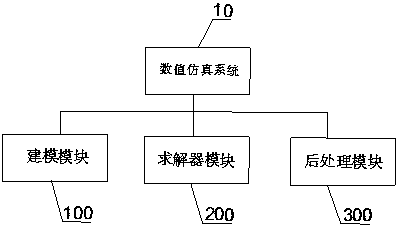
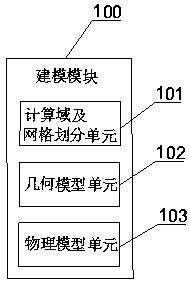
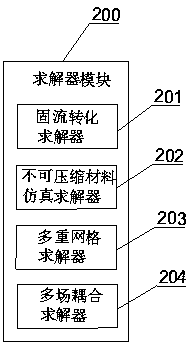
System and method for numerical simulation based on Lagrange integral point finite element
A numerical simulation and finite element technology, applied in the direction of design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve the problems of high calculation cost, time-consuming calculation, and inability to track and calculate the stress-strain history of elastic-plastic materials, so as to improve calculation efficiency and reduce calculation cost. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050] Unless otherwise defined, all technical and scientific terms used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by those skilled in the technical field of the application; the terms used herein in the description of the application are only for the purpose of describing specific embodiments , is not intended to limit the present application; the terms "comprising" and "having" and any variations thereof in the description and claims of the present application and the description of the above drawings are intended to cover non-exclusive inclusion. The terms "first", "second" and the like in the description and claims of the present application or the above drawings are used to distinguish different objects, rather than to describe a specific order.
[0051] Reference herein to an "embodiment" means that a particular feature, structure, or characteristic described in connection with the embodiment can be included in at least one embodiment of the present application....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com