A method for screening and preserving bacterial genetic resources
A gene and bacterial technology, applied in the screening and preservation of bacterial genetic resources, can solve the problems of difficult direct application of haplotype bacterial analysis, high randomness, low accuracy, etc., to achieve stable methods, strong purpose, and low cost little effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
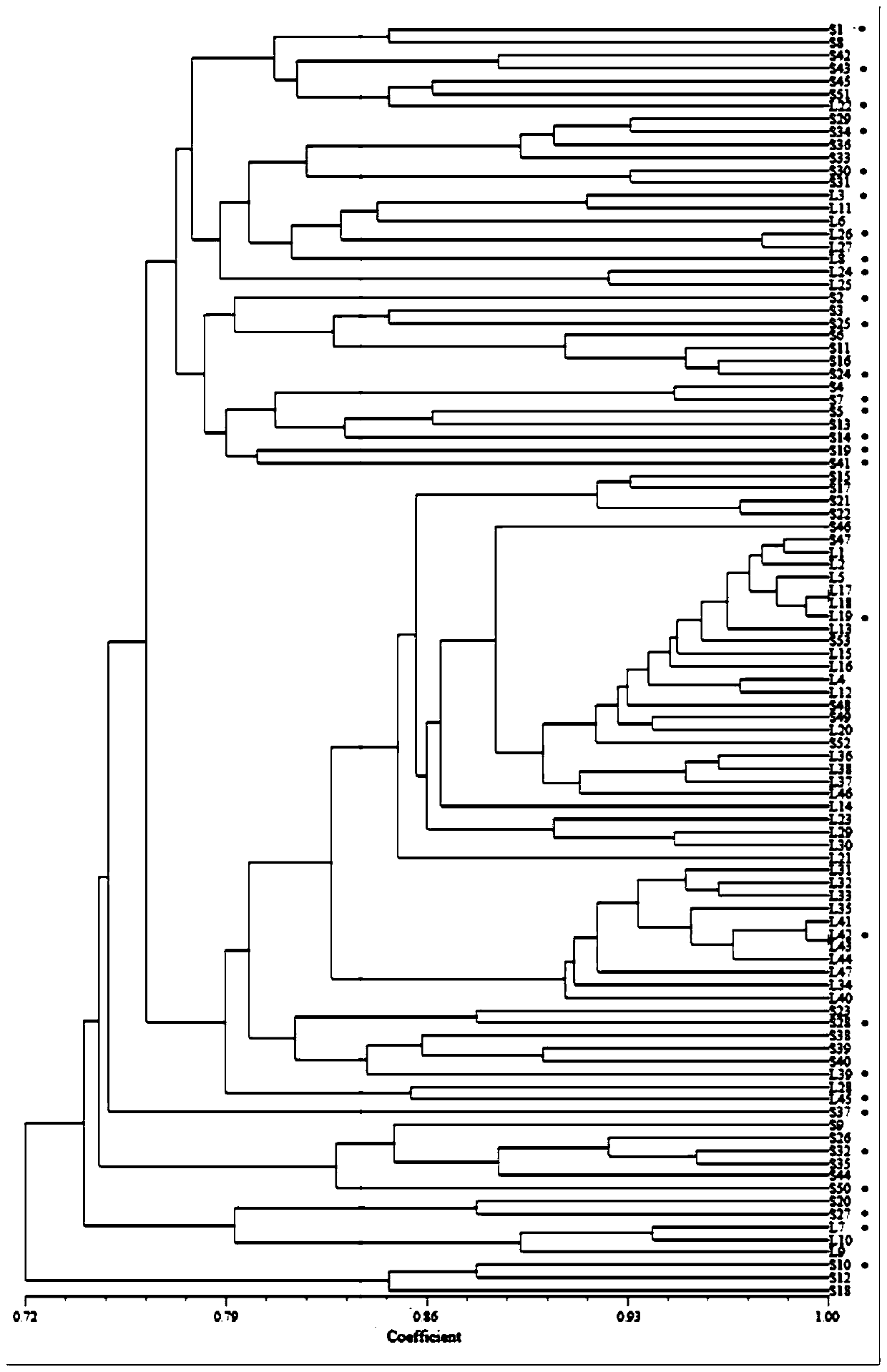
[0043] Isolation of strains
[0044] Take five 12-day cut-flower carnations in vases, cut off the stem ends of about 1cm, and use sterile scalpel tweezers to chop the stem ends and put them into test tubes, add sterilized deionized water until the stem ends are submerged , put the cork on the shaker and shake for 5 minutes. Dilute the bacterial solution by 10 -1 、10 -2、 10 -3 These three concentrations are labeled well. Dip the bacterial liquid with an inoculation needle, and do a streak separation on the LB medium, so as to achieve the purpose of isolating the bacterial species. Each sample has 10 replicates, which are marked and placed in an incubator for cultivation. After cultivating for 12 hours, observe the plate. If there is a single colony on the line marked by the inoculation needle, select the single colony, and then carry out streak plate culture to select a single strain to ensure the purity of the strain, and mark them in order, marked as S1, S2 , S3···S52, a...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Extract the total DNA of the bacterial classification obtained in Example 1, and the specific operations are as follows
[0048] (1) Pipette 2mL of bacterial liquid into a 2mL centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 2min, and discard the supernatant.
[0049] (2) Add 0.5 mL of normal saline, resuspend the bacterial mass, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 2 min, and discard the supernatant.
[0050](3) Add 0.5mL extract, resuspend the bacterial mass, and bathe in water at 65°C for 30min,
[0051] (4) Take it out of the water bath and shake it well for 1 minute, then place it at -20°C for 10 minutes.
[0052] (5) Add 0.5mL chloroform / water-saturated phenol (volume ratio 1:1), shake well for 3 minutes and then centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10 minutes.
[0053] (6) Take about 0.4 mL of the supernatant, add an equal volume of isopropanol to gently mix dozens of times, and then stand at -20°C for more than 30 minutes.
[0054] (7) Discard the supernatant after centrifugation a...
Embodiment 3
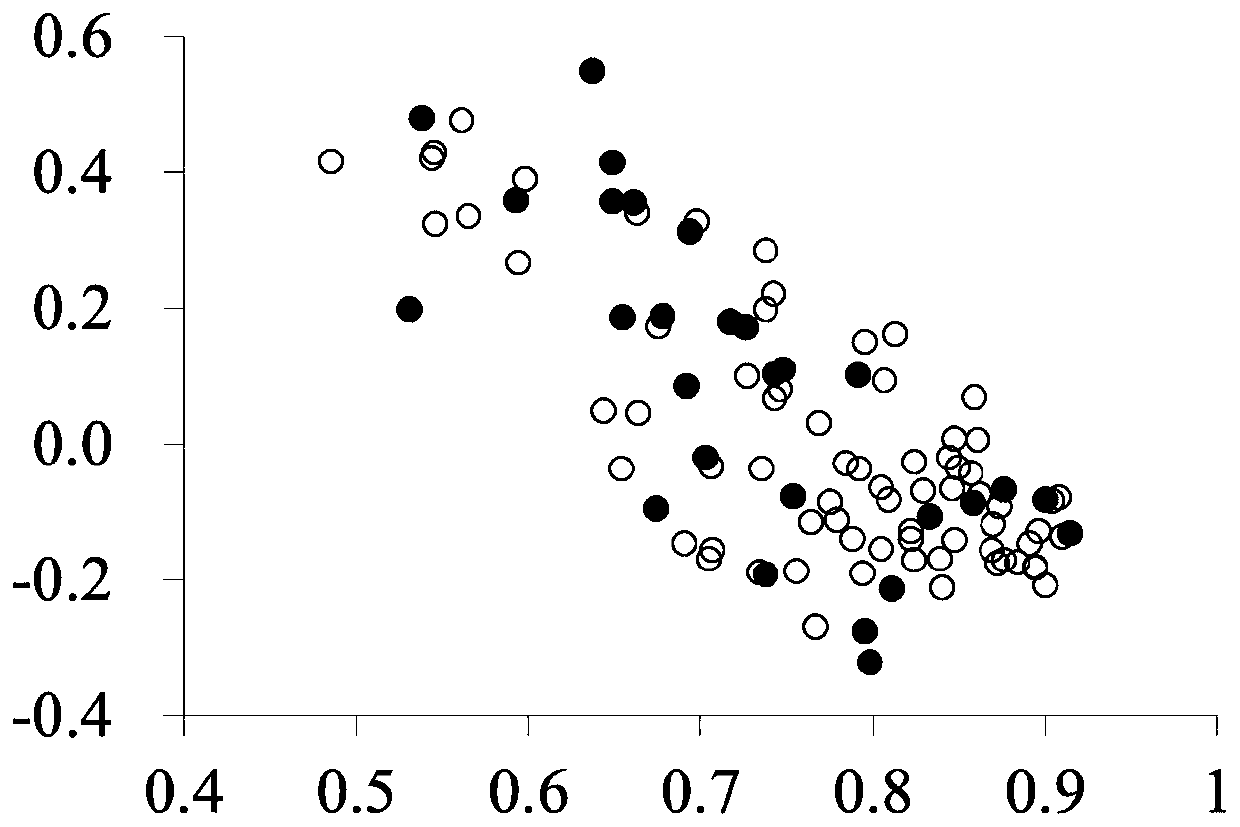
[0057] SRAP PCR and establishment of matrix table: SRAPPCR was carried out using the strain DNA extracted in Example 2 as a template; the primer combinations used in PCR were: F1R1, F1R4, F2R1, F2R2, F3R1, F3R3;
[0058] Said:
[0059] F1 is TGAGTCCAAACCGGATA,
[0060] F2 is TGAGTCCAAACCGGAGC,
[0061] F3 is TGAGTCCAAACCGGAAG,
[0062] R1 is GACTGCGTACGAATTGAC,
[0063] R2 is GACTGCGTACGAATTTGA,
[0064] R3 is GACTGCGTACGAATTCAA,
[0065] R4 is GACTGCGTACGAATTAGC.
[0066] The amplification procedure of described PCR is:
[0067] (1) Preheat at 94°C for 5 minutes;
[0068] (2) Denaturation at 94°C for 45s, primer annealing at 35°C for 1min, extension at 72°C for 1min30s, 5 cycles;
[0069] (3) Denaturation at 94°C for 45s, primer annealing at 50°C for 1min, extension at 72°C for 1min45s, a total of 35 cycles;
[0070] (4) Extend at 72°C for 10 minutes and store at 4°C.
[0071] The PCR product was subjected to polyacrylamide electrophoresis, and the specific operatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com