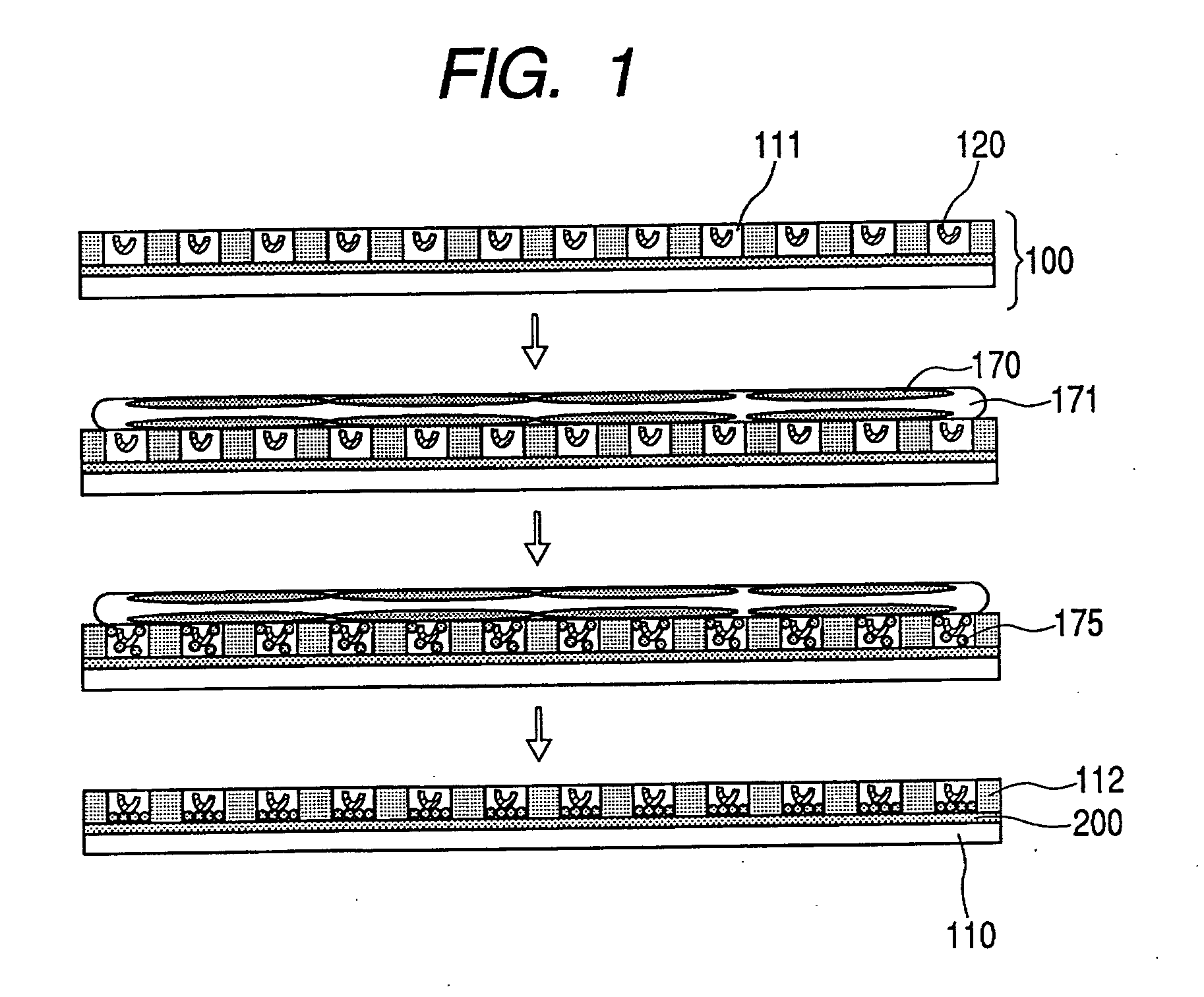
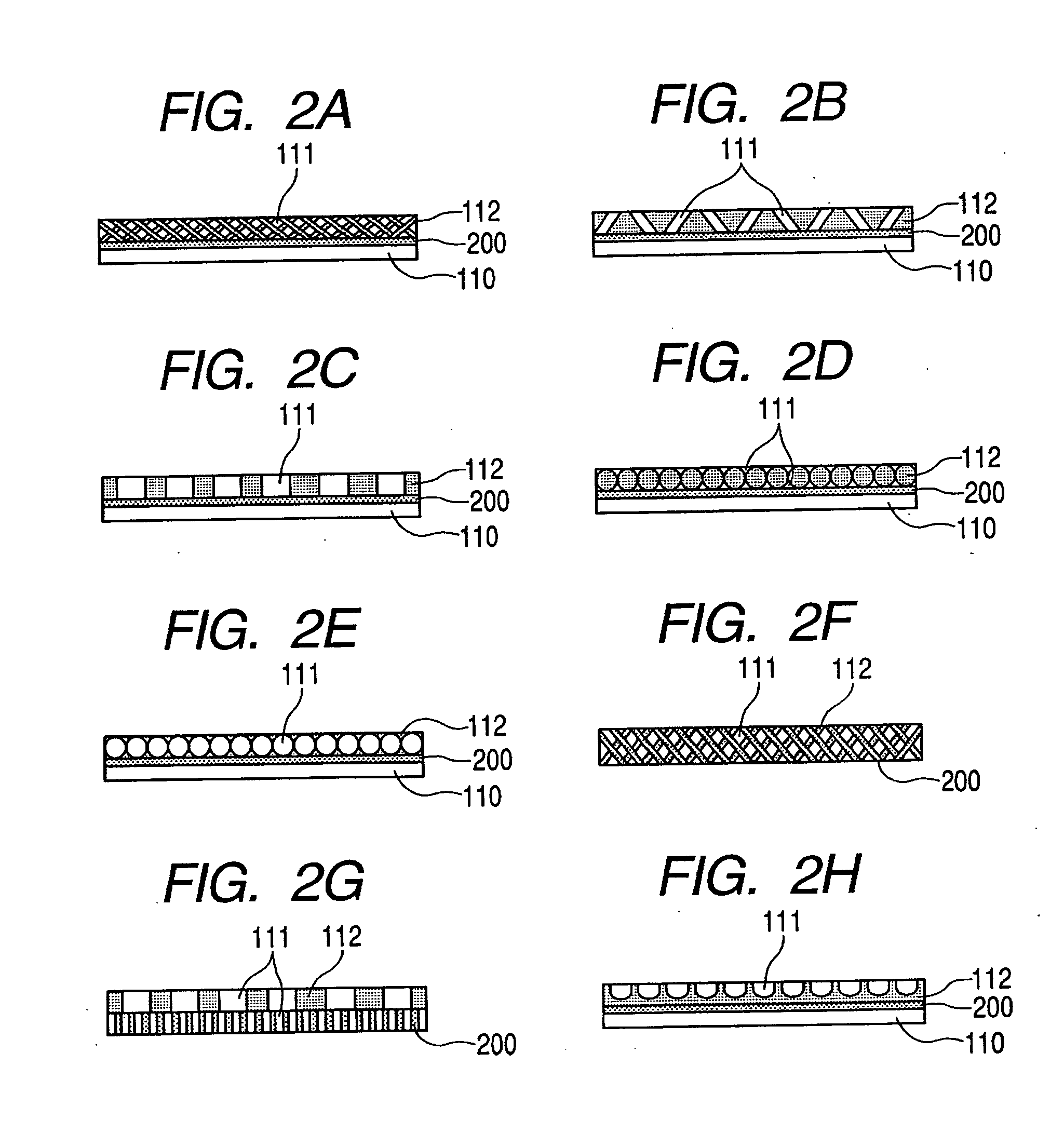
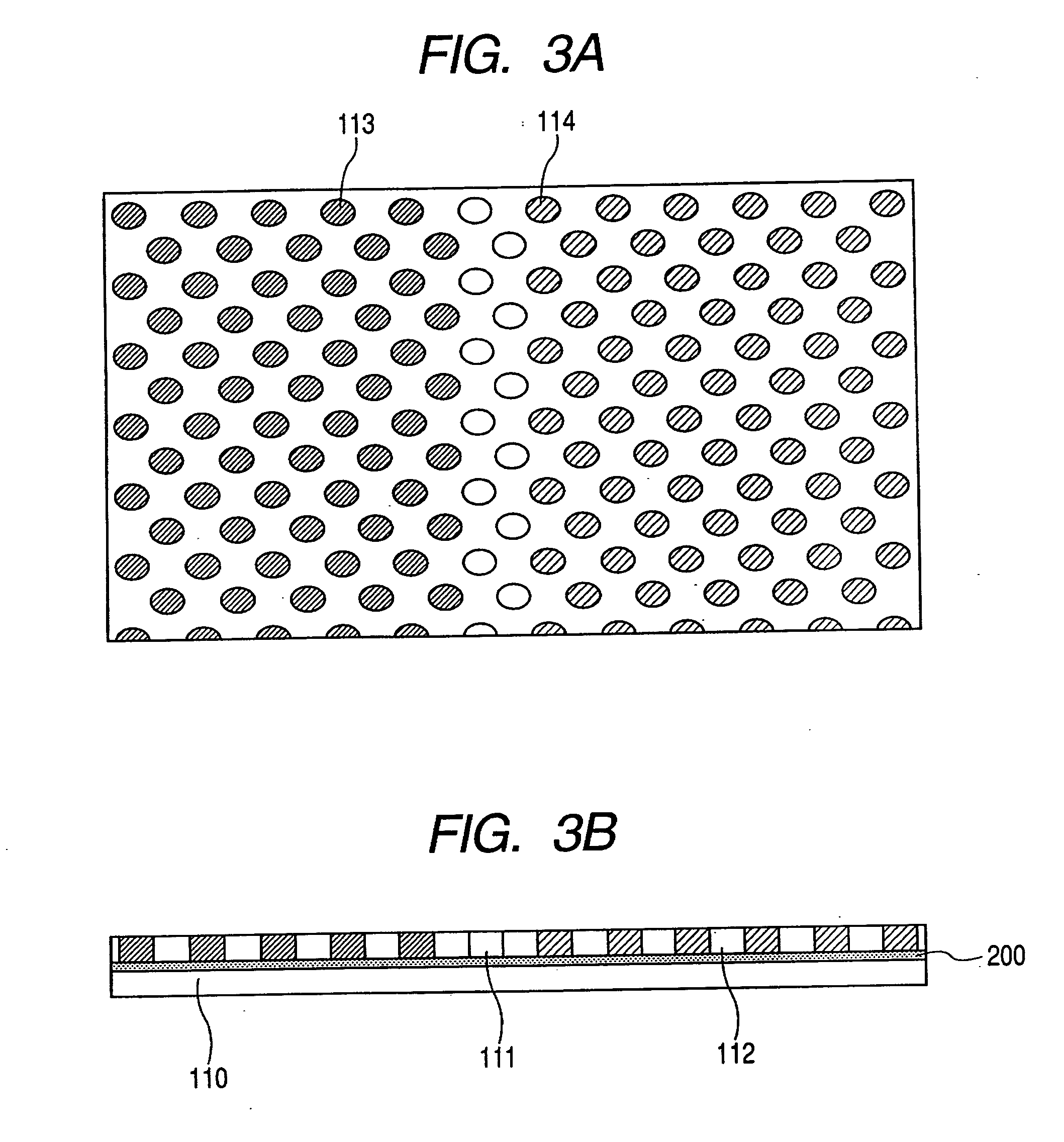
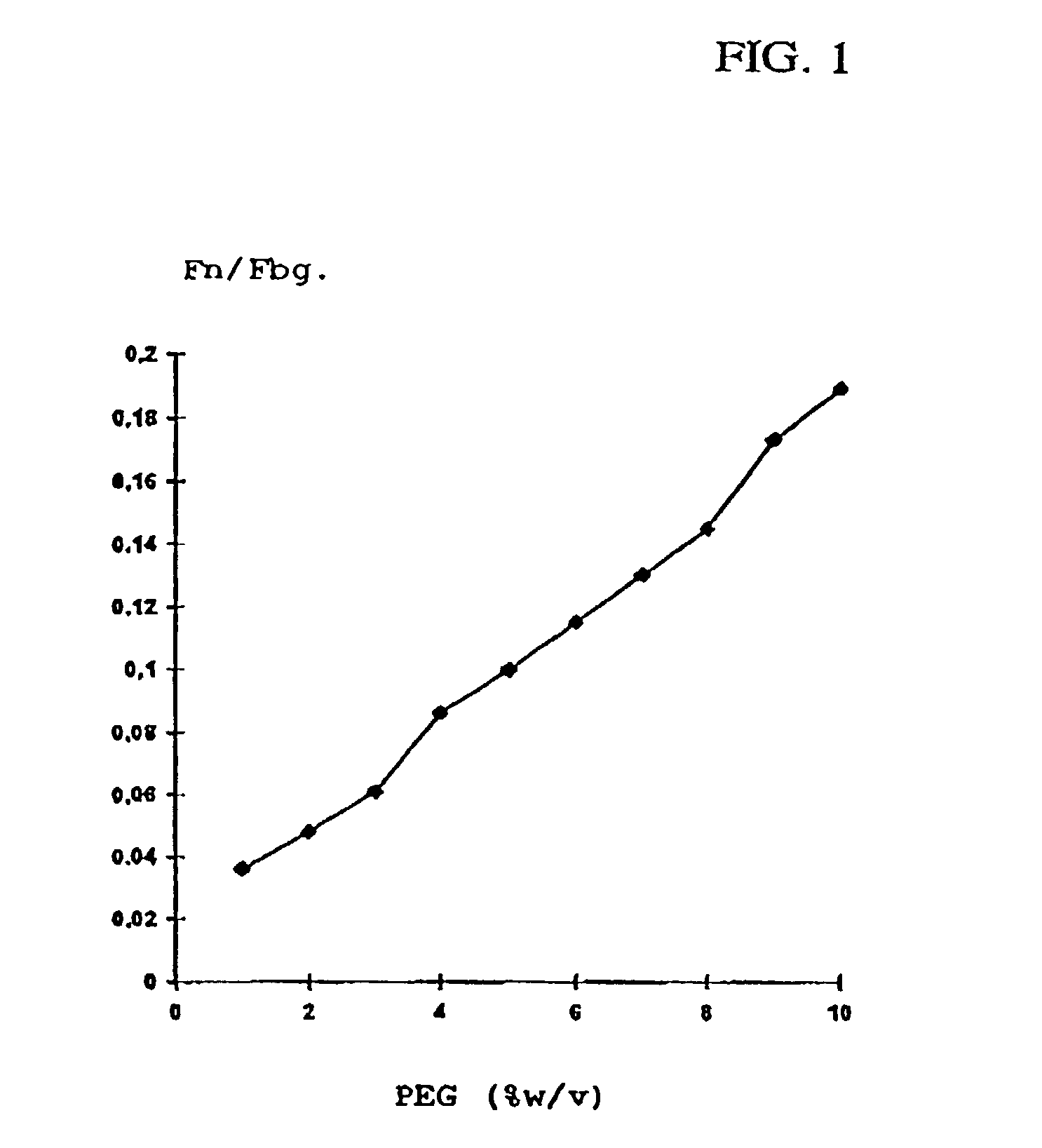
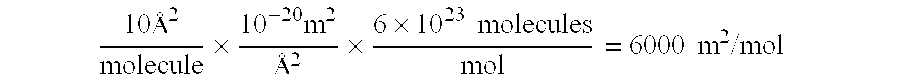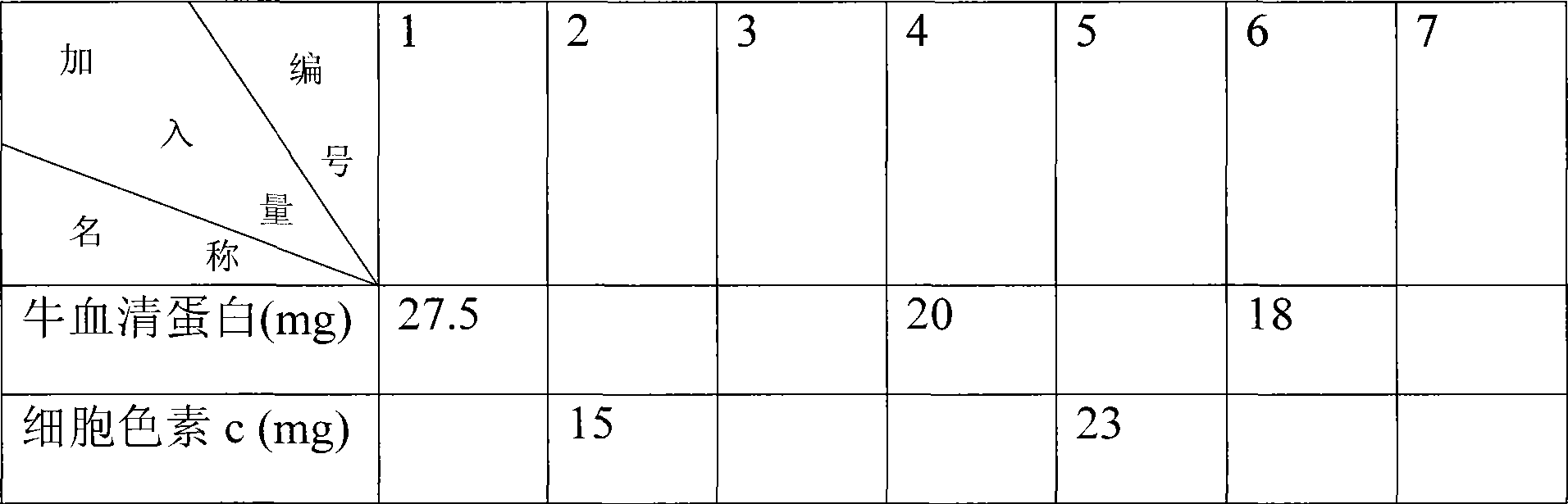Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
95 results about "SAA protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
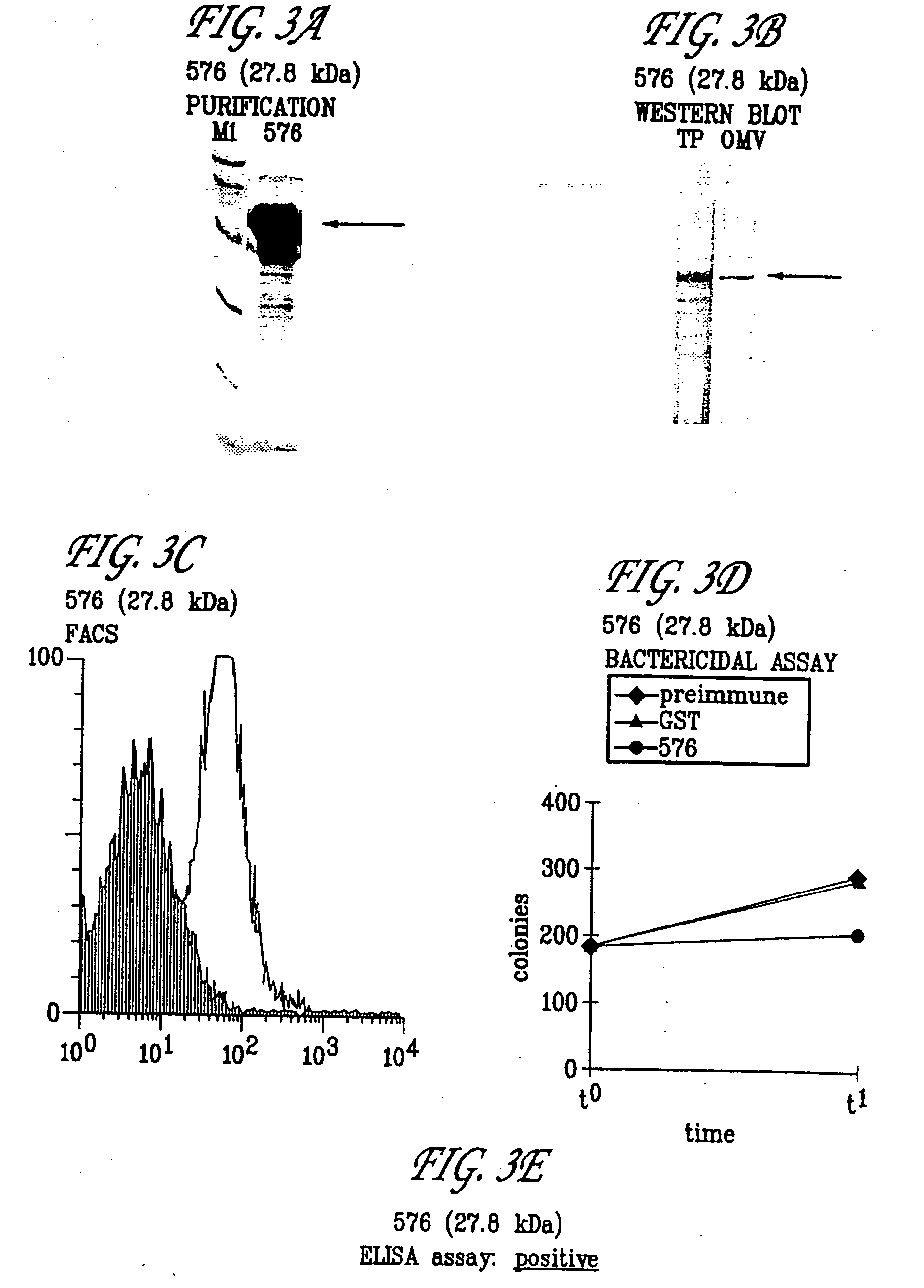
Biological tissue processing substrate, processing apparatus, processing method and processing kit
InactiveUS20070105087A1Improve accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSAA proteinBiology
A biological tissue processing substrate for fixing proteins in a biological tissue or degradation products of the proteins, the substrate comprising: a porous body that forms a contact surface with the biological tissue, the porous body holding in pores an enzyme for obtaining the proteins or the degradation products of the proteins from the biological tissue, wherein the proteins or the degradation products obtained by the action of the enzyme are brought into contact with a member consisting of a metal.
Owner:JACKSON BRAD
Method for producing a preparation based on fibrinogen and fibronectin as well as protein compositions obtainable according to this method
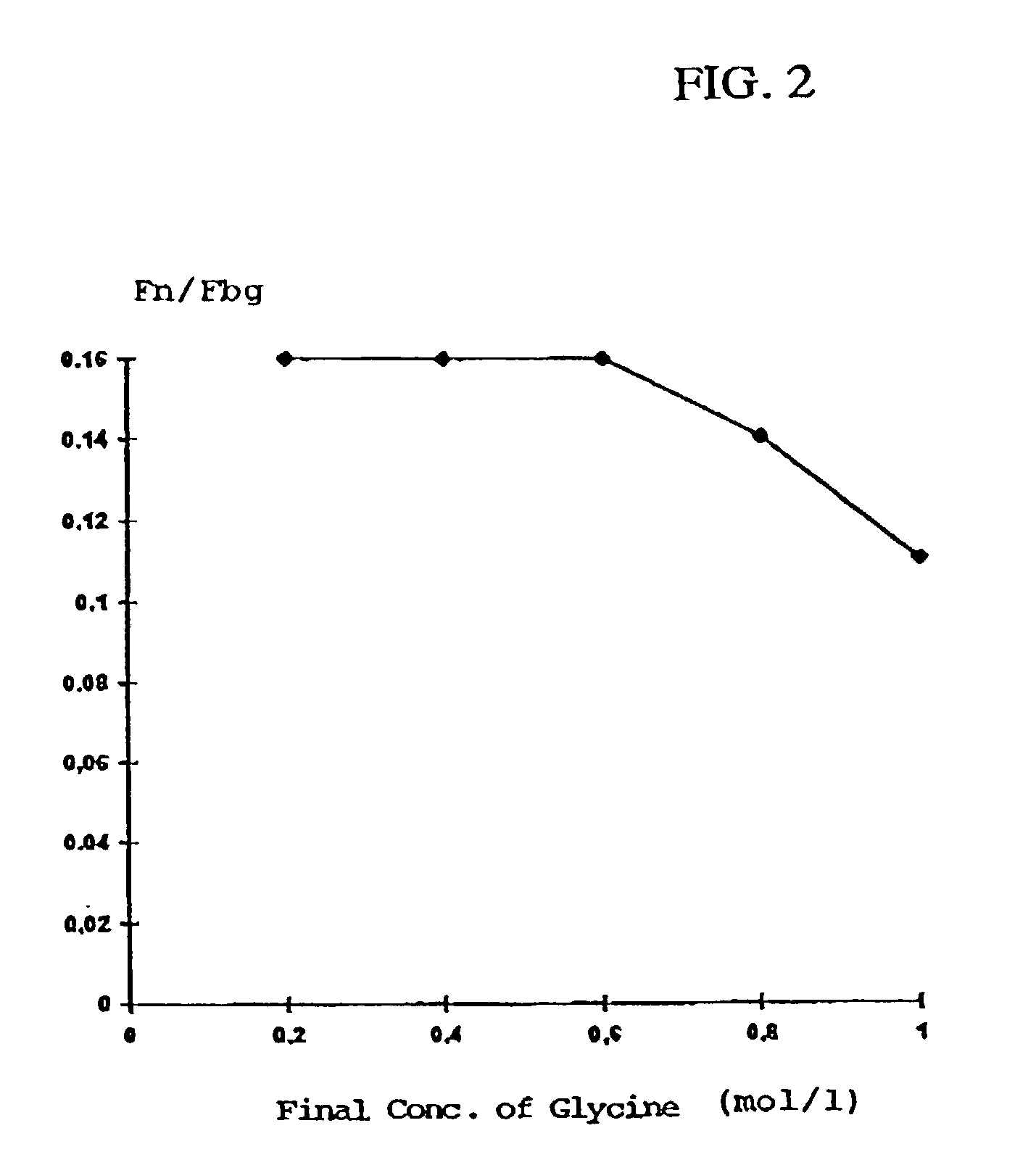
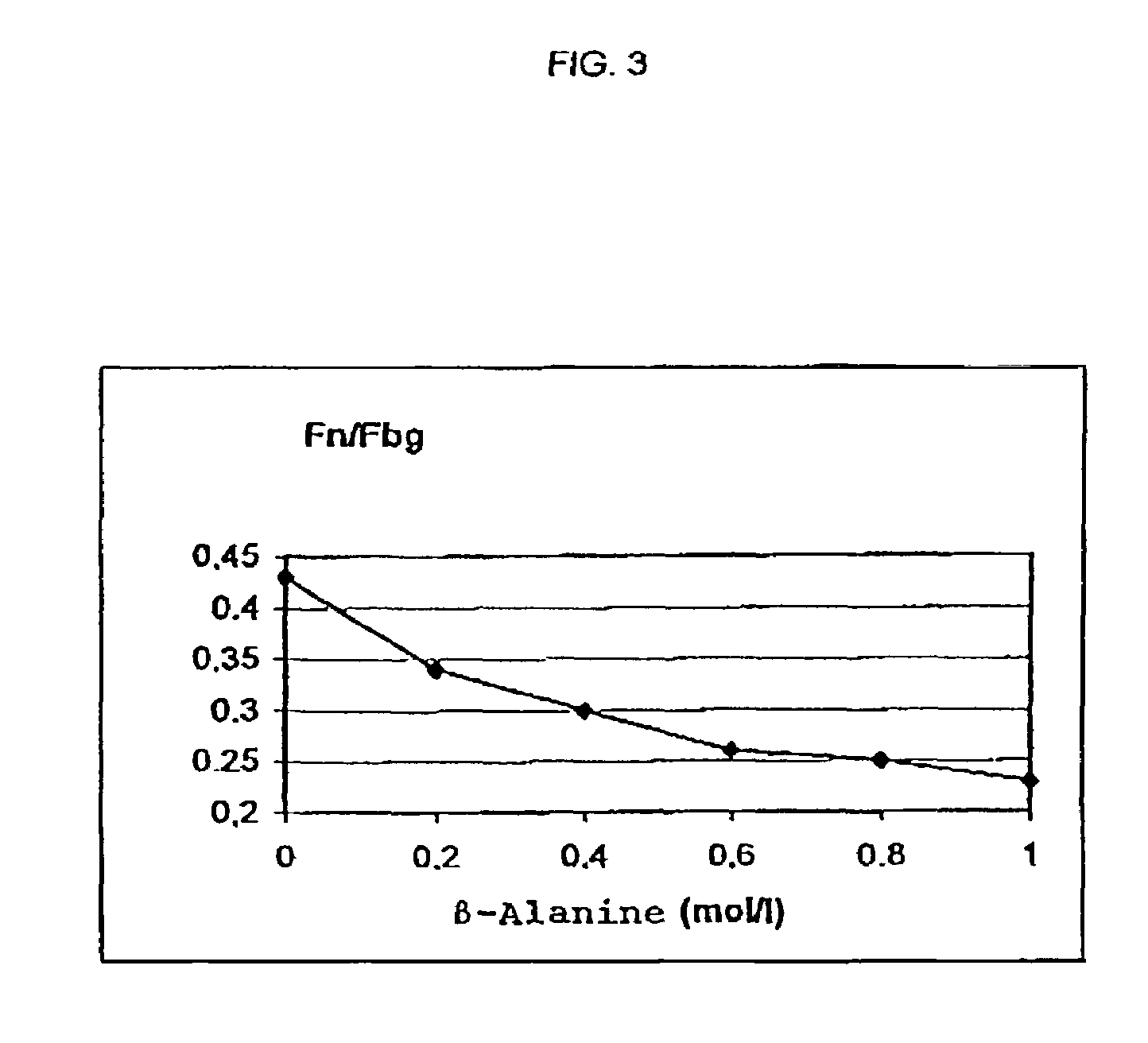
InactiveUS7241603B2Promote wound healingEliminate pollutionFactor VIIConnective tissue peptidesSAA proteinSolubility
A method for producing protein compositions comprising fibrinogen and fibronectin is disclosed, wherein a fibrinogen and fibronectin-containing starting solution is treated with a precipitating composition which comprises two different components that modify the solubility of fibrinogen and / or fibronectin, so that in a single-step precipitation a precipitate is formed which comprises fibrinogen and fibronectin, and the precipitate formed optionally is further treated by methods known per se.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
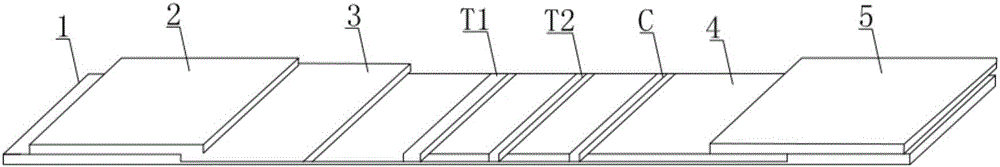
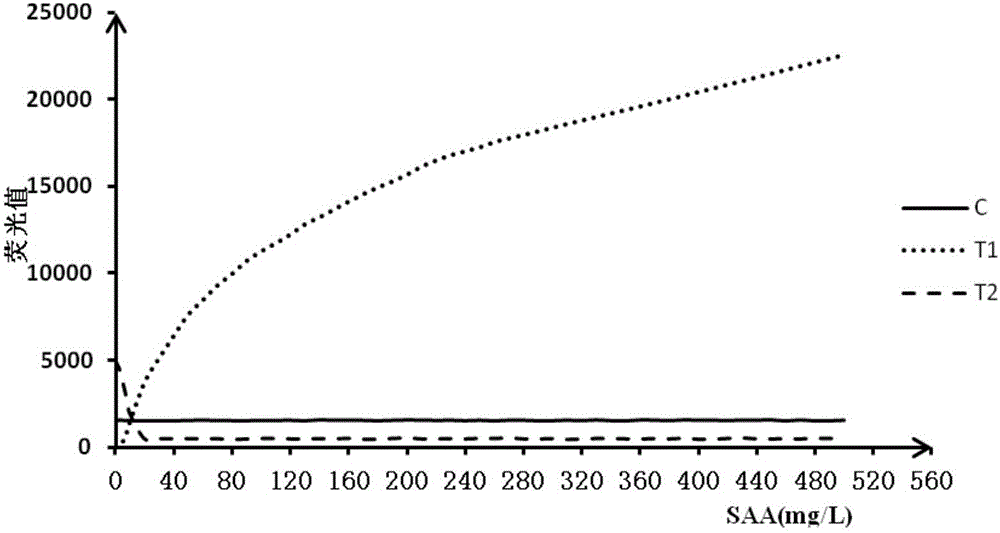
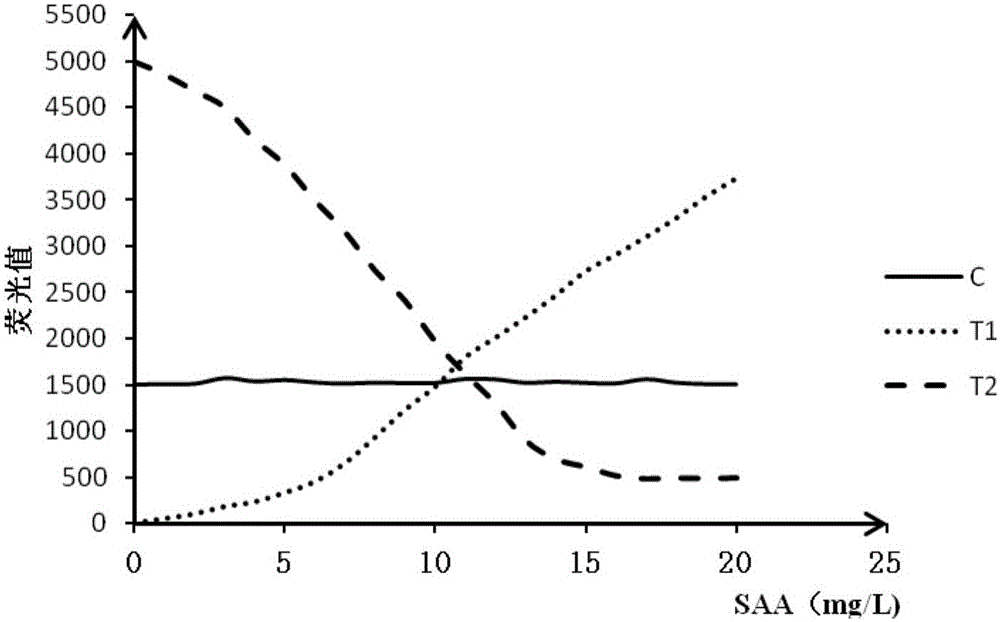
Double detection line SAA (Serum amyloid A protein) immunofluorescence chromatography quantitative detection reagent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105785038AExpand the scope of detectionHigh sensitivityDisease diagnosisBiological testingAntigenSAA protein
The invention discloses a double detection line SAA (Serum amyloid A protein) immunofluorescence chromatography quantitative detection reagent and a preparation method thereof. The double detection line SAA immunofluorescence chromatography quantitative detection reagent can simultaneously promote sensitivity and detection scope and can be applied to clinical detection for SAA level in patients of acute inflammation and chronic inflammation. According to the technical key points, the reagent comprises a base plate, a combining cushion, a coating film and an absorbing cushion, wherein a sample cushion is connected with the base plate; anti-SAA monoclonal antibody 1 and chick IgY are sprayed on the combining cushion and are marked with a same fluorescent microsphere; a detection line T1, a detection line T2 and a quality control C line are arranged on the coating film; anti-SAA monoclonal antibody 2 is coated with the detection line T1; antigen SAA protein is coated with the detection line T2; goat-anti-chick IgY is coated with the quality control C line. The reagent belongs to the technical field of in-vitro diagnostic reagents.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WEIMI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Adherence factors of non pathogenic microorganisms and applications thereof for screening microorganisms for specific probiotic properties; novel pharmaceutical compositions and food additives comprising such microorganisms and adherence factors
A protein obtainable from a non pathgenic microorgansim, said protein having mucosa binding promoting activity and a molecular weight of 20-40 kD is disclosed. Application of such a protein or a peptide derived therefrom in a method of screening non pathogenic microorganisms for a microorganism capable of specifically binding mucosa, said method comprising detection in a manner known per se of the presence of a particular protein on or in a microorganism or in a culture of microorganisms, said particular protein being the already defined protein. Kits suitable for such a screening method are also disclosed. Use of a component selected from the group of components comprising a protein or peptide as defined; an expression vector comprising nucleic acid encoding such protein or peptide; a recombinant microorganism or a part of said microorganism expressing such protein or peptide, said part expressing mucosa binding promoting activity; a non pathogenic microorganism capable of expressing such protein or peptide or a part of said microorganism, said part expressing mucosa binding promoting activity as pharmaceutically active component in a pharmaceutical composition for prophylaxis and / or treatment of disease or illness associated with a mucosa colonizing pathogenic microorganism. Use of such components as food additive and compositions comprising such components are described.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Neisseria genomic sequences and methods of their use
InactiveUS20050191316A1Easy to insertEfficient HarvestingAntibacterial agentsBacteriaSAA proteinNucleotide
The invention provides methods of obtaining immunogenic proteins from genomic sequences including Neisseria, including the amino acid sequences and the corresponding nucleotide sequences, as well as the genomic sequence of Neisseria meningitidis B. The proteins so obtained are useful antigens for vaccines, immunogenic compositions, and / or diagnostics.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
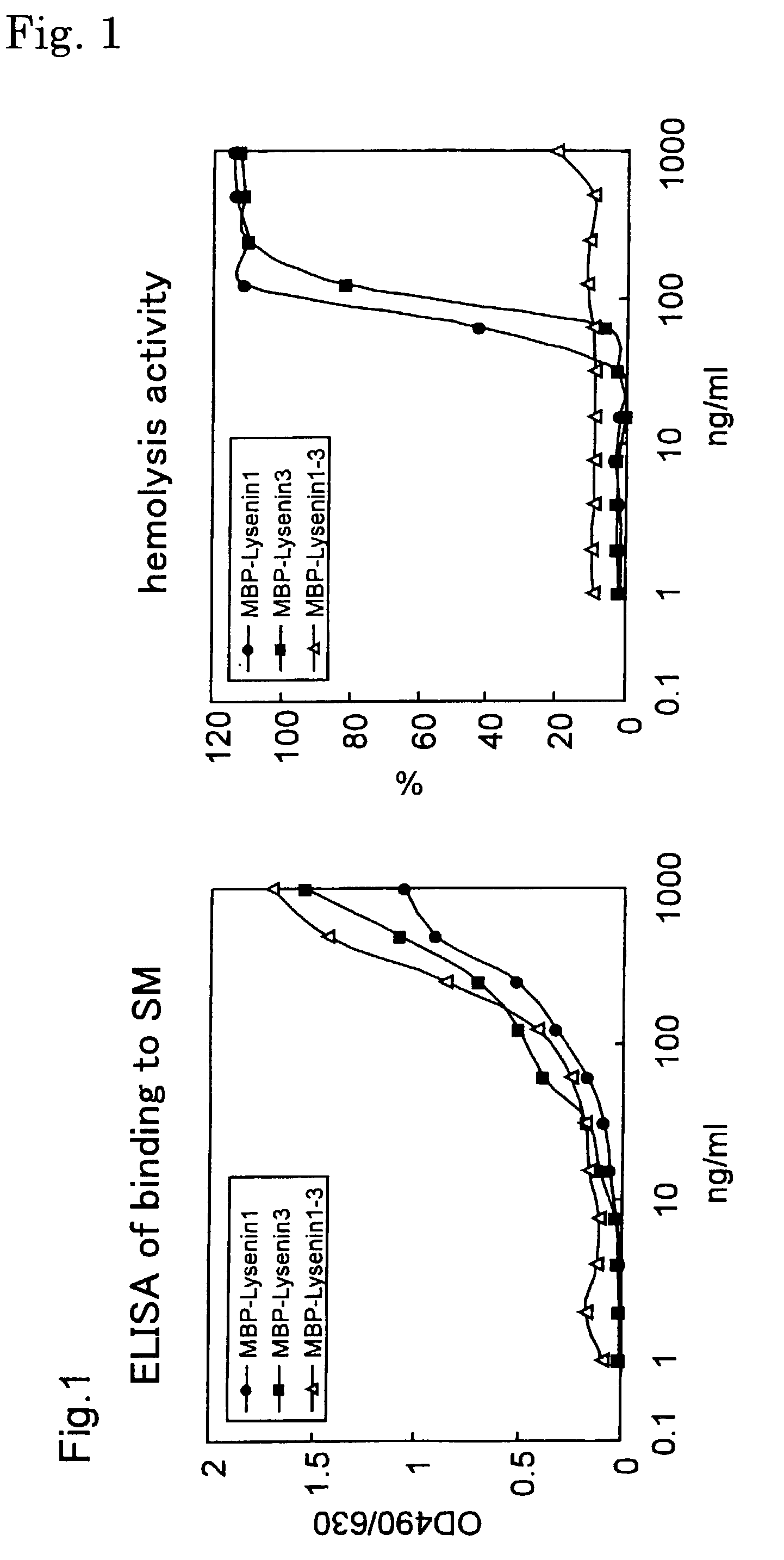
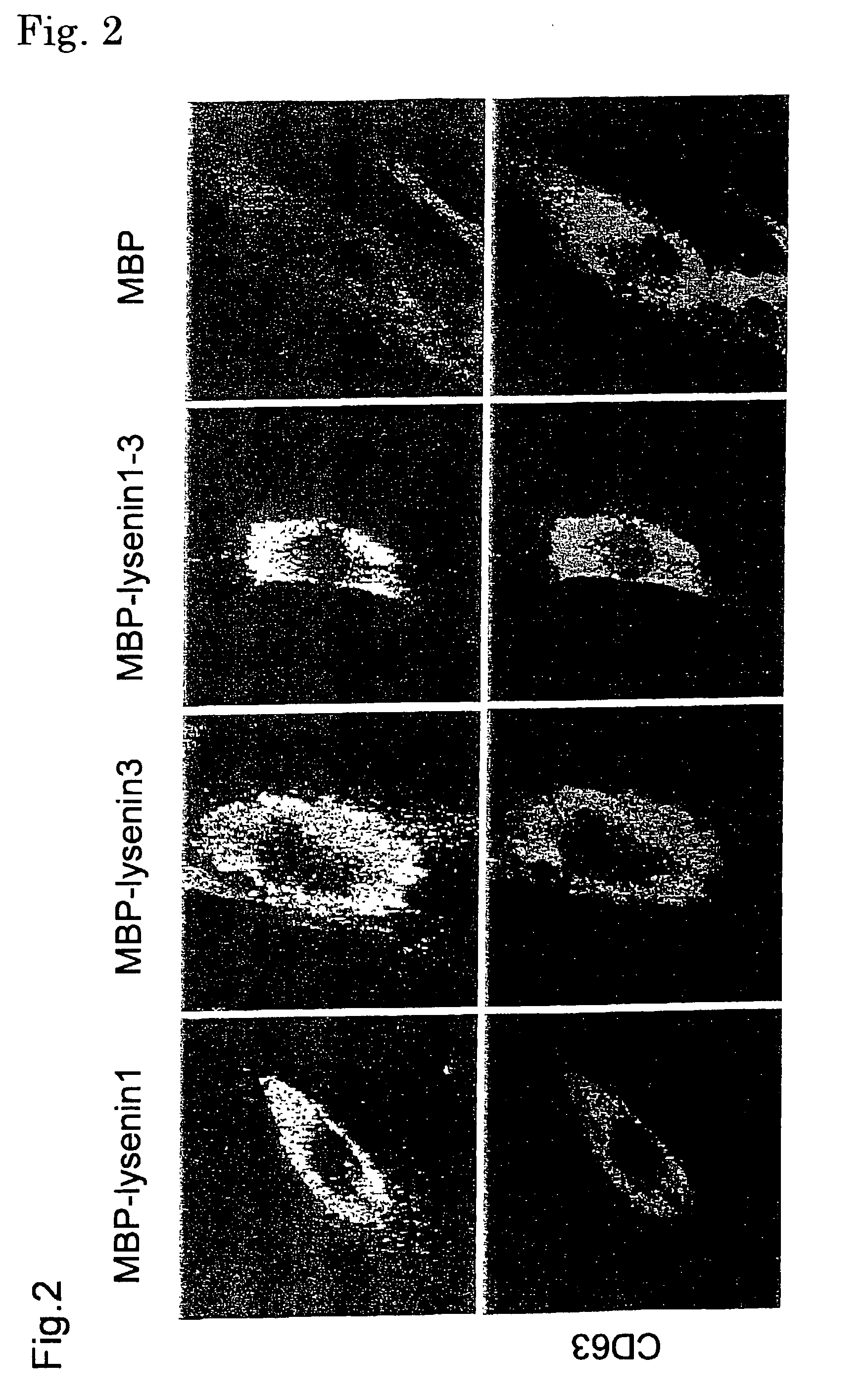
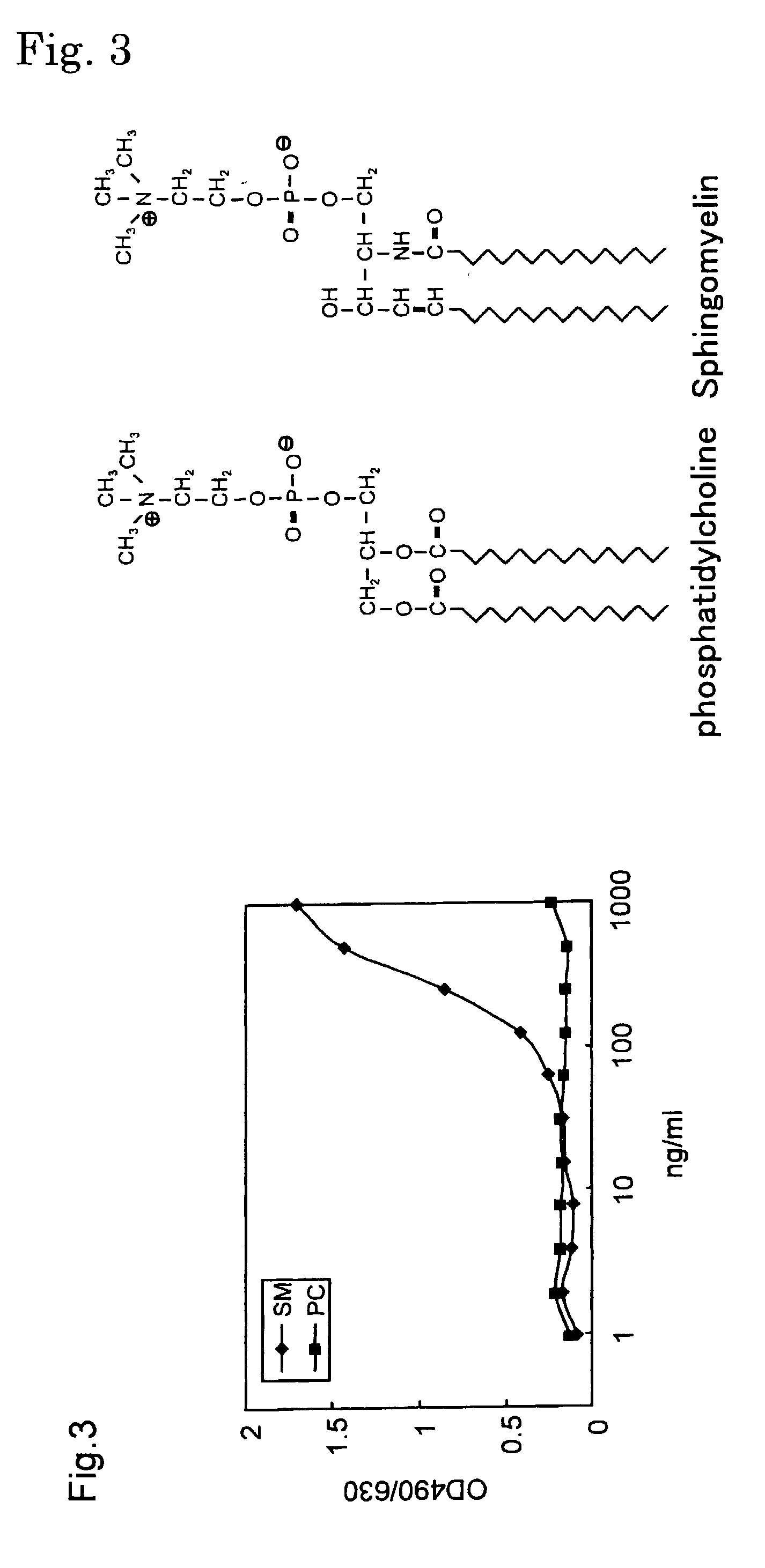
Sphingomyelin detecting probe
An object of the present invention is to provide a protein useful as a sphingomyelin detecting probe, which specifically recognizes sphingomyelin and has low cytotoxicity. The present invention provides a protein which has an amino acid sequence having, as the amino acid sequence from the 1st to the 48th amino acid, the amino acid sequence from the 1st to the 48th amino acid in Lysenin 1, and as the amino acid sequence from the 49th to the 298th amino acid, the amino acid sequence from the 51st to the 300th amino acid in Lysenin 3; and a protein which is obtained by deleting N terminal and / or C terminal from earthworm toxins Lysenin 1 or 3, and which specifically recognizes sphingomyelin.
Owner:RIKEN
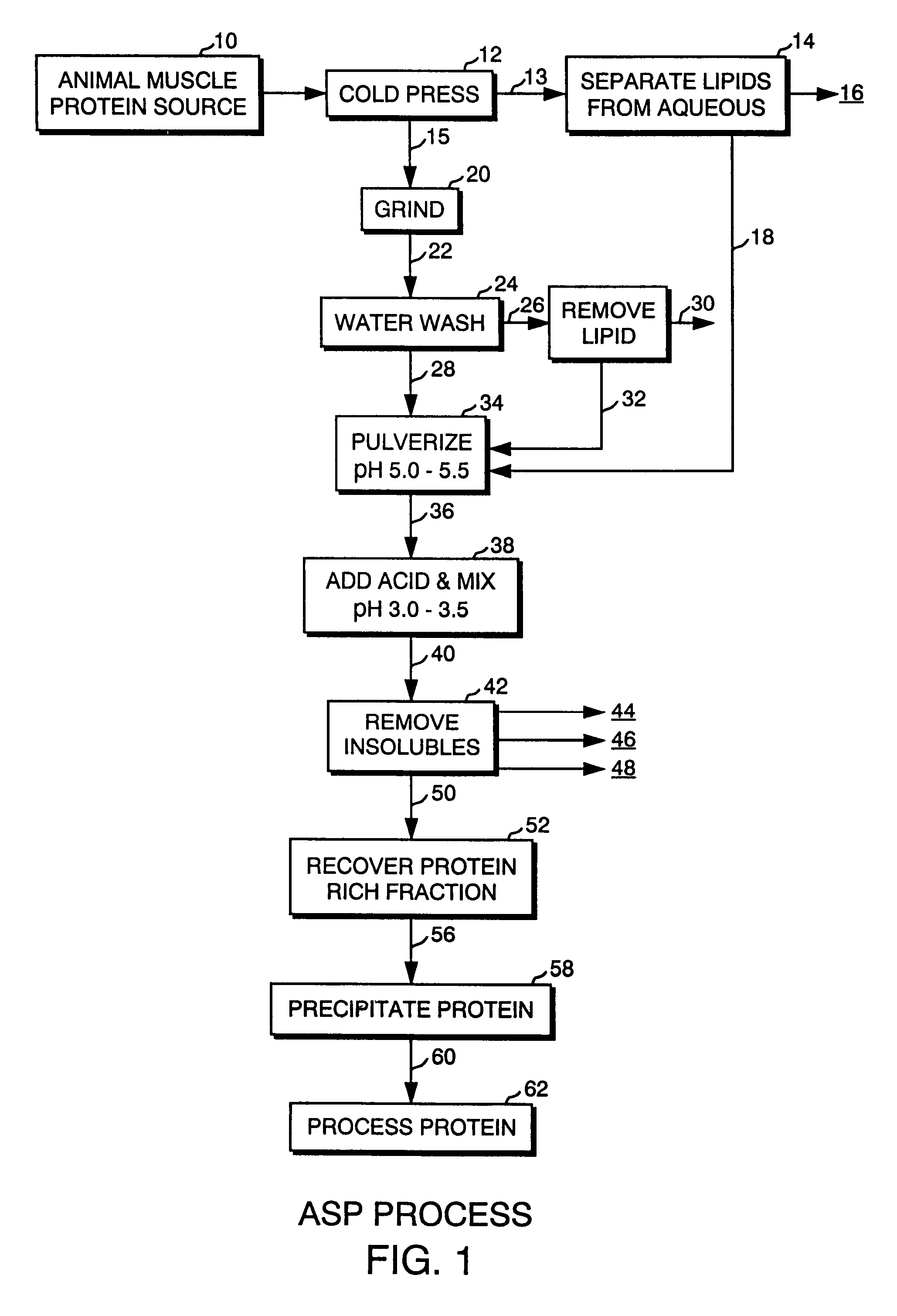
Protein composition obtained from a muscle source
InactiveUS7473764B2Simple treatmentSufficient low viscosityProtein composition from fishDepsipeptidesSAA proteinMuscle tissue
A process is provided for isolating a protein component of animal muscle tissue by mixing a particulate form of the tissue with an acidic aqueous liquid having a pH below about 3.5 to produce a protein rich solution substantially free of myofibrils and sarcomere tissue structure. The protein rich aqueous solution can be treated to effect protein precipitation, followed by protein recovery.
Owner:ADVANCED PROTEIN TECH INC
Mutant Strain of Aspergillus sojae with Enhanced Protease Activity and Preparation Method of Natural Taste Enhancer Using the Same
The present invention relates to a mutant strain of Aspergillus sojae with an enhanced protease activity and a preparation method of a natural taste enhancer using the same. More specifically, the present invention relates to the mutant strain of Aspergillus sojae with an enhanced protease activity is obtained by selecting a strain with high protease activity and treating it with N-methyl-N′-Nitroso-N-nitrosoguanidine (NTG) and inducing a mutation through irradiating, and a preparation method of a natural taste enhancer using protein hydrolysate obtained by hydrolyzing the protein sources with their cultures.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Direct Assay of Skin Protein in Skin Samples Removed by Tape Stripping
InactiveUS20080188387A1Cost effectiveImprove throughputCosmetic preparationsMake-upSAA proteinMedicine
The present invention provides for a method of measuring the amount of skin removed by tape stripping. In one aspect of the invention, the invention provides a method for the direct assay of protein in skin samples removed by tape stripping, with a view to combining the protein measurement obtained with a corresponding skin cholesterol measurement to identify individuals at risk of having atherosclerosis as well as those at risk of developing atherosclerosis and similar diseases associated with and attributable to high cholesterol levels. Moreover, the present invention allows a comparative measurement of the amount of skin removed by tape stripping that does not rely solely on the area of the sample removed. Additionally, in one aspect of the invention, the method of this invention can allow relative levels of skin cholesterol to be compared based on the relative amounts of skin removed.
Owner:MIRACULINS
Method of herding and collection of oil spilled at the aquatic surface
ActiveUS20120074067A1General water supply conservationSolid sorbent liquid separationSAA proteinStress Proteins
Disclosed are methods of removing oil from an aqueous surface, comprising: surrounding an oil spot on the aqueous surface with an oil-absorbing material; and introducing a solution comprising a surfactant to the oil spot. Also disclosed are the above methods where the oil is not mechanically directed towards the oil-absorbing material, or where the oil-absorbing material is not mechanically directed towards the oil. Also disclosed are the above methods further comprising introducing a solution comprising a protein / surfactant complex to the oil spot, where the protein / surfactant complex comprises a protein component obtained from the fermentation of yeast, comprising a mixture of multiple intracellular proteins, at least a portion of the mixture including yeast polypeptides obtained from fermenting yeast and yeast stress proteins resulting from subjecting a mixture obtained from the yeast fermentation to stress.
Owner:ADVANCED BIOCATALYTICS
Method for detecting and/or removing protein and/or peptide comprising a cross-beta structure from an aqueous solution comprising a protein
InactiveUS20070015133A1Prevent and decrease inductionReduce presenceCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHaemoglobins/myoglobinsSAA proteinCompound (substance)
The invention relates to the field of aqueous solutions comprising a protein. More specifically, the invention relates to the detection and / or removal of conformationally altered proteins and / or peptides comprising a cross-β structure from an aqueous solution comprising a protein. The invention provides methods for detecting and / or removing proteins and / or peptides comprising a cross-β structure from an aqueous solution comprising a protein, the method comprising contacting the aqueous solution comprising a protein with at least one cross-β structure-binding compound resulting in a bound protein or peptide with cross-β structure. The invention further provides a aqueous solution comprising a protein obtainable by a method of the invention, and a kit for carrying out the methods of the invention.
Owner:CROSSBETA BIOSCIENCES BV
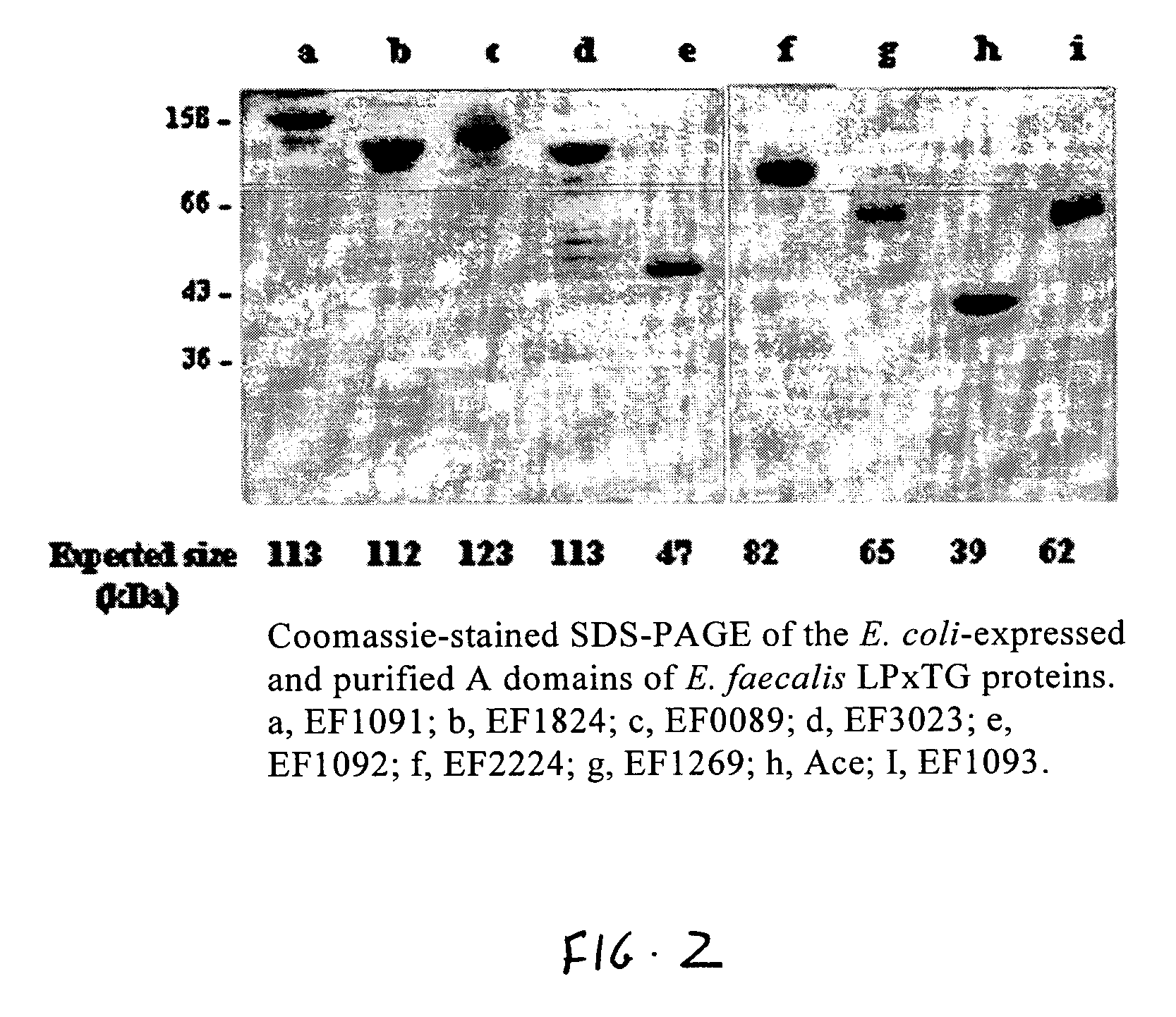
Bioinformatic method for identifying surface-anchored proteins from gram-positive bacteria and proteins obtained thereby
ActiveUS7615616B2Antibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsSAA proteinGram-positive bacterial infections
A bioinformatic method is provided for identifying and isolating proteins with MSCRAMM®—like characteristics from Gram positive bacteria, such as Enterococcus, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus and Bacillus bacteria, which can then be utilized in methods to prevent and treat infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria. The method involves identifying from sequence information those proteins with a putative C-terminal LPXTG (SEQ ID NO:1) cell wall sorting signal and other structural similarities to MSCRAMM® proteins having the LPXTG-anchored cell wall proteins. The MSCRAMM® proteins and immunogenic regions therein that are identified and isolated using the present invention may be used to generate antibodies useful in the diagnosis, treatment or prevention of Gram positive bacterial infections.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +2
Spider silk protein gene designed and synthesized by plant preference codon and its application
InactiveCN1390937AHigh strengthImprove practicalityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSAA proteinCellulose
The present invention relates to a spider silk crystal protein gene synthesized by plant preferance codon, its expression carrier, the plant cells transformed from it, and the transgenic plant and its descendant. Said gene can be effectively expressed in fibrous plant and the obtained protein moleculae can be combined with the cellulose of plant, so improving the strength of plant fibres.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Crystallization of a protein with a sulphur salt
InactiveUS6066481AOxidation stabilityHydrolasesPeptide preparation methodsCrystallographySAA protein
The present invention relates to a method for crystallization of a protein obtained from a protein-containing solution which involves (a) treating the protein-containing solution with a salt containing a sulphur atom having an oxidation state less than 6, and (b) recovering the protein in crystalline form.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
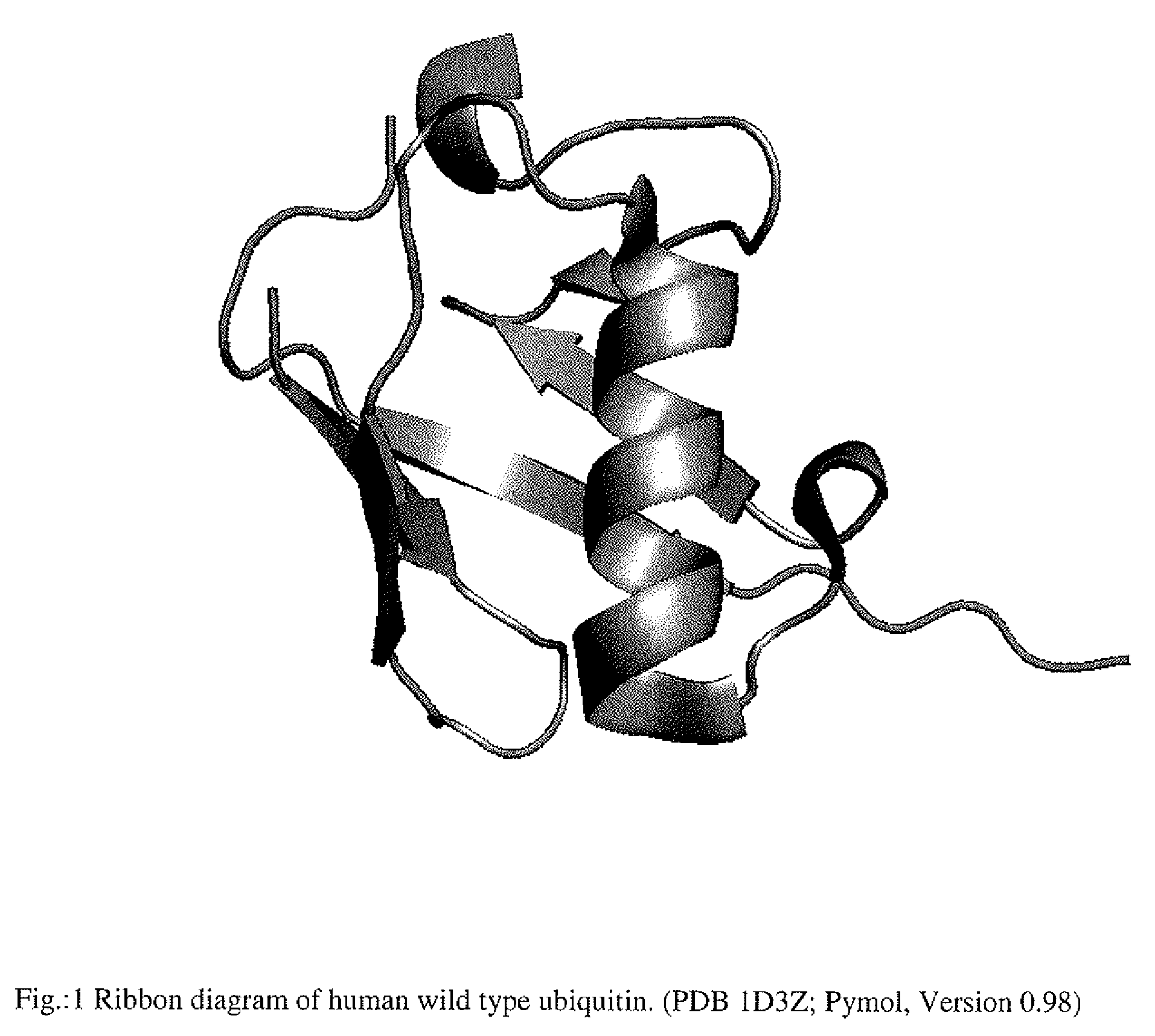
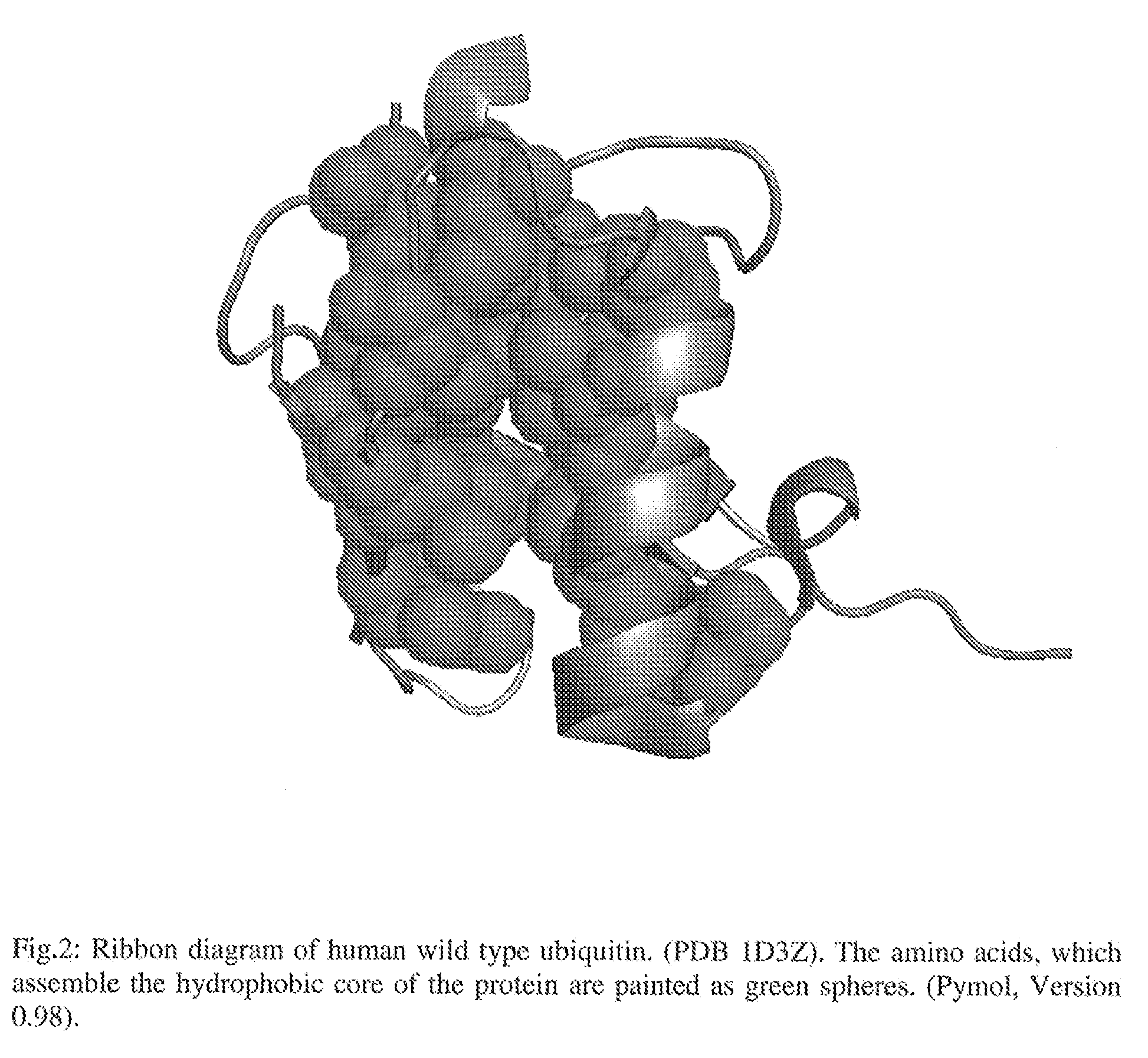
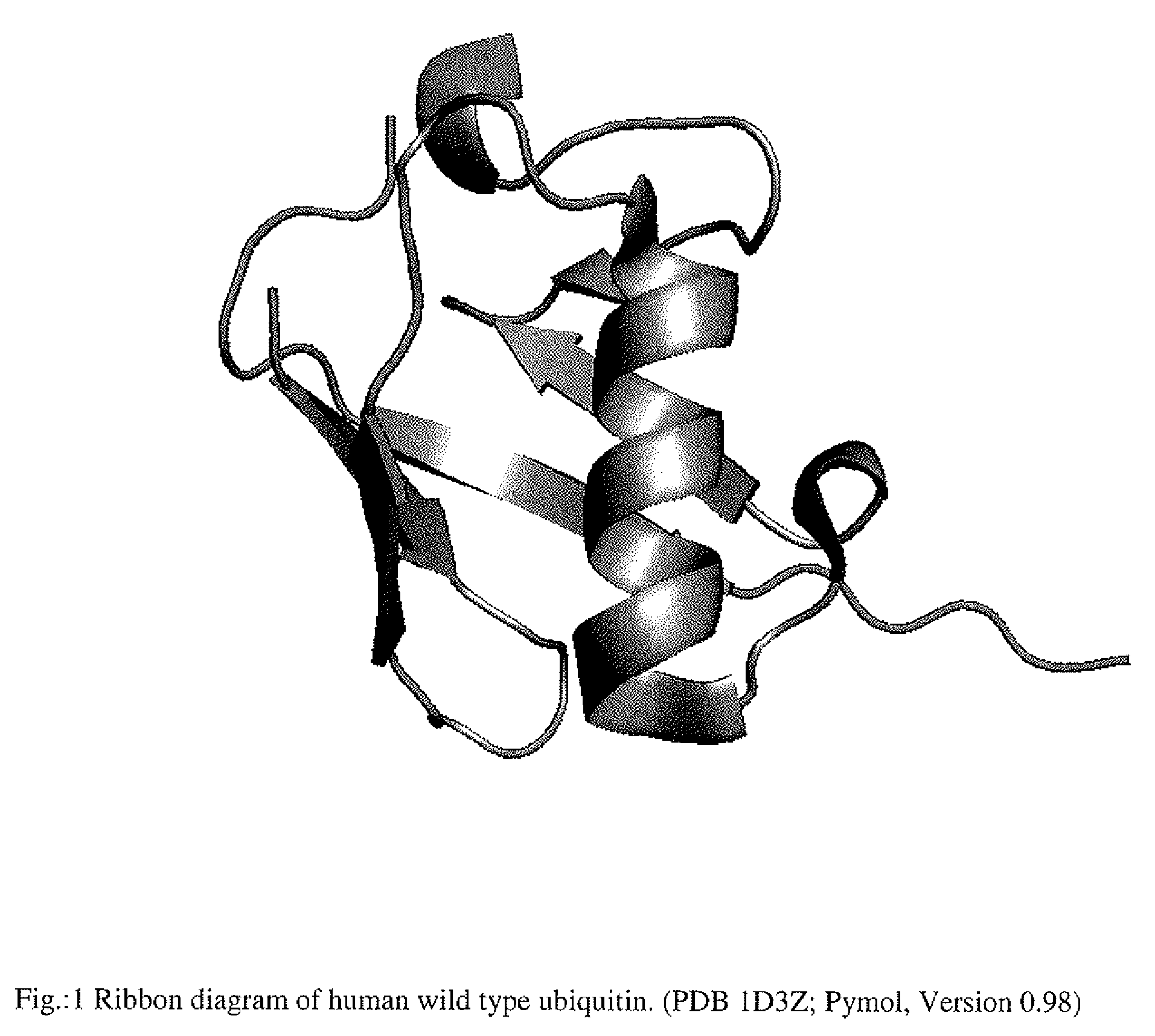
Artificial binding proteins based on a modified alpha helical region of ubiquitin
ActiveUS20100130720A1Raise the possibilitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsSAA proteinDisease
The present invention is directed to a method for the generation of binding proteins derived from the protein super-family of ubiquitin like proteins with modifications in their alpha helical region as well as to a protein obtainable by said method. Furthermore, the invention provides the use of a protein for the specific recognition, binding and neutralization of a predescribed target molecule, for the detection, quantitative determination, separation and / or for the isolation of a corresponding binding partner and the use of a protein of the invention, for diagnosis, prophylaxis and treatment of diseases in which the corresponding binding partner is directly or indirectly involved.
Owner:NAVIGO PROTEINS GMBH
Artificial binding proteins based on a modified alpha helical region of ubiquitin
The present invention is directed to a method for the generation of binding proteins derived from the protein super-family of ubiquitin like proteins with modifications in their alpha helical region as well as to a protein obtainable by said method. Furthermore, the invention provides the use of a protein for the specific recognition, binding and neutralization of a predescribed target molecule, for the detection, quantitative determination, separation and / or for the isolation of a corresponding binding partner and the use of a protein of the invention, for diagnosis, prophylaxis and treatment of diseases in which the corresponding binding partner is directly or indirectly involved.
Owner:NAVIGO PROTEINS GMBH
Enhanced oil recovery compositions comprising proteins and surfactants and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20130281328A1Function increaseReserved functionOrganic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsSAA proteinStress conditions
Owner:PODELLA CARL WALTER +2
Protein/polypeptide-k obtained from Momordica charantia and a process for the extraction thereof
InactiveUS6831162B2Improve immunityGood blood pressurePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSAA proteinDiabetes mellitus
The invention relates to a novel and highly effective hypoglycemic protein called polypeptide-k, extracted from Momordica charantia, provides a method for the extraction of said polypeptide-k from Momordica charantiaand provides novel hypoglycemic compositions employing the said extract, and useful in the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Owner:KHANNA PUSHPA
Preparation of microprotein
The invention relates to a method for preparing microprotein, which takes active sludge generated during biochemical treatment of sewage and waste water, particularly remained active sludge from town sewage treatment plants, as raw materials. The method is characterized in that the active sludge is subjected to concentration regulation, hot basic hydrolysis, residue-liquid separation, filtrate condensation and concentrated solution drying to obtain protein products with different concentrations. The method has the advantages of simple technological process and equipment and easy industrialized production, and protein products prepared have the advantages of good foamability and foaming stability, high yield and low cost.
Owner:天津市裕川置业集团有限公司
Method for Separating Protein from Food
InactiveUS20110305817A1Increase productionHigh protein yieldProtein composition from vegetable seedsDepsipeptidesSAA proteinFood additive
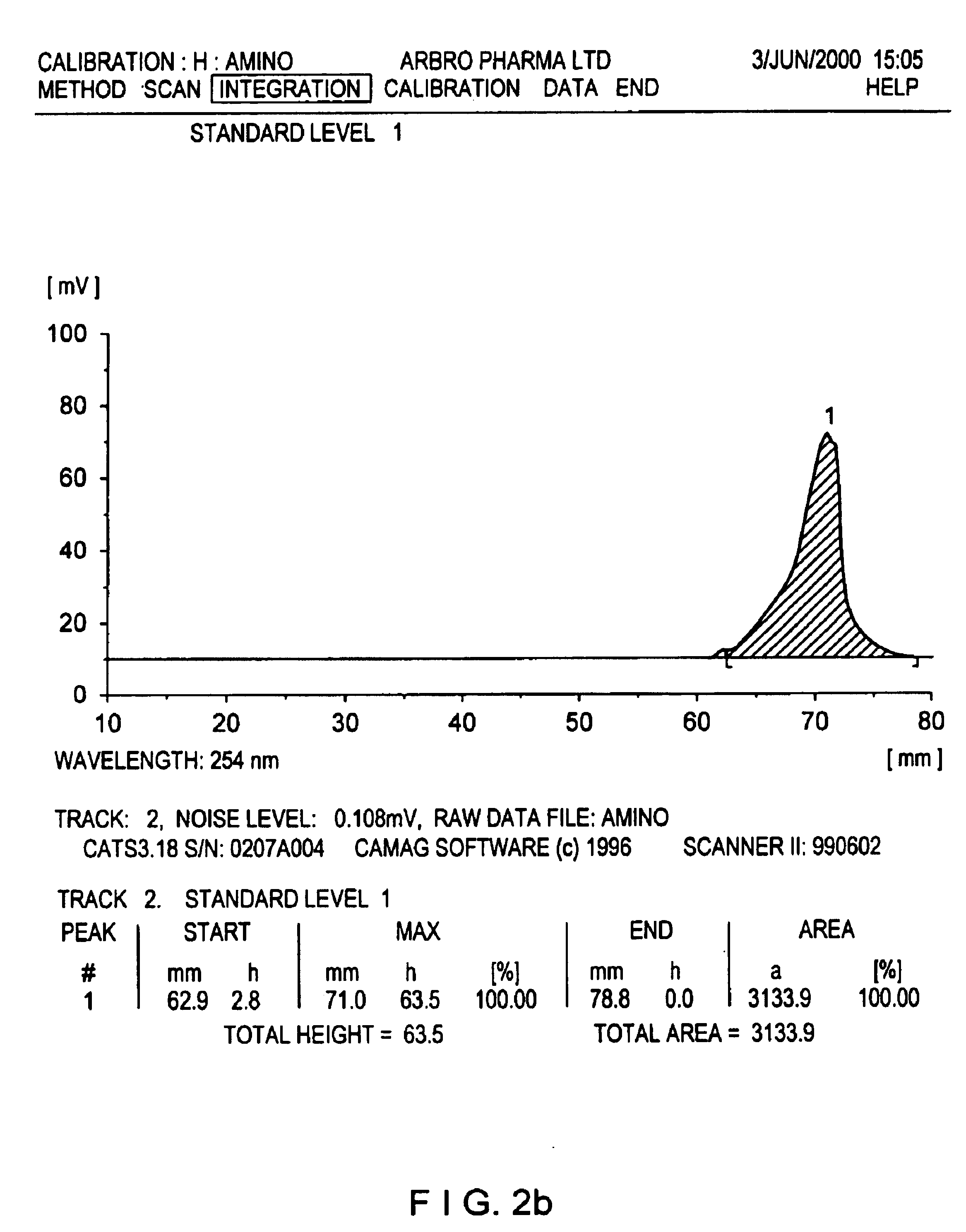
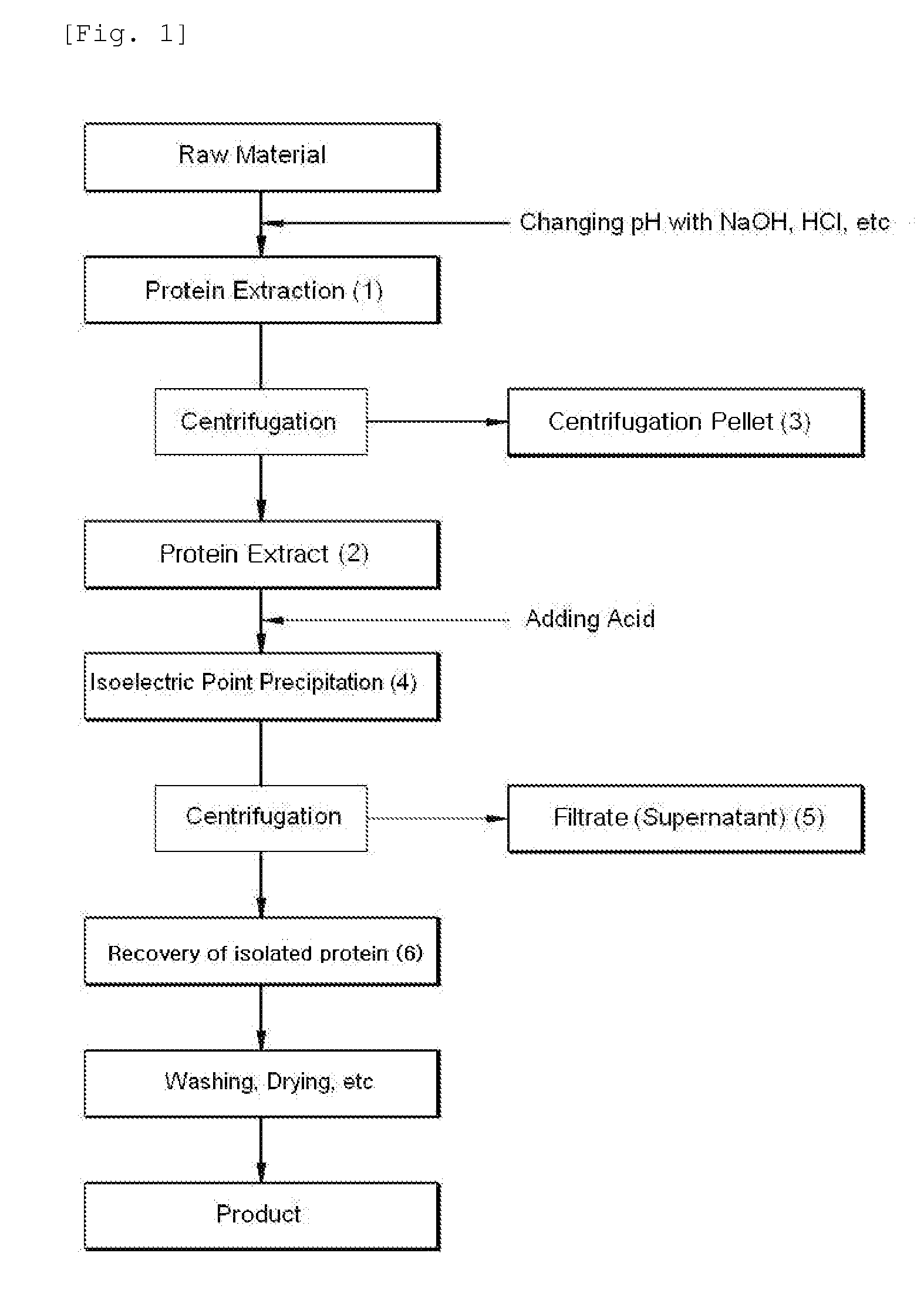
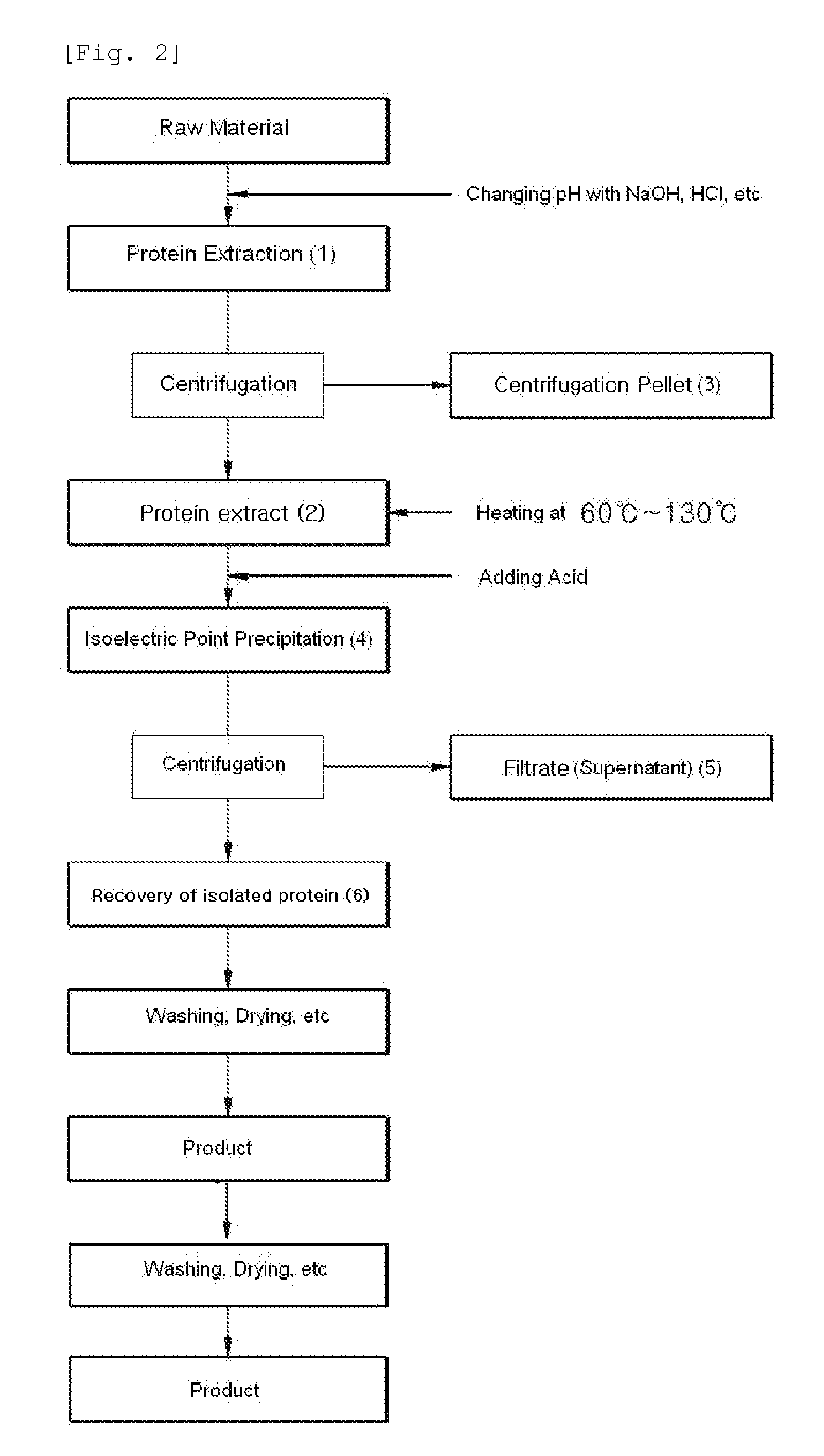
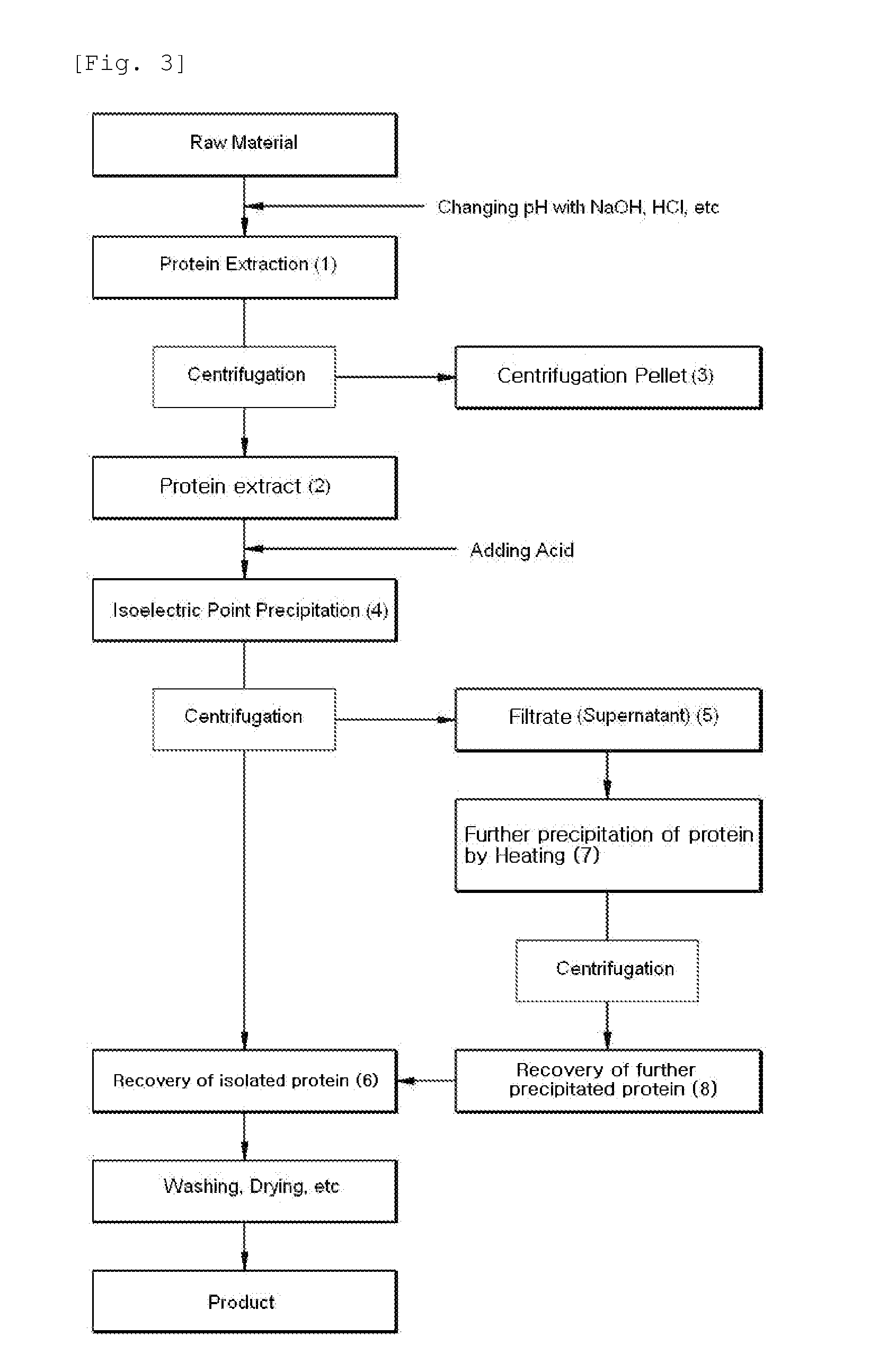
The present invention relates to a method for separating protein from food by using an iso-electric point precipitation, comprising: obtaining a protein extract by adjusting pH of a raw material food in a media; precipitating the protein by adjusting pH of the protein extract to an iso-electric point of the desired protein; and recovering the protein precipitated after separating a protein filtrate through centrifuging the precipitated protein; in which the method may further include a heat-precipitation of the protein by heating the protein extract or the protein filtrate to 60˜145° C. The protein obtained in high yield according to the above method can be used as a food additive or a food nutritional enhancer.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Production method for protein molecule imprinting integral column
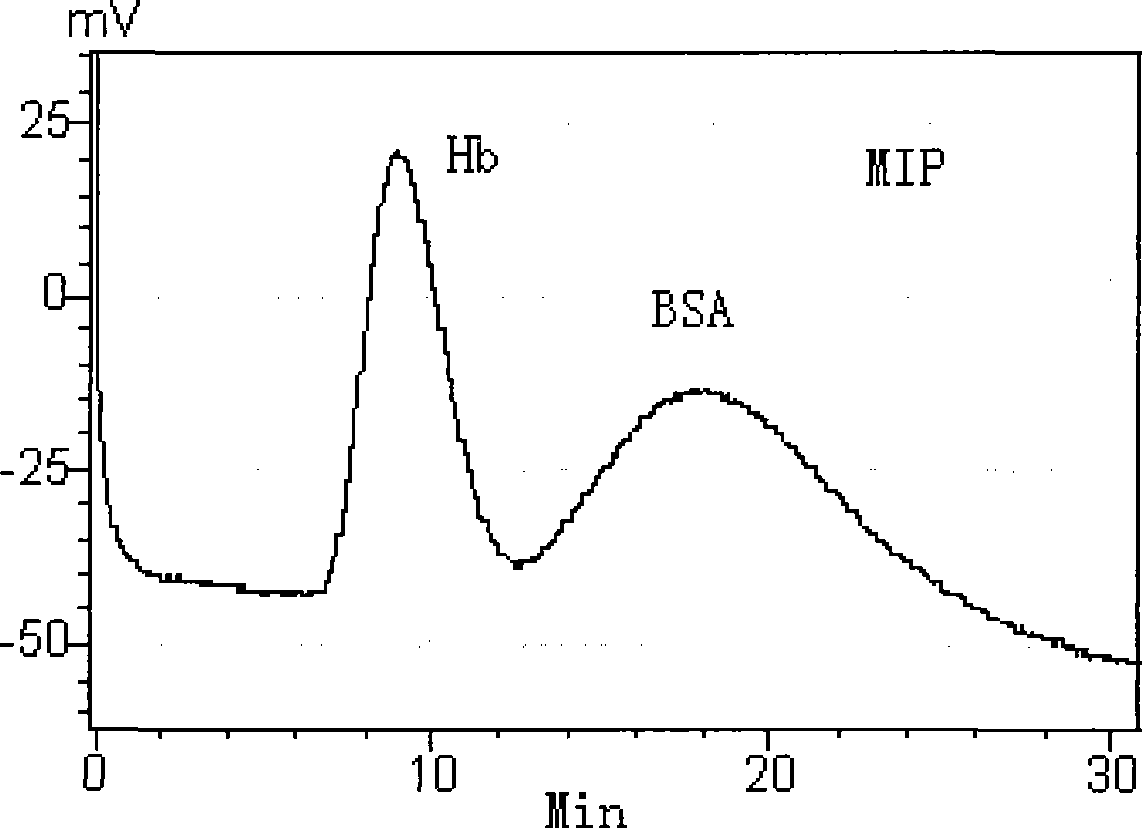
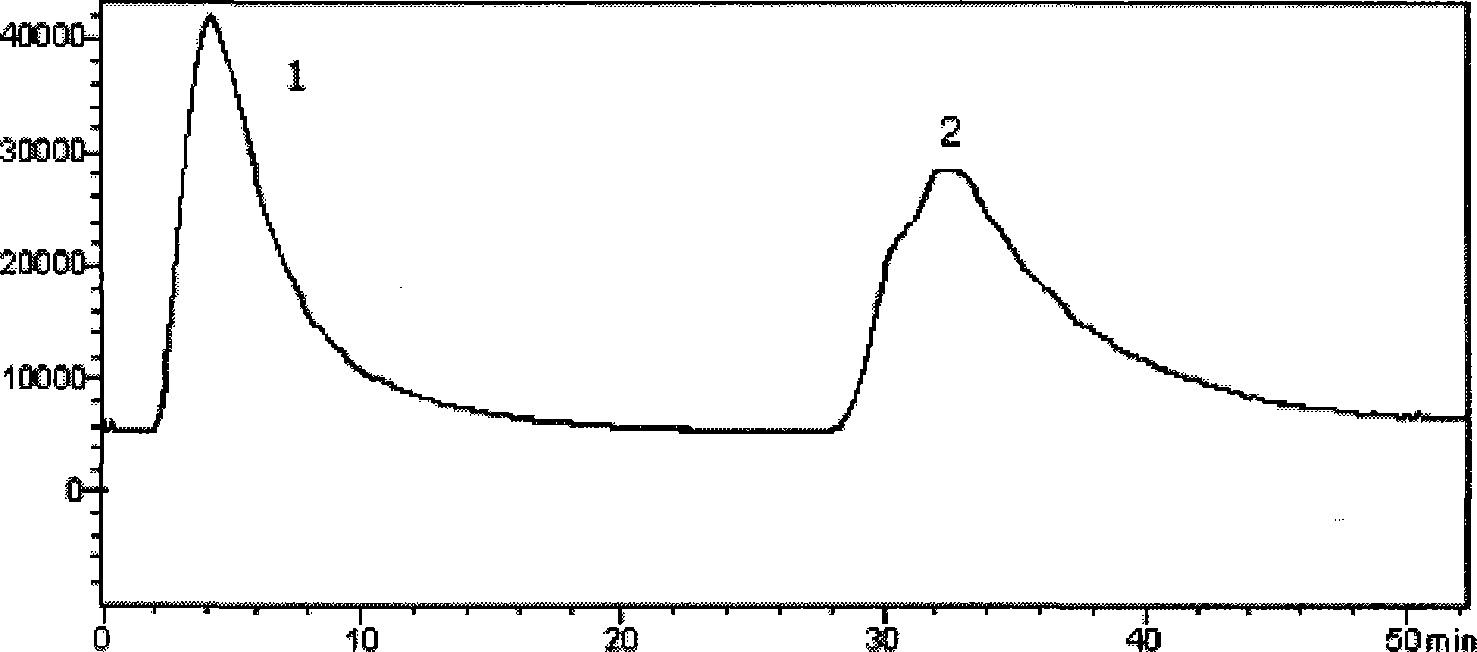
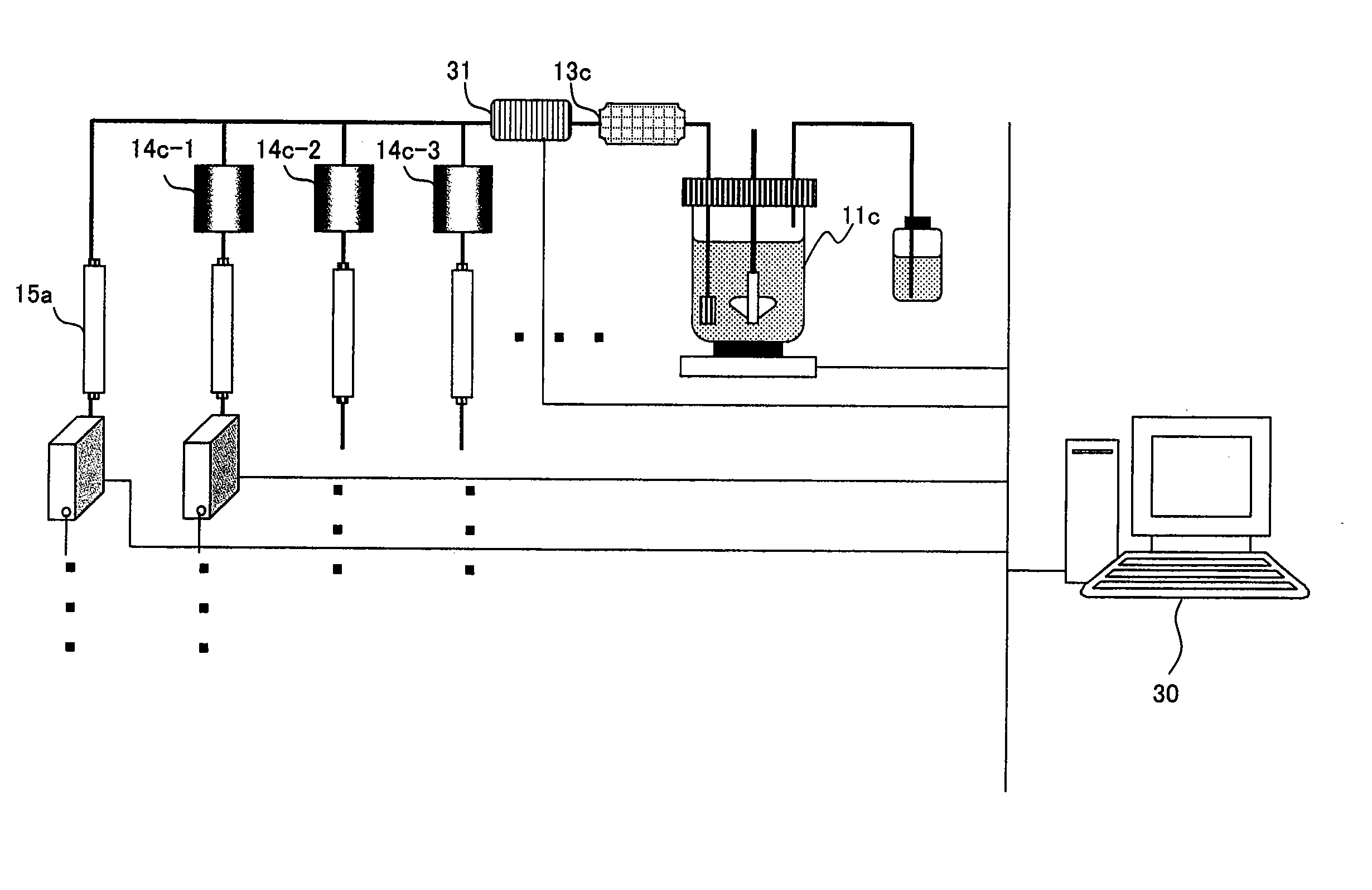
ActiveCN101464439AMass transfer rate is fastStrong molecular recognition propertiesComponent separationSAA proteinFunctional monomer
The invention relates to a method for preparing a protein molecular engram block polymer. Functional monomers, crosslinking agents and model protein molecules in proper proportions stand for 2 to 5 minutes at the temperature ranging from 0 to 4 DEG C, and a certain amount of evocating agents and rate accelerating materials are orderly added later. The mixture is put under the environment whose temperature ranges from minus 5 DEG C to minus 20 DEG C after being rapidly injected into a liquid chromatogram column jacket and polyreaction is completed within 1 to 12 hours. The model protein molecules are eluted by dodecyl sodium sulfate whose weight concentration is 10 percent and acetic acid solution whose volume concentration is 10 percent, namely, a macroporous protein molecular engram monolithic column can be prepared. The invention has the advantages as follows: the preparation method is simple and reliable, and the obtained protein molecular engram monolithic column has stronger template molecule recognition property. The technique provides a novel preparation method for developing protein molecular engram monolithic column.
Owner:中科榆林能源技术运营有限责任公司
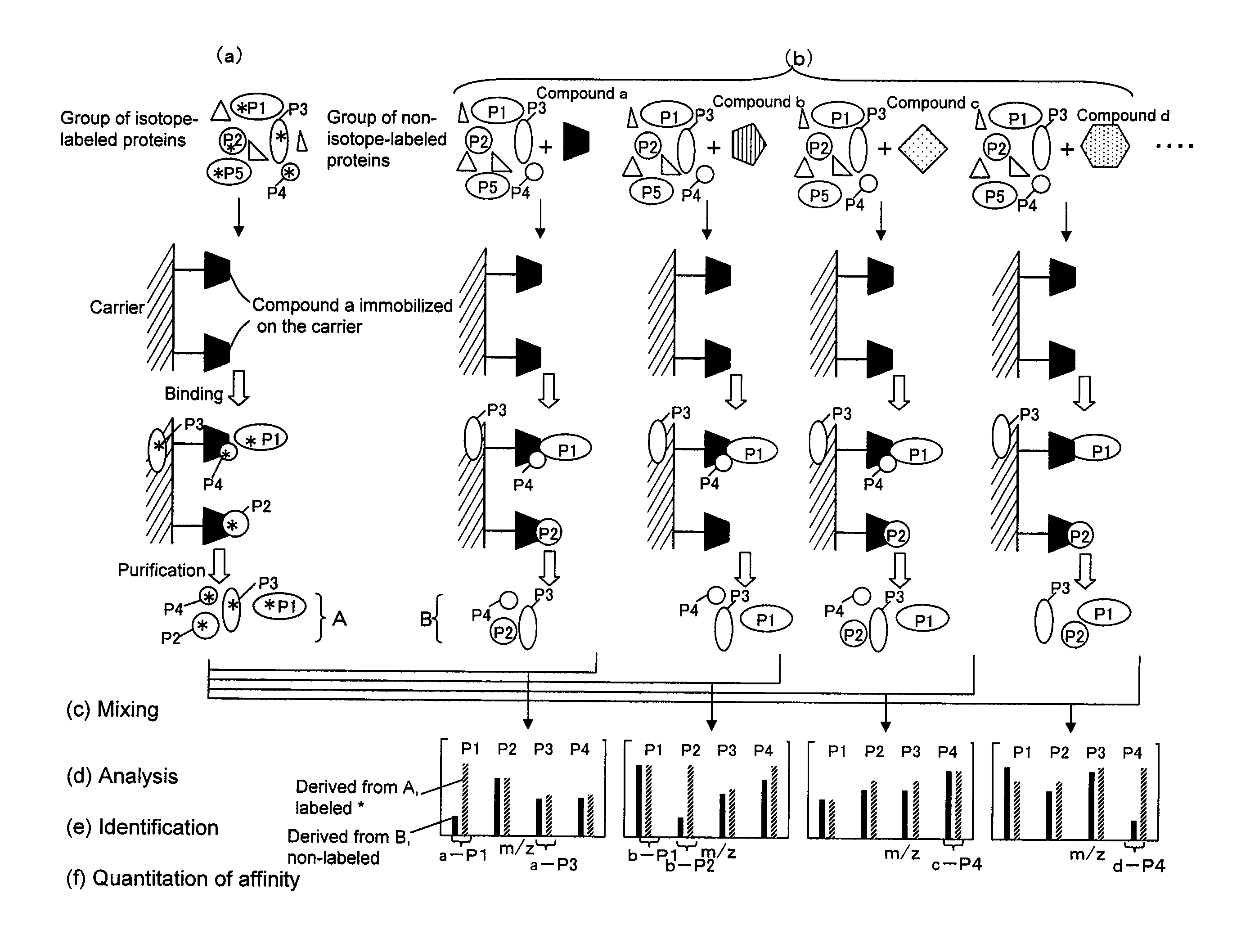
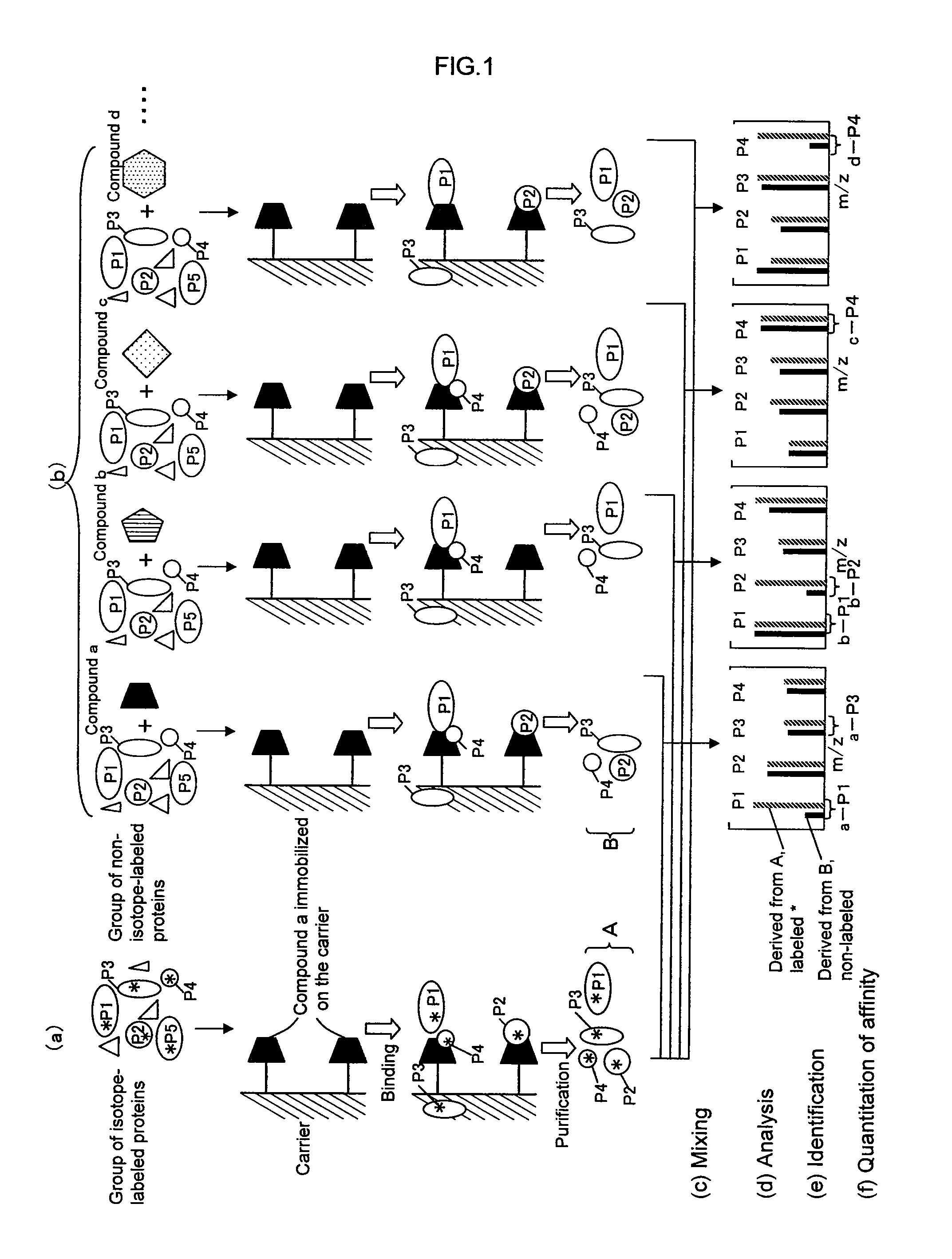
Method of Analyzing Protein Structure Affinity Relationship
InactiveUS20080057592A1Reduce concentrationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSAA proteinProtein markers
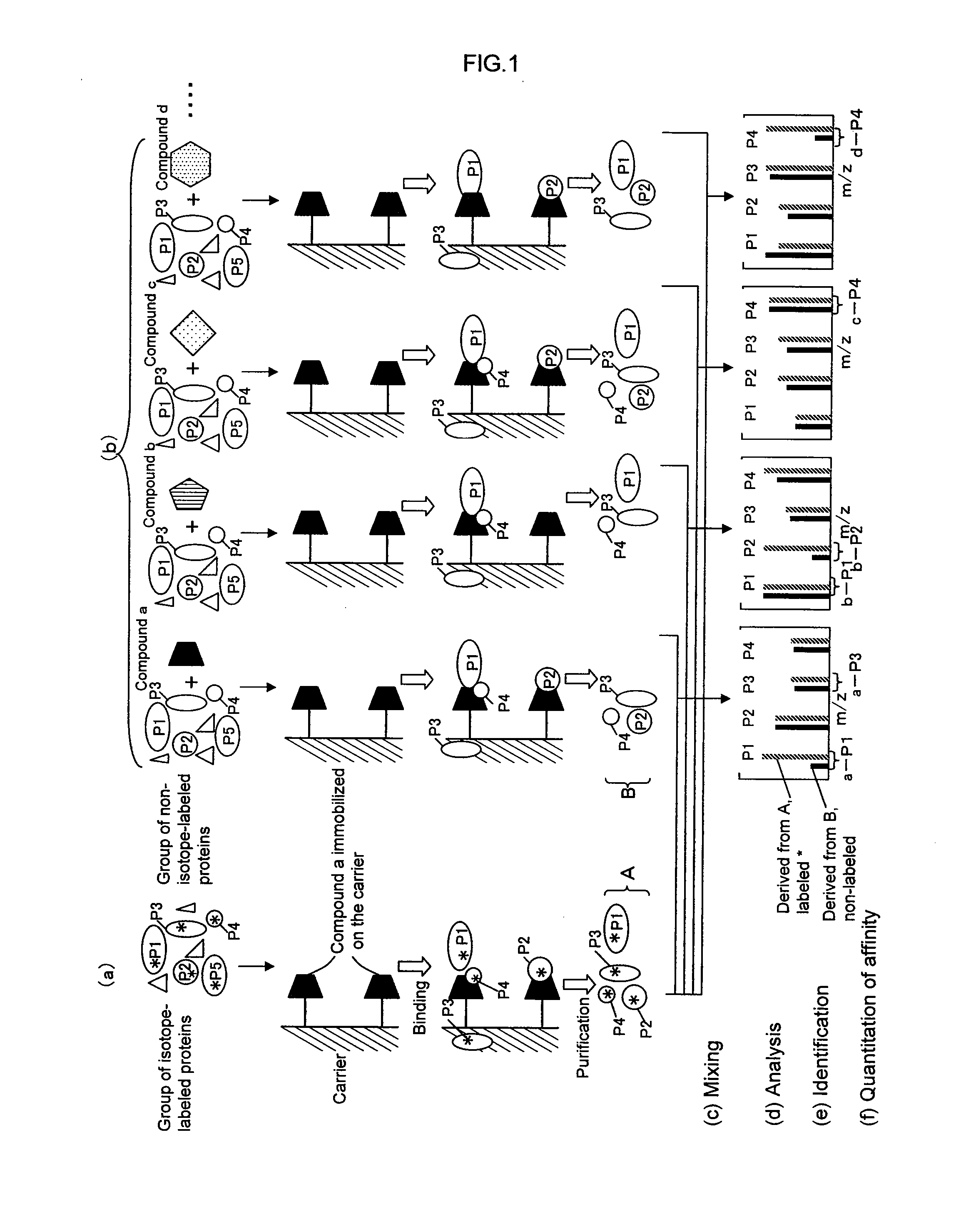
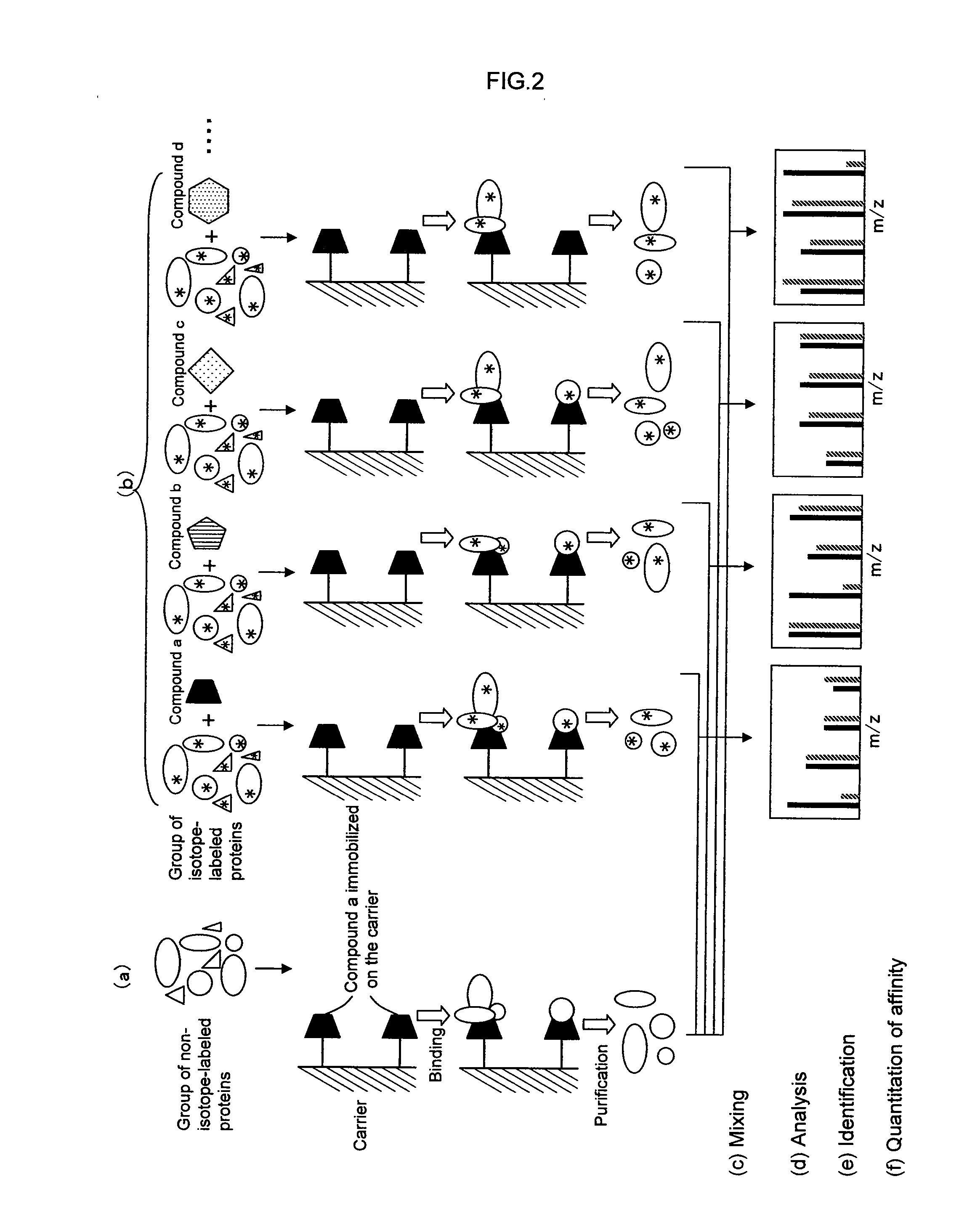
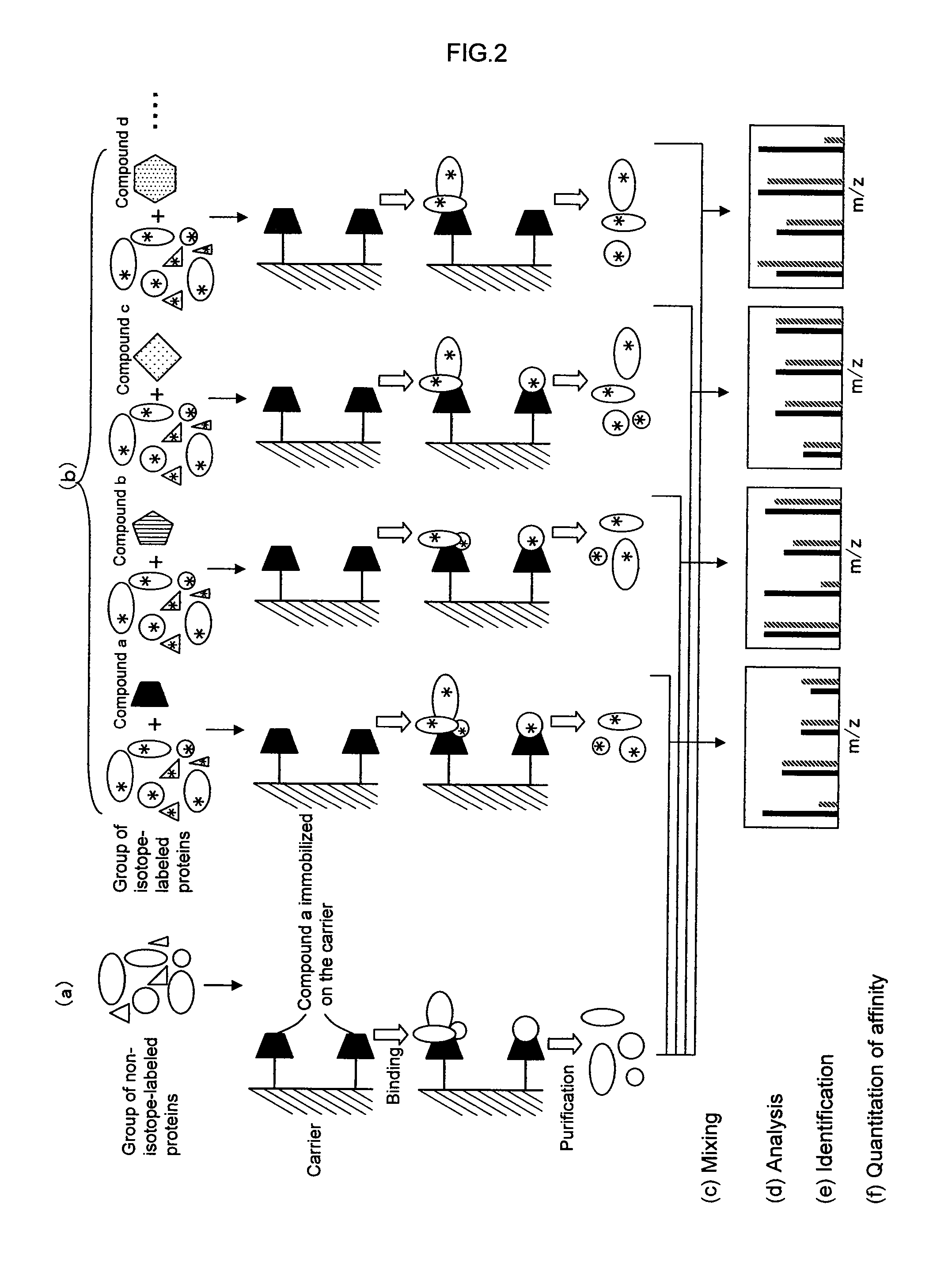
A method for analyzing a structural affinity relationship between plural kinds of proteins and a compound, comprising the steps of (a) using a compound-immobilized carrier to purify plural kinds of proteins bound to the compound on the carrier, from a group of isotope-labeled proteins; (b) using a compound-immobilized carrier to purify plural kinds of proteins bound to the compound on the carrier, from a group of proteins brought into contact with a compound beforehand; (c) mixing the proteins obtained in step (a) and step (b); (d) analyzing the mixture obtained in step (c) with mass spectrometry; (e) identifying each of plural kinds of proteins based on information obtained by the mass spectrometry; and (f) obtaining an intensity ratio between a labeled peak and a non-labeled peak of each protein, thereby quantitating an affinity ratio of the compound to each protein.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Coupling dihedral angle parameter optimization method based on CMAP potential function and protein force field
PendingCN111755064ASimplify the optimization processEasy and convenientSystems biologyInstrumentsSAA proteinProtein molecules
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular dynamics simulation, in particular to a protein force field, and more particularly relates to a coupling dihedral angle parameter optimizationmethod based on a CMAP potential function. According to the optimization method, an existing protein force field is taken as a parent force field, local intrinsic conformation preference in a crimp library is taken as a fitting target, and dihedral angle parameters of amino acid residues in the parent force field are optimized, so that local conformation distribution obtained through molecular dynamics simulation and distribution in the crimp library reach preset similarity. The invention also relates to a protein force field obtained by the optimization method. According to the method, coupled dihedral angles in protein molecules can be simply and efficiently optimized at the same time, the dihedral angle parameter optimization process is simple, efficient and automatic, the residue specific force field RSFF2C with high compatibility is obtained, and the method can be widely applied to various kinds of MD software.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Anti hepatitis B virus chicken yolk immune globulin IgY and its separating method
The invention discloses anti-hepatitis B virus immunoglobulin of yolk and separation method. The separation method includes the following steps: animal immune; separating and purifying yolk; diluting by de-ionized water; adjusting pH; adding sodium chloride; setting for 5-6h; centrifugal separation; removing precipitation; adding sodium sulfate into supernatant to process the first salting out; centrifugalizing out protein precipitation; adding de-ionized water until the precipitation be fully dissolved; adding sodium sulfate to process the second salting out; centrifugal separation; the gained protein precipitation is added into de-ionized water until it is fully dissolved; filtering by gel-column; the eluted protein flow is monitored by ultraviolet photometer to absorb the 280 nm light wave and collect the first spectral band, concentrated by reversal dialysis, dialyzed to remove salt to gain the anti-hepatitis B virus IgY. The invention has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, and better sample quality.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Extraction method of fructus momordicae leaf total protein for proteomics analysis
InactiveCN104877004AHigh purityImprove extraction efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationPeptide preparation methodsSAA proteinProteomics
The invention discloses an extraction method of fructus momordicae leaf total protein for proteomics analysis, which comprises the following steps: mixing pretreated fructus momordicae leaf powder with a first protein extracting solution, standing at -20 DEG C for 10-14 hours, centrifuging at 4 DEG C for 30 minutes at the rate of 12000 r / min, and taking the understratum precipitate to obtain a first precipitate. The preparation method of the first protein extracting solution comprises the following steps: mixing acetone and beta-mercaptoethanol in a volume ratio of 10000:(5-10), adding trichloroacetic acid, mixing and storing at -20 DEG C for later use. The method has the advantages of high total protein extraction efficiency, time saving and low protein degradability, solves the problem that the traditional phenol extraction process for extracting the plant leaf protein can not effectively remove polyphenols and salts, and implements high-efficiency extraction of the fructus momordicae leaf total protein. The obtained protein has high purity, and is suitable for proteomics analysis.
Owner:GUANGXI BOTANICAL GARDEN OF MEDICINAL PLANTS
Antibodies recognizing methyllysine, process for producing the same and utilization thereof
Antibodies capable of recognizing many types of proteins having methyllysine residues are established by immunizing an animal with a chemically methylated protein other than histone and subsequent screening or the like depending on the reactivity to a protein obtained by chemically methylating a protein other than the protein used in the immunization. A process for producing such an antibody is also established. These antibodies are useful in searching for and studying various methylated proteins and are particularly useful in regulating the functions of biological molecules wherein the methylation of a lysine residue plays an important role, and in diagnosing a disease by detecting a methyllysine-containing protein.
Owner:ADVANCED LIFE SCI INST
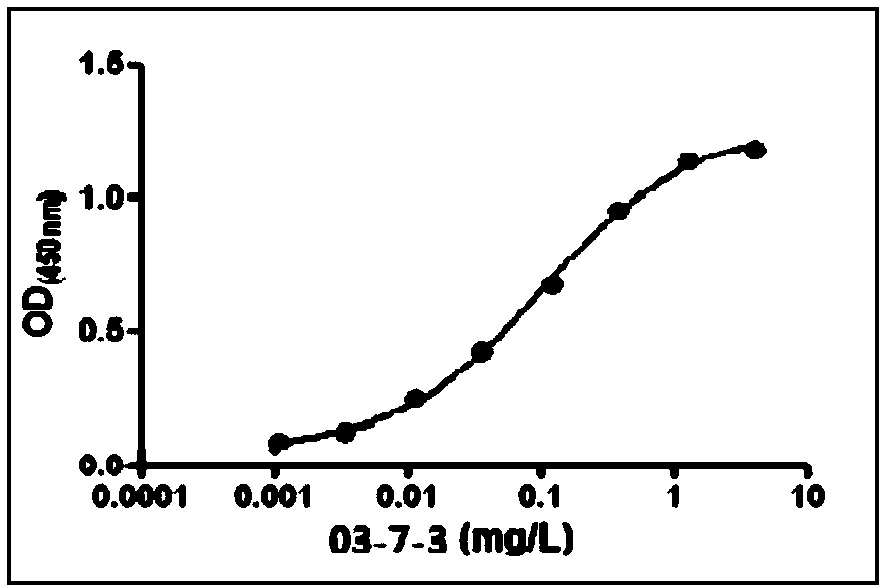
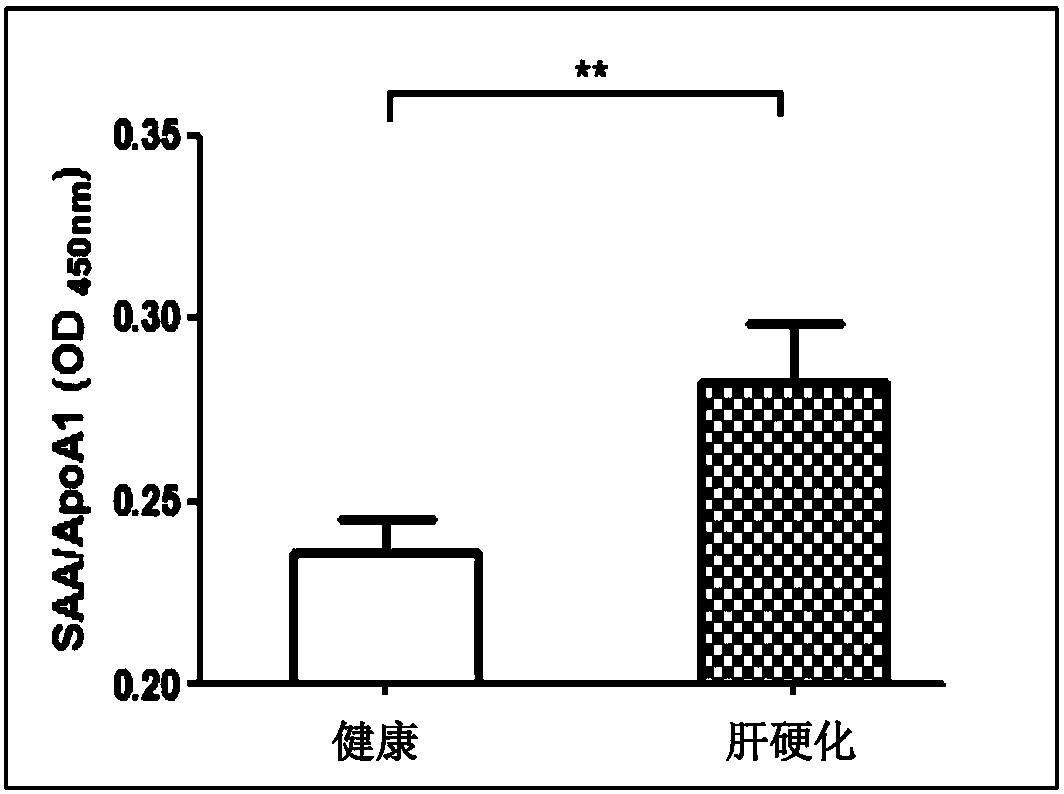
Anti-human SAA (Serum Amyloid A) monoclonal antibody and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109503713AHigh affinityImprove featuresImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesSAA proteinFactor ii
The invention discloses an SAA monoclonal antibody 03-7-3, the heavy chain of the SAA monoclonal antibody 03-7-3 is IgG1, the light chain is k, and the amino acid sequences of the variable regions ofthe heavy chain and the light chain are respectively shown as SEQ ID NO. 3 and SEQ ID NO. 4. The SAA monoclonal antibody 03-7-3 disclosed by the invention can specifically identify disease-related SAA-ApoA1-HDL complex and SAA proteins, and on the basis of the SAA monoclonal antibody 03-7-3, an assay method for the SAA-ApoA1-HDL complex and the SAA proteins is established. The SAA-ApoA1-HDL complex is significantly associated with liver cirrhosis, and is a potential risk factor for the liver cirrhosis; and the concentration of the SAA proteins is significantly associated with the liver cirrhosis due to hepatitis B and liver cancer, and is a potential risk factor for the liver cirrhosis due to hepatitis B and the liver cancer. Therefore, the SAA monoclonal antibody 03-7-3 disclosed by the invention has important clinical value for the prediction of the potential risk of the liver cirrhosis and the liver cancer and the development of diagnostic markers for the diseases.
Owner:DIASYS DIAGNOSTIC SYST SHANGHAI
Method of analyzing protein structural affinity relationship
A method for analyzing a structural affinity relationship between plural kinds of proteins and a compound, comprising the steps of (a) using a compound-immobilized carrier to purify plural kinds of proteins bound to the compound on the carrier, from a group of isotope-labeled proteins; (b) using a compound-immobilized carrier to purify plural kinds of proteins bound to the compound on the carrier, from a group of proteins brought into contact with a compound beforehand; (c) mixing the proteins obtained in step (a) and step (b); (d) analyzing the mixture obtained in step (c) with mass spectrometry; (e) identifying each of plural kinds of proteins based on information obtained by the mass spectrometry; and (f) obtaining an intensity ratio between a labeled peak and a non-labeled peak of each protein, thereby quantitating an affinity ratio of the compound to each protein.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Protein containing material biomass and methods of production
The present invention provides methods and protein compositions having advantageous properties, such as a high uncorrected limiting amino acid score as well as favorable amounts of essential amino acids, branched chain amino acids, as well as other amino acids more difficult to find in the regular diet. The protein composition is obtainable as taught herein from algal or microbial biomass. The protein composition produced according to the methods of the invention provides a proteinaceous food or food ingredient that is more nutritionally balanced (and therefore nutritionally superior) to protein compositions otherwise available. The protein material is advantageously used as a food or food ingredient for humans and / or animals. Also provided are methods of producing the protein material from biomass sources.
Owner:SMALLFOOD INC
Serum amyloid protein A mutant as well as application and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110746499AAntigenic retentionNatural antigenicityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSAA proteinSerum amyloid protein
The invention discloses a serum amyloid protein A mutant which has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and still has antigenicity of serum amyloid protein after several amino acids are replaced, so that a unique mutant is obtained. The SAA mutant is obtained by replacing four amino acids in natural SAA protein, so that the in-vitro stability of the SAA mutant is improved. Experiments prove that obtained SAA protein is soluble mature protein, the activity of the SAA protein is kept to the maximum extent, and the antigenicity of natural SAA protein is reserved. The invention also discloses application and a preparation method of the serum amyloid protein A mutant.
Owner:宁波赛珀生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com