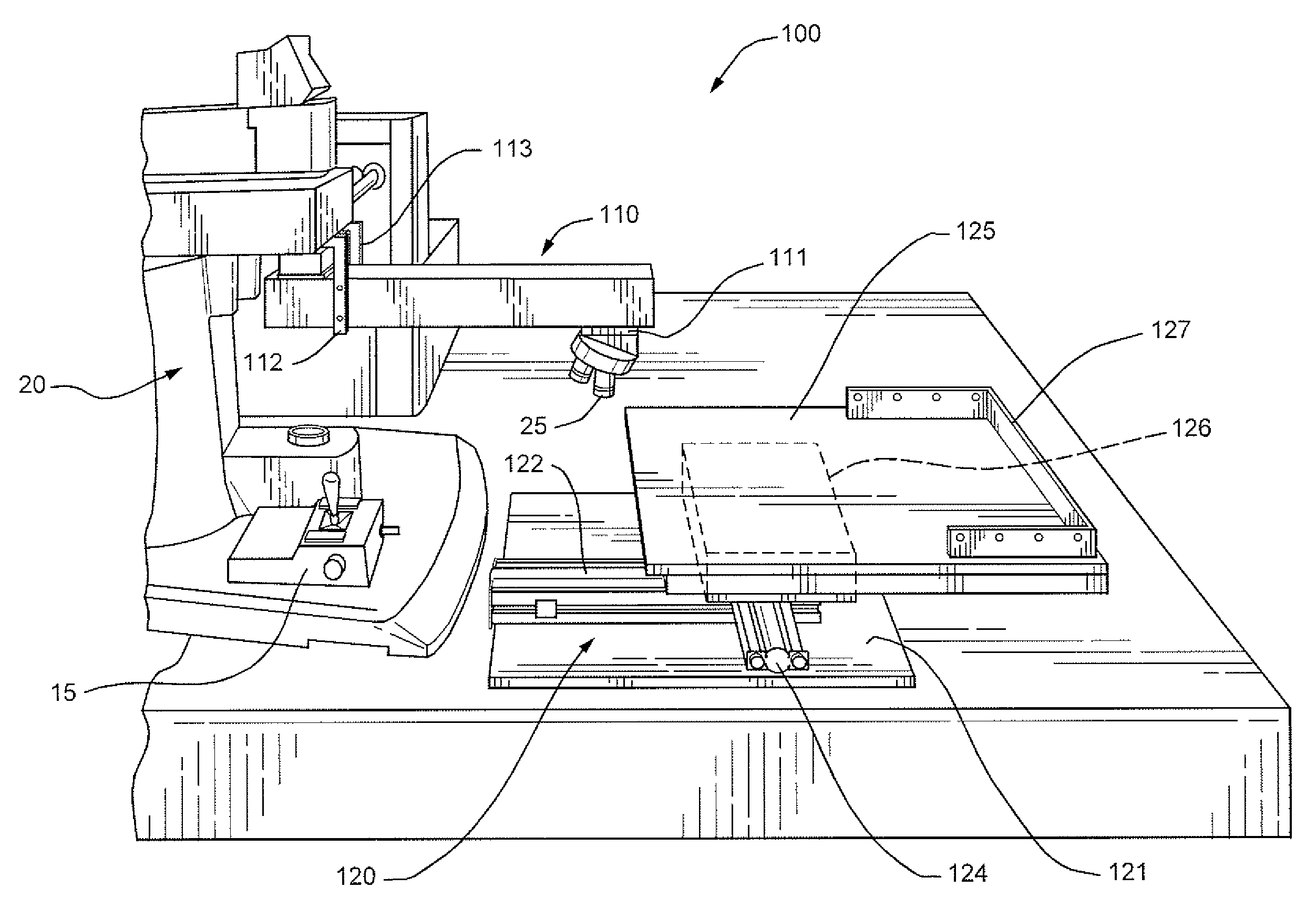
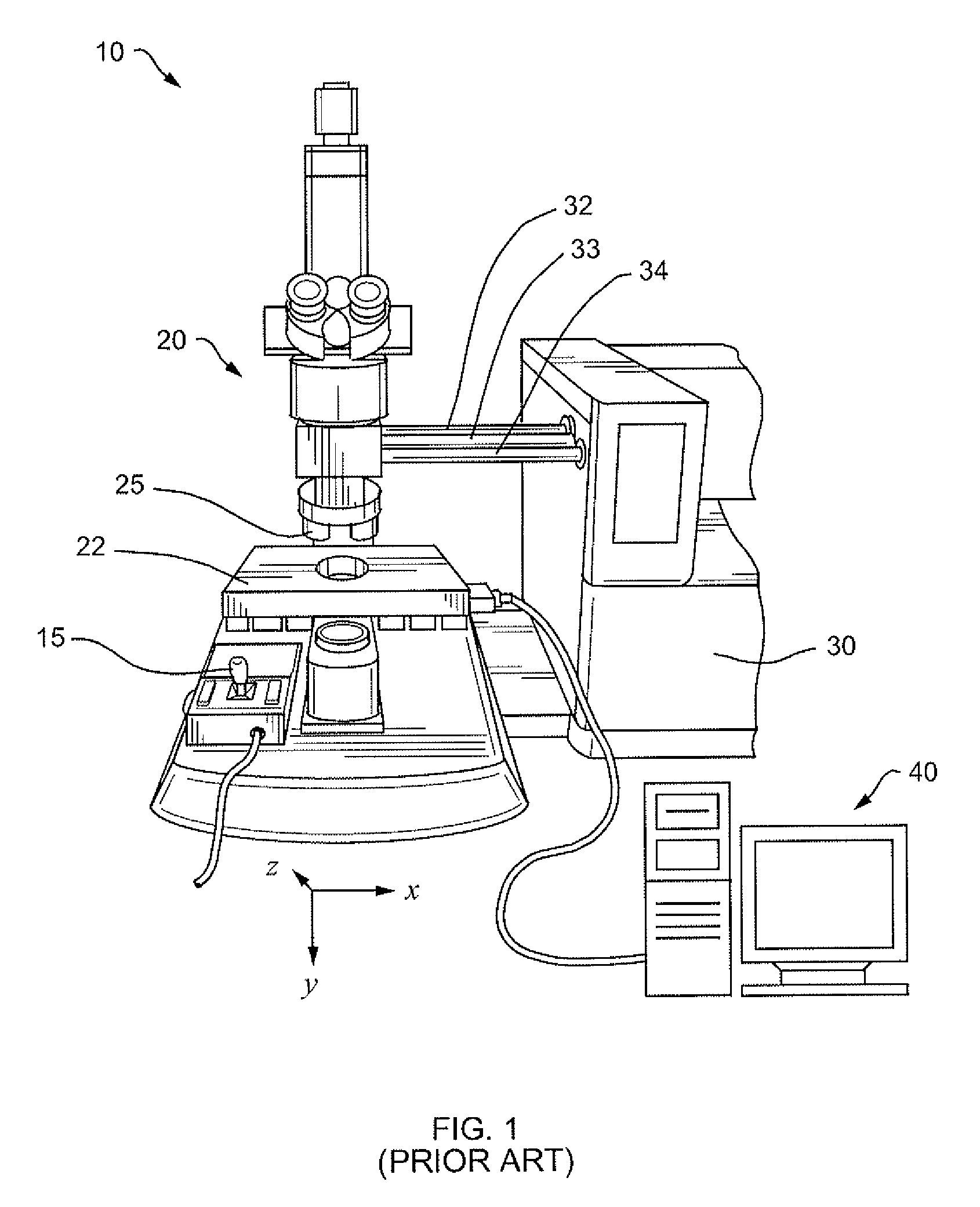
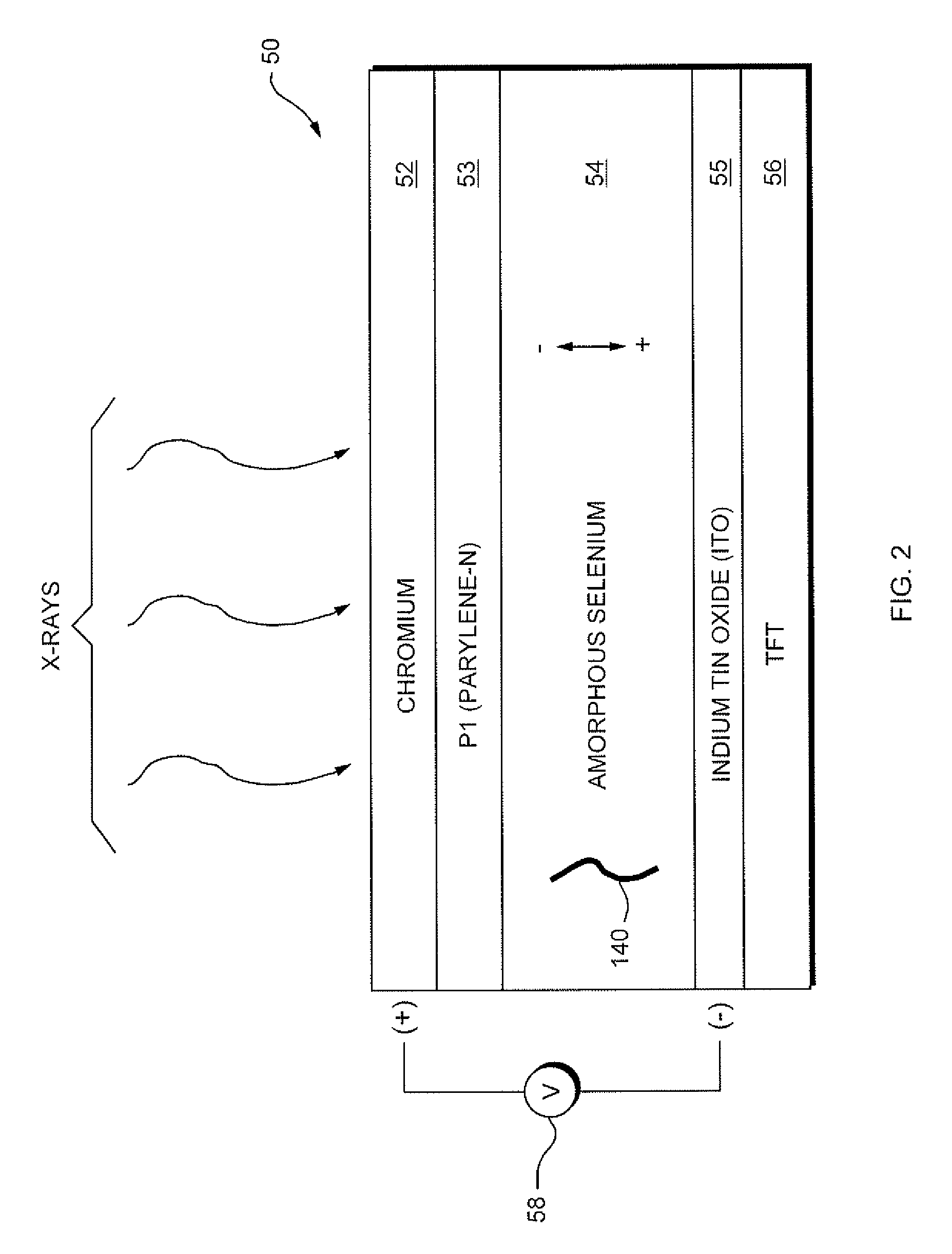
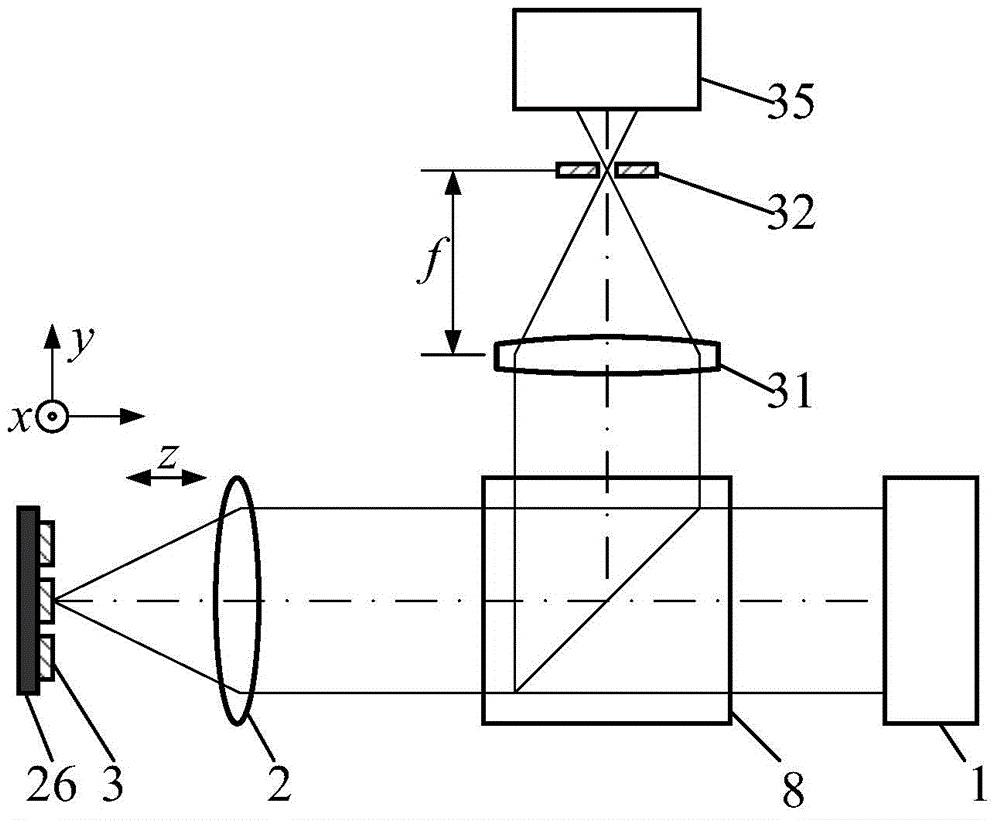
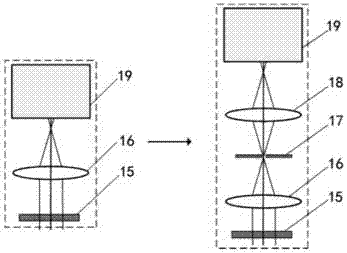
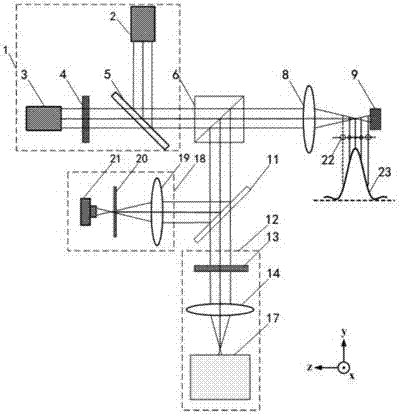
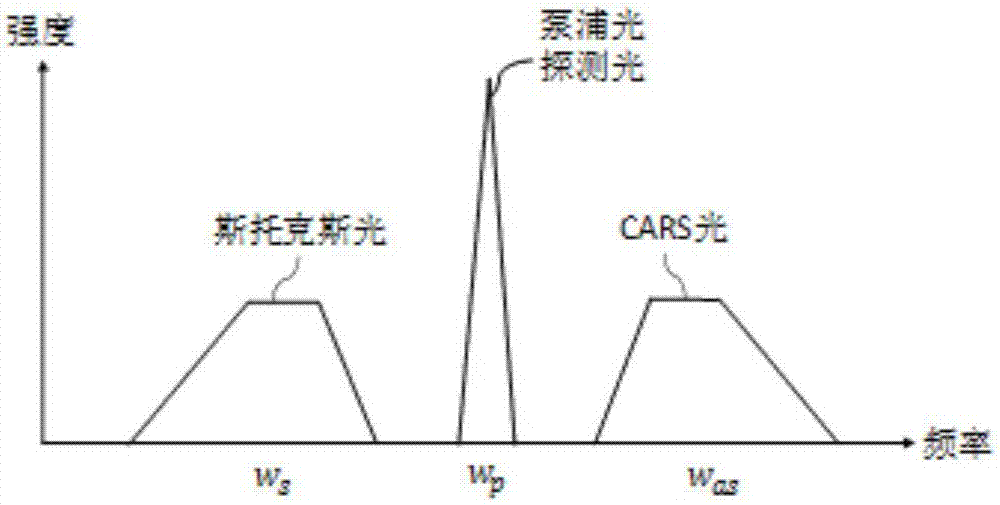
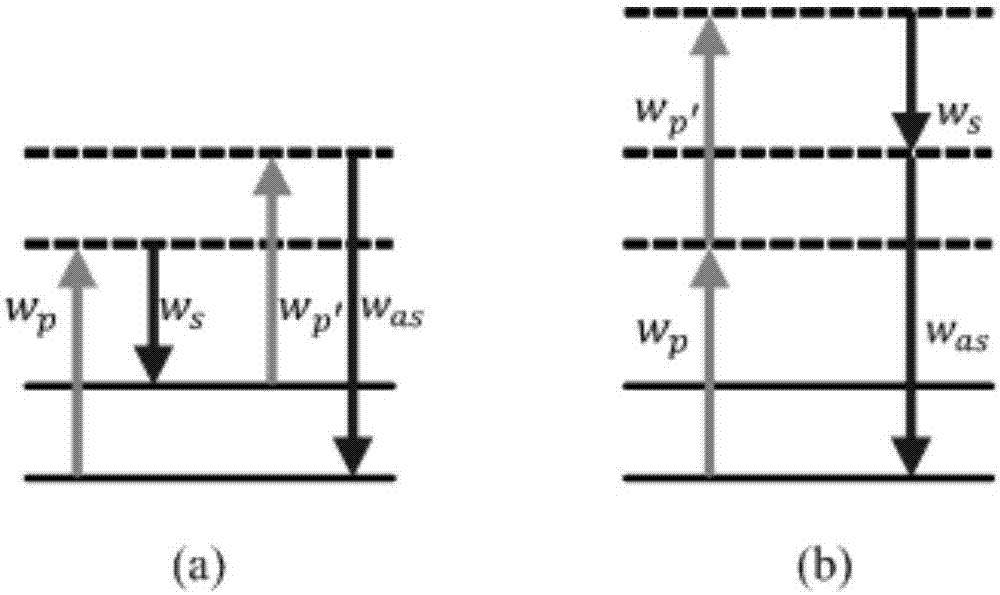
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Micro spectroscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Micro-FTIR Spectroscopy. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) is an important tool in the process of identification of unknown material. FTIR provides specific information about chemical bonding and molecular structure, making it useful for analyzing organic materials and certain inorganic materials.
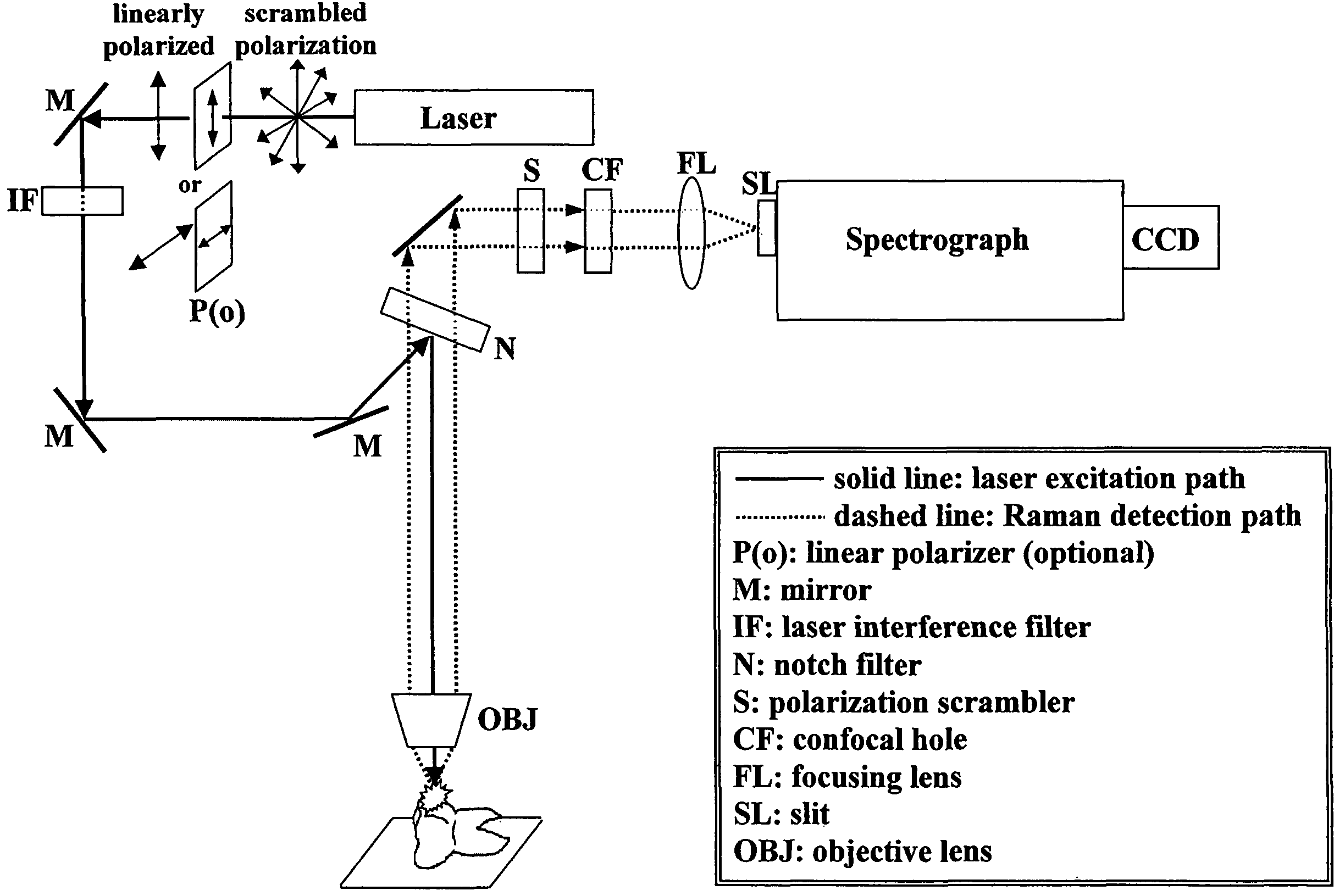
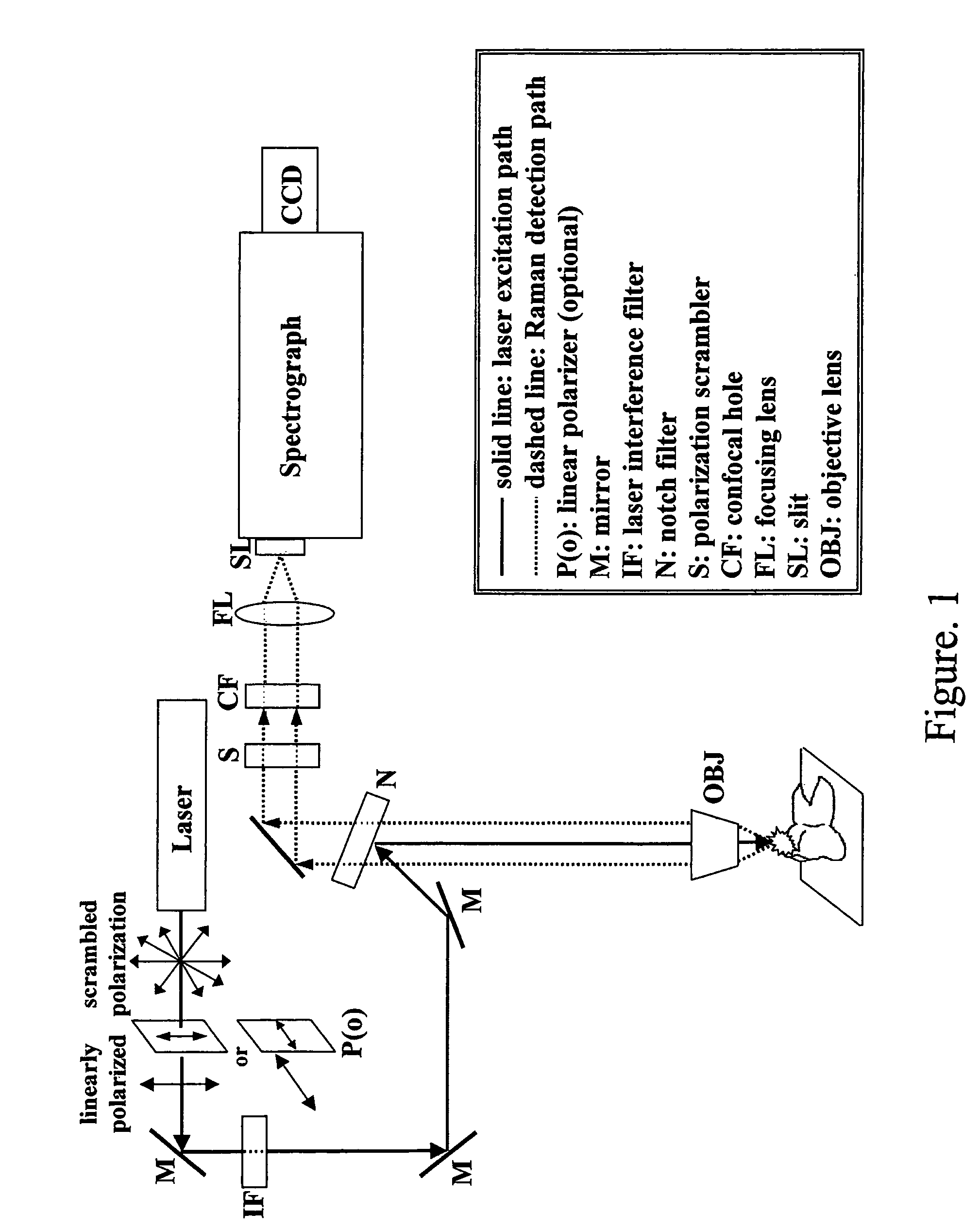
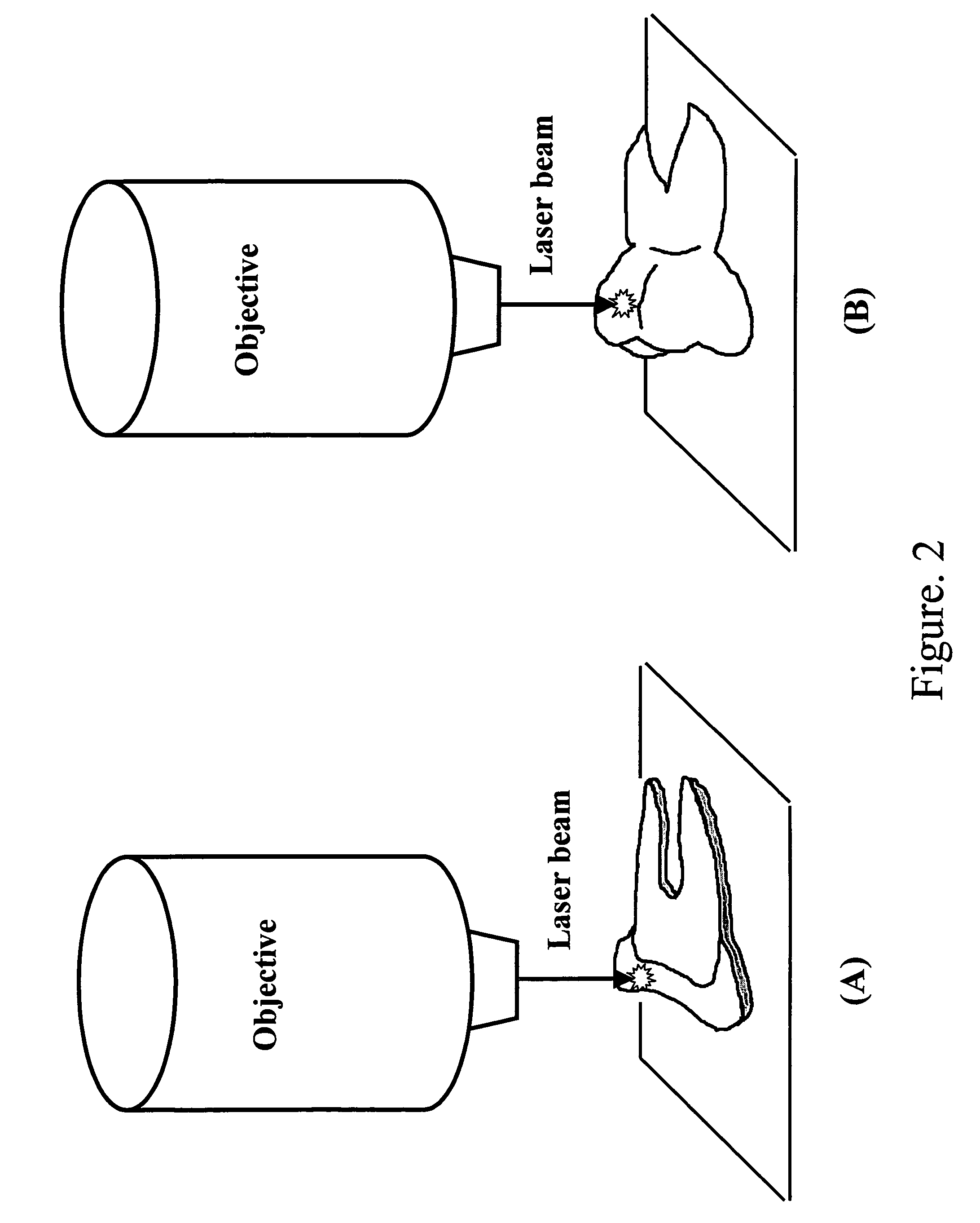
Detection and monitoring of changes in mineralized tissues or calcified deposits by optical coherence tomography and Raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS7796243B2Minimal disruptionHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansCarious lesionTooth Supporting Structures
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA +2
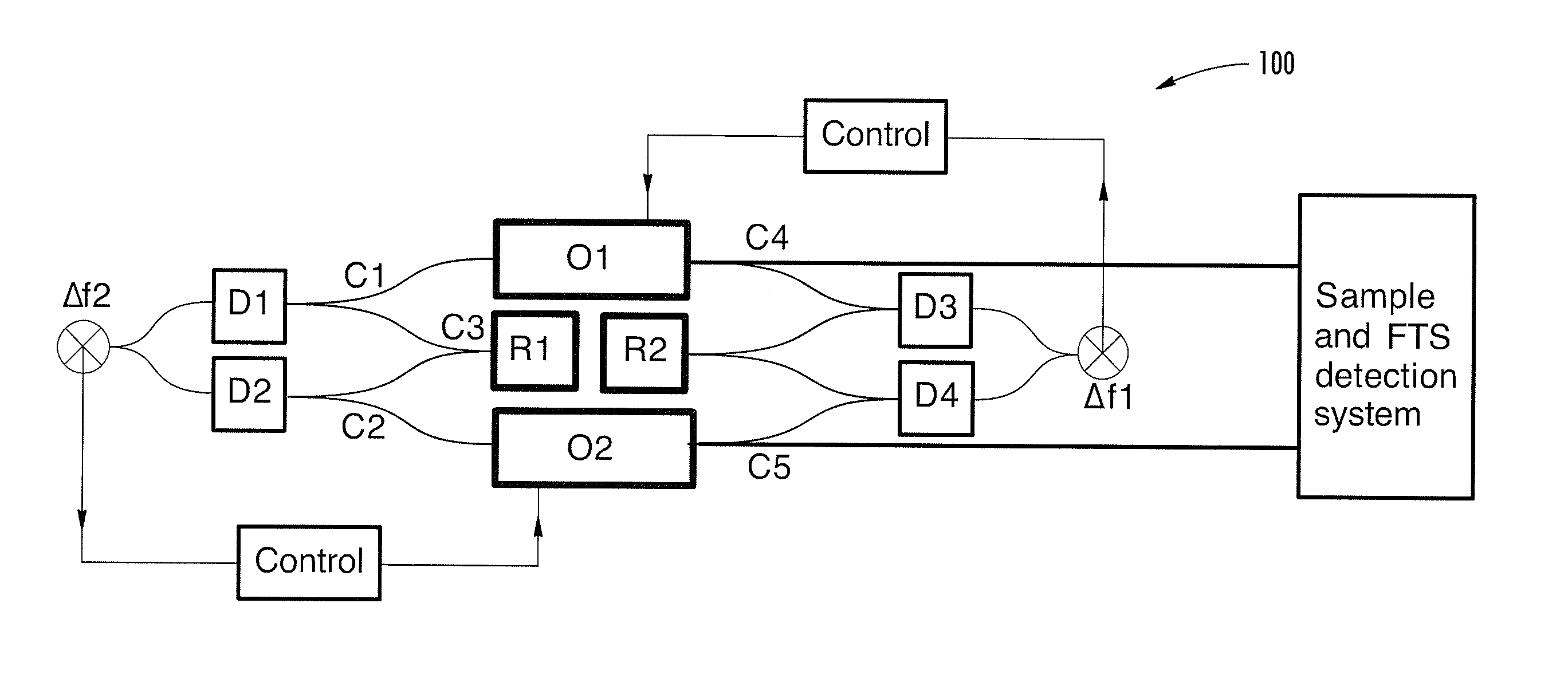
Optical signal processing with modelocked lasers
ActiveUS20110080580A1High resolutionMinimize fluctuationLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryFiberTime delays
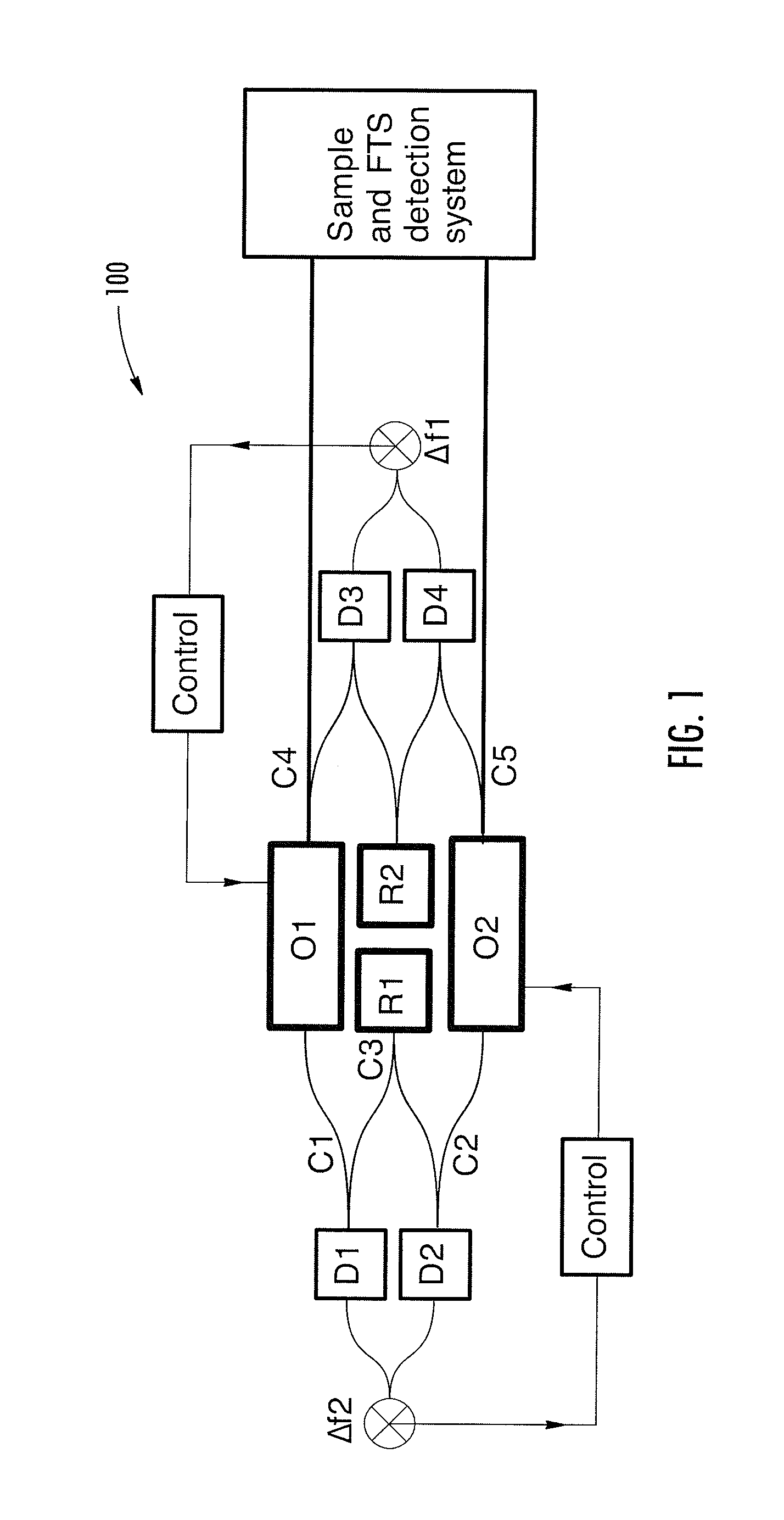
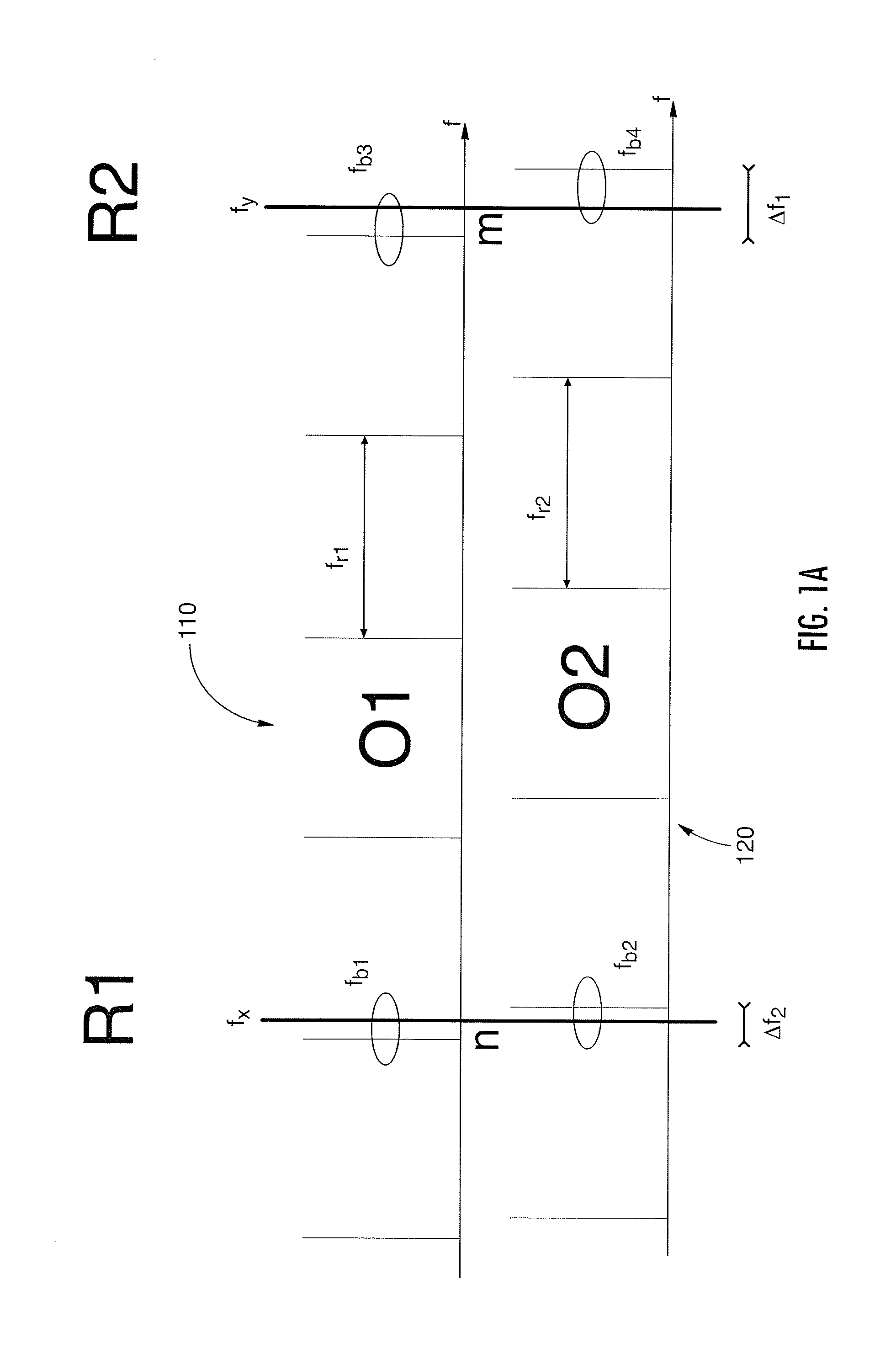
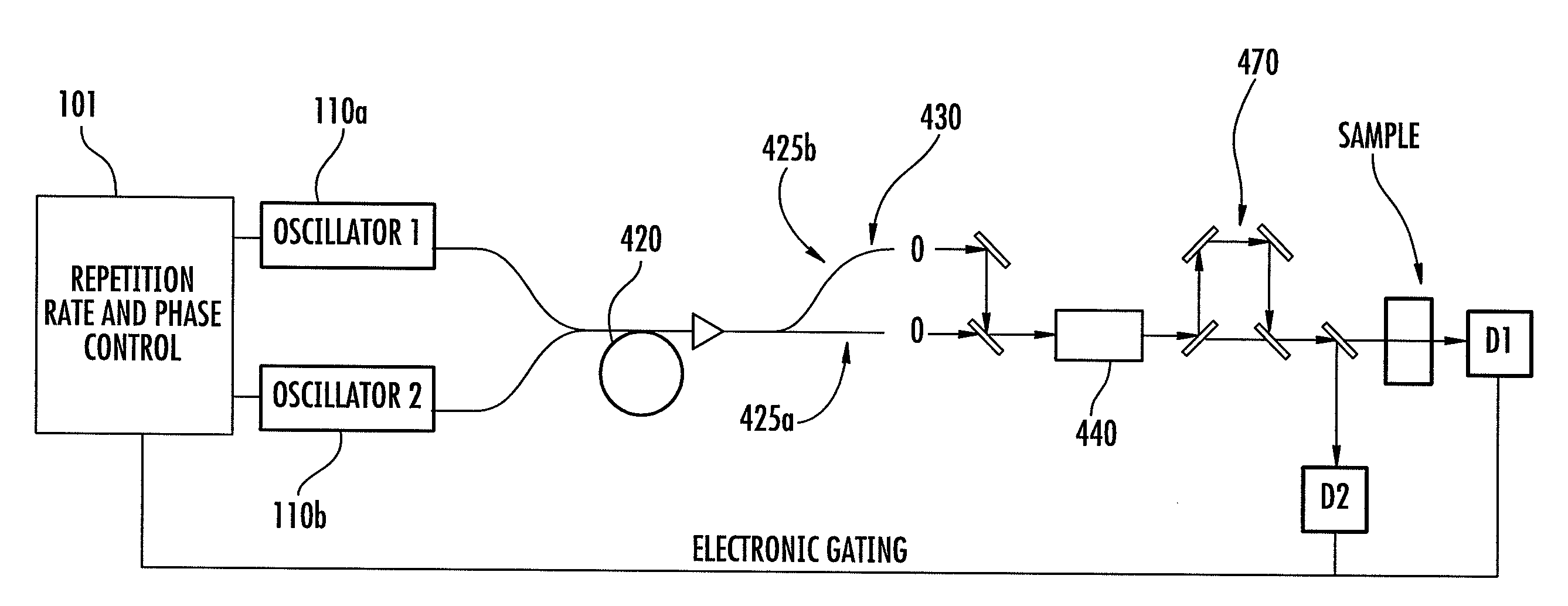
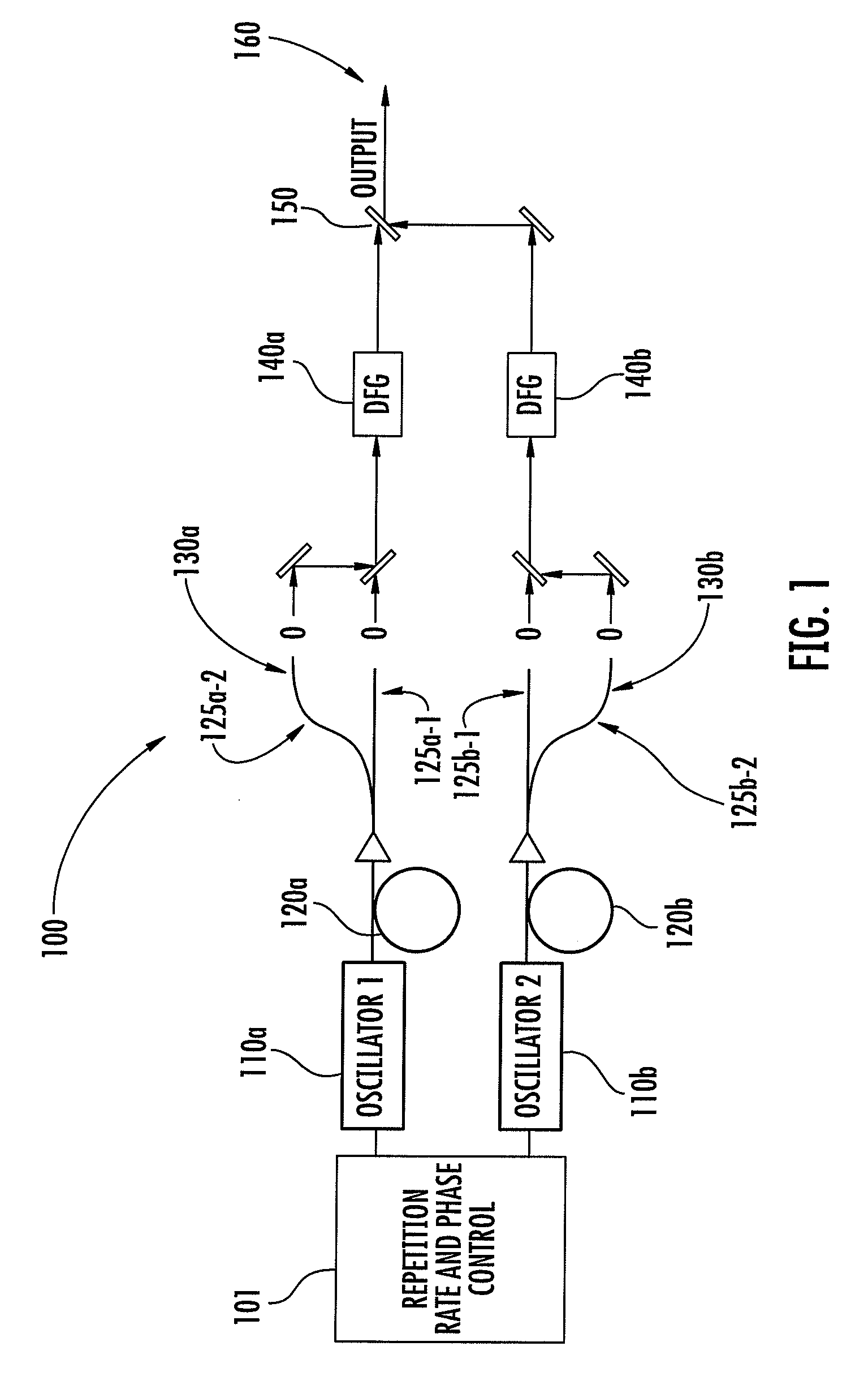
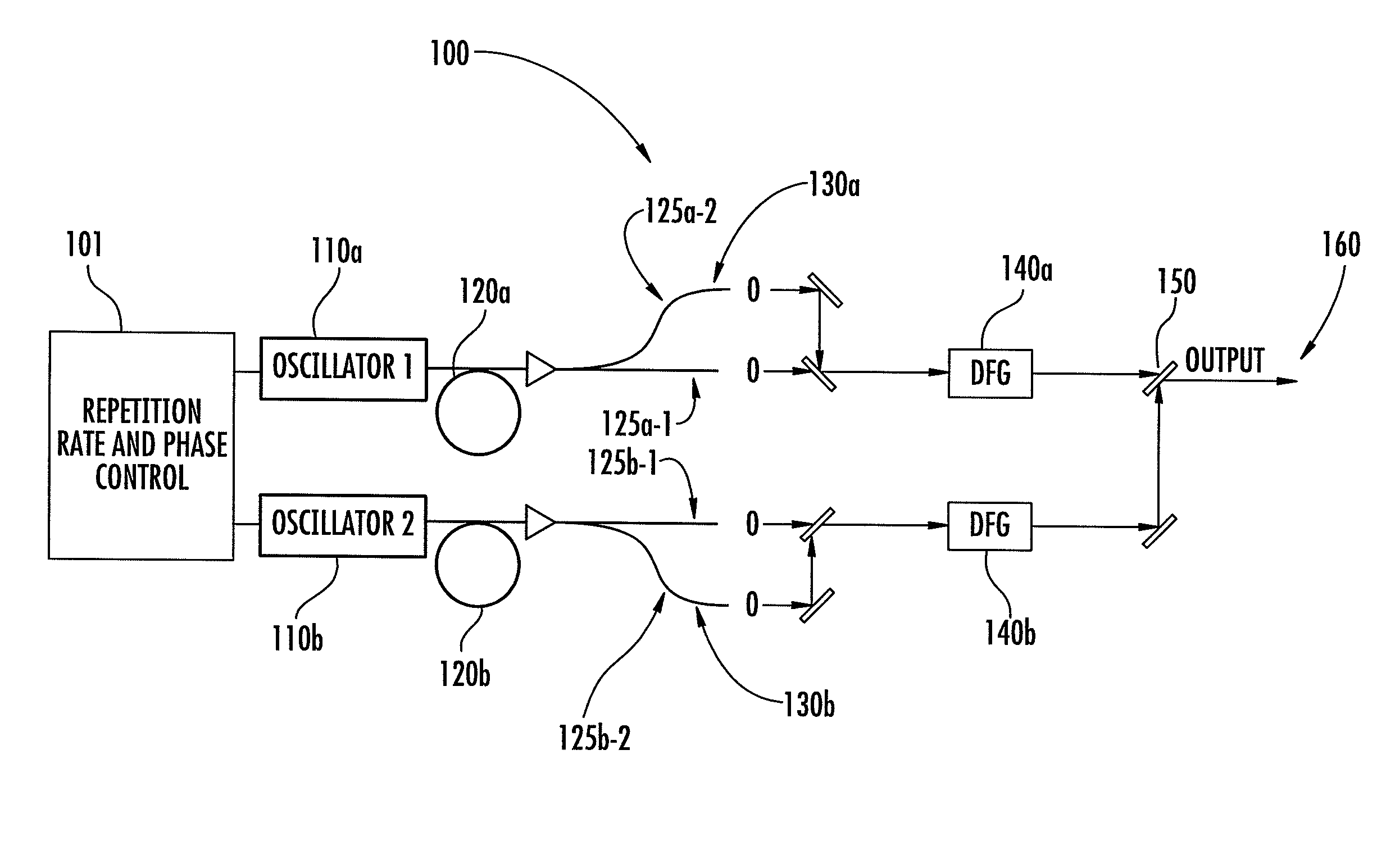
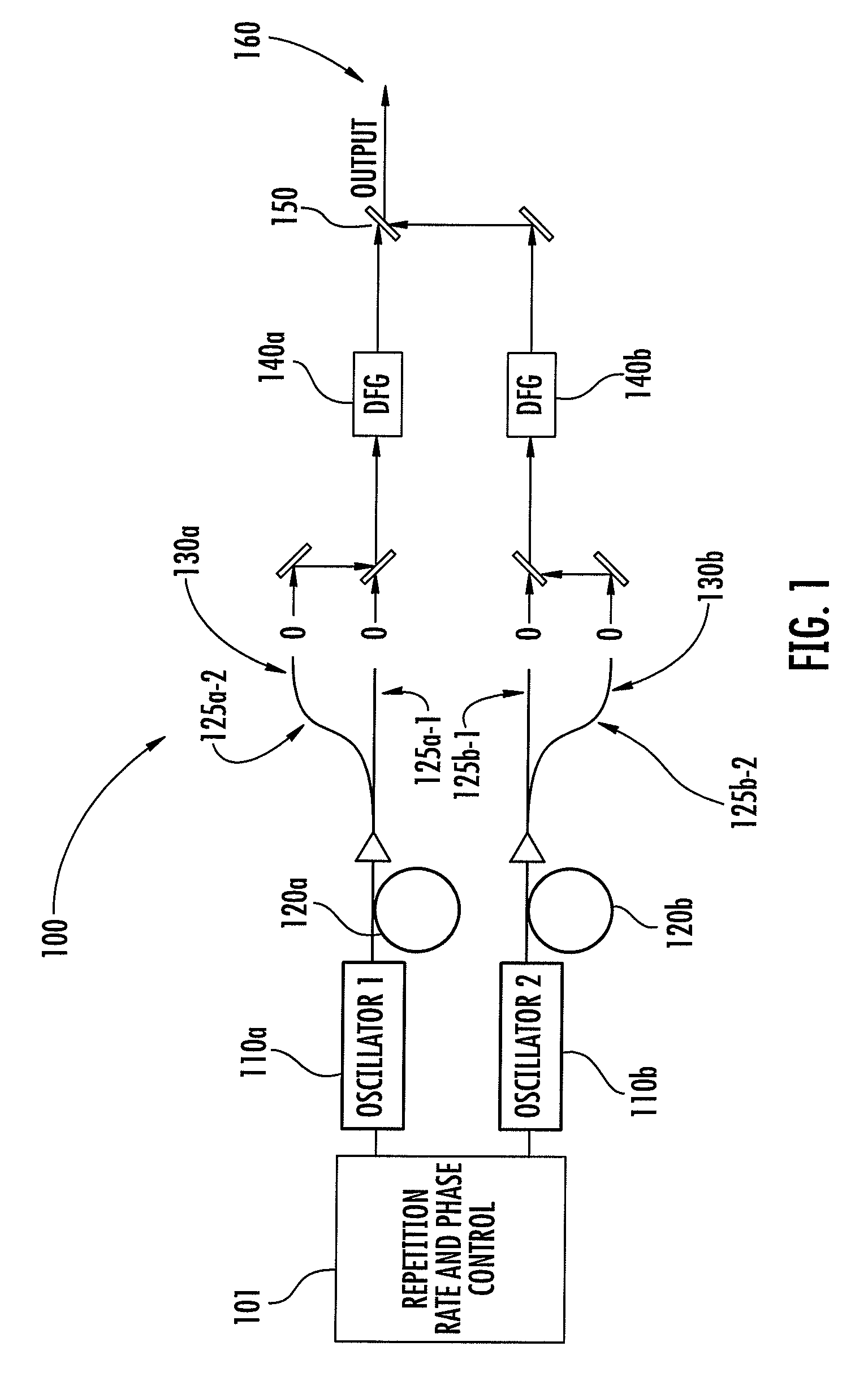
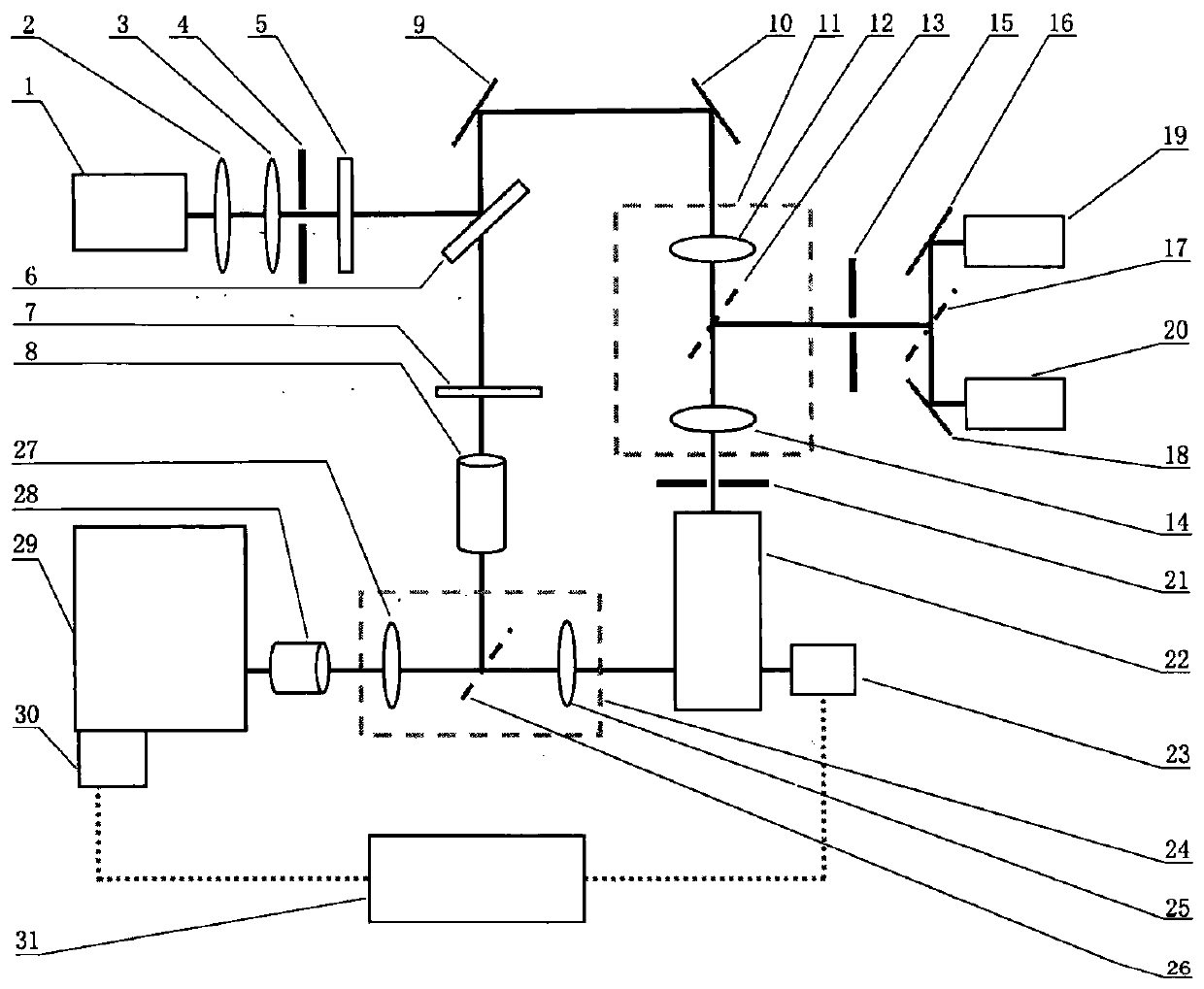
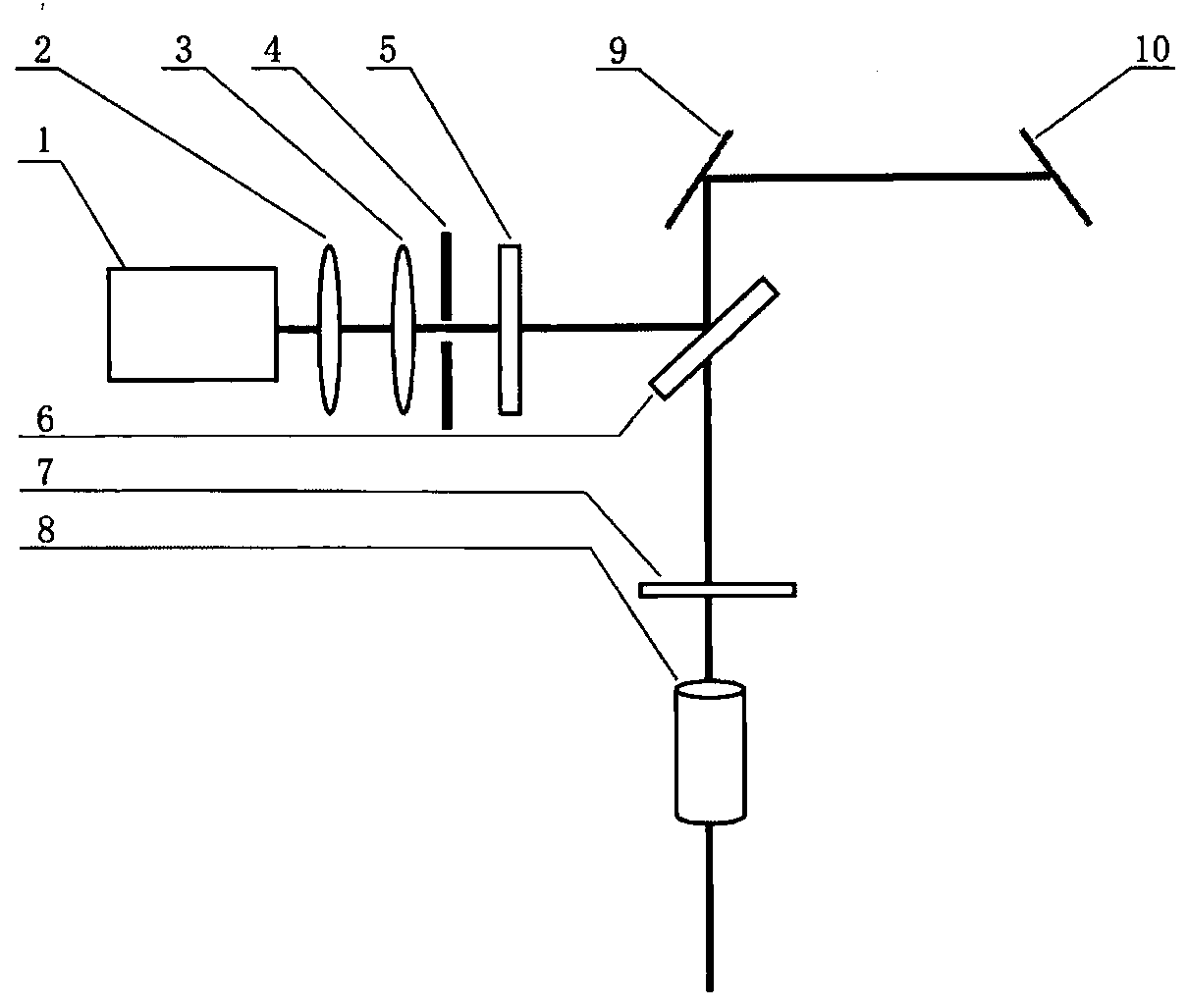
The invention relates to scanning pulsed laser systems for optical imaging. Coherent dual scanning laser systems (CDSL) are disclosed and some applications thereof. Various alternatives for implementation are illustrated. In at least one embodiment a coherent dual scanning laser system (CDSL) includes two passively modelocked fiber oscillators. In some embodiments an effective CDSL is constructed with only one laser. At least one embodiment includes a coherent scanning laser system (CSL) for generating pulse pairs with a time varying time delay. A CDSL, effective CDSL, or CSL may be arranged in an imaging system for one or more of optical imaging, microscopy, micro-spectroscopy and / or THz imaging.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Optical scanning and imaging systems based on dual pulsed laser systems
ActiveUS20100225897A1Noise minimizationEasy to implementRadiation pyrometryLaser detailsFiberFrequency conversion
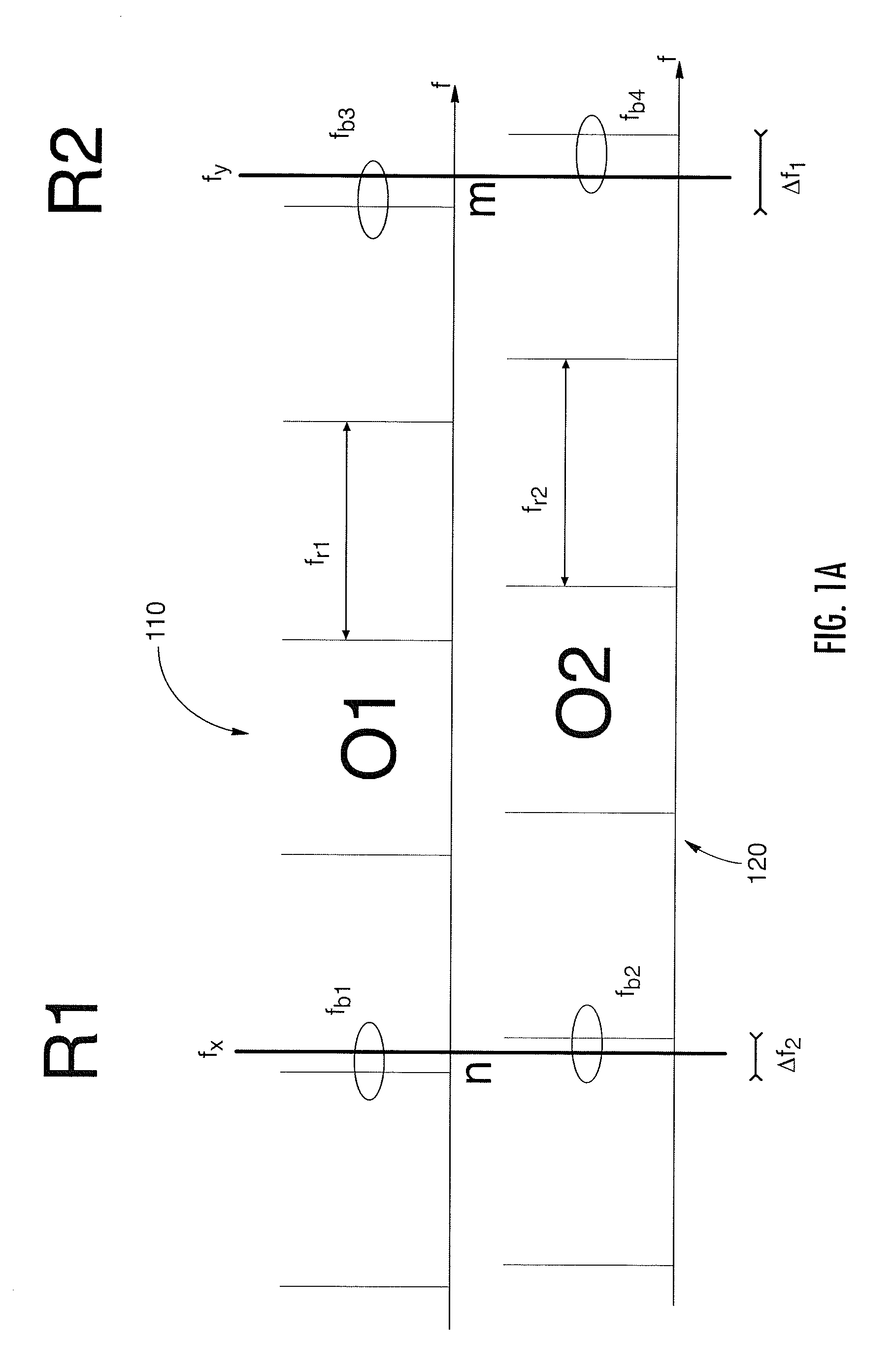
The invention relates to scanning pulsed laser systems for optical imaging. Coherent dual scanning laser systems (CDSL) are disclosed and some applications thereof. Various alternatives for implementation are illustrated, including highly integrated configurations. In at least one embodiment a coherent dual scanning laser system (CDSL) includes two passively modelocked fiber oscillators. The oscillators are configured to operate at slightly different repetition rates, such that a difference δfr in repetition rates is small compared to the values fr1 and fr2 of the repetition rates of the oscillators. The CDSL system also includes a non-linear frequency conversion section optically connected to each oscillator. The section includes a non-linear optical element generating a frequency converted spectral output having a spectral bandwidth and a frequency comb comprising harmonics of the oscillator repetition rates. A CDSL may be arranged in an imaging system for one or more of optical imaging, microscopy, micro-spectroscopy and / or THz imaging.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device
ActiveCN103439254AImproving the Detection Capability of Micro-area Raman SpectroscopyHigh detection sensitivityRaman scatteringRayleigh scatteringHigh resolution imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of microscopic spectrum imaging, and relates to a spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device, wherein a confocal microscopic technology and a Raman spectrum detecting technology are combined. A spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system is constructed by using rayleigh scattering light discarded in confocal Raman spectrum detection, high-resolution imaging and detection of a three-dimensional geometric position of a sample are realized; and a spectrum detection system is controlled by using an extreme point of the spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system to be capable of accurately capturing Raman spectrum information excited by a focusing point of an objective lens, and further spectroscopic pupil confocal Raman spectrum high-space-resolution imaging and detection of image and spectrum integration are realized. The spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device provide a new technical approach for high-space-resolution detection of the three-dimensional geometrical position and spectrum in a microcell, can be widely applied to the fields such as physics, chemistry, biomedicine, material science, environmental sciences, petrochemical engineering, geology, medicines, foods, criminal investigation and jewelry verification, and are capable of carrying out nondestructive identification and deep spectrum analysis of a sample.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Differential confocal Raman spectra test method
InactiveCN101290293AImproved microspectral detection capabilitiesImprove detection performanceRaman scatteringLight beamAbsolute measurement
The invention belongs to the micro-spectrum imaging technical field and relates to a differential confocal raman spectral test method. The method integrates the technical characteristics of the differential confocal detection method and the raman spectral detection method, forms a test method capable of realizing sample microarea spectral detection, precisely catches focus positions of excitation light beams through the differential confocal technology, detects raman spectra of corresponding positions, simultaneously adopts a designed pupil filter, sharpens Airy disc major lobes of a differential confocal raman spectral system, improves the microarea raman spectral detectability and precisely acquires microarea space spectrum information which comprises spectral information and position information of microarea samples. The method obviously improves the microarea spectral detectability of a confocal raman spectromicroscope, has absolute tracking zero points and bipolar tracking characteristics, realizes absolute measurement of physical dimension, can be widely applied in the technical fields such as biomedicine, life sciences, biophysics, biochemistry, industrial precision detection and so on to perform high-precision detection of geometric positions and spectral characteristics of microareas, and has very important application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Infrared microscopic spectrum analysis apparatus and method for analysis of recording media using the same
A microscopic analysis apparatus for analysis of infrared single beam spectrum is composed of an interference light source unit, a measuring unit, and a signal processing unit. The measuring unit is configured such that a semi-spherical prism made from germanium, an incident angle varying device composed of a pair of opposed parabolic mirrors, and a detector for sensing light totally reflected from the surface of a sample are provided in an enclosed sample chamber. According to the method using the analysis apparatus, a profile of a concentration of an organic lubricant contained in a sample in the depth direction of the sample is measured by bringing the surface on the magnetic layer formation side of a floppy disk as the sample into press-contact on the bottom surface of the prism at a low pressure, scanning an incident angle of an infrared light ray on the prism, and analyzing the spectrum of the infrared light ray totally reflected from the surface of the sample.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical scanning and imaging systems based on dual pulsed laser systems
ActiveUS8120778B2Easy to implementEliminate signal interferenceRadiation pyrometryLaser detailsFiberFrequency conversion
The invention relates to scanning pulsed laser systems for optical imaging. Coherent dual scanning laser systems (CDSL) are disclosed and some applications thereof. Various alternatives for implementation are illustrated, including highly integrated configurations. In at least one embodiment a coherent dual scanning laser system (CDSL) includes two passively modelocked fiber oscillators. The oscillators are configured to operate at slightly different repetition rates, such that a difference δfr in repetition rates is small compared to the values fr1 and fr2 of the repetition rates of the oscillators. The CDSL system also includes a non-linear frequency conversion section optically connected to each oscillator. The section includes a non-linear optical element generating a frequency converted spectral output having a spectral bandwidth and a frequency comb comprising harmonics of the oscillator repetition rates. A CDSL may be arranged in an imaging system for one or more of optical imaging, microscopy, micro-spectroscopy and / or THz imaging.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
System and Device for Non-Destructive Raman Analysis
InactiveUS20100020393A1Easy to useLow costRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryNon destructiveEngineering
An improved Raman microspectrometer system extends the optical reach and analysis range of an existing Raman microspectrometer to allow analysis and / or repair of an oversized sample. The improved Raman microspectrometer system includes an extender for extending the optical reach of the existing microspectrometer and a supplemental stage which extends the analysis range of the existing microspectrometer by providing travel capabilities for non-destructive analysis of an entire oversized sample. Such an arrangement decreases manufacturing costs associated with testing oversized samples such as mammography panels, enabling analysis and / or repair to be performed without destruction.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Laser double-shaft differential confocal Brillouin-Raman spectrum measurement method and device
ActiveCN103954602AEasy to testScattering properties measurementsRaman scatteringHigh energyHigh spatial resolution
The invention belongs to the technical field of microscopic spectral imaging, and relates to a laser double-shaft differential confocal Brillouin-Raman spectrum measurement method and device. The laser double-shaft differential Brillouin-Raman spectrum measurement method and device fuse double-shaft differential confocal microscopy and spectrum detection technologies, and use a segmentation focal spot differential detection method to realize precise imaging of geometric position, and Raman spectrum detection and Brillouin spectrum detection technologies are combined to realize united detection on a system high spatial resolution graph spectrum. The laser double-shaft differential Brillouin-Raman spectrum measurement method and device have three modes of three-dimensional tomographic geometric imaging, spectrum detection and micro-region spectrum tomographic imaging, and use the characteristics of complementary advantages of a confocal Raman spectrum detection technology and a confocal Brillouin spectrum detection technology to provide a new solution channel for comprehensive detection of morphology, properties, texture, stress and other parameters of a sample, and have wide application prospect in the fields of biomedicine, high energy production, material chemistry and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
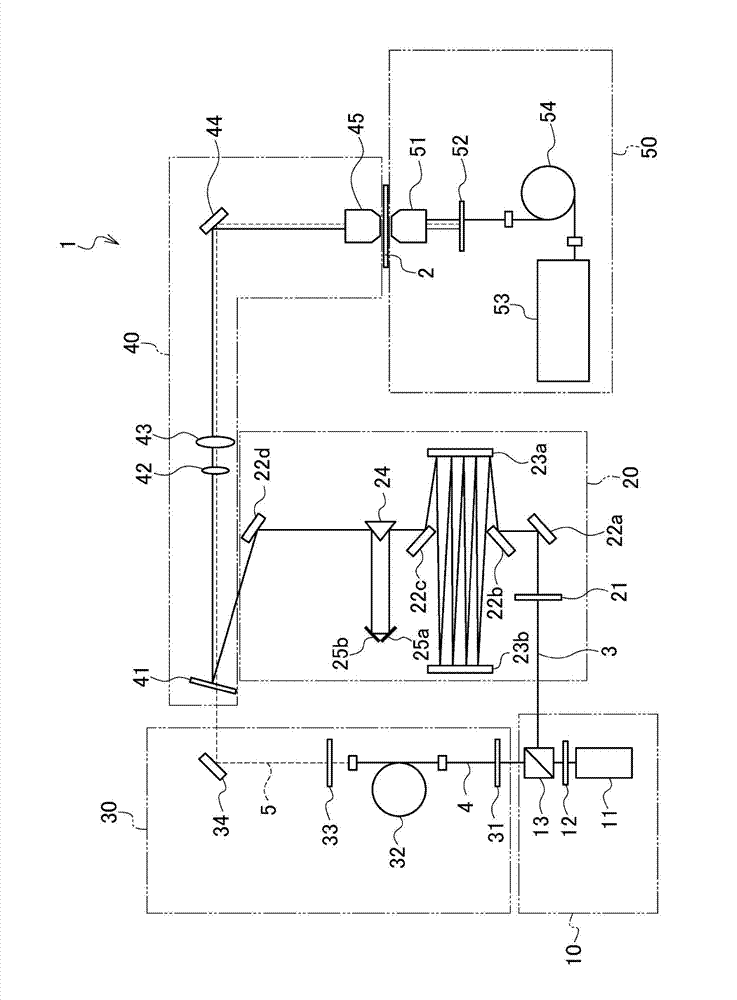
Nonlinear Raman spectroscopic apparatus, microspectroscopic apparatus, and microspectroscopic imaging apparatus
The present invention provides a nonlinear Raman spectroscopic apparatus, a microspectroscopic apparatus, and a microspectroscopic imaging apparatus. The nonlinear Raman spectroscopic apparatus includes two light sources and a pulse control section. The two light sources are each configured to emit short-pulse laser light. The pulse control section is configured to perform time-delay for the short-pulse laser light emitted from one of the light sources.
Owner:SONY CORP
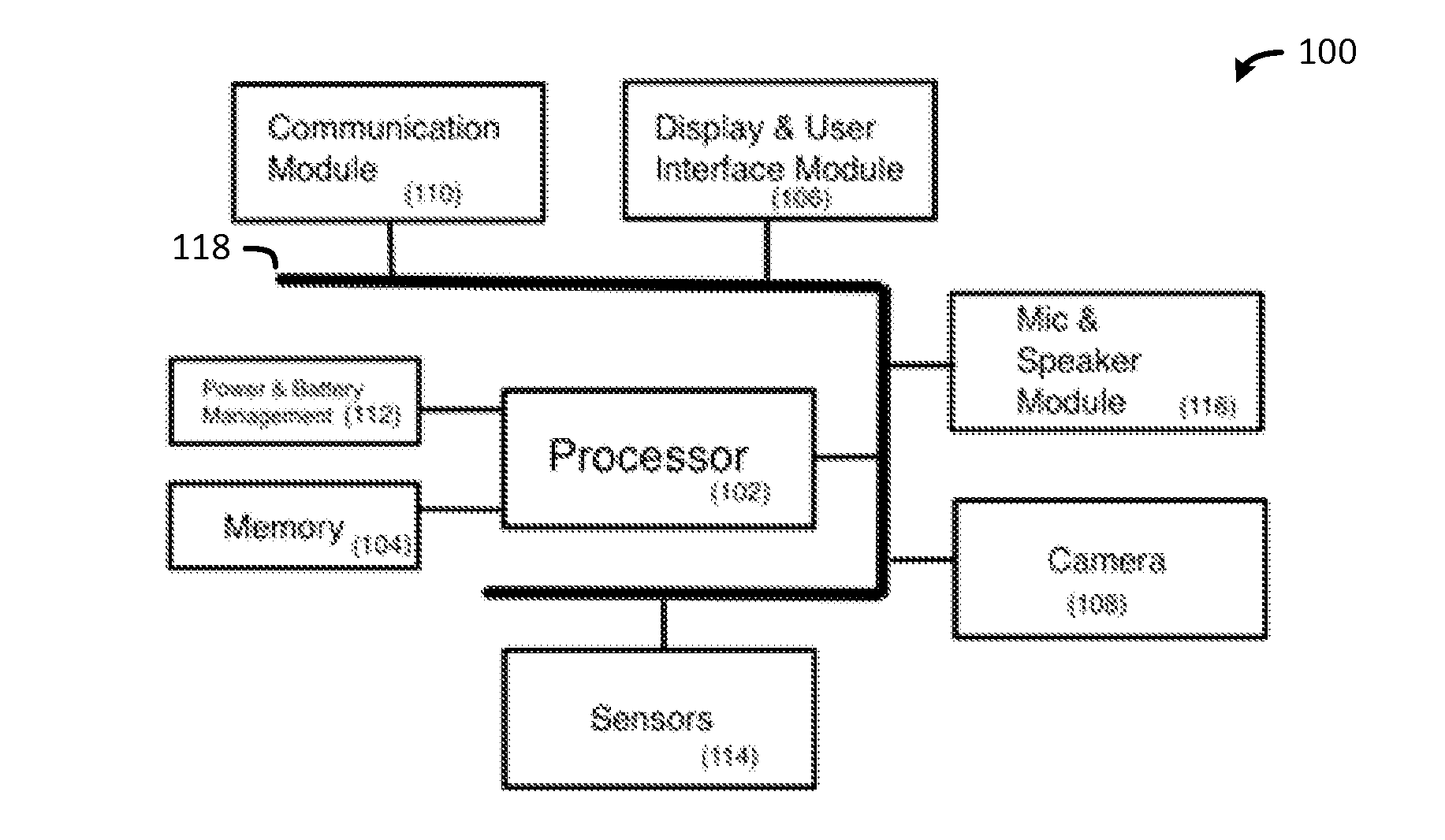
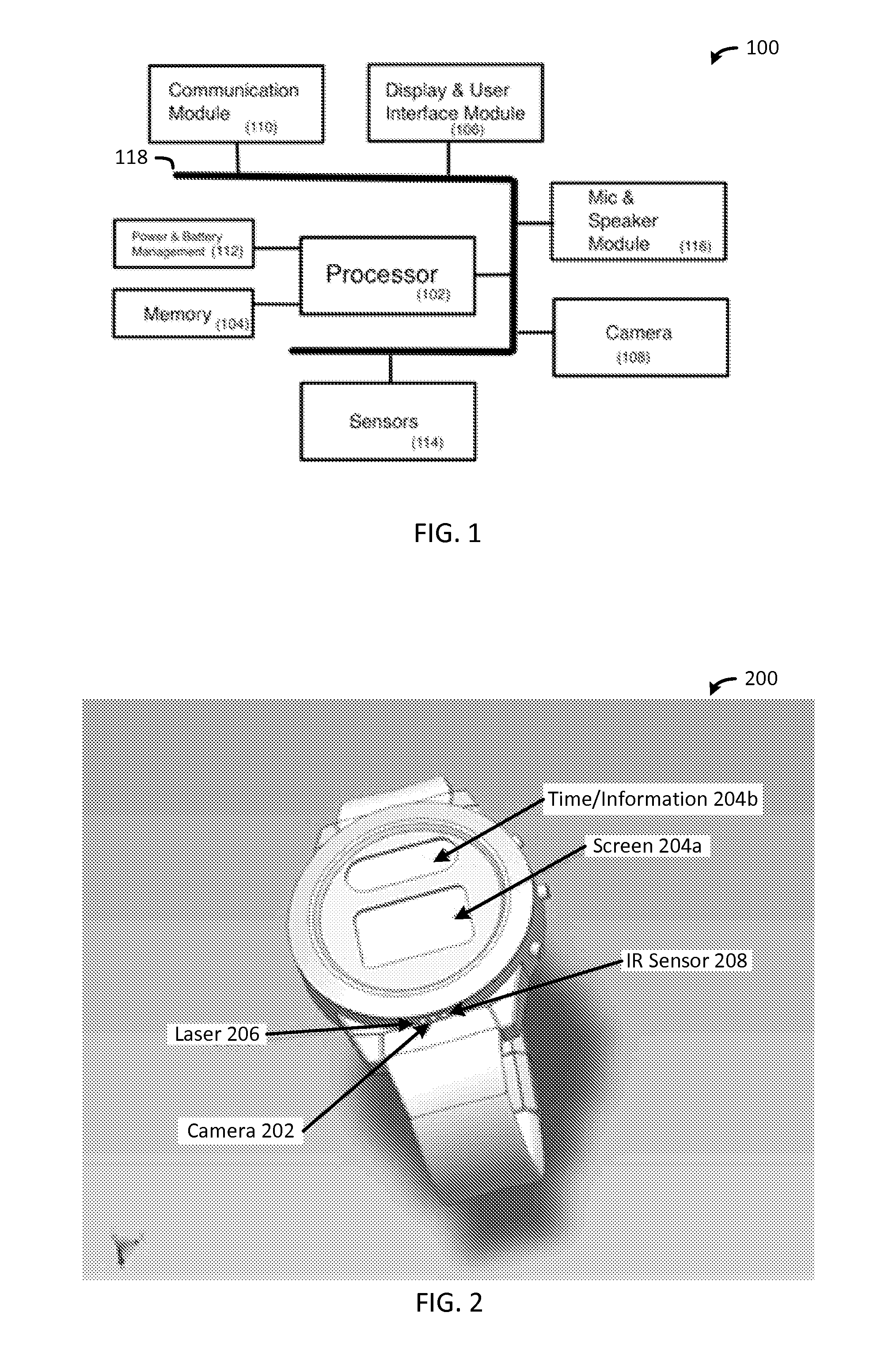
Method and Apparatus for Monitoring Diet and Activity
InactiveUS20150302160A1Increase heightExcessive activityPhysical therapies and activitiesPerson identificationUser inputDisplay device
A method and apparatus includes a memory, a display and user input module, a camera and micro spectroscopy module, and one or more communication modules communicably coupled to a processor. The processor is configured to capture one or more images and spectroscopy data of the food(s) using the camera and micro spectroscopy module, determine a food type and food amount for each of the food(s) using the image(s) and spectroscopy data, perform a dietary analysis of the food(s) based on the food type and food amount determined from the image(s) and spectroscopy data, determine the set of nutritional data for the food(s) based on the dietary analysis, and provide the set of nutritional data for the food(s) to the memory, the display and user input module or the one or more communication modules.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT NEVADA SYST OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF NEVADA RENO
Optical scanning and imaging systems based on dual pulsed laser systems
InactiveUS20120081694A1Easy to implementEliminate signal interferenceLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryFiberFrequency conversion
The invention relates to scanning pulsed laser systems for optical imaging. Coherent dual scanning laser systems (CDSL) are disclosed and some applications thereof. Various alternatives for implementation are illustrated, including highly integrated configurations. In at least one embodiment a coherent dual scanning laser system (CDSL) includes two passively modelocked fiber oscillators. The oscillators are configured to operate at slightly different repetition rates, such that a difference δfr in repetition rates is small compared to the values fr1 and fr2 of the repetition rates of the oscillators. The CDSL system also includes a non-linear frequency conversion section optically connected to each oscillator. The section includes a non-linear optical element generating a frequency converted spectral output having a spectral bandwidth and a frequency comb comprising harmonics of the oscillator repetition rates. A CDSL may be arranged in an imaging system for one or more of optical imaging, microscopy, micro-spectroscopy and / or THz imaging.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
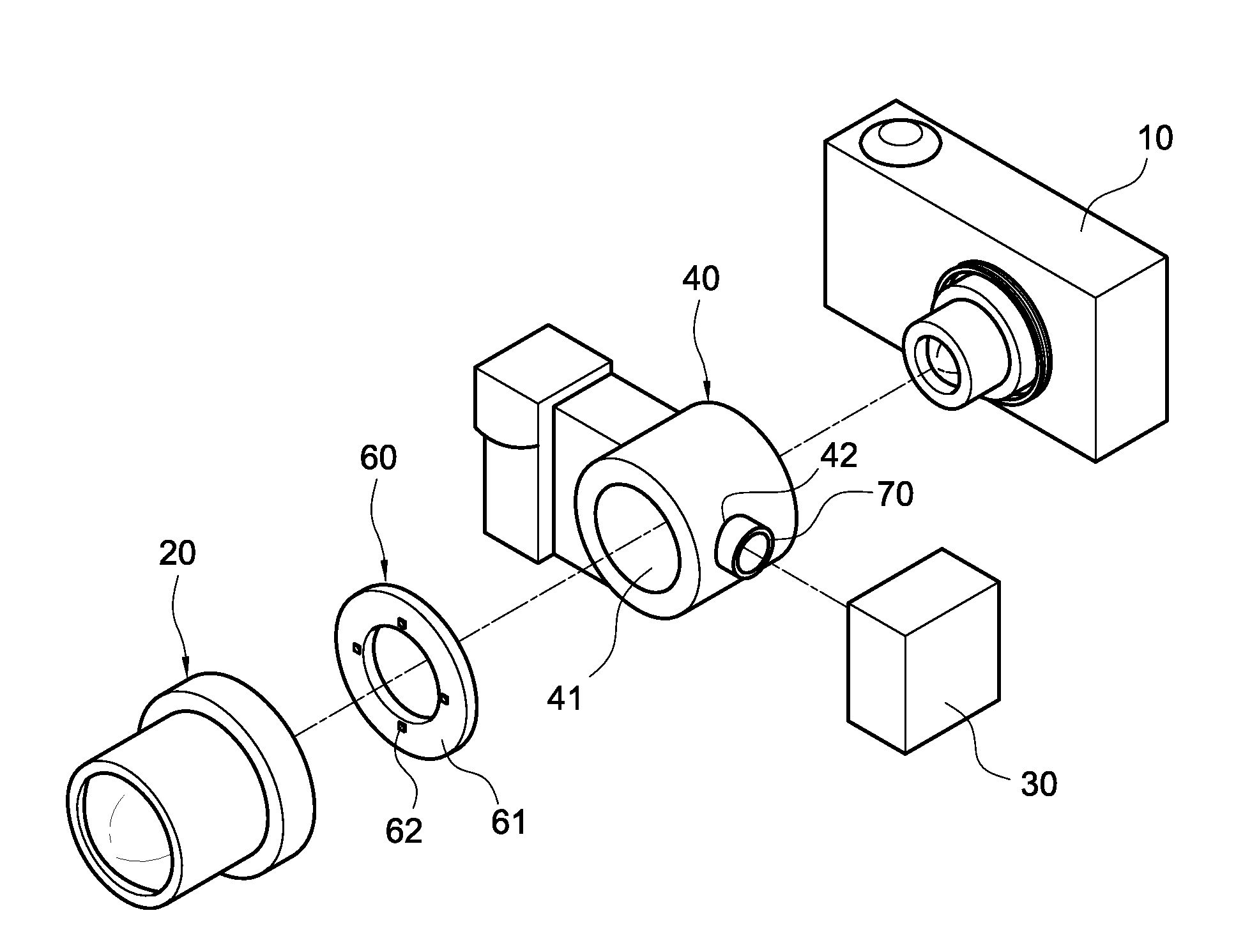
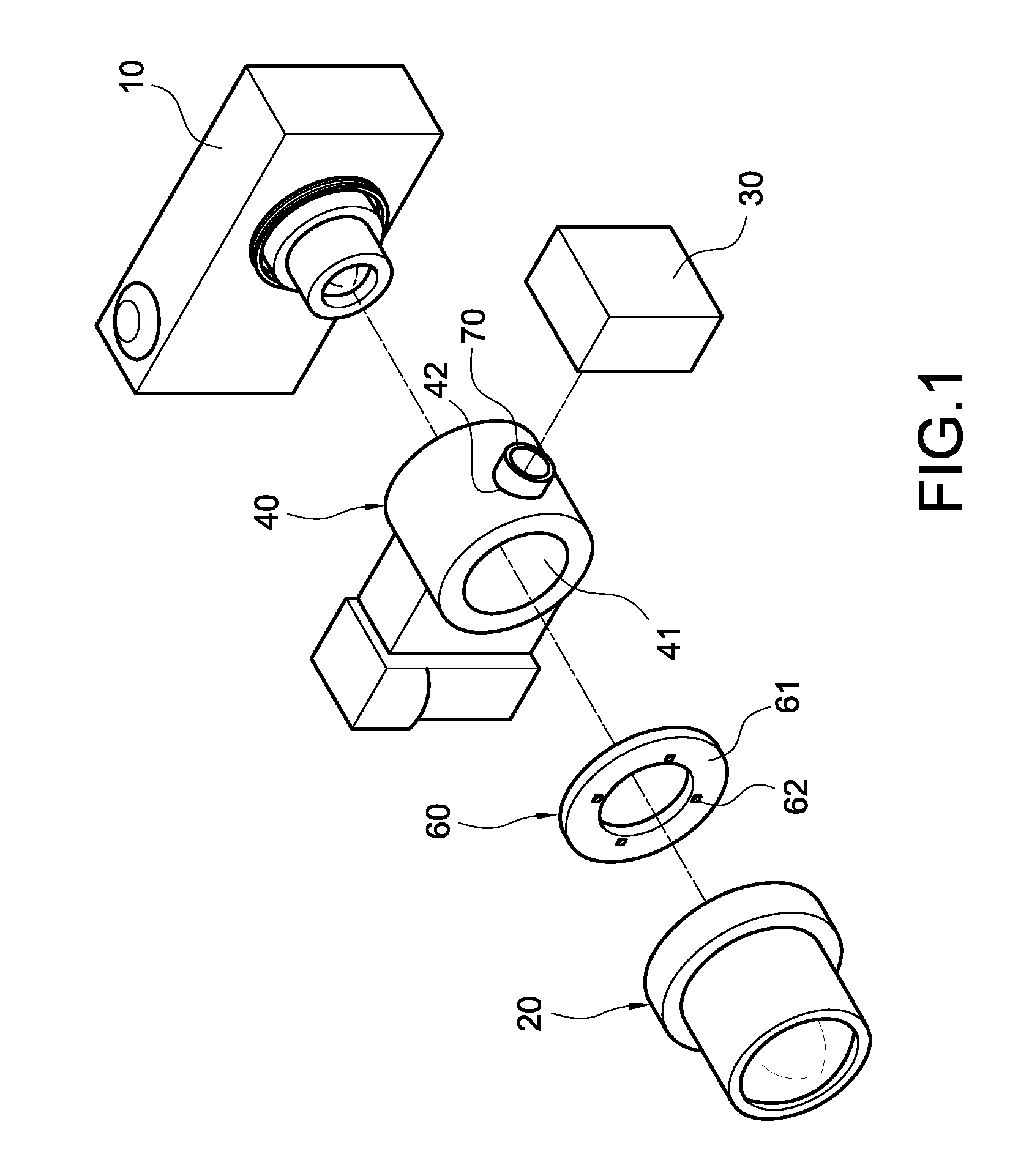
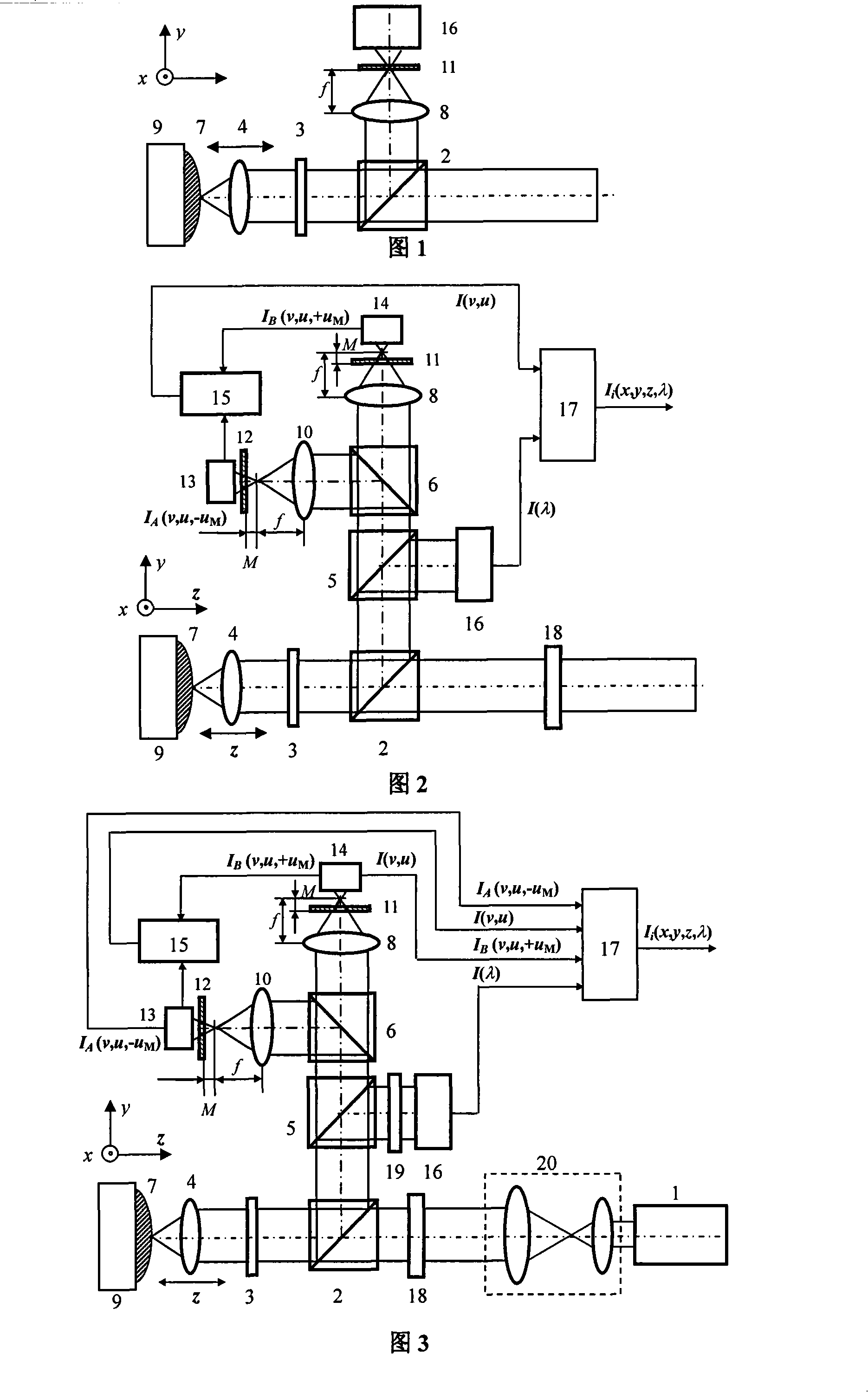
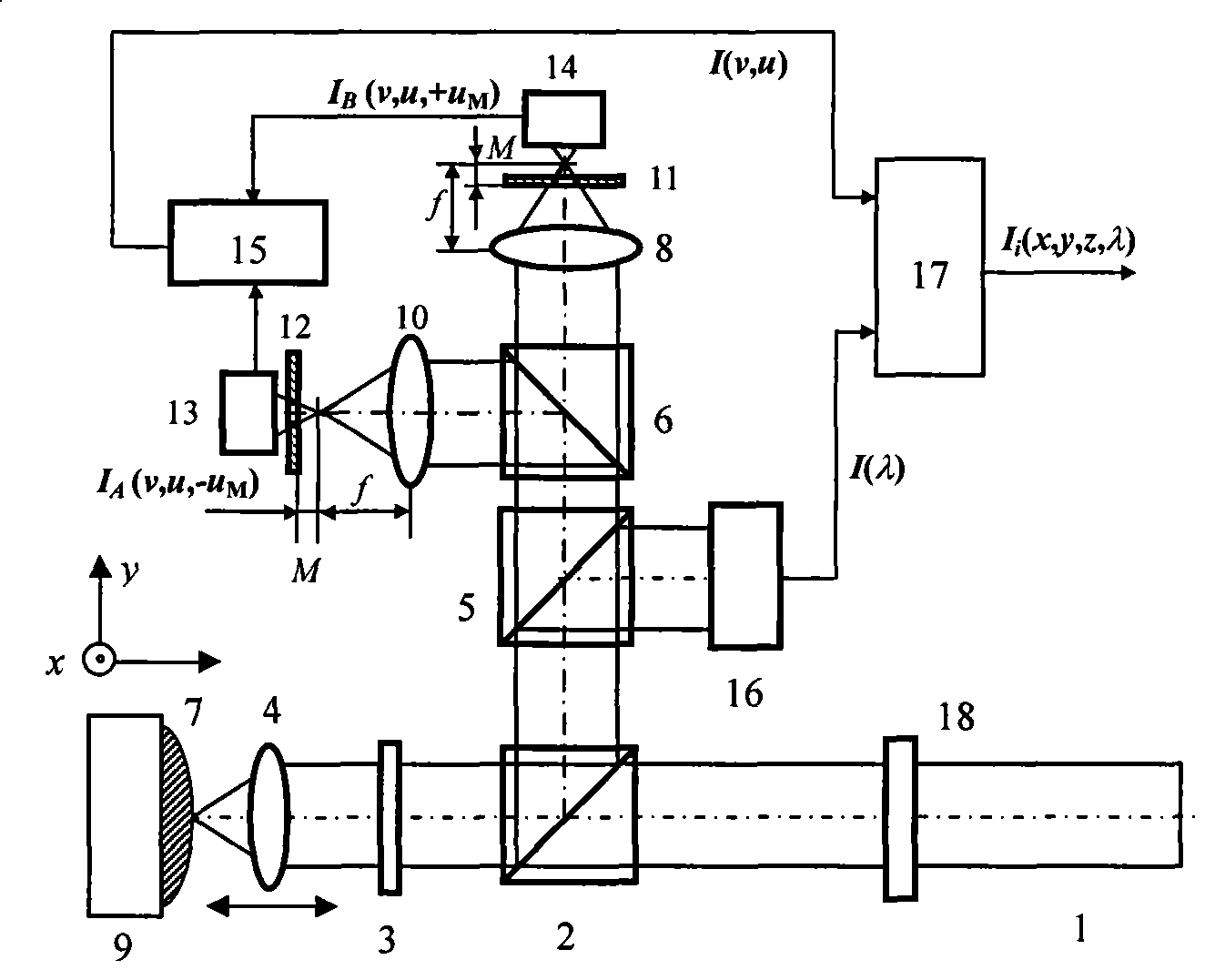
Microscopic spectrum apparatus
A microscopic spectrum apparatus for connecting to an image capturing module which is used for converting external image light into electrical signal is disclosed. The microscopic spectrum apparatus includes a microscopic lens module, a spectrum analyzing module and a light beam splitter. The microscopic lens module is used for collecting the external image light to the image capturing module and magnifying the external image. The spectrum analyzing module is arranged at a side of the microscopic lens module. The light beam splitter is arranged between the microscopic lens module and the image capturing module, and is used for directing part of the external image light from the microscopic lens module to the spectrum analyzing module. In addition, a microscopic spectrum apparatus with image capturing capability is also disclosed.
Owner:LUMOS TECH
Multimode coupling in-situ microscopic spectral imaging system
InactiveCN110441235AAvoid measurement biasAchieve independent acquisitionMaterial analysis by optical meansObservational errorPath switching
The invention discloses a multimode coupling in-situ microscopic spectral imaging system. The system is composed of an inverted microscope, an exciting light source module, a light path switching module, a spectral imaging and spectrum test module, and refers to a plurality of spectrum and imaging measurement functions in the same micron-order area of a sample, comprising measuring microcell Ramanspectrum and microcell fluorescence spectrum, fluorescence microimaging, microcell transmittance spectrum, transmittance microimaging, microcell reflection spectrum and reflection microimaging. The system has the characteristics that multimode and multidimensional in-situ detection and analysis can be performed on the same microcell of the sample with no need to moving the sample to various kindsof detection equipment; the acquired sample microcell information can be represented in situ, namely that various kinds of information such as the Raman spectrum, fluorescence spectrum and imaging, transmittance spectrum and imaging, reflection spectrum and imaging of the same microcell of the sample can be acquired in real time. Measurement errors caused by transferring of the sample are eliminated, and the reliability of the test result is greatly improved.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical signal processing with modelocked lasers
InactiveUS9153928B2High resolutionMinimize fluctuationRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFiberTime delays
The invention relates to scanning pulsed laser systems for optical imaging. Coherent dual scanning laser systems (CDSL) are disclosed and some applications thereof. Various alternatives for implementation are illustrated. In at least one embodiment a coherent dual scanning laser system (CDSL) includes two passively modelocked fiber oscillators. In some embodiments an effective CDSL is constructed with only one laser. At least one embodiment includes a coherent scanning laser system (CSL) for generating pulse pairs with a time varying time delay. A CDSL, effective CDSL, or CSL may be arranged in an imaging system for one or more of optical imaging, microscopy, micro-spectroscopy and / or THz imaging.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
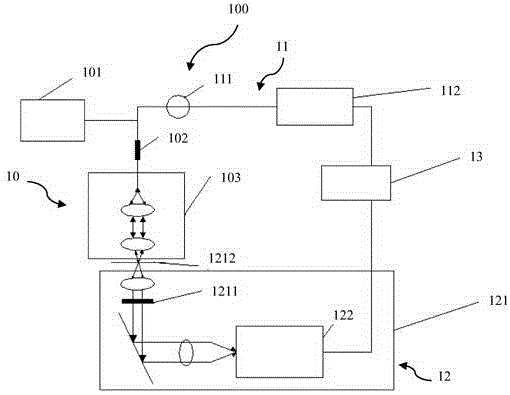
Field electrochemical microspectroscopic imaging analysis method and system
The embodiment of the invention provides a field electrochemical microspectroscopic imaging analysis method and system which are used for solving the problems that the commercially available common working electrode cannot be applied to a spectrum elecrochemical technology, and information on the surface of the working electrode is difficult to acquire. The system comprises light source equipment, electrochemical signal equipment, electrochemical interface equipment and microspectroscopic imaging equipment, wherein the commercially available common working electrode can be vertically arranged in the electrochemical interface equipment; incident light supplied by the light source equipment irradiates to the surface of the working electrode in an inclination manner and is acquired by the microspectroscopic imaging equipment after being reflected; the reflected light comprises the information on the surface of the working electrode; and the microspectroscopic imaging equipment can generate a spectrum according to the reflected light and performs microscopic imaging on the surface of the working electrode, so that the problem that the information on the surface of the working electrode is difficult to acquire on the basis of the existing equipment is solved. Furthermore, an aim of applying the commercially available common working electrode to the spectrum elecrochemical technology is fulfilled.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and system for active-illumination parallel raman microspectroscopy
ActiveUS20140029003A1Improved sampling flexibilityHigh laser power duty cycleRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsRaman imagingWide field
An active-illumination parallel Raman microspectroscopy scheme for simultaneously collecting Raman spectra from multiple points in a full-spectra range. A combination of multi-point laser illumination with wide-field Raman imaging is employed in order to allow for simultaneous imaging of multiple points not aligned on a single line.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Laser dual-axis confocal Brillouin-Raman spectral measurement method and apparatus
ActiveCN103940799ASuppress measurement effectsHigh measurement accuracyRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringDual axis confocalHigh energy
The invention relates to a laser dual-axis confocal Brillouin-Raman spectral measurement method and apparatus realizing integration of images and spectrums, belonging to the technical field of microscopic spectral imaging. According to the invention, dual-axis confocal microscopy and spectral detection technology are organically fused, Rayleigh light is used for assisted detection, Raman spectral detection technology and Brillouin spectral detection technology are cooperatively used to realize high spatial discrimination image-spectrum integrated detection of a system, and high spatial resolution is achieved. The apparatus has three modes, i.e., a three-dimensional chromatographic geometric imaging mode, a spectral detection mode and a micro-area image-spectrum chromatographic imaging mode, obtains basic properties and a plurality of crossing effects of substances by detecting abandoned Brillouin diffusion light in confocal Raman spectral detection, realizes acquisition of a plurality of parameters like the micro-area morphology, state, texture and attributes of a measured sample in virtue of the characteristic that advantages of confocal Raman spectral detection technology and confocal Brillouin spectral detection technology are complementary, and has wide application prospects in fields like biomedicine, high energy manufacturing and material chemistry.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Transmittance type differential confocal CARS (Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) micro-spectrum testing method and device
InactiveCN107167456AAccurate measurementAccurate analysisAnalysis by material excitationHigh spatial resolutionTransmittance
The invention belongs to the technical field of micro-spectrum imaging detection, and relates to a transmittance type differential confocal CARS (Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) micro-spectrum testing method and a device. The key point of the method is that a CARS spectrum detection technique is combined with a differential confocal microtechnique and applied to spectrum detection and geometric measurement on transparent substances, the differential confocal microtechnique is adopted to achieve precise focus fixation and geometric measurement, and after precise focus fixation, an optimal spectrum signal of a transparent sample in a focal position of an objective lens is rapidly detected by using the CARS spectrum detection technique, then spectrum imaging of high spatial resolution is achieved, and a device for geometric morphology measurement, spectrum information measurement and atlas and spectrum integration measurement on micro transparent objects is formed. According to the method, by using the CARS spectrum detection technique, CARS spectrum information with information of a tested transparent sample can be excited within a short time (dozens of milliseconds), possibility is provided for rapidly detecting components of transparent samples, and thus the method has wide application prospects in fields such as biological medicines and material detection.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Reflection-type confocal CARS micro-spectrum test method and device
ActiveCN106990095AIncrease flexibilityImprove spatial resolutionRaman scatteringHigh spatial resolutionBeam splitting
The invention belongs to the technical field of micro-spectrum imaging detection, and relates to a reflection-type confocal CARS micro-spectrum test method and a device. According to the reflection-type confocal CARS micro-spectrum test method, fusion of laser confocal microtechnique and CARS spectrum detection technology is realized, a binary beam splitting system is adopted for nondestructive separation of Reyleigh scattering light and CARS light, wherein CARS light is used for spectrum detection, and Reyleigh scattering light is used for geometric positioning. Accurate capturing and positioning of exciting light focal point position is realized based on the corresponding performance of confocal curve top point to focal point, high precision geometric detection and high spatial resolution spectrum detection are realized, and the method and the device capable of realizing sample microdmain high spatial resolution spectrum detection are constructed. The intensity of sample information-loaded Raman scattering light excited via combination of CARS microtechnique is much higher than that of conventional spontaneous Raman light, excitation time is short, and possibility is provided for rapid detection of biological samples and chemical materials. The reflection-type confocal CARS micro-spectrum test method possesses advantages such as accurate positioning, high spatial resolution, high spectrum detection sensitivity, and controllable measuring focusing spot size; and application prospect in the fields such as biomedicine and material detection is promising.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Transmittance type confocal CARS (Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) micro-spectrum testing method and device
InactiveCN107167457AImplement detectionImproving the ability of micro-region spectral detectionAnalysis by material excitationMicrocellFacula
The invention belongs to the technical field of micro-spectrum imaging detection, and relates to a transmittance type confocal CARS (Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) micro-spectrum testing method and a device. The key point of the method is that a laser confocal microtechnique is combined with a CARS spectrum detection technique, a bidirectional light splitting unit is added to a transmittance type confocal microstructure to implement nondestructive separation on Reyleigh scattering light and CARS light, the CRAS is adopted for spectrum detection, and the Reyleigh scattering light is adopted for geometrtic positioning. By virtue of the characteristic that the top point of a confocal curve precisely corresponds to a focus position, the position of an emitted spot focus is precisely captured and positioned, high-precision geometric detection and spectrum detection of high spatial resolution are achieved, and a method and a device for high spatial resolution spectrum detection on microcells of samples are formed. By using the CARS spectrum detection technique, excited Raman scattering light with information of a transparent sample is far stronger than conventional excited Raman light and is short in excitation time, so that possibility is provided for rapidly detecting biological samples and transparent materials. The method is accurate in positioning, high in spatial resolution, high in spectrum detection sensitivity, controllable in focus spot size measurement and wide in application prospect in fields such as biological medicines and transparent material detection.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
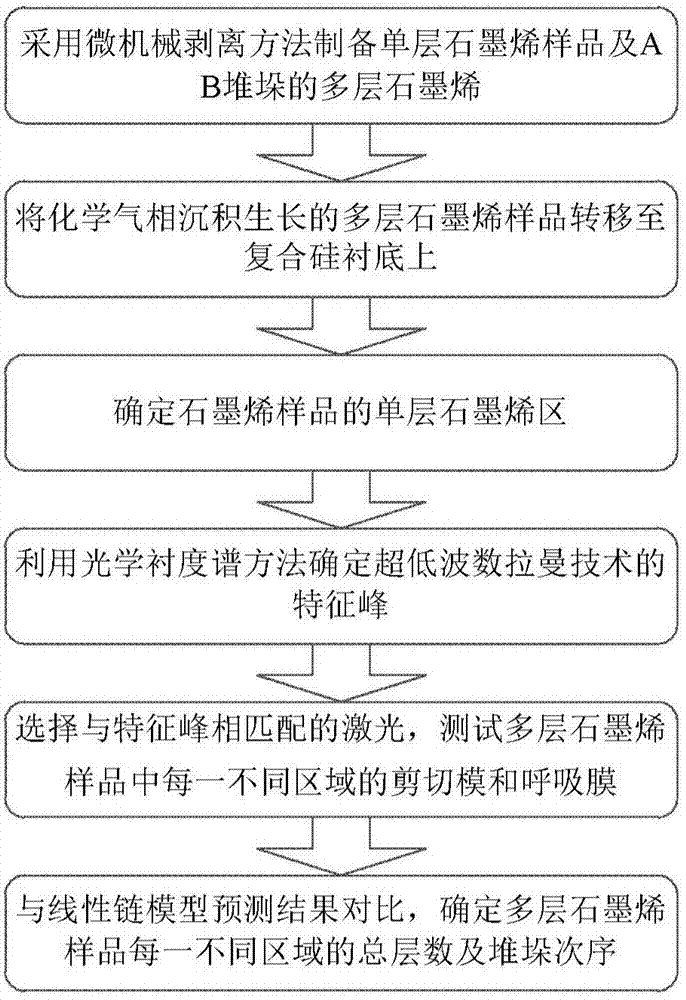
Method for determining stacking sequence of graphene sample containing single-layer graphene areas
ActiveCN107389653AImprove accuracySimple test methodRaman scatteringShear modulusSingle layer graphene
The invention relates to a method for determining stacking sequence of a graphene sample containing single-layer graphene areas. The method comprises the following steps of using a Raman spectrometer to test the Raman G modulus strengths of single-layer graphene and the graphene sample, and determining the single-layer graphene areas in the graphene sample; using a microscope spectrometer to test the optical contrast spectrum of the multi-layer graphene area adjacent with the single-layer graphene area in the graphene sample, and optical contrast spectrum of different areas of the multi-layer graphene in stacks A and B, and comparing the optical contrast spectrum to obtain feature peak; selecting the laser matched with the feature peak, using a Raman spectrometer with ultra low wave number to test the shear modulus and respiration modulus in different areas of the graphene sample, and comparing with the peaks of the shear modulus and respiration modulus and the predicting result of a linear chain module, so as to determine the total layer number and stacking sequence in different areas of the graphene sample. The method has the advantages that the method is simple and clear; the stacking sequence of the graphene sample with four layers or more can be determined; the damage to the sample is avoided.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
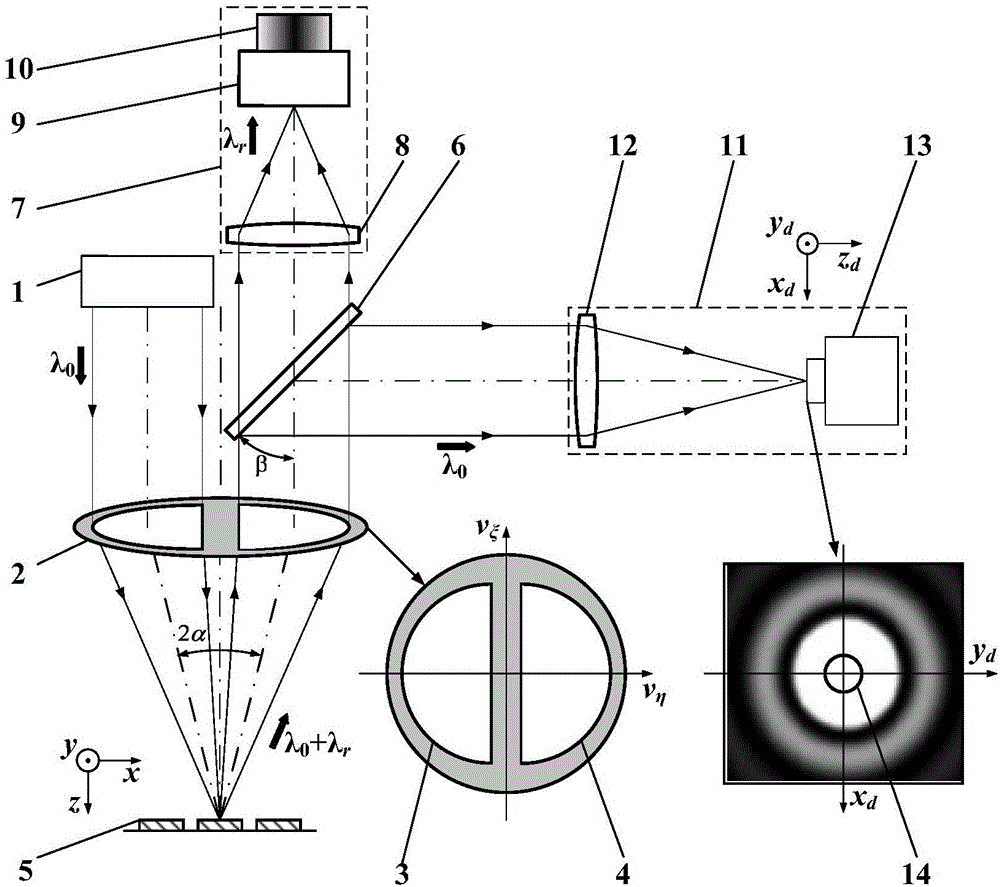
A split-pupil laser confocal Raman spectroscopy testing method and device
ActiveCN103439254BImproving the Detection Capability of Micro-area Raman SpectroscopyHigh detection sensitivityRaman scatteringRayleigh scatteringHigh resolution imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of microscopic spectrum imaging, and relates to a spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device, wherein a confocal microscopic technology and a Raman spectrum detecting technology are combined. A spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system is constructed by using rayleigh scattering light discarded in confocal Raman spectrum detection, high-resolution imaging and detection of a three-dimensional geometric position of a sample are realized; and a spectrum detection system is controlled by using an extreme point of the spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system to be capable of accurately capturing Raman spectrum information excited by a focusing point of an objective lens, and further spectroscopic pupil confocal Raman spectrum high-space-resolution imaging and detection of image and spectrum integration are realized. The spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device provide a new technical approach for high-space-resolution detection of the three-dimensional geometrical position and spectrum in a microcell, can be widely applied to the fields such as physics, chemistry, biomedicine, material science, environmental sciences, petrochemical engineering, geology, medicines, foods, criminal investigation and jewelry verification, and are capable of carrying out nondestructive identification and deep spectrum analysis of a sample.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
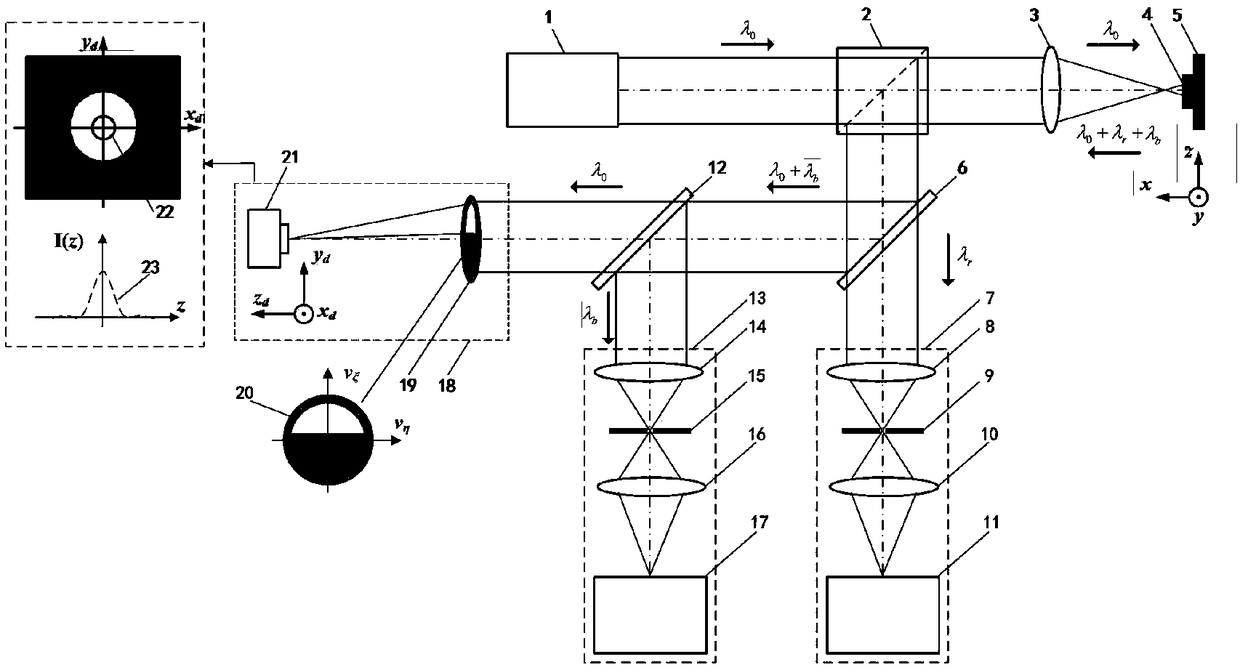
Rear-mounted light splitting pupil laser confocal Brillouin-Raman spectroscopy testing method and device
InactiveCN109187438AImproving the ability of micro-region spectral detectionLight path structure is simpleScattering properties measurementsRaman scatteringRayleigh scatteringSpectroscopy
The invention relates to a rear-mounted light splitting pupil laser confocal Brillouin-Raman spectroscopy testing method and device and belongs to the technical field of microscopy spectroscopy imaging. A light splitting pupil laser confocal microscopy imaging system is established through utilization of abandoned Rayleigh scattering light in a confocal Raman spectroscopy detection system, and high spatial resolution detection of geometrical morphology of a sample is realized. Various basic properties of a tested sample are obtained through detection of abandoned Brillouin scattering light inthe confocal Raman spectroscopy detection system, and parameters such as elasticity and density of a material are measured. Spectroscopy information at a position of a focus of the sample is preciselyobtained through utilization of a focus position obtained by the light splitting pupil laser confocal microscopy imaging system, and further image-spectroscopy integrated light splitting pupil laserconfocal Brillouin-Raman spectroscopy high spatial resolution imaging and detection are realized. Through integration of a confocal Raman spectroscopy detection technology and a confocal Brillouin spectroscopy detection technology, morphology performance multiparameter comprehensive measurement of the sample is realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Rear-mounted beam-splitting pupil laser differential confocal Raman spectroscopy test method and device
InactiveCN109211873ARealize the "unity of graphs"Realization spaceRaman scatteringRayleigh scatteringBeam splitting
The invention relates to a rear-mounted beam-splitting pupil laser differential confocal Raman spectroscopy test method and device, and belongs to the technical field of microscopic spectral imaging.According to the method, a beam-splitting pupil differential confocal microscopic imaging system is constructed trough Rayleigh scattered light abandoned in a confocal Raman spectroscopy detection system to realize high spatial resolution detection for the geometrical morphology of a sample; and Raman spectroscopy information at a focal point of the sample is precisely acquired by using a focal point information acquired by the beam-splitting pupil differential confocal microscopic imaging system, thus realizing "spectrum-in-one" beam-splitting pupil differential confocal Raman spectroscopy high spatial resolution imaging and detection. The method has the advantages of precise positioning, high spatial resolution, high spectroscopy detection sensitivity and the like and can be widely applied to the field of biomedicines, physical chemistry, precision measurement, femtosecond laser machining and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Differential confocal Raman spectra test method
InactiveCN101290293BImproving the ability of micro-region spectral detectionImprove the ability to detect the geometric position of the micro-areaRaman scatteringLight beamAbsolute measurement
The invention belongs to the micro-spectrum imaging technical field and relates to a differential confocal raman spectral test method. The method integrates the technical characteristics of the differential confocal detection method and the raman spectral detection method, forms a test method capable of realizing sample microarea spectral detection, precisely catches focus positions of excitationlight beams through the differential confocal technology, detects raman spectra of corresponding positions, simultaneously adopts a designed pupil filter, sharpens Airy disc major lobes of a differential confocal raman spectral system, improves the microarea raman spectral detectability and precisely acquires microarea space spectrum information which comprises spectral information and position information of microarea samples. The method obviously improves the microarea spectral detectability of a confocal raman spectromicroscope, has absolute tracking zero points and bipolar tracking characteristics, realizes absolute measurement of physical dimension, can be widely applied in the technical fields such as biomedicine, life sciences, biophysics, biochemistry, industrial precision detection and so on to perform high-precision detection of geometric positions and spectral characteristics of microareas, and has very important application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Microspectroscopy device
ActiveUS20170023409A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryContinuous measurementHigh numerical aperture
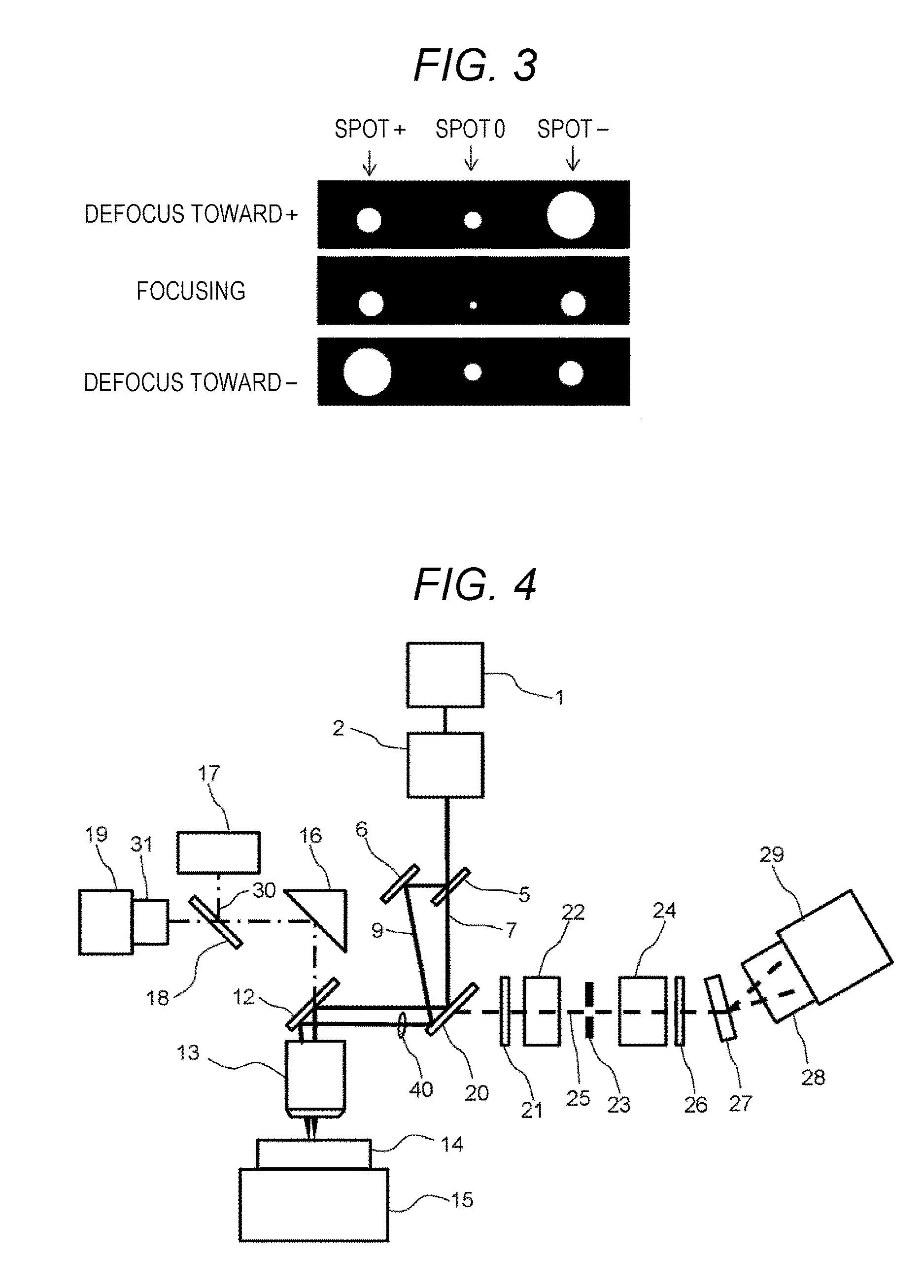
With a microspectroscopy device provided with an objective lens with a high numerical aperture, a defocus arises from thermal drift, etc., necessitating auto-focusing. Conventional auto-focus based on through-focus image acquisition takes time, and thus, it cannot be applied to continuous measurement over a long time wherein high-speed sampling is carried out. The present invention addresses this problem by having a defocus-sensing beam that has either defocus or astigmatism fall incident on the objective lens. Since how the image of the spot of the beam for defocus sensing blurs differs depending on the orientation of the defocus, real-time detection of the amount and orientation of defocus becomes possible, and high-speed realtime auto-focus becomes possible.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
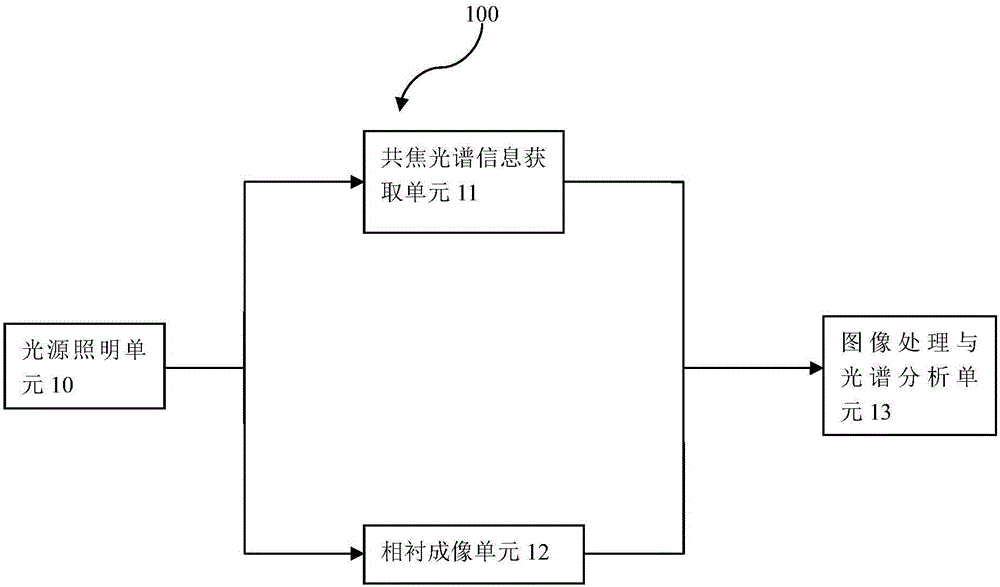
Cell recognition apparatus and method based on phase contrast image and confocal scattering microspectrum
InactiveCN105067617AEasy accessFast 3D MorphologyColor/spectral properties measurementsUsing optical meansImaging processingNormal cell
The invention provides a cell recognition apparatus based on phase contrast image and confocal scattering microspectrum. The cell recognition apparatus is used for detecting early stage cancerous cells in a sample to be detected, and comprises: a light source illumination unit, which is used for emitting and transmitting light; a phase contrast imaging unit, which comprises a phase contrast microscope and a camera; a confocal spectrum information obtaining unit, which comprises a spectrometer for collecting light which is scattered from the sample to be detected, wherein, the light that irradiates the sample is from the other part of light that penetrates from a coupling lens set and the light scattered from the sample is received and transmitted by the coupling lens set again, and obtaining a spectrum containing the component information of the cells; an image processing and spectral analysis unit, which is used for receiving the phase contrast image and the spectrum, and calculating, analyzing and obtaining a qualitative and a quantitative matching result between cells in the sample to be detected and the normal cells; and a control unit for controlling the light source illumination unit, the phase contrast imaging unit, the confocal spectrum information obtaining unit and the image processing and spectral analysis unit to work normally.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
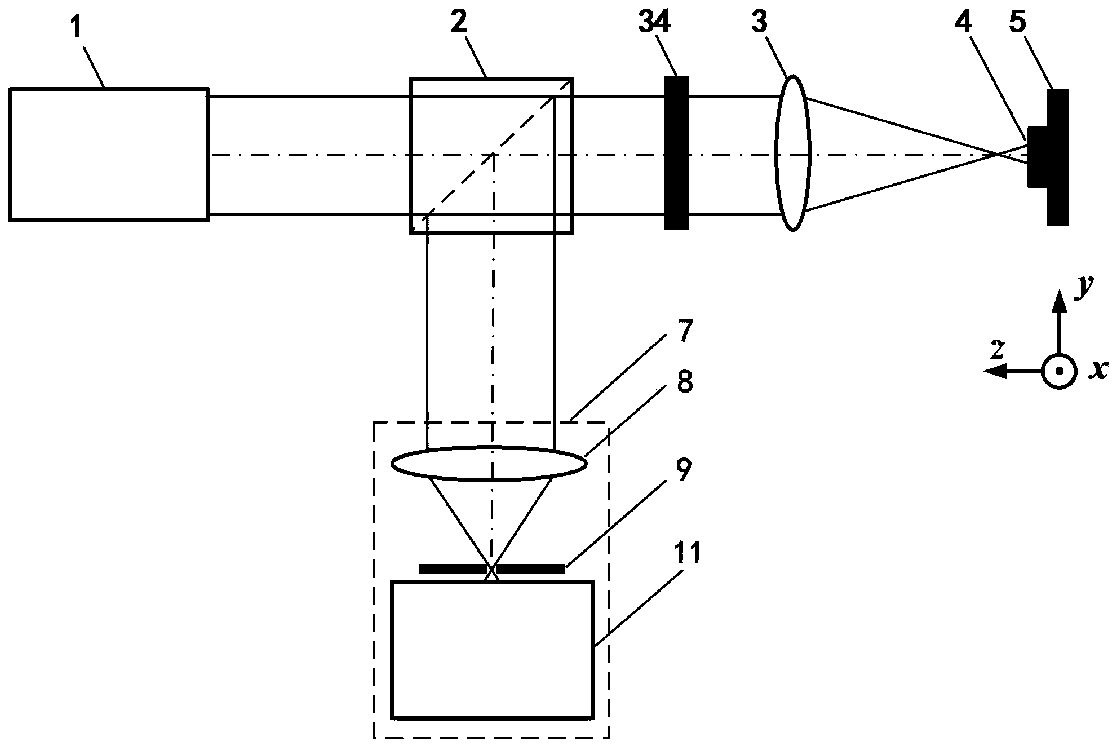
Method and device for testing rear spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum
InactiveCN109211874AImproving the ability of micro-region spectral detectionLight path structure is simpleRaman scatteringRayleigh scatteringFocal position
The invention relates to a method and device for testing a rear spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum, and belongs to the technical field of microscopic spectrum imaging. According to themethod for testing the rear spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum, a spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system is constructed by Rayleigh scattering light abandoned in a confocal Raman spectrum detection system to realize high spatial resolution detection of the geometrical morphology of a sample; and a focal position obtained by the spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system is utilized to accurately obtain Raman spectrum information at the focal point of the sample, so that high spatial resolution imaging and detection of the spectroscopic pupil confocal Raman spectrum of spectrum integration are realized. The method and device for testing the rear spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum have the advantages of accurate positioning, high spatial resolution, high spectrum detection sensitivity and the like, and can be widely applied to the fields of biomedicine, physical chemistry, precision measurement, femtosecond laser processing andthe like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Field electrochemical microspectroscopic imaging analysis method and system
The embodiment of the invention provides a field electrochemical microspectroscopic imaging analysis method and system which are used for solving the problems that the commercially available common working electrode cannot be applied to a spectrum elecrochemical technology, and information on the surface of the working electrode is difficult to acquire. The system comprises light source equipment, electrochemical signal equipment, electrochemical interface equipment and microspectroscopic imaging equipment, wherein the commercially available common working electrode can be vertically arranged in the electrochemical interface equipment; incident light supplied by the light source equipment irradiates to the surface of the working electrode in an inclination manner and is acquired by the microspectroscopic imaging equipment after being reflected; the reflected light comprises the information on the surface of the working electrode; and the microspectroscopic imaging equipment can generate a spectrum according to the reflected light and performs microscopic imaging on the surface of the working electrode, so that the problem that the information on the surface of the working electrode is difficult to acquire on the basis of the existing equipment is solved. Furthermore, an aim of applying the commercially available common working electrode to the spectrum elecrochemical technology is fulfilled.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com