Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
521results about "Cards" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
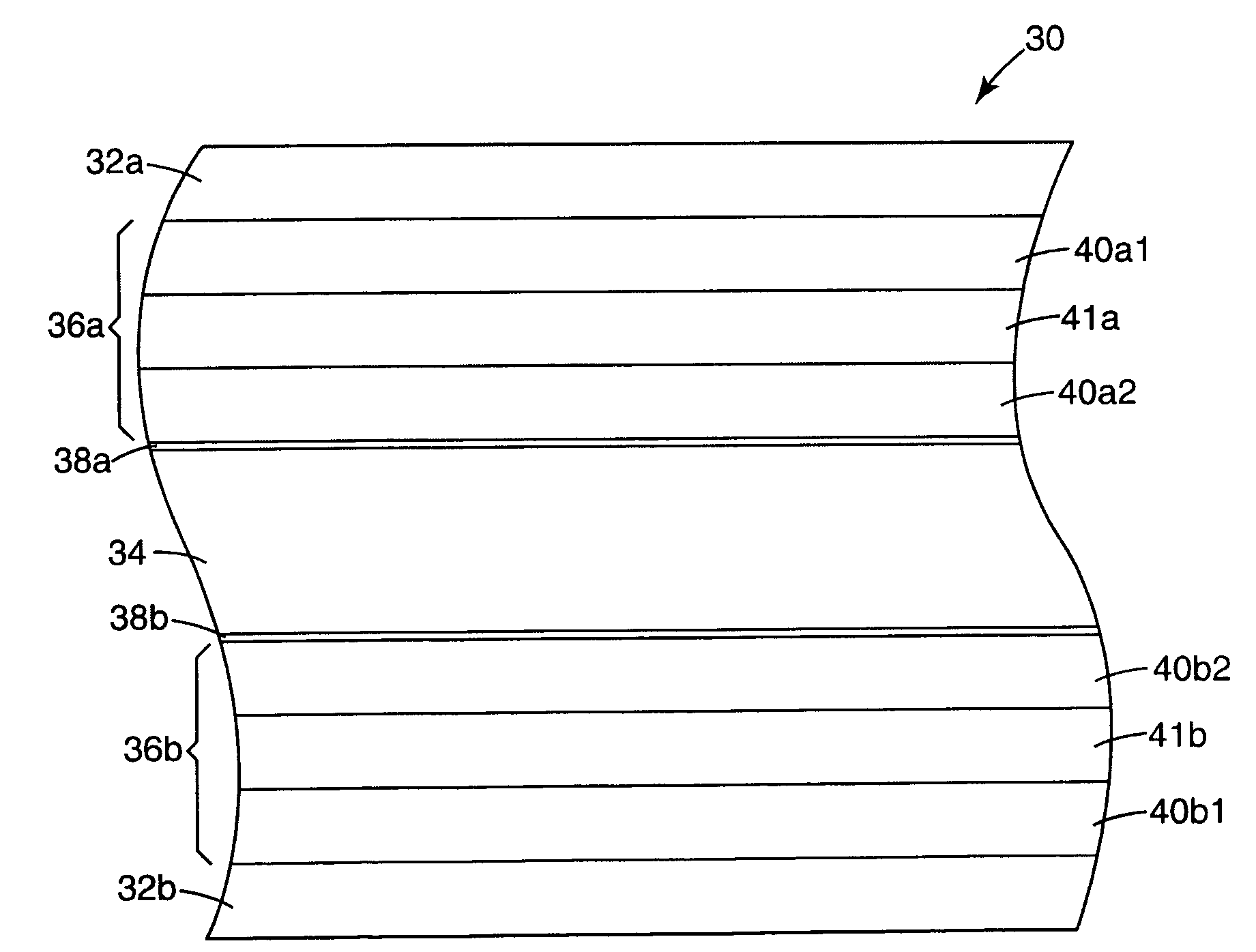
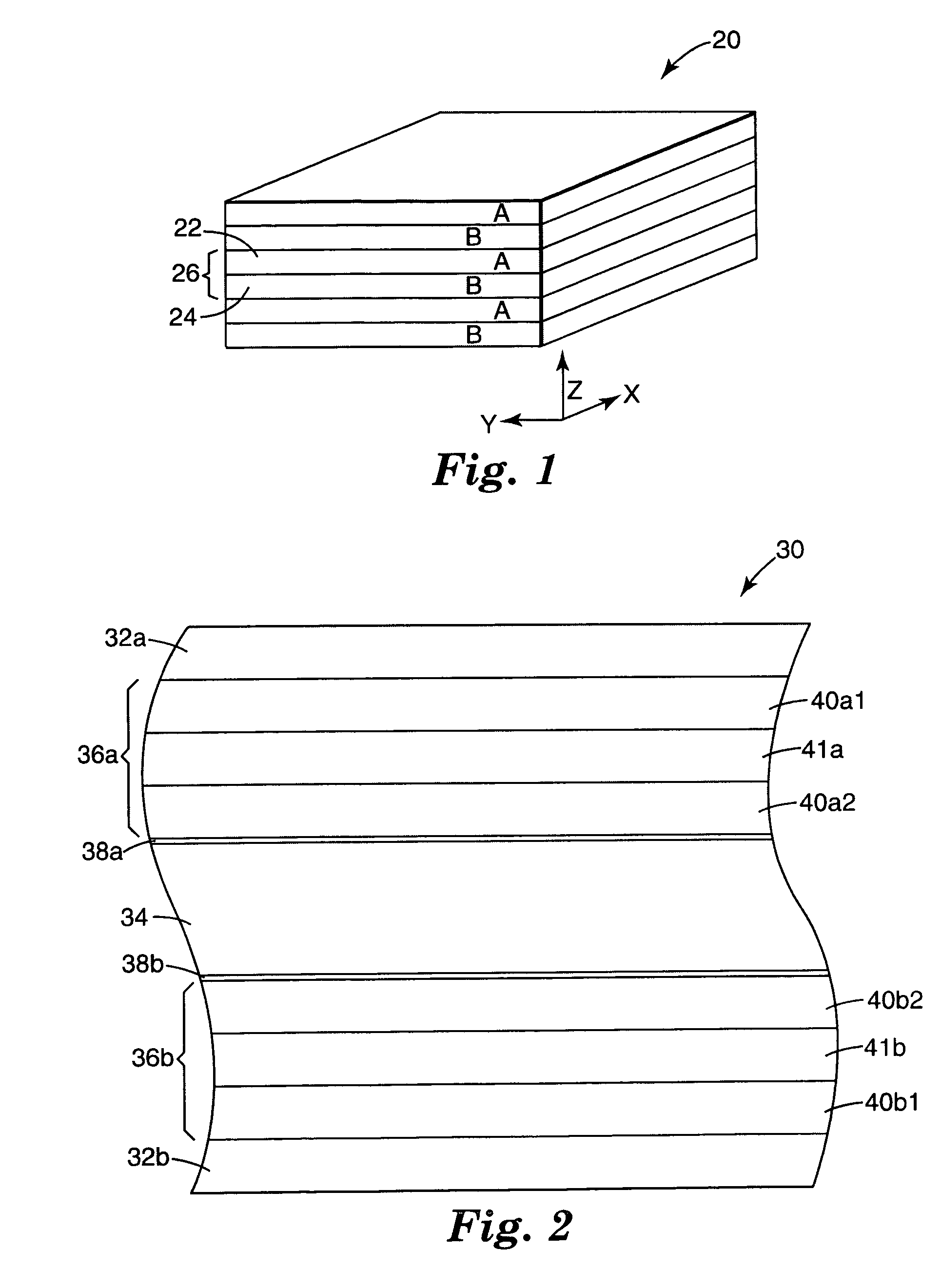
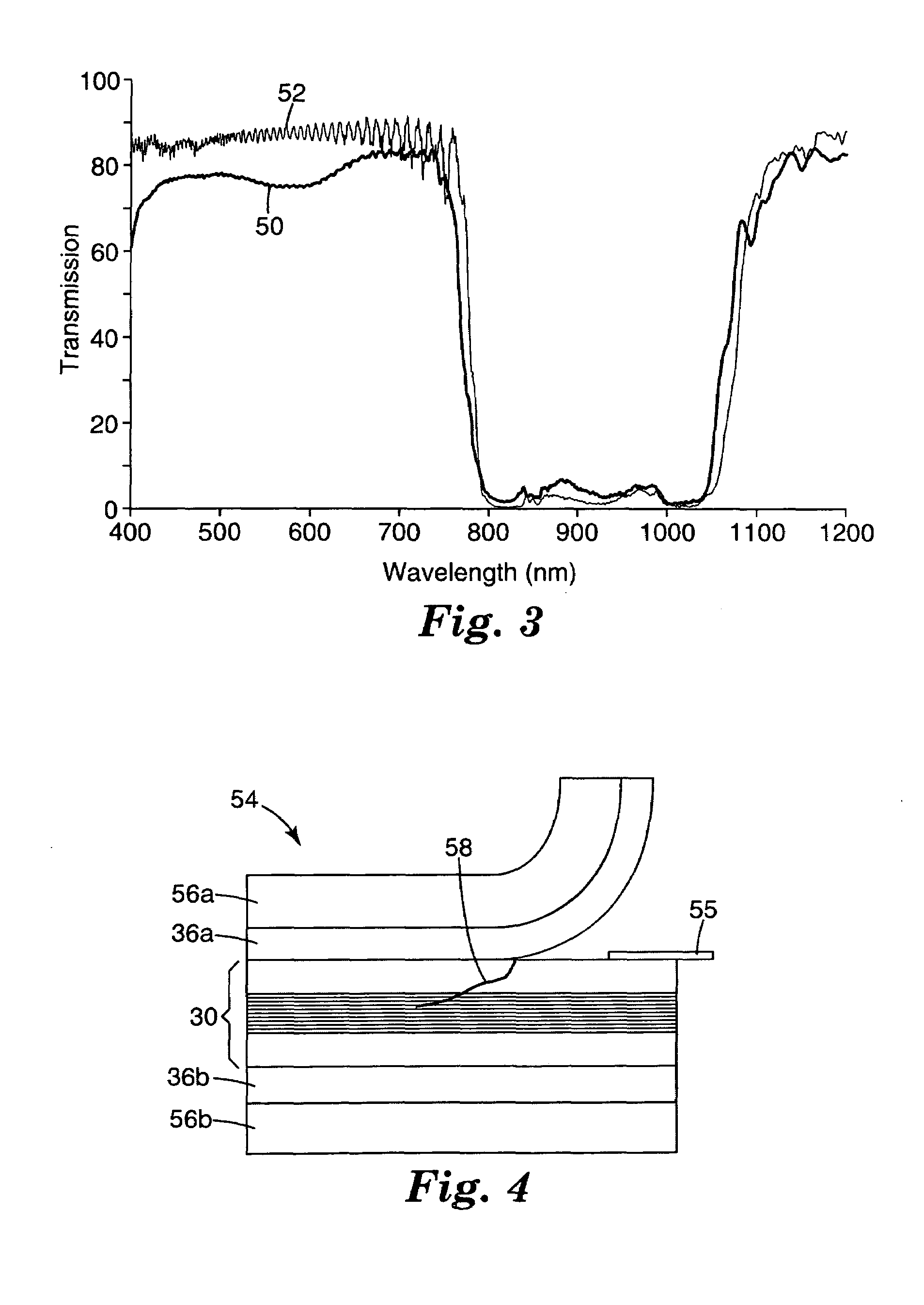
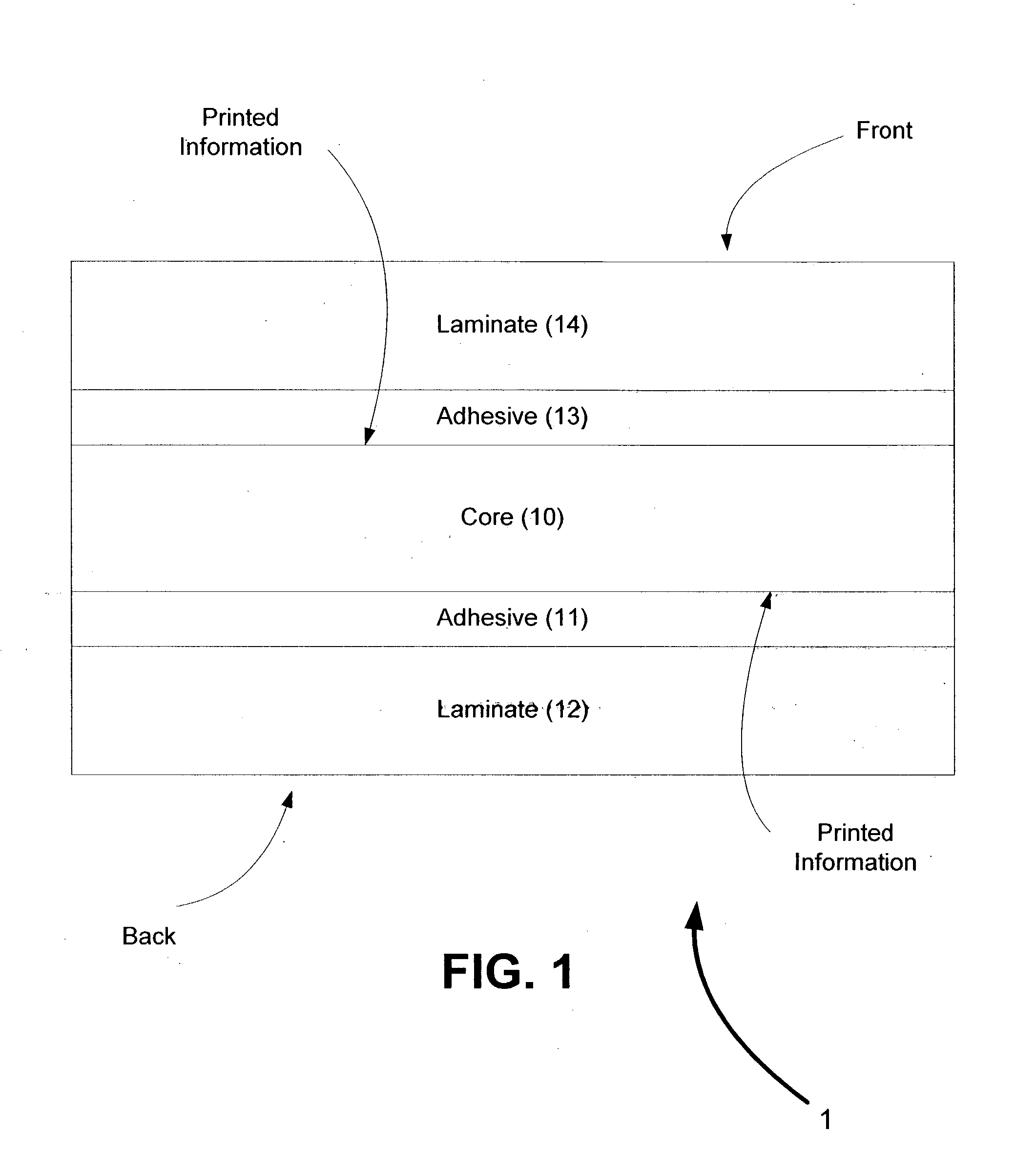
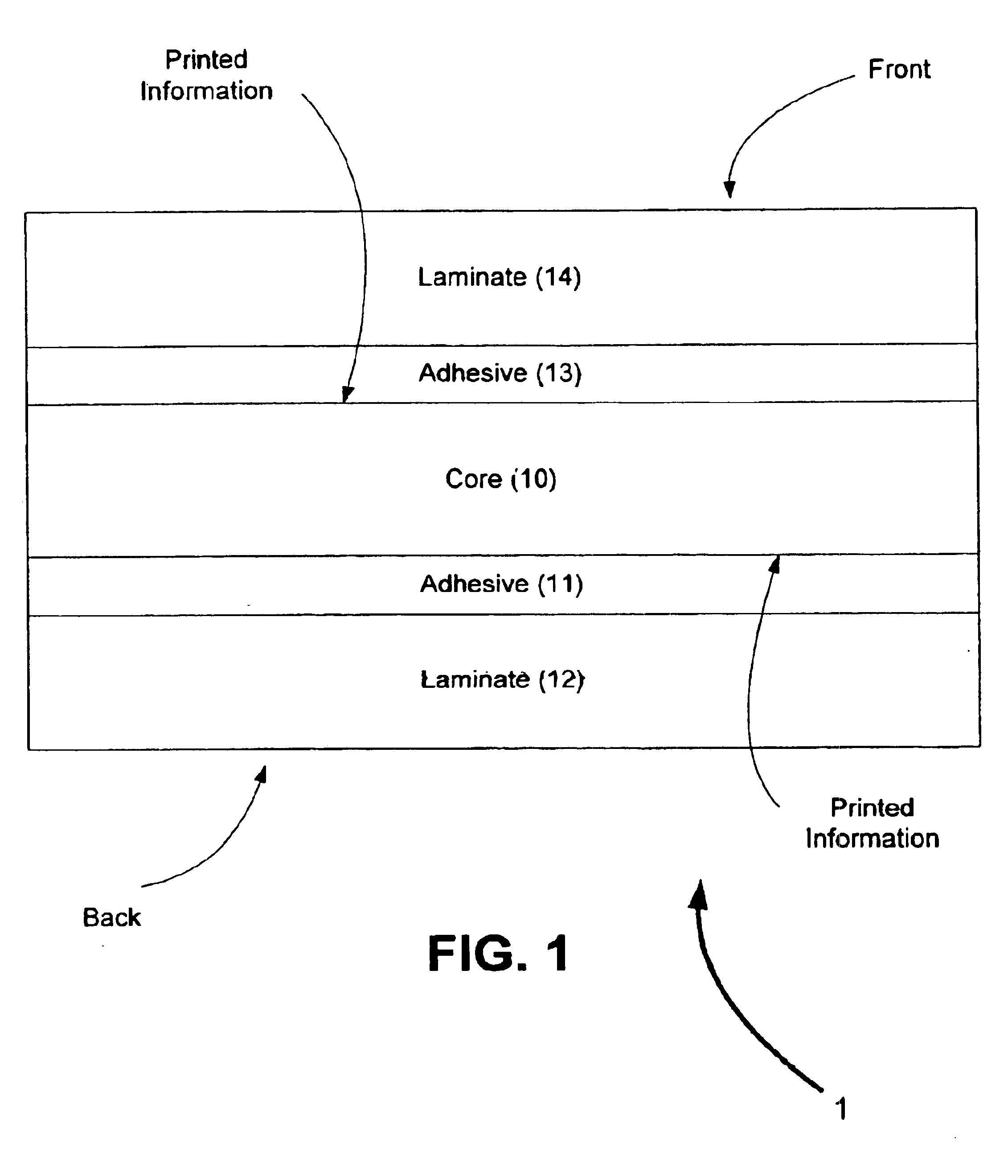
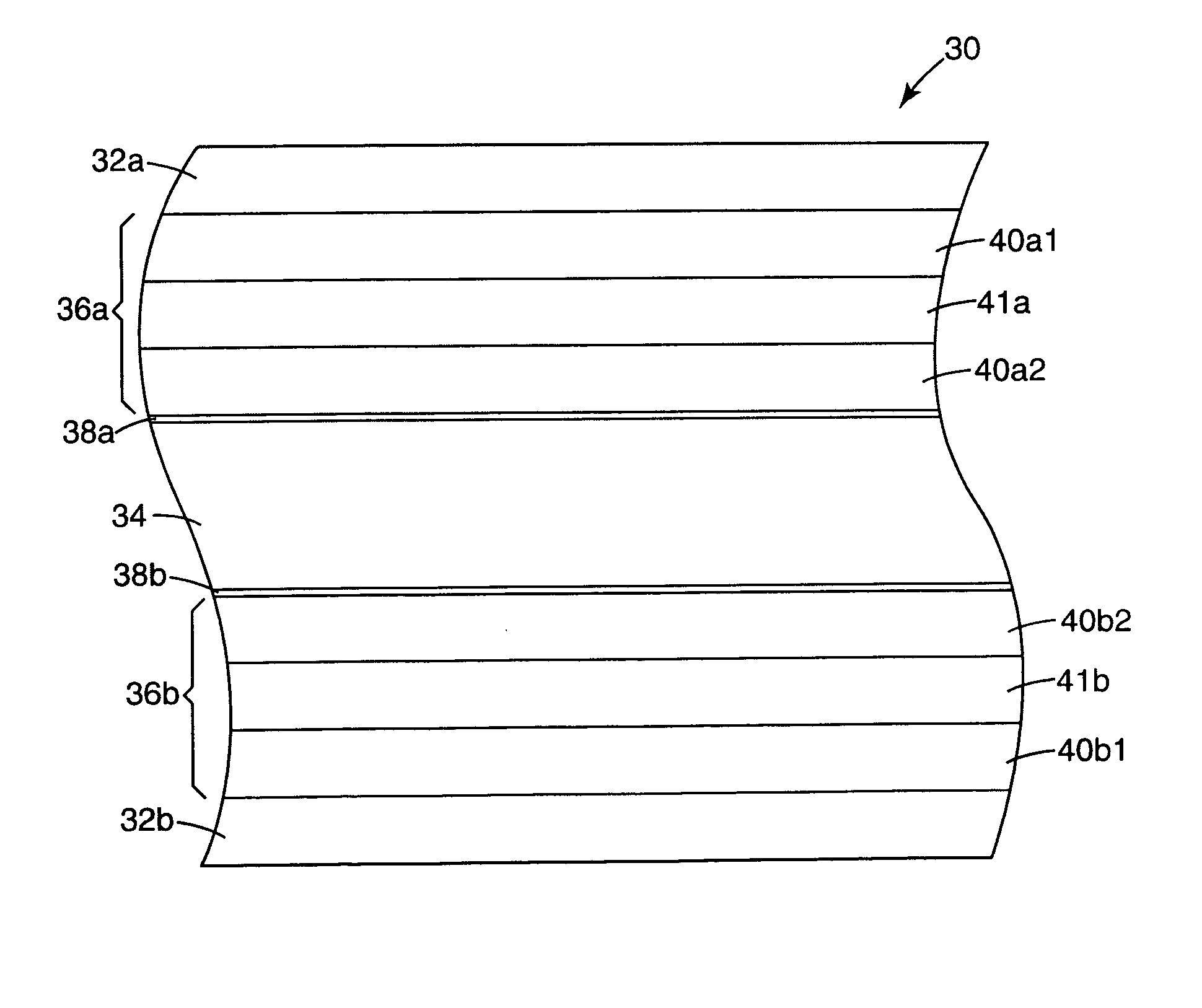
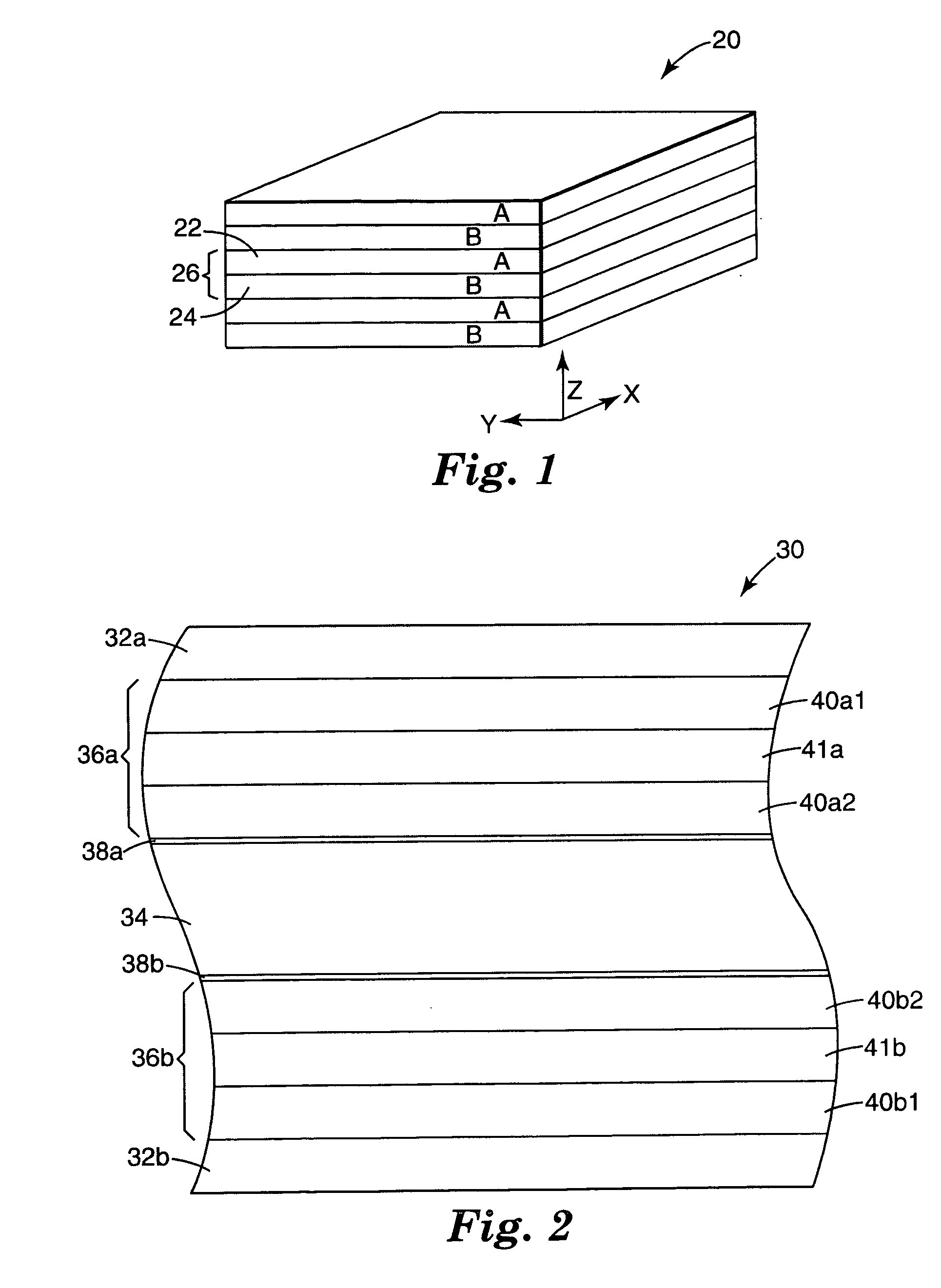
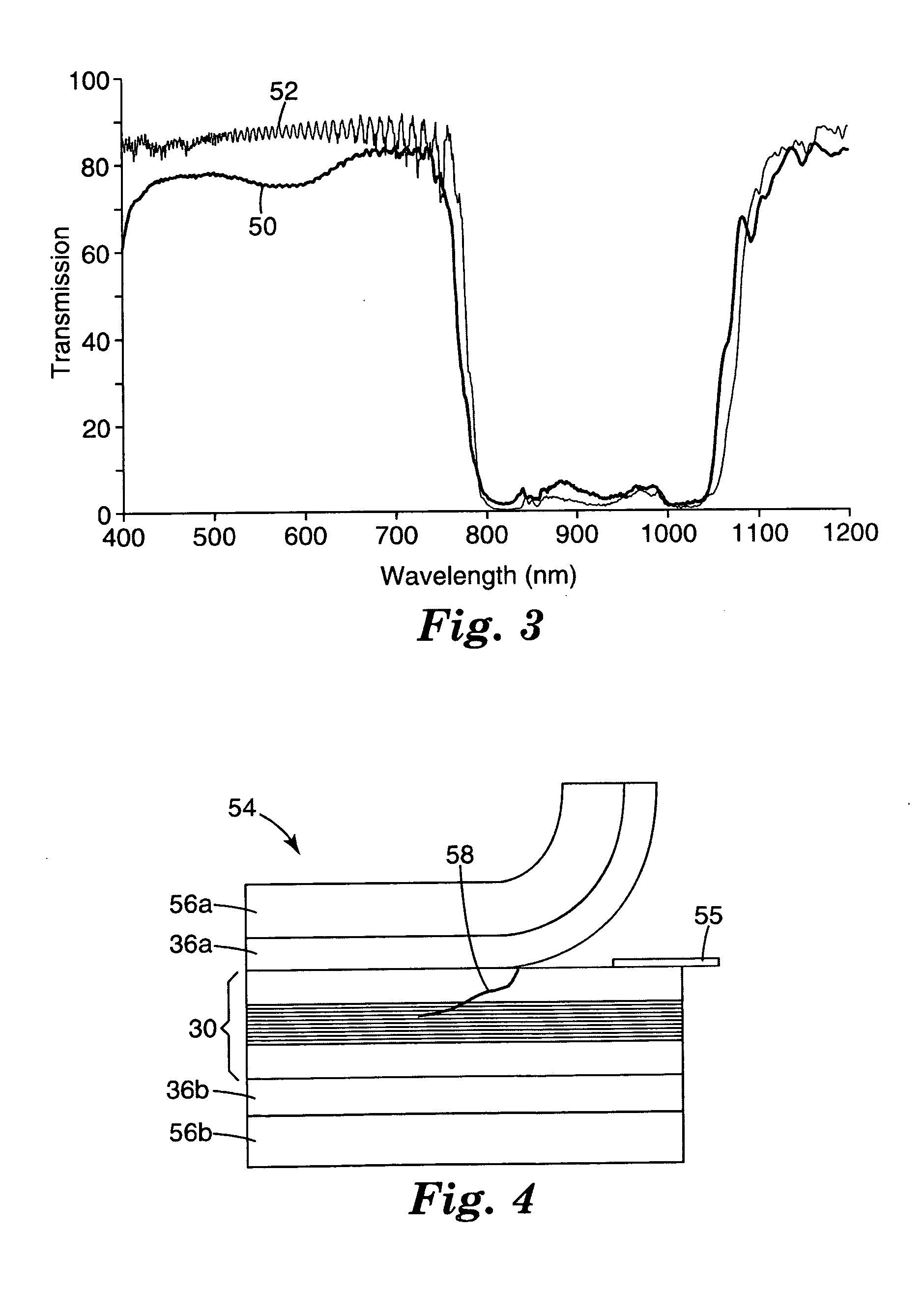
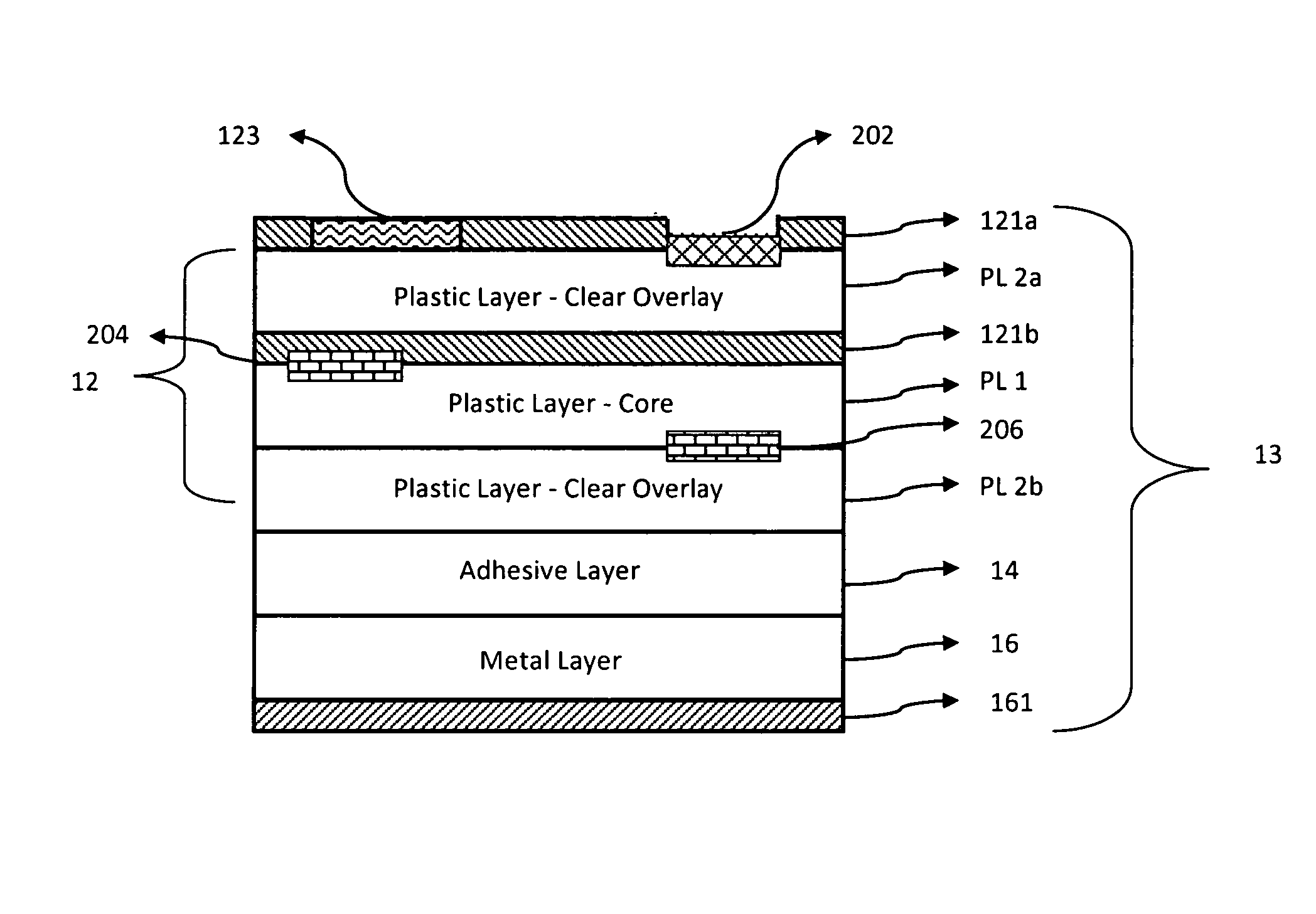
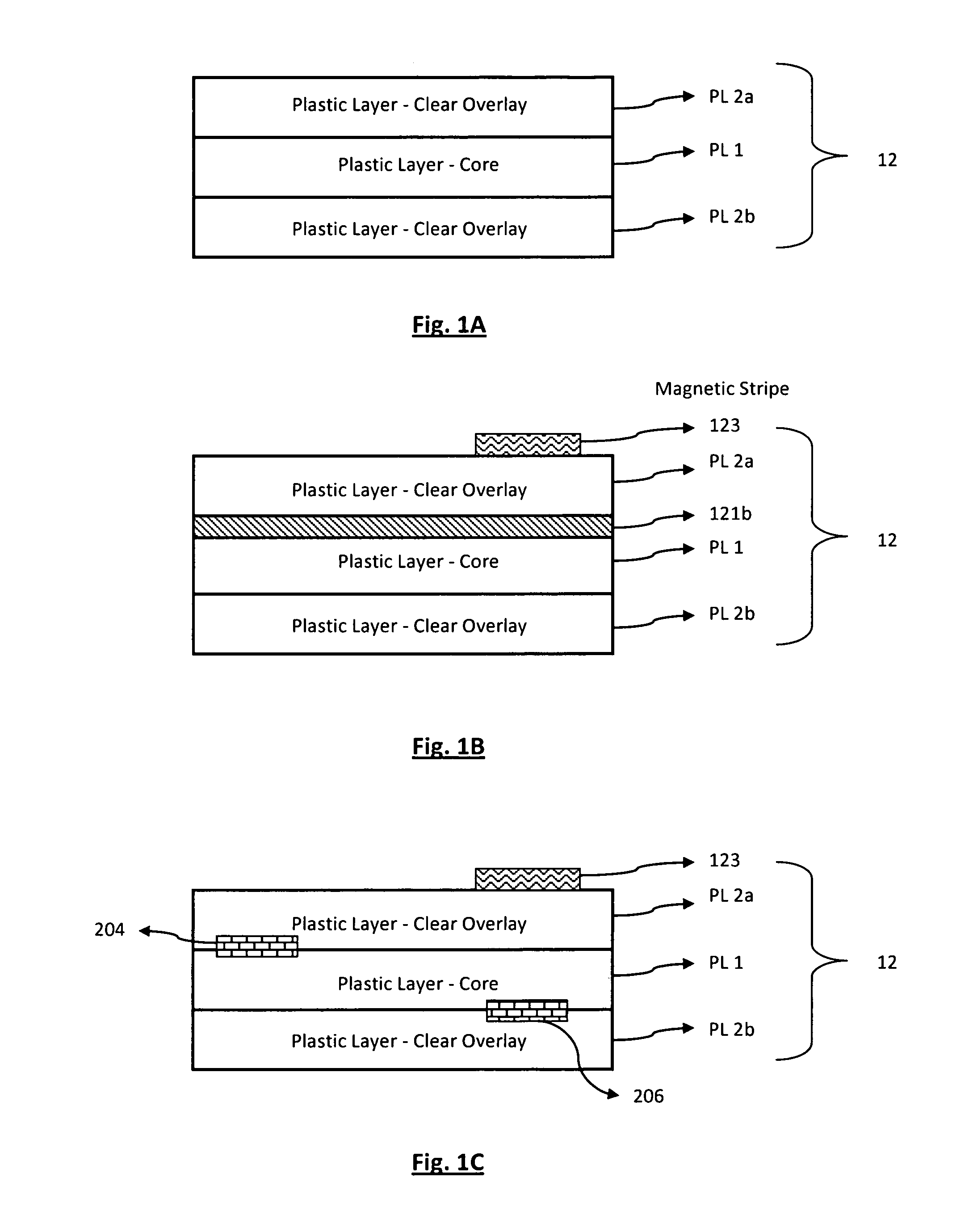
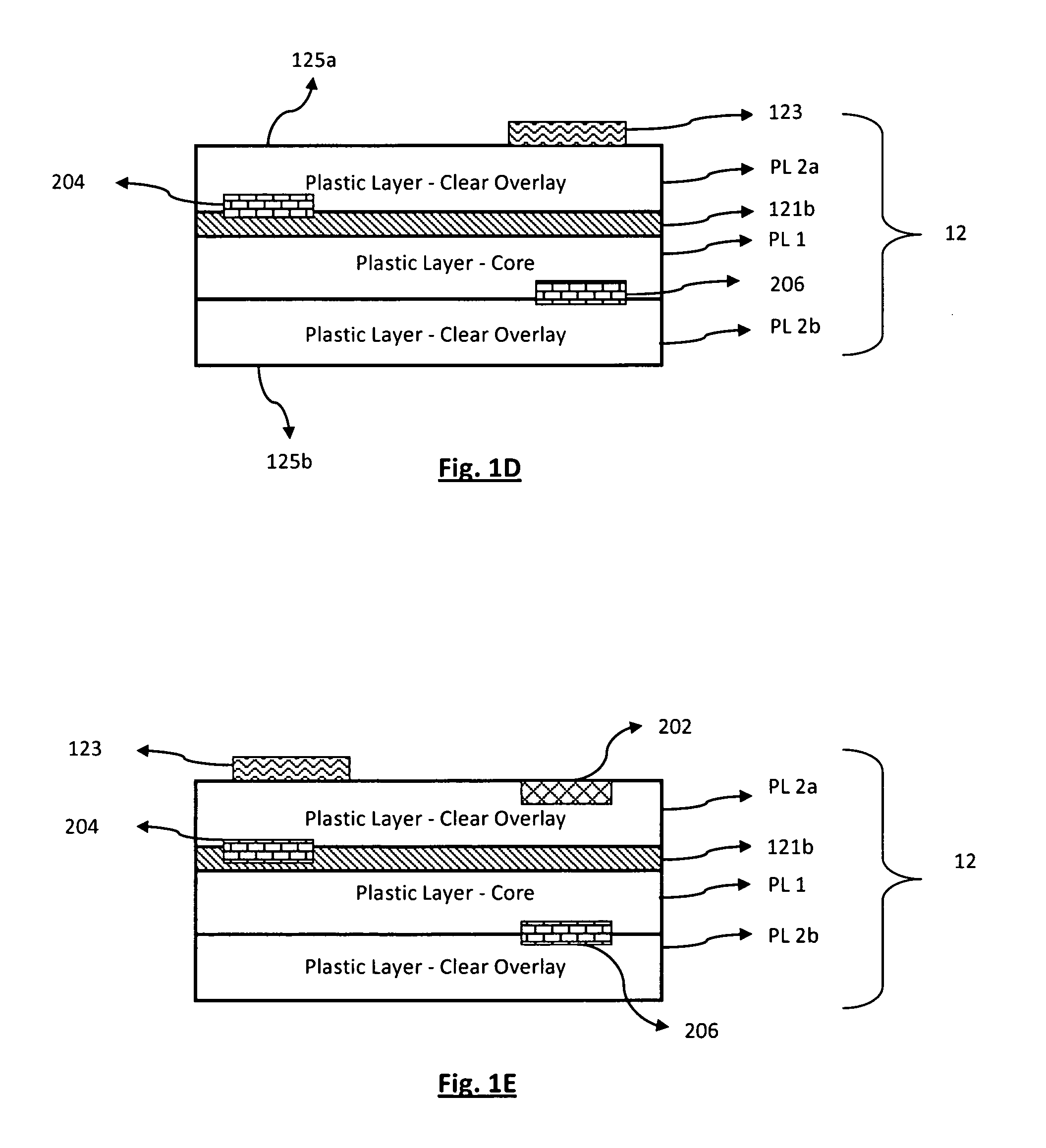
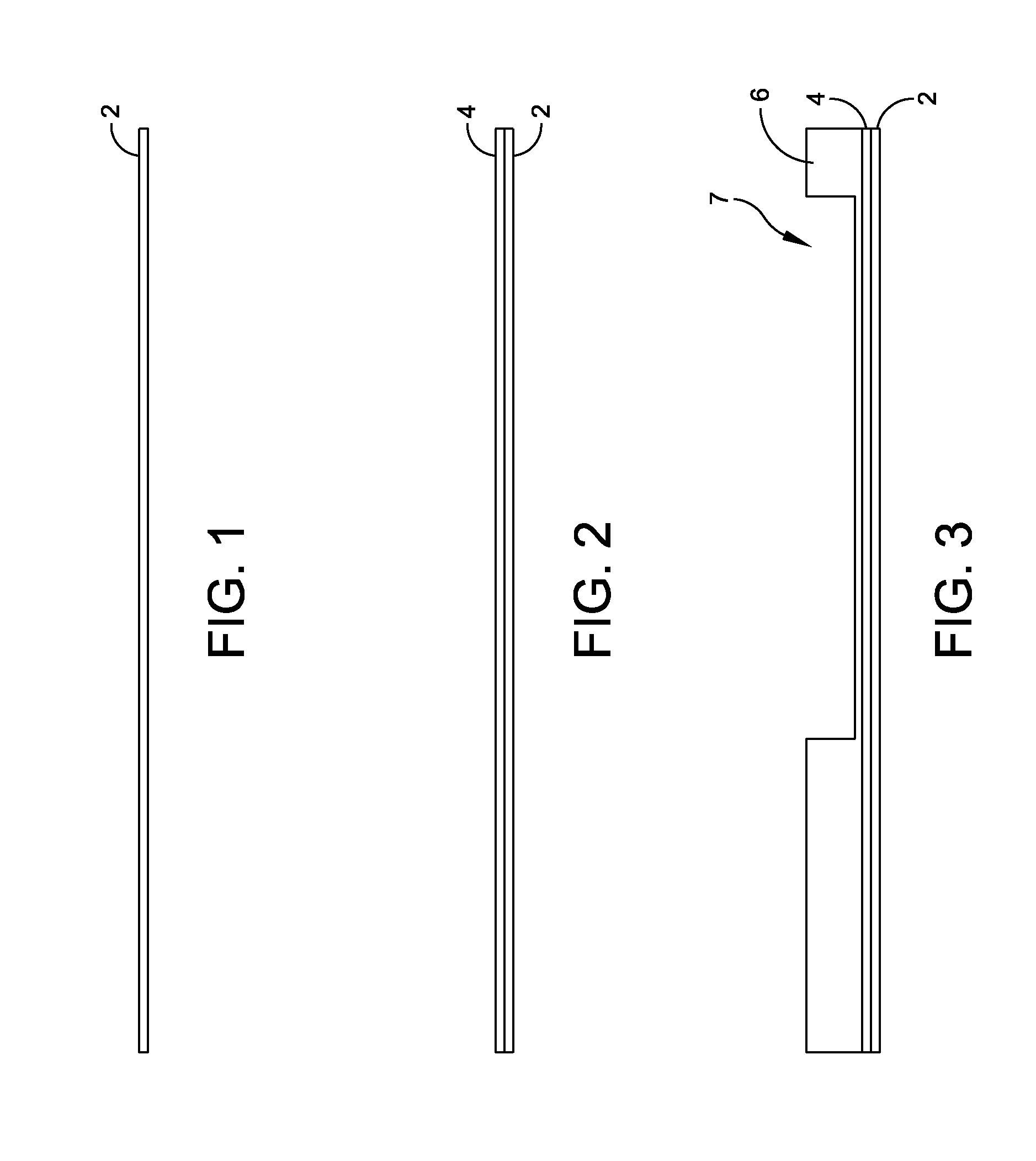
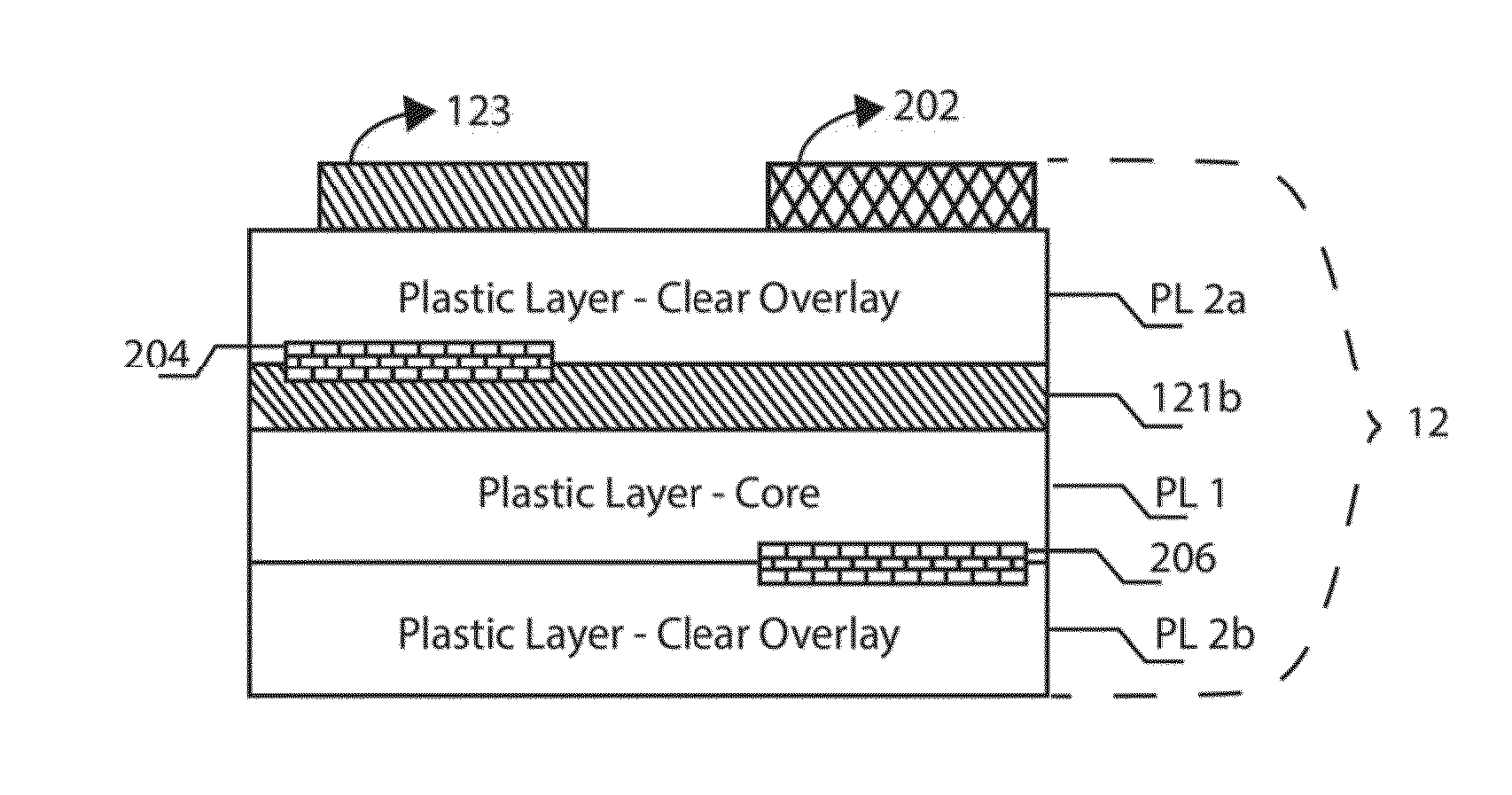
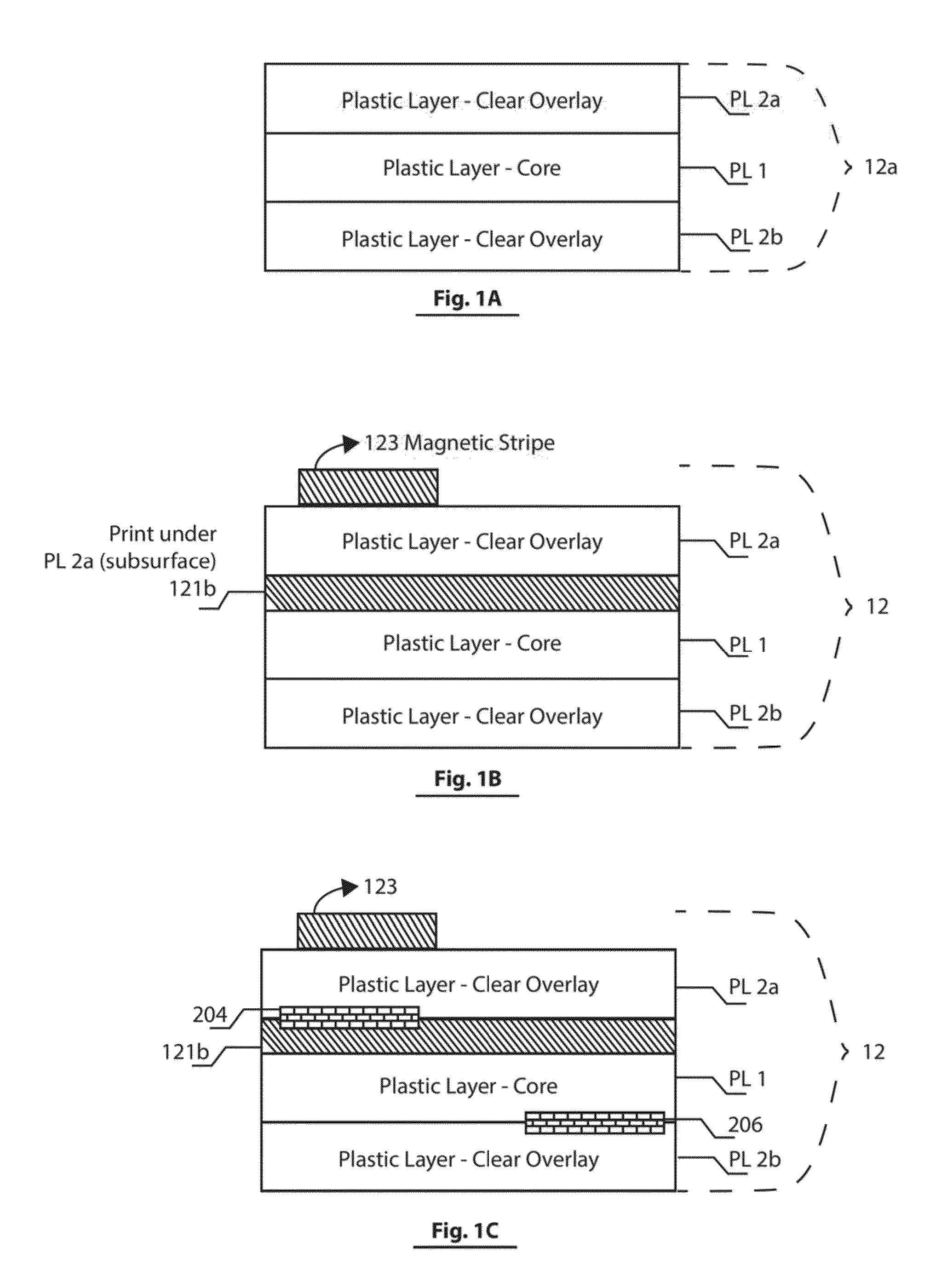
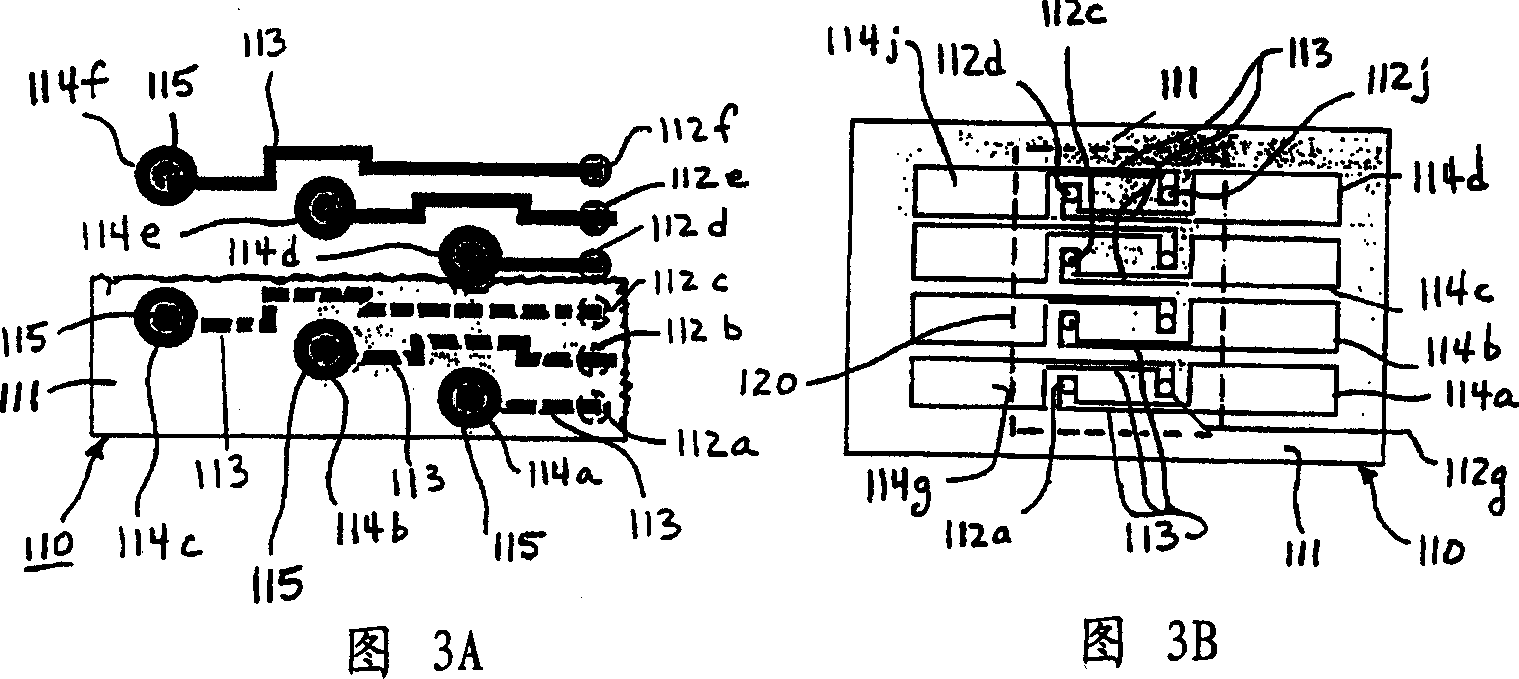
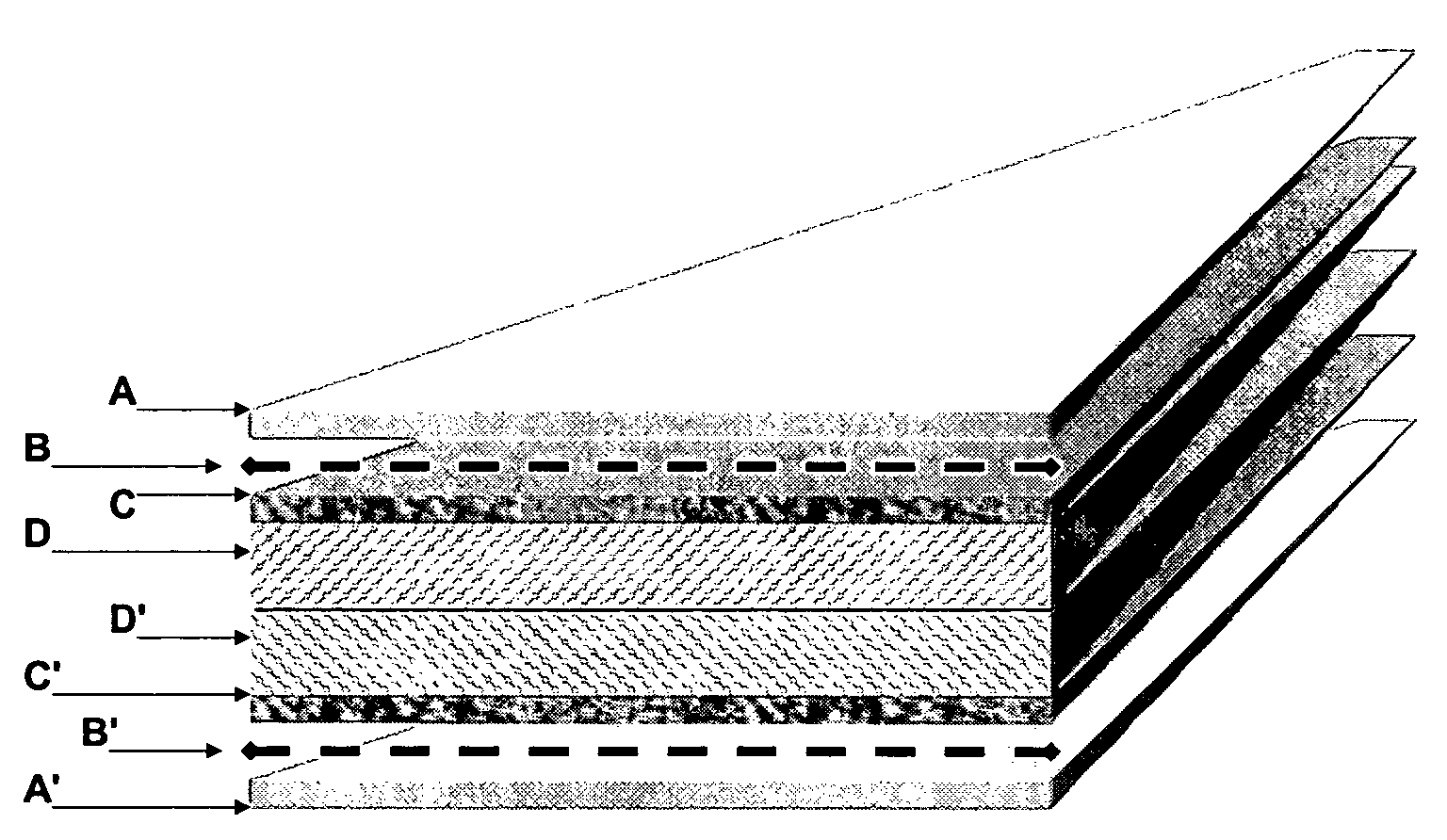
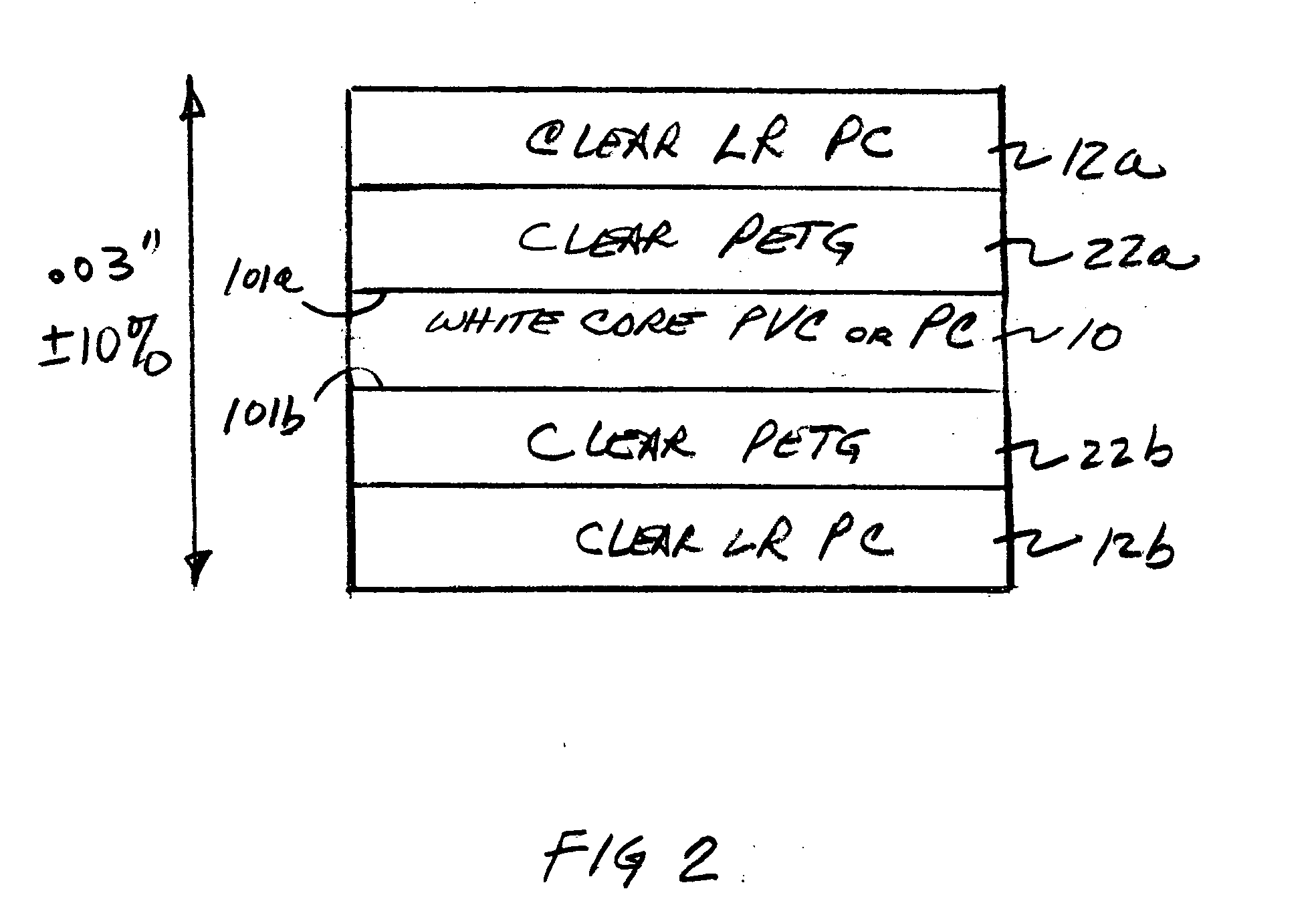
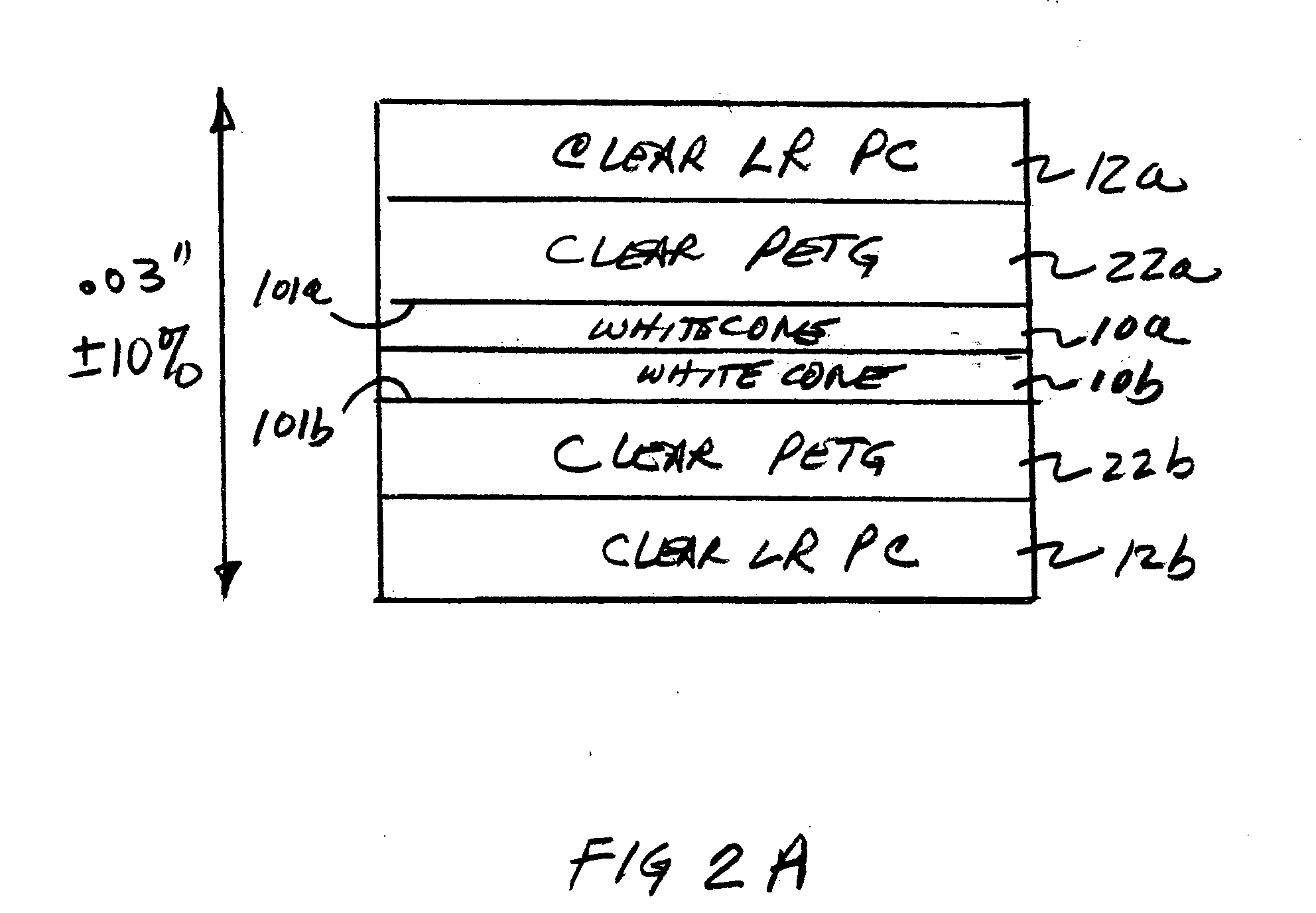
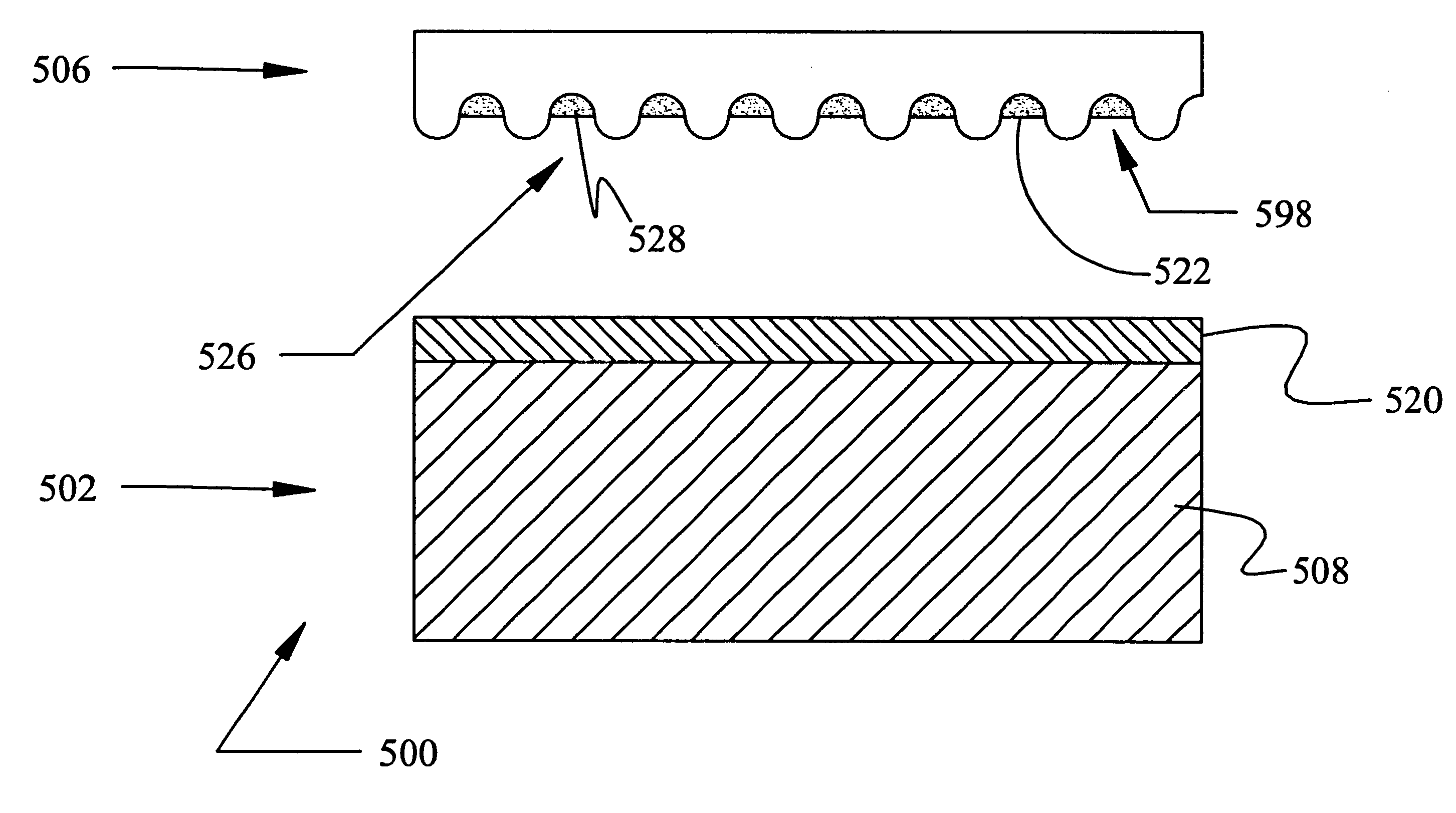
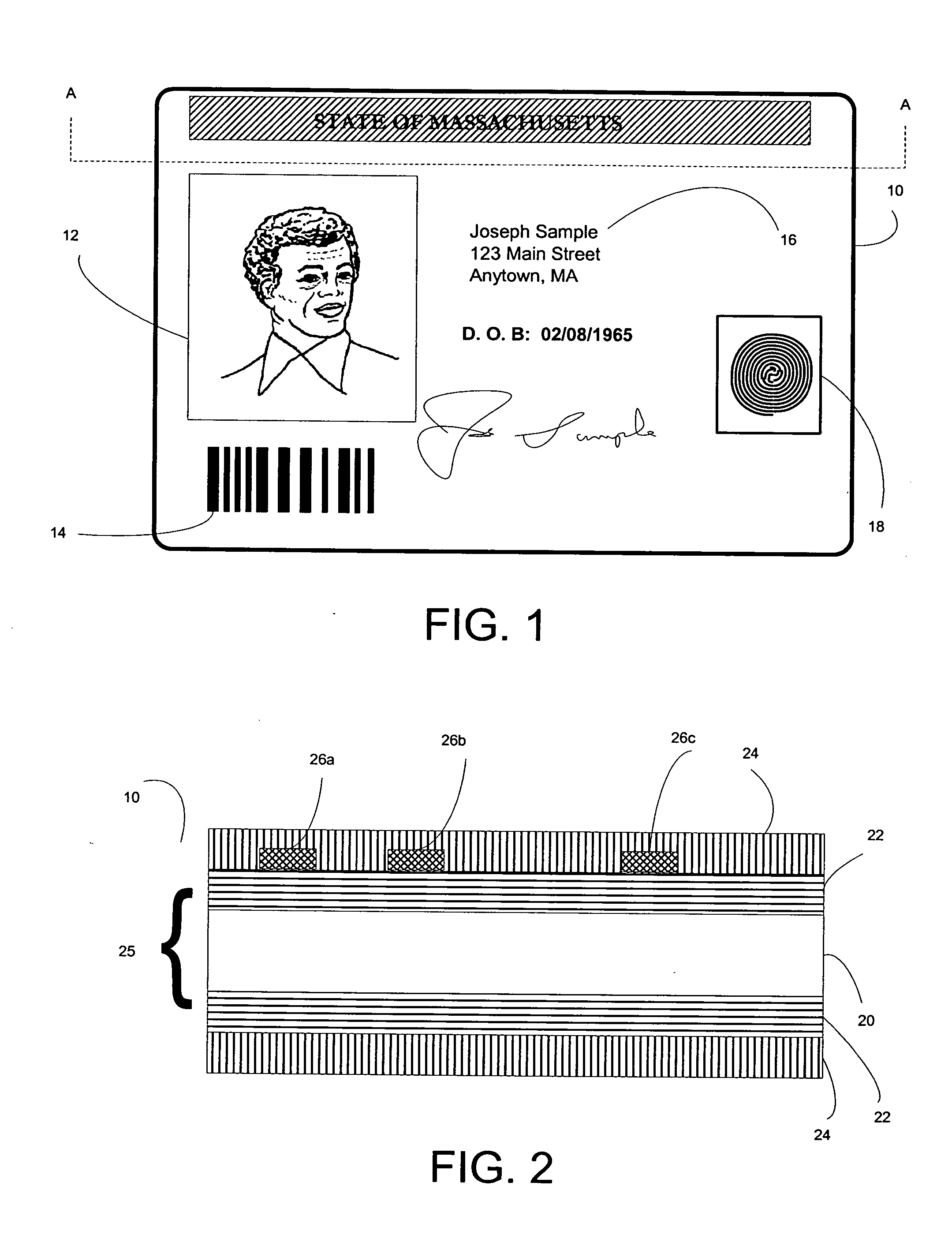
Cards and laminates incorporating multilayer optical films
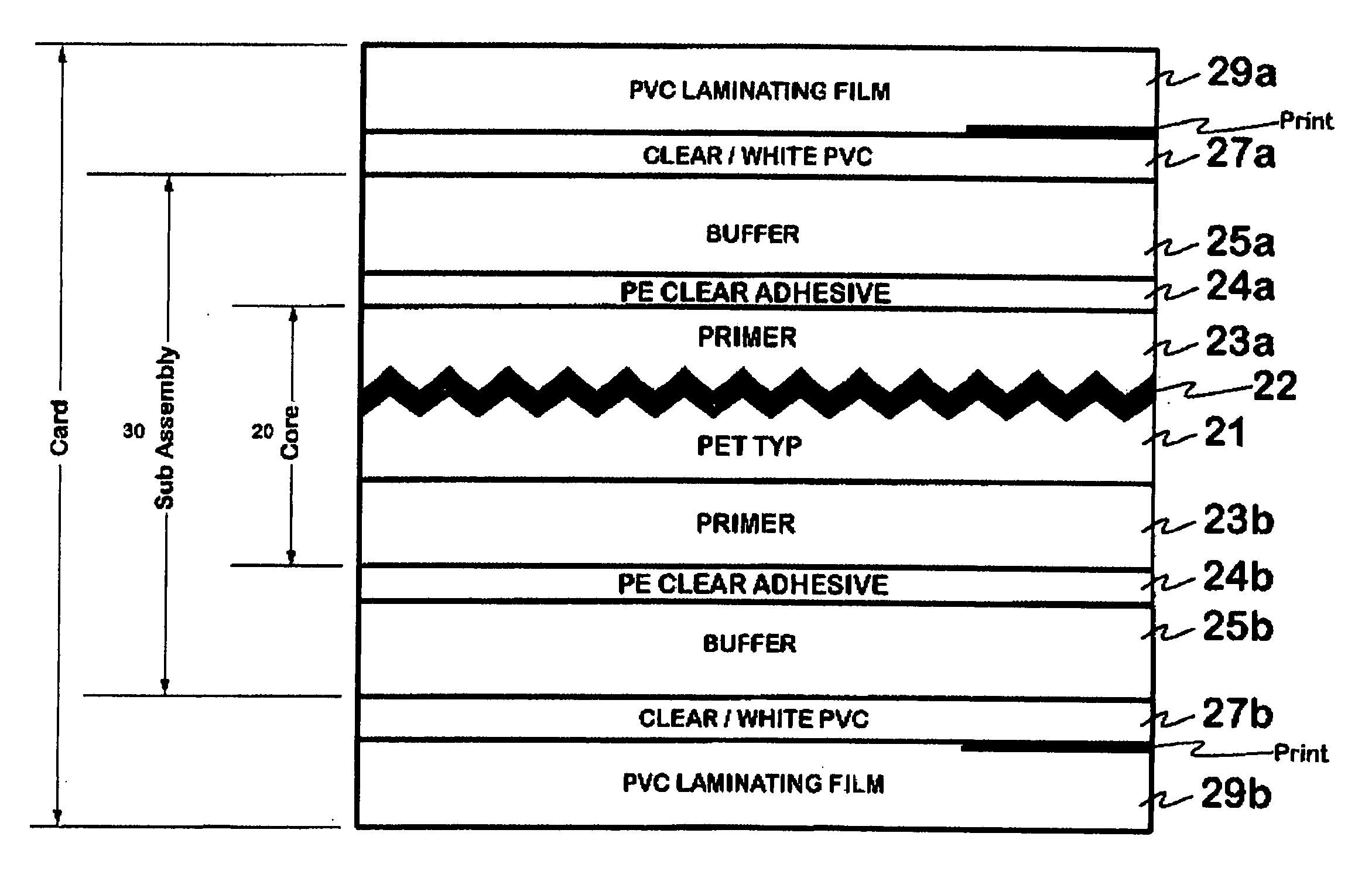
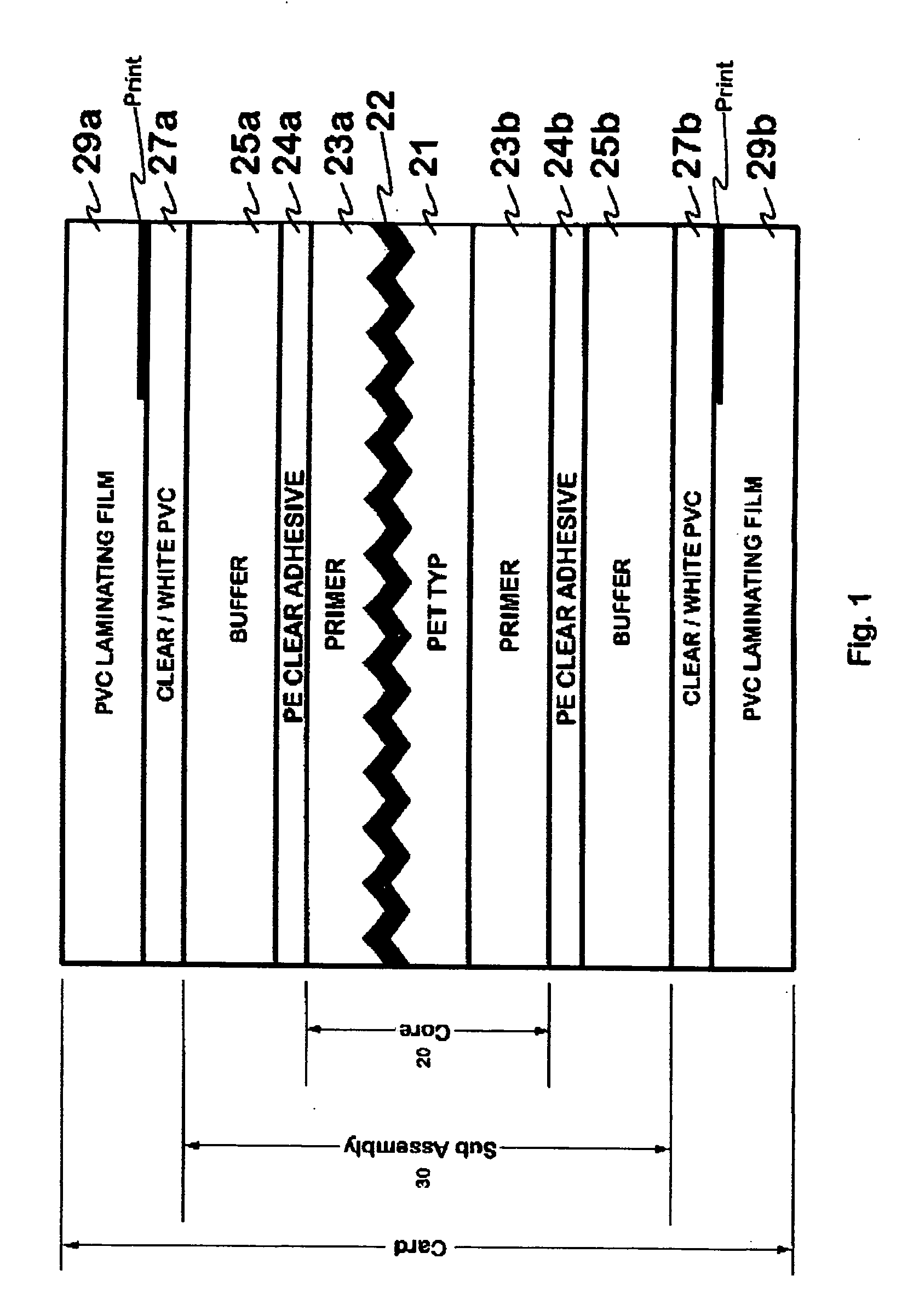
New constructions of multilayer optical films, laminates thereof, and cards incorporating same are disclosed. In a card, the multilayer optical film can be sandwiched between relatively thick polymer layers using adhesive layers that are at least 0.5 mils thick but that may collectively account for no more than 3 mils of thickness. The cards can if desired be highly transmissive in the visible yet highly opaque in portions of the infrared. The resulting cards can have reduced angel hair formation during card stamping, increased resistance to delamination, and reduced haze.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
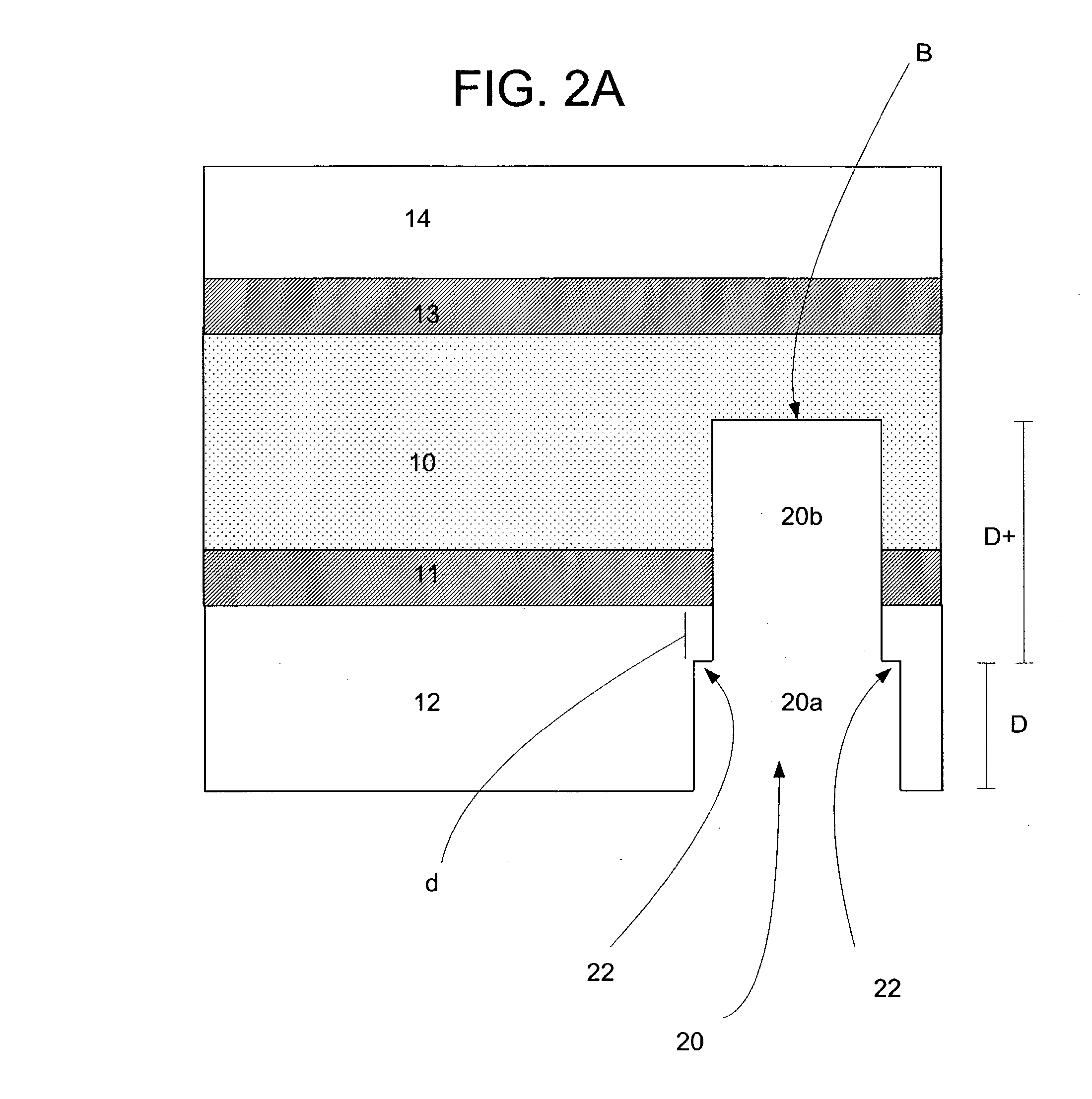
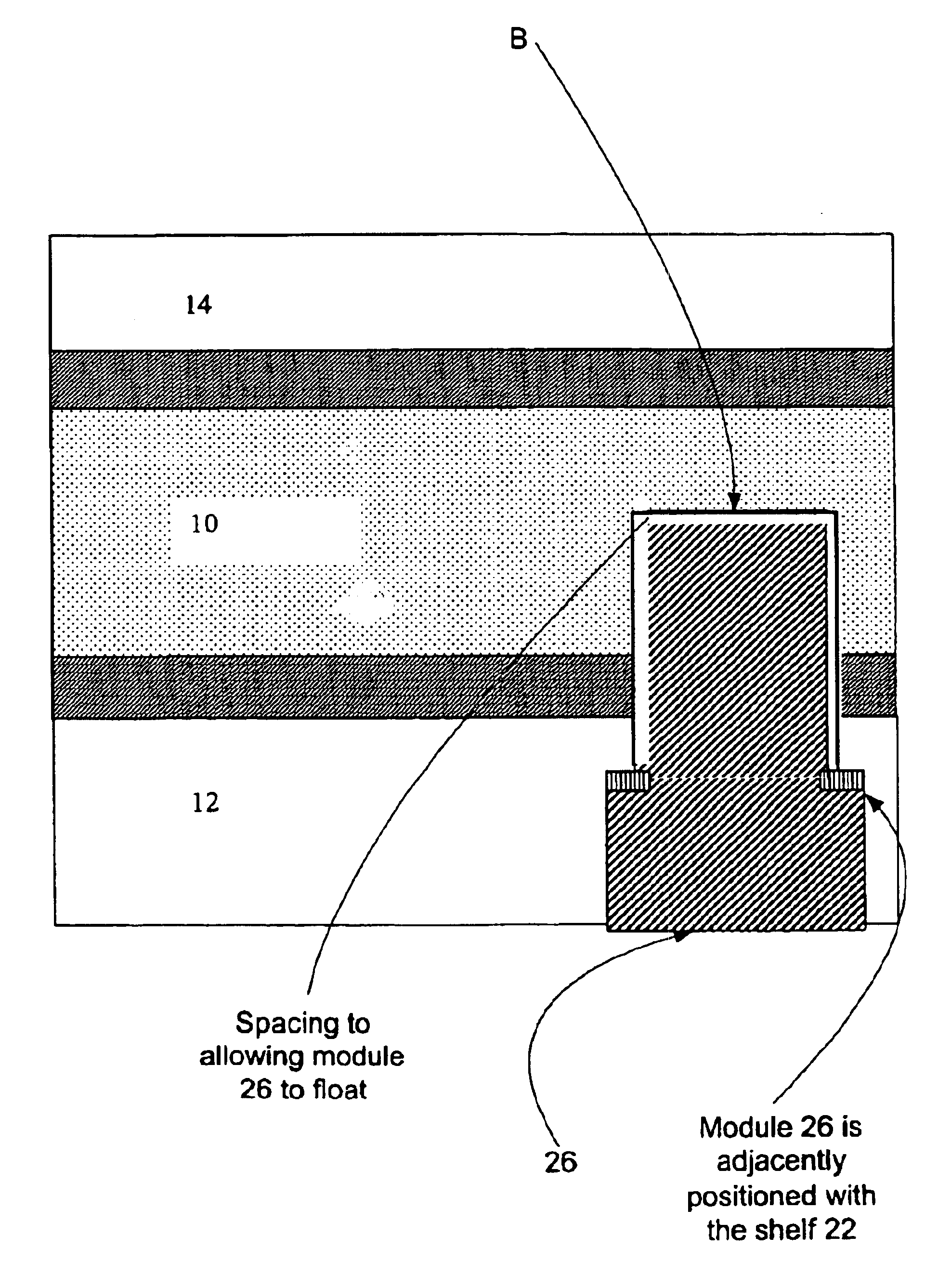
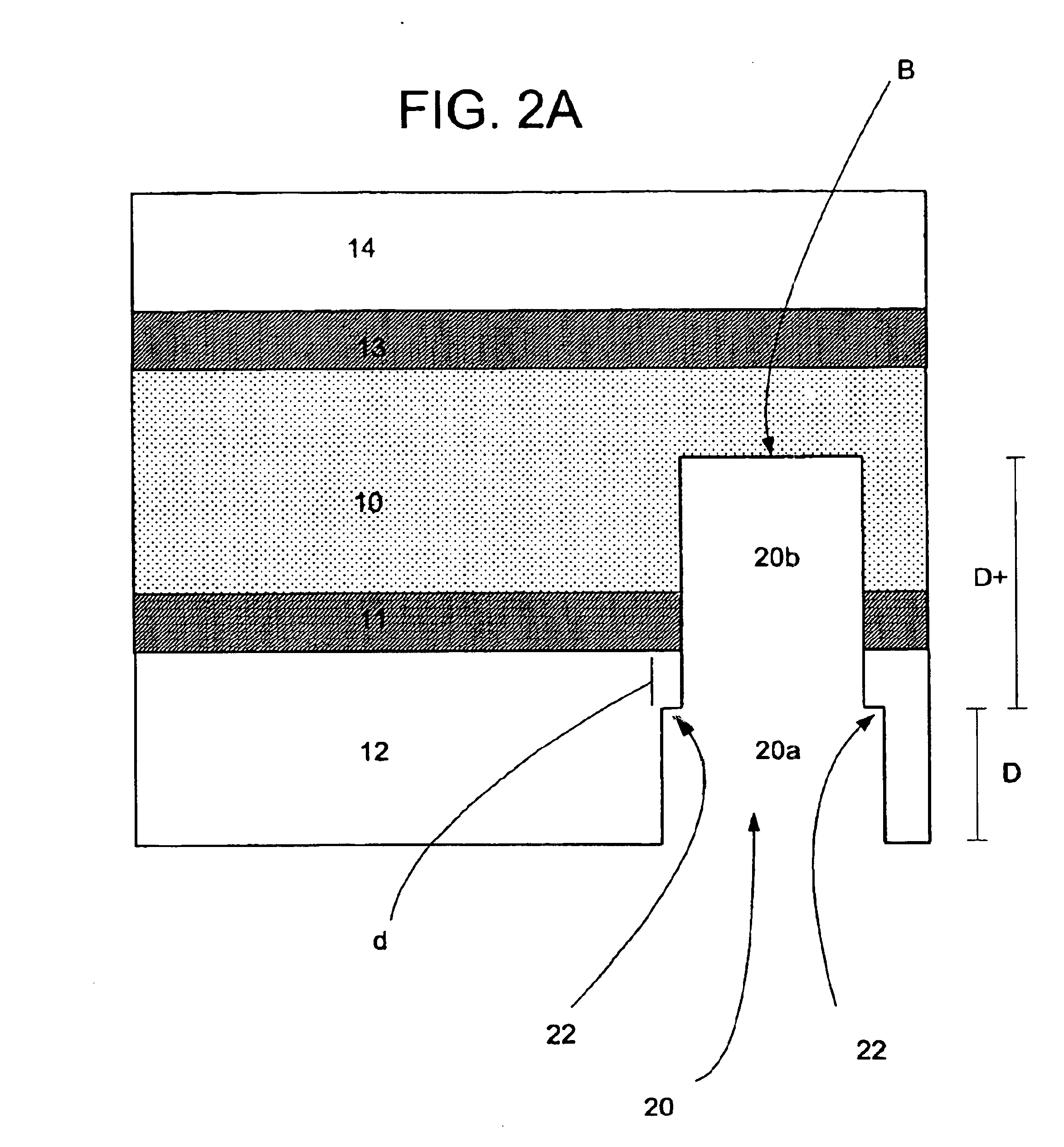
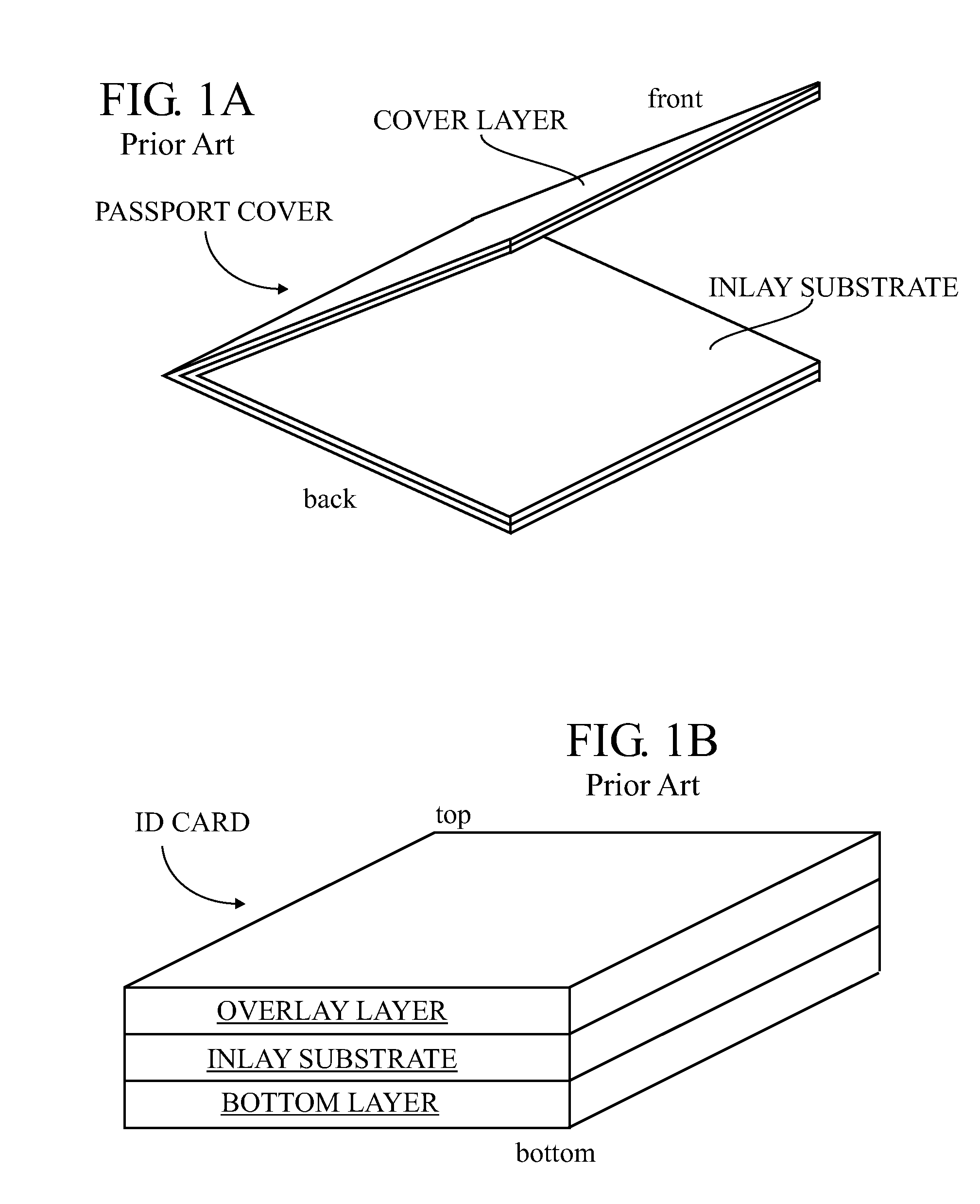
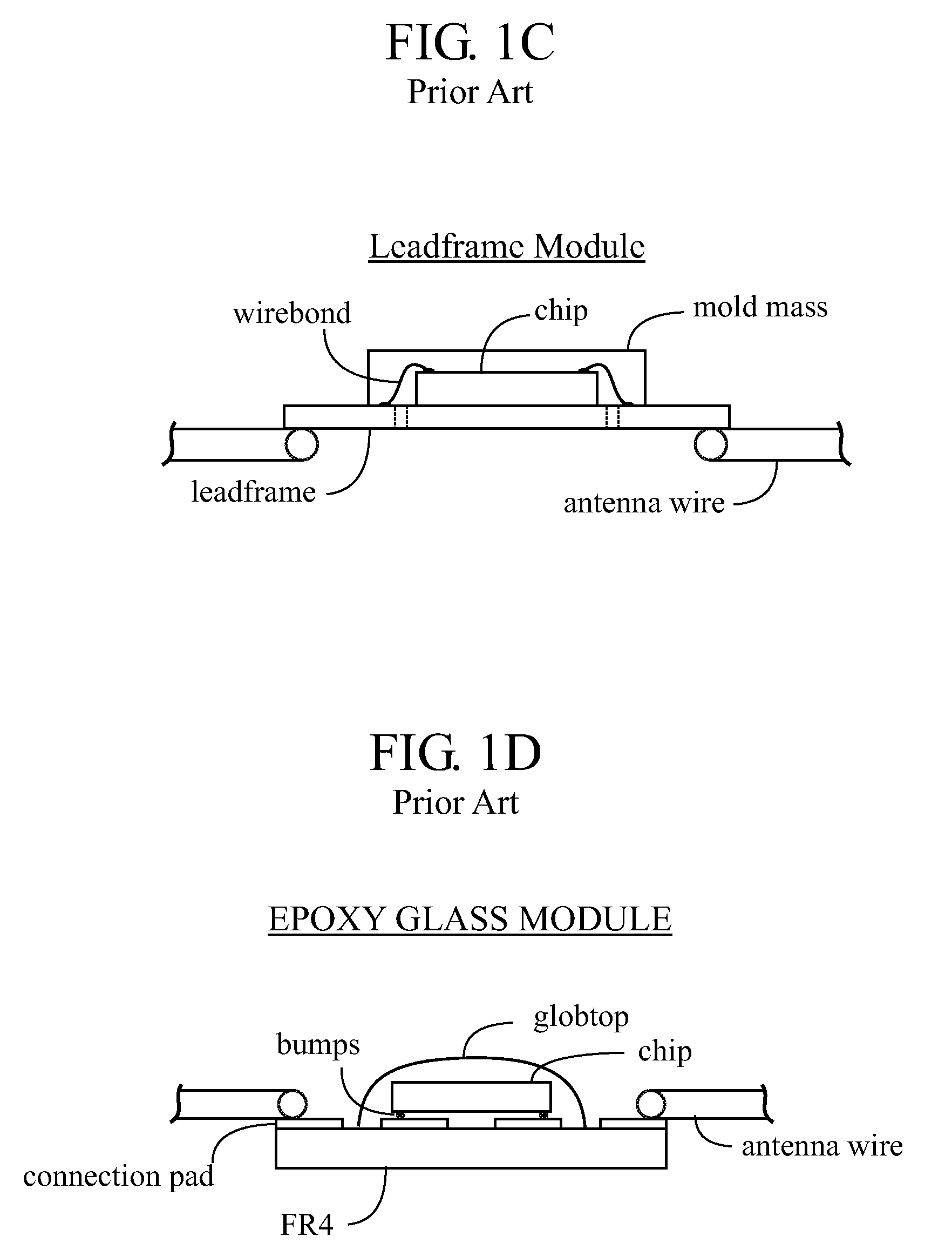
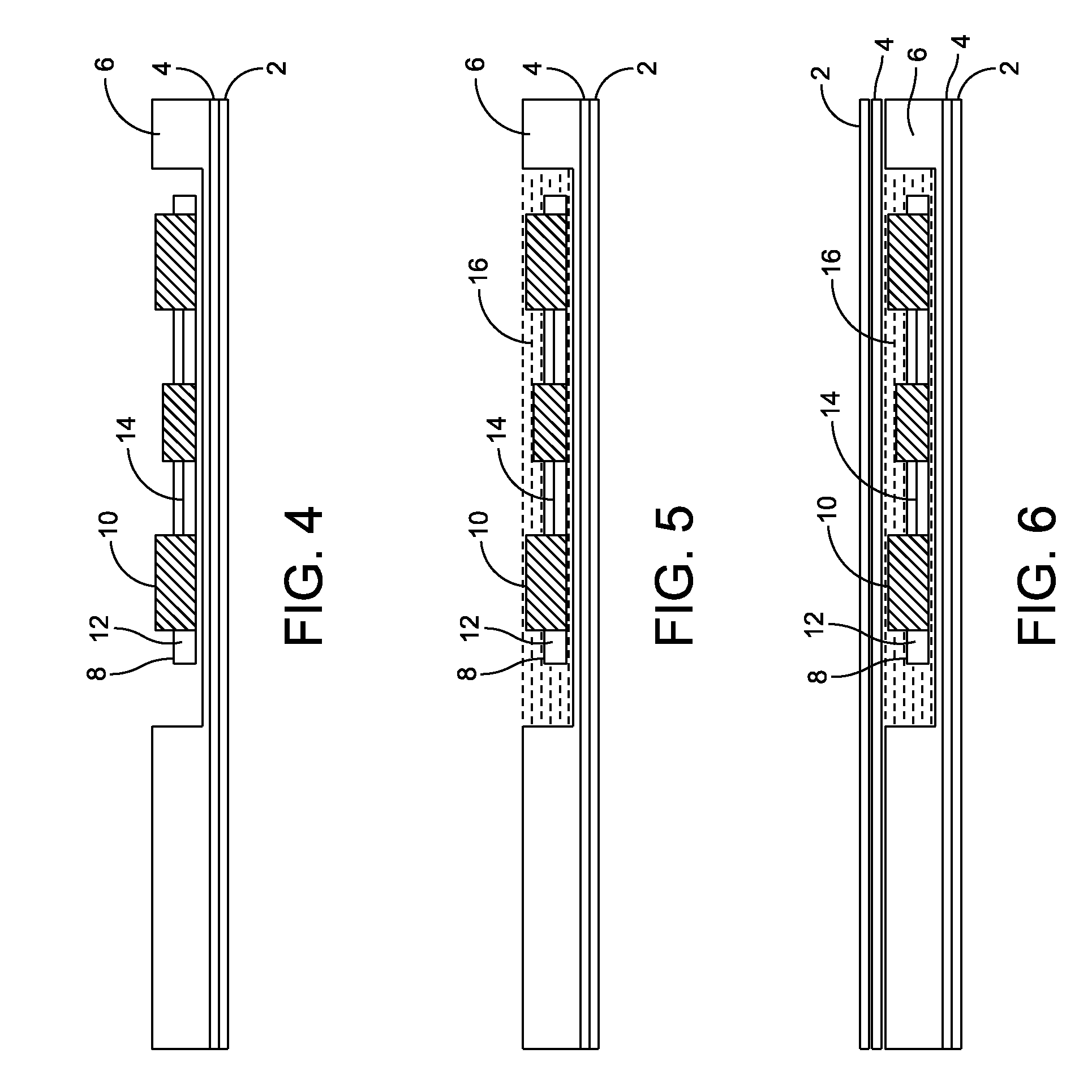
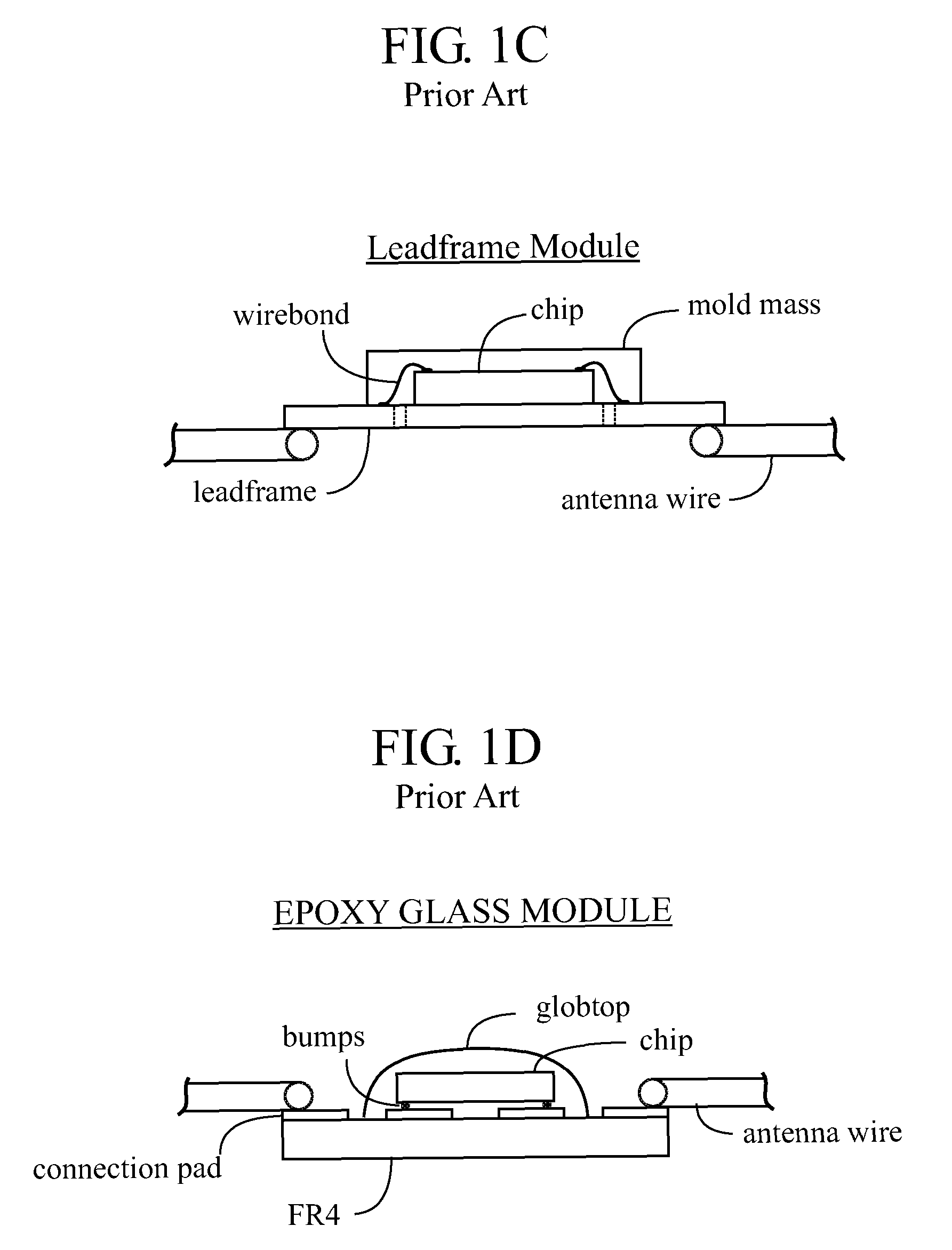
Contact smart cards having a document core, contactless smart cards including multi-layered structure, pet-based identification document, and methods of making same
InactiveUS20030178495A1Improve security levelReduce chanceLayered productsMilling cuttersComputer moduleCompanion animal
The present invention relates to identification documents and smart cards. In one implementation, we provide a smart identification document including a document core. The document core is printed and laminated. The laminated core is milled to create a cavity. An integrated circuitry module is provided in the cavity. In one implementation, the cavity includes an upper cavity and a lower cavity. A laminate layer houses the upper cavity while the lower cavity extends into the document core. The upper cavity's aperture exceeds the aperture of the lower cavity resulting in a ledge in the laminate layer. A portion of the module may rest on the ledge, while another portion of the module may extend into the lower cavity. In another implementation, we provide a contactless smart card including a multi-layered structure. The structure includes a carrier layer including the smart card electronics. The carrier can be permeable (like a mesh or scrim) so that additional layers may be laminated into or through the carrier layer. A multi-layer structure provides a enhanced durability and helps protect the smart card electronics. In still another implementation, we provide a PET-based identification document. The PET-based document includes favorable durability and earth-friendly characteristics.
Owner:L 1 SECURE CREDENTIALING
Contact smart cards having a document core, contactless smart cards including multi-layered structure, pet-based identification document, and methods of making same
InactiveUS6843422B2Reduce crackingQuality improvementLayered productsMilling cuttersComputer moduleCompanion animal
The present invention relates to identification documents and smart cards. In one implementation, we provide a smart identification document including a document core. The document core is printed and laminated. The laminated core is milled to create a cavity. An integrated circuitry module is provided in the cavity. In one implementation, the cavity includes an upper cavity and a lower cavity. A laminate layer houses the upper cavity while the lower cavity extends into the document core. The upper cavity's aperture exceeds the aperture of the lower cavity resulting in a ledge in the laminate layer. A portion of the module may rest on the ledge, while another portion of the module may extend into the lower cavity. In another implementation, we provide a contactless smart card including a multi-layered structure. The structure includes a carrier layer including the smart card electronics. The carrier can be permeable (like a mesh or scrim) so that additional layers may be laminated into or through the carrier layer. A multi-layer structure provides a enhanced durability and helps protect the smart card electronics. In still another implementation, we provide a PET-based identification document. The PET-based document includes favorable durability and earth-friendly characteristics.
Owner:L 1 SECURE CREDENTIALING
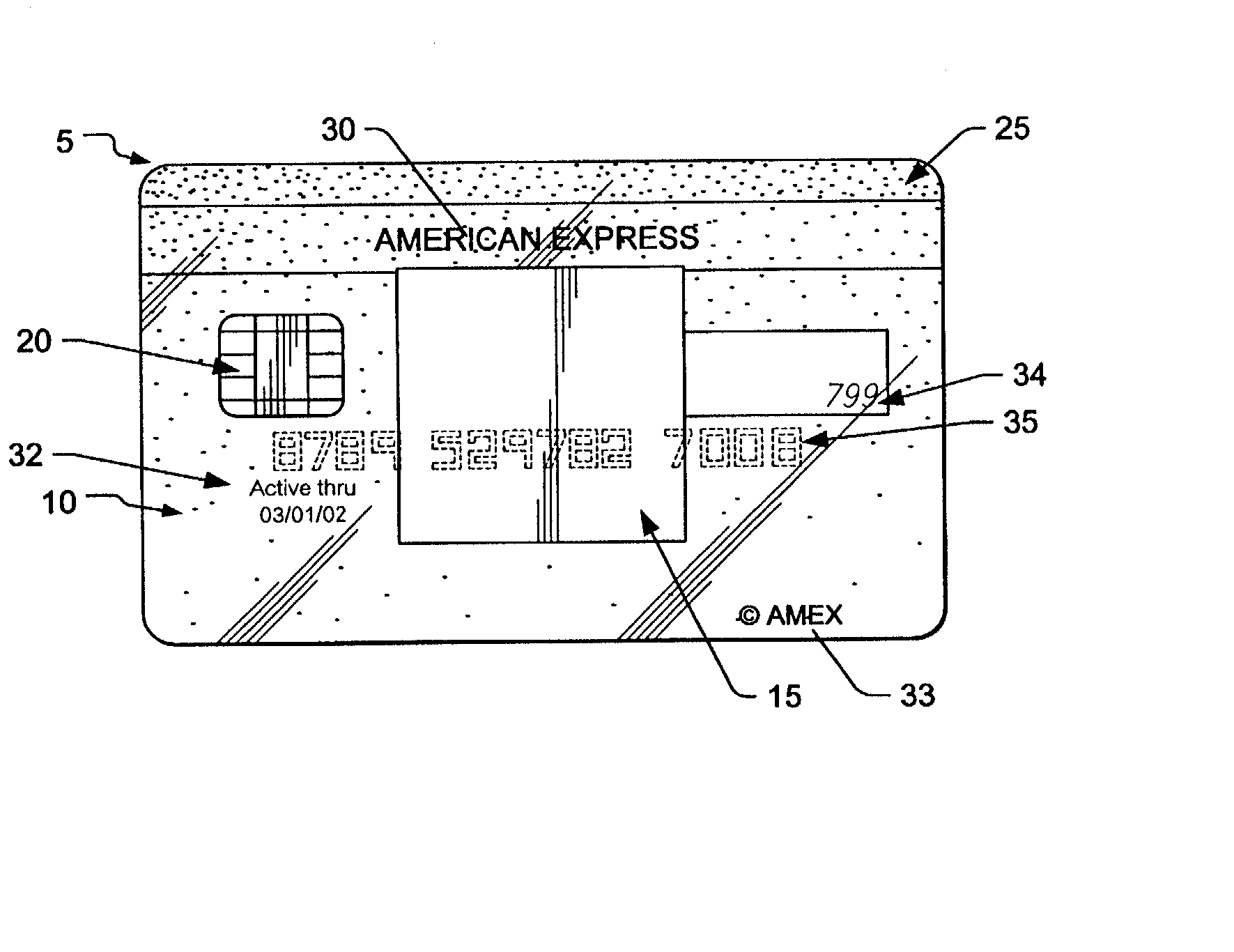
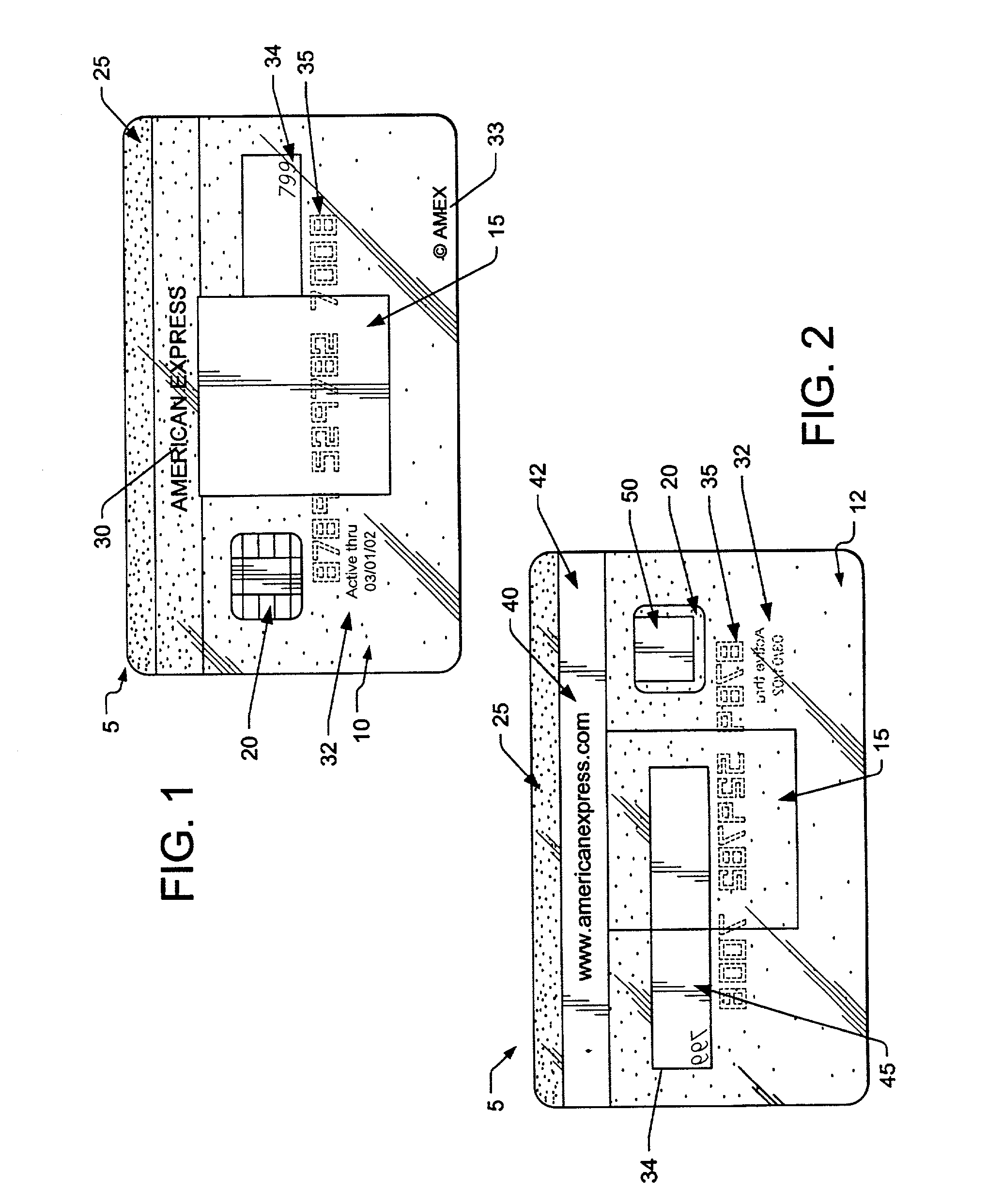
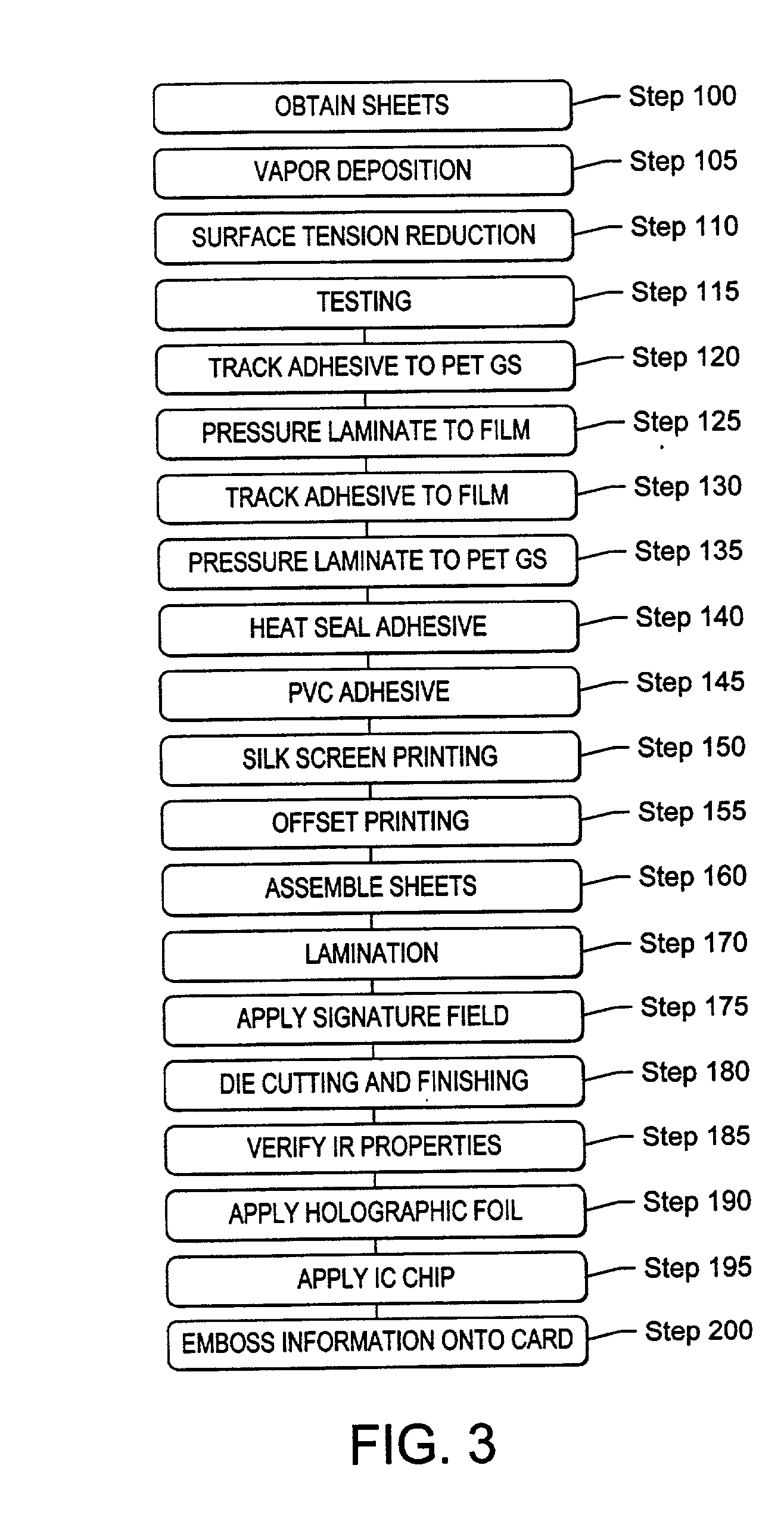
Transaction card
The present invention relates to a process for producing an opaque, transparent or translucent transaction card having multiple features, such as a holographic foil, integrated circuit chip, silver magnetic stripe with text on the magnetic stripe, opacity gradient, an invisible optically recognizable compound, a translucent signature field such that the signature on back of the card is visible from the front of the card and an active thru date on the front of the card. The invisible optically recognizable compound is an infrared ink and / or film, which can be detected by a sensor found in an ATM or card assembly line.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
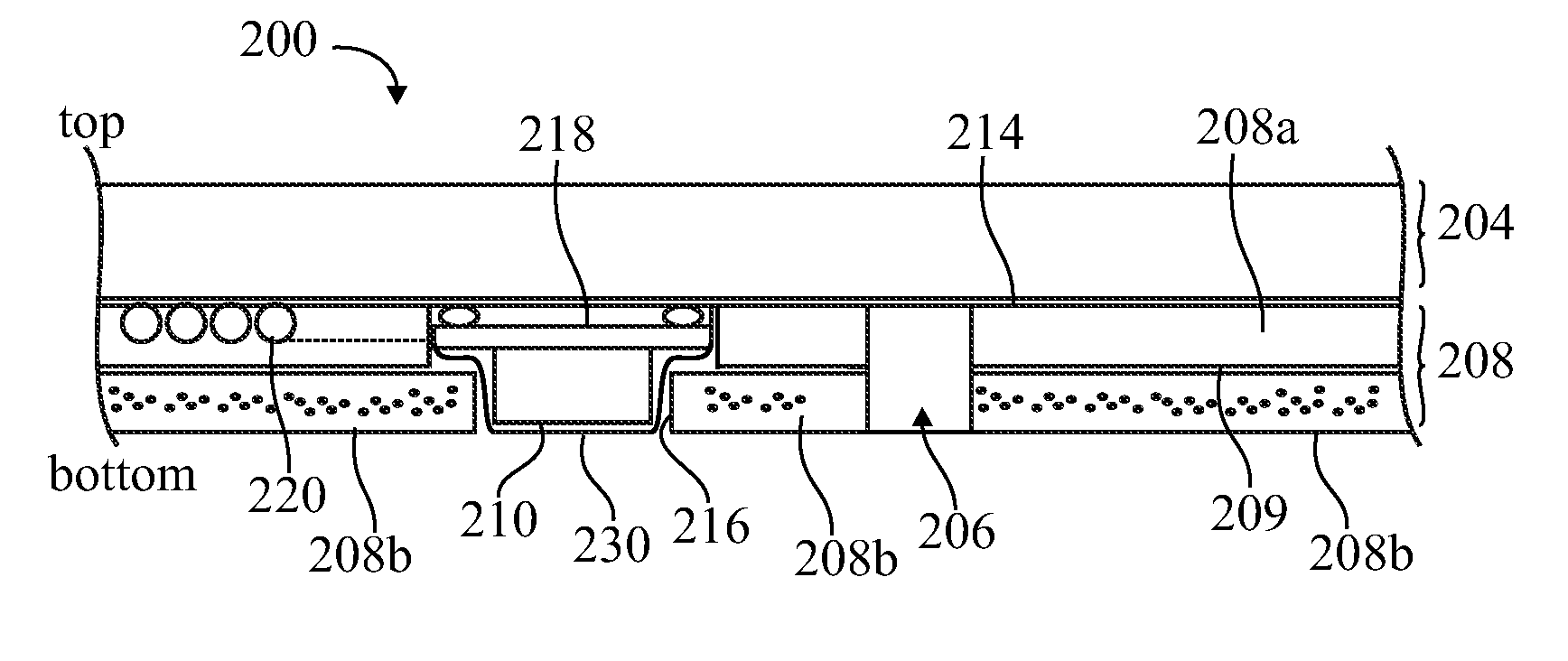
Inlays for security documents
InactiveUS20090315320A1Prevent skimmingReduce warpage and breakageSolid-state devicesRadiating elements structural formsMoisture cure polyurethaneElectromagnetic shielding
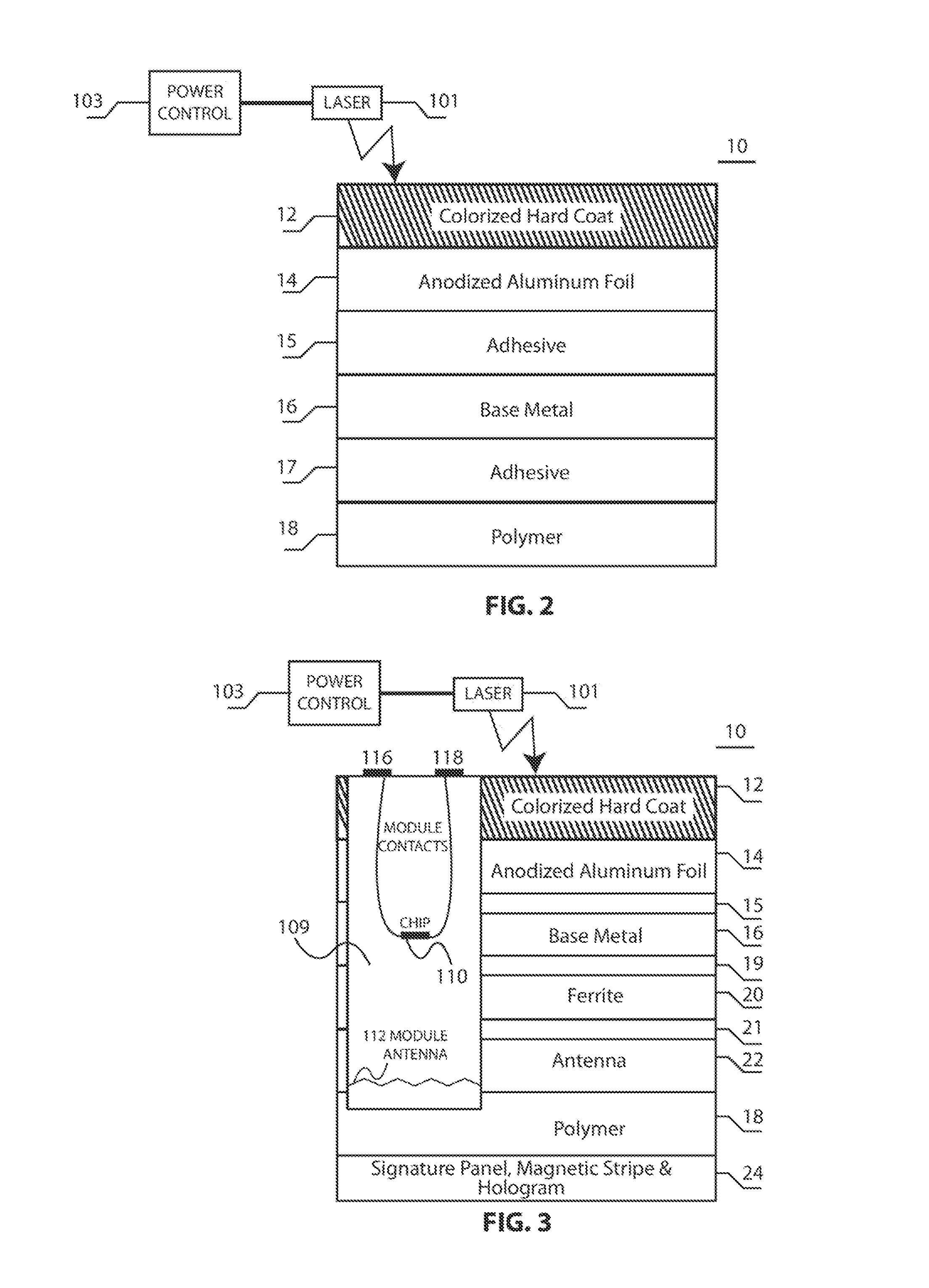
Secure inlays for secure documents such as a passport comprising an inlay substrate may have laser ablated recesses within which a chip module is installed. Channels for an antenna wire may be formed in a surface of the substrate. Instead of using wire, the channels may be filled with a flowable, conductive material. Patches homogenous with the substrate layer may be used to protect and seal the chip and interconnection area. The inlay substrate may include two layers, and the antenna wire may be between the two layers. A moisture-curing polyurethane hot melt adhesive may be used to laminate a cover layer and the additional inlay substrate layers. The adhesive layer may include metal nanoscale powder and ink for electromagnetic shielding. Additional security elements may include material that is optically changeable by an electromagnetic field. Ferrite-containing layers may be incorporated in the inlay substrate.
Owner:ASSA ABLOY AB +2
Laminating System, Ic Sheet, Scroll of Ic Sheet, and Method for Manufacturing Ic Chip
InactiveUS20080042168A1Increase productivityPrevent damage and destructionSolid-state devicesLaminationEngineeringIntegrated circuit
Thin film integrated circuits are peeled from a substrate and the peeled thin film integrated circuits are sealed, efficiently in order to improve manufacturing yields. The present invention provides laminating system comprising transporting means for transporting a substrate provided with a plurality of thin film integrated circuits; first peeling means for bonding first surfaces of the thin film integrated circuits to a first sheet member to peel the thin film integrated circuits from the substrate; second peeling means for bonding second surfaces of the thin film integrated circuits to a second sheet member to peel the thin film integrated circuits from the first sheet member; and sealing means for interposing the thin film integrated circuits between the second sheet member and a third sheet member to seal the thin film integrated circuit with the second sheet member and the third sheet member.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Transaction and id cards having selected texture and coloring
ActiveUS20150339564A1More costAvoid less flexibilityAnodisationWave amplification devicesEpoxyFinancial transaction
Cards made in accordance with the invention include a specially treated thin decorative layer attached to a thick core layer of metal or ceramic material, where the thin decorative layer is designed to provide selected color(s) and / or selected texture(s) to a surface of the metal cards. Decorative layers for use in practicing the invention include: (a) an anodized metal layer; or (b) a layer of material derived from plant or animal matter (e.g., wood, leather); or (c) an assortment of aggregate binder material (e.g., cement, mortar, epoxies) mixed with laser reactive materials (e.g., finely divided carbon); or (d) a ceramic layer; and (e) a layer of crystal fabric material. The cards may be dual interface smart cards which can be read in a contactless manner and / or via contacts.
Owner:COMPOSECURE LLC
Foil composite card
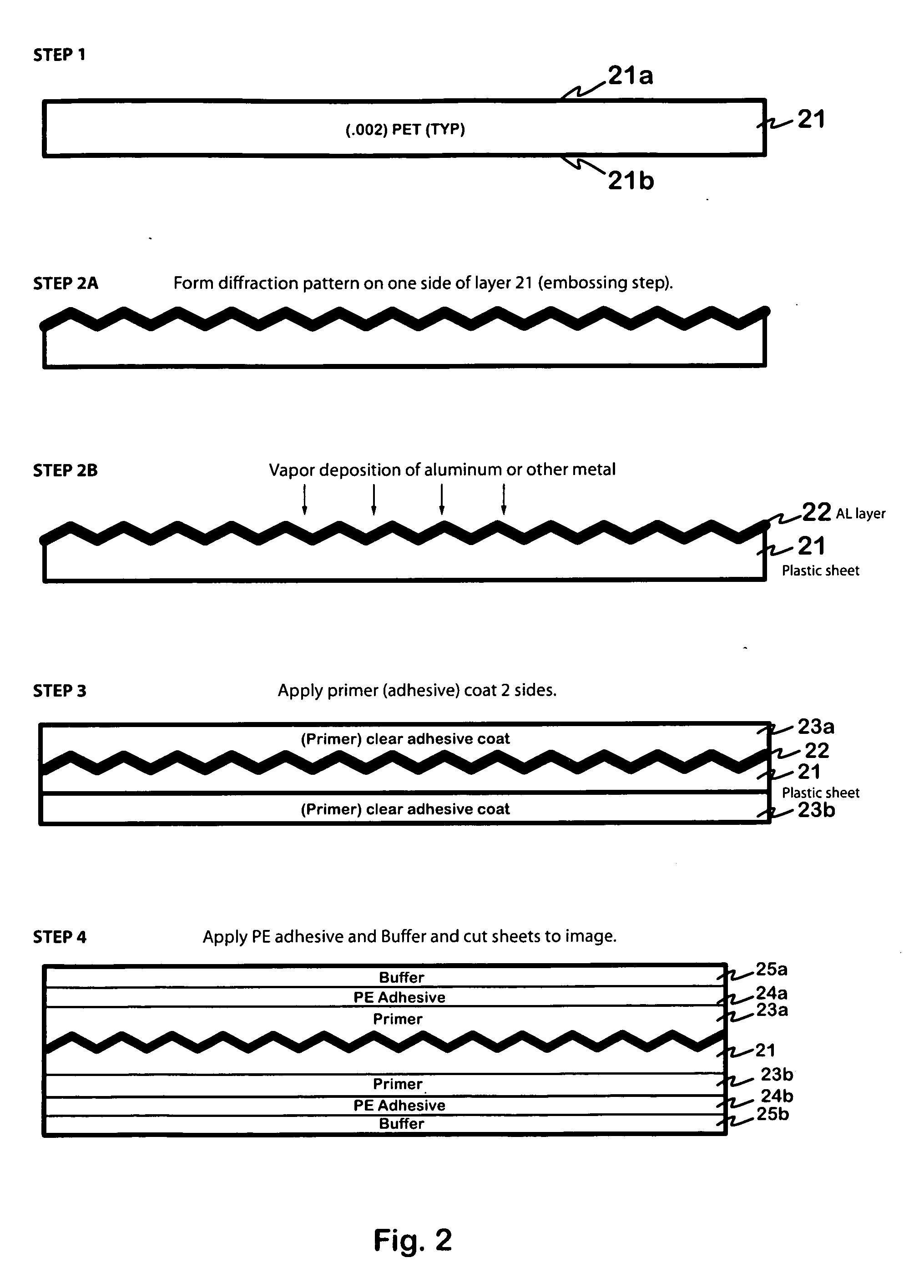
Composite cards formed in accordance with the invention include a security layer comprising a hologram or diffraction grating formed at, or in, the center, or core layer, of the card. The hologram may be formed by embossing a designated area of the core layer with a diffraction pattern and depositing a thin layer of metal on the embossed layer. Additional layers may be selectively and symmetrically attached to the top and bottom surfaces of the core layer. A laser may be used to remove selected portions of the metal formed on the embossed layer, at selected stages of forming the card, to impart a selected pattern or information to the holographic region. The cards may be “lasered” when the cards being processed are attached to, and part of, a large sheet of material, whereby the “lasering” of all the cards on the sheet can be done at the same time and relatively inexpensively. Alternatively, each card may be individually “lasered” to produce desired alpha numeric information, bar codes information or a graphic image, after the sheets are die-cut into cards.
Owner:COMPOSECURE LLC
Cards and laminates incorporating multilayer optical films
New constructions of multilayer optical films, laminates thereof, and cards incorporating same are disclosed. In a card, the multilayer optical film can be sandwiched between relatively thick polymer layers using adhesive layers that are at least 0.5 mils thick but that may collectively account for no more than 3 mils of thickness. The cards can if desired be highly transmissive in the visible yet highly opaque in portions of the infrared. The resulting cards can have reduced angel hair formation during card stamping, increased resistance to delamination, and reduced haze.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Phosphor based authentication system
InactiveUS20100102250A1Eliminate risk of damageMinimize risk of damageOptical radiation measurementDecorative surface effectsPhotoluminescencePhosphor
A phosphor (photo-luminescent) material based authentication system in which a blend (mixture) of at least two, preferably three or more, phosphor materials are used as a photo-luminescent security marking which is applied to or incorporated within an article / document to be authenticated. Preferably, the phosphor materials are each excitable by “eye safe” excitation radiation comprising visible light of wavelength 380 nm to 780 nm. Moreover, when excited the security marking preferably also emits visible light thereby minimizing any risk of damage to an operator's eye in the event of accidental exposure to the excitation radiation and / or light generated by the photo-luminescent marking. The authenticity of the article / document can be authenticated by verification of the composition of the phosphor by exciting the marking and comparing one or more selected parameters of light emitted by the security marking with corresponding parameters of the characteristic emission spectrum of the authentic phosphor blend.
Owner:INTEMATIX
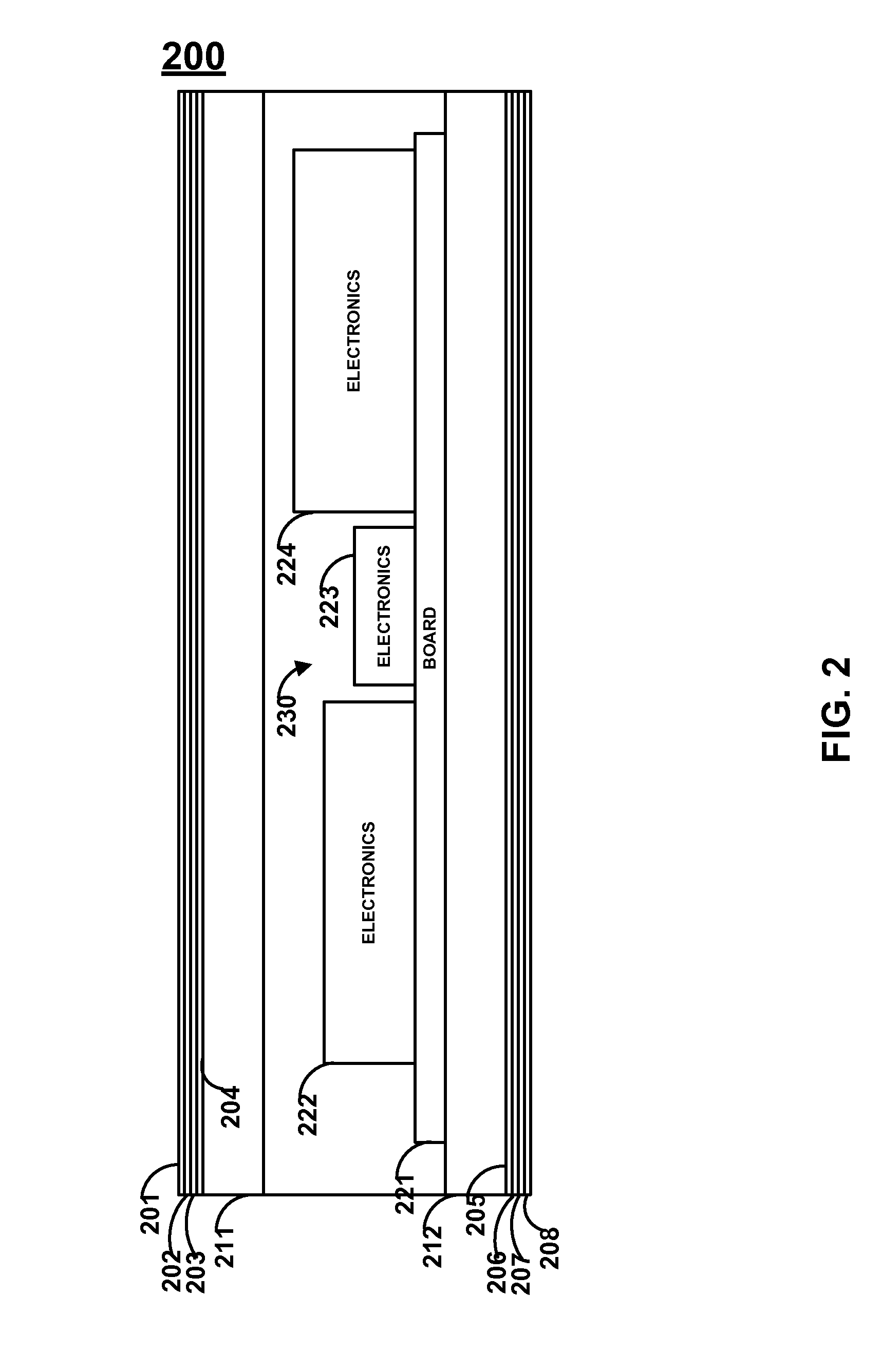
Systems and methods for advanced card printing
ActiveUS8322623B1Decreasing structural integrityIncrease whimsical and festive natureLayered product treatmentLaminationUltravioletWavelength
Layers of colored polymers are applied to a surface of a card and are hardened and adhered to a card via light such as ultraviolet or light having a wavelength in the blue spectrum. The layers may be applied to form three dimensional indicia on the surface of the card. For example, letters, numbers, logos, and other indicia (e.g., pictures) may be printed three dimensionally onto the surface of the card. Troughs may be formed via such layering such that indicia is provided as indentations into the added layers. Extensions may be formed via such layering such that indicia is provided as extensions from the added layers. Indicia may be provided via extensions and / or indentations. As such, embossed and / or engraved indicia may be provided on the surface of a card without impacting the structural integrity of the card.
Owner:DYNAMICS
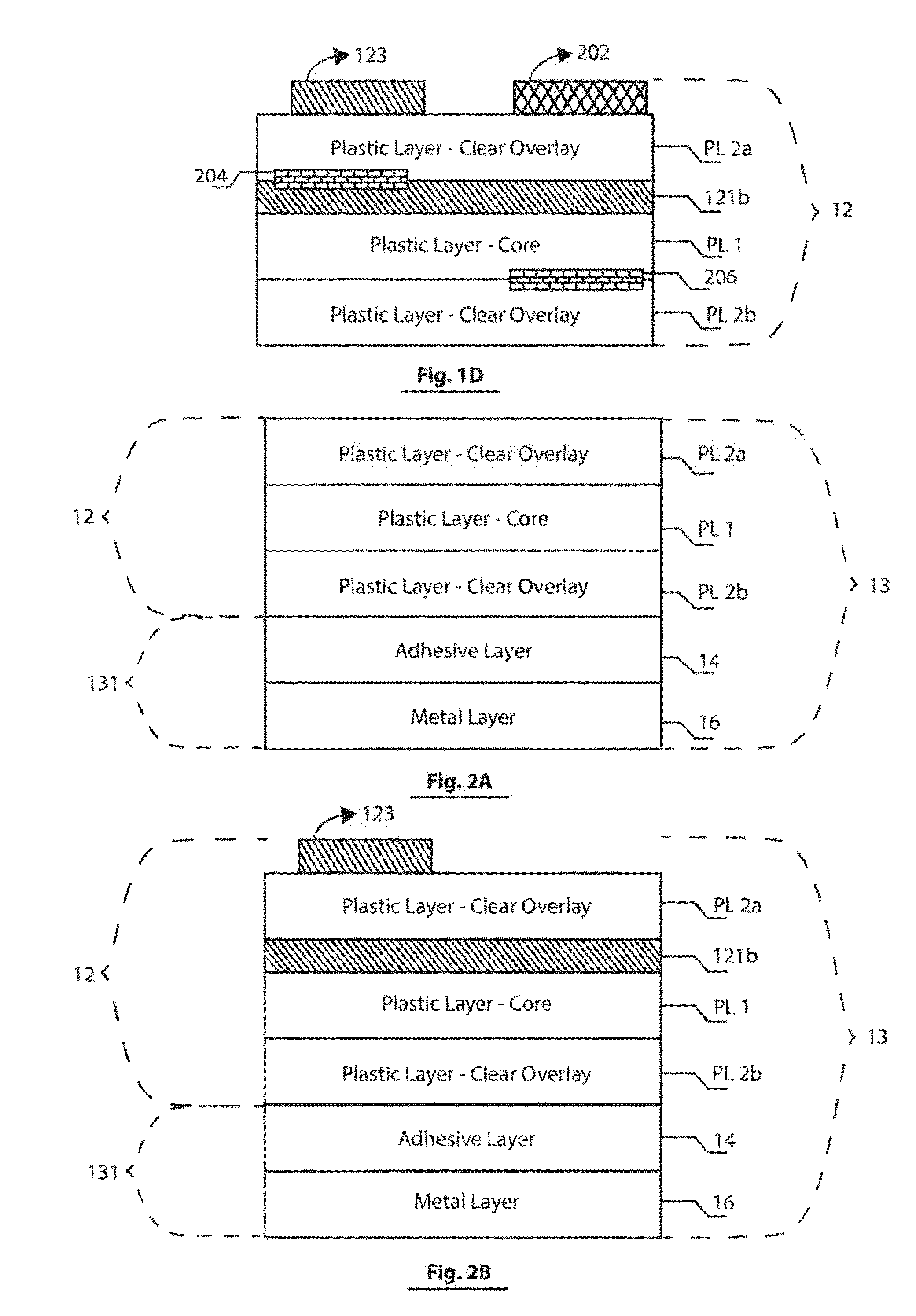
Combination card of metal and plastic
ActiveUS8672232B2Dimensionally stableReduce changesOrnamental structuresSpecial ornamental structuresAdhesiveEngineering
A card formed in accordance with the invention includes a first assembly comprised of multiple plastic layers attached via an adhesive to a metal layer. The multiple plastic layers forming the first assembly are laminated under a first selected temperature and pressure conditions to preshrink the multiple plastic layers, stress relieve the first assembly and render the first assembly dimensionally stable. The laminated first assembly is then attached to a metal layer via an adhesive layer to form a second assembly which is then laminated at a temperature below the first selected temperature to form a card which is not subjected to warpage and delamination.
Owner:COMPOSECURE LLC
Electromagnetic shield sheet and RFID plate
InactiveUS20100096181A1Higher electromagnetic shielding effectImprove efficiencyMagnetic/electric field screeningSynthetic resin layered productsPliabilityElectromagnetic shielding
Provided is an electromagnetic shield sheet having an excellent electromagnetic shielding effect which can be sufficiently exhibited even when the sheet has a reduced thickness and a reduced weight. Furthermore, the electromagnetic shield sheet has an excellent molding efficiency and flexibility and can be used in a desired shape such as various shapes of a power supply box, an inner wall, or an electronic device for electromagnetic shielding. An RFID plate using the electromagnetic shield sheet is also provided. The electromagnetic shield sheet A has a polymer composition layer obtained by mixing a conductive material with a polymer material. The sheet A is formed by layering at least two of polymer composition layers 1, 2, 3 having different dielectric constants. The RFID plate is formed by layering the electromagnetic shield sheet A, an IC, and an antenna circuit.
Owner:ASAHI RUBBER +1
Information carrying card comprising a cross-linked polymer composition, and method of making the same
The disclosure provides a cross-linkable polymer composition, a core layer for an information carrying card comprising such cross-linked composition, resulting information carrying card, and methods of making the same. A crosslinkable polymer composition comprises a curable base polymer resin in a liquid or paste form, and a particulate thermoplastic filler. The base polymer resin is selected from the group consisting of urethane acrylate, silicone acrylate, epoxy acrylate, urethane, acrylate, silicone and epoxy. The particulate thermoplastic filler may be polyolefin, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a copolymer of vinyl chloride and at least another monomer, or a polyester such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a compound or blend thereof.
Owner:X CARD HLDG
Biodegradable card base
InactiveUS6350530B1High strengthReduce rigidityDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsPolyesterPolymer science
The present invention provides a card base which is degradable by microbes in natural environment. The card base is excellent in properties necessary for card bases, such as tensile strength, impact strength, flex temperature, heat resistance, resistance to thermal expansion and contraction, blocking resistance and humidity resistance, and has rigidity, bending resistance and durability. The card base contains, as essential components, a 3-hydroxybutylate / 3-hydroxyvalerate copolymer and a lactic acid polymer, and, where necessary, a polycaprolactone or a high-molecular aliphatic polyester. The card base has a single-layer structure, or a sandwich structure further having overlay layers comprising a composition containing, as essential components, a lactic acid polymer and either or both of a polycaprolactone and a high-molecular alphatic polyester.
Owner:GUNZE LTD
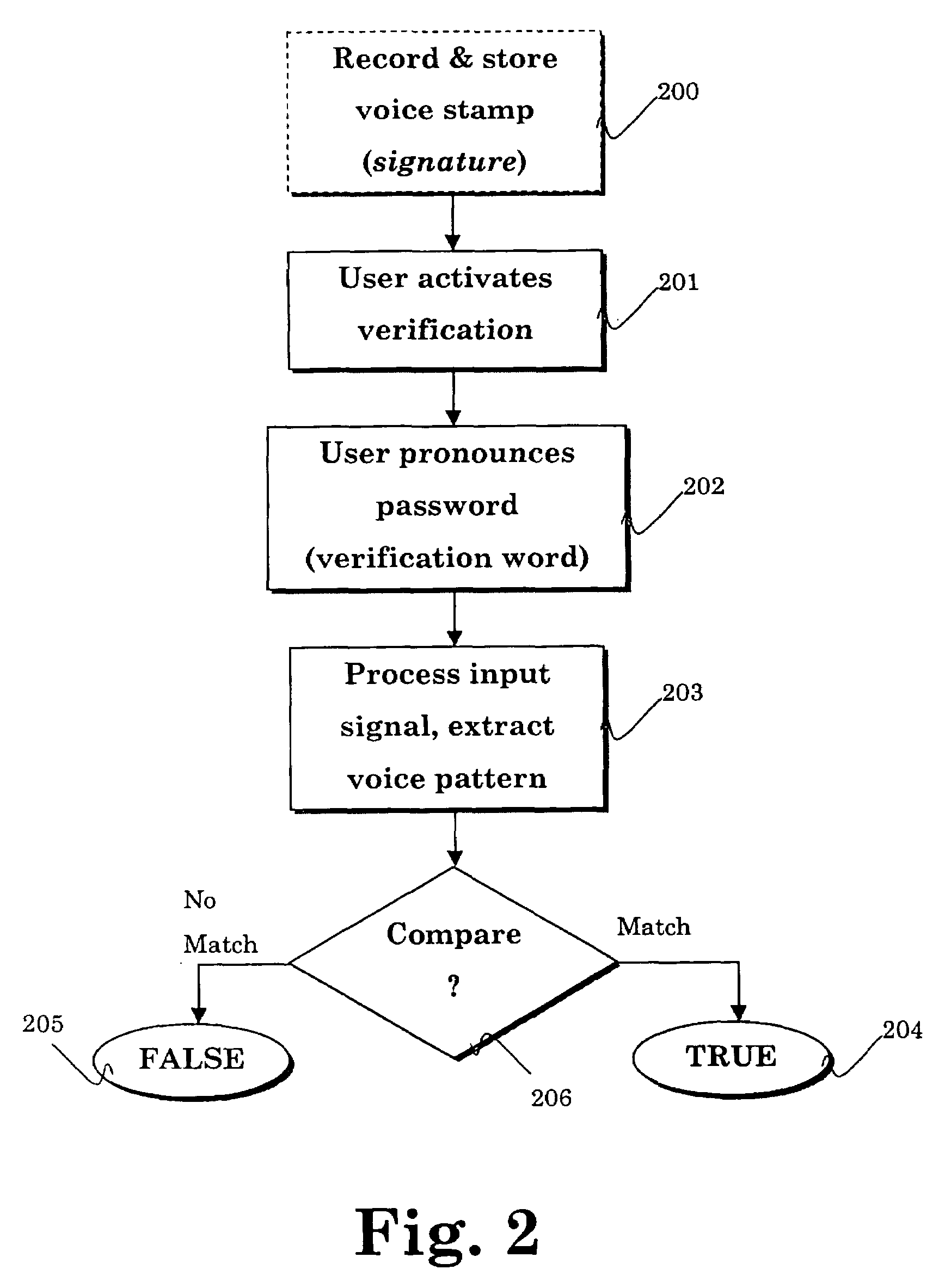
Sonic/ultrasonic authentication device
InactiveUS7280970B2Layered product treatmentSolid-state devicesDigital dataDigital signal processing
A method for verifying and identifying users, and for verifying users' identity, by means of an authentication device capable of transmitting, receiving and recording audio or ultrasonic signals, and capable of converting the signals into digital data, and performing digital signal processing. Voice pattern(s) and user(s) information of one or more authorized user(s) are recorded and stored on the authentication device. User(s) identification is verified by inputting to the authentication device a vocal identification signal from a user, and comparing the voice pattern of the vocal identification signal with the recorded voice pattern(s) of the authorized user(s), and if a match is detected issuing an indication that the user is identified as an authorized user.
Owner:SONIXIO INC
Inlays for security documents
InactiveUS8608080B2Reduce warpage and breakageProduction impossibleSolid-state devicesRadiating elements structural formsElectromagnetic shieldingConductive materials
Owner:ASSA ABLOY AB +2
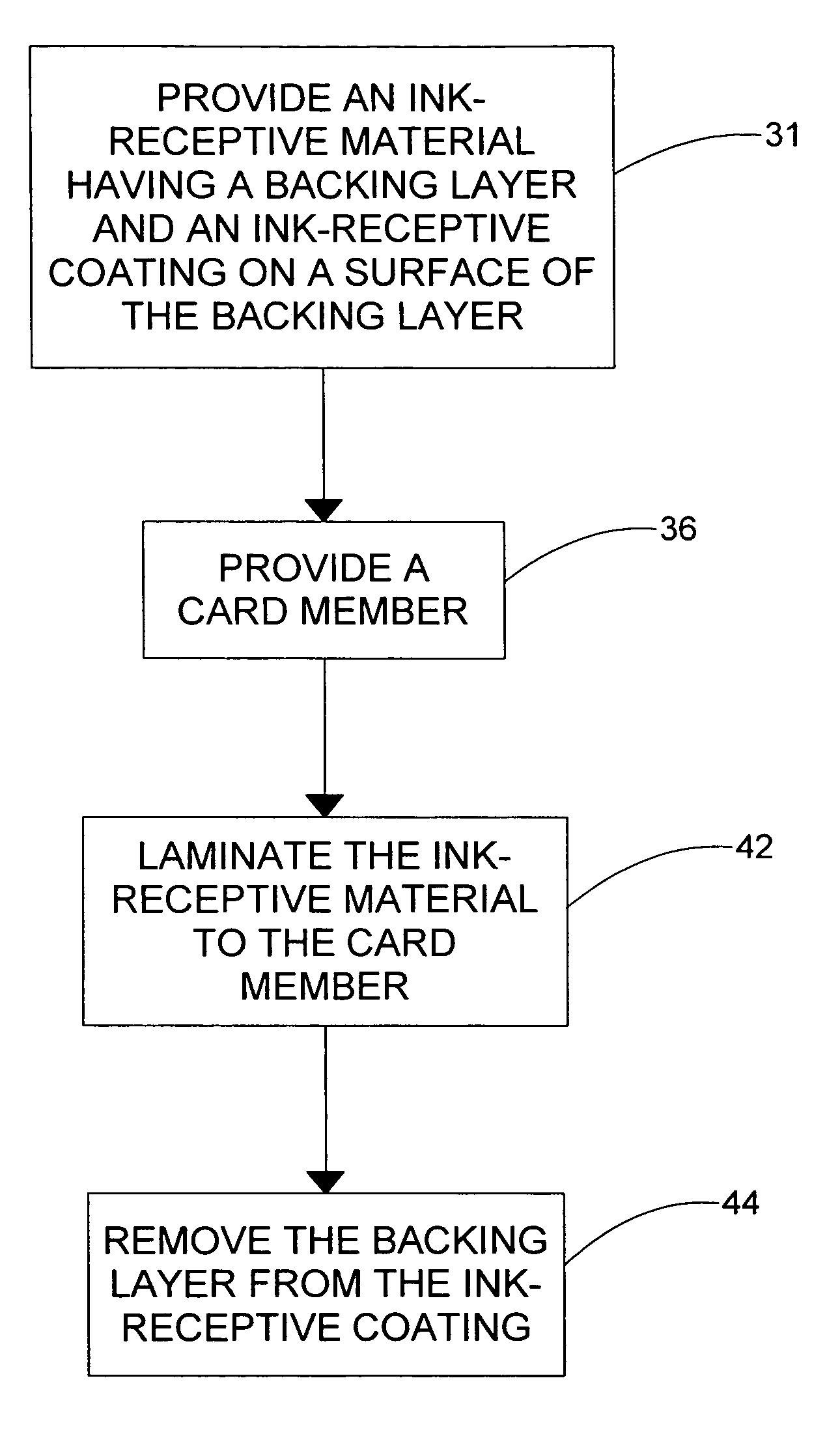
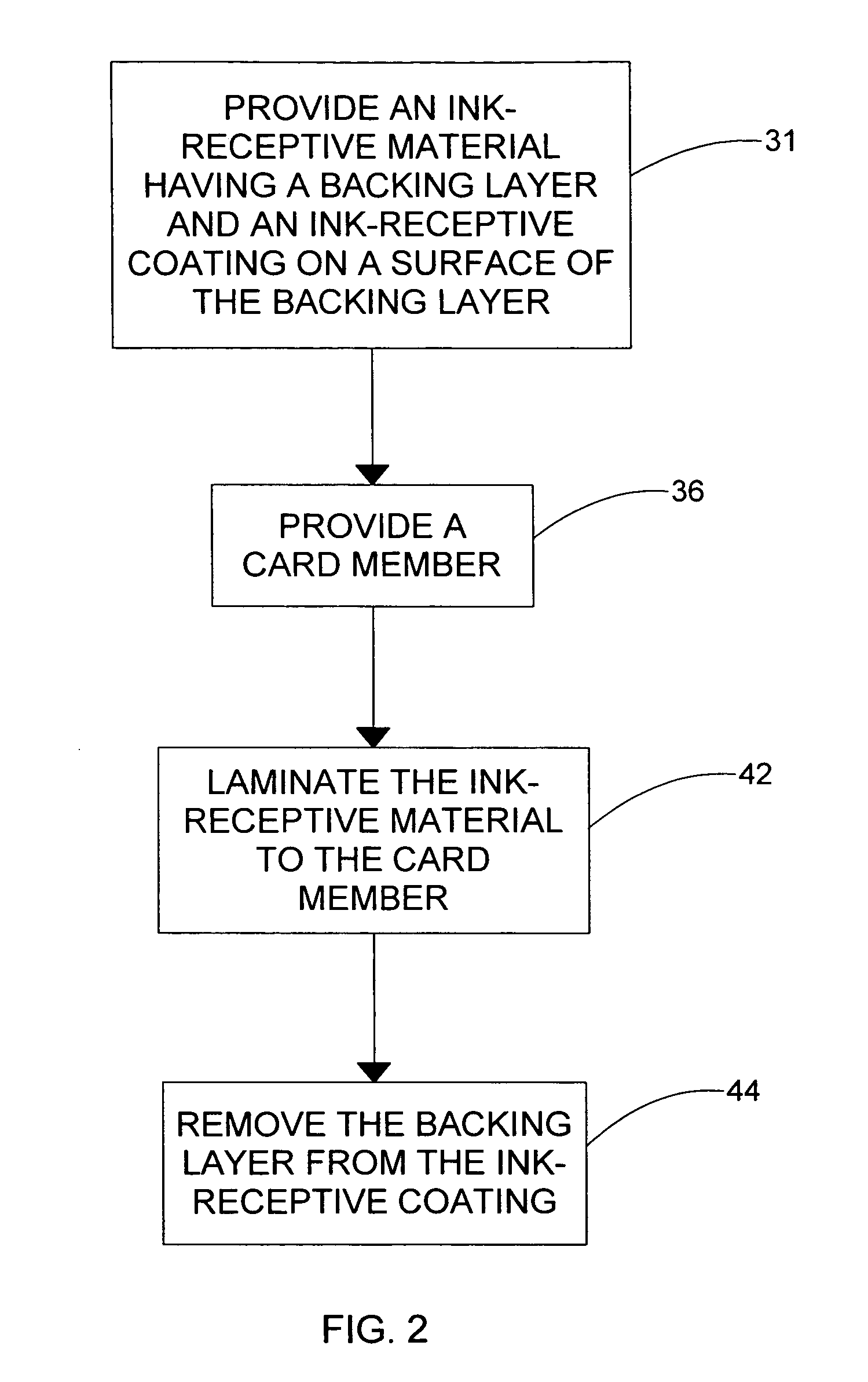
Ink-receptive card substrate
In a method of forming an ink-receptive card substrate, an ink-receptive material is provided. The ink-receptive material includes a backing layer and an ink-receptive coating on a surface of the backing layer. Next, a card member is provided. Finally, the ink-receptive material is laminated to a surface of the card member with the ink-receptive coating facing the surface of the card member. This results in the bonding of the ink-receptive coating to the surface of the card member. Additional embodiments of the present invention are directed to devices that are configured to perform the above-identified method.
Owner:ASSA ABLOY AB
Card with metal layer and electrostatic protection
ActiveUS20150180229A1Minimize the possibilityReduce the possibilityLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsDual stageAcrylic resin
A metal card or a hybrid metal-plastic includes an acrylic resin protective clear coat layer and / or a “hard” nano-particle top-coat layer overlying any exposed metal surface in order to insulate the metal and reduce the likelihood of an electrostatic discharge (ESD) or a short circuit condition. In a particular embodiment the “hard” nano-particle top-coat layer overlies the clear coat layer. The dual stage protective layers which include a clear-coat layer and a top-coat ensure that the problem associated with an ESD and / or a short circuit condition is minimized. In addition, the dual stage protection imparted to a card by forming a clear-coat layer and a top-coat layer ensures that any card surface treatment or card decoration is protected over time from excessive wear or scratching due to use in conjunction with a POS device and / or handling.
Owner:COMPOSECURE LLC
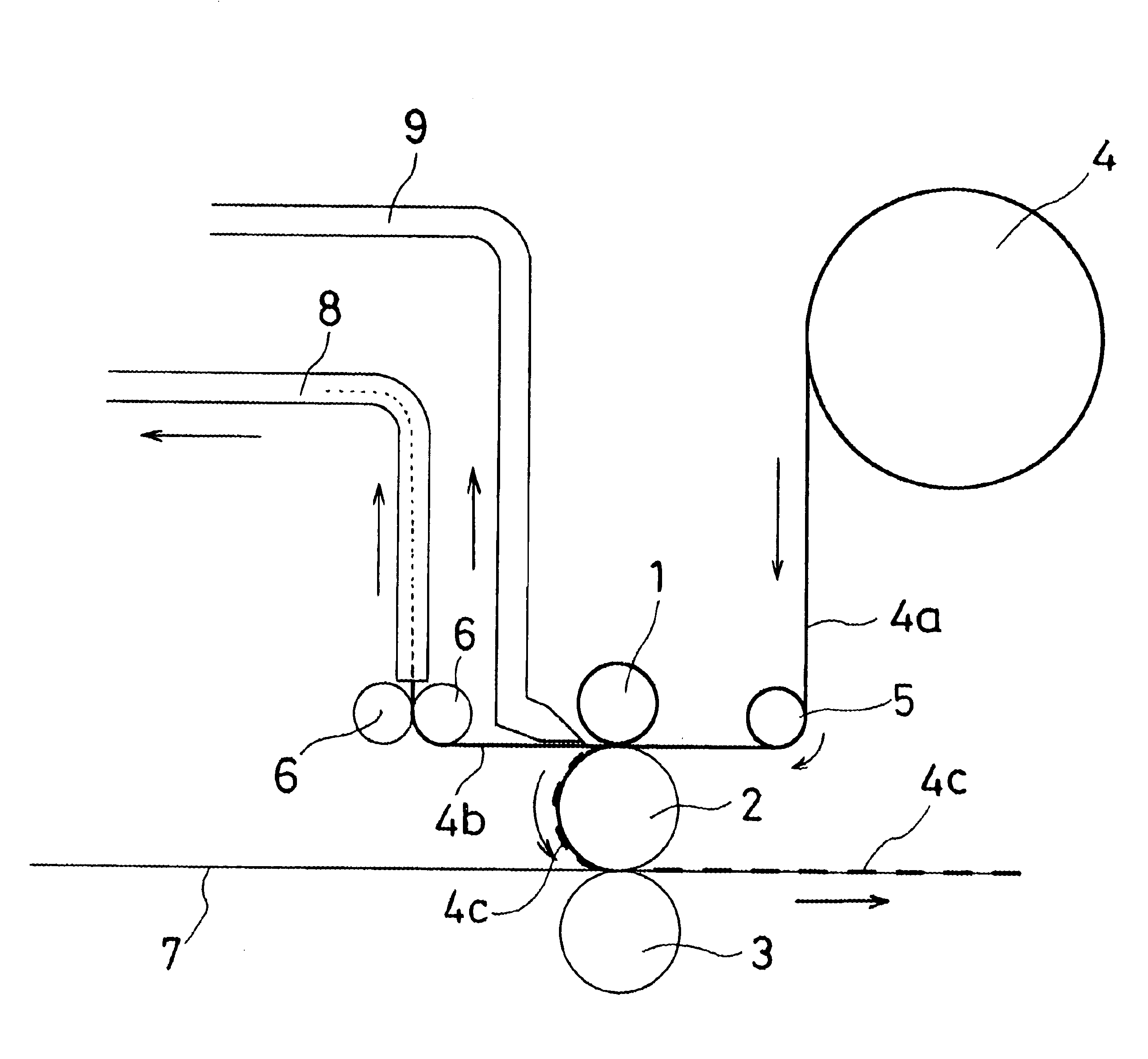
Process for producing resonant tag
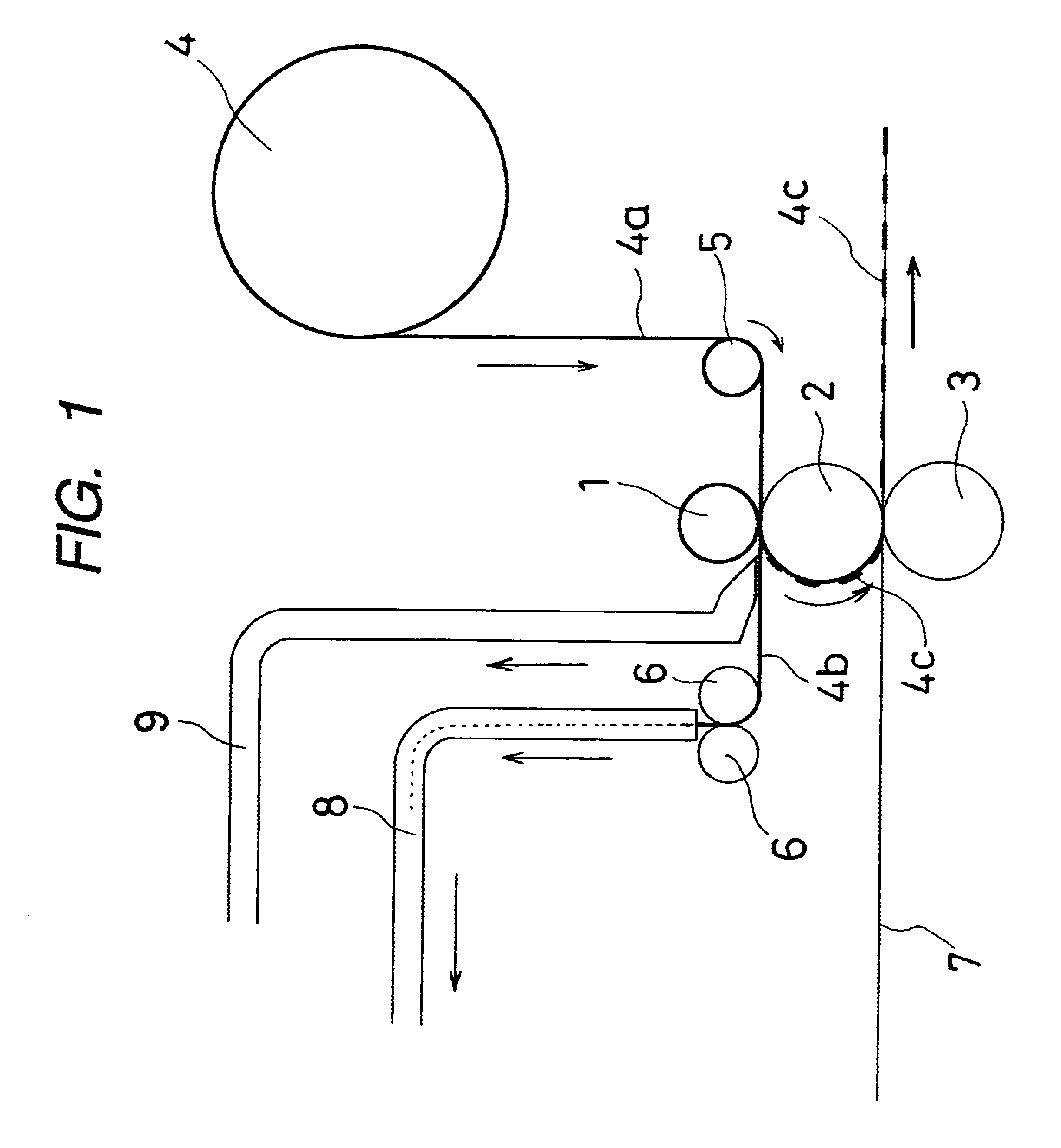
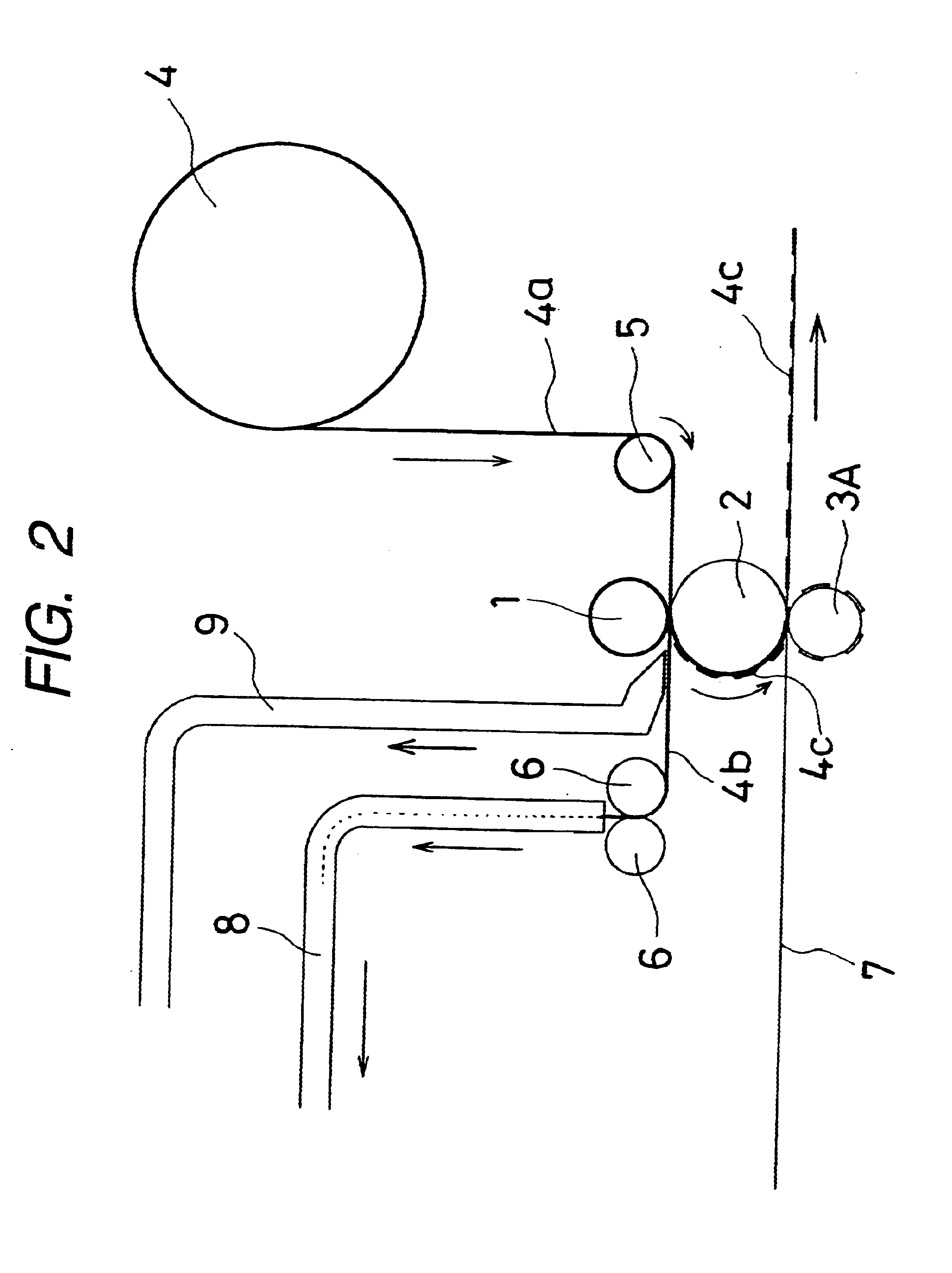
InactiveUS6618939B2Easy to manufactureStable resonant characteristicWave amplification devicesElectrical connection printed elementsMetal foilAdhesive
A process for producing a resonant tag, wherein a metal foil having a thermal adhesion adhesive applied to at least one face thereof is stamped out into a circuit-like shape and is adhered to a base sheet, the process comprising: stamping out the metal foil into a predetermined shaped metal foil portion (4c) while being passed through a die roll (1) having thereon a stamping blade with a predetermined shape and a transfer roll (2) in contact with the die roll (1) which functions also as a die back-up roll; holding this metal foil portion obtained by the stamping-out operation onto the surface of the transfer roll by suction holes formed in the transfer roll; and thermally adhering the stamped metal foil portion to the base sheet (7) in contact with the transfer roll (2) at its another face by an adhesive roll (3) in contact with the transfer roll through the base sheet. The present invention has such advantages as no damage to the base sheet since the stamping-out operation for the metal foil and the thermal adhesion operation thereof to the base sheet are carried out in separate positions, and no requirement of carrier sheet because the resultant metal foil portion obtained by the stamping-out operation is sucked and held onto the surface of the transfer roll.
Owner:NOVATRON ELECTRONICS HANGZHOU
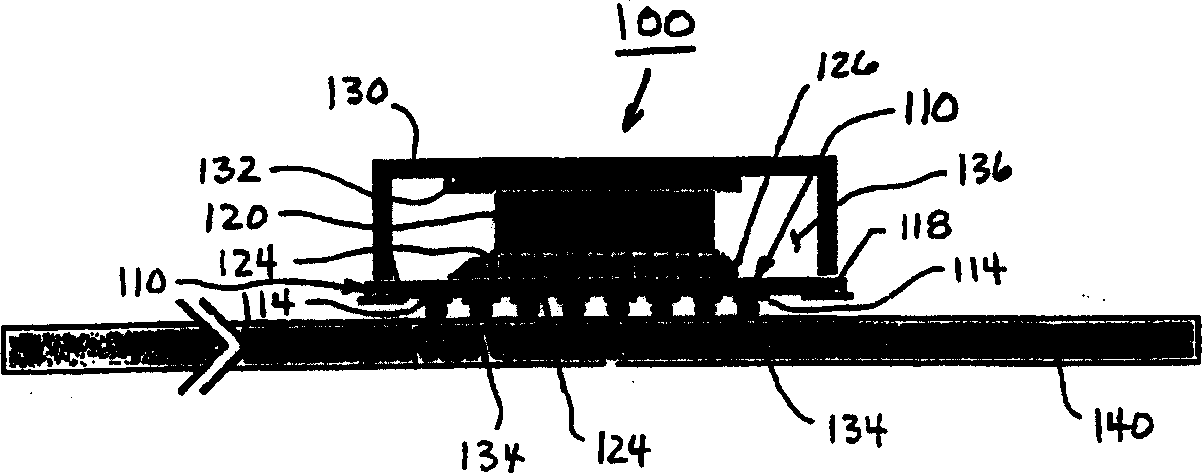
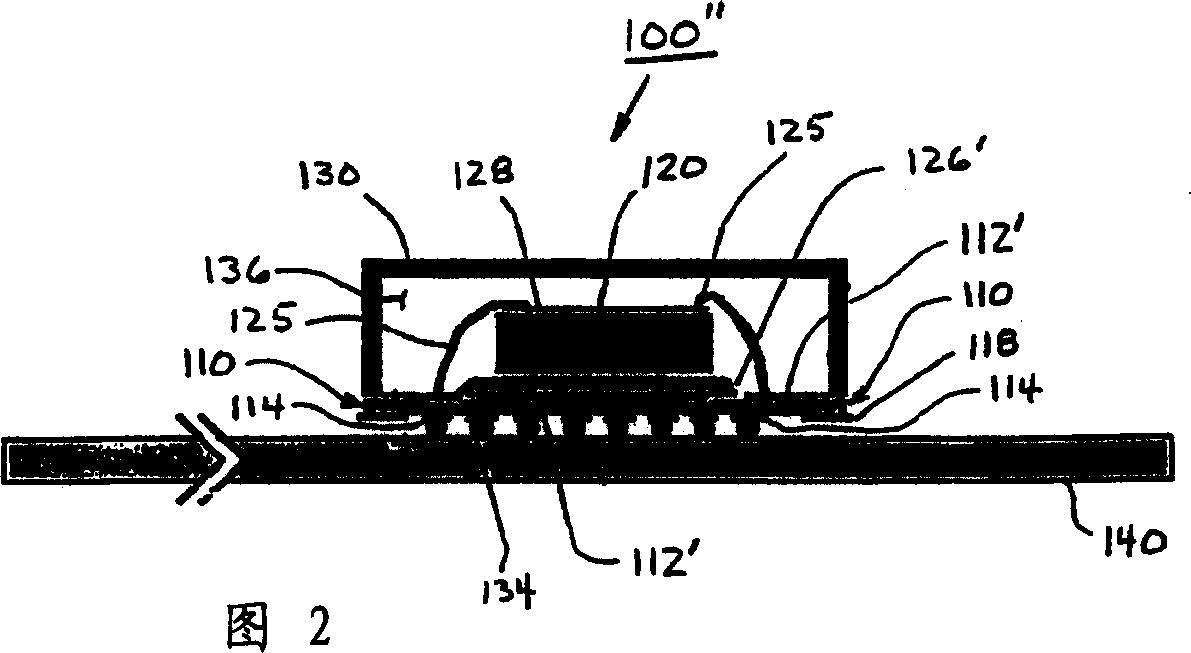
High-density electronic package and method for making same
InactiveCN1352804ARecord carriersSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorHigh density
A high density electronic package includes a low-modulus-of-elasticity flexible adhesive interposer substrate to which an electronic device, such as a semiconductor chip or die or other component, is attached. The flexible adhesive interposer substrate includes a sheet or layer of a molecularly flexible adhesive having via holes therein in which are built up conductive vias to which contacts of the electronic device connect. A thin layer of metal foil on one surface of the flexible adhesive sheet is patterned to provide contacts and to connect electrically to the conductive vias. The electronic device may be covered by a lid or by an encapsulant attached to the flexible adhesive interposer substrate and / or the electronic device. An electronic package may include a plurality of electronic devices and respective flexible adhesive interposers that are electrically interconnected.
Owner:AMERASIA INT TECH
Metal-containing transaction card and method of making the same
Metal-containing transaction cards, useful for the purchase of goods and / or services are disclosed. The metal-containing transaction cards may be standard-sized (i.e., about 3⅜ inches by about 2 14 inches) or any other size yet still usable as a transaction card. Moreover, the metal-containing transaction card may include a pocket having characters embossed therein. Further, the metal-containing transaction card may include a fill panel disposed within the pocket. The metal may be titanium or stainless steel.
Owner:AMERICAN EXPRESS TRAVEL RELATED SERVICES CO INC
Process of making laminated sheet and product made by the process
A process of making an improved sheet / card laminate for packaging, signage, displays, transaction cards, ID cards and the like. The process comprises registering flat sheets to a film and then laminating the film or transferring coating(s) from the film to the individual, generally flat sheets via an adhesive. The film or coating(s) may include layered security, functional and / or decorative features.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Laminated imaged recording media
InactiveUS7022385B1Faithfully reproducedSynthetic resin layered productsPattern printingDigital imagingImage recording
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing an identification document that can contain both common information and unique information describing the specific document holder. The information is in the form of indicia applied by digital imaging means. The document itself is in the form of a laminated article having the information affixed to one or more internal layers. Attempt to gain access to these internally imaged layers causes the image to be sufficiently disrupted as to prevent modifying such images.
Owner:NUCOAT
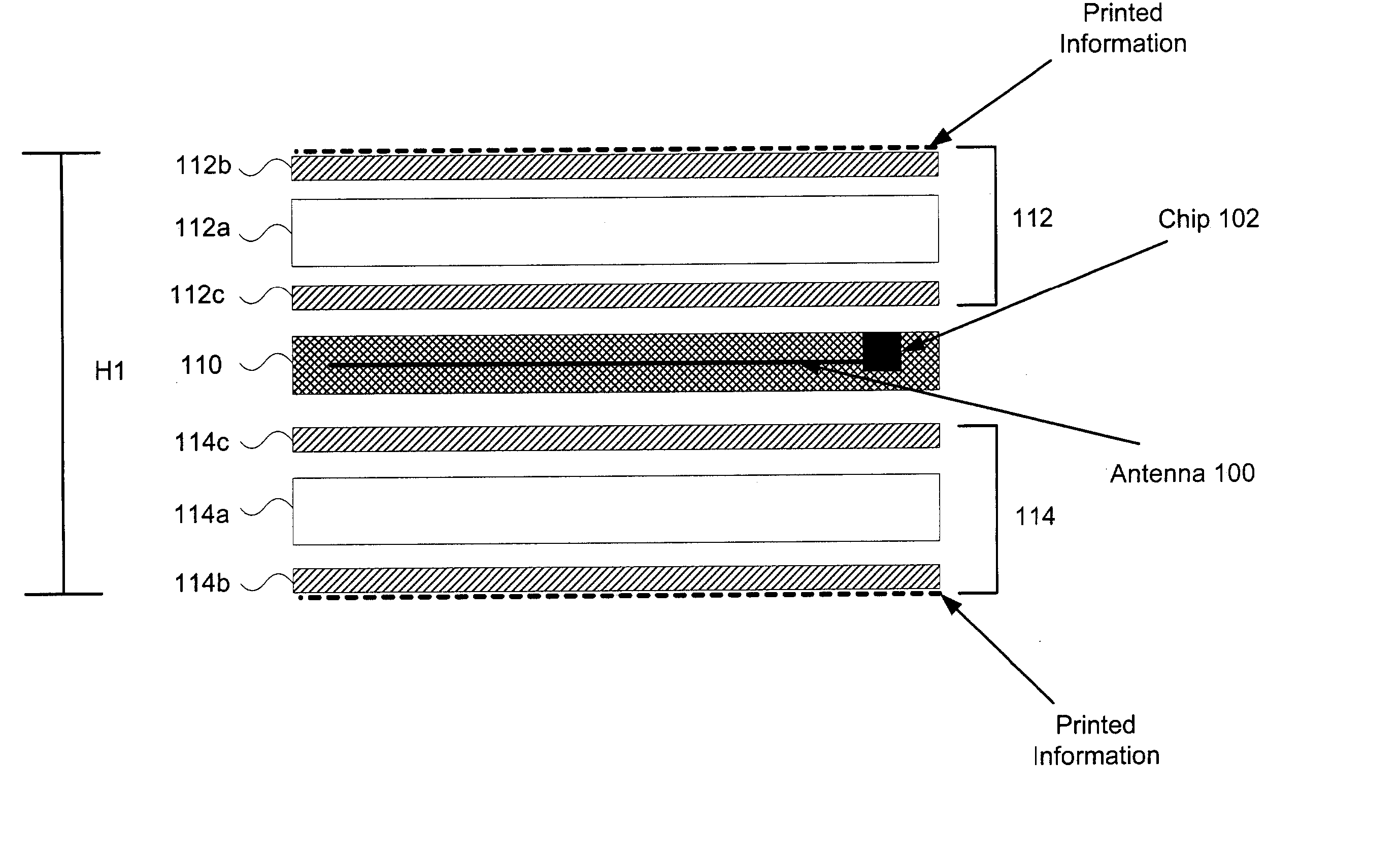
Method for making a smart card antenna on a thermoplastic support and resulting smartcard
InactiveUS20060181478A1Casings/cabinets/drawers detailsRadiating elements structural formsScreen printingThermoplastic
The invention concerns a method for making a hybrid contact / non-contact or non-contact smart card comprising a support (10, 11) whereon is produced the antenna, two card bodies (32, 42, 34, 44) on either side of the support, each of the card bodies consisting of at least one thermoplastic layer, and one chip (30) or module connected to the antenna. Said method comprises the following steps: depositing a layer of a material consisting of a major amount of resin on a predetermined zone (12, 13) of the antenna support; making the antenna which consists in screen-printing turns (14, 15) and two connection pads (16, 18, 17, 19) of conductive polymer ink on the zone previously produced on the support and subjecting the support to a heat treatment to cure the ink.
Owner:ASK SA (FR)
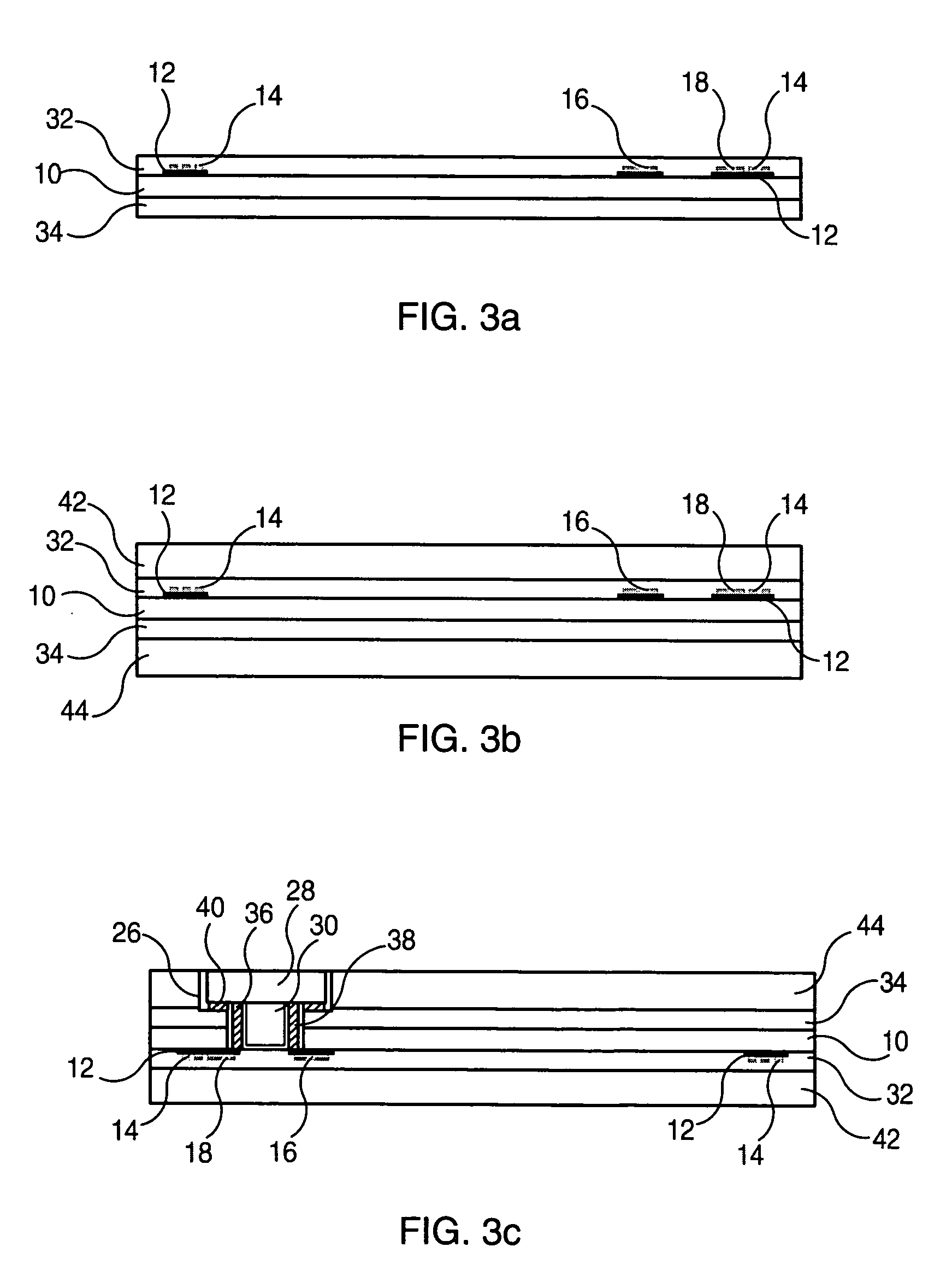
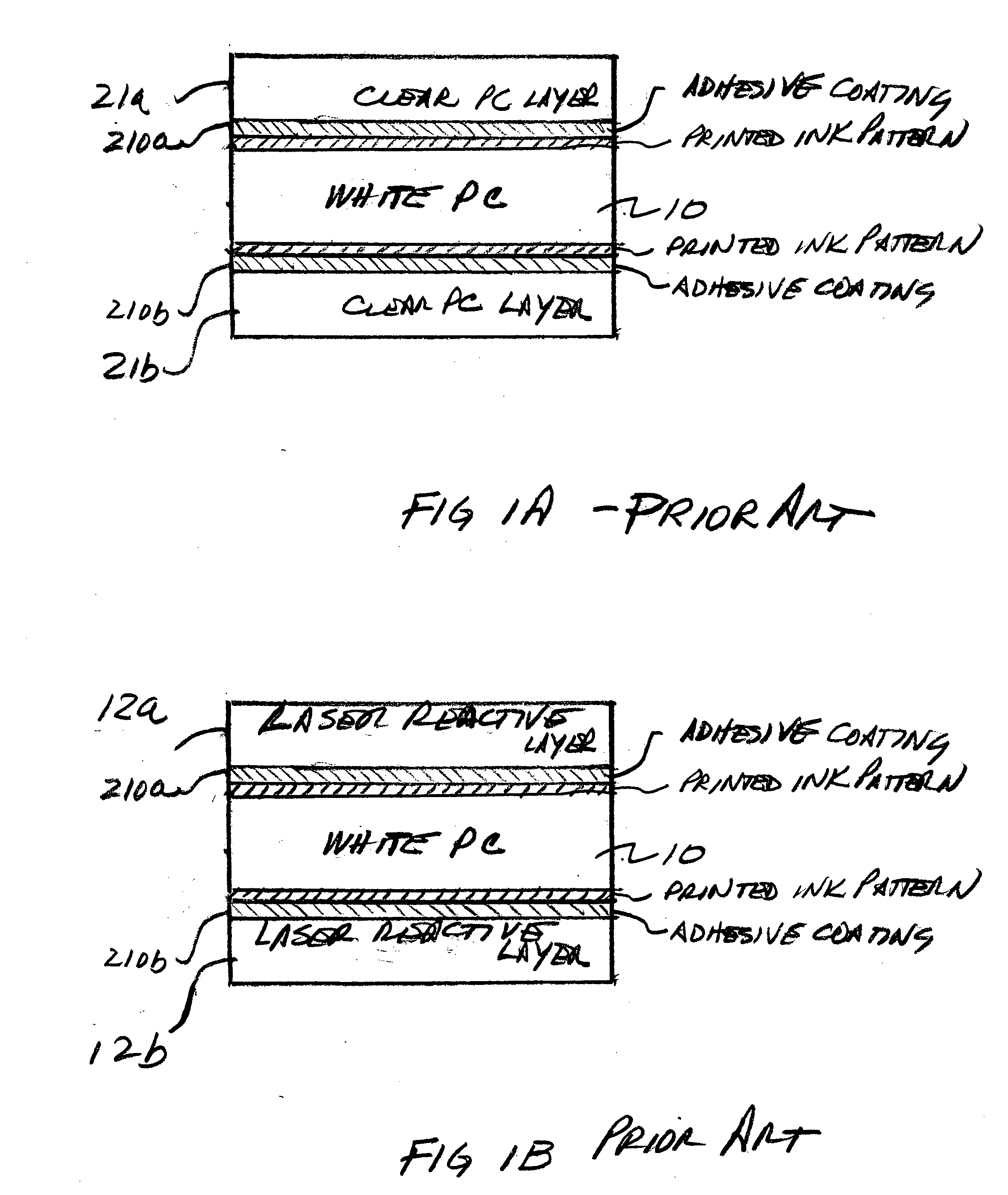
Laser markable secure documents
ActiveUS20060251869A1Reduce heatAvoid problemsSynthetic resin layered productsCardsPolycarbonatePaper document
Documents embodying the invention include a sandwich-like structure comprised of a core layer on which information may be printed using inks, a buffer layer bonded to each surface of the core layer for protecting the printed information and a laser reactive layer on, or in, which information can be written with a laser, bonded to each one of the buffer layers. The core layer may be formed of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) or PC (poly carbonate) material or any other suitable material on which information can be printed. The buffer layer may be formed of amorphous polyester material (e.g., PETG) or any other suitable material which can readily bond to the core layer and the laser reactive layer. The laser reactive layer may be polycarbonate (PC) or may be any other suitable plastic material (e.g., PVC, PET, PC, etc.) which includes a chemical which can react with a laser to produce desirable markings.
Owner:COMPOSECURE LLC
Polypropylene card construction
An image retaining card is disclosed. An image retaining card in accordance with the present invention may be utilized as an identification card, a driver's license, a passport, and the like. An image retaining card in accordance with the present invention comprises a substrate structure, a cover, and an image receptive material disposed between the substrate structure and the cover. The substrate structure comprises a substrate layer and a substrate tie layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Document laminate formed from different polyester materials
InactiveUS20050084693A1Reduce adverse effectsImproved safety and durabilityRecord carriersDecorative surface effectsPolyesterAdhesive
A polyester laminate for an identification document is formed from different polyester materials. One of the polyester materials, such as PCTA, provides a durability property. Another of the polyester materials, such as PETG, provides a layer having a surface with a bonding property for bonding directly to a core without adhesive. The polyester material with the bonding property is selected to enable direct bonding to a printed core layer of TESLIN or polyester through a roll to roll or platen press process.
Owner:L 1 SECURE CREDENTIALING
Process of making laminated sheet and product made by the process
A process of making an improved sheet / card laminate for packaging, signage, displays, transaction cards, ID cards and the like. The process comprises registering flat sheets to a film and then laminating the film or transferring coating(s) from the film to the individual, generally flat sheets via an adhesive. The film or coating(s) may include layered security, functional and / or decorative features.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Apparatus and method for making information carrying cards through radiation curing, and resulting products
A method forms an information carrying card or a core layer of an information carrying card using a radiation curing, and an apparatus configured to provide such a radiation curing. The method includes providing a carrier layer that defines at least one cavity, providing an inlay layer supporting at least one electronic component, and positioning at least a portion of the inlay layer in the at least one cavity. The method further comprises dispensing a radiation crosslinkable polymer composition over the inlay layer, and irradiating the radiation crosslinkable polymer composition.
Owner:X CARD HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com