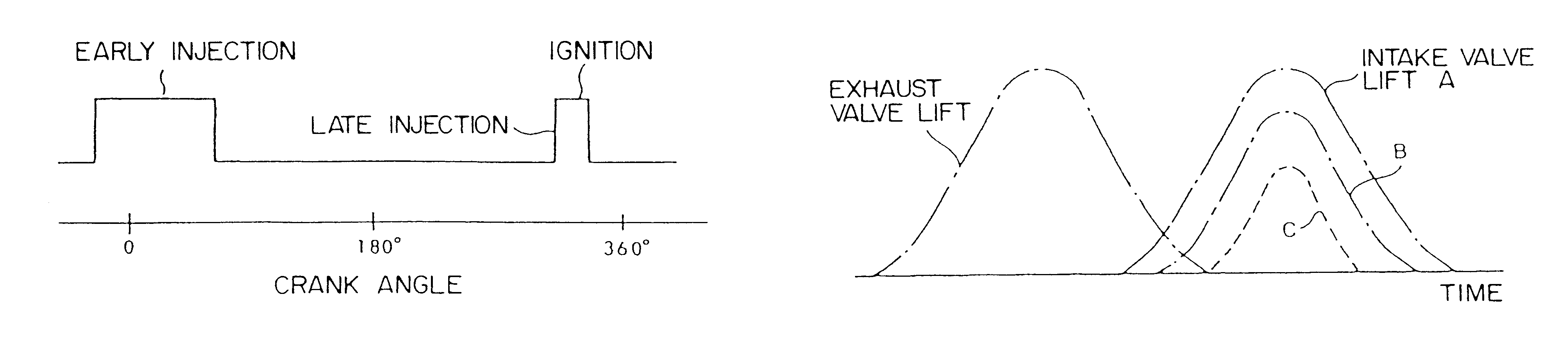Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
187results about "Electronic control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
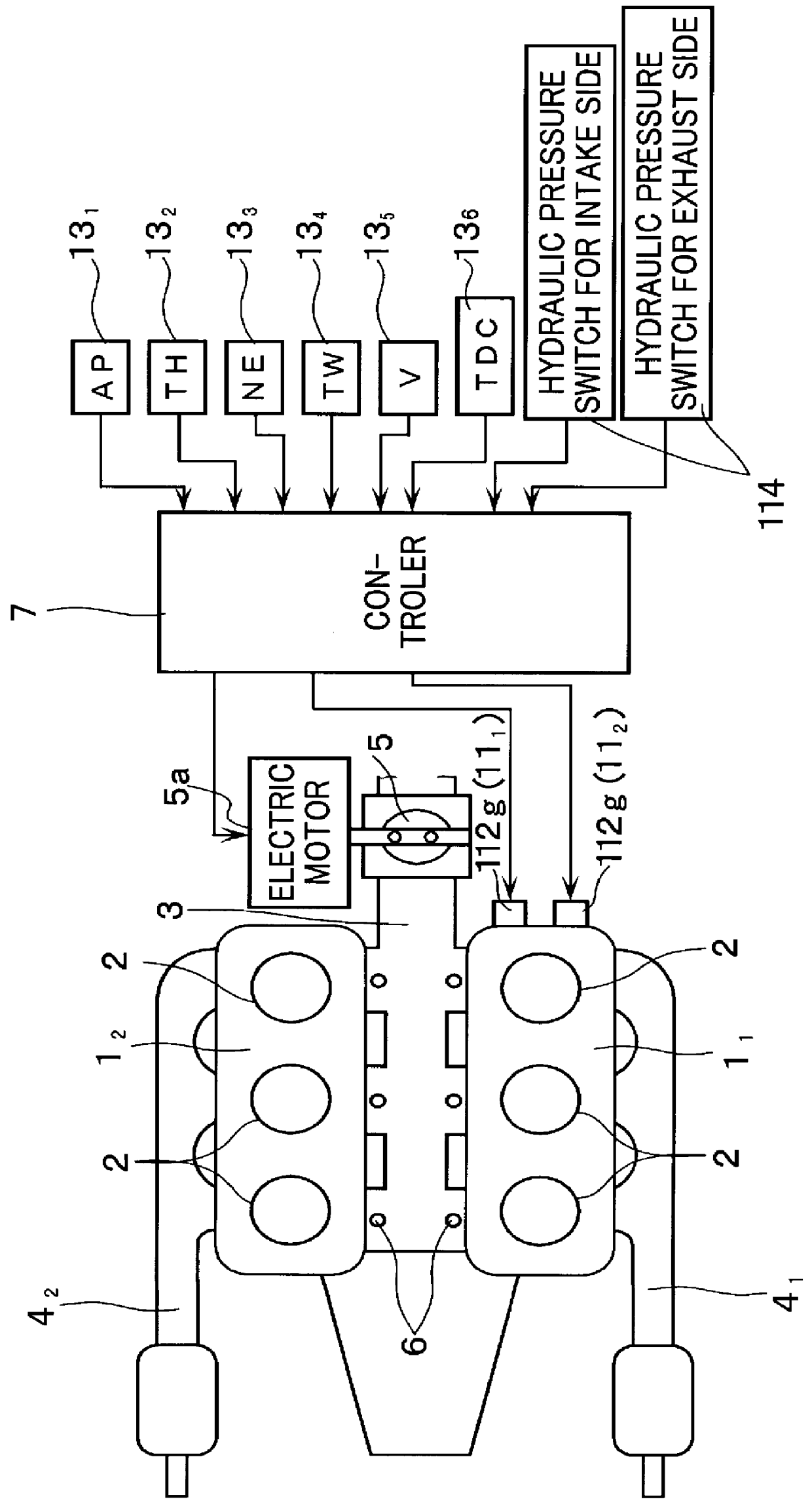
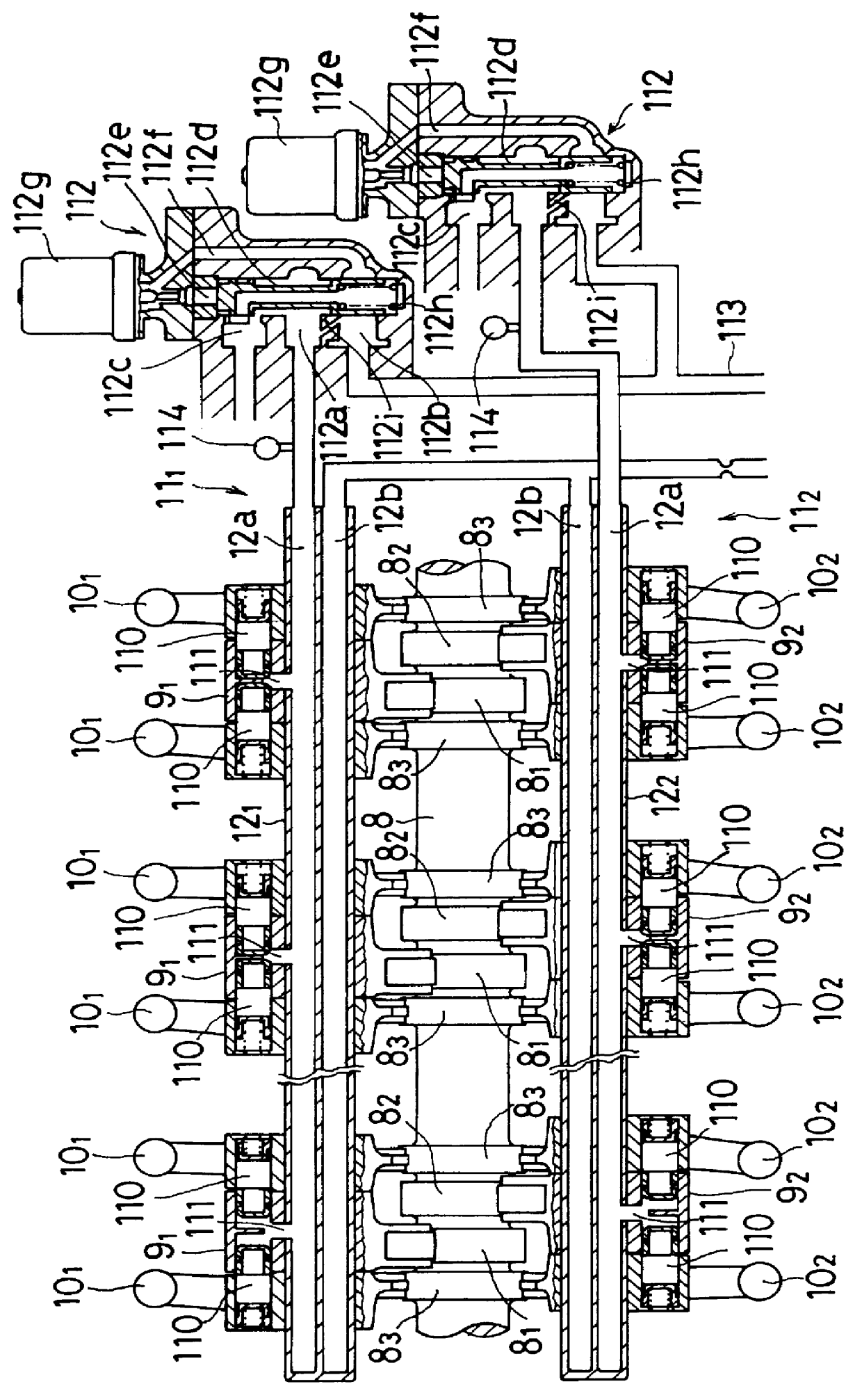
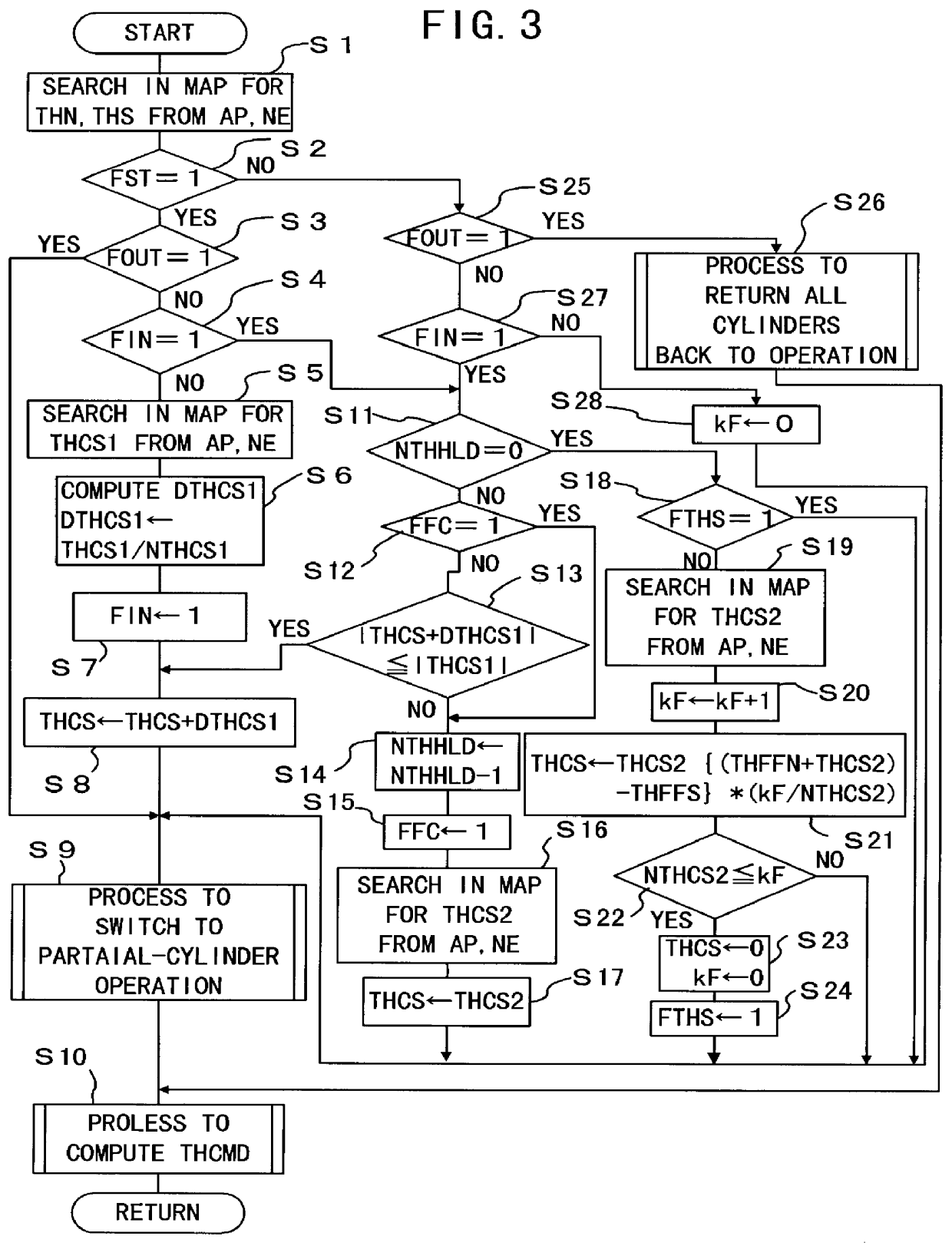
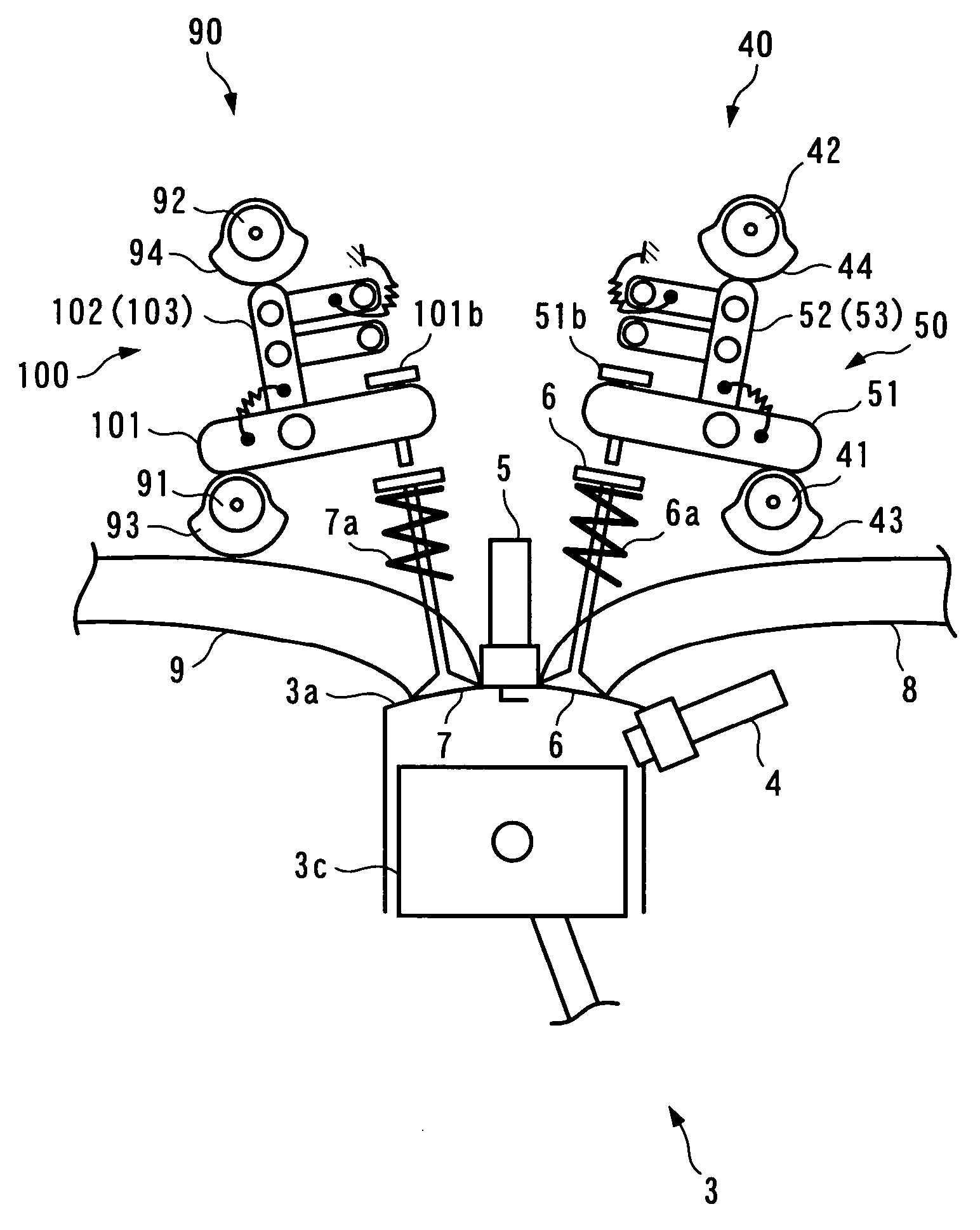
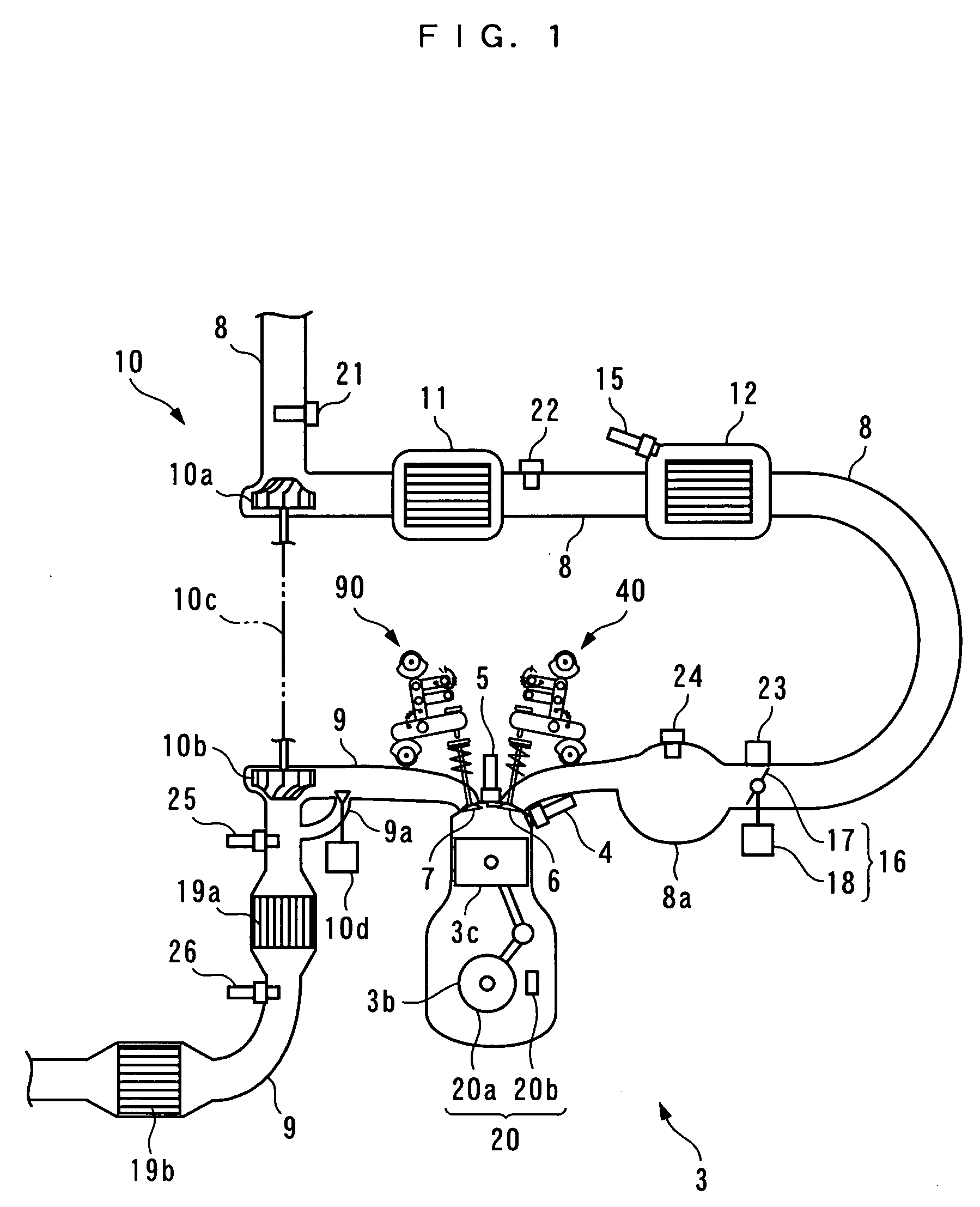
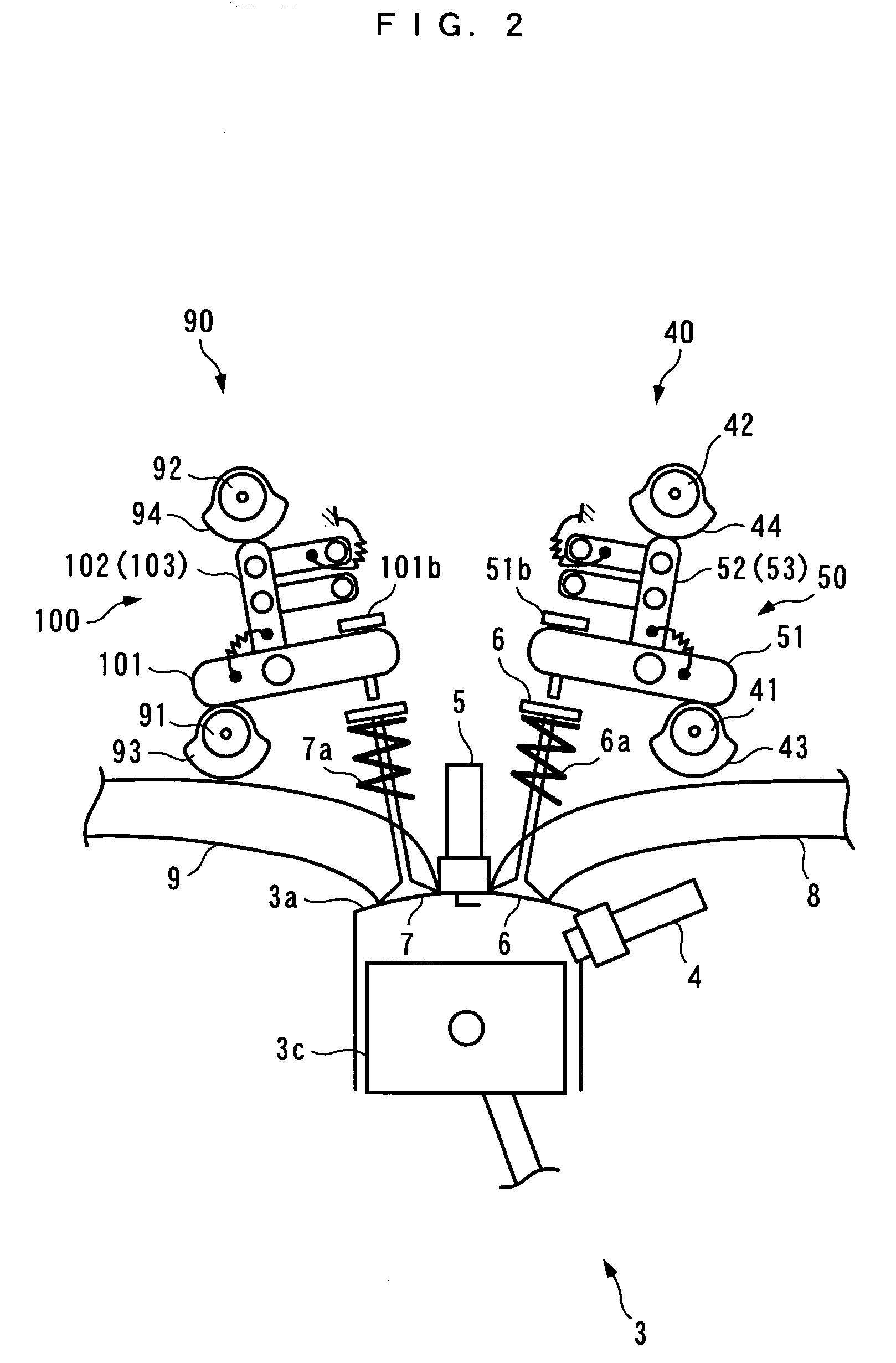
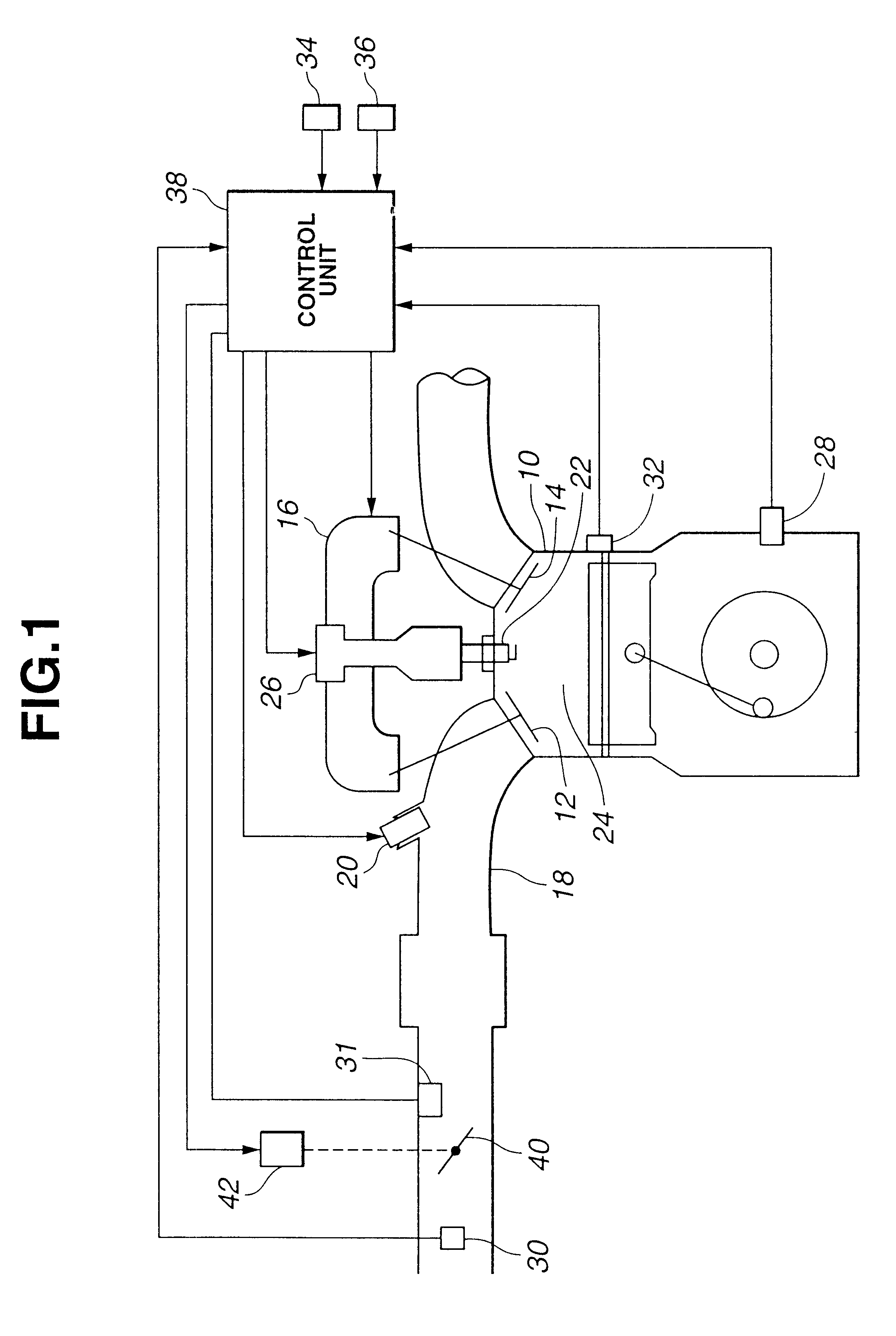
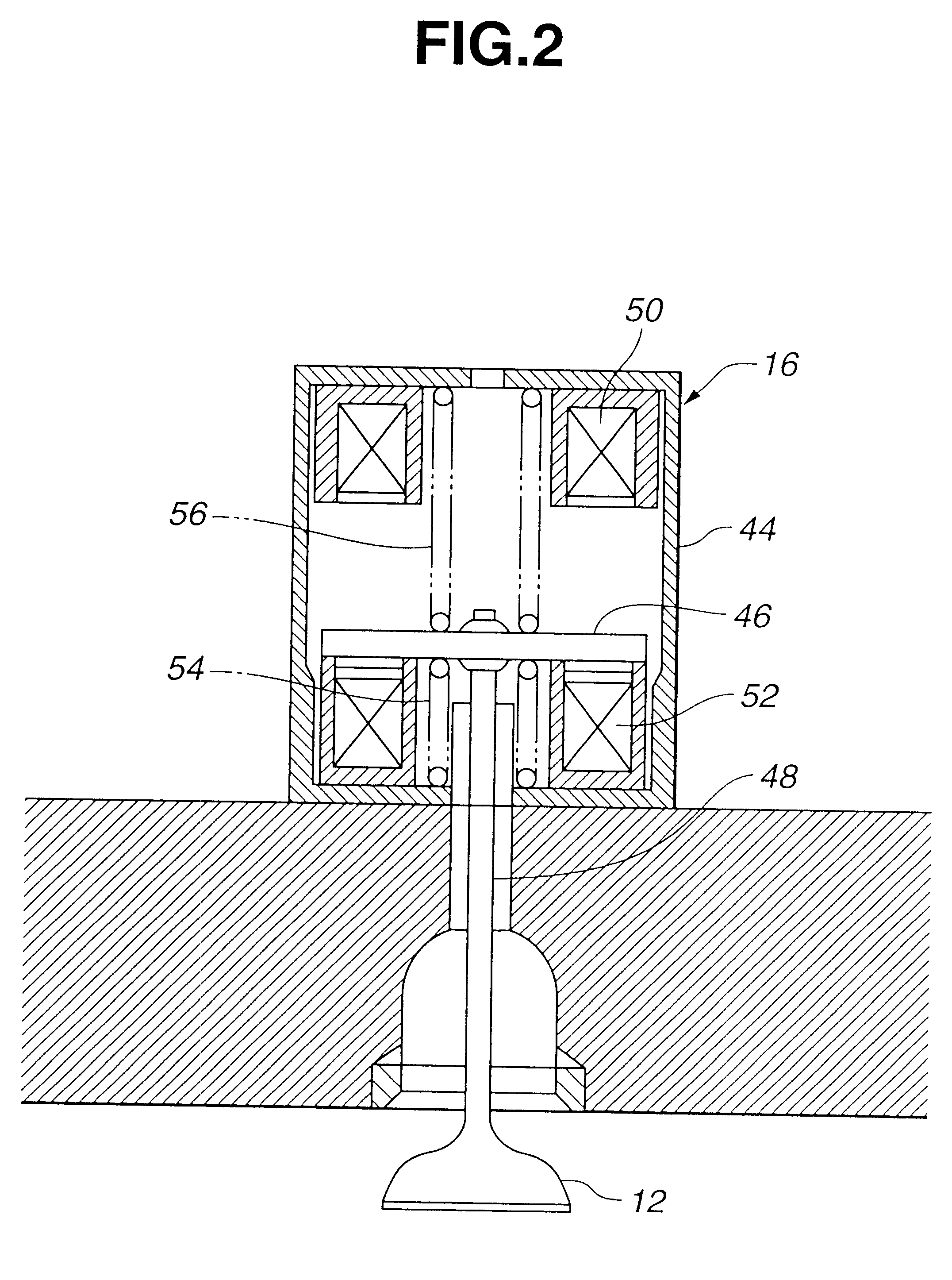
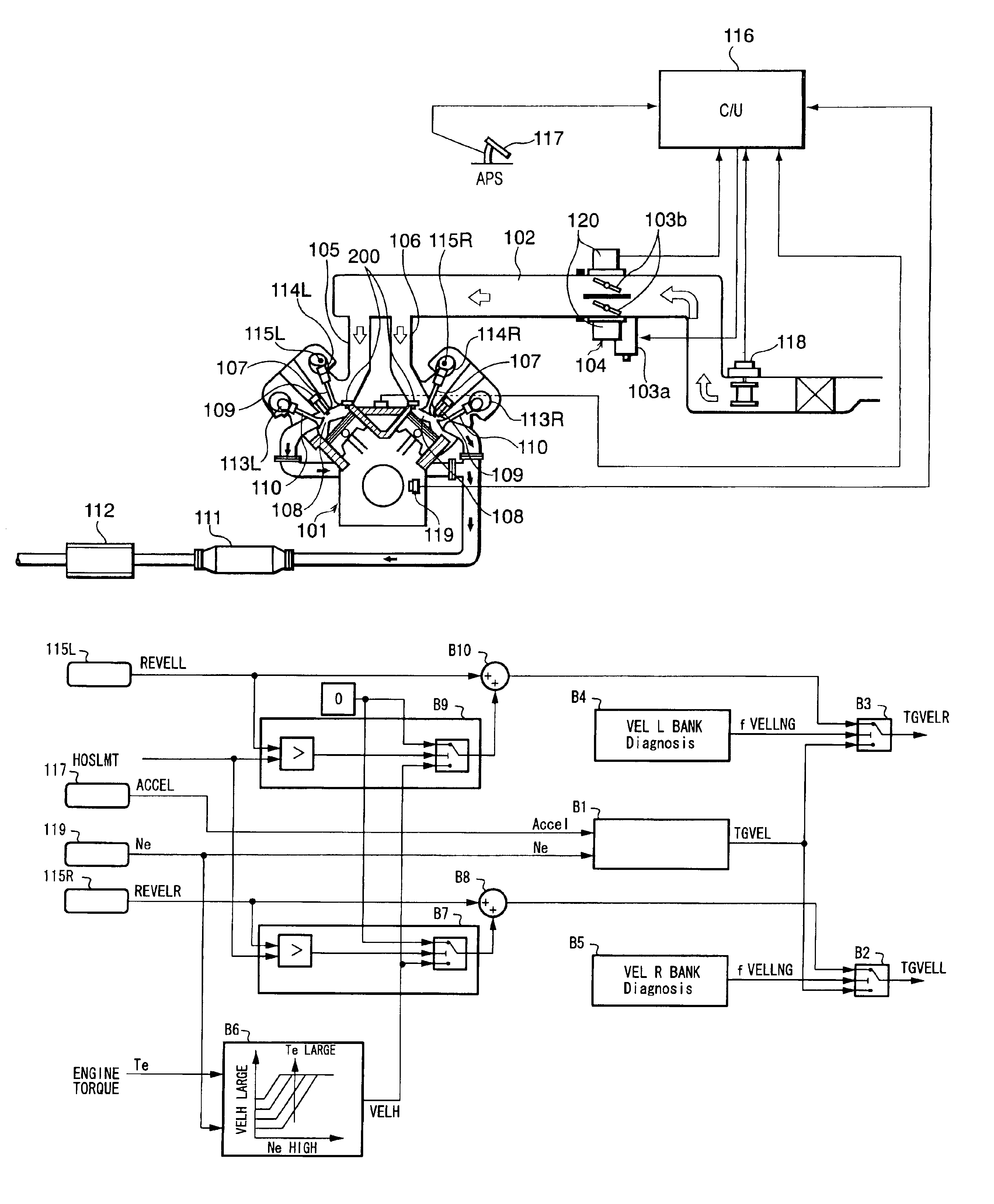
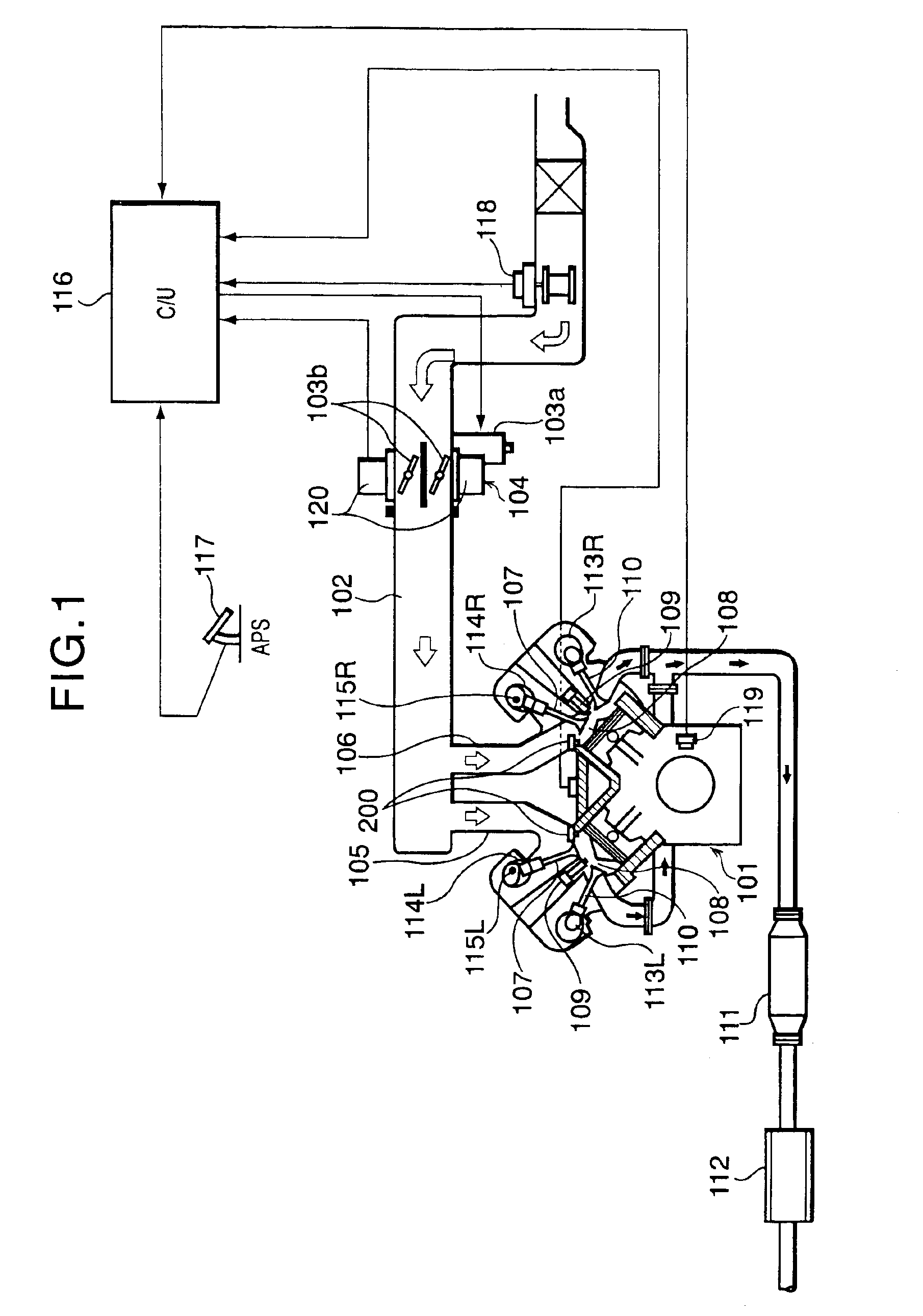
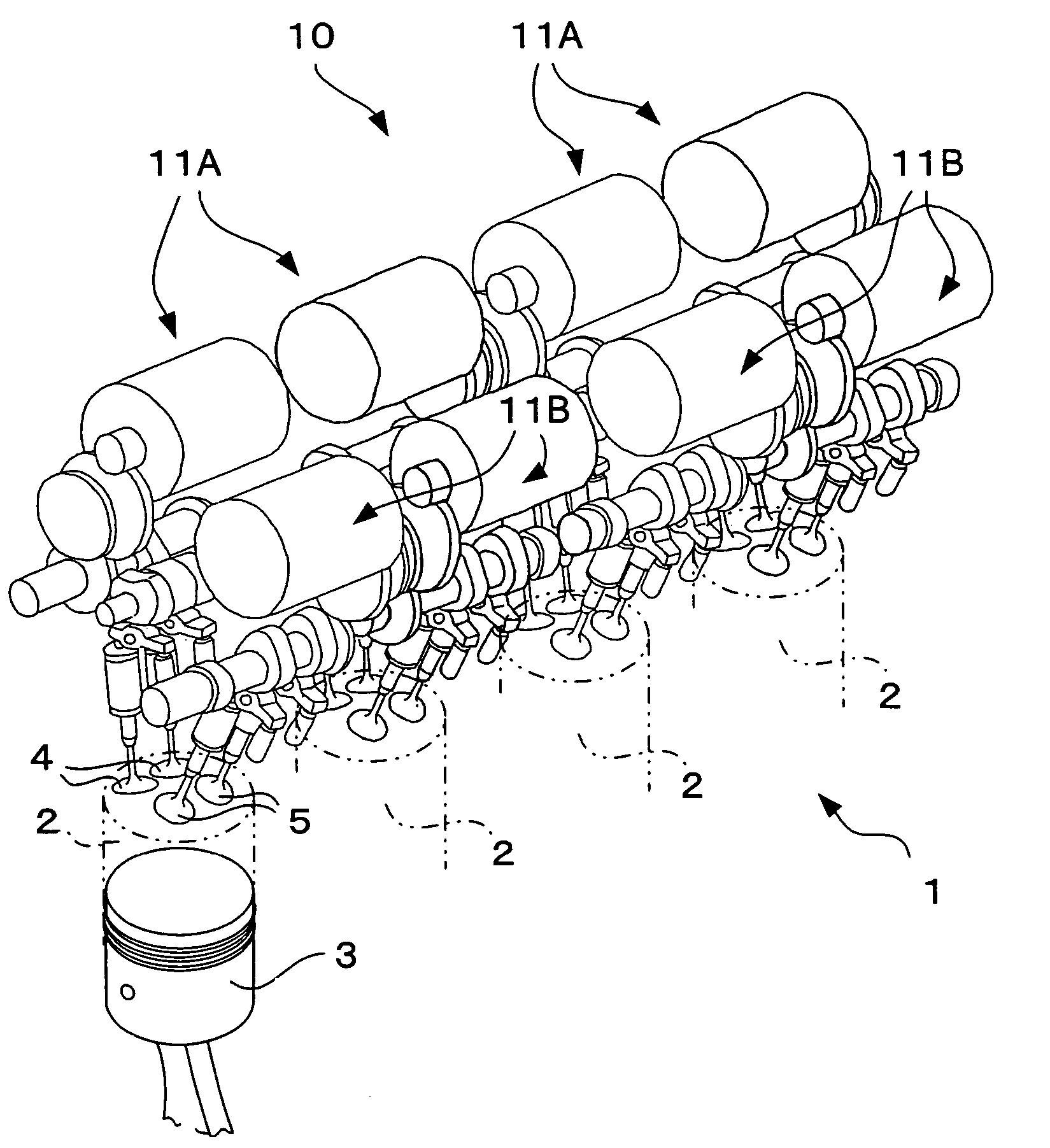
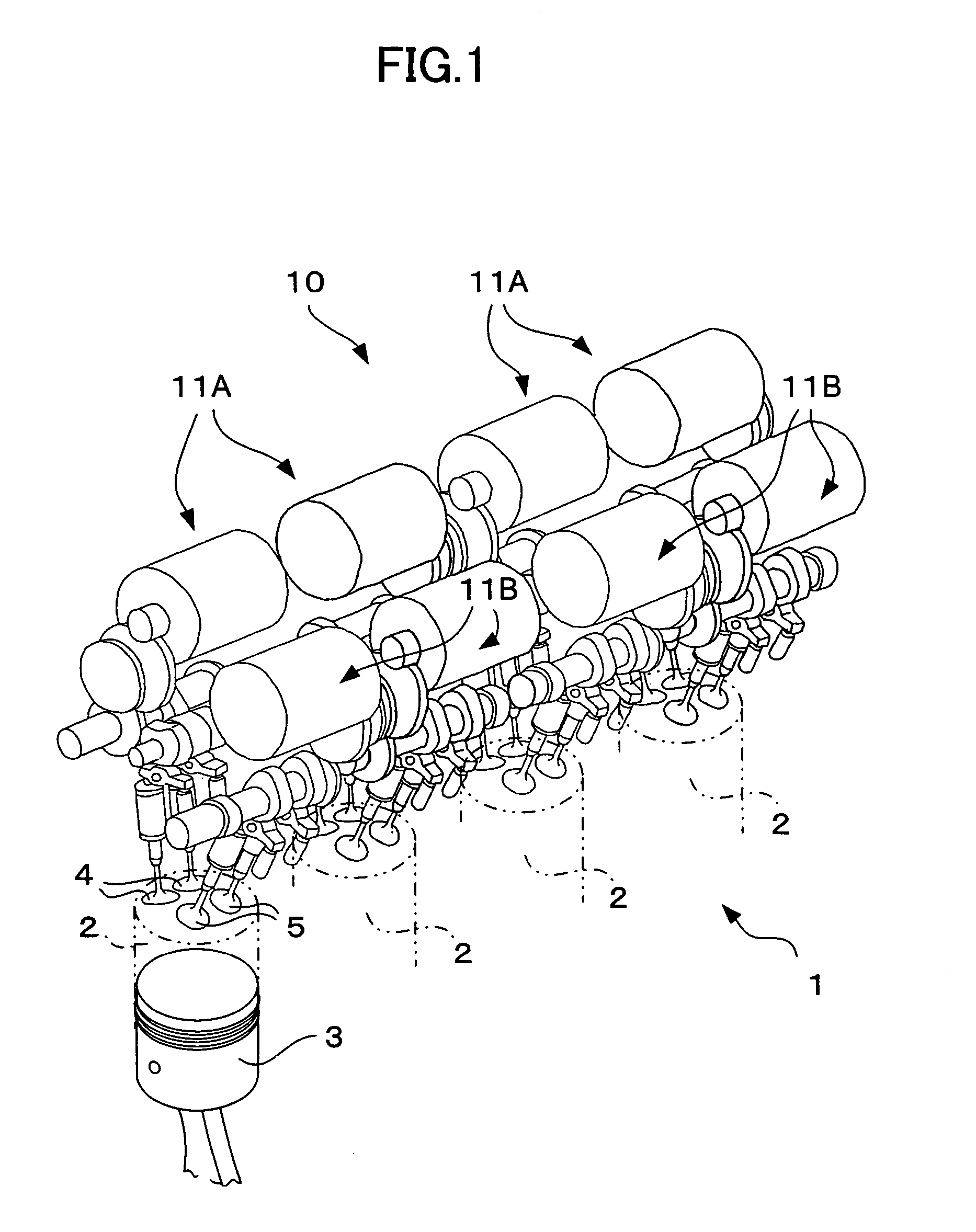
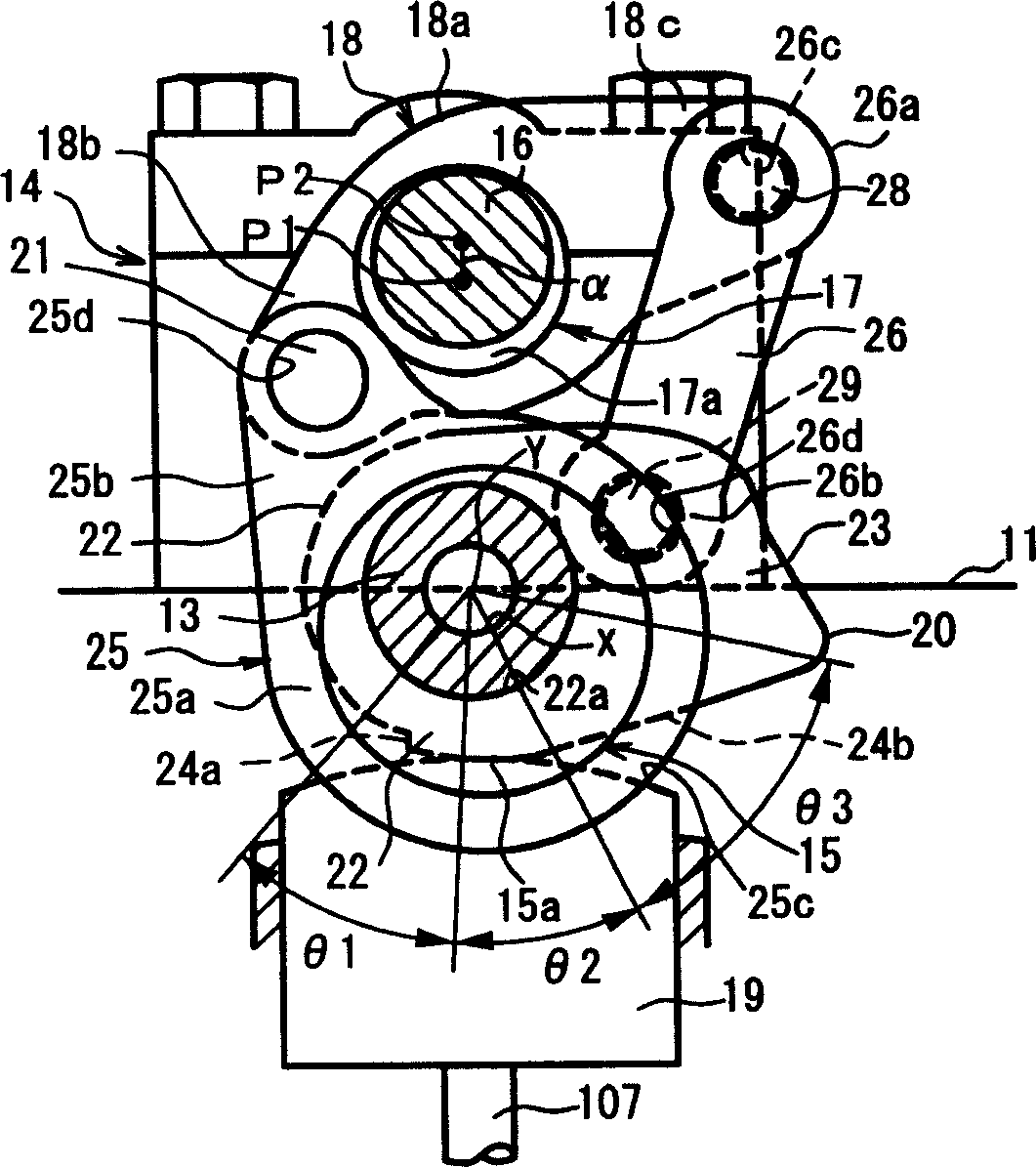
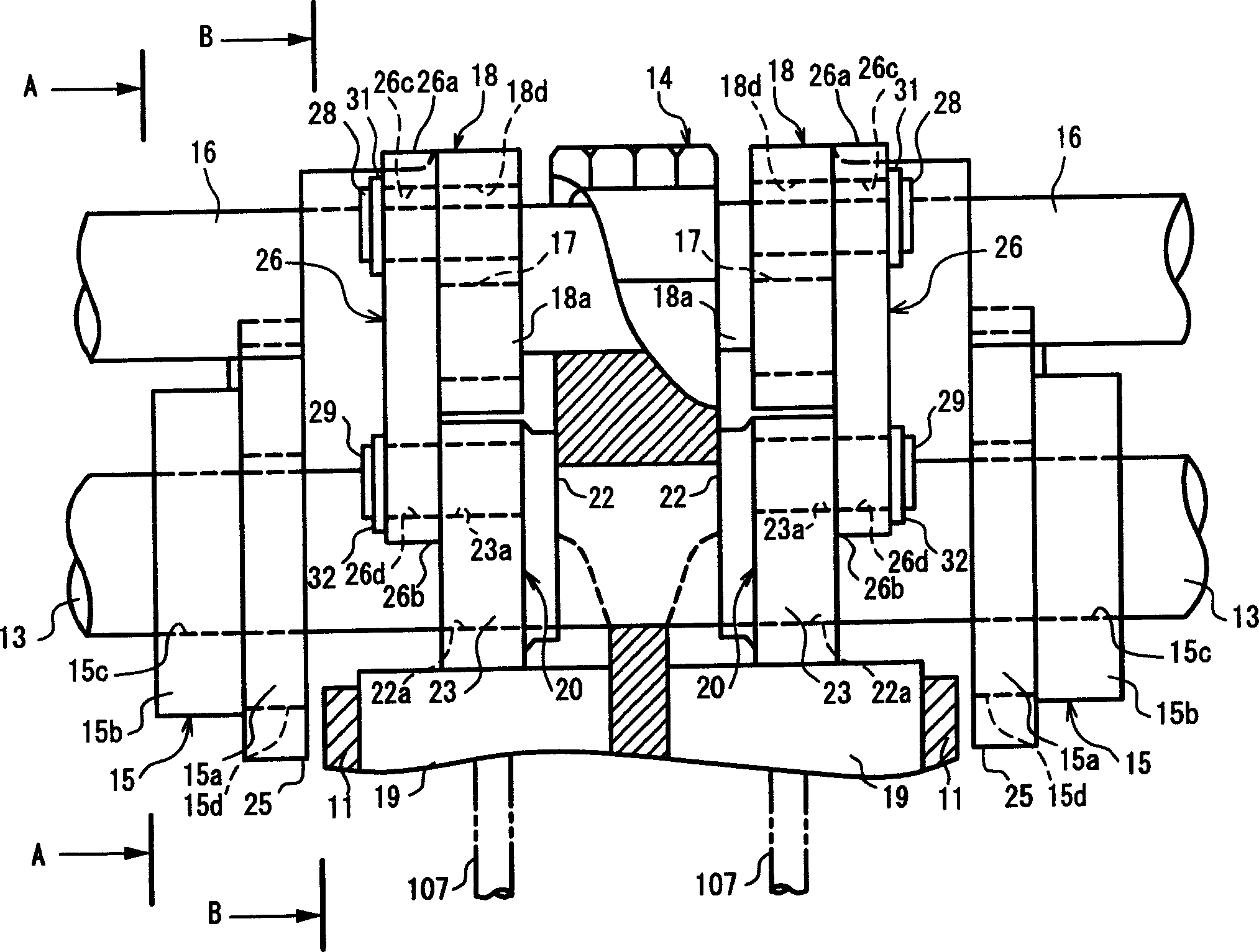
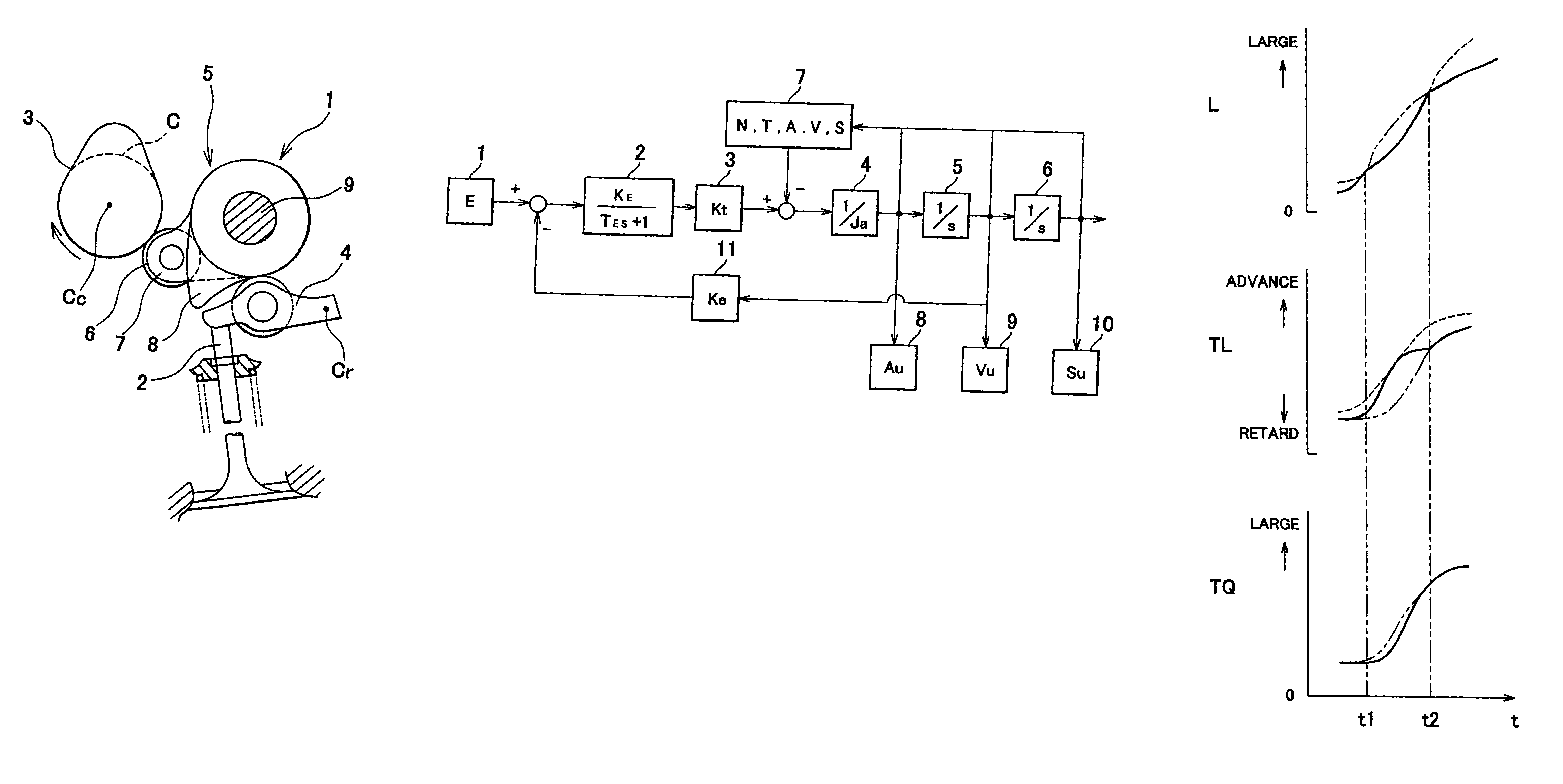
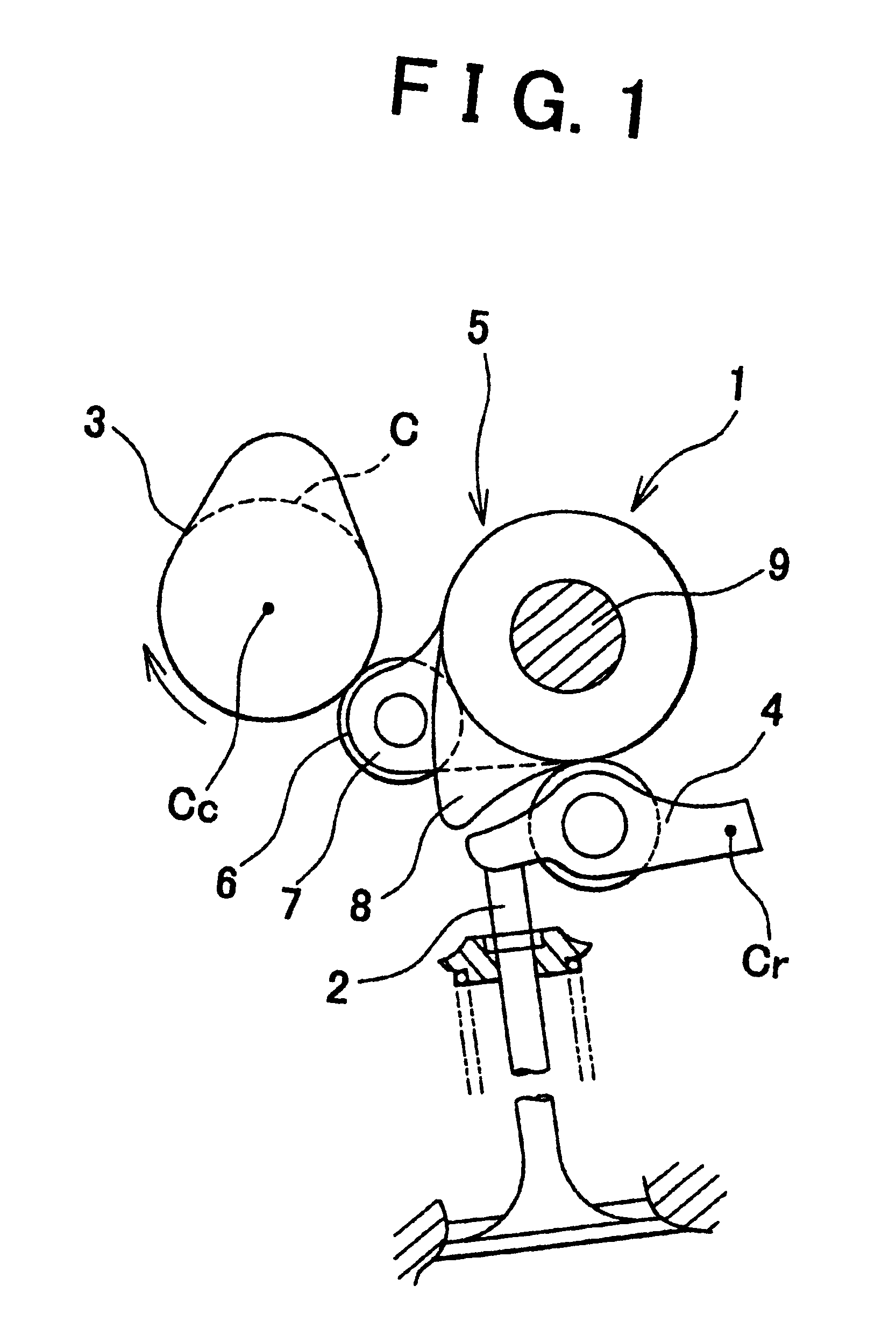
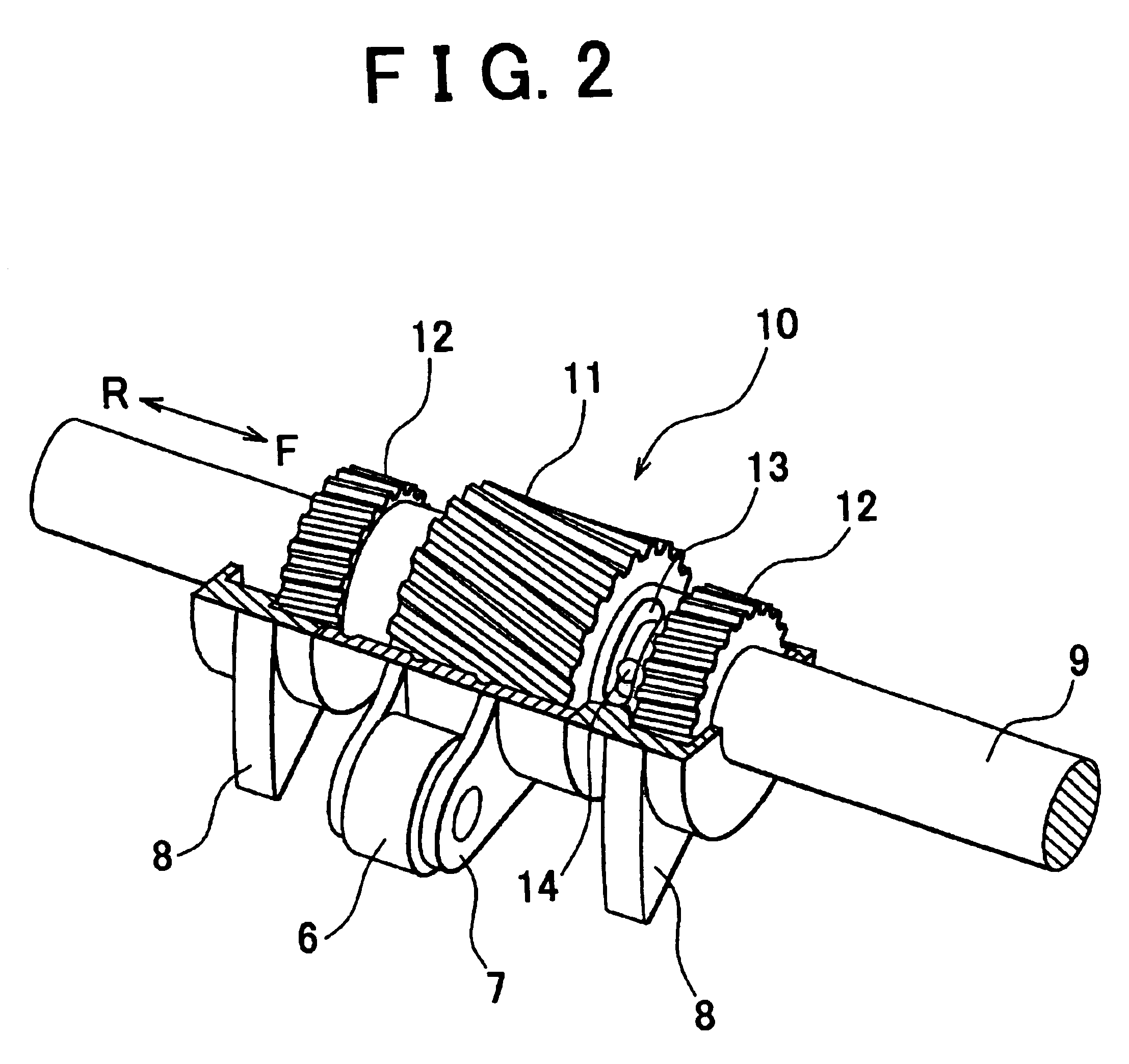
Apparatus for controlling multi-cylinder internal combustion engine with partial cylinder switching-off mechanism
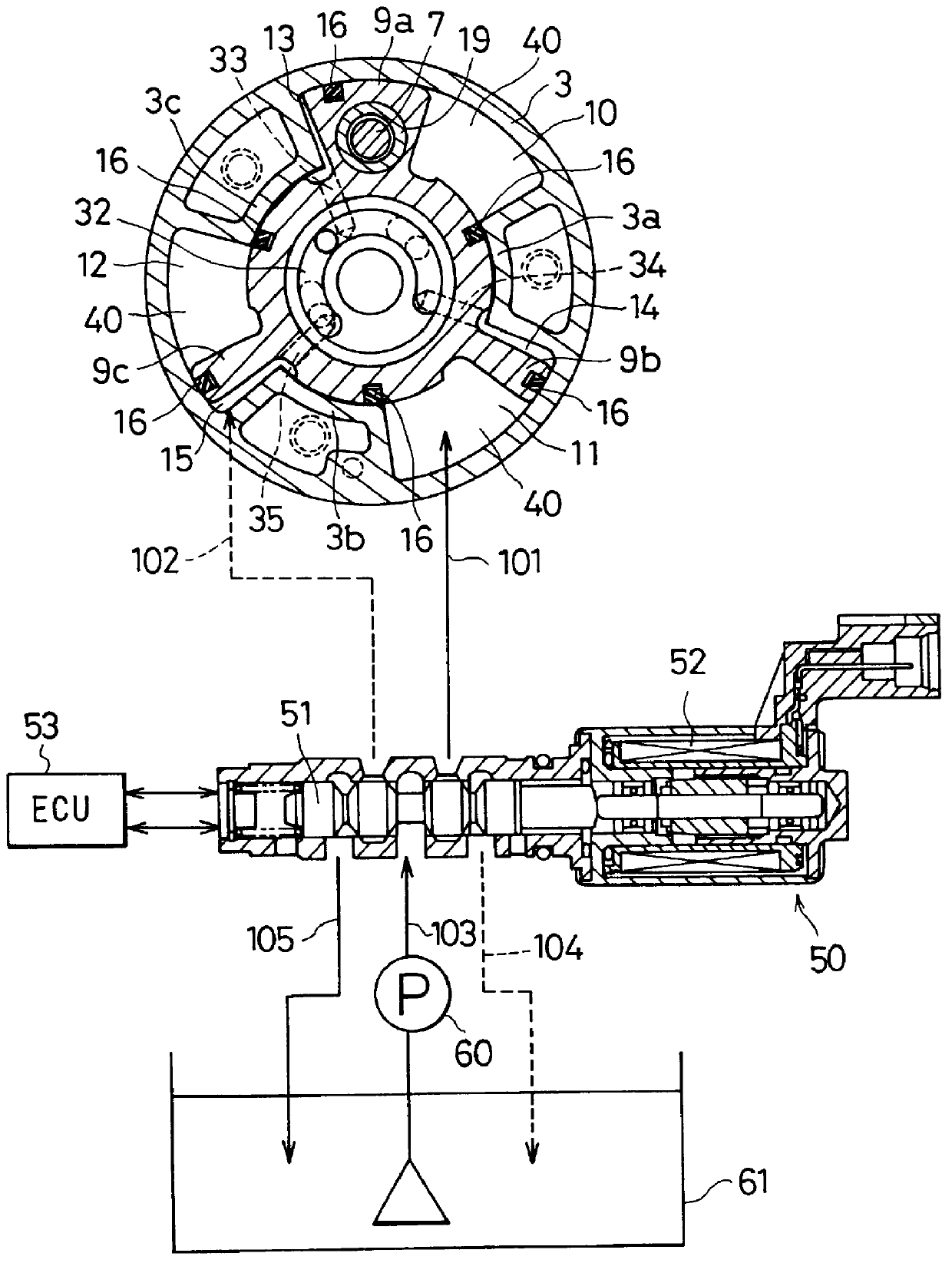
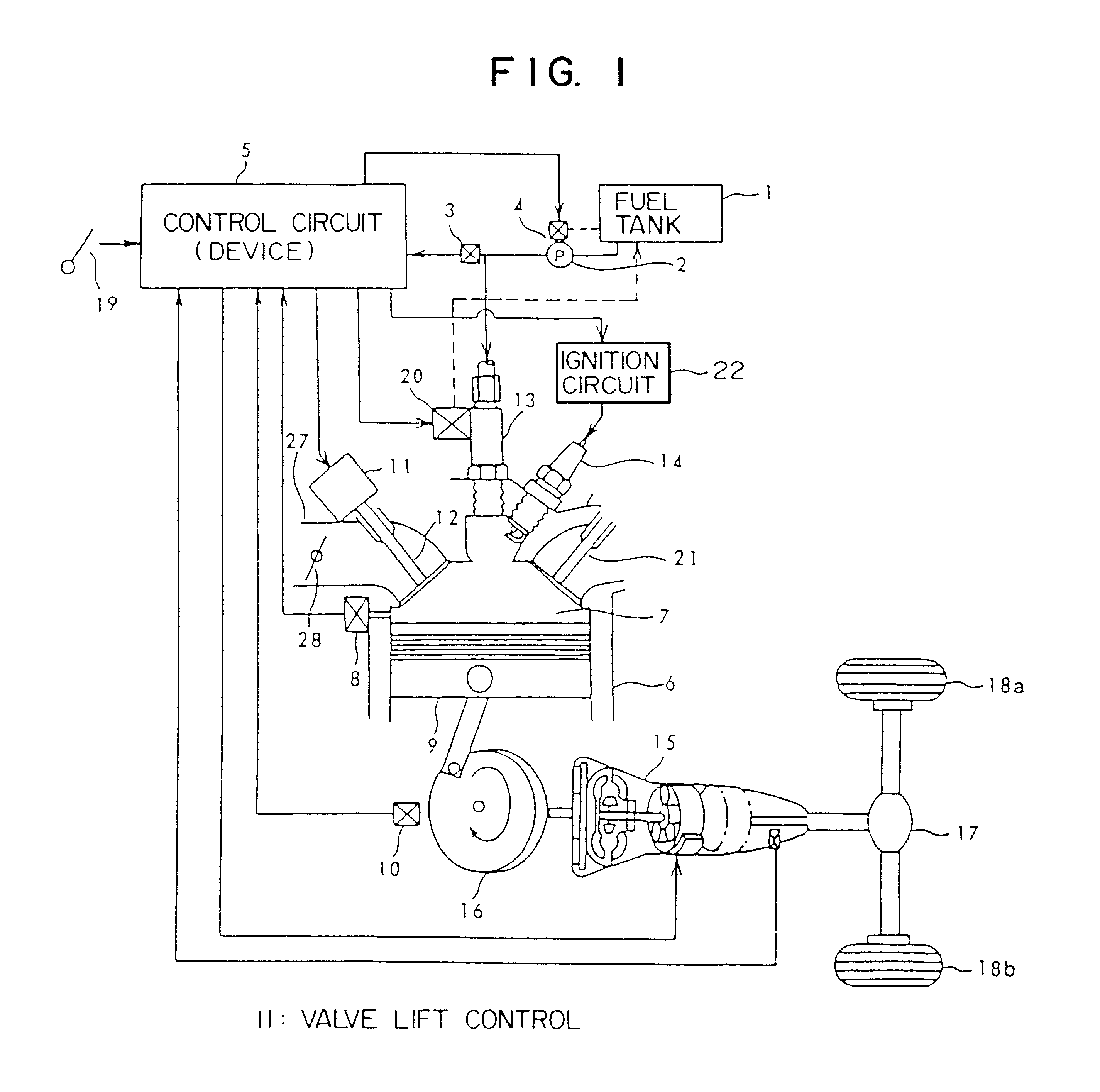
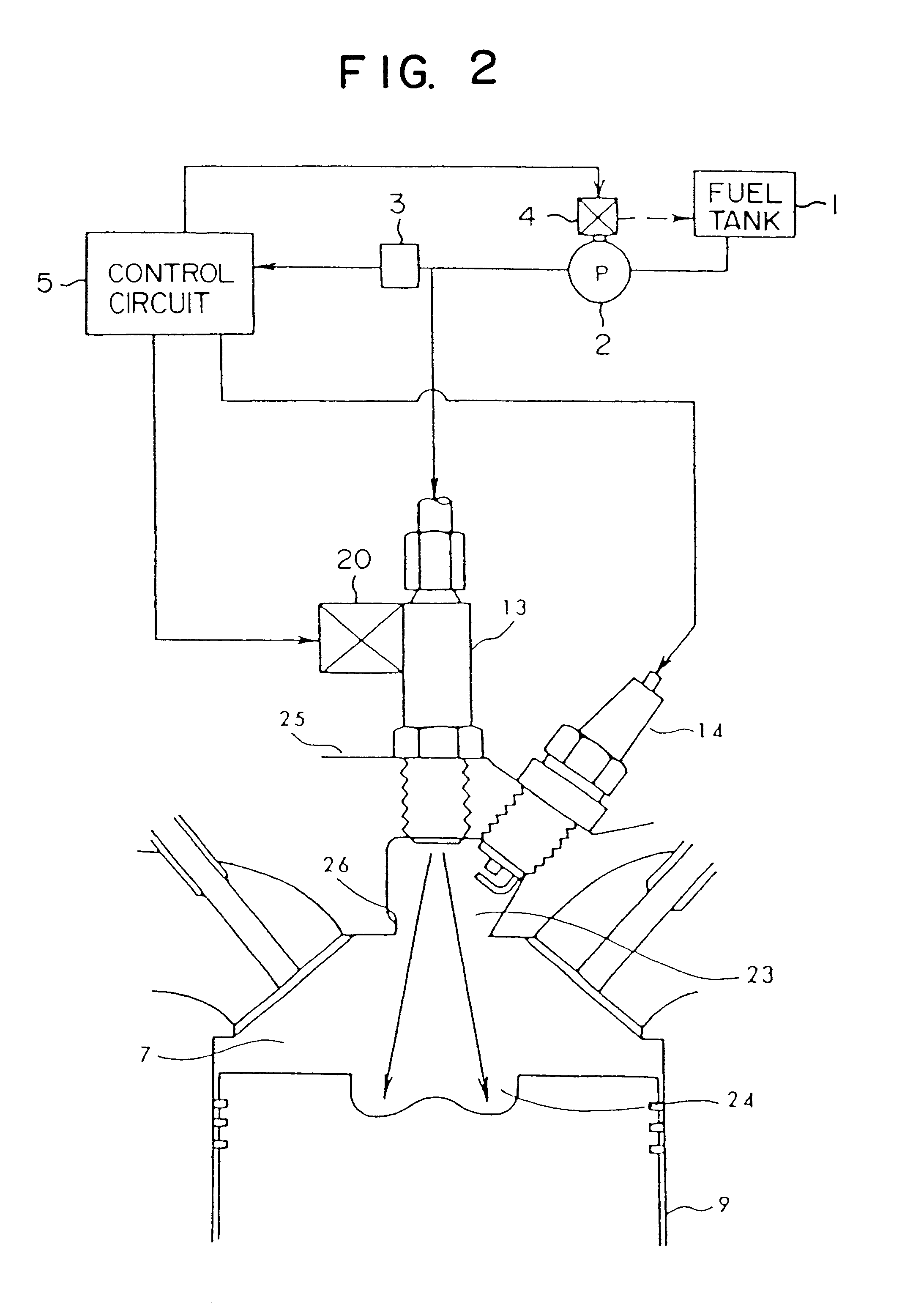
In an apparatus for controlling a multi-cylinder internal combustion engine with partial cylinder switch-off mechanism which is switchable between an all-cylinder operation mode in which all cylinders are operated and a partial-cylinder operation mode in which operation of partial cylinders is suspended, the operation of intake valves and exhaust valves is suspended or resumed in a predetermined order with respect to all of the suspended cylinders irrespective of a rotational frequency of the engine. There are provided a solenoid valve on an intake side and a solenoid valve on an exhaust side for switching input hydraulic pressures for hydraulically operated switching devices respectively on the intake side and on the exhaust side between the driving state and the drive-free state. At the time of switching the operation, one of the solenoid valves on the intake side and the exhaust side is driven in advance. The subsequent number of rotations of a crankshaft is counted. When the number of this counting has reached a predetermined value, the solenoid valve on the other side is driven.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
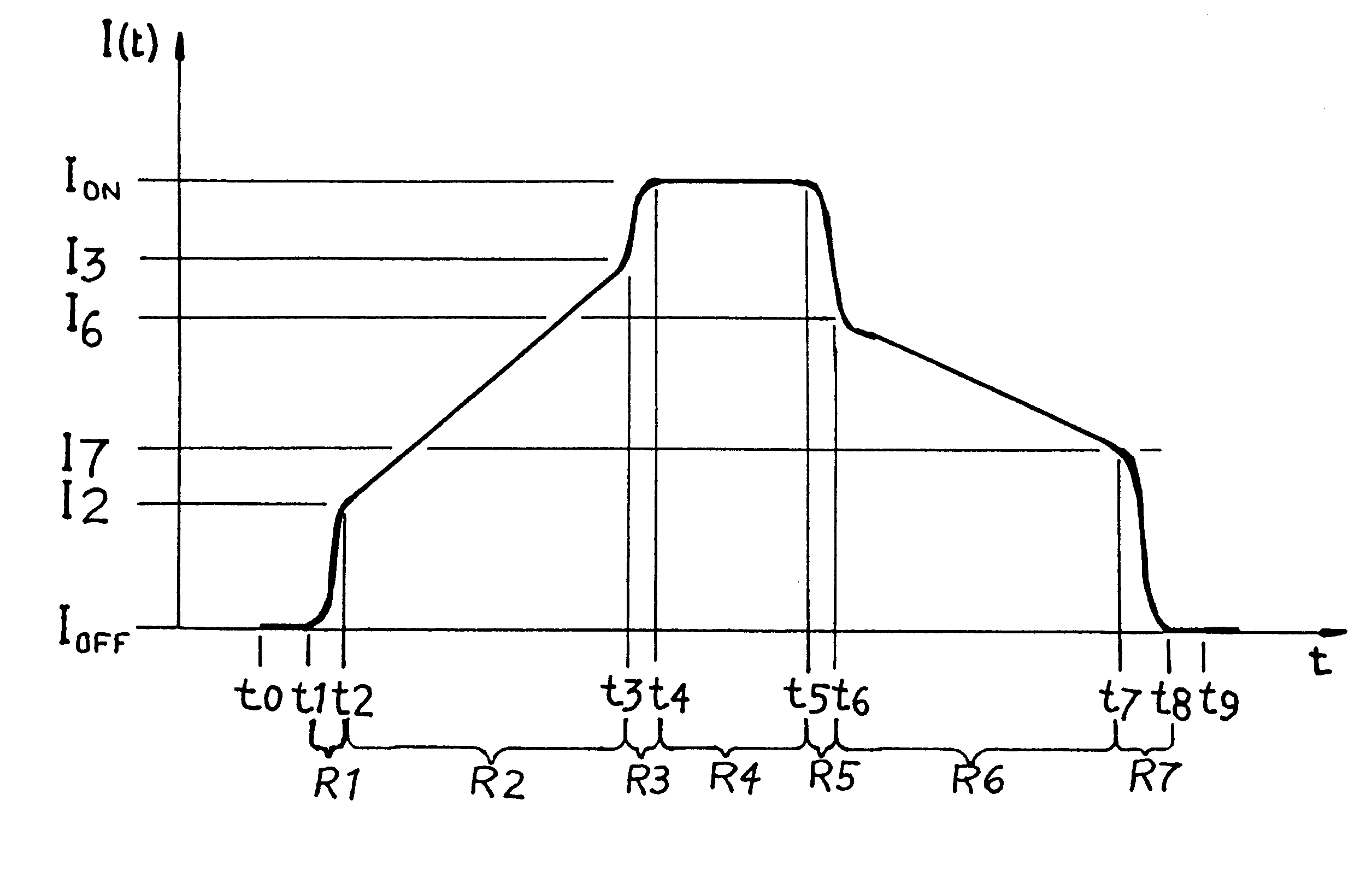
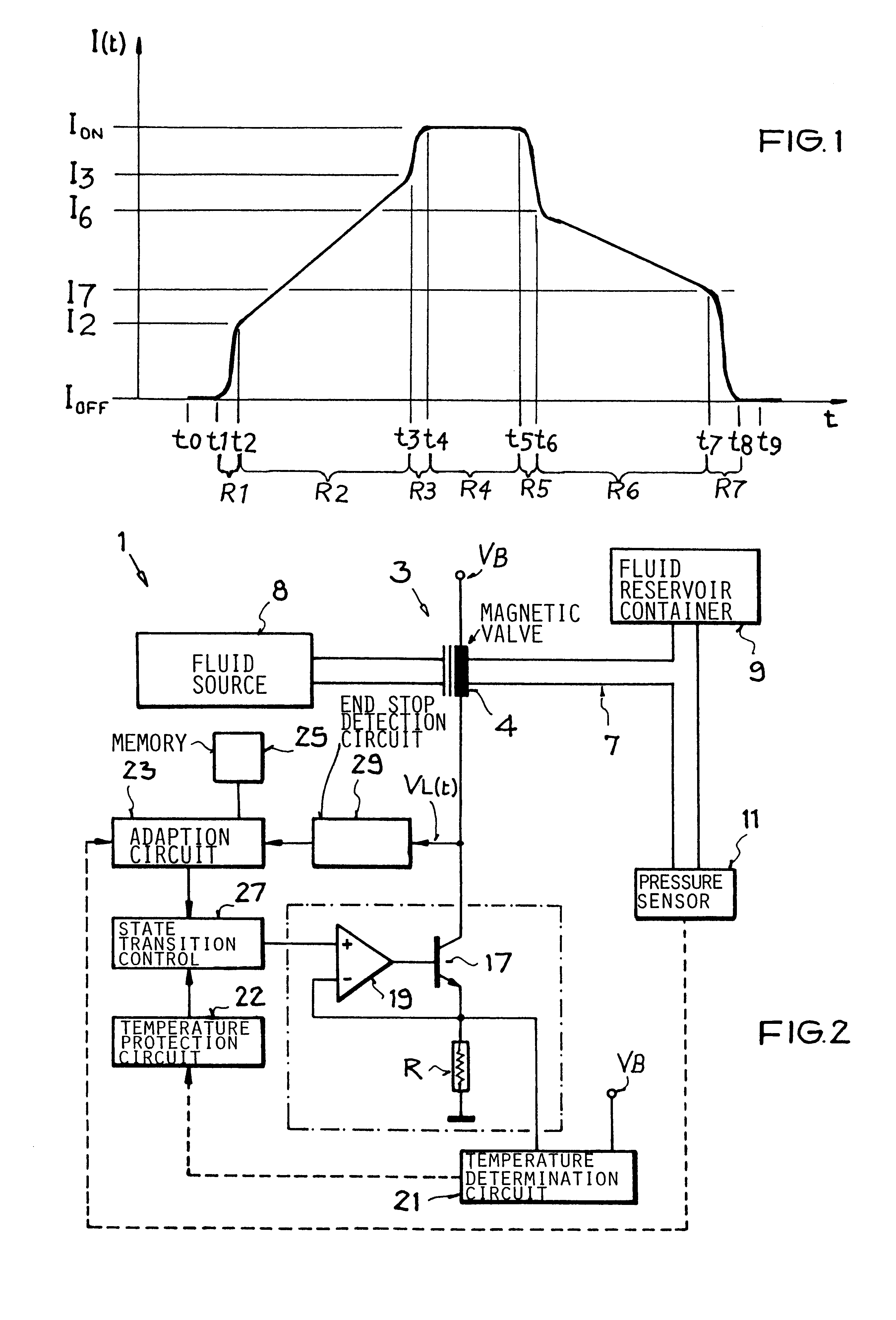
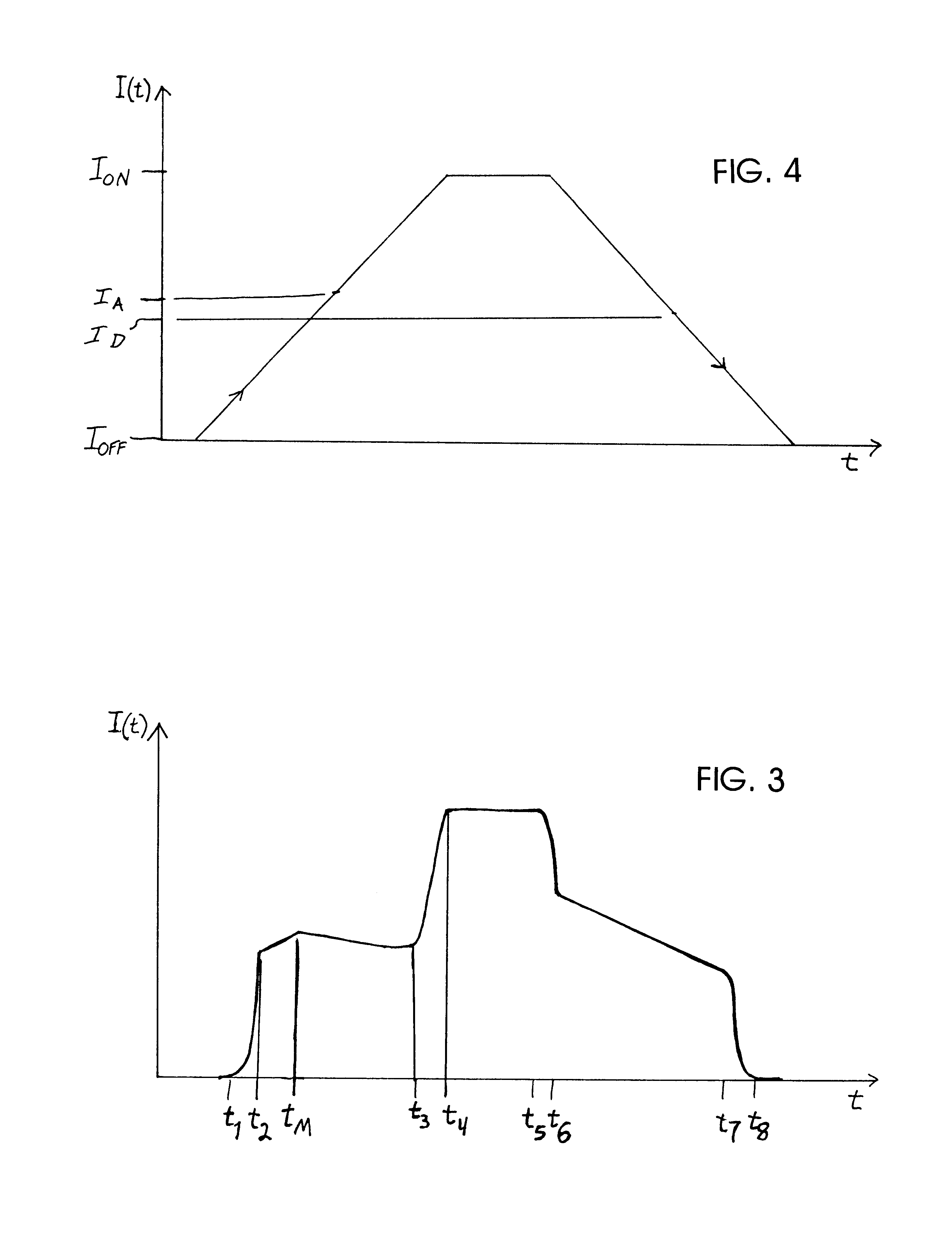
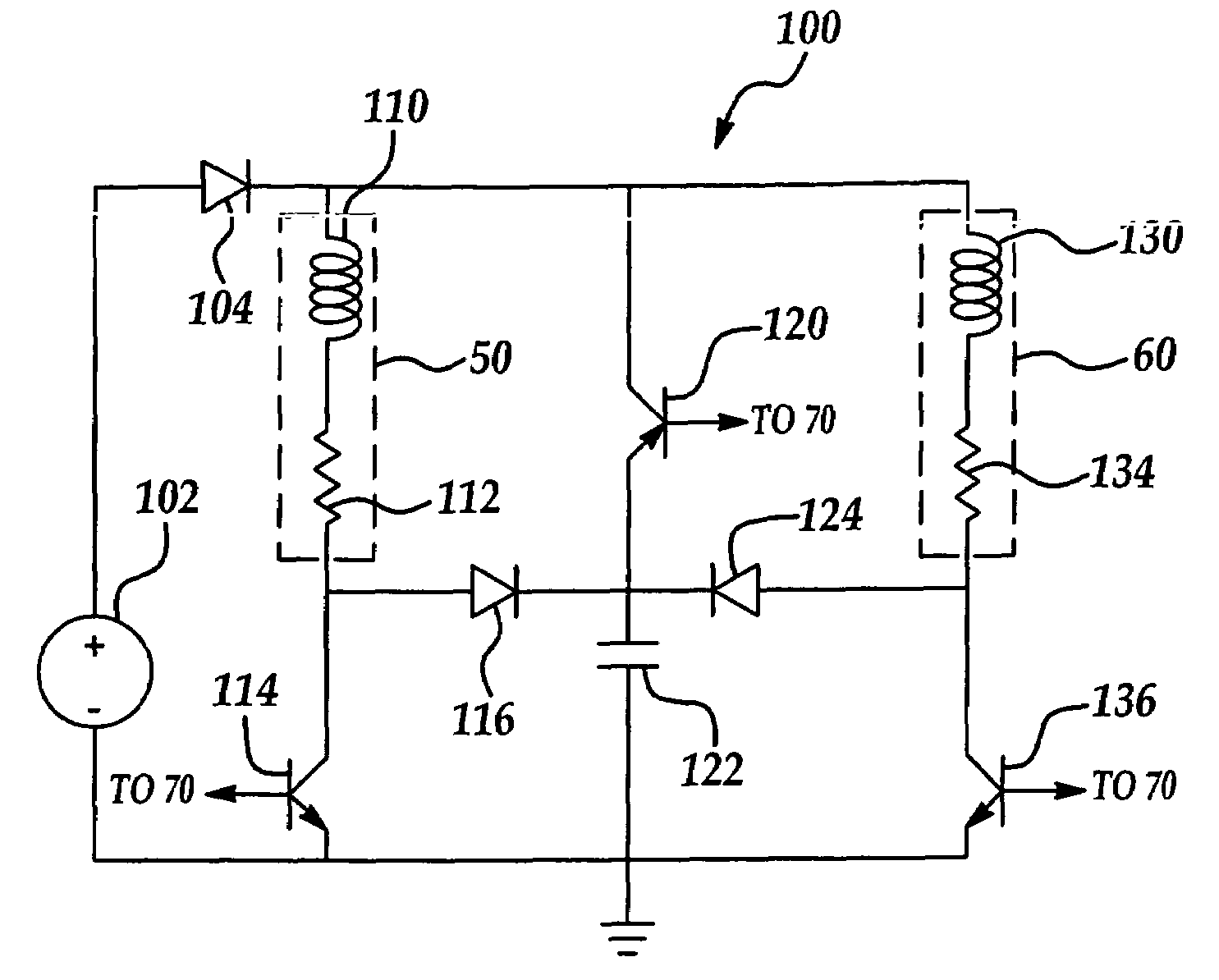
Method and circuit arrangement for reducing noise produced by electromagnetically actuated devices
InactiveUS6560088B1Minimizes excess energyGeneration can be minimizedOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectric switchesEngineeringElectromagnet
In an electromagnetically actuatable device, an electromagnet is driven with a controlled current progression so that the armature of the electromagnet can be actuated at the lowest possible current level while still achieving the most rapid overall increase of the actuating current from zero to maximum amperage. A first portion or range of the current increase is carried out with a steep or jump-like current increasing characteristic. A second portion or range of the current increase is carried out with a more gradual variation of the current. The current levels at the end points of the respective ranges are selected to ensure that the electromagnet is actuated during the second range in which the current varies more gradually. Preferably, two steep or jump-like current increase ranges are respectively provided before and after the second range having the gradual current increase. The armature of the electromagnet is thereby actuated with the lowest possible energy, and the lowest possible acceleration, so that noise and wear are reduced.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
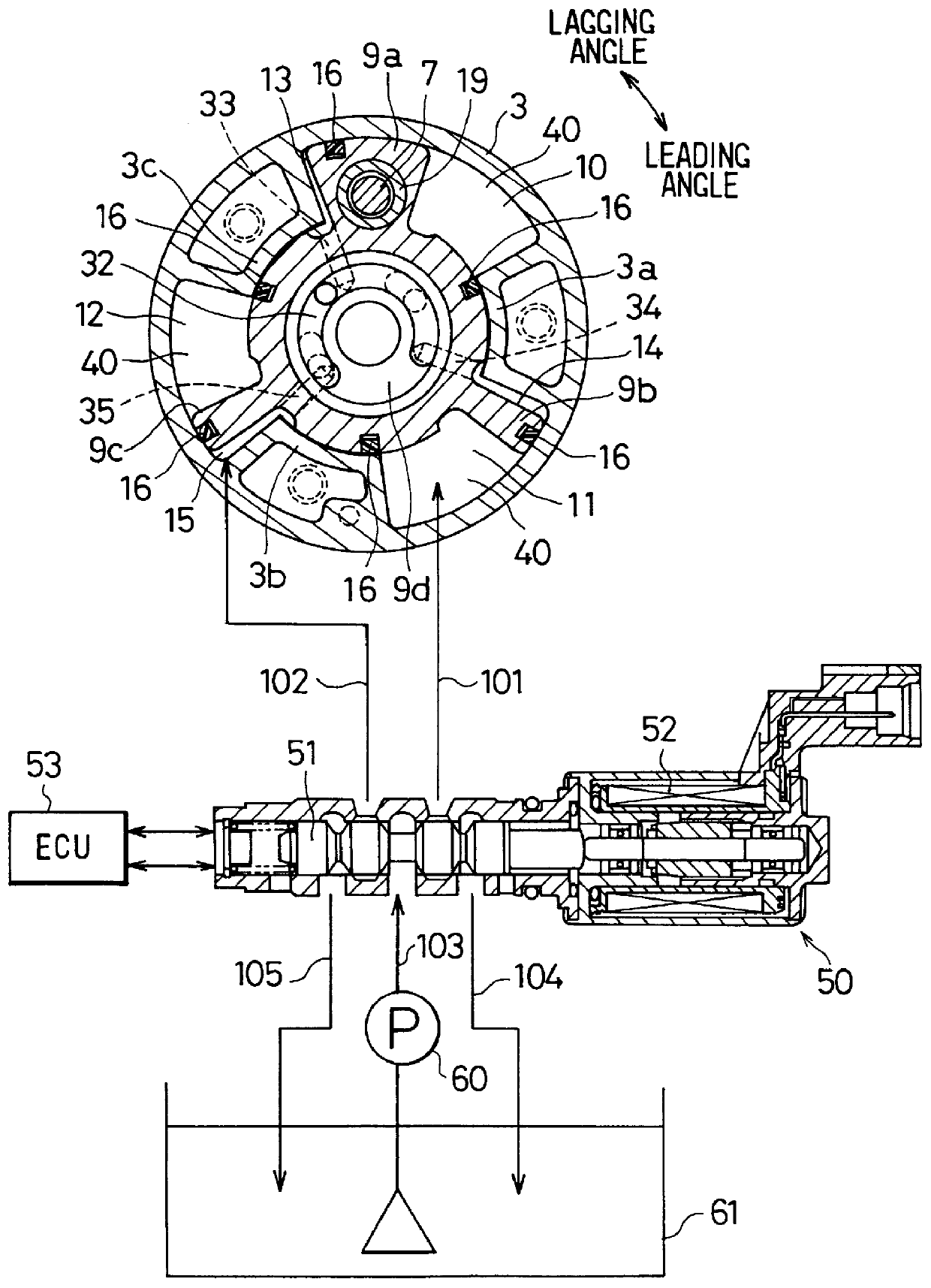
Valve timing adjusting apparatus for internal combustion engines
InactiveUS6024061AEasy to manufactureHigh precisionCamsYielding couplingCombustionExternal combustion engine
A valve timing adjusting apparatus that selectively controls a restraint mechanism for restraining relative rotation between a housing member and a vane member to increase the operational life thereof. When a vane rotor is held at a most lagging angular position, an end holding mode is executed to pull out a stopper piston from a stopper hole by fluid pressures of both a leading angle side and a lagging angle side. As a result, when the vane rotor rotates from the most lagging angular position to the leading angle side, torsional forces on the stopper piston and the stopper hole can be minimized as the vane member direction of rotation changes. Since a fluid pressure has already been applied to each of leading angle fluid pressure chambers in the end holding mode, the vane rotor can be rotated from the most lagging angular position to the leading angle side quickly by increasing fluid pressure applied to each of the leading angle fluid pressure chambers without the need to switch a fluid path. In addition, since the fluid pressure applied to each of the leading angle fluid pressure chambers in the end holding mode is smaller than fluid pressure for rotating the vane rotor to the leading angle side, generation of impact sound due to collisions of vanes can be avoided.
Owner:DENSO CORP
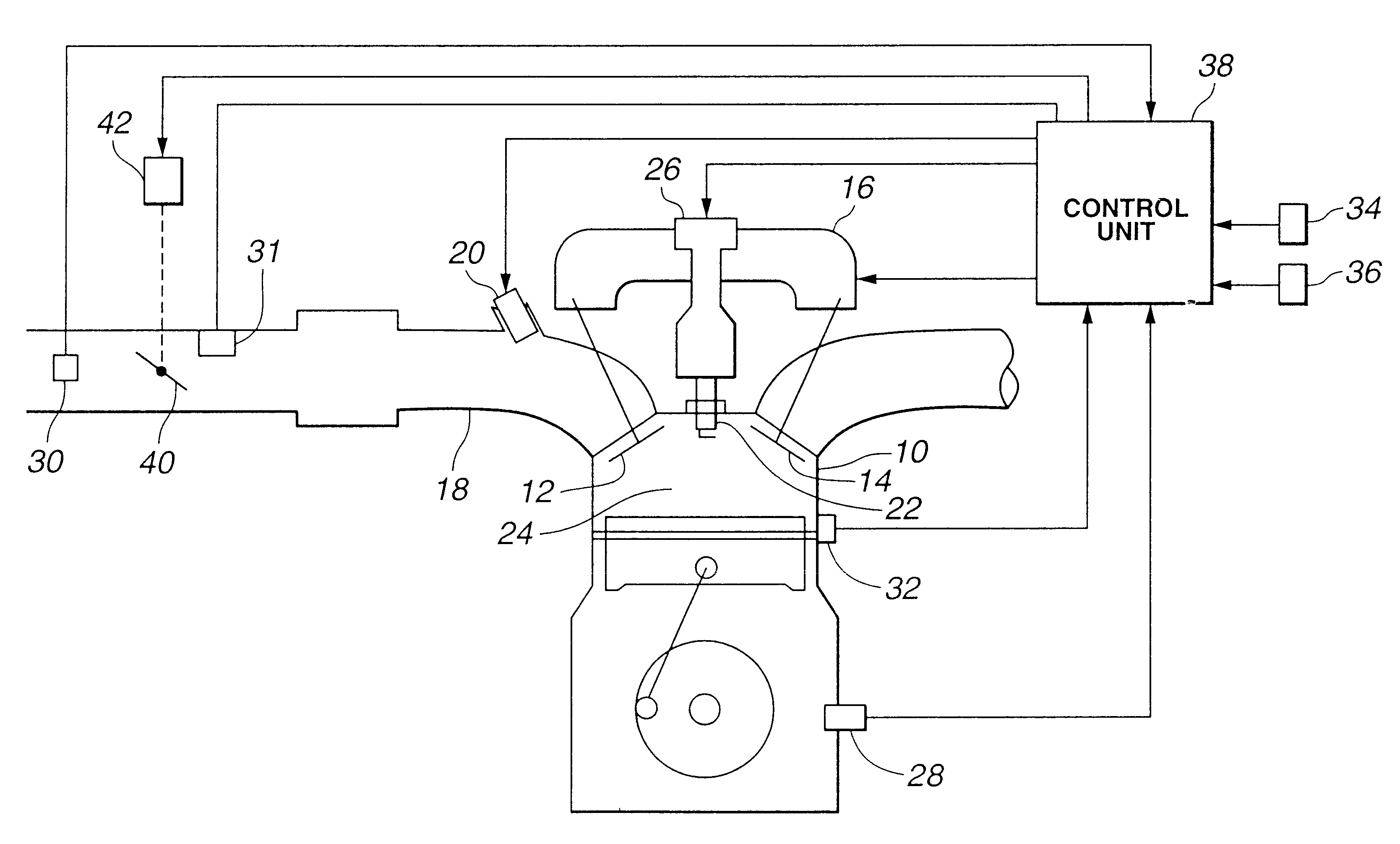
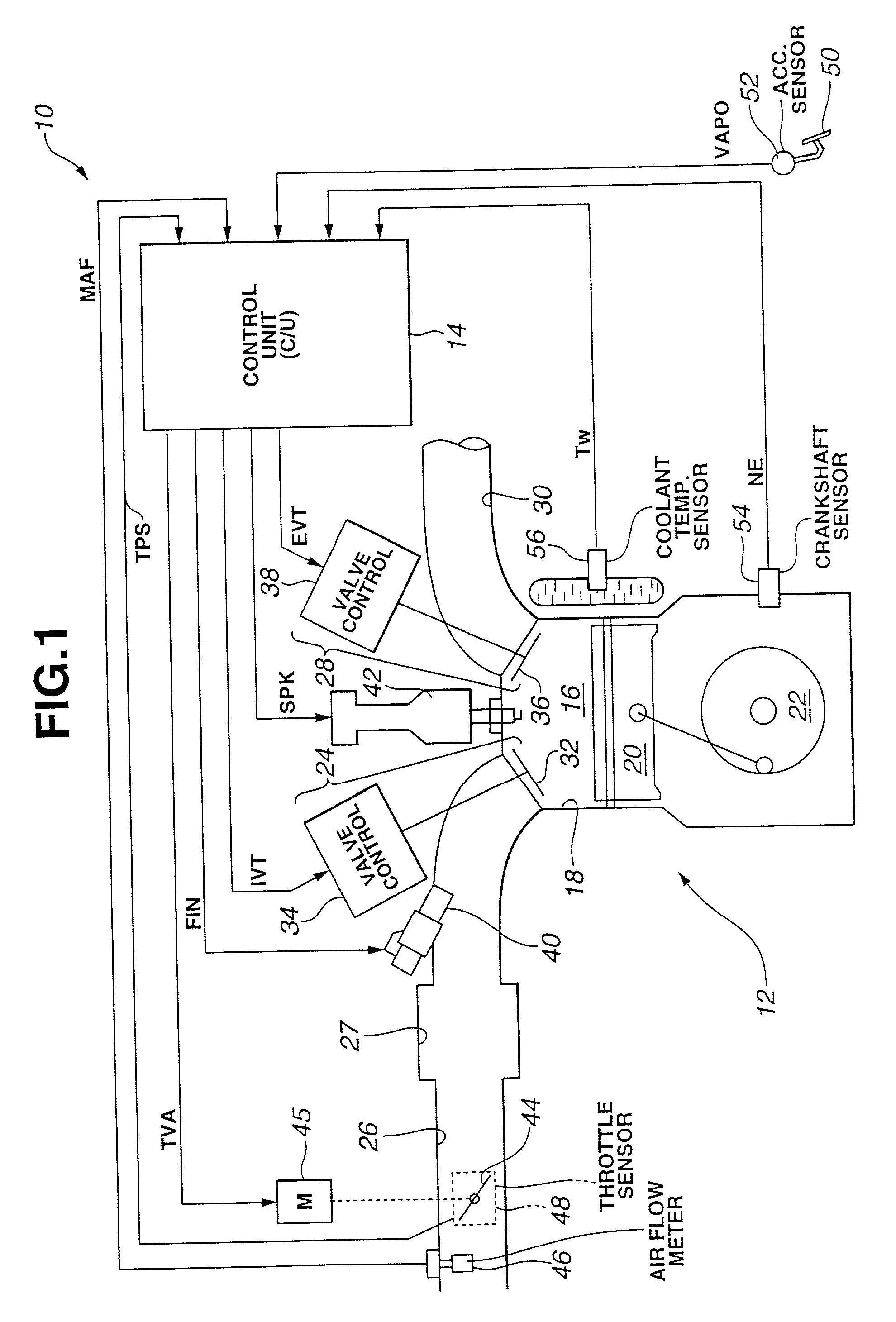
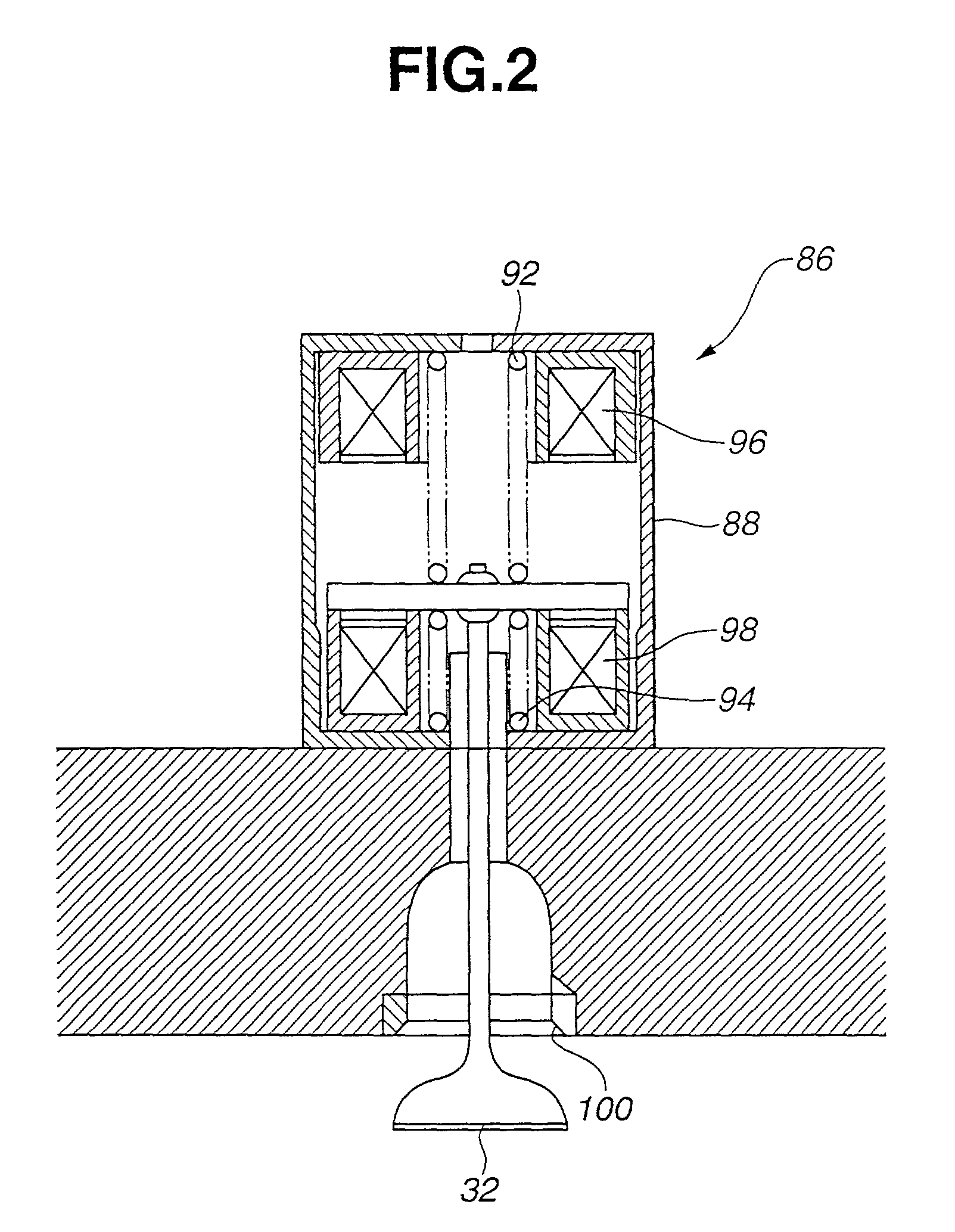
Apparatus for and method of controlling internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6343585B1Increasing produced torqueInjection amount is smallElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveExternal combustion engine
The engine disclosed features an engine cylinder provided with an air intake valve, an injector having a fuel injection port which is directed towards an interior of the engine cylinder, and a control unit which is connected to the air intake valve and to the injector, the control unit effecting changes in the air intake amount by controlling the degree of opening of the air intake valve, and, also, controls the air / fuel ratio by changing the amount of fuel supplied by the injector. The engine also has an exhaust valve in the engine cylinder such that the control unit controls the intake valve and the exhaust valve so that an opening period of the intake valve is overlapped with an opening period of the exhaust valve at least when the opening period of the intake valve is maximum. The period of the overlap is longer when a relatively large amount of air is required than when a relatively small amount of air is required. According to such a scheme, the amount of the air can be changed by the lift of the intake valve. By changing the lift, the overlap with an exhaust valve is also changed. During the high-output or power operation, the period of overlap between the exhaust valve and the intake valve is made longer. When engine torque decreases to a level lower than the target engine torque, the air amount is adjusted by the cam or the throttle valve.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Control system for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20050000480A1Emission reductionQuick activationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemOtto cycle
A control system for an internal combustion engine, which is capable of reducing exhaust emissions during and after the start of the engine. A control system is capable of changing the valve-closing timing of intake valves relative to the valve-opening timing thereof as desired using a variable intake valve actuation assembly. The control system includes an ECU. The ECU sets a target auxiliary intake cam phase to a start value that sets the valve-closing timing of the intake valves to retarded-closing timing, during starting of the engine, and to a catalyst warmup value that sets the same to timing closer to timing in the Otto cycle operation, during catalyst warmup control after the start of the engine.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Electromagnetic valve actuation
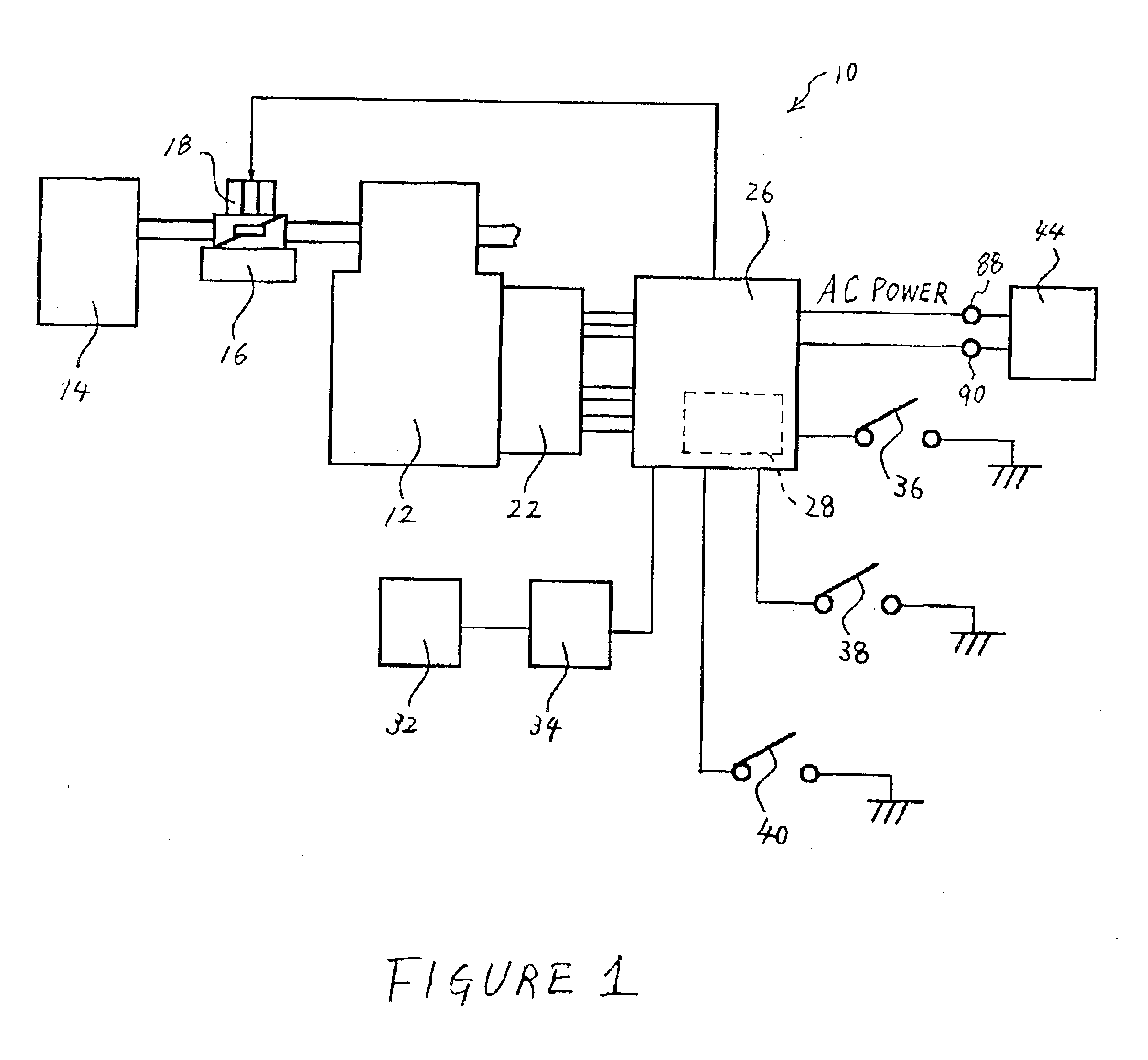
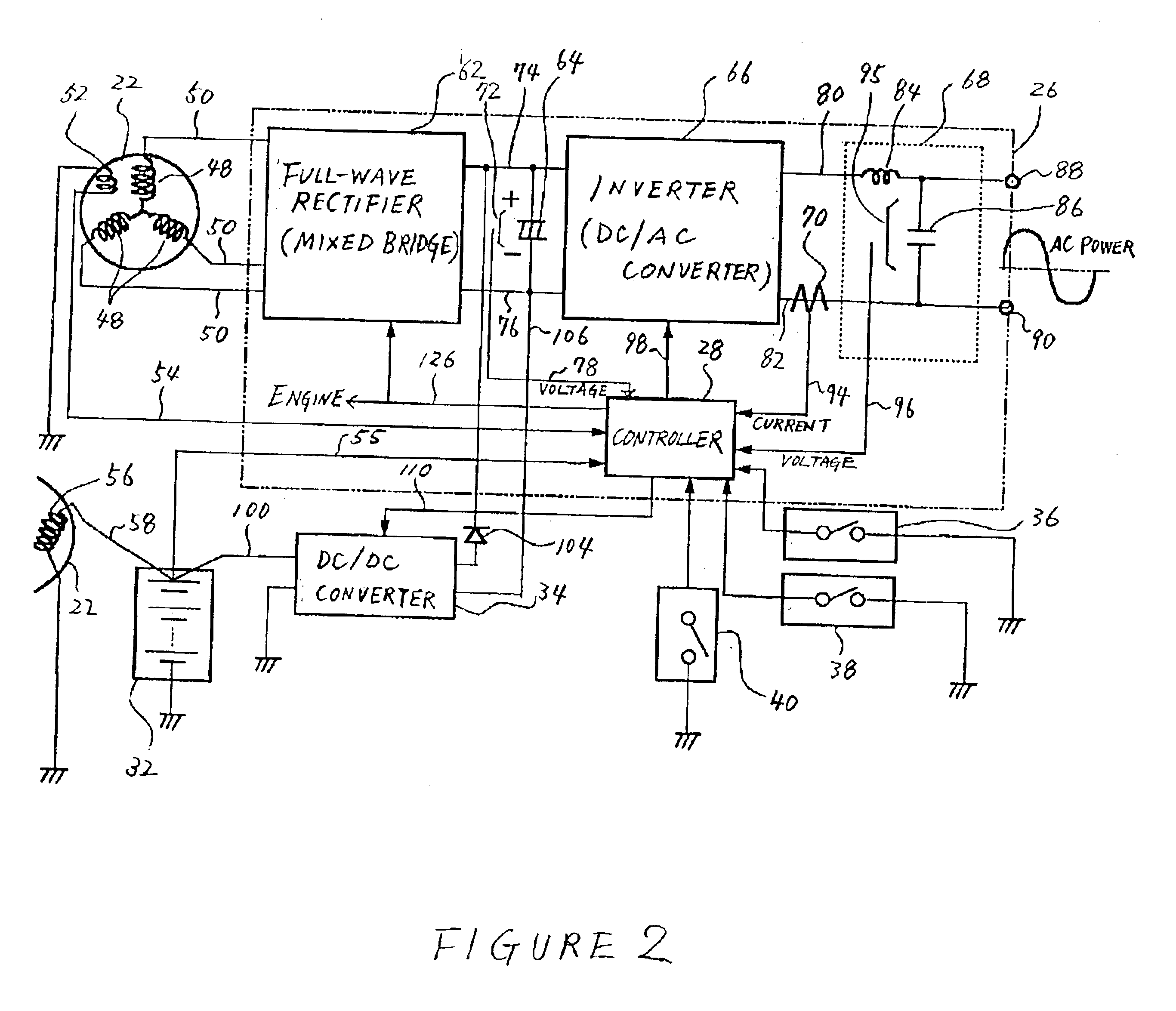
ActiveUS6948461B1Loss of forceRapidly quench the coil currentOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectric switchesCombustion chamberControl system
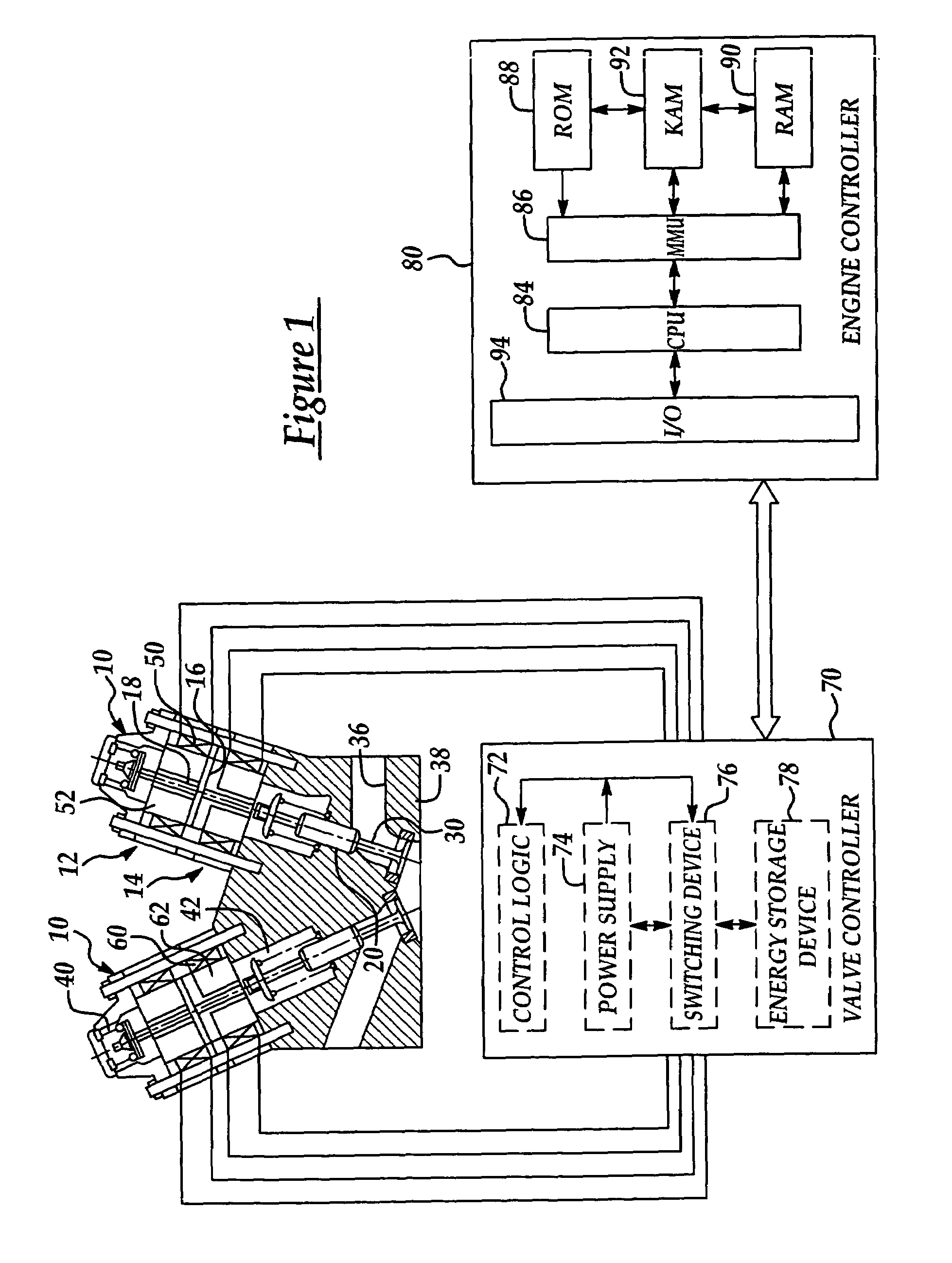
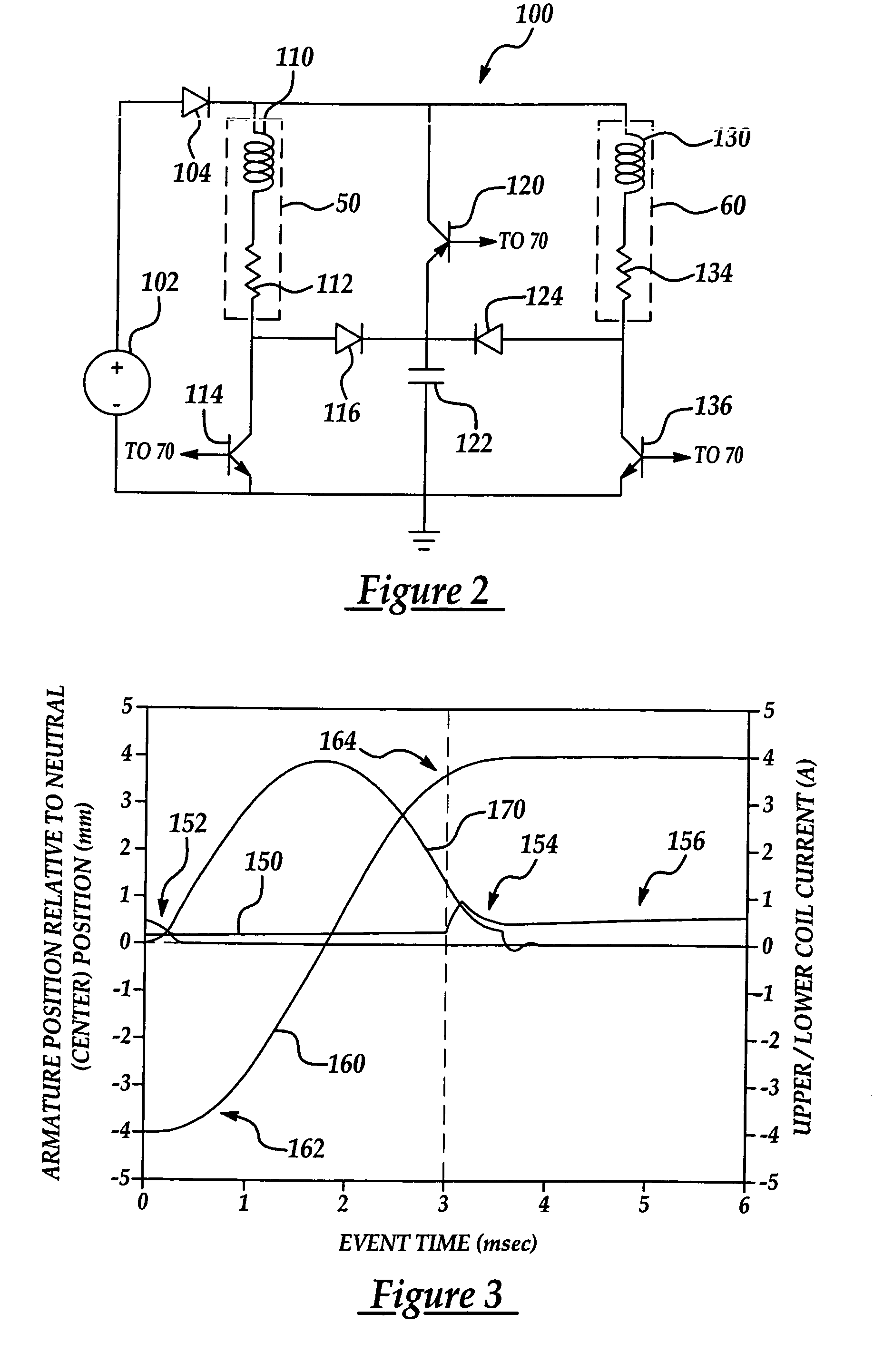
A system and method for controlling an internal combustion engine provide valve actuation that selectively couples an energy storage device to a launching coil to recover energy stored in the magnetic field and valve spring of the launching coil, decouples the energy storage device during a valve opening or closing event to control energy supplied to the catching coil, and couples the energy storage device to the catching coil to transfer energy from the storage device to the catching coil to provide a repeatable soft landing. A nonlinear feedback controller incorporates a feedforward system with an observer to control the rate of energy into the magnetic field of the catching coil while compensating for system losses and work to overcome gas forces within the combustion chamber. Feedback linearization techniques improve stability of the control system.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Control apparatus for drive system
InactiveUS6516264B2Improve acceleration performanceImprove fuel economy performanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl theoryAir–fuel ratio
A drive system composed of an engine and a transmission is controlled in accordance with a desired wheel toque corresponding to a position of an accelerator, and a present vehicle speed in such a way that a speed ratio of the transmission is determined in consideration with torque factors such as an air-fuel ratio on the engine side, thereby it possible to optimize the control in order to reduce the emission of exhaust substance such as NOx and to enhance the acceleration performance and the fuel economy.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Valve timing control device
ActiveUS8220426B2Improve balanceYielding couplingInternal combustion piston enginesPower control systemControl system
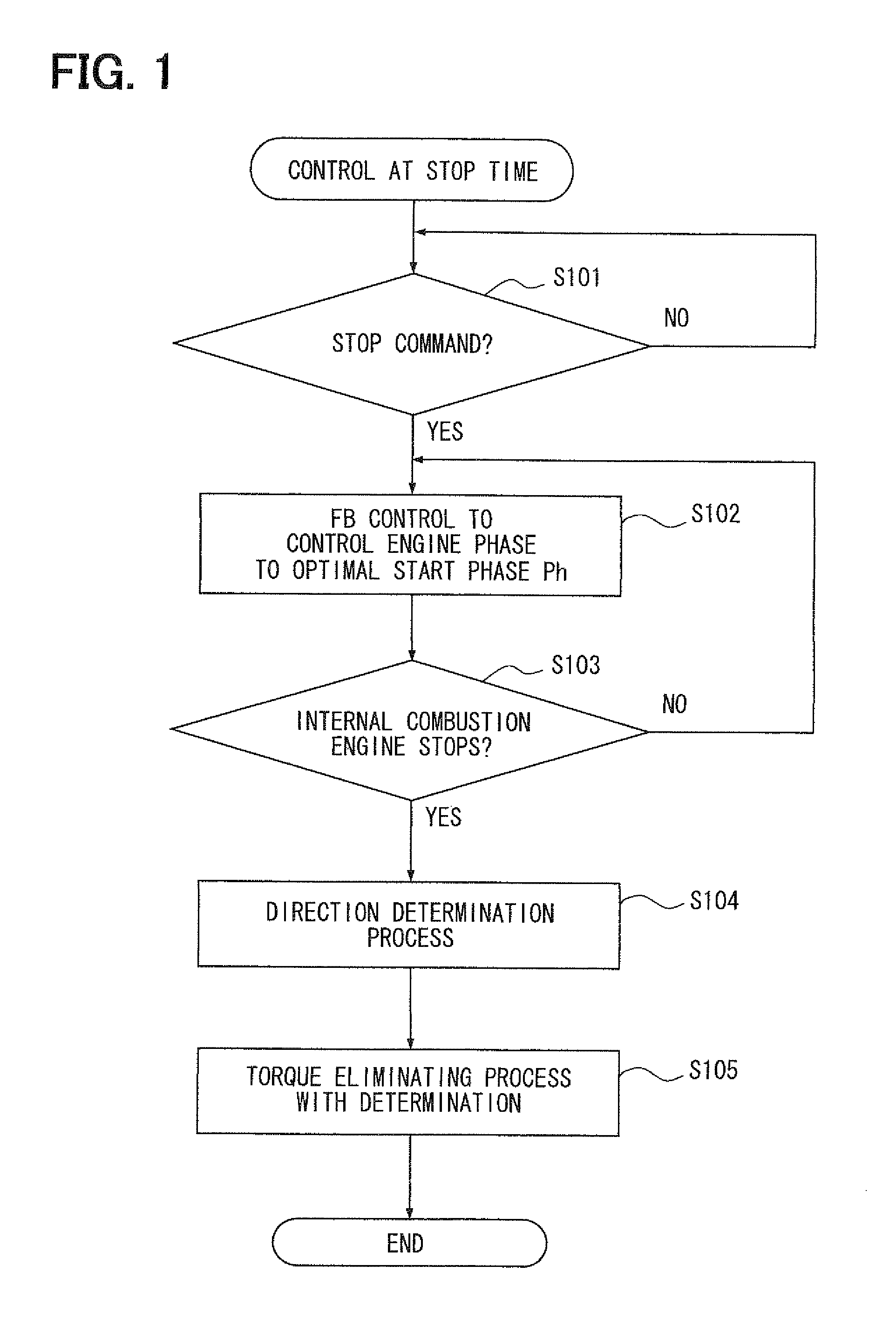
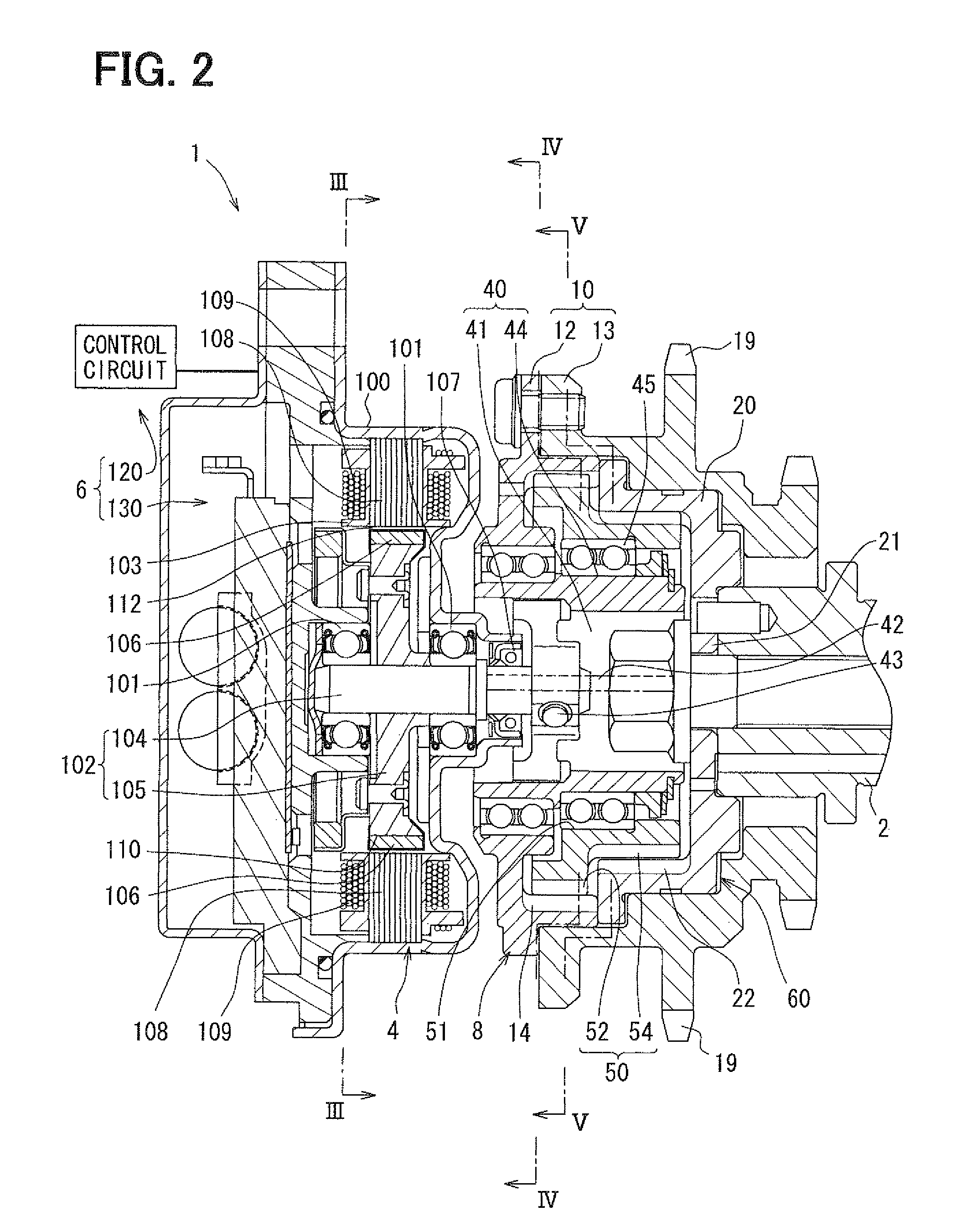
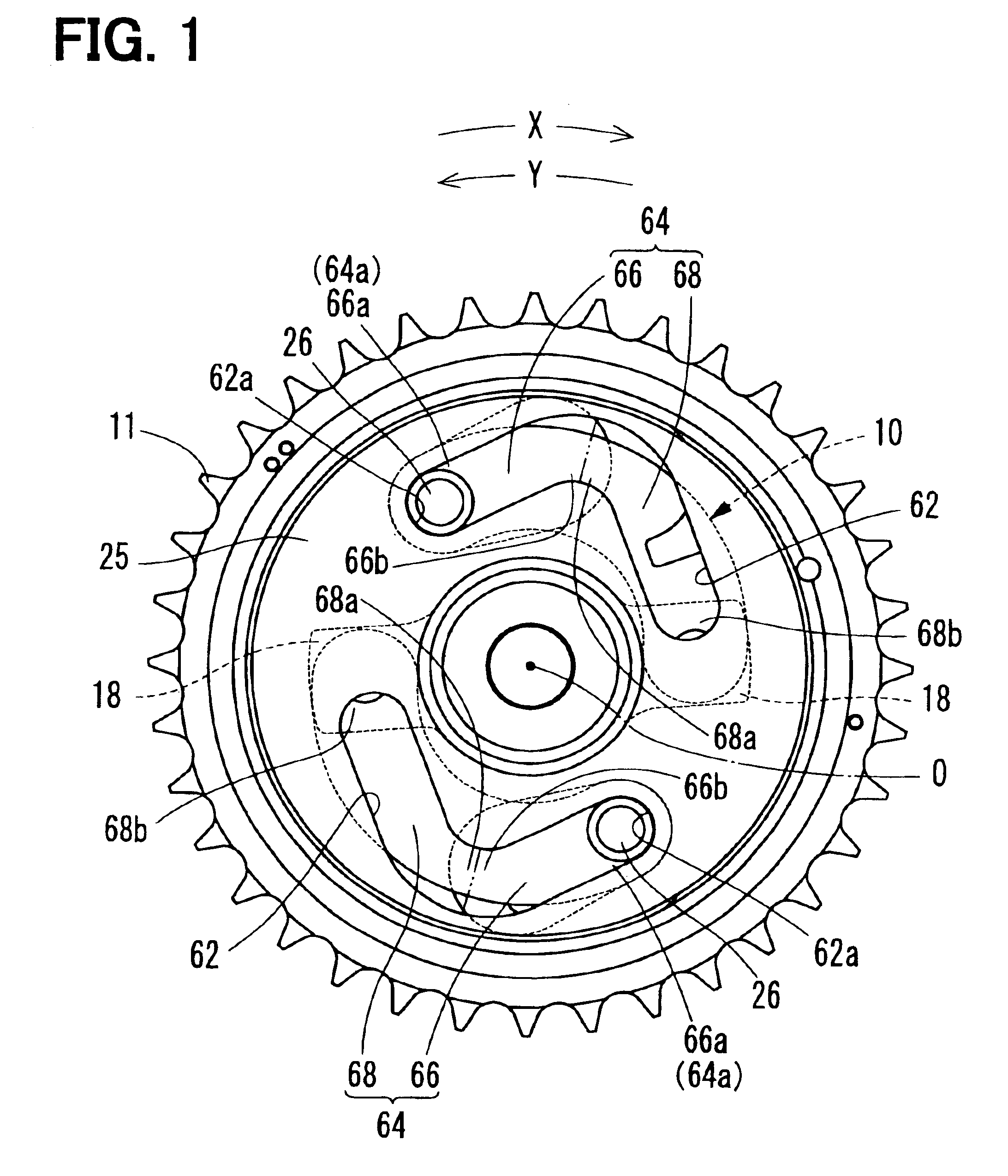
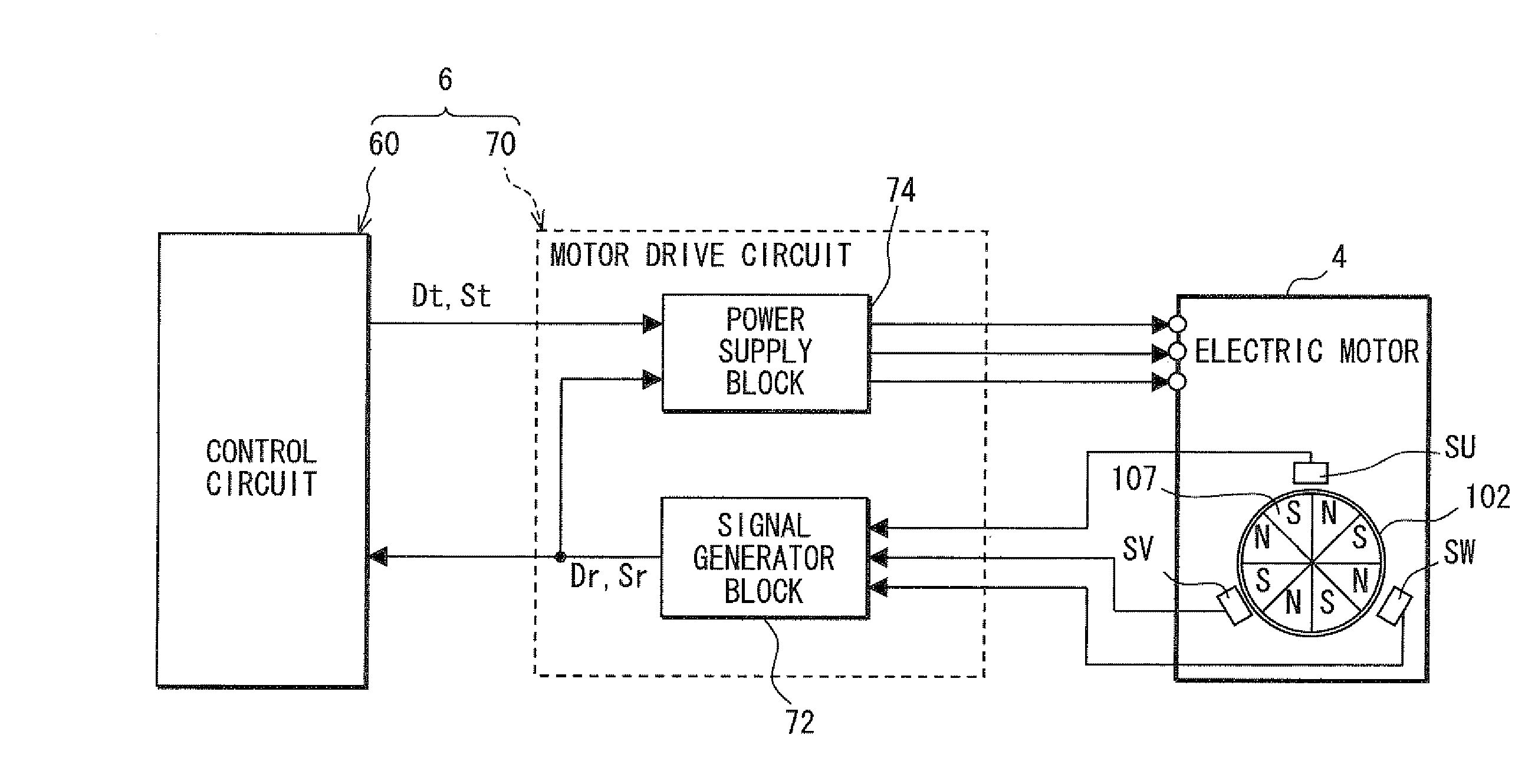
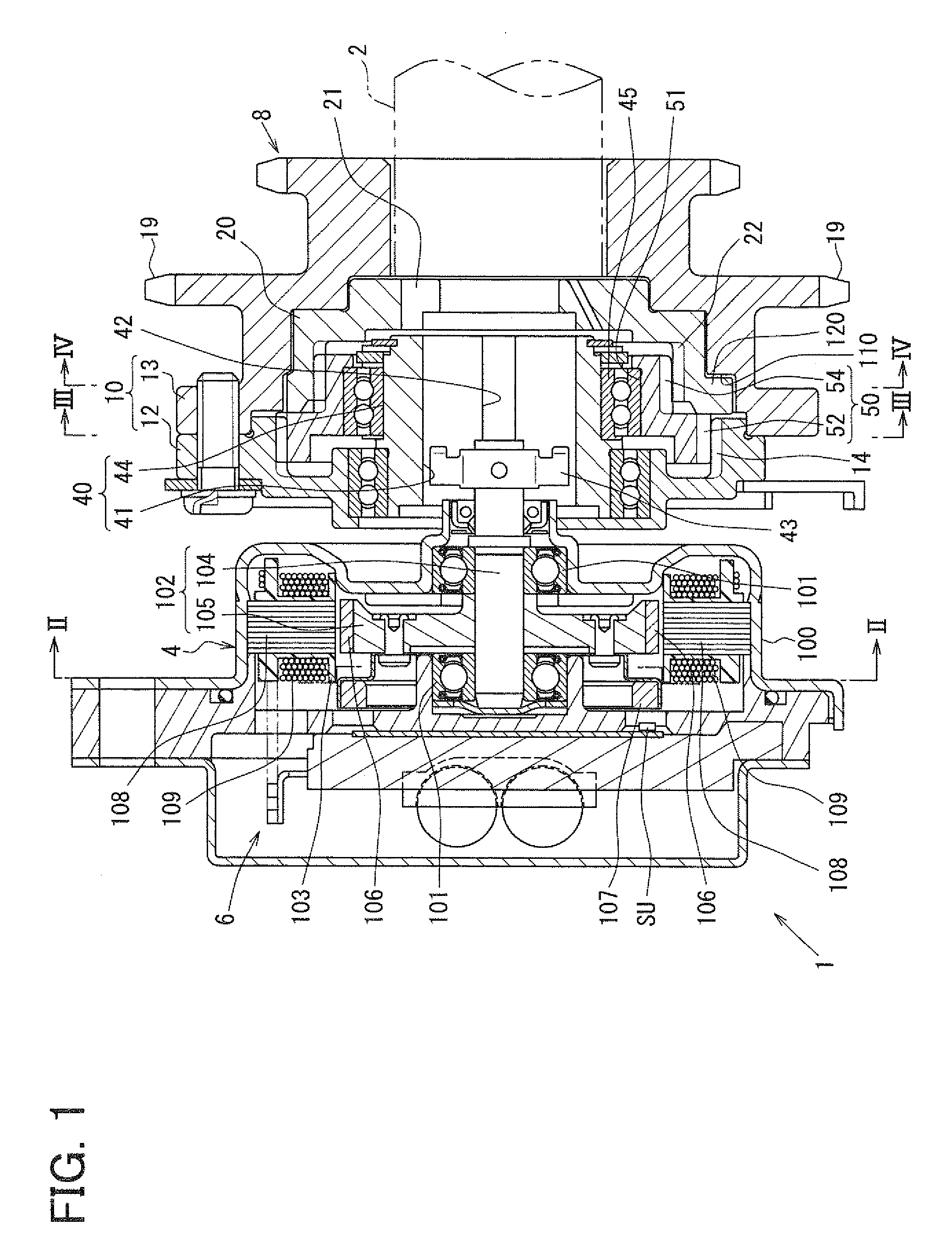
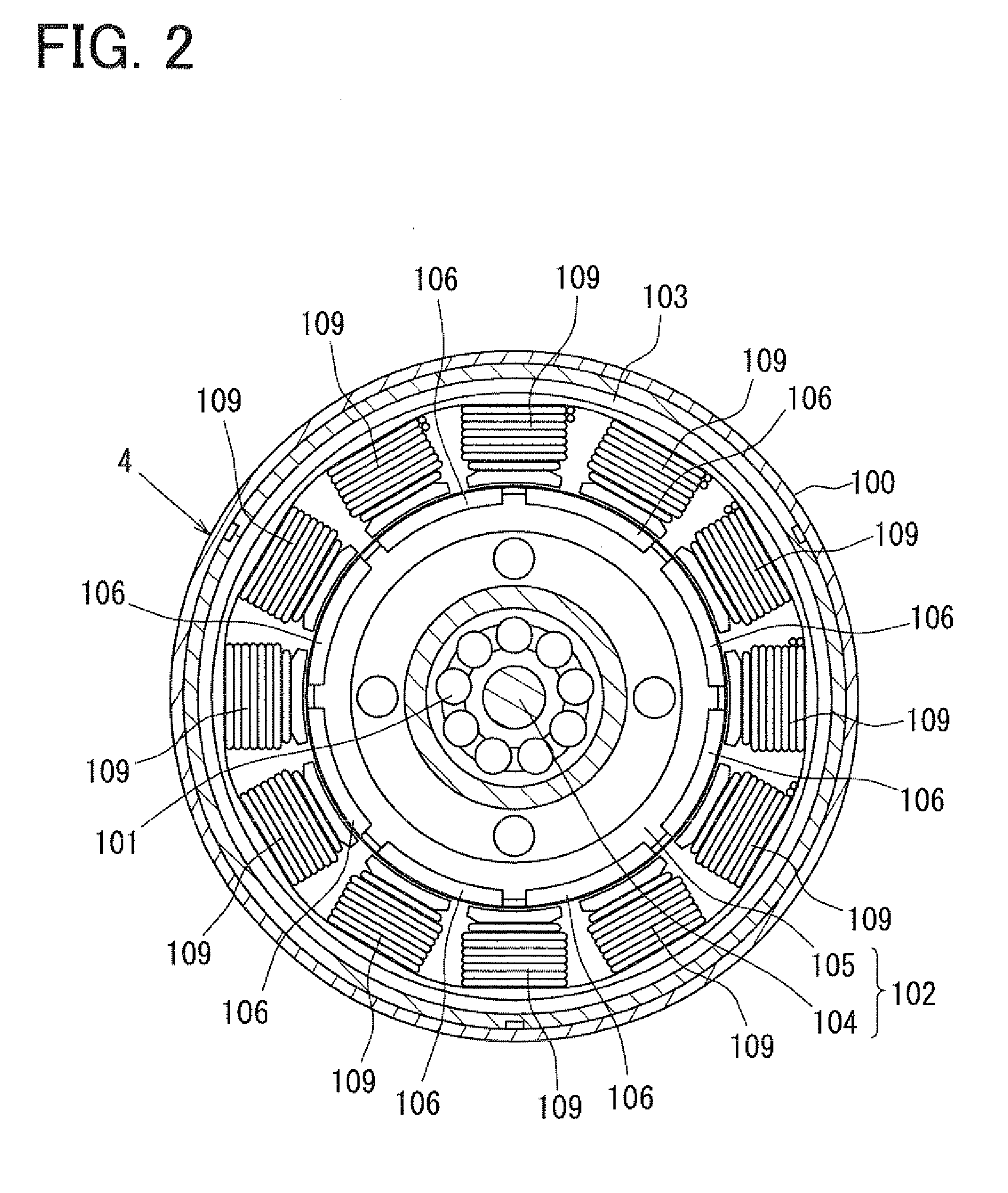
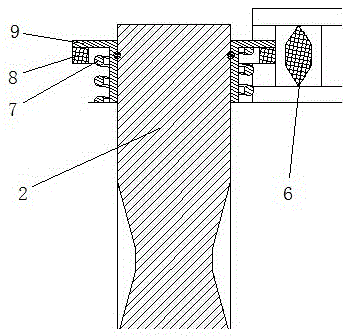
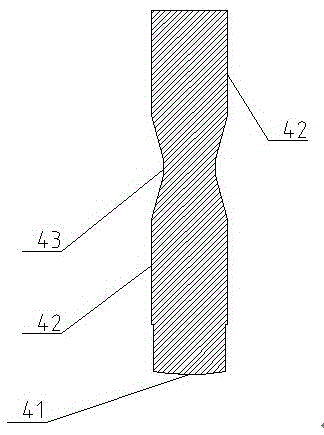
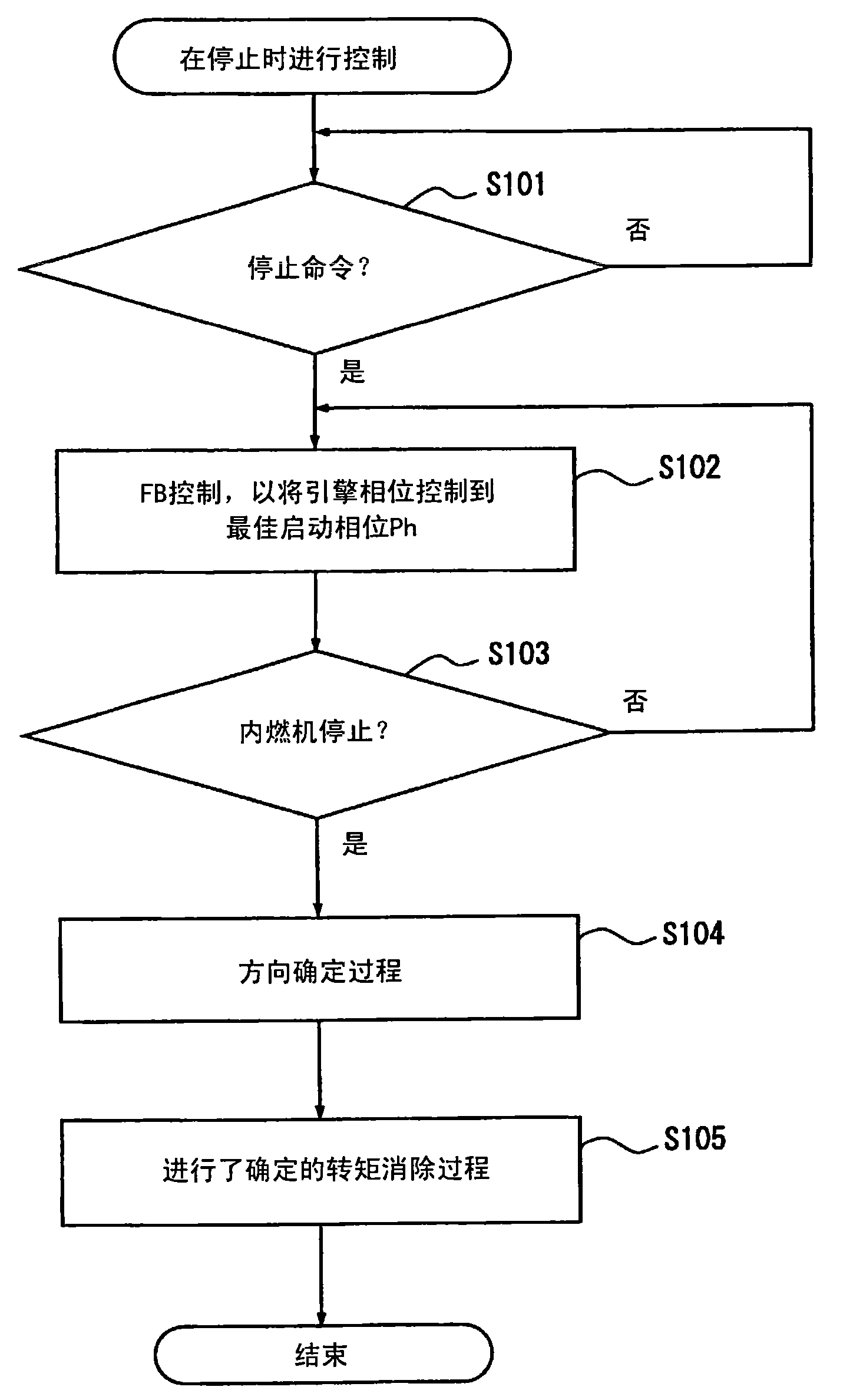
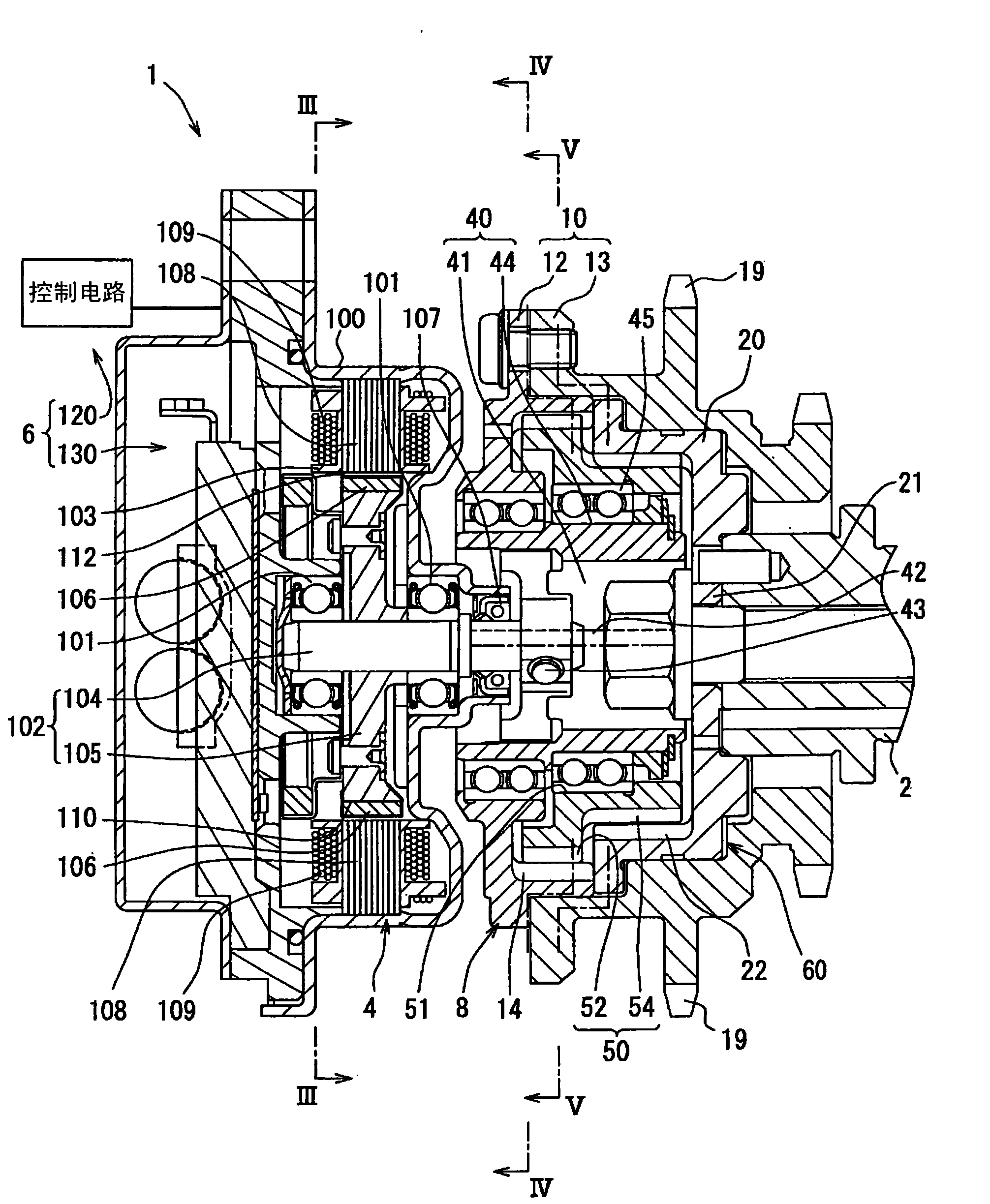
A valve timing control device is provided with an electric motor (4) generating a magnetic retaining torque (Th) and a motor torque (Tm) in a motor shaft (102) based on a power supply. A power supply control system (6) controls the motor torque (Tm) by controlling the power supply supplied to the electric motor (4). A phase control mechanism (8) transmits a cam torque (Tca) that can alternate between a positive and a negative direction in response to rotation of a cam shaft, to the motor shaft (102) and controls a relative phase between the crank shaft and the cam shaft in accordance with a torque balance in the motor shaft (102). The power supply control system (6) eliminates the motor torque (Tm) that is balanced with the magnetic retaining torque (Th) and the cam torque (Tca) after a stop of the internal combustion engine (S105).
Owner:DENSO CORP
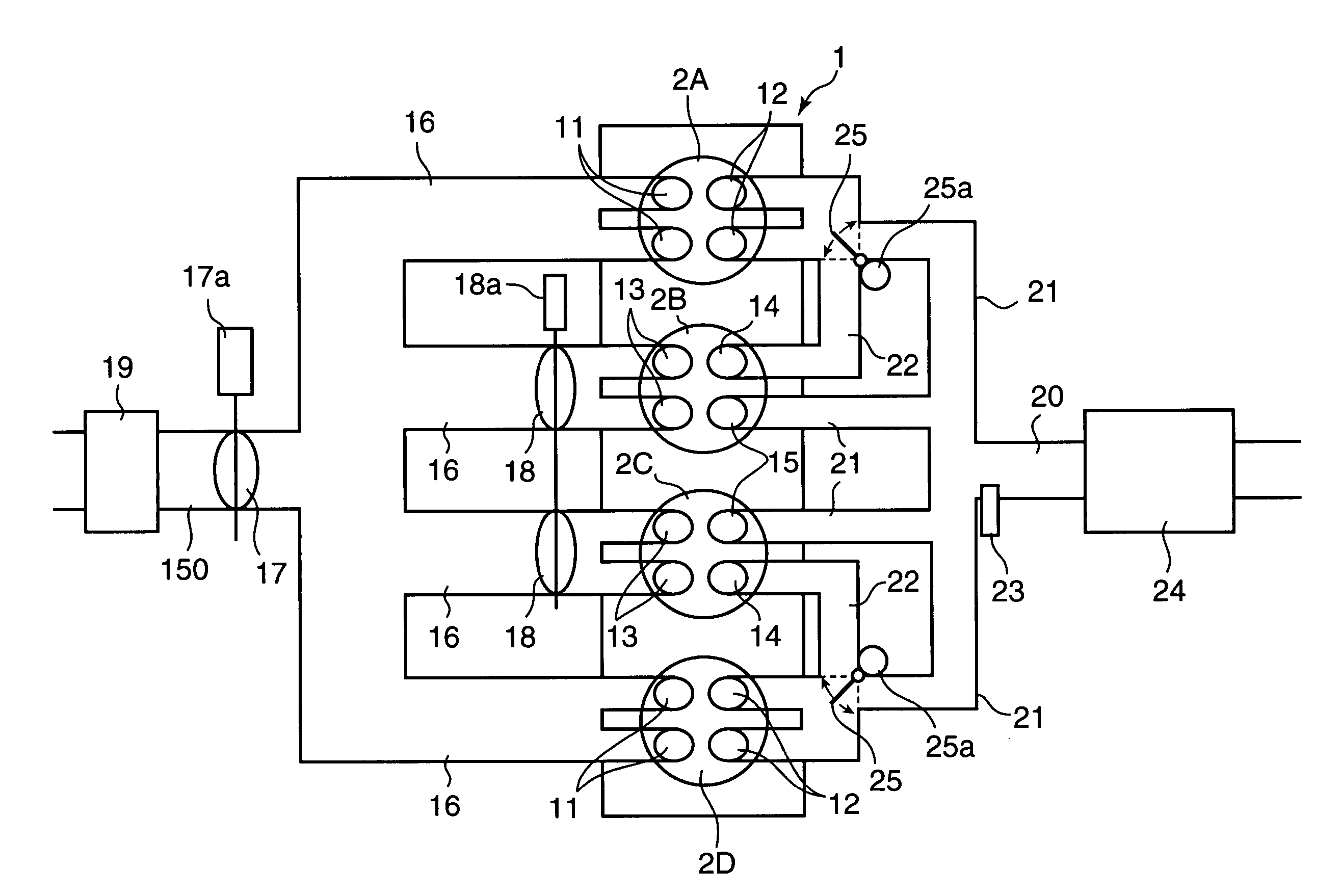
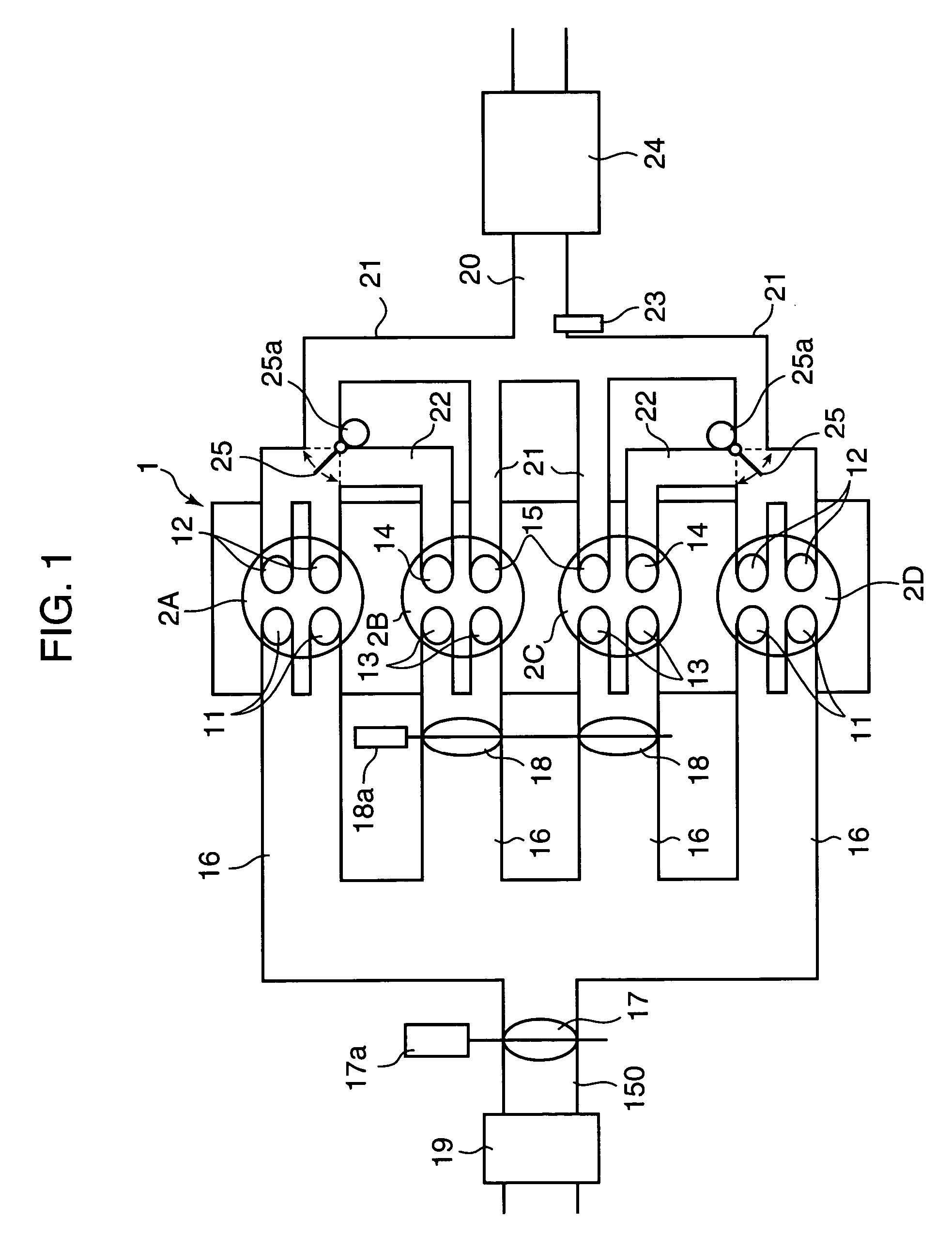
Control unit for spark ignition-type engine
InactiveUS6941905B2Improve thermal efficiencyReduces pumping lossElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionEngineering
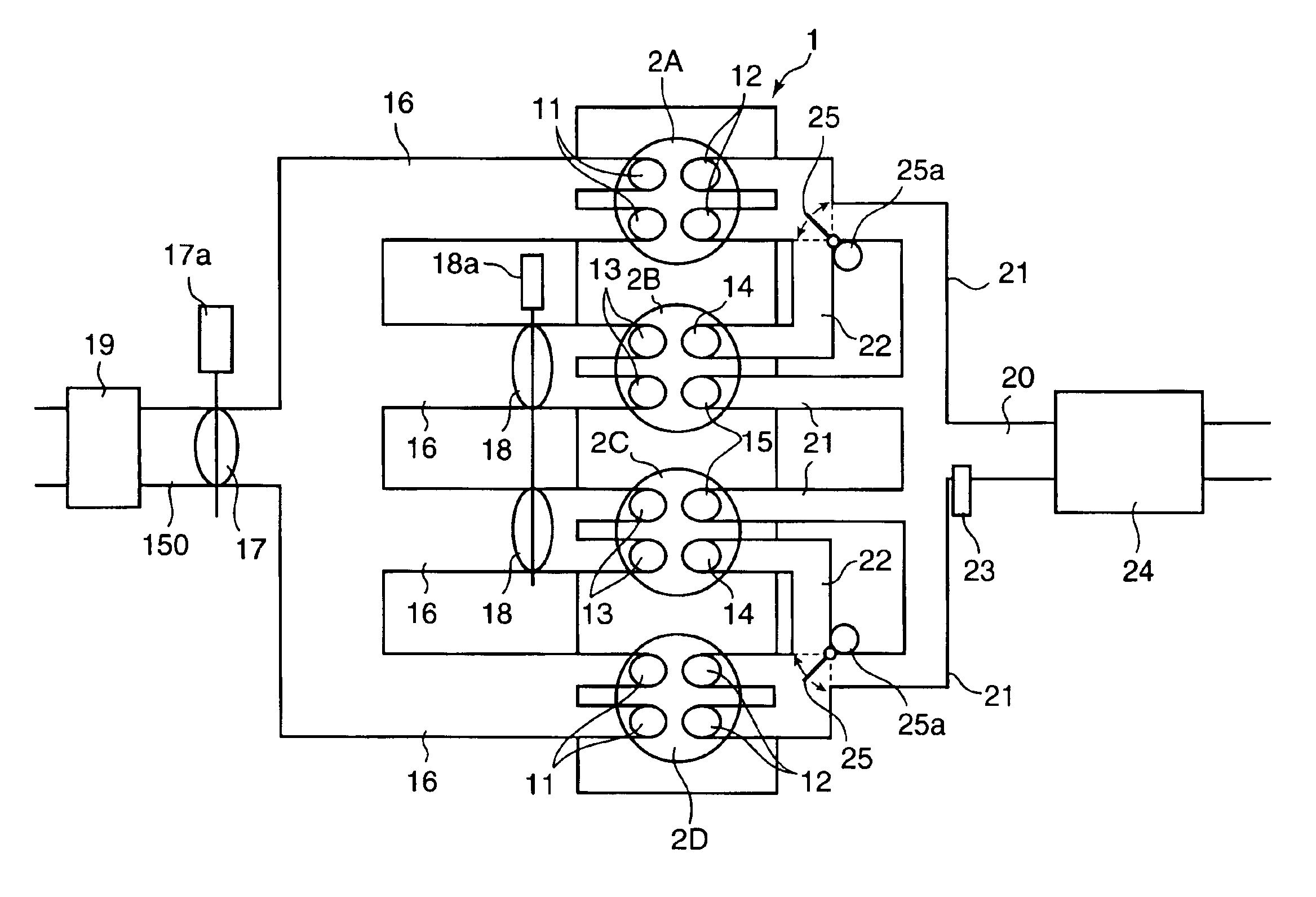
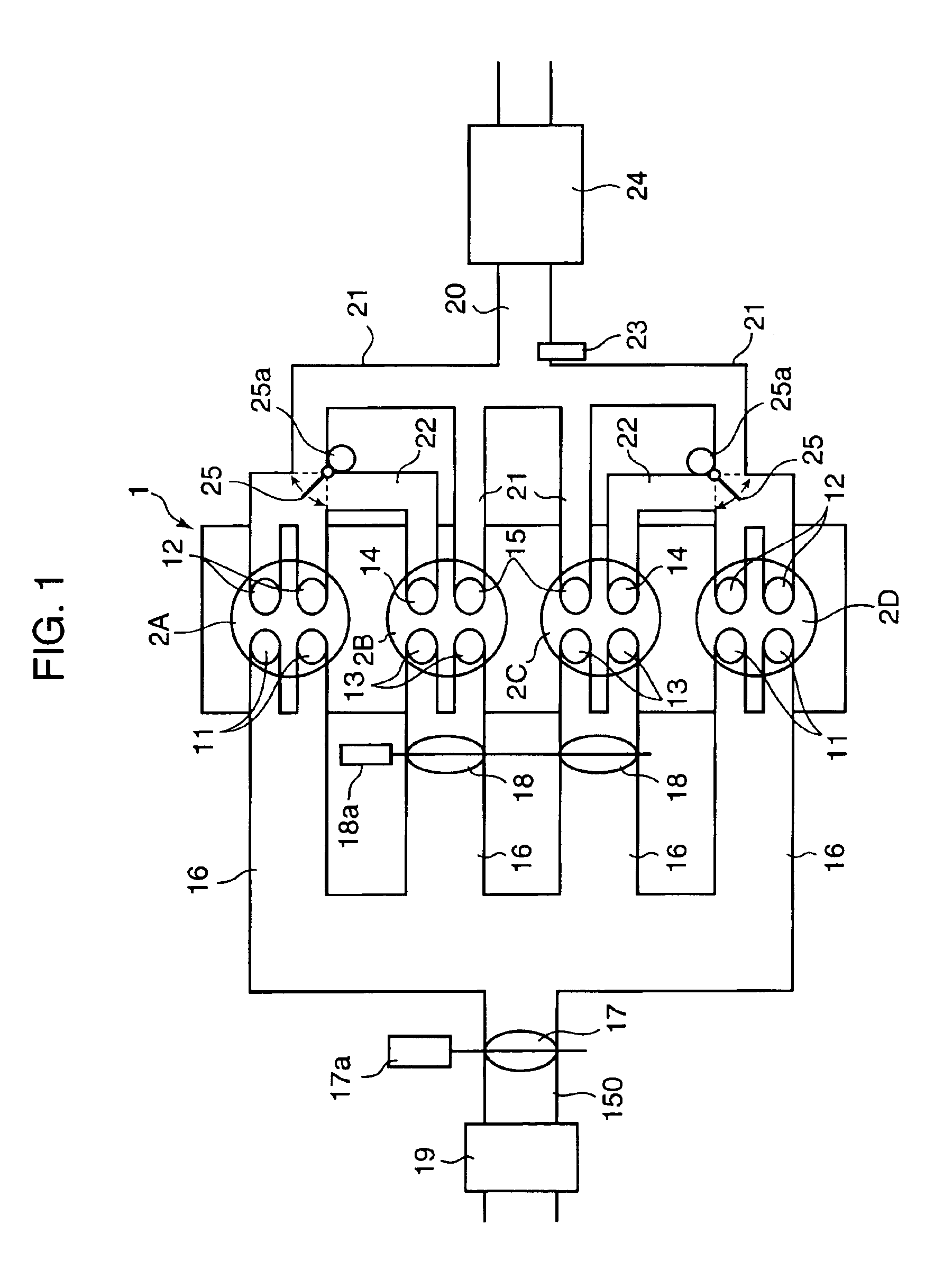
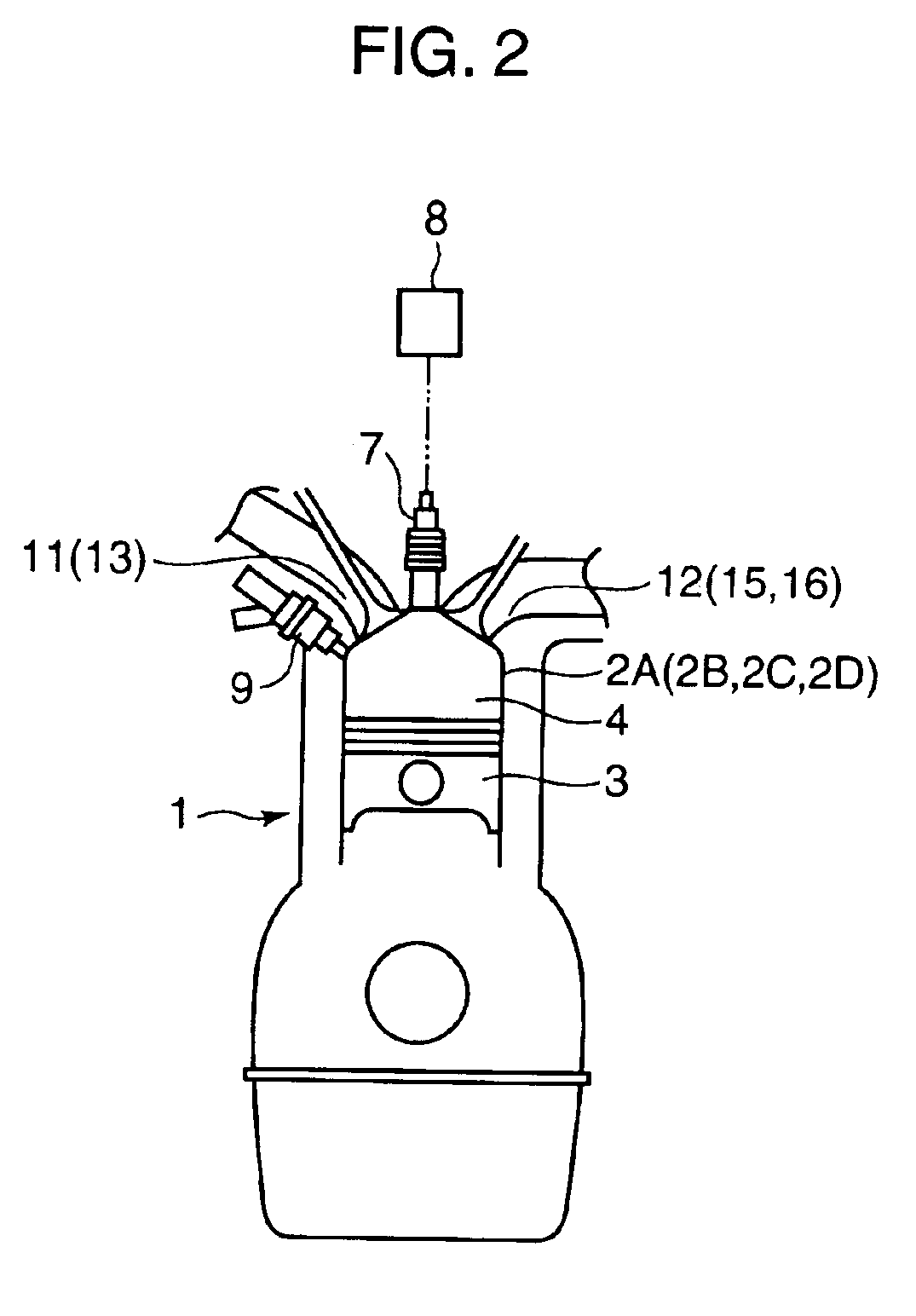
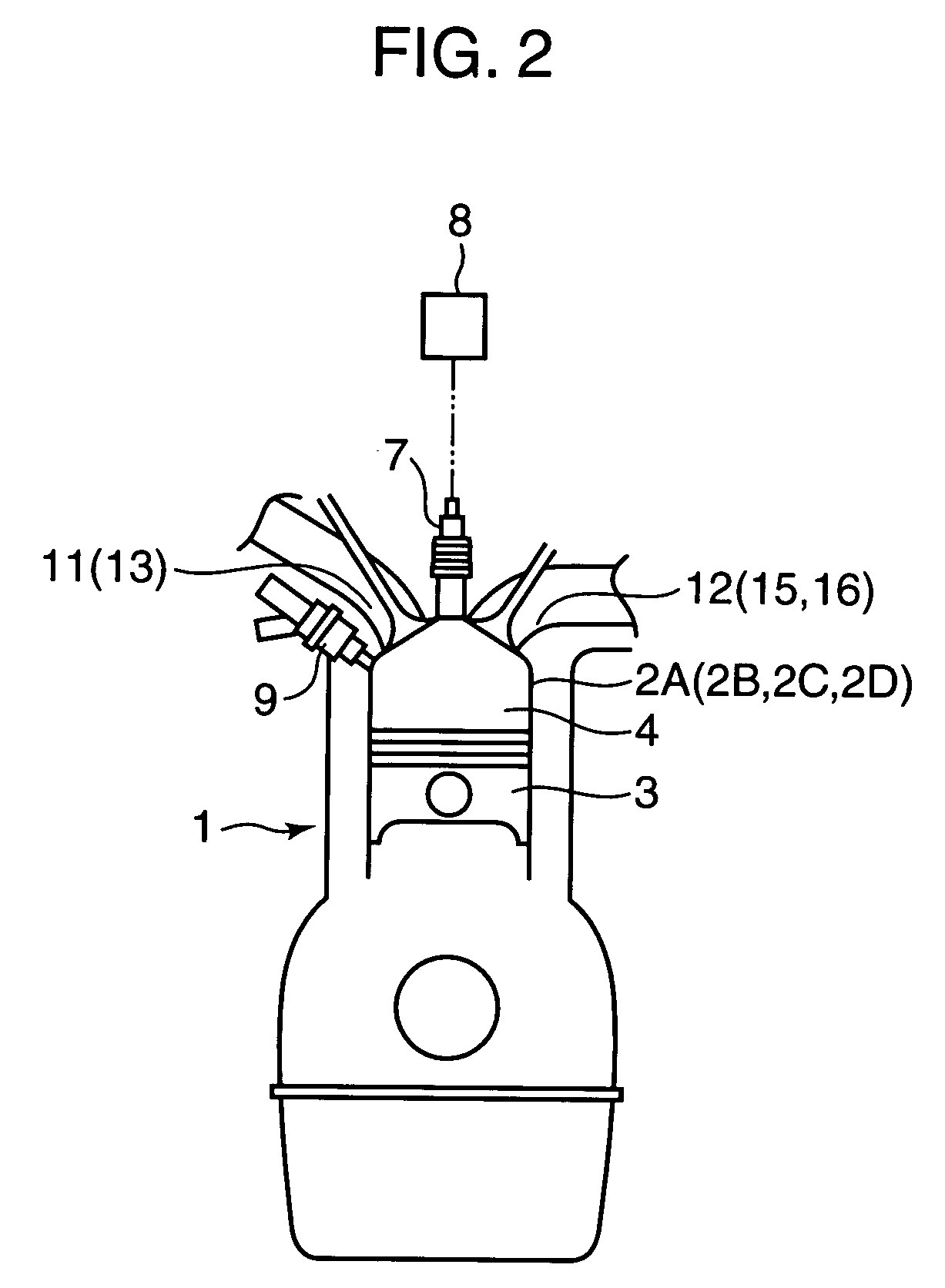
In a partial load range of the engine, control of the flowing state of sucked and discharged gas is executed between a pair of cylinders, an exhaust stroke of one of the cylinders overlapping with an intake stroke of the other, so that burnt gas discharged from preceding cylinders 2A, 2D on the exhaust-stroke side is introduced, in a state where it has been discharged, through an inter-cylindrical gas passage 22 into following cylinders 2B, 2C on the intake stroke side. In a higher load range than the partial load range, control is executed so that a fresh-air introducing valve 18 disposed in a fresh-air introduction passage of the following cylinders 2B, 2C is opened, both the burnt gas and fresh air are introduced into the following cylinders 2B, 2C, and fuel is supplied to conduct combustion in the following cylinders 2B, 2C.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Coordinated valve timing and throttle control for controlling intake air
InactiveUS6553964B2Aggressive response performanceReduction in ride comfortAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlThrottle controlVariable valve timing
A system and method control intake air of an internal combustion engine. The engine has at least one combustion chamber provided with intake valves together with an intake manifold provided with a throttle valve. The opening and closure timings of the intake valves are adjustable entirely independently by electromagnetic drivers from the crankshaft position to control the amount of intake air supplied to the combustion chamber. The system and method provide a response adjustment to variable valve timing and throttle valve position controls of the intake valves for unthrottled intake air control.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
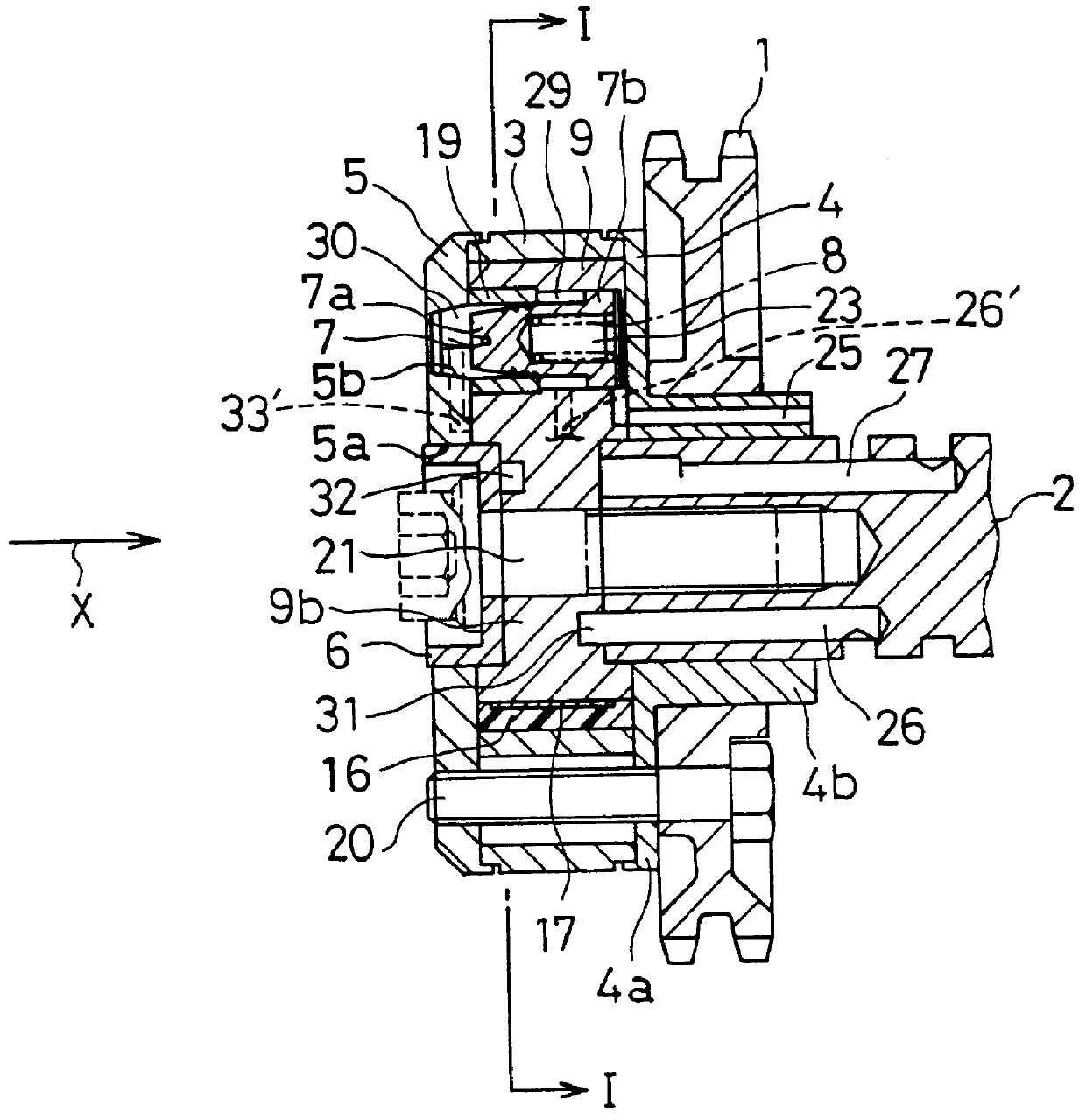
Valve timing adjustment device
InactiveUS20050061277A1Increase freedomFormed with easeOscillating piston enginesOutput powerDrive shaftEngineering
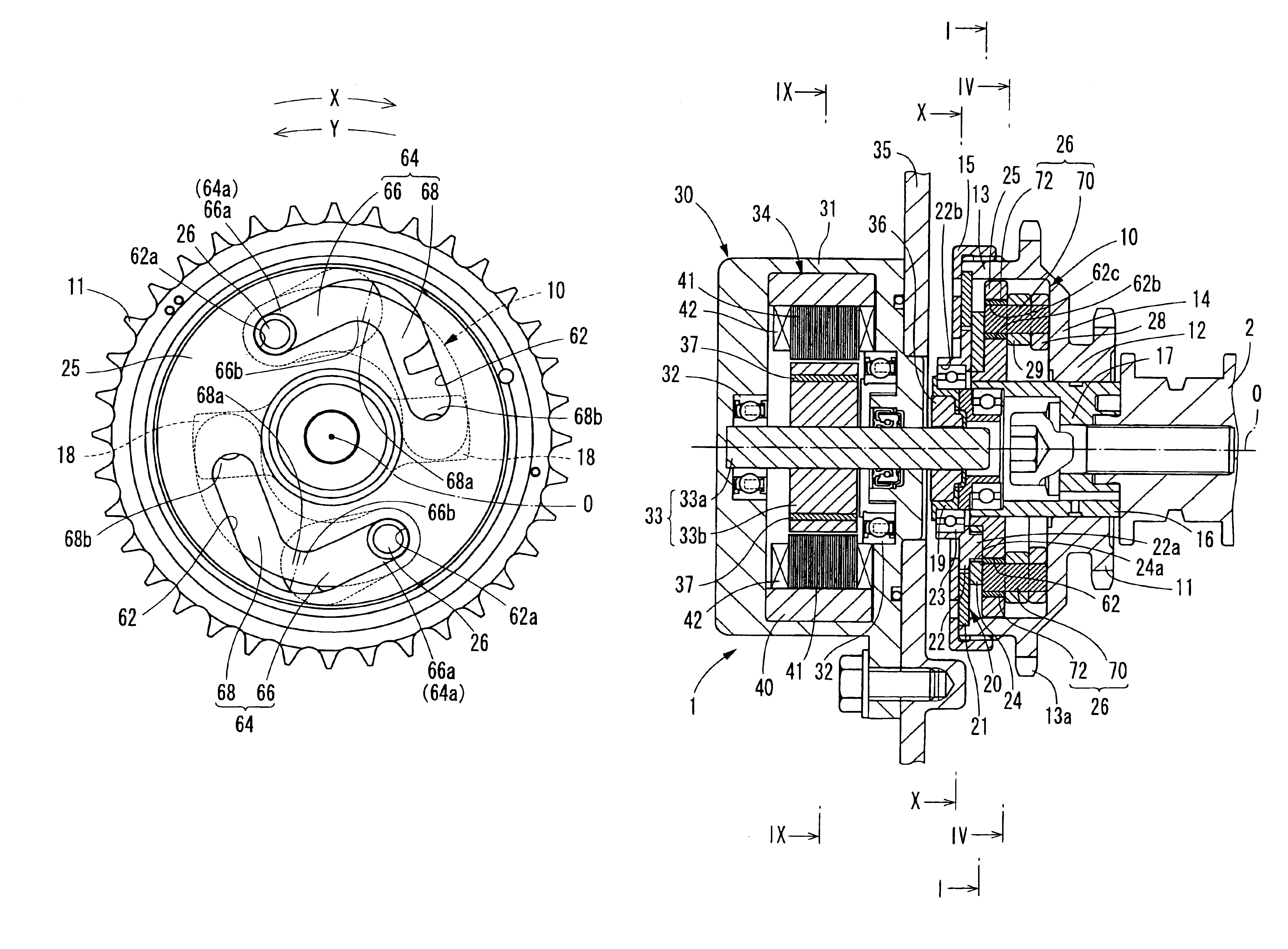
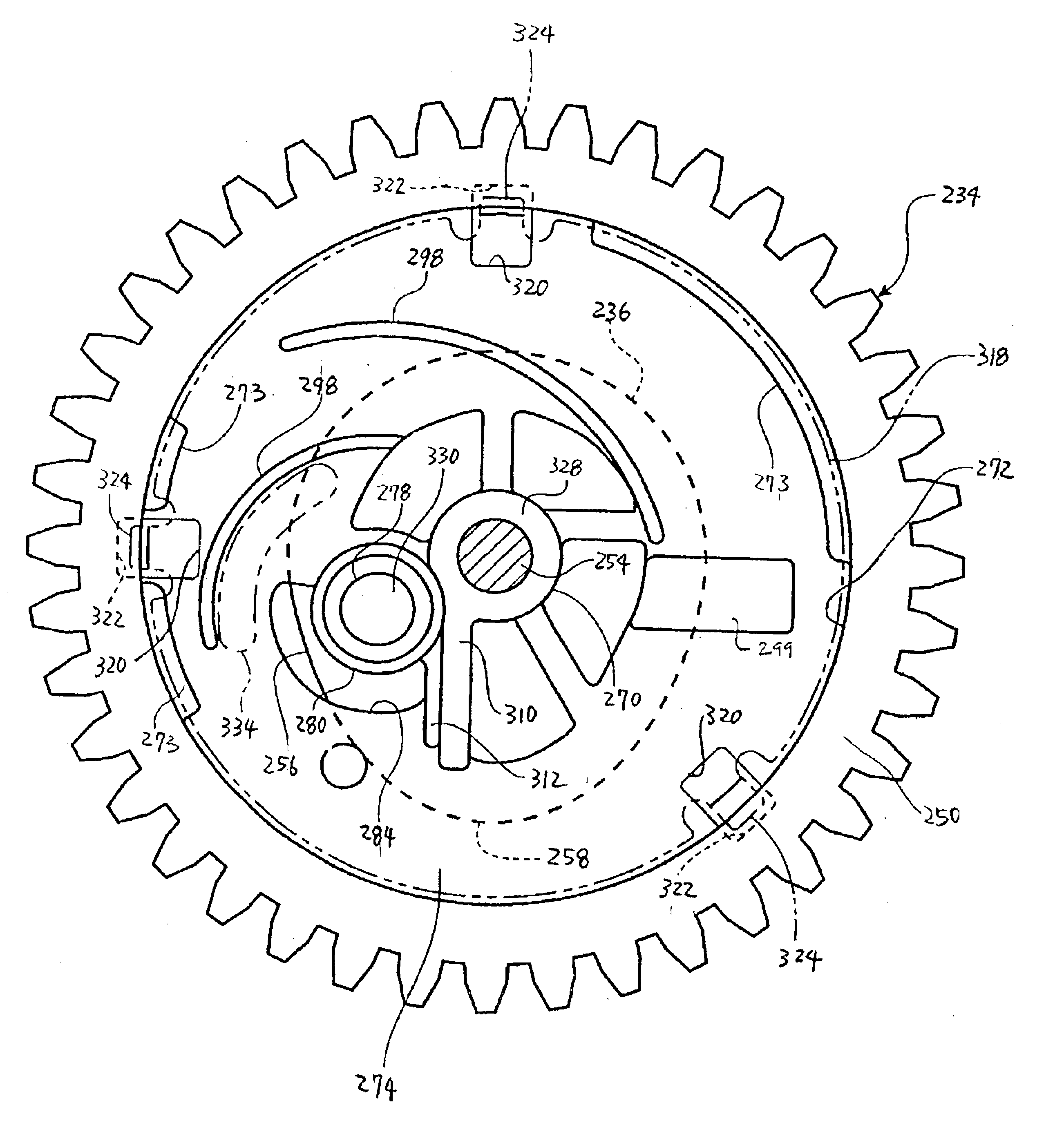
A valve timing adjustment device for promptly switching a rotational phase includes a guide rotary body having a guide passage containing a movable body. The guide passage includes a variable radial dimension relative to a rotational centerline. The guide rotary body rotates relative to a driving rotary body and guides the movable body in the guide passage. A phase change mechanism changes the rotational phase of a driven shaft relative to a drive shaft according to the position of the movable body in the guide passage. The guide passage has a gradually decreasing region and a gradually increasing region. The gradually decreasing region slants toward an axis of the guide rotary body. The gradually increasing region slants relative toward the axis of the guide rotary body. The gradually decreasing region and the gradually increasing region are connected.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Intake air control system of engine
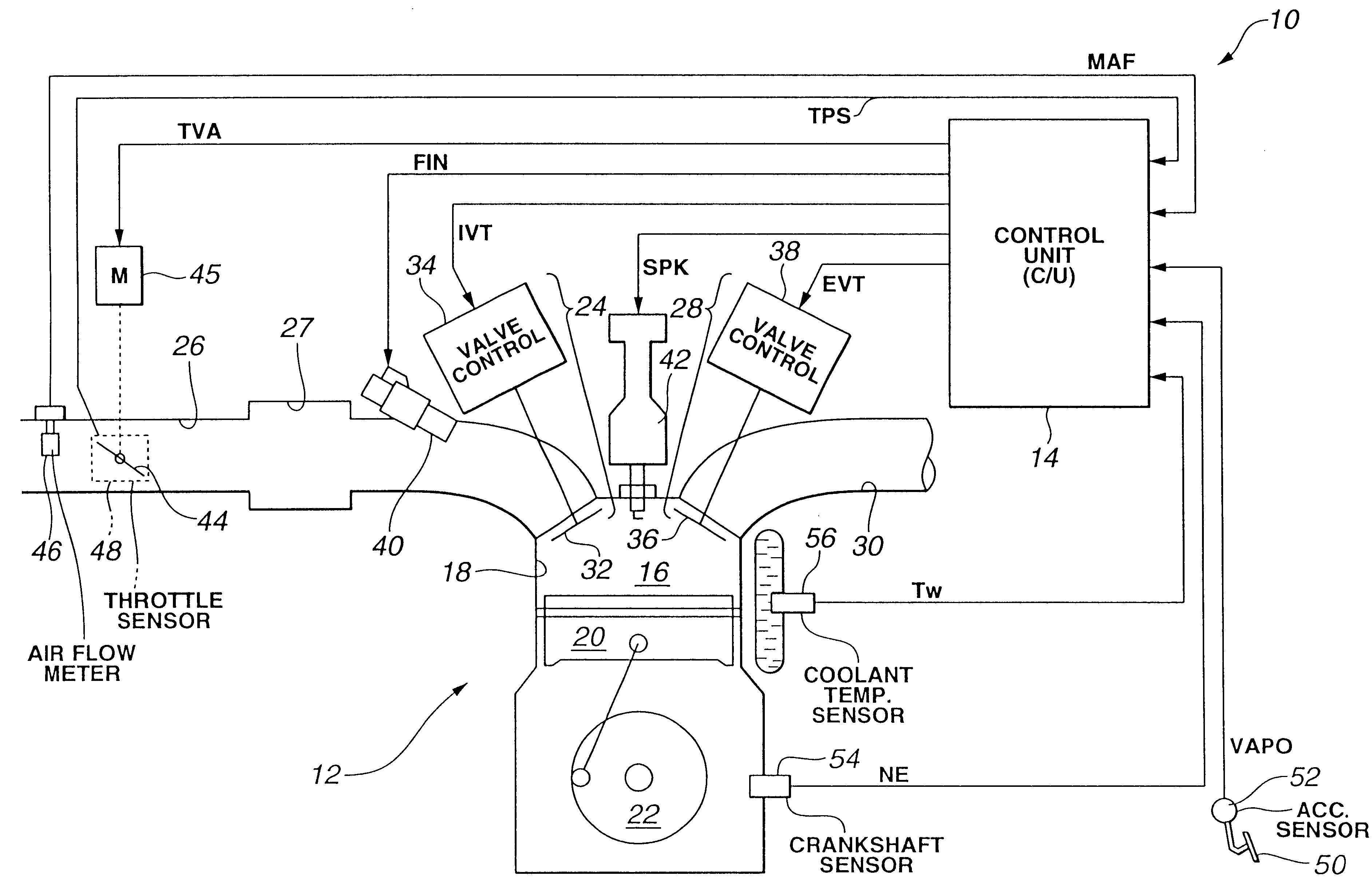
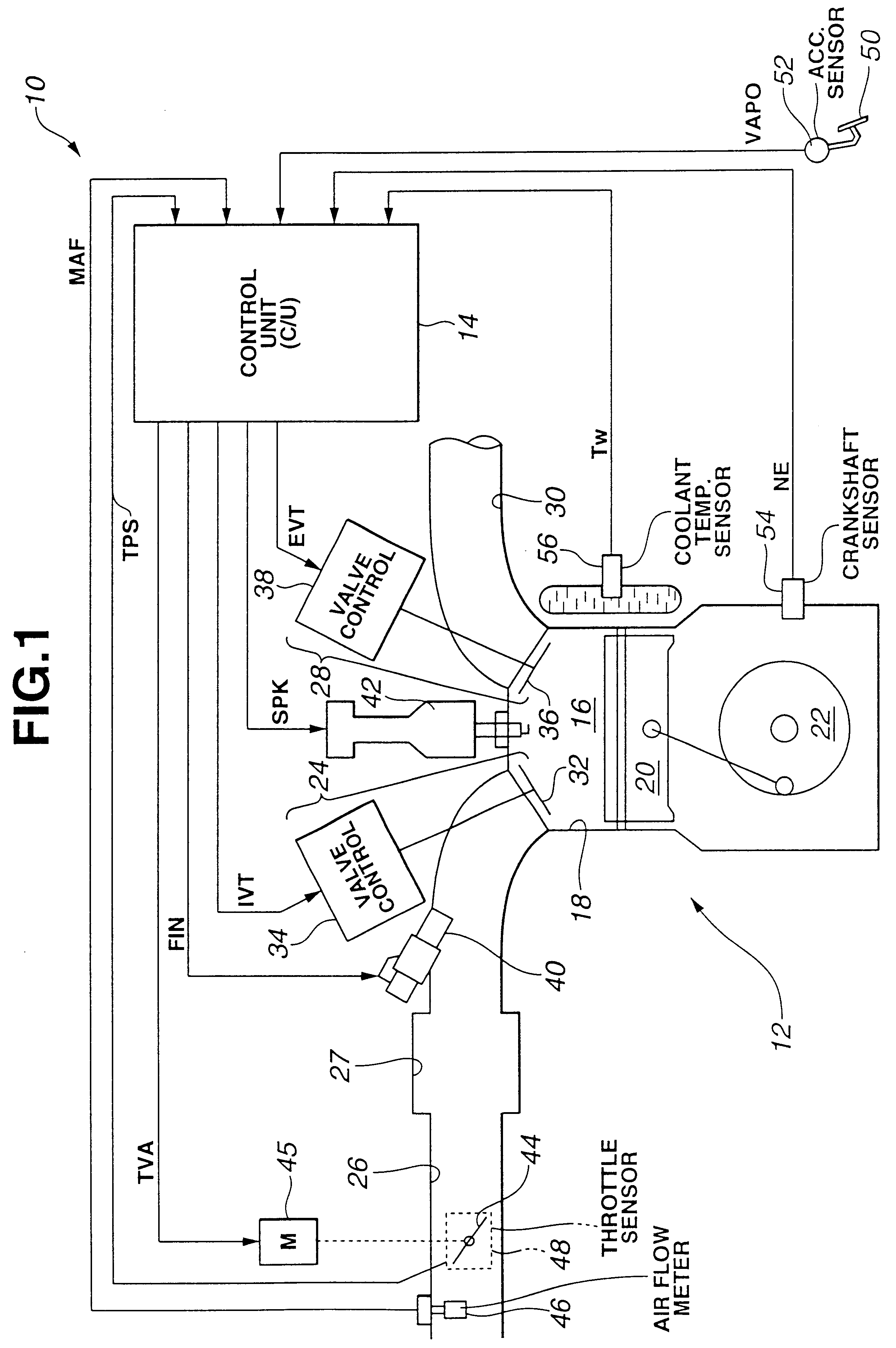
InactiveUS6502546B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemInternal combustion engine
A control unit controls both a motor actuated throttle valve and a magnetically actuated variable valve in accordance with an operation condition of an internal combustion engine. The control unit is configured to provide both a first control mode wherein an intake air control is carried out by controlling the open / close timing of the variable valve while keeping the throttle valve at a full-open or near full-open position and a second control mode wherein the intake air control is carried out by controlling the position of the throttle valve while reducing a controllable range of the open / close timing of the variable valve. The first and second control modes are selectively switched in accordance with the operation condition of the engine. The first and second control modes allow the engine to output the same engine torque under the same operation condition of the engine. The first and second control modes are respectively provided by calculating target intake air amounts for the first and second control modes and feeding the engine with the calculated target intake air amounts respectively.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
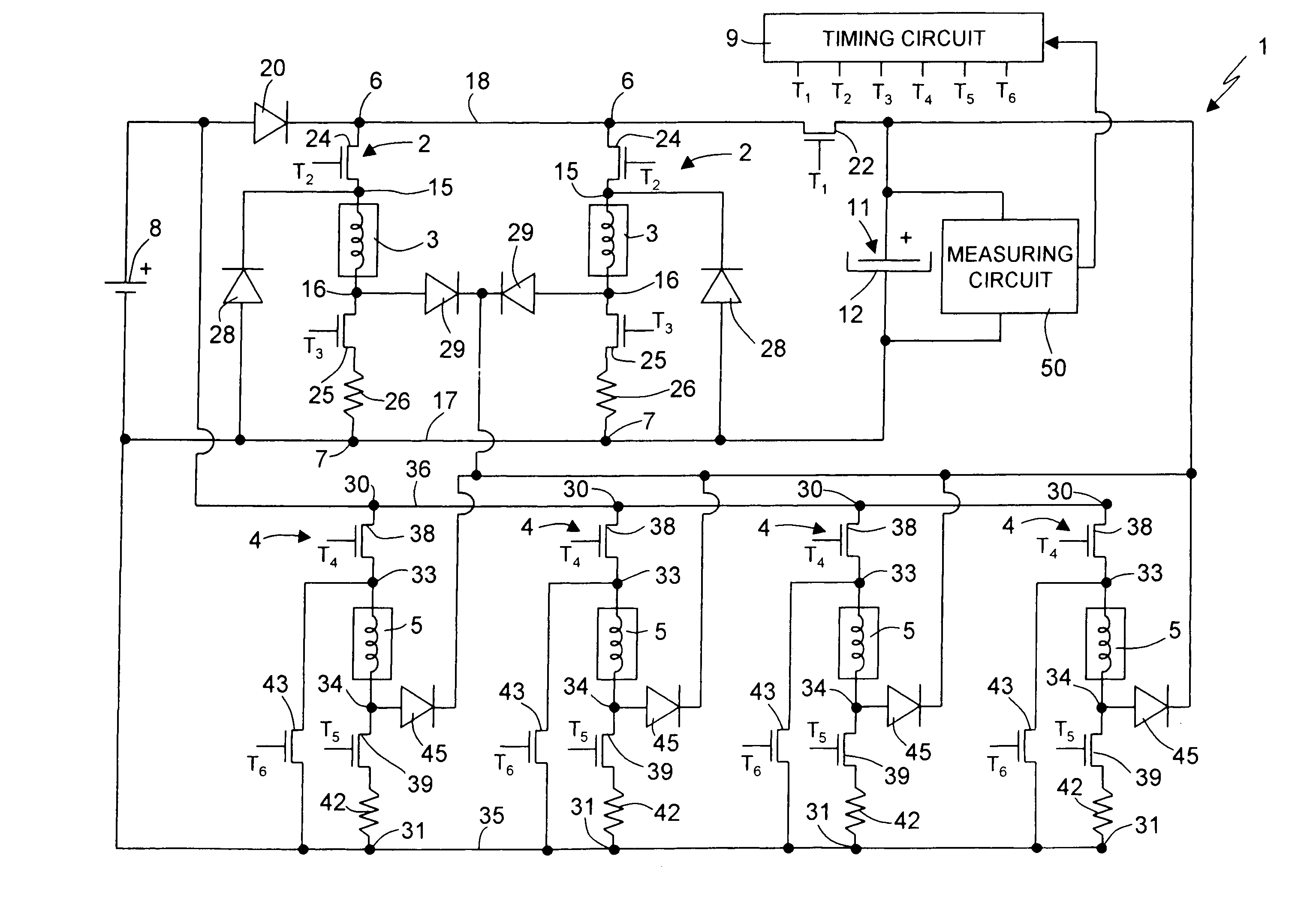
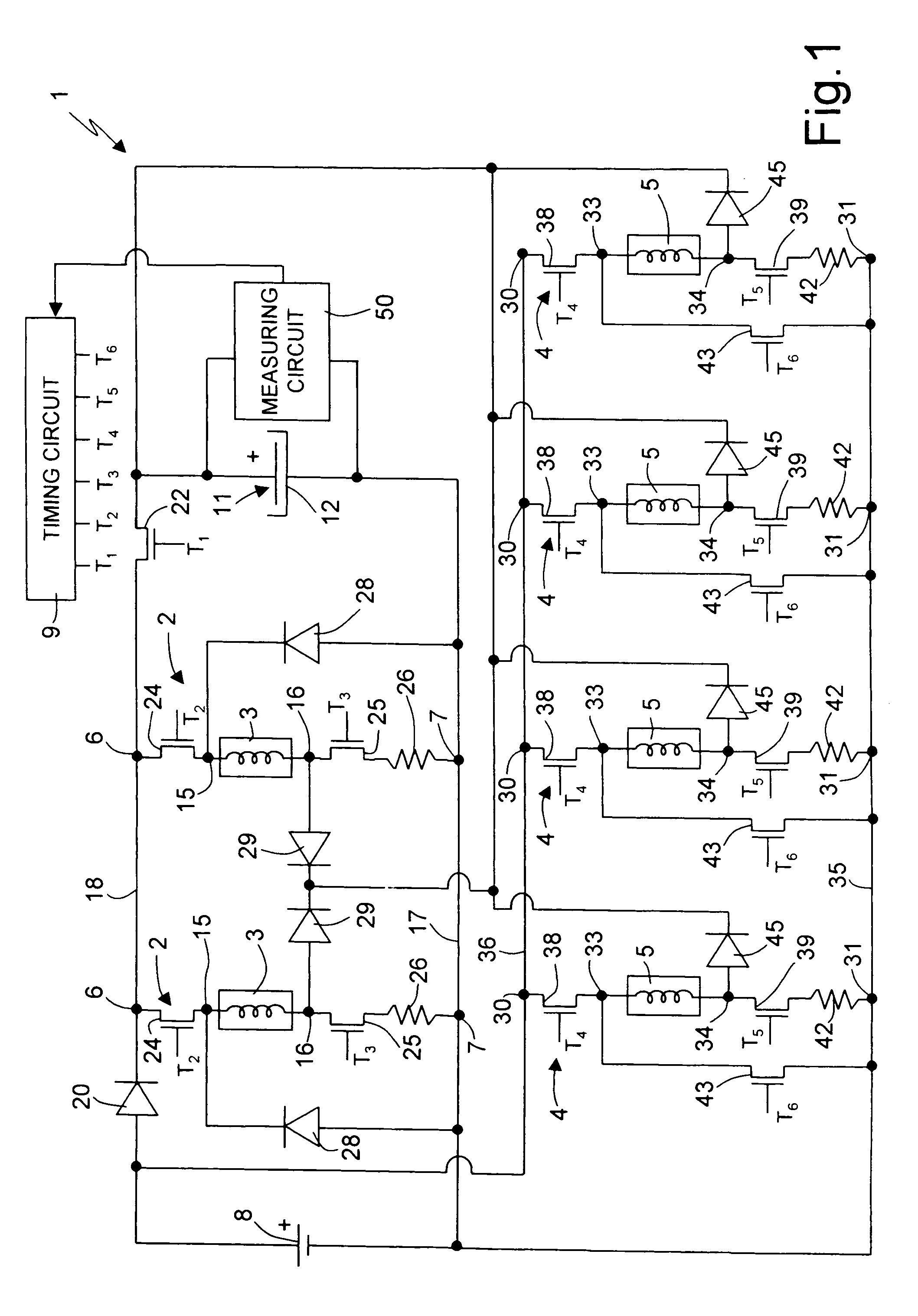
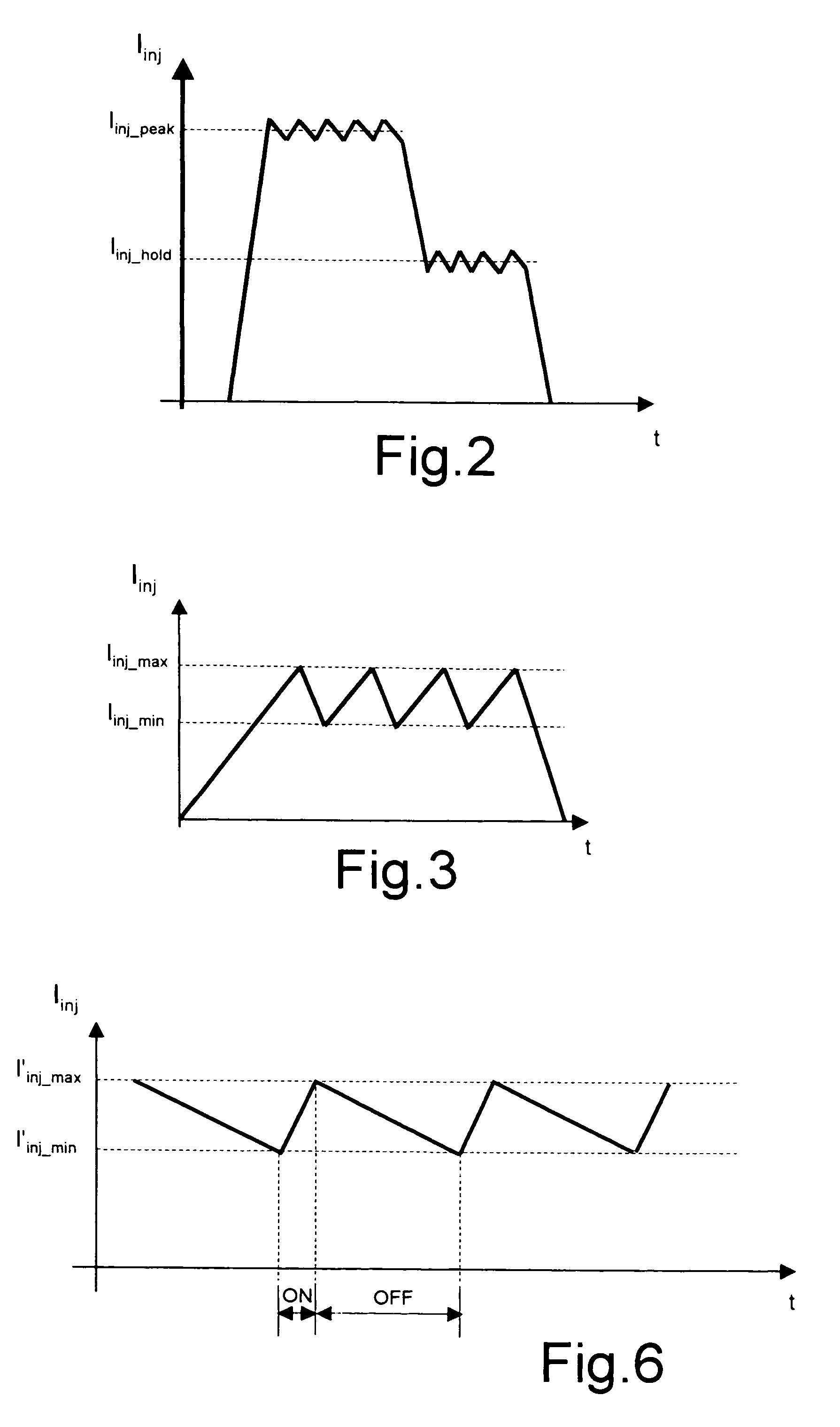
Single device for controlling fuel electro-injectors and electrovalves in an internal-combustion engine, and method of operating the same
ActiveUS7117852B2Overcomes drawbackTransistorElectrical controlInternal combustion engineVoltage source
In a single device for controlling electro-injectors and electrovalves in an internal-combustion engine, a first control circuit for each electro-injector, a second control circuit for each electrovalve, and a timing circuit, supplying timing signals to the first and second control circuits. In the second control circuit, switches selectively connect the respective electrovalve to a first voltage source in certain given operating conditions, and to a boosted voltage source, constituted by a capacitor for accumulation of energy, in certain other given operating conditions. In this way, part of the electrical energy accumulated in the electrovalve during its normal actuation is transferred to the capacitor, thus causing the latter to be recharged.
Owner:CENT RICERCHE FIAT SCPA
Fail-safe control apparatus for internal combustion engine equipped with variable valve characteristic mechanism and method thereof
When it is detected that any one of a plurality of variable valve characteristic mechanisms disposed for every cylinder groups is failed, an effective opening degree (valve lift amount, valve operating angle or the like) in a valve characteristic in the failed state, is obtained. When the effective opening degree is judged to be a predetermined value or above, the valve characteristic of the normal variable valve characteristic mechanism is controlled to be coincident with the valve characteristic in the failed state. When the effective opening degree is judged to be less than the predetermined value, there is performed a control for limiting the control to coincide the valve characteristic of the normal variable valve characteristic mechanism with the valve characteristic in the failed state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Valve timing adjustment device
A valve timing adjustment device for promptly switching a rotational phase includes a guide rotary body having a guide passage containing a movable body. The guide passage includes a variable radial dimension relative to a rotational centerline. The guide rotary body rotates relative to a driving rotary body and guides the movable body in the guide passage. A phase change mechanism changes the rotational phase of a driven shaft relative to a drive shaft according to the position of the movable body in the guide passage. The guide passage has a gradually decreasing region and a gradually increasing region. The gradually decreasing region slants toward an axis of the guide rotary body. The gradually increasing region slants relative toward the axis of the guide rotary body. The gradually decreasing region and the gradually increasing region are connected.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Decompression device for power generator engine
A decompression device for an engine reduces pressure in the engine's combustion chamber thereby reducing the amount of force required to start the engine. The decompression device incorporates a decompression lever that cooperates with a cam surface to hold engine valves open longer than normal while the engine is being started. The decompression lever has a weight section and a lifter section. The lifter section is located near a pivot location on the decompression lever and is generally the same thickness as the weight section. The lifter section protrudes beyond the cam gear to hold the engine valves open longer while starting the engine. After the engine has started, the decompression lever rotates into a retracted position to allow the engine valves to open and close normally.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR POWER PROD KK
Control unit for spark ignition-type engine
In a partial load range of the engine, control of the flowing state of sucked and discharged gas is executed between a pair of cylinders, an exhaust stroke of one of the cylinders overlapping with an intake stroke of the other, so that burnt gas discharged from preceding cylinders 2A, 2D on the exhaust-stroke side is introduced, in a state where it has been discharged, through an inter-cylindrical gas passage 22 into following cylinders 2B, 2C on the intake stroke side. In a higher load range than the partial load range, control is executed so that a fresh-air introducing valve 18 disposed in a fresh-air introduction passage of the following cylinders 2B, 2C is opened, both the burnt gas and fresh air are introduced into the following cylinders 2B, 2C, and fuel is supplied to conduct combustion in the following cylinders 2B, 2C.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Valve timing control apparatus
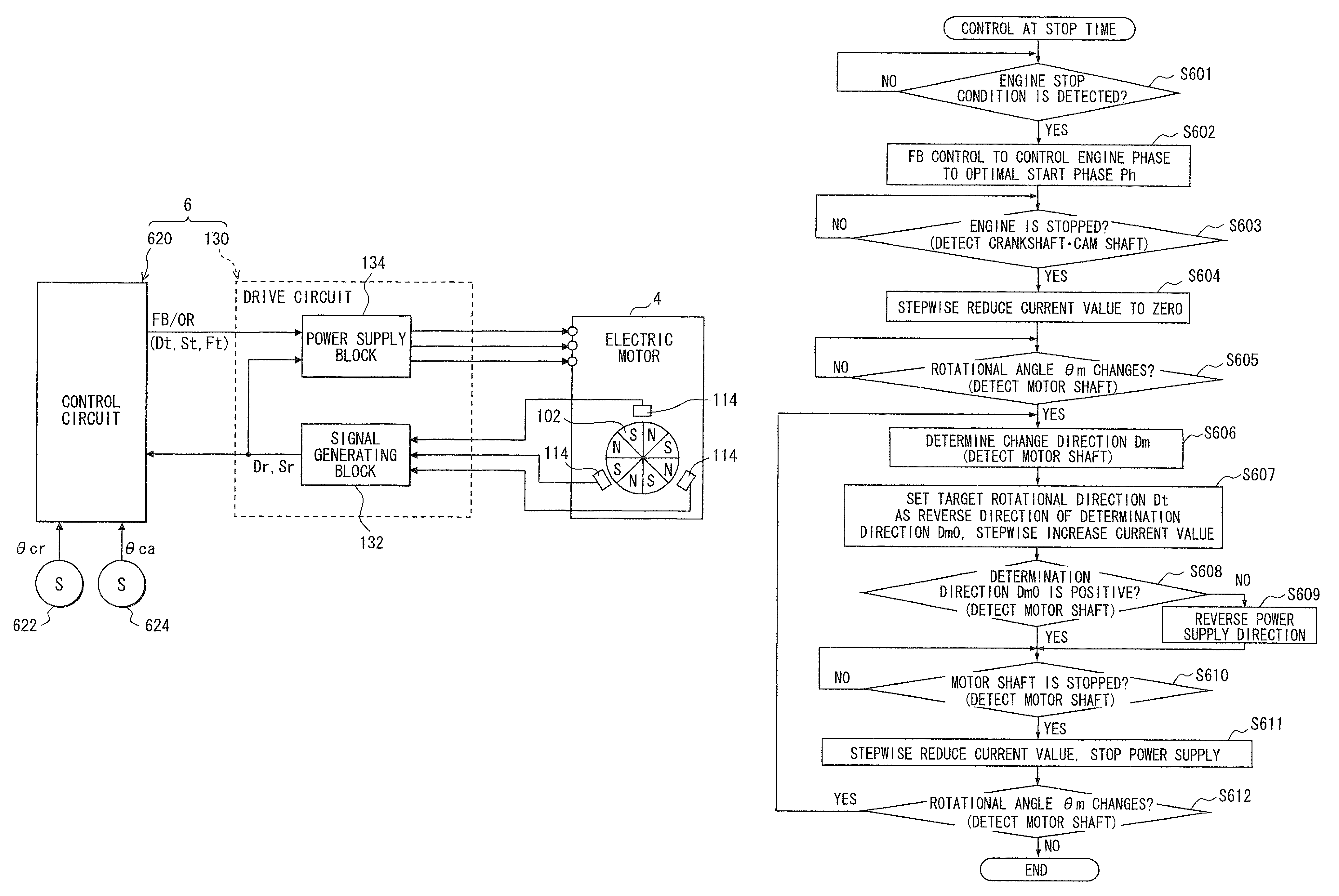
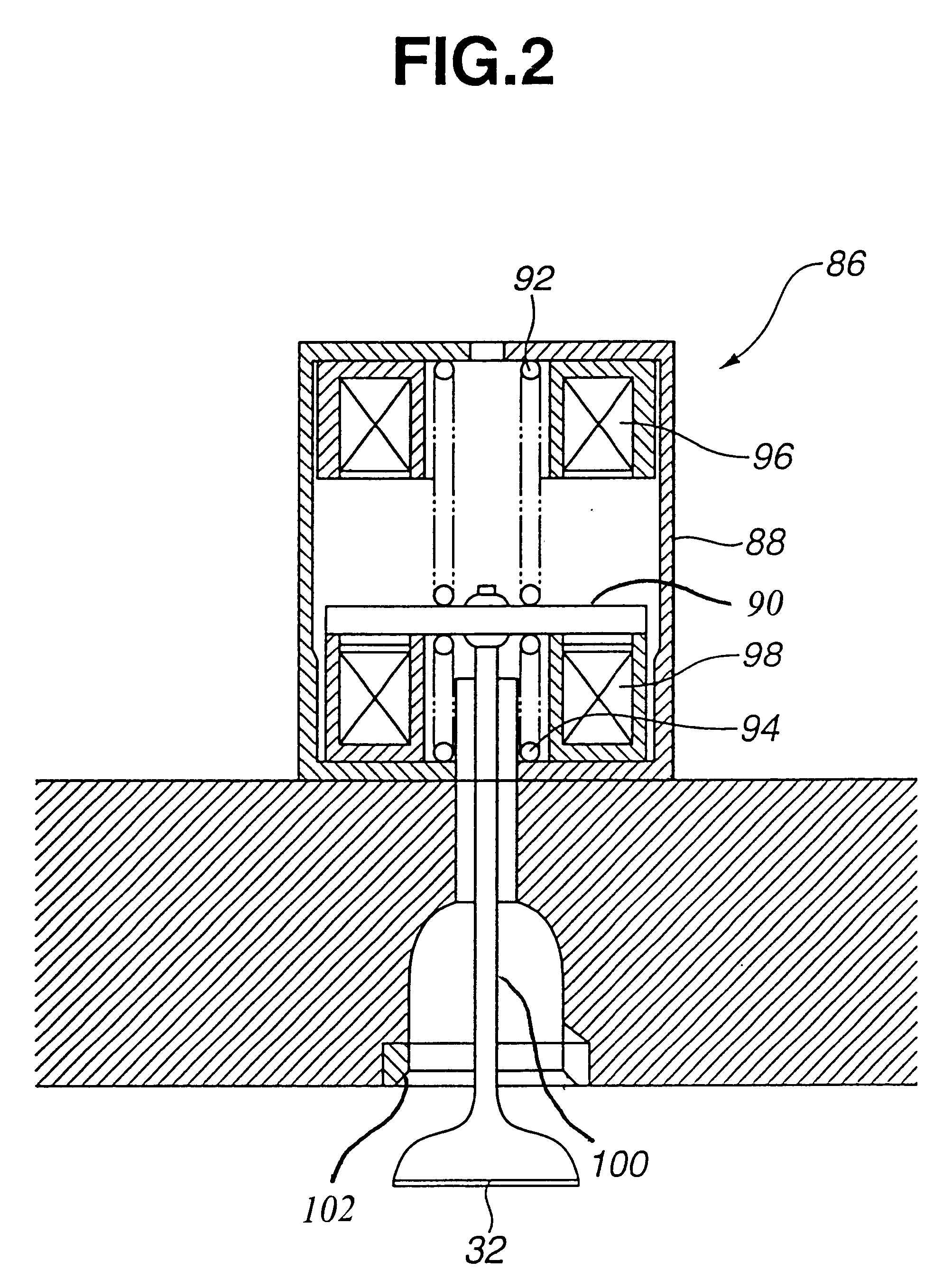
ActiveUS20090121671A1Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersLower limitStator coil
An electric power supply driver executes duty control of turning on and off of a selected switching element to supply electric power to a corresponding stator coil in a case where an actual rotational direction and a target rotational direction of a motor shaft coincide with each other. Furthermore, the driver sets an on-duty ratio of the selected switching element below a lower limit value, which is at least required to rotate the motor shaft through the power supply to each corresponding stator coil in a case where the actual rotational direction and the target rotational direction do not coincide with each other.
Owner:DENSO CORP
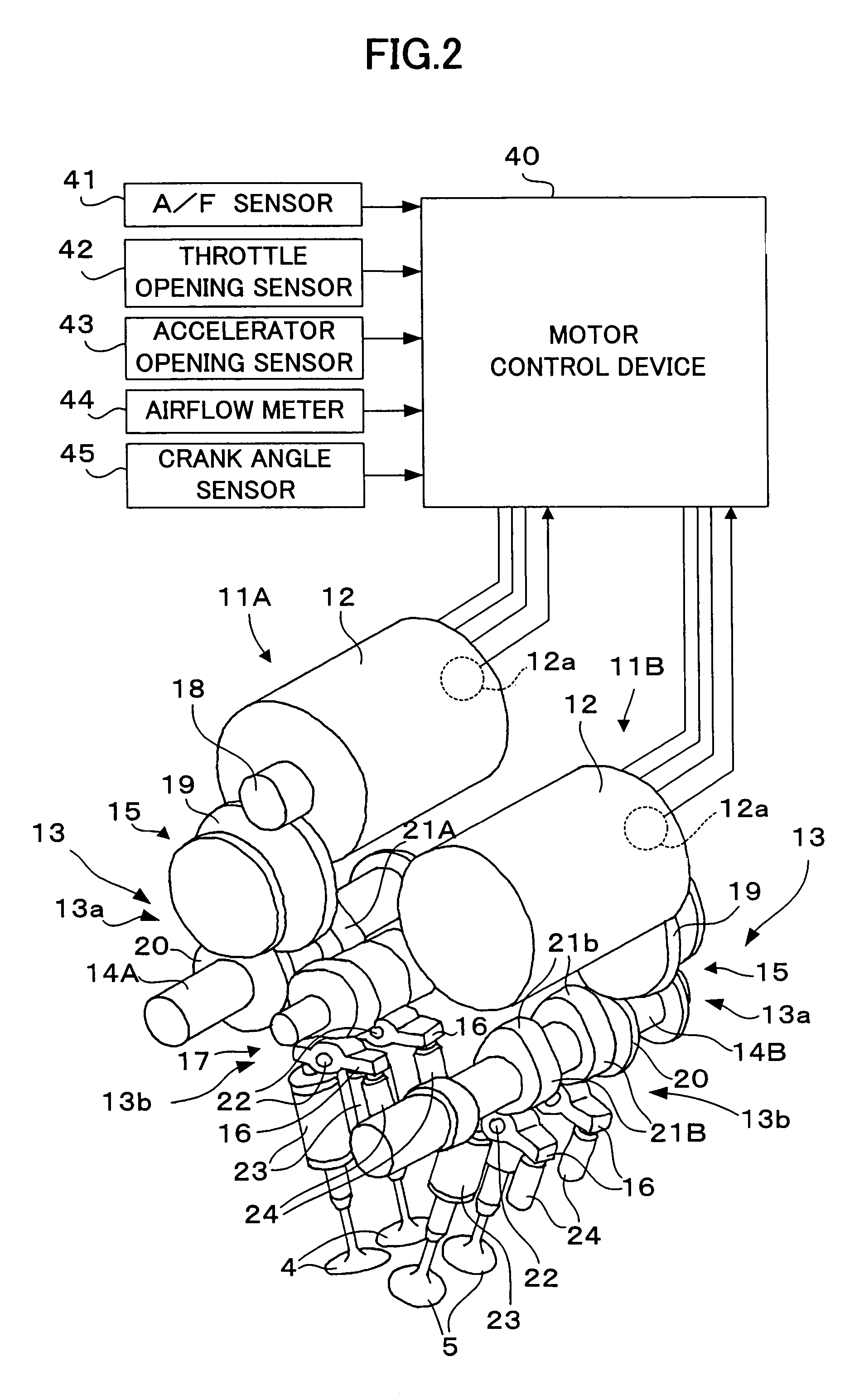
Valve-driving system of internal combustion engine and valve-driving apparatus
InactiveUS7047922B2Open efficientlyEffectively closedOutput powerMachines/enginesExhaust valveExternal combustion engine
A valve-driving system, which is applied to an internal combustion engine having a plurality of cylinders, for driving an intake or exhaust valve provided in each cylinder, comprising: a plurality of valve-driving apparatuses, each of which is provided for at least each one of the intake valve and the exhaust valve, each valve-driving apparatus having an electrical motor as a driving source for generating rotation motion and a power transmission mechanism provided with a transmitting section for transmitting the rotation motion generated by the electrical motor and a converting section for converting the rotation motion transmitted from the transmitting section into opening and closing motion of the valve to be driven; and a motor control device which controls operations of electric motors of the respective valve-driving apparatuses in accordance with the operation state of the internal combustion engine.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fail-safe control apparatus for internal combustion engine equipped with variable valve characteristic mechanism and method thereof
When it is detected that any one of a plurality of variable valve characteristic mechanisms disposed for every cylinder groups is failed, an effective opening degree (valve lift amount, valve operating angle or the like) in a valve characteristic in the failed state, is obtained. When the effective opening degree is judged to be a predetermined value or above, the valve characteristic of the normal variable valve characteristic mechanism is controlled to be coincident with the valve characteristic in the failed state. When the effective opening degree is judged to be less than the predetermined value, there is performed a control for limiting the control to coincide the valve characteristic of the normal variable valve characteristic mechanism with the valve characteristic in the failed state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Coordinated valve timing and throttle control for controlling intake air
InactiveUS20010032613A1Aggressive response performanceReduction in ride comfortAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlThrottle controlVariable valve timing
A system and method control intake air of an internal combustion engine. The engine has at least one combustion chamber provided with intake valves together with an intake manifold provided with a throttle valve. The opening and closure timings of the intake valves are adjustable entirely independently by electromagnetic drivers from the crankshaft position to control the amount of intake air supplied to the combustion chamber. The system and method provide a response adjustment to variable valve timing and throttle valve position controls of the intake valves for unthrottled intake air control.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Intake airvolume controller of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20070006830A1Inhibition of variationStable combustionAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlAir volumeControl system
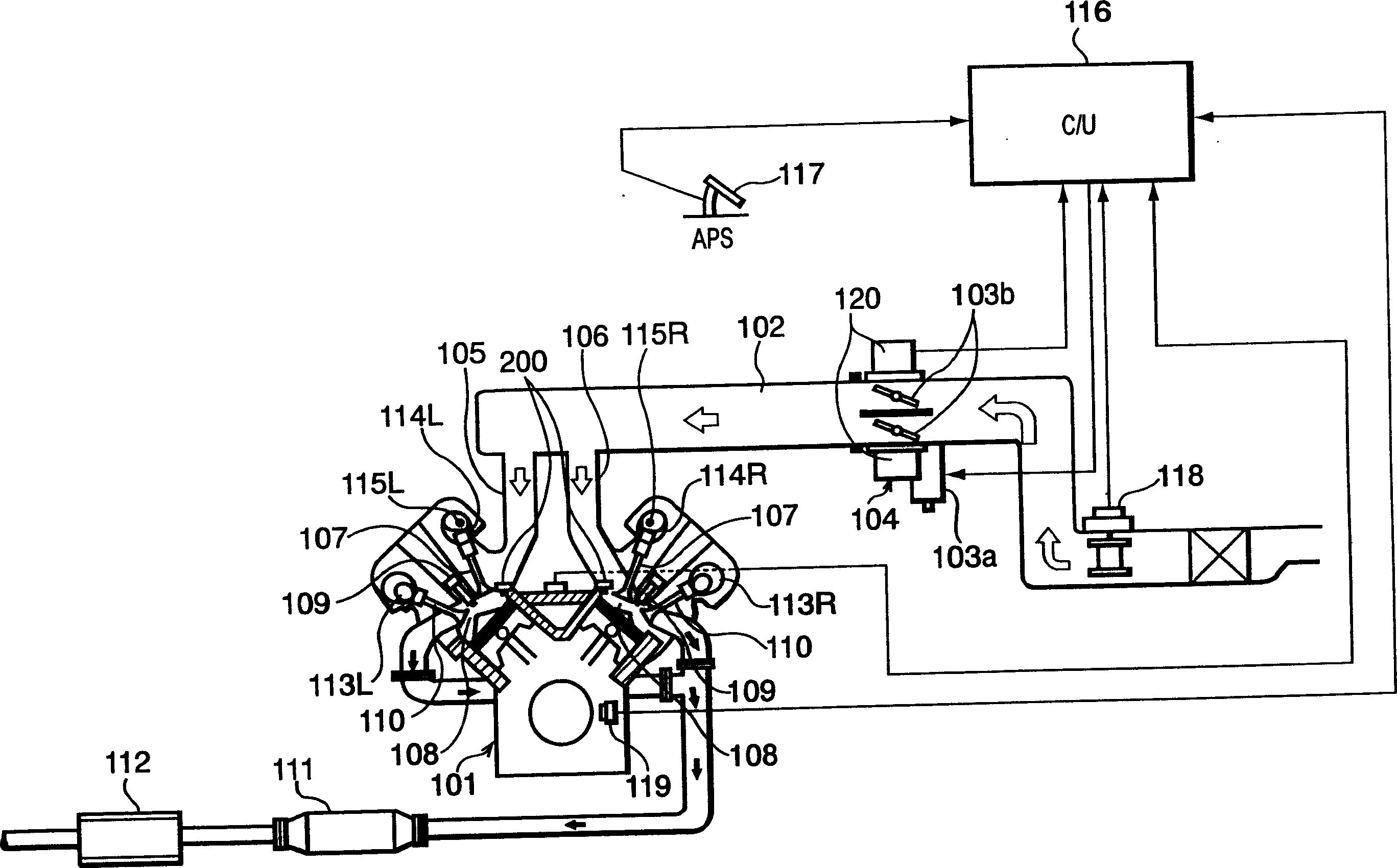
An intake air amount control system for an internal combustion engine, which controls respective amounts of intake air drawn into four cylinders #1 to #4, independently of each other, by variable inter-intake cam phase mechanisms 80, identifies intake air amount variation coefficients Φ#i, based on a model [equation (43)] defining a relationship between an estimated value Gth_est of a TH passing intake air amount and a plurality of simulation values Gcyl_OS#i, such that the estimated value Gth_est becomes equal to the TH passing intake air amount, calculates a target inter-intake cam phase θssi#i_cmd, on a cylinder-by-cylinder basis, according to the identified intake air amount variation coefficients Φ#i (step 81), and calculates control input DUTY_ssi#2 to #4 to the variable inter-intake cam phase mechanisms 80 according to the target inter-intake cam phases θssi#i_cmd (step 75).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Control apparatus and method for valve actuating system of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6782853B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveExternal combustion engine
A control apparatus is provided for a valve actuating system which is operable to lift an intake valve or an exhaust valve of an internal combustion engine and includes a lift characteristic changing mechanism for changing a lift characteristic of the intake valve or the exhaust valve. The control apparatus calculates a target operation value of the lift characteristic changing mechanism, and calculates a realizable range of the operation value which can be realized by the lift characteristic changing mechanism, based on a controlled variable that can be given to the lift characteristic changing mechanism and at least one parameter related to an environment surrounding the lift characteristic changing mechanism. If the target operation value is not within the realizable range of the operation value, the control apparatus calculates a new target operation value to be within the realizable range.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Valve controller
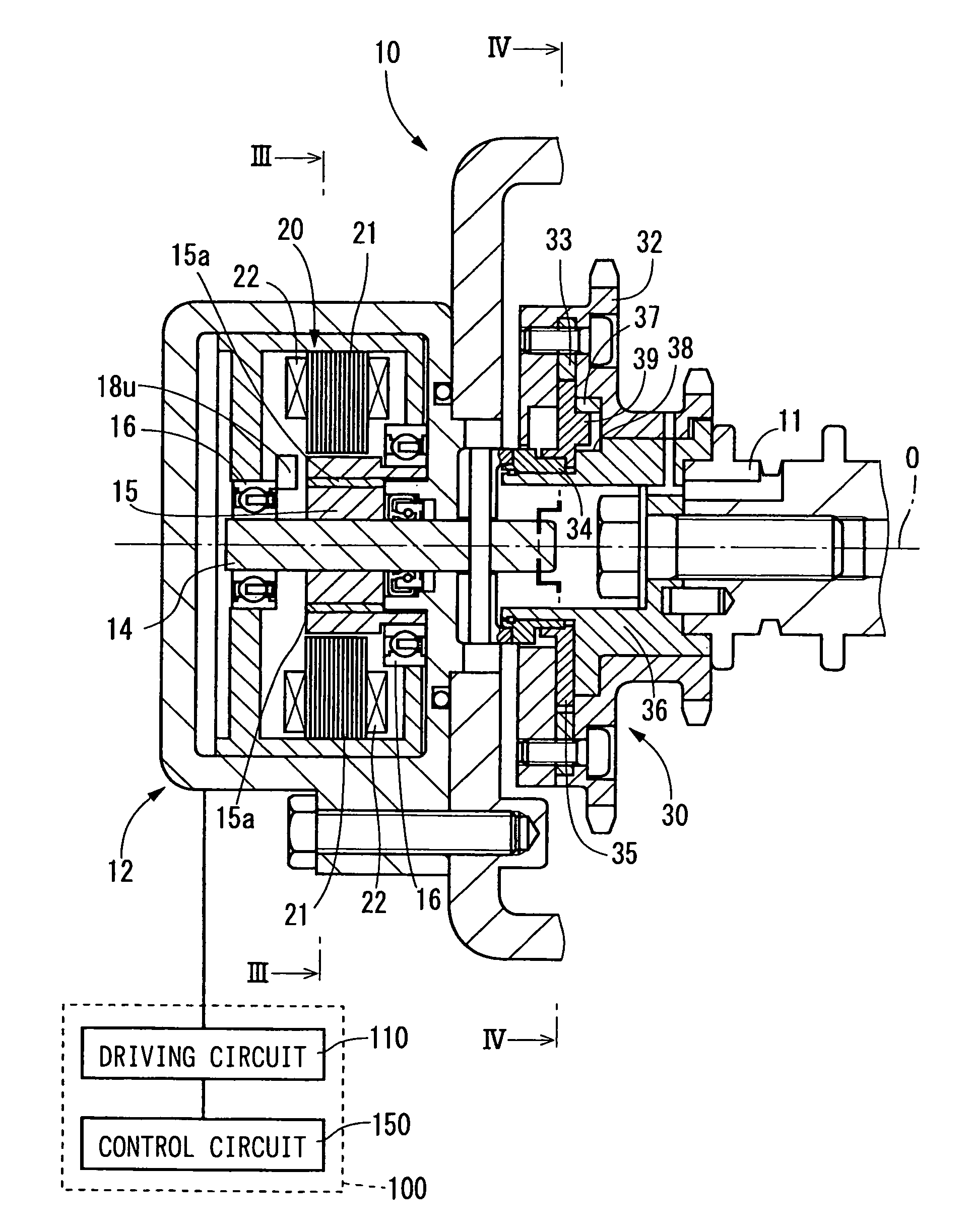
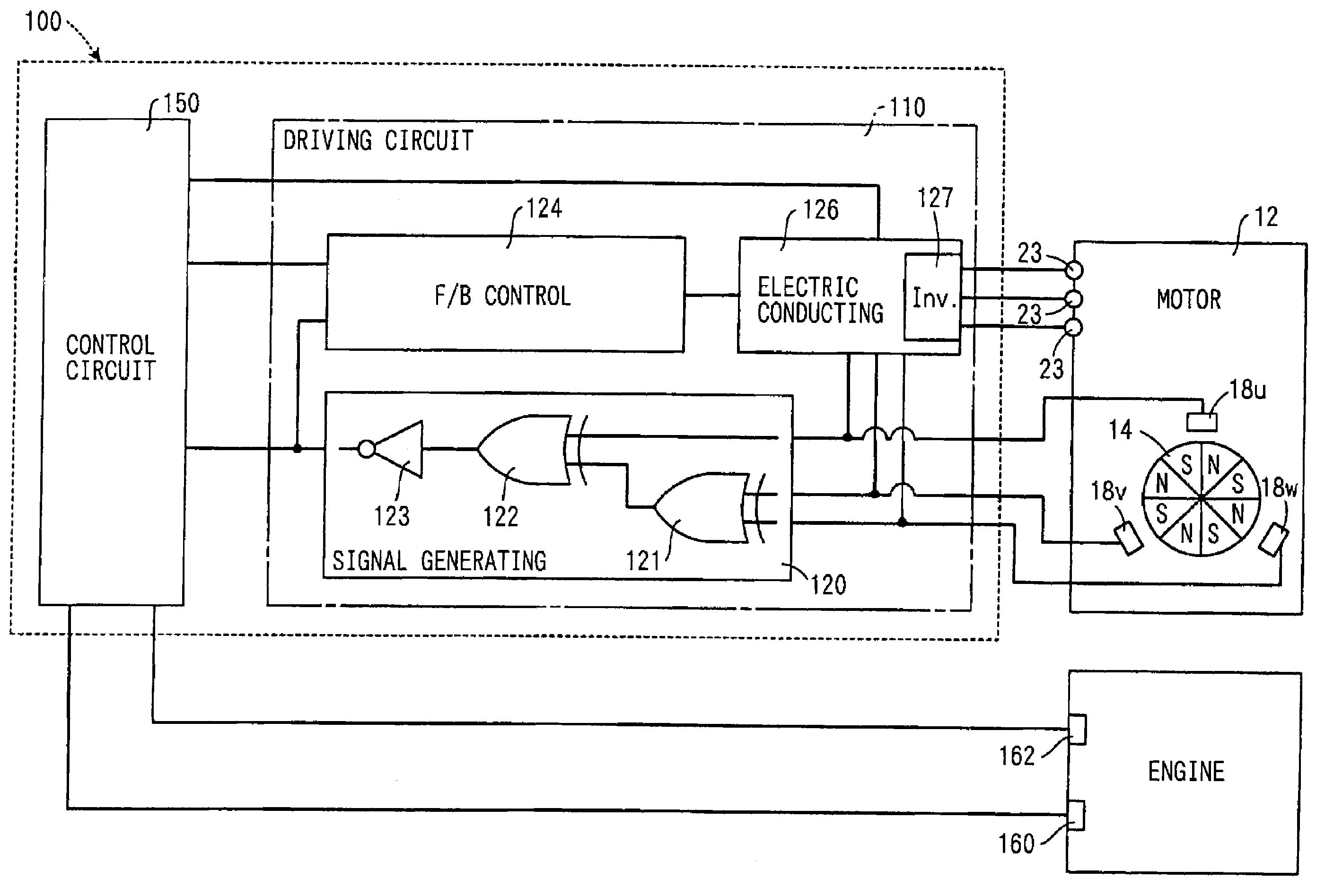
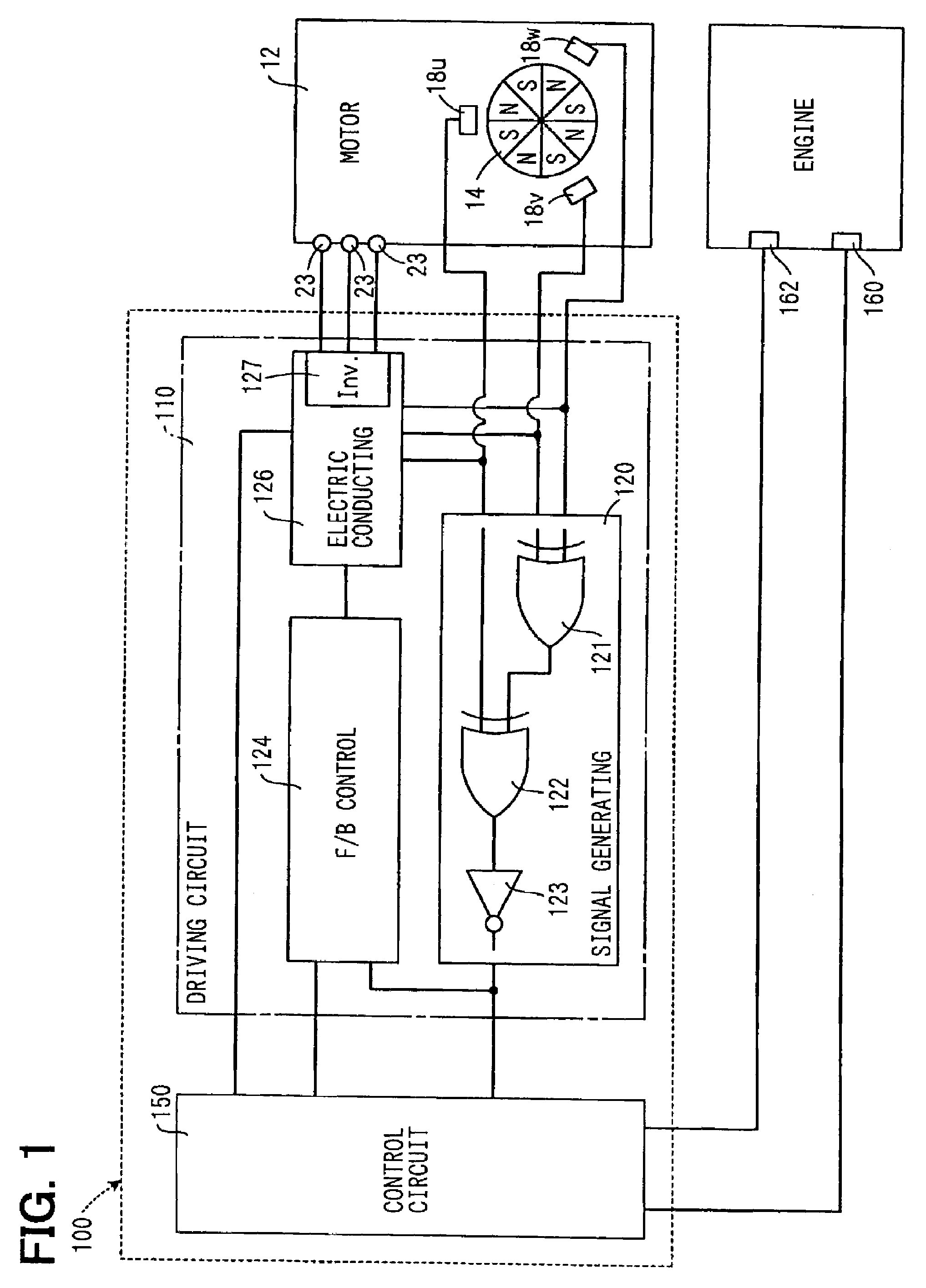
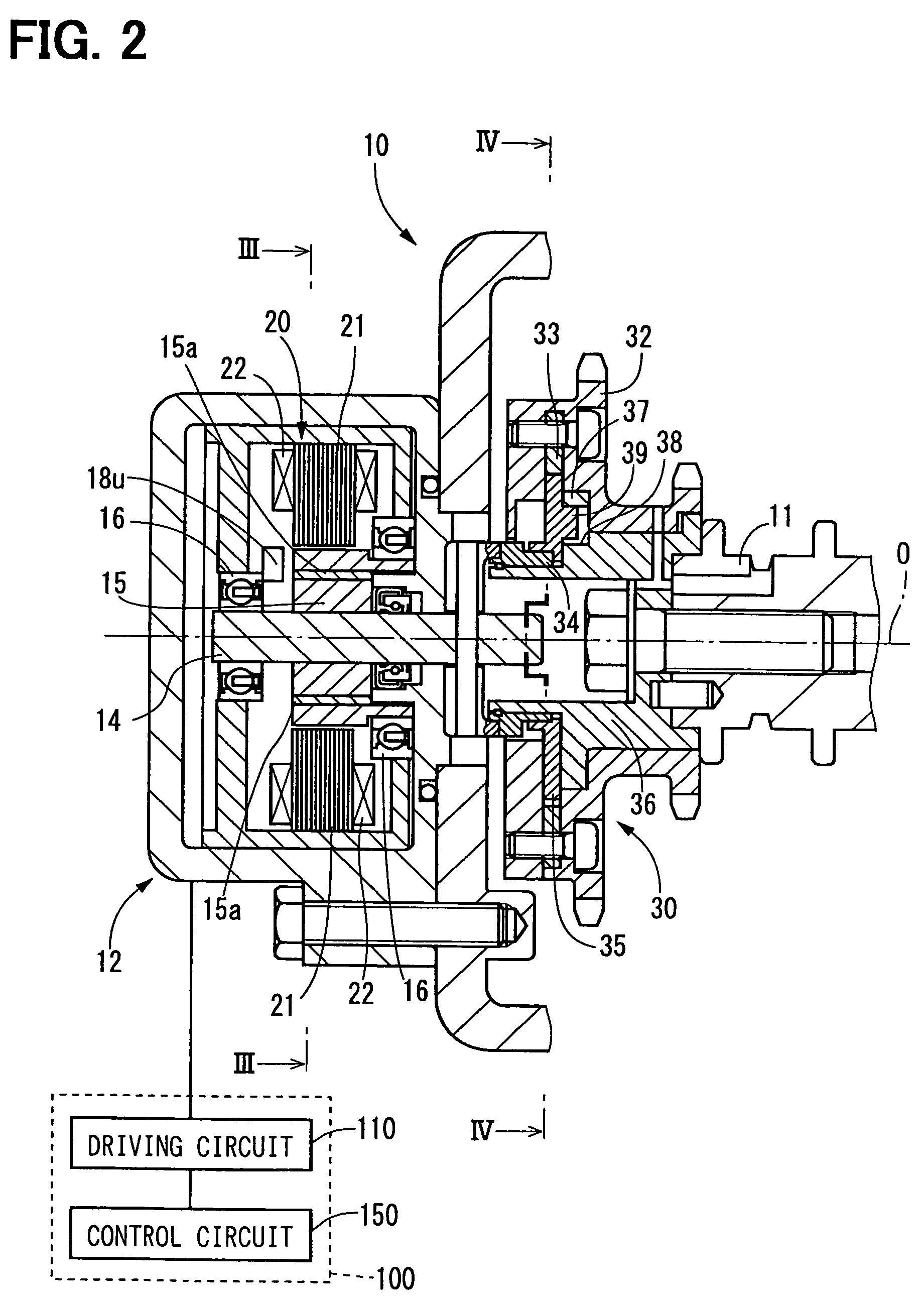
InactiveUS7121240B2Low production costAnalogue computers for vehiclesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesControl signalEngineering
The valve controller is driven by a motor. The valve controller has a control circuit and a driving circuit. The driving circuit drives a motor based on a control signal generated by the control circuit and a rotational position signal generated by a rotational position sensor. The driving circuit generates a rotation number signal representing an actual rotation number of the motor according to the rotational position signal, and transfers the rotation number signal to the control circuit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and apparatus to control a variable valve control device
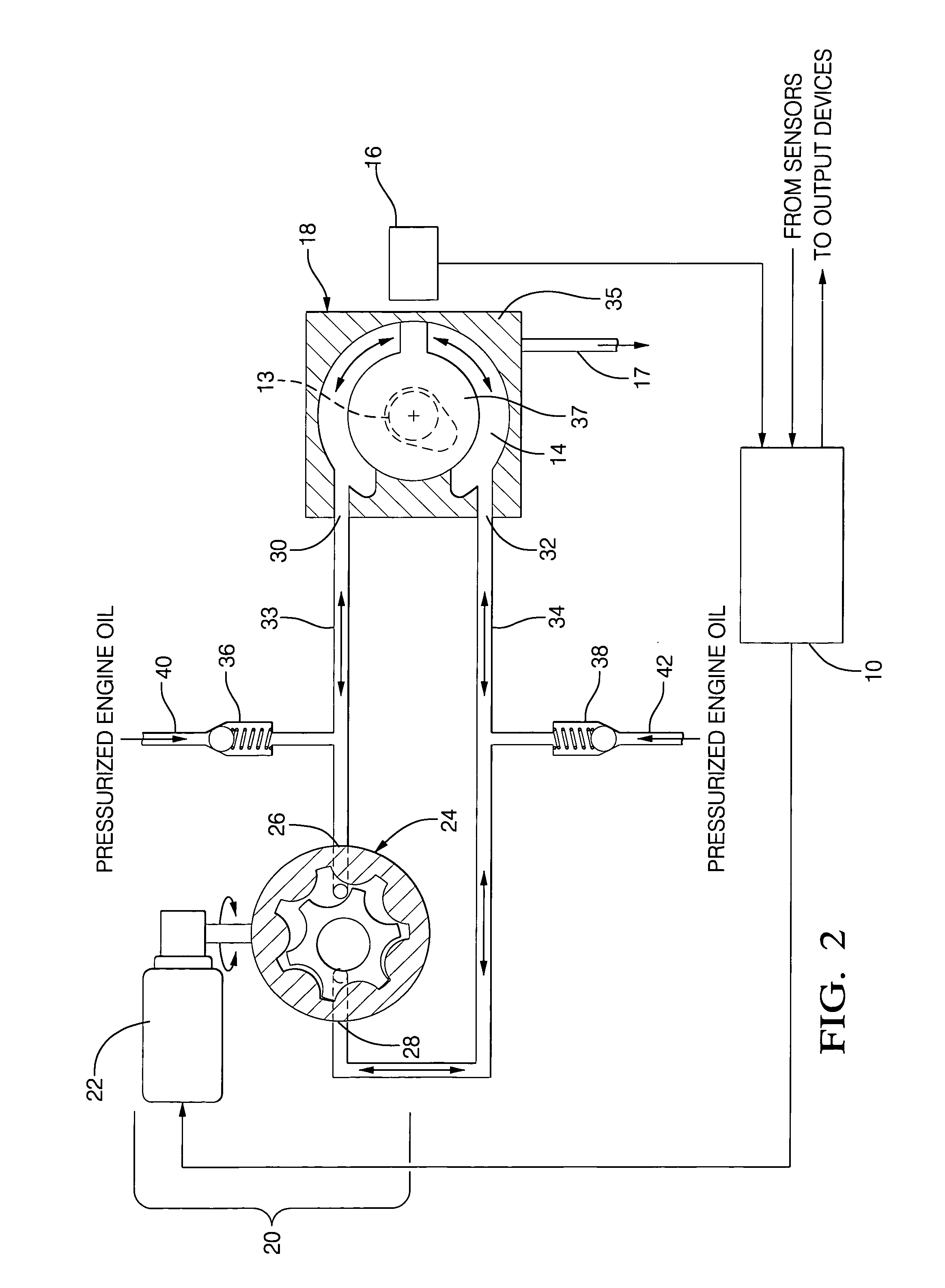
InactiveUS6978746B2Reduce energy consumptionShort response timeMachines/enginesElectronic controlFluid controlControl system
The present invention provides an improvement over conventional engine control systems for variable valve control devices for the valvetrain in that it provides a substantially closed-circuit hydrostatic fluid control system and accompanying method to improve response time of the variable valve control device and reduce energy consumption by an engine oil pump. The hydrostatic fluid control system preferably comprises a bi-directional fluid-pumping device that is fluidly connected to a variable valve control device. A controller is operable to control the bi-directional fluid-pumping device and operable to determine rotational position of the variable valve control device.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Valve timing controller
Owner:DENSO CORP
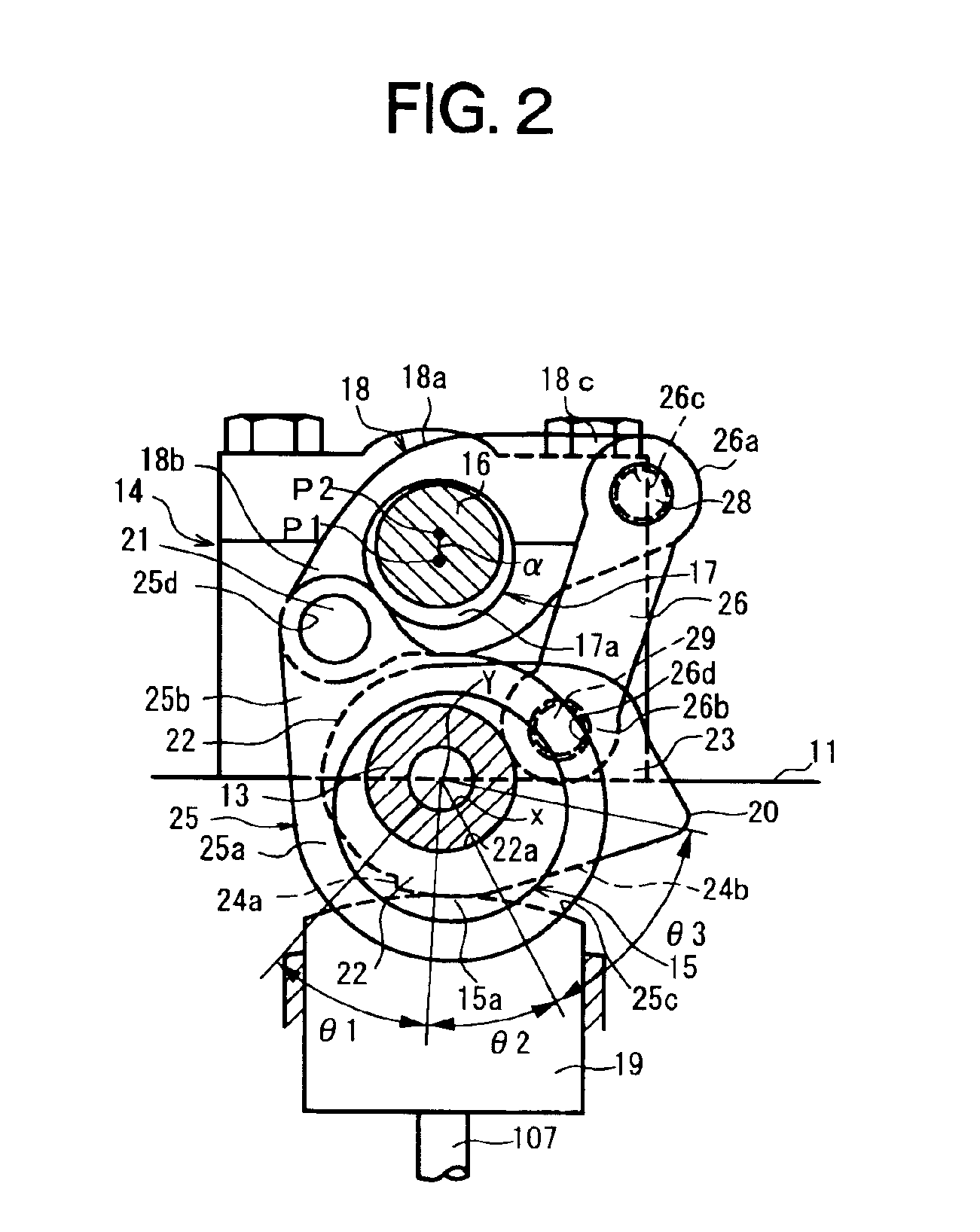
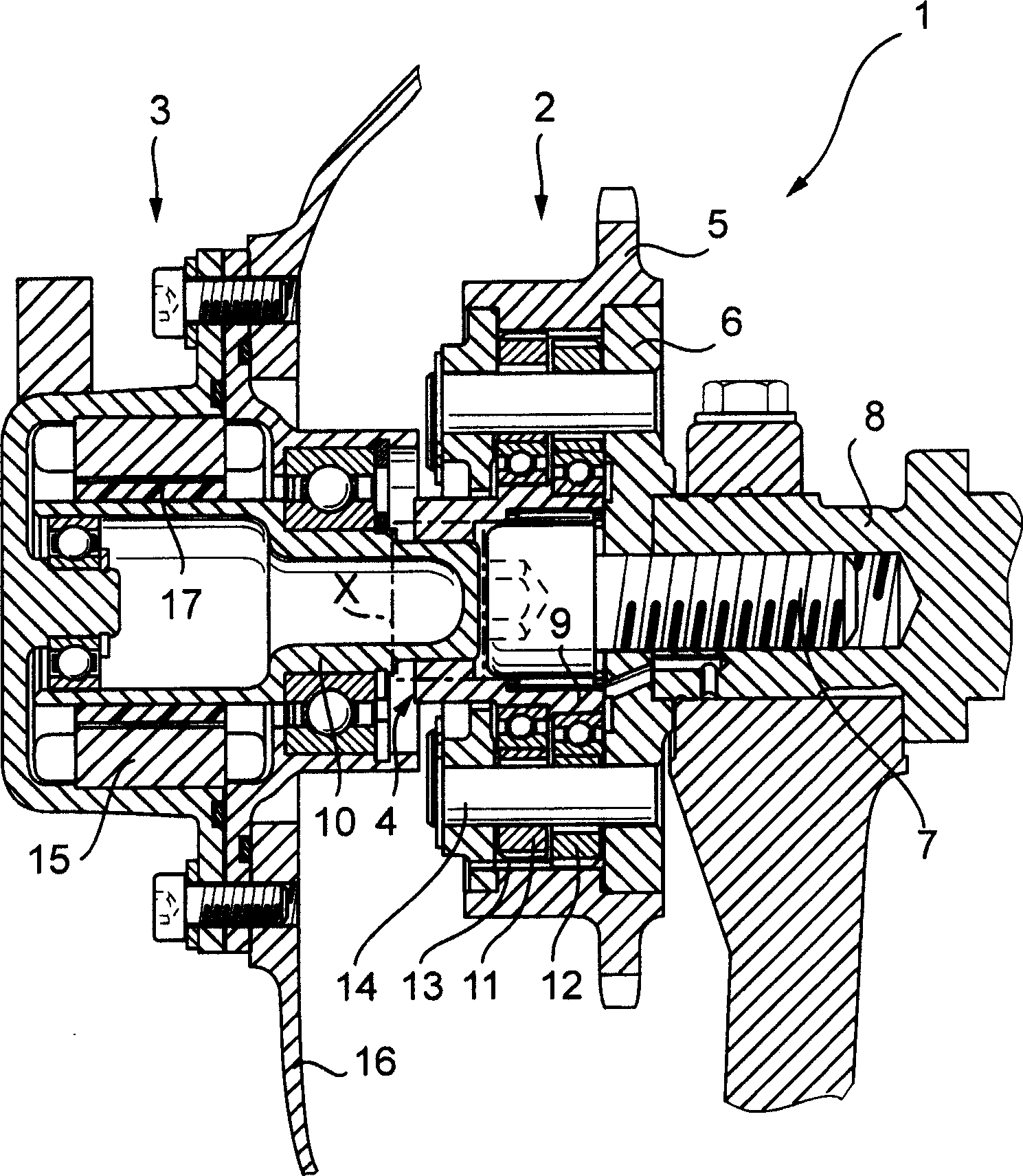
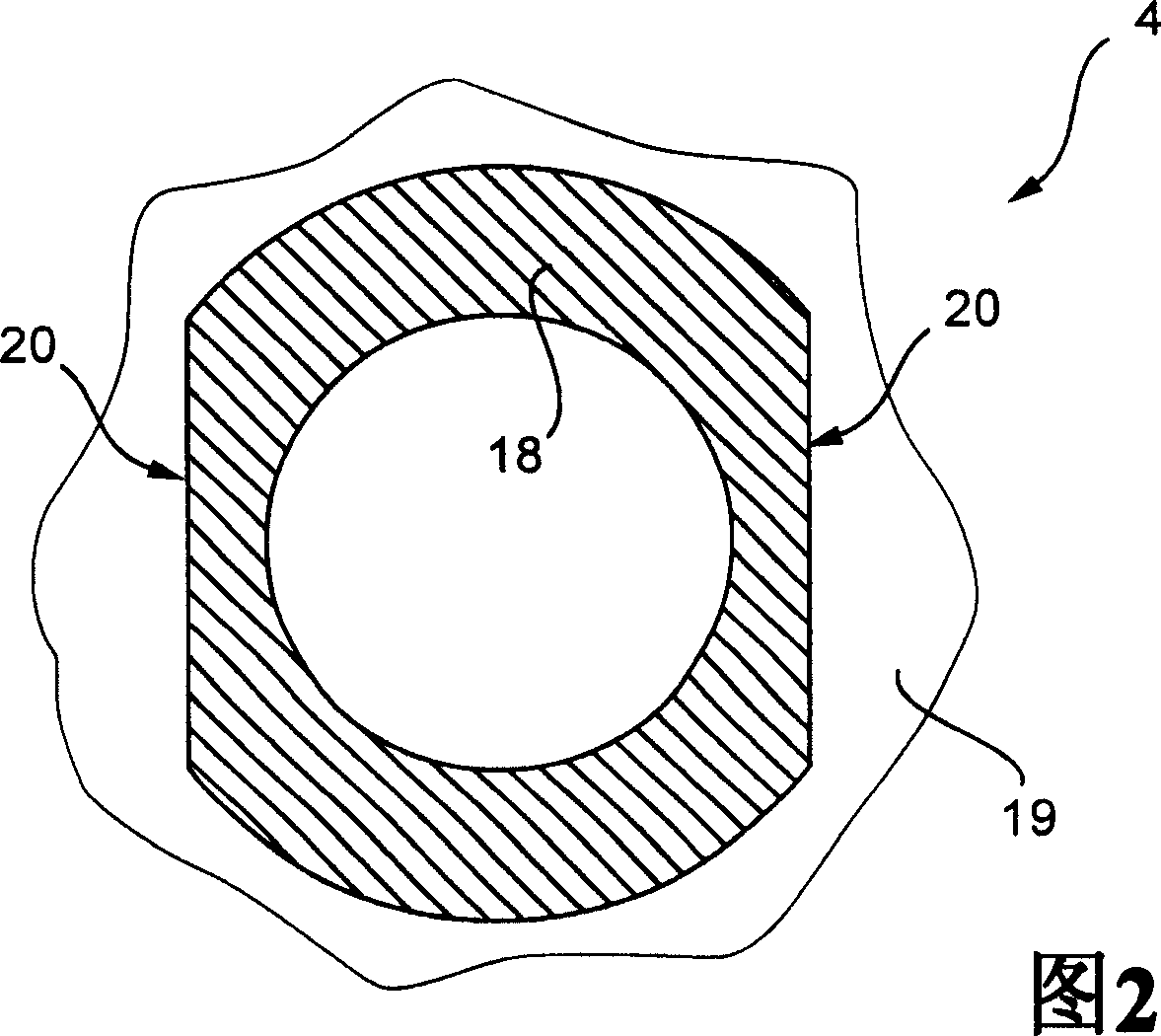
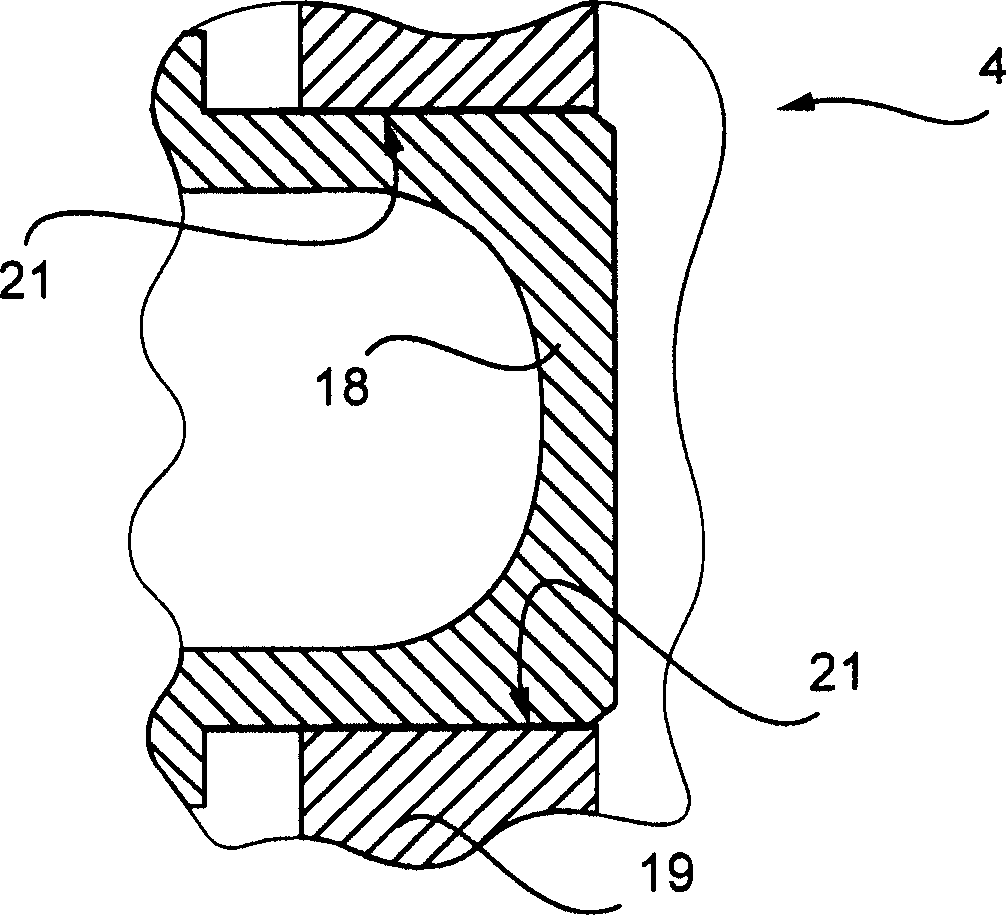
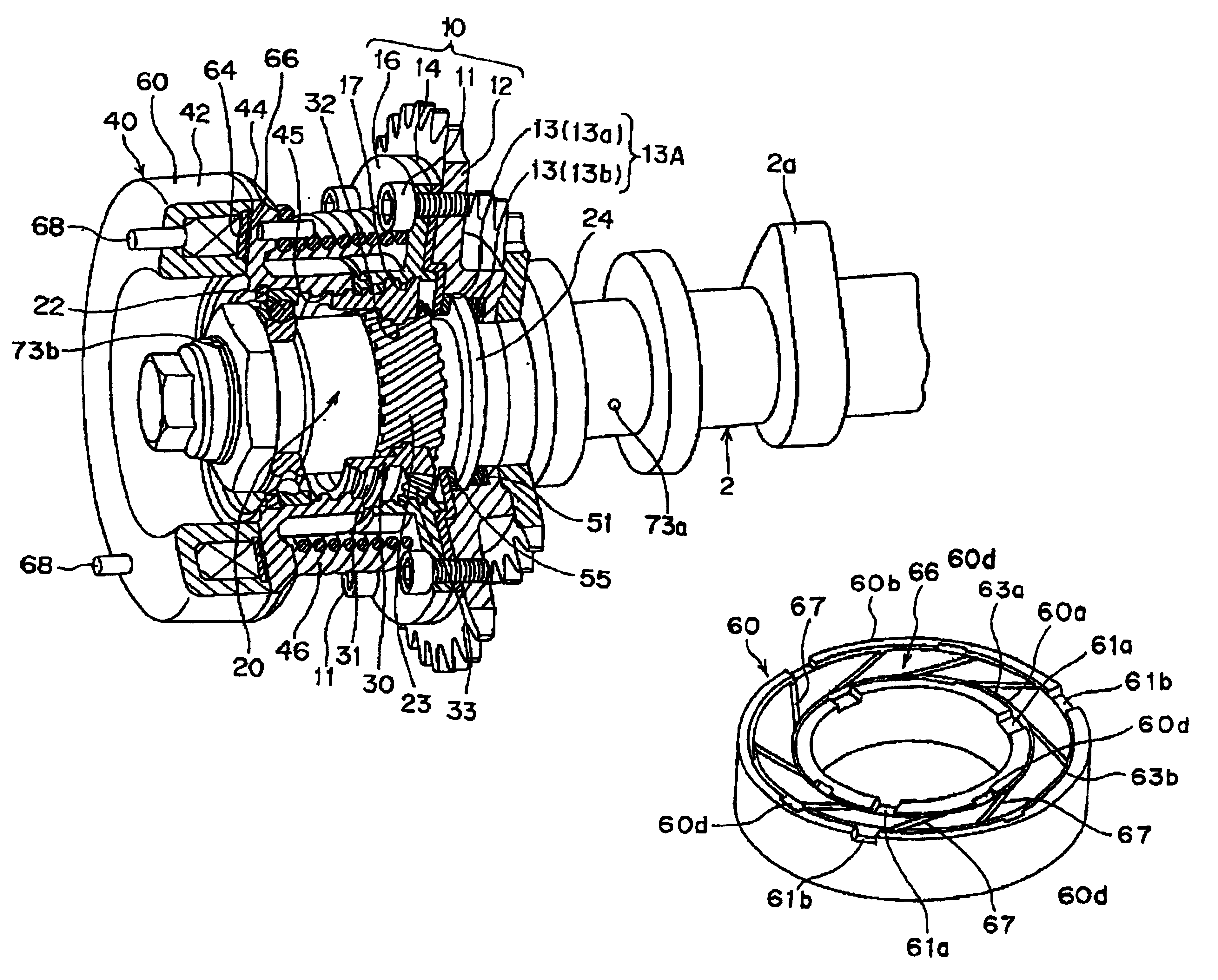
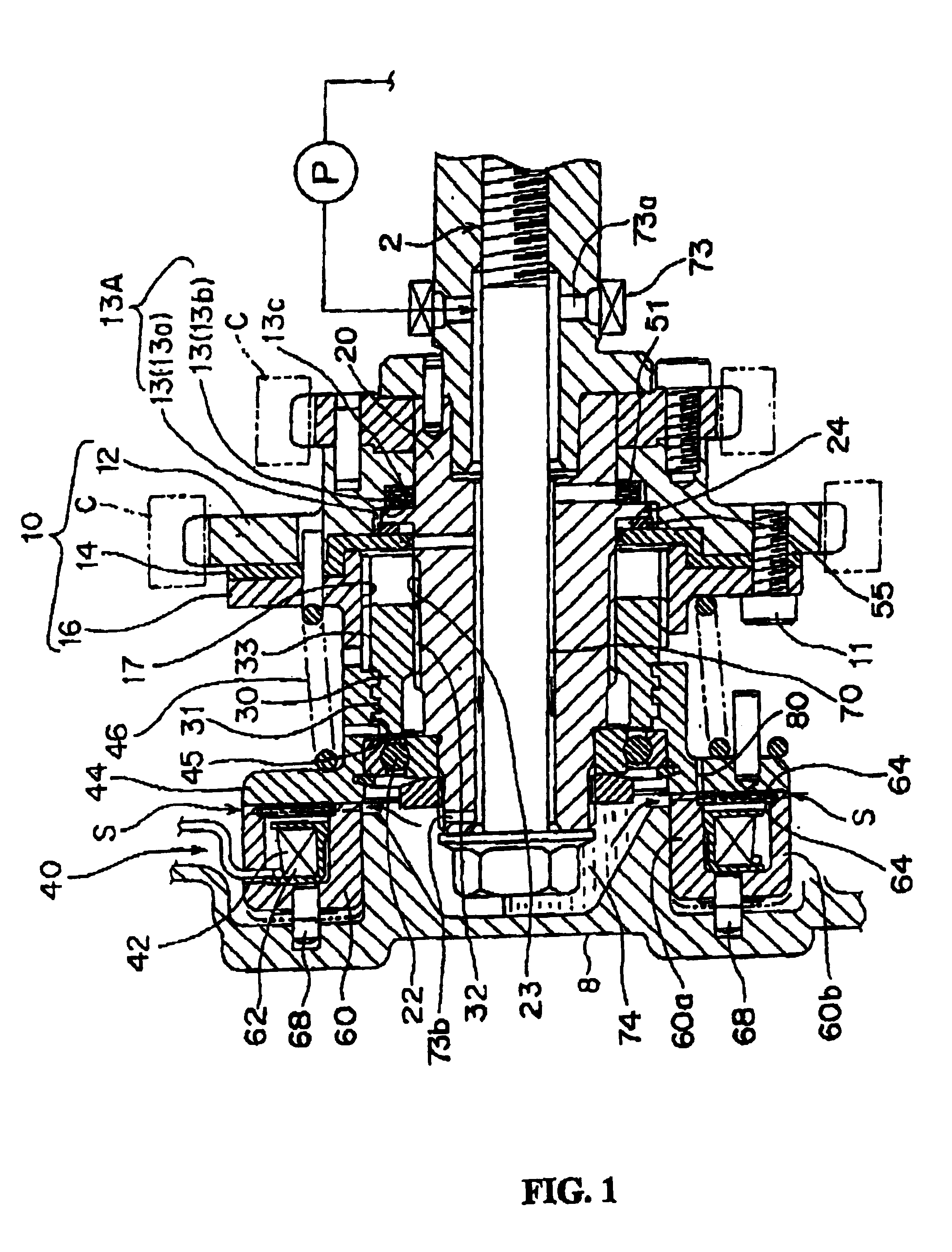
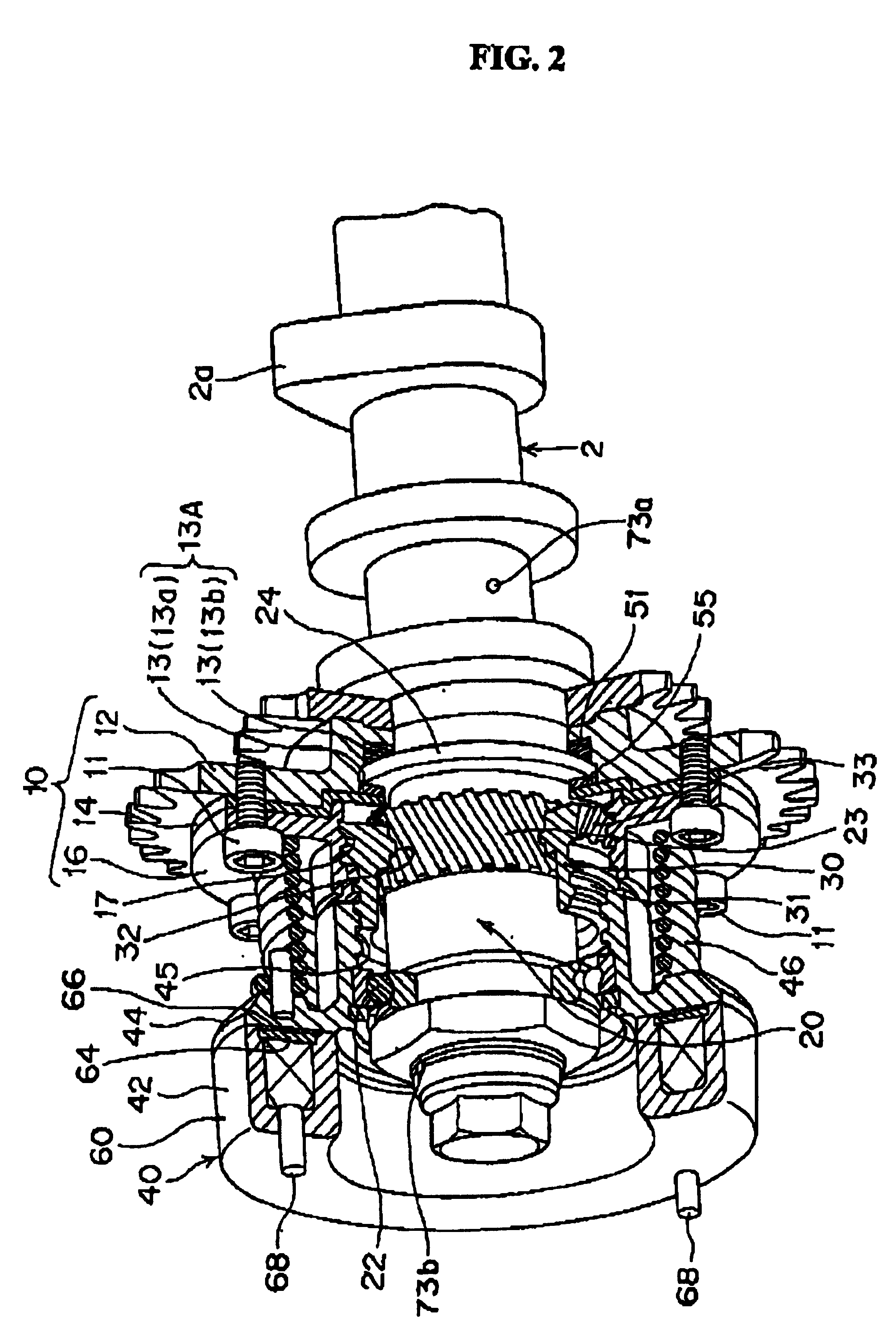
Electrically driven camshaft adjuster
InactiveCN1694999AEliminate gapsReduce manufacturing costYielding couplingCouplings for rigid shaftsExternal combustion engineEngineering
The invention relates to a camshaft adjuster (1) for adjusting and fixing the relative position of the angle of rotation of a camshaft (8) in relation to the crankshaft of a reciprocating piston internal combustion engine. Said adjusting device comprises a high transmission and friction-reduced adjusting gear mechanism (2), comprising a drive shaft which is rotationally fixed to the crankshaft, a driven shaft which is rotationally fixed to a camshaft (8) and an adjusting shaft (9) which is connected to an adjusting motor shaft (10) of an adjusting motor. A camshaft adjuster (1), which is economical to run, can be produced such that the adjusting gear mechanism (2) and the adjusting motor (3) are embodied as separate units and are connected together by a rotational backlash-free, disengaging clutch (4).
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Electric control system two-pin electromagnetic valve for automobile engine
InactiveCN105546196AAccurately judge the movement situationReduce shockOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMachines/enginesSolenoid valveElectric control
The invention provides an electric control system two-pin electromagnetic valve for an automobile engine. According to the scheme, the electric control system two-pin electromagnetic valve comprises a pin sleeve installed on a valve shell, and valve pins are arranged in the pin sleeve; electromagnetic actuators are arranged in the valve shell; each electromagnetic actuator comprises a front yoke sleeve, a rear yoke sleeve, a guide sleeve for connecting the front yoke sleeve with the rear yoke sleeve, a magnetic core and a push rod, wherein the guide sleeve and the front and rear yoke sleeves are wrapped by an electromagnetic solenoid, the magnetic core is arranged in the guide sleeve, the front portion of the magnetic core makes contact with the push rod, the push rod is arranged in the front yoke sleeve, the push rod makes contact with the corresponding valve pin, and a magnetic core reset mechanism is arranged between the rear portion of the magnetic core and the valve shell. By means of the scheme, magnetism can be ensured, it can be ensured that the valve pins can make soft contact with the valve shell and the pin sleeve when moving, the valve pins can be effectively lubricated, and meanwhile whether the valve pins act in place or not can be accurately detected.
Owner:CHENGDU FULIN PRECISION AUTOMOTIVE COMPONENTS CO LTD
Valve timing adjustment device
A valve timing adjustment device has an electric motor (4) where magnetic holding torque (Th) and motor torque (Tm), which is generated by electric current, are generated on a motor shaft (102), an electric current flow control system (6) as a control section that adjusts the motor torque (Tm) by controlling electric current flow to the electric motor (4), and a phase adjustment mechanism (8) that, while transmitting CAM torque (Tca), which alternately takes positive and negative directions according to rotation of a cam shaft, to the motor shaft (102), adjusts relative phases between a crankshaft and the cam shaft according to torque balance on the motor shaft (102). After an internal combustion engine is stopped, the electric current flow control system (6) fades the motor torque (Tm) that is balanced with magnetic holding torque (Th) and the cam torque (Tca) (S105).
Owner:DENSO CORP
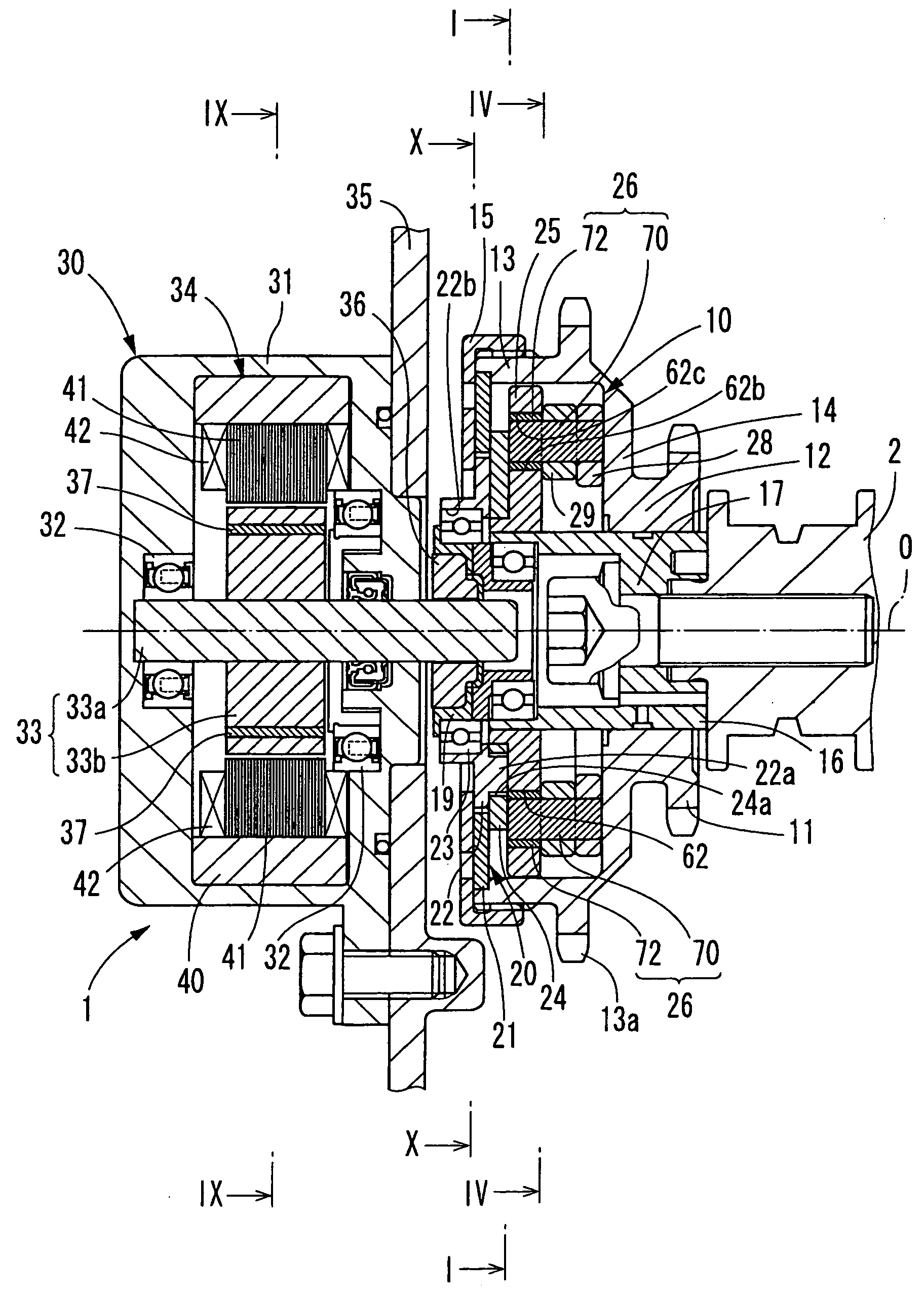
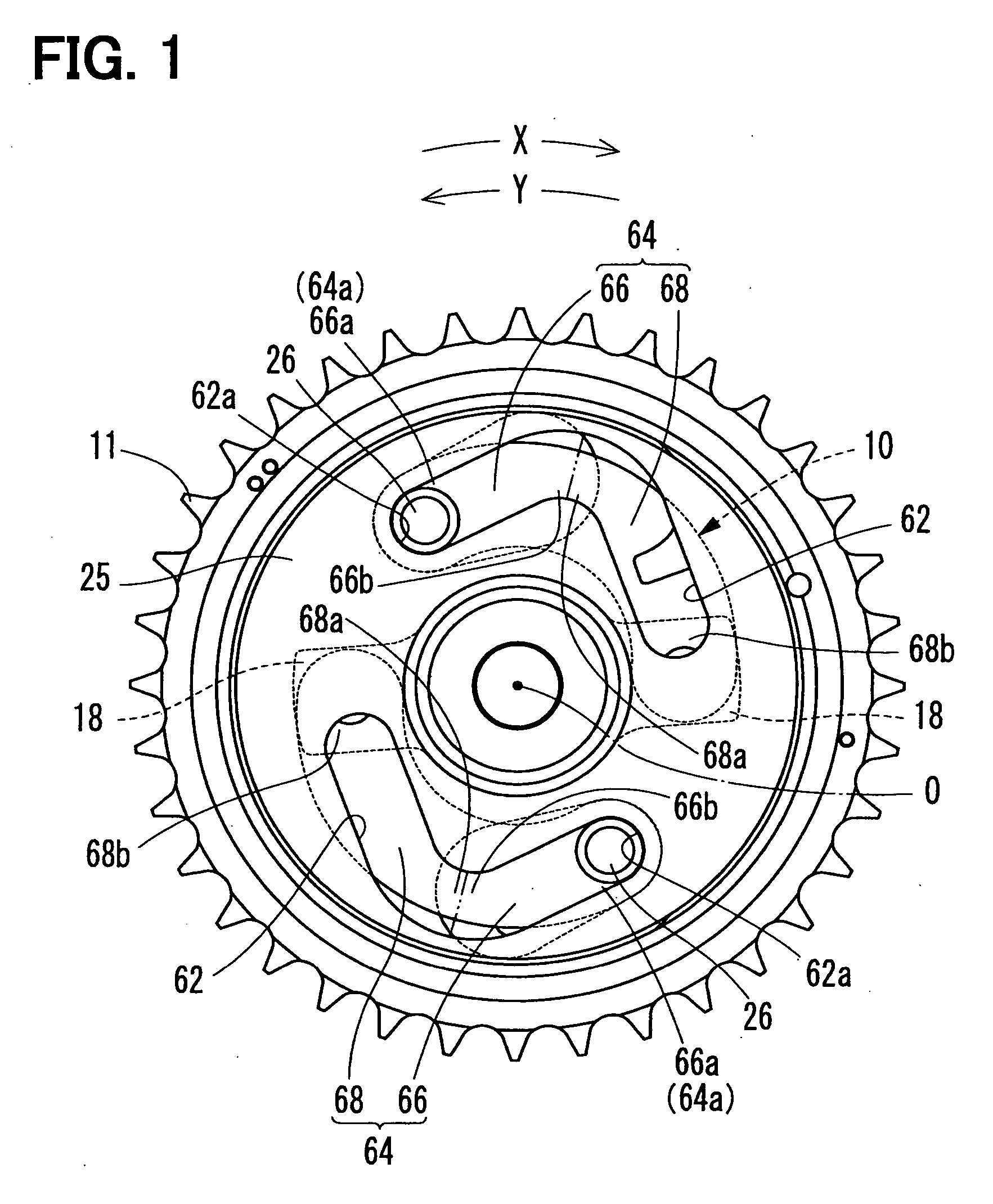
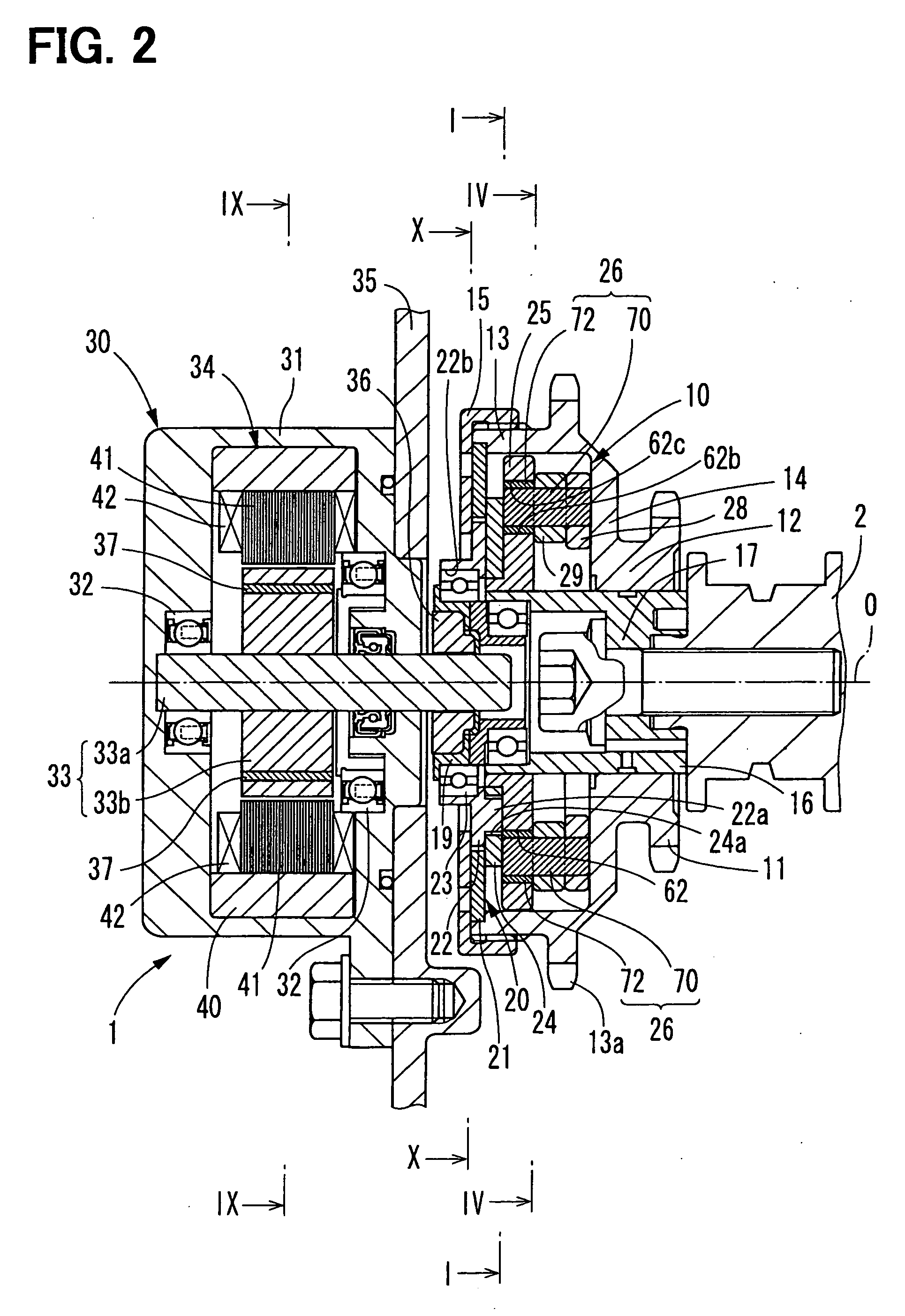
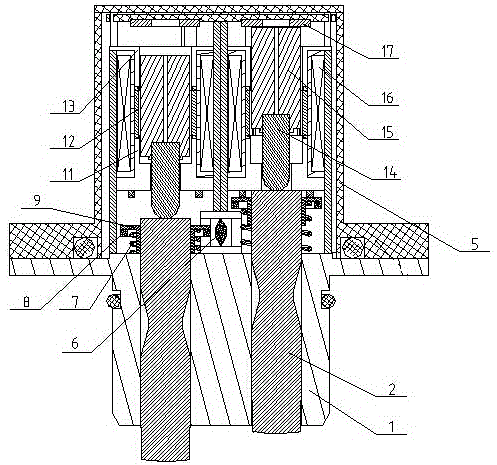
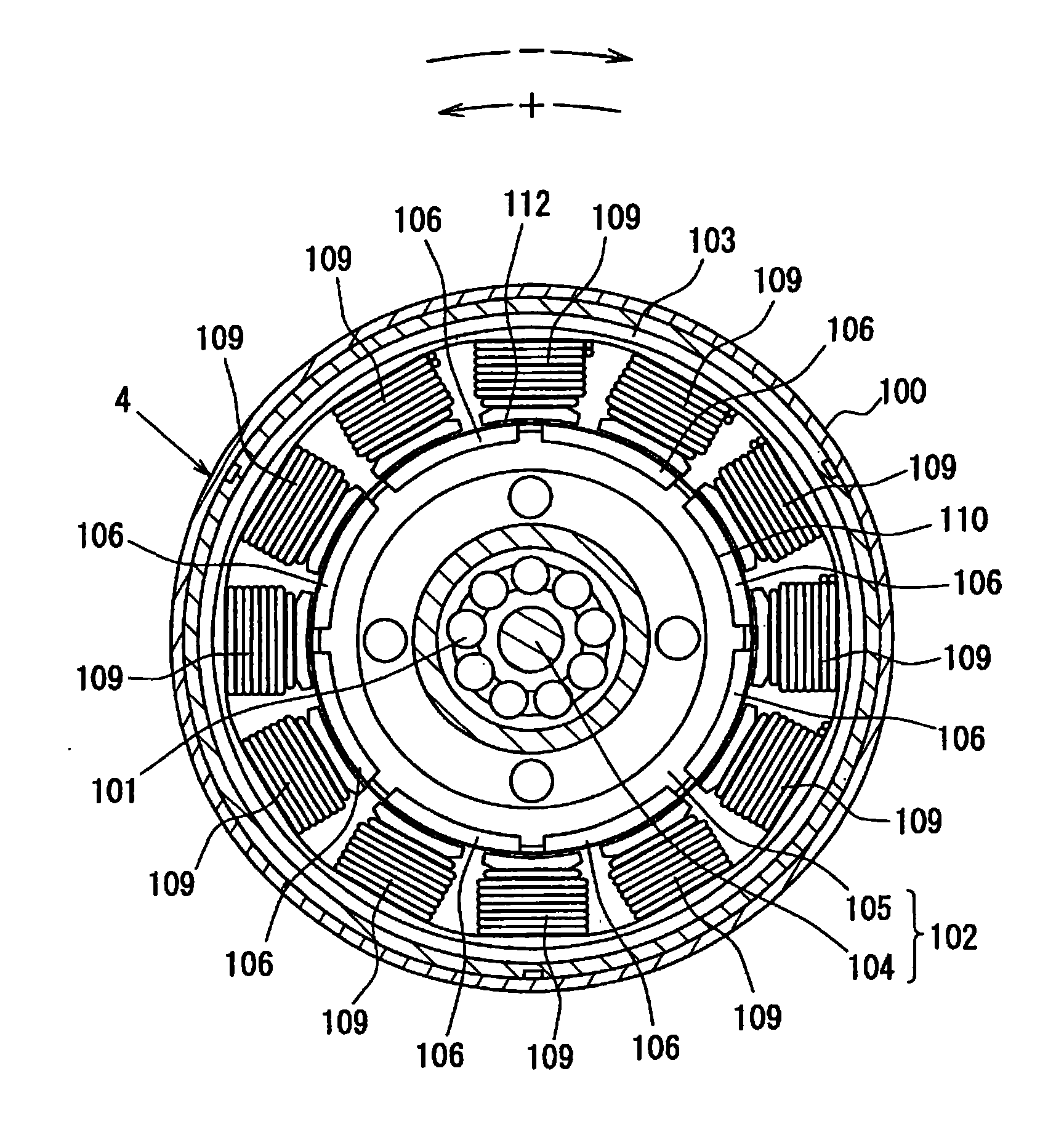
Electromagnetic brake cooling structure of phase variable device in car engine
InactiveUS6932036B2Improve cooling effectIncrease flow rateLiquid coolingYielding couplingCooling effectEngineering
An electromagnetic-brake cooling structure of a phase-variable device having an electromagnetic brake means (40) and varying the phase of a camshaft, wherein engine oil in an oil sump (74) on the radial inner side of a clutch case (60) led to the relative sliding surfaces of a friction material (66) and a rotary drum (44) through a notch (61) provided in the clutch case (60) at the front edge part of the inner peripheral wall of the clutch case (60), a notch (61b) for leading oil to the front edge part of the clutch case outer peripheral wall (60b), the oil on the relative sliding surfaces of the friction material (66) and the rotary drum (44) is discharged positively to the outside, and the circulation of the cooling oil is activated to increase the cooling effect of the sliding surface of the friction material (66).
Owner:NITTAN VALVE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com