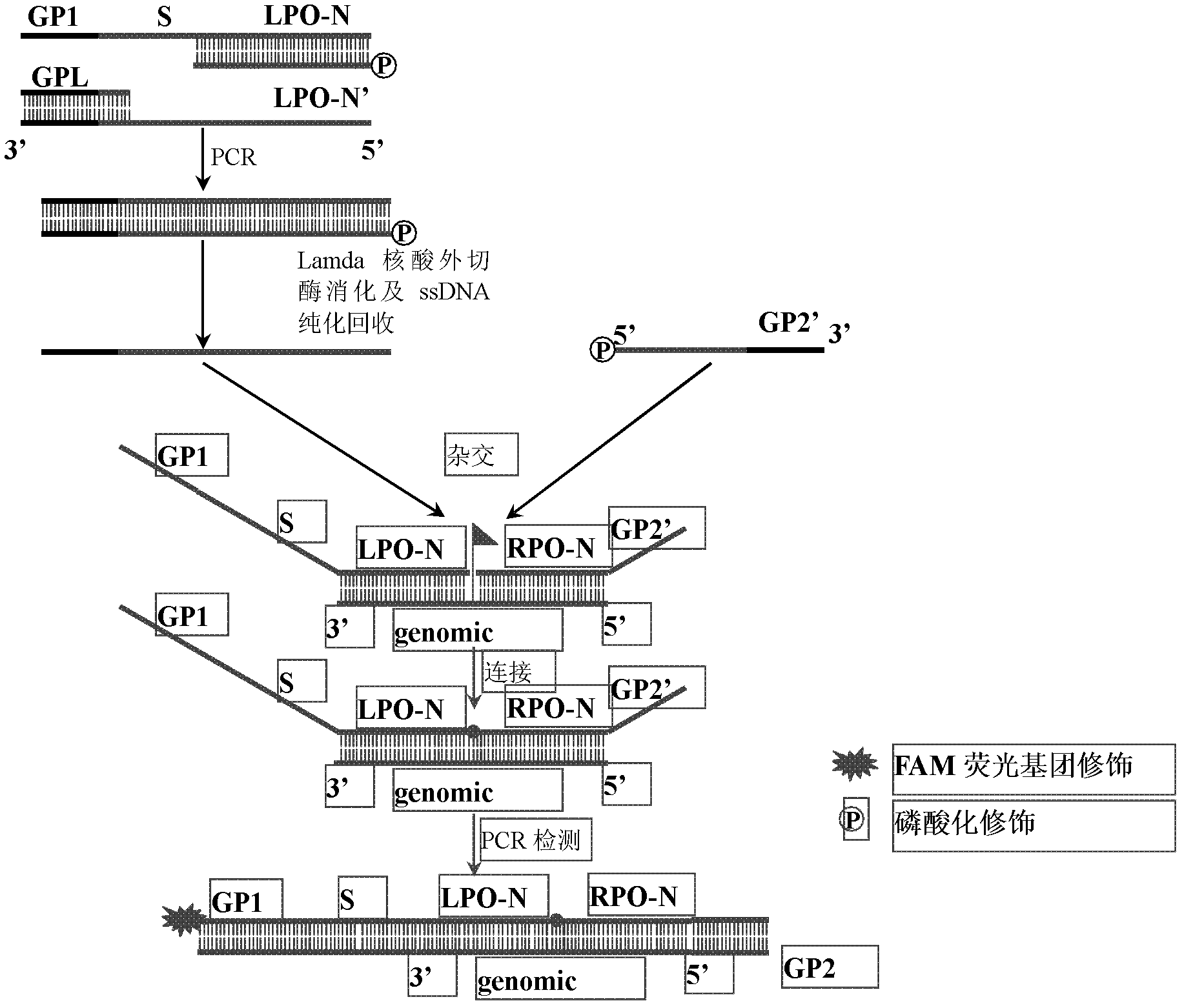
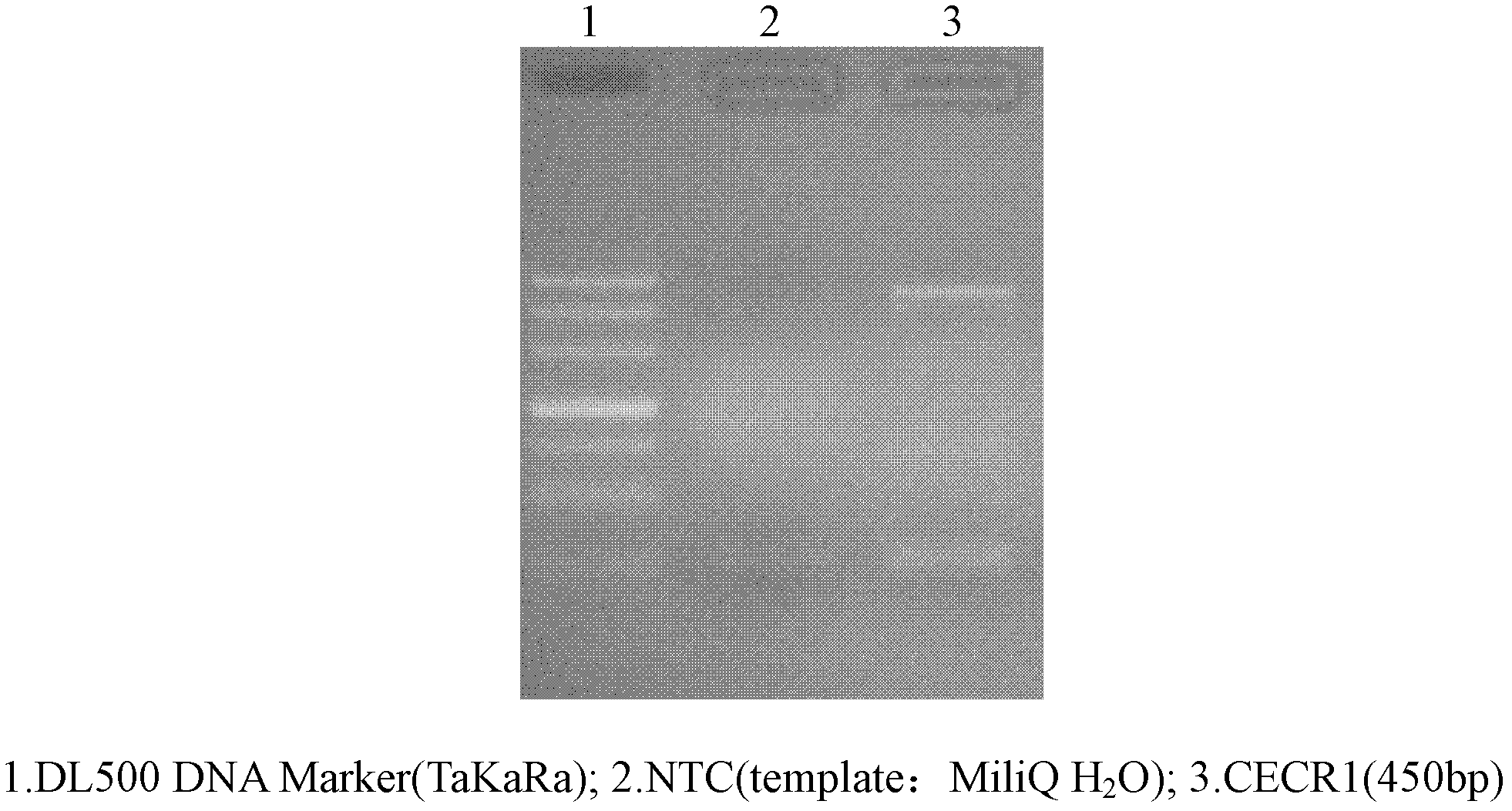
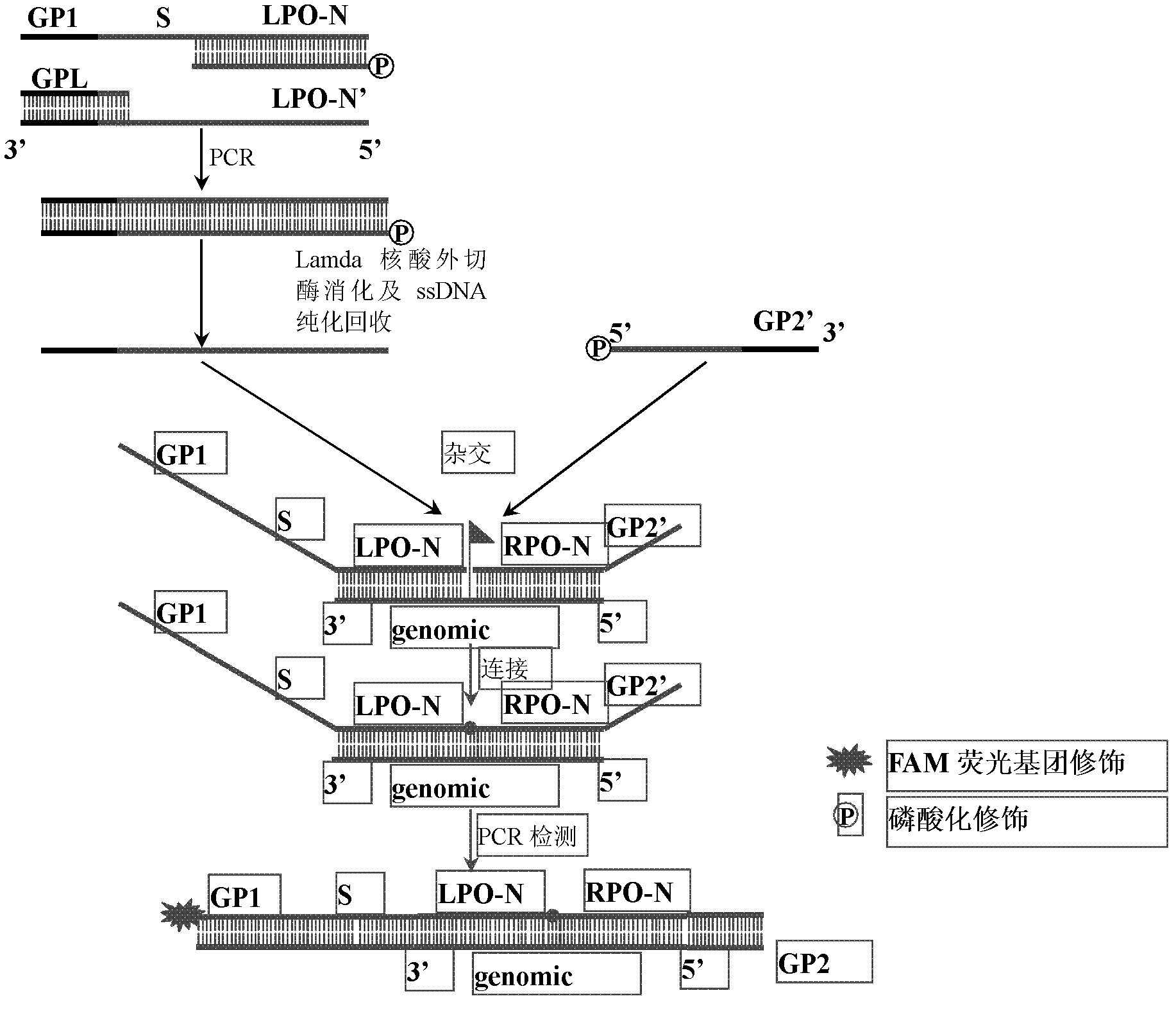
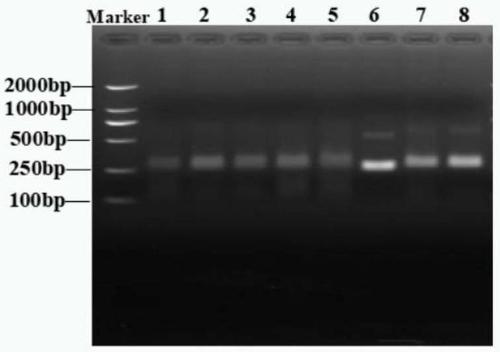
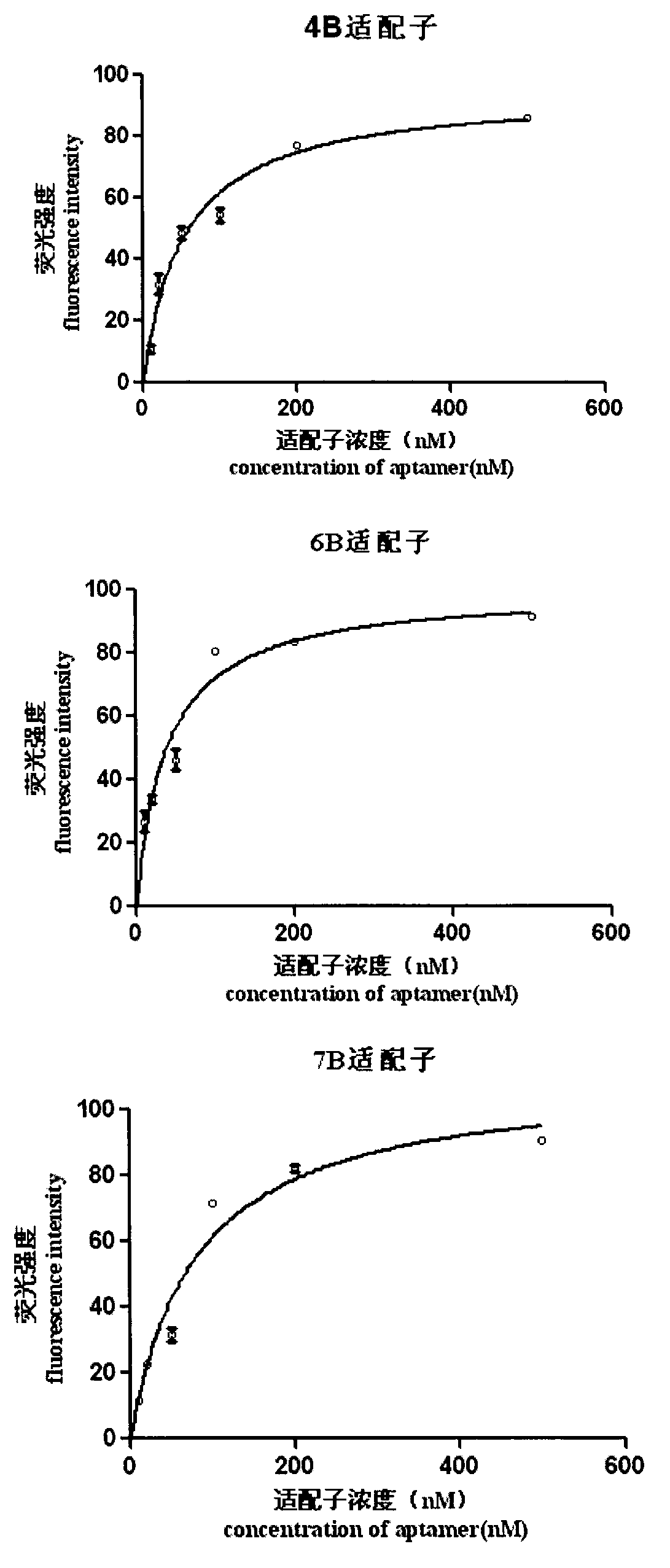
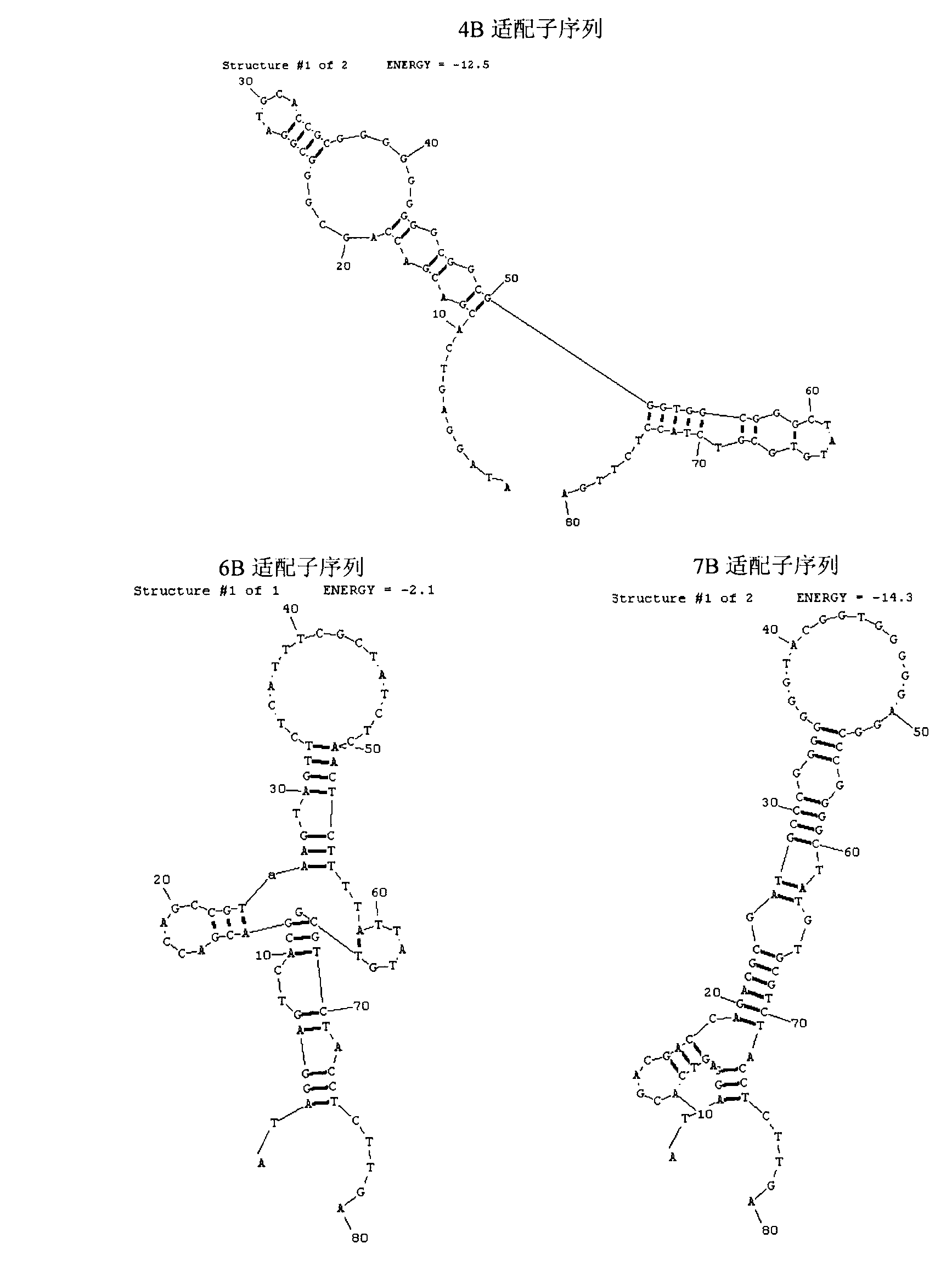
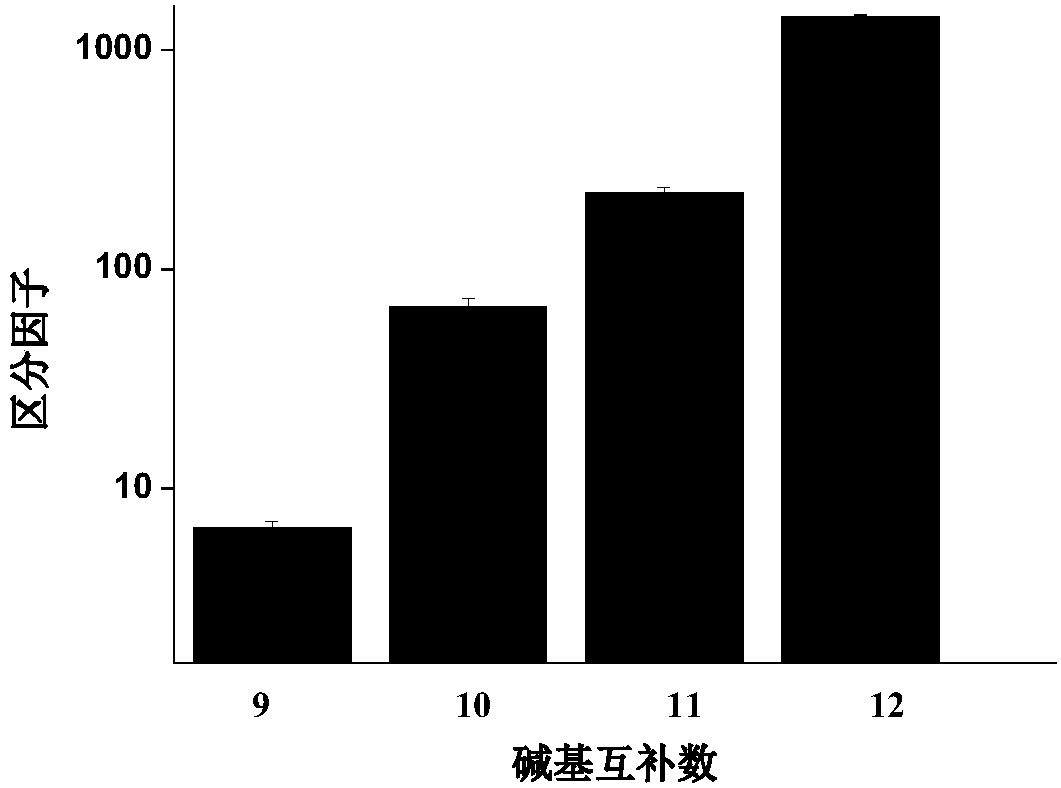
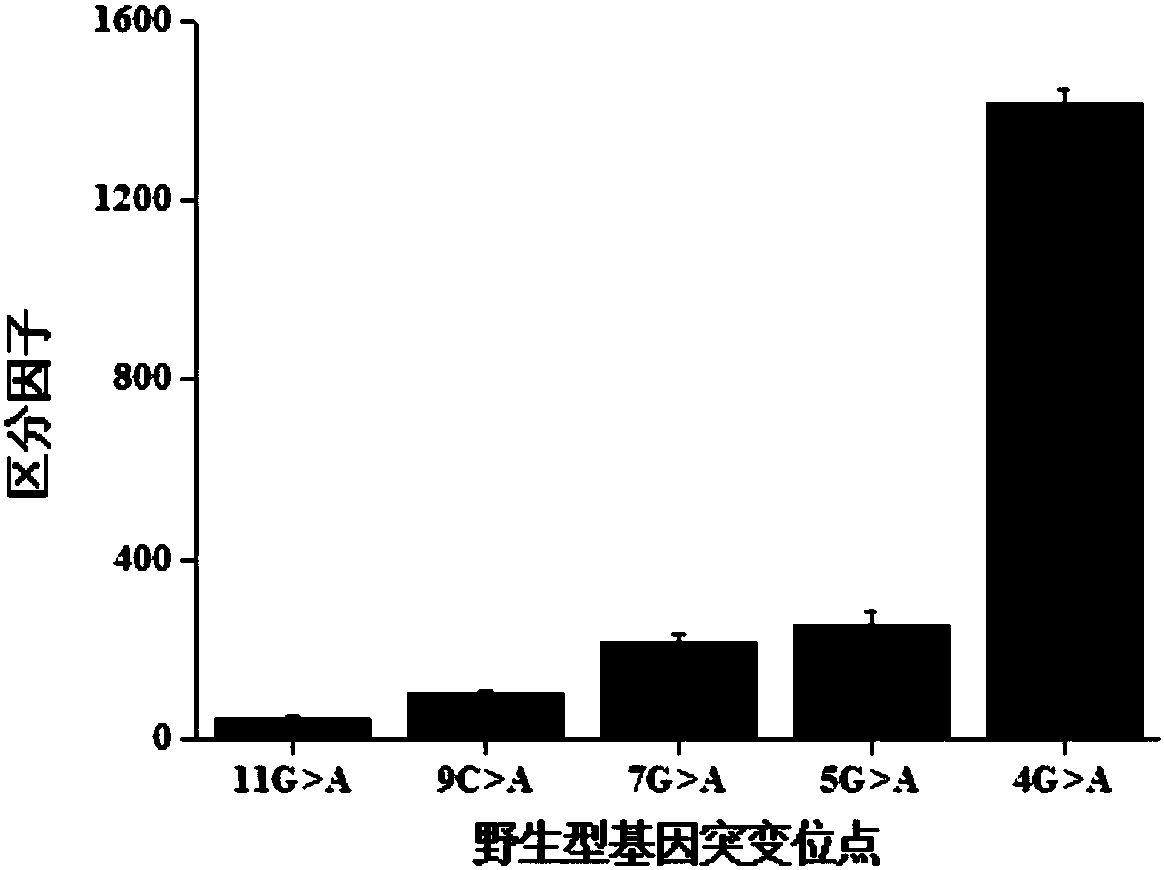
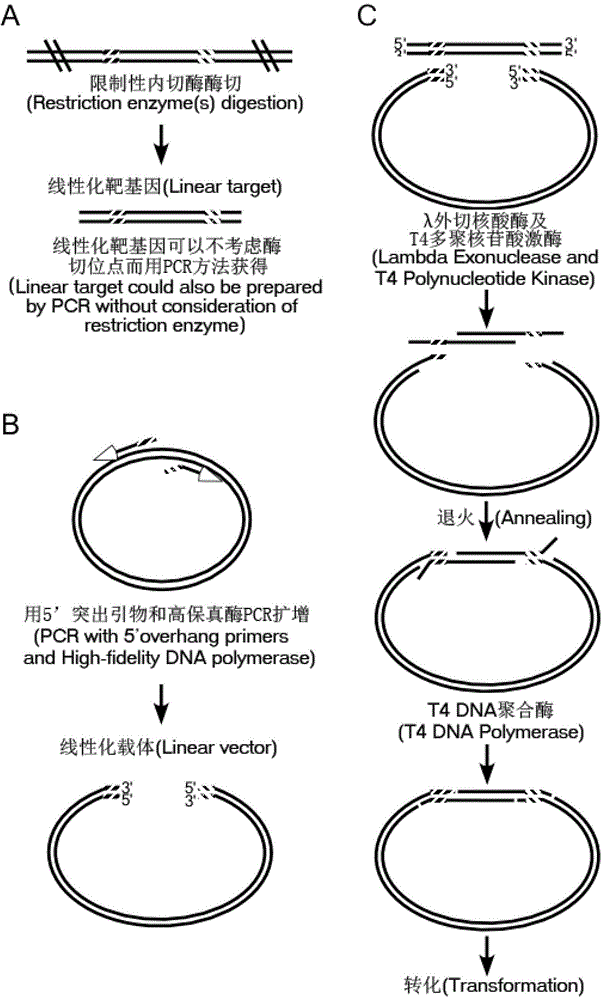
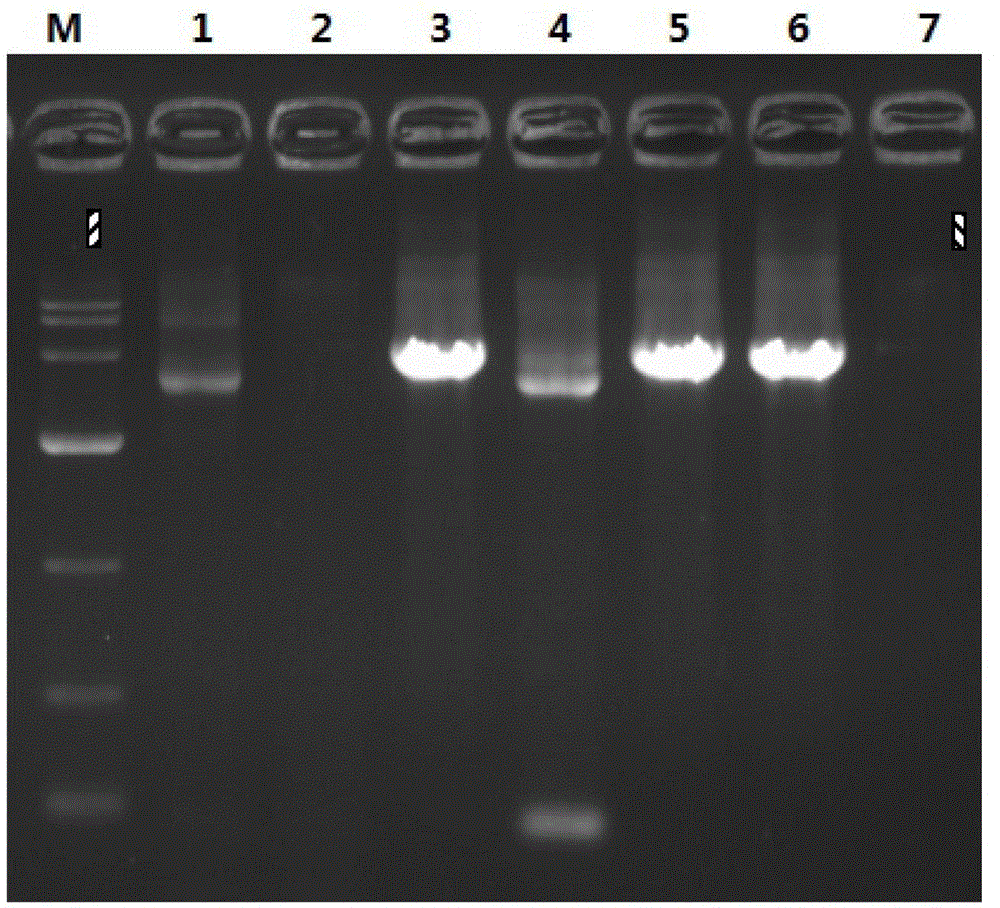
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Lambda exonuclease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
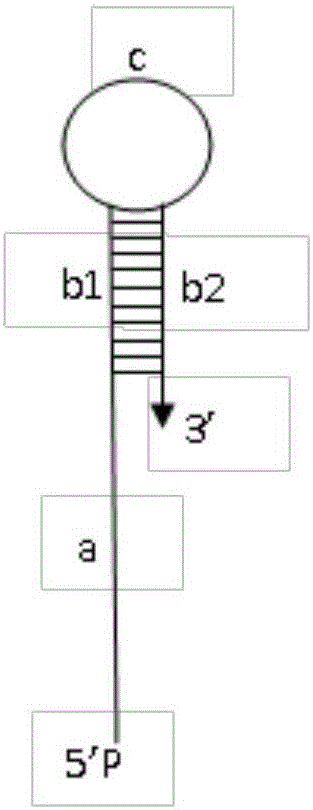
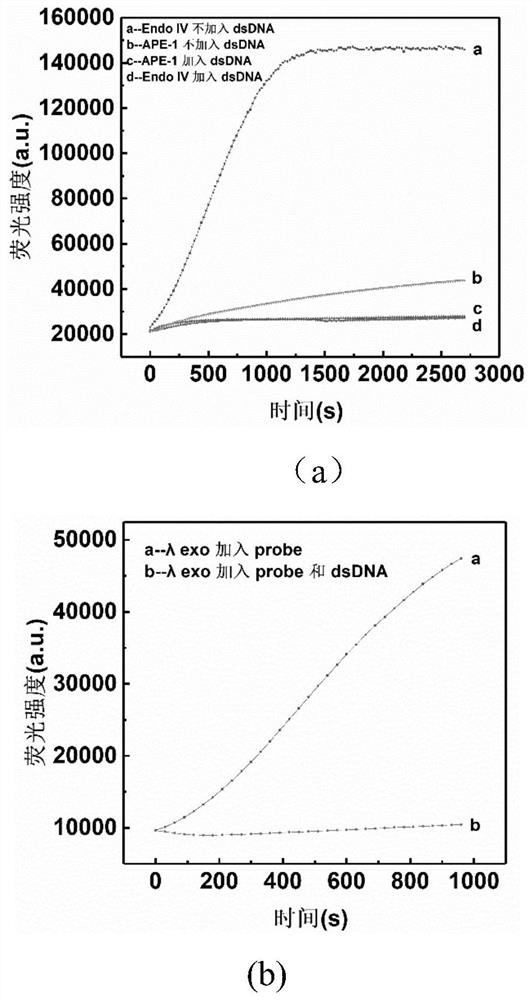
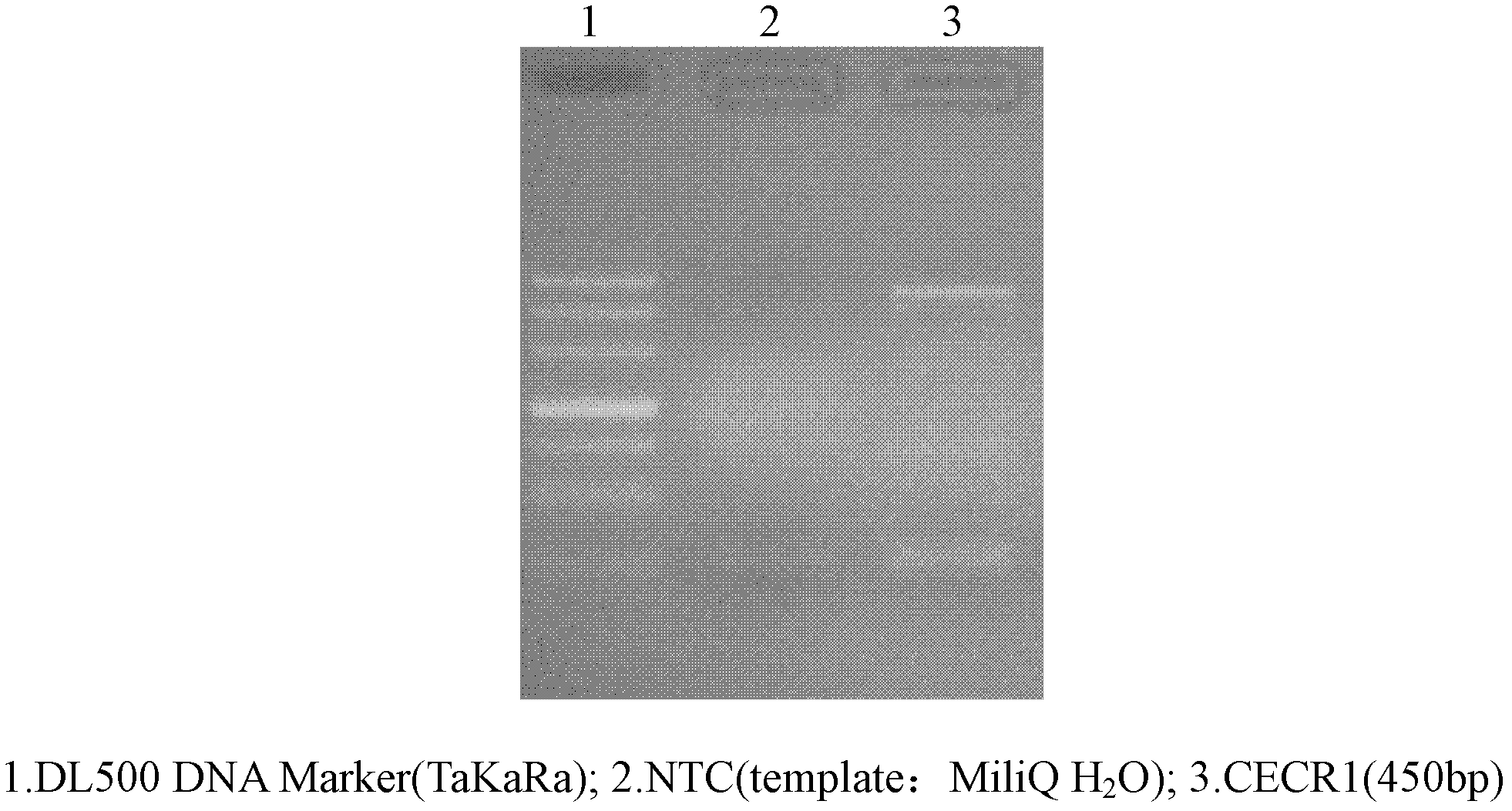
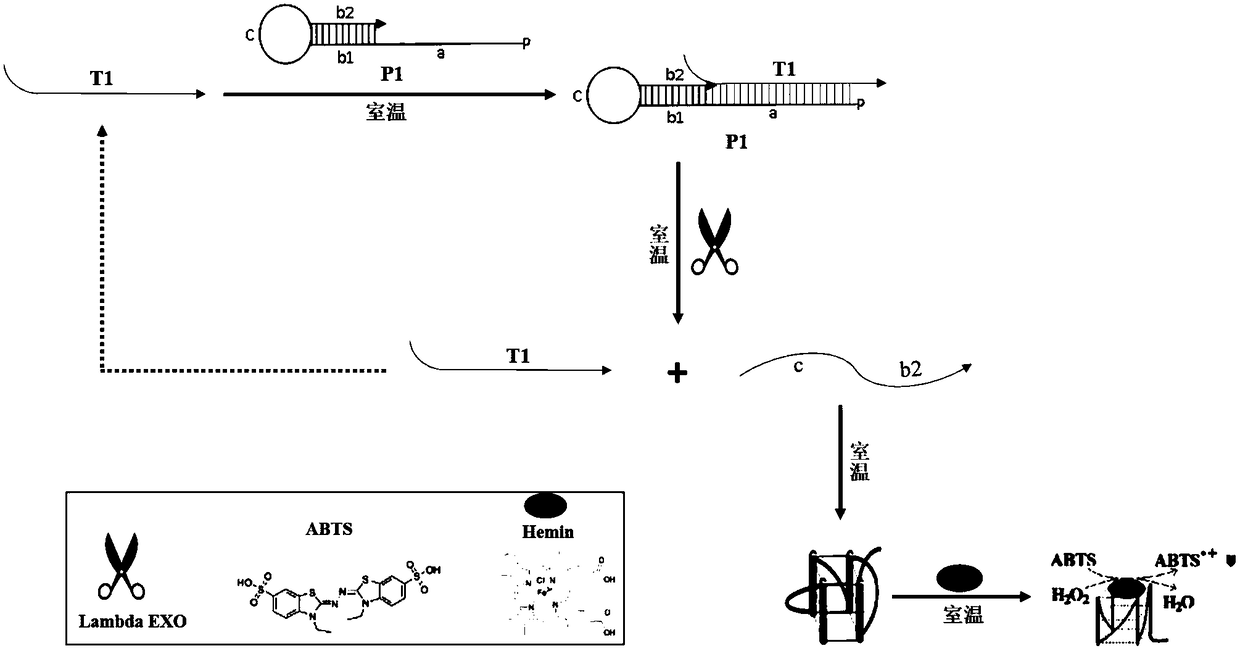
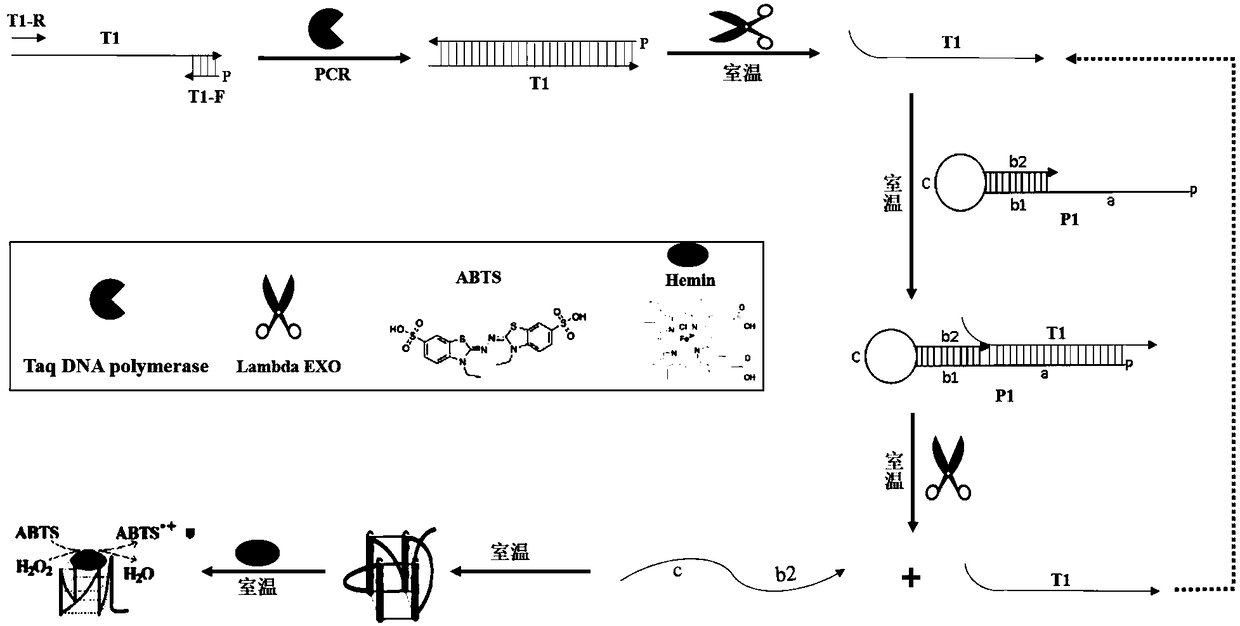
Thermo Scientific Lambda Exonuclease is a highly processive 5'→3' exodeoxyribonuclease. It selectively digests the 5'-phosphorylated strand of double-stranded DNA. The enzyme exhibits low activity on single-stranded DNA and non-phosphorylated DNA, and has no activity at nicks and limited activity at gaps in DNA.
Oligonucleotide probe
ActiveCN105802963AAvoid interferenceEasy to manufactureMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleic Acid ProbesSingle strand
The invention belongs to the technical field of nucleic acid probes and provides an oligonucleotide probe. The probe sequentially comprises a sequence complementary with a target sequence, a G-quadruplex closing sequence and a G-quadruplex sequence from the 5' terminal to the 3' terminal, wherein the G-quadruplex closing sequence is complementary with part of G-quadruplex sequence to form a stable hairpin structure, and the G-quadruplex sequence is closed in the probe. During target molecule detection, the probe firstly recognizes the target sequence and forms a double-stranded structure, then, the hairpin structure is opened under the digestion action of Lambda exonuclease, the G-quadruplex sequence is released, the procedures are repeated, finally, a trace amount of target molecule information is converted into a large quantity of G-quadruplex sequences, and the G-quadruplex sequences are converted into readable light signals, electric signals and the like. The probe has the advantages of good stability, low cost, easiness in preparation, high throughput and high sensitivity and specificity, can directly detect single-stranded nucleic acid and can also indirectly detect double-stranded nucleic acid and other molecules capable of inducing generation of single-stranded nucleic acid.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Manganese dioxide sheet mimic enzyme sensor and preparation method thereof as well as T4PNK detection method
ActiveCN105548167AHigh sensitivityLow detection limitMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsA-DNALambda
The invention discloses a manganese dioxide sheet mimic enzyme sensor and a preparation method thereof as well as a T4PNK detection method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing a MnO2 nanosheet solution with a TMB (3,3',5,5'-tetramethyl benzidine) solution to obtain a MnO2-TMB mixed solution; (2) dissolving hairpin DNA in a Tris-HCl buffer solution, and adding ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and lambda EXO (lambda exonuclease) for mixing to obtain a DNA solution; and (3) mixing the MnO2-TMB mixed solution and the DNA solution to obtain the manganese dioxide sheet mimic enzyme sensor. The preparation method is simple in operation, and the sensor has the characteristics of high sensitivity, low detection limit and simple operation when used for detecting T4PNK.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of modified DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) hybridization probe for targeted hybrid capture
ActiveCN105647907AImprove bindingLow environmental requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHybridization probeEnzyme digestion
Owner:HANGZHOU LC BIOTECH
Colorimetric method for detecting tobramycin based on double strand displacement and three-dimensional DNA structure
ActiveCN110592187AAchieving multiple magnificationsExpand the scope of detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementLinear relationshipGenetics
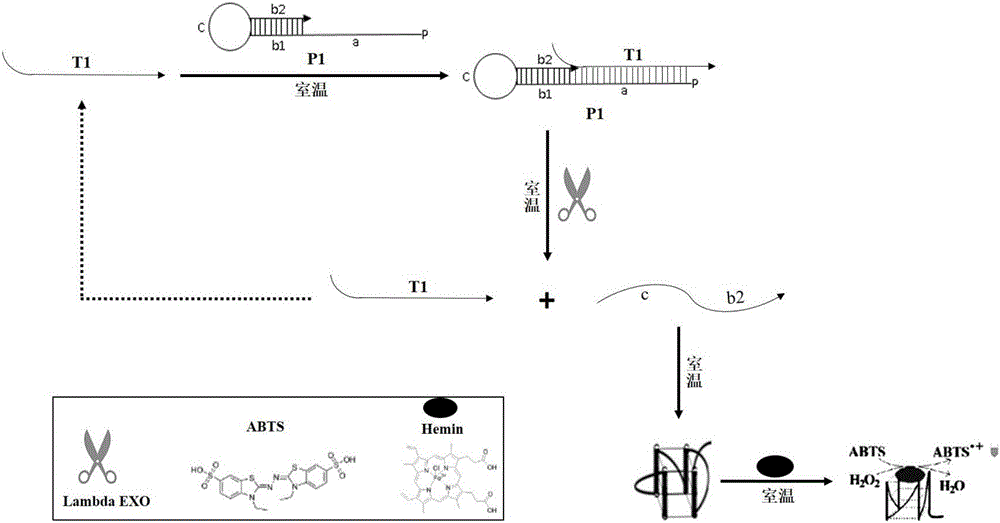
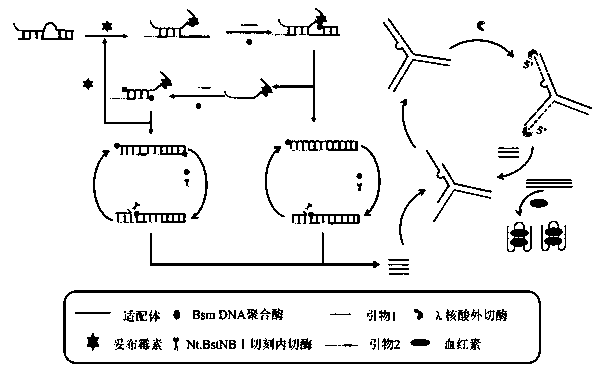
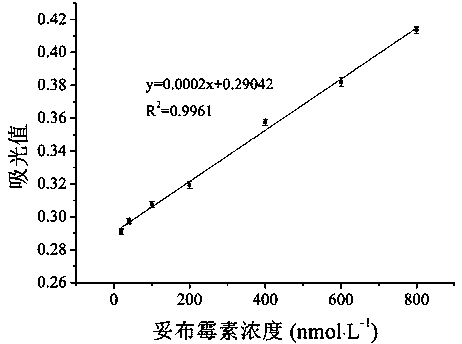
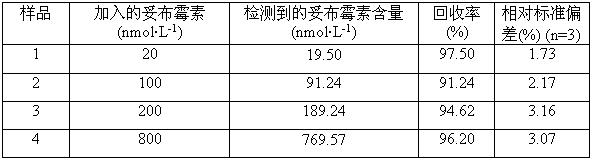
The invention discloses a colorimetric method for detecting tobramycin based on double strand displacement and a three-dimensional DNA structure, and belongs to the field of food safety, medical analysis and environmental pollution detection. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, double strands T1 / T2 are designed; when tobramycin exists, Bsm DNA polymerase synthesizes double strands which are completely complementary through a strong strand displacement reaction, and Nt.BstNBI incision endonuclease cuts recognition sites on the double strands; the three-way DNA structure capture reporter probes, and regenerates and replaces a large number of S1 strands containing G-quadruplex forming sequences. Thereafter, the G-quadruplex / heme catalyzes ABTS<2-> / H2O2 chromogenic reaction, andthe tobramycin content can be determined by using the linear relationship between light absorption value and tobramycin concentration. According to the invention, an aptamer captures tobramycin to trigger double strand displacement reaction which is mediated by the Nt.BstNBI incision endonuclease and the Bsm DNA polymerase so as to generate a large number of reporter probes. Meanwhile, the reporter probes trigger lambda exonuclease-assisted loop amplification, so that multiple amplifications of colorimetric signals are realized, the detection range is widened, and the detection sensitivity isimproved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method for probe used for multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA)
ActiveCN102534004ALower the technical threshold of MLPALower technical barriersMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMultiplex ligation-dependent probe amplificationEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a preparation method for a long probe which can be used for multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA). The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a vector which is irrelevant with a target sequence to be tested to serve as a template, and designing a primer according to the length of a target nucleotide sequence and the length of a target probe; (2) artificially synthesizing the primer; (3) performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification; (4) purifying and recovering PCR products; (5) digesting the PCR products by using Lambda exonuclease; and (6) recovering single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (ssDNA). The preparation method for the probe for the MLPA is low in cost, and all operations, such as the amplification, enzyme digestion and the like, can be finished only by a PCR instrument; recovery is performed by using a special ssDNA recovery kit after the enzyme digestion is finished, thereby, double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and nucleotide which are not completely digested are eliminated, and the hybridization efficiency when an MLPA experiment is conducted is increased; and through full Lambda exonuclease digestion, the dsDNA can be changed into the ssDNA to the maximum degree, and thereby, the preparation efficiency of the probe is increased.
Owner:江西南兴医疗科技有限公司 +1
Application and seamless cloning method of DNA exonuclease
PendingCN107760706AImprove digestion efficiencyFlexible site selectionVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliHomologous sequence
The invention provides application of DNA exonuclease to DNA recombinant seamless cloning and provides a kit capable of being used for DNA recombinant seamless cloning. The DNA exonuclease is T5 exonuclease, T7 exonuclease, exonuclease III or Lambda exonuclease or a mixture thereof. The invention further provides a seamless cloning method applying the DNA exonuclease, which comprises the followingsteps: linearizing a vector through a PCR method or restriction endonuclease digestion; introducing homologous sequences that are respectively homologous to the two ends of the vector at the two endsof a target gene fragment through PCR to obtain an amplified target gene fragment; after the treated target fragment and the treated linearized vector are mixed, adding the DNA exonuclease and a reaction solution for temperature bath to obtain a vector and fragment mixture; converting an echerichia coli receptive cell by using the obtained vector and fragment mixture. The application and the method provided by the invention have the following advantages that the site selection can be flexibly performed, and the gene cloning can be performed in any position of the vector; the vector construction can be quickly, simply and conveniently completed within 10 minutes; meanwhile, the cloning is accurate and efficient.
Owner:NOVOPROTEIN SCI INC
Biosensor and method for detecting salmonella
InactiveCN110205394AImplement triggerRealize detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPhosphorylationHemin
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology, and in particular, relates to a biosensor and method for detecting salmonella. The biosensor includes an RPA reaction reagent, a Lambda nucleic acid exonuclease cutting reaction reagent, an HCR reaction reagent and a chromogenic reagent. A double-stranded nucleic acid of salmonella is amplified by a multi-enzyme system, and dsDNA phosphorylated at the 5' end is obtained. 5'-phosphorylated strands in the dsDNA are digested by Lambda exonuclease, and RPA products become single strands. A universal junction is exposed, an HCR reaction is initiated, and released G-tetrad binds to Hemin to form G4 DNAzyme, colorless TMB is catalyzed to be oxidized into blue oxTMB visible to naked eyes by H2O2, and then salmonella is detected through the change of color and absorbance value. The biosensor has the advantages of visualization, versatility, rapidity and high sensitivity.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
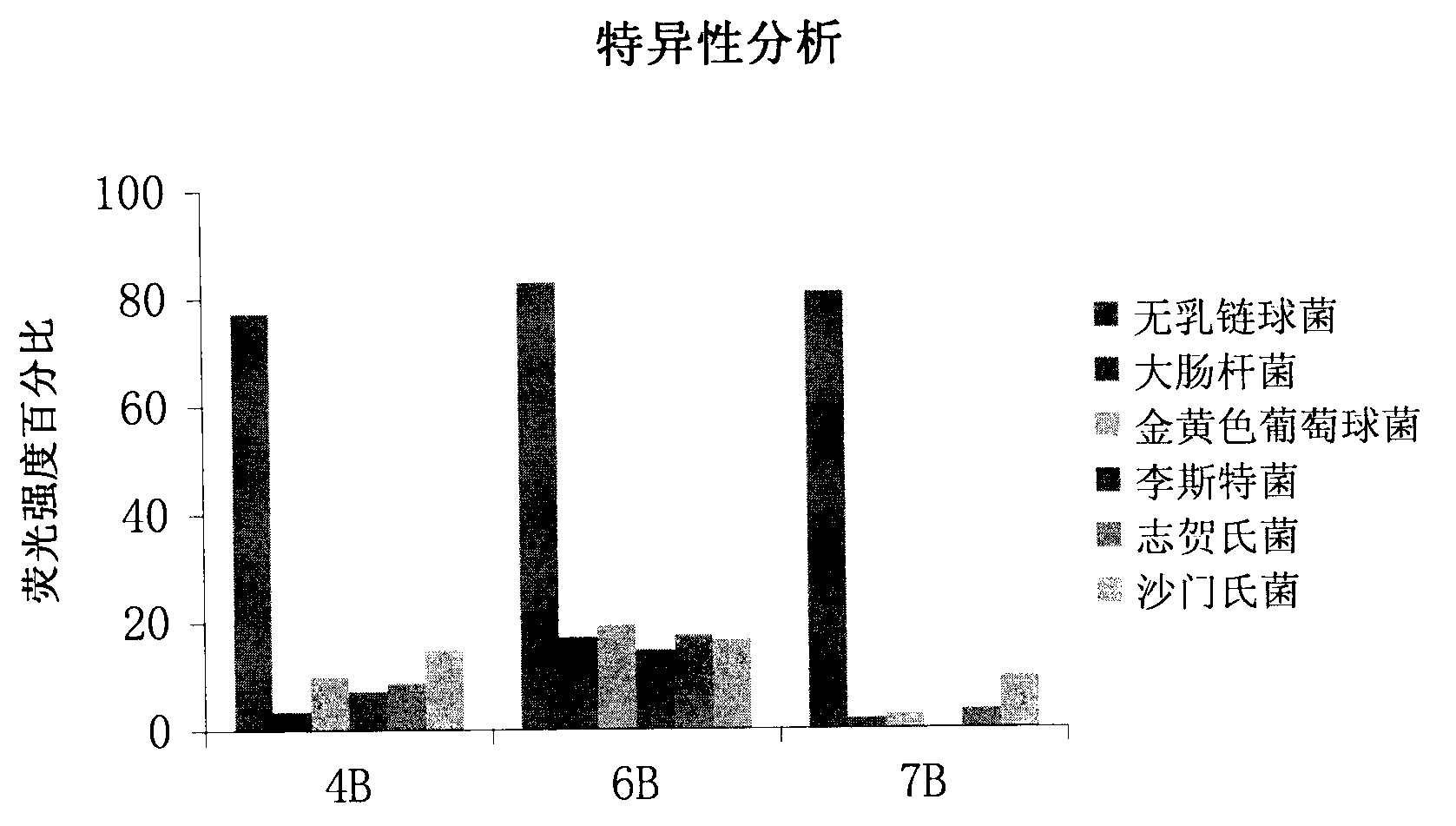
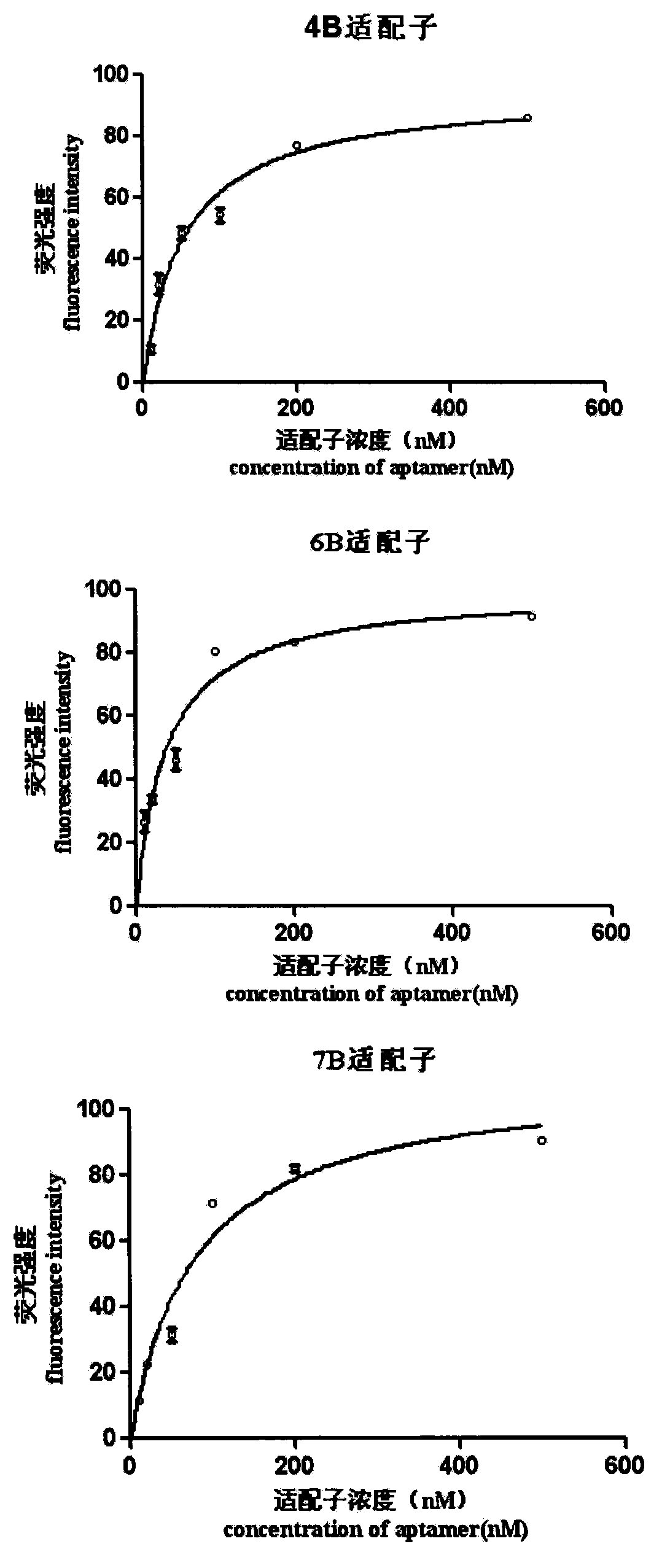
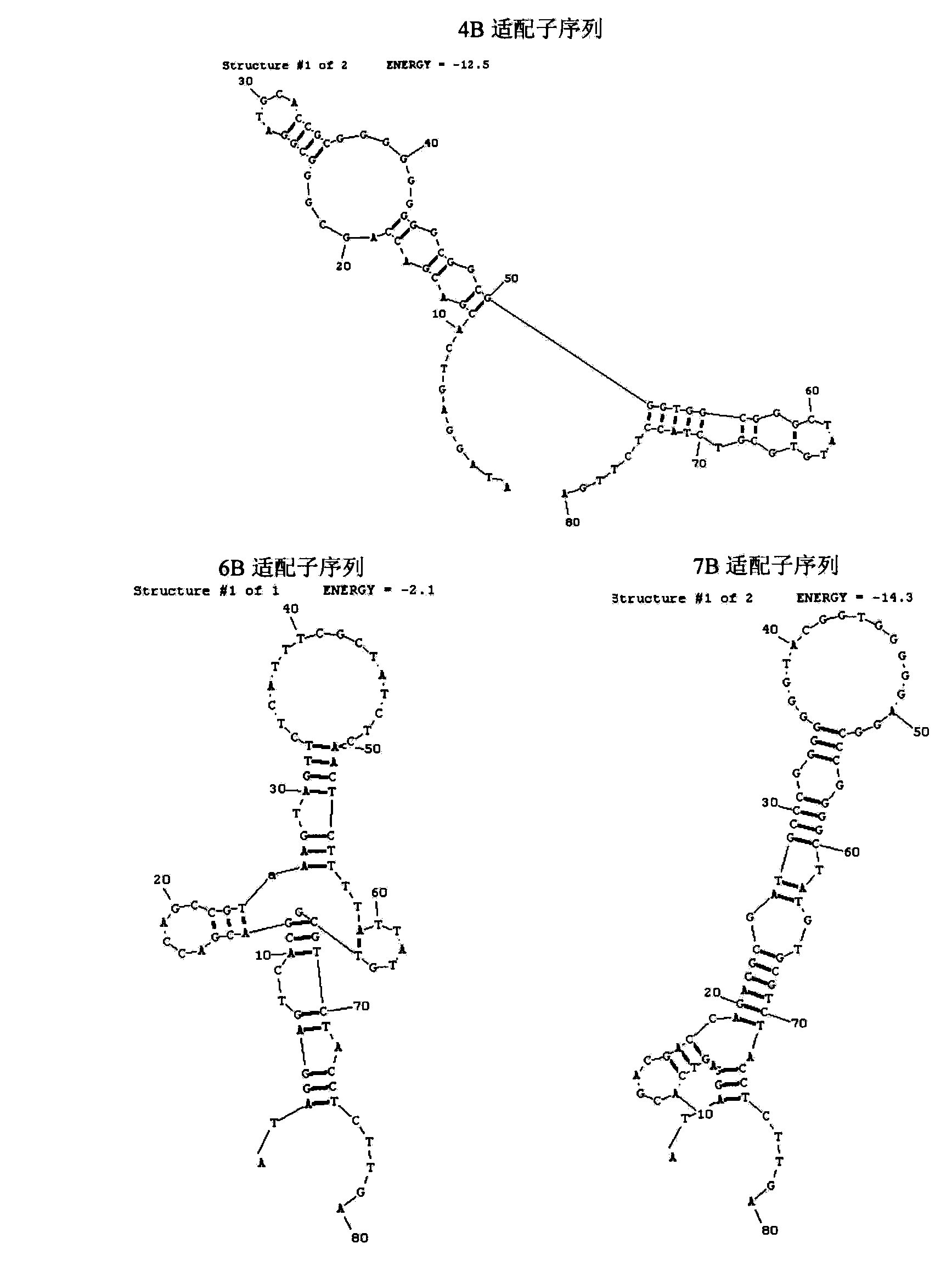
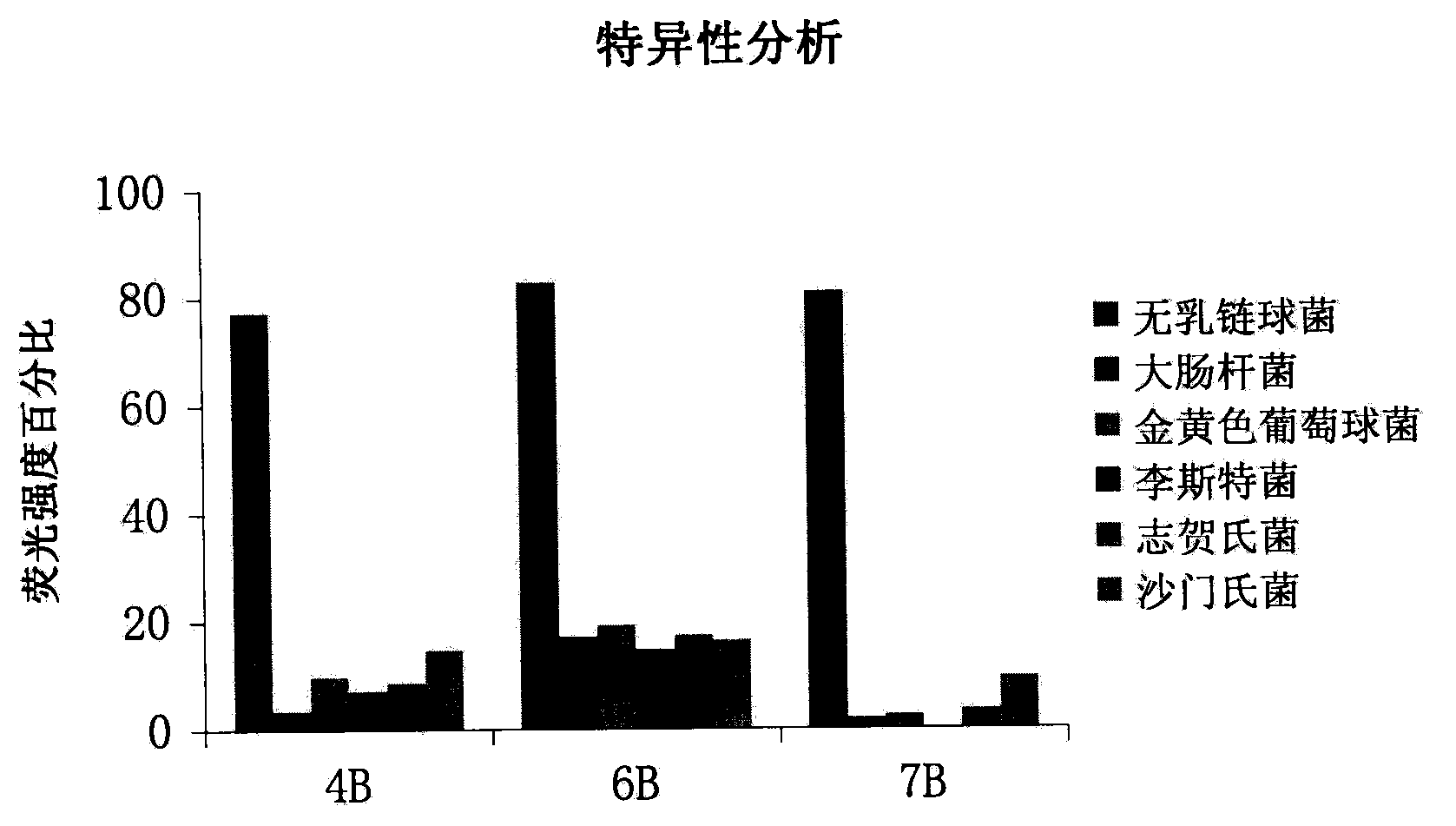
A set of oligonucleotide aptamers capable of specifically recognizing streptococcus agalactiae
ActiveCN103014000AEasy to operateLower synthesis costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStreptococcus agalactiaeNucleotide
The invention discloses a set of oligonucleotide aptamers capable of specifically recognizing streptococcus agalactiae, and belongs to the field of food hygiene and clinical medicine detection. Aiming at the defects that no oligonucleotide aptamers for the streptococcus agalactiae are in the prior art, the oligonucleotide aptamers provided by the invention combine an SELEX technology with the streptococcus agalactiae, a single stranded secondary library is prepared by incubating, cleaning, dissociating, amplifying, and digesting by using lambda exonuclease again and again for 12 rounds, the oligonucleotide aptamers capable of specifically combining with the streptococcus agalactiae are selected from a single stranded DNA random library; and three aptamers with the best effect are obtained by sequencing, affinity analysis and specificity analysis, wherein the nucleotide sequences are selected from 1 to 3 in the sequence table. The set of the oligonucleotide aptamers provide specific and efficient recognition ligands for analyzing and detecting the streptococcus agalactiae in the food hygiene and clinical blood samples and novel choices for developing and replacing a conventional method that detects the streptococcus agalactiae depending on antibodies.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for simulating recombination and non-trace cloning
The invention relates to a method for simulating recombination and non-trace cloning, which is characterized in that when a carrier primer is designed, a fragment of DNA basic group having a same sequence with a target gene is respectively added at 5' terminal of the primer, the obtained carrier DNA terminal and the inner part of the target gene have a coupling area, the carrier DNA and the target gene are mixed, and Lambda Exonuclease and T4 DNA polymerase are used for treatment to obtain recombinant DNA. The method for simulating recombination and non-trace cloning has the following beneficial effects that 1) the target gene amplified through PCR is not required, the mutation caused by PCR is reduced; 2) the target fragment can be specifically cloned in a DNA mixture; and a trace of an enzyme site is not kept.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of capture probe for targeted sequencing of novel coronavirus virus SARS-CoV-2 genome
PendingCN111455102AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesReference genome sequenceEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to genomic targeted sequencing. The preparation method of the capture probe for targeted sequencing of the novel coronavirus virus SARS-CoV-2 genome comprises the following steps: downloading an SARS-CoV-2 virus reference genome sequence NC _ 045512.2 from an NCBI database, adopting an imbricated coverage design strategy, and screening probes with the length of 75-120nt according to parameters such as GC content, a Tm value and homology, carrying out quantitative evaluation on the probe library, filtering out unqualified probe sequences, and leaving 249 probes to cover the whole genome of the novel coronavirus virus; preparing a DNA templates of 249 probe libraries, performing PCR amplification, and purifying PCR products; carrying out enzyme digestion on the purifiedPCR product and smoothly supplementing the tail end of T4 DNA polymerase, and digesting a single strand with 5'end phosphorylation in the double-stranded DNA by using Lambda exonuclease to obtain a single-stranded DNA with a biotin label; and purifying the single-stranded DNA with the biotin label by a magnetic bead enrichment method to obtain the modified probe library. According to the method,the sequencing data volume is reduced, the data analysis process is simplified, and the sensitivity and accuracy of the NGS method for detecting the novel coronavirus virus are improved.
Owner:上海符贝基因科技有限公司
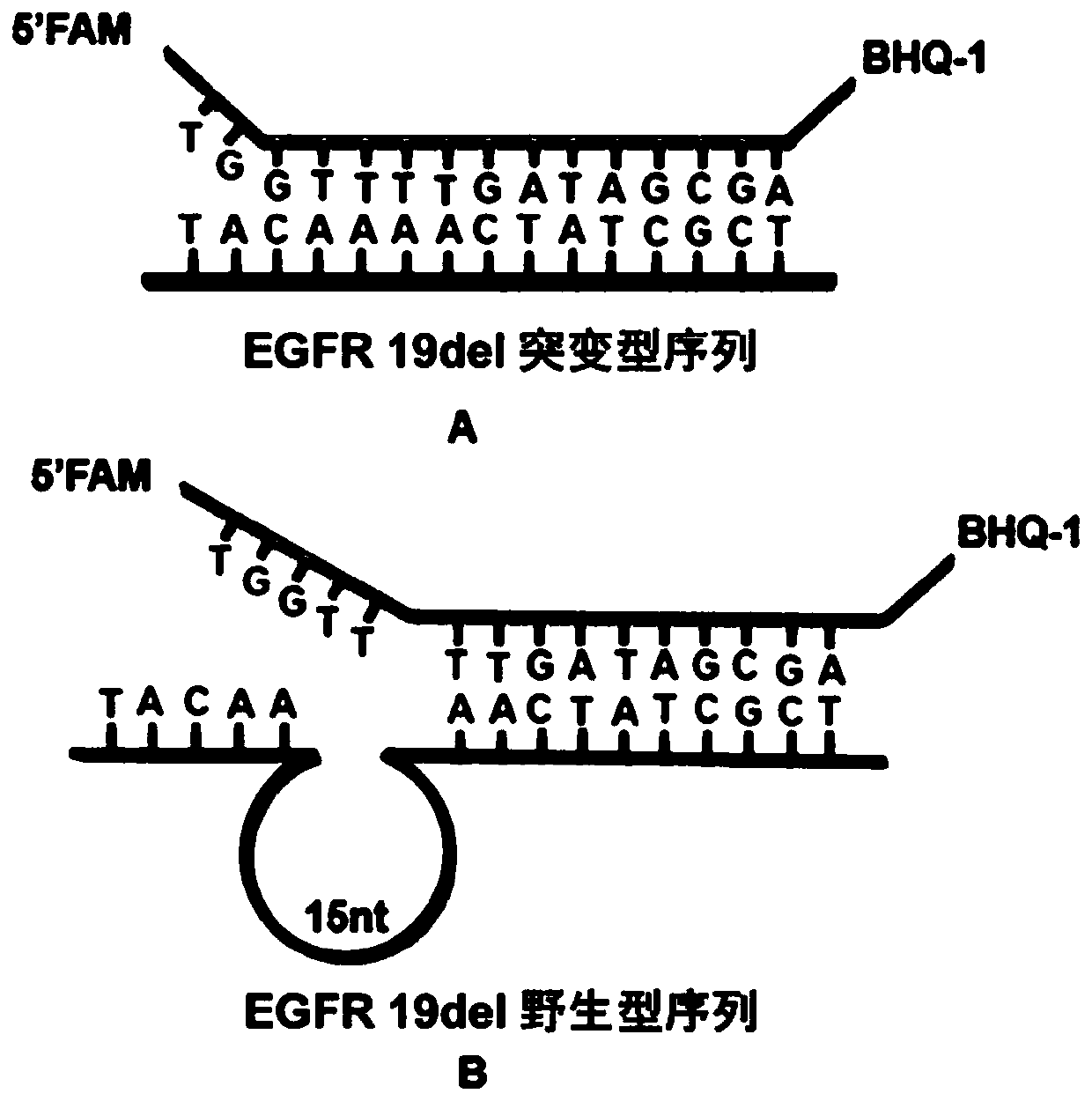
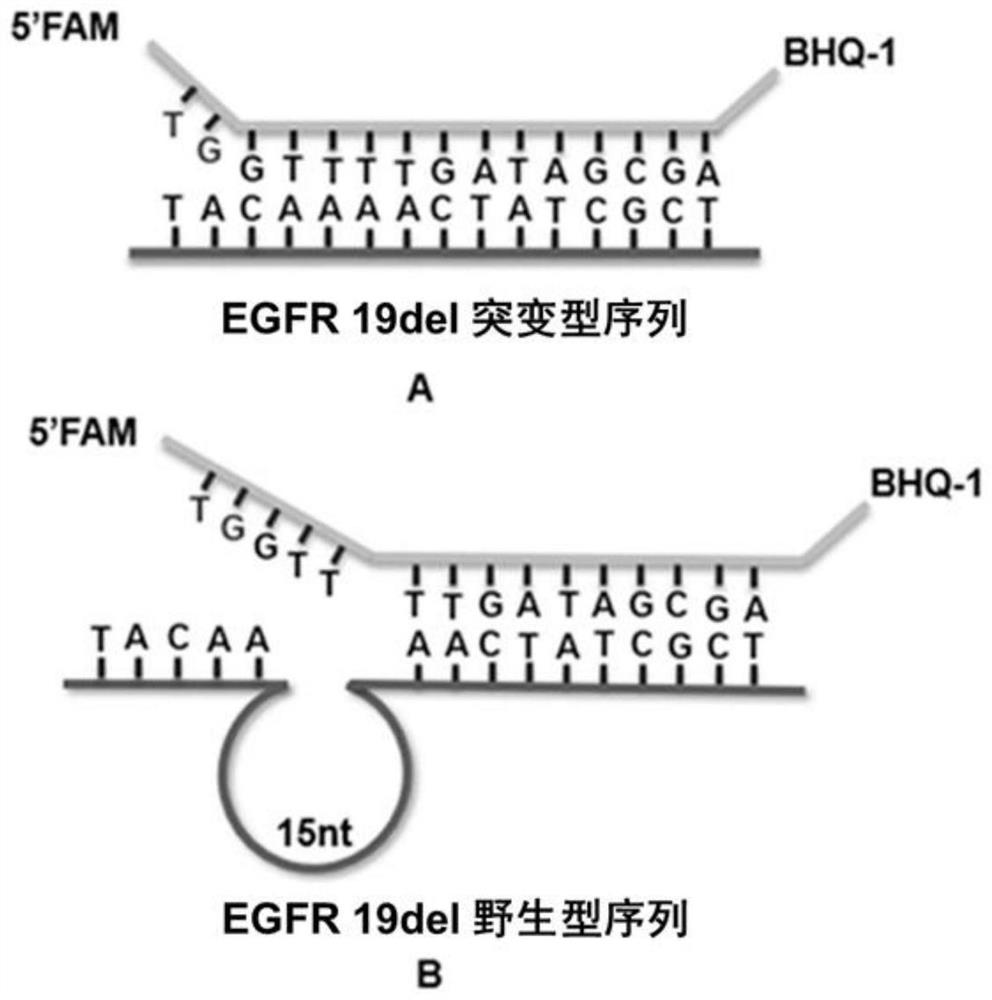
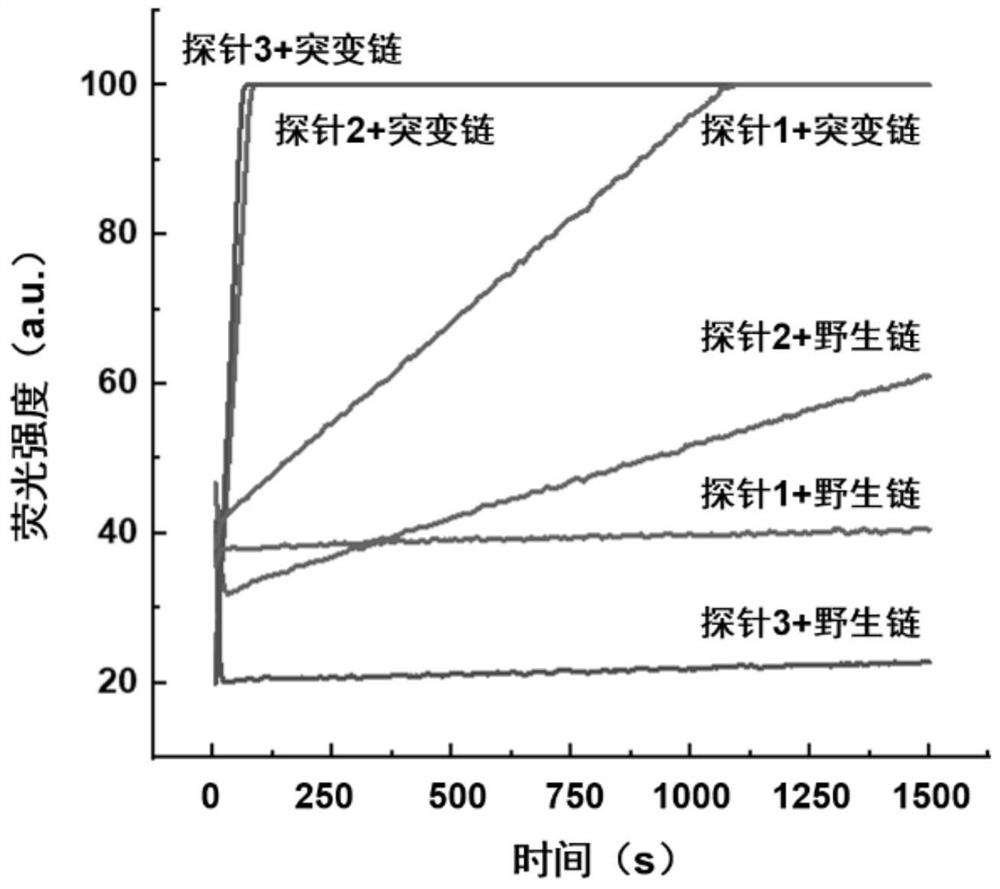
Rapid fluorescence detection method for 19# exon deleted mutation of gene EGFR and application
ActiveCN110511984AReduce abundanceIncrease dosageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPhosphorylationA-DNA
The invention discloses a rapid fluorescence detection method for 19# exon deleted mutation of a gene EGFR and an application. The method disclosed by the invention has the properties that by using Lambda exonuclease, an outstanding structure, of which 5' terminals are two bases, and a single strand labeled with fluorophore in DNA double strands can be rapidly hydrolyzed, and a DNA single strand with a 5' phosphorylated terminal in double-stranded DNA can be continuously hydrolyzed; and mutated base identification, PCR product single-stranding and fluorescence signal amplification processes are completed in a combined manner, so that entire detection flows are greatly simplified, the detection time is shortened, the relative detection limit is lowered to 0.01%, the sensitivity is high, andthus, the method has a very good application prospect in the aspects of clinical diagnosis, targeted medication instruction, postoperative accompanied detection and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
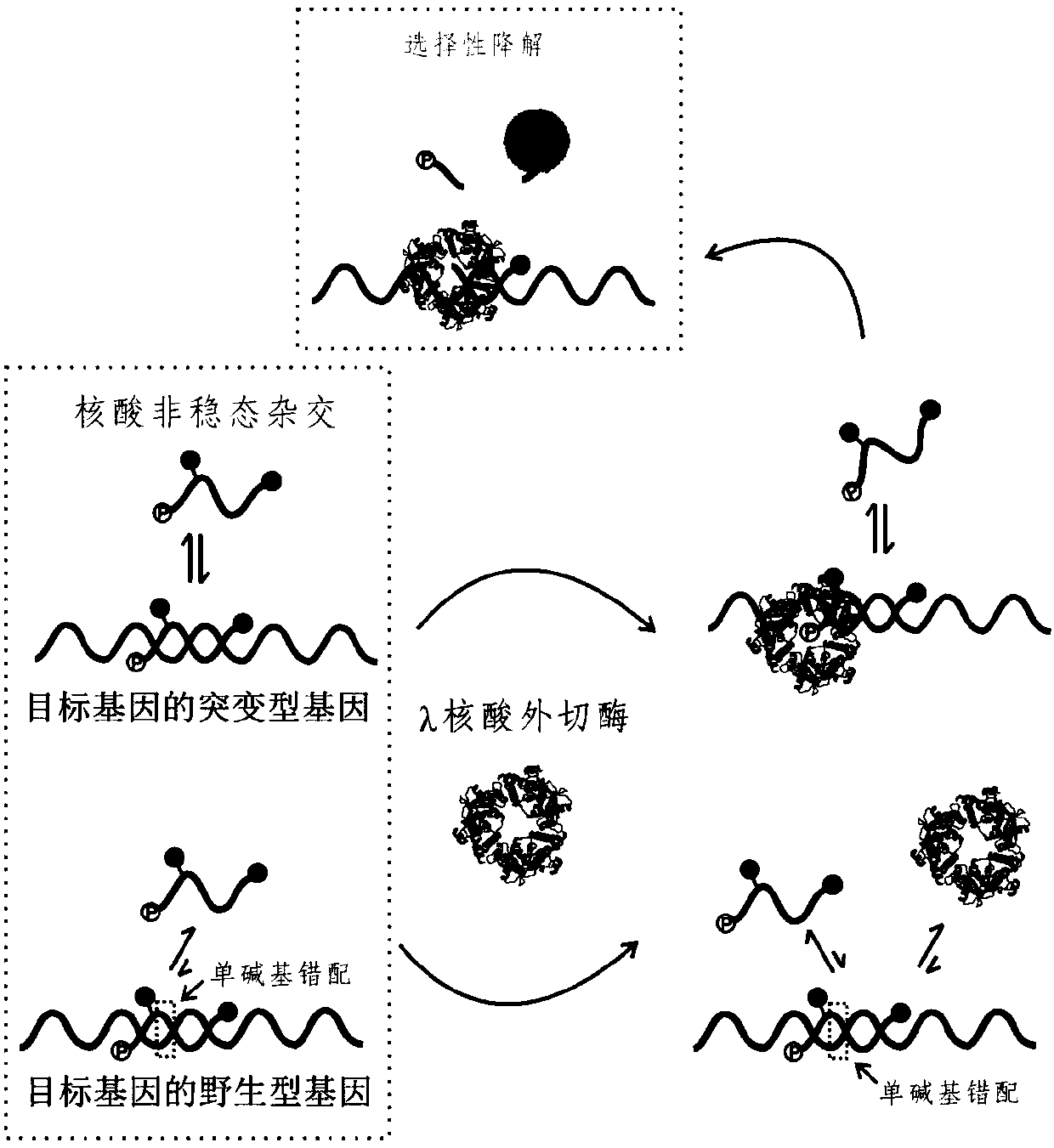
Gene mutation detection method based on selective elimination of wild strand background interference
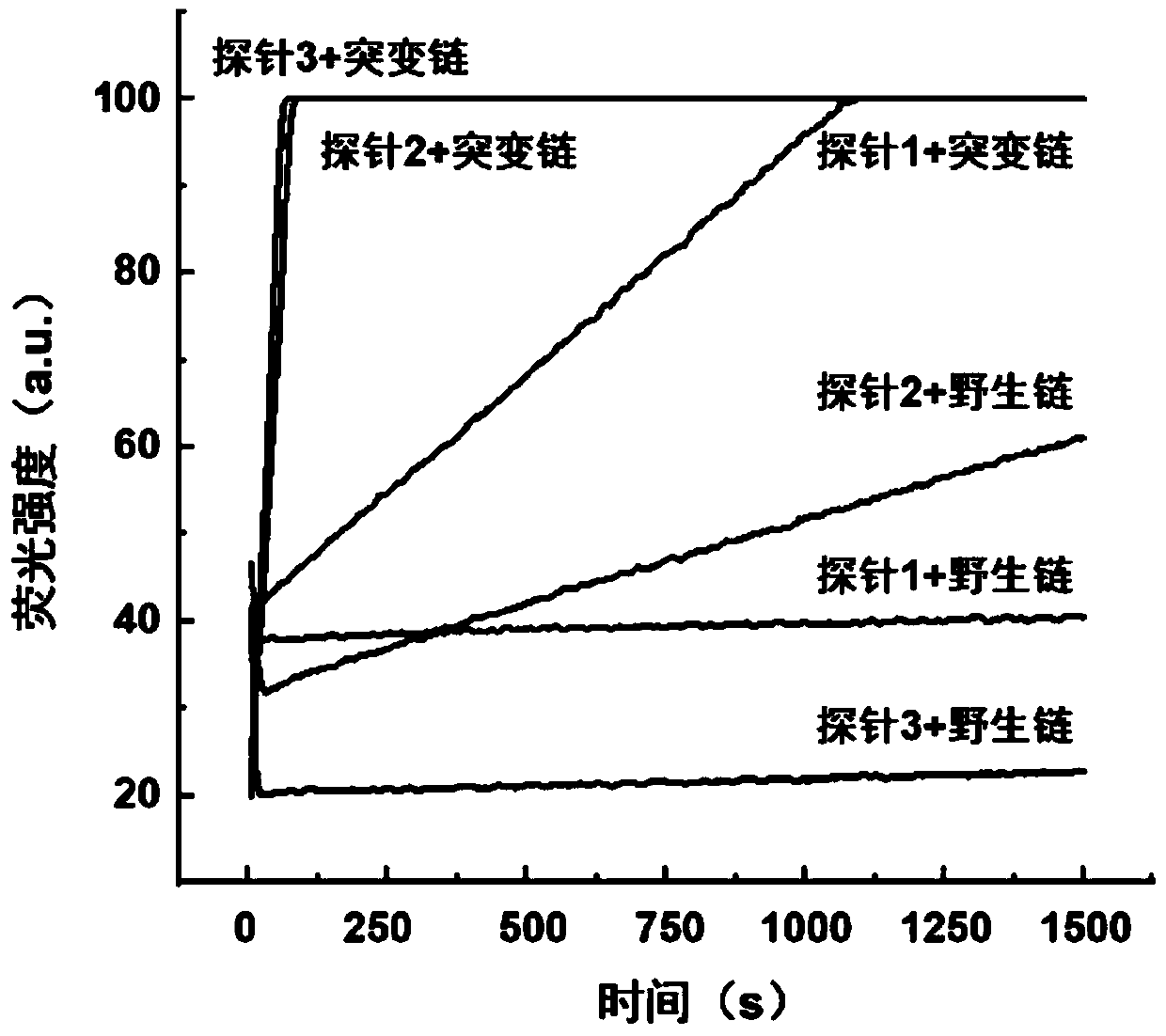
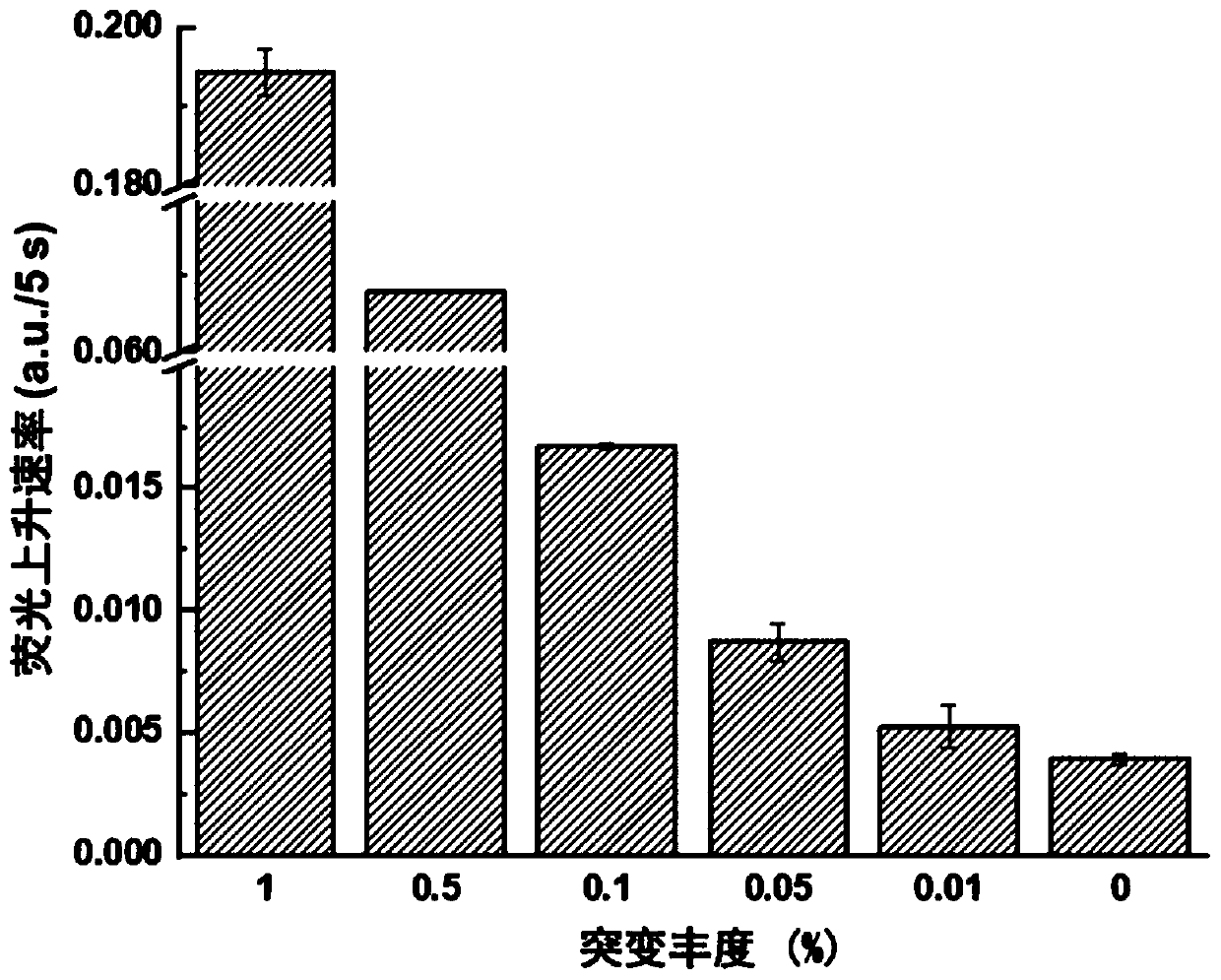
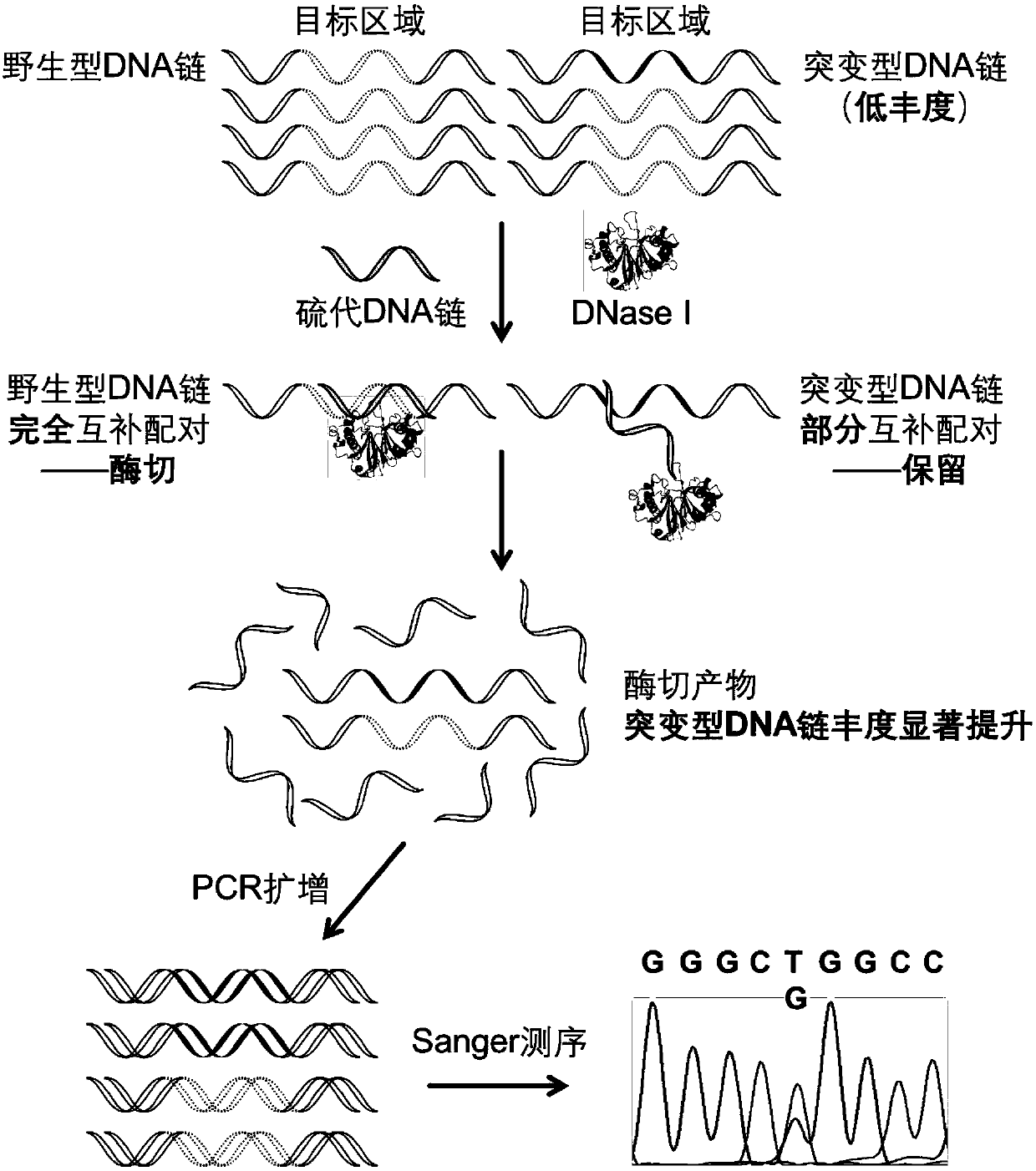
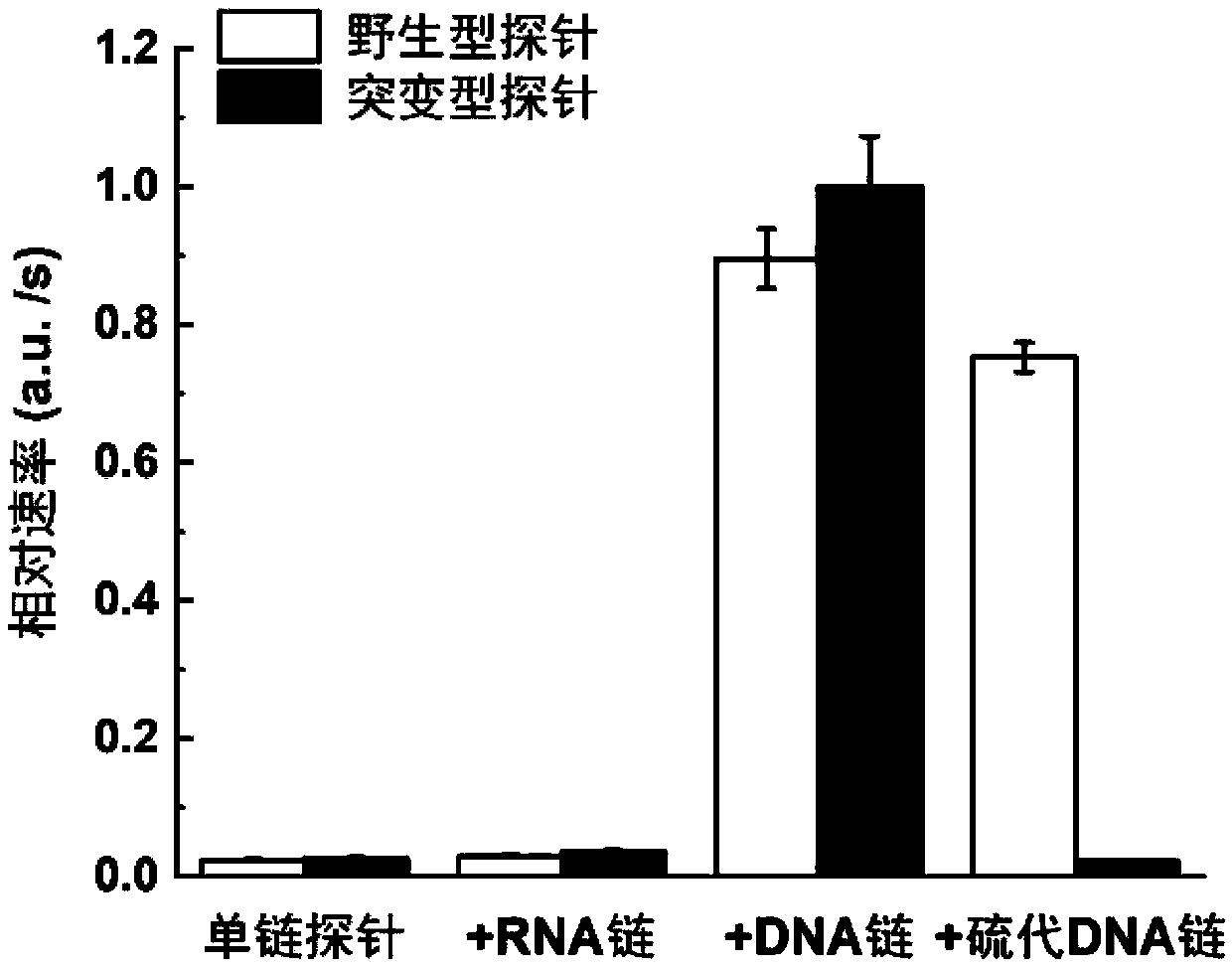
ActiveCN109680044AObvious technical advantagesImprove enrichment effectMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typeLambda exonuclease
The invention discloses a gene mutation detection method based on selective elimination of wild strand background interference. A target sequence to be detected is amplified through PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and then is processed into single-stranded DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) through Lambda exonuclease; a thio-DNA strand which is complementary with a target region of a wild type DNA sequence and an RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) closed strand which is complementary with a non-target region are designed and synthesized; then the thio-DNA strand and the RNA closed strand are mixed with the single-stranded DNA, and DNase I is added to carry out cutting after temperature rising and annealing are carried out; a wild type DNA strand target region sequence is selectively cut off through the DNaseI under the guidance of the thio-DNA strand; a mutation type DNA strand is remained since mispairing exists in the target region and cannot be cut off by the DNase I, so that the abundance of the mutation type DNA strand is remarkably improved and the difficulty in detecting low-abundance gene mutation in the prior art is greatly reduced. The method disclosed by the invention does not need complicated and expensive instruments, is easy to operate and low in cost and can provides a result within 1 day; in-time and reliable gene mutation information can be provided for clinical early screeningof tumors and monitoring the recurrence after operation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
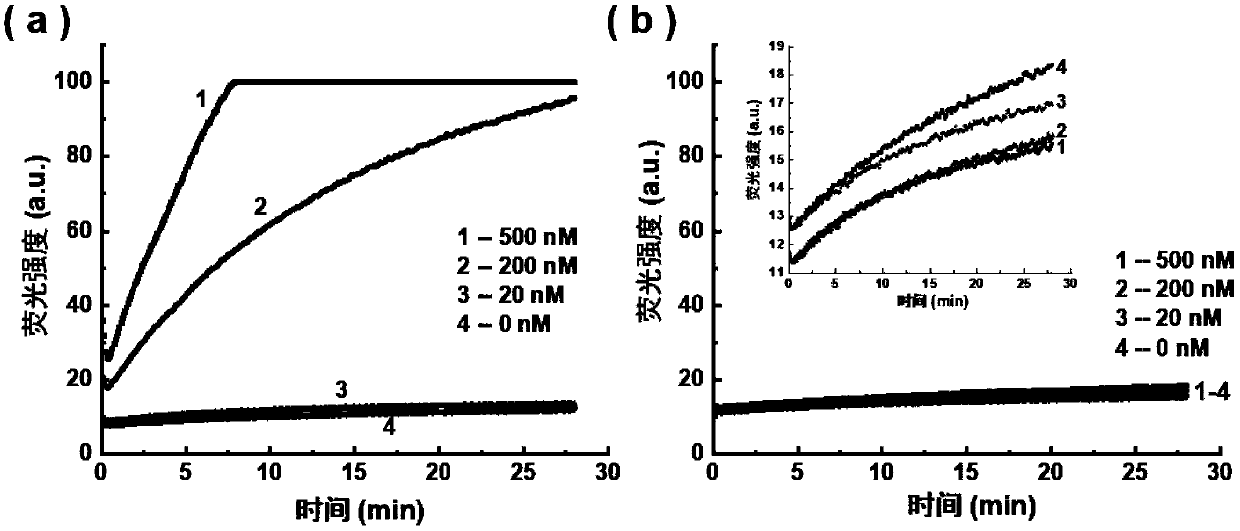
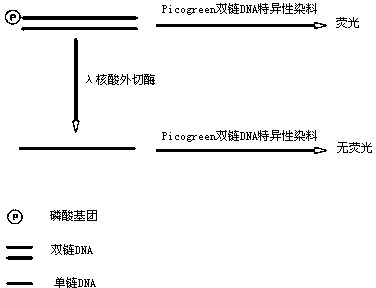
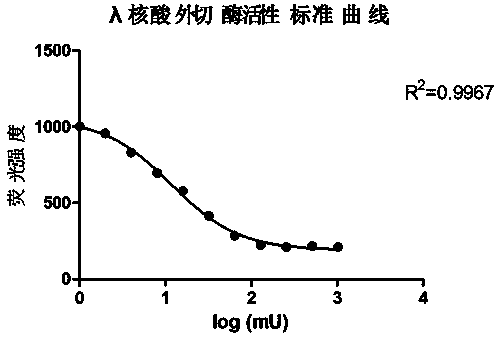
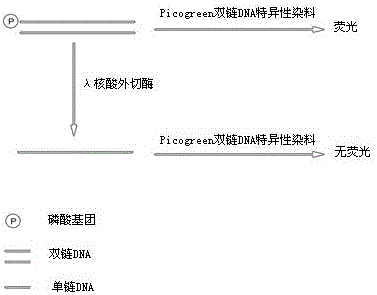
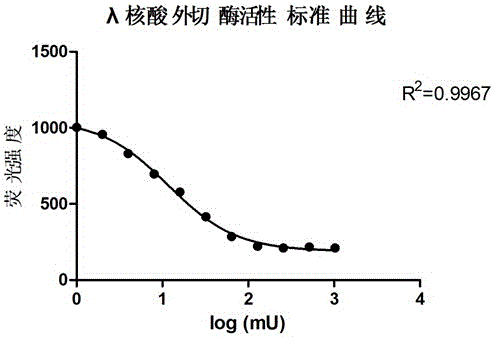
Active determination method for Lambda exonuclease
ActiveCN104297221AEasy to operateImprove throughputFluorescence/phosphorescenceRadioactive contaminationLambda exonuclease
The invention discloses an active determination method for Lambda exonuclease. The active determination method comprises the following steps: obtaining double-chain DNA with a phosphorylated 5' end on one chain, then reacting in a reaction system in the presence of the Lambda exonuclease by adopting the double-chain DNA as a substrate, determining the relative quantity of single-chain DNA or the double-chain DNA in the reaction system after the reaction is finished, and deducing the active degree of the Lambda exonuclease from a detection result. Compared with the method in the prior art, the active determination method has the advantages of no radioactive pollution, simplicity and fastness in operation and high sensitivity.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
Enzyme-based regeneration of surface-attached nucleic acids
InactiveUS7101669B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymatic digestionNucleotide
Enzyme-based regeneration of surface-attached nucleic acids is described herein. Microarrays involving hybridization of a probe to a target are important tools for genetic analysis. Conventionally, a microarray is used for a single analysis, after which it is discarded. The invention relates to a process for regeneration of a microarray through enzymatic digestion of a target from a surface-attached probe using a nuclease to digest a single strand of a nucleic acid duplex with directional specificity starting from the free end of the target strand. For example, a probe oligonucleotide bound to a gene chip at the 5′-end hybridizes to a target nucleic acid, leaving the 5′ end of the target open to 5′–3′ digestion. Lambda-exonuclease (λ-exonuclease) cleaves single nucleotides from the 5′ end of a duplex, progressing in the 5′–3′ direction. Once the target strand is digested, the enzyme is rinsed from the microarray. The microarray is thus regenerated and ready for a subsequent use.
Owner:SENSORCHEM INT
Preparation method of multi-fluorescent nucleic acid probe and application thereof
PendingCN113150769AAchieve improvementHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLuminescent compositionsNucleotidePhosphorylation
The invention relates to the technical field of nucleic acid detection material preparation, in particular to a preparation method and an application of a multi-fluorescent nucleic acid probe, 5-ethynyl-uracil deoxynucleotide (5-EdUTP) is used for replacing thymine deoxynucleotide (dTTP) for nucleic acid amplification, and high-density alkyne double-stranded DNA is obtained; after the obtained double-stranded DNA is treated by an excision enzyme Lambda Exonuclease, the 5'end phosphorylation labeled nucleic acid chain is digested, and the high-density alkyne single-stranded DNA is obtained; through a click reaction catalyzed by copper ions, a dye cy3-azide with an azide group is successfully modified to a single-chain DNA of high-density alkyne, and the multi-fluorescent nucleic acid probe is obtained. The fluorescent groups of the multi-fluorescent nucleic acid probe prepared by the invention are increased, signal amplification is realized structurally, the sensitivity of the fluorescent nucleic acid probe in researches such as analysis and detection, biological imaging and the like can be enhanced, and the practical value of the fluorescent nucleic acid probe is improved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Rapid fluorescence detection method and application of egfr gene exon 19 deletion mutation
ActiveCN110511984BReduce abundanceIncrease dosageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBase JSingle strand
Owner:PEKING UNIV
A kind of lambda exonuclease activity assay method
ActiveCN104297221BNo radioactive contaminationEasy to operateFluorescence/phosphorescenceRadioactive contaminationExonuclease I
The invention discloses an active determination method for Lambda exonuclease. The active determination method comprises the following steps: obtaining double-chain DNA with a phosphorylated 5' end on one chain, then reacting in a reaction system in the presence of the Lambda exonuclease by adopting the double-chain DNA as a substrate, determining the relative quantity of single-chain DNA or the double-chain DNA in the reaction system after the reaction is finished, and deducing the active degree of the Lambda exonuclease from a detection result. Compared with the method in the prior art, the active determination method has the advantages of no radioactive pollution, simplicity and fastness in operation and high sensitivity.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
A method for preparing long dna probes containing multiple repeating units
ActiveCN108728430BHigh magnificationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationElectrophoresisSingle strand
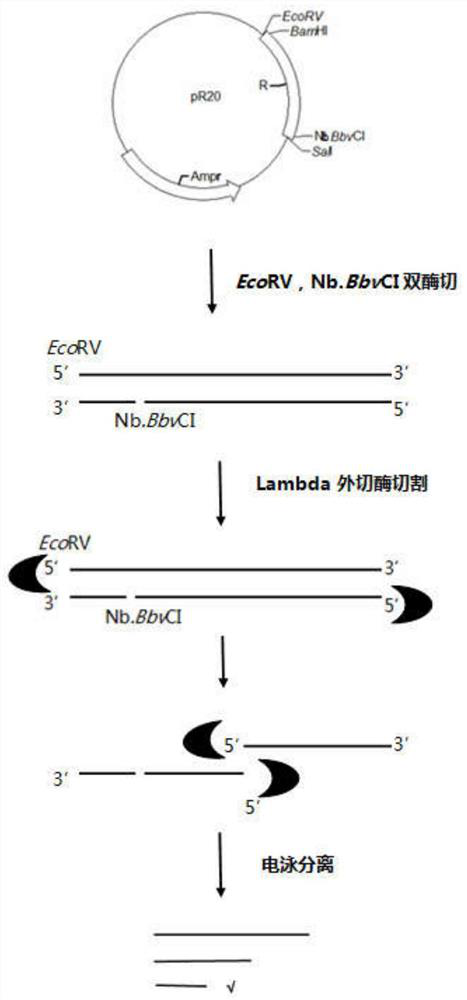
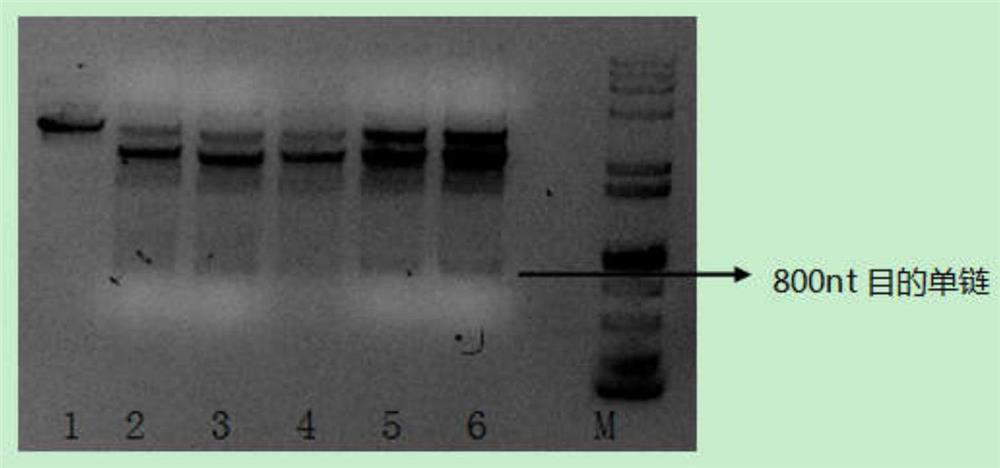
The invention relates to the preparation of oligonucleotide probes, in particular to a method for preparing long DNA probes containing multiple repeating units. Using blunt-end endonuclease and nicking endonuclease to simultaneously cut the plasmid containing multiple repeat unit DNA double strands, and then use the principle of lambda exonuclease to specifically cut, after cutting, separate by electrophoresis to obtain multiple repeat units Single-stranded DNA of interest for the unit. The method of the present invention is suitable for preparing DNA probes of all sequence components, especially for sequences that are difficult to perform PCR amplification, such as those containing multiple repeating units, and the length of the prepared probe can reach 800nt, solving the problem of multiple repeating unit DNA Technical issues in the preparation of long probes.
Owner:沈阳中科赛尔生物科技有限公司
A method for specific regulation of nuclease activity
ActiveCN111172252BSide effects do not affectGuaranteed to workMicrobiological testing/measurementLambda exonucleaseNuclease
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method for probe used for multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA)
ActiveCN102534004BLower the technical threshold of MLPALower technical barriersMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMultiplex ligation-dependent probe amplificationEnzyme digestion
Owner:江西南兴医疗科技有限公司 +1
A preparation method of modified dna hybridization probe for targeted hybridization capture
ActiveCN105647907BImprove bindingLow environmental requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationEnzyme digestionHybridization probe
The invention discloses a preparation method of a modified DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) hybridization probe for targeted hybrid capture. The preparation method mainly includes preparing a DNA template prior to PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification and purifying a PCR product; subjecting the purified PCR product to USER enzyme digestion and T4 DNA polymerase terminal blunting, wherein one of double-stranded DNA of an Lambda exonuclease hydrolysis product has 5'-phosphorylated single strand, so that bioti-labeled single-stranded DNA is obtained; purifying the bioti-labeled single-stranded DNA by a magnetic beads enrichment method to obtain the modified DNA hybridization probe. The preparation method of the modified DNA hybridization probe for targeted hybrid capture has the advantages that production cost is reduced greatly, and the preparation method is wide in application range including exon regions, intron regions, mitochondrion regions and the like of genomes of any species. The obtained DNA hybridization probe can be applied to construction and sequencing of next generation targeting libraries.
Owner:HANGZHOU LC BIOTECH
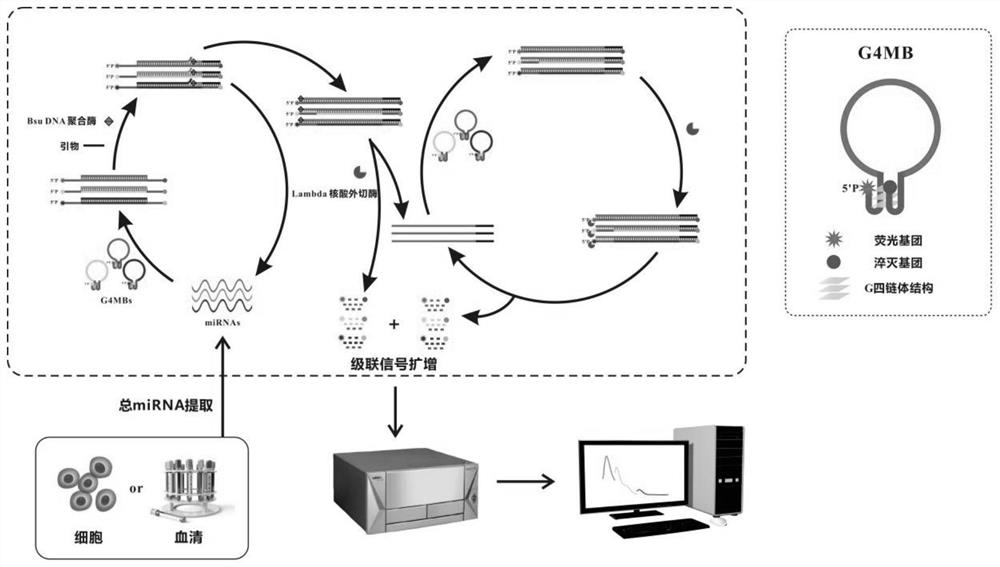
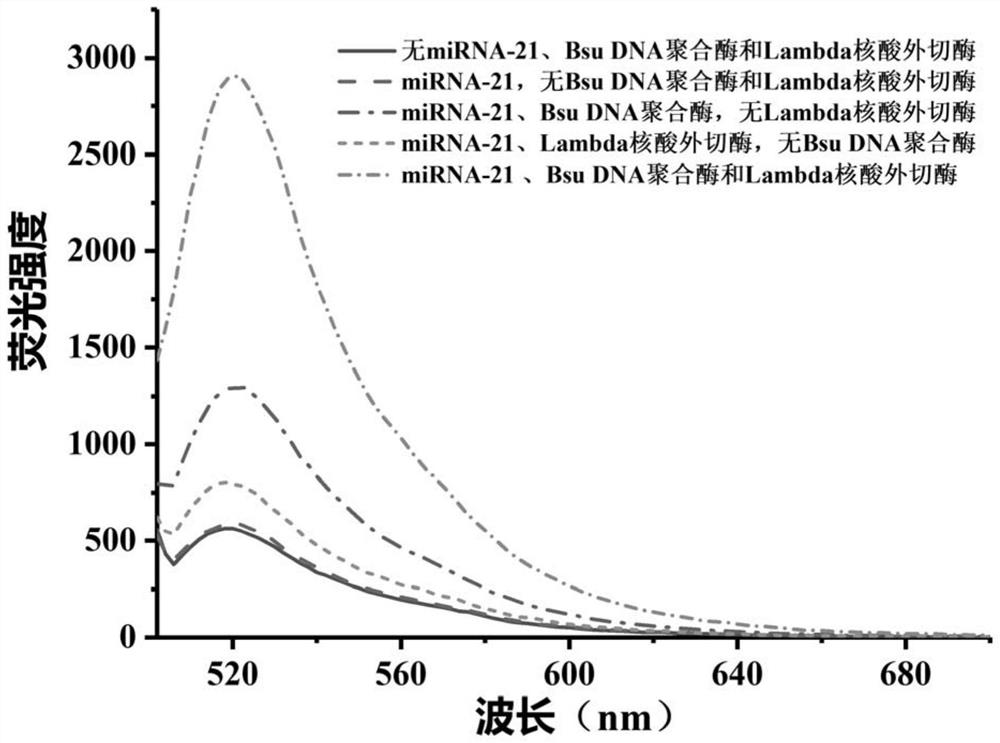
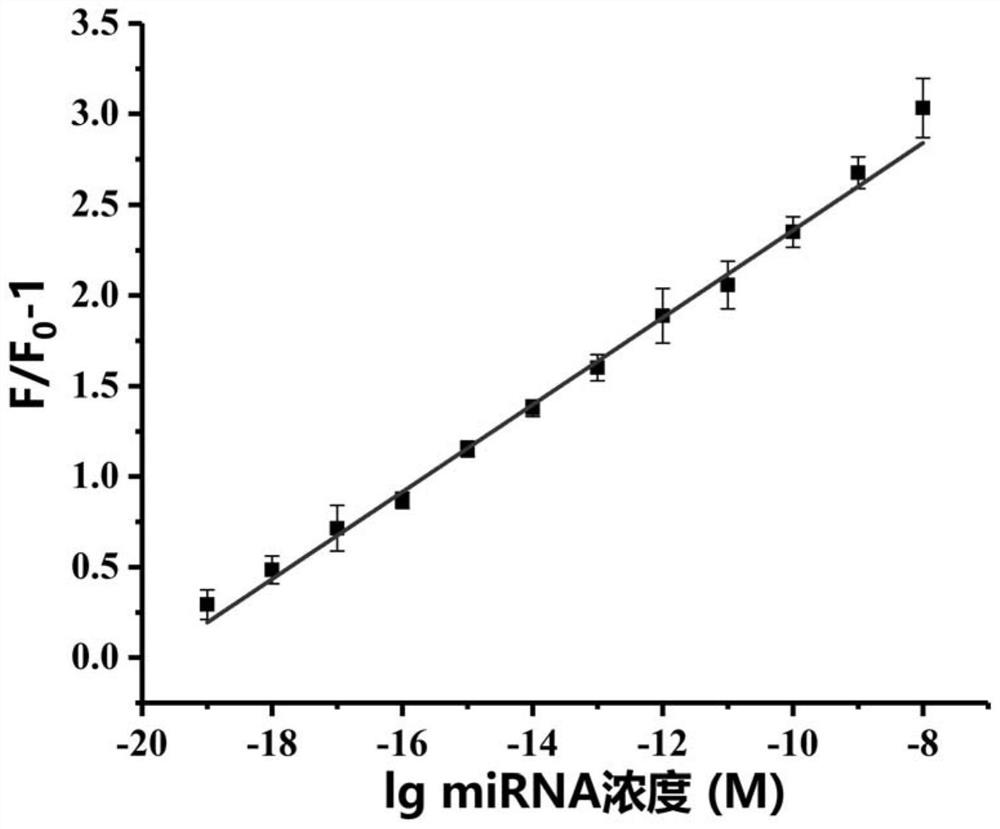
Method for detecting target miRNA based on G-quadruplex molecular beacon double-enzyme cascade isothermal amplification
ActiveCN112080552AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesNucleotideA-DNA
The invention discloses a method for detecting target miRNA based on G-quadruplex molecular beacon double-enzyme cascade isothermal amplification. The method comprises the following steps: taking a reaction system containing miRNA, a reaction buffer solution, Bsu DNA polymerase, Lambda exonuclease and G4MB, and incubating; detecting fluorescence intensity; and judging whether the miRNA contains the target miRNA or the content of the target miRNA according to the fluorescence intensity. The G4MB sequentially comprises a DNA fragment 1, a DNA fragment 2 and a DNA fragment 3 from the 5' end to the 3' end; the nucleotide sequence of the DNA fragment 2 is reversely complementary with the nucleotide sequence of the target miRNA; and one end of the G4MB is modified with a fluorescence marker anda phosphate group, and the other end of the G4MB is modified with a quenching group. Experiments prove that the method provided by the invention can be used for simultaneously detecting multiple target miRNAs, and is high in accuracy, high in sensitivity and good in specificity. The method disclosed by the invention has important application values.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
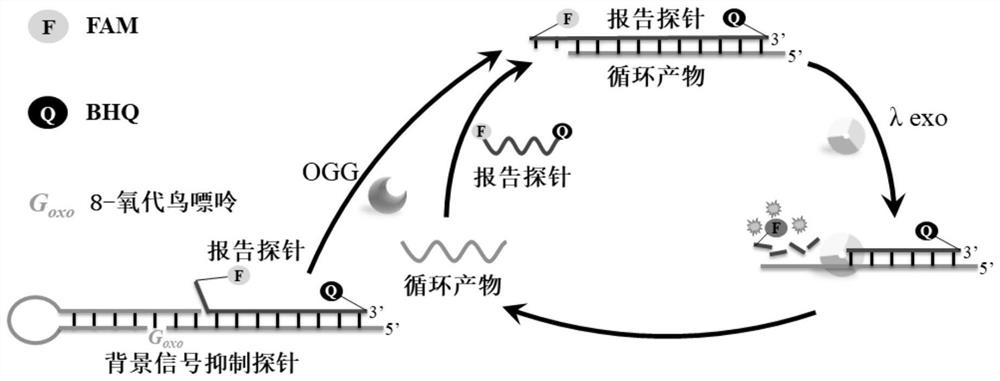
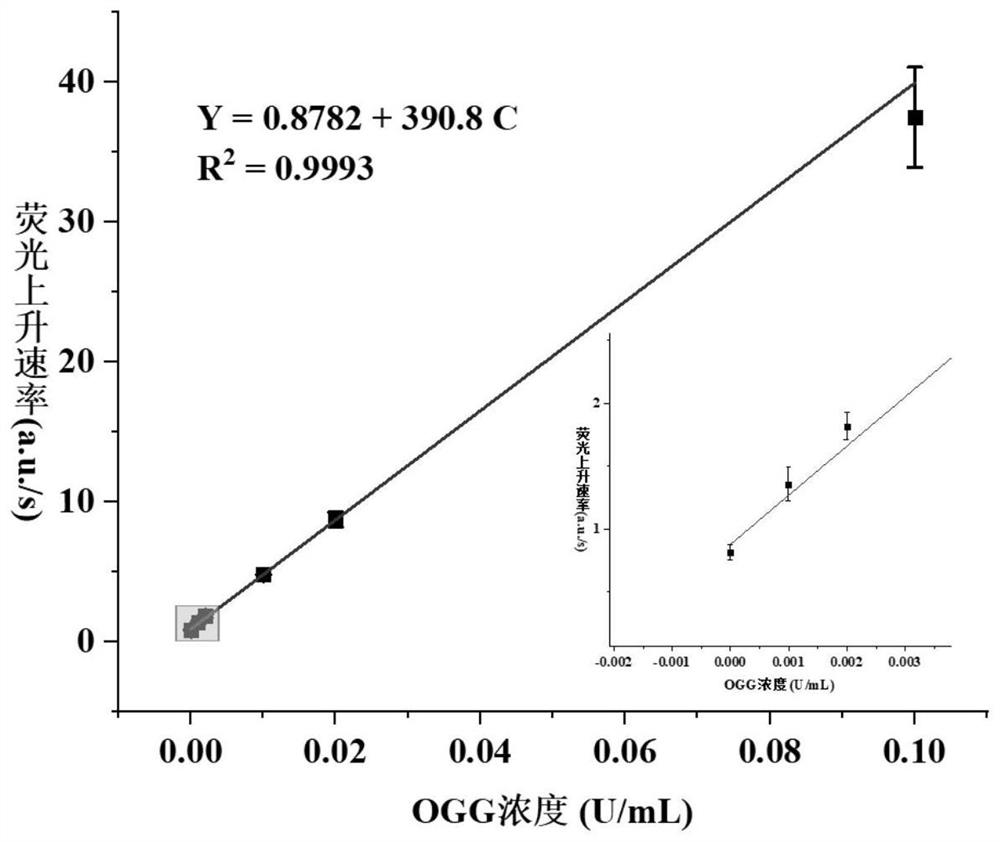
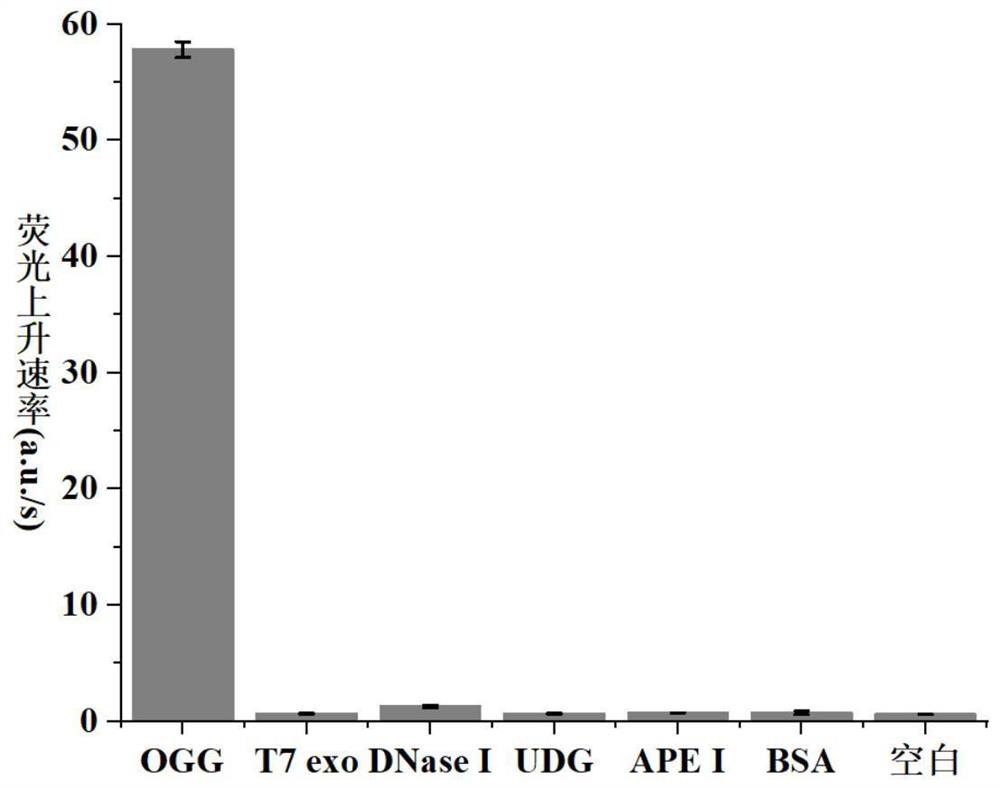
8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase determination method based on background signal inhibition probe, kit and application thereof
ActiveCN113186248AImprove detection limitLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionEnzyme assay
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to an 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase determination method based on a background signal inhibition probe, a kit and an application thereof. According to the present invention, the selectivity of Lambda exonuclease on the substrate structure and the recognition cutting effect of 8-oxo guanine DNA glycosylase on 8-oxo guanine are utilized, and the inhibition effect of the background signal inhibition probe on the lambda exo side activity is combined so as to construct the new 8-oxo guanine DNA glycosylase fluorescence determination method. The method specifically comprises the following steps: mixing a lambda exo buffer solution, a reporter probe sequence containing a fluorophore and a quenching group, and a background signal inhibition probe sequence containing 8-oxo guanine; heating the mixed solution to 85 DEG C, then gradually cooling to 37 DEG C, and adding a sample to be detected; incubating at 37 DEG C; and after incubation is finished, adding lambda exo, carrying out enzyme digestion reaction, and then carrying out fluorescence detection.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Manganese dioxide thin sheet mimic enzyme sensor and its preparation method and detection method of t4pnk
ActiveCN105548167BHigh sensitivityLow detection limitMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsA-DNALambda
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Method for detecting single-base mutation
ActiveCN107723341AAccurate detectionGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceMutation detection
The invention relates to a method for detecting single-base mutation in the field of gene mutation detection. The method comprises the following steps: S1, designing a fluorescent signal probe according to a target gene, wherein the fluorescent signal probe is completely complementary to a mutant gene of the target gene and forms a single-base mismatch with a wild-type gene of the target gene; S2,adding a target gene sample to be detected and lambda exonuclease into a fluorescent signal probe-containing solution to form a reaction system; S3, acquiring a real-time fluorescence curve of the reaction system during the reaction, and judging whether the single-base mutation exists in the target gene sample to be detected. By the method, a single-base mutant gene sequence can be rapidly and accurately detected, and the selectivity to the single-base mutant gene sequence is high, so that the method can be applied to low-abundance mutation detection; in addition, by the method, the detectioncost is low, the preparation is easy, the operation is simple and the repeatability is high, and the method is easily popularized among non-professionals.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for simulating recombination and non-trace cloning
The invention relates to a method for simulating recombination and non-trace cloning, which is characterized in that when a carrier primer is designed, a fragment of DNA basic group having a same sequence with a target gene is respectively added at 5' terminal of the primer, the obtained carrier DNA terminal and the inner part of the target gene have a coupling area, the carrier DNA and the target gene are mixed, and Lambda Exonuclease and T4 DNA polymerase are used for treatment to obtain recombinant DNA. The method for simulating recombination and non-trace cloning has the following beneficial effects that 1) the target gene amplified through PCR is not required, the mutation caused by PCR is reduced; 2) the target fragment can be specifically cloned in a DNA mixture; and a trace of an enzyme site is not kept.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A set of oligonucleotide aptamers capable of specifically recognizing streptococcus agalactiae
ActiveCN103014000BEasy to operateLower synthesis costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAptamerNucleotide
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
an oligonucleotide probe
ActiveCN105802963BEasy to makeEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleic Acid ProbesTrue positive rate
The invention belongs to the technical field of nucleic acid probes and provides an oligonucleotide probe. The probe consists of a sequence complementary to the target sequence, a G-quadruplex blocking sequence and a G-quadruplex sequence from the 5'-3' end. The G-quadruplex blocking sequence is complementary to part of the G-quadruplex sequence, forming a stable hairpin structure, and enclosing the G-quadruplex sequence inside the probe. When detecting target molecules, the probe first recognizes the target sequence and forms a double-stranded structure, then under the digestion of Lambda exonuclease, the hairpin structure is opened, the G-quadruplex sequence is released, and the cycle repeats, and finally the trace target Molecular information is converted into a large number of G-quadruplex sequences, and then converted into readable optical, electrical and other signals through the G-quadruplex sequences. The probe has the advantages of good stability, low cost, easy preparation, high throughput, high sensitivity and specificity, can realize the direct detection of single-stranded nucleic acid, and can also detect double-stranded nucleic acid and other molecules for indirect detection.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
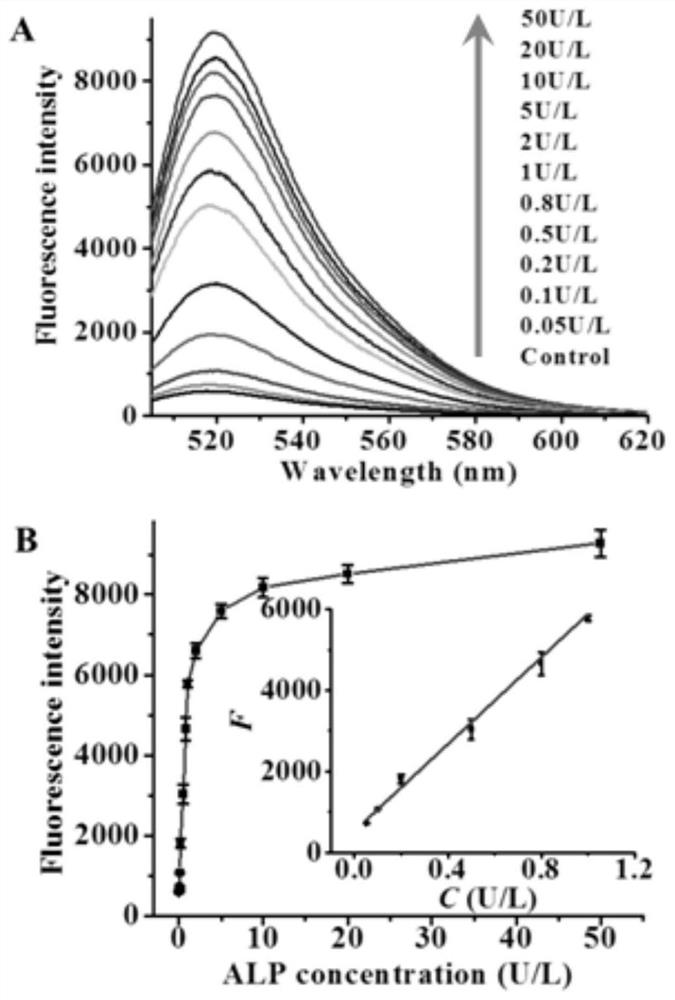
A kit and method for detecting alkaline phosphatase
ActiveCN108588178BAvoid design complexityInhibit synthesisMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellPhosphorylation
The invention relates to a method for sensitively detecting alkaline phosphatase through dual-signal amplification mediated by dephosphorylation-triggered transcription reaction. A 5'-phosphorylated T7 promoter single-chain is designed, and alkaline phosphatase can catalyze The 5'-phosphorylated T7 promoter is dephosphorylated, protecting the T7 promoter chain from digestion by lambda exonuclease, and the remaining T7 promoter can activate the transcription reaction mediated by T7 RNA polymerase, resulting in a large amount of RNA transcripts . Subsequently, these RNA transcripts are complementary paired with Taqman probes to form RNA-DNA duplexes, and duplex-specific nucleases are introduced to trigger cyclic cleavage of Taqman probes, resulting in significantly enhanced fluorescent signals. The method is simple to operate, has high sensitivity and high specificity, and can be applied to the screening of target inhibitors in complex biological samples and the quantitative detection of targets in cervical cancer cells.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com