Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
336 results about "Memory protection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Memory protection is a way to control memory access rights on a computer, and is a part of most modern instruction set architectures and operating systems. The main purpose of memory protection is to prevent a process from accessing memory that has not been allocated to it. This prevents a bug or malware within a process from affecting other processes, or the operating system itself. Protection may encompass all accesses to a specified area of memory, write accesses, or attempts to execute the contents of the area. An attempt to access unowned memory results in a hardware fault, called a segmentation fault or storage violation exception, generally causing abnormal termination of the offending process. Memory protection for computer security includes additional techniques such as address space layout randomization and executable space protection.
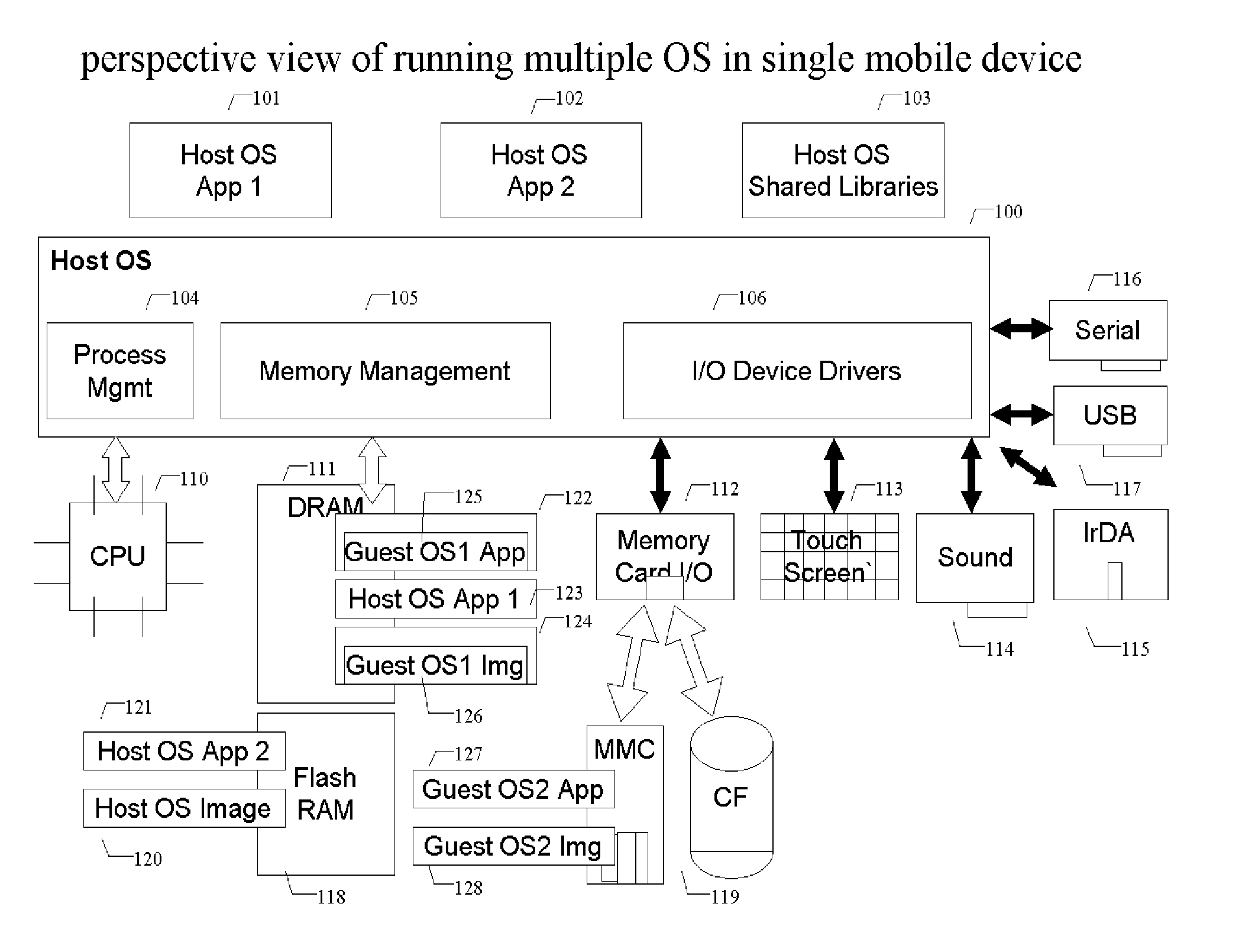
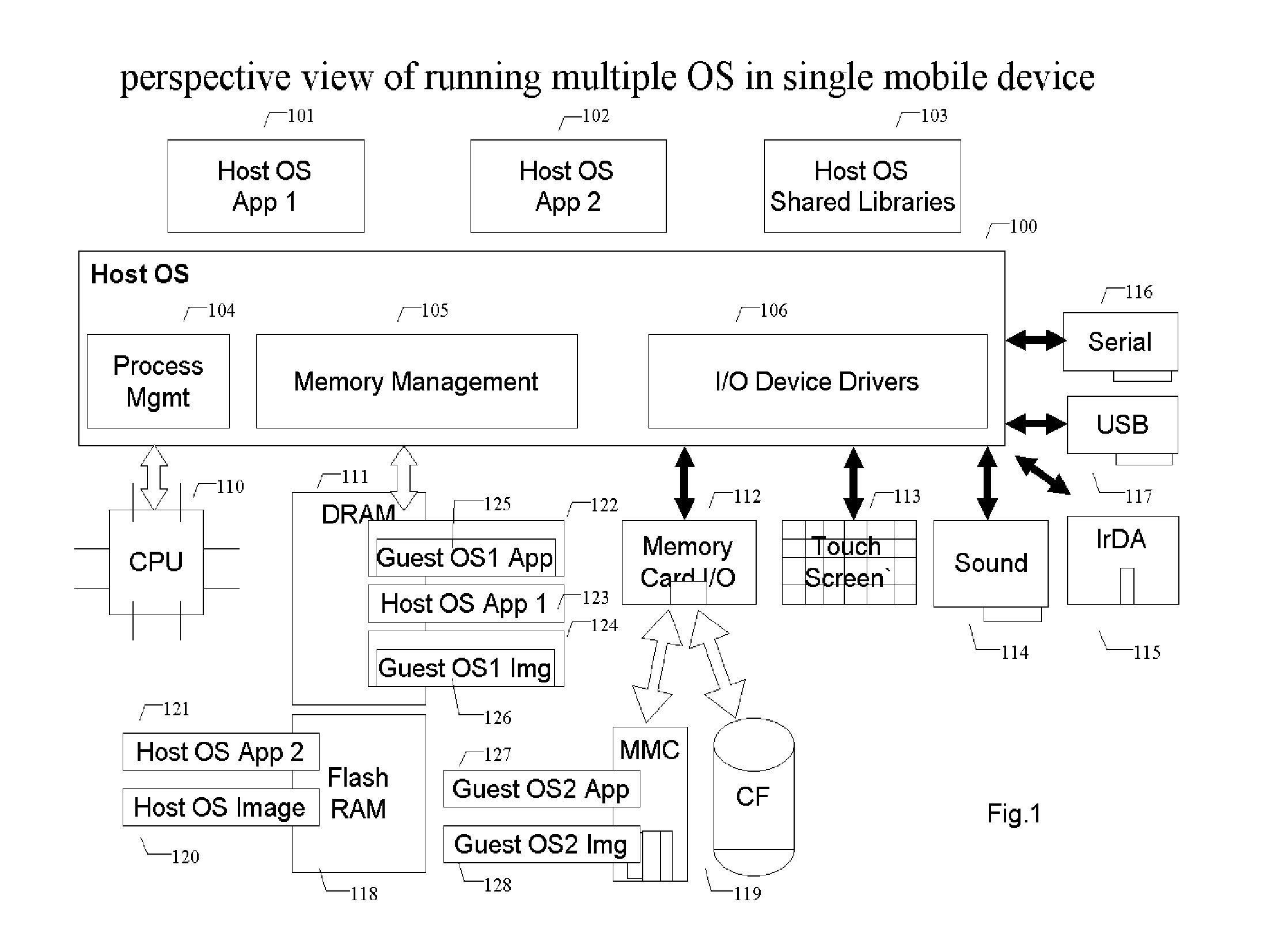
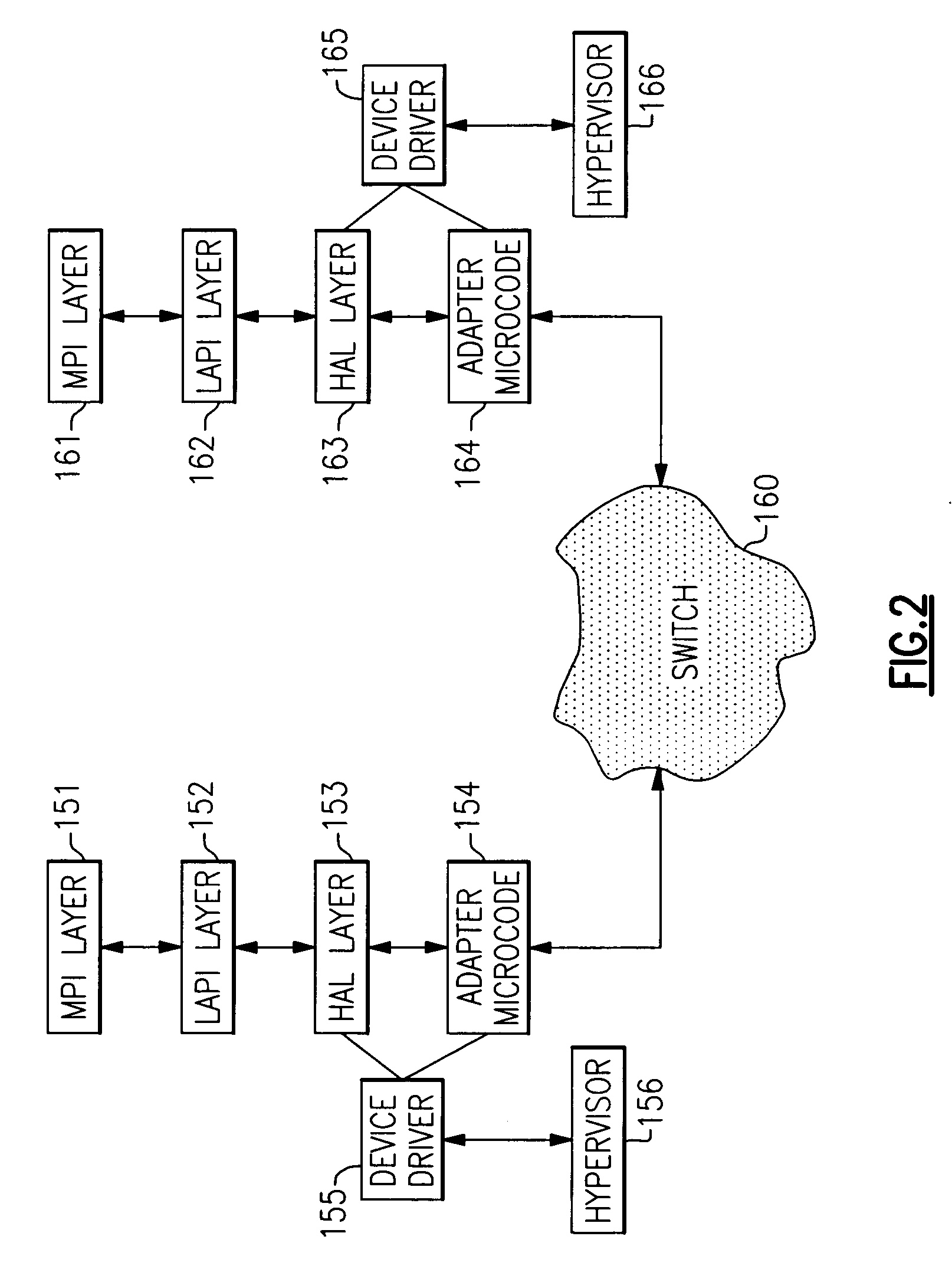
Methods and systems for running multiple operating systems in a single mobile device
ActiveUS20060010314A1Reduce memory usageError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsOperational systemEngineering
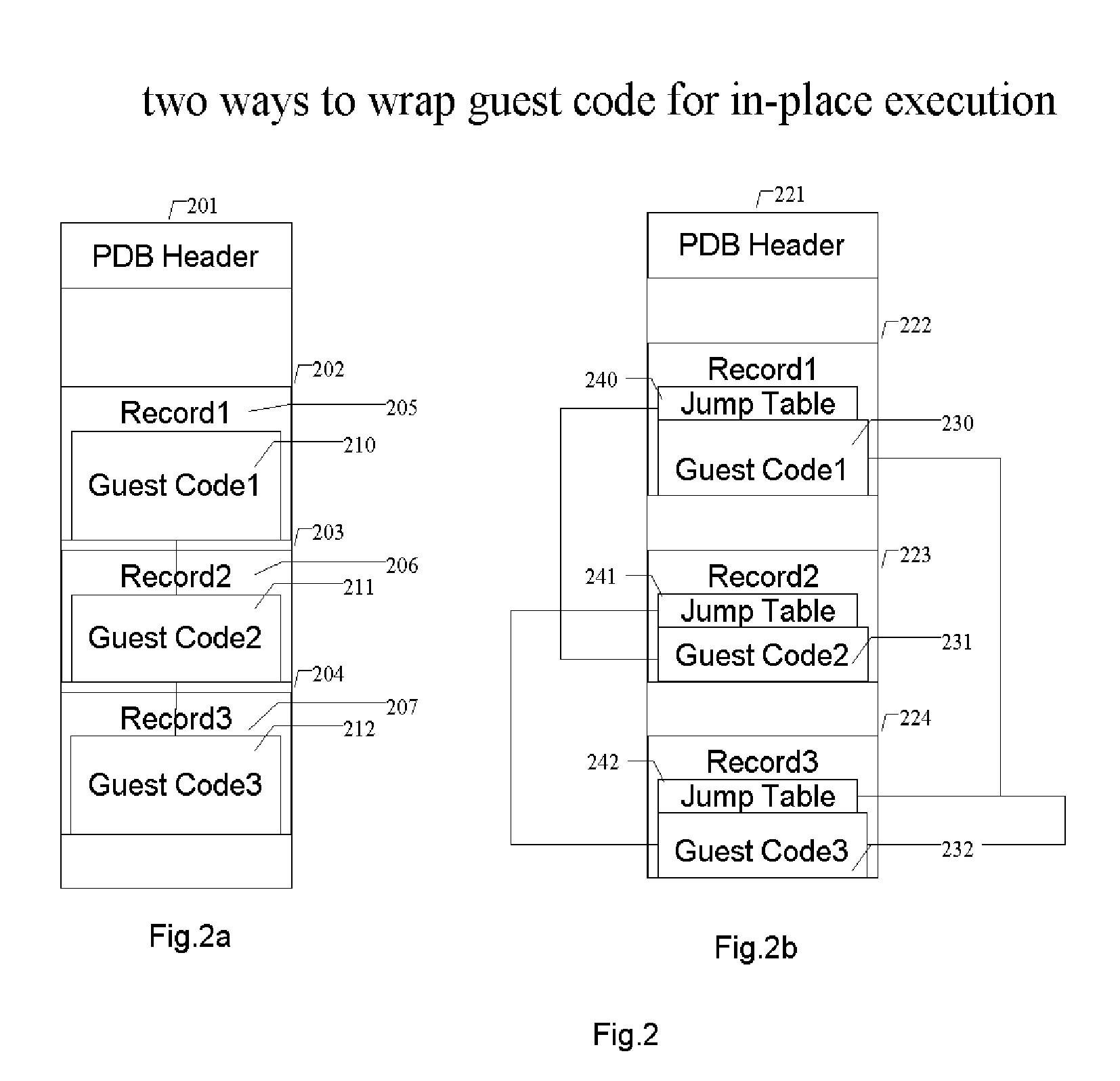
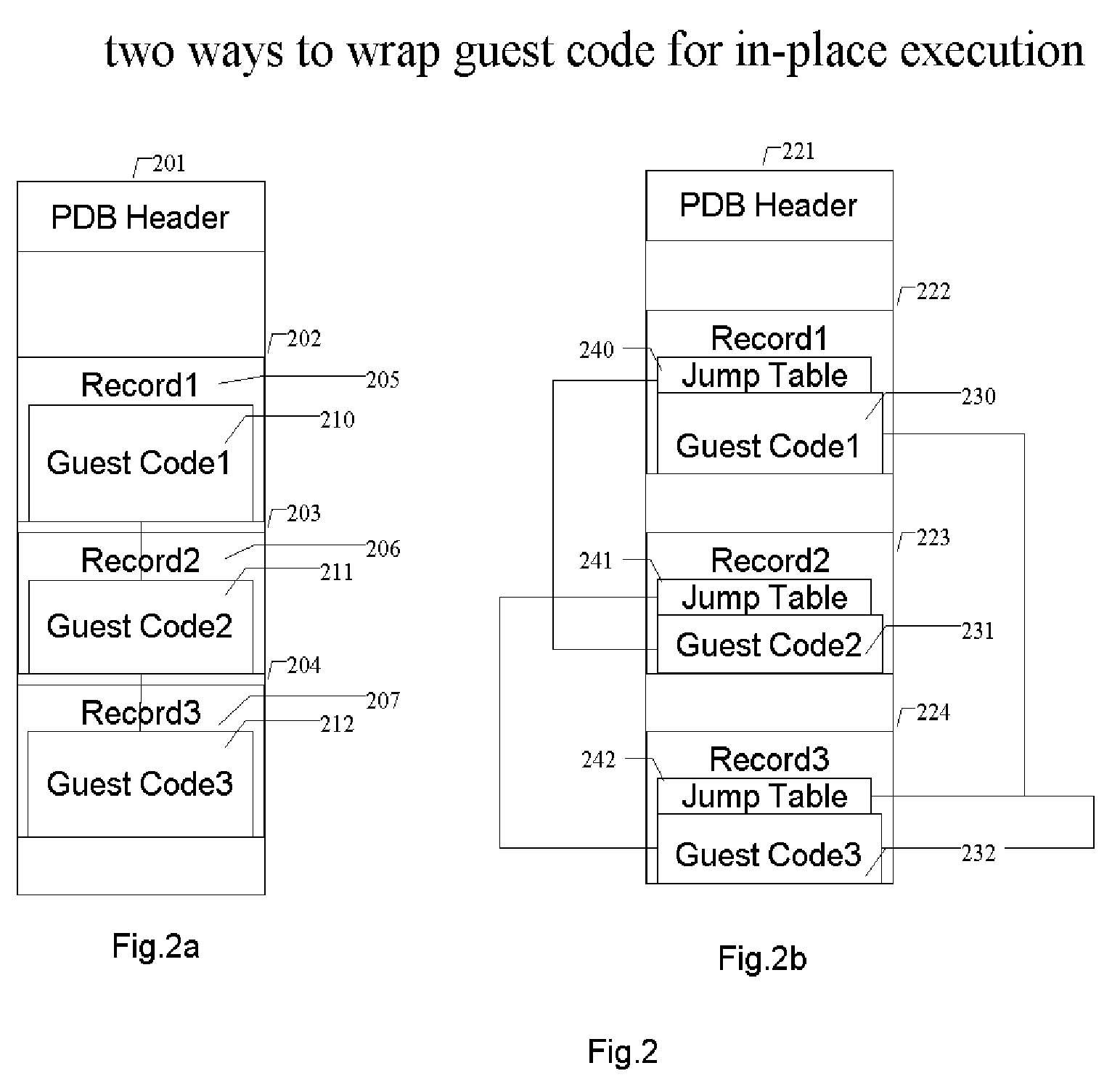
Methods and systems for running multiple operating systems in a single embedded or mobile device (include PDA, cellular phone and other devices) are disclosed. The invention allows a mobile device that normally can only run a single operating system to run another operating system while preserving the state and data of the original operating system. Guest OS is packaged into special format recognizable by the host OS that still can be executed in place by the system. The Methods include: •Change the memory protection bits for the original OS; •Fake a reduced physical memory space for guest OS; •Use special memory device driver to claim memories of host OS; •Backup whole image of the current OS and data to external memory card.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
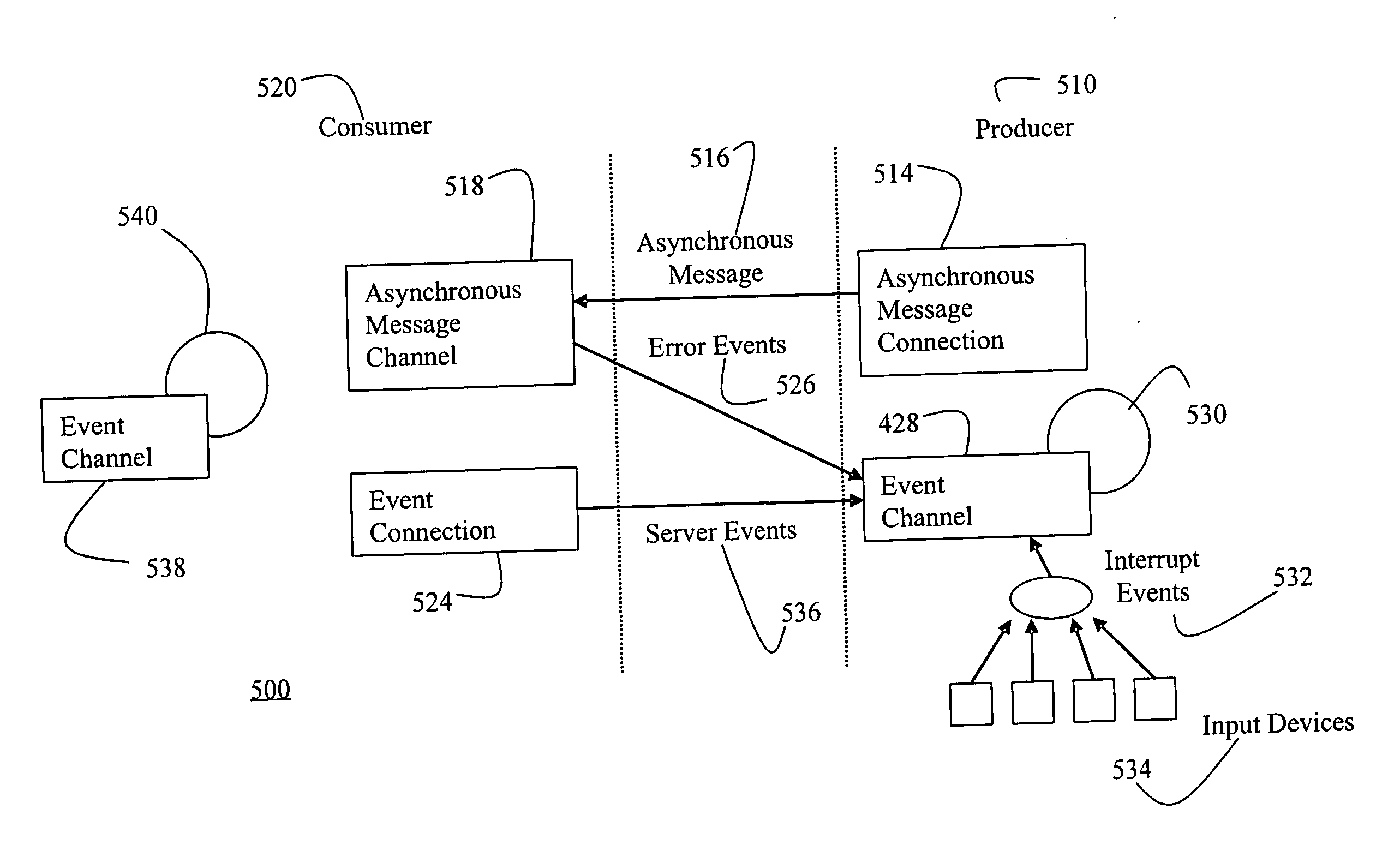
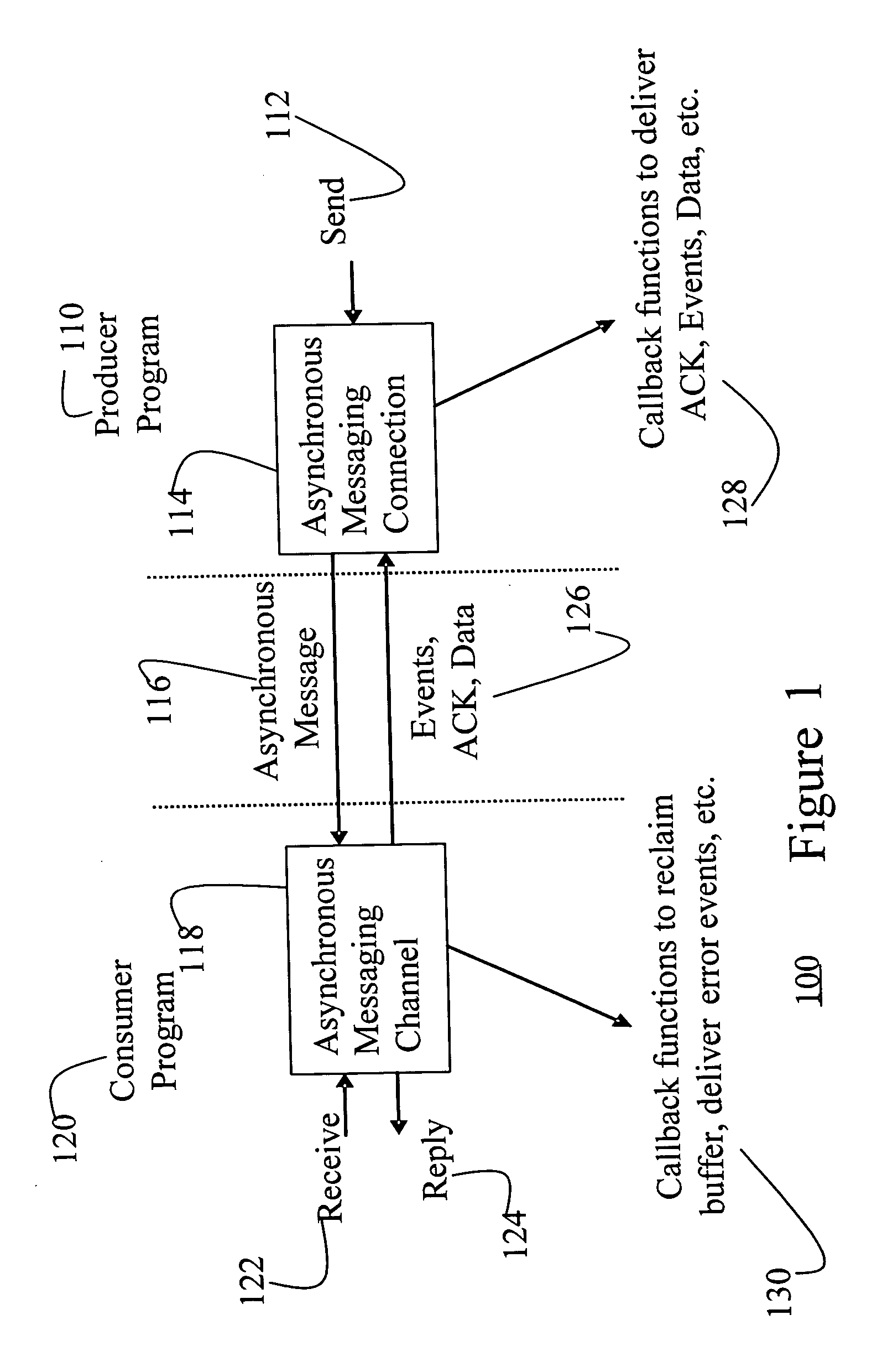
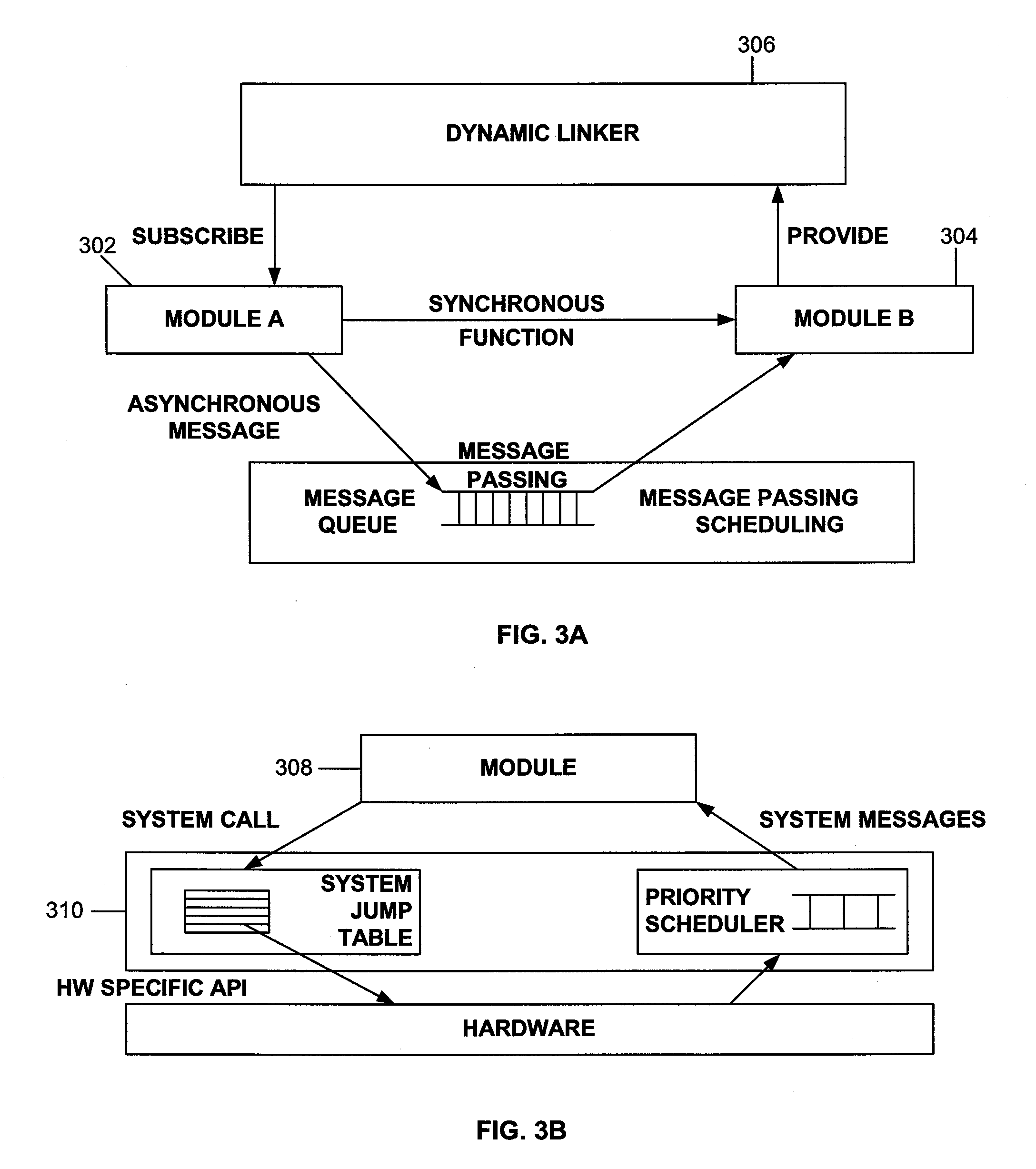
Fast and memory protected asynchronous message scheme in a multi-process and multi-thread environment
ActiveUS20060182137A1Speeding up queue operationSlow performanceTime-division multiplexStore-and-forward switching systemsComputer hardwareData transmission
An asynchronous message passing mechanism that allows for multiple messages to be batched for delivery between processes, while allowing for full memory protection during data transfers and a lockless mechanism for speeding up queue operation and queuing and delivering messages simultaneously.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
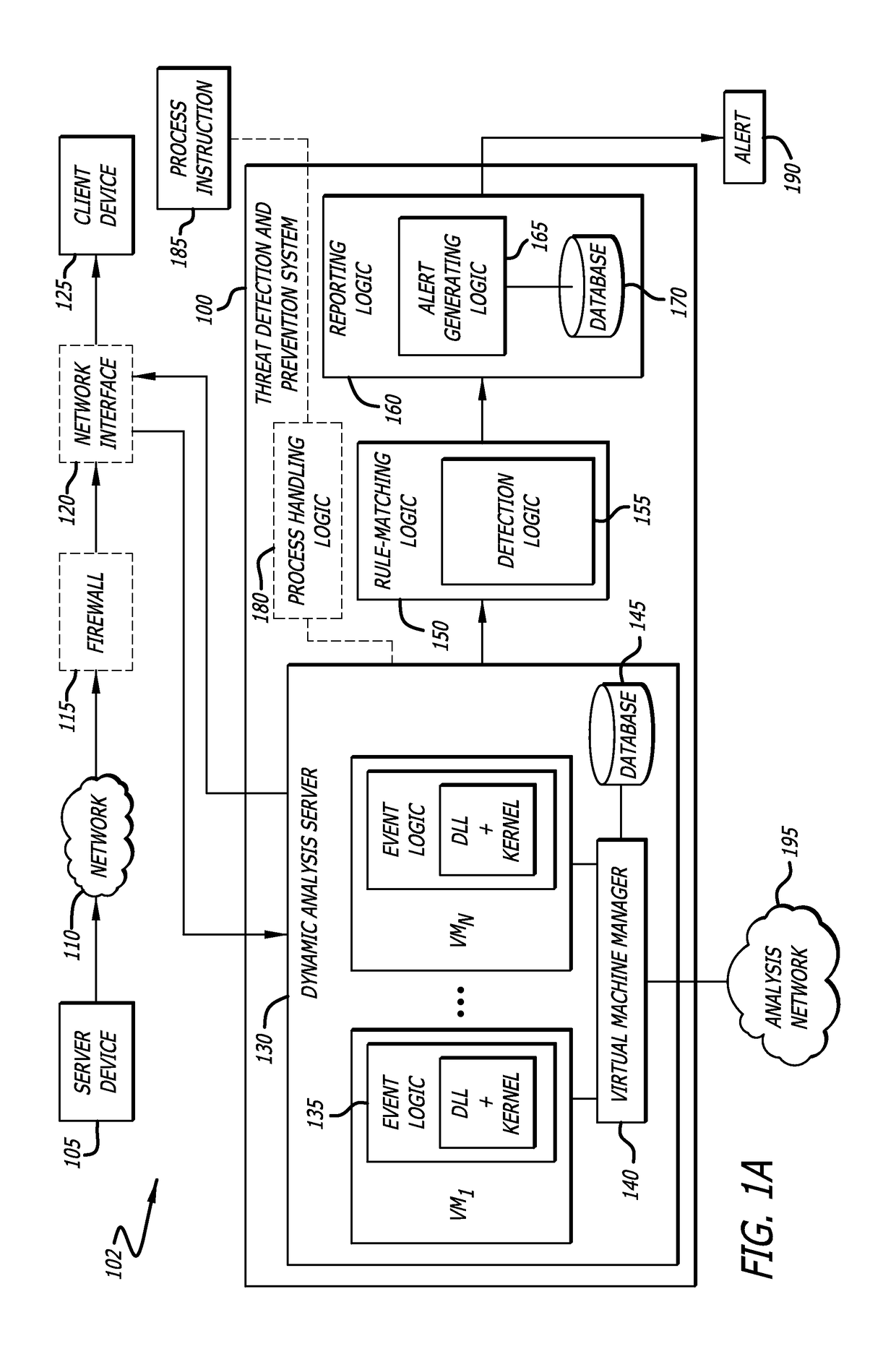
Method to detect application execution hijacking using memory protection
According to one embodiment, a system comprising a dynamic analysis server comprising one or more virtual machines is disclosed, wherein the one or more virtual machines may be configured to execute certain event logic with respect to a loaded module. The virtual machines may be communicatively coupled to a virtual machine manager and a database; and rule-matching logic comprising detection logic, wherein the detection logic is configured to determine (1) whether an access source is attempting to access a protected region such as a page guarded area; and (2) determine whether the access source is from the heap. The system further comprises reporting logic that is configured to generate an alert so as to notify a user and / or network administrator of a probable application-execution hijacking attack.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
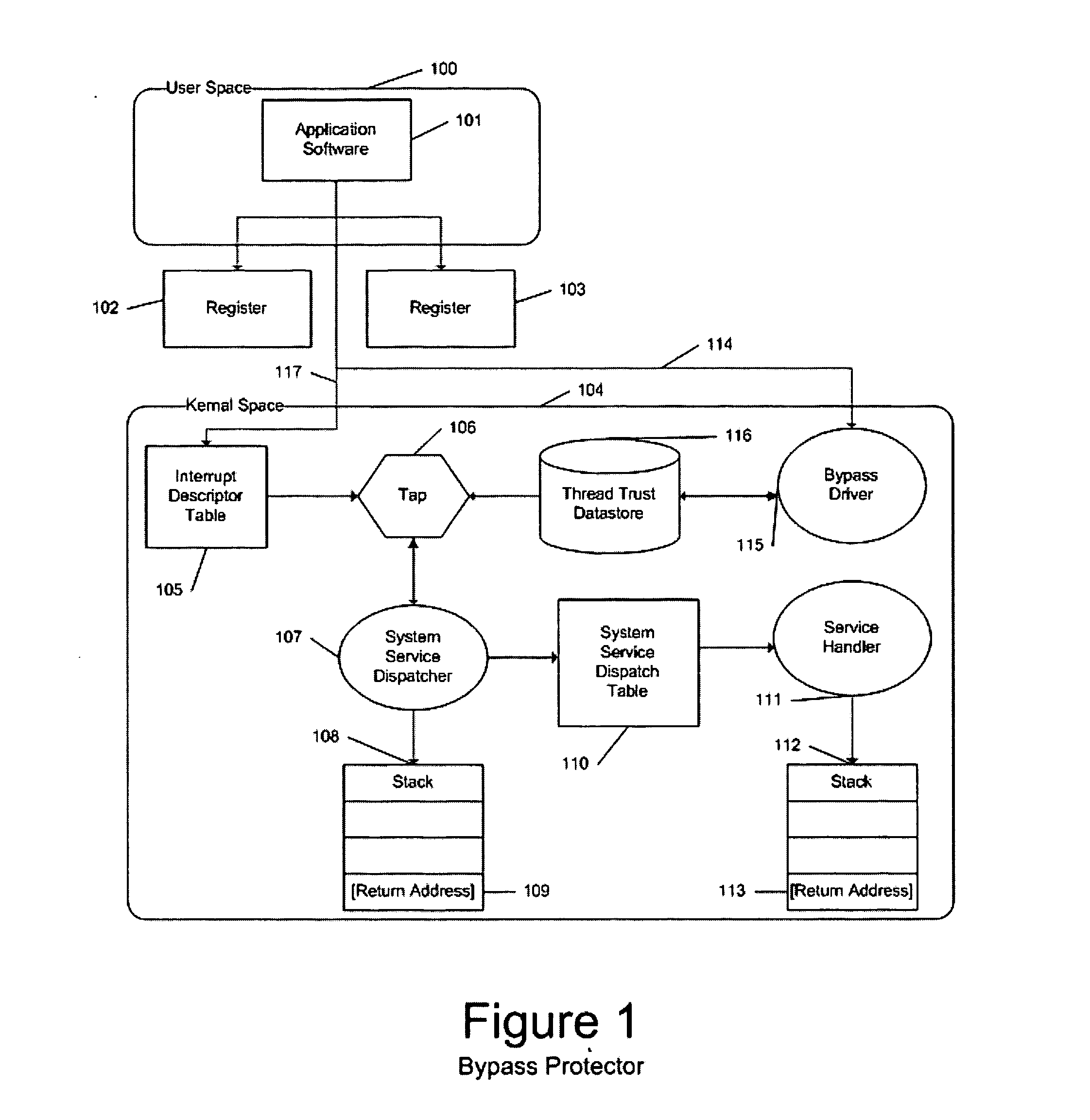
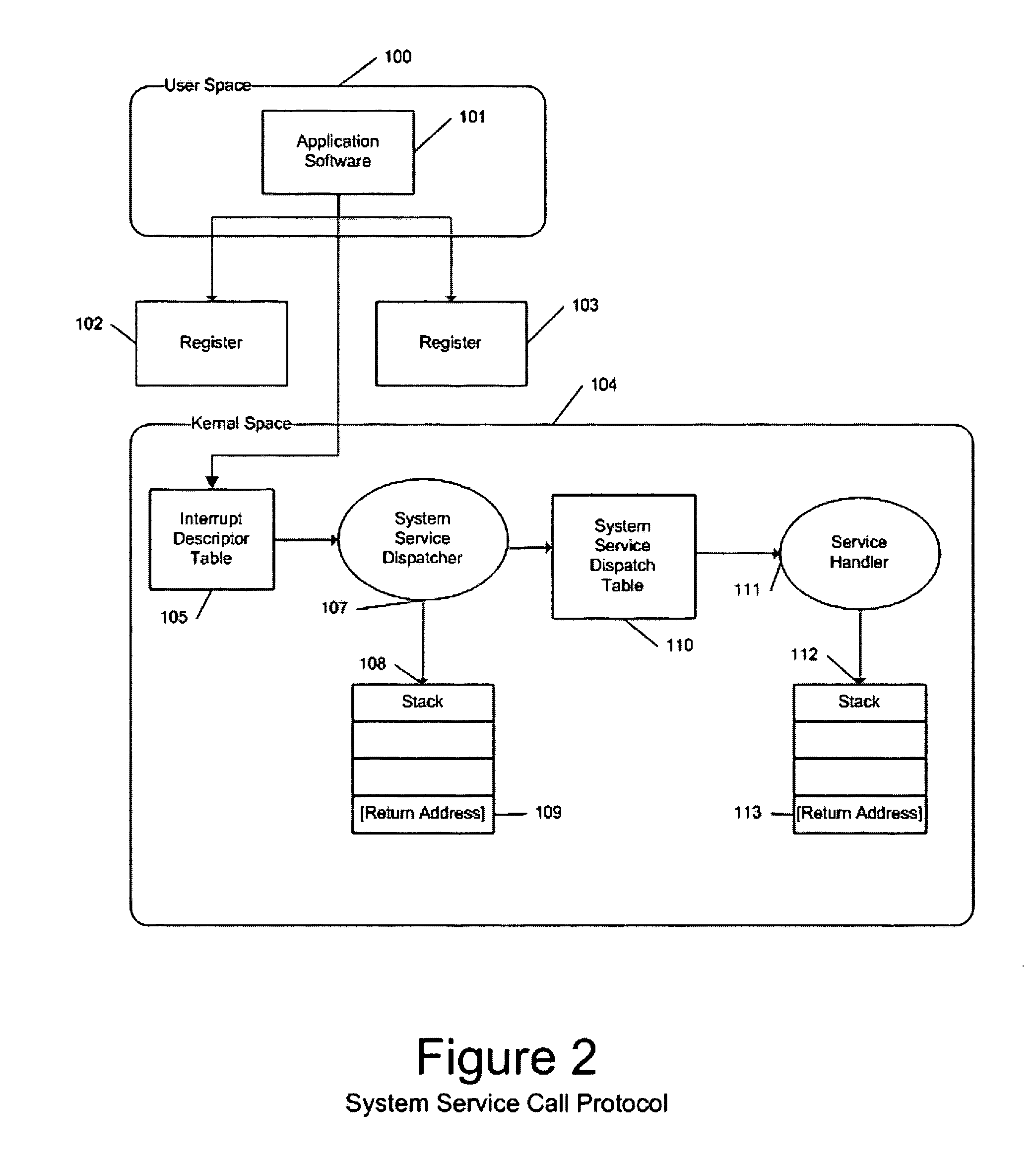
By-pass and tampering protection for application wrappers
InactiveUS20050108516A1Restoration of protectionSpecific access rightsPlatform integrity maintainanceOperational systemHooking
In a computer system with an operating system that supports multiple levels of interfaces (APIs) that application programs (i.e. programs executing outside the operating system kernel in user mode) can invoke to obtain services from the operating system, and the employment of a hooking or mediation technology within a user-mode process (i.e. an instantiation of an application program) to intercept / mediate invocations of selected interfaces of some of those levels, the Tampering Protection protects the code and statically or heap allocated data of the mediators from corruption by the code of the user-mode process being mediated that resides and operates in the same address space as the code and data of the mediators (as such corruption would compromise the integrity of the mediator and could prevent it from accomplishing its intended mediation purpose). It does so by providing memory protection services that allow mediators to define data areas (both static segments and dynamic heaps) to be protected and to temporarily unprotect them during the execution of a mediator so that they can be modified during that execution, thus ensuring that the mediate application does not directly use the operating system services to override Tampering Protection management of these protected segments or protected.
Owner:BALZER ROBERT +1
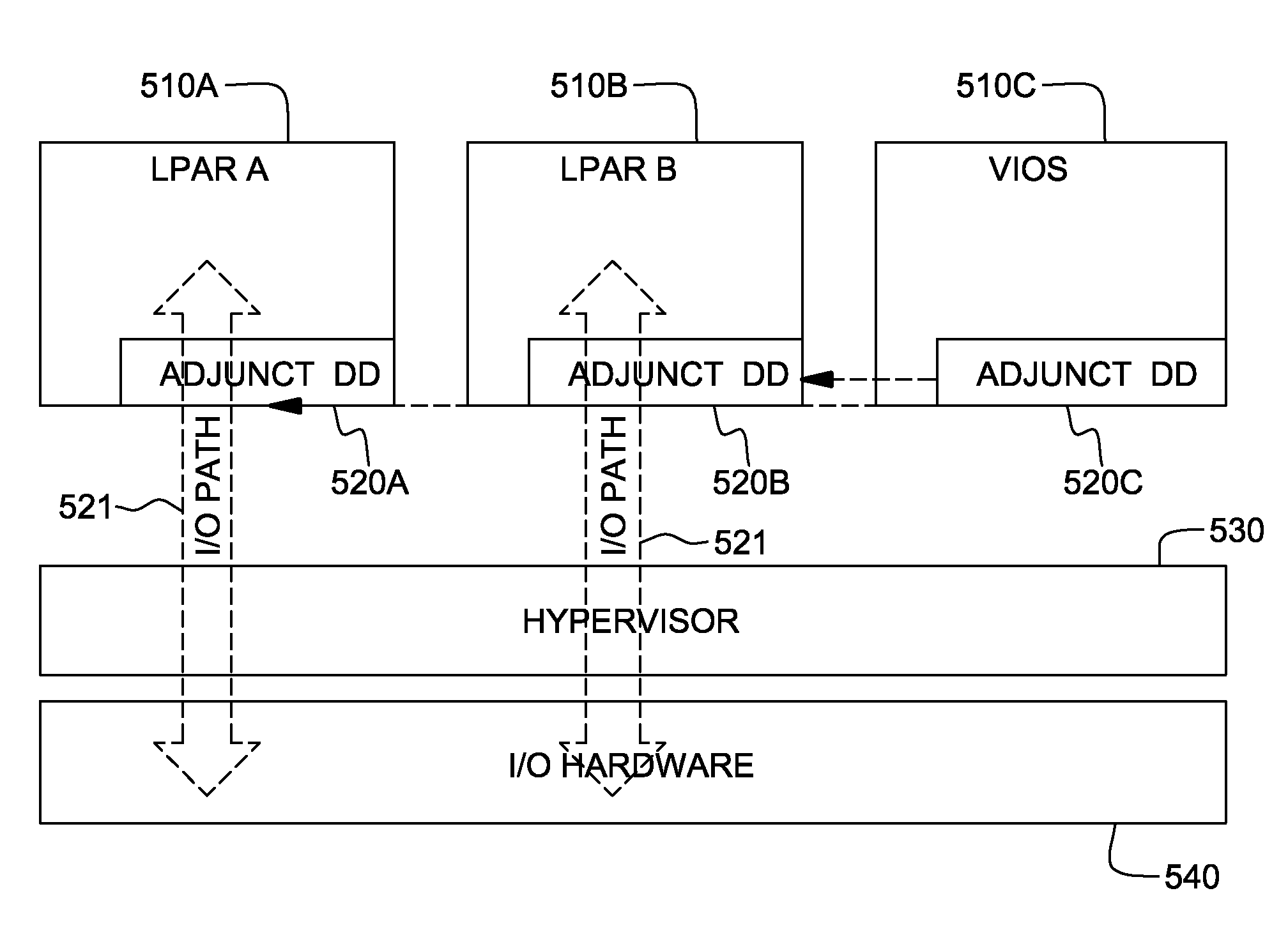
Hypervisor-enforced isolation of entities within a single logical partition's virtual address space
ActiveUS20090037682A1Easy to operateAllow accessMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData processing systemData treatment
Access control to shared virtual address space within a single logical partition is provided. The access control includes: associating, by a hypervisor of the data processing system, a memory protection key with a portion of a single logical partition's virtual address space being shared by multiple entities, the key preventing access by one of the multiple entities to that portion of the virtual address space, and allowing access by another of the entities to that portion of the virtual address space; and locking by the hypervisor the memory protection key from modification by the one entity, wherein the locking prevents the one entity from modifying the key and thereby gaining access to the portion of the single logical partition's virtual address space with the associated memory protection key. In one embodiment, the one entity is the single logical partition itself, and the another entity is a partition adjunct.
Owner:IBM CORP
Memory consistency protection in a multiprocessor computing system
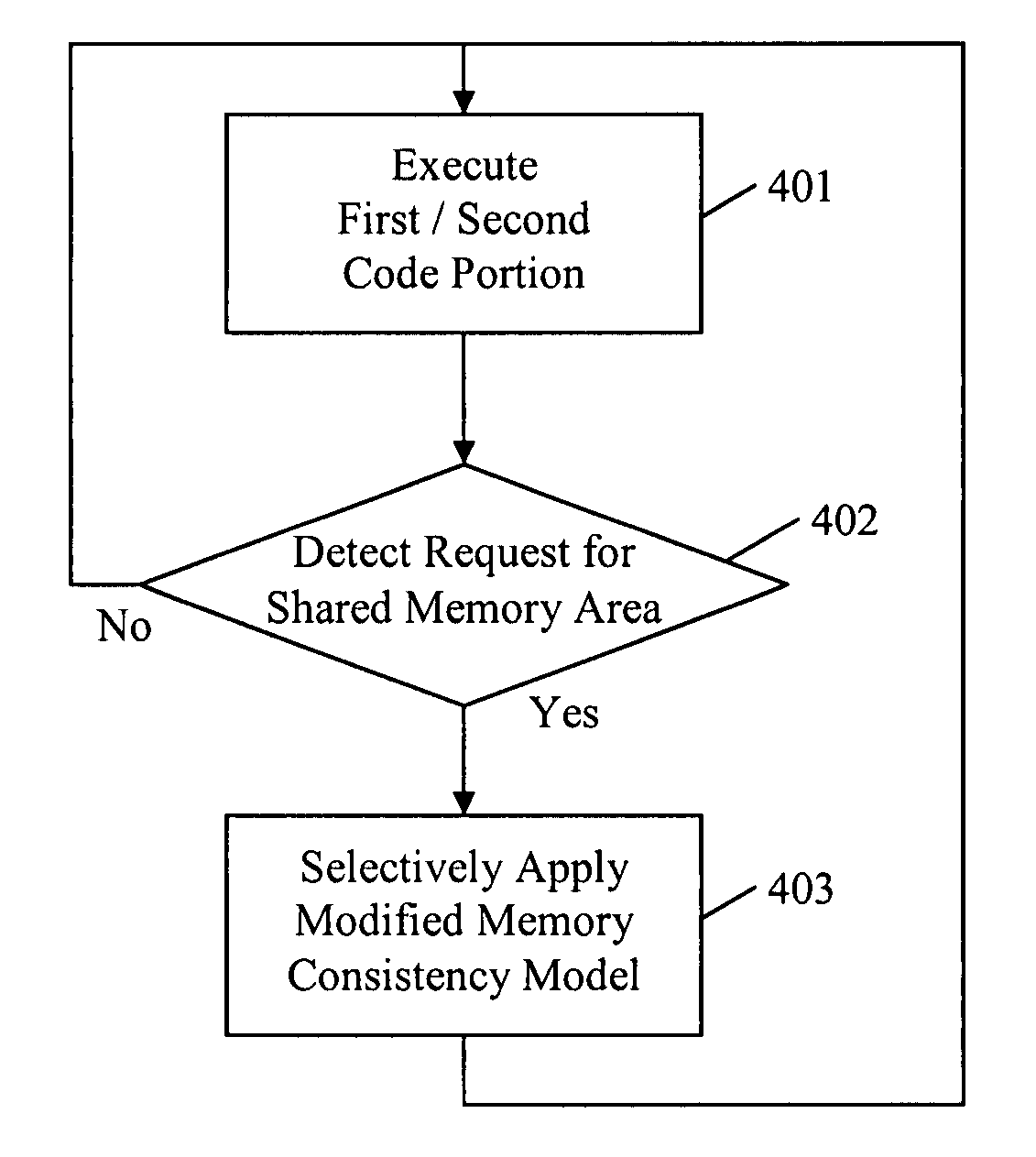
InactiveUS20080140971A1Low-cost and effectiveImproved memory consistencyResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti processorObject code
A method and apparatus to protect memory consistency in a multiprocessor computing system are described, in particular relating to program code conversion such as dynamic binary translation. The exemplary system provides a memory, processors and a controller / translator unit (CTU) arranged to convert subject code into at least first and second target code portions executable on the processors. The CTU comprises an address space allocation unit to provide virtual address space regions and direct the target code portions to access the memory therethough; a shared memory detection unit to detect a request to access a shared memory area, accessible by both target code portions, and to identify at least one group of instructions in the first target code portion which access the shared memory area; and a memory protection unit to selectively apply memory consistency protection in relation to accesses to the shared memory area by the identified group of instructions.
Owner:IBM CORP
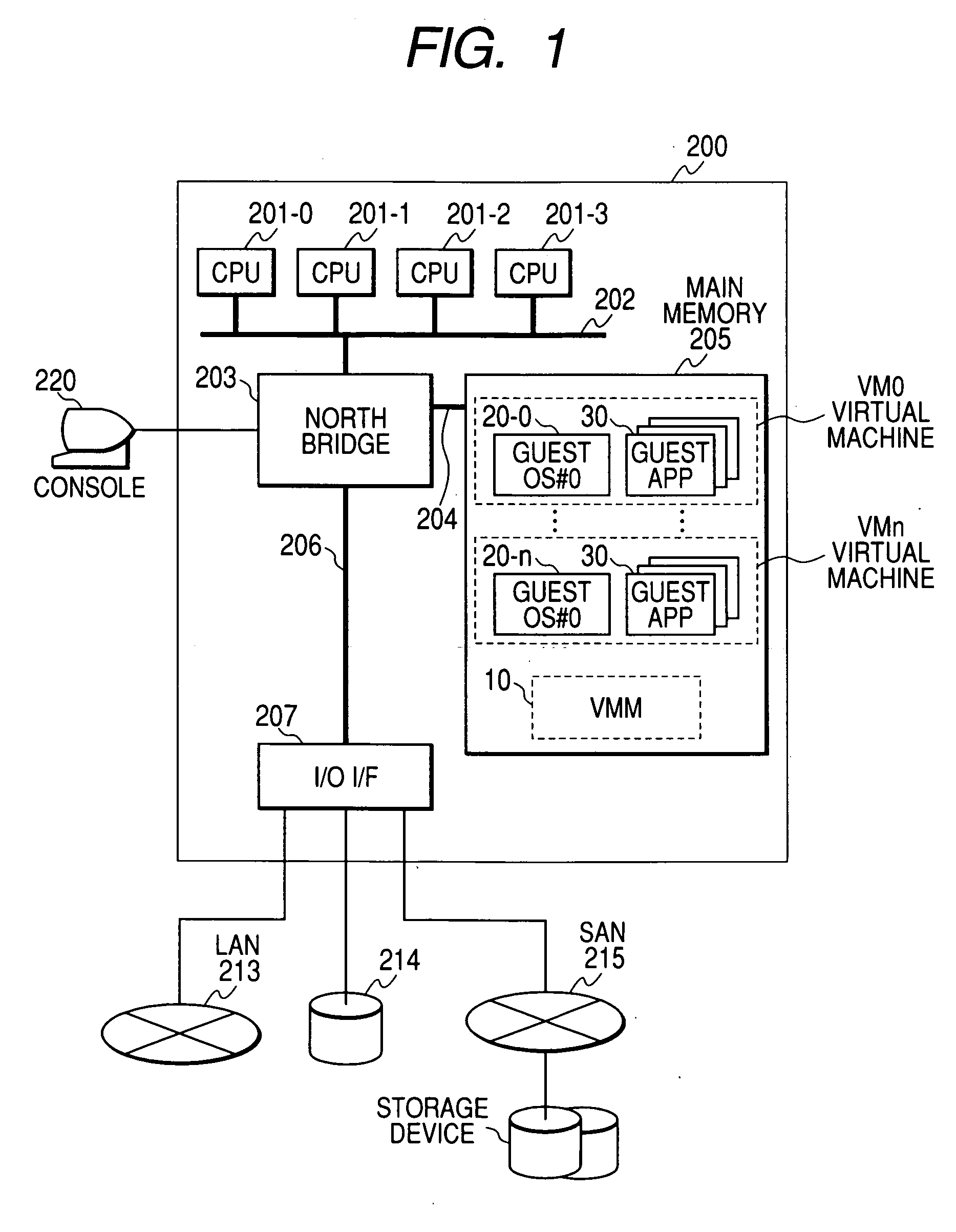
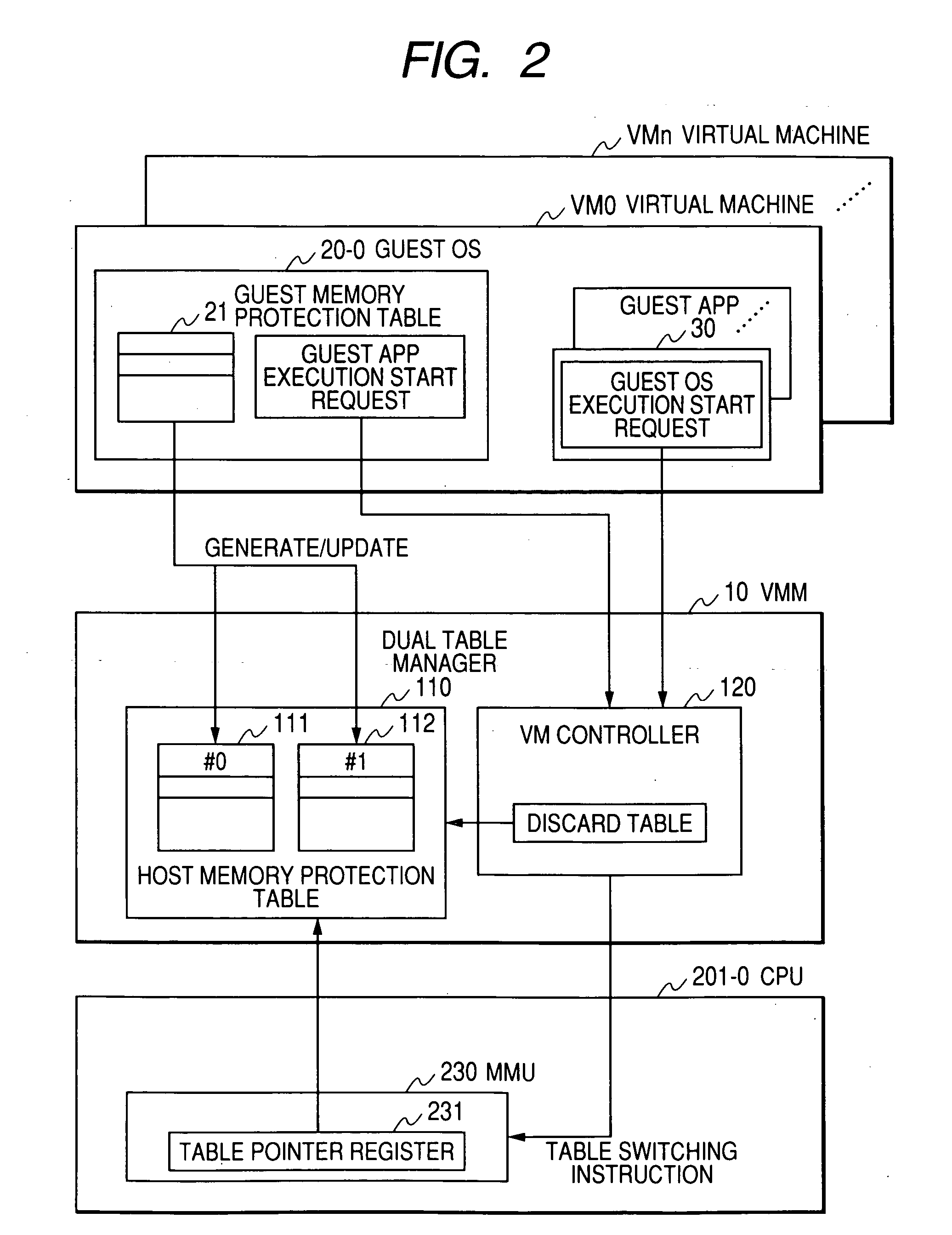
Virtual machine control method and program thereof
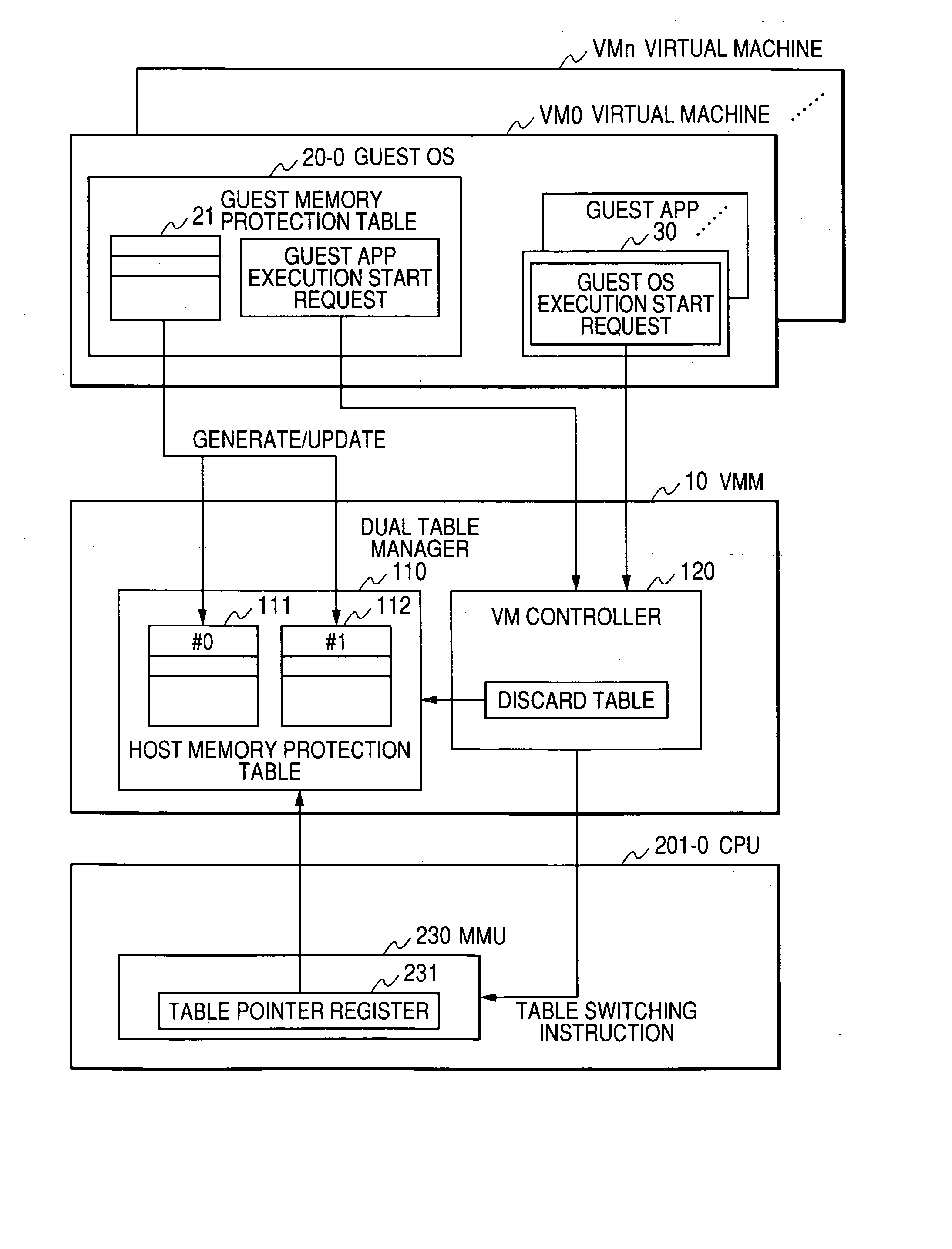
InactiveUS20060294519A1Highly reliable virtual machine systemImprove protectionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsTerm memoryMemory management unit
Disclosed is a virtual machine control method for switching and executing multiple programs jointly shared between at least one CPU and memory. The method is comprised of a process for setting a first memory protection table for defining a memory area accessible by a first program executed on the CPU, a process for setting a second memory protection table for defining a memory area accessible by a second program executed on the CPU, a process for detecting the start of execution of the first or the second program, a process for selecting and switching to either of a first or the second memory protection table according to the detected first or the second program, and a process for checking the first or the second memory protection table with the memory management unit for the CPU, and protecting the memory area defined in the first or the second memory protection table.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
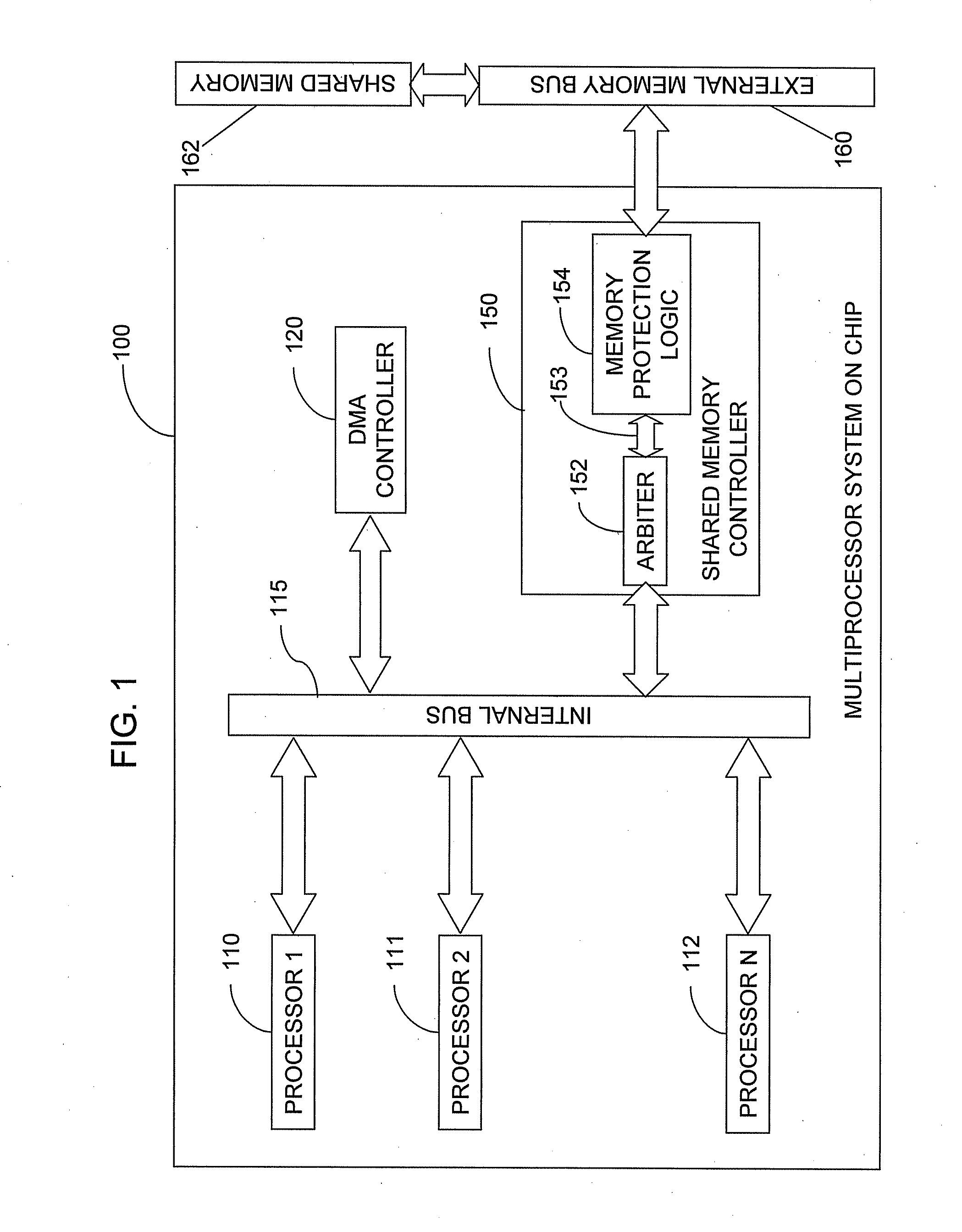
Memory protection system and method
A shared memory controller is provided for controlling access to a shared memory by a plurality of processors. At least one device includes a storage area for storing a respective address range for each of a plurality of memory regions. The at least one device further includes a permission table containing, for each of the plurality of memory regions, read and write permission data for each of the plurality of processors. A memory fault detector is coupled to the at least one device and has an input for receiving a memory access request including a memory address, a processor identification and a read / write indicator. The memory fault detector includes logic for determining whether a memory access according to the memory access request would conflict with the read and write permission data in the permission table.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
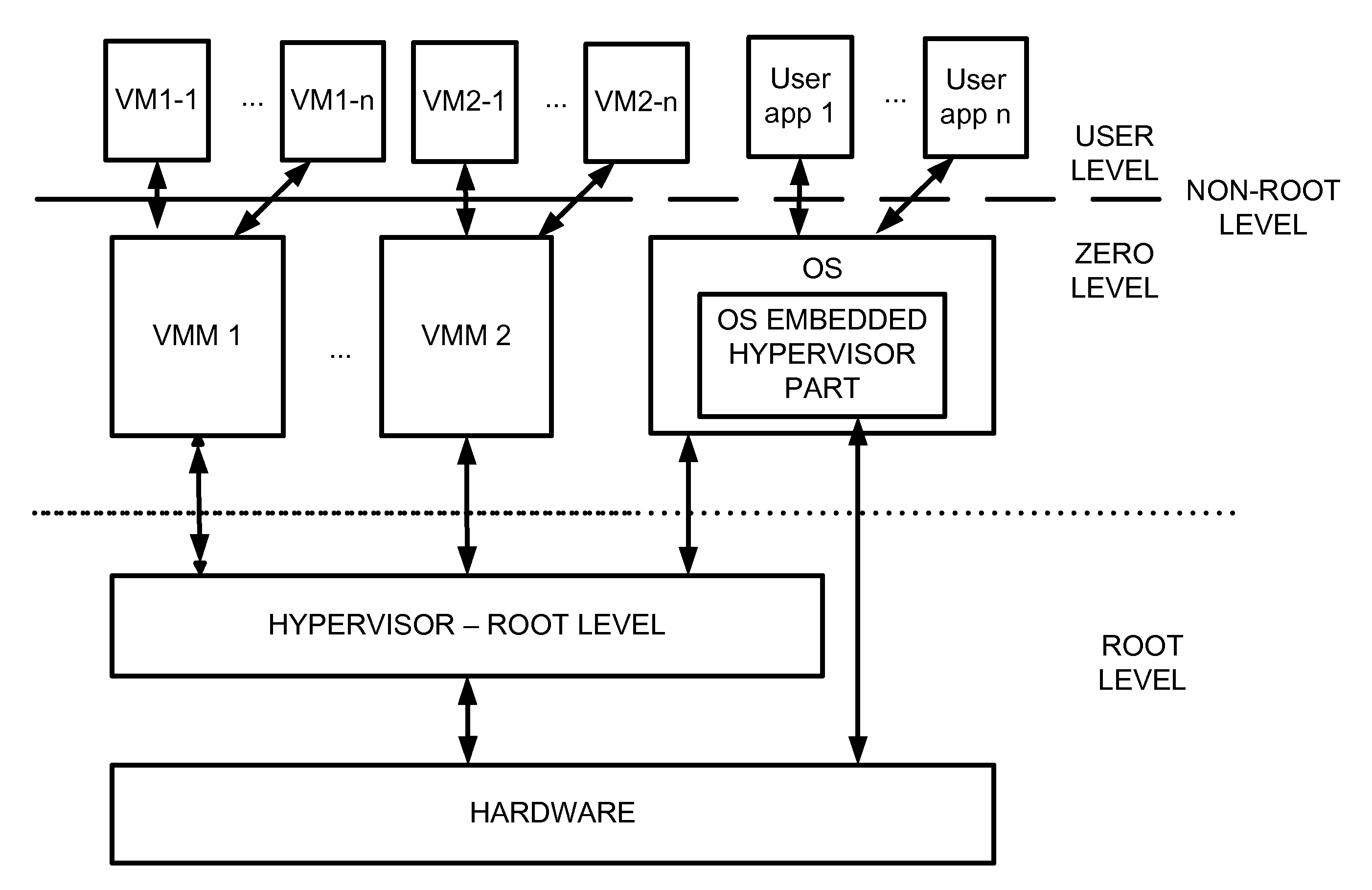
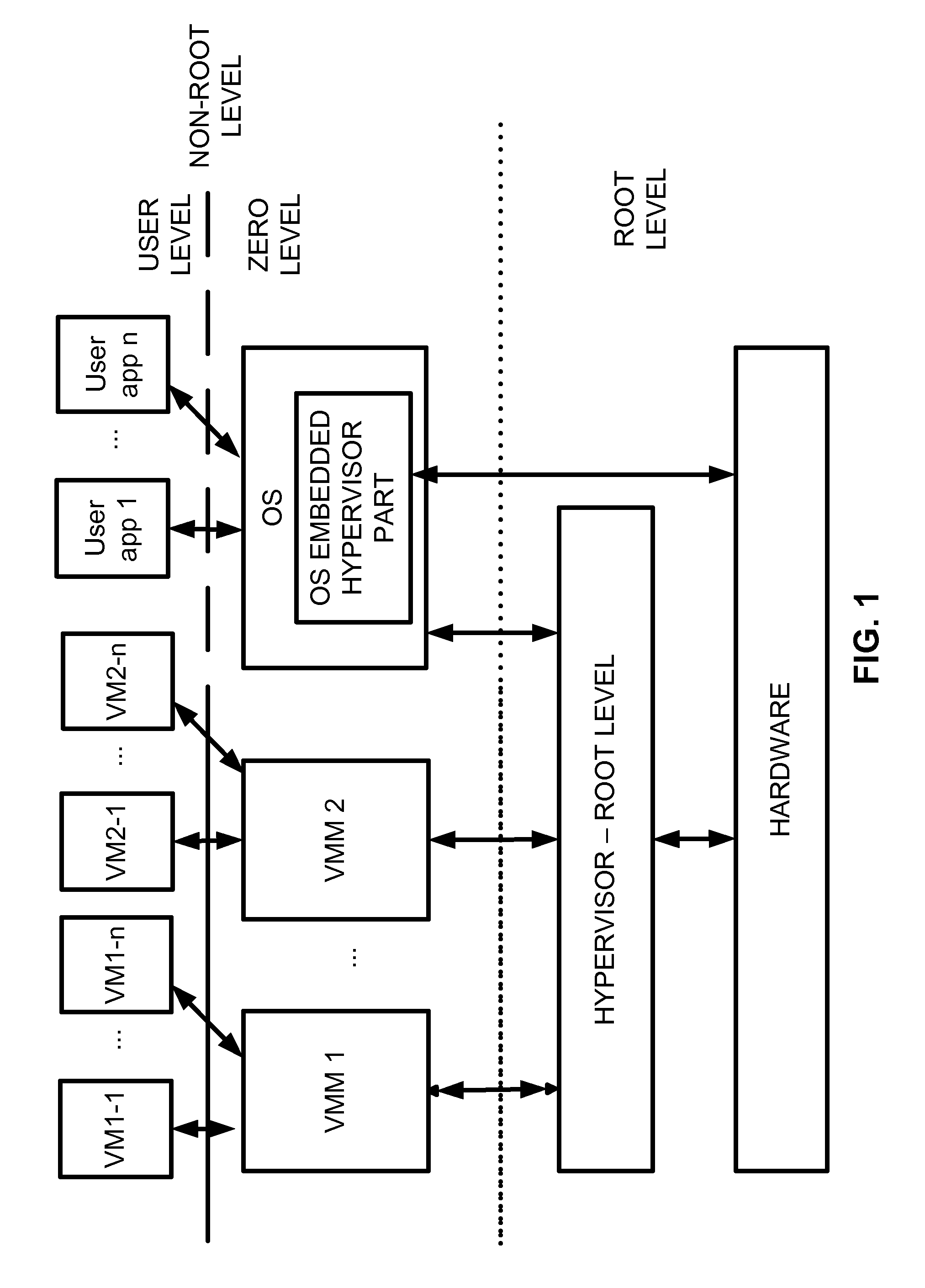
Virtualization system with hypervisor embedded in bios or using extensible firmware interface
A computer system includes a first portion of a Hypervisor is loaded into the memory as a part of an Extensible Firmware Interface upon start up and prior to loading of an operating system. The first portion is responsible for context switching, at least some interrupt handling, and memory protection fault handling. The first portion runs on a root level. An operating system is loaded into a highest privilege level. A second portion of the Hypervisor is loaded into operating system space together with the operating system, and runs on the highest privilege level, and is responsible for (a) servicing the VMM, (b) servicing the VMs, (c) enabling communication between code launched on non-root level with the second portion of the Hypervisor to perform security checks of trusted code portions and to enable root mode for the code portions if allowable. The VMM runs on the highest privilege level. A Virtual Machine is running under control of the VMM. Trusted code runs on non-root level. The first portion of the Hypervisor verifies trusted code portions during their loading or launch time, and the trusted code is executed on root level.
Owner:PARALLELS INT GMBH
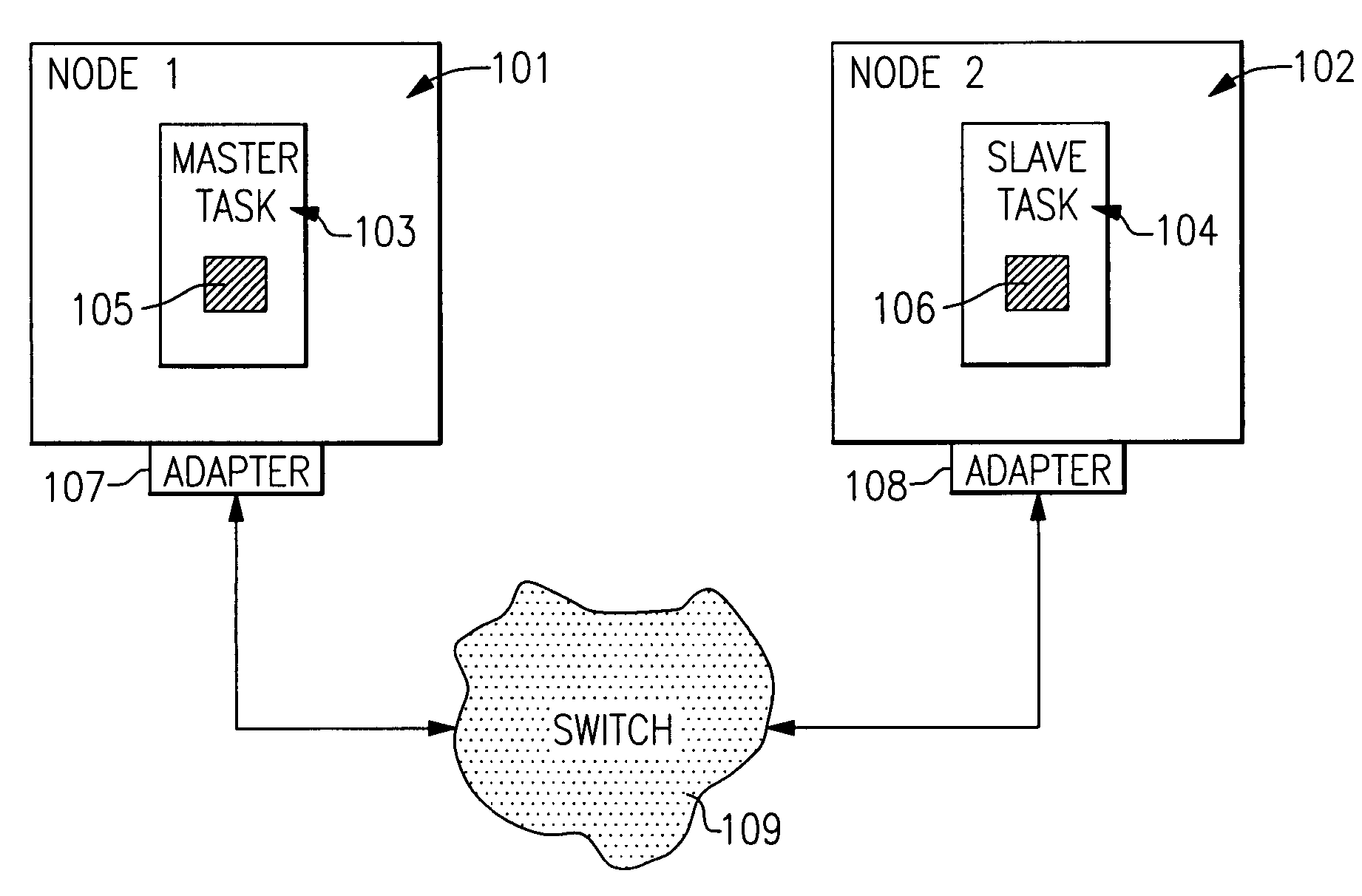
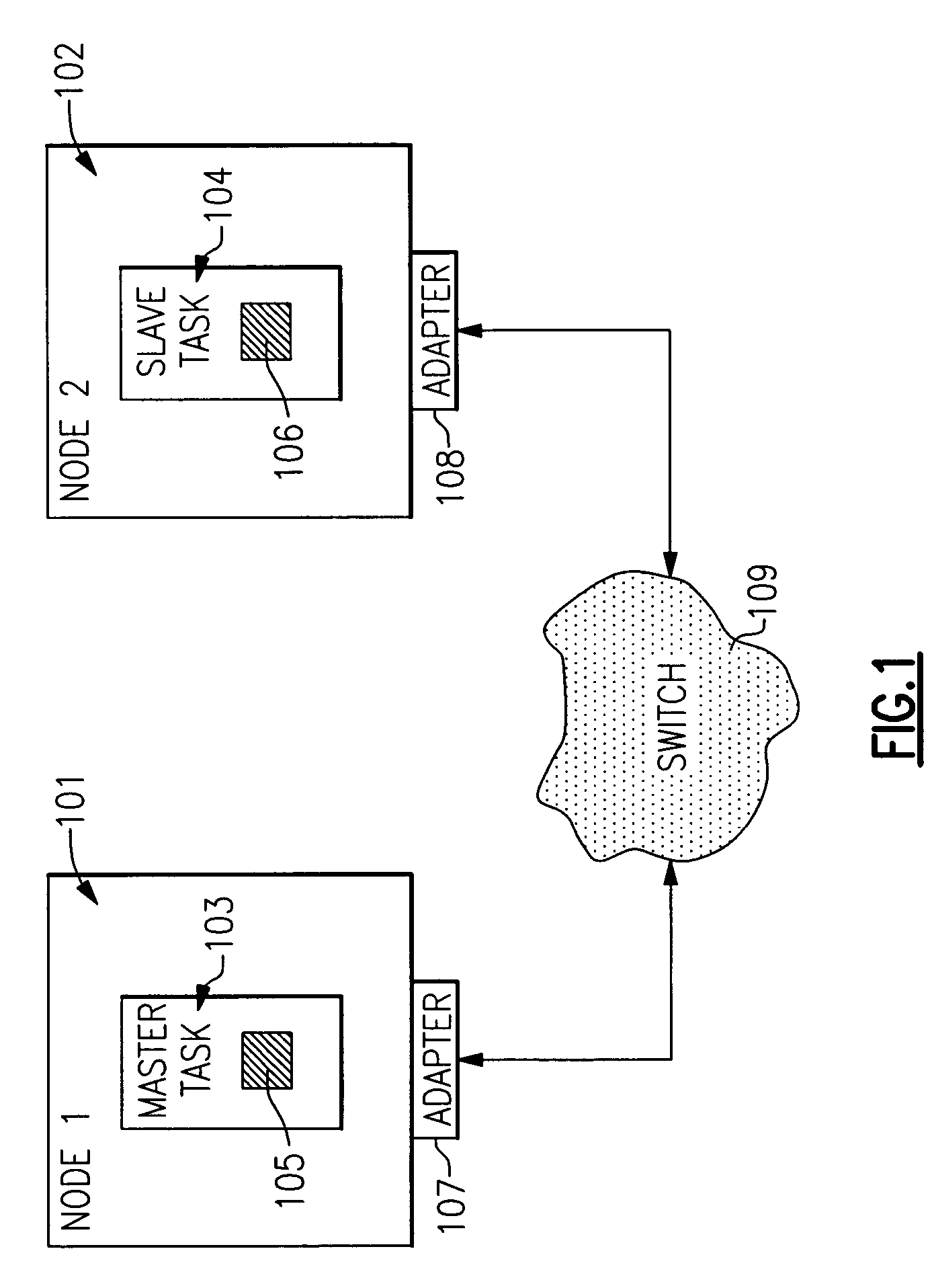
RDMA server (OSI) global TCE tables
ActiveUS20060047771A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionVirtual memoryData processing system
In remote direct memory access (RDMA) transfers in a multinode data processing system in which the nodes communicate with one another through communication adapters coupled to a switch or network, there is a need for the system to ensure efficient memory protection mechanisms across jobs. A method is thus desired for addressing virtual memory on local and remote servers that is independent of the process ID on the local and / or remote node. The use of global Translation Control Entry (TCE) tables that are accessed / owned by RDMA jobs and are managed by a device driver in conjunction with a Protocol Virtual Offset (PVO) address format solves this problem.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and systems for running multiple operating systems in a single mobile device
ActiveUS7424601B2Reduce memory usageError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsExternal storageOperational system
Methods and systems for running multiple operating systems in a single embedded or mobile device (include PDA, cellular phone and other devices) are disclosed. The invention allows a mobile device that normally can only run a single operating system to run another operating system while preserving the state and data of the original operating system. Guest OS is packaged into special format recognizable by the host OS that still can be executed in place by the system. The Methods include: Change the memory protection bits for the original OS; Fake a reduced physical memory space for guest OS; Use special memory device driver to claim memories of host OS; Backup whole image of the current OS and data to external memory card.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
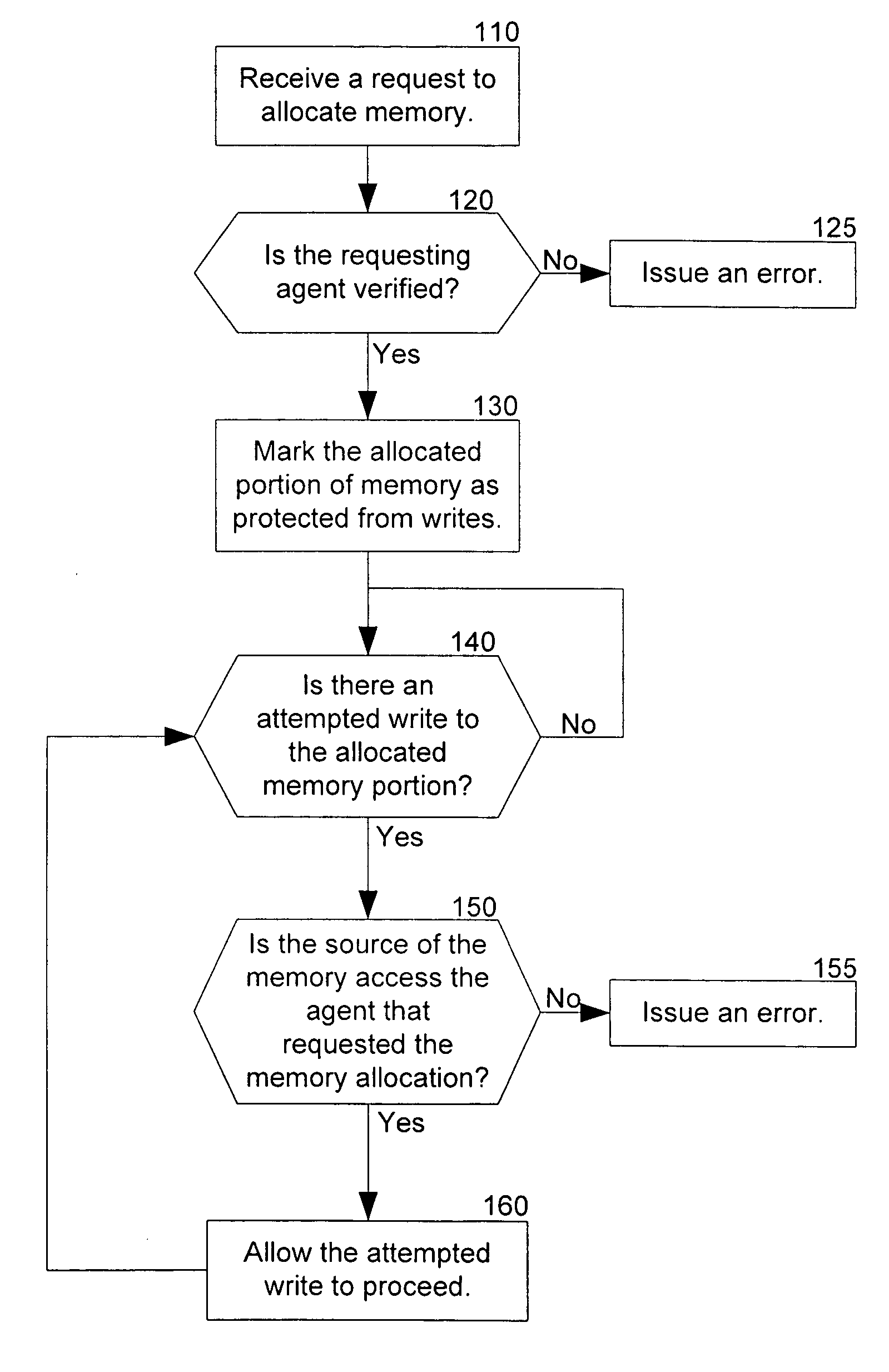
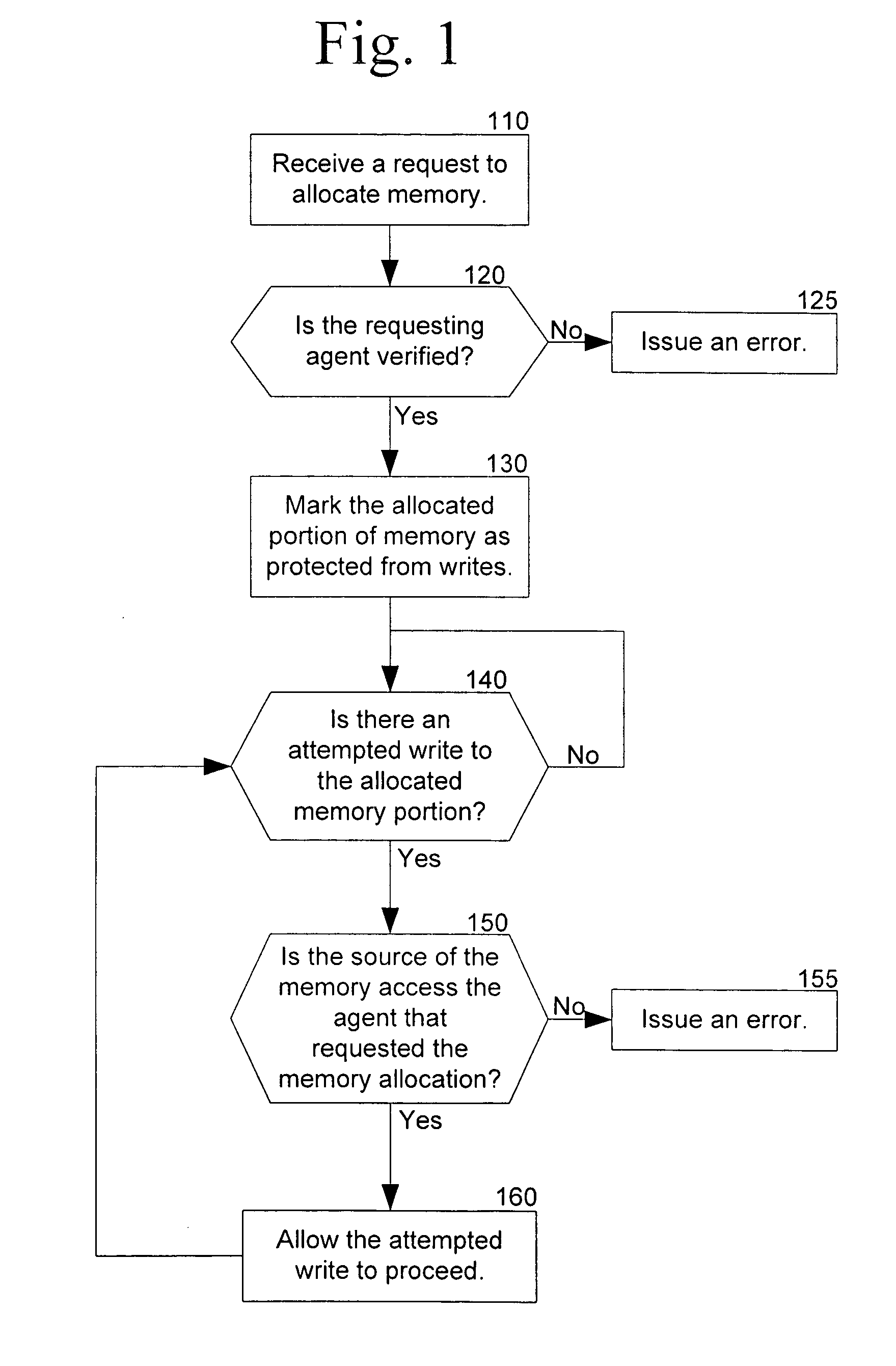
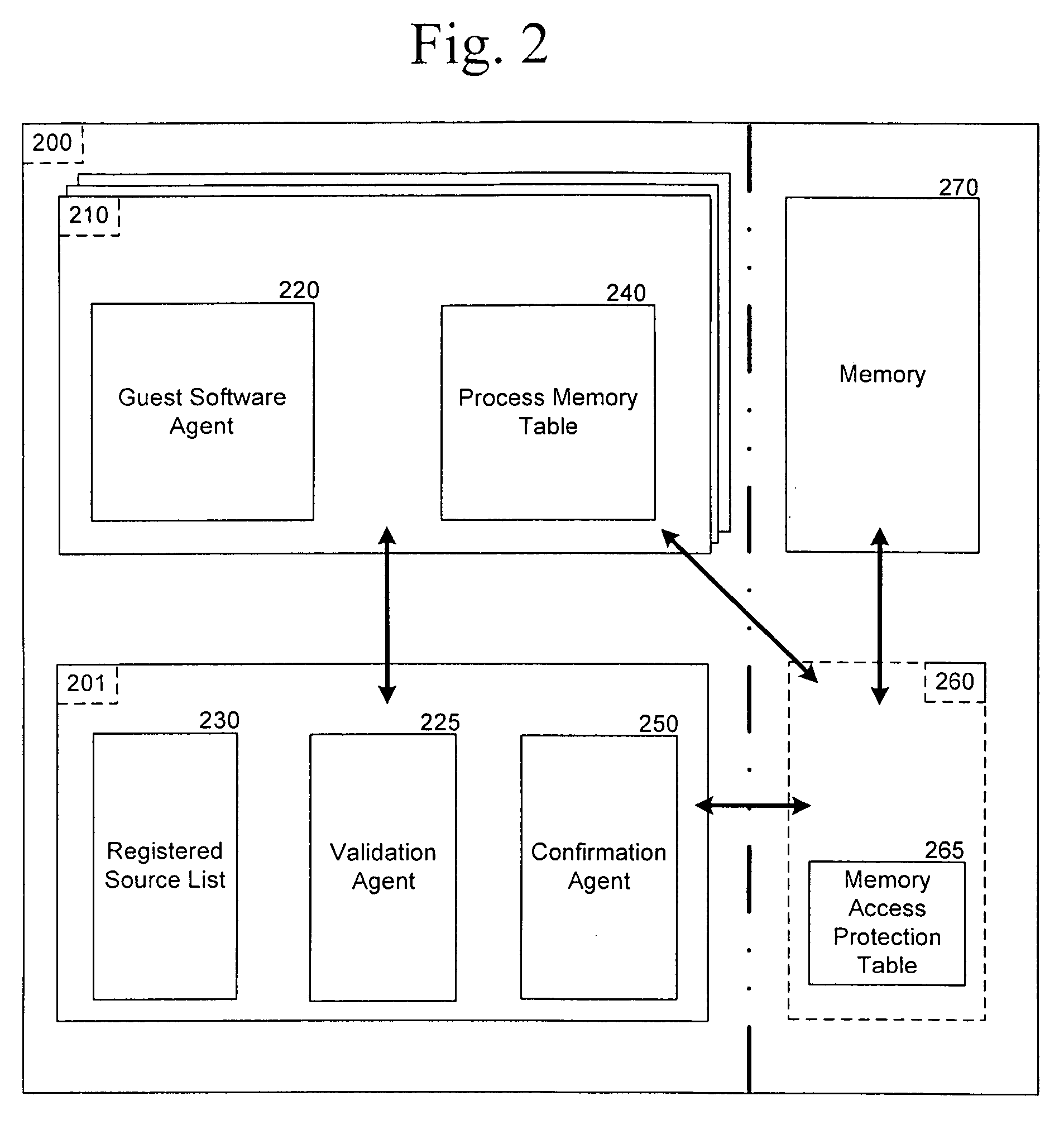
Memory protection within a virtual partition
ActiveUS20070055837A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionTerm memoryControl memory
The present disclosure relates to attempting to monitor and control memory access and, more specifically, to attempting to limit memory access to a specific registered software agent.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
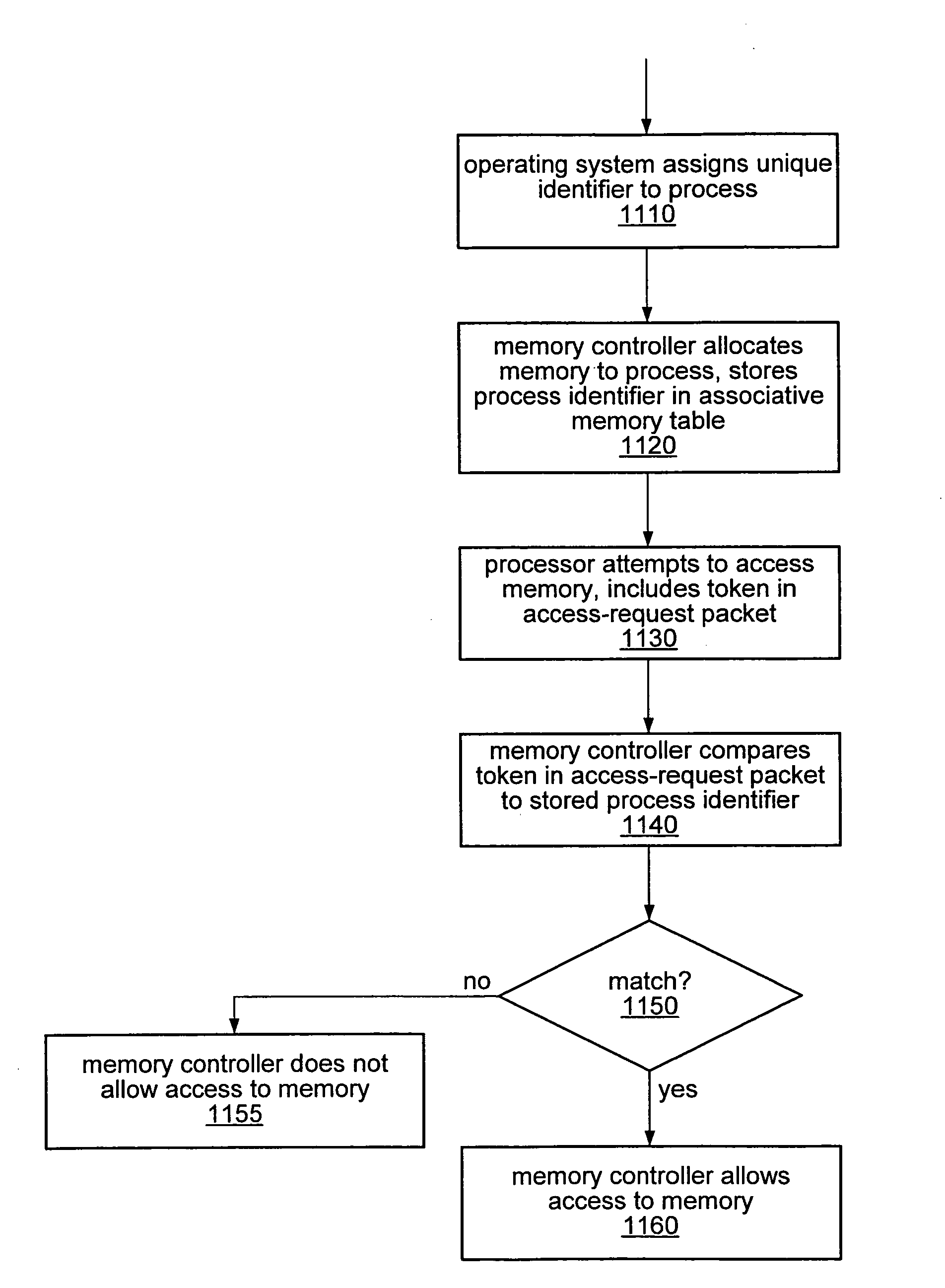
Memory protection in a computer system employing memory virtualization
ActiveUS20070283115A1Unauthorized memory use protectionComputer security arrangementsVirtualizationComputerized system
The use of a token-based memory protection technique may provide memory protection in a computer system employing memory virtualization. A token-based memory protection technique may include assigning a unique identifier to an application, process, or thread, and associating the identifier with a block of memory allocated to that application, process, or thread. Subsequent to assigning the identifier, a packet requesting access to that block of memory may include a token to be compared to the identifier. A memory controller may be configured to associate the identifier with the block of memory and to compare the token in the memory request packet to the identifier before granting access. If a second block of memory is subsequently allocated to the application, process, or thread, the identifier may be disassociated with the first block of memory and associated with the second block of memory.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
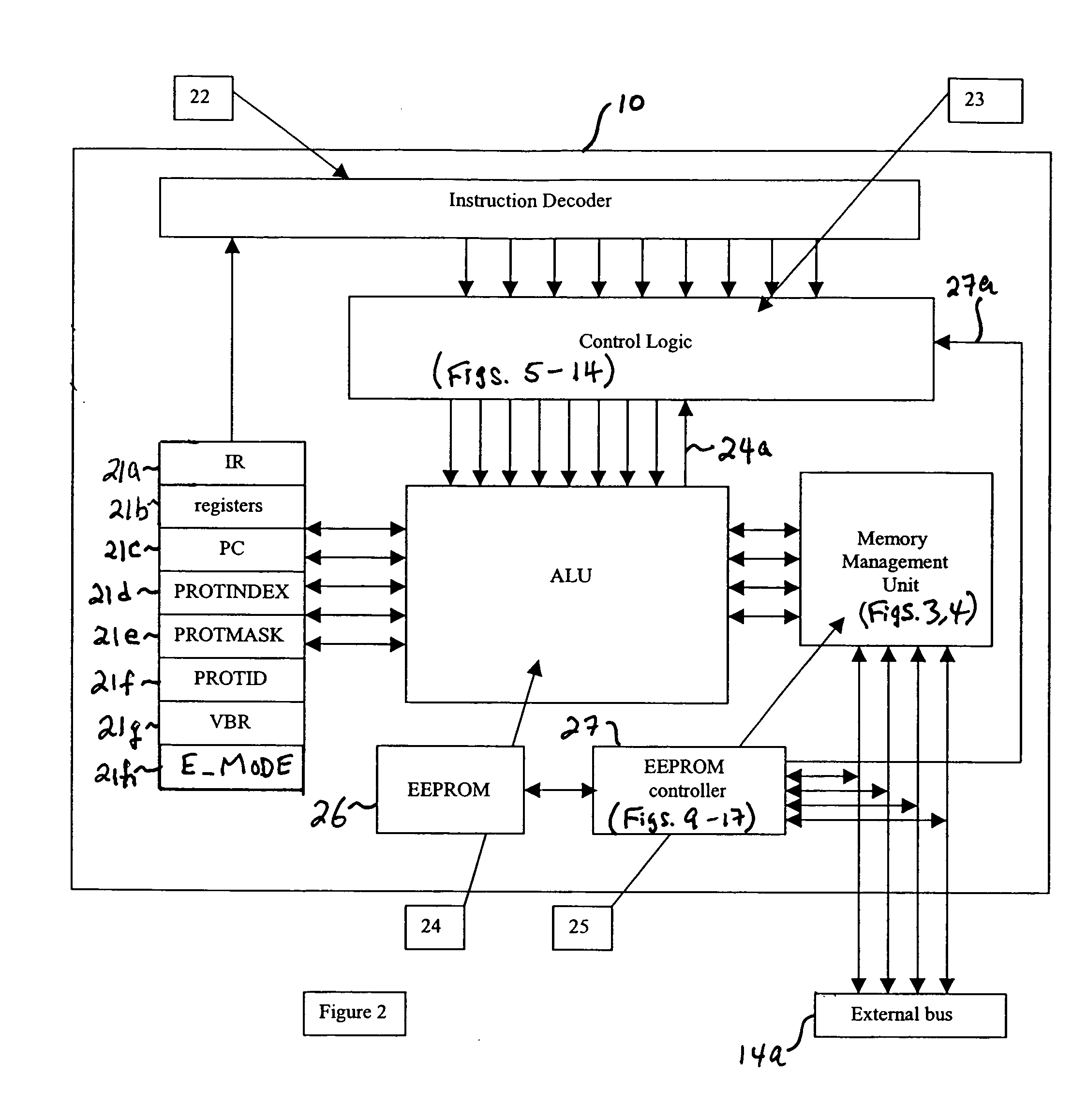
Processor for virtual machines and method therefor
ActiveUS20050091468A1Implement extensionsMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRandom access memoryTerm memory
Apparatus and method are described for a data processing device. The data processor includes features suitable for executing a software virtual machine. The data processor provides an instruction set that supports object-level memory protection suitable for high speed operation. Memory control logic is provided to accommodate a configuration having relatively less random access memory (RAM) as compared to re-programmable, nonvolatile memory, and to improve access to the re-programmable, nonvolatile memory.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS AMERICA
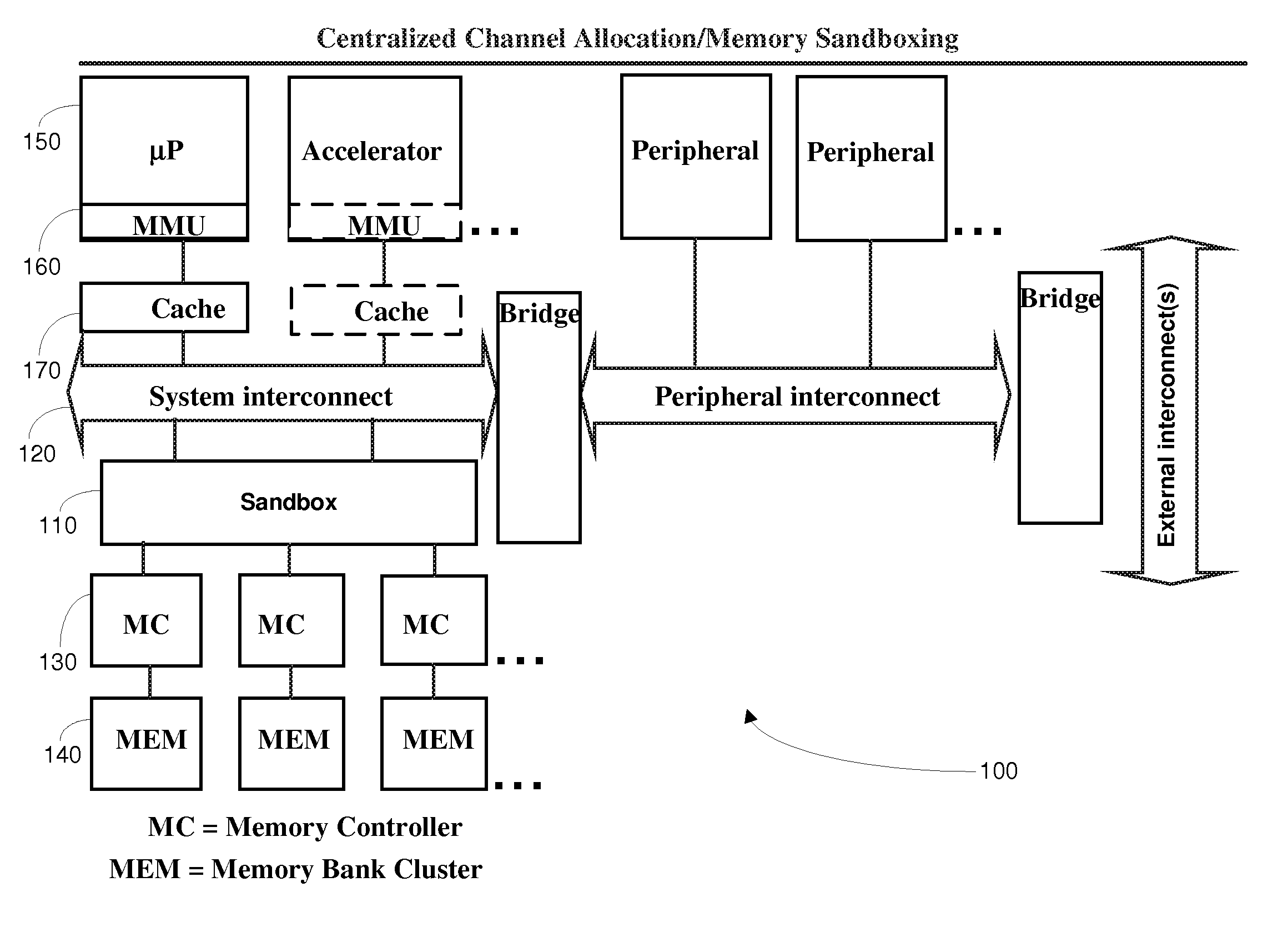
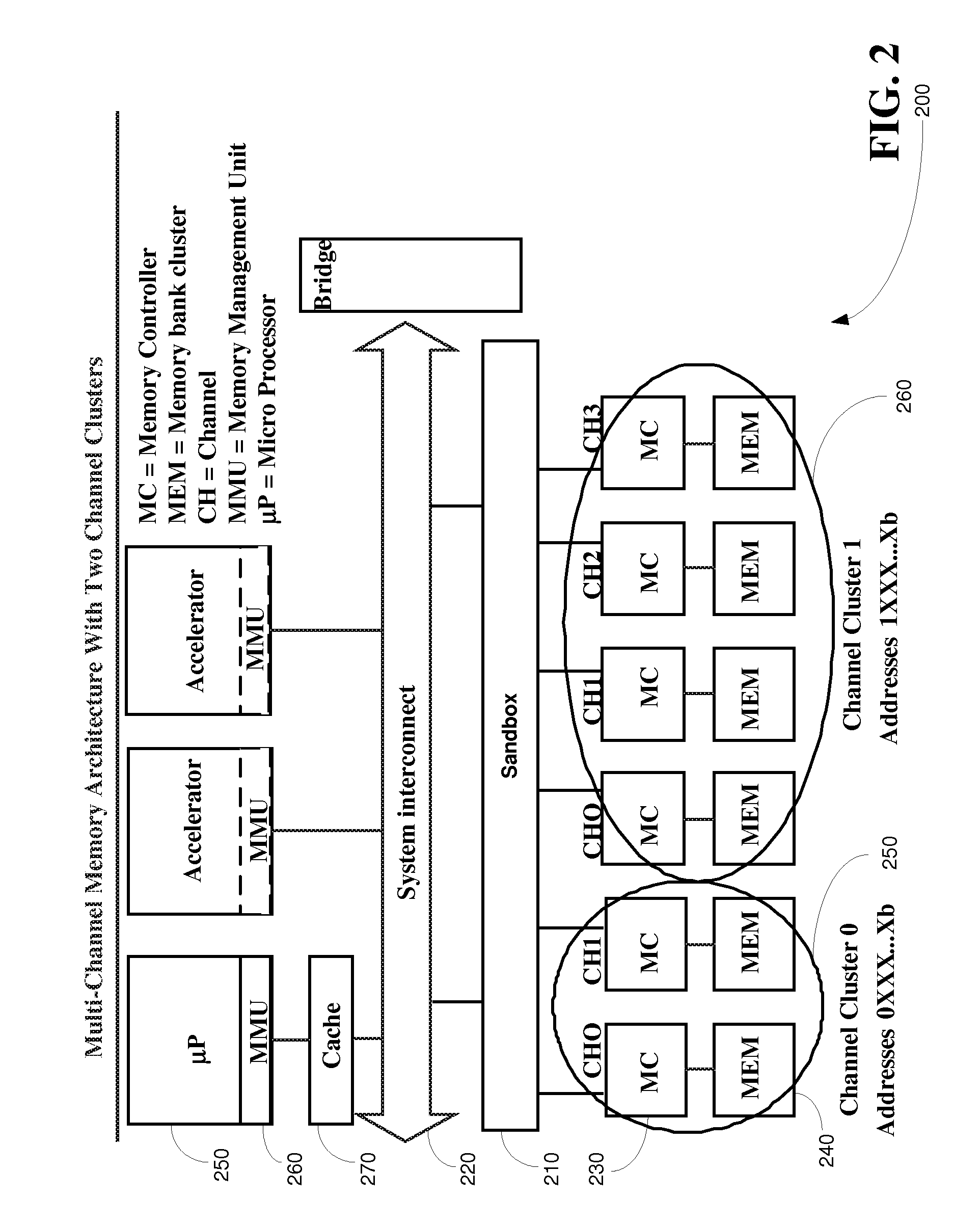
Method, apparatus and software product for multi-channel memory sandbox
InactiveUS20100058016A1Avoid problemsChangeEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationControl memoryMemory protection
A method, apparatus, and software product allow signalling toward a multi-channel memory subsystem within an application processing architecture, and routing of that signalling via a single sandbox which provides memory protection by controlling memory usage and blocking the signalling if it is unauthorized. The signalling via the sandbox leads to a plurality of different memory locations, and the sandbox is an intermediary for substantially all execution memory accesses to the multi-channel memory subsystem.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Hypervisor-enforced isolation of entities within a single logical partition's virtual address space
ActiveUS8010763B2Easy to operateAllow accessMemory architecture accessing/allocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationData processing systemVirtual address space
Access control to shared virtual address space within a single logical partition is provided. The access control includes: associating, by a hypervisor of the data processing system, a memory protection key with a portion of a single logical partition's virtual address space being shared by multiple entities, the key preventing access by one of the multiple entities to that portion of the virtual address space, and allowing access by another of the entities to that portion of the virtual address space; and locking by the hypervisor the memory protection key from modification by the one entity, wherein the locking prevents the one entity from modifying the key and thereby gaining access to the portion of the single logical partition's virtual address space with the associated memory protection key. In one embodiment, the one entity is the single logical partition itself, and the another entity is a partition adjunct.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Apparatus and method for unilaterally loading a secure operating system within a multiprocessor environment
InactiveUS7024555B2Memory loss protectionVolume/mass flow measurementInformation repositoryOperational system
An apparatus and method for unilaterally loading a secure operating system within a multiprocessor environment are described. The method includes disregarding a received load secure region instruction when a currently active load secure region operation is detected. Otherwise, a memory protection element is directed, in response to the received load secure region instruction, to form a secure memory environment. Once directed, unauthorized read / write access to one or more protected memory regions are prohibited. Finally, a cryptographic hash value of the one or more protected memory regions is stored within a digest information repository as a secure software identification value. Once stored, outside agents may request access to a digitally signed software identification value in order to establish security verification of secure software within the secure memory environment.
Owner:INTEL CORP
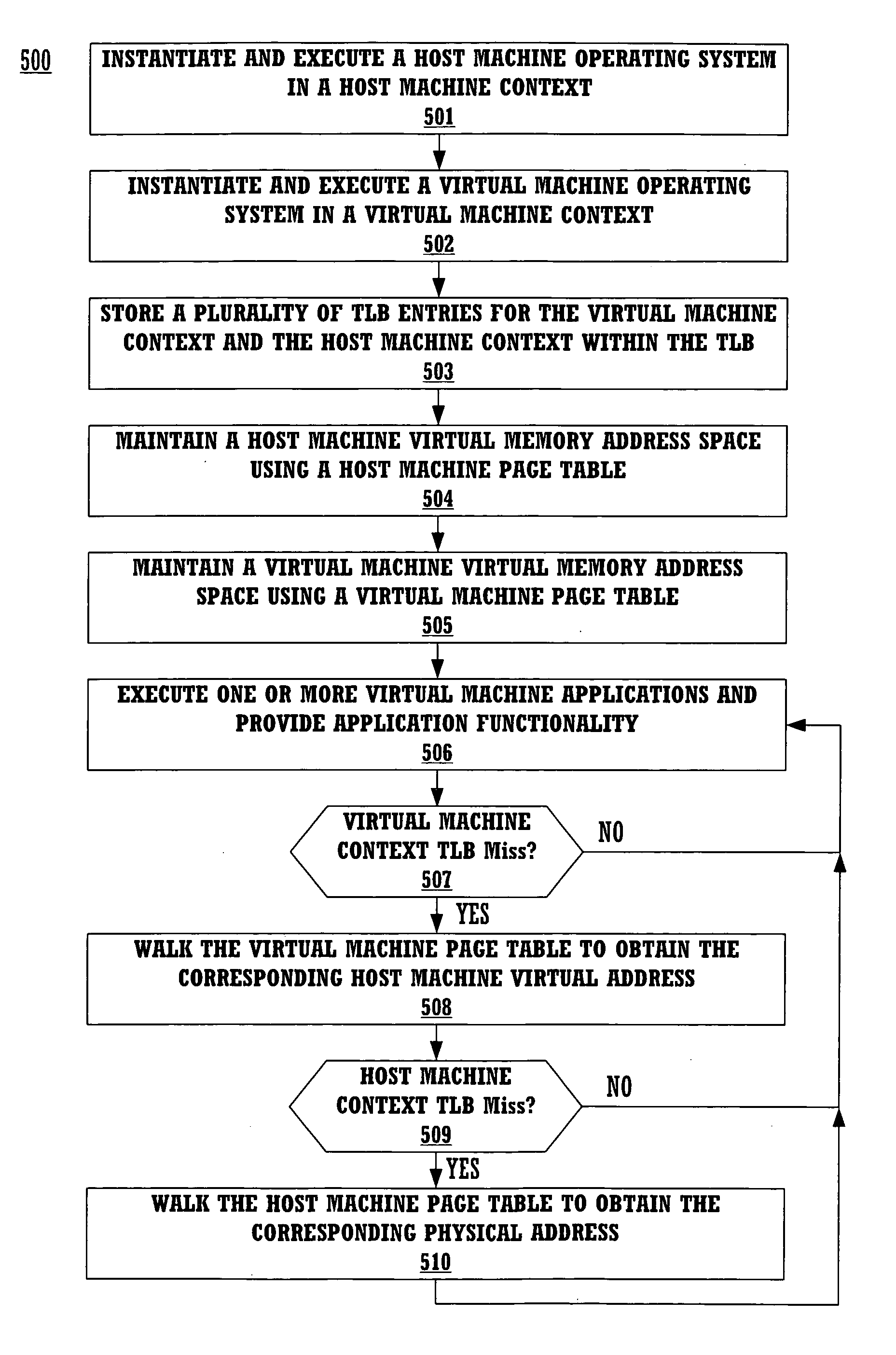
Method and system for providing hardware support for memory protection and virtual memory address translation for a virtual machine
ActiveUS7111146B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionVirtual memoryApplication software
A method for providing hardware support for memory protection and virtual memory address translation for a virtual machine. The method includes executing a host machine application within a host machine context and executing a virtual machine application within a virtual machine context. A plurality of TLB (translation look aside buffer) entries for the virtual machine context and the host machine context are stored within a TLB. Memory protection bits for the plurality of TLB entries are logically combined to enforce memory protection on the virtual machine application.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
System and method to enhance memory protection for programs in a virtual machine environment
ActiveUS20110078361A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiprogramming arrangementsVirtualizationOperational system
Owner:VMWARE INC
Memory protection unit (MPU) having a shared portion and method of operation
In a disclosed embodiment, a data processing system comprises a memory protection unit (MPU); and a plurality of region descriptors associated with the MPU. Each region descriptor is associated with one of multiple subsets of the region descriptors and includes an address range, protection settings, and attributes for a respective region of memory. The subsets include data-only region descriptors, instruction-only region descriptors, and shared region descriptors. The shared region descriptors are used to access memory regions for data and instruction memory requests.
Owner:NXP USA INC
System management interrupt for a desktop management interface/system management basic input output system interface function
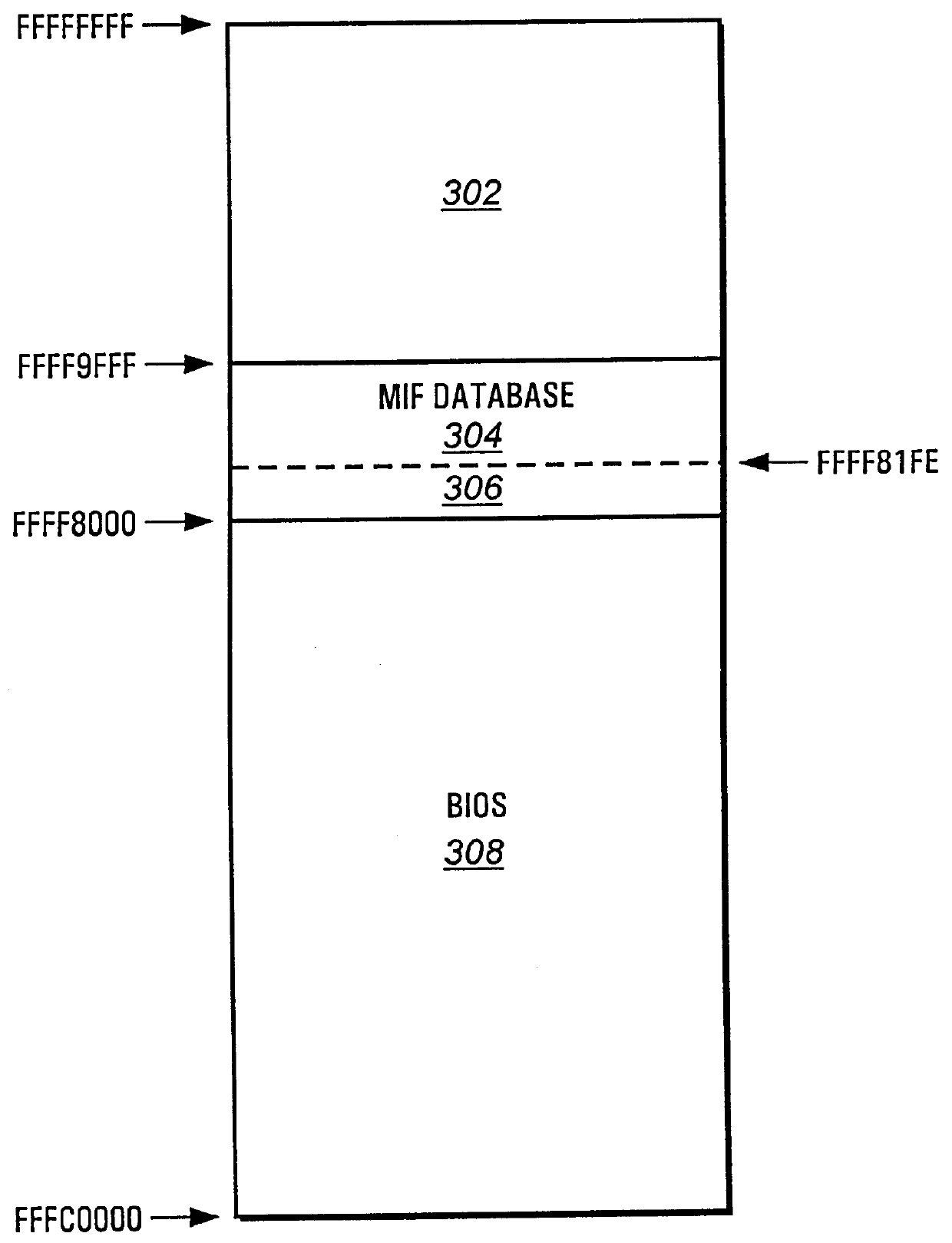
InactiveUS6122732AReduce problemsDigital computer detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionMemory protectionSystem Management Mode
A computing system provides a process for updating a management information format (MIF) database while a processor is operating in a protected mode. The BIOS accesses a protected memory space by utilizing a system management interrupt (SMI). A SMI causes the computing system to enter a system management mode (SMM) and call a Basic Input Output System (BIOS) function, such as the BIOS function 52h (Set Structure), to accomplish an update of the MIF database. An OEM string, for example, may be updated. In SMM, the system is capable of accessing the entire memory address space without risking a memory protection fault.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Selective self-healing of memory errors using allocation location information
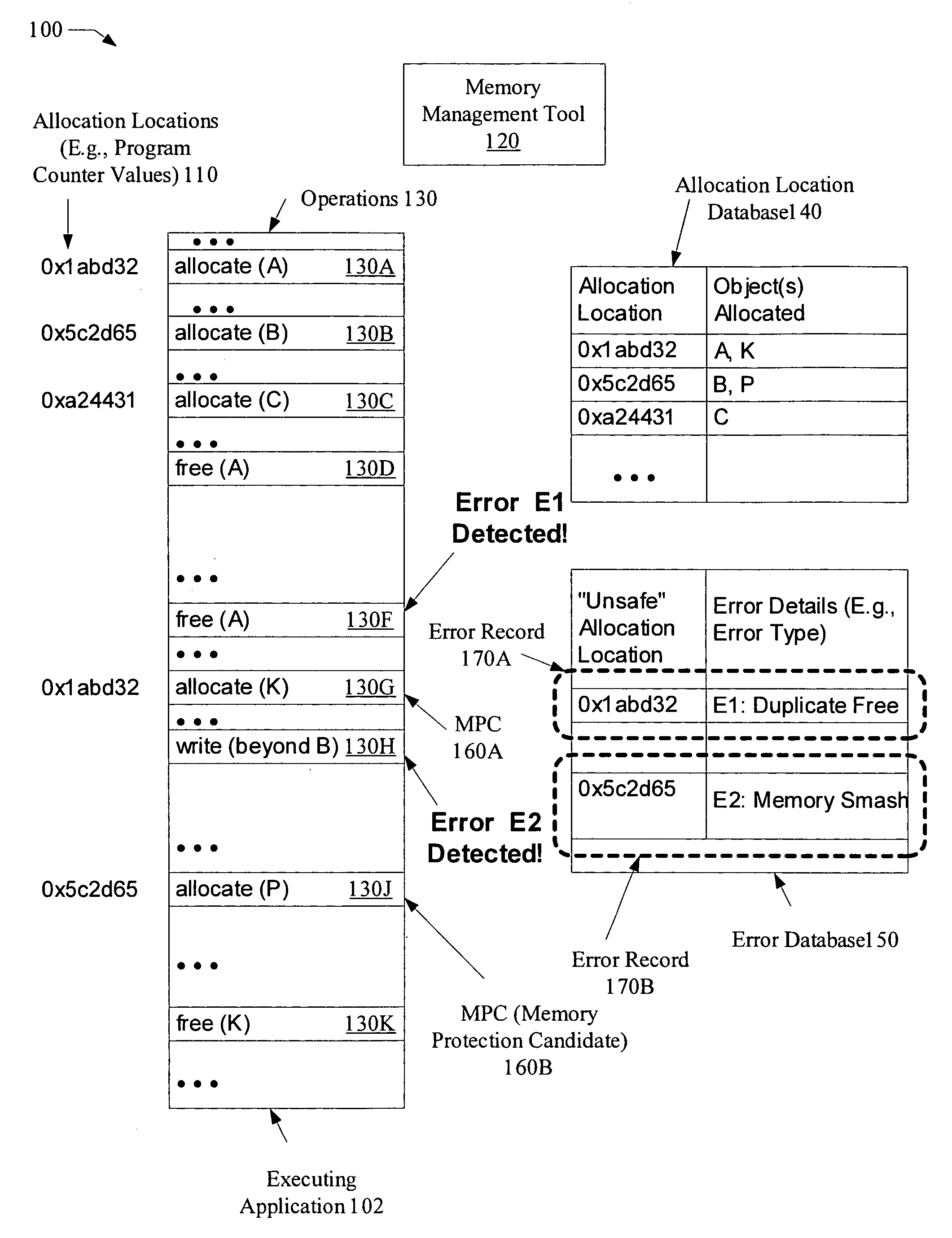
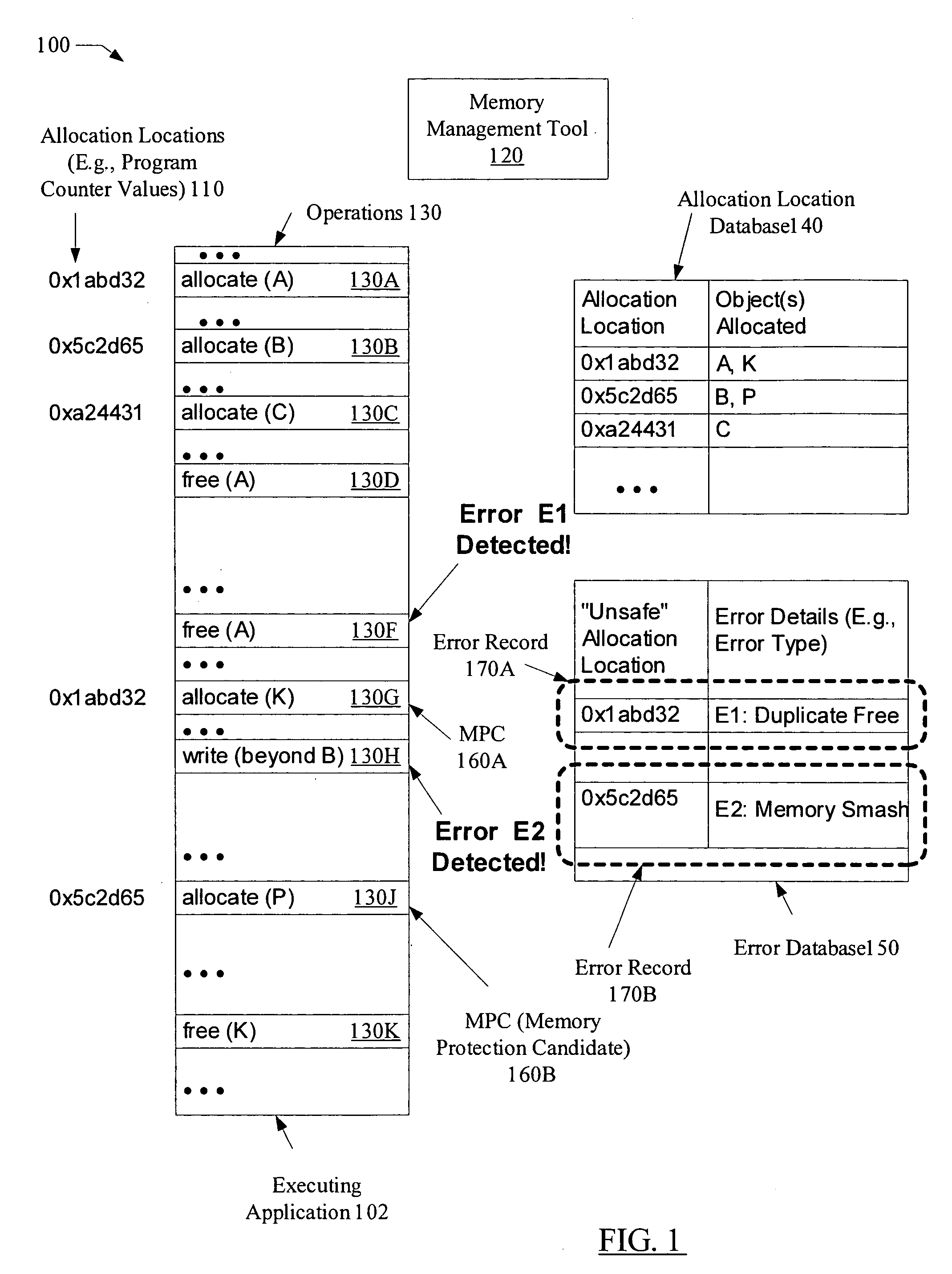
ActiveUS7434105B1Reduce overheadNon-redundant fault processingMemory systemsSelf-healingMemory protection
A system for selective self-healing of memory errors comprises a processor coupled to a memory, where the memory stores instructions executable by the processor to store an error record for each memory management error detected during an execution of the application. The error record identifies an allocation location (e.g., a portion of a stack trace corresponding to the invocation of a memory allocation function such as malloc( )) of an object associated with the memory management error. The instructions are executable to use the error record to identify, during subsequent execution, memory operations performed on objects allocated from the allocation location, and to perform corresponding memory protection operations (e.g., operations to prevent re-occurrences of the memory errors) for the memory operations identified using the error record.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
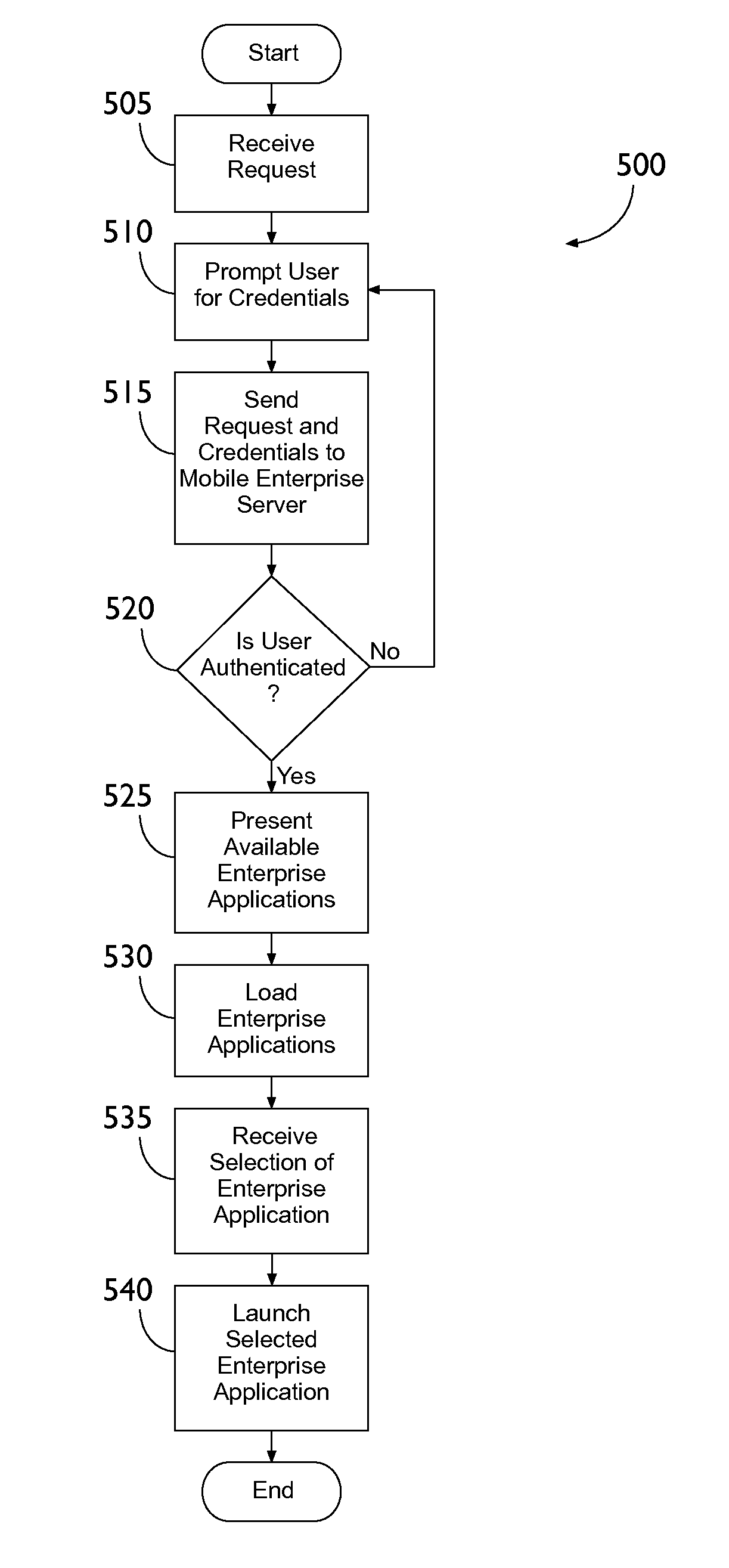
Mobile enterprise server and client device interaction
A system includes an application server that hosts a plurality of enterprise applications and stores enterprise data associated with each of the enterprise applications. A client device executes a client application that can provide access to each of the enterprise applications. The client application includes a memory protection engine that allocates a first memory location for the enterprise data transmitted to the client device so the enterprise data is accessible to each of the plurality of enterprise applications through the client application. A second allocated memory location is allocated for non-enterprise data. A mobile enterprise server transmits the enterprise data to the client device.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Xen-based active defense method
The invention discloses a virtual machine Xen-based active defense method, which comprises the following steps of: generating a virtual machine for a user by using Xen, and making the user perform operation in the virtual machine; simultaneously removing conventional security programs required to be installed in the virtual machine and arranging the removed security programs outside the virtual machine of a system, so that kernel modules of the security programs are invisible for rogue programs; in addition, setting a front-end drive in the virtual machine of the user to make the security modules outside the virtual machine can scan and intervene in the operation in the virtual machine, and simultaneously protecting the front-end drive by using a memory protection module in a monitor layer of the virtual machine to prevent the front-end drive from being attacked by the rogue programs. In the method, the kernel modules are arranged outside the virtual machine, and are invisible for therogue programs, thereby achieving security higher than that of a conventional security program deployment method; in addition, a para-virtualization front / rear-end drive communication way is introduced to greatly reduce system overhead caused by virtualization and make the method highly practicable.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
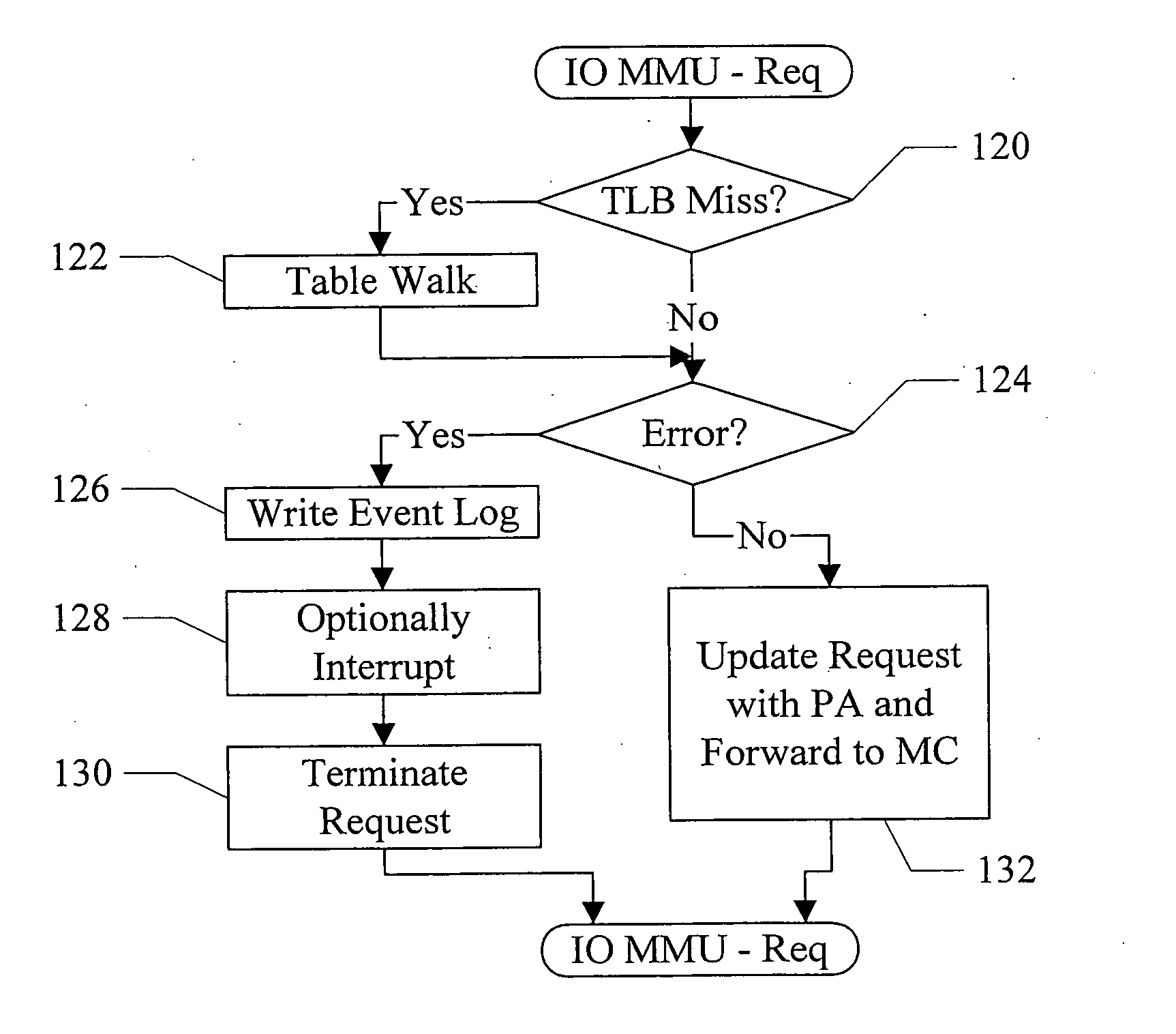
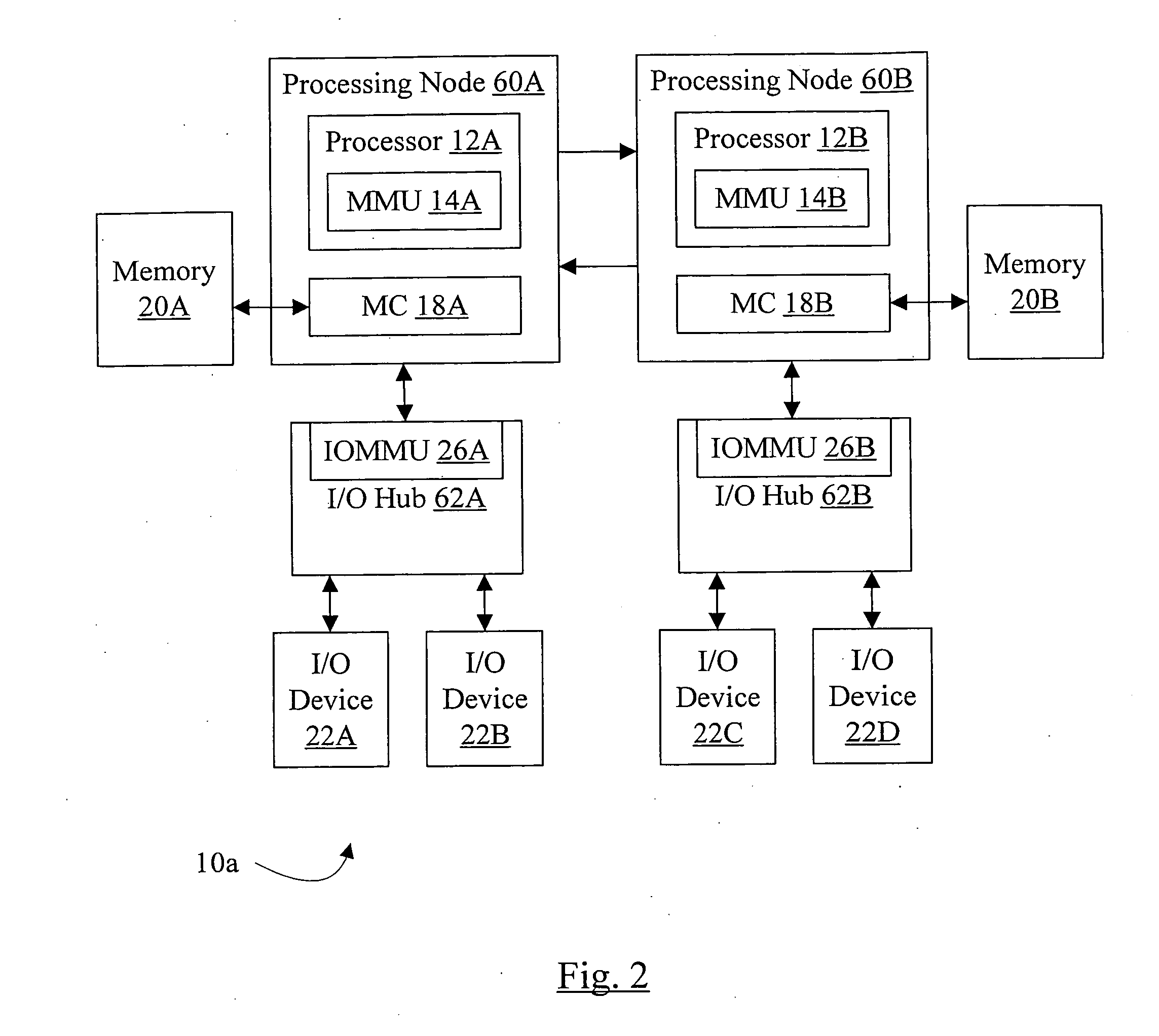
Controlling an I/O MMU
ActiveUS20070038839A1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingTerm memoryExecution control
In an embodiment, a computer system comprises a processor; a memory management module comprising a plurality of instructions executable on the processor; a memory coupled to the processor; and an input / output memory management unit (IOMMU) coupled to the memory. The IOMMU is configured to implement address translation and memory protection for memory operations sourced by one or more input / output (I / O) devices. The memory stores a command queue during use. The memory management module is configured to write one or more control commands to the command queue, and the IOMMU is configured to read the control commands from the command queue and execute the control commands.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Processor for Virtual Machines and Method Therefor
InactiveUS20080313383A1Implement extensionsMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRandom access memoryControl logic
Apparatus and method are described for a data processing device. The data processor includes features suitable for executing a software virtual machine. The data processor provides an instruction set that supports object-level memory protection suitable for high speed operation. Memory control logic is provided to accommodate a configuration having relatively less random access memory (RAM) as compared to re-programmable, nonvolatile memory, and to improve access to the re-programmable, nonvolatile memory.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS AMERICA
Memory protection within a virtual partition
ActiveUS7380049B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsControl memorySoftware agent
The present disclosure relates to attempting to monitor and control memory access and, more specifically, to attempting to limit memory access to a specific registered software agent.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
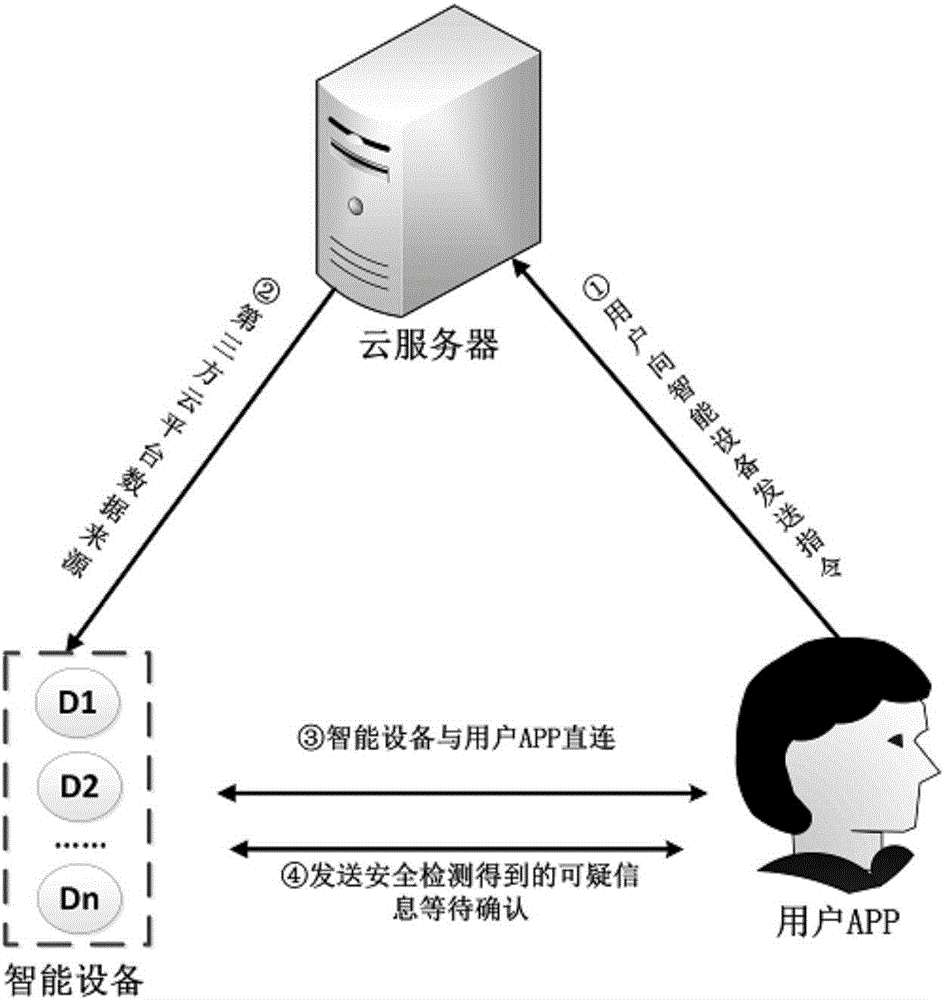
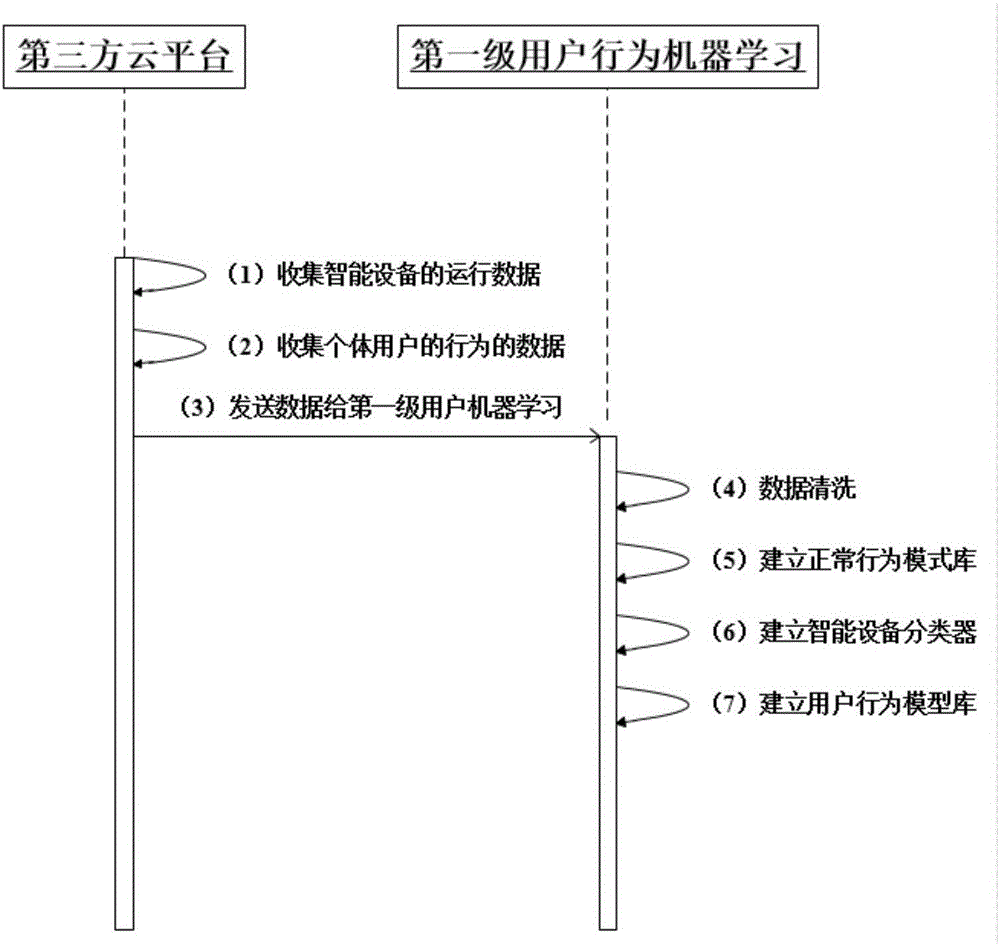
Intelligent equipment machine learning safety monitoring system based on user behavior
InactiveCN106230849AProtection securityAchieve securityDigital data protectionPlatform integrity maintainanceThird partyMonitoring system
The invention discloses an intelligent equipment machine learning safety monitoring system based on a user behavior. The system is characterized by comprising a first-level machine learning model oriented to the third party intelligent equipment user behavior data and a second-level user behavior machine learning model of an intelligent equipment side based on a MPU memory protection mechanism; the first-level learning model performing data cleaning on two types of data on the basis of two types of data, namely, the data of the same intelligent equipment type and the behavior data of the same individual user, by means of the user behavior data of a third party cloud platform, determining the data and the correlation needed to use by the intelligent equipment, and determining a subject of the intelligent equipment user behavior according to the type of the intelligent equipment; the second-level user behavior machine learning model of the intelligent equipment side based on the MPU memory protection mechanism, the intelligent equipment side firstly using the memory protection mechanism of the MPU to divide safety protection regions on a safety monitoring model obtained in the first-level machine learning model, and finally enabling a monitoring system to effectively protect the security of the intelligent equipment and the user.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CAS
Method and system usable in sensor networks for handling memory faults
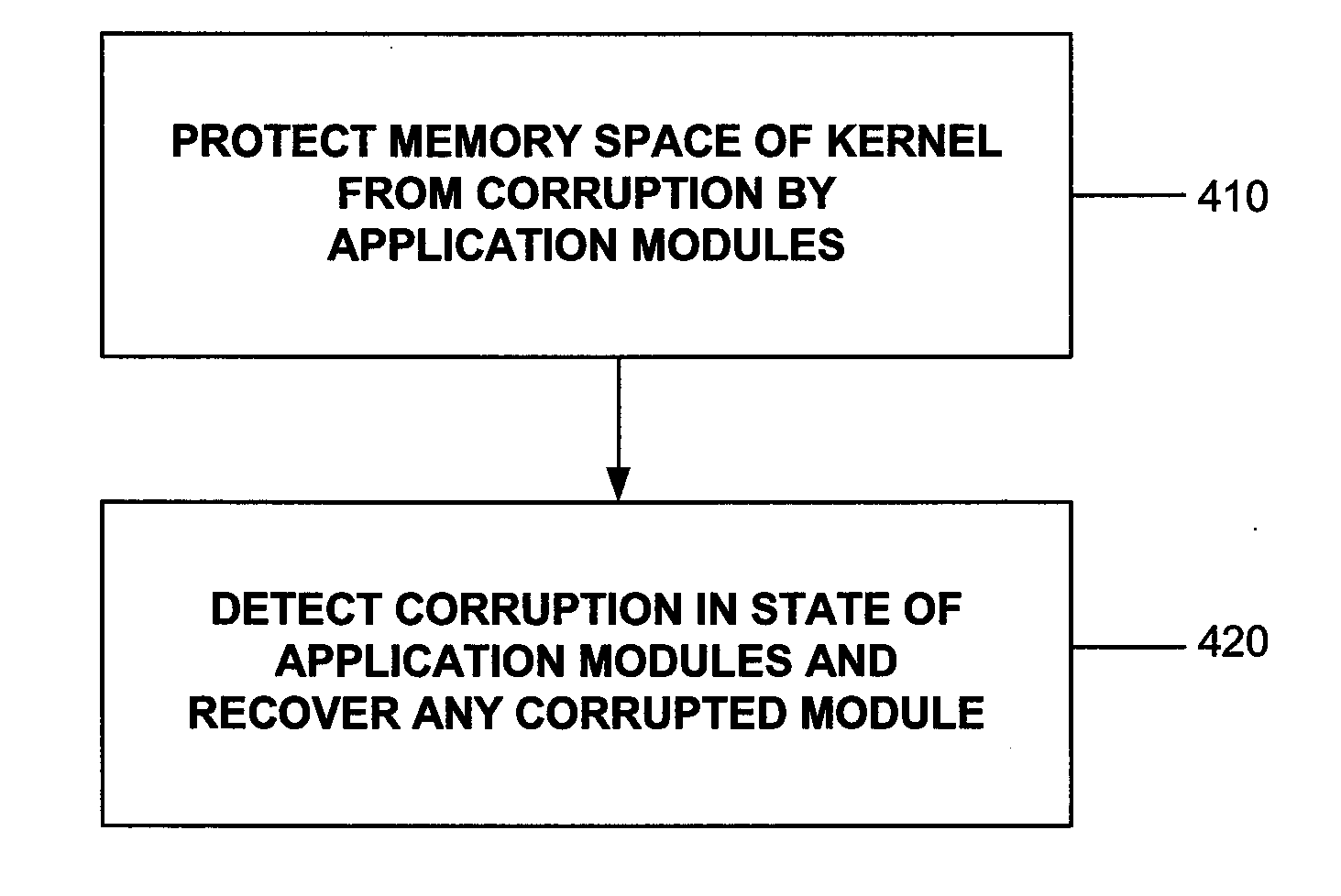
InactiveUS20070156951A1Corrupt stateProtection operationError detection/correctionMemory systemsMemory faultsOperational system
A method and system usable in sensor networks for handling memory faults is disclosed. In order to protect the operating system of a sensor node, coarse-grained memory protection is provided by creating and enforcing an application fault domain in the data memory address space of the sensor node. The data memory accessed by the application modules is restricted to the region (which defines the application fault domain) within the data memory address space. The application modules are prevented from accessing memory outside the application fault domain through software-based run-time checks. The state belonging to the operations system is maintained outside of the application fault domain, and is thus protected from memory corruption from any application module. In order to ensure that an application module does not operate on a corrupted state, fine-grained error detection and recovery is provided within the application fault domain. Any corruption of memory within the application fault domain is detected by a run-time memory integrity verifier implemented in the operating system kernel. Recovery involves purging the corrupted state and restarting only the affected application module to operate on an uncorrupted state.
Owner:NEC CORP
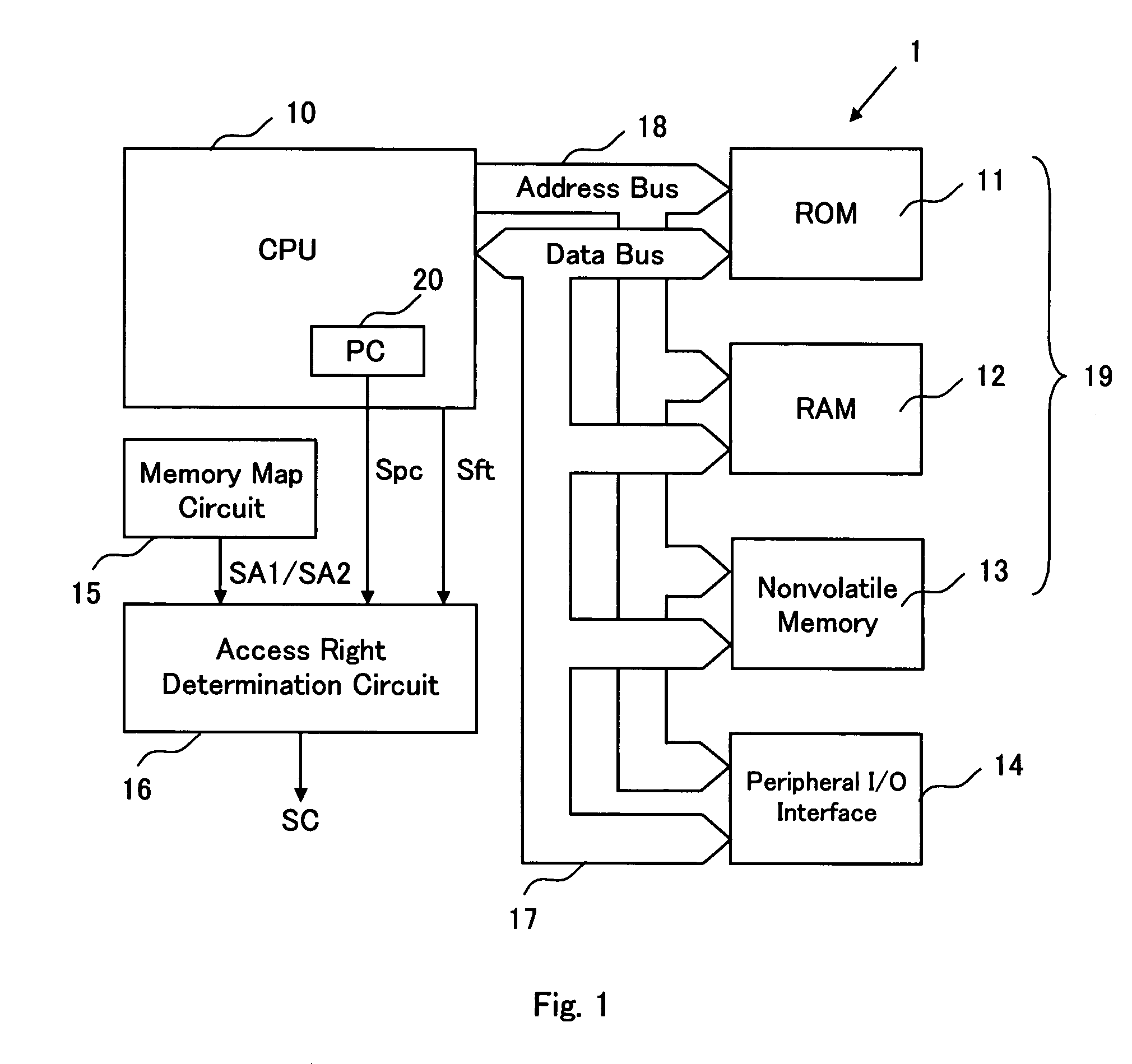
Computer system having memory protection function
InactiveUS20070266214A1Preventing executionUnauthorized memory use protectionPlatform integrity maintainanceBuffer overflowComputerized system
A computer system for preventing secret data in a memory area from being erased, altered or leaked due to a buffer overflow attack and the like comprises a memory map circuit for storing an access control memory map which defines whether the CPU has an access right for executing a program with respect to each address of the memory area, an access right determination circuit for determining whether the CPU has the access right to the memory area of an execution program storage address designated by a program counter based on the access control memory map, and outputting an access prohibition signal which makes the CPU execute a predetermined operation to disable the CPU from accessing the memory area of the execution program storage address when the CPU does not have the access right.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com