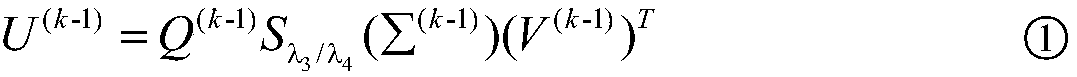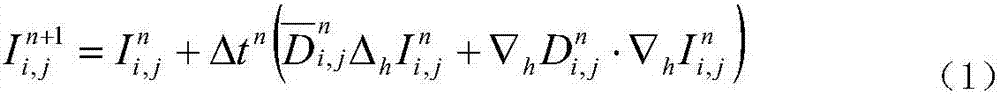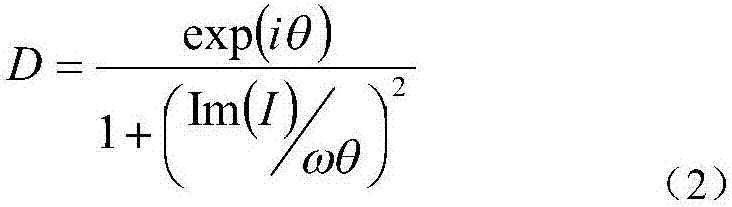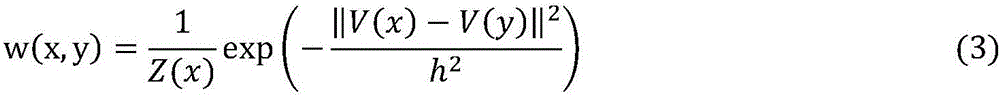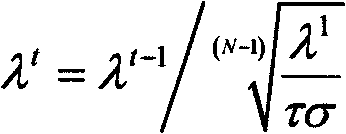Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
112 results about "Multiplicative noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
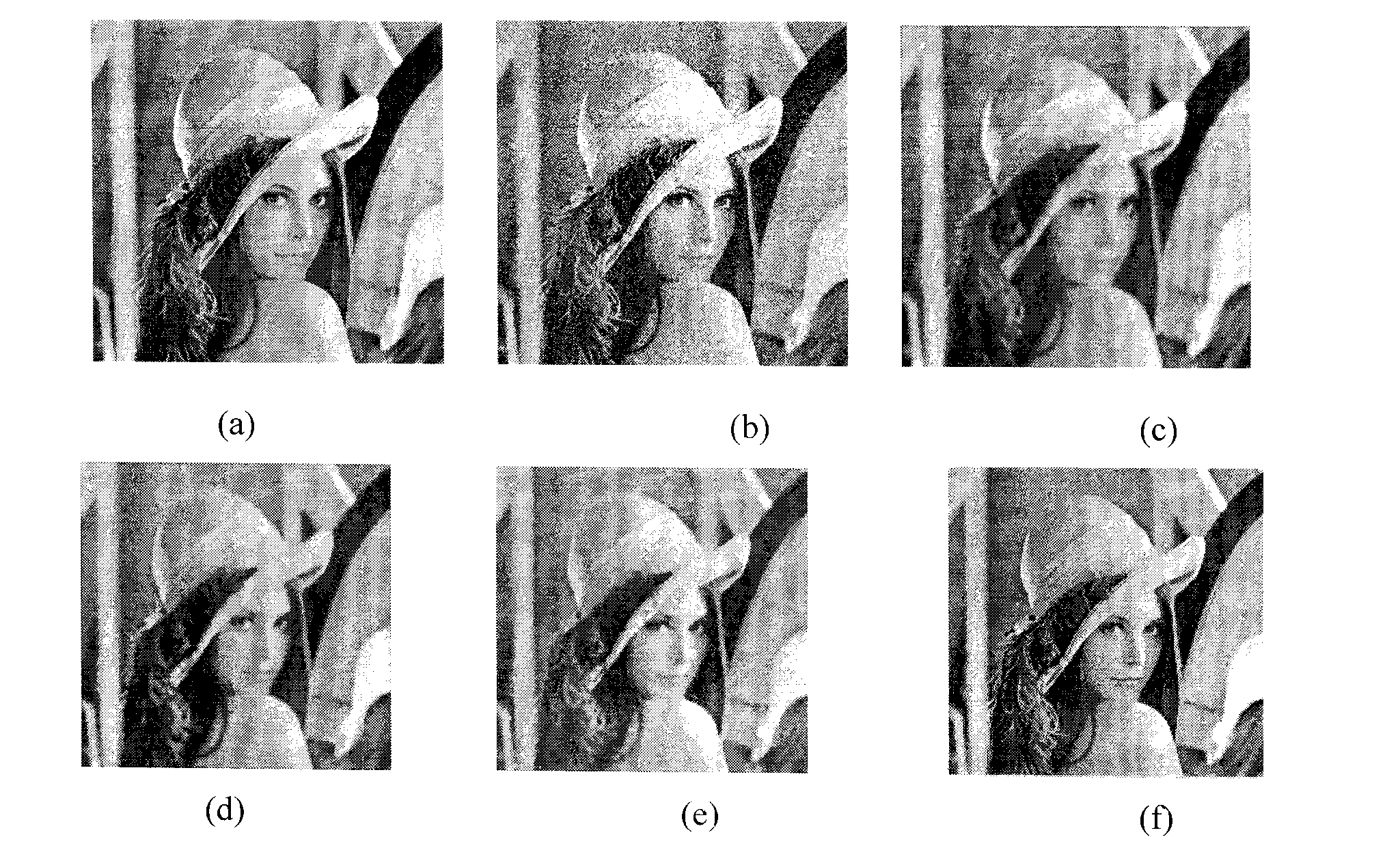
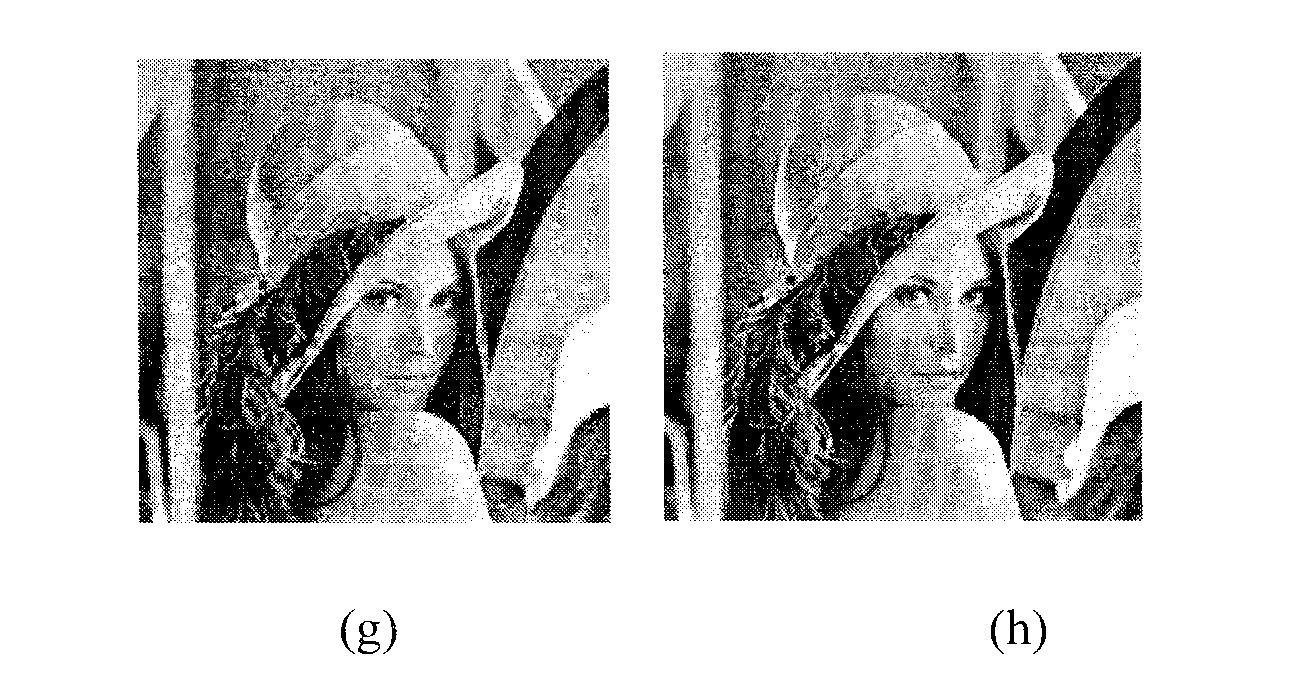
In signal processing, the term multiplicative noise refers to an unwanted random signal that gets multiplied into some relevant signal during capture, transmission, or other processing. An important example is the speckle noise commonly observed in radar imagery. Examples of multiplicative noise affecting digital photographs are proper shadows due to undulations on the surface of the imaged objects, shadows cast by complex objects like foliage and Venetian blinds, dark spots caused by dust in the lens or image sensor, and variations in the gain of individual elements of the image sensor array.
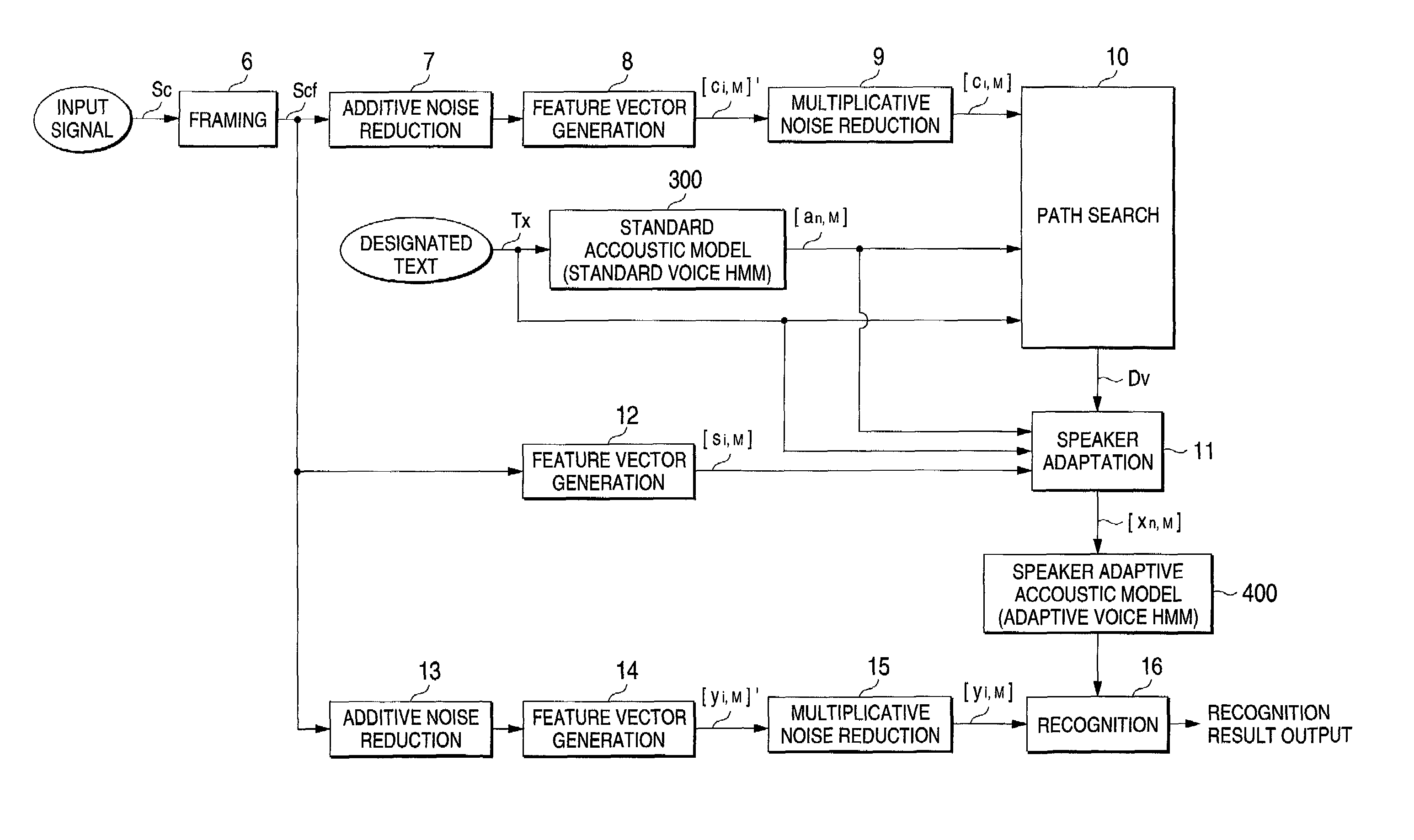
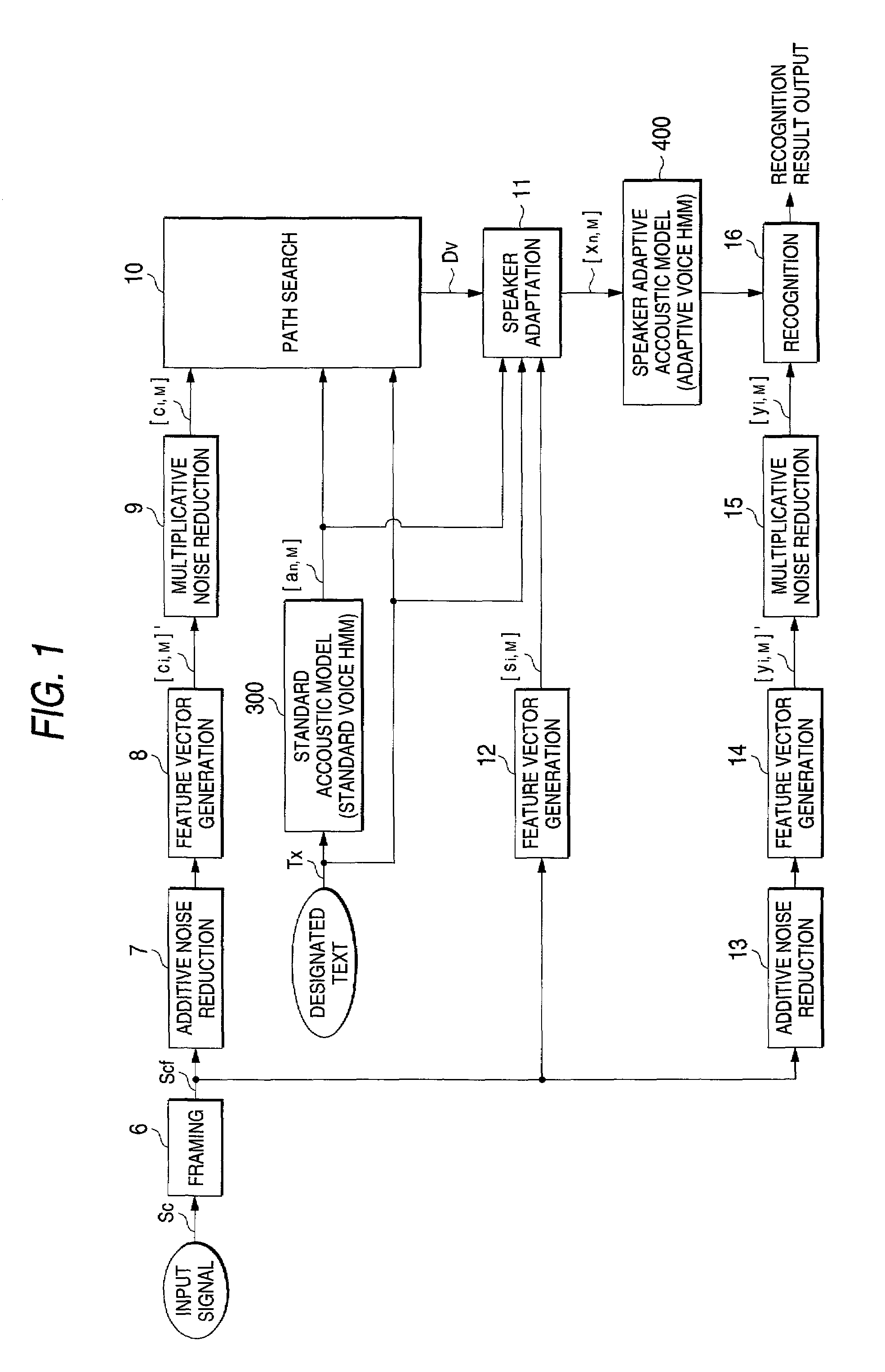
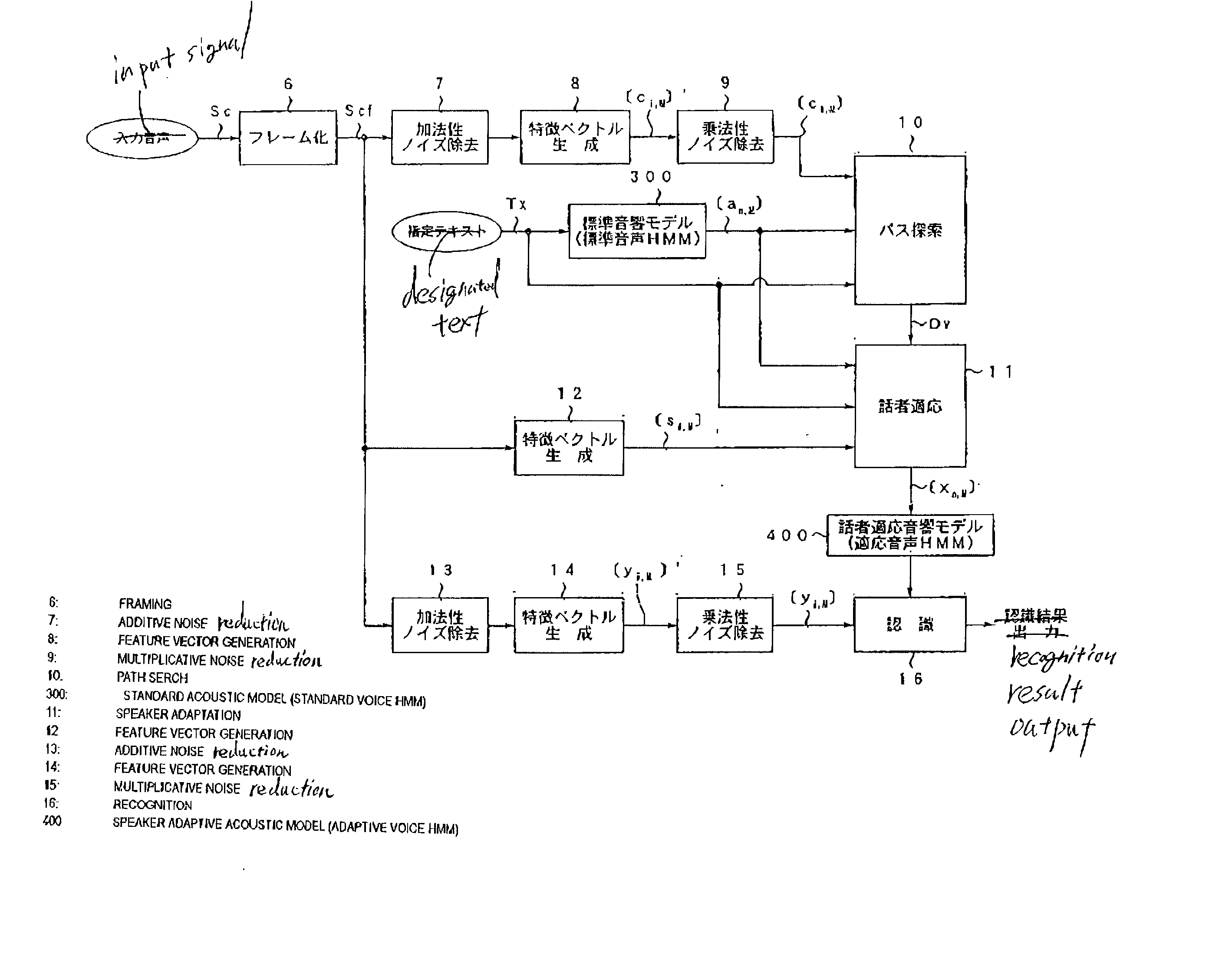
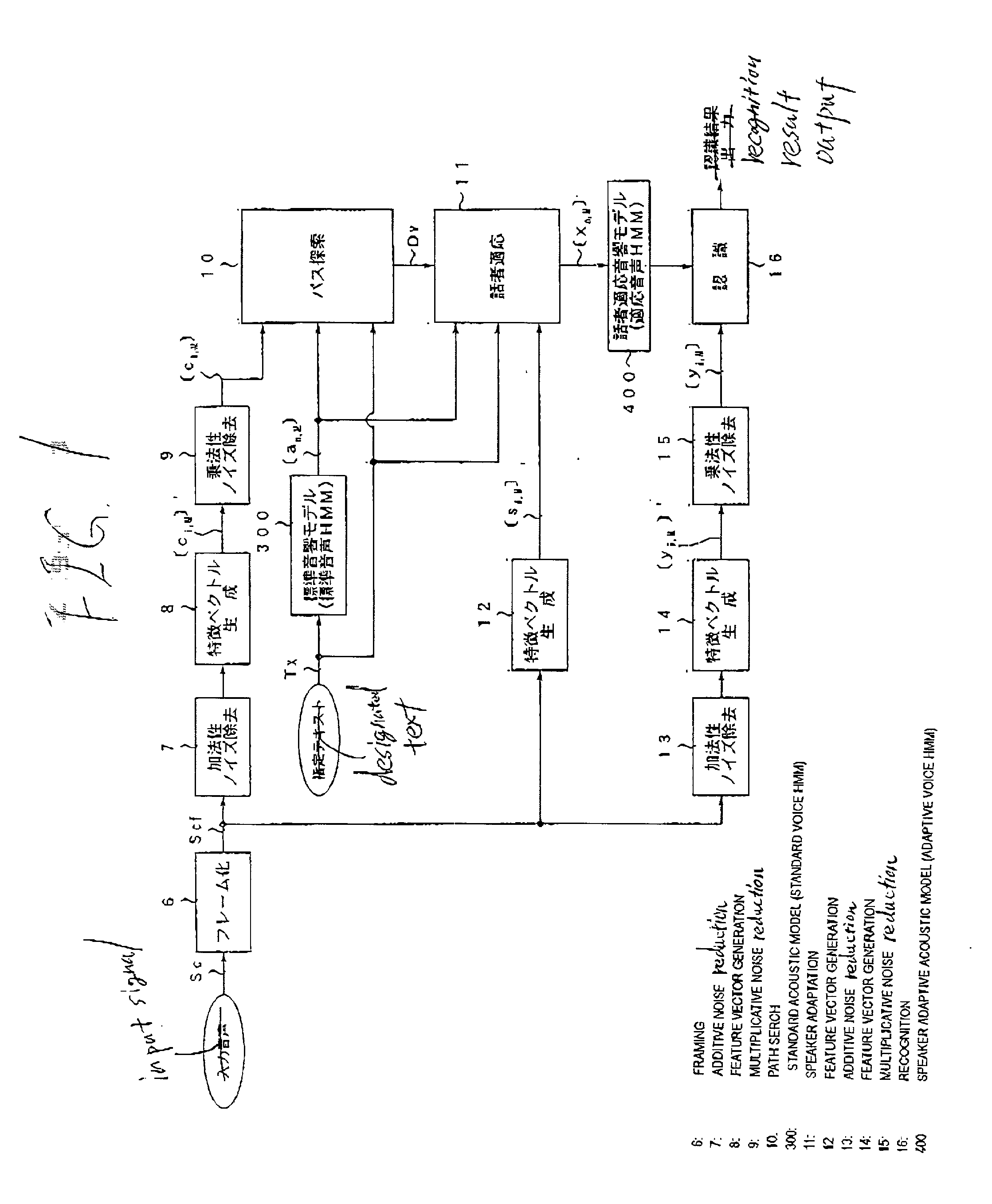
Speech recognition system with an adaptive acoustic model
InactiveUS7065488B2Improve speech recognition performanceReduce noiseSpeech recognitionFeature vectorAcoustic model
At the time of the speaker adaptation, first feature vector generation sections (7, 8, 9) generate a feature vector series [Ci, M] from which the additive noise and multiplicative noise are removed. A second feature vector generation section (12) generates a feature vector series [Si, M] including the features of the additive noise and multiplicative noise. A path search section (10) conducts a path search by comparing the feature vector series [Ci, m] to the standard vector [an, m] of the standard voice HMM (300). When the speaker adaptation section (11) conducts correlation operation on an average feature vector [S^n, m] of the standard vector [an, m] corresponding to the path search result Dv and the feature vector series [Si, m], the adaptive vector [xn, m] is generated. The adaptive vector [xn, m] updates the feature vector of the speaker adaptive acoustic model (400) used for the speech recognition.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Two-dimensional blur polymer based ultrasonic image division method
InactiveCN1924926ACorrect convergence guaranteeCancel noiseImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionDiffusionSonification
This invention relates to one two-dimension fuzzy poly spot noise filter and brightness compensation B type of hypersonic cutting method, which comprises the following steps: extending the image brightness information to the update two-dimension poly fuzzy type near the pixel zone based on image brightness information; leading each heter diffusion spot noise filter to the fuzzy poly aim function to provide near information and to strengthening spot robust property; leading two-dimension fuzzy poly aim function with brightness compensation factor based on the noisy on uneven hypothesis and using image aim and background even to strengthen uneven noise robust.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
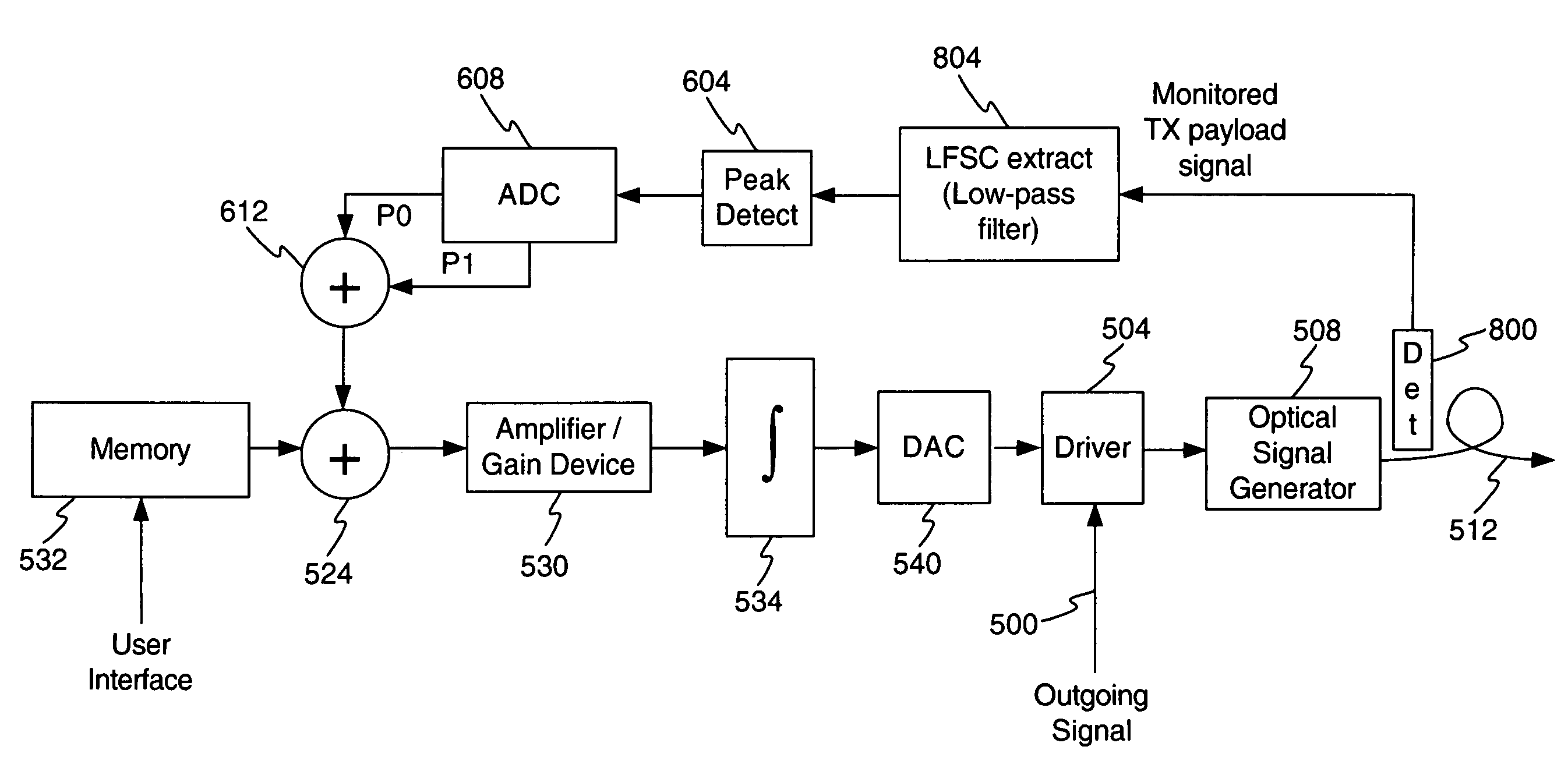
Laser power control with automatic compensation
ActiveUS7265334B2Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansControl systemClosed loop
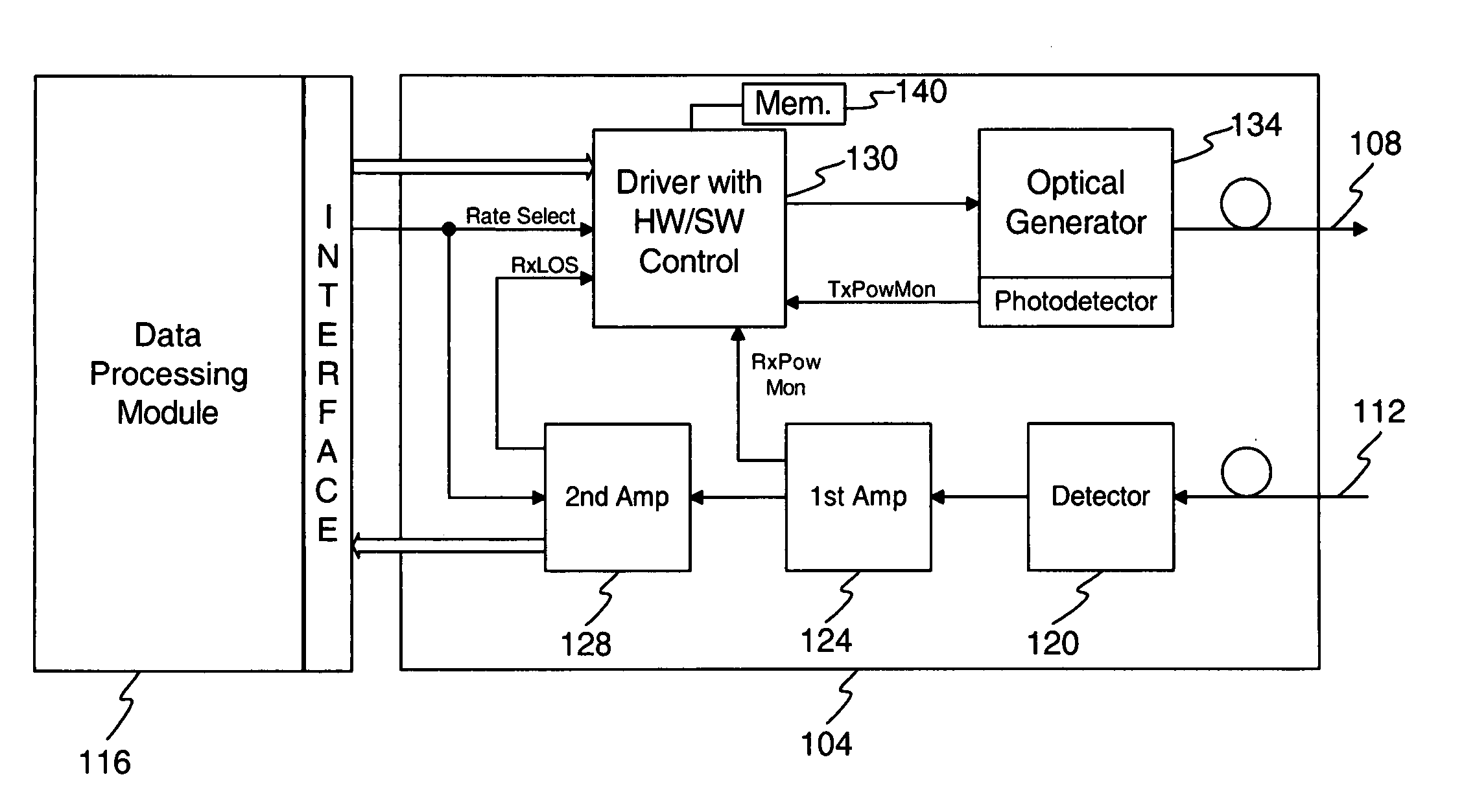
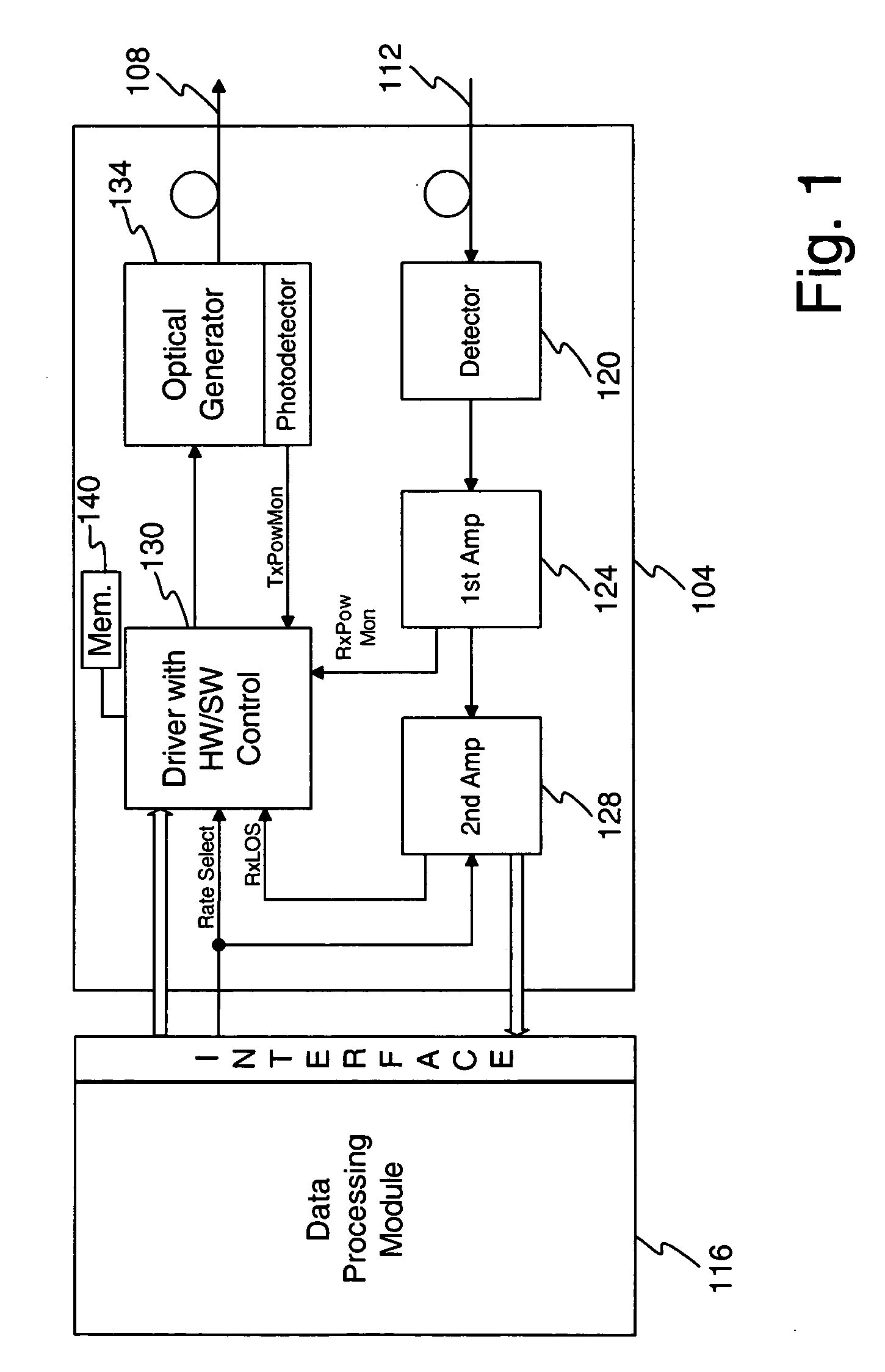
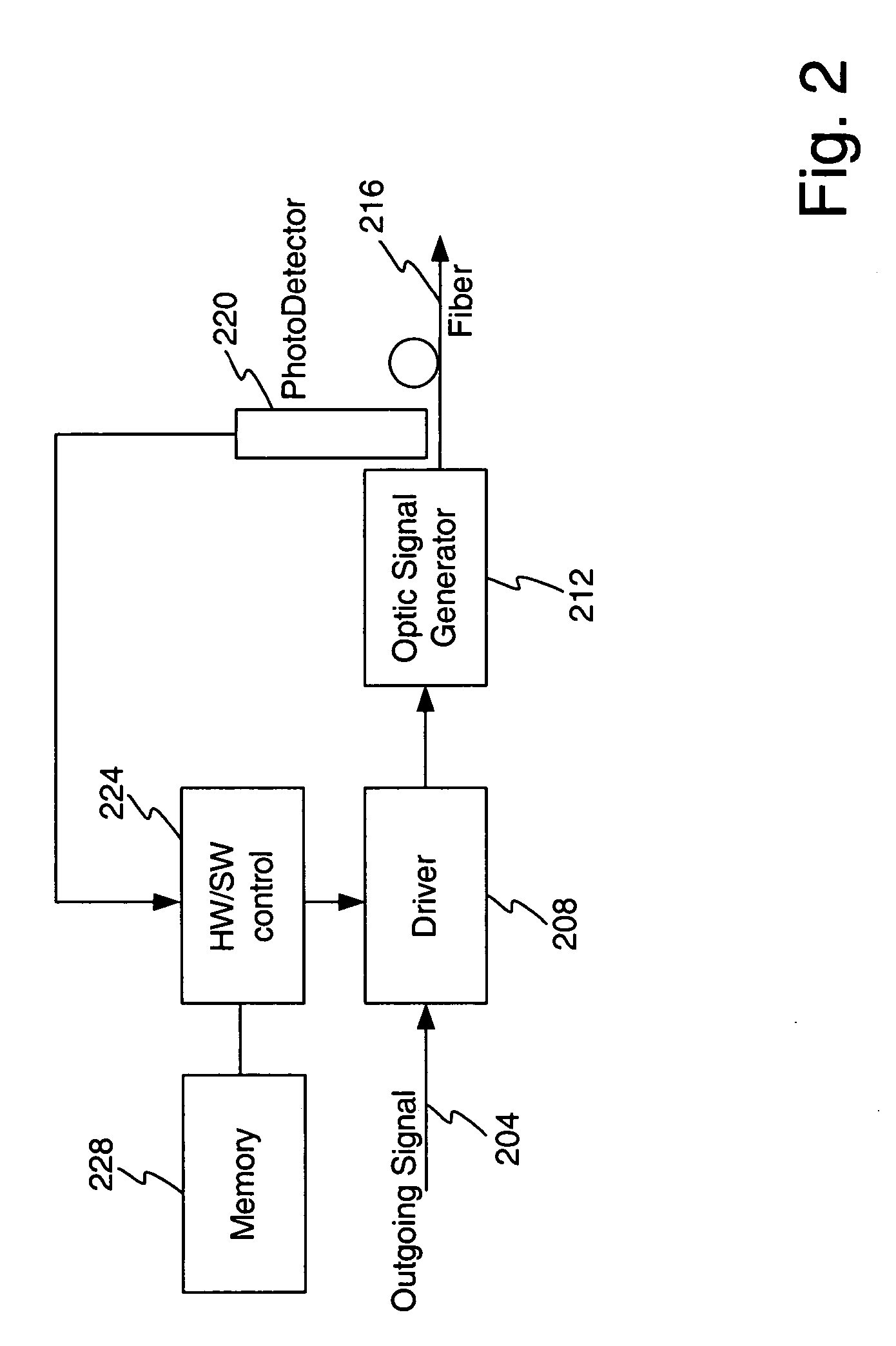
A method and apparatus is disclosed for optic signal power control to maintain a desired or optimum optic signal power level. During start-up, a target value from memory may be utilized to control one or more power levels of an optic signal. There may comprise 2 or more different power levels for the optic signal. During operation, target values may continue to be utilized or an open loop or closed loop control system may be utilized. Compensation may occur for both additive noise / distortion and multiplicative noise / distortion. The compensation for one power level may be expanded or extrapolated to compensate for additive noise / distortion and multiplicative noise / distortion that affect other power levels.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
A nonlinear system filter design method based on a self-adaption event triggering mechanism
ActiveCN107169193AReduce transmission consumptionImprove applicabilityCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsEvent triggerEngineering
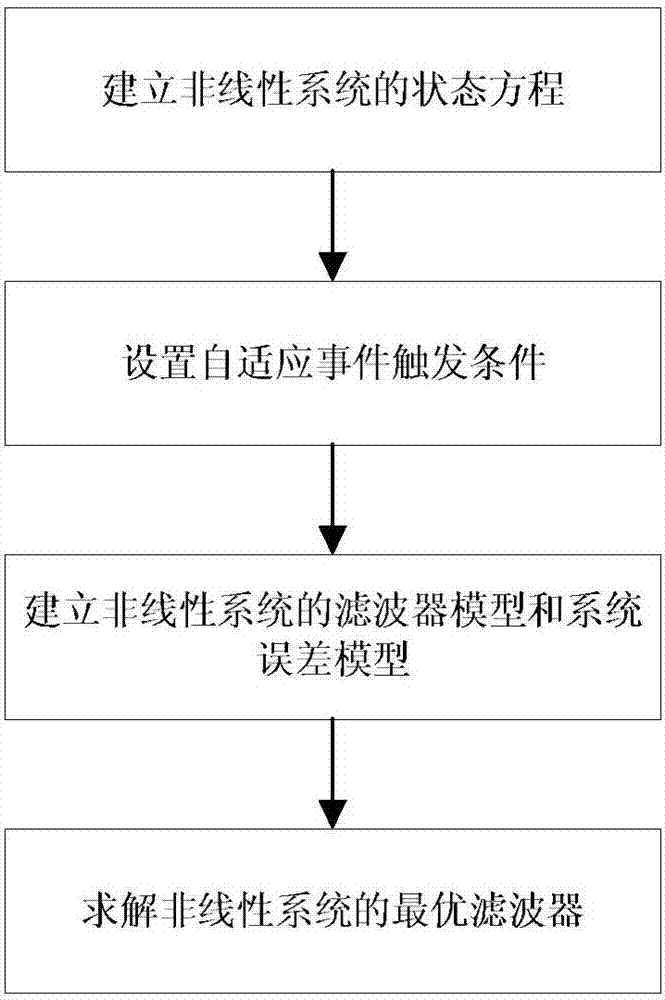
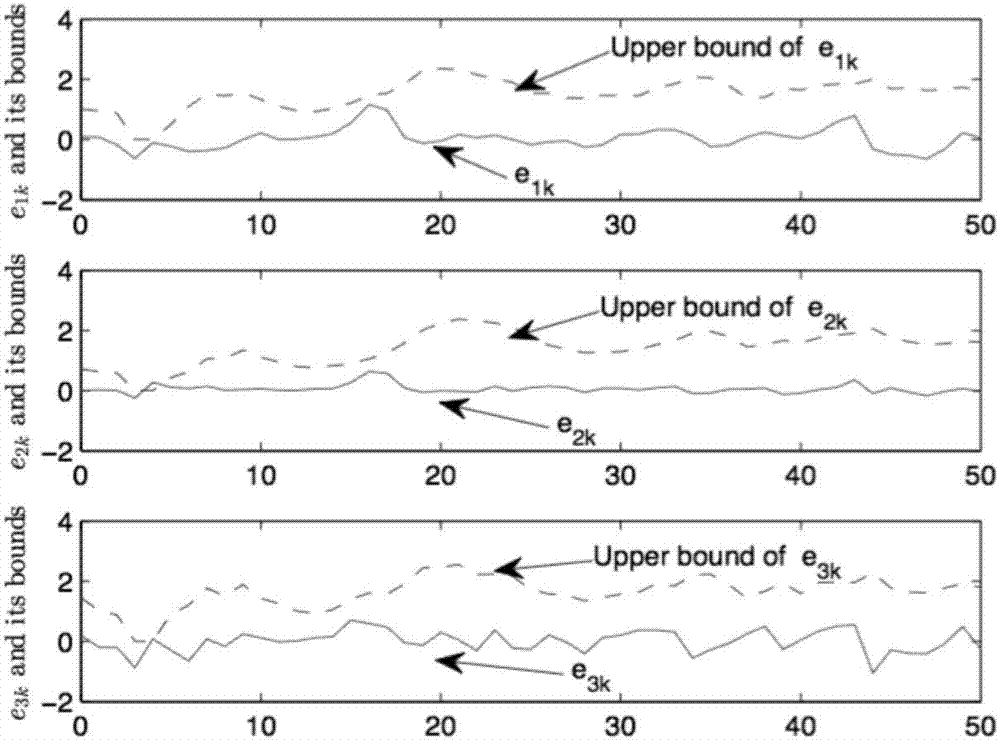
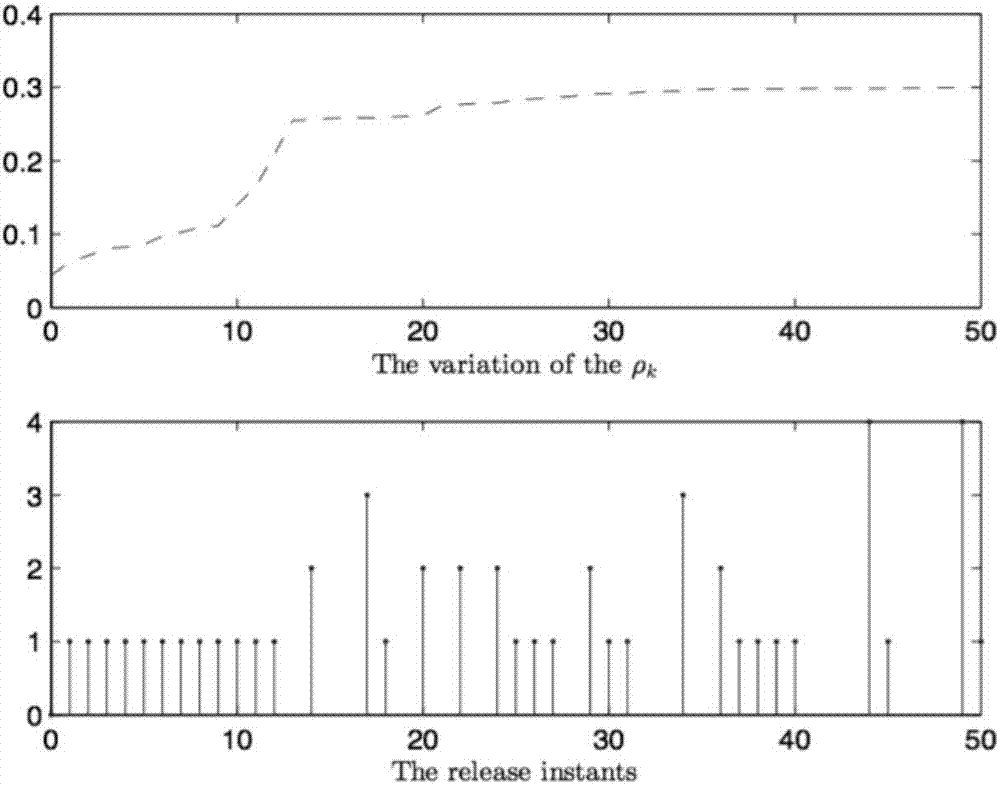
The invention provides a nonlinear system filter design method based on a self-adaption event triggering mechanism. The method comprises the steps of firstly building a state equation of a non-linear system; setting self-adaption event triggering conditions; building a filter model and a system error model of the non-linear system and obtaining an optimal filter of the non-linear system. The method employs the self-adaption event triggering mechanism for the non-linear system which is characterized by random nonlinearity, multiplicative noise and state constraints, so that the performance of filters is improved.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Multiplicative noise removing method based on deep neural network
InactiveCN107644401AAchieve removalHigh speedImage enhancementNeural architecturesImage denoisingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
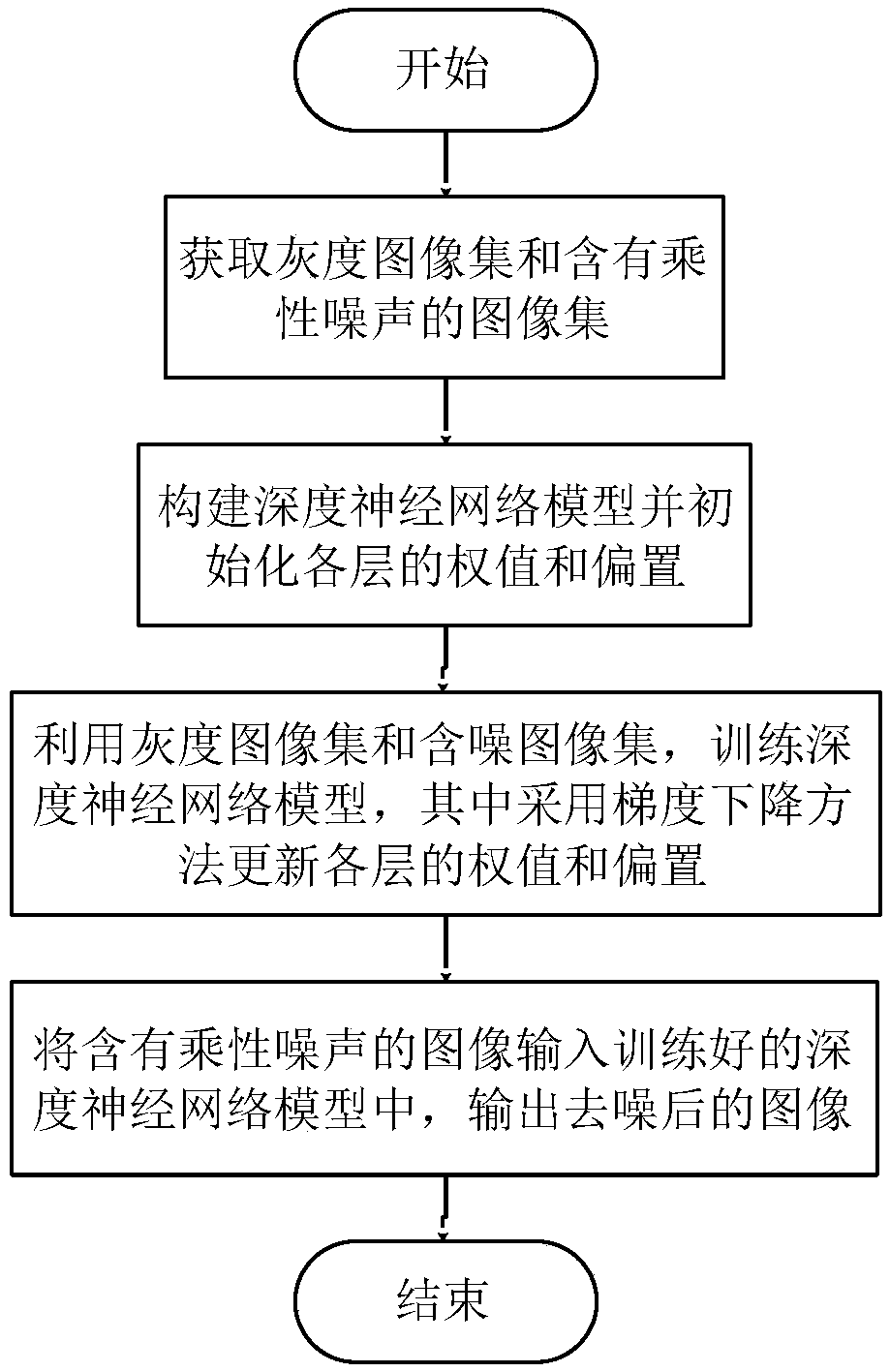
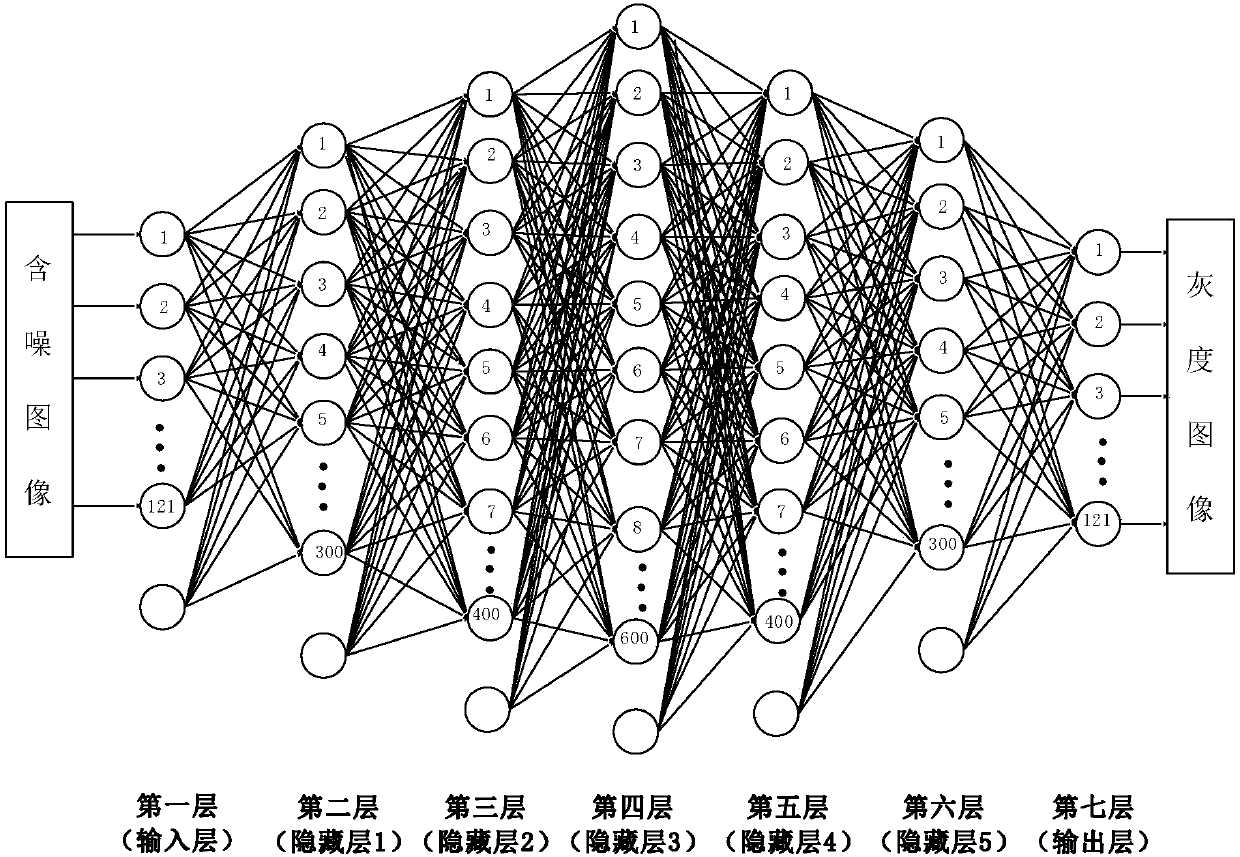
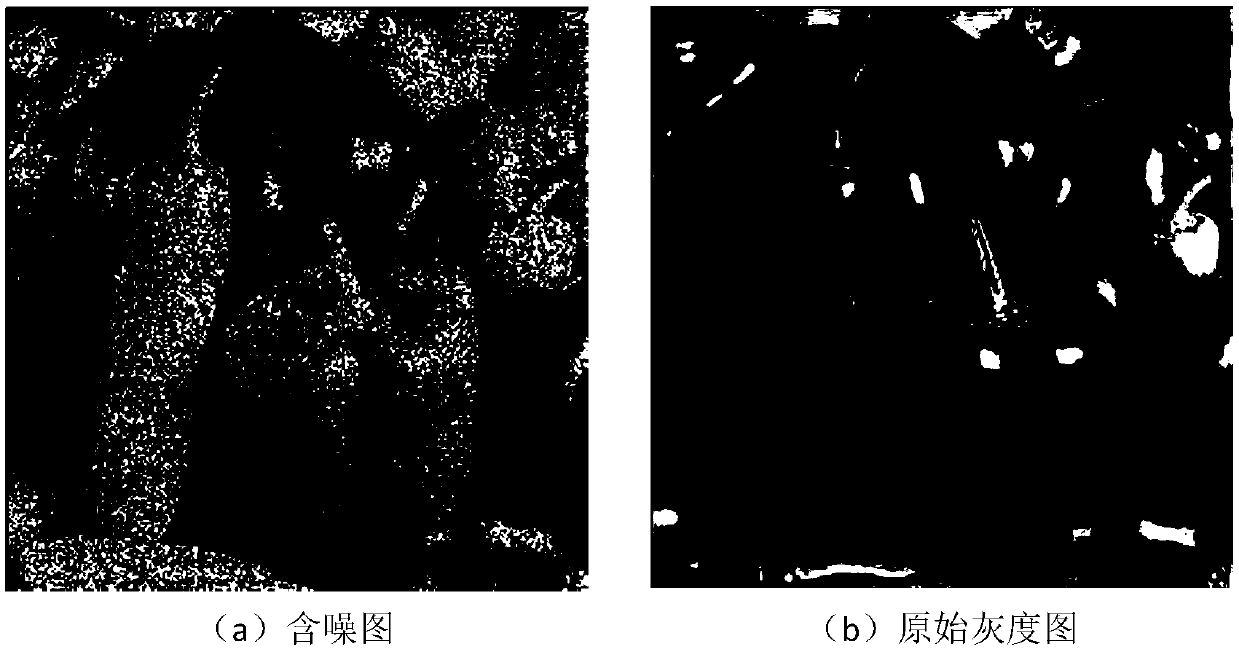
The invention provides a multiplicative noise removing method based on a deep neural network, and mainly solves the problems that the peak signal-to-noise ratio is low and the speed is low when imagemultiplicative noise is removed in the prior art. The method is characterized in that a nonlinear mapping relation between a noisy image and a grayscale image is fitted through a trained deep neural network, and is used for removing the multiplicative noise. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a grayscale image set (X) and a noise-containing image set (Y), constructing a deep neural network model; using the grayscale image set (X) and a noise-containing image set (Y) to train the weight and bias of each layer of the deep neural network model, and inputting a to-be-denoised image into atrained deep neural network model. The output result of the deep neural network model is a denoised grayscale image. According to the method, the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the denoised image is improved, and the speed of removing the multiplicative noise is increased. The method can be applied to the occasions of for image denoising and preprocessing including image classification, object recognition, edge detection and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Semiconductor optical detector
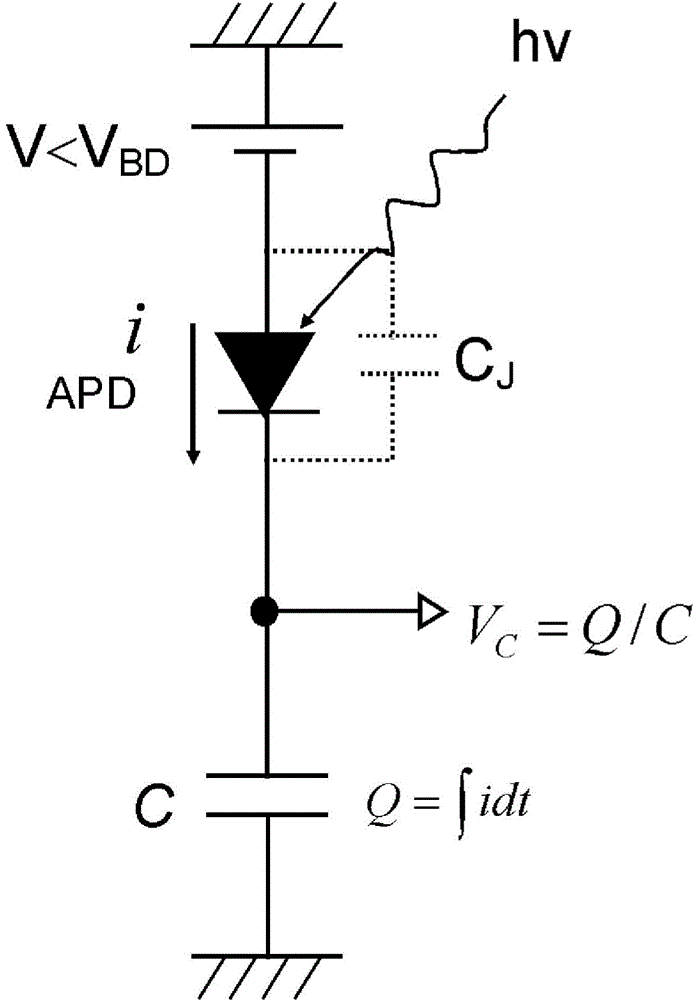
Provided is a semiconductor optical detector that is capable of detecting weak light including random light by significantly reducing dark-time noise and multiplicative noise from those in conventional semiconductor optical detectors. This semiconductor optical detector has at least one unit pixel having a photoelectric conversion section, a charge storage section, and a detecting circuit. The charge storage section photoelectrically converts inputted light, and has a charge multiplying region where charges are multiplied by means of avalanche multiplication. The charge storage section is connected to the photoelectric conversion section, and stores signal charges transmitted from the photoelectric conversion section. The detecting circuit is connected to the charge storage section, converts the signal charges stored in the charge storage section into voltage, amplifies the voltage by means of an amplifying section, and outputs the amplified voltage.
Owner:PANASONIC INTPROP MANAGEMENT CO LTD
De-noising method integrated with gradient histogram and low rank constraint
ActiveCN107358589AEasy to keepTake full advantage of non-local featuresImage enhancementNon localImage gradient
The invention discloses a de-noising method integrated with a gradient histogram and low rank constraint. Based on sparse priori and other non-local self similar priori, sparse expression advantages are utilized, and a non-local regular item, a gradient regular item and a low rank constraint item are added to remove multiplicative noise. The method is advantaged in that a multiplicative noise model is converted through logarithmic transformation into an additive noise model of a logarithm domain, a training dictionary of the noise image in the logarithm domain is utilized, image gradient histogram estimation and low rank constraint are combined, local and non-local image connection is enhanced, on the condition that de-noising is effectively realized, the image texture information is better reserved; the experiment result is relatively good in subjective vision and objective evaluation indexes, the precise texture structure of the image is reserved to a great degree, and the image after de-noising is more intelligible.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Method for reducing synthetic aperture radar smudges noise
InactiveCN101398487AImage enhancementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarFiltration
The invention discloses a method used for reducing the noise of image stain of synthetic aperture radar (SAR), comprising the steps as follows: the image is logarithmically transformed so as to change the multiplicative noise into the additive noise; mean correction is carried out on transformed image so as to lead the correction result to meet the hypothesis premise of zero mean Gauss white noise; the image after mean correction is circularly translated, thus eliminating image visible effect aberrance possibility caused by Contourlet transformation; Contourlet transformation is carried out on a series of gained translation images and filtration processing is carried out by a Contourlet domain filter; Contourlet transformation is carried out on all filtrated translation images; subsequently, inverse translation conversion is carried out on all images after the inverse transformation; subsequently, the images after inverse translation transformation are averaged; exponential transform is carried out on the averaged images, thus gaining the filtrated images; the method can greatly reduce the noise of image stain of SAR.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Multiplicative noise removal method for image
InactiveCN104657951AEfficient removalReduce workloadImage enhancementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Noise removal
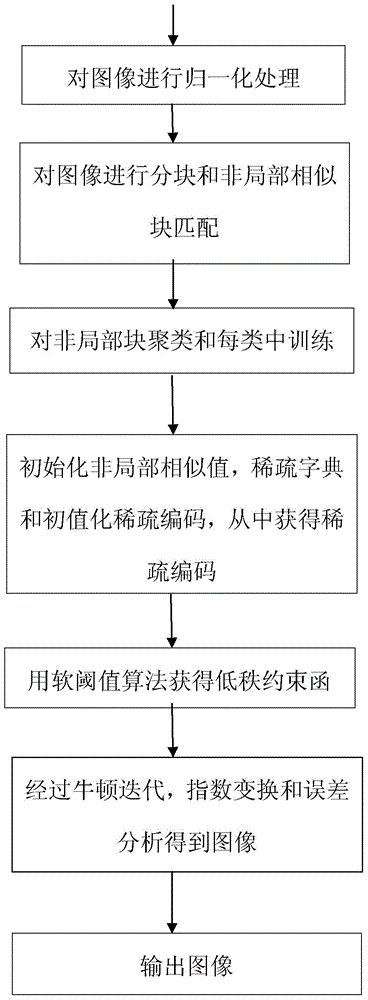
The invention discloses a multiplicative noise removal method for an image. According to the method, calculus of variations and low rank constraint condition are embedded on the basis of a non-local learned dictionary based on sparse representation, non-local similar patches are subjected to weight matching, a sparse coding is solved with an iterated function, and a soft threshold algorithm is applied to low rank solution. The multiplicative noise removal method has the advantages that very good noise removal effect and high peak signal to noise ratio are realized, edge information and textural features of the image are reserved well to be more close to an original image visually, and the similarity is improved greatly.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
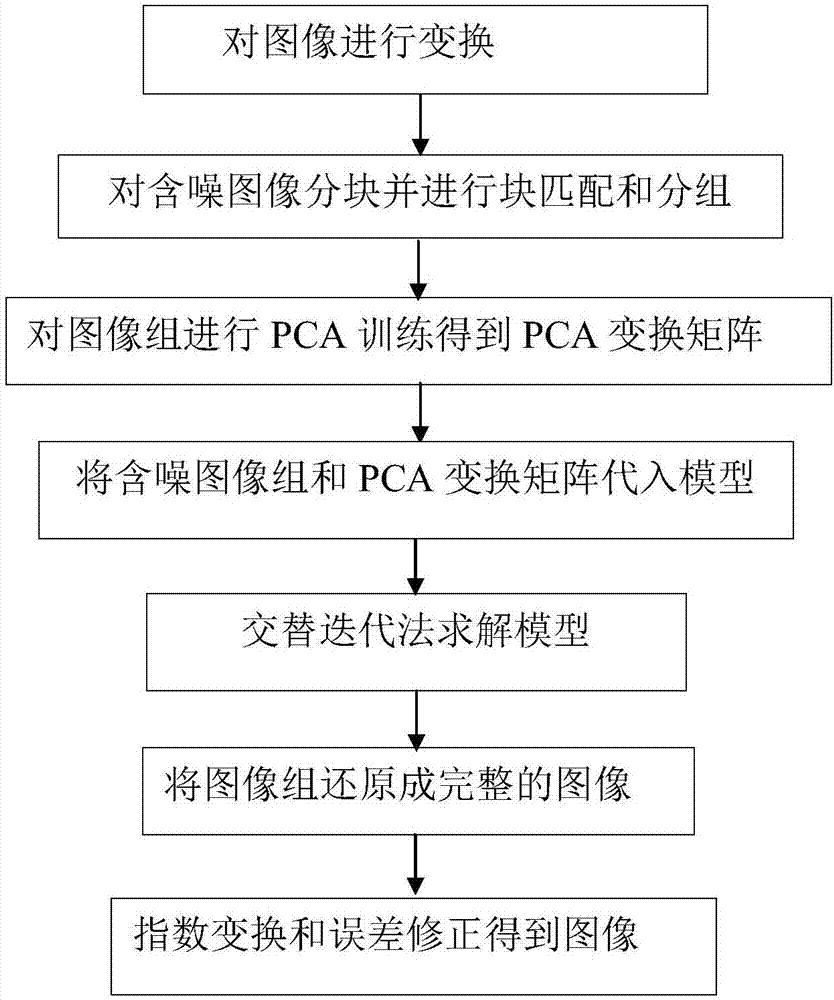
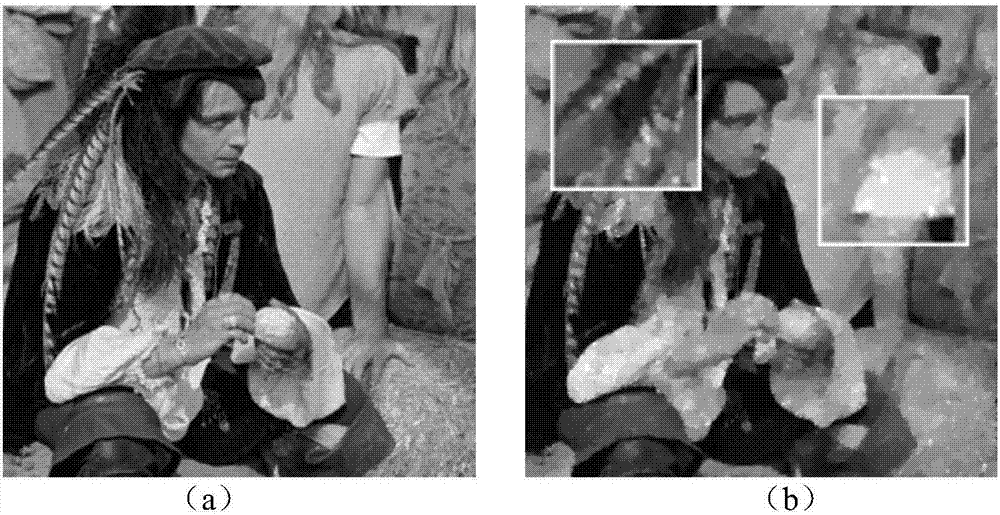
Multiplicative noise removal method based on non-local adaptive dictionary
ActiveCN106204483AGood for preserving edgesGood for retaining detailed informationImage enhancementImage analysisNoise removalPrincipal component analysis
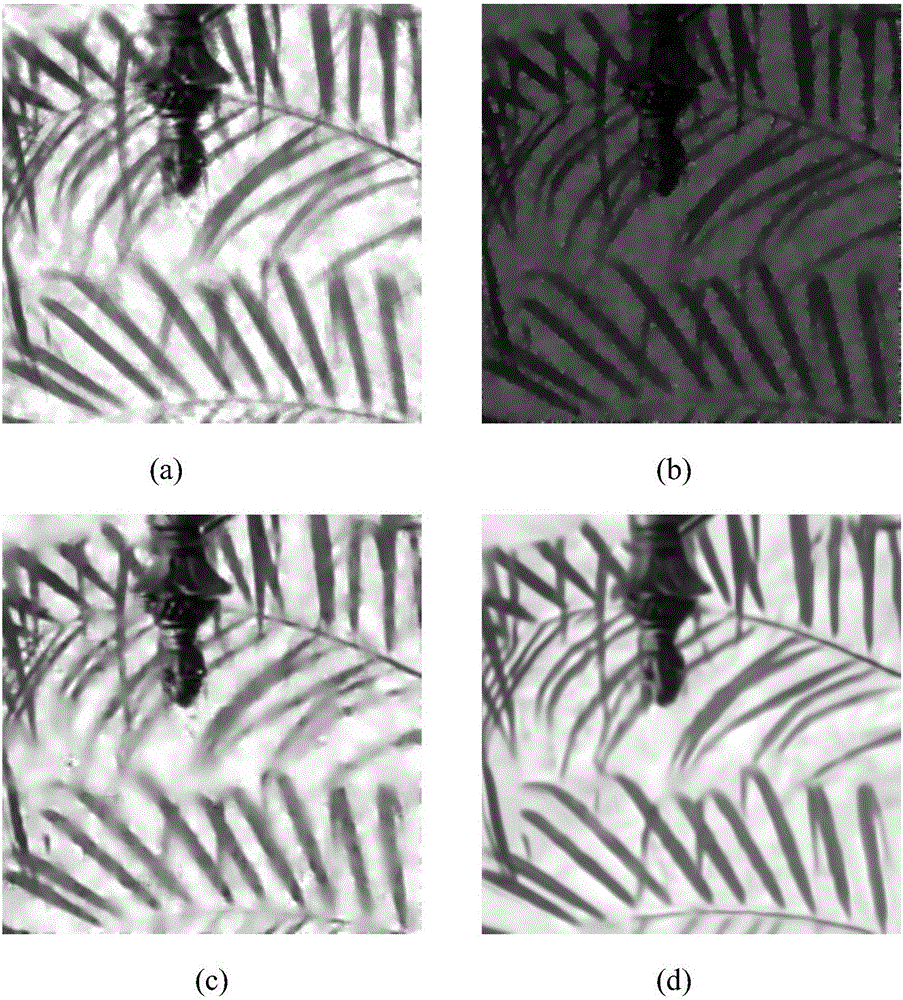
The invention discloses a multiplicative noise removal method based on a non-local adaptive dictionary. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, utilizing logarithm transformation to convert multiplicative noise into additive noise; then combining a PCA (Principal Component Analysis) sparse dictionary with an iteration shrinkage algorithm to update sparse coding, and utilizing a Newton iteration method to obtain a noise removal image in a log domain; and finally, through an exponential function and error correction, obtaining the noise removal image in a real number field. By use of the method, the edge, detail and texture information of the image can be favorably kept while noise can be effectively removed.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
A finite-time-domain Hinfinite control method for time-varying systems under the influence of high-rate communication networks is proposed
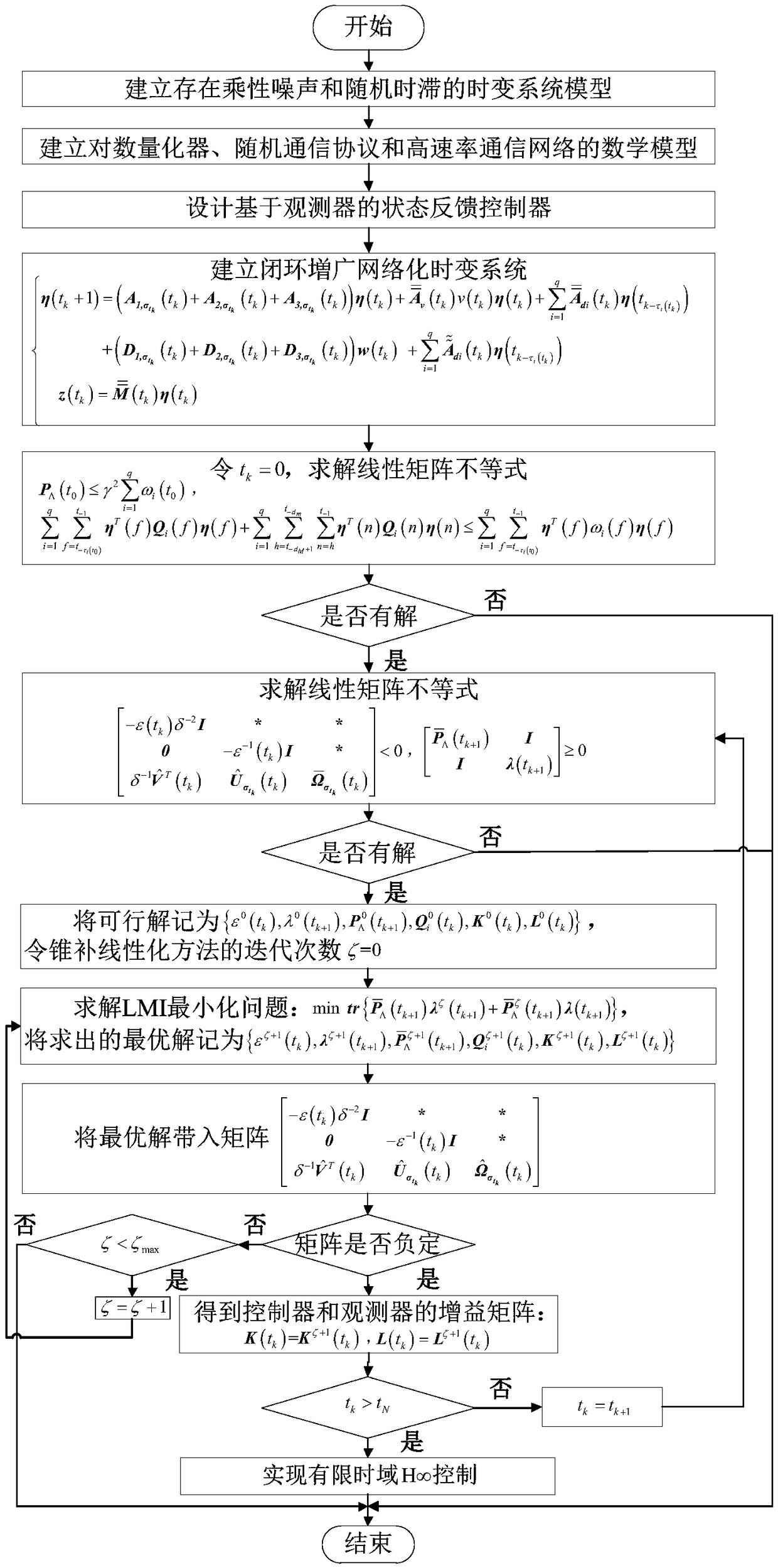
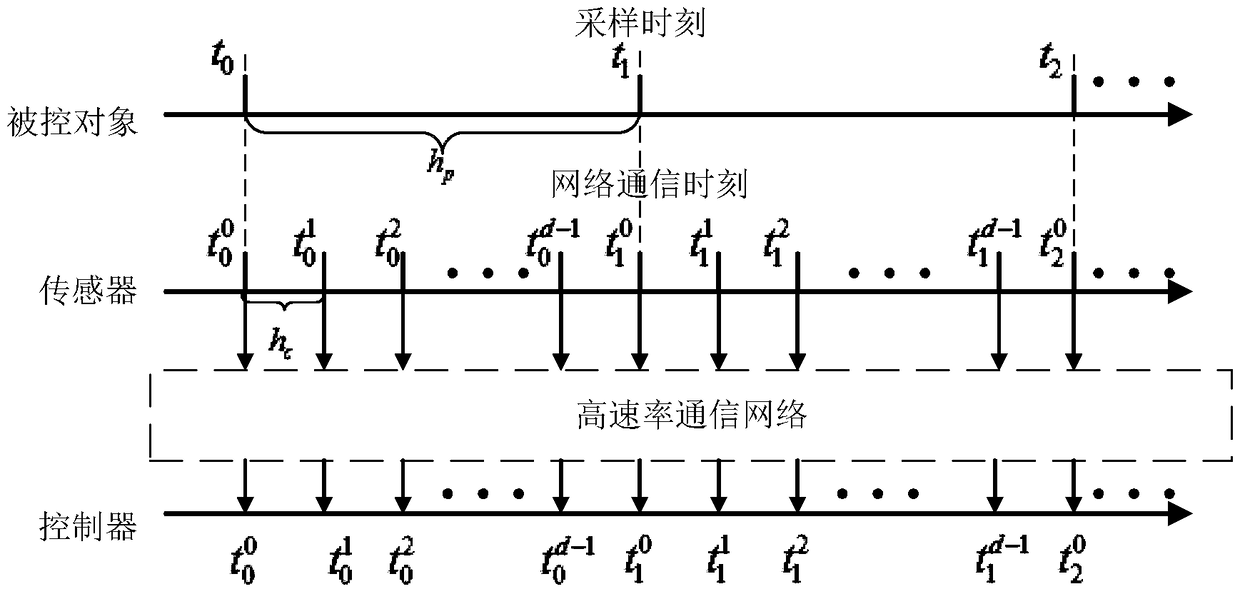
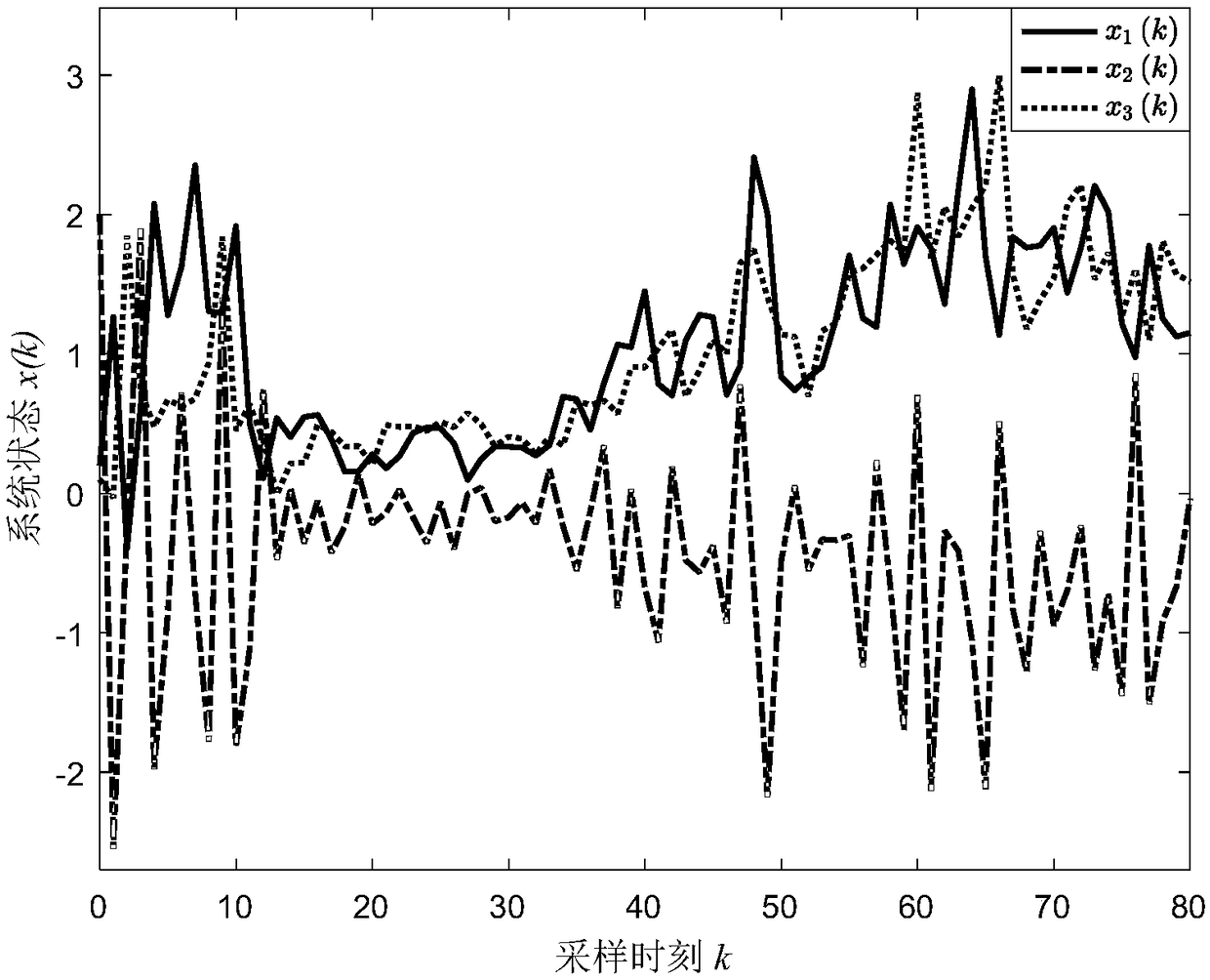
The invention provides a finite time domain Hinfinite control method of a time-varying system under the influence of a high-speed communication network, belonging to the networked control system field. At first, under the influence of random communication protocol and high-speed communication network, a networked time-varying system model with multiplicative noise, stochastic time delay and quantization error is proposed. Then observer-based state feedback controller is designed. By using Lyapunov stability theory and linear matrix inequality analysis method, the sufficient conditions for theclosed-loop system to satisfy the Hinfinite performance requirement are obtained. Finally, a finite-time-domain Hinfinite controller design algorithm based on cone-complementary linearization is proposed, and the time-varying gain matrices of the observer and the controller are obtained by using Matlab LMI toolbox. The invention considers the influence of the stochastic communication protocol andthe high-speed communication network on the networked time-varying system under the actual situation, and the existence of multiplicative noise, the stochastic time delay and the quantization error ofthe system, and is suitable for the finite time domain Hinfinite control of the general networked time-varying system, and reduces the conservatism.
Owner:单旭
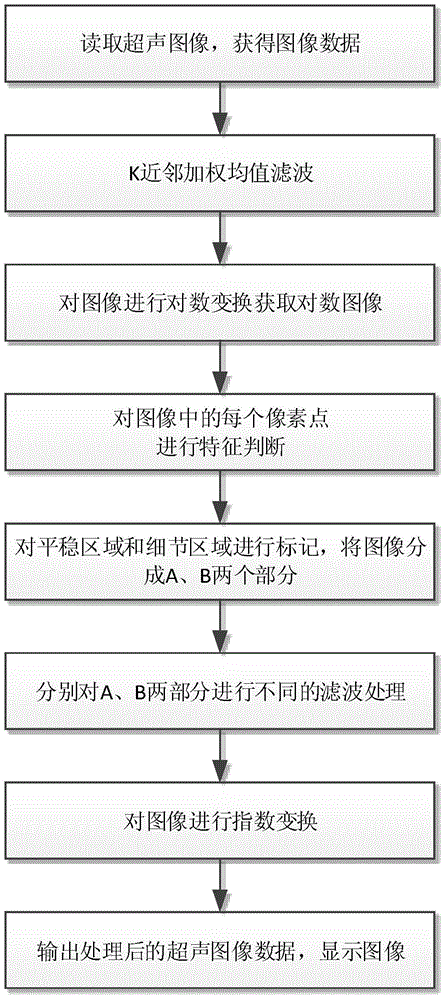
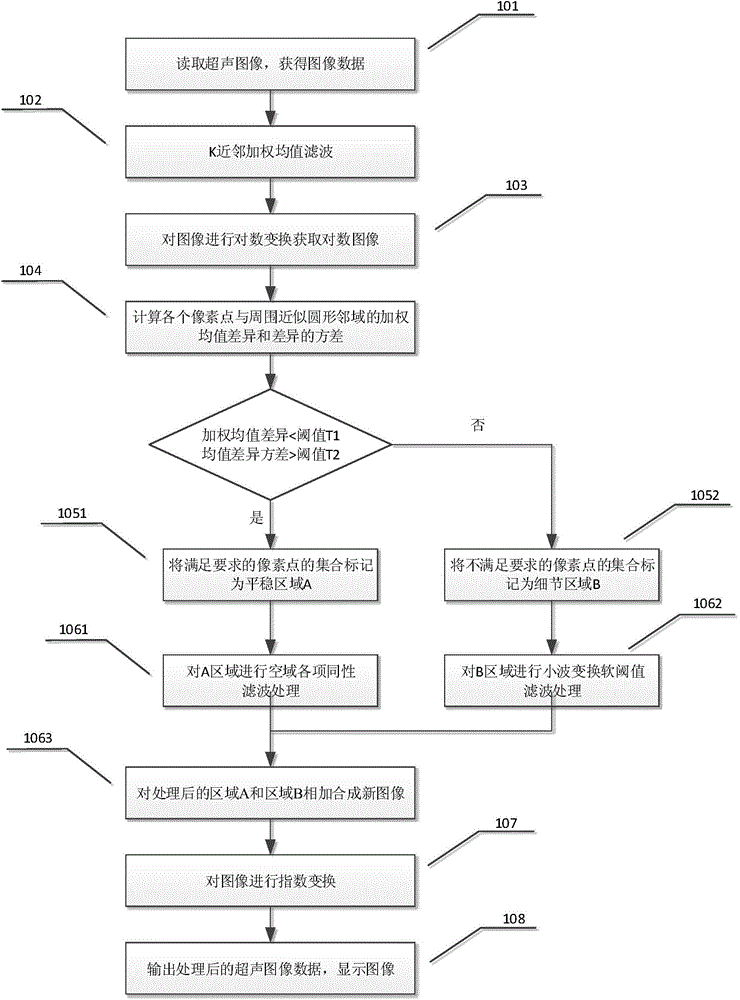
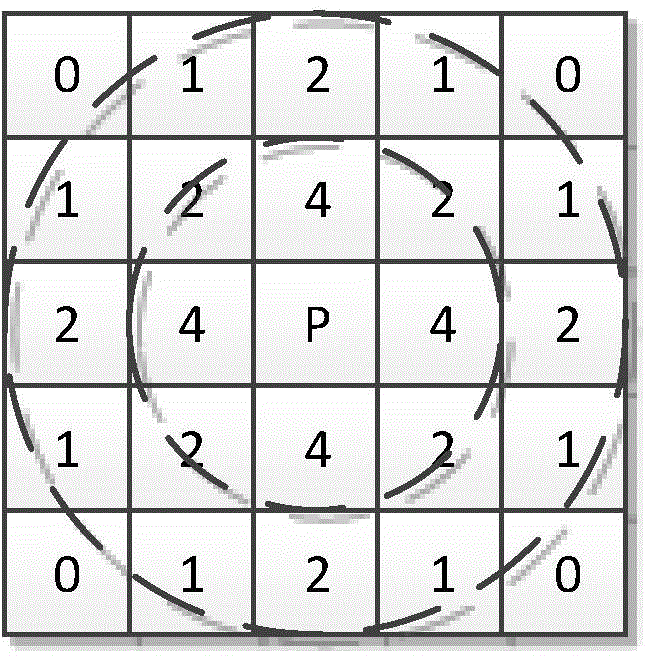
Ultrasonic image mixed noise self-adaptive suppression method
ActiveCN104103041AValid reservationImprove protectionImage enhancementPattern recognitionMixed noise
The invention provides an ultrasonic image mixed noise self-adaptive suppression method. According to the method, additive noise and multiplicative noise in an image are removed respectively; logarithmic transformation is carried out on the image after being subjected to the additive noise removing to enable the multiplicative noise to be converted into the additive noise; then, weighted average difference values of pixel points and neighbourhood points in the image as well as the variance of the difference values are calculated; noise judgment is carried out based on the difference values and the variance and the image is divided into a smooth area and a detail area; and after the different areas are respectively subjected to space-domain filtering and transform-domain filtering, the processed areas are added to obtain a de-noised image. Therefore, the advantages of the two filtering processing can be fully utilized to realize the self-adaptive processing that for different pixel points, different filtering methods are used. The method is simple and convenient; neighbourhood domain section is reasonable; de-noising effect is more obvious than that of single domain processing; and the method is high in practicality.
Owner:BEIJING HUACO HEALTHCARE TECH CO LTD +1
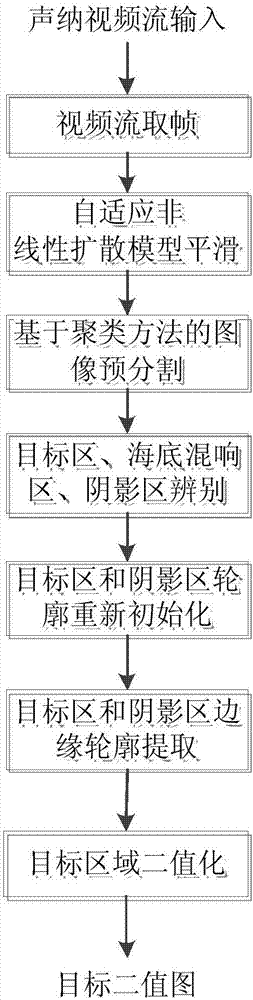
Underwater target rapid extraction method for side-scan sonar imaging
ActiveCN107167810AImprove the noise problemUnderstand the purposeAcoustic wave reradiationReal time analysisComputer vision
The present invention discloses an underwater target rapid extraction method for side-scan sonar imaging. The method can perform real-time analysis on a side-scan sonar image and quickly extract an underwater target. According to the method, adaptive non-linear complex diffusion model filtering is performed on a side-scan sonar image of which the multiplicative noises are prominent, so that a noise problem in the side-scan sonar image can be improved; the de-noised sonar image is pre-segmented, and the target region, seabed reverberation region and shade region of the side-scan sonar image are automatically determined; the contours of the pre-segmentation results are redefined, so that time for constantly re-defining an initial level set in level set model evolution can be decreased in a segmentation process; a variation level set model-based evolution and segmentation are performed on the target region and the shade region; and binarization is performed on a target to be extracted, clear segmentation results of the three regions are displayed for an operator. According to the underwater target rapid extraction method for the side-scan sonar imaging of the invention, target extraction is performed on a real-time side-scan sonar, and therefore, the method has the advantages of high detection real-time performance, high detection stability and high accuracy, provides a reliable guarantee for underwater detection and target tracking.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Method for estimating aircraft attitudes based on capacity quaternion estimation
ActiveCN106767837ATake advantage ofImprove estimation accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationGyroscopeQuaternion
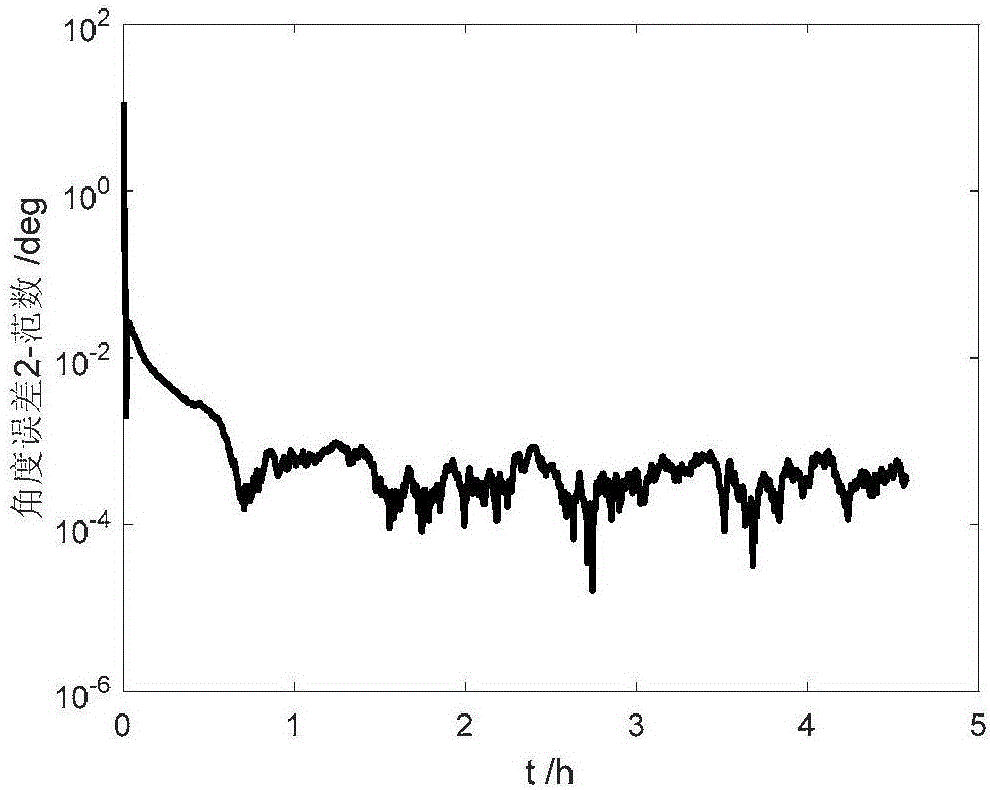
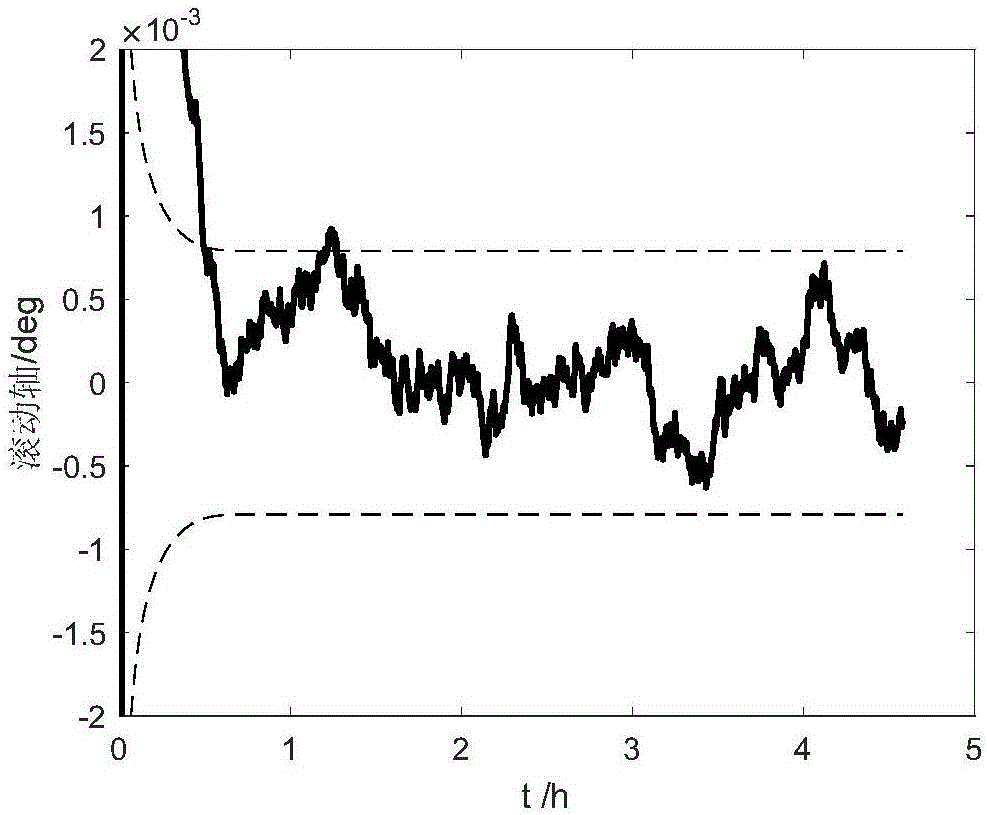
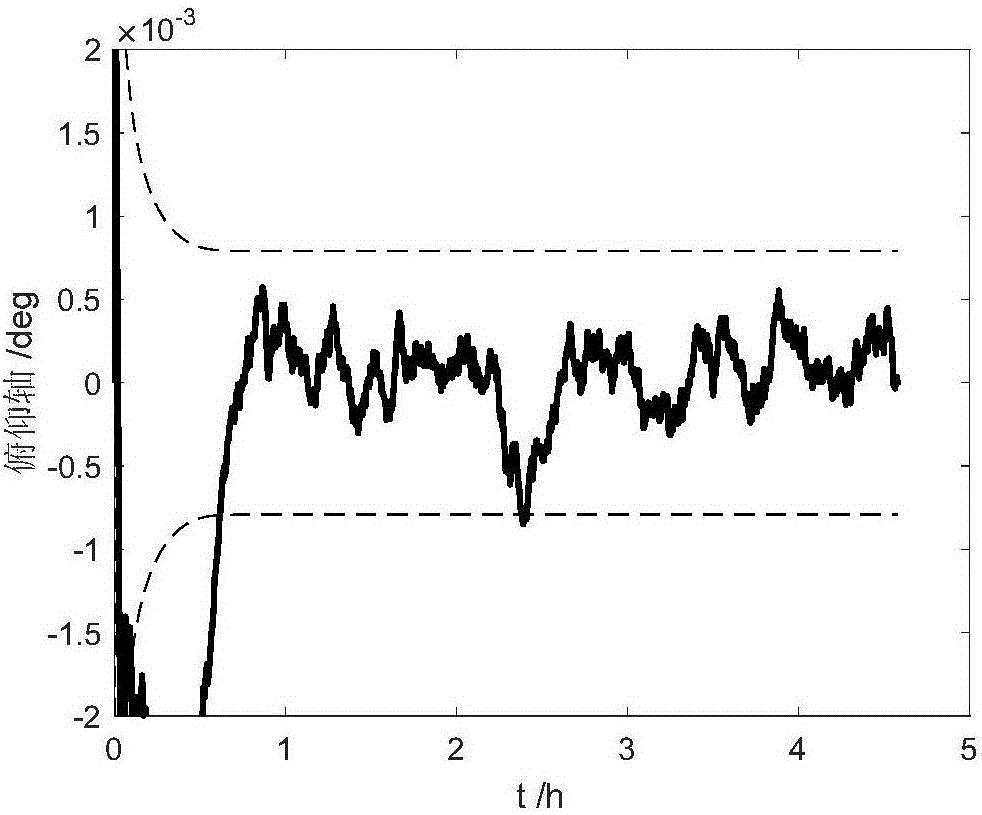
The invention provides a method for estimating aircraft attitudes based on capacity quaternion estimation, and relates to a method for estimating aircraft attitudes based on capacity quaternion estimation and satellite sensor and gyroscopic combination, which aims at solving the problem of low estimation accuracy of aircraft attitudes due to multiplicative noise and noise correlation in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of 1, establishing an aircraft attitude kinematics model and an observing model; 2, using a Gaussian filtering algorithm to remove the noise in the aircraft attitude kinematics model and the observing model established in step 1; 3, using a capacity quaternion attitude estimator to estimate the aircraft attitudes. Compared with the CQE (cubature quaternion estimator) algorithm, a CQE-MCNS (cubature quaternion estimator for multiplicative correlated noises system) method has the advantage that the angle estimation error is reduced by about 0.0002 degree, and the gyroscope drift estimation error is reduced by about 0.002 degree per hour, so that the CQE-MCNS method is more suitable for the problem of aircraft attitude estimation with multiplicative noise and related to noise correlation. The method is applied to the aerospace field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
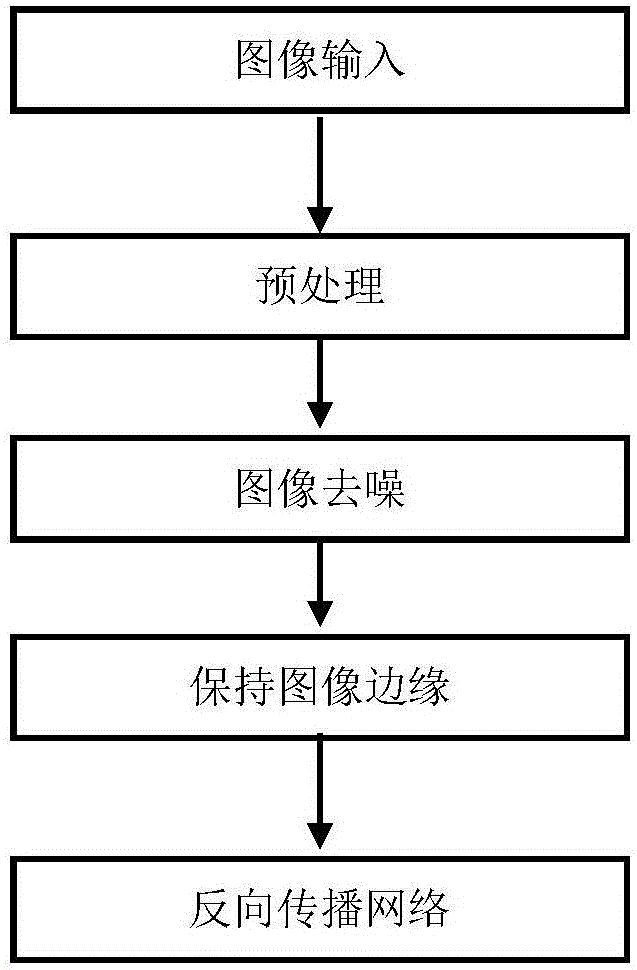
Image super-resolution reconstruction method based on back-propagation neural network
InactiveCN106846253AImage enhancementGeometric image transformationPattern recognitionReconstruction method
The invention discloses an image super-resolution reconstruction method based on a back-propagation neural network. The contents of the method mainly include image input, preprocessing, image denoising, image-border maintaining and the back-propagation neural network. The method includes the steps that first, a synthetic aperture radar image is preprocessed, multiplicative noise of the image is converted into additive noise, an improved non-local mean value is adopted to conduct the denoising, and an exponentiation operation is adopted to restore the image; then, a kernel function is adopted to maintain clear borders of a reduced image; finally, through the treatment of the back-propagation neural network, a super-resolution reconstruction result is obtained. According to the method, a neural network model is adopted, and a large number of computing resources and a large amount of calculation time are saved; according to the improved non-local mean value method, a low-resolution image is reconstructed into a high-resolution image, speckle noise of the synthetic aperture radar image is denoised, and the combination of the modified non-local mean value method and the back-propagation neural network greatly improves the reconstruction effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
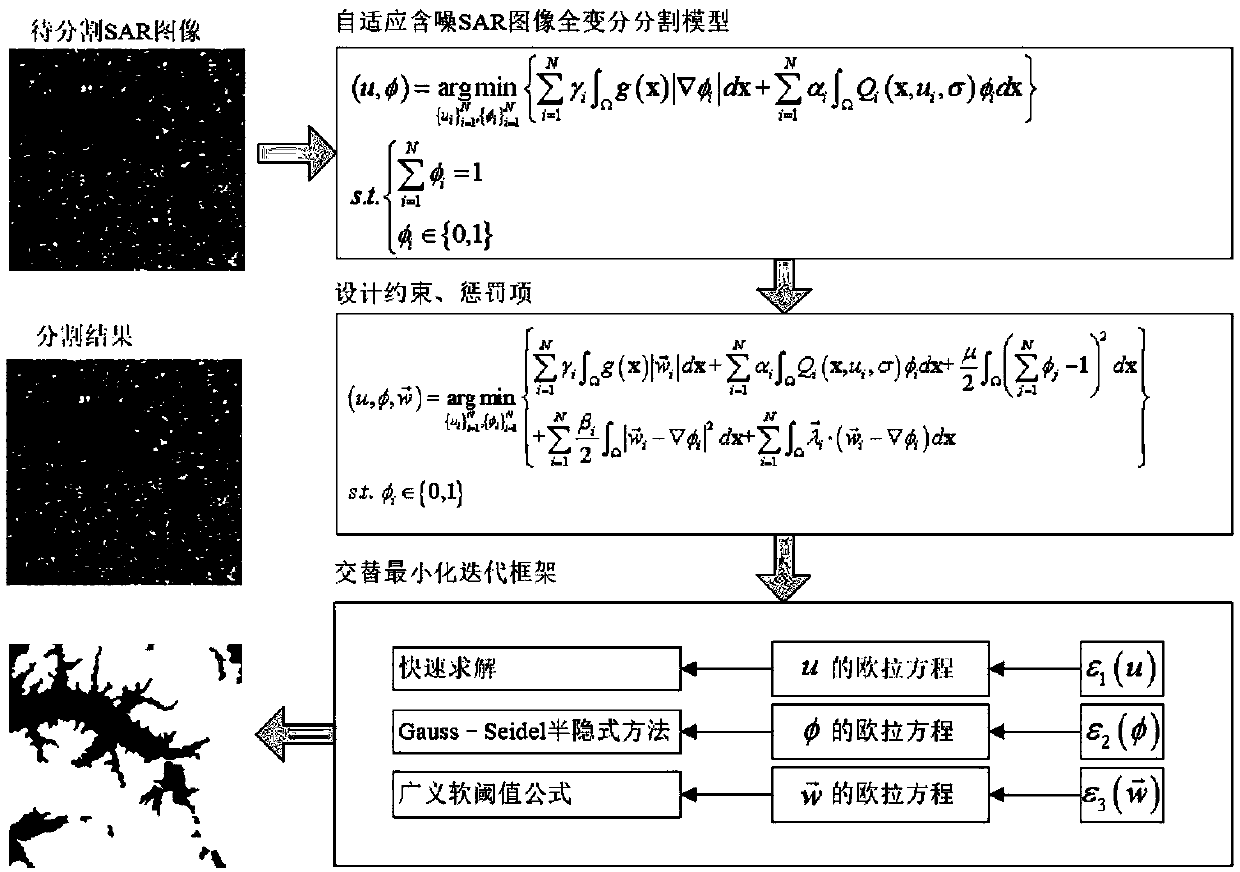
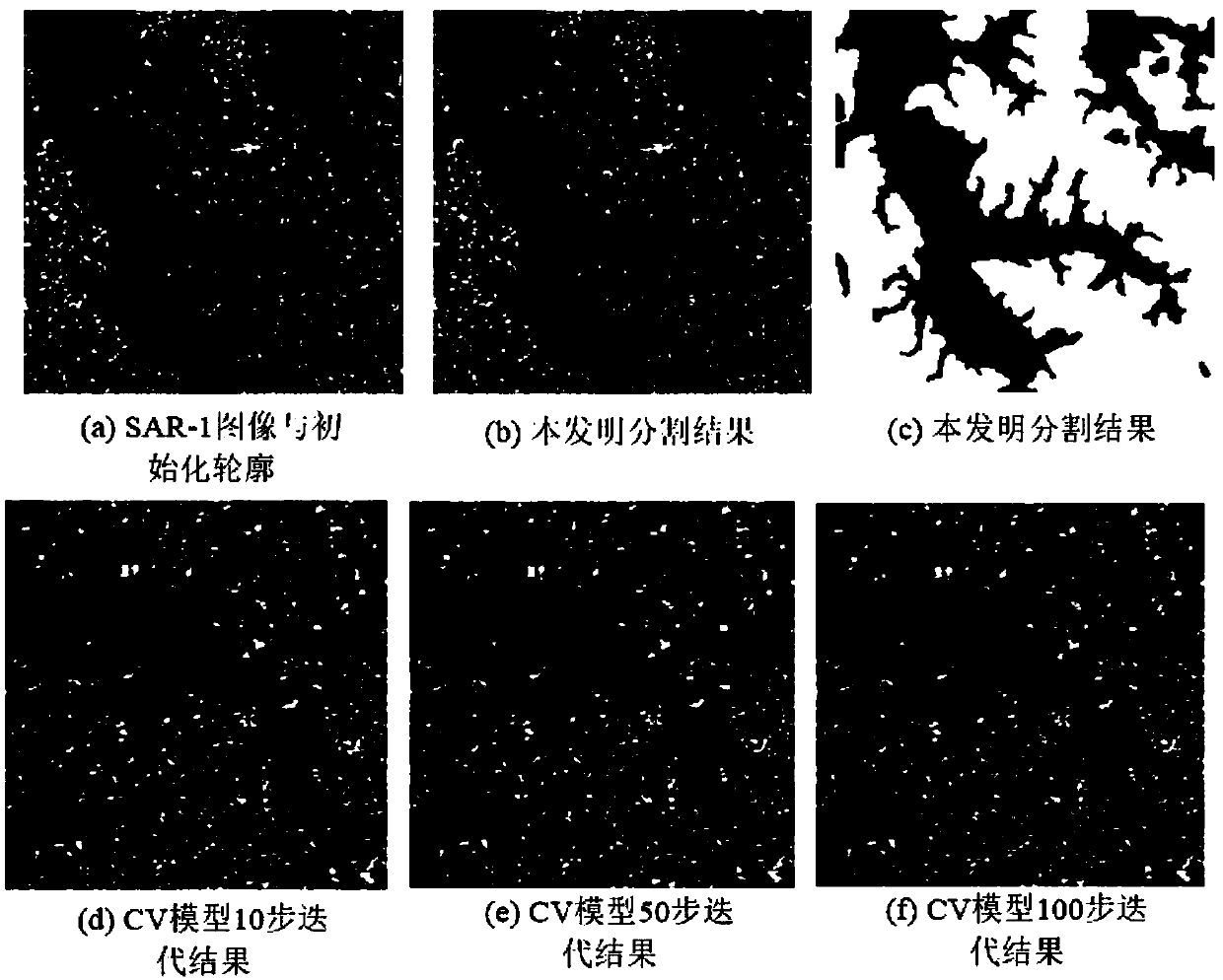
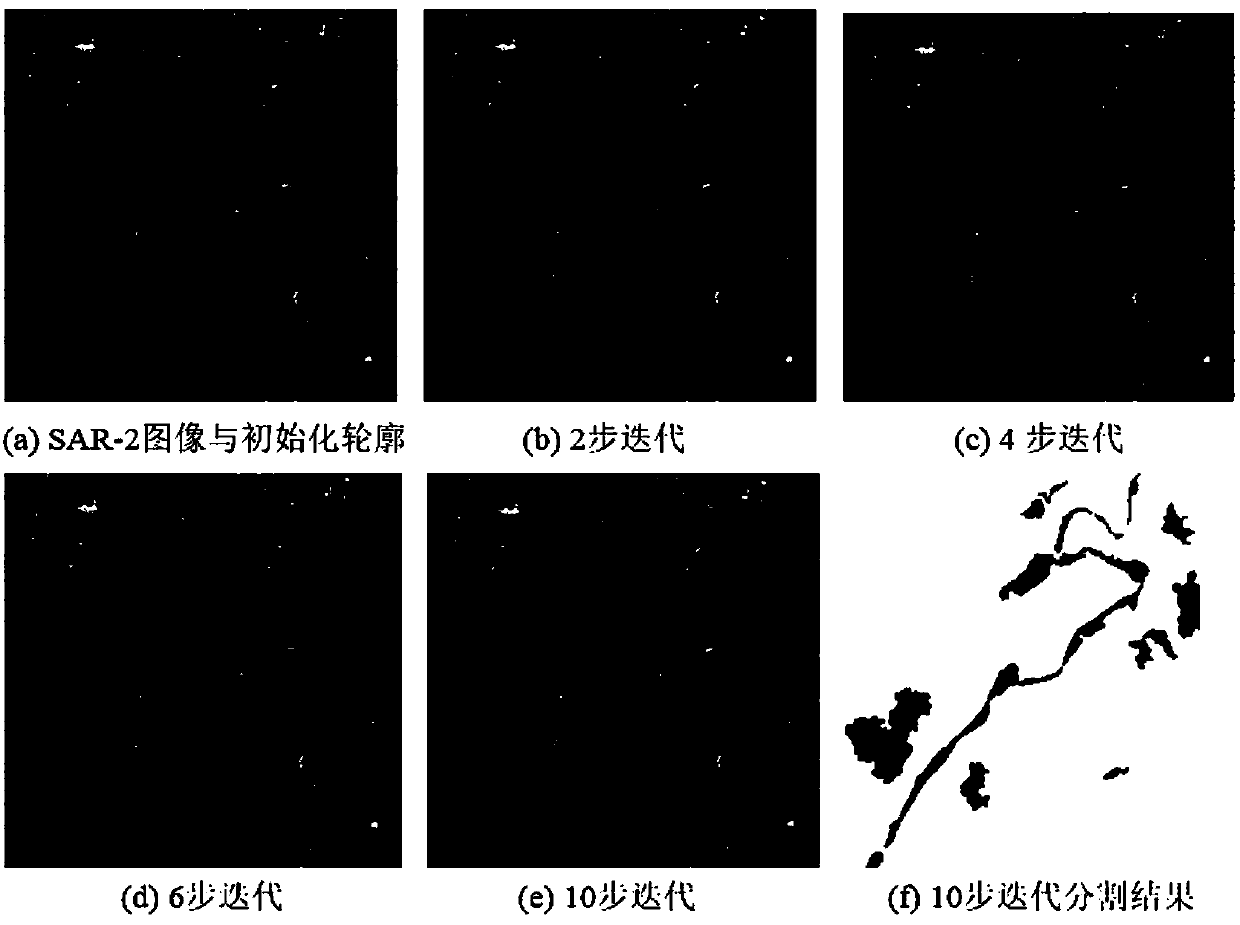
Self-adaptive noise-containing SAR image full-variation segmentation method
InactiveCN107665494AQuality improvementImprove efficiencyImage analysisPattern recognitionEnergy functional
The invention belongs to the technical field of digital image processing, and particularly relates to a self-adaptive noise-containing SAR image variational segmentation method. According to the invention, a self-adaptive edge detection operator is introduced to control the diffusion of all-variation rule items, and a noise-containing SAR image segmentation variation model is built according to the reconstructed data items of a multiplicative noise distribution function. The model has the characteristics of non-linear, non-convex and non-smoothness performances, and is difficult to solve. According to a curve evolution theory and a operator splitting method, the minimization energy functional problem is formalized as the minimum value problem with the constraint. Meanwhile, a fast numerical approximation iterative solution method is designed to carry out SAR image segmentation. According to the invention, the self-adaptive noise-containing SAR image full-variation segmentation method is good in robustness for the multiplicative noise of SAR images, and the edge details can be well kept. The noise-containing SAR image segmentation is realized. Meanwhile, the method lays a foundationfor the interpretation analysis and other subsequent applications on SAR images. The method is friendly in application environment and wide in market prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
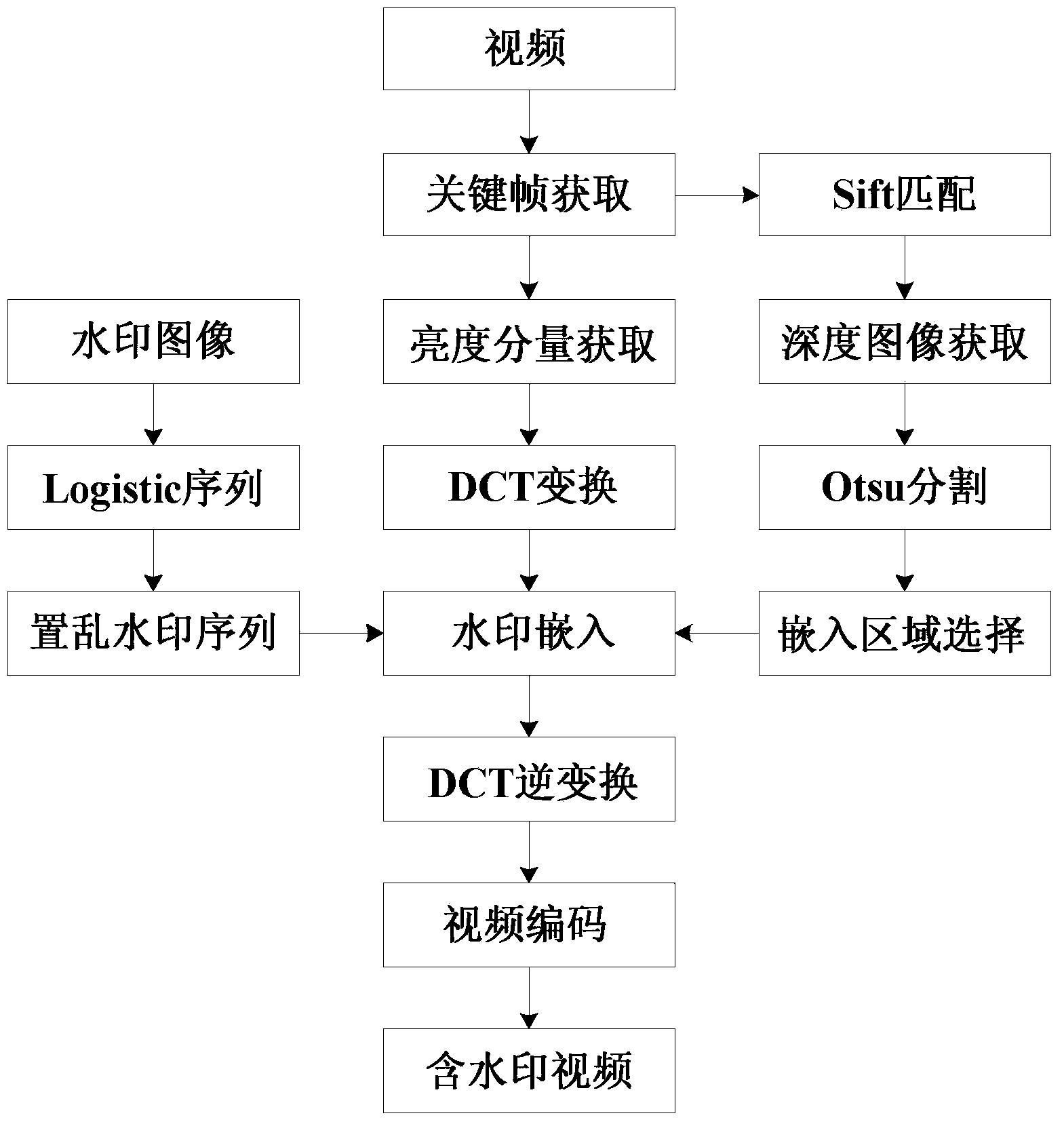
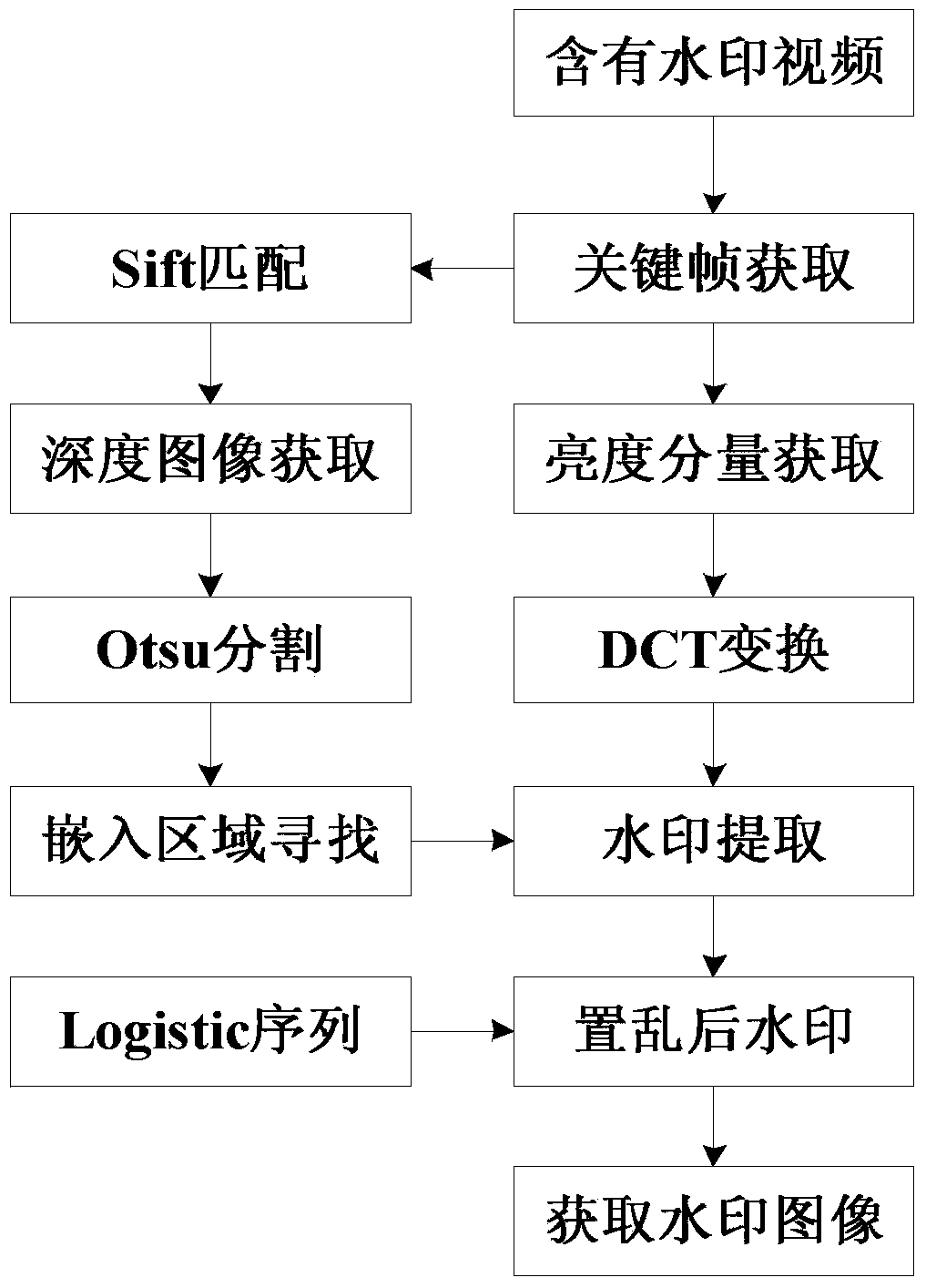
Video watermarking method based on depth image and Otsu segmentation
InactiveCN104053074AResistant to processing attacksImage data processing detailsSelective content distributionDepth of fieldMultiplicative noise
The invention discloses a video watermarking method based on a depth image and Otsu segmentation. The method comprises the steps of obtaining the depth image of a video keyframe, scrambling a watermark picture through Logistic mapping to generate disordered one-dimensional watermark information, segmenting the depth image into a foreground region and a background region through an Otsu threshold segmentation method according to depth-of-field information provided by the depth image, judging the foreground region of the video keyframe, embedding the watermark information in a DCT coefficient of luminance component subblocks belonging to the foreground region, judging the foreground region and the background region of a video containing a watermark and extracting the watermark information from the DCT coefficient of the luminance component subblocks belonging to the foreground region. According to the video watermarking method, the embedded region of the watermark is determined according to the depth information of the video keyframe, so the problem that scene spatial position relativity is not considered in a human visual system is effectively solved, and good robustness to attacks of pepper and salt noise, multiplicative noise, gaussian noise, luminance contrast adjustment and the like is achieved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Voice recognition system
At the time of the speaker adaptation, first feature vector generation sections (7, 8, 9) generate a feature vector series [ci, M] from which the additive noise and multiplicative noise are removed. A second feature vector generation section (12) generates a feature vector series [si, M] including the features of the additive noise and multiplicative noise. A path search section (10) conducts a path search by comparing the feature vector series [ci, M] to the standard vector [an, M] of the standard voice HMM (300). When the speaker adaptation section (11) conducts correlation operation on an average feature vector [s<custom-character file="US20020042712A1-20020411-P00900.TIF" wi="20" he="20" id="custom-character-00001" / >n, M] of the standard vector [an, M] corresponding to the path search result Dv and the feature vector series [si, M], the adaptive vector [xn, M] is generated. The adaptive vector [xn, M] updates the feature vector of the speaker adaptive acoustic model (400) used for the voice recognition.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Method for regulating human face image illumination based on multilevel wavelet disintegrating and spline interpolation
InactiveCN101201900AQuick estimateEffective estimateCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingWavelet decomposition
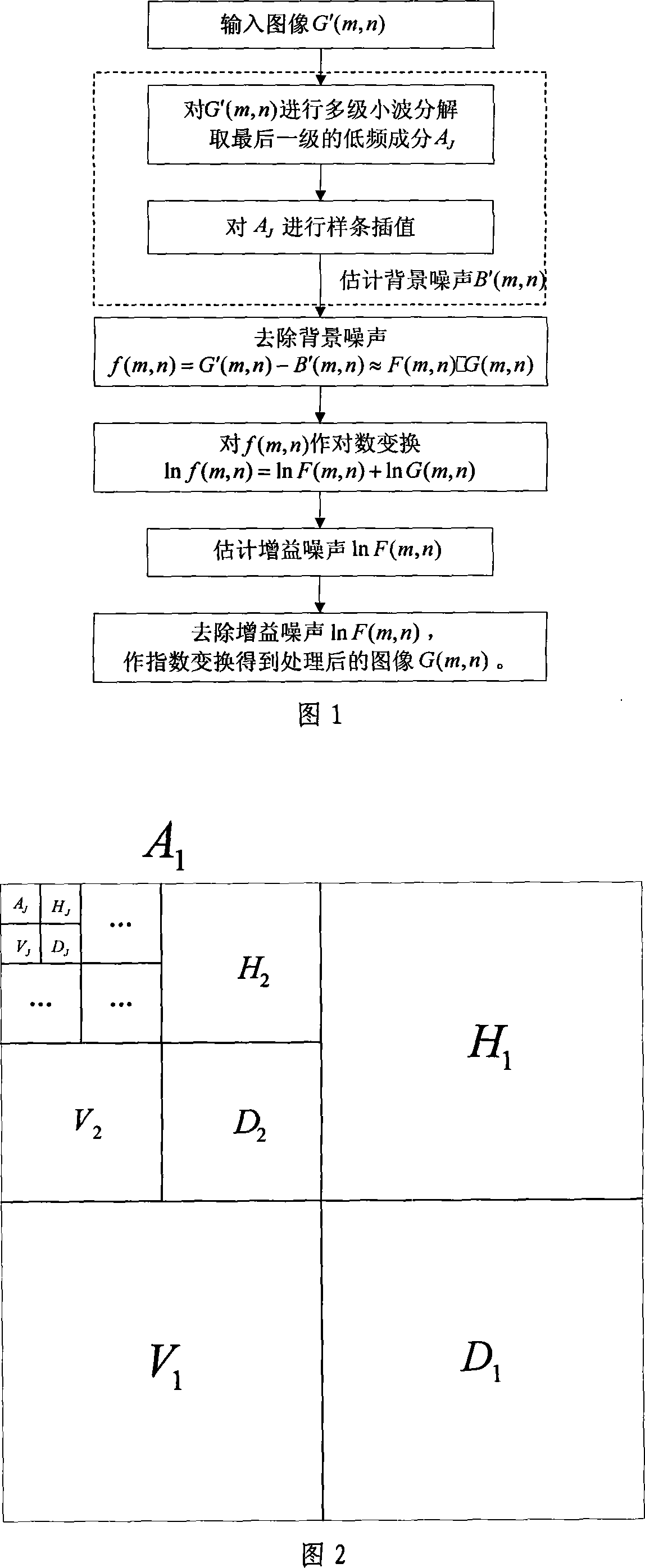
The invention relates to an adjustment method of light on human face, based on multi-level wavelet decomposition and spline interpolation, pertaining to the technical field of image processing. Illumination variations can add into an image with two noises that are background noise and gain noise. The invention, by taking advantages of direct decomposition multi-level wavelet and spline interpolation, estimates and removes the background noise and the gain noise; the background noise belongs to additive noise, which is estimated and removed through the direct multi-level wavelet decomposition and the spline interpolation; while, the gain noise pertains to multiplicative noise; through logarithmic transformation of the imagines removed background noise and by taking advantage of the decomposition multi-level wavelet and the spline interpolation, the gain noise is removed. The invention has the advantages that the invention can quickly and effectively estimate picture illumination situation, remove the background noise and gain noise introduced by illumination as much as possible, and effectively adjust human face image under different illumination conditions. The method of the invention can be applied to real-time human face identification system under illumination variations and can reduce the influence of human face identification system performance caused by illumination variations.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Morphological component analysis (MCA)-based synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image noise suppression method
InactiveCN101908206AEnhance expressive abilityDescribe wellImage enhancementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMorphological component analysisSynthetic aperture radar
The invention relates to a morphological component analysis (MCA)-based synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image noise suppression method. The method is technically characterized in that: an MCA method is applied to the suppression of multiplicative noises in an SAR image; and because the image generally comprises the two morphological components of edge / contour and texture, in the method, the dictionary assembly of curvelet and local discrete cosine transform (LDCT) is utilized under the uniform frame of MCA according to the good edge / contour representation characteristics of the curvelet and the high partial texture expression capability of the LDCT to fulfill the aim of suppressing the noises in the SAR image. Therefore, for a noise image, effective components of the image can be separated and the noises are kept in the remnant image by the method to fulfill the aim of suppressing the noises. Experimental results on both simulated and real SAR images show that the method has the advantage of relatively better noise suppression effect compared with the conventional wavelet-based methods and curvelet-based methods.
Owner:HAIAN TEXTILE MACHINERY +1
Laser power control with automatic compensation
ActiveUS20060108501A1Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityControl system
A method and apparatus is disclosed for optic signal power control to maintain a desired or optimum optic signal power level. During start-up, a target value from memory may be utilized to control one or more power levels of an optic signal. There may comprise 2 or more different power levels for the optic signal. During operation, target values may continue to be utilized or an open loop or closed loop control system may be utilized. Compensation may occur for both additive noise / distortion and multiplicative noise / distortion. The compensation for one power level may be expanded or extrapolated to compensate for additive noise / distortion and multiplicative noise / distortion that affect other power levels.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
An optimal distributed state estimation method based on sensor network
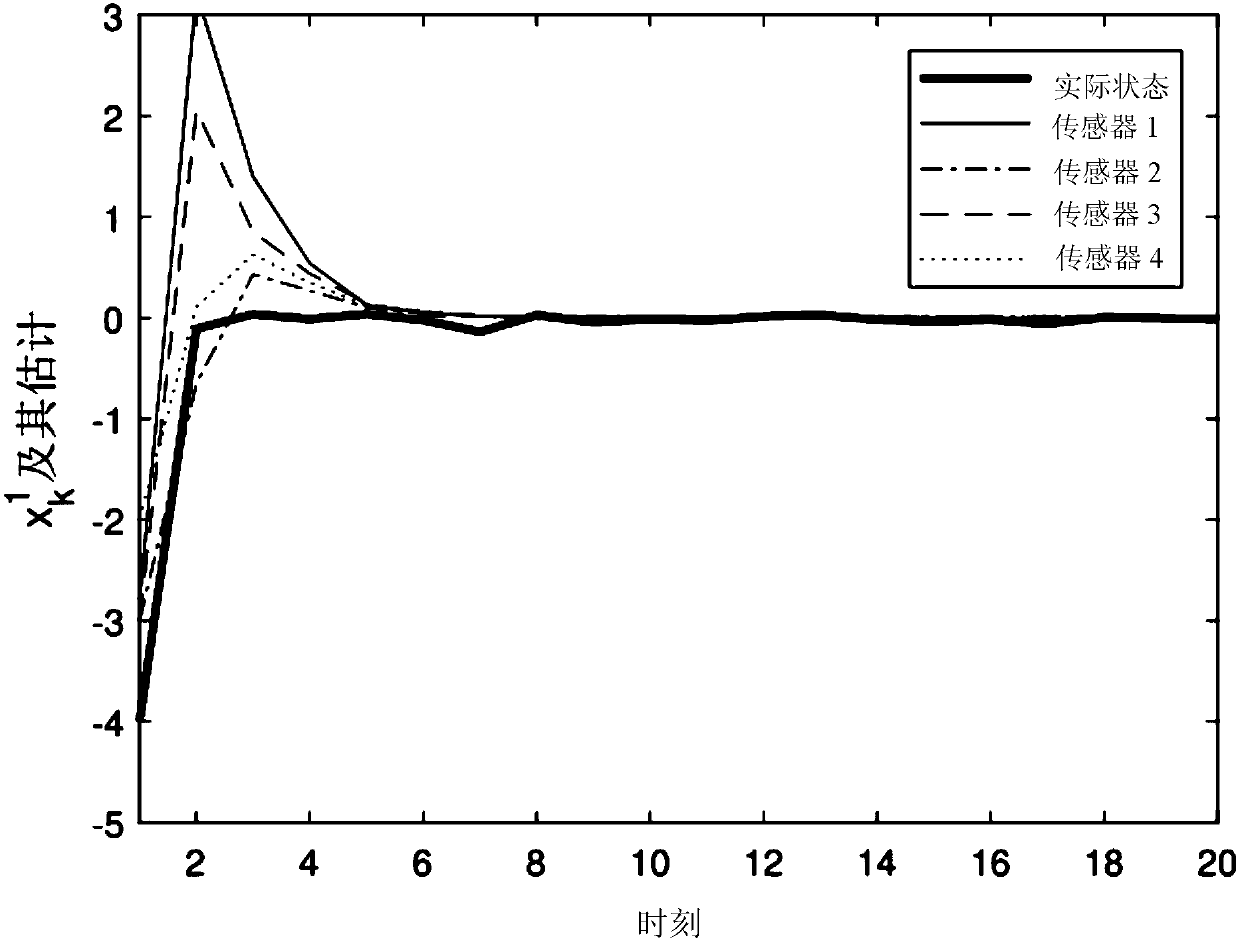
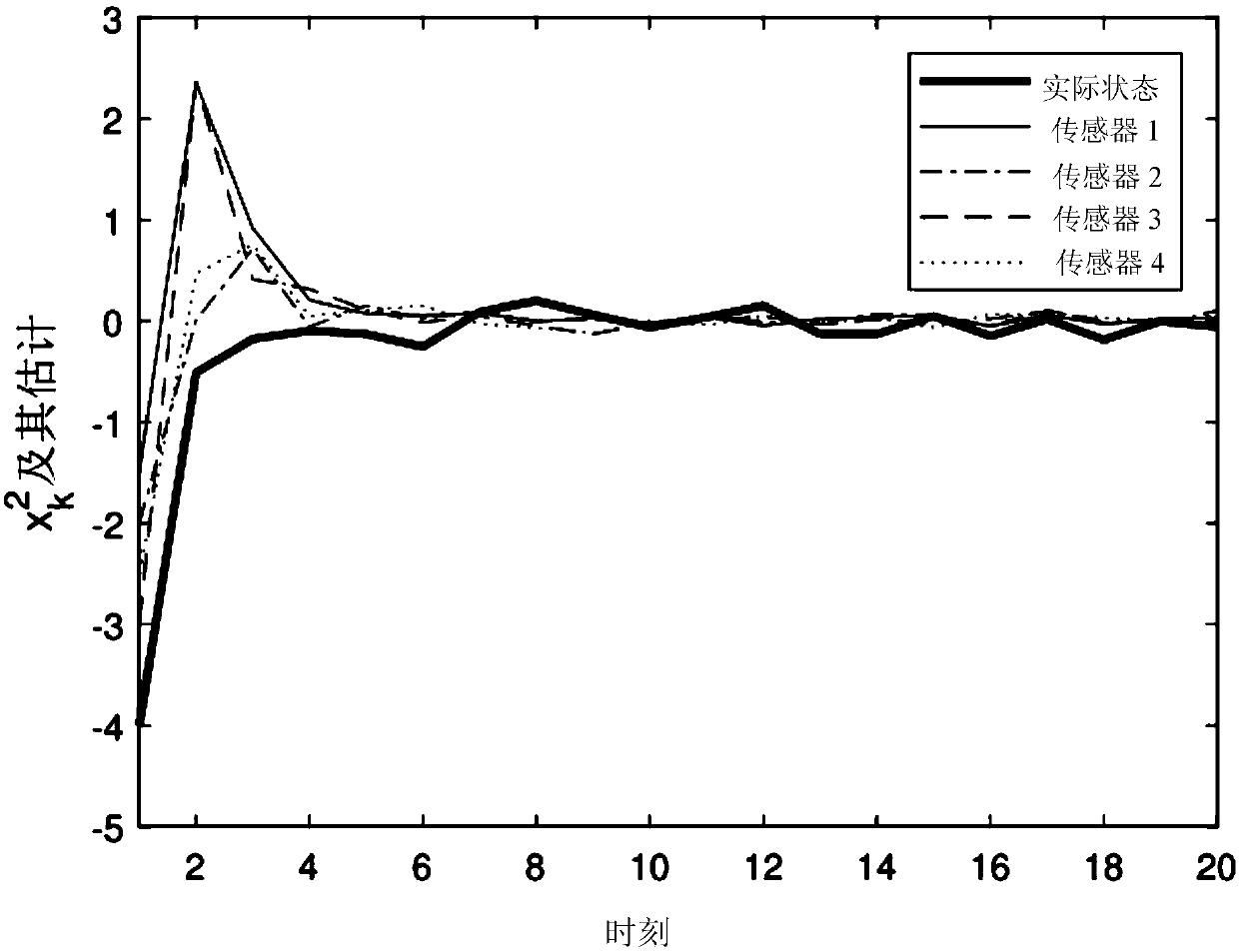
ActiveCN108959808ATo achieve the purpose of resisting external disturbancesReduce estimation errorGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationInterference phenomenonControl system
An optimized distributed state estimation method based on a sensor network is used in the field of control system and signal processing technology. The present invention solves the problem that existing conventional state estimation method cannot simultaneously process the state estimation of a sensor network with multiplicative noise and a non-linear interference phenomenon randomly occurring. Atthat same time, the method considers the influence of multiplicative noise and randomly occurring non-linearity on the state estimation performance, and a distributed filtering method based on Riccati-Riccati difference equation is obtained. Compared with existing conventional state estimation method of a nonlinear time-varying system, the method of the invention can control the estimation errorin a very small range, and can improve the estimation accuracy by more than 10% while being easy to solve. The invention can be applied to the field of control system and signal processing technology.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for measuring large linear range data fusion by compound color ultra-resolved differential confocal
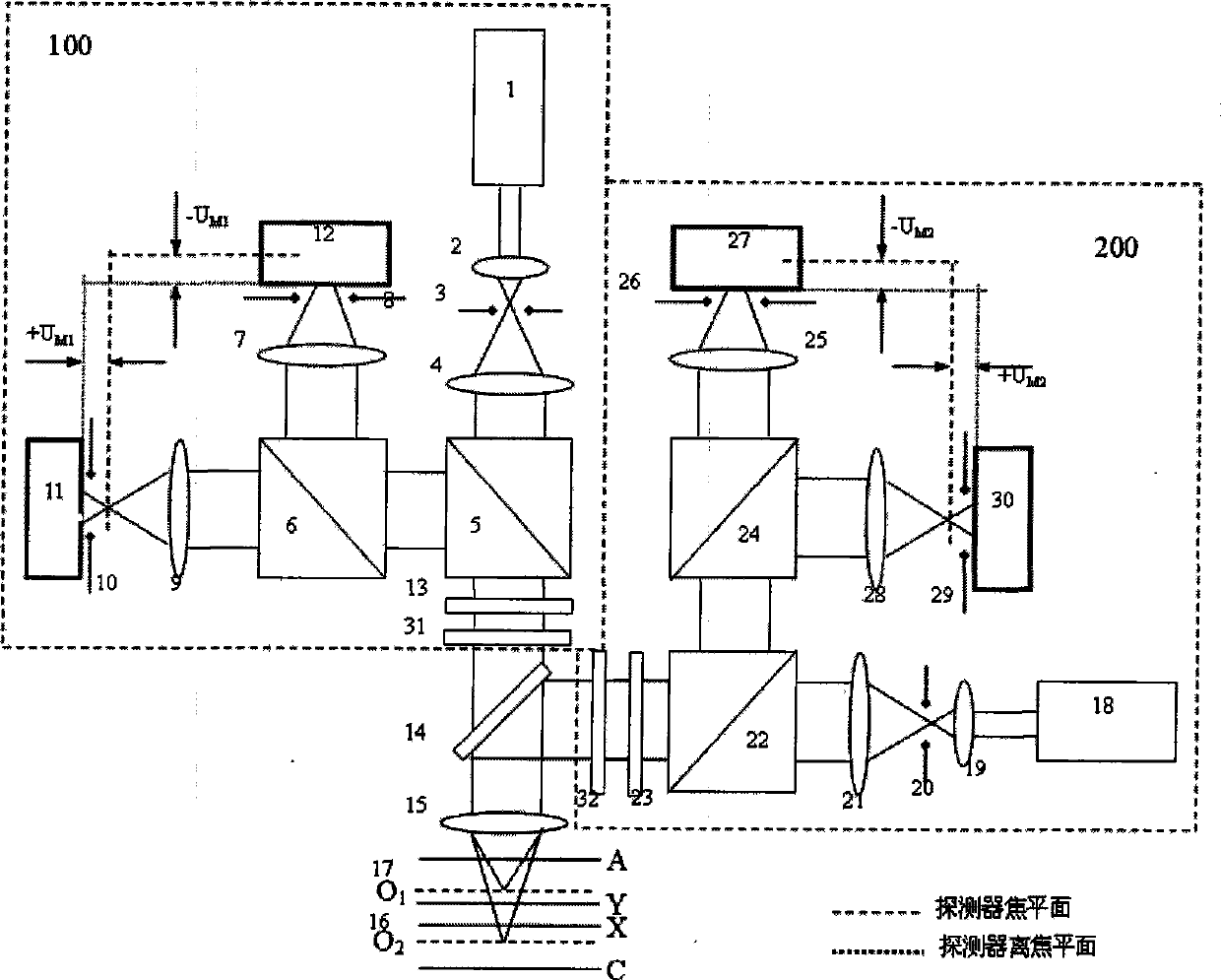
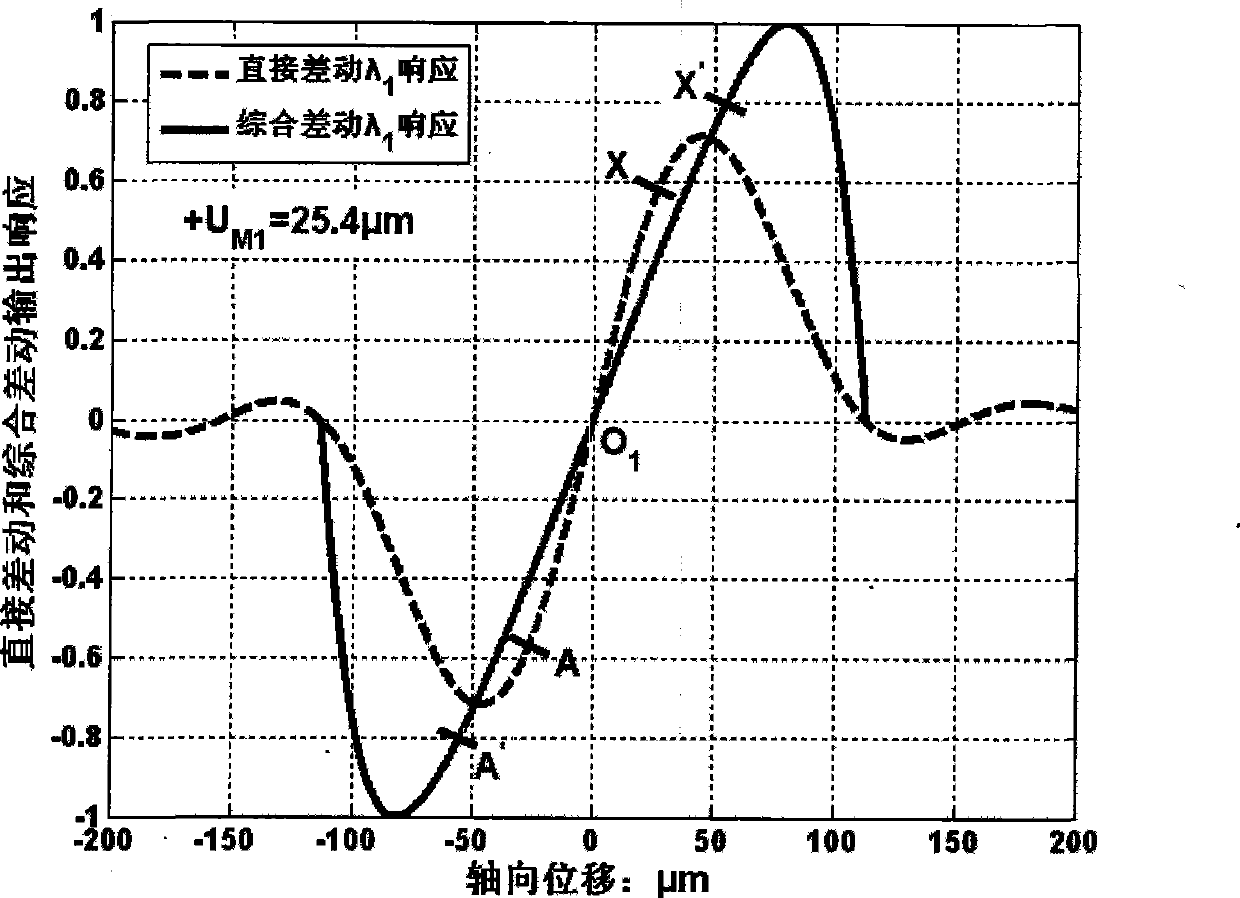
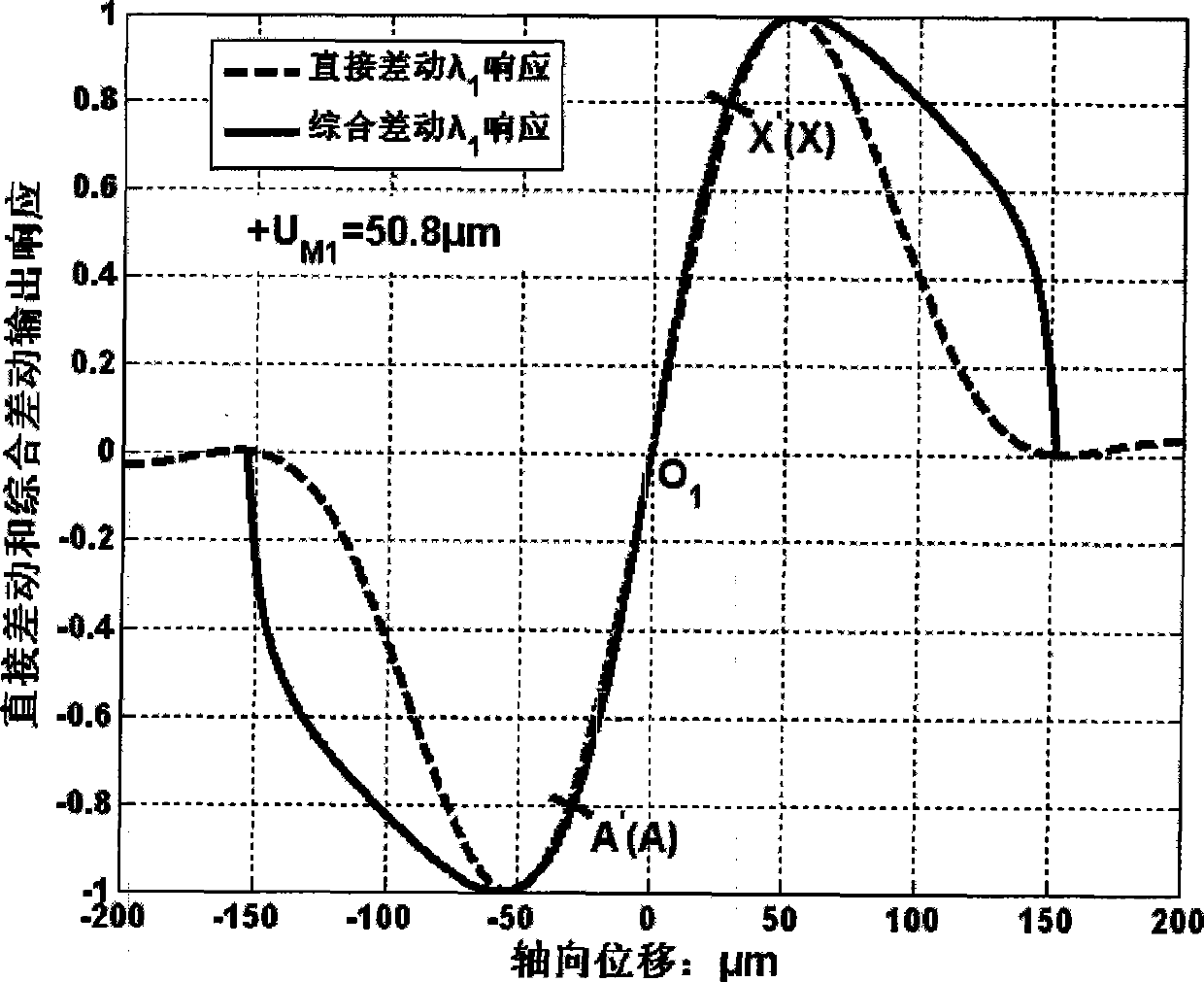
ActiveCN101413784AImprove linearityLarge linear rangeUsing optical meansThree dimensional microstructureMeasurement device
The invention relates to a method for measuring large linearity measuring range data fusion by means of compound color super resolution differential confocal measurement, belonging to the ultraprecise three-dimensional microstructure surface measuring field; firstly, formula 1 and formula 2 are utilized to respectively calculate output information of a first and a second super resolution differential confocal measuring branches, wherein, formula 3 is the actual output light intensity information of a first and a second measuring branches which are respectively obtained by adopting a compound colour super resolution differential confocal measuring device, (the formula 1, the formula 2 and the formula 3 are shown at the upper right side); Gamma1 and Gamma2 are intercepted to obtain effective output Gamma1 and Gamma2, and finally a systemic linear output fusion function (see the formula 4) is constructed and is output as the systemic final displacement response, wherein, GammaB' is a shift factor, lambda1and lambda2 are the wavelength of the first and the second measuring branches. The method remains the advantages of high space resolution and inhibiting common mode additive noise and linear range extension of the compound colour super resolution differential confocal measuring, can inhibit interference of multiplicative noise, and can obtain output characteristic curve with better linearity and larger linear measurement range.
Owner:NANTONG MINGGUANG ELECTRIC WIRE
Medical ultrasound image speckle removing method through quantum inspiration
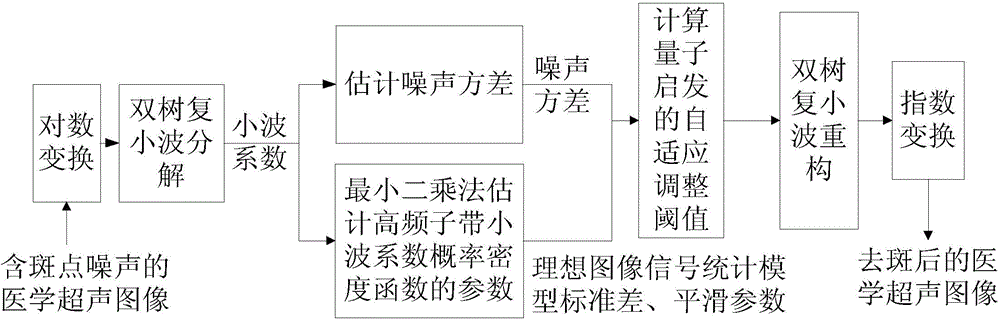
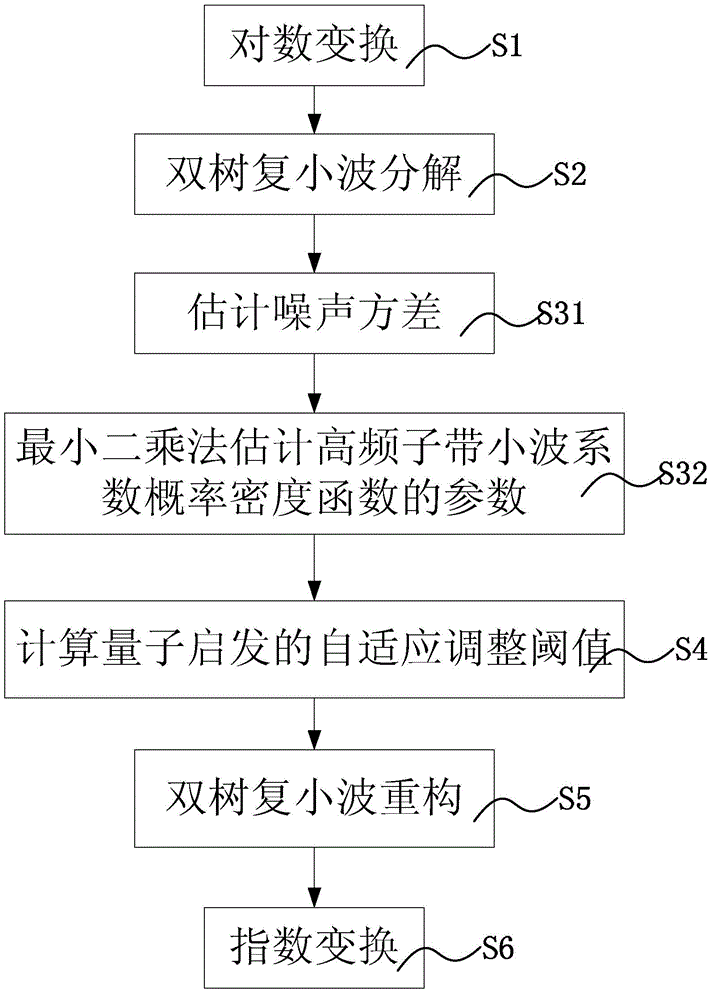
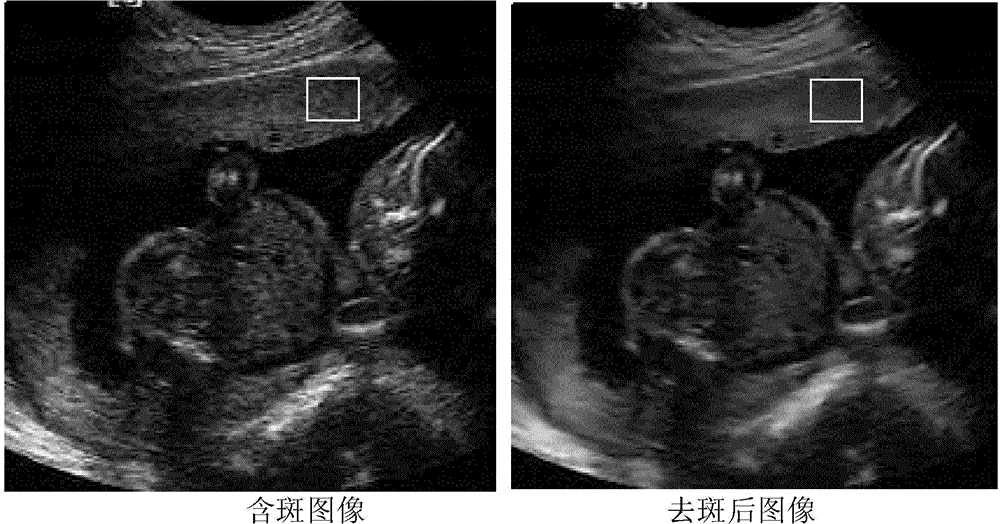
ActiveCN103955894AGood auxiliary effectKeep Organizational DetailsImage enhancementUltrasonographySonification
The invention discloses a medical ultrasound image speckle removing method through quantum inspiration. The method comprises the steps that a medical ultrasound image containing speckle noise is input; logarithm transformation is carried out to convert the multiplicative noise image into the additive noise image; complex wavelet transformation is carried out to convert a grey value of the image into a wavelet coefficient; noise variance, and variance and smoothing parameters of a probability density function of an ideal image signal are estimated to obtain a noise statistic model and a statistic model of the ideal image signal; an adaptive adjustment threshold value is calculated according to the theory of quantum inspiration, and soft threshold processing is carried out on the wavelet coefficient to obtain a wavelet coefficient estimation value of the ideal image signal; the wavelet coefficient estimation value of the ideal image signal is used for wavelet reconstruction to obtain the image; exponential transformation is carried out on the image to compensate the logarithm transformation in the first step, and the image with speckles removed is obtained. The method can keep organization details in the image well on the basis of effectively removing the speckle noise of the medical ultrasound image, and play a good role in assisting in medical treatment.
Owner:SUZHOU ZIGUANG WEIYE LASER TECH CO LTD
Fractal-wavelet self-adaptive image denoising method based on multivariate statistic model
InactiveCN102938138AEliminate Mixed NoiseWith multiple resolutionsImage enhancementImage denoisingMixed noise
The invention discloses a fractal-wavelet self-adaptive image denoising method based on a multivariate statistic model. The method includes: step one, subjecting a noisy image to homomorphic transform through which an original image IB containing multiplicative noise is transformed into an image IB' only containing additive noise; step two, performing fractal-wavelet transform on a noisy signal f (k), selecting a wavelet basis and a wavelet decomposition layer j to obtain corresponding wavelet coefficients; step three, selecting an MGGD multivariate statistic model for self-adaptive solution of a parameter alpha and a parameter beta, and obtaining the most suitable parameter value alpha and beta after analysis for the distribution condition of the wavelet coefficient of a natural image; step four, for the wavelet coefficients obtained through decomposition, performing noise-free predictive coding on the noisy image by using a fractal-wavelet coding method; and step five, performing wavelet reconstruction by using the wavelet coefficients to obtain estimation signals which are image signals after denoising. Compared with other algorithms, the method has better denoising effect and high edge preserving capacity, and is particularly suitable for eliminating Gaussian-impulse mixed noise.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Star sensor and gyro combined attitude determining method for processing multiplicative noise
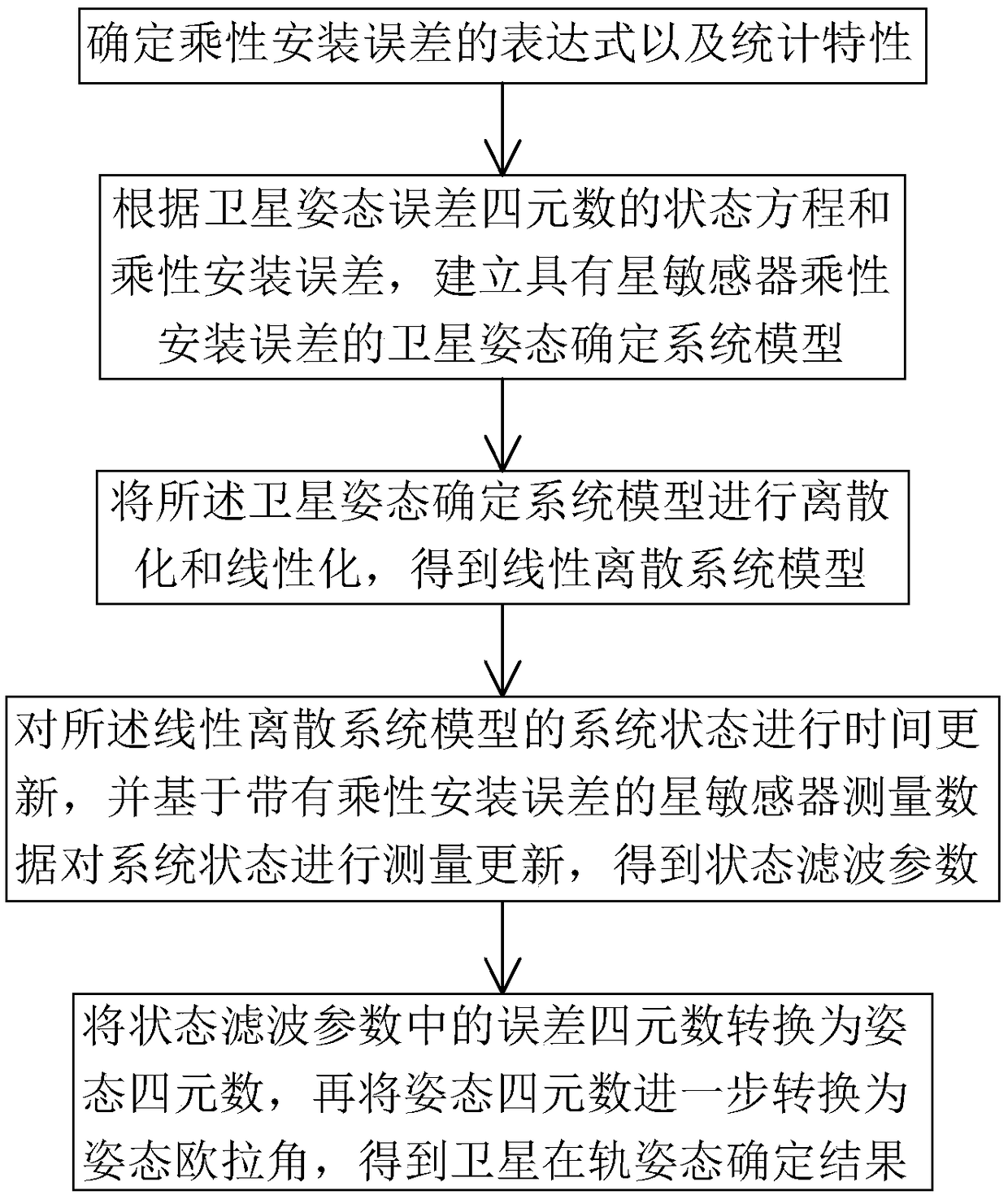
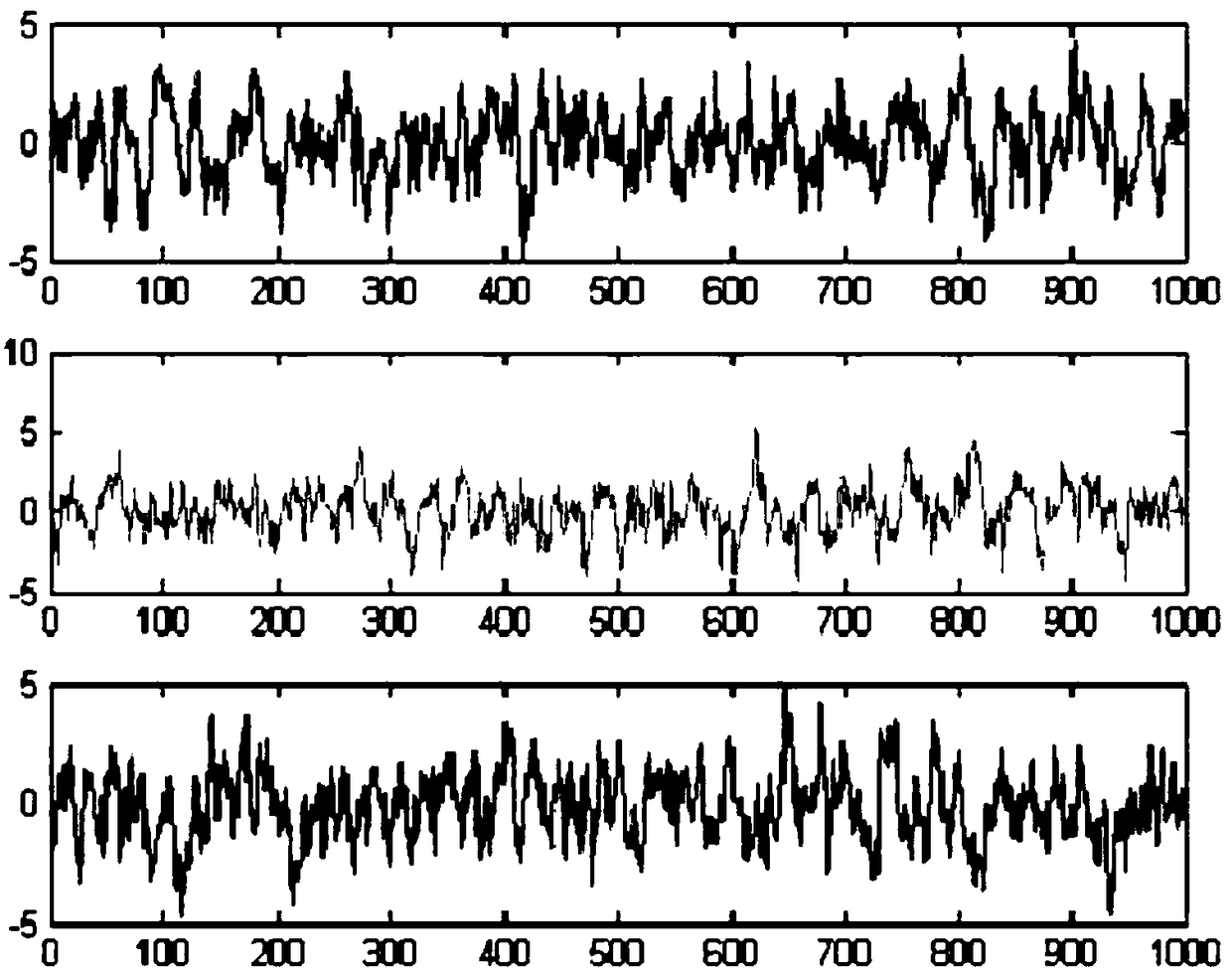
InactiveCN109470266AThe impact of reducing the accuracy of attitude determinationMeasurement devicesFilter algorithmDiscretization
The invention discloses a star sensor and gyro combined attitude determining method for processing multiplicative noise. The star sensor and gyro combined attitude determining method comprises the following steps: determining an expression of multiplicative installation errors and counting characteristics; establishing a satellite attitude determination system model with star sensor multiplicativeinstallation errors; discretizing and linearizing the satellite attitude determination system model to obtain a linear discrete system model; carrying out time updating on the system state of the linear discrete system model to obtain state filter parameters; transferring an error quaternion in the state filter parameters into an attitude Euler angle. According to the star sensor and gyro combined attitude determining method disclosed by the invention, the satellite attitude determination system model with the multiplicative installation errors of a star sensor and gyro combination is established on the basis of the error quaternion; an optimal attitude filtering algorithm based on linear minimum variance is designed by utilizing a linear minimum variance estimation and projection theorem; by use of an algorithm, suppression of multiplicative measurement noise of the star sensor and estimation of the satellite triaxial motion posture are realized, and the influence of the multiplicative measurement noise on posture determination precision is effectively reduced.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Image denoising method through combination of adaptive nonlocal samples and low rank
ActiveCN107292855AClear structureOvercome the edgeImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionPeak value
The invention discloses an image denoising method through combination of adaptive nonlocal samples and low rank. Firstly an image is transformed to a logarithmic domain by using logarithmic transformation, and a multiplicative noise model is transformed into an additive noise model; the image is partitioned and grouping is performed according to the similarity so as to obtain image groups having similar blocks; then low-tank approximation processing is performed on the image groups so as to obtain an initial estimation value; then adaptive nonlocal sample model processing is performed on the initial estimation value so as to obtain a logarithmic domain recovery result; and finally the logarithmic domain image is restored to a real number domain by using exponential transformation and corrected so as to obtain a final denoised image. The experiment result indicates that the method has great robustness for the multiplicative noise, and the great peak signal-to-noise ratio and the structural similarity can be obtained and the visual quality of the image can be greatly improved for the image having the multiplicative noise.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
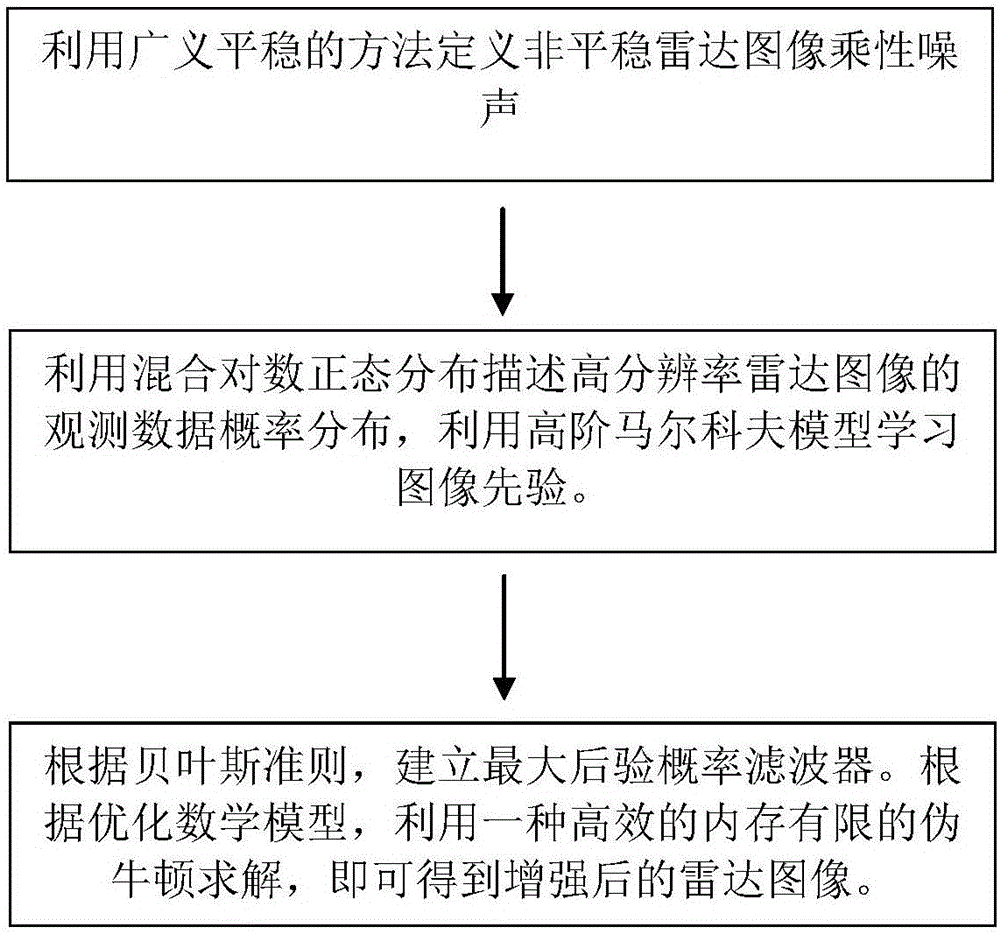
High-resolution radar image enhancement method for aiming at vehicle observation scene
InactiveCN106600558AOvercoming the problem of non-stationary noise filtering failureEnhanced high-resolution radar image qualityImage enhancementImage analysisMaximum a posteriori estimationRadar
The invention provides a high-resolution radar image enhancement method for aiming at a vehicle observation scene. The high-resolution radar image enhancement method comprises the following steps of 1), defining multiplicative noise in a non-stationary radar image according to a generalized stationary method; 2), leading an image prior probability according to a high-order Markov model, describing observation data probability distribution of the high-resolution radar image according to the prior probability through logarithm normal distribution description, and deriving likelihood probability function distribution of an image according to the observation data probability distribution and the multiplicative noise model; and 3), establishing a Maximum-a-posteriori filter according to a Bayes principle, and performing optimization problem processing for obtaining a reinforced radar image. The high-resolution radar image enhancement method has beneficial effects of overcoming a problem of filtering failure to non-stationary noise of the high-resolution image according to a traditional method, and effectively improving quality of the high-resolution radar image in a vehicle observation scene.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY +1
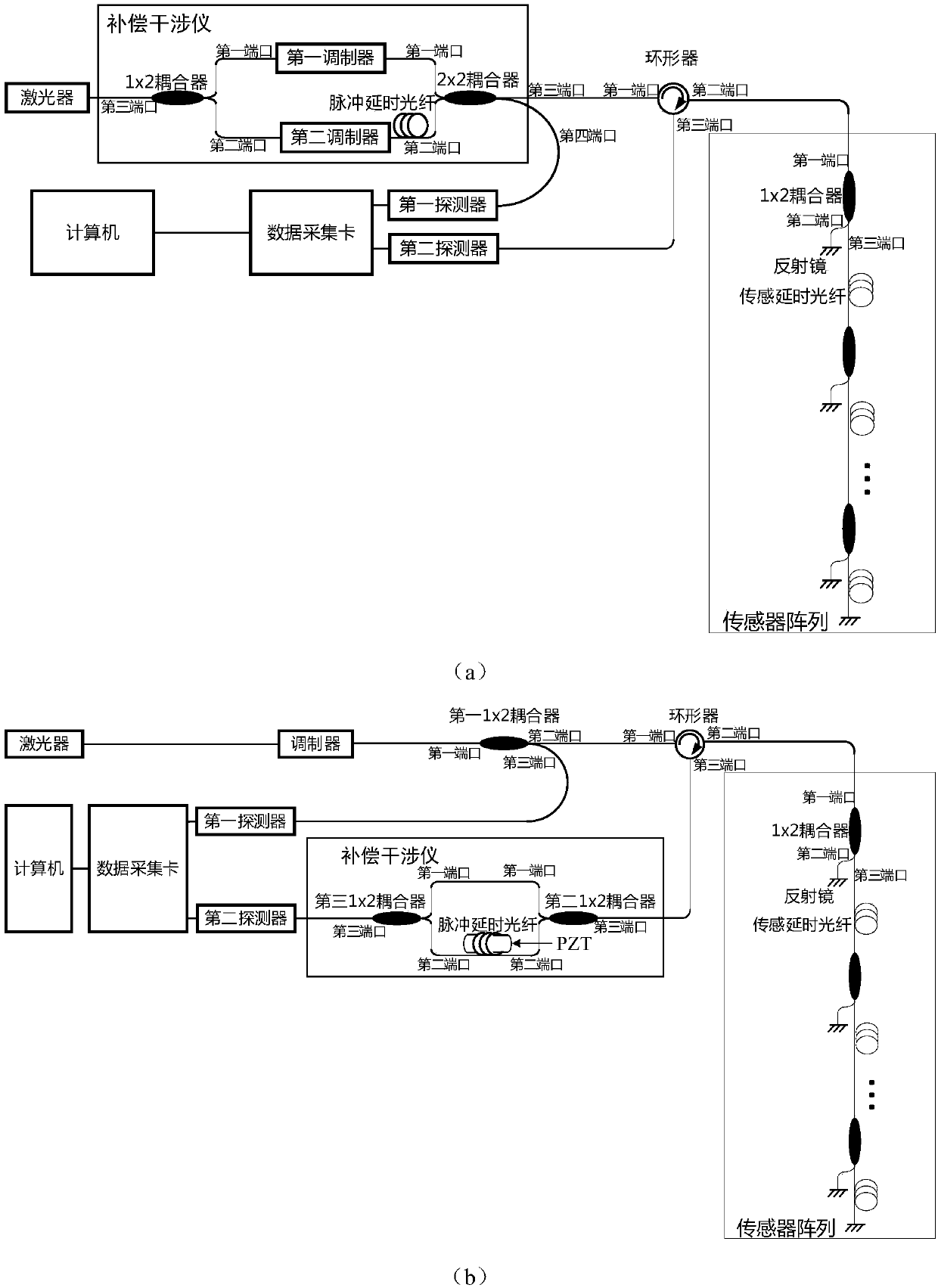
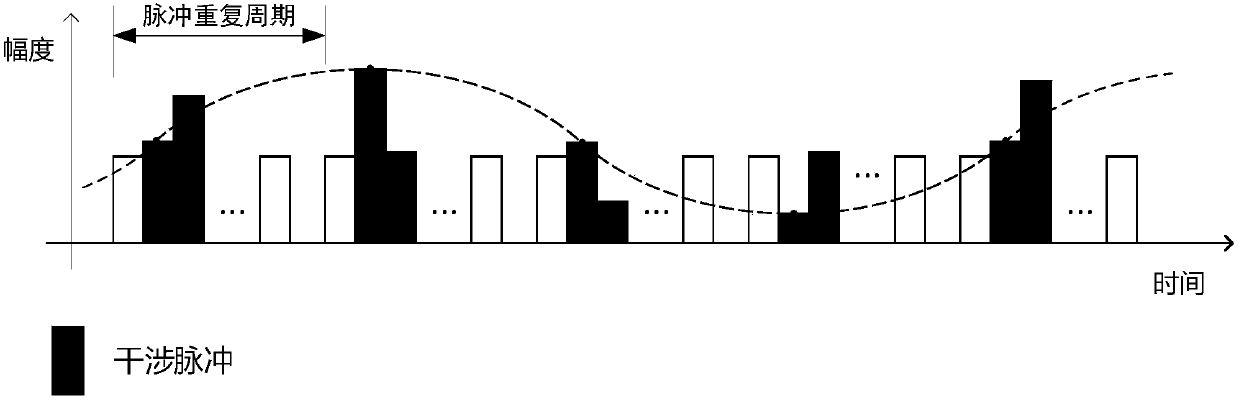
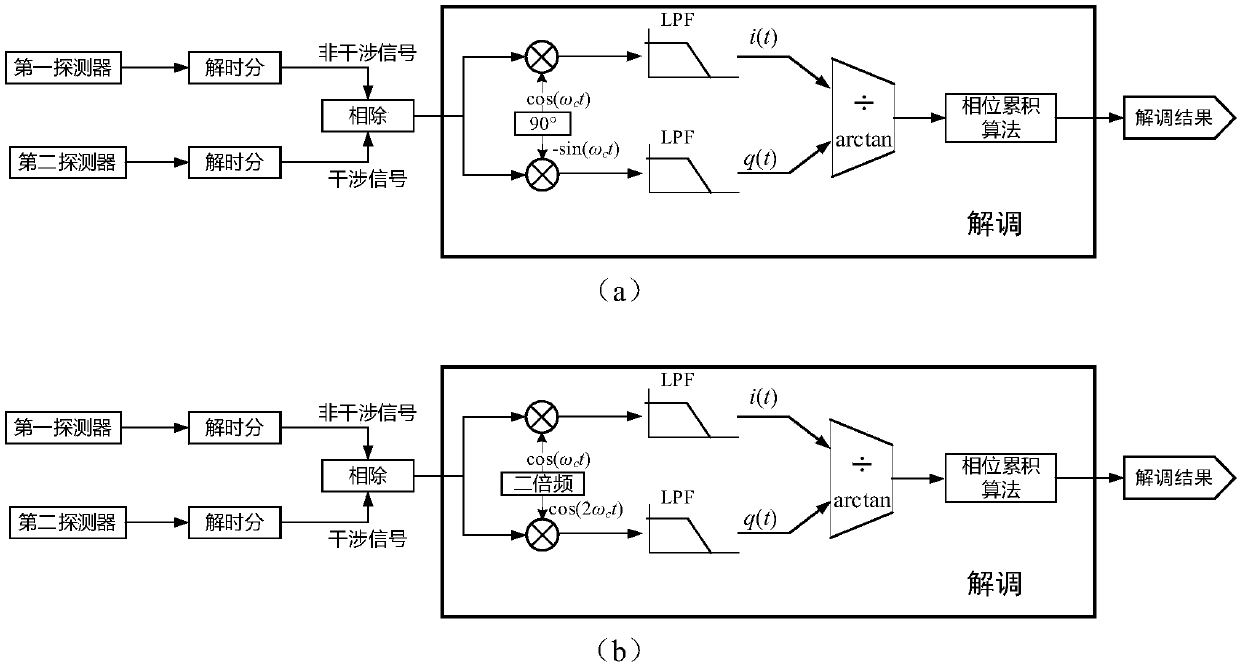
Method for restraining multiplicative noise of time division multiplexing optical fiber sensing system, and system thereof
ActiveCN108592963AEnough punchSuppress multiplicative noiseConverting sensor output opticallyEngineeringNoise suppression
The invention discloses a method for restraining the multiplicative noise of a time division multiplexing optical fiber sensing system. Two detectors receive a non-interference pulse and an interference pulse, by means of the non-interference pulse of the time division multiplexing optical fiber sensing system, and through the adoption of a division method, the multiplicative noise in the sensor interference pulse is restrained, and on the premise that the conditions that the impulse amplitude of the non-interference pulse of the system is sufficient and the additive noise is lower than the multiplicative noise are guaranteed, and a good noise suppression effect can be obtained; in addition, the method is also applicable to a phase generation carrier method and a heterodyne method.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
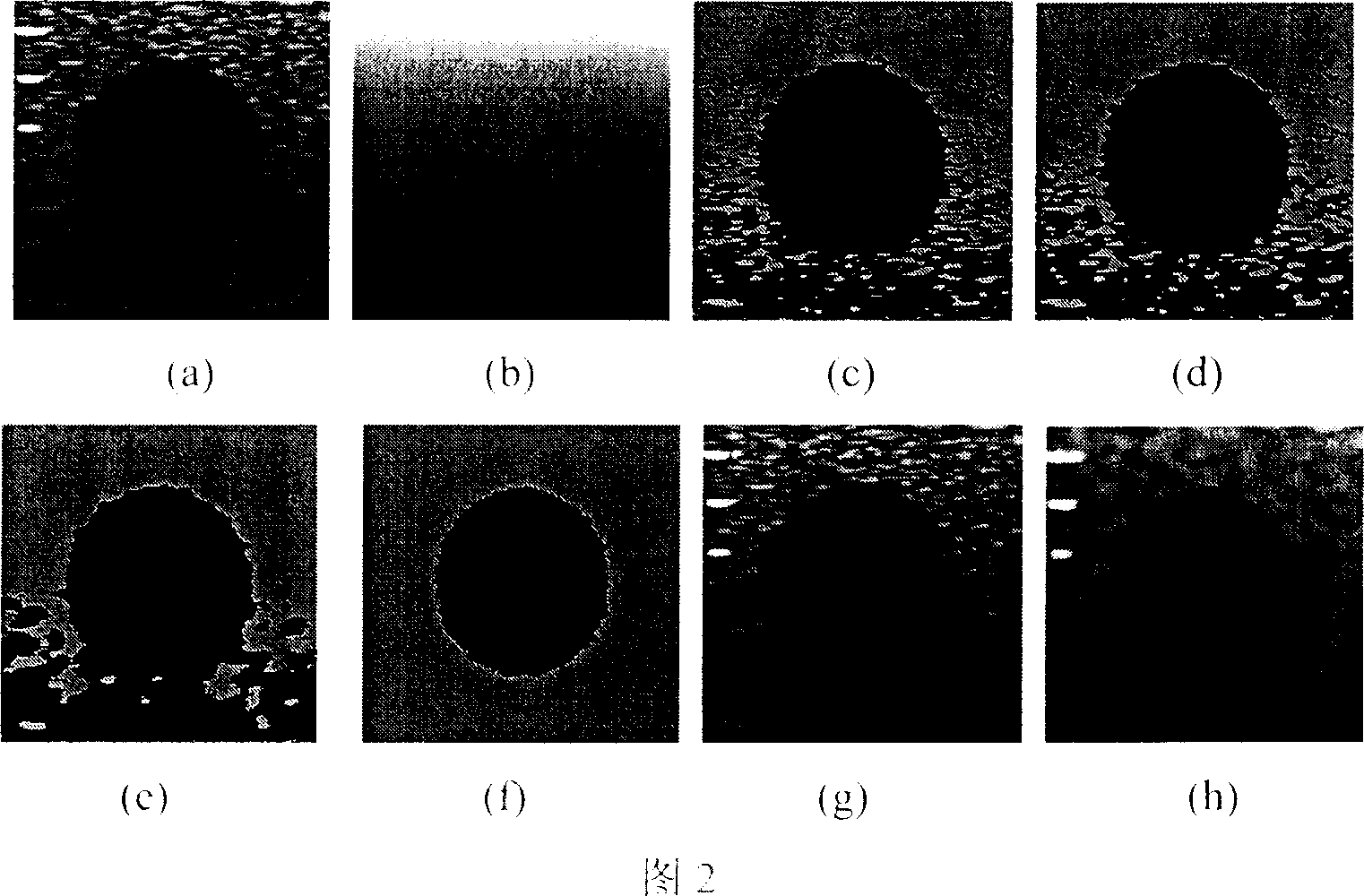
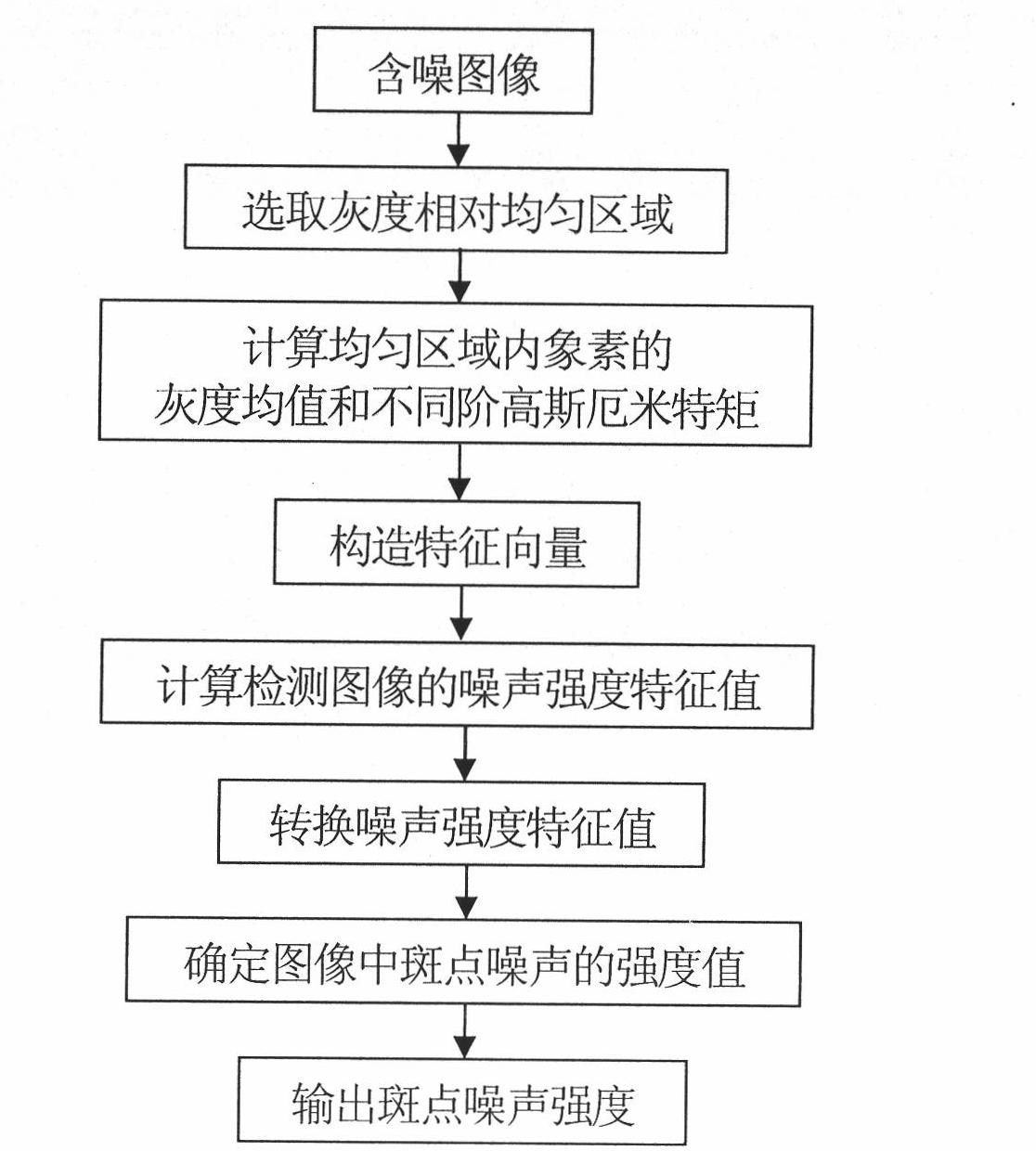
Method for determining intensity of speckle noise in images
The invention relates to a method for determining the intensity of speckle noise in images, which comprises the six steps of: selecting an area of which the gray scale is relatively uniform; calculating the grayscale mean value of pixels in the relatively-uniform area and different orders of Gaussian-Hermite moments of all pixels; constructing feature vectors; calculating and detecting noise intensity characteristic values of the images; converting the noise intensity characteristic values; and determining intensity values of speckle noise in the images. In the method, on the basis of a multiplicative noise module, the intensity of the noise is determined under the condition of no any priori knowledge, and thus the method has the characteristics of high precision, high speed and strong practical applicability and generality, and can be used for determining the intensity of the noise of the images containing the speckle noise, such as visible light images with grayscale uniform areas, synthetic aperture radar images, medical ultrasound images and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com