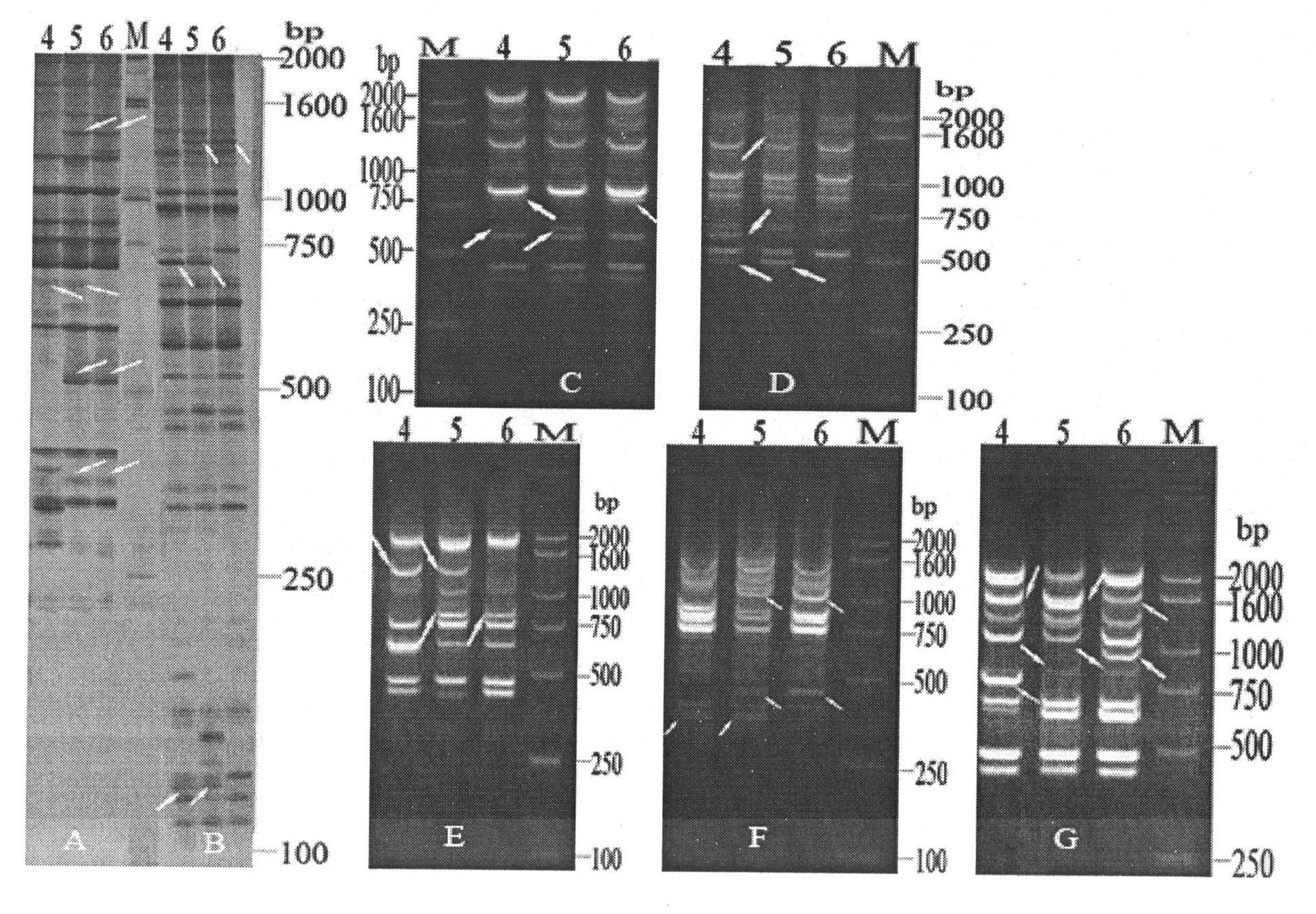
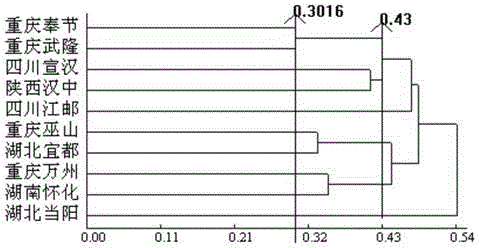
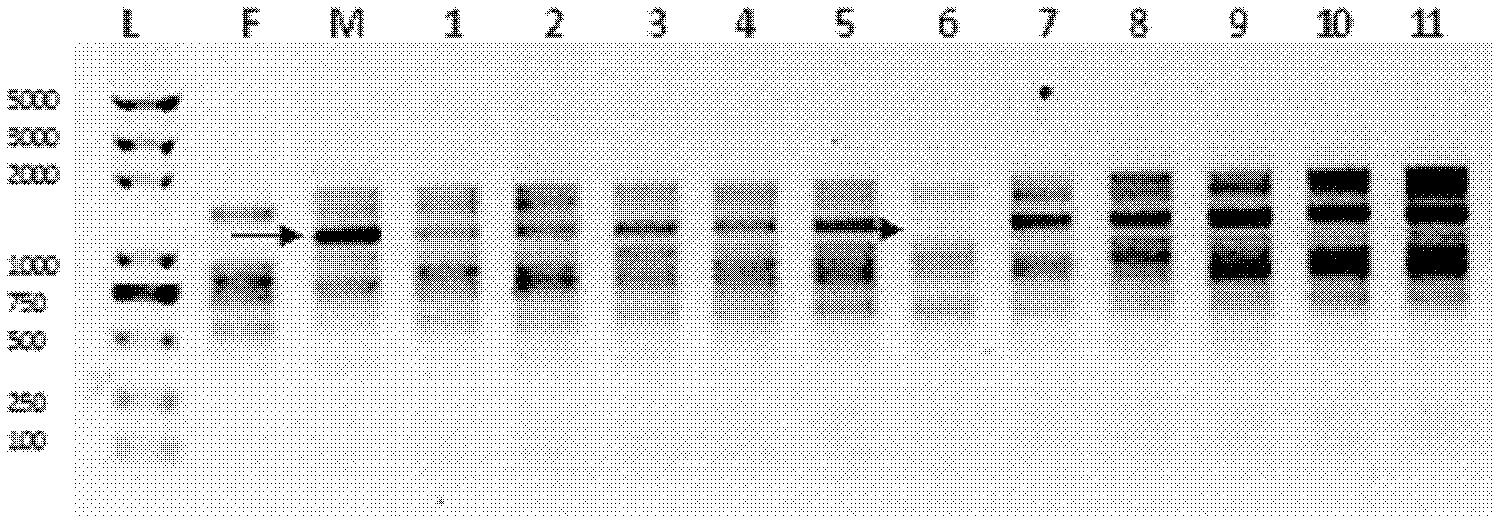
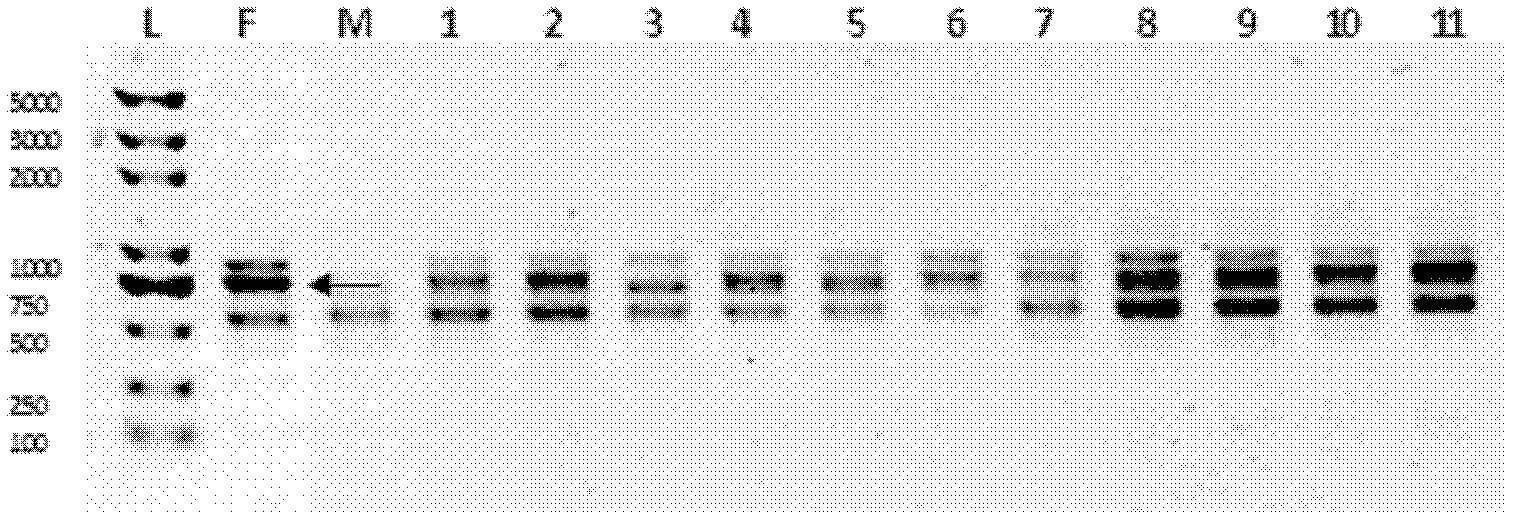Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Sequence-related amplified polymorphism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A sequence related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) is a molecular technique, developed by G. Li and C. F. Quiros in 2001, for detecting genetic variation in the open reading frames (ORFs) of genomes of plants and related organisms.
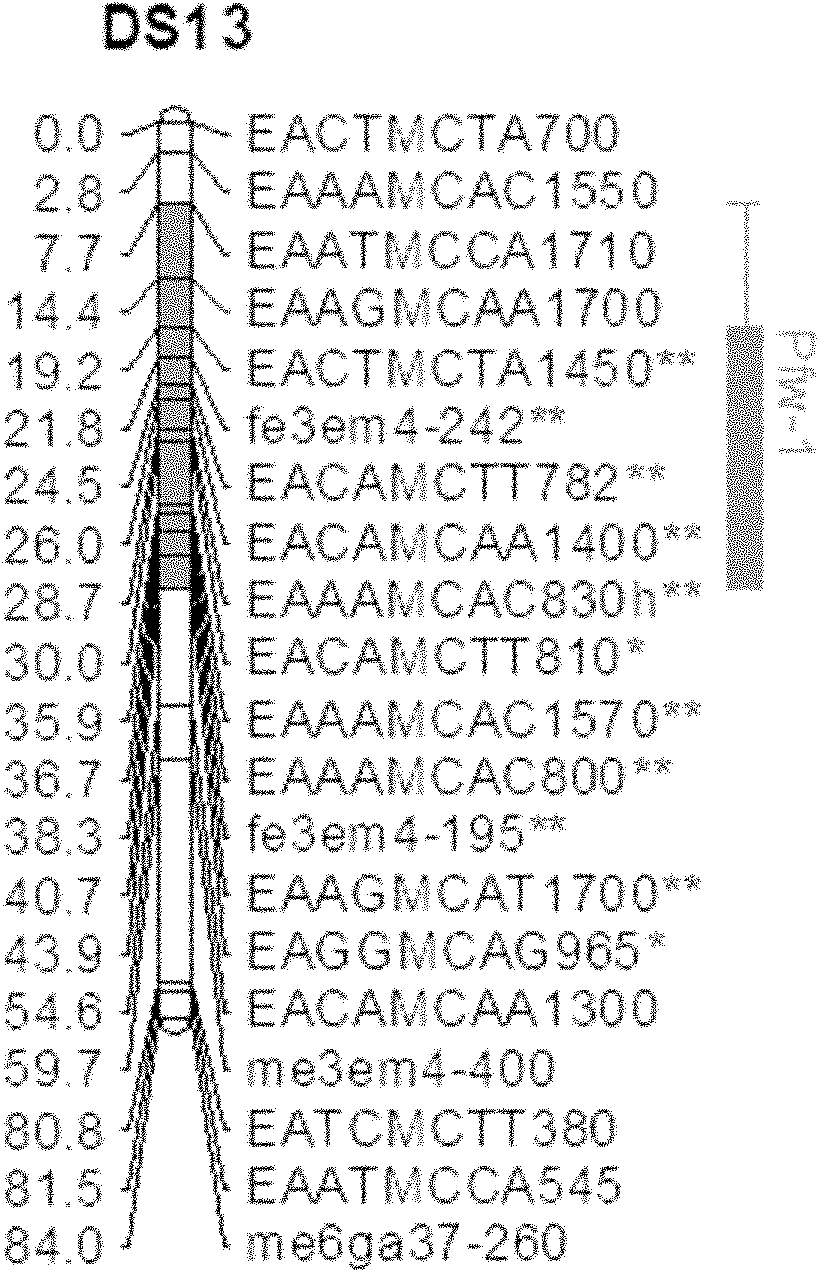
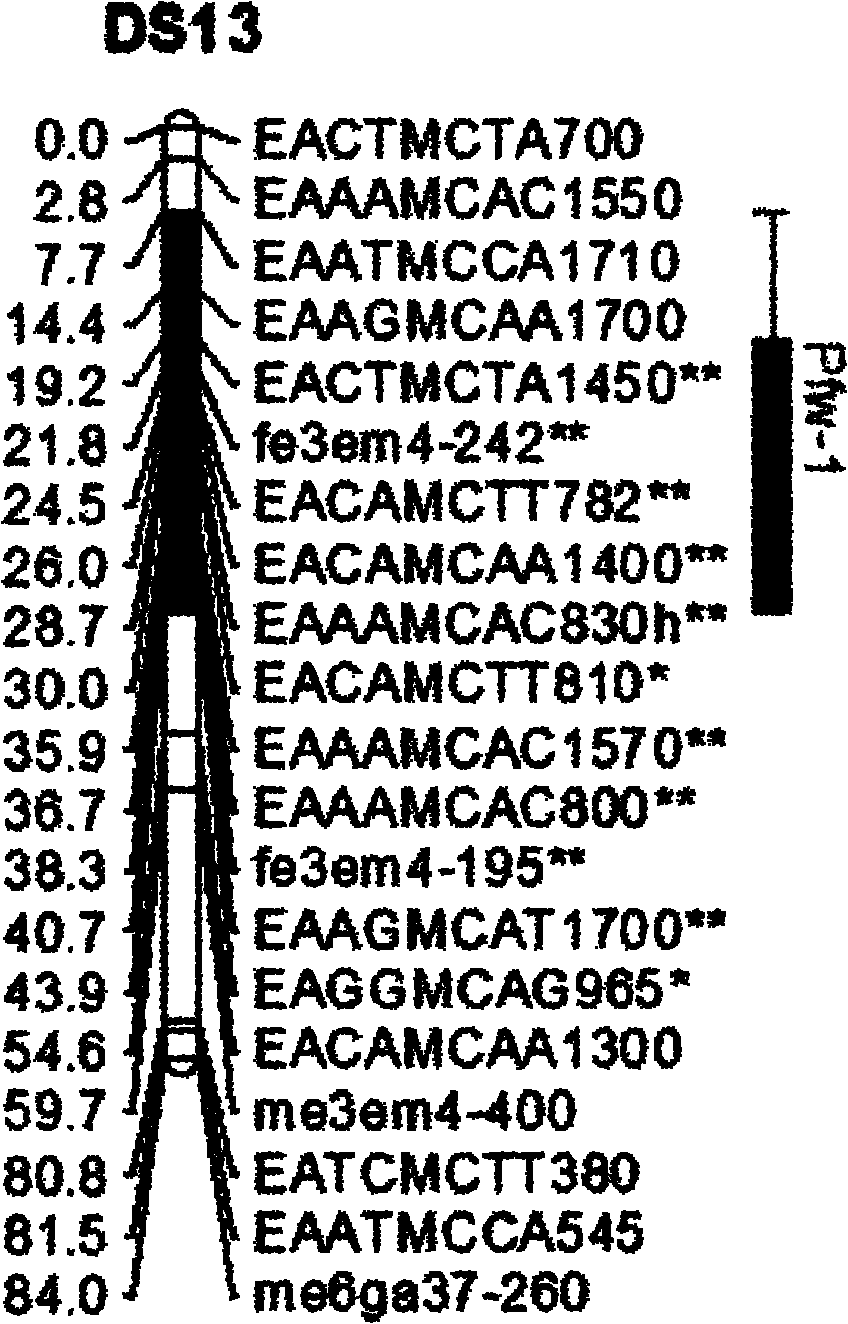
Molecular marker for single fruit weight main-effect quantitative trait loci (QTL) of Dangshansu pear fruit and application thereof
ActiveCN102140455AHigh contribution rateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationPEARAgricultural science
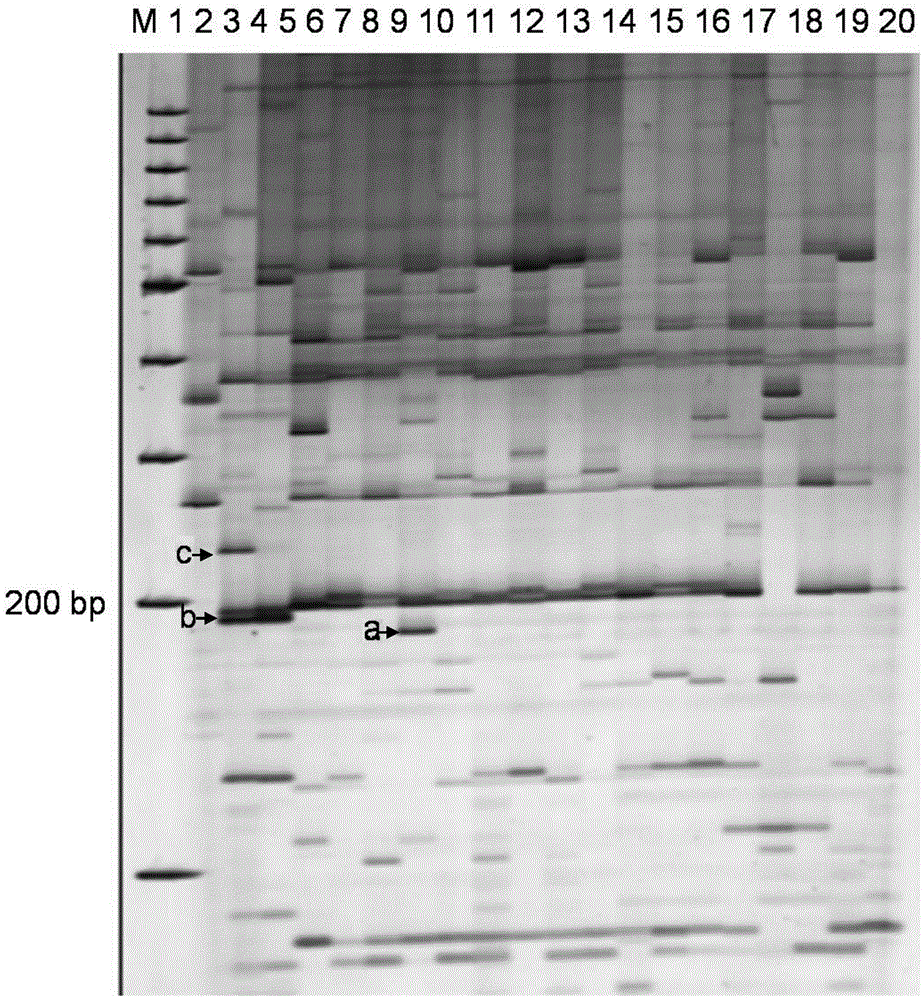
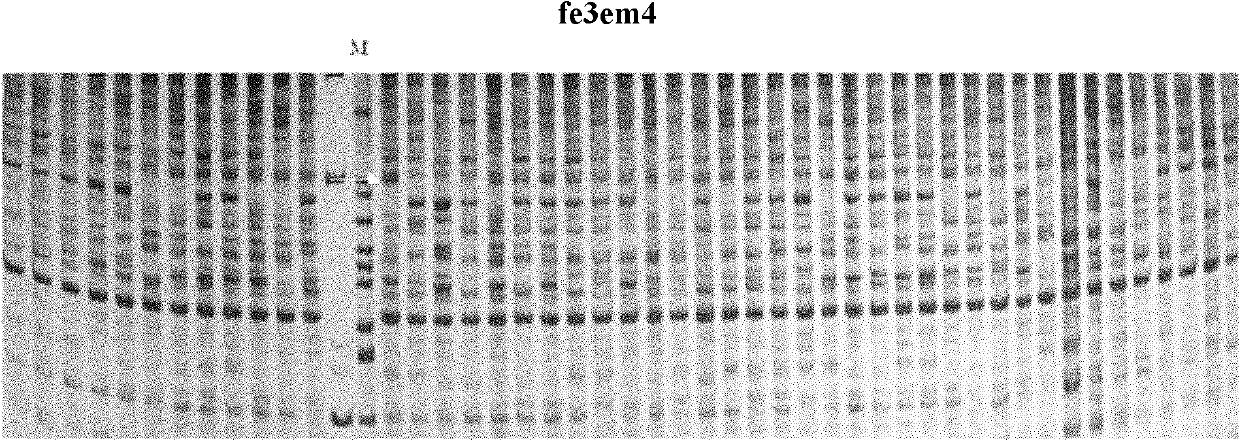
The invention belongs to the field of inheritance breeding, and relates to a molecular marker for a single fruit weight main-effect quantitative trait loci (QTL) of Dangshansu pear fruit and application thereof. A genetic linkage map of Dangshansu pear is constructed by utilizing sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), simple sequence repeats (SSR) and amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP), phenotypic identification on the single fruit weight of the fruit is combined, a group is analyzed through interval mapping, the presence of the main-effect QTL is detected on the 13th linkage group of the Dangshansu pear, and the 48.8 percent of single fruit weight can be interpreted. A molecule closest to the main-effect QTL Pfw-1 is marked as fe3em4-242p* and the distance is 0cM. The obtained molecular marker for the single fruit weight main-effect QTL has important theoretical and practical guidance significance for quickening the genetic improvement progress of pear varieties and improving breeding selection efficiency.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
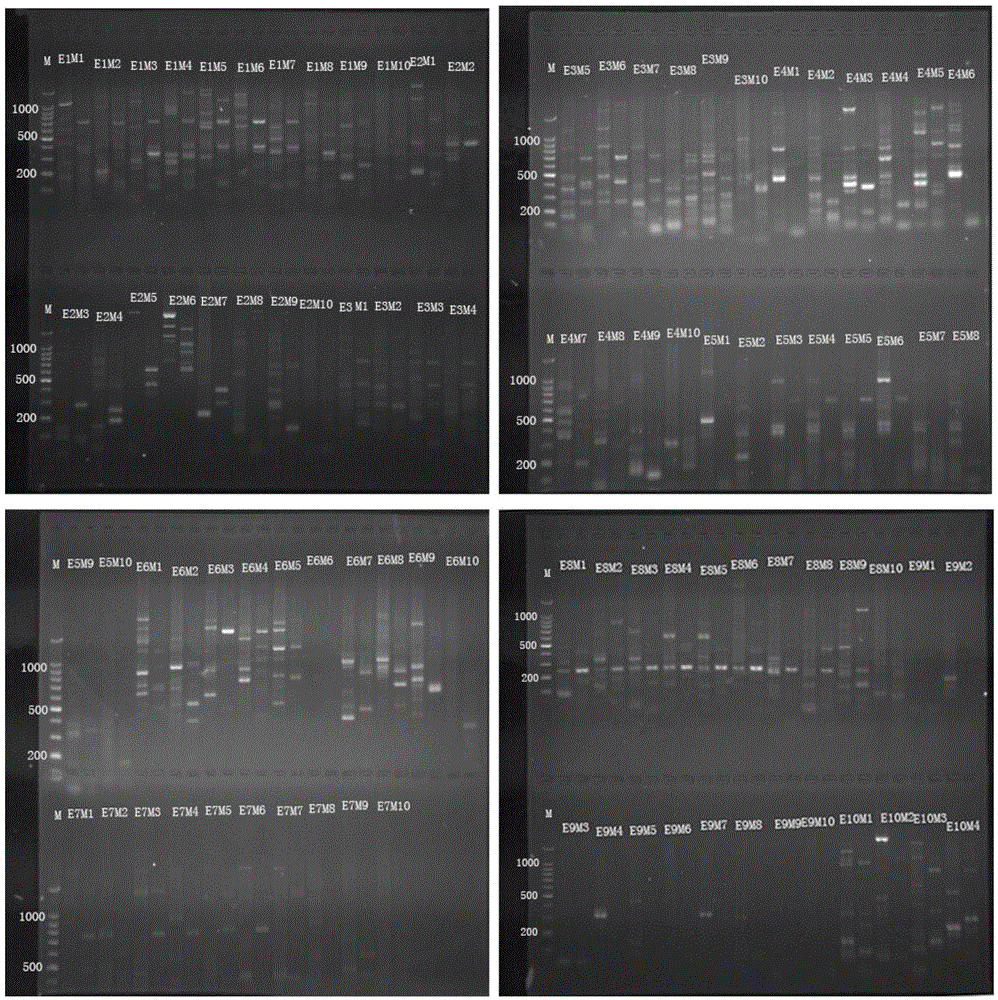
SRAP (Sequence Related Amplified Polymorphism) molecular marker primer for identifying common cynodon dactylon and cynodon arcuatus as well as method and application of SRAP molecular marker primer
PendingCN105420406AEasy to operateIncrease usageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceCynodon arcuatus
The invention discloses an SRAP (Sequence Related Amplified Polymorphism) molecular marker primer for identifying common cynodon dactylon and cynodon arcuatus. The SRAP molecular marker prime is selected from one of primer combinations of E1M4, E1M5, E1M6, E1M7, E1M8, E2M3, E2M4, E2M5, E2M6, E2M7, E3M1, E3M3, E3M4, E3M6, E3M9, E4M1, E4M3, E4M4, E4M5, E4M6, E5M9, E6M1, E6M2, E6M3, E6M4, E6M7, E6M8, E6M9, E7M2, E7M3, E7M4, E7M5, E7M7 and E10M9, wherein various primers are as shown in sequence. The SRAP molecular marker primer disclosed by the invention is used for identifying the cynodon richard; an obtained band is clear, good in polymorphism and high in repeatability; in addition, the SRAP molecular marker primer is simple in operation and wide in application prospect.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method for selecting specific SRAP marking tapes for coilia ectenes genders and gender determination method
InactiveCN102899321AGender identification is validDoes not affect normal growthMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationCoiliaBiology
The invention discloses a method for selecting specific SRAP (Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism) marking tapes for coilia ectenes genders and a gender determination method. The specific SRAP marking tapes for coilia ectenes genders are selected through SRAP-PCR reaction of 49 primer sets; and then the DNA sample of the coilia ectene which is not clear in gender is amplified through a specific primer set; and the gender of the coilia ectenes is differentiated according to whether the corresponding specific marking tapes can be amplified or not. The method provided by the invention overcomes the limits and shortcomings of the existing coilia ectenes gender differentiation technology, and therefore, an accurate and convenient gender differentiation method is provided.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Molecular marker of single fruit weight major quantitative trait loci (QTL) of August red pyrus L. fruits and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN102154273AHigh contribution rateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGeneticsAmplified fragment length polymorphism
The invention belongs to the field of genetic breeding, and provides a molecular marker of single fruit weight major quantitative trait loci (QTL) of August red pyrus L. fruits and application of the molecular marker. The genetic linkage map of August red is constructed by using SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism), SSR (simple sequence repeats) and AFLP (amplified fragment length polymorphism), phenotype identification on single fruit weight of pyrus L. is combined, and an interval mapping method is used to analyze linkage groups, thus major QTL is detected on the seventh linkage group of August red and can explain 30.9% of characteristics of single fruit weight. The point which is the nearest to the major QTL site Pfw-1 is marked to be EACAMCAC-2000m, and the nearest distance is 1.019cM. The obtained titratable acid major QTL molecular marker has significant theoretical and practical means for quickening genetic improvement process of pyrus L. varieties and improving breeding selection efficiency.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
SRAP (Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism) molecular marking method related to color character of Ulmus pumila cv.jinye. and application thereof
InactiveCN103993098AAchieve standardizationAvoid errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementTotal rnaComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses an SRAP (Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism) molecular marking method related to color character of Ulmus pumila cv.jinye. and an application thereof, and relates to an SRAP molecular marking method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: I, collecting leaves of different colors of Ulmus pumila cv.jinye. and calibrating the colors; II, respectively extracting total RNAs (Ribonucleic Acid) of golden and forest green leaves on each Ulmus pumila cv.jinye.; III, detecting RNA concentration; IV, carrying out cDNA-SRAP (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) amplification on differential fragments; and V, recovering, sequencing and analyzing the differential fragments. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simplicity in operation, accuracy in result, visualized result, practicality and the like. The method provided by the invention is used for researching genes related to different colors of Ulmus pumila cv.jinye.
Owner:DAQING BRANCH OF HEILONGJIANG ACAD OF SCI
Method for establishing cauliflower hybrid seed DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fingerprint spectrum and application thereof
InactiveCN102108395AProtection of legal rightsAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementHybrid seedTest material
The invention discloses a method for establishing a cauliflower hybrid seed and a parent DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fingerprint spectrum and the application thereof. The establishment method comprises the following steps: 1) extracting and purifying cauliflower DNA; 2) using the obtained high-purity cauliflower DNA as a template for performing RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) and SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) analysis; and 3) selecting selective polymorphism amplified bands to construct the DNA fingerprint spectrum of a tested material; and the cauliflower hybrid seed and parents thereof in the DNA fingerprint spectrum have specific DNA fingerprints which can be mutually differentiated. The DNA fingerprint spectrum is represented in the form of a diagram, thereby being relatively intuitive to look and being easy to understand; and the DNA fingerprint spectrum is converted to the digital representation form, thereby being convenient to be identified, read and analyzed by a computer. The method can be applied in identification of seed purity of the cauliflower hybrid seed, the result is accurate and reliable, and the detection is rapid.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
Molecular marker for Fenneropenaeus chinensis with high-pH resistance character and identification method using same
InactiveCN102154287AQuick filterLong screening periodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceFenneropenaeus chinensis
The invention provides a molecular marker for Fenneropenaeus chinensis with a high-pH resistance character and an identification method using the same. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) identification method for the high-pH resistance character of Fenneropenaeus chinensis is established based on a specific sequence responsible for the high-pH resistance character of Fenneropenaeus chinensis and designed specific primers, and the specific sequence responsible for the high-pH resistance character of Fenneropenaeus chinensis is obtained by SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) marker screening, cloning, sequencing, specific primer design and specific marker verification. The method for screening the specific SRAP marker to the high-pH resistance character of Fenneropenaeus chinensis is established to select one primer pair composition from 110 SRAP primer pair compositions to produce a high-pH resistance specific SRAP fragment. The PCR identification method for the high-pH resistance character of Fenneropenaeus chinensis is established for the first time. The identification method is advanced, stable and reliable; and has significance and wide prospects in application for stress resistance breeding of Fenneropenaeus chinensis, enhancement of environmental adaptability of Fenneropenaeus chinensis, and large-area farming of Fenneropenaeus chinensis.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for establishing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fingerprint of green vegetable hybrid and application thereof
InactiveCN102108393AProtection of legal rightsAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNATest material
The invention discloses a method for establishing a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fingerprint of green vegetable hybrid and parents thereof, and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) extracting and purifying a green vegetable DNA; 2) carrying out RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA), ISSR (inter-simple sequence repeat) and SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) analysis by using the acquired high-purity green vegetable DNA as a template; and 3) choosing a typical polymorphism amplification strip to establish the DNA fingerprint of tested material, wherein both the green vegetable hybrid and the parents thereof in the DNA fingerprint have specific DNA fingerprints which can be distinguished. The DNA fingerprint disclosed by the invention is presented in a graphic mode, so the DNA fingerprint is visualized and can be easily understood. The graphic mode of the DNA fingerprint can be converted into a digital code presenting mode, thereby being conveniently read and analyzed by a computer. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the seed purity of the green vegetable hybrid can be identified from the heredity nature, the result is accurate and reliable, and the detection can be quickly performed.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
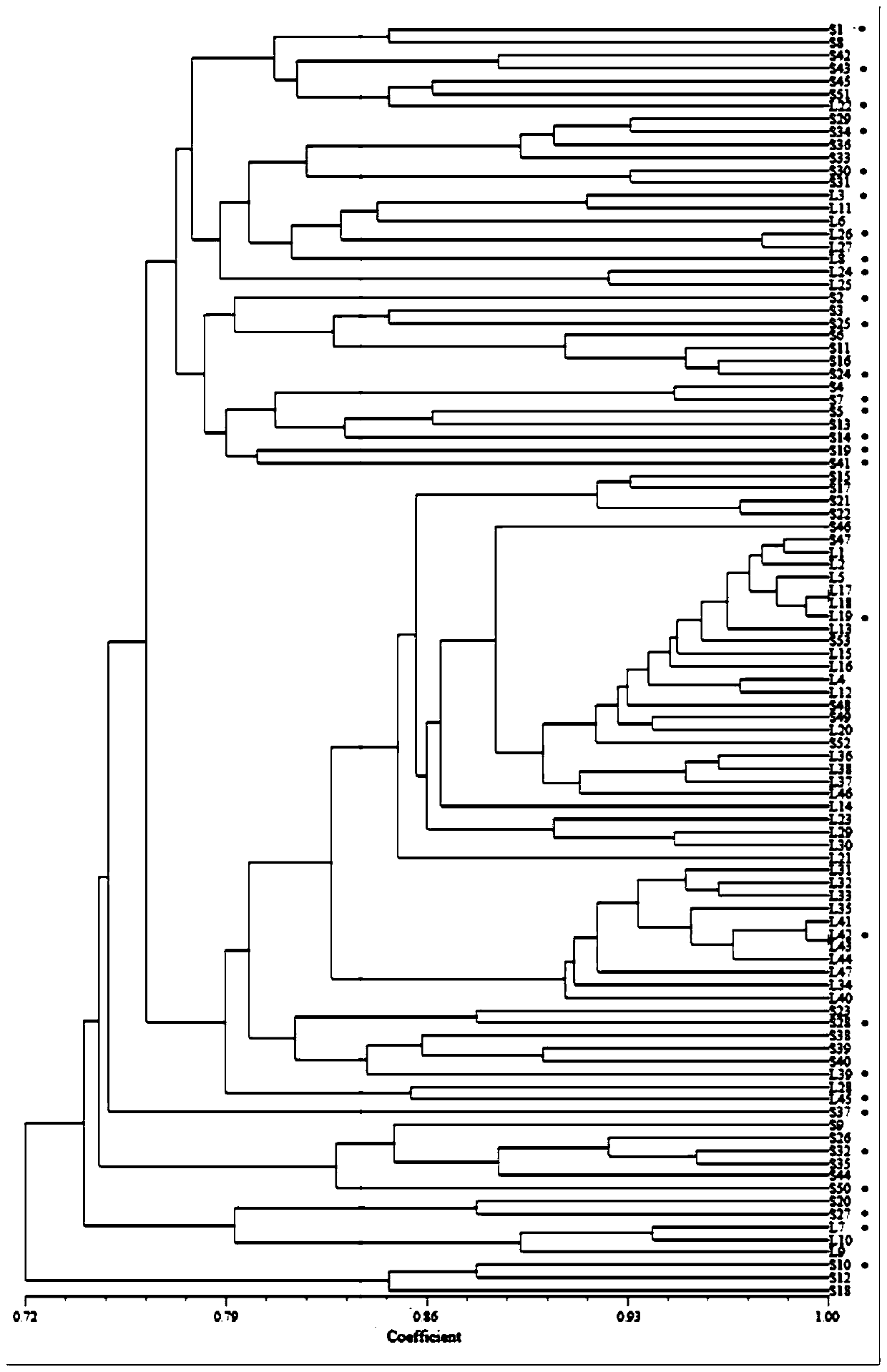
Molecular marking method for carrying out genetic relationship and clustering analysis on citrus fruit flies
InactiveCN104087664AFast cluster analysisAccurate cluster analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDendrogramSequence-related amplified polymorphism
The invention relates to a molecular marking method for carrying out genetic relationship and clustering analysis on citrus fruit flies and belongs to the technical field of molecular marking. The molecular marking method for carrying out genetic relationship and clustering analysis on the citrus fruit flies comprises the following steps: carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on DNA of citrus fruit flies by utilizing seven RAPD (random amplification polymorphism DNA) primers and 10 pairs of SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) primer combinations, carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis on amplification products, taking pictures, recording results, and carrying out statistics on an amplification zone of a detected material; and analyzing with genetic analysis software to obtain genetic distance between individuals, and drawing a dendrogram of citrus fruit flies in different geographical populations for distinguishing different class groups. The molecular marking method for carrying out genetic relationship and clustering analysis on the citrus fruit flies has the advantages of stable reaction, clear amplified fragments and high polymorphism, a molecular reaction system for population genetic diversity of the citrus fruit flies is constructed, genetic diversity among populations can be shown, clustering analysis can be rapidly and accurately carried out on the citrus fruit flies, different populations can be distinguished, and the molecular marking method for carrying out genetic relationship and clustering analysis on the citrus fruit flies has an important significance on prevention and control of the citrus fruit flies.
Owner:CITRUS RES INST SOUTHWEST UNIV
Dendrobium DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) fingerprint spectrum and special primer and establishment method for dendrobium DNA fingerprint spectrum
InactiveCN104894288AAccurate identificationReliable identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic DNAA-DNA
The invention discloses a dendrobium DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) fingerprint spectrum and a special primer and an establishment method for the dendrobium DNA fingerprint spectrum. A nucleotide sequence of the special primer is as shown in a sequence table. The special primer is selected from one or more pairs in the following primer pairs: SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.7; SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.8; SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.5; SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.6; SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.8; SEQ ID NO.4 and SEQ ID NO.5. A genomic DNA of a dendrobium material serves as a template, and any special primer is used for SRAP-PCR (Sequence Related Amplified Polymorphism-Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification; an obtained SRAP-PCR amplification product is subjected to modified polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and a DNA strip is displayed by silver staining to obtain the dendrobium DNA fingerprint spectrum. The dendrobium DNA fingerprint spectrum is created, and dendrobium strains can be subjected to germplasm identification in genetic essence accurately and reliably.
Owner:上海孙桥现代农业联合发展有限公司
Method for quickly identifying genetic purity of glutinous corn hybrid
InactiveCN102505044AAccurate identificationImprove the efficiency of genetic purity identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisDNA fragmentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a method for quickly identifying the genetic purity of a glutinous corn hybrid. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from glutinous corn, performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using the screened sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) effective primer combination NAUSRem7 / NAUSRpm1 and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) effective primers NAUSR709 and NAUSR712, respectively performing non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and agarose gel electrophoresis on a PCR product obtained through amplification, and shooting a DNA electrophoresis pattern; and comparing and analyzing the size and position difference of polymorphism amplified fragments formed due to the difference of DNA fragment sequences in the electrophoresis pattern, and identifying the genetic purity of the glutinous corn F1 hybrid, namely a Suyunuo 2 seed. The detection method has the advantages of marking stability, high accuracy, no influence of the growth stage and environment of a sample to be detected, low cost, capability of being performed in thewhole growth season, and the like.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Cultivating method of hyriopsis cumingii with golden yellow shell
ActiveCN103478025AShell color genetically stableHigh postoperative survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTotal rnaGlochidium
The invention relates to a cultivating method of hyriopsis cumingii with a golden yellow shell. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1), selecting 4-6 parent hyriopsis cumingii; (2) taking the margin tissues of the pallium of the parent hyriopsis cumingii, extracting the total RNA (ribonucleic acid) and synthetic single stranded c RNA, performing SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) amplification by adopting primer combination, and selecting male and female individuals with specific strip sequences with the golden yellow shells after the amplification products are subjected to electrophoresis; (3) using the selected male and female parent hyriopsis cumingii to build a family and cultivating in a water flowing pool; (4) periodically examining the pregnant condition of the female hyriopsis cumingii, and if mature glochidiums are found, selecting the mature female hyriopsis cumingii to reproduce to obtain infant hyriopsis cumingii; cultivating the infant hyriopsis cumingii in the water flowing pool until the shell reaches 1-2cm long, removing into to a net cage, and suspending the net cage into a pond to perform second stage cultivating on the infant hyriopsis cumingii until the shell length reaches 5-8cm; (5) removing the family parent hyriopsis cumingii with the non-golden yellow shells, and using the rest parent hyriopsis cumingii to build a core cultivating population with the golden yellow shells. According to the cultivation method of the hyriopsis cumingii with the golden yellow shell, the ratio of the hyriopsis cumingii with the golden yellow shell can reach more than 99.0%, the shell color is stable in heredity and the postoperative survival rate is high.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for identifying porphyra yezoensis high-temperature-resistant strain TM-18, molecular marker and construction method for same
InactiveCN103343122AAccurate identificationJudgment criteria are simple and intuitiveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyElectrophoresis
The invention belongs to the fields of molecular biology DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) marking technology and applications, and relates to a molecular marker for porphyra yezoensis high-temperature-resistant strain TM-18 and a construction method for the same. Specifically, a porphyra yezoensis strain obtained by artificial selection and breeding is analysed by virtue of an SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) marking technology, and the specific bands of the high-temperature-resistant strain TM-18 are found via PCR (polymerase chain reaction) electrophoresis detection; and specific primers are designed via recovering and sequencing, and converted to SCAR (sequence characterized amplified regions) markers for extension and strain verification. A method for identifying porphyra yezoensis high-temperature-resistant strain TM-18 by the molecular marker comprises the following steps of: extracting the total DNA of porphyra yezoensis; performing PCR amplification by the specific primers; performing electrophoresis detection on amplification products; and performing result judgement, specifically, if amplification products with a length of 341 bp are generated, then judging that the strain is a high-temperature-resistant strain TM-18. In the method, identification can be performed only by one-time simple PCR and agarose electrophoresis; and the method is simple and rapid to operate, and free from the influence of environmental factors, and is an ideal means of strain identification.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for identifying peach bud mutation
InactiveCN103820542AIncrease the chances of screeningIncrease economic benefitsMicrobiological testing/measurementBudMaterial resources
The invention discloses a method for identifying peach bud mutation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out continuous three-generation grafting identification, observing the stability of phenotypic character, collecting tender leaves and parental tender leaves of suspected bud mutation with stable characters after the continuous three-generation grafting, extracting genome DNA, carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the DNA by using an SSR (Signal Sequence Repeat) primer and an SRAP (Sequence Related Amplified Polymorphism) primer respectively, carrying out bud mutation distinguishing on amplification products through agarose gel electrophoresis, and if electrophoresis bands of parent and the suspected bud-mutant breed are different, identifying the suspected bud-mutant breed as bud mutation. By means of the method disclosed by the invention, 'small white peach' and early-maturing bud-mutant 'Jinliuzaohong' peach are successfully identified. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient in operation, wide in application and convenient to popularize, and saves a lot of human and material resources.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Molecular marker for raphanus sativus L. downy mildew resistant gene close linkage
InactiveCN102978207ARapid identificationMolecular markers are stable and accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationHigh resistanceGene selection
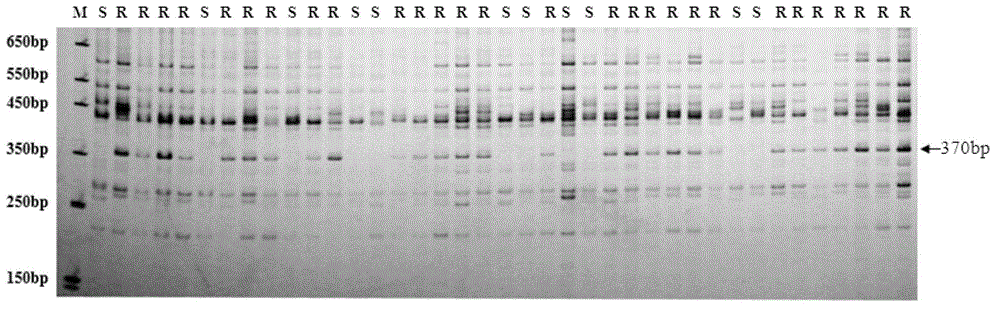
The invention belongs to the field of crop genetic breeding, and discloses a molecular marker for raphanus sativus L. downy mildew resistant gene close linkage. A sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) molecular marker method is used for carrying out marker genotyping on high-resistance downy mildew raphanus sativus L. parents (NAU-dhp08), high-sensitive downy mildew raphanus sativus L. parents (half green from autumn fields) and a second filial generation (F2) group single plant which is prepared through resistance and sensitive parent hybridization, through the F2 single plant resistance phenotype and marker gene linkage analysis, a resistance marker Em9 / ga24370 of 370-base pair (bp) close linkage is identified, a distance from a resistance locus and a marker genetic distance is 2.3 centimeters. The molecular marker method provided by the invention can be used for the marker assisted selection of raphanus sativus L. downy mildew resistance breeding, quickly and accurately identifies the raphanus sativus L. downy mildew resistance, overcomes the limitations of heavy workload, long period, easily influenced results by environment and the like of the conventional resistance identification method, the high-resistance gene selection efficiency can be obviously improved, so that a breeding process of a new high raphanus sativus L. downy mildew-resistant variety can be accelerated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Reaction system and kit for analyzing moringa oleifera genetic relationship and application method thereof
ActiveCN108456719AGood polymorphismGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGermplasmBiology
The invention provides a reaction system and kit for analyzing a moringa oleifera genetic relationship and application thereof. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, 13 pairs ofprimers with good polymorphism and high definition are screened from 170 pairs of primers through an SRAP (Sequence Related Amplified Polymorphism) molecular marker technology and 18 parts of moringaoleifera DNAs (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) are marked; NTSYS software is used for finishing data analysis and UPGMA (Unweighted Pair-group Method with Arithmetic means) clustering; furthermore, the moringa oleifera genetic relationship and the genetic diversity are researched. A result shows that different moringa oleifera lines have abundant genetic diversity and an SRAP molecular marker is an effective means for analyzing themoringa oleifera germplasm genetic relationship; important technical supports are provided for moringa oleifera molecular assisted breeding and establishment of a genetic map database.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF TROPICAL CROPS
Molecular identification method of clerodendranthus spicatus
ActiveCN105483223AEnhancing the Ability to Discriminate Similar Varieties of Kidney TeaImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a molecular identification method of clerodendranthus spicatus. The molecular identification method disclosed by the invention, by screening an SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) primer combination, can enhance the capacity of identifying the clerodendranthus spicatus of approximate varieties, and through amplification and comparison on the approximate varieties, primers can effectively distinguish the various clerodendranthus spicatus varieties and can conduct molecular identification on the clerodendranthus spicatus varieties. Meanwhile, the method disclosed by the invention, through the direct identification of genetic materials of the clerodendranthus spicatus, can greatly improve the accuracy of identification. The molecular identification method disclosed by the invention can conduct the identification of the clerodendranthus spicatus varieties on a DNA level and can avoid errors caused by such indirect identification methods as expression identification; the method has the characteristics of convenient operation and good repeatability; and the method is high in reliability and authority.
Owner:中国医学科学院药用植物研究所云南分所
Sodium azide mutagenizing method for juvenile citrus internodal stem segments
ActiveCN108307915AFacilitate progress in creating variantsPromote progressBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSodium azideBud
The invention discloses a sodium azide mutagenizing method for juvenile citrus internodal stem segments, comprising: I, taking citrus young plantlets more than 1 mm in stem thickness and 5-10 cm in plantlet height, cutting to obtain internodal stem segments, soaking the internodal stem segments in a mutagenizing liquid, mutagenizing in darkness for 1-3 h, wherein the mutagenizing liquid includes sodium azide having a concentration of 0.5-2 mmol / L; II, subjecting the mutagenized internodal stem segments to tissue culture until sectional wounds of the internodal stem segments grow regenerated buds; III, using an SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) molecular markup method to detect the regenerated buds that vary, and subjecting the varied regenerated buds to rooting culture to obtain complete citrus variant plants. It is clarified that sodium azide-mutagenized juvenile citrus internodal stem segments may produce stable variant plants. The method of the invention has mutagenizing efficiency of greater than 10% and has significant mutagenizing effect and good operating convenience.
Owner:HUNAN INST OF GARDENING
Molecular marker and screening method of gift strain nile tilapia oreochromis niloticus streptococcus iniae infection resistant family
InactiveCN103642802AGuaranteed stabilityAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationScreening methodNile tilapia
The invention discloses a molecular marker and a screening method of gift strain nile tilapia oreochromis niloticus streptococcus iniae infection resistant family. The molecular marker is a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.20; the screening method comprises five steps of streptococcus iniae infection, genome DNA extraction, primer screening, SRAP-PCR (Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism-Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and sequencing and analyzing, by the method, a parent family with stronger resistance to streptococcus iniae disease can be found more accurately and quickly, after enhanced cultivation, the parent family can be used as the parent for fingerlings propagation. The molecular marker screened out is prepared into a probe for detecting different parent families, the probe can sort out the streptococcus iniae disease resistant parent more simply and accurately, and selection of parent among different families is facilitated. Meanwhile, by using the bred disease-resistant parent as the propagation parent, quality of fingerlings can be improved further, and culture benefit of gift strain nile tilapia oreochromis niloticus can be increased.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Multi-PCR primer, method and kit for identifying authenticity of filial generations of stylosanthes guianensis
InactiveCN105296667AReduce dosageLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWorkloadMultiplex pcrs
The invention provides a multi-PCR primer, a method and a kit for identifying the authenticity of filial generations of stylosanthes guianensis. The multi-PCR primer, method and kit disclosed by the invention are used for carrying out SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) molecular marker identification on filial generations of stylosanthes guianensis, and achieve the effects of rapidness, accuracy and low cost; when more identified samples exist, in case that the multi-PCR primer for identifying the authenticity of filial generations of stylosanthes guianensis provided by the invention is adopted, an operation of configuring a set of PCR system, then dividing the system into multiple pipes, and respectively adding the DNAs of to-be-detected filial generations is only required to be performed, and an operation of configuring different PCR systems for different filial generations and then respectively adding the DNAs of to-be-detected filial generations is not required to be performed, thereby greatly reducing the workload and reducing the probability of human errors introduced in the process of sample adding.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Molecular detection method aiming at Asia fusarium and application thereof
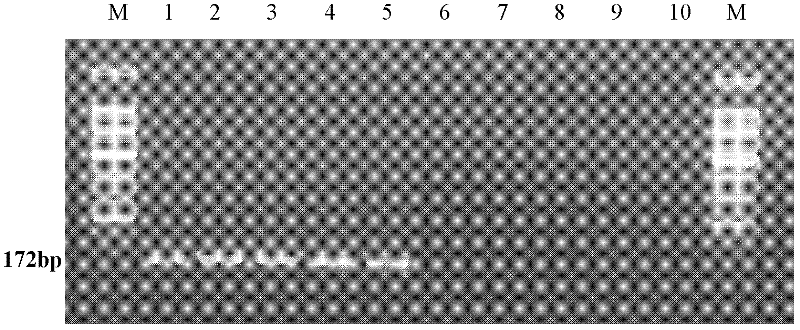
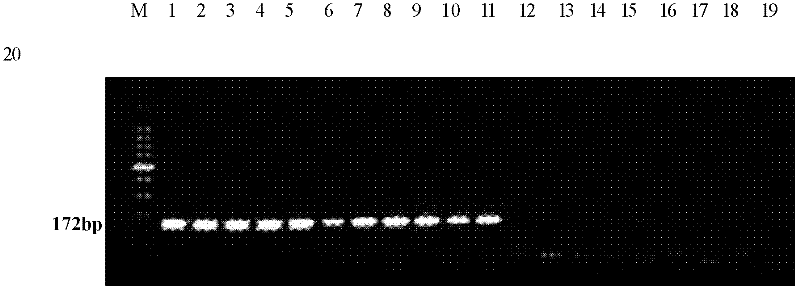
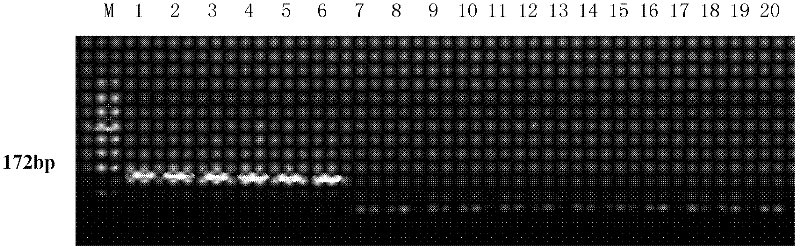
ActiveCN102559873AReduce stepsEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisImaging analysis
The invention relates to a molecular detection method aiming at Asia fusarium and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on sample-extracted DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) by use of a pair of specific primers to Asia fusarium, and carrying out electrophoresis gel imaging analysis on an amplified product, wherein the pair of specific primers are an upstream primer SEQ ID NO.1 and a downstream primer SEQ ID NO.2; in the step of carrying out electrophoresis gel imaging analysis on the PCR amplified product, judging whether the sample is correlated with the Asia fusarium or not according to the condition of whether a specific stripe exists at 172bP or not; and amplifying a polymorphic SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) label by virtue of the pair of specific primers based on the related sequence of the Asia fusarium, wherein the sequence of the SRAP label is SEQ ID NO.3, and the size of the SRAP label is 172bp. The method provided by the invention can be used for identifying the Asia fusarium, or monitoring the pollution of the Asia fusarium to crops or feeds.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for identifying diospyros species based on SRAP (Sequence Related Amplified Polymorphism) molecular marker
InactiveCN104059967AQuick distinctionAccurate distinctionMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a method for identifying diospyros species based on an SRAP (Sequence Related Amplified Polymorphism) molecular marker. A primer for identifying diospyros species (varieties) is a primer combination formed by screening and verifying 357 pairs of primers in a large scale, wherein the primer combination comprises an upstream primer and a downstream primer respectively having the concrete nucleotide sequences as follows: the nucleotide sequence of the upstream primer is TGA GTC CAA ACC GGACA, and the nucleotide sequence of the downstream primer is GAC TGC GTA CGA ATT CAA. The SRAP primer for rapidly distinguishing diospyros species is obtained by strictly screening in a large scale so as to have relatively high stability and repeatability; five diospyros species (varieties) can be easily distinguished through one pair of primers and one PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), so that the method is convenient to operate, rapid and accurate; the method disclosed by the invention can be used for rapidly and accurately distinguishing the five diospyros species under any condition, and can also be used for realizing the taxonomic identification of wild diospyros resources by combining a morphological feature.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Establishing method of blue honeysuckle sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) reaction system
InactiveCN109251966AEasy to operateGood research resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementGene mappingPcr ctpp
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and provides an establishing method of a blue honeysuckle sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) reaction system. SRAP serves as a novel molecular marker, has the characteristics of being simple in operation, stable and efficient, and is widely applied to researches of map construction, gene mapping and genetic diversity analysis ofdifferent crops; similar to other PCR technologies, the amplified results can be affected by reaction factors such as Tag DNA polymerase, template DNA, dNTPs, Mg<2+> and primers, so that optimizationof the SRAP system is the precondition to obtain a good research result. The blue honeysuckle SRAP reaction system is established, abundant polymorphism DNA can be acquired simply, stably and efficiently, and therefore the establishing method is applied to map construction, gene mapping and genetic diversity analysis and the like of the blue honeysuckle.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Identification method of loquat SRAP marking system and loquat dwarf hybrid variety
InactiveCN105400872AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiologySequence-related amplified polymorphism
The invention relates to the field of agricultural application, in particular to an identification method of a loquat SRAP (Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism) marking system and a loquat dwarf hybrid variety. The method comprises the steps that optimization is conducted on the annealing temperature in an SRAP amplification program and the content of four main factors of DNA, dNTPs, a Taq enzyme and Primers in an amplification system, and on the basis, SRAP marking identification and analysis are conducted on the authenticity of a loquat dwarf hybrid variety 861 strain and genetic far and near relationships between the loquat dwarf hybrid variety 861 strain and eight white flesh loquat varieties. According to the identification method of the loquat SRAP marking system and the loquat dwarf hybrid variety, it is indicated that the optimized SRAP system can be well applied to loquat molecular assistant breeding work such as loquat hybrid variety identification, genetic relationship classification and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU POLYTECHNIC INST OF AGRI
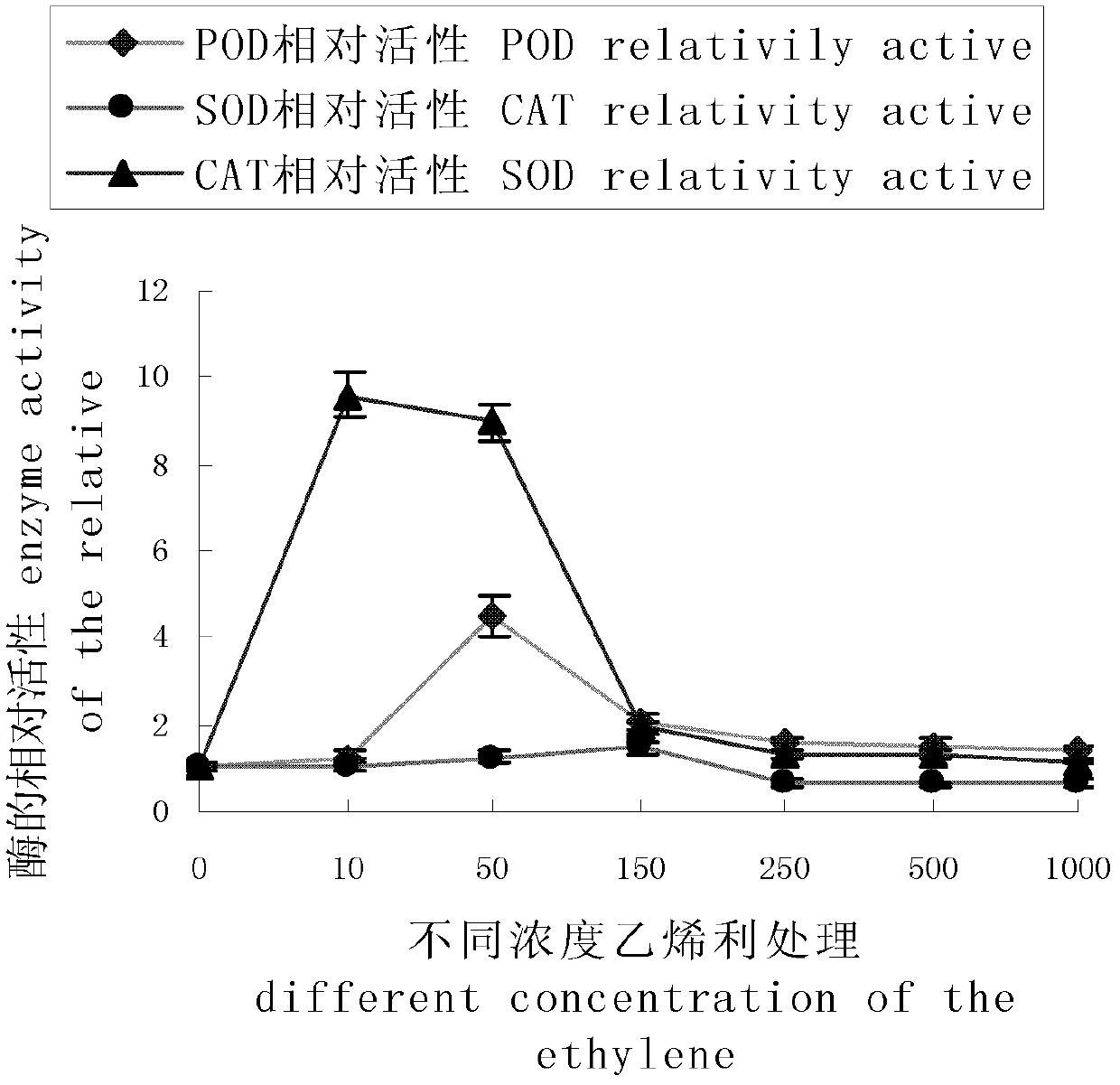
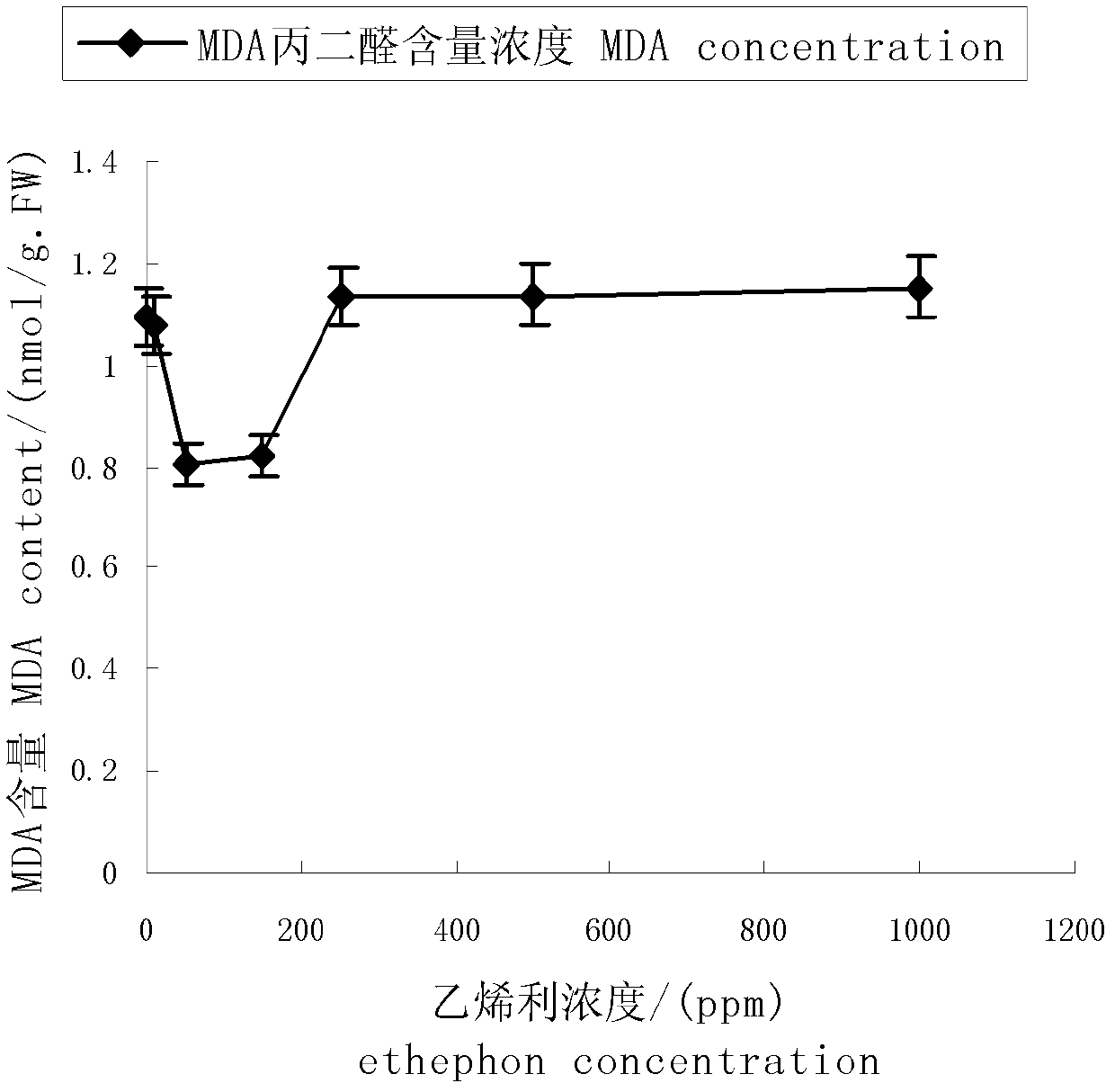
Method for analyzing differential expression of cotyledon senescence-associated gene of brown cotton by use of cDNA-SRAP (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid-sequence-related amplified polymorphism) technique
InactiveCN102605073ADeepen understandingSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementTotal rnaComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses a method for analyzing differential expression of cotyledon senescence-associated genes of brown cotton by use of a cDNA-SRAP (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid-sequence-related amplified polymorphism) technique. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, spraying ethylene with concentration of 450-550ppm on a to-be-analyzed material to process for 18-24h and extracting total RNA (ribonucleic acid) in cotyledon; and performing cDNA-SRAP PCR (polymerase chain reaction), recovering and purifying specific bands obtained in a reaction product and analyzing functions of sequences. According to the invention, cDNA-SRAP technique is utilized to analyze differential expression of the related genes on a molecular level, so as to explore the molecular mechanism of cotyledon senescence of brown cotton, deepen understanding of the leaf senescence of brown cotton, and provide a theoretical basis for artificial control of leaf senescence process of colorful cotton.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A method for screening and preserving bacterial genetic resources
ActiveCN106191289BPrimer specificMethod stableMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyBacterial strain
The invention discloses a bacterial gene resource screening and storing method which includes the steps: (1) separating strains; (2) extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of the strains; (3) building a matrix table; (4) acquiring a screening scheme; (5) storing representative bacterial strains. An SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) molecular marker method based on bacterial genome information adopts specific primers and is stable and high in purposefulness.
Owner:大襟岛海洋生物谷(深圳)有限公司
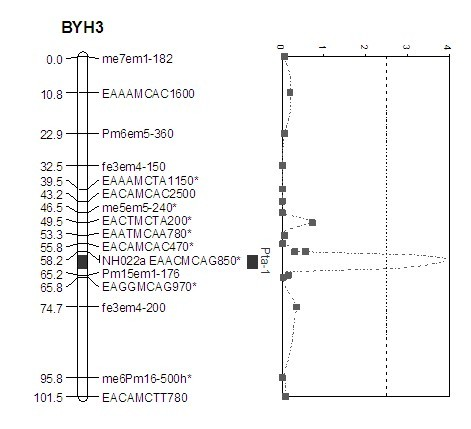
Molecular marker of Pyrus communis L. fruit titratable acid content
InactiveCN102121055AHigh contribution rateImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsAmplified fragment length polymorphism
The invention provides a molecular marker of the Pyrus communis L. fruit titratable acid content, belonging to the genetic breeding field. Sequence related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), simple sequence repeat (SSR) and amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) are utilized to construct the genetic linkage maps of Pyrus communis L., the phenotypic identification of the fruit titratable acid content is combined, the interval mapping method is adopted to analyze the colony, a main effect quantitative trait locus (QTL) exists in the third linkage group of Pyrus communis L. through detection, and the characteristic that the titratable acid content is 49.3% can be explained. The marker EAACMCAG-850m* is most near the main effect QTL Pta-1, and the distance between the marker and the locus is 2cm. The obtained molecular marker of titratable acid main effect QTL has important theoretical and practical significances for accelerating the genetic improvement process of Pyrus L. cultivars and increasing the breeding selection efficiency.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Cultivating method of hyriopsis cumingii with golden yellow shell
ActiveCN103478025BShell color genetically stableHigh postoperative survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTotal rnaGlochidium
The invention relates to a cultivating method of hyriopsis cumingii with a golden yellow shell. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1), selecting 4-6 parent hyriopsis cumingii; (2) taking the margin tissues of the pallium of the parent hyriopsis cumingii, extracting the total RNA (ribonucleic acid) and synthetic single stranded c RNA, performing SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) amplification by adopting primer combination, and selecting male and female individuals with specific strip sequences with the golden yellow shells after the amplification products are subjected to electrophoresis; (3) using the selected male and female parent hyriopsis cumingii to build a family and cultivating in a water flowing pool; (4) periodically examining the pregnant condition of the female hyriopsis cumingii, and if mature glochidiums are found, selecting the mature female hyriopsis cumingii to reproduce to obtain infant hyriopsis cumingii; cultivating the infant hyriopsis cumingii in the water flowing pool until the shell reaches 1-2cm long, removing into to a net cage, and suspending the net cage into a pond to perform second stage cultivating on the infant hyriopsis cumingii until the shell length reaches 5-8cm; (5) removing the family parent hyriopsis cumingii with the non-golden yellow shells, and using the rest parent hyriopsis cumingii to build a core cultivating population with the golden yellow shells. According to the cultivation method of the hyriopsis cumingii with the golden yellow shell, the ratio of the hyriopsis cumingii with the golden yellow shell can reach more than 99.0%, the shell color is stable in heredity and the postoperative survival rate is high.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Molecular marking method for identifying variety of Suzhi No.1 hybrid zoysia
ActiveCN103602742BReliable identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentGenetics
The invention relates to a method for molecularly identifying the genetic markers and the variety of a plant, and specifically discloses a group of SRAP (Sequence-Related Amplified Polymorphism) marking primers and an identification method for identifying Suzhi No.1 hybrid zoysia. The group of primers is used for PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) to obtain the amplified fragments of each pair of primers; the obtained fragments are compared with genome fragments disclosed by the invention; consequently, whether the zoysia variety is the Suzhi No.1 hybrid zoysia can be identified accurately.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for identifying porphyra yezoensis high-temperature-resistant strain TM-18, molecular marker and construction method for same
InactiveCN103343122BNot affected by environmental factorsThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyAgarose electrophoresis
The invention belongs to the fields of molecular biology DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) marking technology and applications, and relates to a molecular marker for porphyra yezoensis high-temperature-resistant strain TM-18 and a construction method for the same. Specifically, a porphyra yezoensis strain obtained by artificial selection and breeding is analysed by virtue of an SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) marking technology, and the specific bands of the high-temperature-resistant strain TM-18 are found via PCR (polymerase chain reaction) electrophoresis detection; and specific primers are designed via recovering and sequencing, and converted to SCAR (sequence characterized amplified regions) markers for extension and strain verification. A method for identifying porphyra yezoensis high-temperature-resistant strain TM-18 by the molecular marker comprises the following steps of: extracting the total DNA of porphyra yezoensis; performing PCR amplification by the specific primers; performing electrophoresis detection on amplification products; and performing result judgement, specifically, if amplification products with a length of 341 bp are generated, then judging that the strain is a high-temperature-resistant strain TM-18. In the method, identification can be performed only by one-time simple PCR and agarose electrophoresis; and the method is simple and rapid to operate, and free from the influence of environmental factors, and is an ideal means of strain identification.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com