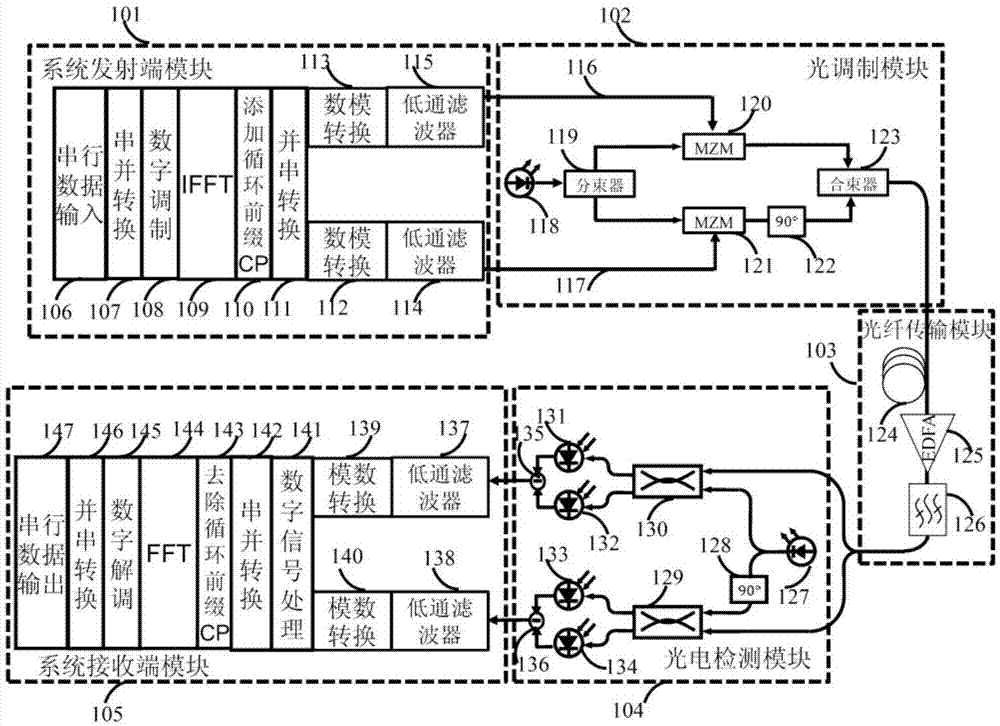
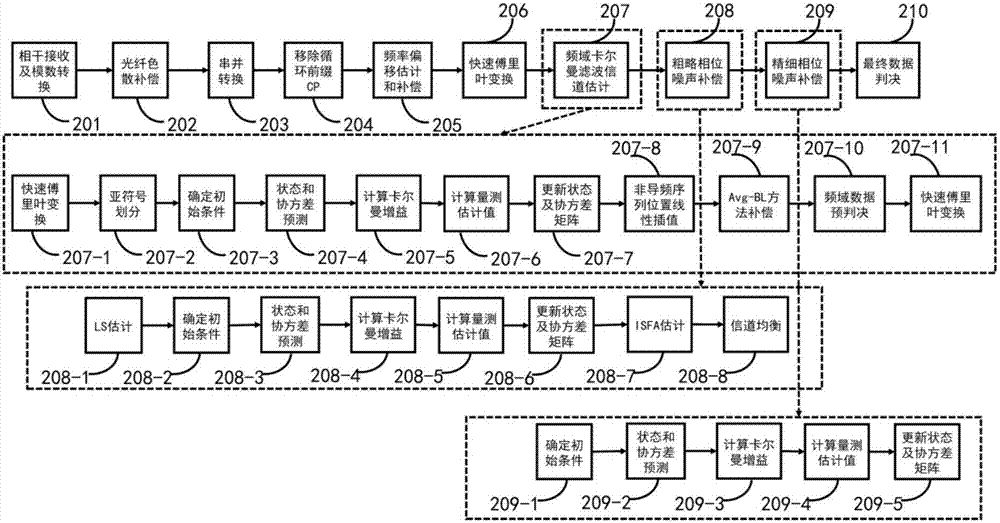
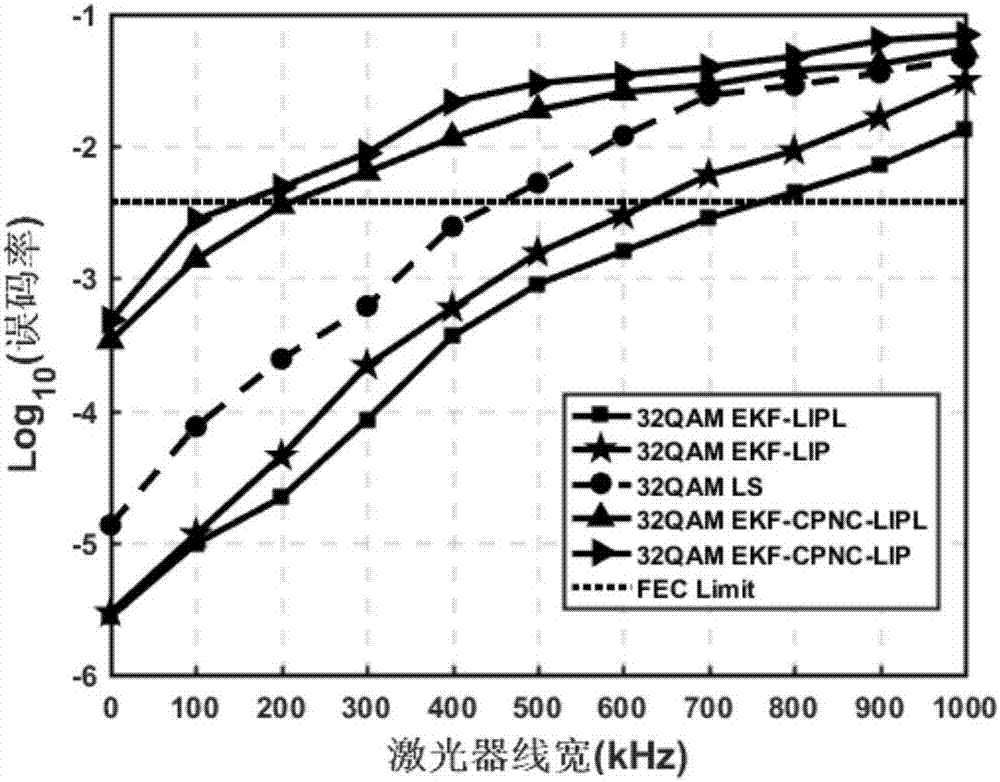
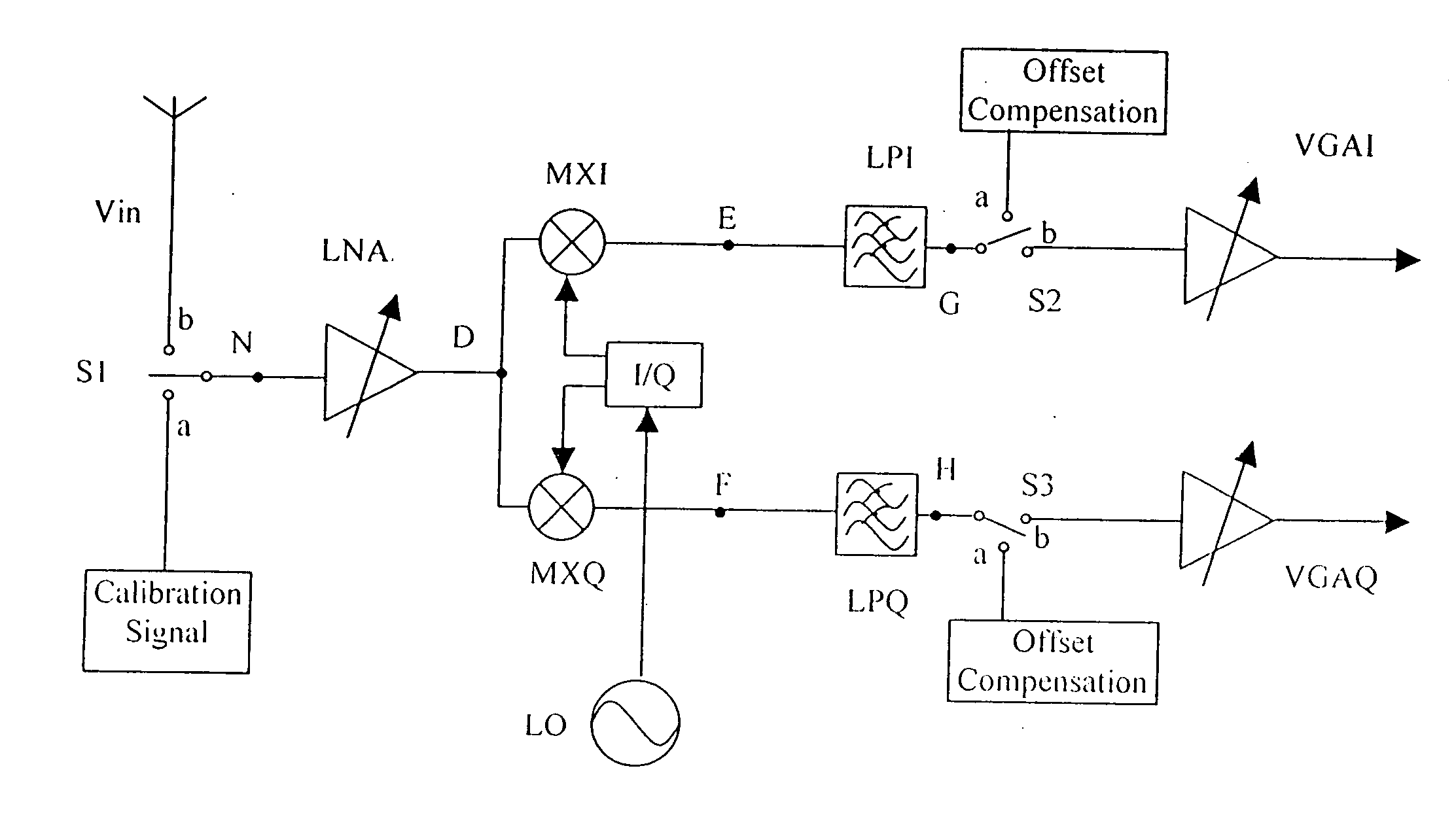
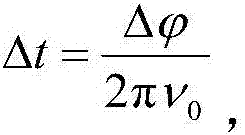Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
280 results about "Noise compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
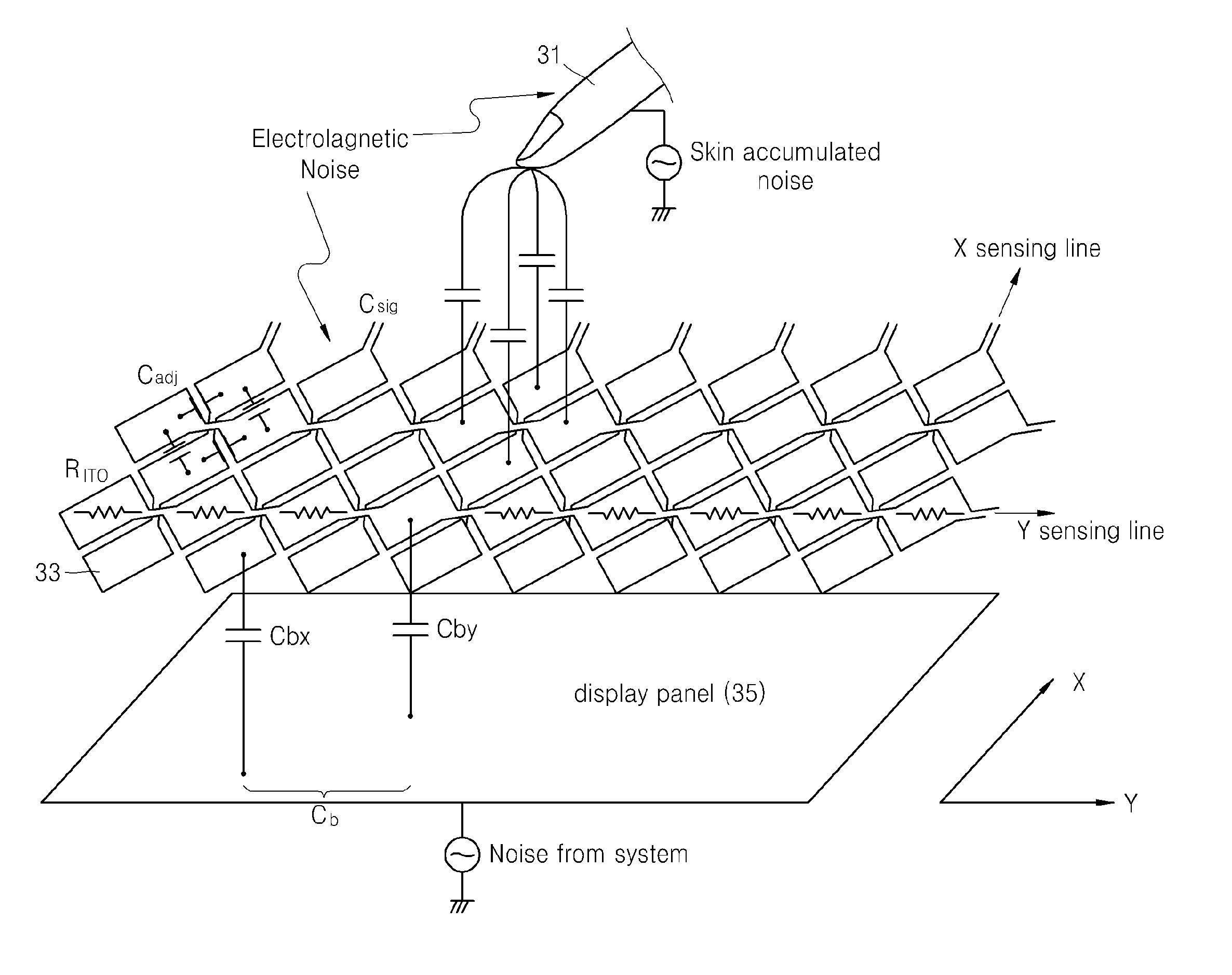
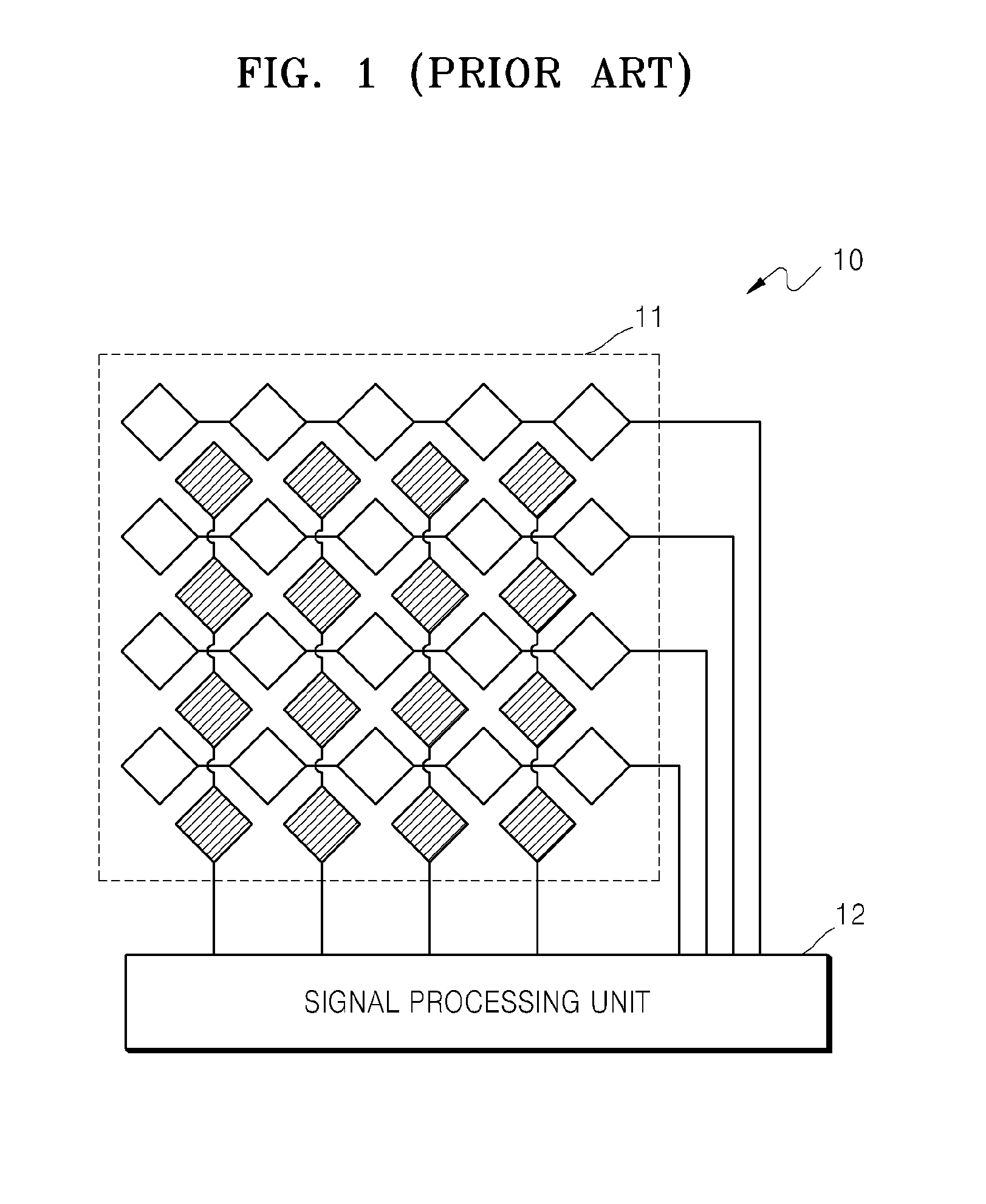
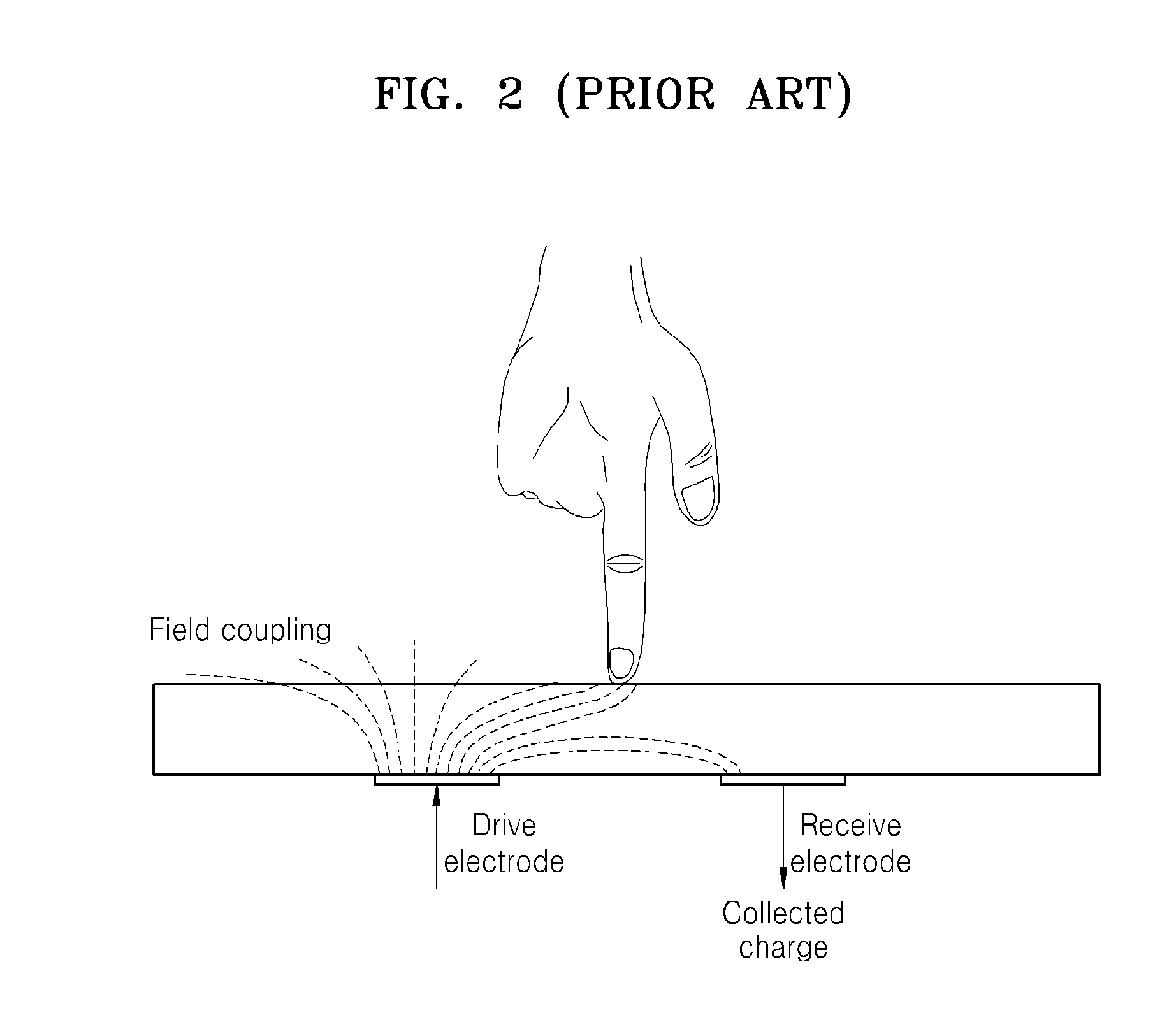
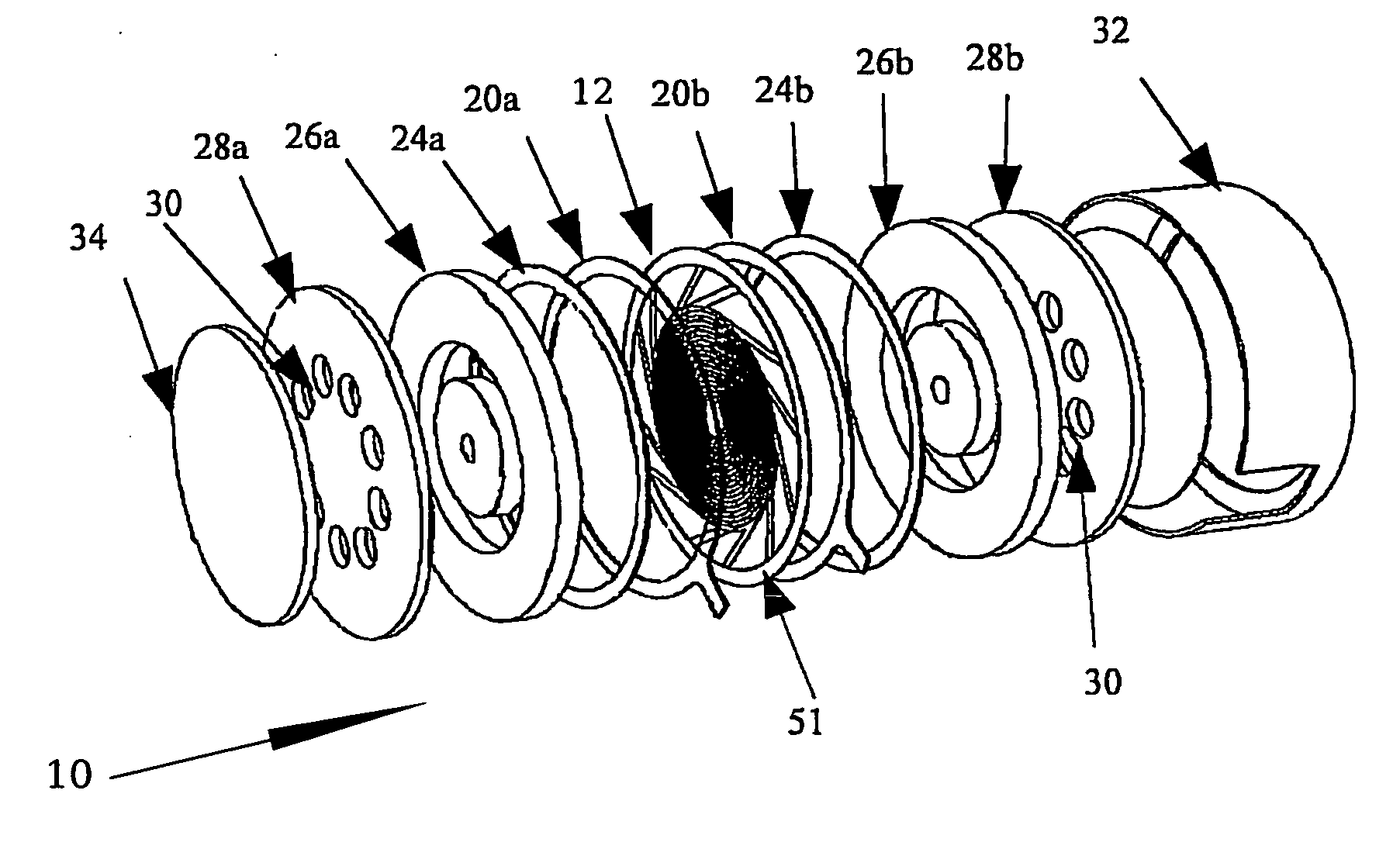
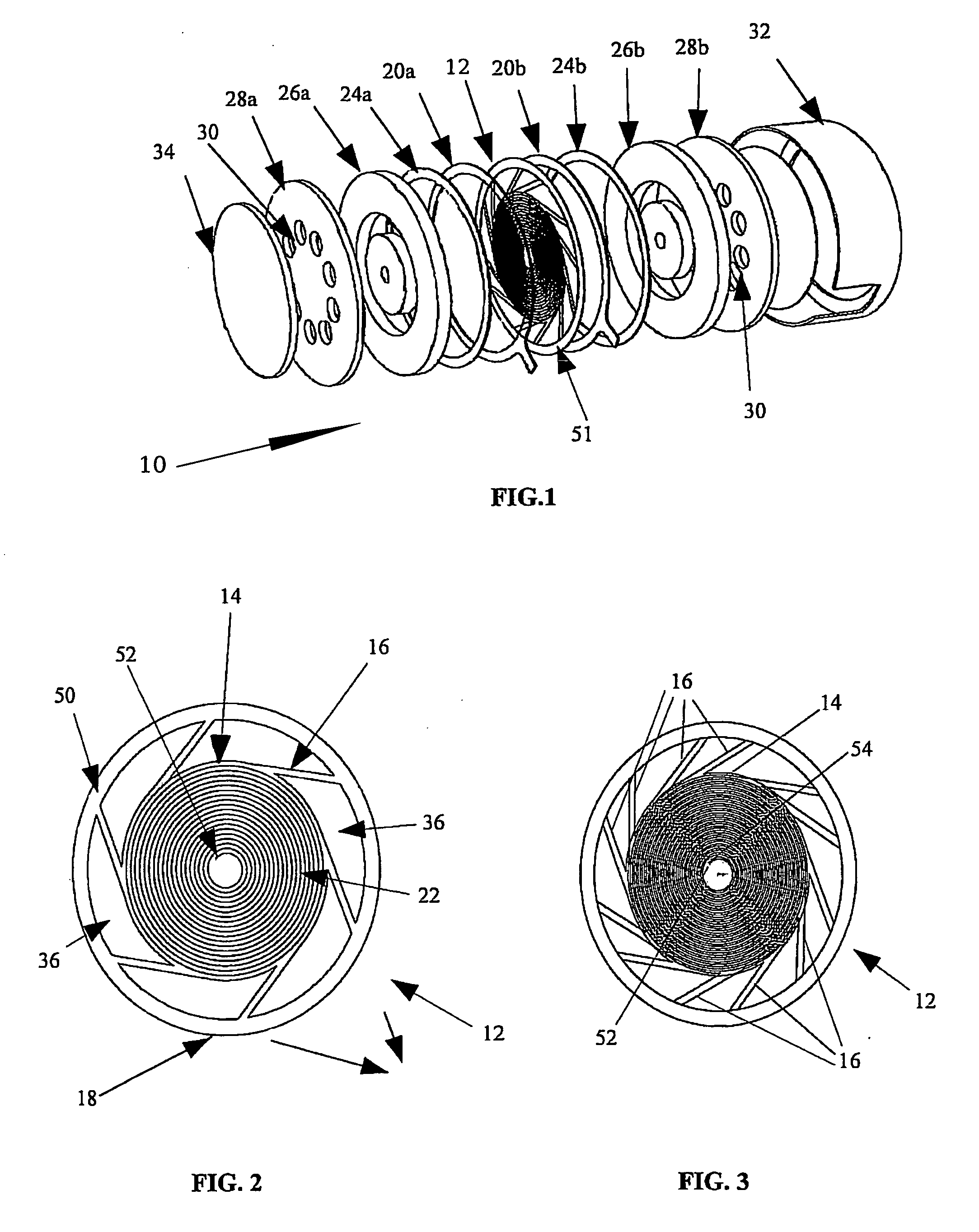
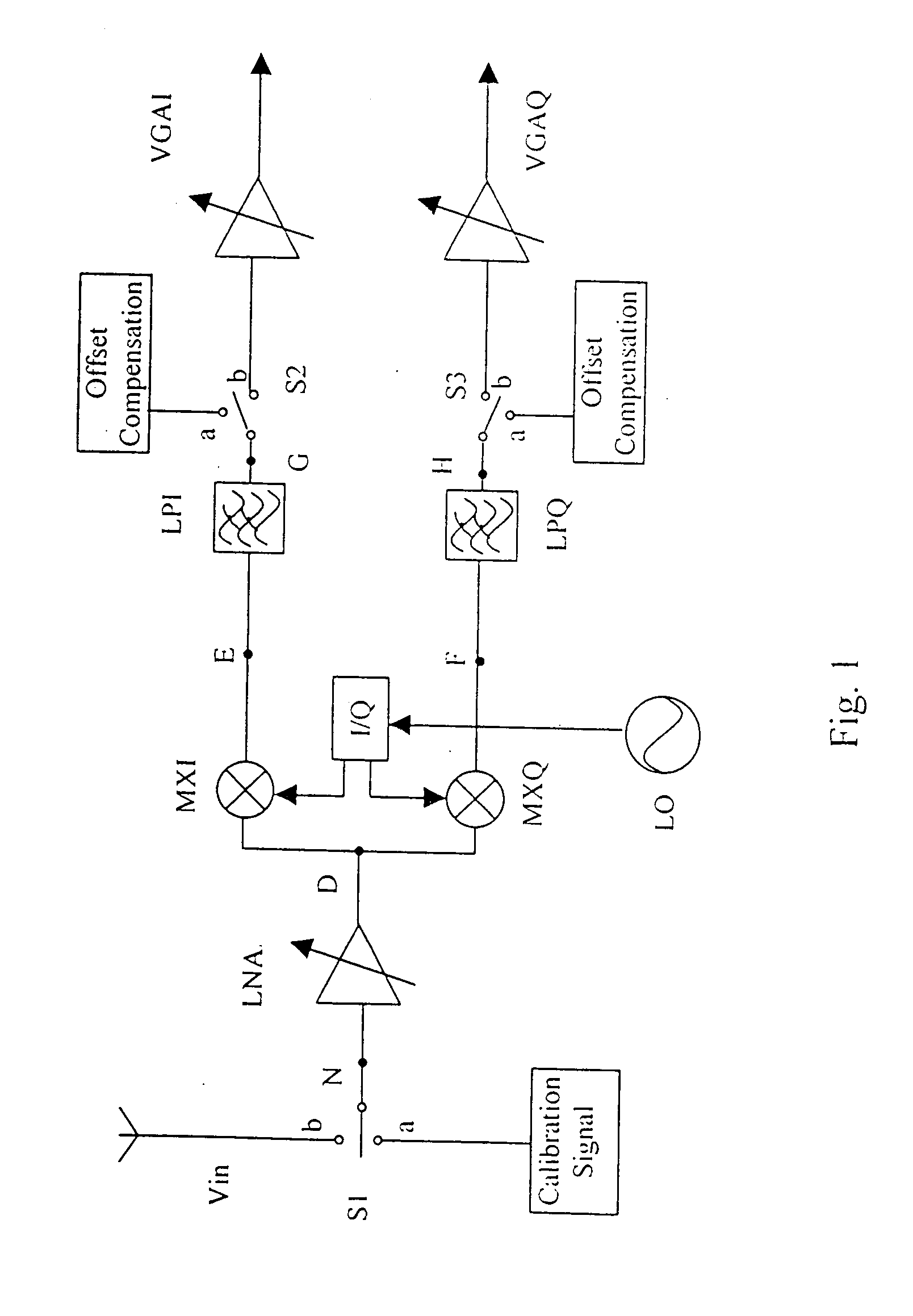
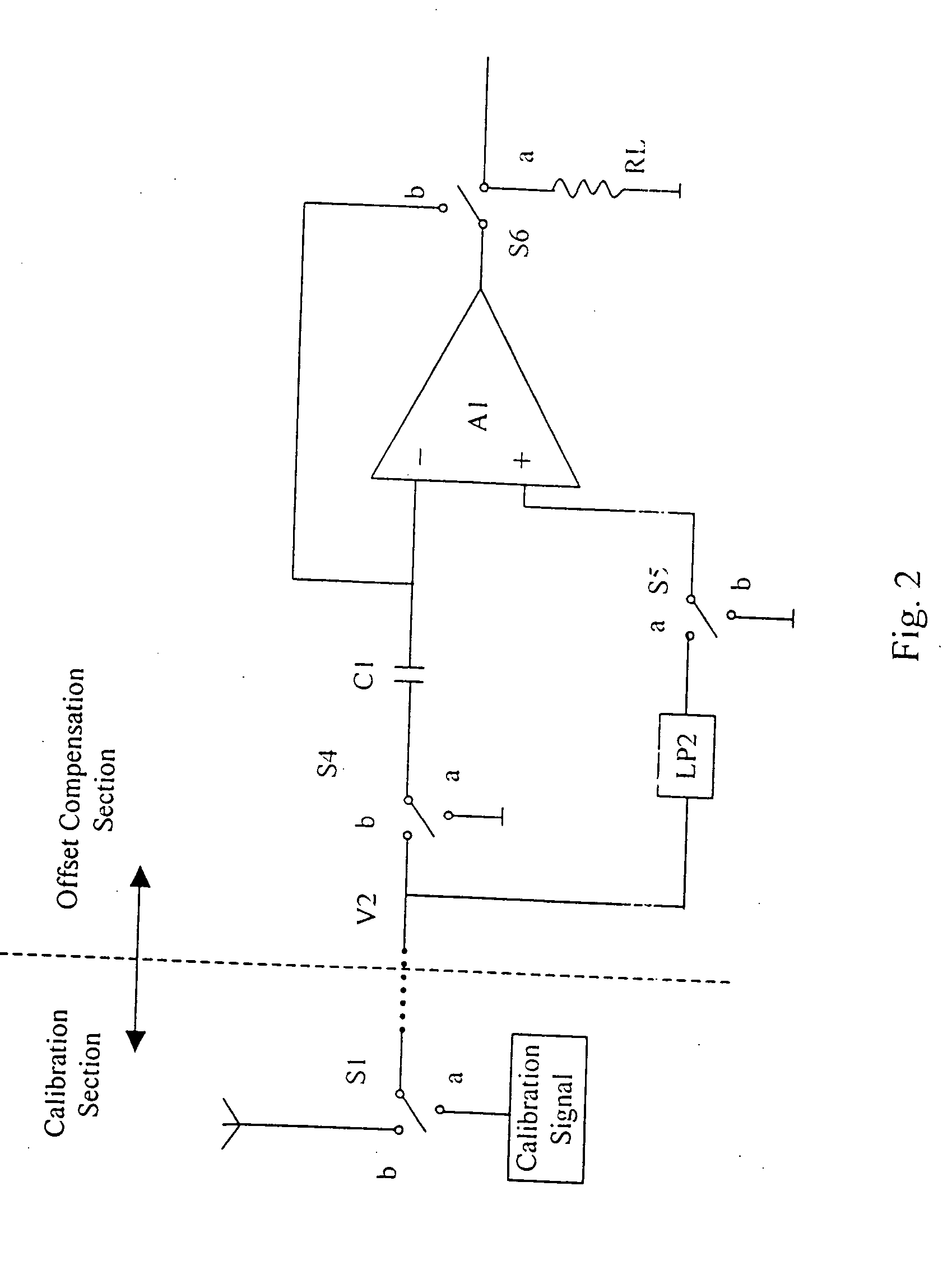
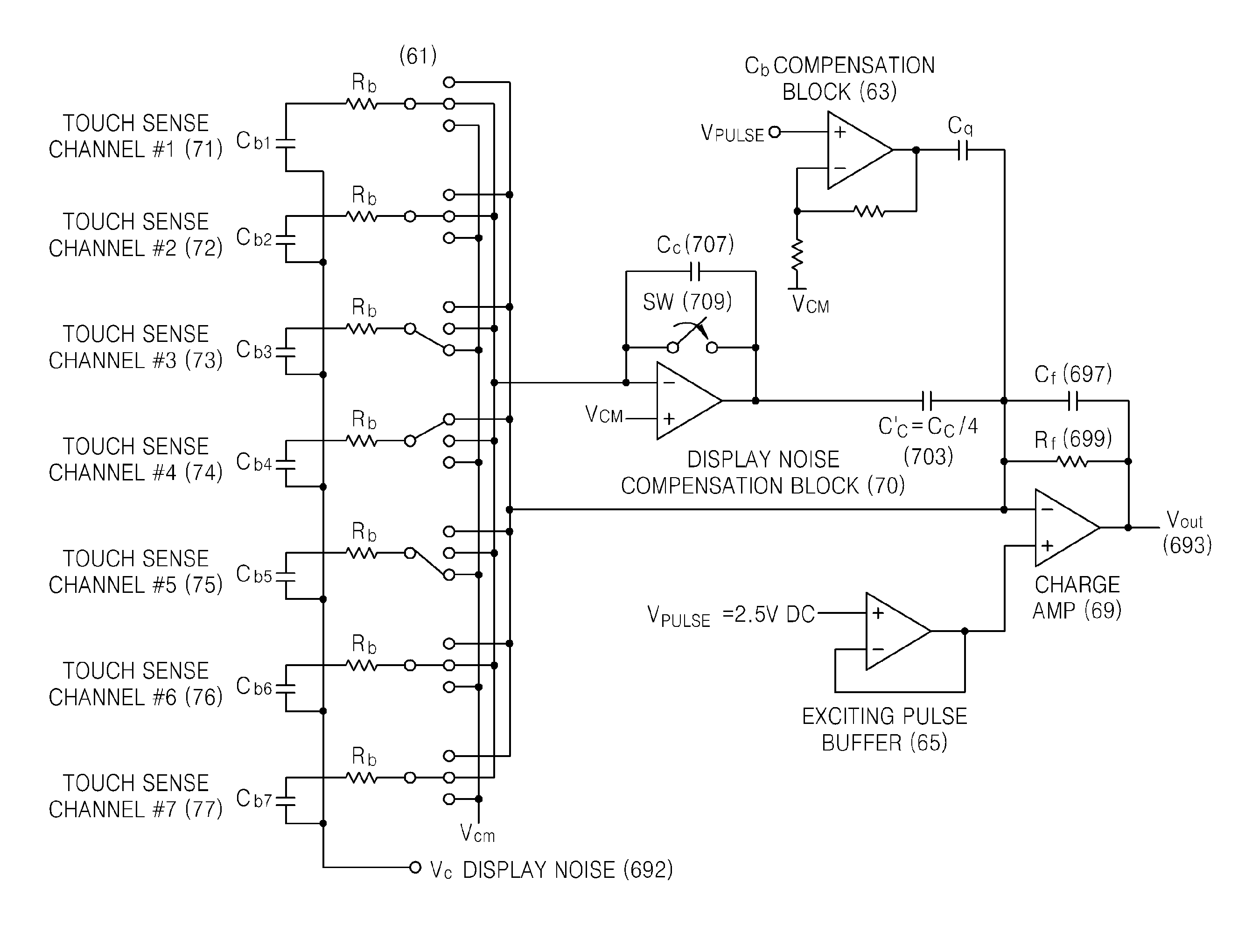
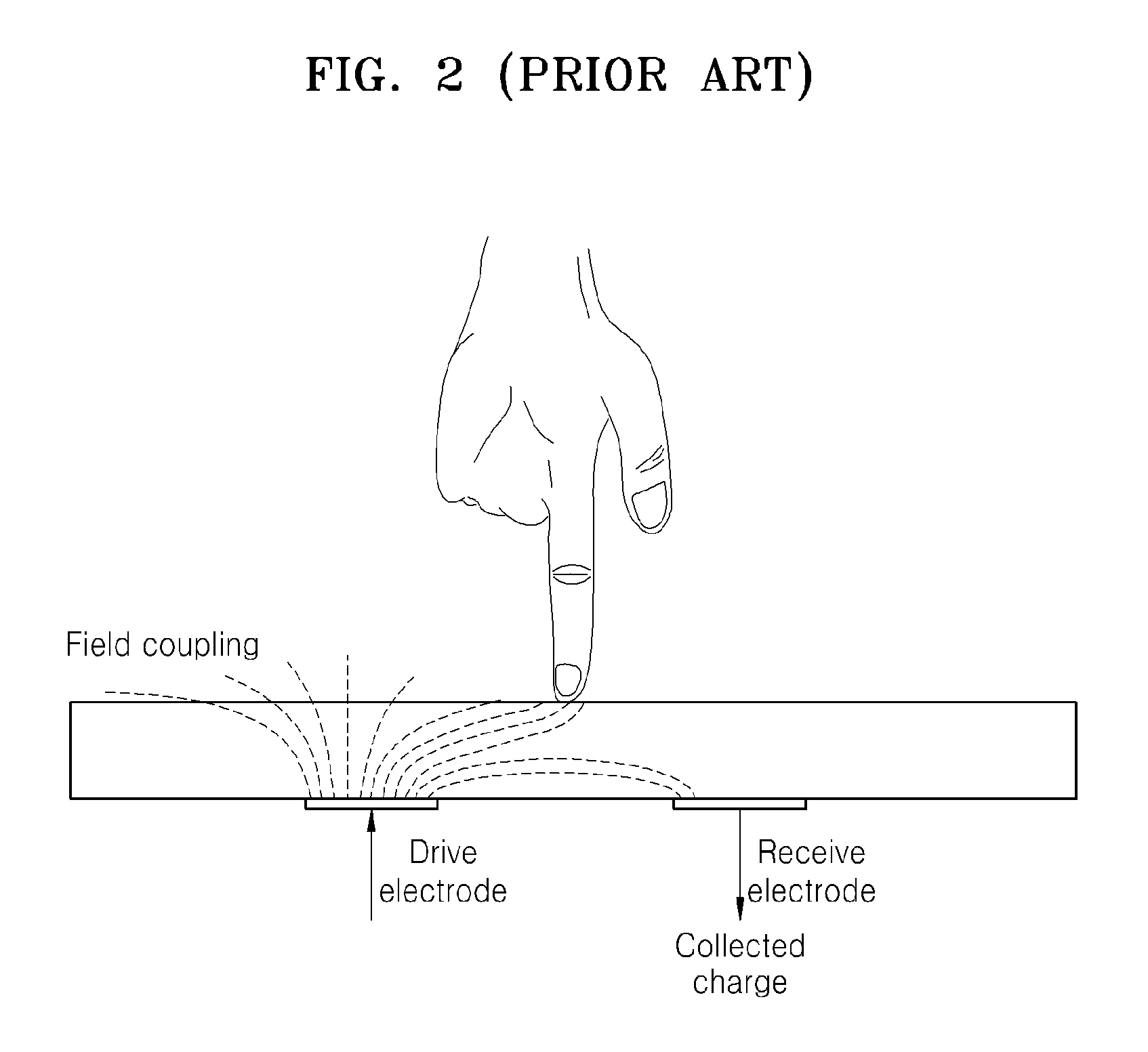
Method and apparatus compensating noise in touch panel
ActiveUS20110193817A1Reduce the impactReduce impactInput/output processes for data processingParasitic capacitanceTouchscreen
Touch screen systems and method of compensating noise in same are presented. One touch screen system includes; a touch screen panel having sense channels providing a sense output corresponding to a capacitance variation associated with an applied touch input as detected by one or more sensing units connected to the sense channels. A parasitic capacitance is accumulated in the sense channels as the touch input is applied. The touch screen system also includes a touch controller receiving the sense output and including; a noise compensation block configured to generate a compensation capacitance to compensate for the parasitic capacitance and provide a compensation output, and a signal conversion unit that receives the sense output and the compensation output and generates a noise compensated sense output.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
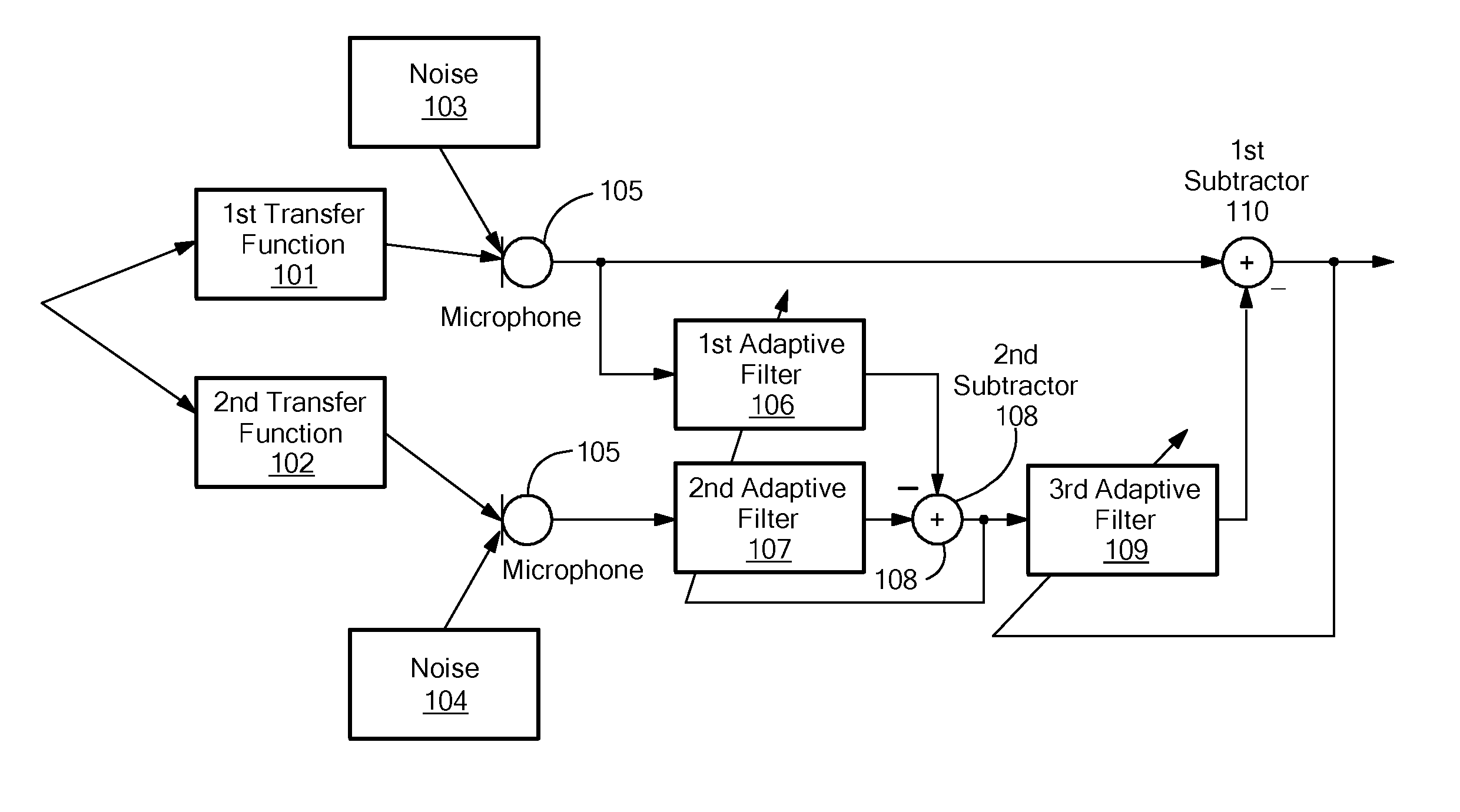
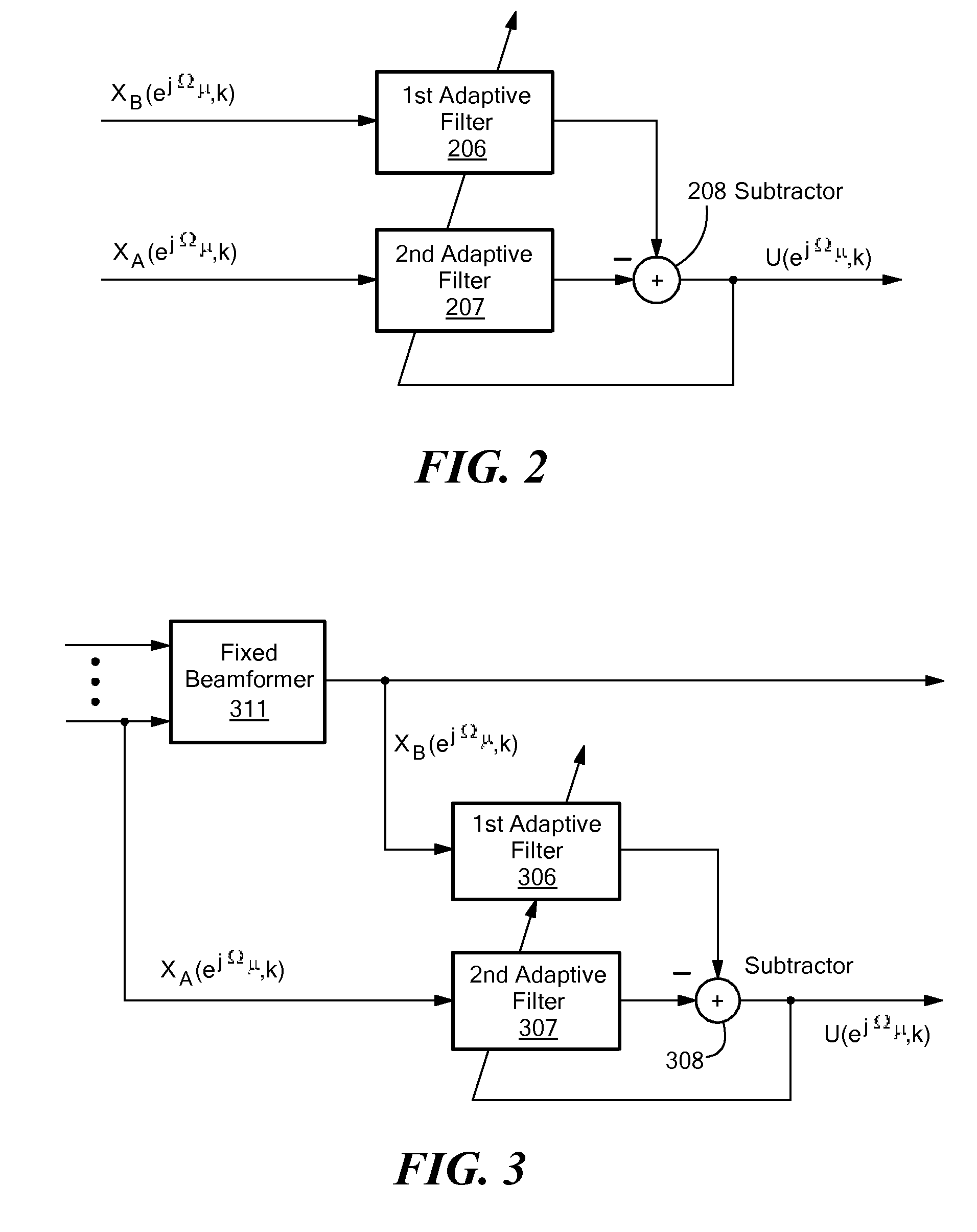
Method for determining a noise reference signal for noise compensation and/or noise reduction
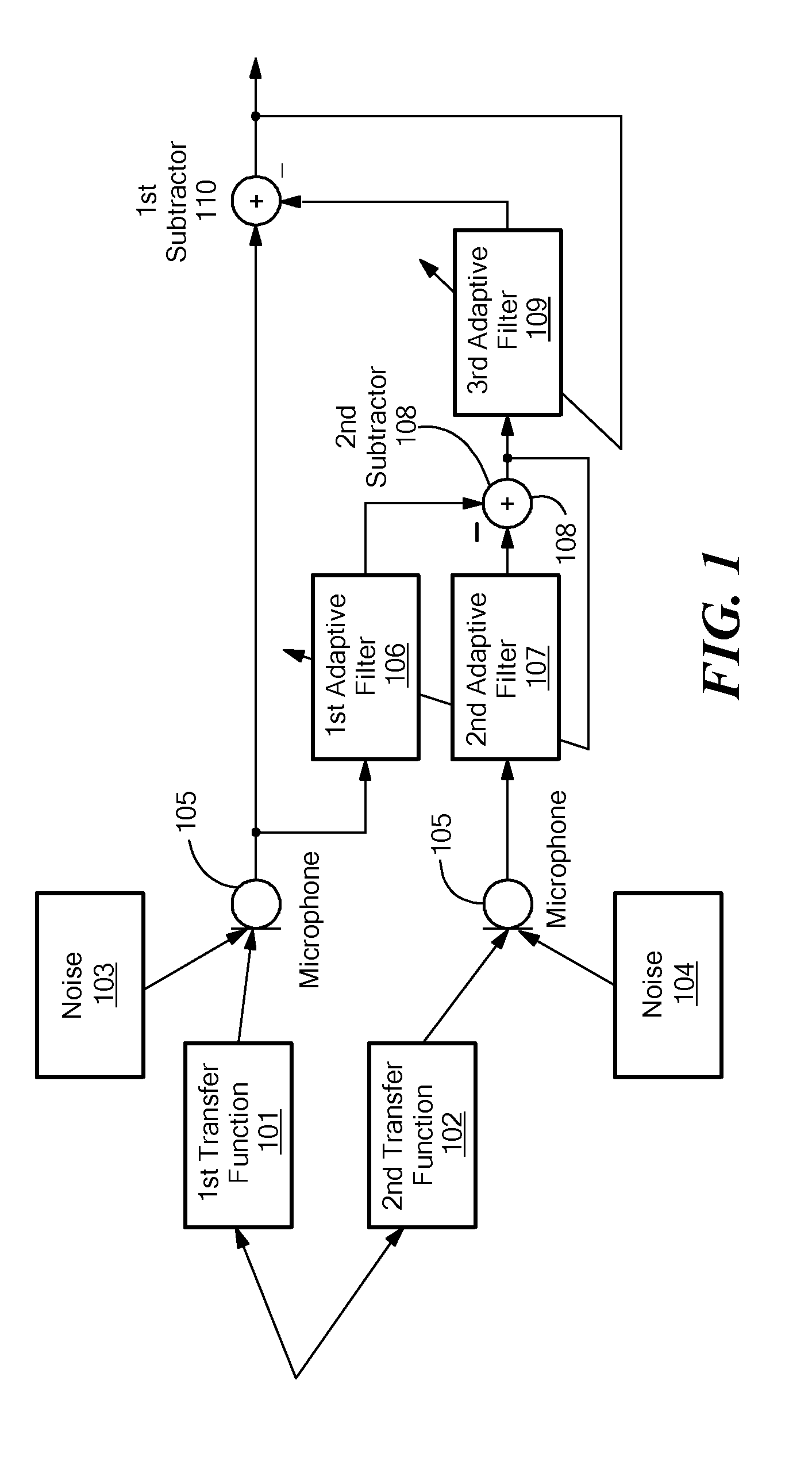
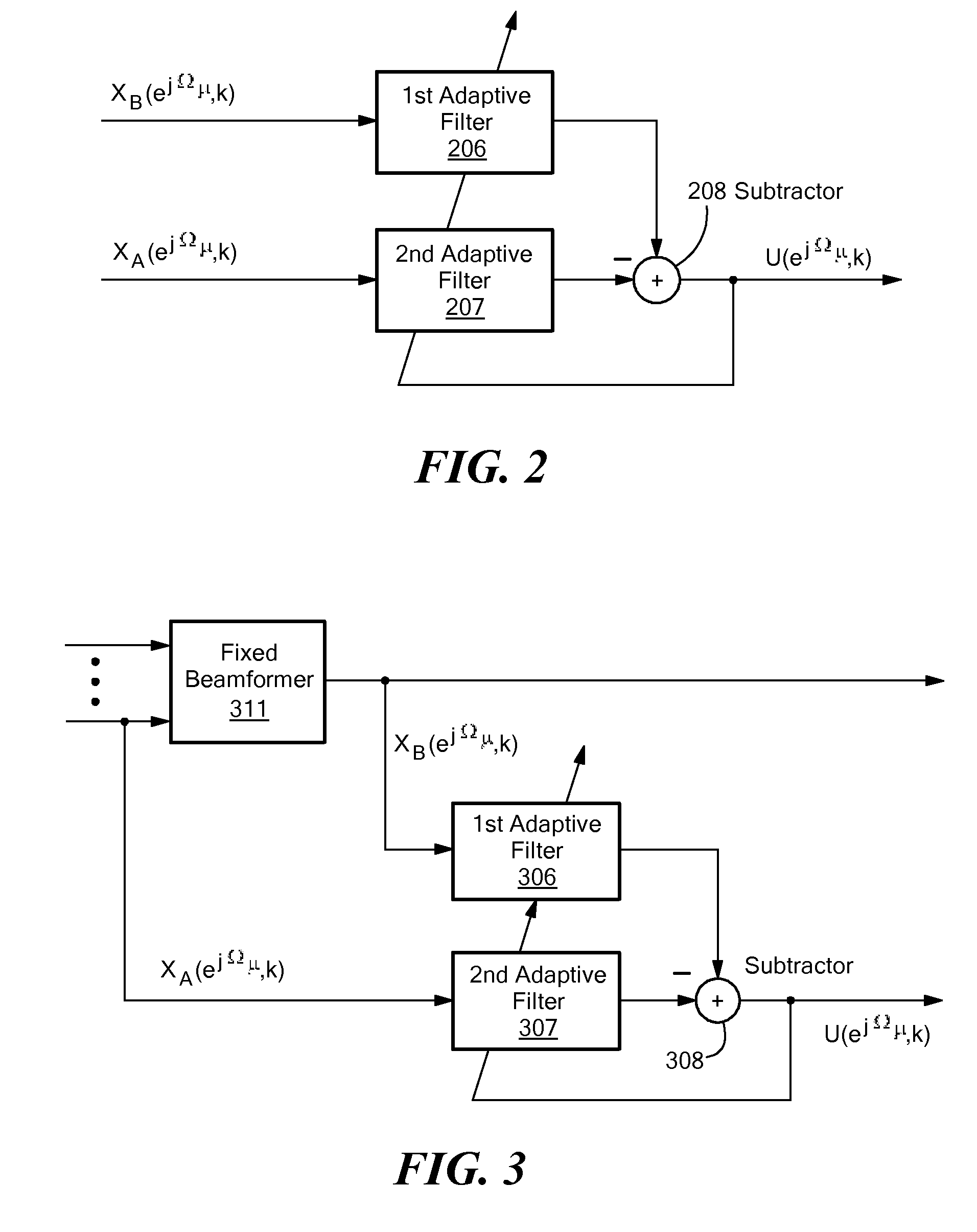
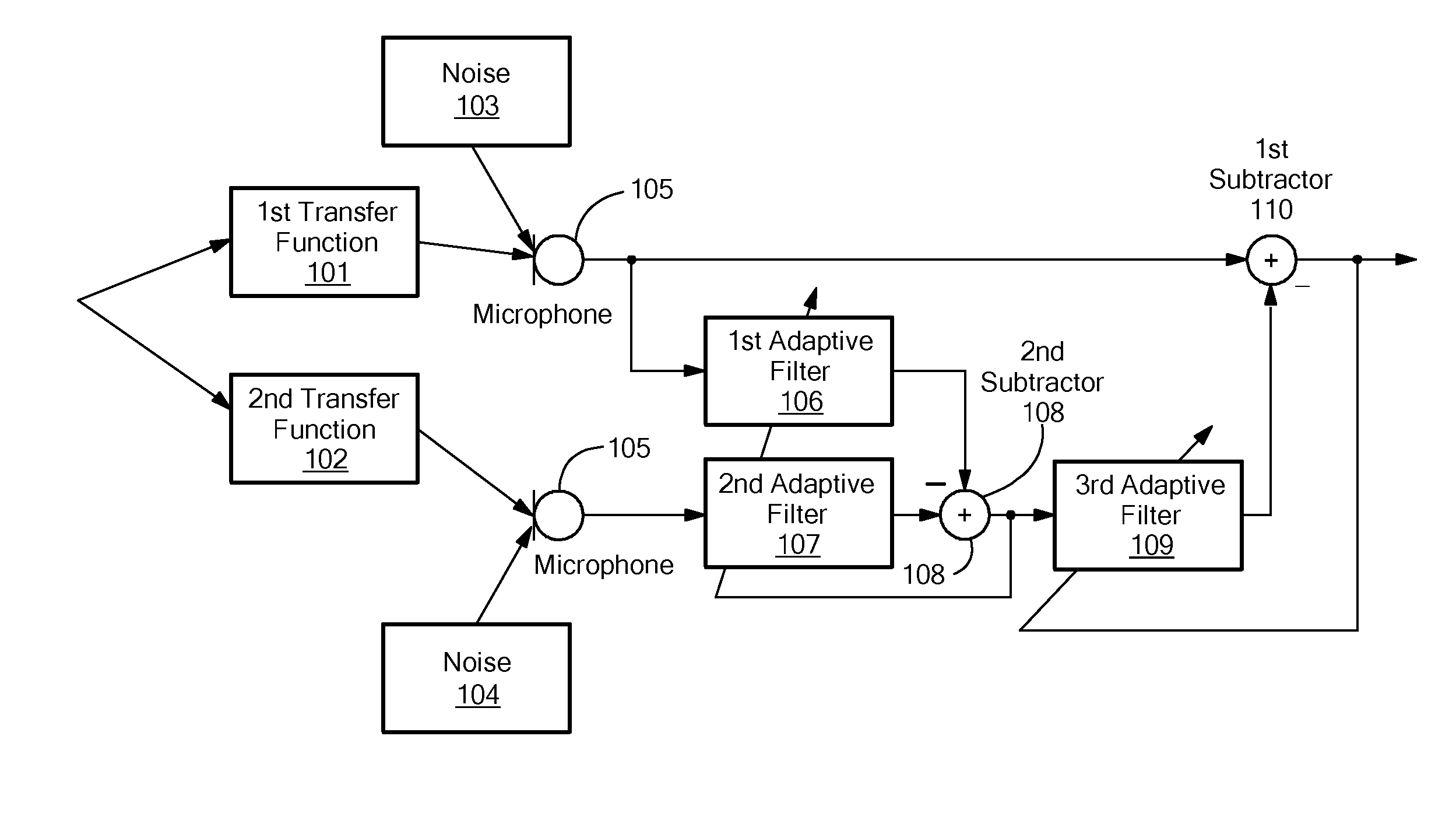
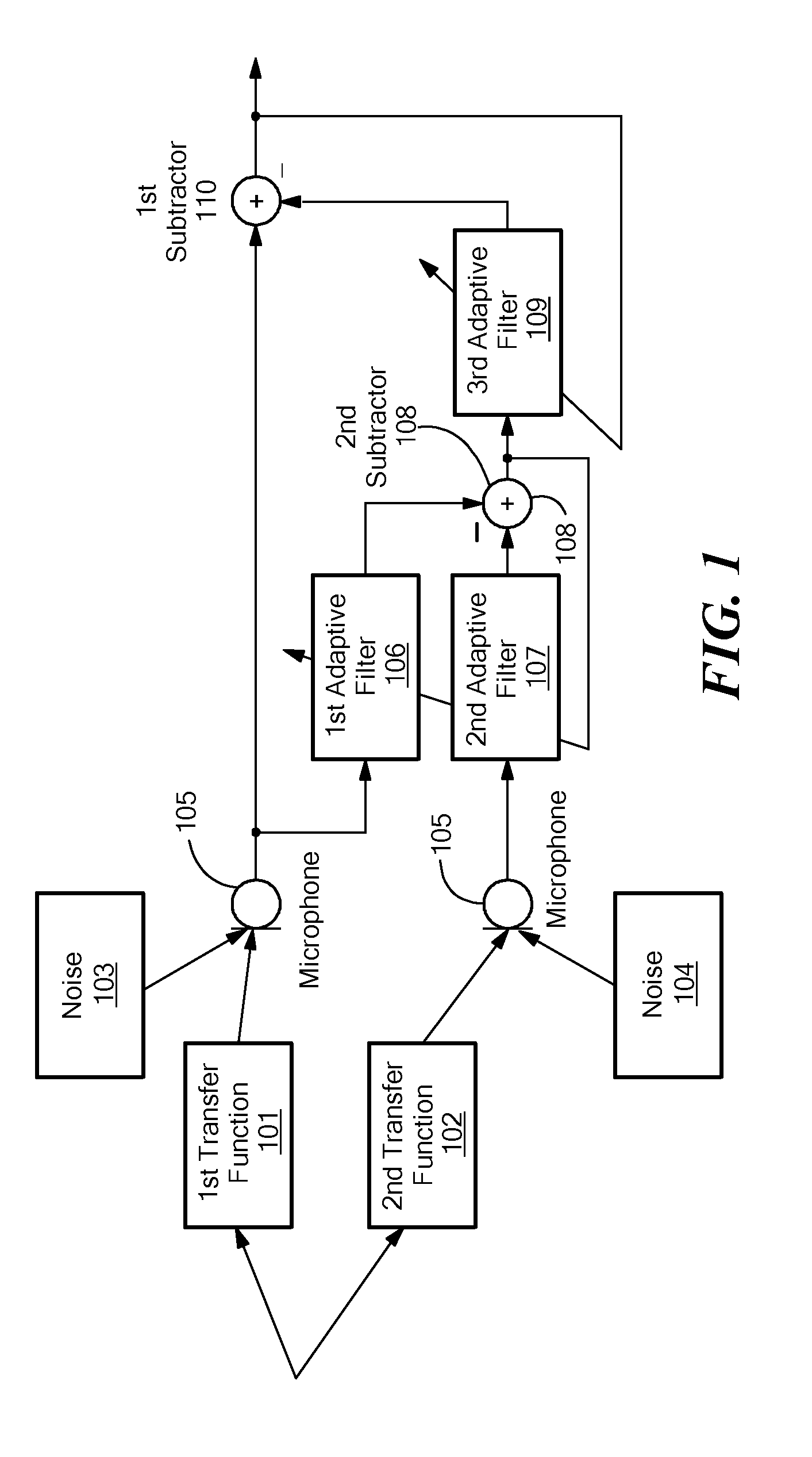
ActiveUS8374358B2Improve noise qualityMinimizing componentSpeech analysisMicrophones signal combinationAdaptive filterNoise reduction
The invention provides a method for determining a noise reference signal for noise compensation and / or noise reduction. A first audio signal on a first signal path and a second audio signal on a second signal path are received. The first audio signal is filtered using a first adaptive filter to obtain a first filtered audio signal. The second audio signal is filtered using a second adaptive filter to obtain a second filtered audio signal. The first and the second filtered audio signal are combined to obtain the noise reference signal. The first and the second adaptive filter are adapted such as to minimize a wanted signal component in the noise reference signal.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Method for Determining a Noise Reference Signal for Noise Compensation and/or Noise Reduction
ActiveUS20100246851A1Reduce noiseNoise component can be minimizedSpeech analysisMicrophones signal combinationAdaptive filterNoise
The invention provides a method for determining a noise reference signal for noise compensation and / or noise reduction. A first audio signal on a first signal path and a second audio signal on a second signal path are received. The first audio signal is filtered using a first adaptive filter to obtain a first filtered audio signal. The second audio signal is filtered using a second adaptive filter to obtain a second filtered audio signal. The first and the second filtered audio signal are combined to obtain the noise reference signal. The first and the second adaptive filter are adapted such as to minimize a wanted signal component in the noise reference signal.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
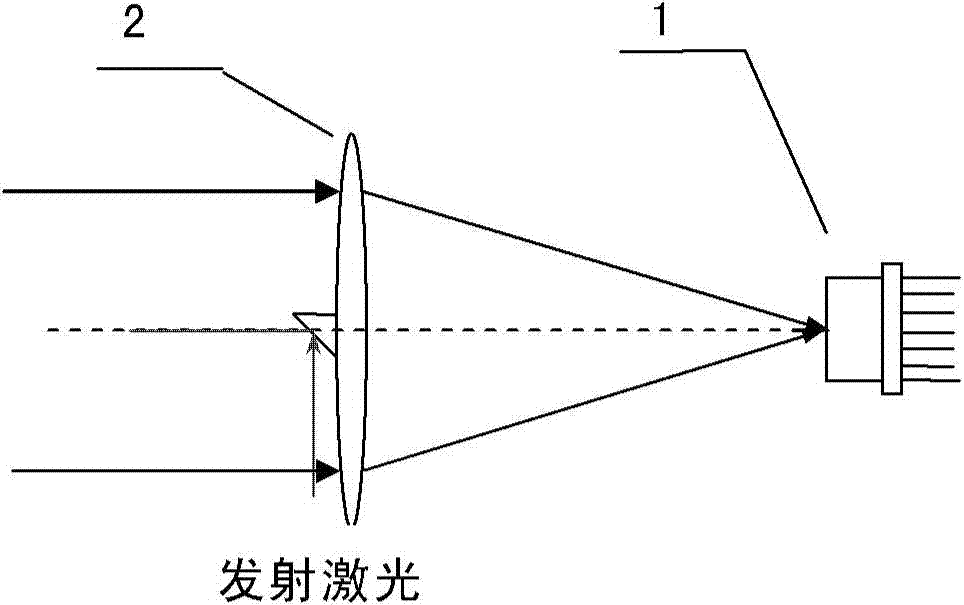
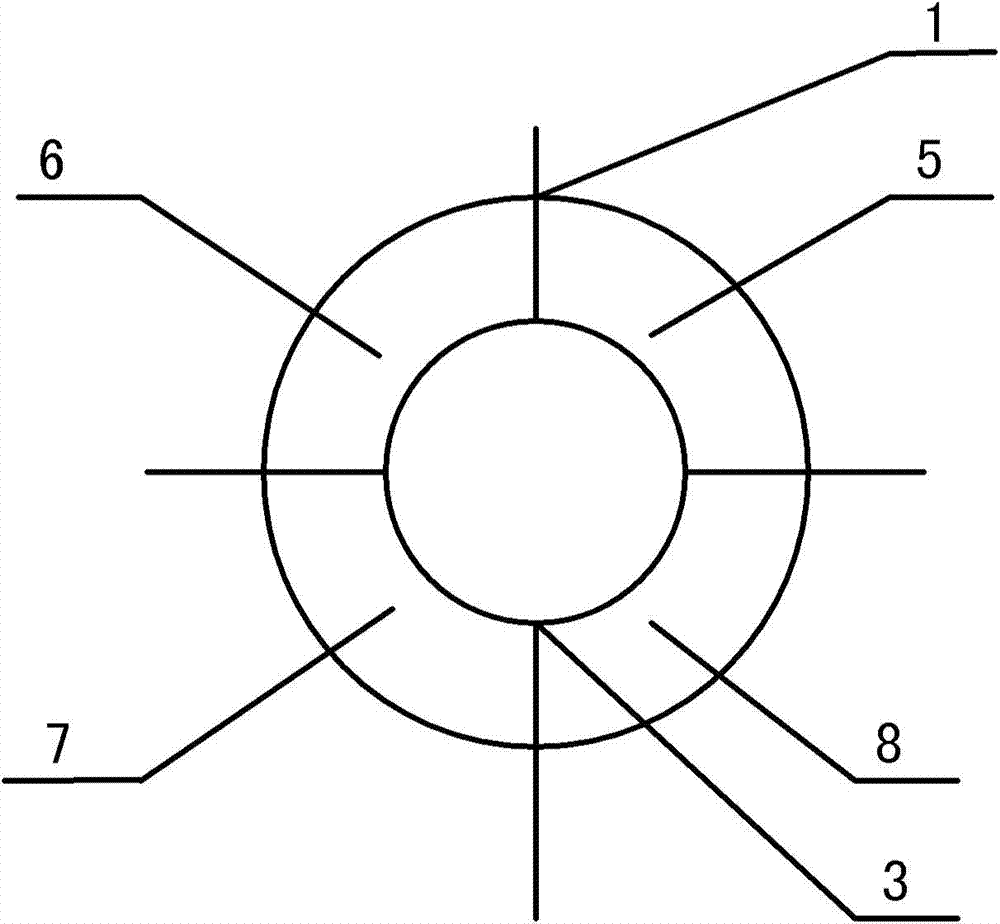
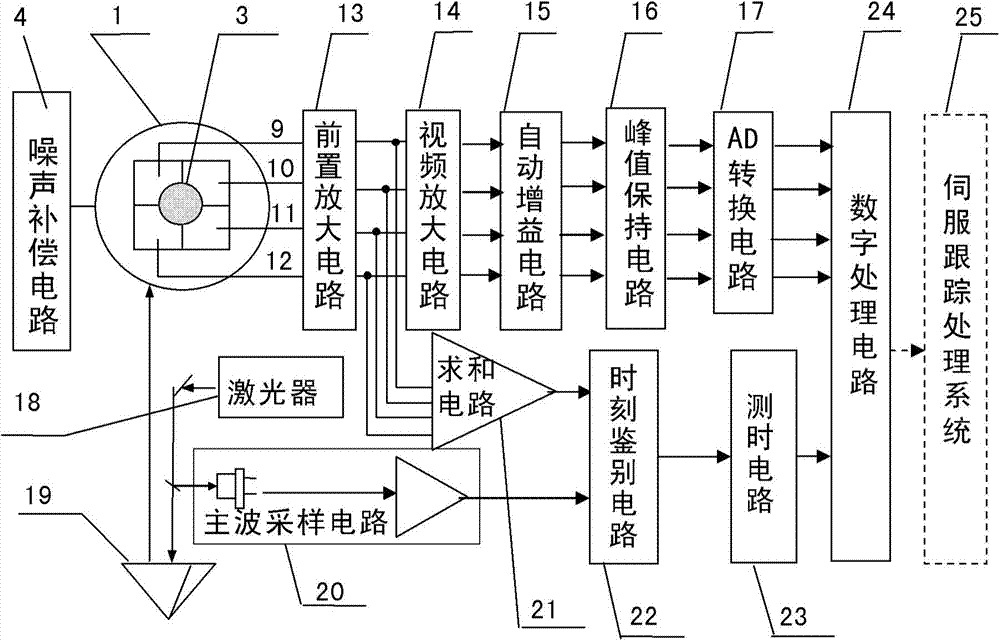
Measuring device and method for target line-of-sight angel offset and distance
ActiveCN103499819AHigh sensitivityEnsuring Gain StabilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationMeasurement devicePhotodetector
The invention provides a measuring device and method for the target line-of-sight angel offset and distance. The device is composed of a four-quadrant avalanche photodetector, a receiving and sending optical unit, a noise compensation circuit, a four-circuit front amplification circuit, a video amplification circuit, an automatic gain amplification circuit, a peak keeping circuit, an AD conversion circuit, a laser, a dominant wave sampling circuit, a summing circuit, a time identifying circuit, a time test circuit and a digital processing circuit, wherein the receiving and sending optical unit enables narrow pulse laser rays emitted by the laser to be converged on the photoelectric detector to form echo light spots after target reflection, photovoltaic conversion of the four-quadrant avalanche photodetector, front amplification, video amplification and automatic gain amplification are conducted, narrow-pulse peak keeping is conducted, transmission of the AD conversion circuit is conducted, and the digital processing circuit extracts the digital line-of-sight angel offset; summing is conducted on the four-circuit front amplification circuit, the dominant wave sampling circuit is combined, the time identifying circuit determines laser emitting and echo coming and returning time, the time is transmitted to the time identifying circuit to be measured, and the digital processing circuit decodes the corresponding distance.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
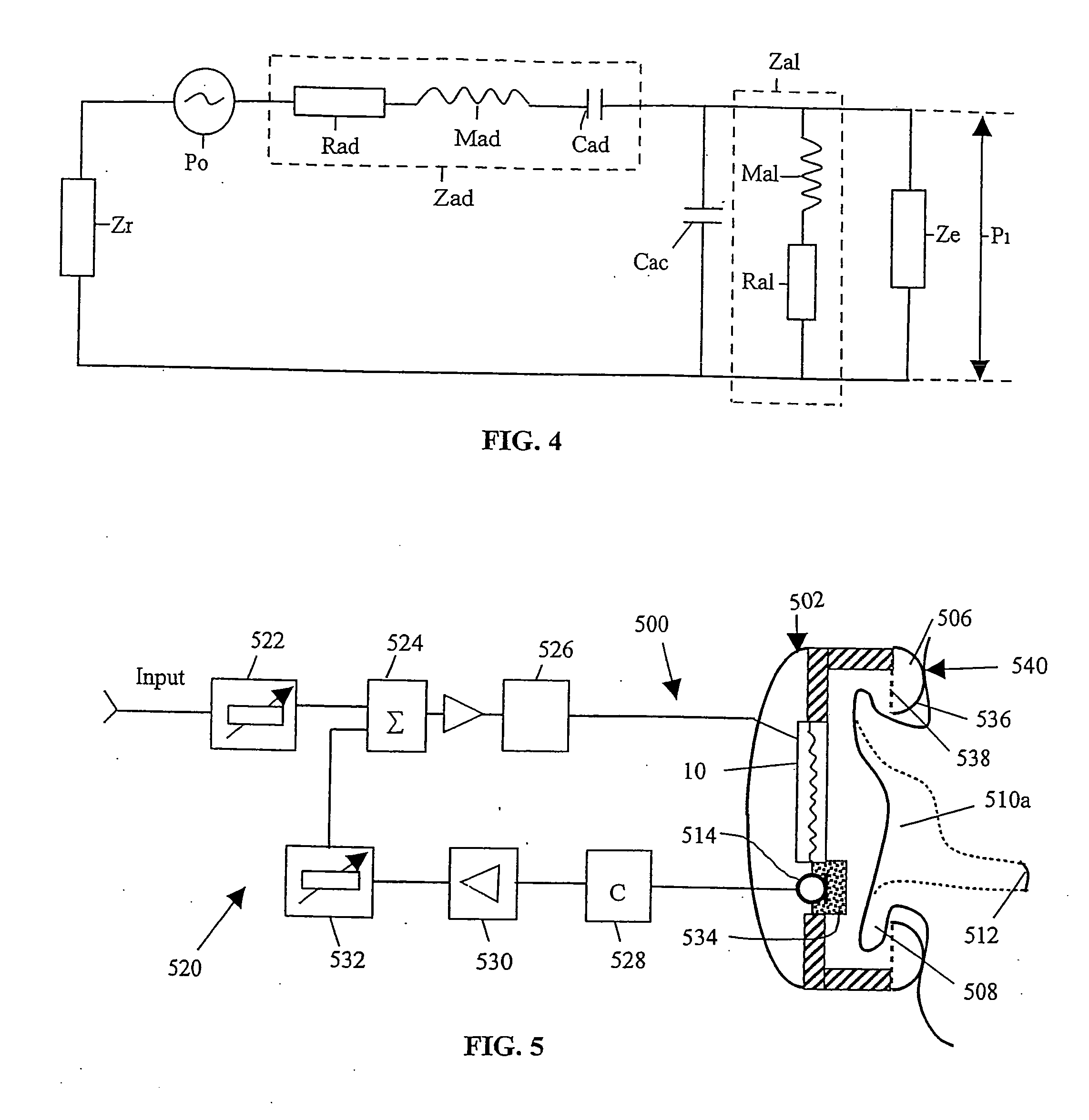
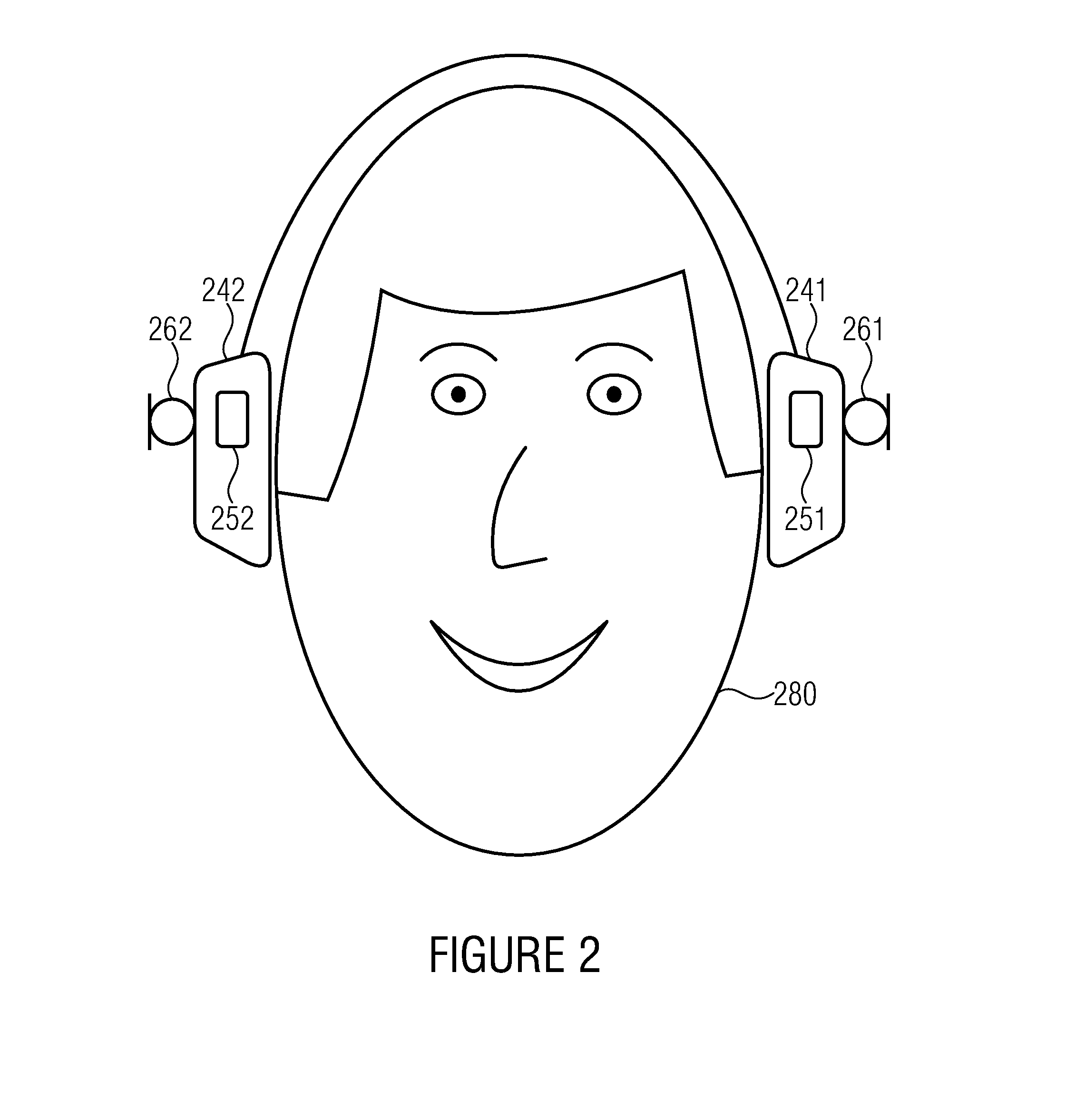
Transducer, headphone and method for reducing noise
InactiveUS20070154049A1Reduce noiseSuppress noiseMicrophonesHeadphones for stereophonic communicationElectrical conductorAcoustic noise reduction
A transducer, a headphone and a method reduce noise and / or ambient sounds. The headphone has a microphone, a transducer and / or an electrical circuit for producing and / or for transmitting an anti-noise sound wave and / or a noise compensation signal inside an ear cup of the headphone. The anti-noise sound wave and / or the noise compensation signal cancels, dampens and / or reduces a sound wave of the noise and / or of the ambient sounds inside the ear cup. The transducer produces and / or transmits an audio signal which is received by an ear of a user. The microphone and the transducer are connected to, are attached to and / or are in communication with the electrical circuit within the headphone. The transducer has a double-sided diaphragm with concentric circular corrugations and / or foil spiral conductors on each side of the diaphragm. The microphone inside the ear cup is covered by and / or is connected to a sound absorbing material inside the ear cup of the headphone. An ear cushion having a inner side and an outer side is attached to and / or is connected to the ear cup for receiving an ear of a user. The inner side and the outer side of the ear cushion are made from an acoustically resistive material and an acoustically isolating material.
Owner:SLS INT
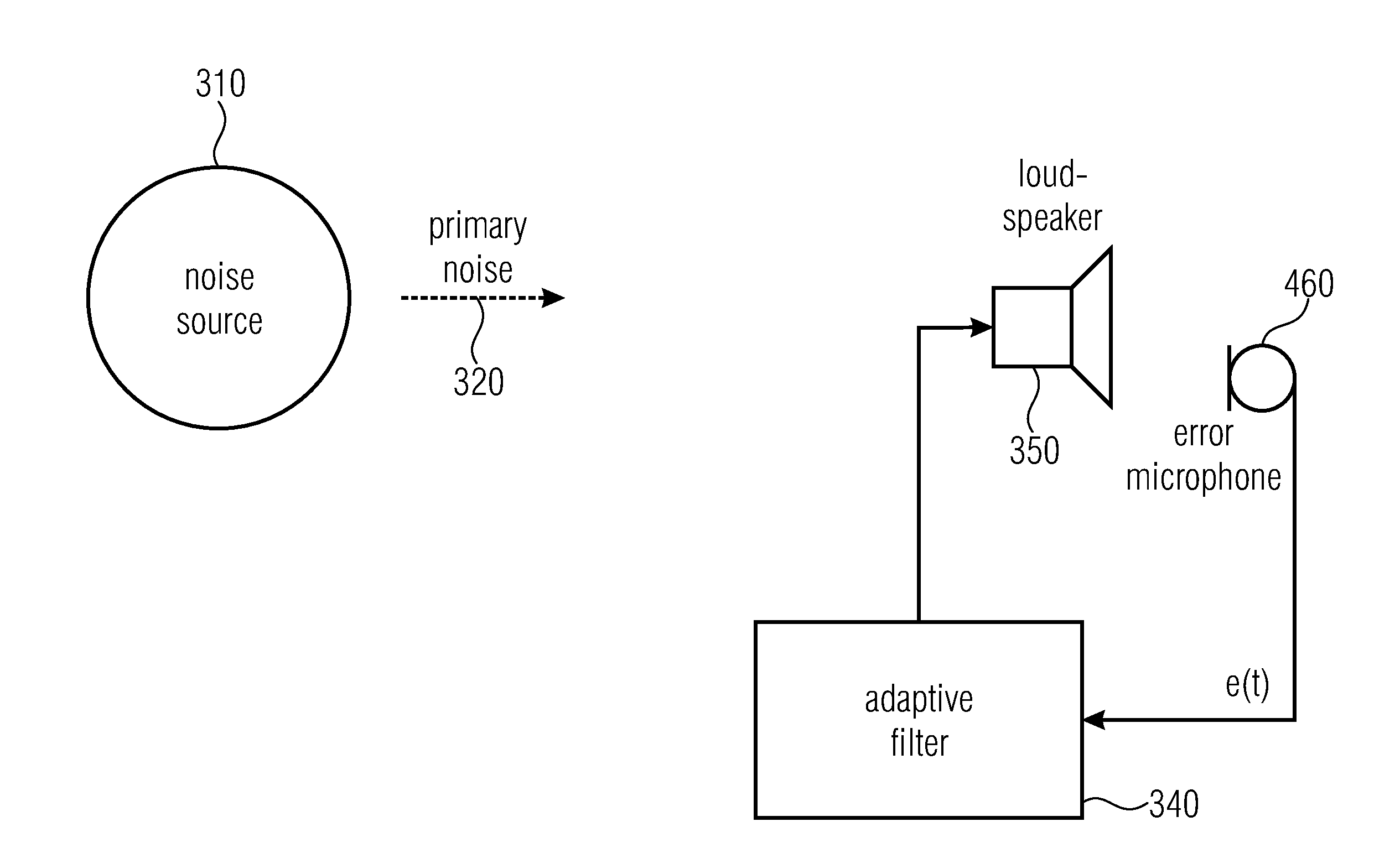
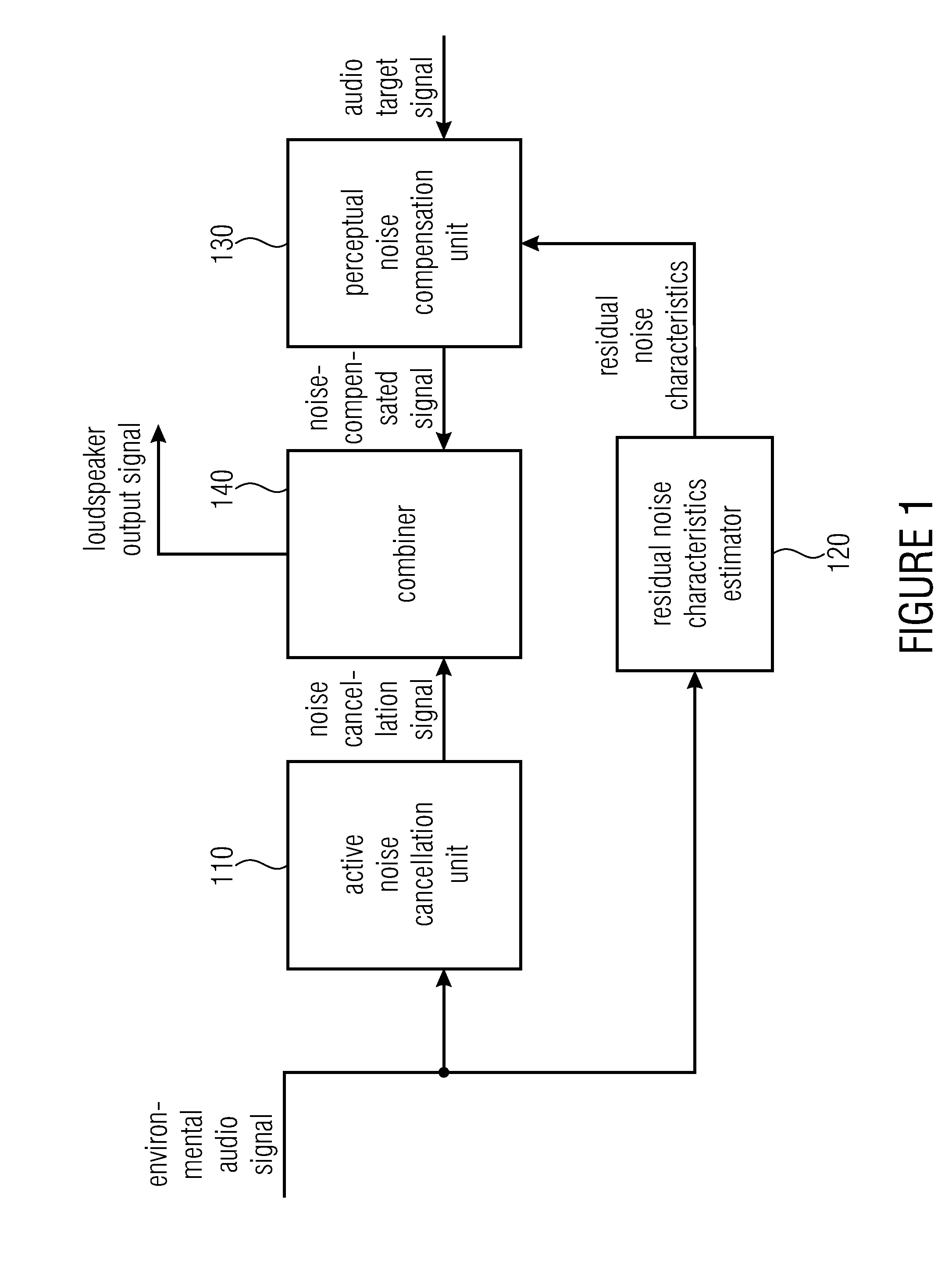
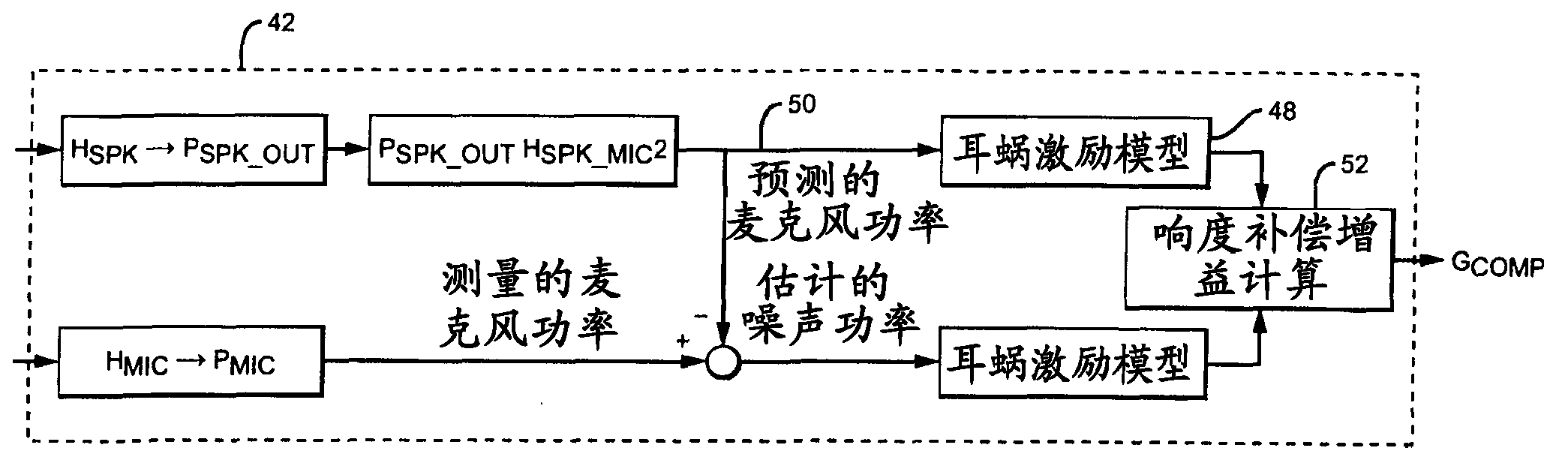
Apparatus and method for improving the perceived quality of sound reproduction by combining active noise cancellation and a perceptual noise compensation
ActiveUS20150003625A1Improve sound qualityEar treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationEnvironmental noiseTarget signal
An apparatus for improving a perceived quality of sound reproduction of an audio output signal is provided. The apparatus has an active noise cancellation unit for generating a noise cancellation signal based on an environmental audio signal, wherein the environmental audio signal has noise signal portions, the noise signal portions resulting from recording environmental noise. Moreover, the apparatus has a residual noise characteristics estimator for determining a residual noise characteristic depending on the environmental noise and the noise cancellation signal. Furthermore, the apparatus has a perceptual noise compensation unit for generating a noise-compensated signal based on an audio target signal and based on the residual noise characteristic. Moreover, the apparatus has a combiner for combining the noise cancellation signal and the noise-compensated signal to obtain the audio output signal.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
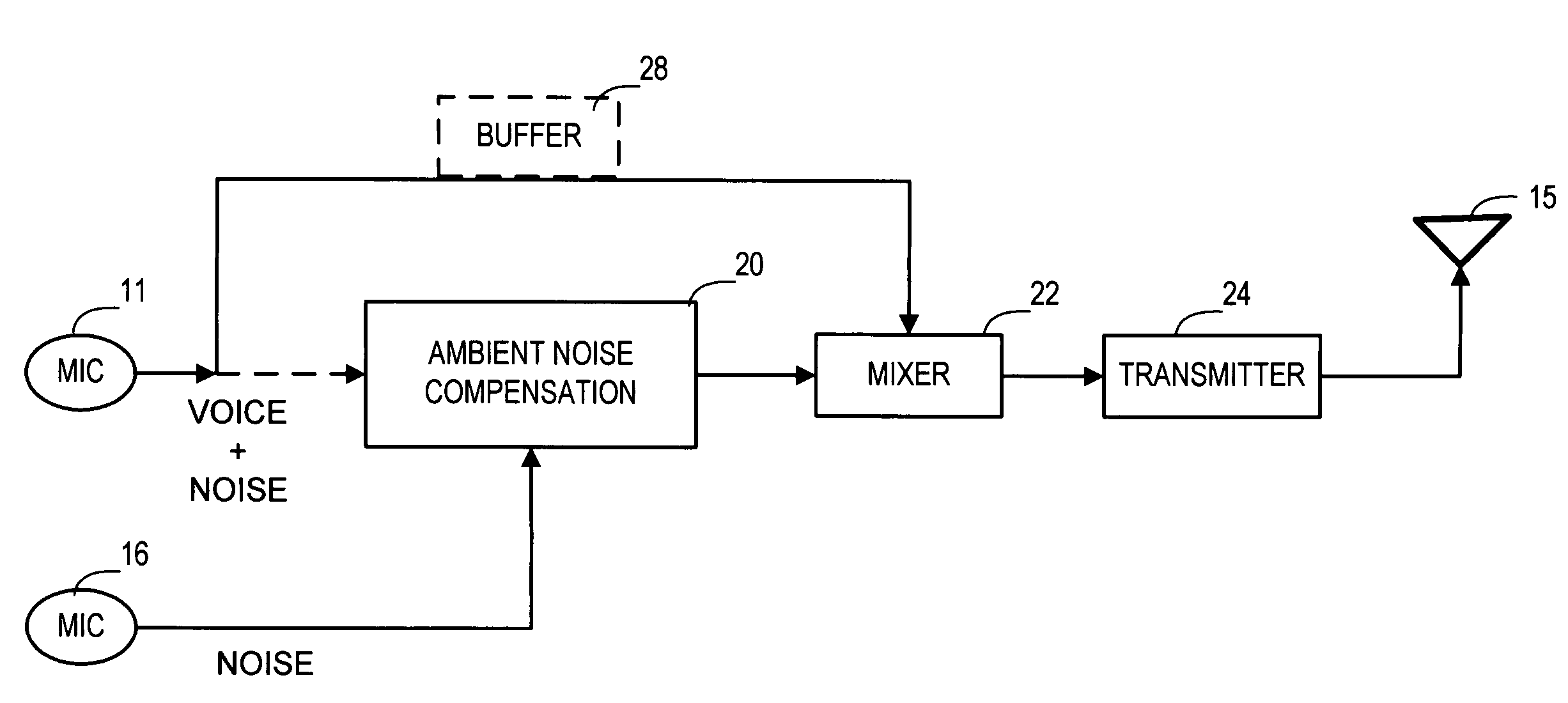
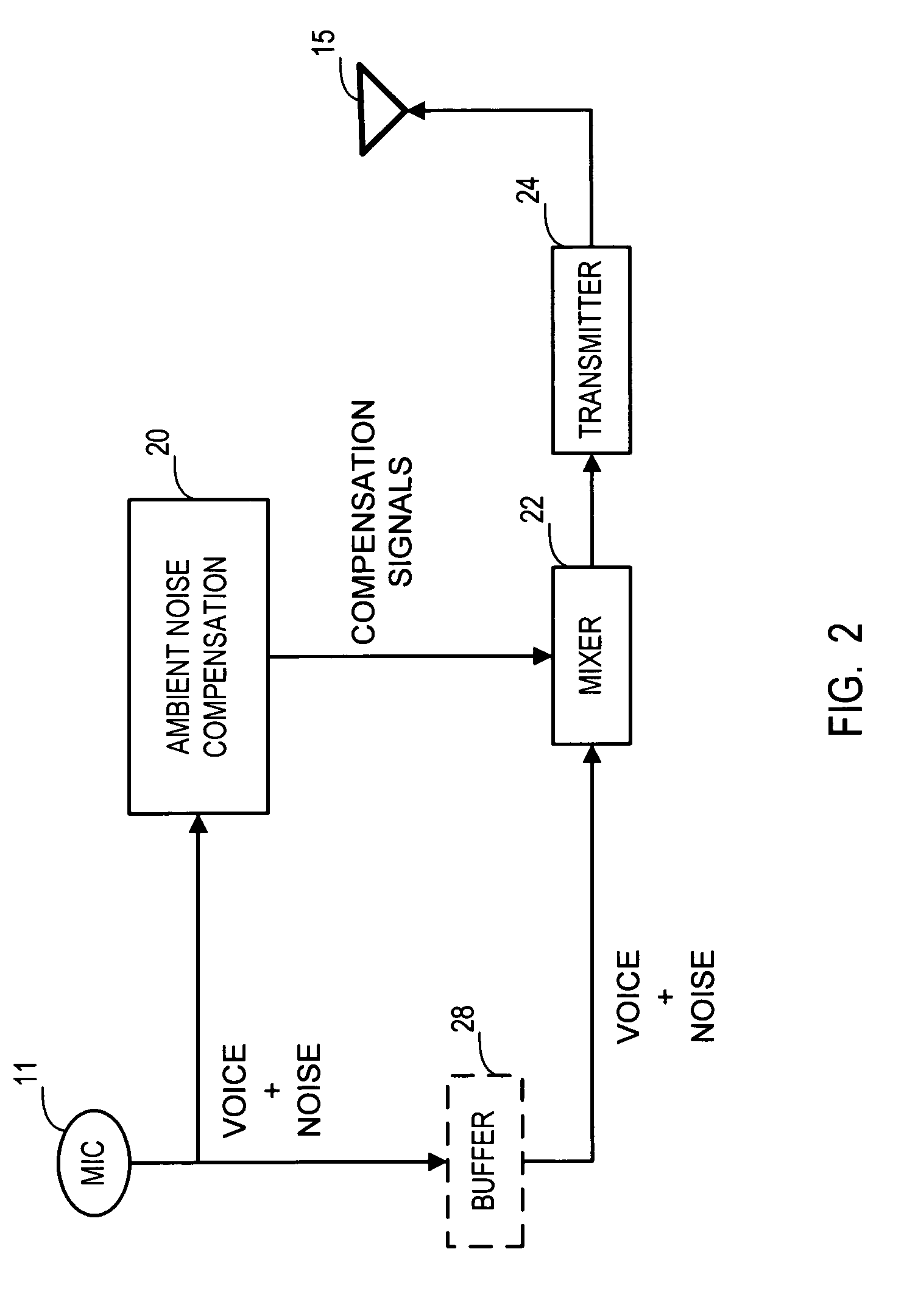
Ambient noise cancellation for voice communication device
InactiveUS6978010B1Easy to hearReduce background noiseInterconnection arrangementsSubstation speech amplifiersVoice communicationFrequency mixer
A system and method for reducing or entirely canceling background or ambient noise from a voice transmission from a communications device. A communications device, such as a mobile telephone, is configured with an ambient noise compensation signal generator that is connected between a microphone and a mixer. The original output of the microphone and a compensation signal generated by the ambient noise compensation signal generator are mixed together prior to being passed to a transmitter. In one embodiment a buffer is provided between the microphone and the mixer to help synchronize the timing of the signals to be mixed. In another embodiment a second microphone is employed to detect ambient noise.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
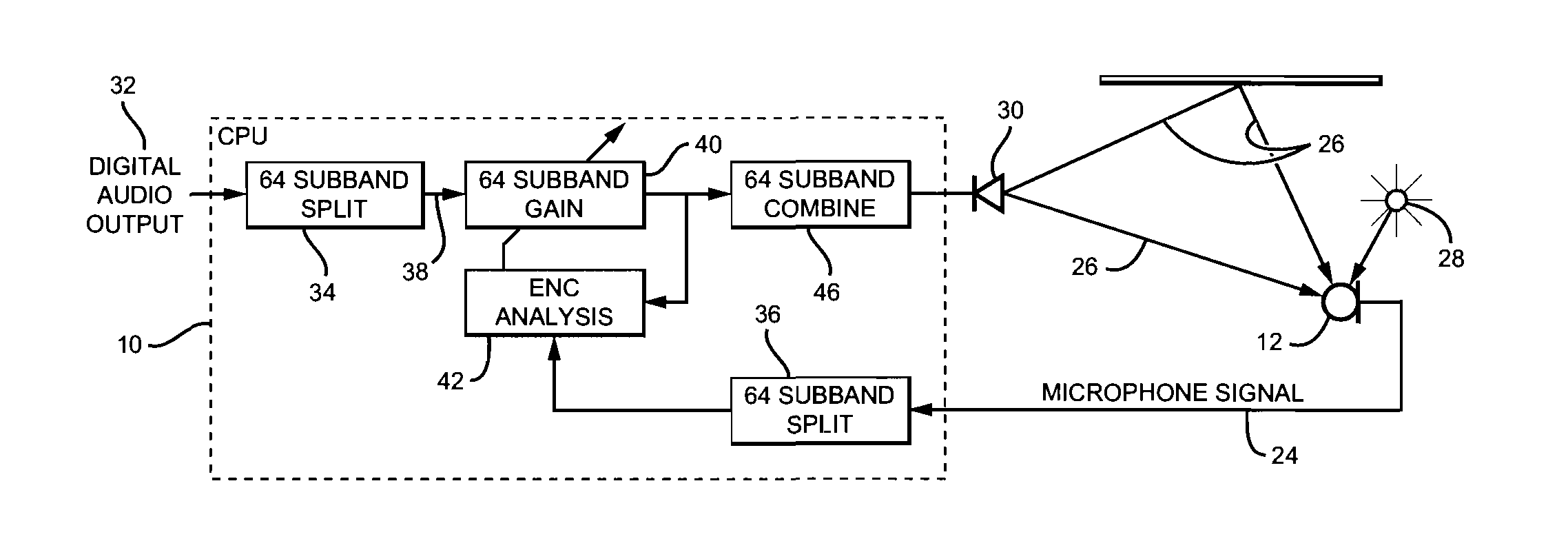
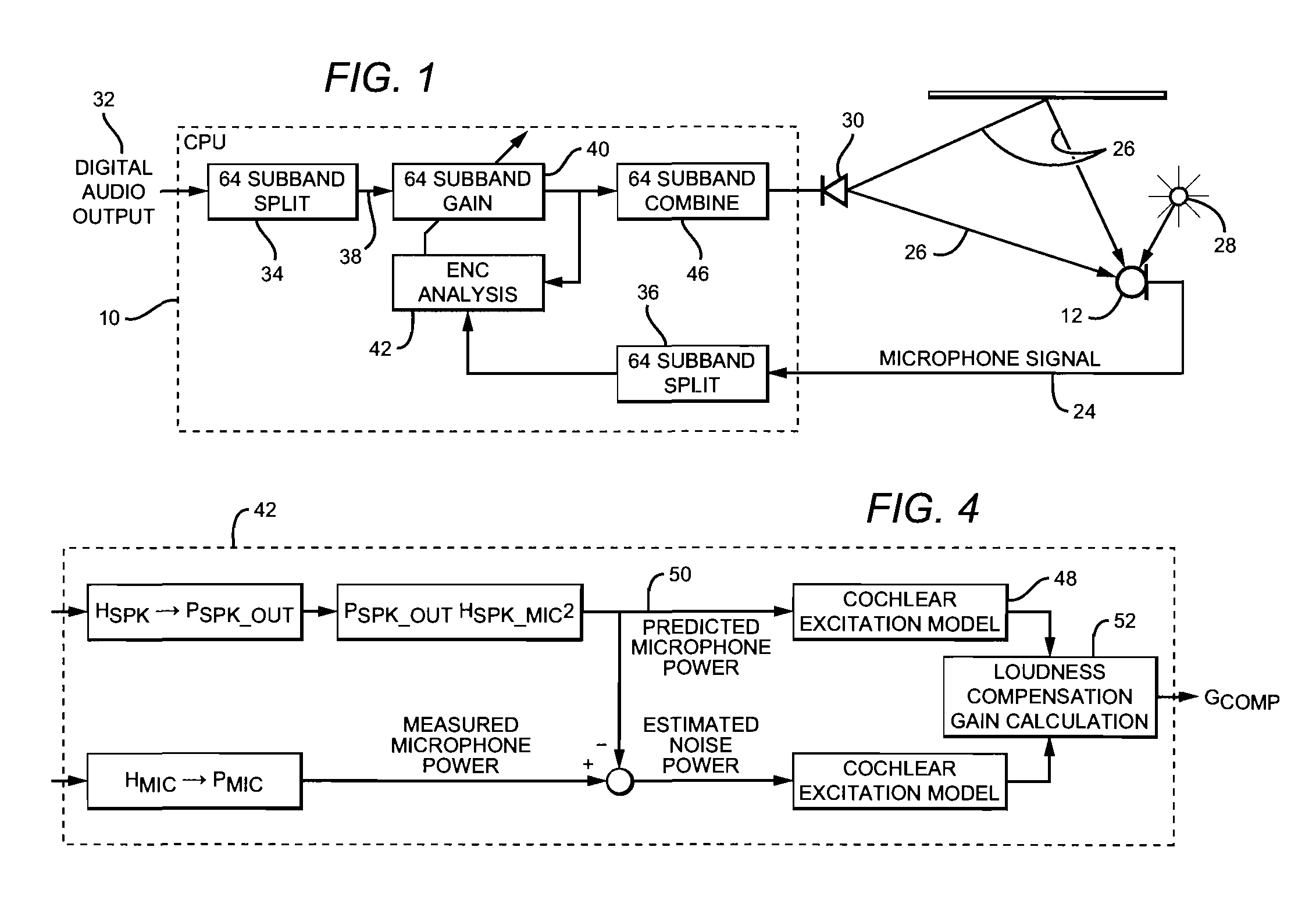
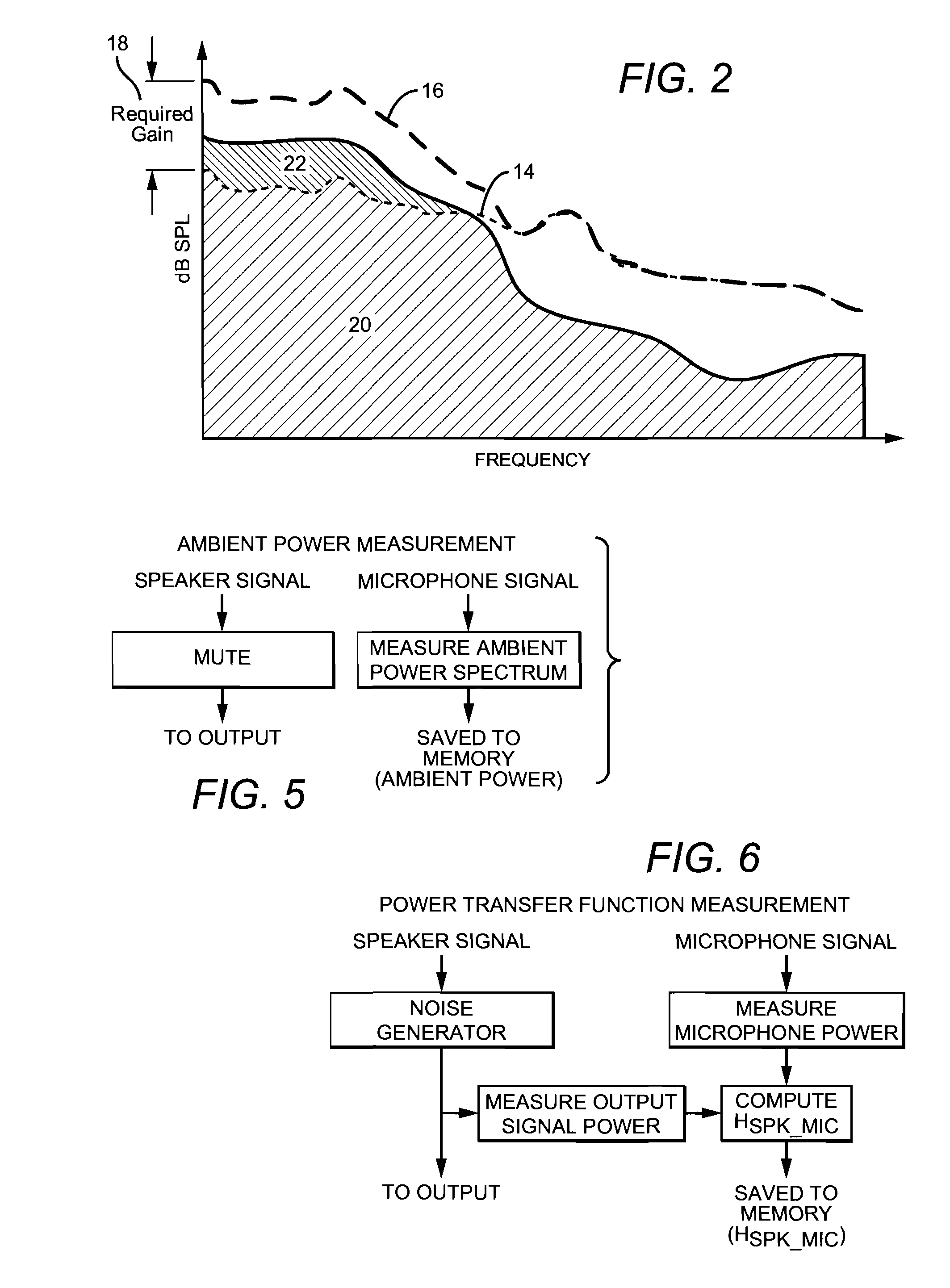
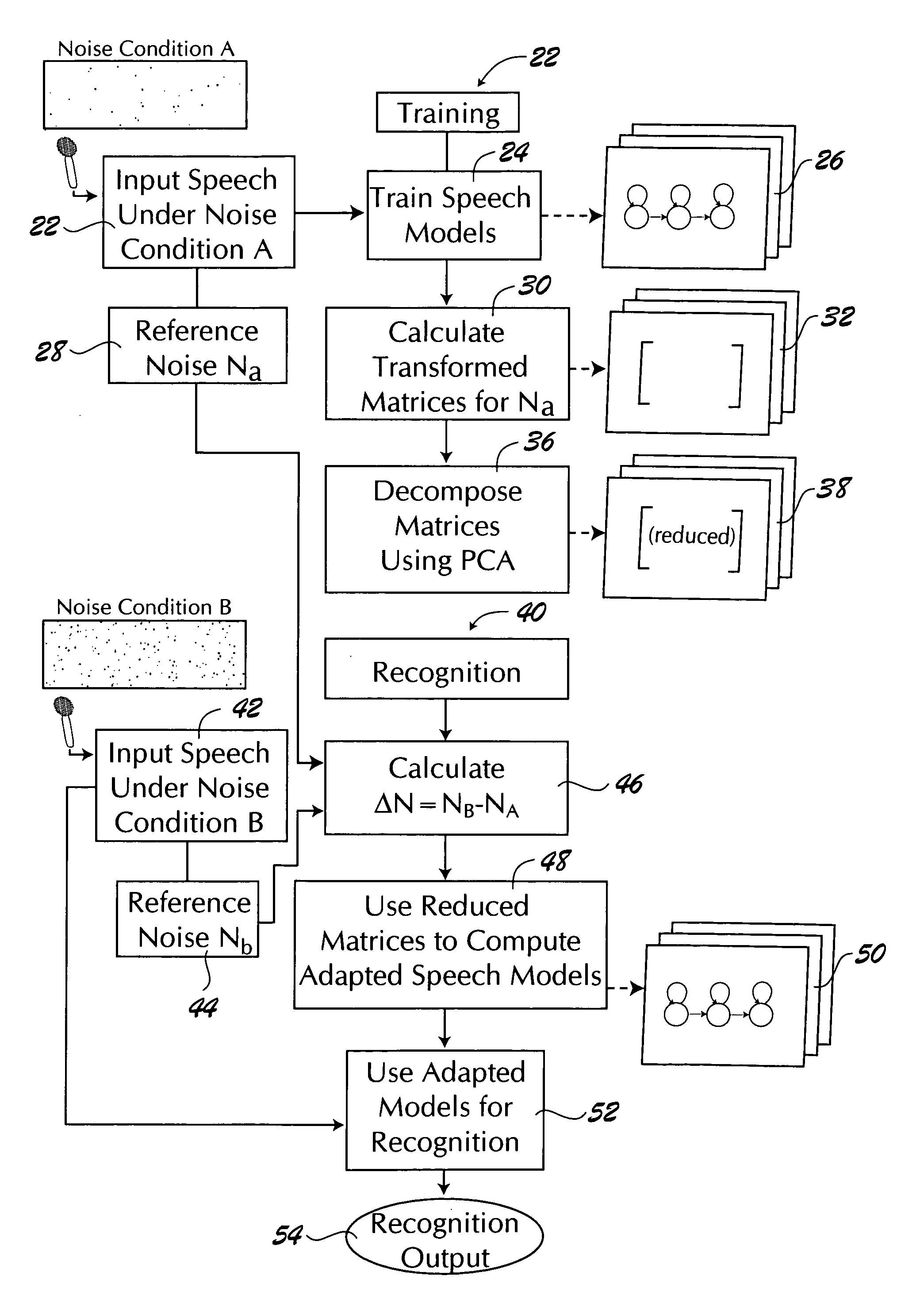
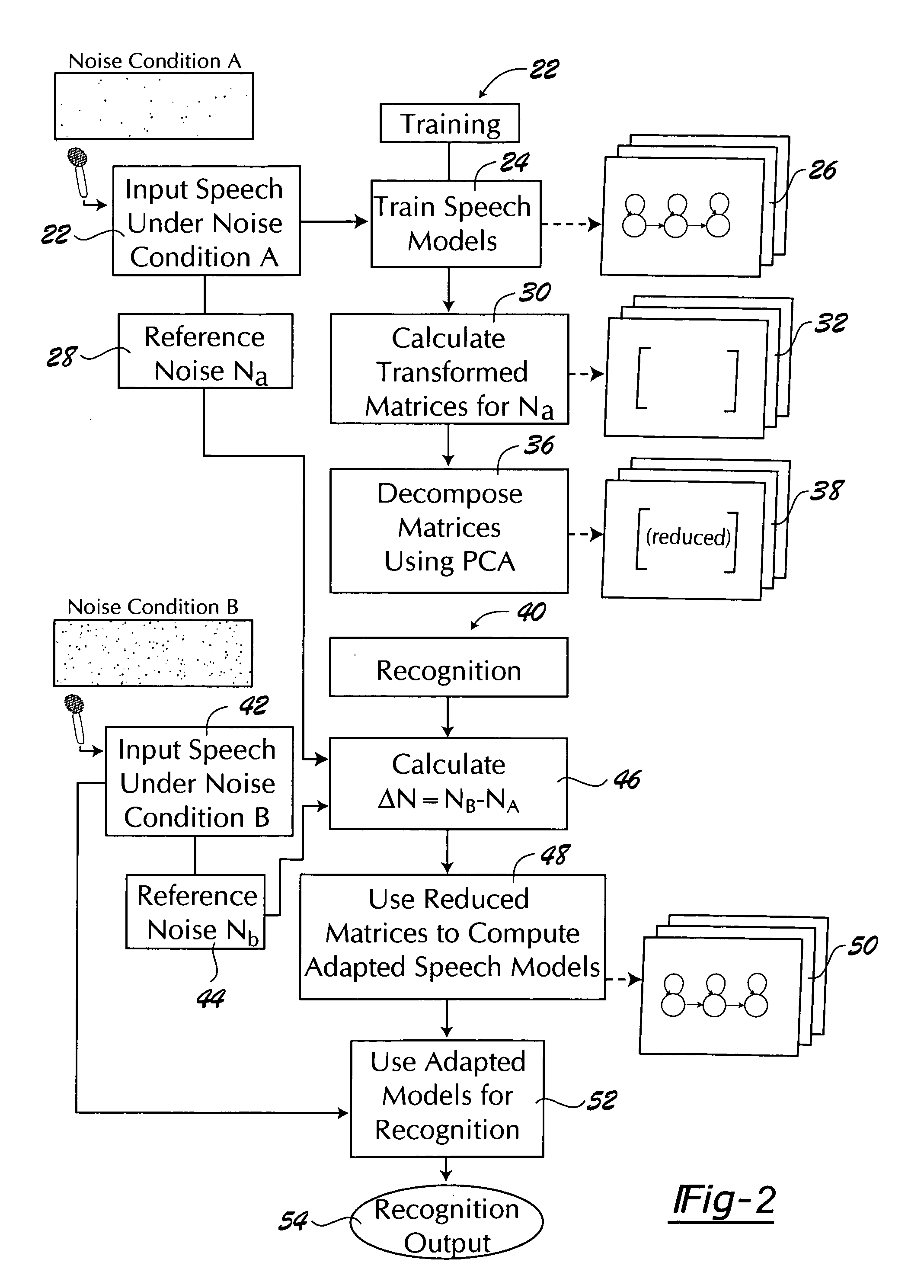
Adaptive environmental noise compensation for audio playback
InactiveUS20110251704A1Prevent maskingSignal processing for reducing noiseSpeech analysisEnvironmental noiseNoise level
The present invention counterbalances background noise by applying dynamic equalization. A psychoacoustic model representing the perception of masking effects of background noise relative to a desired foreground soundtrack is used to accurately counterbalance background noise. A microphone samples what the listener is hearing and separates the desired soundtrack from the interfering noise. The signal and noise components are analyzed from a psychoacoustic perspective and the soundtrack is equalized such that the frequencies that were originally masked are unmasked. Subsequently, the listener may hear the soundtrack over the noise. Using this process the EQ can continuously adapt to the background noise level without any interaction from the listener and only when required. When the background noise subsides, the EQ adapts back to its original level and the user does not experience unnecessarily high loudness levels.
Owner:DTS
Method for driving liquid crystal display having multi-channel single-amplifier structure
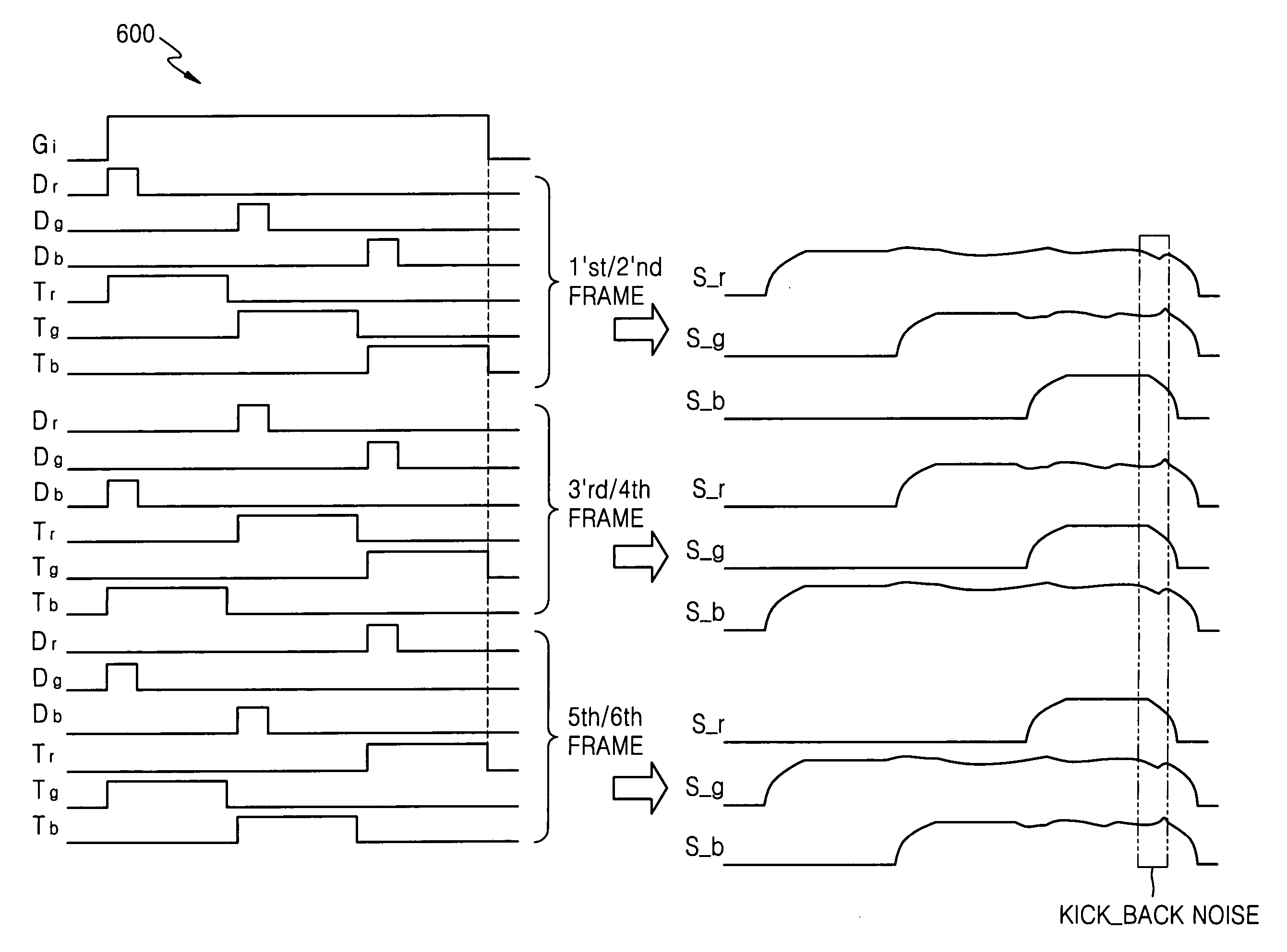
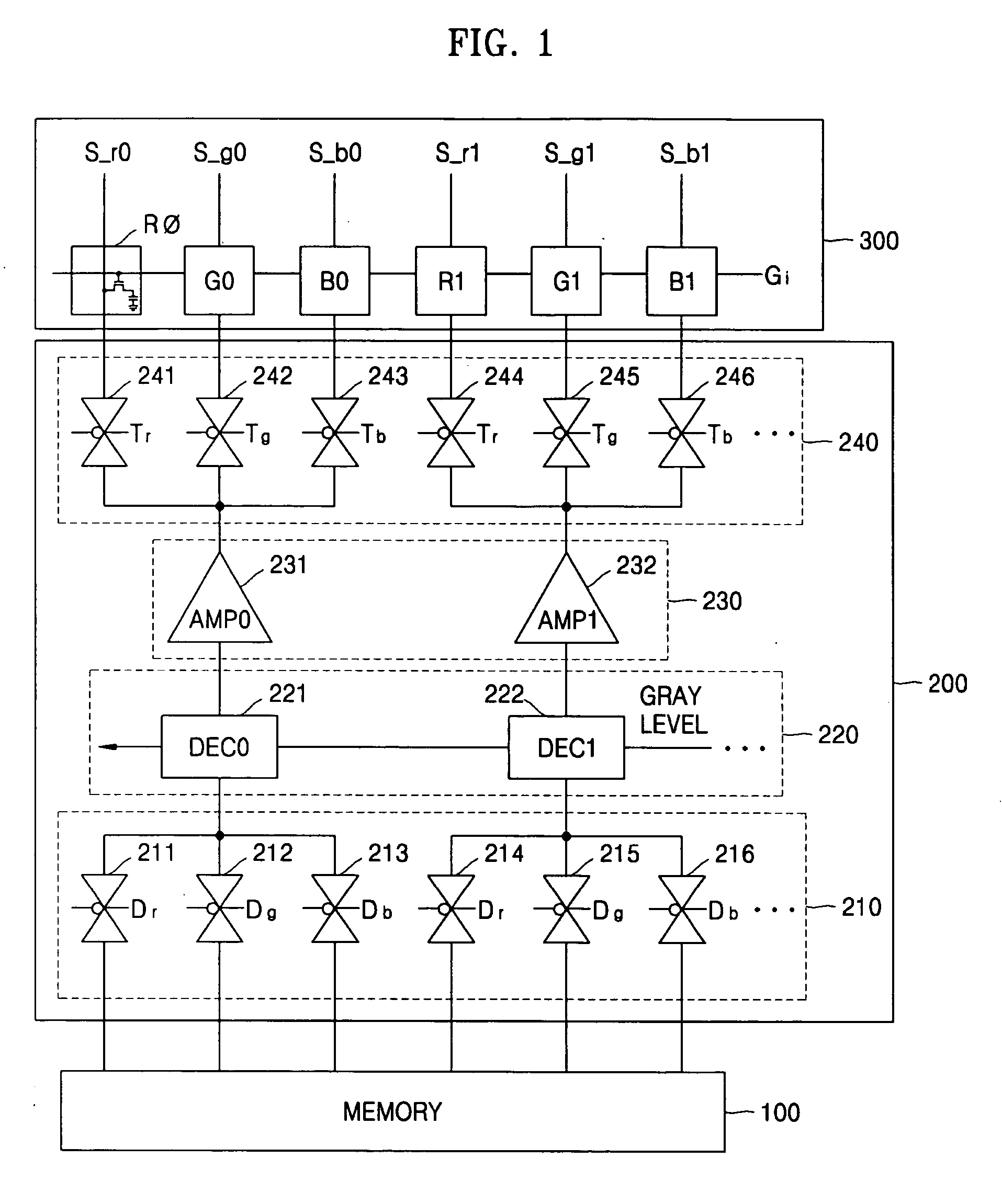
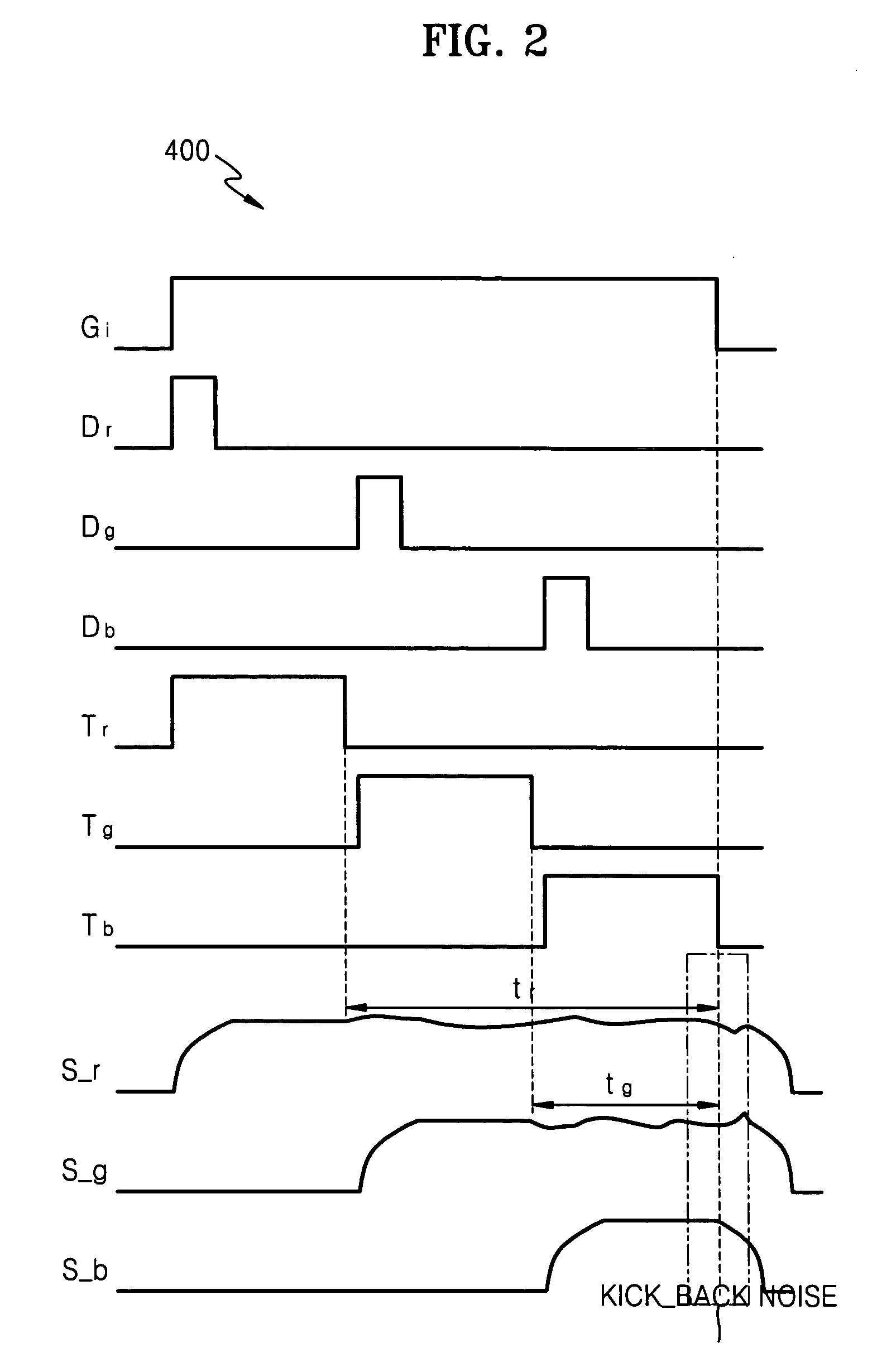
A method is provided for driving a liquid crystal display having a multi-channel single-amplifier structure, where the number of times of coupling according to video signals transmitted to adjacent source lines while the source lines are floated is 3 and it is equal for the respective source lines for 6 frames, noise aspects of the respective source lines are similarly repeated for every 6 frames, kick-back noise compensation is uniformly applied to the source lines S_r, S_g and S_b with noise of the 6 frames averaged, and charge sharing time of parasitic capacitors between the source lines and charge sharing time of capacitors of liquid crystal cells become similar to each other.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
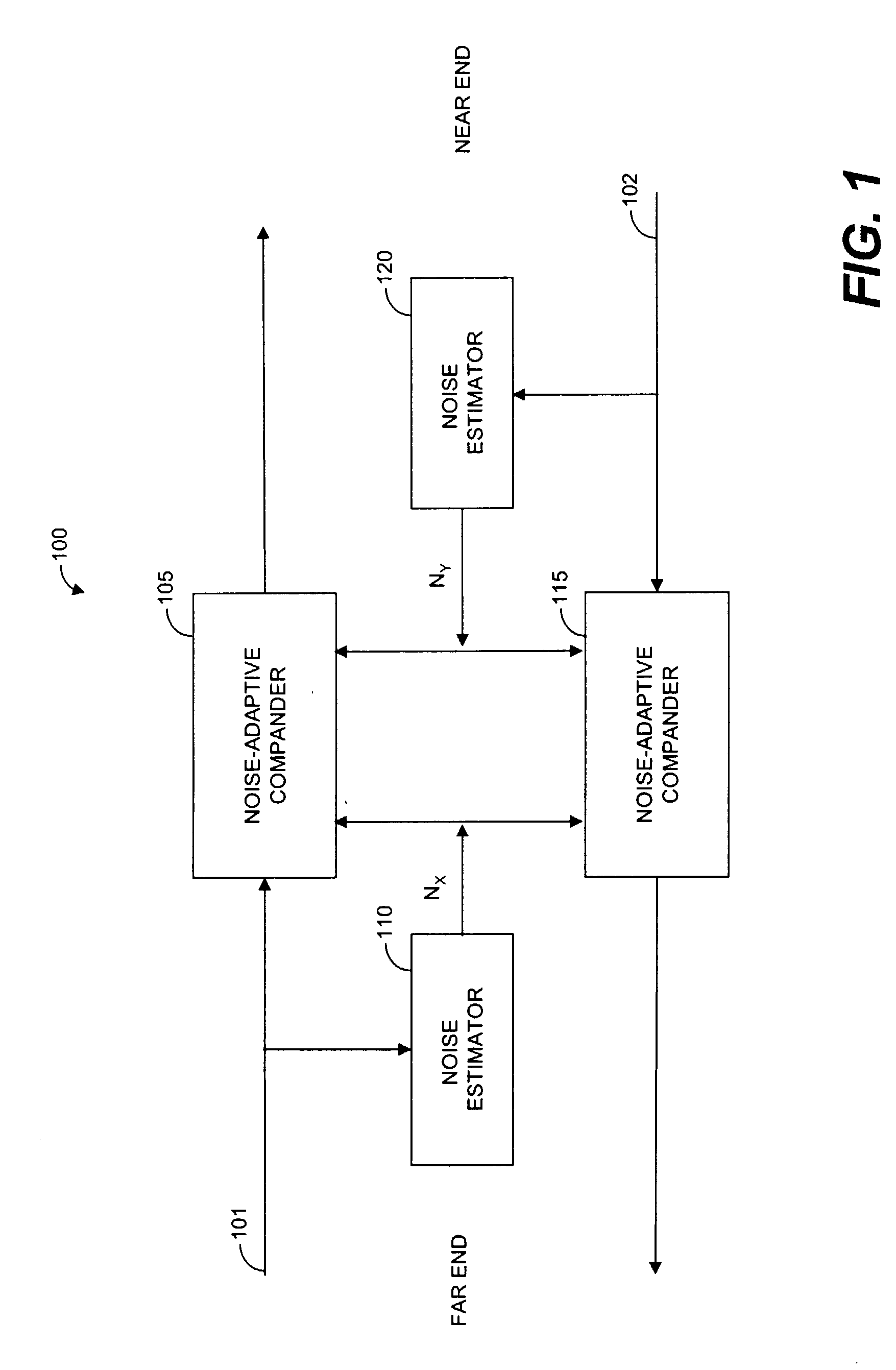
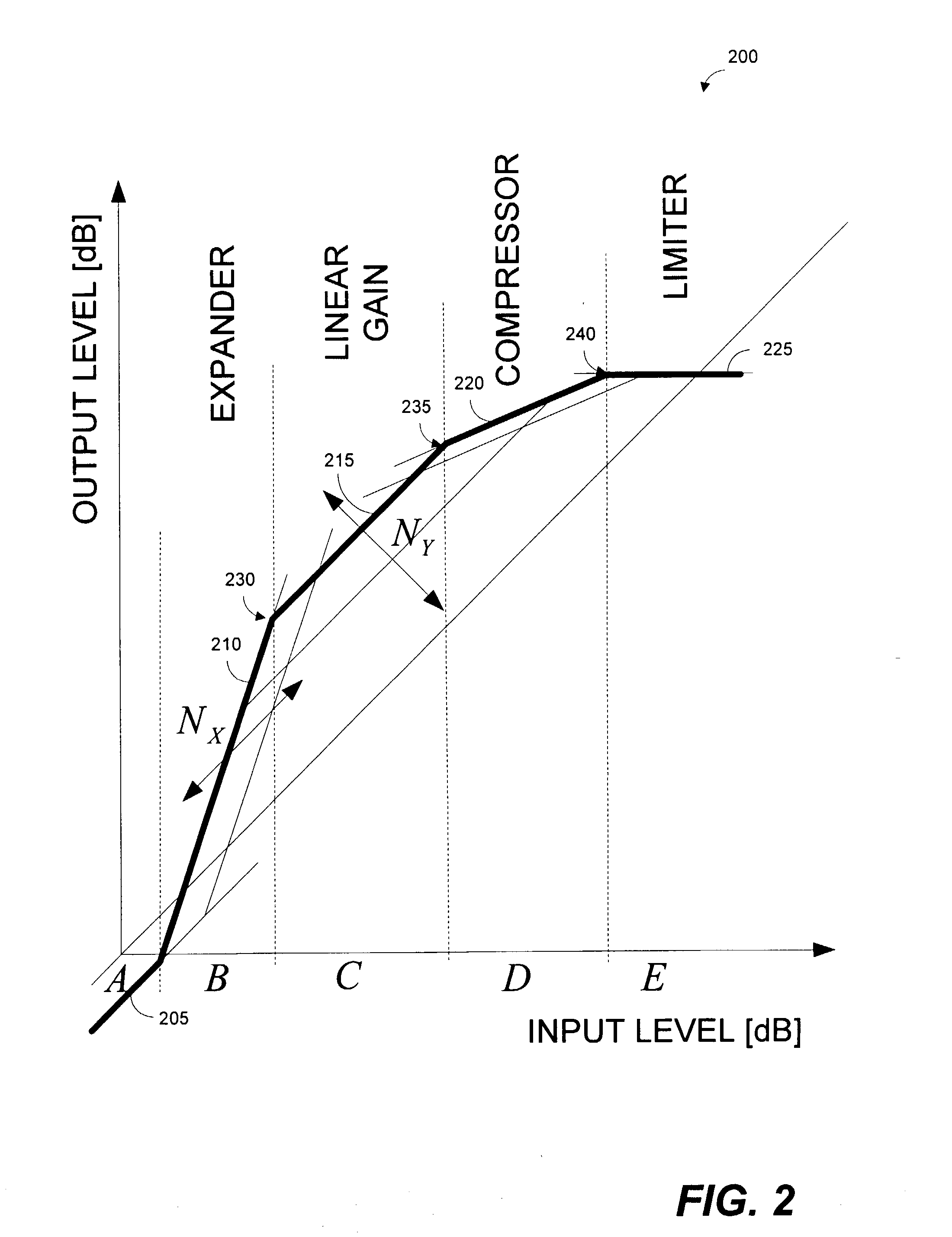
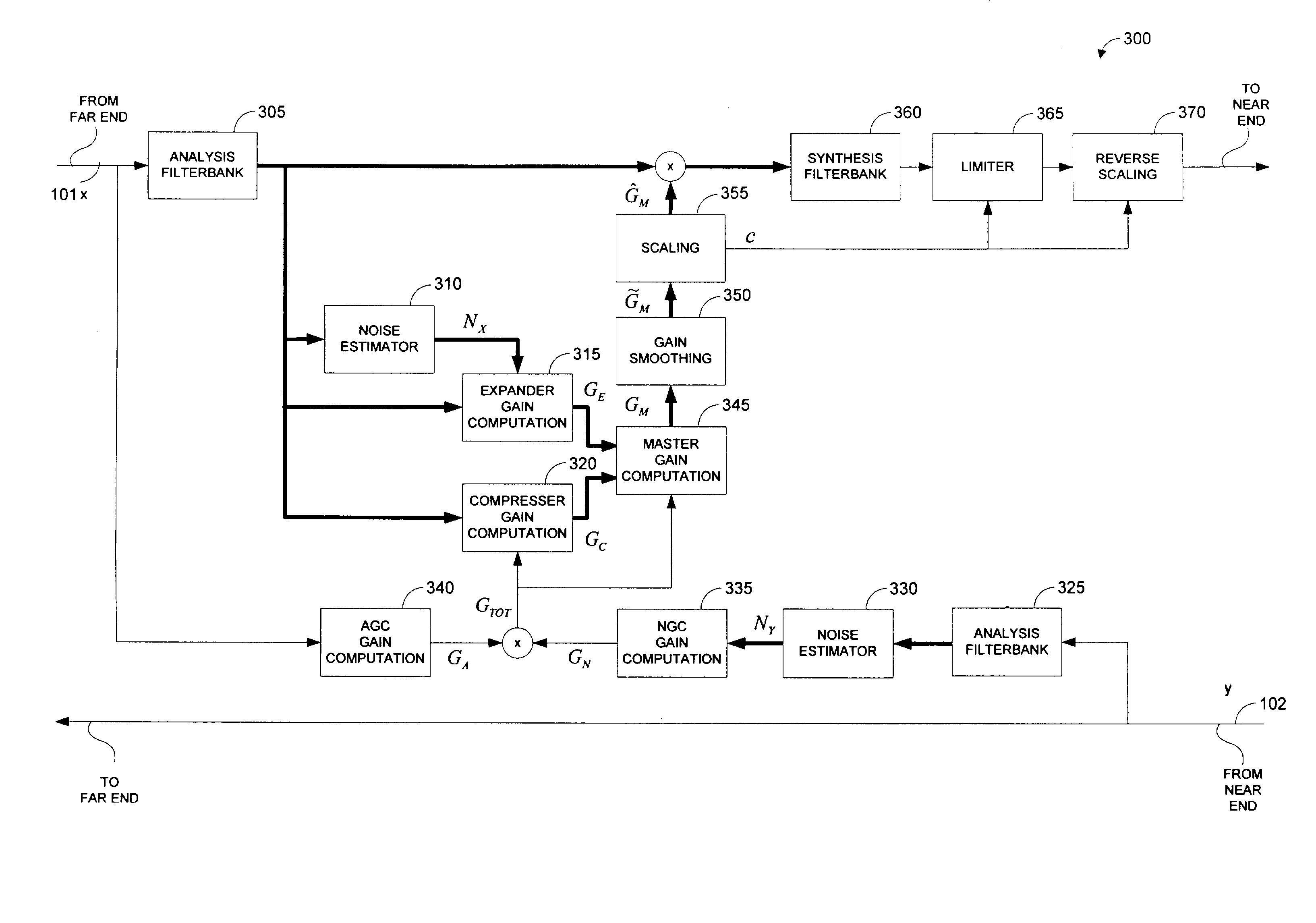
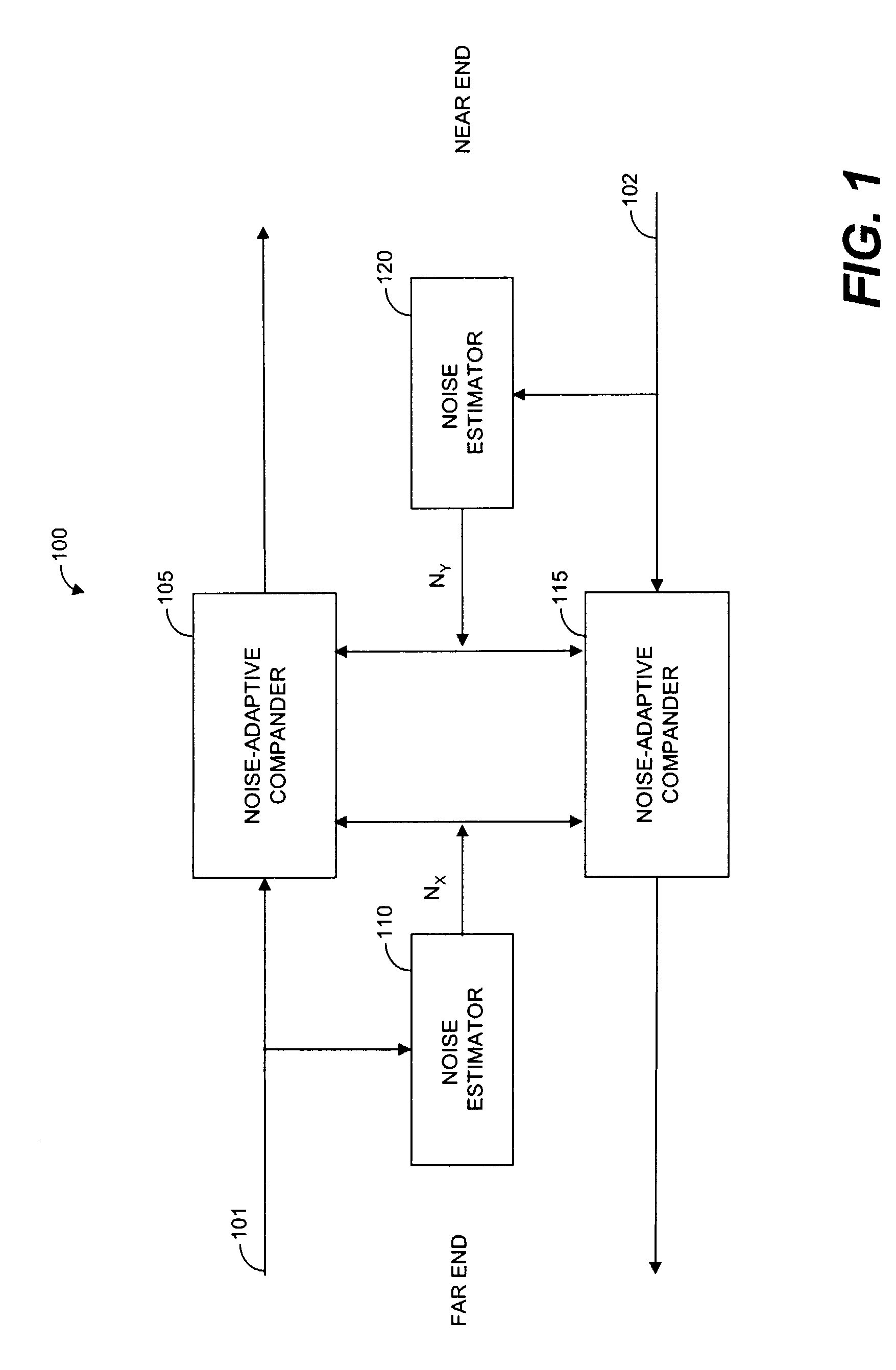
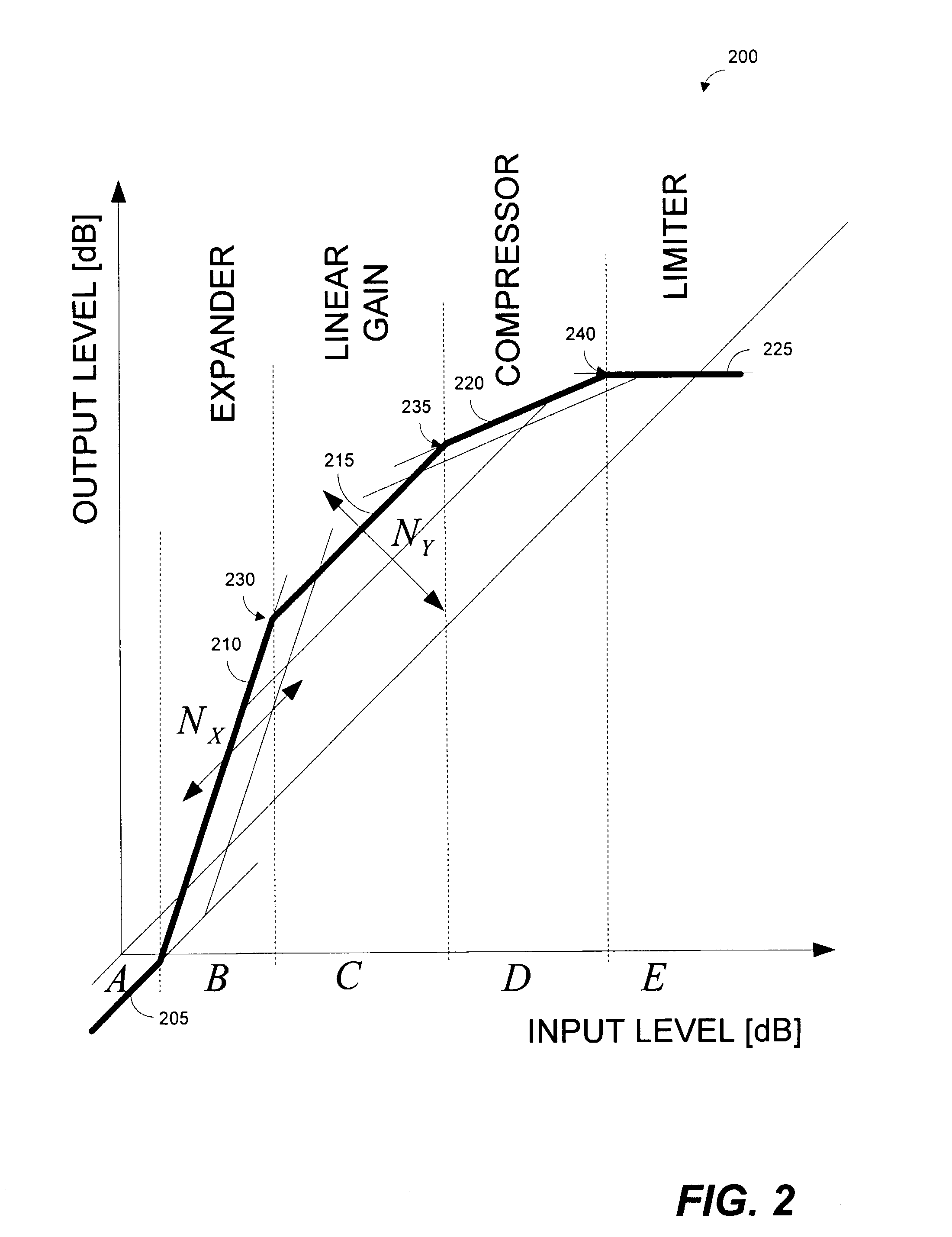
Systems and methods for far-end noise reduction and near-end noise compensation in a mixed time-frequency domain compander to improve signal quality in communications systems
InactiveUS20040101038A1Improve clarityReduce inconvenienceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTime domainCommunications system
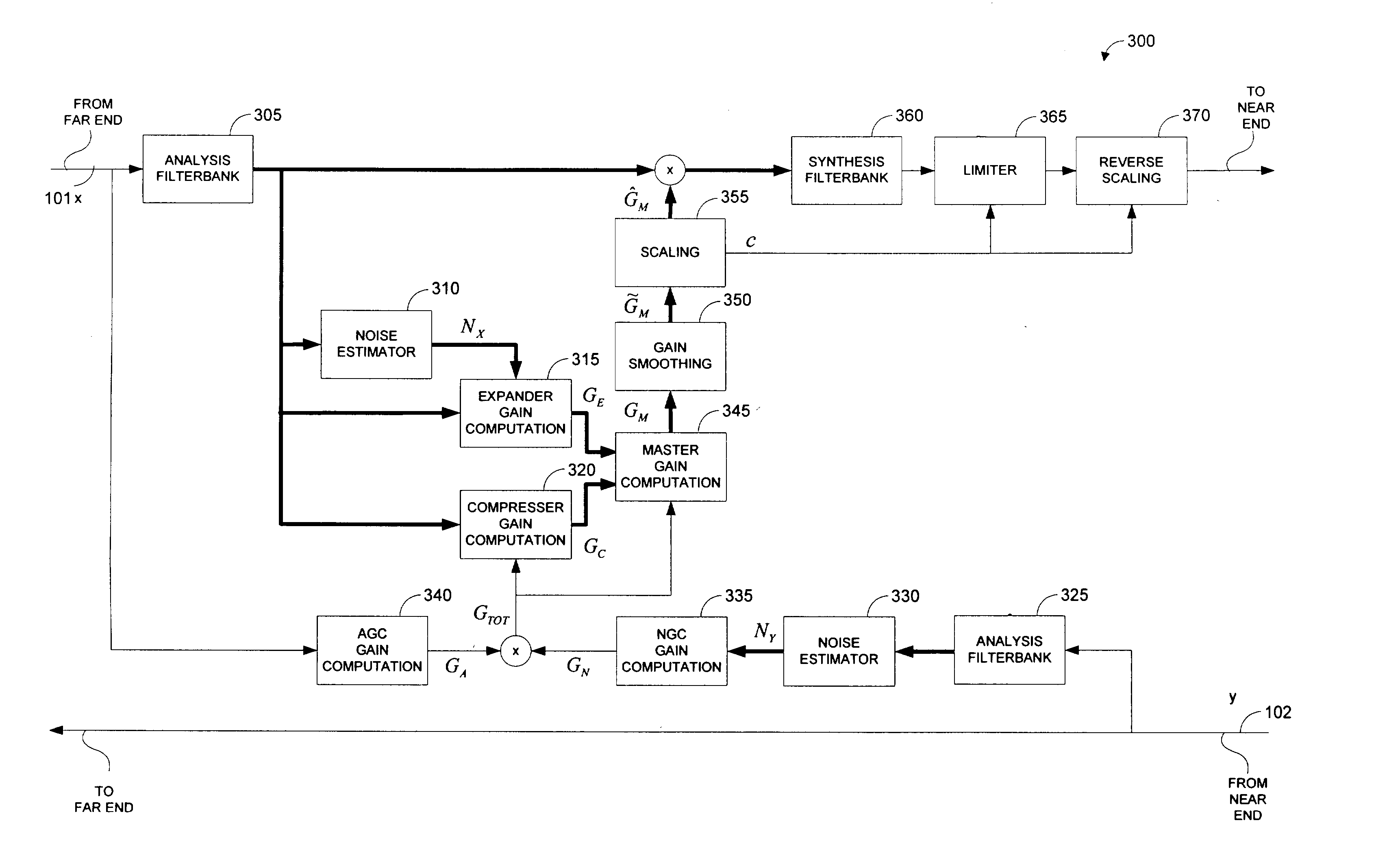
Methods and systems for a mixed time-frequency domain compander, where the expander and compressor are applied in the frequency domain (subbands), while the limiter and the linear gain are applied in the time-domain (full band). Far-end noise reduction is achieved by adapting the expander gain to the far-end noise, near-end noise compensation is achieved by adapting the linear gain and the compressor gain to the near-end noise. The range of the linear gain section is set individually for each subband, but the linear gain is essentially applied to the full band signal via a scaling procedure. The scaling procedure first reduces the compander gain in the frequency domain by a scaling factor and then performs the reciprocal reverse scaling in the time domain. Far-end noise reduction is coupled to near-end noise compensation in order to avoid cross-modulation of the far-end noise by the near-end noise.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
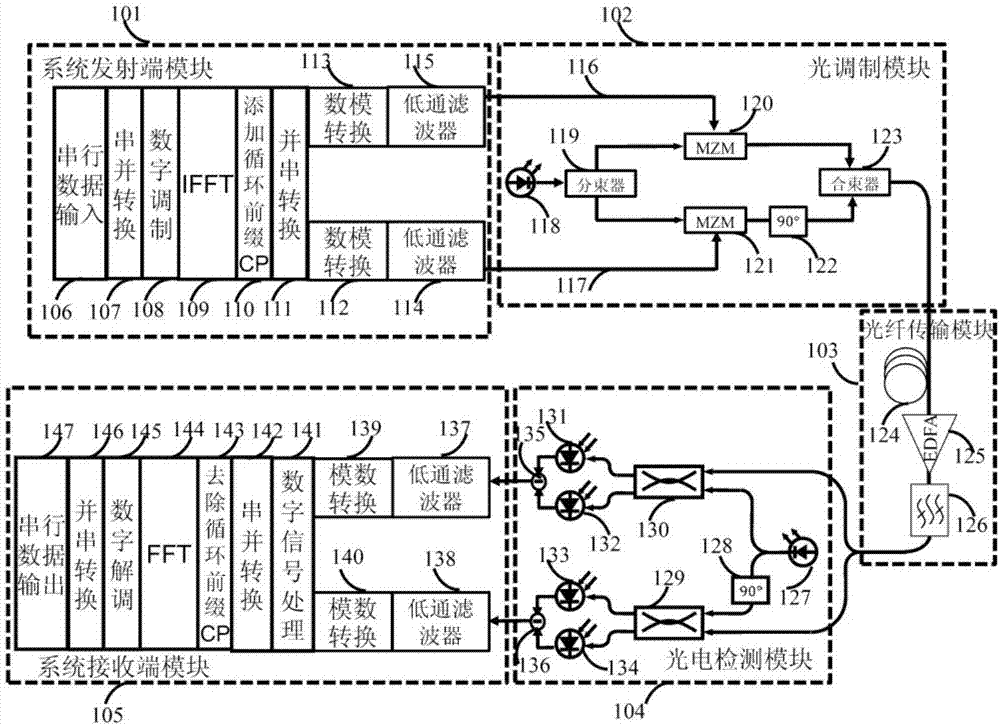
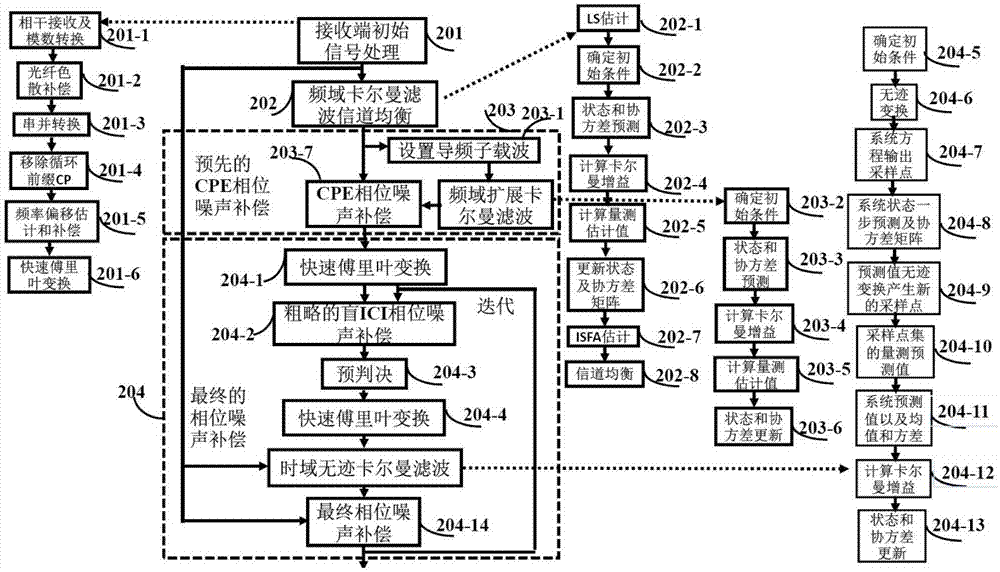
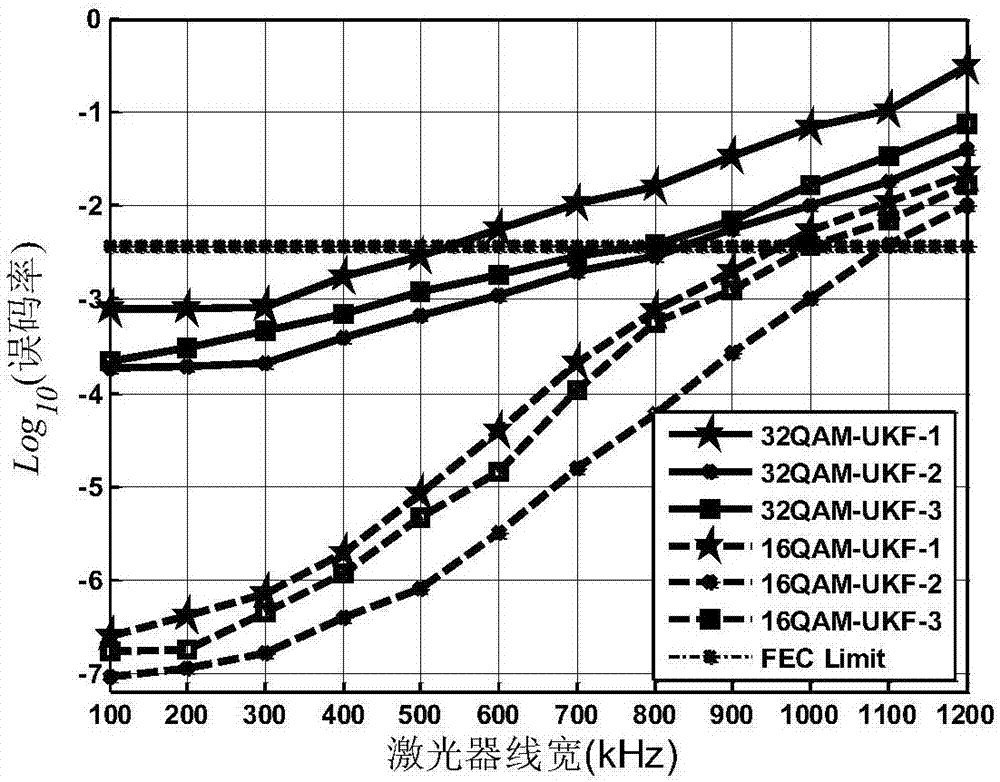
Large line width CO-OFDM system phase noise compensation method of time domain unscented Kalman filter
ActiveCN107395282ALess carrierGood phase noise equalizationDistortion/dispersion eliminationMulti-frequency code systemsPhase noiseFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a phase noise compensation method suitable for large line width and high order modulation CO-OFDM system. The method comprises the following steps: performing channel equalization on training symbol data of a receiving terminal after performing Kalman filter on the same in the frequency domain; setting pilot frequency subcarrier data with certain intervals for each OFDM symbol on a transmitting terminal, and performing preset CPE phase noise estimation and compensation at pilot frequency subcarriers in the frequency domain based on extended Kalman filter (EKF); and finally, converting frequency domain data subjected to CPE phase noise compensation into the time domain, and realizing blind ICI phase noise compensation by using the Avg-BL method, then performing pre- judgment, converting the frequency domain data subjected to the judgment into the time domain, applying time domain data and original time domain data of the receiving terminal to time domain unscented Kalman filter, calculating a final phase noise compensation value, and performing compensation. By adoption of the phase noise compensation method, a better phase noise equalization effect is obtained, and the spectrum utilization rate of the system is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Systems and methods for far-end noise reduction and near-end noise compensation in a mixed time-frequency domain compander to improve signal quality in communications systems
InactiveUS7242763B2Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstation equipmentTime domainCommunications system
Methods and systems for a mixed time-frequency domain compander, where the expander and compressor are applied in the frequency domain (subbands), while the limiter and the linear gain are applied in the time-domain (full band). Far-end noise reduction is achieved by adapting the expander gain to the far-end noise, near-end noise compensation is achieved by adapting the linear gain and the compressor gain to the near-end noise. The range of the linear gain section is set individually for each subband, but the linear gain is essentially applied to the full band signal via a scaling procedure. The scaling procedure first reduces the compander gain in the frequency domain by a scaling factor and then performs the reciprocal reverse scaling in the time domain. Far-end noise reduction is coupled to near-end noise compensation in order to avoid cross-modulation of the far-end noise by the near-end noise.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
High-precision fiber frequency transmission system
ActiveCN106877930AImprove response bandwidthImprove stabilityFibre transmissionDiscriminatorInjection locked
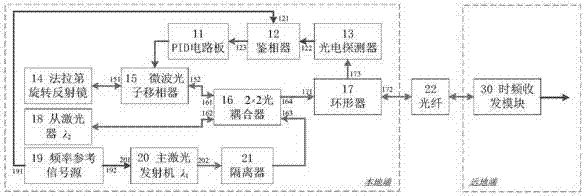
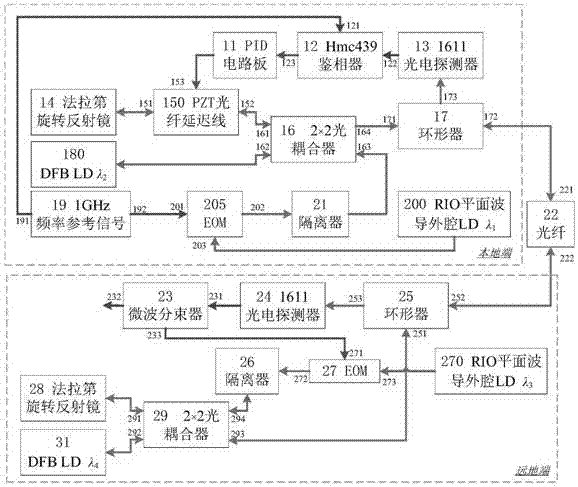
The invention discloses a high-precision fiber frequency transmission system, and the system comprises a PID circuit board, a phase discriminator, a photoelectric detector, a Faraday rotary reflector, a microwave photon phase shifter, a 2*2 optical coupler, a circulator, a slave laser, a frequency reference signal source, a main laser emitter, an isolator, an optical fiber link, and a time frequency receiving and transmitting module. On the basis of a single-fiber bidirectional return error signal obtaining mode, the system carries out the optical fiber link noise compensation based on injection locked coherent detection and the microwave photon phase shifter, thereby achieving the high-precision fiber frequency transmission. The system can achieve the high-precision recovery of a frequency reference signal of a local end at a far end. The system can achieve the two features, needed by phase change, on the same microwave photon phase shifter at the same time: large-bandwidth response and large dynamic range, facilitates the reduction of the complexity, and improves the stability and adaptability. The system can be used in the fields of comparison of the optical clock / atomic clock and the frequency transmission.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coherent optical transceiver and coherent communication system and method for satellite communications
InactiveUS20080025728A1Fast elimination of additive noiseSatellite communication transmissionTransmission monitoringDigital signal processingTransceiver
An optical transceiver is provided for optical communications with additive noise compensation. The system and method are disclosed for the additive noise cancellation, which is typically a vibration noise, caused by moving platform, where the transceiver is located. The transceiver comprises an additive noise sensor and a digital signal processing (DSP) unit which implements variable step size technique to adjust the filter weight in the least square estimate of the noise signal. In the preferred embodiment the digital signal processing is applied both at the transmission and the receiving side. The optical device is packed for ground-satellite and inter-satellite communications applications with resistance to high-energy X-rays, gamma rays and cosmic rays. The optical device sustains its operation characteristics under launch load.
Owner:CELIGHT
Optical amplifiers with a simple gain/output control device
InactiveUS20010040720A1Automatically suppressesMinimize impactWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectronic controllerAudio power amplifier
An optical fiber amplifier includes an optical system and an electronic controller. The optical system includes: an optical gain medium; at least one pump source coupled to the optical gain medium; an input port for in-coming signal; and an output port for an out-going signal. It also includes an input optical signal tap coupled to a first optical detector; and an output optical signal tap coupled to a second optical detector. The electronic controller is adapted to utilize inputs received from the tabs to control optical power provided by the pump source. The controller includes a user interface that allows a user to control at least one of the following available functions: desired amplifier gain value; amplifier output power value; ASE noise compensation.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Implementing a high accuracy continuous speech recognizer on a fixed-point processor
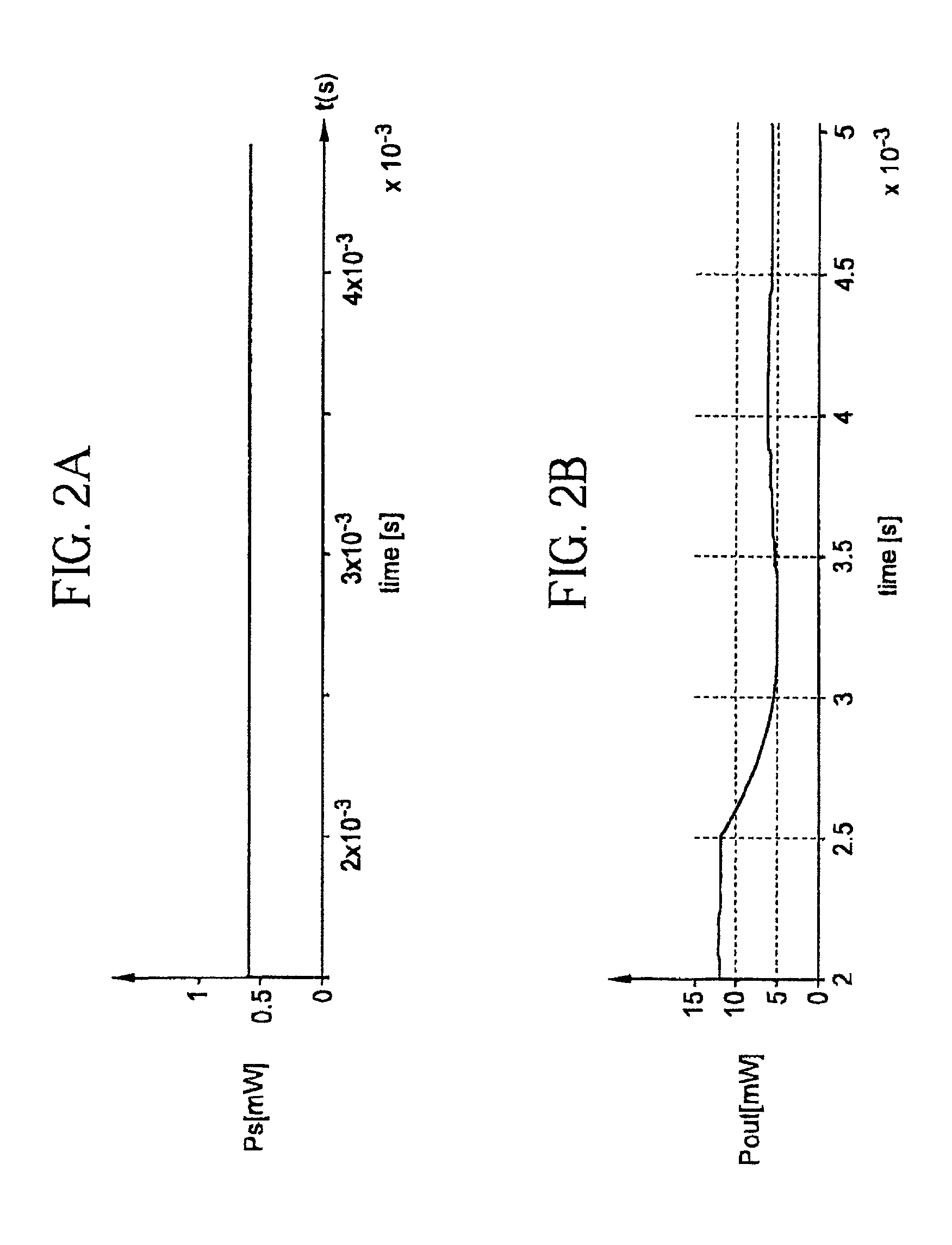
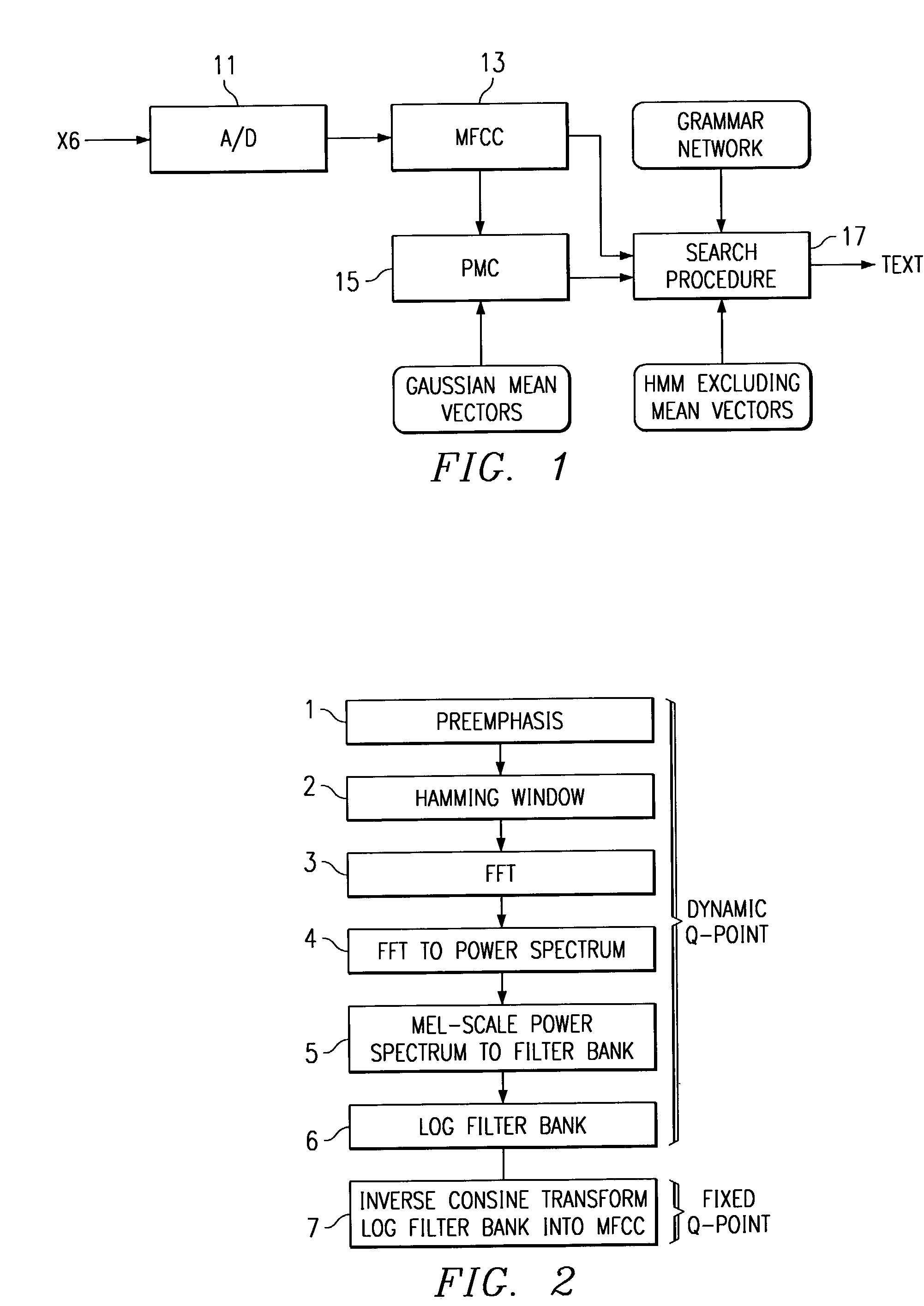
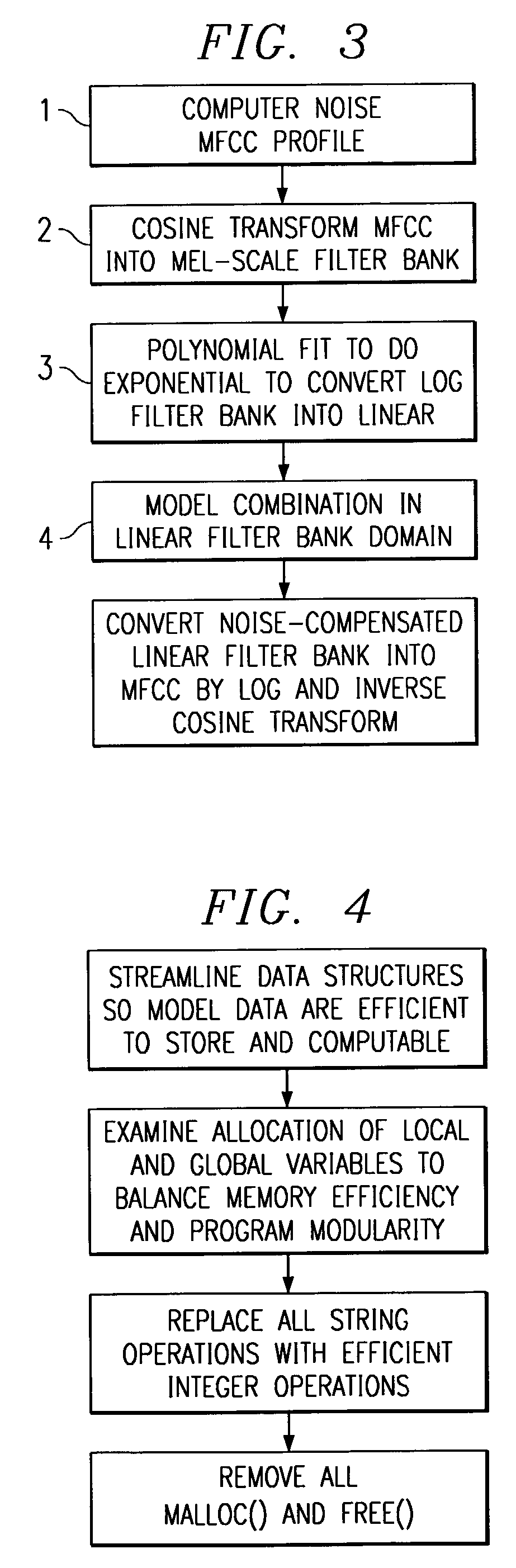
A small vocabulary speech recognizer suitable for implementation on a 16-bit fixed-point DSP is described. The input speech xt is sampled at analog-to-digital (A / D) converter 11 and the digital samples are applied to MFCC (Mel-scaled cepstrum coefficients) front end processing 13. For robustness to background noises, PMC (parallel model combination) 15 is integrated. The MFCC and Gaussian mean vectors are applied to PMC 15. The MFCC and PMC provide speech features extracted in noise and this is used to modify the HMMs. The noise adapted HMMs excluding mean vectors are applied to the search procedure to recognize the grammar. A method of computing MFCC comprises the steps of: performing dynamic Q-point computation for the preemphasis, Hamming Window, FFT, complex FFT to power spectrum and Mel scale power spectrum into filter bank steps, a log filter bank step and after the log filter bank step performing fixed Q-point computation. A polynomial fit is used to compute log2 in the log filter bank step. The method of computing PMC comprises the steps of: computing noise MFCC profile, computing cosine transform MFCC into mel-scale filter bank, converting log filter bank into linear filter bank with an exponential wherein to compute exp2 a polynomial fit is used, performing a model combination in the linear filter bank domain; and converting the noise compensated linear filter bank into MFCC by log and inverse cosine transform.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System for quickly measuring surface quality
InactiveCN101718520AShort reaction timeFast measurementUsing optical meansEnvironmental noiseAcousto-optics
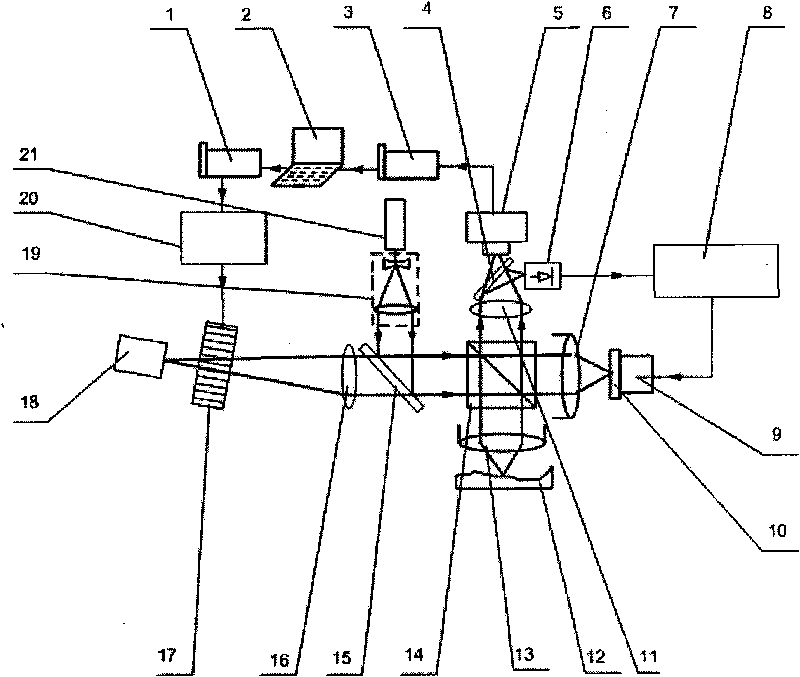
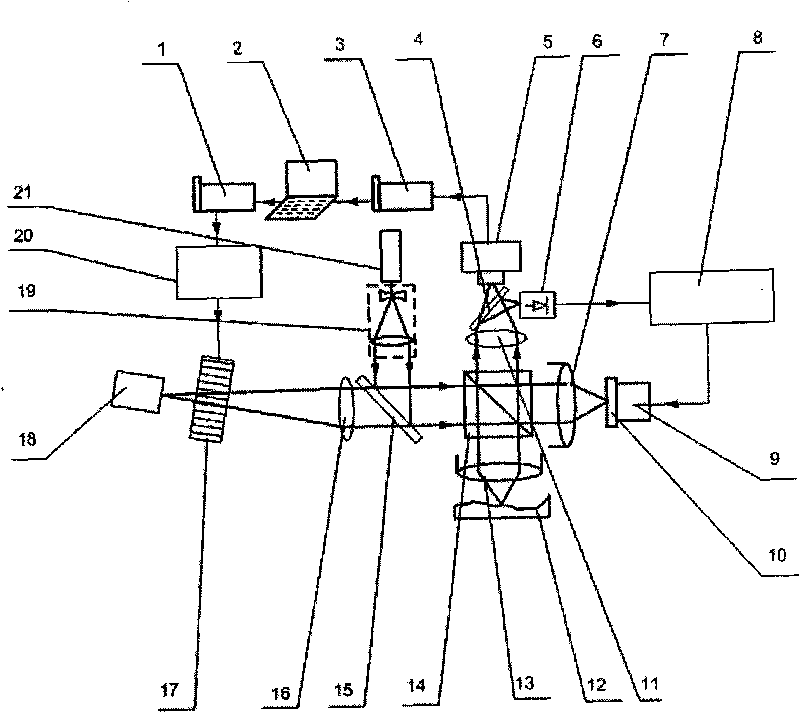
The invention discloses a system for quickly measuring surface quality. The system comprises two sets of common-path interferometers, wherein one set of reference interferometer for noise compensation is specially used for detecting noises such as vibration, air disturbance and the like in environment, and eliminating the influence of interference of the background noises through negative feedback; and the other set of main interferometer for measurement controls wavelength of optical wave incident to the interferometers by using an acousto-optic filter, and can quickly acquire a three-dimensional feature of a surface to be measured by processing a generated interference signal by using large-scale parallel computation based on GPGPU. The system can measure the surface quality in real time, does not need mechanical light path scanning in the process of measurement, and can reach a high measurement speed. The system can be updated one time in 1 to 2 seconds on average, and can be updated more frequently after being optimized. The system can reduce influence of environmental noise on the measurement by adding the active optical path compensation technology, achieves measurement accuracy of sub-nano range, reduces cost, saves a usually expensive high-precision translation stage and can be used for processing workshops with more interference.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for feature domain joint channel and additive noise compensation
InactiveUS7089182B2More robustLess memorySound input/outputSpeech recognitionSpeech identificationSpeech sound
A method for performing noise adaptation of a target speech signal input to a speech recognition system, where the target speech signal contains both additive and convolutional noises. The method includes estimating an additive noise bias and a convolutional noise bias; in the target speech signal; and jointly compensating the target speech signal for the additive and convolutional noise biases in a feature domain.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Ambient noise compensation system
InactiveUS20100329471A1Eliminate the problemVolume andGain controlTransducer protection circuitsEnvironmental noiseEngineering
An ambient noise compensation system having an automatic gain control to adjust the volume of a desired sound in a listening area. A sound pick-up may be placed in the listening area to capture the sound level, including both the desired sound and ambient noise. A measured value is then determined based on the sound level received by the sound pick-up. The measured value may then be compared to a predictive value to determine an acceptable range. The gain control automatically adjusts the volume of the desired sound to maintain the measured sound within the acceptable range.
Owner:MFG RESOURCES INT INC
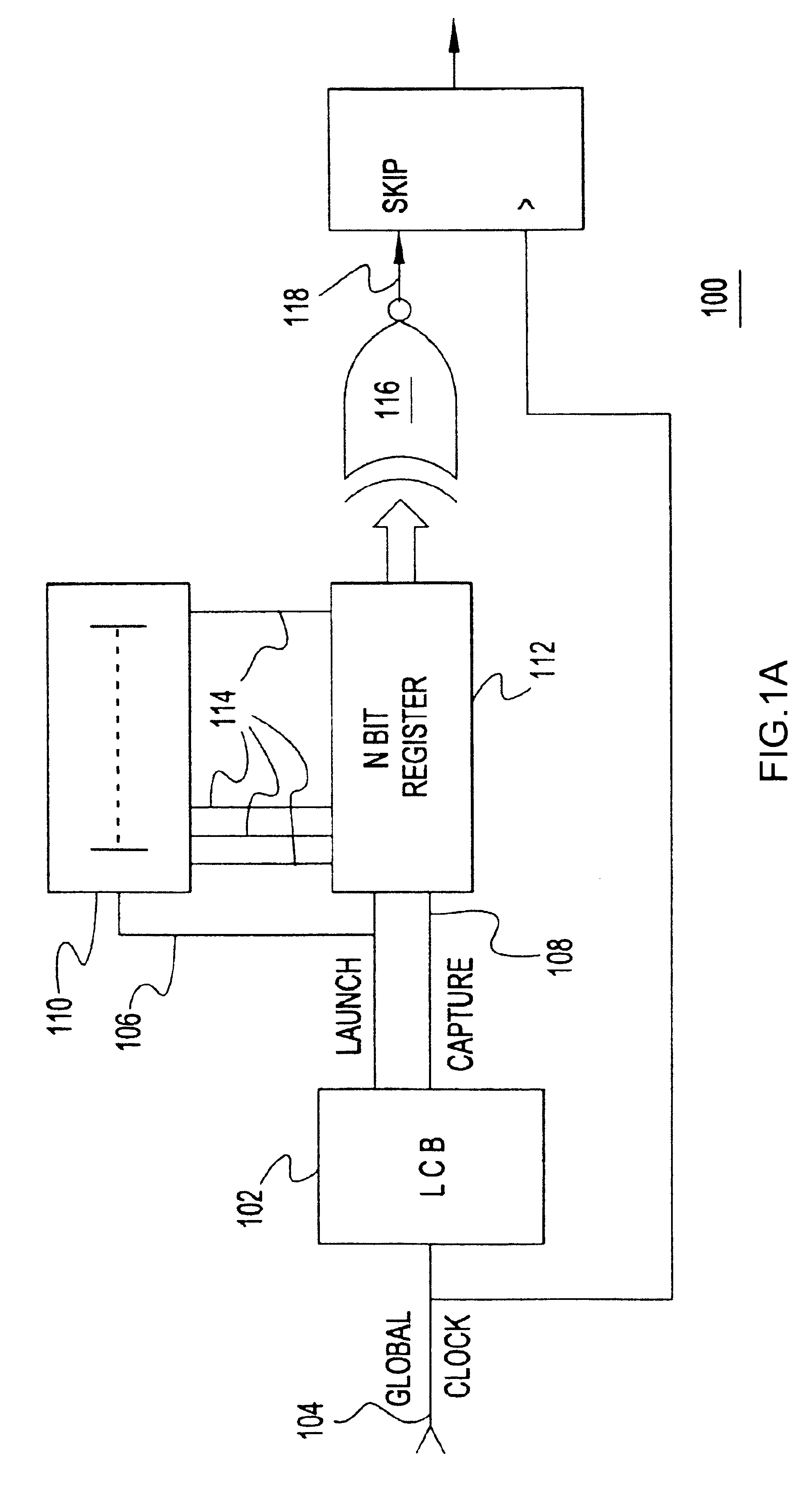
Clock gated power supply noise compensation
InactiveUS6933754B2Reduce impactMinimize how it affects circuit performanceMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlEngineeringClock gating
Owner:IBM CORP
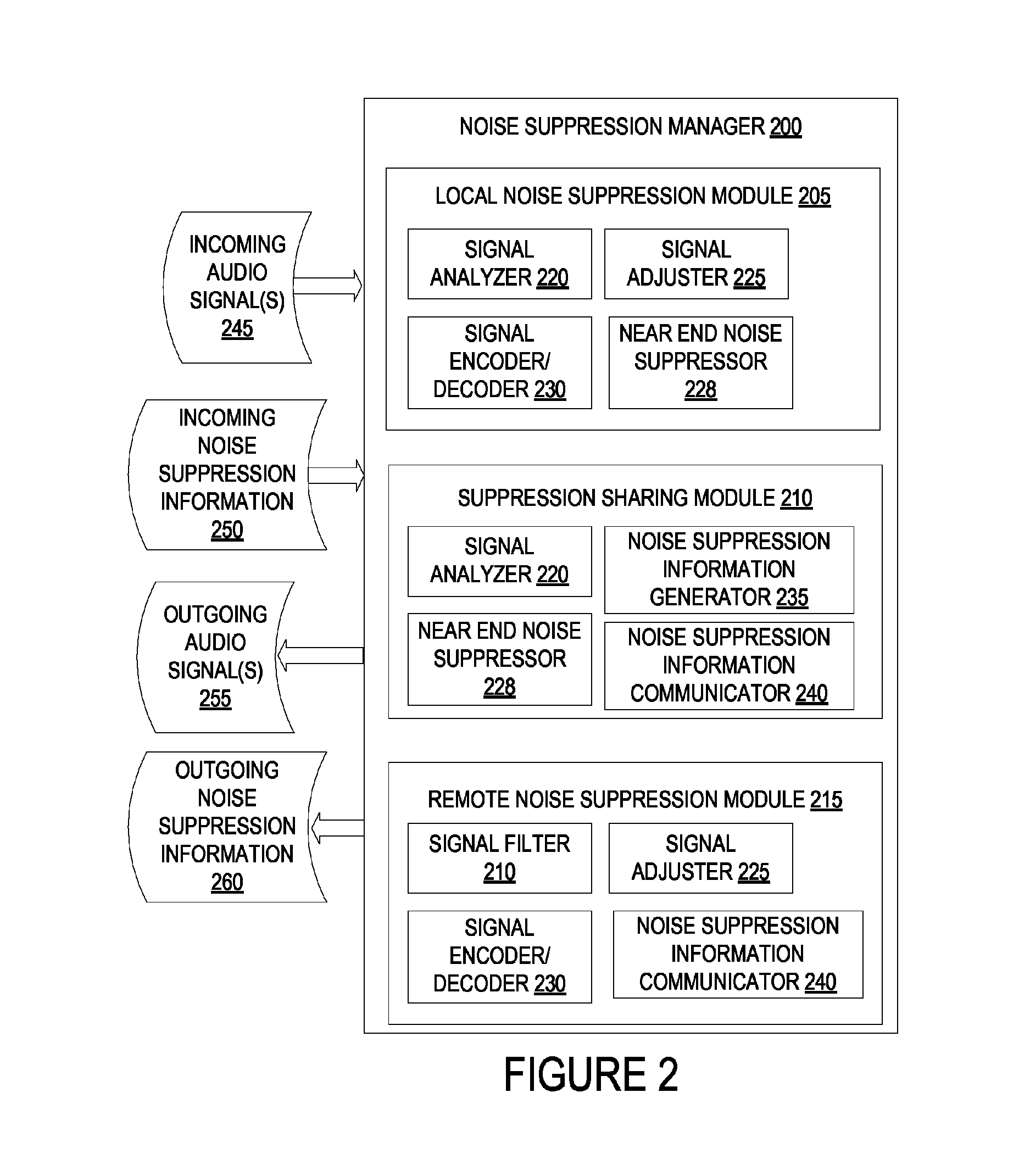
Transmission of noise compensation information between devices
One or more microphones of a first devices receive a first audio. The first device generates a first audio signal from the received first audio. The first device analyzes the first audio signal to determine noise characteristics included in the first audio received by the first device. The first device generates noise compensation information based at least in part on the noise associated with the first audio. The first device transmits the noise compensation information to at least one of a second device or a third device that is intermediate to the first device and the second device. The first device receives a second audio signal generated by the second device, wherein the second audio signal is based at least in part on the noise compensation information transmitted by the first device. The first device then outputs the second audio signal to a speaker of the first device.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Method and apparatus for detecting marine deposits
InactiveUS20110013481A1High sensitivityAccurate detectionMagnetic gradient measurementsSeismology for water-covered areasMagnetic gradientMagnetic measurements
Noise compensation in controlled source electromagnetics (CSEM) comprises measuring time-varying magnetic gradients of the marine environment subjected to CSEM. From the measured magnetic gradients, oceanographic electric and magnetic field noise is determined and used for noise compensation of CSEM measurements of electric and magnetic fields. Selection of magnetic gradient measurement provides improved measurement of oceanographic magnetic noise as other electromagnetic noise sources produce negligible magnetic gradients in the marine environment. Electric field noise is then predicted from the magnetic measurements.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Large line width CO-OFDM phase noise compensation method of time-frequency domain Kalman filtering
ActiveCN107171735AGood phase noise equalizationOvercoming problems caused by sign decision errorsDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic receiversComputation complexityPhase noise
The invention provides a large line width CO-OFDM phase noise compensation method of time-frequency domain Kalman filtering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing Kalman filtering on receiving end training symbol data in the frequency domain, and performing channel equalization, then dividing each OFDM symbol into a plurality of sub-symbols, performing time domain extended Kalman filtering at a pilot frequency sequence in each sub-symbol to obtain a rough phase noise estimation value of each time domain sampling point, and compensating the rough phase noise estimation value; performing linear interpolation between the rough phase noise estimation values at the last pilot frequency sequence of the adjacent sub-symbol to obtain the rough phase noise estimation value of each time domain sampling point, compensating the rough phase noise estimation value, and performing pre- judgment after performing phase noise compensation by using the Avg-BL method; and finally converting the frequency domain data into the time domain to combine with the initial time domain data after the pre- judgment, performing extended Kalman filtering at each sampling point to calculate a precise phase noise estimation value, and compensating the precise phase noise estimation value. The large line width CO-OFDM phase noise compensation method has the advantages of better phase noise equalization effect, good compensation effect and small calculation complexity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
DC offset and 1/f noise compensation of a direct conversion receiver
InactiveUS20050221781A1Minimize noisePulse automatic controlTransmission monitoringIntermediate frequencyDirect-conversion receiver
In a direct conversion receiver with zero-frequency intermediate frequency (IF) signal, the DC offset and 1 / f noise of the IF signal is compensated by means of double-sampling. The first period of the doubling-sampling is a calibration phase, which stores the DC offset and the 1 / f noise. The second period is a signal flow phase during which the stored DC offset and 1 / f noise is connected in opposition with the IF signal to cancel the DC offset and 1 / f noise.
Owner:MARYLAND SEMICON
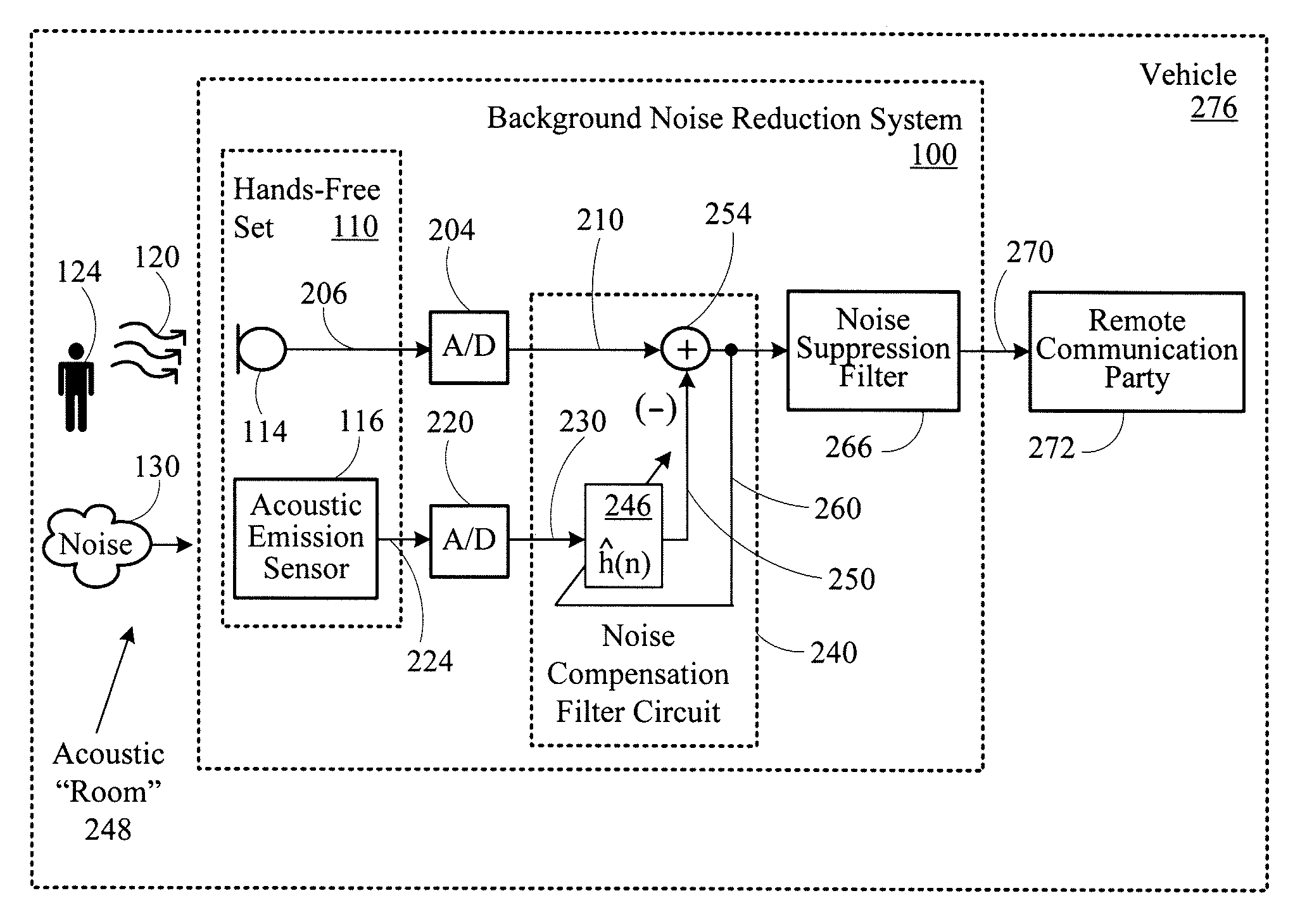
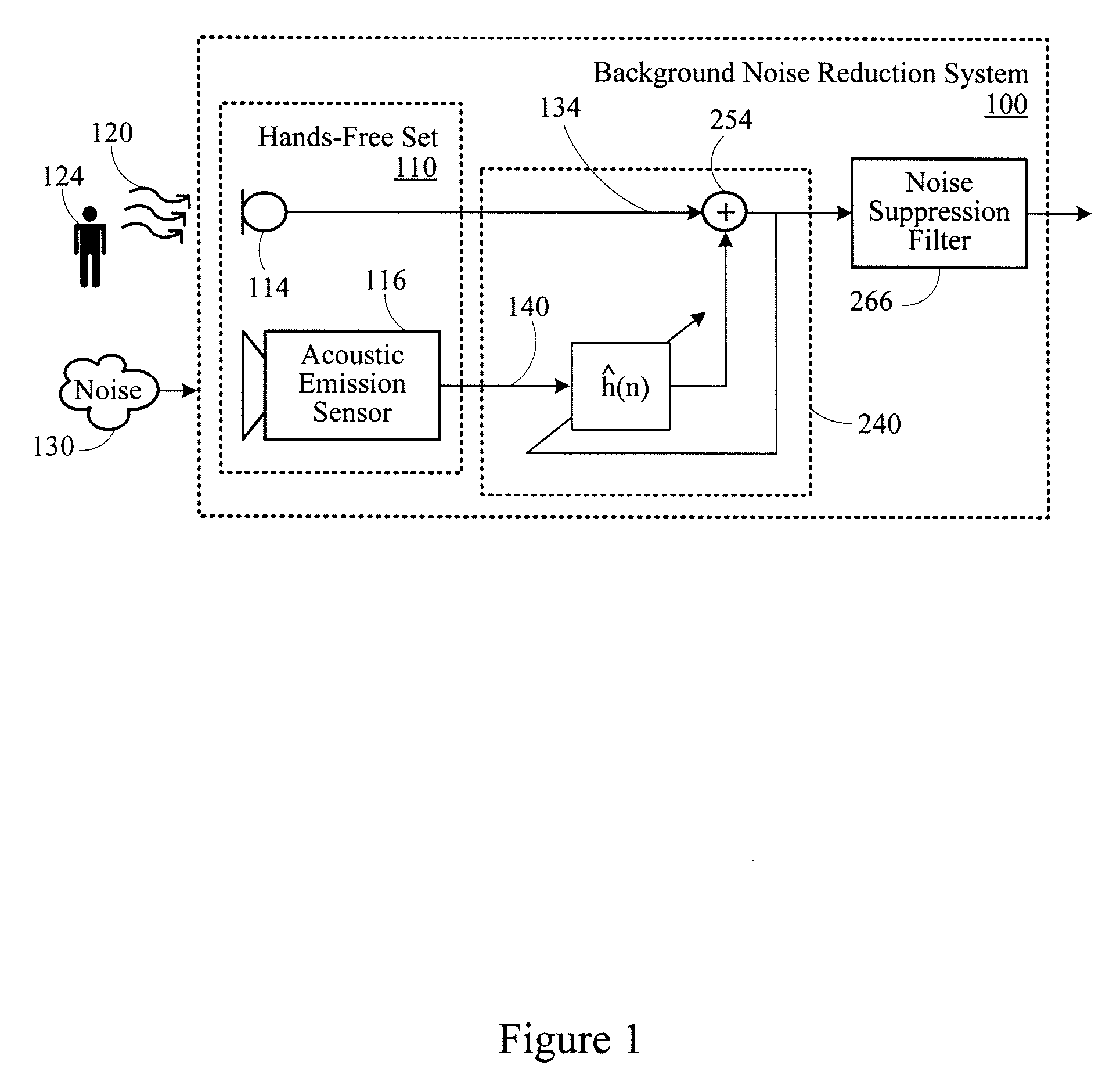
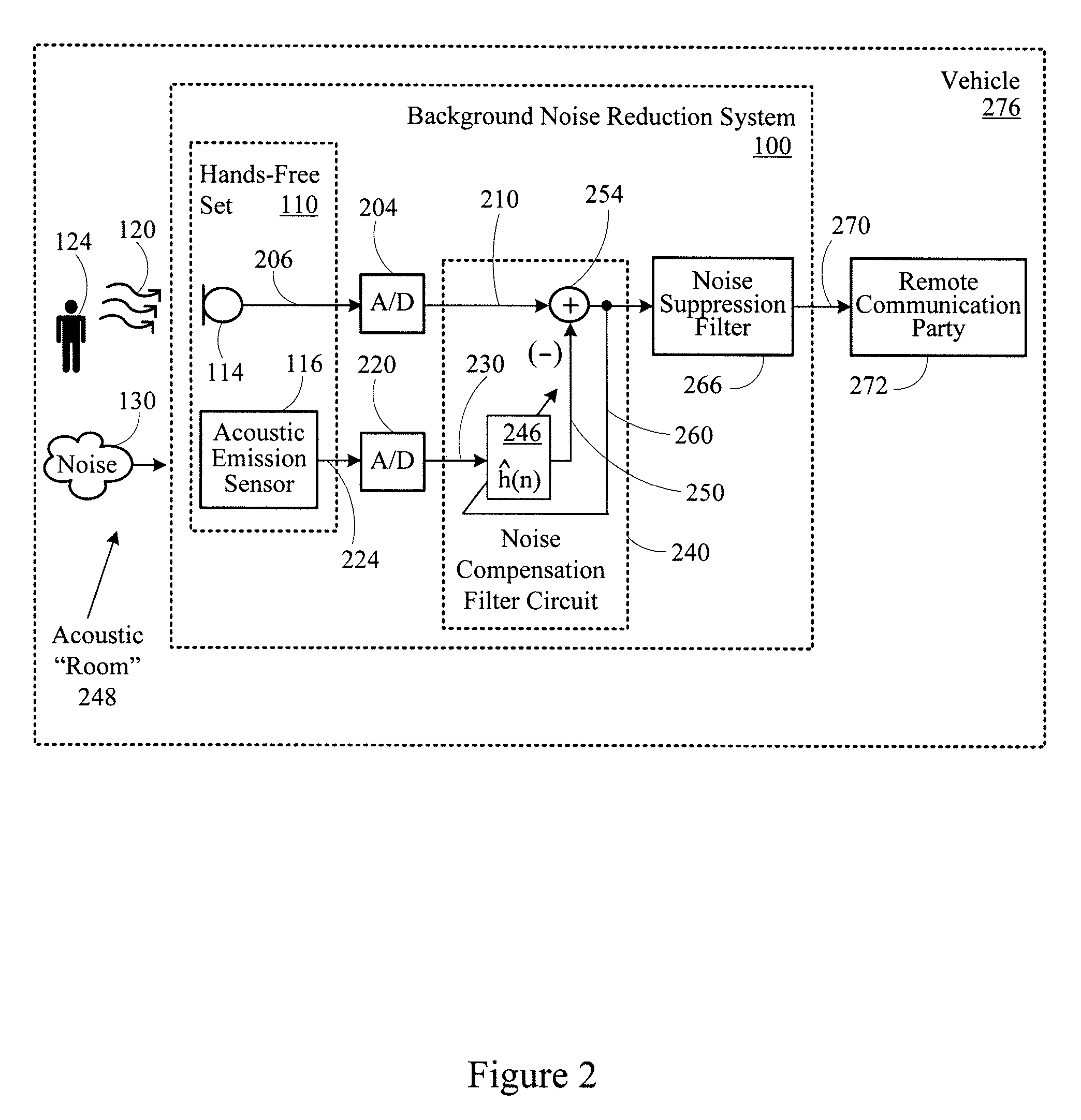
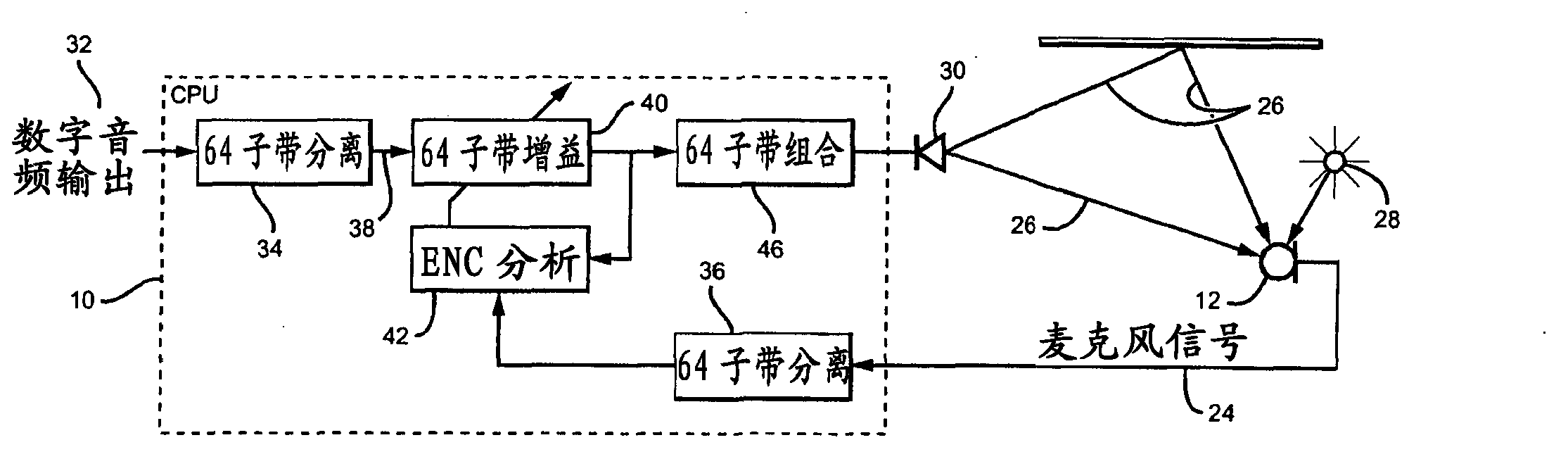
Background noise reduction system
A noise reduction system includes a microphone configured to detect an acoustic signal. A first digitizer converts an output of the microphone into a discrete output signal. An acoustic sensor detects structure-borne noise, and a second digitizer converts an output of the acoustic sensor into a discrete acoustic noise reference signal. A noise compensation circuit processes the discrete output signal based on the discrete acoustic noise reference signal.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
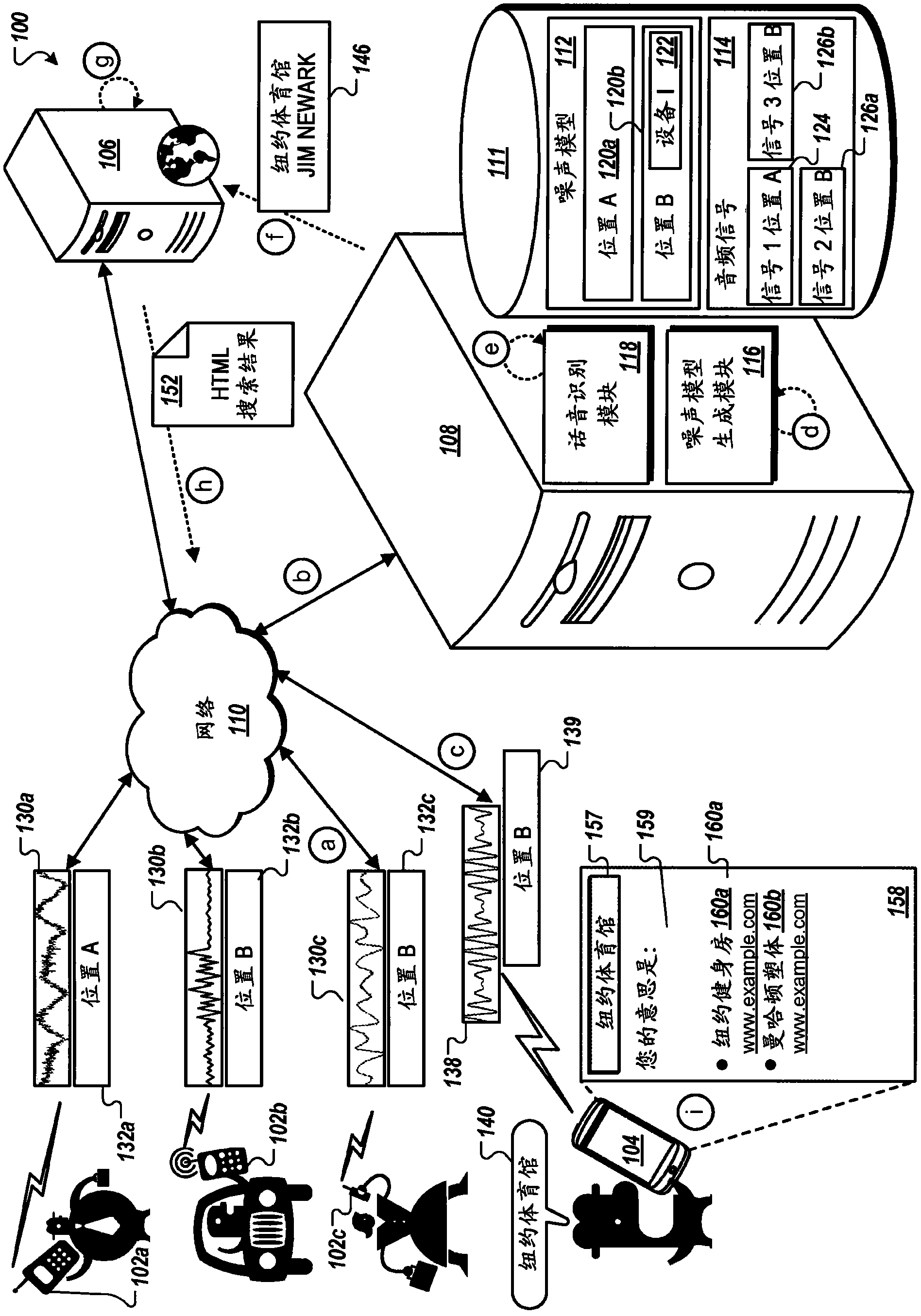
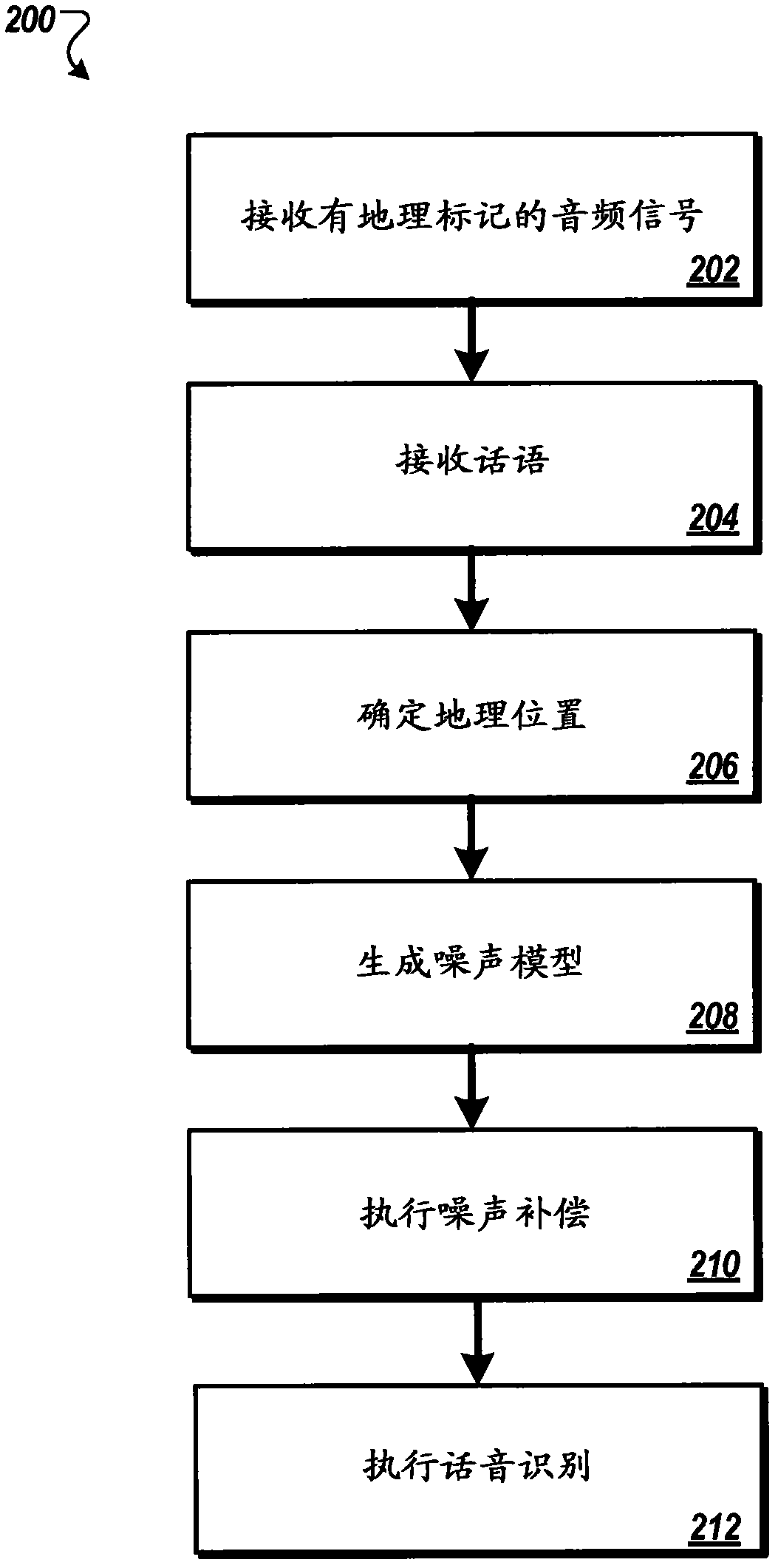
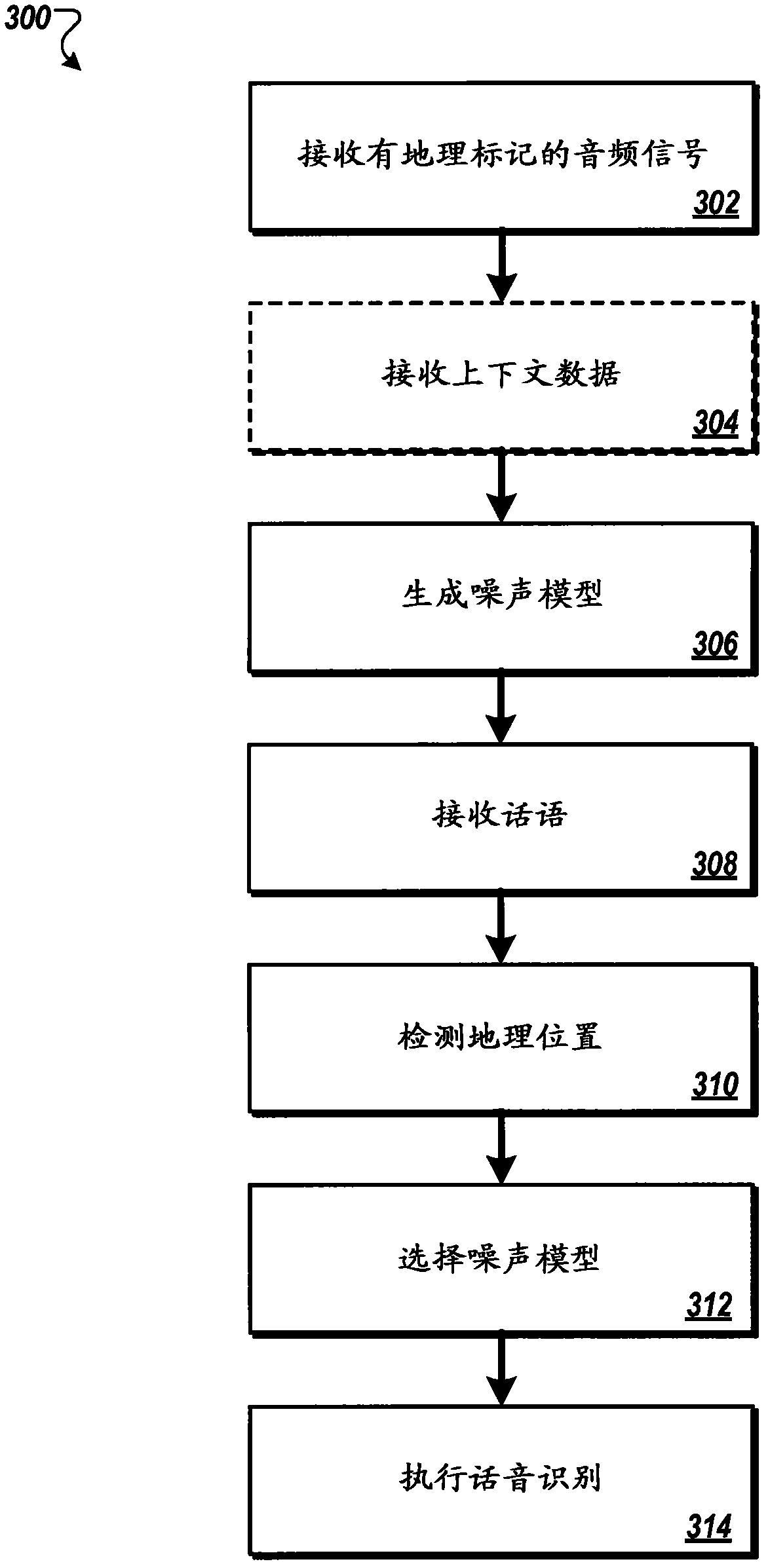
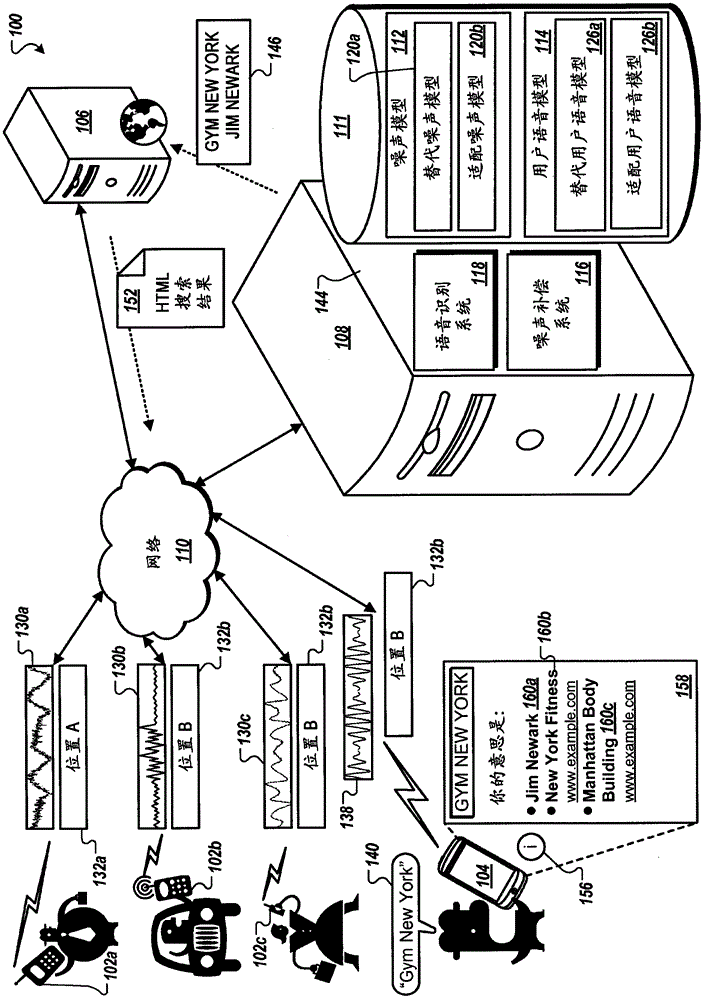
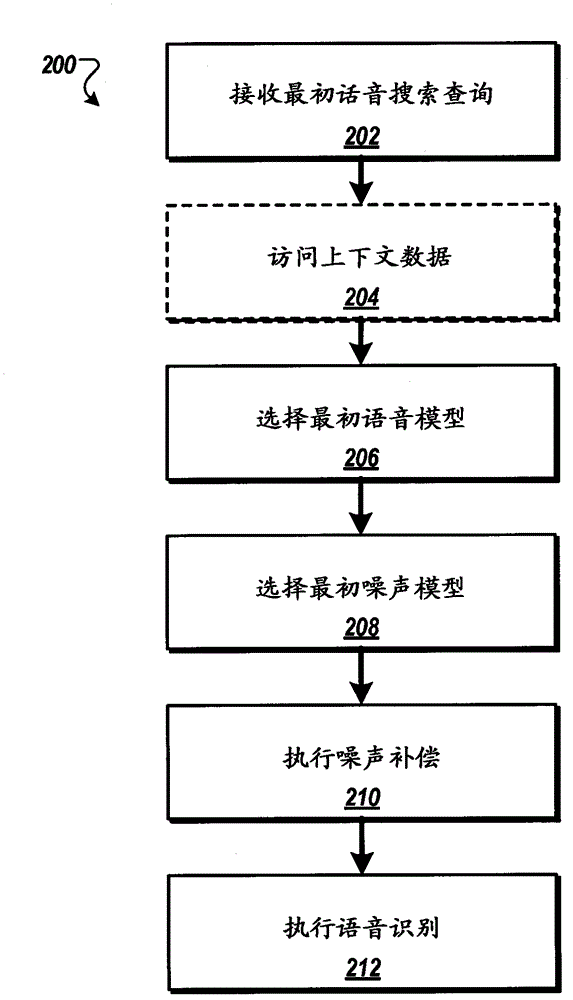
Geotagged environmental audio for enhanced speech recognition accuracy
ActiveCN102918591AImproved noise suppressionEasy to optimizeSpeech recognitionGeolocationAudio signal flow
Methods, systems, and apparatus, including computer programs encoded on a computer storage medium, for enhancing speech recognition accuracy. In one aspect, a method includes receiving geotagged audio signals that correspond to environmental audio recorded by multiple mobile devices in multiple geographic locations, receiving an audio signal that corresponds to an utterance recorded by a particular mobile device, determining a particular geographic location associated with the particular mobile device, generating a noise model for the particular geographic location using a subset of the geotagged audio signals, where noise compensation is performed on the audio signal that corresponds to the utterance using the noise model that has been generated for the particular geographic location.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
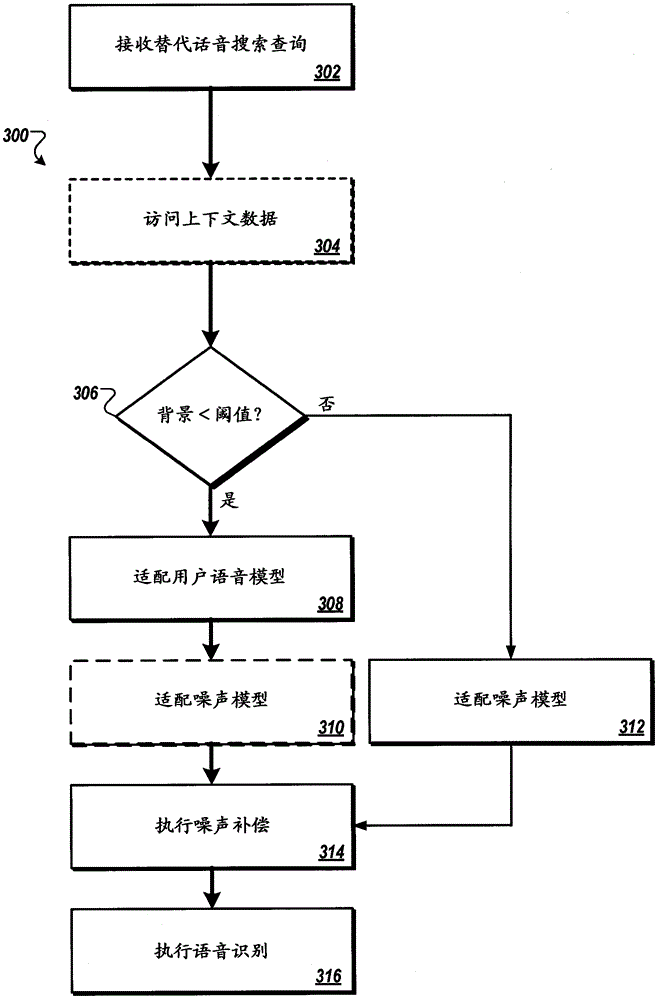
Speech and noise models for speech recognition
An audio signal generated by a device based on audio input from a user may be received. The audio signal may include at least a user audio portion that corresponds to one or more user utterances recorded by the device. A user speech model associated with the user may be accessed and a determination may be made background audio in the audio signal is below a defined threshold. In response to determining that the background audio in the audio signal is below the defined threshold, the accessed user speech model may be adapted based on the audio signal to generate an adapted user speech model that models speech characteristics of the user. Noise compensation may be performed on the received audio signal using the adapted user speech model to generate a filtered audio signal with reduced background audio compared to the received audio signal.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Adaptive environmental noise compensation for audio playback
InactiveCN103039023ASignal processing for reducing noiseSpeech analysisEnvironmental noiseEqualization
The present invention counterbalances background noise by applying dynamic equalization. A psychoacoustic model representing the perception of masking effects of background noise relative to a desired foreground soundtrack is used to accurately counterbalance background noise. A microphone samples what the listener is hearing and separates the desired soundtrack from the interfering noise. The signal and noise components are analyzed from a psychoacoustic perspective and the soundtrack is equalized such that the frequencies that were originally masked are unmasked. Subsequently, the listener may hear the soundtrack over the noise. Using this process the EQ can continuously adapt to the background noise level without any interaction from the listener and only when required. When the background noise subsides, the EQ adapts back to its original level and the user does not experience unnecessarily high loudness levels.
Owner:DTS
Method and apparatus compensating noise in touch panel
ActiveUS8736573B2Reduce impactInput/output processes for data processingParasitic capacitanceEngineering
Touch screen systems and method of compensating noise in same are presented. One touch screen system includes; a touch screen panel having sense channels providing a sense output corresponding to a capacitance variation associated with an applied touch input as detected by one or more sensing units connected to the sense channels. A parasitic capacitance is accumulated in the sense channels as the touch input is applied. The touch screen system also includes a touch controller receiving the sense output and including; a noise compensation block configured to generate a compensation capacitance to compensate for the parasitic capacitance and provide a compensation output, and a signal conversion unit that receives the sense output and the compensation output and generates a noise compensated sense output.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
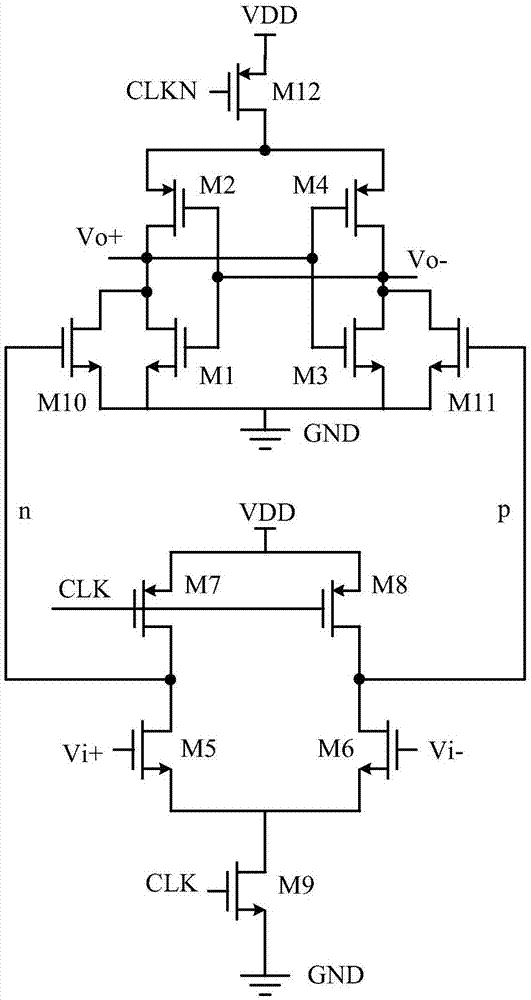
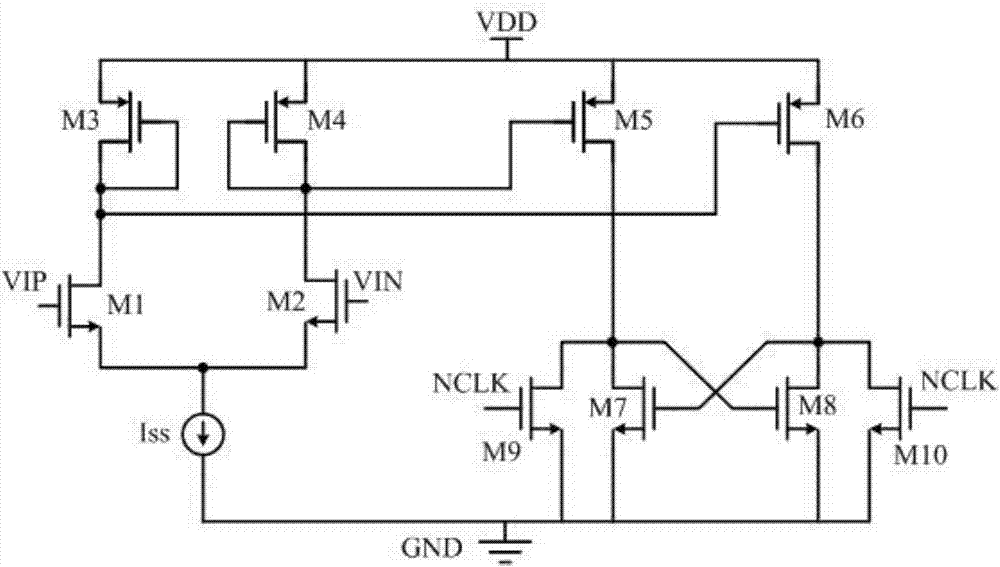
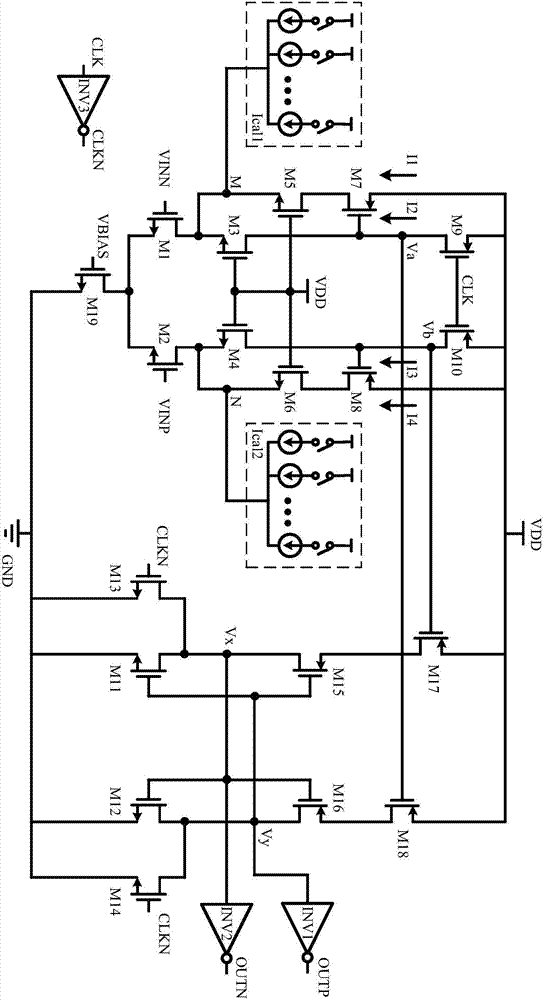
High-speed low-kickback-noise dynamic comparer and circuit
InactiveCN107888171AReduce reset timeShorten the working cycleMultiple input and output pulse circuitsUltrasound attenuationDynamic noise
The invention discloses a dynamic comparator with high speed and low kick noise, which belongs to the field of analog integrated circuits. Its structure includes: pre-amplification stage, current compensation branch for suppressing kickback noise, positive feedback regeneration stage composed of N-channel transistor and P-channel transistor cross-coupling unit, current between pre-amplification stage and positive feedback regeneration stage A control unit, a reset control unit, an offset calibration unit, and an inverter output driver stage. The two current compensation branches that suppress the kickback noise compensate the current attenuation of the main channel to ensure a constant working current of the input pair tube, thereby suppressing the influence of the kickback noise on the input signal, thereby increasing the size of the input pair tube and reducing offset voltage, increasing the response speed. Compared with the traditional comparator, the invention satisfies the requirement of high speed and low power consumption, and exhibits excellent kickback noise suppression ability.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF MICROELECTRONICS SHRIME PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com