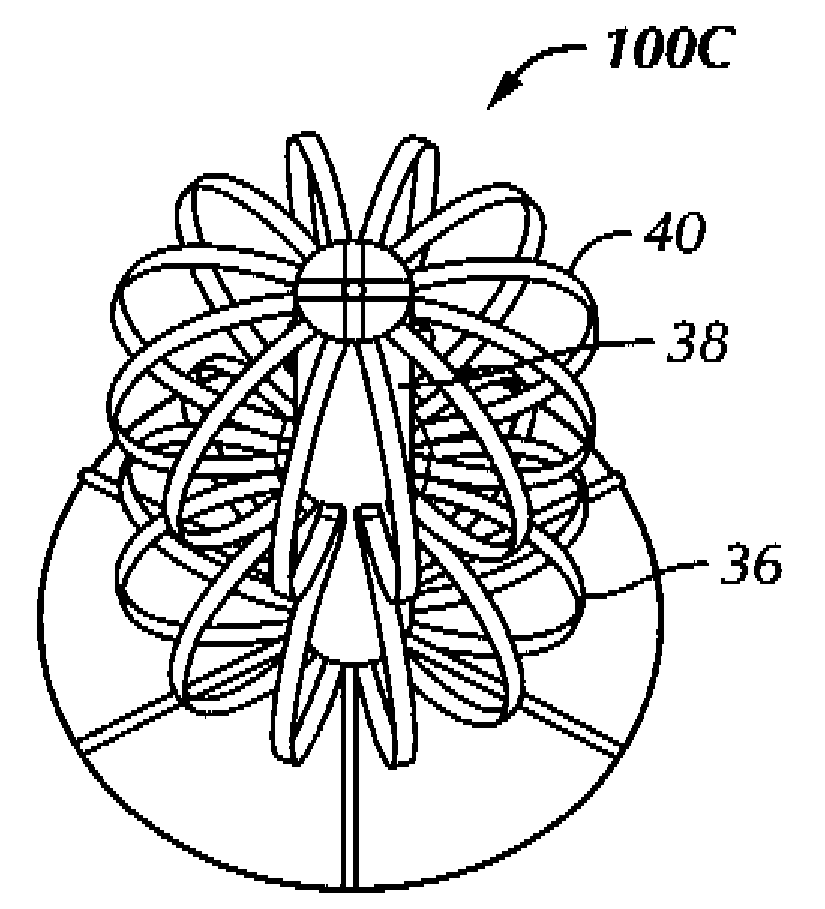
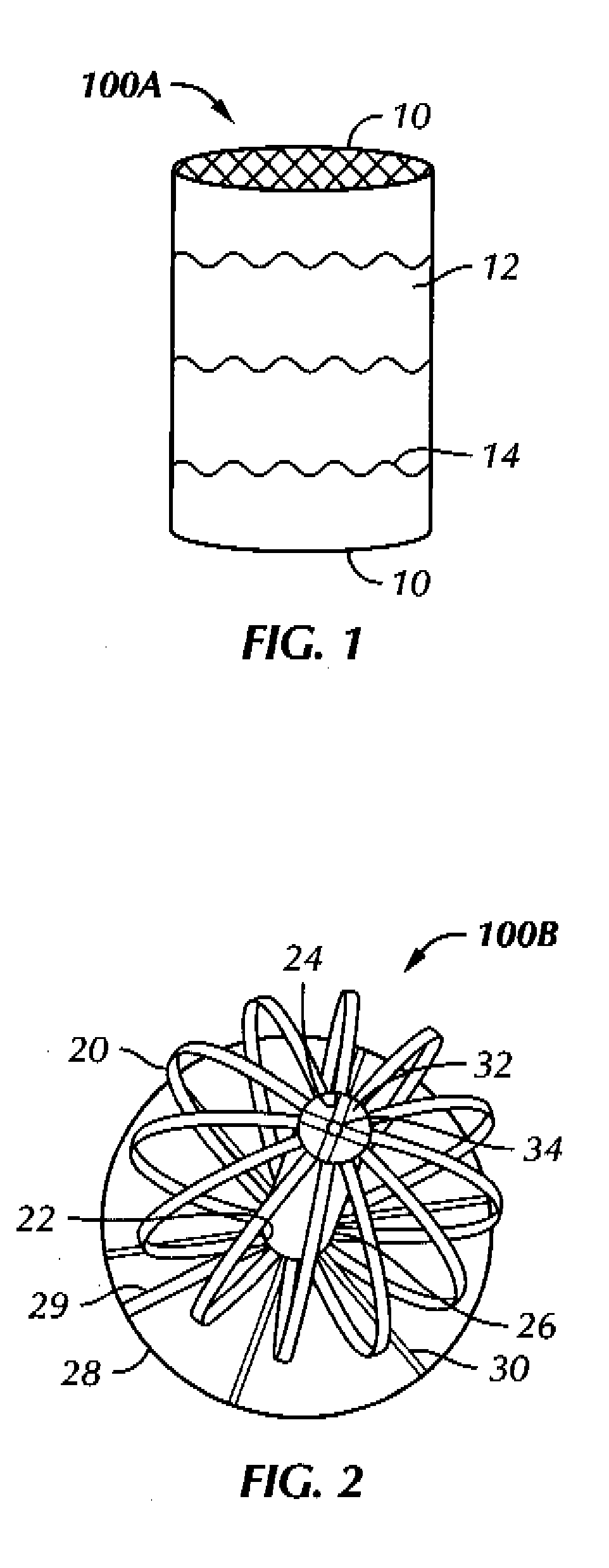
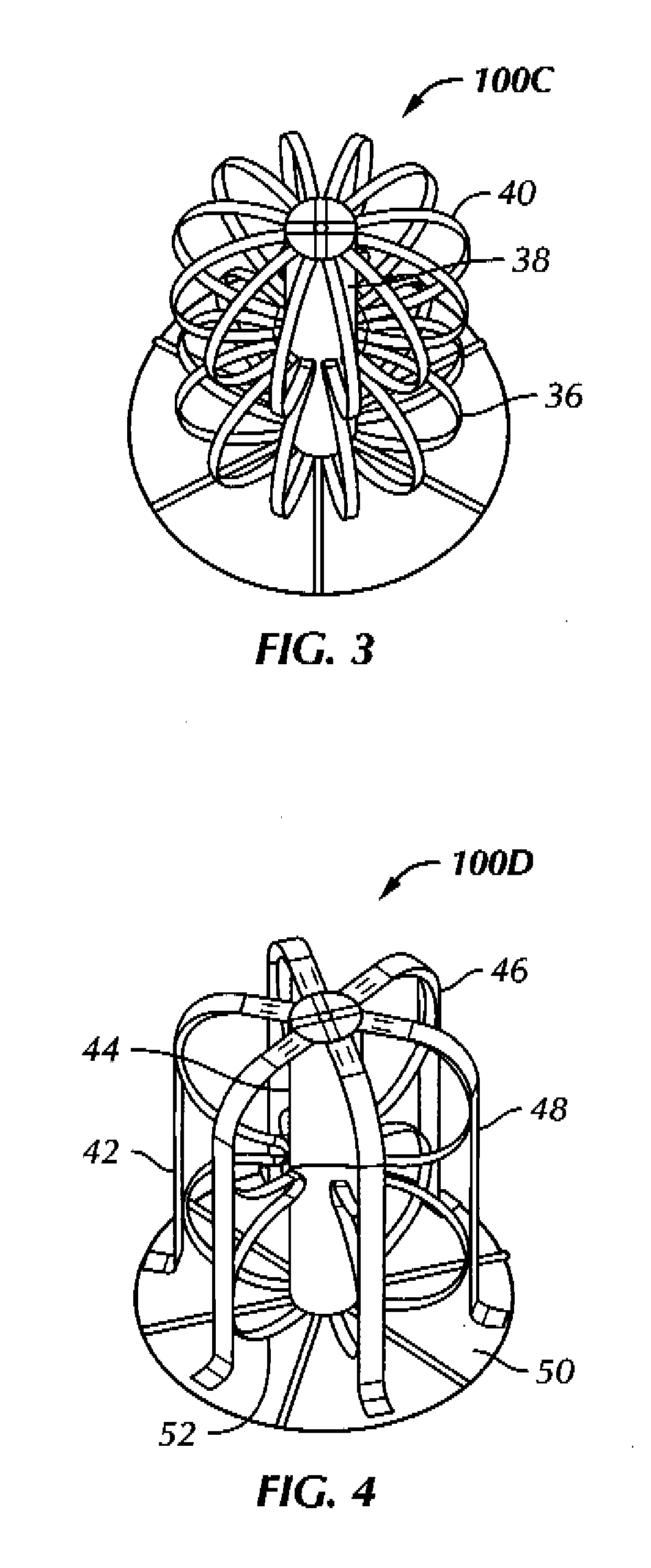
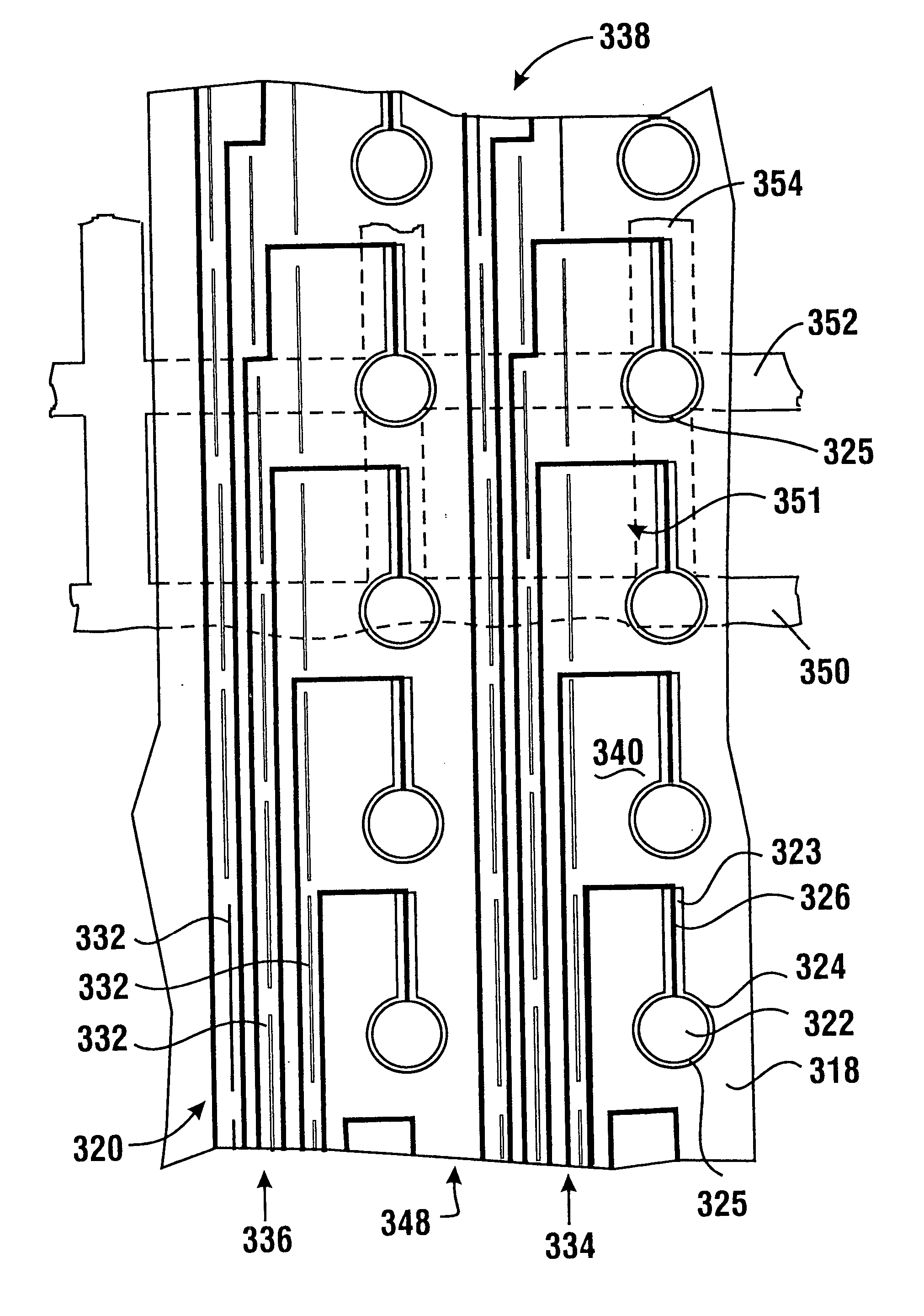
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Muscle architecture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Muscle architecture is the physical arrangement of muscle fibers at the macroscopic level that determines a muscle’s mechanical function. There are several different muscle architecture types including: parallel, pennate and hydrostats. Force production and gearing vary depending on the different geometries of the muscle. Some parameters used in architectural analysis are muscle length (Lm), fiber length (Lf), pennation angle (θ), and physiological cross-sectional area (PCSA).
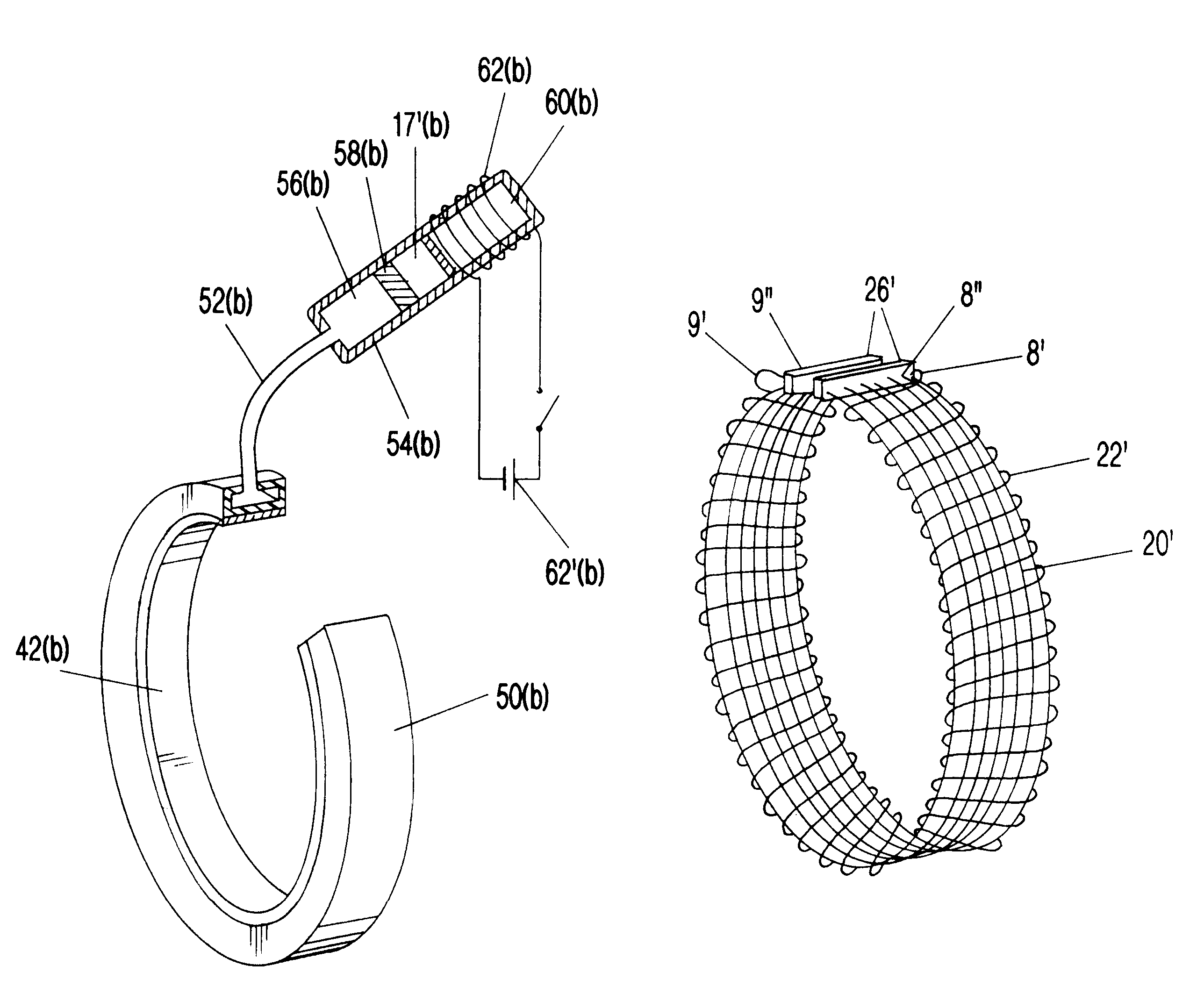
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and stigmatism by using transcutaneously inductively energized artificial muscle implants to either actively change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe. This brings the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants use transcutaneously inductively energized scleral constrictor bands equipped with composite artificial muscle structures. The implants can induce enough accommodation of a few diopters, to correct presbyopia, hyperopia, and myopia on demand. In the preferred embodiment, the implant comprises an active sphinctering smart band to encircle the sclera, preferably implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, similar to a scleral buckle band for surgical correction of retinal detachment, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing (decreasing) the active length of the globe. In another embodiment, multiple and specially designed constrictor bands can be used to enable surgeons to correct stigmatism. The composite artificial muscles are either resilient composite shaped memory alloy-silicone rubber implants in the form of endless active scleral bands, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscle structures, electrochemically contractile endless bands of ionic polymers such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), thermally contractile liquid crystal elastomer artificial muscle structures, magnetically deployable structures or solenoids or other deployable structures equipped with smart materials such as preferably piezocerams, piezopolymers, electroactive and eletrostrictive polymers, magnetostrictive materials, and electro or magnetorheological materials.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
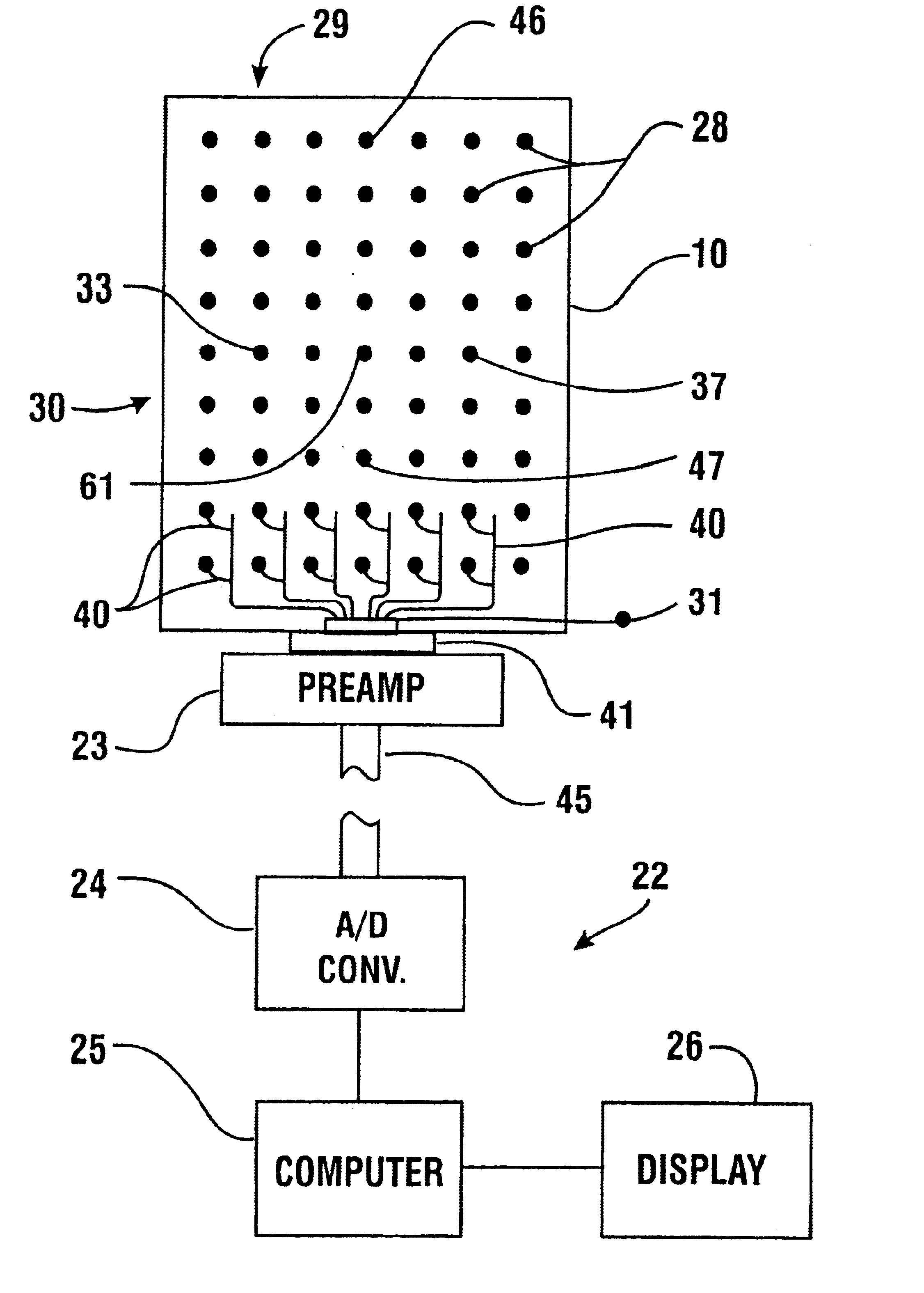
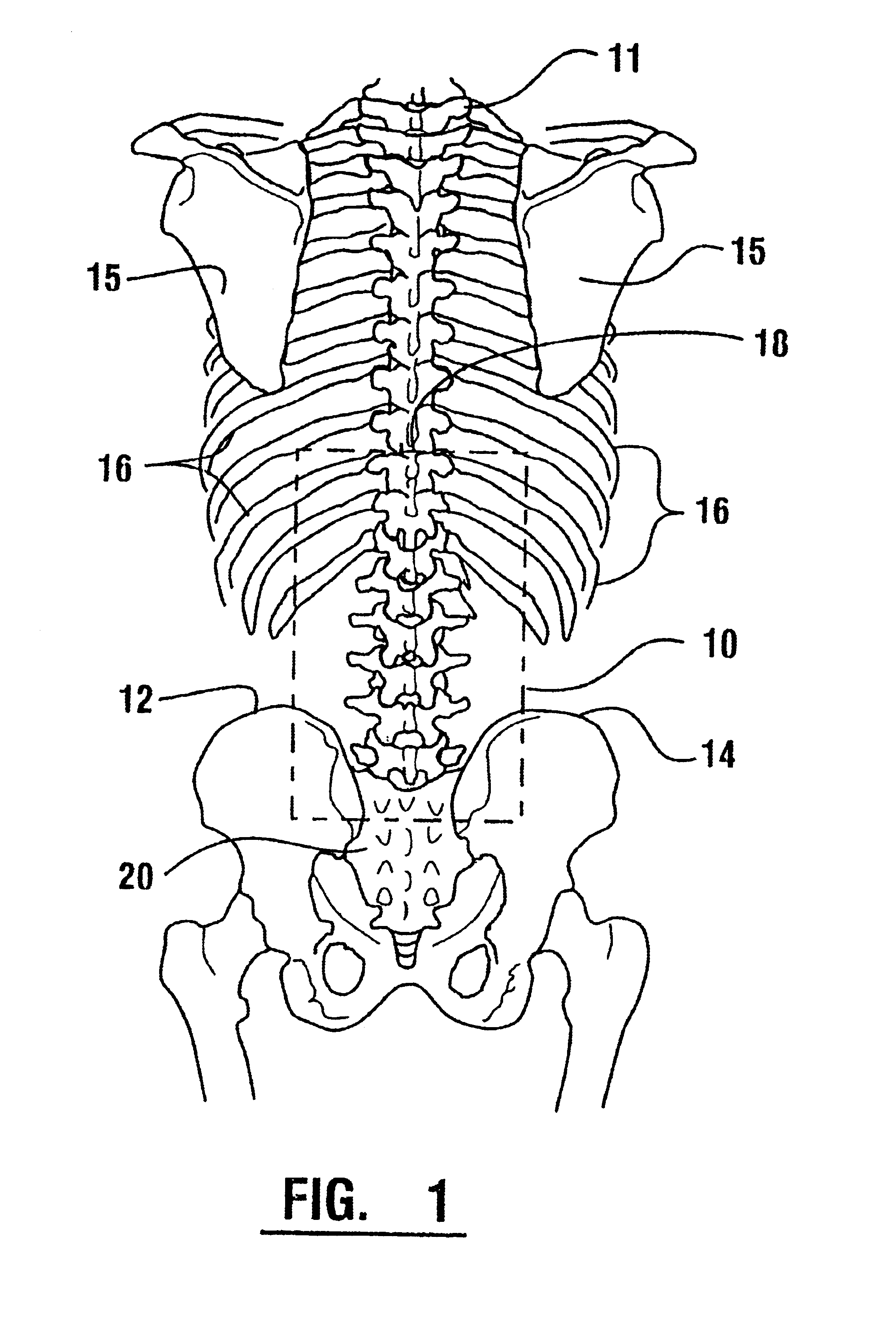
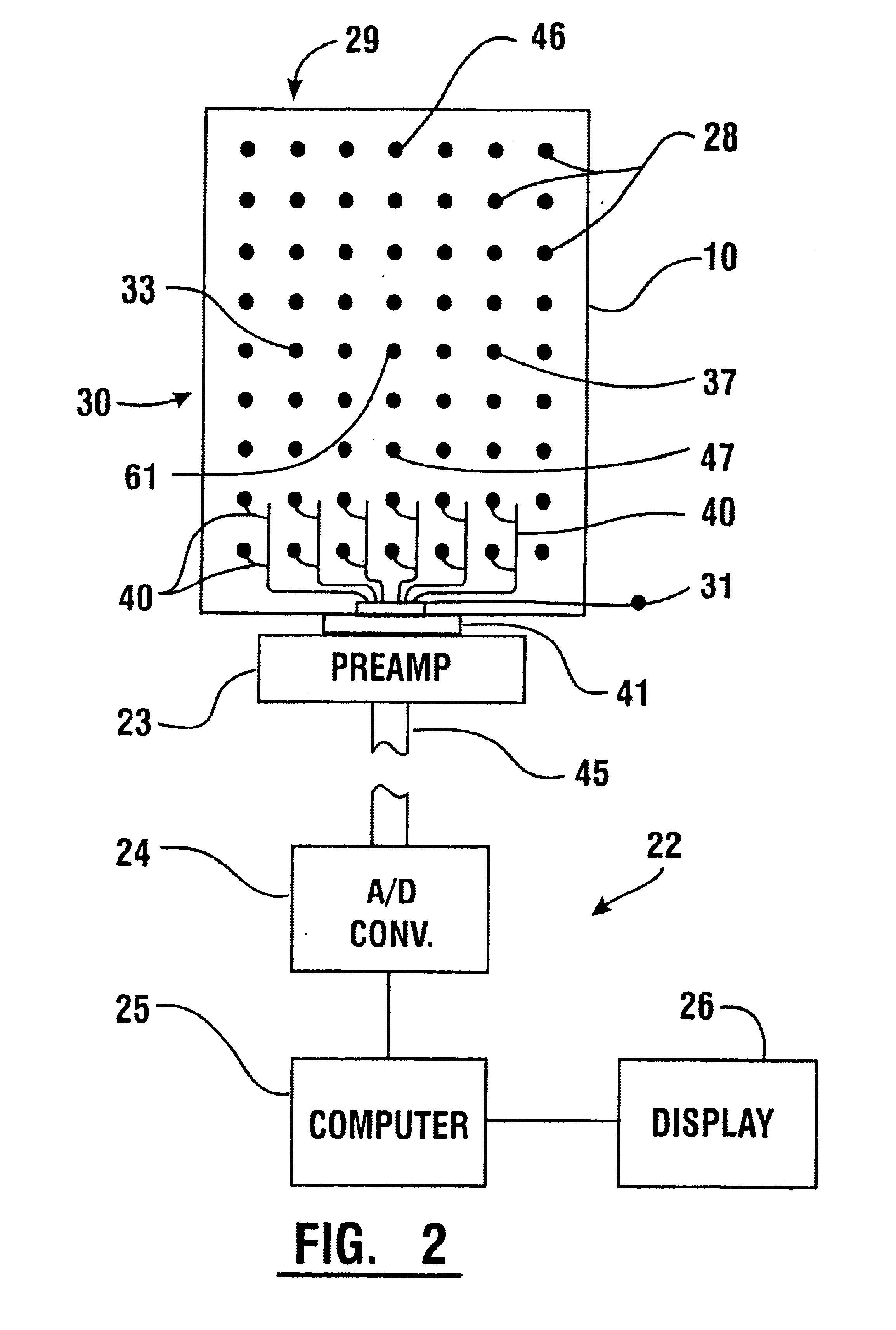
Emg electrode apparatus and positioning system
InactiveUS6745062B1Enhancing flexibility and extensibilityElectromyographySensorsElectricityBiological body
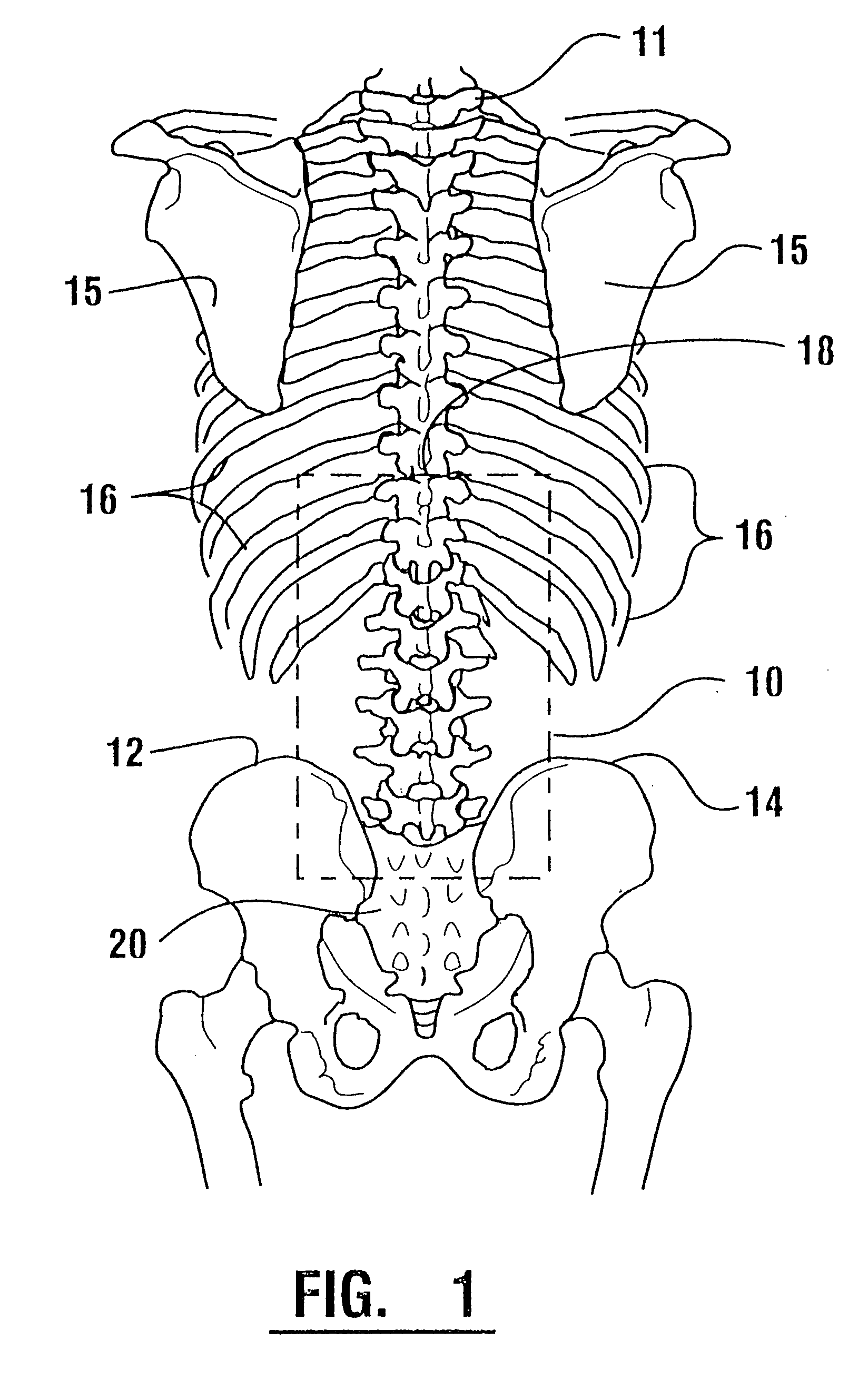
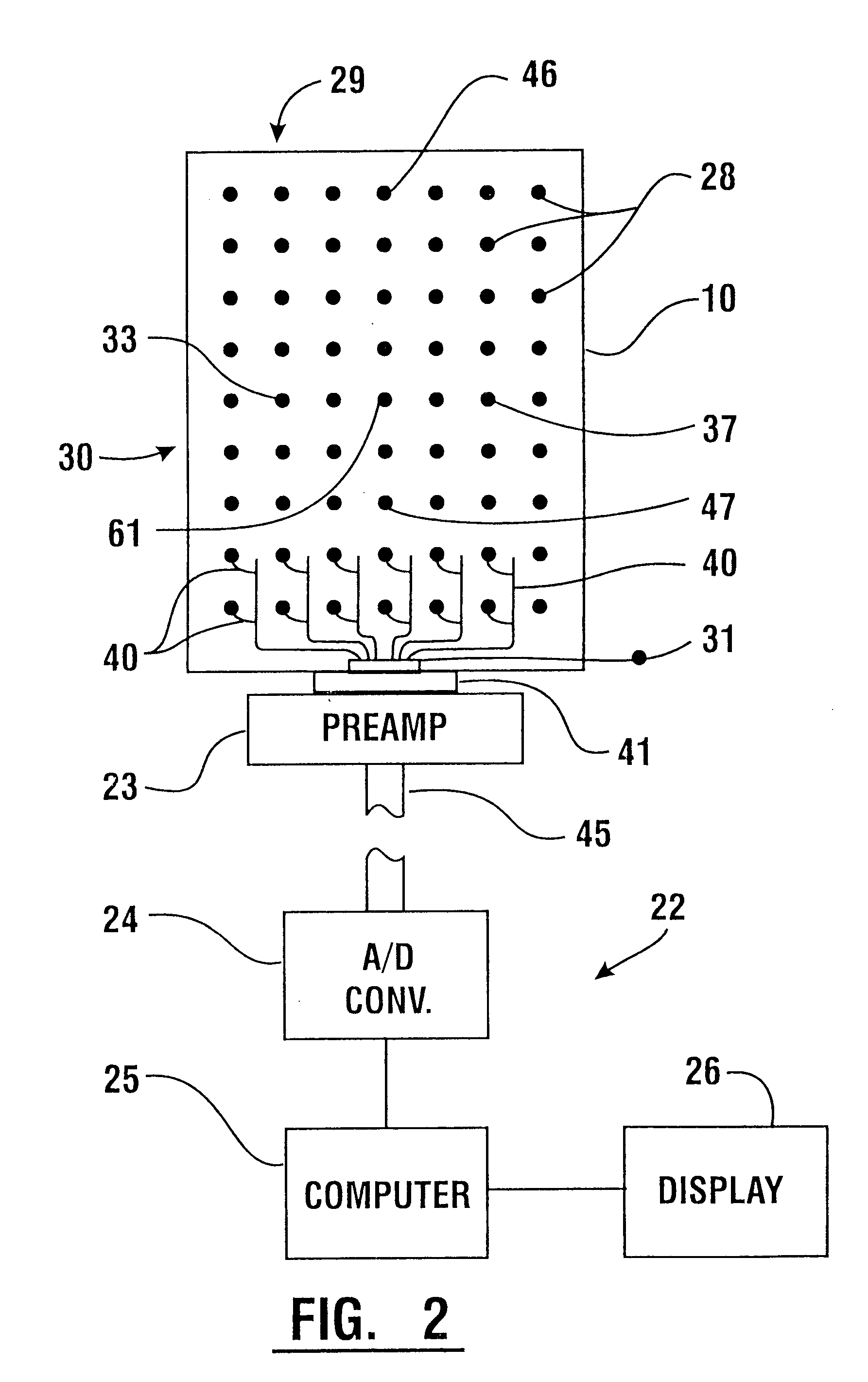
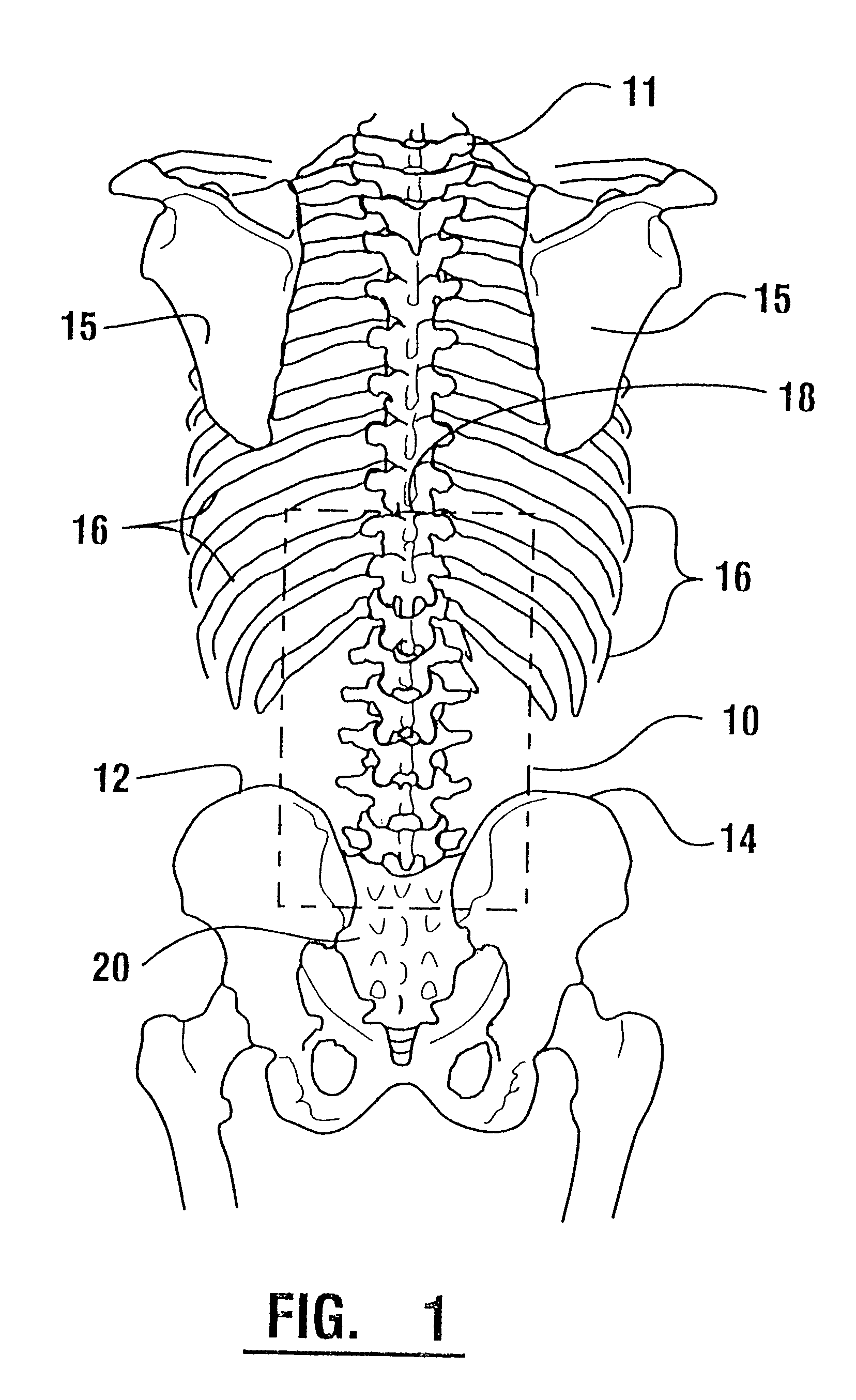
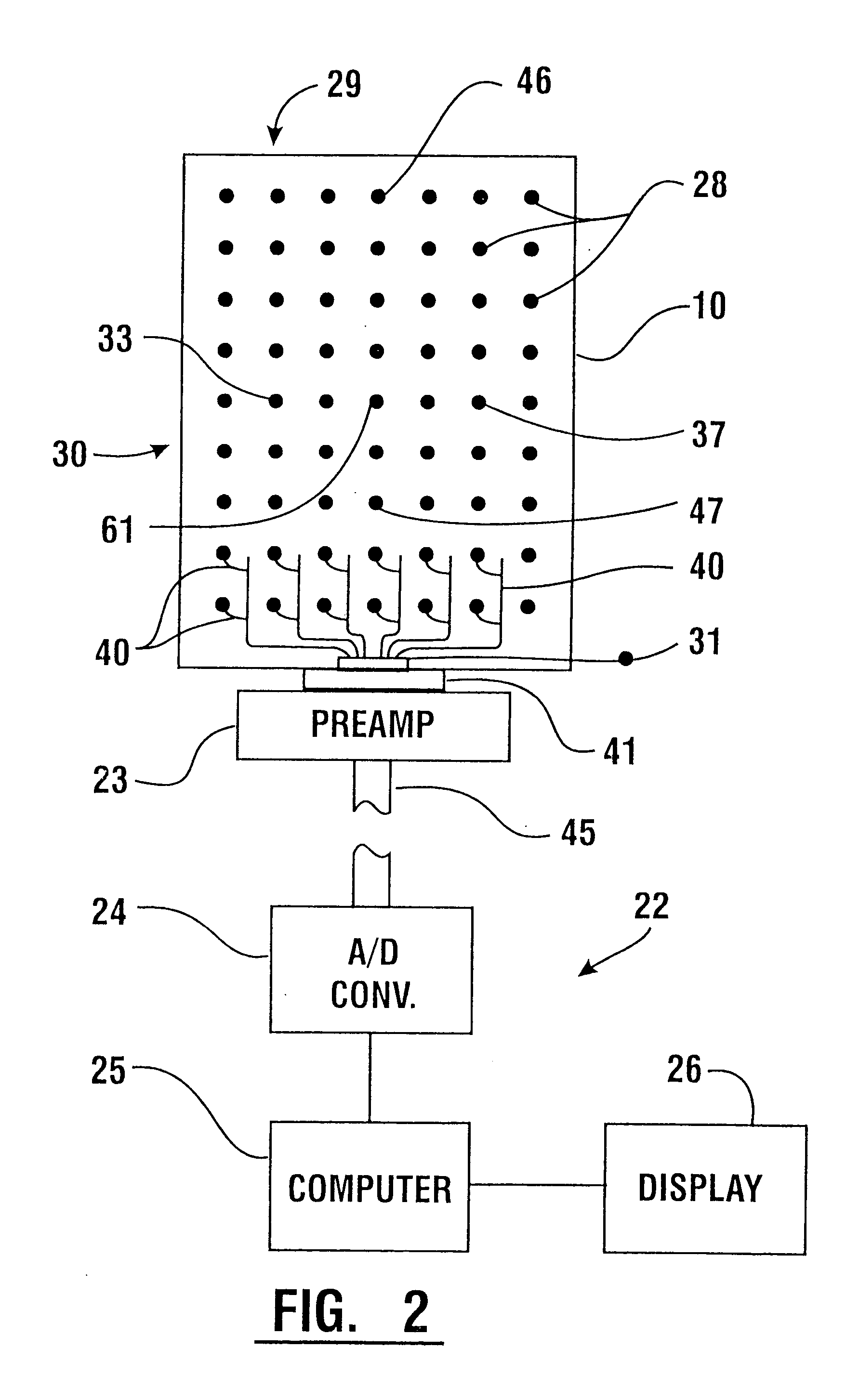
A system for detecting and analyzing electrical activity in the anatomy of an organism underlying an electrode array provides signals corresponding to electrical activity adjacent each electrode. Such signals are correlated to the underlying anatomy of the organism and representative outputs presented through various types of output devices. Such outputs may include variations in coloration or other qualities in correspondence with representations of underlying anatomical structures. The system includes novel electrode structures (200, 224, and 284) and methods for producing and attaching electrode arrays (240 and 280) to the organism. The exemplary form of the invention is used in connection with the diagnosis of muscle activity in the lower lumbar regions of humans. Levels of muscle activity detected are analyzed by correlation with the muscular structures underlying the electrode array. Forms of the invention may be used in other applications.
Owner:SPINEMATRIX
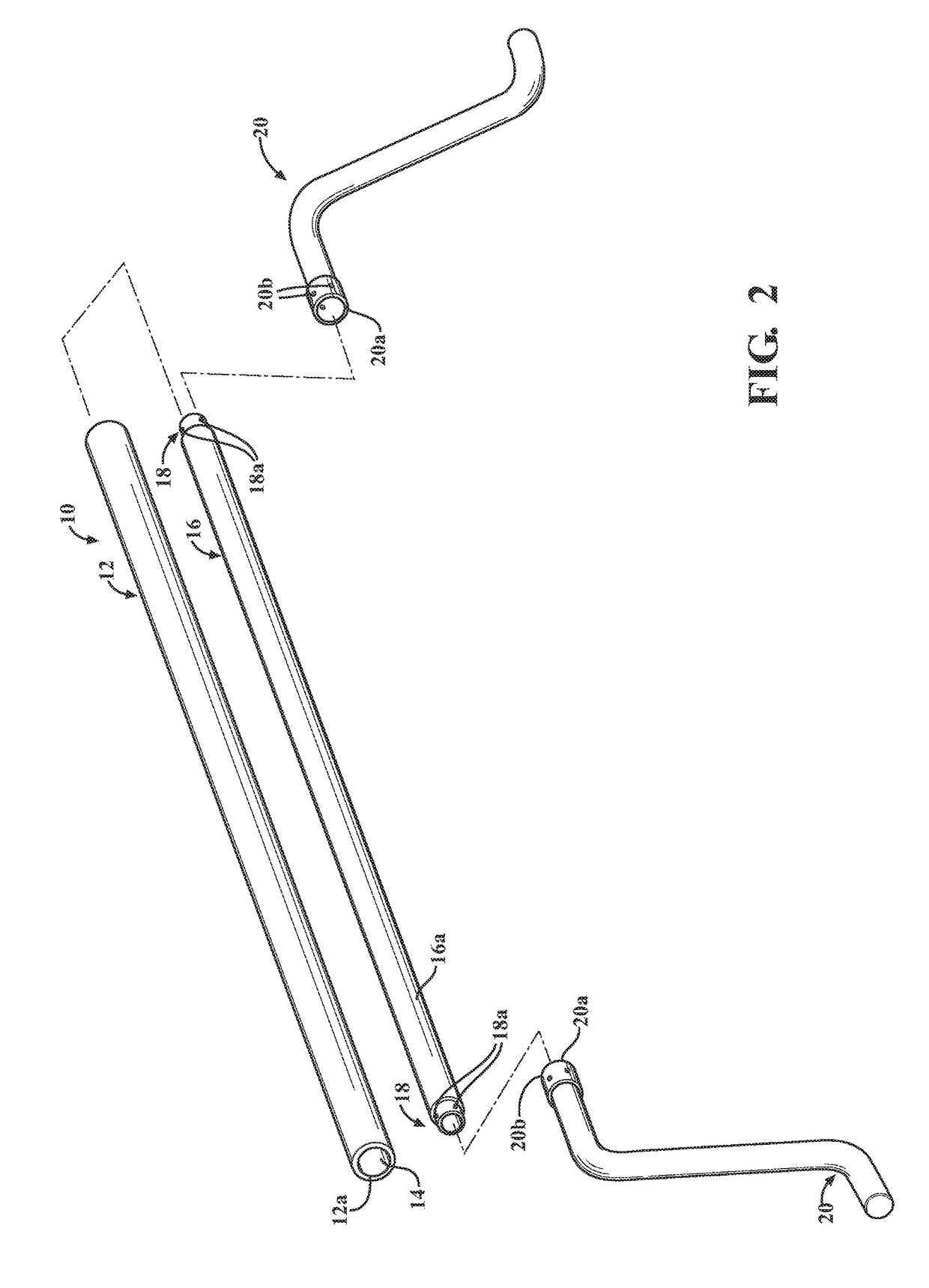
Repair of defect in inguinal canal and other muscular structures
InactiveUS20080287970A1Restore contractibilityAvoid compressionDilatorsProsthesisFibrosisEngineering
A space in a muscle wall such as the inguinal canal is dilated to break up fibrotic bands by divulsion. While the space is dilated a dynamic plug is advanced into it, with the plug expanding and contracting with the space. Shields may be placed against opposite sides of the wall surrounding the space.
Owner:AMATO
EMG electrode apparatus and positioning system
A system for detecting and analyzing electrical activity in the anatomy of an organism underlying an electrode array provides signals corresponding to electrical activity adjacent each electrode. Such signals are correlated to the underlying anatomy of the organism and representative outputs presented through various types of output devices. Such outputs may include variations in coloration or other qualities in correspondence with representations of underlying anatomical structures. The system includes novel electrode structures (200, 224, and 284) and methods for producing and attaching electrode arrays (240 and 280) to the organism. The exemplary form of the invention is used in connection with the diagnosis of muscle activity in the lower lumbar regions of humans. Levels of muscle activity detected are analyzed by correlation with the muscular structures underlying the electrode array. Forms of the invention may be used in other applications.
Owner:SPINEMATRIX
Endovascular electrode system for tissue stimulation
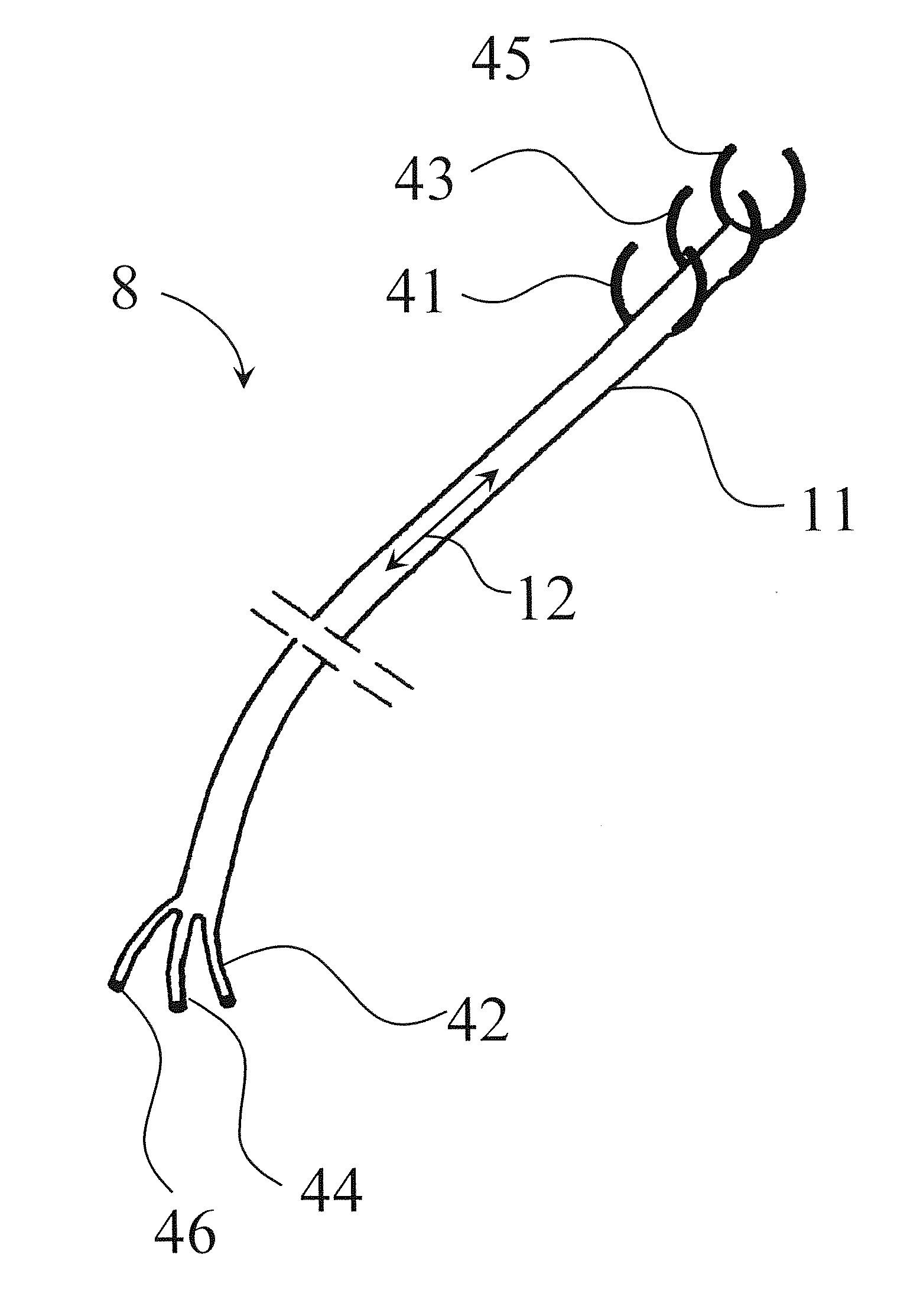
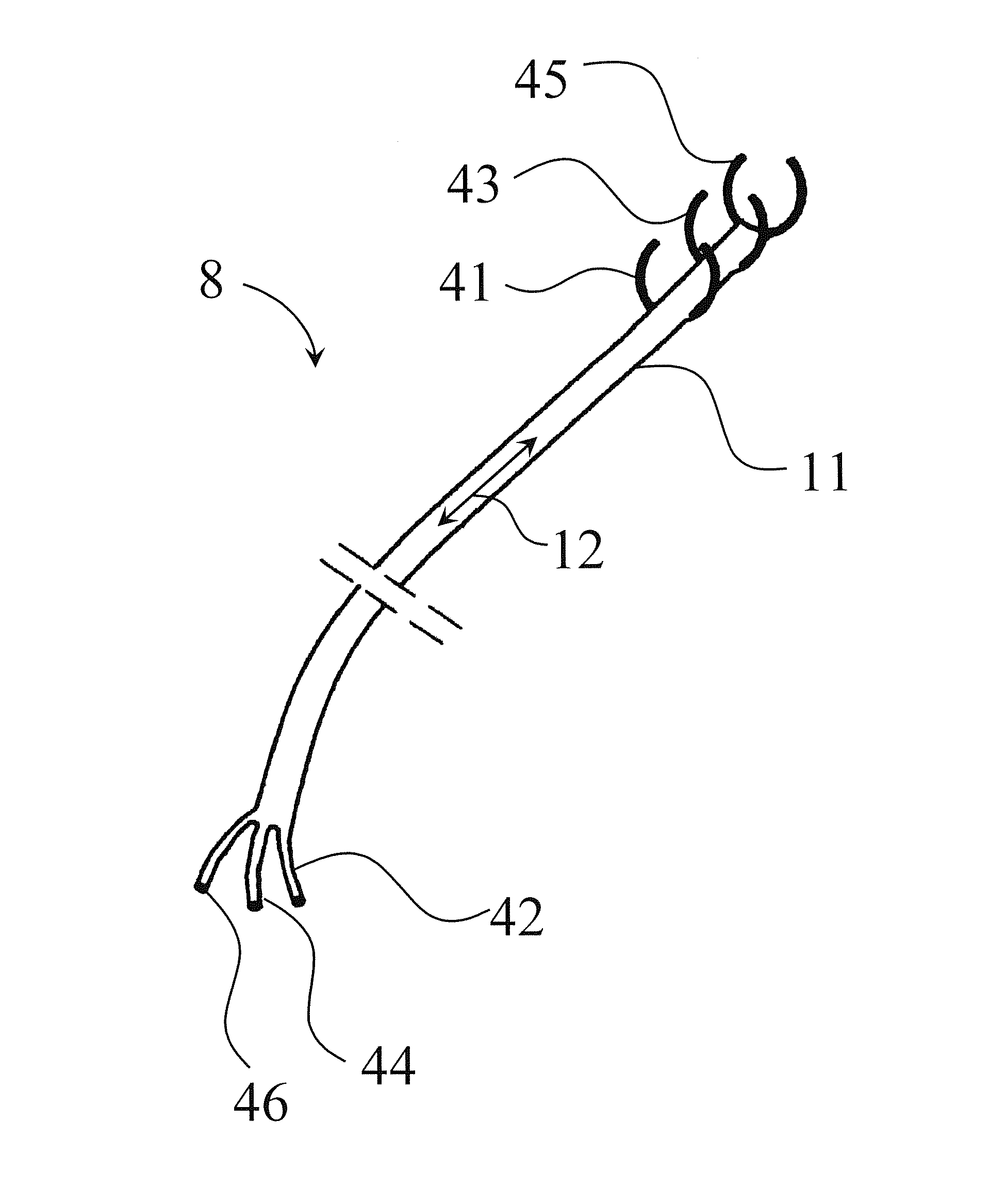
An electrical lead system includes a shaft to which a series of expandable ring electrodes are attached that follows the contour of the vascular or muscular structures of the heart, such as cardiac veins, arteries, atrial appendages and trabeculae, and provides sensing of electrical cardiac impulses, pacing and high voltage shock or defibrillation. The lead system uses a variety of energy sources to stimulate the heart, such as ultrasound, electromagnetic and electric impulses.
Owner:PHYSICIAN ELECTRONICS NETWORKS LLC
Structure decoupling driven variable-stiffness soft hand
InactiveCN108177156AAchieving Variable StiffnessReduce riskProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsVariable stiffnessShape-memory alloy
The invention relates to the technical field of intelligent robots, in particular to a structure decoupling driven variable-stiffness soft hand, which comprises a palm base. A long finger and two short fingers are arranged on three electrical interfaces in the front end of the palm base; each finger comprises a fingertip, a plurality of finger knuckles and a finger root arranged sequentially at intervals; a framework structure is connected among the fingertip, the plurality of finger knuckles and the finger root; muscle-like structures and muscular tissues are arranged on the fingers; and theframework structures, the muscle-like structures and the muscular tissues are made of SMA (shape memory alloy) materials. The structure decoupling driven variable-stiffness soft hand provided by the invention is reasonable in structure; and the SMA drives various parts of the fingers to act, and meanwhile, an electric current changes a temperature of the shape memory alloy so as to control a Youngmodulus, so that the stiffness of the fingers is variable, a more accurate grabbing action can be obtained; and the structure decoupling driven variable-stiffness soft hand has a simpler structure and solves the problems of mechanical fatigue and wear, and risks caused during an interaction process of a manipulator and people can be further reduced, so that a practicable structure model for softhand development is provided.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
EMG electrode apparatus and positioning system
A system for detecting and analyzing electrical activity in the anatomy of an organism underlying an electrode array provides signals corresponding to electrical activity adjacent each electrode. Such signals are correlated to the underlying anatomy of the organism and representative outputs presented through various types of output devices. Such outputs may include variations in coloration or other qualities in correspondence with representations of underlying anatomical structures. The system includes novel electrode structures (200, 224, and 284) and methods for producing and attaching electrode arrays (240 and 280) to the organism. The exemplary form of the invention is used in connection with the diagnosis of muscle activity in the lower lumbar regions of humans. Levels of muscle activity detected are analyzed by correlation with the muscular structures underlying the electrode array. Forms of the invention may be used in other applications.
Owner:SPINEMATRIX
Endovascular electrode system for tissue stimulation
ActiveUS9289593B1Transvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesLead systemElectromagnetic pulse
An electrical lead system includes a shaft to which a series of expandable ring electrodes are attached that follows the contour of the vascular or muscular structures of the heart, such as cardiac veins, arteries, atrial appendages and trabeculae, and provides sensing of electrical cardiac impulses, pacing and high voltage shock or defibrillation. The lead system uses a variety of energy sources to stimulate the heart, such as ultrasound, electromagnetic and electric impulses.
Owner:PHYSICIAN ELECTRONICS NETWORKS LLC
Infant mannequin
A novel infant mannequin system for documenting features of a specific human infant comprises a infant head form with two eye members, a nose member, a mouth aperture having two lips, and a head form having a facial image of a specific human infant. The system comprises an infant body form, a skeletal structure, a muscular structure, a skin covering, and a hair receptacle system located on the head form. The system comprises an abdomen compression diaphragm located underneath the skin covering. A function simulation system comprises a microprocessor, a power source, a data port and an activation switch located in the torso. The function simulation system comprises a heartbeat output simulator, a thermal circulation system, an abdominal expansion system, and a sound generator. A body weight distribution member is located in the skeletal structure.
Owner:HUNT ANGIE +1
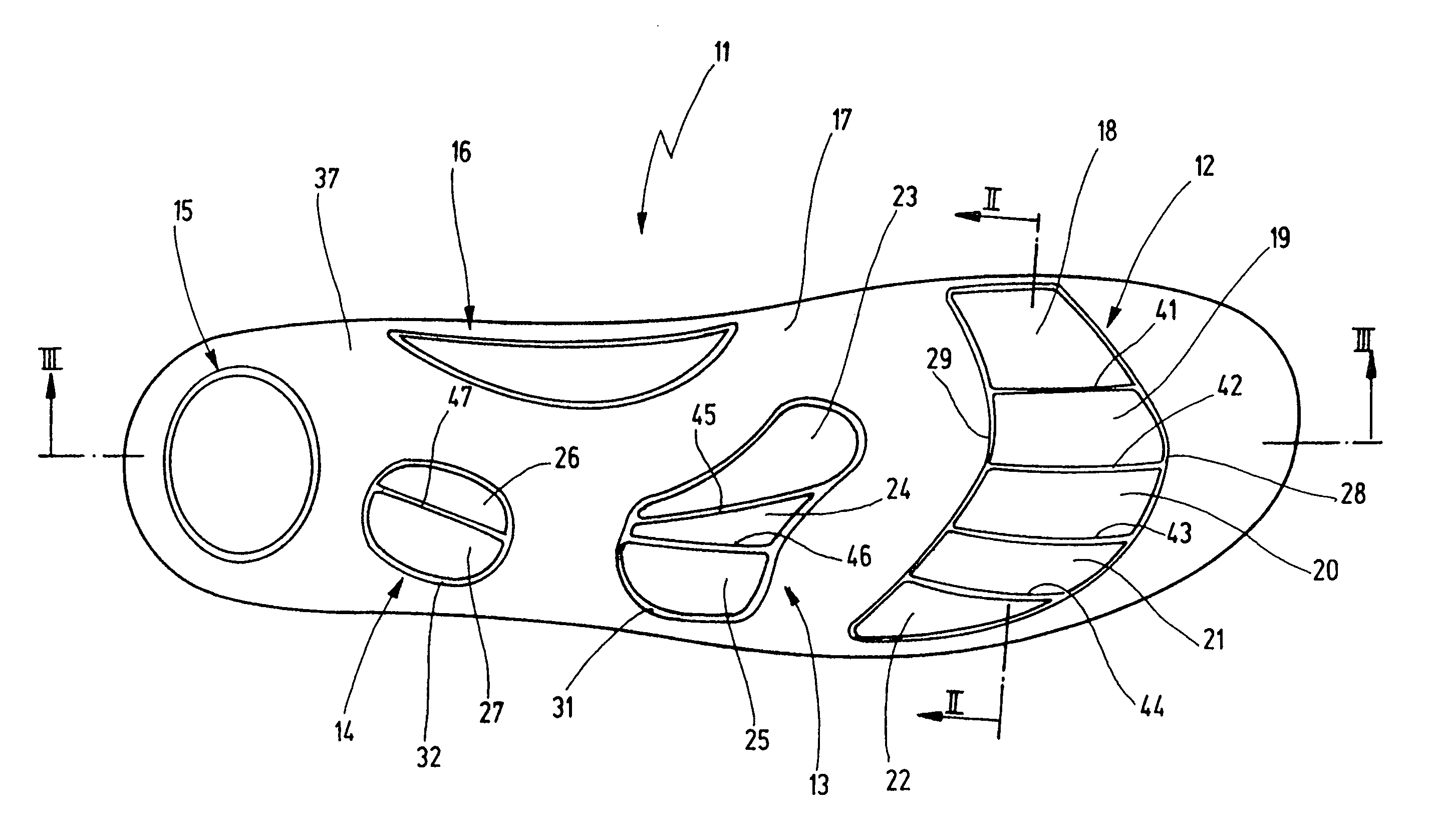
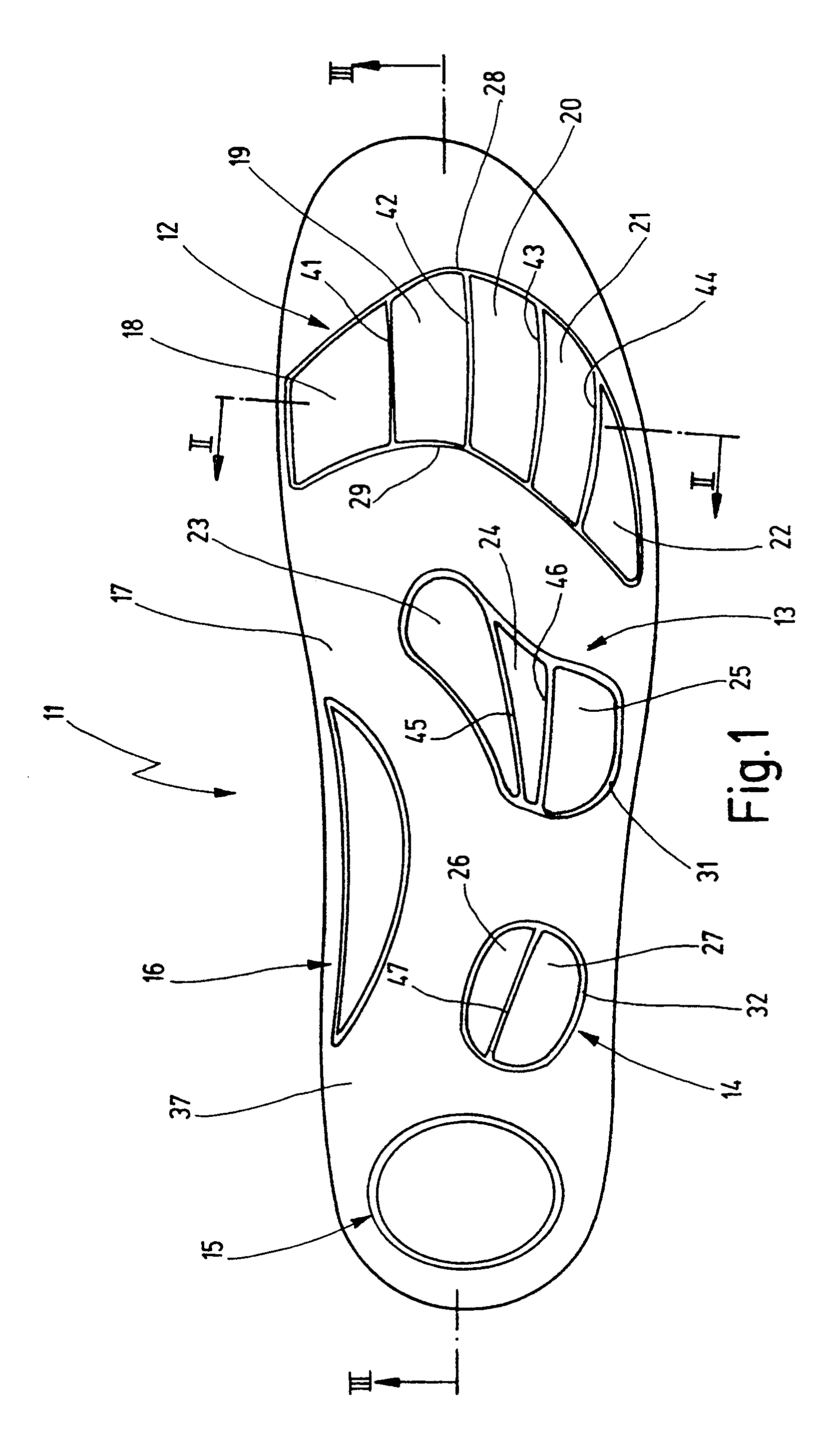
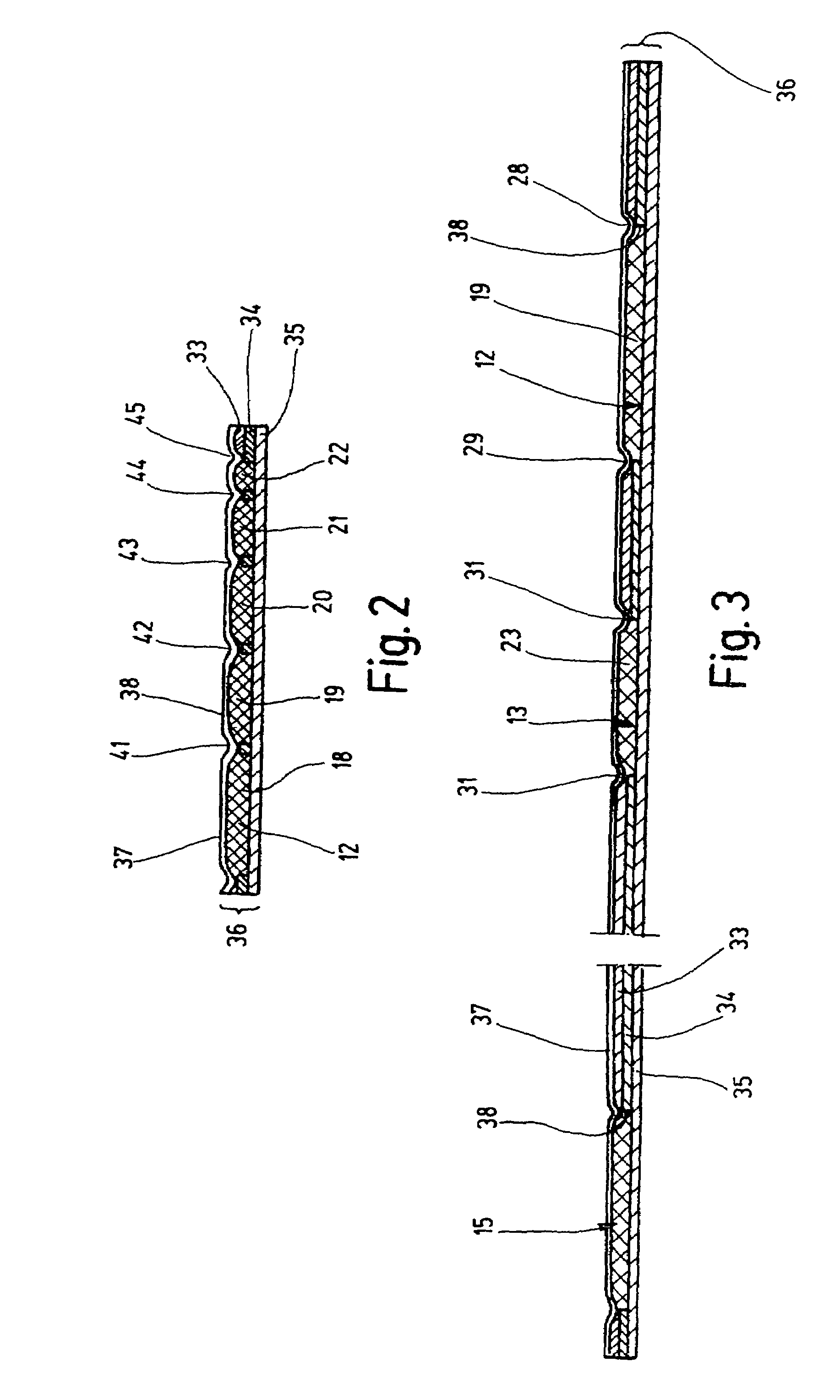
Inner sole for a shoe
InactiveUS7322130B2Increase return flowSignificant positive effectSolesInsolesFoot jointsLymphatic vessel
The present invention relates to an inner sole for a shoe, comprising a base body, a covering layer and several cushioned layers arranged on the surface of the sole. A first cushioned layer is provided in the ball area of the forefoot, a second cushioned layer is included in the transition area of the metatarsus and the tarsus and a third cushioned area is provided between the metatarsus and the heel. The cushioned layers are subdivided into individual, separate plateau-like fields which are located close to each other in the transversal direction of the sole surface. This provides an inner sole which brings about a substantial improvement in the transport of fluids in the venous and lymphatic vessel system in the legs during movement of the foot joints and ankle joints by means of synergistic support of the muscle structure.
Owner:SEITER HANS
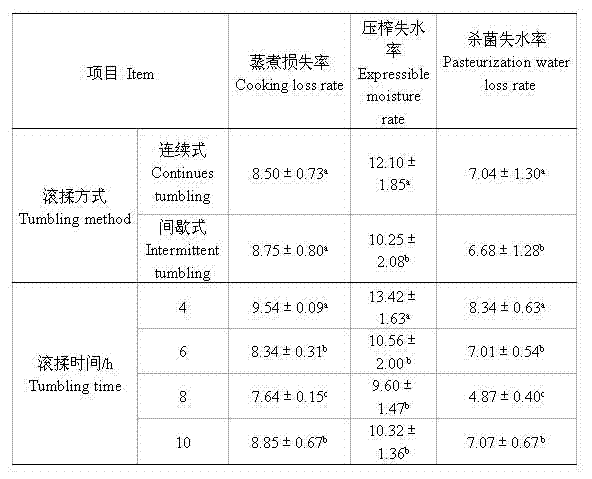
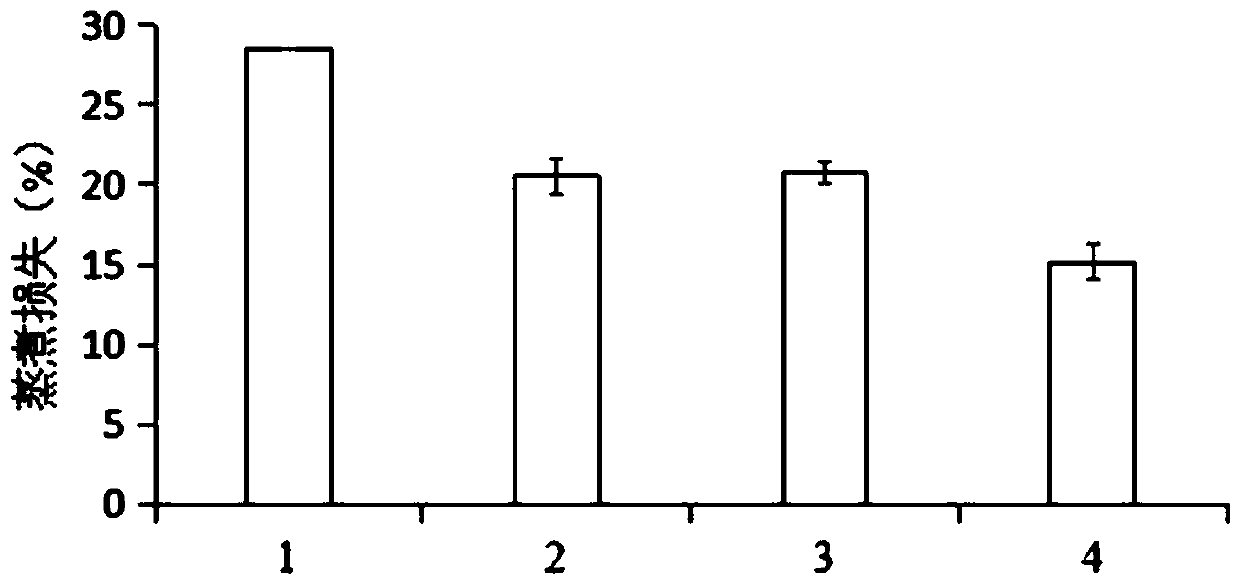
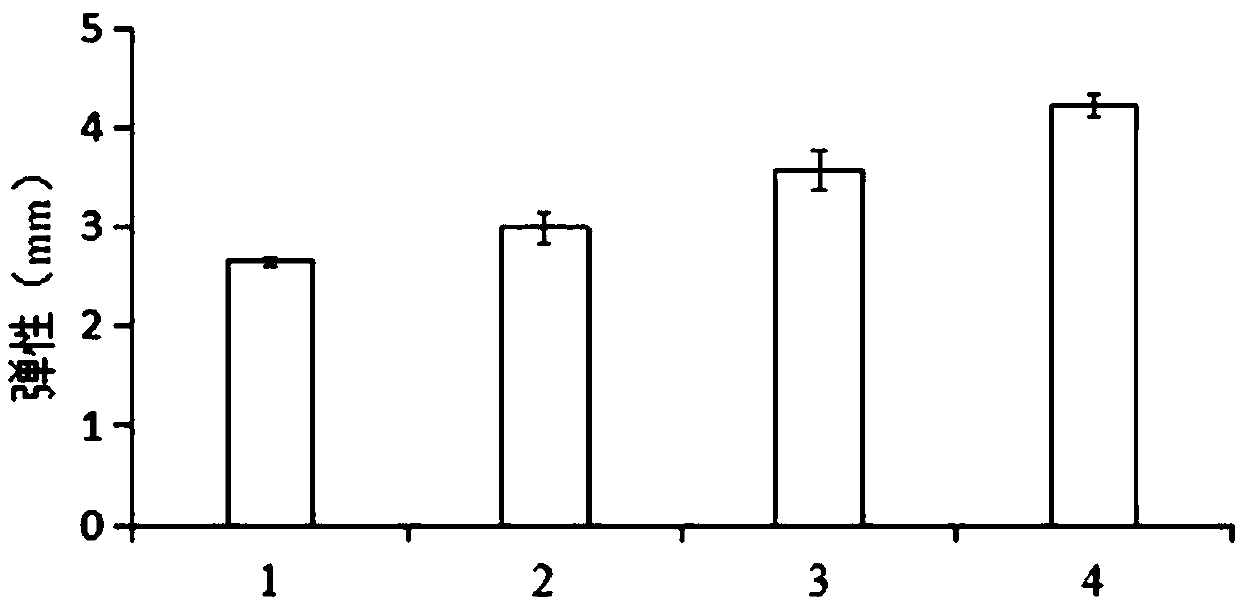
Processing method for improving quality of pork sliced ham
InactiveCN102754840AImprove textural propertiesFully efficient distributionFood preparationLoss rateDissolution
The invention discloses a processing method for improving quality of pork sliced ham. The processing method is characterized by comprising the steps of: thawing freezing-stored pork hindquarter, cutting, trimming, injecting, tenderizing, interval-tumbling for 6-10h, canning, smudging, steaming and cooking, cooling, slicing and vacuum-packaging. The pork sliced ham prepared by adopting the processing method has the characteristics of little steaming and cooking loss, small squeezing water loss rate and sterilization water loss rate, and good water holding capacity; and because the interval-tumbling process is carried out by adopting an aspiration tumbling mode under the conditions that meat loaves are in a vacuum state for a long time in a tumbling stage and a vacuum pump vacuumizes at intervals in a suspending stage, a preserving solution is more completely and effectively distributed in a muscle structure to be beneficial to the dissolution of salt soluble protein. Compared with the continuous tumbling mode, the interval-tumbling mode has the advantages that more salt soluble protein is generated, so that the binding among the meat loaves is facilitated; and during thermal processing, a stable protein gel structure is formed, thus the texture of the ham is improved.
Owner:NANJING YURUN FOOD
EMG electrode apparatus and positioning system
A system for detecting and analyzing electrical activity in the anatomy of an organism underlying an electrode array provides signals corresponding to electrical activity adjacent each electrode. Such signals are correlated to the underlying anatomy of the organism and representative outputs presented through various types of output devices. Such outputs may include variations in coloration or other qualities in correspondence with representations of underlying anatomical structures. The system includes novel electrode structures (200, 224, and 284) and methods for producing and attaching electrode arrays (240 and 280) to the organism. The exemplary form of the invention is used in connection with the diagnosis of muscle activity in the lower lumbar regions of humans. Levels of muscle activity detected are analyzed by correlation with the muscular structures underlying the electrode array. Forms of the invention may be used in other applications.
Owner:SPINEMATRIX
A system for processing carcass parts
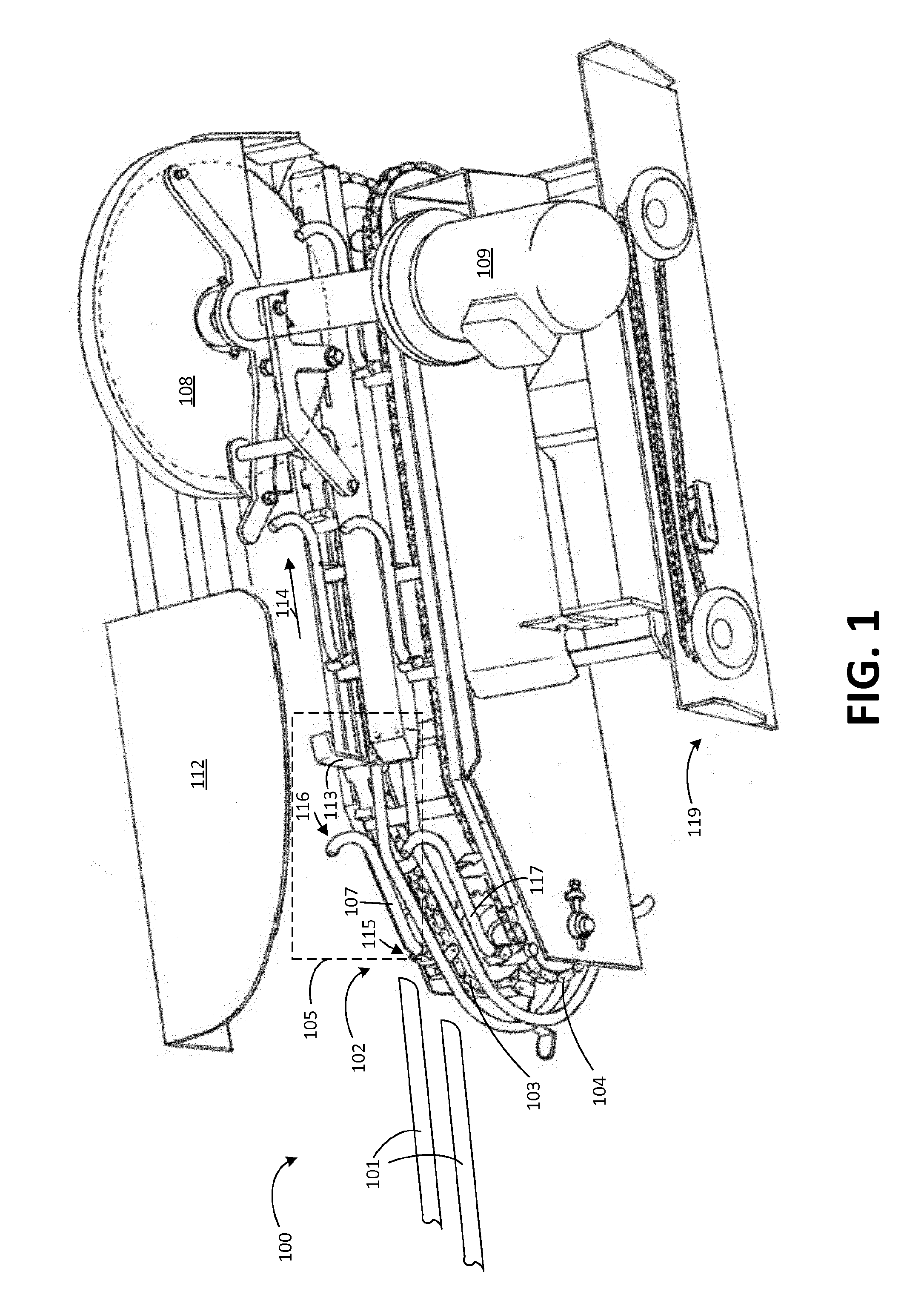
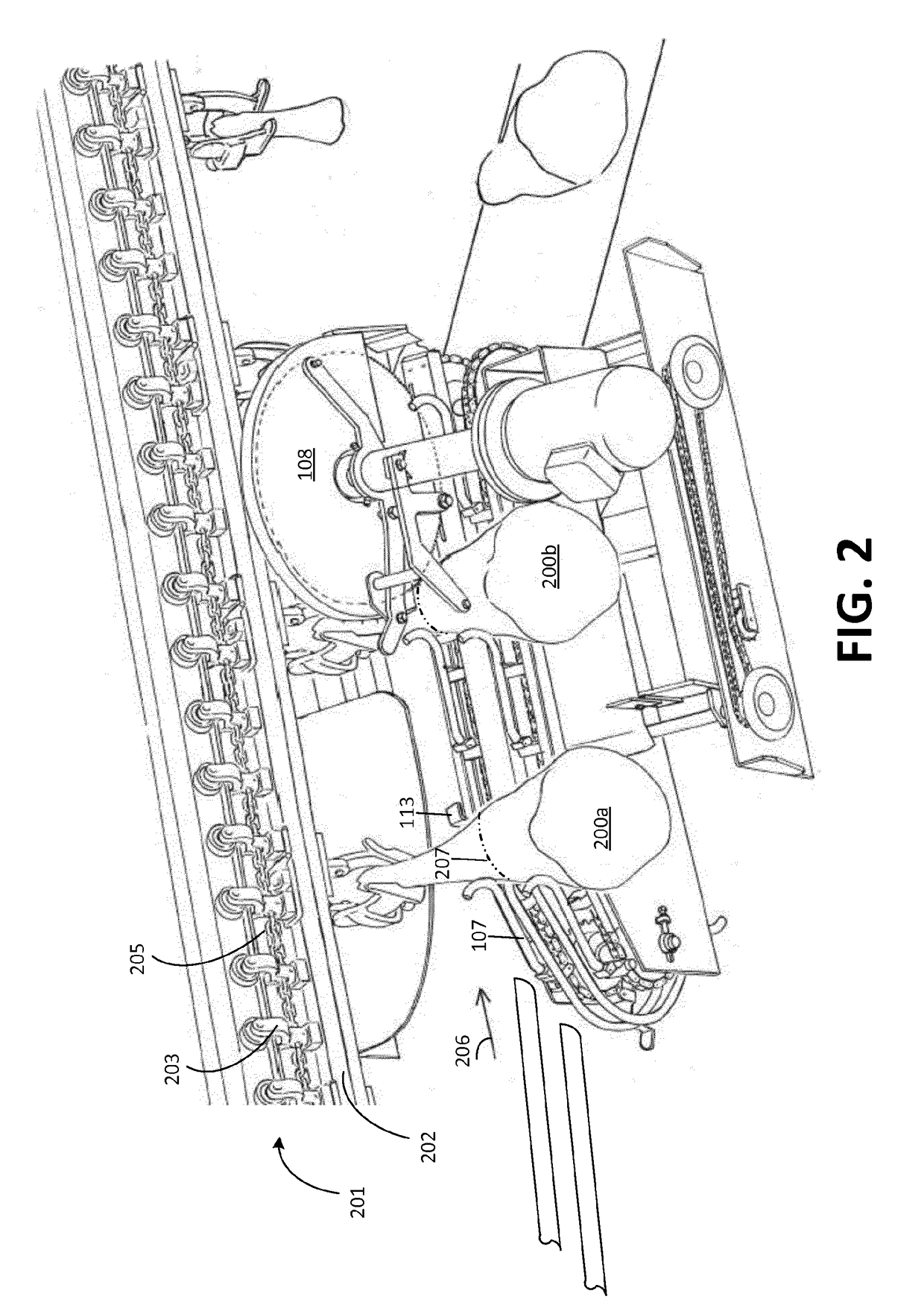
ActiveUS20160106113A1Smooth transferAccurate guideMeat holding apparatusMeat processing plantsMechanical engineeringMuscle architecture
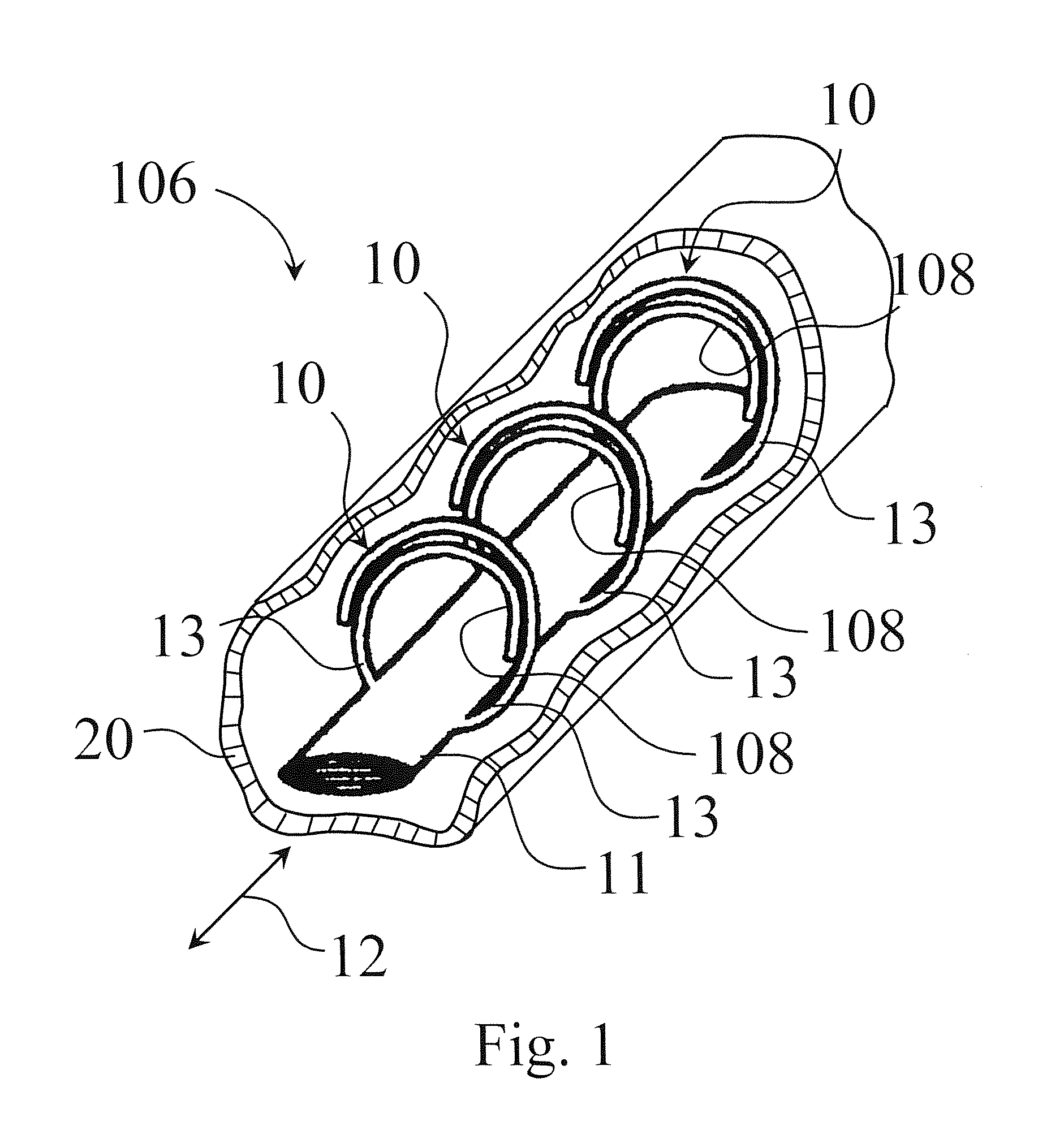
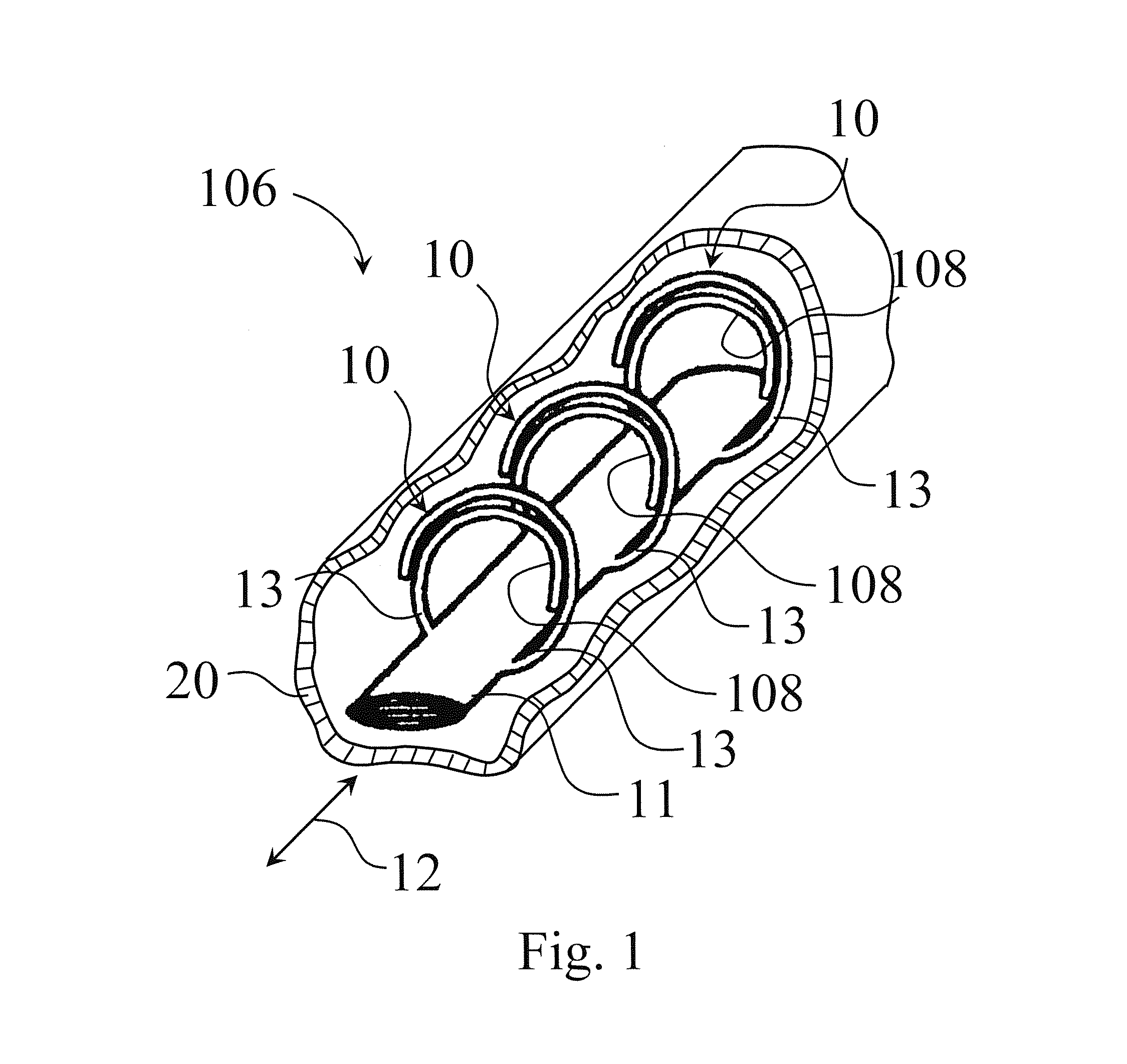
A system for processing carcass parts includes an overhead conveyor and a saw module comprising supporting means for interacting with a lower end portion of each incoming carcass part, the supporting means adjusting an angular position of the carcass parts as a result of the carcass parts resting at least partly on the supporting means while being conveyed by the overhead conveyor. A positioning conveyor having a plurality of spaced-apart positioning pair structures arranged below the overhead conveyor and adjacent to the supporting means receives the carcass parts from the supporting means. Each carcass part is guided into a predetermined position within the positioning pair structures and cut at a predetermined position, e.g. defined by a 360° cut through skin and muscle structures of each of the carcass parts.
Owner:MAREL MEAT PROCESSING
Bionics artificial thews material based on electro spinning superfine fibre and method for making same
InactiveCN101081313ALow efficiencySmall contraction forceFilament/thread formingProsthesisFiberHigh energy
The present invention is process of preparing bionic artificial muscle material based on superfine electrically spun fiber and capable of being used in sensor, executor robot and other fields. The bionic artificial muscle material is film comprising oriented superfine fiber of 20 nm-10 micron diameter. It is prepared through an electrical spinning process including the following steps: 1. forming solution or melt of polymer material for the artificial muscle; 2. electrically spinning to form oriented superfine fiber film; and 3. treating the superfine fiber film for raised stretching function. The bionic artificial muscle material has high response speed, high energy converting efficiency and other advantages.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Compound water retaining agent capable of improving bullfrog quality and application method of compound water retaining agent
InactiveCN109588645AImprove water retentionImprove qualityFood ingredient as antioxidantFood ingredient as raising agentSodium bicarbonateSolubility
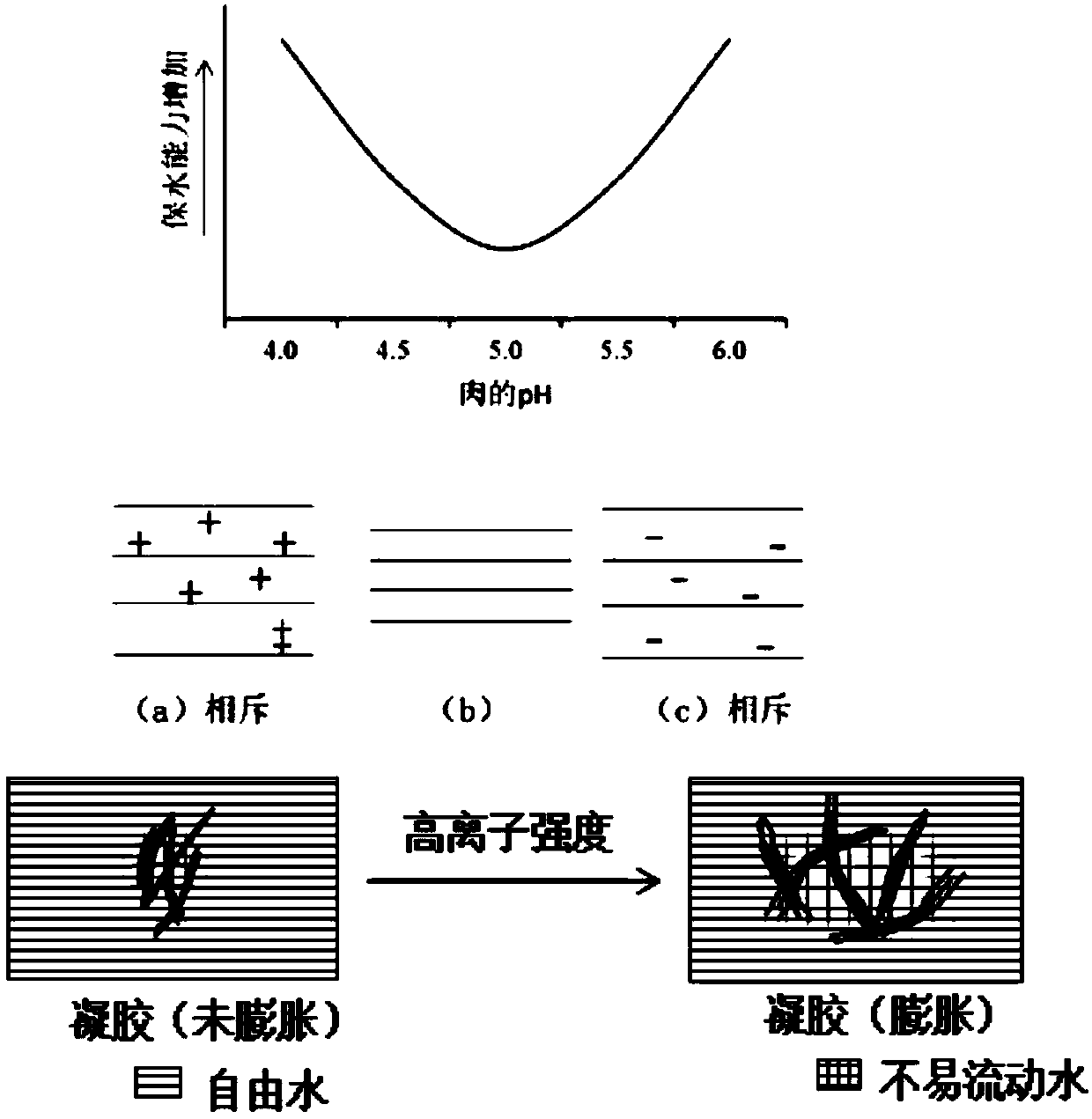
The invention provides a compound water retaining agent capable of improving bullfrog quality and an application method of the compound water retaining agent. Raw materials of the compound water retaining agent comprise polyphosphate and sodium bicarbonate, polyphosphate is basic, can increase pH of bullfrog and can also binds with polyvalent metal ions binding with structural protein of muscle, so that carboxyl groups get free from protein, the protein is enabled to be negatively charged, and electrostatic repulsion between the carboxyl groups is increased. Polyphosphate can provide higher ionic strength, can improve solubility of myofibrillar proteins and the like, is beneficial to transformation of muscle protein into a loose state and can also dissociate actomyosin, water retention ofmeat is improved, and tenderness of the meat is improved. Sodium bicarbonate can also provide a basic environment and improve meat bulkiness, so that the protein structure of the treated bullfrog getslooser, the water retention is improved substantially, the tenderness is improved, eating quality of the bullfrog is improved, and the market of the bullfrog is further expanded.
Owner:新派(上海)餐饮管理有限公司
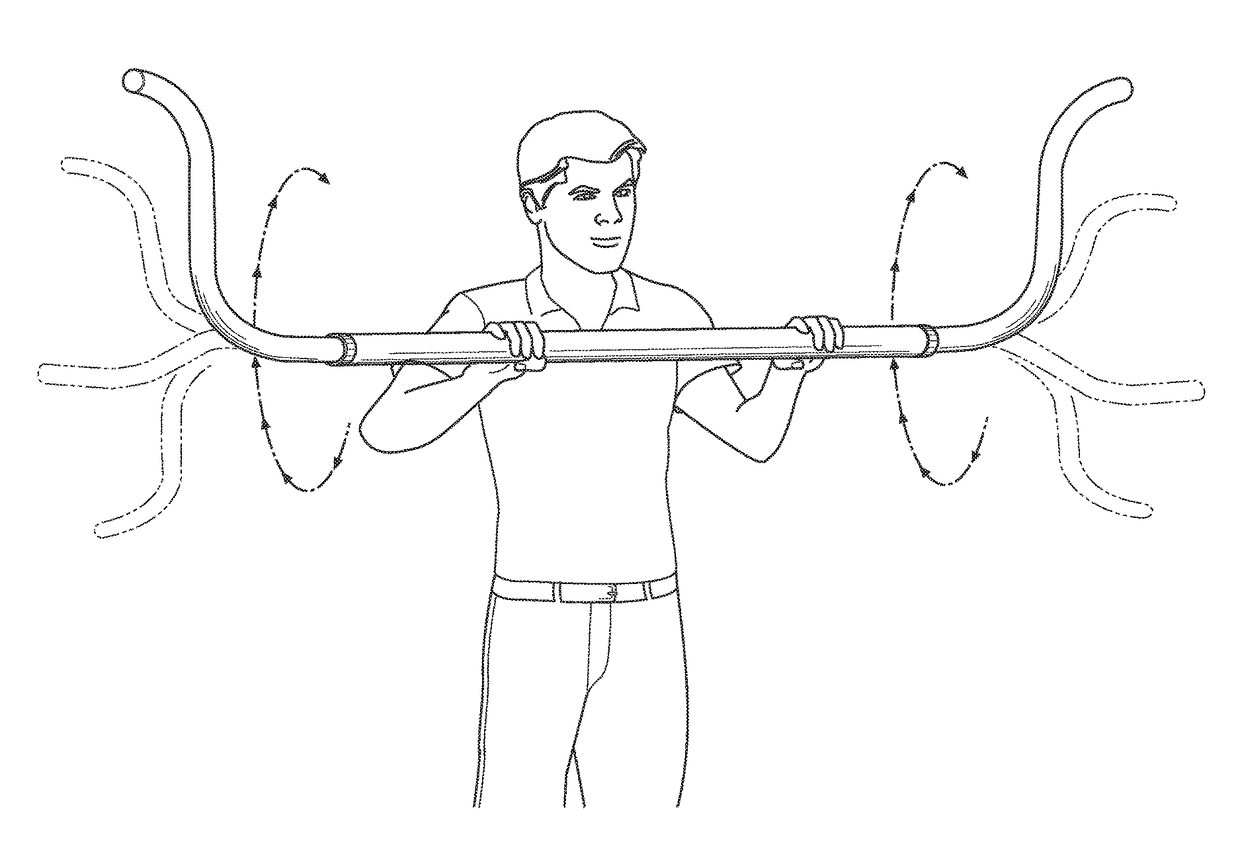
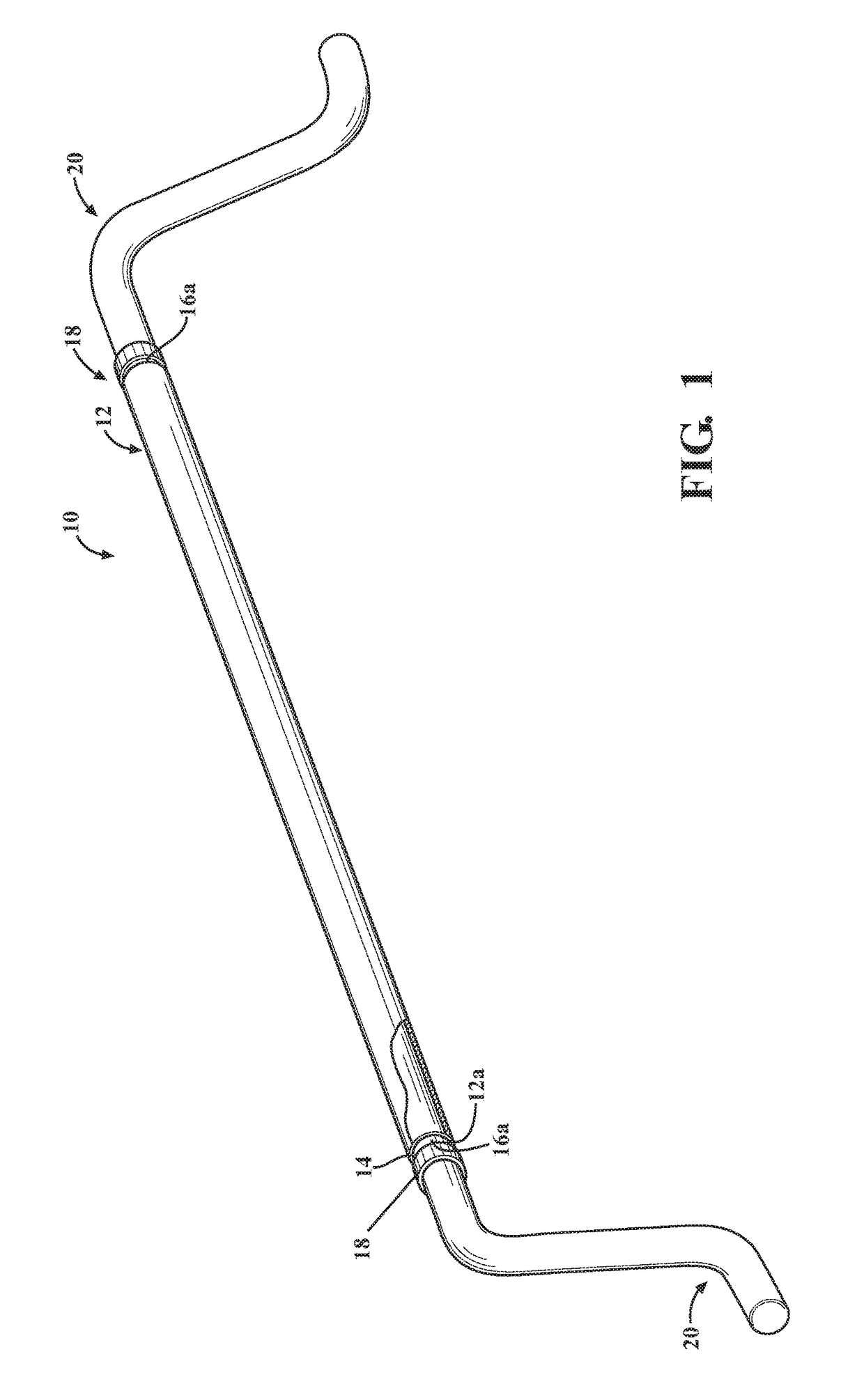
Exercise equipment and method of exercising utilizing a pulse generation
An exercise equipment configured to exercise muscles by require the muscles to generate torque intermittently is provided. The exercise equipment includes a sleeve. A pipe is slidably disposed within the sleeve. The sleeve is concentric to the pipe wherein the outer surface of the pipe is spaced apart the inner surface of the sleeve. A counterweight is mounted to at least one end of the pipe wherein the rotation of the pipe along an orbital path causes the pipe to turn within the bore of the sleeve. The turning of the pipe is a result of the counterweights completing a revolution as the counterweights rotate about the longitudinal axis of the pipe. The turning of the pipe generates a pulse so as to actuate muscular structure within the body of the user.
Owner:PARR ROBERT
Repair of defect in inguinal canal and other muscular structures
InactiveUS20120065650A1Restore contractibilityAvoid compressionProsthesisWound clampsFibrosisEngineering
A space in a muscle wall such as the inguinal canal is dilated to break up fibrotic bands by divulsion. While the space is dilated a dynamic plug is advanced into it, with the plug expanding and contracting with the space. Shields may be placed against opposite sides of the wall surrounding the space.
Owner:AMATO
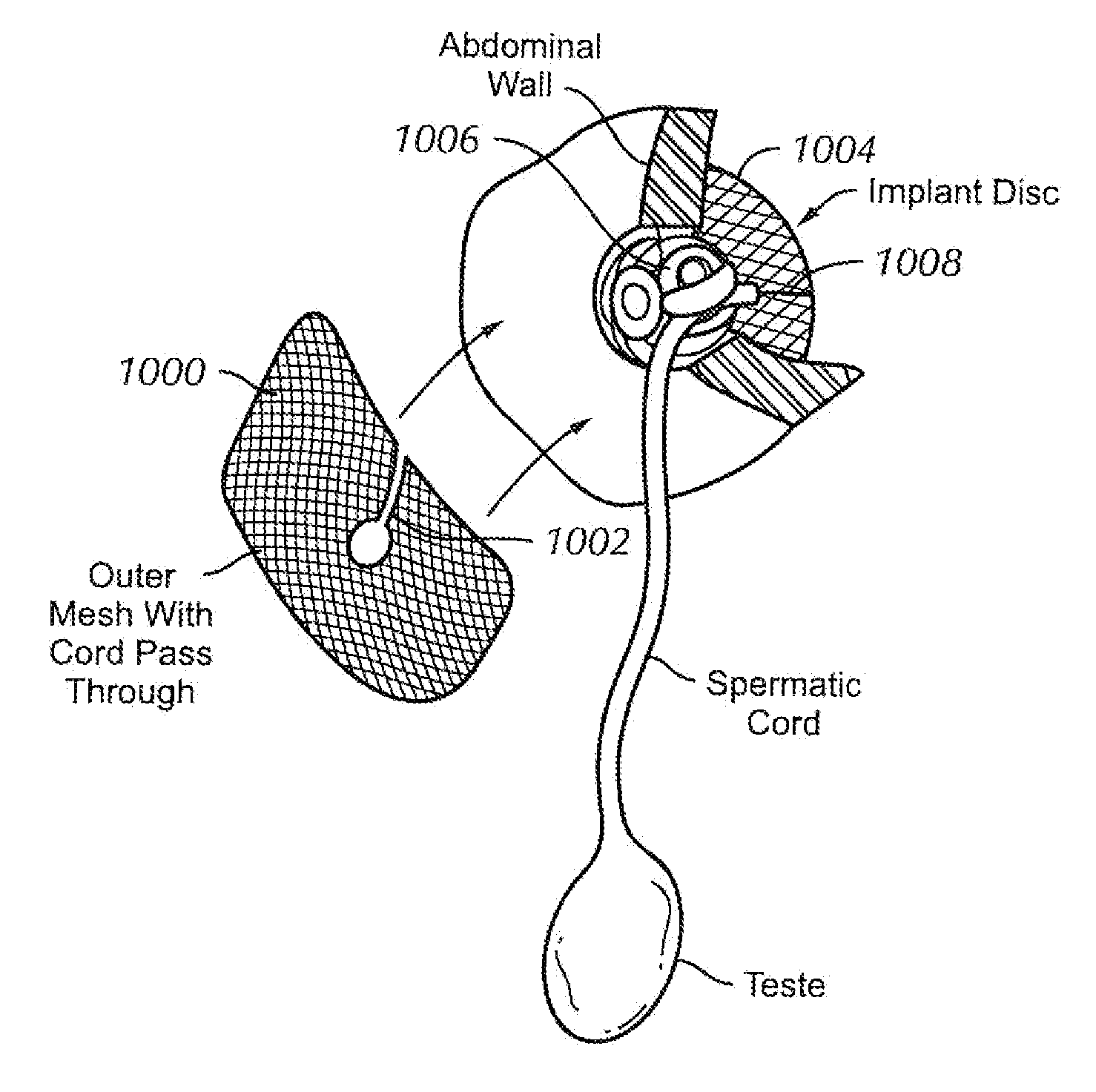
Innervation Of Engineered Structures
Methods of generating an innervated muscle structures are disclosed as well as bioengineered structures for tissue repair or regeneration. The methods can include the steps of obtaining populations of smooth muscle cells and neuronal progenitor cells and then seeding the cells together onto a matrix material, followed by culturing the seeded cells to form an innervated smooth muscle cell construct of directionally oriented smooth muscle cells. In one embodiment, the neuronal progenitor cells can be seeded first as neurospheres in a biocompatiable solution, e.g., a collagen / laminin solution, and allowed to gel. Next, a second suspension of smooth muscle cells can be deposited as separate layer. Multiple layer structures of alternating muscle or neuron composition can also be formed in this manner. Differentiation of the neuronal progenitor cells can be induced by exposure to a differentiation medium, such as Neurobasal A medium and / or exposure to a differentiating agent, such as B-27 supplement. The innervated muscle structures can be disposed around a tubular scaffold, e.g., a chitosan-containing tube and further cultured to form tubular, bioengineered structures and two or more innervated muscle structures can be joined together to form an elongate composite structure.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Treatment prostheses for edentulous dental patients
InactiveUS20080038695A1Easily and efficiently fabricatedEasy to installFastening prosthesisDental articulatorsDental patientsDentures
A treatment prosthesis is specifically designed to be efficiently fabricated without the use of bite rims or interocclusal records, thus resulting in a device that is beneficial in the development and training of patient tissues and muscular structures prior to the fitting of actual dentures. The treatment prosthesis, and the related method for fabrication, is efficiently designed using mathematical formulas and reference planes such that very little adjustment is necessary when incorporated into a patient's mouth. The treatment prosthesis includes several anterior teeth, thus providing some level of realism, while also including only occlusion rims on the posterior portions so that muscular development can be achieved without having to deal with natural interference created by typical cusp structures of molar teeth.
Owner:CARLSON JAMES E
Stretching type pneumatic artificial muscle
PendingCN108527353AReduce frictionIncrease flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringPneumatic artificial muscles
The invention discloses the stretching type pneumatic artificial muscle. The pneumatic artificial muscle comprises an upper fixing disc, an inner layer rubber tube, an I-shaped connector, an upper sliding shaft, fixed rods, a mesh grid, an outer layer rubber tube, an upper moving disc, a lower moving disc, a lower sliding shaft and a lower fixing disc, wherein the outer surface of the fixed rods are smooth, the two ends of the fixed rods are provided with threads, one ends of the fixed rods are connected with the upper fixing disc, and the other ends of the fixed rods are connected with the lower fixing disc, and the four fixed rods, the upper fixing disc and the lower fixing plate form a fixing structure; the pneumatic muscle is composed of the inner layer rubber tube, an oblique crossingmesh grid and the outer layer rubber tube, the pneumatic muscles at the upper end are fixedly connected with the upper fixing disc and the upper moving disc, and the pneumatic muscle at the lower endis fixedly connected with the lower moving disc and the lower fixing disc; and the pneumatic muscles are inflated and then expands and then drives the moving discs to move in the axial direction. Thestretching type pneumatic artificial muscle is connected between the moving discs and the sliding shafts through the I-shaped connector, so that the complexity of the artificial muscle structure is greatly reduced, the overall structure is more compact, and the stability is high.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Bionics artificial muscle material based on electro spinning superfine fibre and method for making same
The present invention is process of preparing bionic artificial muscle material based on superfine electrically spun fiber and capable of being used in sensor, executor robot and other fields. The bionic artificial muscle material is film comprising oriented superfine fiber of 20 nm-10 micron diameter. It is prepared through an electrical spinning process including the following steps: 1. formingsolution or melt of polymer material for the artificial muscle; 2. electrically spinning to form oriented superfine fiber film; and 3. treating the superfine fiber film for raised stretching function. The bionic artificial muscle material has high response speed, high energy converting efficiency and other advantages.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Pneumatic muscle
InactiveCN110840713ASimple structureImprove flexibilityWalking aidsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of bionic drivers, particularly relates to a pneumatic muscle, and solves the problems of complicated structure and high production cost of an existing pneumatic muscle. The pneumatic muscle comprises an air bag, a woven mesh pipe is arranged on the outer side of the air bag, the air bag is connected with one end of the woven mesh pipe through a first connector component and connected with the other end of the woven mesh pipe through a second connector component, an air guide pipe is arranged in the air bag, the first connector component comprises an inflatable channel, and the air guide pipe penetrates the inflatable channel. The pneumatic muscle is a capsule-type artificial pneumatic muscle. Compared with an existing pneumatic muscle, an air bag structure of the capsule-type artificial pneumatic muscle is inflated and deformed, a space without needing to be inflated is formed in the middle of an inflated air bag, compressed gas is saved bythe structure, pressure applied onto the air bag is reduced, response time is shortened, and working efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A force-controlled joint device that keeps the output force constant
The invention discloses a force control joint device, which comprises a base, an elastic mechanism component, a pneumatic muscle structure component, a displacement sensor component and an output end. It is characterized in that two sets of symmetrically arranged elastic mechanism components output thrust, and pneumatic muscle structure components output pulling force. The resultant force of the two is used to jointly control the output force of the joint, and the displacement sensor is used to monitor the real-time deformation of the current joint in real time, so as to facilitate follow-up Data processing and real-time control of joint output force. The invention is used for pressure control, wherein the special structural design enables the joint to keep the contact pressure between the grinding tool head and the workpiece surface constant even when the joint is disturbed by the unevenness of the grinding tool head on the working surface.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
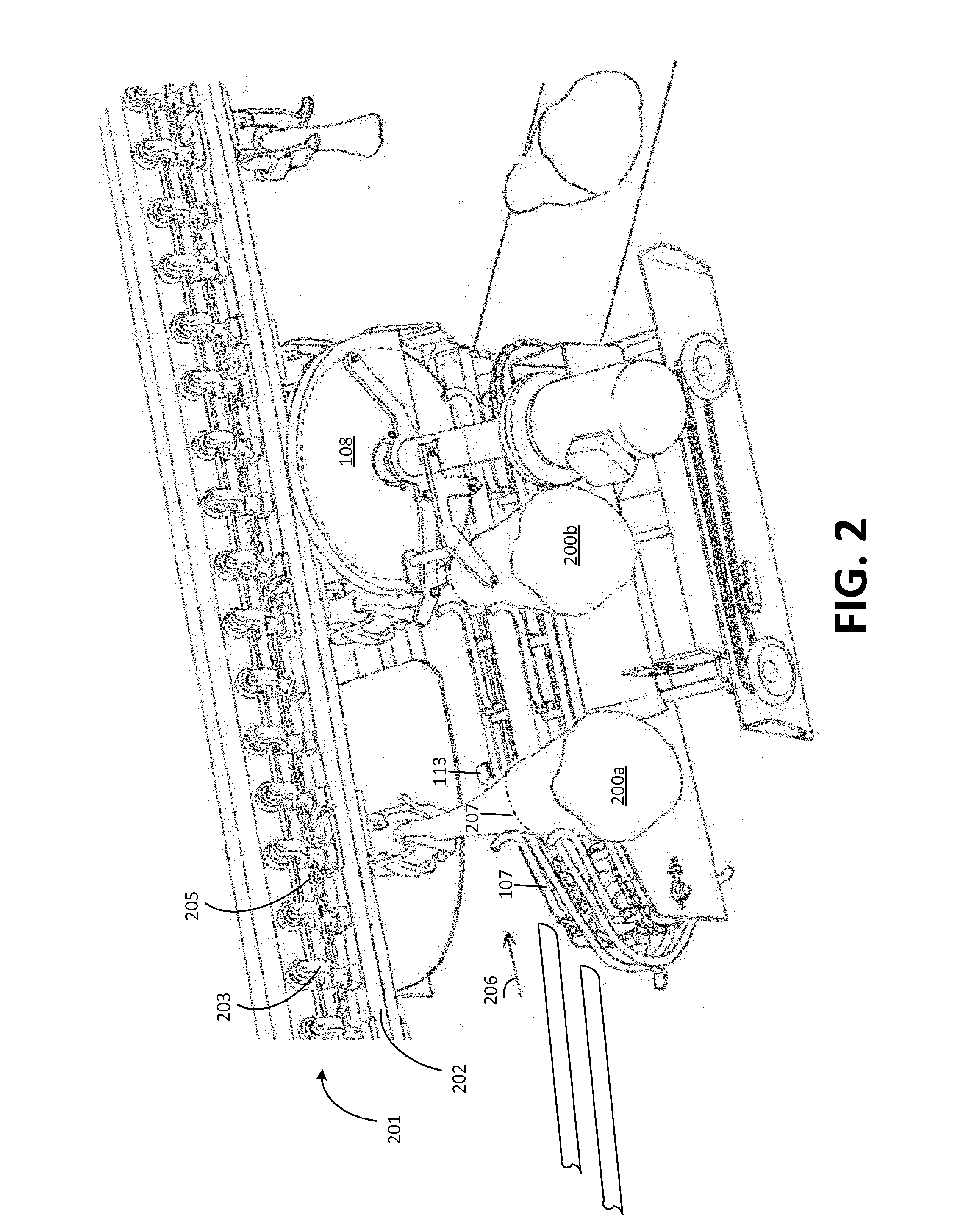
System for processing carcass parts
ActiveUS9596868B2The effect is accurateIncrease valueMeat holding apparatusSlaughtering accessoriesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A system for processing carcass parts includes an overhead conveyor and a saw module comprising supporting means for interacting with a lower end portion of each incoming carcass part, the supporting means adjusting an angular position of the carcass parts as a result of the carcass parts resting at least partly on the supporting means while being conveyed by the overhead conveyor. A positioning conveyor having a plurality of spaced-apart positioning pair structures arranged below the overhead conveyor and adjacent to the supporting means receives the carcass parts from the supporting means. Each carcass part is guided into a predetermined position within the positioning pair structures and cut at a predetermined position, e.g. defined by a 360° cut through skin and muscle structures of each of the carcass parts.
Owner:MAREL MEAT PROCESSING
Nested Shape Memory Alloy Pneumatic Artificial Muscle
InactiveCN106514645BImprove performancePerformance improvements and enrichmentsProgramme-controlled manipulatorMuscle fascicleShape-memory alloy
The invention discloses a nested shape memory alloy pneumatic artificial muscle. The invention includes upper fixed plate, fixed rod, axial SMA wire, sliding plate, pneumatic muscle, PM lower mounting plate, lower fixed plate, sliding square shaft, rotating shaft, PM upper mounting plate, spring, radial SMA wire, drive circuit , upper fixed plate threading hole, rotating shaft hole, sliding plate threading rod hole, sliding plate threading hole, lower fixed plate threading hole, square hole; the pneumatic muscle is nested inside the fixed frame to achieve a compact structure of the device; axial Through multiple windings, SMA wire increases the effective length, produces large deformation, pulls the muscle bundle, and increases its contraction, and the hysteresis cycle effect of the wire during superelasticity can alleviate the impact of load vibration; through the radial SMA wire Contraction realizes the rotation of muscle bundles and changes the stiffness of the pneumatic muscle; compared with the same model of pneumatic muscle on the market, the pneumatic muscle has a compact structure, a large contraction amount, and a wide range of variable stiffness.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
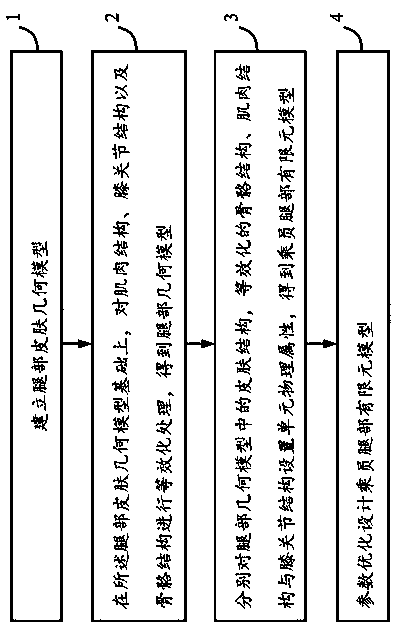
Design method and system for constructing rapid parametric model of passenger's legs
InactiveCN106372349BImprove computing efficiencyImprove the calculation efficiency of safety simulation analysisDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMuscle tissueElement model
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Eel-like robot based on electromagnetic artificial muscle and its working method
InactiveCN111360801BStable reversing abilityBody adjustmentProgramme-controlled manipulatorPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
The invention provides an eel-like robot based on electromagnetic artificial muscles and its working method. The eel-like robot includes a robot head, a robot tail and a robot skeleton composed of several joints connected in series. The robot head and the robot tail have the same structure and are symmetrical. Installed at both ends of the robot skeleton; each joint of the robot skeleton includes the rear ribs, the first right electromagnetic muscle, the front ribs, the front spine, the pin shaft, the first left electromagnetic muscle and the rear spine; between two adjacent joints of the robot skeleton They are connected in series by sharing the same rib; the head of the robot includes the second right electromagnetic muscle, auxiliary electromagnetic muscle, second left electromagnetic muscle and head ribs; all the electromagnetic muscles have the same structure, including two electromagnets, magnetically conductive rubber and magnetic liquid; the swimming of the eel-like robot is realized through the coordinated actions of multiple joints and the electromagnetic muscles at the head and tail of the robot. The invention has high maneuverability and can be used in places with narrow spaces and complex structures.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
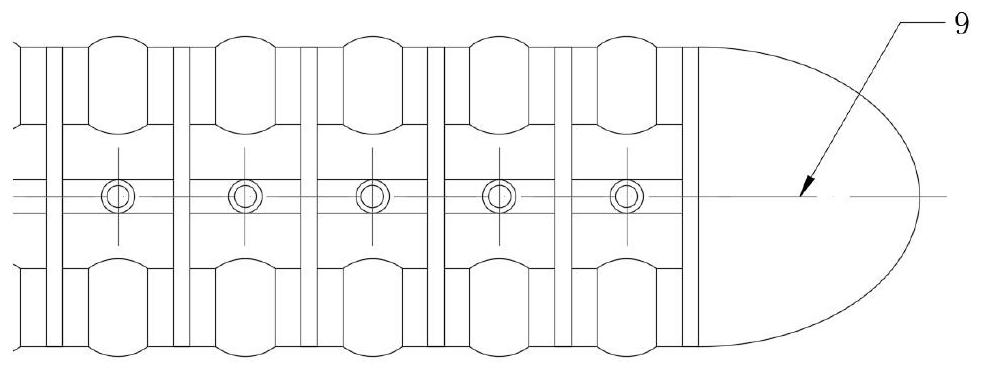
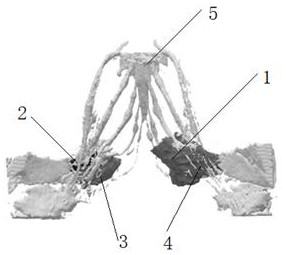
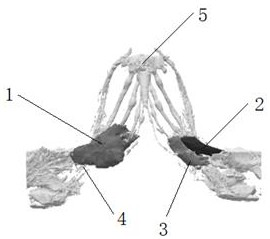
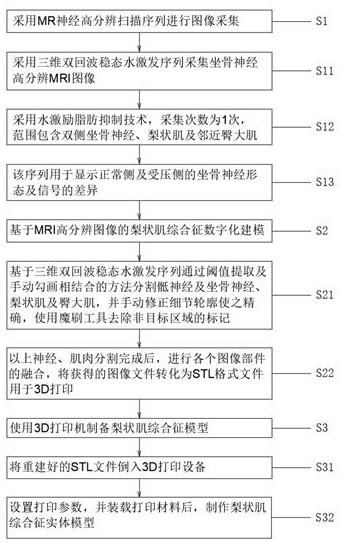
MR image-based piriformis syndrome model and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112562470AImproving Precise Preoperative UnderstandingImprove effectivenessImage enhancementAdditive manufacturing apparatusPiriform muscleComputer printing
The invention provides an MR image-based piriformis syndrome model and a preparation method thereof, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining 3D high-resolution MRI scanning images of sciatic nerves, piriformis and adjacent muscles through an MR nerve imaging sequence, importing the obtained original image data into modeling post-processing software, perfroming image fusion, segmentation andreconstruction on pressed sciatic nerves, piriformis and adjacent muscle structures to obtain a piriformis syndrome three-dimensional anatomical model, importing the piriformis syndrome three-dimensional anatomical model into a color 3D printer to print an individualized 3D printing entity model, and effectively displaying the sciatic nerve compression form, walking and the spatial relation between the walking and the adjacent piriformis structures; so that the product meets the requirements of precise medical evaluation and operation, is used for preoperative planning, operation simulation and medical teaching training, and improves the teaching effect of medical training.
Owner:天津市第一中心医院
Exercise equipment and method of exercising utilizing a pulse generation
An exercise equipment configured to exercise muscles by require the muscles to generate torque intermittently is provided. The exercise equipment includes a sleeve. A pipe is slidably disposed within the sleeve. The sleeve is concentric to the pipe wherein the outer surface of the pipe is spaced apart the inner surface of the sleeve. A counterweight is mounted to at least one end of the pipe wherein the rotation of the pipe along an orbital path causes the pipe to turn within the bore of the sleeve. The turning of the pipe is a result of the counterweights completing a revolution as the counterweights rotate about the longitudinal axis of the pipe. The turning of the pipe generates a pulse so as to actuate muscular structure within the body of the user.
Owner:PARR ROBERT
Magnetic simulation muscle structure
InactiveCN109676599AScalability can be controlledHigh accelerationProgramme-controlled manipulatorTime extensionLow noise
The invention discloses a magnetic simulation muscle structure which is provided with a first module, and a second module arranged in the first module; and the first module and the second module can be moved relatively through electromagnetic repulsion force. The simulation muscle structure is a simulation muscle device using the electromagnetic repulsion force, and a traditional driving mode using a servo motor as a robot is changed completely. Compared with another driving mode using electromagnetic attraction, the magnetic simulation muscle structure has the effects that the controllable expansion degree is achieved on the expansion stroke of simulation muscle is achieved, while the electromagnetic attraction can only attract and release once, namely that only one-time extension and contraction can be achieved, and the expansion degree of the electromagnetic attraction can not be controlled. Thus, the magnetic simulation muscle structure is achieved by using the repulsion force of amagnetic field, namely that not only can any expansion degree of the simulation muscle be achieved, but also control over the size of the required force can be achieved. Therefore, the magnetic simulation muscle structure has the advantages of high acceleration, low mechanical wear, small size, light weight, low noise, energy saving, high response speed, controllable expansion degree and other excellent driving characteristics.
Owner:广东协禾医业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com