Method for separating unmodified hemoglobin from cross-linked hemoglobin
a technology of unmodified hemoglobin and cross-linked hemoglobin, which is applied in the field of separating unmodified hemoglobin from cross-linked hemoglobin, can solve the problems of patient death, complex patient recovery, and a significant fraction of unmodified tetrameric hemoglobin, and achieves the reduction or elimination of significant renal elimination of hemoglobin, improve intravascular retention time, and suitable oncotic pressure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Diafiltration of Deoxygenated Hb Solution Containing a Higher Concentration Dissociation Buffer
[0069] A polymerized Hb solution was formed according to the method described in Example I of U.S. Pat. No. 5,084,558, issued to Rausch et al. This Hb solution was analyzed by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) and found to comprise about 45% Hb dimers, about 15% unmodified Hb tetramers, and about 40% polymerized Hb molecules which were larger than unmodified tetramers. One liter of a dissociation buffer containing 1.5 M MgCl2, 0.1 M Bis-Tris and 0.2 mM EDTA (pH 6.5) was added to one liter of the Hb solution. This mixture was then recirculated through a 100 kD polysulfone ultrafilter (Millipore Catalog No. PTHK 000C5) to concentrate the mixture to a volume of one liter. The concentrated mixture was subsequently diafiltered with 11 volumes of a dissociation buffer comprising 0.7 M MgCl2, 0.05 M Bis-Tris and 0.1 mM EDTA (pH 6.5). The filtered Hb solution was then washed and equilibrated wi...
example ii
Diafiltration of Deoxygenated Hb Solution Containing a Lower Concentration Dissociation Buffer
[0071] One hundred seventy milliliters (ml) of a dissociation buffer containing 0.75 M MgCl2, 0.05 M Bis-Tris and 0.1 mM EDTA (pH 7.5) was added to 15 ml of the initial polymerized Hb solution of Example I and then 15 ml of a two-fold concentrate of the dissociation buffer was added. The Hb solution was then recirculated through a Chemineer, Inc. / Kenics static mixer and then diafiltered by a 100 kD ultrafilter (Amicon YM 100, Catalog No. 14451) to obtain 200 ml of Hb solution.
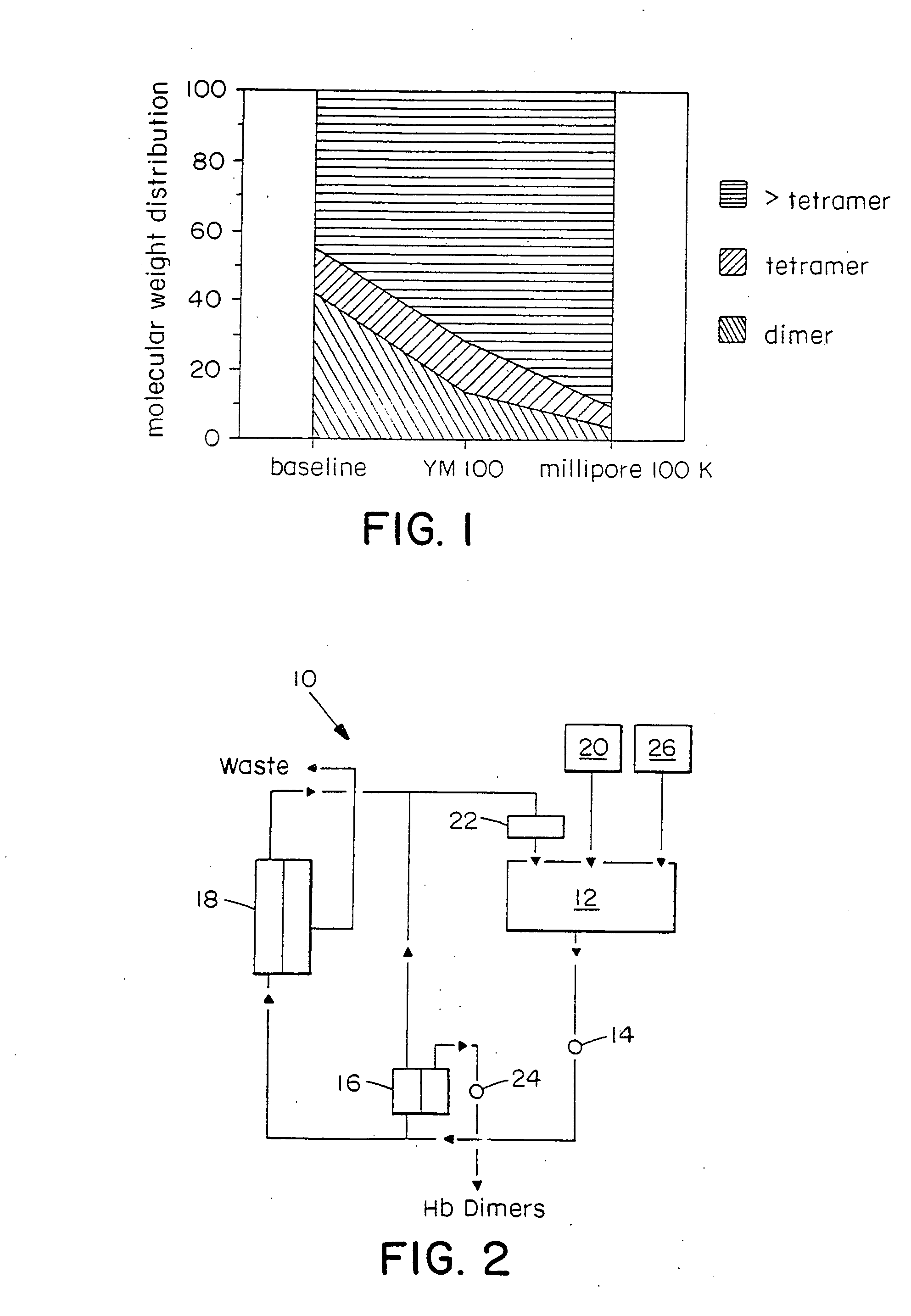
[0072] The Hb solution was then diafiltered with 3 volume exchanges of the dissociation buffer and lastly washed and equilibrated with a deoxygenated buffer containing 27 mM sodium lactate, 12 mM N-acetyl cysteine, 115 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, and 1.36 mM CaCl2 in WFI. The molecular weight distribution of the resulting Hb solution was then analyzed by GPC.
[0073] The results of these analyses are shown in FIG. 2. The Hb so...
example iii
Diafiltration of Oxygenated and Deoxygenated Hb Solutions Without a Dissociation Buffer
[0074] A polymerized Hb solution was formed according to the method described in Example 1 of U.S. Pat. No. 5,955,581, issued to Rausch et al. This Hb solution was analyzed by GPC and found to comprise about 3.5% Hb dimers, 31% unmodified Hb tetramers and about 65.5% polymerized Hb molecules which were larger than unmodified tetramers.
[0075] Two liters of the Hb solution were oxygenated through an oxygenation cartridge with a gaseous mixture, comprising 98% oxygen and 2% carbon dioxide, until 95% oxygenated Hb valves were obtained by a co-oximeter (Co-Oximeter Model #482; Instrumentation Laboratory, Lexington, Mass.).
[0076] The oxygenated Hb solution was then diafiltered with 7 volumes of an oxygenated buffer solution containing 27 mM solution lactate, 12 mM N-acetyl-L-cysteine, 115 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl and 1.4 mM CaCl2 in WFI against a 100 kD ultrafilter. Throughout this process, the Hb solution ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com