Nonlinear equalization method based on weighted principal component analysis
A technique of weighted principal components and equalization method, applied in the fields of instruments, optical fiber transmission, computing, etc., which can solve the surge in the number of Volterra second-order and third-order expansion terms, the inability to improve the transmission capacity of communication systems, and the inability to deploy short-range receivers, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of convergence, facilitate real-time processing, and increase complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
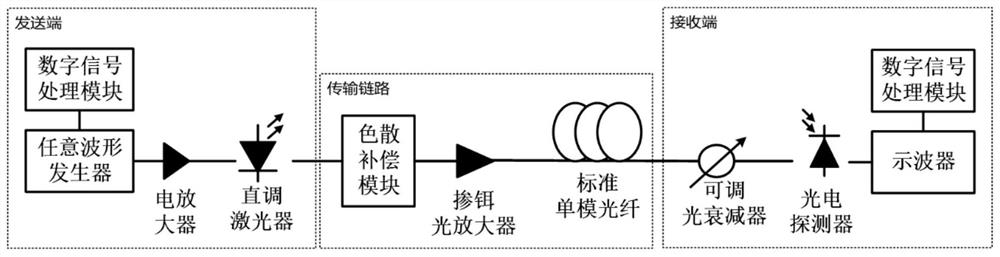
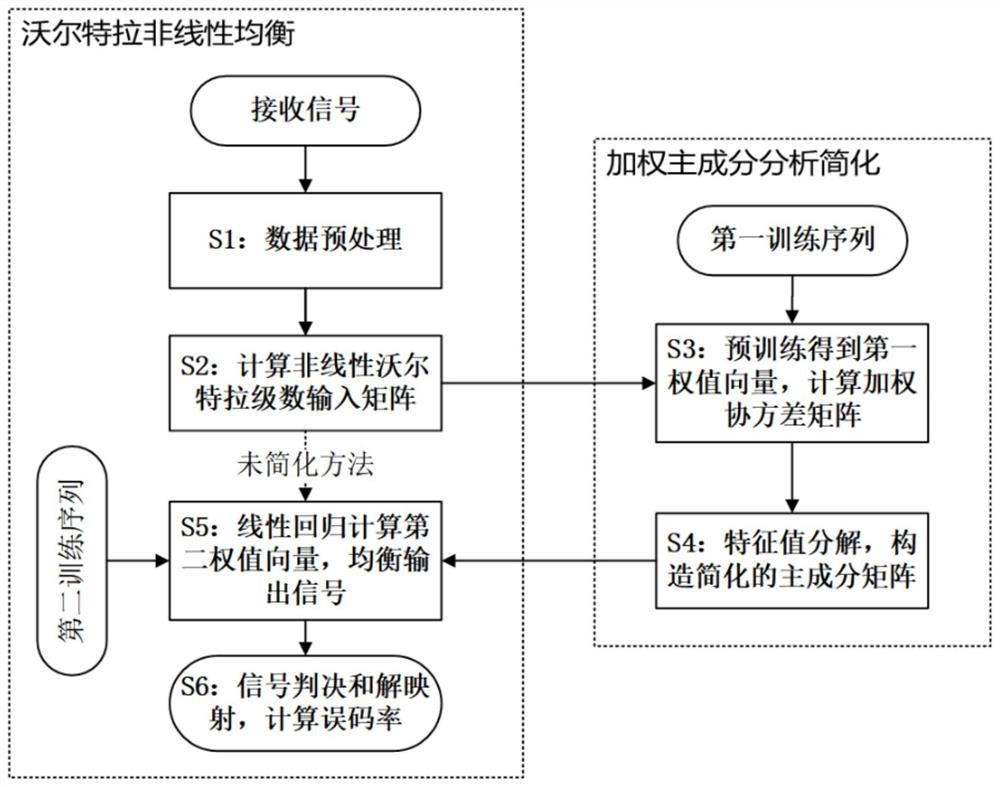
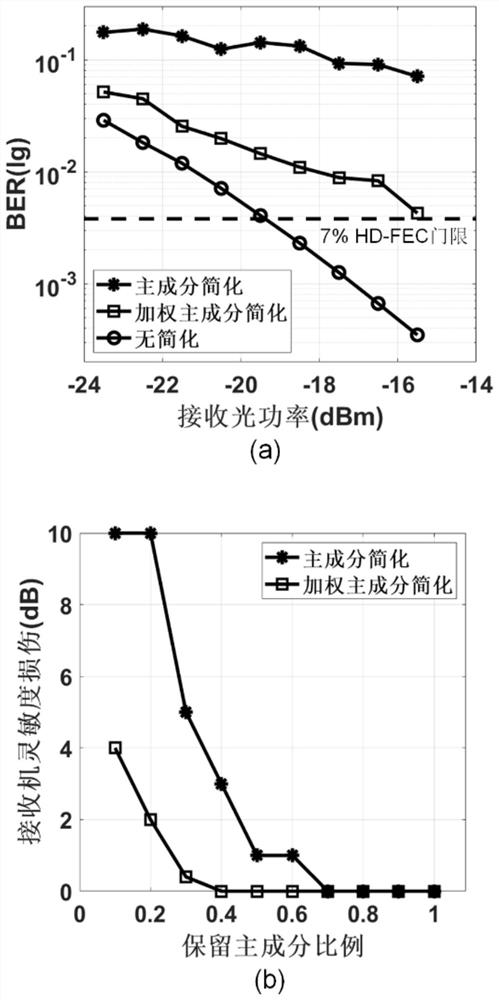
[0051] A nonlinear equalization method based on weighted principal component analysis for compensating channel impairments at the receiving end of fiber optic communication systems, such as figure 2 As shown, the method includes: a nonlinear mapping step, a principal component projection step and a nonlinear equalization step;
[0052] Such as figure 2 As shown, the nonlinear mapping steps specifically include:
[0053] S1: Data preprocessing: downsampling and amplitude normalization of the sequence to be processed;
[0054] As a preferred implementation, in this embodiment, in the nonlinear mapping step, after downsampling the sequence to be processed, the sampling rate of the sequence to be processed is the same as the sampling rate of the transmitted signal;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com