Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Mesh geometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
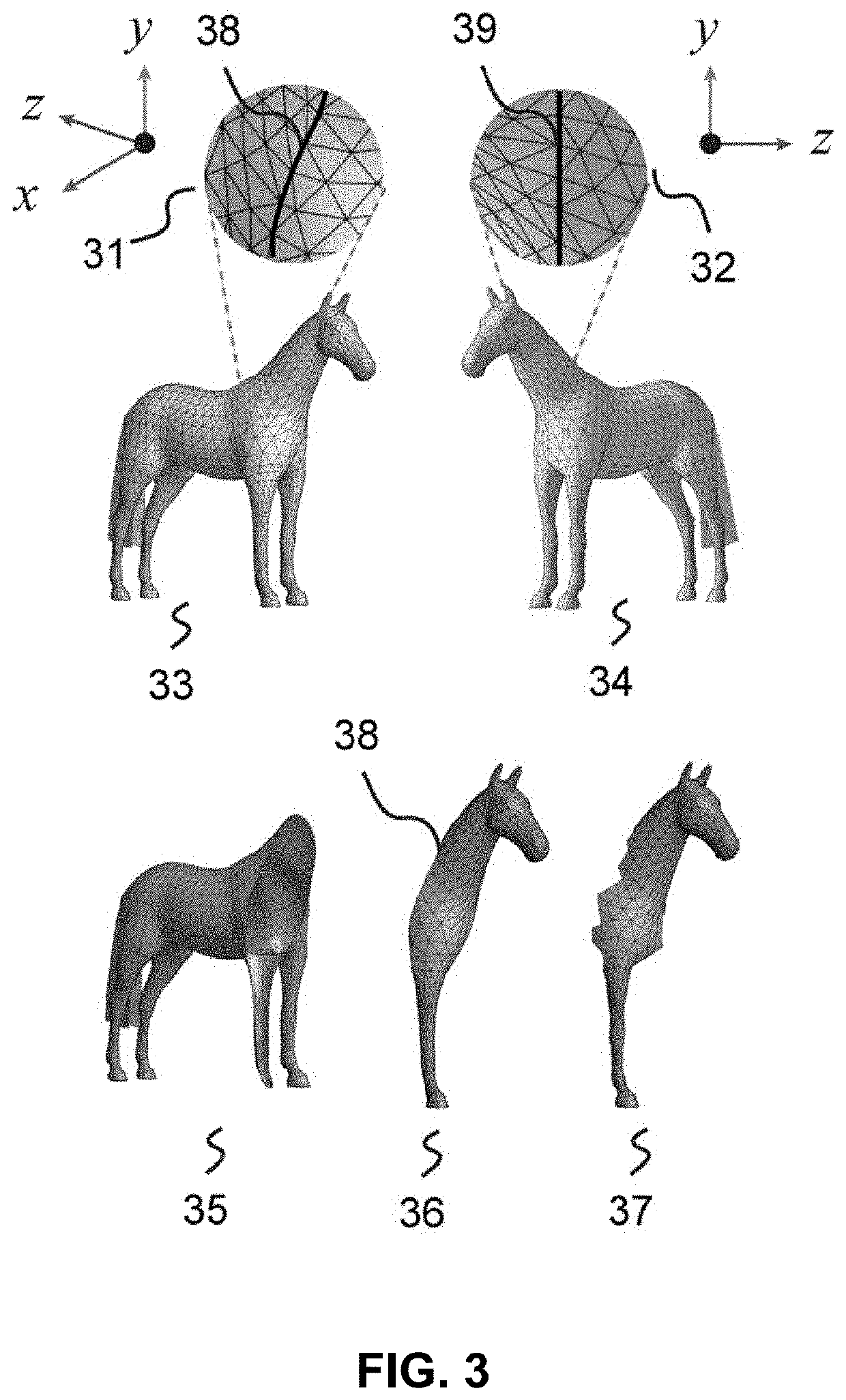
A mesh is typically a collection of polygons/geometric objects. For instance triangles, quads or a mixture of various polygons. A mesh is simply a more complex shape. From Wikipedia: Geometry is a part of mathematics concerned with questions of size, shape, and relative position of figures and with properties of space.
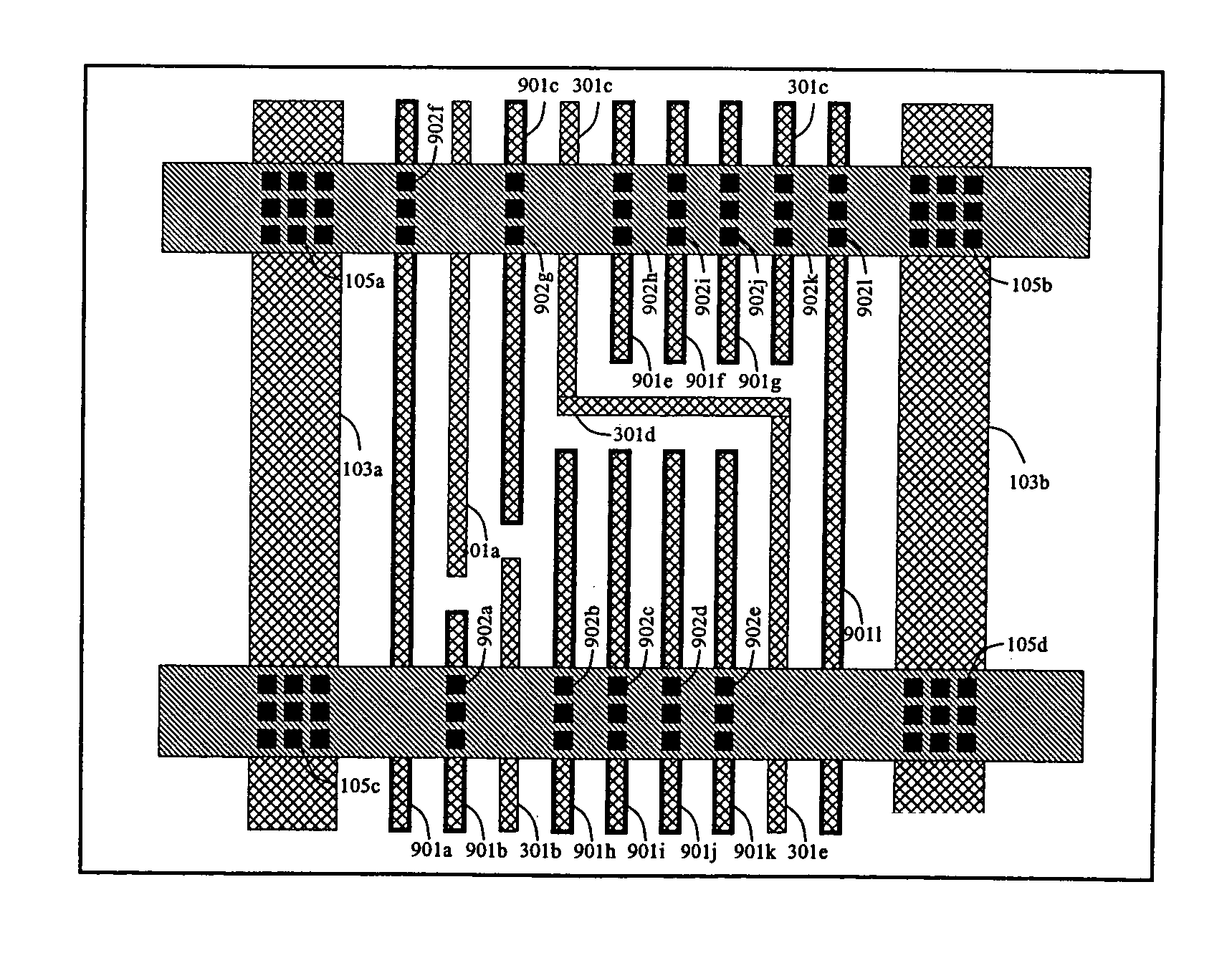
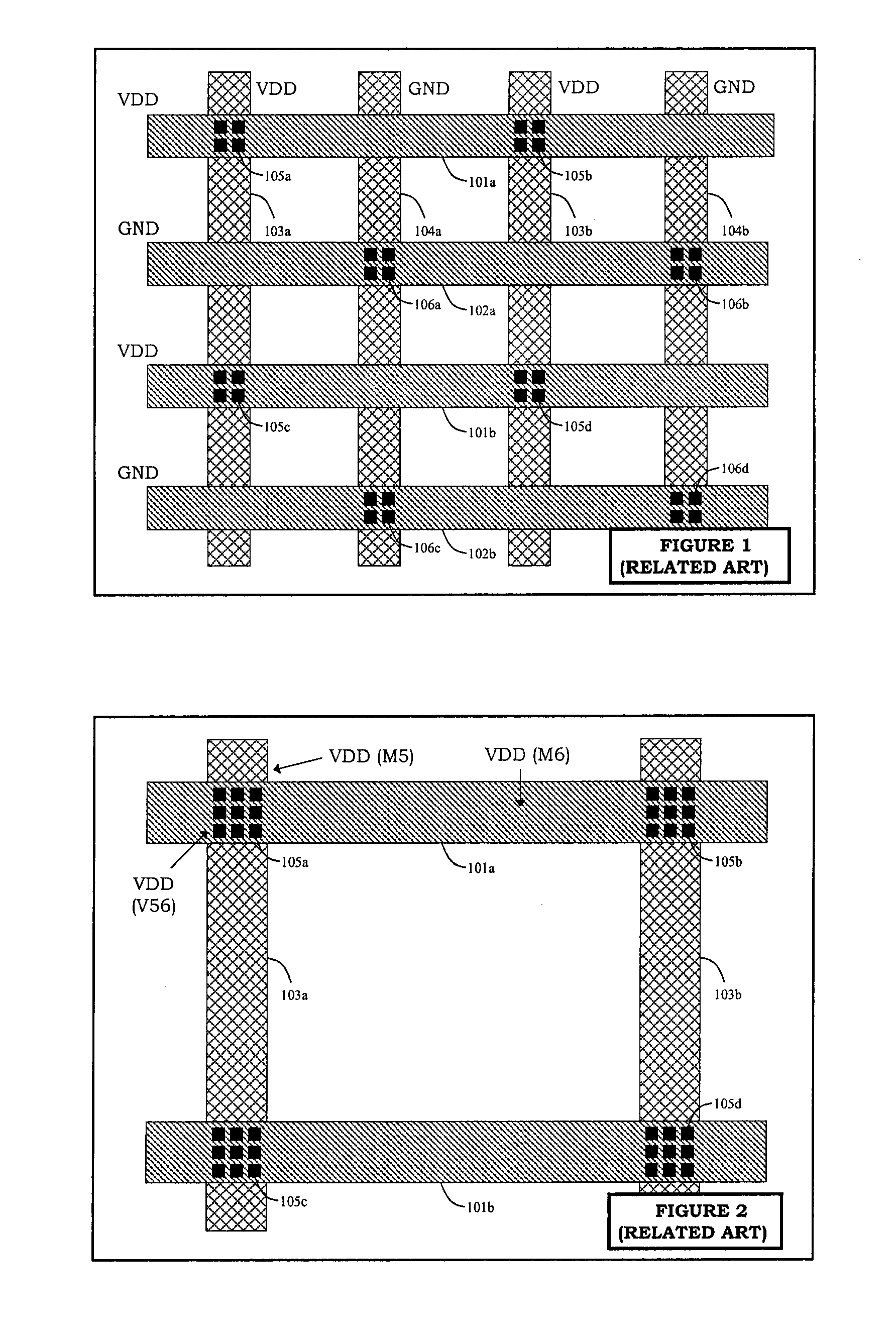
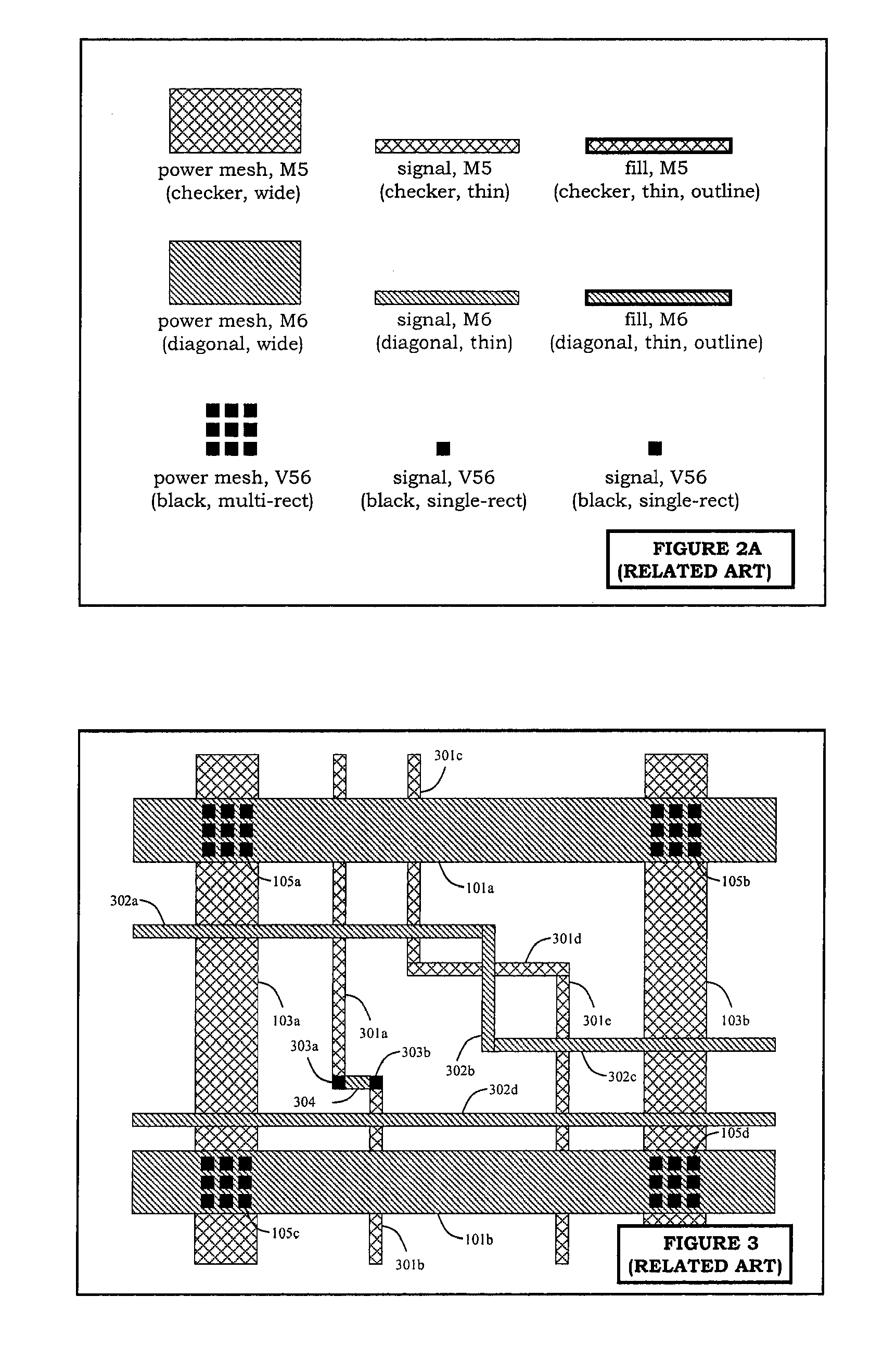
Redundantly tied metal fill for IR-drop and layout density optimization
ActiveUS7240314B1Reduce voltage dropAvoid volume increaseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage drop
An integrated circuit and a method for using metal fill geometries to reduce the voltage drop in power meshes. Metal fill geometries are connected to the power mesh using vias or wires at multiple locations. Metal fill geometries are connected to other floating metal fill geometries using vias or wires at multiple locations. The circuit design introduces maximum redundancy between metal fill geometries and power mesh geometries, but partial redundancy between metal fill geometries and metal fill geometries. In particular, the redundancy in connectivity between metal fill geometries and metal fill geometries is kept minimal to reduce the number of geometries introduced. The high redundancy between metal fill geometries and power mesh geometries and the partial redundancy among metal fill geometries result in a smaller IR-drop by reducing the effective resistance on a power mesh. Hence, the invention use redundancy carefully and advantageously to achieve simultaneous metal density and IR-drop optimization without introducing excessive number of metal fill geometries.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method of visualizing geometric uncertainties
InactiveUS20100268515A1Rapid assessmentEfficient executionComputation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsMesh geometryTest procedures
A method of constructing an enveloping mesh geometry (EMG) for a plurality of sample mesh geometries (MG). The enveloping mesh geometry is a geometric representation of the mean of the probability distribution underlying the sample space from which the enveloping mesh geometry (MG) have been drawn. The method is based on estimating probability densities fj using the kernel density method. The method further comprises constructing, based on the enveloping mesh geometry (EMG) so constructed, further enveloping mesh geometries (EMG-α) related to the α-Quantiles of the probability distribution. The enveloping mesh geometries (EMG, MG-α) are suitable for development and test procedures in aircraft and automotive manufacturing processes.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
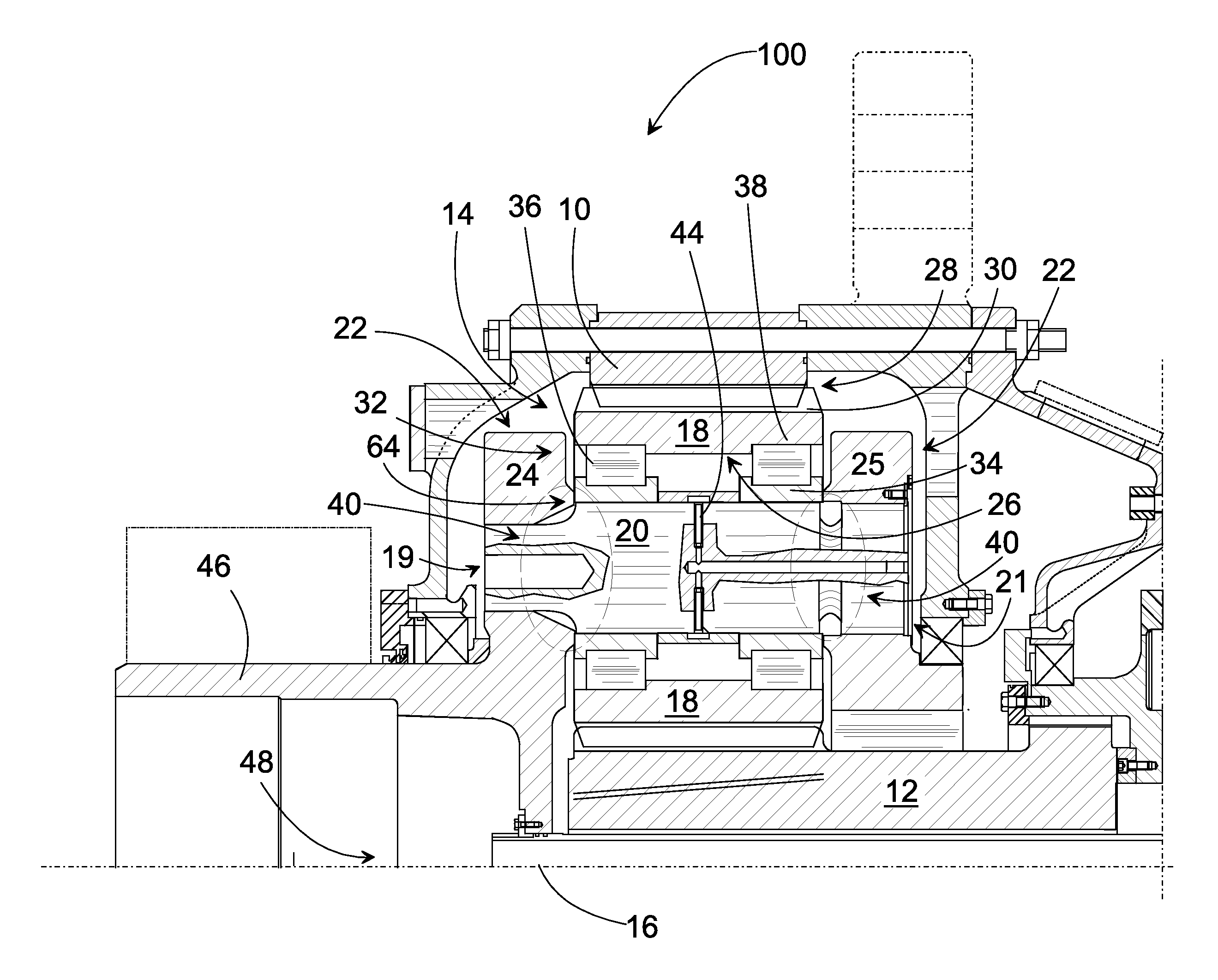
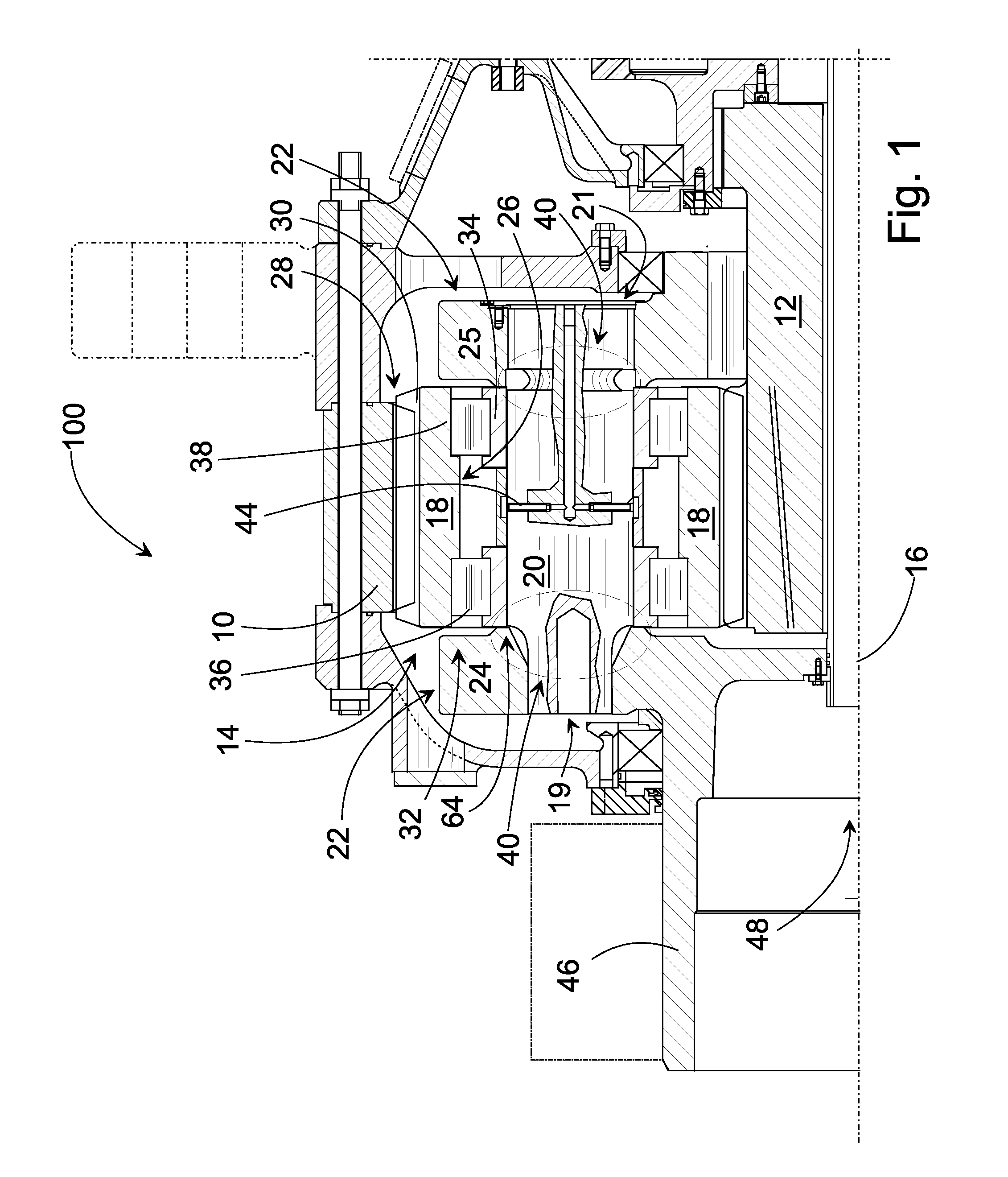
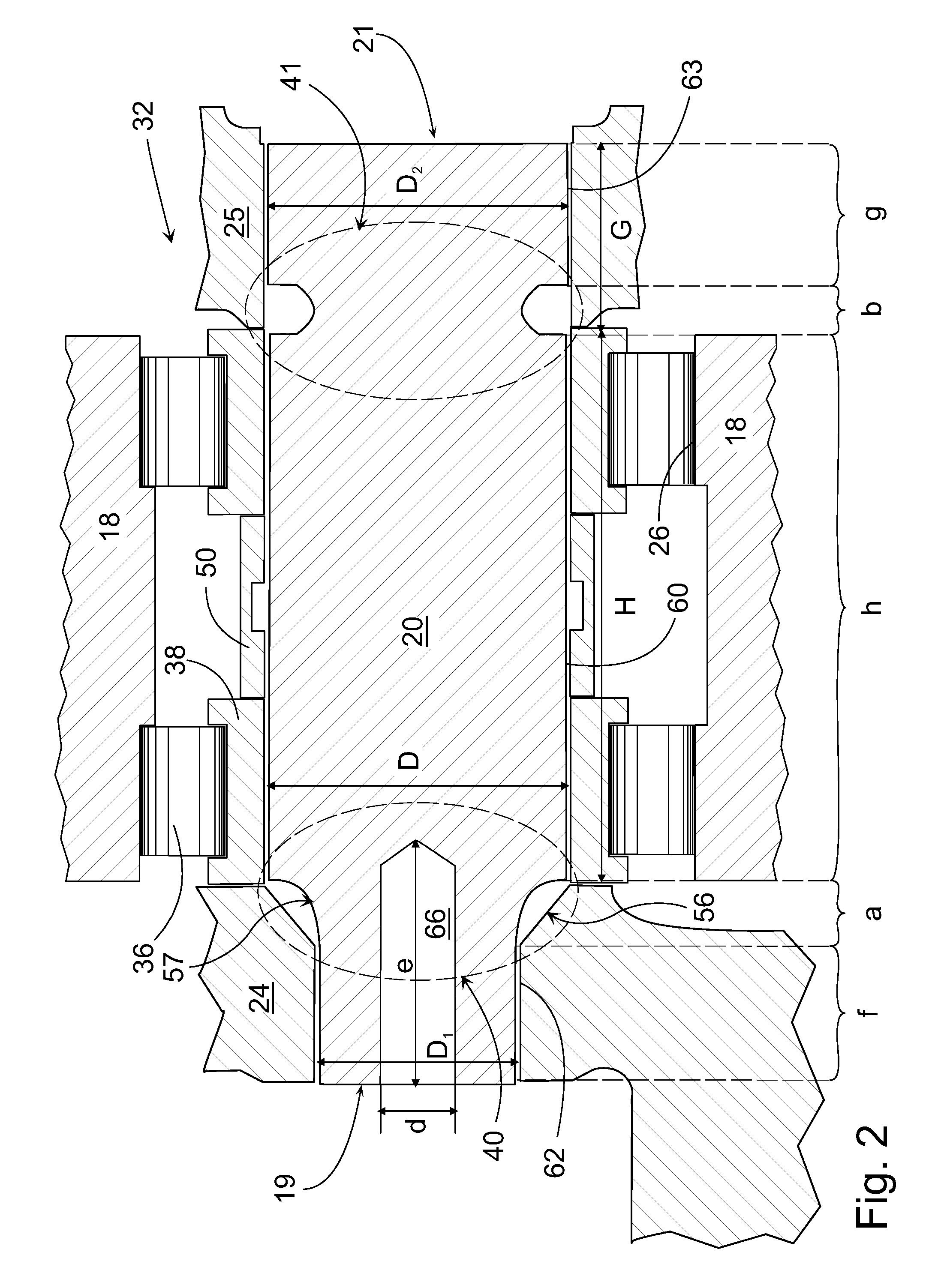
Arrangement in a Planetary Gearing and a Planetary Gear
ActiveUS20100292044A1Reduce the total massEliminate the effects ofEngine fuctionsToothed gearingsGear wheelMesh geometry
The invention relates to an arrangement and a corresponding planetary gear for increasing the rotation speed including a sun wheel (12), a gear rim (10), a planet gear (14), a power input shaft (46), and a planet carrier. A construction (40) allowing flexing is placed between the support length (f) of the first fastening end (62) of the shaft (20) of the planet wheel (18) and the closest bearing for dynamically adapting the mesh geometry.
Owner:MOVENTAS GEARS
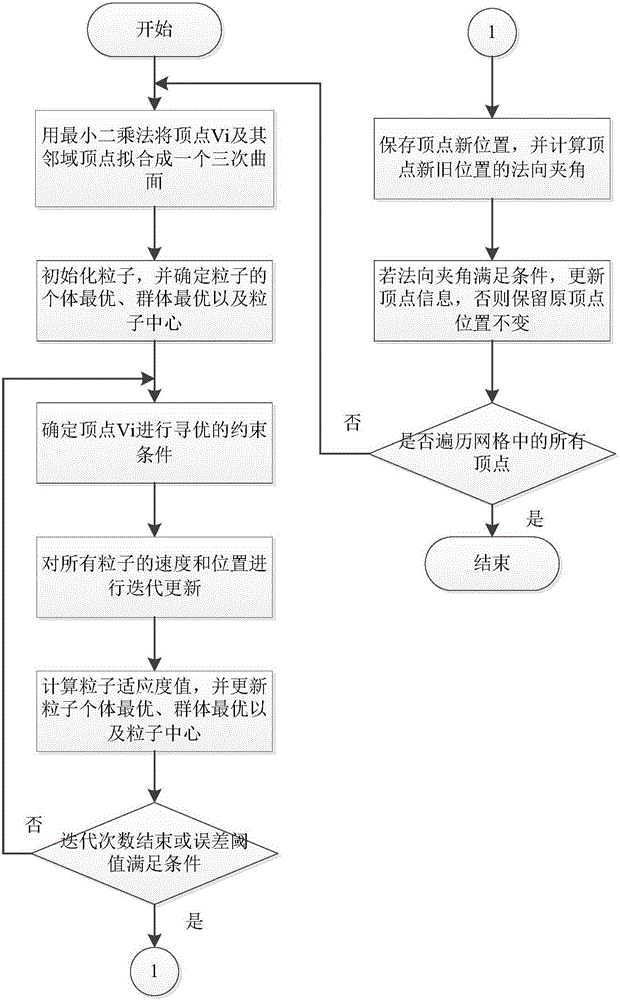
Particle swarm algorithm-based triangular mesh normalization method
ActiveCN106157370AImprove triangle qualitySolve the problem of volume shrinkageDetails involving 3D image data3D modellingLocal optimumAlgorithm
The invention discloses a particle swarm algorithm-based triangular mesh normalization method. With the method adopted, the quality of triangles in a mesh model can be effectively improved with the geometric characteristics of meshes ensured. According to the method, a particle center position Pc, a constraint factor Xi and an adaptive inertia factor Omega a are introduced to improve a particle swarm algorithm, and therefore, a situation that the algorithm is trapped in local optimum when operating can be avoided effectively, the convergence speed of the algorithm can be increased, and the search range of the algorithm is adjusted in real time; the local fitting surface of vertexes is adopted as the search domain of particle swarms, and therefore, the problem of volume shrinkage of a triangular mesh model after normalization existing in most of algorithms can be solved; and whether a certain vertex is required to be adjusted can be confirmed through judging whether the included angle of the normal directions of the vertex before and after adjustment, and therefore, the detail features of the mesh model after normalization will not lose.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
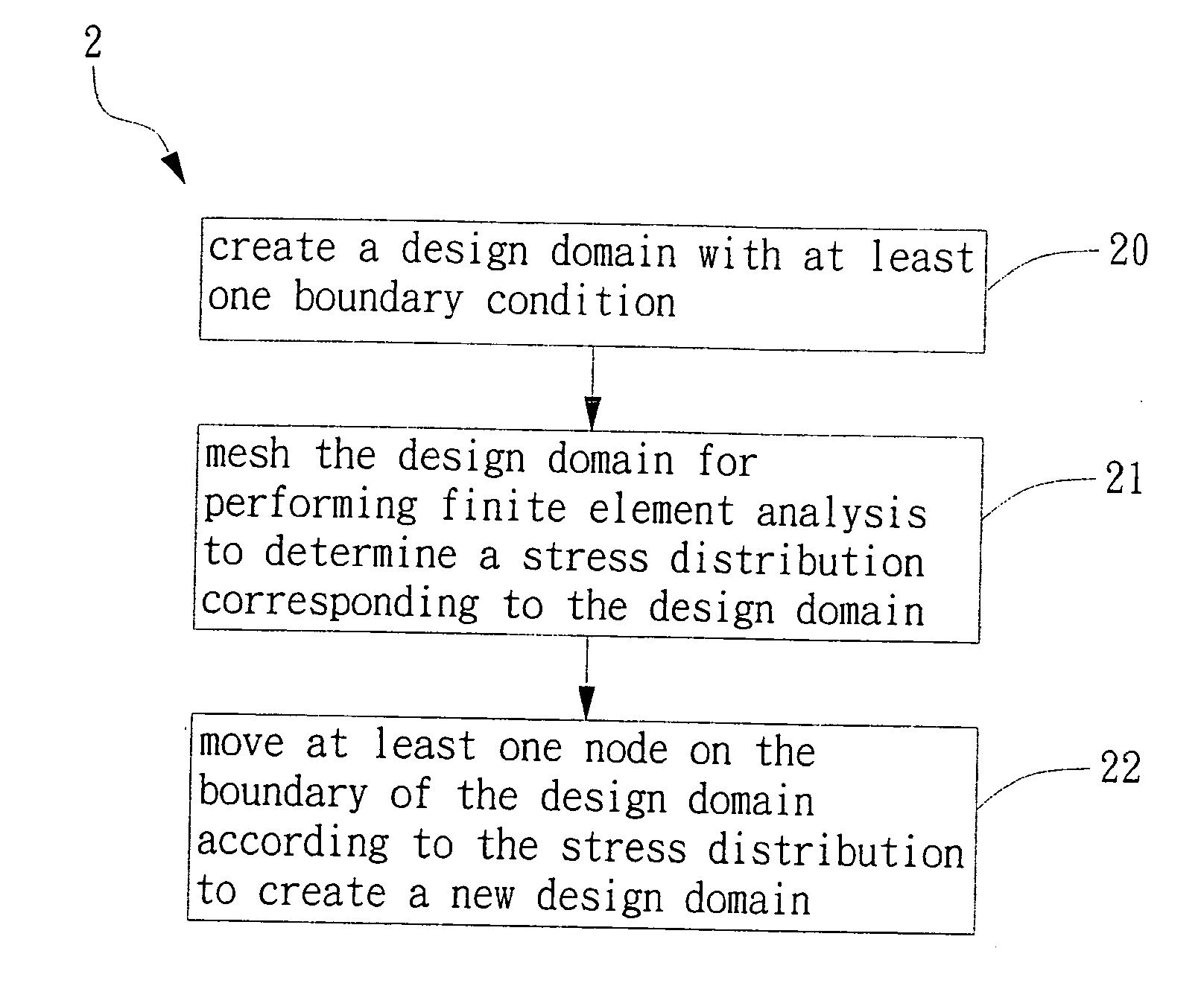
Method of evolutionary optimization algorithm for structure design
InactiveUS20080183436A1Geometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStress distributionElement analysis
The present invention discloses a method of evolutionary optimization algorithm for structure design which comprises steps of: meshing a geometric structure with applied geometric boundary conditions; analyzing the meshed geometric structure by finite element analysis to determine the relative stress distribution of the structure; and evolving the geometric structure by migrating geometric boundary nodes. During evolution, meshing and finite element analysis are repeated to perform structural optimization evolutionally till the evolving design converged to an optimum. The present invention overcomes the mesh-dependency problem in most of structural optimization algorithms in the field of structure topology optimization. In addition, the optimized design of the present invention possesses smooth geometric boundaries. Moreover, structure topology resolutions can be controlled and capable of producing designs that are very close to exact theoretical analysis.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Capturing and stylizing hair for 3D fabrication
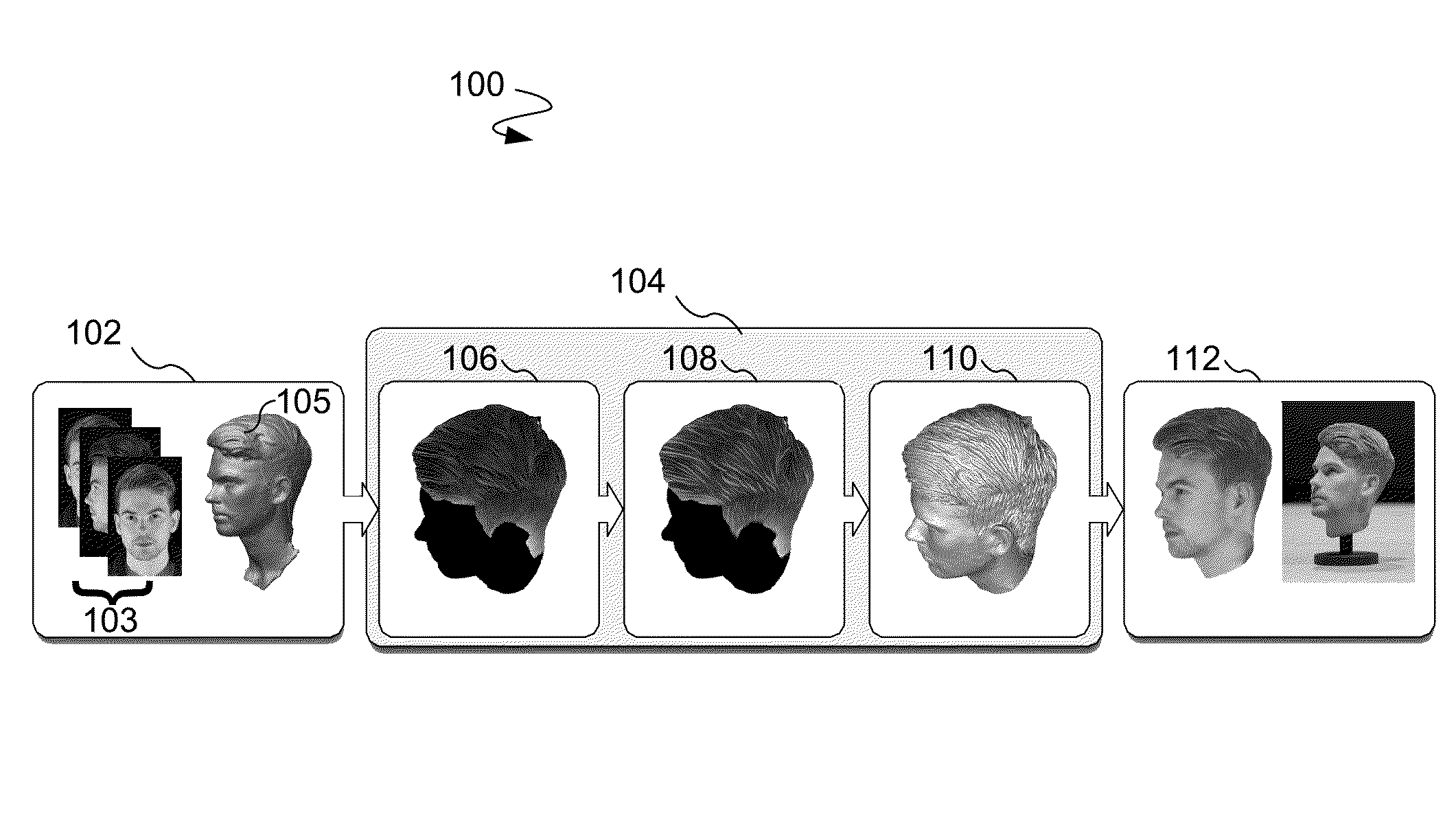
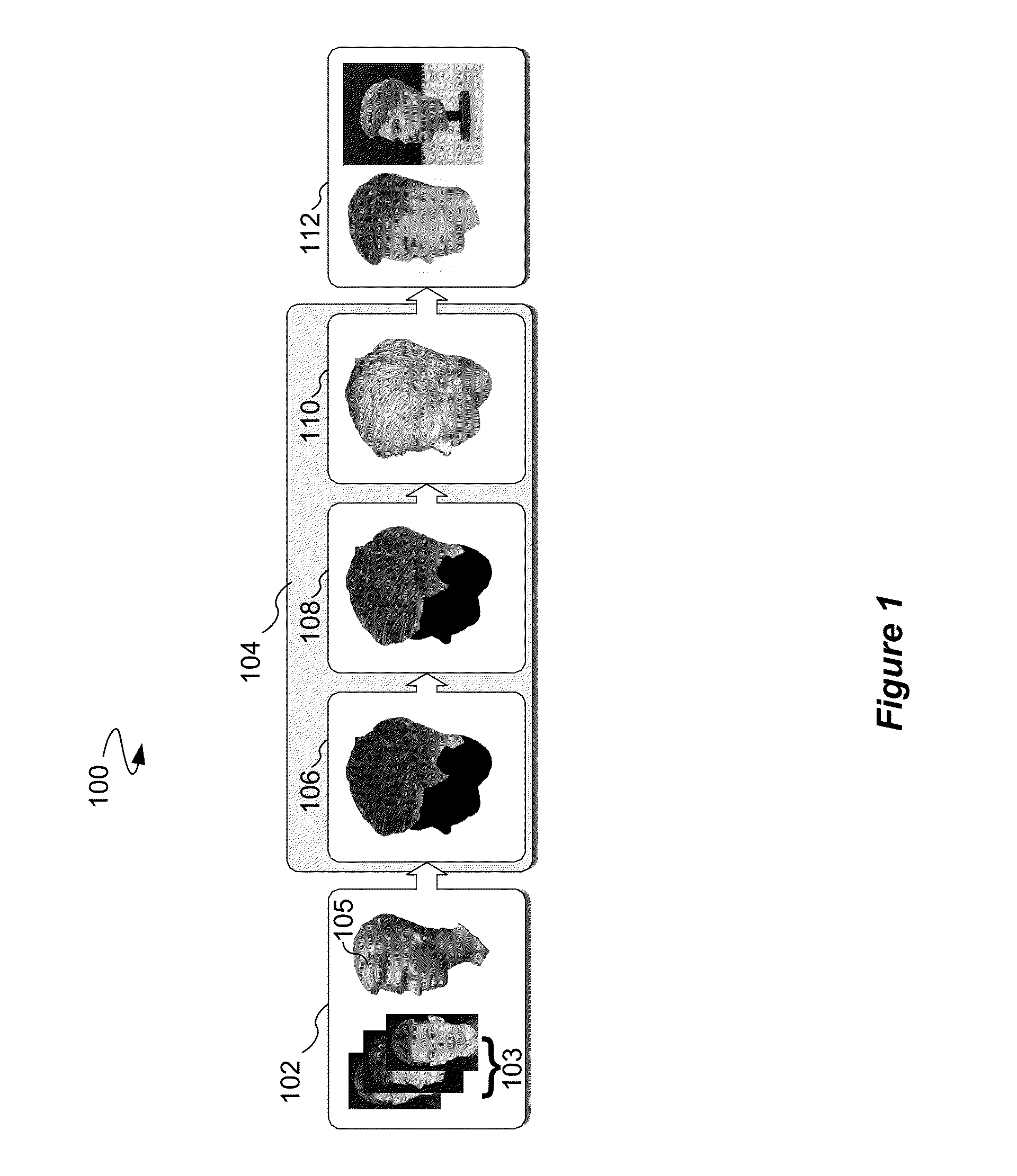
ActiveUS20160071316A1Reduce complexityAdd dimension3D-image rendering3D modelling3d fabricationComputer graphics (images)
A process, computer program product, and apparatus provide color and shape stylization for a captured hairstyle. The process, computer program product, and apparatus receive a plurality of images of a hairstyle in an n dimensional space at a plurality of different angles. Further, the process, computer program product, and apparatus generate a mesh surface in an n−1 dimensional space. In addition, the process, computer program product, and apparatus combine color data from the plurality of images at the plurality of different angles with mesh geometry data of the mesh surface. The process, computer program product, and apparatus also stylize the color data with an n dimensional filter that projects the color data to the n−1 dimensional space of the mesh surface. The process, computer program product, and apparatus may also stylize the geometric shape details in a coherent manner with the color.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Volumetric Grid Generation in a Domain with Heterogeneous Material Properties
Method for generating a 3D grid, and for defining a material property model on the grid, to use, for example, in a reservoir simulator. A mapping is defined (61,71) to a design space in which the material property is described as a piecewise smooth implicit or explicit function in three dimensions. Grid geometry is constructed only in the physical space of the model (62-65,73-76), and no grid is required in the design space. The material property, for example permeability, is sampled in the design space (66,77) to populate the cells in the grid constructed in the physical domain. Prismatic grid cells may be truncated based on faults and horizons (65), or maybe conformed to fault surfaces using a 3D parameterization of the model (76). Only forward mapping, i.e. from the physical domain to the design space, is required.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
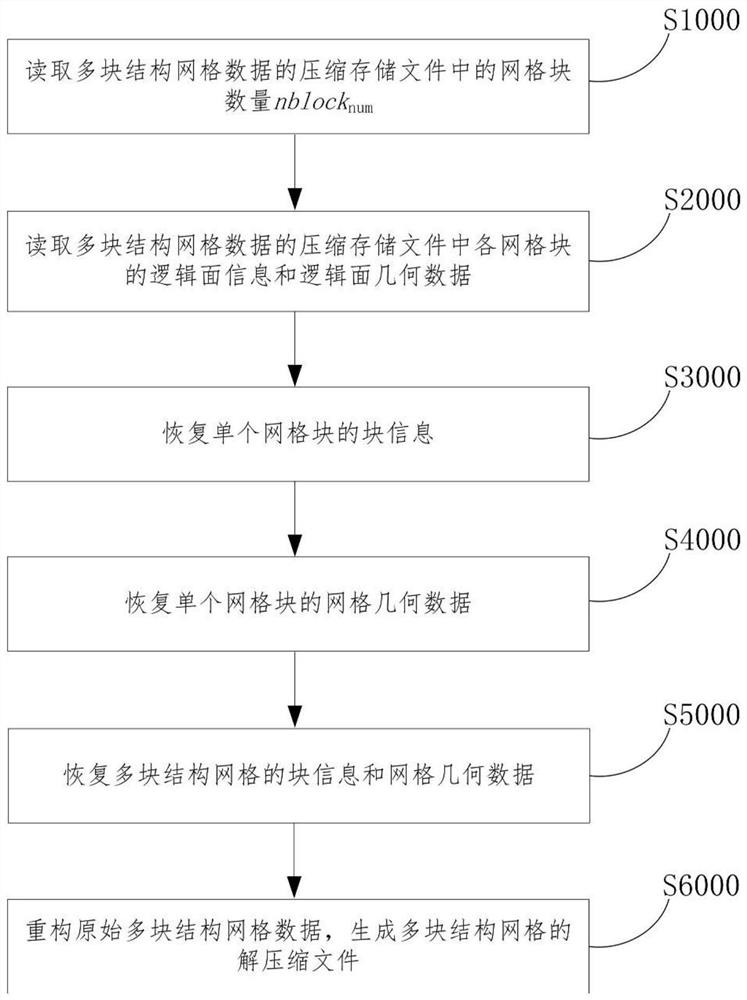
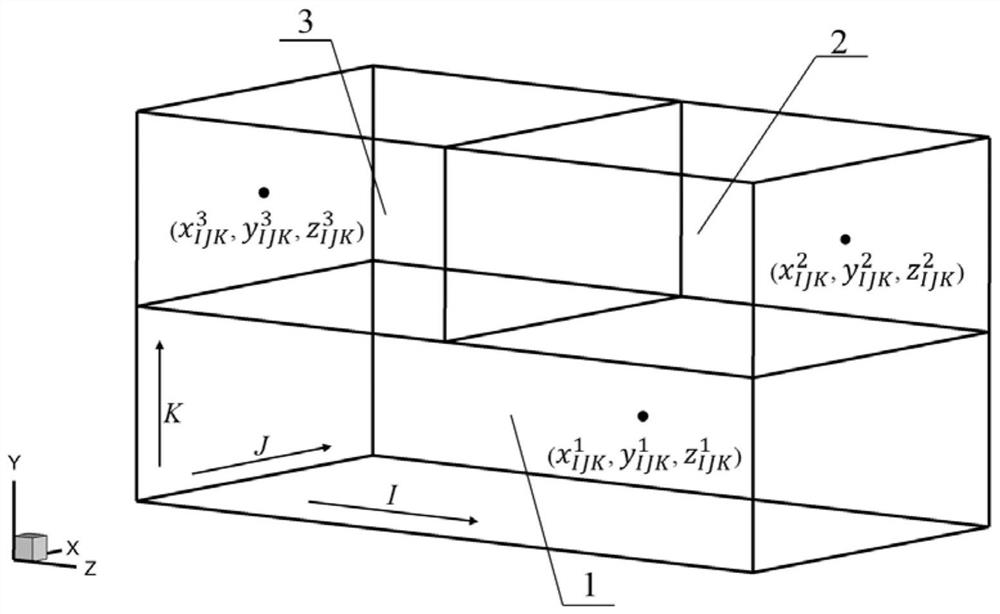
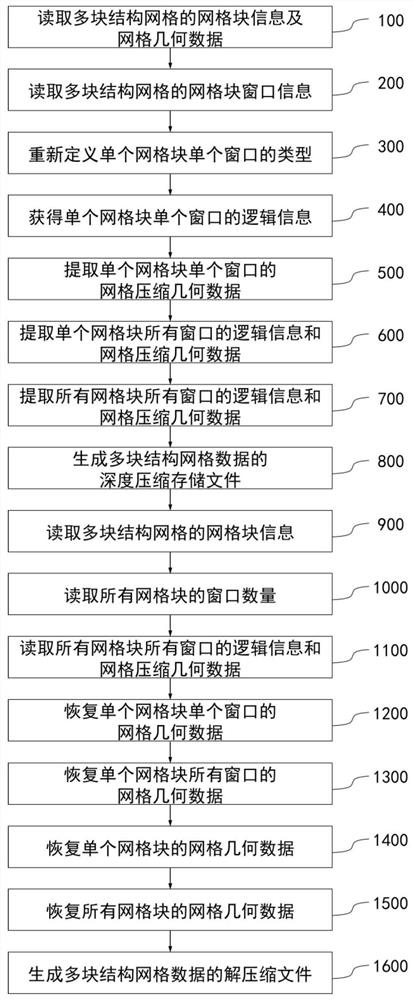
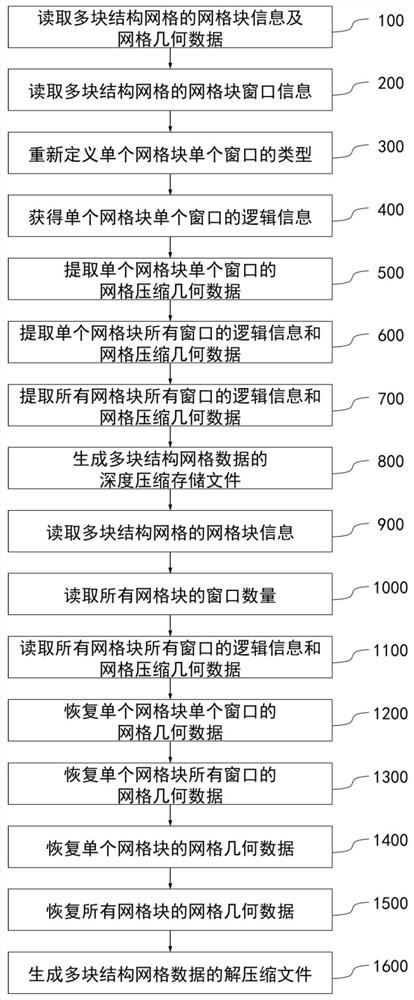
Multi-block structure grid data compression and storage method and device and multi-block structure grid data decompression method and device
ActiveCN112162957AImprove storage efficiencyReduce bandwidth requirementsGeometric CADDigital data information retrievalData compressionEngineering
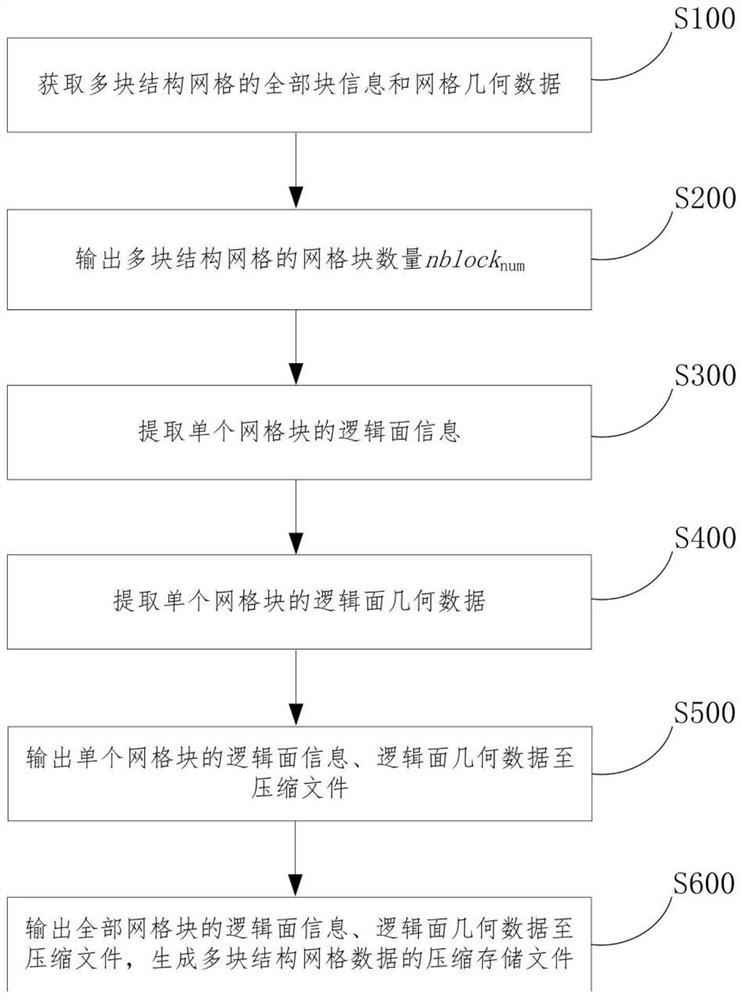
The invention discloses a multi-block structure grid data compression and storage method. The method comprises the following steps: extracting block information and grid geometric data of a pluralityof block structure grids; outputting the number nblocknum of the grid blocks to a file; extracting logic surface information and logic surface geometric data of six logic surfaces of a single grid block; sequentially outputting the logic surface information and the logic surface geometric data of the six logic surfaces of the single grid block to a compressed file, and completing output of the logic surface information and the logic surface geometric data of the single grid block; and completing output of logic surface information and logic surface geometric data of all grid blocks of the plurality of structural grids, and generating a compressed storage file of the plurality of structural grids. According to the method, the logic surface information and the logic surface geometric data ofthe single-block structure grid are extracted, the geometric data of the original grid are encoded and compressed, and then the logic surface information and the logic surface geometric data of the grid are stored, so that the storage space of the grid data is reduced, all grid geometric data can be recovered in a lossless manner, the storage space is small, and the storage efficiency is high.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Volumetric grid generation in a domain with heterogeneous material properties
Method for generating a 3D grid, and for defining a material property model on the grid, to use, for example, in a reservoir simulator. A mapping is defined (61,71) to a design space in which the material property is described as a piecewise smooth implicit or explicit function in three dimensions. Grid geometry is constructed only in the physical space of the model (62-65,73-76), and no grid is required in the design space. The material property, for example permeability, is sampled in the design space (66,77) to populate the cells in the grid constructed in the physical domain. Prismatic grid cells may be truncated based on faults and horizons (65), or maybe conformed to fault surfaces using a 3D parameterization of the model (76). Only forward mapping, i.e. from the physical domain to the design space, is required.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
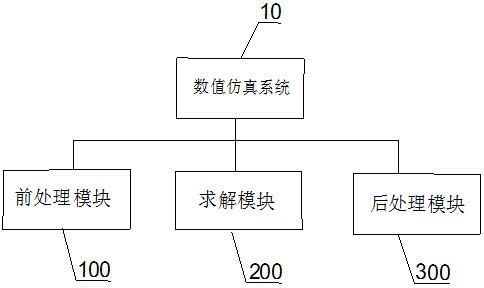
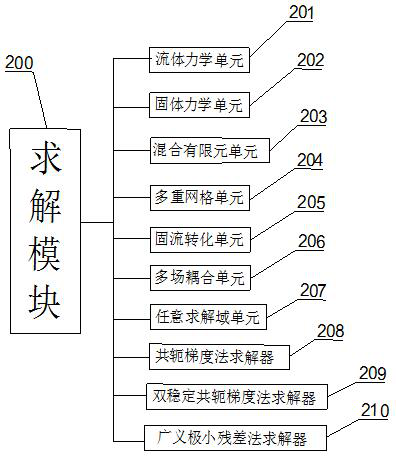
Variable calculation domain Lagrange integral point finite element numerical simulation system and method
PendingCN111859766ASolving Mesh Distortion ProblemsFast and accurate modeling and analysisDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a variable calculation domain Lagrange integral point finite element numerical simulation system and method, and the system comprises a preprocessing module which is used for sequentially generating a calculation domain, a calculation grid, a geometric model and a physical model according to the data inputted by a user, and storing the numerical model data; a solving modulewhich is used for receiving the numerical model data, establishing a unit matrix and a large sparse total stiffness matrix according to the input geometric physical parameters and boundary conditions, performing total numerical calculation and local calculation, and storing and outputting a simulation analysis result; and a post-processing module which is used for drawing a cloud chart and a curve chart and storing text data according to the output simulation analysis result. According to the method, large deformation problems such as landslide can be analyzed, the calculation precision and the calculation efficiency can be remarkably improved, and the storage cost is reduced.
Owner:福建省拳石科技发展有限公司
Grid creation method and device, and distribution method and device
ActiveCN109146360ADigital data information retrievalLogisticsGeographic regionsComputer graphics (images)
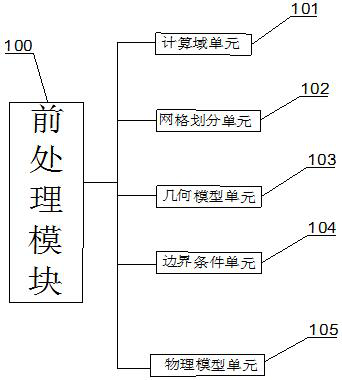
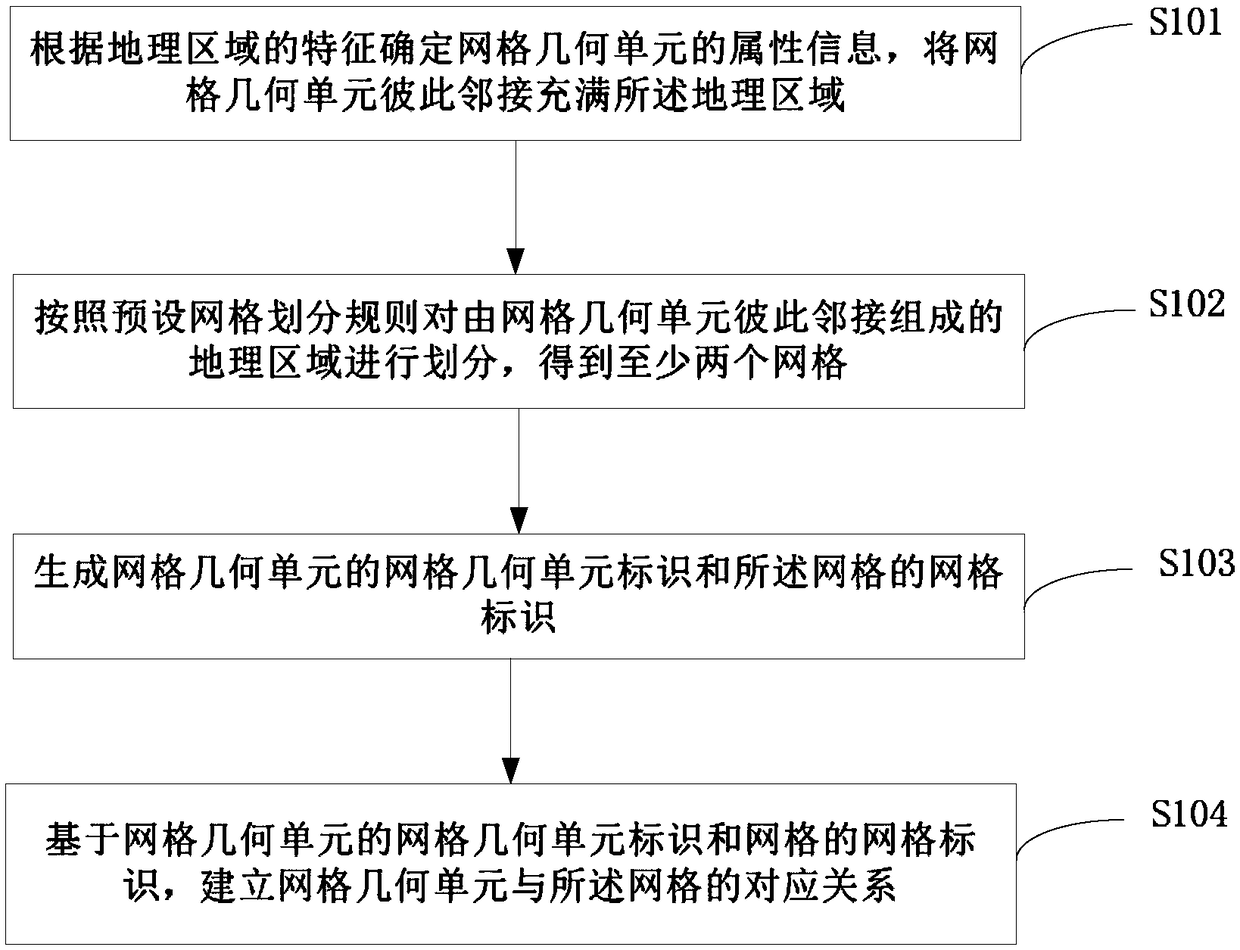
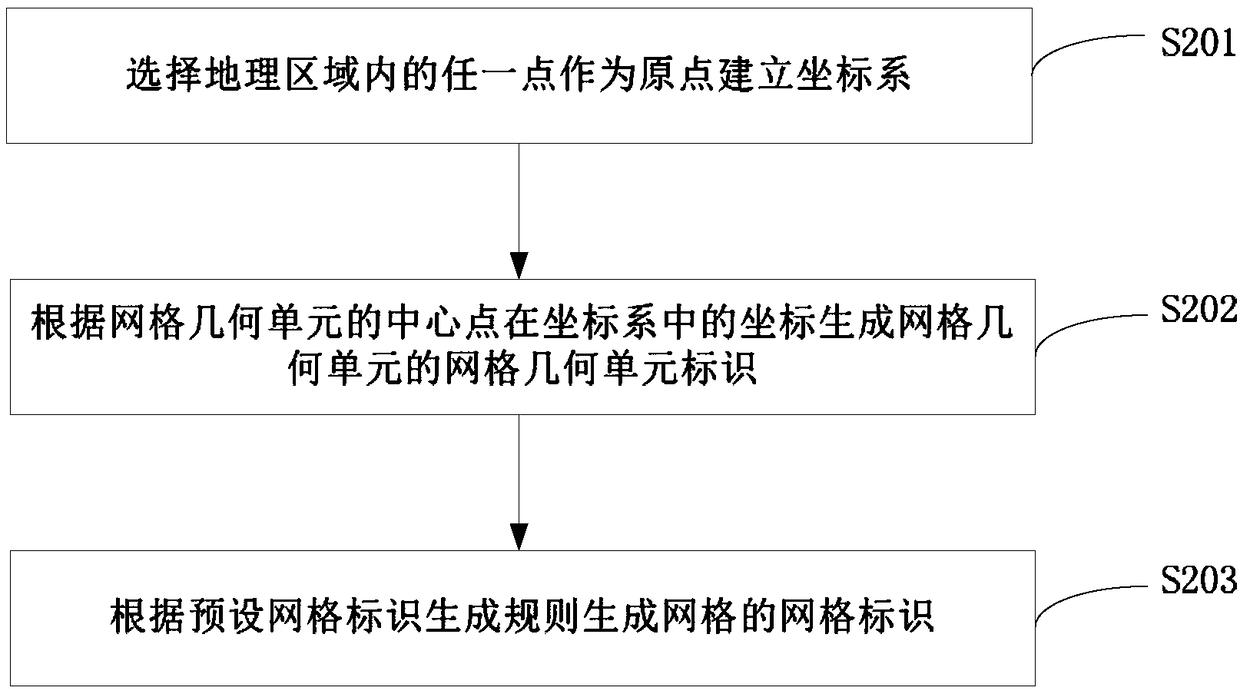
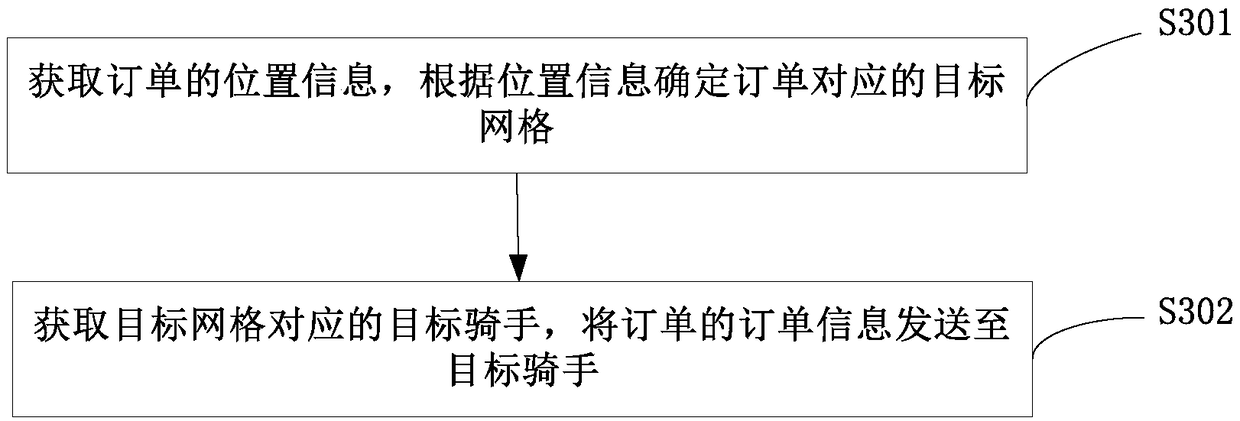
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide a grid creation method and apparatus, and a distribution method and apparatus. The mesh building method comprises the following steps of: determining attribute information of a mesh geometric unit according to characteristics of a geographic region, and filling the geometric region with the mesh geometric units adjacent to each other; at least two meshes being obtained by dividing the geographic region composed of the mesh geometric elements adjacent to each other according to a preset mesh division rule; generating a mesh geometry cell identification of the mesh geometry cell and a mesh identification of the mesh; based on the mesh geometric unit identification of the mesh geometric unit and the mesh identification of the mesh, the corresponding relationship between the mesh geometric unit and the mesh being established, thereby saving the tedious operation of manually selecting points to construct a mesh, improving the efficiency of constructing a mesh, and saving a lot of labor costs. The mesh geometric unit identification of the mesh geometric unit and the mesh identification of the mesh are used to establish the corresponding relationship between the mesh geometric unit and the mesh. Moreover, each mesh geometric element is adjacent to each other, thus solving the problem that the mesh has gaps and providing a solution for 100%coverage of the business.
Owner:RAJAX NETWORK &TECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Efficient data mapping technique for simulation coupling using least squares finite element method
The coupling of geomechanics to reservoir simulation is essential for many practical situations in the exploitation of hydrocarbons. Such coupling requires cross-mapping block-centered data in reservoir model to nodal data in geomechanical finite element model. If different grid geometries and grid densities between two models are used, this data mapping will become considerably challenging. In this invention, an innovative method is proposed to achieve remarkable accuracy of data mapping from reservoir model to the geomechanical model with ease and quite efficiently using least squares finite element method. The achievement of accurate data mapping will enable efficient simulation coupling between reservoir simulation and geomechanical simulation to investigate some engineering problems in the exploitation of hydrocarbons.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
2d-3d sculpture paintings
ActiveUS20200027279A1Guaranteed smoothMinimize the differenceModifying/creating image using manual inputEditing/combining figures or textComputer graphics (images)Engineering
We disclose a method for synthesizing by computer an artwork where 2D and 3D contents are integrated within a same composition. Such an artwork creates plausible effects for the viewers by showing a different relationship between 2D and 3D at each viewing angle. Methods are proposed for ensuring the continuity between the 2D and the 3D parts in terms of mesh geometry and reflected colors. The user selects from a given scene a region of interest (ROI) to be reproduced in 3D. A flat rendering grid is created that matches the topology and tesselation of the ROI. The ROI is attached to the rendering grid. To enhance the continuity between the 2D and the 3D parts of a scene object, the 2D part of the object can be represented as bas-relief. Designers can create 2D-3D sculpture paintings for decoration, exhibitions, and homes.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Damping and support in high-temperature superconducting levitation systems
Methods and apparatuses to provide improved auxiliary damping for superconducting bearings in superconducting levitation systems are disclosed. In a superconducting bearing, a cryostat housing the superconductors is connected to a ground state with a combination of a damping strip of material, a set of linkage arms to provide vertical support, and spring washers to provide stiffness. Alternately, the superconducting bearing may be supported by a cryostat connected to a ground state by posts constructed from a mesh of fibers, with the damping and stiffness controlled by the fiber composition, size, and mesh geometry.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
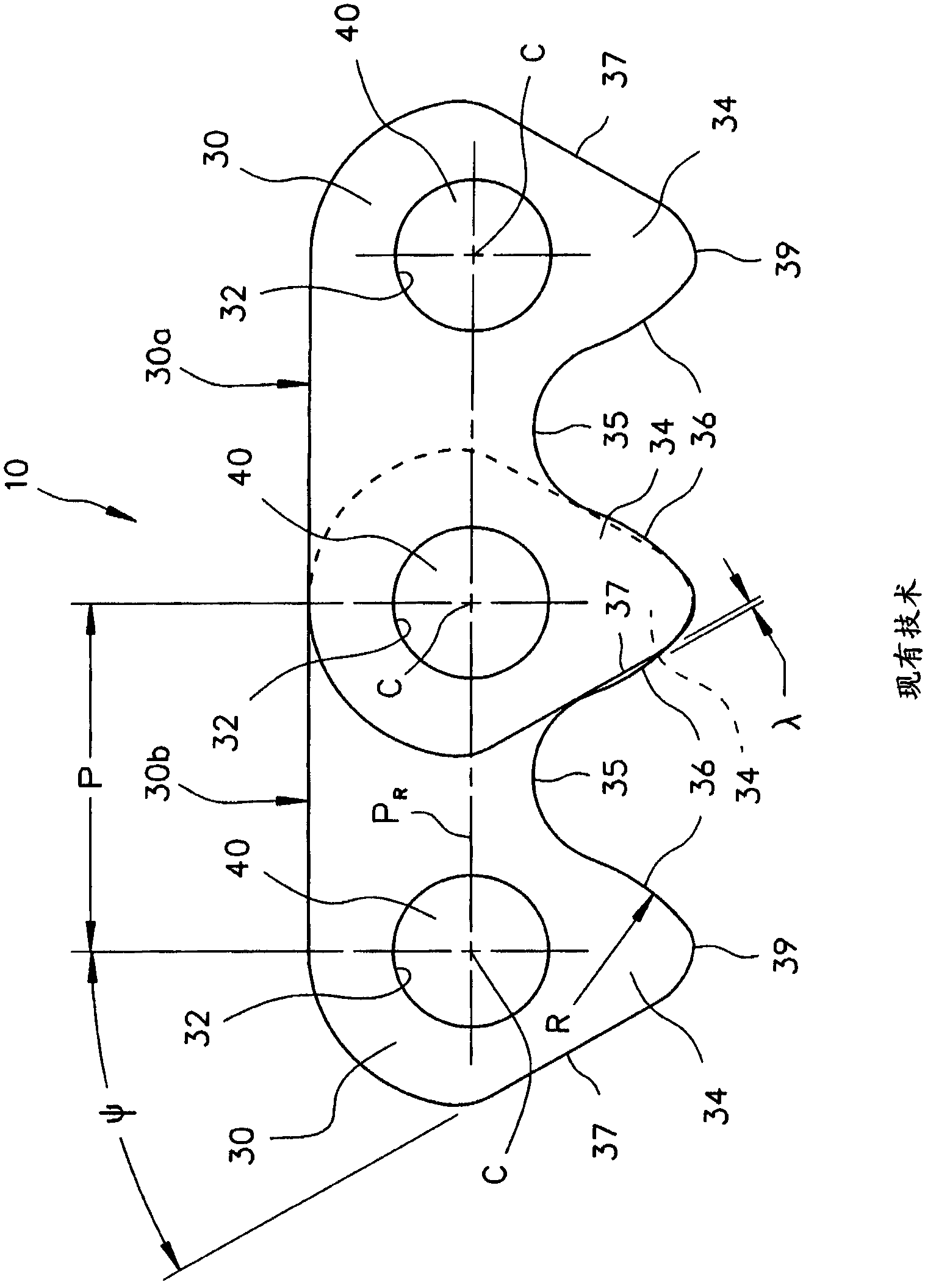
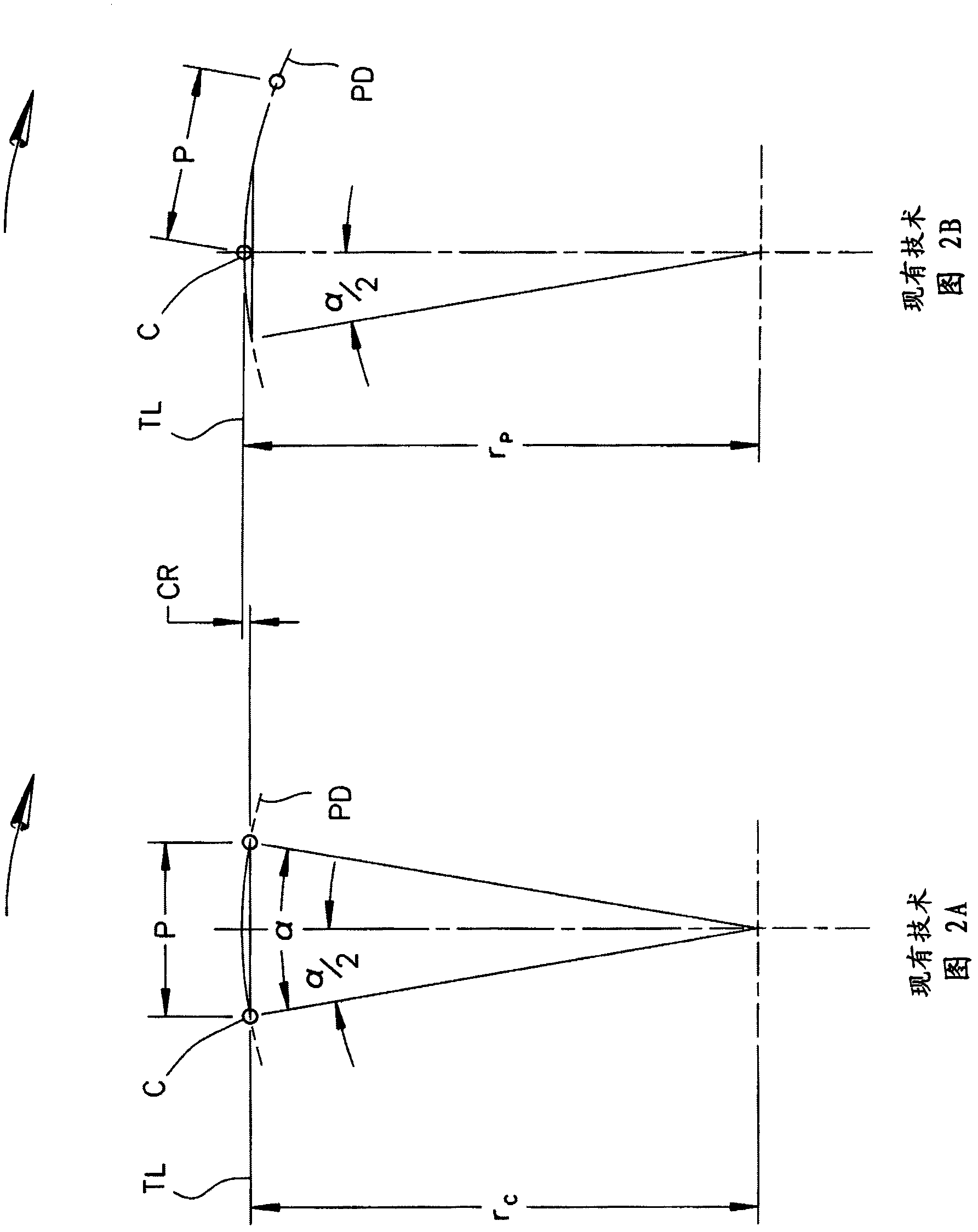
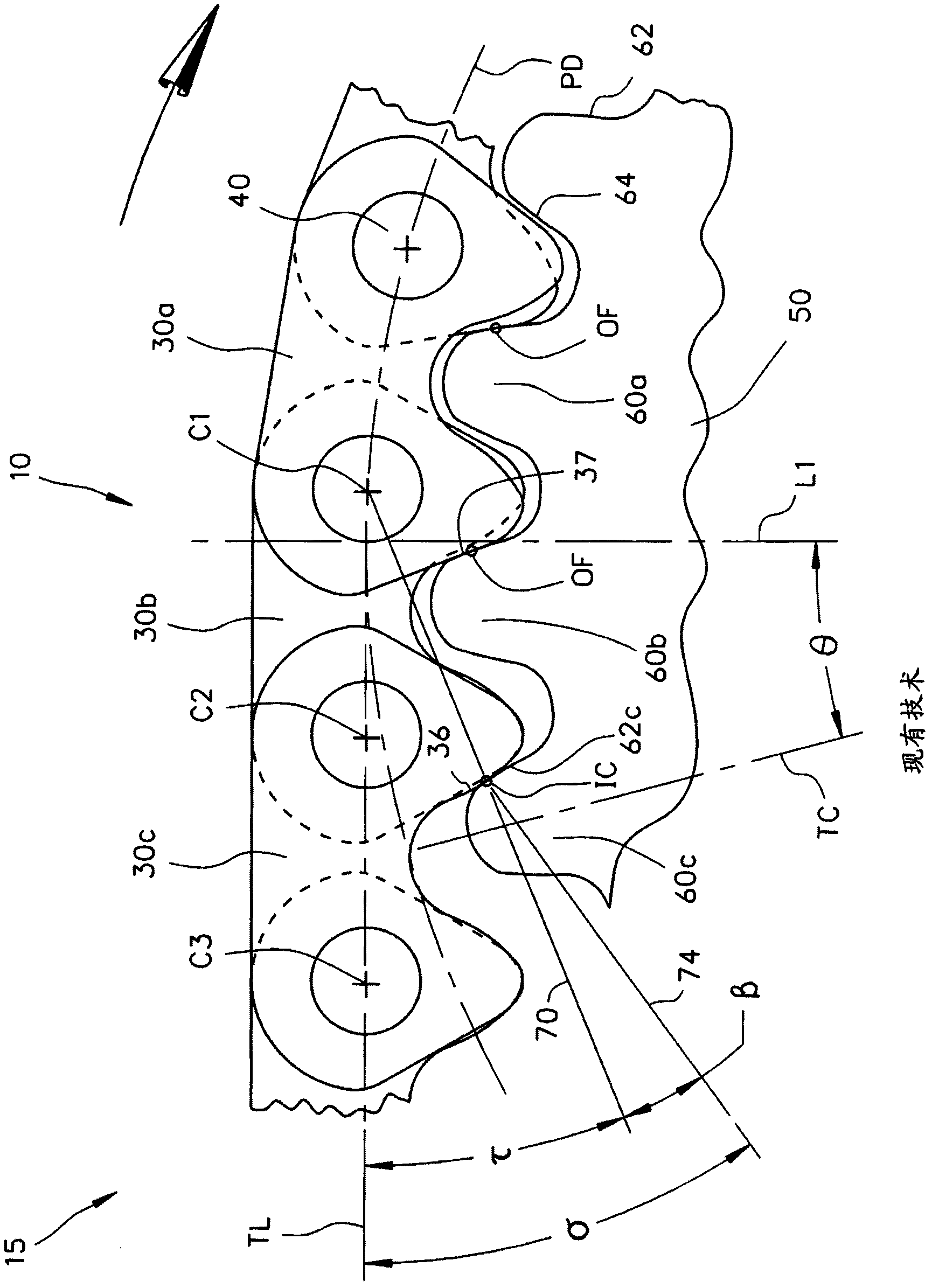
Inverted tooth chain and sprocket drive system with reduced meshing impact
An inverted tooth chain and sprocket drive system in which the initial contact distance ICD, the meshing impact angle Sigma (s), the link plate entrance angle Beta (ss), and other aspects of the meshing geometry are controlled and optimized to reduce noise and vibration by using a particular chain link plate form and, in preferred cases, by modifying the sprocket tooth pressure angle. The system can include first and second sprockets for which the pressure angle can be controlled to ensure that the desired values for the initial contact distance ICD, the meshing impact angle Sigma (s), and the link plate entrance angle Beta (ss) are equal for both sprockets even though the sprockets have different tooth counts. For a chain pitch P in the range of 6.35mm to 7.7mm, the initial contact distance IC0 is controlled such that 0.49P = IC0 = 0.53P, the meshing impact angle Sigma (s) is controlled such that s < 34 DEG , and the link plate entrance angle Beta (ss) is controlled such that ss = 9 DEG . For certain chain and sprocket configurations, s < 31 DEG and ss < 7 DEG .
Owner:CLOYES GEAR & PRODS INC
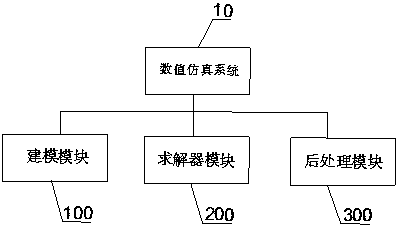
System and method for numerical simulation based on Lagrange integral point finite element
PendingCN111125963AFast and accurate modeling and analysisResolve distortionDesign optimisation/simulationSustainable transportationComputational scienceAlgorithm
The invention discloses a system and a method for numerical simulation based on a Lagrange integral point finite element. The system for numerical simulation comprises: a modeling module which is usedfor sequentially generating a calculation domain, a calculation grid, a geometric model and a physical model according to data inputted by a user, and storing numerical model data; a solver module which is used for receiving the numerical model data, establishing a unit matrix and a large sparse total stiffness matrix according to input geometric physical parameters and boundary conditions, performing total numerical calculation and local calculation, and storing and outputting a simulation analysis result; and a post-processing module which is used for drawing a cloud chart and a curve chartaccording to the output simulation analysis result, and storing text data. Finite element analysis of fluid and incompressible materials can be carried out, the calculation efficiency is greatly improved, and the calculation cost is reduced.
Owner:福建省拳石科技发展有限公司
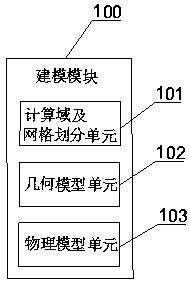
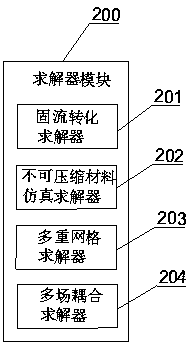
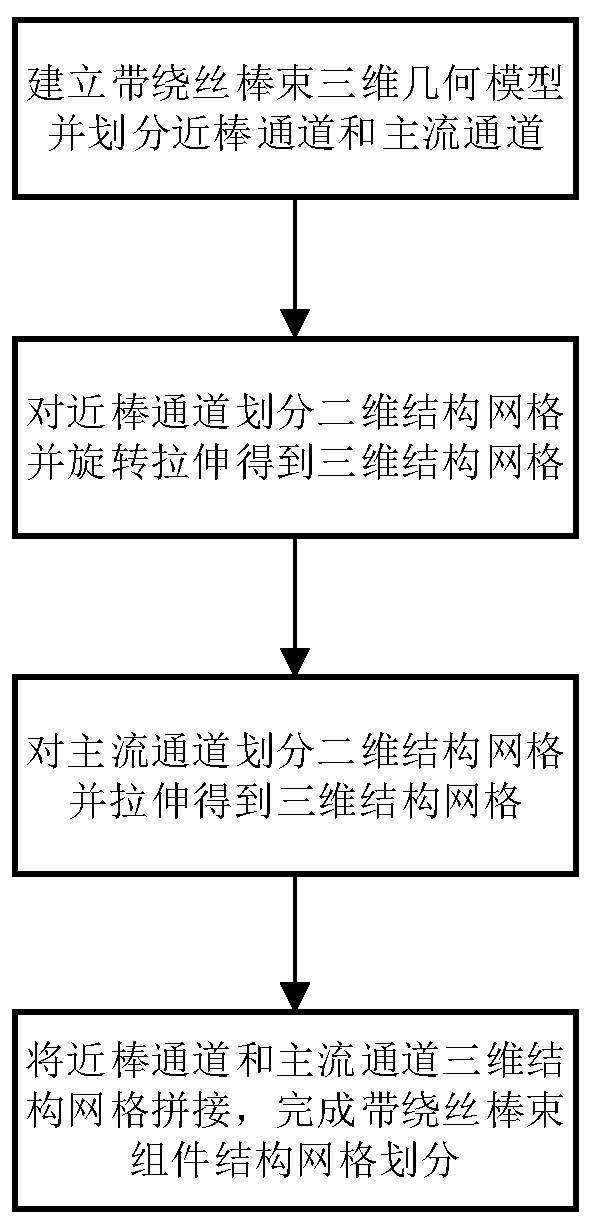
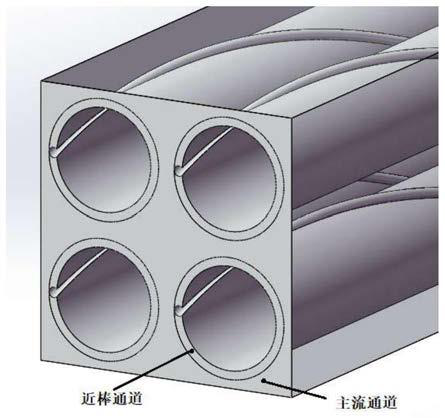
Structured grid division method for rod bundle assembly with wire winding function
InactiveCN111046614AQuality improvementFast convergenceDesign optimisation/simulation3D modellingStructural engineeringMesh geometry
The invention discloses a structured grid division method for a rod bundle assembly with a wire winding function. The method comprises the following steps: building a three-dimensional geometric modelof a flow channel of the rod bundle assembly with the wire winding function, and dividing the three-dimensional geometric model into a near-rod channel containing a wire winding feature and a main flow channel not containing the wire winding geometric feature; establishing a two-dimensional plane topological structure for the flow section of the near-rod channel, setting grid node parameters, dividing a two-dimensional structure grid, and performing rotary stretching to obtain a three-dimensional structure grid of the near-rod channel; dividing the flow cross section of the main flow channelinto two-dimensional structure grids and stretching to obtain three-dimensional structure grids of the main flow channel; and finally, splicing the three-dimensional structure grids of the near-rod channel and the main flow channel to finish the structure grid division of the rod bundle assembly with the winding wire. According to the method, the problems of low geometric reduction degree, poor grid quality, difficulty in controlling the number of grids and the like of non-structural grids of the rod bundle assembly with the winding wires are solved; meanwhile, the number and distribution of grids are easy to adjust, and high-quality grids can be provided for CFD calculation of the rod bundle assembly with the winding wires.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of visualizing geometric uncertainties
InactiveUS8698801B2Statistically accurateEfficient executionCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsMesh geometryTest procedures
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
Finite element grid geometric structure contour recognition method and device and medium
ActiveCN114781233AAutomatically realize the contour recognitionImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationPattern recognitionMesh geometry
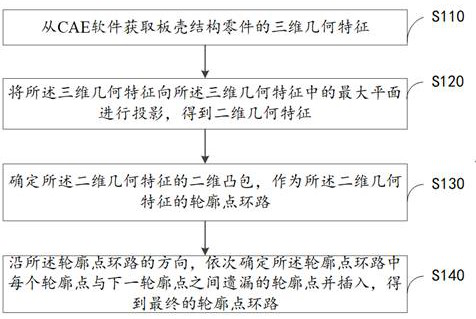
The embodiment of the invention discloses a finite element grid geometric structure contour recognition method and device and a medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring three-dimensional geometrical characteristics of a plate shell structure part from CAE software; projecting the three-dimensional geometric features to a maximum plane in the three-dimensional geometric features to obtain two-dimensional geometric features; determining a two-dimensional convex hull of the two-dimensional geometric feature as a contour point loop of the two-dimensional geometric feature; sequentially determining and inserting missing contour points between each contour point and the next contour point in the contour point loop along the direction of the contour point loop to obtain a final contour point loop; wherein the direction of the contour point loop comprises a clockwise direction and an anticlockwise direction. According to the embodiment, the contour of the complex geometric feature is automatically identified.
Owner:CATARC TIANJIN AUTOMOTIVE ENG RES INST CO LTD
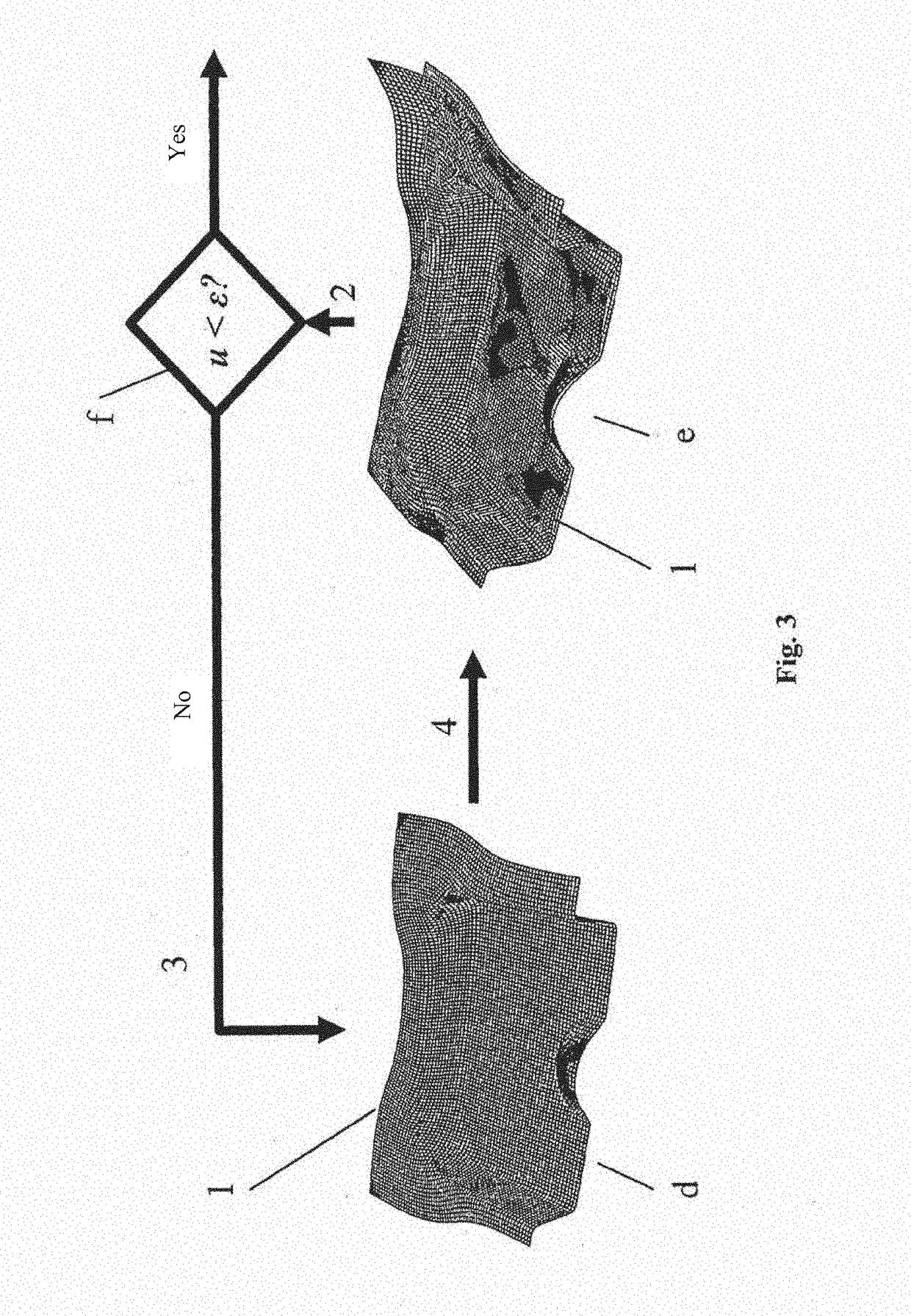
Method for transferring a stress state (stress sensor) of an FE simulation result to a new FE mesh geometry of a modeled construction system in a simulation chain of production operations
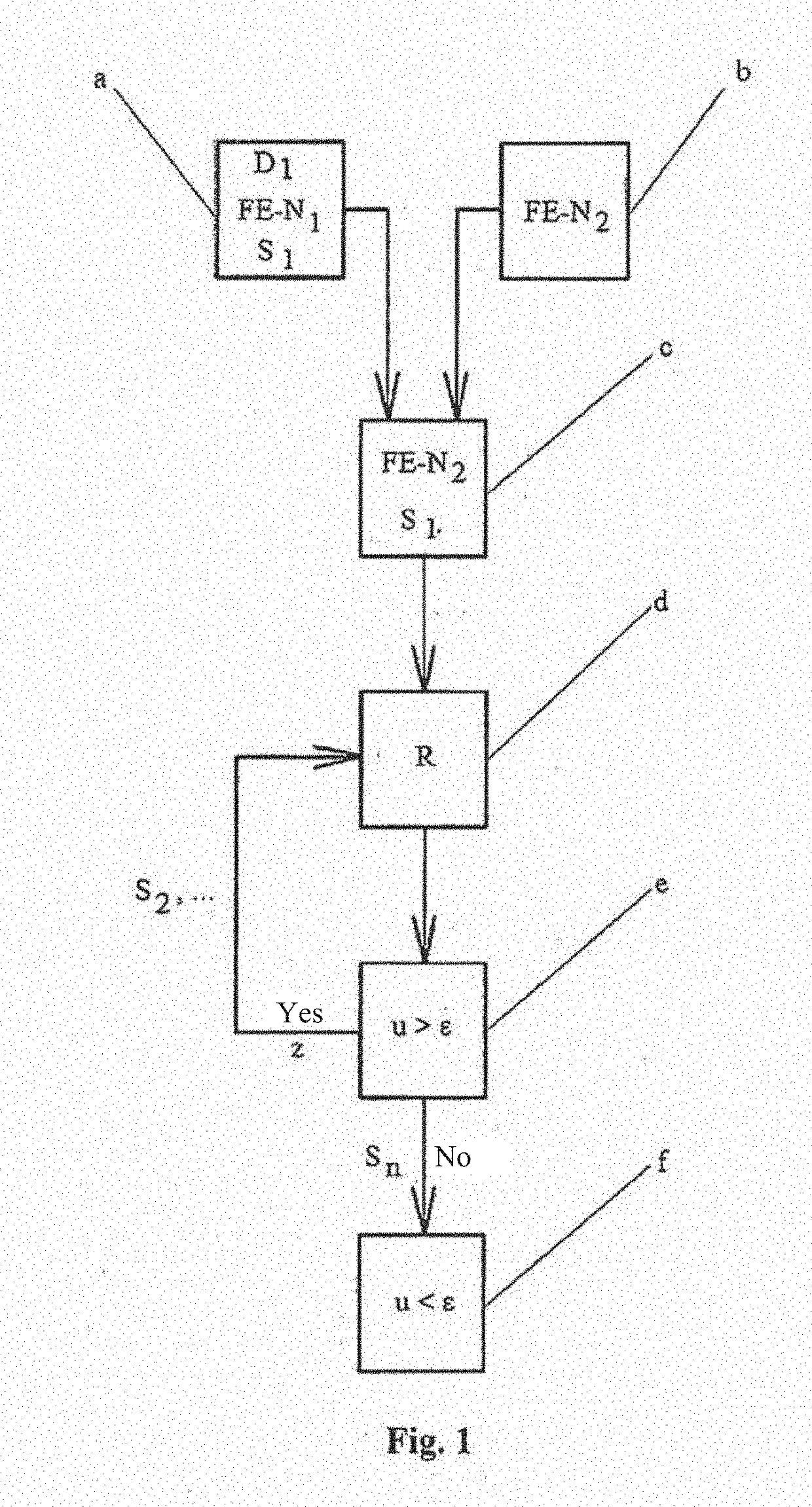
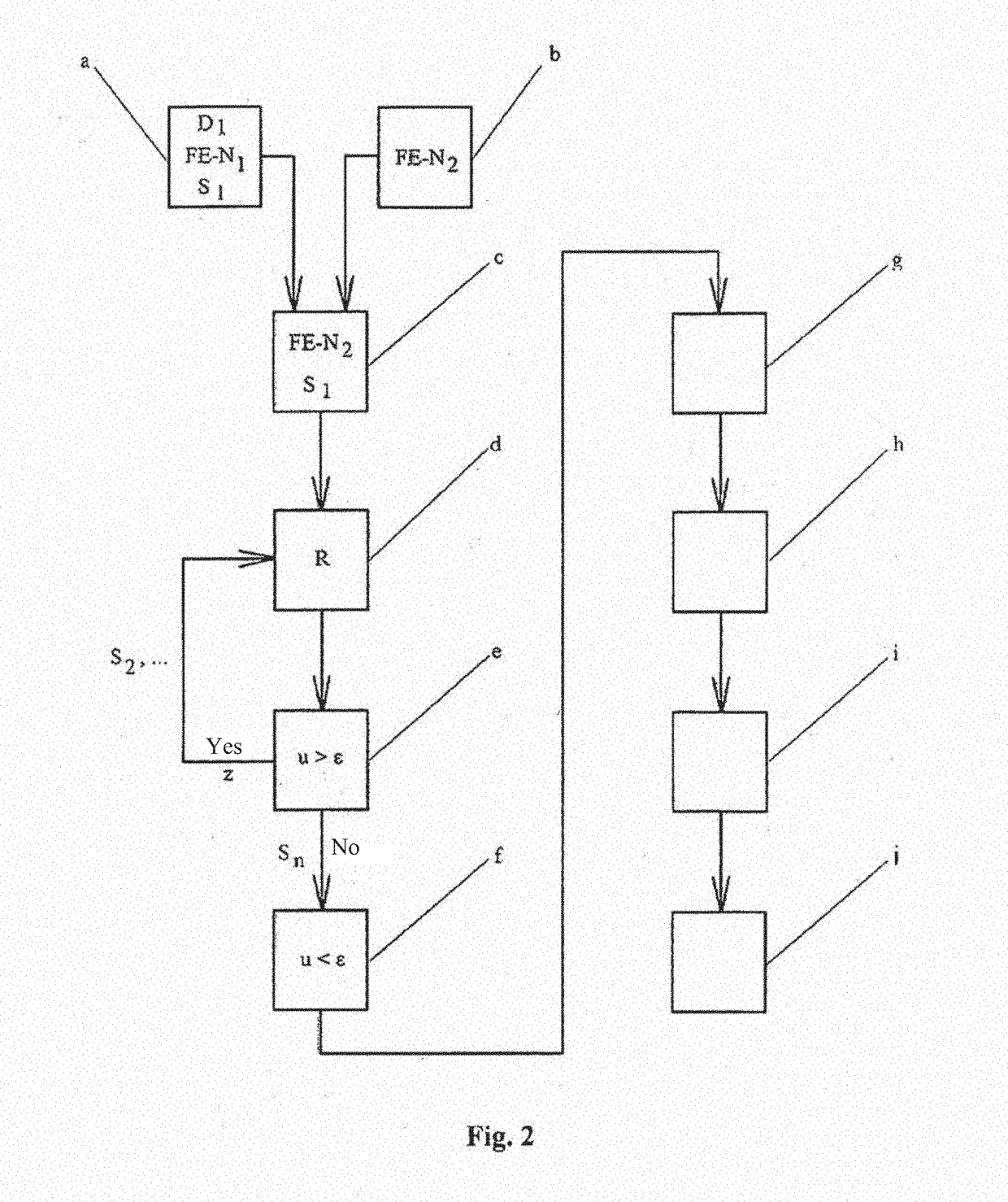
The invention relates to a method for transferring a stress state of an FE simulation result to a new FE mesh geometry of a simulated construction system, such as a component for motor vehicles that has a 3-D shape, in a simulation chain of production operations, comprising: a) providing a first data set, which describes the FE simulation result with a stress state of the FE simulation of the construction system or component of a first production operation, b) creating the new FE mesh geometry of the simulated construction system or component, which new FE mesh geometry is associated with a second production operation, c) transferring the stress state of the provided first data set to the new FE mesh geometry of the construction system or component, d) performing an equilibrium calculation by using the stress tensor in the FE mesh geometry, wherein deformation of the construction system or component results, which deformation differs from the deformation in the FE mesh by a shape alteration u>tolerance value ε, e) iteratively repeating the equilibrium calculation as a cyclic equilibrium iteration in the new FE mesh geometry (in the new target FE mesh) of the construction system or component, wherein, in each cycle, a new stress state is applied to the FE mesh geometry of the construction system or component and stress components that lead to undesired shape alterations are decreased until a displacement / termination criterion of shape alteration u<tolerance value ε is achieved, and f) displaying the fulfilled condition of u<ε.
Owner:INNOVATIONSGES FUR FORTGESCHRITTENE PRODN SSYST & DER FAHRZEUGIND
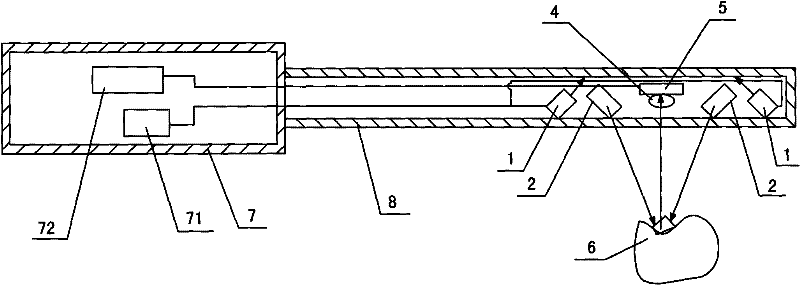
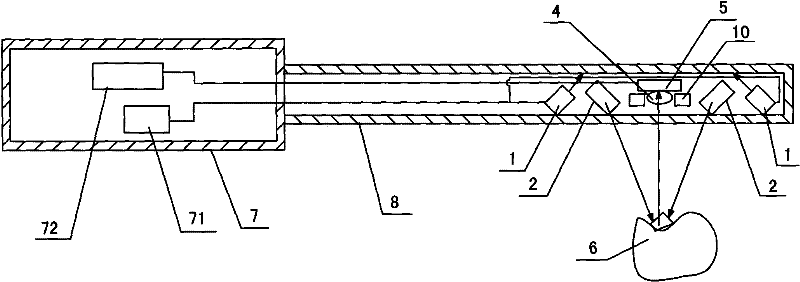
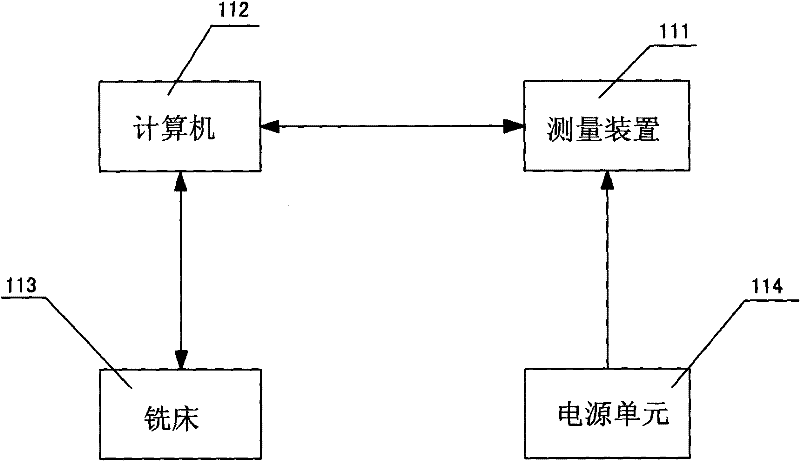
Device for Measuring Tooth Geometry
InactiveCN101711675BHigh resolutionAvoid shadowsDentistryDiagnostic recording/measuringGraphicsProjection image
The invention discloses a device for measuring the geometric shape of teeth. The device includes a handle and a probe. The probe is provided with a light source, a projection head and an imaging unit. The projection head is provided with a mesh geometric image; the light source emits incident light to illuminate On the projection head, the projection head alternately projects the same-shaped mesh geometric images onto the tooth surface at the angle of a symmetrical triangle to form different distorted mesh geometric images. Through the tooth surface, two different distorted mesh images Shaped geometric figure images are reflected into the imaging unit, and the perspective angle range between the projection light and the imaging light is ±10°~±30°. The characteristic is that the camera is set between the two projection heads and between the projection light and the imaging light. The perspective angle range is ±10°~±30°, and the distorted mesh geometric image is formed at a large perspective angle (greater than 30 degrees), which effectively avoids the shadow phenomenon of the mesh geometric image and improves the measurement sensitivity and precision.
Owner:宁波思达利光电科技有限公司
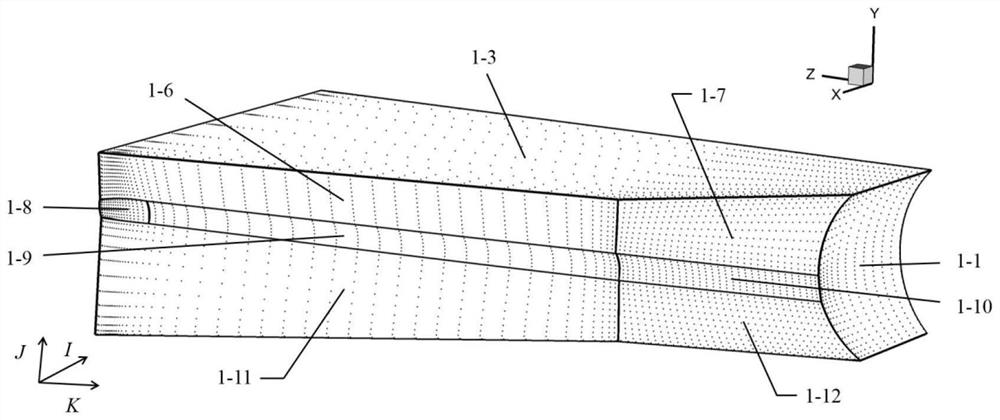
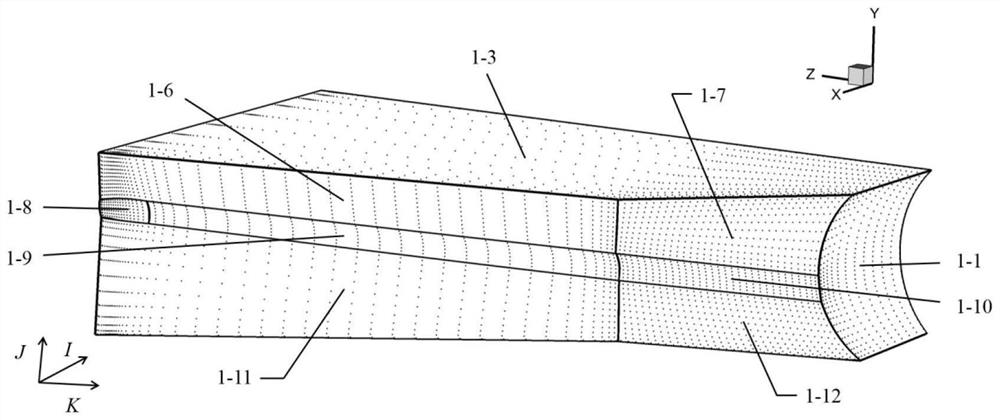
Deep compression storage and decompression method for multi-block structured grid data
ActiveCN112906314AGood compressibilityConformalDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingData compressionSimulation
The invention discloses a multi-block structured grid data deep compression storage and decompression method. According to the multi-block structure grid data deep compression storage and decompression method, by judging the type of each window in a grid block, grid window boundary ridge line grid points or grid window surface grid points of the grid block are extracted and stored in a classified mode so as to achieve shape preserving of an original grid, geometric data of the original grid are coded and compressed, and the data compression efficiency of the original grid is improved. The compression performance of the grid data is improved, and when the grid is to be used, the over-limit interpolation algorithm is utilized, and quick recovery of different storage formats of all the grid geometric data is realized through decompression. According to the multi-block structured grid data deep compression storage and decompression method, the storage and transmission crisis caused by the fact that current mainstream software adopts all geometric data storage formats can be solved, and the problem of insufficient compression caused by a surface grid data storage method is solved.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
2D-3D sculpture paintings
ActiveUS10593125B2Guaranteed smoothMinimize the differenceModifying/creating image using manual inputEditing/combining figures or textComputer graphics (images)Engineering
We disclose a method for synthesizing by computer an artwork where 2D and 3D contents are integrated within a same composition. Such an artwork creates plausible effects for the viewers by showing a different relationship between 2D and 3D at each viewing angle. Methods are proposed for ensuring the continuity between the 2D and the 3D parts in terms of mesh geometry and reflected colors. The user selects from a given scene a region of interest (ROI) to be reproduced in 3D. A flat rendering grid is created that matches the topology and tesselation of the ROI. The ROI is attached to the rendering grid. To enhance the continuity between the 2D and the 3D parts of a scene object, the 2D part of the object can be represented as bas-relief. Designers can create 2D-3D sculpture paintings for decoration, exhibitions, and homes.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Interactive self-penetrating grid deformation method based on proxy geometries
ActiveCN111932597ACalculation speedImage analysis3D-image renderingGrid deformationThree-dimensional space
The invention provides an interactive self-penetrating grid deformation method based on proxy geometries, which comprises the following steps: generating a corresponding proxy geometry according to manually selected patches on active collision grid geometries; taking the proxy geometry as an active collision geometry, and recording the initial three-dimensional space position of the active collision geometry as an initial position, wherein the vertexes of the surface patches, facing the direction of a passive collision geometry, of the proxy geometry emit rays towards all directions, and interpenetration calculation is carried out between the vertexes and the passive collision geometry; and when interpenetration is calculated, recording the three-dimensional space displacement of the active collision geometry, and applying the displacement to the vertexes of the surface of the passive collision geometry, so that a real-time deformation process is realized. The limitation of a self-penetrating problem is effectively and reasonably avoided, and the calculation speed is greatly improved.
Owner:江苏原力数字科技股份有限公司
Capturing and stylizing hair for 3D fabrication
ActiveUS9710965B2Reduce complexity3D-image rendering3D modelling3d fabricationComputer graphics (images)
A process, computer program product, and apparatus provide color and shape stylization for a captured hairstyle. The process, computer program product, and apparatus receive a plurality of images of a hairstyle in an n dimensional space at a plurality of different angles. Further, the process, computer program product, and apparatus generate a mesh surface in an n−1 dimensional space. In addition, the process, computer program product, and apparatus combine color data from the plurality of images at the plurality of different angles with mesh geometry data of the mesh surface. The process, computer program product, and apparatus also stylize the color data with an n dimensional filter that projects the color data to the n−1 dimensional space of the mesh surface. The process, computer program product, and apparatus may also stylize the geometric shape details in a coherent manner with the color.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Multi-block structure grid data deep compression storage and decompression method
ActiveCN112906314BGood compressibilityConformalDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingComputational scienceMesh geometry
The invention discloses a method for deeply compressing, storing and decompressing multi-block structured grid data. The multi-block structure grid data deep compression storage and decompression method of the present invention judges the type of each window in the grid block, classifies, extracts and stores the grid window boundary ridgeline grid point or grid window surface of the grid block Grid points, in order to keep the shape of the original grid, and encode and compress the geometric data of the original grid to improve the compression performance of the grid data. Fast recovery of mesh geometry data in different storage formats. The multi-block structure grid data deep compression storage and decompression method of the present invention can resolve the storage and transmission crisis caused by the use of all geometric data storage formats in current mainstream software, and solve the problem of insufficient compression caused by surface grid data storage methods question.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
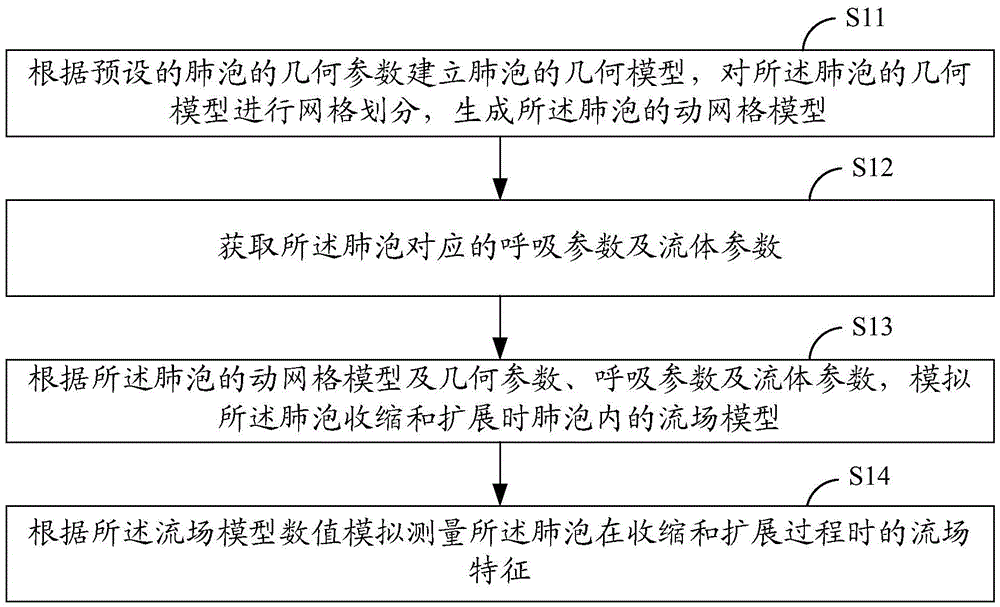
Flow field numerical simulation measurement method and system for alveolar contraction and expansion process
ActiveCN104027114BAccurate acquisitionShort measuring cycleRespiratory organ evaluationANA measurementMesh geometry
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
An interactive self-penetrating mesh deformation method based on proxy geometry
ActiveCN111932597BCalculation speedImage analysis3D-image renderingGrid deformationThree-dimensional space
The invention provides an interactive self-penetrating grid deformation method based on proxy geometries, which comprises the following steps: generating a corresponding proxy geometry according to manually selected patches on active collision grid geometries; taking the proxy geometry as an active collision geometry, and recording the initial three-dimensional space position of the active collision geometry as an initial position, wherein the vertexes of the surface patches, facing the direction of a passive collision geometry, of the proxy geometry emit rays towards all directions, and interpenetration calculation is carried out between the vertexes and the passive collision geometry; and when interpenetration is calculated, recording the three-dimensional space displacement of the active collision geometry, and applying the displacement to the vertexes of the surface of the passive collision geometry, so that a real-time deformation process is realized. The limitation of a self-penetrating problem is effectively and reasonably avoided, and the calculation speed is greatly improved.
Owner:江苏原力数字科技股份有限公司
A Dynamic Mesh Perturbation Domain Update Method for Simulation of Aircraft Maneuvering Process
ActiveCN114218878BImprove computing efficiencySmall amount of calculationGeometric CADSustainable transportationFlight vehicleClassical mechanics
The invention relates to the technical field of computational fluid dynamics, and provides a method for updating a dynamic grid disturbance domain for simulating the maneuvering process of an aircraft. In this method, the influence of grid element velocity and dynamic grid geometry conservation law is considered in the solution of the flow governing equations, and only the unsteady unconverged disturbed elements are solved under the framework of the dynamic grid technology. The solution method of the viscous effect can effectively avoid the invalid calculation of the discrete equation in the traditional numerical simulation method based on the dynamic mesh unit. Secondly, the idea of local updating in the region dominated by unsteady effects is introduced in the update of the coordinates, surface quantities, volumes, and grid unit speeds of the moving grid unit, thereby effectively avoiding the traditional numerical simulation method based on the moving grid unit. Invalid calculation of update grid cell parameters in .
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Damping and support in high-temperature superconducting levitation systems
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com