Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
76 results about "Nonlinear equalization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
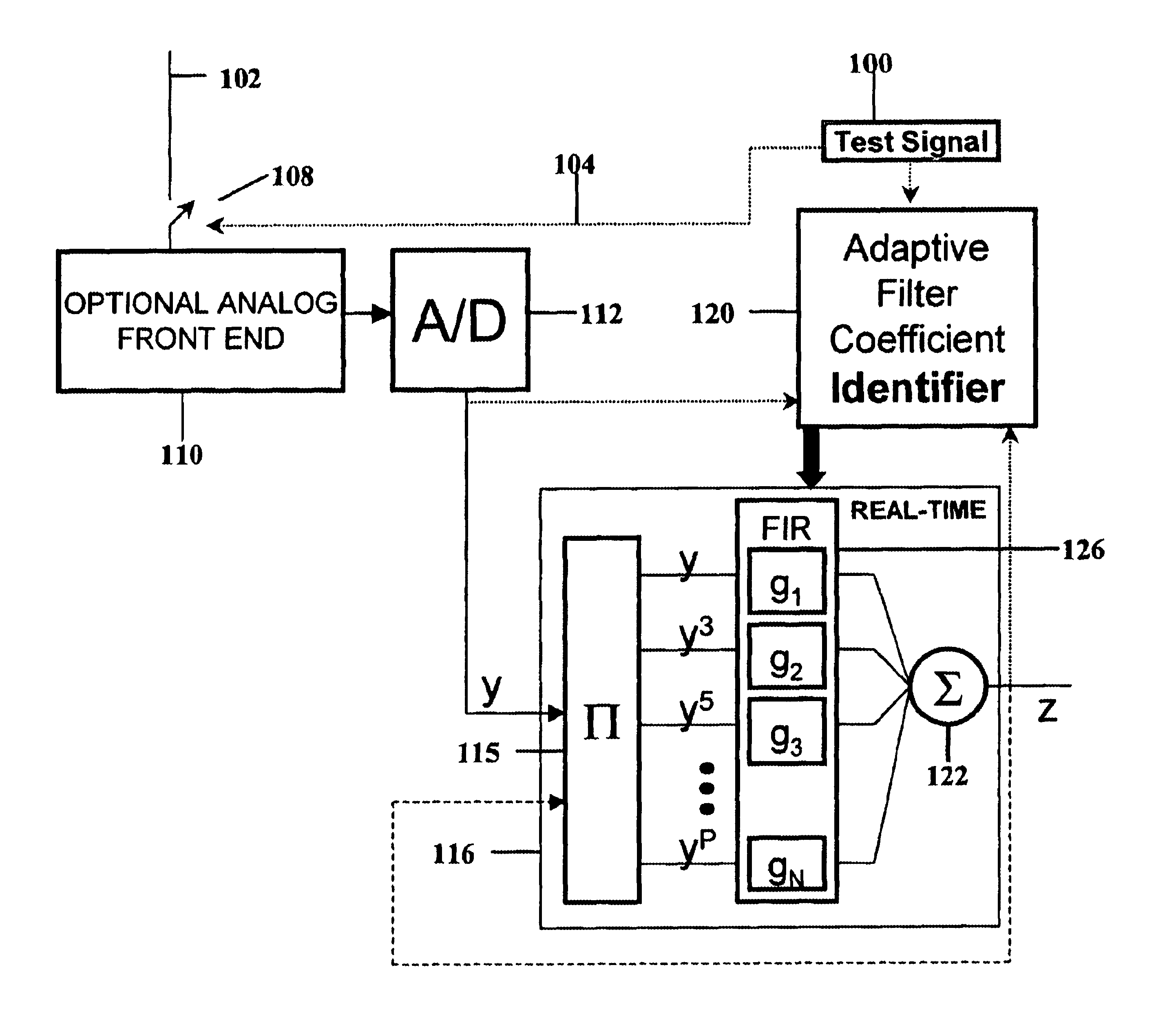
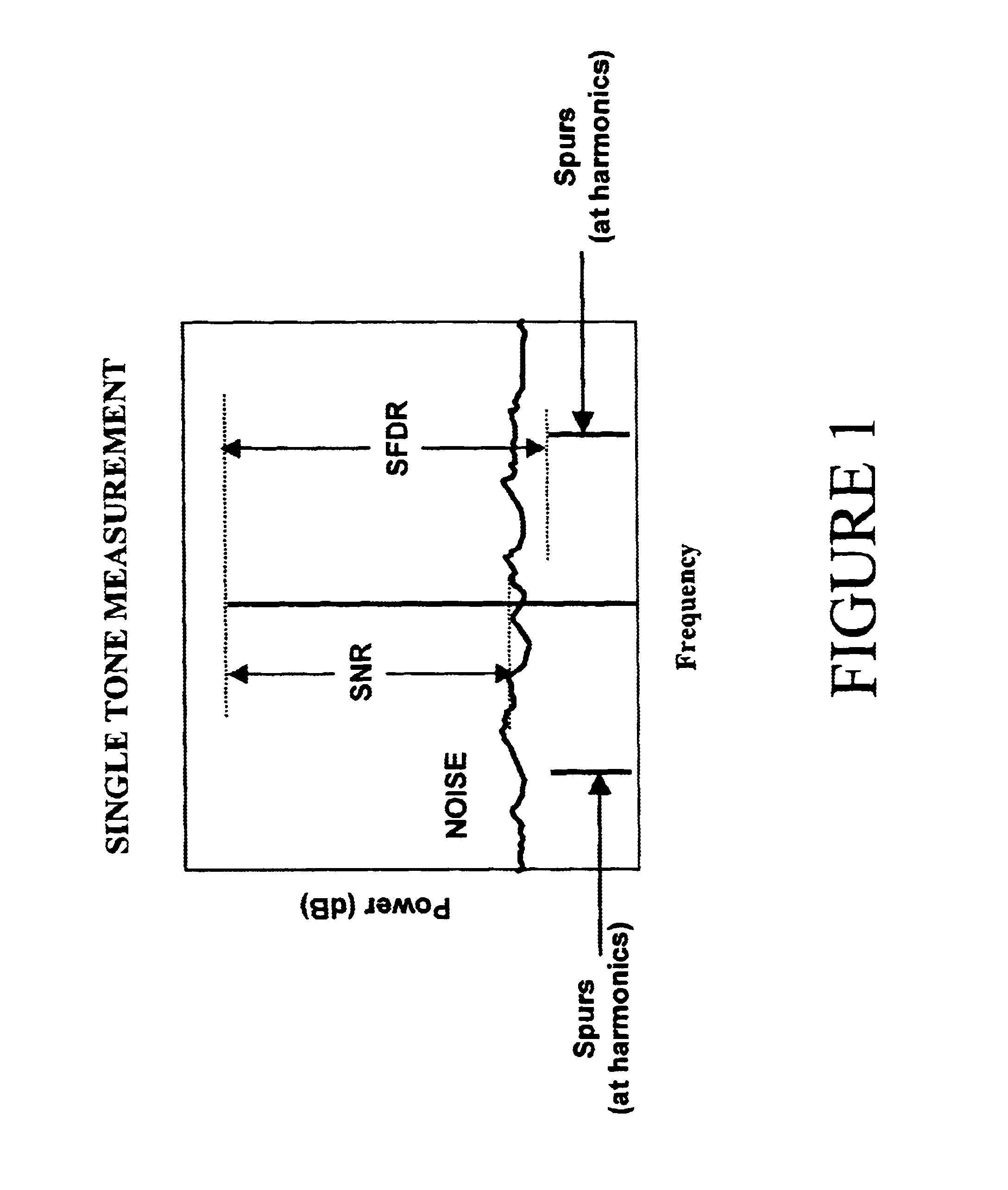
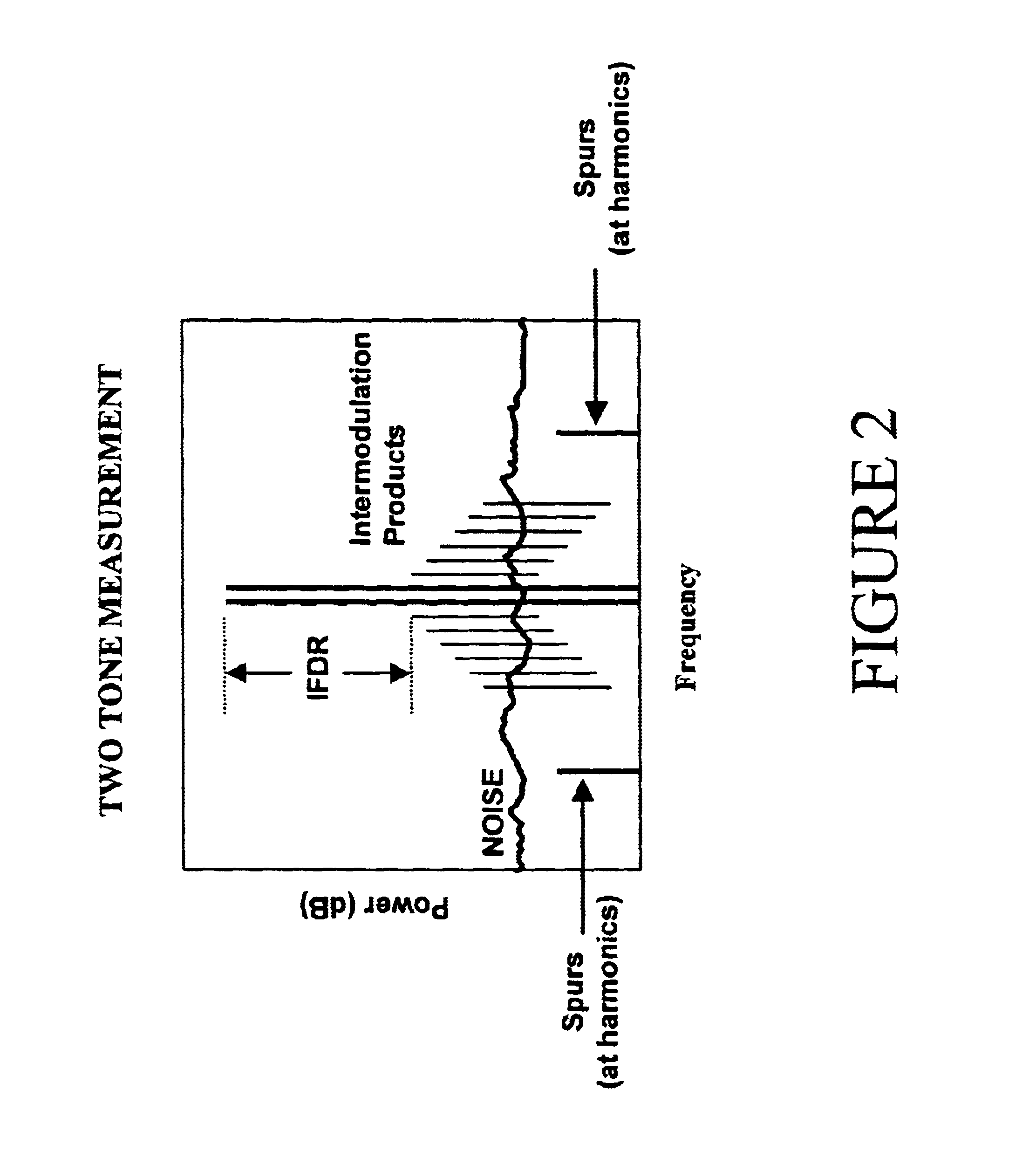
Highly linear analog-to-digital conversion system and method thereof
InactiveUS6639537B1Reduce nonlinear distortionMinimizes non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionFinite impulse responseNonlinear distortion
A highly linear analog-to-digital (ADC) conversion system has an analog front-end device in cascade with a standard ADC converter, and a tunable digital non-linear equalizer. The equalizer corrects the quantization distortion, deviations from ideal response, and additive noises generated by the analog front-end device and ADC converter. The equalizer is formed by three main parts: Generate Function Streams Unit, Finite Impulse Response FIR filters and a summer. The equalizer receives the unequalized output from the ADC converter and generates a plurality of monomial streams in a systolic fashion. Each of the monomial streams is passed through a corresponding linear finite impulse response FIR filter. A convolution sum of all outputs from the FIR filters produces a unique equalized output with the non-linear distortion reduced to a satisfactory level. The FIR filter coefficients are determined by an Identity Equalizer Coefficient Unit, and a Test Signal Generator with different types of test signals. The FIR filter coefficients are set to minimize an error function.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
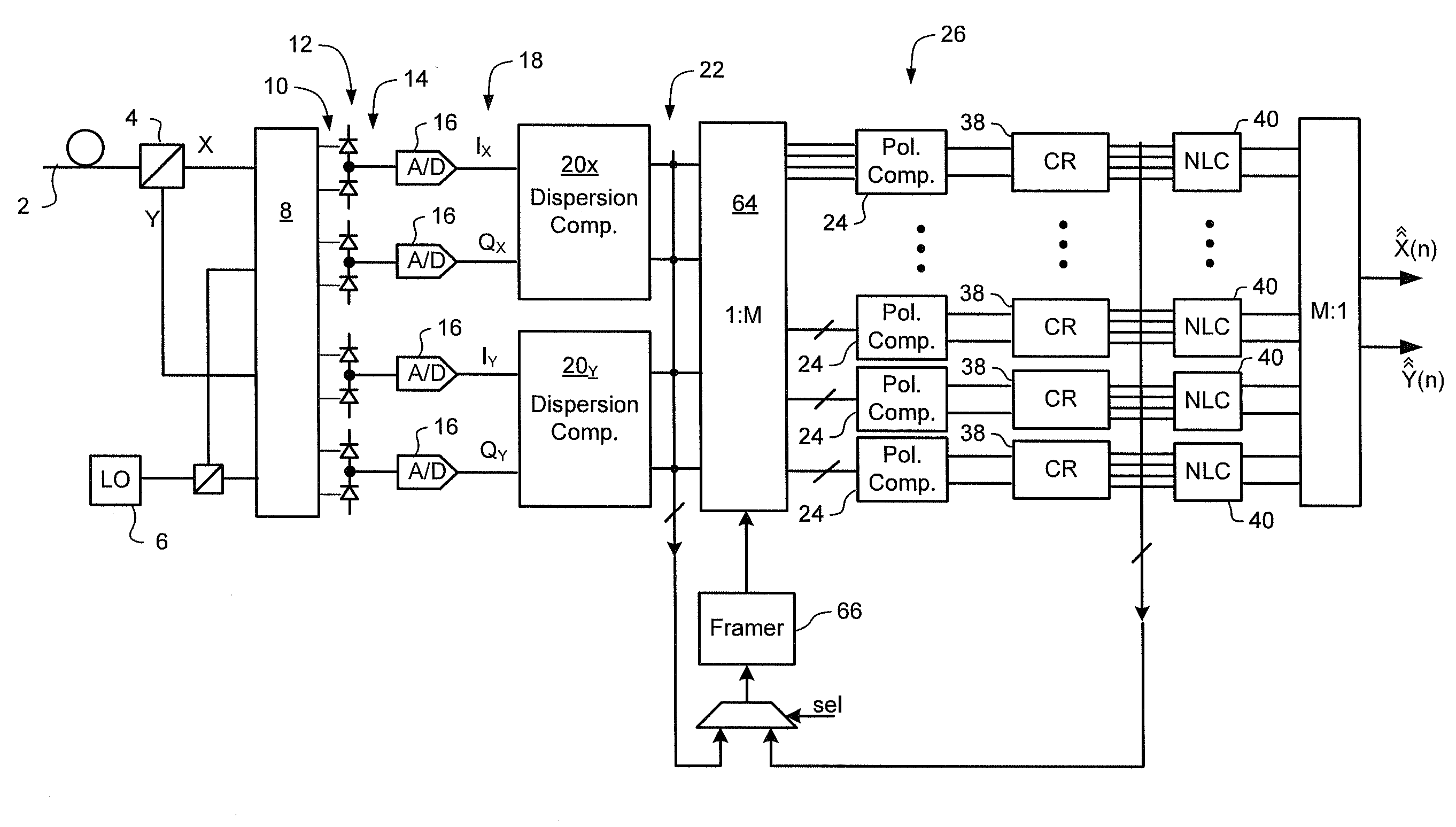
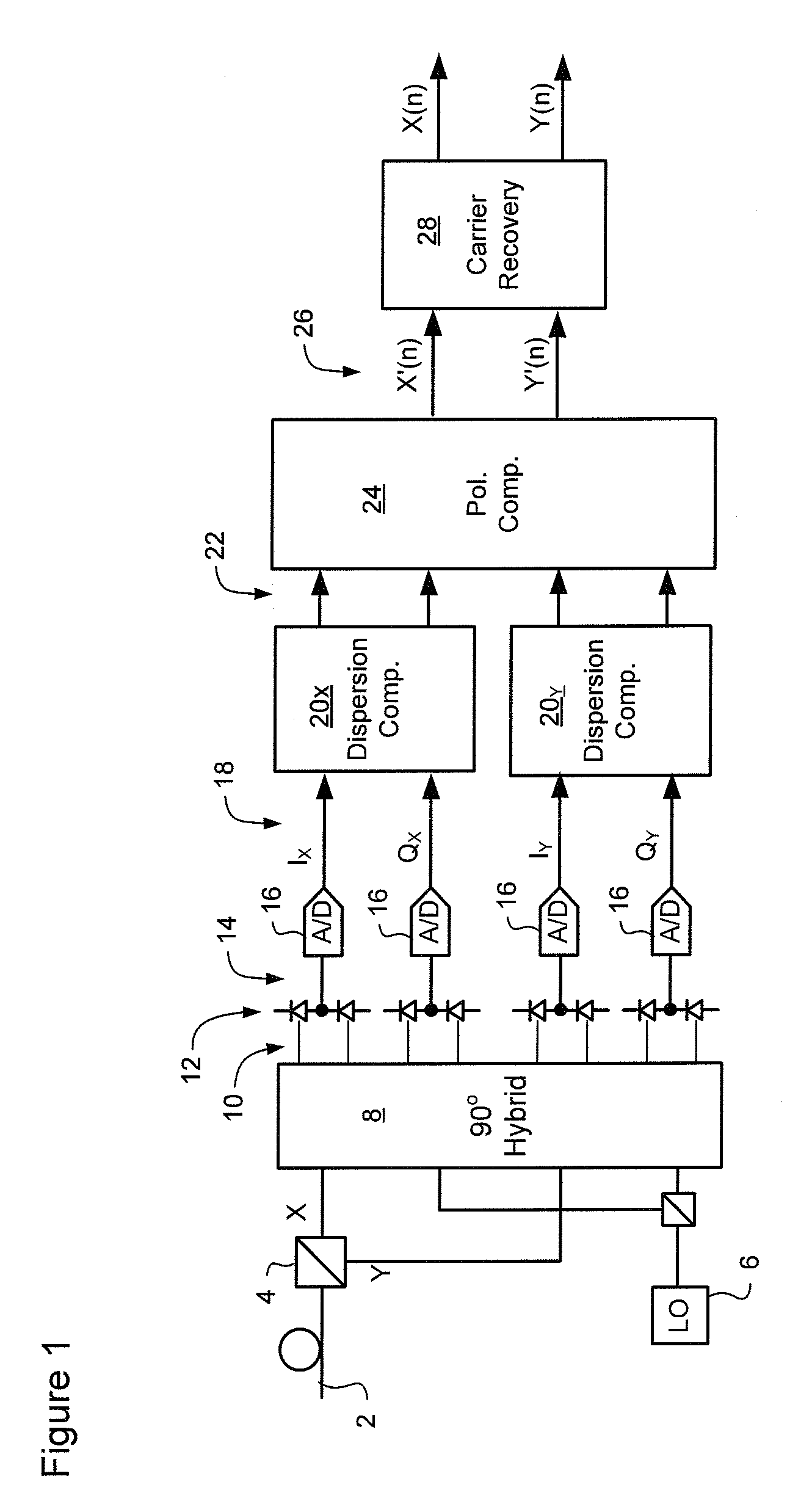
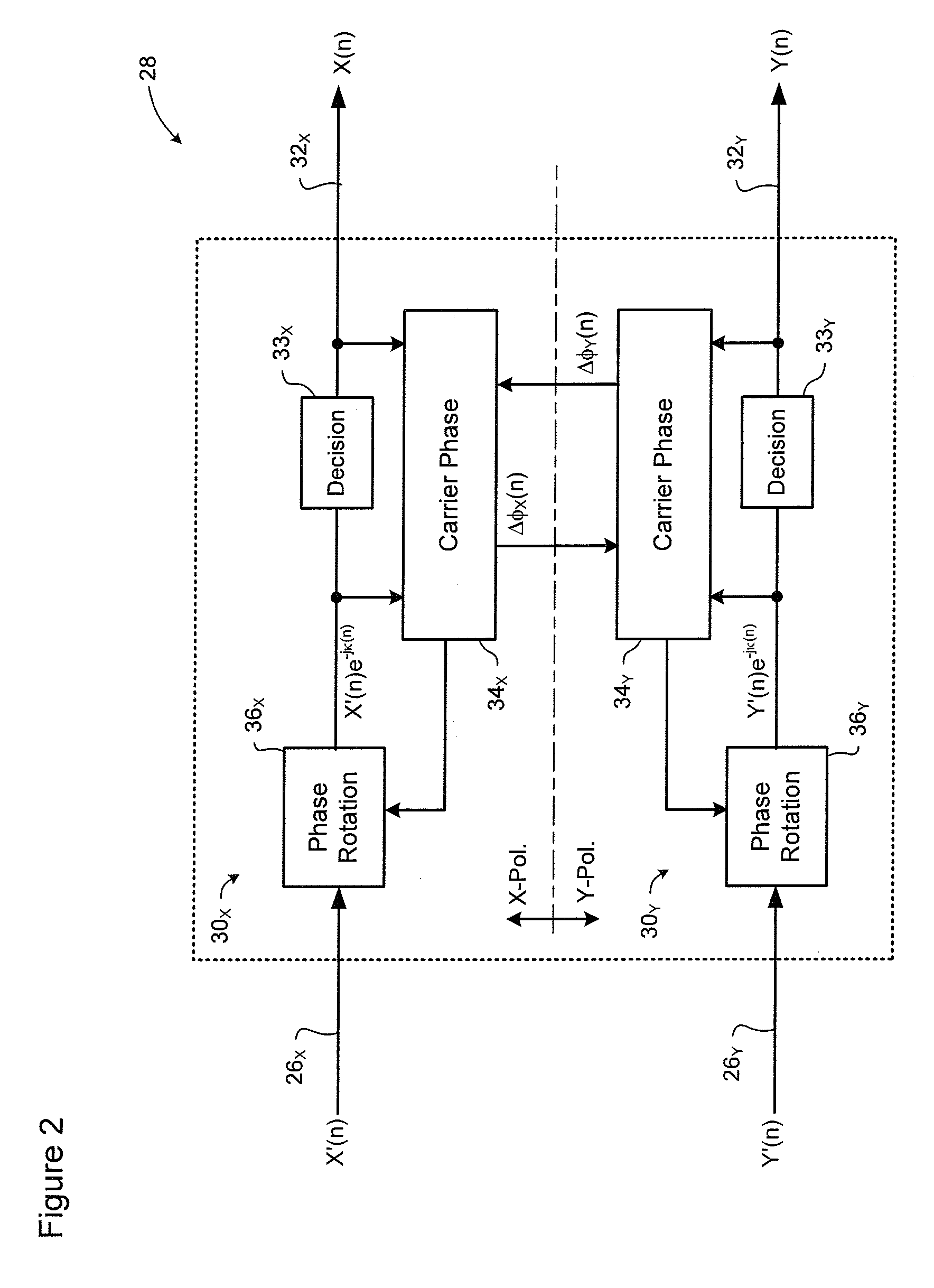
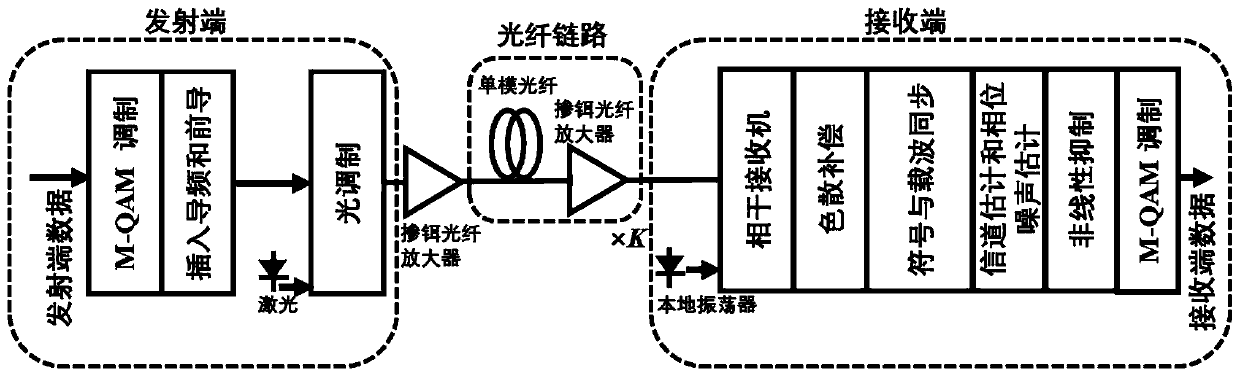
Non-linear equalizer in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS7684712B1Receiver initialisationSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansSignal restorationComputer science
A method of recovering a most likely value of each symbol transmitted through an optical communications network using a high speed optical signal. A stream of multi-bit digital samples of the optical signal is processed to generate a respective multi-bit estimate X′(n) of each transmitted symbol. A first function is applied to each symbol estimate X′(n) to generate a corresponding soft decision value {tilde over (X)}(n). Each soft decision value {tilde over (X)}(n) is processed to generate a corresponding hard decision value. {circumflex over (X)}(n) having an ideal amplitude and phase. A plurality of successive soft decision values and hard decision values are processed to determine a second function, which is applied to each soft decision value {tilde over (X)}(n) to generate a most likely symbol value {circumflex over ({circumflex over (X)}(n).
Owner:CIENA CORP
Frequency-domain multi-user access interference cancellation and nonlinear equalization in CDMA receivers
ActiveUS20050249269A1Reduce accessImprove performanceModulated-carrier systemsSoil-shifting machines/dredgersCommunications systemInterference cancelation
A method for canceling interference at a wireless code division multiple access (CDMA) communication receiver is provided. The wireless CDMA communication system receiver receives a stream of chips generated by spreading data symbols formed by grouping bits of information at a wireless CDMA communication transmitter which are broadcast at a certain chip-rate. The received chips are de-spread and symbols pertaining to respective users are reconstructed. The method includes formatting the stream of chips into blocks of chips, and performing an iterative block decision feedback equalization in a frequency domain at the chip-rate of the broadcast stream of chips to remove inter-symbol interference by defining a transfer function. The transfer function is defined based upon iteration cycles as a function of data detected in a preceding iteration cycle. The chips generated are interleaved by spreading each data symbol being transmitted before broadcasting the stream of interleaved chips in distinct blocks of chips.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
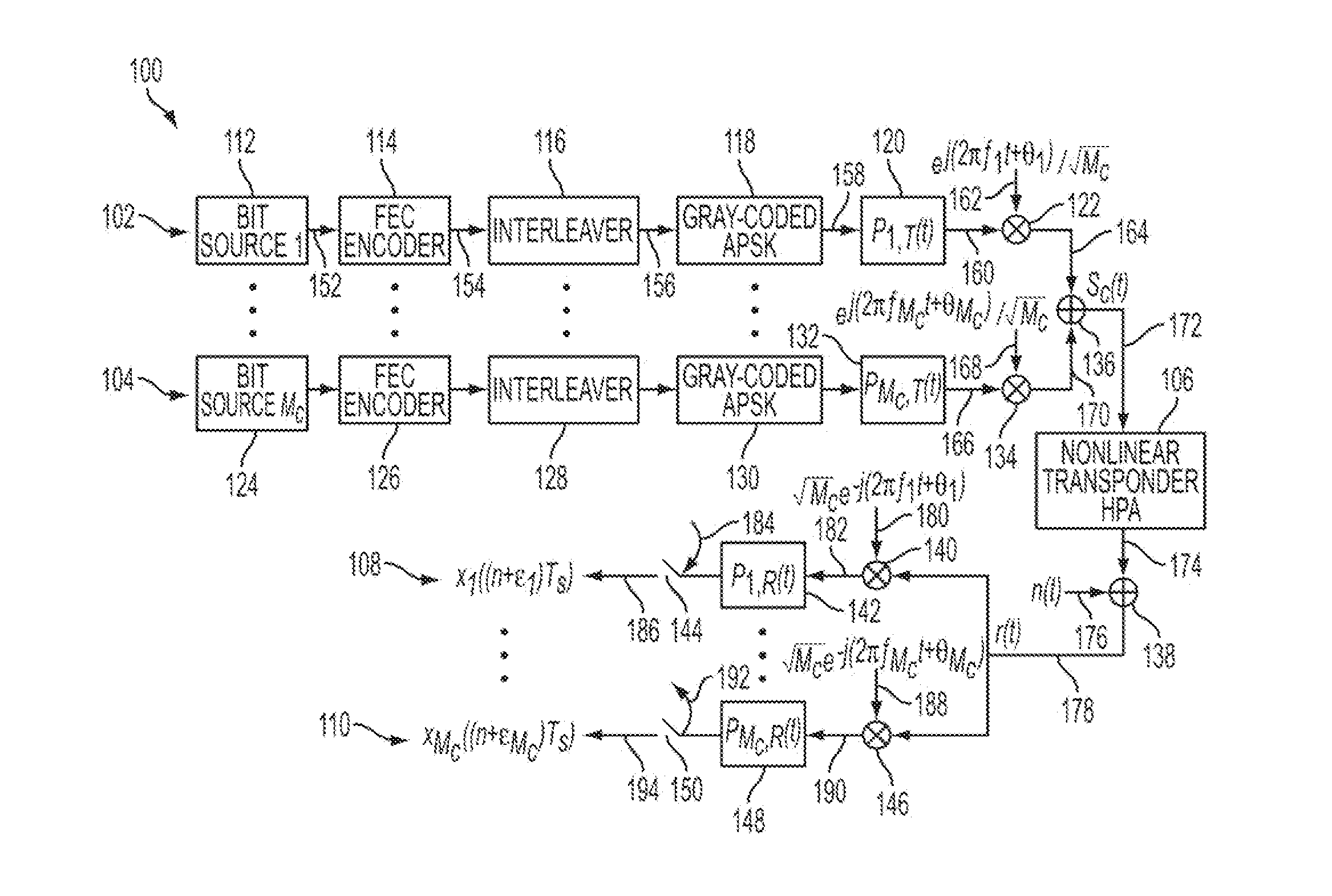
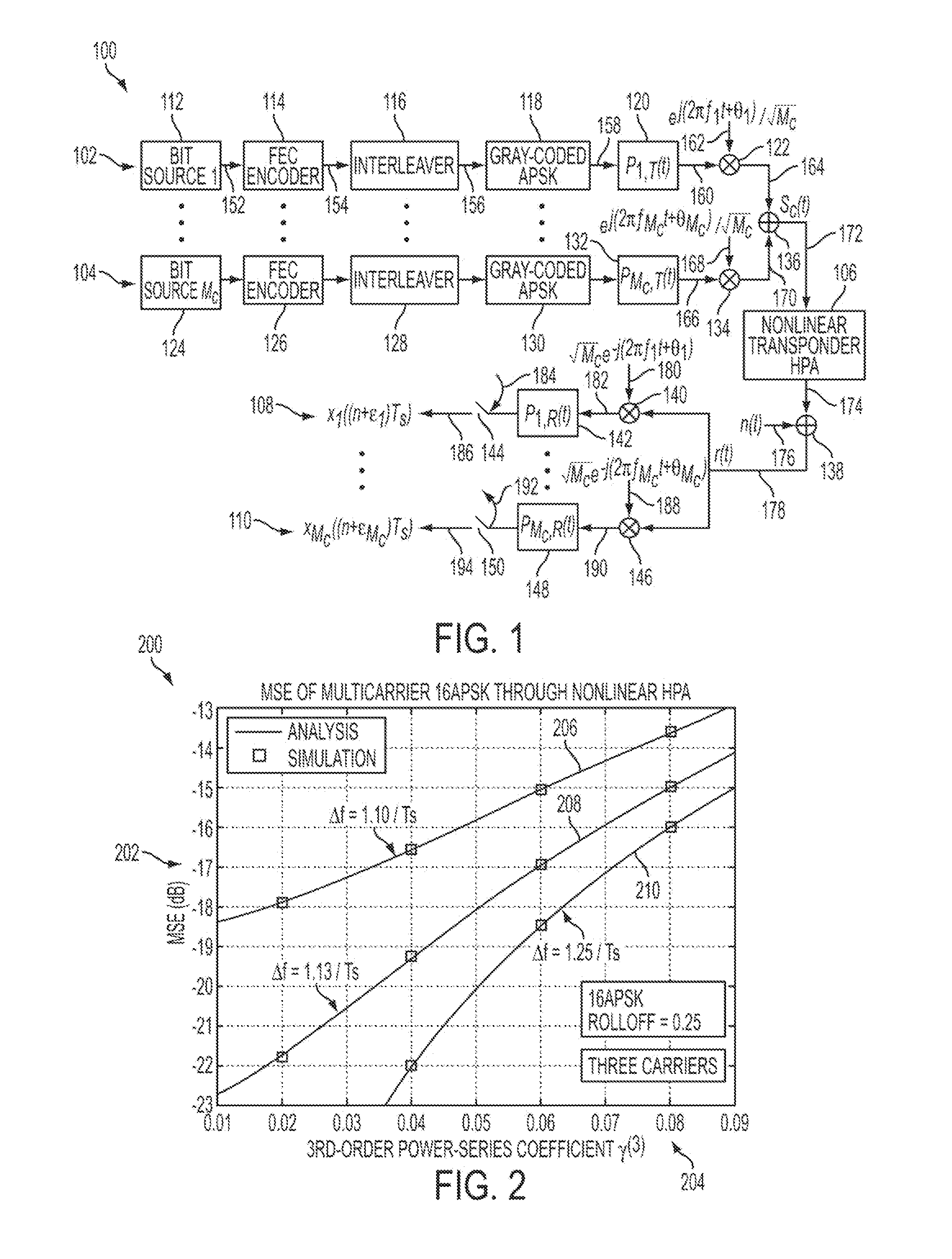
System and method for iterative nonlinear compensation for intermodulation distortion in multicarrier communication systems
ActiveUS20120027070A1Multiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionCommunications systemCarrier signal
A receiver is provided that can receive a first signal transmitted on a first carrier and a second signal transmitted on a second carrier. The receiver includes a channel estimation portion, a multicarrier nonlinear equalizer, a first log likelihood computing portion and a second log likelihood computing portion. The channel estimation portion can output a first estimation. The multicarrier nonlinear equalizer can output a first equalized signal and a second equalized signal. The first log likelihood ratio computing portion can output a first log likelihood ratio signal based on the first equalized signal. The second log likelihood ratio computing portion can output a second log likelihood ratio signal based on the second equalized signal. The multicarrier nonlinear equalizer can further output a third equalized signal and a fourth equalized signal. The third equalized signal is based on the first signal, the second signal and the first estimation. The fourth equalized signal is based on the first signal, the second signal and the first estimation.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
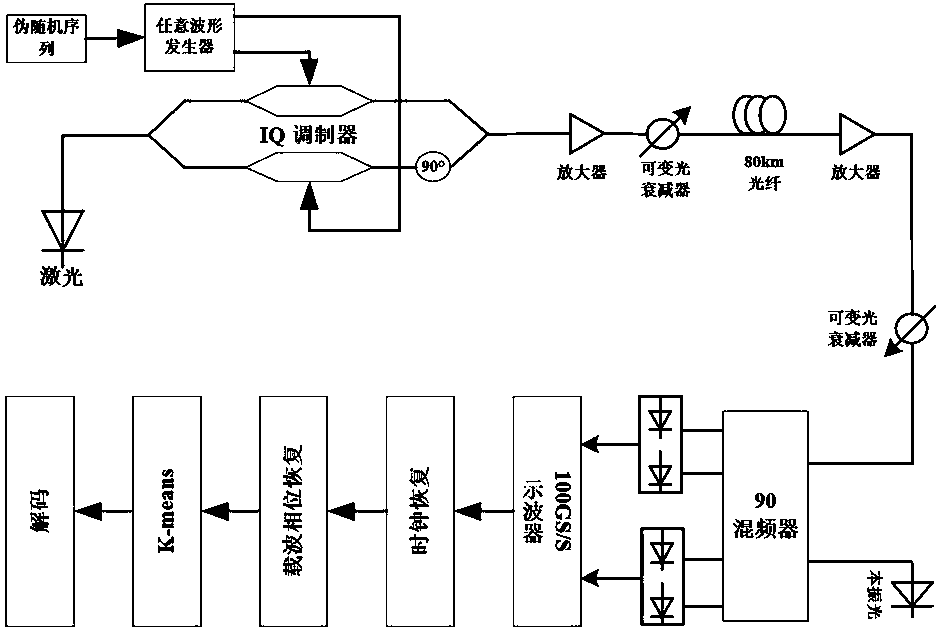
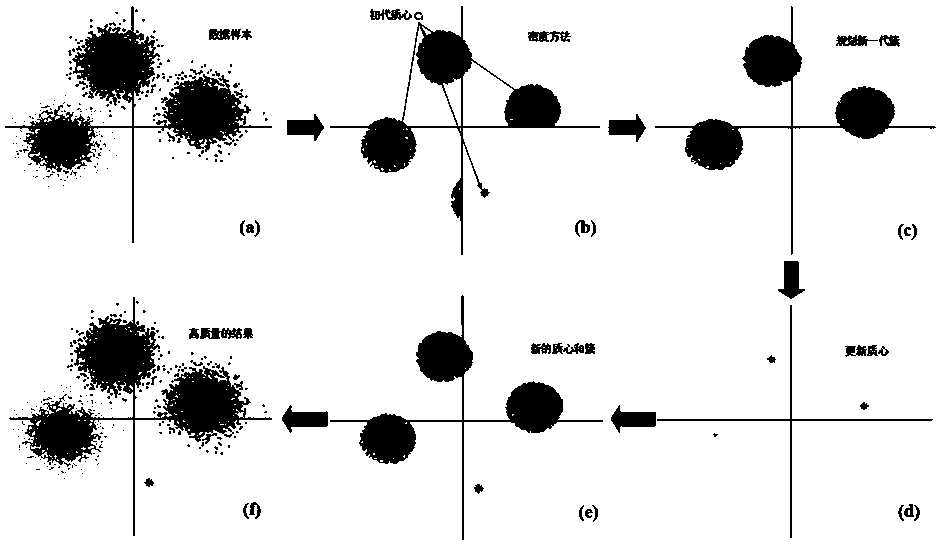
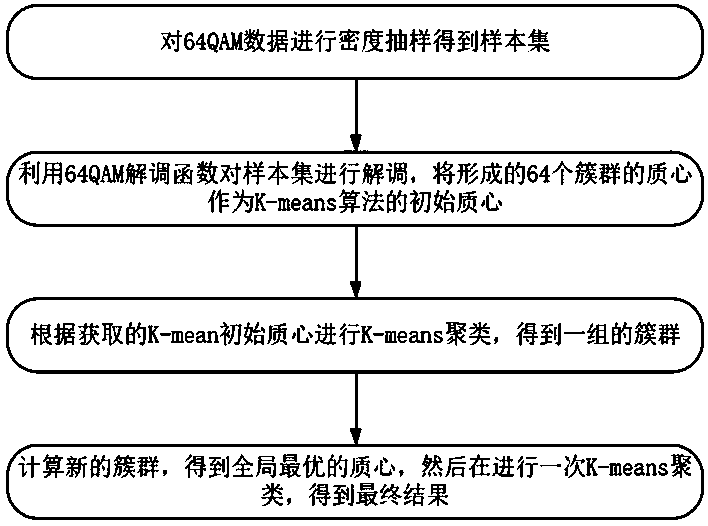
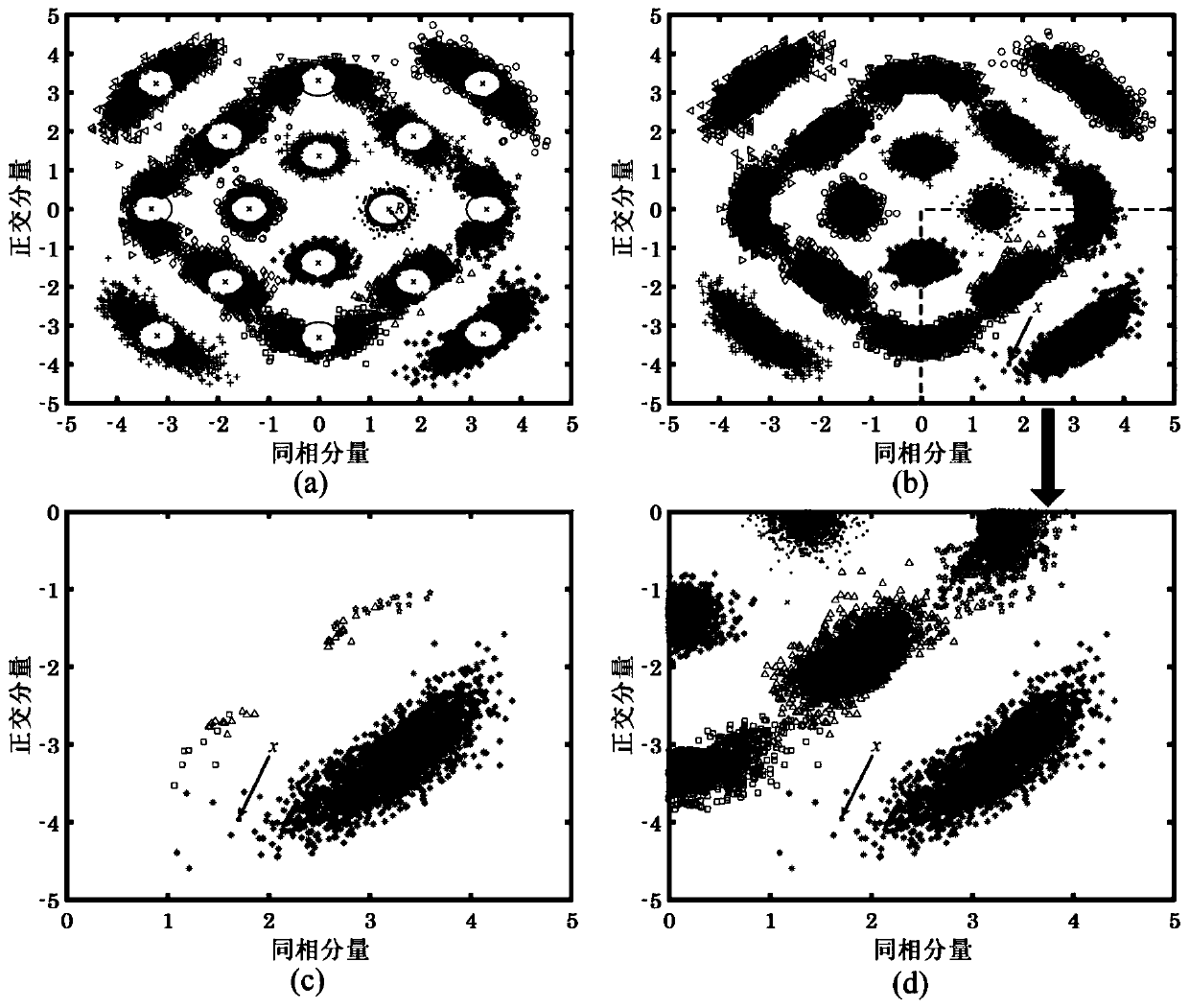
Optical fiber nonlinear equalization method for 64-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) coherent optical communication system
ActiveCN107707494AReduce the impactReduce the effect of Kerr nonlinearityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksElectromagnetic receiversData setOptimal control
The invention discloses an optical fiber nonlinear equalization method for a 64-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) coherent optical communication system used for processing received 64-QAM data. The method comprises the following steps: setting a received data set as a first-level data set, calculating the density parameter of each data point, setting a threshold, and selecting the data with the density parameter exceeding the specified threshold as a second-level data set; demodulating second-level data set points, dividing the second-level data set points into 64 clusters, and obtaining 64 centroids; according to the obtained centroids, classifying data in the second-level data set into a corresponding cluster according to the nearest Euclidean distance, and using 64 centroids of a newly obtained cluster to update; and allocating the first-level data set to the corresponding cluster according to the nearest Euclidean distance, obtaining the classified 64 clusters, and calculatingto obtain an optimal centroid of each cluster. The optical fiber nonlinear equalization method for the 64-QAM coherent optical communication system provided by the invention can quickly and accuratelyselect a global optimal centroid of a K-means cluster without the need of iteration, well reduce the influence of Kerr nonlinearity in an optical fiber, and the obtained bit error rate performance isone half an order of magnitude higher than the performance that is not processed before.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method and apparatus for adaptive nonlinear equalization in a polarization multiplexing optical communication system
ActiveUS20130108260A1Effective compensationTransmission monitoringDistortion/dispersion eliminationCommunications systemPolarization multiplexed
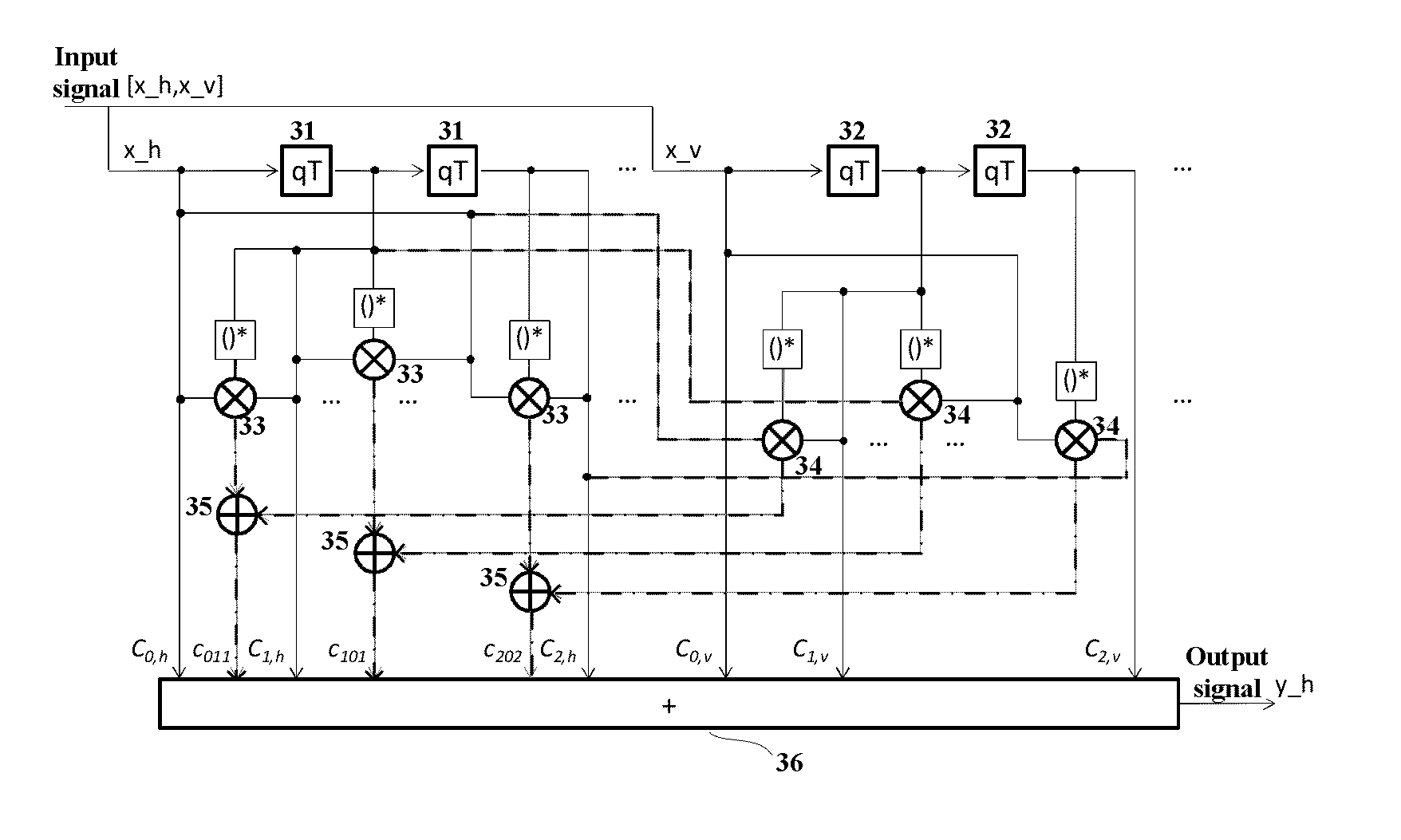
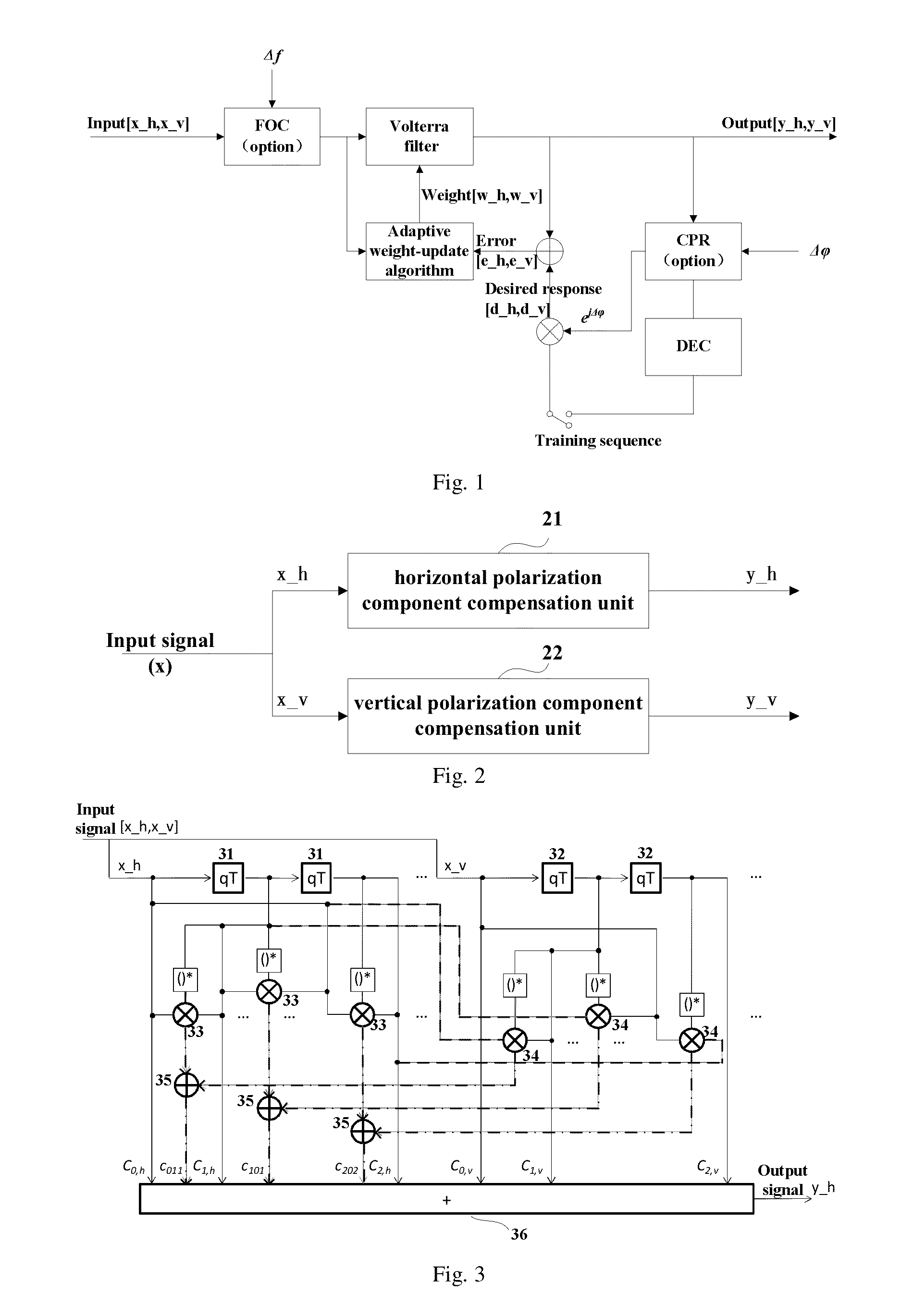
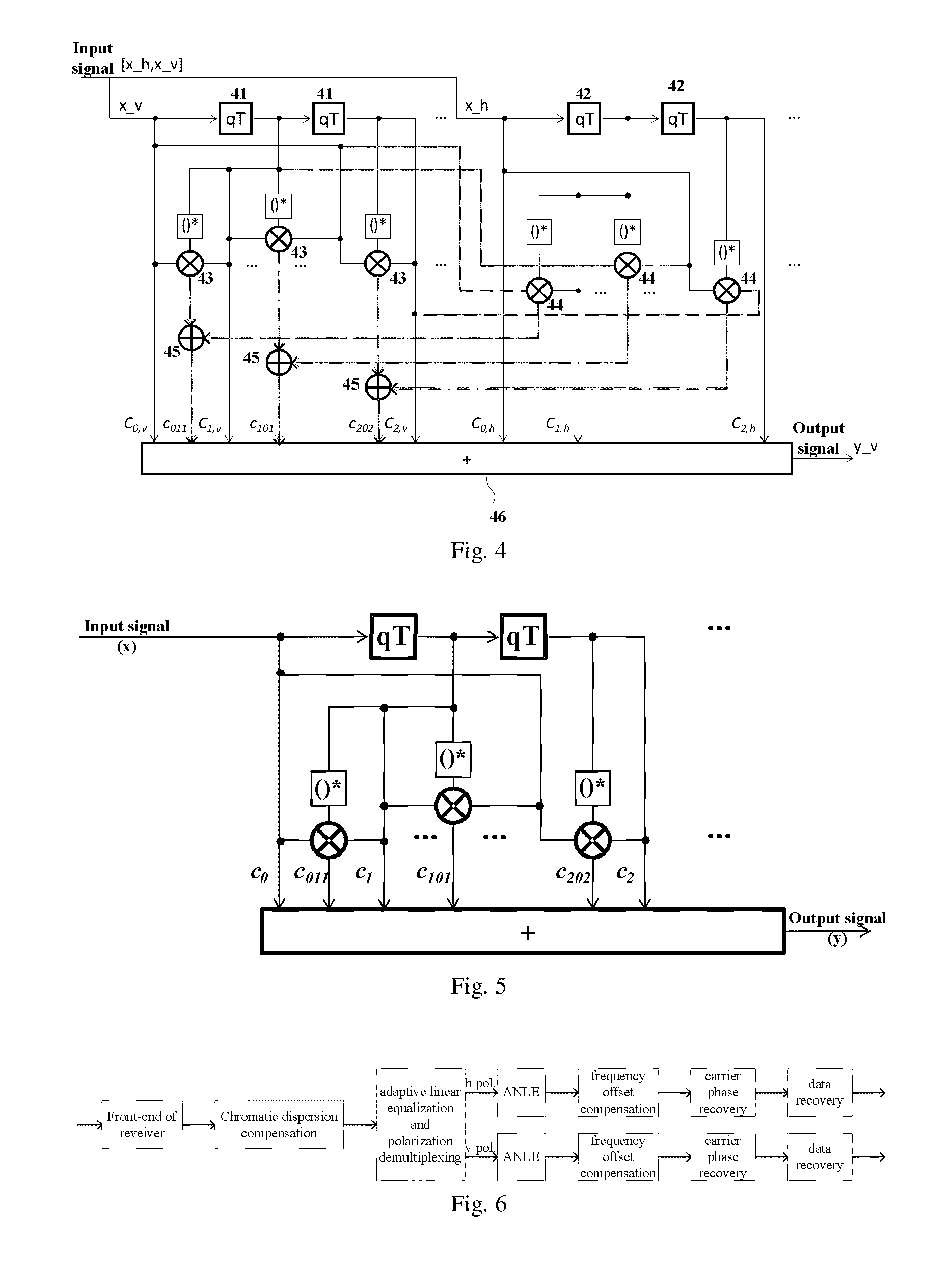
A method and apparatus for adaptive nonlinear equalization in a polarization multiplexing optical communication system, having a horizontal polarization compensation unit calculating a linear damage value of an input signal, a nonlinear damage value of a horizontal component of the signal, and a crosstalk value caused by a vertical component of the signal to the horizontal component of the signal, and compensate the horizontal component of the signal according to the damage values, and the crosstalk value; and, a vertical polarization component compensation unit calculating a linear damage value of the signal, a nonlinear damage value of a vertical component of the signal, and a crosstalk value caused by a horizontal component of the signal to the vertical component of the input signal, and compensate the vertical component of the signal according to the damage values and the crosstalk value. Intra-channel nonlinear damage is effectively compensated.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Nonlinear equalization method for high-order QAM coherent light system
ActiveCN110190906AReduce computational complexityReduce running timeCharacter and pattern recognitionElectromagnetic receiversPhase noiseCompensation effect
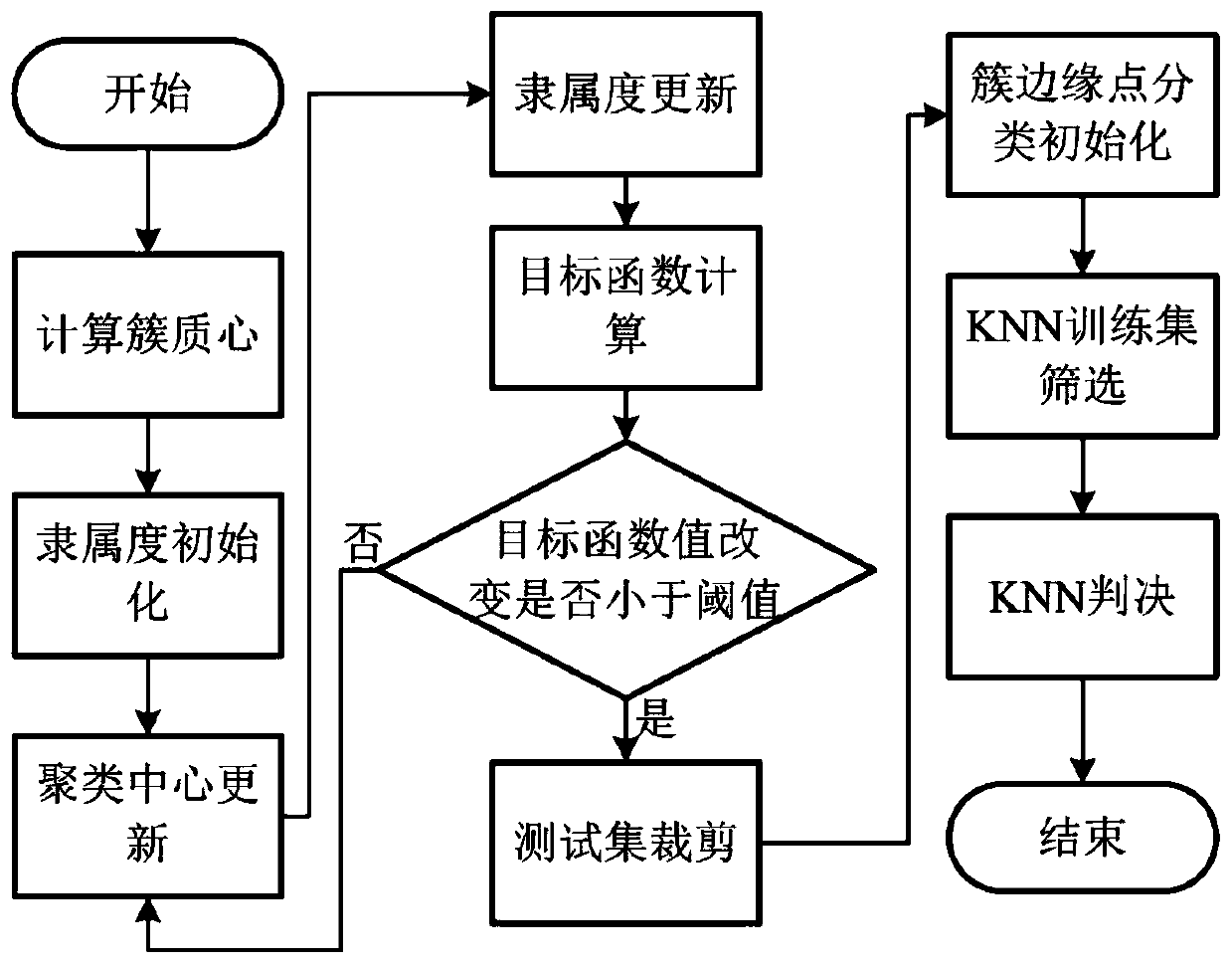
According to the nonlinear equalization method for the high-order QAM coherent light system, after receiving end data is subjected to phase noise compensation, an FCM algorithm is firstly used for achieving effective clipping of training data, meanwhile, test data is subjected to classification judgment, and therefore a test set and a training set of a follow-up KNN algorithm are greatly reduced.The method is based on a coherent light 16QAM system with the transmission rate of 112 Gb / s and the transmission distance of 160 km, and non-linear equalization simulation verification is carried out.Simulation results show that the same system nonlinear damage compensation effect as a traditional KNN algorithm can be obtained, but the algorithm complexity of the method is far lower than that ofthe traditional KNN algorithm, and the algorithm running time is far shorter than that of the KNN algorithm. According to the invention, the application of the coherent light QAM system in medium andlong distance optical fiber transmission can be greatly promoted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
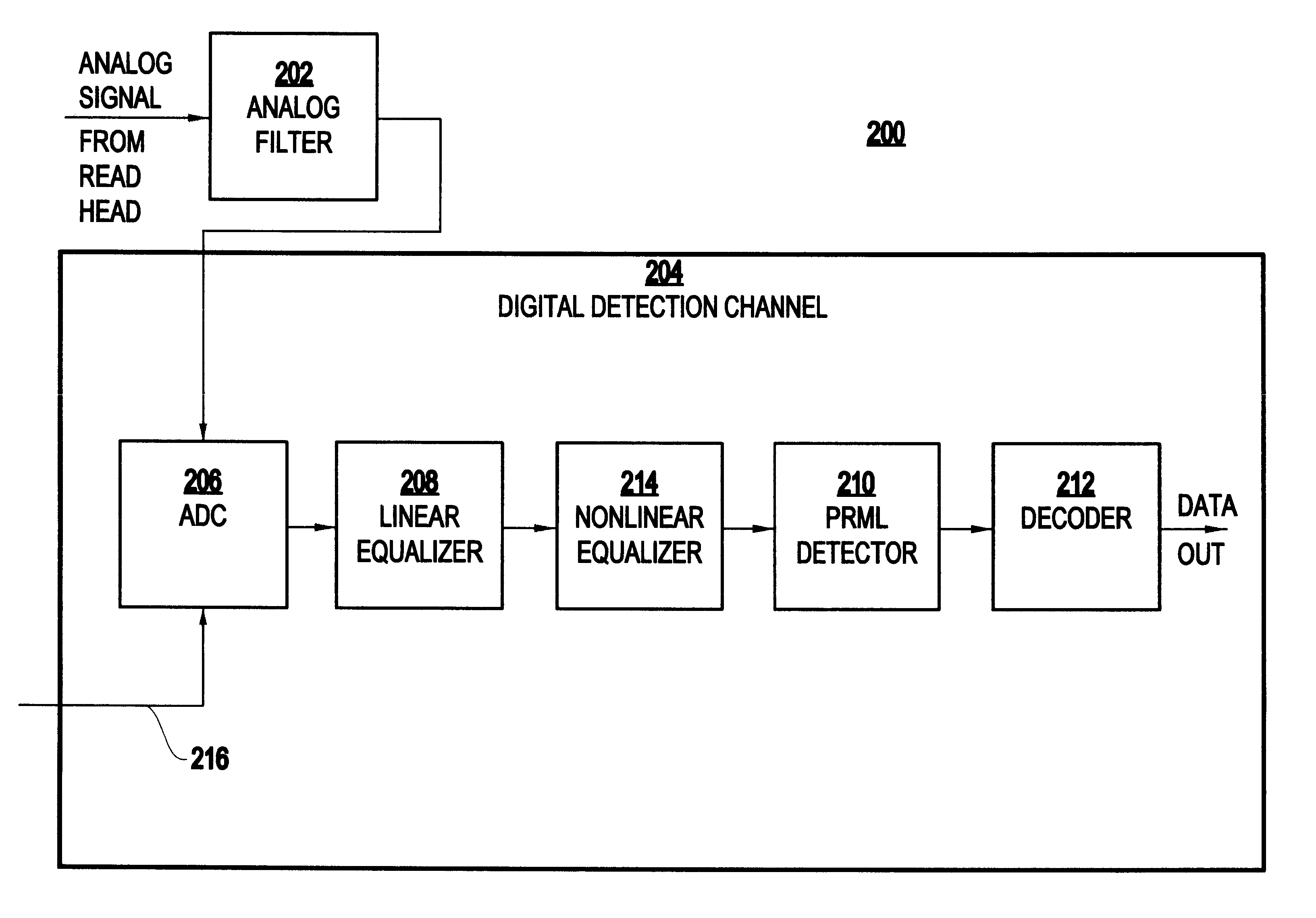
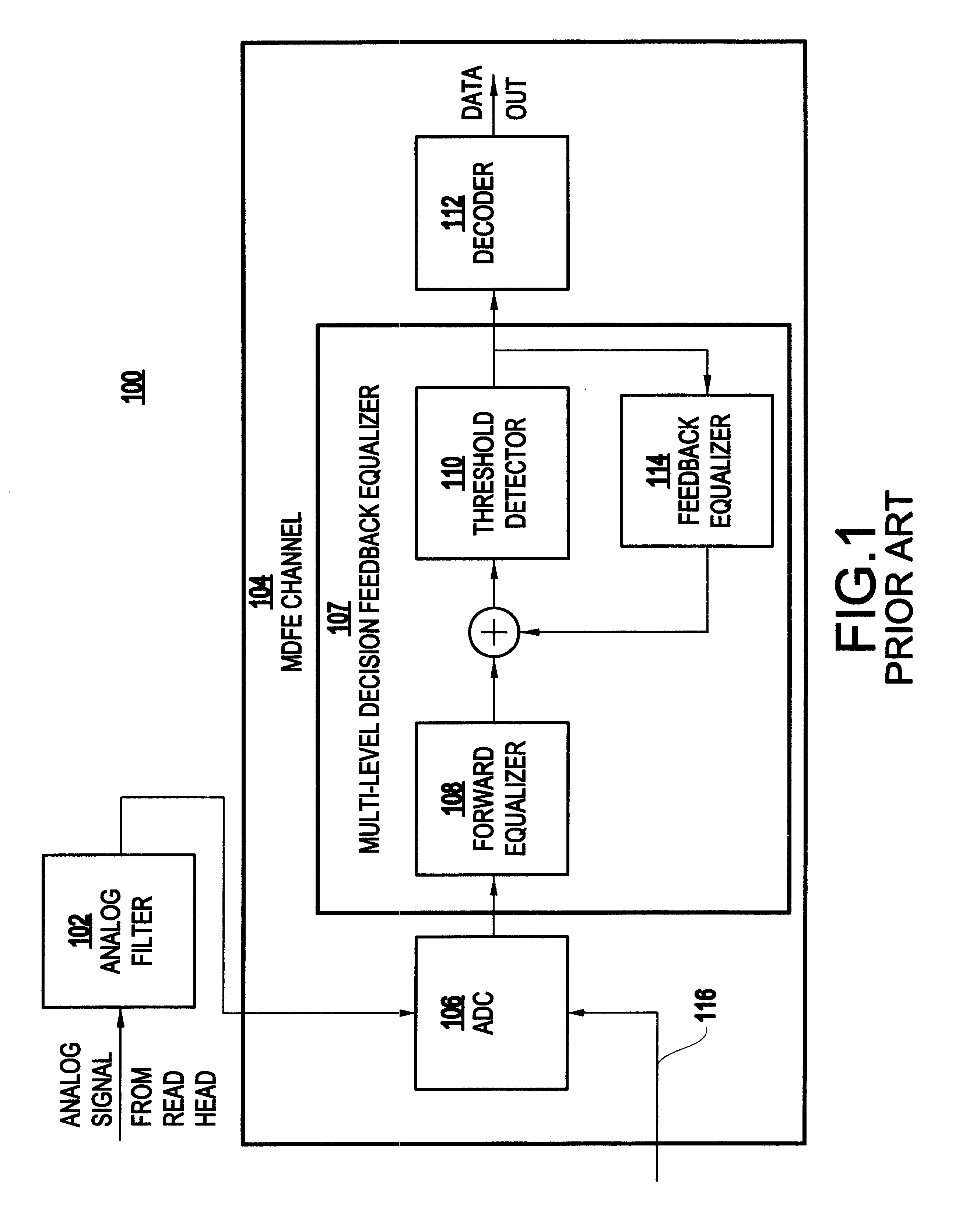
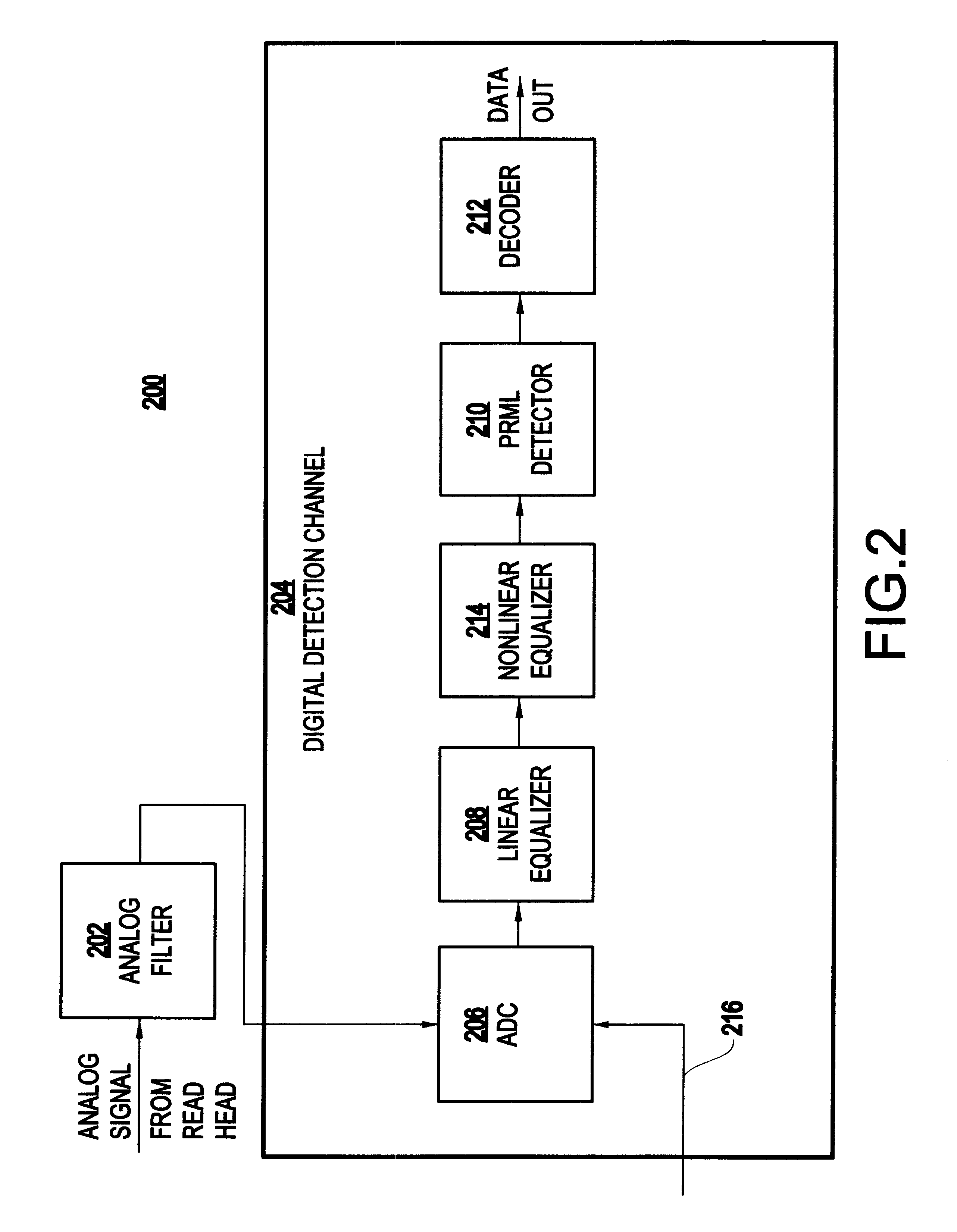
Nonlinear equalizer and decoding circuit and method using same
InactiveUS6678105B2Eliminate interferenceLess memoryMultiple-port networksModification of read/write signalsSignal conditioningAnalog signal
A decoding circuit has a nonlinear equalizer which employs a signal conditioning algorithm for conditioning a partial response sampled signal to eliminate intersymbol interference. The inventive decoding circuit has an analog-to-digital converter for sampling an analog signal, a linear equalizer for adjusting the amplitude and phase relations of the sampled signal, a nonlinear equalizer for conditioning the sampled signal and outputting a partial response sampled signal having two nonzero samples, and a partial response maximum likelihood detector, for detecting the partial response sampled signal having two nonzero samples.
Owner:IBM CORP
Optical nonlinear equalization method based on transfer learning
ActiveCN110505020ARapid modelingReduce resource overheadElectromagnetic receiversNeural learning methodsNonlinear phase noiseNerve network
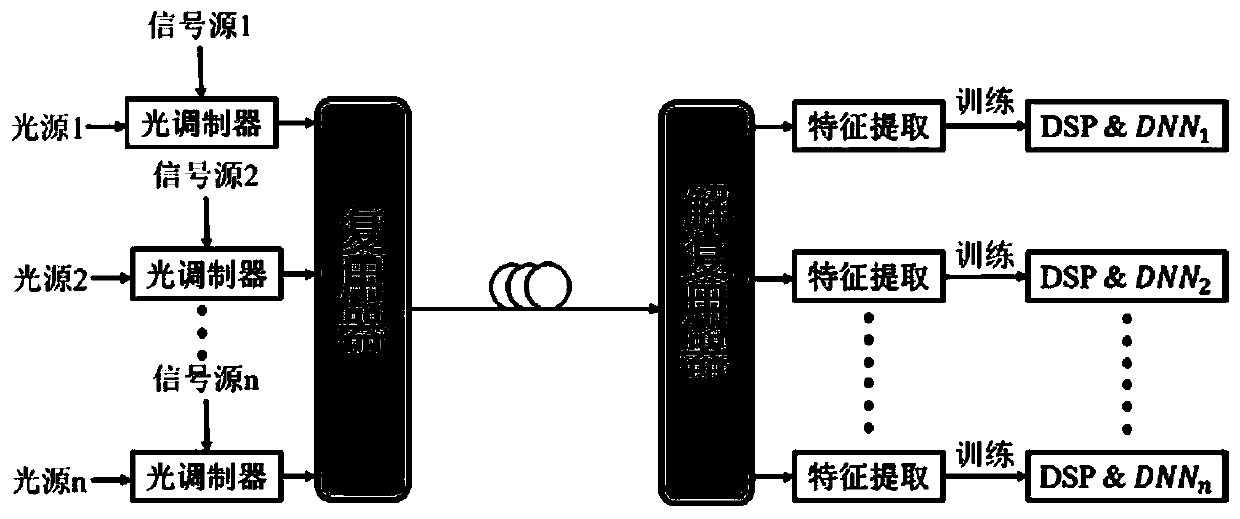
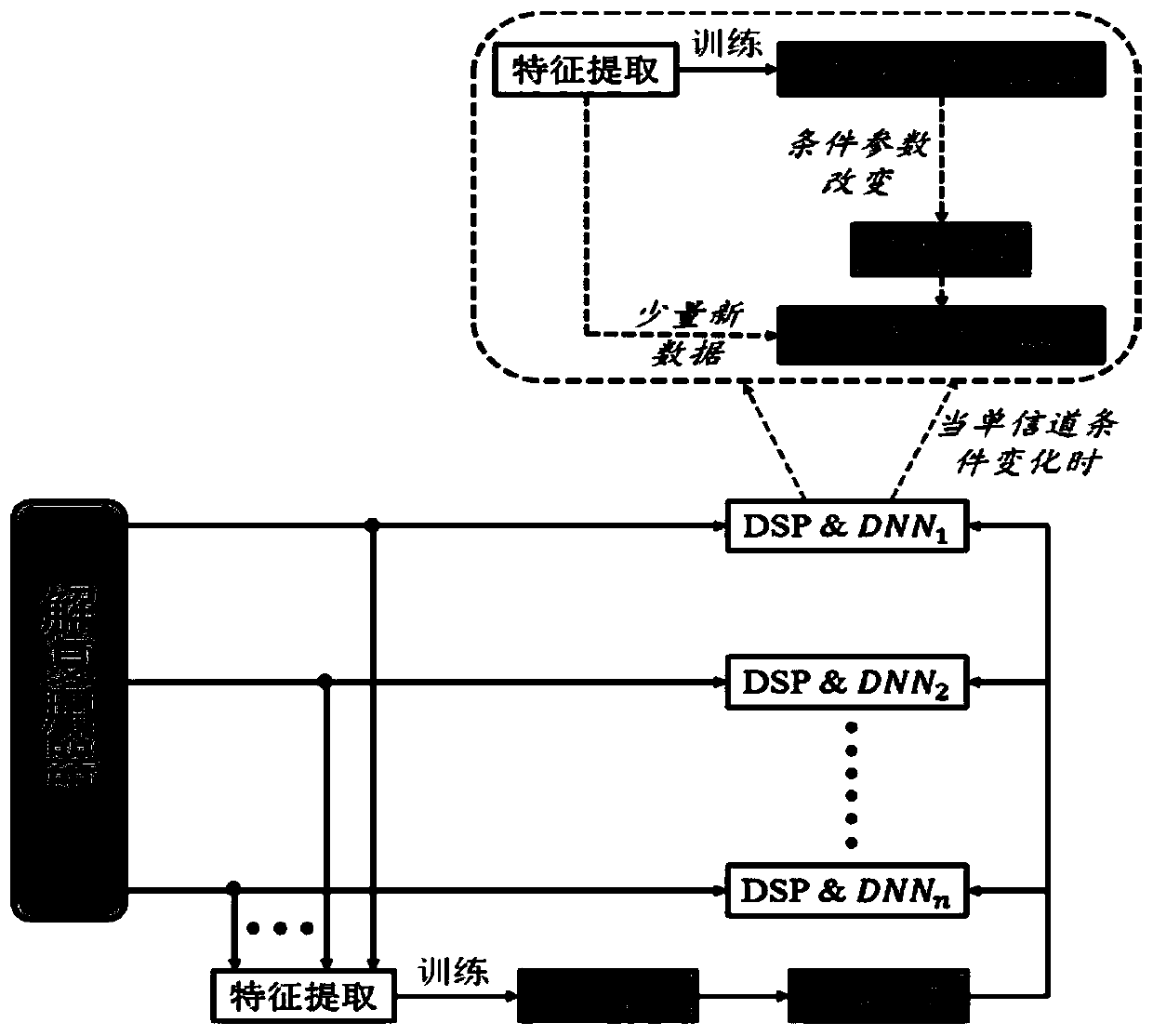
The invention provides an optical nonlinear equalization method based on transfer learning. Trained initialized neural network parameters are migrated to a neural network of each channel through transfer learning, and each channel is assisted to quickly establish the neural network equalizer, so that quick modeling is realized, and the resource overhead, such as less new training data and less iterative compensation, is reduced. Meanwhile, once the channel state is changed, such as the optical power and the transmission distance, the nonlinear phase noise is correspondingly changed, and at themoment, if each channel is retrained respectively, huge expenditure is also corresponding. At the moment, by initializing migration of neural network parameters and supplementing a small amount of new data, rapid neural network remodeling is realized, and then updated parameters are migrated to each channel for updating, so that the response capability to channel change is improved. According tothe invention, nonlinear equalization efficiency under different channels is improved, and high tolerance to optical fiber nonlinearity is maintained.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
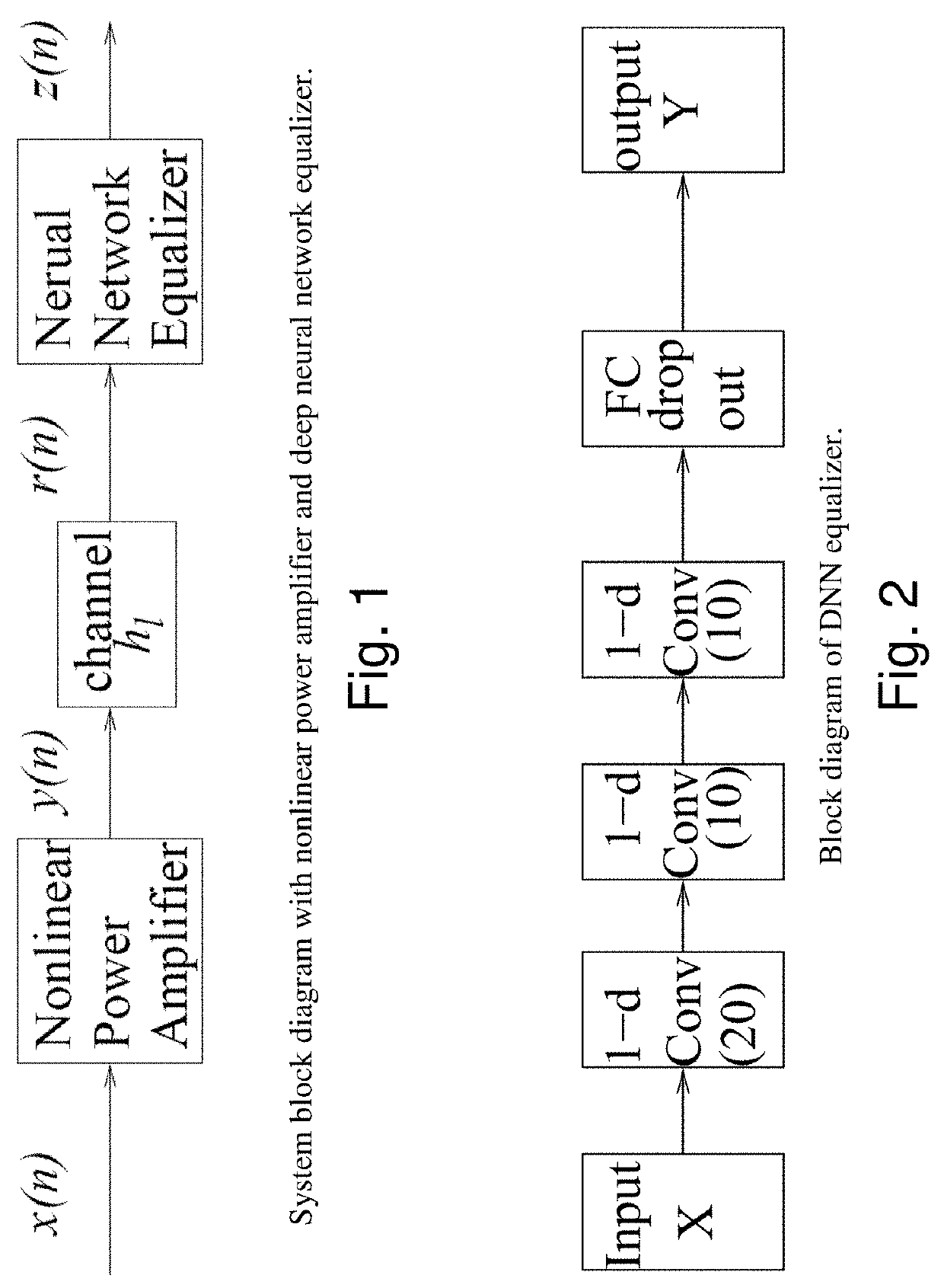
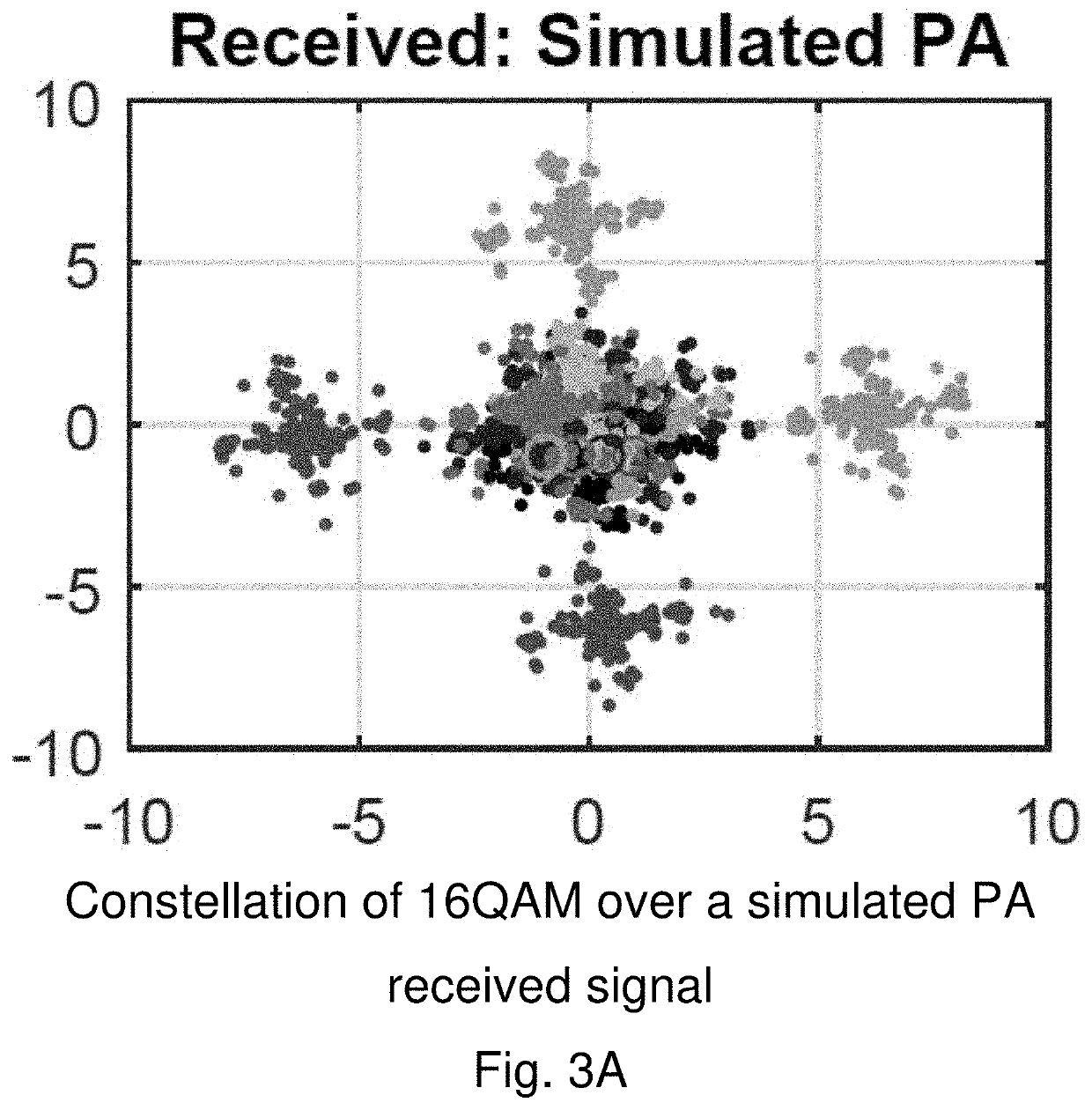
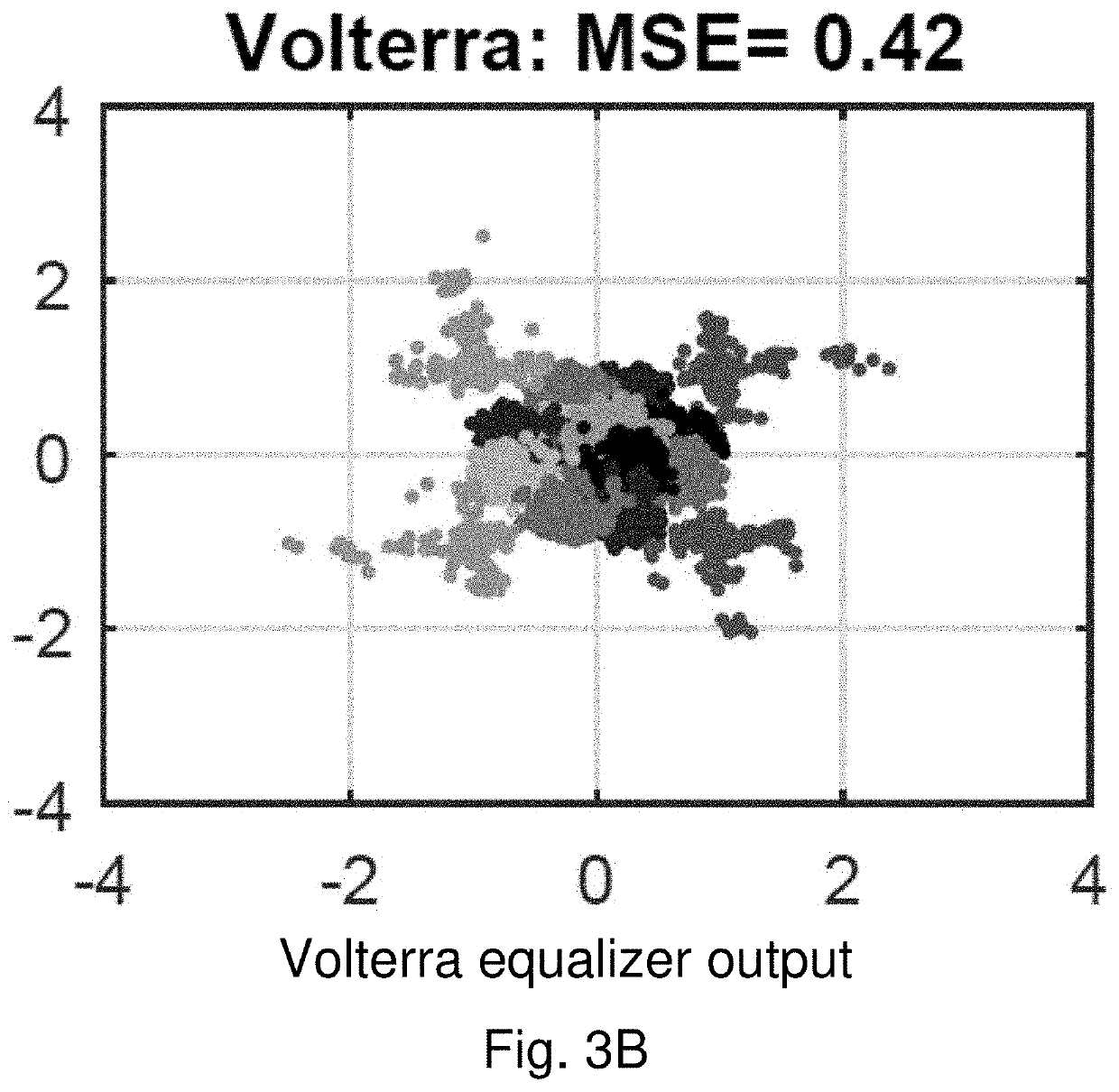
Integrating volterra series model and deep neural networks to equalize nonlinear power amplifiers
ActiveUS20200295975A1Fast convergenceMore efficientAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersNonlinear distortionWireless transceiver
The nonlinearity of power amplifiers (PAs) has been a severe constraint in performance of modern wireless transceivers. This problem is even more challenging for the fifth generation (5G) cellular system since 5G signals have extremely high peak to average power ratio. Nonlinear equalizers that exploit both deep neural networks (DNNs) and Volterra series models are provided to mitigate PA nonlinear distortions. The DNN equalizer architecture consists of multiple convolutional layers. The input features are designed according to the Volterra series model of nonlinear PAs. This enables the DNN equalizer to effectively mitigate nonlinear PA distortions while avoiding over-fitting under limited training data. The non-linear equalizers demonstrate superior performance over conventional nonlinear equalization approaches.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
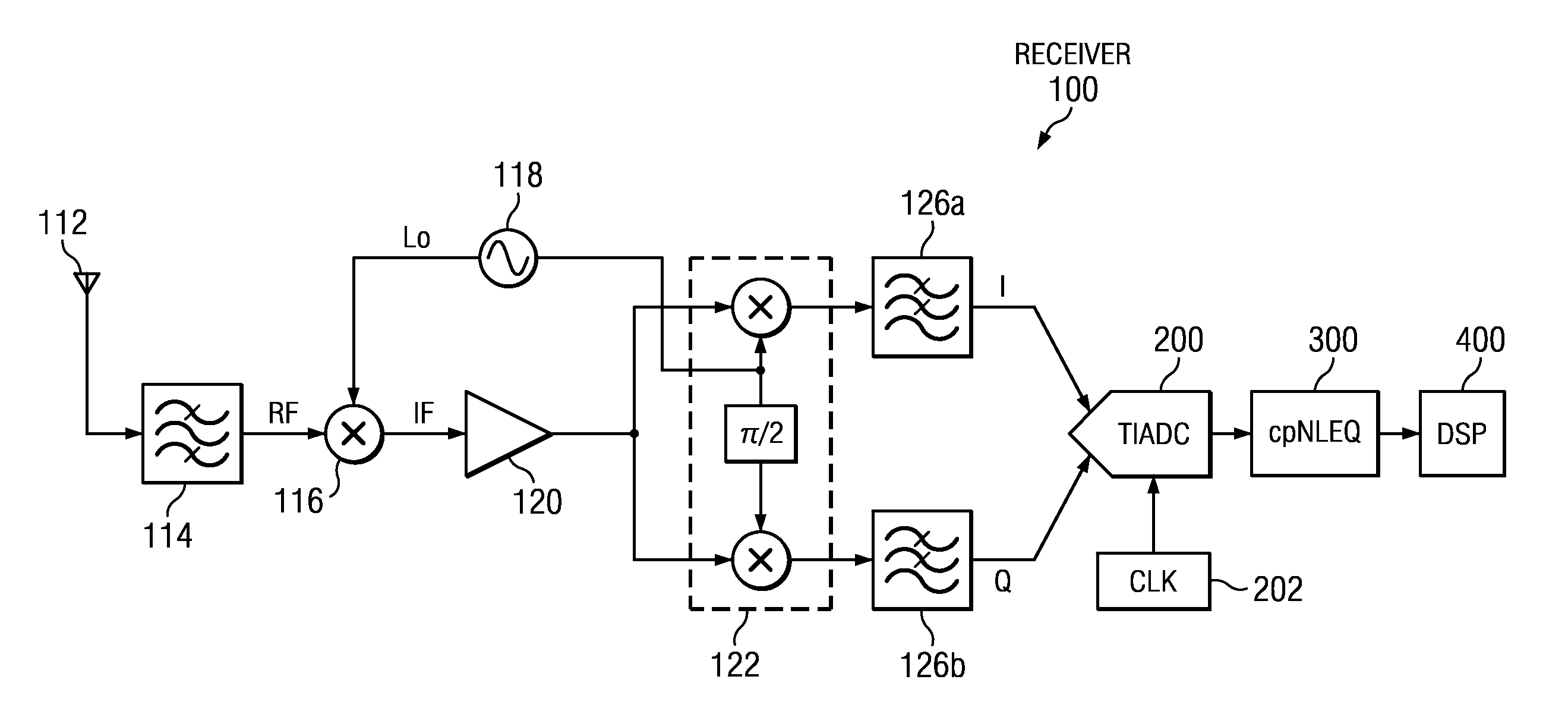
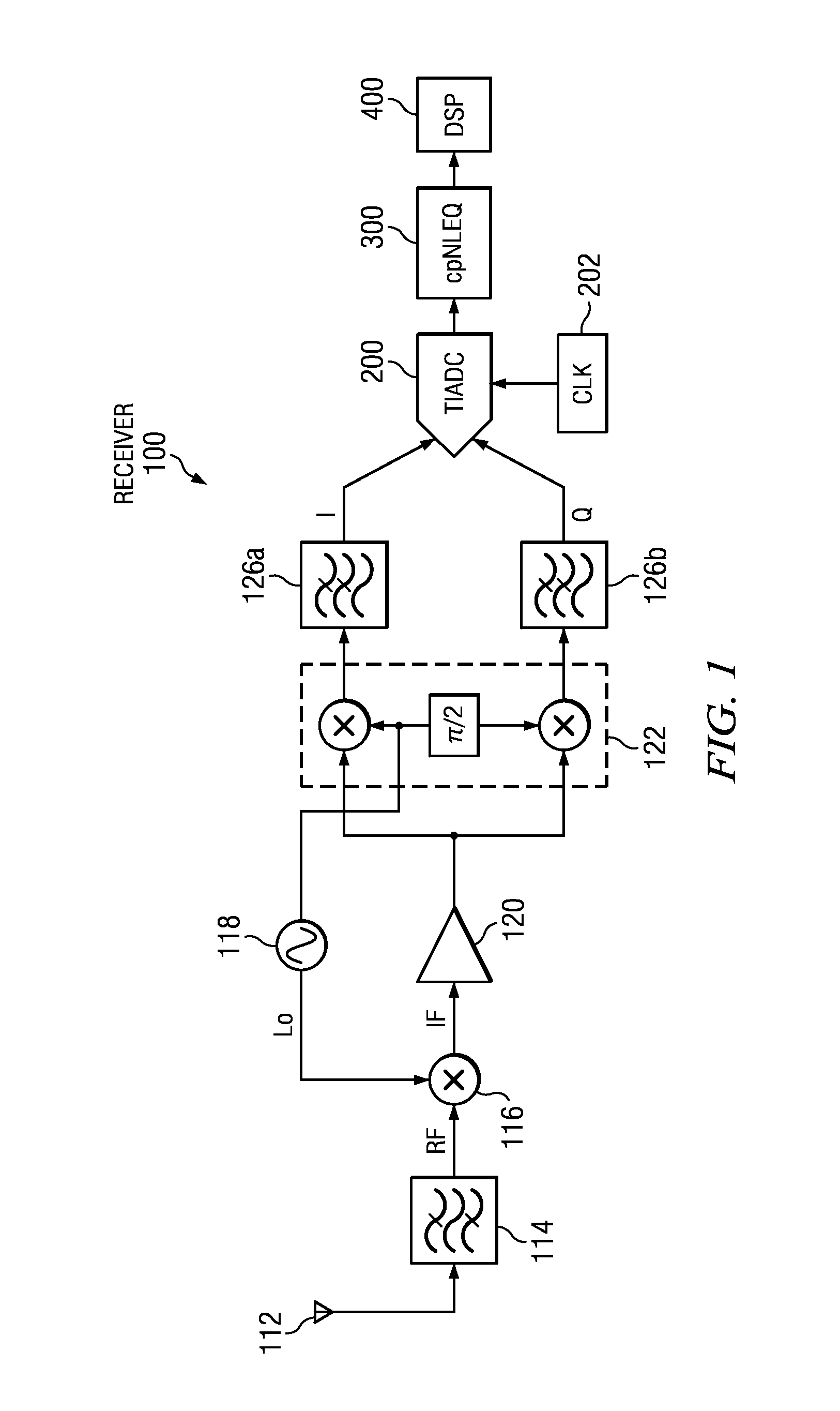
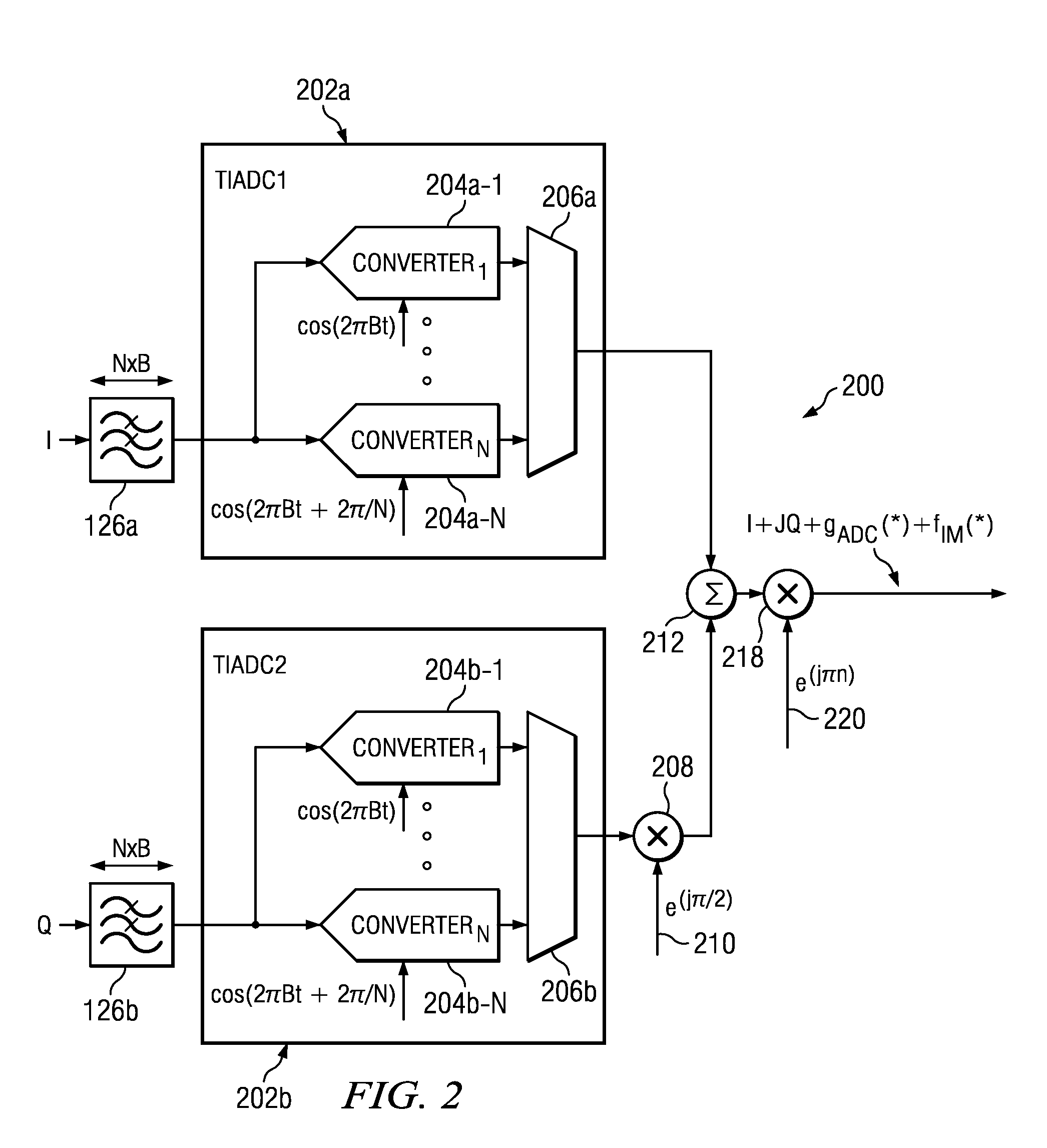
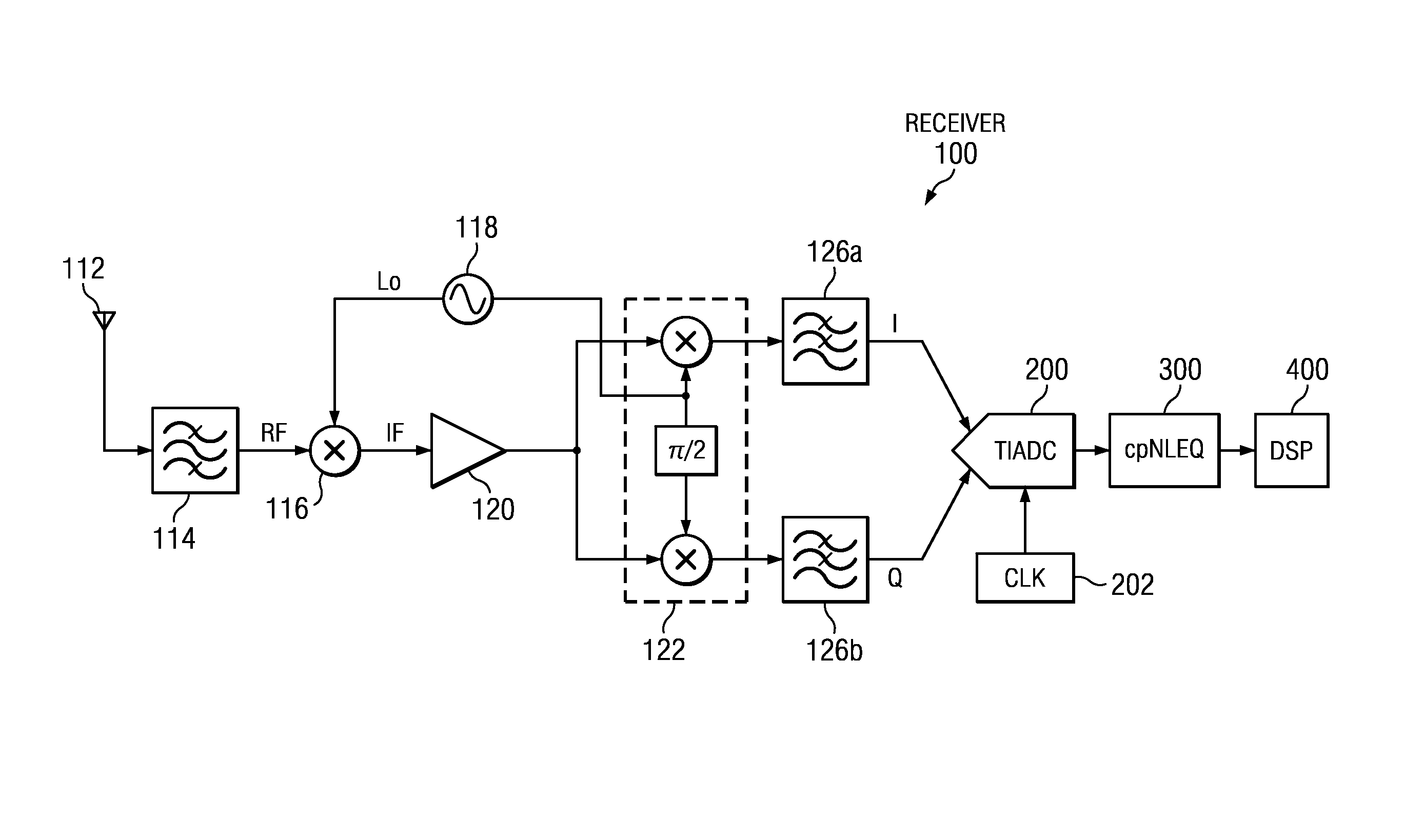
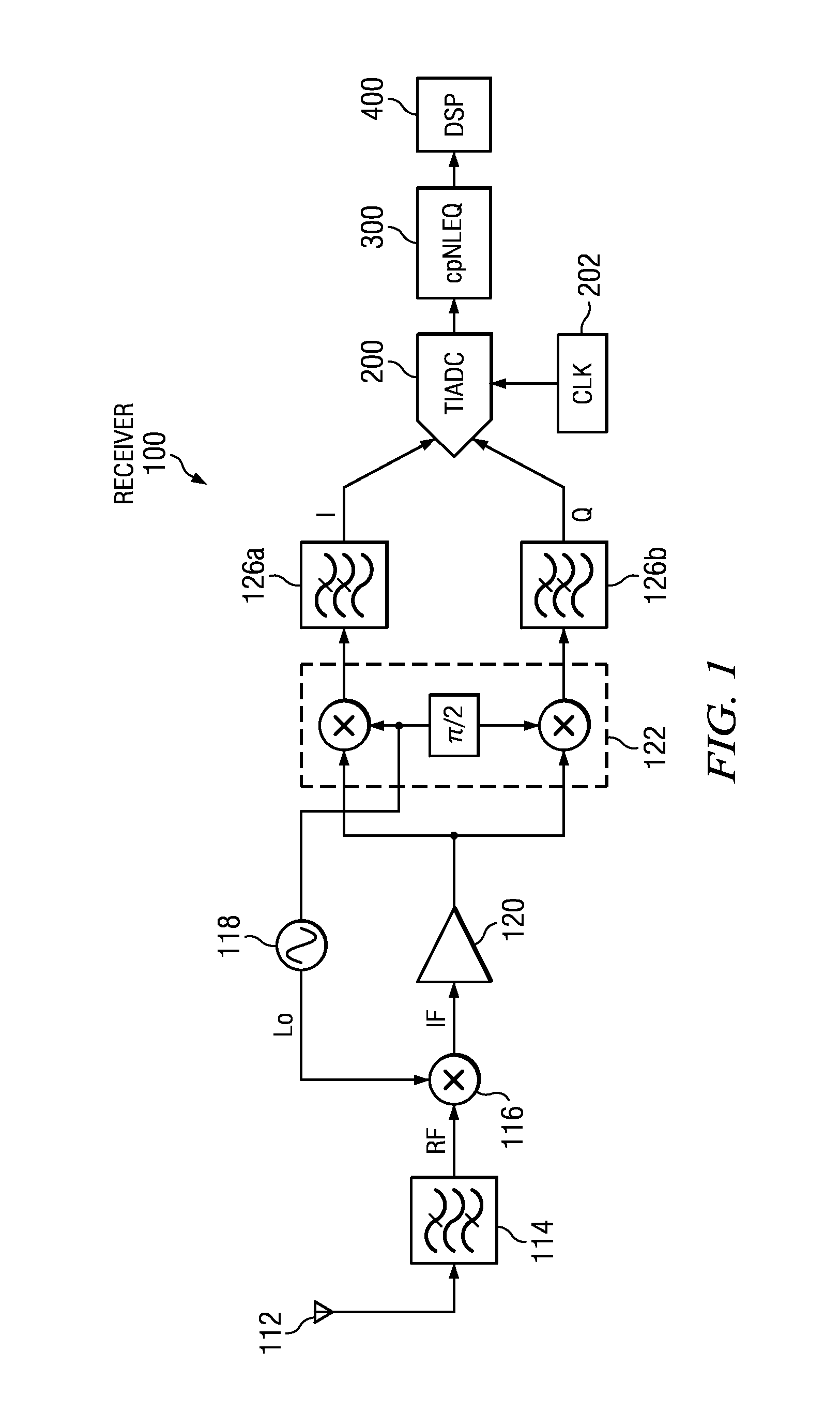
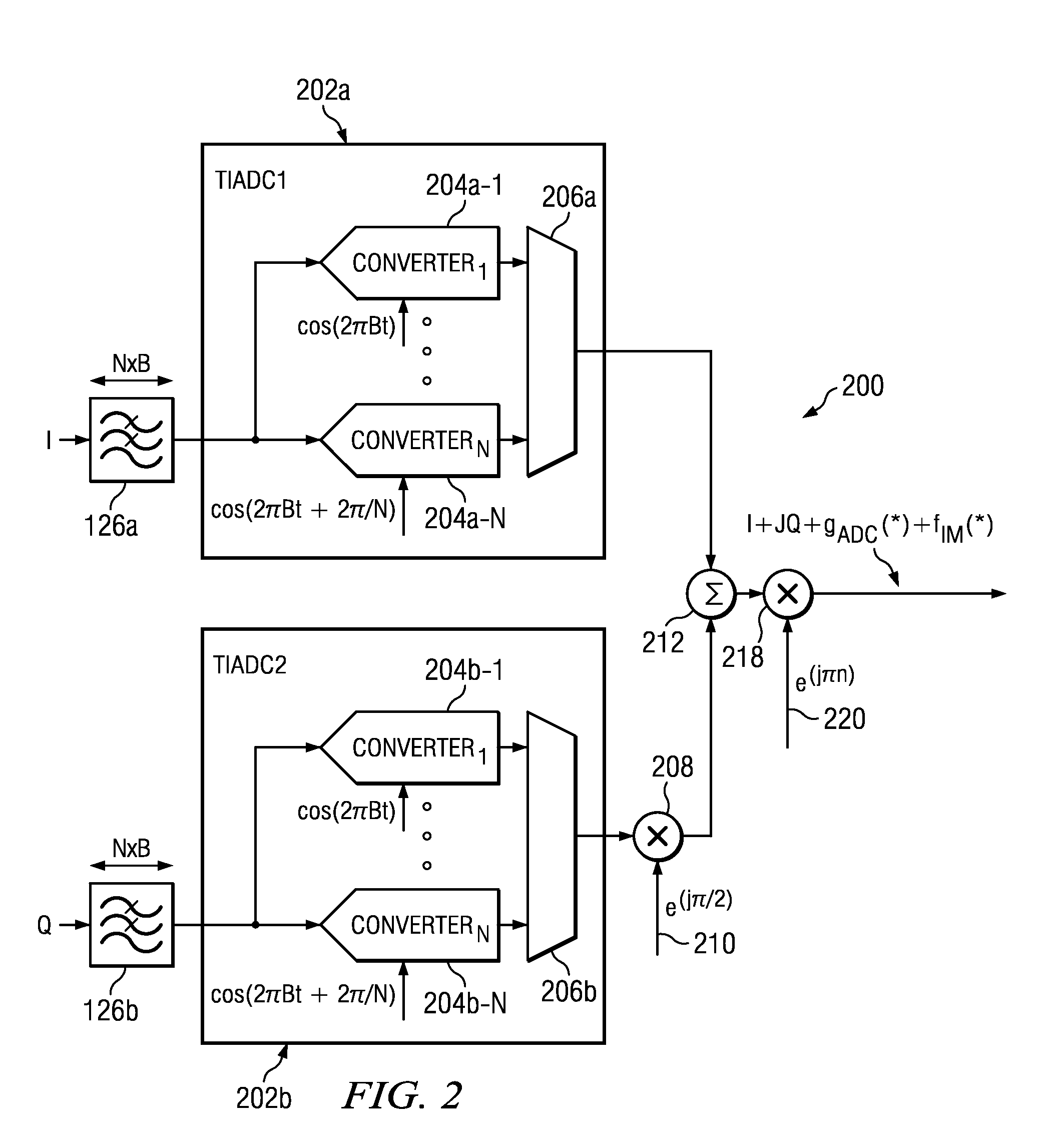
Method and Apparatus for Complex In-Phase/Quadrature Polyphase Nonlinear Equalization
Complex polyphase nonlinear equalizer (cpNLEQs) mitigate nonlinear distortions generated by complex in-phase / quadrature (I / Q) time-interleaved analog-to-digital converters (TIADCs). Example cpNLEQs upsample the digital waveform emitted by the TIADC, e.g., by a factor of two, then separate the upsampled digital waveform into upsampled in-phase and quadrature components. Processors in the cpNLEQs create real and imaginary nonlinear compensation terms from the upsampled in-phase and quadrature components. The nonlinear compensation terms are downsampled, and the downsampled imaginary nonlinear compensation term is phase-shifted, then combined with the downsampled real component to produce an estimated residual distortion. Subtracting the estimated residual distortion from the digital waveform emitted by the TIADC yields an equalized digital waveform suitable for further processing.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
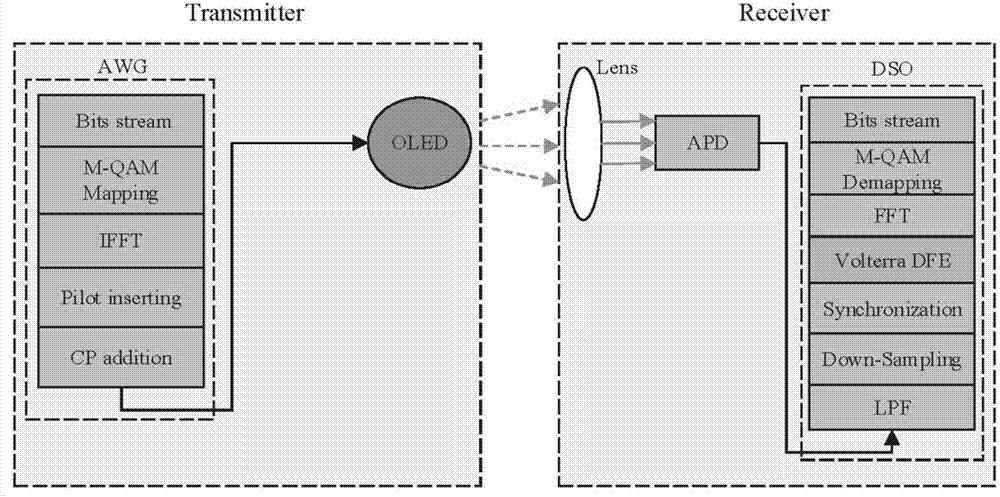
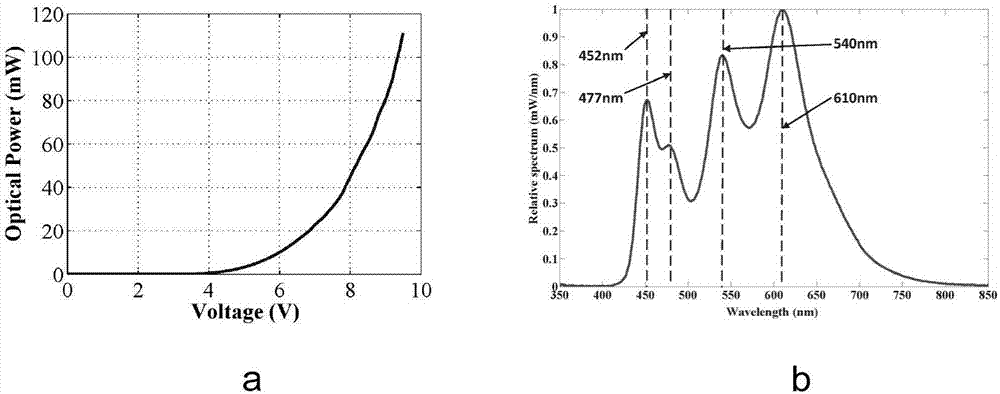
Organic visible light communication system and adaptive nonlinear equalizer based on Volterra series
InactiveCN107317627ASuppress nonlinear distortionImprove performanceClose-range type systemsElectromagnetic receiversNonlinear distortionPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses an organic visible light communication system and an adaptive nonlinear equalizer based on Volterra series. The organic visible light communication system comprises a white light OLED arranged on a sending end, and an optical lens, a photoelectric detector and the adaptive nonlinear equalizer based on Volterra series, which are arranged on a receiving end and are connected in sequence; the white light OLED is used as a light source, the optical lens and the photoelectric detector perform photoelectric signal conversion on a received optical signal and output an electric signal to the adaptive nonlinear equalizer based on Volterra series; and the adaptive nonlinear equalizer based on Volterra series is used for inhibiting the nonlinear distortion of the white light OLED having a memory effect and improving the effective SNR of the electric signal. The scheme can inhibit the nonlinear distortion of the organic visible light communication system to a certain extent, so that the effective SNR can be effectively improved, the transmission distance is increased while satisfying a certain error rate threshold, and thus the overall performance of the organic visible light communication system is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and method for iterative nonlinear compensation for intermodulation distortion in multicarrier communication systems
ActiveUS8467438B2Multiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionCommunications systemCarrier signal
A receiver is provided that can receive a first signal transmitted on a first carrier and a second signal transmitted on a second carrier. The receiver includes a channel estimation portion, a multicarrier nonlinear equalizer, a first log likelihood computing portion and a second log likelihood computing portion. The channel estimation portion can output a first estimation. The multicarrier nonlinear equalizer can output a first equalized signal and a second equalized signal. The first log likelihood ratio computing portion can output a first log likelihood ratio signal based on the first equalized signal. The second log likelihood ratio computing portion can output a second log likelihood ratio signal based on the second equalized signal. The multicarrier nonlinear equalizer can further output a third equalized signal and a fourth equalized signal. The third equalized signal is based on the first signal, the second signal and the first estimation. The fourth equalized signal is based on the first signal, the second signal and the first estimation.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
System and Method for Chromatic Dispersion Tolerant Direct Optical Detection
Embodiments are provided to improve direct detection for optical transmissions. In an embodiment, a method by a transmitter includes adjusting, using a nonlinear equalizer (NLE), a drive voltage for an optical modulator in accordance with a mapping between the drive voltage and an output of the optical modulator. The mapping is an inverse function of a nonlinear transfer function at the optical modulator between the output and to the drive voltage. The method further includes driving, using the adjusted drive voltage, the output of the optical modulator. The output is a single-side band (SSB) signal and is sufficiently linear with respect to the drive voltage for allowing direct detection at a receiver.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Ultra wideband interference suppression technique of minimum bit error rate criterion
InactiveCN101969419AApproximation effect is goodReduce bit error rateTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSlide windowBroadband
The invention discloses an ultra wideband interference suppression technique of minimum bit error rate criterion, which comprises the following steps of: 1, establishing a nonlinear equalizer model; 2, establishing a target function by using minimum bit error rate as criterion; and 3, adjusting the equalizer parameter by adopting a sliding window random gradient algorithm. The bit error rate of asystem is lower, the interference suppression capability of the system is stronger, the nonlinear function has better approximation performance, and the nonlinear equalizer has more excellent interference suppression capability; the system is simple to control, and the nonlinear equalizer can be switched between the minimum bit error rate criterion and the minimum mean square error criterion; thetechnique is simple to implement, the parameter can be adaptively adjusted, and the parameter of the equalizer can be adaptively adjusted on line by using the sliding window random gradient algorithm; and the technique has wide application range, is used for narrowband interference suppression of an ultra wideband communication system, and is also used in the fields of interference suppression, mode identification and the like of other communication systems.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
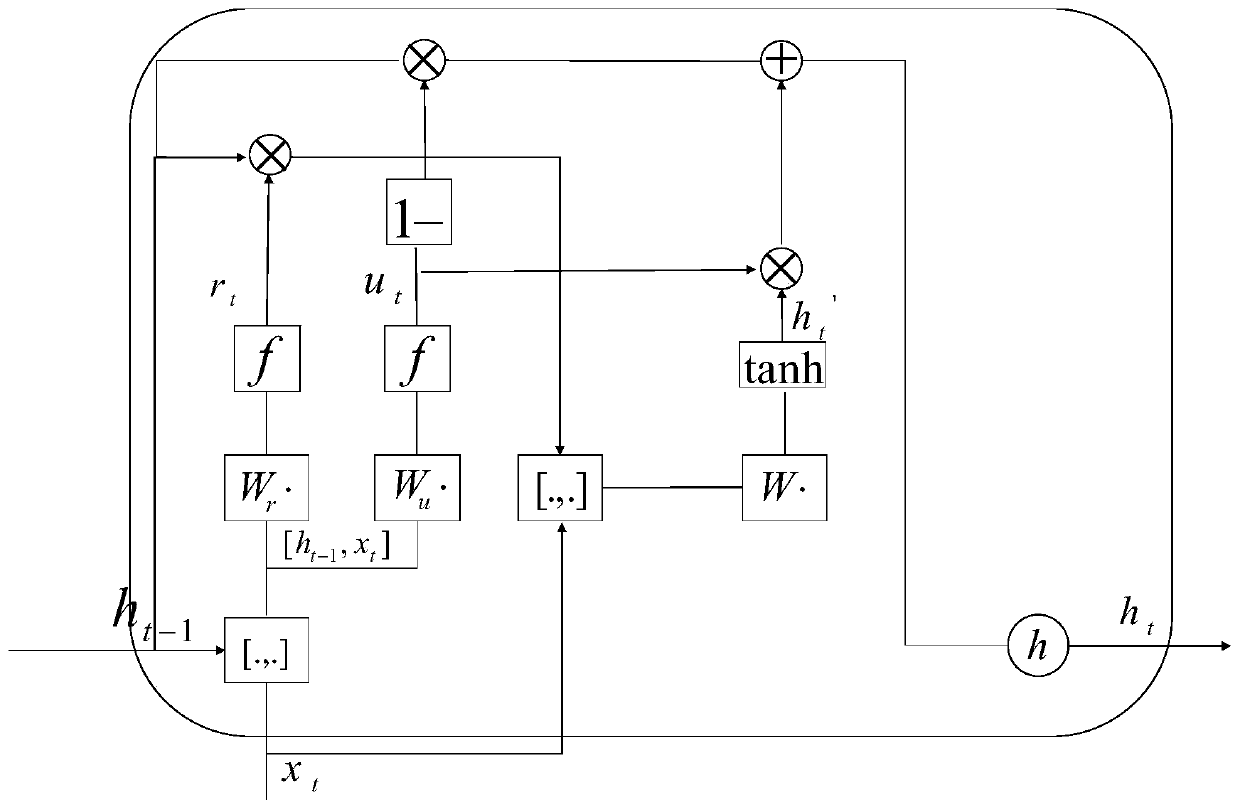
Nonlinear equalization method based on gated recurrent neural network
ActiveCN110598859ARealize nonlinear loss compensation functionImprove performanceNeural architecturesPhysical realisationNetwork modelEqualization
The invention discloses a nonlinear equalization method based on a gated recurrent neural network. The method comprises the steps of determining a gated recurrent neural network model, training the gated recurrent neural network model by using the training sample data, and obtaining a gated recurrent neural network model after preliminary training; performing optimization processing on the gatingrecurrent neural network model generated by the preliminary training; trimming the gated recurrent neural network model after optimization processing; retraining the trimmed gated recurrent neural network model by using the training sample data to obtain a trained gated recurrent neural network model; and carrying out nonlinear estimation or equalization processing by using the trained gated recurrent neural network model, thereby realizing a high-performance and low-complexity nonlinear loss compensation function.
Owner:北京光锁科技有限公司 +1
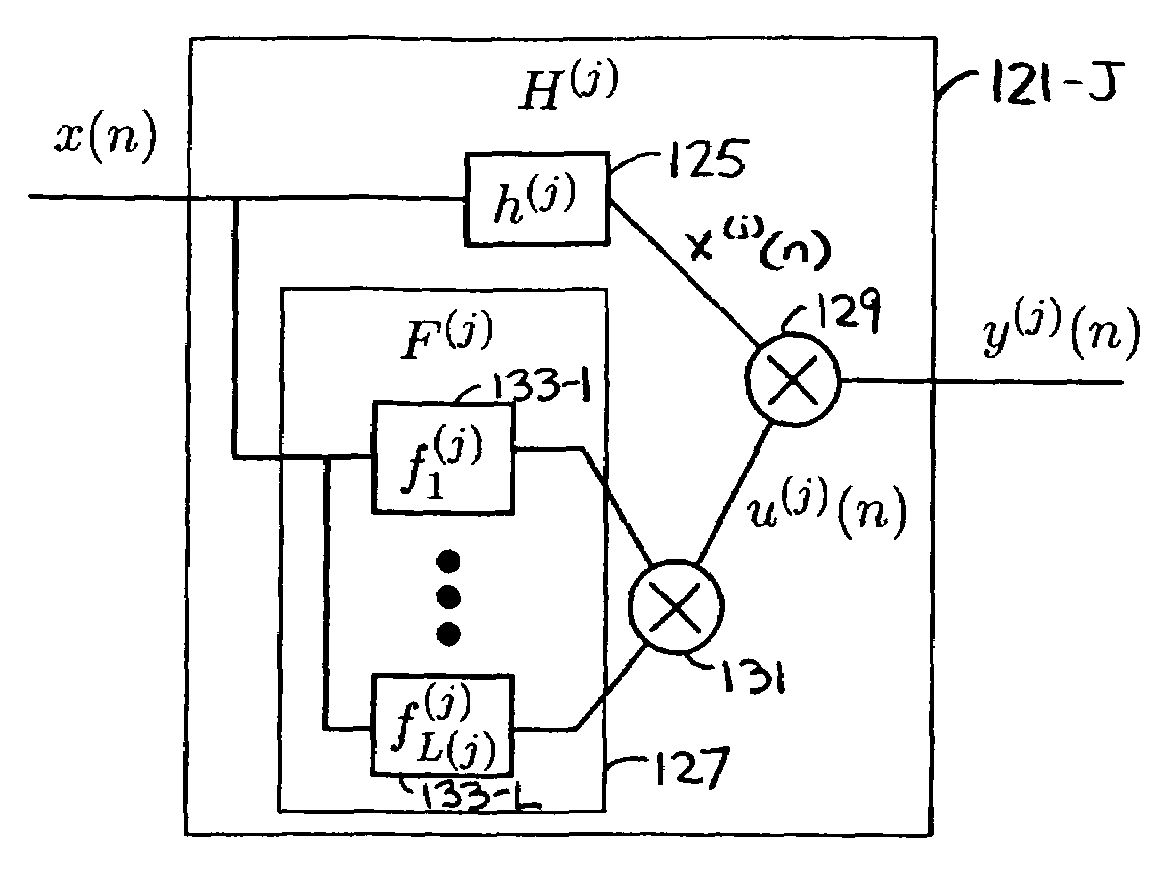
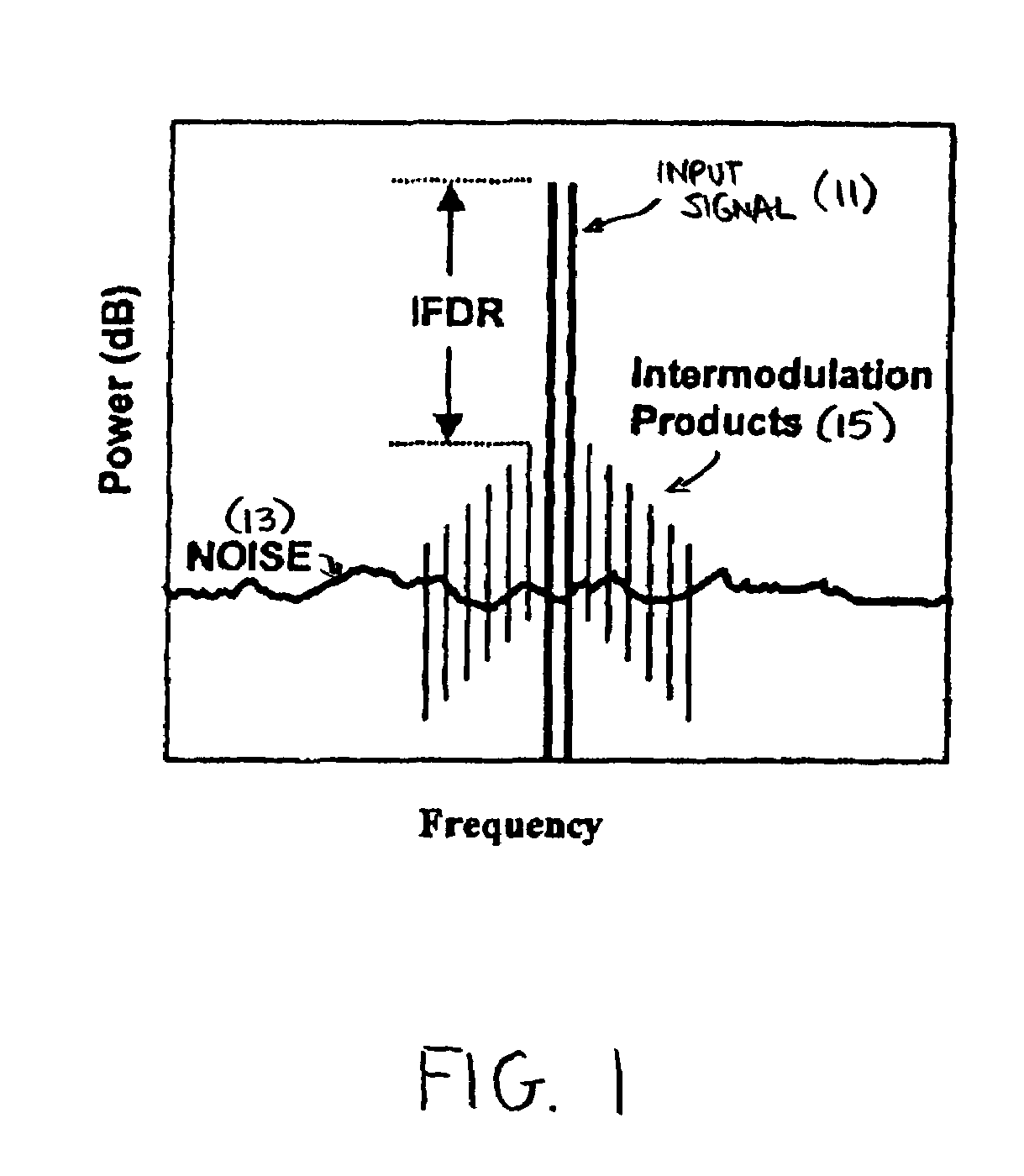
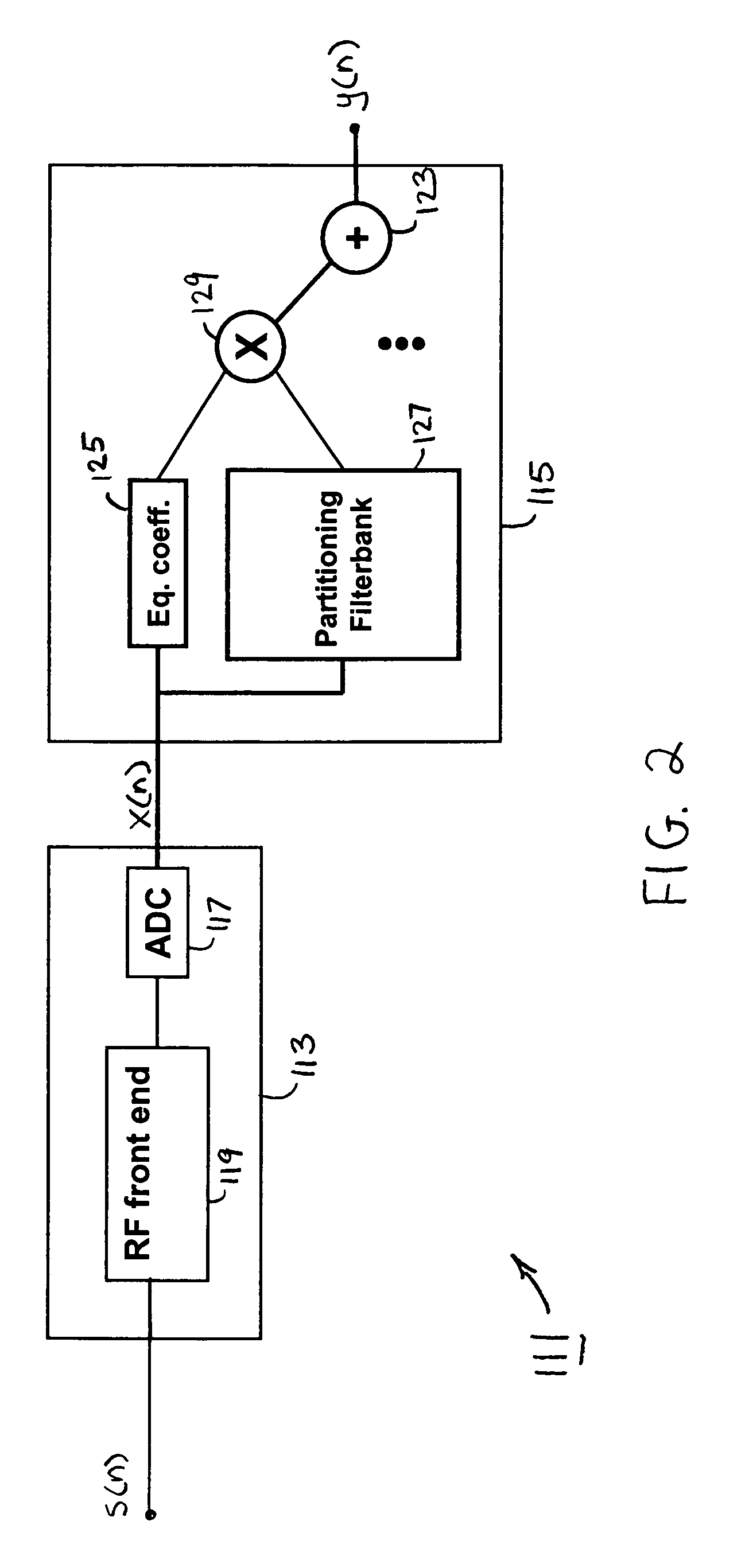
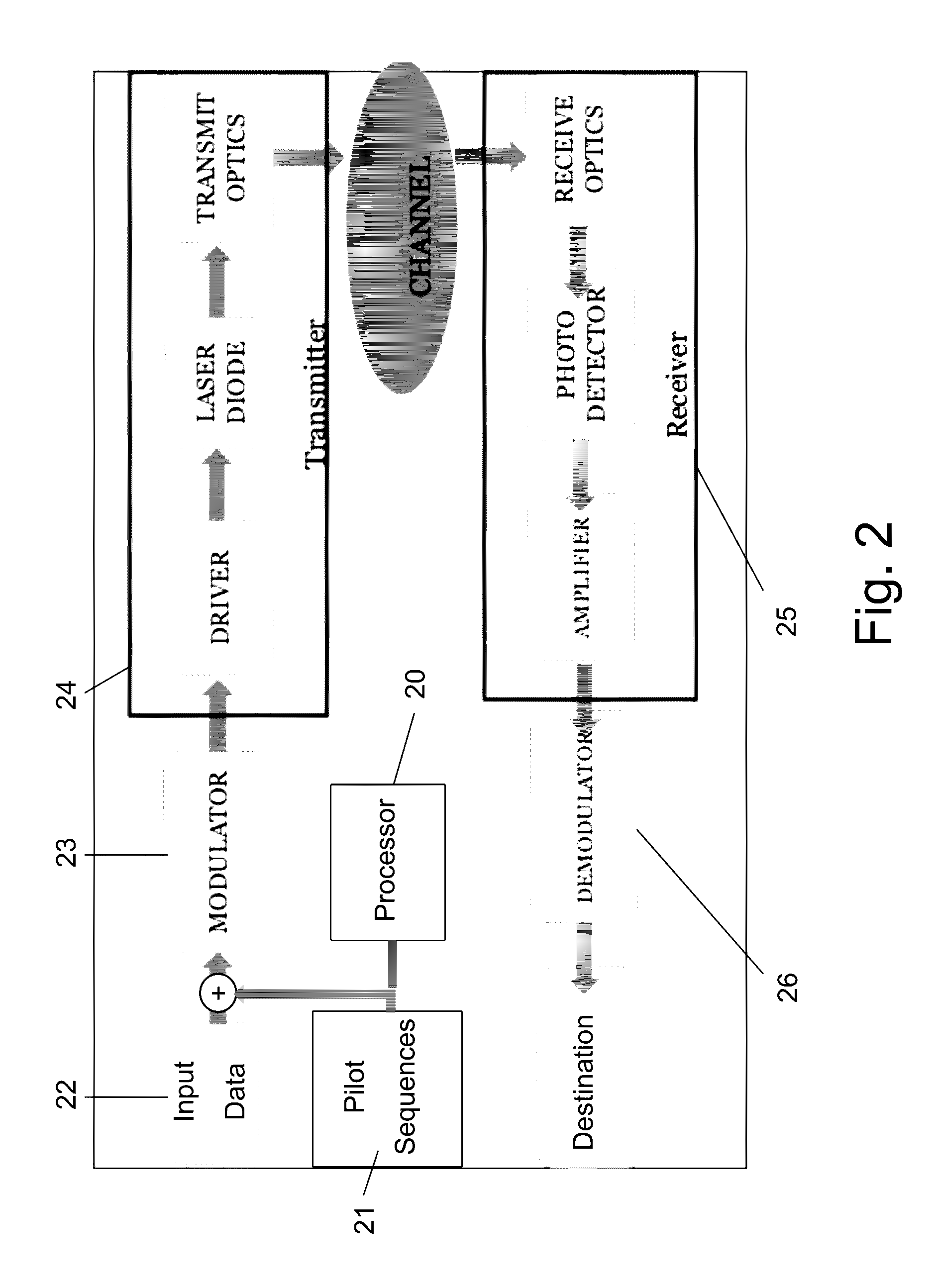
Method and system of nonlinear signal processing
InactiveUS7609759B2Reduce non-linearityThe implementation process is simpleMultiple-port networksError preventionLinear filterEngineering
A nonlinear equalizer for treating the nonlinear component of a distorted digital signal includes a first processing unit adapted to receive the distorted digital signal and yield an appropriate output signal in response thereto, a second processing unit adapted to receive the distorted digital signal and yield an appropriate output signal in response thereto, and a summation module for summing together the output signals from the first and second processing units so as to yield an equalized digital signal. In one embodiment, each of the first and second processing units comprises a linear filter, a partitioning filterbank for partitioning the distorted digital signal, and a multiplier for multiplying together the output of said linear filter with the output of said partitioning filterbank. In use, the nonlinear equalizer can be used to adaptively partition the distorted digital signal so as to allow for nonlinear equalization in a highly efficient manner. Prior to its use in this manner, the coefficient of each linear filter is optimized through the injection of multiple sets of test tones into the nonlinear system.
Owner:RAZ GIL M +1
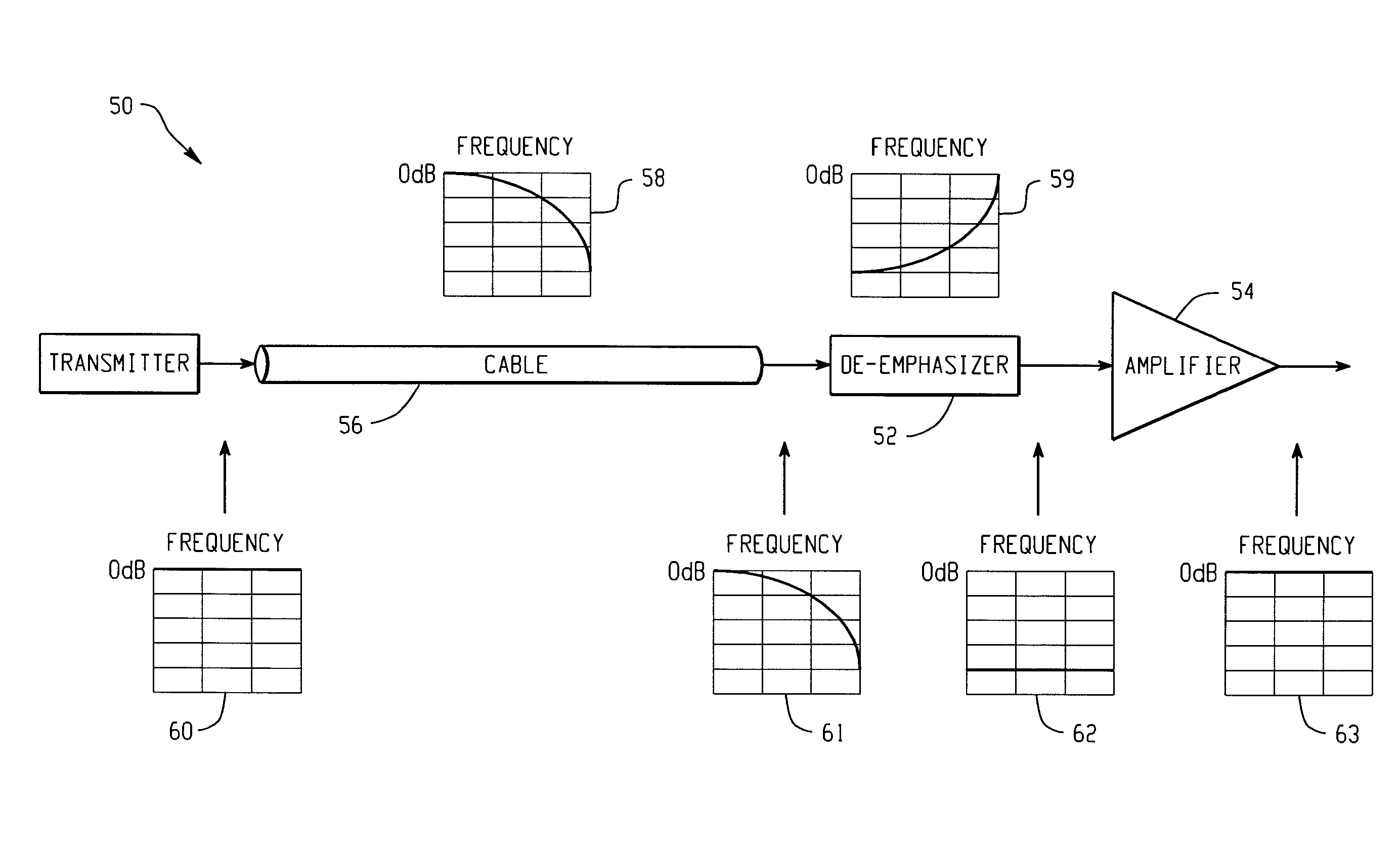
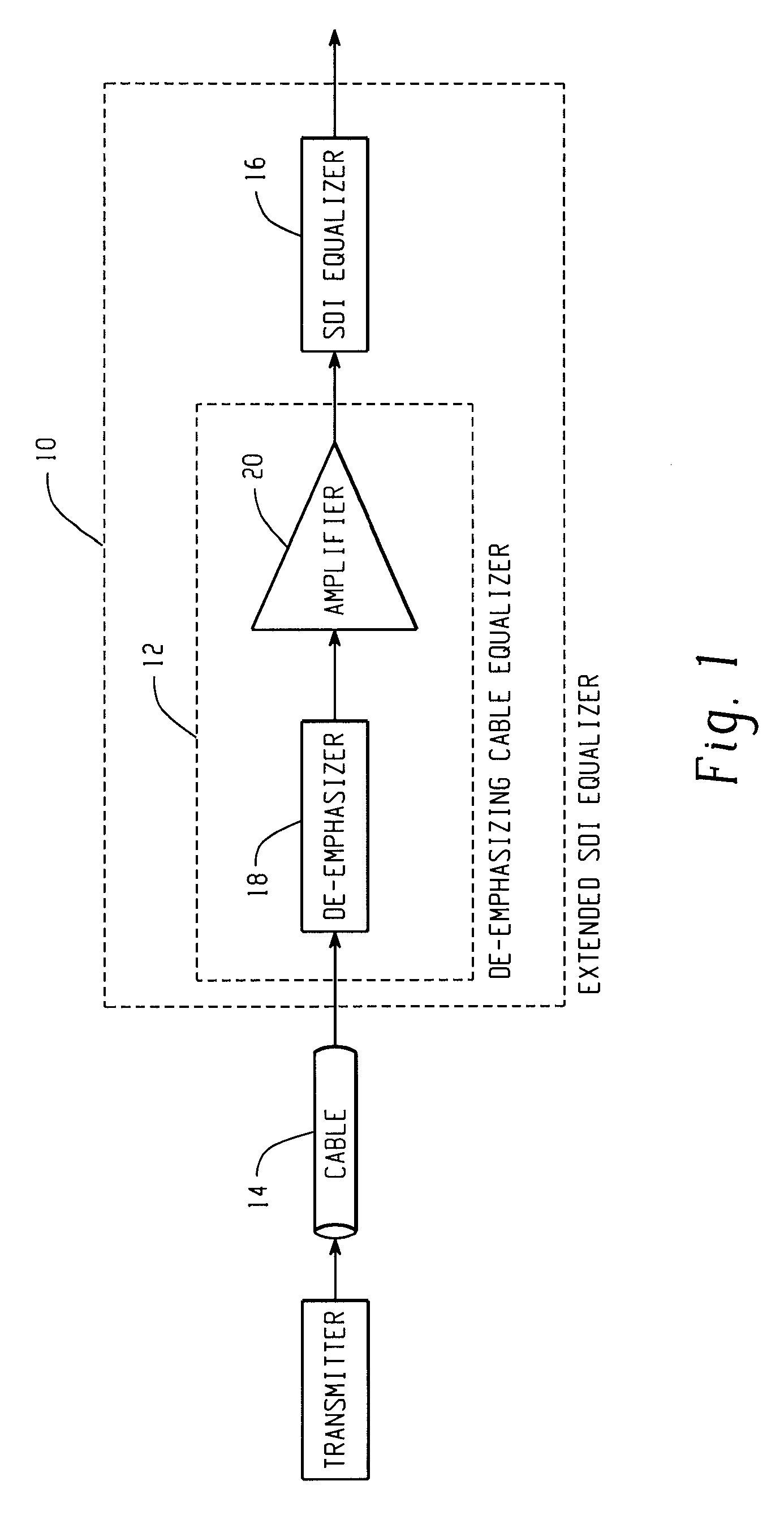
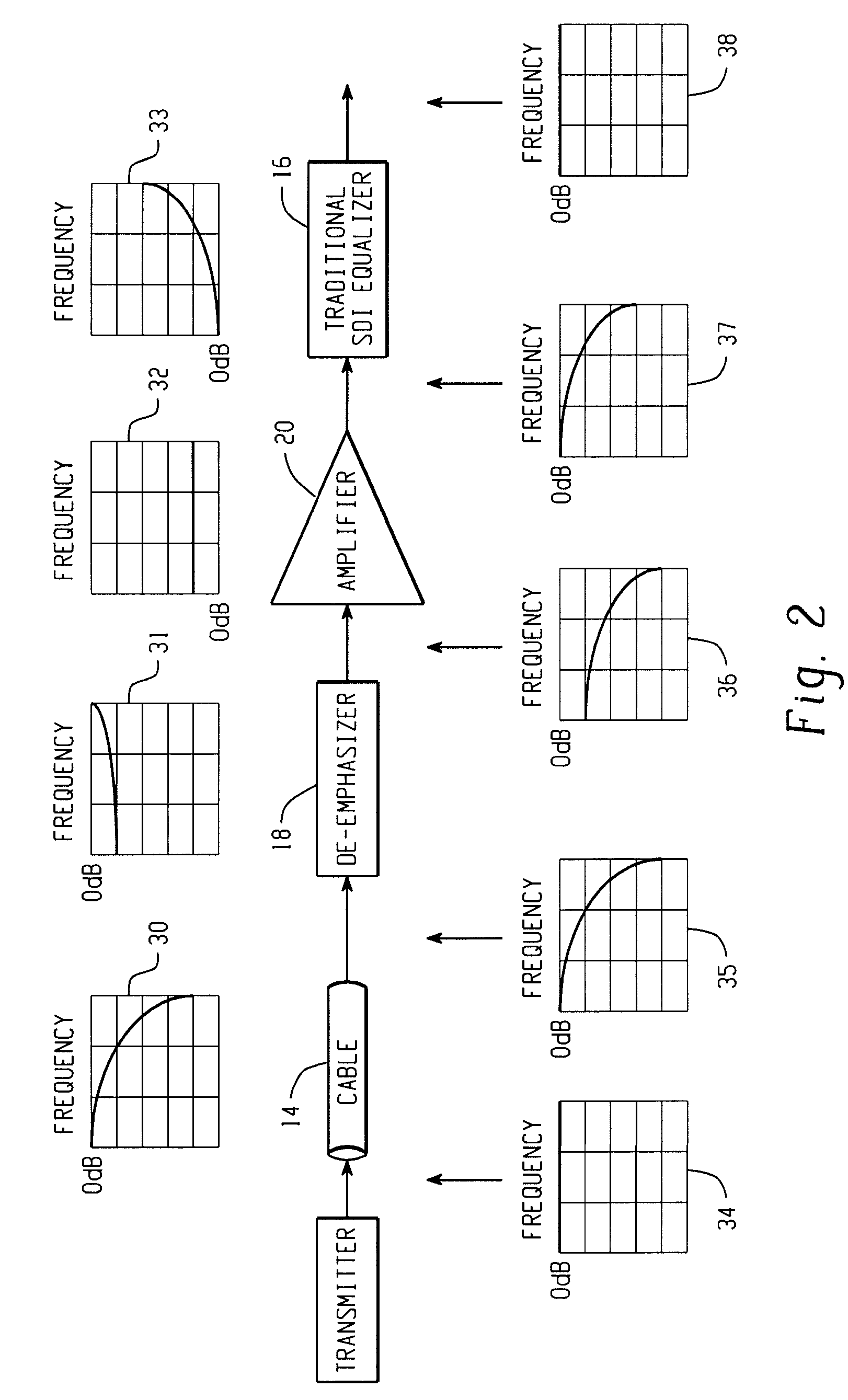
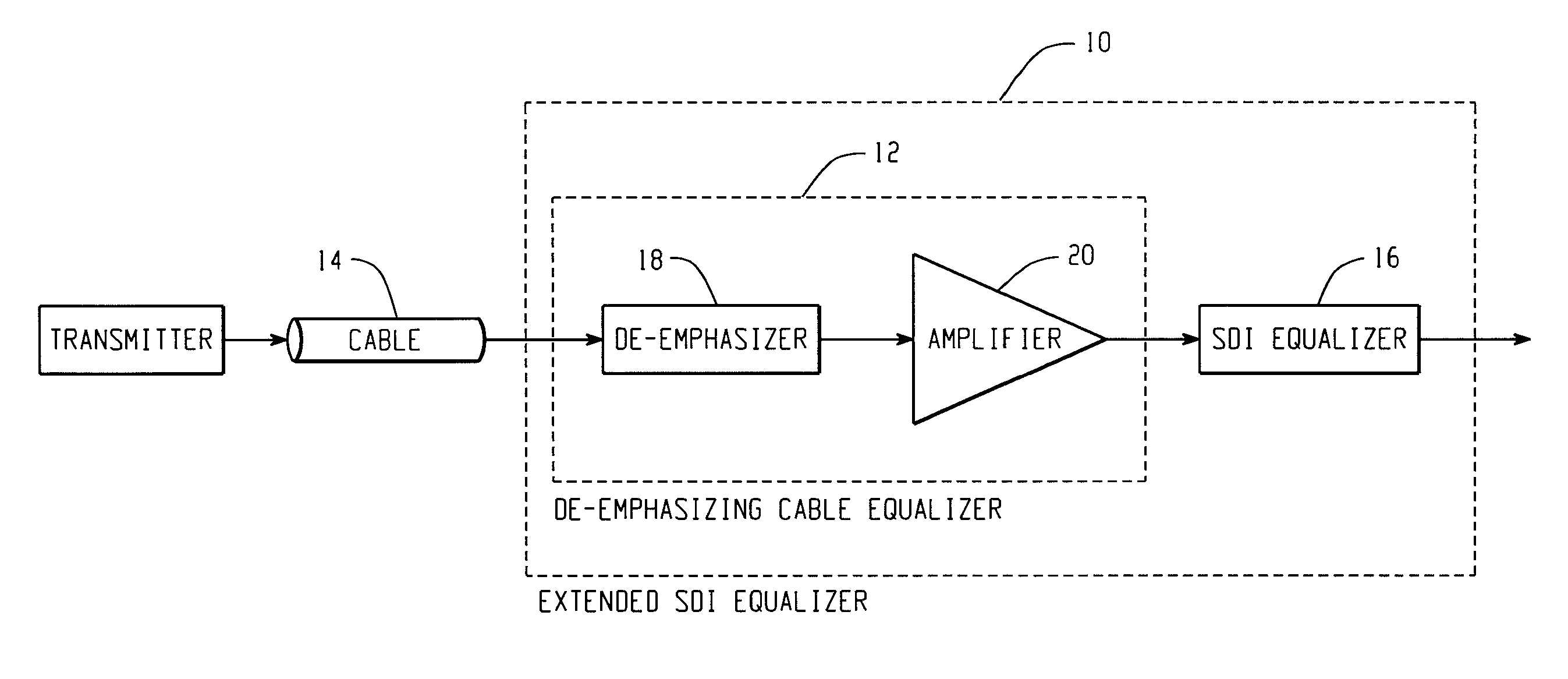
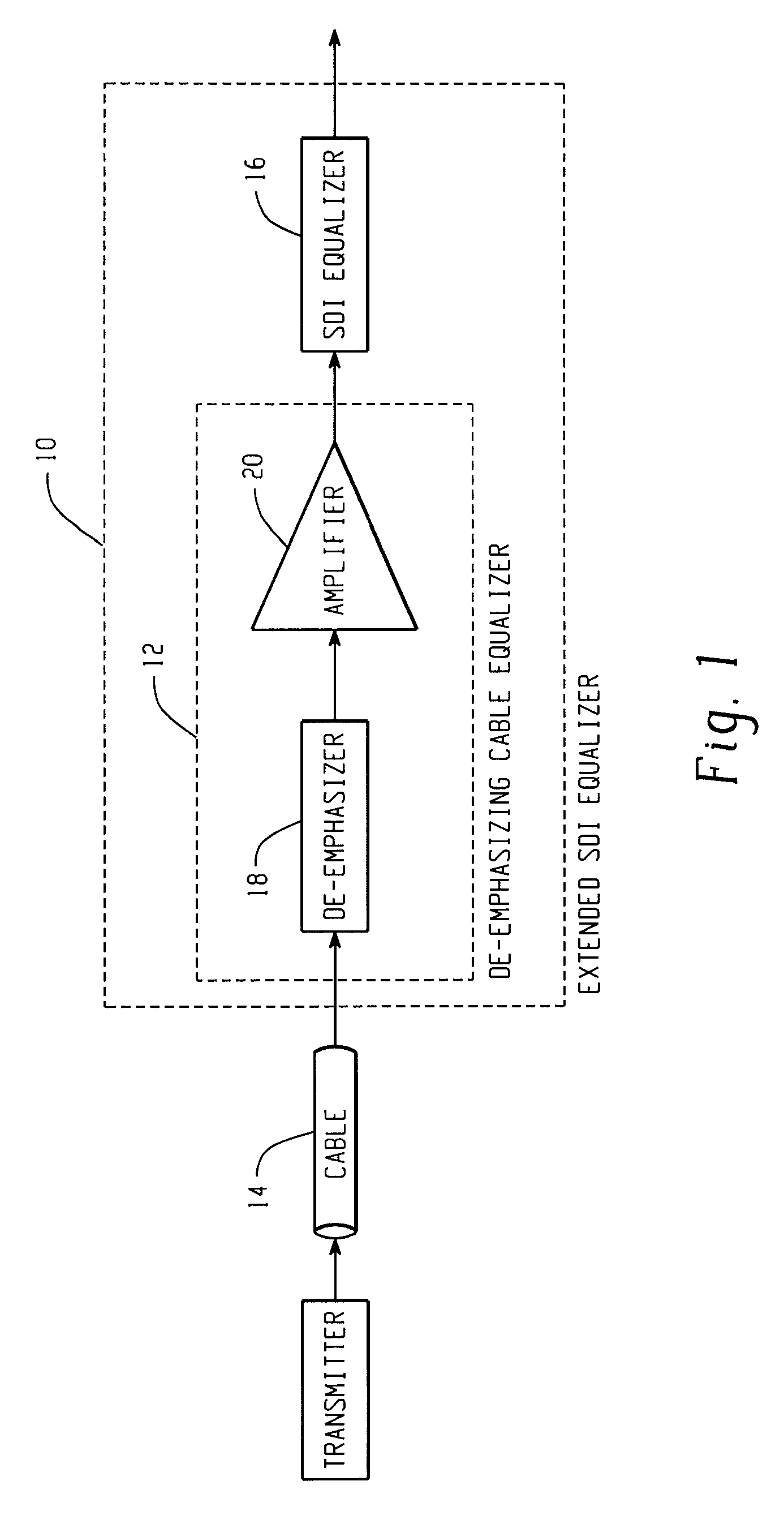
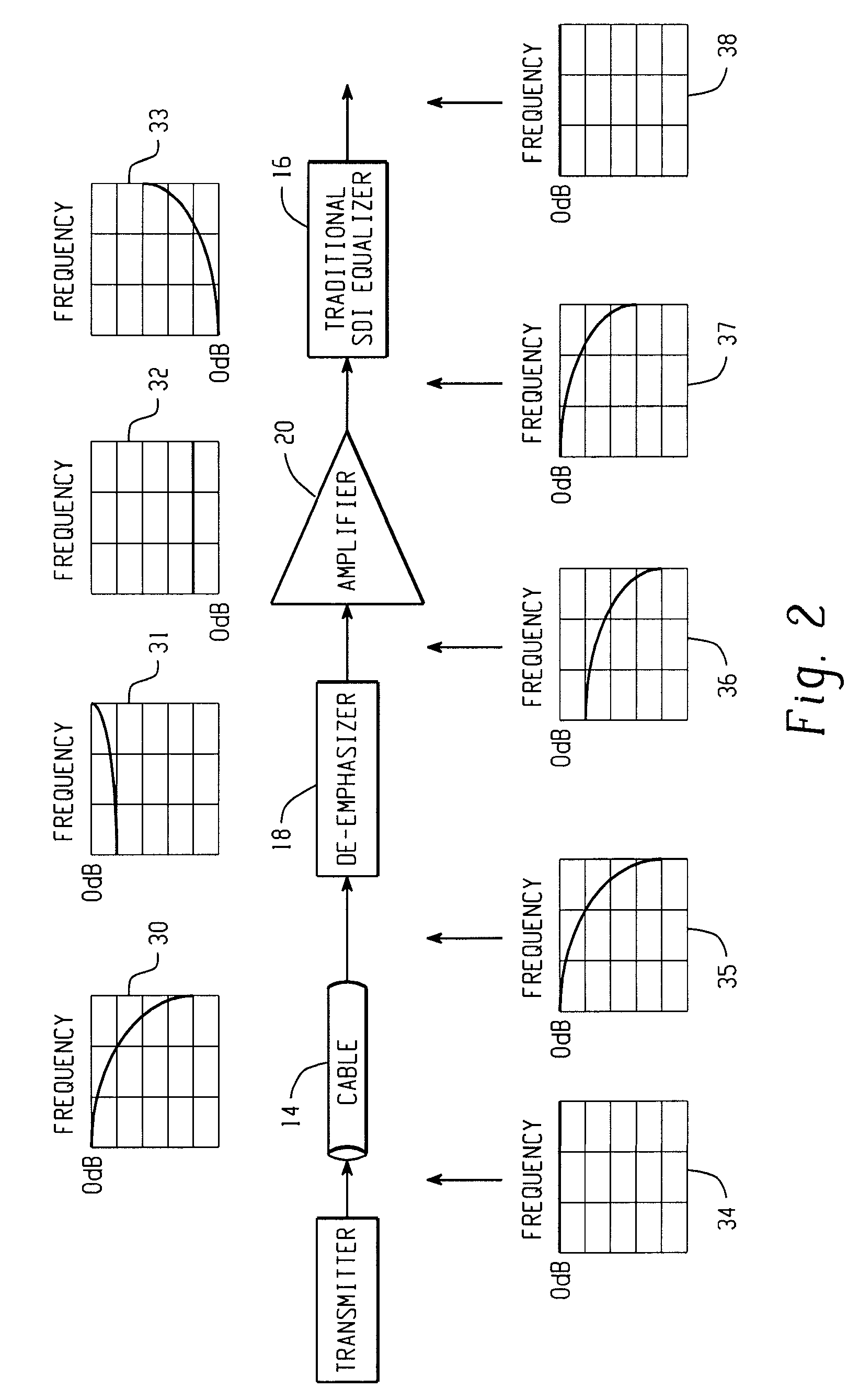
De-emphasizing cable equalizer
In accordance with the teachings described herein, an extended equalizer circuit is provided for equalizing a digital communication signal transmitted over a transmission medium that causes a frequency-dependent attenuation of the digital communication signal. An equalizer may be used that includes a linear equalization circuit and a non-linear equalization circuit, the linear equalization circuit being configured to apply a linear filter to the digital communication signal to compensate for the frequency-dependent attenuation caused by a first portion of the transmission medium, and the non-linear equalization circuit being configured to apply one or more non-linear operations to the digital communication signal. A de-emphasizing equalizer circuit may be coupled in series between the transmission medium and the equalizer and configured to apply an additional linear filter to the digital communication signal in order to compensate for the frequency-dependent attenuation caused by a second portion of the transmission medium
Owner:SEMTECH CANADA
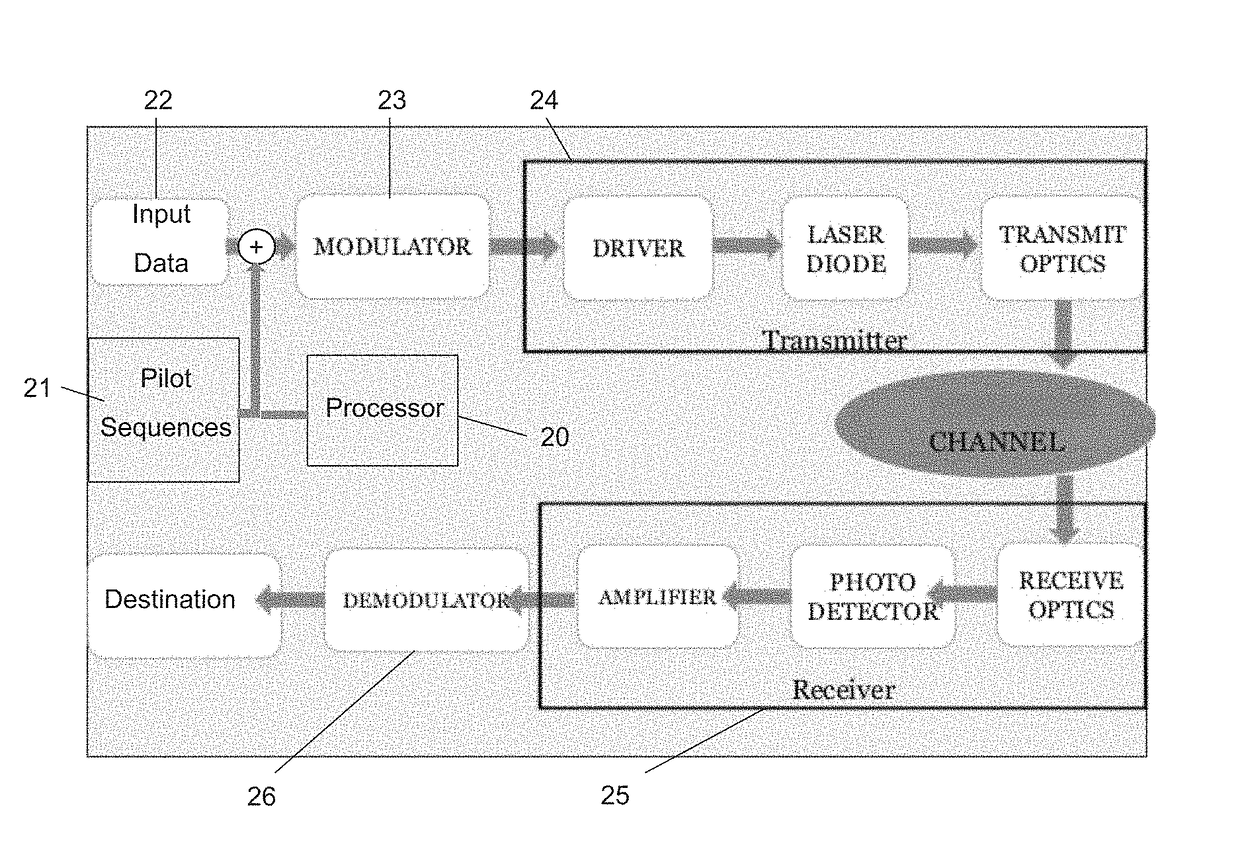
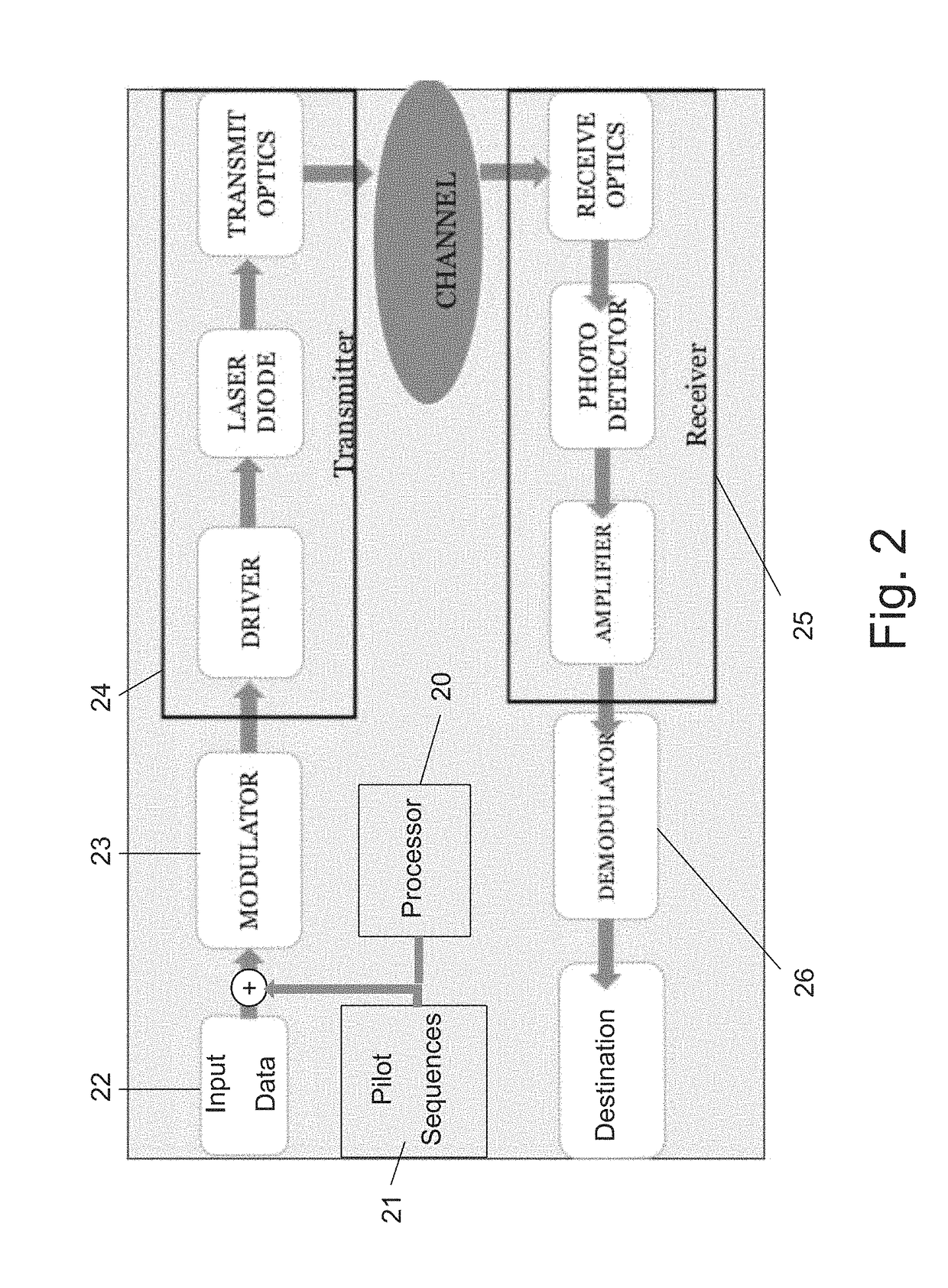
Framing scheme for continuous optical transmission systems
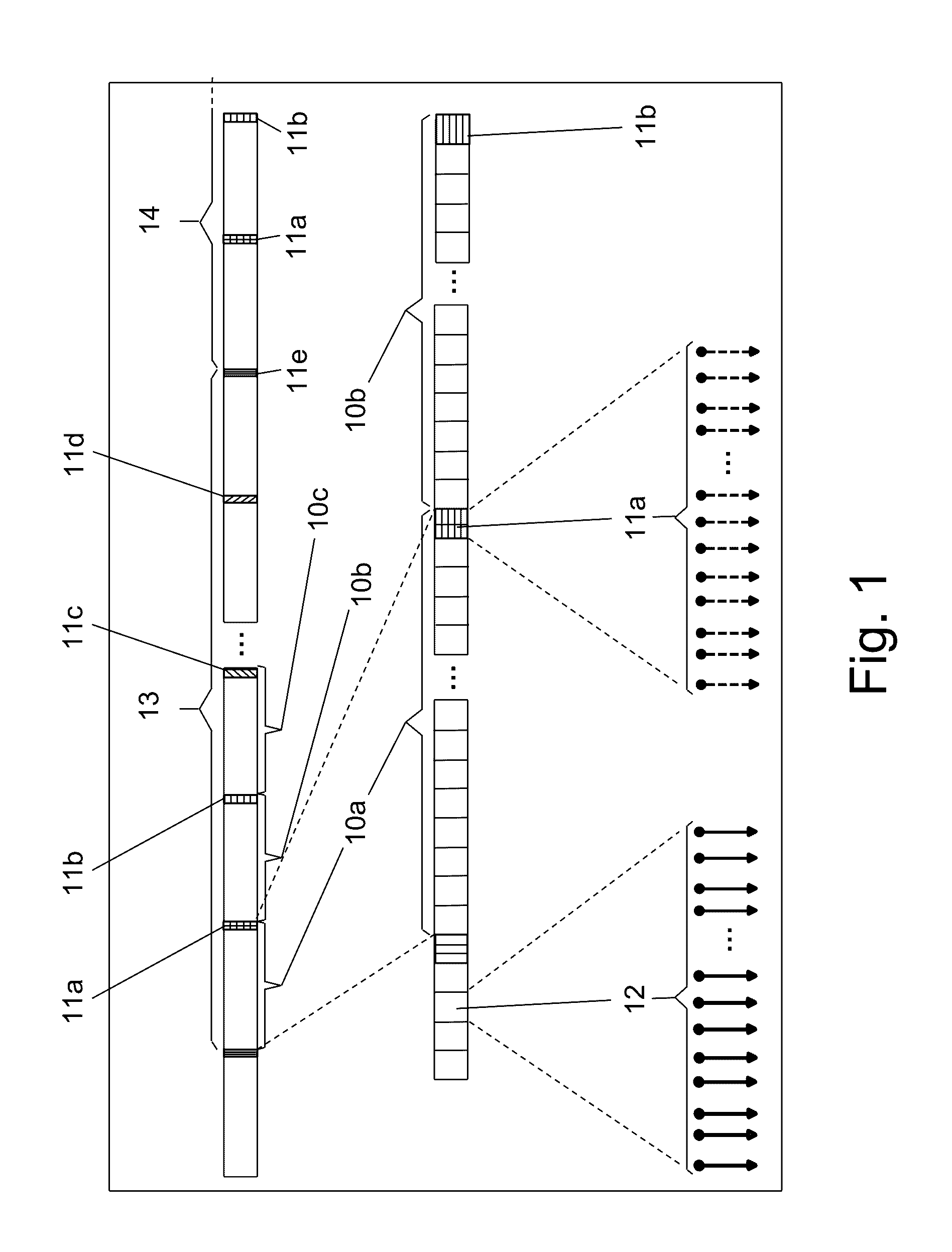
ActiveUS20160359644A1Robustness against pattern depended effects is increasedElectromagnetic network arrangementsDistortion/dispersion eliminationChannel state informationData segment
An optical communication system with nonlinear equalization capability for equalizing distortions of a data communication channel, which comprises a processor for periodically gathering a predetermined number of consecutive data segments from an input data stream to a group and adding a known pilot sequence to the group, thereby forming a data frame; an optical transmitter at the input of the channel, for transmitting the data frames to a receiver, over the channel; a receiver at the output of the channel, for detecting the transmitted frames, the receiver including a demodulator. The demodulator is adapted to recover the pilot sequence of each frame; compare each recovered pilot sequence which its corresponding original transmitted pilot sequence; extract the current Channel State Information indicative of changes in the channel distortion, using the comparison results; use changes in the Channel State Information for updating the coefficients of the estimator and of the equalizer, every time a frame is received; and equalize the channel estimator and of said equalizer, every time a frame is received; and equalize the channel using the equalizer coefficients, and based on the current Channel State Information.
Owner:MULTIPHY
Method and apparatus for complex in-phase/quadrature polyphase nonlinear equalization
ActiveUS8705604B2Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationNonlinear distortionPhase shifted
Complex polyphase nonlinear equalizer (cpNLEQs) mitigate nonlinear distortions generated by complex in-phase / quadrature (I / Q) time-interleaved analog-to-digital converters (TIADCs). Example cpNLEQs upsample the digital waveform emitted by the TIADC, e.g., by a factor of two, then separate the upsampled digital waveform into upsampled in-phase and quadrature components. Processors in the cpNLEQs create real and imaginary nonlinear compensation terms from the upsampled in-phase and quadrature components. The nonlinear compensation terms are downsampled, and the downsampled imaginary nonlinear compensation term is phase-shifted, then combined with the downsampled real component to produce an estimated residual distortion. Subtracting the estimated residual distortion from the digital waveform emitted by the TIADC yields an equalized digital waveform suitable for further processing.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Frequency-domain multi-user access interference cancellation and nonlinear equalization in CDMA receivers
ActiveUS7720134B2Reduce accessImprove performanceModulated-carrier systemsSoil-shifting machines/dredgersInterference cancelationEqualization
A wireless CDMA communication system receiver receives a stream of chips generated by spreading data symbols formed by grouping bits of information at a wireless CDMA communication transmitter which are broadcast at a certain chip-rate. The received chips are de-spread and symbols pertaining to respective users are reconstructed. The stream of chips are formatted into blocks of chips, and an iterative block decision feedback equalization is performed in a frequency domain at the chip-rate of the broadcast stream of chips to remove inter-symbol interference by defining a transfer function. The chips generated are interleaved by spreading each data symbol being transmitted before broadcasting the stream of interleaved chips in distinct blocks of chips.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
De-emphasizing cable equalizer
In accordance with the teachings described herein, an extended equalizer circuit is provided for equalizing a digital communication signal transmitted over a transmission medium that causes a frequency-dependent attenuation of the digital communication signal. An equalizer may be used that includes a linear equalization circuit and a non-linear equalization circuit, the linear equalization circuit being configured to apply a linear filter to the digital communication signal to compensate for the frequency-dependent attenuation caused by a first portion of the transmission medium, and the non-linear equalization circuit being configured to apply one or more non-linear operations to the digital communication signal. A de-emphasizing equalizer circuit may be coupled in series between the transmission medium and the equalizer and configured to apply an additional linear filter to the digital communication signal in order to compensate for the frequency-dependent attenuation caused by a second portion of the transmission medium.
Owner:SEMTECH CANADA
Receiver for optical communications, comprising a nonlinear equaliser
Owner:UNIV POLITECNICA DE CATALUNYA
Optical communication channel equalization using a kernel
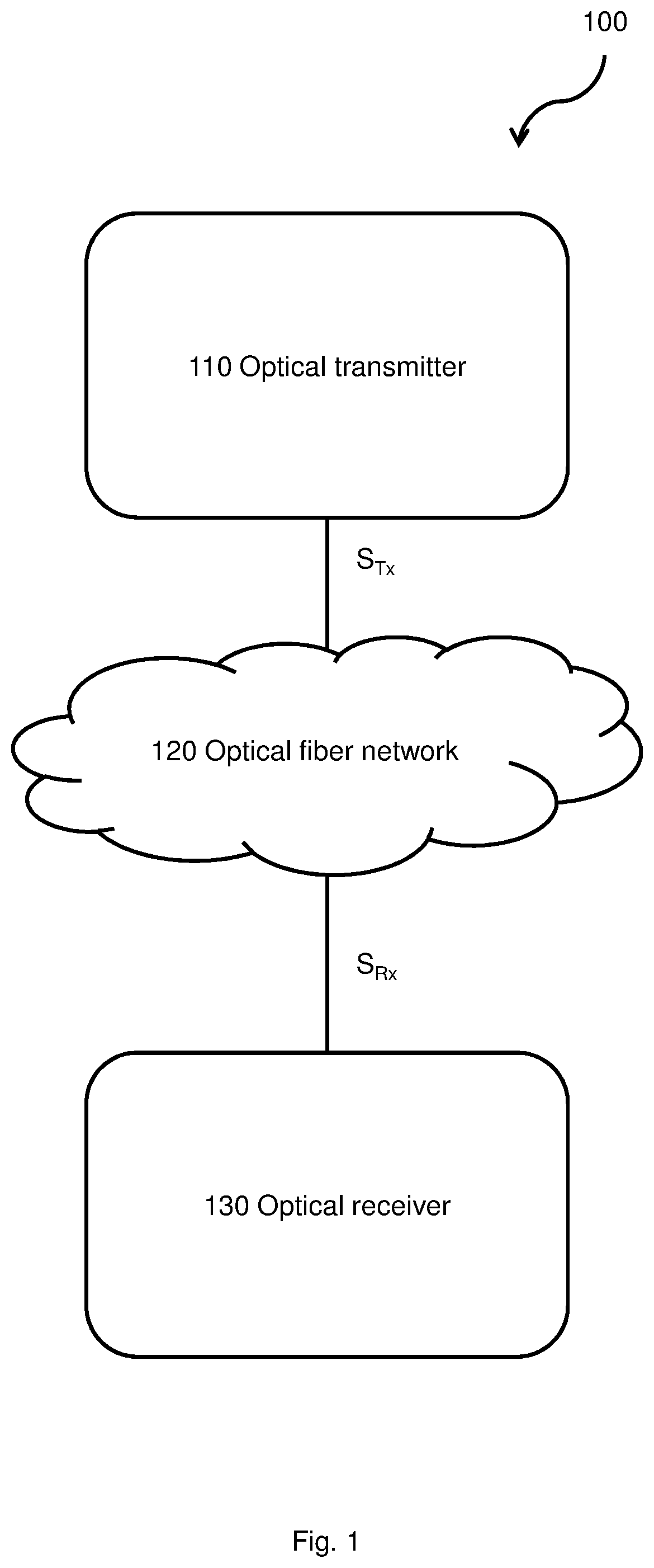
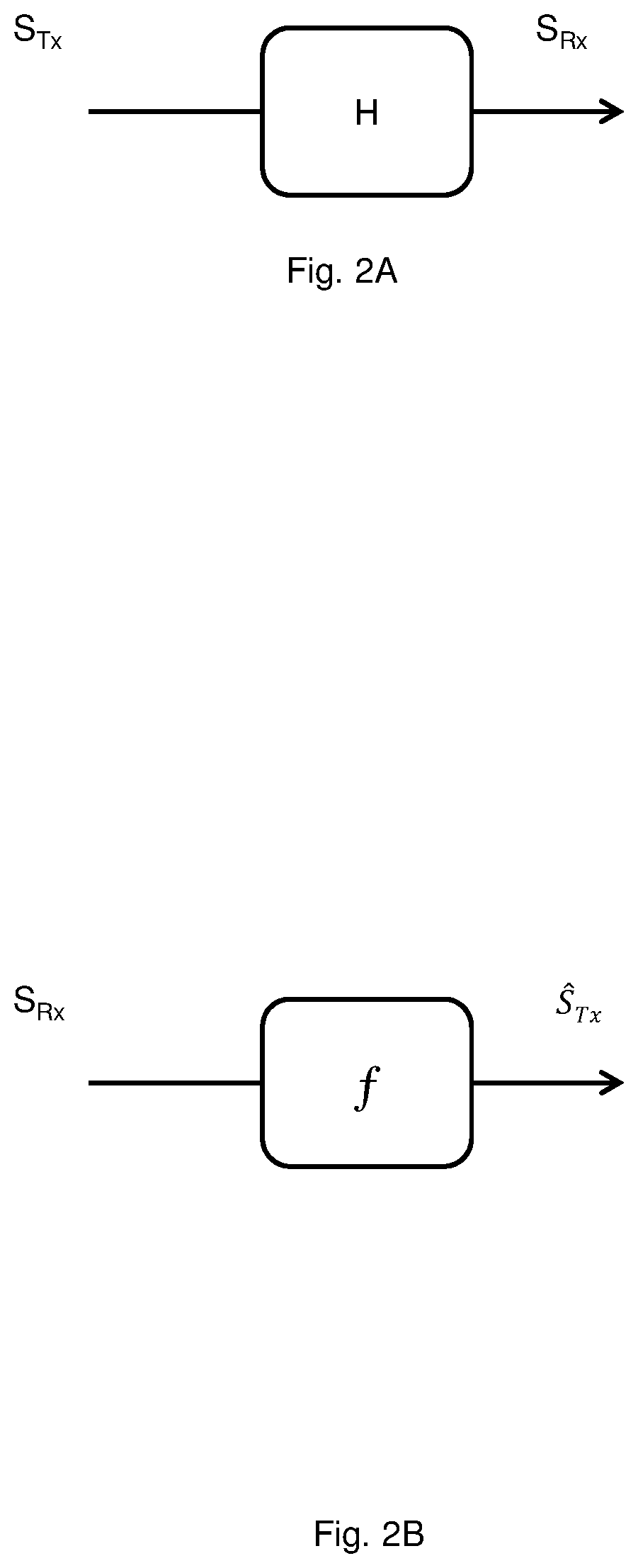
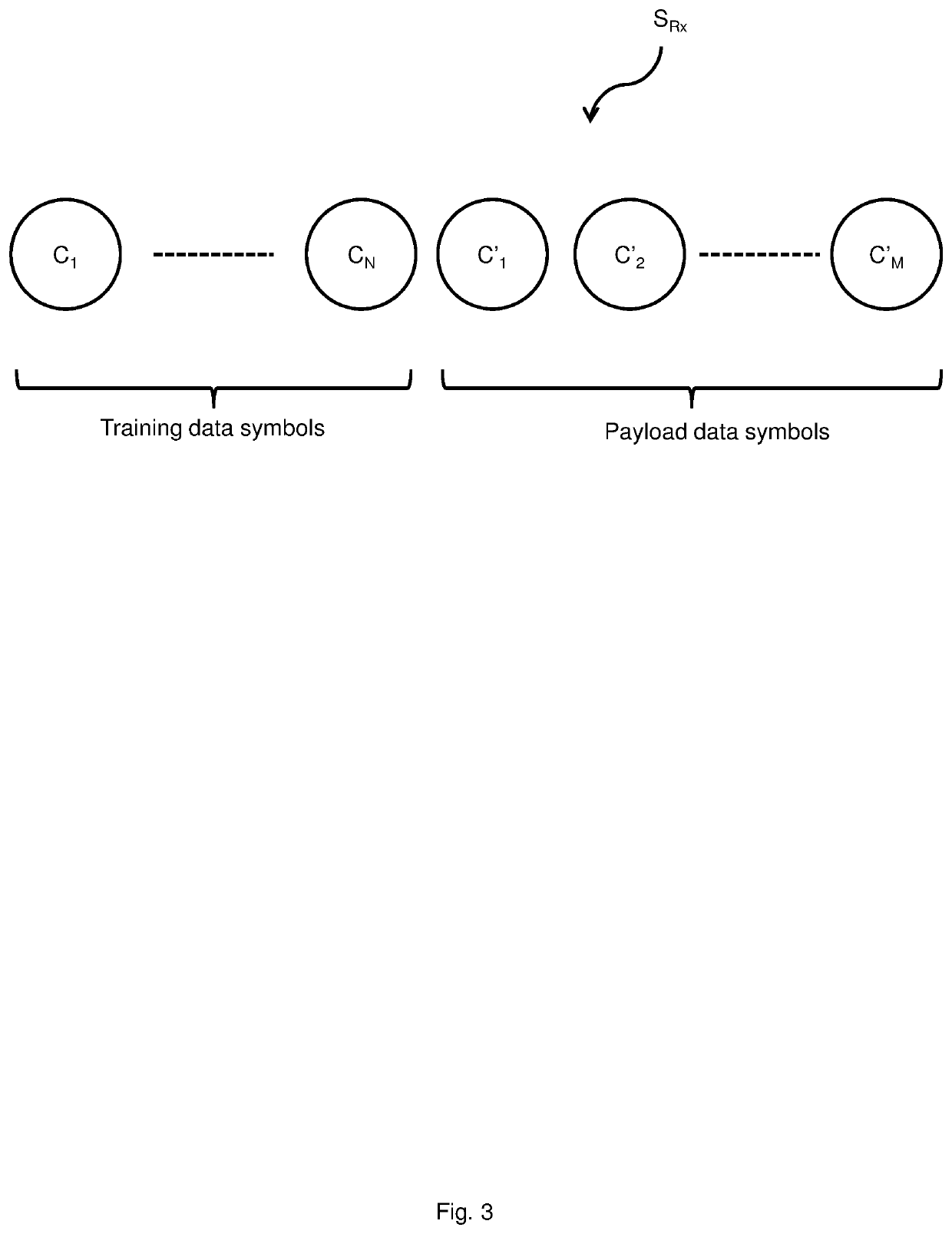
InactiveUS20200028593A1Mitigates and solves drawbackMitigates and solves and problemElectromagnetic receiversAlgorithmSymbol mapping
The disclosure relates to a method performed by an optical receiver, the method comprising receiving an optical communication signal comprised in a signal space, the signal comprising a set of received training symbols and a set of received payload symbols, determining a kernel operating in a feature space by using the set of training symbols and a reference set of training symbols indicative of an undistorted version of the training symbols, wherein determining a kernel further comprises determining at least an equalization mapping function ƒ configured to map received symbols to channel equalized symbols, and determining an error function (e) configured to generate a measure indicative of an error between symbols mapped by the equalization mapping function ƒ and an ideal equalization mapping function, performing nonlinear equalization of the payload symbols (C′1 to C′M) by performing linear equalization of the payload symbols (C′1 to C′M) in the feature space using the received training symbols (C1 to CN) and the error function (e). The disclosure further relates to an optical receiver
Owner:CHEN JIAJIA +1
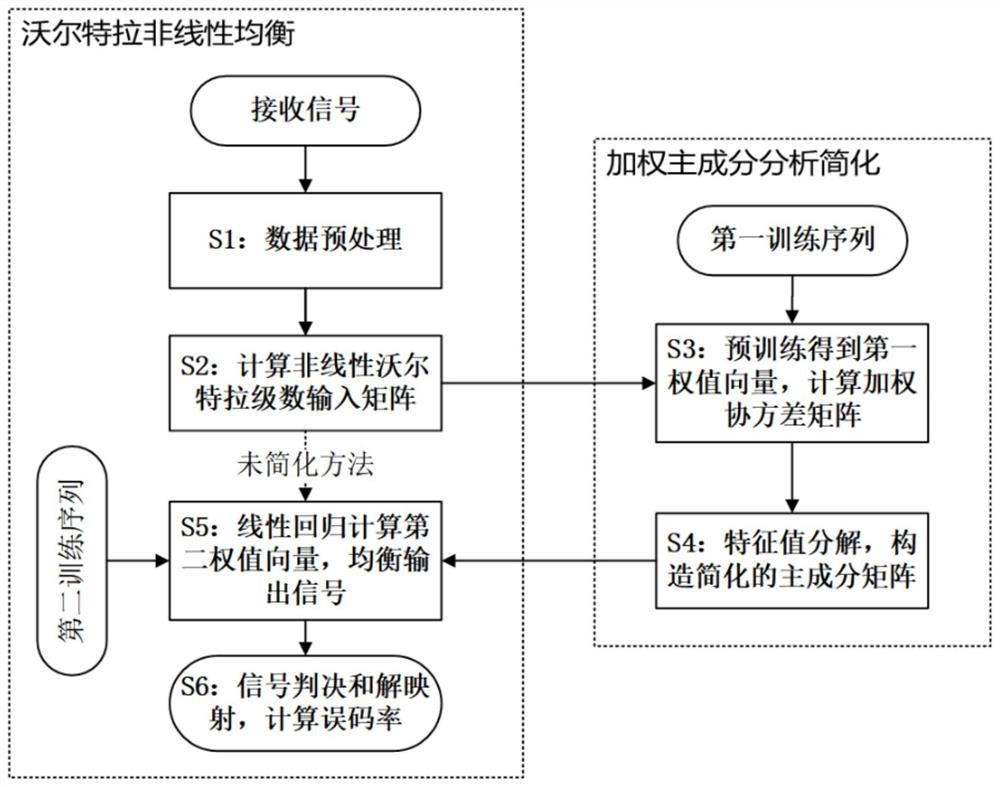
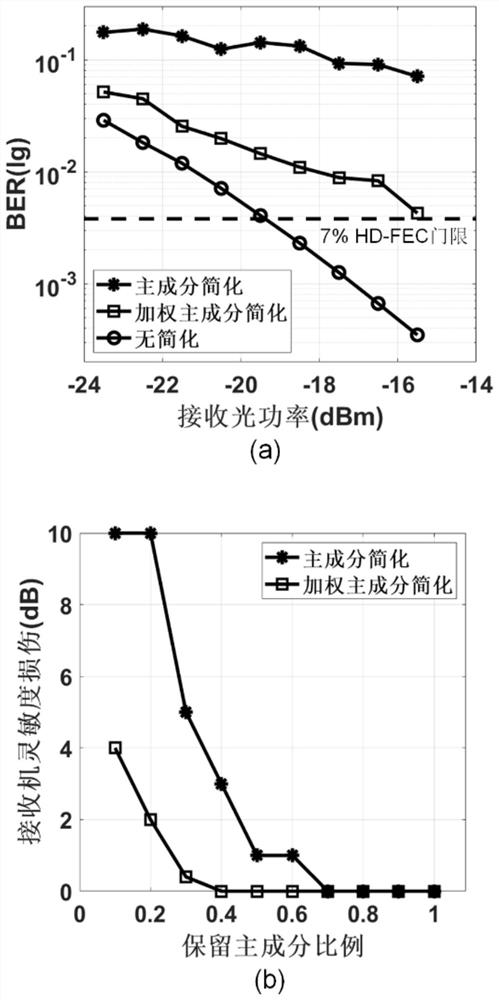
Nonlinear equalization method based on weighted principal component analysis
ActiveCN112613538AAdd effective balance informationAvoid performance degradationCharacter and pattern recognitionFibre transmissionHat matrixMaximum eigenvalue
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Receiver For Optical Communications, Comprising a Nonlinear Equaliser
InactiveUS20080159757A1Enhanced advantageMitigate and eliminate negative effectElectromagnetic receiversOptical communicationQuadratic nonlinearity
The present development includes a first element of an optical fibre entrance by which an information carrying signal is transmitted, an optical detector block, a non-linear equalizer block and a final processor block. The development includes an electrical non-linear equalizer block, connecting the output of the optical detector block and the input of the final processor block that compensates the quadratic non-linear characteristic of the optical detector block. Both blocks thus may present a more linear joint characteristic between the electrical field envelope of the information carrying signal in the optical fibre and the electrical signal. Consequently, the final processor block can compensate, in a more effective form, for the linear distortions that the information carrying signal suffers in the transmission through the fibre. The result may be an optical receiver with non-linear compensation of the photo-detection process and with approximate linear compensation of the linear distortions of the optical fibre transmission.
Owner:UNIV POLITECNICA DE CATALUNYA
Visible light communication equalization method and system based on sparse Bayesian learning
ActiveCN111525955AImprove transmission performanceImprove noise immunityCharacter and pattern recognitionClose-range type systemsPattern recognitionAlgorithm
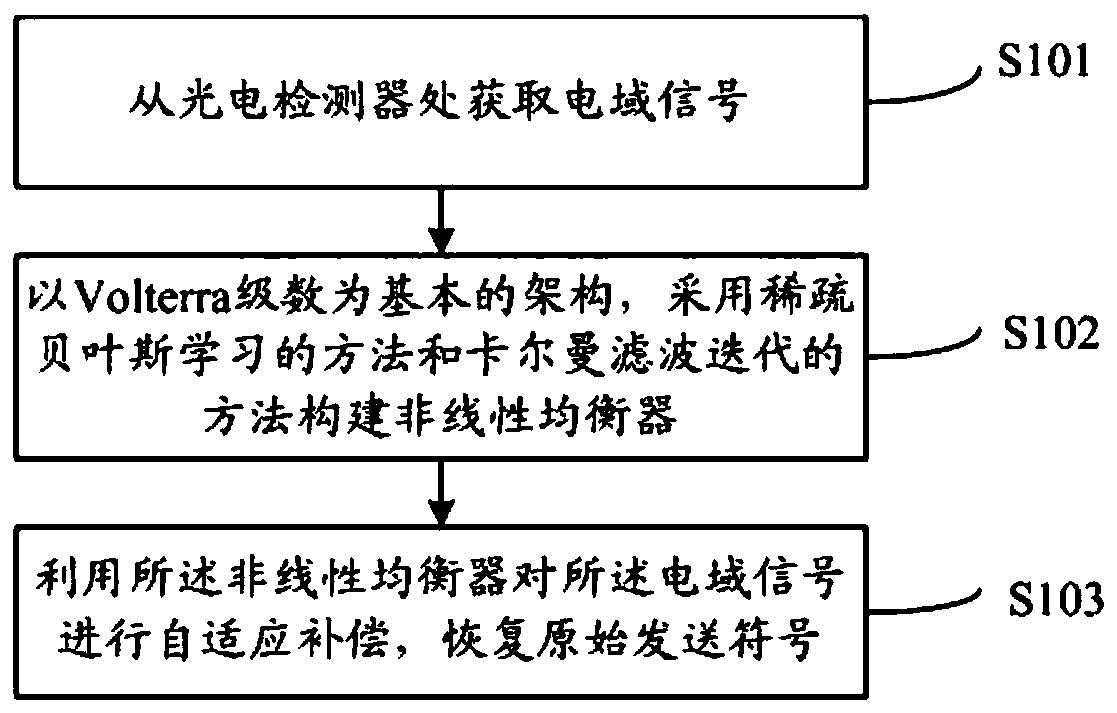
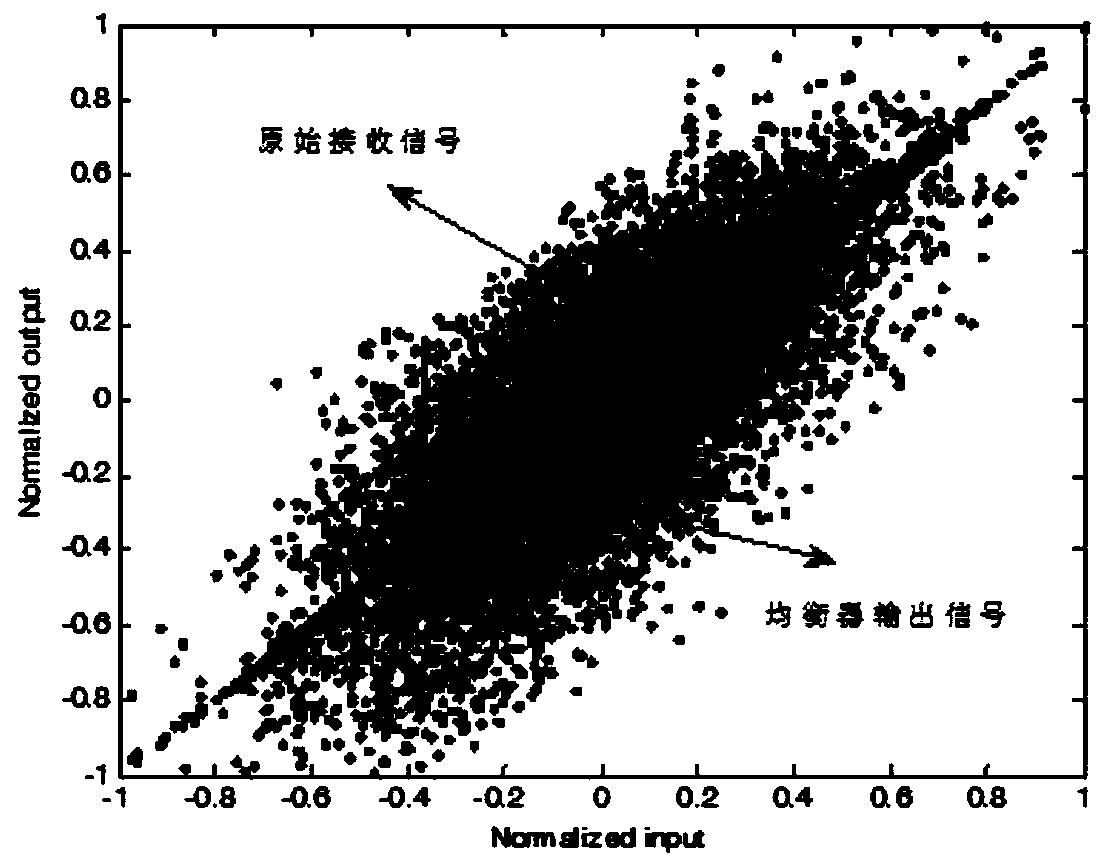
The invention relates to a visible light communication equalization method and system based on sparse Bayesian learning. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an electric domain signal from a photoelectric detector; constructing a nonlinear equalizer by taking Volterra series as a basic framework and adopting a sparse Bayesian learning method and a Kalman filtering iteration method;performing adaptive compensation on the electric domain signal by using the nonlinear equalizer, and recovering an original sending symbol. According to the visible light communication equalization method and system based on sparse Bayesian learning provided by the invention, the adaptive compensation of complex dynamic nonlinearity and multipath transmission damage of a VLC system can be realized, and the communication performance of the VLC system is improved.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
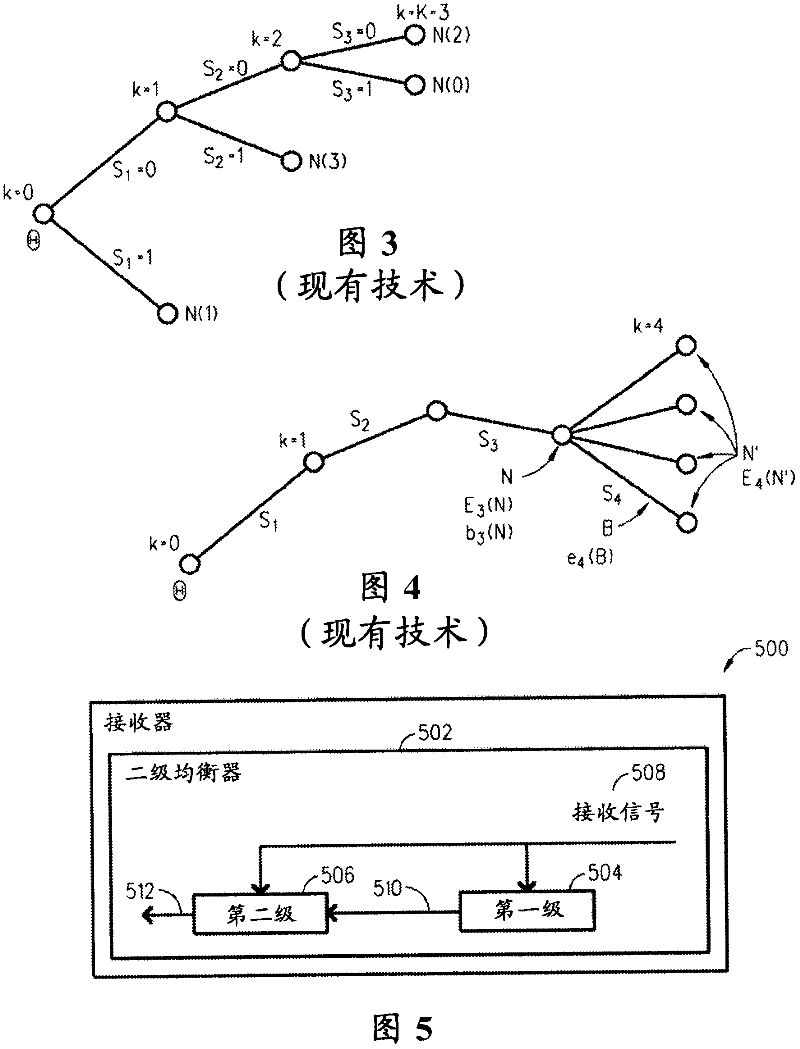
Receiver and method for two-stage equalization with sequential tree search
A receiver (500) and a method are described herein that address inter-symbol interference in a received signal (508) by using a two-stage equalizer (502) which includes a first demodulation stage (504) that processes the received signal and produces initial symbol decisions (510), and a non-linear equalization second stage (506) that uses the received signal to perform a sequential search in an attempt to improve upon the initial symbol decisions; wherein, if able to improve upon the initial symbol decisions then an output sequence (512) is obtained from the sequential search and if not able to improve upon the sequence metric threshold then the output sequence is the initial symbol decisions.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Framing scheme for continuous optical transmission systems
ActiveUS9716603B2Robustness against pattern depended effects is increasedElectromagnetic network arrangementsDistortion/dispersion eliminationChannel state informationData segment
An optical communication system with nonlinear equalization capability for equalizing distortions of a data communication channel, which comprises a processor for periodically gathering a predetermined number of consecutive data segments from an input data stream to a group and adding a known pilot sequence to the group, thereby forming a data frame; an optical transmitter at the input of the channel, for transmitting the data frames to a receiver, over the channel; a receiver at the output of the channel, for detecting the transmitted frames, the receiver including a demodulator. The demodulator is adapted to recover the pilot sequence of each frame; compare each recovered pilot sequence which its corresponding original transmitted pilot sequence; extract the current Channel State Information indicative of changes in the channel distortion, using the comparison results; use changes in the Channel State Information for updating the coefficients of the estimator and of the equalizer, every time a frame is received; and equalize the channel estimator and of said equalizer, every time a frame is received; and equalize the channel using the equalizer coefficients, and based on the current Channel State Information.
Owner:MULTIPHY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com