Multiplicative noise removal method for image
A multiplicative noise and image technology, applied in the field of digital image processing, can solve problems such as poor adaptability and loss of details, and achieve the effect of reducing workload and strengthening removal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
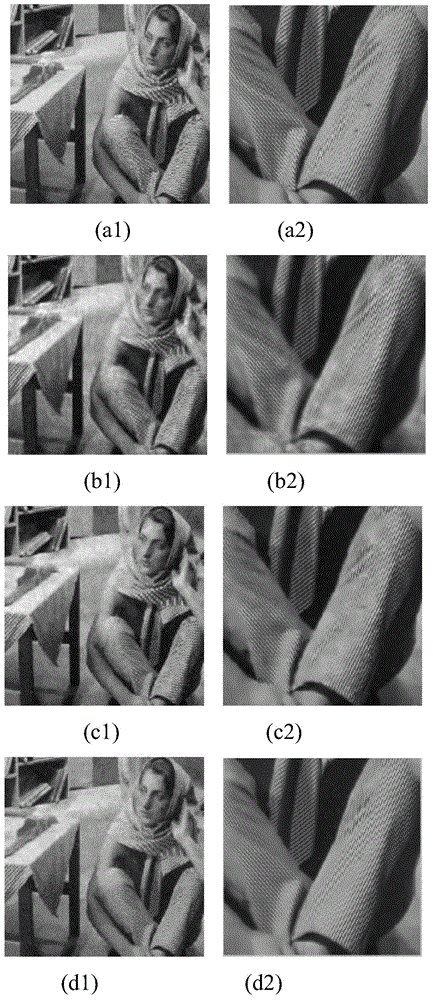
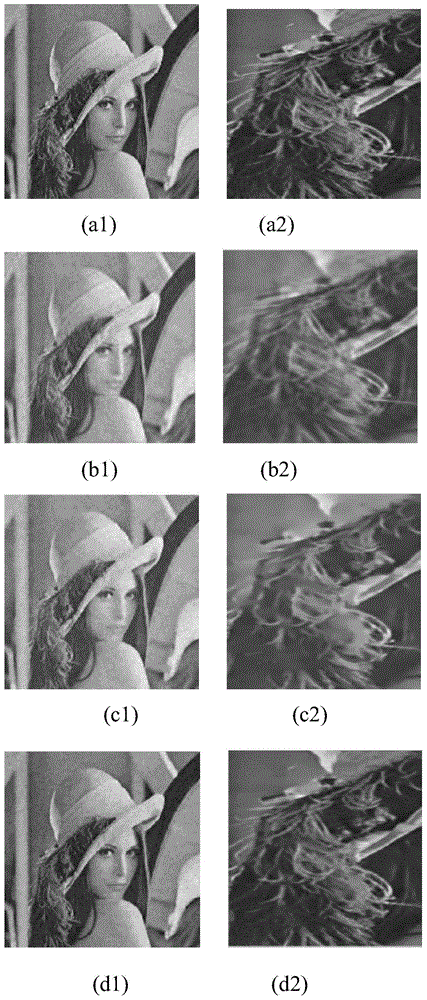
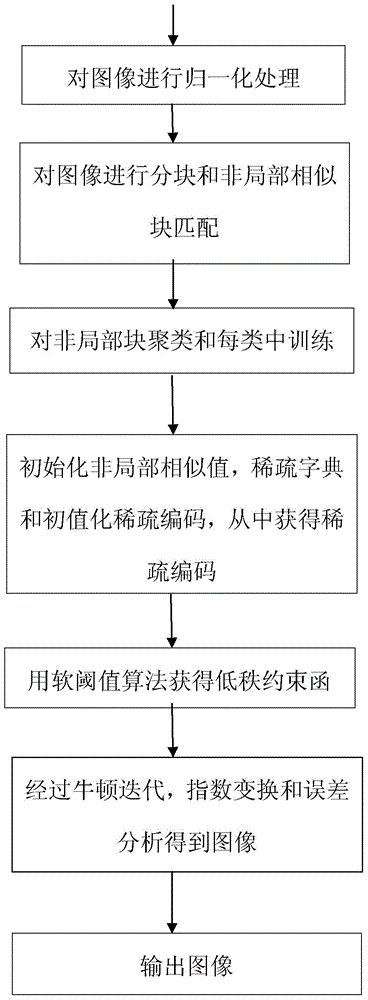
[0029] An image multiplicative noise removal method, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0030] Step 1: Perform normalized preprocessing on the original image with multiplicative noise, that is, the noisy image, that is, perform logarithmic transformation on the noisy image.
[0031] In order to simplify the calculation amount, the image is normalized, and the multiplicative noise is converted into additive noise through logarithmic transformation, that is, the noise is removed in the logarithmic domain. The logarithmic transformation model is Where y is the observed image, x is the denoised image to be obtained, v is the multiplicative noise obeying the Gamma distribution, f is the observed image after logarithmic transformation, and z is the denoised image after logarithmic transformation The ideal image of w is the logarithmically transformed noise.
[0032] Step 2: Divide the image in the logarithmic domain into blocks, and then perform non-local si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com