Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
197 results about "Plant cell culture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
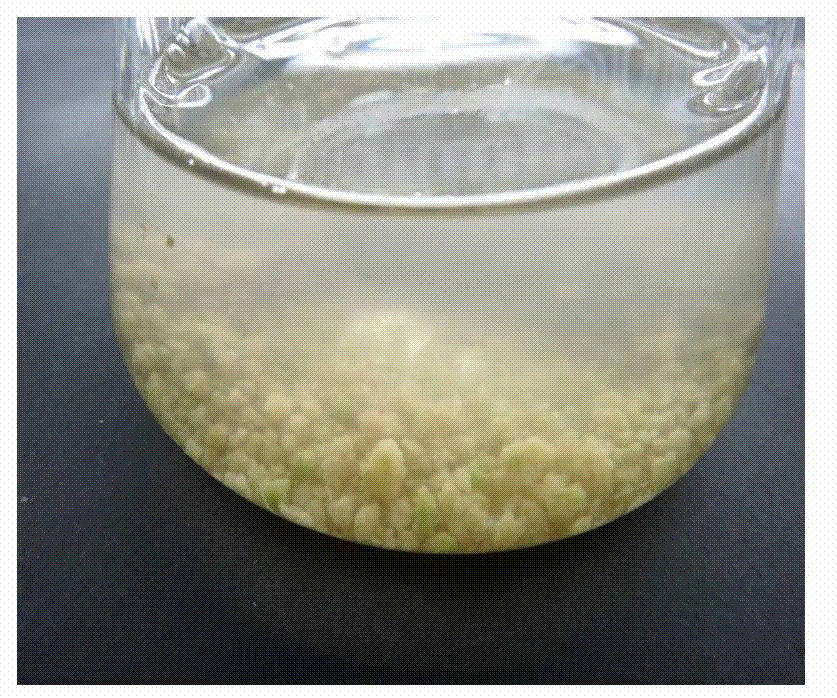
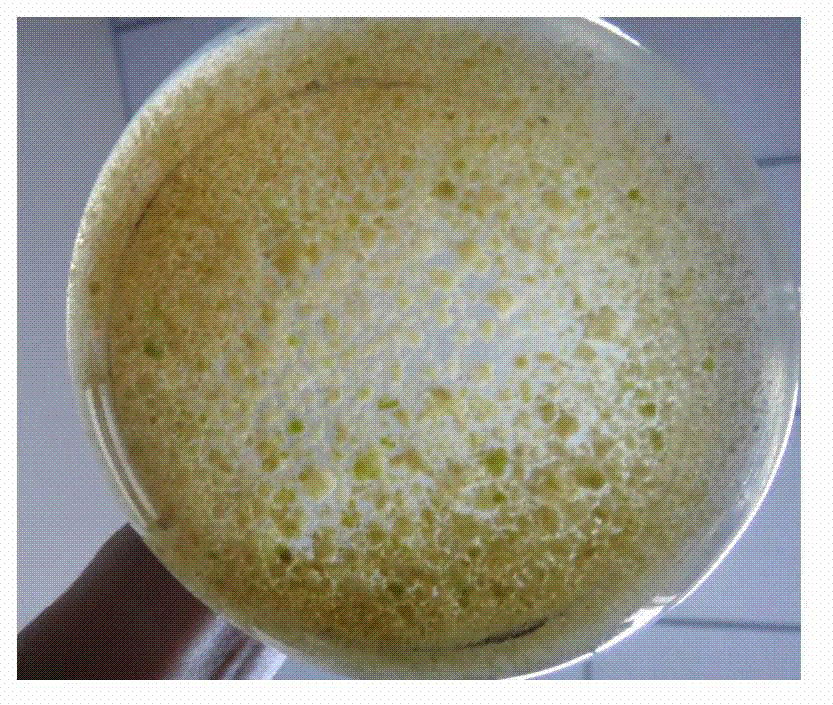
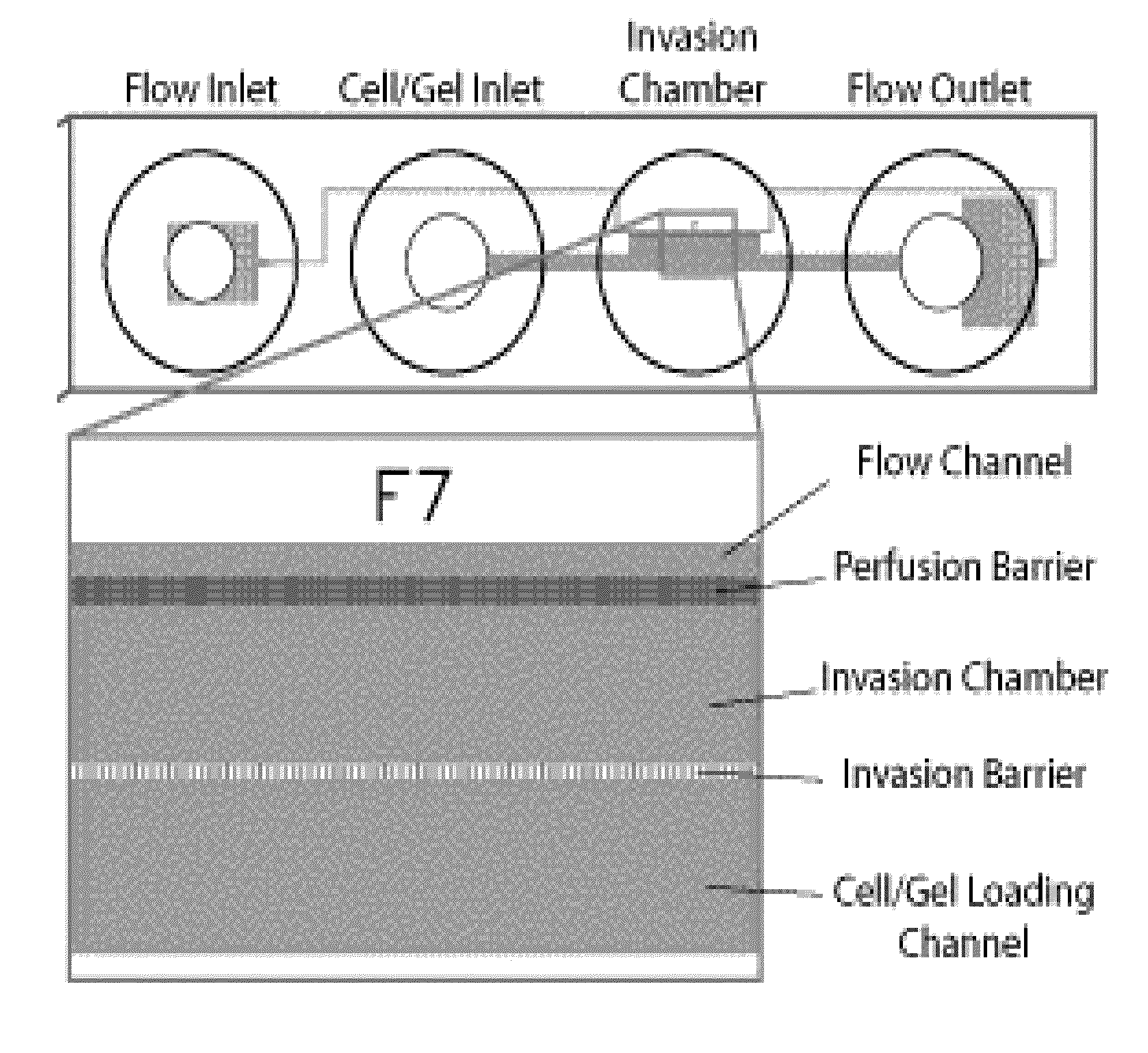
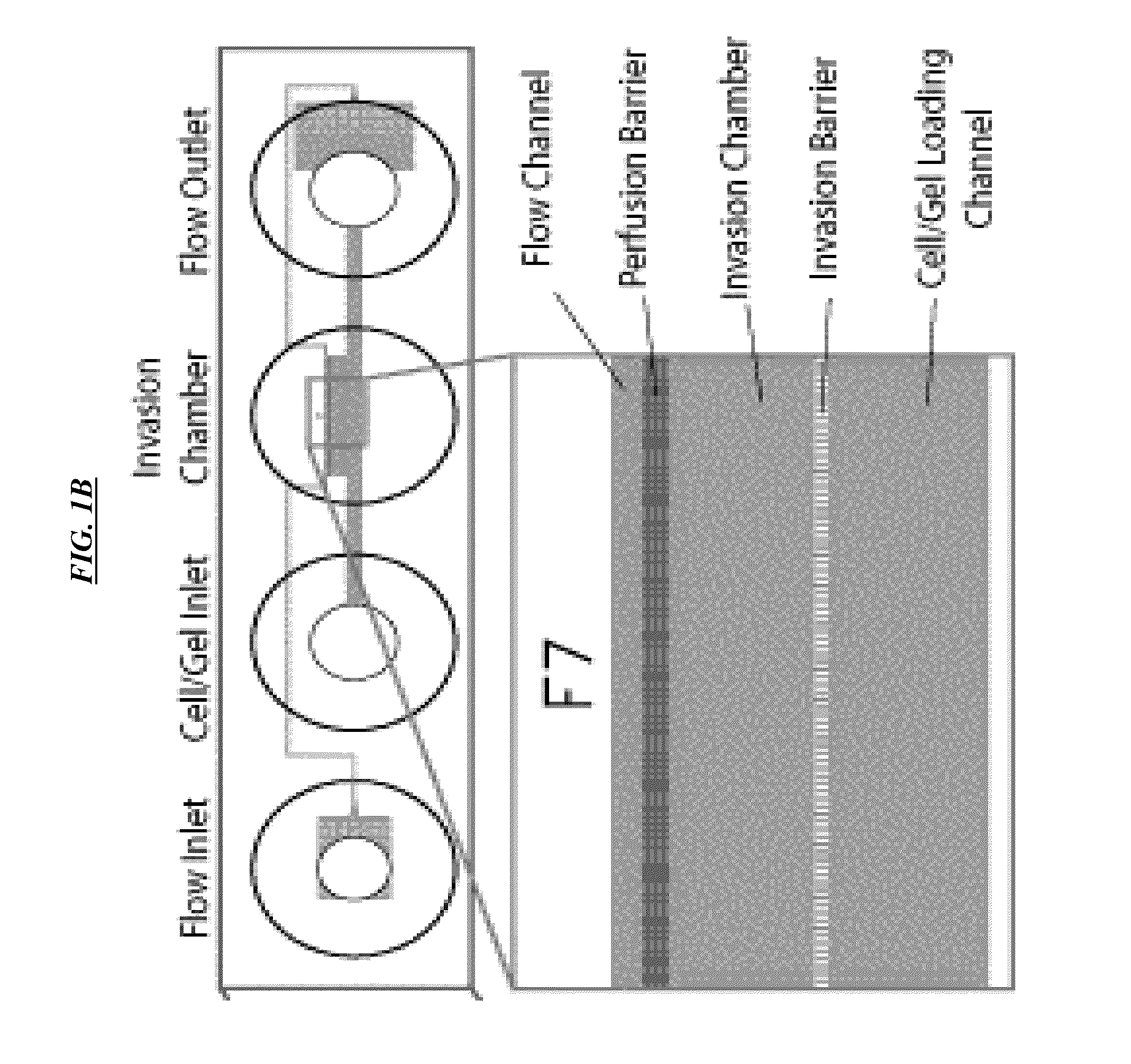
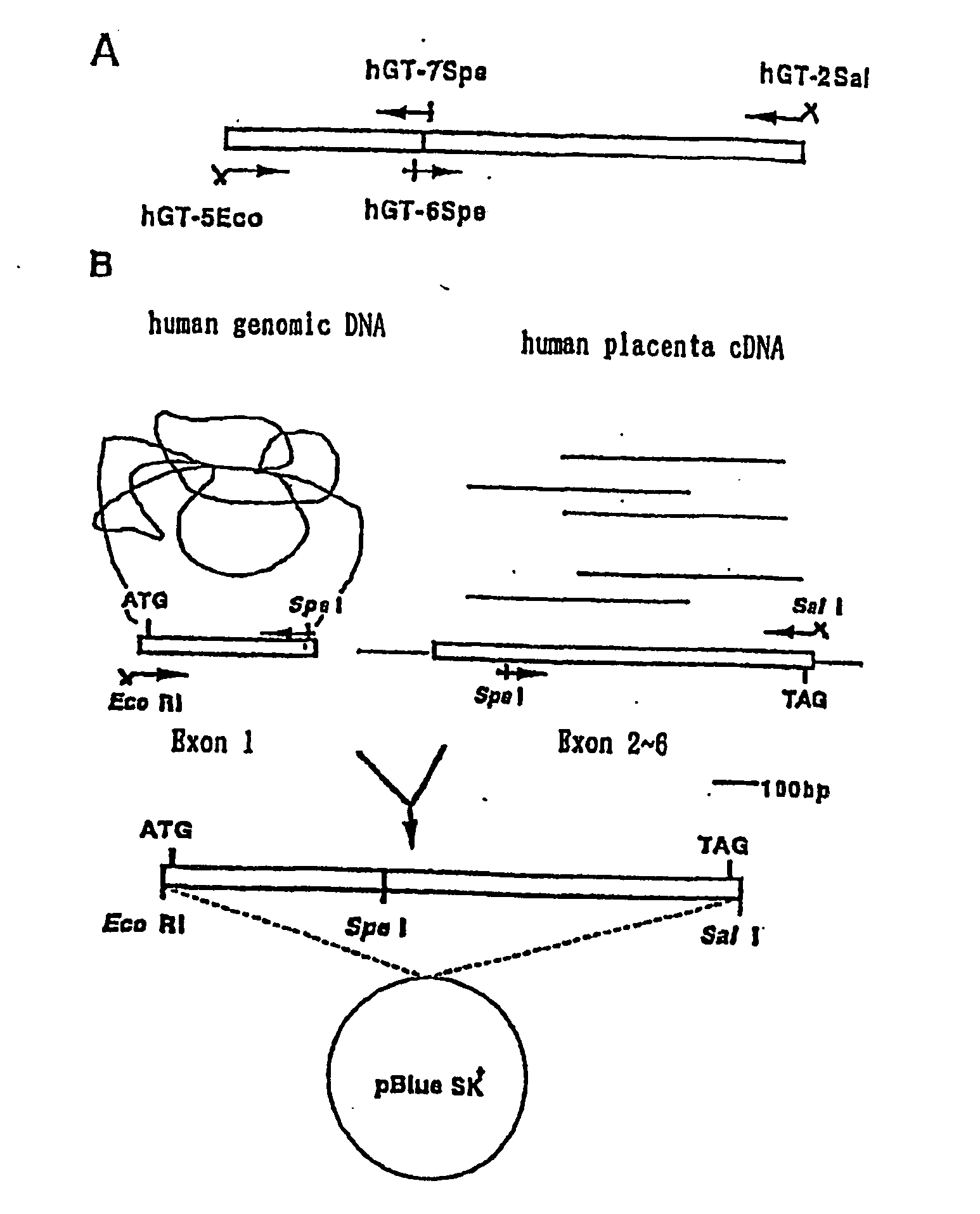
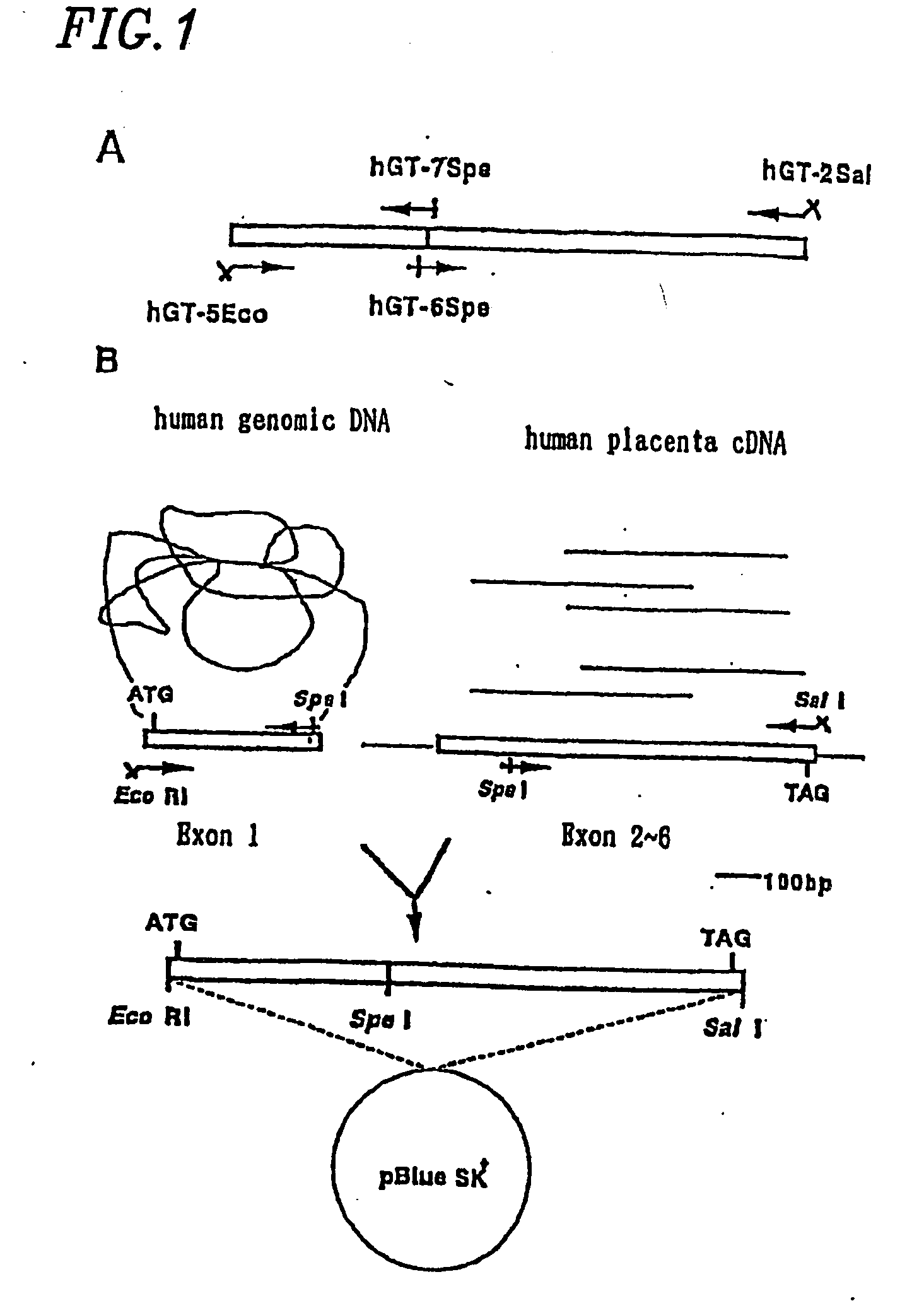
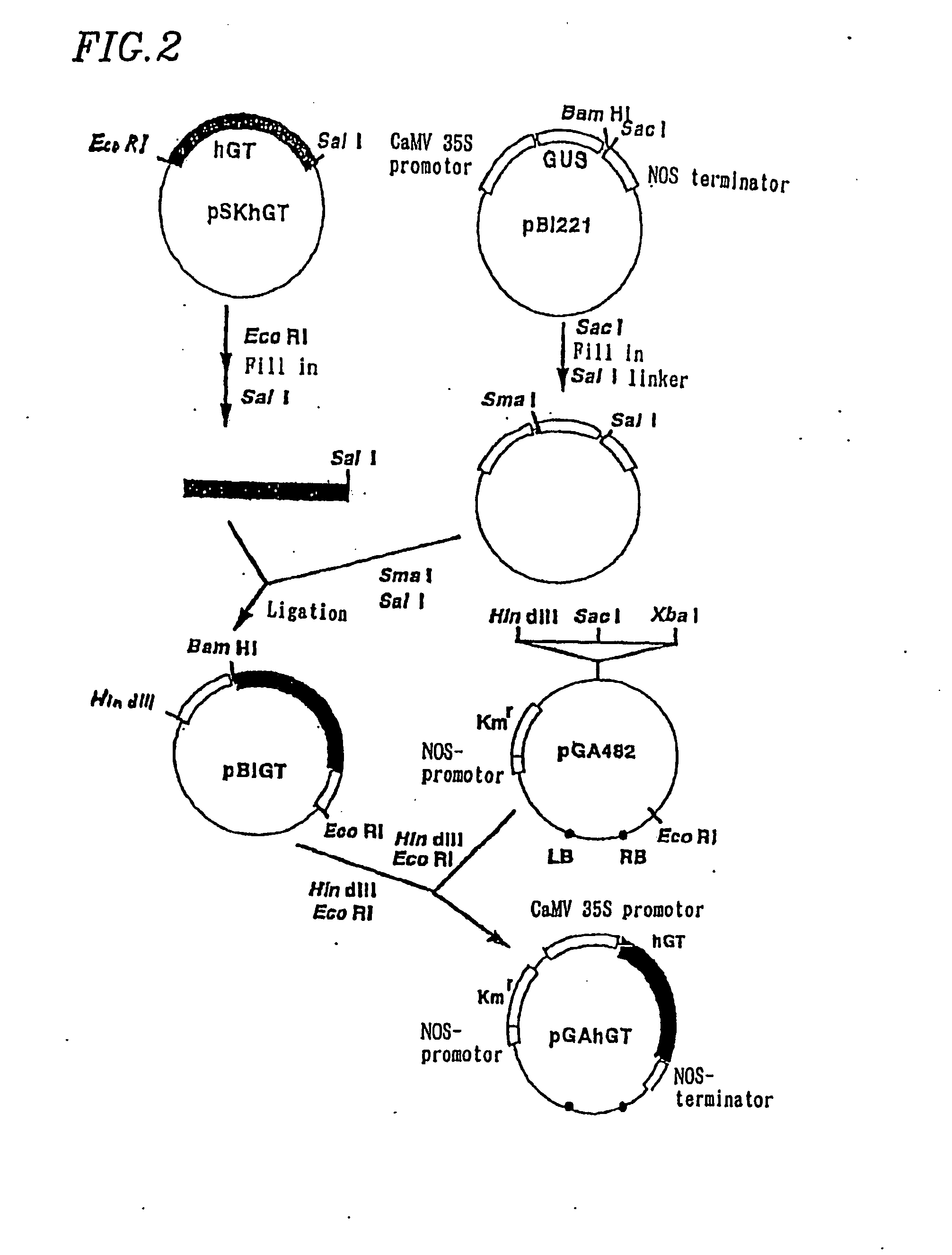
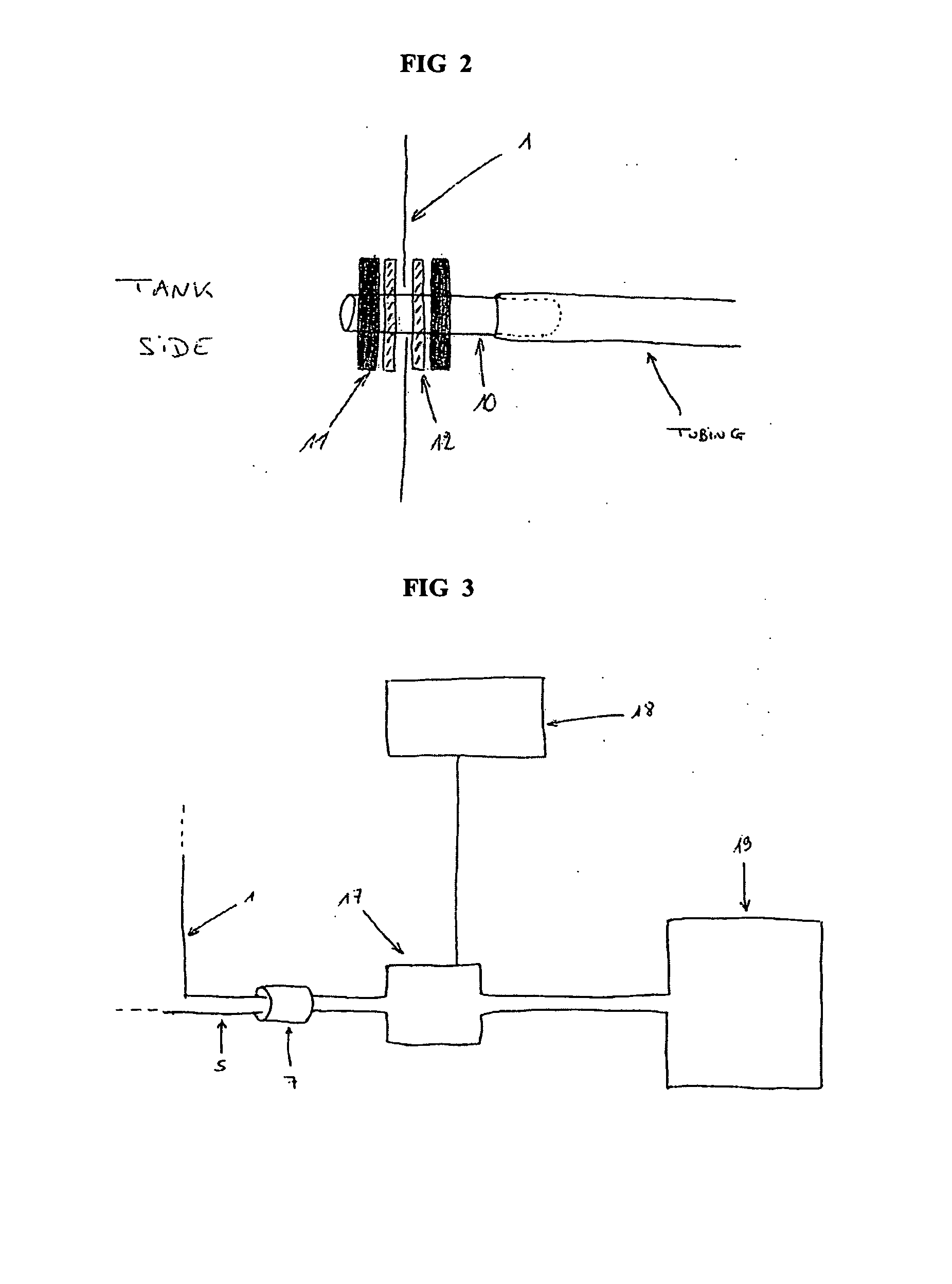
Cell culture and invasion assay method and system
ActiveUS20130059322A1Effectively handle gel culture mediaBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPlant cell cultureBiophysics
Microfluidic devices, systems, and methods providing for an invasion assay using microfluidic culture systems.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
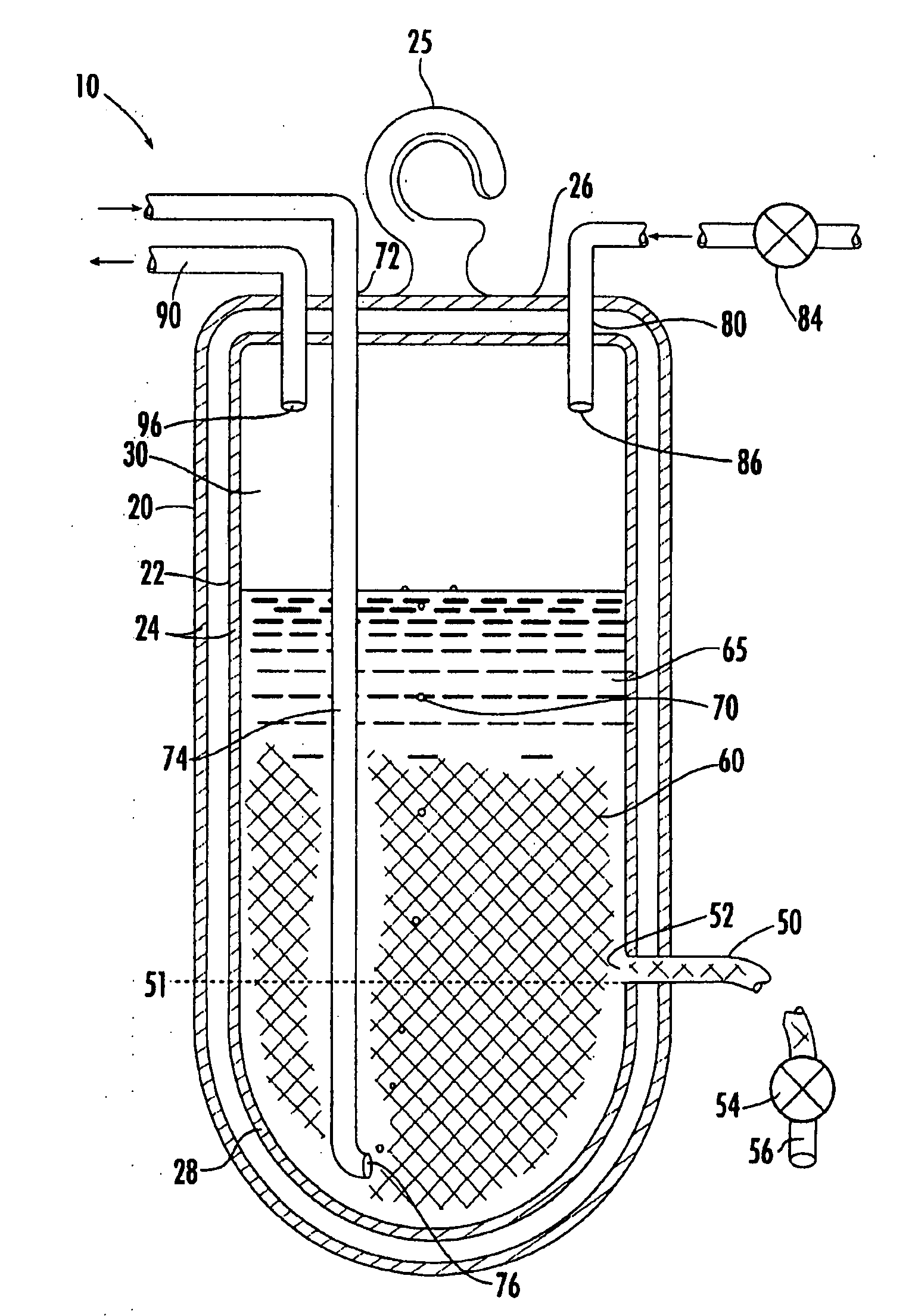
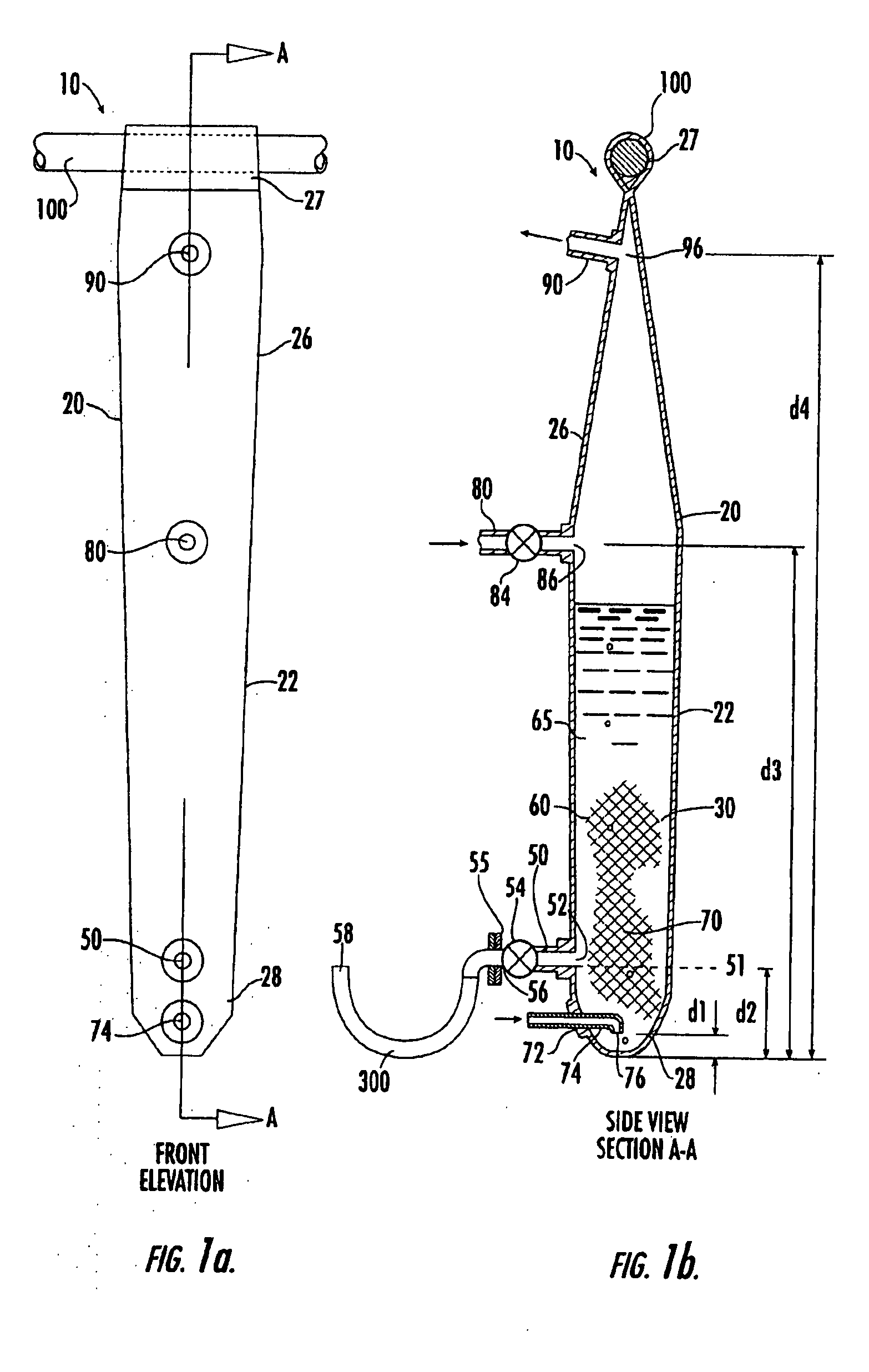
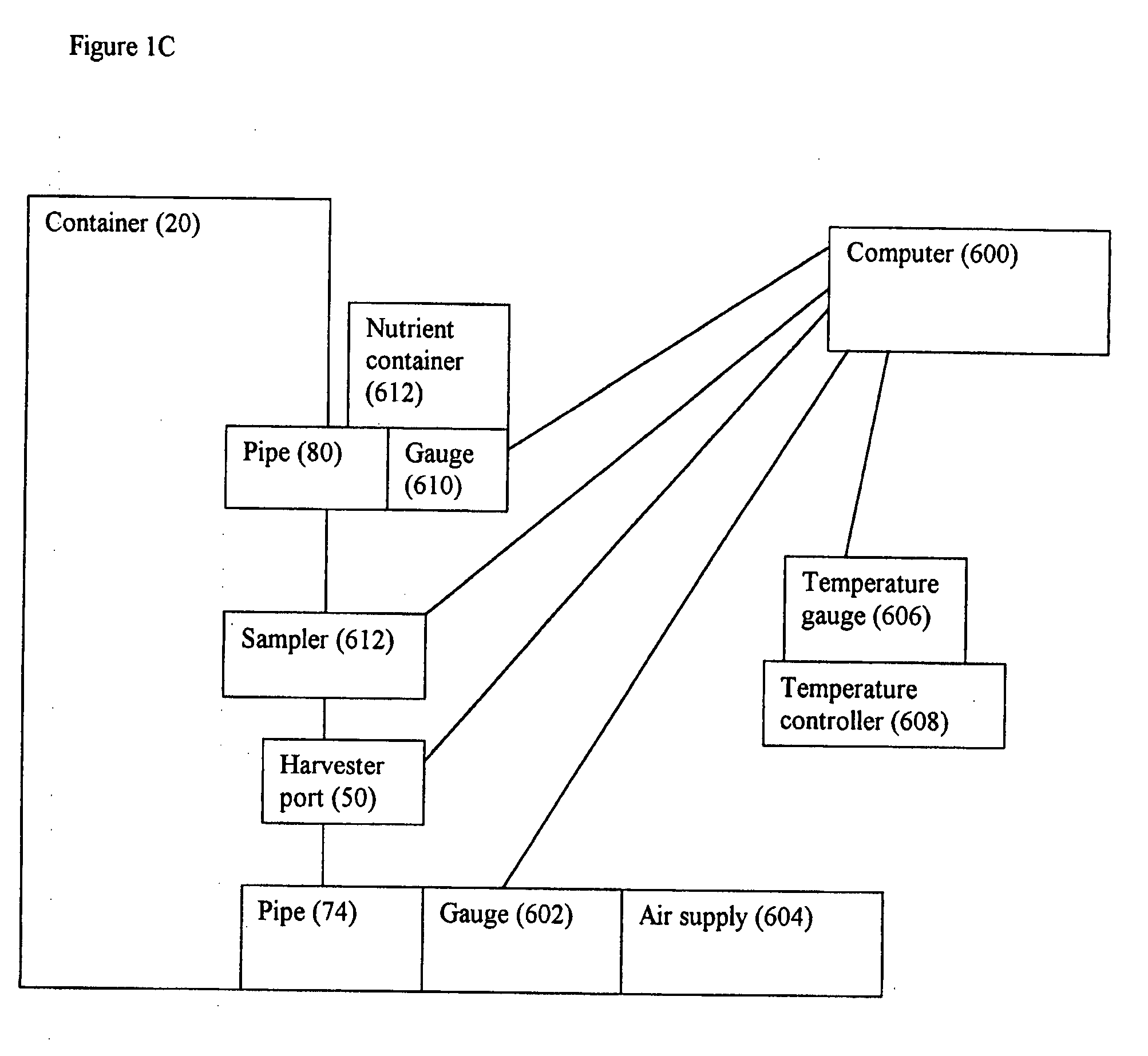
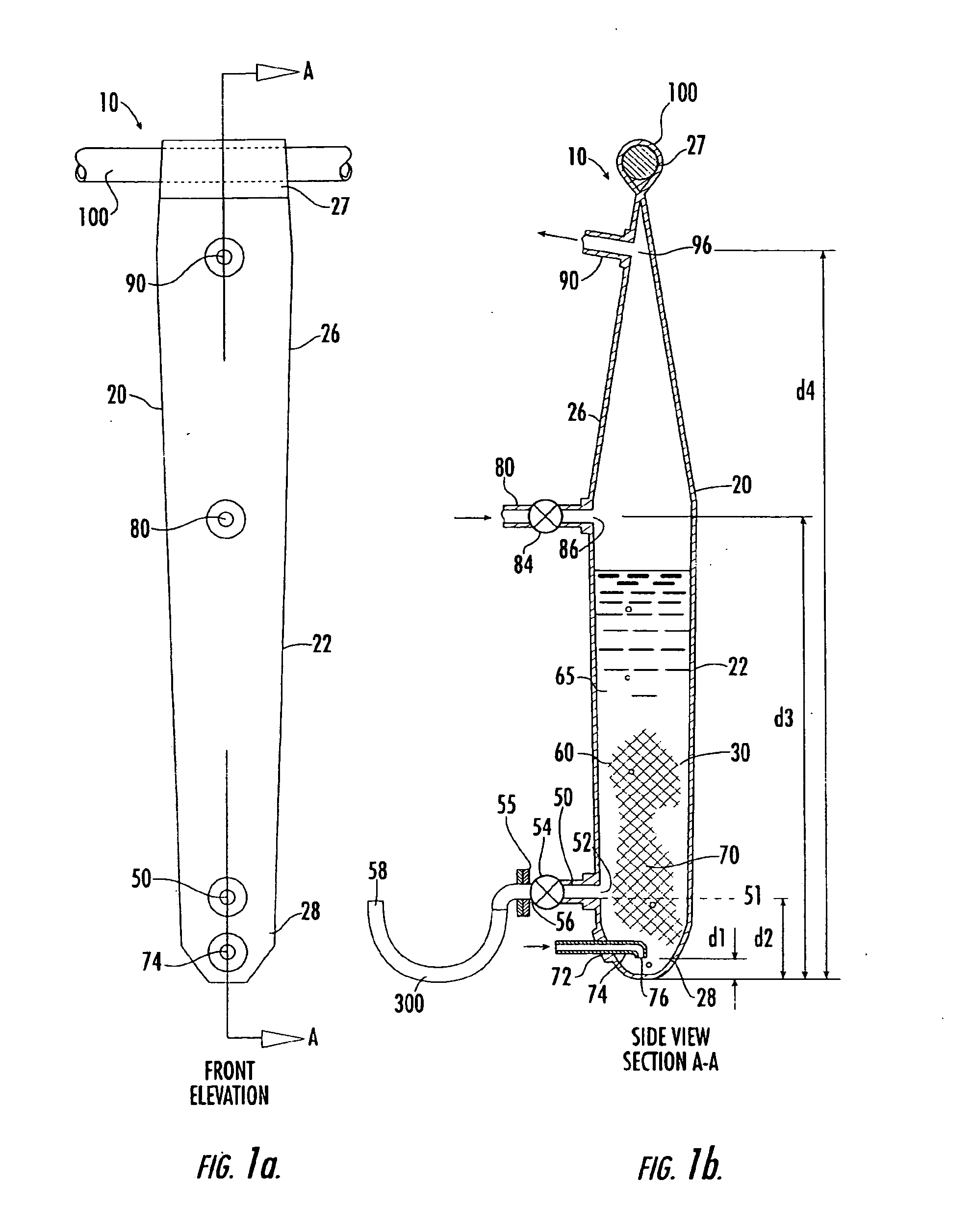
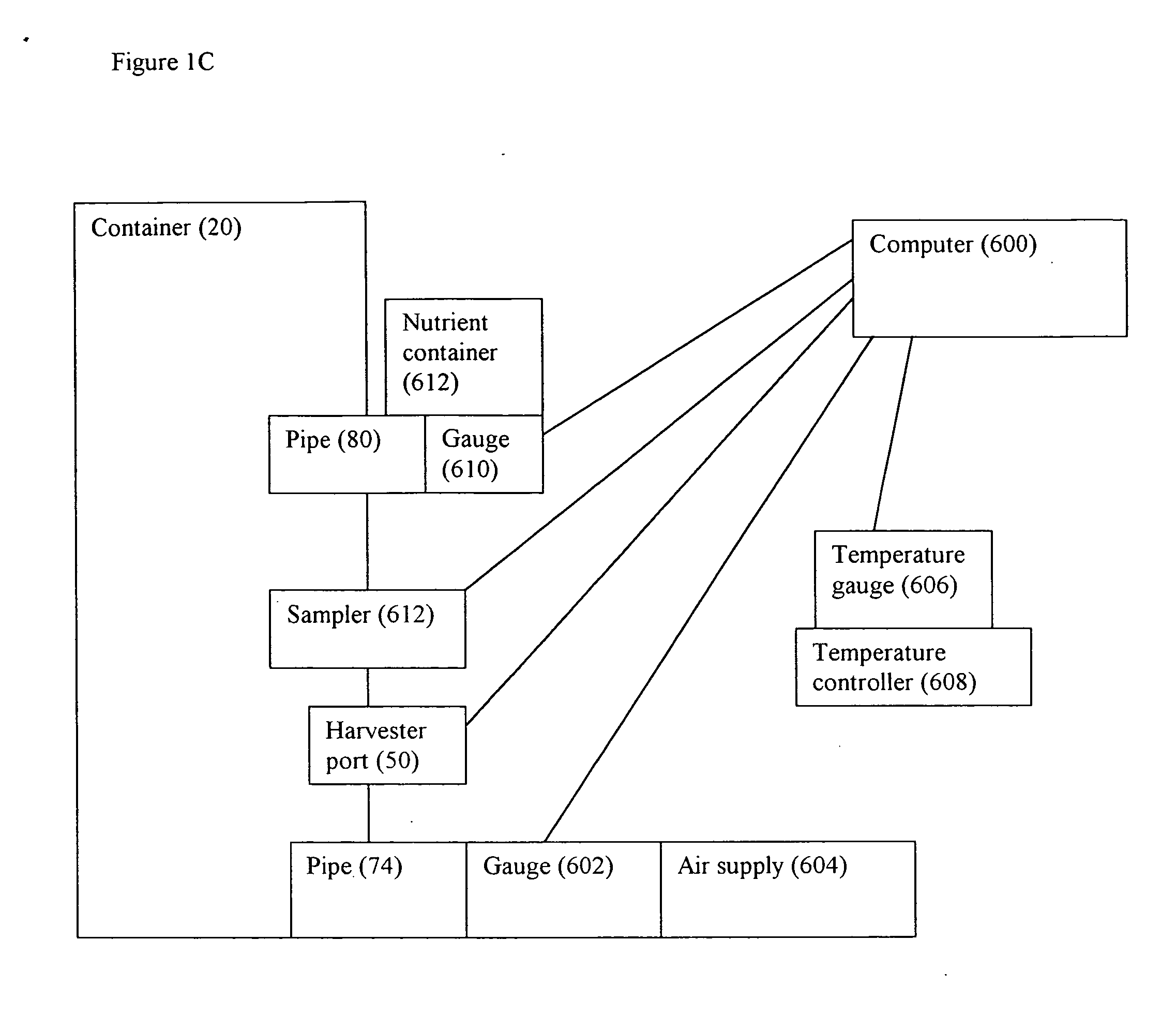
Cell/tissue culturing device, system and method
InactiveUS20090053762A1Reduce shear forceReduce maintenanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyContinuous use
A device, system and method for axenically culturing and harvesting cells and / or tissues, including bioreactors and fermentors. The device is preferably disposable but nevertheless may be used continuously for a plurality of consecutive culturing / harvesting cycles prior to disposal of same. This invention also relates to batteries of such devices which may be used for large-scale production of cells and tissues. According to preferred embodiments of the present invention, the present invention is adapted for use with plant cell culture.
Owner:PROTALIX
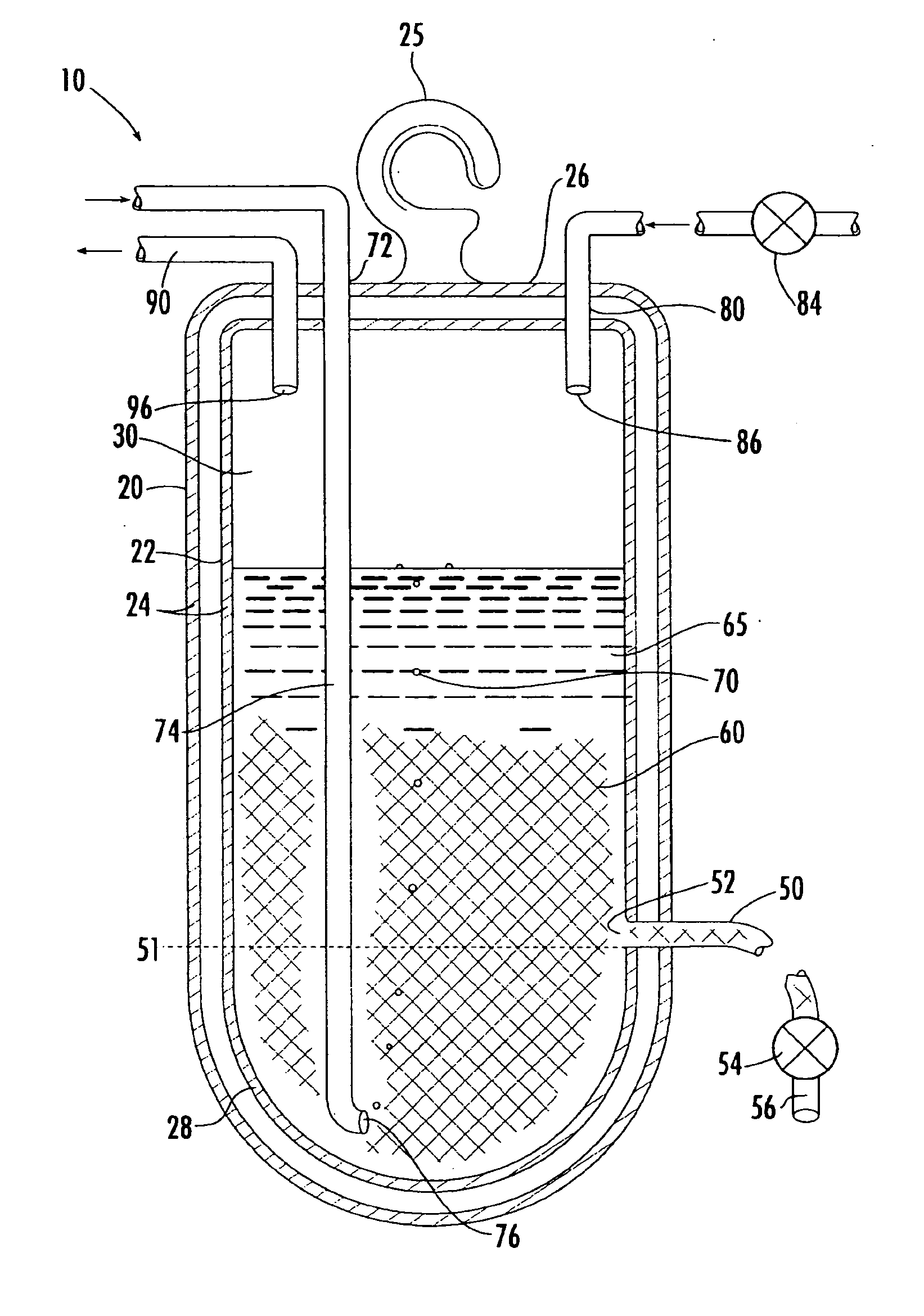
Cell/tissue culturing device, system and method
InactiveUS20050032211A1Avoid introducingReduce shear forceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsContinuous usePlant cell culture
A device, system and method for axenically culturing and harvesting cells and / or tissues, including bioreactors and fermentors. The device is preferably disposable but nevertheless may be used continuously for a plurality of consecutive culturing / harvesting cycles prior to disposal of same. This invention also relates to batteries of such devices which may be used for large-scale production of cells and tissues. According to preferred embodiments of the present invention, the present invention is adapted for use with plant cell culture.
Owner:PROTALIX
System and method for production of antibodies in plant cell culture
ActiveUS20090082548A1Rapid and consistent reproductionLack of uniformityVaccinesFused cellsBiotechnologyHigh level expression
A system and method for production of antibodies in plant cell culture, which results in highly functional antibodies, produced with a high level of expression efficiency. The present invention also encompasses host cells, vectors and methods for mass production of full size assembled immunoglobulins.
Owner:PROTALIX
High-rate perfusion bioreactor
InactiveUS20090280565A1Prevent extractionStable settlementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPerfusion bioreactorMetabolite
The present invention relates to a novel perfusion bioreactor allowing continuous medium feed and extraction of metabolites or other desired products from cells. The invention is useful for plant cell cultures but may also be used for mammalian cell cultures, insect cell cultures and bacterial cell cultures. The design of the reactor includes sedimentation columns mounted inside the bioreactor to separate single cells and cell aggregates from the culture medium at a very low shear stress. The operating conditions allow a stable cell / medium separation by maintaining the medium upward velocity equal to or slightly lower than the cell sedimentation velocity.
Owner:CORP DE LECOLE POLYTECHIQUE MONTREAL
Cosmetic preparation and method for preparing the same
The present invention relates to the use of dedifferentiated plant cells in cosmetic preparations for protecting of stem cells against intrinsic and extrinsic stress factors, in particular for promoting proliferation of stem cells and for protecting them against apoptosis. In particular, the invention relates to the use of dedifferentiated plant cells from fruits of Malus domestica (Apple) cultivar Uttwiler Spaetlauber. Further, the invention relates to a method for cultivating of dedifferentiated plant cells, as well as to the preparation of extracts of plant cell cultures which are suitable for such applications.
Owner:MIBELLE
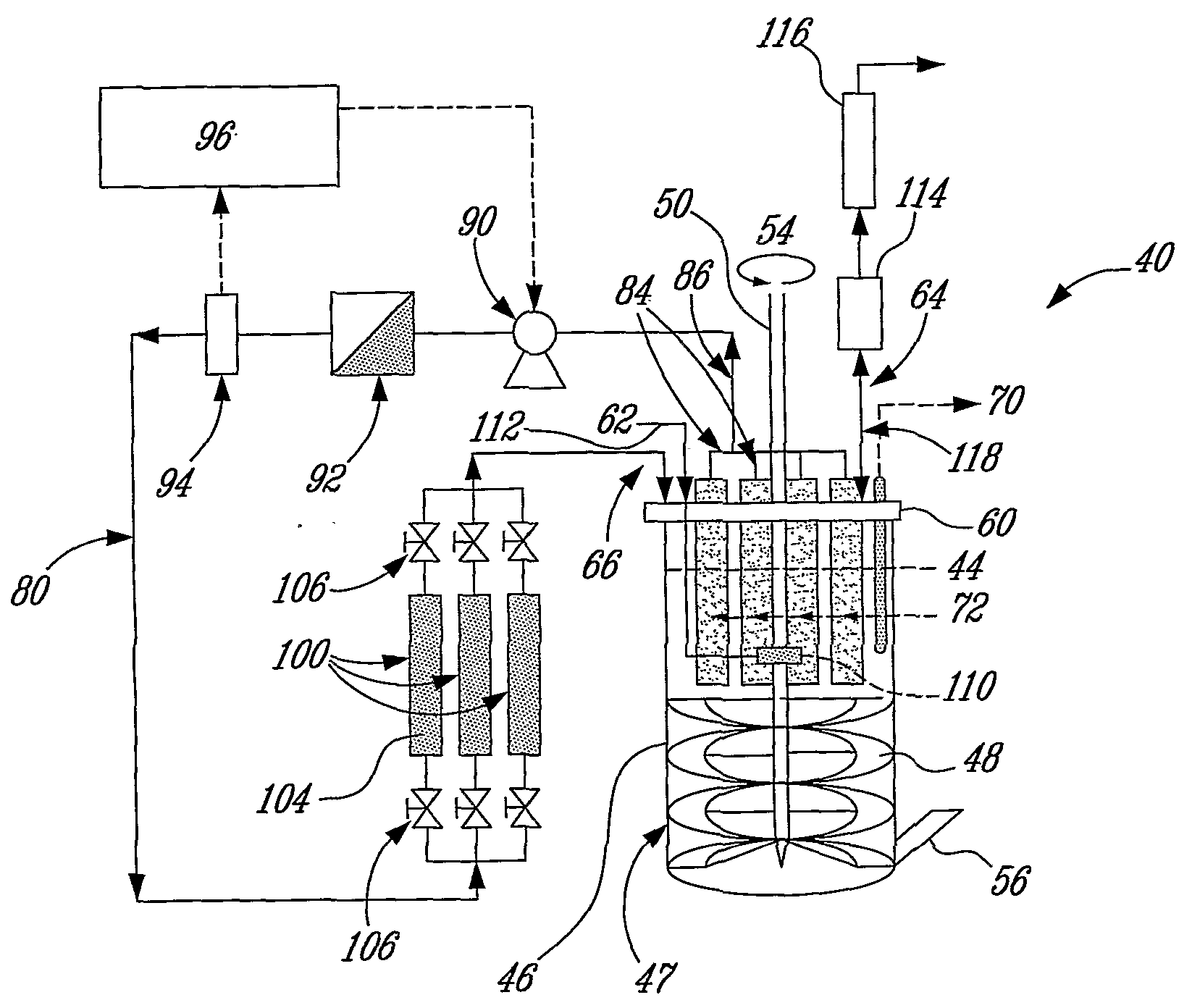
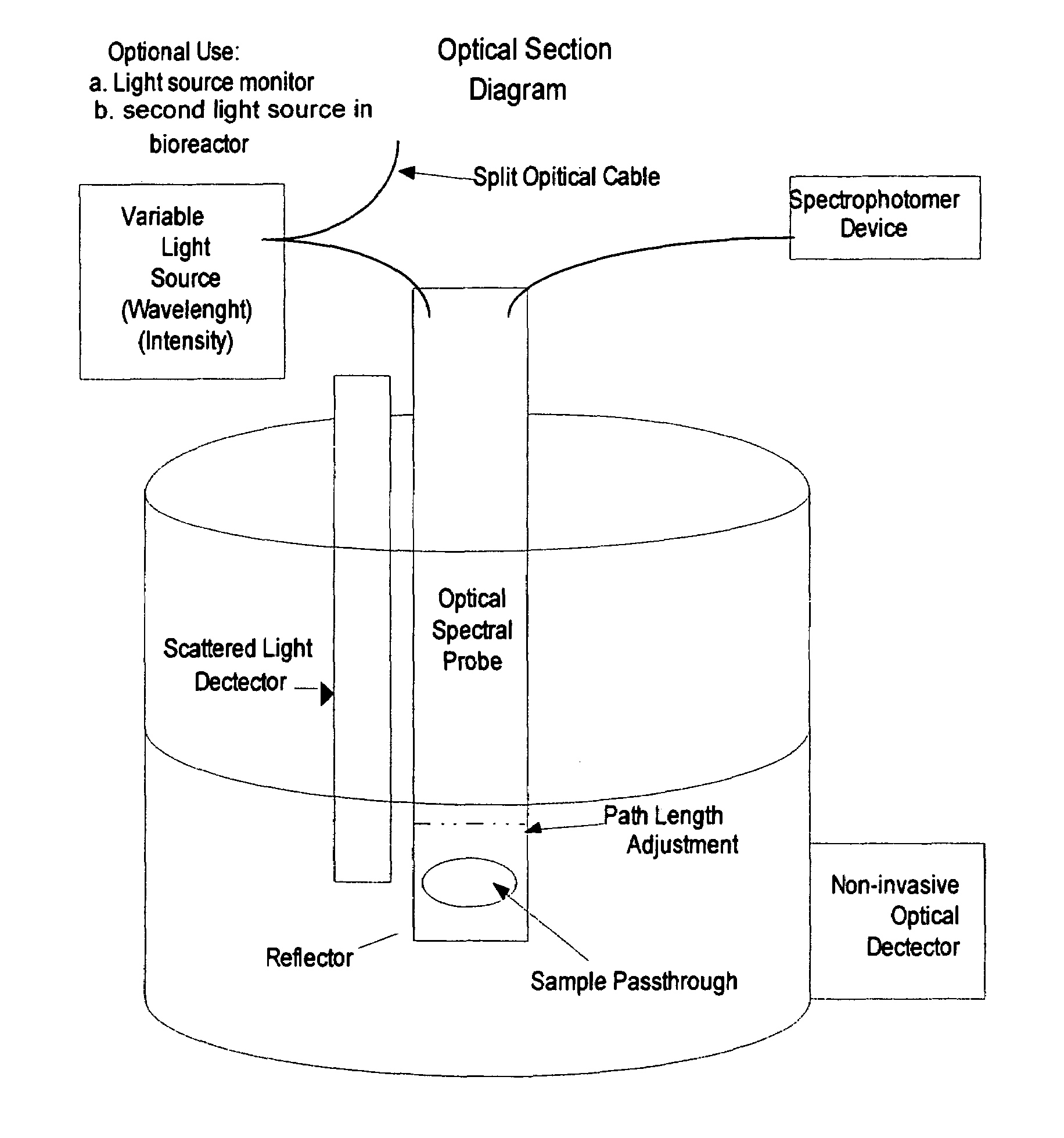
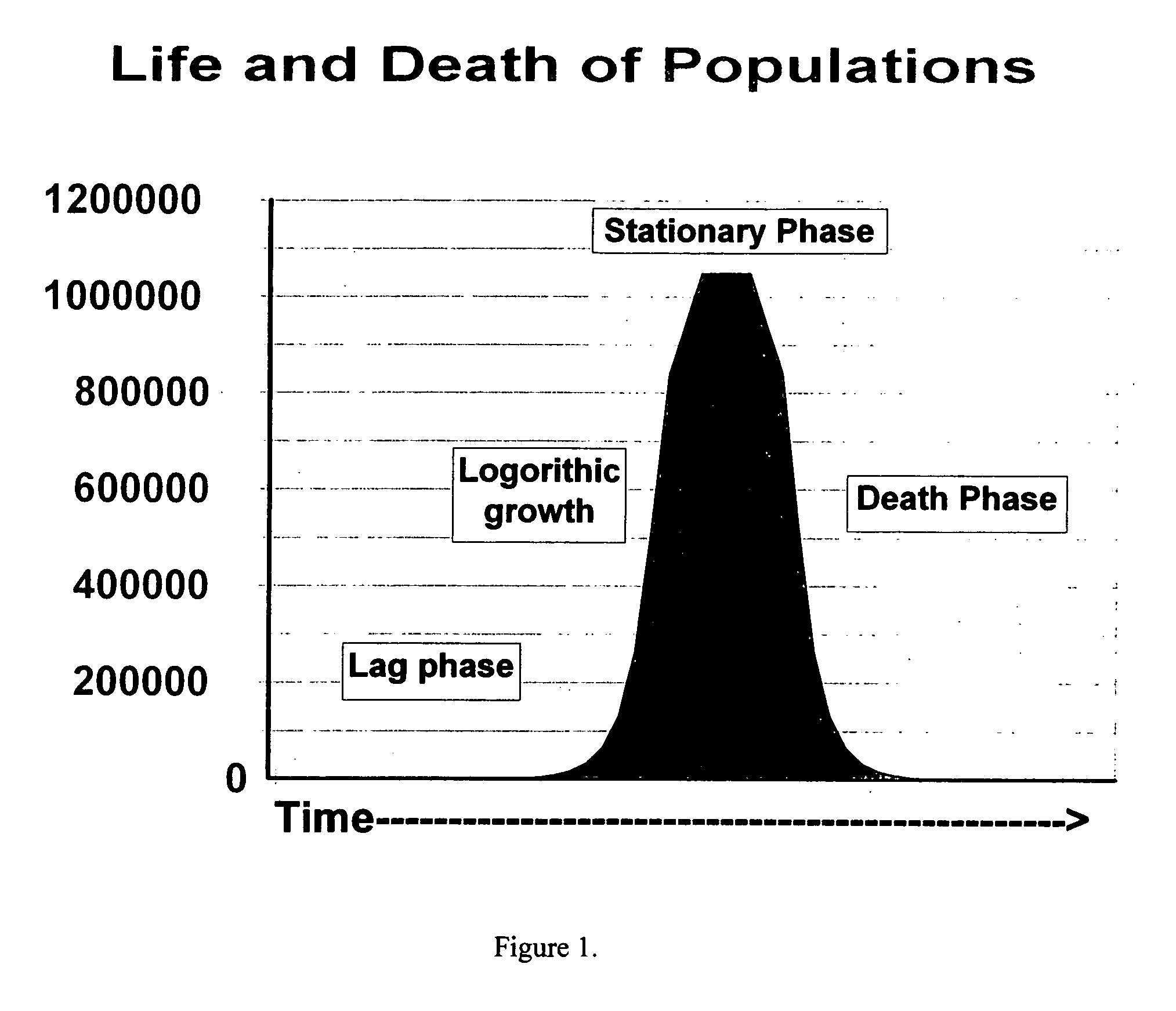
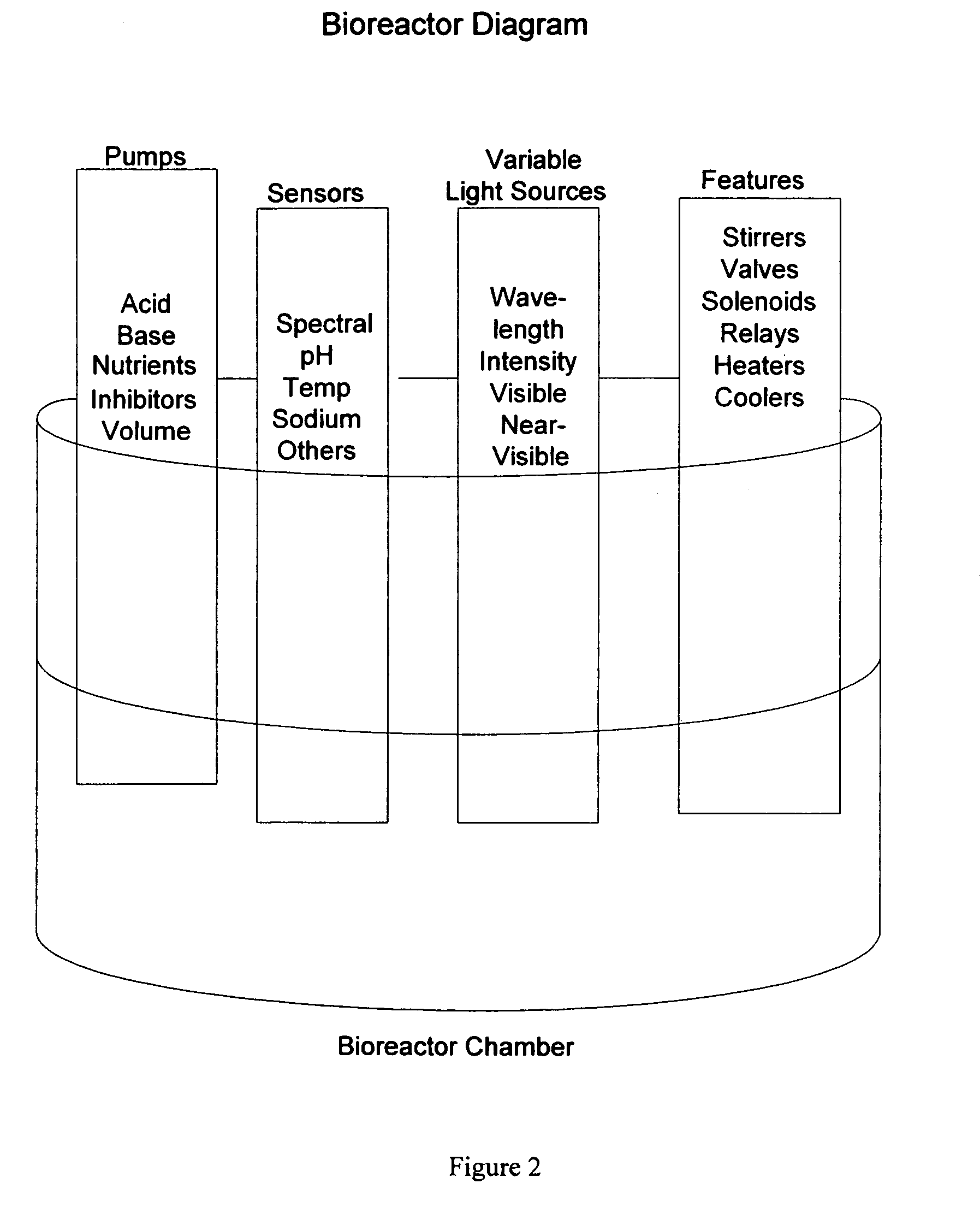
Decision-making spectral bioreactor
InactiveUS7510864B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMetaboliteLaboratory scale
This invention fills several voids in bioreactor technology that allows efficient connection of aspects of physical science (optics, electronics, physical chemistry, sensors) to aspects of microbial and cell culture physiology in a uniquely interactive manner. This is accomplished mathematically through decision making software that utilizes detected changes in the course of fermentation. Decisions are aimed at determining the optima for cellular growth, optimizing for production or degradation of metabolites or substrates, or determining the limits of growth under various combinations of conditions. The invention determines optima or limits in a manner more quickly and at less cost than traditional methods. The basis for the computer generated decisions may be first or second derivative changes observed such as inflection points, limits on allowable rates of change, or the like. The most common measured parameter controlling the decision making process is the optically observed growth of the cells (e.g. microbial, animal, or plant cell cultures) under study. Any other measurable parameter (e.g. pH, temperature, pigment production) may be used to control the process (i.e., the independent variable). This process and variations of this process on a laboratory scale are valuable for research and development, education, pilot plant models, and bio-manufacturing optimization, including scale up to production volumes.
Owner:KRICHEVSKY MICAH I +4
Methods for the production of apolipoproteins in transgenic plants
InactiveUS20050172359A1Readily apparentApolipeptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleic acid sequencingAdemetionine
Methods for the production of an apolipoprotein in plants are described. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a method for the expression of apolipoprotein in plants comprising: (a) providing a chimeric nucleic acid construct comprising in the 5′ to 3′ direction of transcription as operably linked components: (i) a nucleic acid sequence capable of controlling expression in plant cells; and (ii) a nucleic acid sequence encoding an apolipoprotein polypeptide; (b) introducing the chimeric nucleic acid construct into a plant cell; and growing the plant cell into a mature plant capable of setting seed wherein the seed expresses apolipoprotein.
Owner:MOLONEY MAURICE M +1
Plant cell culture and selection system
InactiveUS20030082580A1Improve stabilityImprove thermal stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods of selecting and transforming plant cells in large scale in vitro liquid cultures. In some methods of the invention, cells are selected that comprise a suppressive nucleic acid sequence that suppresses the effect of a target gene that impairs cellular function in the cell. In other embodiments, the methods are directed to identifying nucleic acids that encode polypeptides that physically interact with one another.
Owner:DNA PLANT TECHNOLOGY
Method for culturing siraitia grosvenorii callus cell suspension system
The invention relates to a method for culturing a siraitia grosvenorii callus cell suspension system. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) inoculating and inducing siraitia grosvenorii stem calluses, performing subculture on MS liquid medium added with 1-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) hormone, sucrose and agar, and selecting the calluses; 2) transferring the calluses obtained in the step 1) to a sterile triangular flask, putting the triangular flask into a shaking incubator, performing suspension culture for 24 hours under the dark condition of 25 DEG C, transferring the culture medium of the upper layer, single cells and small cell masses to a triangular flask, and continuously performing shaking culture, performing transfer again after 3 days by adopting the same method, filtering the suspended cells through a screen with meshes of 40 microns after 7 days, inoculating the suspended cells to fresh culture medium for culturing, transferring the cultured cells to a big triangular flask after a certain volume is reached, and continuously adding the culture medium and performing shaking culture by using the same method; and 3) culturing for 21 days, harvesting, flushing for 3 times, performing vacuum filtration, weighing and drying. The method has the characteristics of high propagation speed and large culture scale, and provides a large amount of uniform plant cell cultures.
Owner:浙江康德药业集团股份有限公司
LED light source bioreactor
ActiveCN101629142AReduce volumeIncrease brightnessPhotobioreactorsTissue/virus culture apparatusPhotobioreactorEngineering
The invention relates to microorganism production equipment which is photosynthetic reaction equipment for photosynthetic bacteria and plant cell culture, in particular to an LED light source bioreactor. The bioreactor comprises a pot body and a luminous tube inserted in the pot body, wherein the luminous tube comprises a transparent glass tube case with a closed lower end and a tubular LED bracket inserted in the transparent glass tube case. The upper end of the transparent glass tube case is fixed on a top cover of the pot body; a plurality of LED mounting holes are distributed on the tube wall of the LED bracket; and LEDs are arranged in the LED mounting holes. The invention has the advantages of small size of a light source arranged in a culture pot, easy regulation, little heat radiation in work, strong radiating ability, high utility ratio of the light source, low energy consumption and long service life.
Owner:王科
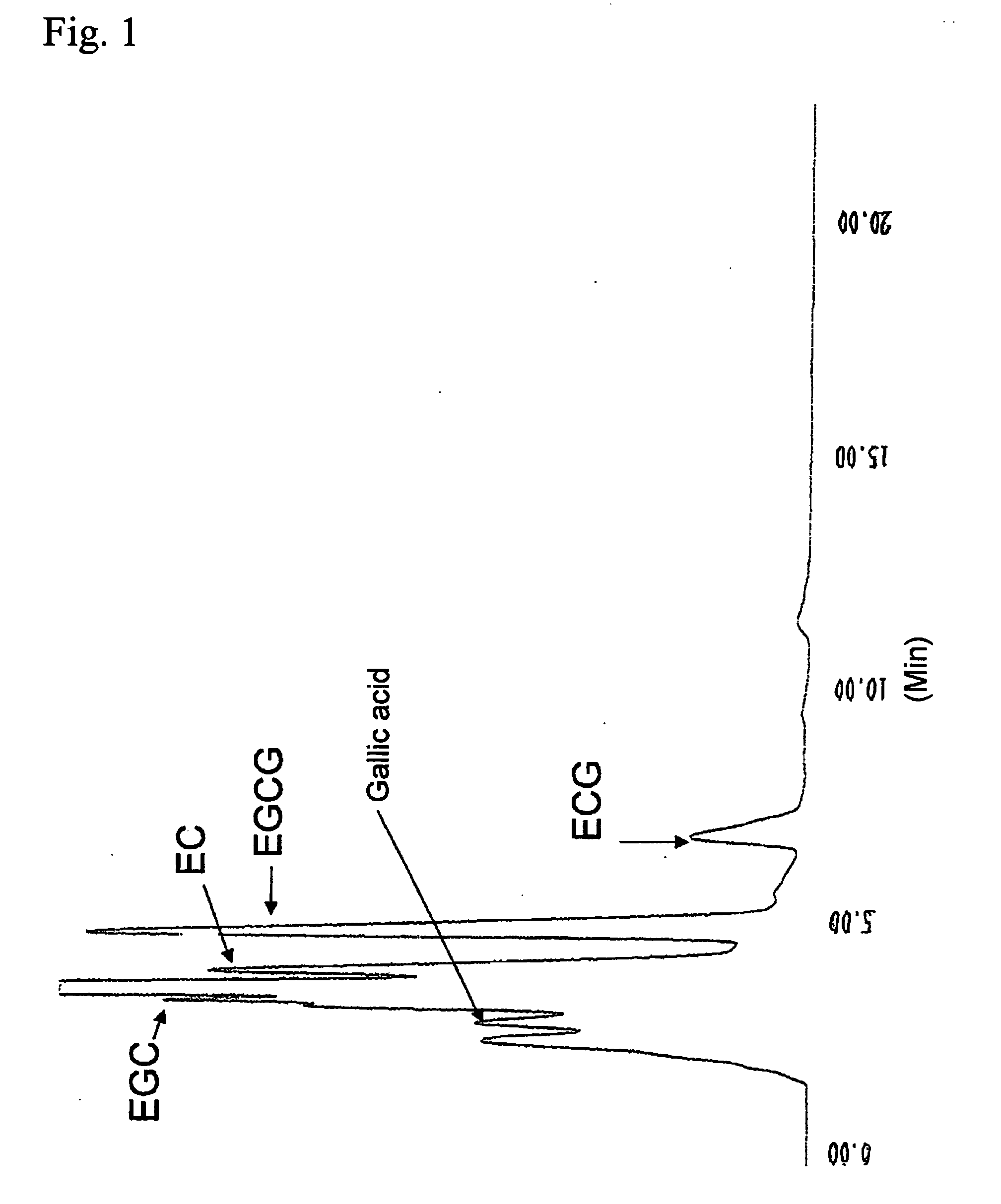
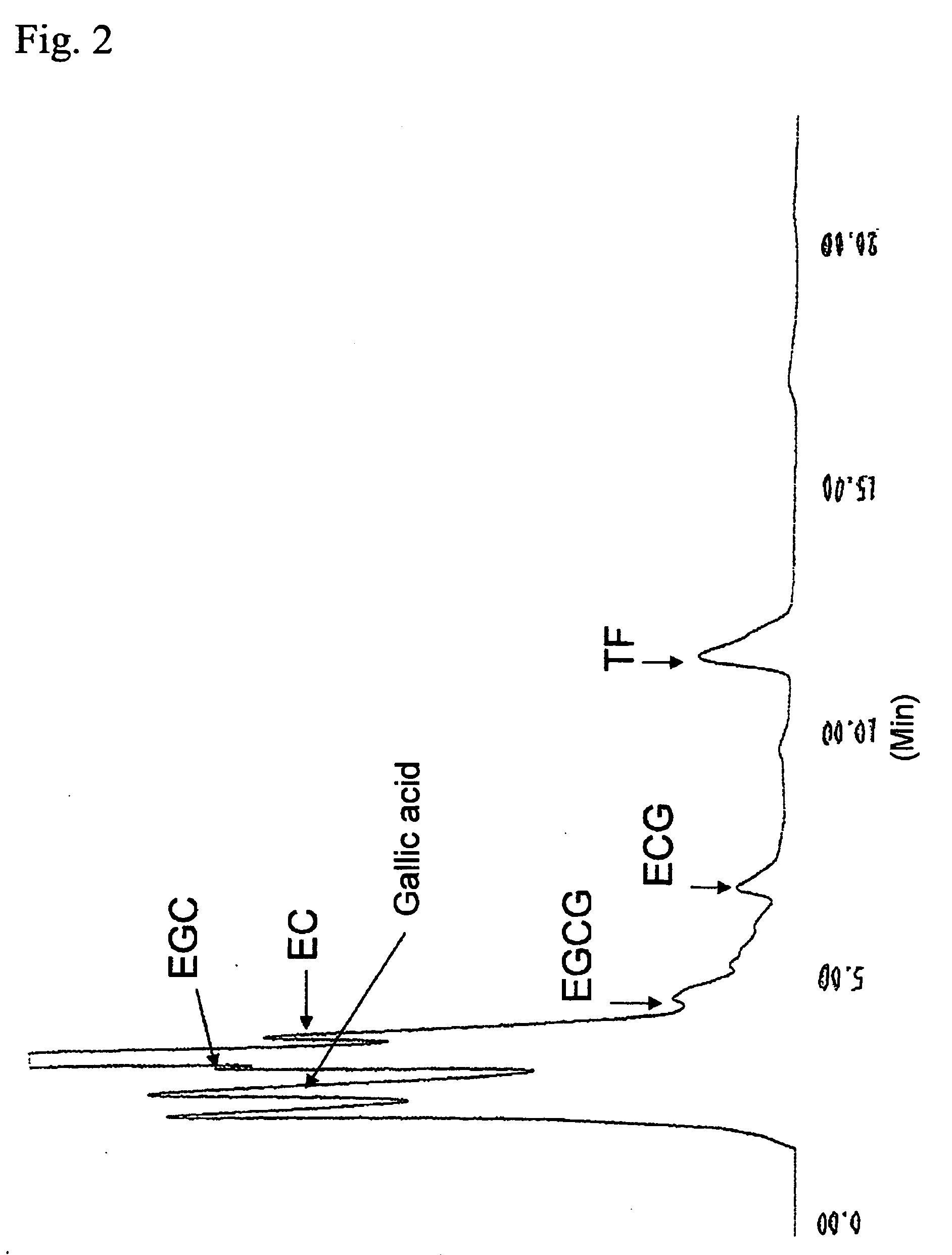
Process for selective production of theaflavin
InactiveUS20100136636A1Produced inexpensively and efficientlyIncrease volumeFermentationPlant cellsBiotechnologyTheaflavin
The present invention provides a method for selective production of theaflavin in large amounts at high yield, and in an easy and inexpensive manner. Specifically, it relates to a method for selective production of theaflavin whereby a processed plant extract containing epicatechin, epigallocatechin, epicatechin-3-O-gallate and epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate is combined with a plant cell culture having peroxidase activity for selective production of theaflavin.
Owner:HAMAMATSU FOUNDATION FOR SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY PR
Method for secretory production of glycoprotein having human-type sugar chain using plant cell
A method for the secretory production of a glycoprotein having a human-type sugar chain, comprising a step of introducing a gene of an enzyme capable of performing a transfer reaction of a galactose residue to a non-reducing terminal acetylglucosamine residue, and a gene of heterologous glycoprotein, to obtain a transformed plant cell, a step of culturing the plant cell, and a step of recovering the culture medium of the plant cell.
Owner:PHYTON HLDG
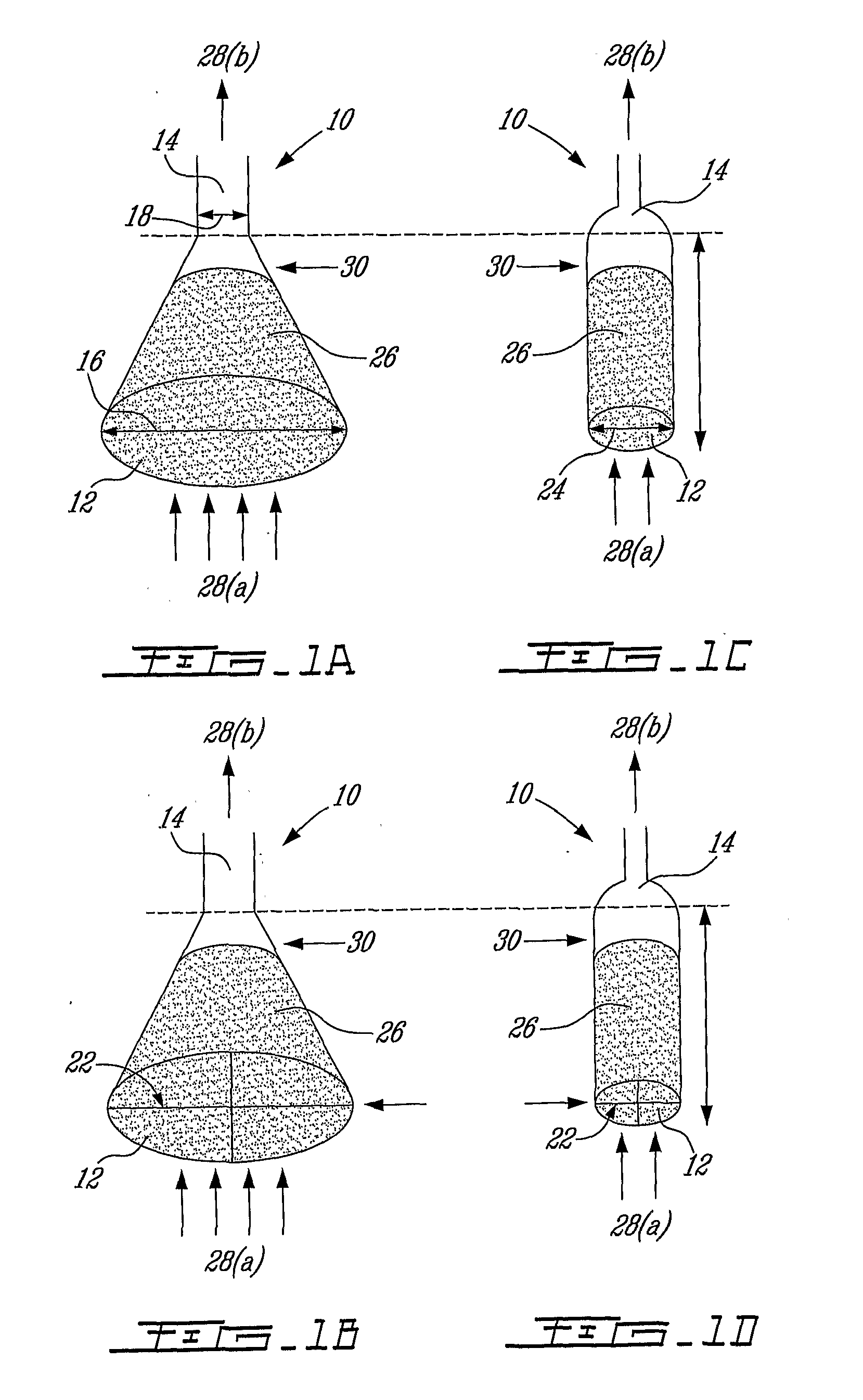
Cell culture system
InactiveUS20070037279A1Convenient mixingConvenient aerationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCulture cellShear stress
The present invention provides a novel apparatus to grow cells where the cultivation chamber (1) is partially filled with liquid cultivation medium and cells. Mixing and aeration is achieved by generating intermittently one single large gas bubble (6) at the bottom of the column bioreactor, the single large bubble width representing from 50 99% of the tank width, preferably from 60 to 99%, more preferably 98.5%. The culture medium flows out as a film between the large bubble and the inner wall of the bioreactor. This rising bubble allows mixing and aeration of the bulk. As the design of the invention is very simple, it is possible to manufacture it with flexible plastic material and use the apparatus as a disposable system. Moreover, such a mixing / aeration principle minimizes cell damages usually due to shear stress and small bubbles and allows easy and efficient scale-up from small scale to a larger one. Such a large-scale, efficient and disposable culture system can largely reduce production costs.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Method for establishing adventitious root cultivation system of Psammosilene tuniceoides W. C. Wu et C. Y. Wu and expanding cultivation method of Psammosilene tuniceoides W. C. Wu et C. Y. Wu
ActiveCN102771397AContinuous productionBalanced productionPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsPlantletCallus
According to the invention, young leaves or stems of plants of Psammosilene tuniceoides W. C. Wu et C. Y. Wu are taken as an explant to successfully induce callus of the Psammosilene tuniceoides W. C. Wu et C. Y. Wu, and a callus culture system of the Psammosilene tuniceoides W. C. Wu et C. Y. Wu under the conditions of light and dark cultivation is established to induce the differentiation of the callus to produce adventitious roots, thus establishing an adventitious root cultivation system of the Psammosilene tuniceoides W. C. Wu et C. Y. Wu. Moreover, the content of total saponins of the Psammosilene tuniceoides W. C. Wu et C. Y. Wu is determined, and the conditions and parameters of plant cell culture are further optimized, thus establishing a high-yield cell culture system of the Psammosilene tuniceoides W. C. Wu et C. Y. Wu. Therefore, the plant cells of the Psammosilene tuniceoides W. C. Wu et C. Y. Wu are cultured in a large scale to produce the adventitious roots which substitute for the original plant of the Psammosilene tuniceoides W. C. Wu et C. Y. Wu to be used as medicine.
Owner:成都市三禾田生物技术有限公司
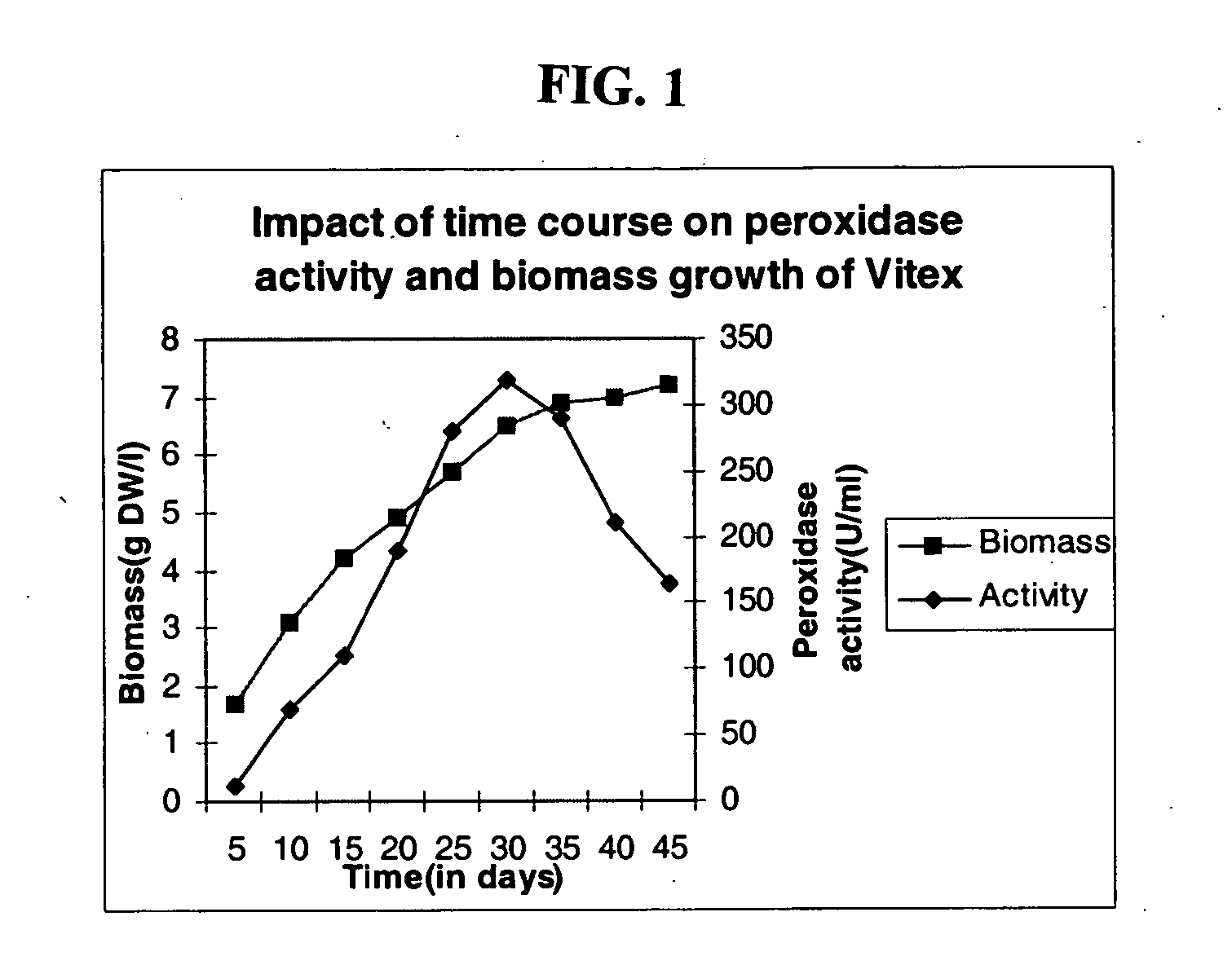
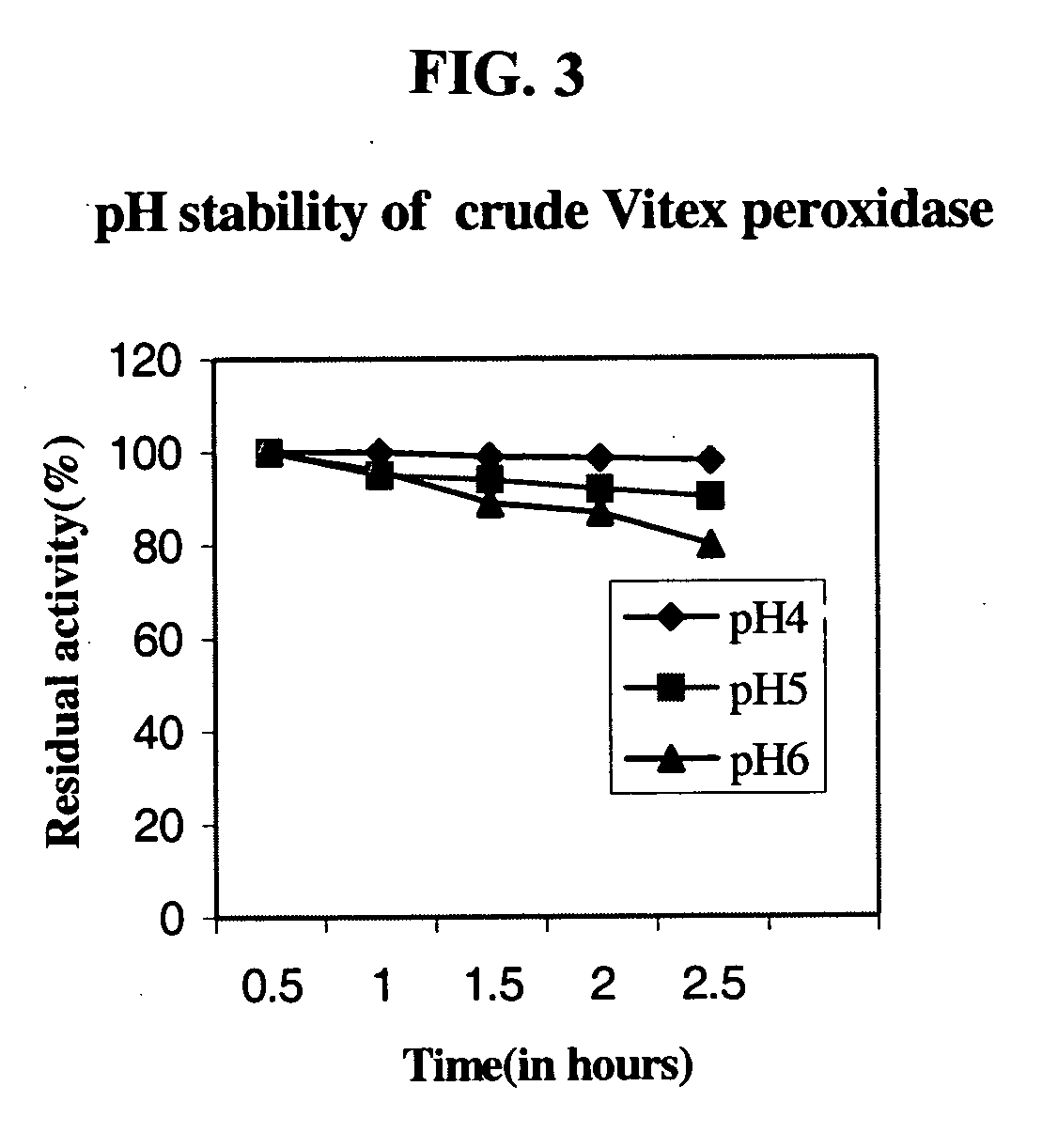
Production of peroxidase from plant cell and callus cultures
InactiveUS20060021084A1Simplifying recovery of enzymePromote recoveryOther foreign material introduction processesEnzymesPeroxidaseVitex negundo
A process for the production of peroxidase which comprises of establishing a plant cell culture producing cells from neem (Azardiracta indica) and nirgundi (Vitex negundo) wherein the peroxidase has higher enzymatic activity not reported earlier.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
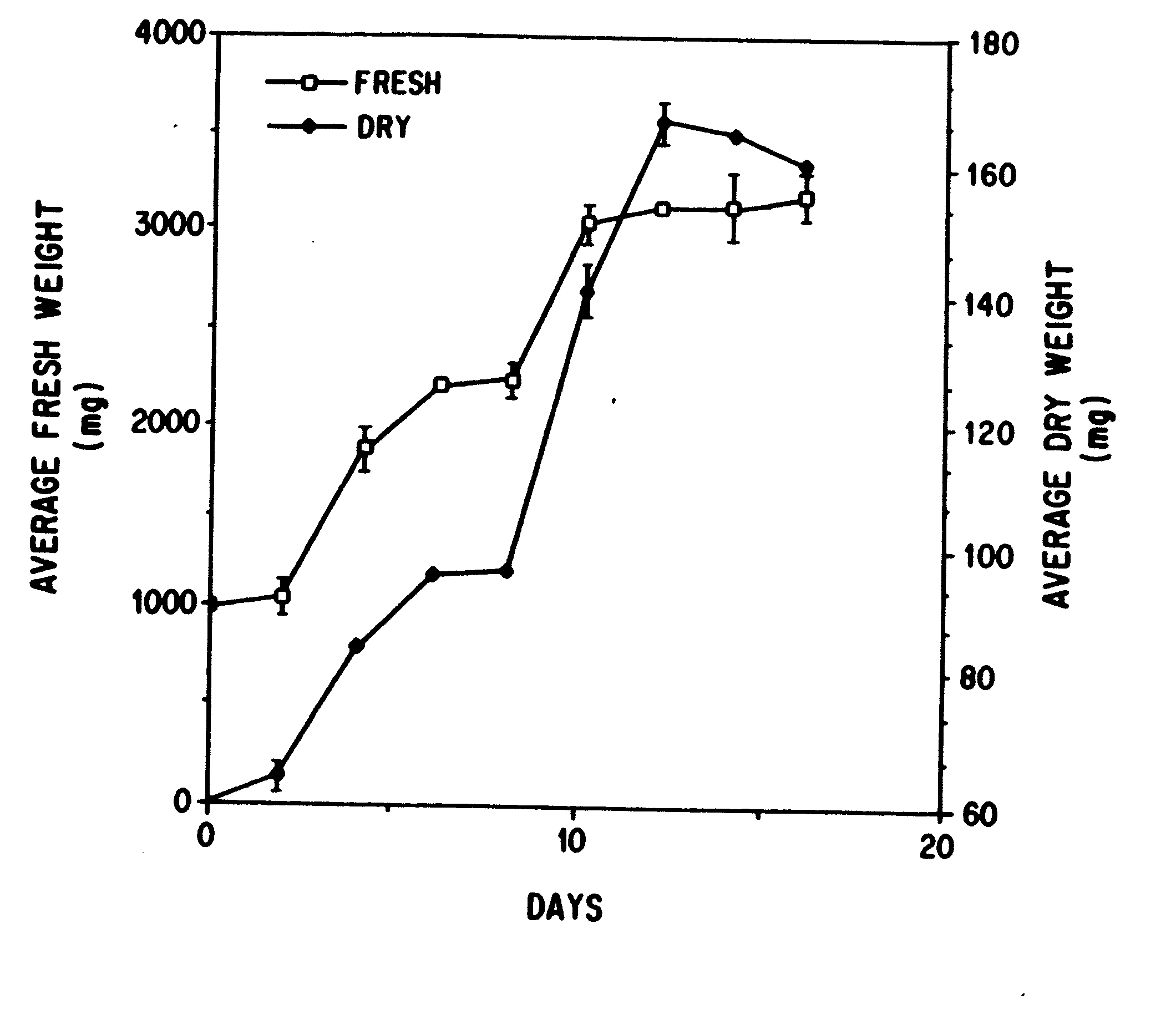
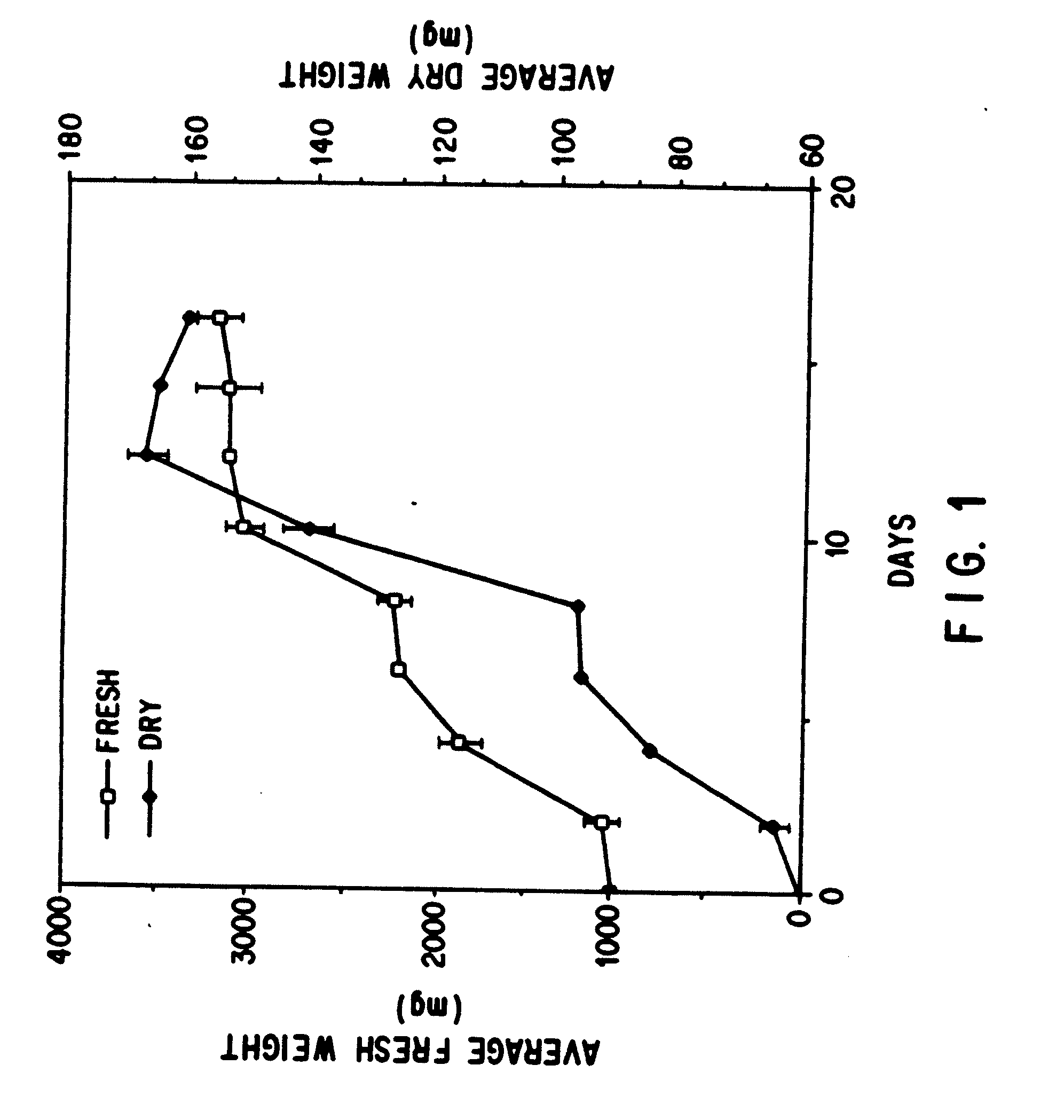
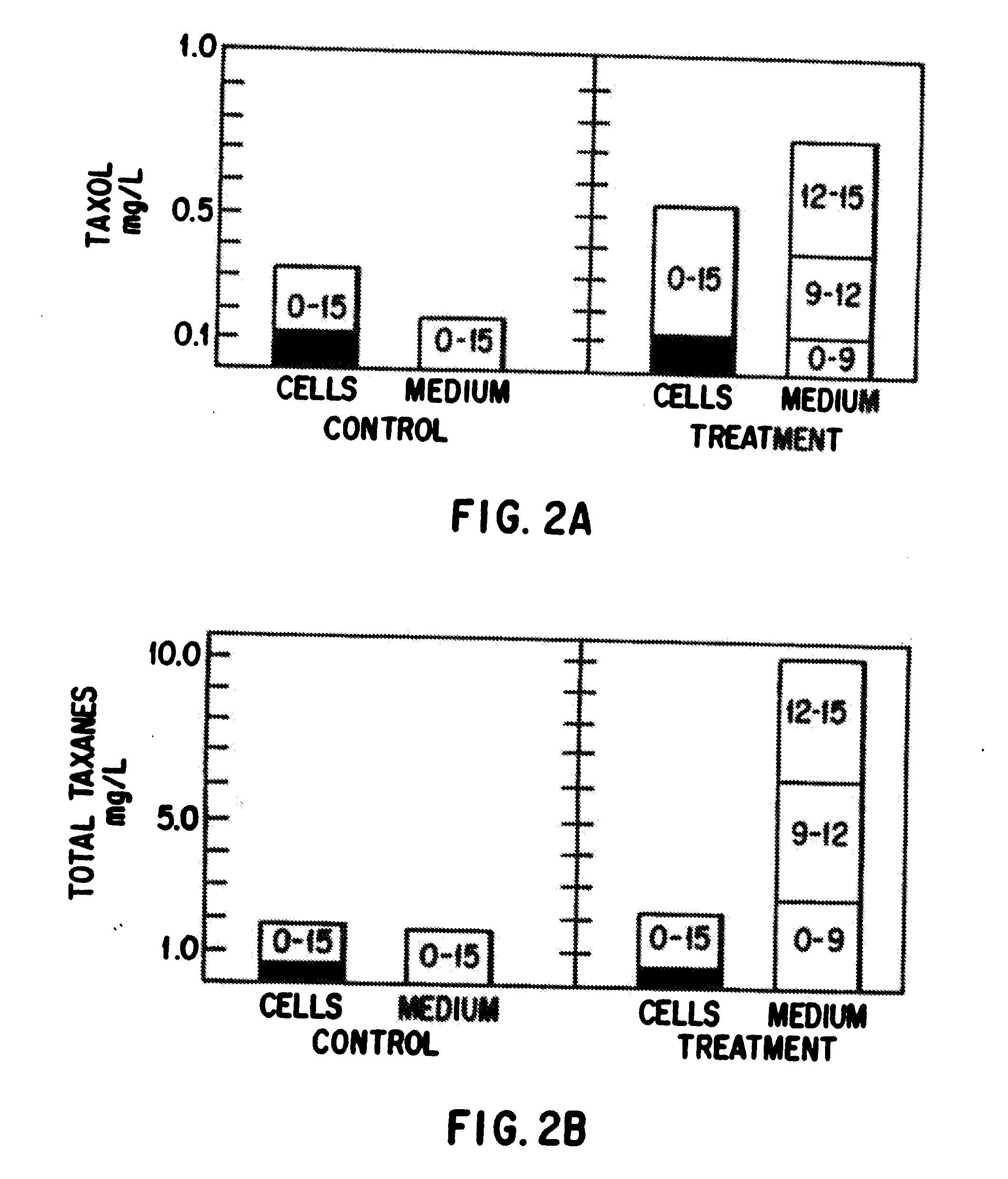
Enhanced production of taxol and taxanes by cell cultures of Taxus species
InactiveUS7264951B1Promote rapid growthIncrease cell densityOrganic chemistryTissue cultureBiotechnologyTaxus species
This invention provides methods whereby taxol, baccatin III, and other taxol-like compounds, or taxanes, can be produced in very high yield from all known Taxus species, e.g., brevifolia, canadensis, cuspidata, baccata, globosa, floridana, wallichiana, media and chinensis. Particular modifications of culture conditions (i.e., media composition and operating modes) have been discovered to enhance the yield of various taxanes from cell culture of all species of Taxus. Particularly preferred enhancement agents include silver ion or complex, jasmonic acid (especially the methyl ester), auxin-related growth regulators, and inhibitors of the phenylpropanoid pathway, such as 3,4-methylenedioxy-6-nitrocinnamic acid. These enhancement agents may be used alone or in combination with one another or other yield-enhancing conditions. While the yield of taxanes from plant cell culture of T. chinensis is particularly enhanced by use of one or more of these conditions, yield of taxanes for all Taxus species has been found to benefit from use of these conditions.
Owner:PHYTON HLDG
Method for biosynthesizing abietane diterpenoids by culturing cells from cloverleaf
InactiveCN102295545ARealize artificial controllable productionEasy to separate and purifyOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationAlkaneOrganism
The invention relates to a plant cell culture technology, in particular to a method for biosynthesizing abietane diterpenoid compounds by using cephalotaxus fortune culture cells. The method comprises the following steps of: placing cephalotaxus fortune cells in a common culture medium, and culturing, wherein50 to 150g of the cells are inoculated in each liter of wet weight of the culture medium; and adding an inducer at the final concentration of 10 to 2,000 mu M and 50 to 200g of adsorbent into each liter of culture medium at the initial stage of cell exponential growth, wherein the inducer is an abiological inducer or fungal elicitor. The method is a biosynthesis method and is stable and environment-friendly; and products are completely adsorbed onto the adsorbent, so that the operation process of separation and purification is greatly simplified, the cost is reduced and industrial production is easy to realize. Meanwhile, seven abietane diterpenoid compounds comprising a new compound are synthesized. The abietane diterpenoid compounds have high bioactivity, and are important lead compounds, and the technology has important commercial application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
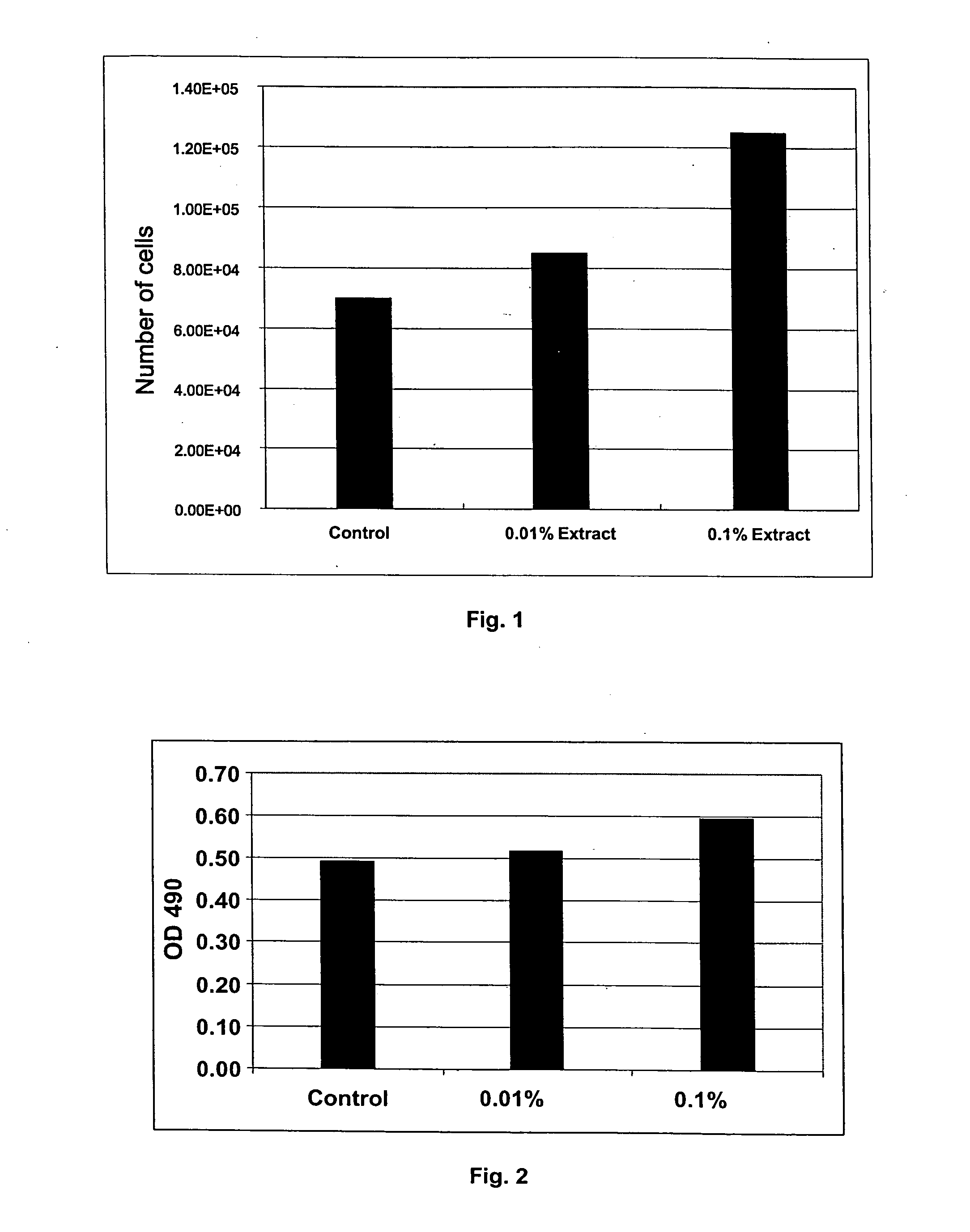
Production and Extraction of Procyanidins from Plant Cell Cultures
InactiveUS20120021080A1High yieldIncrease productionCosmetic preparationsBiocideTheobromaBetacyanins
Provided herein are methods of making cocoa polyphenol preparations, which methods comprises harvesting cocoa polyphenols, for example, procyanidins, from the cell suspension culture. In examples of these methods, the resultant cocoa polyphenol preparation is substantially (or in some cases, completely) free of detectable caffeine and theobromine, and more generally substantially free of xanthine alkaloids. Methods of producing a cell suspension culture of cacao cells are also described, including cell suspension cultures useful for making cocoa polyphenol and, more specifically, procyanidin preparations. Theobroma and Herrania sp cell suspension cultures and cocoa polyphenol preparations made therefrom are also provided, in particular xanthine alkaloid-free (or caffeine- and / or theobromine-free) cocoa polyphenol preparations.
Owner:CALIFORNIA CULTURED INC
Rna virus-derived plant expression system
ActiveUS20070044170A1Reduced expression levelHigh frequencyMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesHeterologousVirus
A process of expressing a sequence of interest in a plant, plant part, or plant cell culture, comprising: (a) providing a plant, plant part, or plant cell culture containing in cell nuclei a heterologous DNA having a sequence encoding an RNA replicon operably linked or linkable to a transcription promoter, wherein said sequence encoding an RNA replicon contains (i) sequences for replicon function of said RNA replicon, said sequences being derived from a sequence of a plant RNA virus, (ii) a sequence of interest, whereby said sequences for replicon function exhibit at selected localities of said sequences of said plant RNA virus functionconservative differences from said sequence of said plant RNA virus, said differences causing an increased frequency of replicon formation compared to an RNA replicon not exhibiting said differences; and (b) causing expression of said sequence of interest.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP +1
Method for gaining panax japonicus secondary metabolite by using panax japonicus cell culture and biological transformation technique
The invention discloses a method by using panax japonicus cell culture and biological transfer technology to obtain secondary metabolites and pertains to plant cell culture engineering field. An improved RW culture medium is added with crane sugar, plant growth hormone and cytokinin and then coagulant; the obtained mixture is made into an induction culture medium after being disinfected in high temperature and then cooled; explants of panax japonicus are inoculated in the induction culture medium under an aseptic condition to be inducted to form callus; after an expansion, a plurality of cells are obtained; the expanded callus in the synthetic medium is inoculated into synthetic culture solution and then panax japonicus saponin crude extracts and byproducts thereof can be obtained through the extraction of cells from the solvent, thereafter the panax japonicus saponin, panax japonicus polysaccharide and other compounds can be obtained through purification. By adopting the method of the invention, secondary metabolites of the panax japonicus can be produced with low cost, short culture cycle, year-round production and no natural environmental limit.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Cosmetic Preparation and Method for Preparing the Same
The present invention relates to the use of dedifferentiated plant cells in cosmetic preparations for protecting of stem cells against intrinsic and extrinsic stress factors, in particular for promoting proliferation of stem cells and for protecting them against apoptosis. In particular, the invention relates to the use of dedifferentiated plant cells from fruits of Malus domestica (Apple) cultivar Uttwiler Spaetlauber. Further, the invention relates to a method for cultivating of dedifferentiated plant cells, as well as to the preparation of extracts of plant cell cultures which are suitable for such applications.
Owner:MIBELLE
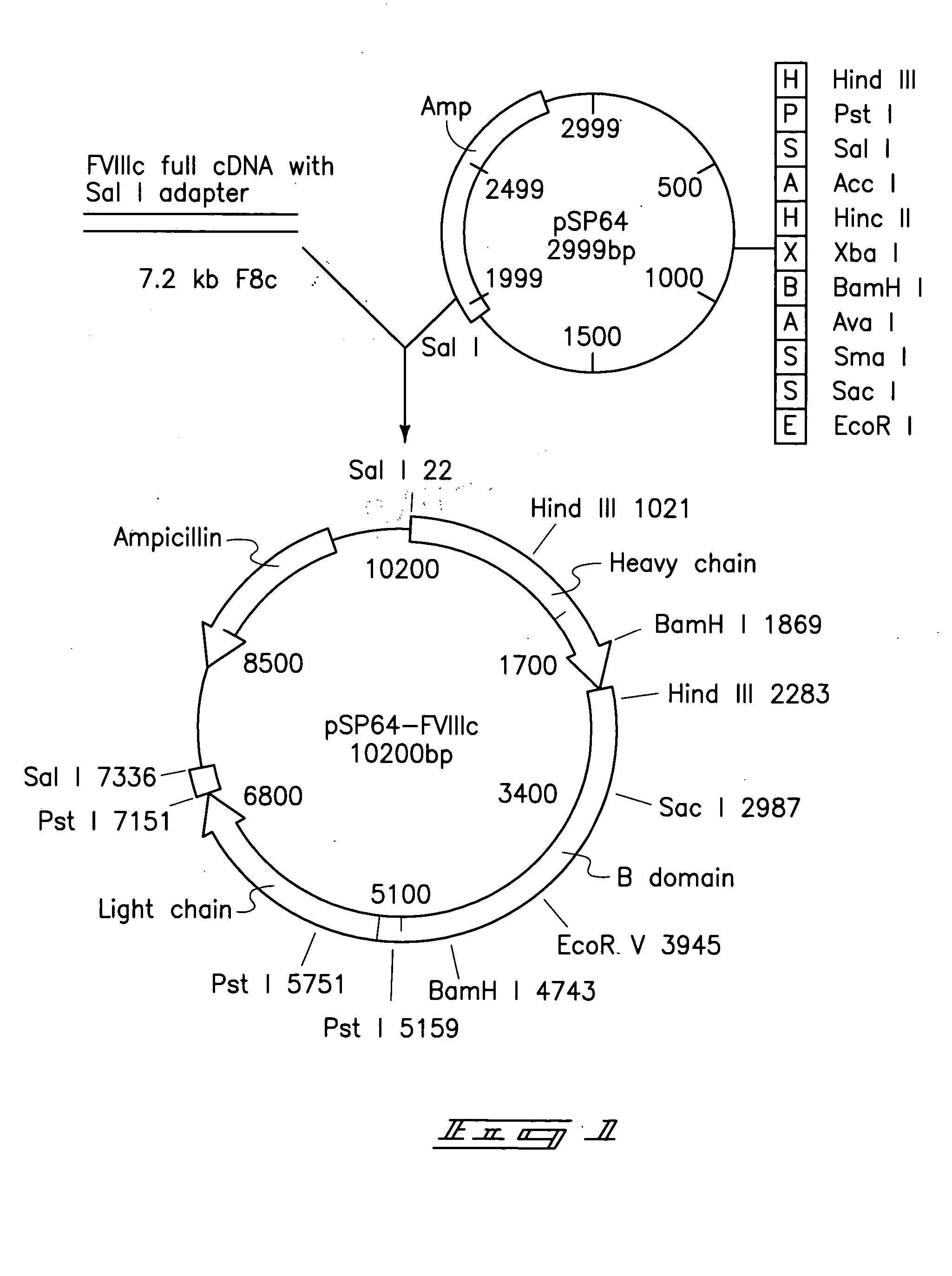
Production of human coagulation factor VIII from plant cells and whole plants
InactiveUS20050060775A1Mammal material medical ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsFactor VIII ActivityPlant tissue
The invention includes methods for production of a polypeptide having factor VIII activity by introduction of a polynucleotide construct into a plant cell. The construct includes an encoding sequence for a polypeptide of coagulation factor VIII or a functional variant thereof. The plant cell is cultured or regenerated into a plant and the polypeptide or functional variant of factor VIII is expressed therein. The invention also includes vectors, plant cells, plant tissues, plants and seeds containing a polynucleotide sequence encoding a functional variant of human coagulation factor VIII. The invention further includes a recombinant DNA molecule having a promoter which is functional in plants operably linked to a coding sequence which codes for a polynucleotide having coagulation factor VIII activity.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Enhanced production of taxol and taxanes by cell cultures of taxus species
This invention provides methods whereby taxol, baccatin III, and other taxol-like compounds, or taxanes, can be produced in very high yield from all known Taxus species, e.g., brevifolia, canadensis, cuspidata, baccata, globosa, floridana, wallichiana, media and chinensis. Particular modifications of culture conditions (i.e., media composition and operating modes) have been discovered to enhance the yield of various taxanes from cell culture of all species of Taxus. Particularly preferred enhancement agents include silver ion or complex, jasmonic acid (especially the methyl ester), auxin-related growth regulators, and inhibitors of the phenylpropanoid pathway, such as 3,4-methylenedioxy-6-nitrocinnamic acid. These enhancement agents may be used alone or in combination with one another or other yield-enhancing conditions. While the yield of taxanes from plant cell culture of T. chinensis is particularly enhanced by use of one or more of these conditions, yield of taxanes for all Taxus species has been found to benefit from use of these conditions.
Owner:DFB BIOTECH
Method for establishing fraxinus mandshurica suspension culture system
InactiveCN102888379AReduce manufacturing costCan realize industrial productionMicroorganism based processesPlant cellsFraxinusCulture mediums
The invention provides a method for establishing a fraxinus mandshurica suspension culture system. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) using a fraxinus mandshurica stem section as an explant, inducing callus, and obtaining the callus on a WPM solid culture medium added with hormone TDZ and BA, cane sugar and agar; 2) inoculating the callus obtained in the step 1) into the WPM liquid culture medium added with hormone BA and 2, 4-D and cane sugar, and oscillating and culturing; and 3) carrying out subculture for 10-15days, and continuously carrying out subculture for 3-5 times to obtain a suspension cell line which uniformly grows and is rapidly propagated. The method has the characteristics that the propagation speed is high, the culture scale is large and a great amount of uniform plant cell cultures are provided.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +2
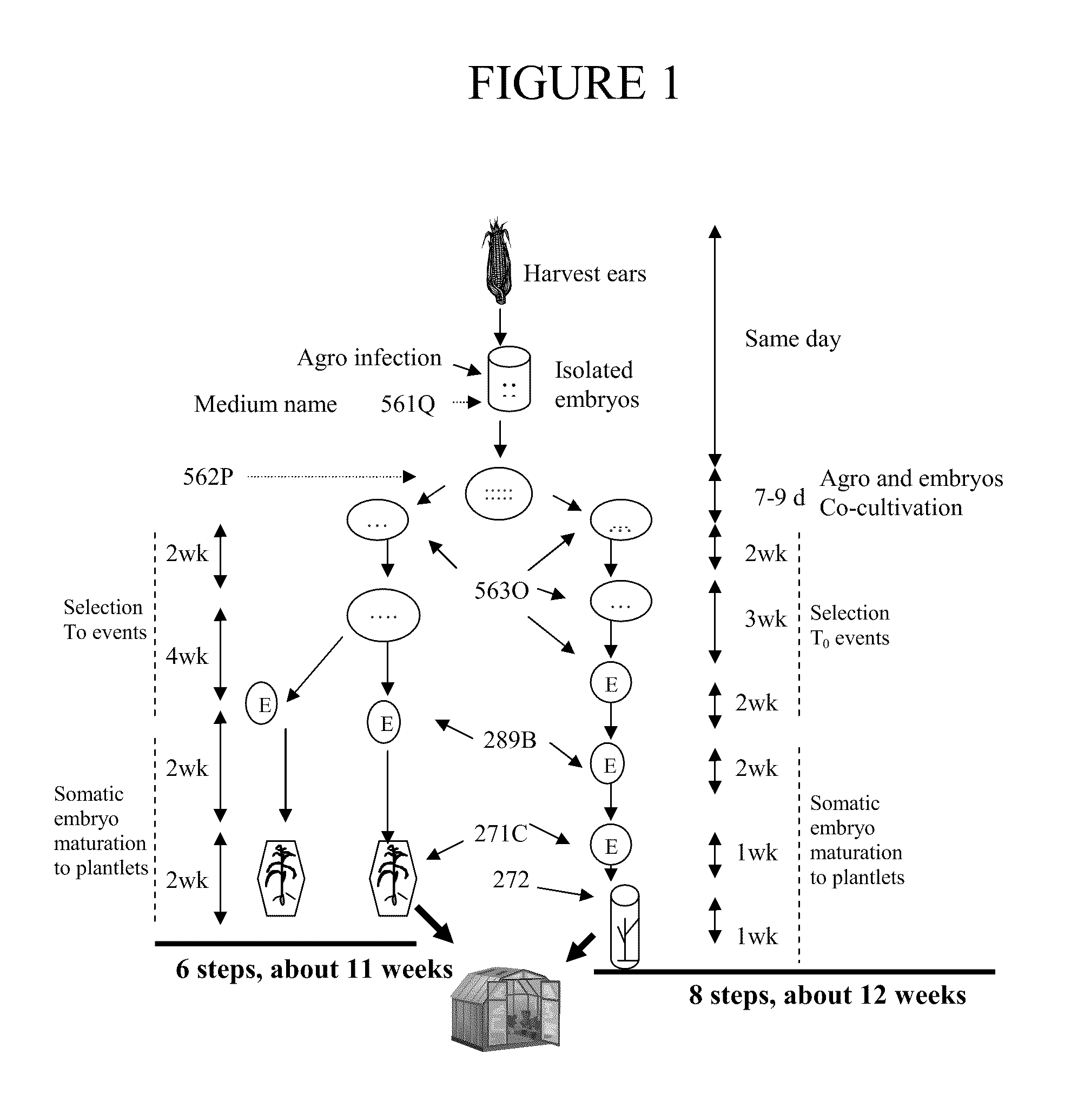
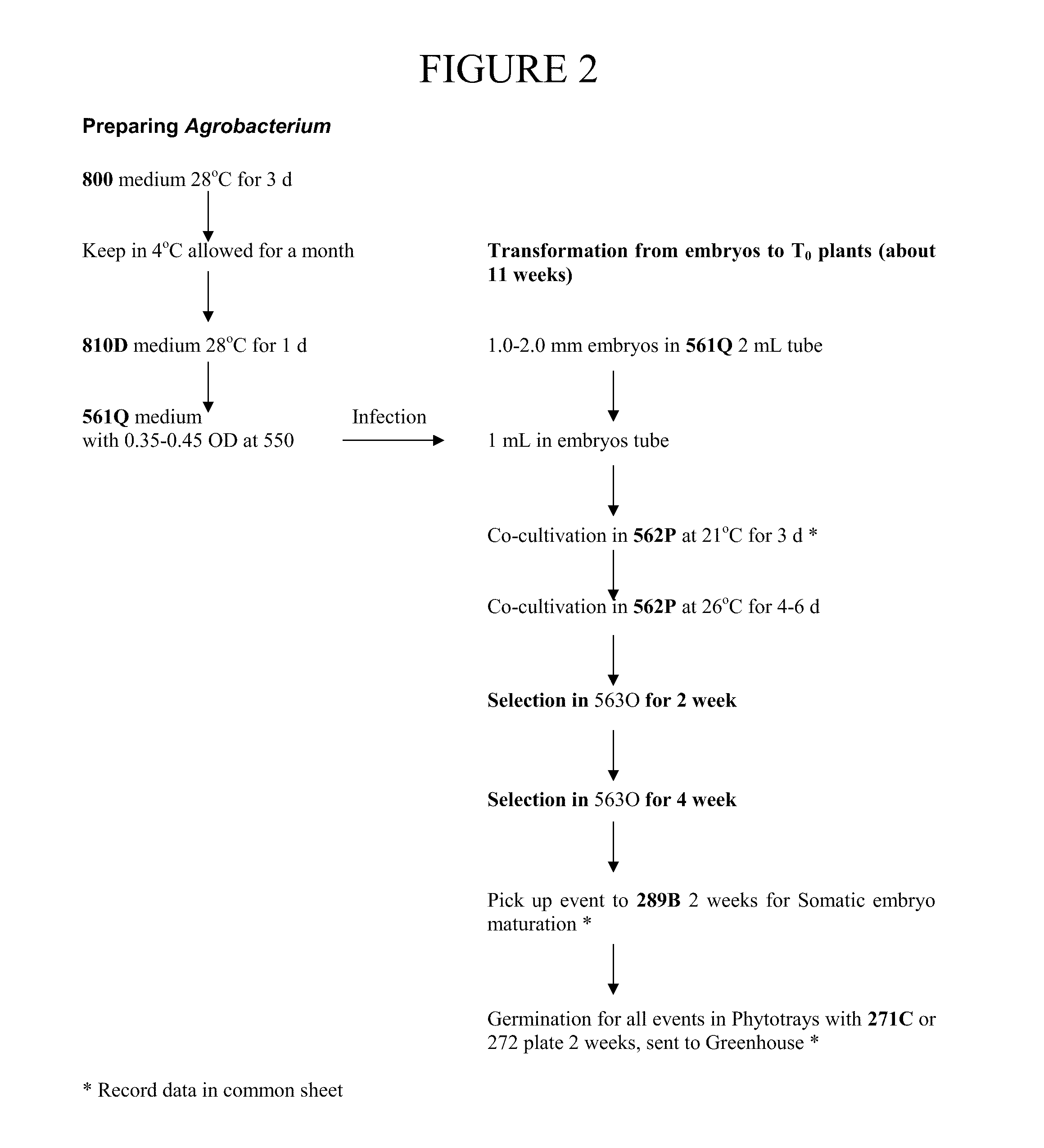
Increasing time-efficiency of high-throughput transformation processes
The methods provided relate to efficient methods for transforming isolated, immature maize embryos and for producing transgenic maize plantlets. The time required for the production of the transgenic plantlets and subsequent plants is significantly decreased compared to conventional methods. The methods also relate to decreasing the selection time of transgenic events and regenerating a transgenic maize plantlet from transgenic somatic embryos from the events in a plant cell culture vessel that allows for root formation and plantlet elongation in the same plant cell culture vessel.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Antiglyphosate gene and its use
A roundup-resisting gene, its related protein polypeptide, protein, plasmid and plant cell and their uses are disclosed. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ ID NO:3. It has better roundup resistance and can remove weed selectively. It can be used to breed and culture plant cell.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Skin external-use preparation composition comprising edelweiss plant cell culture extracts and preparation method of skin external-use preparation composition
ActiveCN106924316AImprove wrinklesHeal woundsCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsNon toxicityMedicine
The invention relates to a skin external-use preparation composition with anti-inflammation and anti-ageing effect, comprising edelweiss plant cell culture extracts and a preparation method of the skin external-use preparation composition, in particular to a skin external-use preparation composition with the anti-inflammation and anti-ageing effect, comprising plant cell cultures and adventitious-root cultures induced from edelweiss fronds, or extracts of the cultures, and a preparation method of the skin external-use preparation composition. The skin external-use preparation composition comprising the edelweiss plant cell or adventitious-root cultures or the extracts of the cultures has the advantages of non-toxicity on skin cells and effects such as improving skin wrinkles, curing wounds, shrinking pores, inhibiting sebum secretion and improving acne.
Owner:BIO FD&C CO LTD
Method for induction and subculture of taxus chinensis leaf callus and culture medium used by method
InactiveCN102640710AHigh induction rateFast growth ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsTaxus wallichiana var. maireiPlant cell culture
The invention discloses a method for induction and subculture of taxus chinensis leaf callus. The method comprises the following steps of: disinfecting tender leaves (which are taken as an explants) of south taxus chinensis growing in the current year, inoculating to a specific induced culture medium, selecting loosen and flaxen callus after culturing for 20 days in dark at the temperature of 20-22 DEG C, transferring into a specific subculture medium, and subculturing 20 days at the temperature of 20-22 DEG C, thus obtaining the taxus chinensis leaf callus. The method for the induction and subculture of the taxus chinensis leaf callus provided by the invention has the characteristics of high inductivity, short callus time, rapid growth rate, low pollution rate and the like; and the method achieves the purpose that the taxus chinensis callus is cultured on large scale through a plant cell culture technology.
Owner:SHANGHAI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation of vaccine master cell lines using recombinant plant suspension cultures
InactiveUS20070107086A1Overcome the lack of robustnessImprove stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesCell culture mediaCryopreservation
The subject invention provides a plant cell culture for producing proteinaceous agents comprising a plant cell line stably transformed to express a transgene encoding a proteinaceous agent and a growth medium which supports the growth of said plant cell culture but which does not support the growth of Mycoplasmataceae and contains no materials of animal origin. The plant cell line is capable of being continuously passaged such that consistent transgene expression is maintained during passaging. The plant cell line is also capable of being cryopreserved such that consistent transgene expression is recovered upon recovery from cryopreservation.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com