Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
730 results about "Optical communication networks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
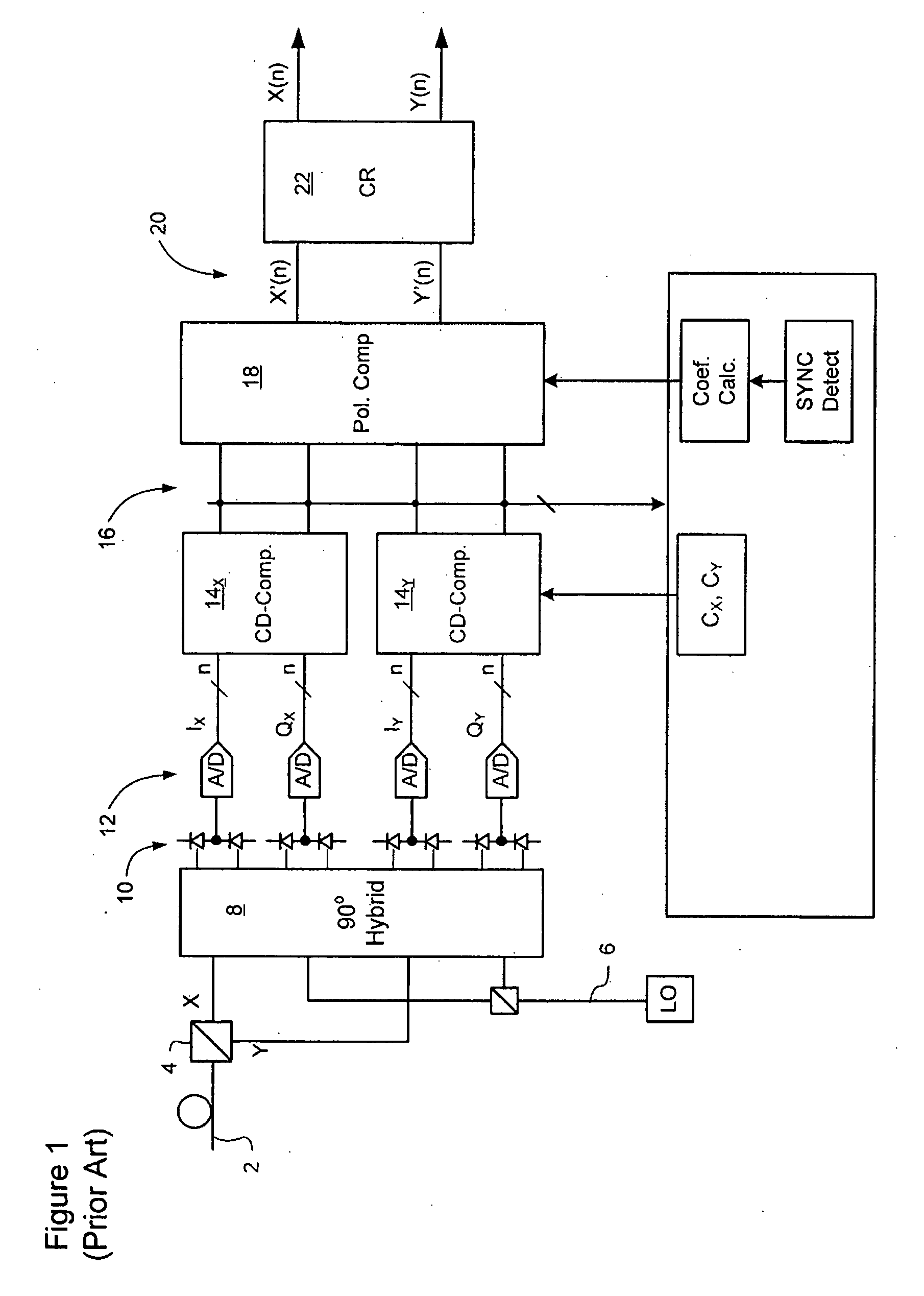
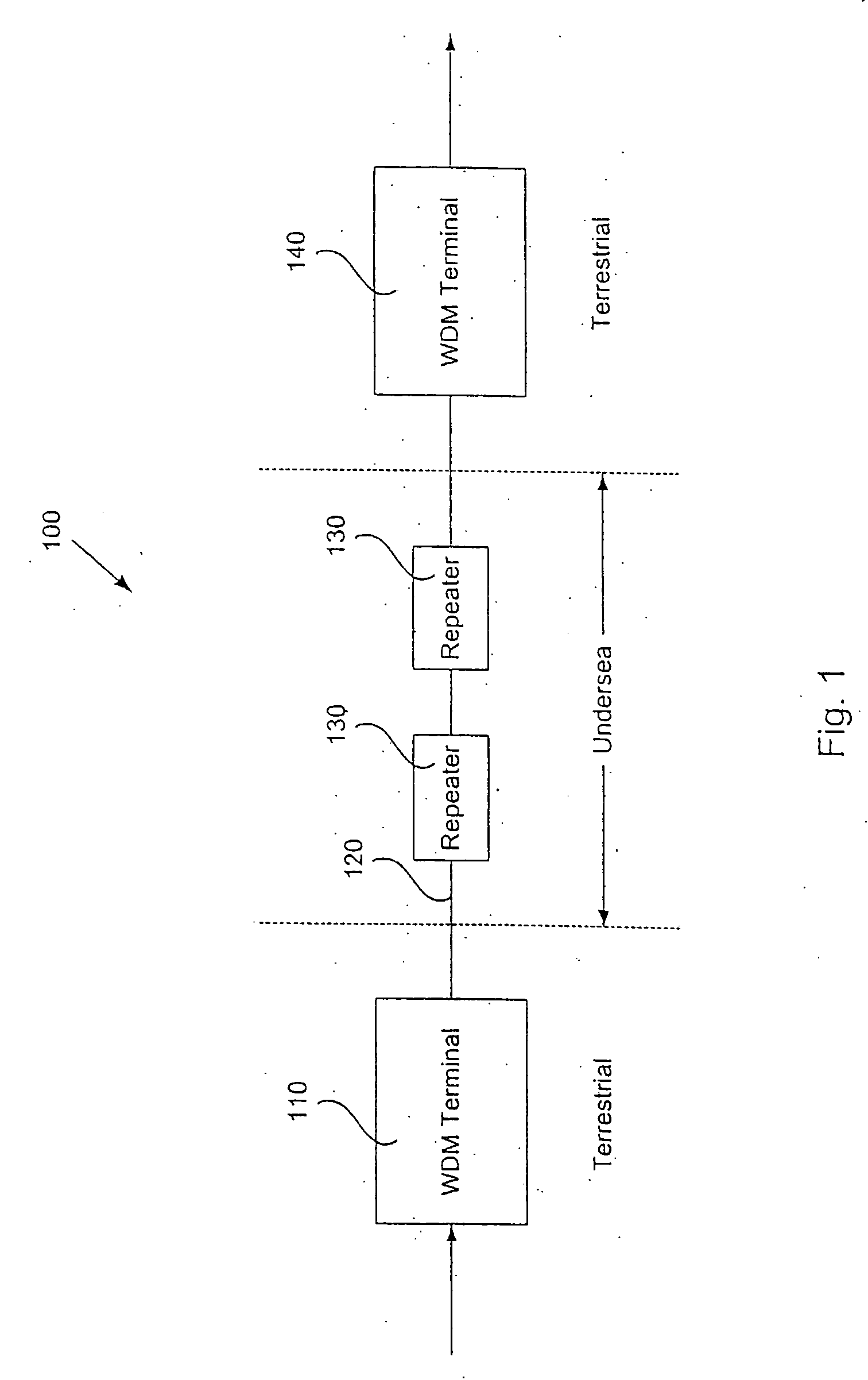
An optical network is a type of data communication network built with optical fiber technology. It utilizes optical fiber cables as the primary communication medium for converting data and passing data as light pulses between sender and receiver nodes. An optical network is also known as an optical fiber...
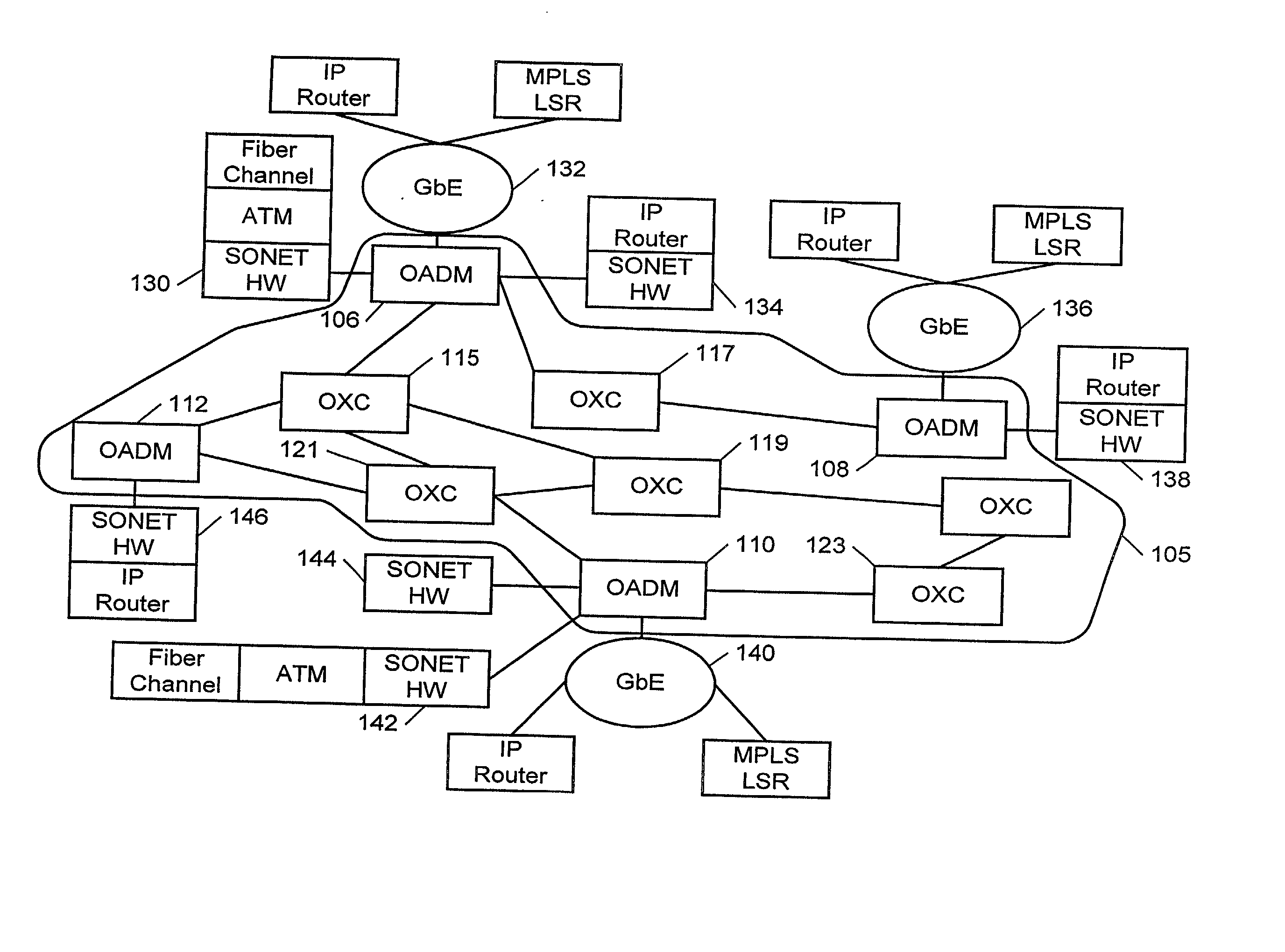
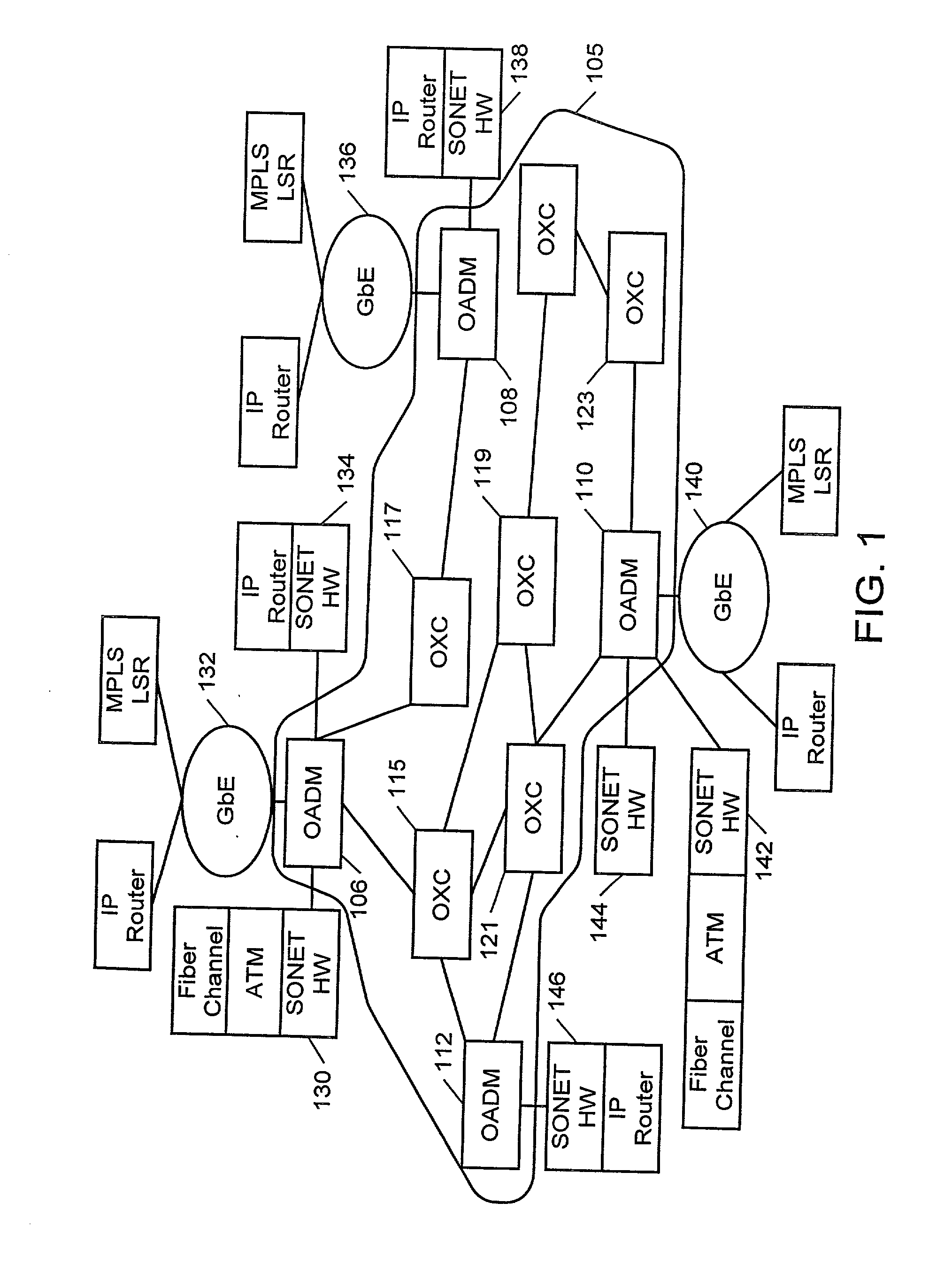
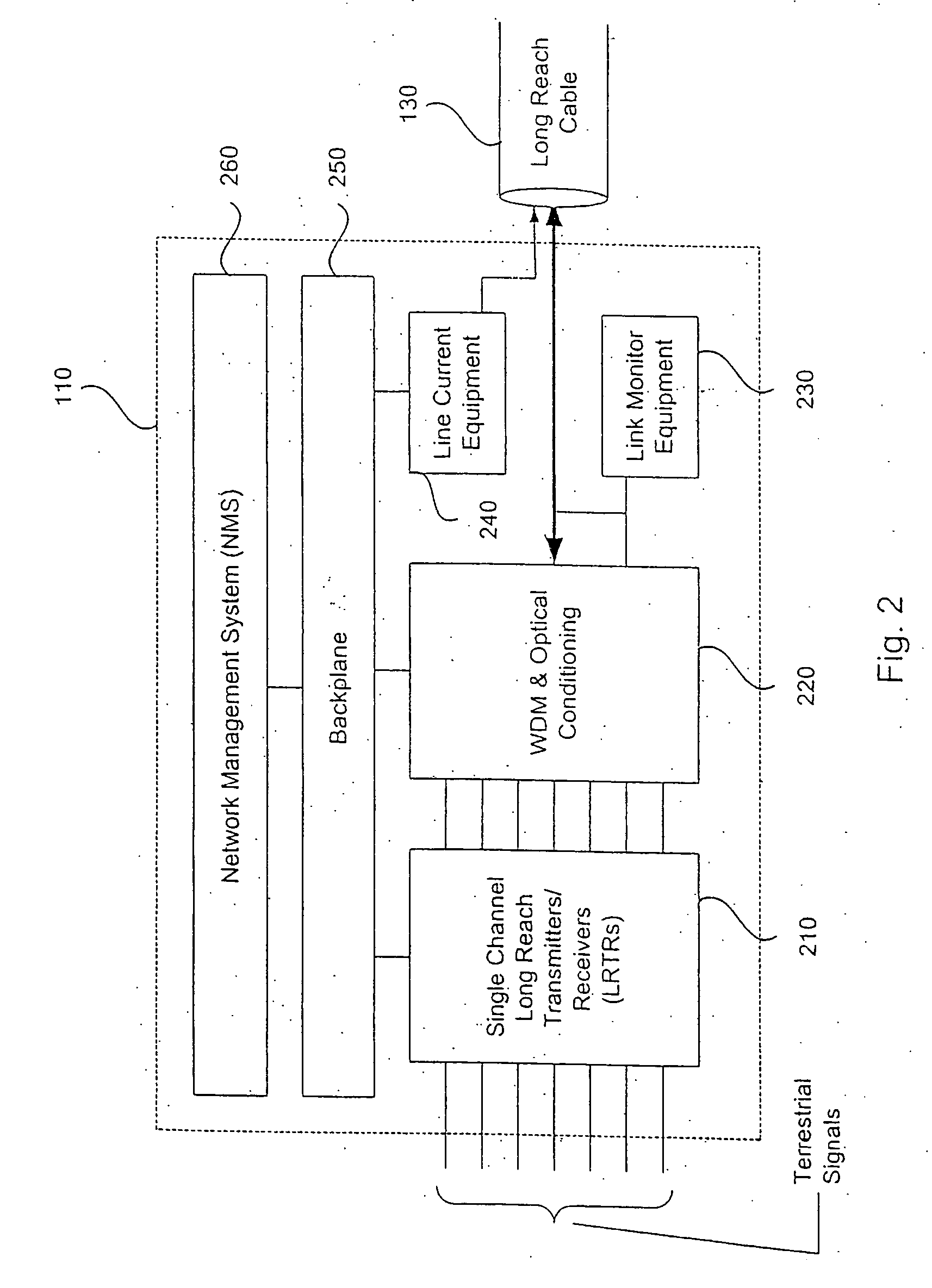
Protection switching for an optical network, and methods and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20020176131A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsTraffic capacityLine card
An optical communications network having at least one optical switch connected to a network access device. The optical switch includes a first line card disposed along a first communications path over which a first optical signal is transmitted. The first line card is connected to the network access device. A second line card is disposed along a second communications path over which a second optical signal is transmitted. An inter-card communication channel is provided for bridging the second path to the first line card. The system enables the rapid switching of traffic from the first optical path to the second optical path.
Owner:FIRSTWAVE SECURE INTELLIGENT OPTICAL NETWORKS
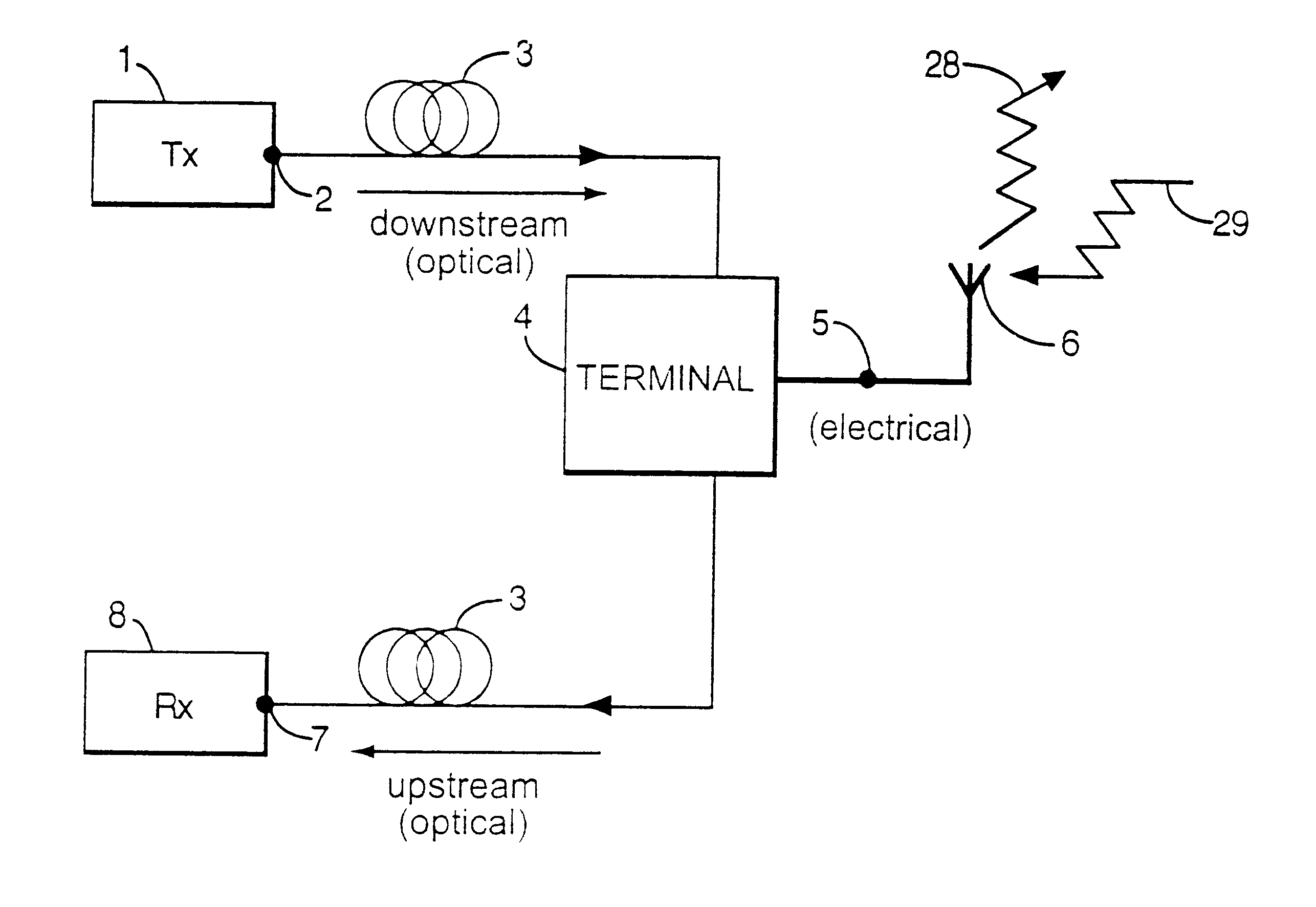
Telecommunications system
InactiveUS6731880B2Low-cost equipmentElectromagnetic transmittersRadio-over-fibreComputer terminalBroadcast communication network
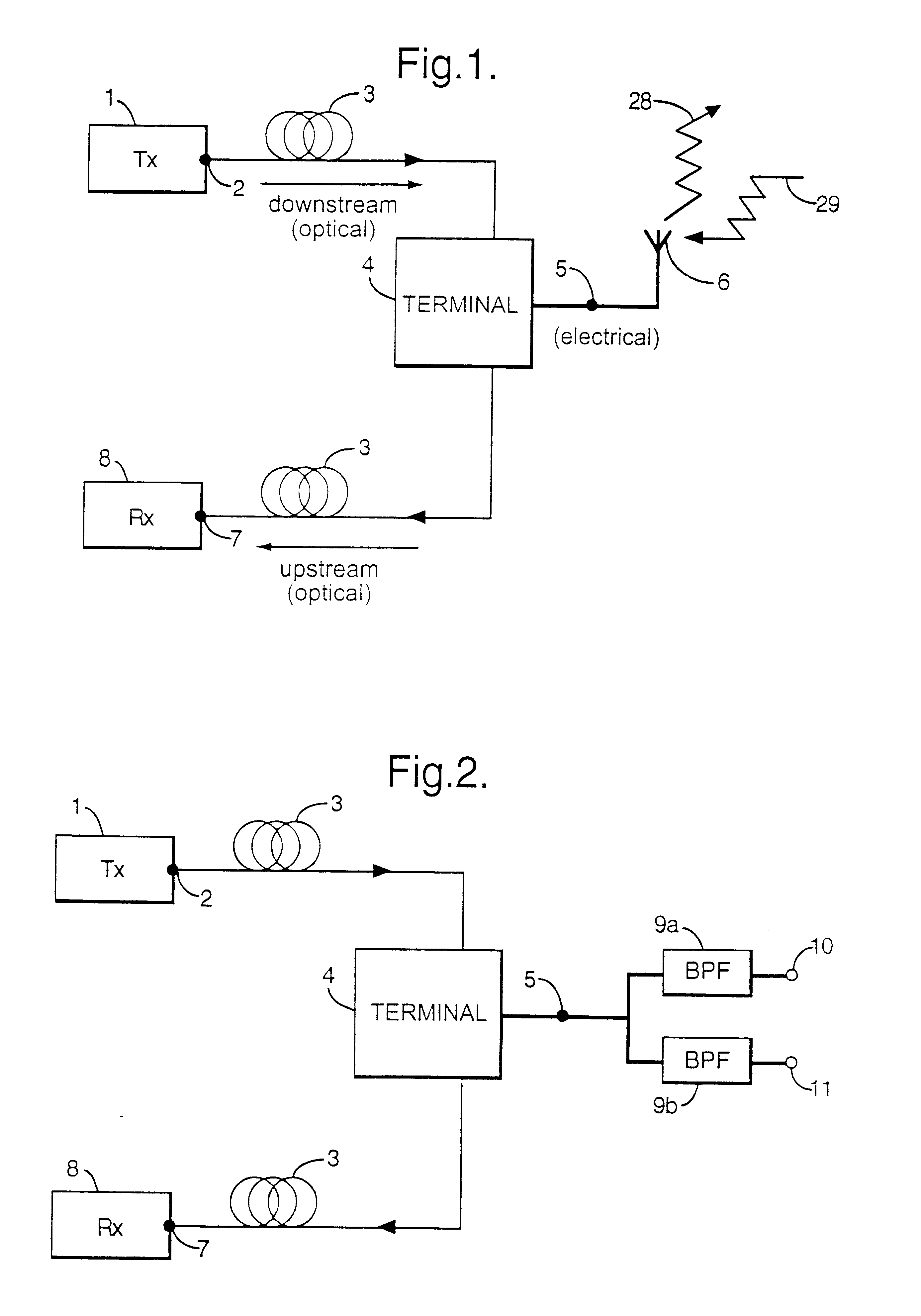
An optical communications network includes a terminal which can simultaneously receive and modulate an optical signal. The terminal includes an optical modulator which is controlled by varying the bias voltage applied to it.
Owner:NEXTG NETWORKS INC
Systems and methods for managing optical fibers and components within an enclosure in an optical communications networks
ActiveUS20050105873A1Minimize and preferentially eliminate congestionFlexible and convenientOptical fibre/cable installationFibre mechanical structuresFiberRibbon cable
The preferred embodiments of the present invention include an optical splitter module having connectorized pigtails that are stored on the bulkhead faceplate of the module. The module includes an optical splitter output harness, for example, a ribbon cable assembly attached to the bulkhead with rugged strain relief mechanism. The ribbon harness is converted to individual pigtails with connectors which are stored on adapter receptacles on the faceplate. Adapter receptacles used may optionally be half receptacles when storage is the only desired function or may be full receptacles when access to the pigtail ferrule tip is required. Access to the ferrule tip may be required for attaching fiber optic terminators to eliminate undesirable reflections caused by unterminated connectors. The module provides an administrative location for splitter outputs prior to being connected individually into service. The module also provides an administrative storage location for splitter outputs taken out of service as a temporary staging area before being reassigned and connected individually into service again.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
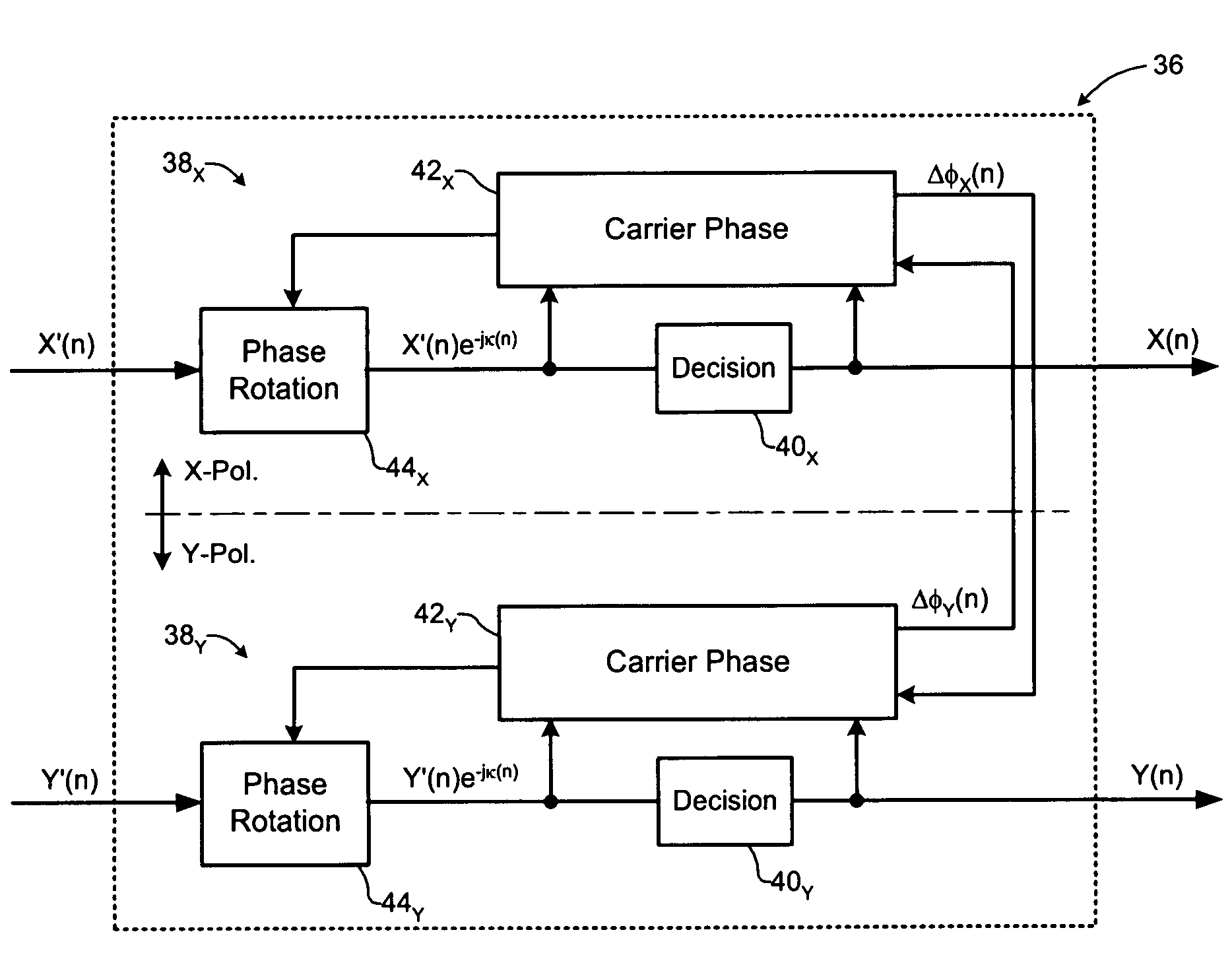
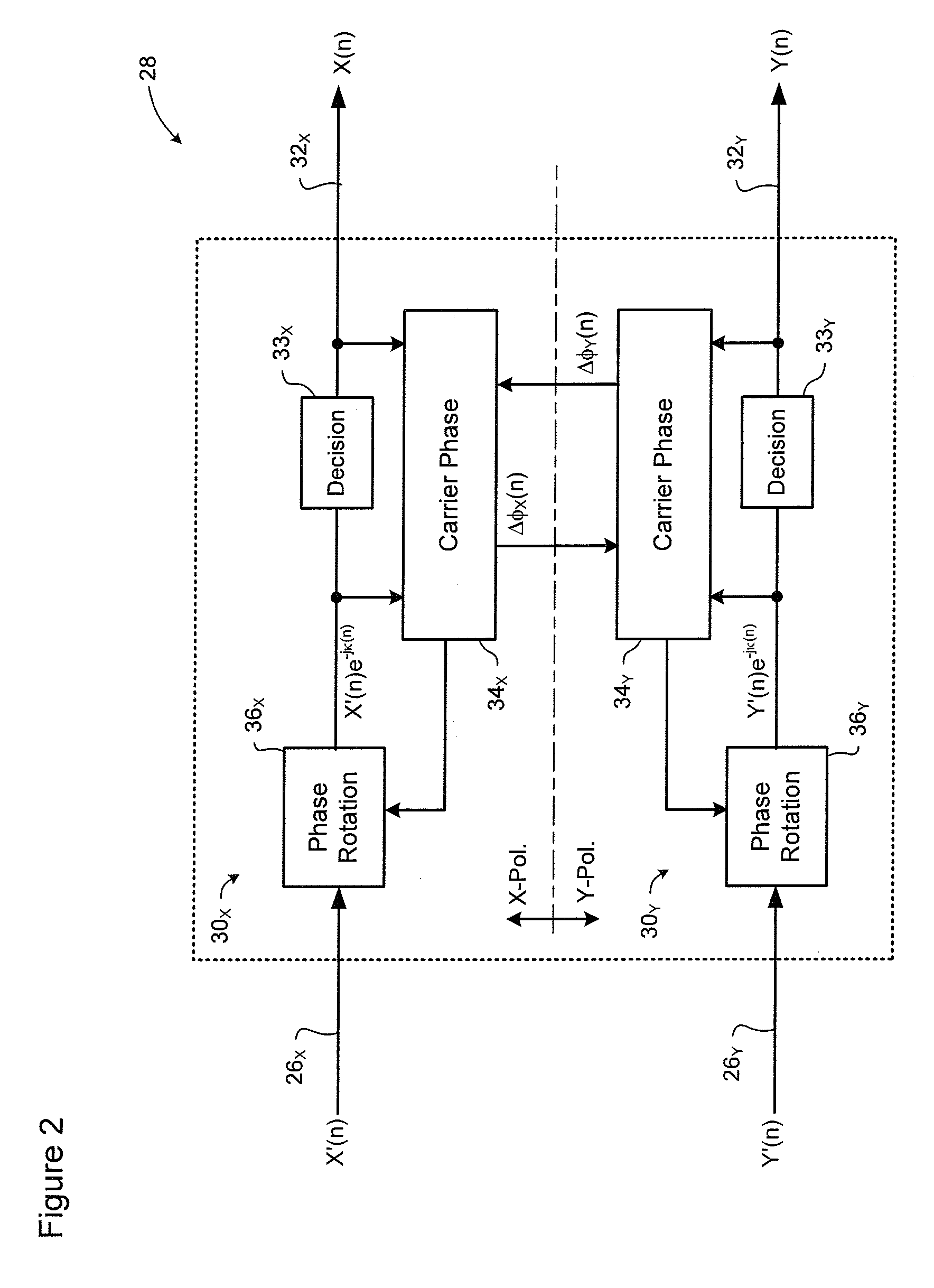
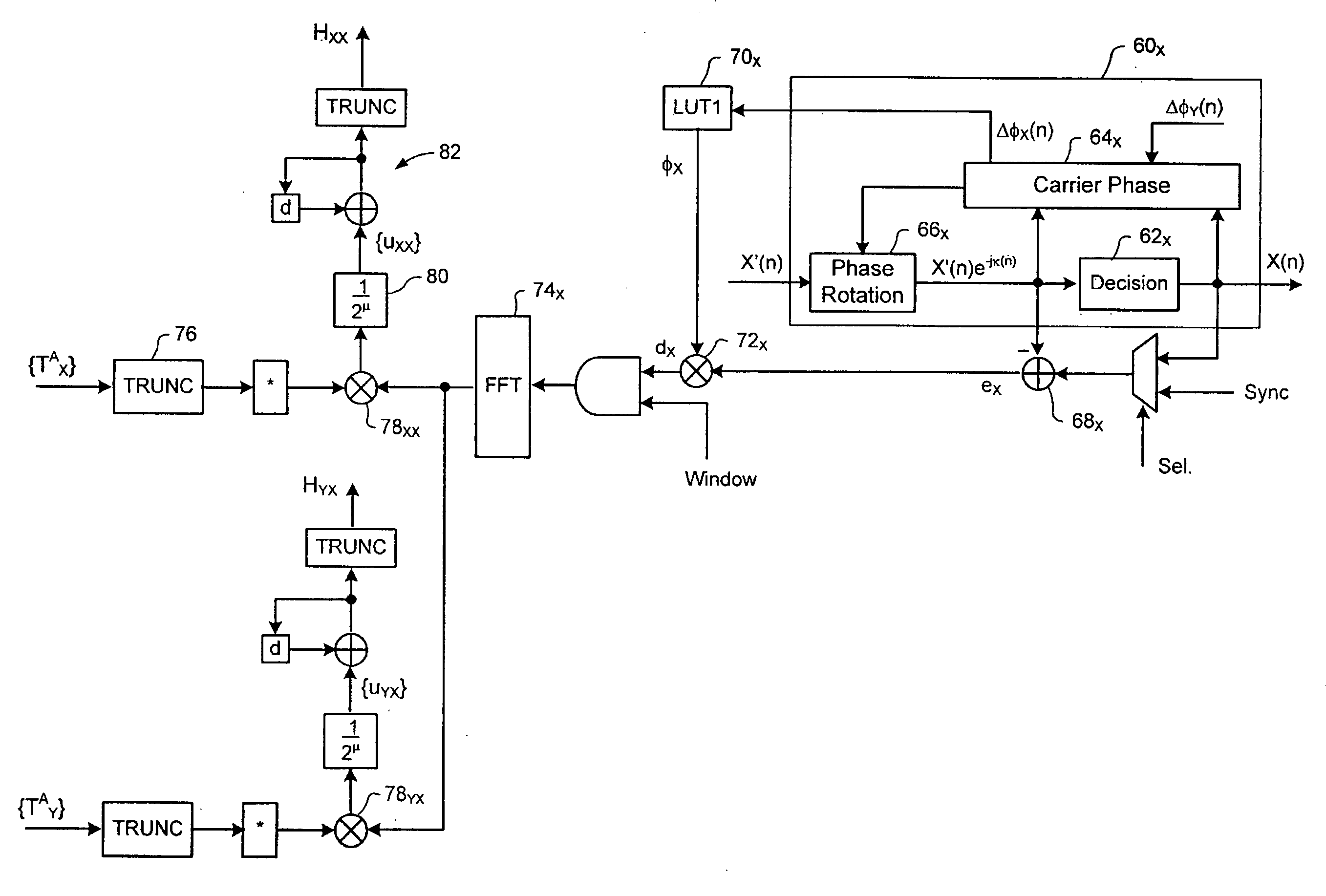
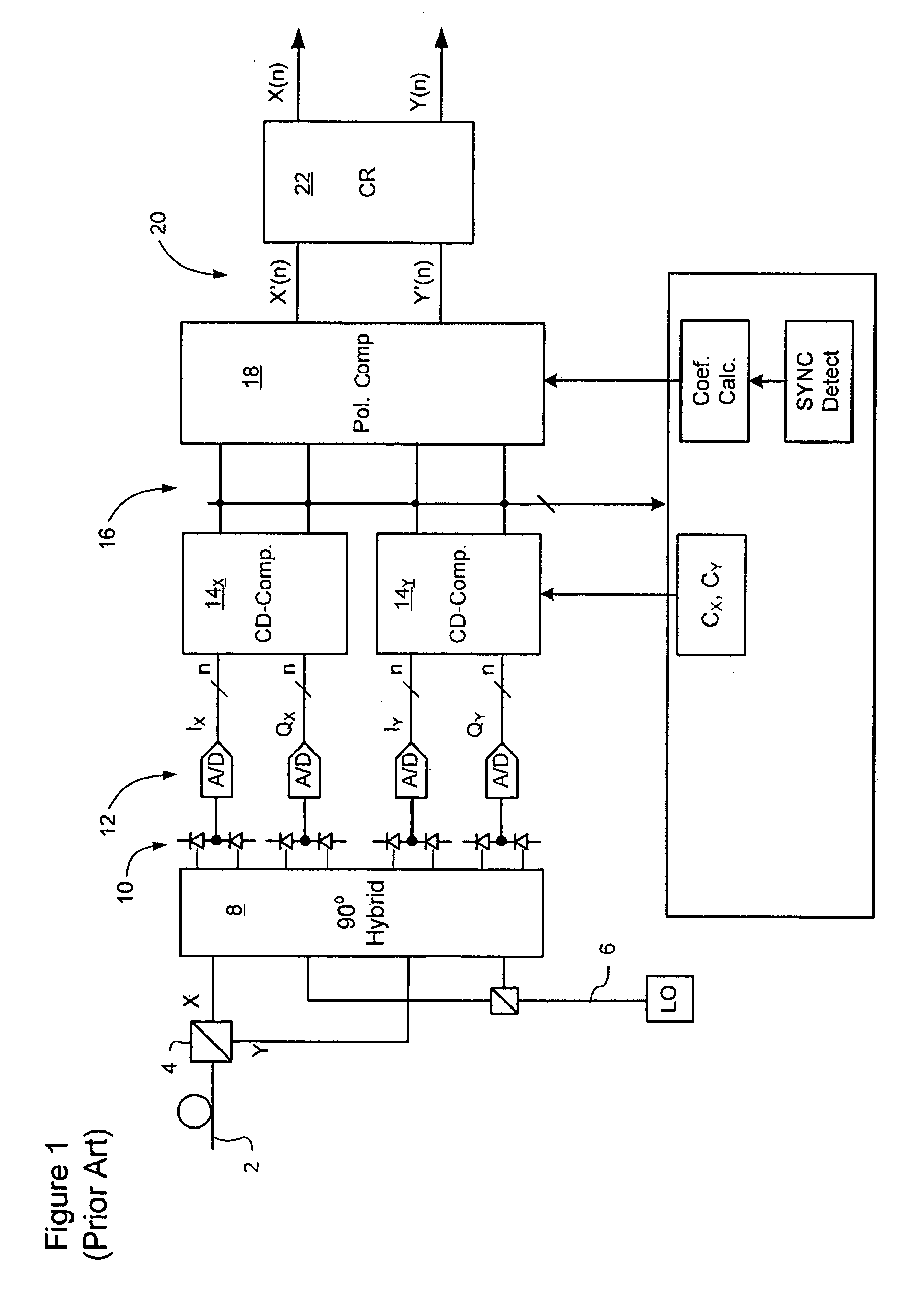
Carrier recovery in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS7606498B1Receiver initialisationSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansCarrier recoveryOptical receivers
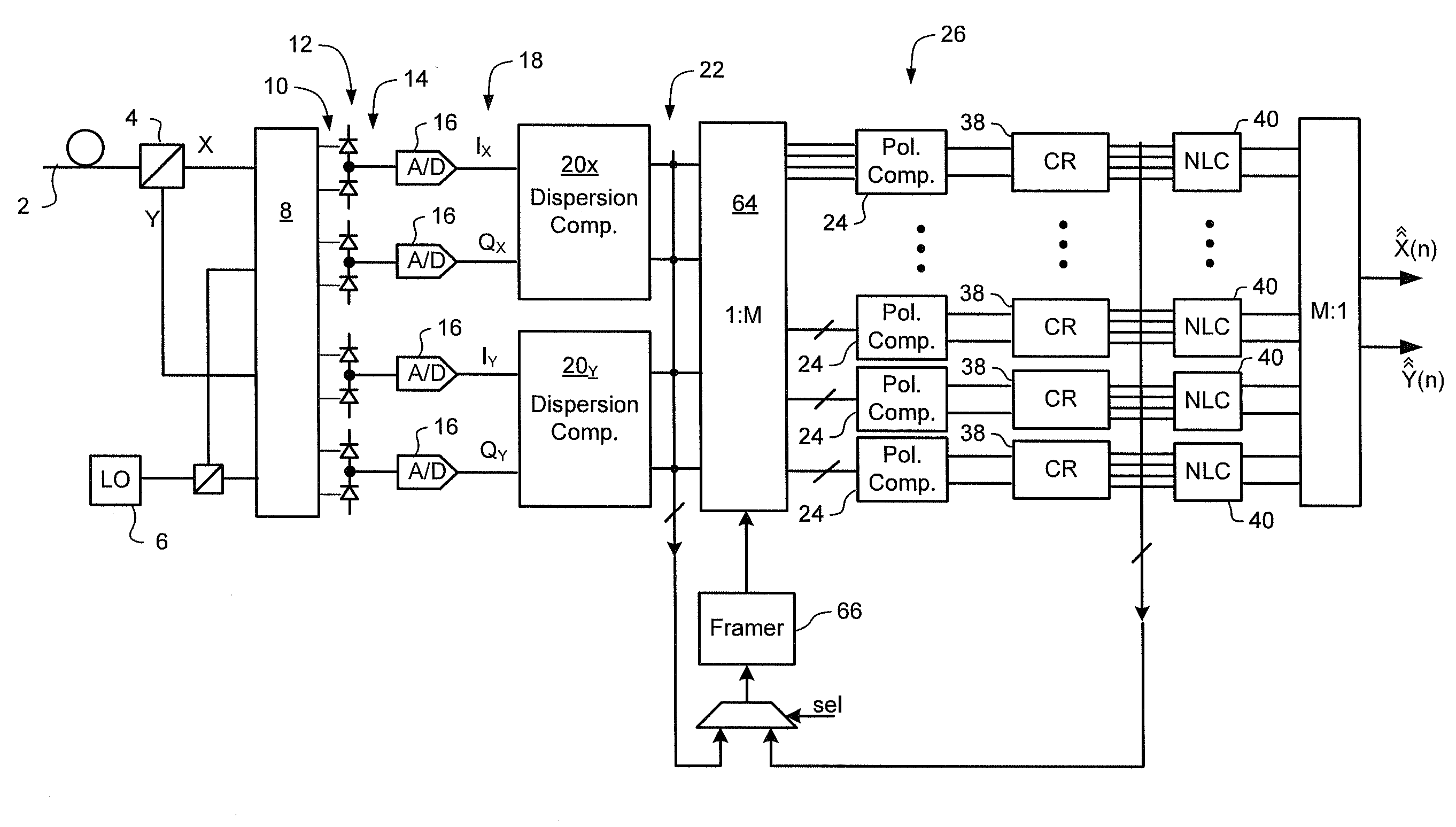
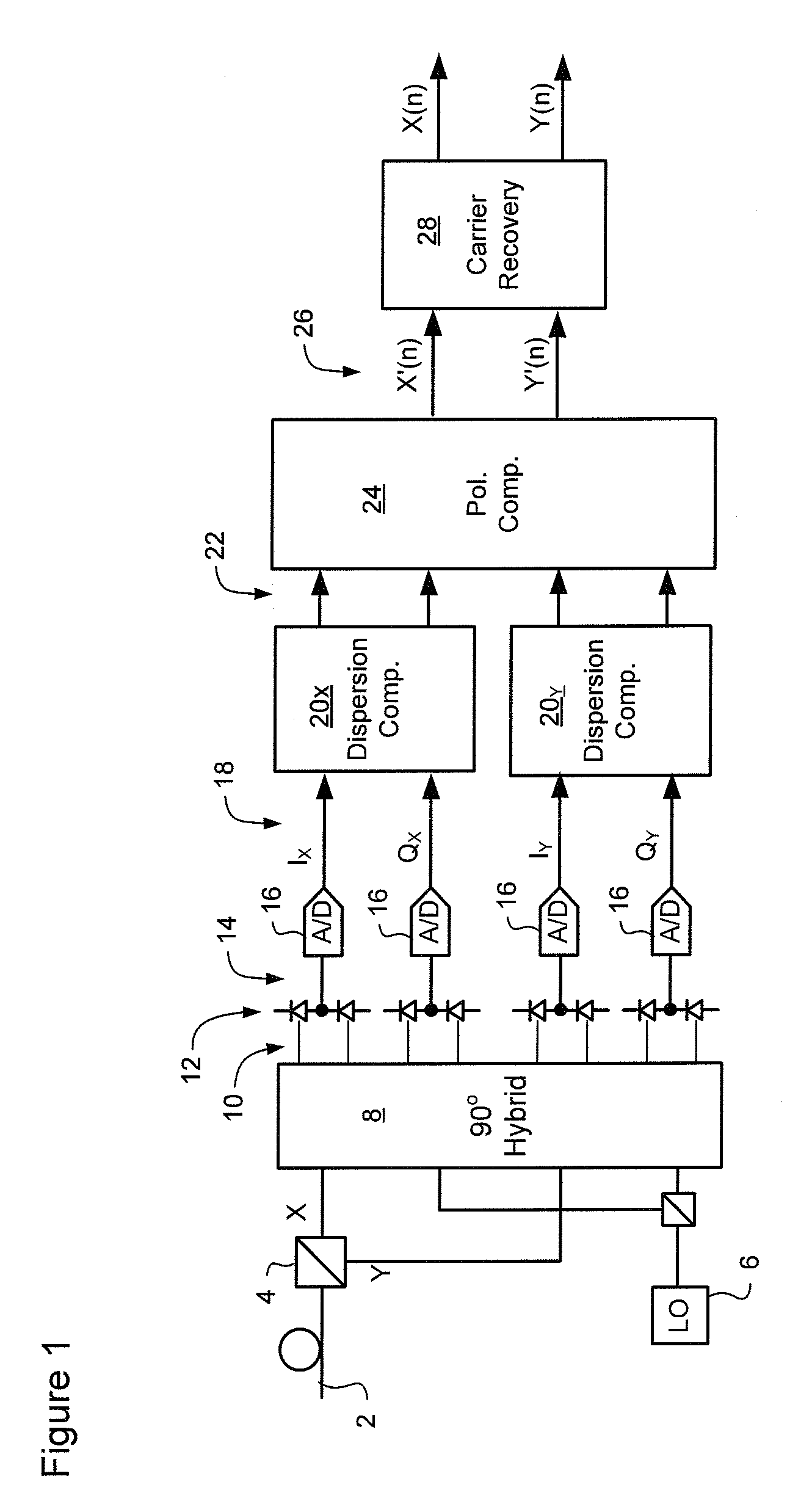
A method of carrier recovery from a high speed optical signal received through an optical communications network. A stream of multi-bit digital samples of the optical signal is processed to generate a multi-bit estimate X′(n) of each one of a plurality of transmitted symbols. A phase of each symbol estimate X′(n) is rotated, and a respective symbol phase error Δφ(n) of the rotated symbol estimate determined.
Owner:CIENA
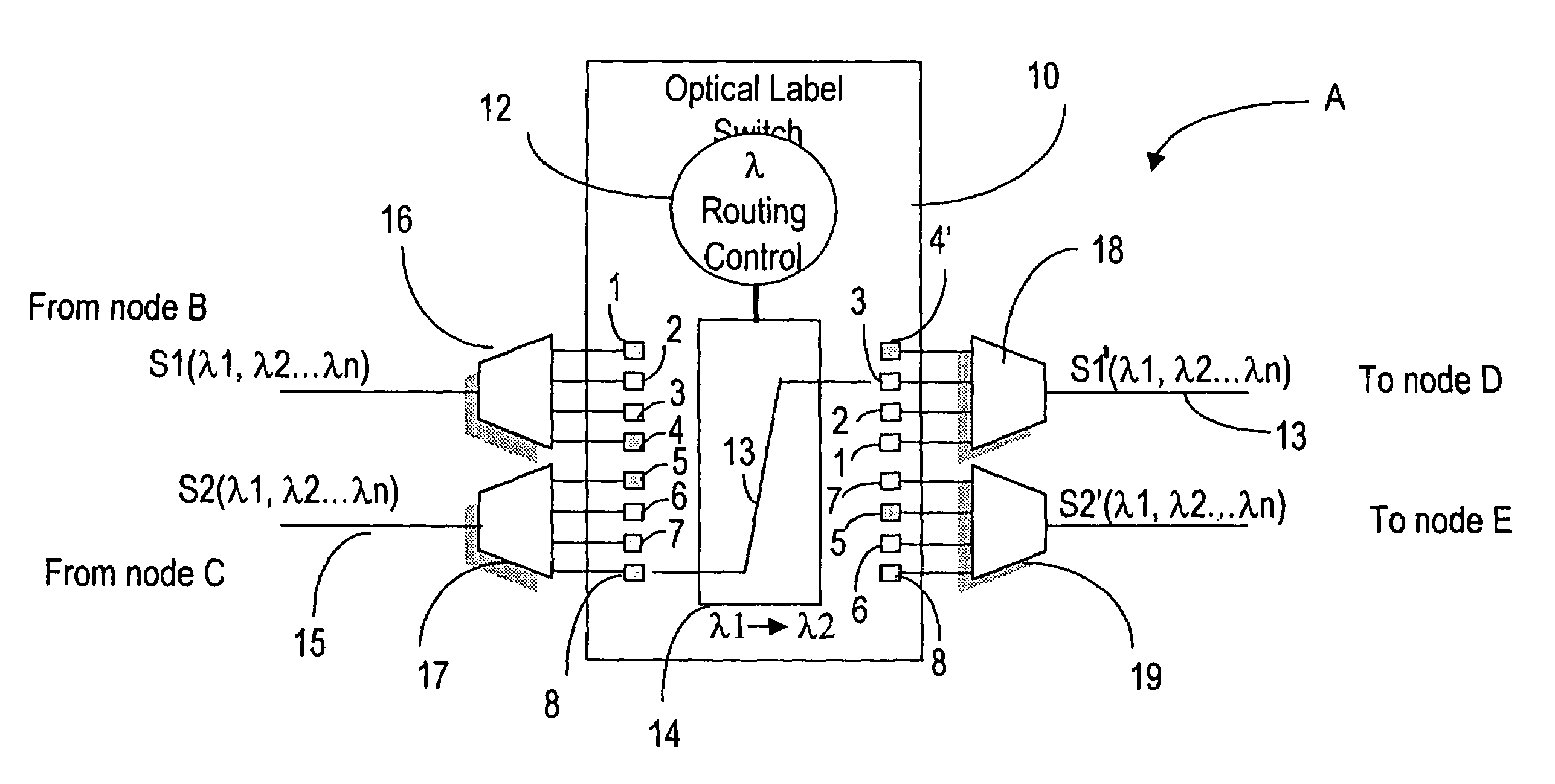
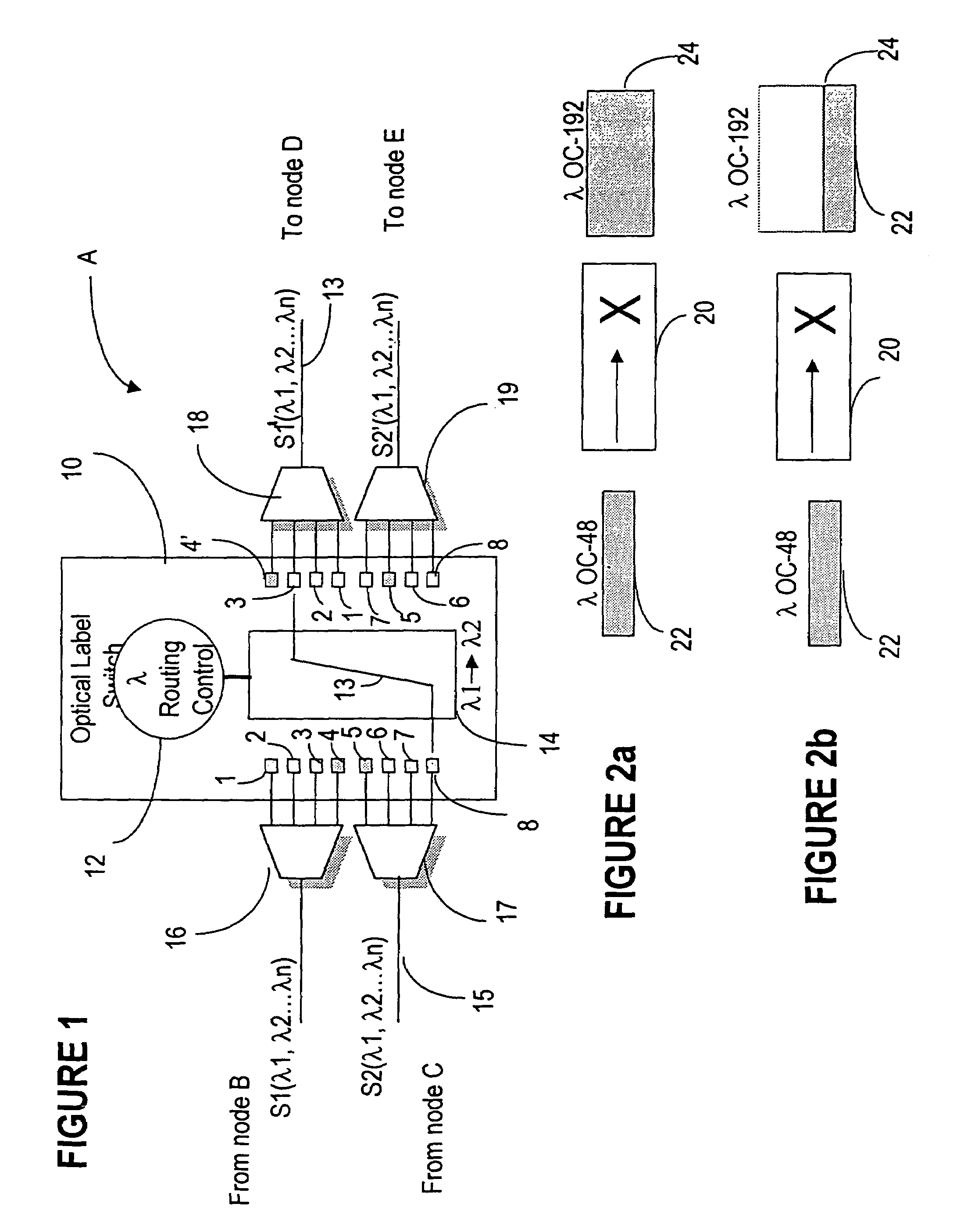
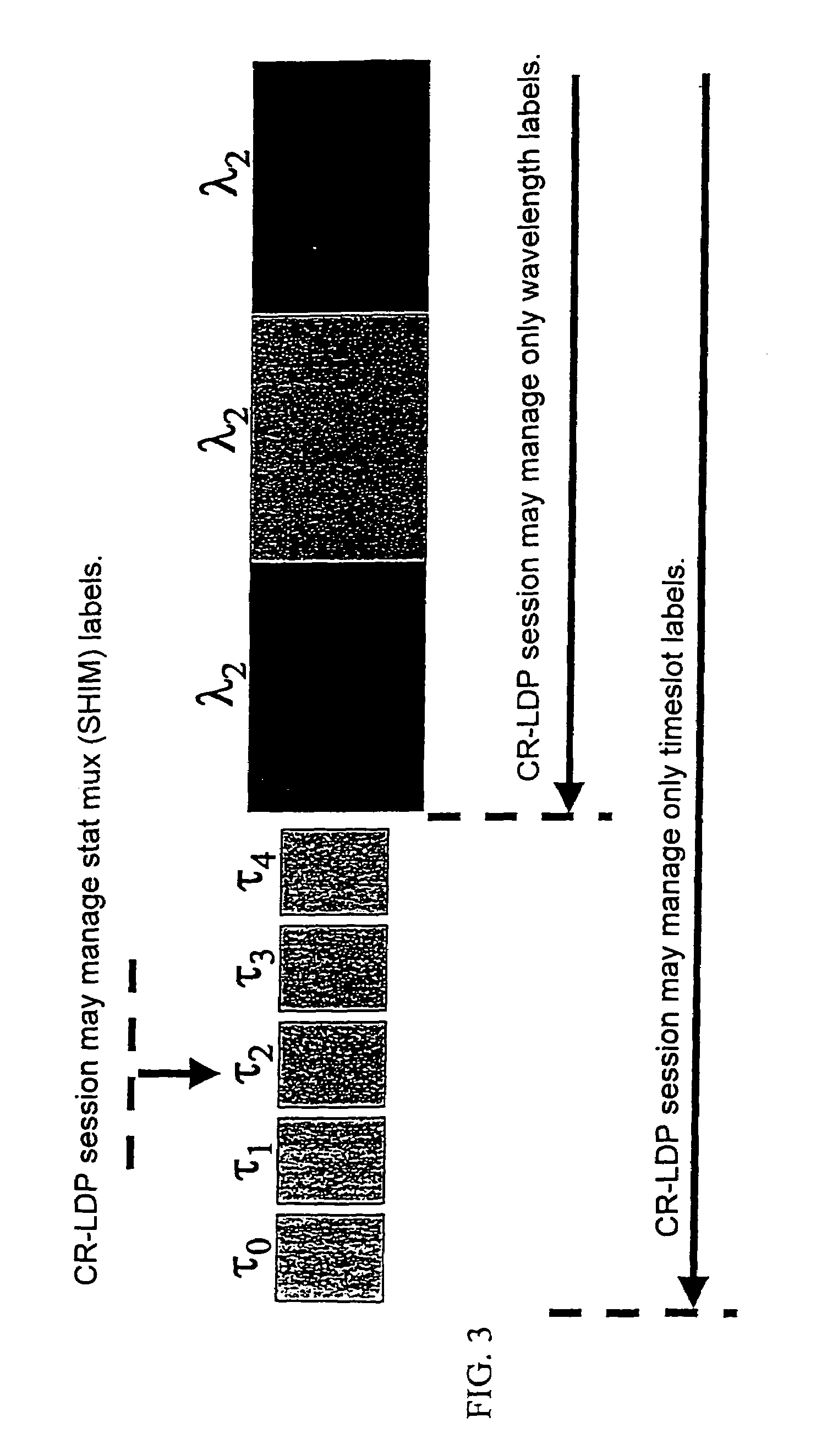
MPLS application to optical cross-connect using wavelength as a label
InactiveUS7031607B1Easy networkingMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexCross connectionMulti protocol
A label switching routing protocol for establishing a datapath as a sequence of locally unique labels in an optical communications network, is provided. A wavelength on an optical cross-connect is considered as a label, or one portion of a label. Timeslots may be assigned to designated wavelengths so as to form the second portion of a composite label. An optical / time cross-connect (OTXC) capable of wavelength conversion from an input to an output interface creates the datapath based on wavelength to wavelength substitution, under the control of a multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) protocol.
Owner:CIENA
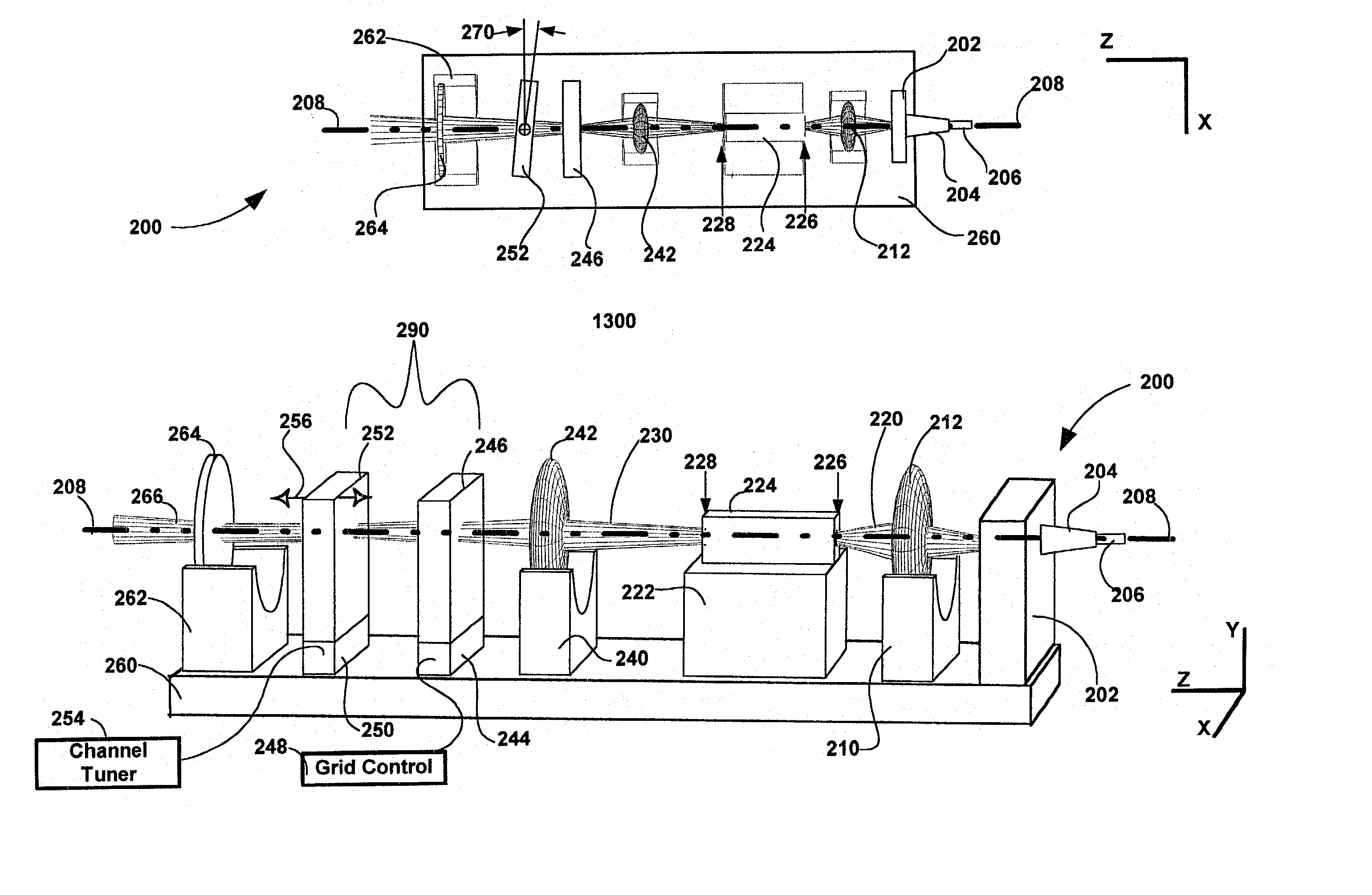
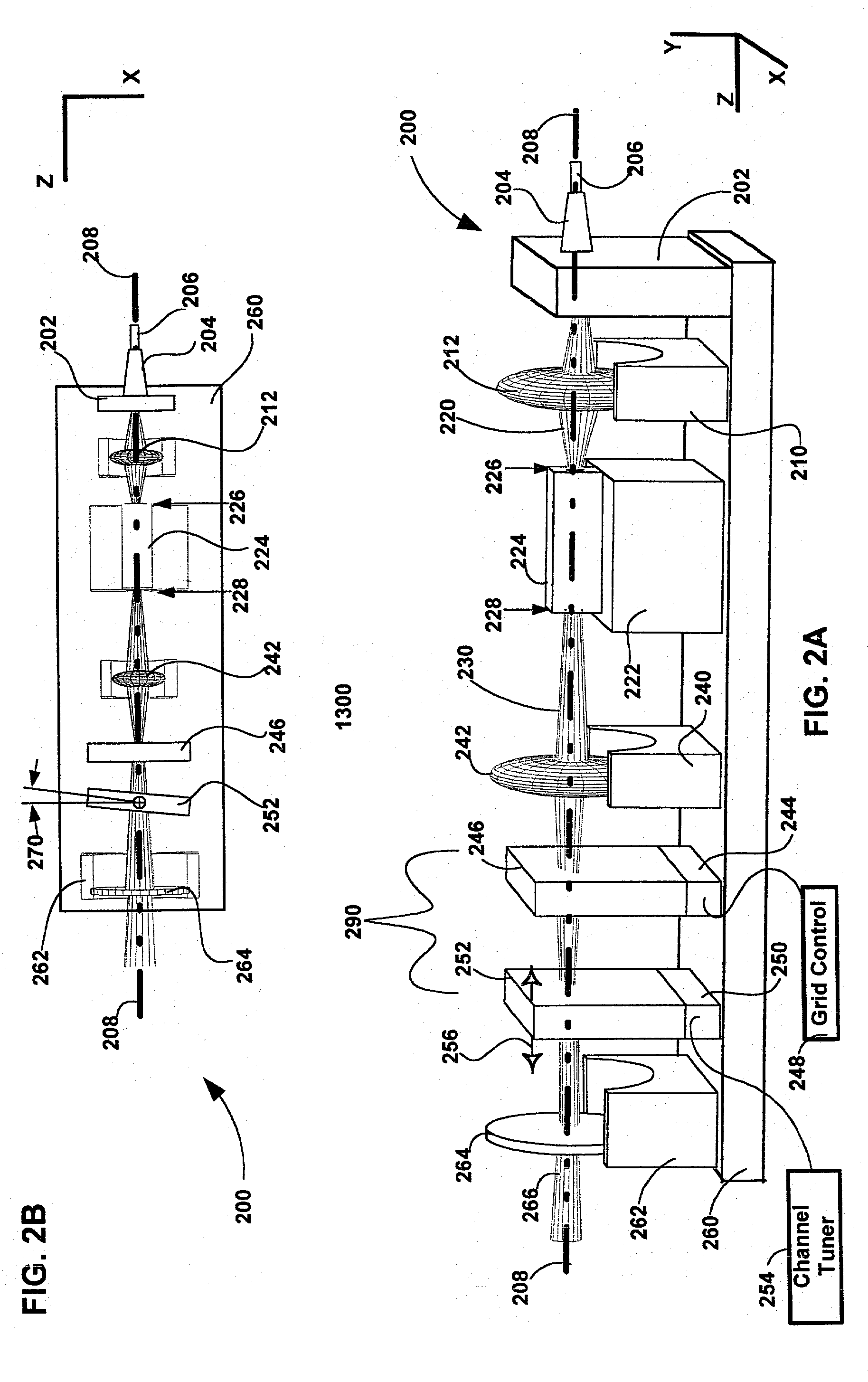
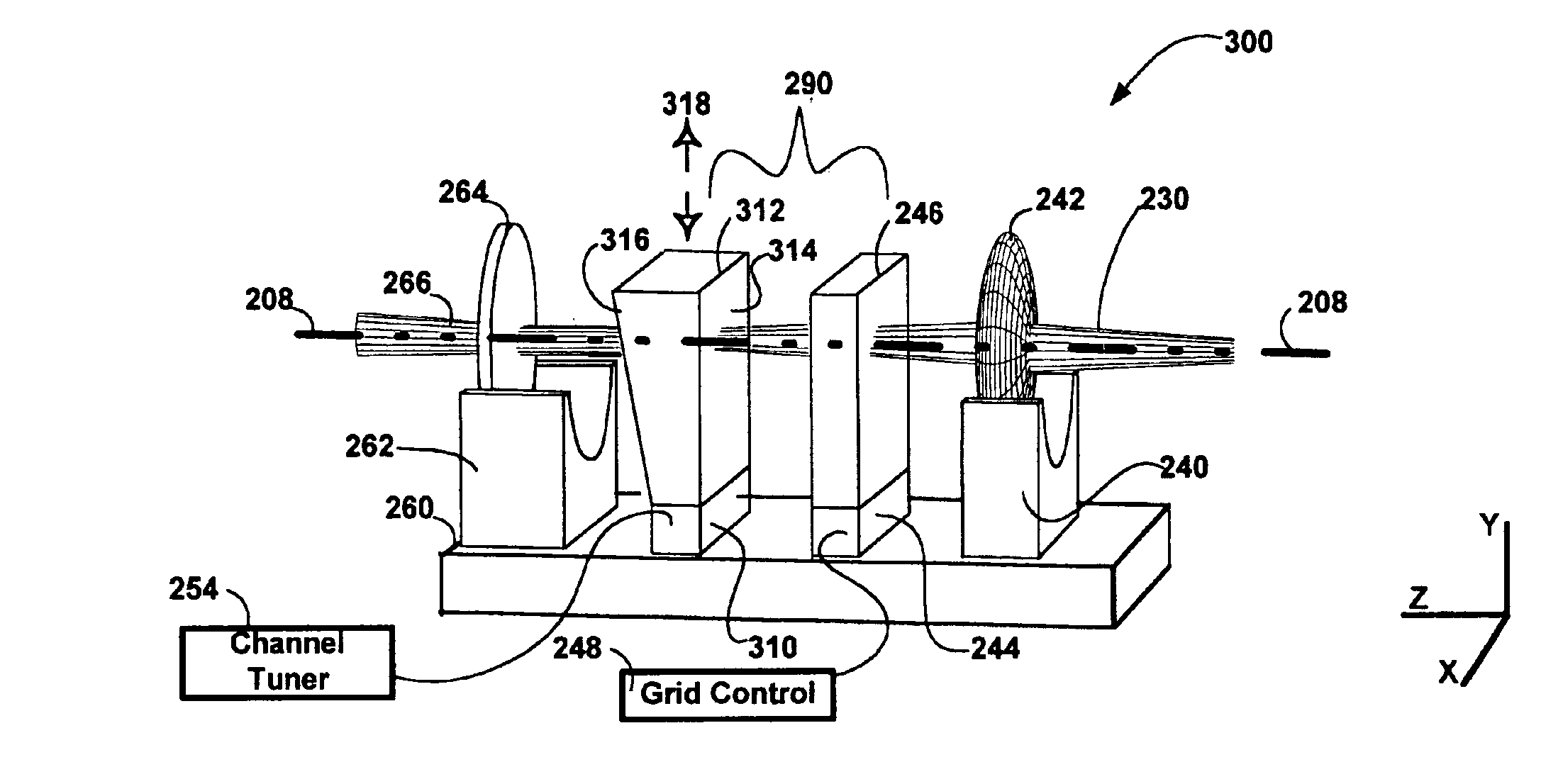
Method and apparatus for filtering an optical beam
InactiveUS20020126345A1Compact form factorEasy to tuneLaser optical resonator constructionPolarisation multiplex systemsExternal cavity laserMesh grid
The invention pertains to wavelength-agile optical filters suitable for wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) optical communications networks. More particularly, the invention pertains to optical filters with a wavelength reference that can be remotely switched to arbitrarily selectable channels on a standard grid, and to re-configurable optical communications networks employing same. The present invention provides a communication apparatus with a tunable filter which may be used in a wide range of applications including tuning an external cavity laser (ECL), selecting a wavelength for an add / drop multiplexer and providing channel selection and feedback for a wavelength locker. The filter may be utilized as a discrete component or in combination with circulators, wavelength lockers and gain medium. The filter may be implemented in whole or in part as part of a gain medium. The tunable filter exhibits a compact form factor and precise tuning to any selected wavelength of a predetermined set of wavelengths comprising a wavelength grid. The tunable filter may thus be utilized in telecom applications to generate the center wavelengths for any channel on the ITU or other optical grid.
Owner:INTEL CORP
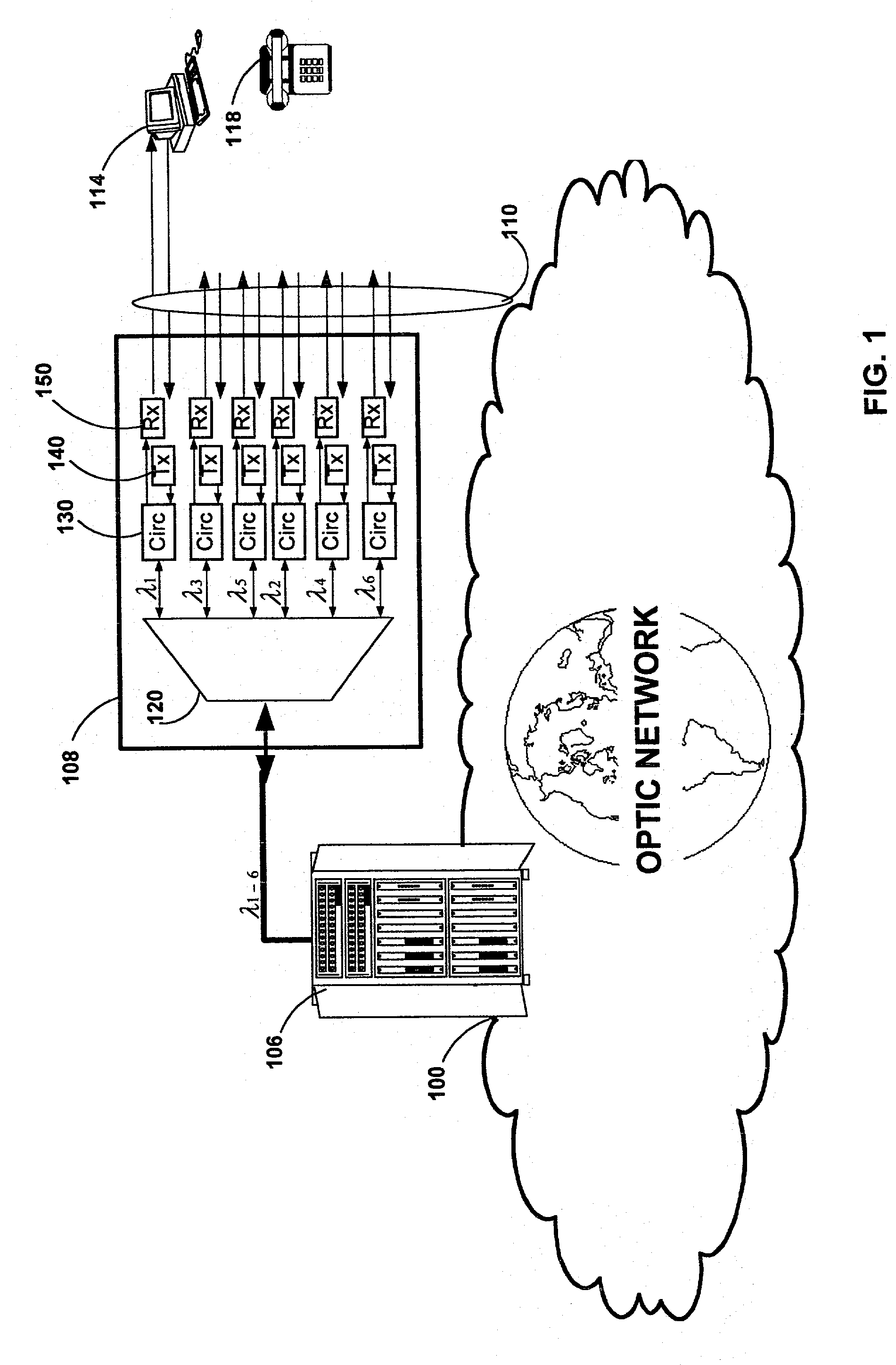
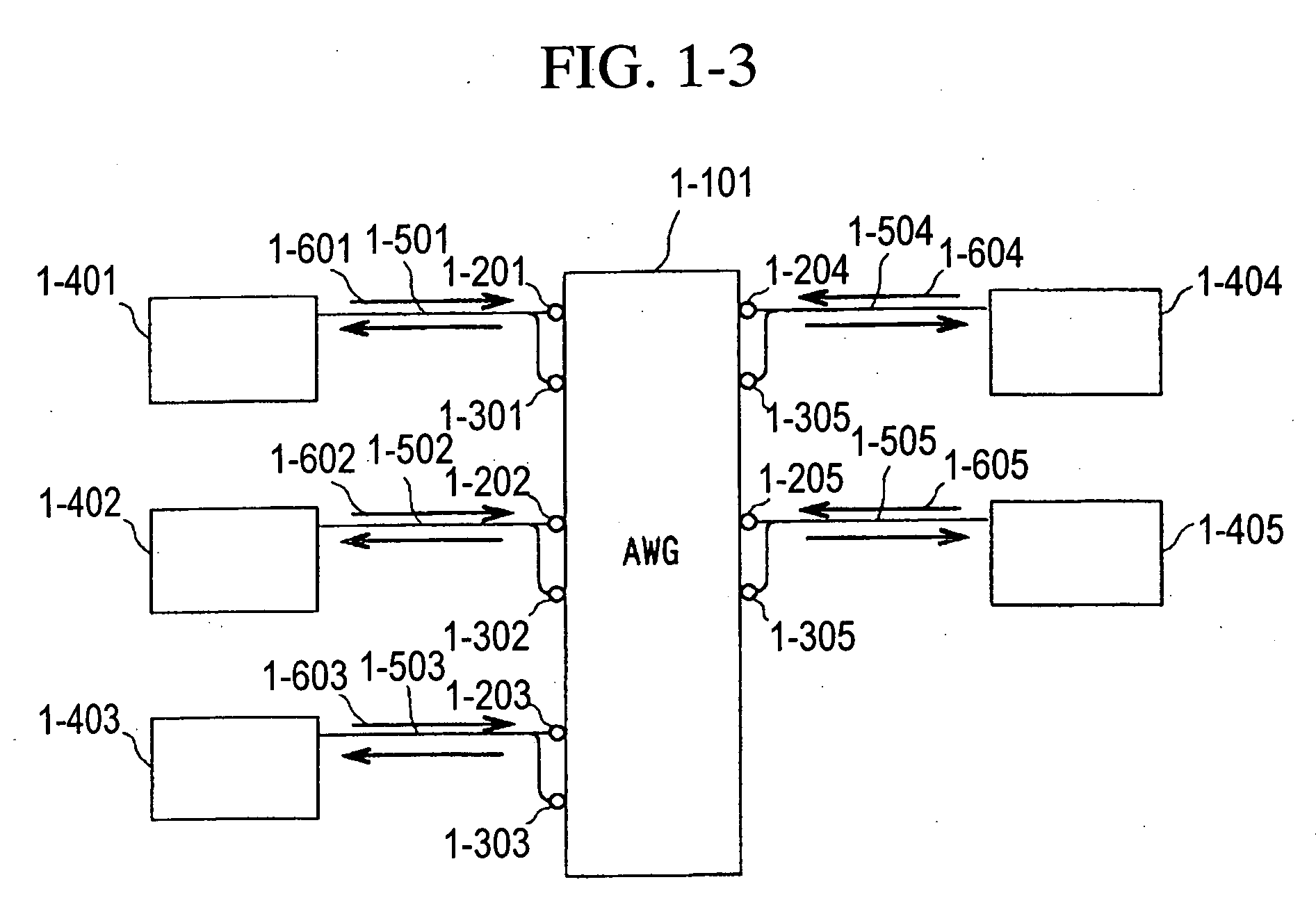
Optical communication network system
ActiveUS20060153496A1Quickly reconfiguredOptimizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksGratingLength wave
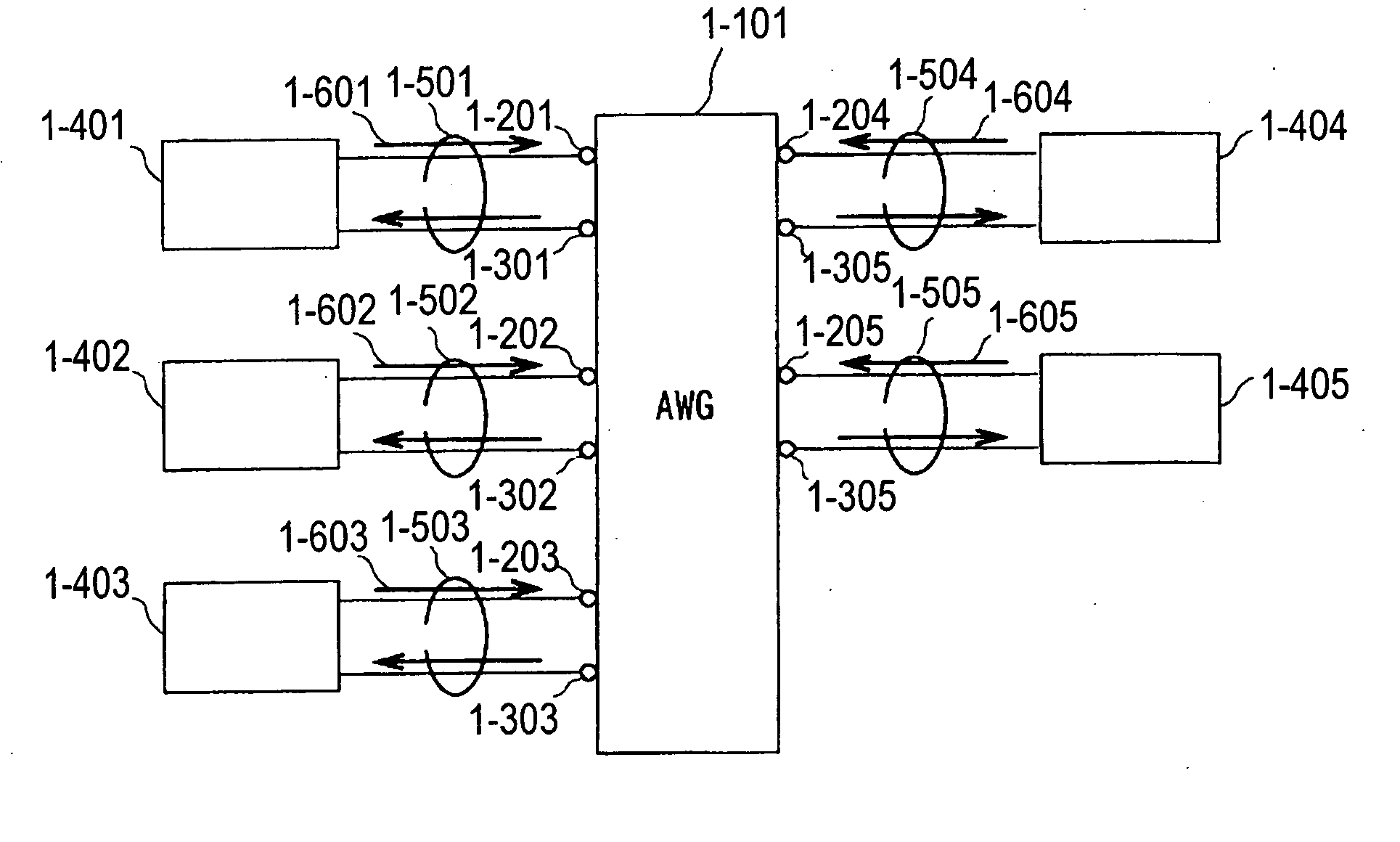
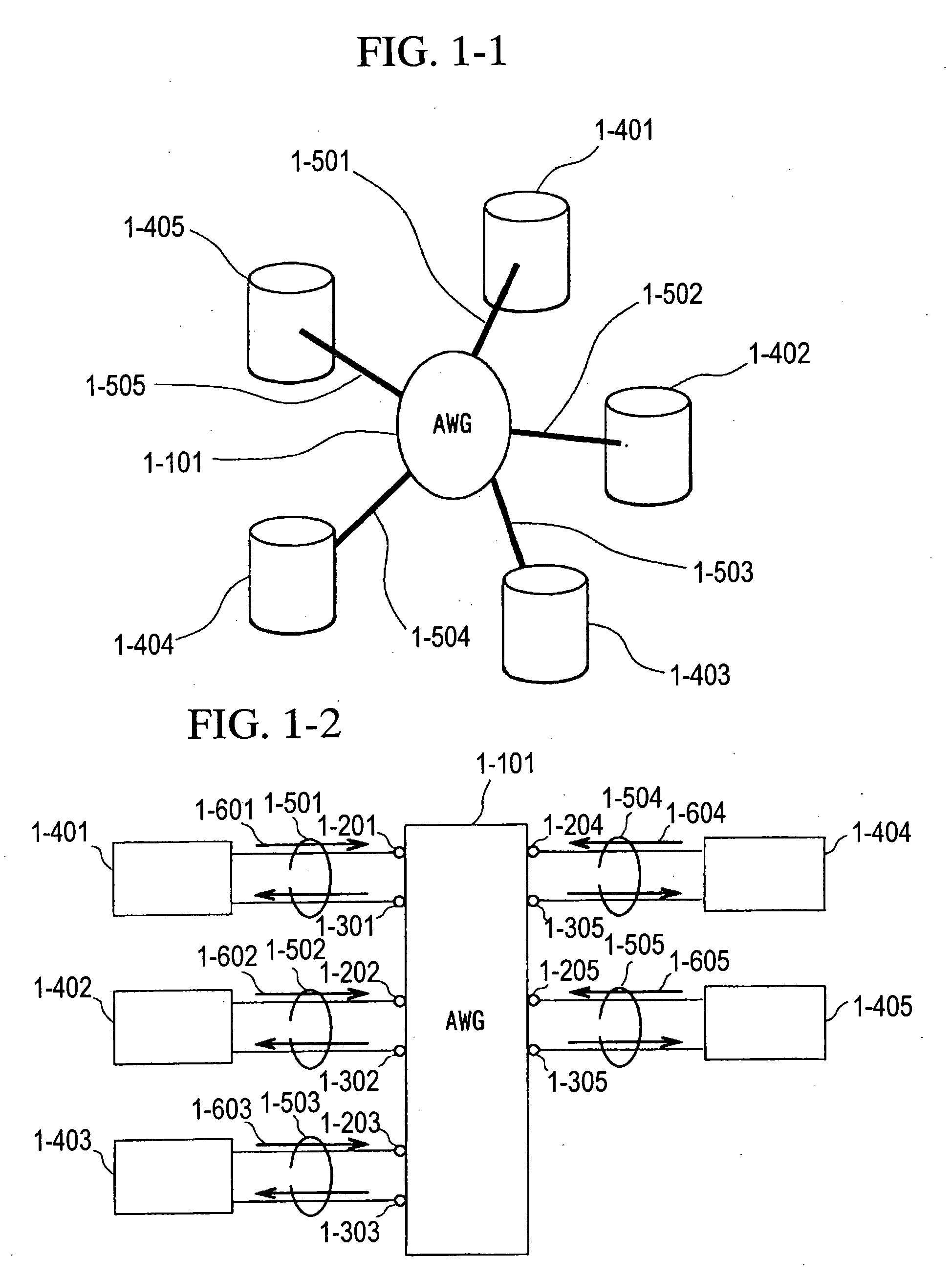
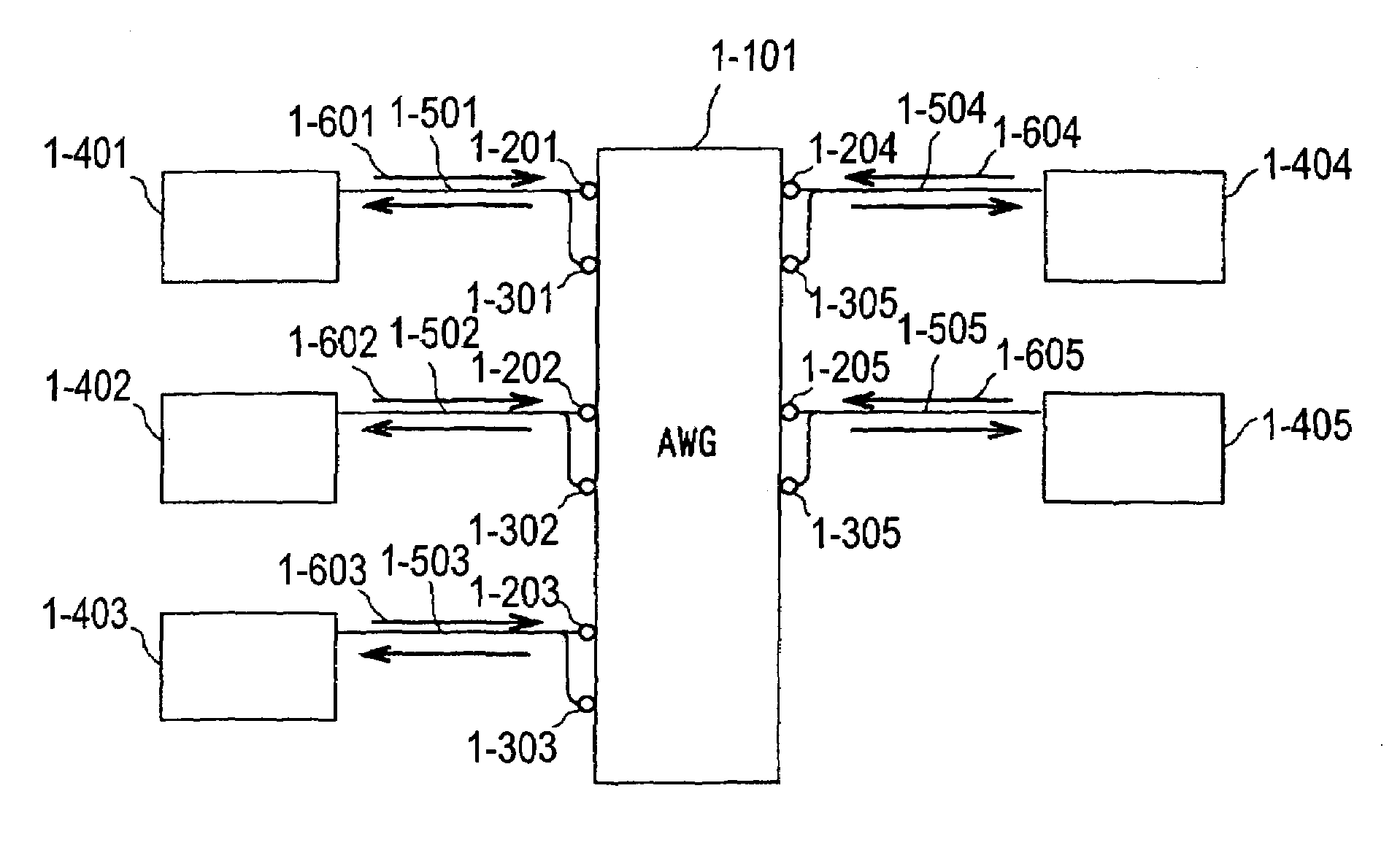
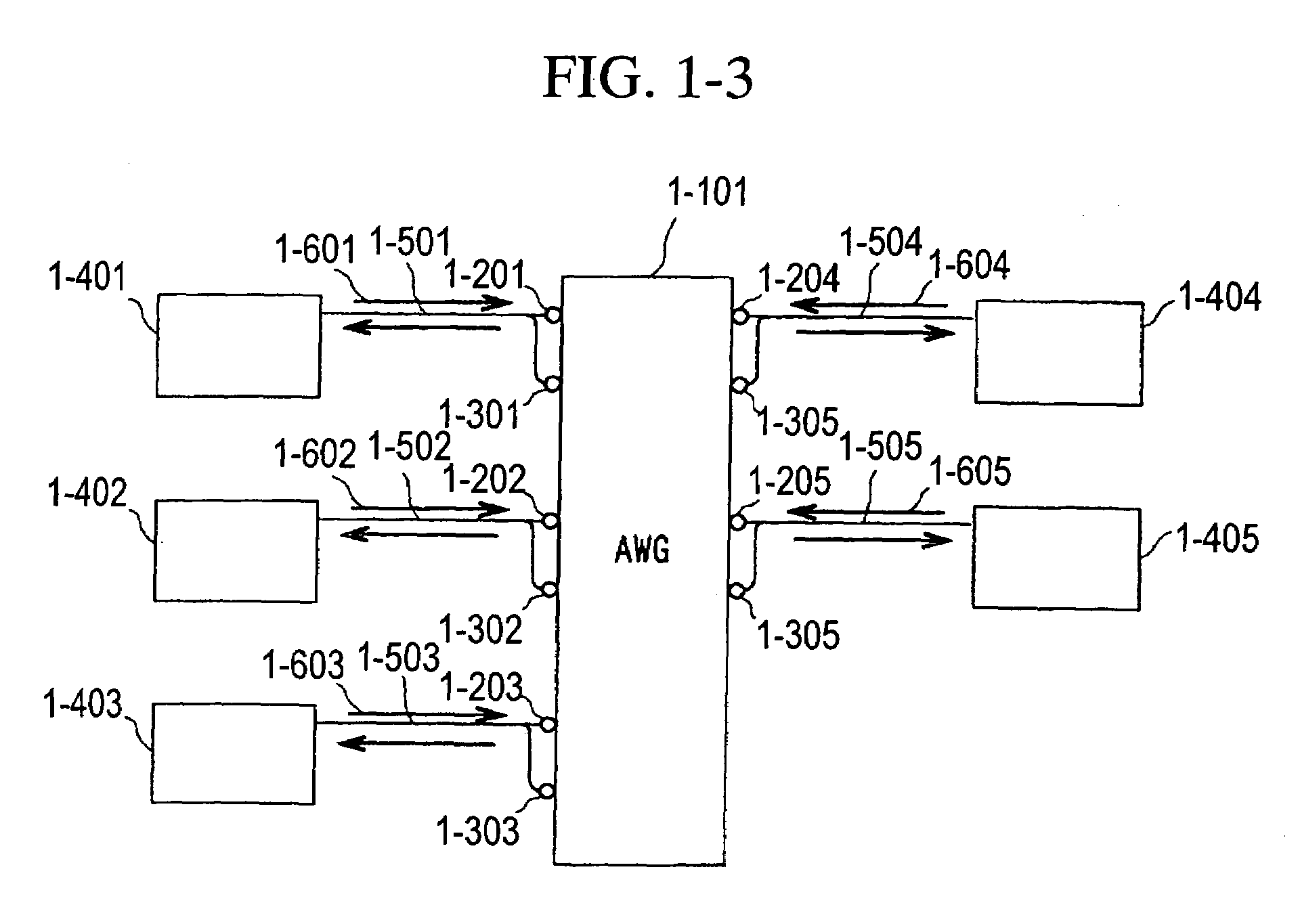
A fiber optic communication system includes a device of switching and setting wavelength of optical signals used in communication by network-node equipments, which sets the mapping of the wavelength of the optical signal used in communication by the network node equipments, and the input / output ports of an array waveguide grating (AWG), so as to construct a predetermined logical network topology by a plurality of network node equipments which are connected via optical fibers to the array waveguide grating that outputs optical signals inputted to optical input ports, to predetermined optical output ports in accordance with the wavelength thereof. As well as enabling a simple construction, it is easy to realize flexible network design, construction, and operation, and different network groups can also be easily connected to each other. Moreover, a fiber optic communication system having robust security and which can be stably operated even at the time of failure is realized at low cost.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
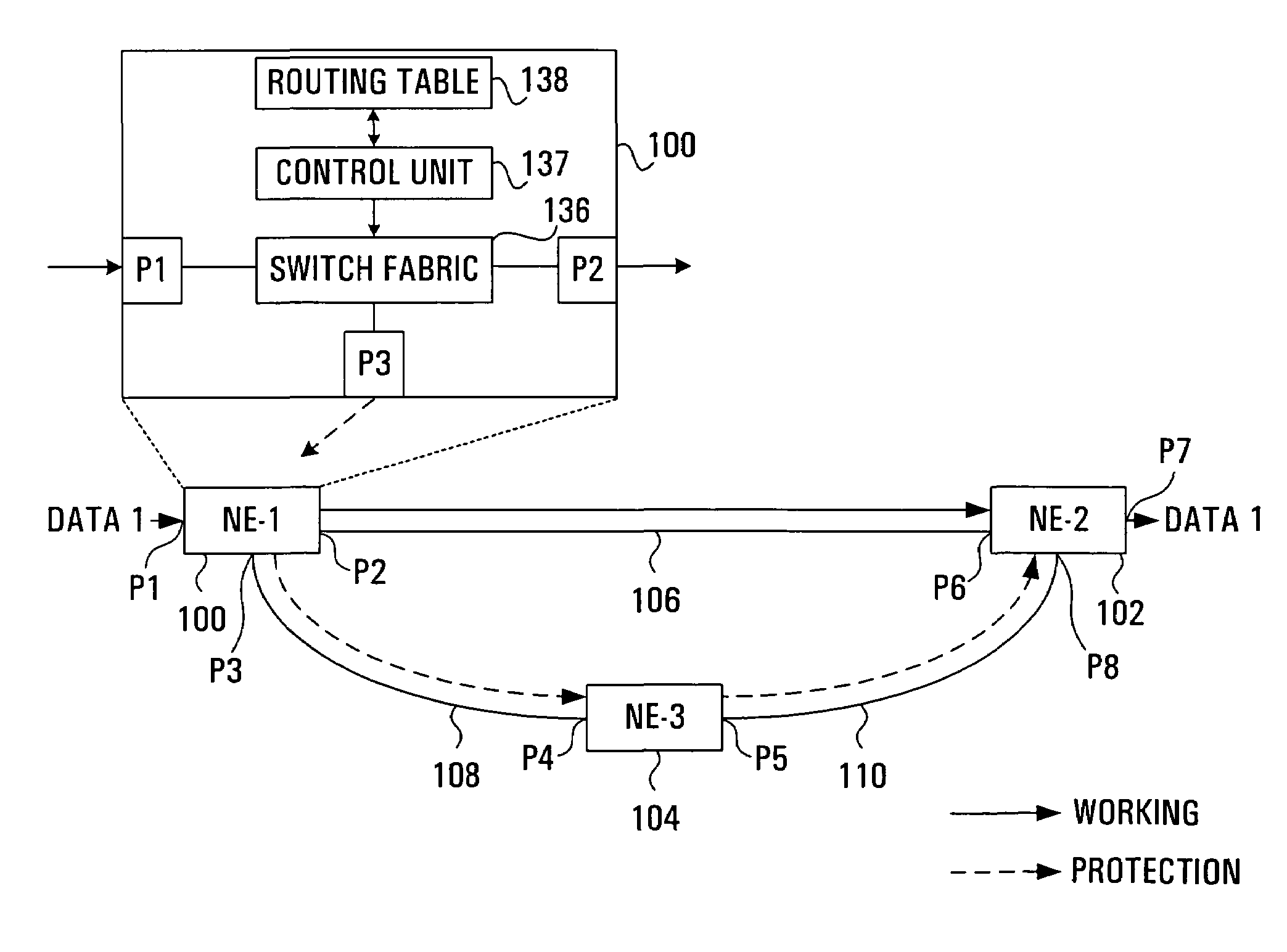
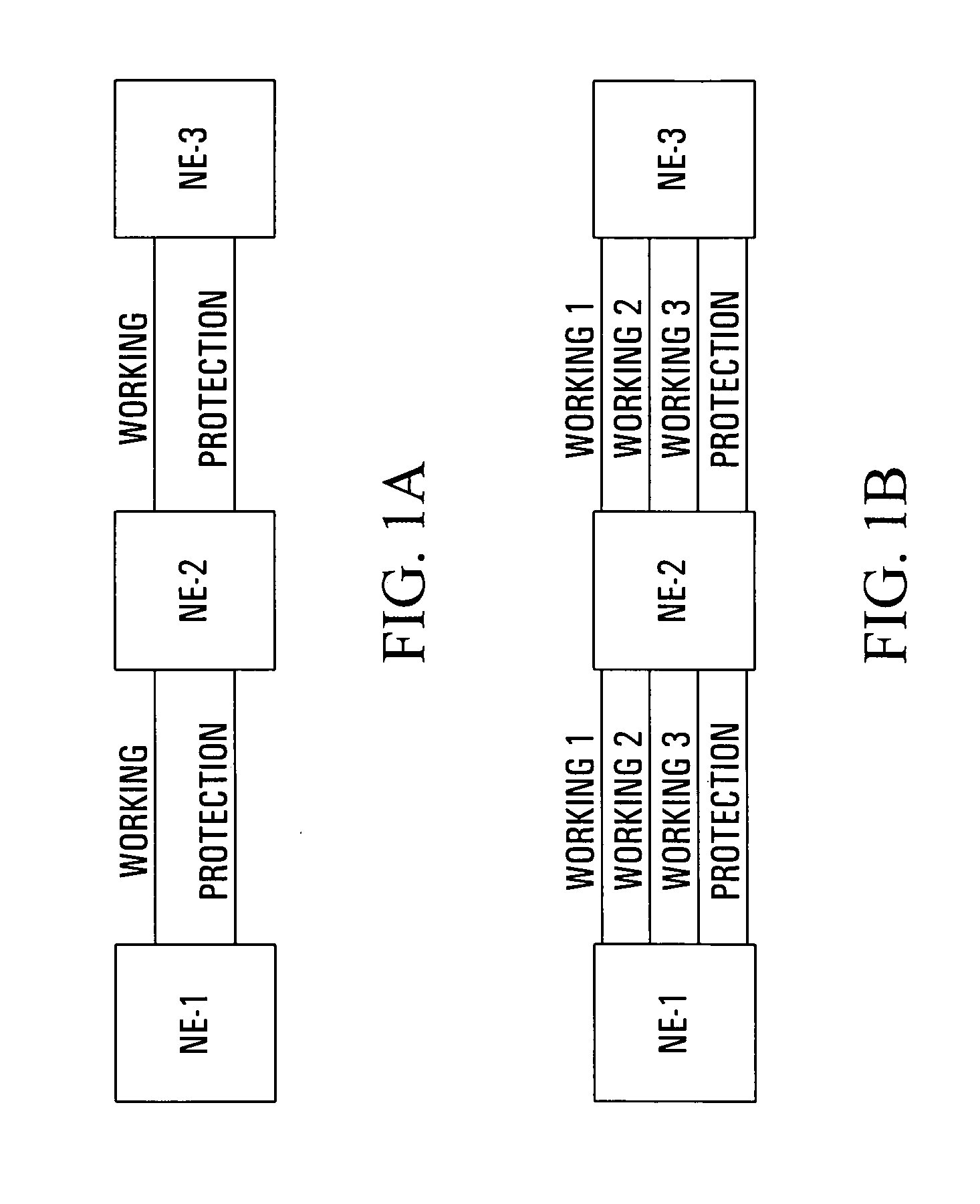
Apparatus and method for optical communication protection
InactiveUS6934248B1Improve efficiencyRing-type electromagnetic networksError preventionTraffic capacityRouting table
Protection techniques within optical communication networks are extremely important. An alternative to a line protection scheme, as most current optical communication networks use, is to utilize a path protection technique in which working and protection paths that are desired are assigned during network setup. During normal operations, only the working path is configured within the network elements' switch fabric with protection paths being left unconfigured. If a failure indication is detected in the working path by a network element, a protection entry within a routing table of the network element is looked up to determine protection switching data that is required to switch the data traffic to the pre-assigned protection path. This protection switching data is inserted within the path overhead for the data traffic so that it can be communicated to all of the network elements that require their switch fabrics reconfigured to establish the protection path of communications. This protection technique allows for similar switching speed to that of line switching protection such as BLSR designs, but with an increase in efficiency in terms of protection bandwidth.
Owner:CIENA
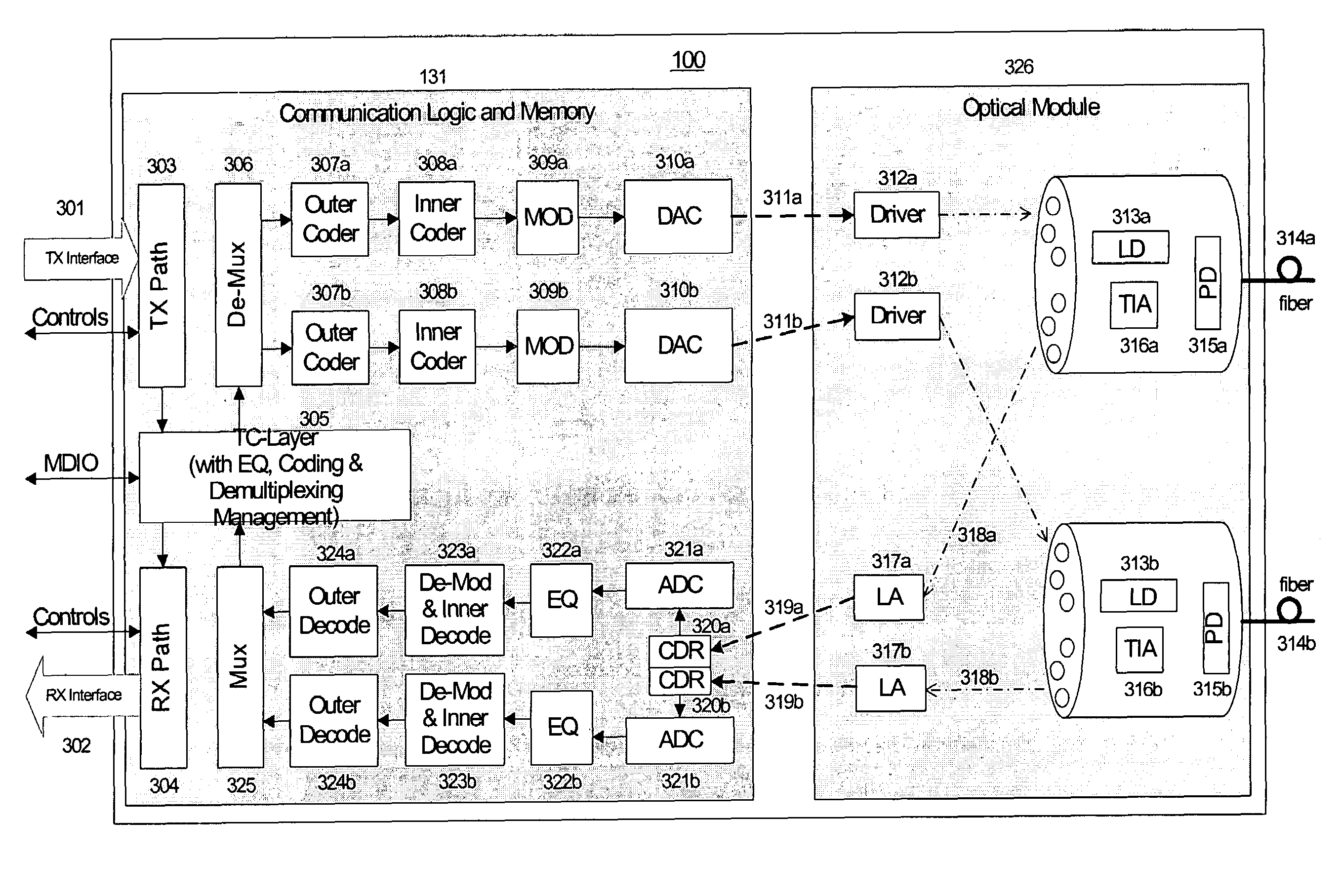
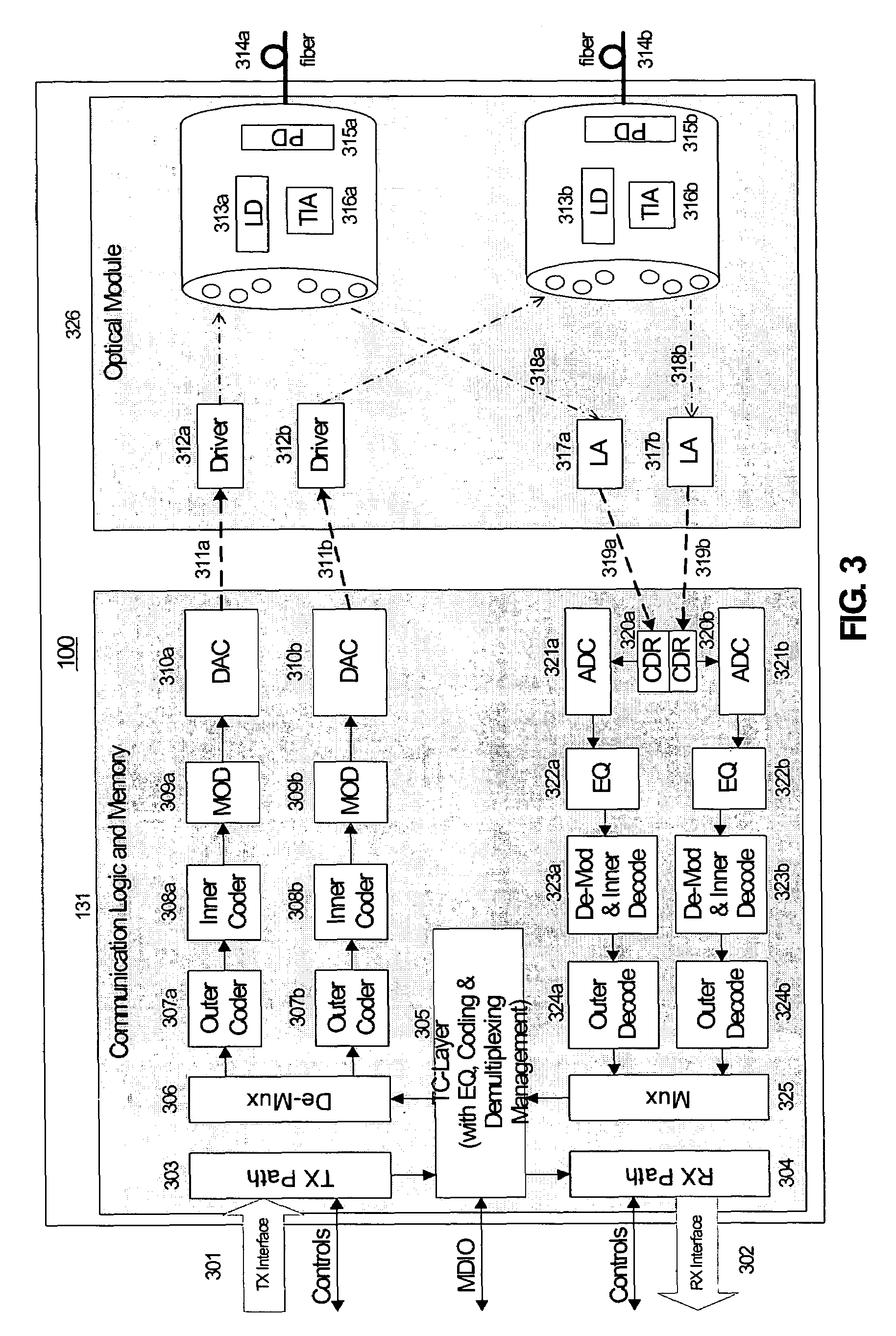
System and method for performing high-speed communications over fiber optical networks
ActiveUS20050019036A1Remove distortionHigh speed communicationMultiple-port networksTransmission path divisionFiberWaiting period
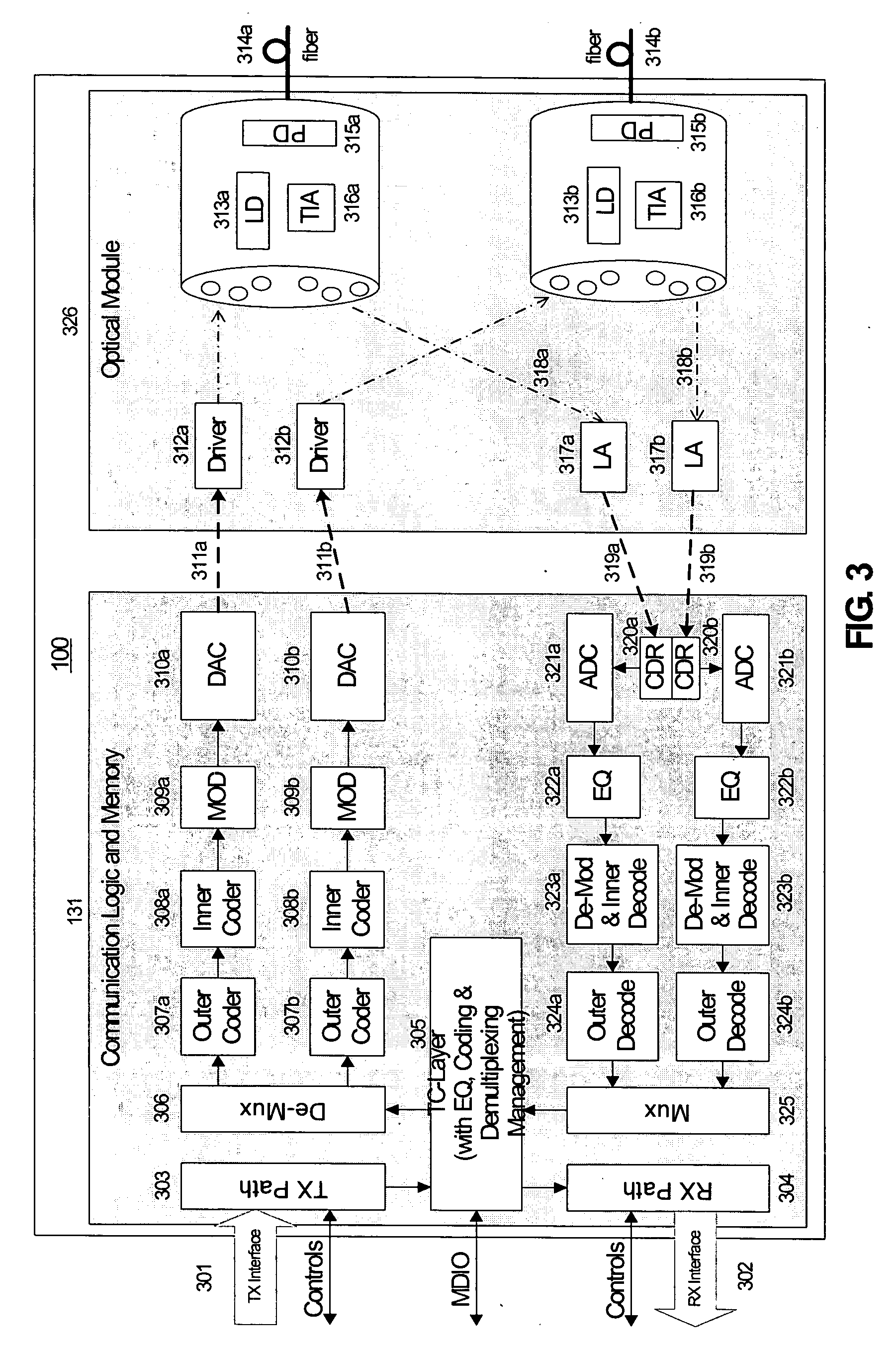
Processing a received optical signal in an optical communication network includes equalizing a received optical signal to provide an equalized signal, demodulating the equalized signal according to an m-ary modulation format to provide a demodulated signal, decoding the demodulated signal according to an inner code to provide an inner-decoded signal, and decoding the inner-decoded signal according to an outer code. Other aspects include other features such as equalizing an optical channel including storing channel characteristics for the optical channel associated with a client, loading the stored channel characteristics during a waiting period between bursts on the channel, and equalizing a received burst from the client using the loaded channel characteristics.
Owner:SOTO ALEXANDER I +1
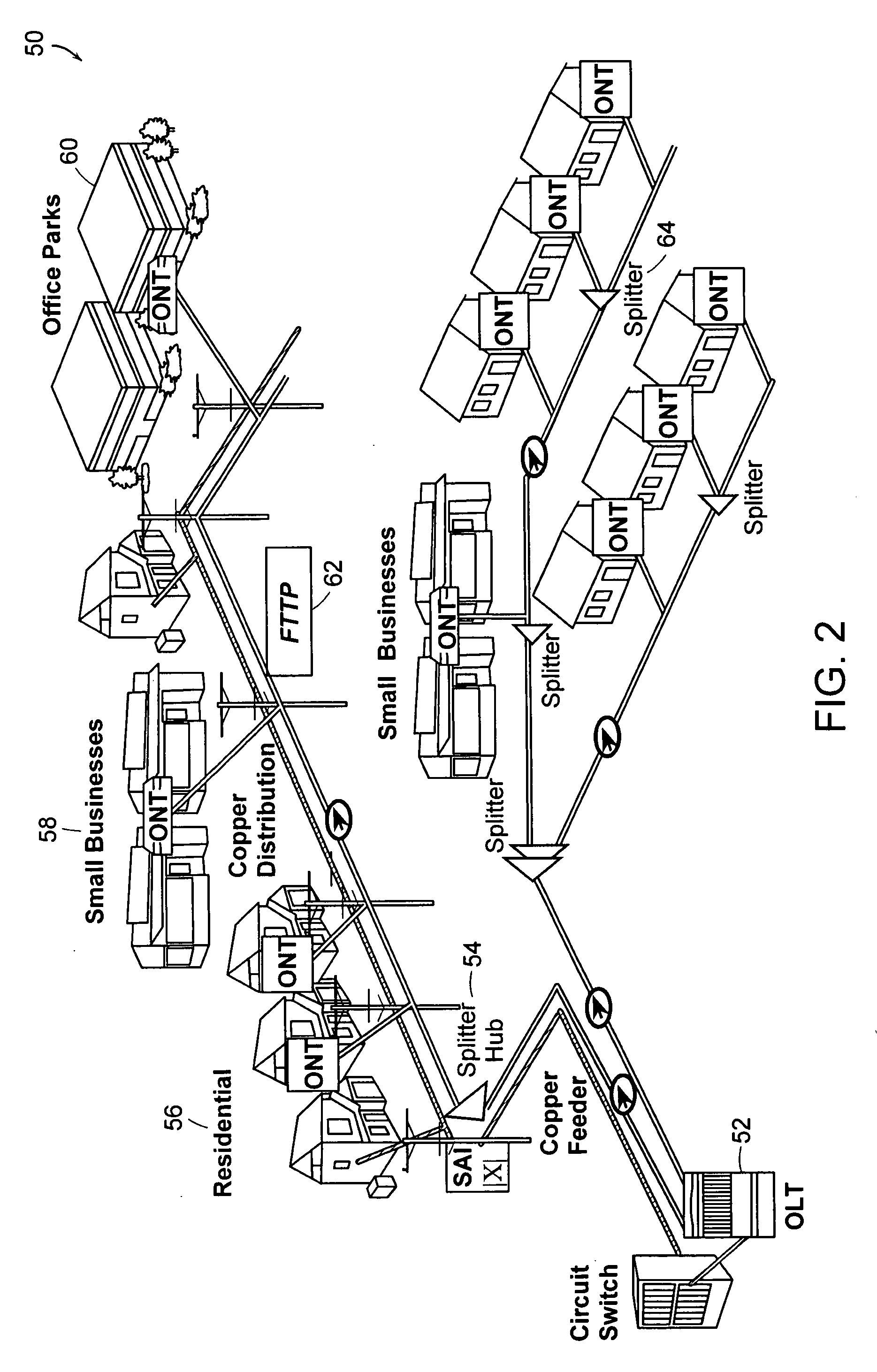
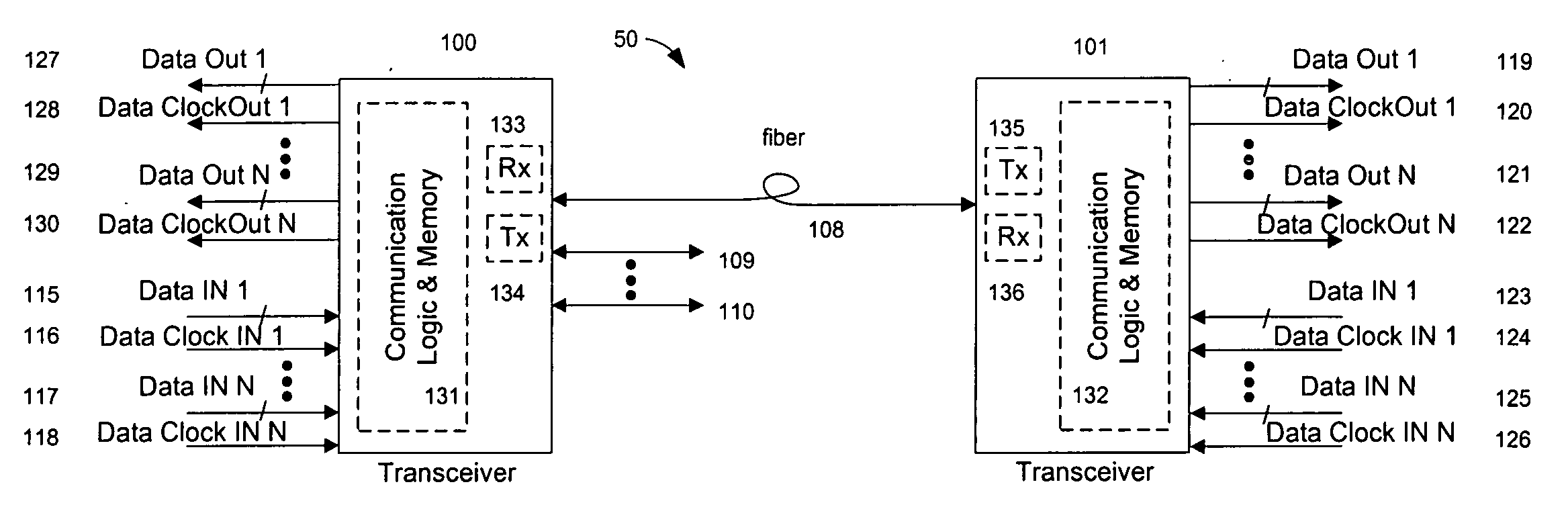
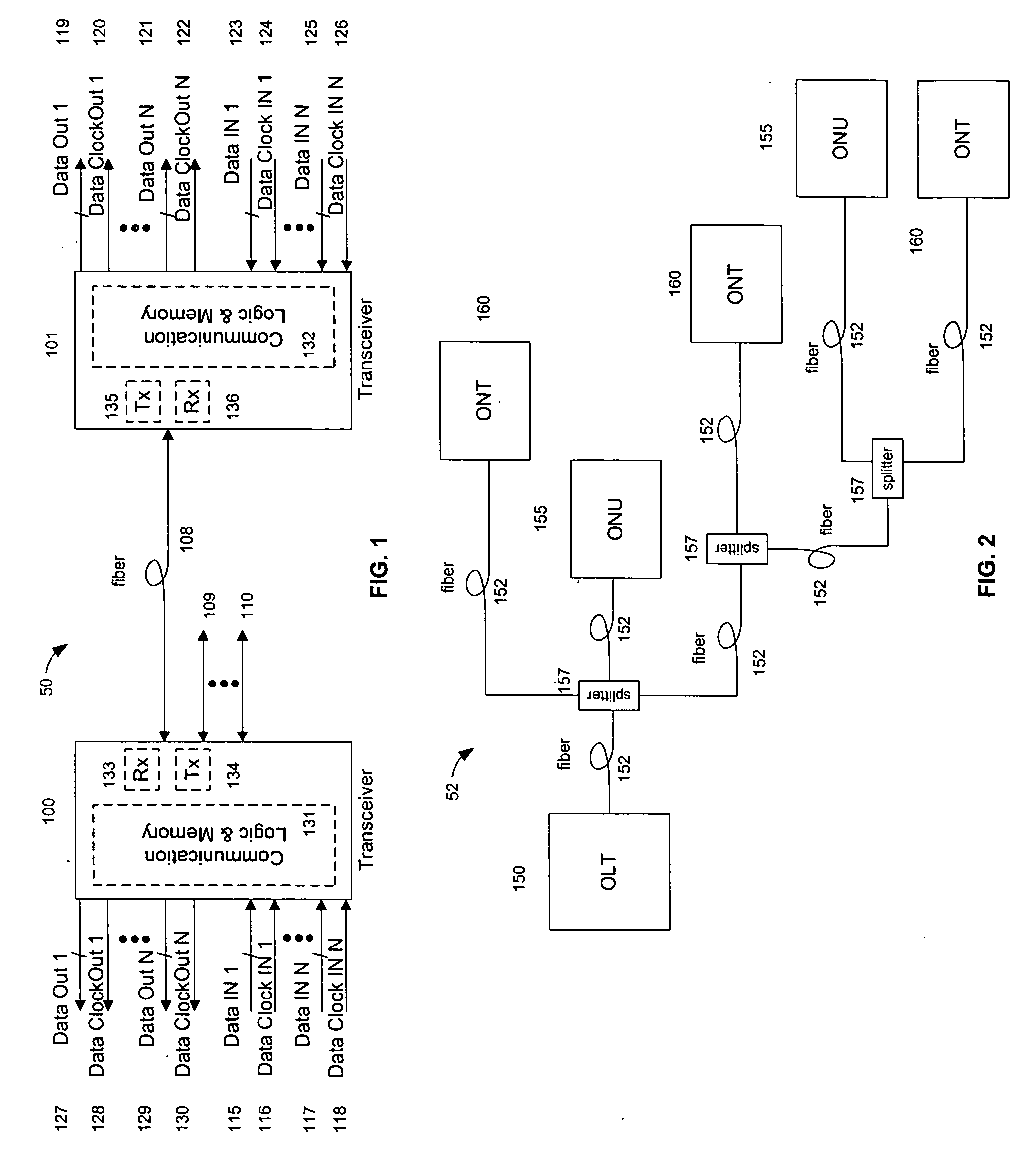
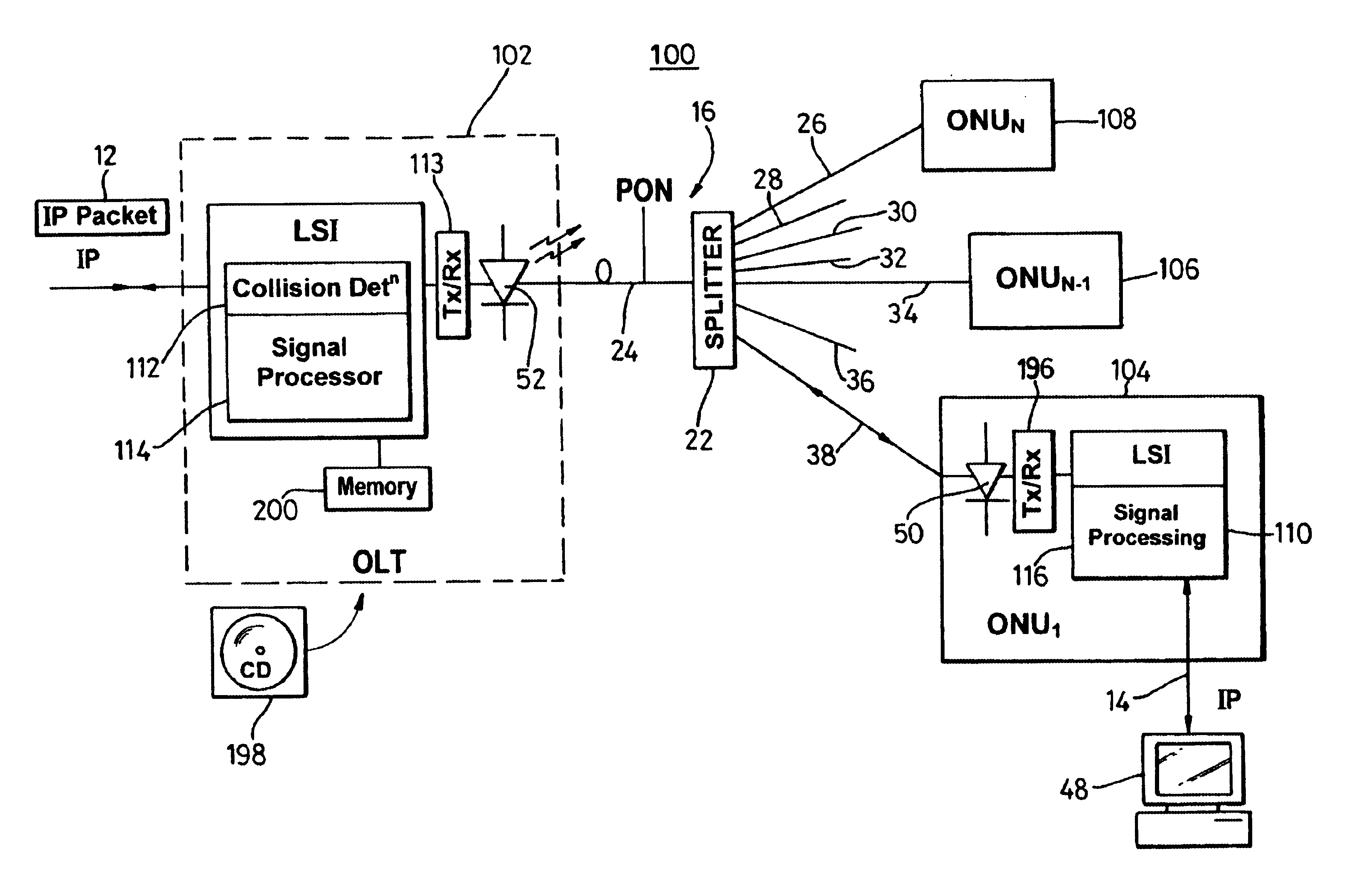
System and method for transfer of IP data in an optical communication networks
InactiveUS6870836B1Reduce complexityHigh complexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsCollision detectionMedia access control
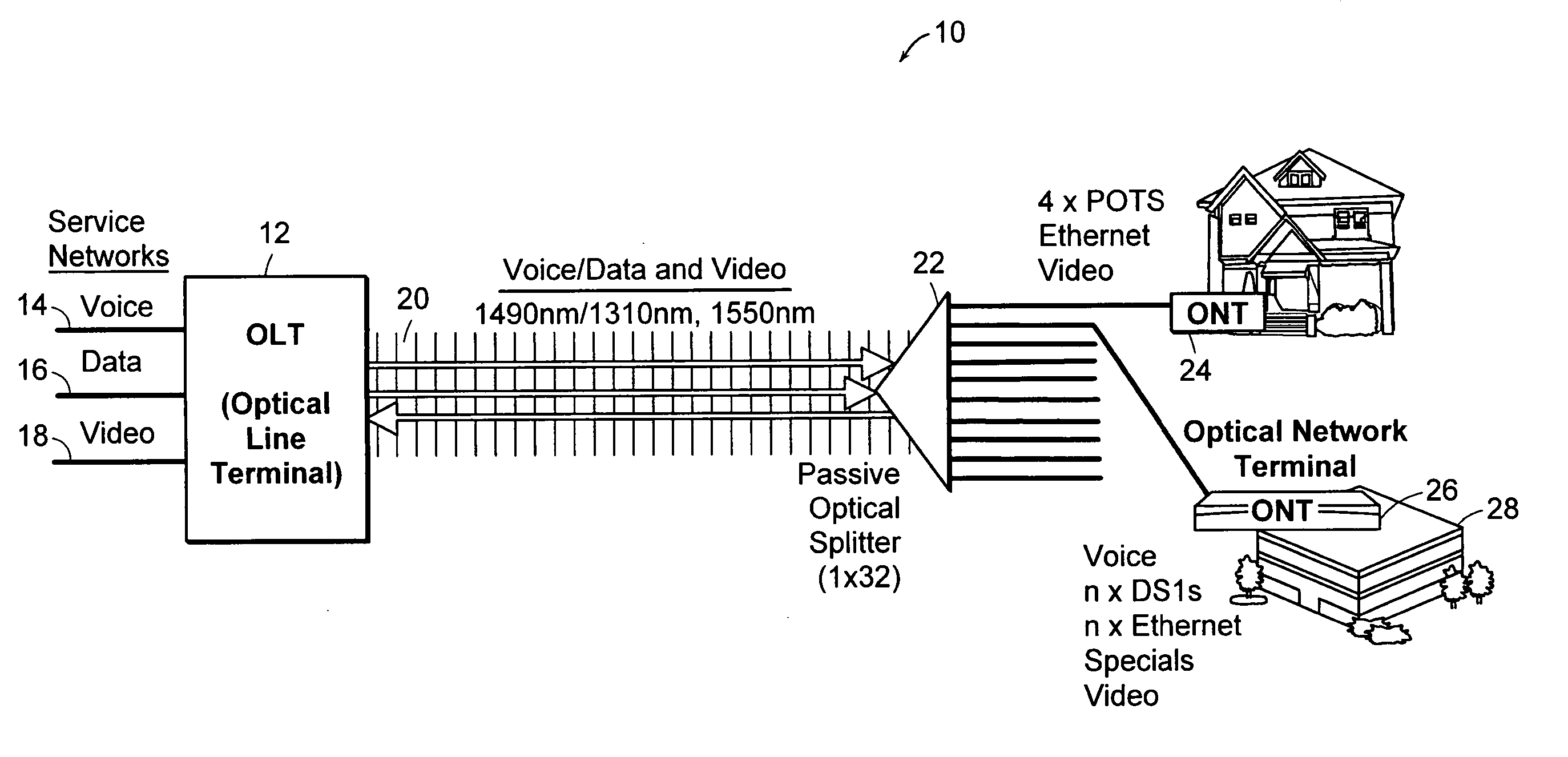
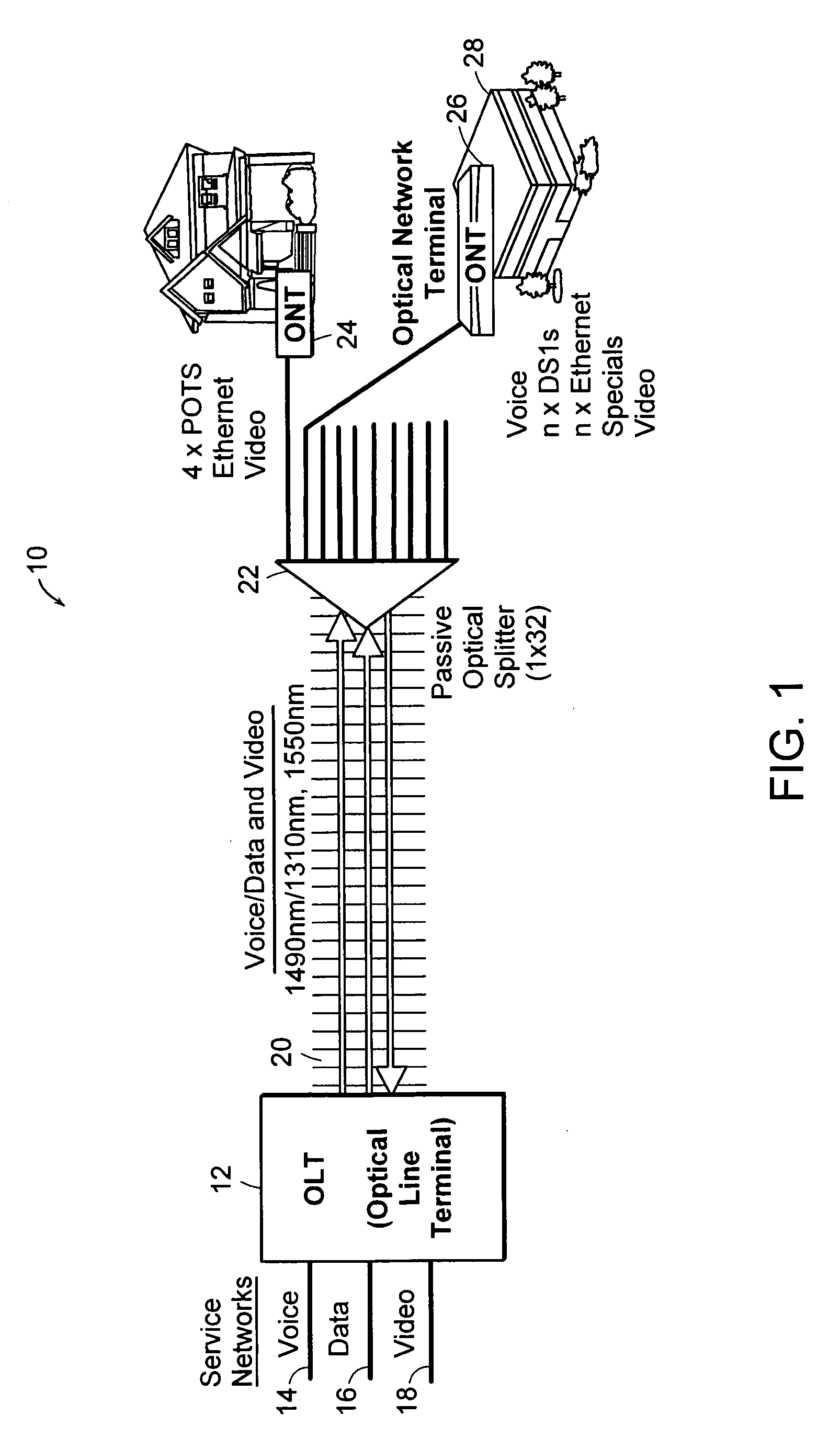
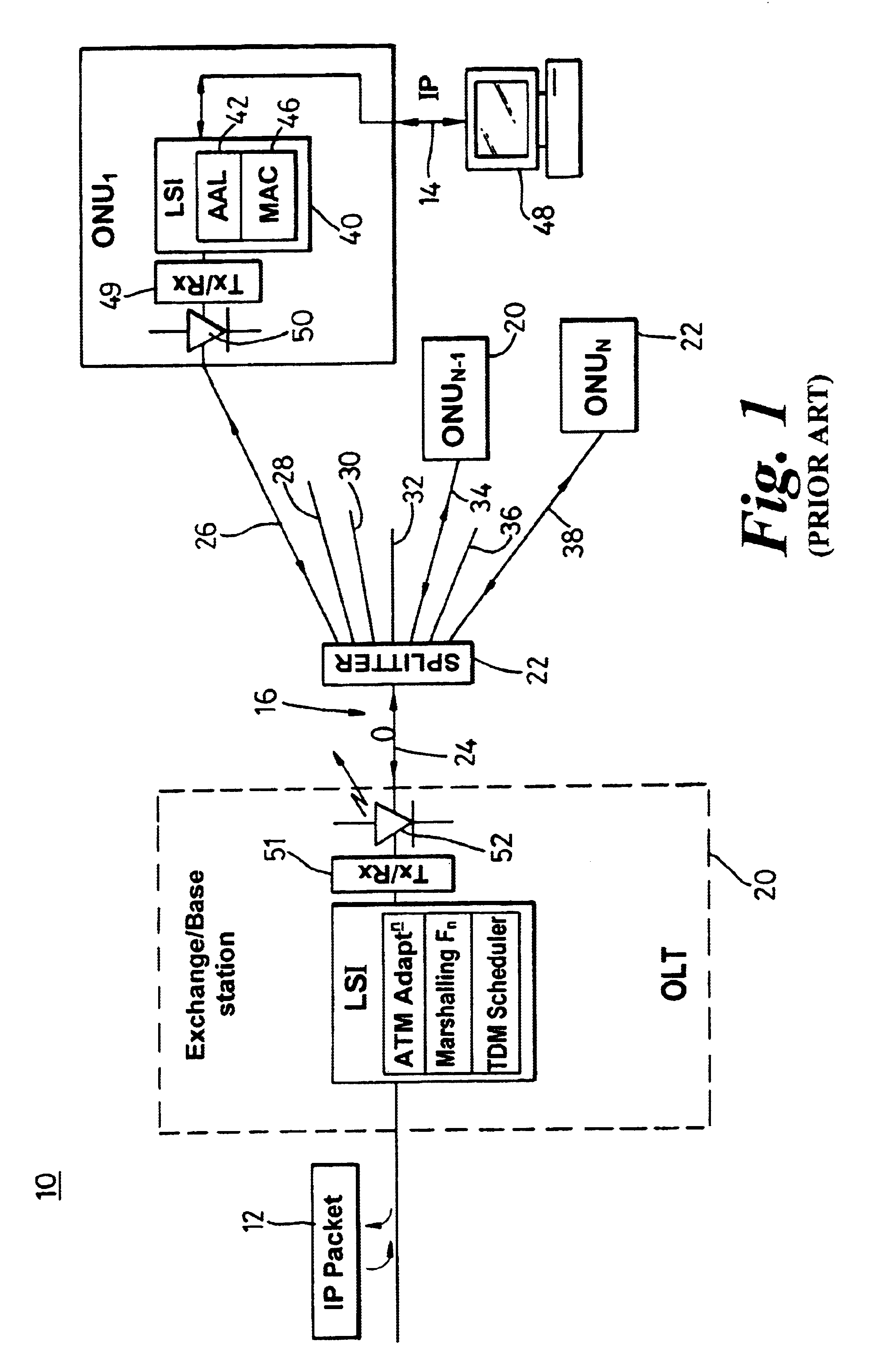
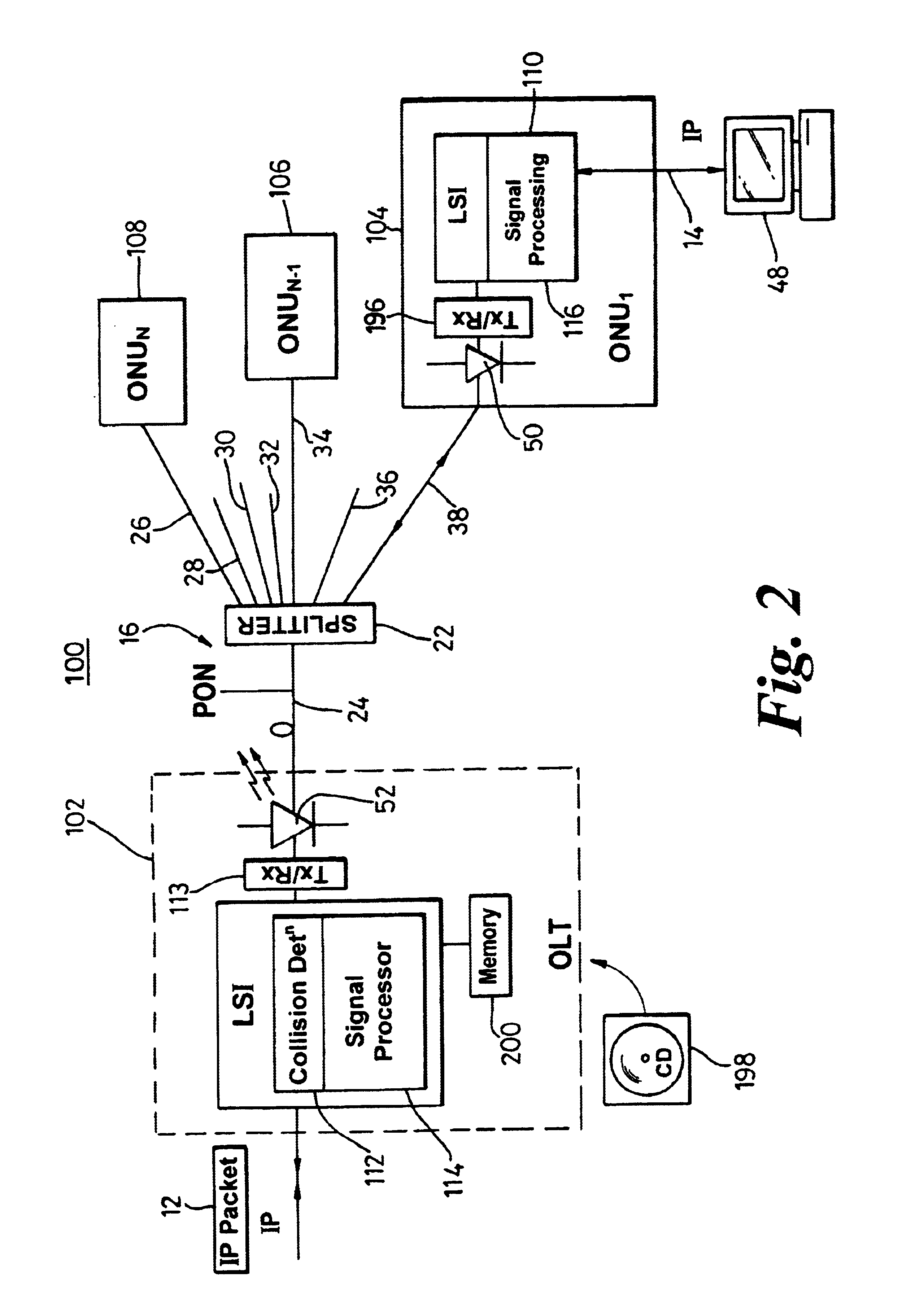
A system (100) to enable the transfer of Internet protocol (IP) format data (12, 14) over a point-to-multipoint passive optical network (PON, 16) is illustrated in FIG. 2. An exchange (102) is connected to a plurality of outstations (104-108) via an optical communication resource (24, 26-38) including a passive optical splitter (22) providing isolation to individual outstations. Media access control of the plurality of outstations is administered by the exchange (102), with collision detection logic (112) in the exchange determining collision (158) of Internet protocol (IP) encoded data communicated thereto through the PON (16). The IP encoded data realises a transport mechanism through the PON. Each of the plurality of outstations (104-108) and the exchange (102) is adapted to pass data in an IP format to and from the optical communication resource such that IP encoded data is transported, in use, directly between the outstation and the exchange.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Non-linear equalizer in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS7684712B1Receiver initialisationSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansSignal restorationComputer science
A method of recovering a most likely value of each symbol transmitted through an optical communications network using a high speed optical signal. A stream of multi-bit digital samples of the optical signal is processed to generate a respective multi-bit estimate X′(n) of each transmitted symbol. A first function is applied to each symbol estimate X′(n) to generate a corresponding soft decision value {tilde over (X)}(n). Each soft decision value {tilde over (X)}(n) is processed to generate a corresponding hard decision value. {circumflex over (X)}(n) having an ideal amplitude and phase. A plurality of successive soft decision values and hard decision values are processed to determine a second function, which is applied to each soft decision value {tilde over (X)}(n) to generate a most likely symbol value {circumflex over ({circumflex over (X)}(n).
Owner:CIENA CORP
System and method for performing high-speed communications over fiber optical networks
ActiveUS7242868B2Remove distortionHigh speed communicationMultiple-port networksTransmission path divisionFiberWaiting period
Processing a received optical signal in an optical communication network includes equalizing a received optical signal to provide an equalized signal, demodulating the equalized signal according to an m-ary modulation format to provide a demodulated signal, decoding the demodulated signal according to an inner code to provide an inner-decoded signal, and decoding the inner-decoded signal according to an outer code. Other aspects include other features such as equalizing an optical channel including storing channel characteristics for the optical channel associated with a client, loading the stored channel characteristics during a waiting period between bursts on the channel, and equalizing a received burst from the client using the loaded channel characteristics.
Owner:SOTO ALEXANDER I +1
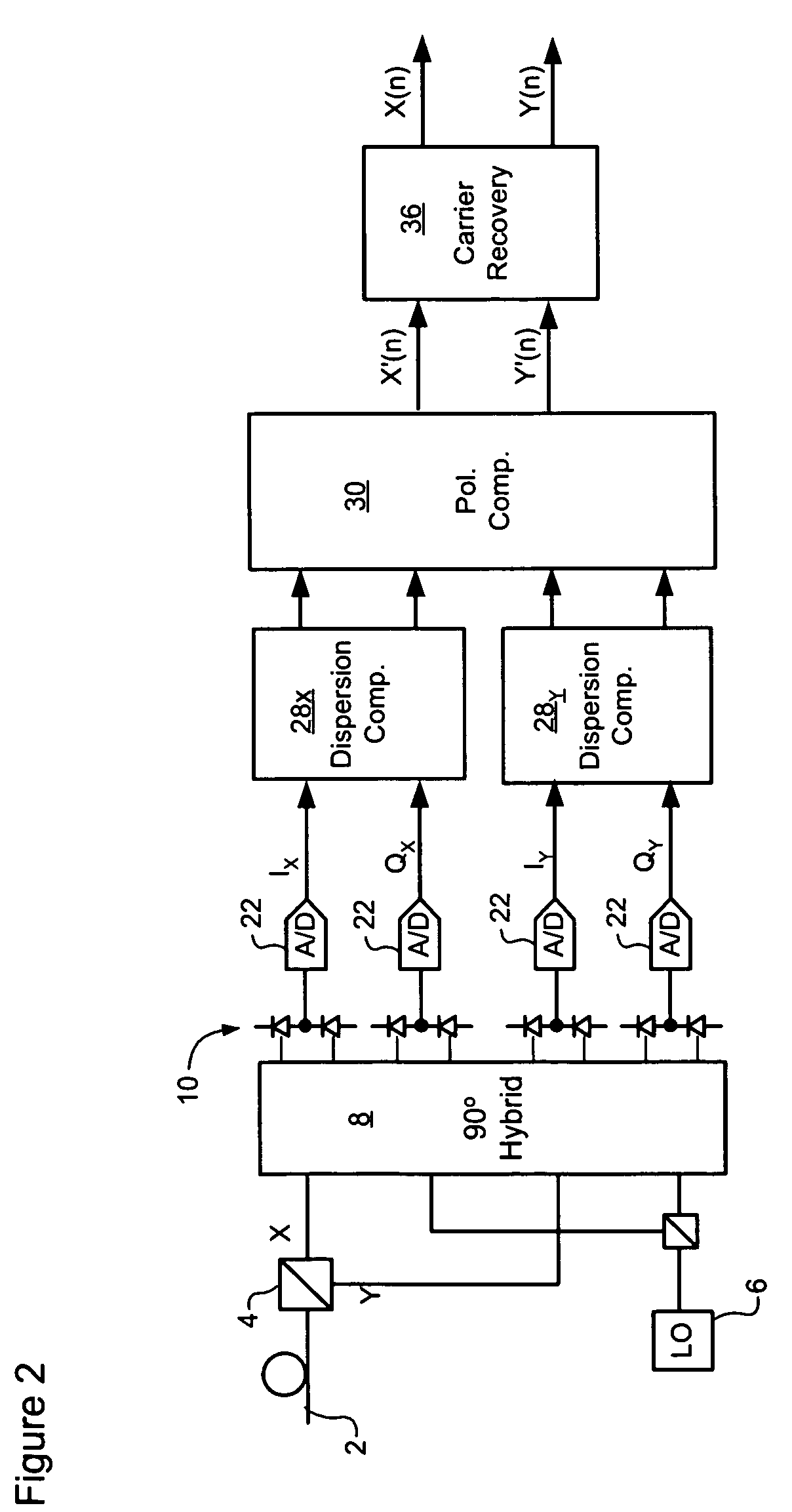
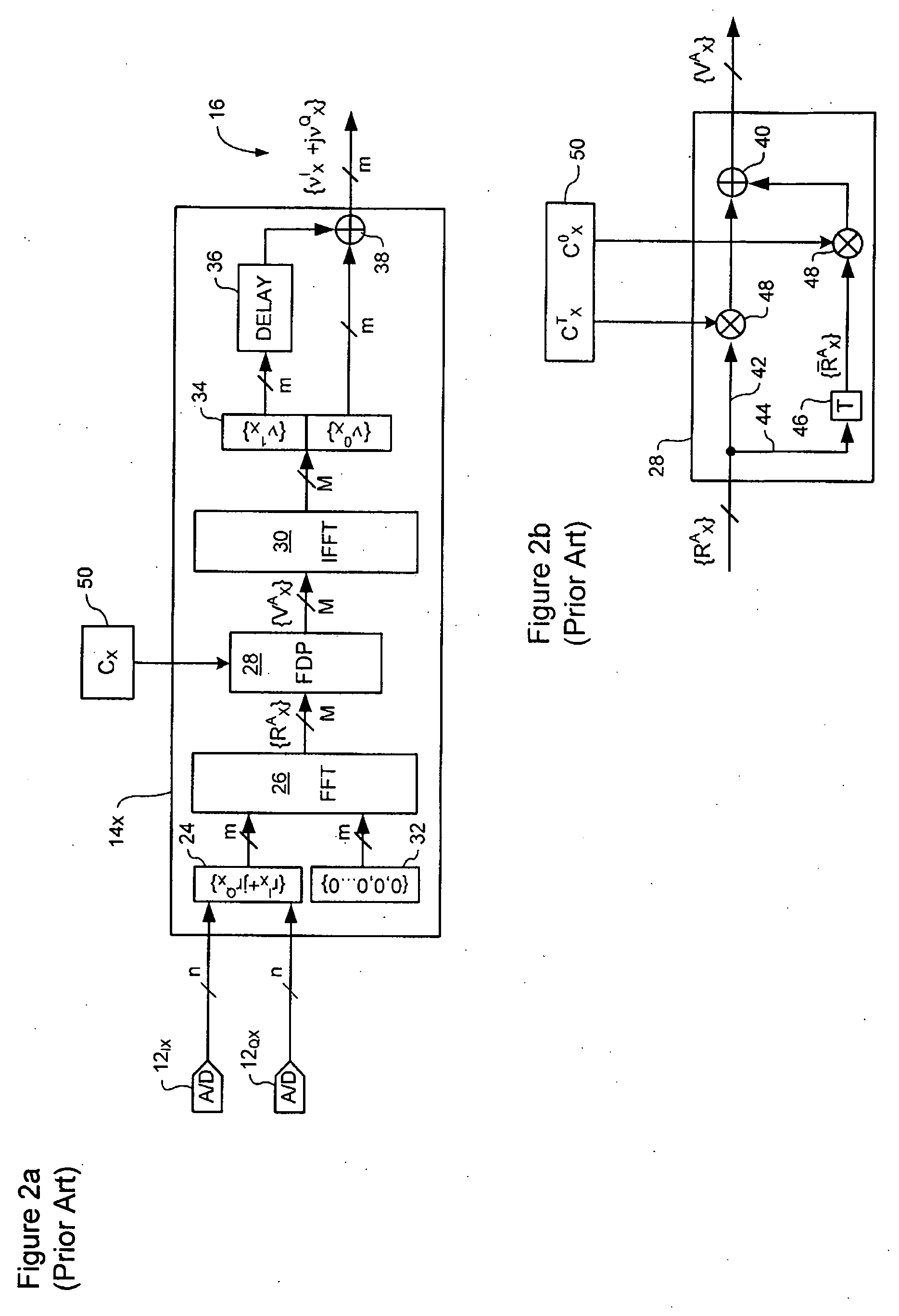
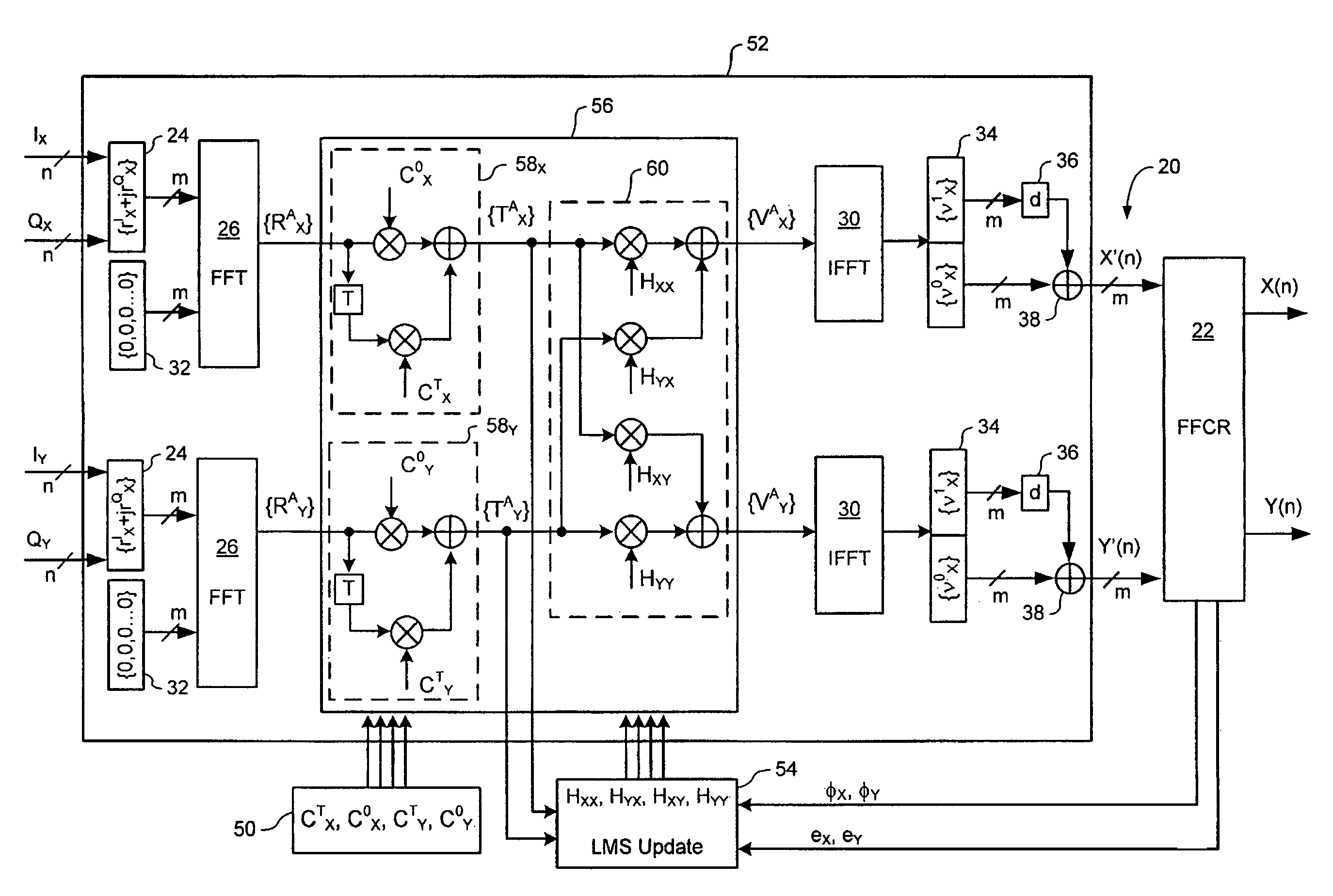
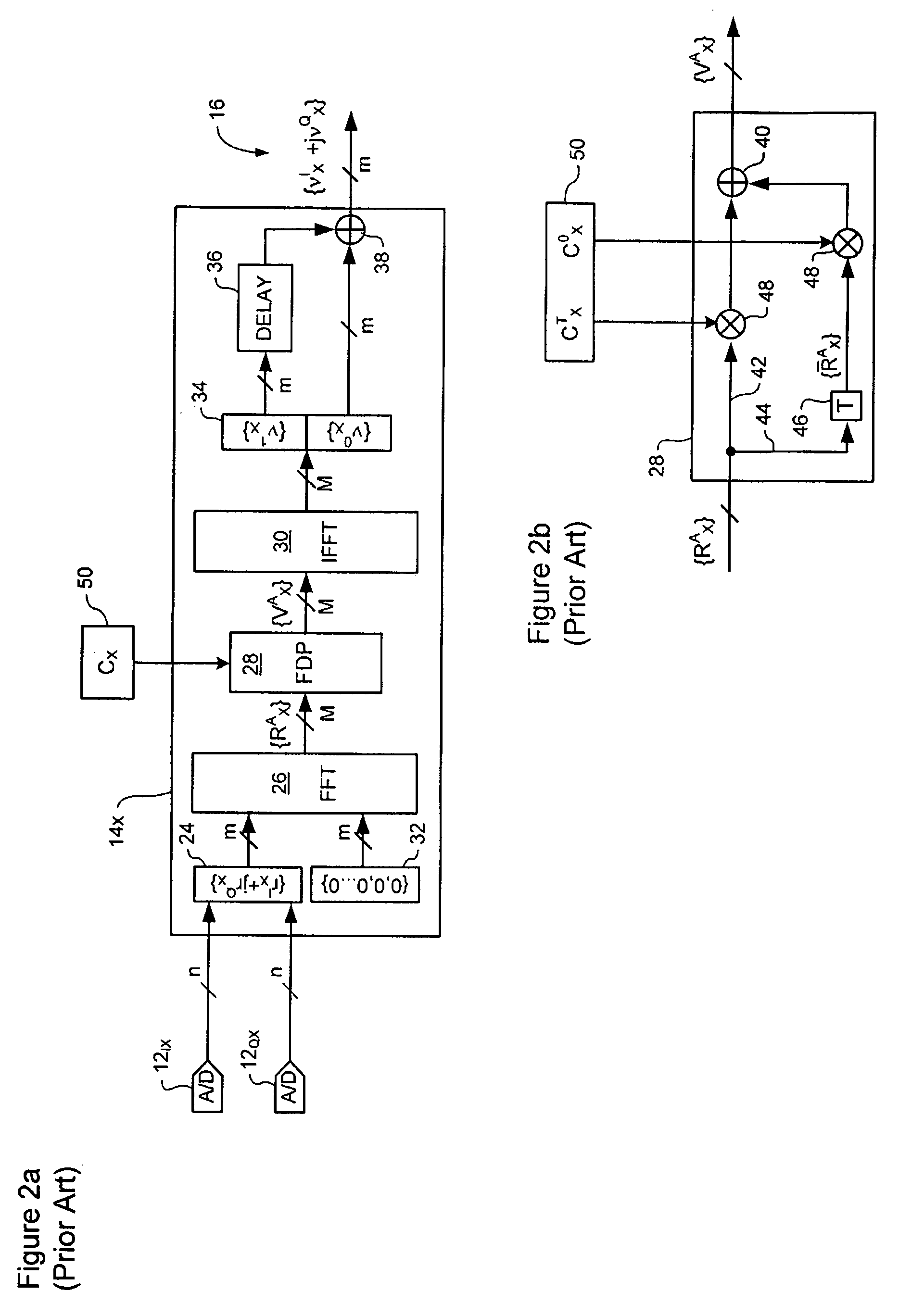
Signal equalizer in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS20090148164A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringFrequency domain
A signal equalizer for compensating impairments of an optical signal received through a link of a high speed optical communications network. At least one set of compensation vectors are computed for compensating at least two distinct types of impairments. A frequency domain processor is coupled to receive respective raw multi-bit in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) sample streams of each received polarization of the optical signal. The frequency domain processor operates to digitally process the multi-bit sample streams, using the compensation vectors, to generate multi-bit estimates of symbols modulated onto each transmitted polarization of the optical signal. The frequency domain processor exhibits respective different responses to each one of the at least two distinct types of impairments.
Owner:CIENA
Optimized Dynamic Routing in a network, in particular in an optical telecommunication network
ActiveUS20100014859A1Guaranteed feasibilityLow costMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionTelecommunications networkAdaptive routing
A routing method for a network including a first type of nodes and a second type of nodes, in particular an optical telecommunication network including transparent codes and regenerating nodes, includes: constructing a simplified network topology including the given node, the second nodes, first paths between the given node and the second nodes and second paths between each couple of second nodes, wherein the first and second paths pass only through first nodes and have an acceptable run-through cost, and, if the given node receives a routing request specifying a destination node that is reachable only through a second node, constructing an enhanced network topology by adding to the simplified network topology the destination node and third paths between the destination node and the second nodes that pass only through first nodes and have an acceptable run-through cost; and searching for a path having the lowest run-through cost from the given node to the destination node in the enhanced network topology.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Fiber communication systems and methods
ActiveUS20170294966A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsInjection lockedFiber
An injection locked transmitter for an optical communication network includes a master seed laser source input substantially confined to a single longitudinal mode, an input data stream, and a laser injected modulator including at least one slave laser having a resonator frequency that is injection locked to a frequency of the single longitudinal mode of the master seed laser source. The laser injected modulator is configured to receive the master seed laser source input and the input data stream, and output a laser modulated data stream.
Owner:CABLE TELEVISION LAB
Method and apparatus for filtering an optical beam
InactiveUS6888856B2Compact formEasy to tuneLaser optical resonator constructionPolarisation multiplex systemsExternal cavity laserMesh grid
The invention pertains to wavelength-agile optical filters suitable for wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) optical communications networks. More particularly, the invention pertains to optical filters with a wavelength reference that can be remotely switched to arbitrarily selectable channels on a standard grid, and to re-configurable optical communications networks employing same. The present invention provides a communication apparatus with a tunable filter which may be used in a wide range of applications including tuning an external cavity laser (ECL), selecting a wavelength for an add / drop multiplexer and providing channel selection and feedback for a wavelength locker. The filter may be utilized as a discrete component or in combination with circulators, wavelength lockers and gain medium. The filter may be implemented in whole or in part as part of a gain medium. The tunable filter exhibits a compact form factor and precise tuning to any selected wavelength of a predetermined set of wavelengths comprising a wavelength grid. The tunable filter may thus be utilized in telecom applications to generate the center wavelengths for any channel on the ITU or other optical grid.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Optical communication network system
ActiveUS7298974B2Quickly reconfiguredOptimizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksNetworked systemFiber-optic communication
A fiber optic communication system includes a device of switching and setting wavelength of optical signals used in communication by network-node equipments, which sets the mapping of the wavelength of the optical signal used in communication by the network node equipments, and the input / output ports of an array waveguide grating (AWG), so as to construct a predetermined logical network topology by a plurality of network node equipments which are connected via optical fibers to the array waveguide grating that outputs optical signals inputted to optical input ports, to predetermined optical output ports in accordance with the wavelength thereof. As well as enabling a simple construction, it is easy to realize flexible network design, construction, and operation, and different network groups can also be easily connected to each other. Moreover, a fiber optic communication system having robust security and which can be stably operated even at the time of failure is realized at low cost.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
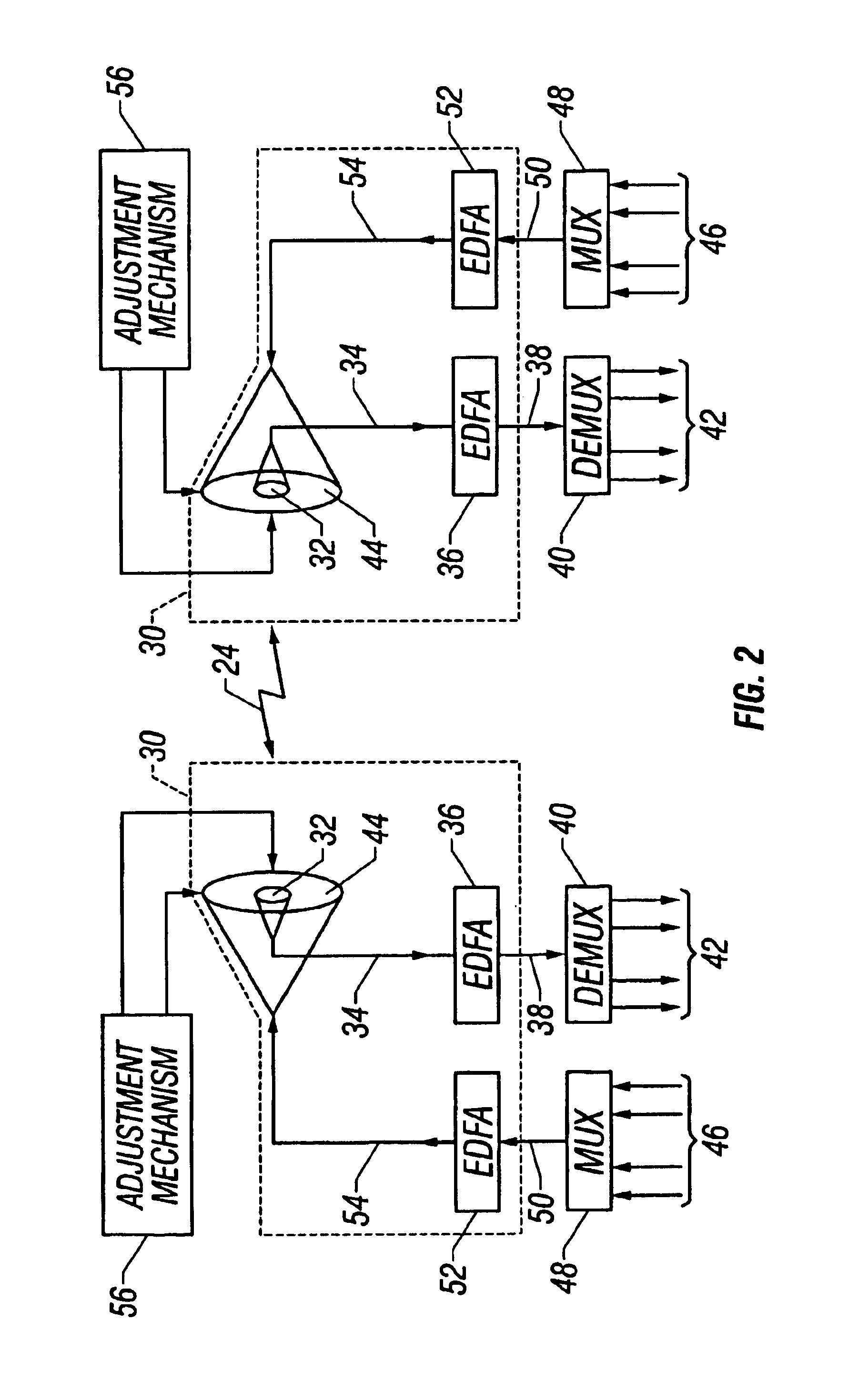
Multi-wavelength locking method and apparatus for wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) optical communication system
InactiveUS7068949B2Suppressing frequency offsetSuppression frequencyLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFast Fourier transformCommunications system
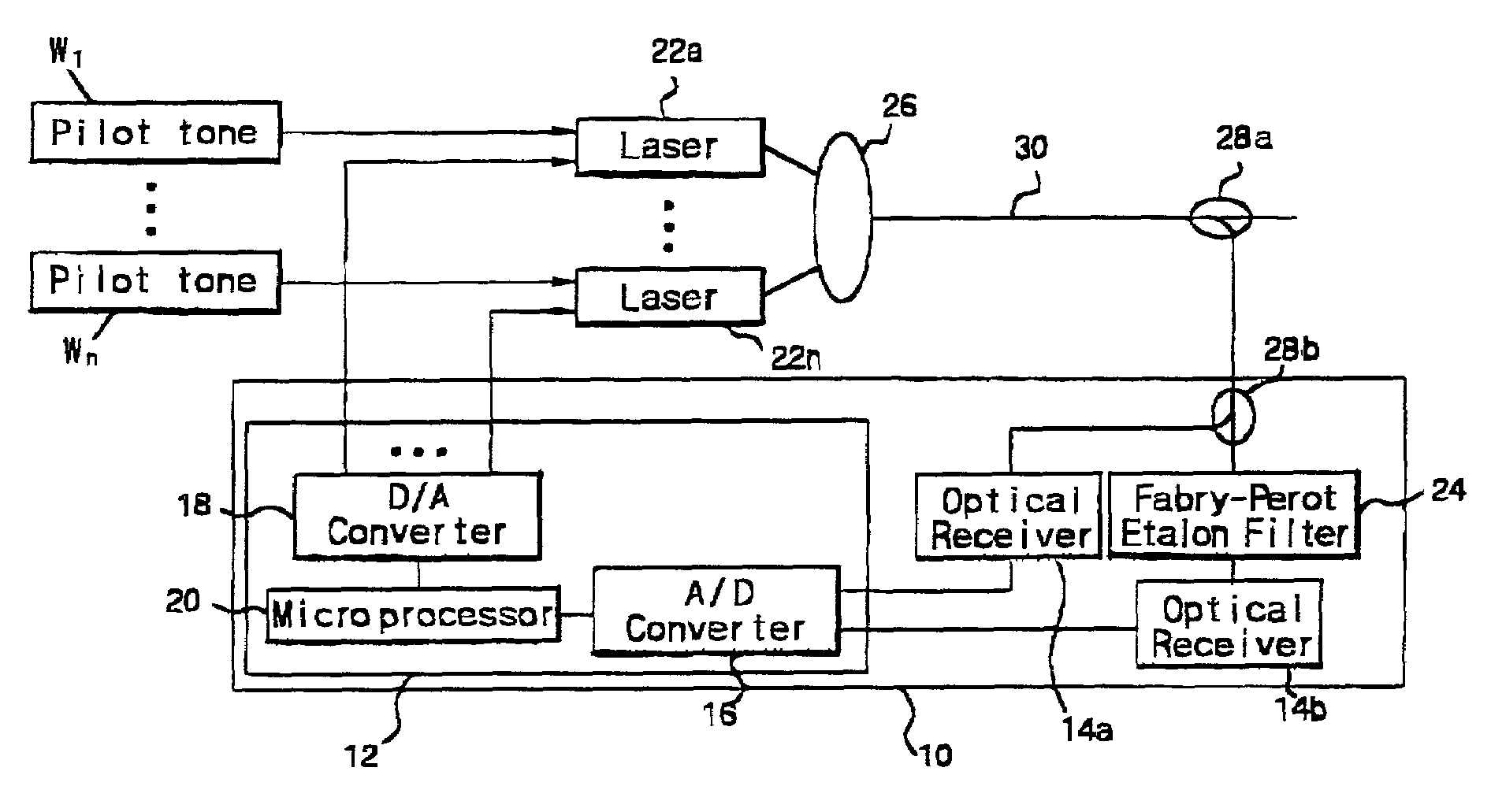
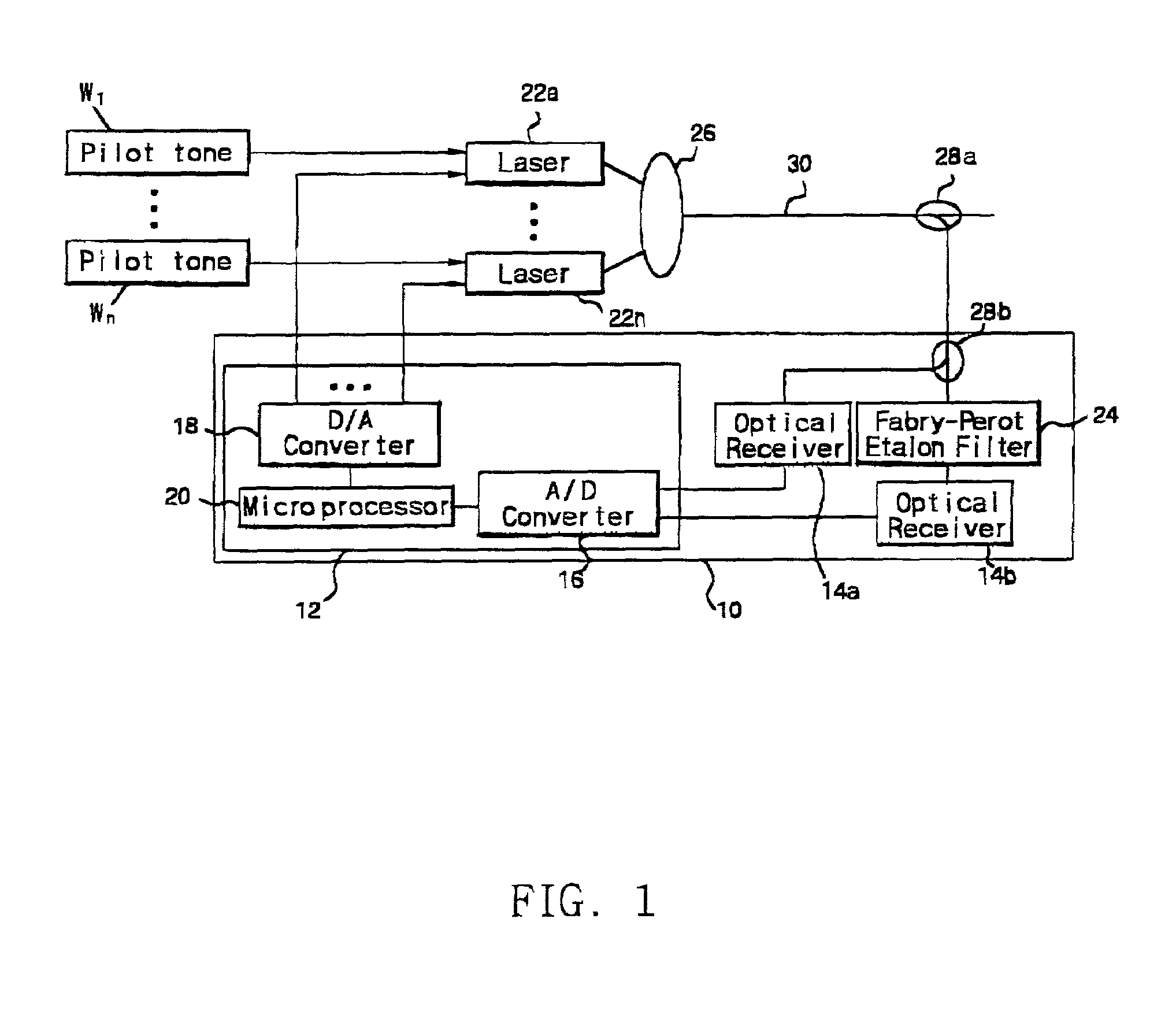
Disclosed is a multi-wavelength locking method for a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) optical communication network, and in particular, a multi-wavelength locking method and apparatus for a WDM optical communication system that can lock wavelengths of optical signals by producing pilot tones by applying a sine-wave current to a plurality of transmission lasers having different wavelengths, passing the optical signal through a Fabry-Perot etalon filter, and then Fourier-transforming the filtered optical signal. The multi-wavelength locking method includes frequency-modulating an optical signal by applying a small and specified sine-wave current to a bias current for driving WDM lasers, detecting pilot tones produced after filtering the optical signal through a filtering section and converting the detected signal into a digital signal by performing a sampling of the detected signal, detecting a magnitude and phase of the pilot tones by performing a fast Fourier transform, providing Fourier-transformed data as a first derivative signal of the filtering section, and locking an operation wavelength of WDM channels by controlling the temperature or current if resonance frequencies of the filtering section coincide with respective standard frequency.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
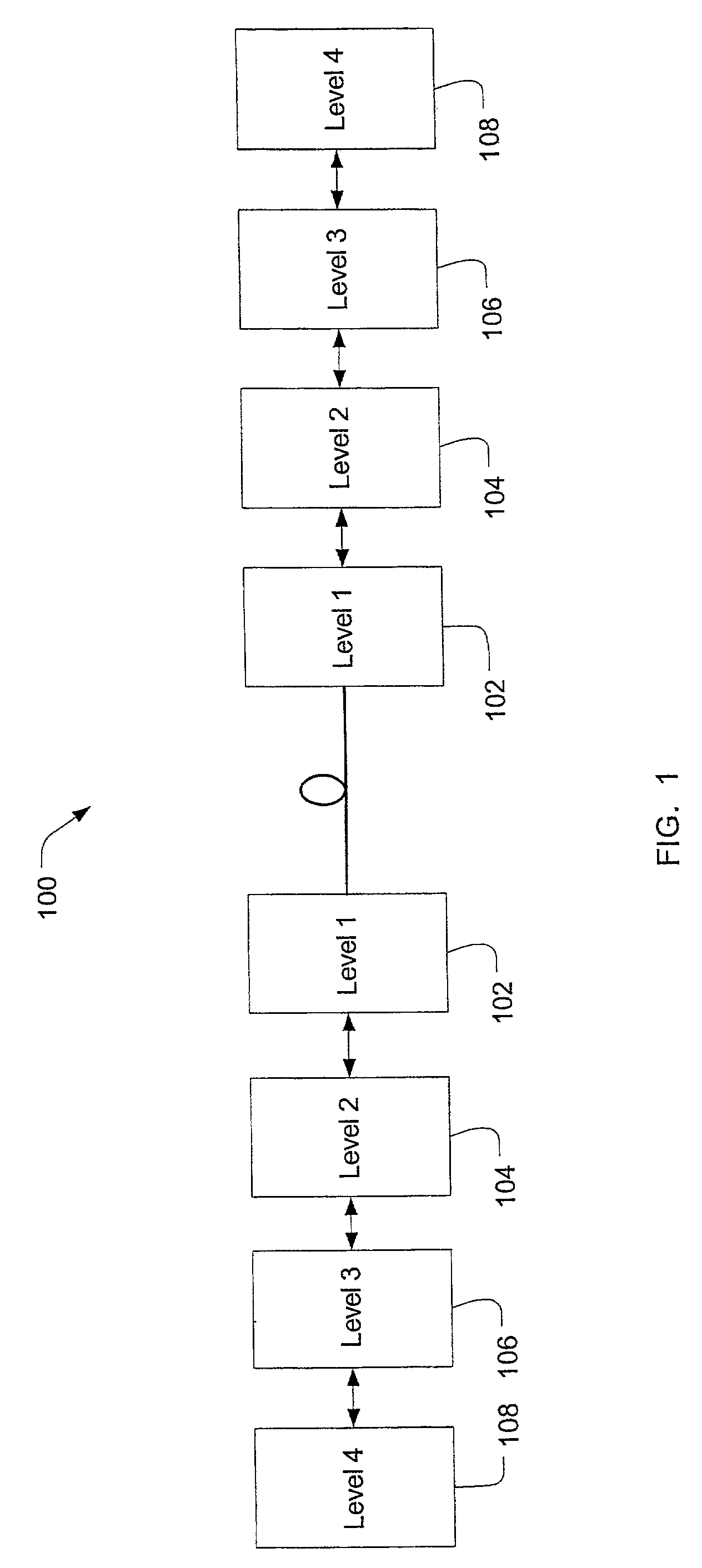
Multi-rate transparent mux for optical communications networks
InactiveUS20080075113A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationLine rateData rate
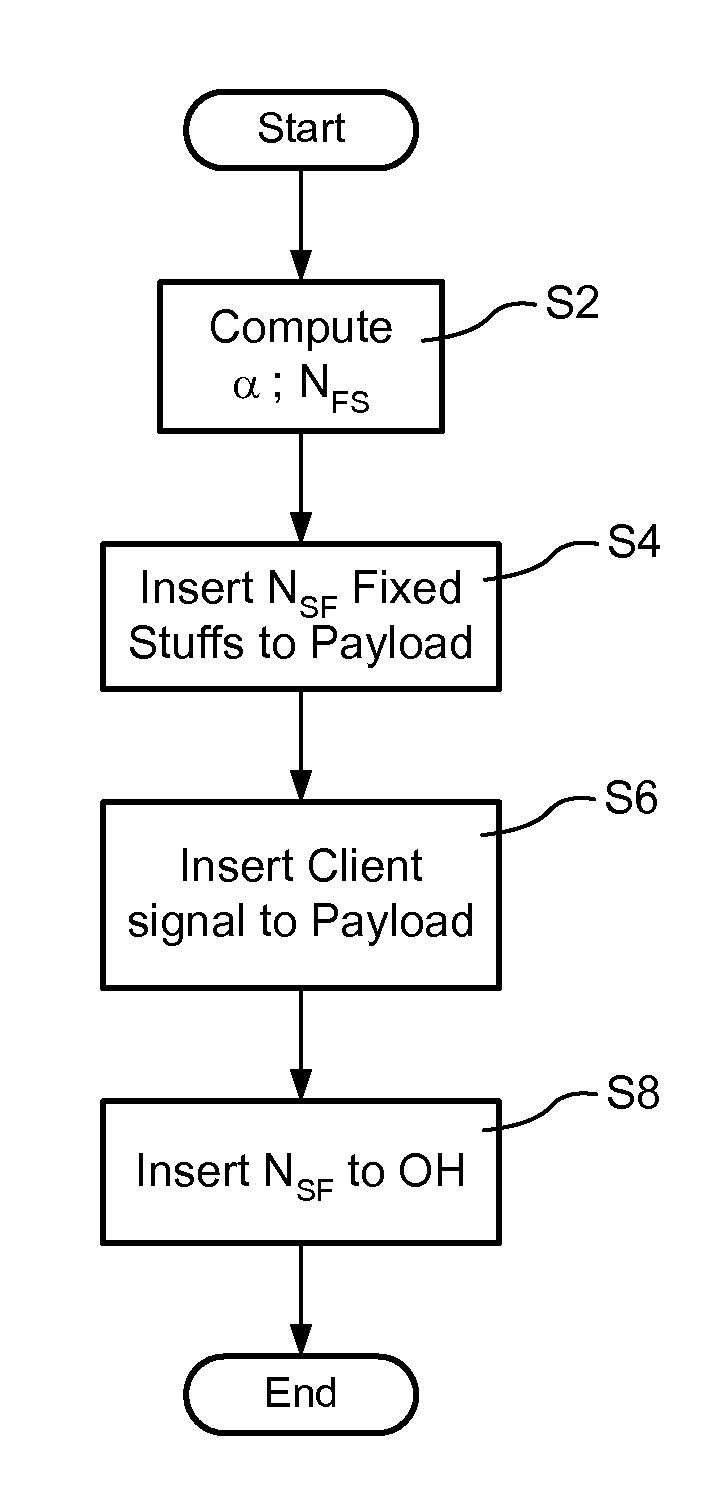
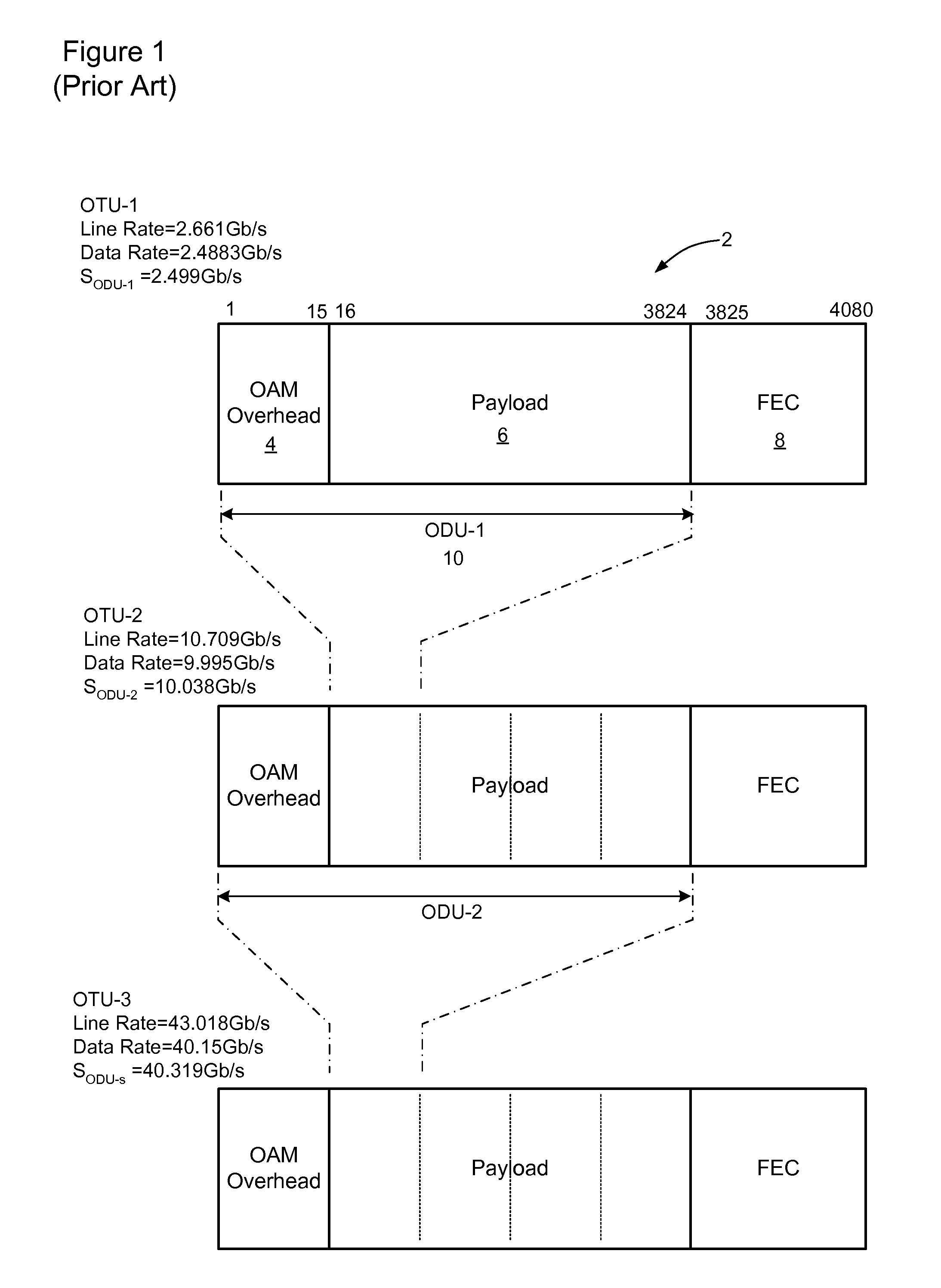
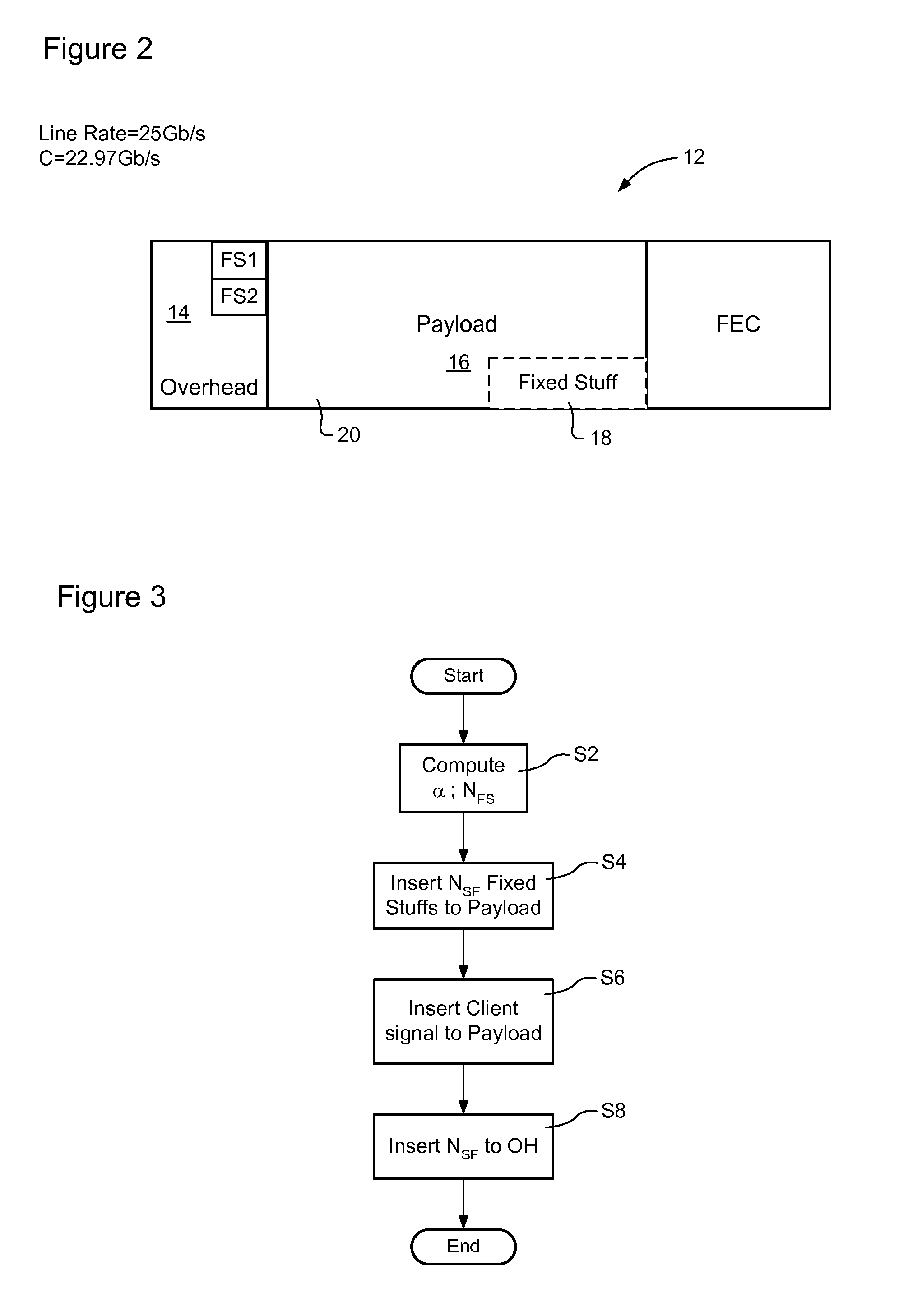
Bit-transparent muxing of an input signal for transport through an optical communications network. A fixed length container of the optical communications network is defined, which includes an overhead and a payload. A stuffing ratio (α) is based based on a line rate of the input signal and a data rate of the container. A number (NFS) of fixed stuffs is computed based on the stuffing ratio (α). The input signal and NFS fixed stuffs are inserted into the payload of the container, and the computed number NFS stored in the container's overhead. In some embodiments, the container is an overclocked OTU-3 (OTU3+) frame having a line rate of 44.6 Gb / s. This enables bit-transparent mux / demux of four nominal 10-Gig signals having line rates within a range of between 7.6 Gb / s and 10.4 Gb / s, or a single nominal 40-Gig signal having a line rate within a range of between 38.8 Gb / s and 41.6 Gb / s.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
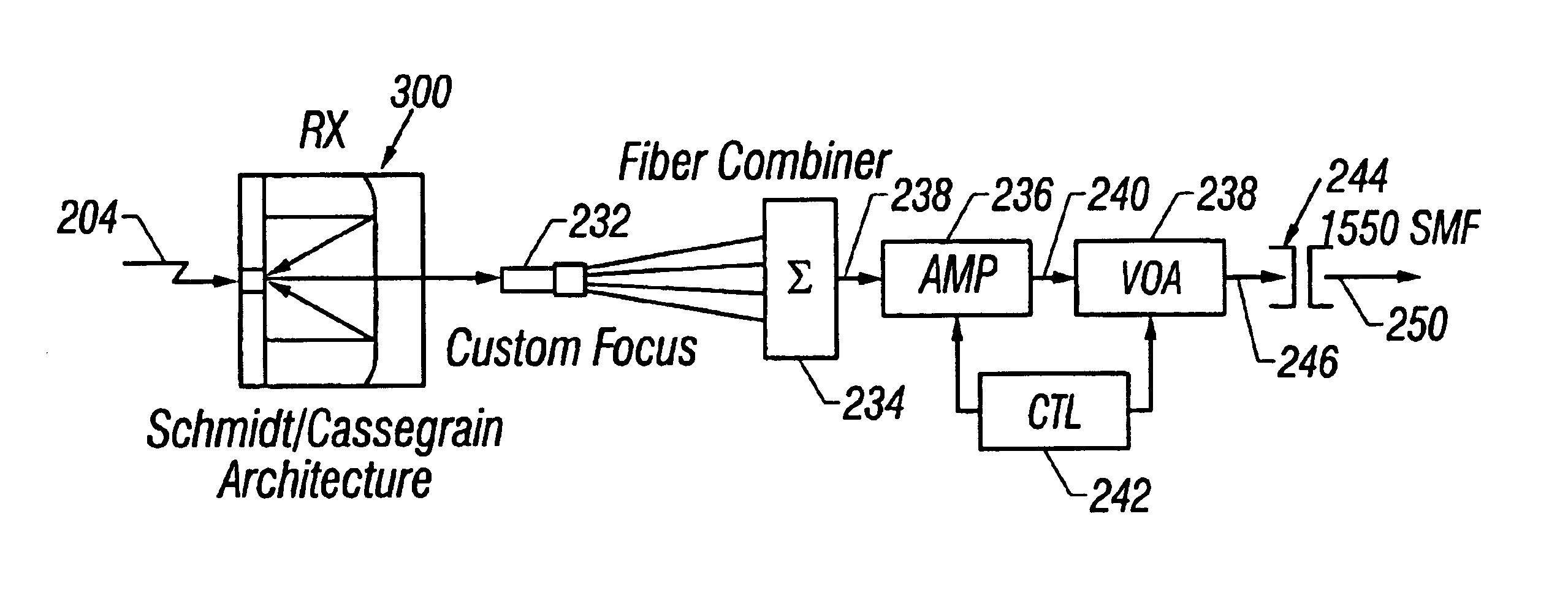
Terrestrial optical communication network of integrated fiber and free-space links which requires no electro-optical conversion between links
InactiveUS6868237B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsUltrasound attenuationLight beam
Optical signals are received from a free-space link by directing received light onto a plurality of microlenses and then directing light received through each of the microlenses into a respective single mode optical fiber (SMF). Light beams from the SMFs are combined into a single light beam in one SMF. The single light beam is amplified with a multi-wavelength fiber amplifier and attenuated with a variable optical attenuator. The power gain of the multi-wavelength fiber amplifier and the attenuation of the variable optical attenuator are controlled. The single light beam is directed into a fiber optic communication system that is optically coupled to the variable optical attenuator.
Owner:LIGHTPOINTE COMM
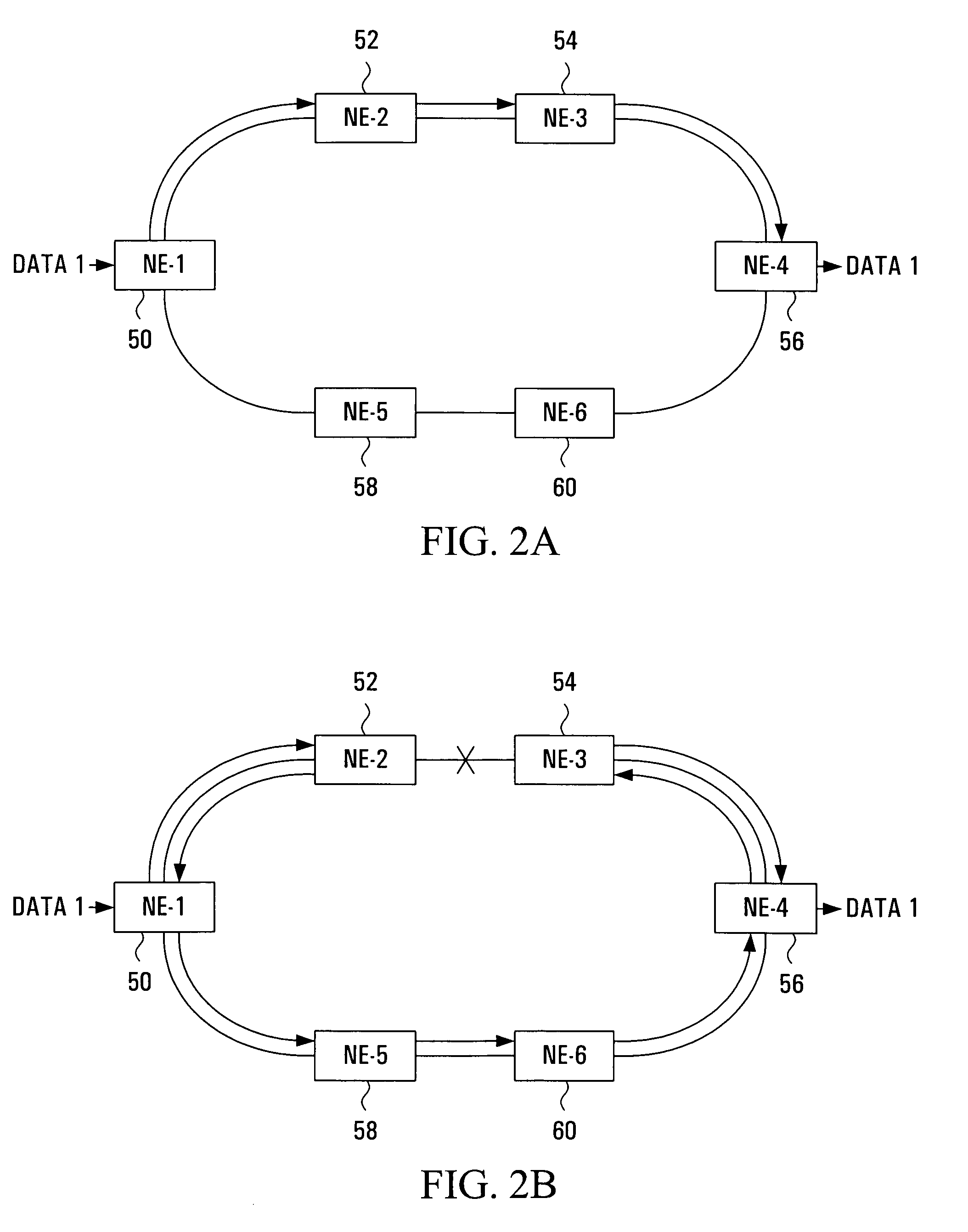
Method and system for providing protection in an optical communication network
InactiveUS20040114925A1Laser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemSignal quality
A method and system for providing tandem protection in a communication system. Path protection is provided using at least two redundant communication paths and selecting the communication path having a higher signal quality. Interface protection is provided through a protection transceiver. The interface protection may be delayed while the path protection attempts to restore communication.
Owner:CIENA
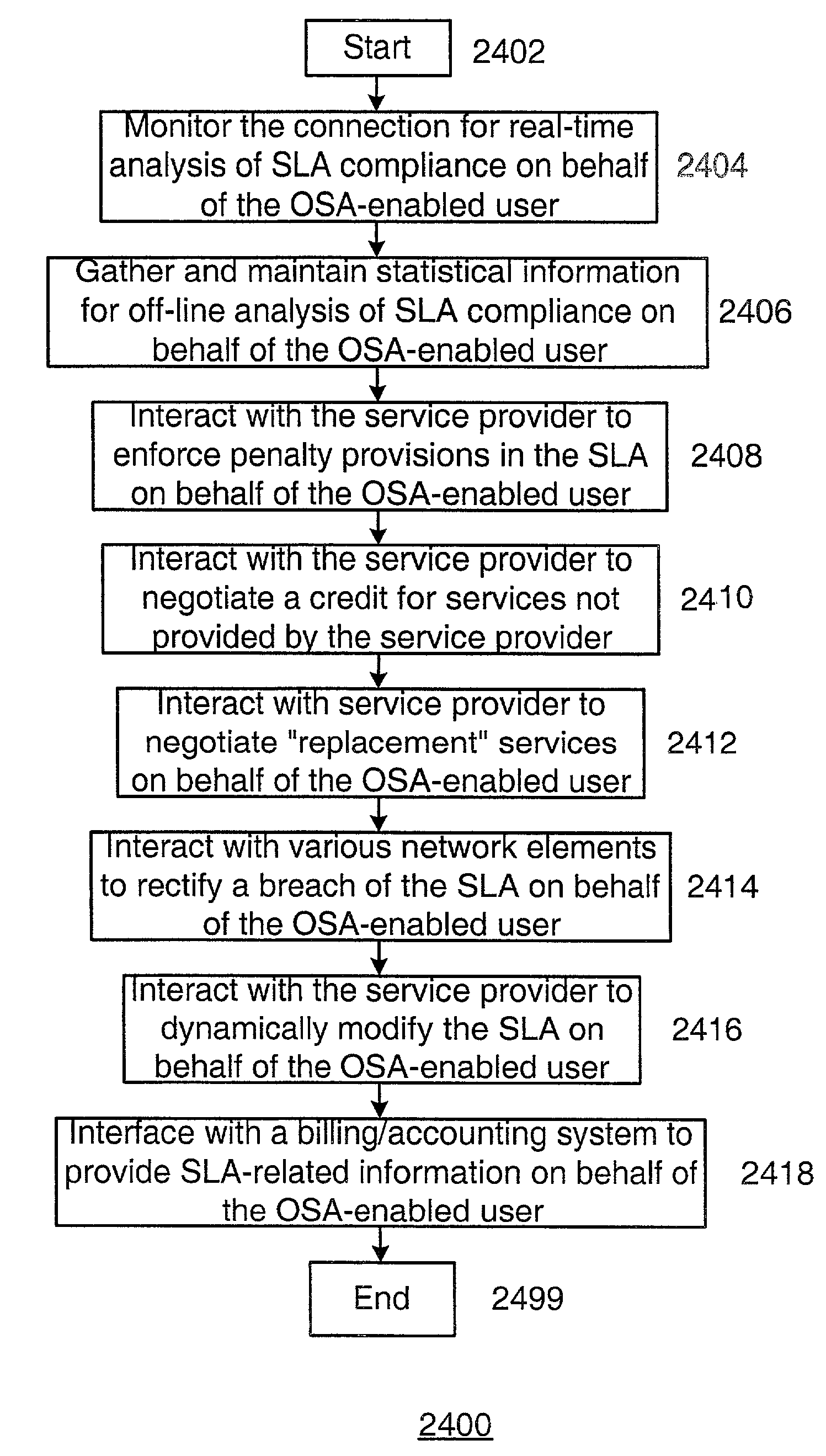
System, device, and method for managing service level agreements in an optical communication system
InactiveUS7437449B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionService-level agreementCommunications system
A system, device, and method for managing service level agreements in an optical communication system uses an optical service agent to manage a service level agreement (SLA) for a user. The optical service agent can perform both real-time and off-line analysis for the user, and can interact with various network elements (including the core optical communication network) to handle billing, penalty, and other issues associated with a SLA breach. Among other things, the optical service agent may monitor and analyze a connection in real-time for determining SLA compliance, gather and maintain statistical information relating to a connection, analyze the statistical information off-line for determining SLA compliance, patterns, and trends, interact with a service provider to enforce penalty provisions in the SLA, interact with a service provider to negotiate a credit for services not provided by the service provider in accordance with the SLA, interact with a service provider to negotiate “replacement” services for a breach of the SLA, interact with various network elements to rectify a breach of the SLA, interact with the service provider to dynamically modify the SLA based upon changing user requirements, and interface with a billing / accounting system to provide SLA-related information.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Signal equalizer in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS8005368B2Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringVIT signals
A signal equalizer for compensating impairments of an optical signal received through a link of a high speed optical communications network. At least one set of compensation vectors are computed for compensating at least two distinct types of impairments. A frequency domain processor is coupled to receive respective raw multi-bit in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) sample streams of each received polarization of the optical signal. The frequency domain processor operates to digitally process the multi-bit sample streams, using the compensation vectors, to generate multi-bit estimates of symbols modulated onto each transmitted polarization of the optical signal. The frequency domain processor exhibits respective different responses to each one of the at least two distinct types of impairments.
Owner:CIENA
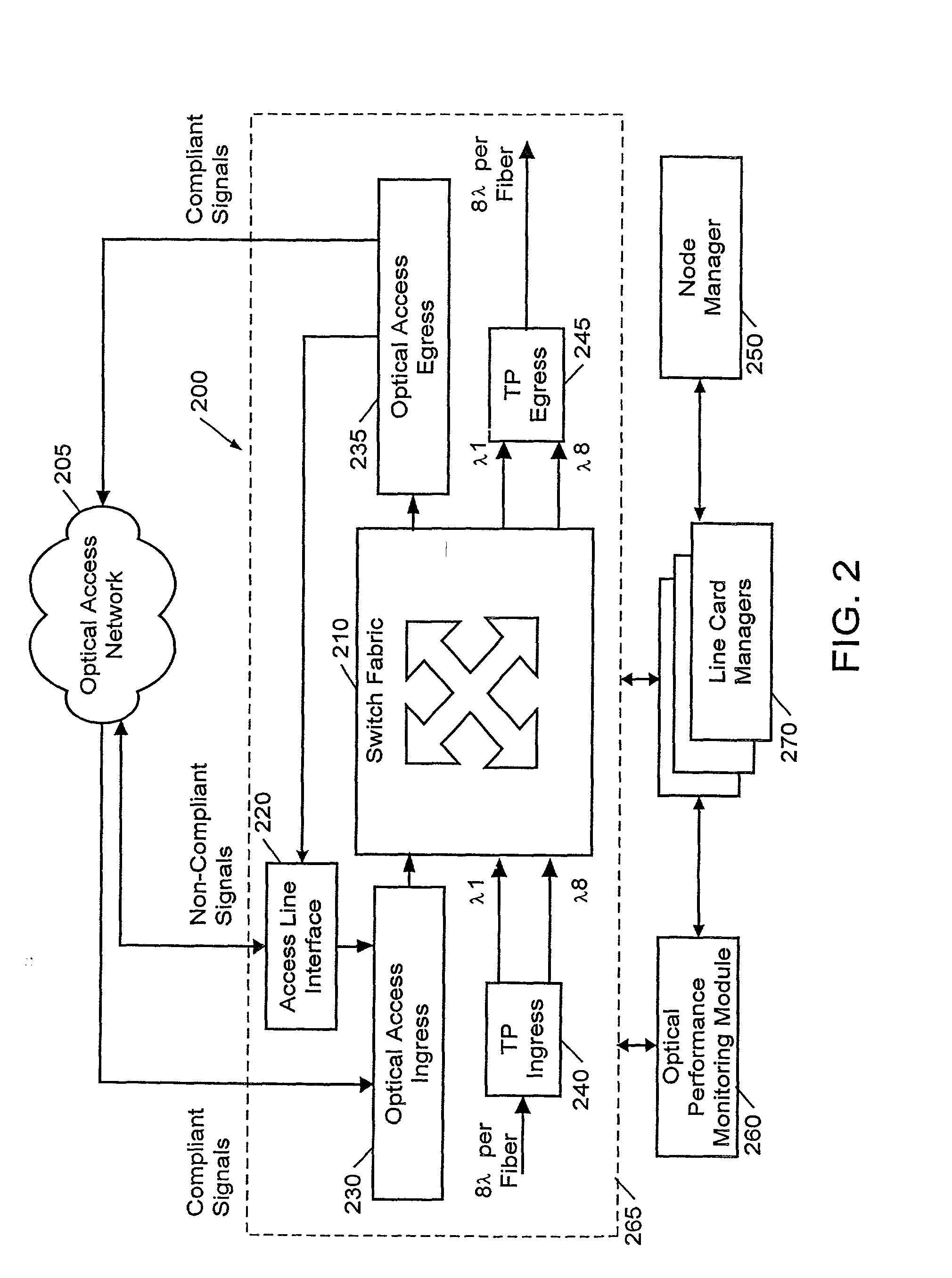
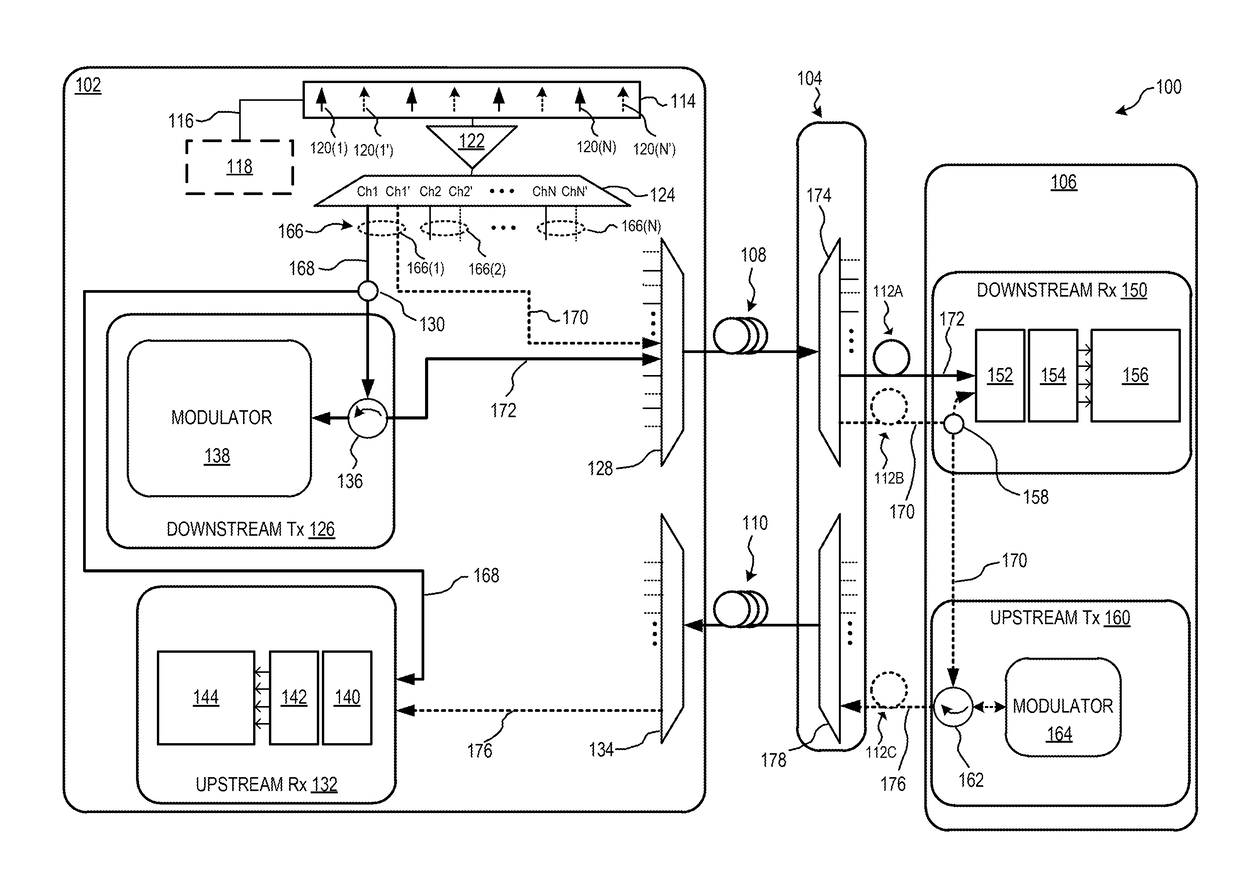
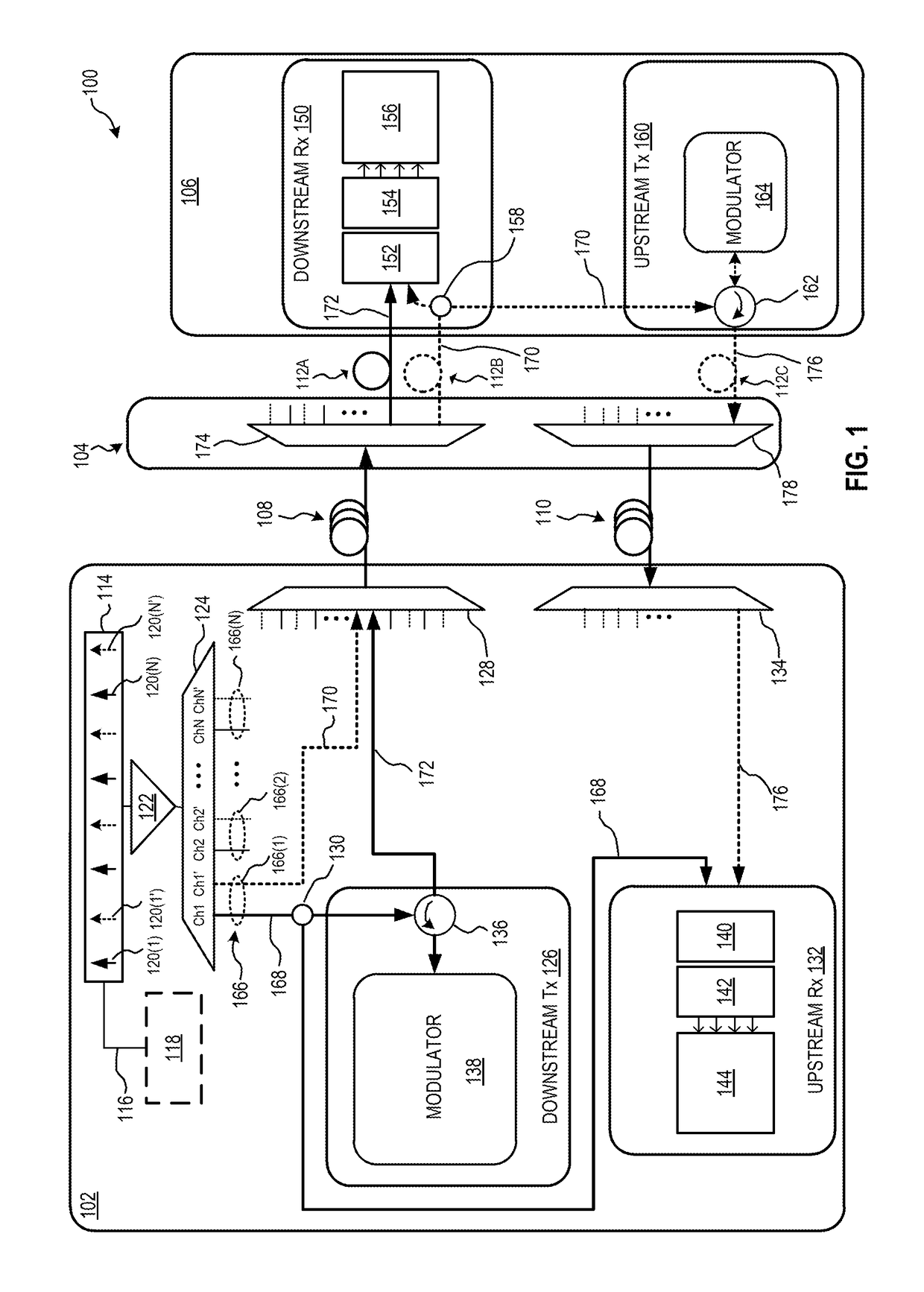
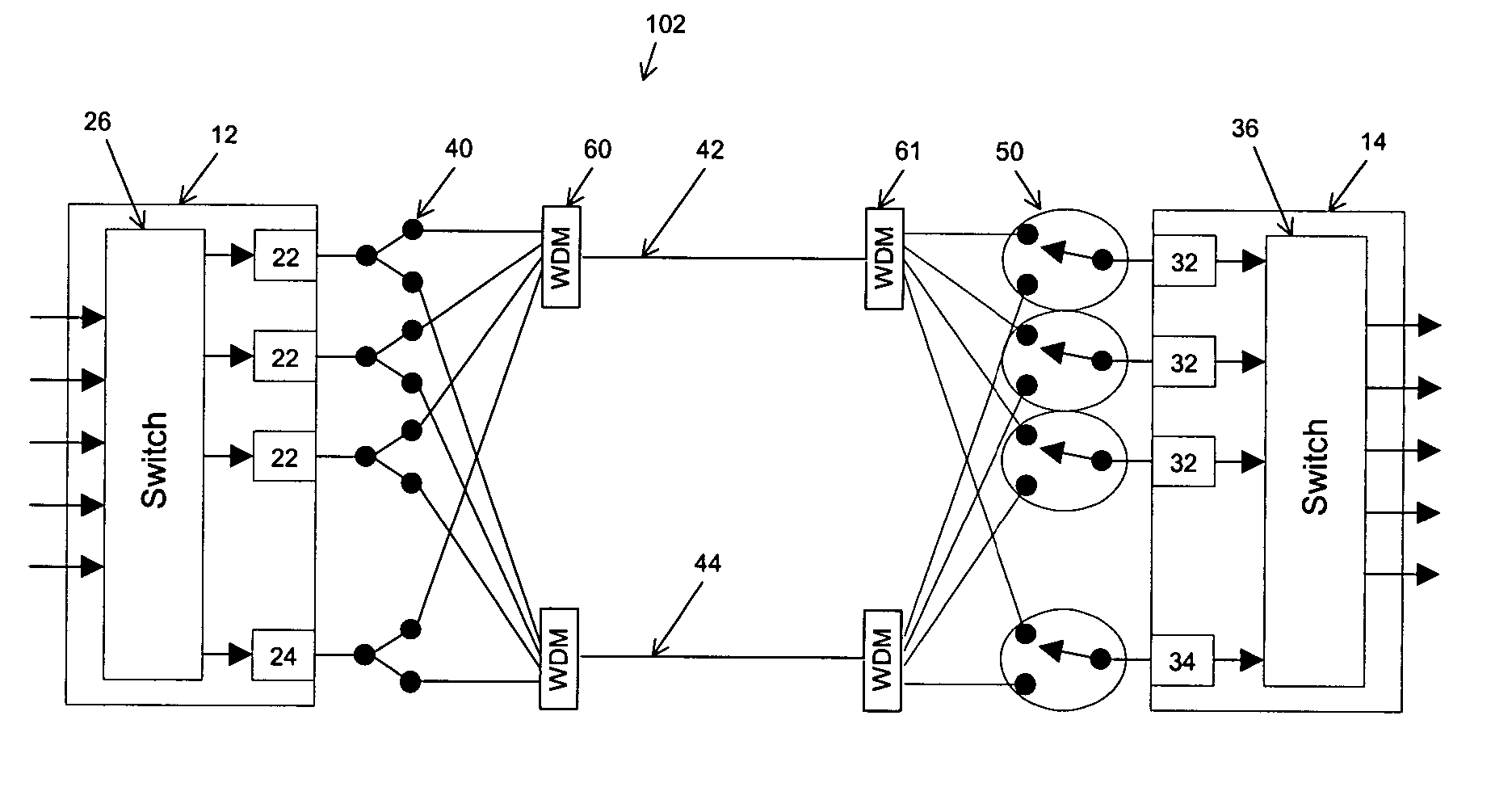
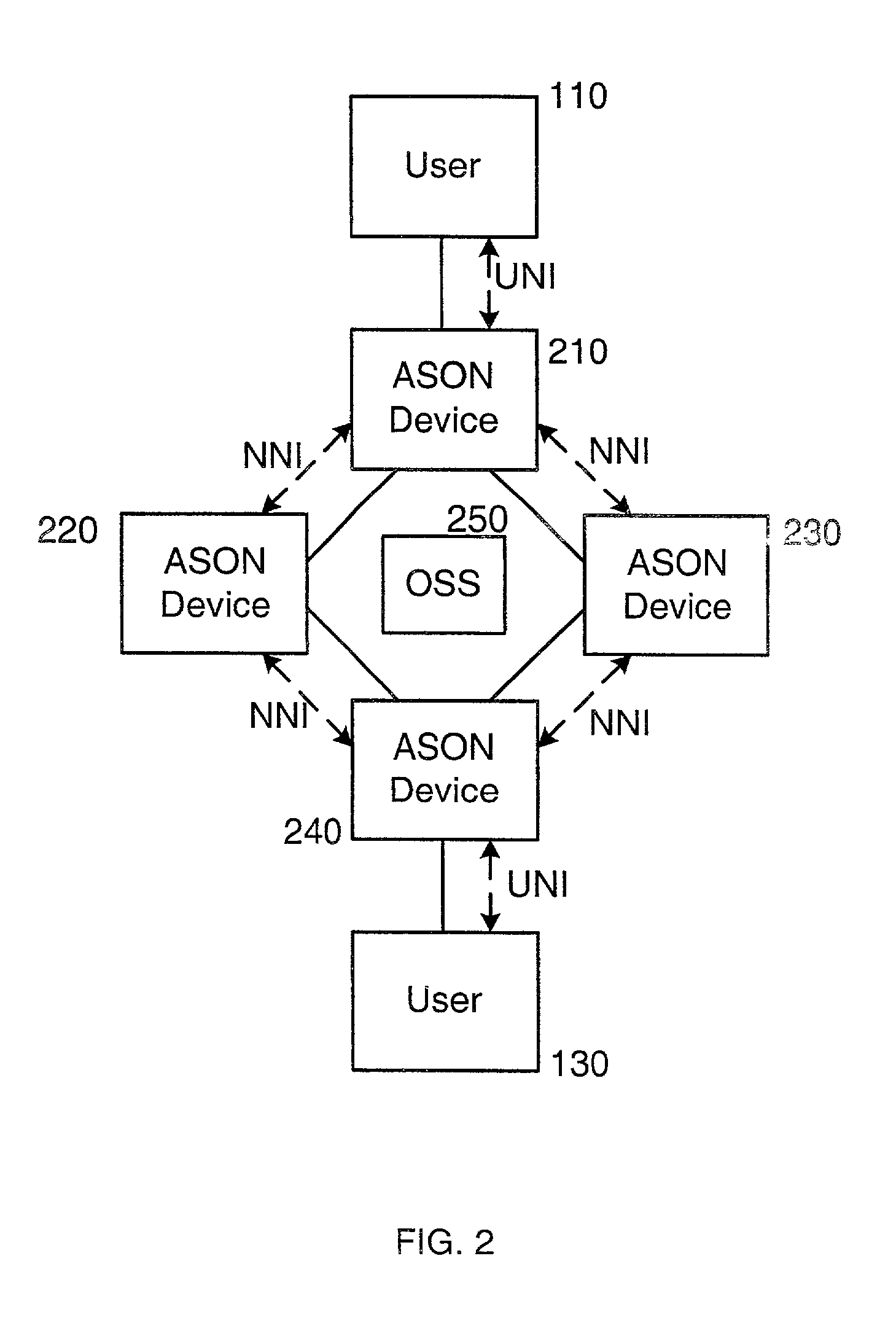
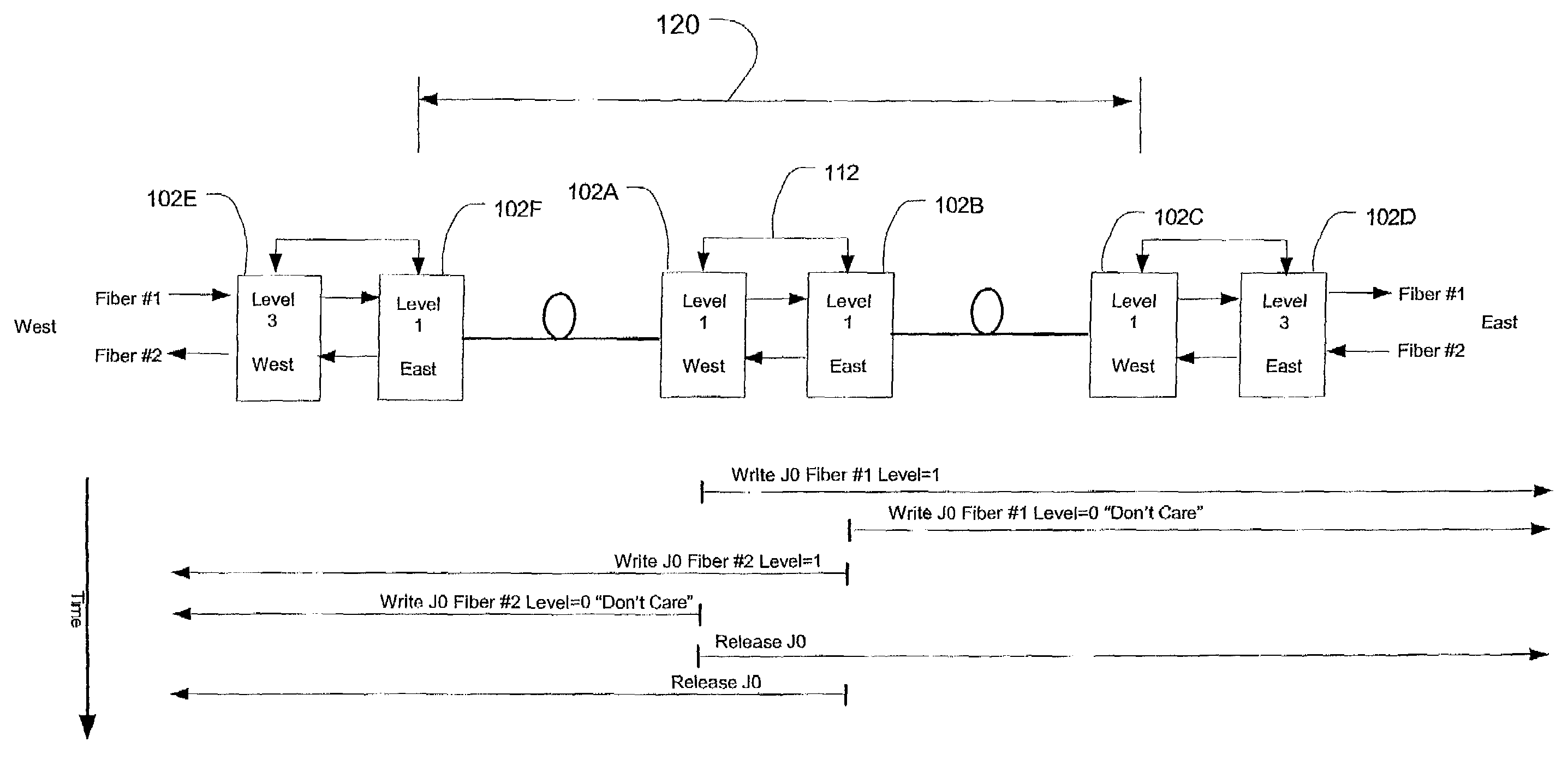
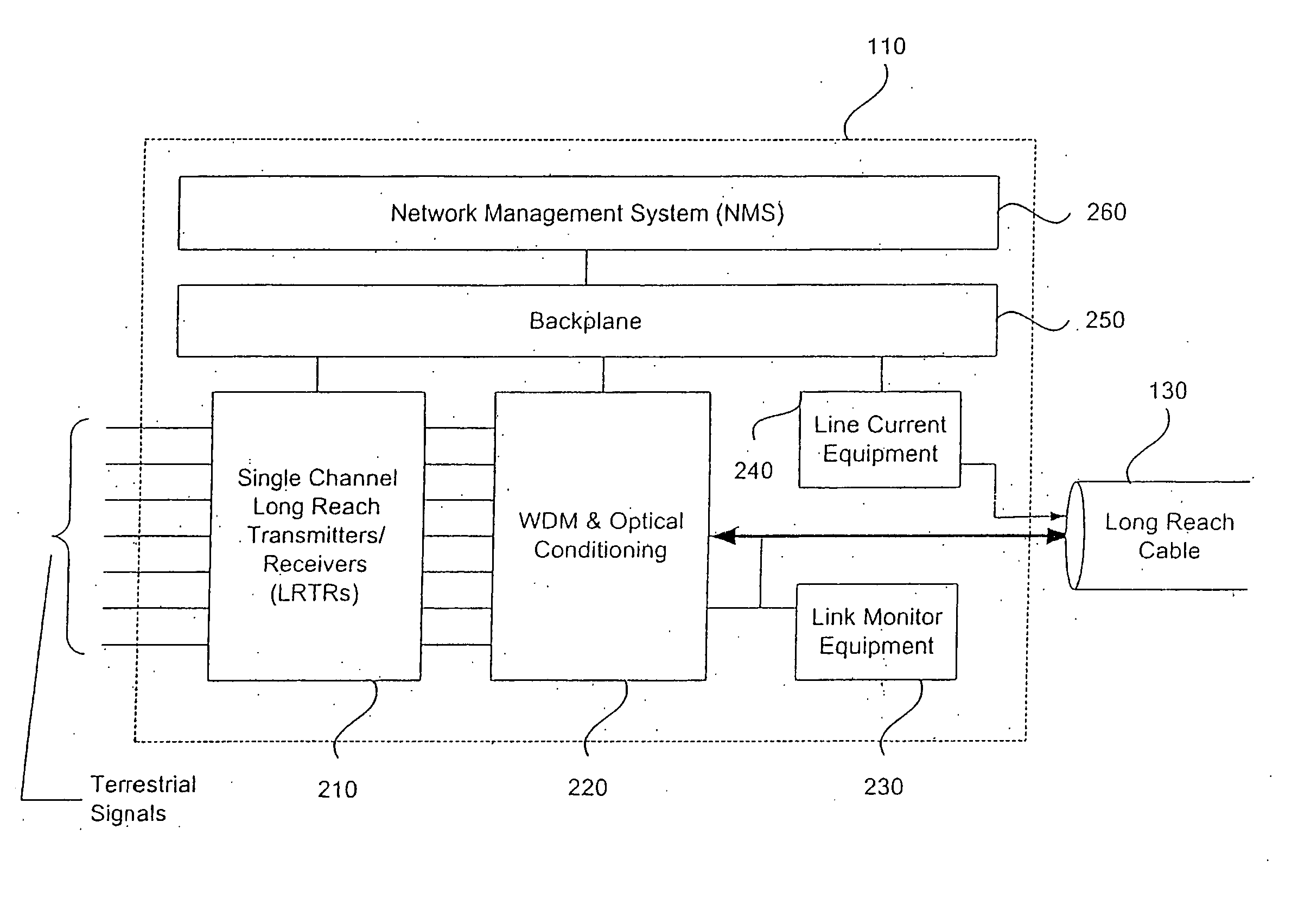
Method and system for detecting network elements in an optical communications network
ActiveUS7054554B1Multiplex communicationData switching by path configurationNetwork elementOptical communication networks
An exemplary embodiment of the invention is a method of detecting network elements in an optical communications network. The method includes an initiating network element generating a neighbor discovery message including a requested hierarchy level at which neighbor discovery is requested and transmitting the neighbor discovery message downstream along the optical communications network. A downstream network element receives the neighbor discovery message, determines if the downstream network element operates at the requested hierarchy level. The downstream network element generates a responding neighbor discovery message if the downstream network element operates at the requested hierarchy level and transmits the responding neighbor discovery message to the initiating network element. Alternate embodiments include a system and storage medium for implementing the method.
Owner:CIENA
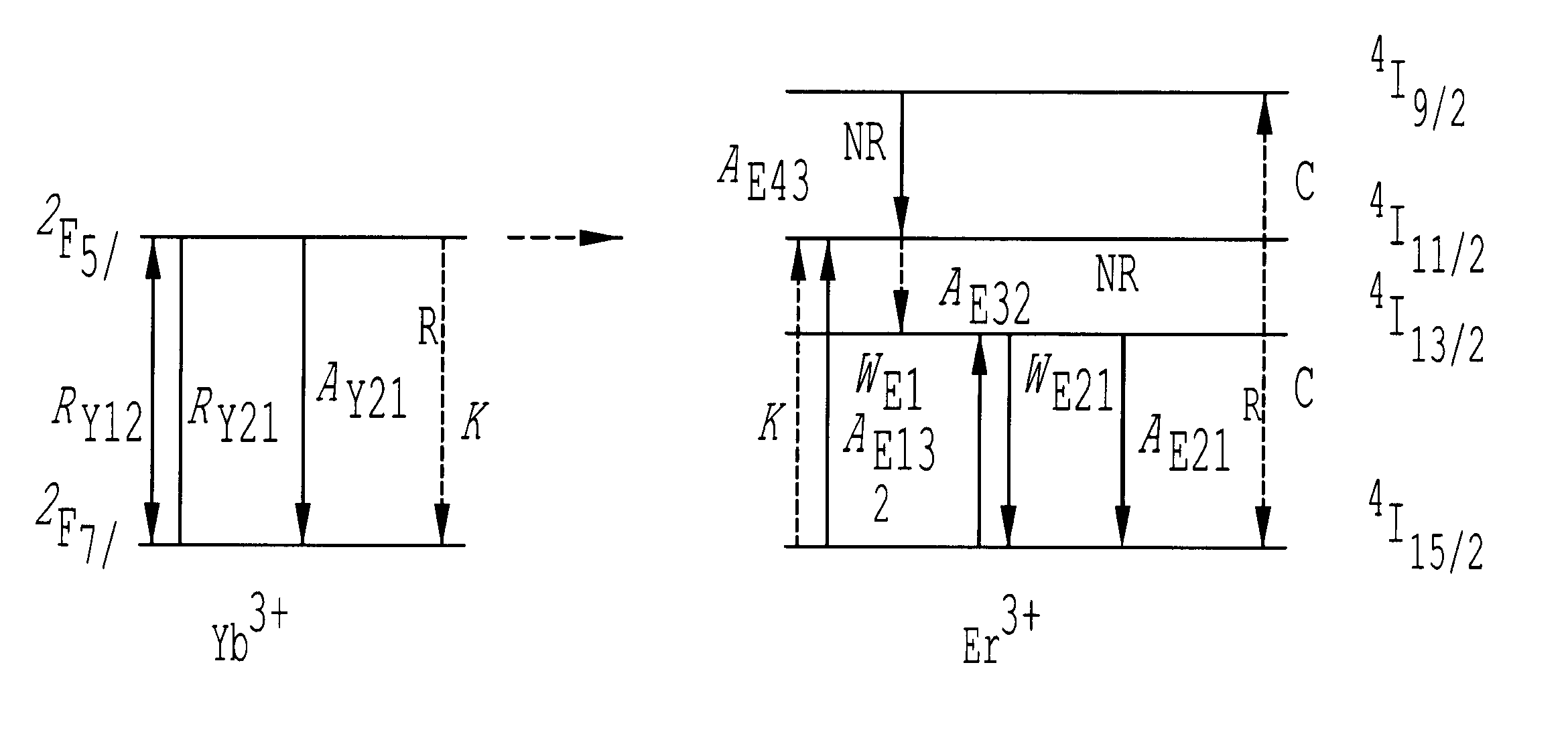
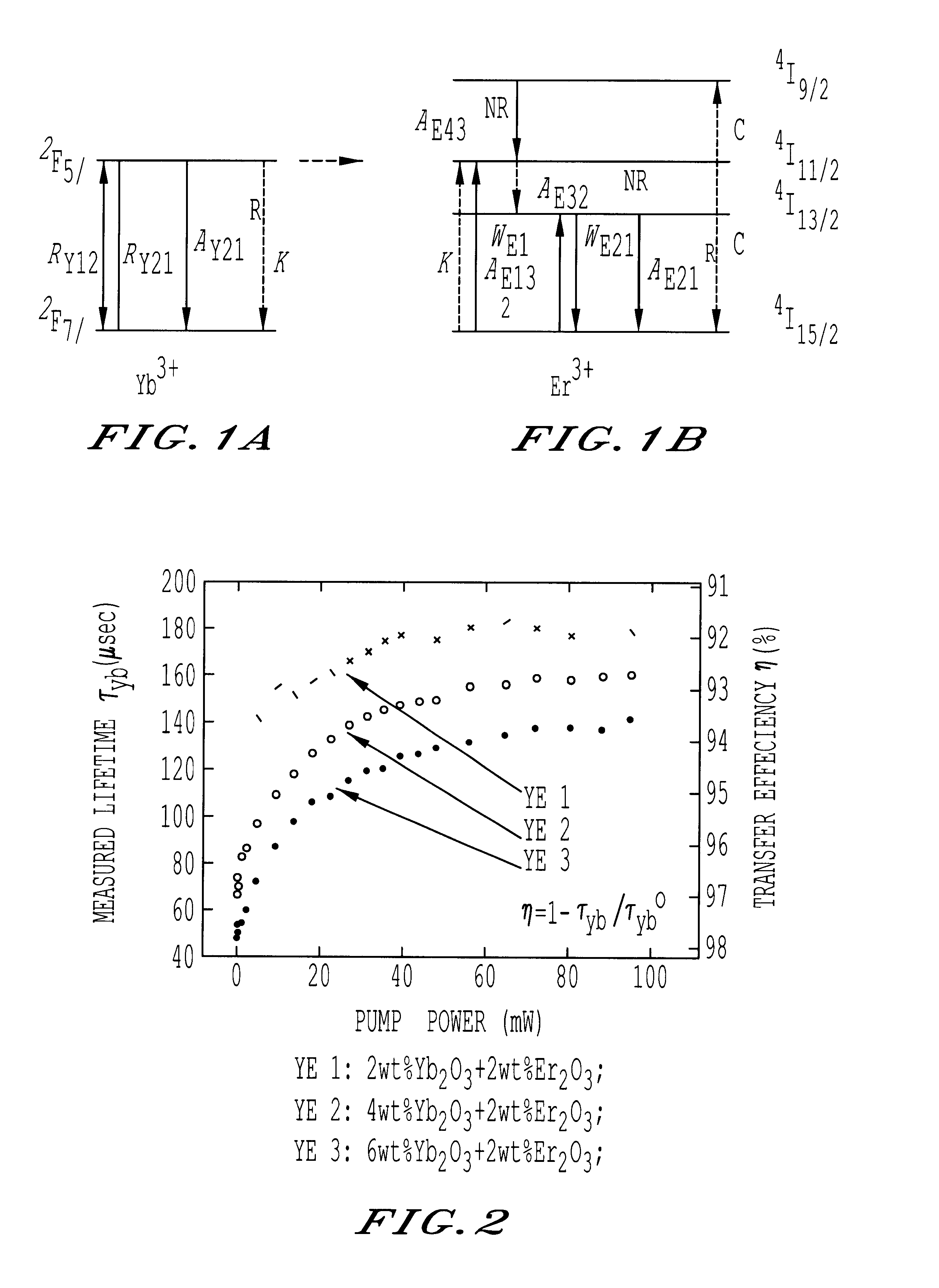
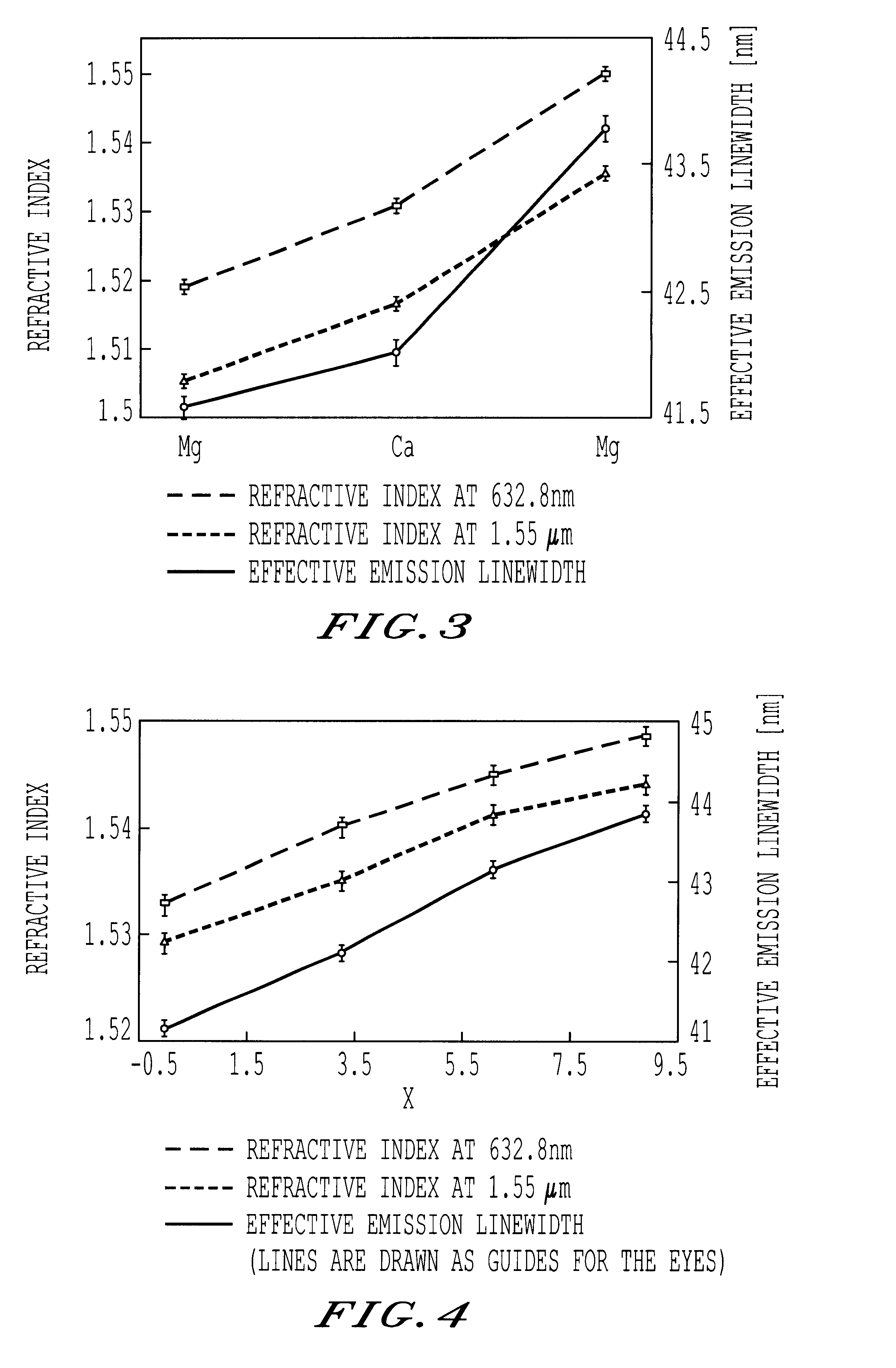
Erbium and ytterbium co-doped phosphate glass optical fiber amplifiers using short active fiber length
InactiveUS6611372B1High gain per unit lengthHigh gain amplificationLaser arrangementsActive medium materialErbium dopingPhosphate glass
An optical fiber amplifier utilizing a phosphate glass optical fiber highly doped with rare-earth ions such as erbium to exhibit high gain per unit length, enabling the use of short fiber strands to achieve the needed gain in practical fiber optical communication networks. The high-gain phosphate optical glass fiber amplifiers are integrated onto substrates to form an integrated optics amplifier module. An optical pump such as a semiconductor laser of suitable wavelength is used to promote gain inversion of erbium ions and ultimately provide power amplification of a given input signal. Gain inversion is enhanced in the erbium doped phosphate glass fiber by co-doping with ytterbium. A phosphate fiber amplifier or an integrated optics amplifier module utilizing this power amplification can be combined with other components such as splitters, combiners, modulators, or arrayed waveguide gratings to form lossless or amplified components that do not suffer from insertion loss when added to an optical network. The fiber amplifier can be a single fiber or an array of fibers. Further, the phosphate glass fibers can be designed with a temperature coefficient of refractive index close to zero enabling proper mode performance as ambient temperatures or induced heating changes the temperature of the phosphate glass fiber. Large core 50-100 .mu.m fibers can be used for fiber amplifiers. The phosphate glass composition includes erbium concentrations of at least 1.5 weight percentage, preferably further including ytterbium at 1.5 weight percentage, or greater.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
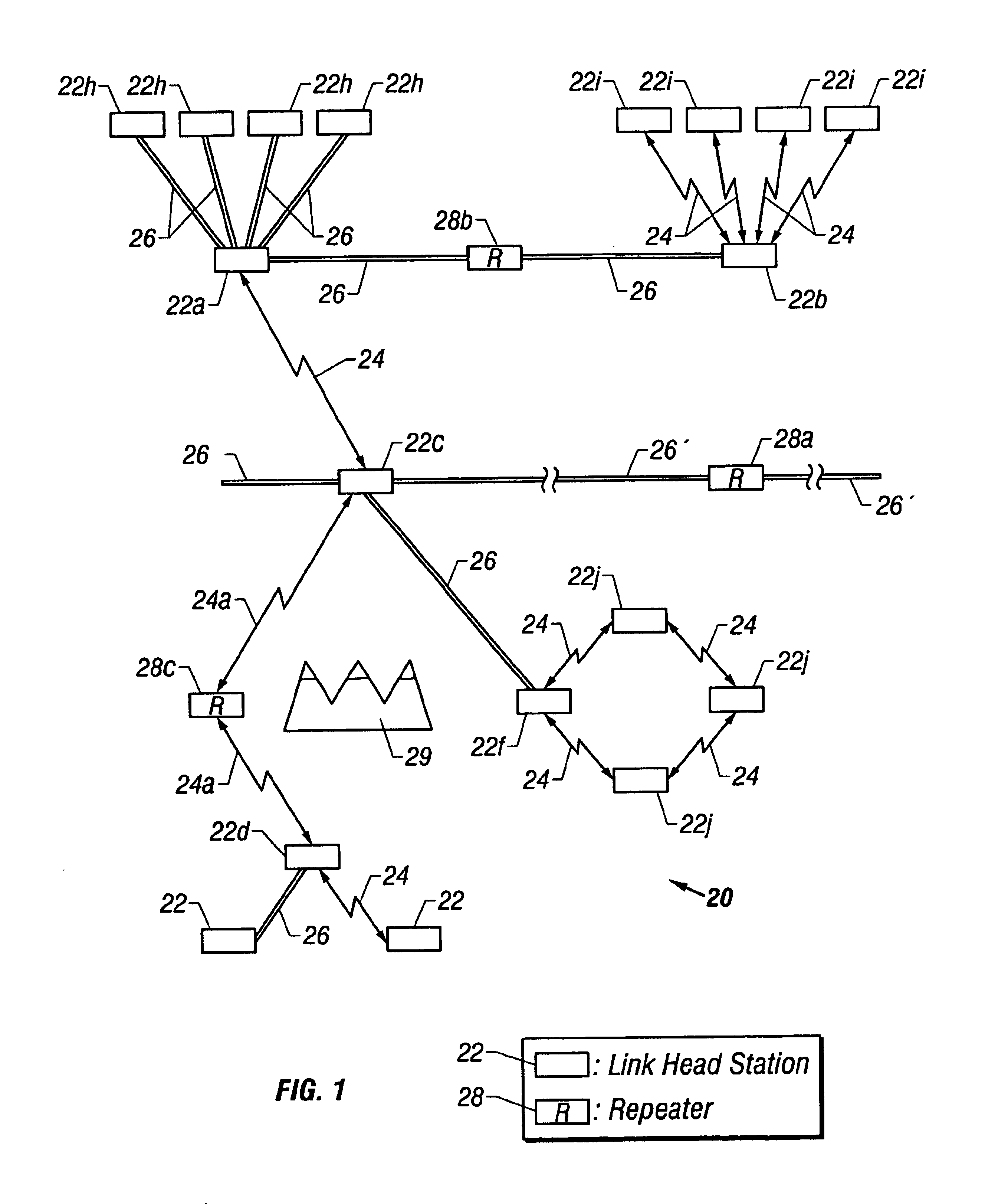
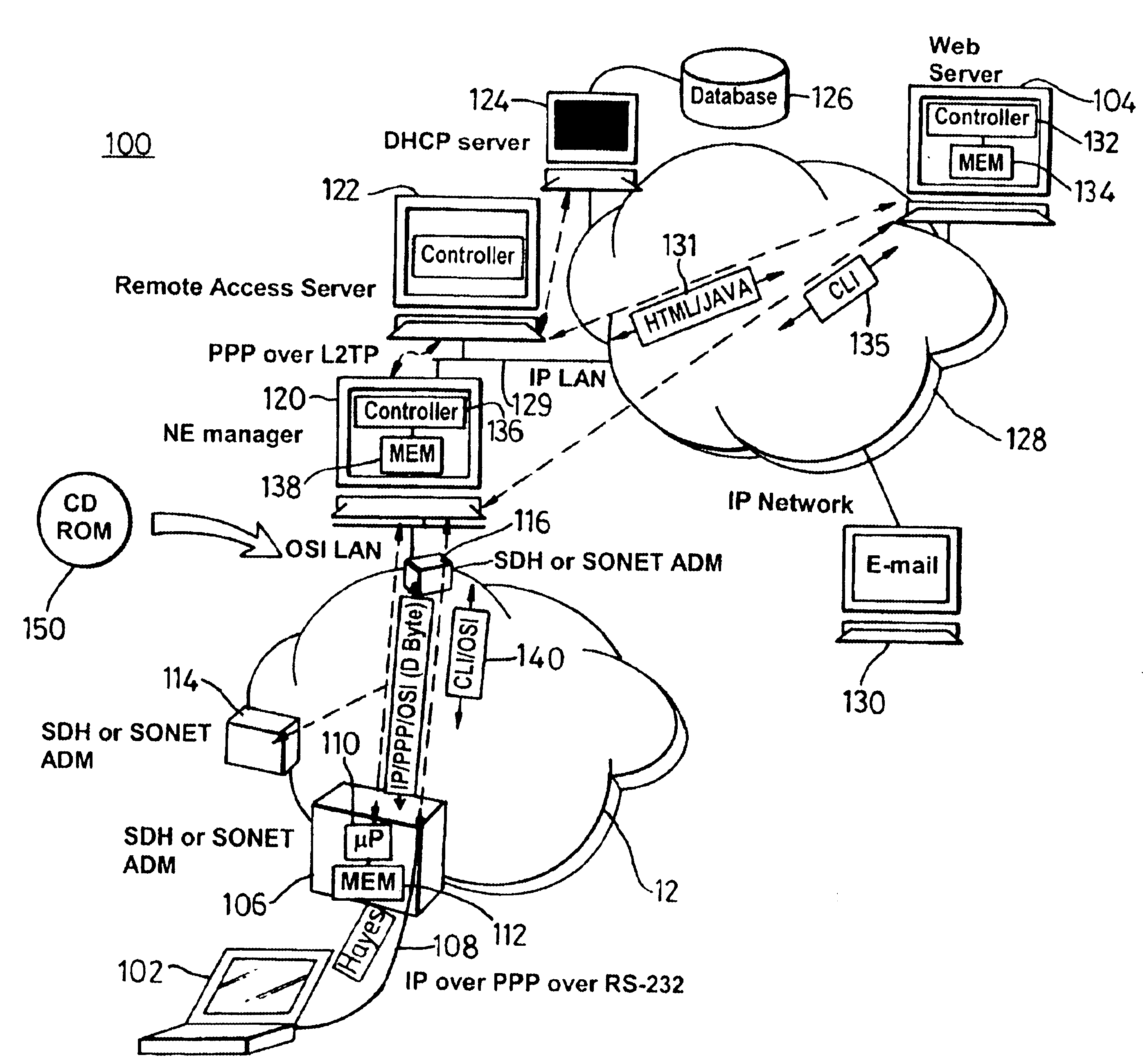
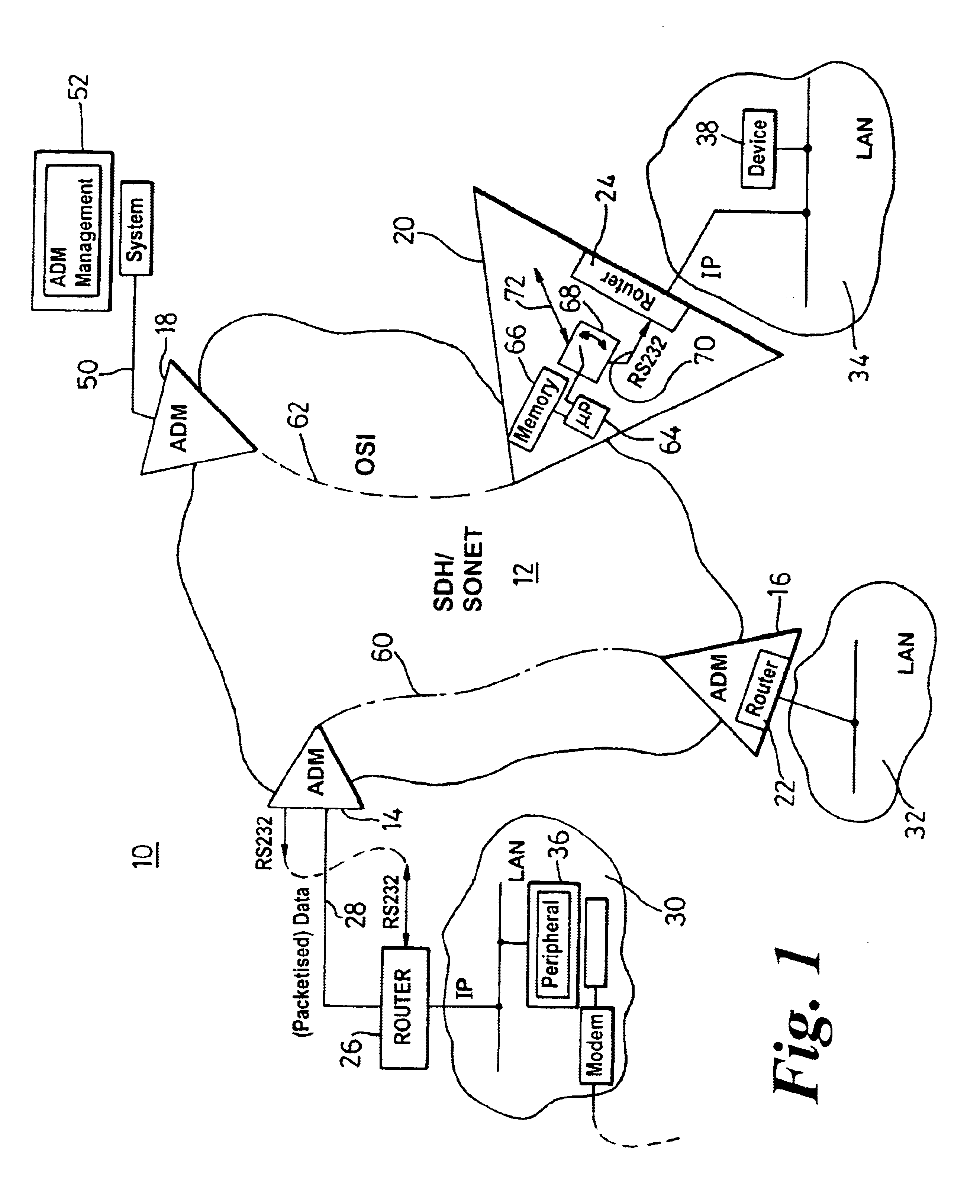
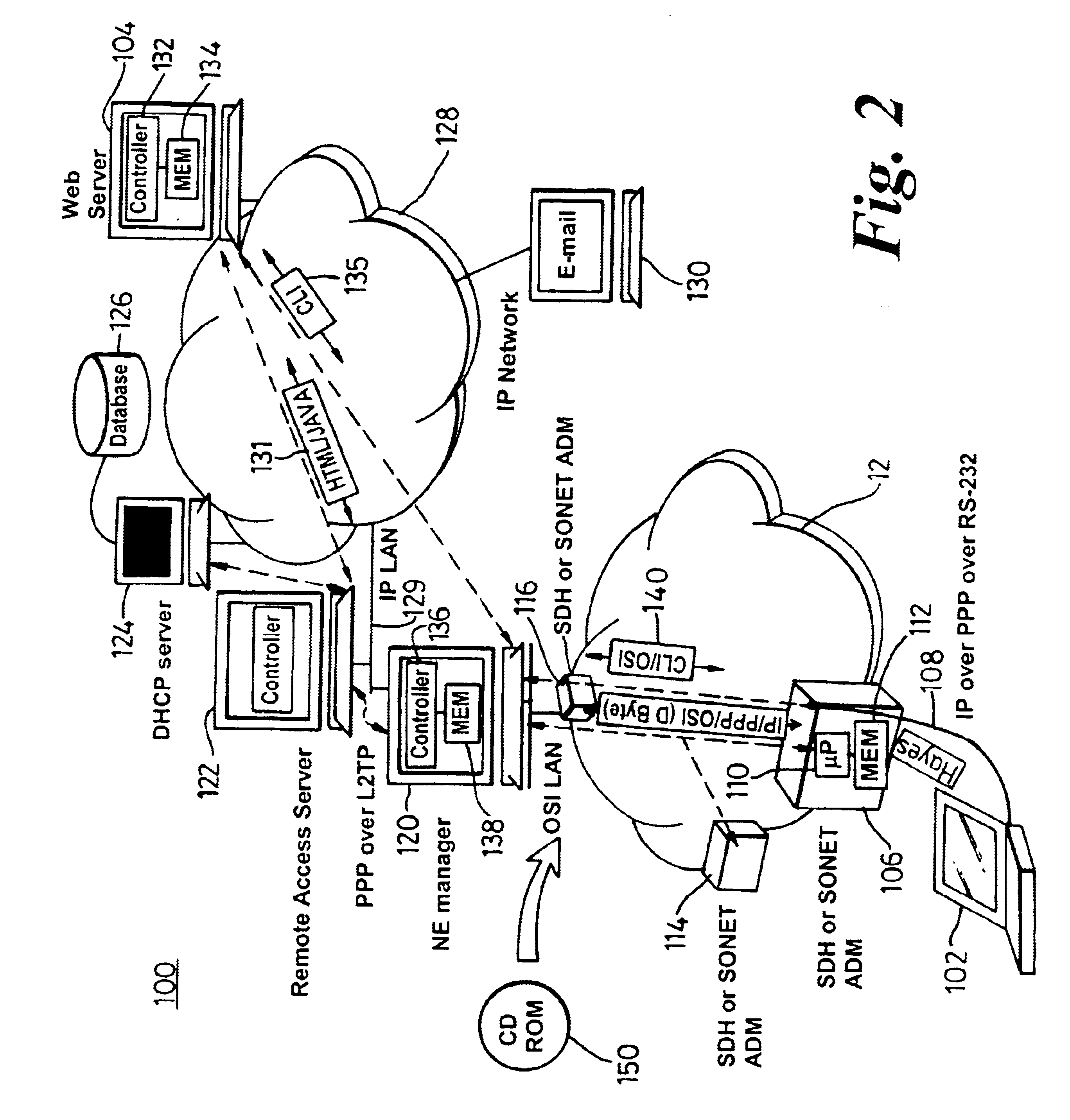
Optical communication network and method of remotely managing multiplexers
InactiveUS6892233B1Simplified user interfaceSimple interfaceMultiplex communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsCommand-line interfaceModem device
To provide a graphic user interface, supported by HTML or Java script, to a personal computer (102) for the control of SONET / SDH network elements (106), an RS-232 port of a PC is used to establish a PPP session to a remote access server, RAS (122). The network element (106) is therefore configured to imitate a modem, and to route PPP packets into its related management system across an optical ring (12). The management system may include an intermediate network manager (120) and a DHCP server (124). Once legitimacy of the PC is established through the IP session, the PC is provided with an IP address to invoke the PC's IP stack. Subsequently, IP is communicated across the PPP session, with the RAS (120) configured to terminate the PPP session and forward IP packets into an IP network (128). IP packets (131), received at a web server (140), are converted into command line interface (CLI) messages 135 and are sent directly to the network manager (120) within an IP packet. The network manager (120) terminated the IP packet and re-packages the CLI messages into an optical carrier format (140) for relay to an addressed network element (106). The addressed network element (106), which is responsive to the CLI messages from a management perspective, then alters its set-up or functionality accordingly. Complex text-based CLI instructions are thus avoided by a field-based engineer through the use of a GUI supported by a PC having web-browser capabilities, with an typical architecture shown in FIG. 2.
Owner:CIENA
Method and apparatus for filtering an optical beam
InactiveUS6879619B1Compact formEasy to tuneLaser optical resonator constructionWavelength-division multiplex systemsExternal cavity laserMesh grid
Owner:INTEL CORP
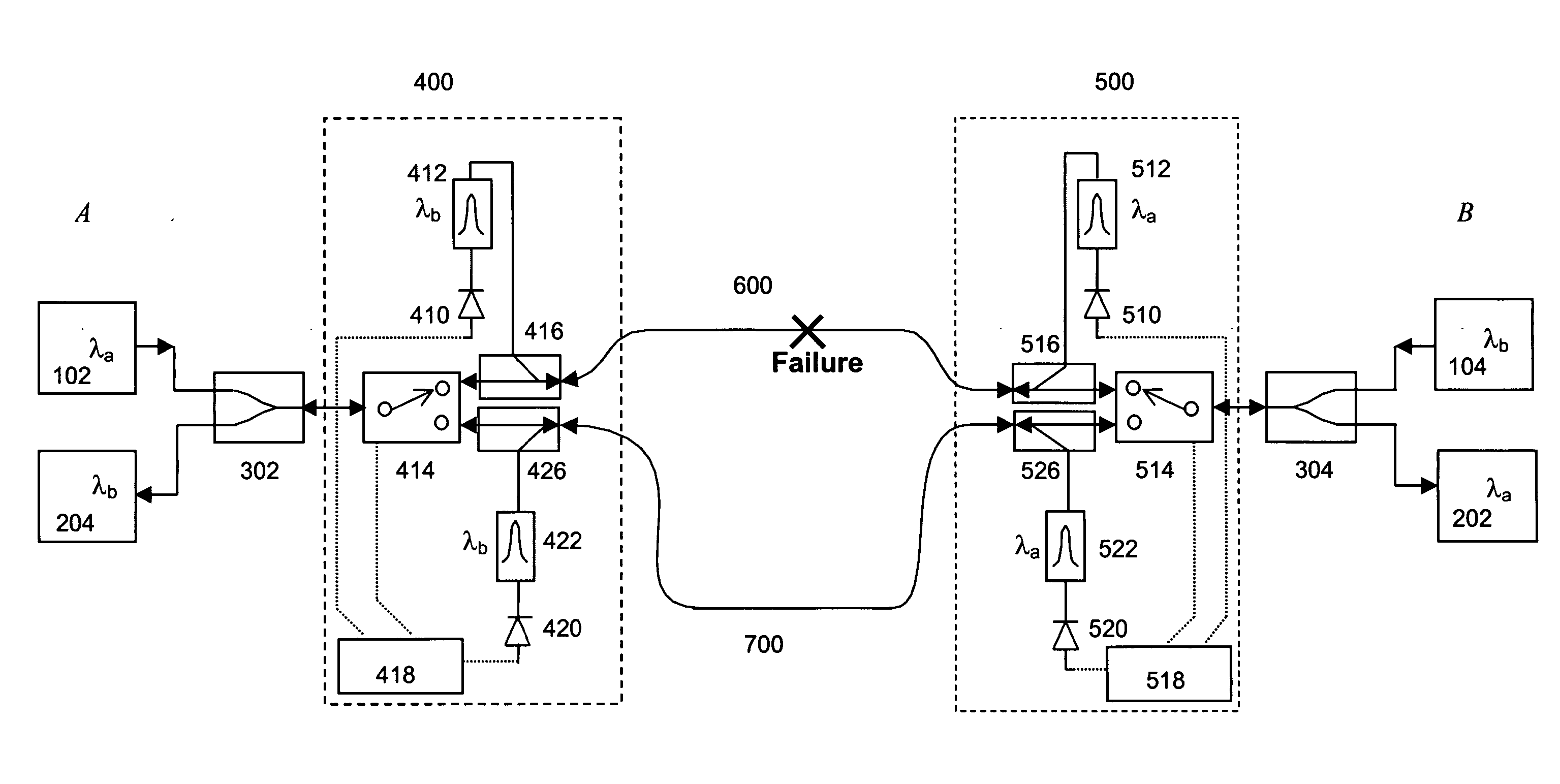
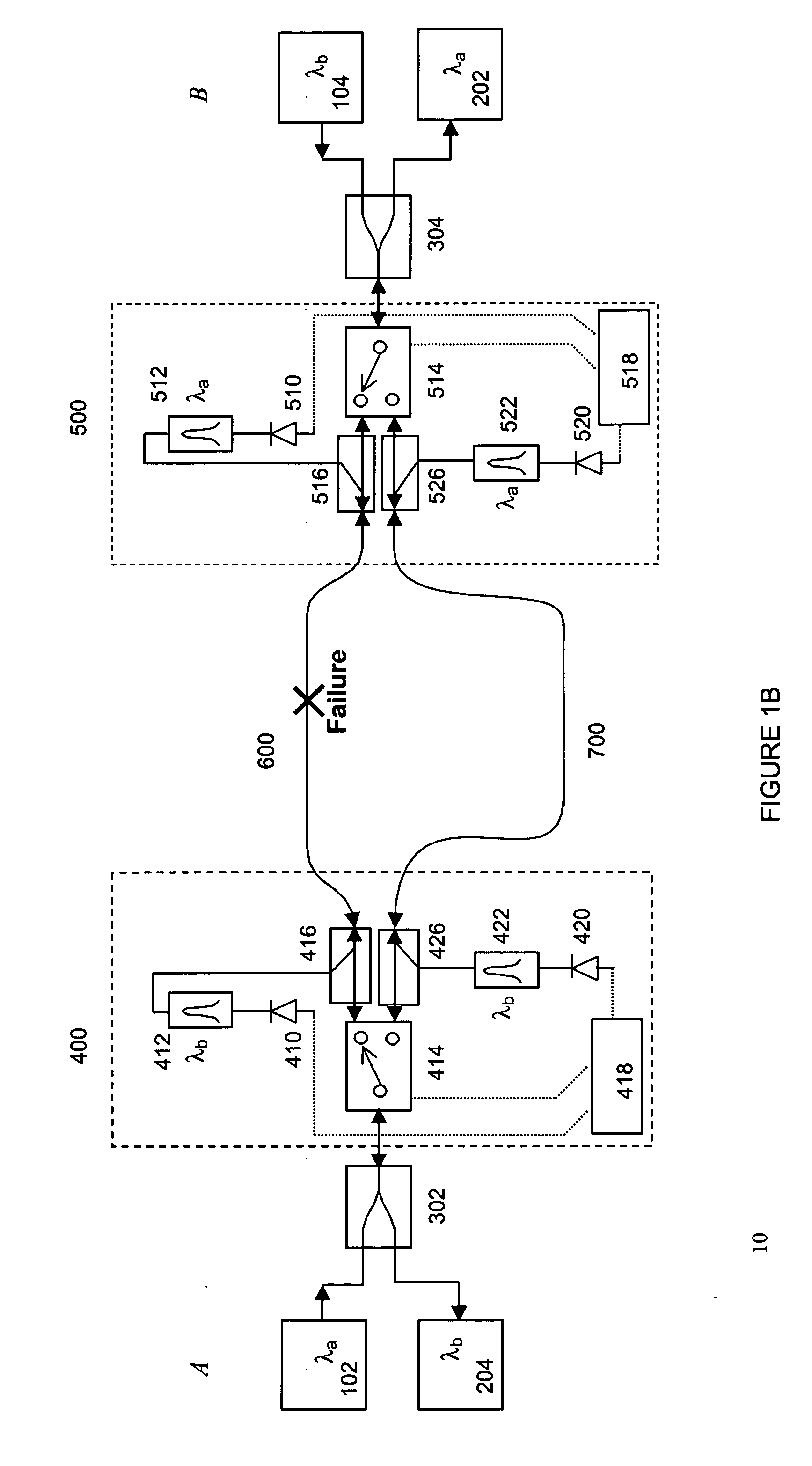
Protection for bi-directional optical wavelength division multiplexed communications networks
A bi-directional wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) optical communications network that includes components for automatically detecting a fault along a primary optical waveguide in a link forming part of a bi-directional WDM communication network and switching the transmission path of the optical signals propagated along that link from that waveguide to a second standby waveguide whenever a fault is detected in the first waveguide using 1×2 optical switches, optical filters, photodetectors and electronics in a configuration designed to avoid silent event failures. Replacing the 1×2 optical switches with 2×2 optical switches in conjunction with other equipment can allow either the constant monitoring of the standby waveguide, provide back up for optical transmitters, receivers and couplers on the path containing the primary waveguide and / or allow carriage of low priority traffic on the standby waveguide as long as it is in standby mode. No handshaking mechanism is required between the opposite ends of the waveguides for the switchover protection.
Owner:GO4FIBER
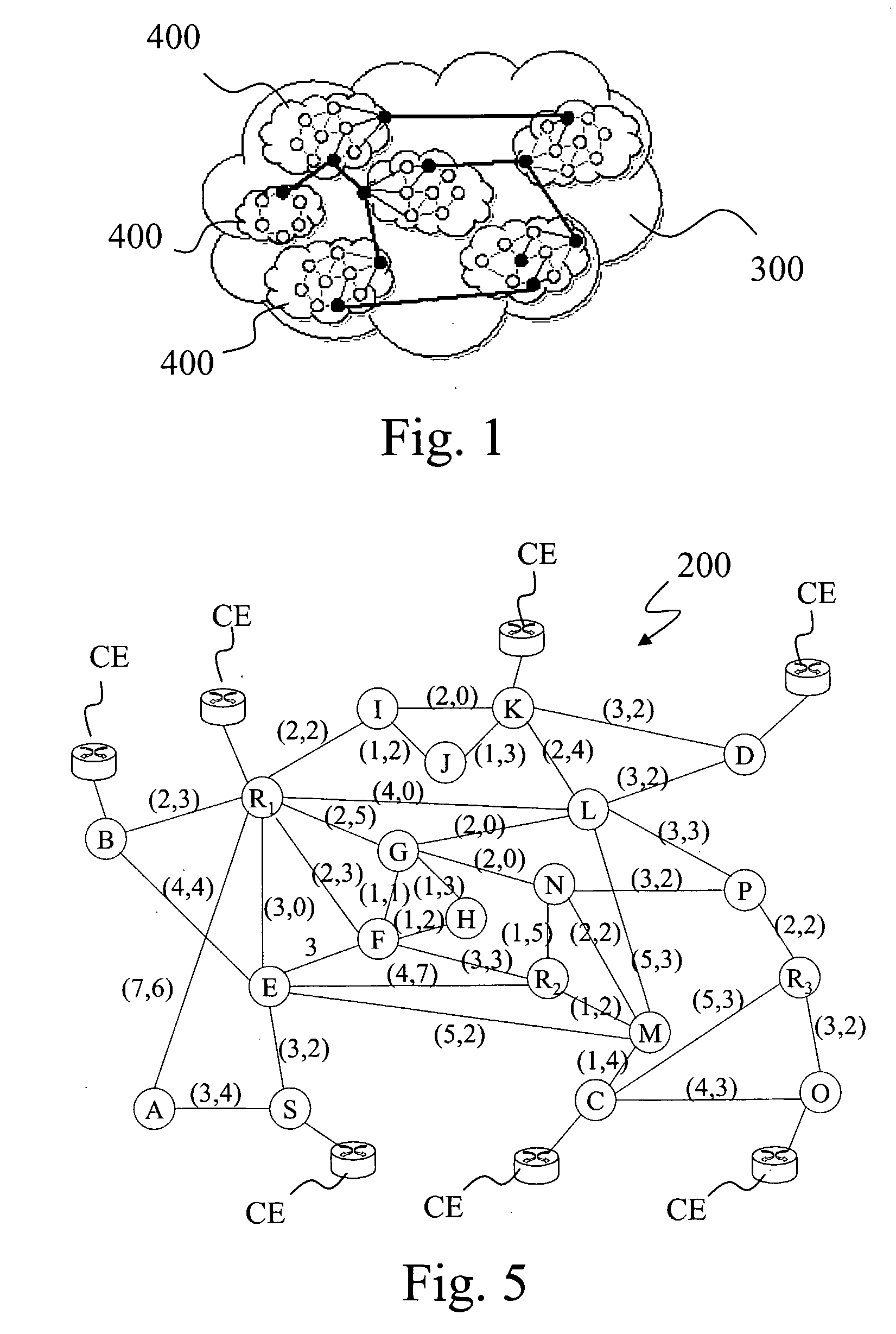
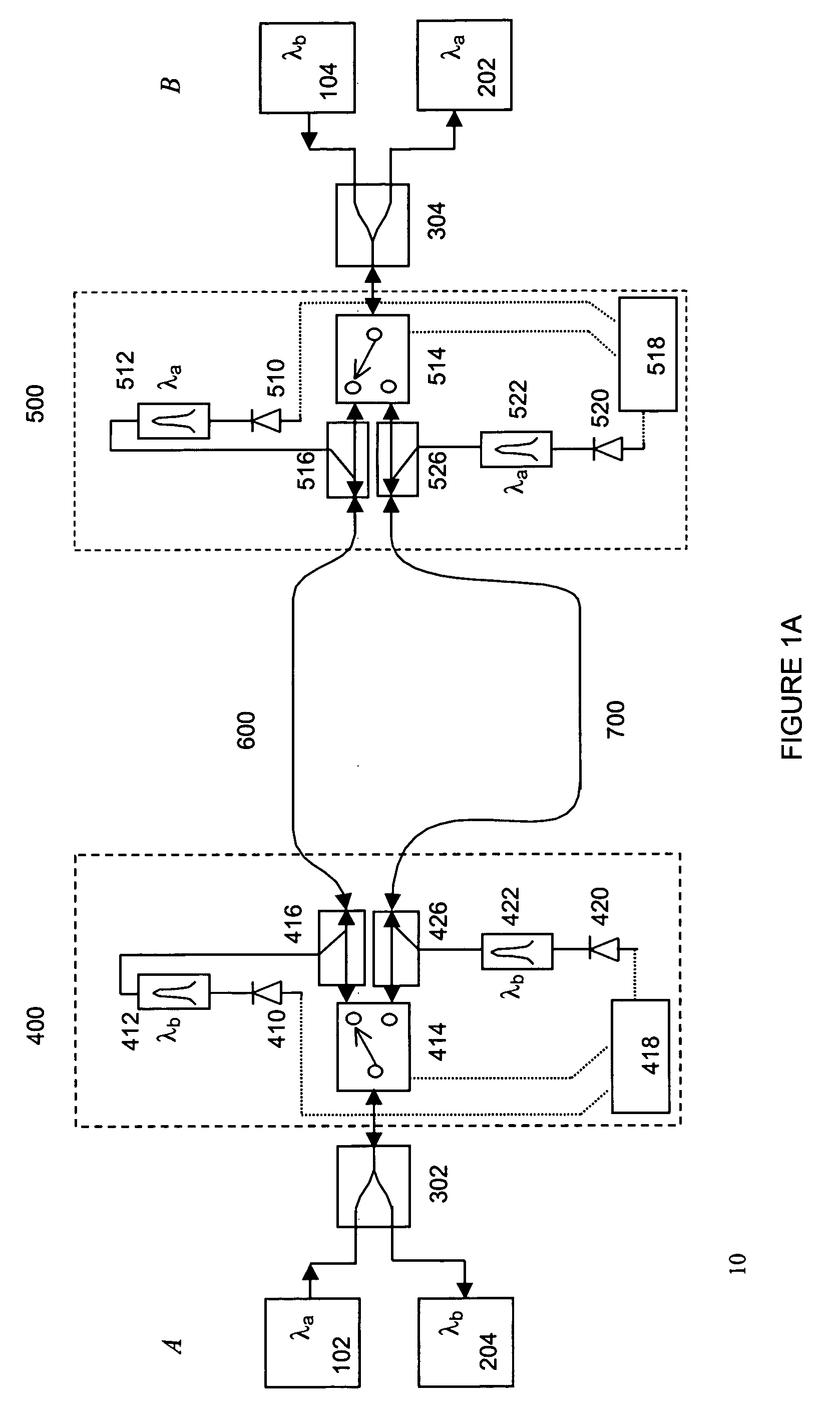
Interconnections and protection between optical communications networks
InactiveUS20070154219A1Optical multiplexElectromagnetic transmissionCommunications systemInterconnection
An optical communications system including a submarine optical communications system, a landing station associated with the submarine optical communications system, a terrestrial optical communications system, a point of presence associated with the terrestrial optical communications system, a first wavelength division multiplexed optical connection between the point of presence and the landing station, and a second wavelength division multiplexed optical connection between the point of presence and the landing station and routed diversely from the first wavelength division multiplexed optical connection.
Owner:OPTIC153 LLC
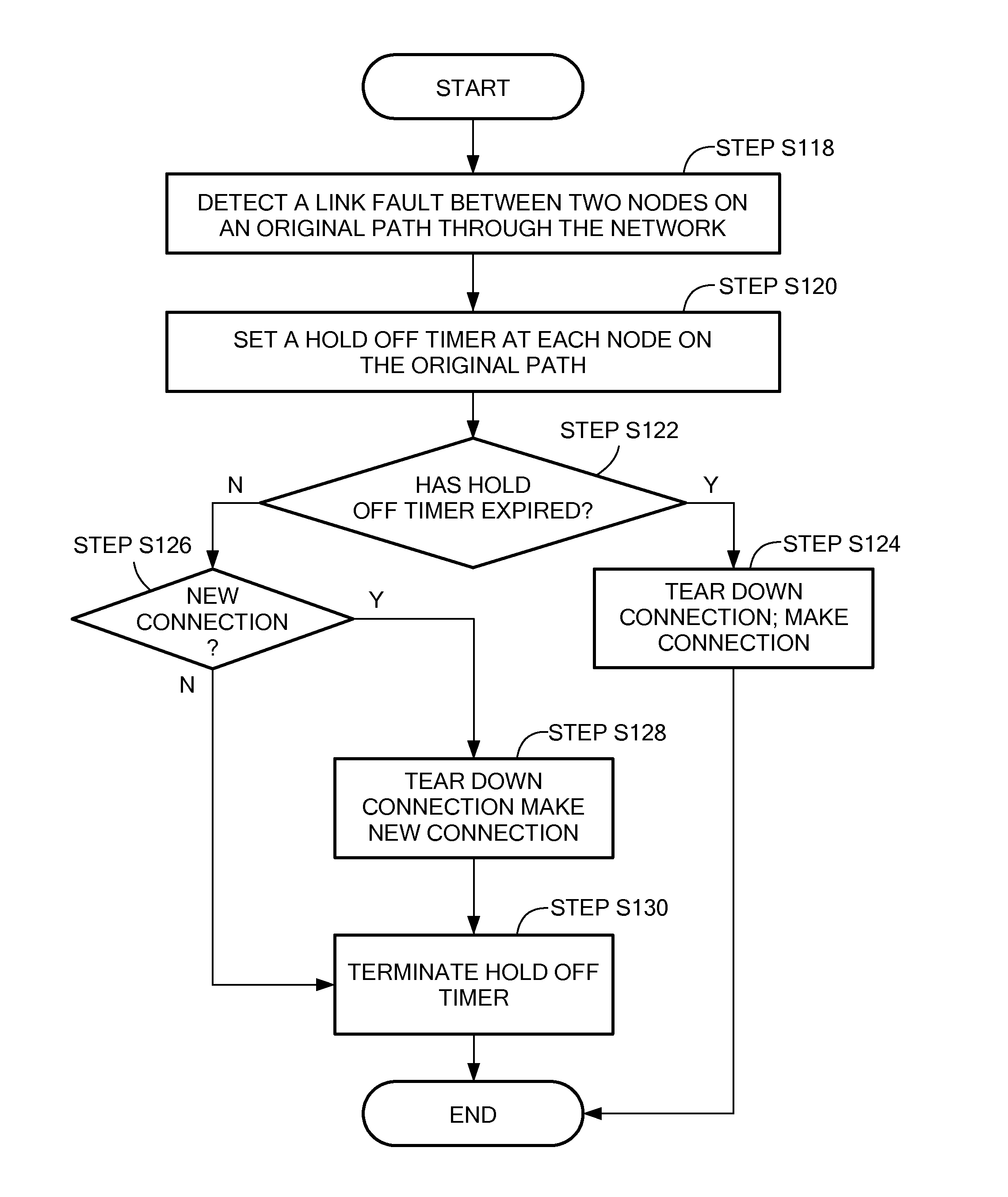
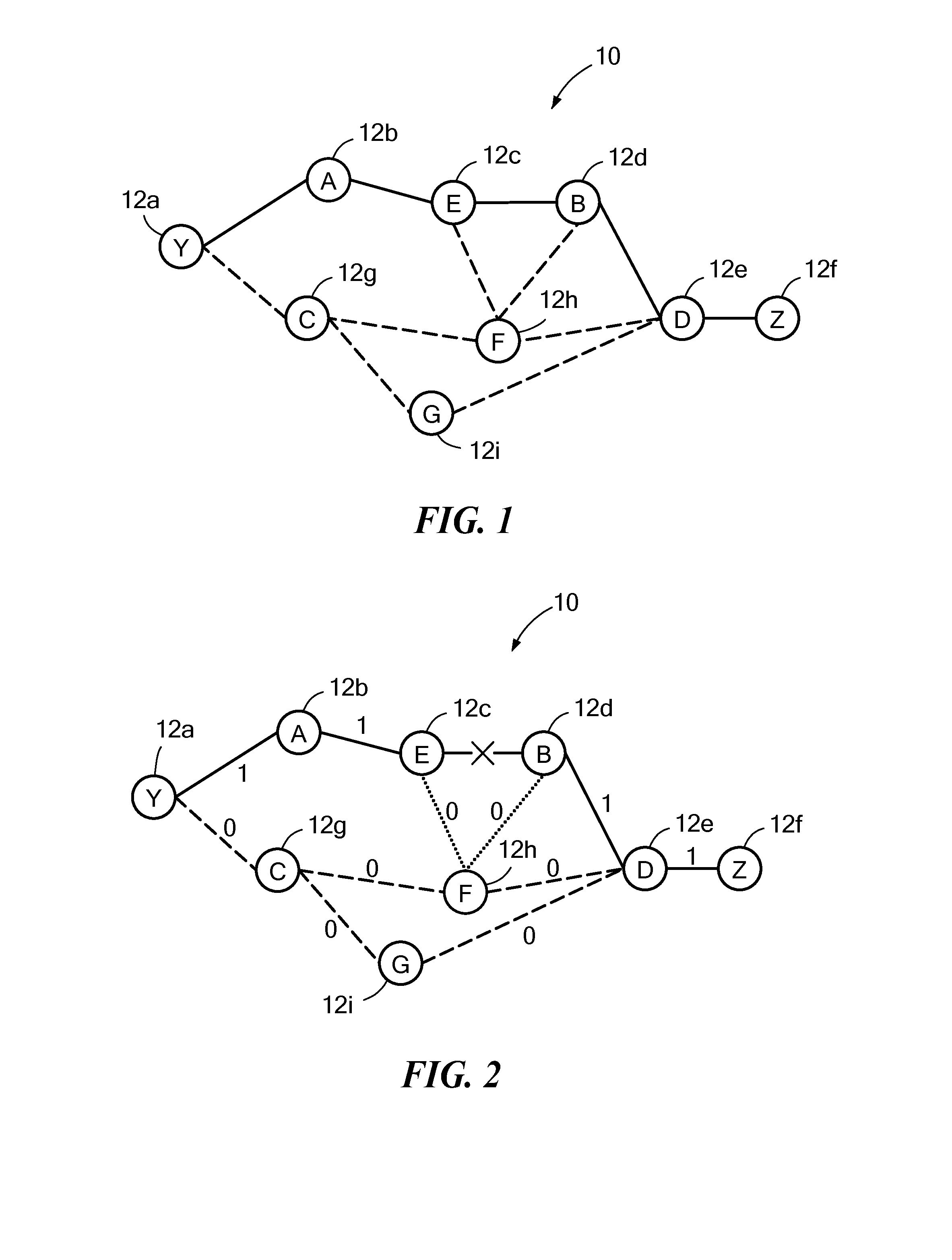
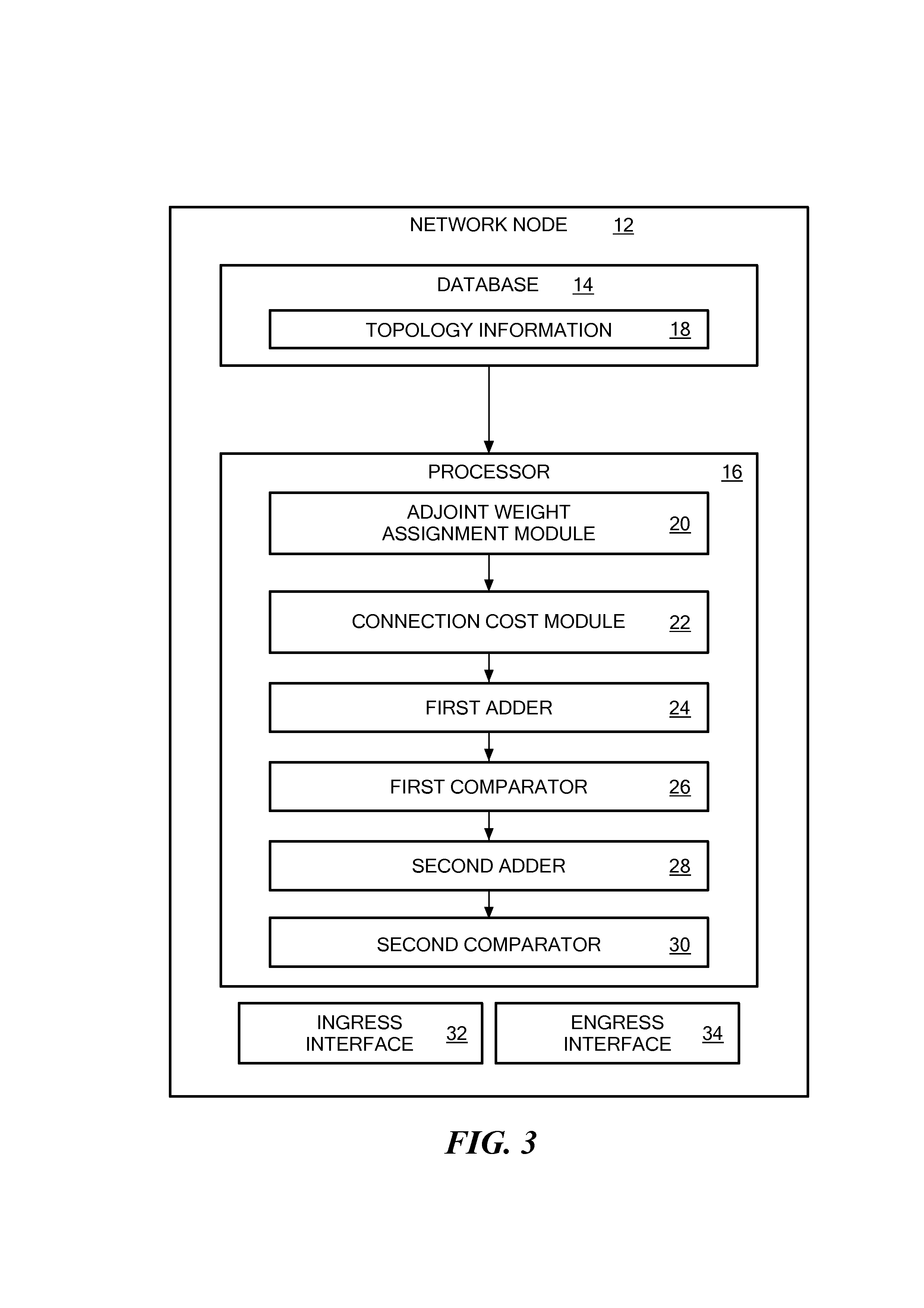
Optical communication network path restoration
ActiveUS20130177305A1Laser detailsOptical multiplexDistributed computingOptical communication networks
A method and system of determining a new path through an optical network from a source node to a destination node when a link in an original path fails are disclosed. When a fault on a link is detected, adjoint weights are assigned to each operational link for each node on the original path. A connection cost is determined for each node based on the adjoint weights of the links connected to the node. A new path through the optical network is determined based at least in part on the adjoint weights and the connection costs.
Owner:CIENA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com