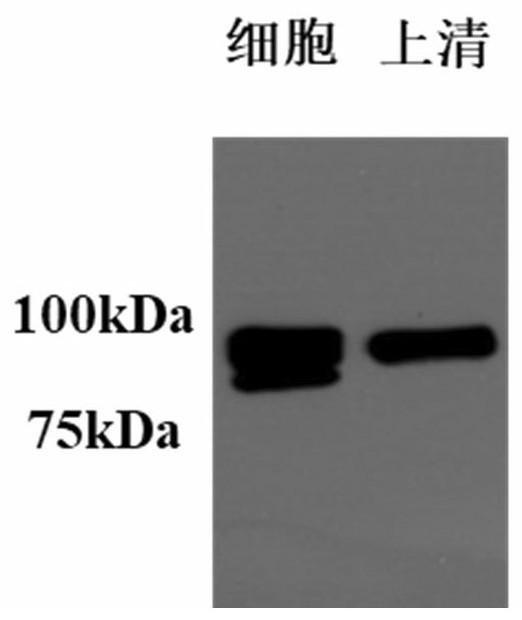
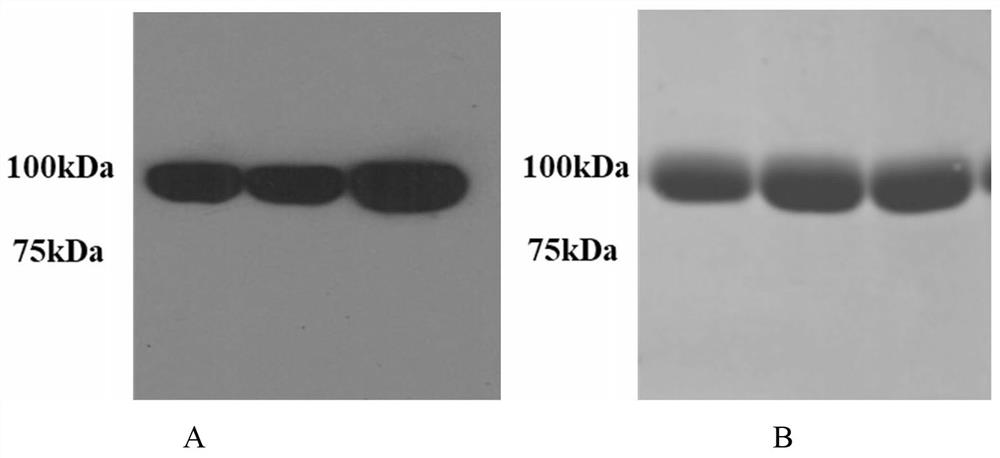
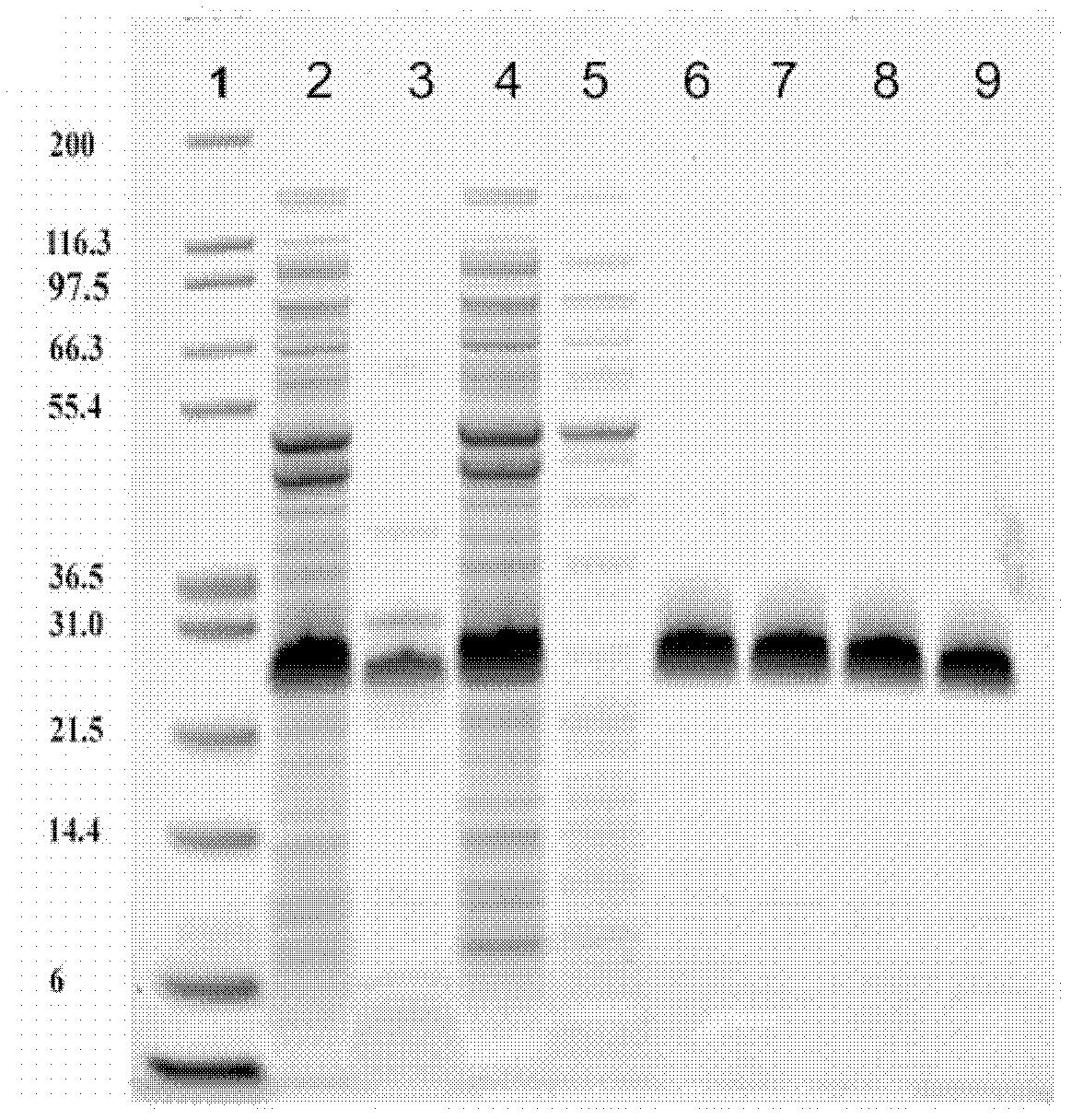
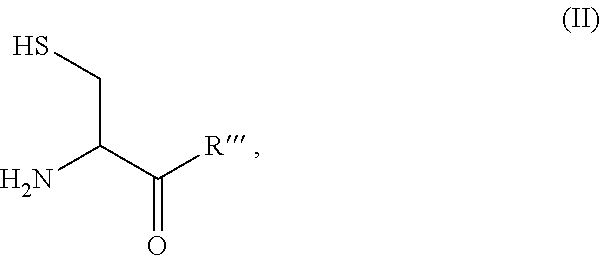Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Protein dimer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
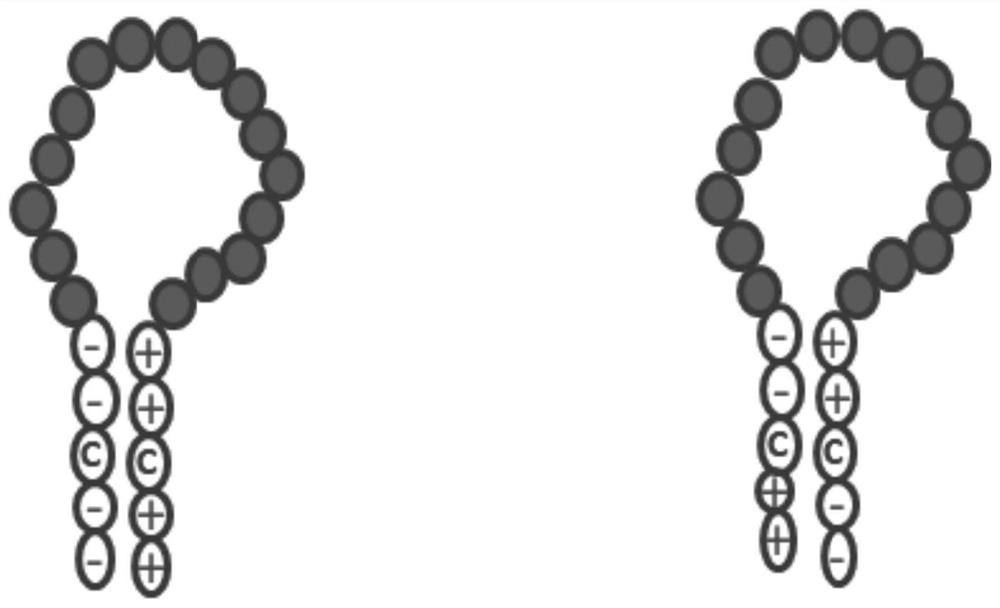
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word dimer has roots meaning "two parts", di- + -mer. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure.
Subunit coronavirus vaccine for dimerization-based receptor binding domains
ActiveCN106928326AOvercoming the disadvantage of insufficient immunogenicityIncrease neutralizing antibody productionSsRNA viruses positive-senseBacteriaCoronavirus vaccinationMiddle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
The invention discloses a subunit coronavirus vaccine for dimerization-based receptor binding domains and belongs to the technical field of medicine. A baculovirus expresses RBD (receptor binding domain (E367-Y606) of MERS-CoV (middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus) protein and RBD (R294-F515) of SARS-CoV (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus) in insect cells, the RBDs may form a dimer through cysteine residue at 603 of S (spike) protein or form a dimer through cysteine residue at 512 of the S protein, and purified RBD protein dimer and monomer are used respectively to immunize Bald / c mice. The dimerized RBDs have the advantages that the defect that RBD monomers have poor immunogenicity is overcome and the generation of neutralizing antibodies in against MERS-CoV is increased greatly.
Owner:ANHUI ZHIFEI LONGCOM BIOPHARM CO LTD
Fusion protein of divisive ranilla luciferase and HBC (hepatitis B core) and application of fusion protein
InactiveCN106188310AInhibition of replicationVirus peptidesBiological testingBiologyHepatitis b core
The invention discloses fusion protein of divisive ranilla luciferase and HBC (hepatitis B core). The fusion protein is obtained by joint connection of 1 to 229 amino acids of the N-terminal of the ranilla luciferase and core protein of hepatitis B virus (HBV), or obtained by joint connection of 229 to 311 amino acids of the N-terminal of the ranilla luciferase and the core protein of the HBV, the sequence of the amino acids is as shown in SEQ (sequence) ID (identity) No: 1 and No: 3 respectively, and nucleotide sequence encoding the two fusion protein is as shown in SEQ ID No: 2 and No: 4 respectively. The invention further discloses a carrier containing the nucleotide sequence as is shown in the SEQ ID No: 2 and No: 4. and discloses an application about whether the fusion protein as is shown in the SEQ ID No: 1 or the No: 3 is formed or not in indication of core protein dimers of the HBV. An importation foundation is laid for establishing cell models for drug screening in formation of the anti-HBC dimers.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Site-specific modification of proteins through chemical modification enabling protein conjugates, protein dimer formation, and stapled peptides
ActiveUS20110263832A1Diminishment of extentAvoid spreadingHormone peptidesHybrid immunoglobulinsLupus erythematosusAdduct
The present invention generally provides methods for the site-specific modification of peptides, polypeptides, and proteins, e.g., granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor, human superoxide dismutase, annexin, leptin, antibodies and the like, cytokines and chemokines, at their N-termini and at sites at which unnatural aminoacids have been introduced along the protein framework. The modifications described herein can be used for the synthesis and application of the adducts in radio-labeling, molecular imaging and protein therapeutic applications, and the treatment of disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, type-1 diabetes, Crohn's disease, and systemic sclerosis, Alzheimer disease, cancer, liver disease (e.g., alcoholic liver disease), and cachexia.
Owner:ADVANCED PROTEOME THERAPEUTICS
Renaturation of reconstituted human bone protein-1 and making method of its preparation
The present invention discloses a recombinant human osteoplastic protein-1 renaturation and its preparation preparation method. It utilizes chromatography to obtain rh OP-1 monomer protein whose purity is above 95%. Said invention also provides the concrete steps of said preparation method, including: in 2M-6M urea or 1M-4M guanidine hydrochloride buffer solution making dialysis and renaturation, pH value of renaturation buffer solution is 8.0-10, renaturation temperature is room temperature or 4deg.C and renaturation time is 24-96 hr, then further making chromatographic purification, dialysis, sterilization, packaging and freeze-drying so as to obtain the renaturation preparation of recombinant human osteoplastic protein-1. Besides, said invention also provides the application method of said renaturation preparation of recombinant human osteoplastic protein-1.
Owner:SHANDONG MEDICAL BIO TECH RES CENT
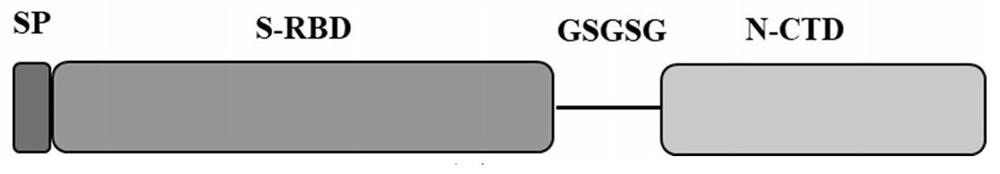
Stable coronavirus recombinant protein dimer and expression vector thereof
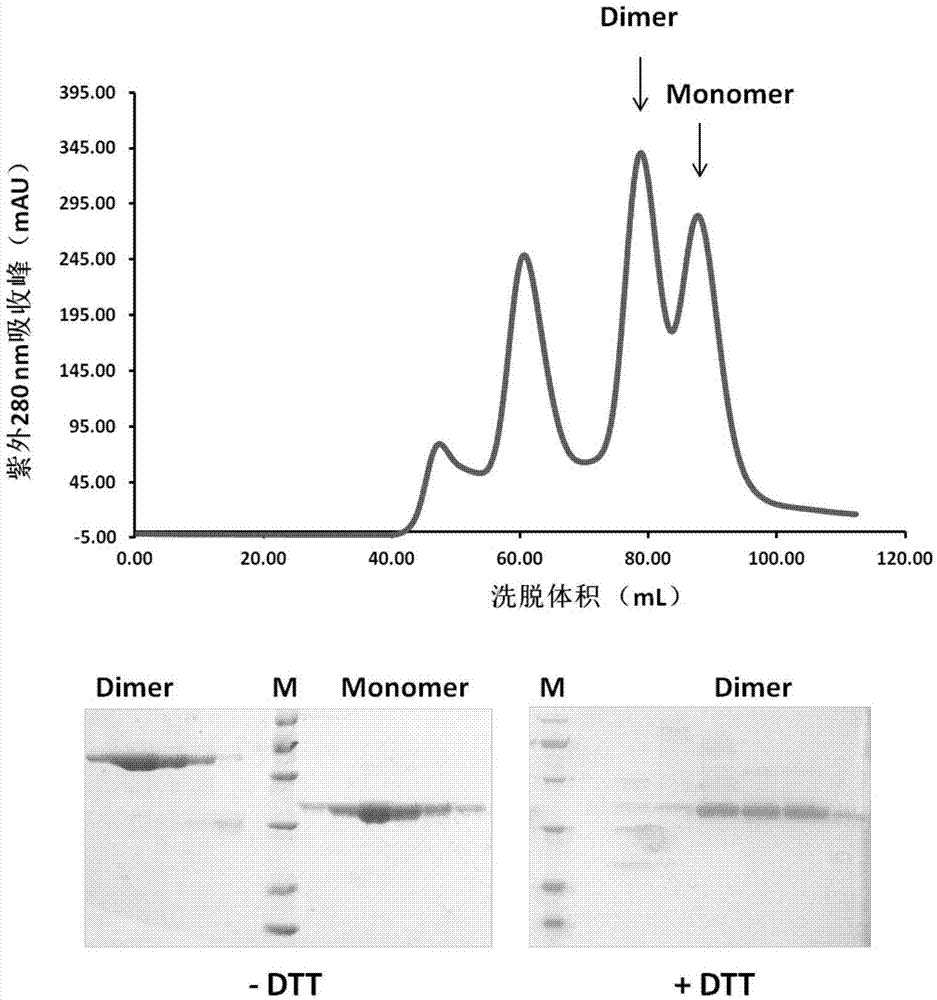
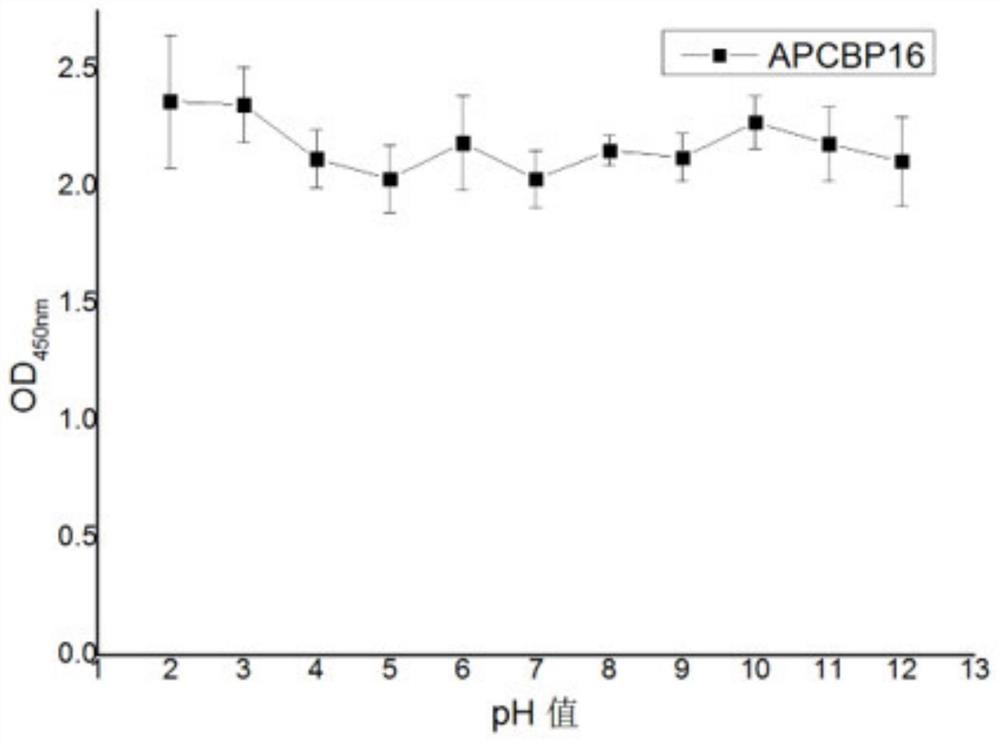
ActiveCN112321688AImproving immunogenicityAvoid degradationSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsDimerMedicine
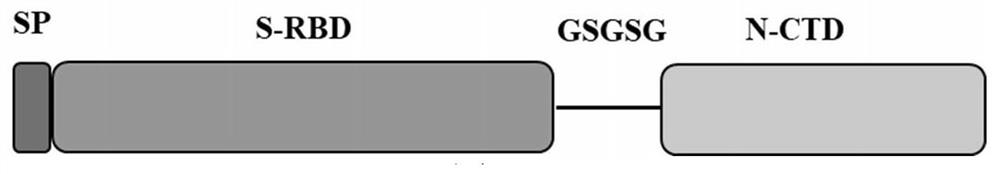
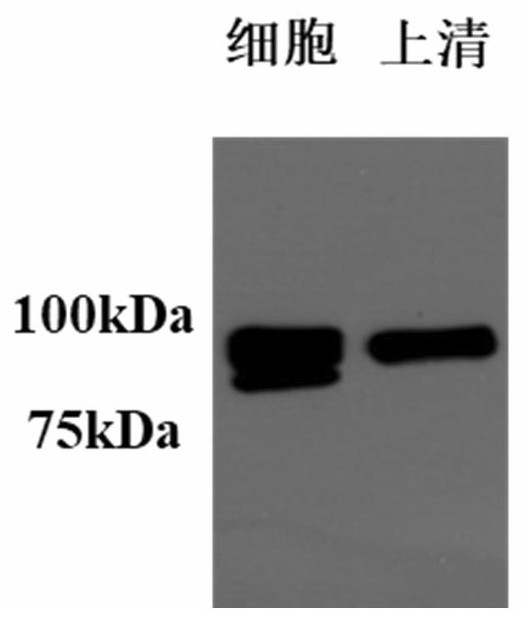
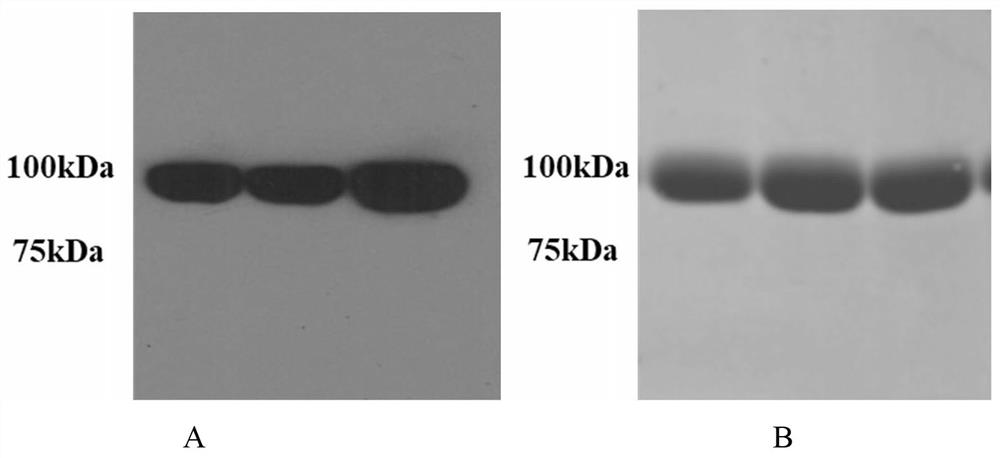
The invention discloses a stable coronavirus recombinant protein dimer and an expression vector thereof. Coronavirus recombinant protein is composed of coronavirus S protein S-RBD, coronavirus N protein CTD region N-CTD and a linker for coupling the coronavirus S protein S-RBD and the coronavirus N protein CTD region N-CTD. The coronavirus recombinant protein in some embodiments can form and maintain a stable dimer structure, avoids monomer S-RBD degradation, is beneficial to improving the immunogenicity of the coronavirus recombinant protein, and is expected to be used for preparing detectionreagent raw materials, vaccines, antibodies and preventive or therapeutic drugs. The coronavirus recombinant protein dimers in some embodiments have good immunogenicity and have wide application prospects in the vaccine development field. Expression vectors in some embodiments can easily express the coronavirus recombinant protein dimers and have high expression quantity.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNITED VACCINE INST
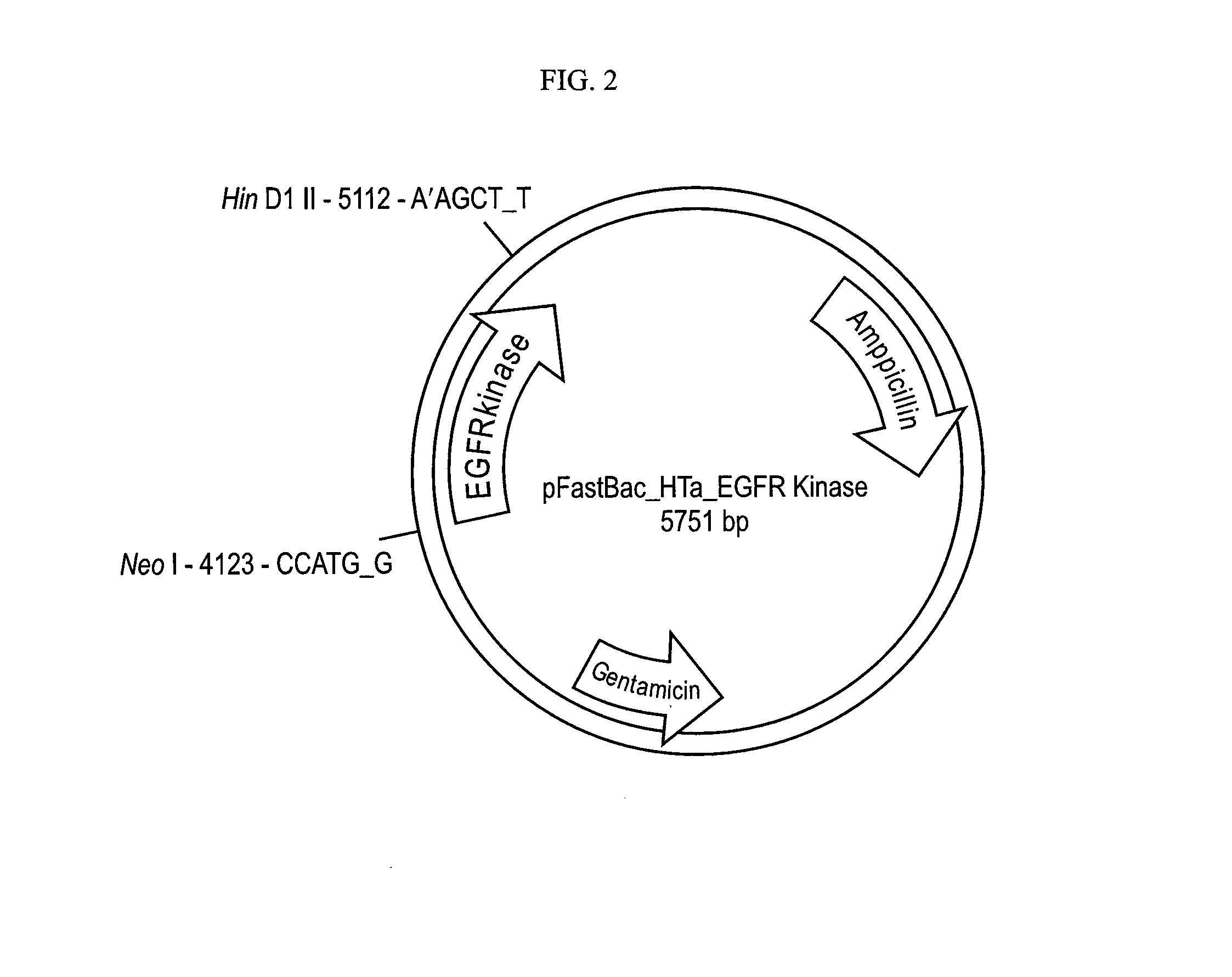
Inhibitors of the EGFR kinase targeting the asymmetric activating dimer interface
The invention provides methods and compositions for the modulation of EGFR activity. In particular, inhibition of EGFR activation through an allosteric mechanism is discloses, as is a method for targeted drug discovery and design based on models of the three dimensional structure of the kinase domains of the protein dimers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bispecific egfr/igfir binding molecules
The present invention relates to bispecific molecules comprising an EGFR binding domain and a distinct IGFIR binding domain for use in diagnostic, research and therapeutic applications. The invention further relates to cells comprising such proteins, polynucleotide encoding such proteins or fragments thereof, and vectors comprising the polynucleotides encoding the innovative proteins. Exemplary bispecific molecules include antibody-like protein dimers based on the tenth fibronectin type III domain.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Novel inhibitors of the EGFR kinase targeting the asymmetric activating dimer interface
The invention provides methods and compositions for the modulation of EGFR activity, in particular, inhibition of EGFR activation through an allosteric mechanism is discloses, as is a method for targeted drug discovery and design based on models of the three dimensional structure of the kinase domains of the protein dimers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for labeling protein through quantum dots
InactiveCN102924564AAvoid instabilityEasy to operateDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsDimerNanobiotechnology
The invention discloses a method for labeling protein through quantum dots and belongs to the field of nano-biotechnology. The method is characterized by expressing a Histag on protein, obtaining a protein dimer containing two Histags through protein dimerization, mixing the protein with the quantum dots according to a certain ratio, and oscillating to enable the two Histags to combine with the quantum dots simultaneously so as to improve the stability of combination. The method is simple in operation, and the quantum dots can be applied to biomarker widely as a nano fluorescent probe.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
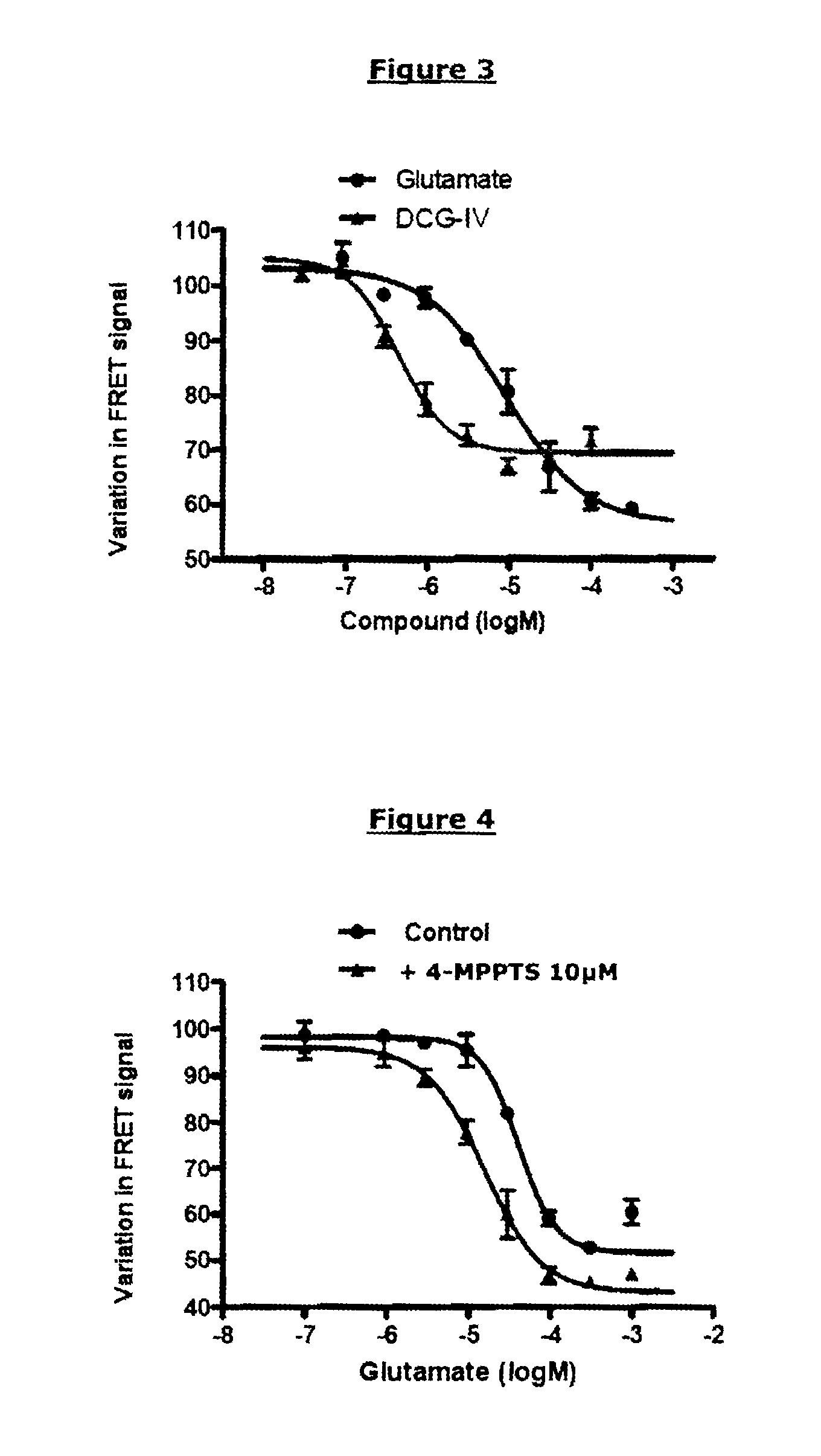
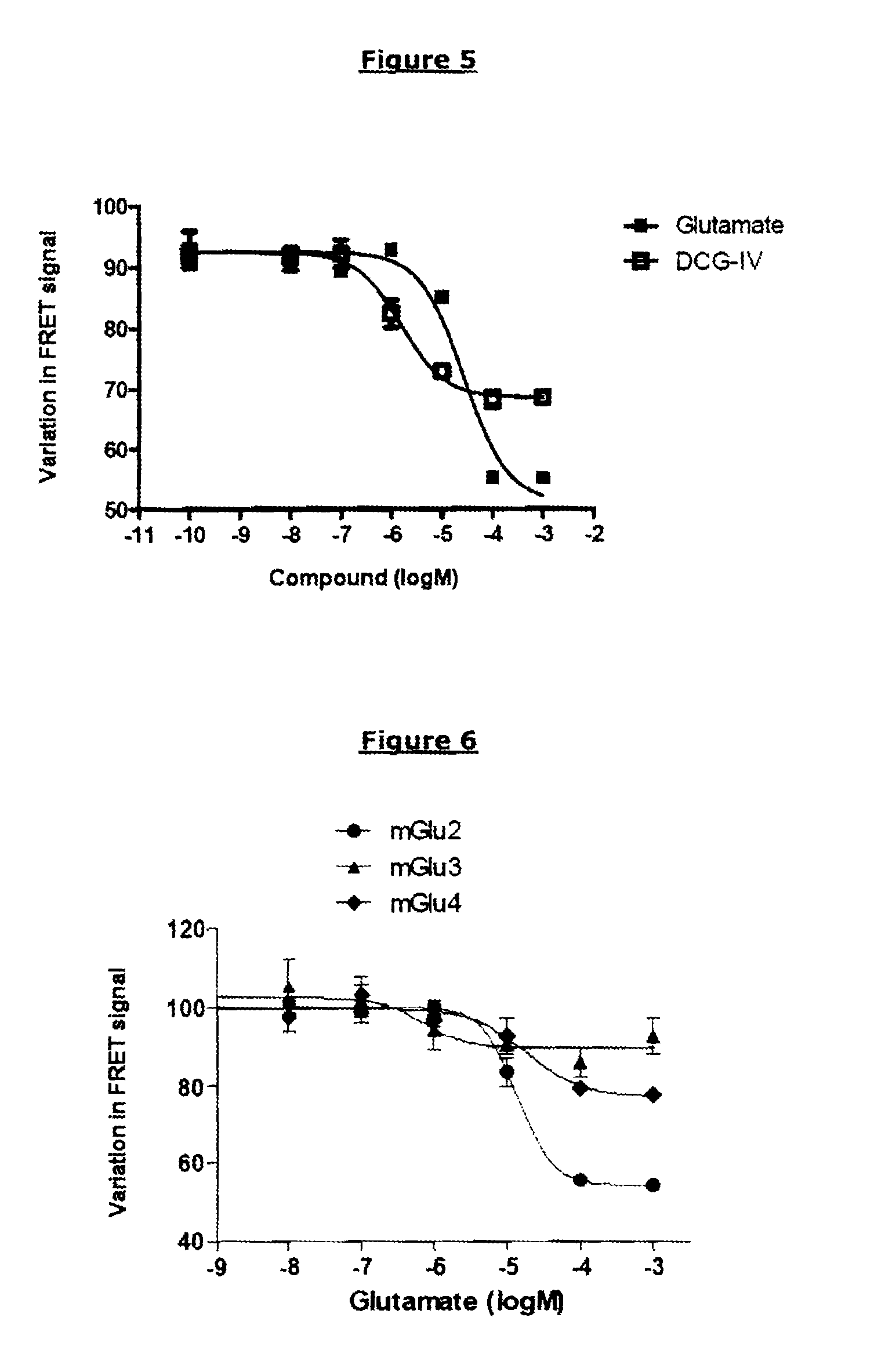
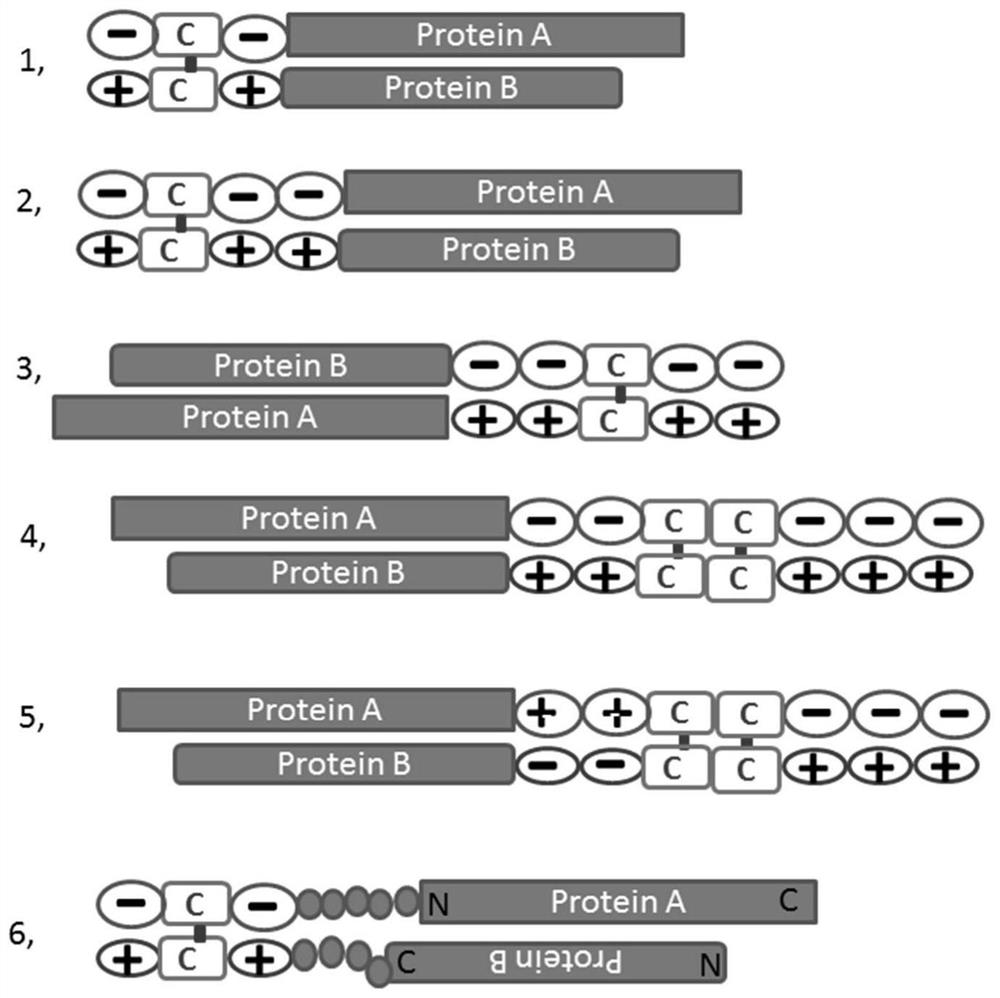
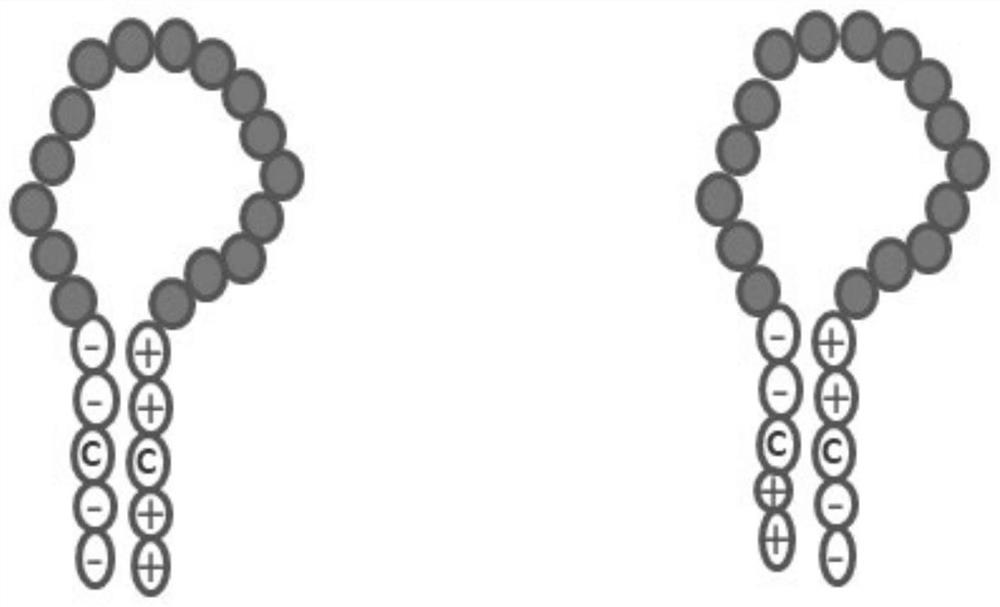
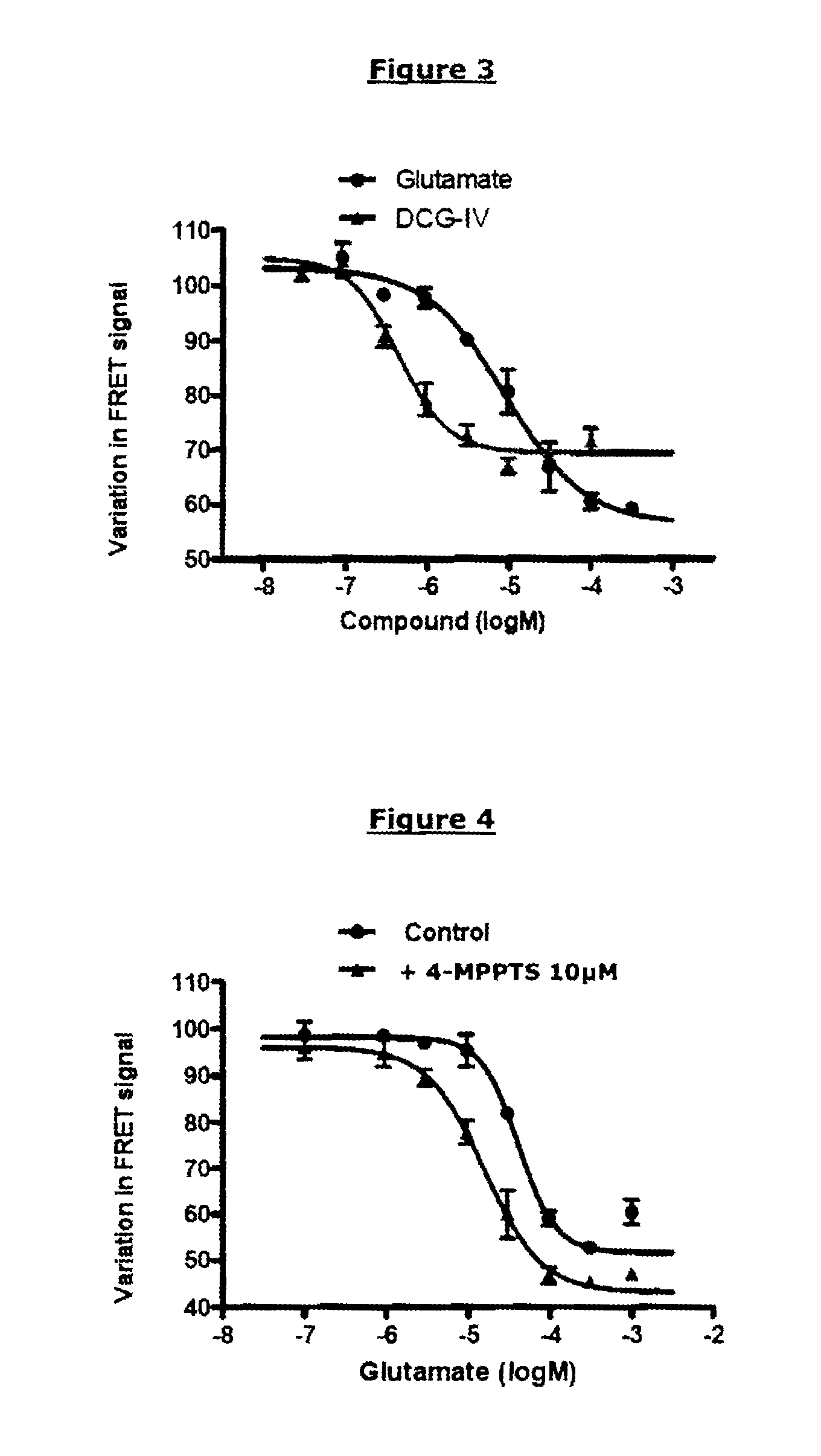
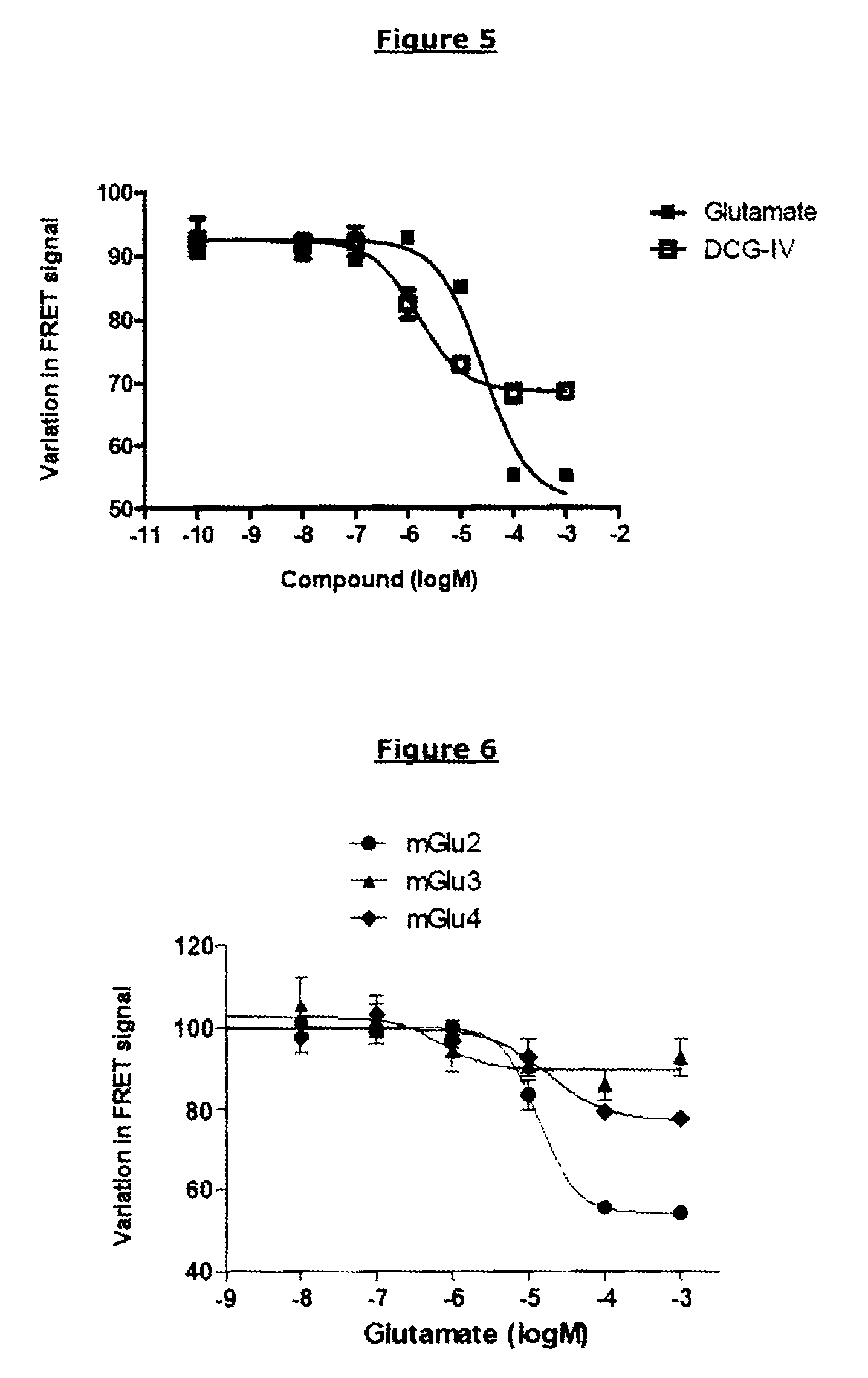
Method for detecting compounds modulating dimers of VFT domain membrane proteins
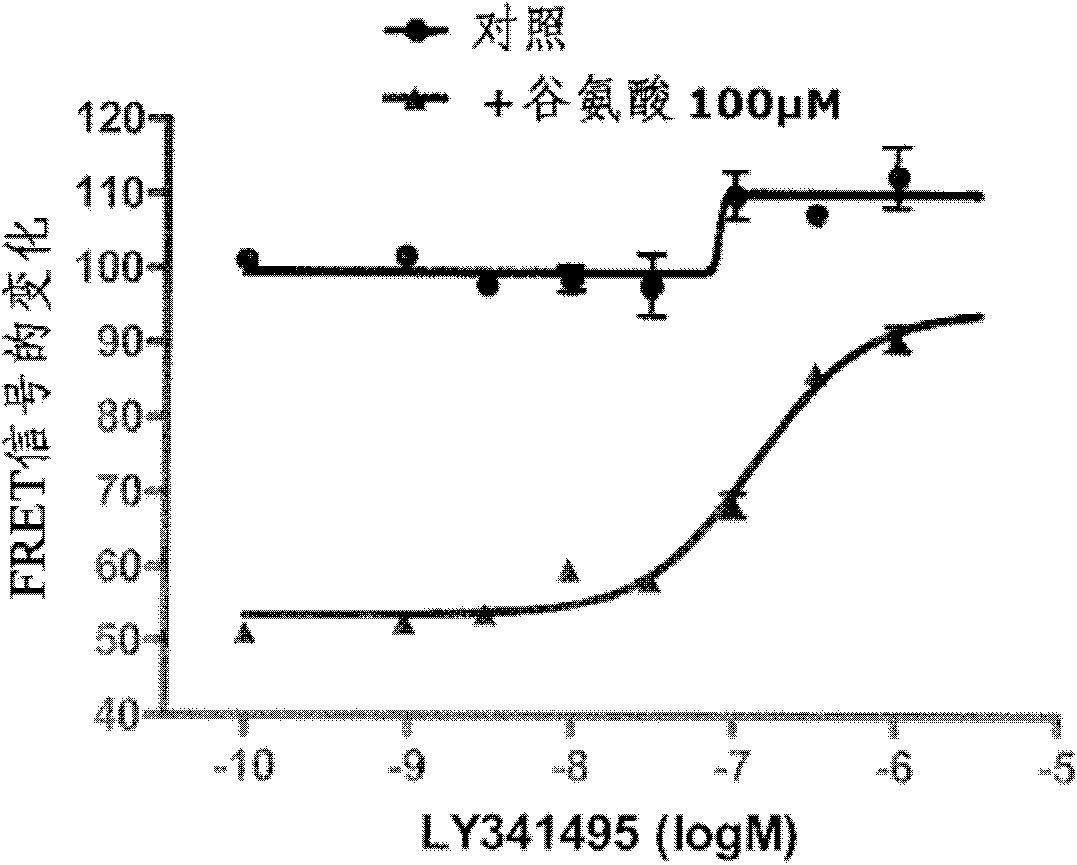
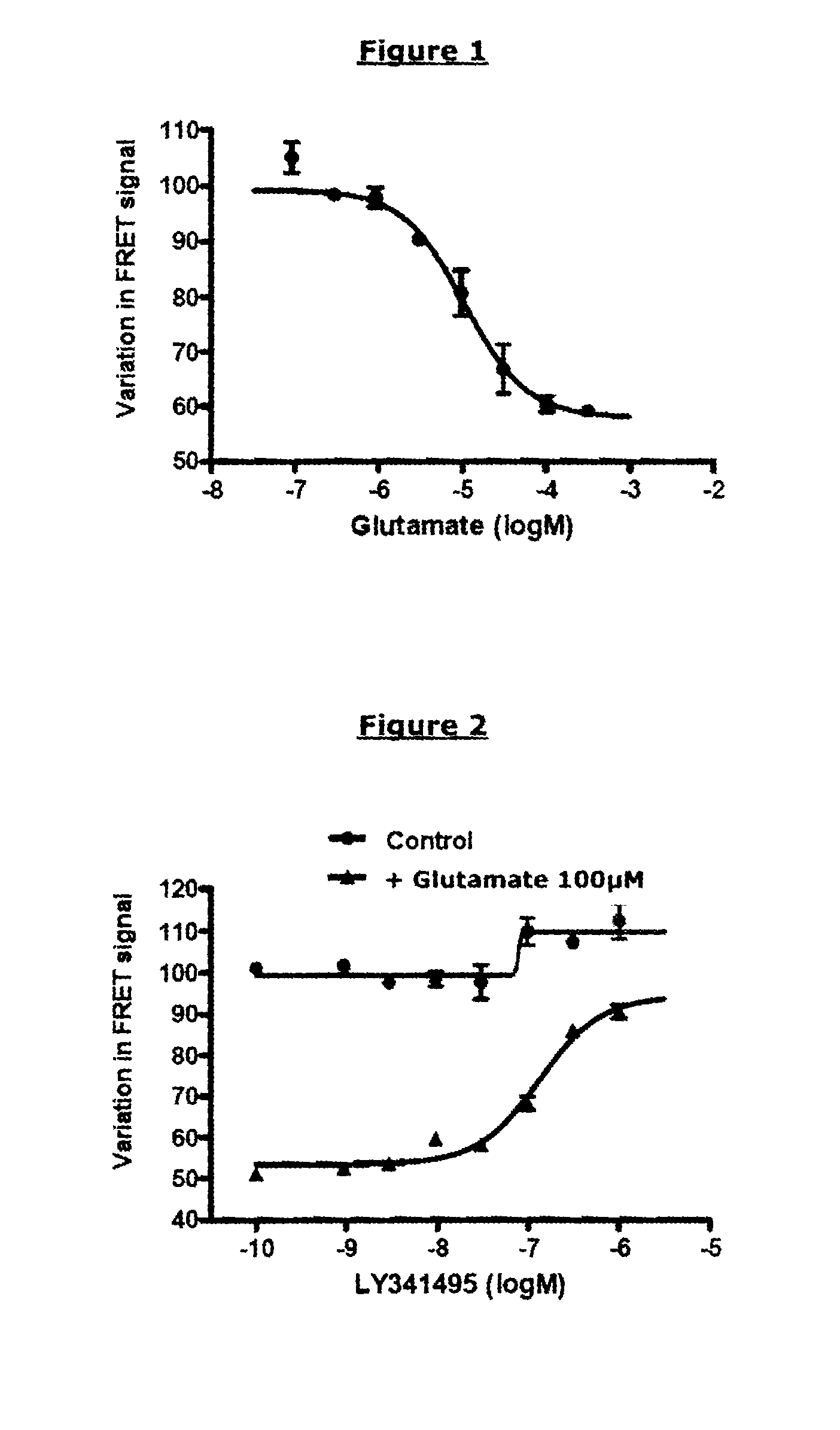
The invention relates to a method for selecting compounds having a modulating effect on the activation state of a dimer of VFT domain proteins expressed in cellular membranes in a measuring medium, said dimer including a first protein and a second protein which are identical or different, wherein the method includes the following steps: (a) marking the first and second proteins in the N-terminal portion of the VFT domain by members of a FRET partner pair, the Forster radius (R0) of said pair ranging between 20 and 55 Angstrom; (b) measuring the FRET signal in the absence and in the presence of the compound to be tested within a predetermined time window; (c) selecting the compound to be tested as a modulating compound if a difference in the FRET signal in the absence and in the presence of the compound to be tested is measured during step (b). The invention can be used in the research for new drugs and new taste modulators.
Owner:CIS BIO INT +1
Method for detecting compounds modulating dimers of vft domain membrane proteins
The invention relates to a method for selecting compounds having a modulating effect on the activation state of a dimer of VFT-domain proteins expressed in cell membranes present in a measuring medium, said dimer consisting of a first protein and of a second protein, said proteins being identical or different, wherein this method comprises the following steps:(a) labeling the first and second proteins in the N-terminal portion of their VFT domains with the members of a pair of FRET partners, the Förster radius (R0) of said pair being between 20 and 55 Å;(b) measuring the FRET signal in the absence and in the presence of the test compound within a predetermined time window;(c) selecting the test compound as a modulating compound if a difference in FRET signal in the absence and in the presence of test compound is measured in step (b).The invention can be used in the search for new medicaments and new taste modulators.
Owner:CIS BIO INT +1
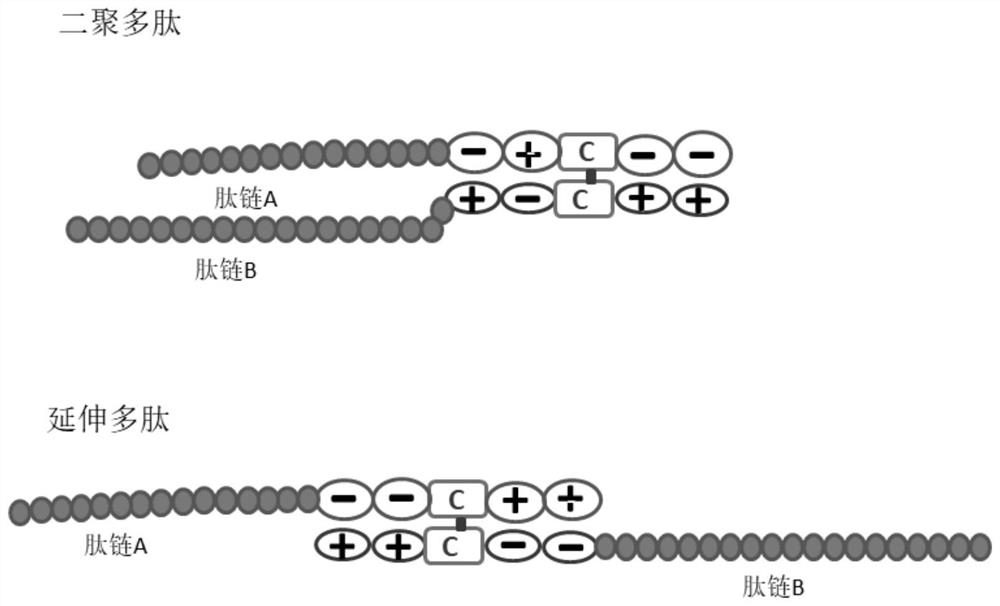
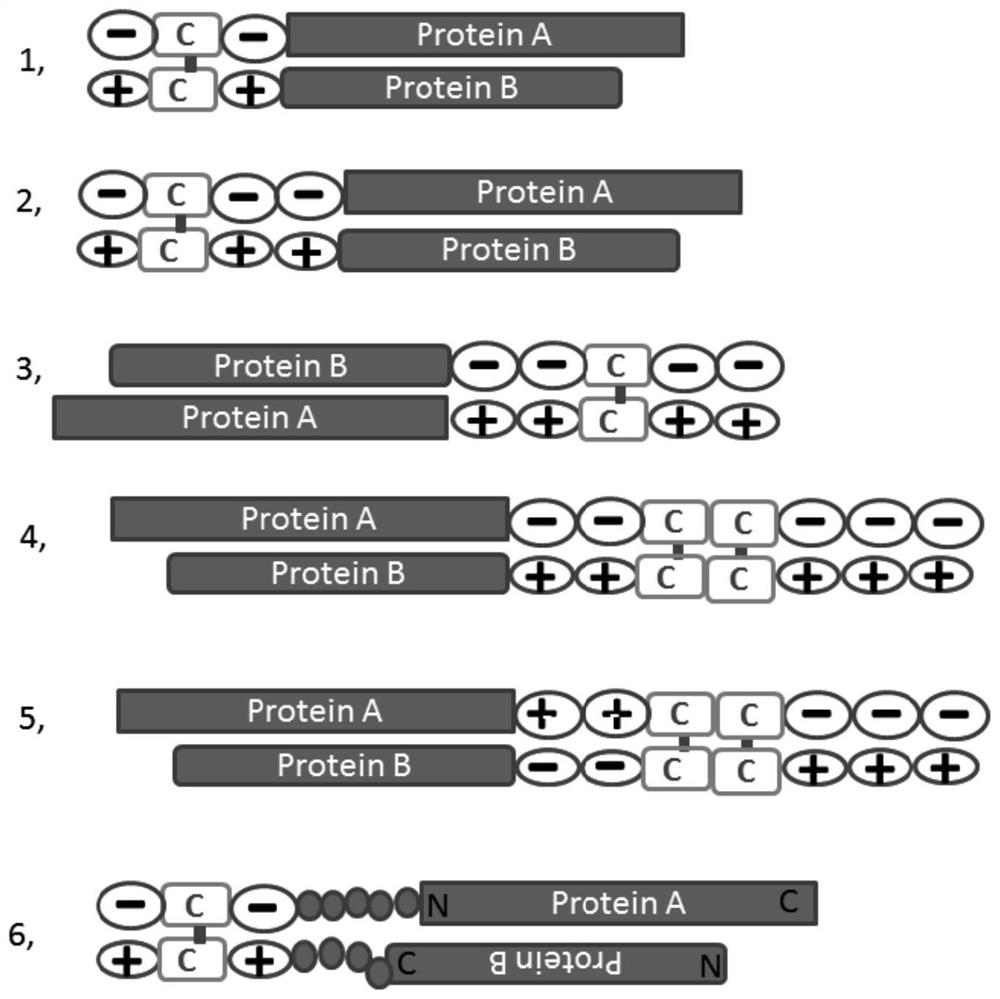
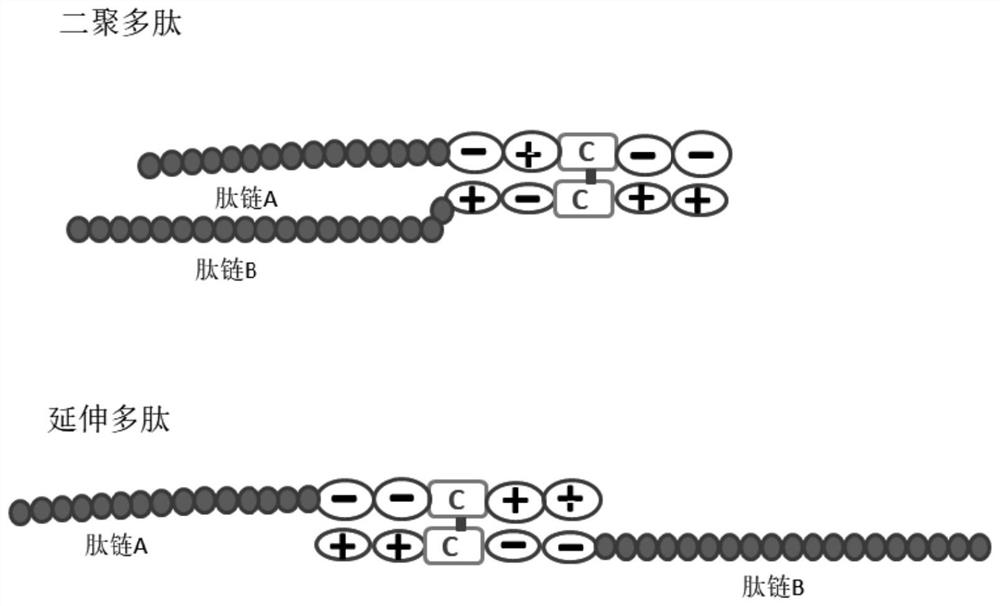
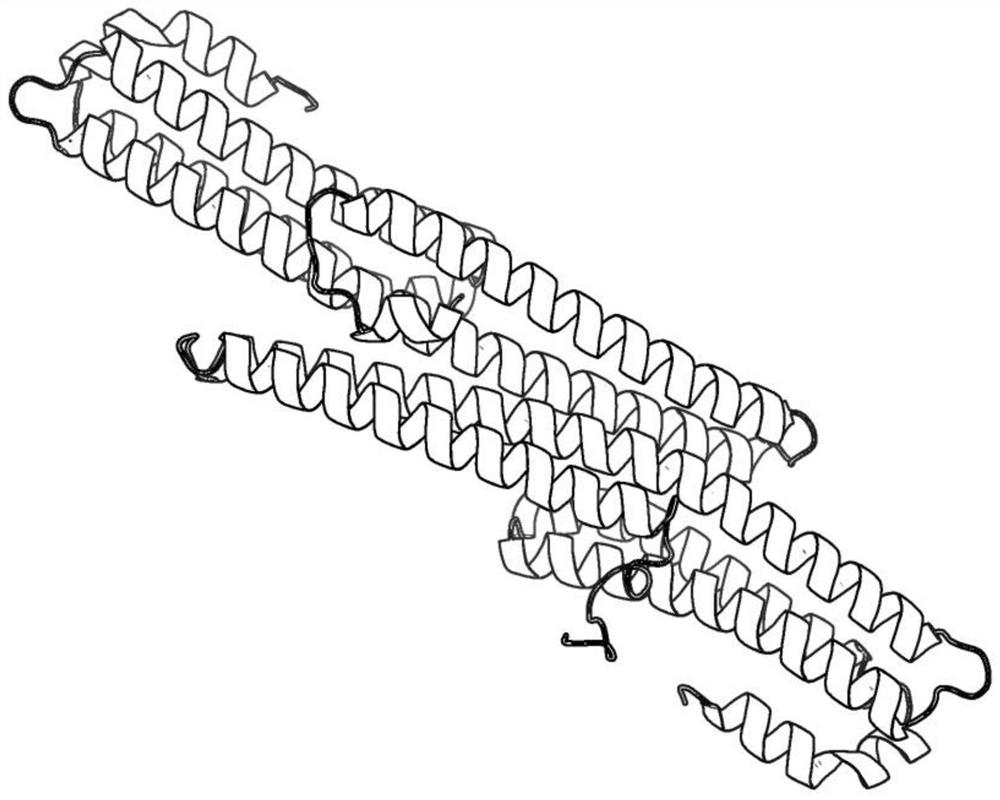
Zipper fastener structure for promoting formation of protein dimers and application thereof
PendingCN111655734AReduce the chance of formationAuxiliary formationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDepsipeptidesDimerAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and relates to a zipper fastener structure for promoting formation of protein dimers and an application thereof, and the zipper fastener can beused for dimerization of homologous proteins and dimerization of heterologous proteins, and can also be used for polypeptide cyclization, dimerization of polypeptides and extension of polypeptides. Some examples can obtain an ESAT6-CFP10 dimer close to native conformation, wherein the dimer has better solubility and has a better stimulation effect on memory T cells than ESAT6-CFP10 protein expressed by linear fusion. The inventor also finds that the dimer zipper fastener can help to form more stable cyclic polypeptide, and the CCP polypeptide added with the dimer fastener can increase the detection rate of citrullinated antibody in serum of rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Owner:GUANGZHOU LDEBIO TECH CO LTD
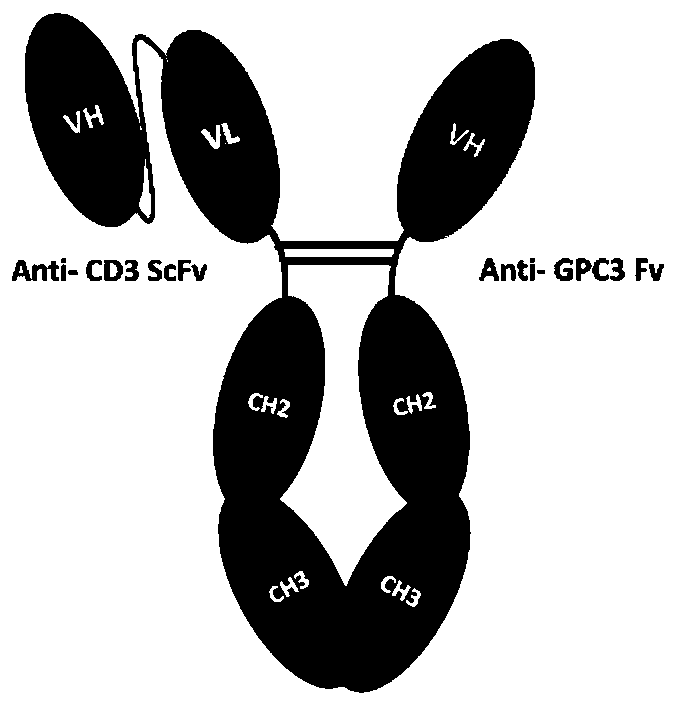
Novel bifunctional antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN110551222AIndustrial Application LimitationsEfficient purificationHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeavy chainAntibody combining site
The invention provides an antibody. The antibody comprises a protein dimer, wherein the protein dimer comprises a first functional domain including an immunoglobulin chain or an antibody combining site of a specifically-recognized specific antigen and a second functional domain including an immunoglobulin chain or an antibody combining site of a specifically-recognized specific antigen. The antibody is characterized in that the first functional domain consists of a first VH structural domain and a first VL structural domain, and the second functional domain consists of a second VH structural domain. The VH is a heavy chain variable zone, and the VL is a light chain variable zone. The bifunctional antibody provided by the invention has the advantages that a half-life period is greatly prolonged; and a homodimer is extremely less, so that identification and removal can be carried out only through primary purification even if aggregates occur.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF ANIMAL SCI +1
Monomer protein with bone morphogenetic activity and medicinal agent containing the same for preventing and treating diseases of cartilage and bone
InactiveUS20060019886A1High purityHigh yieldBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliCysteine thiolate
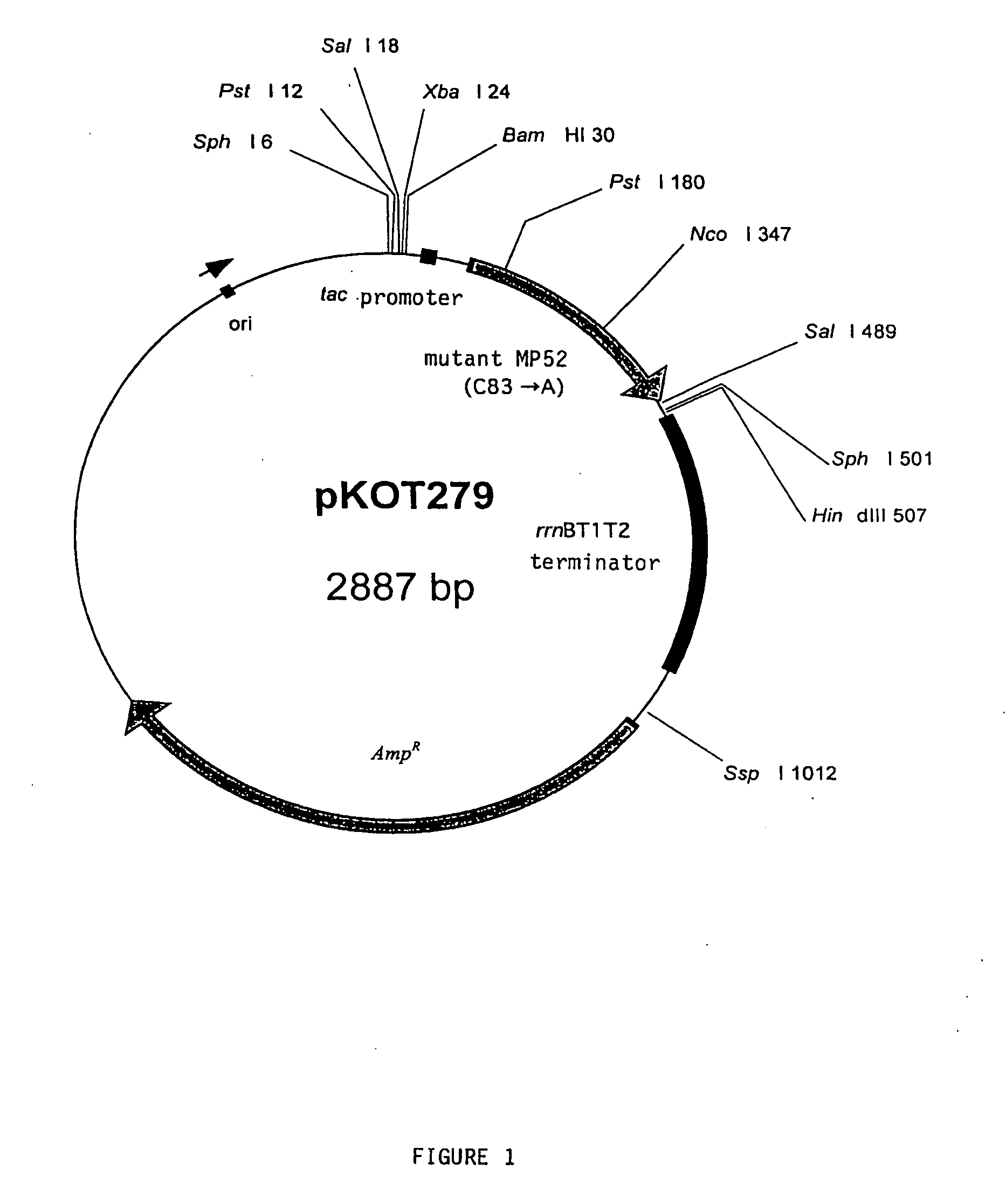
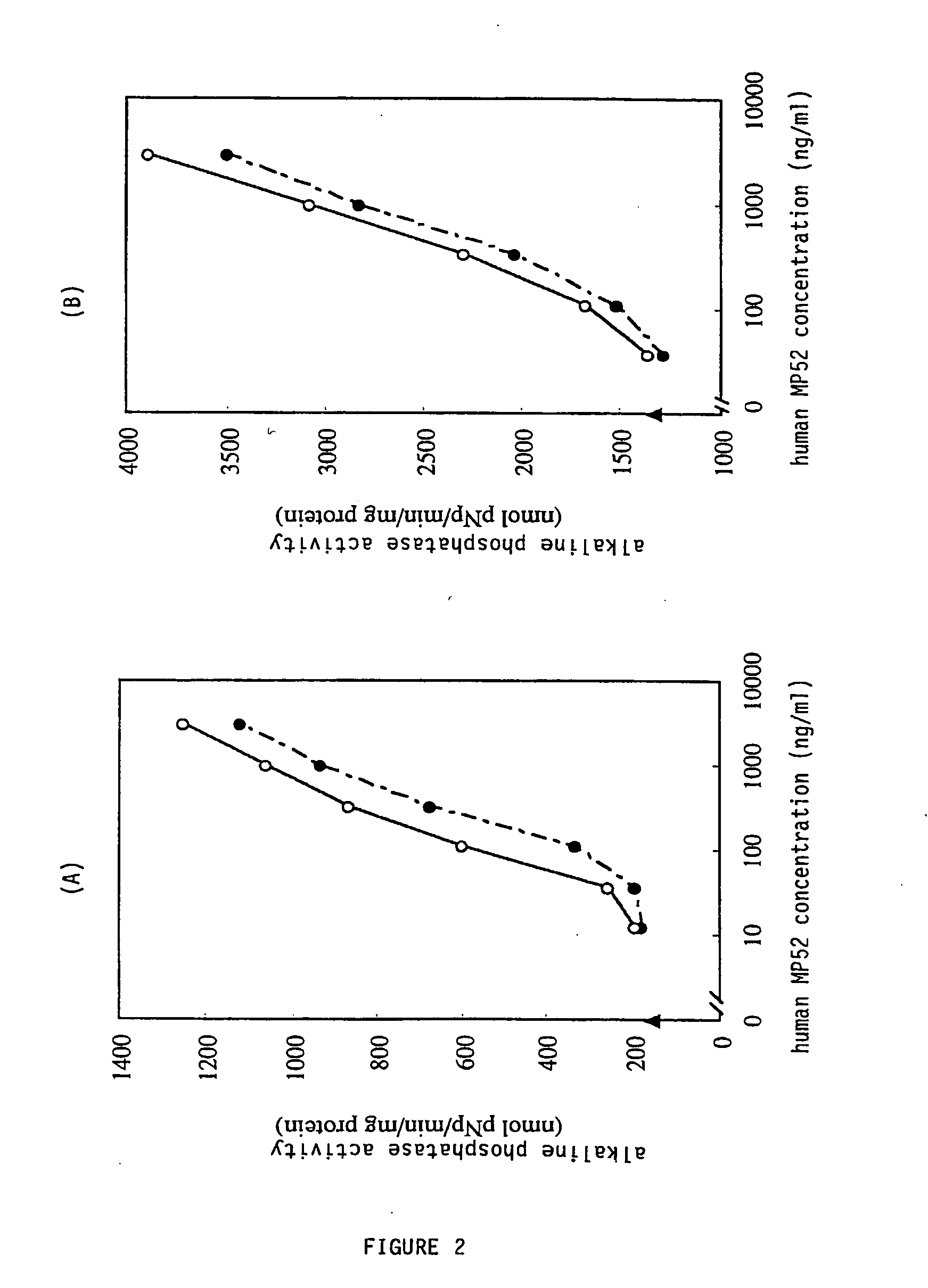
This invention provides for a protein of the TGF-β superfamily in which the cysteine involved in the normal formation of homodimers is changed to another amino acid. These mutant proteins, as monomers, display higher bone morphogenetic activity than the wild-type protein dimers. Also provided is a method for producing and isolating these monomers by plasmid driven expression in various host systems including E. coli. In addition, the invention discloses the use of an agent containing purified monomers in preventing and treating diseases and problems affecting bone and / or cartilage.
Owner:BIOPHARM GES ZUR BIOTECHNOLOGISCHEN ENTWICKLUNG VON PHARMAKA
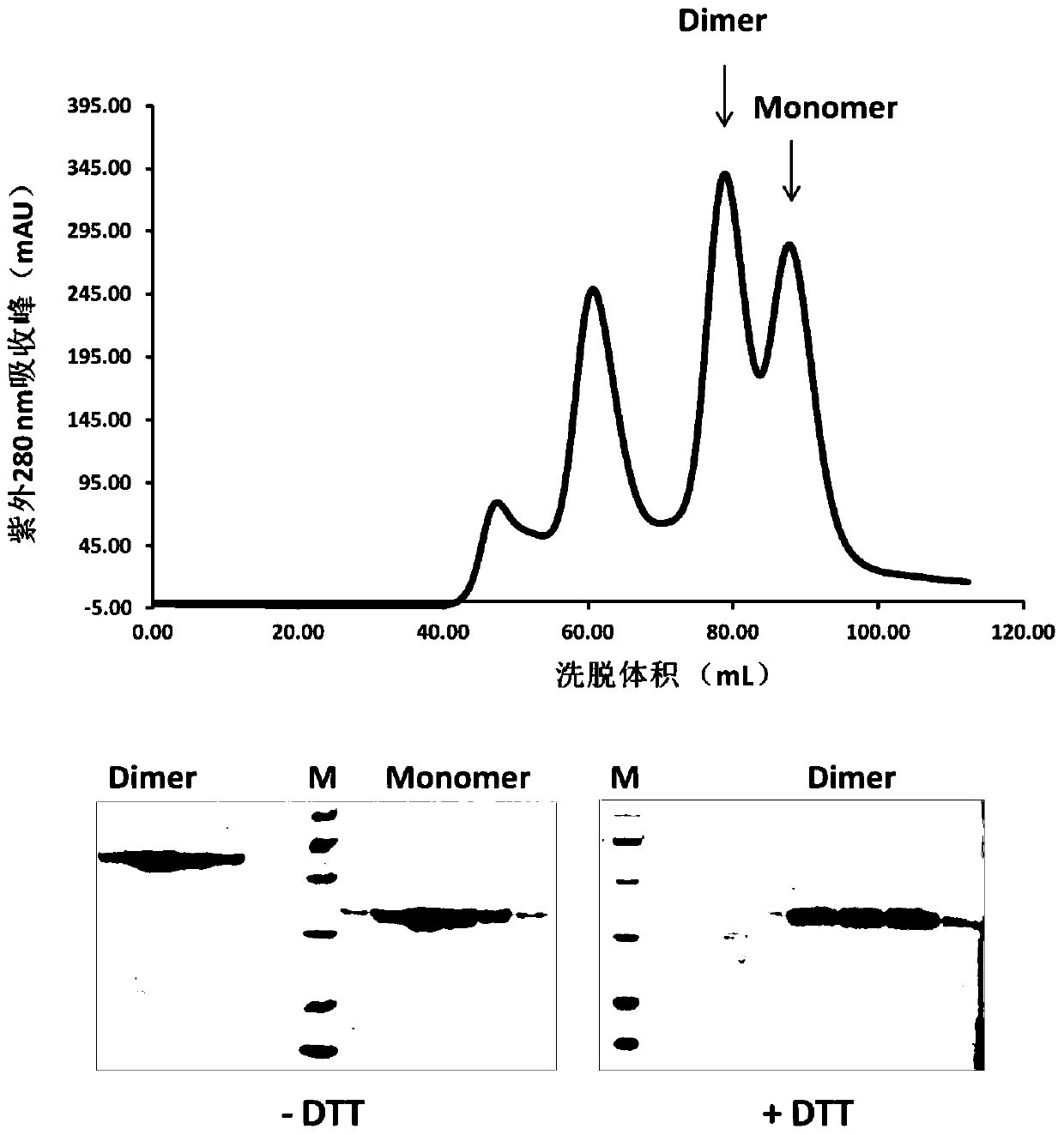
System and method for characterizing protein dimerization
ActiveUS20190242877A1Reduced level of dimerizationReduced dimerization and noncovalent interactionSerum immunoglobulinsArtificial cell constructsProtein DimerizationProtein
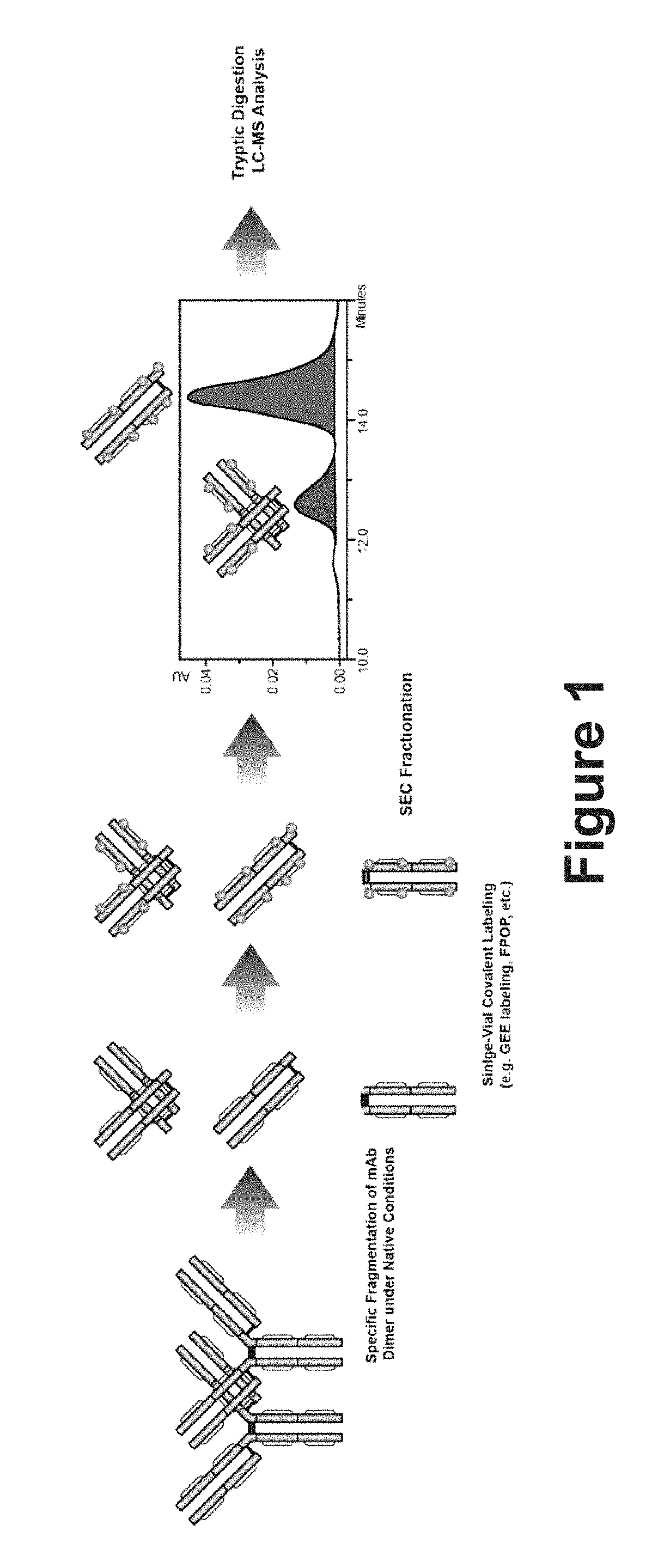
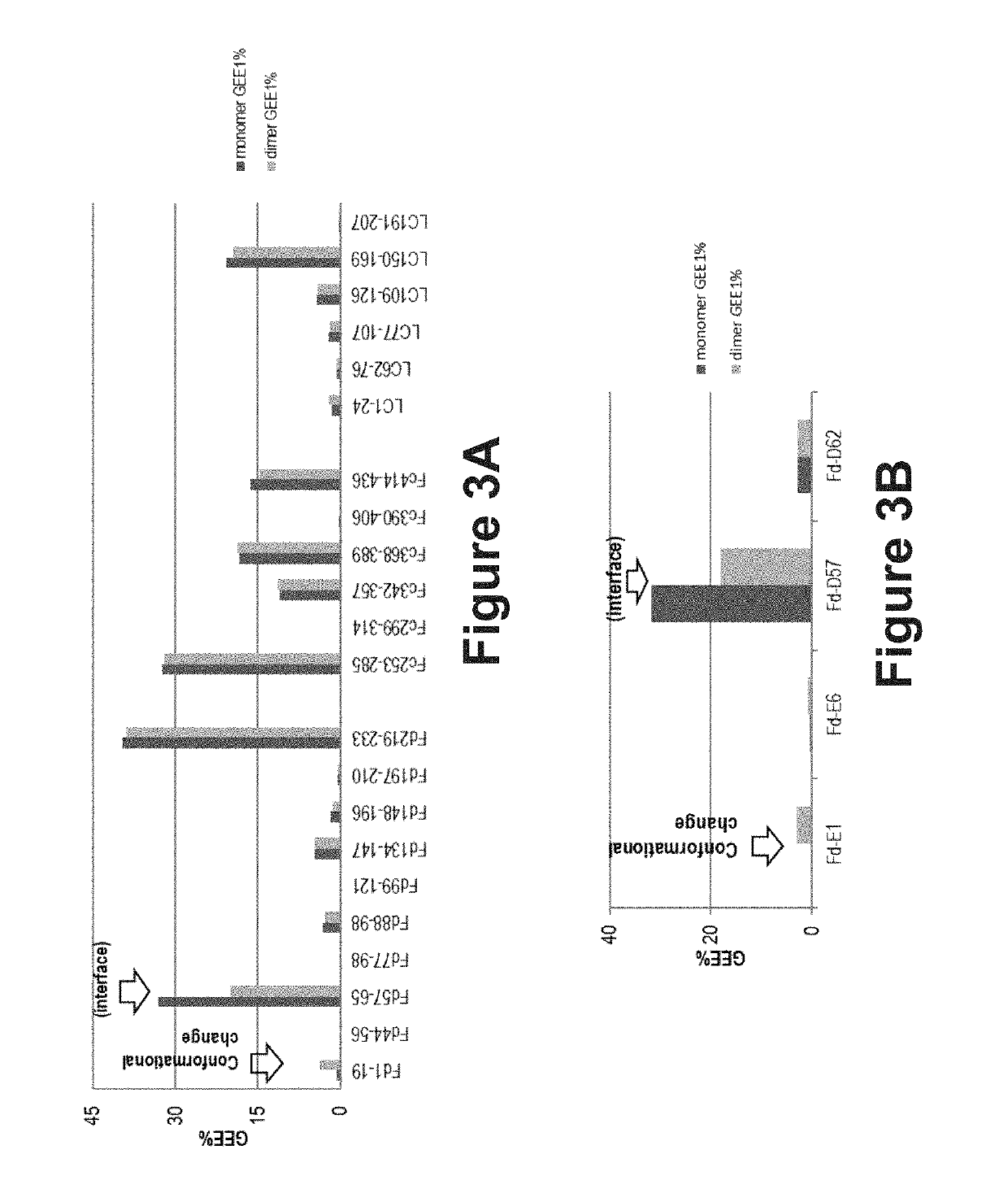
Systems and methods to characterize dimerization interfaces at the subdomain level of a protein are provided. An exemplary method includes digesting a protein dimer sample into subdomains, labeling the digested protein sample, isolating labeled dimeric and monomeric subdomain fragments, and peptide mapping the labeled sample to determine where the dimer fragments are labeled and where the dimer fragments are not labeled. Regions that show decreased labeling extents in the dimer fraction than that in the monomer fraction are likely involved or in close proximity to the dimerization interface.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Site-specific modification of proteins through chemical modification enabling protein conjugates, protein dimer formation, and stapled peptides
ActiveUS8927485B2Diminishment of extentAvoid spreadingPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesDiseaseDimer
Owner:ADVANCED PROTEOME THERAPEUTICS
Method for detecting compounds modulating dimers of VFT domain membrane proteins
The invention relates to a method for selecting compounds having a modulating effect on the activation state of a dimer of VFT-domain proteins expressed in cell membranes present in a measuring medium, said dimer consisting of a first protein and of a second protein, said proteins being identical or different, wherein this method comprises the following steps:(a) labeling the first and second proteins in the N-terminal portion of their VFT domains with the members of a pair of FRET partners, the Förster radius (R0) of said pair being between 20 and 55 Å;(b) measuring the FRET signal in the absence and in the presence of the test compound within a predetermined time window;(c) selecting the test compound as a modulating compound if a difference in FRET signal in the absence and in the presence of test compound is measured in step (b).The invention can be used in the search for new medicaments and new taste modulators.
Owner:CIS BIO INT +1
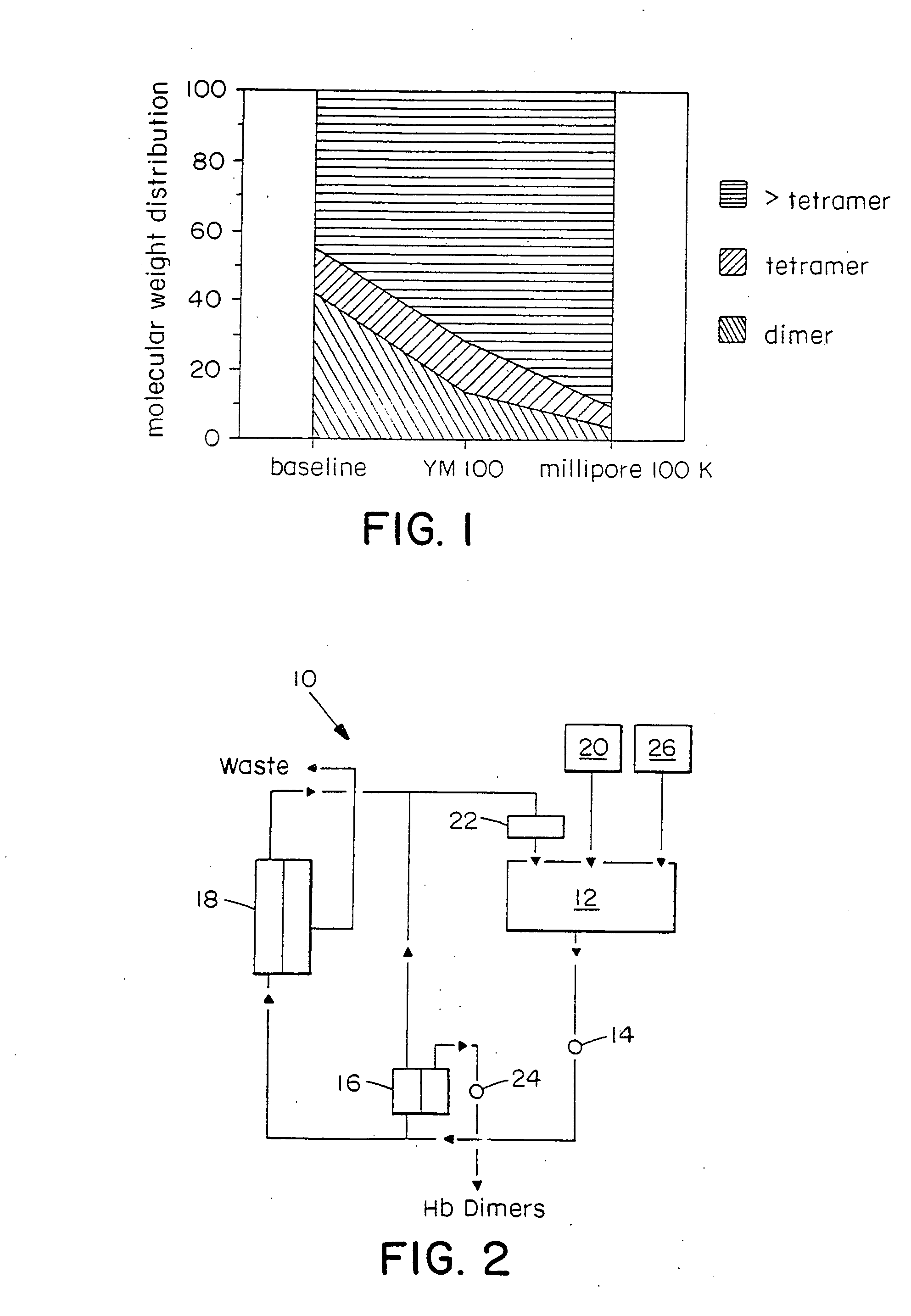
Method for separating unmodified hemoglobin from cross-linked hemoglobin
InactiveUS20050143565A1Improved intravascular retention timeReduction and elimination of significant renal eliminationHaemoglobins/myoglobinsMammal material medical ingredientsPhysical chemistryCross linked hemoglobin
A method for separating unmodified hemoglobin from cross-linked hemoglobin in a hemoglobin solution. The method involves contacting the hemoglobin solution with a least one dissociating agent to form a dissociation solution wherein unmodified tetrameric hemoglobin is dissociated to form hemoglobin dimers. The hemoglobin dimers are then separated from the dissociation solution, while retaining the cross-linked hemoglobin in the dissociation solution.
Owner:OPK BIOTECH
A coronavirus vaccine based on dimerized receptor binding domain subunits
ActiveCN106928326BOvercoming the disadvantage of insufficient immunogenicityIncrease neutralizing antibody productionSsRNA viruses positive-senseBacteriaCoronavirus vaccinationMiddle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
The invention discloses a subunit coronavirus vaccine for dimerization-based receptor binding domains and belongs to the technical field of medicine. A baculovirus expresses RBD (receptor binding domain (E367-Y606) of MERS-CoV (middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus) protein and RBD (R294-F515) of SARS-CoV (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus) in insect cells, the RBDs may form a dimer through cysteine residue at 603 of S (spike) protein or form a dimer through cysteine residue at 512 of the S protein, and purified RBD protein dimer and monomer are used respectively to immunize Bald / c mice. The dimerized RBDs have the advantages that the defect that RBD monomers have poor immunogenicity is overcome and the generation of neutralizing antibodies in against MERS-CoV is increased greatly.
Owner:ANHUI ZHIFEI LONGCOM BIOPHARM CO LTD
Artificial binding protein capable of specifically recognizing allophycocyanin and acquisition method
ActiveCN111690045AAntigen-binding activityStrong specificityBiological material analysisDepsipeptidesDimerAntigen binding
The invention discloses an artificial binding protein capable of specifically recognizing allophycocyanin. The amino acid sequence is as follows: HMVDNKFNKEIVNAITEIHHLPNLNLEQRWAFIFSLFDDPSQSANLLAEAKKLNDAQAPKSGGGGSGGGGIGVDNKFNKEWQNAHNEIIWLPNLNWEQKWAFINSLYDDPSQSANLLAEAKKLNDAQAPKAAASDYKDDDDKLEHHHHHH. The protein has the characteristics of strong specificity, high affinity, strong thermal stability, strong acid-base tolerance and the like, and can be applied to the fields of detection, purification and the like of allophycocyanin. In addition, the invention also relates to a DNA fragment for encoding the artificial binding protein and an acquisition method of the artificial binding protein. According to the invention, a protein A dimer with high stability and high solubility is selected as a skeleton protein, and on the basis of the skeleton protein, the protein with antigen binding activity is finally obtained through the processes of genetic engineering modification, mutant library construction, affinity screening and the like.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Yeast transformant for screening protein with interaction with G protein beta-gamma dimer and screening method of yeast transformant
The invention relates to yeast transformant for screening a protein with interaction with G protein beta-gamma dimer and a screening method of the yeast transformant. Yeast transformant has encoding genes of a beta-subunit and a gamma-subunit of mulberry, a mulberry cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) library is converted into the yeast transformant capable of simultaneously expressing thebeta-subunit and the gamma-subunit, two types of nutrition defect screening of His and Met are carried out to obtain positive cloning with interaction with beta-gamma dimer, and finally the protein with interaction with the G protein beta-gamma dimer of the mulberry can be successfully screened. By adopting the method, a protein dimer interaction protein can be efficiently screened, and the methodcan be successfully applied to screening on a mulberry G protein beta-gamma dimer interaction protein.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Bispecific EGFR/IGFIR binding molecules
The present invention relates to bispecific molecules comprising an EGFR binding domain and a distinct IGFIR binding domain for use in diagnostic, research and therapeutic applications. The invention further relates to cells comprising such proteins, polynucleotide encoding such proteins or fragments thereof, and vectors comprising the polynucleotides encoding the innovative proteins. Exemplary bispecific molecules include antibody-like protein dimers based on the tenth fibronectin type III domain.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
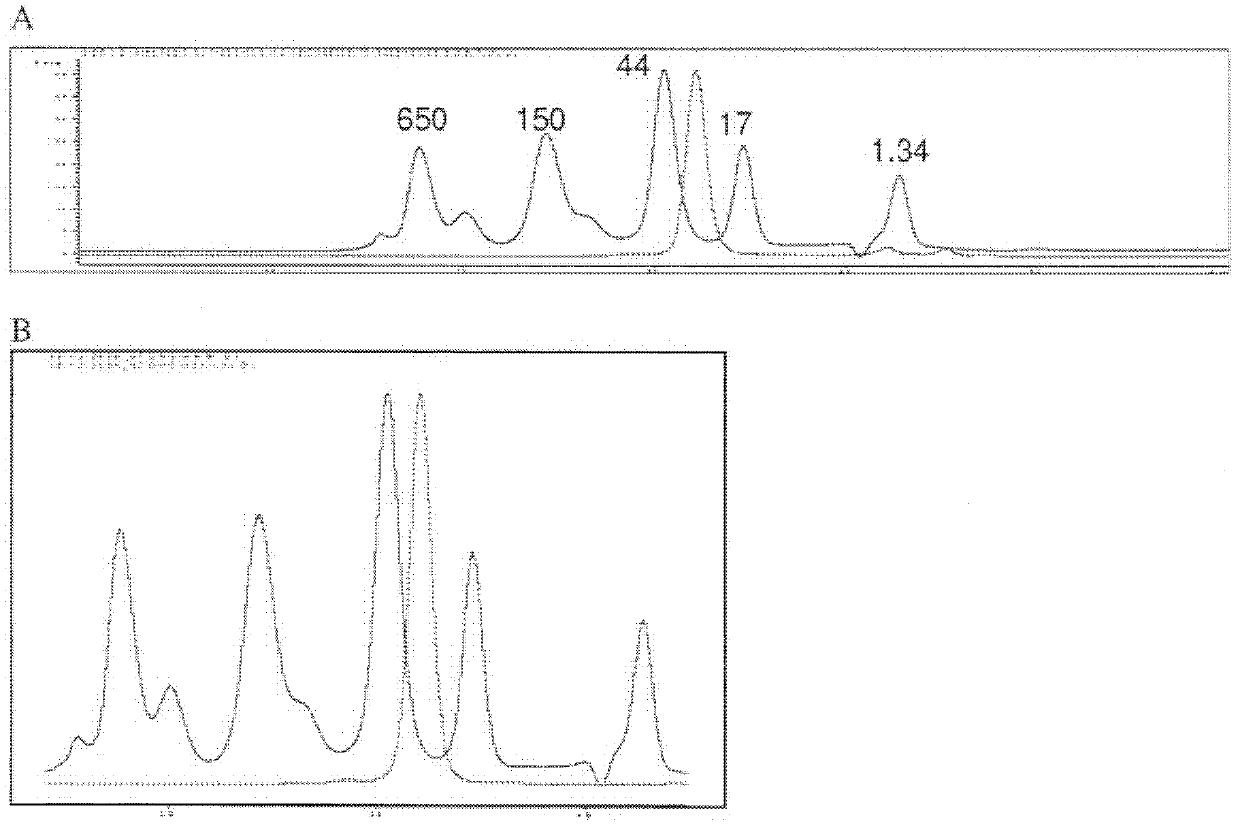
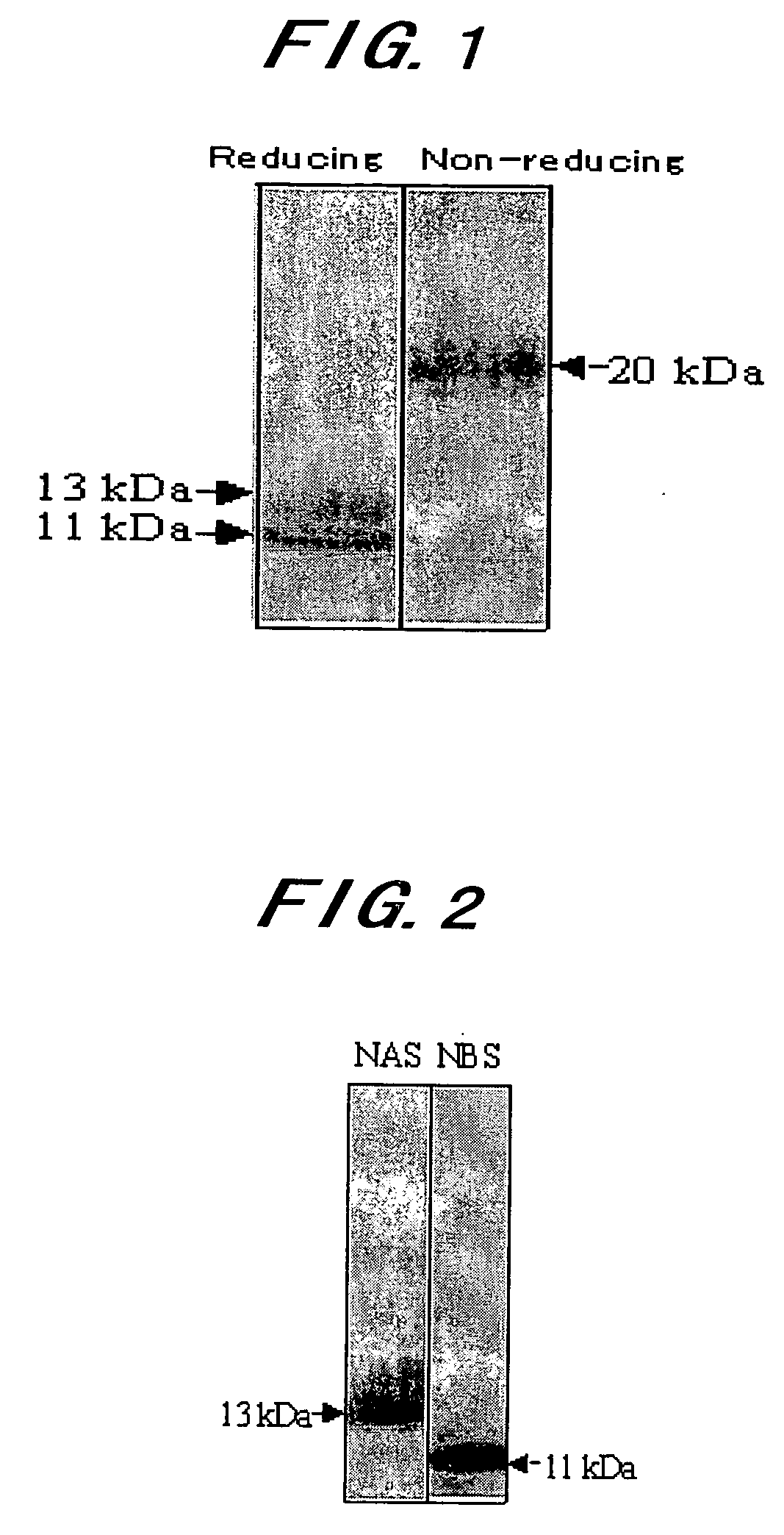
Novel Taste-Modifying Polypeptide Nas, Dna Thereof and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20080305522A1Excellent taste-modifying activityEfficiently provideFungiNervous disorderGeneDNA
It is an object of the invention to find a substance with a better taste-modifying function and determine the structure of the taste-modifying substance, as well as to elucidate the structure thereof at a gene level and determine the primary structure of the substance and obtain the gene encoding the substance. Additionally, it is an object of the invention to provide a novel taste-modifying composition characteristically containing the taste-modifying substance.Specifically, the invention provides the polypeptide shown below in (A) or (B), a protein dimer neoculin comprising the polypeptide NAS and the polypeptide NBS and having a taste-modifying activity:(A) a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 in the sequence listing;(B) a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence with the substitution, deletion, insertion, addition or inversion of one or several amino acids in the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 in the sequence listing, which polypeptide can form the neoculin dimer having a taste-modifying activity together with the polypeptide NBS.
Owner:MITSUKAN GROUP CORP
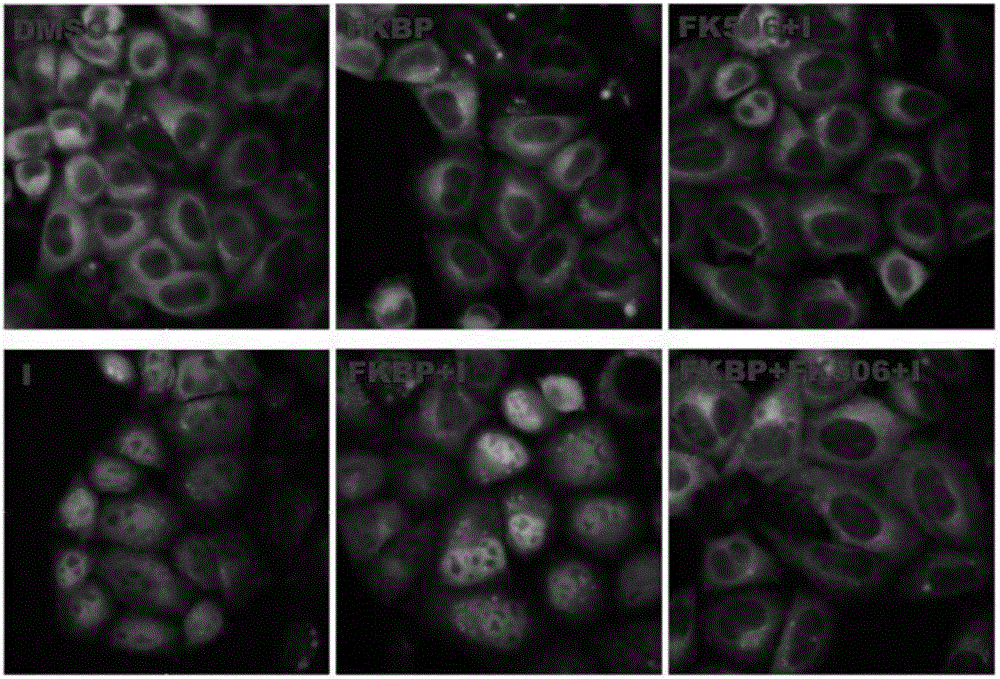
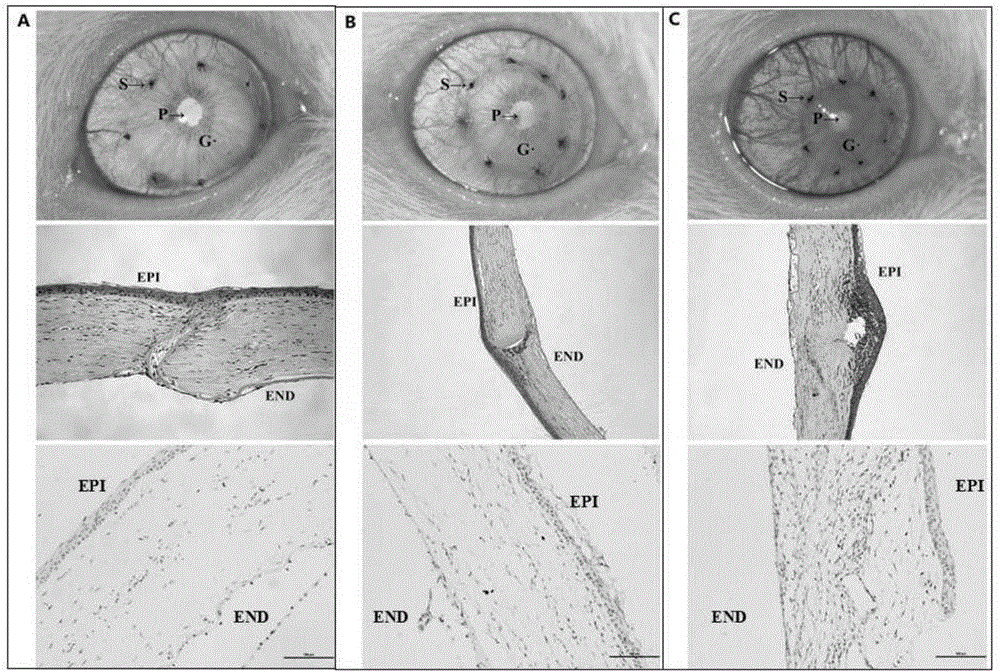
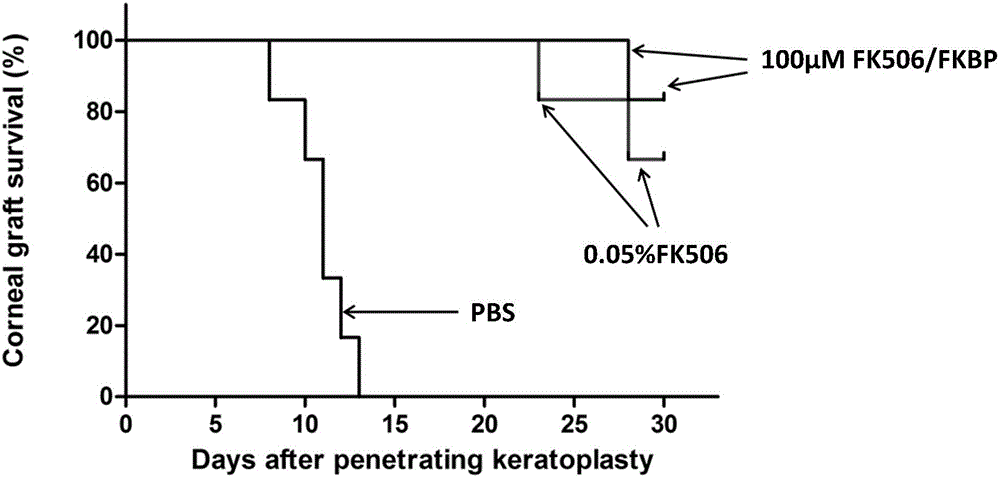
FK506 compound/FKBP protein dimer containing pharmaceutical composition and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106074367ASolve the following shortcomingsImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderFKBPSolubility
The invention discloses an FK506 compound / FKBP protein dimer containing pharmaceutical composition and a preparation method thereof. FK506 and hFKBP12a protein in the FK506 compound / FKBP protein dimer containing pharmaceutical composition are combined according to a mass ratio of 1:1, and a PBS buffer solution with pH being 6-8 serves as a solvent. A dimer formed by FK506 and endogenous binding protein hFKBP12a of FK506 can greatly improve solubility of FK506 in a water solution, and accordingly efficacies of an FK506 water solution are enhanced while storage time of the FK506 water solution is prolonged.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN OPHTHALMIC CENT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
An artificial binding protein capable of specifically recognizing allophycocyanin and its obtaining method
ActiveCN111690045BAntigen-binding activityStrong specificityBiological material analysisDepsipeptidesDimerActive protein
An artificial binding protein that can specifically recognize allophycocyanin, its amino acid sequence is: HMVDNKFNKEIVNAITEIHHLPNLNLEQRWAFIFSLFDDPSQSANLLAEAKKLNDAQAPKSGGGGSGGGGIGVDNKFNKEWQNAHNEIIWLPNLNWEQKWAFINSLYDDPSQSANLLAEAKKLNDAQAPKAAASDYKDDDDKLEHHH. The protein has the characteristics of strong specificity, high affinity, strong thermal stability, strong acid-base tolerance and the like, and can be applied in the fields of detection and purification of allophycocyanin and the like. In addition, the present invention also relates to a DNA fragment for encoding the above-mentioned artificial binding protein and a method for obtaining the artificial binding protein. In the present invention, by selecting highly stable and highly soluble protein A dimer as the backbone protein, on the basis of it, through processes such as genetic engineering transformation, construction of mutant library, affinity screening, etc., the finally obtained class has antigen binding active protein.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Stable coronavirus recombinant protein dimer and its expression vector
ActiveCN112321688BImproving immunogenicityAvoid degradationSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsDimerProtein S
The invention discloses a stable coronavirus recombinant protein dimer and its expression vector. The coronavirus recombinant protein consists of the coronavirus S protein S-RBD, the CTD region N-CTD of the coronavirus N protein and the connection connecting the two Sub composition. The coronavirus recombinant protein of some examples of the present invention can form and maintain a stable dimer structure, avoid the degradation of the monomer S-RBD, help improve the immunogenicity of the coronavirus recombinant protein, and is expected to be used for the preparation of raw materials for detection reagents and vaccines , antibodies, prophylactic or therapeutic drugs. The coronavirus recombinant protein dimers of some examples of the present invention have good immunogenicity. It has broad application prospects in the field of vaccine development. The expression vectors of some examples of the present invention are easy to express coronavirus recombinant protein dimers and have high expression levels.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNITED VACCINE INST
Therapeutic compounds and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS11504381B1Avoid accumulationPrevent proliferationHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsDimerDisease
There are provided new heterobifunctional agents designed to mediate formation of protein-protein dimers and promote ubiquitination of a protein of interest component of the dimer. Also provided are methods of synthesizing the agents, pharmaceutical formulations including the agents, and methods of using the agents to treat, ameliorate or cure diseases characterized by protein over-expression or malfunction.
Owner:LIGATURE THERAPEUTICS PTE LTD
Zipper fastener structure for promoting formation of protein dimer and application of zipper fastener structure
PendingCN114805598AReduce the chance of formationAuxiliary formationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDepsipeptidesDimerAutoantibody
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and relates to a zipper fastener structure for promoting formation of protein dimer and application thereof, and the zipper fastener structure can be used for dimerization of homoprotein and heteroprotein, and can also be used for polypeptide ring formation, dimerization polypeptide and polypeptide extension. Some examples can obtain the ESAT6-CFP10 dimer close to native conformation, the dimer has better solubility, and the memory T cell stimulation effect of the dimer is better than that of ESAT6-CFP10 protein of linear fusion expression. The inventor also finds that the dimer zipper buckle can help to form a more stable cyclic polypeptide, and the CCP polypeptide added with the dimer buckle can increase the detection rate of citrullinated autoantibody in the serum of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis.
Owner:GUANGZHOU LDEBIO TECH CO LTD
A Differential Evolution-Based Method for Predicting the Structure of Protein Dimers
A protein dipolymer structure predicting method based on differential evolution includes the steps of firstly, predicting structural information of two chains of protein dipolymers through an I-TASSERsever so as to improve the prediction precision of the space structure of each single chain of protein; secondly, converting the existing protein dipolymer structure predicting problem into the optimal individual search optimizing problem through the design of population individuals so as to reduce the calculation price; thirdly, searching for the optimal individual through a differential evolution algorithm so as to improve the prediction precision of the protein dipolymer structure. The protein dipolymer structure predicting method based on differential evolution is low in calculation priceand high in search efficiency.
Owner:深圳新锐基因科技有限公司
Renaturation of reconstituted human bone protein-1 and making method of its preparation
The present invention discloses a recombinant human osteoplastic protein-1 renaturation and its preparation preparation method. It utilizes chromatography to obtain rh OP-1 monomer protein whose purity is above 95%. Said invention also provides the concrete steps of said preparation method, including: in 2M-6M urea or 1M-4M guanidine hydrochloride buffer solution making dialysis and renaturation, pH value of renaturation buffer solution is 8.0-10, renaturation temperature is room temperature or 4deg.C and renaturation time is 24-96 hr, then further making chromatographic purification, dialysis, sterilization, packaging and freeze-drying so as to obtain the renaturation preparation of recombinant human osteoplastic protein-1. Besides, said invention also provides the application method of said renaturation preparation of recombinant human osteoplastic protein-1.
Owner:SHANDONG MEDICAL BIO TECH RES CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com