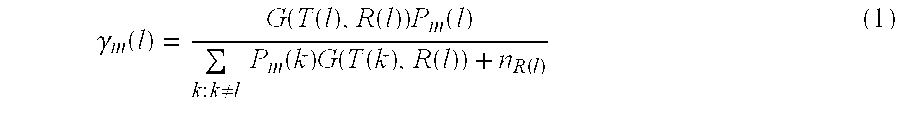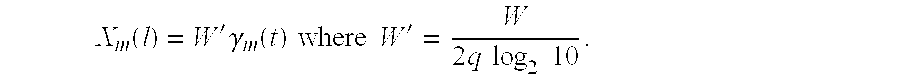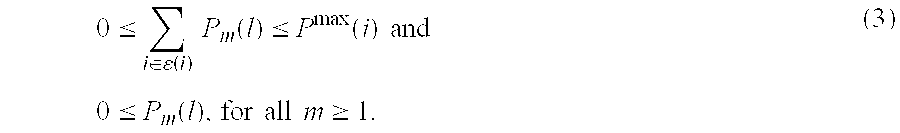Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
226 results about "Throughput maximization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
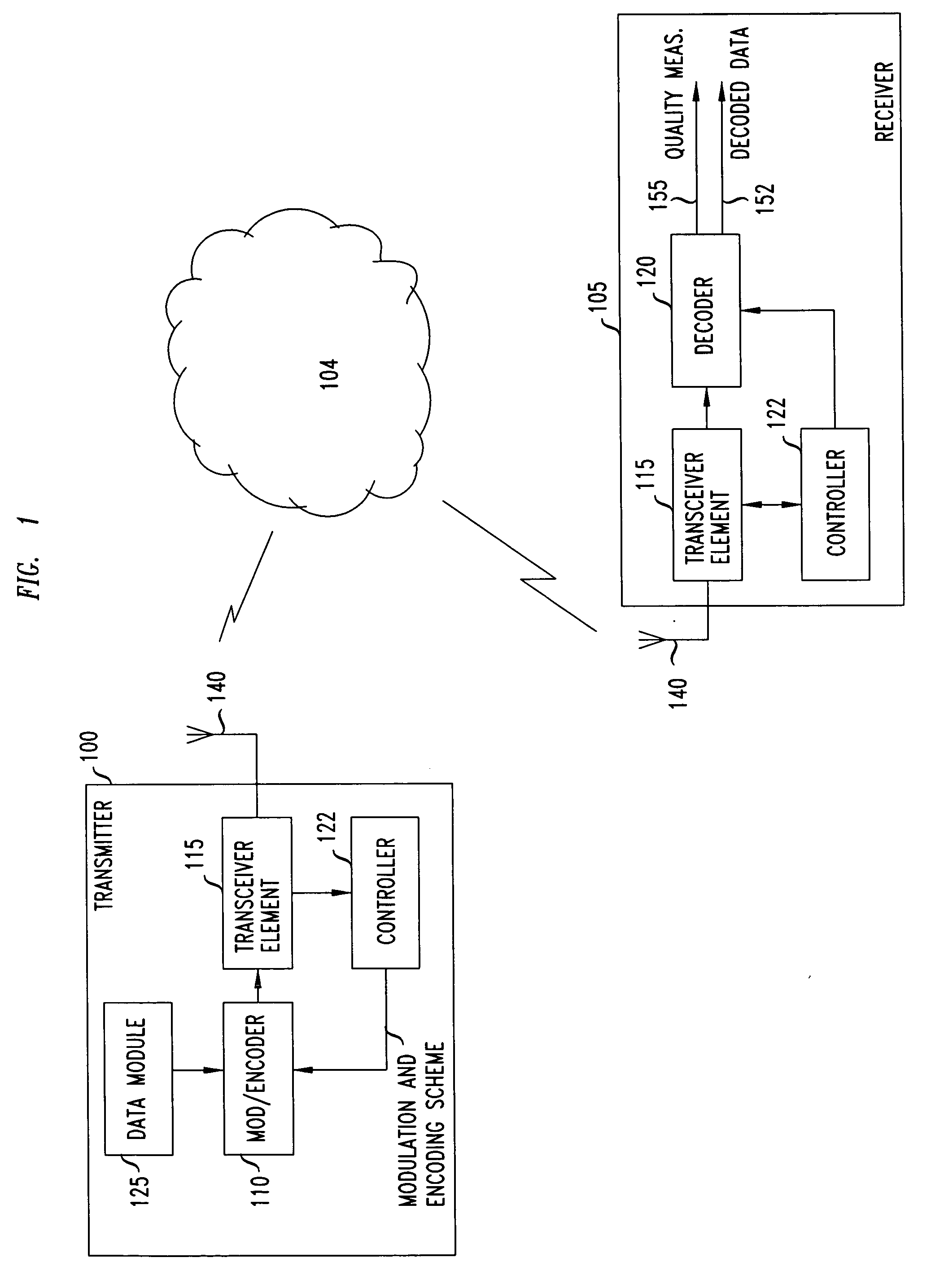
Throughput Maximization in Wireless Communications Systems Current theory tells us the ultimate throughput, or ergodic capacity, of an idealized communications system. The ergodic capacity is achieved in idealized systems by using codewords that are infinitely long and thus averaged over an infinite number of instances of the fading channel.
Scheduling methods for wireless networks
InactiveUS20060046658A1Minimize powerMaximize throughputPower managementEnergy efficient ICTThroughput maximizationPower control
The invention concerns routing, scheduling, and power control methods for single and multi-hop wireless networks. A multi-hop network is one in which source and destination nodes may communicate directly or through relay nodes. Nodes in single hop networks communicate without use of relay nodes. Embodiments of the invention may produce an optimal schedule to provide for the best-case goal for a given parameter. In a preferred embodiment, total power is the parameter and total power is minimized for the network. In another preferred embodiment, data throughput is the parameter, and throughput is maximized for the network.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
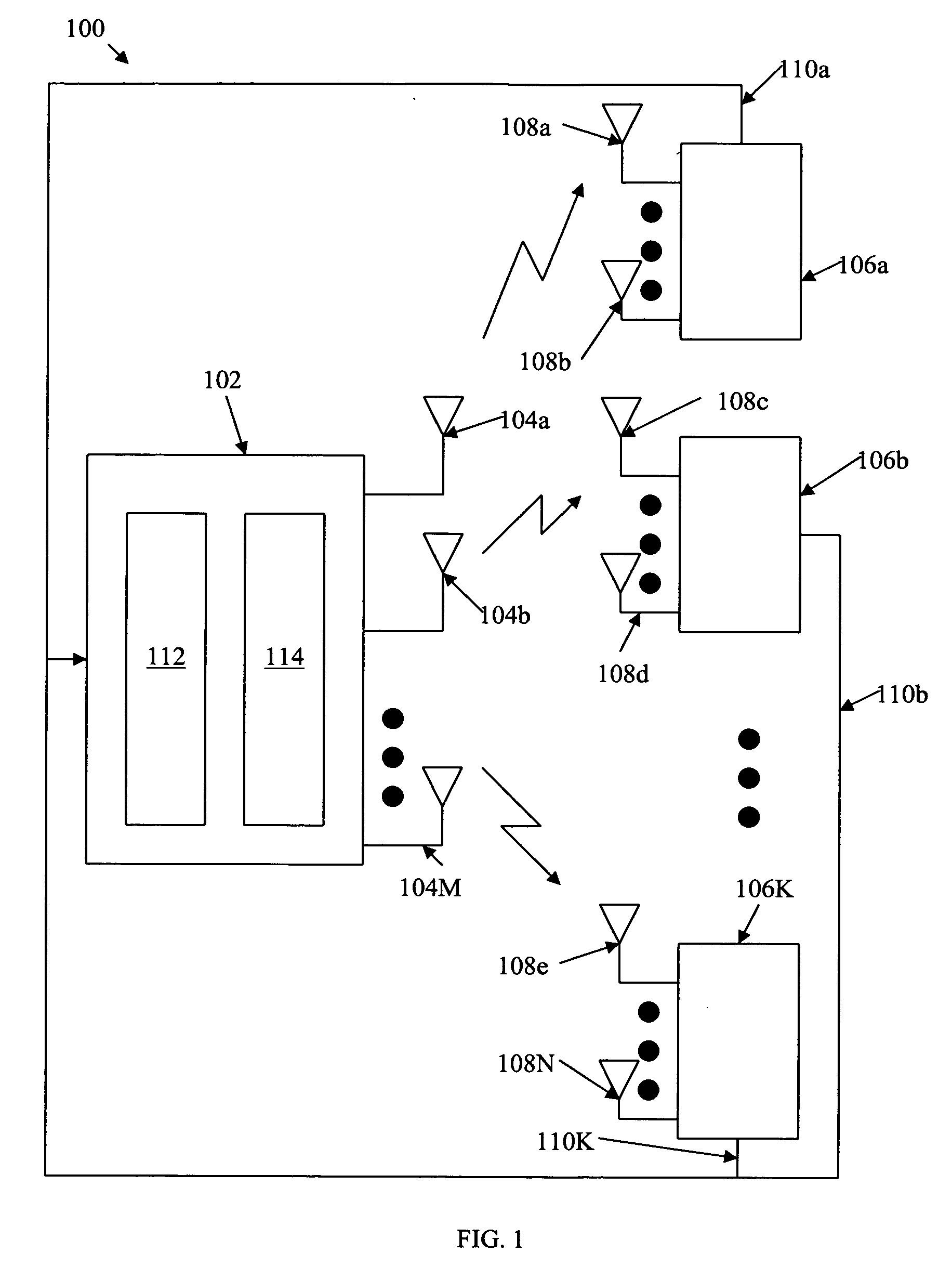
Design of multi-user downlink linear MIMO precoding systems
ActiveUS20080159425A1Maximize throughputSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityEngineeringMimo systems
Multi-user (MU-) MIMO systems with quantized feedback are designed to maximize the sum-rate via scheduling and linear precoding. To maximize throughput over the network, quantized CSIT is sent through a low-rate feedback link feedback from a plurality of users back to a base station. The base station then determines a subset of the plurality of users to transmit one or more signals to based on the received feedback and determines a preceding matrix based on the received feedback from the plurality of users wherein the precoding matrix maximizes a sum-rate throughput for the subset of the plurality of users. Additionally, based on the received feedback, the base station designs a quantization codebook. This codebook may be designed off-line and / or online. The codebook and / or precoding matrix are used to transmit signals to the users.
Owner:NEC CORP
Base station apparatus and transmission assignment control method
InactiveUS7257423B2Maximize throughputError prevention/detection by using return channelModulated-carrier systemsTerminal equipmentEngineering
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Unmanned aerial vehicle network hovering position optimization method based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN111786713AReduce energy consumptionEnsure fairnessRadio transmissionNeural learning methodsSimulationUncrewed vehicle
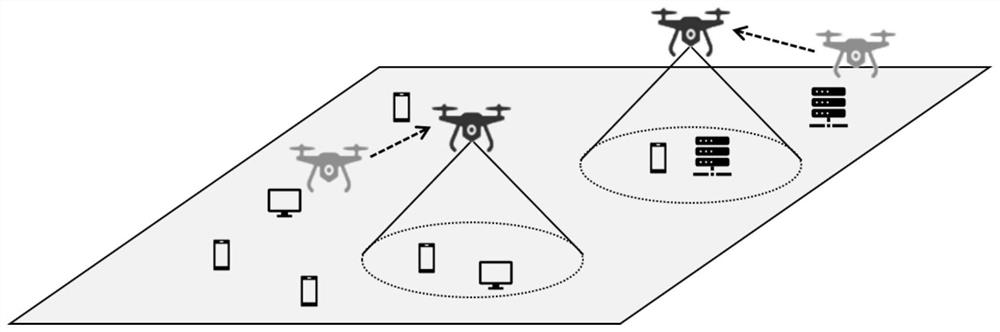
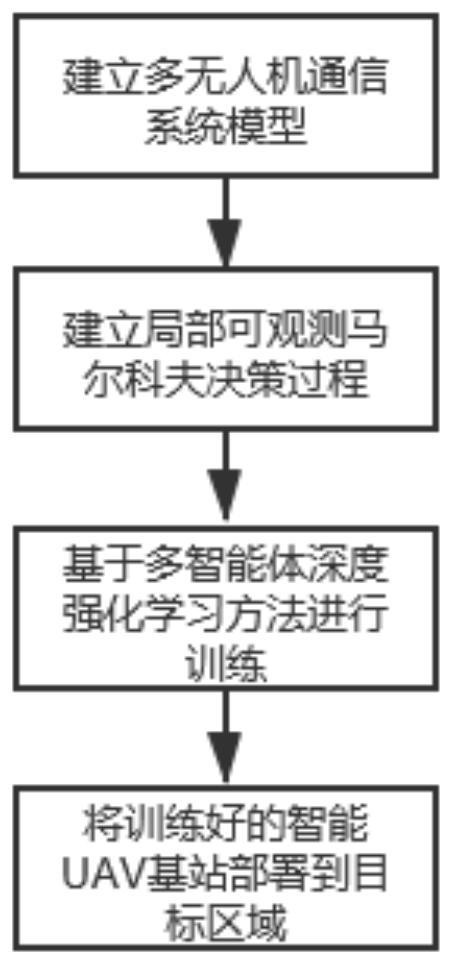
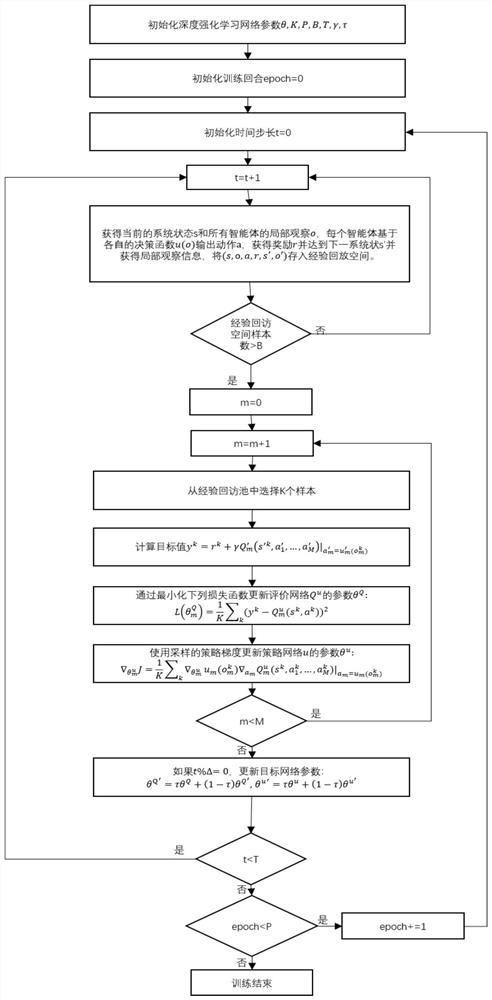
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle network hovering position optimization method based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, modeling a channel model, a coverage model and an energy loss model in an unmanned aerial vehicle to ground communication scene; modeling a throughput maximization problem of the unmanned aerial vehicleto ground communication network into a locally observable Markov decision process; obtaining local observation information and instantaneous rewards through continuous interaction between the unmanned aerial vehicle and the environment, conducting centralized training based on the information to obtain a distributed strategy network; deploying a strategy network in each unmanned aerial vehicle, so that each unmanned aerial vehicle can obtain a moving direction and a moving distance decision based on local observation information of the unmanned aerial vehicle, adjusts the hovering position, and carries out distributed cooperation. In addition, proportional fair scheduling and unmanned aerial vehicle energy consumption loss information are introduced into an instantaneous reward function,the fairness of the unmanned aerial vehicles for ground user services is guaranteed while the throughput is improved, energy consumption loss is reduced, and the unmanned aerial vehicle cluster can adapt to the dynamic environment.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Heterogeneous cloud wireless access network resource allocation method based on deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN110493826AMaximize total throughputMeet stability requirementsNetwork traffic/resource managementNonlinear approximationSmall sample
The invention relates to a heterogeneous cloud wireless access network resource allocation method based on deep reinforcement learning, and belongs to the technical field of mobile communication. Themethod comprises the following steps: 1) taking queue stability as a constraint, combining congestion control, user association, subcarrier allocation and power allocation, and establishing a random optimization model for maximizing the total throughput of the network; 2) considering the complexity of the scheduling problem, the state space and the action space of the system are high-dimensional,and the DRL algorithm uses a neural network as a nonlinear approximation function to efficiently solve the problem of dimensionality disasters; and 3) aiming at the complexity and the dynamic variability of the wireless network environment, introducing a transfer learning algorithm, and utilizing the small sample learning characteristics of transfer learning to enable the DRL algorithm to obtain an optimal resource allocation strategy under the condition of a small number of samples. According to the method, the total throughput of the whole network can be maximized, and meanwhile, the requirement of service queue stability is met. And the method has a very high application value in a mobile communication system.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
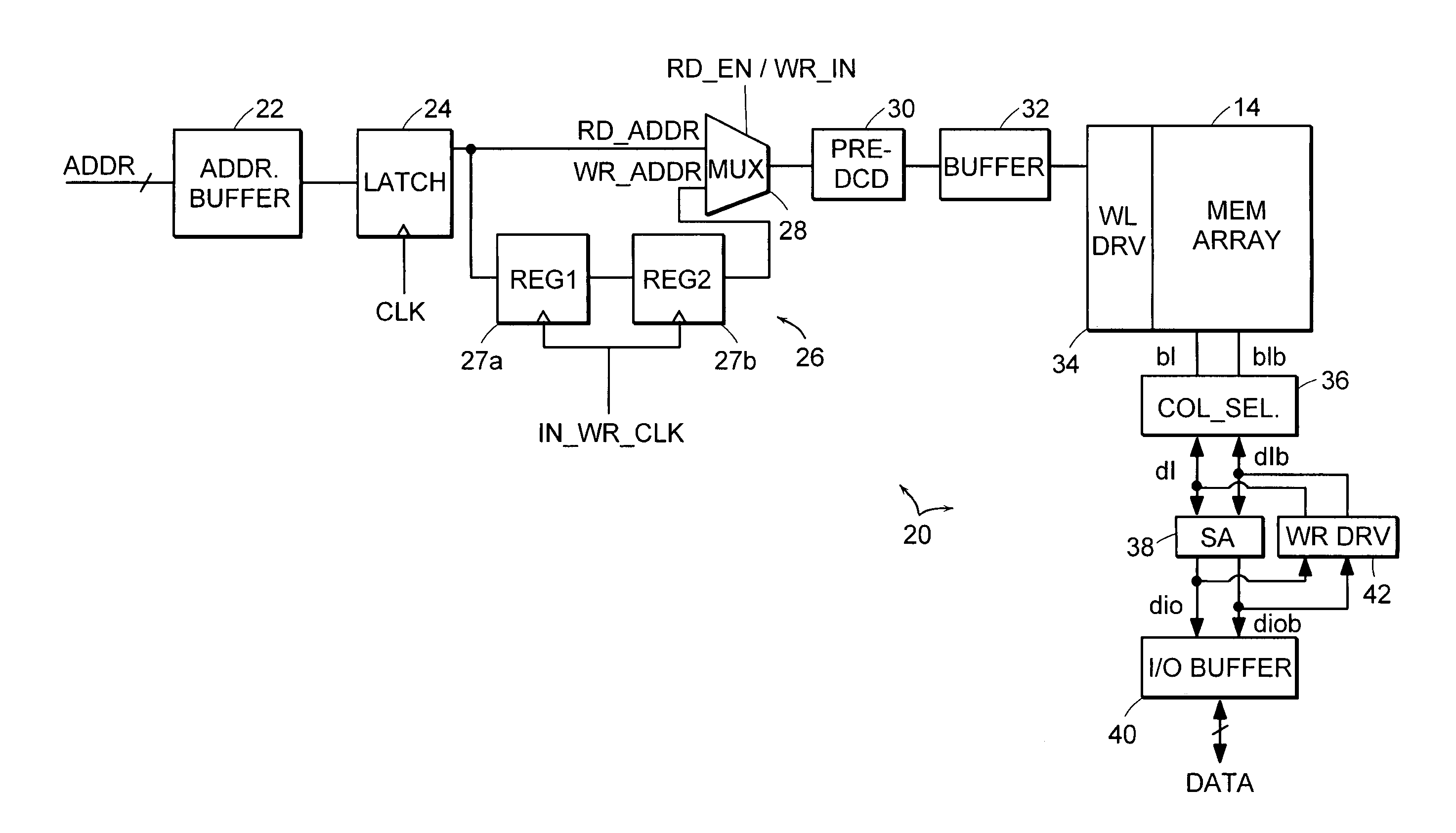
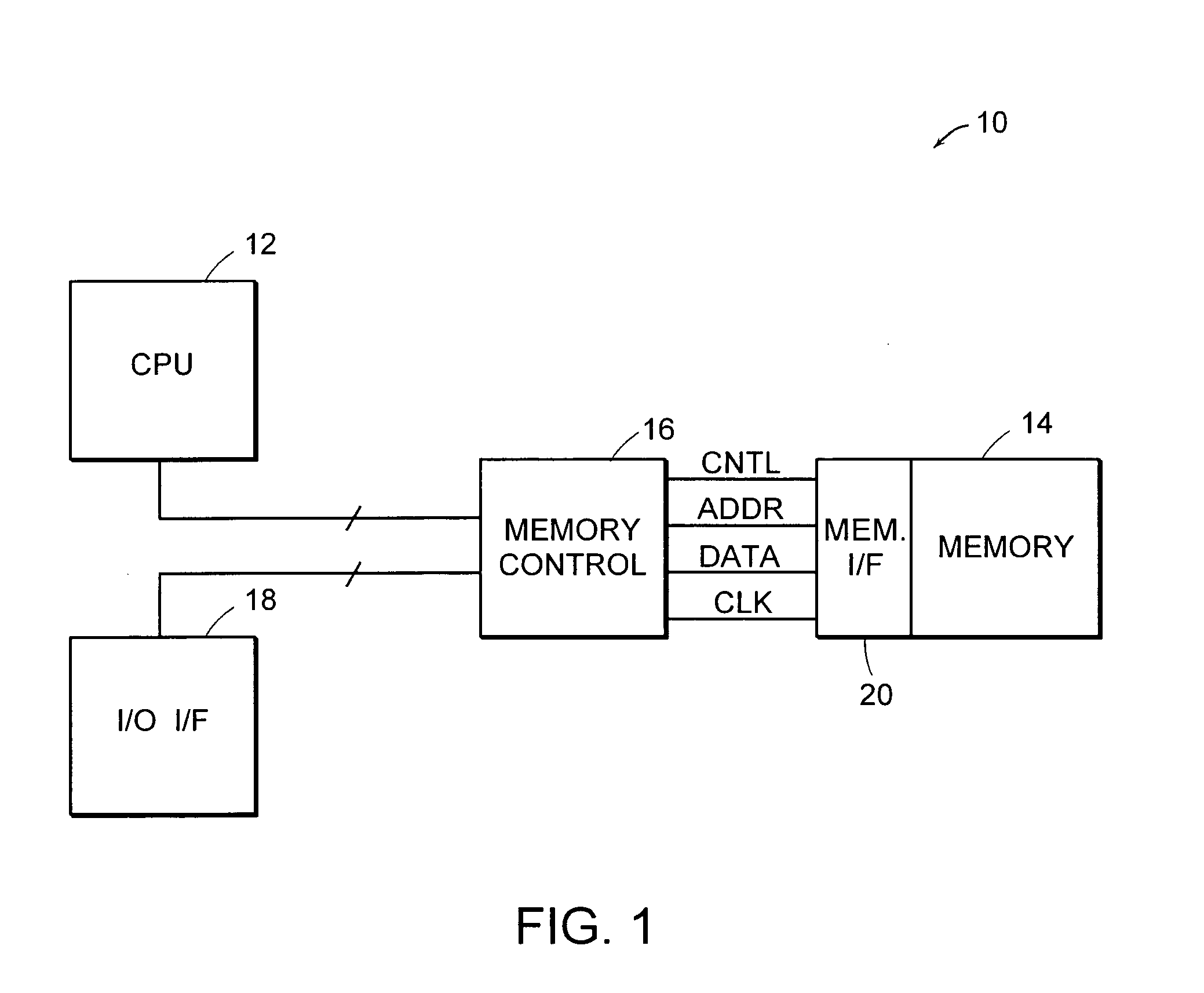
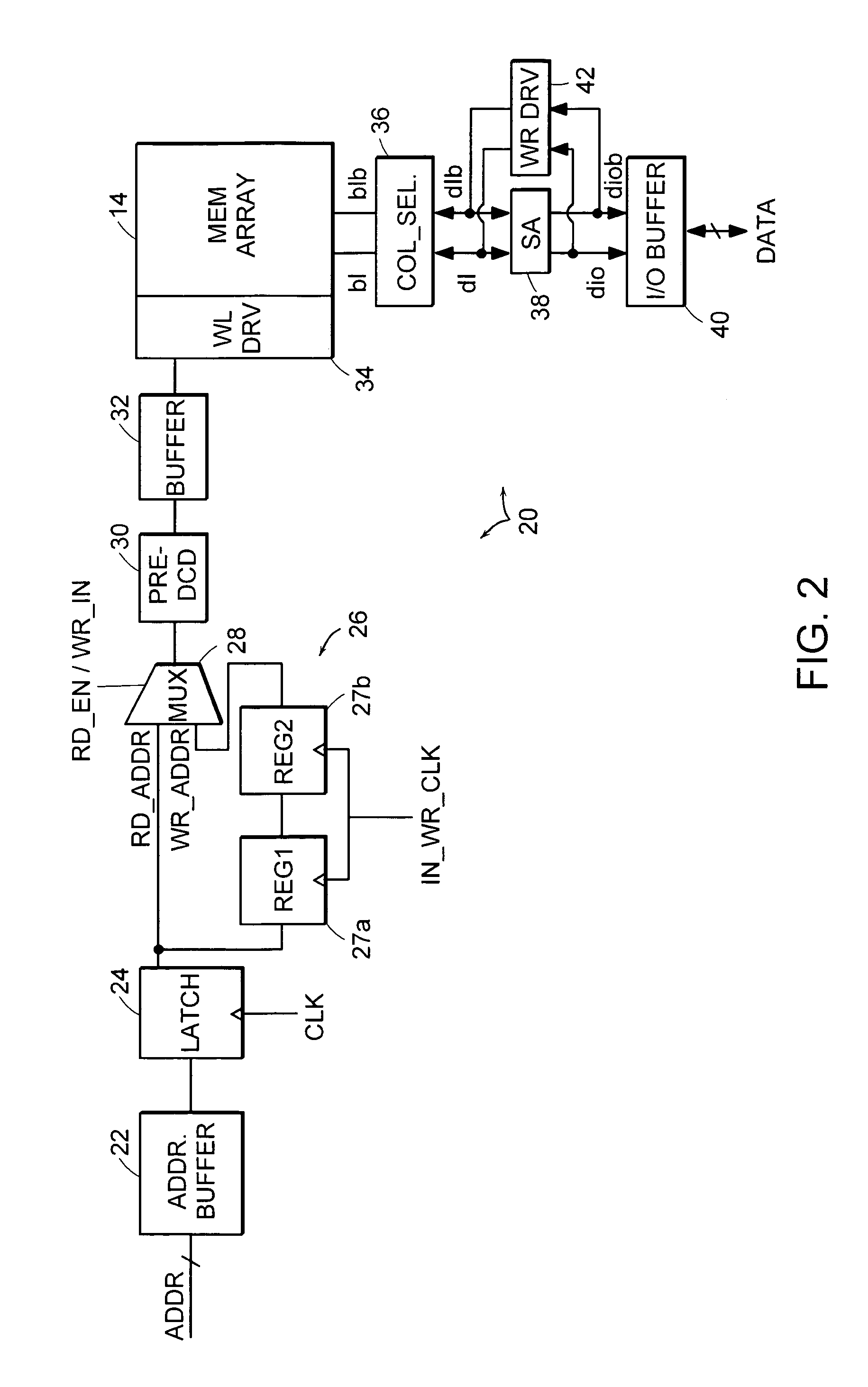
Memory interface system and method for reducing cycle time of sequential read and write accesses using separate address and data buses
ActiveUS7142477B1Improve data throughputImprove throughputDigital storageDouble data rateMemory interface
A memory interface system and method are provided for transferring data between a memory controller and an array of storage elements. The storage elements are preferably SRAM elements, and the memory interface is preferably one having separate address bus paths and separate data bus paths. One address bus path is reserved for receiving read addresses and the other address bus path is reserved for receiving write addresses. One of the data bus paths is reserved for receiving read data from the array, and the other data bus path is reserved for receiving data written to the array. While bifurcating the address and data bus paths within the interface is transparent to the memory controller, the separate paths afford addressing phases of a read and write address operation to be partially overlapped, as well as the data transfer phases. This will essentially reduce the cycle time between a read and write memory access, and proves useful when maximizing the data throughput across the data bus when implementing double data rate (QDR) mechanisms.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
Method and system FPOR transferring data to improve responsiveness when sending large data sets
ActiveUS9509802B1Improve data throughputWithout impacting responsivenessMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksWide areaTimestamp
Most of the internet traffic today is carried out via the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). The main advantage of TCP is that it provides reliable data transfer to the application layer and simplifies programming. The protocol maximizes data throughput but may also lead to noticeable transmission delay in wide area networks (WAN). A client-server based medical image viewing system is disclosed that achieves high data throughput over TCP without impacting responsiveness. Special timestamp messages inserted into the data stream allow the system to detect situations where network latency increases noticeably and to obtain a reliable estimate of sustained transfer bandwidth. The system applies a feedback scheme that avoids network delays by limiting send bandwidth. In addition other parameters, in particular image compression settings, are dynamically adjusted depending on current network quality.
Owner:PME IP
Transmit power allocation in a distributed MIMO system
ActiveUS20070149236A1Maximise equal throughput rateEqual throughput ratePower managementDiversity/multi-antenna systemsTelecommunicationsTransmitted power
Allocate power so as to maximise the throughput of each user of a multi-user MIMO group, with the constraint that over time all users in the group have equal throughput. This differs from equal capacity per slot in that each user may be assigned multiple slots as well as unequal power. This is illustrated in FIG. 4. Total throughput is maximised on any given slot for any two users. Power is shared between the spatial modes such that the total number of slots used by the two users is minimised. The membership of the MIMO group may change between slots and thus throughput is not necessarily equalised on a slot by slot basis.
Owner:APPLE INC
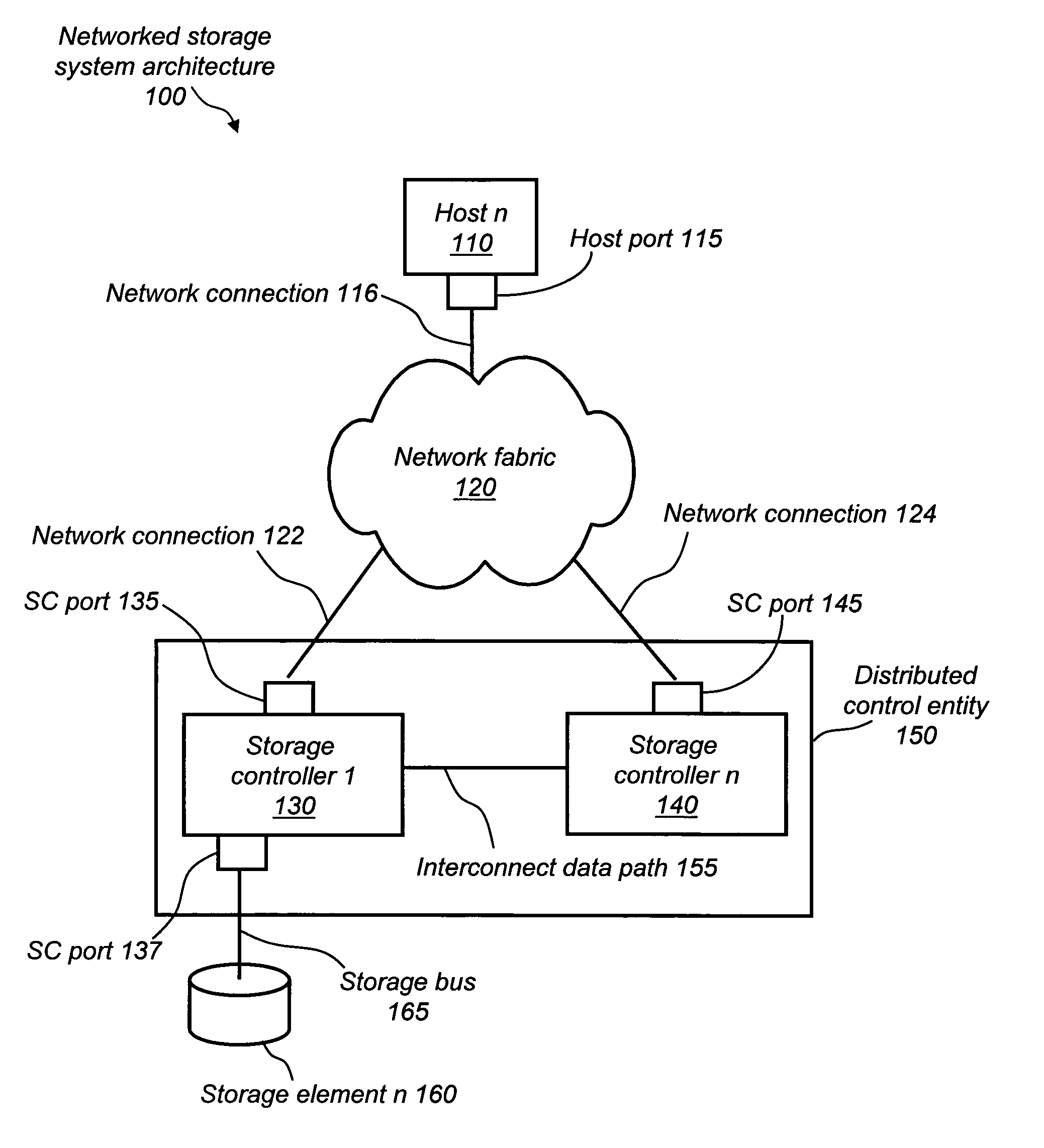
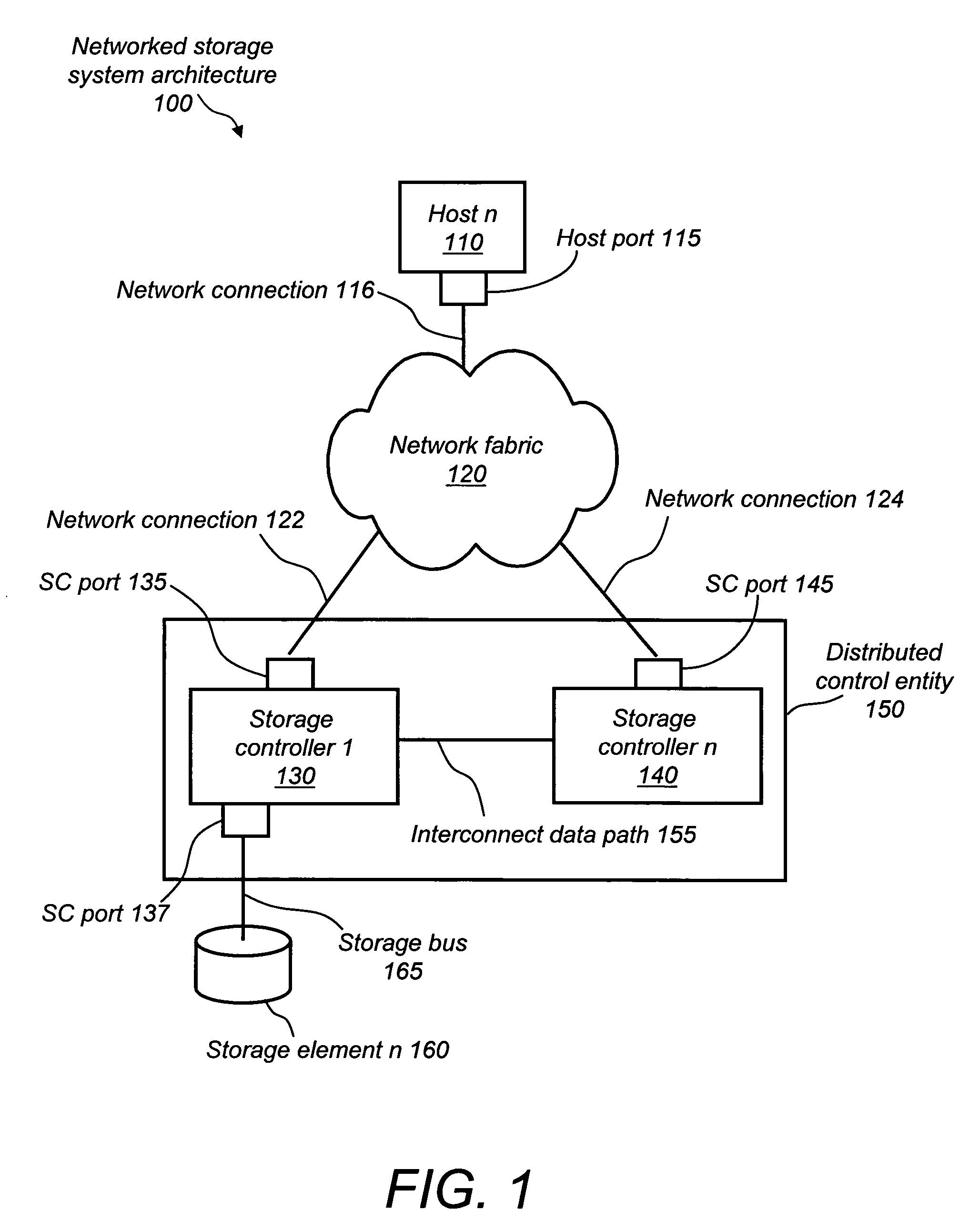
Optimized port selection for command completion in a multi-ported storage controller system
InactiveUS20050091426A1Good choiceInput/output to record carriersTransmissionStorage area networkLoop bandwidth
A multi-ported storage area network (SAN) controller system with command completion that utilizes optimal port selection. The system determines the optimal port for command completion based on criteria such as loop bandwidth utilization or port throughput maximization, and allows data and response information to occur via the optimal port regardless of the receiving port. This is accomplished through port aliasing (spoofing) of port identities, in which the receiving port identity is substituted into a sending port identity by a distributed control entity. In this way, any port within the SAN may return data or status to the originating host.
Owner:ARISTOS LOGIC
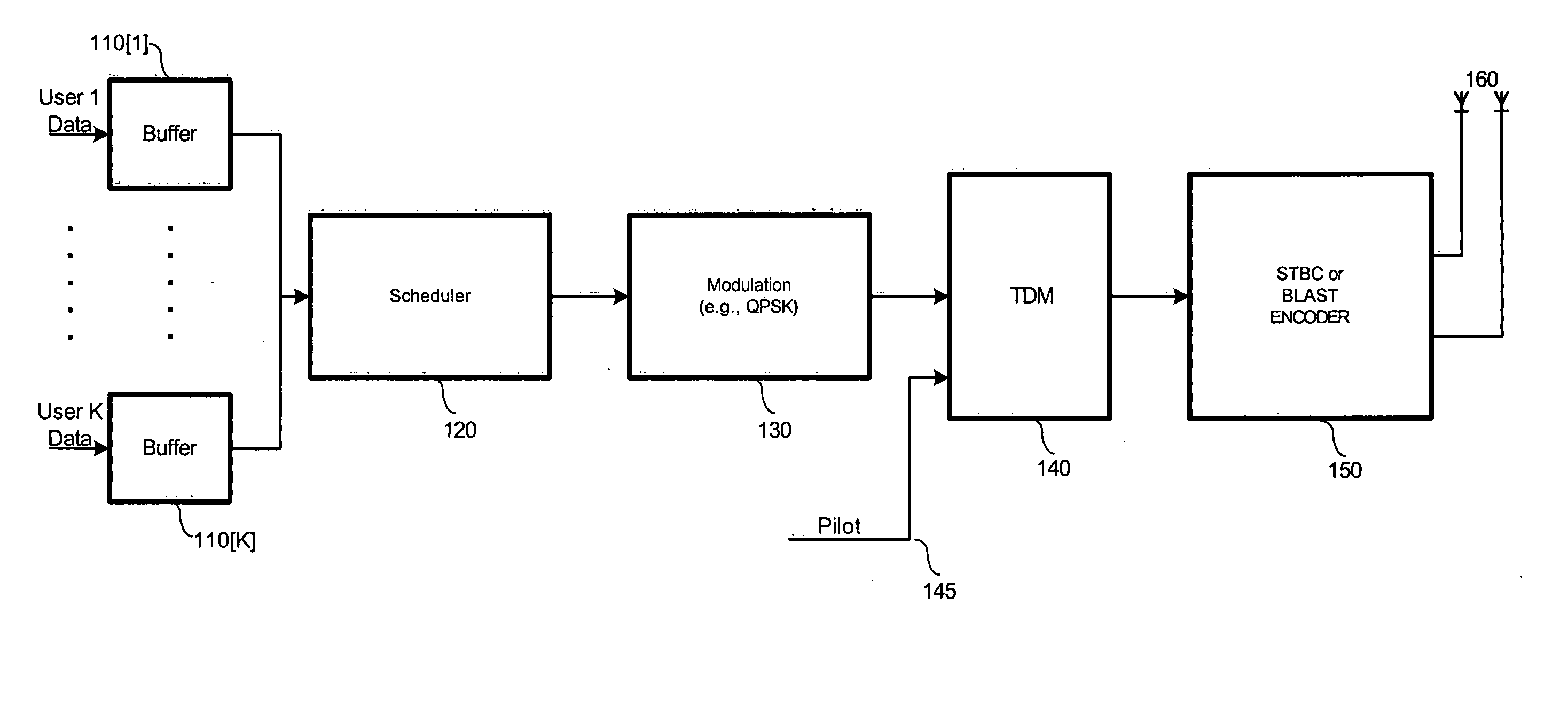
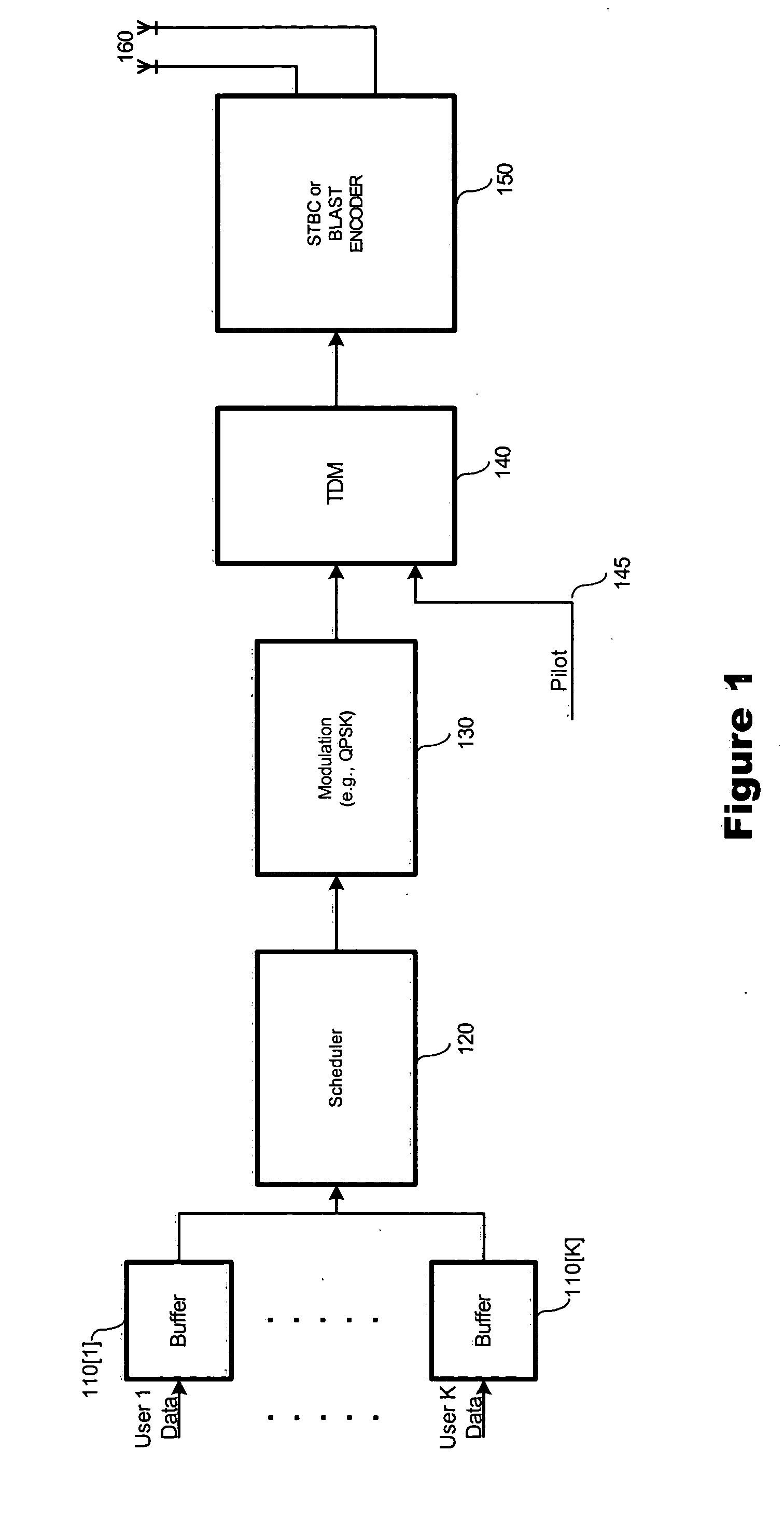
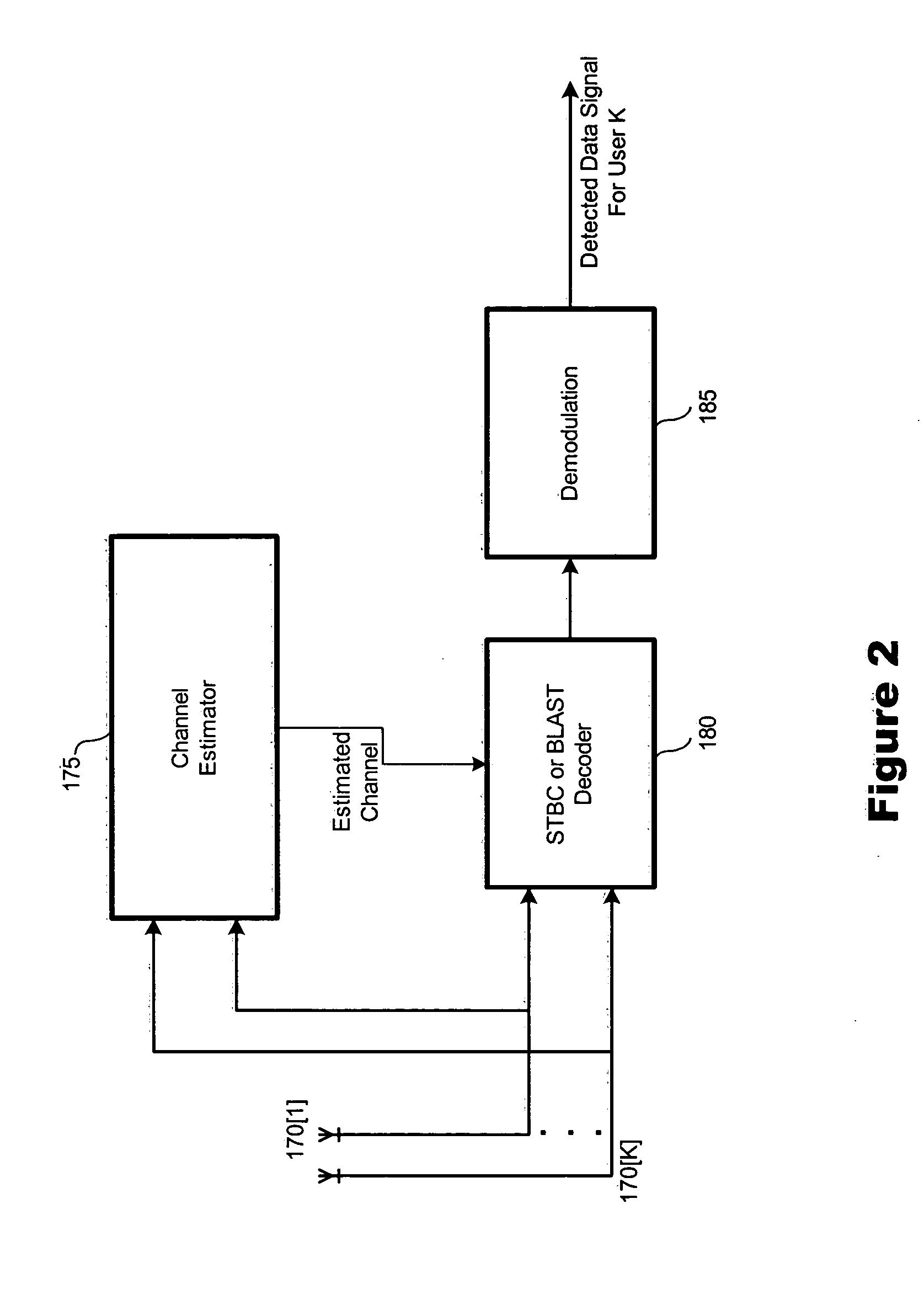
Scheduling method with tunable throughput maximization and fairness guarantees in resource allocation
ActiveUS20050130664A1Effectively fairnessEffectively throughputError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsHigh rateFlexible scheduling
A flexible scheduling method with tunable throughput maximization and fairness guarantees in resource allocation is required and suitable for high-rate packet data and other services. Our inventive method, named Alpha-Rule, employs a control variable α, that permits dynamic and / or real-time adjustment / tradeoff between aggregate throughput, per-user throughput, and per-user resource allocation. Our method advantageously operates in conjunction with Multiple-input Multiple-Output techniques such as Space-Time Block Coding (STBC), Bell Labs Layered Space-Time (BLAST) and others, while offering greater flexibility than existing scheduling techniques, e.g., max-C / I or Proportionally Fair (PF).
Owner:NEC CORP
Throughput-based rate adaptation for wireless transmissions
ActiveUS20100034106A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRate adaptationWireless transmission
A system and method of throughput-based transmission rate adaptation for wireless transmissions is provided. An adapted transmission rate is determined based on transmission feedback from previous wireless frame transmissions. The adapted transmission rate is determined by comparing nominal throughputs derived from packet success rate (PSR) estimates at the current rate and other rates, such that the adapted transmission rate chosen is one that maximizes the nominal throughput. The PSR estimates can include those associated with the current rate, a fallback rate, and other rates. The PSR estimates are updated after each frame transmission. The PSR estimates can be saved and used for calculating future estimates, and they can also be time-stamped so as not to use them if they are older than a predetermined age.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
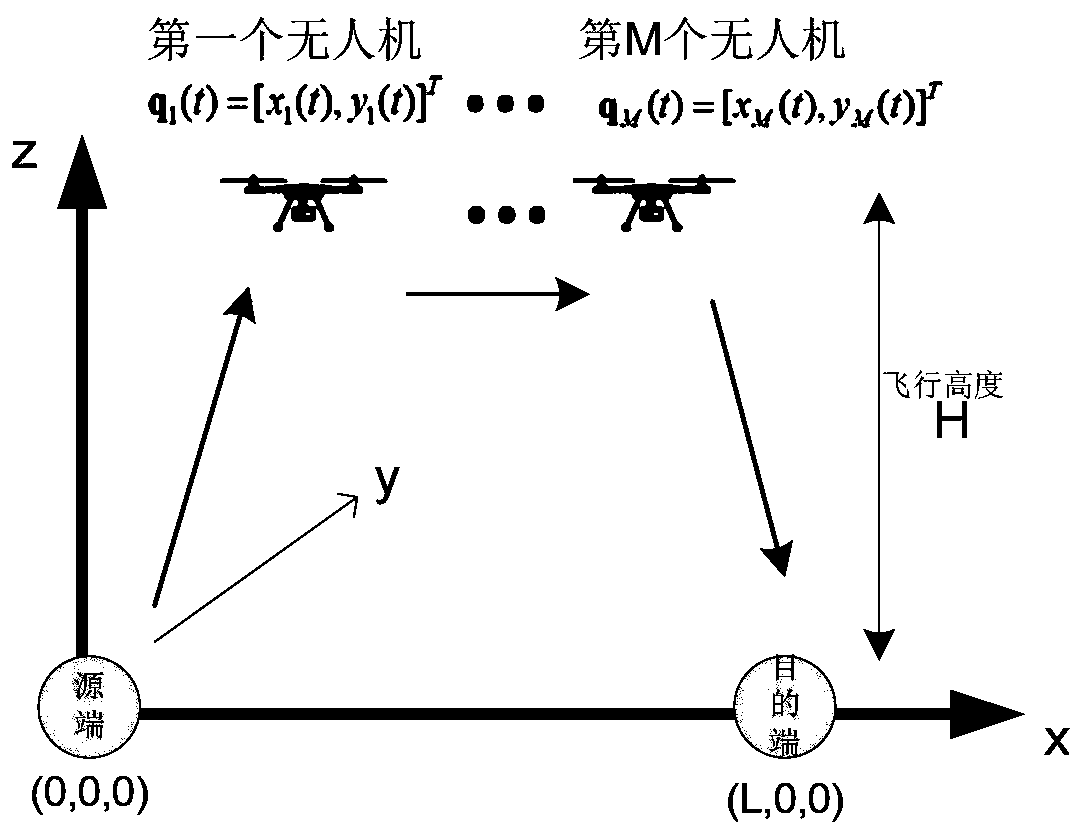
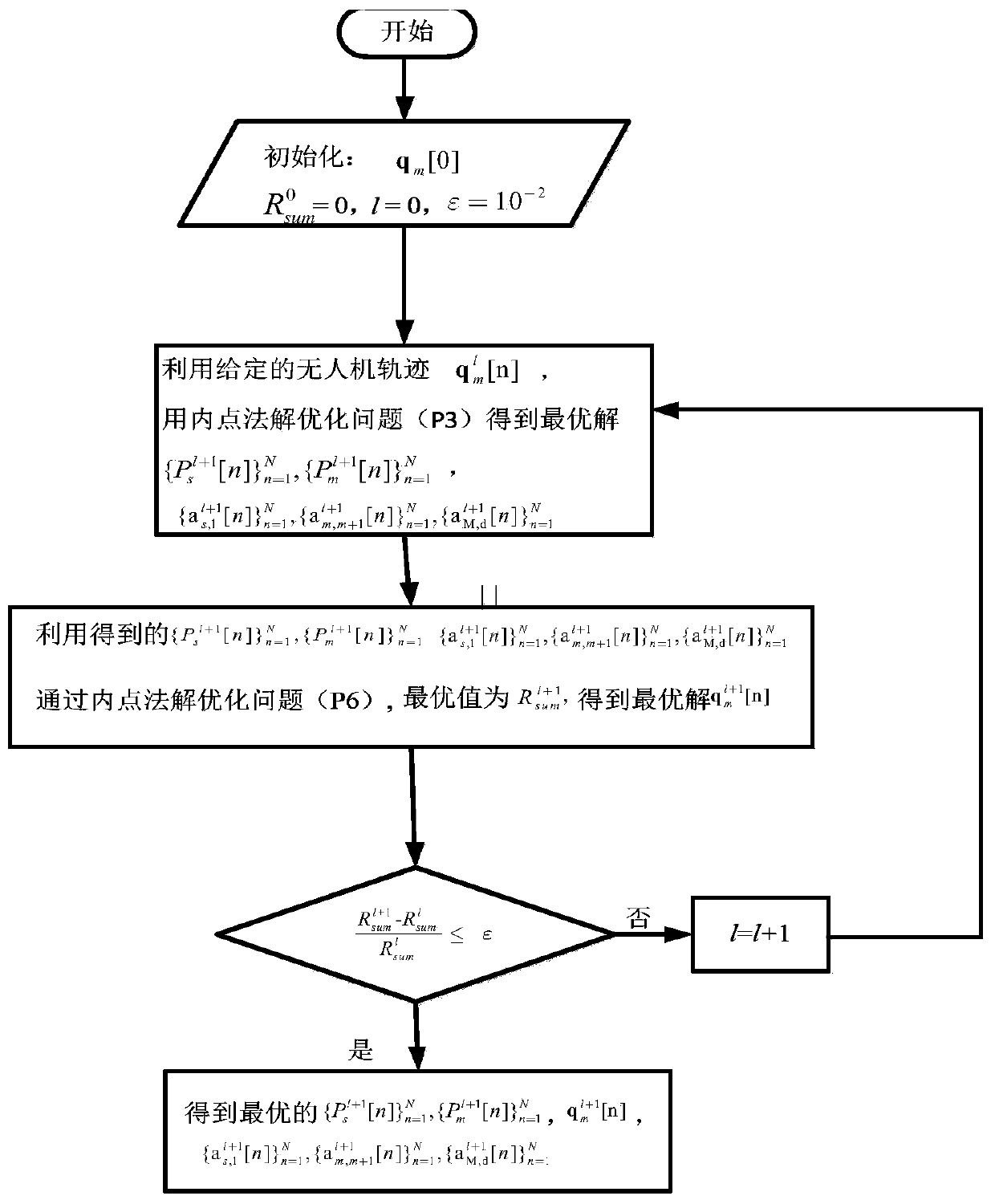
Trajectory optimization and resource allocation method of unmanned aerial vehicle multi-hop relay communication system
ActiveCN110380773AEasy to useImprove throughputRadio transmissionData switching networksCommunications systemMulti hop relay
The invention relates to a trajectory optimization and resource allocation method of an unmanned aerial vehicle multi-hop relay communication system. The method comprises the following steps: S1, modeling a trajectory optimization and resource allocation problem based on the unmanned aerial vehicle multi-hop relay communication system; S2, calculating the maximum system throughput by allocating power and bandwidth under the condition of giving an unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory; S3, under the condition of given unmanned aerial vehicle power and bandwidth allocation, optimizing the trajectory by using continuous convex programming; and S4, maximizing the throughput of the system by adopting a joint optimization unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory and source / unmanned aerial vehicle transmitting power and bandwidth allocation alternating optimization algorithm. According to the method, the multiple unmanned aerial vehicles are used as the multi-hop relay to assist the communication, thethroughput of the system is maximized by jointly optimizing flight paths, bandwidths and power of the multiple unmanned aerial vehicles, and the throughput of the system can be improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
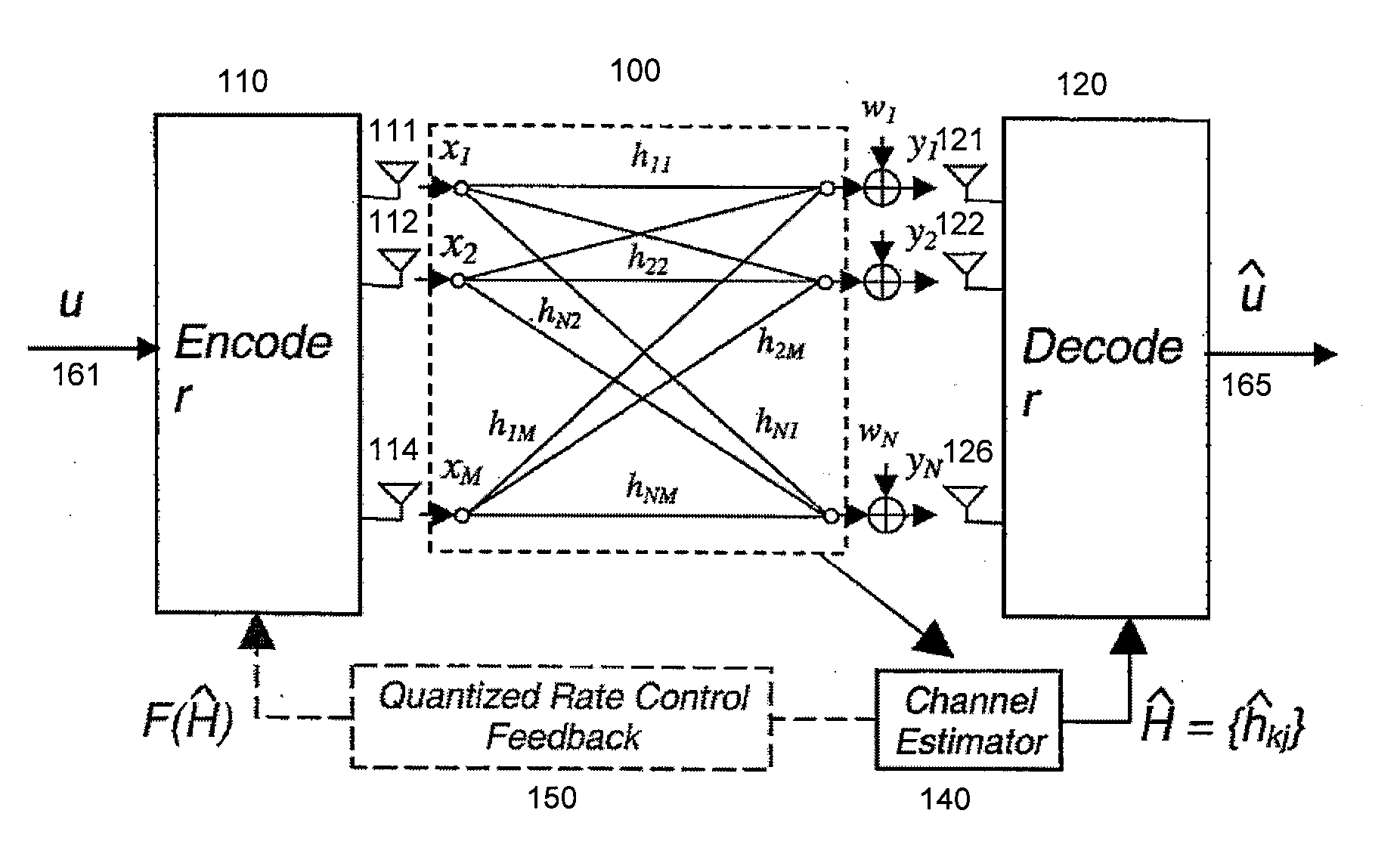
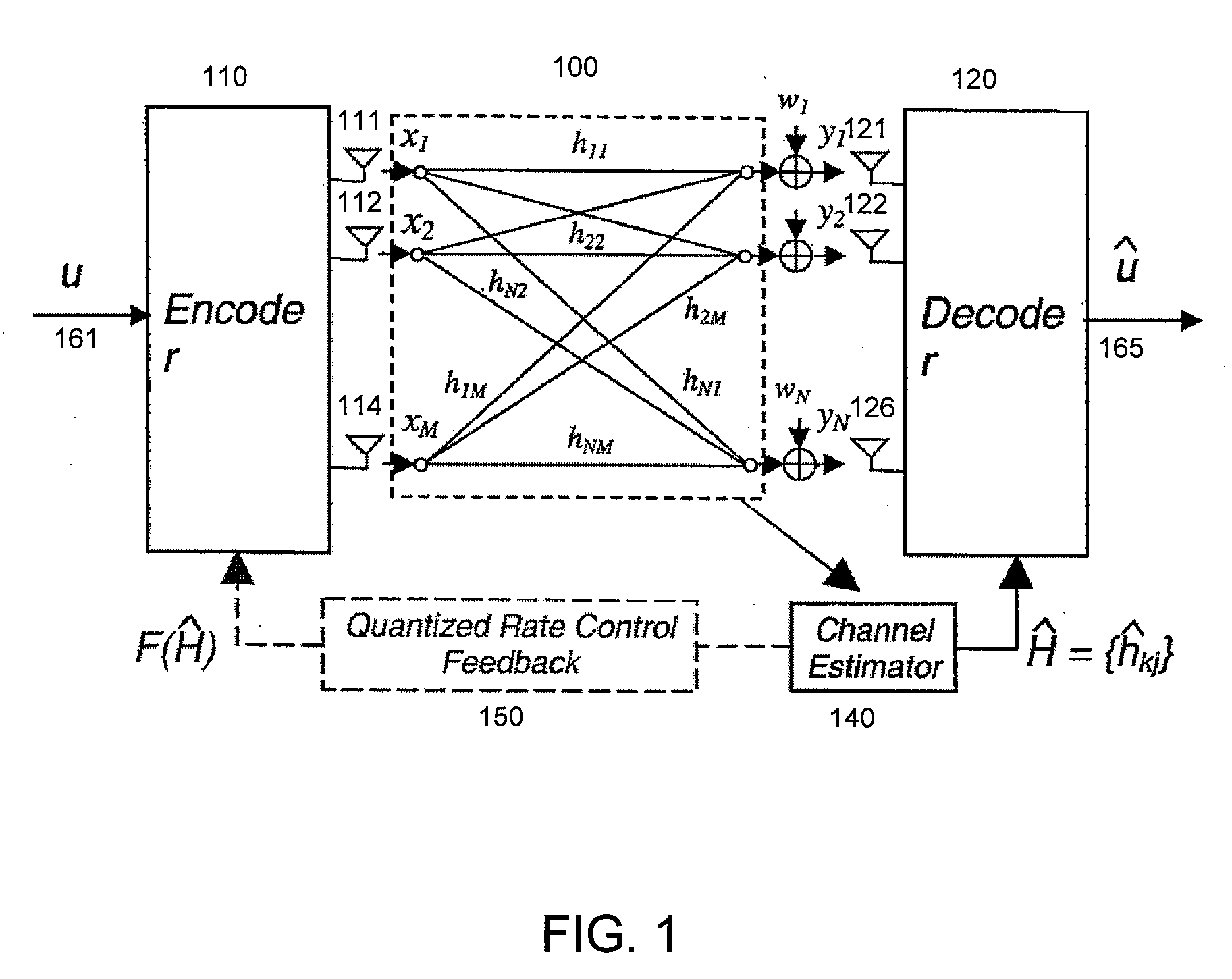
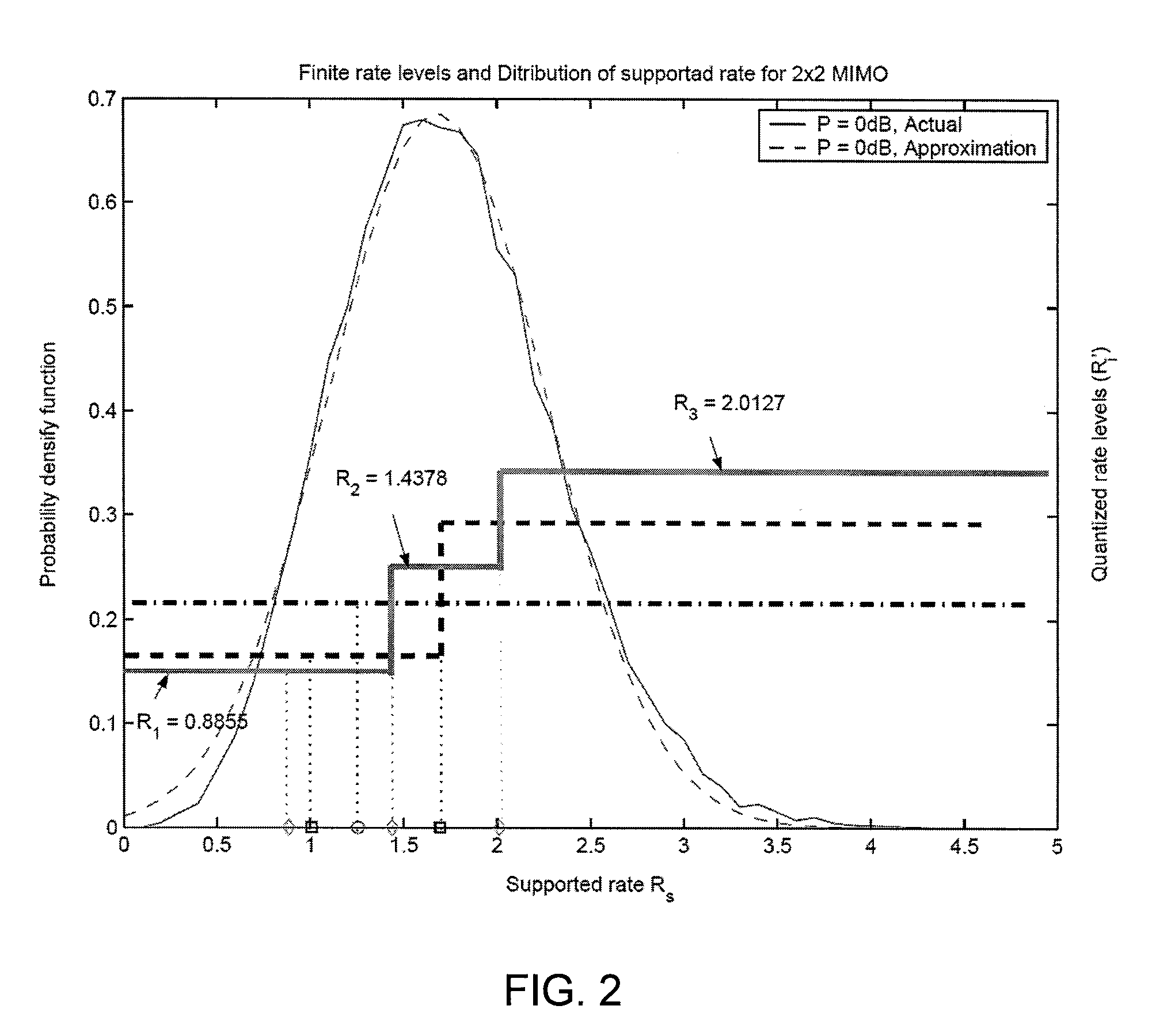
Throughput Maximization Using Quantized Rate Control in Multiple Antenna Communication
InactiveUS20060276217A1Improve system throughput performanceEfficiently findPower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemEngineering
A feedback link between a receiver and a transmitter in a multiple antenna communication system is used to control the transmission rate and thereby improve system throughput performance.
Owner:NEC CORP
Fast transmission method of internet larger file
InactiveCN101616077AFlexible use of reliabilityFlexible use of speedData switching networksTraffic capacityTransfer procedure
The invention relates to the technical field of network communication, in particular to a fast transmission method of an internet larger file. In the invention, a server is connected with a client by TCP protocol, the transmission of the larger data file is carried out by UDP protocol, during transmission, network flow and congestion control mechanism are adopted to self-adaptively adjust the magnitude of data blocks and the transmission intervals among the data blocks so as to realize the maximization of throughput during transmission, and finally lost packet re-transmission mechanism is adopted to re-transmit the data packets lost during transmission. The invention has the characteristics of reliability of flexible use of TCP protocol and fastness of UDP protocol, and obvious enhancement of transmission speed of the large file in case of limit bandwidth.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Computer system management and throughput maximization in the presence of power constraints
InactiveUS20080109811A1Control power consumptionMinimal degradationEnergy efficient ICTResource allocationComputer architectureComputation complexity
Methods are provided for maximizing the throughput of a computer system in the presence of one or more power constraints. Throughput is maximized by repeatedly or continuously optimizing task scheduling and assignment for each of a plurality of components of a computer system. The components include a plurality of central processing units (CPUs) each operating at a corresponding operating frequency. The components also include a plurality of disk drives. The corresponding operating frequencies of one or more CPUs of the plurality of CPUs are adjusted to maximize computer system throughput under one or more power constraints. Optimizing task scheduling and assignment, as well as adjusting the corresponding operating frequencies of one or more CPUs, are performed by solving a mathematical optimization problem using a first methodology over a first time interval and a second methodology over a second time interval longer than the first time interval. The first methodology comprises a short term heuristic solver for adapting to computer system changes that occur on a short time scale, and the second methodology comprises a long term solver having greater accuracy and greater computational complexity than the first methodology.
Owner:IBM CORP
Joint scheduling and grouping for sdma systems
InactiveUS20070105595A1Reduce complexityMinimize complexitySpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentChannel state informationRound complexity
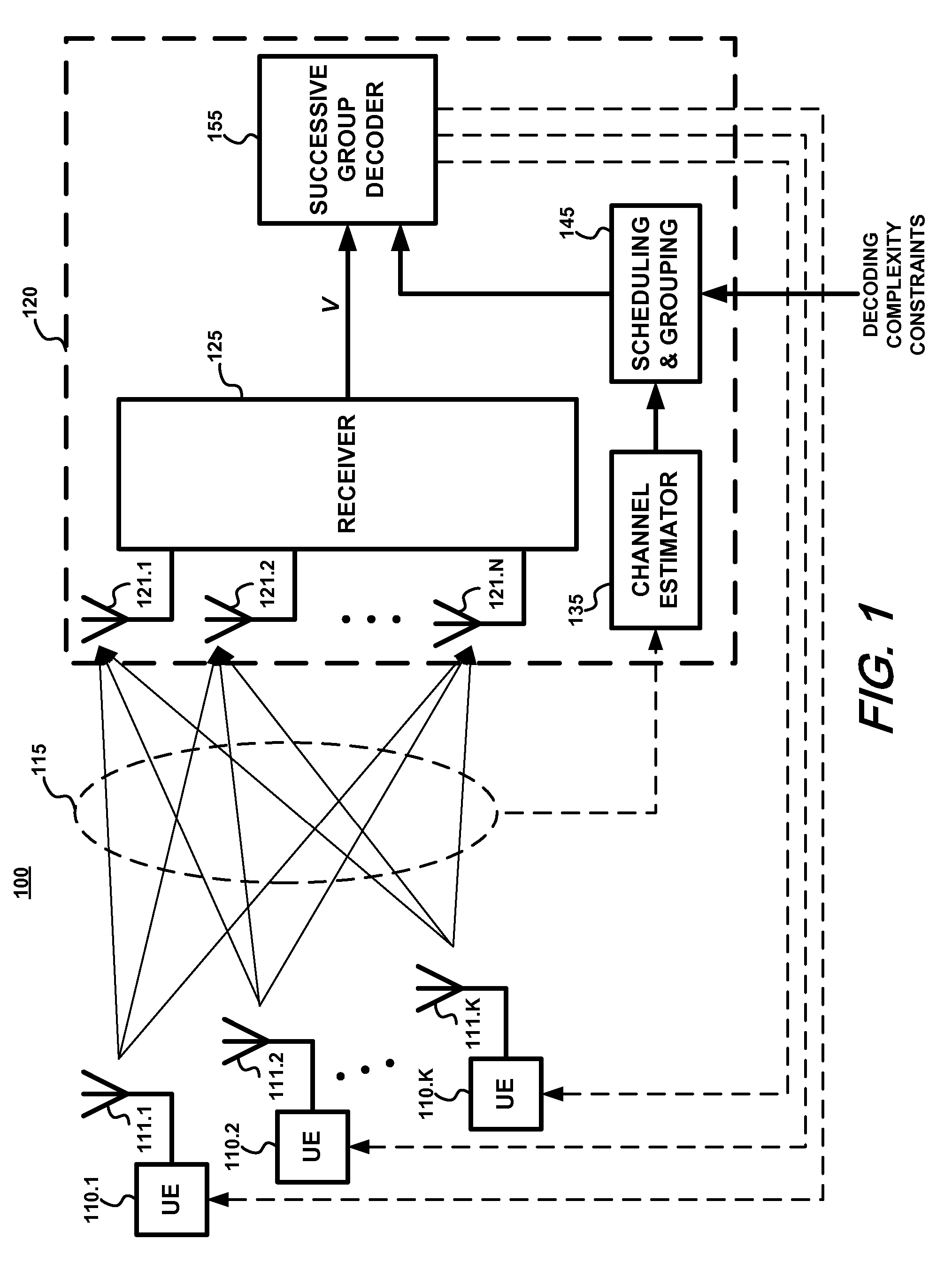
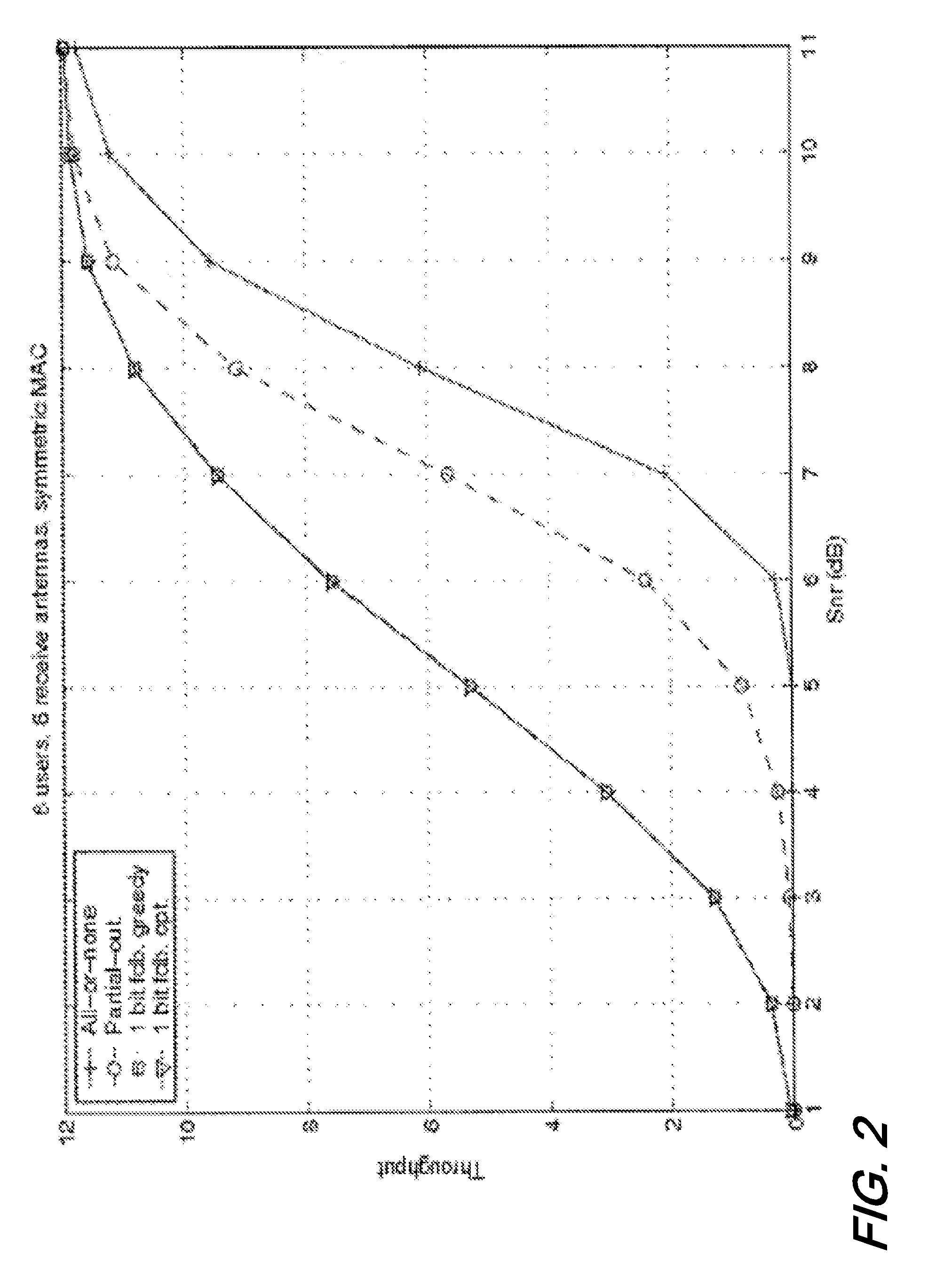
A joint scheduling and grouping technique for throughput maximization is disclosed for an uplink space-division multiple access (SDMA) system under proportional fairness constraints, when the receiver employs successive group decoding. We consider a slow-fading narrowband MIMO multiple access channel (MAC) in which multiple users, each equipped with multiple transmit antennas, communicate to a receiver equipped with multiple receive antennas. The users are unaware of the channel state information (CSI) whereas the receiver has perfect CSI and employs a successive group decoder (SGD). For an open-loop system, achievable outage probabilities are obtained for the case where an outage must be declared simultaneously for all users (common outage) as well as the case where outages can be declared individually for each user (individual outage). We then derive the optimum successive group decoder (OSGD) that simultaneously minimizes the common outage probability and the individual outage probability of each user, over all SGDs of permissible decoding complexity. For each channel realization, the OSGD is also shown to maximize the error exponent of the decodable set of users. An adaptive SGD is derived which not only retains the outage optimality of the OSGD but also minimizes the expected decoding complexity. Asymptotically tight (in the limit of high SNR) affine approximations are then obtained for the weighted sum common and individual outage capacities and the symmetric outage capacities. Limiting expressions for the relevant capacities as the number of users and the number of receive antennas approach infinity are also obtained and it is shown that the SGD yields symmetric capacity gains commensurate with the decoding complexity allowed. Simulation results with practical LDPC outer codes show that the OSGD offers significantly improved performance at low decoding complexity.
Owner:NEC CORP
System and method for combining relay selection and power distribution
InactiveCN102223644AImprove throughputPower managementNetwork planningMulti hop relayTransmitted power
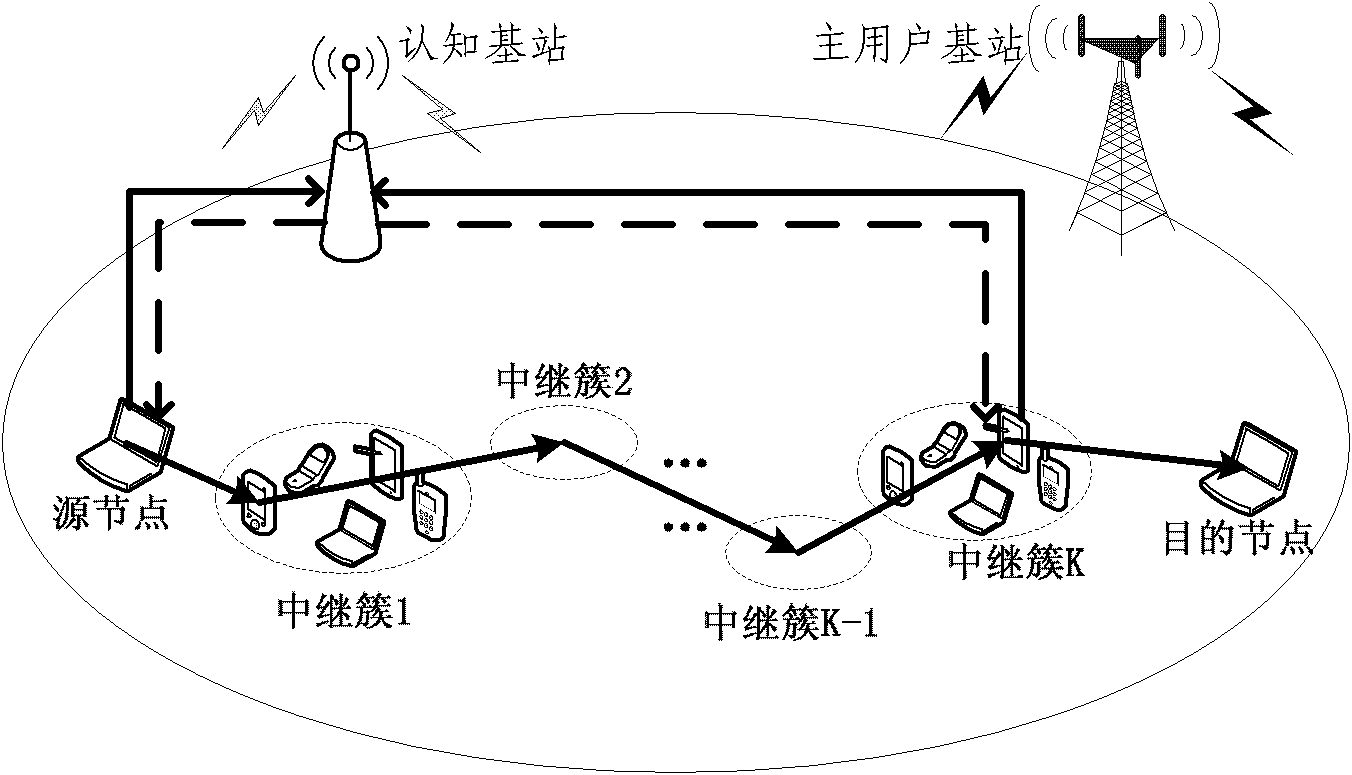
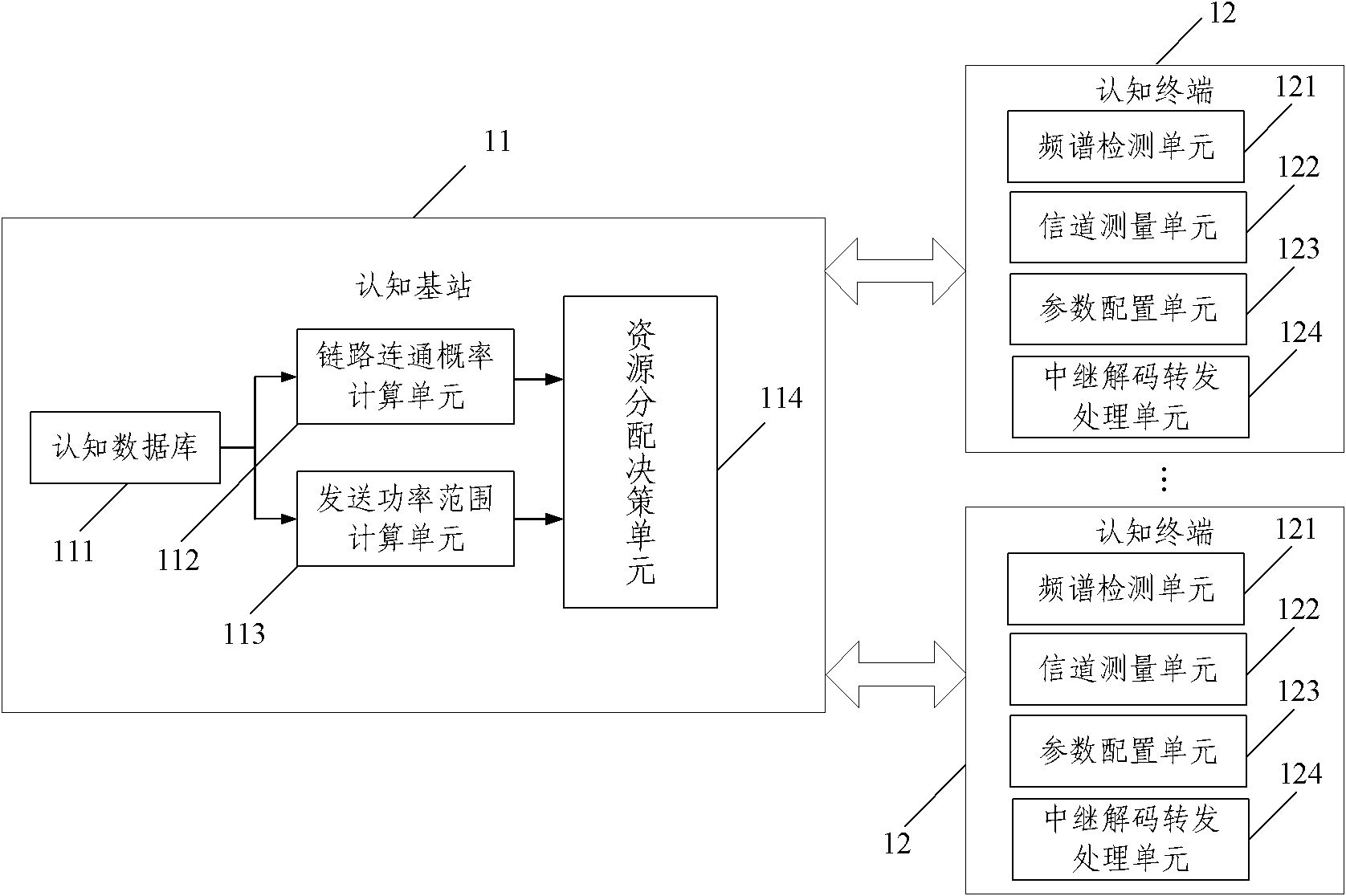
The invention relates to the technical filed of wireless communication, and provides a system and method for combining relay selection and power distribution, and is used for solving the problem that the combined application of cognitive radio and wireless relay does not exist in the prior art. Through selecting optimal multi-hop relay links, and distributing proper transmitted power to each relay node, the throughput maximized target of the system is realized under the condition that the total transmitted power of the system does not exceed certain threshold value.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Link adaptation in wireless networks for throughput maximization under retransmissions
InactiveUS20050054296A1Maximize throughputEffective distributionLine-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude demodulation detailsWireless mesh networkWireless data
The present invention implements a method and system for dynamically adapting the modulation and coding scheme for radio links in a wireless communications network based on a retransmission environment model in order to maximize throughput and most efficiently allocate bandwidth resources. The present invention encompasses a refined calculus and methodology for deriving the link adaptation thresholds in a retransmission environment using a complex model and analysis of the retransmission environment. The present invention holds particular application for wireless data communications as opposed to real time data services because it is based on a retransmission model applicable primarily for data services. A critical component of this new link adaptation system is a “no transmission” cutoff mode that is selected for SIR below a base threshold value. This new mode prevents system instability and misallocation of bandwidth in a wireless communication system.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method and system for sharing and using frequency spectrum resources
The invention discloses a method and a system for sharing and using frequency spectrum resources. The method and the system solve the technical problems that frequency spectrum resources of other radio communication technologies cannot be shared and used in an existing radio communication system and utilization rate of the frequency spectrum resources is low. By utilizing frequency spectrum of other systems in a gathering manner, an LTE (long term evolution) system can carry out data transmission by means of frequency spectrum resources which are not used in the LTE system originally, and especially for two operating modes in the LTE system, the frequency band of the TDD (time division duplex) can be sufficiently used in the FDD (frequency division duplex) network of the LTE system. By the aid of the method and the system for sharing and using frequency spectrum resources, frequency spectrum resources can be utilized sufficiently, and throughput of the LTE system can be maximized as far as possible.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Spectral efficiency estimation in coherent receivers
ActiveUS8285148B2Maximize throughputTransmission monitoringElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency spectrumSpectral density estimation
The present invention relates to optical transmission systems. In particular, the present invention relates to a method and system for estimating the spectral efficiency which may be achievable in an optical transmission network and for adapting the parameters of the transmission network to the achievable spectral efficiency. A method and system for controlling an optical transmission system comprising a first and a second optical transmission channel is described. The first optical transmission channel is affected by the second optical transmission channel. The method comprises the steps of measuring the inverse signal-to-noise ratio of the first channel for a plurality of input power levels used by the first and second channel; determining a contribution of the second channel to the inverse signal-to-noise ratio; and determining the input power to the second channel, such that an overall throughput of the first and second channel is maximized.
Owner:RPX CORP
Scheduling method with tunable throughput maximization and fairness guarantees in resource allocation
ActiveUS7230991B2Effectively fairnessEffectively throughputError preventionTransmission systemsHigh rateFlexible scheduling
A flexible scheduling method with tunable throughput maximization and fairness guarantees in resource allocation is required and suitable for high-rate packet data and other services. Our inventive method, named Alpha-Rule, employs a control variable α, that permits dynamic and / or real-time adjustment / tradeoff between aggregate throughput, per-user throughput, and per-user resource allocation. Our method advantageously operates in conjunction with Multiple-Input Multiple-Output techniques such as Space-Time Block Coding (STBC), Bell Labs Layered Space-Time (BLAST) and others, while offering greater flexibility than existing scheduling techniques, e.g., max-C / I or Proportionally Fair (PF).
Owner:NEC CORP
Dynamic reuse partitioning and subchannel allocation scheme in multicell OFDMA downlink systems
InactiveUS20070077934A1Less amount of communication overheadLess computing powerRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork planningRadio networksComputation complexity
The reuse partitioning problem for a cellular orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) system with dynamic subcarrier allocation is considered. One objective is to allocate the network resources in an efficient way in order to maximize the system's total throughput under individual user's quality-of-service (QoS) constraint. A suboptimal two-step approach is used where the radio network controller (RNC) solves the network planning problem and each base station (BS) solves the cell throughput maximization problem. Compared with the optimal resource allocation scheme, the approach described herein has much lower computational complexity in the RNC. Moreover, the communication overhead between each BS and the RNC is reduced substantially which renders our approach more practical for delay sensitive applications. Throughput increase is demonstrated
Owner:SIEMENS CORP RES INC
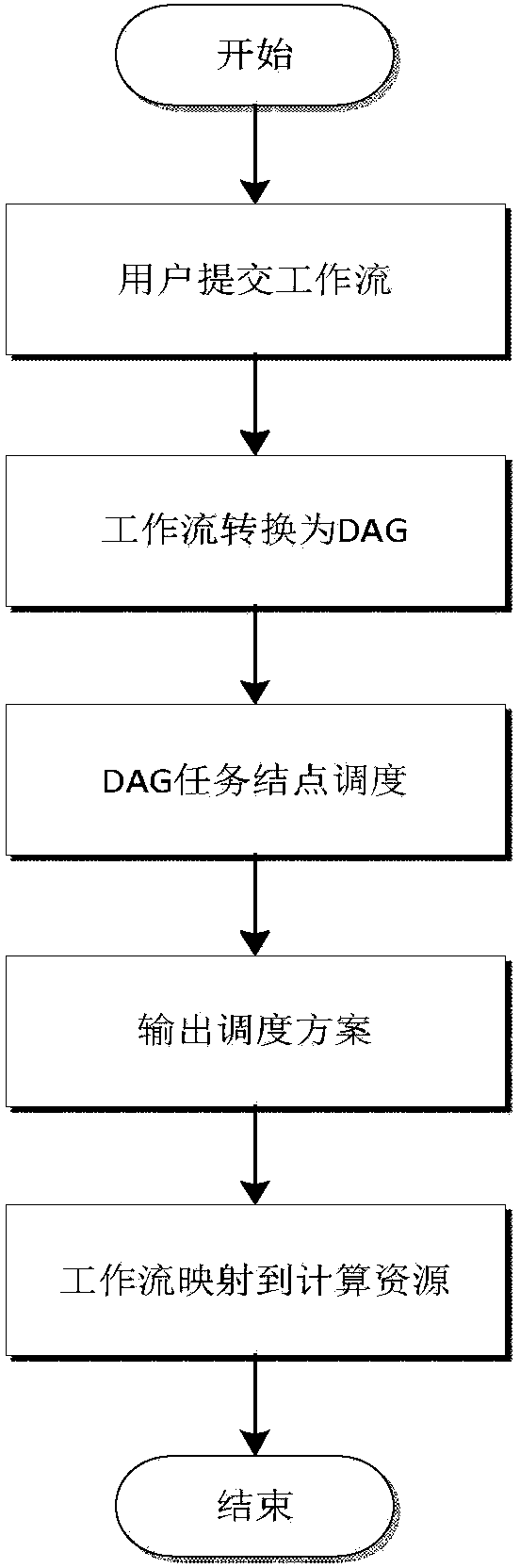
Workflow dispatching method based on workflow throughput maximization
ActiveCN103838627AIncrease flexibilityImprove experienceResource allocationTime limitSoftware engineering
The invention relates to a workflow dispatching method based on workflow throughput maximization. The workflow dispatching method comprises the steps that a user submits a workflow with executing deadline restraint; the workflow is converted into a DAG; DAG task nodes are dispatched; a workflow output maximization dispatching scheme is output and returned to the user; the workflow submitted by the user is mapped to a specific calculating resource to be executed, and then workflow dispatching is finished. According to the workflow dispatching method, dispatching of a plurality of workflows on isomerism distribution type calculating resources is taken into consideration, the workflows are finished as much as possible, the calculating resources are utilized as much as possible, the defect that according to an existing EDF method, the dispatching sequence cannot be determined according to different characteristics of the DAG is overcome, the efficiency of a workflow dispatching system is greatly improved, the loss caused by the fact that calculation is not finished within the regulated time is reduced, and the user experience of the system is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Transmission mode adaptation in a wireless network
InactiveUS20130028309A1Good choiceChoose accuratelyError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorRadio transmissionTransfer modeAntenna gain
Conventional mode adaptation does not account for the gain imbalance between channels for measurement and for data reception. Therefore, the precoder, which is selected based on the measurement channel, may not be the optimal precoder for the data reception channel. By maintaining relative SINR ordering between transmission modes, a receiver may select the transmission mode for a transmitter that maximizes the actual throughput even in the presence of inter-antenna gain increase or decrease.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Mobile communication apparatus including transceiving multi-antennas and mobile communication method
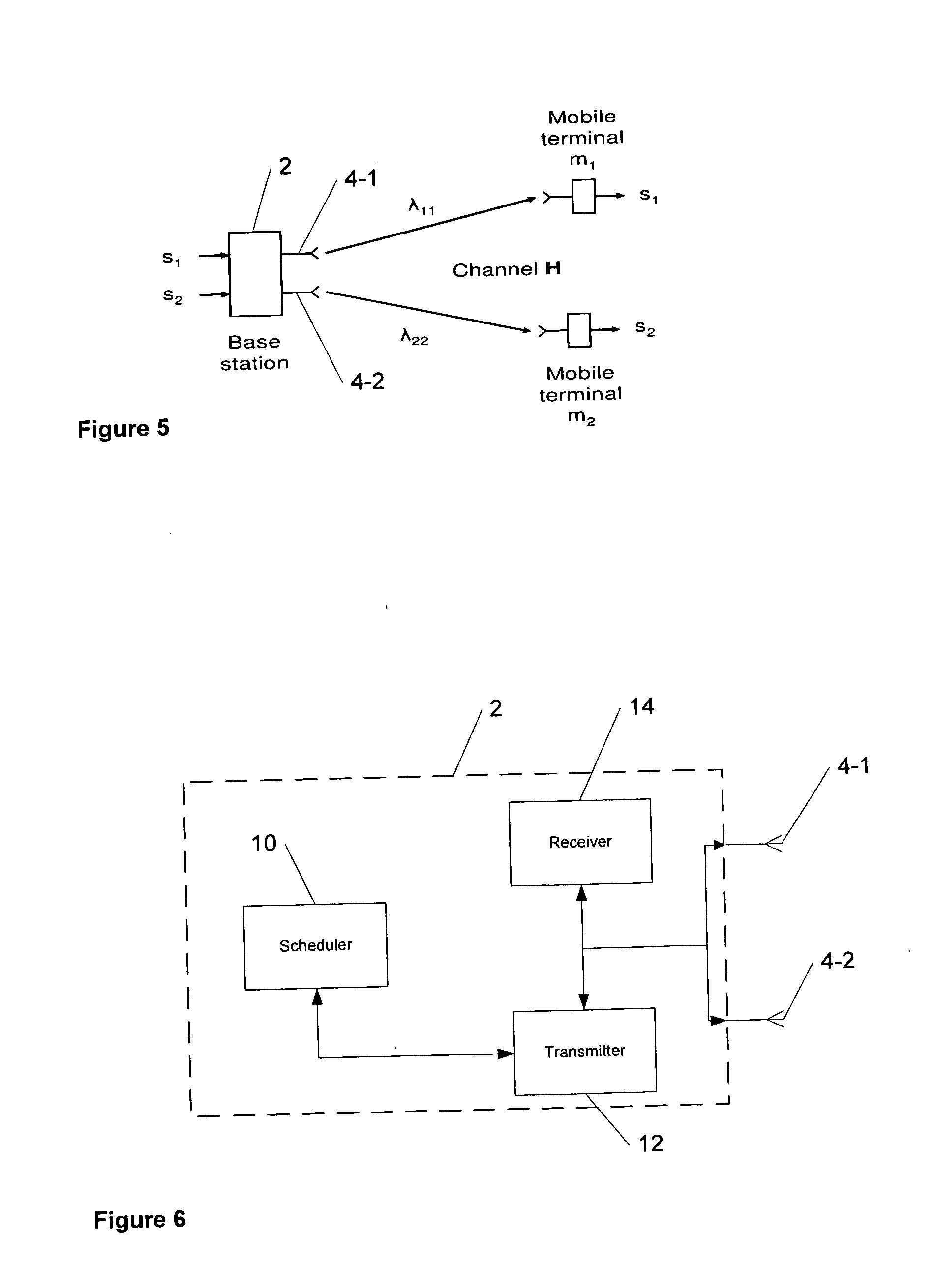
ActiveUS7050776B2Minimize impactMaximize throughputPower managementSpatial transmit diversityMobile stationShort terms
A mobile communication apparatus having multiple transmission antennas and multiple reception antennas and a mobile communication method used in the mobile communication apparatus, wherein a base station, which has at least one reception antenna, restores long-term and short-term information determined in consideration of first characteristics in a mobile station, which has at least one transmission antenna, from a feedback signal received from the mobile station, spatially processes dedicated physical channel signals using basis information produced from the restored long-term and short-term information, and transmits the results of addition of the spatially-processed signals to pilot signals to the mobile station, wherein the first characteristics are the characteristics of the downlink channels of the respective transmission and reception antennas. Accordingly, the feedback of long-term and short-term information from the mobile station to the base station minimizes the effects of fading, interference, and noise and maximizing throughput.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Self-adaptive antenna mode control method and device thereof
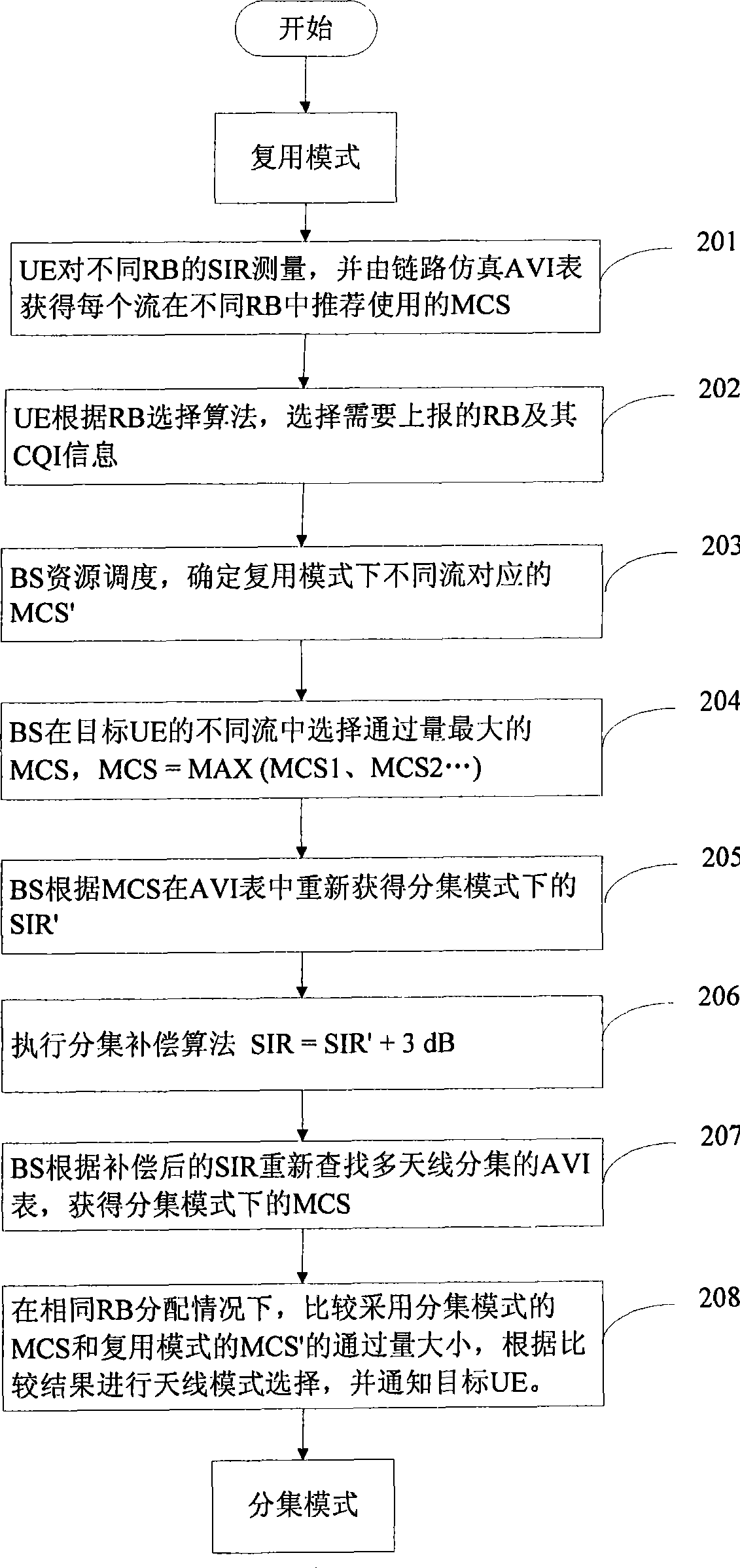
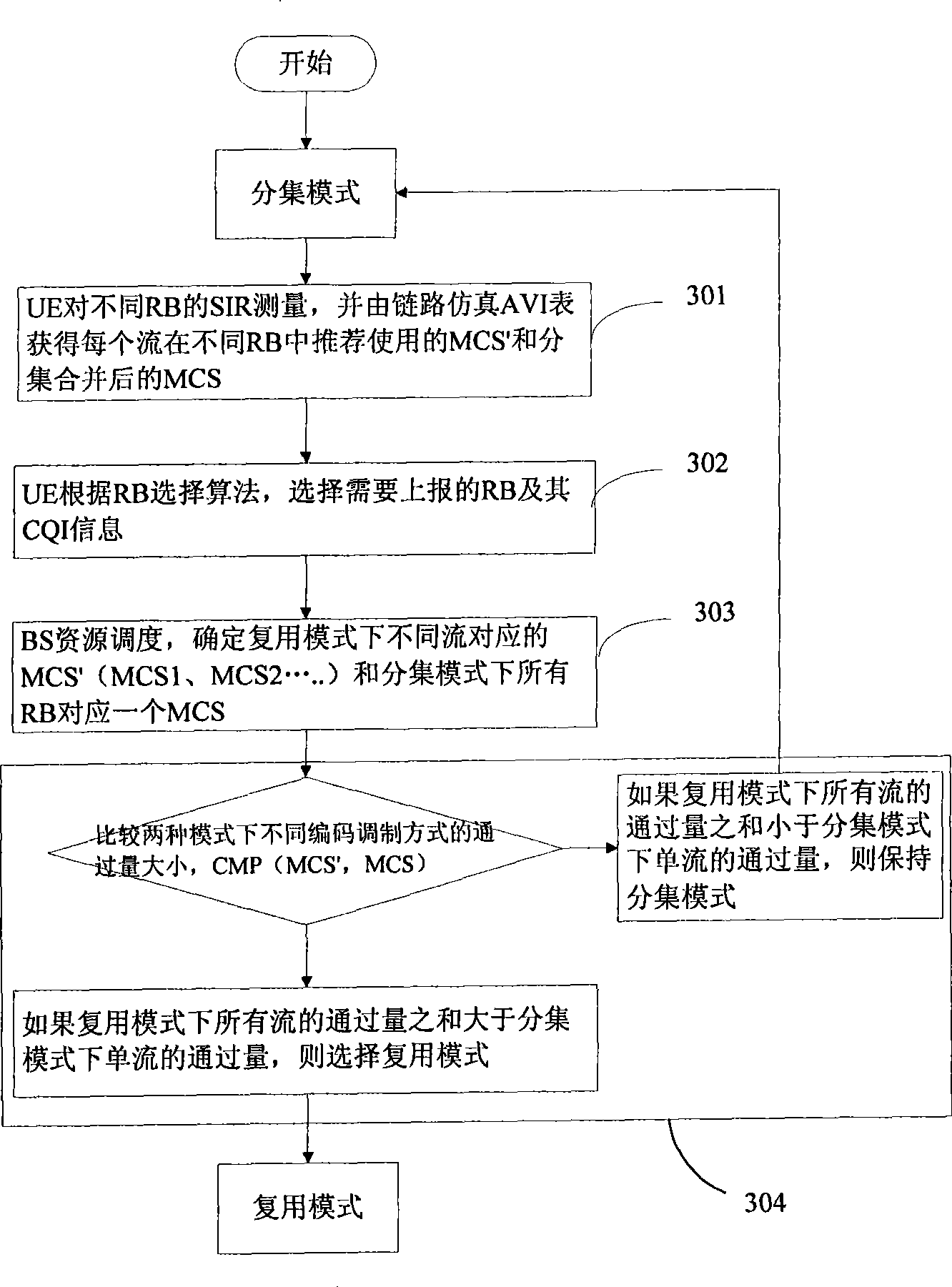
InactiveCN101534176ASolving the Adaptive Selection ProblemImprove system performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelMulti-frequency code systemsMode controlModulation coding
The invention provides a self-adaptive antenna mode control method and a device thereof. The method is characterized by comprising an external ring control process and an internal ring control process. The external ring control process comprises the steps of: setting an aggregate value threshold and a successive value threshold and judging whether the aggregate statistic value of confirmation or denial information is larger than the aggregate value threshold, if so, directly switching the antenna mode; if not, judging whether the successive statistic value of the confirmation or denial information is larger than the successive value threshold, if so, entering the internal ring control process, and if not, keeping the current antenna mode. The internal ring control process comprises the steps of: carrying out return treatment under a plurality of antennas according to channel quality instructions fed back by different user terminals and an interface table of link layer simulated true values, and determining the antenna mode and a code modulation mode selected by the target user terminal according to the rule of throughput maximization. The invention effectively solves self adaptiveselection problem of different antenna modes in an MIMO system and can obtain optimum system performance.
Owner:冯丽红
D2D communication throughput maximization method and device based on intelligent reflecting surface
PendingCN111954190AImprove throughputReduce distractionsSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringTelecommunications linkCommunications system
The invention relates to a D2D communication throughput maximization method and device based on an intelligent reflecting surface. A D2D communication system based on the intelligent reflecting surface comprises cell users, D2D communication pairs, a base station and an intelligent reflecting surface arranged in a cell, wherein the D2D communication pair comprises a D2D sending end and a D2D receiving end; the intelligent reflecting surface is provided with a plurality of reflecting elements, and a phase shift matrix is designed according to the precision and the number of the reflecting elements. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring cell user throughput and D2D communication link throughput; constructing a maximum throughput optimization model according to the cell user throughput and the D2D communication link throughput; and solving an optimal parameter of the maximum throughput optimization model. According to the invention, the intelligent reflecting surface is introduced into a D2D (Device to Device) communication system, and the beamforming of the base station, the power distribution of the base station and the D2D transmitting end and the phase shift matrix of the intelligent reflecting surface are optimized, so that the communication quality of cellular users is ensured while the throughput of D2D communication is maximized.
Owner:深圳恩步通信技术有限公司
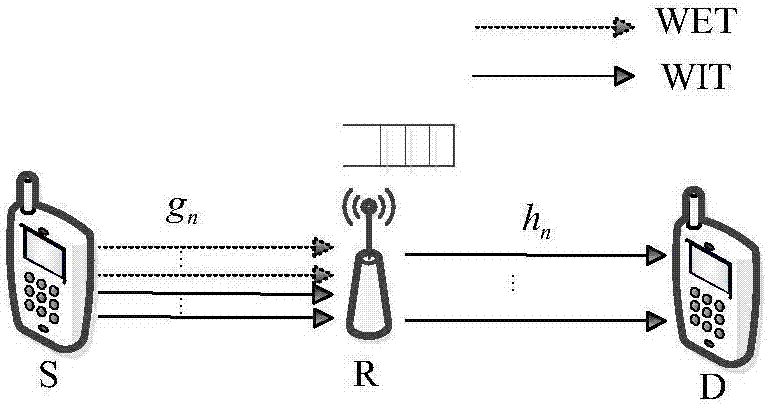
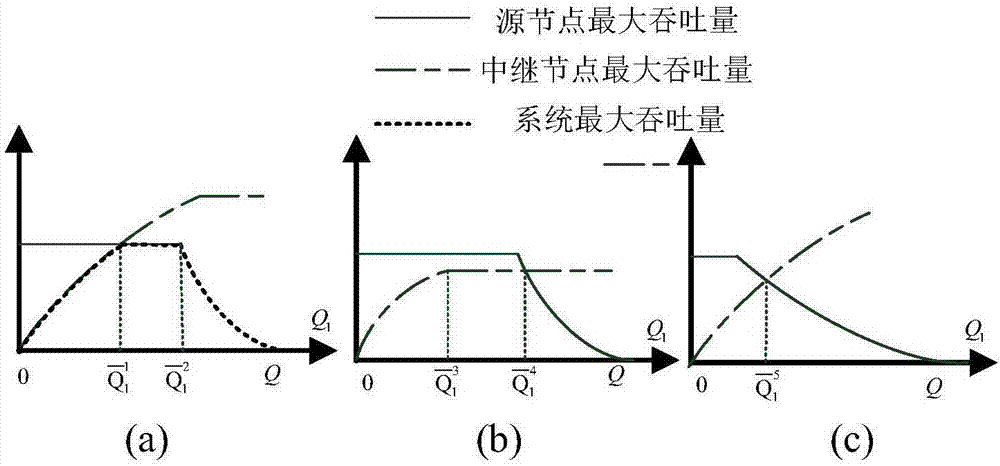
OFDM relay network resource allocating method based on the information-and-energy-simultaneous-wireless-transmission
ActiveCN106961322AThe method is close to realityIncrease coveragePower managementTransmission path divisionWireless transmissionCarrier signal
The invention discloses an OFDM relay network resource allocating method based on the information-and-energy-simultaneous-wireless-transmission. This method constructs an optimization model for the system throughput under the condition that the peak power of a source node is restricted, the peak power of each subcarrier is restricted and the energy causality of the relay node is restricted. In the case that the subcarrier allocation strategy of the source node is given, the optimal criteria for the original problem are sought. Then, through the arrangement of the general energy transmission power of the source node, the original problem is decoupled as two separate sub-problems of the maximization of the throughput, which reduces the complexity of the original problem for solutions considerably. The decoupled sub-problems are then solved according to a water injection manner. Finally, the invention provides four subcarrier allocation schemes, referred to as the energy optimizing scheme, the information optimizing scheme, the equilibrium allocation scheme and the exhaustion scheme with the first three schemes reducing the complexity of the sub-carrier allocation significantly.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
Frequency spectrum admission control method based on cooperative frequency spectrum sensing
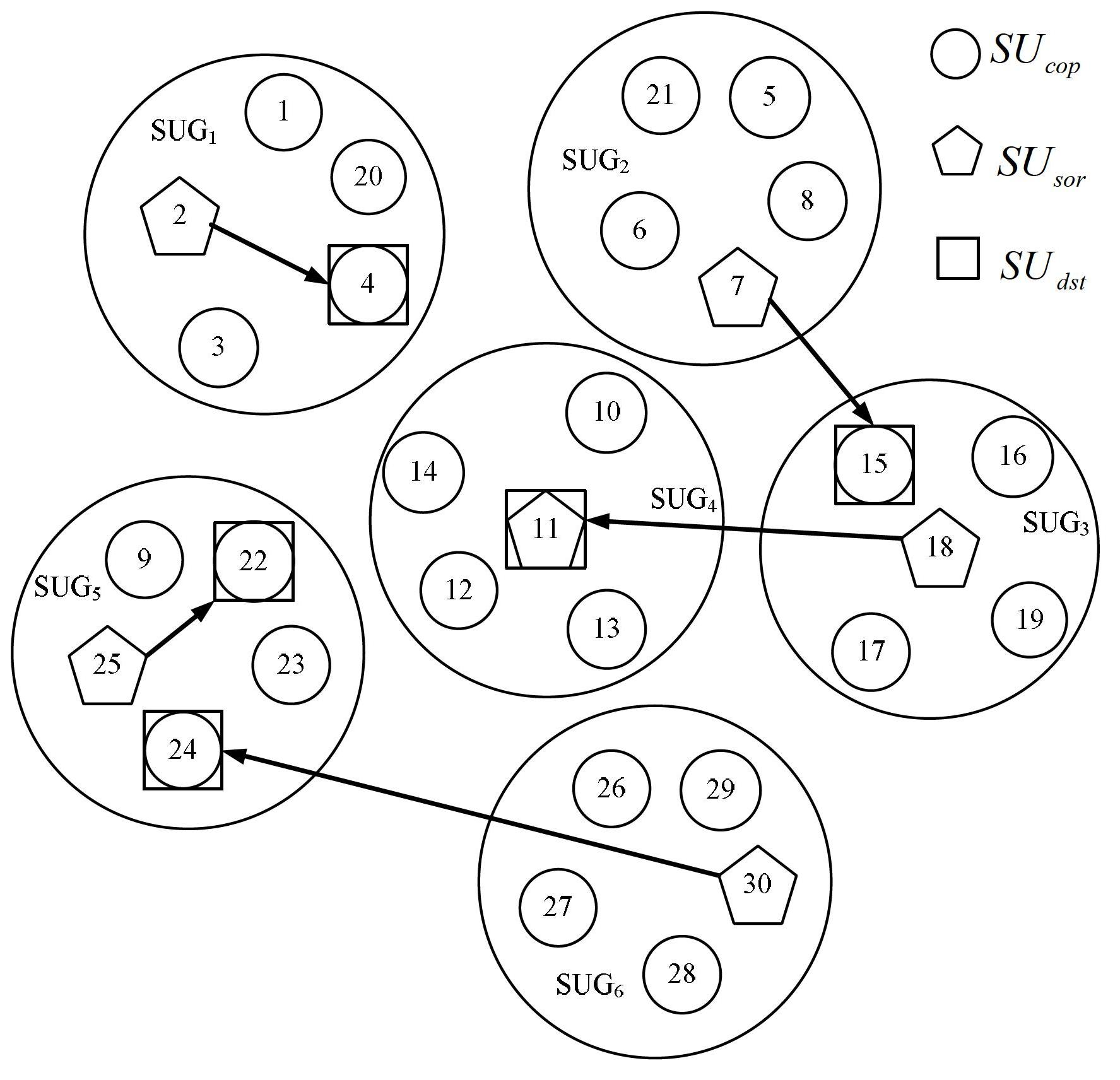
InactiveCN102685754AGuarantee service quality requirementsReduce the probability of forced interruptionNetwork planningFrequency spectrumSpectral efficiency
The invention provides a frequency spectrum admission control method based on cooperative frequency spectrum sensing. The method comprises the following steps: (1) through a cooperative scheme based on a secondary user group (SUG), self-adapting each secondary user SU to form SUGs; (2) for a cooperative sensing fusion strategy, carrying out calculation on a source node SUsor through a cooperative frequency spectrum sensing scheme so as to obtain an optimal value k under the situation of a given n value; and (3) for an acceptance control threshold of a cognitive radio network, analyzing an optimal acceptance control threshold, which can maximize throughput of the SUGs under the restriction condition of global false alarm probability, through a frequency spectrum acceptance control scheme based on cooperative sensing; and through solving of the optimal acceptance control threshold, finishing the whole optimizing process. According to the invention, the frequency spectrum frequency of the network is very well improved and the throughput of the SUGs can be also effectively increased; and the frequency spectrum acceptance control method based on cooperative frequency spectrum sensing, provided by the invention, is applicable to frequency spectrum access and frequency spectrum switching strategies in the cognitive radio network as well as corresponding performance analysis.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Throughput-maximized cognitive radio system
InactiveCN101800623AEfficient use ofImprove throughputError preventionData switching networksData terminalFrequency spectrum
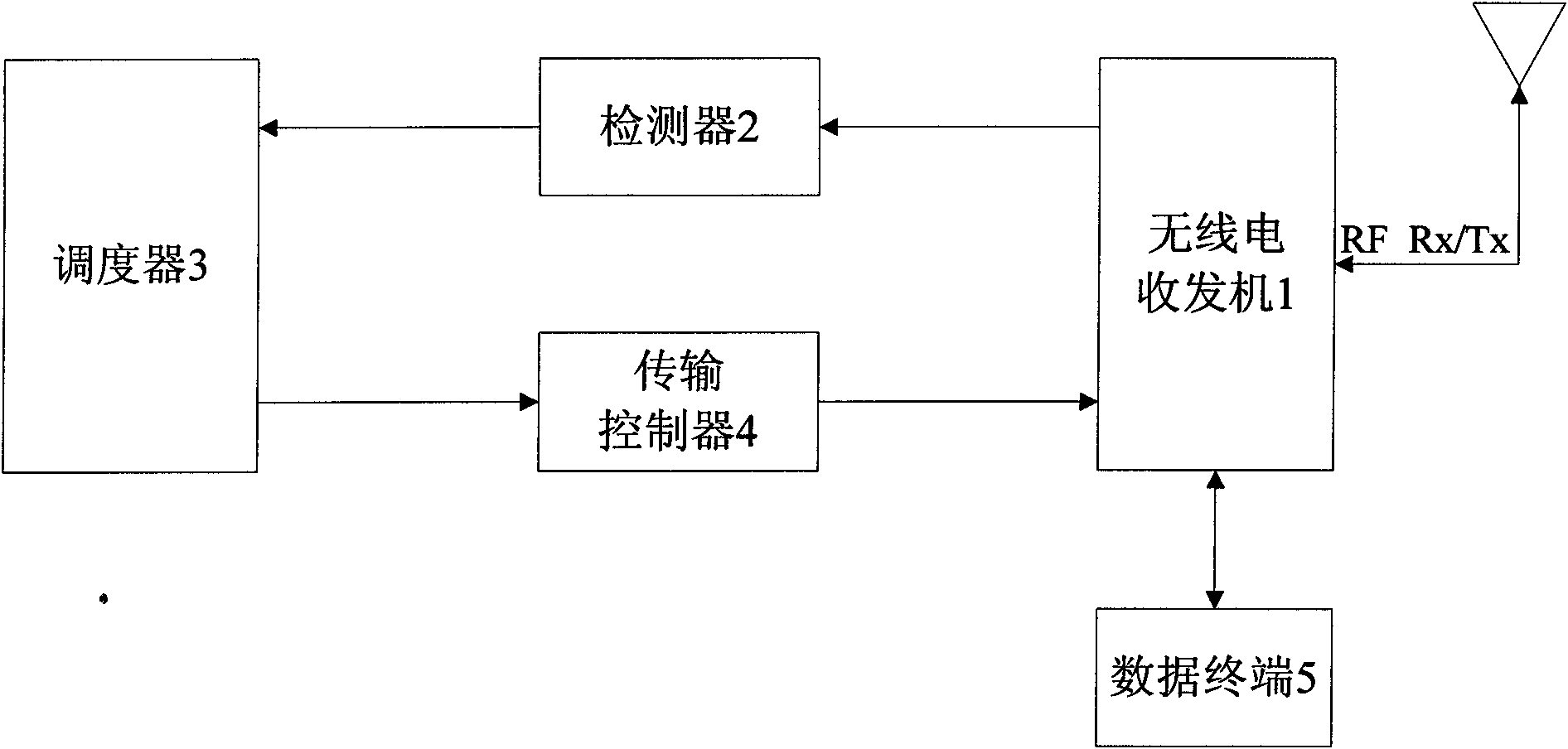
The invention belongs to the radio communication field, and relates to a throughput-maximized cognitive radio system which aims at enabling secondary users to maximize the radio frequency spectrum not made full use by major users and simultaneously effectively controlling the interference on the major users by the secondary users. The invention uses the collision probability as the measure gauge and control target of the interference on the major users by the secondary users. The system comprises a radio transceiver, a detector, a dispatcher, a transmission controller and a data terminal. By optimally dispatching the secondary-user transmission probability on each transmission sub-time slot in each frequency spectrum idle area, the system maximizes the secondary-user throughput on a single channel and simultaneously limits the collision probability of the major-user data packets within the range of a preset threshold. The system acquires the major-user channel occupying characteristic in a prediction mode, and simultaneously, the performance of the system can be optimized for any secondary-user time slot length.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com