Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Packet scheduling algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
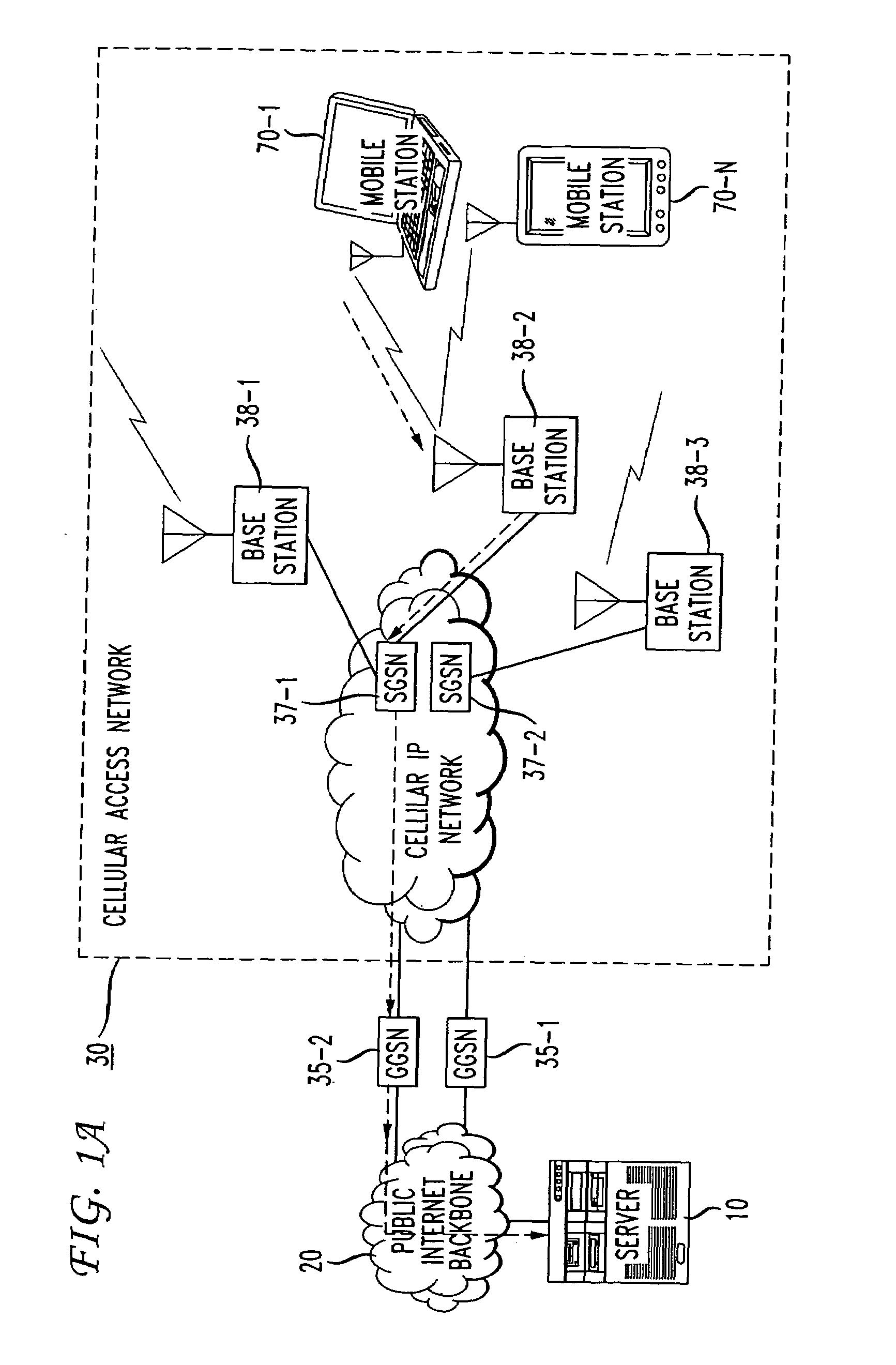
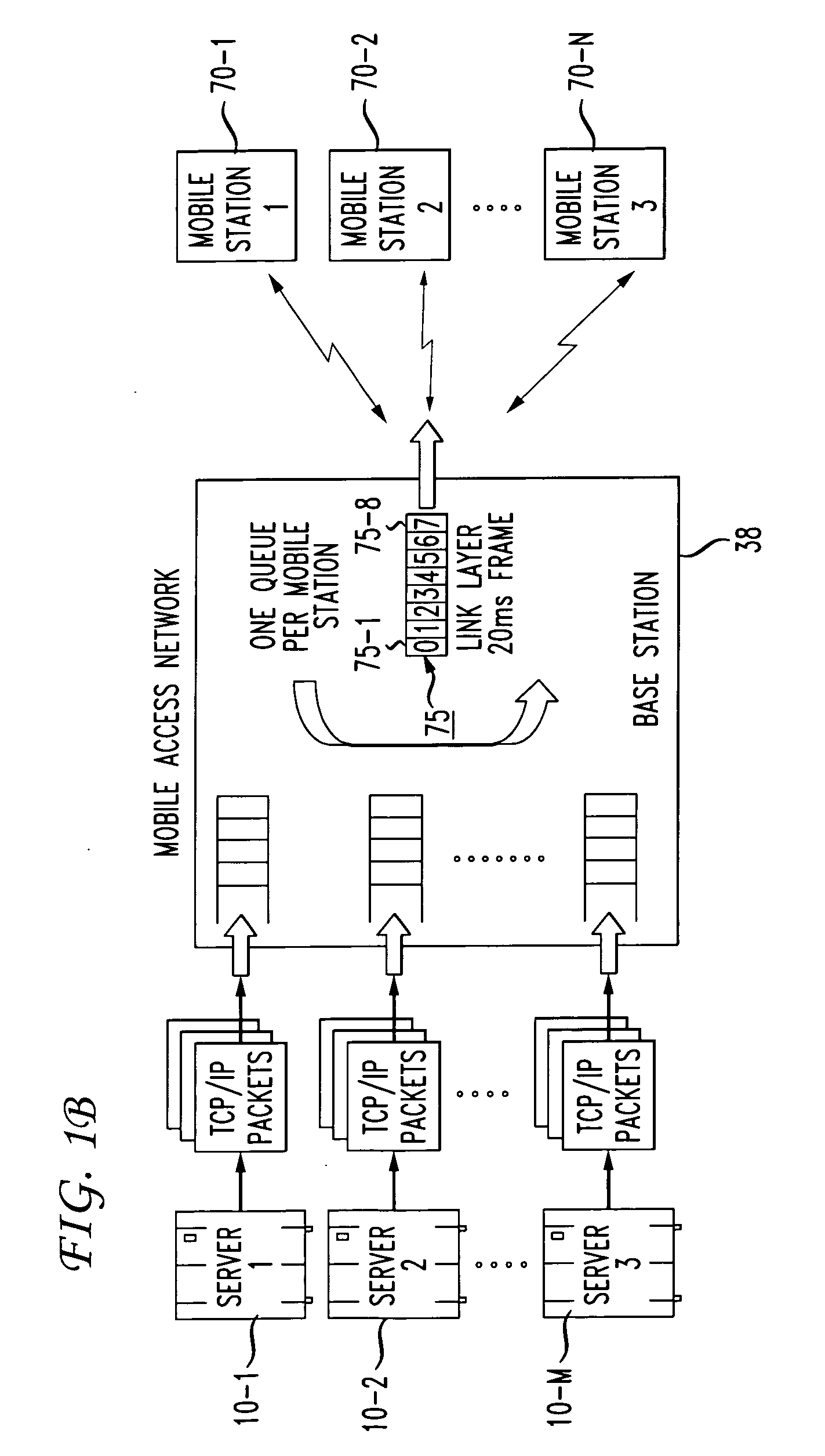
Integrated packet latency aware QoS scheduling using proportional fairness and weighted fair queuing for wireless integrated multimedia packet services
ActiveUS20070041364A1Network traffic/resource managementIn VoIP networksPacket communicationPacket scheduling
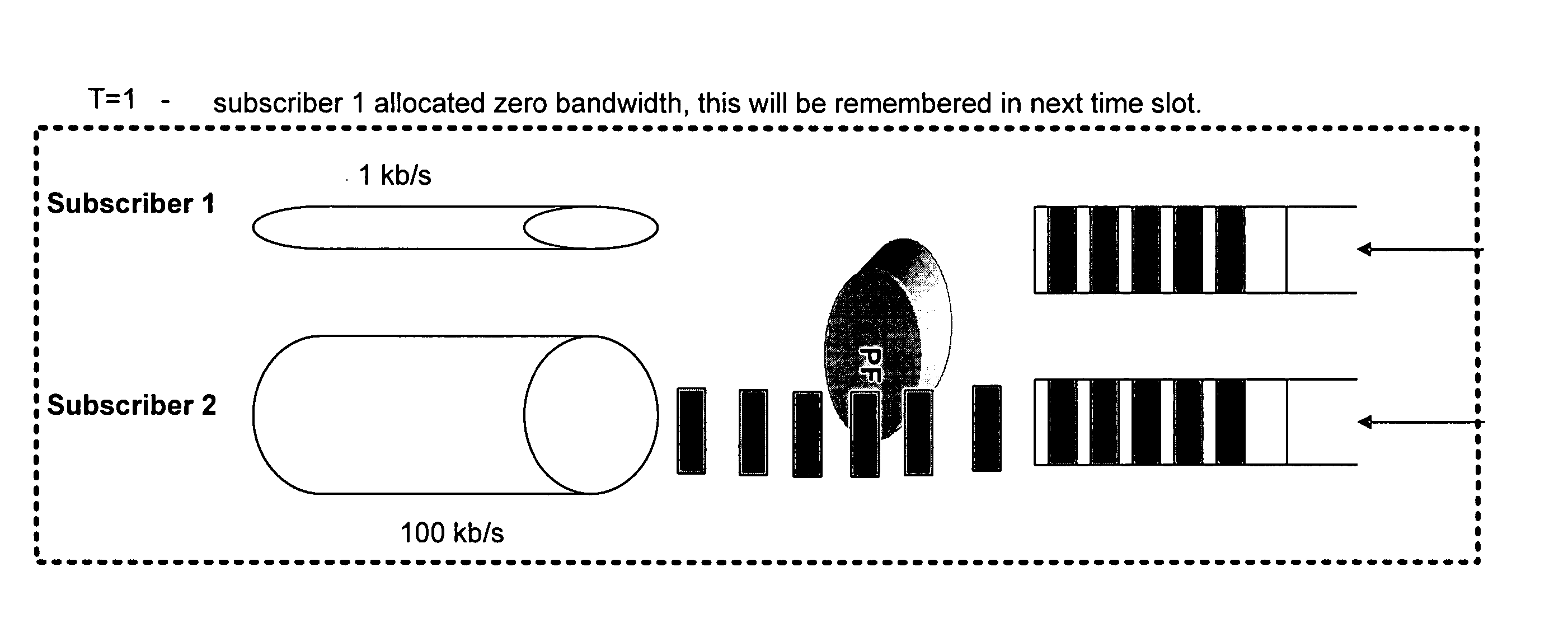
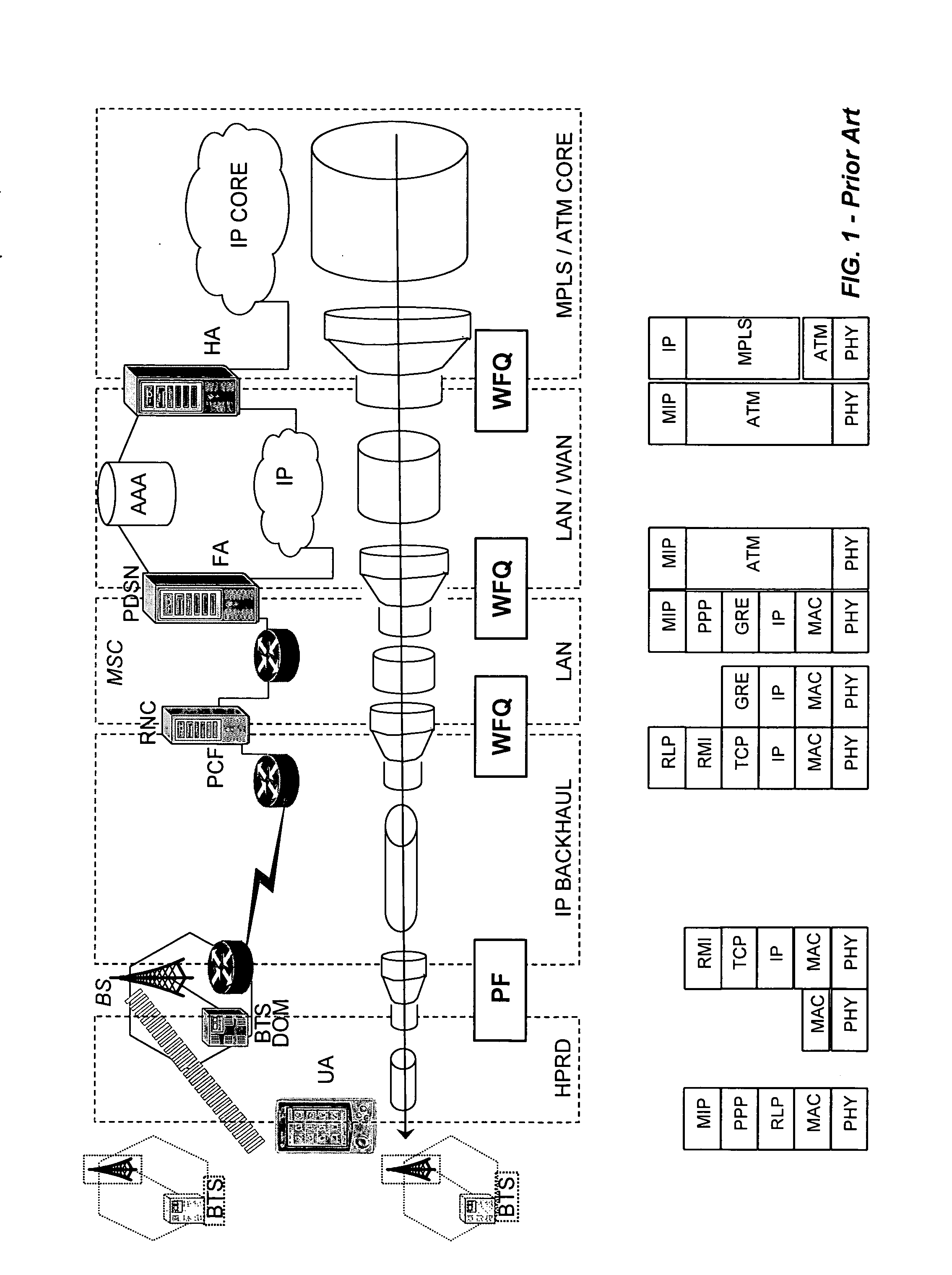
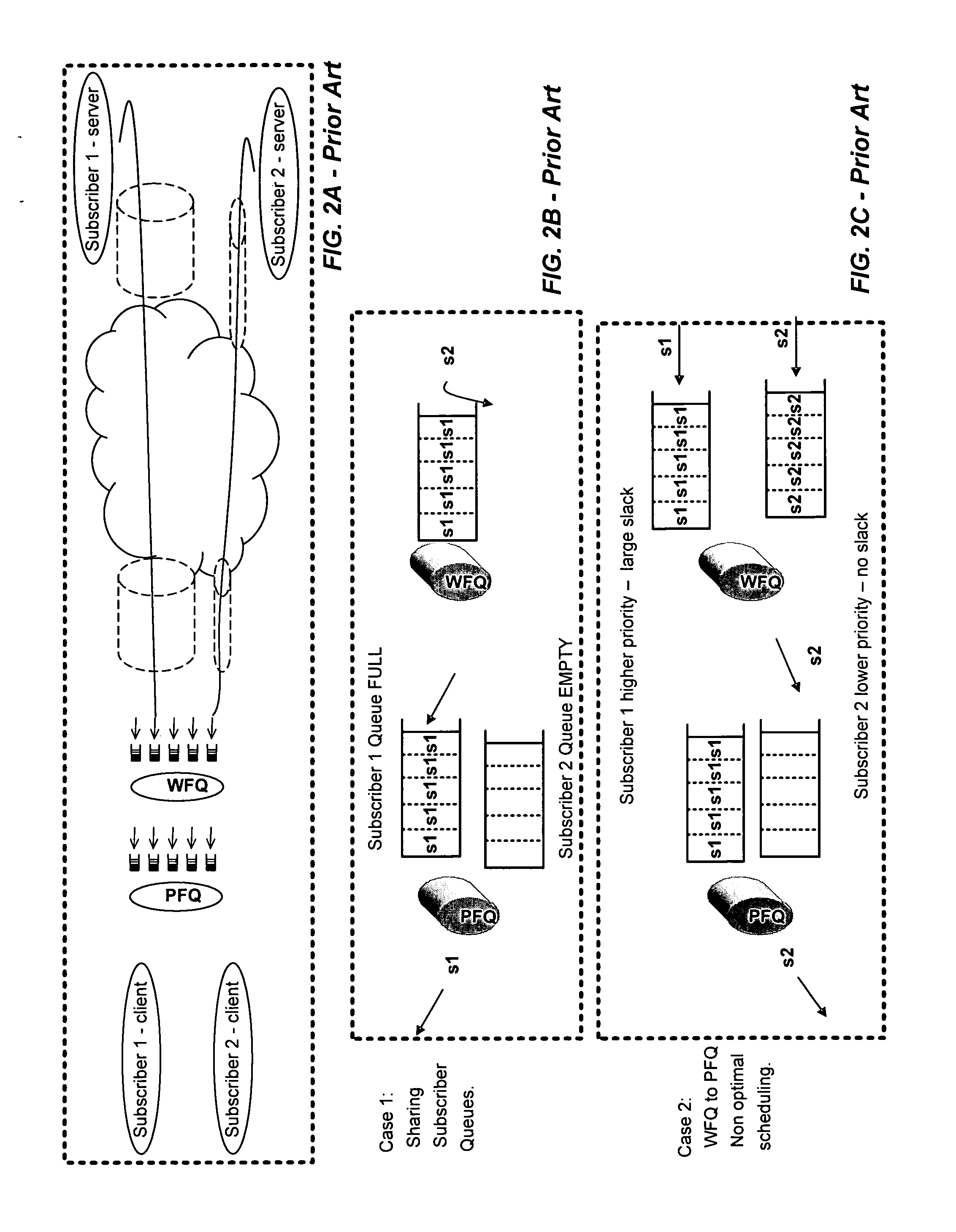
Packet communication networks for transmission to wireless subscriber devices utilize both wireline and wireless packet routing components. The routing elements of these two different types often implement different packet scheduling algorithms, typically a form of Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ) in the wireline portion of the network and Proportional Fairness (PF) queuing in the wireless domain. To improve resource allocation and thus end to end quality of service for time sensitive communications, such as integrated multimedia services, the present disclosure suggests adding the notion of slack time into either one or both of the packet scheduling algorithms. By modifying one or more of these algorithms, e.g. to reorder or shuffle packets based on slack times, global optimal resource allocations are possible, at least in certain cases.
Owner:CELLCO PARTNERSHIP INC
Channel efficiency based packet scheduling for interactive data in cellular networks
InactiveUS7046678B2More modulation schemeEffectively channelError preventionTransmission systemsTrade offsLink adaptation
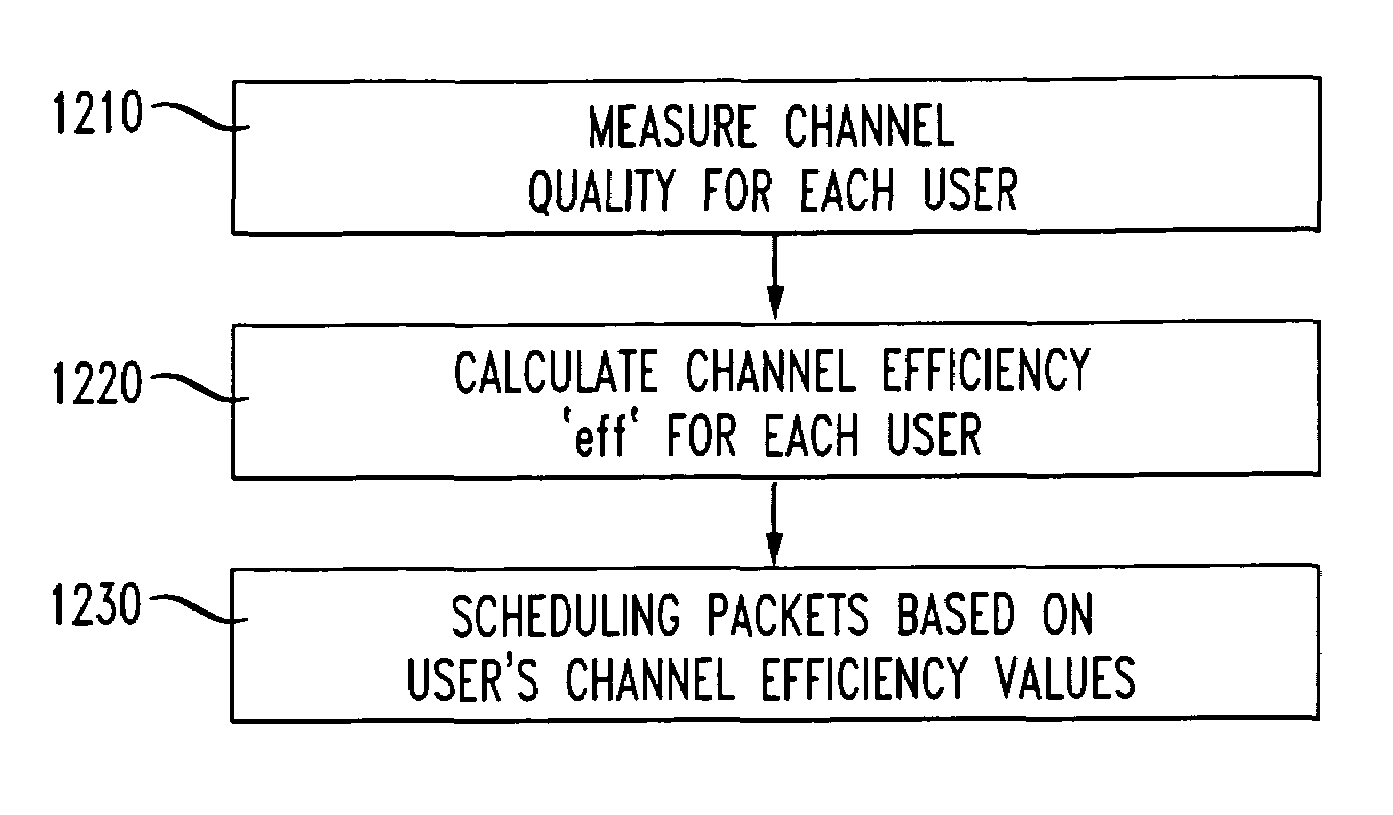
The present packet scheduling algorithm gives cellular network operators greater flexibility in adjusting the way resources are allocated among interactive best-effort data users. Best effort data users with different radio link qualities may have different amounts of data delivered to them using the same amount of radio resource. In the context of link adaptation, this characteristic complicates the fairness issue in cellular environments and has a profound impact on the overall system performance. As a result, the present packet scheduling algorithm is capable of allocating radio resource dynamically, not only based on channel conditions, but also to achieve different performance trade-offs among users with different link qualities. According to the algorithm, channel quality is determined for each user, channel efficiency is calculated and the channel efficiency value is used as the primary factor in weighting the delivery of packets to (or from) a given user. In a packet schedule weighting equation, a value of exponent may be varied from negative to positive to give good (or bad) users better service. However, performance of users with bad channel qualities degrades the performance of good channel users in a disproportionate manner. It is shown that it is frequently preferable to favor users with good channel qualities.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
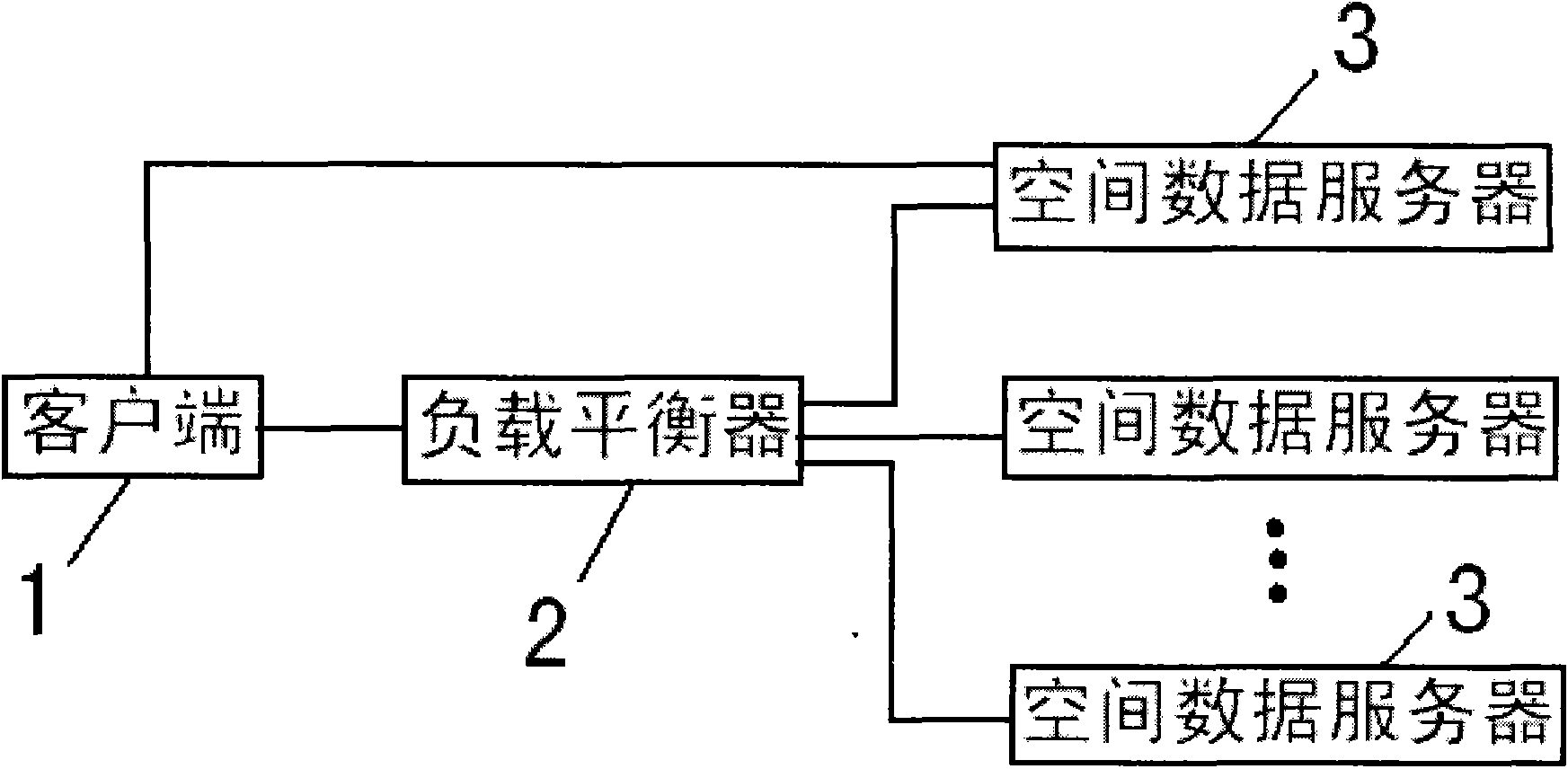
Dynamic load balancing method based on spatial geographical locations
InactiveCN101557344AImprove load balancing effectImprove Cache utilizationData switching networksDynamic load balancingLoad distribution
The invention relates to a dynamic load balancing method based on spatial geographical locations. The method comprises the following steps: a redirection load distribution model is adopted and a load indicator is selected; a dynamic packet-scheduling algorithm based on spatial geographical locations is adopted to realize the load balance of a spatial data server cluster. The method has the advantages: the dynamic load balancing method based on spatial geographical locations is adopted to optimize the load balancing performance of spatial data servers; the redirection load distribution model is adopted, which eliminated the bottleneck of a load balancing unit; and the dynamic packet-scheduling algorithm based on spatial geographical locations is adopted, thereby improving the Cache utilizing rate of the spatial data servers. The implementation of the dynamic load balancing method provides a solid network basis for the promotion and application of global geographic information and brings great convenience to applying geographic information in every aspect of human life.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
A packet dispatching method based on avoidance mechanism in WLAN
InactiveCN101150469AIncrease profitImprove compatibilityData switching by path configurationWireless communicationGroup schedulingNetworked system
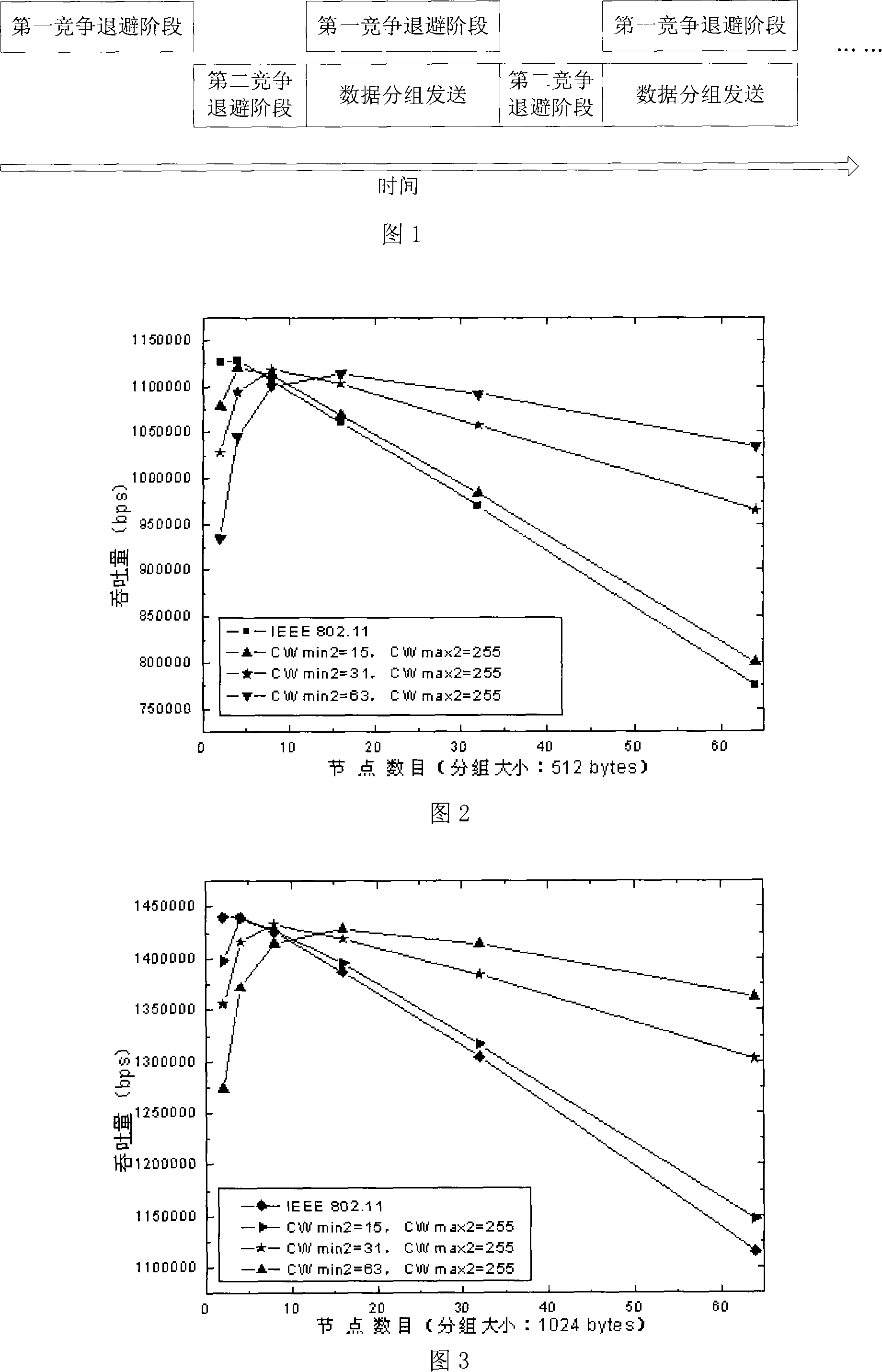
The invention discloses a group scheduling method adopted in the wireless LAN based on a back-off system. The group scheduling method includes a first competition back-off phase and a second competition back-off phase which are respectively provided with a corresponding competition window. The competition window for the first competition back-off phase has a broader range (1023 as the maximum value) while the competition window for the second competition back-off phase has a smaller range (255 as the maximum value). The nodes cannot visit the channels unless the data groups complete the two back-off phases in order. The group scheduling algorithm for the invention is characterized in that when the two nodes in the network are connected by using RTS / CTS frames, other nodes in the network detect the CTS frame. At the same time, the back-off timers which are not zero in the nodes during the first competition phase continue to back off. The invention includes two back-off phases, while the transmission of data groups and competition back-off are carried out simultaneously. Therefore, the utilization ratio of channels in the highly loaded network system can be greatly increased.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Systems and methods for mutiplexing MPEG services for IP networks
InactiveUS20100150182A1Time-division multiplexSelective content distributionTraffic capacityMultiplexer
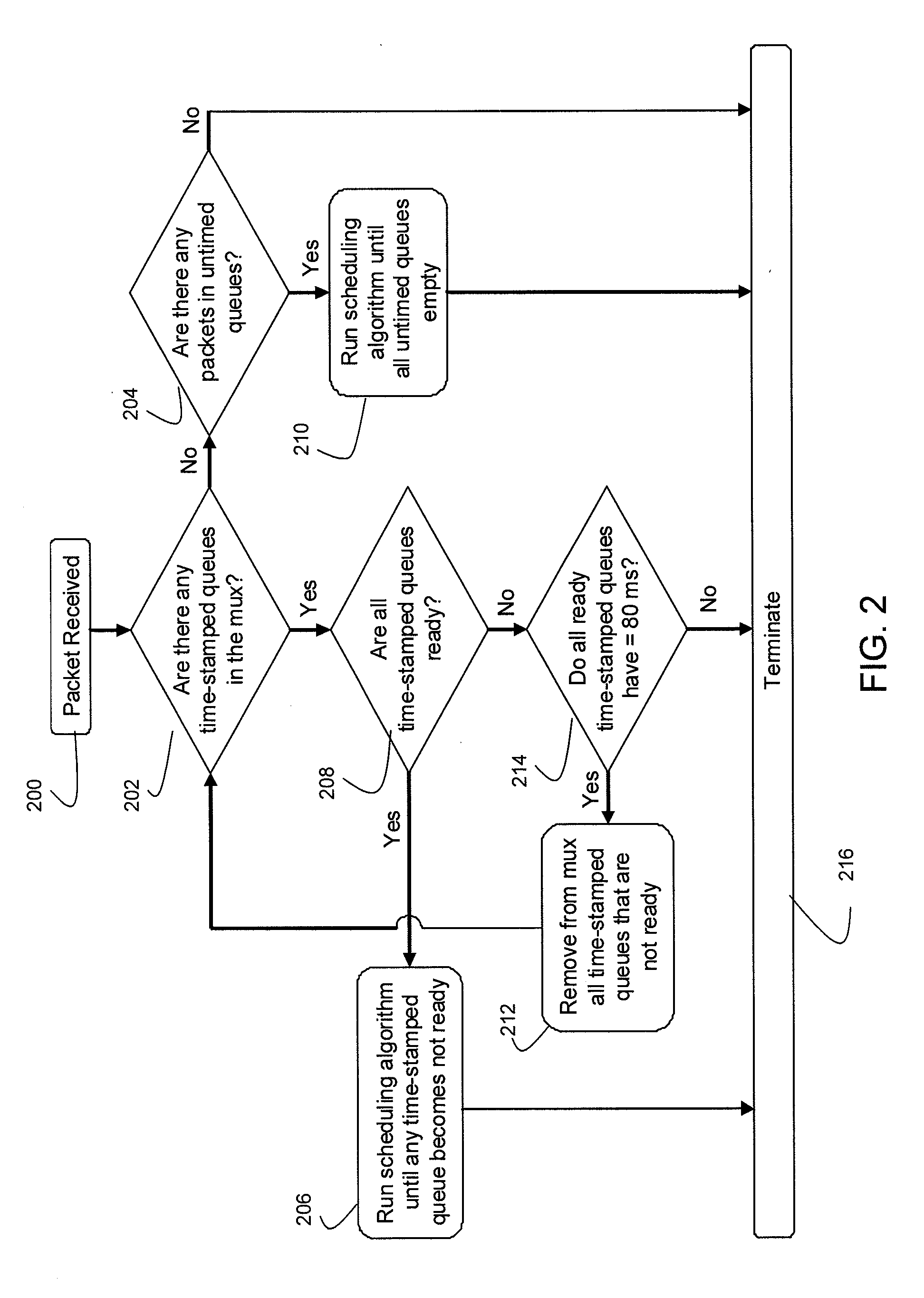
A multiplexer handling different types of traffic in different queue types, including in one embodiment time-stamped content such as in the form of MPEG service data, untimed content such as in the form of other variable bit rate data, and periodic tables, such as in the form of MPEG program specific information, allocates a tag to each packet, which is used to schedule packets for transmission. A tagging algorithm tags each packet in the queue, and a packet scheduling algorithm uses the tag to determine which packet is next to be transmitted, and a control algorithm determines when the scheduling algorithm will be executed. The algorithms cooperate to allow the multiplexer to handle traffic without requiring an internal clock to be synchronized with the input streams, nor stuffing of packets to pad out the contents of the variable bit rate traffic.
Owner:ERICSSON TELEVISION
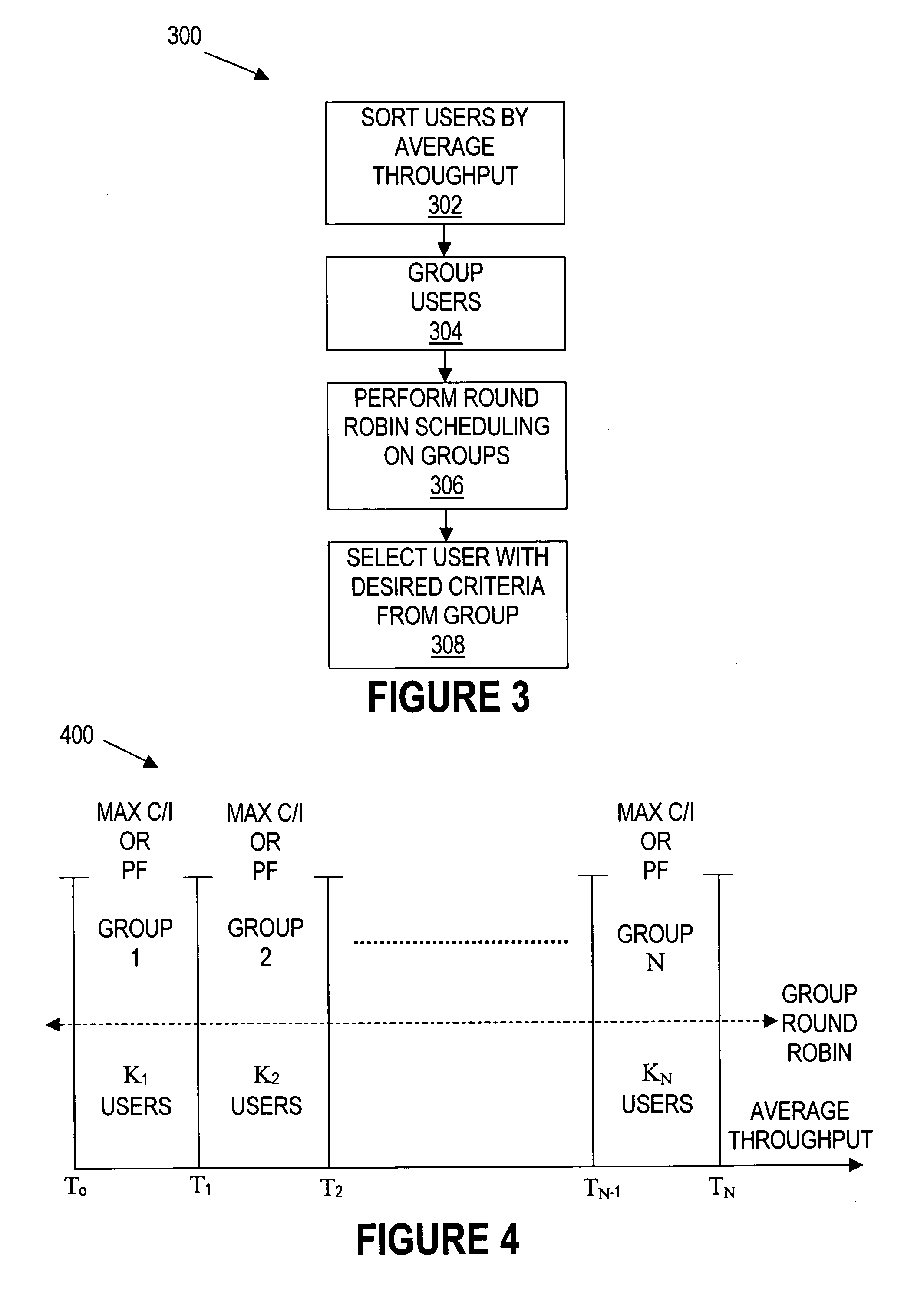
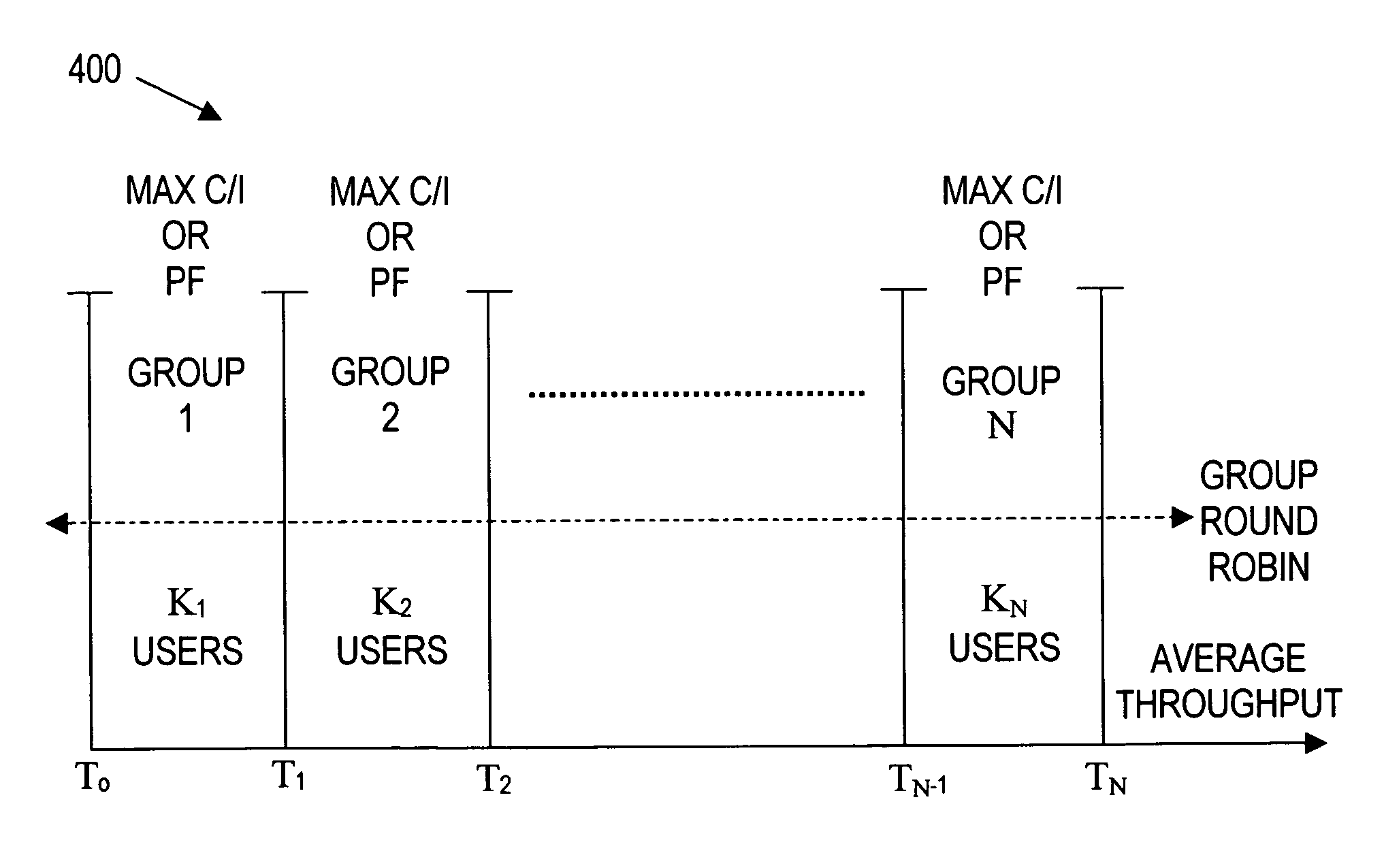
Group based packet scheduling algorithm
ActiveUS20050195843A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMobile stationDistributed computing
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
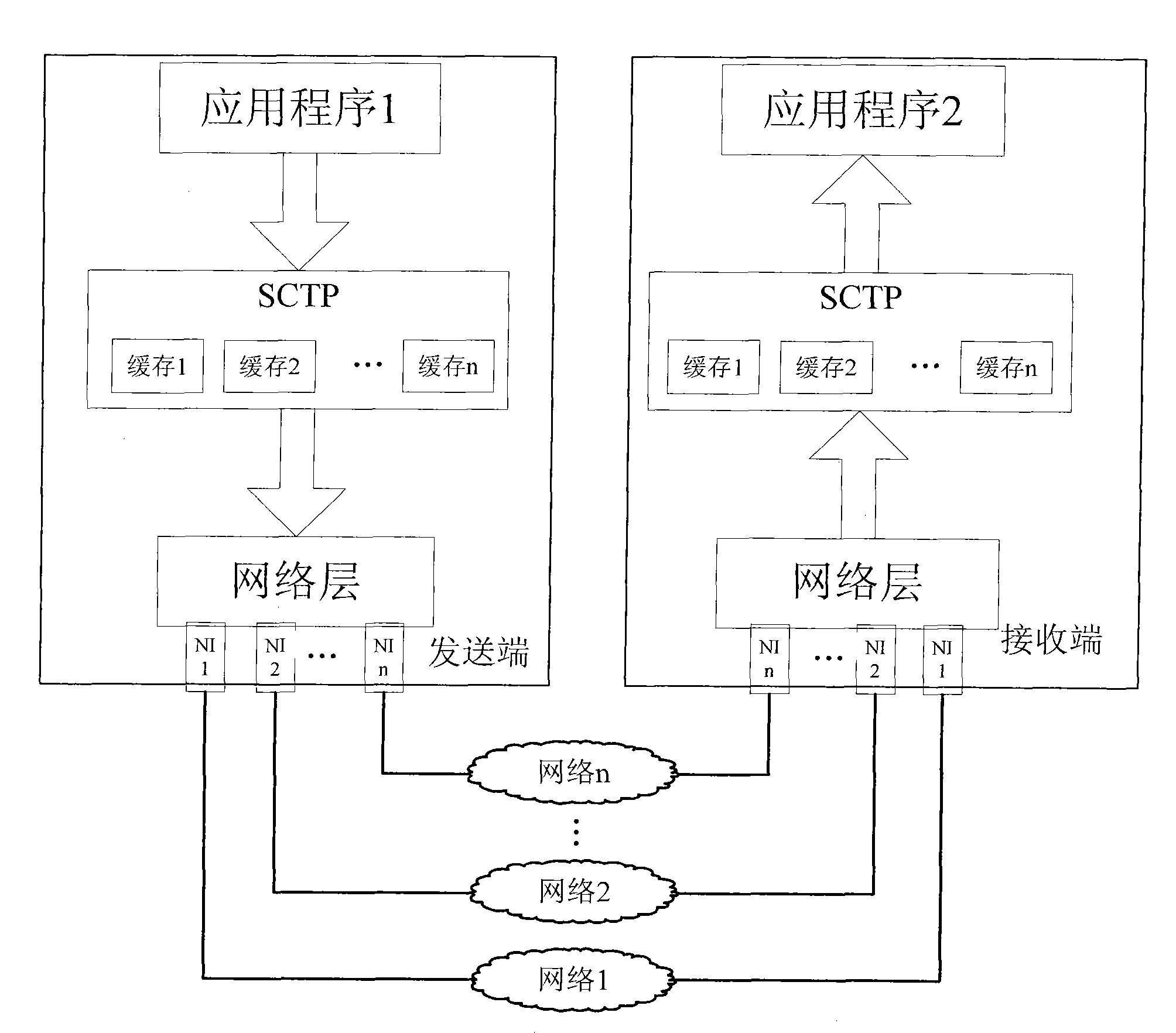
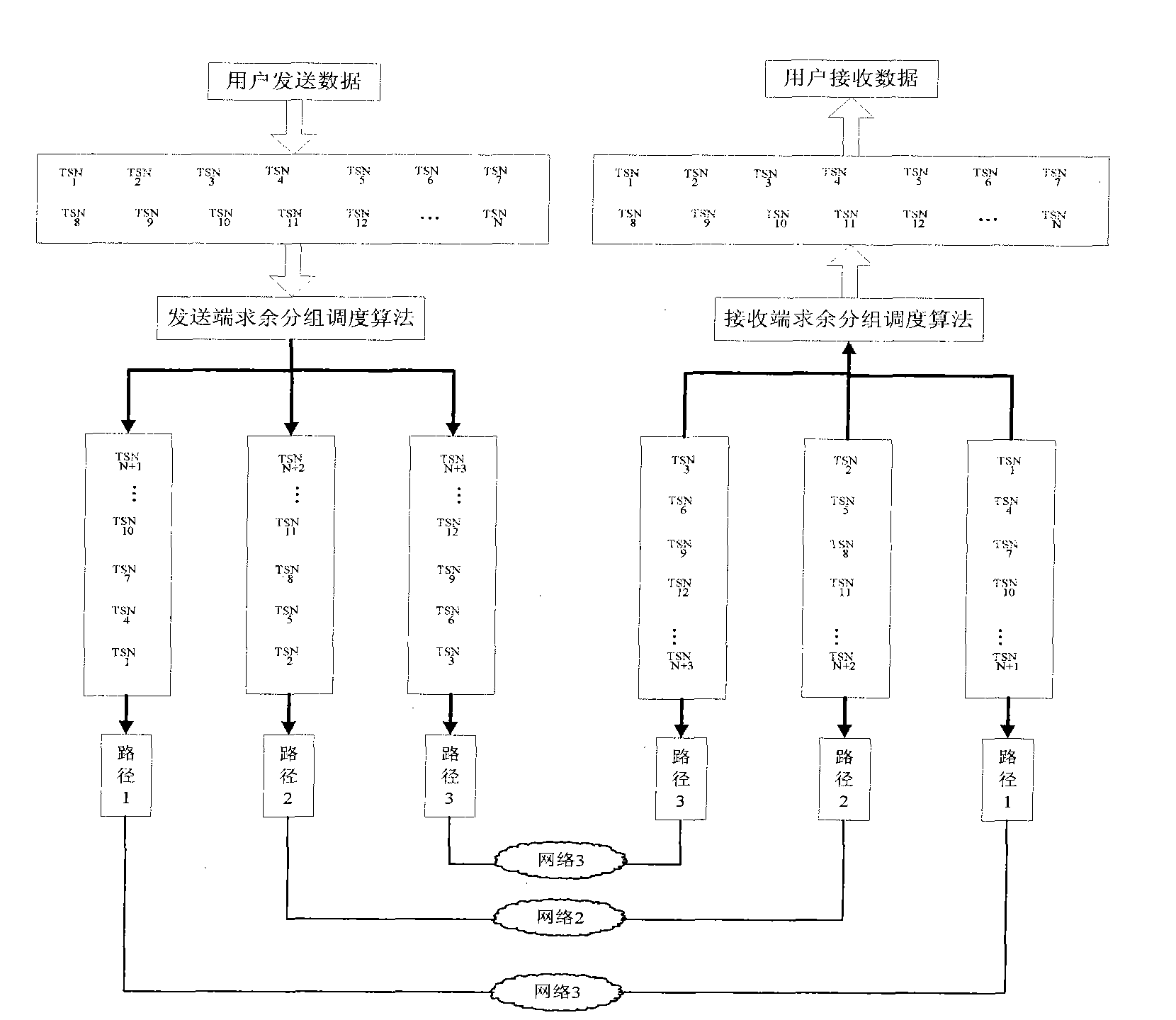
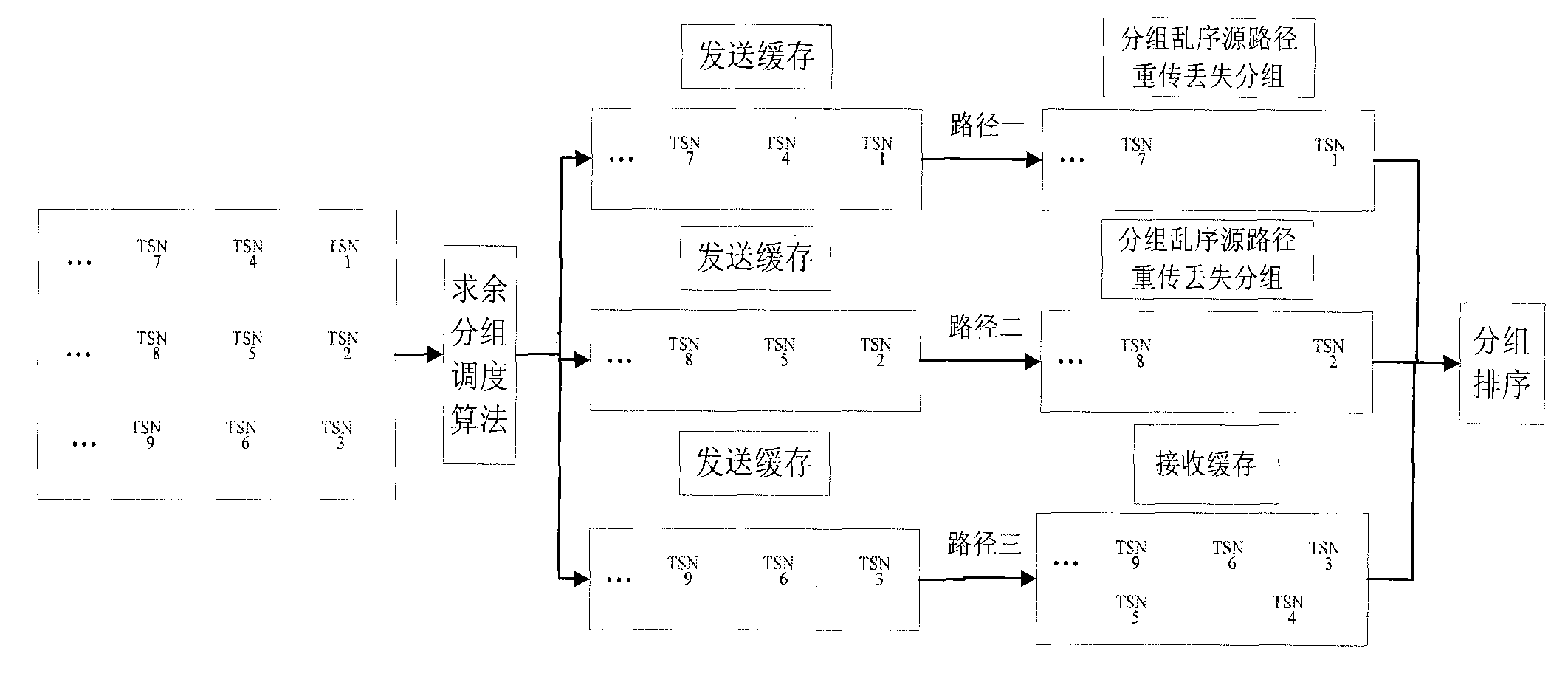
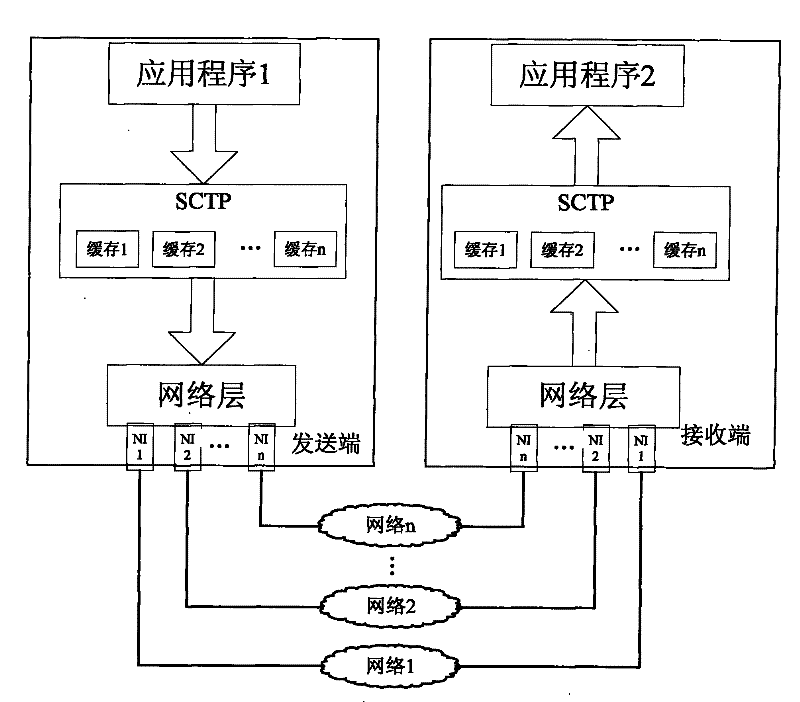
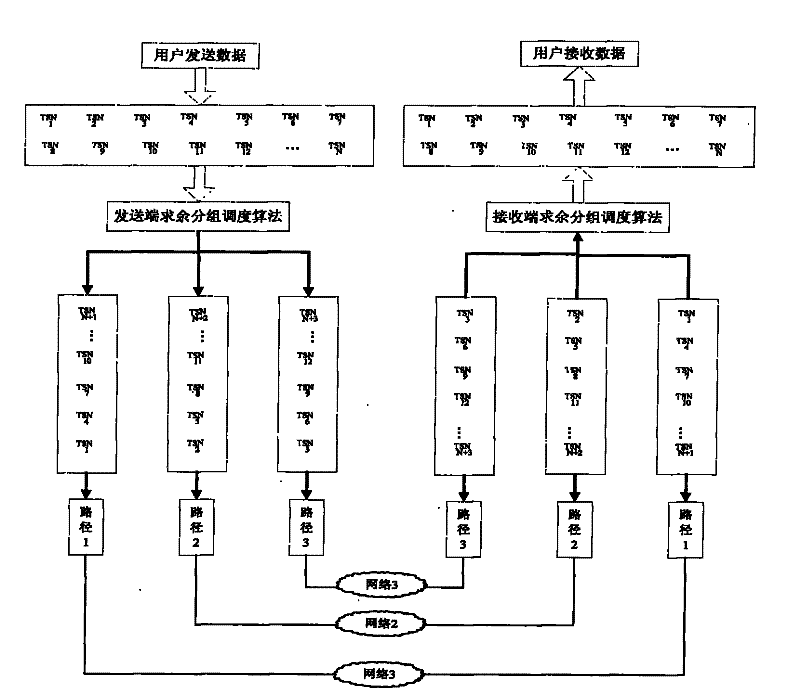
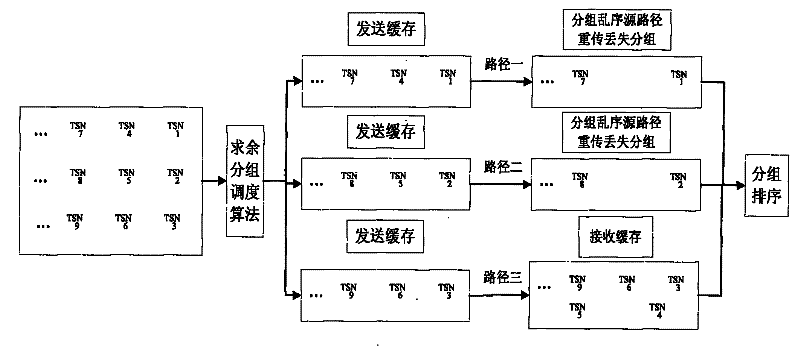
Data concurrency transmission method of multi-network interface device
InactiveCN101883047ASolve rationalityResolve out-of-order receptionError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksNetwork interface deviceSerial code
The invention belongs to the technical field of network, in particular relates to a data concurrency transmission method of a multi-network interface device. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a transmission end and a reception end detect the amount of network interfaces for communication and label the network interfaces so that each network interface for communication has a serial number; (2) the transmission end divides the data to be transmitted into a plurality of message segments and adds transmission serial number for each message segment; (3) the transmission end remainders the transmission serial number of the message segment to the amount of the network interfaces and transmits the message segment according to the obtained remainder by selecting the corresponding network interface; and (4) the reception end orders the received message segments. The invention can fully utilize the traditional network to solve the problems of unreasonable data distributing and dispatching, disordered reception, low retransmission efficiency, and the like by an improved grouping dispatching algorithm.
Owner:黄宏程
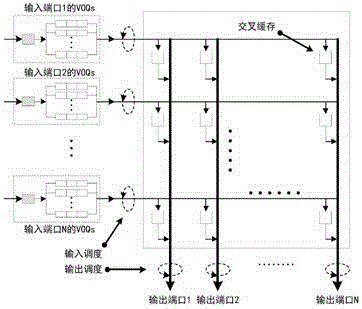
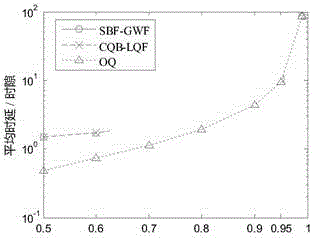
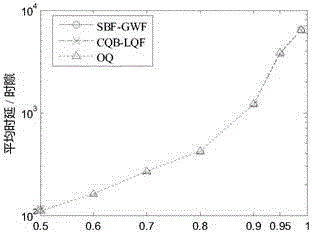
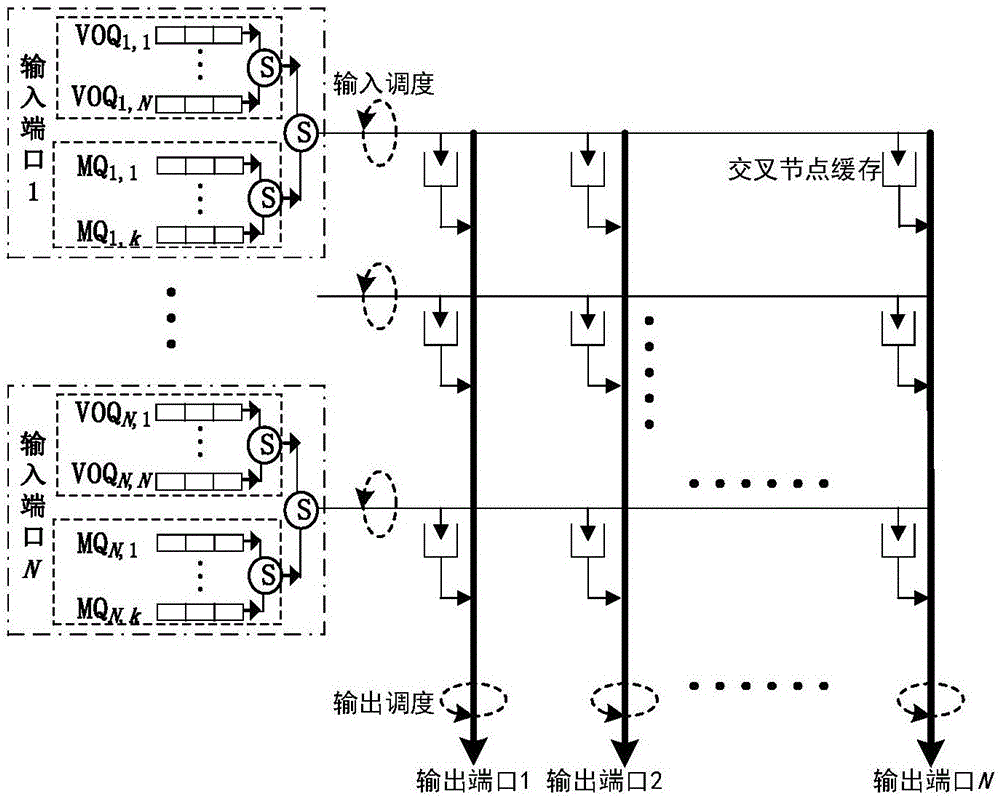
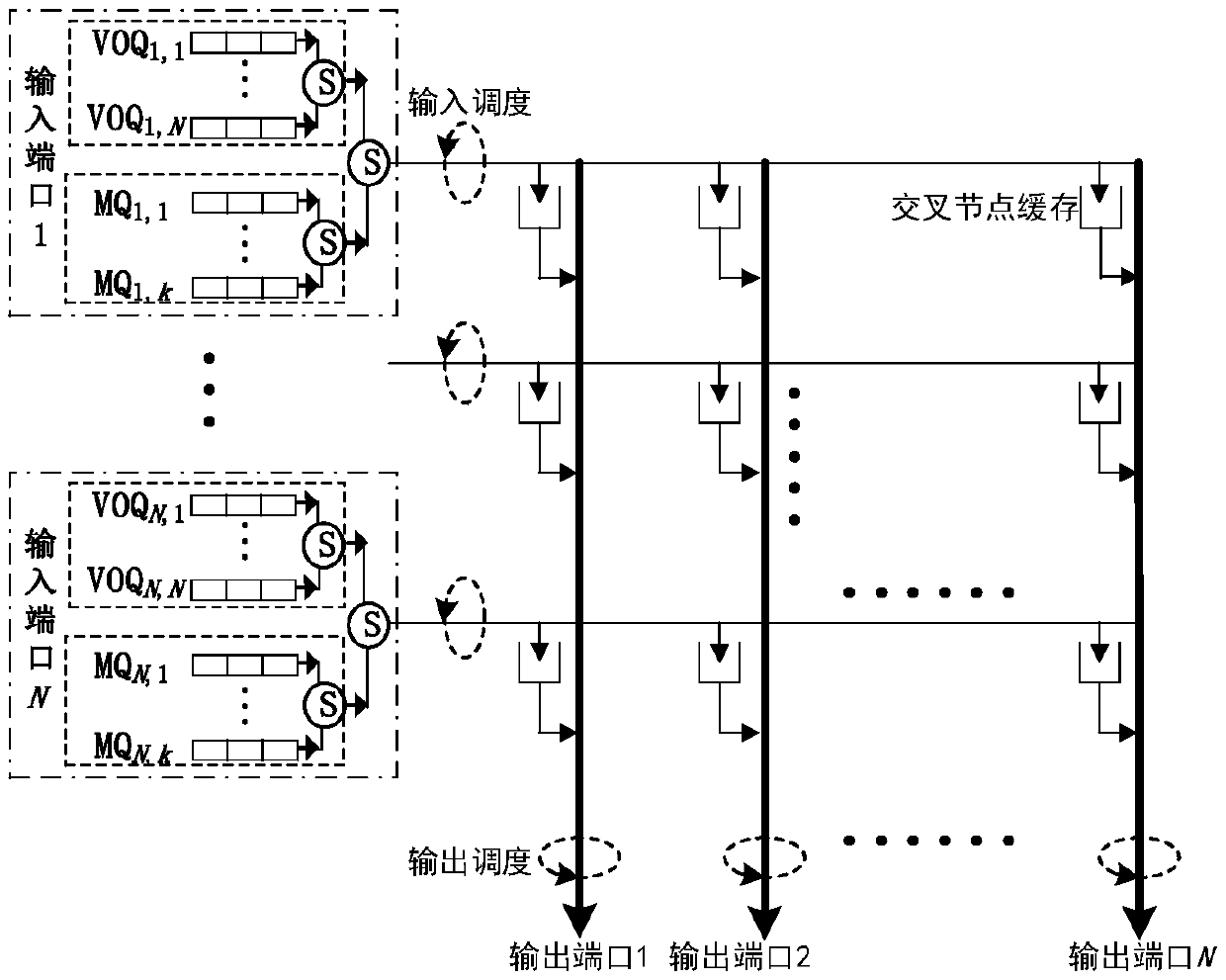
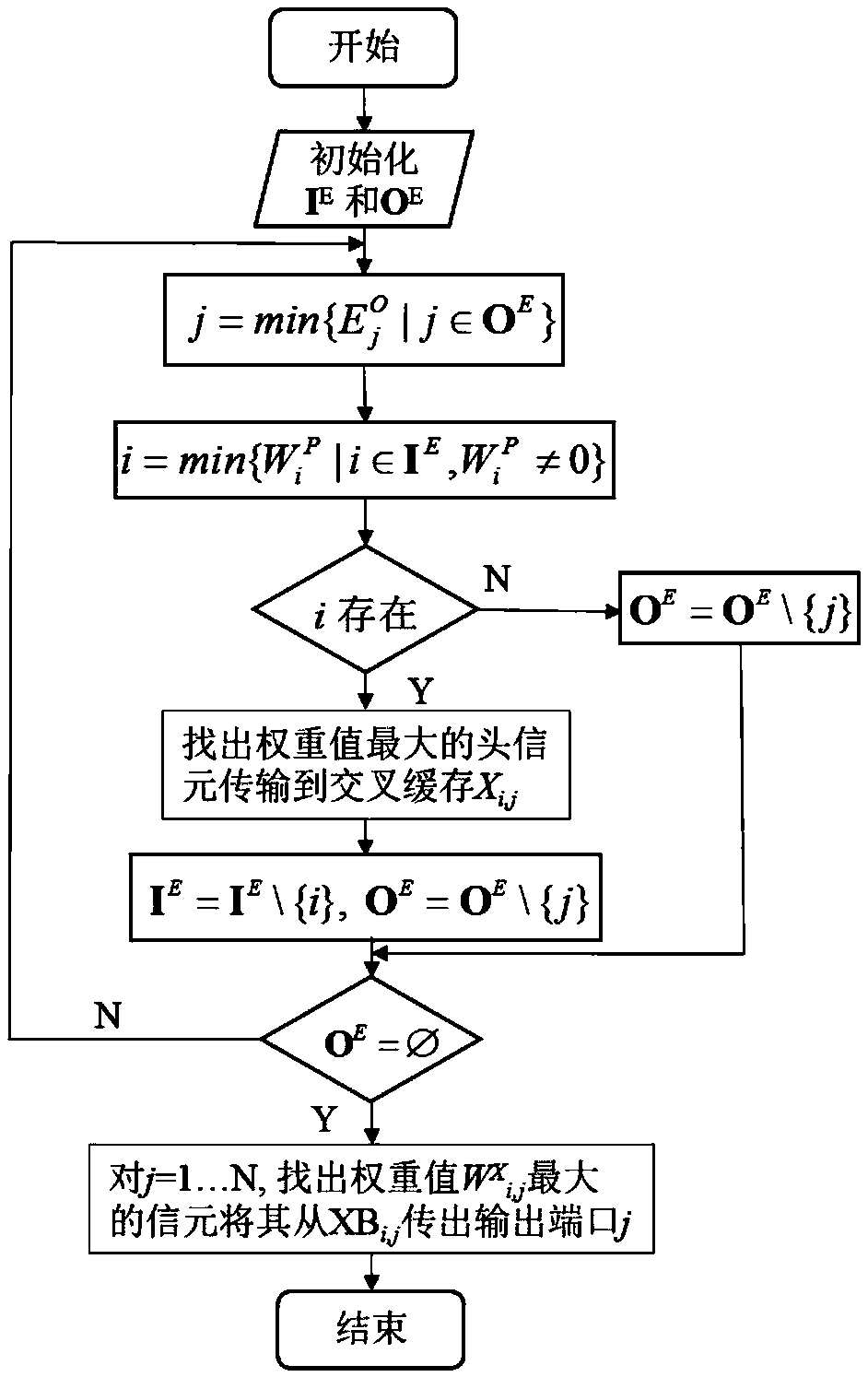
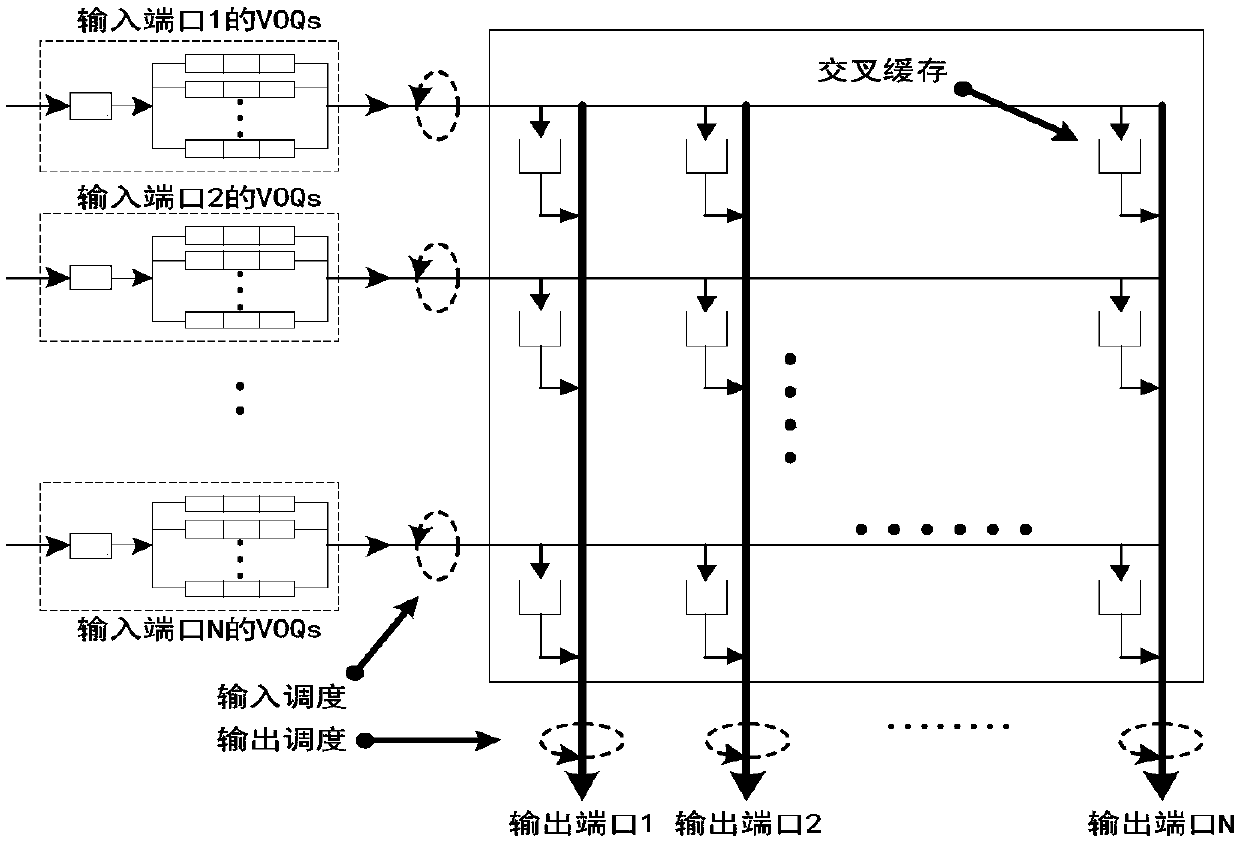
CICQ structure crossbuffer queue balance packet scheduling algorithm
InactiveCN105429898AImprove pass rateGood practical valueData switching networksReal-time computingTime delayed
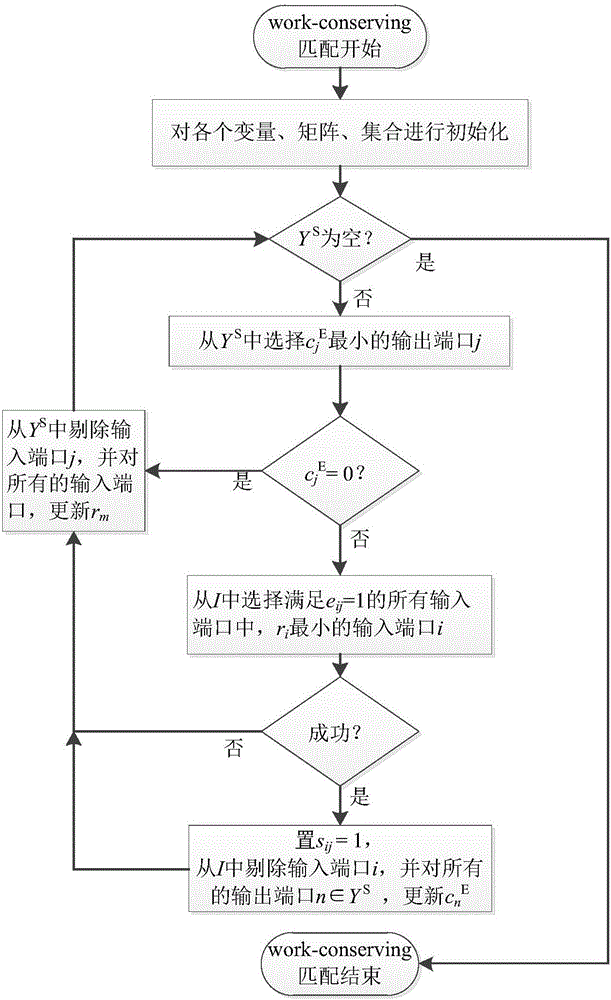
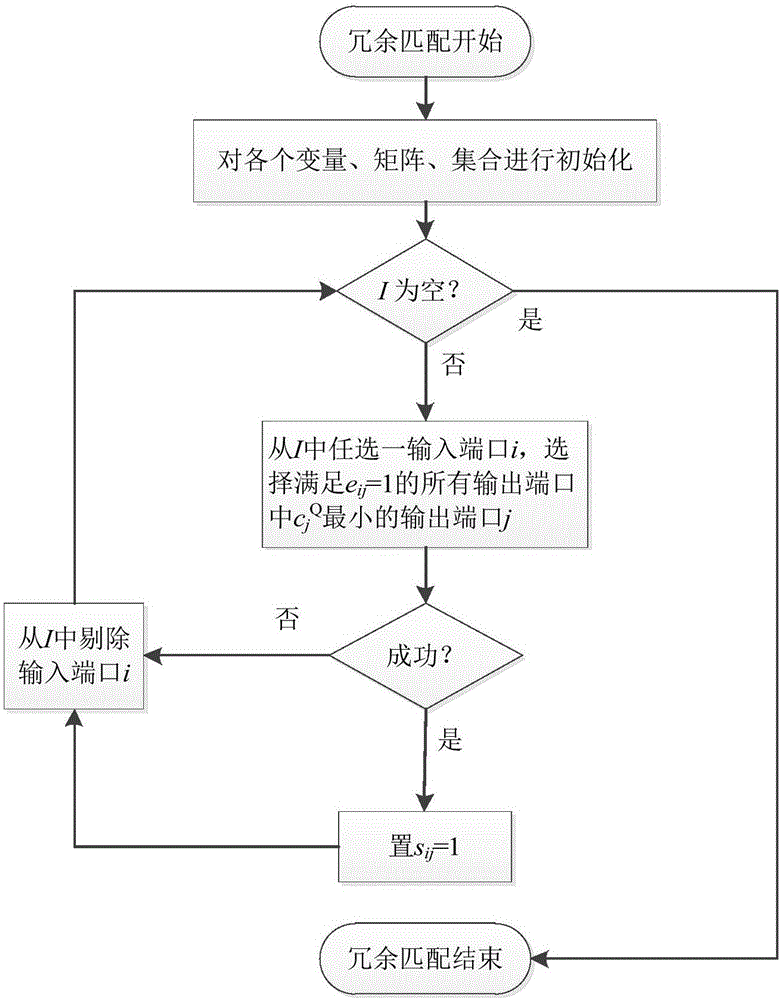
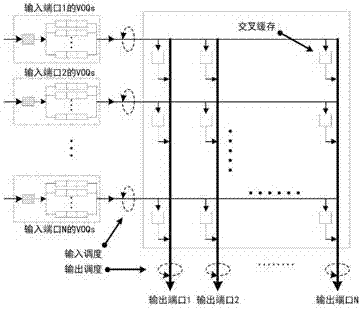
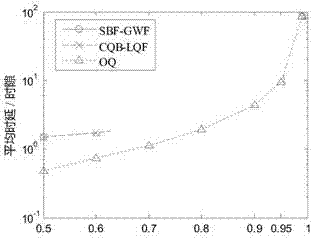
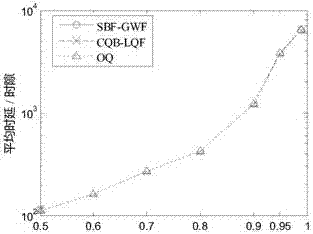
The invention discloses a CICQ structure crossbuffer queue balance packet scheduling algorithm. According to the CICQ structure crossbuffer queue balance packet scheduling algorithm, making a switch work in a work-conserving state as a core is realized or is approached to a maximum degree, output ports are taken as matching reference, output ports having smallest crossbuffer queue length are selected for priority matching, crossbuffer packet occupation of all output ports is balanced, so working in the work-conserving state is made to realize or approach to a maximum degree, the passing percentage is improved, and average packet time delay is further reduced. As is shown in simulation result comparison, for the CICQ switch with crossbuffer as one packet, the algorithm is better than known mainstream algorithms in the average packet time delay, and excellent practical values in large-scale high performance CICQ switches are realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for scheduling packet
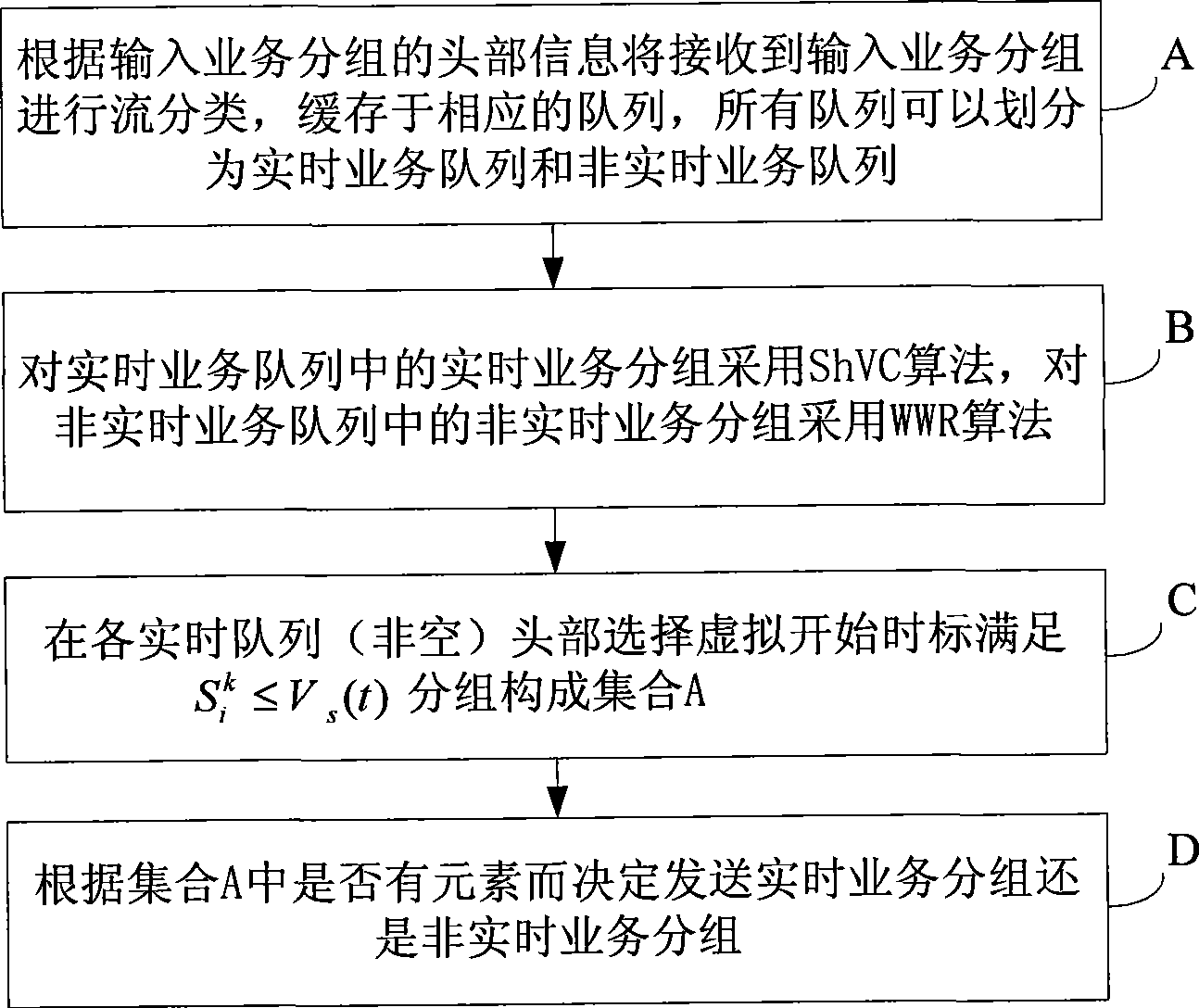
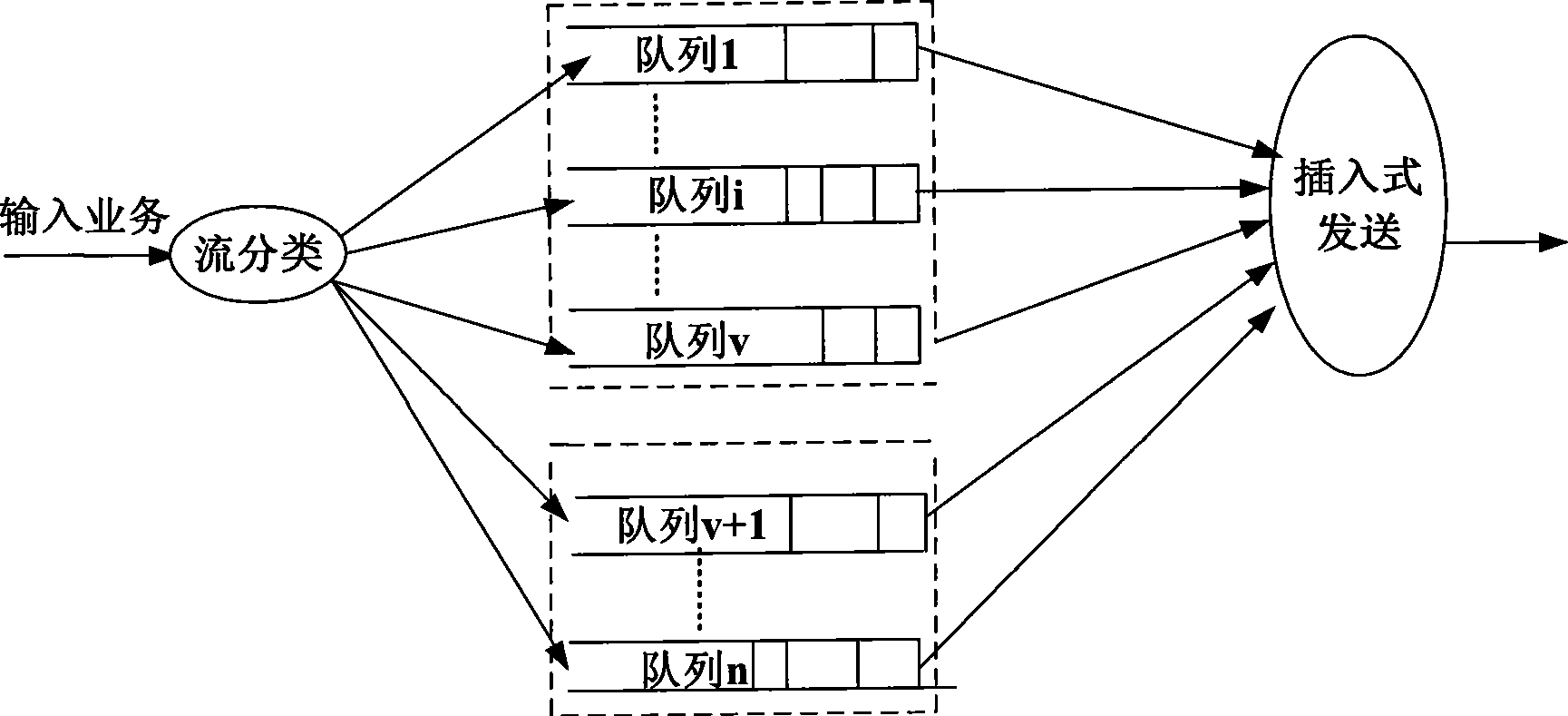
InactiveCN101465794AUniform outputTimely outputData switching networksNon real timeReal time services
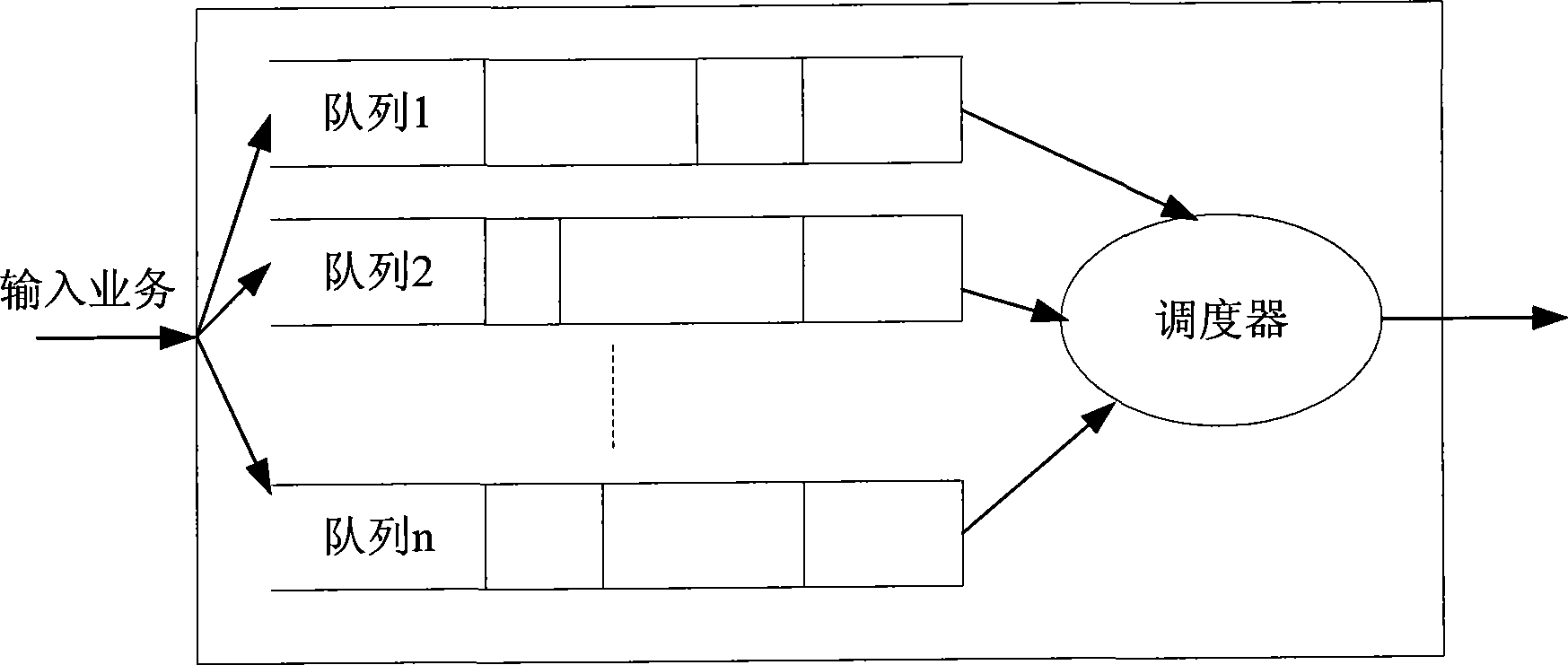
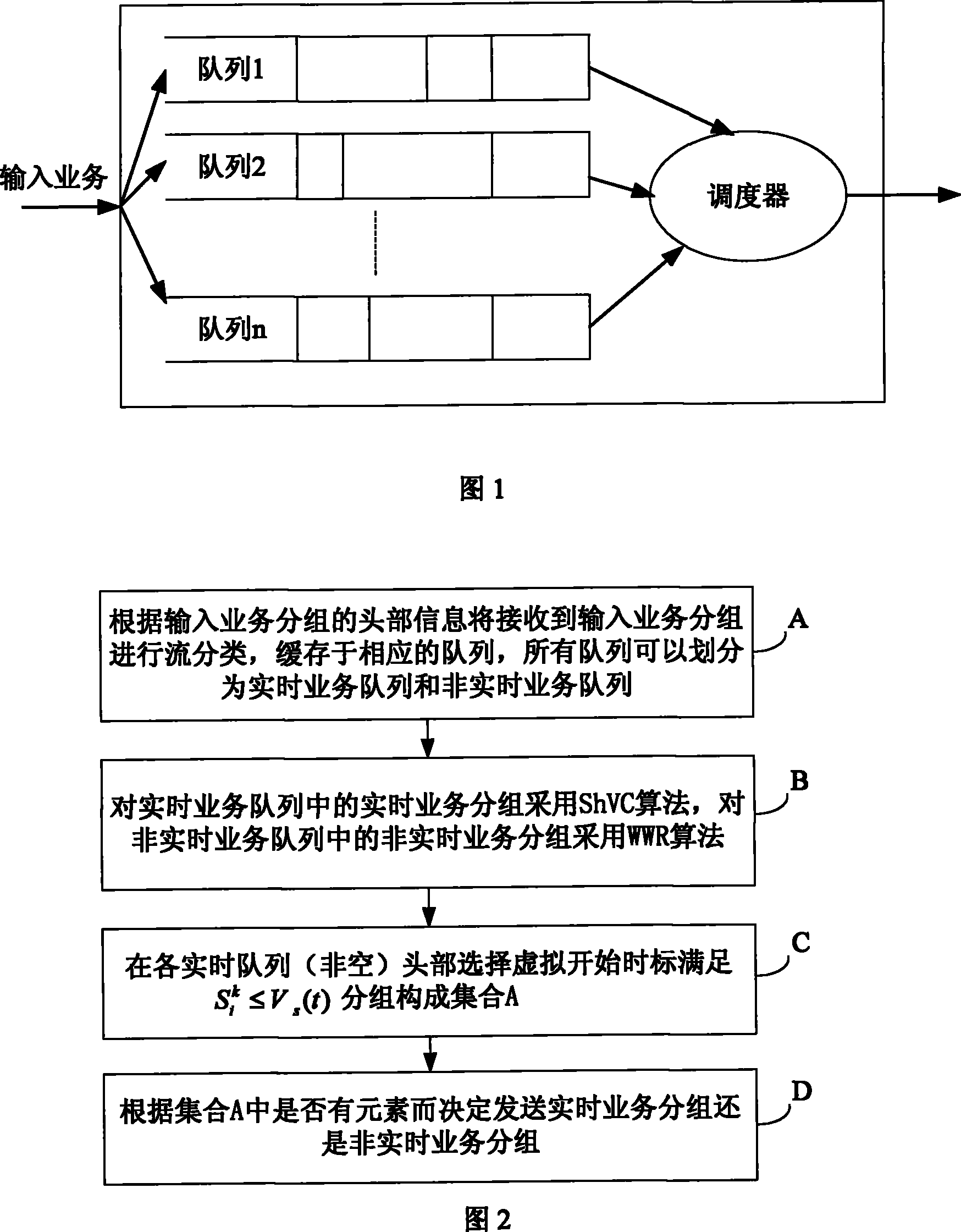
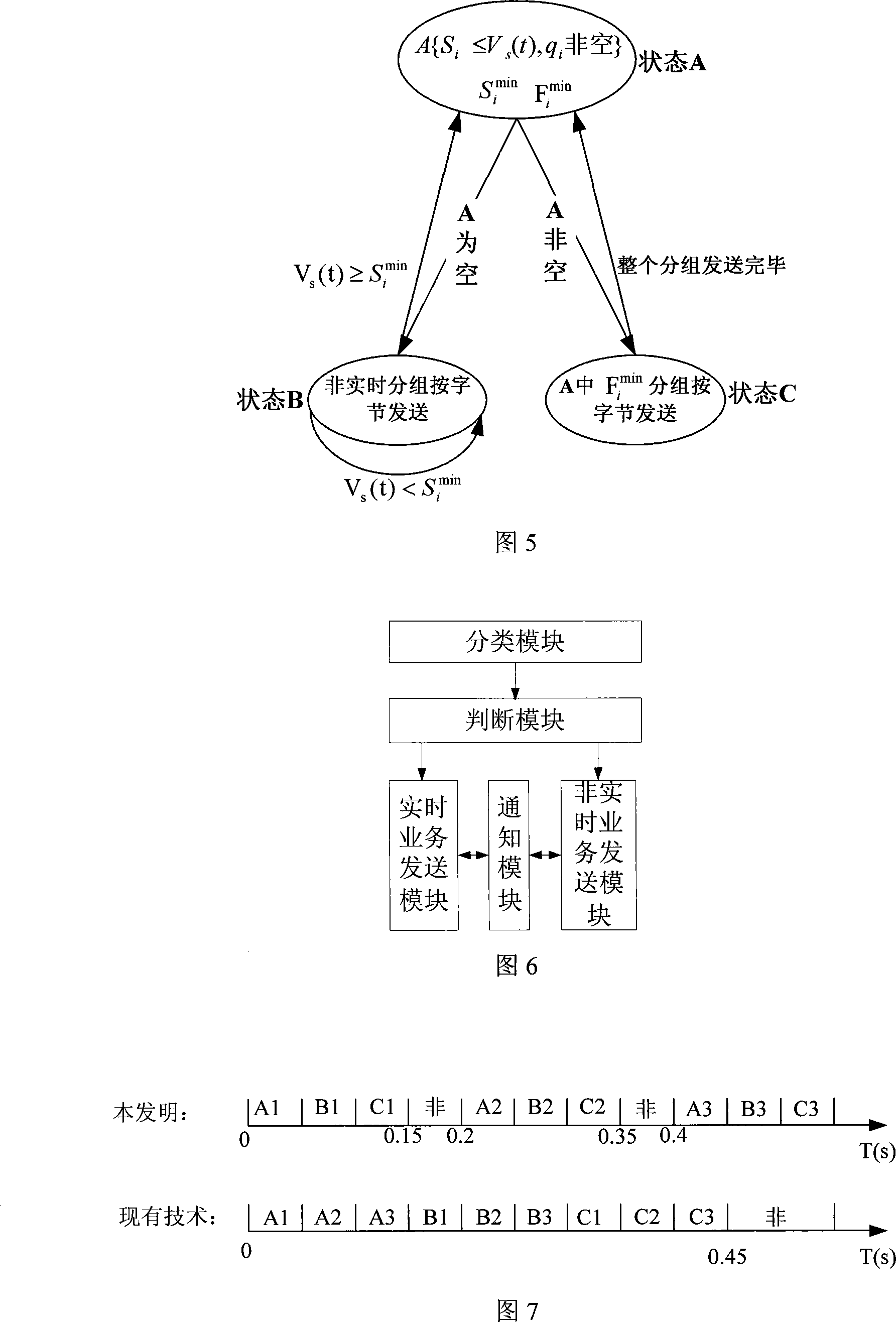
The embodiment of the invention discloses a packet scheduling algorithm and a device thereof, belonging to communication field. The packet scheduling algorithm includes the following steps: partitioning the service packets into real-time service packets and non-real-time service packets according to headers of the service packets; judging whether legal real-time service packets exist in the real-time service packets according to shaping virtual clock algorithm, if yes, sending out the legal real-time service packets, and if no, sending out the non-real-time service packets; if new legal real-time service packets appear during the process of sending out the non-real-time service packets, suspending the sending of the non-real-time service packets and sending out the new legal real-time service packets. The device comprises a sort module, a judge module, a real-time service sending module, a non-real-time sending module and a notification module. The packet scheduling algorithm and the device can ensure that the sending of the real-time service packets is free from the influence of the non-real-time service packets and can avoid the occasion that the non-real-time service packets wait for too long. Therefore, the packet scheduling algorithm and the device have strong practicability, reliability and effectiveness.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Adaptive dynamic telemetering packet scheduling method
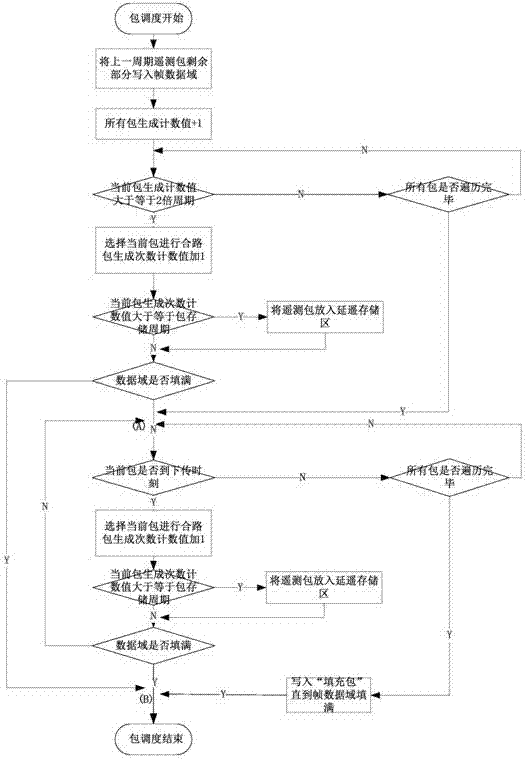
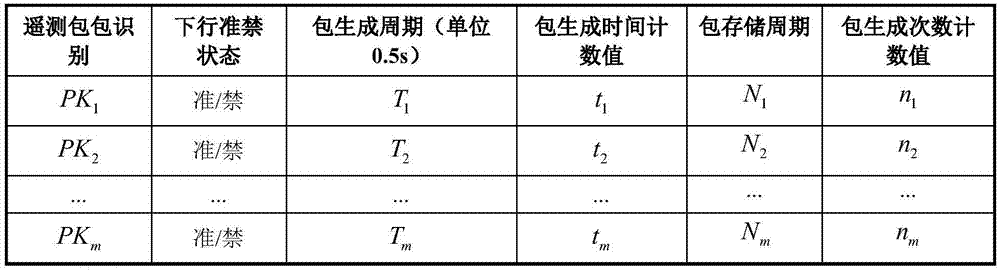
ActiveCN105450545AImprove general performanceAdaptableData switching networksData domainPacket scheduling
The invention discloses an adaptive dynamic telemetering packet scheduling method. The method comprises the following steps of writing remaining telemetering packets failing to be written in a frame data domain in the last period in a current frame data domain; ranking all telemetering packets in an ascending order of periods; traversing all the telemetering packets, and determining a count value of packet generation time; determining whether it is time to transmit each packet in a sequence of ranked packets in each period; and filling the frame data domain with organized telemetering packets, and waiting for the next clock period to fill the remaining telemetering packets failing to write in the frame data domain completely. The adaptive dynamic telemetering packet scheduling method is realized through automatic replacement of a telemetering packet scheduling table or data injection adjustment of telemetering table parameters and a telemetering packet scheduling algorithm, has high universality and adaptation, and has a positive role on ground test, on-orbit experiment, troubleshooting and so on.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
All-optical sharing cache router based on optical fiber delay lines and working method of all-optical sharing cache router
InactiveCN103685078AImplement priority schedulingRealize Optical Packet Space SwitchingFibre transmissionData switching networksOptical packetParallel computing
The invention discloses an all-optical sharing cache router based on optical fiber delay lines and a working method of the all-optical sharing cache router. The router comprises a sharing cache queue and a logic control unit. The sharing cache queue is composed of N input ports, N output ports, N discarding ports, a (N + M) * (N + M) non-blocking optical switching matrix and the M optical fiber delay lines. By arranging the lengths of the optical fiber delay lines and using an optical packet schedule algorithm based on sorting, according to the router and the working method thereof, the priority dispatch sharing cache optical router function under any optical grouping reaching situation can be simulated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
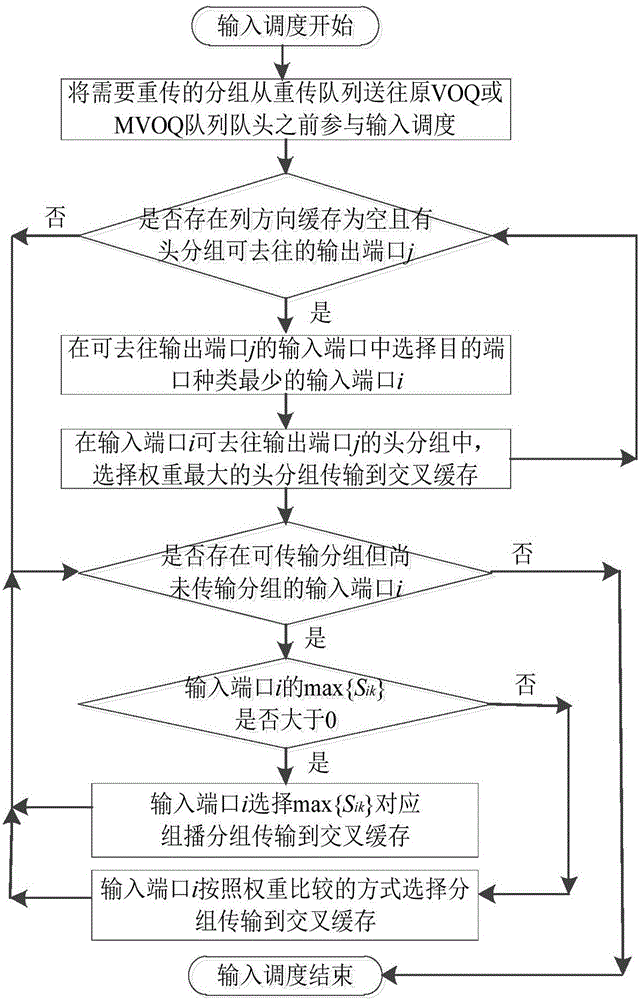
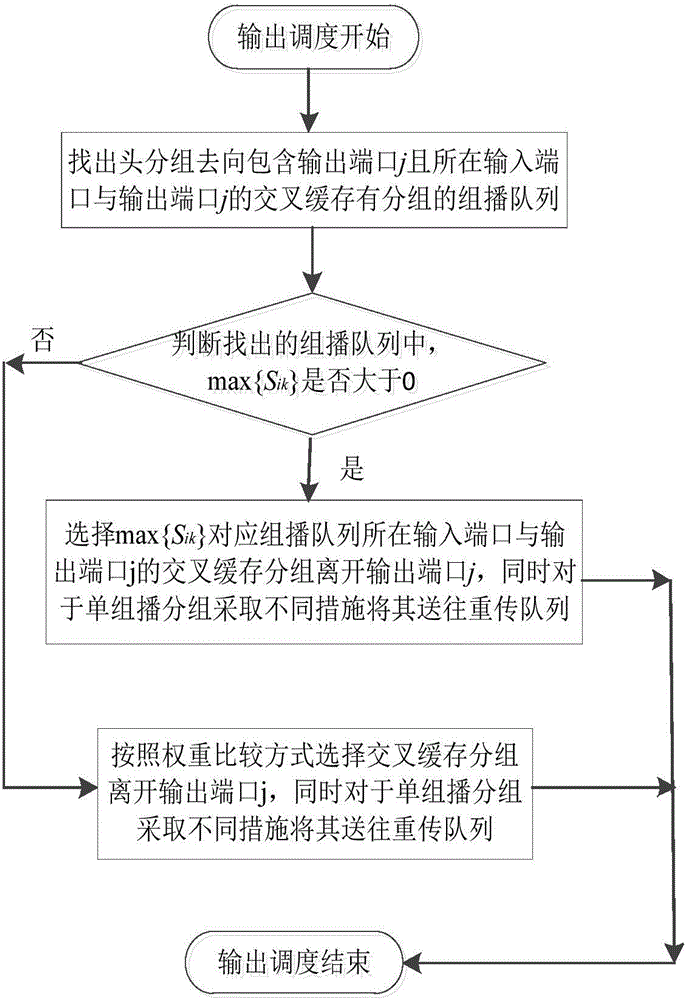
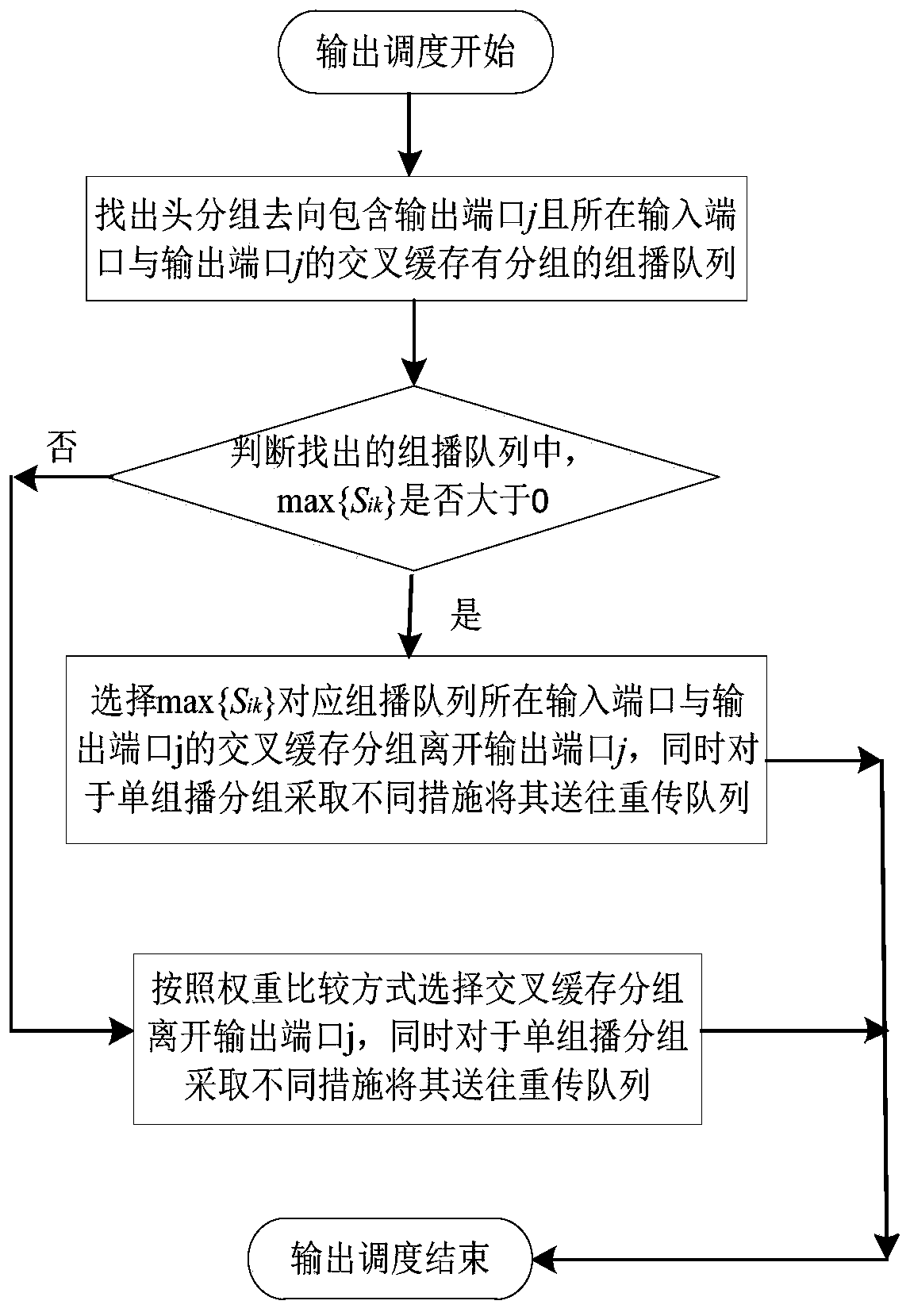
Unicast and multicast service packet scheduling algorithm for satellite-borne CICQ structural switch under GEO channel environment
ActiveCN106789738AError prevention/detection by using return channelRadio transmissionPacket schedulingMulticast packets
The invention discloses a unicast and multicast service packet scheduling algorithm for a satellite-borne CICQ structural switch under a GEO channel environment, belonging to the technical field of satellite network and high-performance packet switching. The algorithm aims at relieving the multicast HOL Blocking problem in CICQ switch packet scheduling from input / output scheduling algorithm, and compensating the packet which fails in transmission and requires retransmission due to the GEO channel problem. The method takes relieving blockage of head packet on next packet of a multicast queue as a target on the premise that a CICQ switch works in work-conserving as far as possible in input scheduling, takes the number of packet retransmission times in a channel as the principle concerning factor in unicast and multicast packet decision, and takes relieving blockage of head packet for next packet of a cross buffer corresponding multicast queue in output scheduling. The method sufficiently takes GEO satellite network characteristics and requirement into consideration, and has an excellent practical application value.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
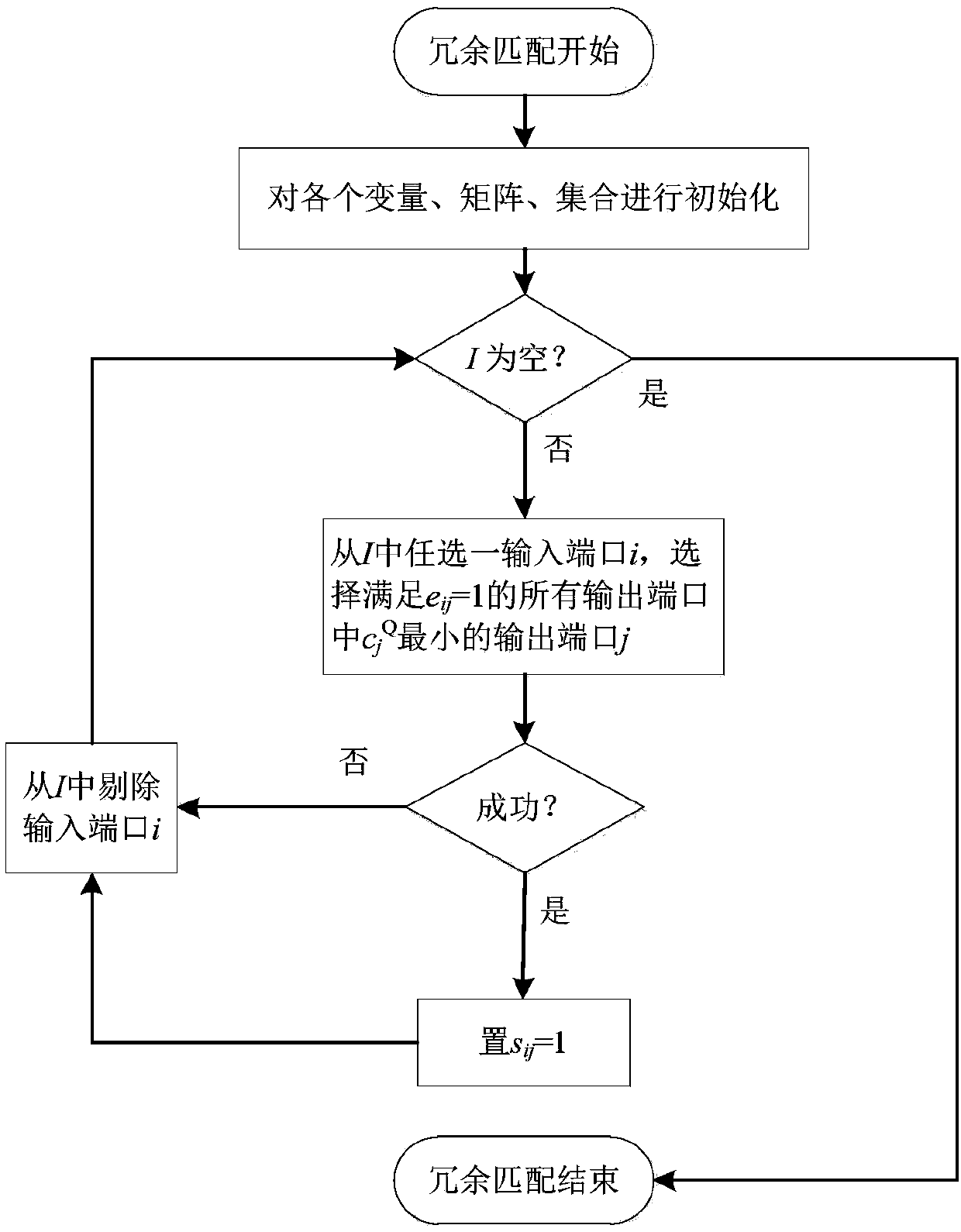
Packet scheduling algorithm of CICQ structure switches based on virtual queue length coordination single multicast competition
ActiveCN106453134AImprove versatilityImprove practicalityData switching networksPass rateDistributed computing
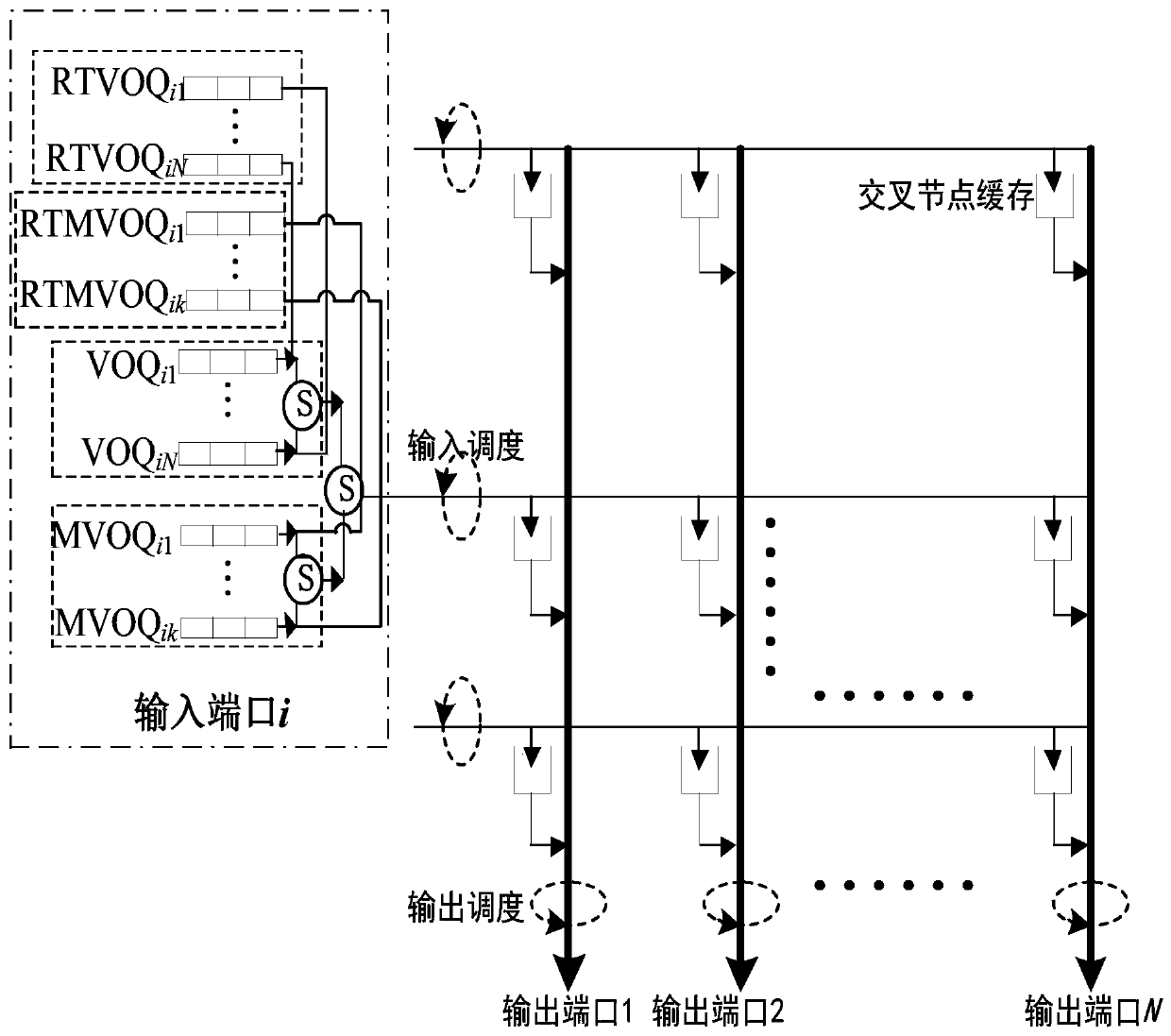
The invention discloses a packet scheduling algorithm of CICQ structure switches based on virtual queue length coordination single multicast competition. The algorithm provided by the invention comprises two parts of input scheduling and output scheduling. In the input scheduling, an output port having the minimum sum of column cross node cache packets is found at first, then an input port having the least union set elements of destination ports of unicast head cells and multicast head cells from the input ports having cells transmitted to the output port is selected, weights of the unicast head cells and the multicast head cells are calculated, and the head cell having the maximum weight is selected and transmitted to the corresponding cross node cache. In the output scheduling, the weight of the cross node cache is set to be equal to the sum of a corresponding unicast queue length and the virtual queue lengths of all multicast queues of the corresponding output ports where the head cells are transmitted to, and the packet in the cross node cache having the maximum weight leaves the output port. Compared with the typical method, the algorithm provided by the invention has better pass rate and packet average delay performance.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Fair flow scheduling algorithm based on smooth time window
InactiveCN101800696AImprove network experienceReduce collisionData switching networksTraffic capacityPacket scheduling
The invention relates to a fair flow scheduling algorithm based on a smooth time window, which is a packet scheduling algorithm under the busy state of a network, the fair flow scheduling algorithm has higher control precision and fairness and can be used in IP network optimization fields such as harmful network flow purification, flow shaping, service quality assurance and the like.
Owner:莱克斯科技(北京)有限公司
Downstream packet scheduling Ethernet energy-saving scheme based on a hybrid sleep mode
InactiveCN108964931AReduce energy savingMinimize consumptionSubstation remote connection/disconnectionHigh level techniquesLow loadPacket scheduling
The invention relates to an energy-saving scheme of Ethernet, in particular to a downstream packet scheduling Ethernet energy-saving scheme based on a hybrid sleep mode. The downstream packet scheduling Ethernet energy-saving scheme mainly comprise downstream packet scheduling and a hybrid sleep mode. A downstream packet scheduling algorithm combines an inter-frame scheduling algorithm and intra-frame scheduling algorithm to ensure that delays of downstream packets can meet requirements. An Ethernet energy-saving mode adopts a hybrid sleep mode, which includes a deep sleep mode of a low-load Ethernet network unit and independent sleep modes of a transmitter and a receiver, so as to ensure the minimum energy consumption of idle periods of Ethernet. In this way, Ethernet can be in a low energy consumption mode for a long time in idle periods so as to be reduced in energy consumption. The scheme of the invention is mainly applied to energy conservation of Ethernet with a large scale network scale and a large network topological structure.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Group based packet scheduling algorithm
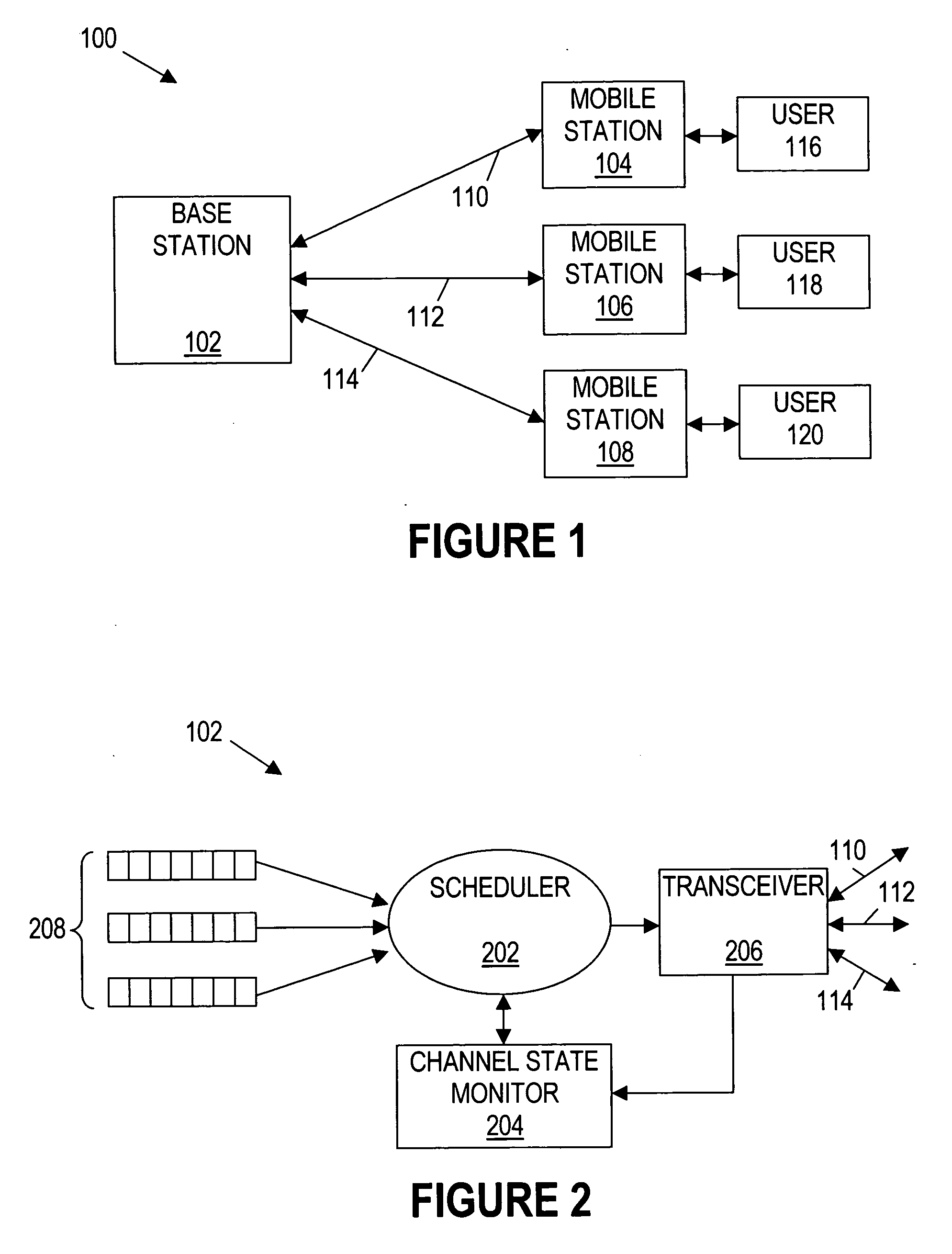
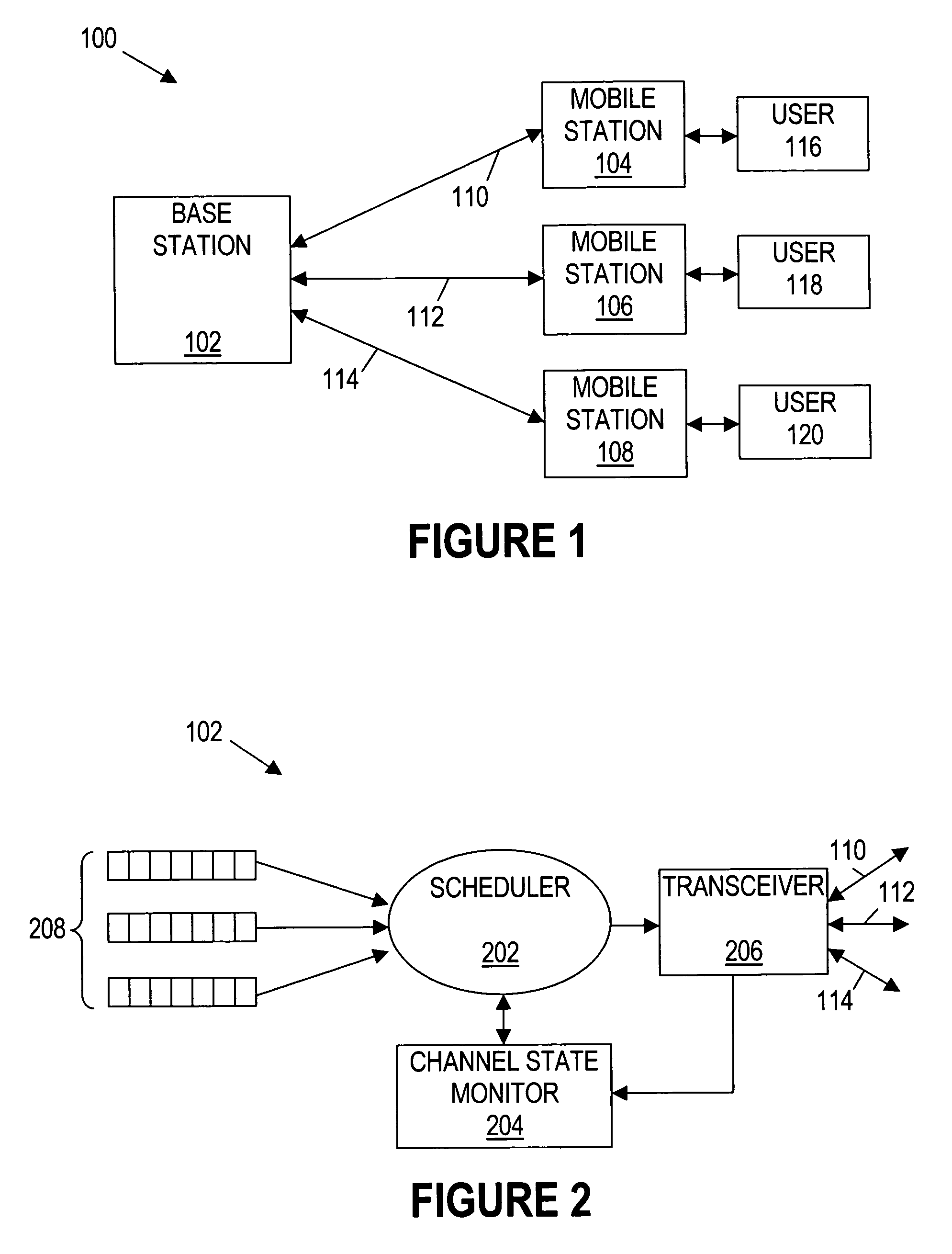
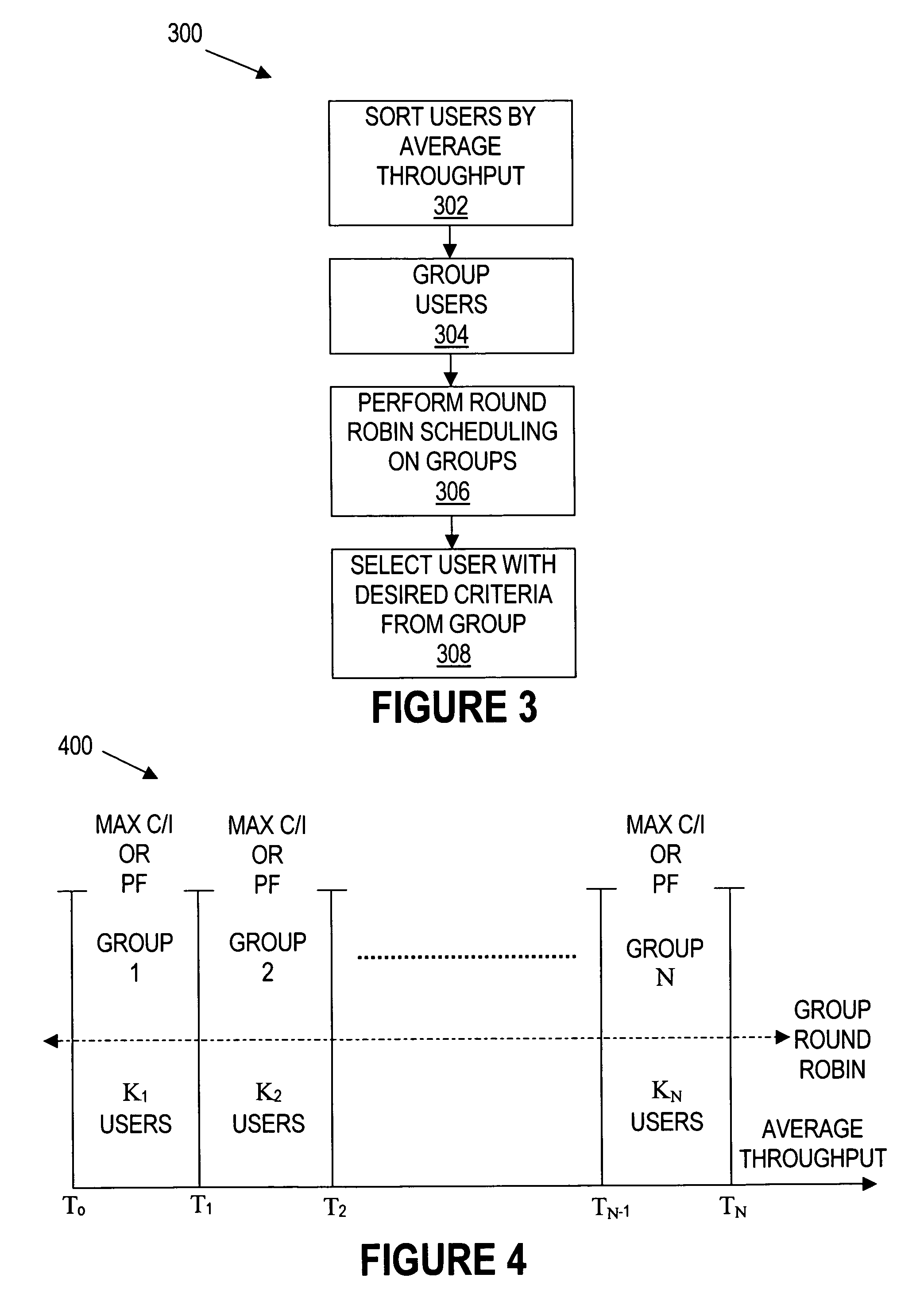
A system comprises a base station, a plurality of mobile stations, and a packet scheduling algorithm that operates on the base station. The packet scheduling algorithm groups the plurality of mobile stations into a plurality of groups based on average throughput with the base station. The packet scheduling algorithm selects one of the plurality of groups for applying a scheduling metric.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
VOQ switch packet scheduling algorithm based on packet accumulation effect
InactiveCN103888385AImprove practicalityImprove good performanceData switching networksExtensibilityRound complexity
The invention discloses a VOQ switch packet scheduling algorithm based on a packet accumulation effect. The VOQ switch packet scheduling algorithm based on the packet accumulation effect is an algorithm based on frames. According to the VOQ switch packet scheduling algorithm based on the packet accumulation effect, N completely-matched matrixes are selected for a switch with N*N ports on the basis of a round robin matching mode; the matched matrixes are multiplied by the lengths of virtual output queues of input ports of the switch at the beginning of a frame boundary so that occupation of the matched matrixes can be obtained; the matched matrix with the maximum occupation value is selected as a matching scheme for the ports of the frame switch. Stability of the VOQ switch packet scheduling algorithm is theoretically certified; according to comparison of simulation results, the VOQ switch packet scheduling algorithm is better than a typical scheduling algorithm in the aspect of packet average delay; meanwhile, iteration complexity of the VOQ switch packet scheduling algorithm is only O(1), and the VOQ switch packet scheduling algorithm can be applied to large-scale high-speed networks, and have good extensibility.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
FIFO cache sharing router based on fiber delay lines and working method thereof
InactiveCN103731359AUnlimited cache sizeImprove resource utilizationData switching networksFiberParallel computing
The invention discloses a FIFO cache sharing router based on fiber delay lines and a working method of the FIFO cache sharing router. The cache sharing router allows sharing of N packets and structurally comprises a (N+M)*(N+M) non-blocking optical switching matrix, the M fiber delay lines and a logic control unit. By setting optical fiber delay line lengths (img file='23068dest_path_image002.TIF', wi='216', he='24' / ) and adopting the packet scheduling algorithm based on sorting, the FIFO light cache sharing function can be simulated under the condition of the arrival of any packet by the FIFO cache sharing router based on the fiber delay lines according to the working method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
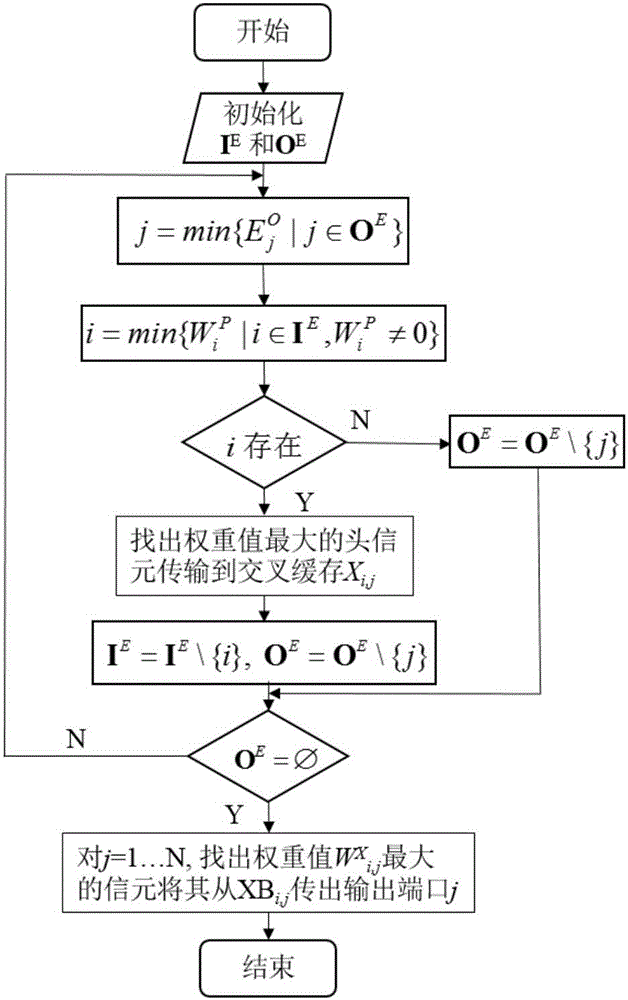
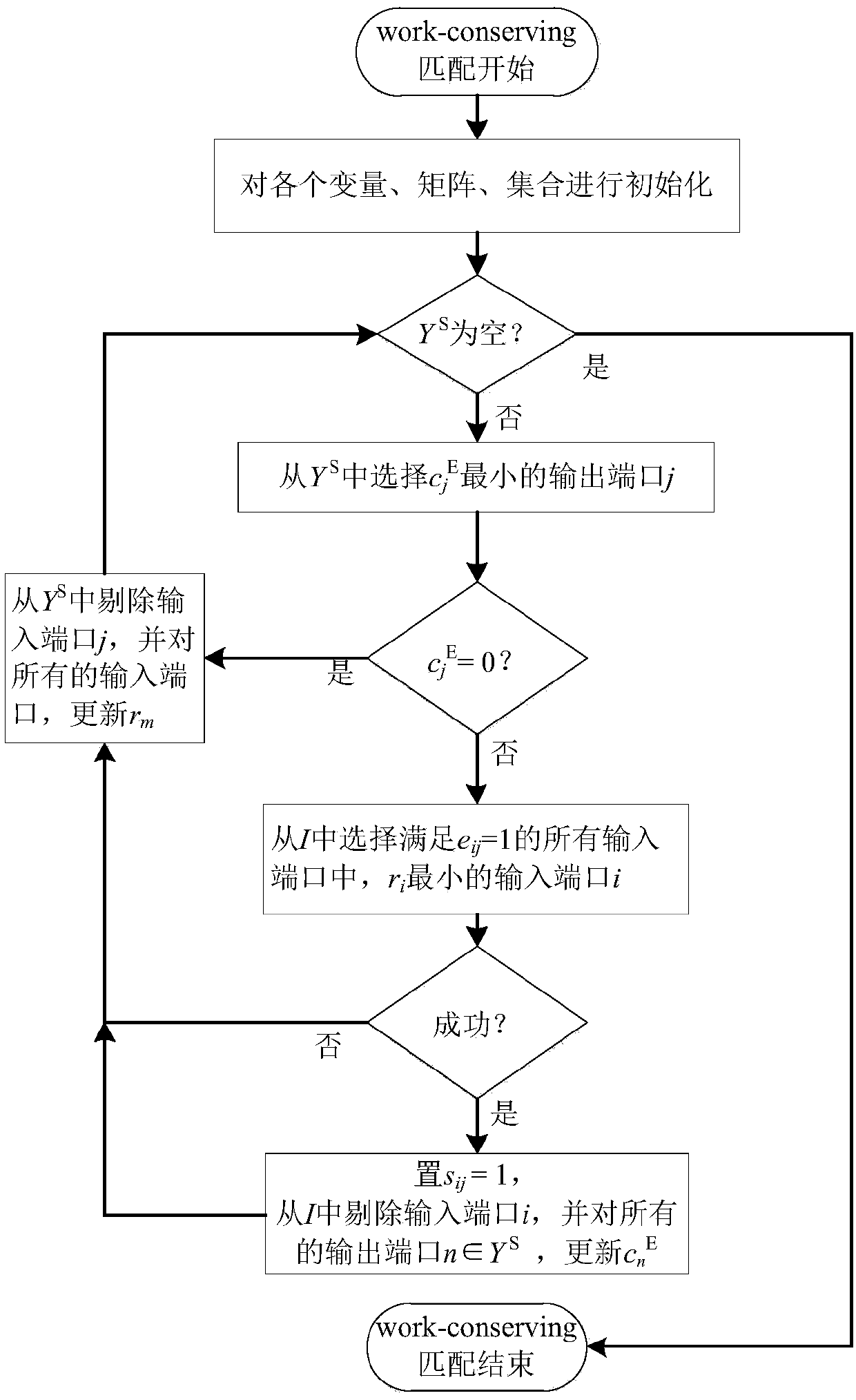
GEO satellite-borne CICQ structure switch packet schedule algorithm considering channel state
ActiveCN106603145AImprove pass rateImprove channel utilizationRadio transmissionData switching networksPass ratePacket schedule
The invention discloses a GEO satellite-borne CICQ structure switch packet schedule algorithm considering channel states. To make a switch work in a work-conserving state or work in the maximum work-conversing state and also to increase a channel utilization rate, the algorithm enables output ports of normal channel states to gain the most matching numbers while ensuring that the maximum matching number keeps unchanged, increases a passing rate and reduces average time delays of packets. A comparison of simulation result shows that for a GEO satellite-borne CICQ switch with one packet as cross cache capacity, the algorithm is superior to conventional mainstream algorithms in terms of the passing rate and packet average time delays in various common satellite channel states, and has great practical values for a GEO high-performance satellite-borne CICQ switch.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
MPQUIC data packet rapid transmission method and system based on priority level queue
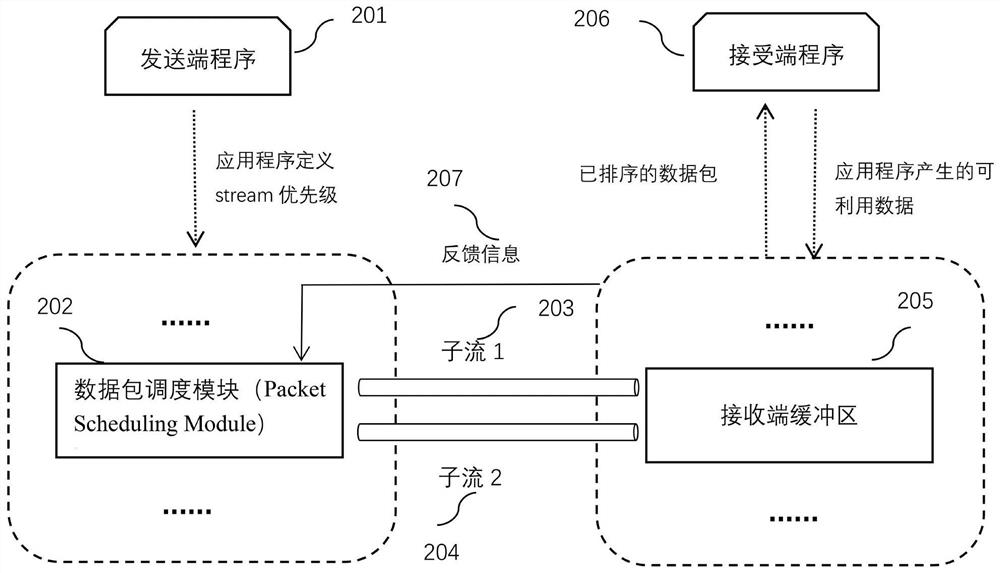
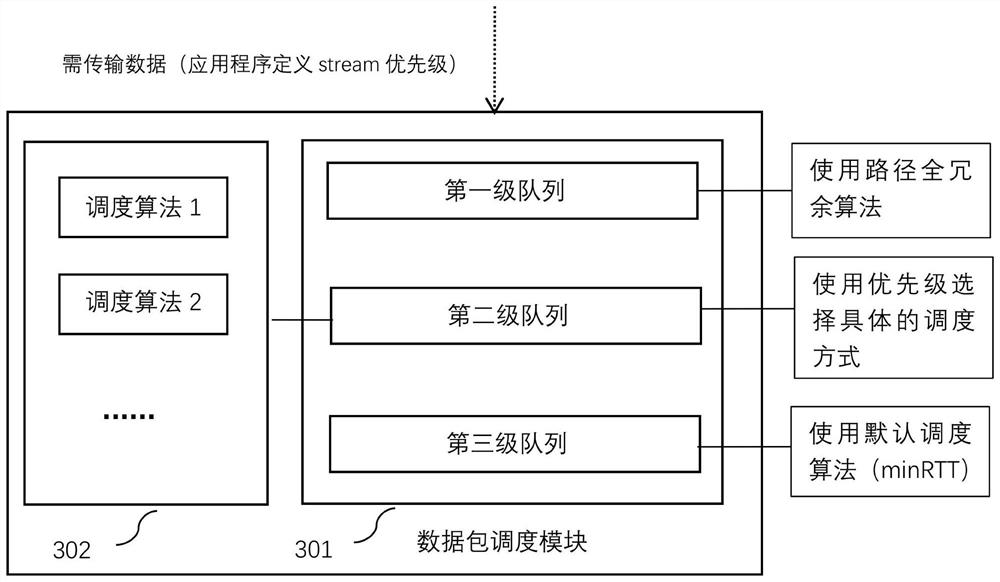
The invention provides an MPQUIC data packet rapid transmission method and system based on a priority level queue, and the method comprises the steps: 1, enabling a transmitting end application program to generate a to-be-transmitted MPQUIC data packet, and putting the data packet into a scheduling queue corresponding to the priority level of the data packet; 2, transmitting the data packet to a receiving end cache region according to a scheduling strategy corresponding to a scheduling queue in which the data packet is located; 3, enabling the receiving end cache region to arrange the data packets in sequence to obtain to-be-operated data and the size of an out-of-order queue, and enabling a receiving end application program to extract the to-be-operated data to complete services corresponding to the data packets to obtain service quality; 4, updating and optimizing the scheduling strategy according to the size of the out-of-order queue and / or the service quality. Compared with a traditional single scheduling mode, the method has the advantages that a data packet scheduling algorithm can be combined with an actual application scene and user requirements, and subsequent integration of the data packet scheduling algorithm is facilitated.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A packet scheduling method for cicq-structured switches based on virtual queue length to coordinate single-multicast contention
ActiveCN106453134BImprove versatilityImprove practicalityData switching networksEngineeringPacket scheduling
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
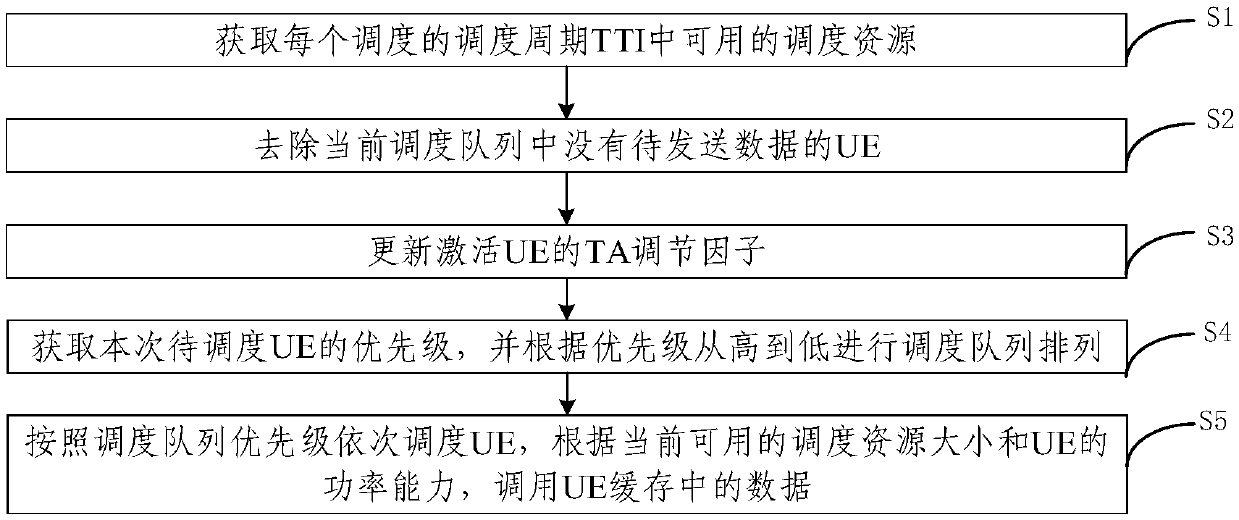
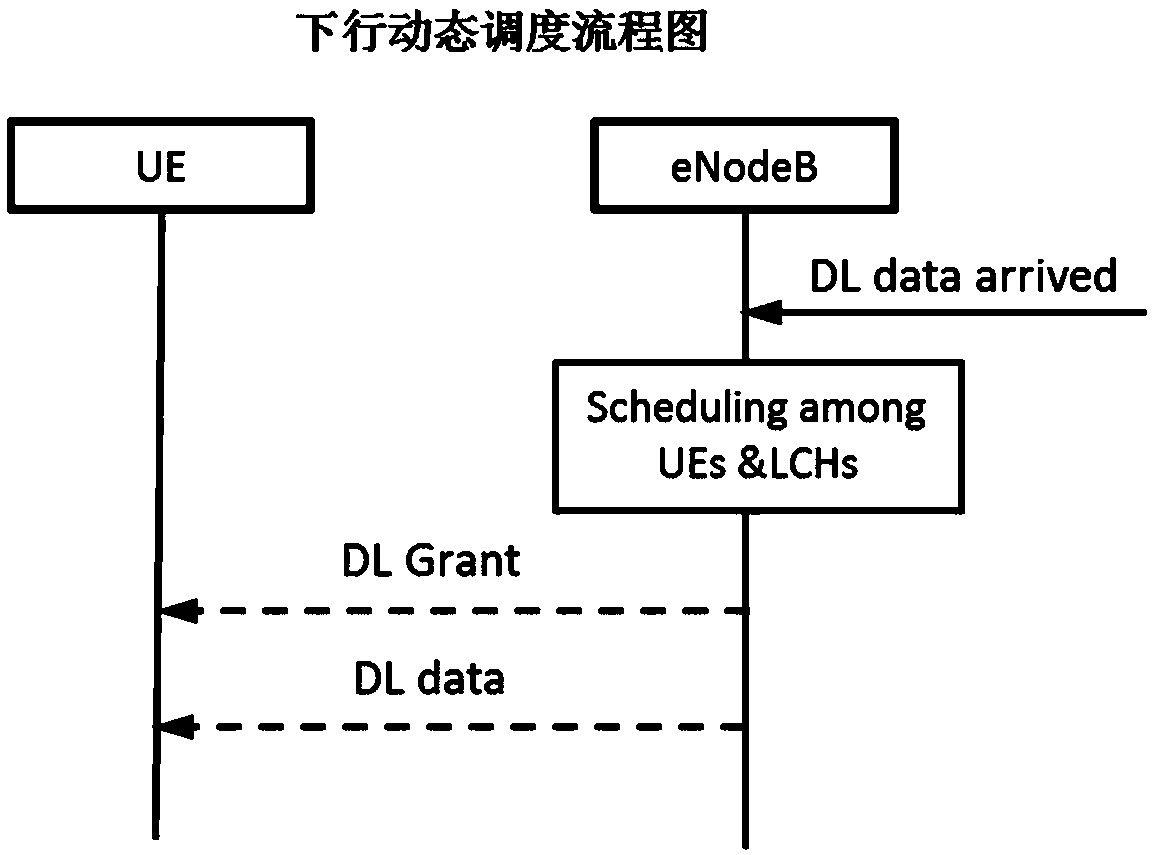
Uplink and downlink scheduling method and device based on user perception
ActiveCN111372315AMeet the experienceHigh level techniquesWireless communicationPower capabilityUser perception
The embodiment of the invention provides an uplink and downlink scheduling method and device based on user perception. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining available scheduling resources in a scheduling period TTI of each scheduling; removing the UE without the to-be-sent data in the current scheduling queue; updating a TA regulation factor for activating the UE; acquiring the priority of the UE to be scheduled at this time, and performing scheduling queue arrangement from high to low according to the priority; and scheduling the UE in sequence according to the priority of the scheduling queue, and calling the data in the UE cache according to the size of the currently available scheduling resource and the power capability of the UE. According to the embodiment of the invention, the defect of low throughput or non-uniform resource allocation of the device in the existing packet scheduling algorithm is overcome.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP ZHEJIANG +1
Data concurrency transmission method of multi-network interface device
InactiveCN101883047BImplement concurrent transfersImprove the efficiency of parallel transfersError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksNetwork interface deviceSerial code
The invention belongs to the technical field of network, in particular relates to a data concurrency transmission method of a multi-network interface device. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a transmission end and a reception end detect the amount of network interfaces for communication and label the network interfaces so that each network interface for communication has a serial number; (2) the transmission end divides the data to be transmitted into a plurality of message segments and adds transmission serial number for each message segment; (3) the transmission end remainders the transmission serial number of the message segment to the amount of the network interfaces and transmits the message segment according to the obtained remainder by selecting the corresponding network interface; and (4) the reception end orders the received message segments. The invention can fully utilize the traditional network to solve the problems of unreasonable data distributing and dispatching, disordered reception, low retransmission efficiency, and the like by an improved grouping dispatching algorithm.
Owner:黄宏程
A Packet Scheduling Algorithm for Cicq Structured Cross Buffer Queue Balance
InactiveCN105429898BImprove pass rateGood practical valueData switching networksEqualizationTime delayed
The invention discloses a CICQ structure crossbuffer queue balance packet scheduling algorithm. According to the CICQ structure crossbuffer queue balance packet scheduling algorithm, making a switch work in a work-conserving state as a core is realized or is approached to a maximum degree, output ports are taken as matching reference, output ports having smallest crossbuffer queue length are selected for priority matching, crossbuffer packet occupation of all output ports is balanced, so working in the work-conserving state is made to realize or approach to a maximum degree, the passing percentage is improved, and average packet time delay is further reduced. As is shown in simulation result comparison, for the CICQ switch with crossbuffer as one packet, the algorithm is better than known mainstream algorithms in the average packet time delay, and excellent practical values in large-scale high performance CICQ switches are realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A single-multicast mixed-service packet scheduling method for space-borne cicq-structured switches under geo-channel environment
ActiveCN106789738BError prevention/detection by using return channelRadio transmissionBroadcast packetOn board
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A packet scheduling method for geo-satellite on-board cicq structured switches considering channel state
ActiveCN106603145BImprove pass rateImprove channel utilizationRadio transmissionData switching networksGroup schedulingPass rate
The invention discloses a GEO satellite-borne CICQ structure exchange group scheduling algorithm considering the channel state. The algorithm of the present invention takes realizing or maximally approaching the switch to work in the work-conserving state as the core, with the goal of improving the channel utilization rate, and under the condition that the maximum matching number remains unchanged, the output port with a normal channel state can obtain the largest matching number , to reduce the average delay of packets while increasing the pass rate. The comparison of the simulation results shows that for the GEO satellite on-board CICQ switch with a cross-buffer capacity of one packet, under various common satellite channel states, the algorithm of the present invention is superior to the existing mainstream in terms of pass rate and average packet delay The algorithm has good practical value in GEO high-performance spaceborne CICQ switches.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
An Online Certificate Status Query Method Based on Limited Priority Dynamic Scheduling Grouping Algorithm
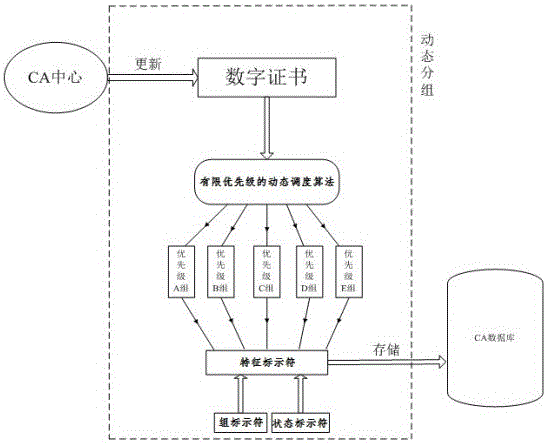
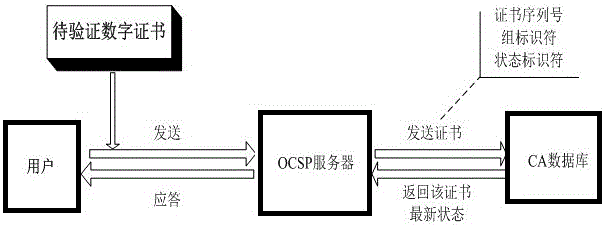
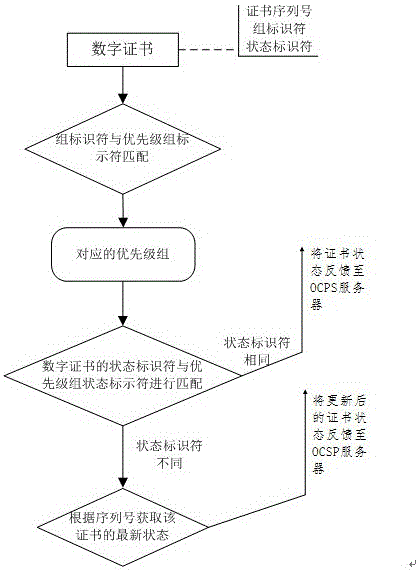
InactiveCN103281307BReduce the number of queriesImprove applicabilityUser identity/authority verificationSpecial data processing applicationsCertificate authorityOperating system
The invention provides the technical scheme of an on-line certificate state query method for a dynamic packet scheduling algorithm on the basis of a limited priority level. The scheme is based on the limited priority level dynamic packet scheduling algorithm; when a CA (certificate authority) center issues an updated-state digital certificate, the algorithm is utilized to dynamically group and store the updated digital certificate into a CA database, and a characteristic identifier is correspondingly added; and when the digital certificate state is queried, the characteristic identifier is matched to look up the priority level group corresponding to the digital certificate to obtain the real-time state of the digital certificate. According to the method, the query time of the data base is reduced, the query time is shortened, the query efficiency is improved, and the on-line certificate state query method has a good applicability for the financial stock exchange and the bank in which the effectiveness of the digital certificate is frequently verified and the state of the digital certificate changes frequently.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method and apparatus for scheduling packet
InactiveCN101465794BUniform outputTimely outputData switching networksNon real timeReal time services
The embodiment of the invention discloses a packet scheduling algorithm and a device thereof, belonging to communication field. The packet scheduling algorithm includes the following steps: partitioning the service packets into real-time service packets and non-real-time service packets according to headers of the service packets; judging whether legal real-time service packets exist in the real-time service packets according to shaping virtual clock algorithm, if yes, sending out the legal real-time service packets, and if no, sending out the non-real-time service packets; if new legal real-time service packets appear during the process of sending out the non-real-time service packets, suspending the sending of the non-real-time service packets and sending out the new legal real-time service packets. The device comprises a sort module, a judge module, a real-time service sending module, a non-real-time sending module and a notification module. The packet scheduling algorithm and the device can ensure that the sending of the real-time service packets is free from the influence of the non-real-time service packets and can avoid the occasion that the non-real-time service packets wait for too long. Therefore, the packet scheduling algorithm and the device have strong practicability, reliability and effectiveness.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
A method for multi-service coexistence and ip-layer data packet scheduling in industrial internet of things
ActiveCN112822268BOvercome the problem that real-time performance cannot be guaranteedReduce the probability of packet lossData switching networksNetwork ConvergenceData pack
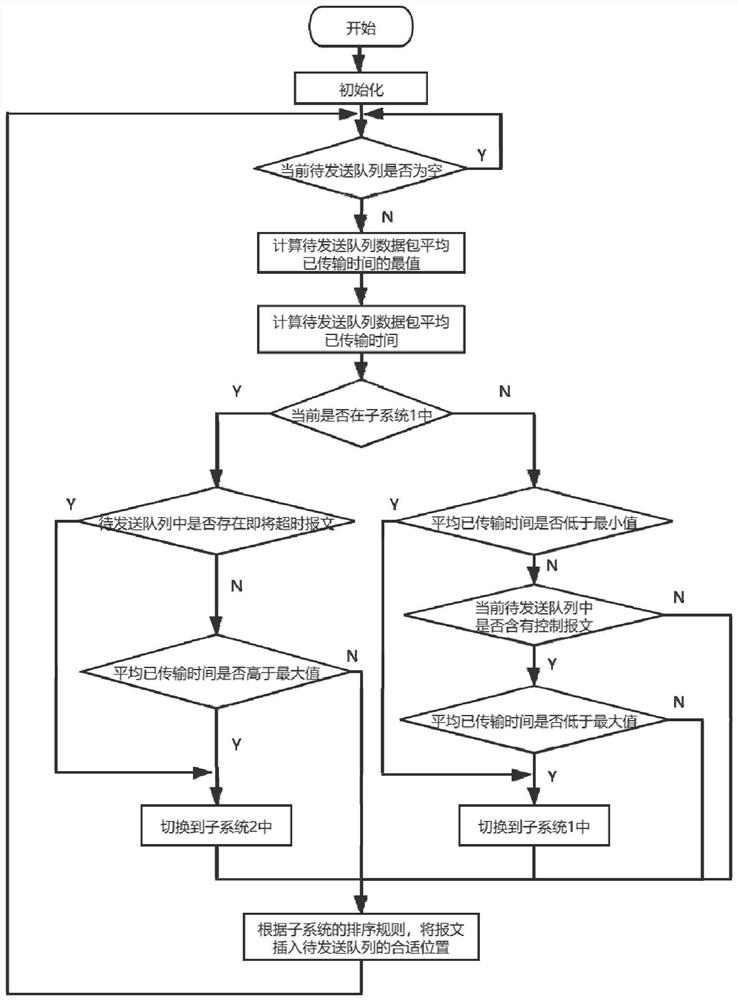
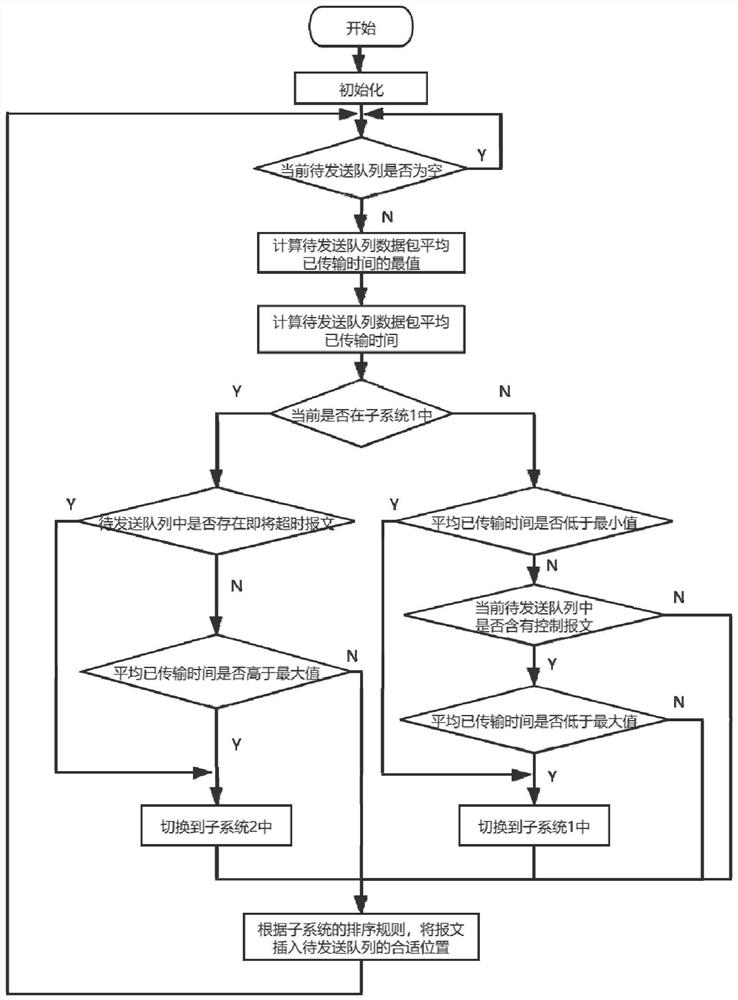
An IP layer data packet scheduling algorithm oriented to multi-service coexistence and deterministic network requirements in the Industrial Internet of Things belongs to the technical field of real-time data transmission and multi-network integration of the Industrial Internet of Things. Current packet scheduling algorithms lack the analysis of the coexistence of continuous periodic data and discrete control data in the Industrial Internet of Things. The algorithm considers the priority and transmission delay of the data packets at the same time, and obtains the partial switching conditions of the hybrid switching system through the calculation formula of the maximum transmission delay of the data packets of each priority, and uses the hybrid switching system model to carry out the packet scheduling process Based on the analysis, the packet scheduling algorithm of IP layer is designed. The algorithm of the invention can be used to schedule data packets from different types of networks, realize multi-network integration, meet the real-time requirements of data packets in the industrial internet of things, and reduce the packet loss rate.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
IP layer data packet scheduling algorithm oriented to multi-service coexistence and deterministic network requirements in industrial Internet of Things
ActiveCN112822268AOvercome the problem that real-time performance cannot be guaranteedReduce the probability of packet lossData switching networksNetwork ConvergenceAlgorithm
The invention discloses an IP layer data packet scheduling algorithm oriented to multi-service coexistence and deterministic network requirements in an industrial internet of things, and belongs to the technical field of real-time data transmission and multi-network convergence of the industrial internet of things. An existing data packet scheduling algorithm lacks analysis of the coexistence problem of continuous periodic data and discrete control data in the industrial Internet of Things. According to the algorithm, the priorities and the transmission delays of data packets are considered at the same time, partial switching conditions of a hybrid switching system are obtained through a calculation formula of the maximum transmission delays of the data packets of all the priorities, a hybrid switching system model is used for analyzing the data packet scheduling process, and therefore a data packet scheduling algorithm of the IP layer is designed. By using the algorithm provided by the invention, data packets from different types of networks can be scheduled, multi-network fusion is realized, meanwhile, the real-time requirement of the data packets in the industrial Internet of Things can be met, and the packet loss rate is reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com