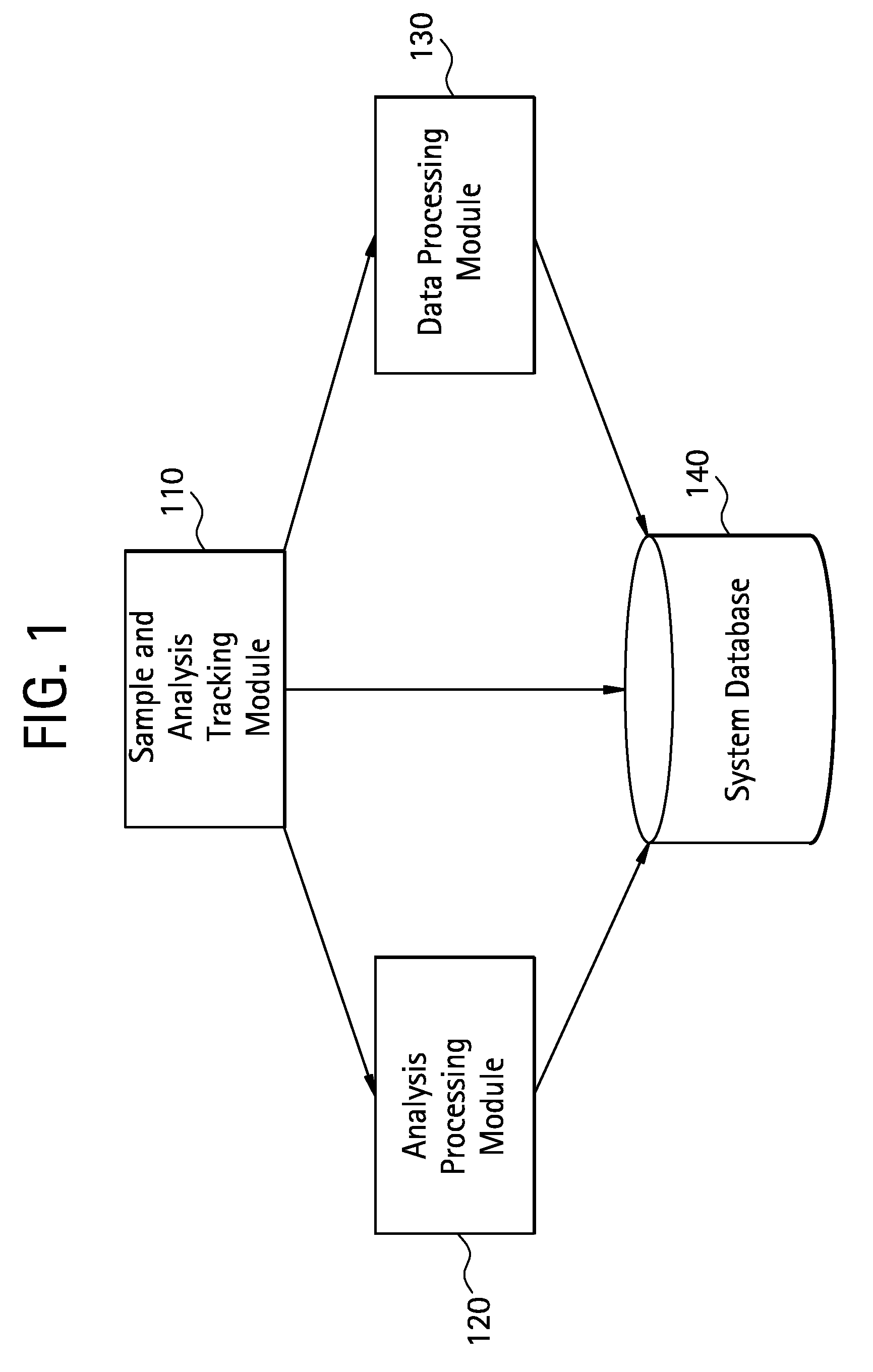
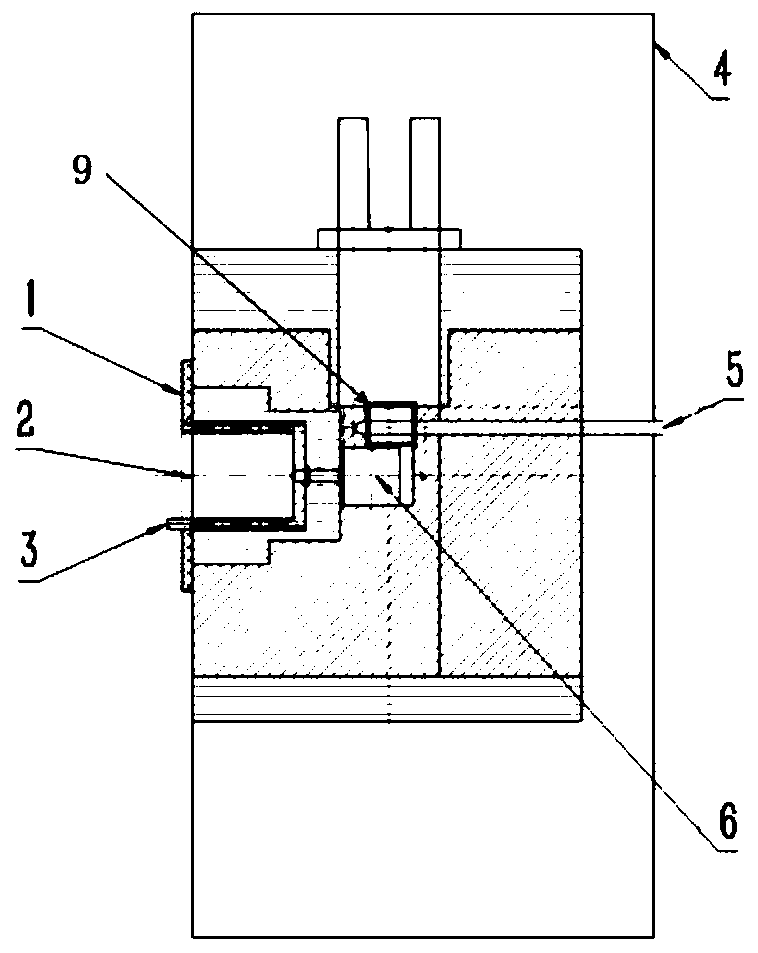
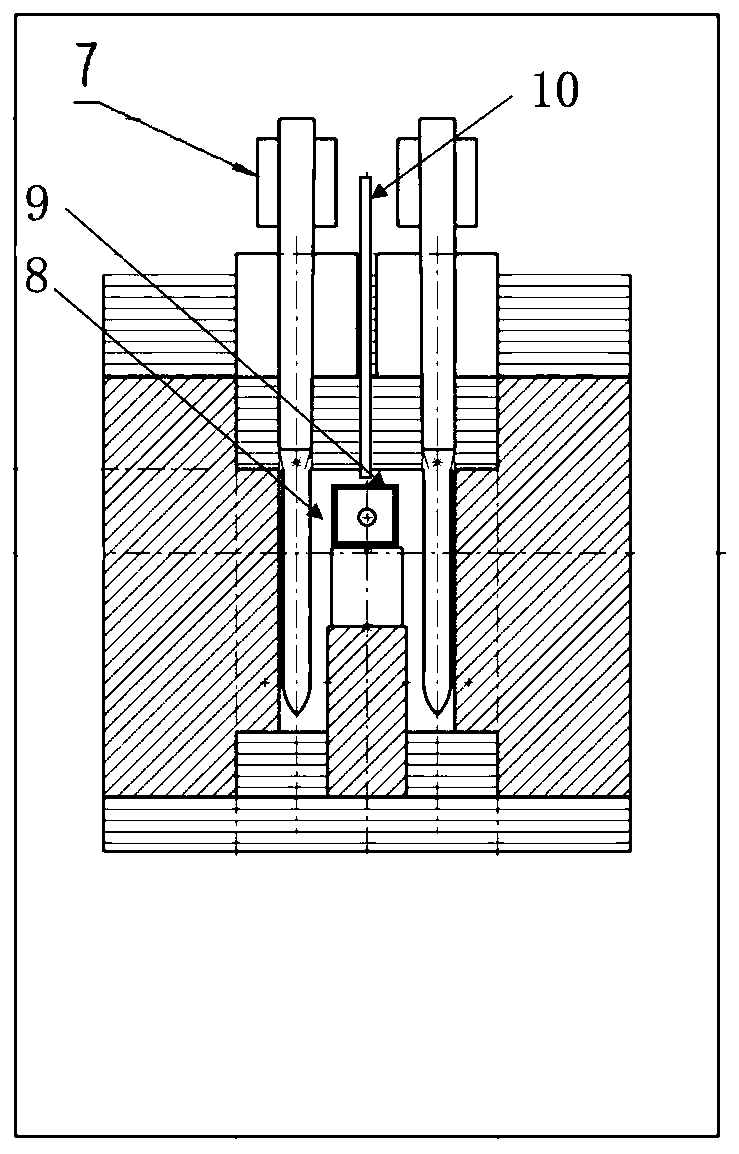
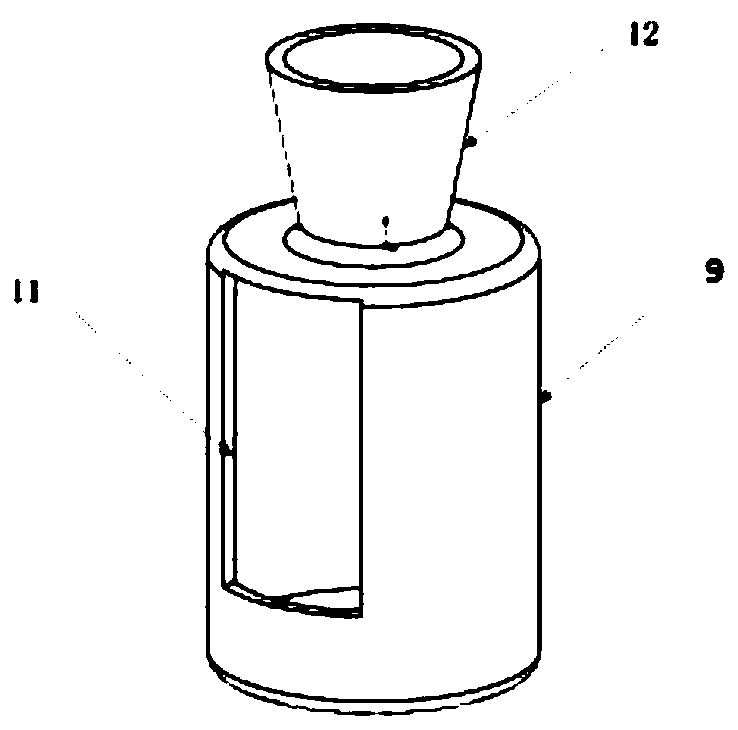
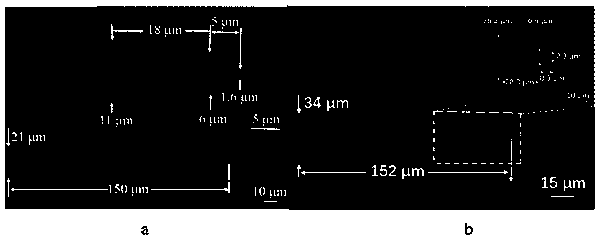
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Raman microscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
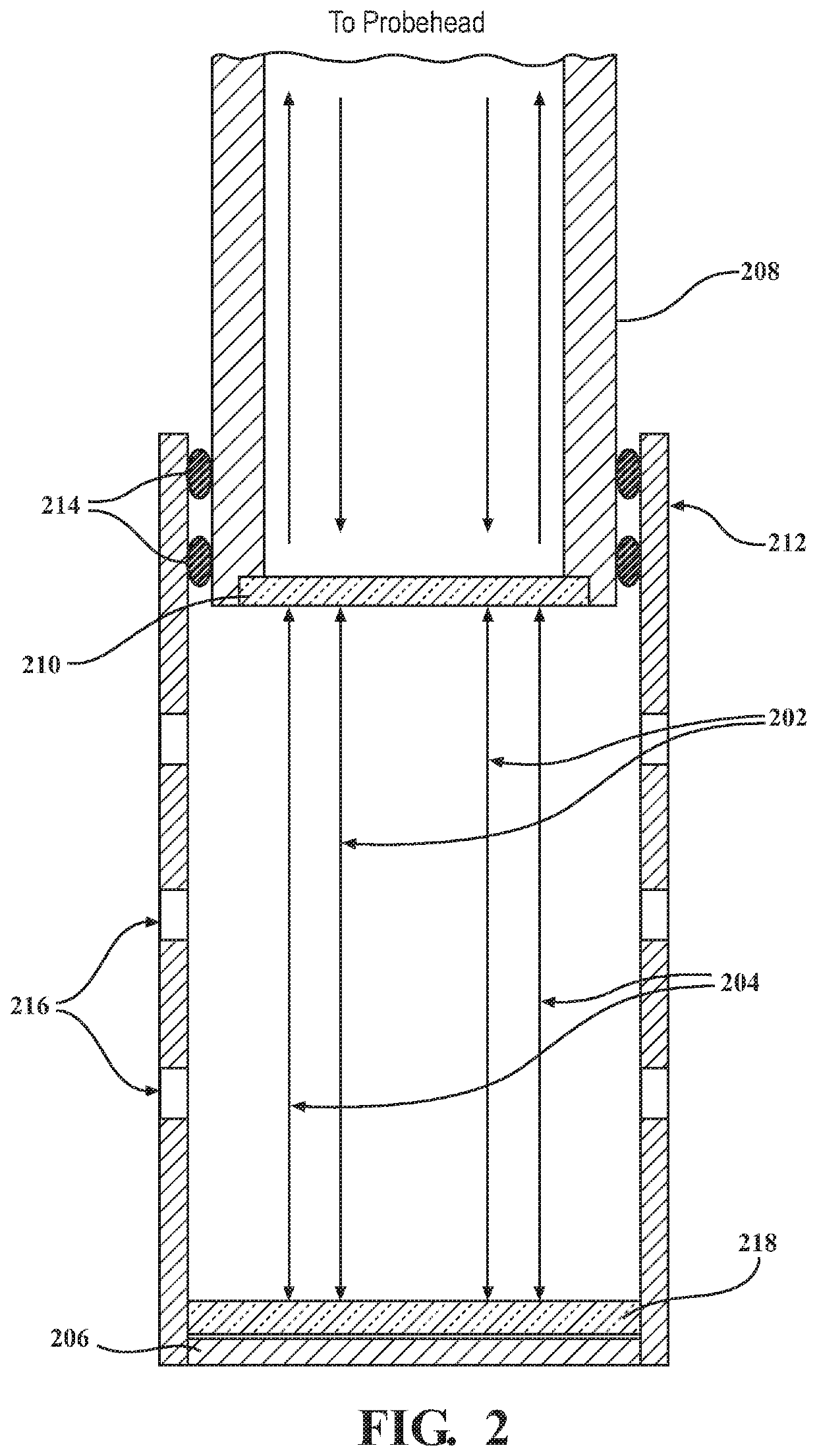
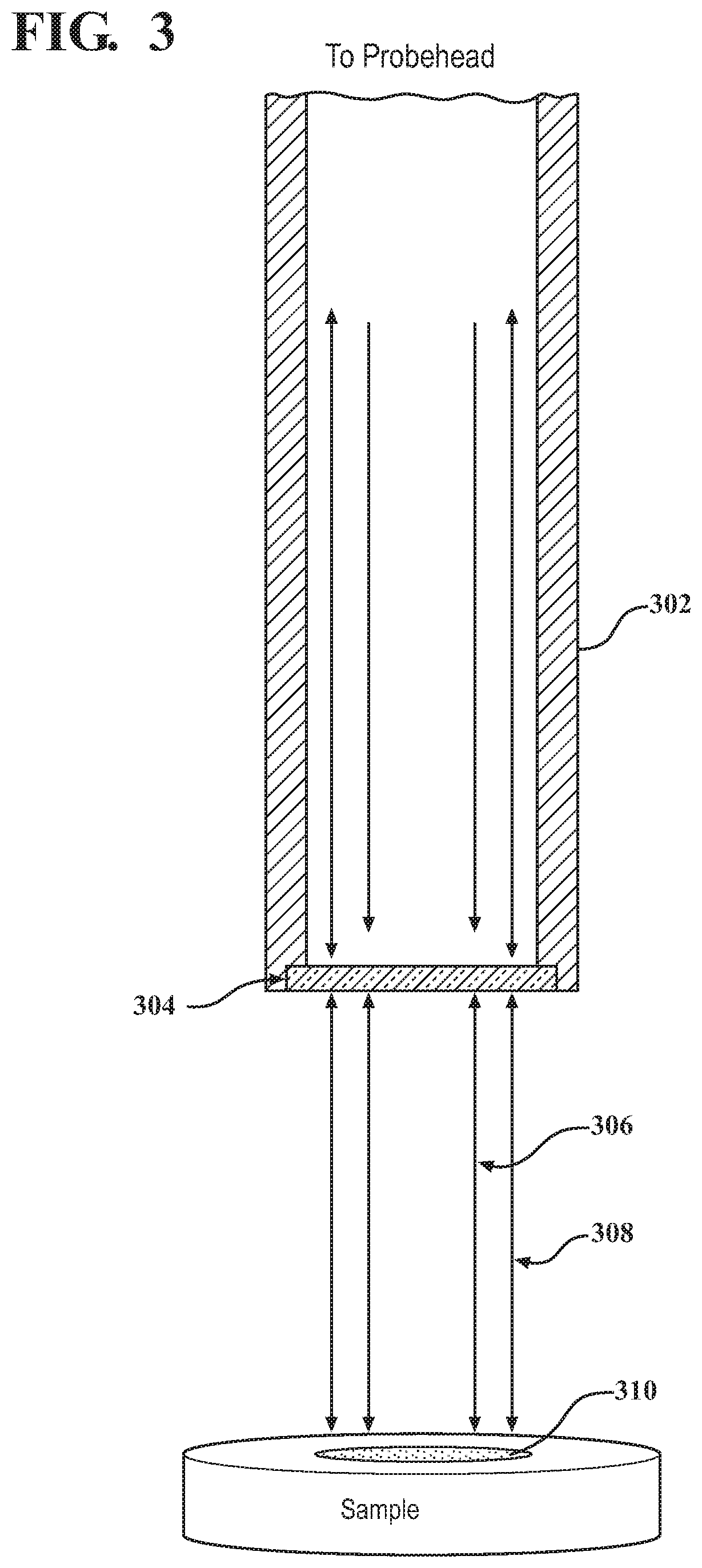
The Raman microscope is a laser-based microscopic device used to perform Raman spectroscopy. The term MOLE (molecular optics laser examiner) is used to refer to the Raman-based microprobe. The technique used is named after C. V. Raman who discovered the scattering properties in liquids.
Near-field Raman spectroscopy
Near-field Raman imaging is performed by holding a dielectric microsphere (e.g. of polystyrene) on or just above the surface of a sample in a Raman microscope. An illuminating laser beam is focused by the microsphere so as to produce a near-field interaction with the sample. Raman scattered light at shifted wavelengths is collected and analysed. The microsphere may be mounted on a cantilever of an atomic force microscope or other scanning probe microscope, which provides feedback to hold it in position relative to the sample surface. Alternatively, the microsphere may be held on the sample surface by an optical tweezer effect of the illuminating laser beam.
Owner:RENISHAW PLC
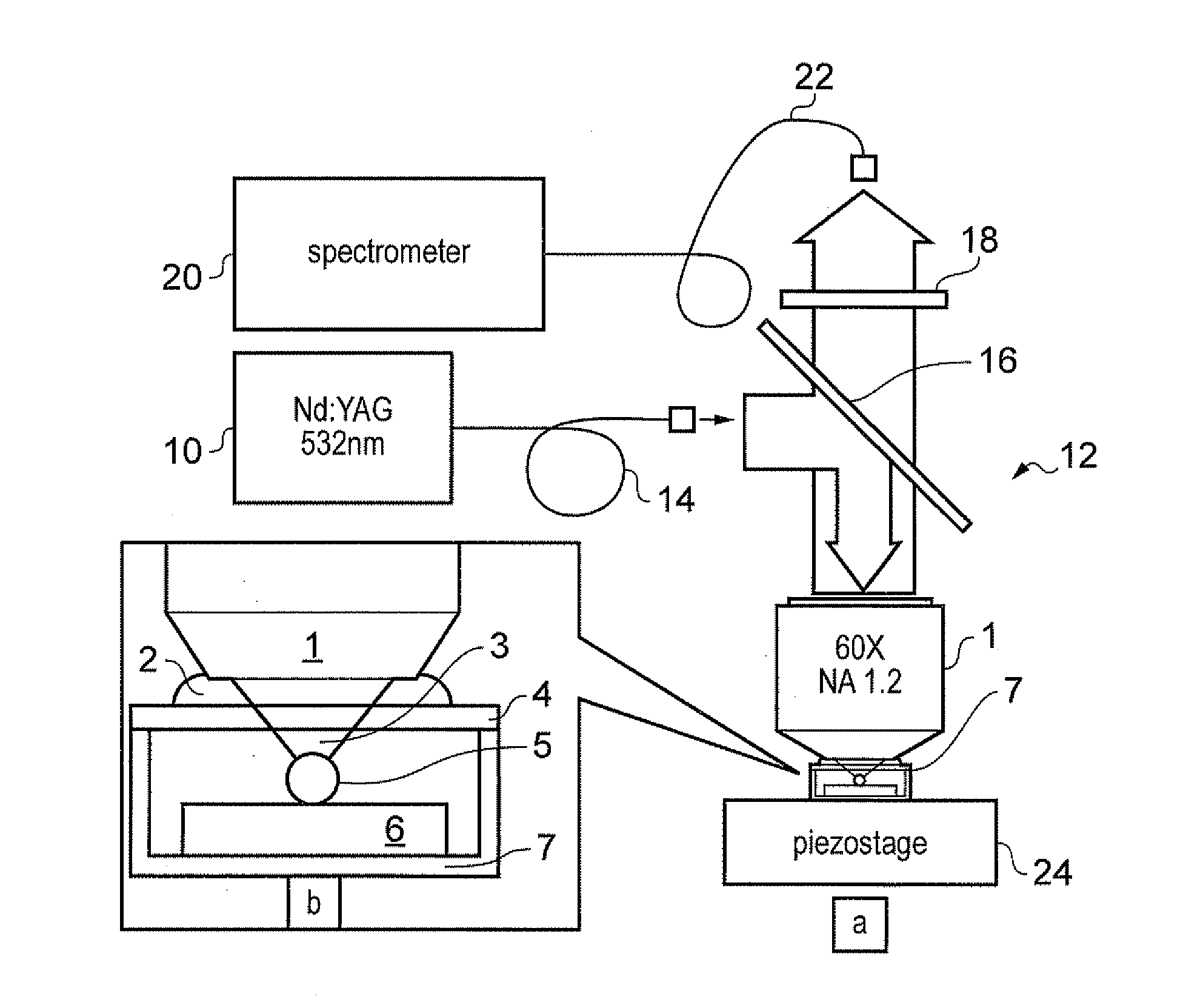
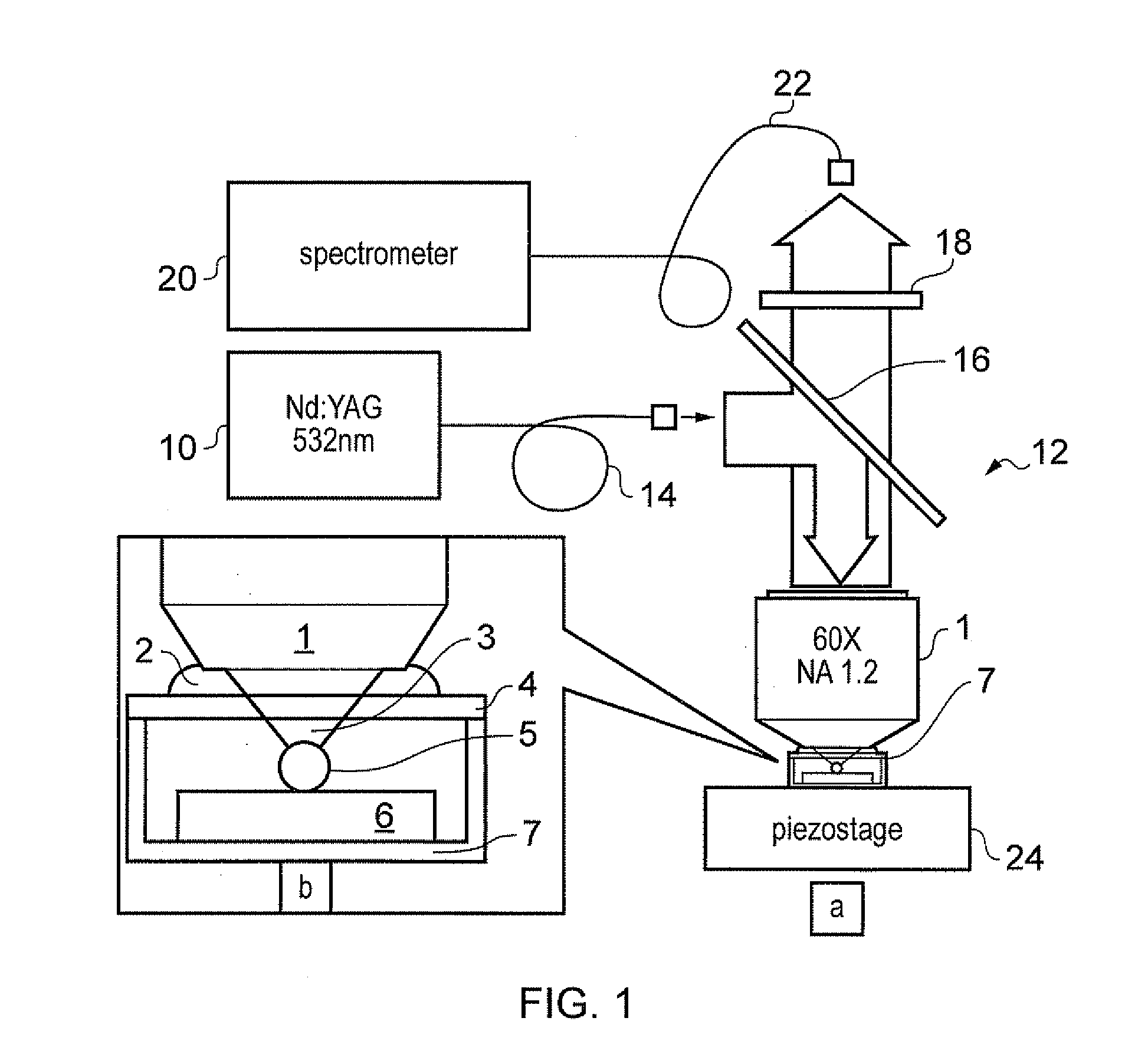
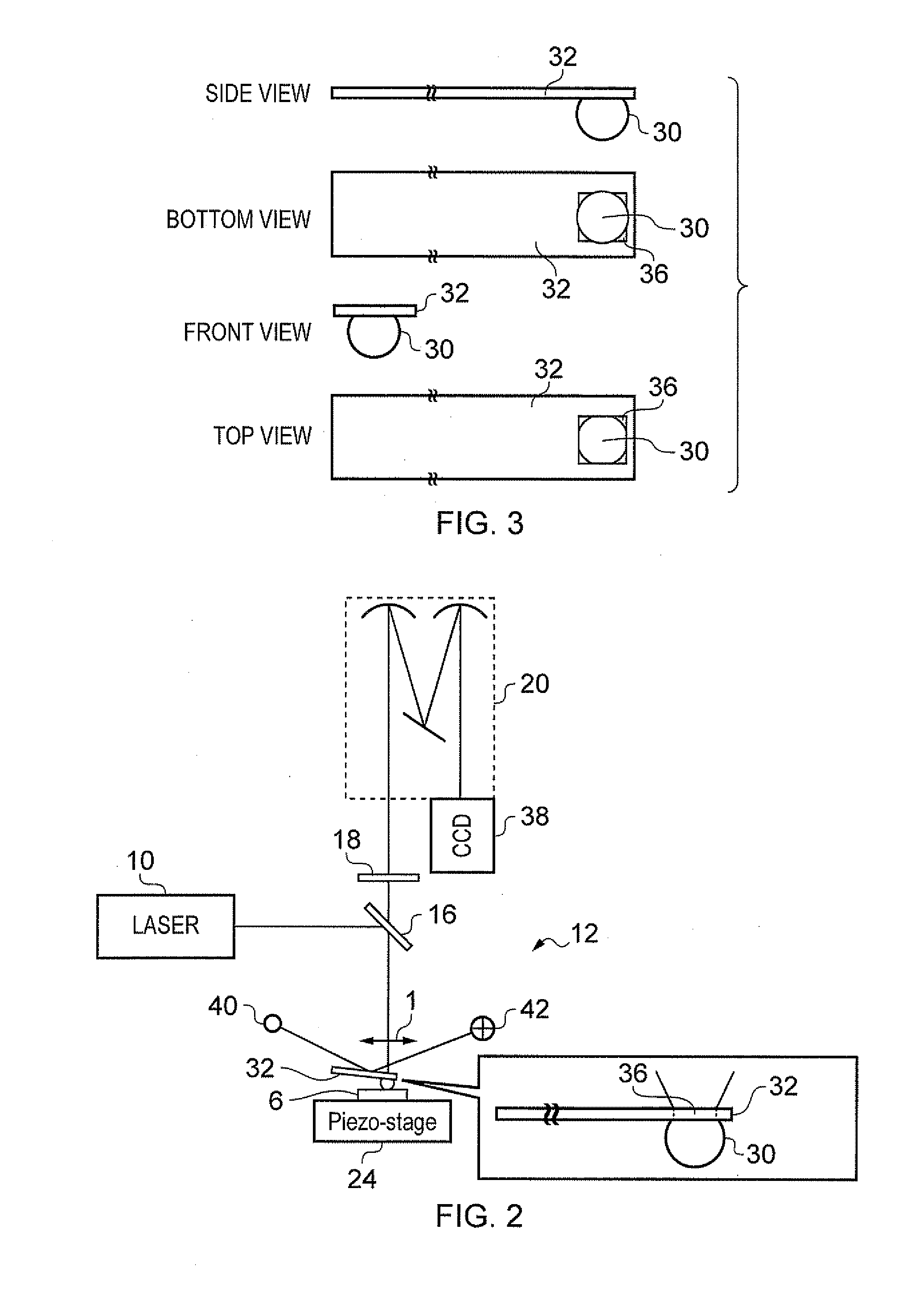
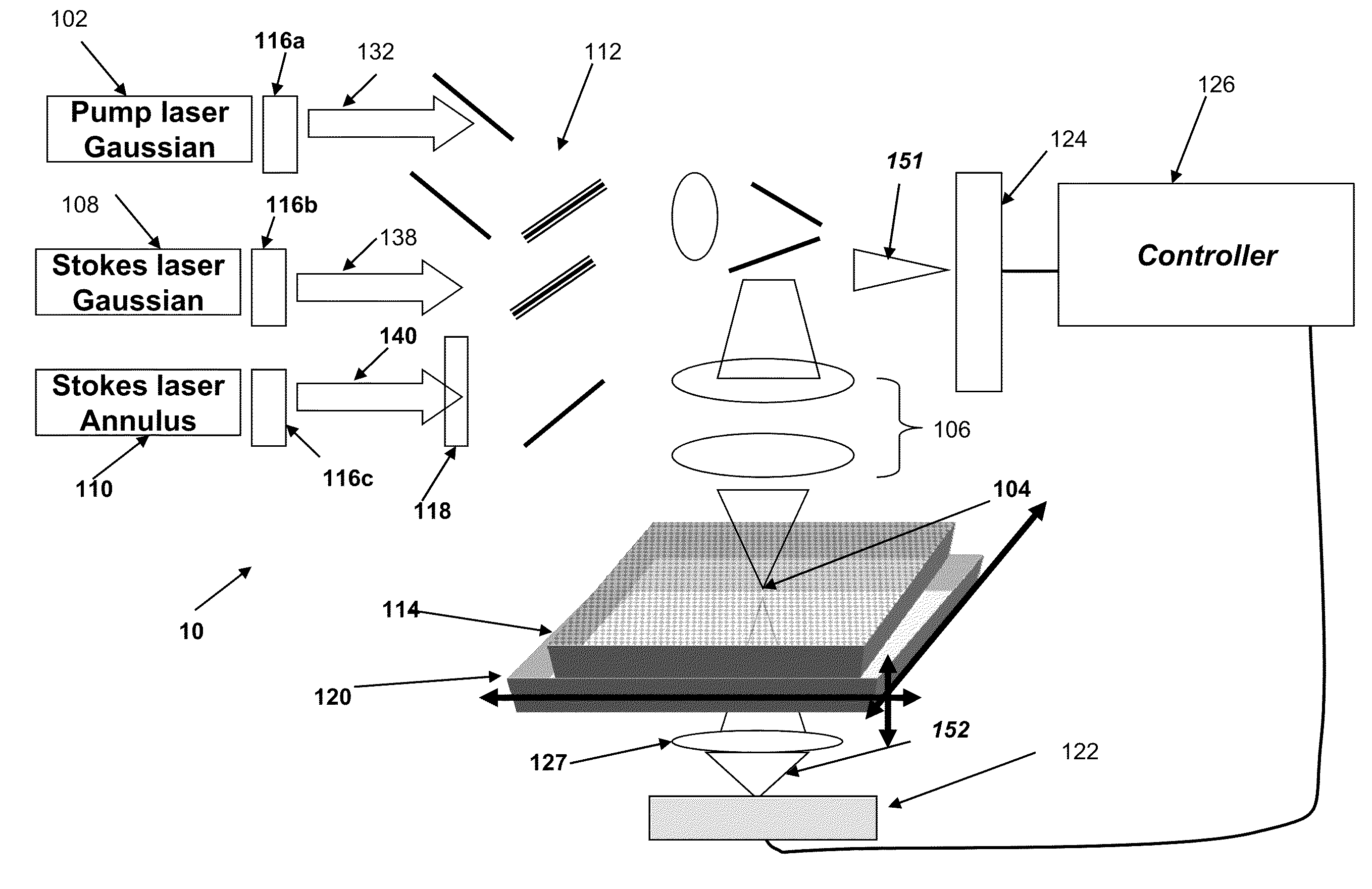
Method and system for stimulated Raman microscopy beyond the diffraction limit
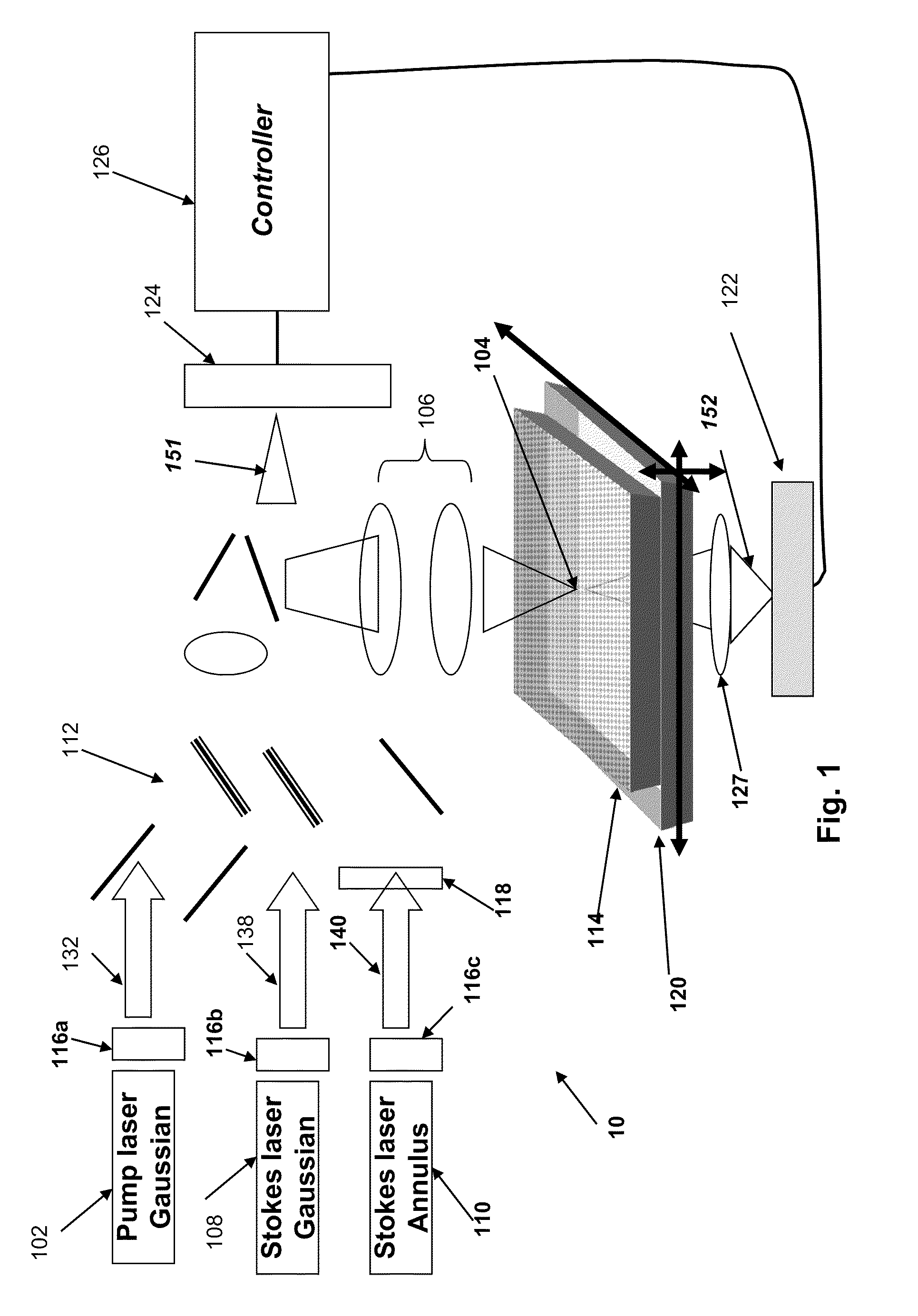
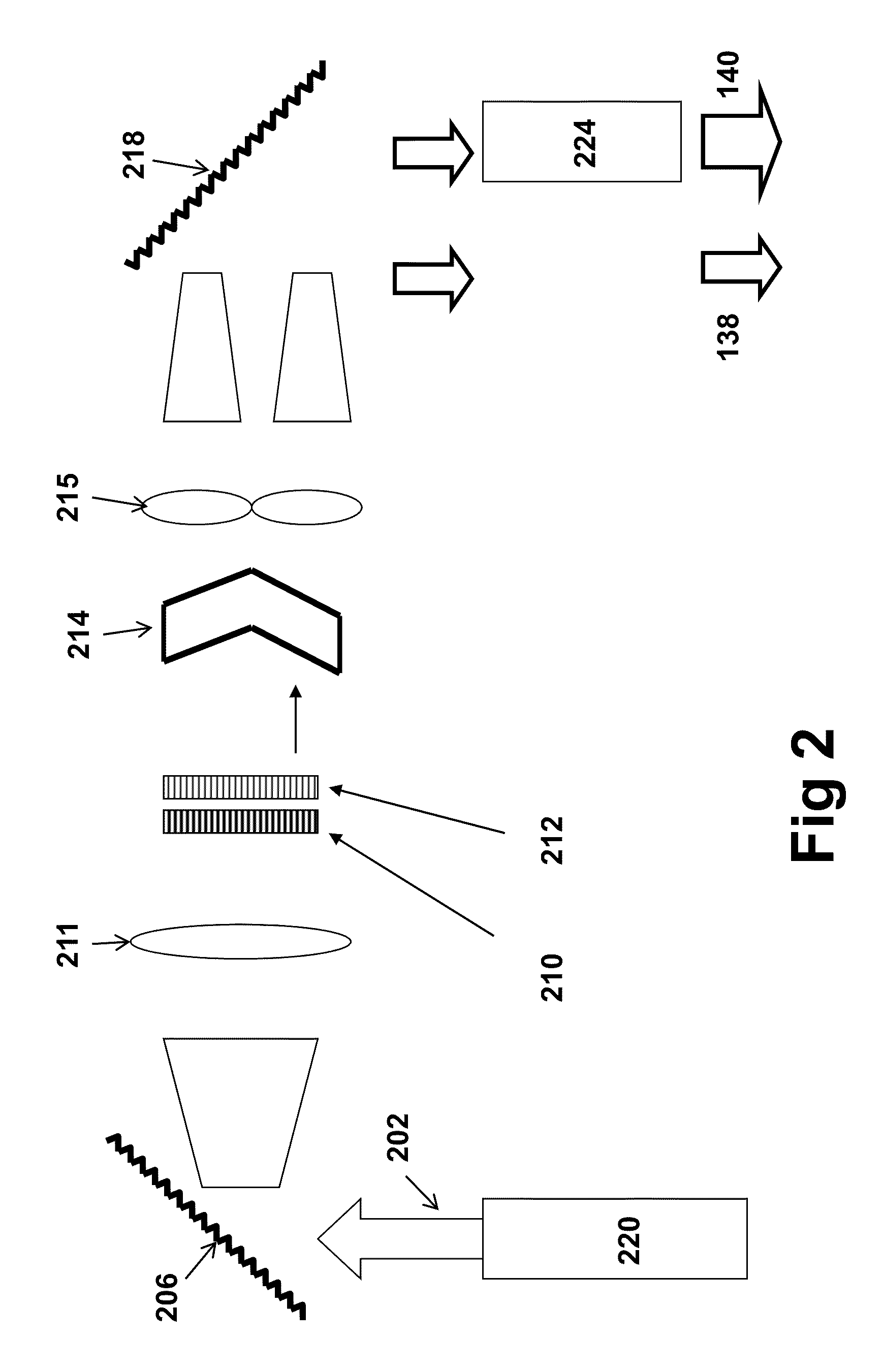
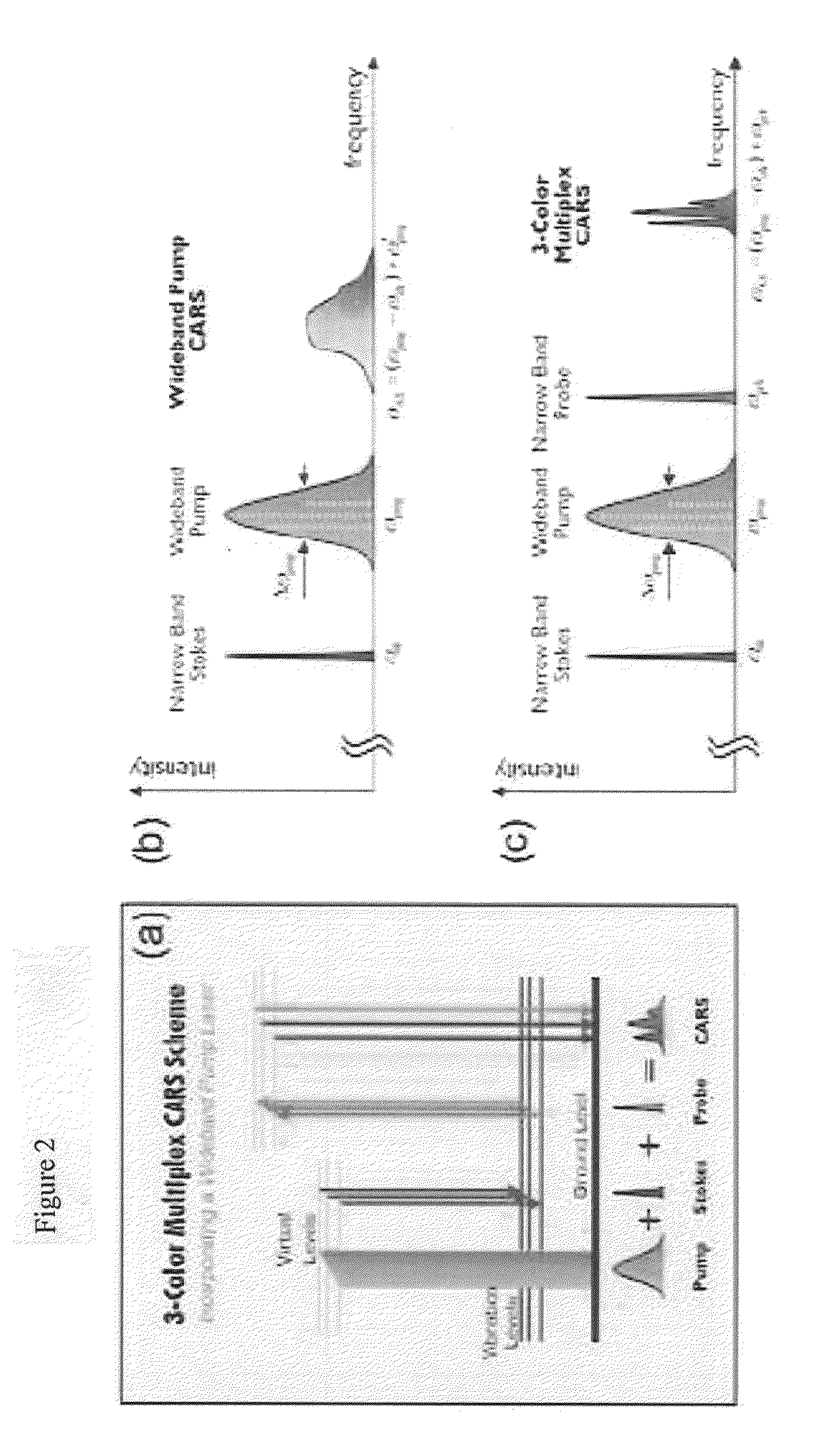
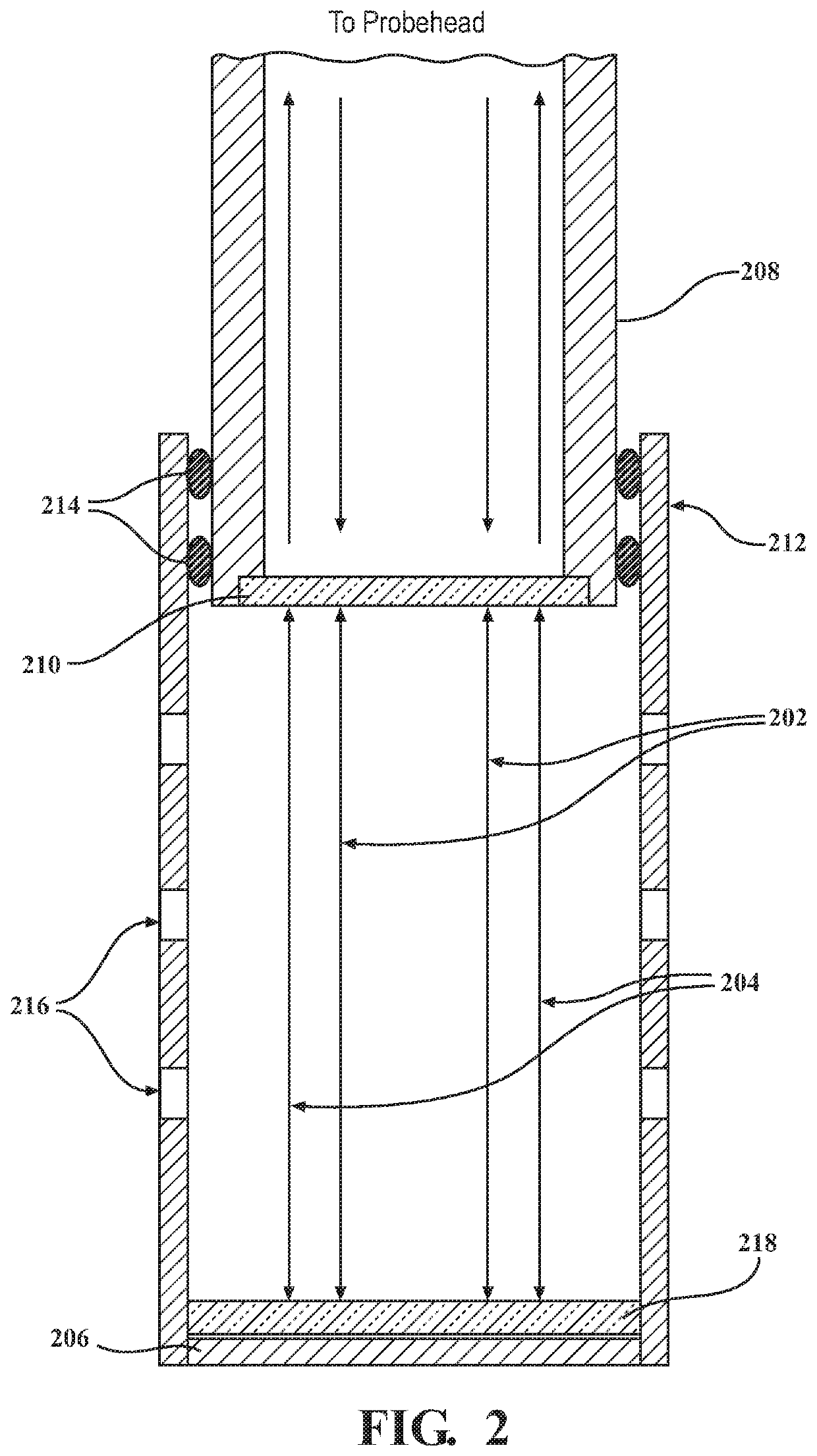
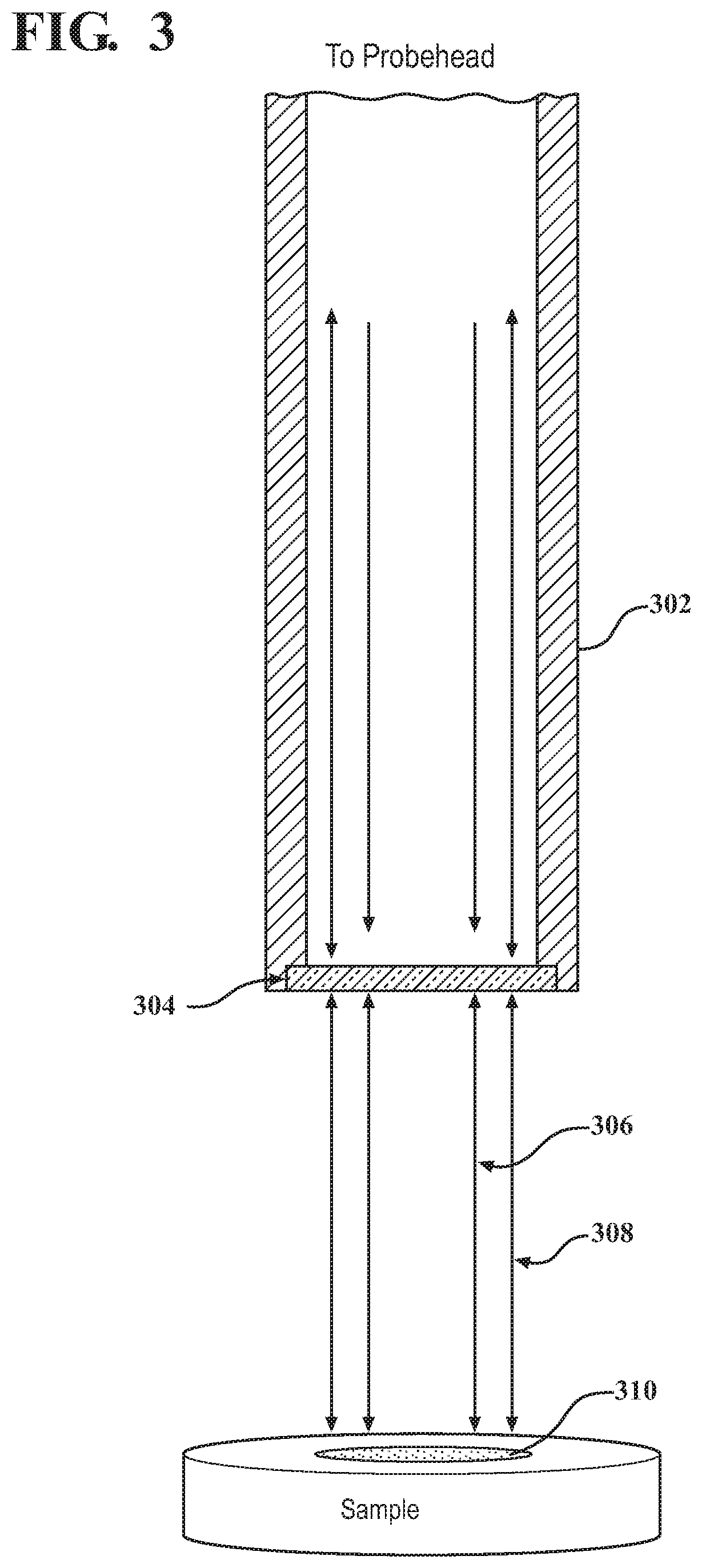
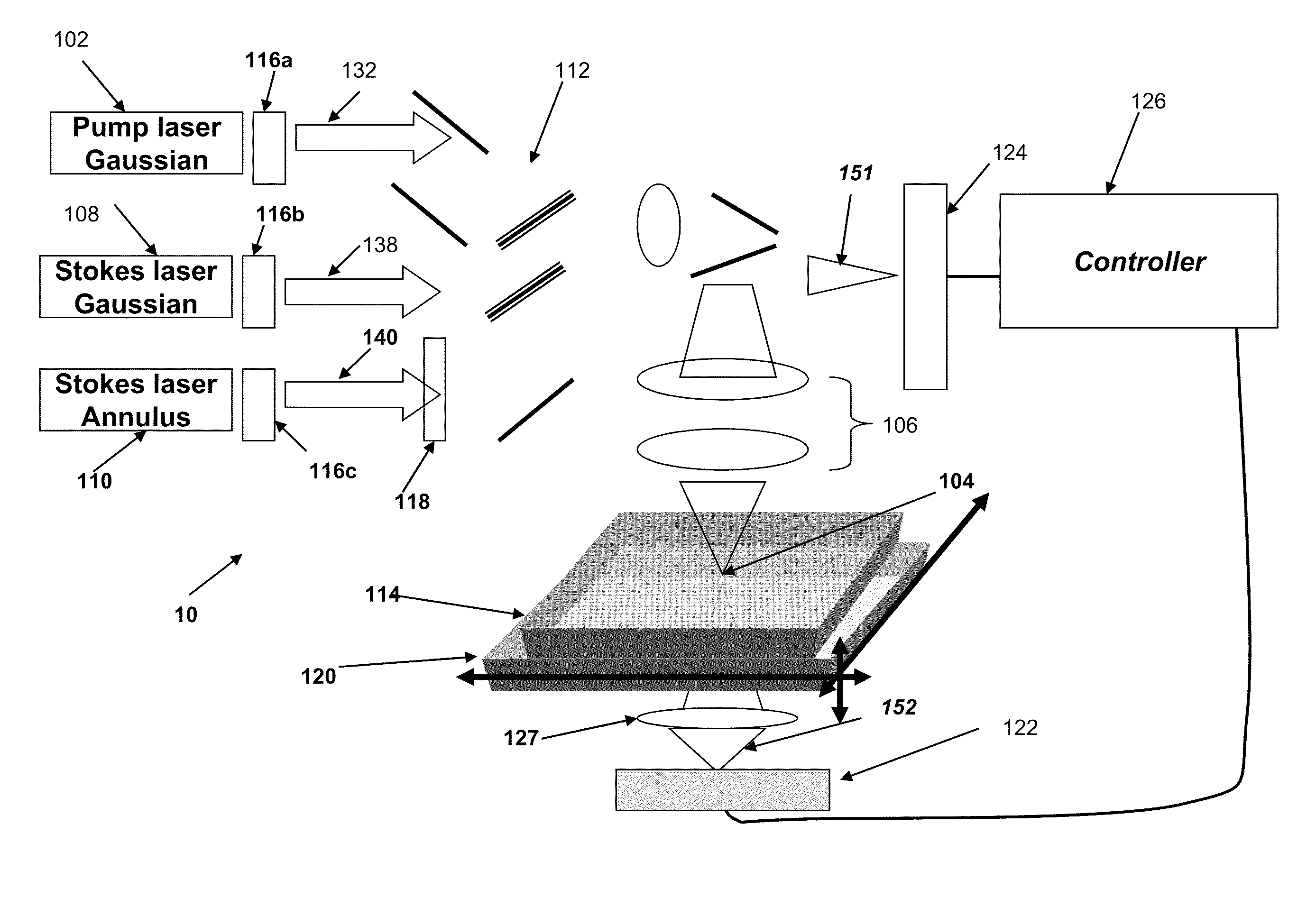
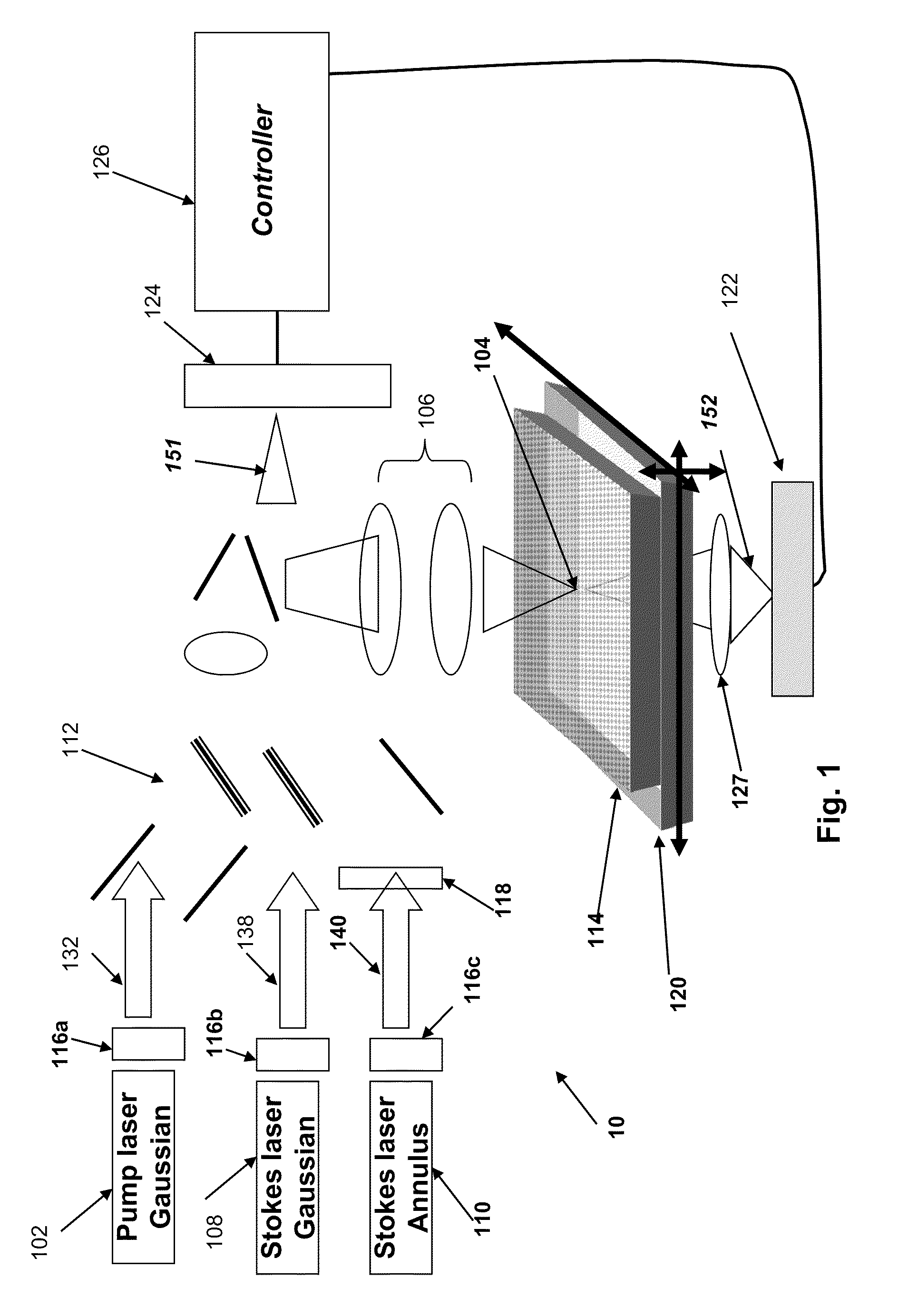
Systems and methods for probing a Raman signature of a sample with a resolution exceeding the diffraction limit are described. These systems, called GASSE (Gain Saturated Stimulated Emission) and iGASSE (interferometric GASSE), are detecting a Raman signal produced in a sample located at the focal spot of a Gaussian pump pulse. Two additional pulsed laser beams (Stokes beams), a central Stokes beam having a Gaussian beam profile and another Stokes beam having an annular beam profile, are also focused to the focal spot. The spatial and temporal phases of the laser pulses are adjusted to produce destructive interference over most of the temporal width of Stokes pulses, which causes emission from the central Stokes beam to narrow well below the diffraction limit. A two-dimensional image of the sample is produced by scanning the combined beams across the sample. The system may find applications in biomedical and semiconductor technology.
Owner:FREL ROBERT D
Method for testing lignification degrees of plant cell walls
InactiveCN102435594AEasy to makeOvercome limitations of preparationPreparing sample for investigationRaman scatteringPlant cellRaman microscope
The invention discloses a method for testing lignification degrees of plant cell walls based on a confocal Raman microscopic technology. The method comprises the following steps of: testing Raman spectrums of the plant cell walls under the in-situ state by using a confocal Raman microscope to obtain Raman spectrum imaging graphs of lignin in the cell walls; and determining the content of the lignin in the cell walls according to Raman signal intensities, and determining the lignification degrees of different secondary cell walls and different form areas of fiber cell walls. The testing method is based on a pure spectrum method, samples are quickly prepared, chemical pollutants are not generated, and the information of the lignification degrees of the plant cell walls can be acquired under the in-situ state.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for reducing auto-fluorescence signals in confocal Raman microscopy
InactiveUS20060084876A1Strong potentialEasy to useRaman scatteringDiagnostic recording/measuringDirect observationRaman microscope
The present invention relates to a method for reducing auto-fluorescence signals from a sample tissue in confocal Raman microscopy and to a method for diagnosing skin cancers using the same method. Raman spectroscopy has strong potential for providing non-invasive diagnosis of skin cancer. Auto-fluorescence signals from tissues, which interfere with the Raman signals, were greatly reduced using a confocal slit adjustment. Distinct Raman band differences between normal and BCC tissues for the amide I mode, the amide III mode and the PO2− symmetric stretching mode, showed that the present invention has strong potential for use as a dermatological diagnostic tool without the need for statistical treatment of spectral data. It was also possible to precisely differentiate BCC tissue from surrounding non-cancerous tissue using the confocal Raman depth profiling technique. According to the present invention, confocal Raman microscopy can provide a novel method for dermatological diagnosis since direct observations of spectral differences between normal and BCC tissues are possible.
Owner:HANBAT NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
System and method for the non-destructive assessment of the quantitative spatial distribution of components of a medical device
ActiveUS7478008B2Molecular entity identificationDigital computer detailsRaman microscopeRaman Optical Activity Spectroscopy
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Raman microscope and electron microscope analytical system
InactiveUS20150279616A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesMutual correlationIon beam
A system uses number of analytical devices such as an electron microscope a Raman microscope, an ion beam column and a scanning probe microscope for sample analysis concurrent, consecutive or with the mutual correlation of the analysis performed by the different devices in the same sample area using the connection of the Raman microscope optical objective lens and objective manipulator, that significantly reduces time needed for analyzing by Raman microscope together with other devices and maintains high quality of the sensed signals comparable to stand alone analytical devices.
Owner:TESCAN ORSAY HLDG AS +1
Probe for dual-mode bio-imaging
ActiveCN110234735AOrganic chemistryDiagnostics using spectroscopyFluorescence microscopeRaman microscope
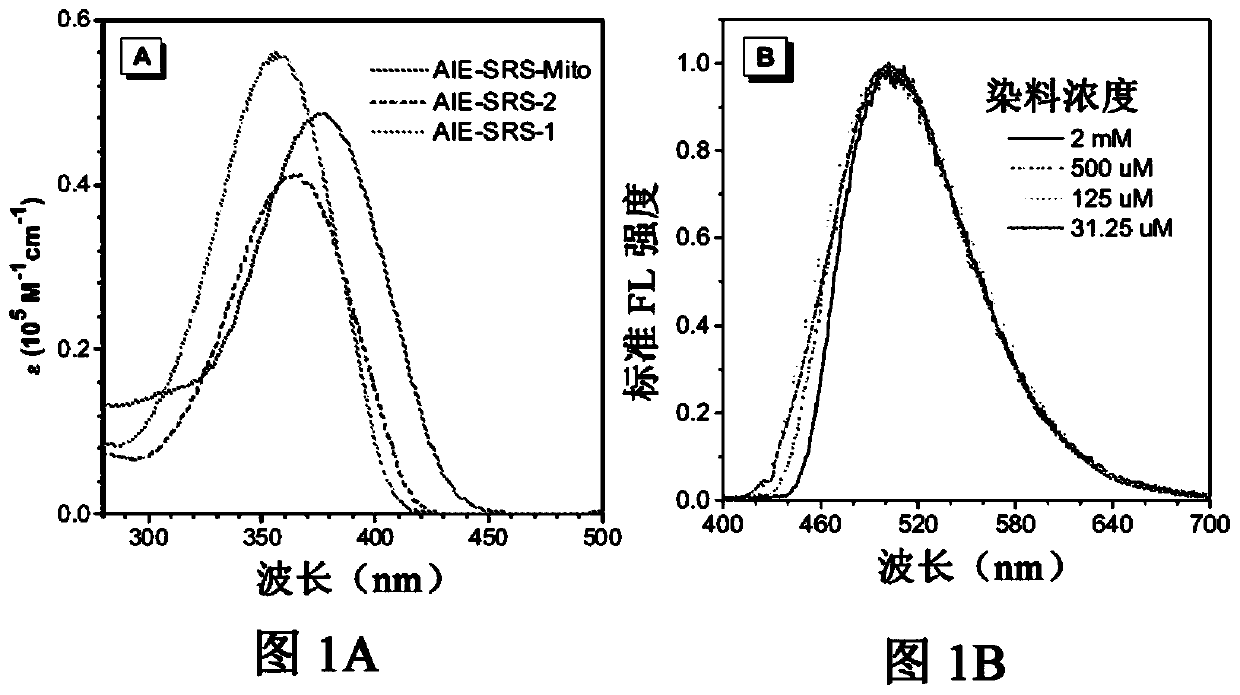
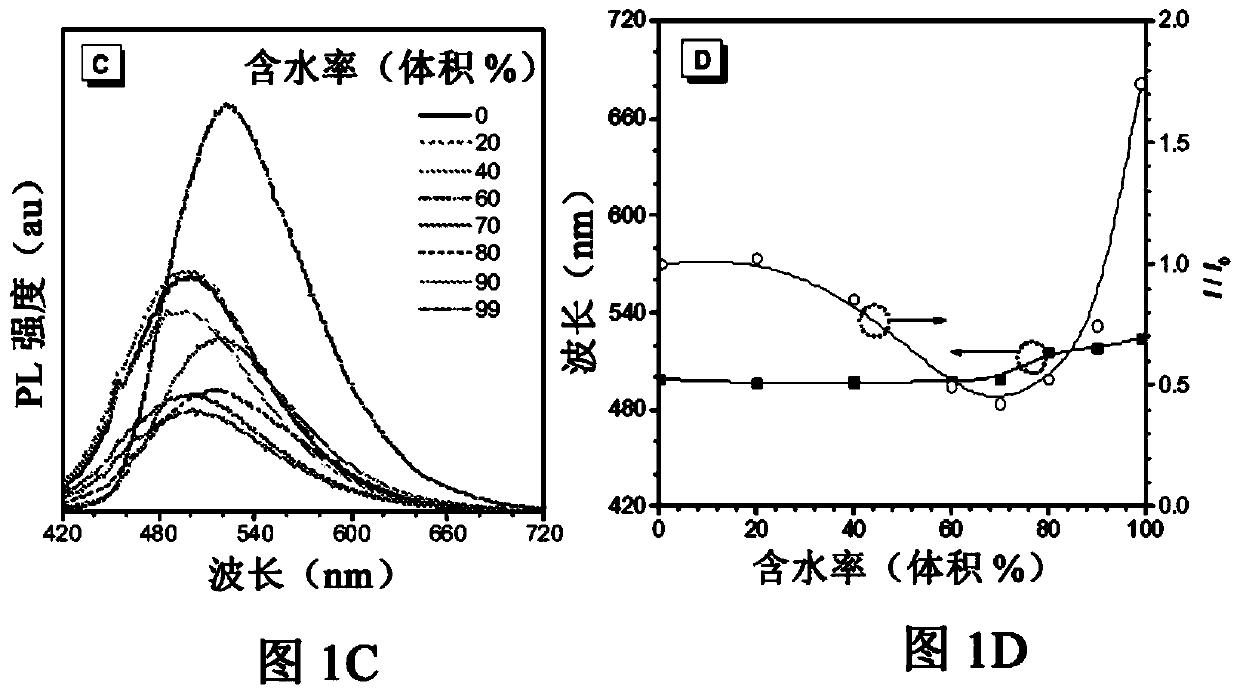
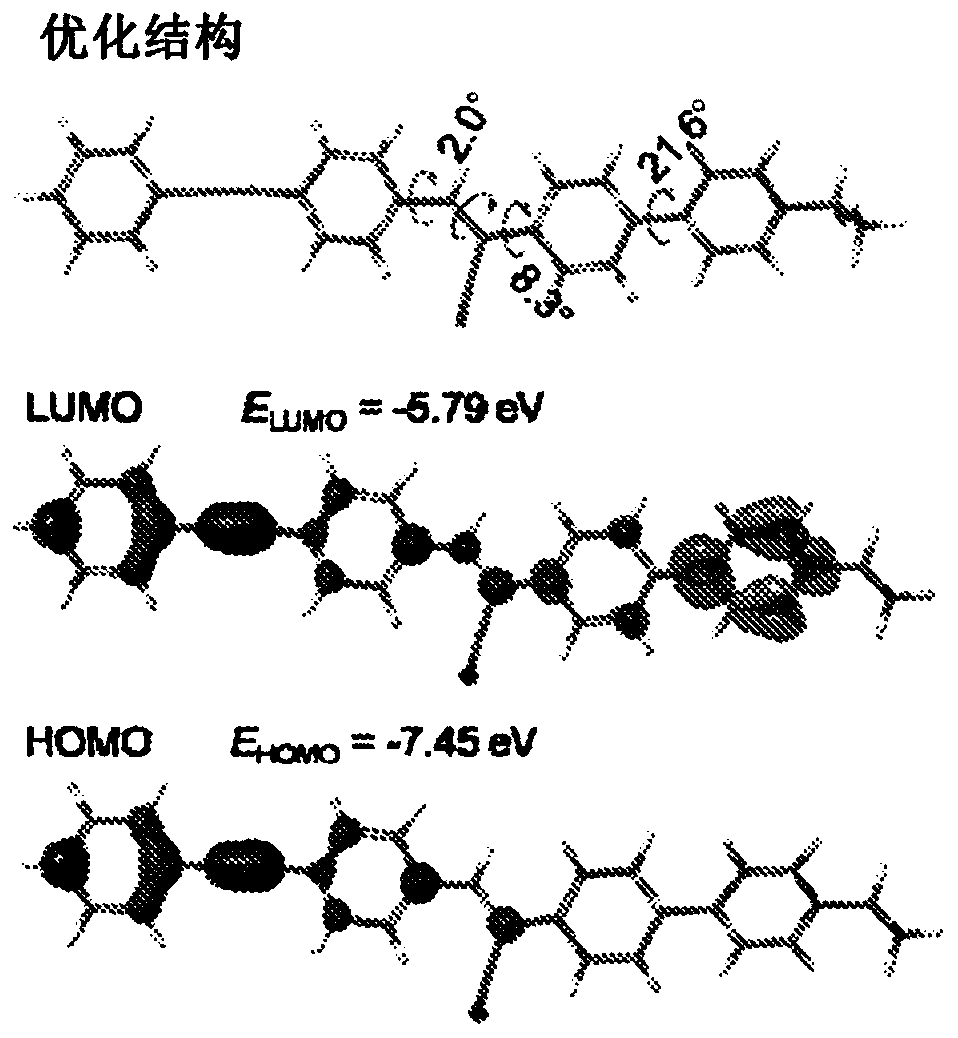
The present subject matter relates to compounds that have aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics and are capable of generating Raman signals in the Ramancell-silent region (1800 cm -1-2800cm -1). The compounds can be used in dual-mode cell imaging by fluorescence and Raman microscopes.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
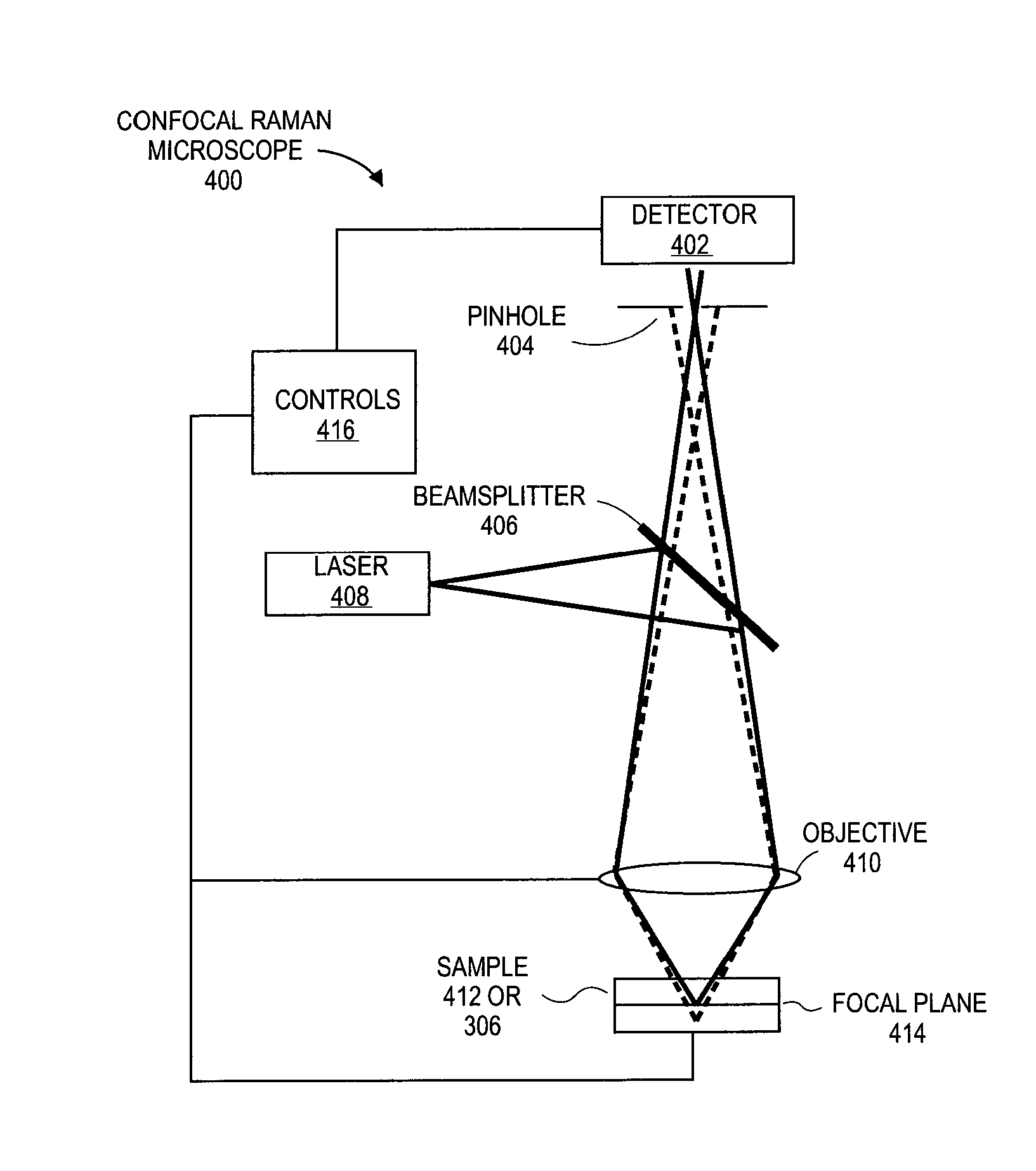
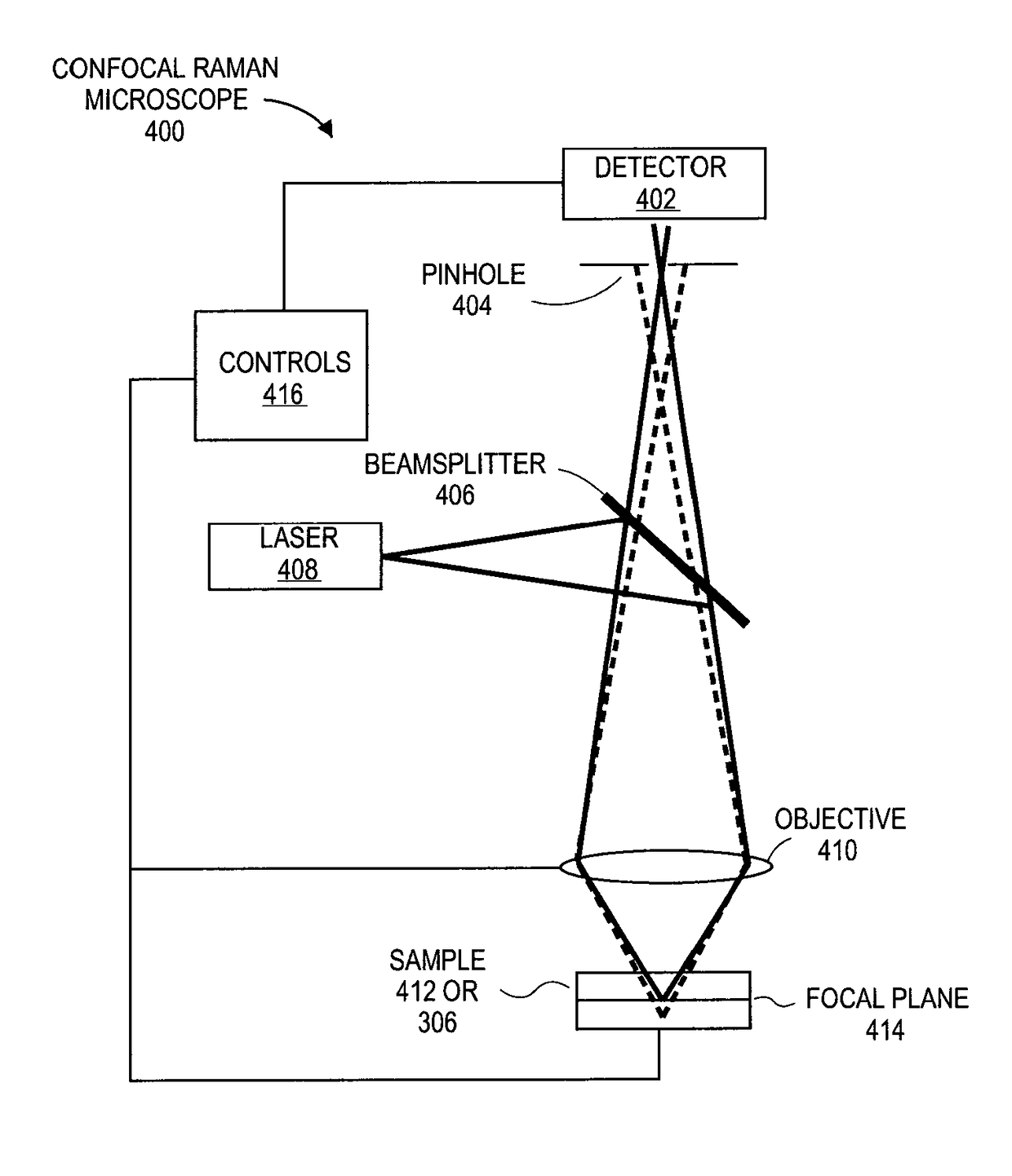
Non-Destructive 3-Dimensional Chemical Imaging Of Photo-Resist Material
Embodiments include devices, systems and processes for using a combined confocal Raman microscope for inspecting a photo resist film material layer formed on the top surface of a layer of a substrate package, to detect border defects between regions of light exposed (e.g., cured) and unexposed (e.g., uncured) resist film material. Use of the confocal Raman microscope may provide a 3D photo-resist chemical imaging and characterization technique based on combining (1) Raman spectroscopy to identify the borders between regions of light exposed and unexposed resist along XY planes, with (2) Confocal imaging to select a Z-height of the XY planes scanned. Such detection provides fast, high resolution, non-destructive in-line inspection, and improves technical development of polymerization profiles of the resist film material.
Owner:INTEL CORP
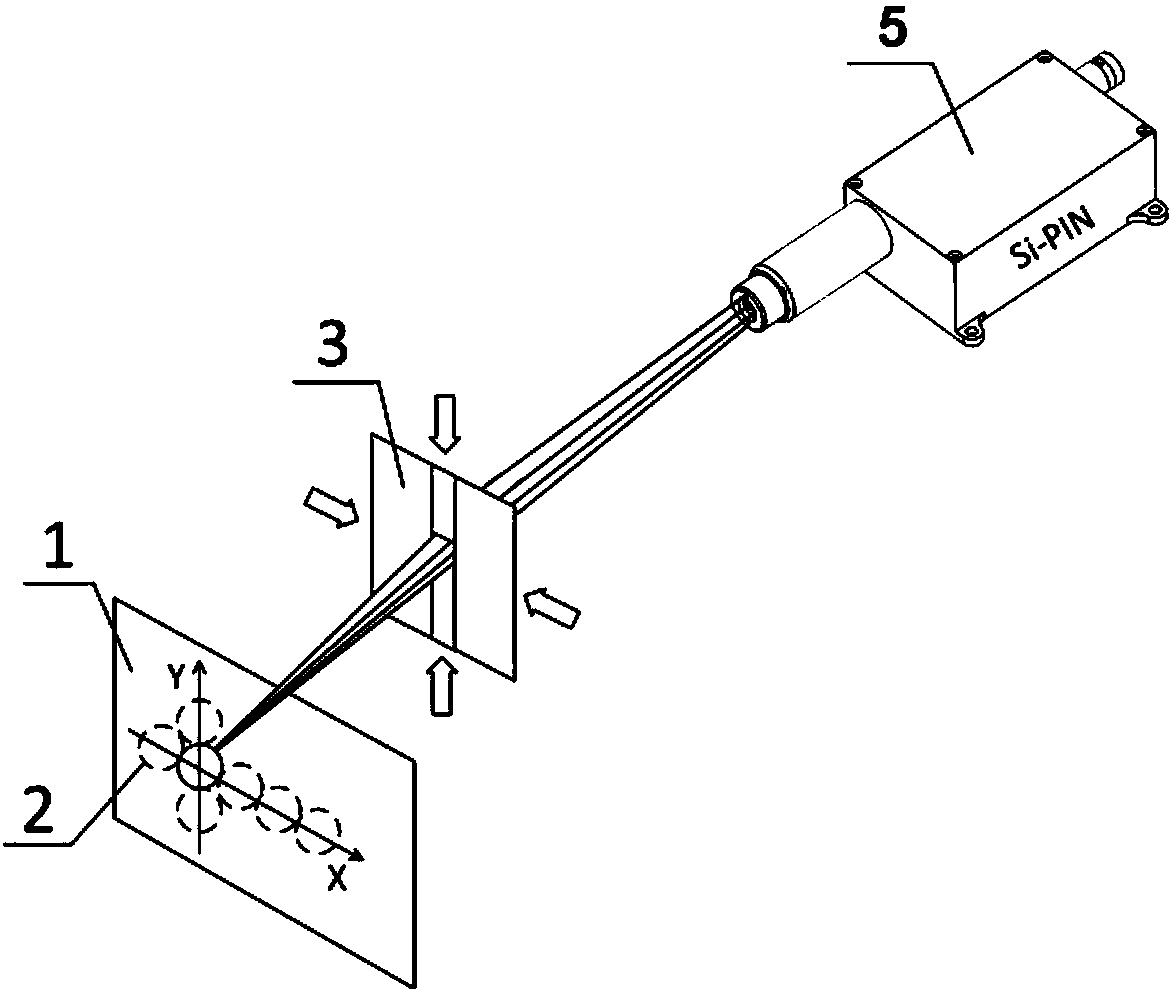
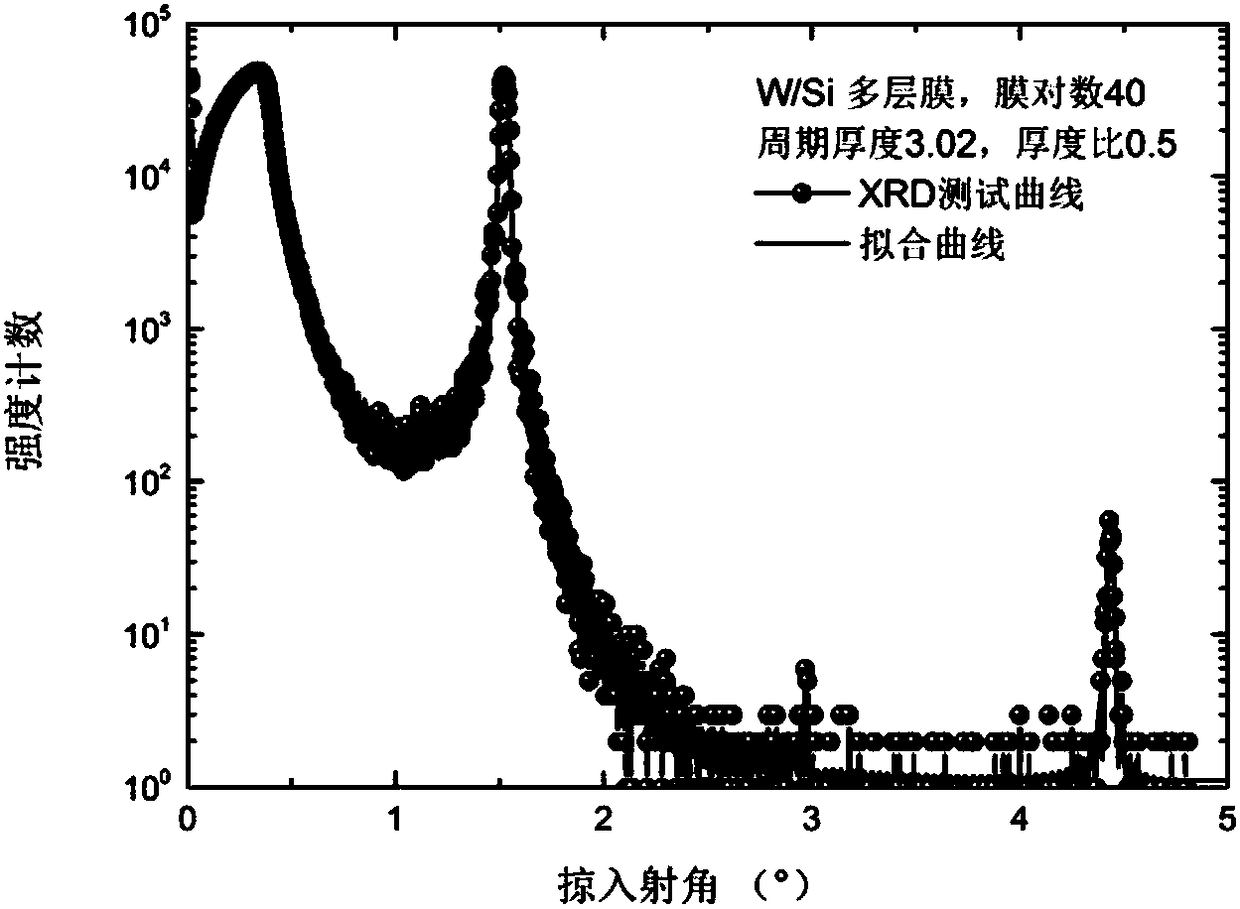
Intensity calibration method of grazing incidence X-ray microscope
ActiveCN108169790ARealize full spectrum measurementIncrease brightnessRadiation measurementRaman microscopeEnergy spectrum
The present invention relates to an intensity calibration method of a grazing incidence X-ray microscope. The method comprises the following steps of: installing each experiment part in a system and performing regulation of the experiment parts to allow the system to achieve an optimal resolution; moving a pin hole diaphragm to measure the emitting spectrum of each field-of-view position; moving out an X-ray microscope from an optical path, and measuring the incident spectrum of the system in each field of view at the rear portion of the aperture diaphragm; employing the measured emitting spectrums and the incident spectrums to perform counting of photons in an energy resolution range, and calculating the object lens reflectivity of each field of view; and employing the object lens reflectivity to calculate the system response efficiency; and according to the system response efficiency of the microscope, the filter disc transmittance and the camera quantum efficiency, calculating and obtaining the source intensity of an implosion pellet. Compared to the prior art, the intensity calibration method of the grazing incidence X-ray microscope considers the consistency of the fields of view, completes the calibration of the optical system energy spectrum response efficiency, and is more suitable for laboratories.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
System for diagnosing pathological change of lipid in blood vessels using non-linear optical microscopy
InactiveUS20120050720A1Diagnose stage of progressionRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringLipid formationTunica intima
Disclosed is a system for diagnosing the pathological change in lipids in blood vessels using coherent anti-strokes raman microscopy which can image lipids abnormally deposited on the deep intima of blood vessels and analyze the components of the imaged lipids, without labeling or destroying blood vessels, to diagnose minute pathological changes in the blood vessels, whereby the stage of progression of lipid-related diseases can be determined.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Test apparatus and method of observing biopsy specimen sampled by using test apparatus
InactiveUS20140354987A1High intrusion performanceRadiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMedicineRaman microscope
A test apparatus includes a biopsy needle for sampling a biopsy specimen. The biopsy needle includes a specimen holder that holds the sampled biopsy specimen, and an optical window disposed in the specimen holder and configured to allow optical detection. A biopsy specimen held by the specimen holder of the test apparatus is measured by using a third-order nonlinear Raman microscope.
Owner:CANON KK
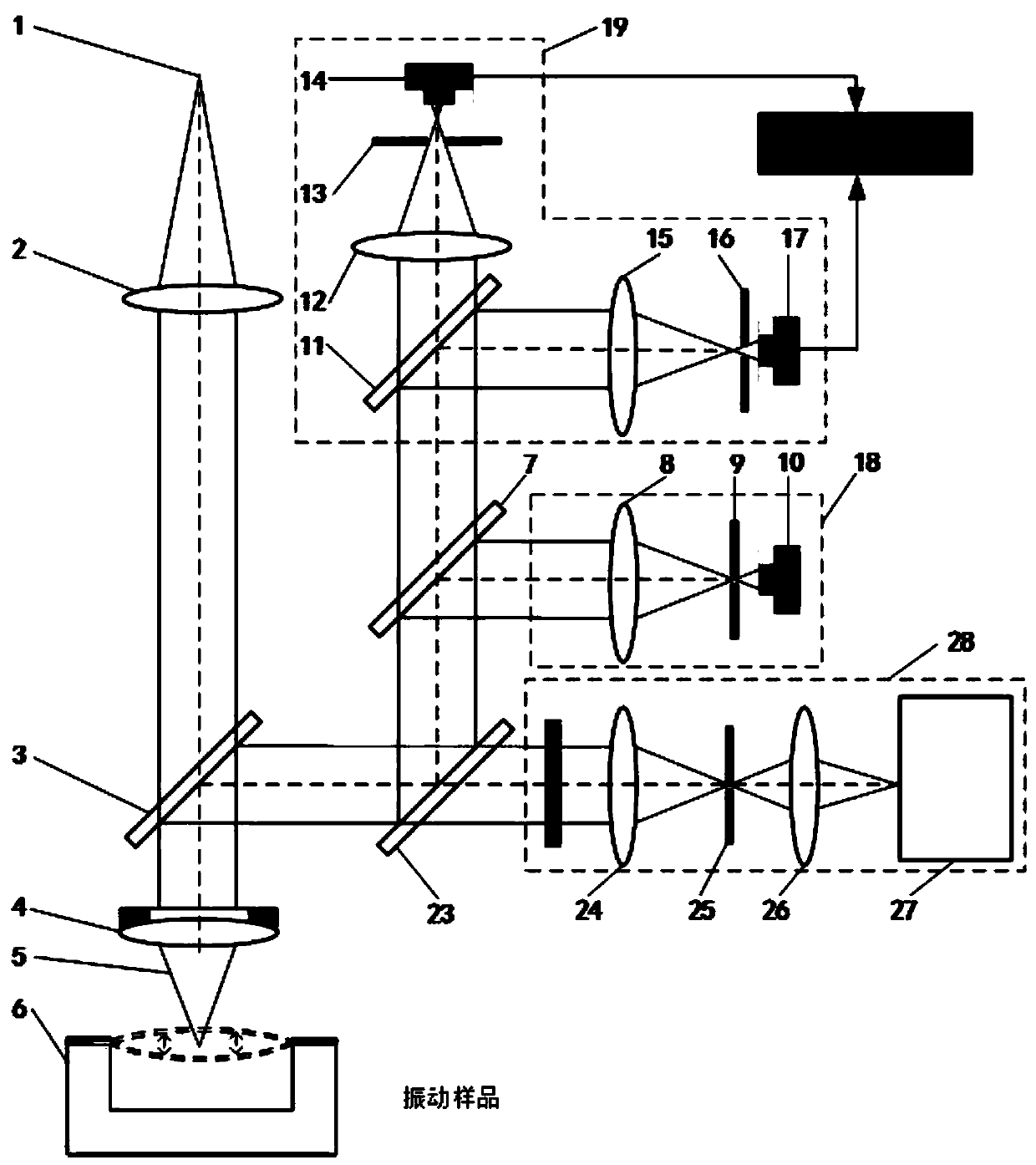
Laser confocal/differential confocal Raman spectrum vibration parameter measurement method
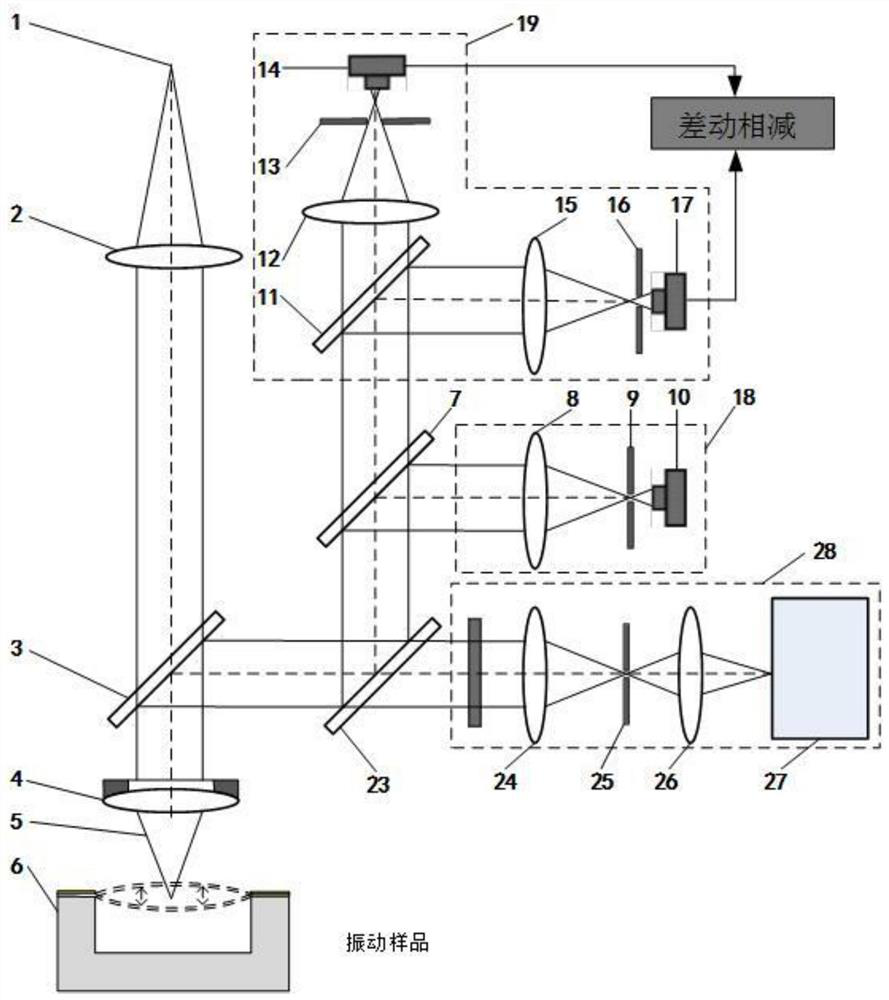
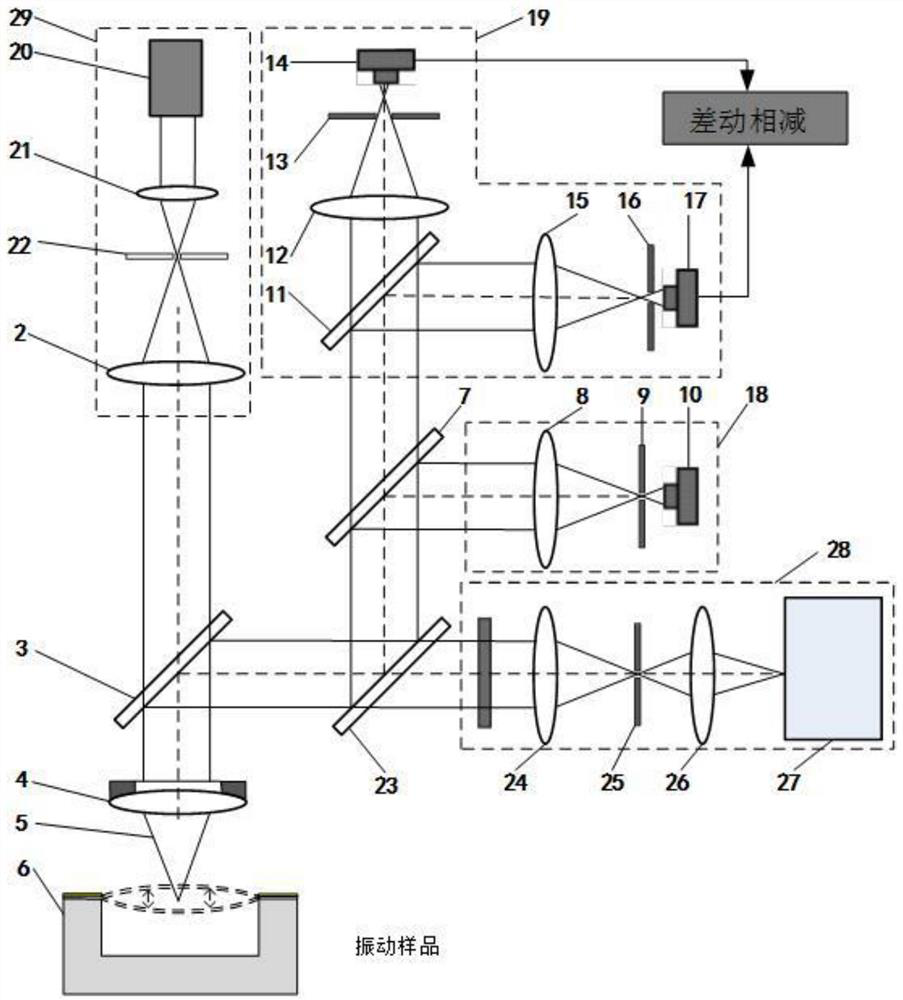
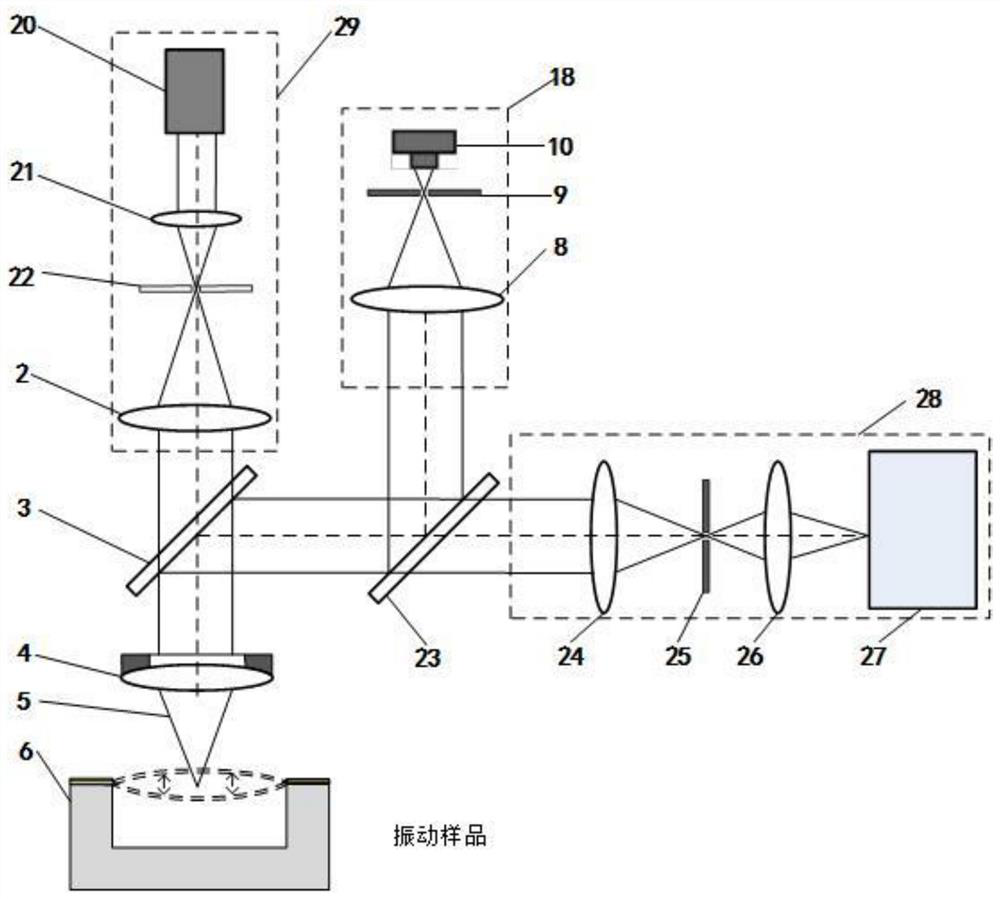
ActiveCN111307269AHigh sensitivityHigh precisionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansVibration amplitudeRaman microscope
The invention discloses a laser confocal / differential confocal Raman spectrum vibration parameter measurement method, and belongs to the technical field of optical precision measurement. Confocal vibration detection, differential confocal vibration detection and Raman spectrum detection technologies are fused, nondestructive separation is carried out on Rayleigh light and Raman scattered light byutilizing a dichroic light splitting system, spectrum detection is carried out on the Raman scattered light, and vibration parameter detection such as amplitude and frequency is carried out on the Rayleigh light. Therefore, the vibration information testing method capable of simultaneously detecting the vibration parameters of the sample micro-area and the Raman spectrum of the vibration of the sample micro-area is formed. According to the invention, the confocal Raman microscope and the differential confocal Raman microscope have the capability of simultaneously detecting micro-area vibrationparameter information and the Raman spectrum of micro-area vibration. The method has the advantages of high vibration measurement precision, wide amplitude measurement range, high frequency measurement bandwidth, high spectrum detection sensitivity, capability of measuring periodic motion and aperiodic motion, high environmental interference resistance and the like. Meanwhile, high-precision detection of micro-area vibration parameters and vibration spectral characteristics is carried out, and the method has a wide application prospect in the technical field of optical precision measurement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
An imaging method of tumor targeting based on enhancement effect of zinc ion signals
ActiveCN103099604AEnhanced autofluorescenceRealize targeted tracking imagingOrgan movement/changes detectionEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsFluorescence microscopeChemical constituents
The invention discloses an imaging method of tumor targeting based on enhancement effect of zinc ion effects. When the imaging method of the tumor targeting based on the enhancement effect of the zinc ion signals is applied at the cellular level, a zinc saline solution is manufactured firstly. Then the saline solution is arranged into a cell incubator together with cancer cells or cancer tissues for incubation. After high resolution fluorescence microscopic imaging and Raman imaging are carried out, qualitative and quantitative analysis is performed on the structure or chemical constituents of the cancer cells or the cancer tissues through the signal data of a fluorescence spectrum and a Raman spectrum. When the imaging method of the tumor targeting based on the enhancement effect of the zinc ion signals is applied at the animal model level, a tumor animal model is constructed and the zinc saline solution is manufactured, after part of the tumor location of an experimental animal is injected with the zinc saline solution, a confocal fluorescence microscope, an ultrasonic imaging device, a fluorescence imaging device, a Raman spectrometer or a Raman microscope are used for monitoring the signal information of the tumor cells or the cancer tissues and processing and analyzing the signal information. Due to the fact that the zinc ions are adopted as the imaging signal enhancer, the imaging method of the tumor targeting based on the enhancement effect of the zinc ion signals has small toxicity on a living body, and has tumor targeting capability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
System for biomolecule sequencing through Raman spectroscopy
PendingCN110628599ARealize detectionLimit sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGratingMeasurement device
The invention provides a system for biomolecule sequencing through Raman spectroscopy. The system comprises a nanopore device, a laser Raman microscope, a spectral measurement device and a data acquisition and analysis device. The nanopore device is located below the laser Raman microscope; the nanopore device mainly comprises a nanopore cavity, a nanopore, a grating and a metal layer; the nanopore is an opening in one end of the nanopore cavity, and the nanopore cavity is a reduced cavity and extends towards the nanopore; the grating surrounds the nanopore cavity; the metal layer is used fordecreasing the size of the nanopore to 1-100 nm; and when to-be-measured biomolecules pass through the nanopore, the laser Raman microscope emits lasers to the biomolecules to generate a Raman spectrum signal, the spectral measurement device measures data, and the data acquisition and analysis device analyzes and outputs a result. By using a surface enhanced Raman spectrum detection strategy, thesystem has the technical effect so that the sub-nano spatial resolution can be detected; and a vibration spectrum of molecular specific fingerprint information is provided, all base spectrum signals are not overlapped, and excellent discrimination and chemical sensitivity are achieved.
Owner:上海近观科技有限责任公司
Biomolecule sequencing method by Raman spectrum method
ActiveCN110628597ARealize detectionLimit sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopyData acquisition
The present invention provides a biomolecule sequencing method by a Raman spectroscopy method. The biomolecule sequencing method comprises the following steps: I, a nanopore device is provided and comprises a flexible substrate nanopore structure, and the flexible substrate nanopore structure comprises nanopores and a metal layer to reduce sizes of the nanopores to be 1-100 nm; II, biomolecules move towards the nanopores, a laser Raman microscope emits laser to the nanopores, and Raman spectrum signals are generated when the biomolecules pass through the nanopores; III, a spectrum measuring device measures Raman spectrum signals to obtain measurement data; and IV, a data acquisition and analysis device analyzes the measured data and outputs results. A detection strategy of using the surface-enhanced Raman spectrum has a technical effect of realizing detection of sub-nanometer spatial resolution and provides vibration spectrum of molecule specificity fingerprint information, the spectrum signals of all bases are not overlapped, and the biomolecule sequencing method has excellent discrimination and chemical sensitivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI IND U TECH RES INST
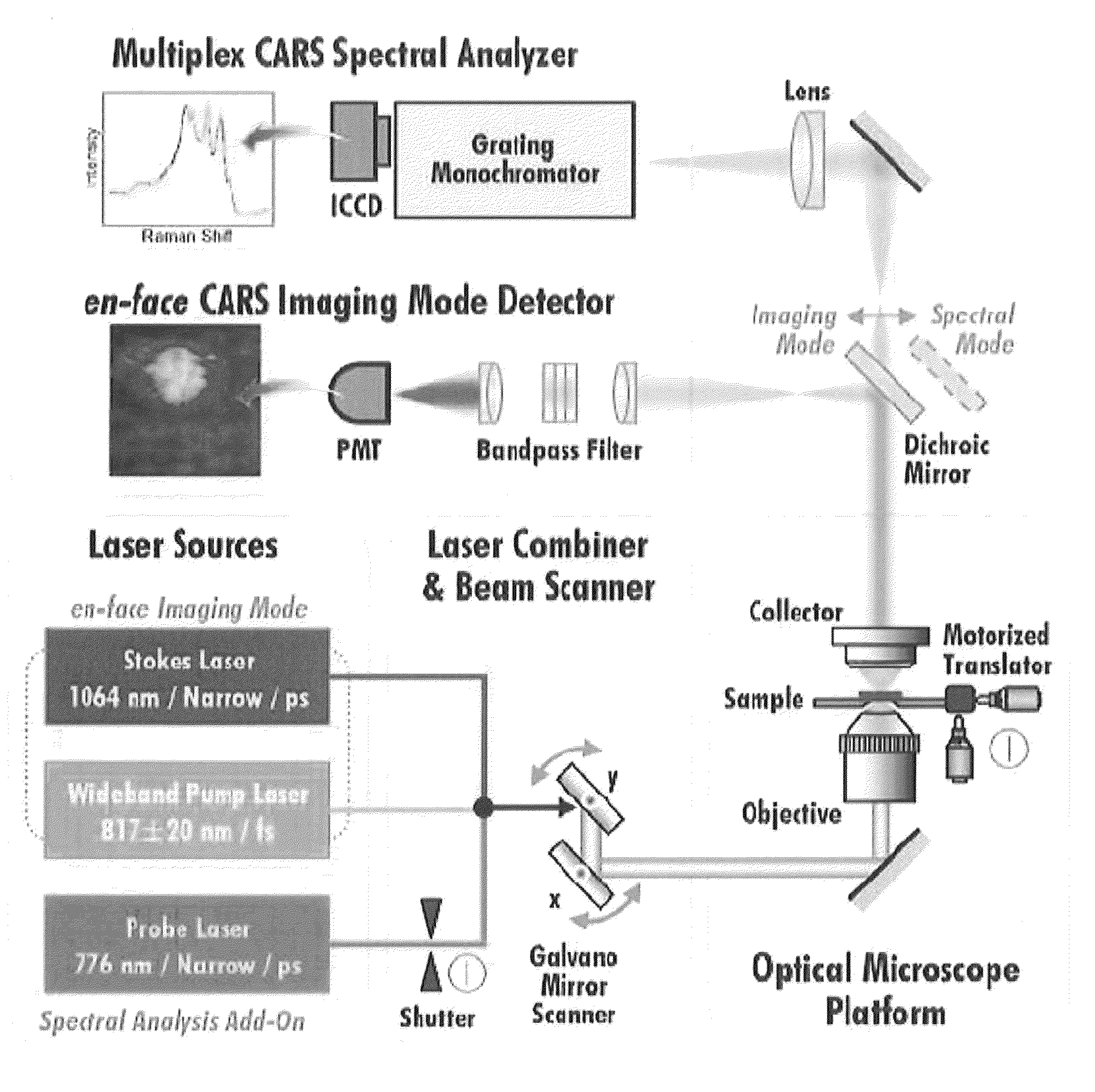
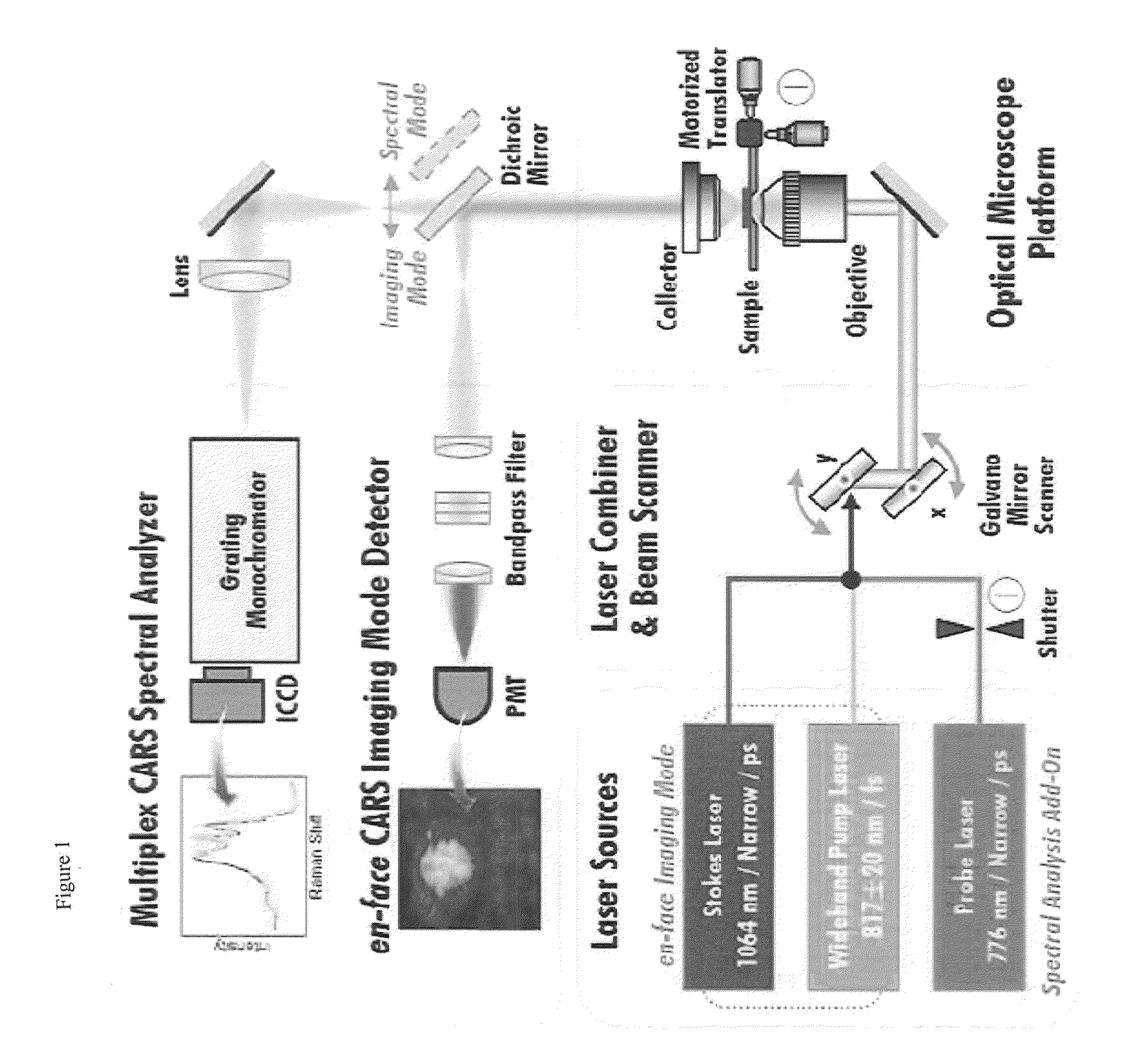
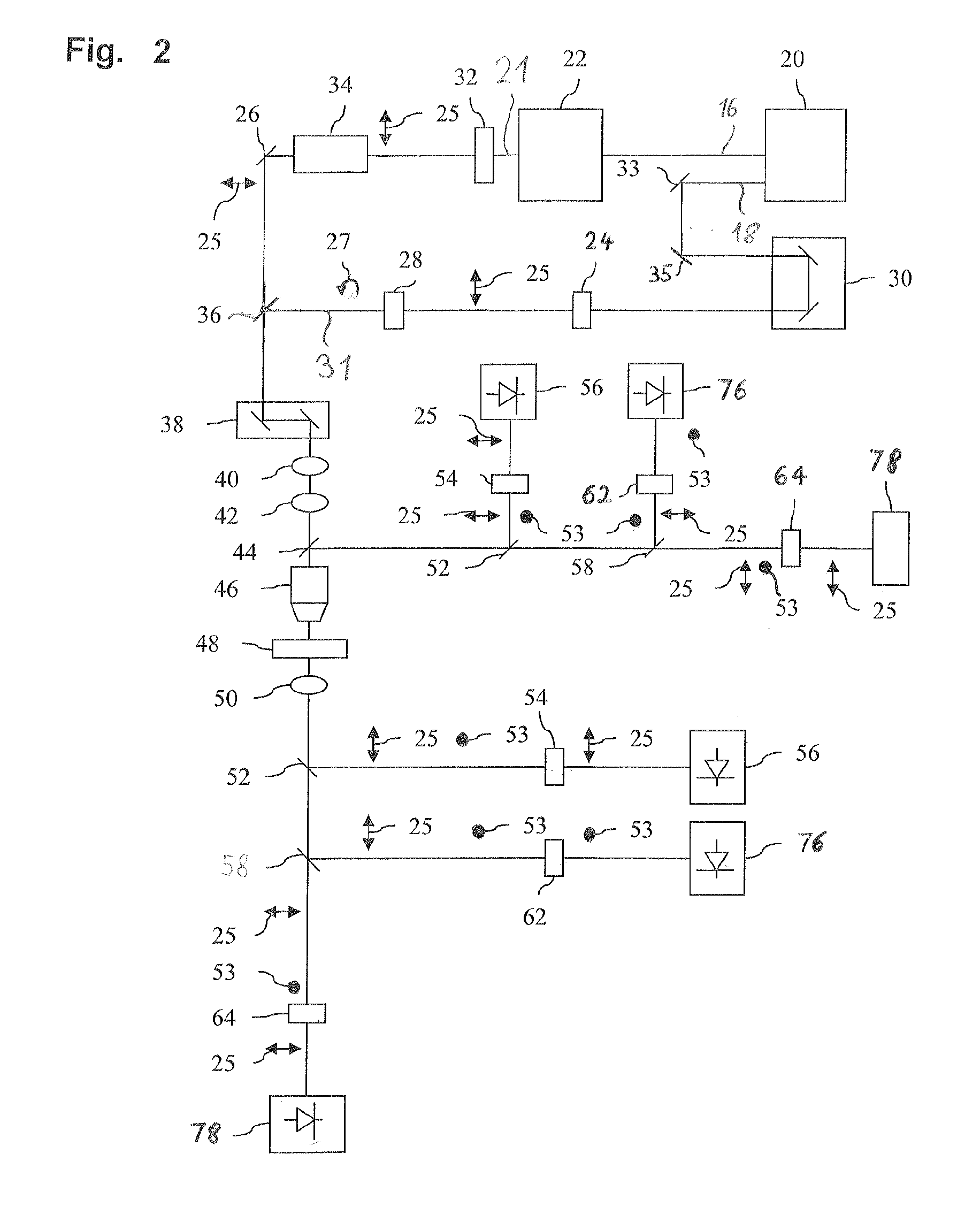
Raman microscopic imaging device
ActiveUS20160363537A1Avoid light lossReduce the numberRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringSignal onLight beam
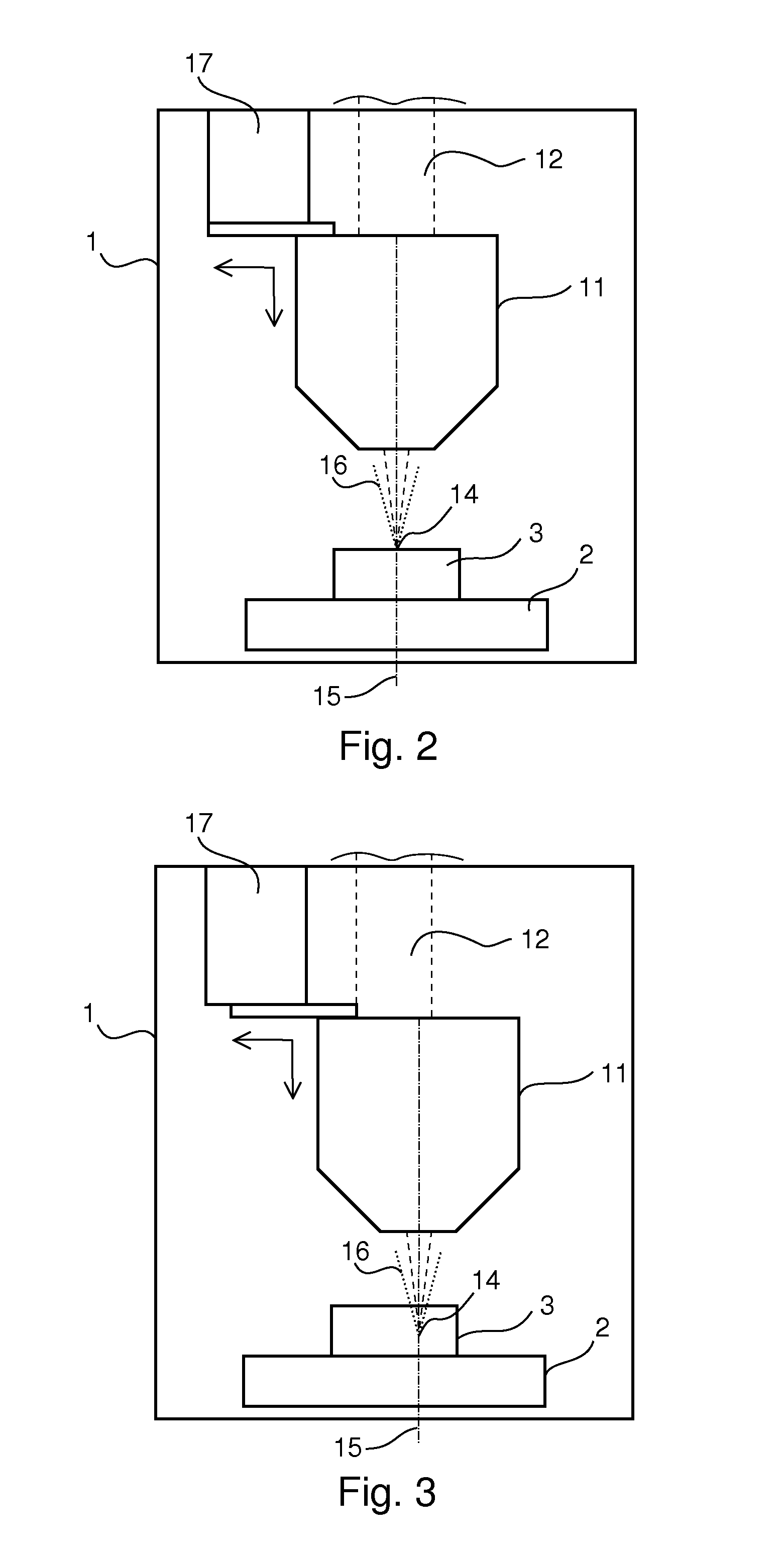
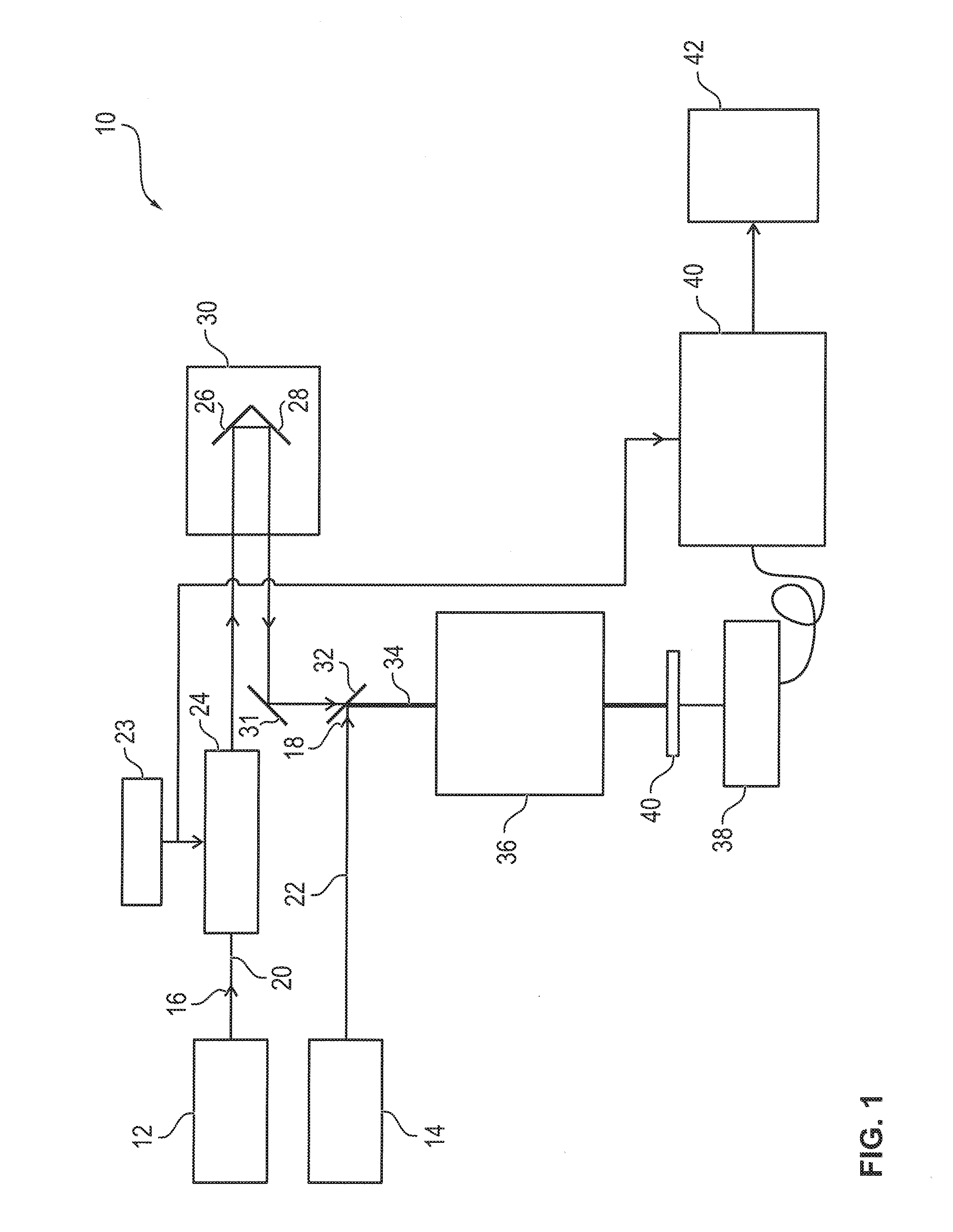
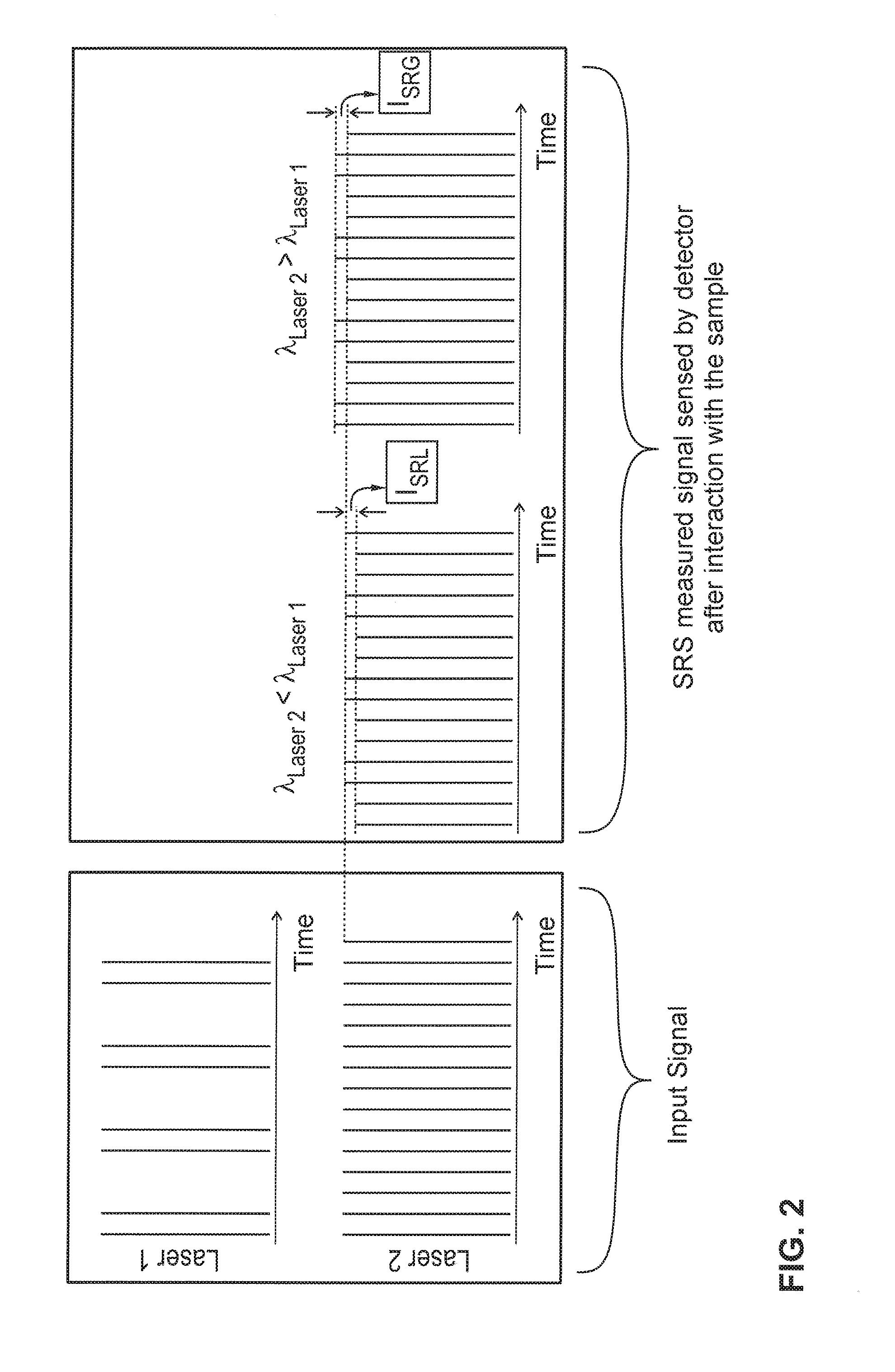
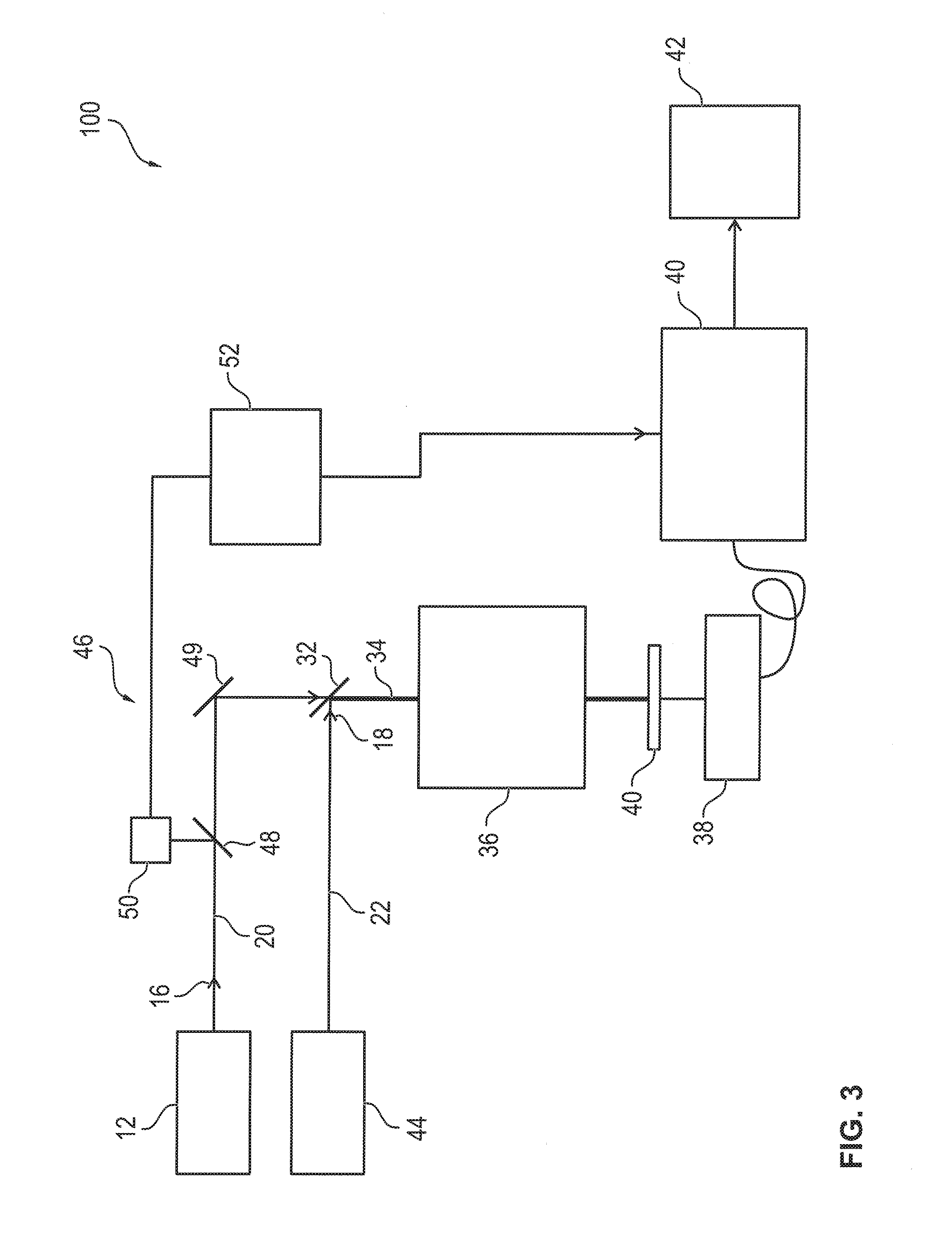
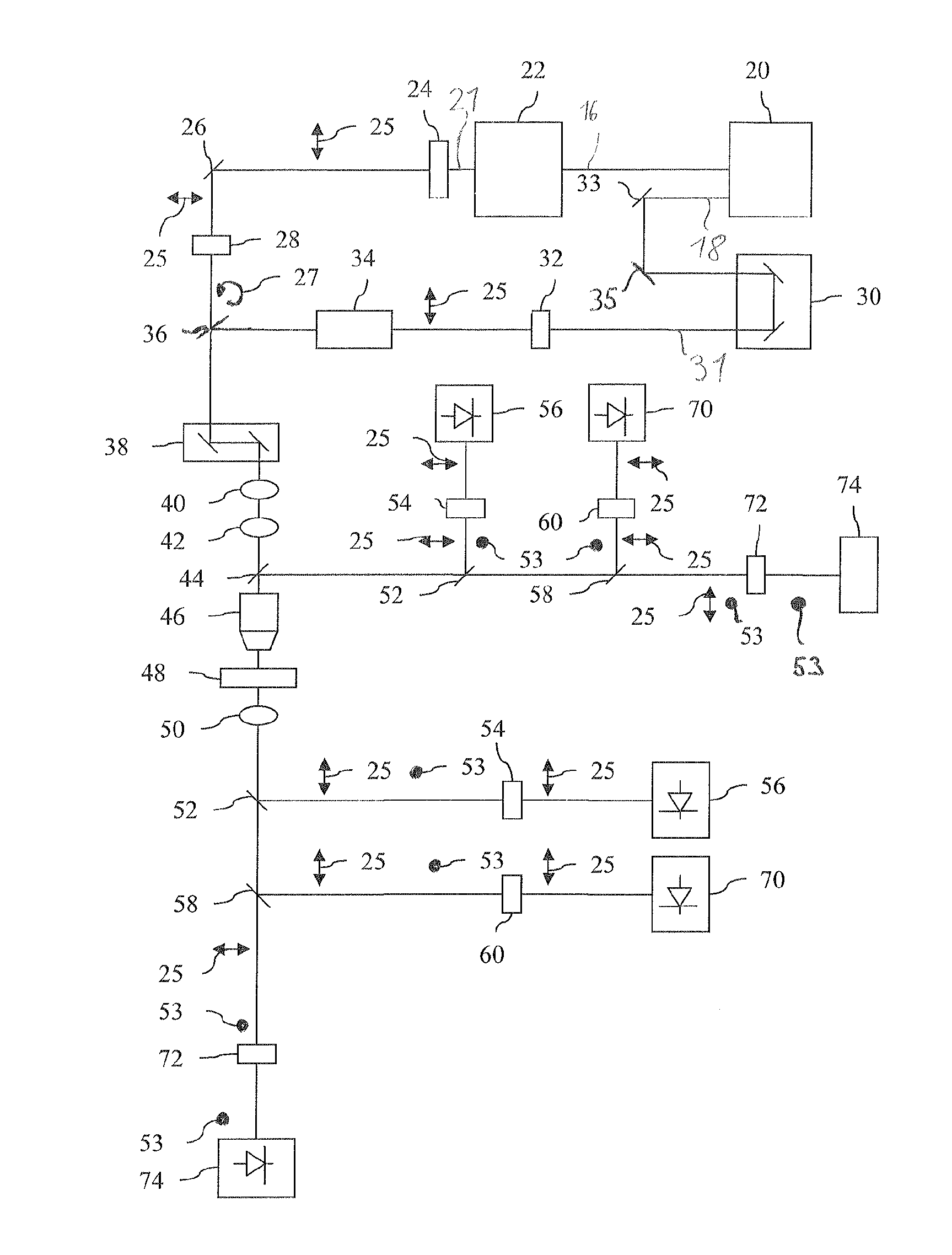
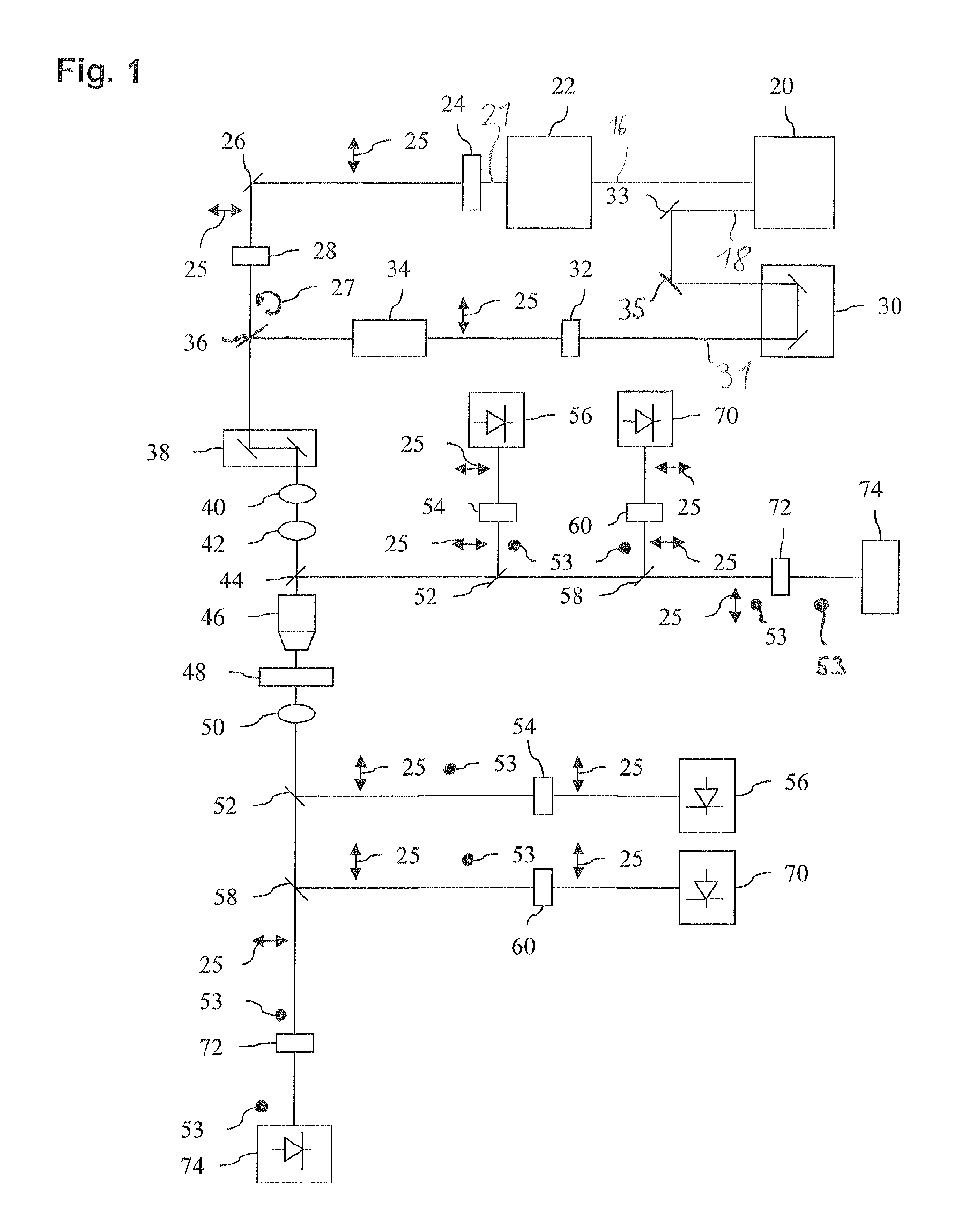
A Raman microscopy imaging device (100) is described, having: a first laser light source (12) for emitting a first laser beam (16) having a first wavelength along a first light path (20); a second laser light source (44) for emitting a second laser beam (18) having a second wavelength, different from the first wavelength, along a second light path (22) physically separated from the first light path (20); a beam combining element (32) for collinearly combining the two laser beams (16, 18) in one shared light path (34) directed onto a sample; a detector (38) for sensing a measured signal on the basis of the two laser beams (16, 18) interacting with the sample; and an evaluation unit (40) for evaluating the measured signal sensed by the detector (38). According to the present invention the first laser light source (12) is embodied as a pulsed source, and the second laser light source (44) as a continuous source.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Raman immersion probe systems and methods
ActiveUS10976259B2Minimize cross-contaminationFacilitate path length adjustmentRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringFiber bundleLight beam
Immersion Raman probes use collimated light as opposed to a diverging fiber bundle or lens-based focusing geometry to deliver and collect light to and from a sample, thereby eliminating problems associated with chromatic aberration. The probes convey counter-propagating excitation and collection beams to and from a distally sealed, signal-transmissive optical component such as a window immersed, in contact with, or otherwise exposed to a sample volume. The counter-propagating excitation and collection beams pass directly through the sealed optical component and into the sample volume in collimated form for Raman analysis thereof. The probe may further include a baffled sample chamber coupled to the distal end of the probe optic body, with one or more optical elements to reflect the counter-propagating beams. The sample chamber may be fixed or axially movable to facilitate path length adjustment. The invention finds utility in process Raman, microscopy and other applications.
Owner:OWEN HARRY
Apparatus and method for multi-modal imaging in nonlinear raman microscopy
ActiveUS8488118B2Improve accuracyAccurate displayRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLight beamRaman microscope
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
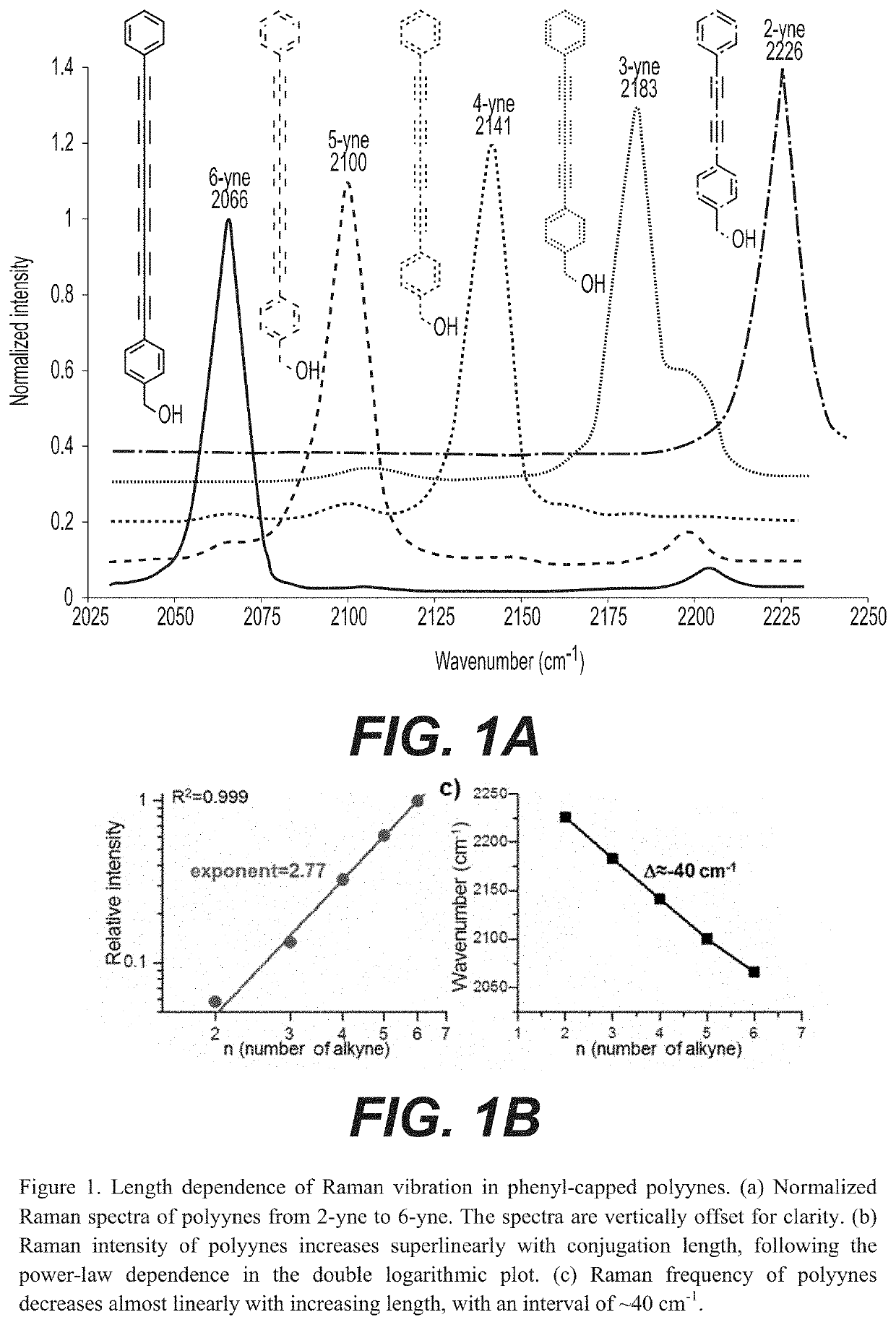
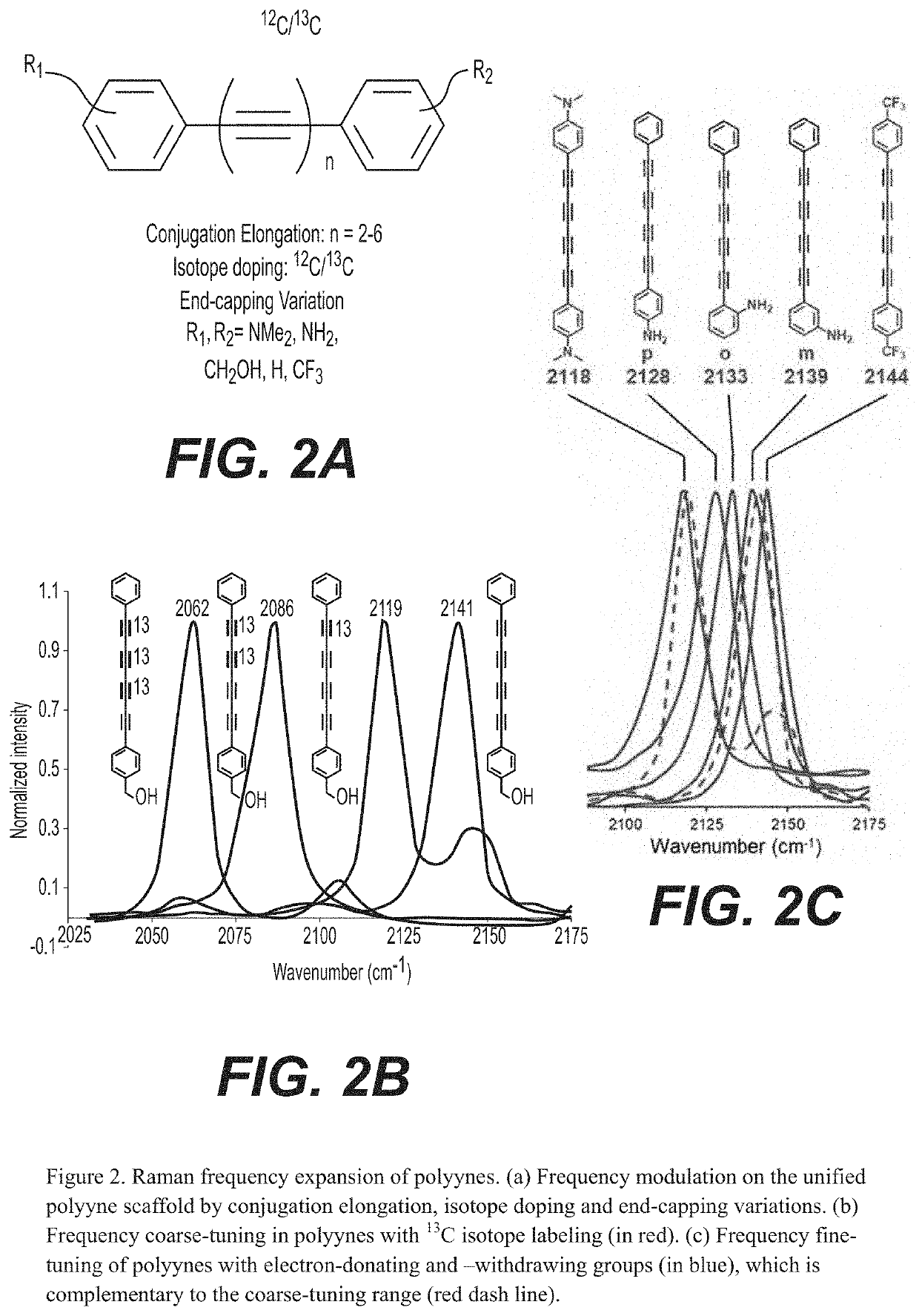
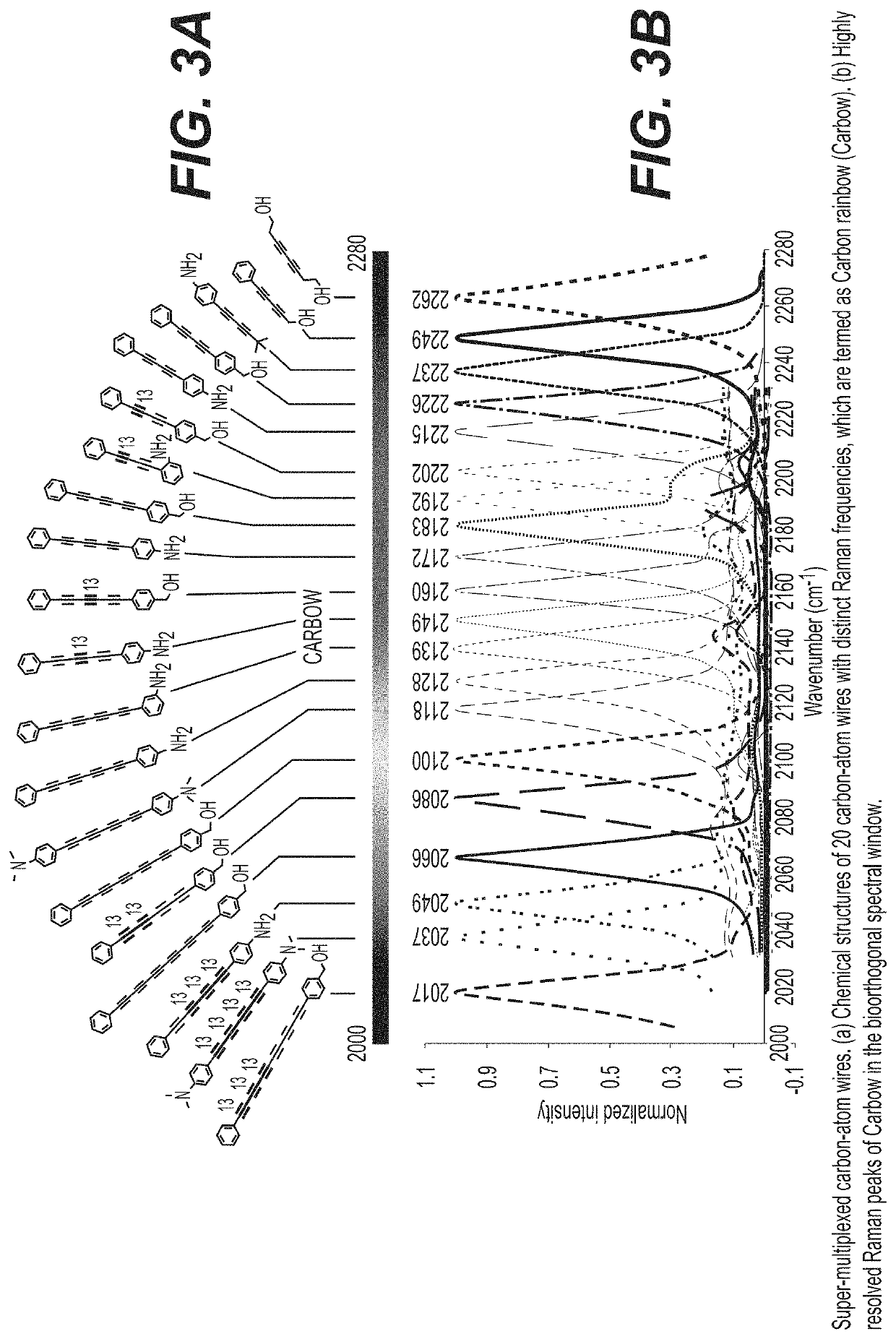
Optical super-multiplexing by polyynes
PendingUS20200199657A1Enhance the imagePromote generationMultiplex system selection arrangementsMaterial nanotechnologyBarcodeRaman microscope
A method for optical super-multiplexing using polyynes to provide enhanced images from stimulated Raman microscopy is disclosed. In some exemplary embodiments, the polyynes are organelle-targeted or spectral barcoded. Imaging can be enhanced by using the polyynes to image whole live cells or specific organelles within live cells. The polyynes can also be used in optical data storage (i.e., encoding) and identification (i.e., decoding) applications.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Test apparatus and method of observing biopsy specimen sampled by using test apparatus
InactiveUS9107651B2High intrusion performanceSurgical needlesDiagnostics using spectroscopyMedicineRaman microscope
A test apparatus includes a biopsy needle for sampling a biopsy specimen. The biopsy needle includes a specimen holder that holds the sampled biopsy specimen, and an optical window disposed in the specimen holder and configured to allow optical detection. A biopsy specimen held by the specimen holder of the test apparatus is measured by using a third-order nonlinear Raman microscope.
Owner:CANON KK
Raman immersion probe systems and methods
ActiveUS20200116639A1Facilitate path length adjustmentMinimize cross-contaminationRaman scatteringFiber bundleLight beam
Immersion Raman probes use collimated light as opposed to a diverging fiber bundle or lens-based focusing geometry to deliver and collect light to and from a sample, thereby eliminating problems associated with chromatic aberration. The probes convey counter-propagating excitation and collection beams to and from a distally sealed, signal-transmissive optical component such as a window immersed, in contact with, or otherwise exposed to a sample volume. The counter-propagating excitation and collection beams pass directly through the sealed optical component and into the sample volume in collimated form for Raman analysis thereof. The probe may further include a baffled sample chamber coupled to the distal end of the probe optic body, with one or more optical elements to reflect the counter-propagating beams. The sample chamber may be fixed or axially movable to facilitate path length adjustment. The invention finds utility in process Raman, microscopy and other applications.
Owner:OWEN HARRY
Method and system for stimulated Raman microscopy beyond the diffraction limit
Systems and methods for probing a Raman signature of a sample with a resolution exceeding the diffraction limit are described. These systems, called GASSE (Gain Saturated Stimulated Emission) and iGASSE (interferometric GASSE), are detecting a Raman signal produced in a sample located at the focal spot of a Gaussian pump pulse. Two additional pulsed laser beams (Stokes beams), a central Stokes beam having a Gaussian beam profile and another Stokes beam having an annular beam profile, are also focused to the focal spot. The spatial and temporal phases of the laser pulses are adjusted to produce destructive interference over most of the temporal width of Stokes pulses, which causes emission from the central Stokes beam to narrow well below the diffraction limit. A two-dimensional image of the sample is produced by scanning the combined beams across the sample. The system may find applications in biomedical and semiconductor technology.
Owner:FREL ROBERT D
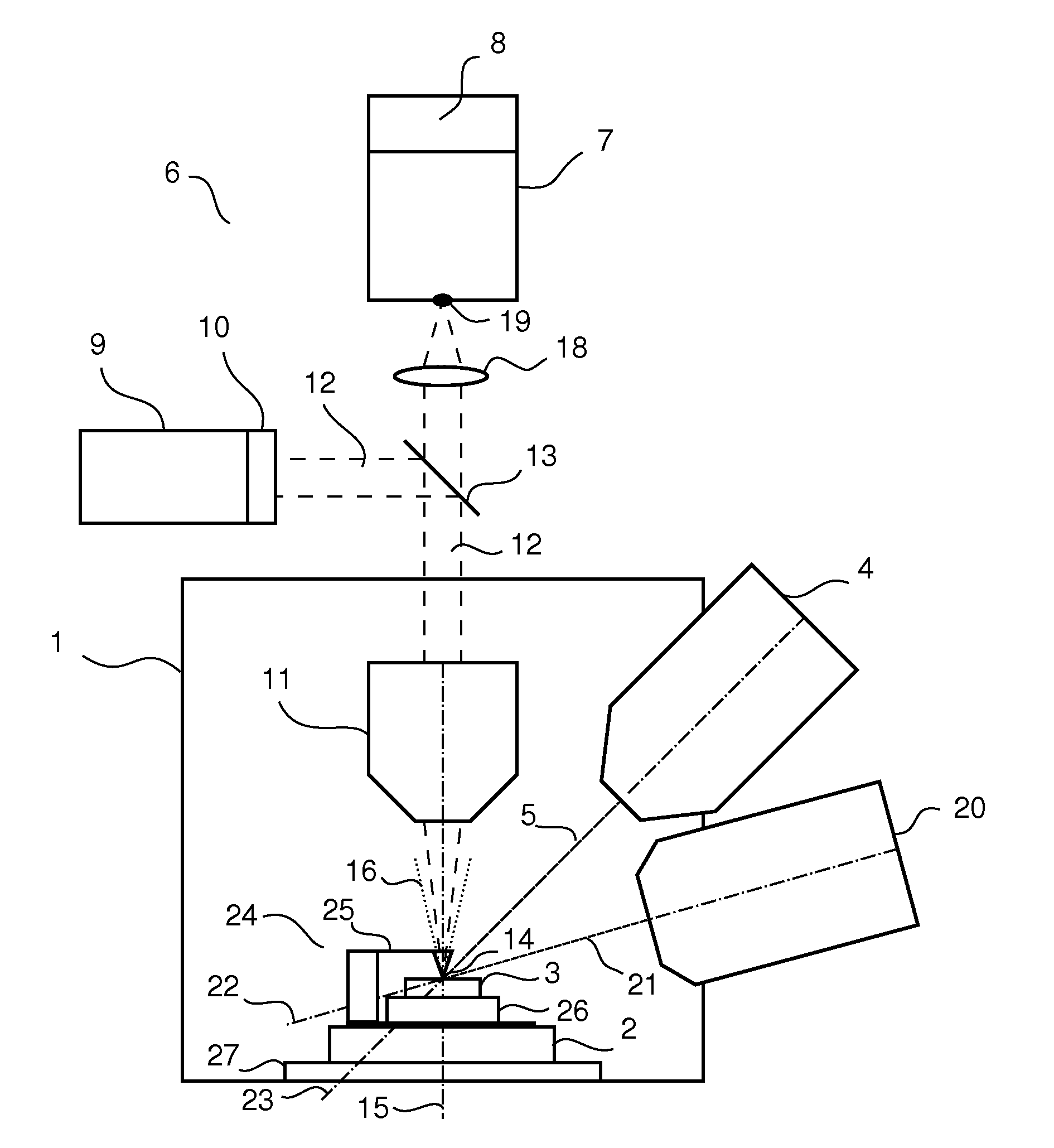
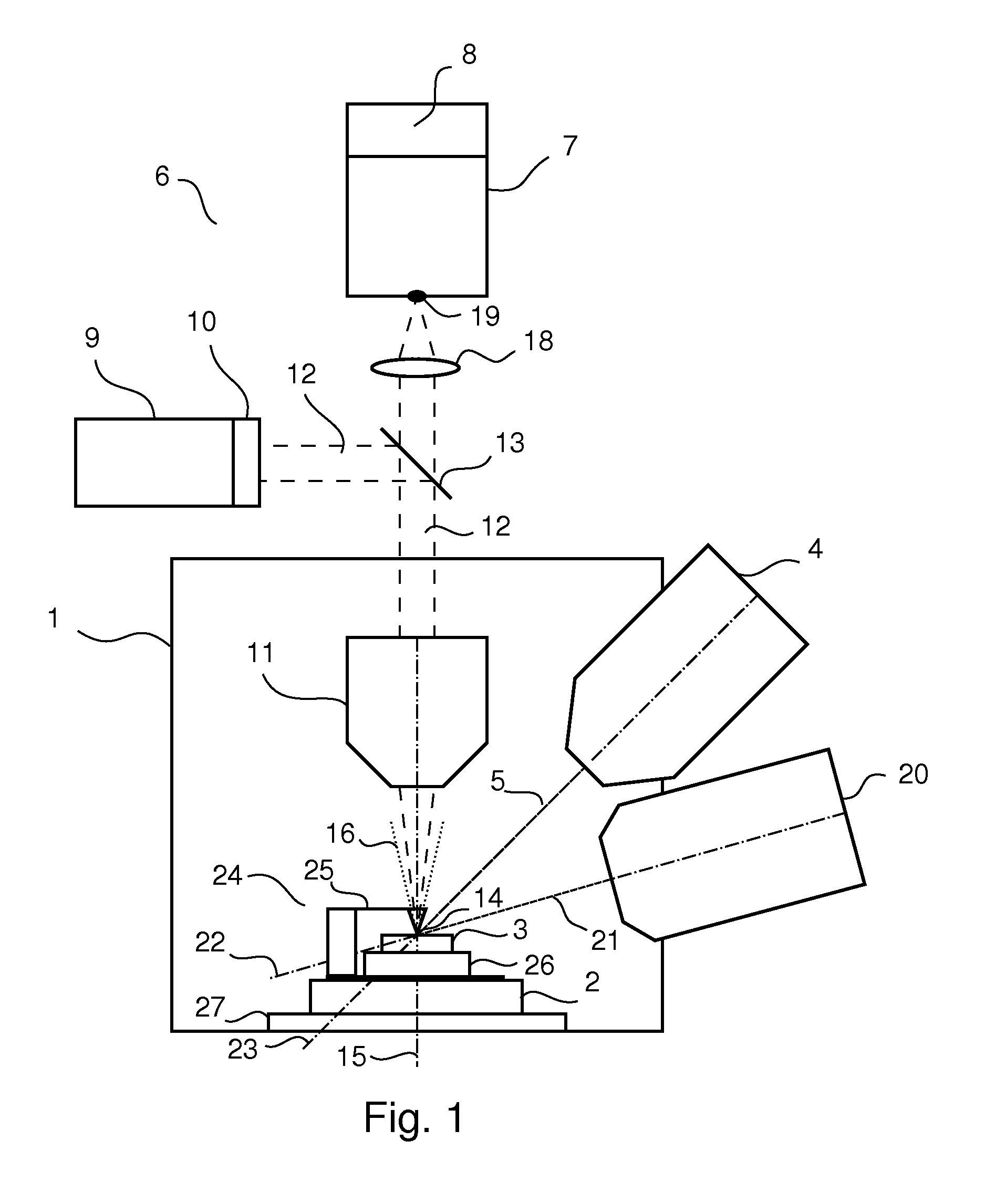
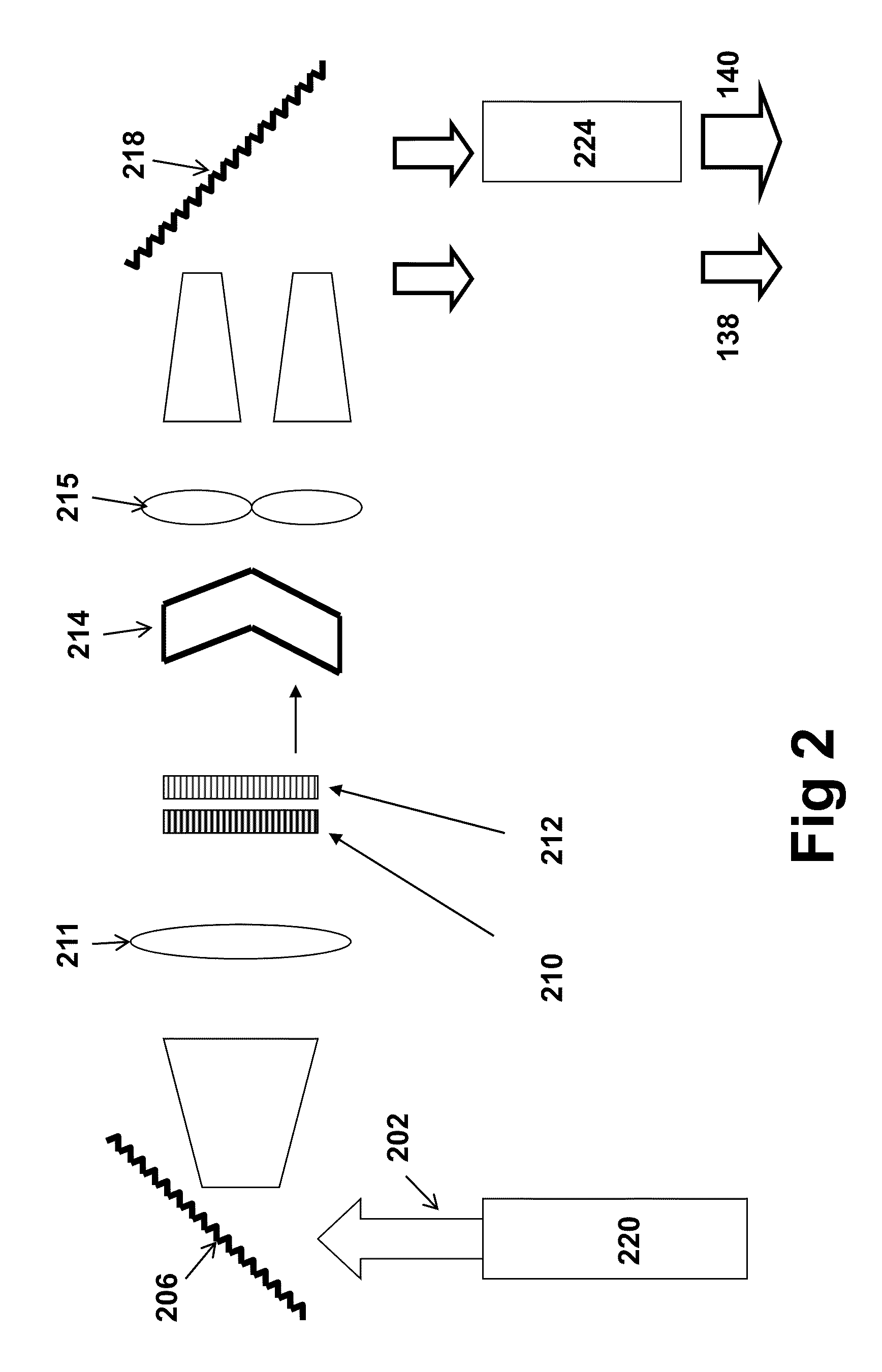
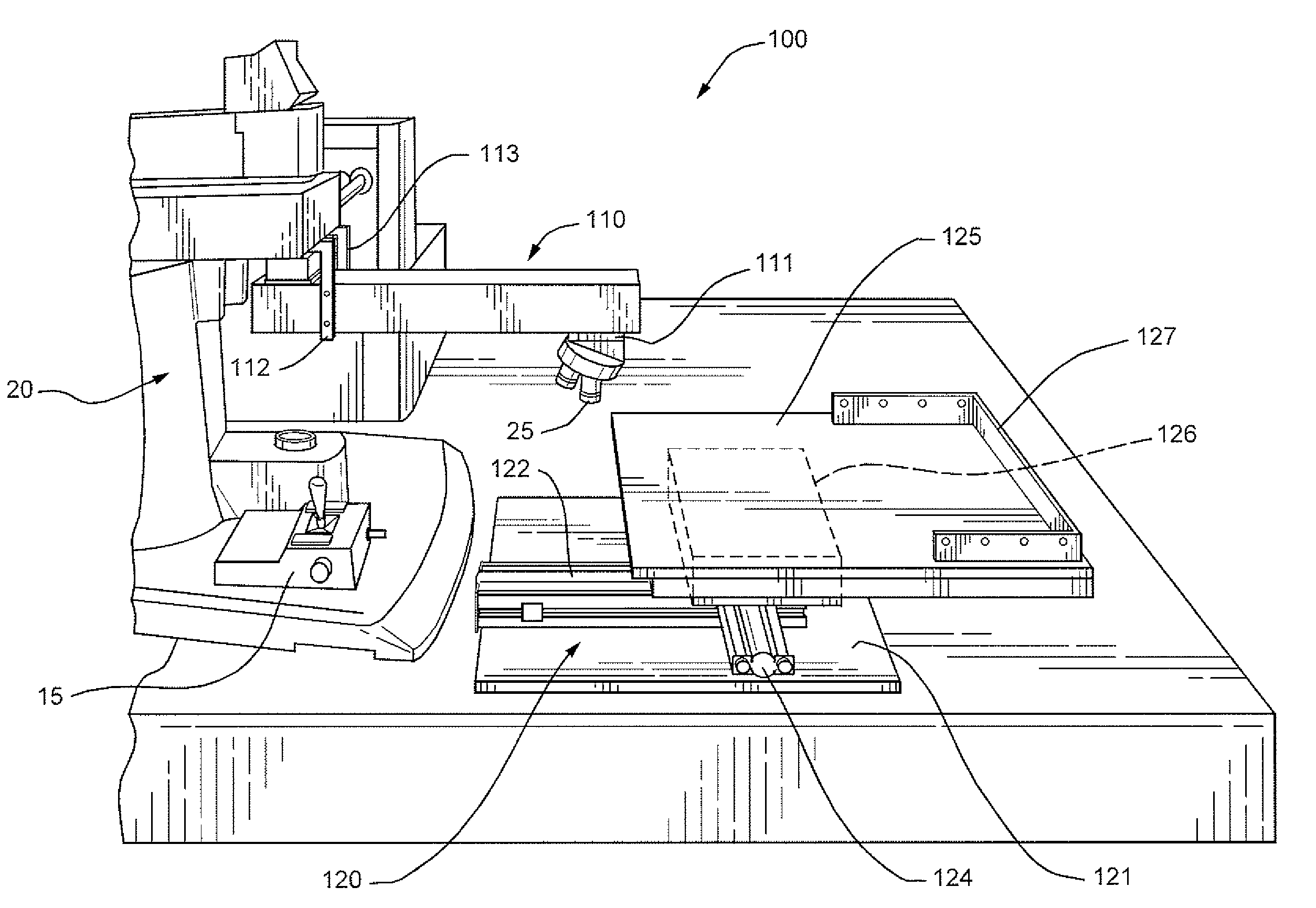
Method for Characterizing X-Ray Detector Materials Using a Raman Microscope
An improved Raman microspectrometer system extends the optical reach and analysis range of an existing Raman microspectrometer to allow analysis and / or repair of an oversized sample. The improved Raman microspectrometer system includes an extender for extending the optical reach of the existing microspectrometer and a supplemental stage which extends the analysis range of the existing microspectrometer by providing travel capabilities for non-destructive analysis of an entire oversized sample. Such an arrangement decreases manufacturing costs associated with testing oversized samples such as mammography panels, enabling analysis and / or repair to be performed without destruction.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Raman Spectroscopy In-Situ Measurement Method and Measurement Device of High Temperature Volatile Corrosive Molten Salt
The invention discloses a device and method for in-situ measurement of the Raman spectrum of high-temperature volatile corrosive molten salt, including: a DXR-Raman Microscope and its matching long-angle objective lens, and There are external heating furnaces (including furnace body, heating elements, thermocouples, cooling water furnace doors, temperature control equipment components, etc.) and quartz sealed crucibles. The design of the external heating furnace and quartz crucible eliminates the limitation of sample amount during the test of volatile corrosive molten salt samples and expands the measurement temperature range to ambient temperature -1873.5K. The use of the external heating furnace with the Raman long corner objective lens can avoid Damage to Raman optical instruments caused by high temperature and volatile and corrosive molten salts during high-temperature in-situ testing. The method of the invention is simple, and the required equipment, the external heating furnace, is cheaper than the micro-microscopic heating stage of the Raman spectrometer, and is more suitable for high-temperature in-situ Raman measurements of volatile corrosive molten salts.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
All-optical method capable of simultaneously achieving single-cell targeted drug transferring and real-time detection
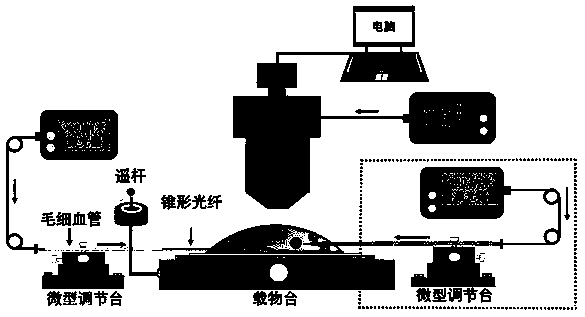
The invention discloses an all-optical method capable of simultaneously achieving single-cell targeted drug transferring and real-time detection. Targeted drug transferring at a single-cell level andreal-time Raman detection of a micronano drug are achieved by assembling a Raman microscopy, a specially-fabricated fiber, a three-dimensional hexagonal adjustment rack and a laser. Micronano drug targeted transferring achieved by an optical control method has the advantages of rapid transfer rate and good targeting ability, quantitative transfer can be achieved, moreover, the all-optical method is wide in applicability and is flexible, simple and convenient to operate, the all-optical method can be applied to an adherent cell, and the problem that targeted drug transfer is difficult due to Brownian movement of a suspension cell also can be solved; by Raman detection, activity detection of a single cell can be achieved, a chemical reagent is not needed to dye or mark during the detection process, no damage is generated, and the all-optical method is simple, convenient and efficient; and single-cell synchronous targeted drug transfer and Raman detection which are achieved by the deviceis of important significance to the fields of cytological study, drug research and development and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
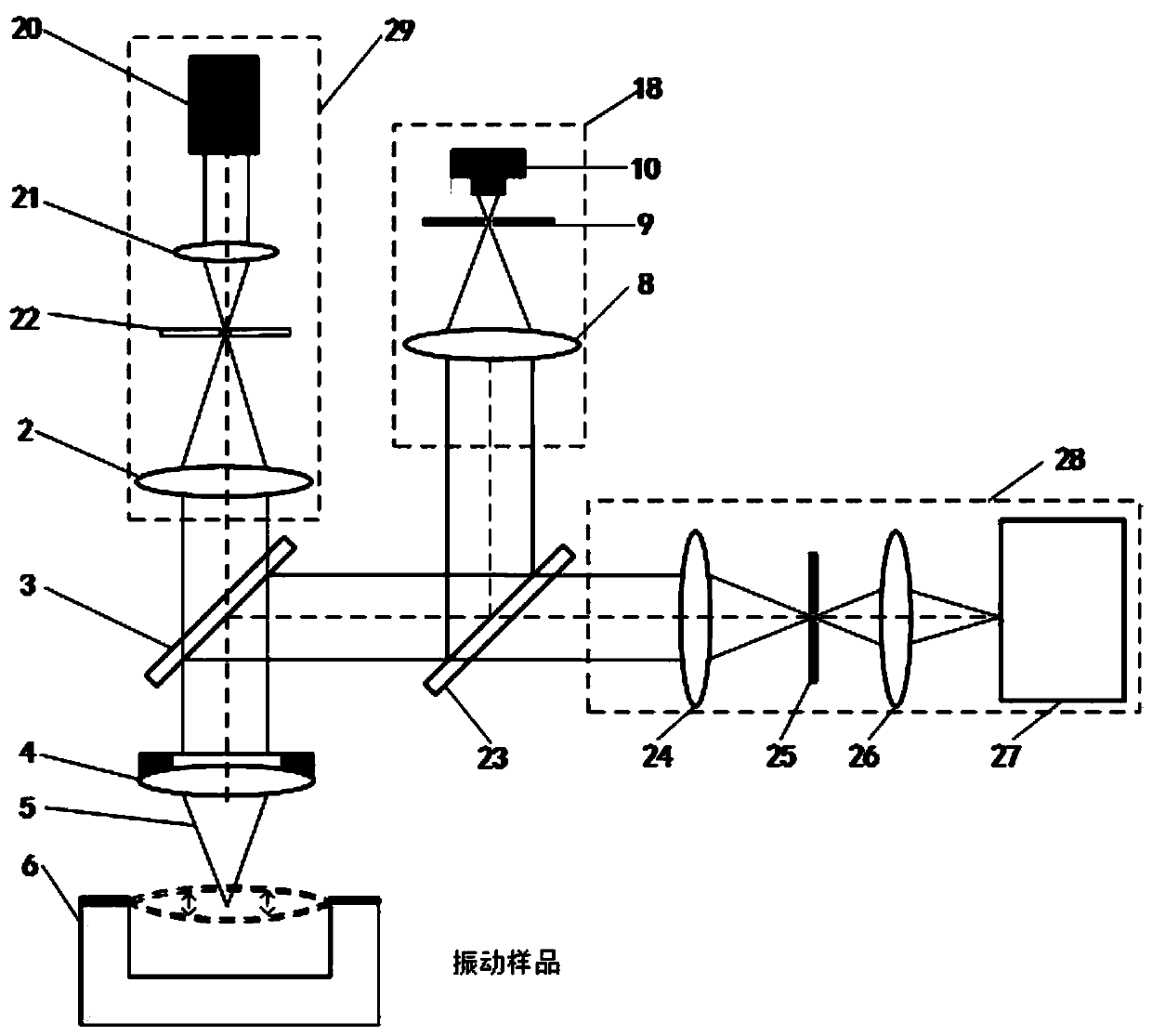
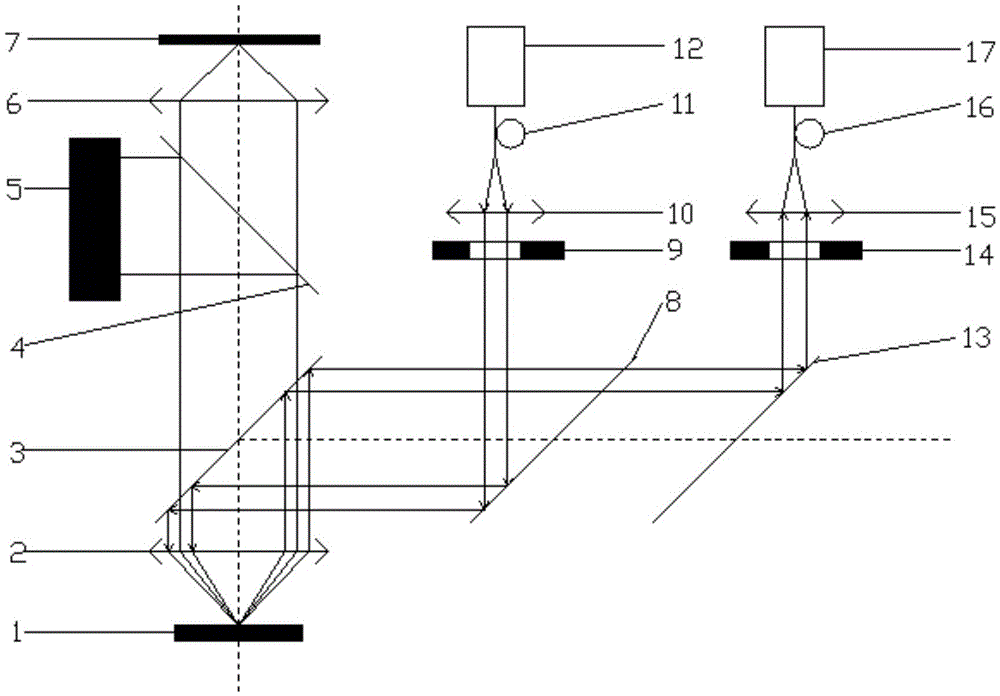
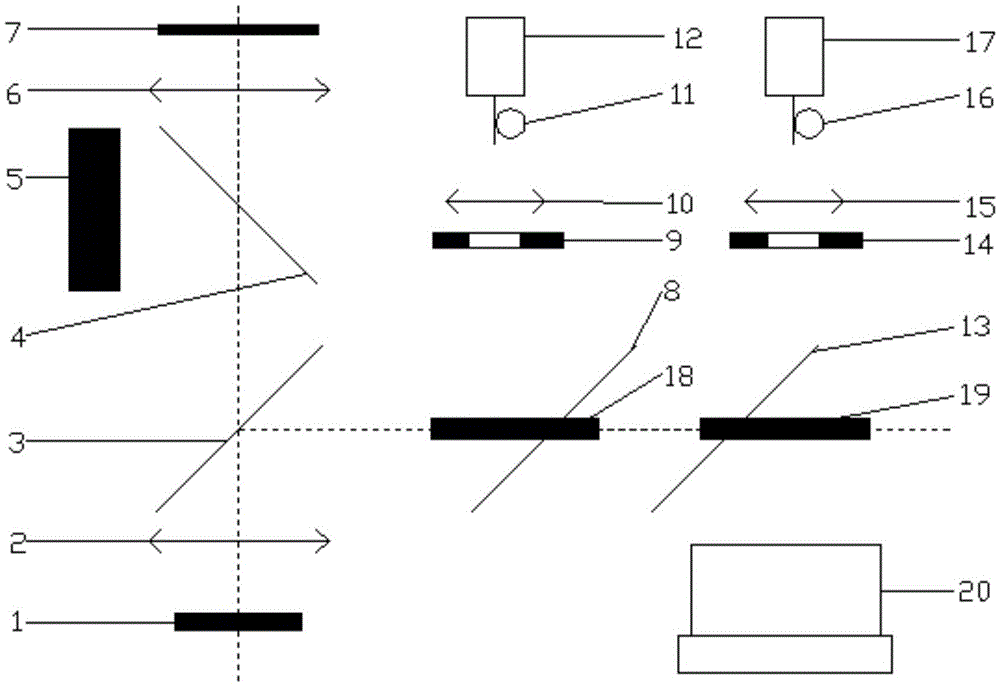
A confocal Raman microscope with angular resolution
The invention discloses a confocal microscopic Raman spectrometer with angle resolution capacity and relates to Raman spectrometers. The confocal microscopic Raman spectrometer comprises a microscope objective, a low-pass light filter, a high-pass light filter, a reflector, a beam splitter, adjustable diaphragms, a collimating lens, an optical fiber and a corresponding laser light source, a spectral signal detector, an illuminating light source and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, wherein light emitted by the laser light source enters the microscope objective through the optical fiber, the collimating lens, the high-pass light filter and the low-pass light filter, the positions of the incident parallel beams can be adjusted by moving the high-pass light filter from left to right along the horizontal direction, and an angle of exciting light which reaches the sample surface is adjusted. The first adjustable diaphragm can control the pore diameter of the incident parallel beams, and the positions of emergent parallel beams can be adjusted by moving the reflector from the left to right along the horizontal direction, so that an angle of Raman scattering light collected from the sample surface is adjusted; and the second adjustable diaphragm can control the pore diameter of the Raman scattering light beams, and the sample can be imaged through the illuminating light source, the beam splitter and the CCD camera.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Solids analysis using raman spectroscopy
PendingUS20220178830A1Low applicabilityImprove performanceRaman scatteringTesting medicinal preparationsSpectrographRaman microscope
Raman systems and methods use advantages offered by increased laser mobility / path length and photon migration to analyze diffusively scattering solids, including pharmaceuticals. A collimated laser excitation beam having a first diameter induces from a sample a backscattered collimated Raman collection beam with a second diameter. The collimated laser excitation beam and the collimated Raman collection beam form a counter-propagating collimated optical path, and the collimated laser excitation beam is preferably smaller in diameter than the diameter of the backscattered collimated Raman beam. The collection beam to a spectrograph for Raman analysis of the sample. A Raman calibration standard may be placed in the collimated optical path, and / or the sample may be supported in a reflective holder that may be at least partially spherical and / or may form part of a multi-well plate. The counter-propagating collimated optical path may be contained within a Raman microscope.
Owner:OWEN HARRY
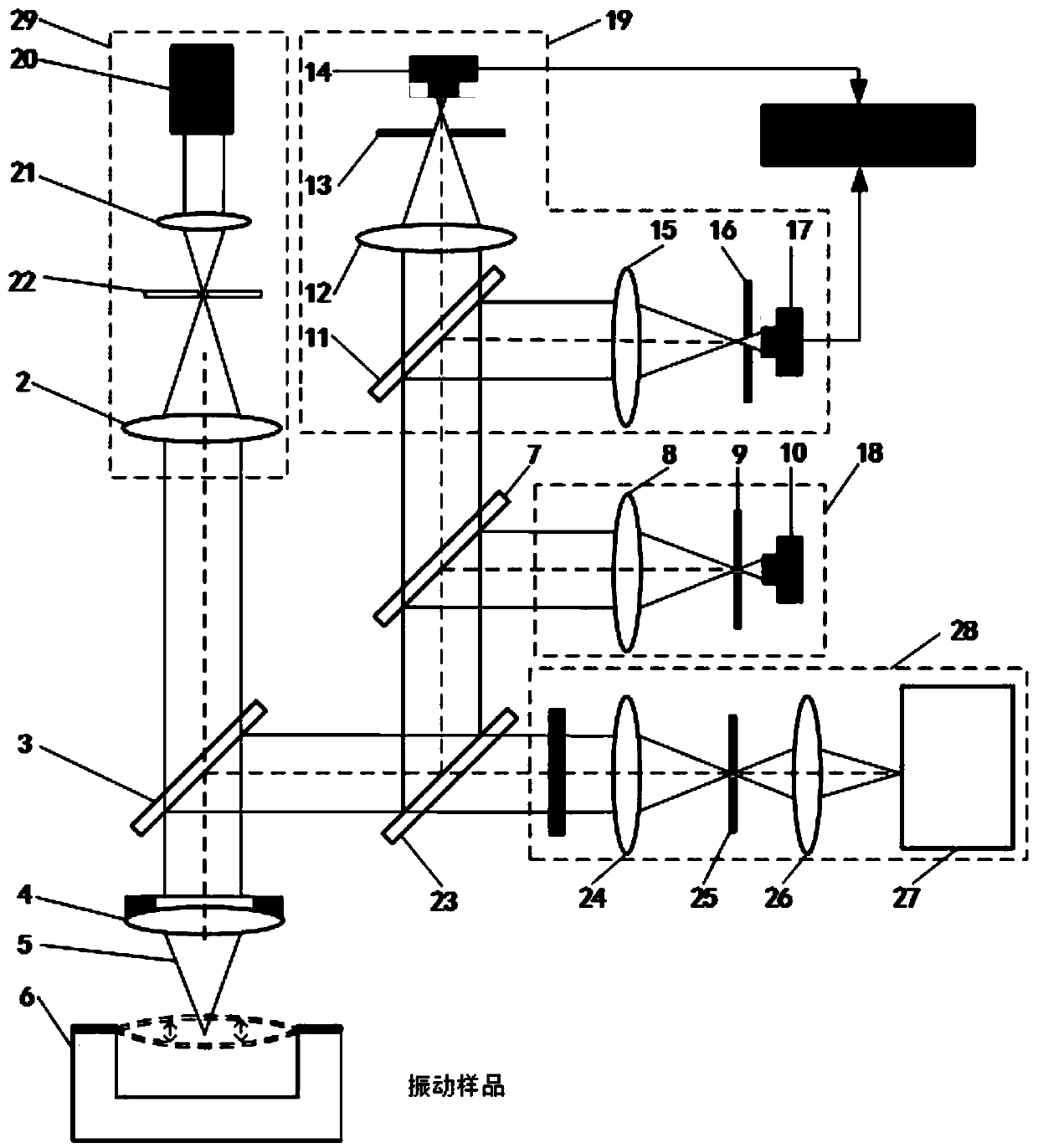
Laser Confocal/Differential Confocal Raman Spectroscopy Vibration Parameter Measurement Method
ActiveCN111307269BHigh precisionAchieve high-precision extractionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansVibration amplitudeRaman microscope
The invention discloses a laser confocal / differential confocal Raman spectrum vibration parameter measurement method, and belongs to the technical field of optical precision measurement. Confocal vibration detection, differential confocal vibration detection and Raman spectrum detection technologies are fused, nondestructive separation is carried out on Rayleigh light and Raman scattered light byutilizing a dichroic light splitting system, spectrum detection is carried out on the Raman scattered light, and vibration parameter detection such as amplitude and frequency is carried out on the Rayleigh light. Therefore, the vibration information testing method capable of simultaneously detecting the vibration parameters of the sample micro-area and the Raman spectrum of the vibration of the sample micro-area is formed. According to the invention, the confocal Raman microscope and the differential confocal Raman microscope have the capability of simultaneously detecting micro-area vibrationparameter information and the Raman spectrum of micro-area vibration. The method has the advantages of high vibration measurement precision, wide amplitude measurement range, high frequency measurement bandwidth, high spectrum detection sensitivity, capability of measuring periodic motion and aperiodic motion, high environmental interference resistance and the like. Meanwhile, high-precision detection of micro-area vibration parameters and vibration spectral characteristics is carried out, and the method has a wide application prospect in the technical field of optical precision measurement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
An imaging method of tumor targeting based on enhancement effect of zinc ion signals
ActiveCN103099604BLow toxicityTumor targetingOrgan movement/changes detectionEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsFluorescence microscopeChemical constituents
The invention discloses an imaging method of tumor targeting based on enhancement effect of zinc ion effects. When the imaging method of the tumor targeting based on the enhancement effect of the zinc ion signals is applied at the cellular level, a zinc saline solution is manufactured firstly. Then the saline solution is arranged into a cell incubator together with cancer cells or cancer tissues for incubation. After high resolution fluorescence microscopic imaging and Raman imaging are carried out, qualitative and quantitative analysis is performed on the structure or chemical constituents of the cancer cells or the cancer tissues through the signal data of a fluorescence spectrum and a Raman spectrum. When the imaging method of the tumor targeting based on the enhancement effect of the zinc ion signals is applied at the animal model level, a tumor animal model is constructed and the zinc saline solution is manufactured, after part of the tumor location of an experimental animal is injected with the zinc saline solution, a confocal fluorescence microscope, an ultrasonic imaging device, a fluorescence imaging device, a Raman spectrometer or a Raman microscope are used for monitoring the signal information of the tumor cells or the cancer tissues and processing and analyzing the signal information. Due to the fact that the zinc ions are adopted as the imaging signal enhancer, the imaging method of the tumor targeting based on the enhancement effect of the zinc ion signals has small toxicity on a living body, and has tumor targeting capability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com