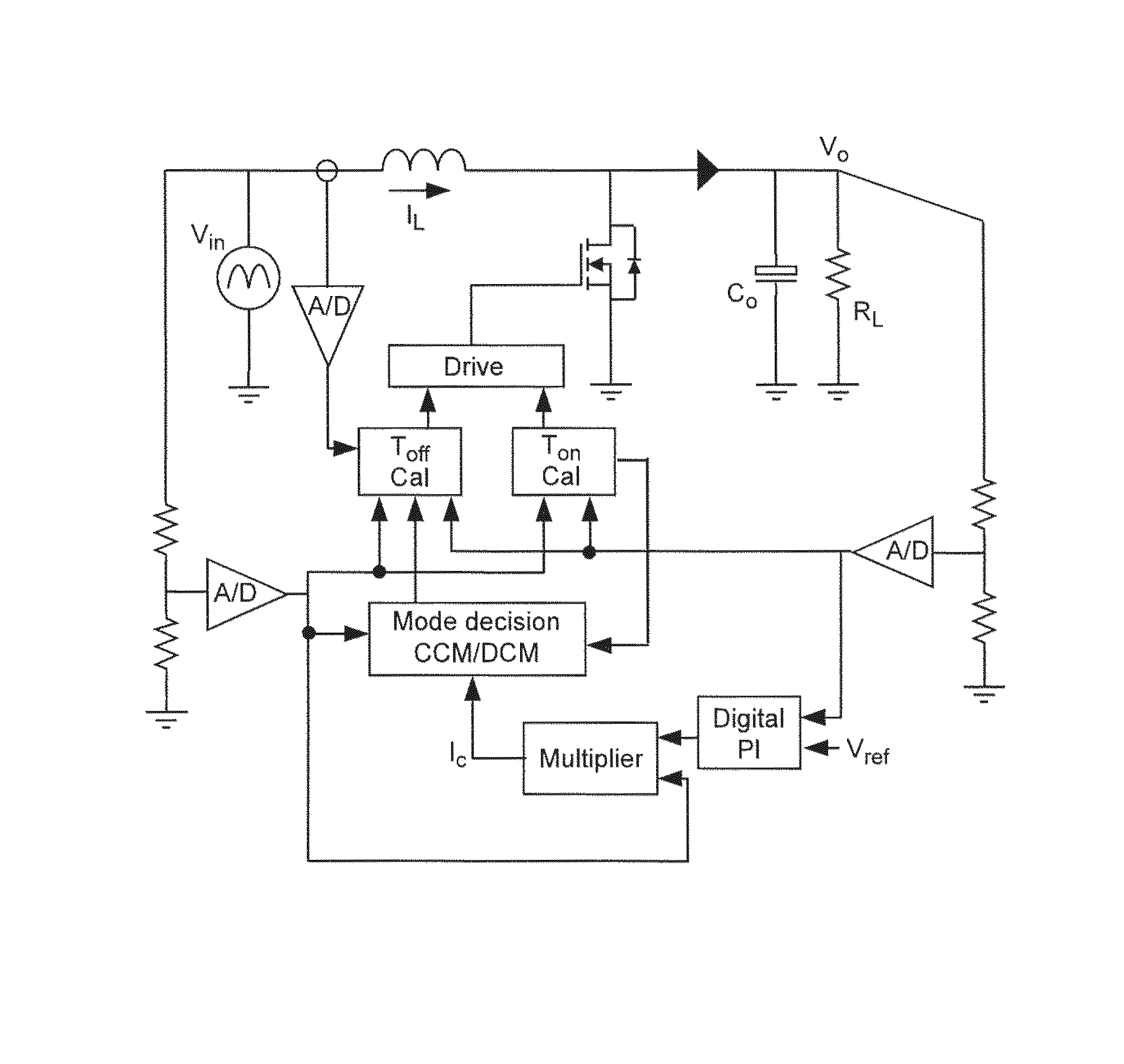
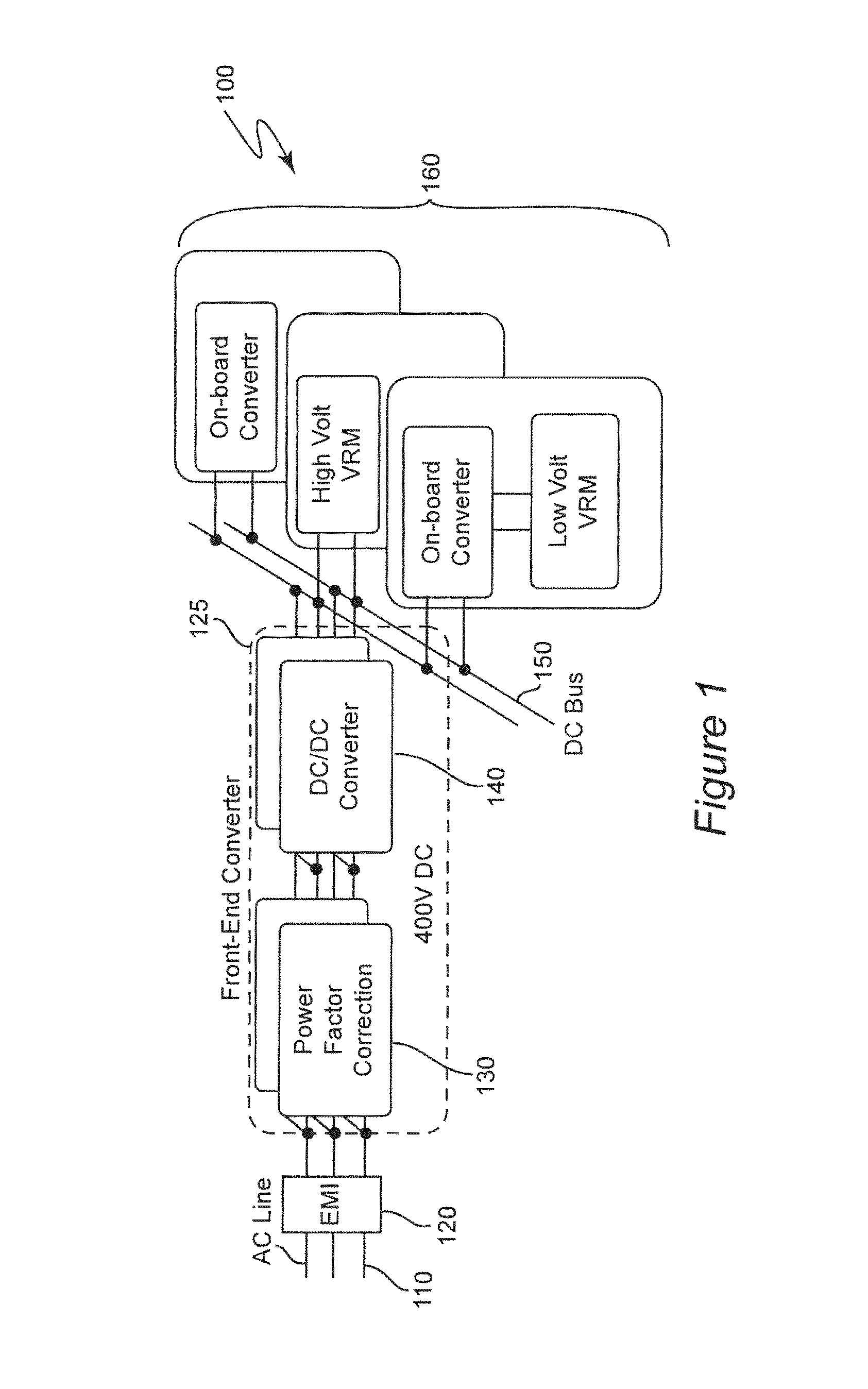
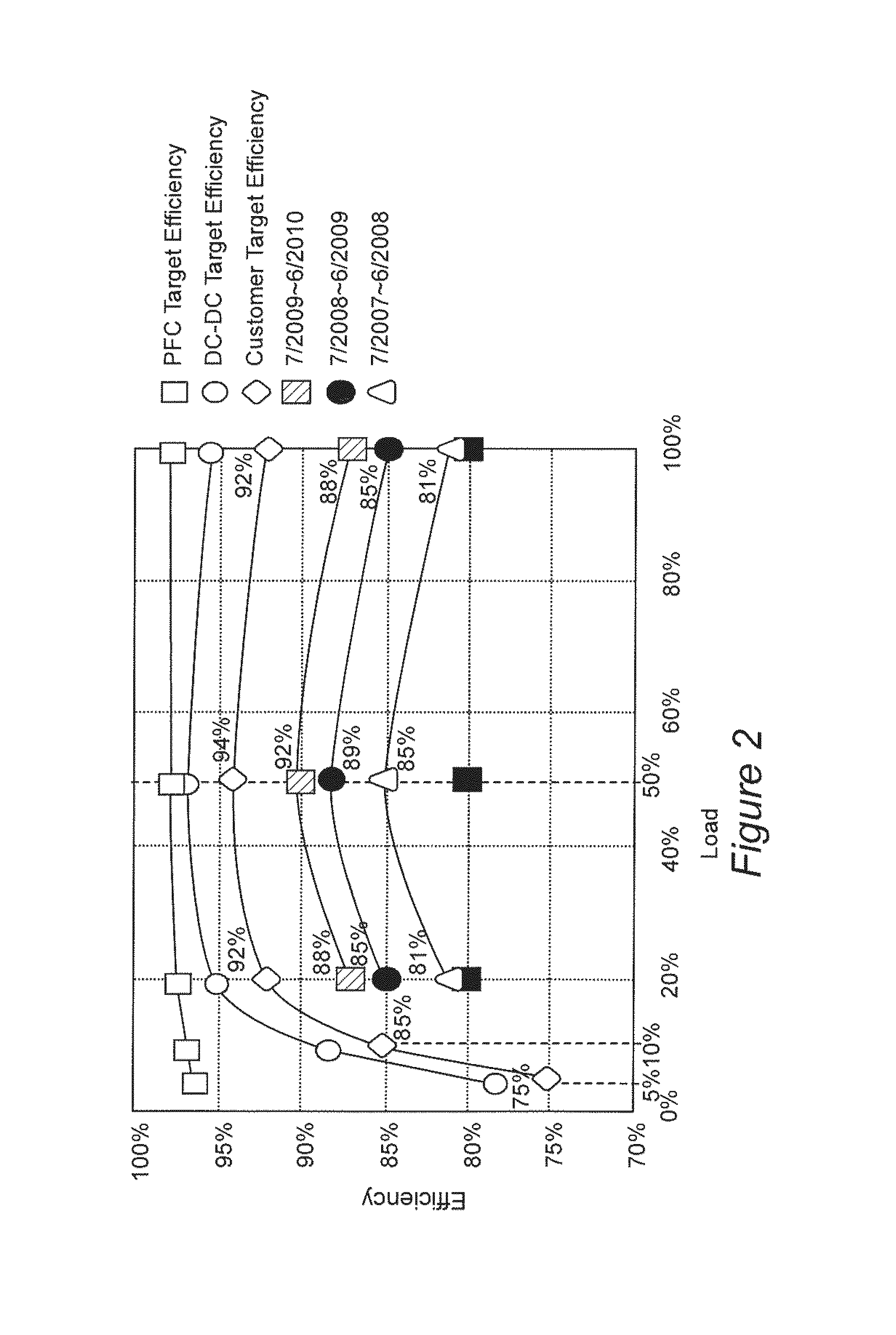
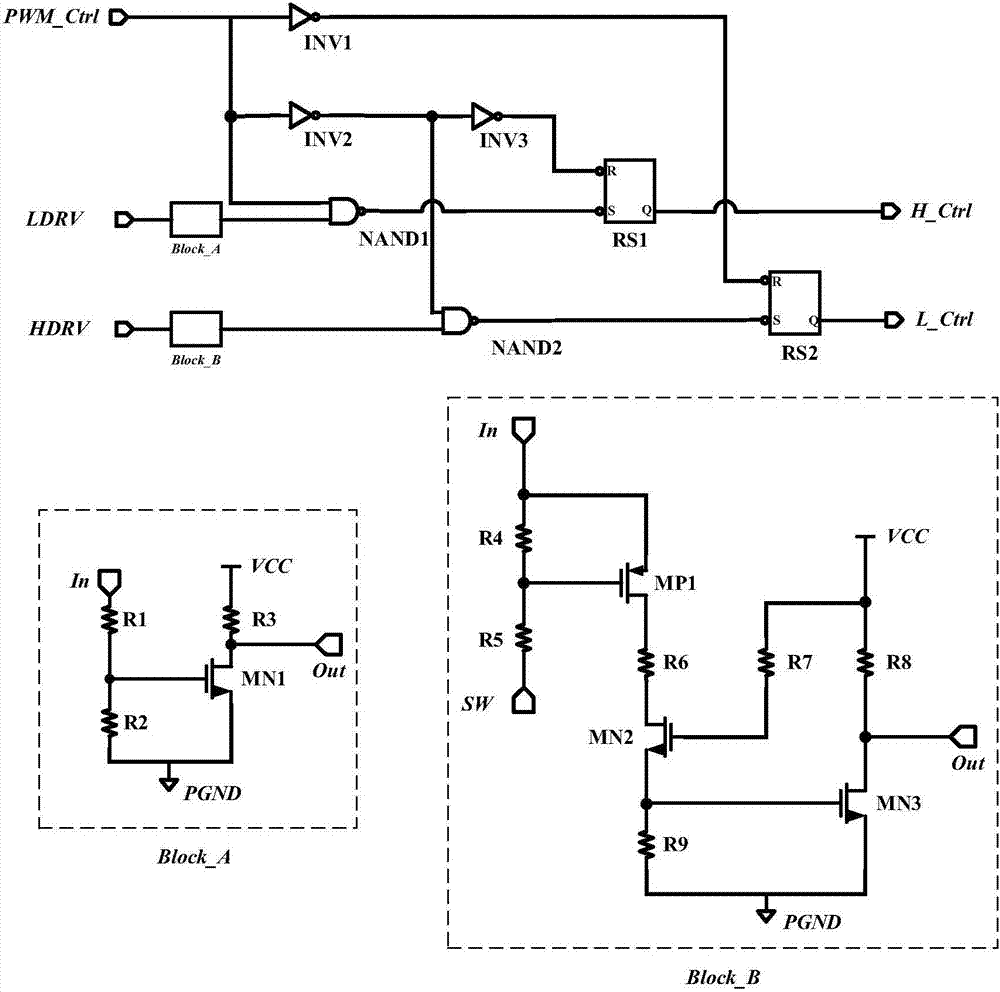
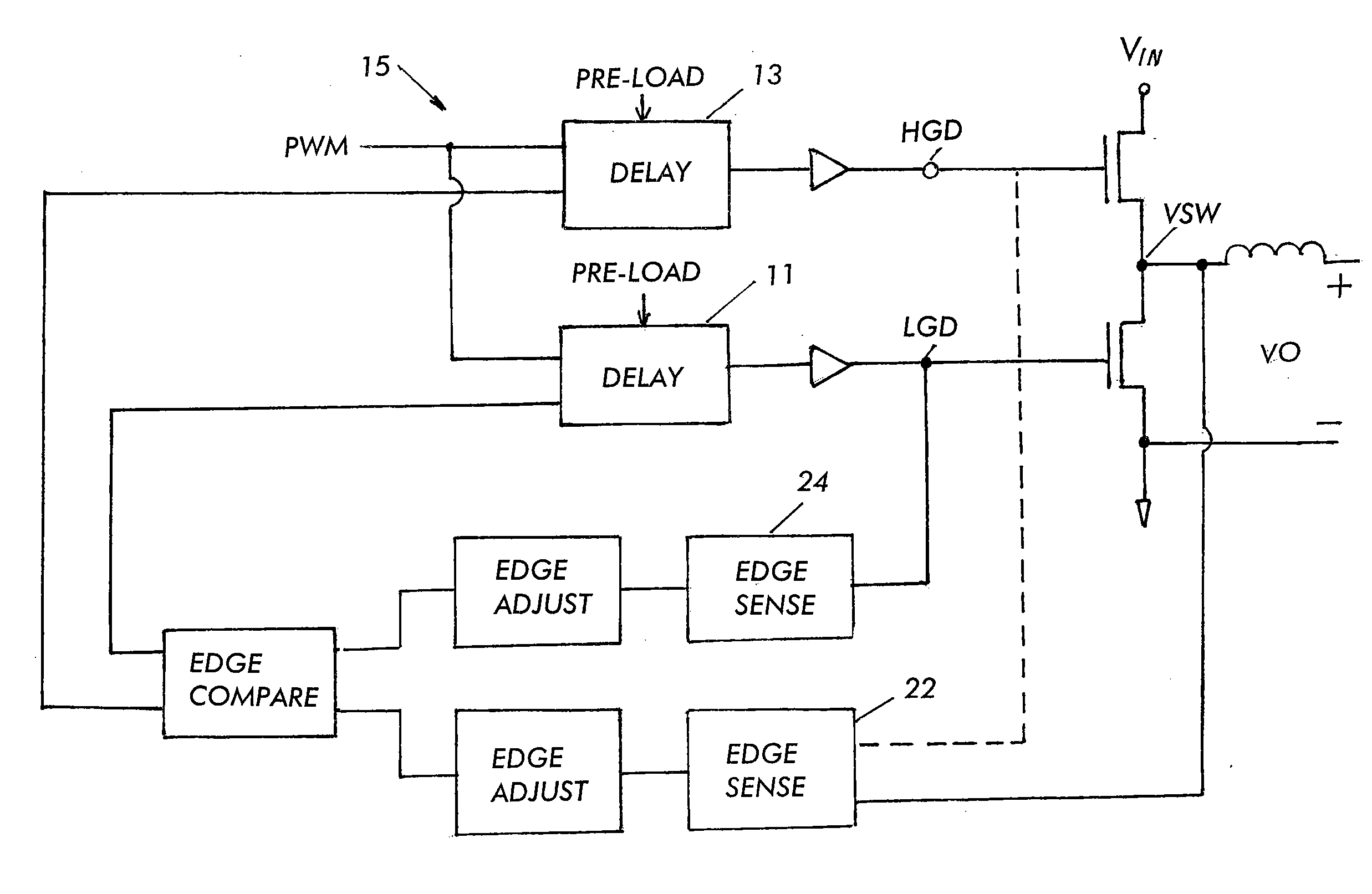
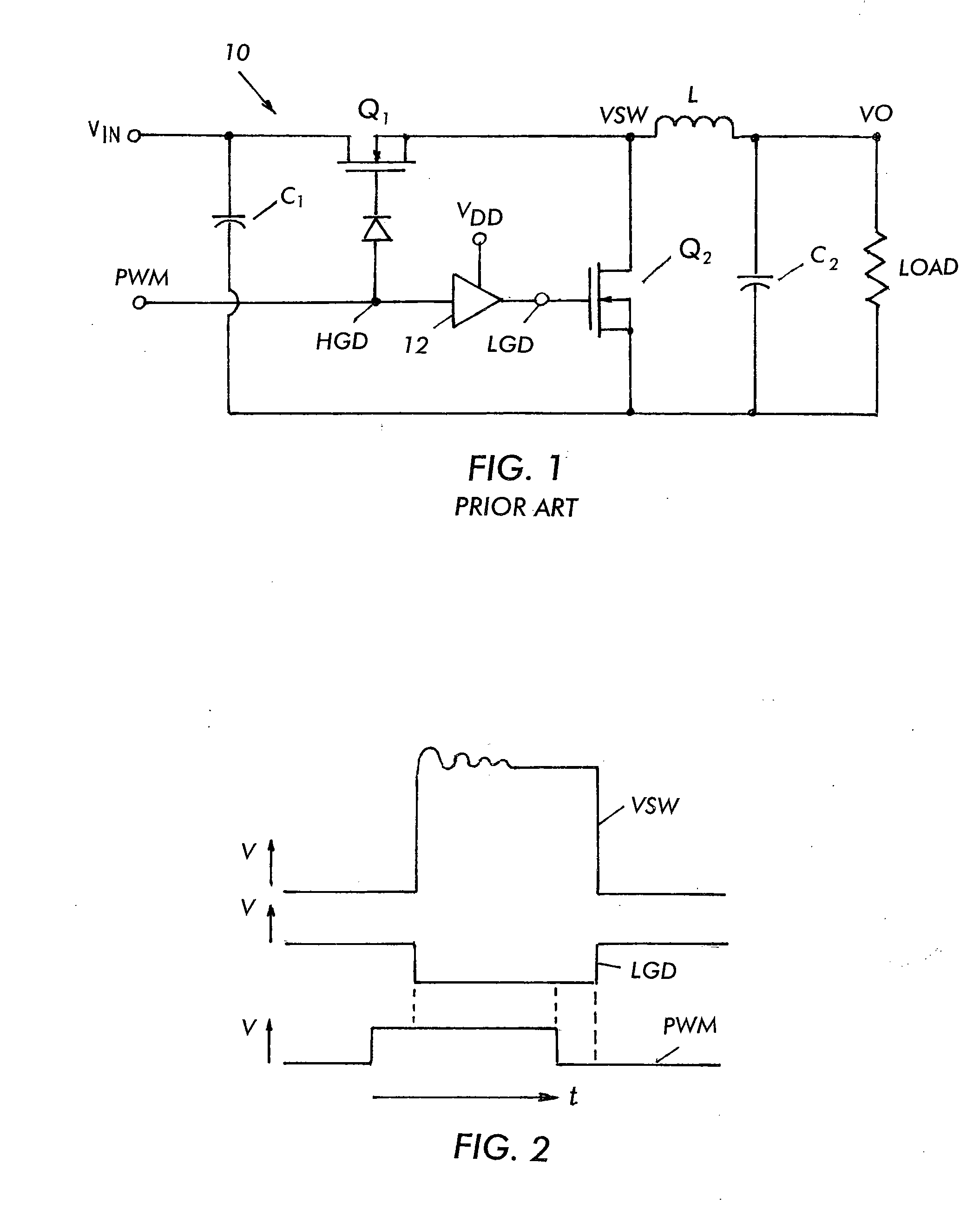
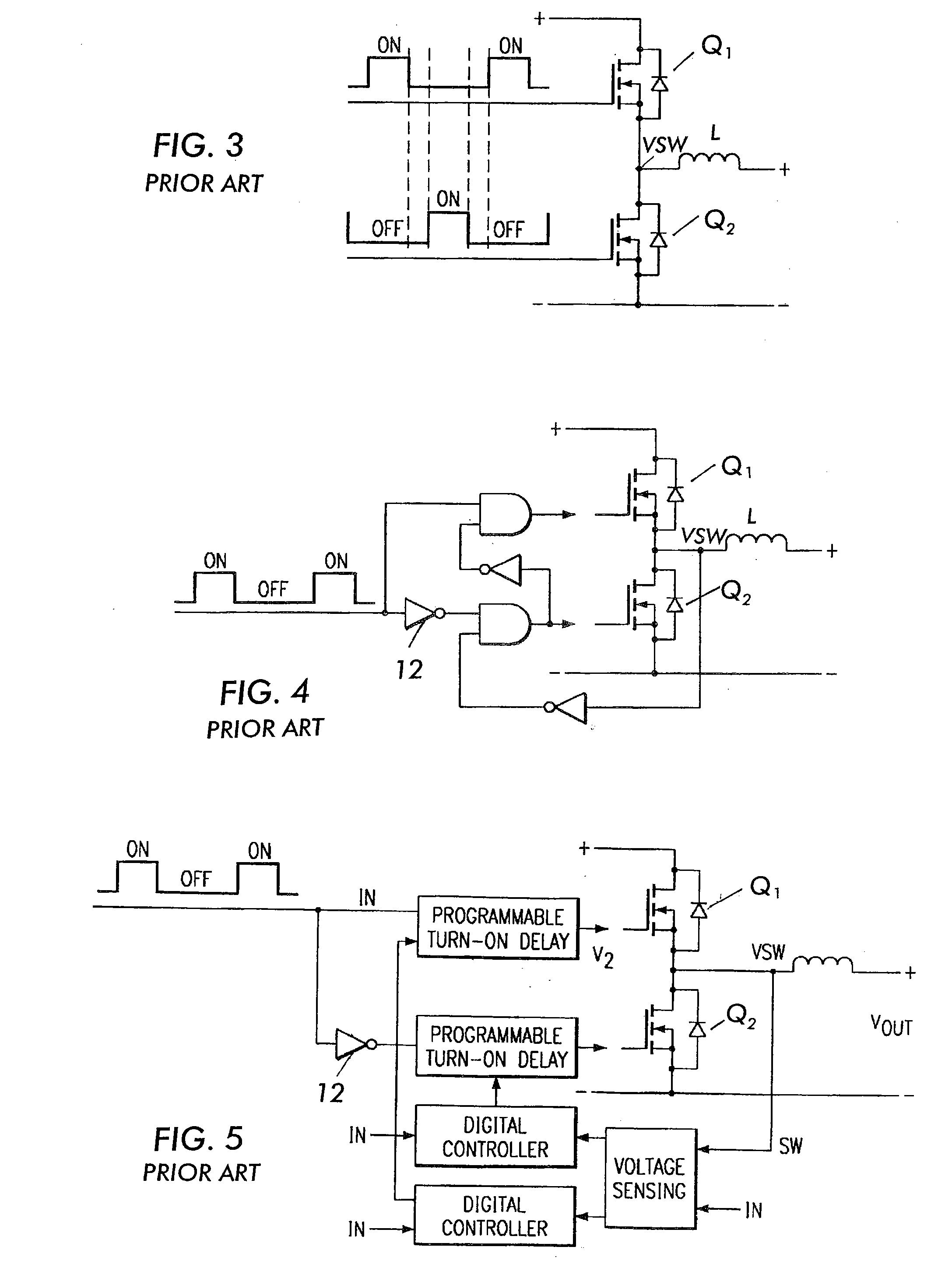
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
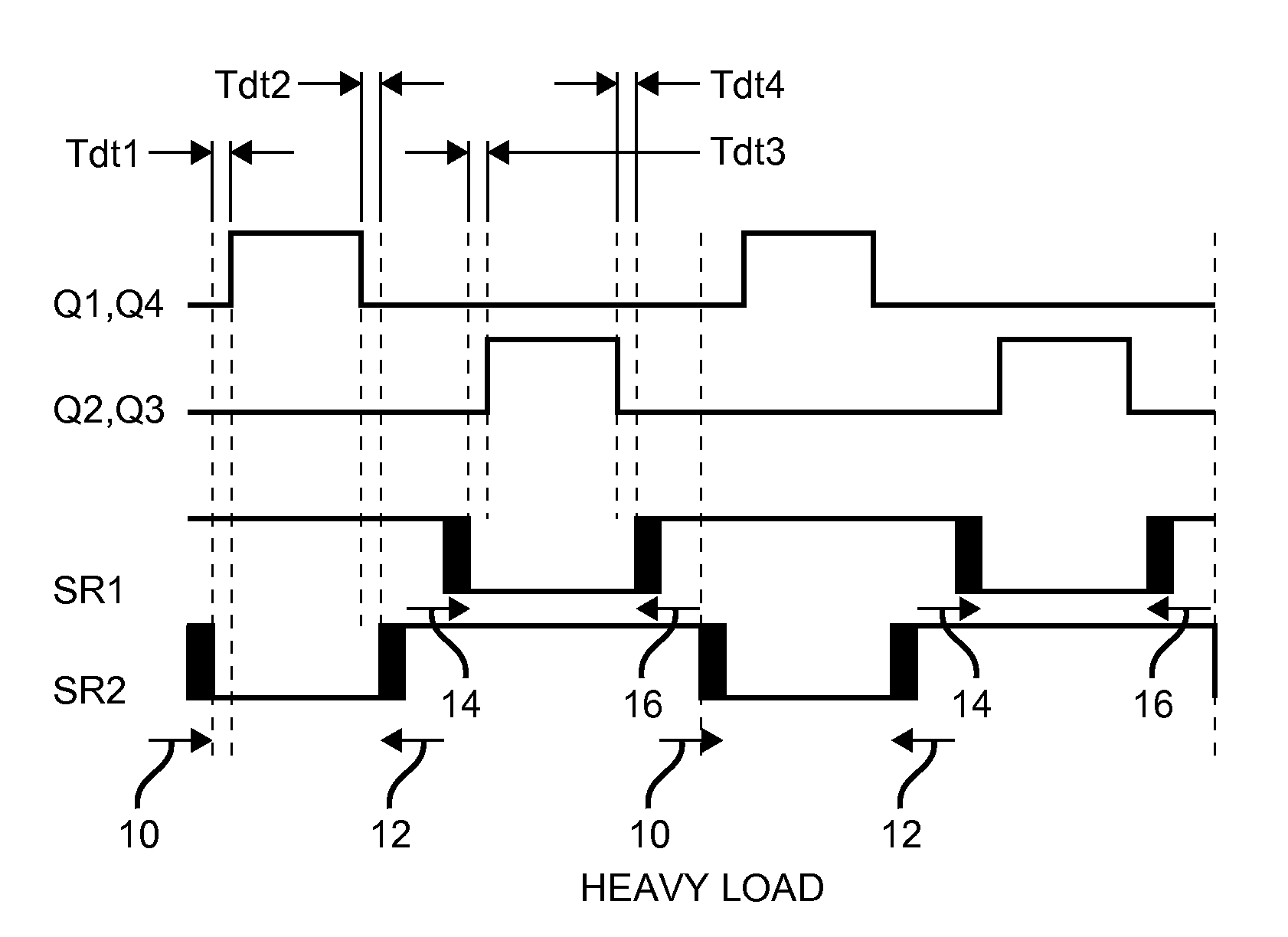
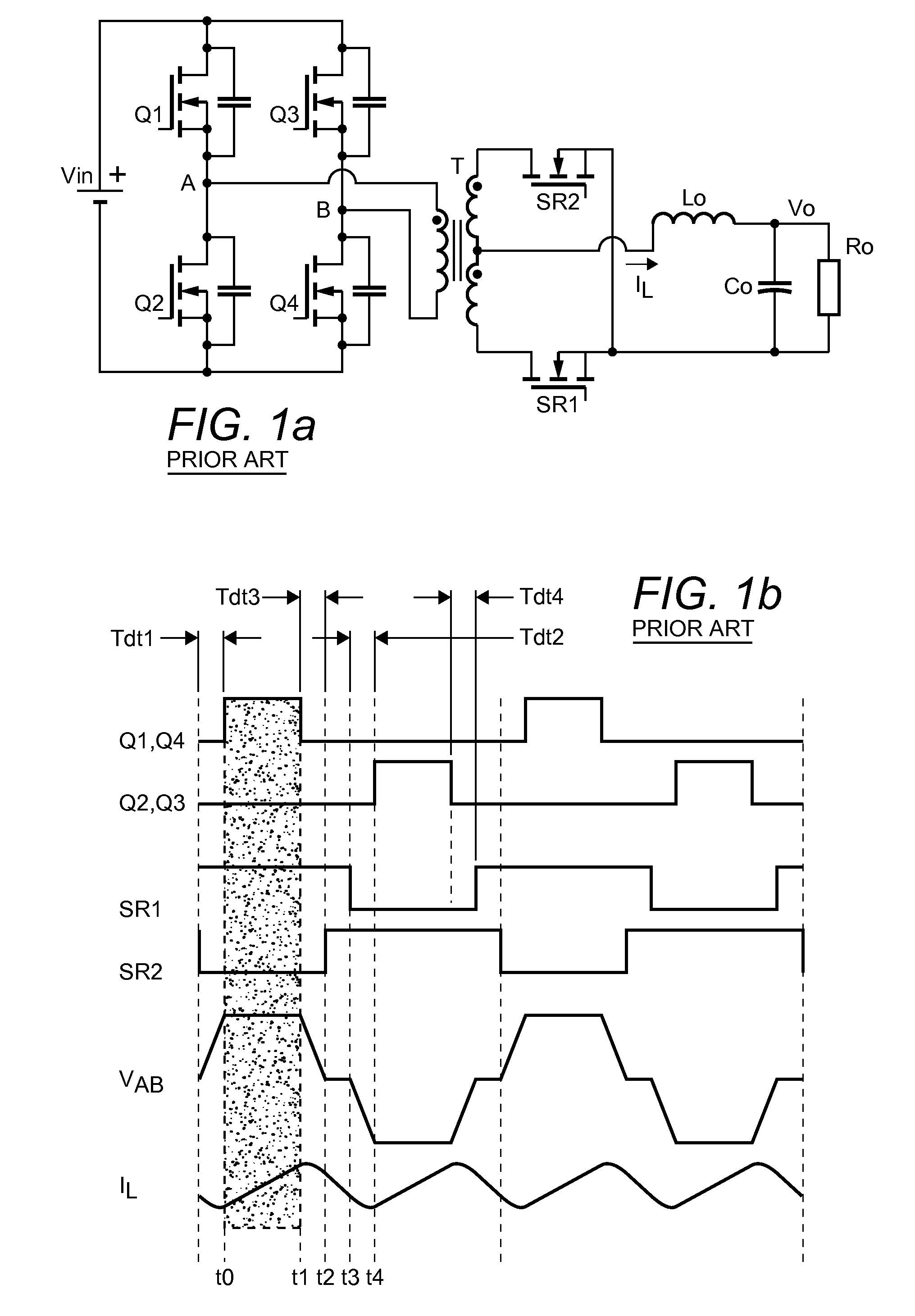
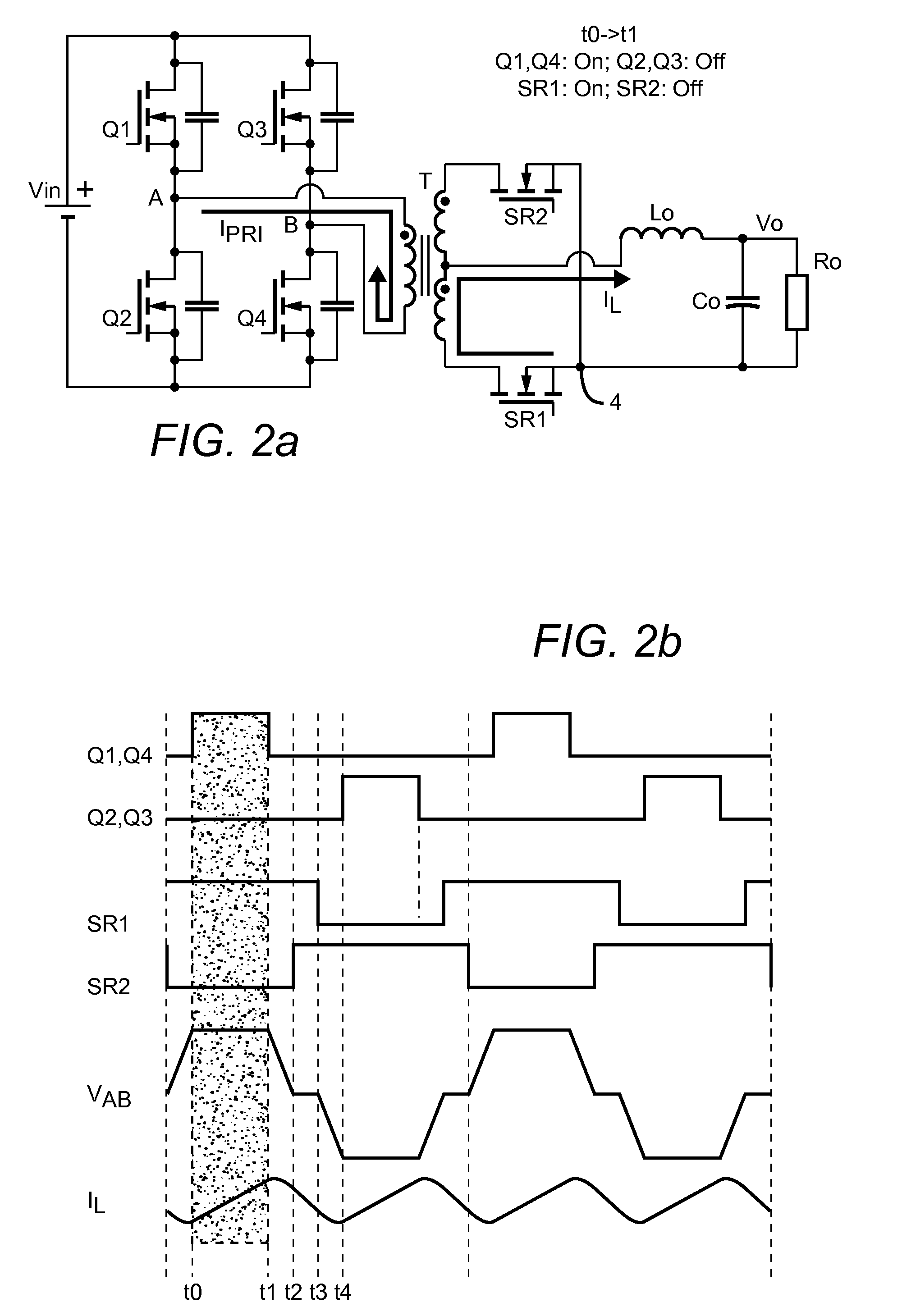
114 results about "Dead time control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
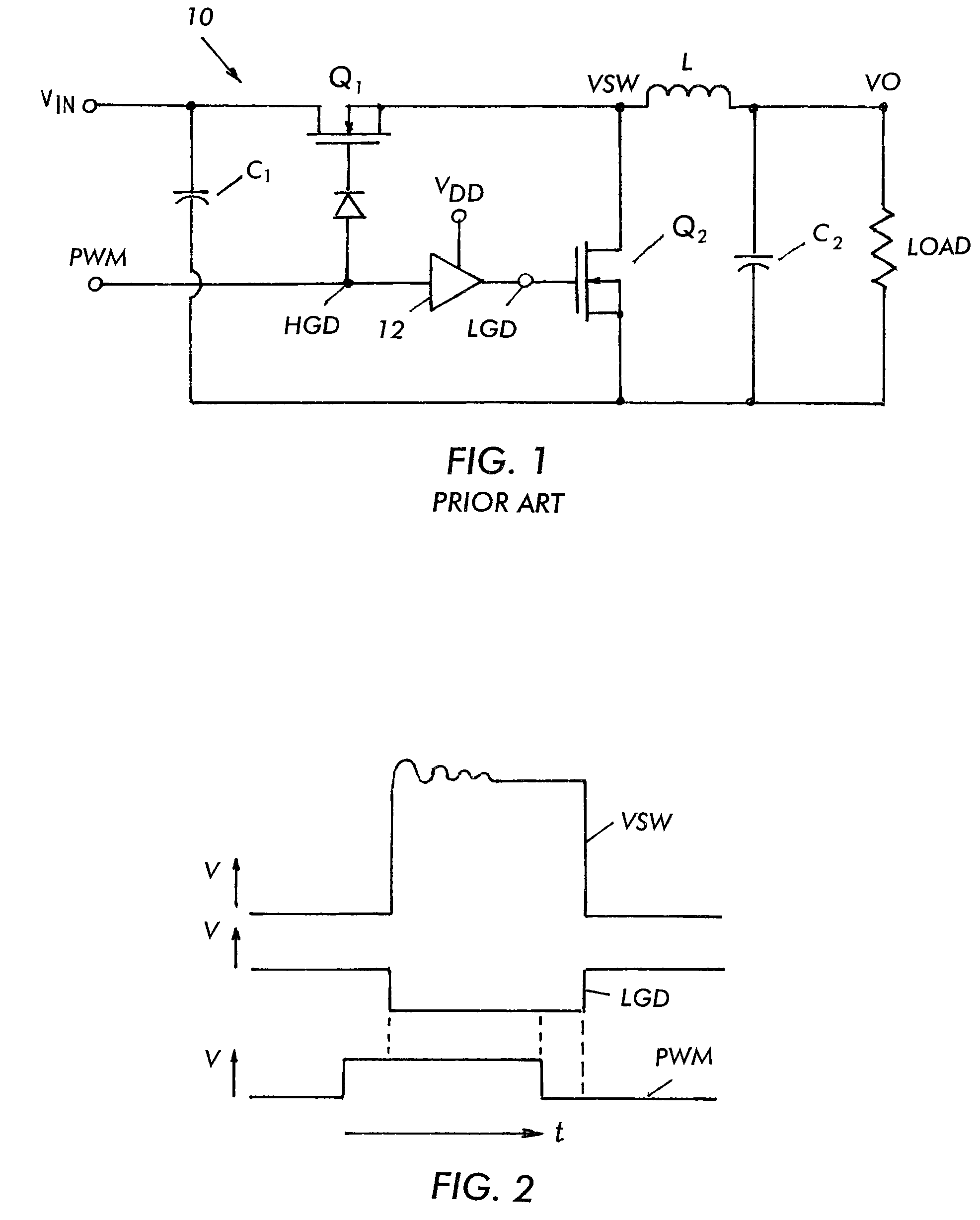
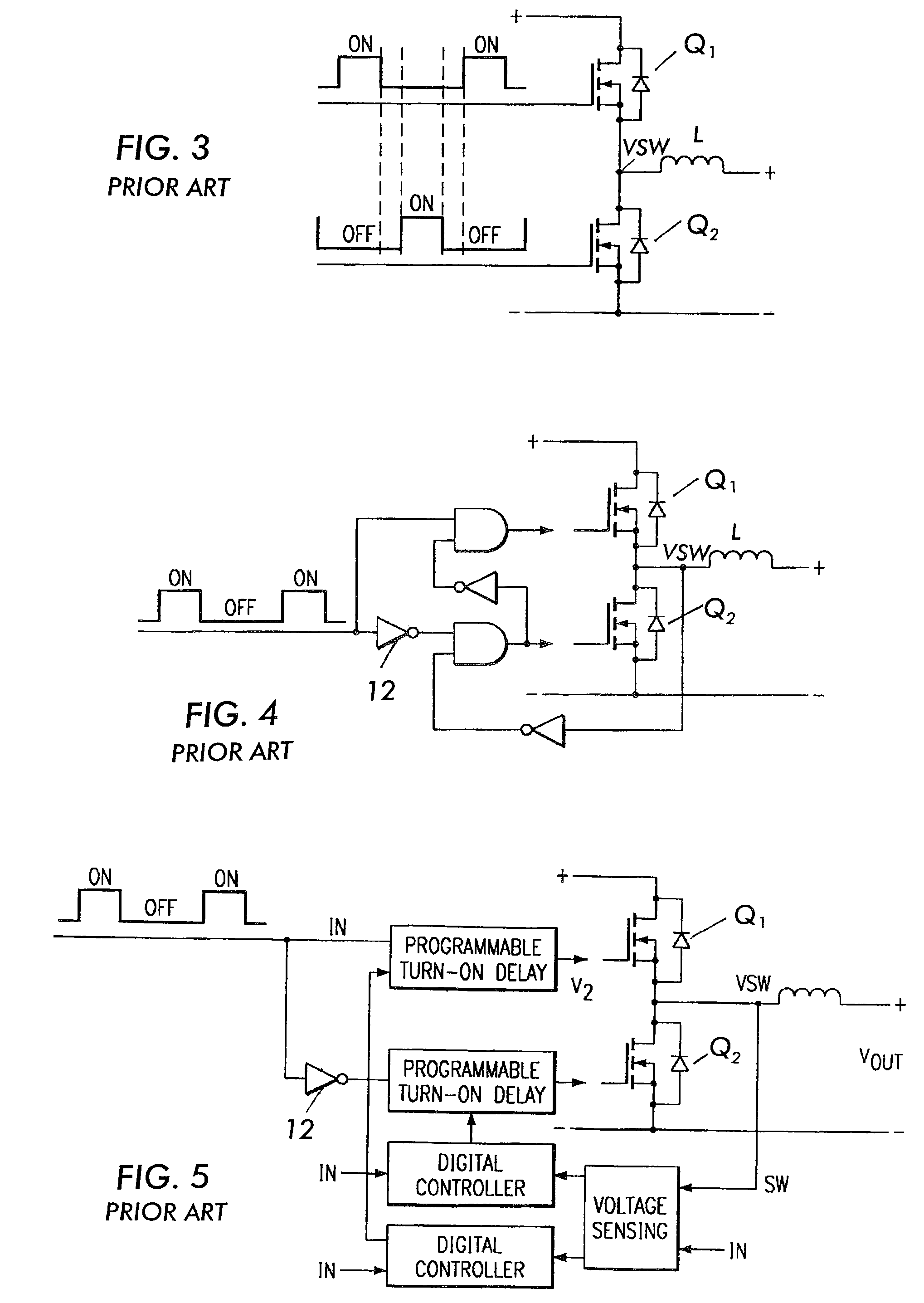
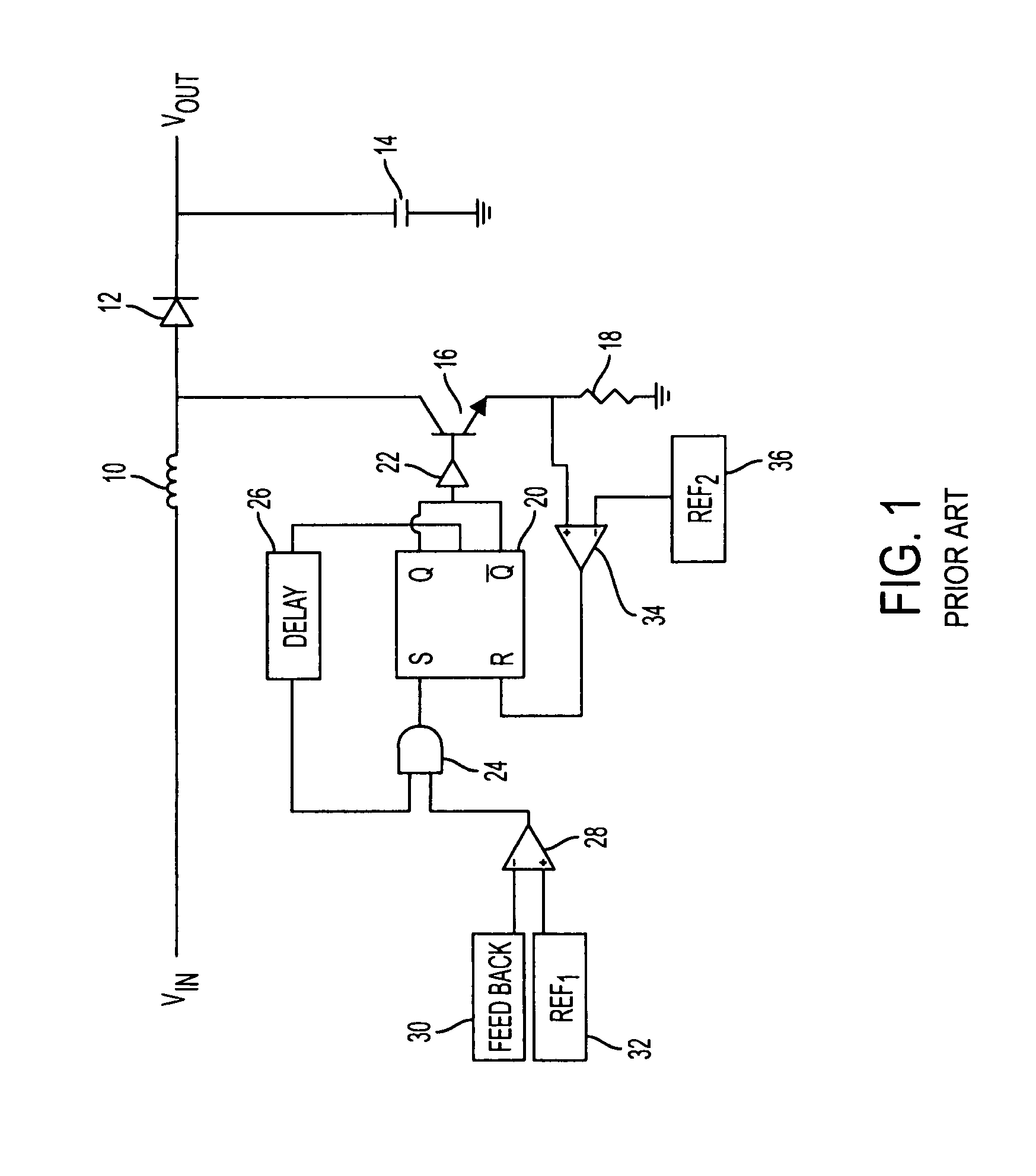
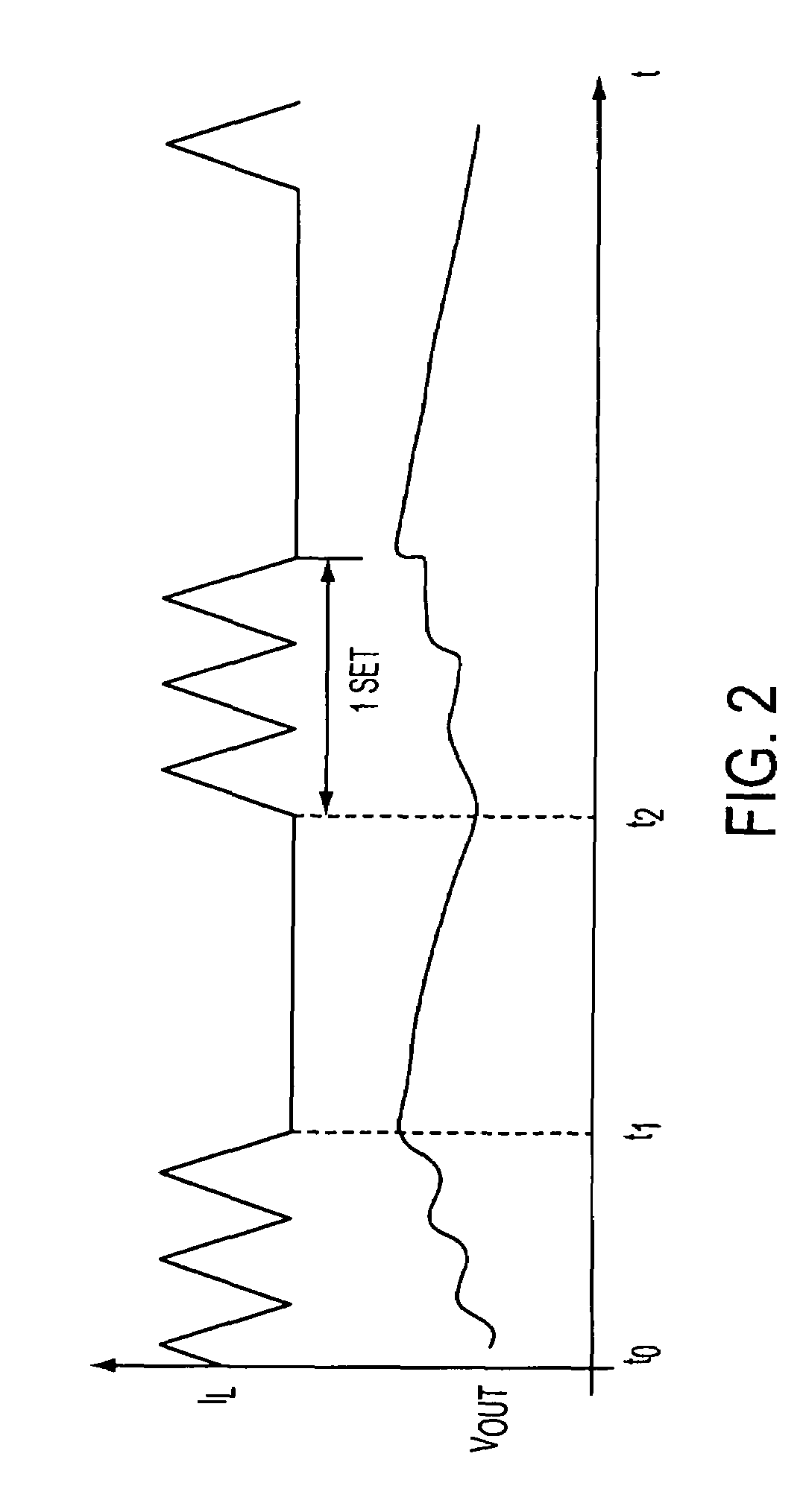
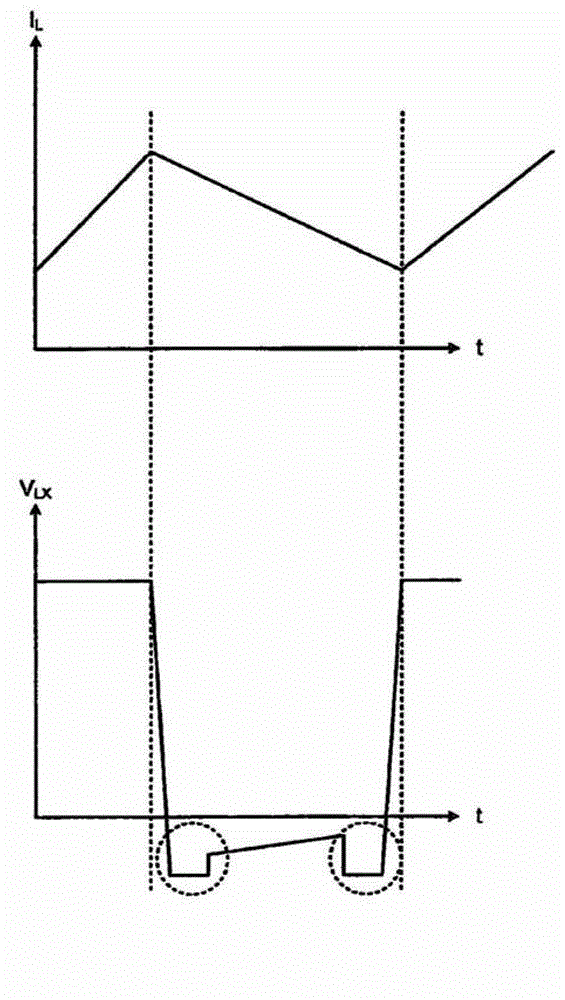
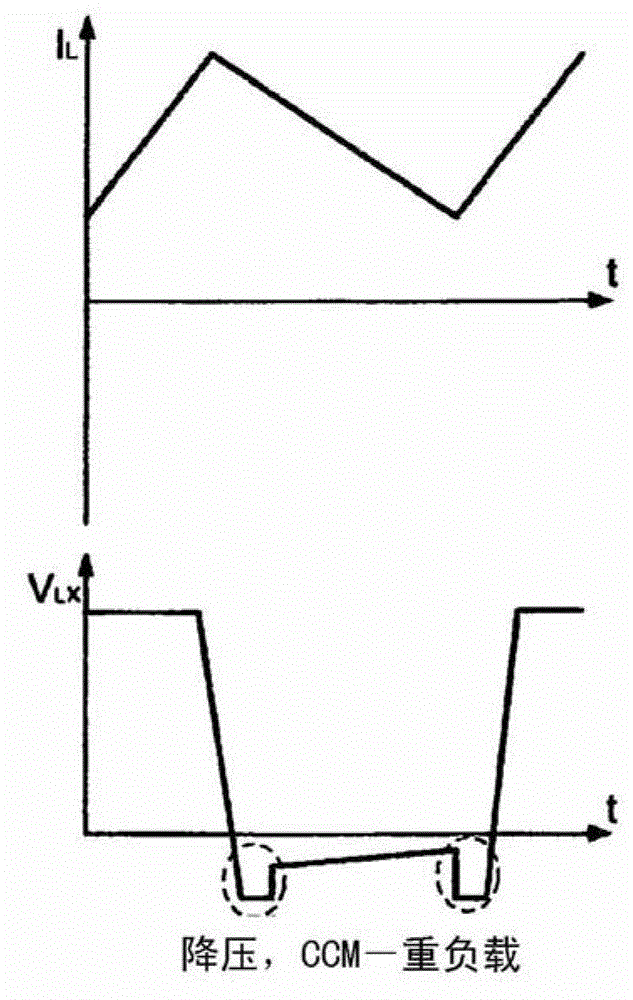
Dead Time is the Killer of Control. Dead time is the delay from when a controller output (CO) signal is issued until when the measured process variable (PV) first begins to respond. The presence of dead time,Өp, is never a good thing in a control loop.
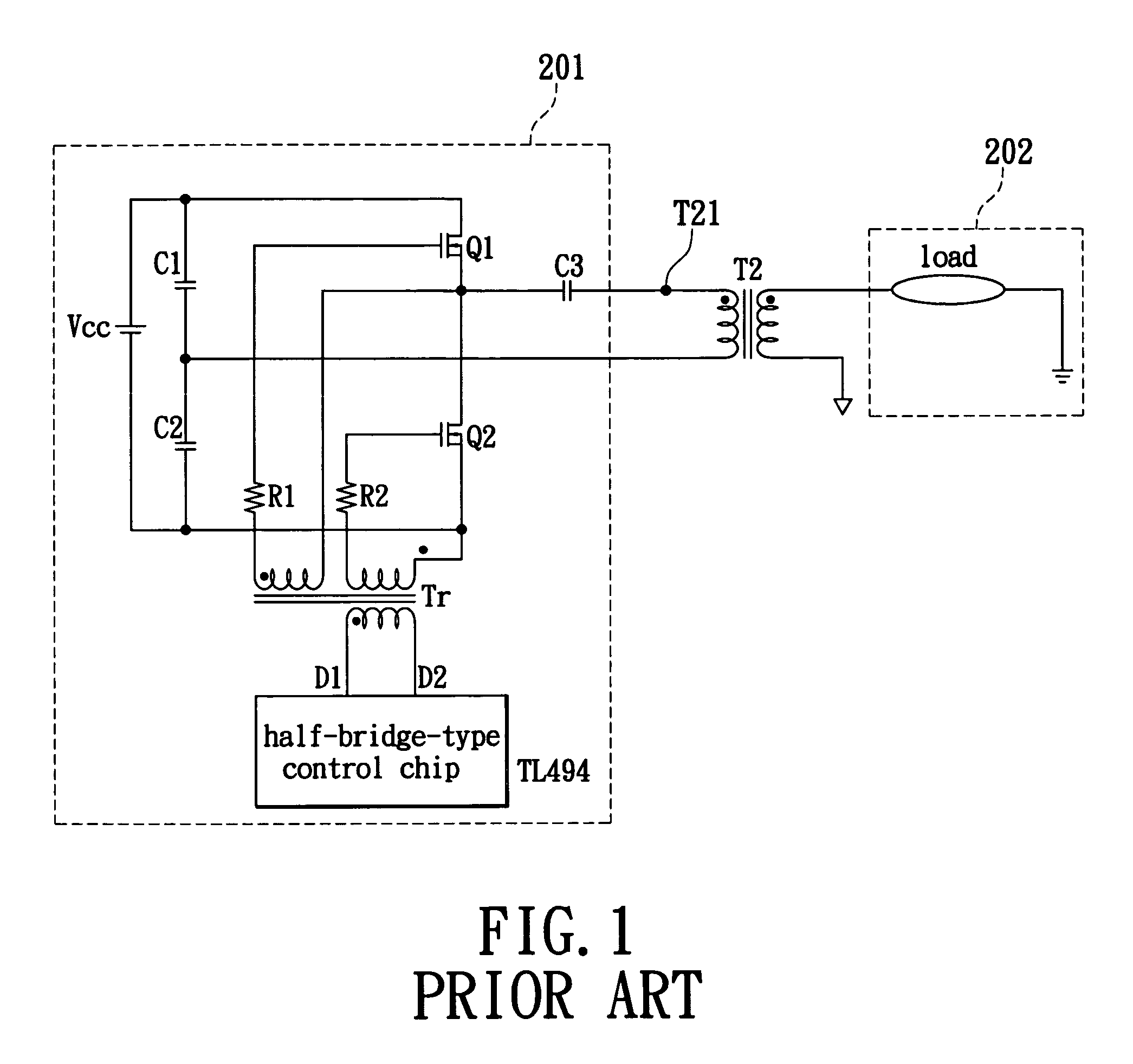
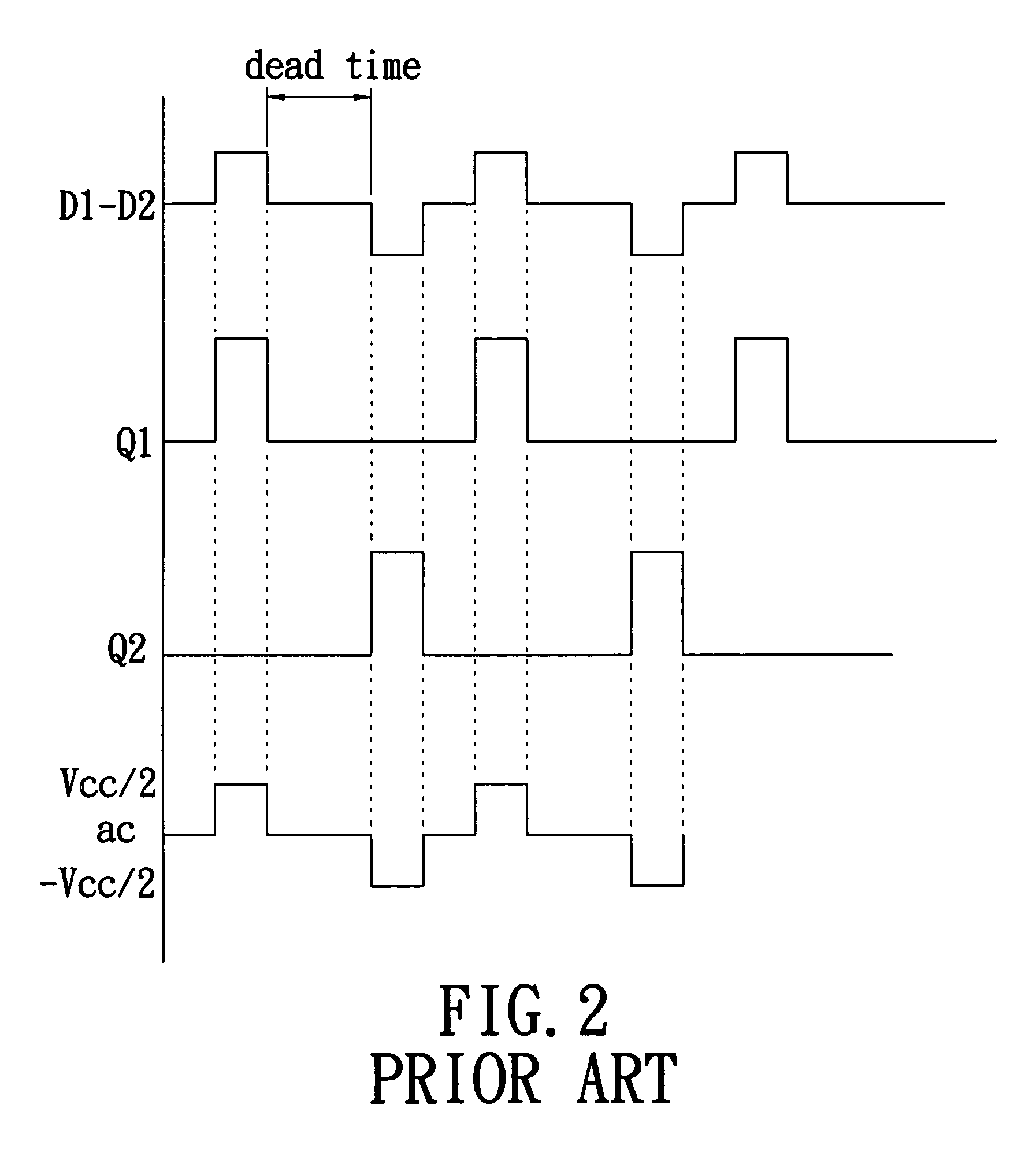
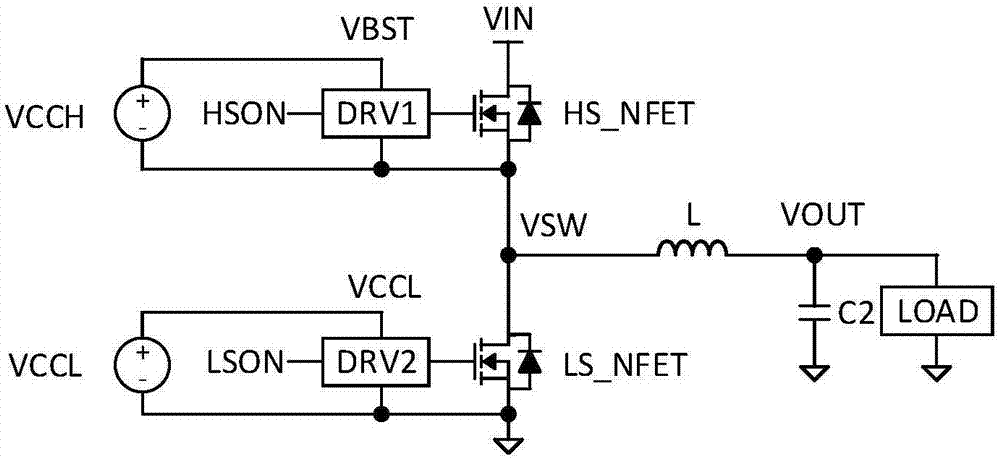
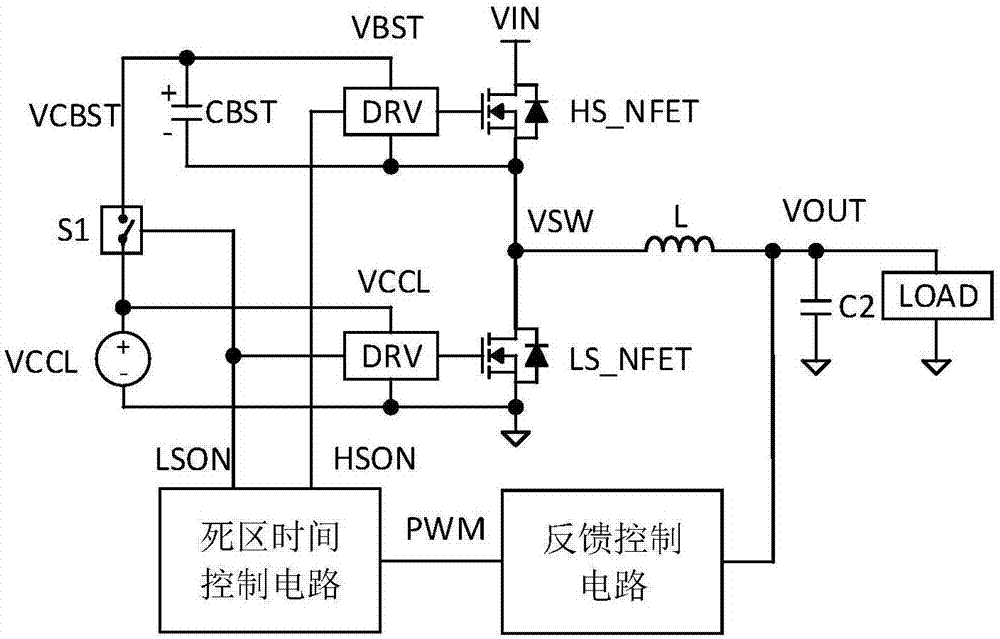
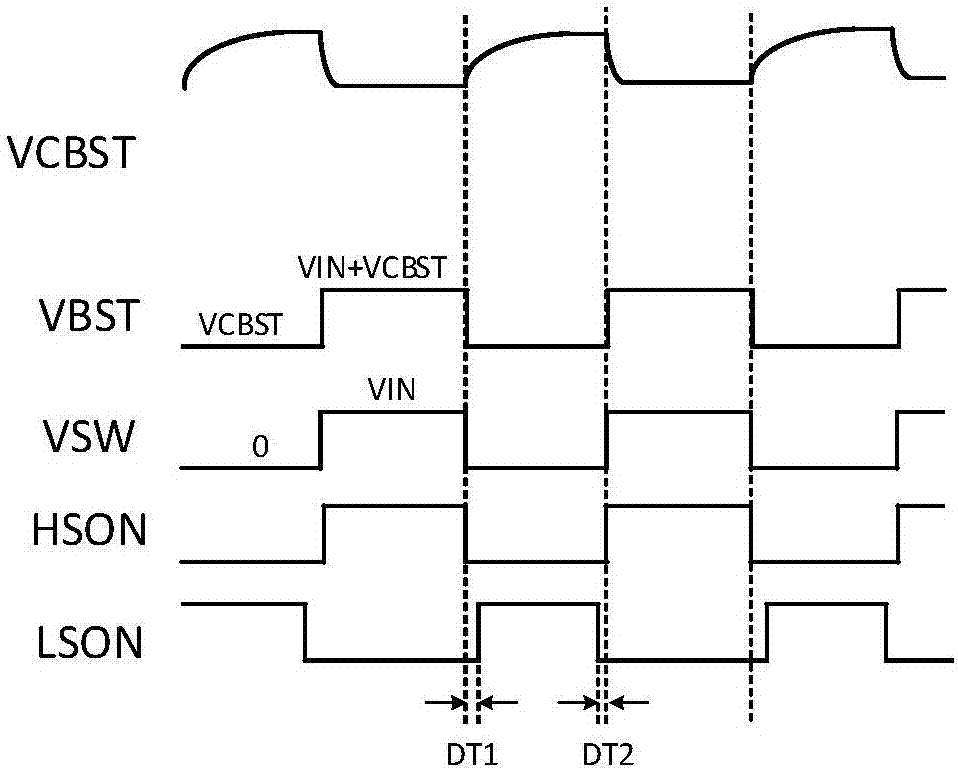
Resonant switching power converter with adaptive dead time control
InactiveUS20100020569A1Improve efficiencyRelieve pressureTransformersEfficient power electronics conversionTransverterEngineering
A resonant switching power converter having adaptive dead time control provides improved efficiency along with reduced EMI / audible noise and component stresses. A dead time between pulses generated by a switching circuit is adaptively set in conformity with a value of the input voltage to the resonant switching power converter and an indication of a magnitude of the current passing through inductive element of the resonant tank of the converter. The indication of the current magnitude may be the switching frequency of the converter, or a measure of line or load current levels. The dead time can be obtained from a look-up table or computed from the current magnitude and input voltage values.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Adaptive Dead Time Control Apparatus and Method for Switching Power Converters
ActiveUS20130063985A1Decreases conduction timeImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringDead time control
An embodiment apparatus comprises a secondary synchronous rectifier and a secondary gate drive controller coupled to a transformer winding. The secondary gate drive controller is configured to generate a forward gate drive signal for the forward switch and generate a freewheeling gate drive signal for the freewheeling switch, wherein the secondary gate drive controller generates a dead time between the forward gate drive signal and the freewheeling gate drive signal.
Owner:HUAWEI DIGITAL POWER TECH CO LTD
PWM-based DC-DC converter with assured dead time control exhibiting no shoot-through current and independent of type of FET used
ActiveUS6940262B2High voltageEfficient power electronics conversionElectronic switchingDc dc converterDead time control
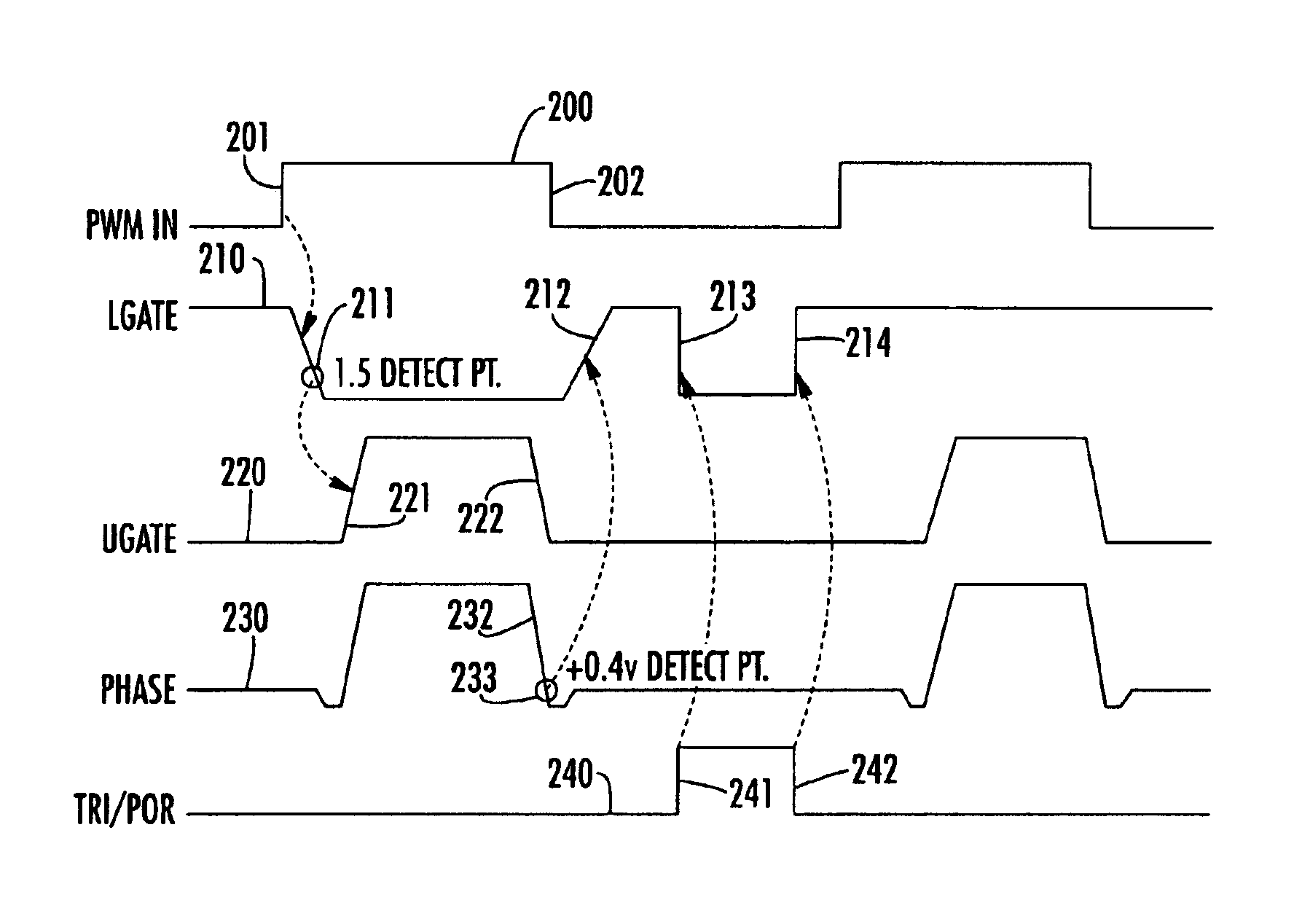
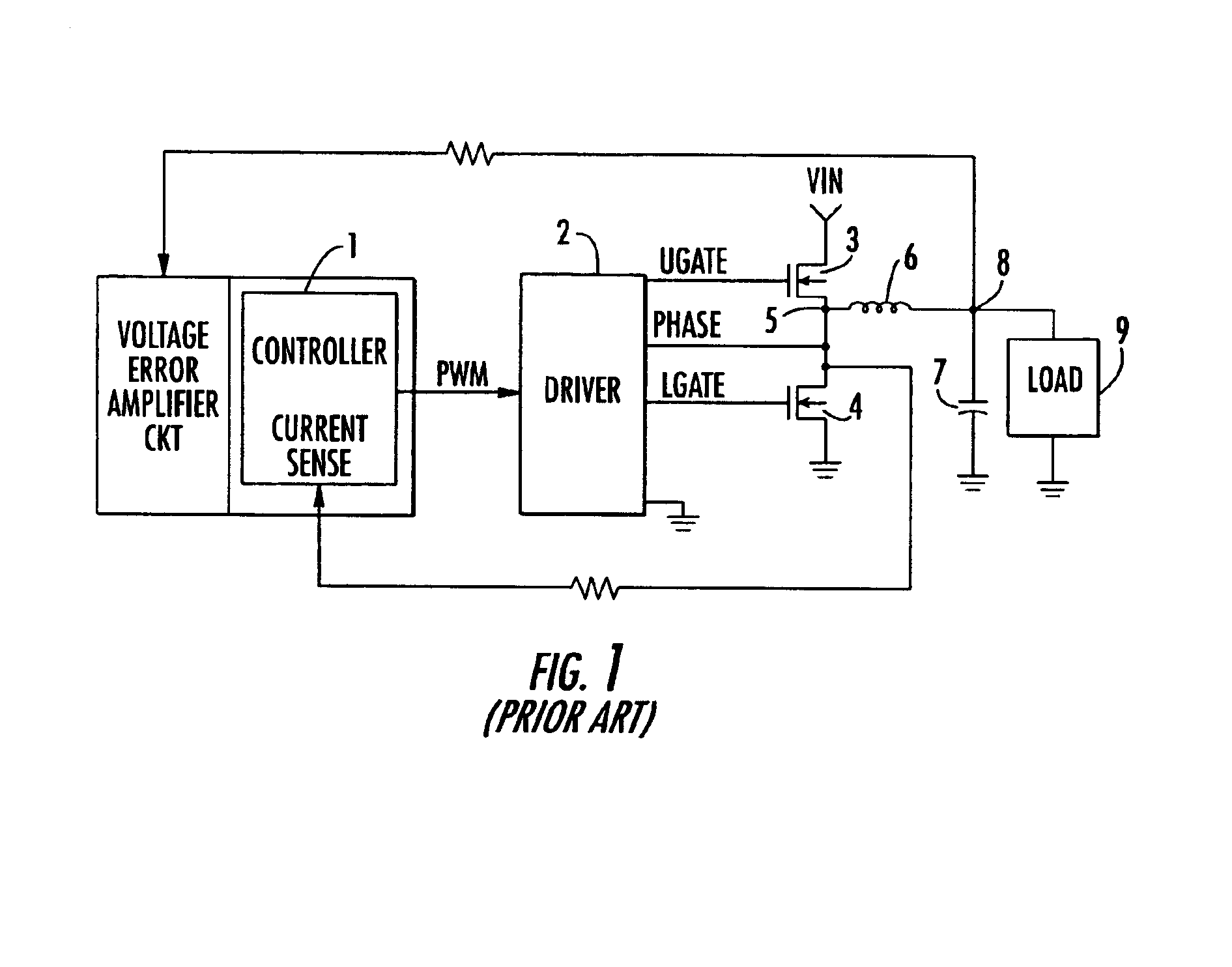
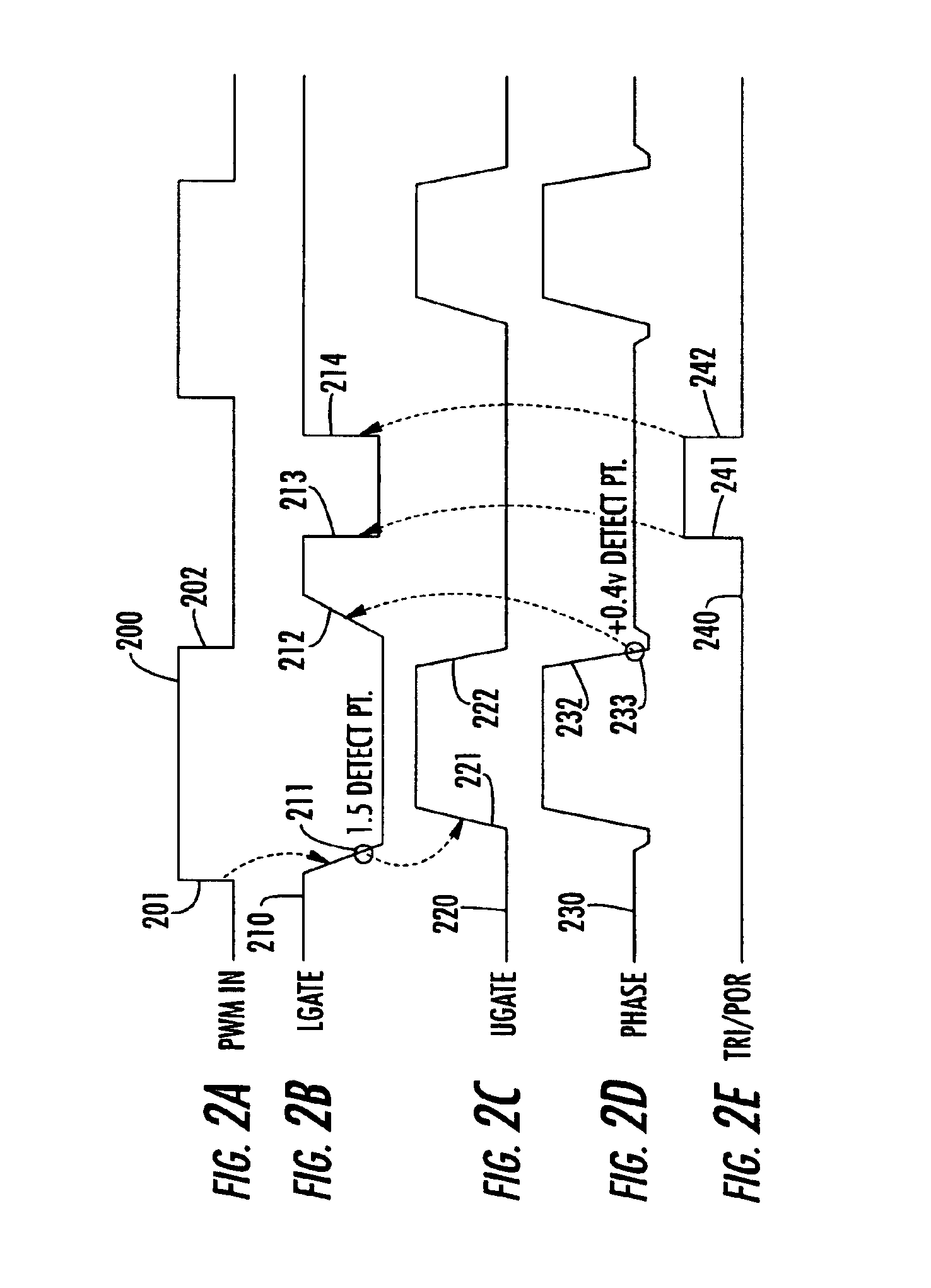
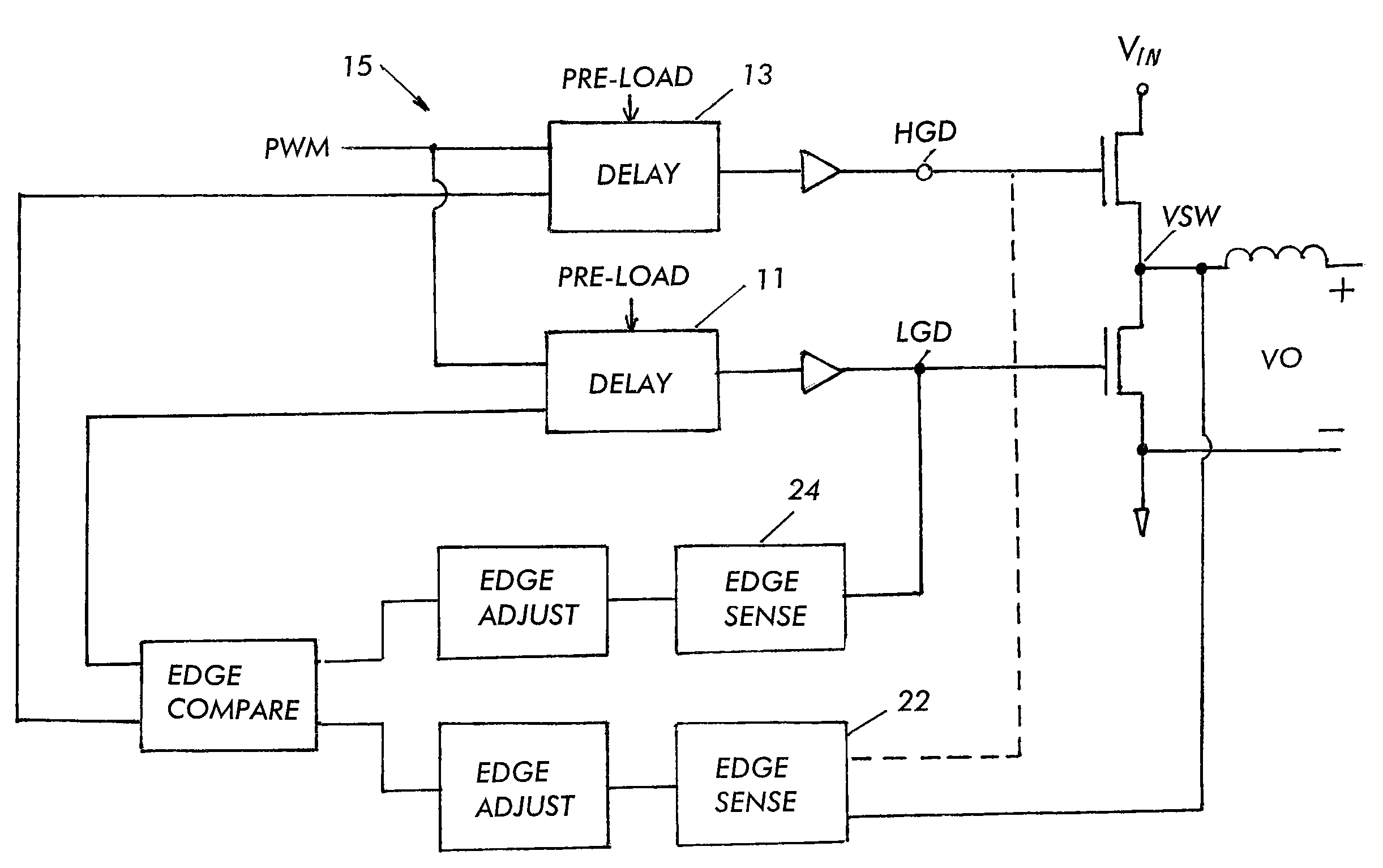
A control circuit for a switch mode DC-DC converter contains an arrangement of monitored LGATE, UGATE and PHASE node condition threshold detectors, outputs of which are processed in accordance with a switching control operator to ensure that each of an upper FET (UFET) and a lower FET (LFET) is completely turned off before the other FET begins conduction, thereby maintaining a dead time that exhibits no shoot-through current and is independent of the type of switching FET.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Intelligent dead time control
ActiveUS7683594B2Convenient timeReduce power lossAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDead timeDead time control
A circuit for reducing switching losses in a synchronous rectifier of a switching stage including a high-side control transistor and a low-side synchronous transistor coupled at a switching node, the switching stage receiving an input voltage and providing a controlled output voltage at an output node. The circuit including a first circuit portion for sensing waveshape edges of a first signal at a gate terminal of the low-side synchronous transistor and a first voltage to determine a delay between the waveshape edge of the first signal and the waveshape edge of the first voltage; and a second circuit portion for calibrating the first signal and the first voltage to align the waveshape edge of the first signal and the waveshape edge of the first voltage, with an optional offset to achieve minimal power loss.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
A dead time control circuit used in a DC-DC converter
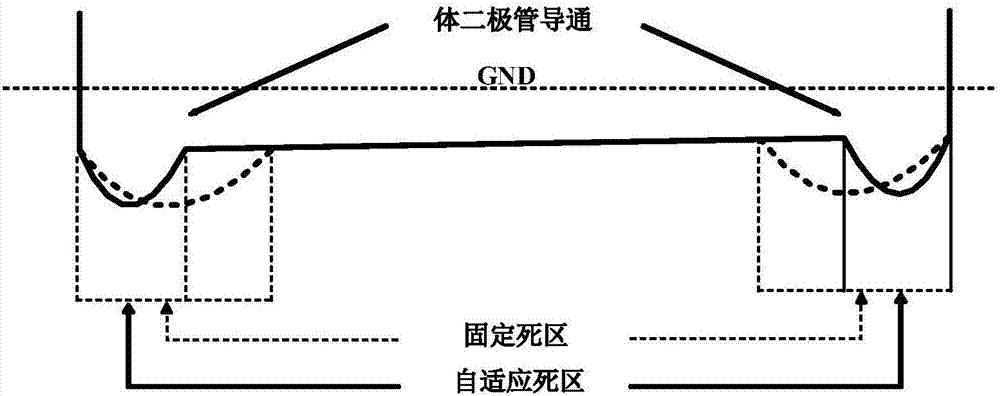
ActiveCN102170228AShort transmission delaySmall sizeDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationDc dc converterReverse recovery
The invention discloses a dead time control circuit used in a DC-DC converter. In allusion to unnecessary power loss brought by conduction loss and reverse recovery in the DC-DC converter, the dead time control circuit used in the DC-DC converter enables a body diode conduction to be detected quickly along the two edges of PWM signal through a dead time detector, thereby turning off a power tube or a rectifying tube to make the body diode conduction time be reduced to be close to the transmission delay time of a drive unit, reducing the power loss brought by the body diode conduction substantially and improving efficiency substantially. The improved efficiency brought by employing the structure enables a higher switch frequency to be feasible, thereby reducing the size of a passive device. Moreover, the circuit of the invention can adjust the dead time adaptively in accordance with different load currents.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Adaptive on-time control for power factor correction stage light load efficiency
ActiveUS8803489B2Improve efficiencyWide load rangeAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionHigher order harmonicsDead time control
Light load efficiency of a power factor correction circuit is improved by adaptive on-time control and providing for selection between a continuous conduction mode and a discontinuous conduction mode wherein the discontinuous conduction mode increases time between switching pulses controlling connection of a cyclically varying voltage to a filter / inductor that delivers a desired DC voltage and thus can greatly reduce the switching frequency at light loads where switching frequency related losses dominate efficiency. The mode for controlling switching is preferably selected for each switching pulse within a half cycle of the cyclically varying input voltage. A multi-phase embodiment allows cancellation of EMI noise at harmonics of the switching frequency and adaptive change of phase angle allows for cancellation of dominant higher order harmonics as switching frequency is reduced.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Self-tuning adaptive dead time control for continuous conduction mode and discontinuous conduction mode operation of a flyback converter
ActiveUS20170222569A1Readily apparentEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionPower flowSelf-tuning
A flyback converter includes a primary-side switch that controls conduction of current on a primary side of a transformer and a synchronous rectifier on a secondary side of the transformer. A synchronous rectifier driver controls the conduction of the synchronous rectifier by adaptively adjusting a turn-off threshold of the synchronous rectifier.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
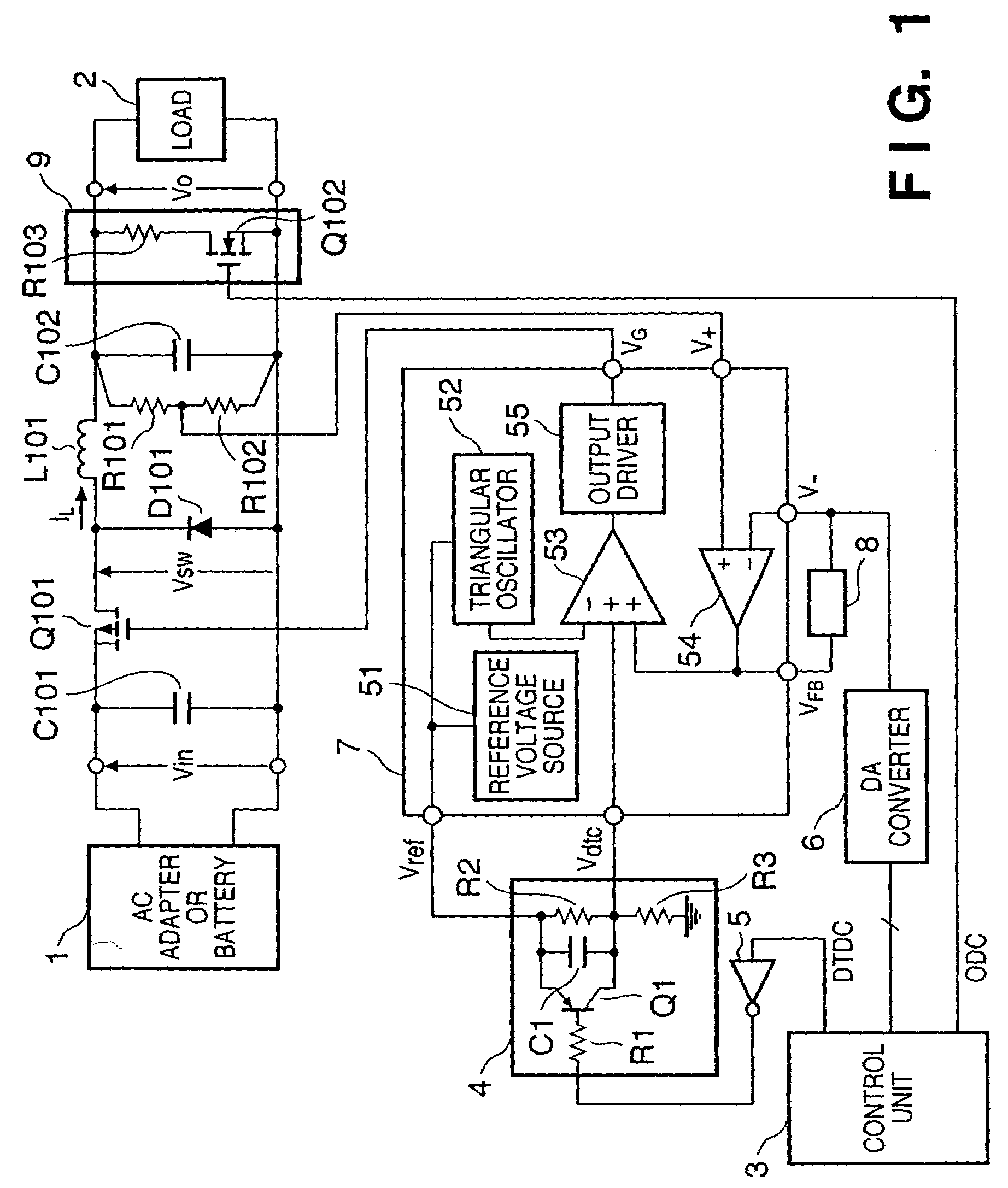
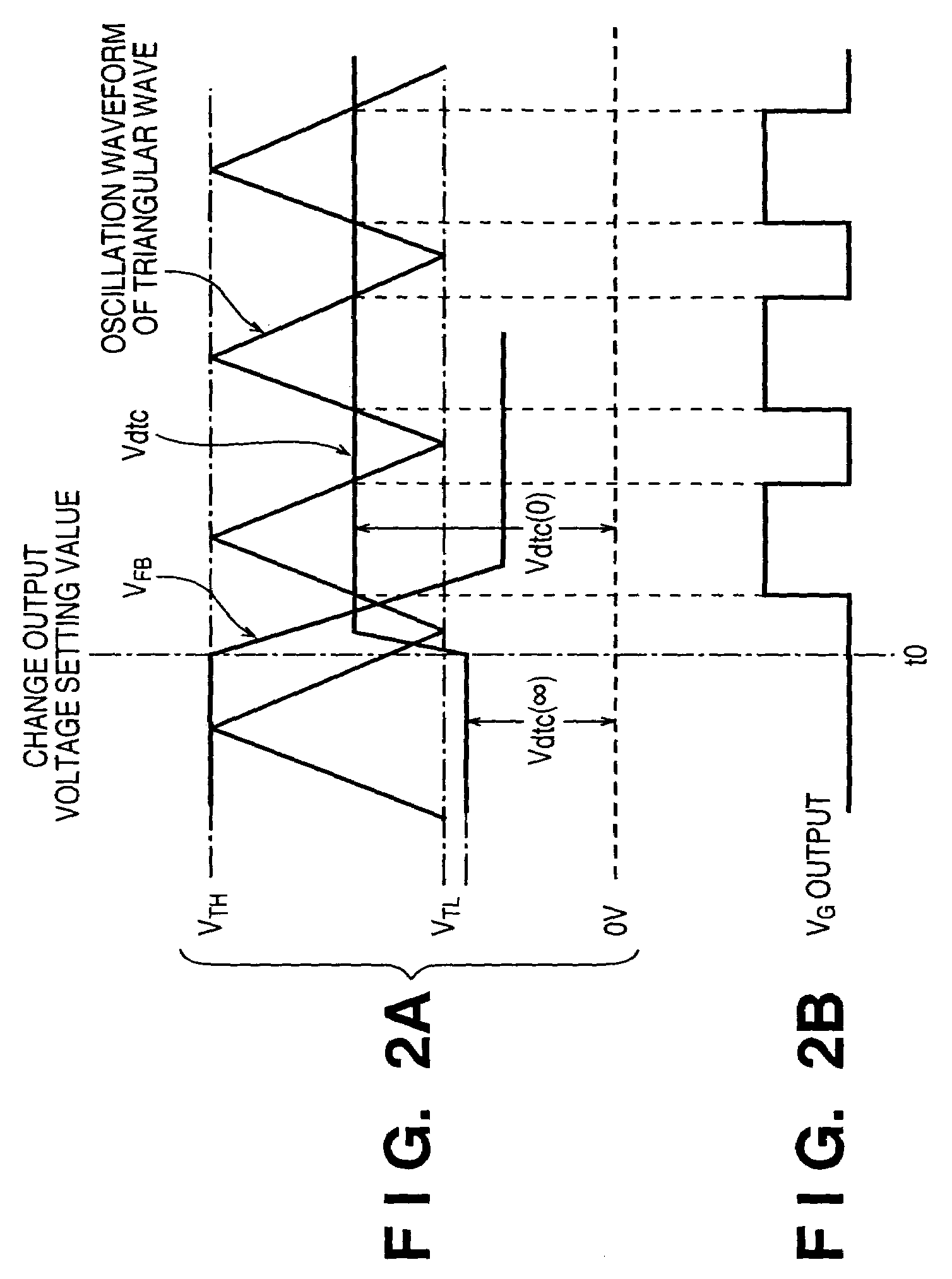
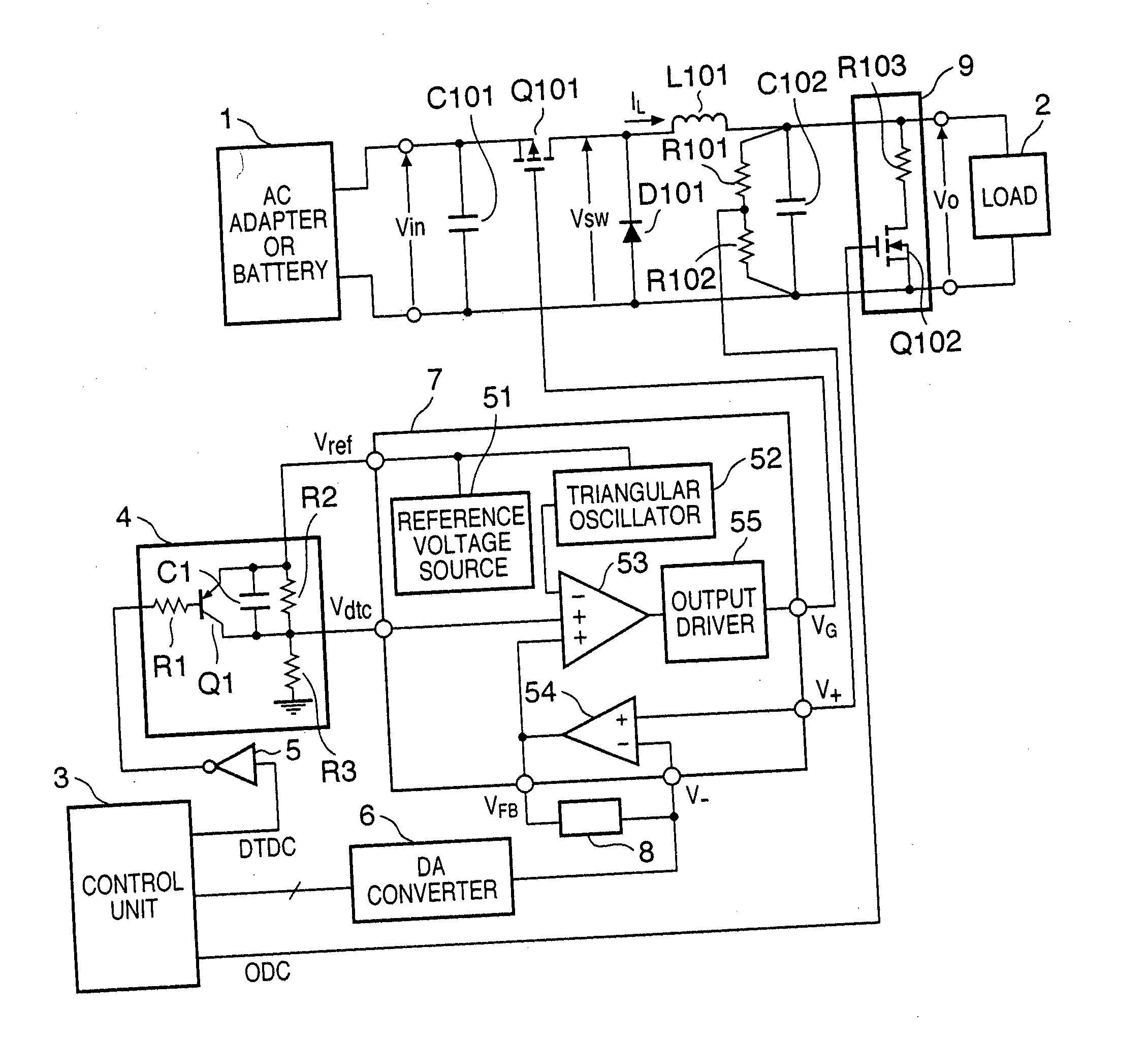
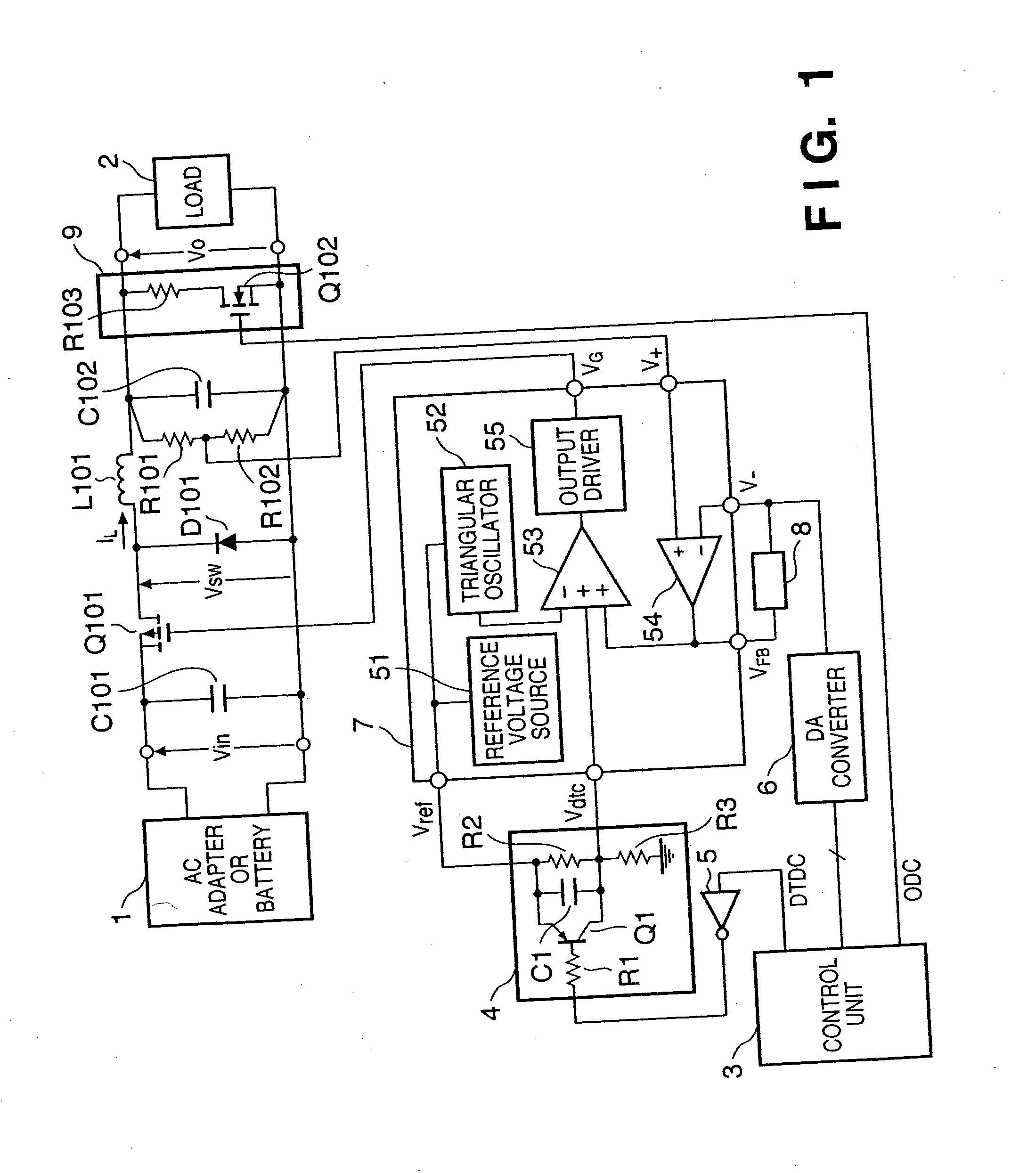
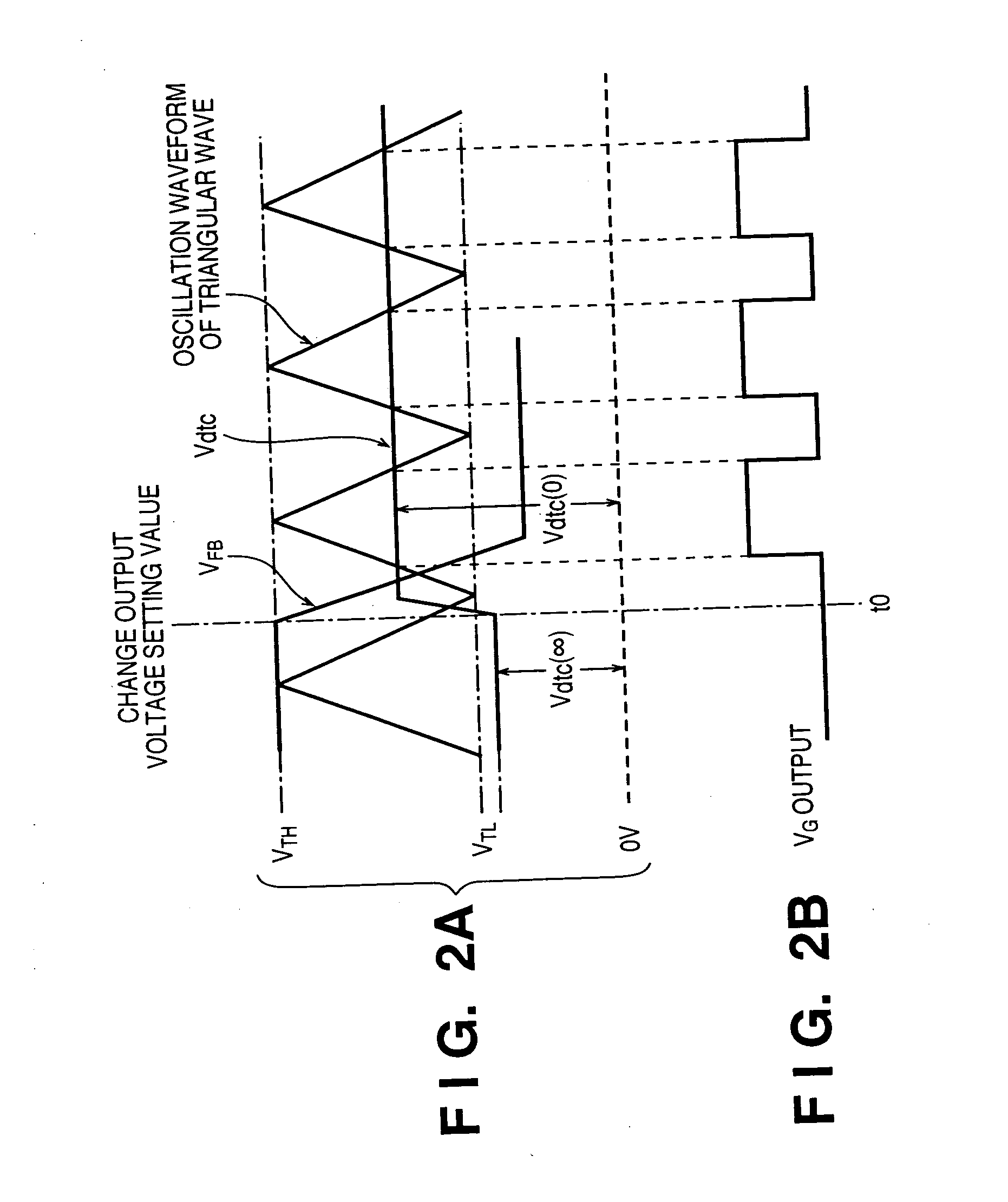
Power supply device with dead-time control and printing apparatus having the same
InactiveUS7279874B2Total current dropShorten the timeDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationControl signalEngineering
In a power supply device including a PWM-controlled DC / DC converter which changes an output voltage on the basis of a setting signal, and a control unit, the DC / DC converter includes a circuit for changing a dead-time control voltage in accordance with a control signal. A dead-time control circuit is arranged, which sets the ON duty of a PWM main switching element at a predetermined time constant in accordance with the dead-time control voltage. The control unit outputs the setting signal and control signal. In this arrangement, an input rush current generated in changing the output voltage during operation can be reduced, and the time required for causing the output voltage to reach the setting value can also be shortened.
Owner:CANON KK
Gate driving circuit with self-adaptive dead time
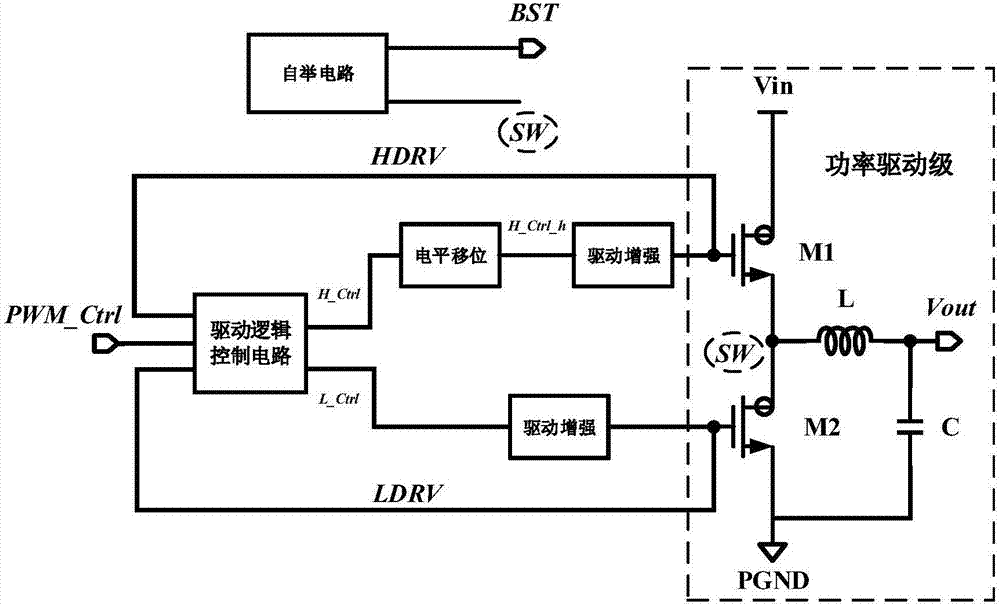
InactiveCN107359787APrevent punch-throughSimple controlPower conversion systemsControl signalControl manner
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of electronic circuits, provides a gate driving circuit with self-adaptive dead time, wherein the gate driving circuit is suitable for a switch power supply circuit. With control by a drive logic control circuit, crossed condition of high-end and low-end driving units is realized, so that the self-adaptive dead time function is realized. A level shift circuit enables a control signal generated by the drive logic control circuit to be lifted to a power rail with high-end driving; and a bootstrap circuit generates the power rail with high-end driving by means of a charge pump. A first driving enhancement circuit and a second driving enhancement circuit enhance drive control signals to be gate drive signals with ampere levels. A power drive stage of the switch power supply circuit is connected to a gate drive signal generated by a gate drive circuit and an output voltage Vout is generated. According to the invention, the dead time is adjusted adaptively based on the dimension of the power tube to avoid penetration; and the control way is simple and self-adaptive dead time control is realized with low costs; and the universality is high.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Intelligent dead time control
ActiveUS20080298101A1Convenient timeReduce power lossAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDead timeWave shape
A circuit for reducing switching losses in a synchronous rectifier of a switching stage including a high-side control transistor and a low-side synchronous transistor coupled at a switching node, the switching stage receiving an input voltage and providing a controlled output voltage at an output node. The circuit including a first circuit portion for sensing waveshape edges of a first signal at a gate terminal of the low-side synchronous transistor and a first voltage to determine a delay between the waveshape edge of the first signal and the waveshape edge of the first voltage; and a second circuit portion for calibrating the first signal and the first voltage to align the waveshape edge of the first signal and the waveshape edge of the first voltage, with an optional offset to achieve minimal power loss.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Digital self-adaptive dead-time control circuit
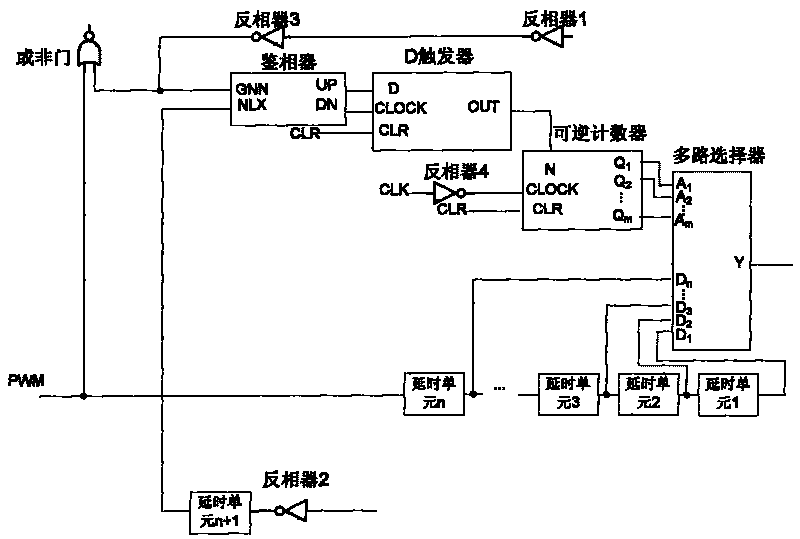
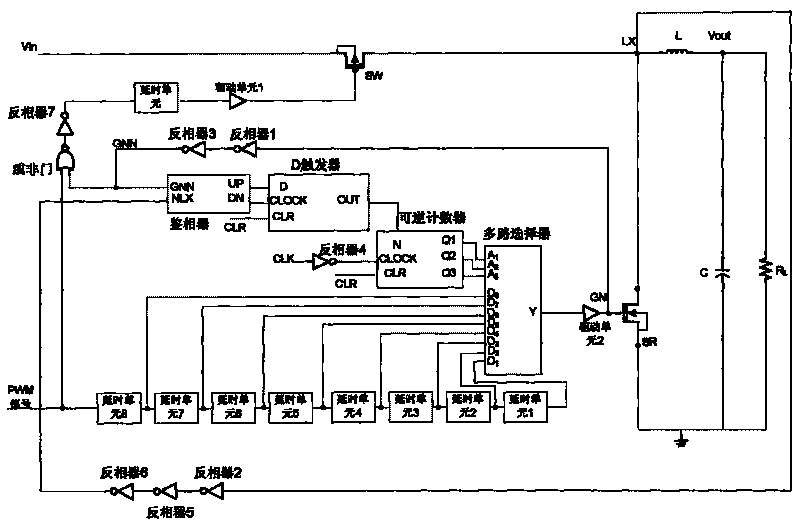
InactiveCN101694992AImprove efficiencyReliability increasing modificationsAc-dc conversion without reversalDiscriminatorDead time
The invention relates to a digital self-adaptive dead-time control circuit, belonging to the electronic technical field and relating to an integrated circuit technology and power conversion and motor-driving circuits which adopt a synchronous rectification technology. The digital self-adaptive dead-time control circuit comprises a phase discriminator, a D-trigger, a reversible counter, an n-to-1 multiple selector, (n+1) delay units, two low-flip level inverters, two common inverters and an NOR gate. The phase demodulation comparison of starting signals of an NMOS transistor SR is continued to control the reversible counter to carry out add-subtract count, so as to adjust a delay time unit and control the multiple selector to start the NMOS transistor SR in a suitable clock to further realize the self-adaptive adjustment of dead time. The invention not only avoids the simultaneous conduction of two power tubes caused by overshot dead time, but also avoids the conduction of a body diode caused by overlong dead time, thereby decreasing additional loss caused by the unsuitably set dead time and improving the whole efficiency of the power converter.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Synchronous rectifying DC-DC converter
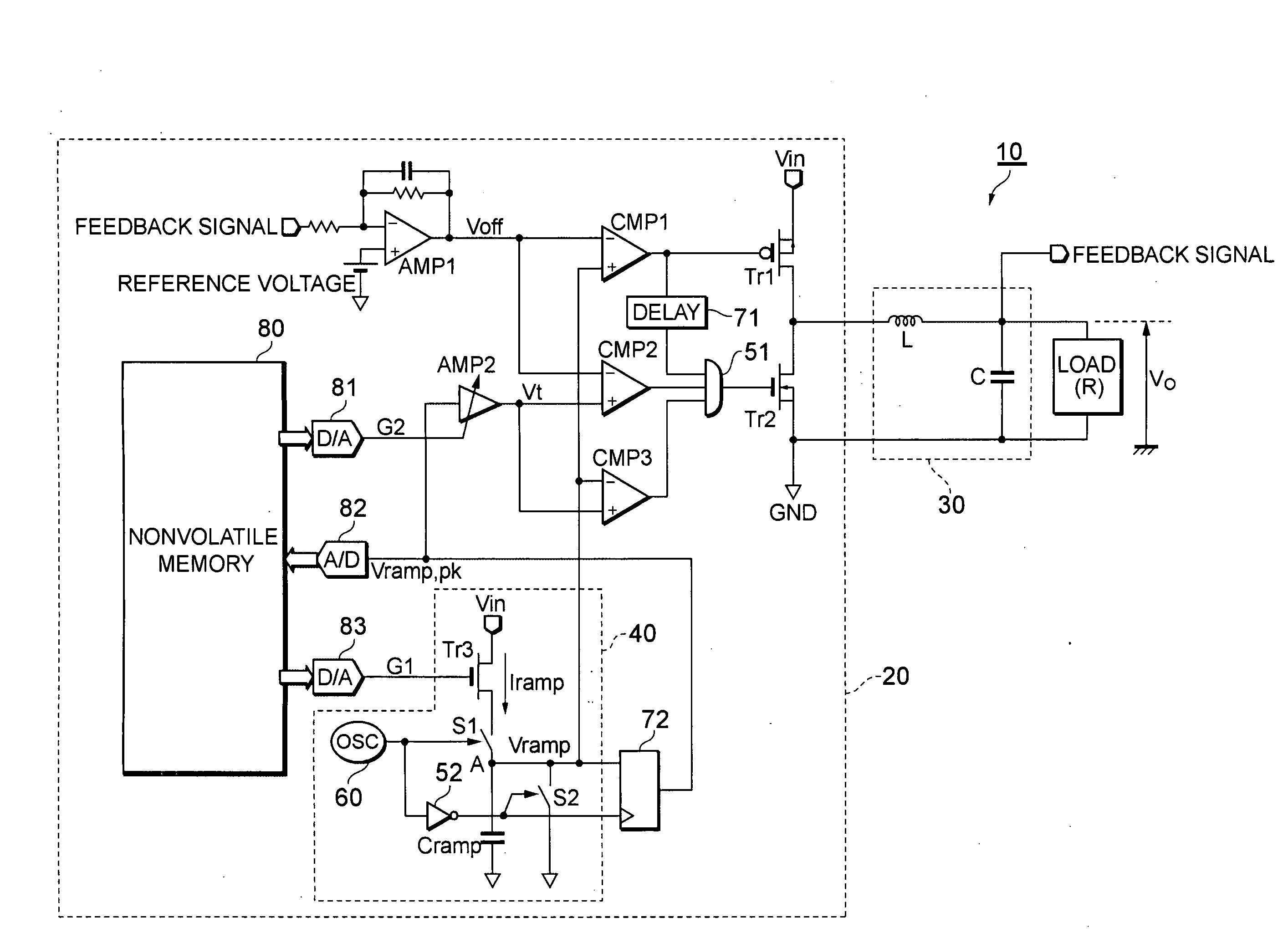
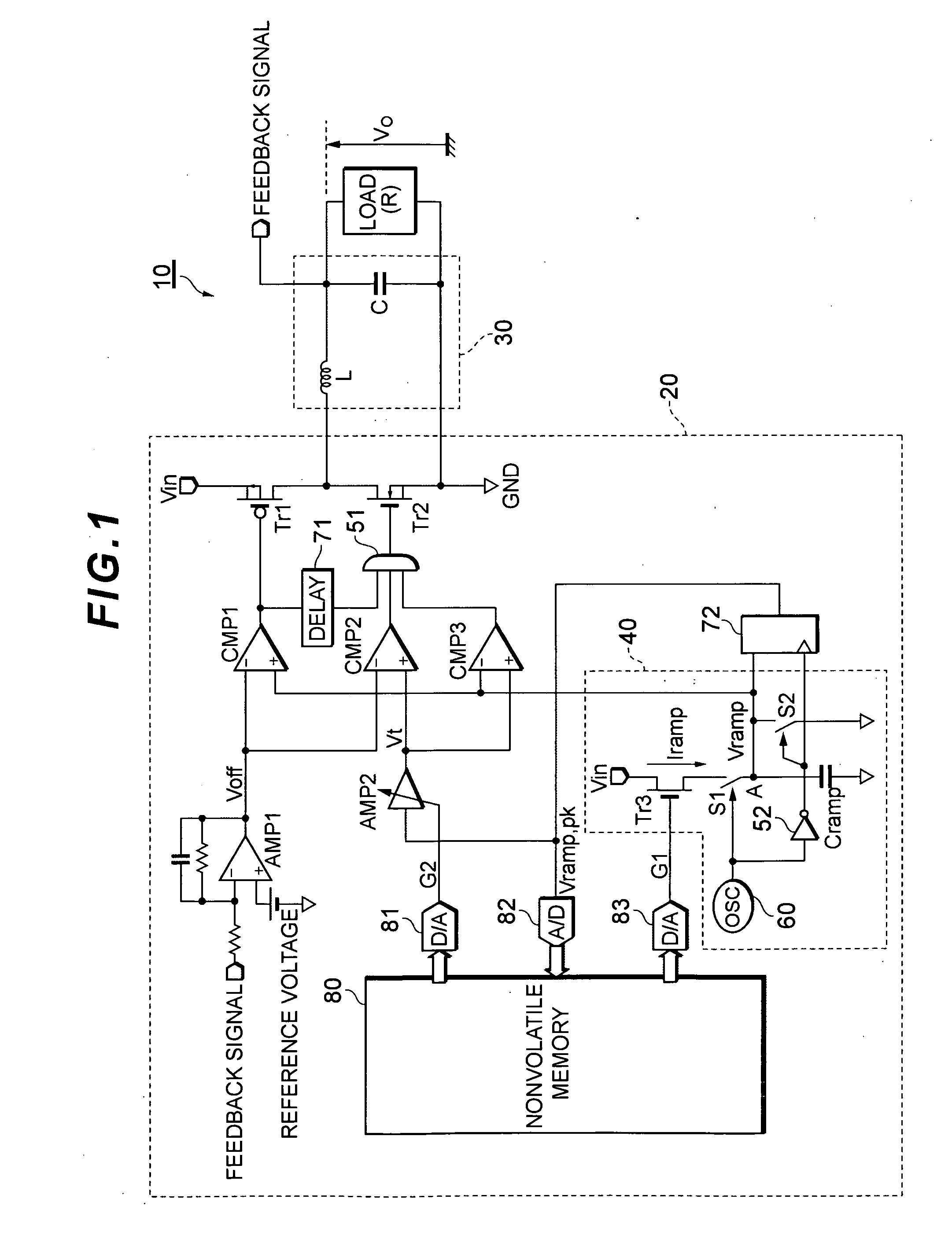
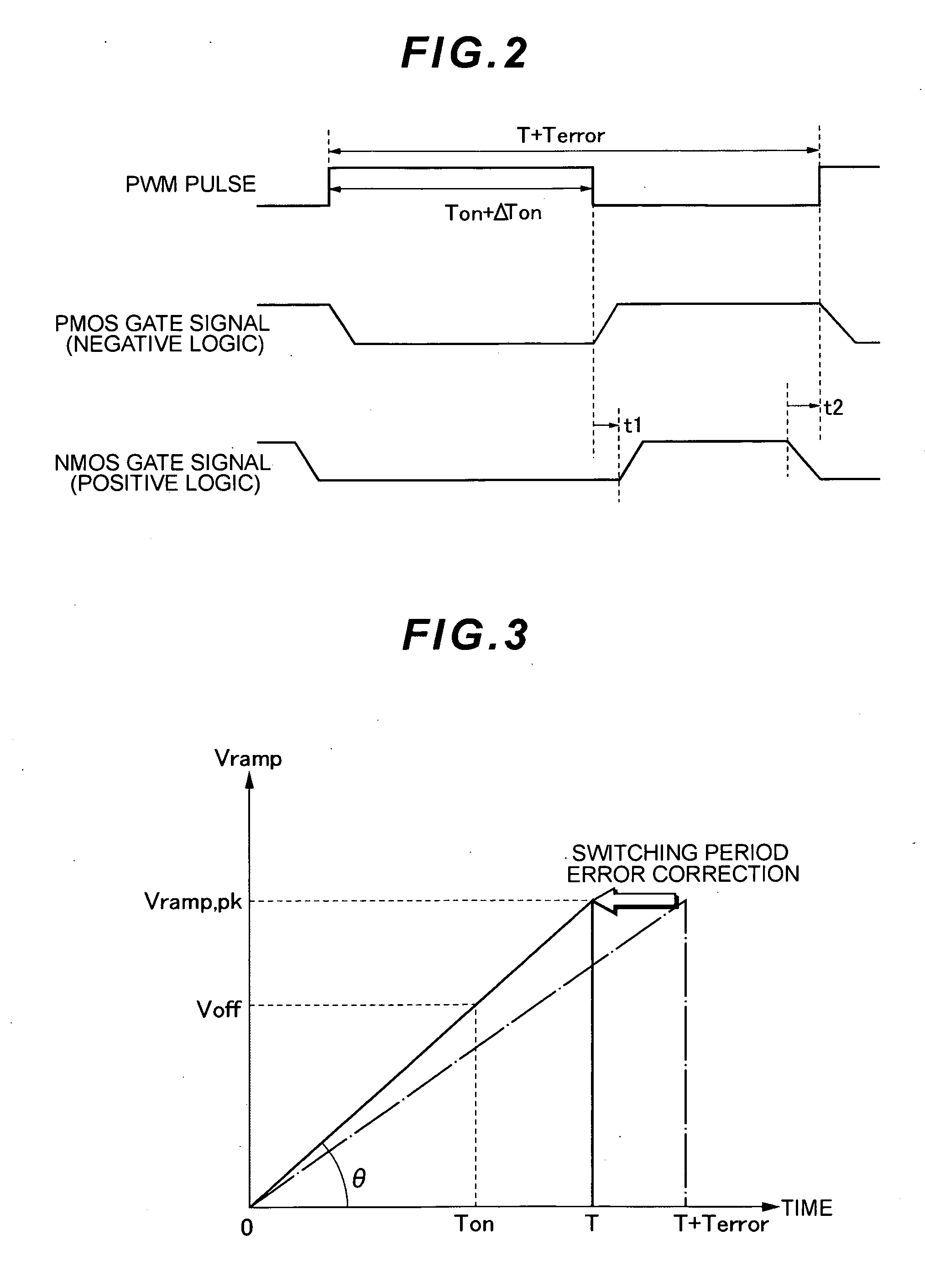
ActiveUS20090237059A1Adaptively prevented from being turnedShorten convergence timeEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterDead time control
There is provided a dead time control method capable of recognizing a critical situation in which a commutating transistor cannot be turned on because of a temporary variation in an output voltage of a synchronous rectifying DC-DC converter and adaptively preventing the commutating transistor from being turned on. The synchronous rectifying DC-DC converter compares an output Voff of an error amplifier with a voltage Vt obtained by multiplying the peak voltage of a ramp by G2. When Voff becomes greater than or equal to Vt, the converter determines that dead time is insufficient to control the switching of the commutating transistor and prevents the commutating transistor from being turned on.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
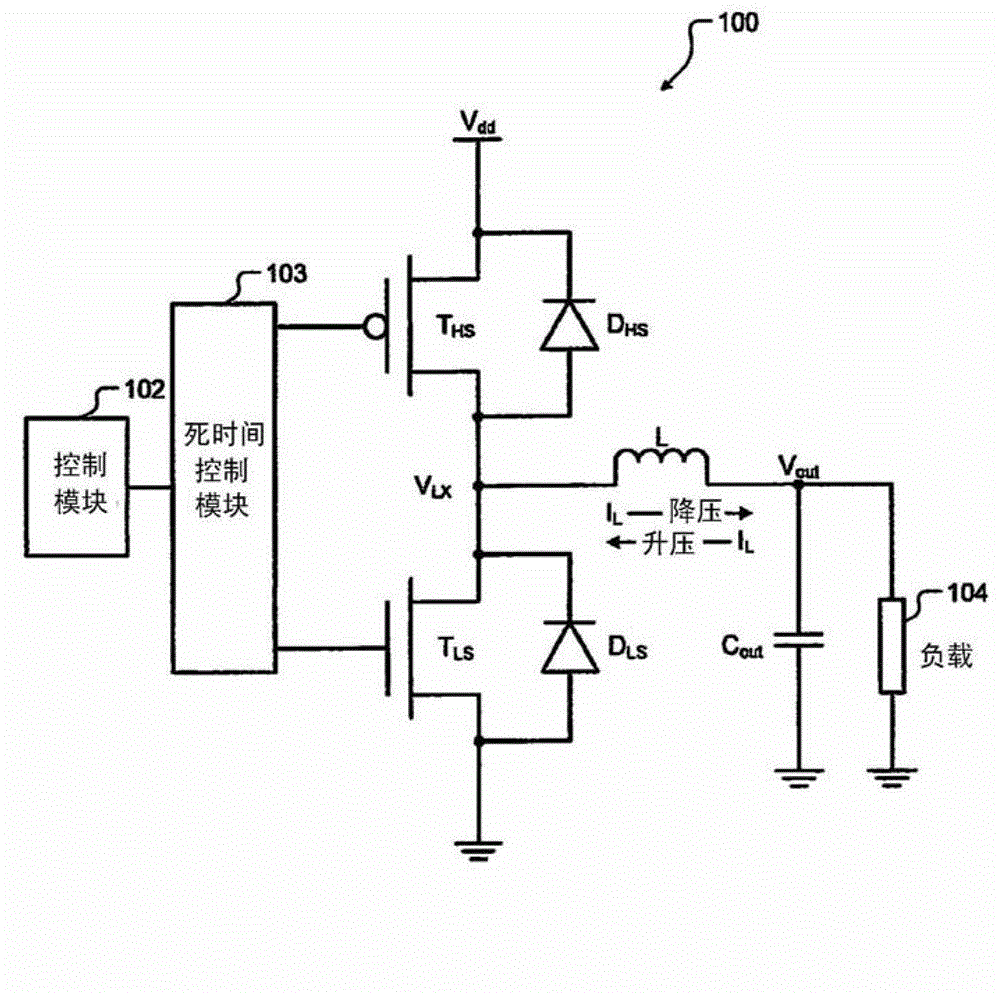
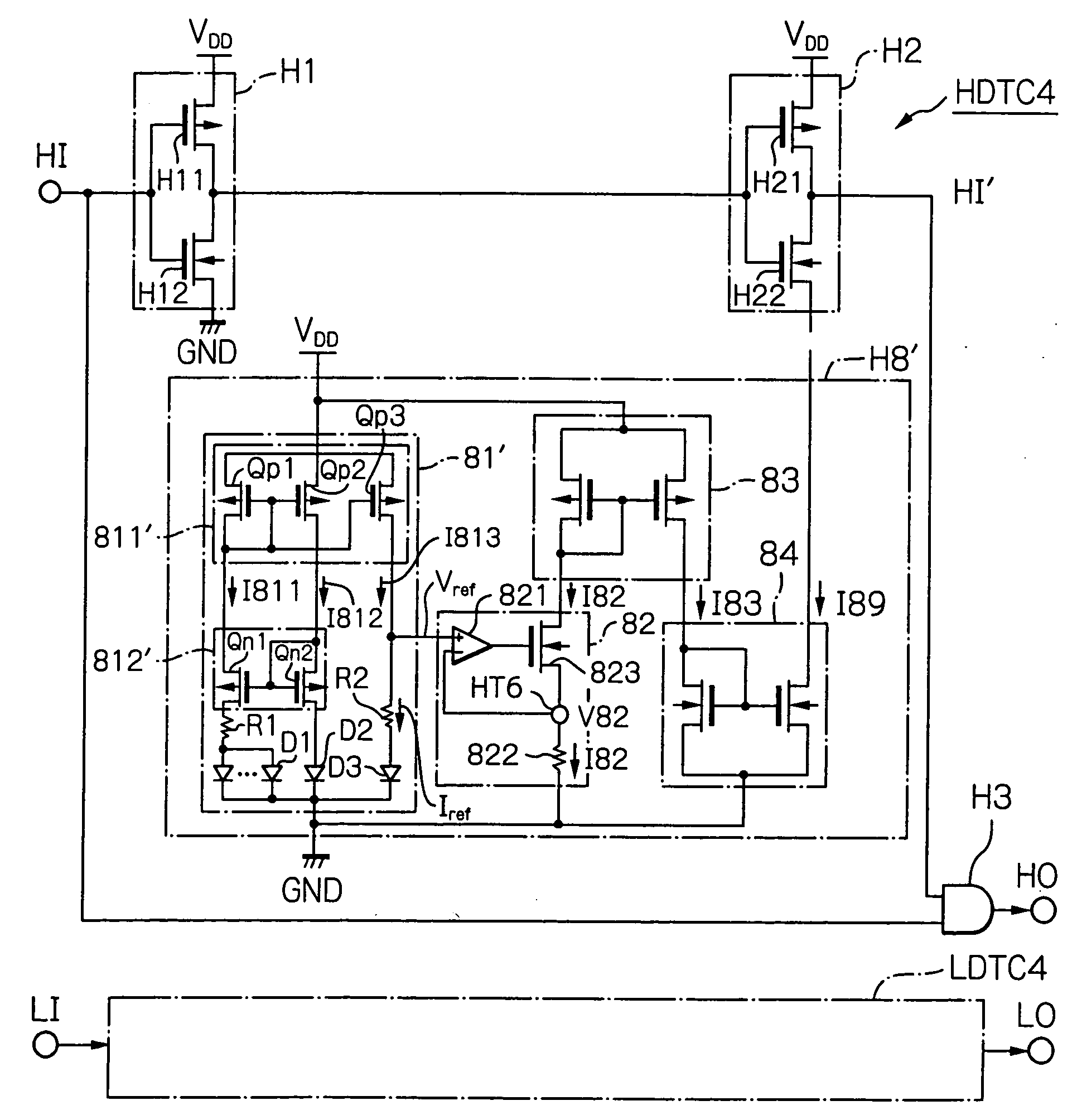
Dead time control circuit capable of adjusting temperature characteristics of dead time
In a dead time control circuit, a delay circuit is connected to an input terminal and adapted to delay signals therethrough by a delay time corresponding to a dead time. A logic circuit has a first input connected via the delay circuit to the input terminal, a second input connected directly to the input terminal, and an output connected to an output terminal. The dead time having adjustable temperature characteristics.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Dual-mode synchronous rectification control circuit for DCM and CCM
ActiveCN107346943AAchieve high efficiencyAvoid accidental openingEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionDual modeDead time control
The invention provides a dual-mode synchronous rectification control circuit for a DCM and a CCM, belonging to the technical field of power management. The structure of the circuit is simple, the rectification conduction loss can be effectively reduced, and high efficiency of synchronous rectification is realized. Minimum dead time control is realized by a second negative level detector. A turn-off time shielding module prevents the wrong turn-on of a synchronous rectifier tube M2, and a turn-on time shielding module prevents the wrong turn-off of the synchronous rectifier tube M2. Drain electrodes of LDMOS and DEMOS high voltage devices are used by a first sampling end to bear high voltage, the clamping of a drain end VD of the synchronous rectifier tube M2 by a Zener is avoided, and the current leakage to the ground by the drain end VD of the synchronous rectifier tube M2 is prevented. The high efficiency of synchronous rectification is realized by the above measures together. In addition, a synchronous control module is introduced, and the synchronous rectification in a current continuous mode CCM is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Switched converter with variable peak current and variable off-time control
ActiveUS7528587B2Avoid deactivationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionMaximum levelLow load
A converter coupled to a DC voltage input and connectable to a load, includes a signal responsive switch coupled between a first circuit point and a second circuit point. In lieu of burst mode operation during low load conditions, the peak switch current is varied directly with load condition and a switch deactivation interval is varied inversely with load condition. The switch deactivation level is within a maximum level to avoid audio frequency band interference, while maintaining high efficiency operation throughout the load range.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
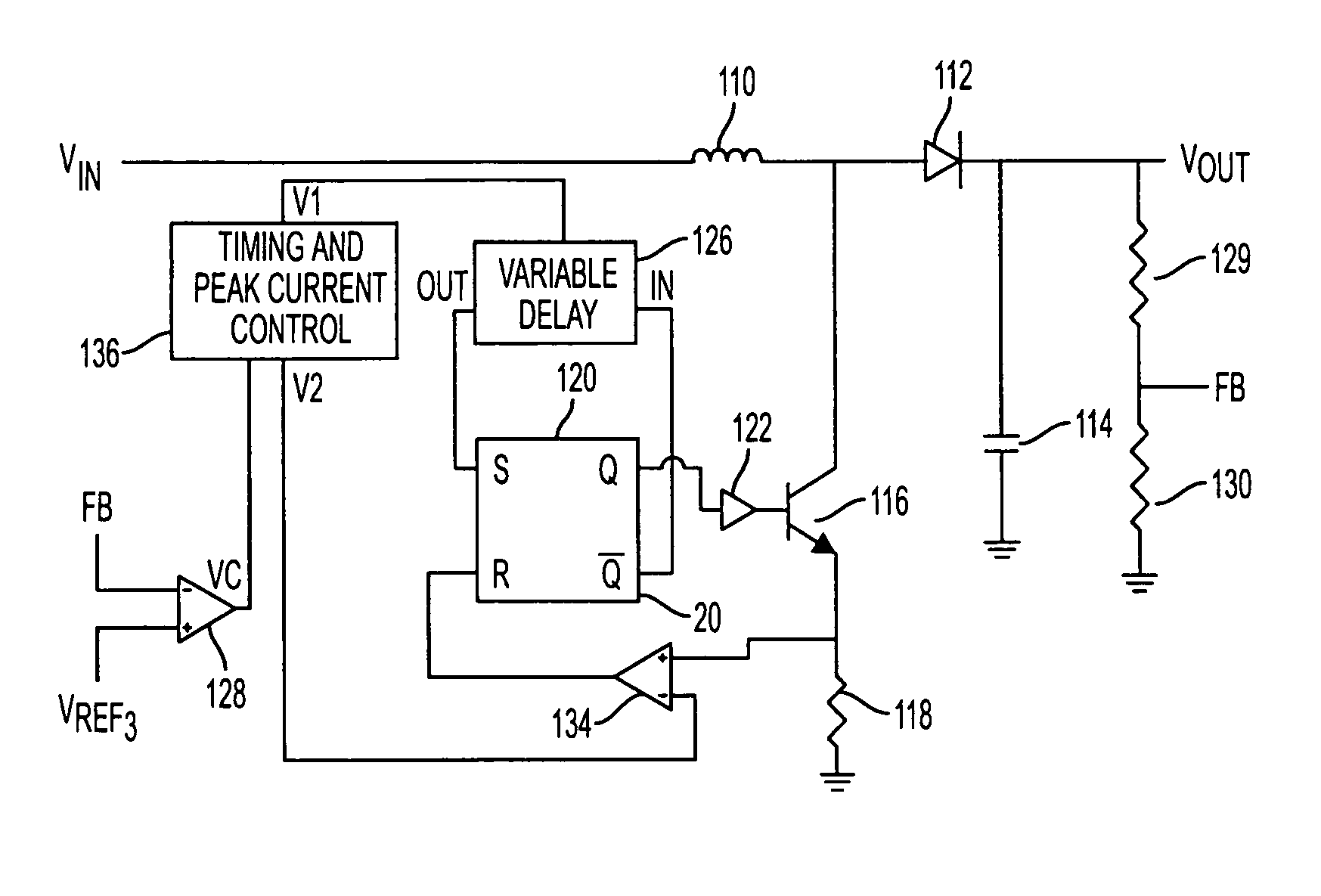
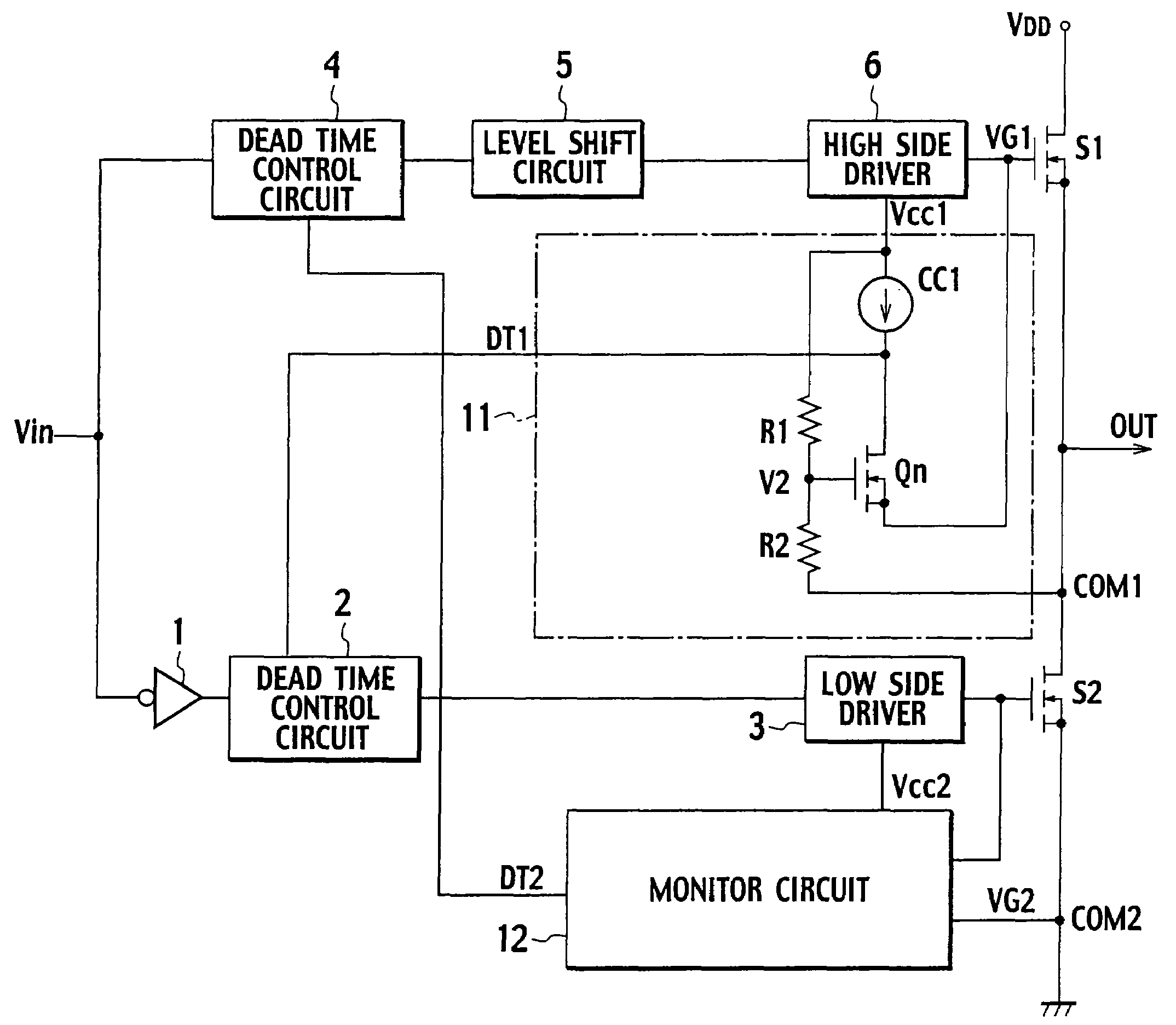
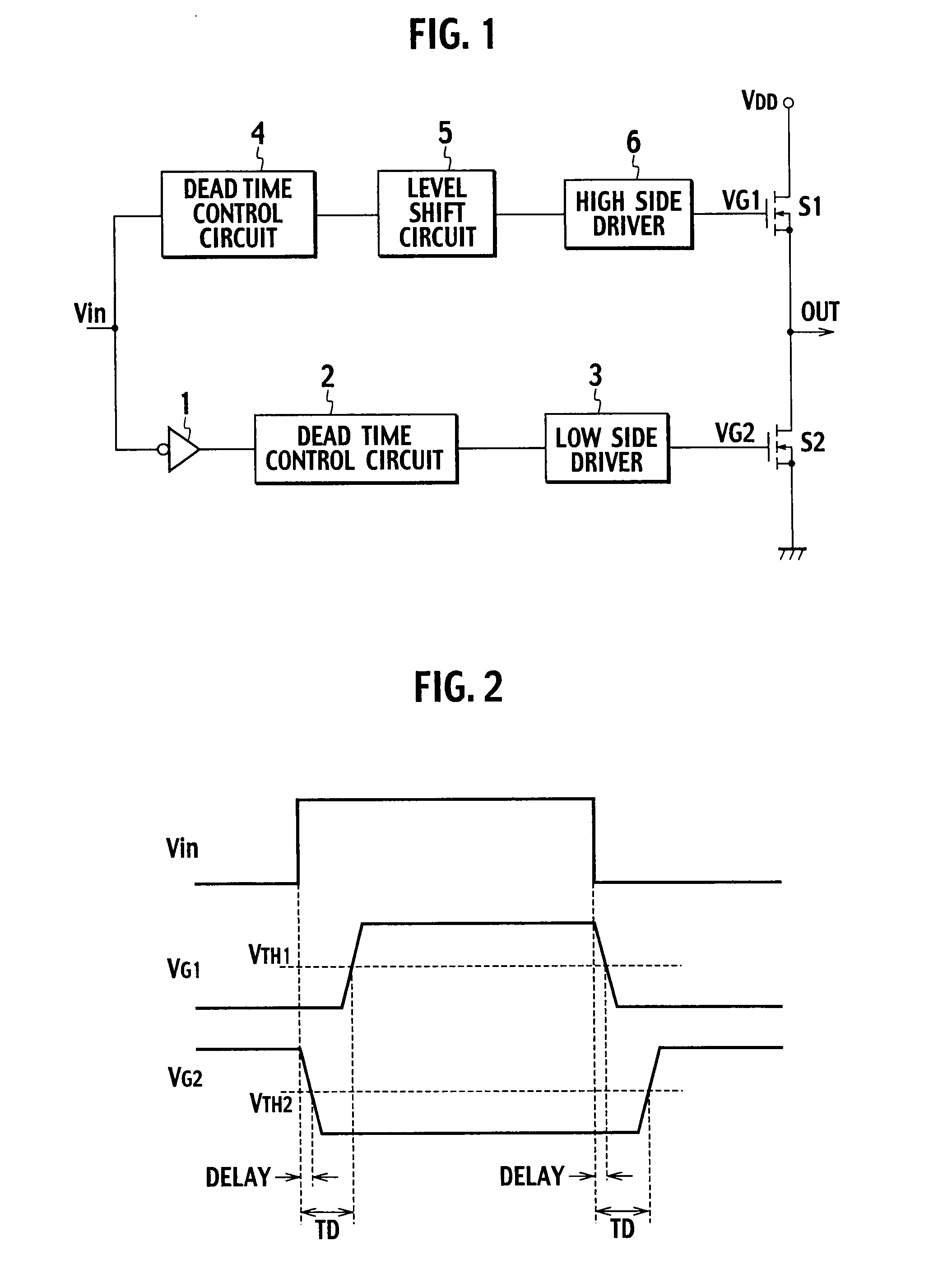
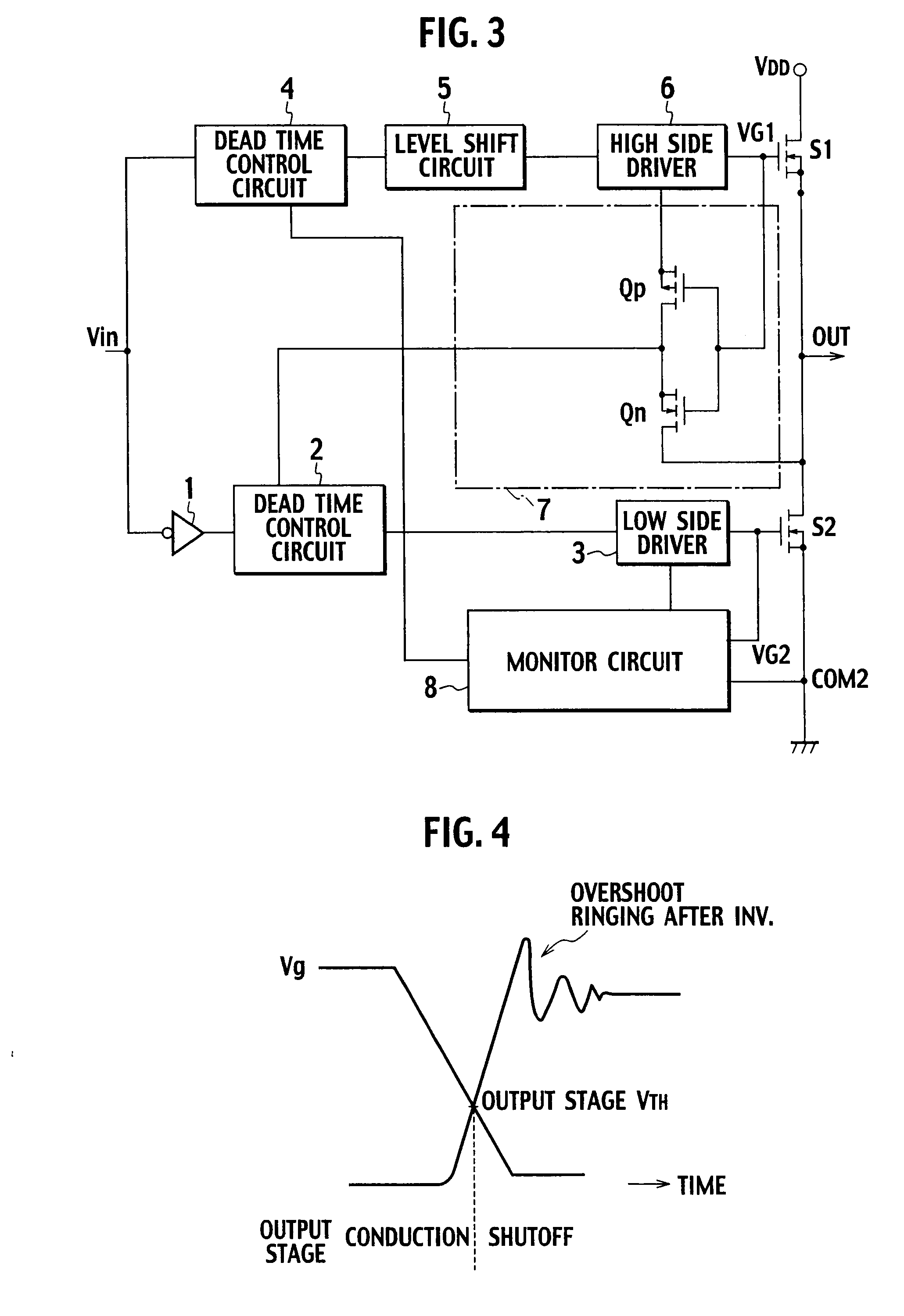
Gate drive circuit
InactiveUS20080246519A1Simple structurePulse automatic controlElectronic switchingControl signalCircuit delay
A gate drive circuit including dead time control circuits delaying on periods of switching elements S1, S2 based on a control signal; driving circuits; and monitor circuits. Each of the monitor circuits includes a current source and an N-type FET in which the source is connected to the gate of one of the switching elements; the drain is connected to the current source; and a predetermined voltage is applied to the gate. When an off state of one of the switching elements is detected, the N-type FET Qn outputs an off signal to the dead time control circuit on the other switching element side. Based on the off signal, the dead time control circuit on the other switching element side terminates an operation of delaying the on period of the other switching element.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
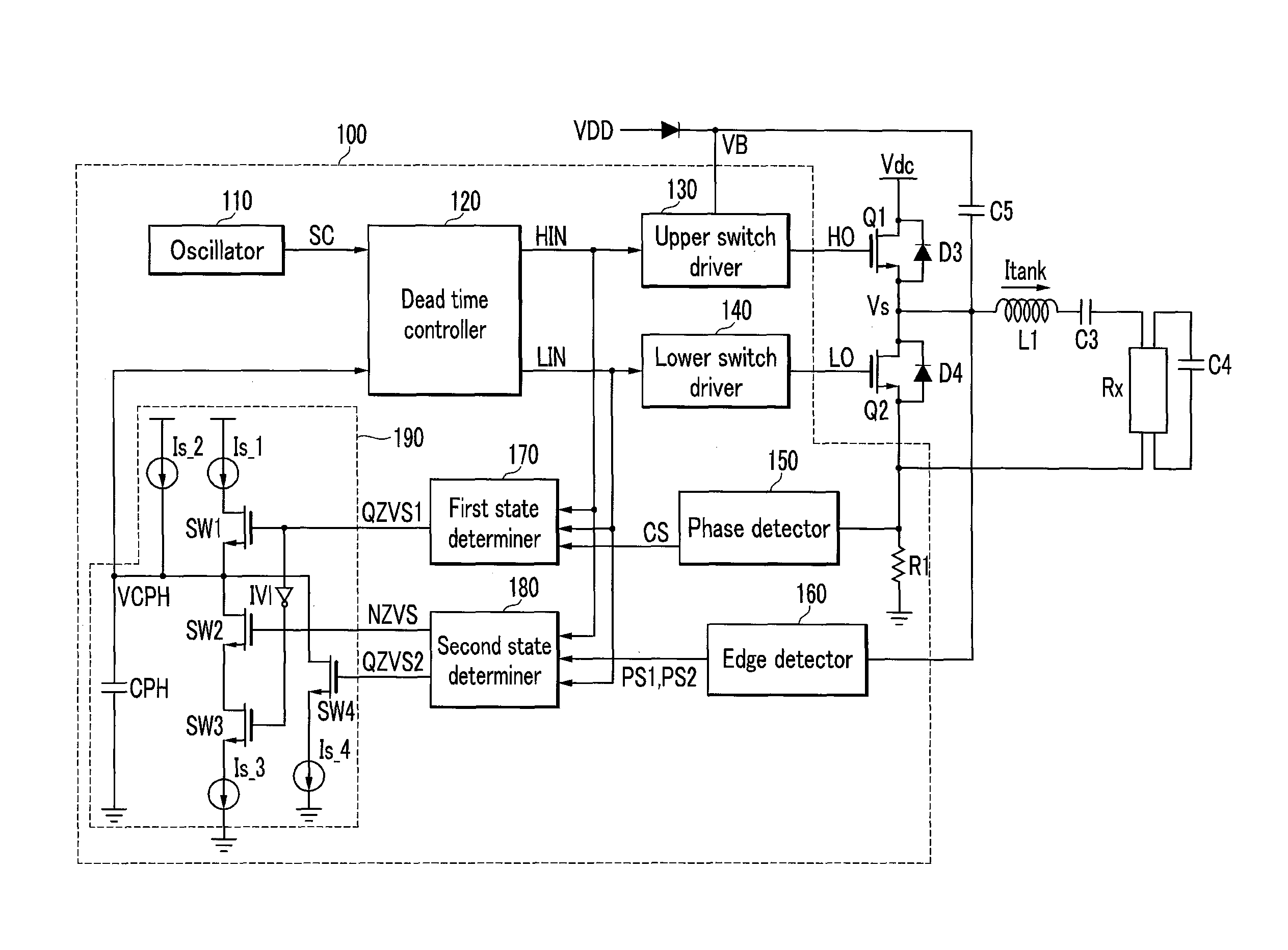
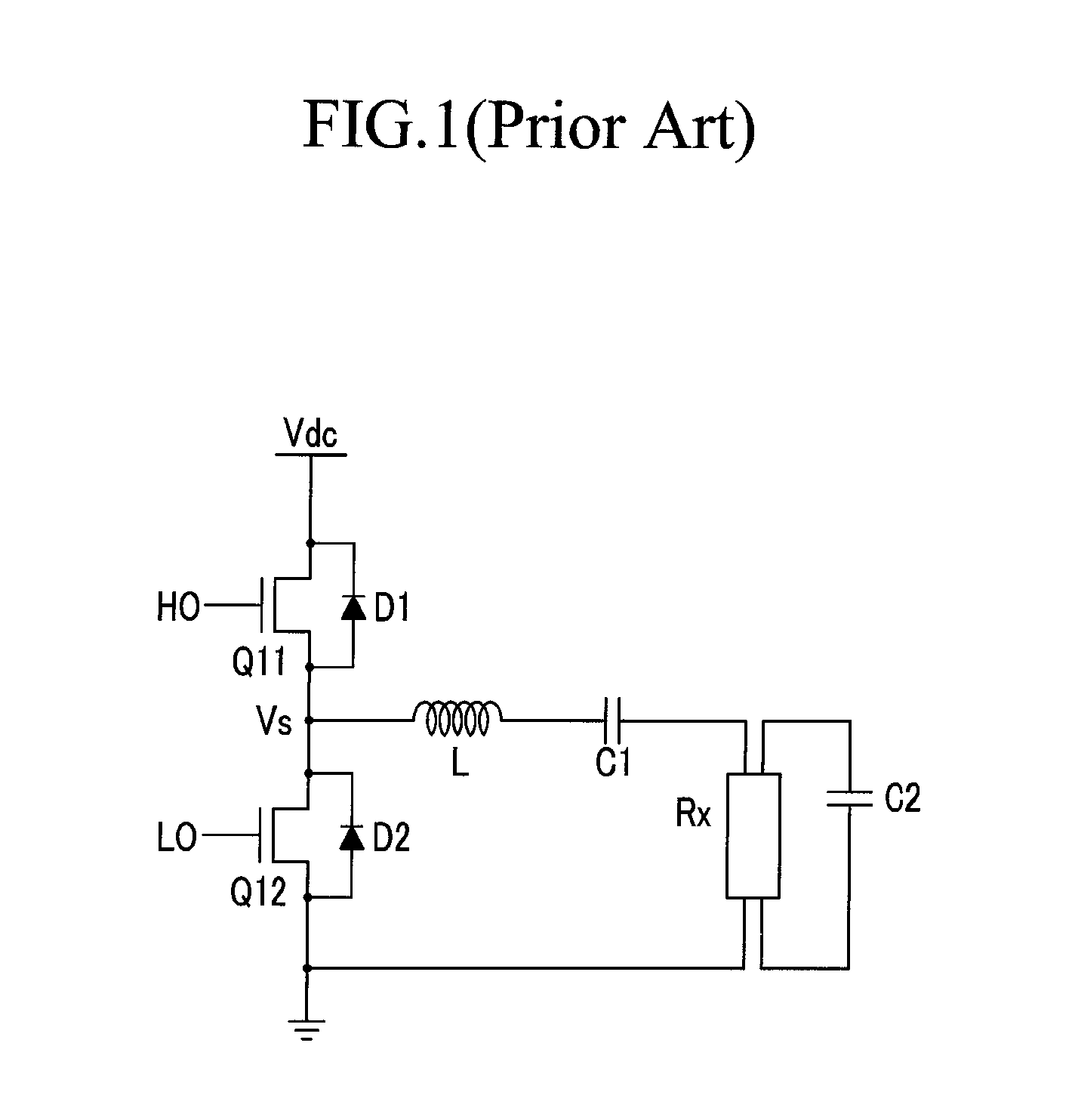
Switch driving circuit and switch driving method
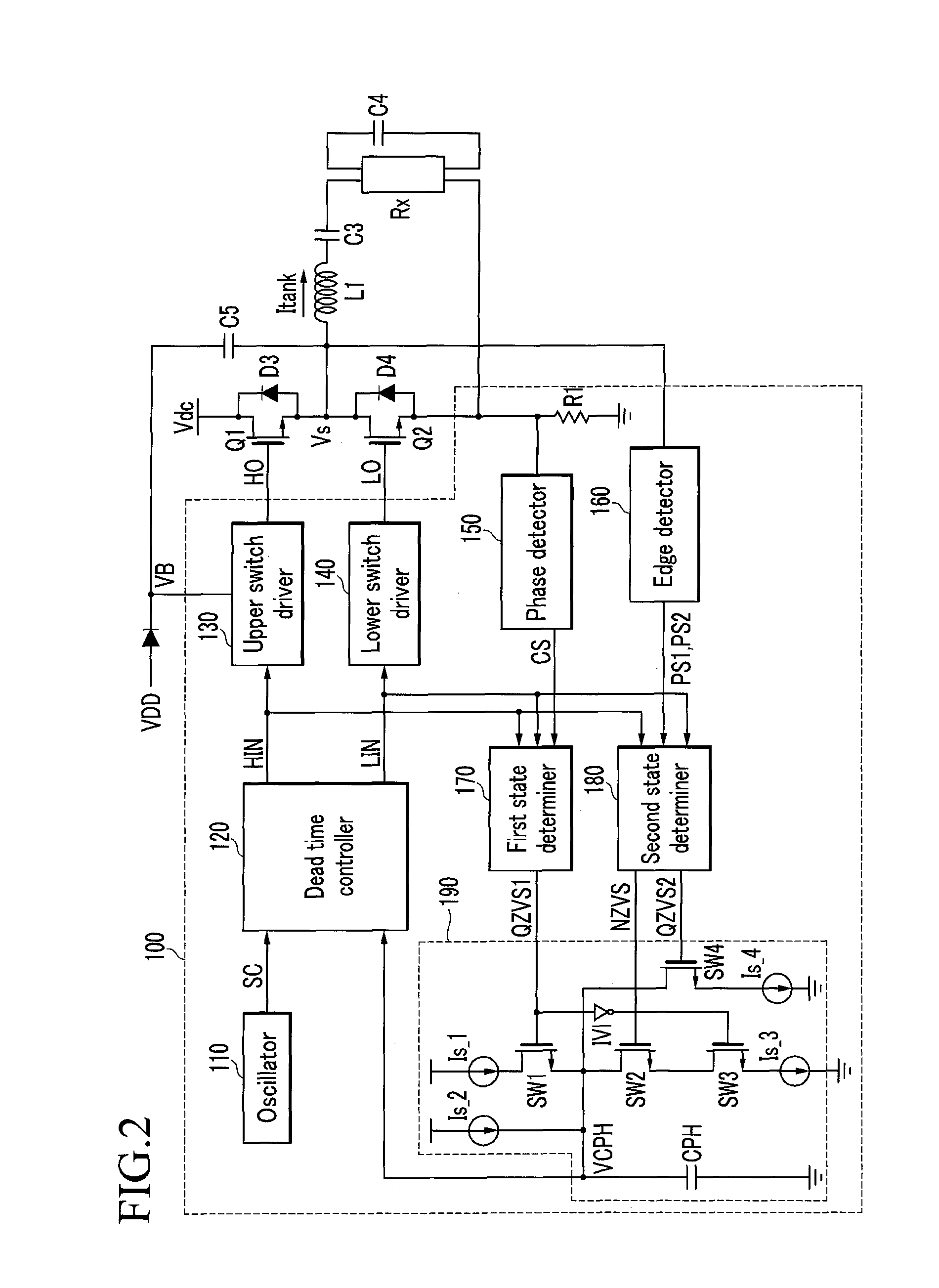
ActiveUS8737101B2Avoid hard switchingReduce dead timeEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPhase detectorDead time
The present invention relates to a switch driving circuit and a driving method thereof that are capable of preventing hard switching. The present invention includes: a dead time controller generating an high-side switching driver controlling signal and a low-side switching driver controlling signal controlling the switching operation of the high-side switch and the low-side switch according to a dead time controlling signal; and a phase detector detecting a phase of a resonance current flowing into the second power voltage terminal to generate a phase information signal, wherein one of the high-side switch driver controlling signal and a signal corresponding thereto, and the phase information signal are compared, and if the turn-on time of the high-side switch is later than the phase change of the resonance current, the dead time is controlled for the turn-on time of the high-side switch to advance the phase change of the resonance current.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Power supply device and printing apparatus having the same
InactiveUS20050135132A1Total current dropShorten the timeDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationControl signalEngineering
In a power supply device including a PWM-controlled DC / DC converter which changes an output voltage on the basis of a setting signal, and a control unit, the DC / DC converter includes a circuit for changing a dead-time control voltage in accordance with a control signal. A dead-time control circuit is arranged, which sets the ON duty of a PWM main switching element at a predetermined time constant in accordance with the dead-time control voltage. The control unit outputs the setting signal and control signal. In this arrangement, an input rush current generated in changing the output voltage during operation can be reduced, and the time required for causing the output voltage to reach the setting value can also be shortened.
Owner:CANON KK
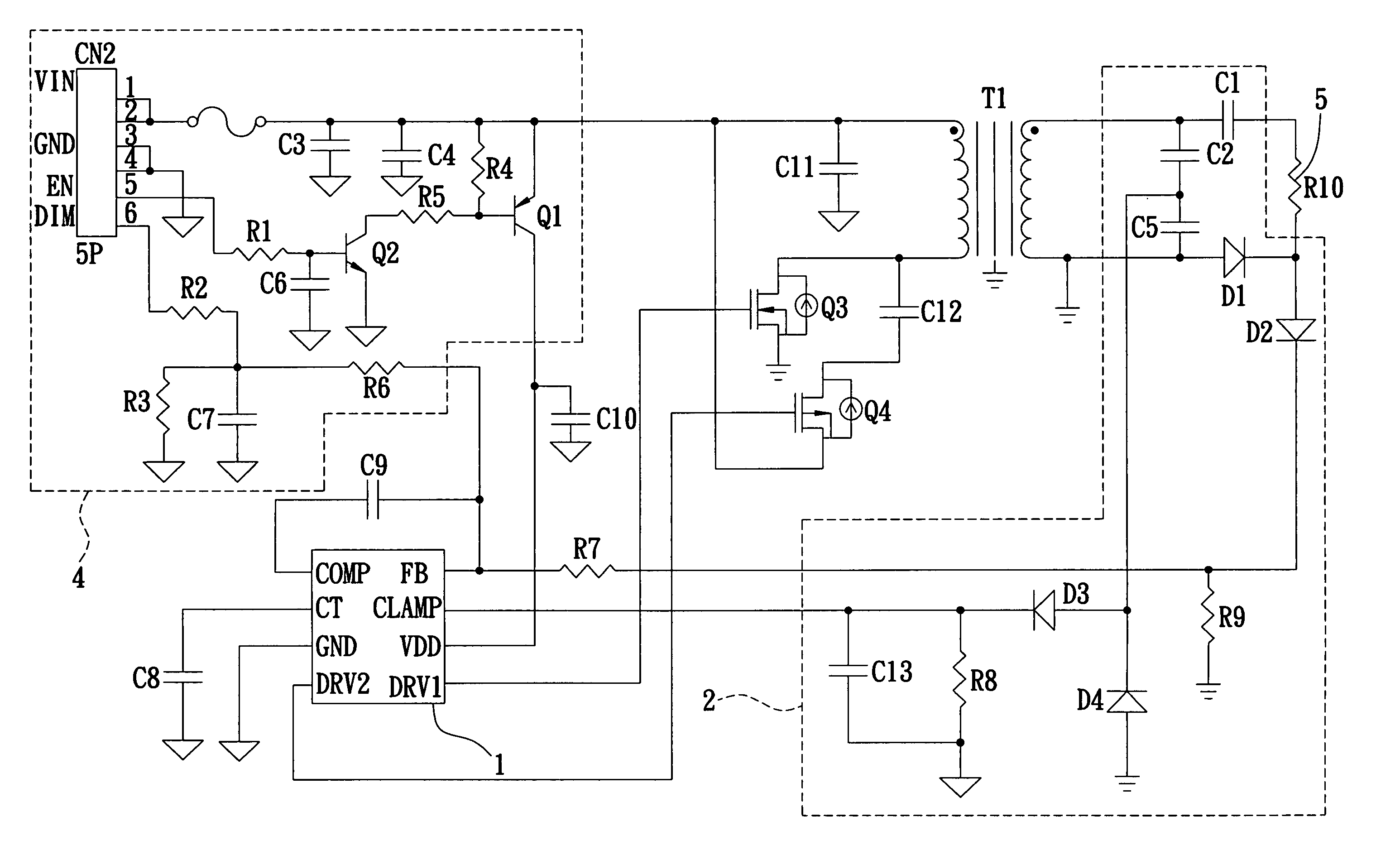
Half-bridge-type control signal generating circuit and method thereof
InactiveUS6995989B1Prevent burnoutExtend lamp lifeConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protective circuit arrangementsControl signalElectronic switch
A half-bridge-type control signal generating circuit outputs two control signals to control directly and drive switching actions of two electronic switches of a half-bridge-type circuit architecture. The half-bridge-type control signal generating circuit comprises an AND-gate logic unit, a NAND-gate logic unit, a circuit protection unit, a function generator, a clock generator, a soft boot unit connected to the clock generator, a sample and hold unit, a first comparator connected to the soft boot unit and the function generator, an OR-gate logic unit connected to the soft boot unit, the first comparator, the AND-gate logic unit and the NAND-gate logic unit, a second comparator connected to the sample and hold unit, the function generator, the AND-gate logic unit and the NAND-gate logic unit, and a dead time control unit connected to the function generator, the AND-gate logic unit and the NAND-gate logic unit.
Owner:NIKO SEMICON
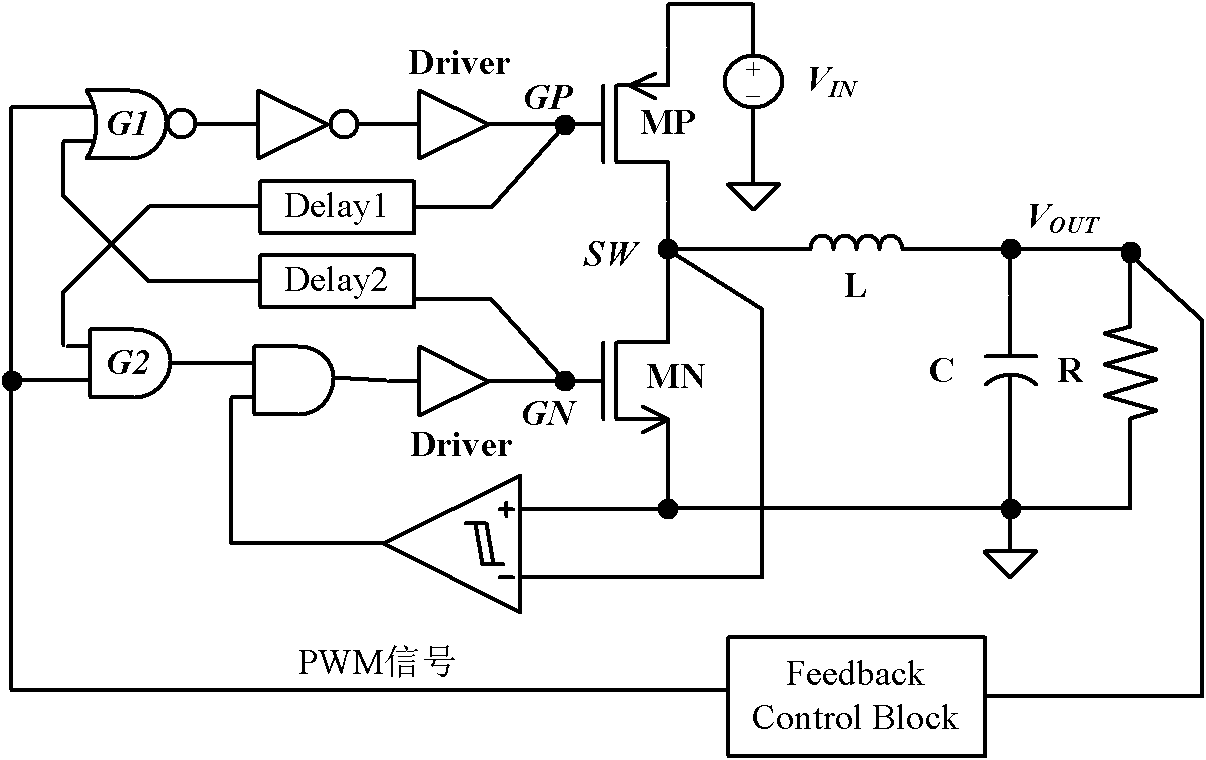
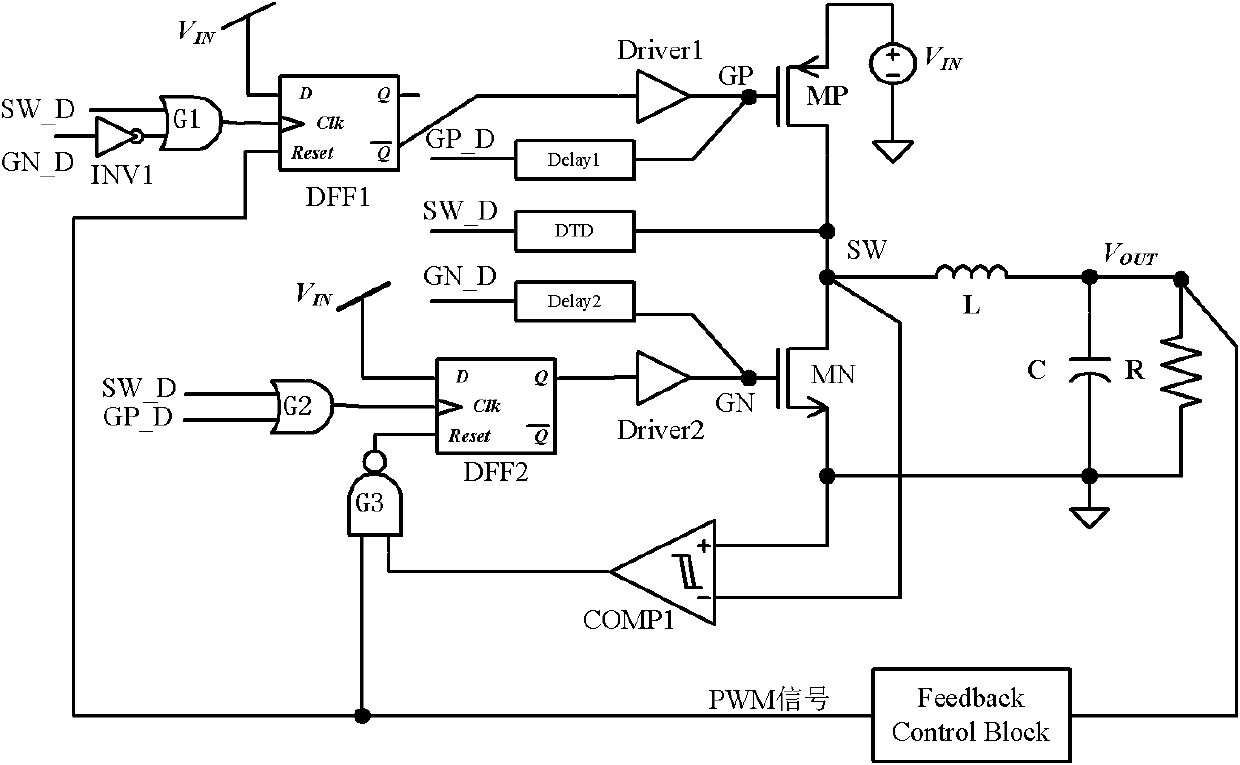
Self-adaptive dead time control
The invention relates to self-adaptive dead time control. A DC-DC converter comprises a first transistor and a second transistor which are in series connection between a power voltage and the ground and are driven by PWM pulses. A connecting point between the two transistors is connected to an inductor that is in series connection with a load. A first timing module is used for determining a first time difference between a first edge of a first signal at the connecting point and a first edge of a second signal at a control terminal of the first transistor. A second timing module is used for determining a second time difference between a second edge of the first signal and a second edge of the second signal. The first edge and the second edge of the second signal respectively corresponds to a first edge and a second edge of one pulse among the PWM pulses. A delay module is used for delaying the first edge and the second edge of the second signal respectively based on the first time difference and the second time difference.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
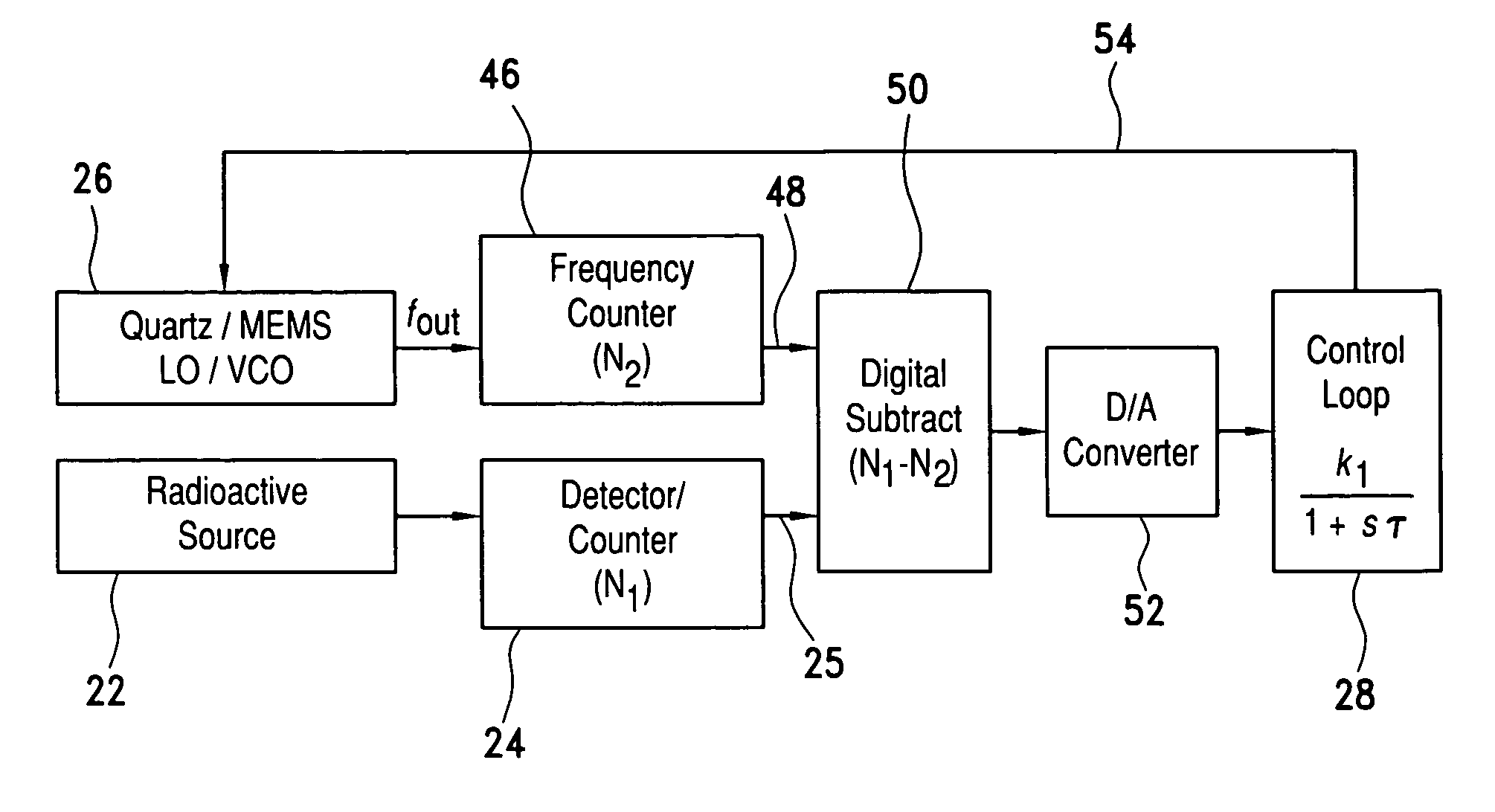
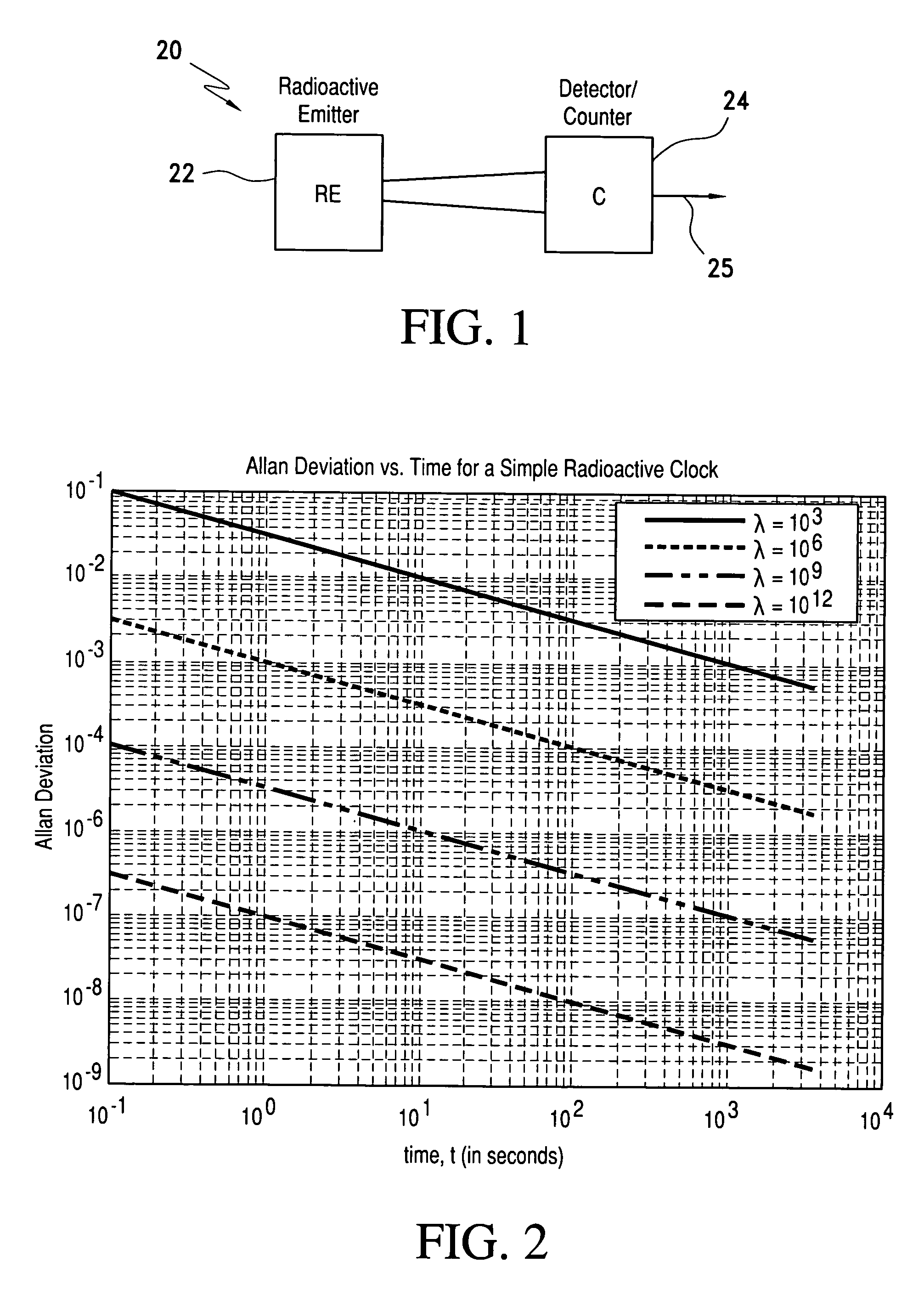
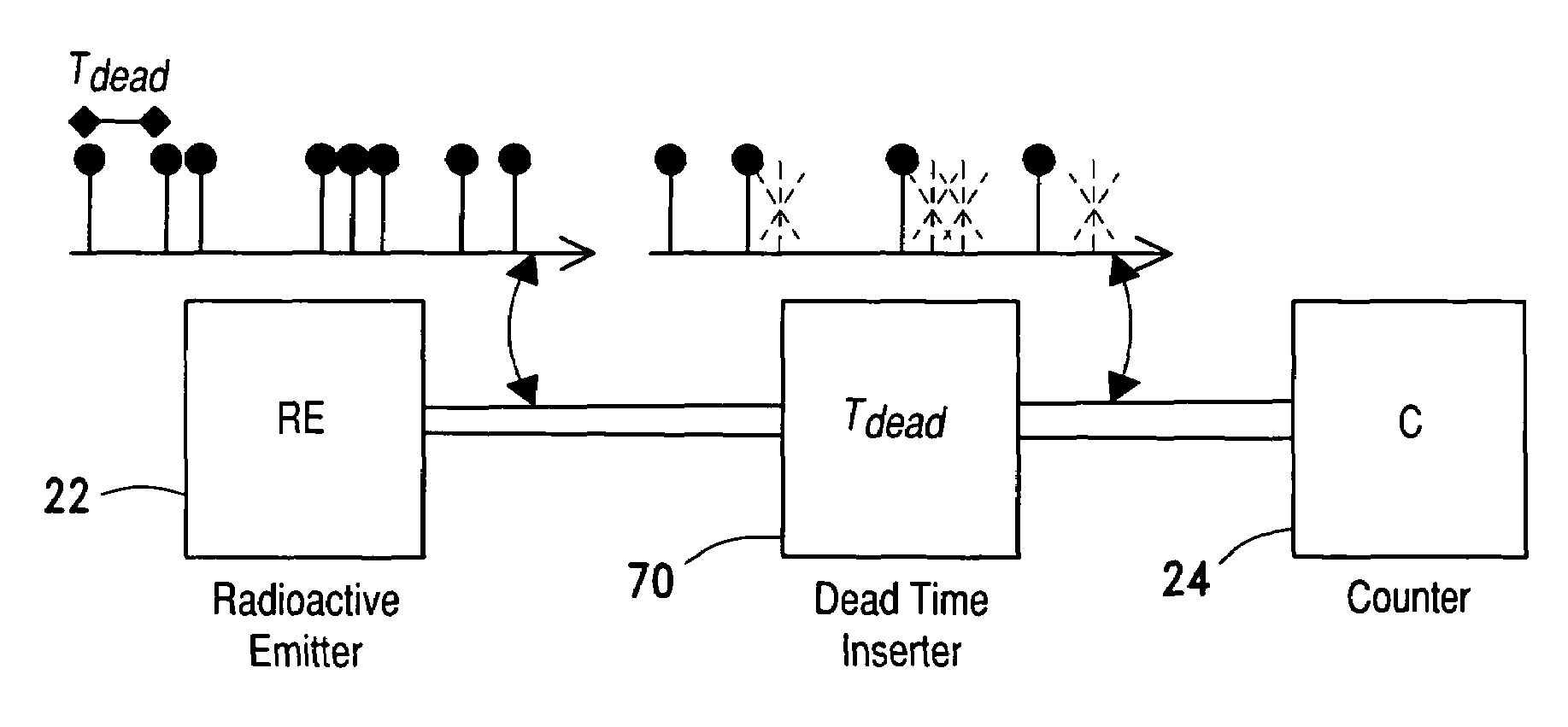
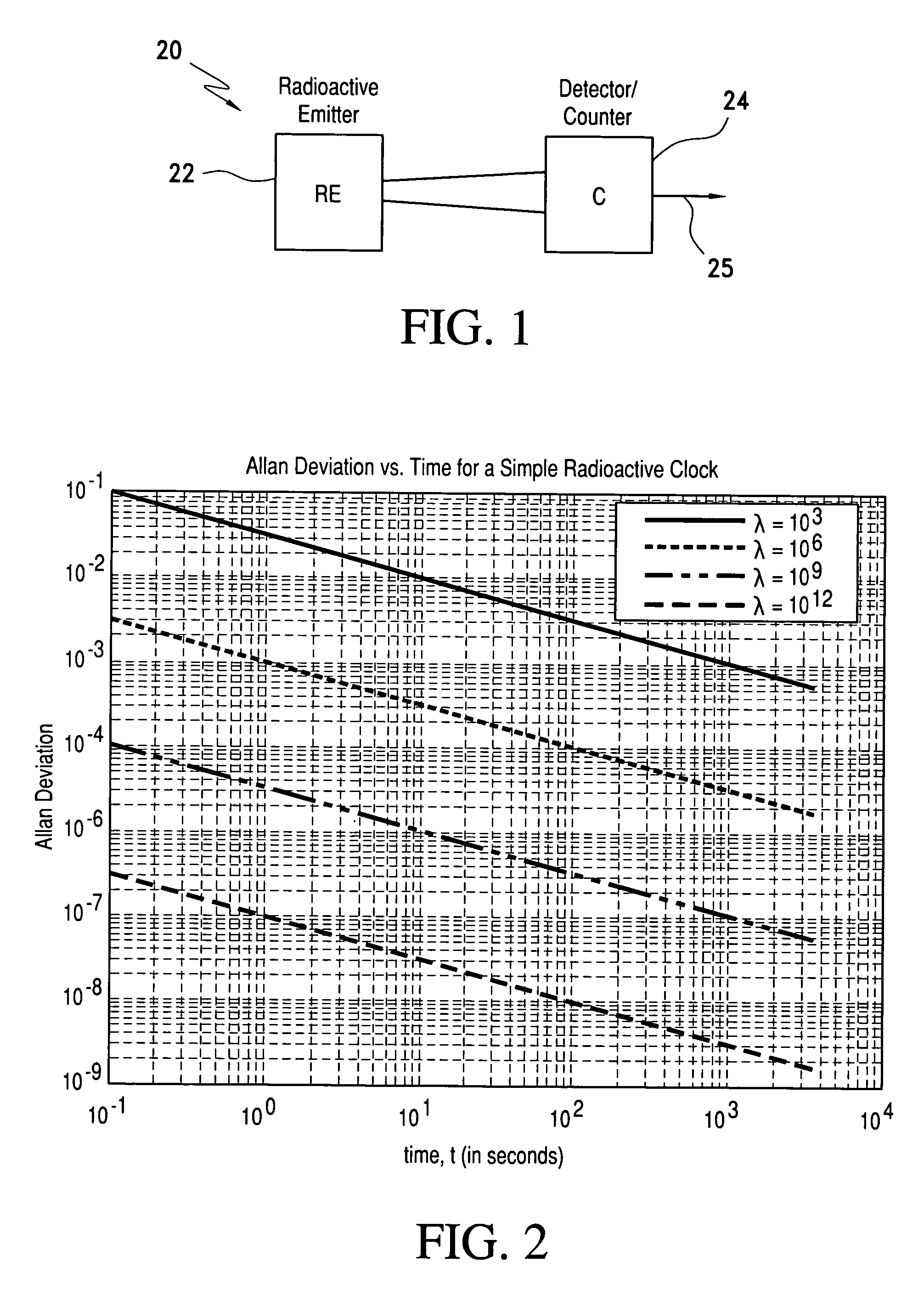
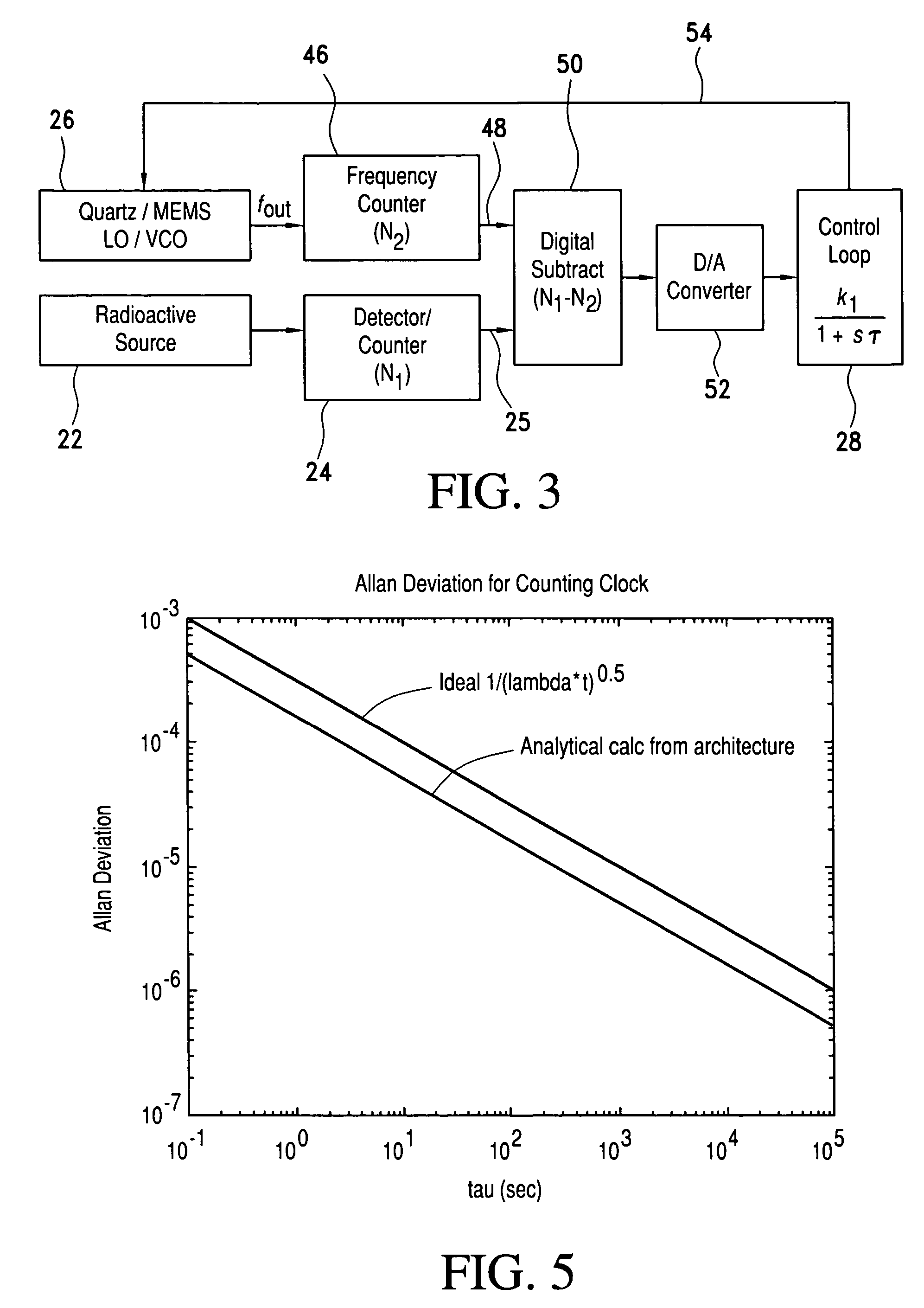
Radioactive decay based stable time or frequency reference signal source
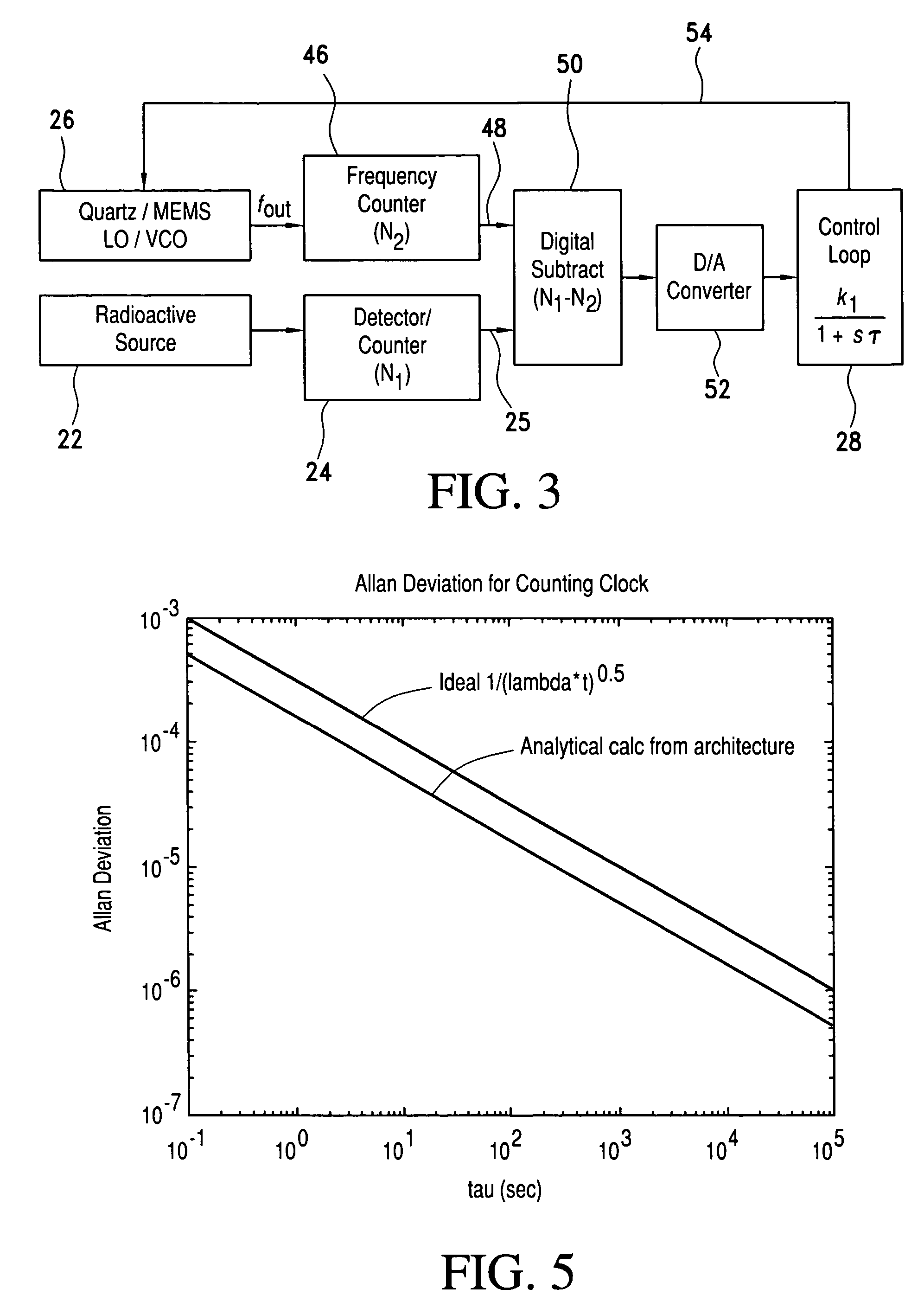
InactiveUS20060255281A1Energy efficient and stable and preciseStable and precise and referenceApparatus using radioisotope pulsesSynchronous motors for clocksDead timeRadioactive agent
A signal source for use as a frequency source or time keeping signal source includes a radioactive emission source generating a substantially periodic signal corresponding to a radioactive material's disintegration rate. A radioactive emission detector generates a radioactive emission detection signal and, to stabilize the detected periodic signal, a dead time controlling attenuator blanks or shuts off the radioactive emission detection signal for a selected dead time interval in response to each detected radioactive emission (i.e., a detected signal pulse or signal component) generated by the source. The dead time controlling attenuator output provides a long-term and short-term a stable periodic signal.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Dead time control circuit capable of adjusting temperature characteristics of dead time
ActiveUS20060290401A1Reliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingDead timeDead time control
In a dead time control circuit, a delay circuit is connected to an input terminal and adapted to delay signals therethrough by a delay time corresponding to a dead time. A logic circuit has a first input connected via the delay circuit to the input terminal, a second input connected directly to the input terminal, and an output connected to an output terminal. The dead time having adjustable temperature characteristics.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Adaptive dead time control scheme for switch mode power converter with synchronous rectifiers topology
ActiveUS9083255B2Improve efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFull bridgeTransverter
An adaptive dead time (ADT) control scheme for use with a switch mode power converter having a full bridge with synchronous rectifiers topology. A controller which implements the control scheme includes an input circuit arranged to receive a signal representative of the converter's output voltage, and an output circuit arranged to operate the converter's switching elements and synchronous rectifiers to produce a desired output voltage. The controller is further arranged such that the converter's “dead time” is adaptively varied in an inverse relationship to the magnitude of the load current. In a preferred embodiment, the signals used to operate the synchronous rectifiers are PWM signals, and the controller adaptively varies the dead time in a linear inverse relationship to the magnitude of the load current by modulating the rising and falling edges of the signals used to operate the synchronous rectifiers.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
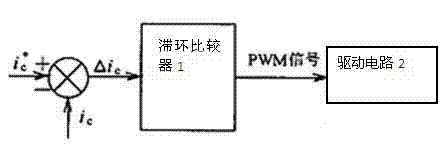
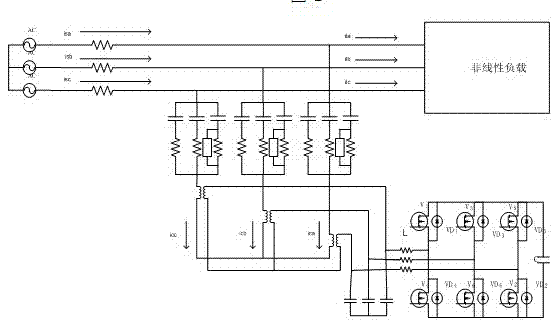
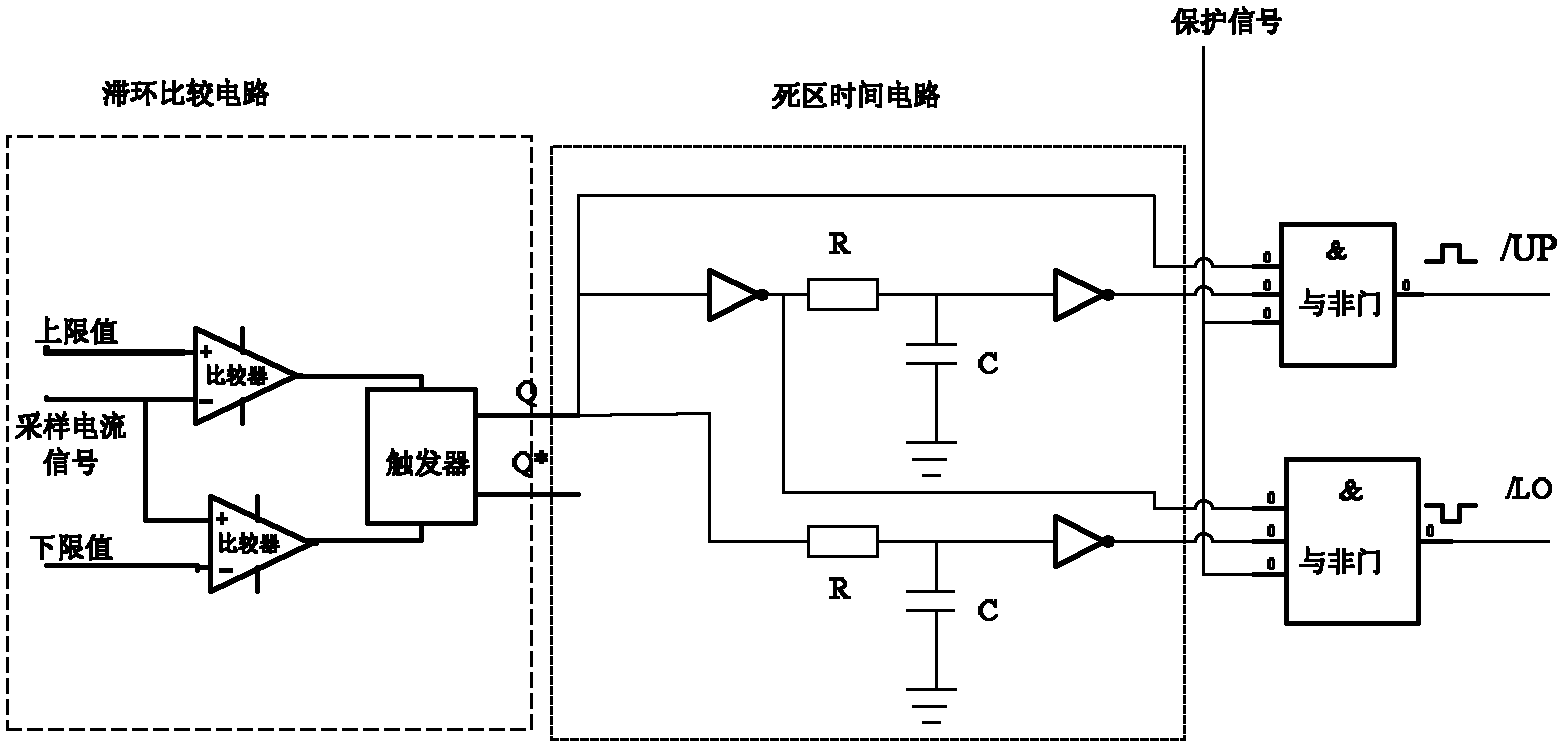
Current control method for active power filter
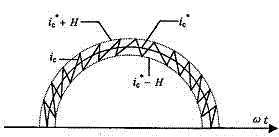
InactiveCN102684192AWide output spectrum rangeEasy to filterActive power filteringHarmonic reduction arrangementHysteresisFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a current control method for an active power filter. The current control method comprises the following steps of: comparing a compensating current command signal ic* with a practical compensating current signal ic; generating a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal for controlling the switch-on / off of a main circuit by the hysteresis comparator by taking a difference delta ic of the two signals as an input of a hysteresis comparator; and controlling the switch-on / off of a switch by the PWM signal through a driving circuit, thereby controlling the change in the compensating current ic, wherein the width H of the hysteresis comparator is designed to be capable of automatically adjusting following the magnitude of ic; the hysteresis comparator is replaced by a comparator under timing control of a clock; the delta ic is judged for one time within each clock period; and the PWM signal changes for one time within at least one clock period. The hysteresis current control is the control based on the transient state of current and has the advantages of high dynamic response speed and excellent robustness; the hysteresis current control essentially is a frequency conversion SPWM (Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation) modulation mode for implied carrier wave; in a three-phase high-power factor rectifier, the wave frequency of the implied carrier wave under hysteresis control periodically changes following the voltage of a power grid; the change frequency is two times of the power frequency; the hysteresis current control is wide in output spectral range and is better in filtering property; and harmonic energy is uniformly distributed in a wider frequency band scope.
Owner:RUGAO TOTEM ELECTRIC POWER TECH
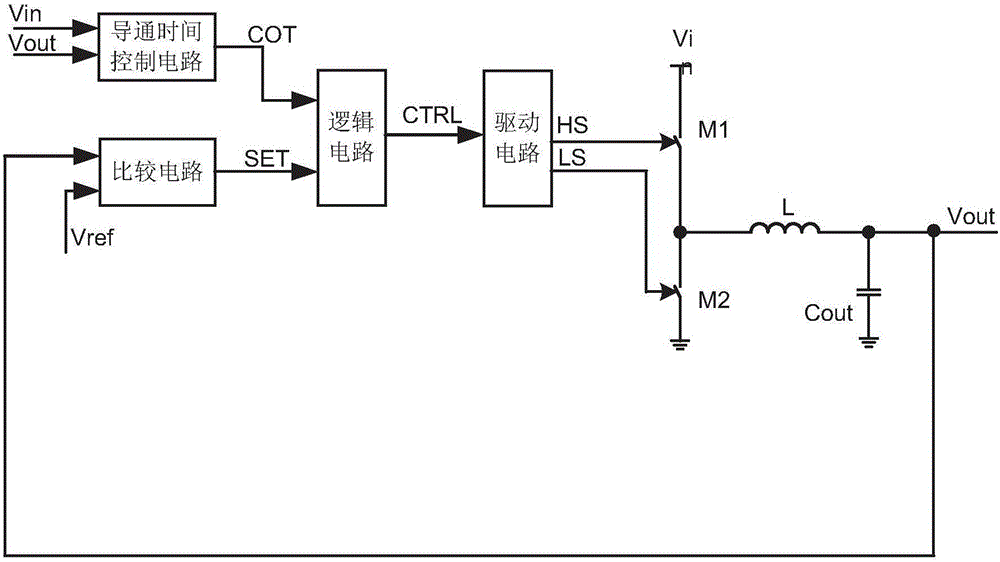
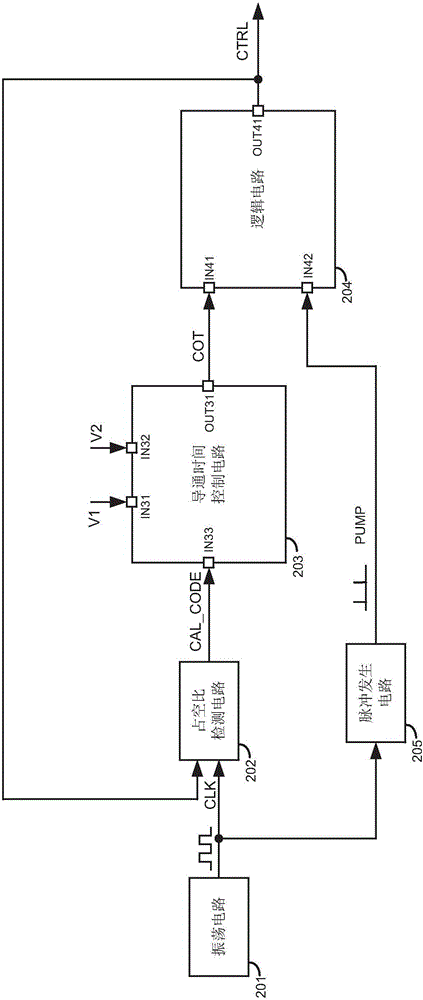
Switching converter for constant turn-on time control and automatic calibration method thereof
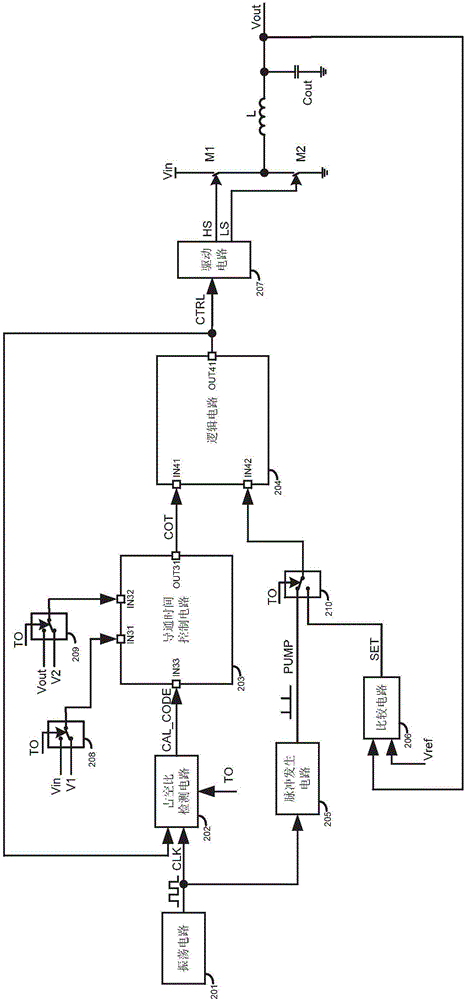
ActiveCN105978303ARealize automatic calibrationAnalogue/digital conversionEfficient power electronics conversionControl signalDead time control
The invention discloses a switching converter for constant turn-on time control as well as a controller, a control method and an automatic calibration method thereof. The switching converter comprises a main transistor, a turn-on time control circuit for determining the turn-on time of the main transistor, and a logic circuit for controlling the main transistor. The automatic calibration method comprises the steps of: generating periodic clock signals with a preset duty cycle; providing a first voltage and a second voltage to the turn-on time control circuit, so that the turn-on time control circuit generates turn-on time control signals based on the first voltage and the second voltage; providing the clock signals and the turn-on time control signals to the logic circuit, so that the logic circuit generates switching control signals based on the clock signals and the turn-on time control signals; comparing the duty cycle of the switching control signals with the duty cycle of the clock signals to generate correction code signals; and adjusting circuit parameters in the turn-on time control circuit based on the correction code signals.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
Bidirectional current alternate control circuit for AC rectification power source
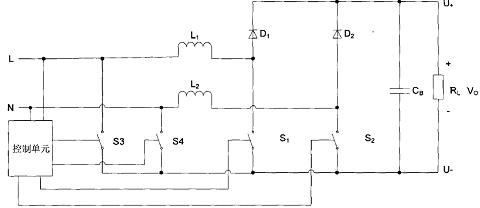
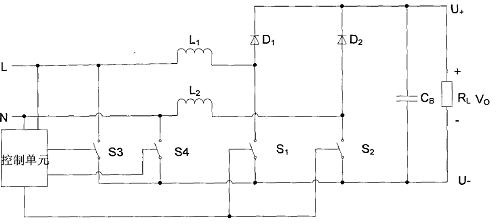
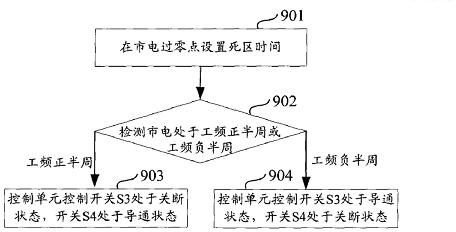
ActiveCN102208876AAchieve powerRealize functionEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionPower factorEngineering
The invention relates to a bidirectional current alternate control circuit for an AC rectification power source. The circuit comprises a PFC (Power Factor Correction) control circuit unit, a split-phase and dead time control circuit, an AC bidirectional current detection and control circuit and the like, wherein the AC bidirectional current detection and control circuit is connected with an AC power source and controls and drives two low-frequency switches, two high-frequency PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) switches and two synchronous rectifier tubes to work according to detected forward and reserve current signals of the AC power source, alternately output working frequency signals and high-frequency PWM signals as well as synchronous rectification signals; the split-phase and dead time control circuit receives and processes signals from the PFC control circuit unit and outputs the signals to a high-frequency PWM driving control circuit unit and a synchronous rectification driving control circuit unit to realize power factor correction; and the high-frequency PWM driving control circuit unit and the synchronous rectification driving control circuit unit ensure that the AC rectification power source has the highest efficiency while having the characteristic of high power factor. The AC bidirectional current detection and control circuit in the invention is simple and reliable and has low cost.
Owner:TEN PAO ELECTRONICS HUIZHOU
Method of manufacturing color metal zipper and apparatus therefor
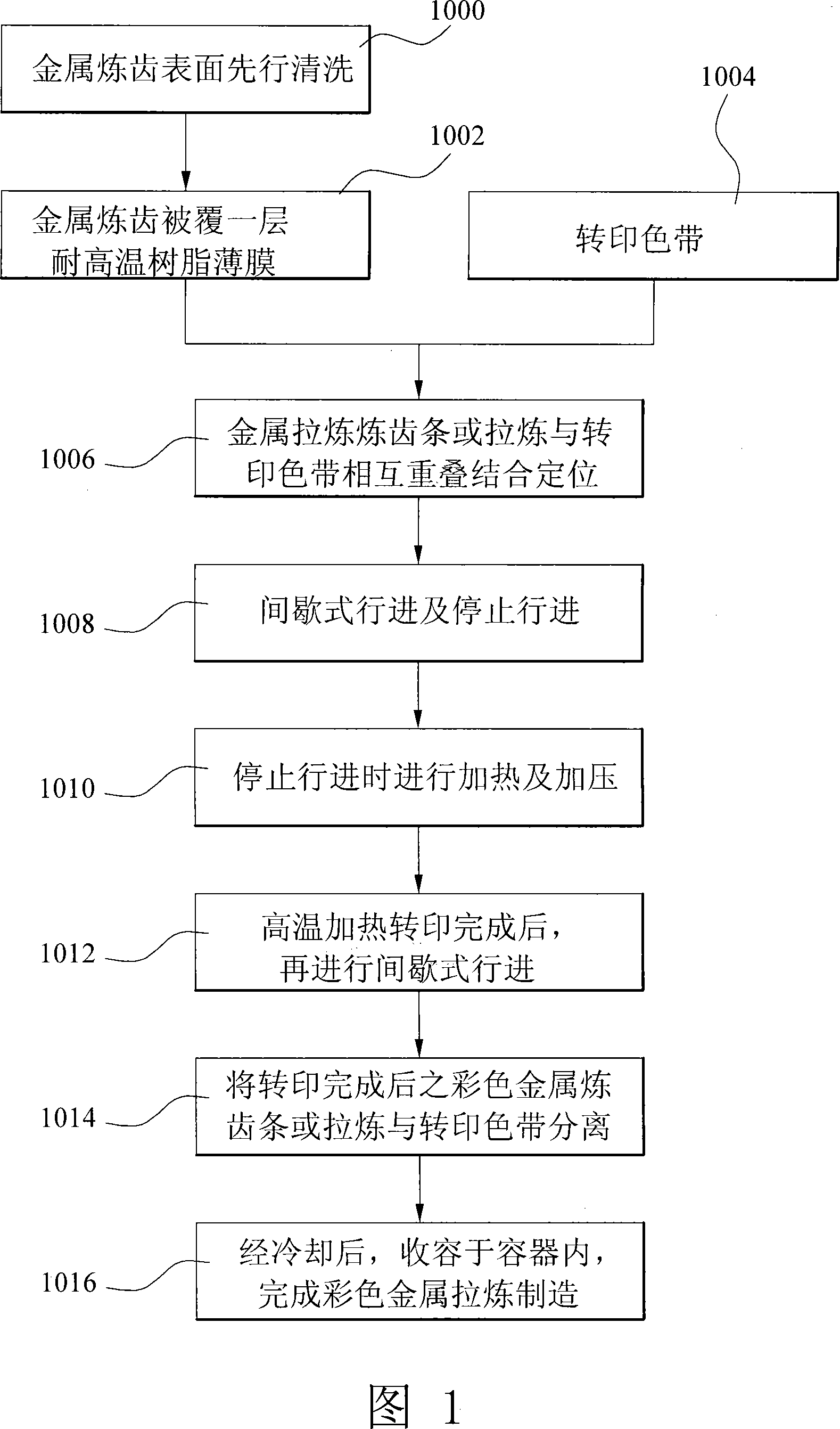
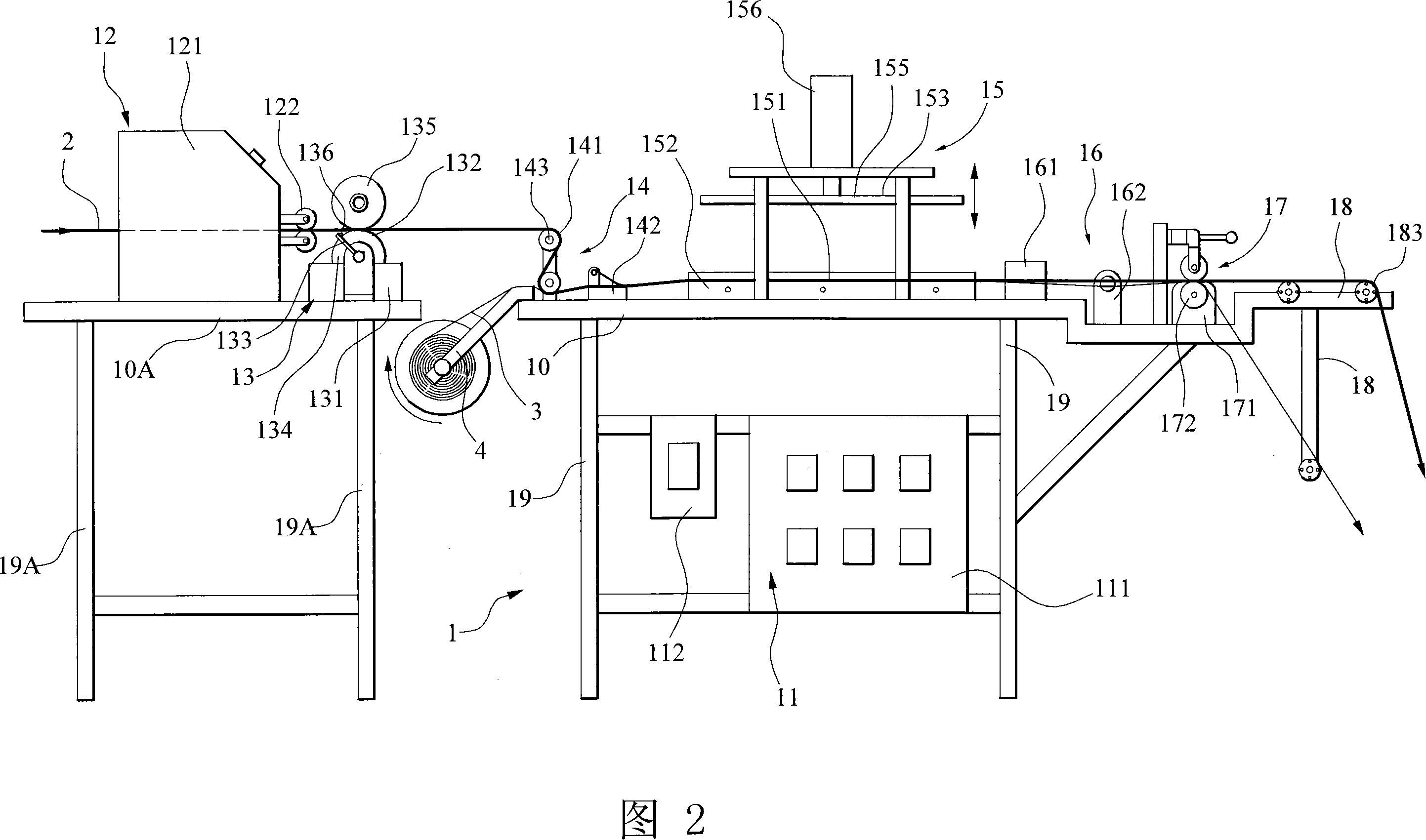
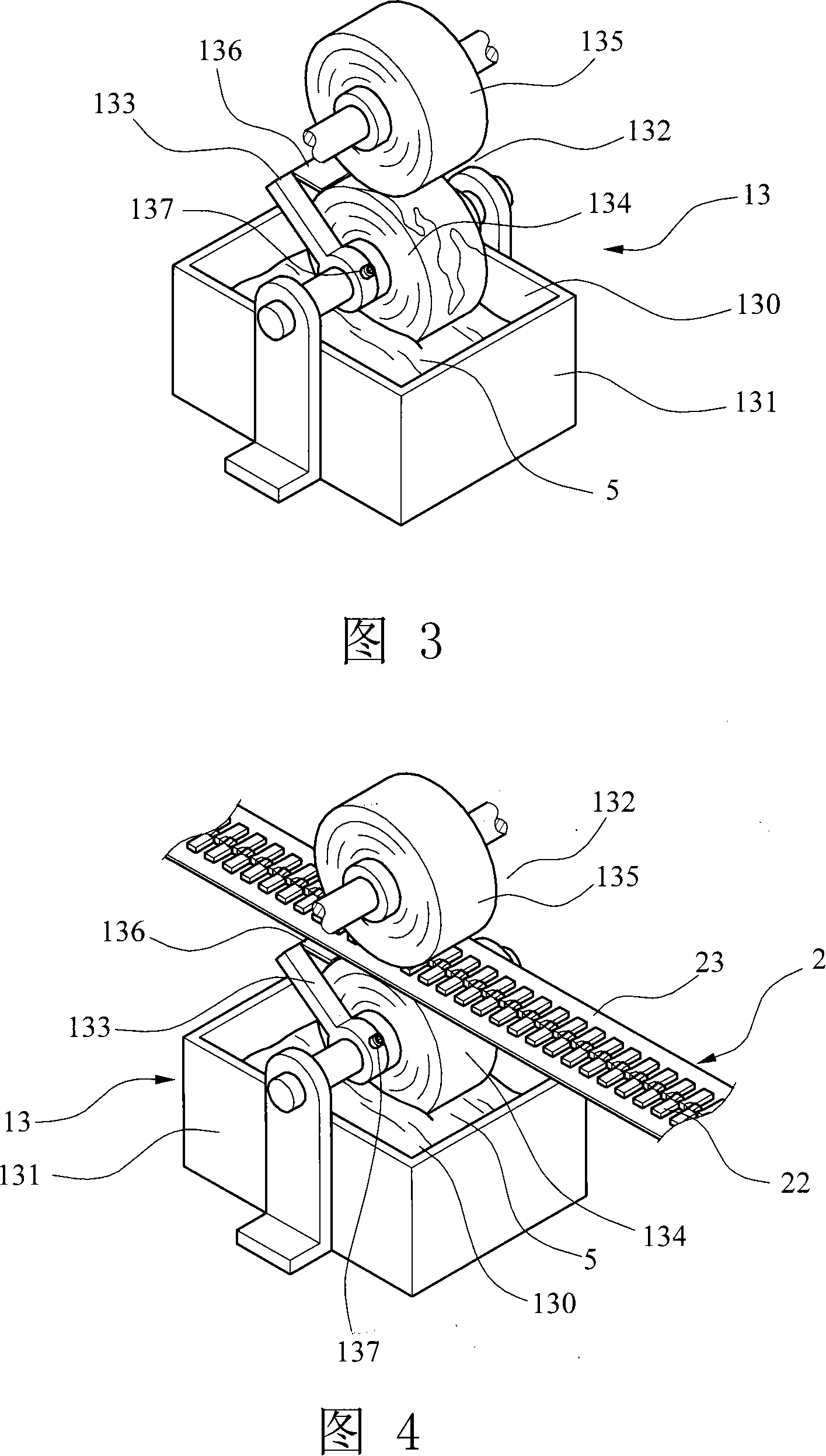
InactiveCN101125508AImprove efficiencyImprove yieldSlide fastenersDecorative surface effectsMetallurgyDead time control
Method and apparatus of manufacturing color metal zipper are disclosed. The method includes washing half-finished metal zipper; overlaying a thin film on the upper surface of half-finished metal zipper; feeding color transfer paper; overlaying the half-finished metal zipper on the color transfer paper and positioning same; intermittently advancing the overlaid half-finished metal zipper and the color transfer paper; heating and pressing the overlaid half-finished metal zipper and the color transfer paper in an interval when the advancing stops for uniformly transferring color of the color transfer paper to a portion of the half-finished metal zipper; intermittently advancing the half-finished metal zipper and the color transfer paper again; separating the finished color metal zipper from the color transfer paper while intermittently advancing; and cooling and storing the finished color metal zipper and color transfer paper.
Owner:IRIS ZIPPER
Step-down DC-DC converter system
PendingCN107370366ARealize switch controlNot affected by duty cycleApparatus without intermediate ac conversionEfficient power electronics conversionCapacitanceControl signal
The invention relates to the technical field of step-down DC-DC converters and particularly relates to a step-down DC-DC converter system, which comprises an upper MOS transistor, an upper MOS transistor driving circuit, a lower MOS transistor, a lower MOS transistor driving circuit, a first capacitor, an inductor, a switch, a power supply, a dead time control circuit, a feedback control circuit, a second capacitor, a first capacitor charging control circuit and a pulse integrating circuit, wherein the feedback control circuit is used for generating PWM control signals; when the duty cycle of the PWM control signals is close to or equal to 100%, the first capacitor charging control circuit is used for generating a switching signal to control the conduction time and the conduction frequency of the lower MOS transistor, and thus, the first capacitor is charged and enough voltage is acquired to ensure normal switching control on the upper MOS transistor by the upper MOS transistor driving circuit. The first capacitor charging control circuit is used to enable the first capacitor to have enough charging time when the duty cycle is large or equal to 100%, and control on the upper MOS transistor by the system is thus ensured.
Owner:LEN TECH LTD
Radioactive decay based stable time or frequency reference signal source
InactiveUS7476865B2Energy stable and preciseStable and precise referenceApparatus using atomic clocksApparatus using radioisotope pulsesDead timeRadioactive agent
A signal source for use as a frequency source or time keeping signal source includes a radioactive emission source generating a substantially periodic signal corresponding to a radioactive material's disintegration rate. A radioactive emission detector generates a radioactive emission detection signal and, to stabilize the detected periodic signal, a dead time controlling attenuator blanks or shuts off the radioactive emission detection signal for a selected dead time interval in response to each detected radioactive emission (i.e., a detected signal pulse or signal component) generated by the source. The dead time controlling attenuator output provides a long-term and short-term a stable periodic signal.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
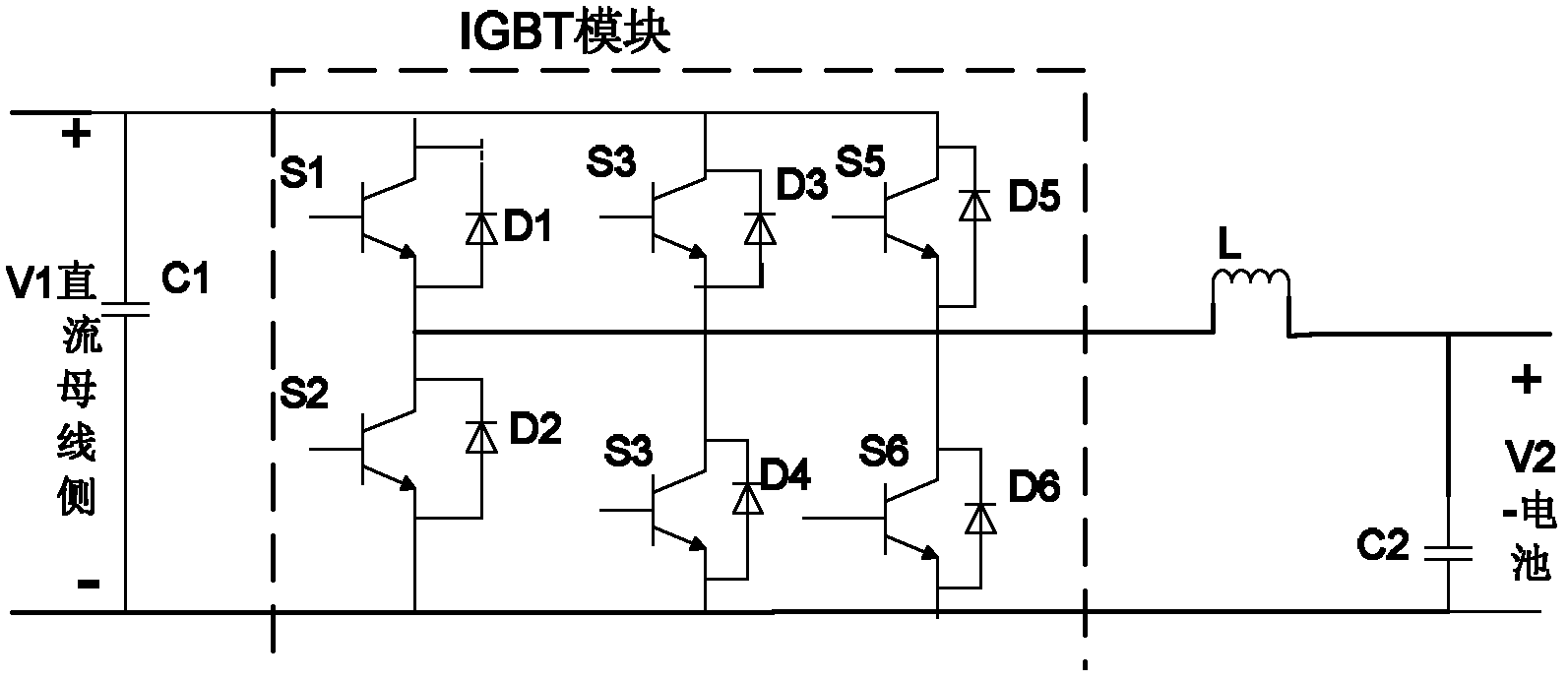
Pulse-width modulation (PWM) phase-shifting control device for bi-directional direct current (DC)-DC converter
InactiveCN102594138AReduce switching lossesReduce switching noiseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPhase shift controlDc dc converter
The invention provides a PWM phase-shifting control device for a bi-directional DC-DC converter. The control device comprises a dead time control unit, a PWM phase-shifting control circuit and a bi-directional DC-DC converter which are sequentially connected. According to the PWM phase-shifting control device for the bi-directional DC-DC converter, the PWM phase-shifting control technology is adopted to enable a control strategy to be simple and easy to achieve. For multi-PWM control technology, drive signals of each unit circuit need to be staggered with each other to guarantee smooth conversion between Insulated Gate Bipolar Translators (IGBT), therefore switching frequency can be decreased, and switching loss can be reduced.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com