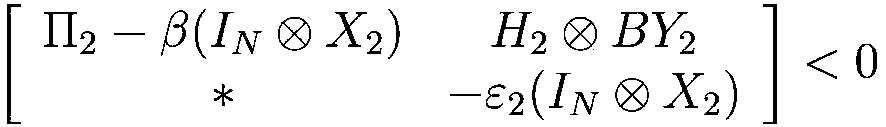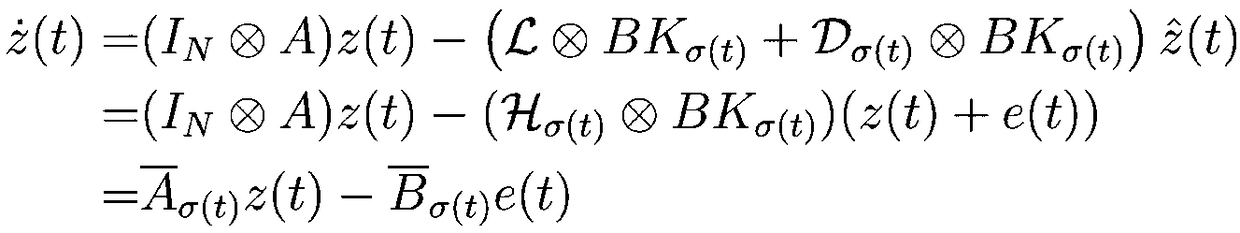Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
246 results about "Networked control system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
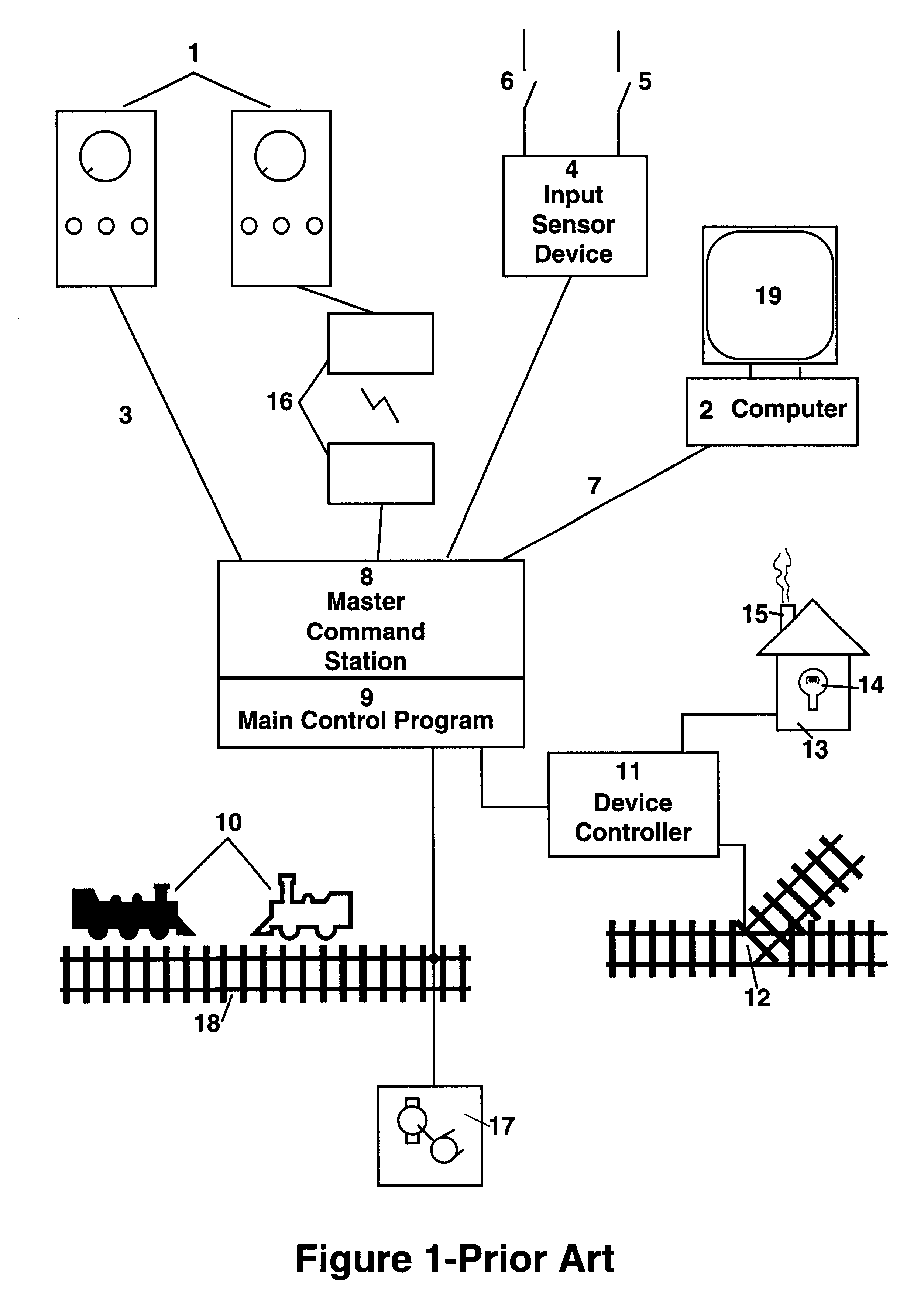
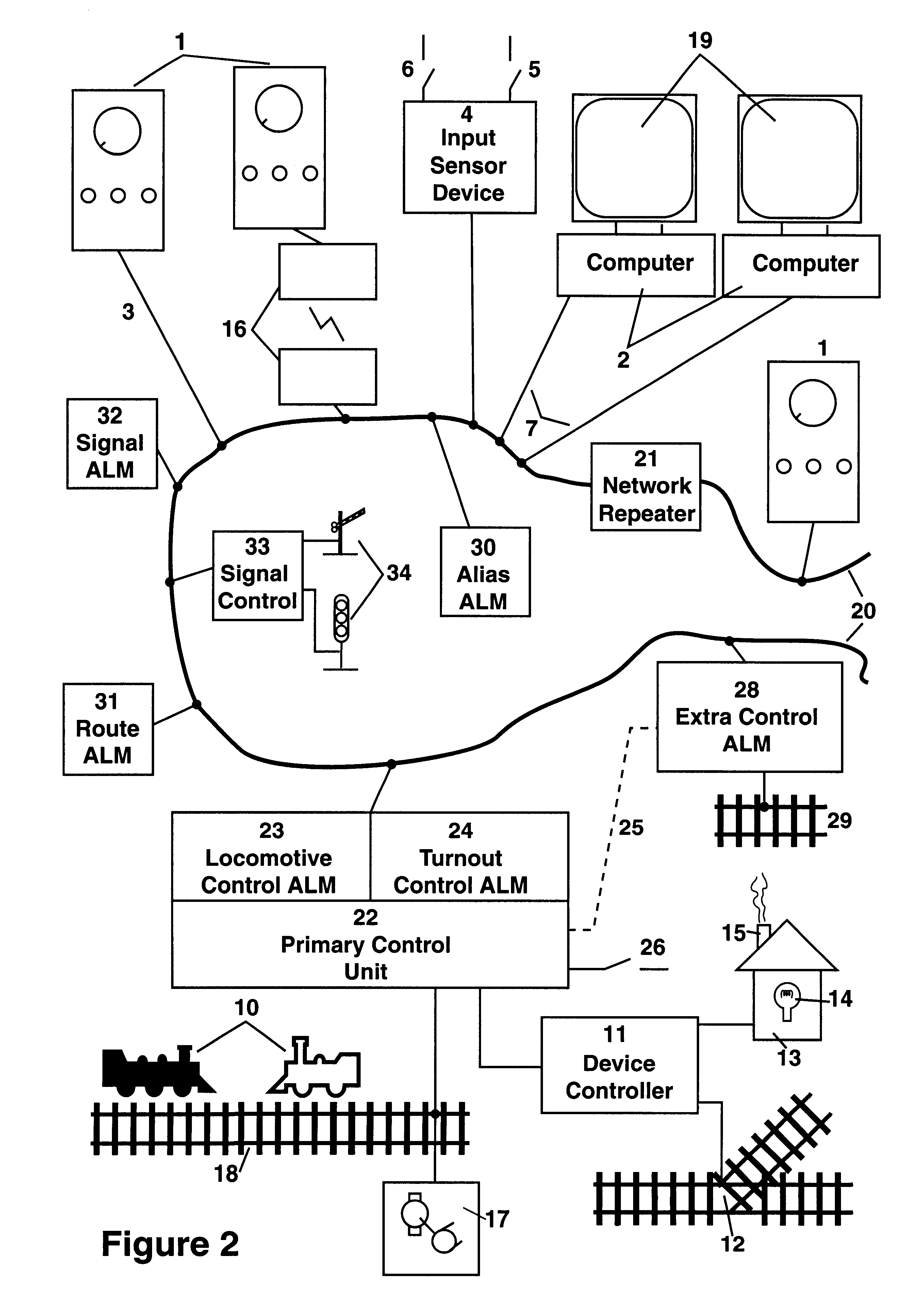
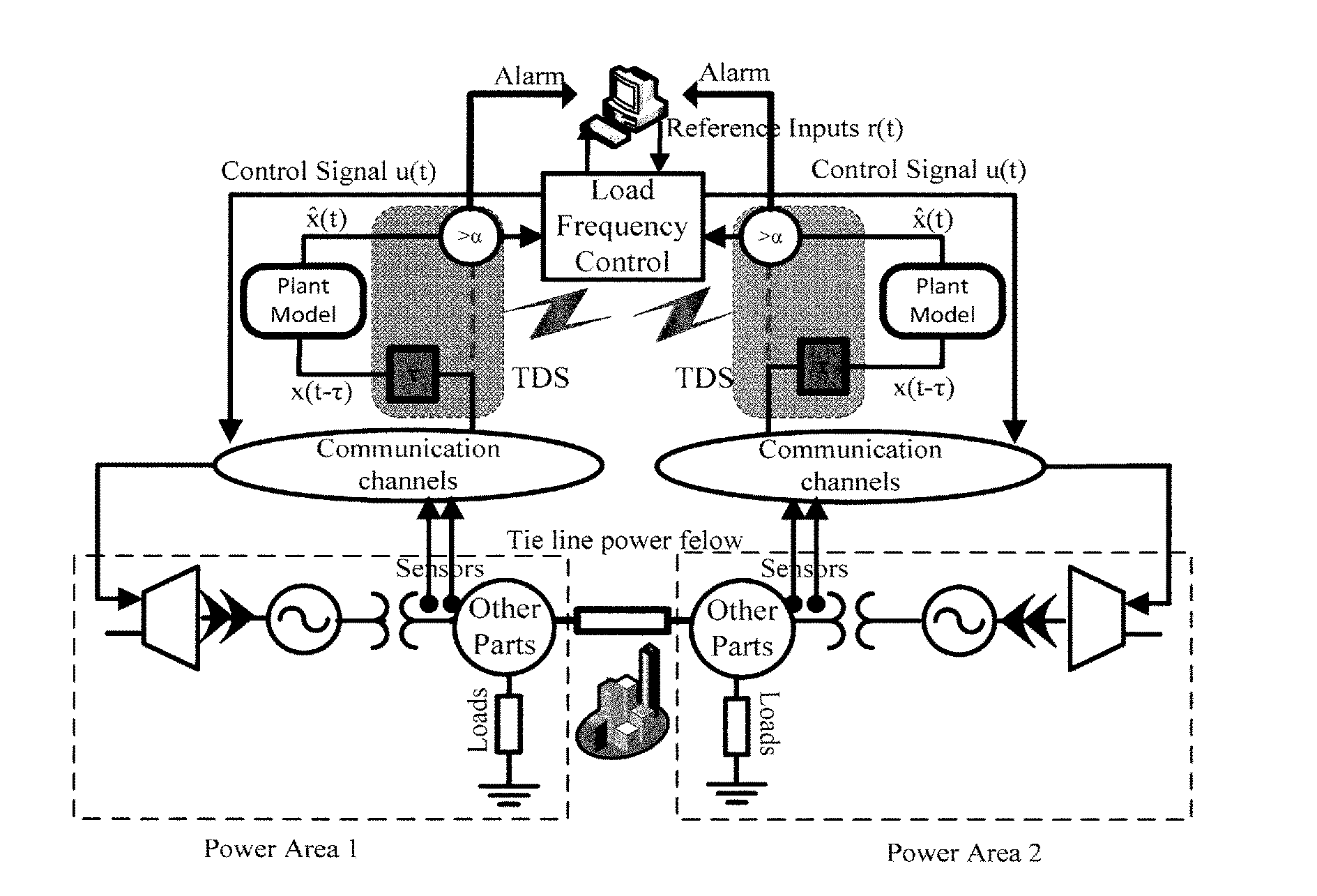
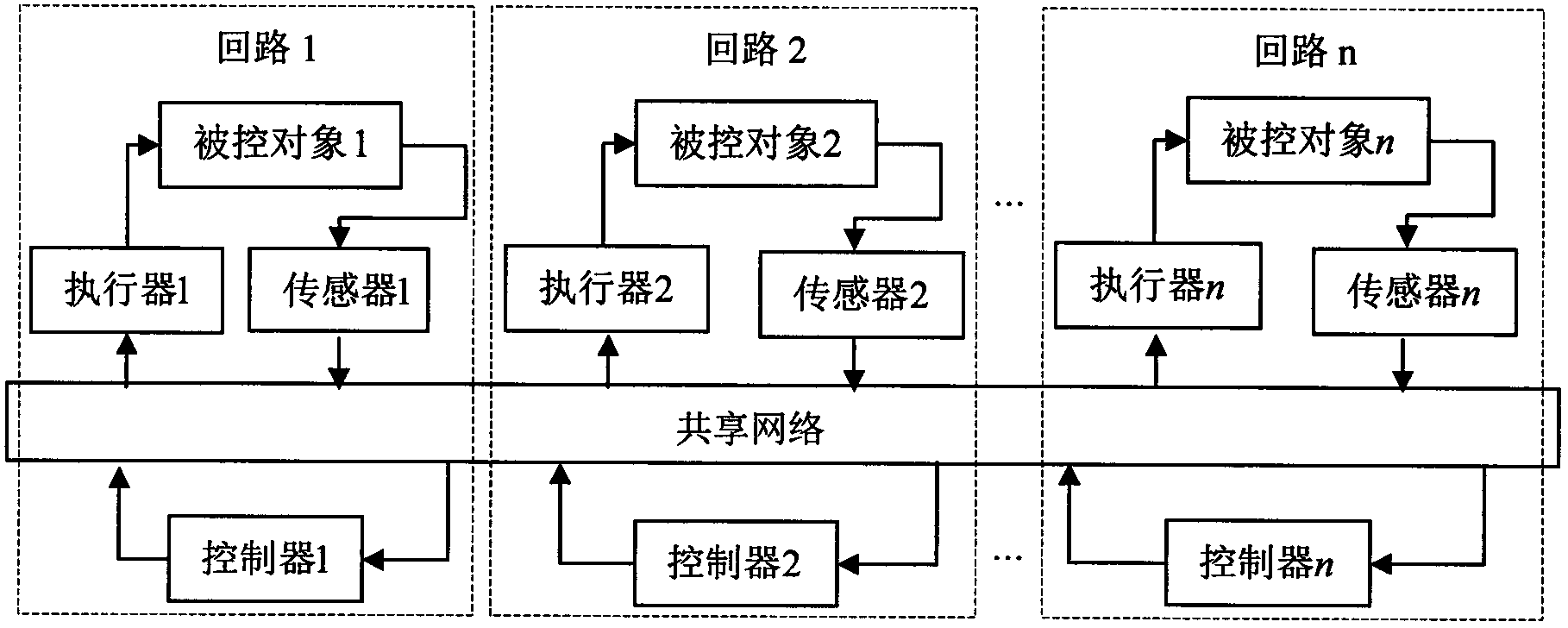
A Networked Control System (NCS) is a control system wherein the control loops are closed through a communication network. The defining feature of an NCS is that control and feedback signals are exchanged among the system's components in the form of information packages through a network.
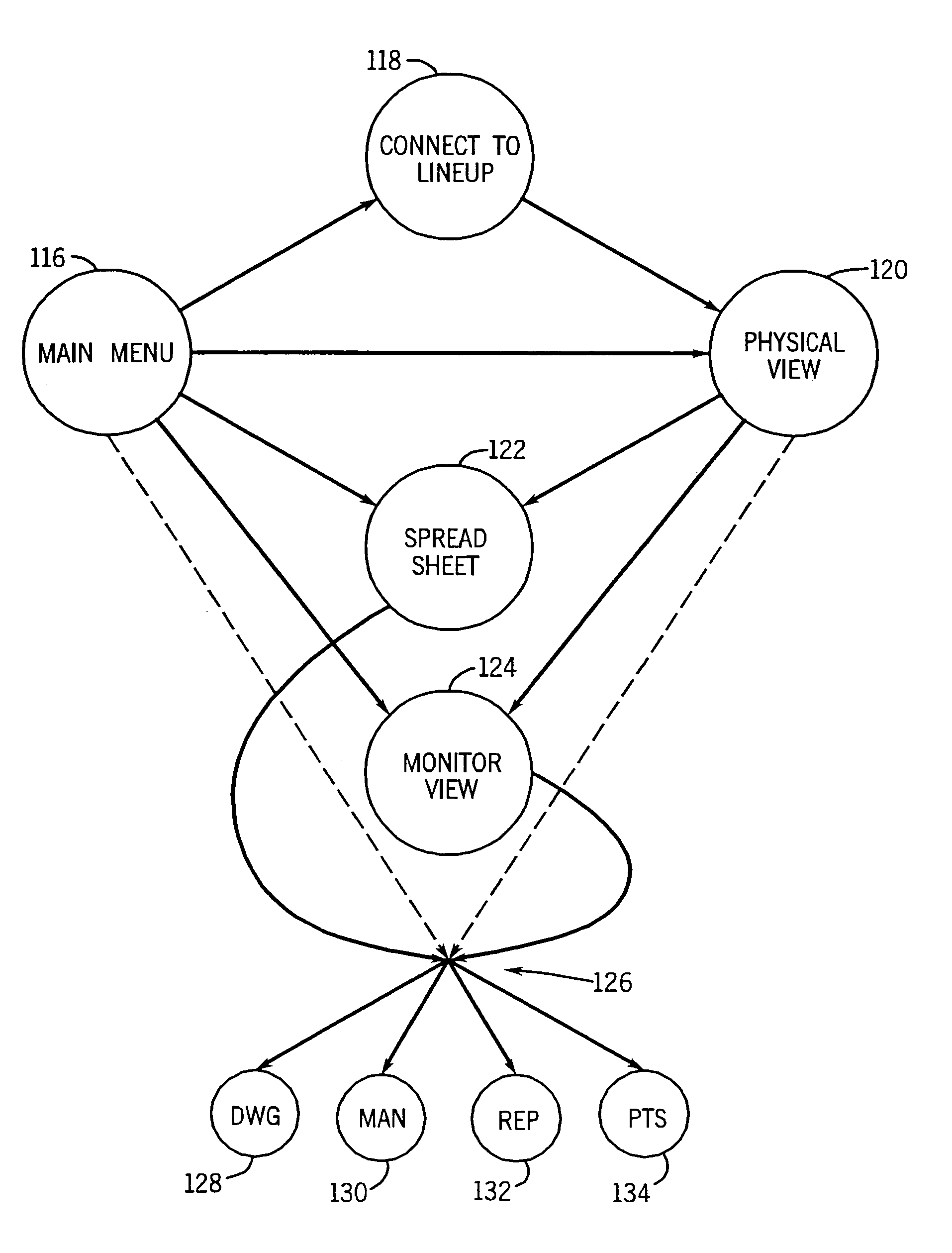
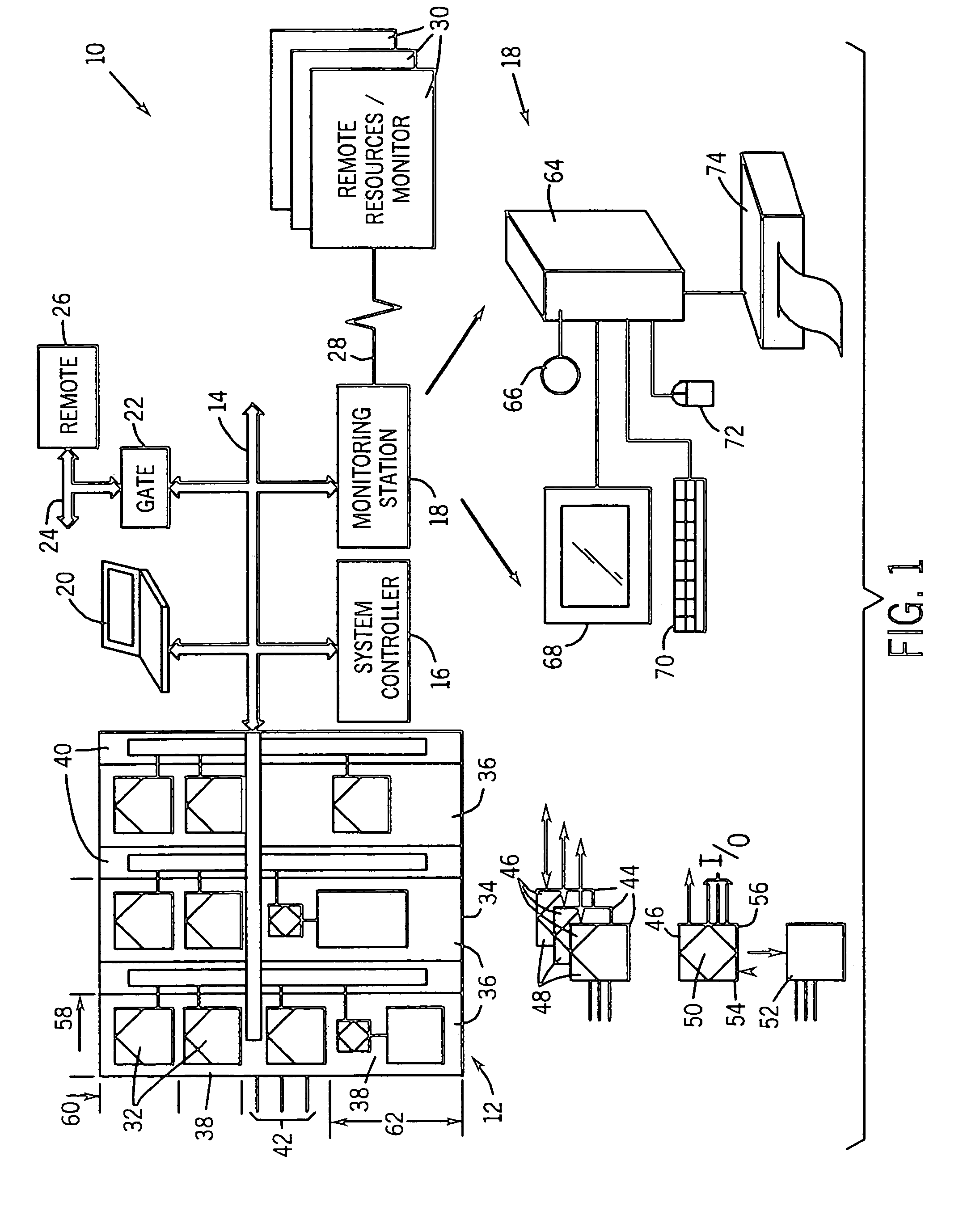
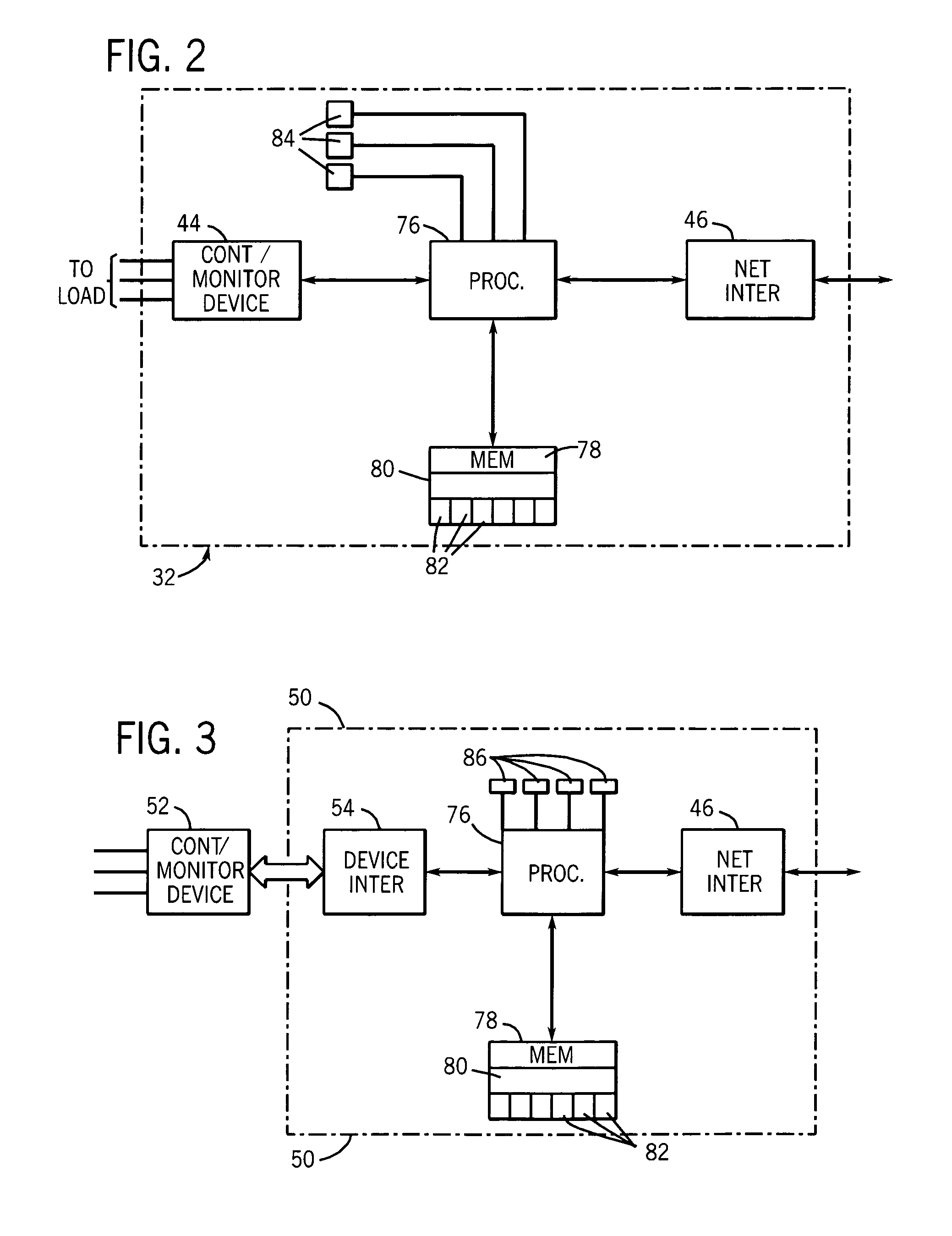
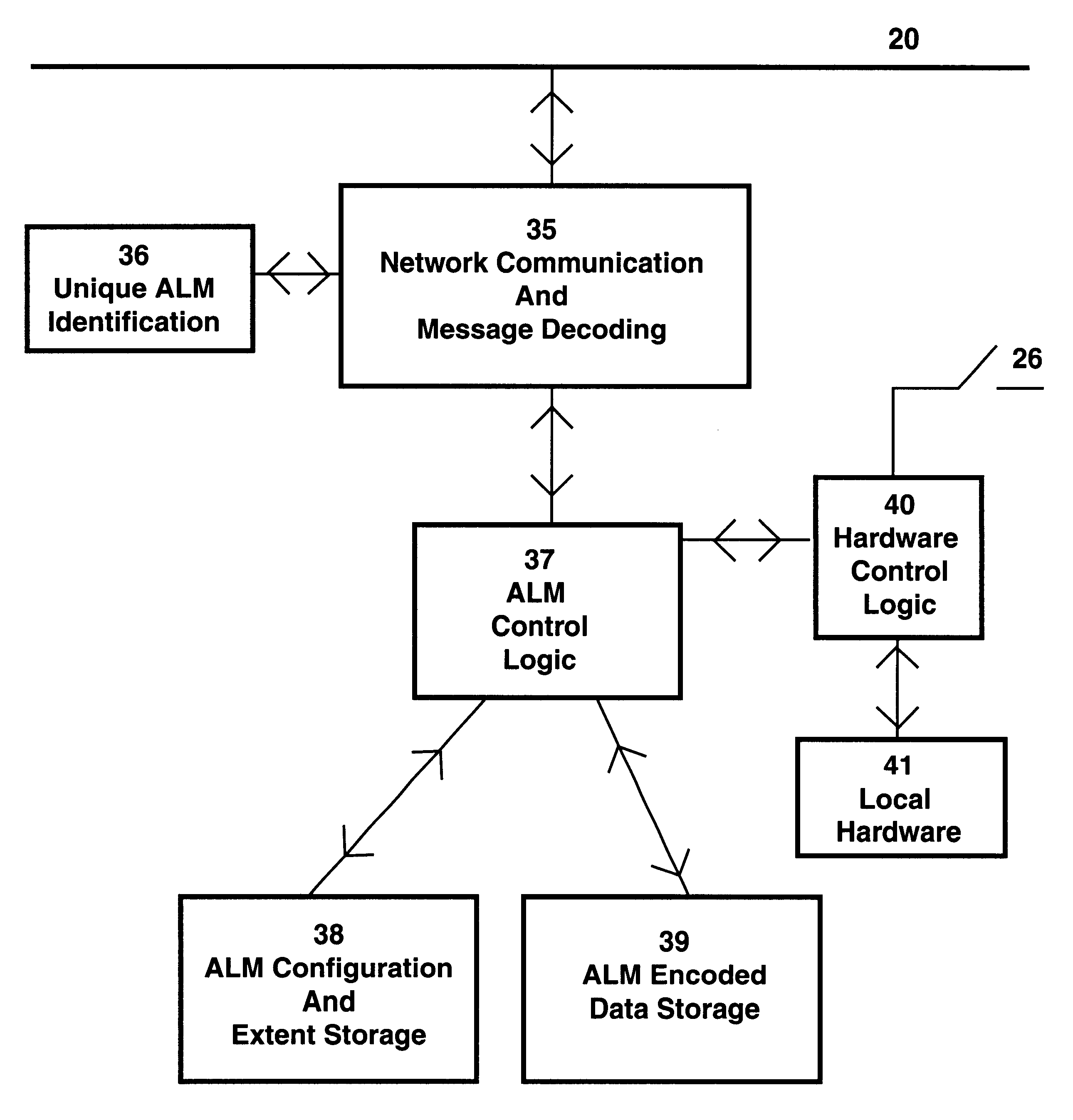
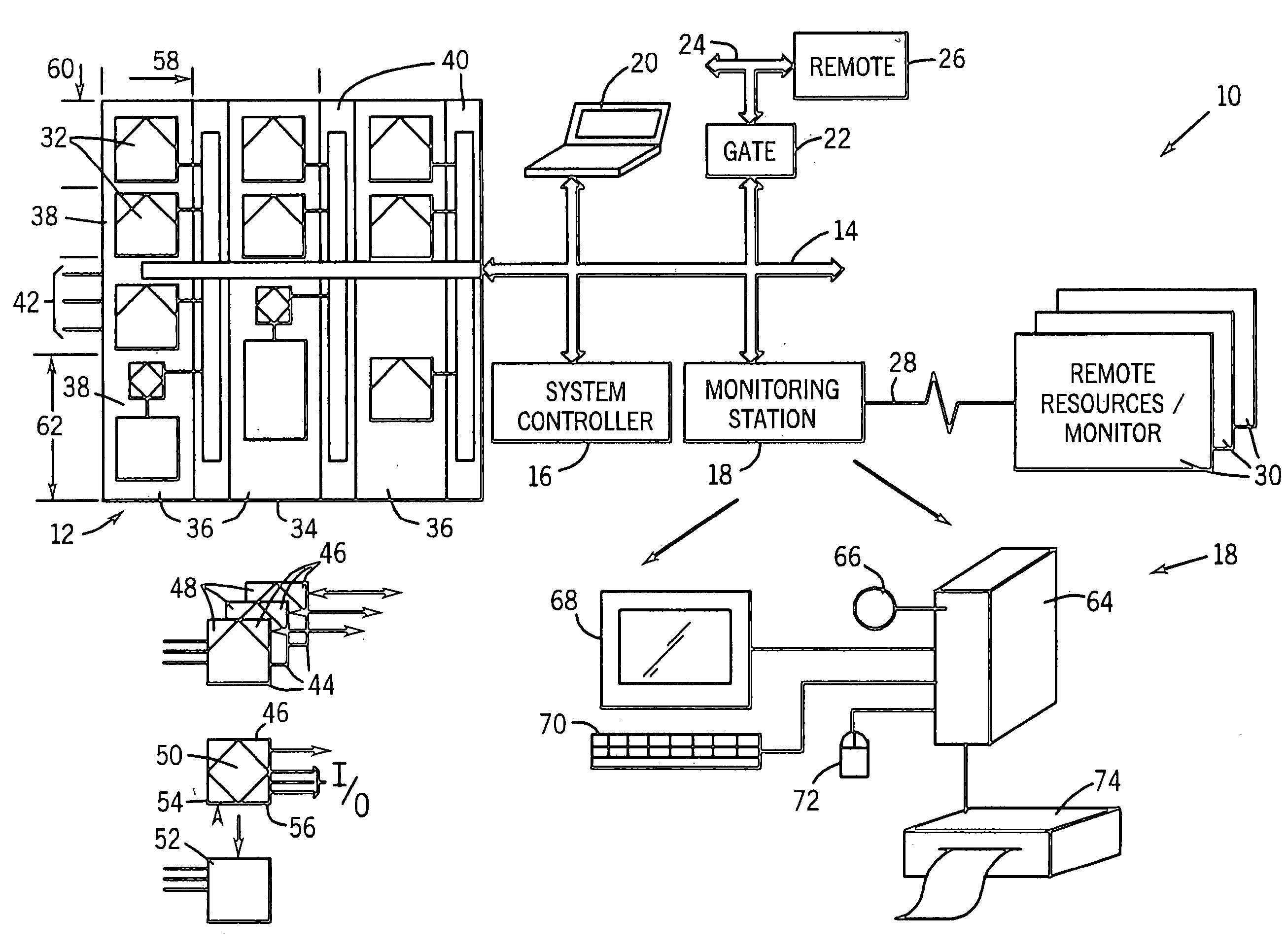
Networked control system with real time monitoring
InactiveUS6978225B2Electrical measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionNetwork controlParameter control
A technique for monitoring operational parameters of networked components includes storing data within each component descriptive of the component. The data is polled by a monitoring station and provides a basis for monitor views compiled in real time. The monitor views provide a view of current levels of parameters controlled or monitored by each device, such as on virtual meters. Historical levels of operational parameters may be presented in virtual strip chart output. Textual descriptions of the components are provided, along with listings of key settings. More detailed data may be accessed by links between the monitor views and other user viewable representations for the system and the specific components.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION
Attached logic module technique for control and maintenance in a distributed and networked control system
InactiveUS6275739B1Easy to modifyEasy to upgradeComputer controlSimulator controlNetwork controlComputer module
A local area network based control system for model railroad layout control that may be readily modified, upgraded, dynamically reconfigured or expanded with minimum physical or functional interruption to the operation of the model railroad layout. This allows for the expansion and improvements to the layout control system to be effected with least effort, time and risk of failure.
Owner:IRELAND ANTHONY JOHN
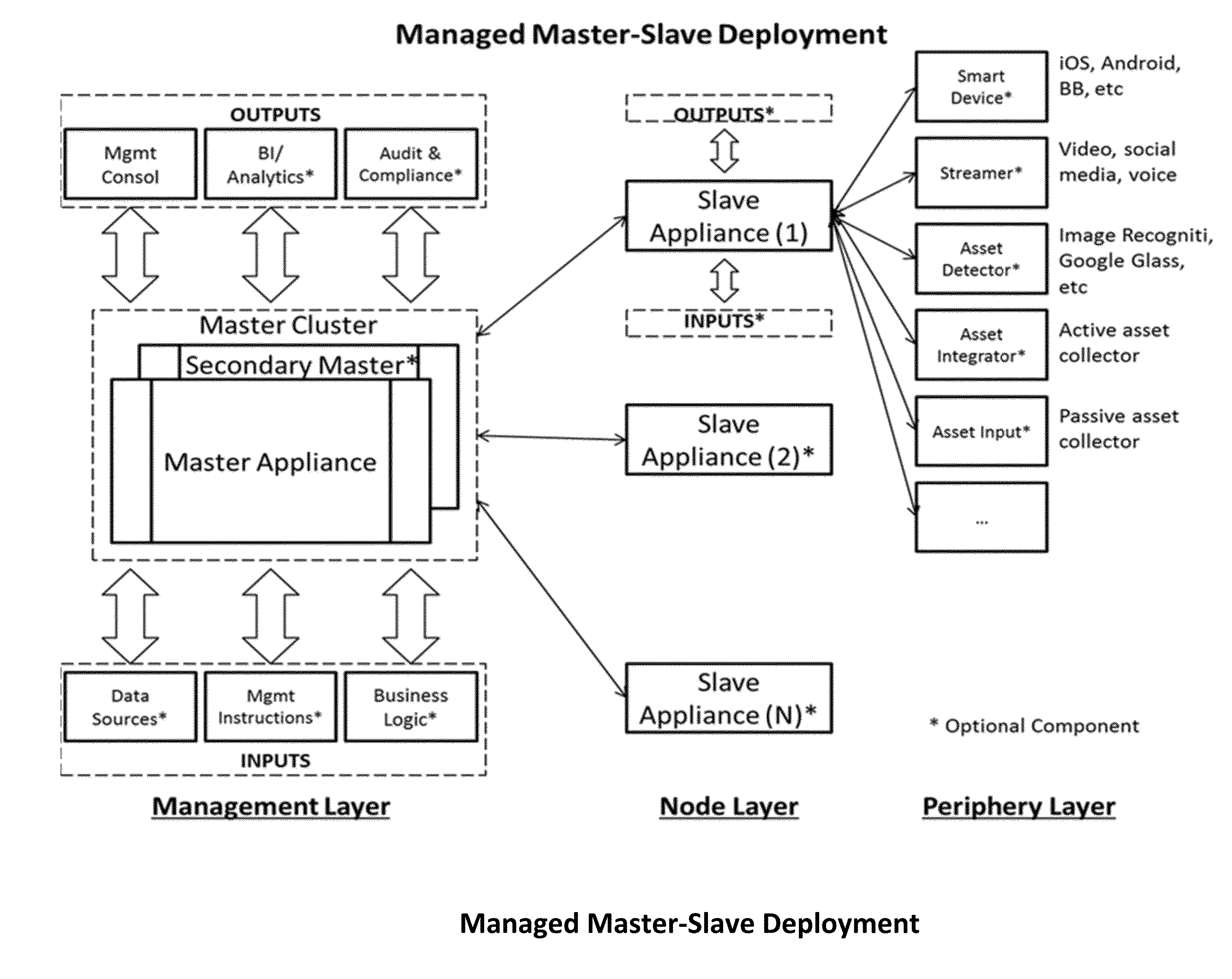
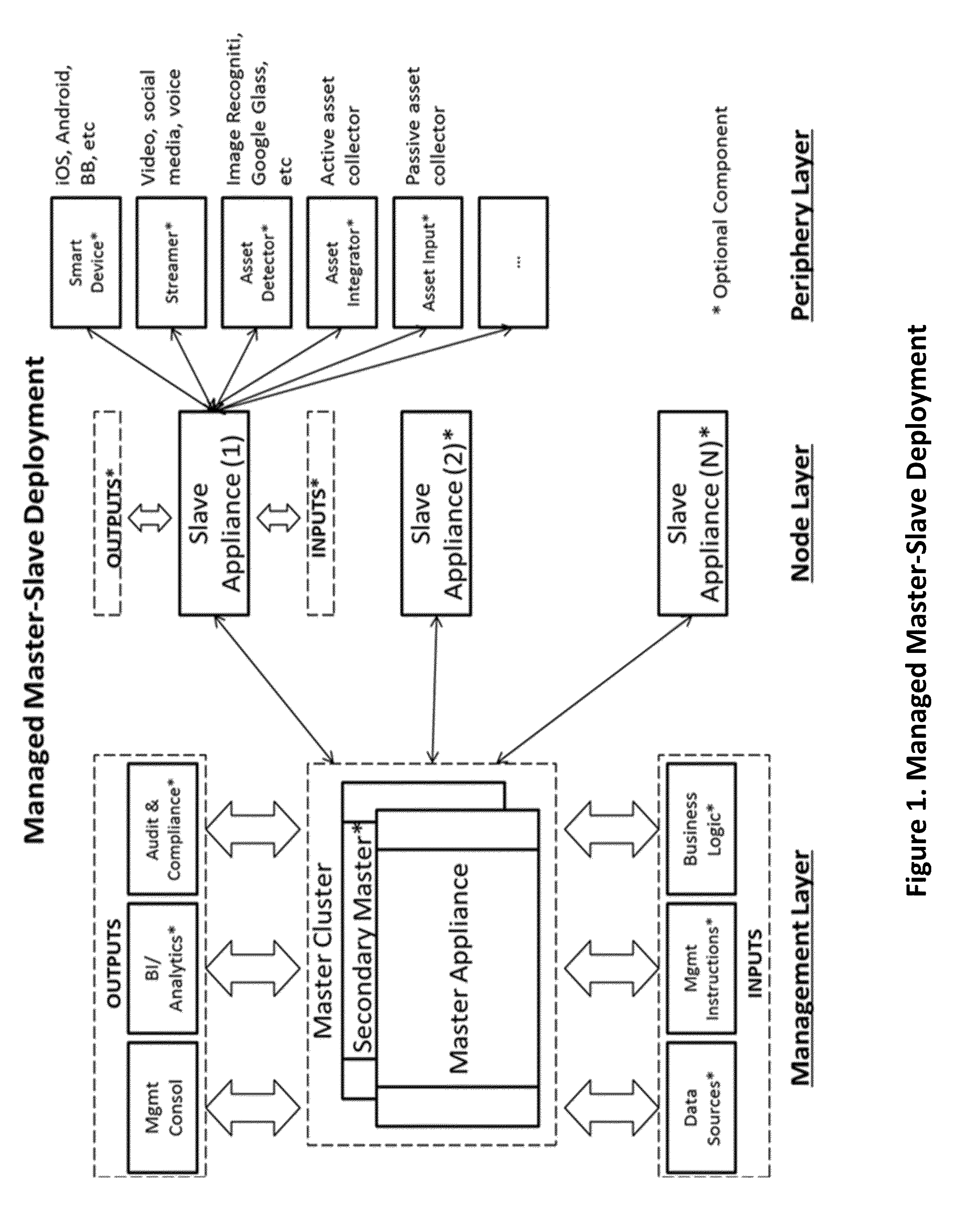
Appliance clearinghouse with orchestrated logic fusion and data fabric - architecture, system and method
InactiveUS20160006629A1Facilitate acquisitionEasy to manageDigital computer detailsInternal/peripheral component protectionUnstructured dataNetworked control system
A computerized method for controlling or connecting a plurality of computer appliances in a networked control system comprised of control center, computer appliance and peripherals for the purposes of establishing an automated framework and technical devices for intelligent integration of two or more applications, logic rules, data repositories and / or services together to automate, manage, synchronize or monitor knowledge or business solutions in real-time. The control center, computer appliances or peripherals can store and process structured or unstructured data; the control center is communicating with each appliance or periphery across a communication network; the control center can determine when an appliances or peripheral requires maintenance or update; the control center controls the current inventory of computer appliances and peripherals; the control center can add or reinitialize a new computer appliance or peripheral; the computer appliance can also add peripherals. A user can interact with the control center, computer appliance or a peripheral to perform monitoring, management or analysis functions.
Owner:IANAKIEV GEORGE +1
Automatically commissioning of devices of a networked control system
InactiveUS20110310621A1Avoid problemsReduce the numberElectrical apparatusDigital computer detailsComputer networkLighting system
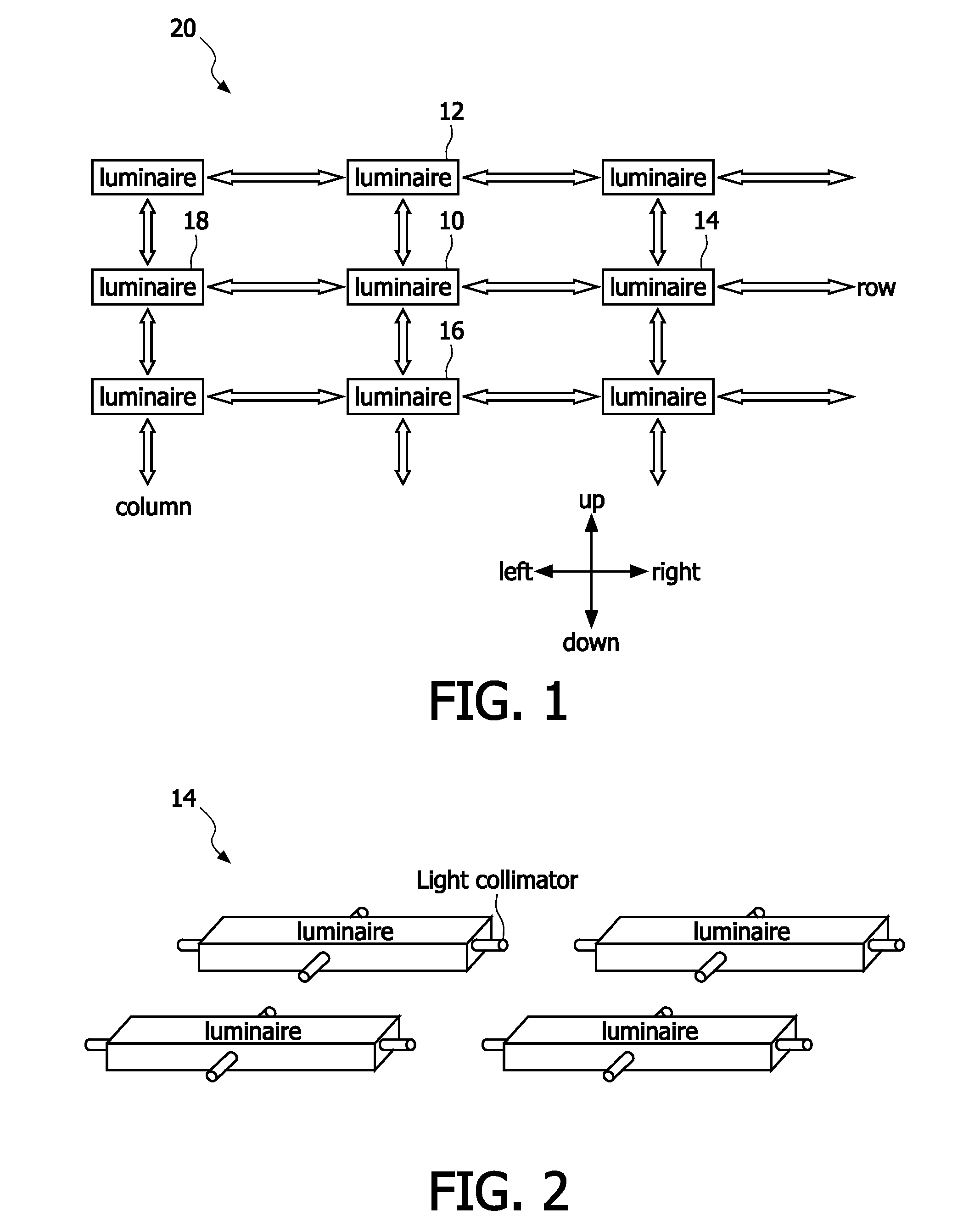
The invention relates to automatically commissioning of devices of a networked control system, particularly to automatically commissioning (auto-commissioning) of light sources of a lighting system, where a control of light sources on an individual and local basis is required. A basic idea of the invention is to route commissioning messages through a grid, particularly an approximately rectangular grid of devices in that each device is able to receive commissioning messages from and to transmit commissioning messages to directly neighbored devices in the grid via light. An embodiment of the invention relates to a method for automatically commissioning of devices (10, 12, 14, 16, 18) of a networked control system, which comprises several devices arranged in a grid (20), wherein each device is adapted for routing messages, which were received from directly neighbored devices in the grid, to directly neighbored devices in the grid via light, wherein the commissioning comprises the acts oftransmitting a commissioning message (S10), which comprises a hops counter, by a first device (10) to a second device (12), which is neighbored to the first device in a predetermined direction (22) in the grid,receiving the commissioning message (S12) from the first device by the second device,updating the hops counter (S14) by the second device and a location counter of the second device andtransmitting the commissioning message (S16) with the updated hops counter to one or more third devices.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Design method of multi-agent system event trigger controller when DoS attack exists
The invention relates to the technical field of networked control systems, in particular to a method for determining a consistent event trigger controller aiming at the condition that a multi-agent system with a leader has denial of service attack (DoS) by utilizing a modal dependent average residence time method, comprises the following steps of: step one, establishing a leader-follower multi-agent system model and a design event triggering condition; step two, establishing a DoS attack model and a switching system model; step 3, designing an event trigger controller and corresponding switching conditions. The average residence time method adopting modal dependence solves the design problem of the consistent event trigger controller in a leader-follower multi-agent system with DoS networkattack.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
Networked control system with real time monitoring
InactiveUS20050021291A1Electrical measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsNetwork controlParameter control
A technique for monitoring operational parameters of networked components includes storing data within each component descriptive of the component. The data is polled by a monitoring station and provides a basis for monitor views compiled in real time. The monitor views provide a view of current levels of parameters controlled or monitored by each device, such as on virtual meters. Historical levels of operational parameters may be presented in virtual strip chart output. Textual descriptions of the components are provided, along with listings of key settings. More detailed data may be accessed by links between the monitor views and other user viewable representations for the system and the specific components.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION
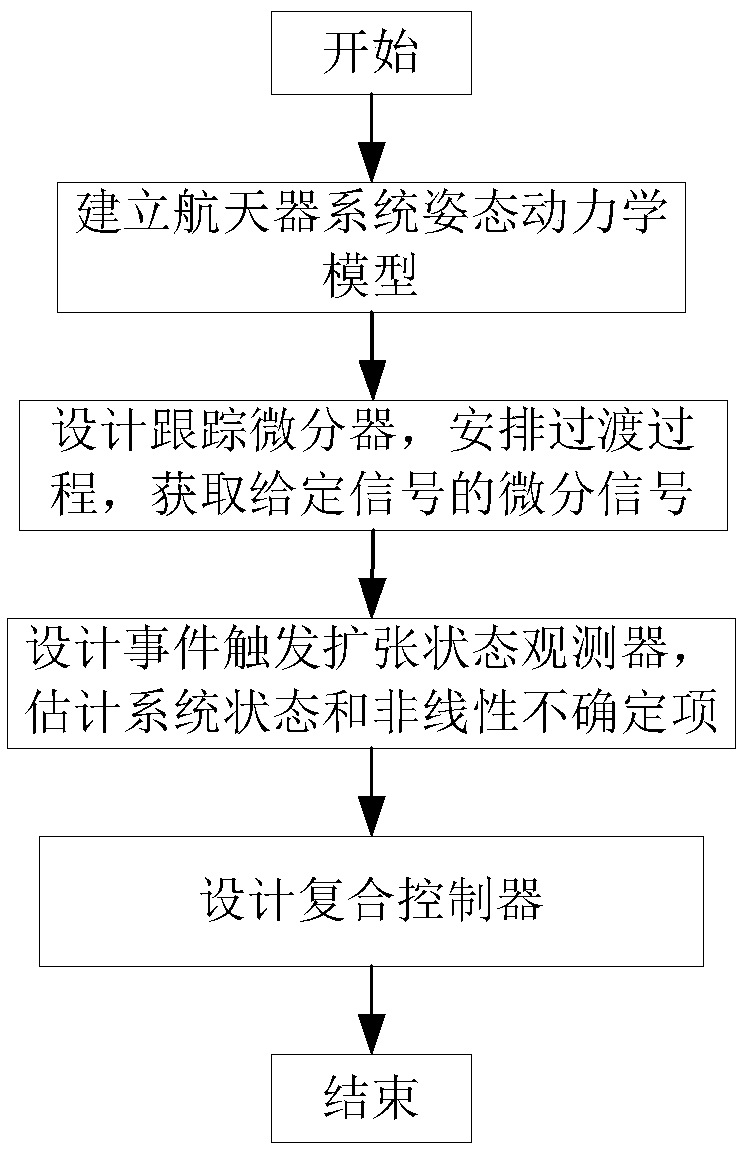
Attitude control method for spacecraft networked system based on event trigger
ActiveCN109189085APlay a protective effectAvoid output overshootAttitude controlDifferentiatorAttitude control
The invention discloses an attitude control method for a spacecraft networked system based on event trigger, belonging to the field of system servo control for space robot networked control systems. The method comprises the following steps: firstly arranging a suitable transition process for the desired attitude of the system by designing a tracking differentiator to avoid a serious overshoot on the output of the system caused by an over-large initial error, and at the same time, acquiring a differential signal of the desired value for preparation for subsequent controller design; then, considering the network transmission signals, designing an event-triggered expansion state observer by using an attitude-angle measurement signal output by an event trigger mechanism, estimating the nonlinear uncertainties formed by the state in the spacecraft system, coupling, external disturbances and the like in real time, and compensating the estimated values of the nonlinear uncertainties into an error feedback control rate to form a composite controller. Finally, the method provided by the invention prevents nonlinear factors such as internal and external interferences from adversely affectingthe system, improves the robustness of the system, and provides guarantee for the smooth completion of space operations tasks.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Fault-tolerant control method for networked control system with time-varying delay
ActiveCN105988368ASufficient conditions for stabilityReduce conservatismAdaptive controlLyapunov stabilityMatrix method
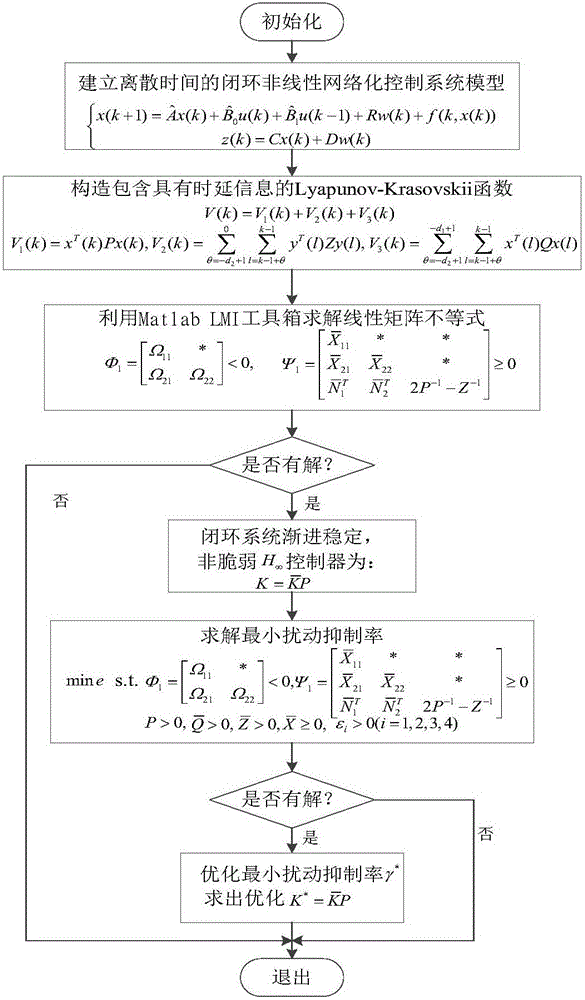
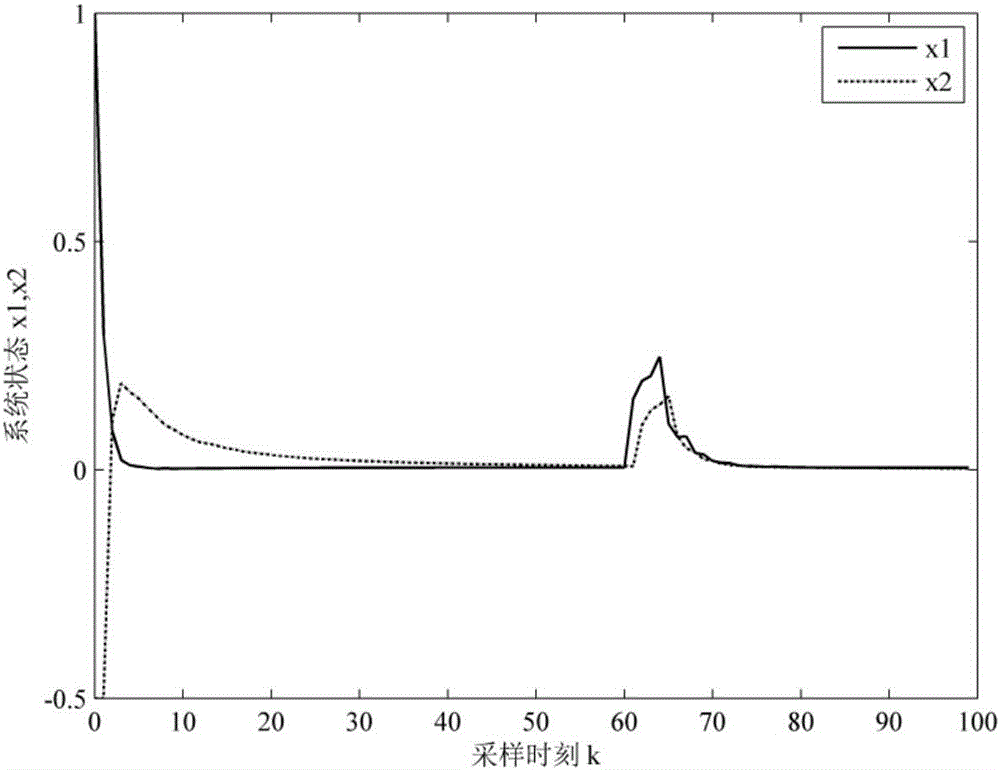
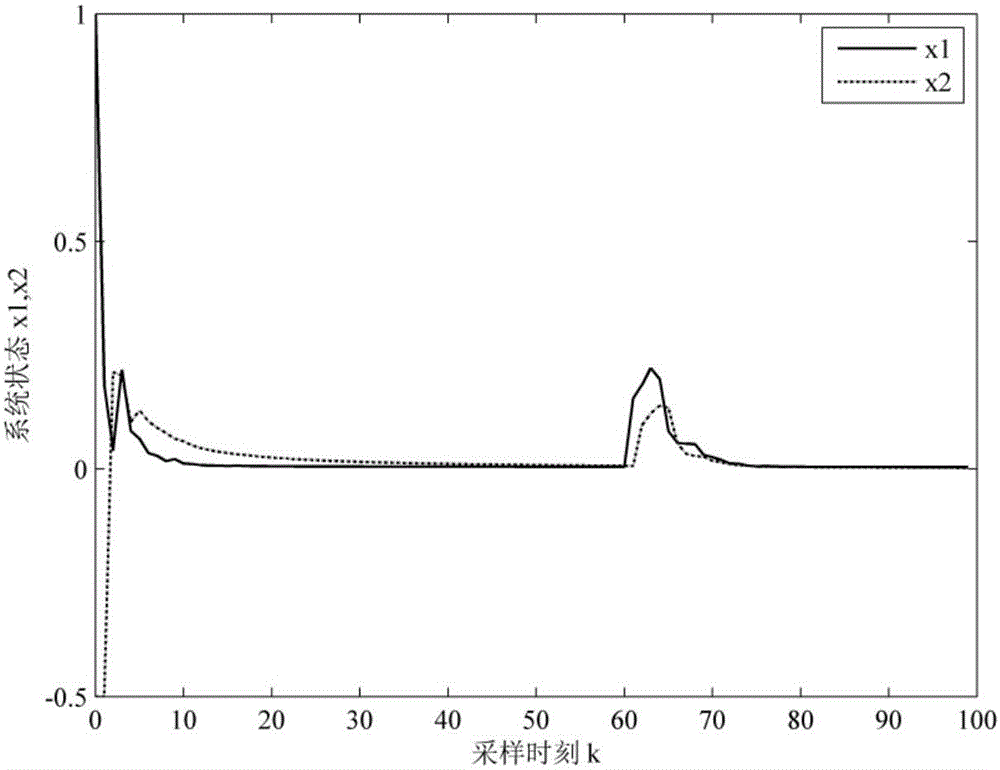
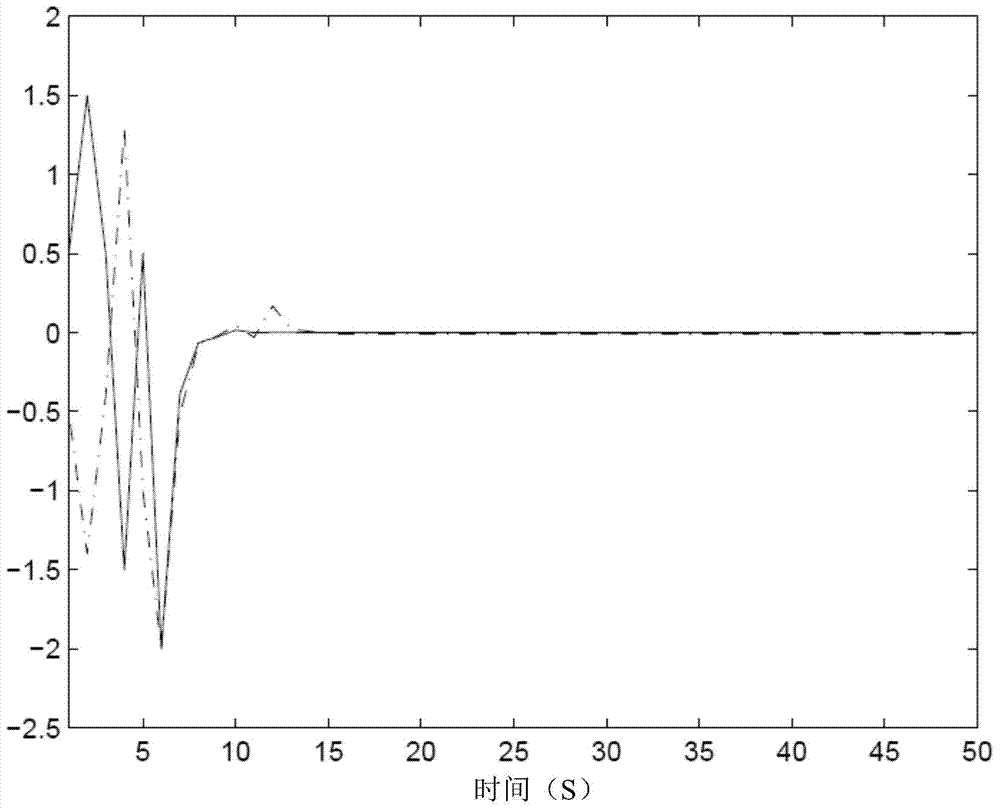
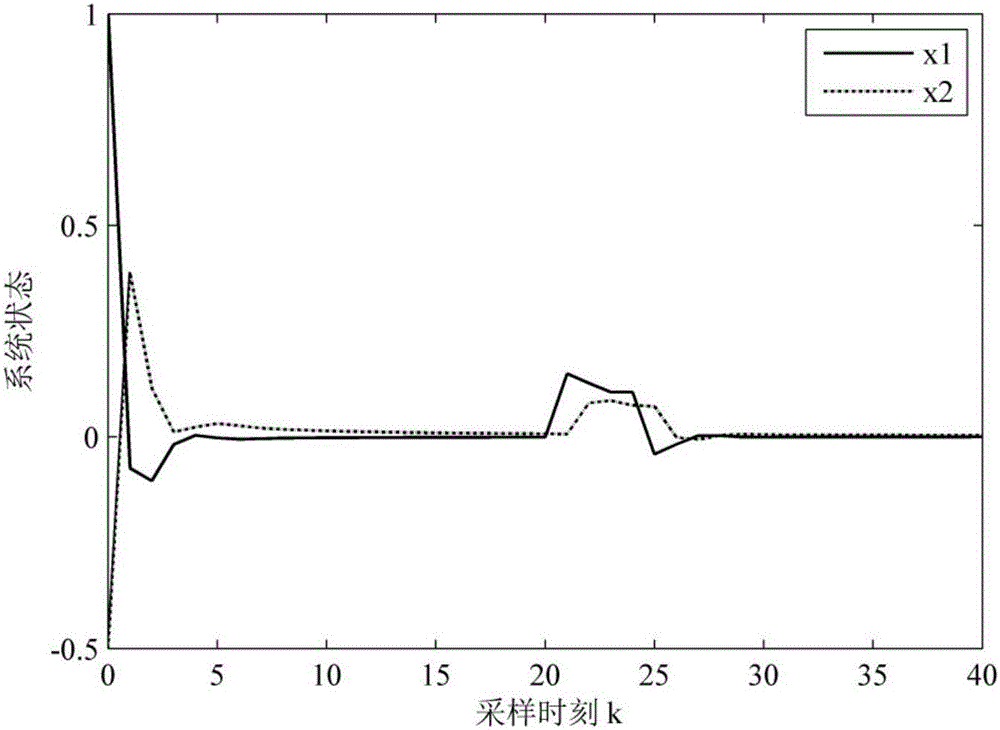
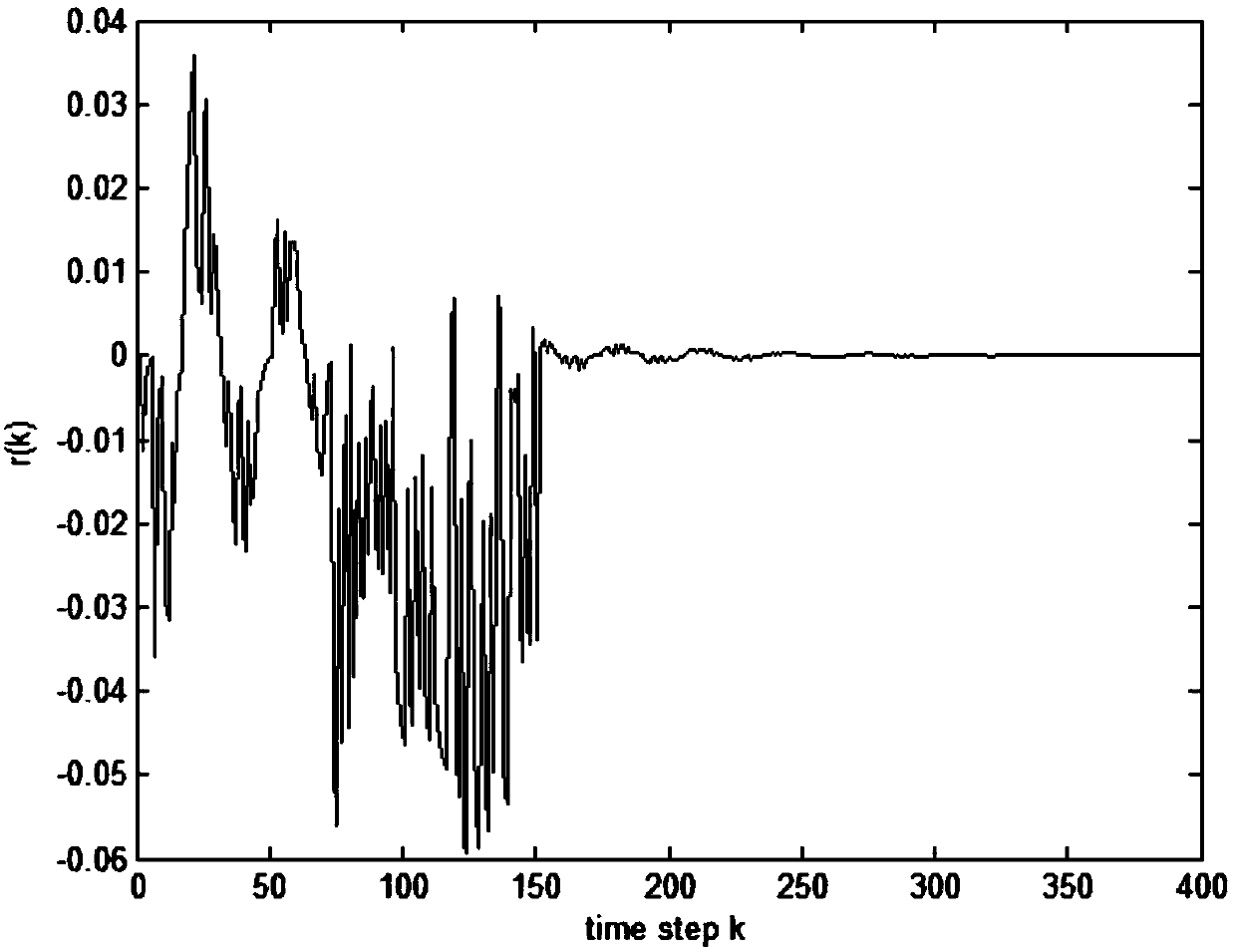
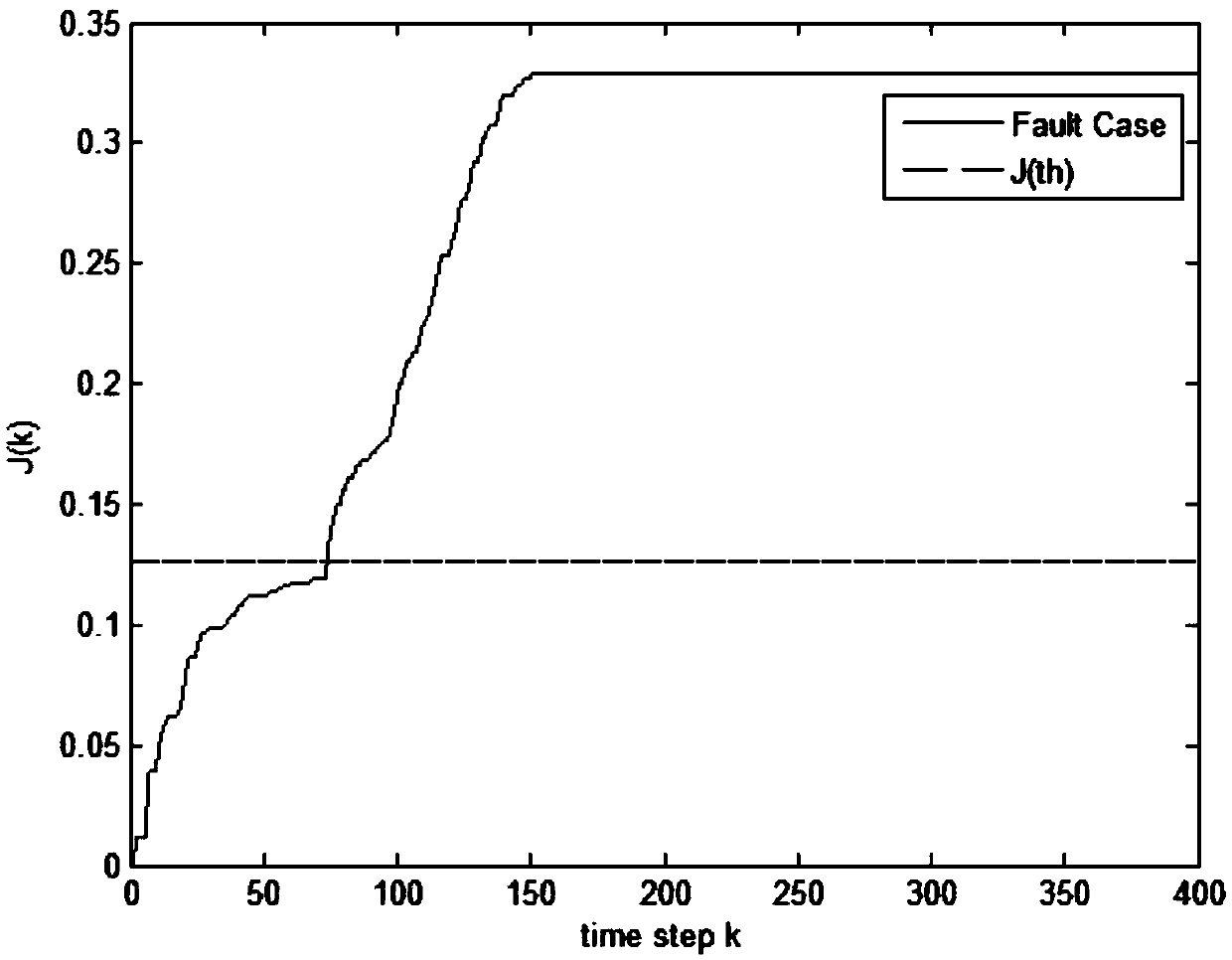
The invention discloses a fault-tolerant control method for a networked control system with time-varying delay. In view of conditions of parameter perturbation, time-varying delay, external disturbance and random failure happening to an actuator, a discrete time closed-loop nonlinear networked control system model is firstly built, a Lyapunov-Krasovskii function with the delay information is then built, a Lyapunov stability theory and a linear matrix inequality analysis method are used, sufficient condition for asymptotic stability of the nonlinear networked control system and existence of an H-infinity fault-tolerant controller are obtained, a Matlab LMI toolbox is used for solution, and a gain matrix for a non-fragile fault-tolerant controller is: K=K<->P; and conditions for optimizing the minimum disturbance rejection rate gamma is given, and the controller gain matrix K<*> optimized under the minimum disturbance rejection rate gammamin= square root of e is acquired. The condition of time-varying delay existing in the system is considered, the time-varying delay is analyzed and processed based on a free-weighting matrix method, and the conservation is reduced.
Owner:嘉兴琥珀科技有限公司
Methods for automatically commissioning of devices of a networked control system
ActiveUS20140088772A1Improve reliabilityMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlNetwork controlEngineering
The invention relates to automatically commissioning of devices of a networked control system, particularly to automatically commissioning of wireless switches in lighting control systems. A basic idea of the invention is to derive from an installation constraints with regard to a networked control system and to consider these constraints during an automatic commissioning process based on signal strength processing. This may help to improve the reliability of commissioning based on signal strengths. An embodiment of the invention relates to a method for automatically commissioning of devices of a networked control system, which comprises one or more first devices (S1-S3) and several second devices (RC1-RC3) being able to communicate wirelessly, wherein wireless signals from first devices (S1-S3) are received by one or more second devices (RC1-RC3) and for each received wireless signal the signal strength is determined, and wherein the commissioning comprises the following steps: processing the determined signal strengths considering constraints derived from an installation of the networked control system for commissioning, and assigning the first devices (S1-S3) to one or more of the second devices (RC1-RC3) depending on the processing result.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Lighting control systems and methods
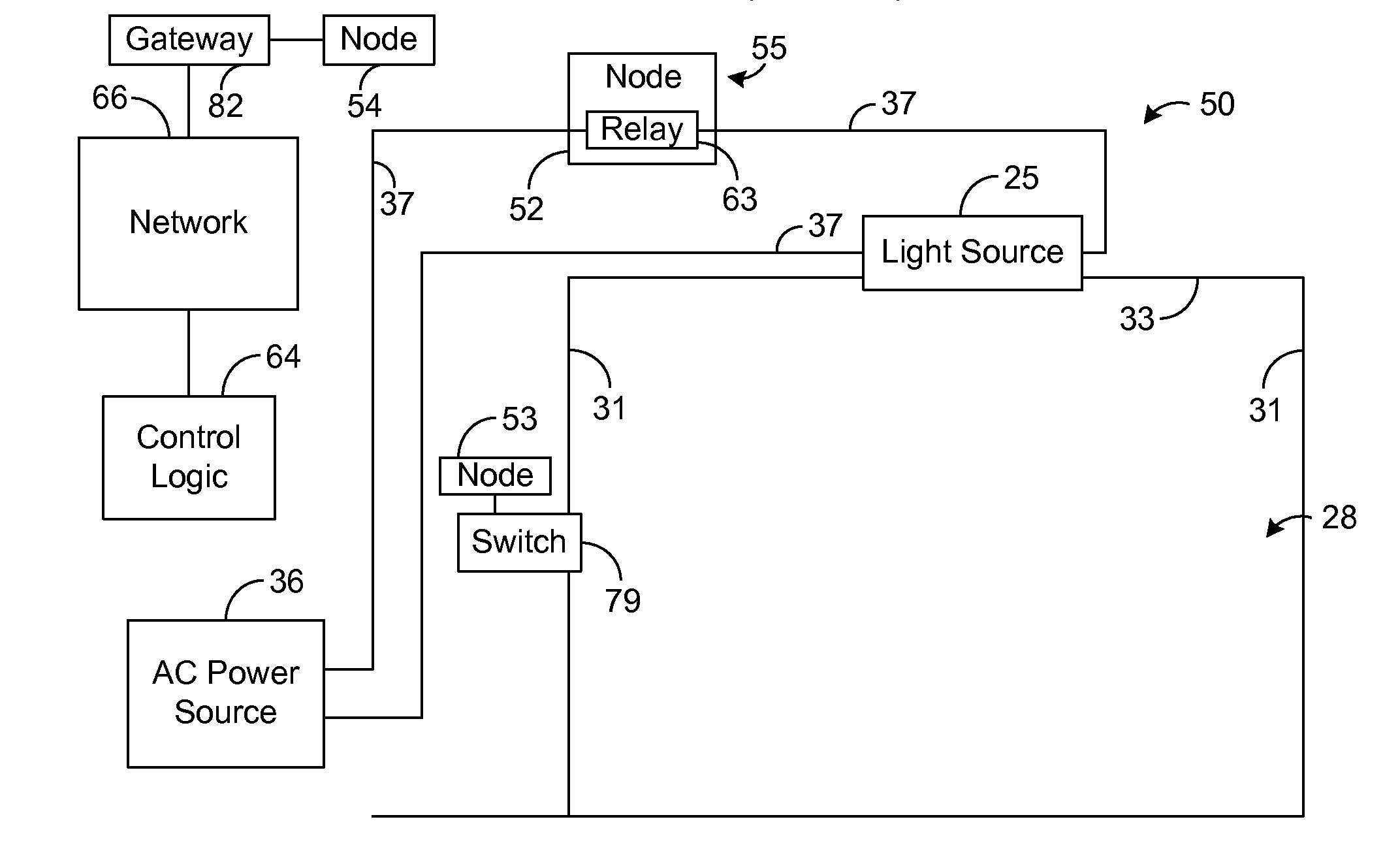
InactiveUS20110316453A1Electrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementNetwork controlEngineering
The present disclosure generally pertains to lighting control systems and methods. In one exemplary embodiment, a building having at least one light source controlled by a manually-actuated switch is retrofitted with a networked control system. In this regard, the manually-actuated switch is decoupled from a power line that provides power to the light source, and the power line is coupled to a node of a wireless network to provide in-line control of the light source. Another node of the network is coupled to the manually-actuated switch so that the node can receive inputs from such switch. Such node uses the wireless network to transmit data indicative of the inputs from the manually-actuated switch. Logic then uses such data to control the activation state of the light source via the in-line relay coupled to the power line.
Owner:SYNAPSE WIRELESS
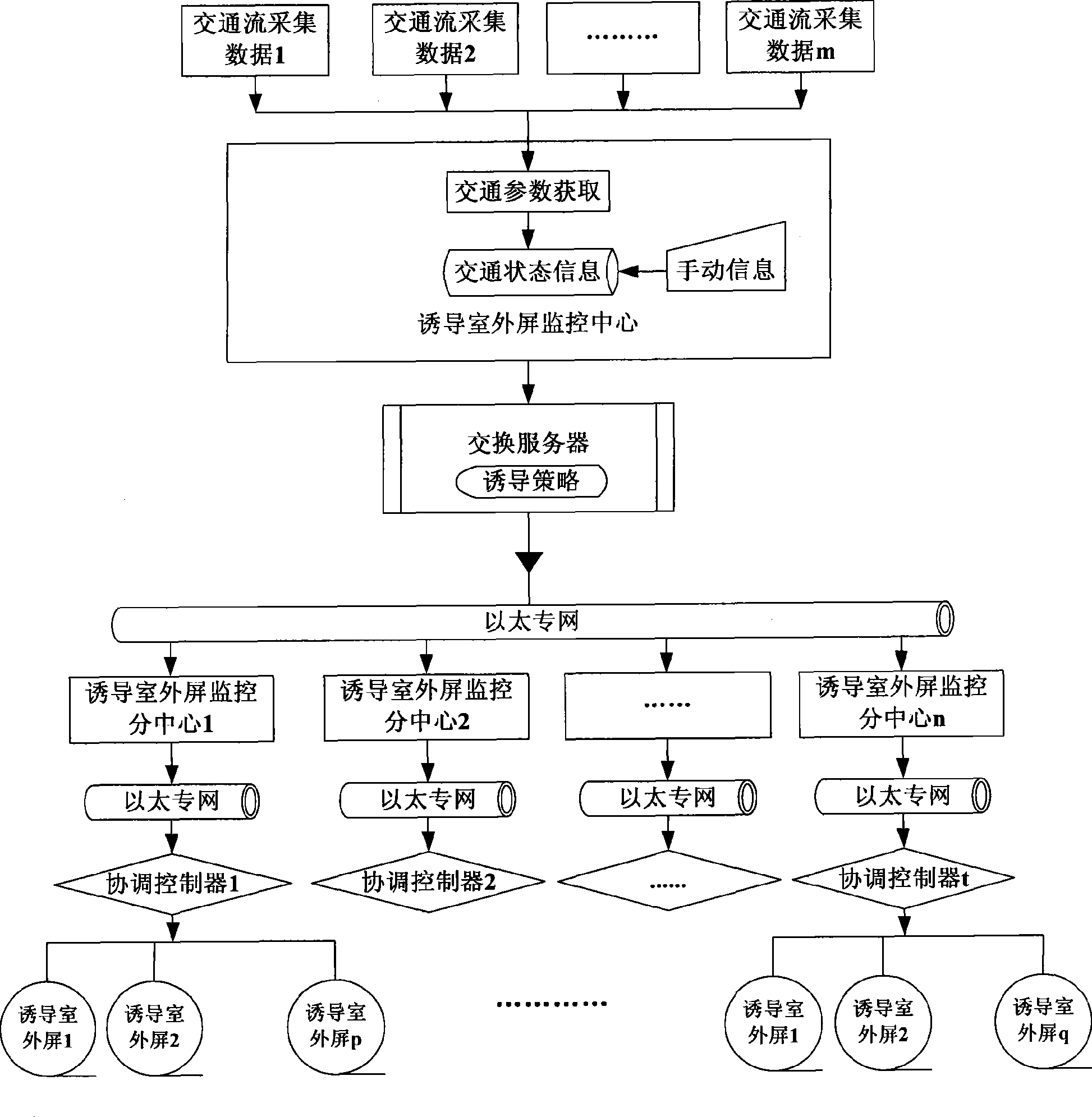
Network control system for traffic induction outdoor screen
InactiveCN101383091ARestrict work rightsDoes not affect network loadRoad vehicles traffic controlNetwork controlIndex system
The invention provides a networking control system of traffic inducing outdoor screens. The distributed Ethernet is used as the fundamental architecture of the system, and a monitoring center is set; sections to which the traffic inducing outdoor screens belong are divided according to urban administrative regions, and the outdoor screens in the sections are controlled by monitoring sub-centers, are not interfered by one another, and are coordinated through an exchange server to construct the unified network control system. Control policies provided by the invention comprise a data processing policy and a display policy for issuing information. The invention provides an addressing module based on performance analysis and provides an assessment indicator system and a module solving algorithm based on a heuristic algorithm. The content of the invention relates to a plurality of key links, such as the architecture of the networking control system of the traffic inducing outdoor screens, the control policies, the addressing, and the like. The invention has the advantages of the completeness and the flexibility of the system architecture, the compatibility of data processing and the validity of the optimized addressing and improves the whole efficiency of constructing the networking control system of the traffic inducing outdoor screens.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for estimating state of networked control system with random uncertainty and delay of distributed sensors
ActiveCN103676646ATo achieve the purpose of resisting nonlinear disturbanceEasy to solveAdaptive controlComplex dynamic systemsComputer science
The invention relates to a method for estimating the state of a networked control system with random uncertainty and delay of distributed sensors, particularly to a method for estimating the state of random uncertainty and delay of distributed sensors. The method solves the problem that the existing method for state estimation can not treat the random uncertainty and the delay of distributed sensors at the same time, so the performance of state estimation is influenced. According to the method of the invention, the influence of random uncertainty and delay of distributed sensors on the performance of state estimation is considered at the same time, and a Lyapunov function is used to fully consider the effective information of the delay. Compared with the existing method for estimating the state of a nonlinear complex dynamic system, the method for state estimation of the invention can be used to treat random uncertainty, delay of distributed sensors and bounded time-varying delay at the same time so as to obtain a method for state estimation on the basis of the solution of a linear matrix inequality; therefore, the purpose of resisting nonlinear perturbation can be achieved. The method is suitable for estimating the state of the nonlinear complex dynamic system.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
QoS-based sampling period adjusting method for networked control system
InactiveCN104486166AImprove dynamic characteristicsImprove dynamic stabilityData switching networksTimestampPacket loss
The invention provides a QoS-based sampling period adjusting method for a networked control system. According to the sampling period of the current network QoS adjusting system, the quality of network service (QoS) is improved, and the network average transmission delay and the packet loss probability are reduced, so that the control performance and the stability of the networked control system are improved. The QoS-based sampling period adjusting method for the networked control system includes the steps that a network QoS measurement module measures the communication service condition of the current network, measures the loop delay of data packets in a timestamp mode, and calculates the packet loss probability of the current data packet by carrying out statistics on the transmitting and receiving conditions of the data packets; according to network QoS measure data, a sampling period control module obtains the sampling period which the system should adopt at the moment by the adoption of a static adjustment or dynamic adjustment method.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and apparatus for altering the behavior of a networked control system
ActiveUS20110144773A1Easy and more comfortableElectric controllersElectric light circuit arrangementNetwork controlLighting system
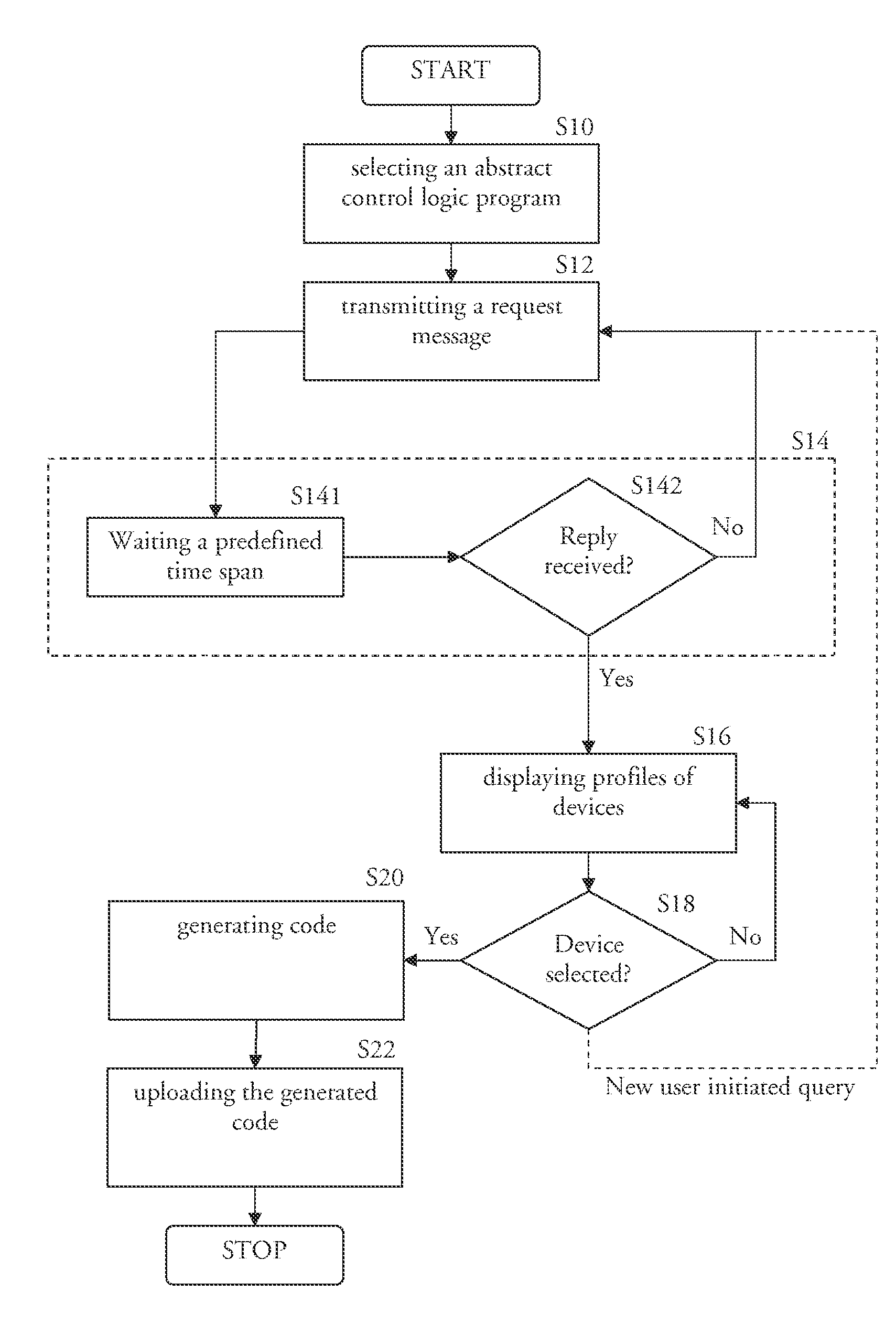
The invention relates to altering the behavior of a networked control system such as the integrating of a device such as a light unit or a light switch in a networked control system such as a networked lighting system. An embodiment of the invention provides a method for altering the behavior of a networked control system, which comprises several devices, wherein the method comprises the steps of—selecting an abstract control logic program from a list of several abstract control logic programs (SIO), —transmitting a message for requesting replies from devices (S 12), —waiting for receiving a reply from at least one device (S 14), —displaying the profile of at least one device of the devices (S 16), from which replies were received, —waiting for a selection of at least one device from the displayed profiles (S 18), —generating code establishing the behavior of the selected abstract control logic program for the selected one or more devices (S20), and—uploading the generated code to one or more devices in the networked control system such that the selected devices will behave according to the selected abstract control logic program (S22). The invention allows creating a behavior alteration procedure for a networked control system, which is very intuitive for users, who merely have to perform some easy and comfortable interactions such as selecting the abstract control logic program.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Nonlinear networked control system non-fragile H-infinity fault tolerance control method
ActiveCN106257873AImprove anti-interference abilityData switching networksLyapunov stabilityPacket loss
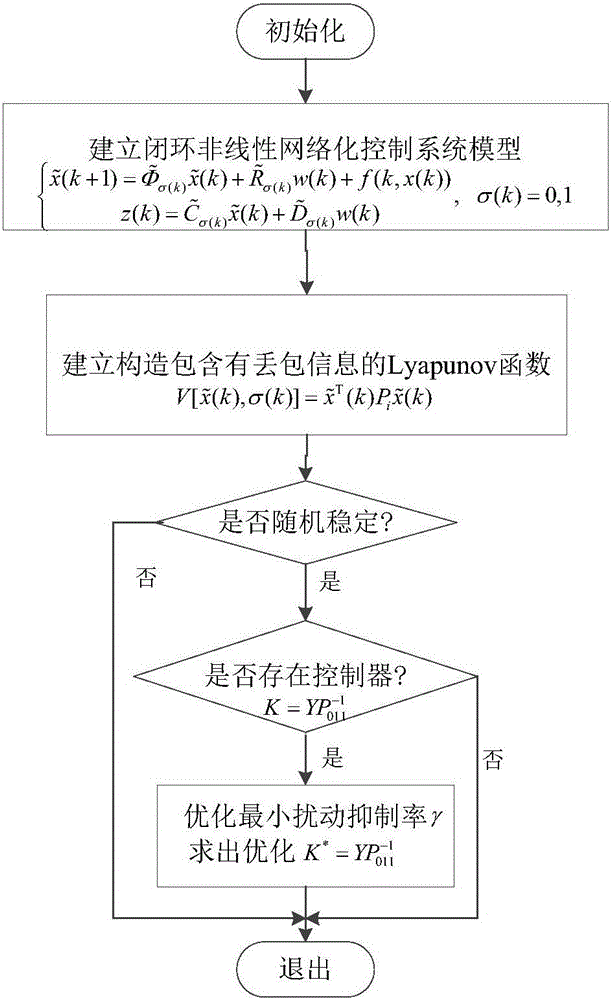
The invention discloses a nonlinear networked control system non-fragile H-infinity fault tolerance control method. Firstly a closed-loop nonlinear networked control system model is established for considering the situation of parameter perturbation, time delay and packet loss of the nonlinear networked control system and random fault of an actuator, and then a Lyapunov function including packet loss information is constructed. The sufficient conditions of nonlinear networked control system stochastic stability and existence of an H-infinity fault tolerance controller are obtained by using the theory of Lyapunov stability and a linear matrix inequality analysis method. Solving is performed by using a Matlab LMI tool box, a non-fragile fault tolerance controller gain matrix K=YP<-1><011> is given, the conditions for optimization of the minimum disturbance suppression ratio gamma are given, and the optimized controller gain matrix K* under the minimum disturbance suppression ratio gamma<min> (the square root of e) is acquired. The situation of the random fault of the actuator is considered, and the probability of the random fault meets BerRoulli distribution so as to have more practical meaning.
Owner:北京新桥信通科技股份有限公司
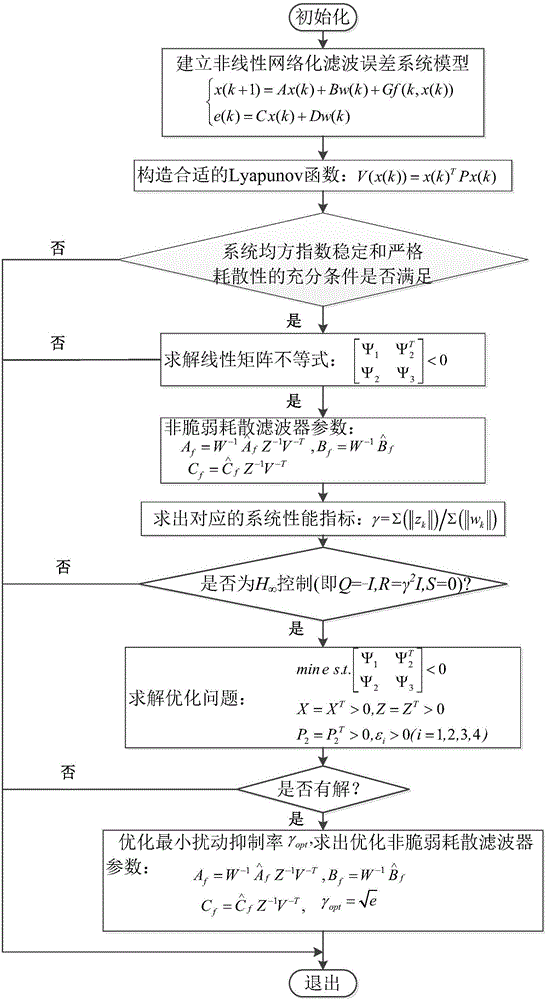
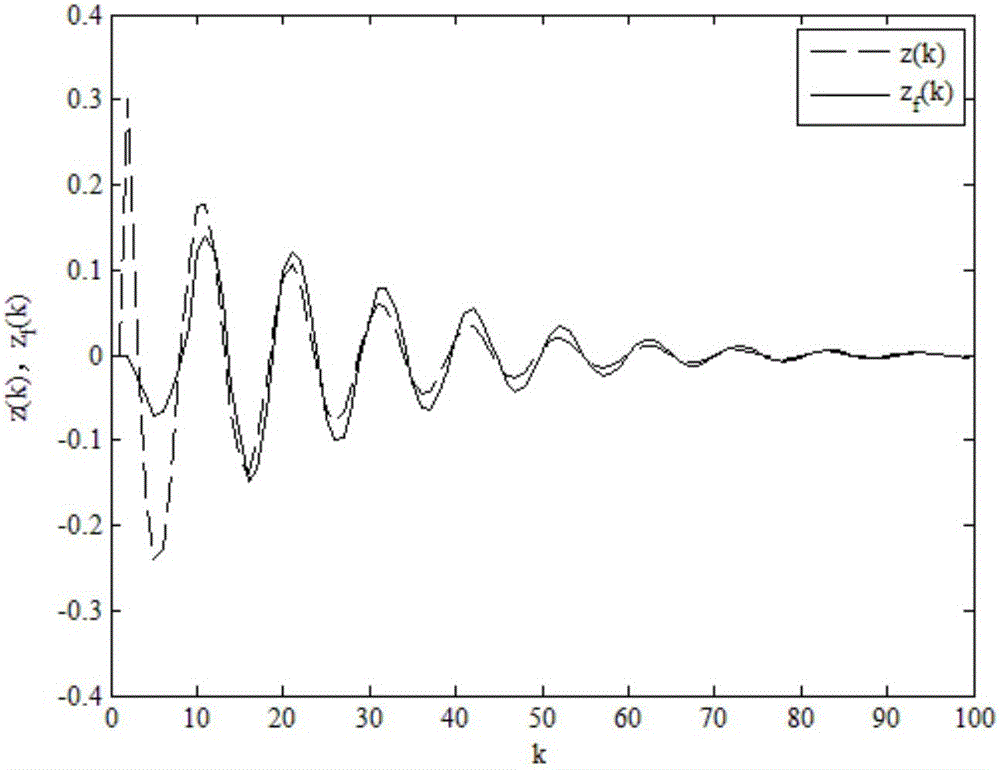
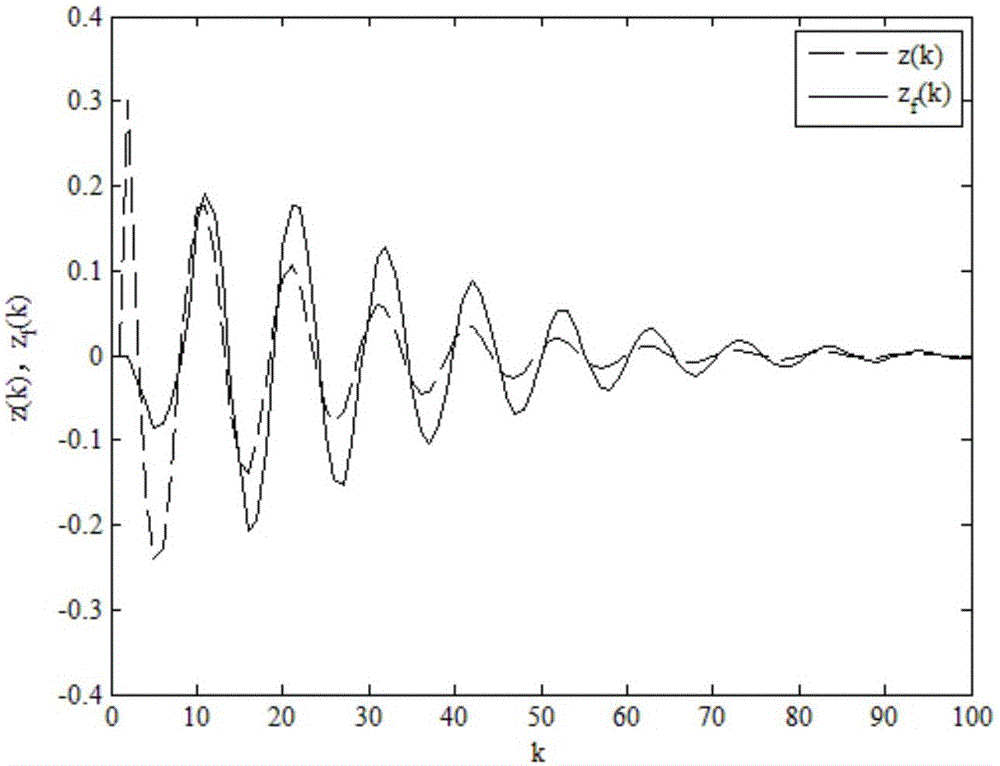
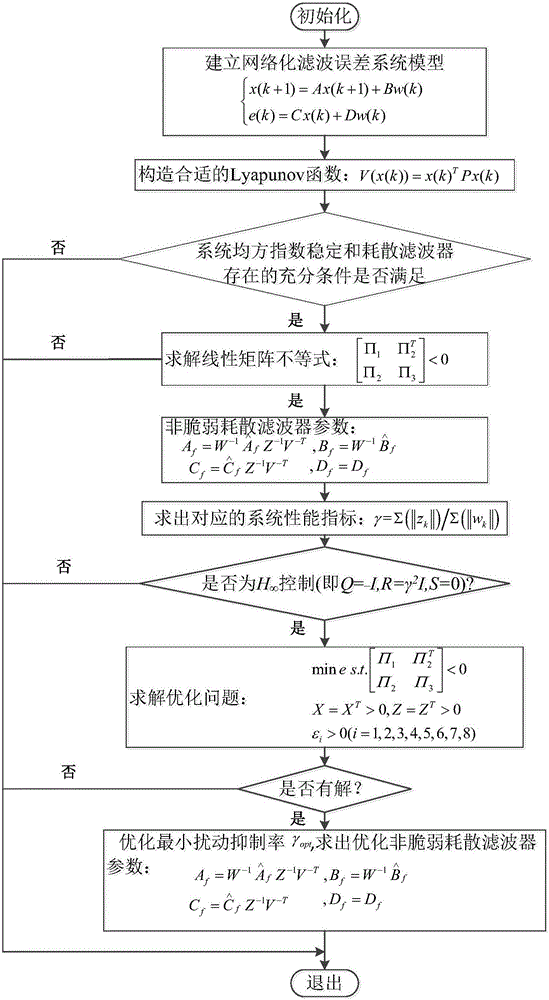
Non-fragile dissipative filtering method of nonlinear networked control system
ActiveCN106529479AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove performance indicatorsCharacter and pattern recognitionLyapunov stabilityPacket loss
The present invention discloses a non-fragile dissipative filtering method of a nonlinear networked control system. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing a nonlinear networked filtering error system model on the conditions of considering the time delay and the packet loss of the nonlinear networked control system and the perturbation of the filter parameters, then constructing a Lyapunov function, and then utilizing a Lyapunov stability theory and a linear matrix inequality analysis method to obtain the sufficient conditions of the mean square exponential stability of a nonlinear networked filtering error system and the existence of a non-fragile dissipative filter, utilizing a Matlab LMI tool kit to solve, and definding a non-fragile dissipative filter parameter matrix. The method of the present invention considers the random time delay and the pocket loss situations between the sensors and the filters, is suitable for the general dissipative filtering including the H-infinite filtering, and enables the conservatism of the non-fragile dissipative filter design to be reduced. Moreover, a non-modeling state of the system is considered when a full-order filter is designed, thereby being able to reduce the calculation burdens and the design cost.
Owner:毛国全
Electric power system wide-area output feedback control method considering WAMS (Wide Area Measurement System) signal time delay
InactiveCN103279035ASolve the problem of nonlinear term LR-1LEasy to solveAdaptive controlWide areaTime delays
The invention provides an electric power system wide-area output feedback control method considering WAMS (Wide Area Measurement System) signal time delay. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, building a closed-loop wide-area electric power system general model considering feedback signal time lag on the basis of a networked control system theory; then introducing an improved free-weighting matrix approach to obtain a theorem and a deduction for time lag stability analysis of a wide-area electric power system networked control system; meanwhile, converting a non-linear matrix inequality (NLMI) into a linear matrix inequality (LMI) which is convenient to resolve by adopting an improved cone compensation algorithm, and obtaining the maximum time lag boundary of a wide-area electric power system networked controller with lower conservative property and a corresponding state feedback controller via a non-linear iterative optimization algorithm; and finally, realizing time lag output feedback control of an electric power system in combination with a mature state observer theory. The electric power system wide-area output feedback control method has the advantages of simple calculating process, higher running speed, capability of obtaining the maximum time lag upper bound of a wide-area electric power system rapidly, and easiness in implementing on the aspect of engineering.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Fault detection method for networked control system
ActiveCN107070734ATroubleshooting fault detection issuesData switching networksMarkov chainFilter gain
The invention provides a fault detection method for a networked control system. The fault detection method comprises the following steps: firstly, two independent Markov chains are used to respectively describe a sensor-to-controller delay and a controller-to-actuator delay, and the networked control system is modeled as a control system with two Markov chains; on the basis, a fault detection filter is constructed and a closed-loop system model is established by using a state augmentation method; and after that, the condition that the closed-loop system is stochastically stable and satisfies the H infinity performance is obtained in the form of a matrix inequality, a controller and filter gain matrix and a solution method of the H infinity reduction level are given, and the relation between the transition probability and the minimum H infinity reduction level is obtained. Examples show that a fault filter obtained by the proposed method is not only sensitive to faults, but also has good robustness to external disturbance, so that the H infinity fault detection problem of the networked control system under the condition that the transition probabilities of the sensor-to-controller delay and the controller-to-actuator delay are both partially unknown is solved.
Owner:卫士通(广州)信息安全技术有限公司
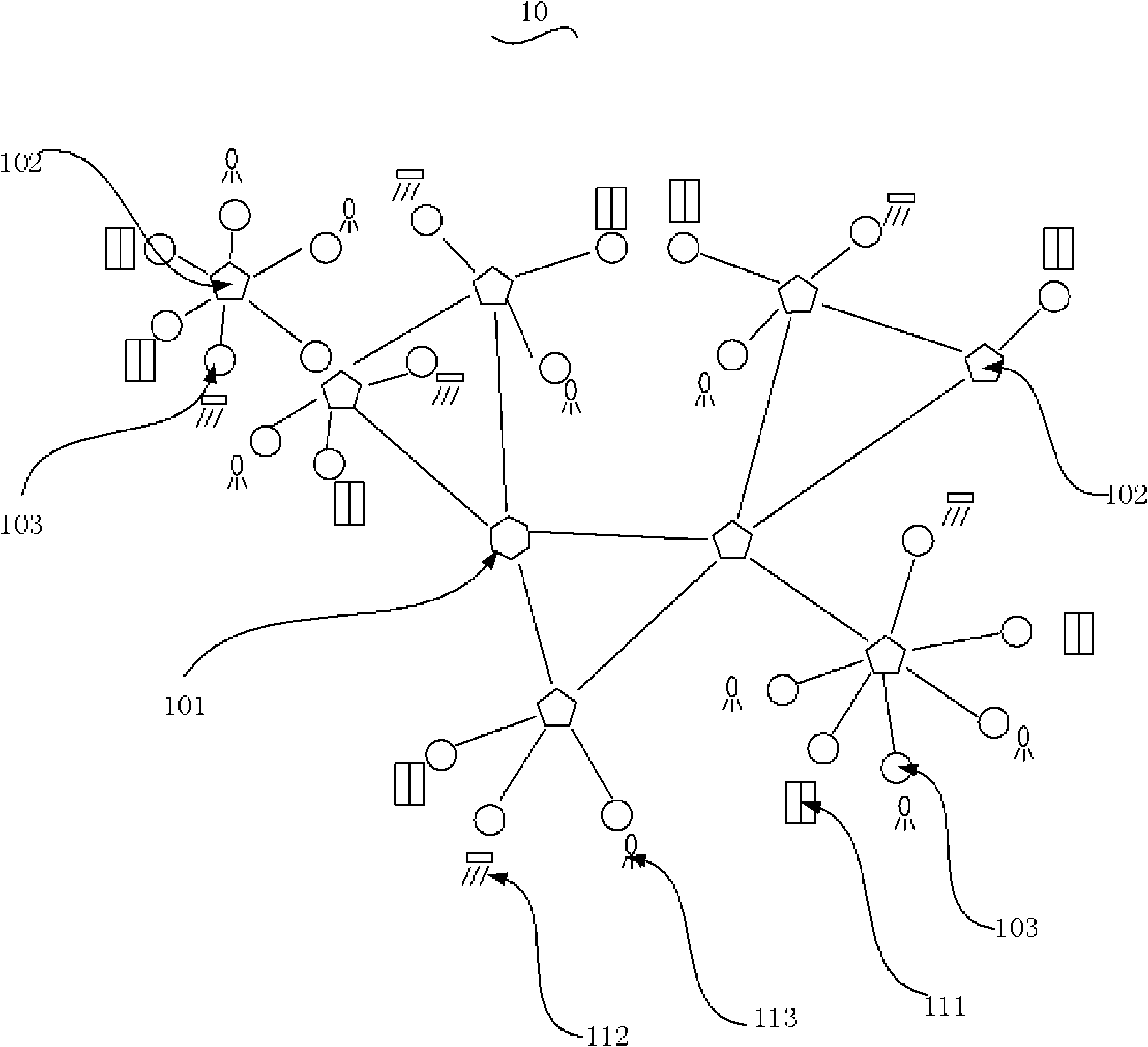
Intelligent building networking control system
InactiveCN101639695AReduce management costsGuaranteed real-timeEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesNetwork controlEngineering
The invention provides an intelligent building networking control method which comprises the following steps: arranging a detection sensor outside a building; arranging a stepped Zigbee network system in the building; arranging tenement equipment in the building; collecting weather signals outside the building and sending the weather signals to the Zigbee network system by the detection sensor; and sending out a command by the Zigbee network system to adjust the use condition of the tenement equipment. The invention has the advantages of adjusting the use condition of the tenement equipment according to actual weather conditions, scientifically realizing energy-saving management, meeting the requirement on normal and comfortable uses of people and reducing the management cost of staff. Inaddition, a network topological structure of a cluster connection mode guarantees the real time and the stability of a network.
Owner:SHENZHEN POLYTECHNIC
Detection of and responses to time delays in networked control systems
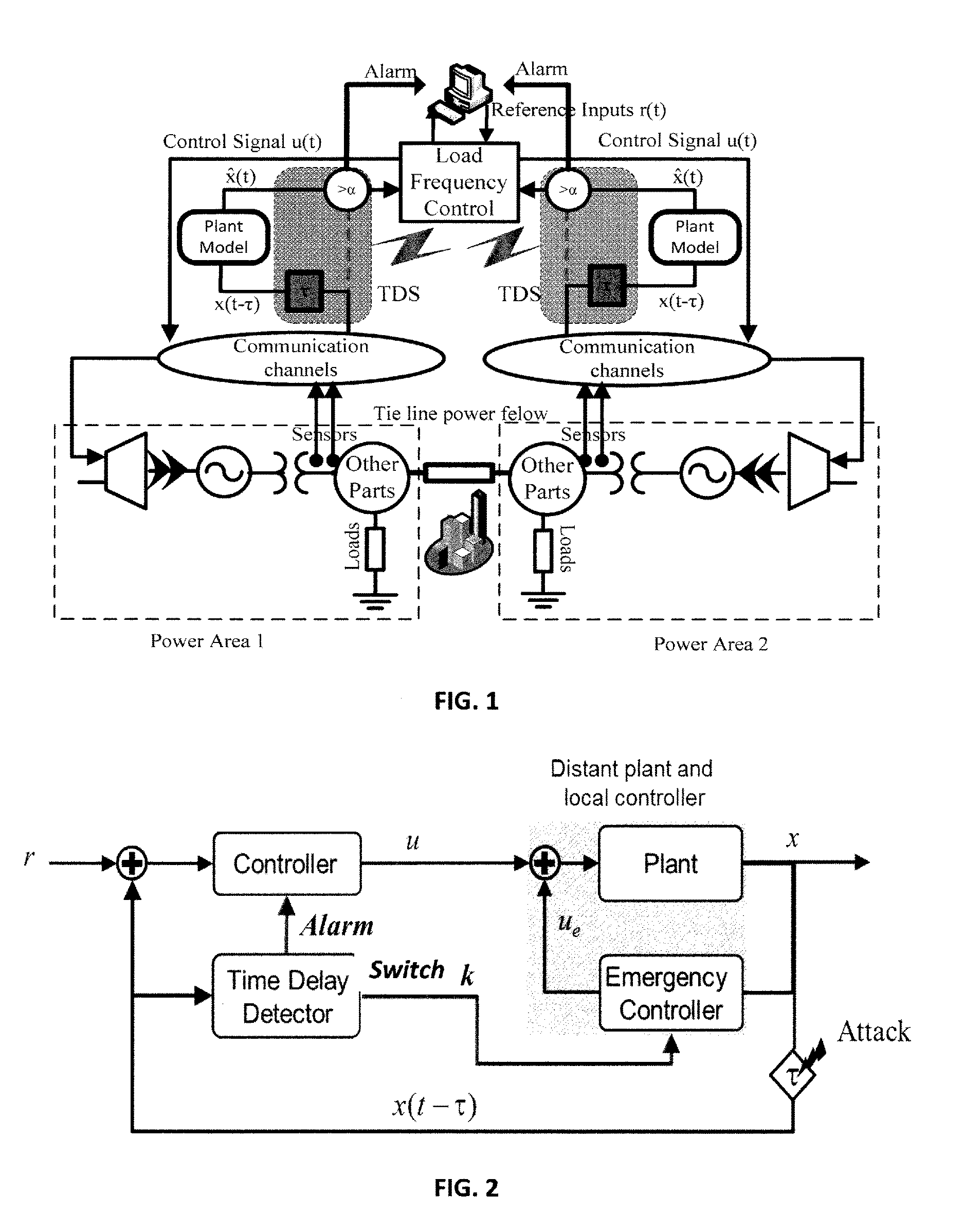
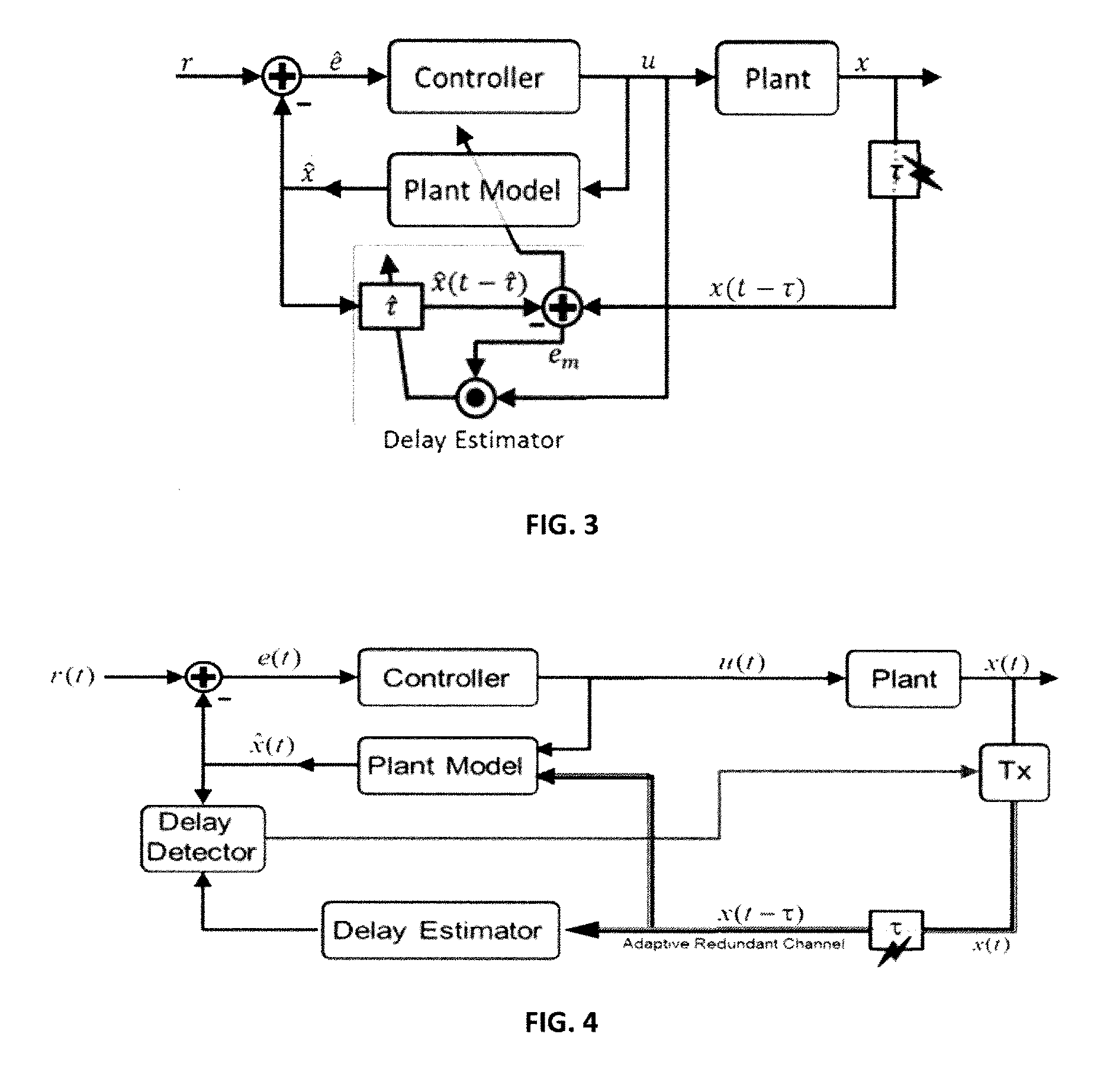
ActiveUS20170060102A1Improve adverse effectsProgramme controlAdaptive controlNetworked control systemTime delays
To ameliorate the detrimental effects of time delays, techniques and systems are disclosed for detecting time delays in a plant, facility, or environment (such as a power system) controlled by an NCS, and for providing more resilient control capabilities for adapting to the detected time delays. A time delay estimate can be determined by comparing the expected state of the plant, calculated from a plant model, with the state of the plant described by its telemetry data. Techniques for adapting to a time delay include: switching to an emergency controller and acting in accordance with a local reference model; sending adjusted control commands in accordance with an expected plant state; and instructing a transmitter to transmit subsequent communications packets over multiple redundant communication channels.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
System and method for controlling the access to a networked control system
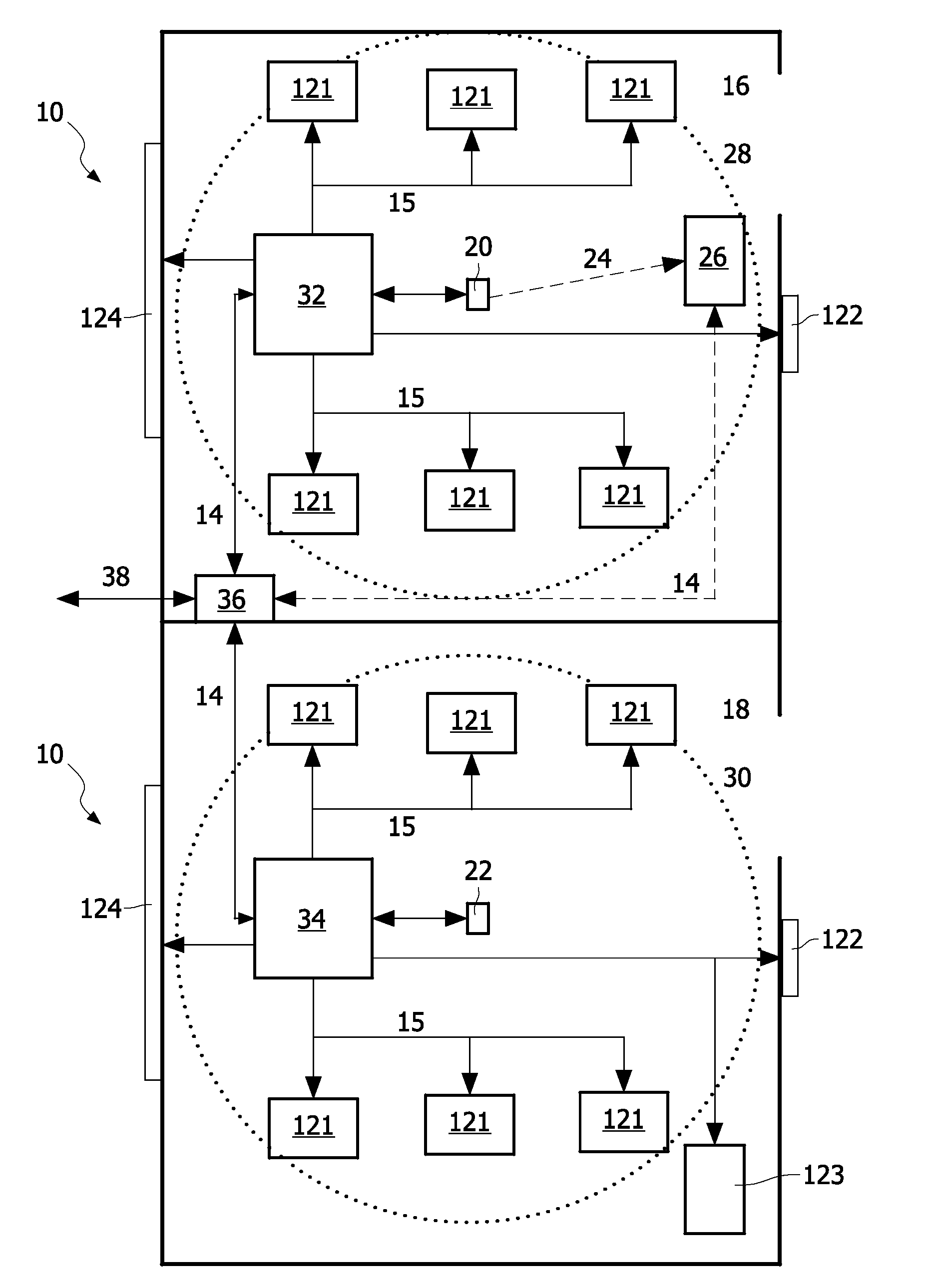
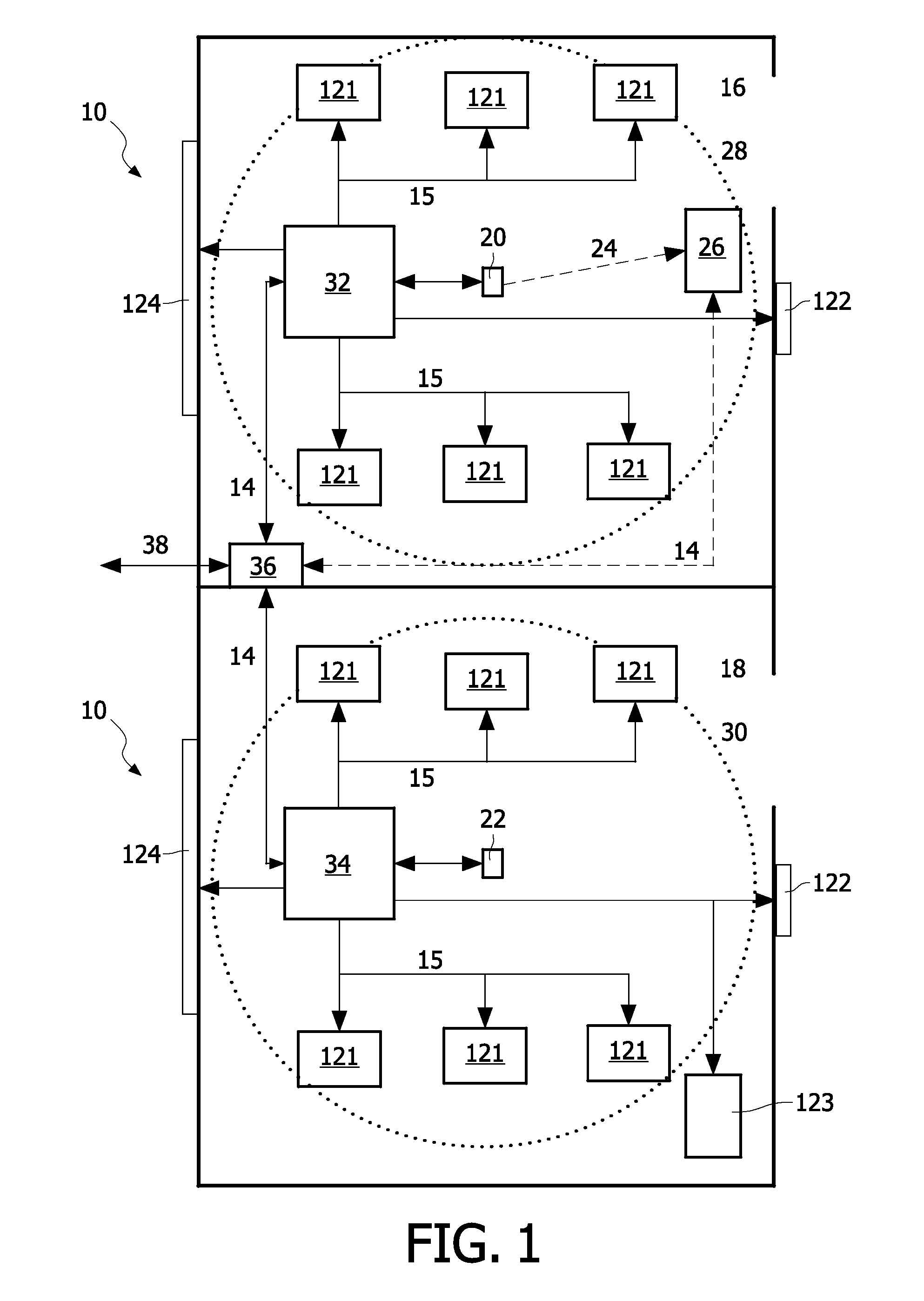
InactiveUS20120062360A1Firmly connectedEasy to controlElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsNetwork controlTransmission channel
The invention relates to controlling the access to a networked control system such as a lighting control system or a home control system. According to an embodiment of the invention, a system for controlling the access to a networked control system (10), whereindevices (121-124) of the networked control system are connected to the same network (14) and are assigned to the same delimited space (16, 18),a transmitter device (20, 22) transmits access information for the devices within the delimited space over a range restricted transmission channel (24, 28) differing from the transmission channel(s) of the networked control system and in a manner that substantially limits the reception of the access information to the delimited space, wherein the access information comprises an access identifier for obtaining access for controlling one or more of the devices in the delimited space, anda receiver device (26) receives the transmitted access information and controls a device assigned to the delimited space over the network (14) by using the access identifier contained in the received access information.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
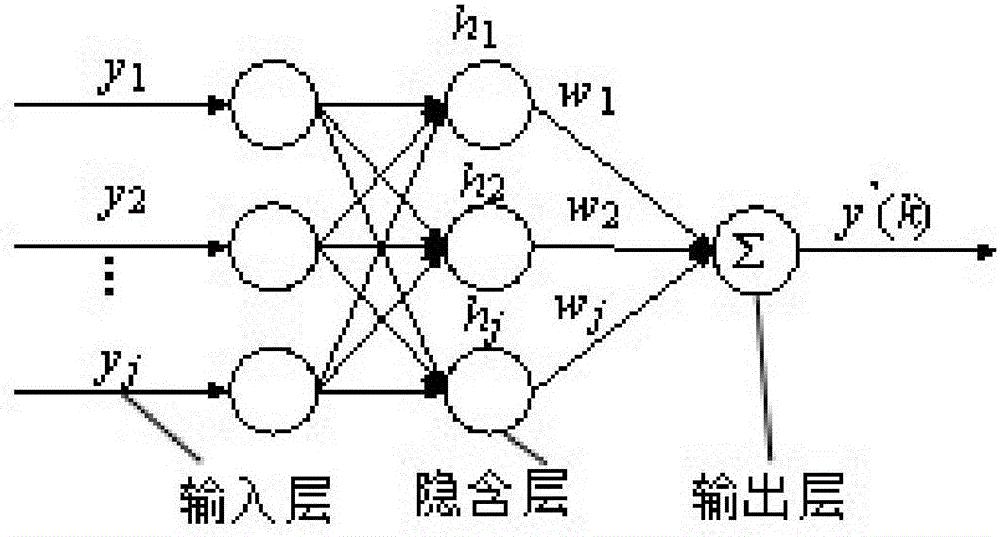
Networked control system fault detection method based on neural network prediction
ActiveCN106249599ASimple compositionSimple calculationAdaptive controlNetworked control systemNeural network system
The invention discloses a networked control system fault detection method based on neural network prediction, which comprises four steps of RBF neural network system building, system fault detection function building, system stability judgment and operation and system fault judgment and operation function building. The system building and operation process is simple, the operation efficiency and the operation precision are relatively high, an improved RBF neural network prediction controller is adopted to effectively predict system output data information, and thus, bad influences on the system by packet loss can be effectively cancelled, errors are smaller and training times are reduced through adjusting learning efficiency on the basis of adopting feedback correction on the obtained predicted output value for correction, and better convergence and quicker prediction speed can be obtained. Meanwhile, when fault happens to the system, happening of the fault can be quickly detected according to a designed fault observer and a judgment criterion.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
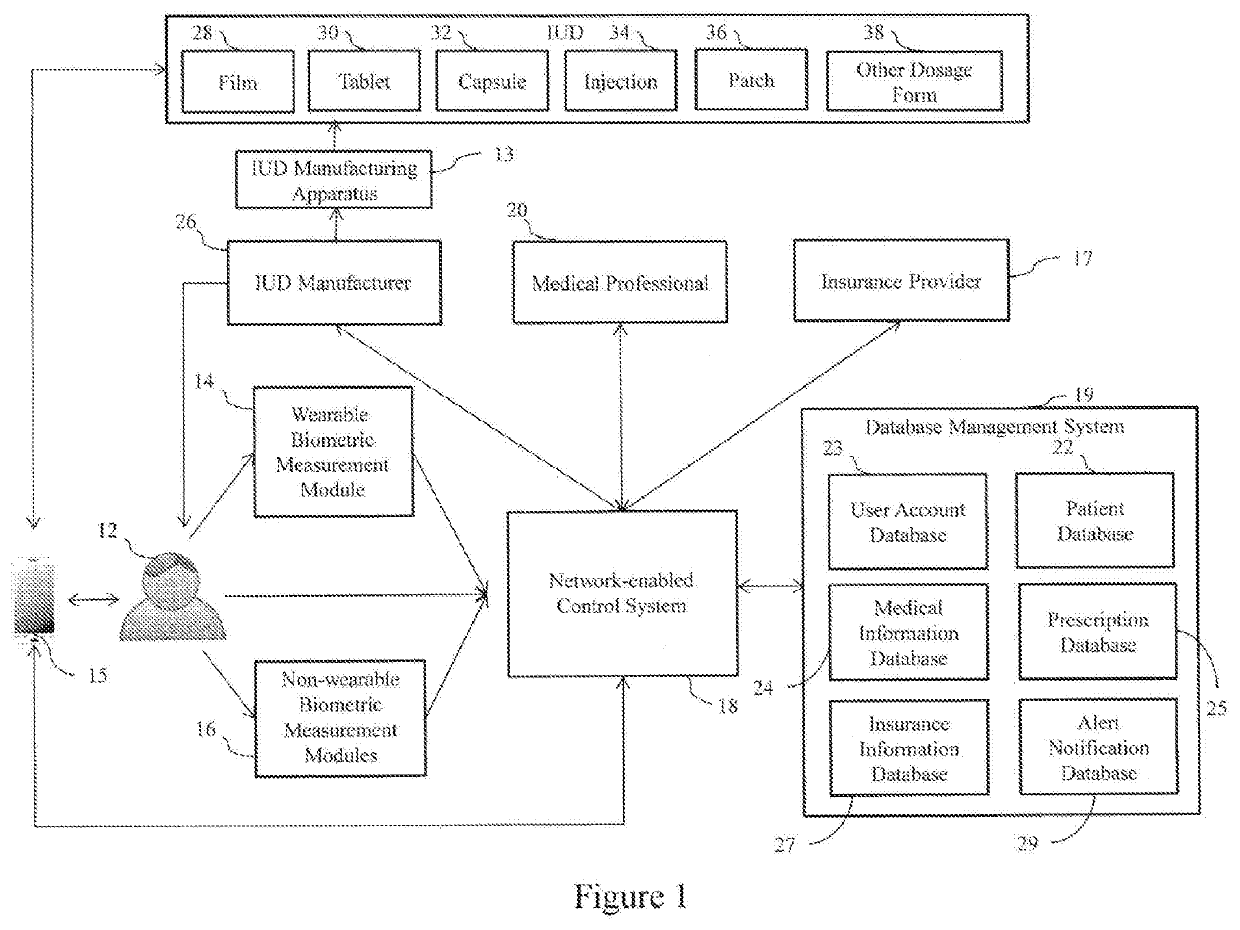
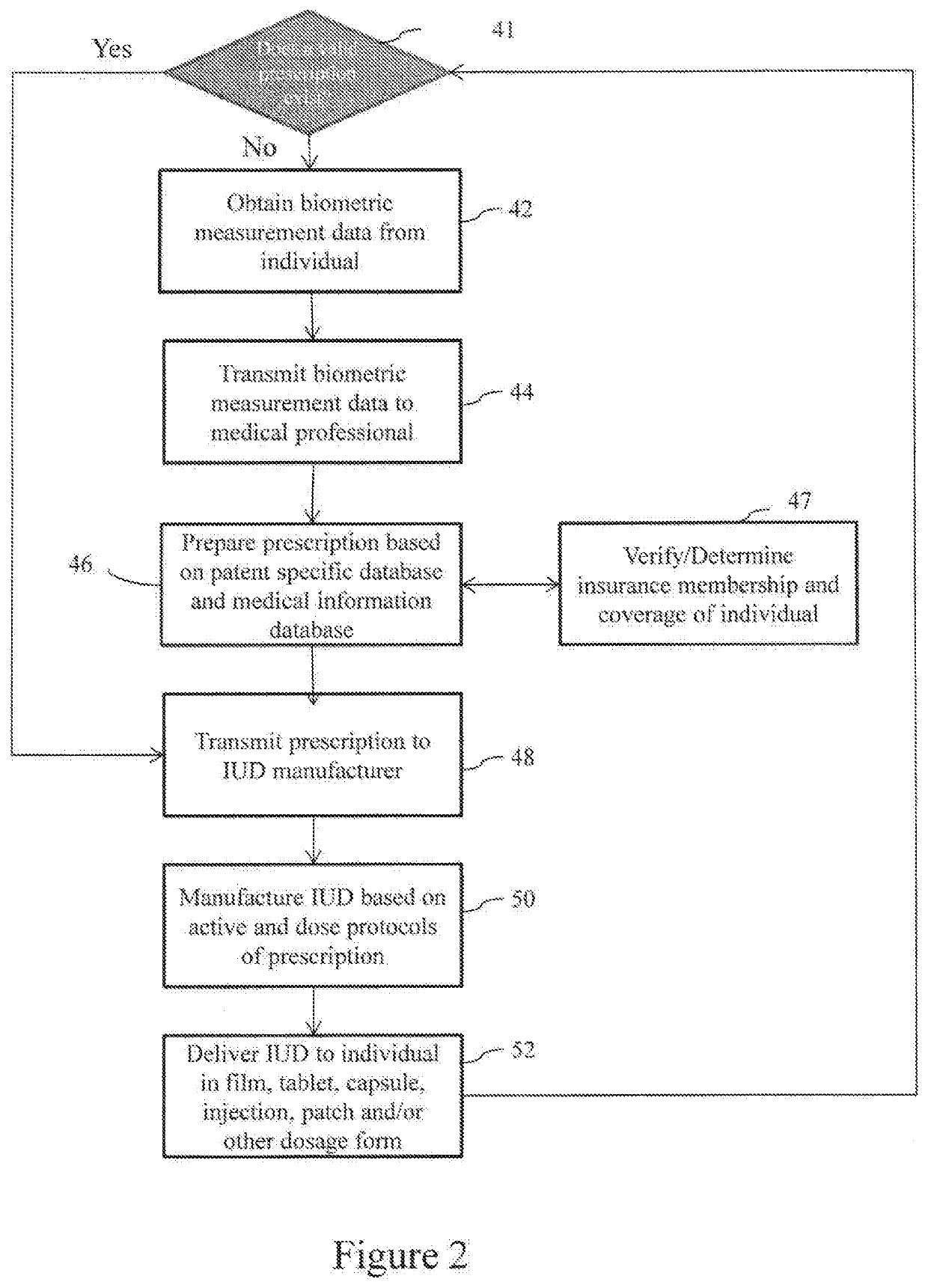
System and method for making personalized indvidual unit doses containing pharmaceutical actives
Systems and methods for making and delivering personalized, medically prescribed pharmaceuticals to an individual patient are described. Individual unit doses (IUDs) of medicine may be prepared specific to the individual in need of same, by using a system, which includes a networked control system in combination with manufacturing assemblies specific to the IUDs and delivering the medicine to the patient directly from the manufacturer.
Owner:AQUESTIVE THERAPEUTICS INC
Tracking control method of networked control systems based on predictive compensation
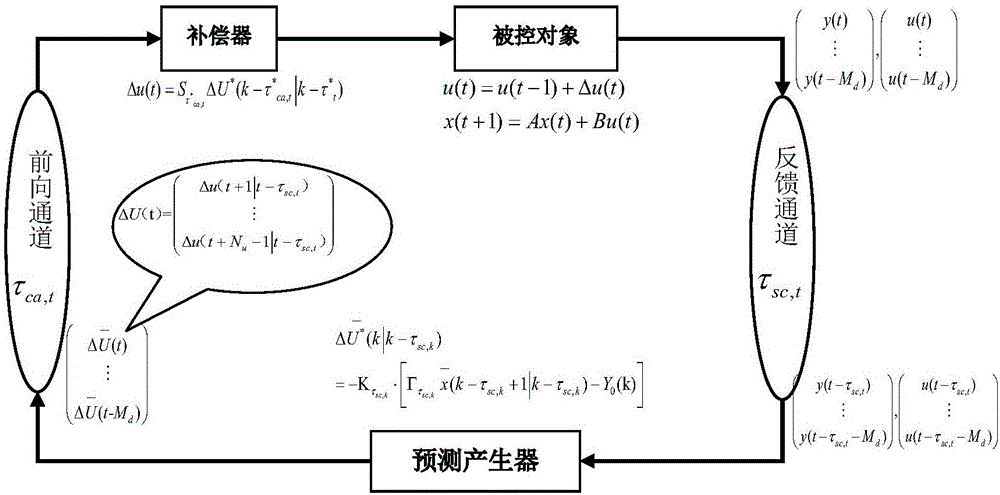
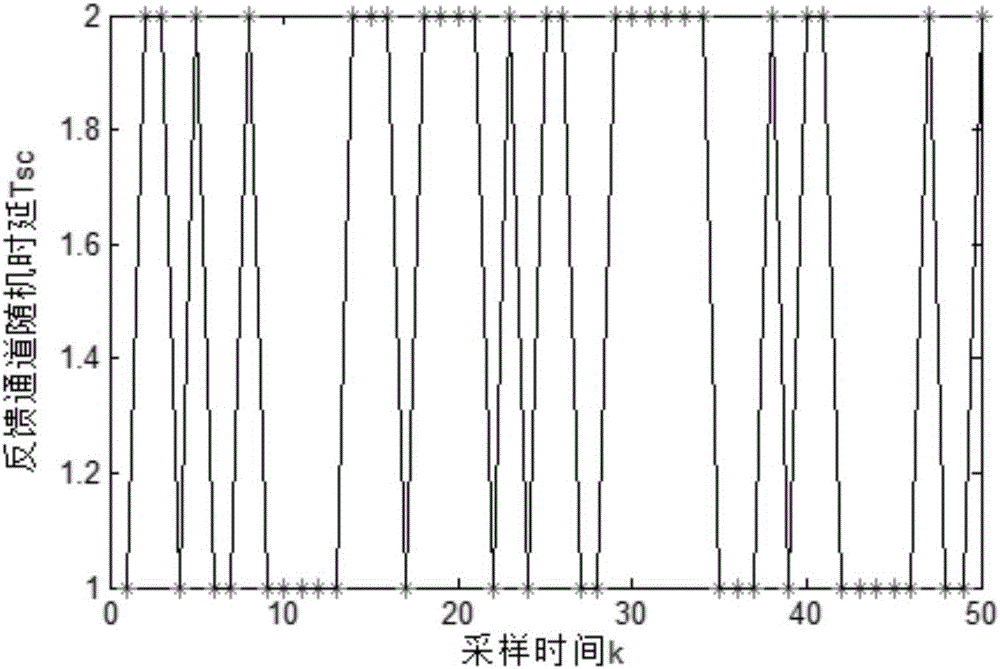
ActiveCN106209474AImprove the compensation effectShorten the forecast step sizeData switching networksSynchronising arrangementCompensation effectPredictive controller
This invention discloses a tracking control method of networked control systems based on predictive compensation. A network predictive controller consists of a predictive generator and a time delay compensator; a control increment sequence outputted by the network predictive generator at time k is as shown in the description; and, the control increment of the time delay compensator at time t is as shown in the description. The method reduces the predictive step length at the cost of introducing a slight prediction error, and improves the compensation effect of the predictive controller to the network time delay; and, compared with the traditional network predictive control, the method is easier to be realized.
Owner:上海牛巨微网络科技有限公司
Random fault detection method of networked control system with packet loss
ActiveCN107272660AReduce conservatismProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringLyapunov stabilityPacket loss
The invention discloses a random fault detection method of a networked control system with packet loss. The method, which takes into account the fact that a networked control system has the problems of random packet loss, quantization error and random faults, includes the following steps: building a model of a networked control system with random faults; building a model of a fault detection filter; introducing a residual evaluation mechanism to detect whether there is a fault; obtaining sufficient conditions for the exponential stability in mean square of an augmented system and the existence of a fault detection filter through the Lyapunov stability theory and a linear matrix inequality analysis method; using a Matlab LMI tool kit to solve the optimization problem, and giving optimal parameters (as shown in the description) of the fault detection filter; and judging whether there is a fault according to the established residual mechanism. The method takes into account the fact that a fault occurs randomly and the occurrence probability of faults satisfies the Bernoulli distribution. The technical scheme is suitable for general fault detection methods. The conservative property is reduced.
Owner:西安四向互联网络科技有限公司
Network control system co-simulation method based on NS3 and MATLAB
ActiveCN110457747AEfficient and realistic simulationTotal factory controlSpecial data processing applicationsOperational systemMATLAB
The invention discloses a network control system co-simulation method based on NS3 and MATLAB. The method comprises the following steps: designing an overall scheme of a networked control system co-simulation platform; determining a collaborative simulation platform composition module of the networked control system and determining a collaborative simulation platform data exchange and transmissionscheme; establishing running environments of two kinds of simulation software in a linux operating system; designing a time synchronization scheme of the networked control system collaborative simulation platform; wherein the collaborative simulation system is a simulation system with strict requirements for real-time performance and time sequence. Two simulators need to be synchronously propelled for execution. Three collaborative simulation time synchronization schemes are designed, two of the three collaborative simulation time synchronization schemes are selected to be realized, the design of a synchronous interaction model is improved, then, each module program of NS3 is designed, an NS3 simulation script is designed, and finally, each module program of MATLAB / Simulink is designed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
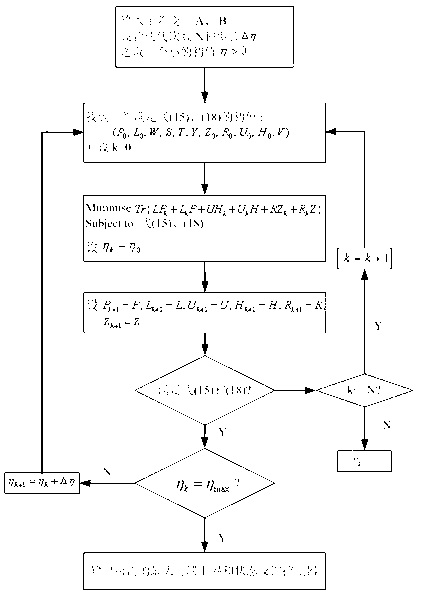
Non-fragile dissipative filter method implemented by networked control systems
ActiveCN106227700AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove performance indicatorsComplex mathematical operationsNetworked control systemLyapunov stability
The invention discloses a non-fragile dissipative filter method implemented by networked control systems. The non-fragile dissipative filter method includes building networked filter error system models under the condition that the availability of delay and packet loss of the networked control systems and perturbation of parameters of filters is taken into consideration; constructing Lyapunov functions; acquiring sufficient conditions for the availability of mean square exponential stability of networked filter error systems and non-fragile dissipative filters by the aid of Lyapunov stability theories and linear matrix inequality analysis processes; solving the parameters of the filters by the aid of Matlab LMI tool boxes; providing parameter matrixes (as shown in the specifications) of the non-fragile dissipative filters. The non-fragile dissipative filter method has the advantages that sensor-filter packet loss and delay conditions are taken into consideration, Bernoulli distribution requirements can be met by the probability of packet loss and delay, accordingly, the non-fragile dissipative filter method has practical significance and is applicable to general dissipative filter including H8 filter, and the conservative property of designs of non-fragile filters can be lowered.
Owner:嘉兴企远网信息科技有限公司
Deadband scheduling method applicable to networked control systems
InactiveCN102710515AControl Performance Quality AssuranceEfficient use ofData switching networksStable stateNetwork packet
The invention relates to a deadband scheduling method applicable to network control systems and belongs to the technical field of networked control systems (NCS). The deadband scheduling method is characterized in that the deadband scheduling method aims to ensure that the output of a plurality of NCSs sharing a same network is satisfied to enter plus or minus 5 percent or plus or minus 2 percent of fluctuation range of a steady-state value of each system, a threshold value delta of each NCS deadband is selected as 0.05 or 0.02, a deviation rate ec(k) threshold value gamma are selected as 0.025, and whether a controller node needs to transmit a data pocket to an actuator node is determined through taking e(k) and ec(k) as double constraints; when the |e(k)| is less than Delta, and the |ec(k)| is more than Gamma, each system is in a stable state, and the controller node is not required to transmit a new data packet to the actuator node through the shared network; and when the |e(k)| is more than or equal to delta or the |ec(k)| is more than or equal to gamma, each system is in a transition process, the controller node is required to transmit a new data pocket to the actuator node through the shared network. With the adoption of the deadband scheduling method, network bandwidth resources can be saved, the bandwidth utilization rate is improved, and meanwhile, the systems not only can stabilize, but also can satisfy the steady-state quality requirements.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
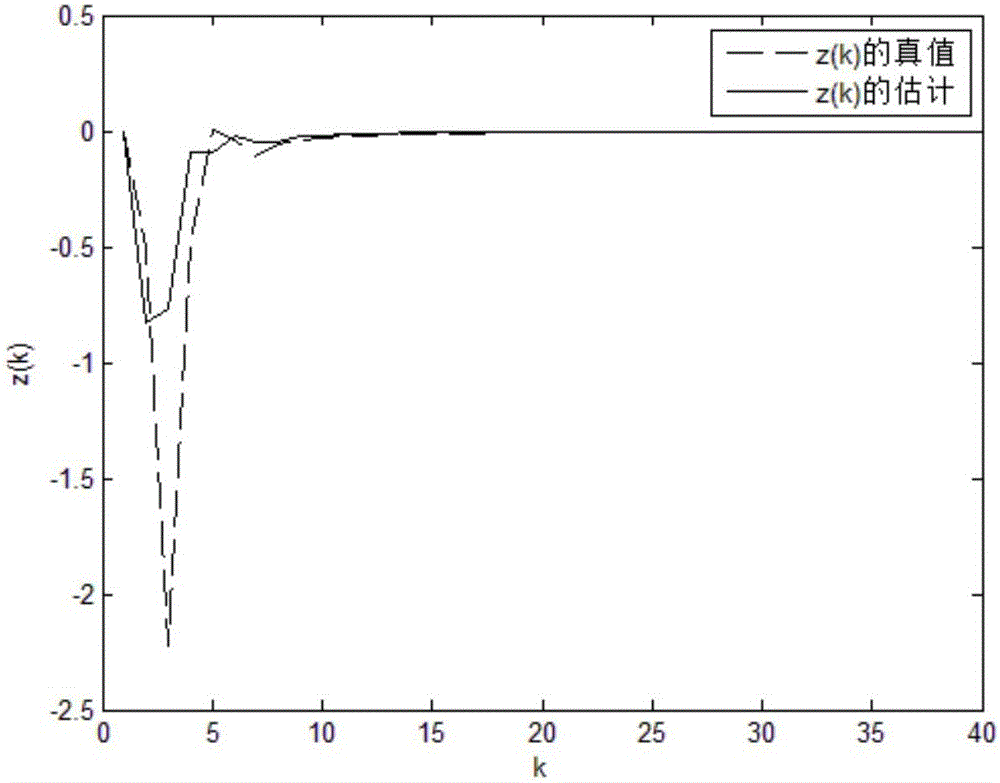
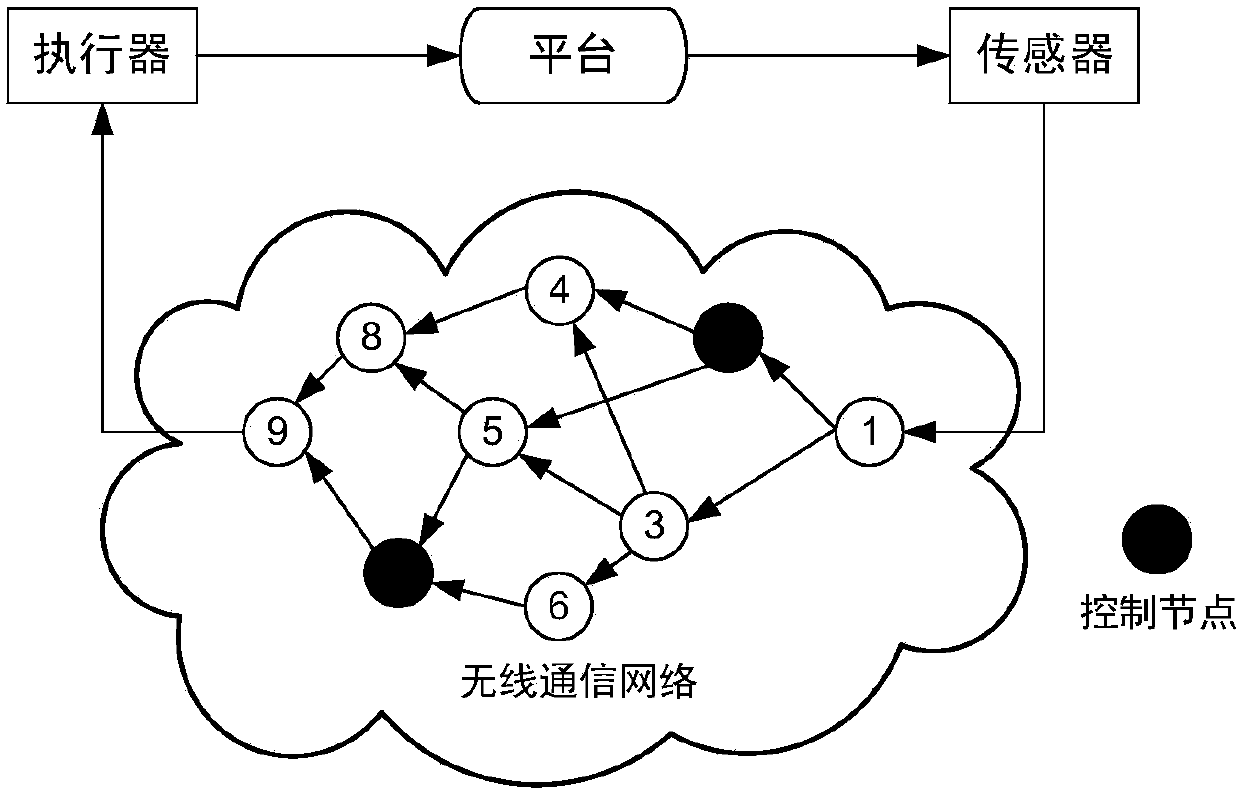
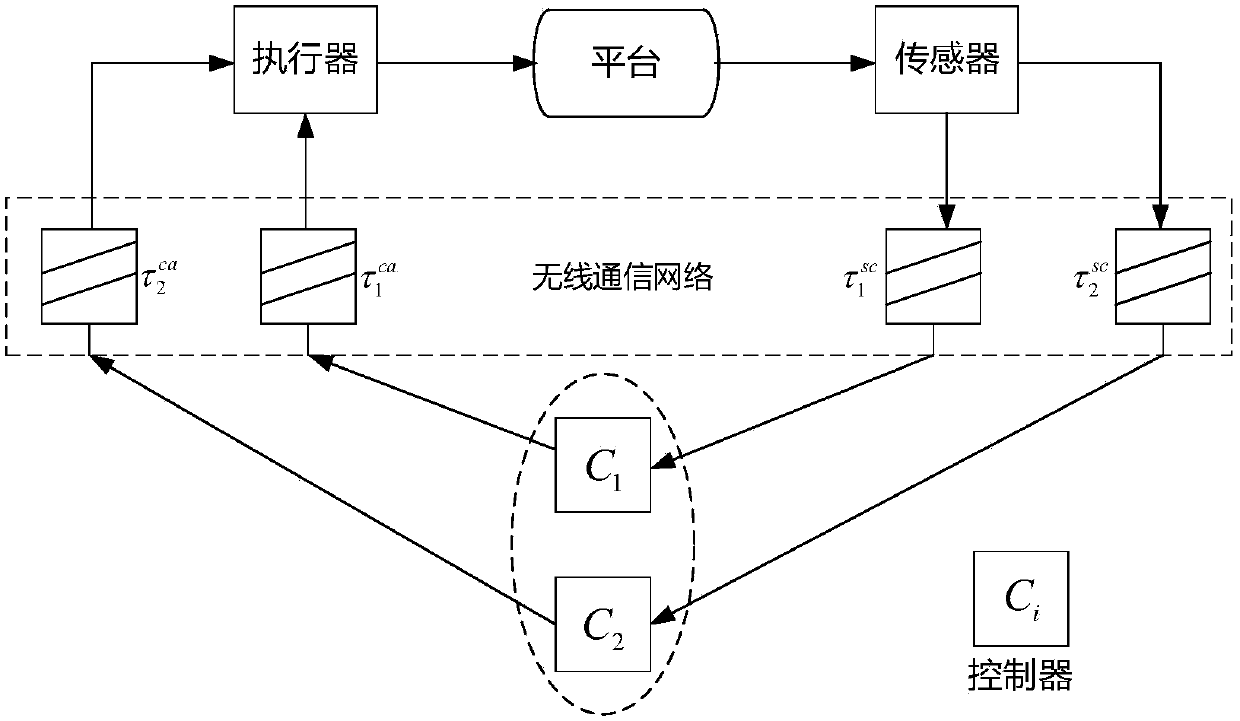
Multi-controller optimal state estimation control strategy design method based on Kalman filtering
ActiveCN108153259ATotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlClosed loopInformation integration
The invention discloses a multi-controller optimal state estimation control strategy design method based on Kalman filtering, and the method comprises the steps: firstly carrying out the system modeling of a wireless networking control system, and analyzing the impact on the closed-loop control of the system when there is network transmission time delay in the wireless networking control system; secondly carrying out the research of the information fusion of distributed controllers, and constructing a network control optimization problem based on double distributed controllers; finally carrying out the Kalman filtering analysis of the platform state information received by the two controllers through employing a Kalman filtering algorithm, solving an optimal state estimation control strategy through an iteration regression method, and verifying the feasibility through a simulation experiment. The method solves a problem of an optimal state estimation control strategy of the distributedcontrollers when there is the transmission time delay in a wireless communication network and the accurate platform state information cannot be obtained because of the noise interference, thereby achieving a purpose of improving the stability of the networking control system and reducing the system loss through the cooperative control of the distributed controllers.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
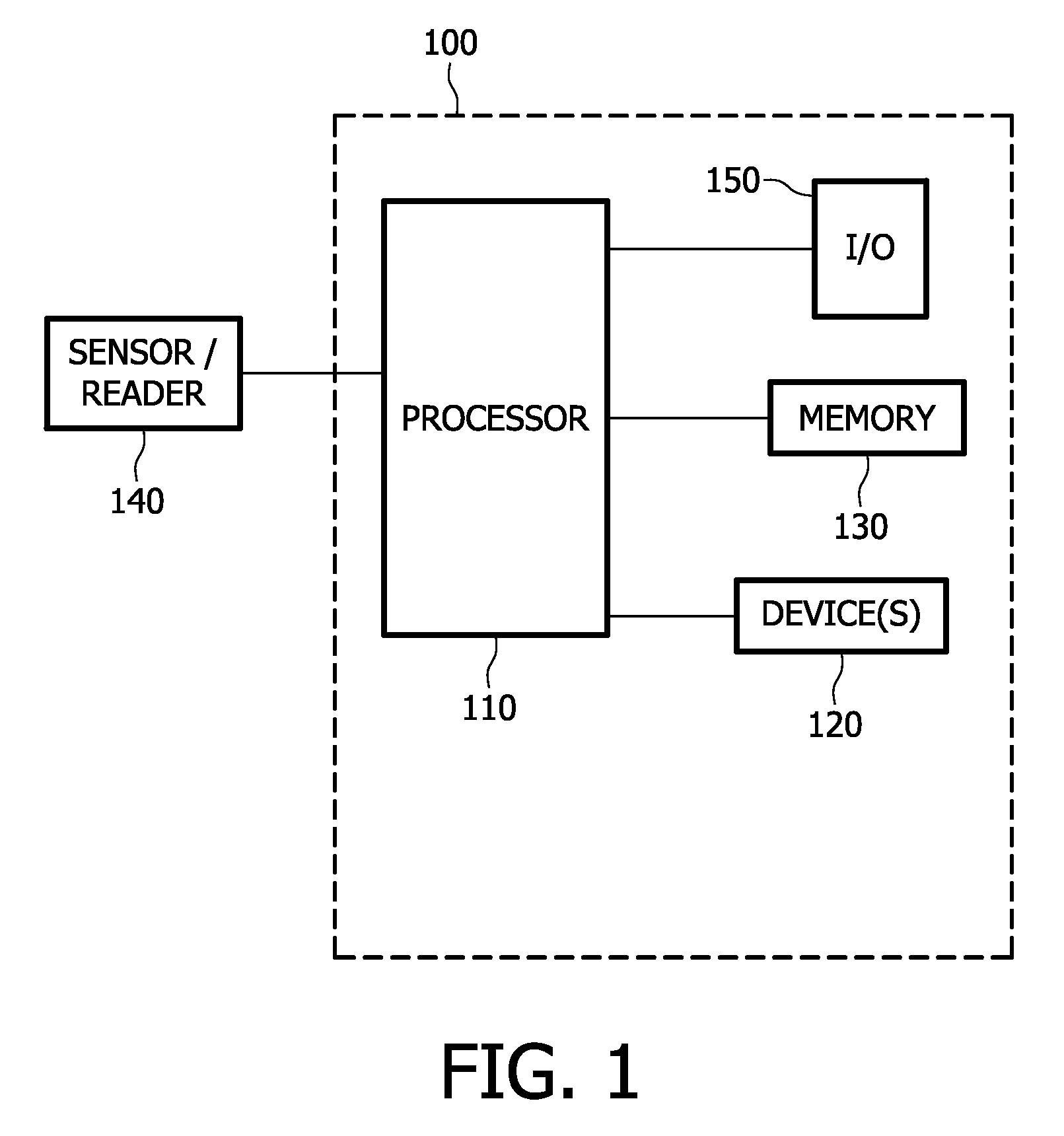
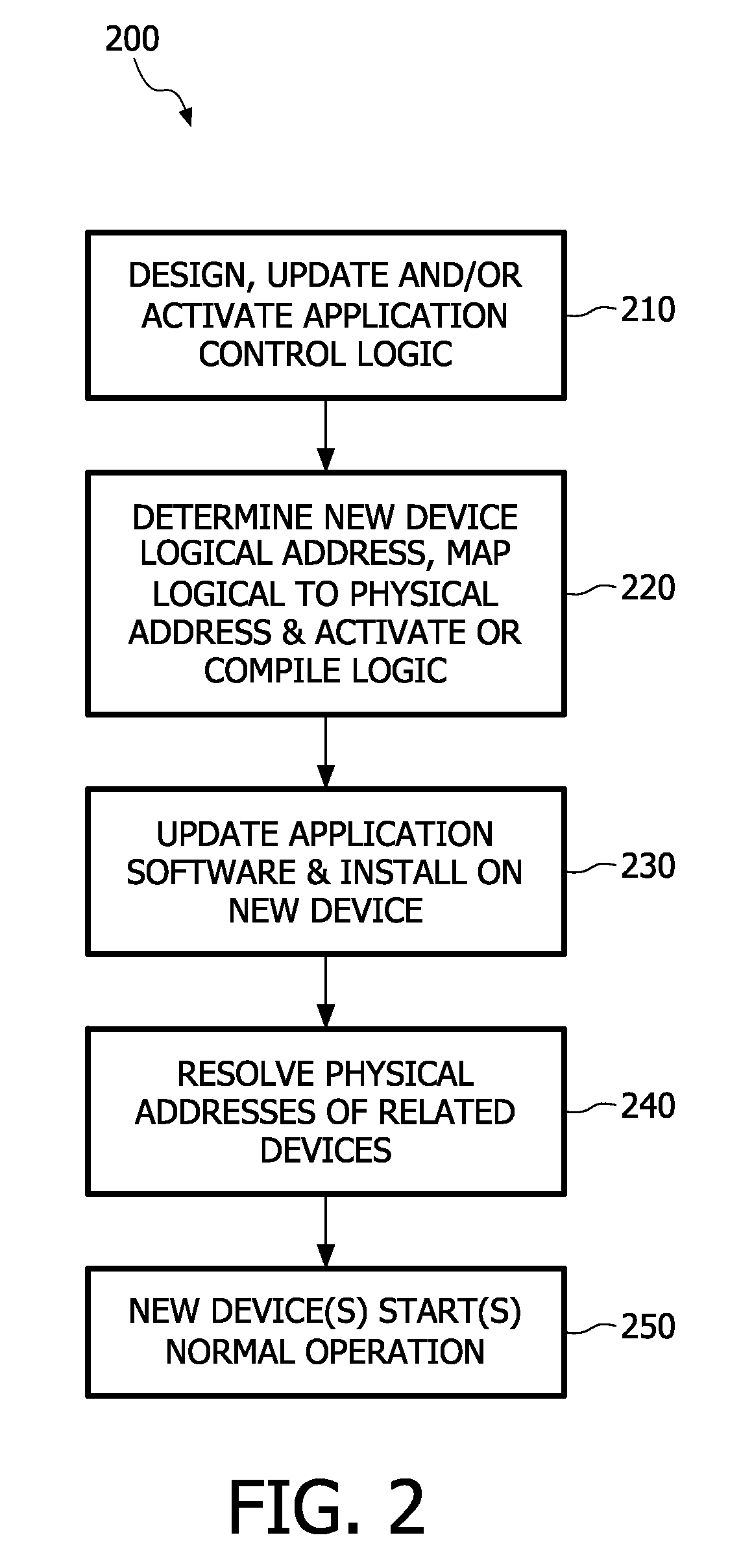
Networked control system using logical addresses
ActiveUS8218547B2Overcome disadvantagesLocation information based serviceNetwork connectionsDevice typeNetwork control
Networked control systems and methods include a plurality of devices connected to a network. At least one device has a logical address that includes a device type and a device location in an environment of the device in a user readable and understandable format, such as English or other languages. The system further includes a processor connectable to the network and configured to execute control logic using the logical addresses. A memory is provided for storing a mapping from the logical address to a physical network address of the device.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com