Rapid fluorescence detection method and application of egfr gene exon 19 deletion mutation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1
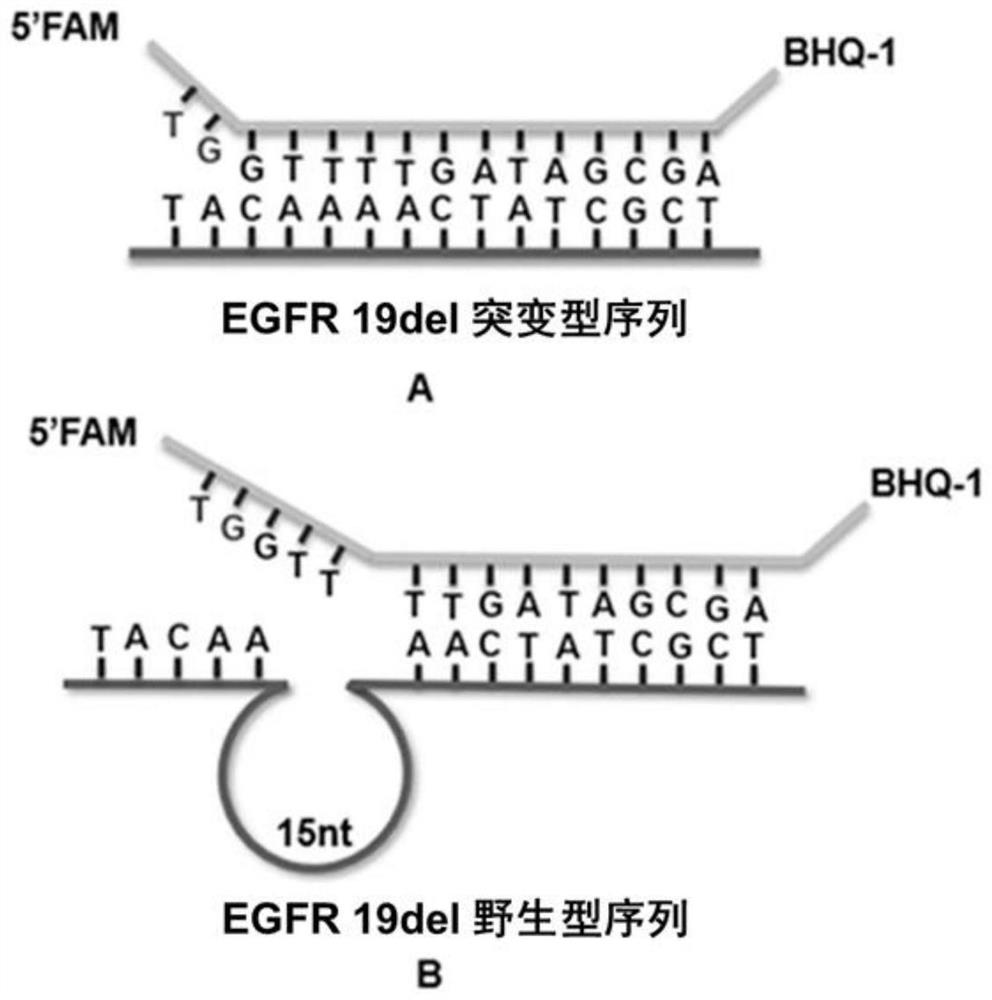
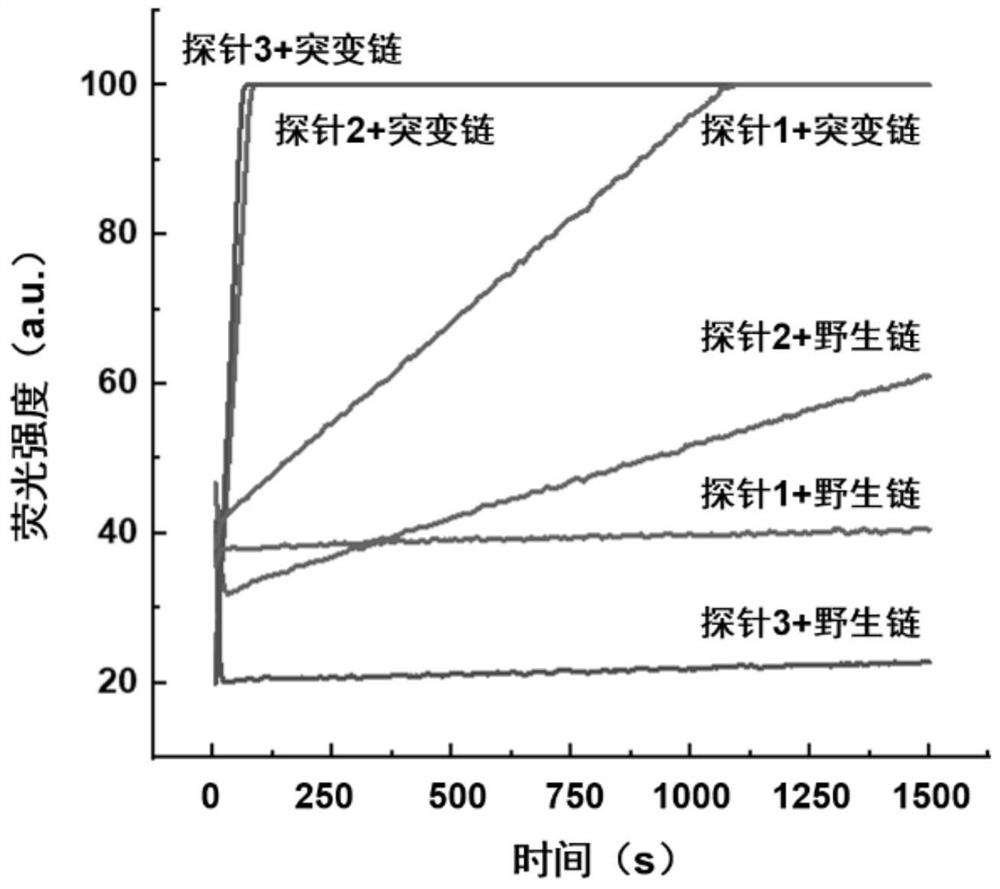
[0052] In order to achieve high-sensitivity detection of low-abundance mutant chains, the most critical issue is to improve the ability of the probe to distinguish between wild and mutant chains. In the design of the present invention, the main factors affecting the discrimination of the probes are: the relative position of the 5' end of the probe and the mutation region, the opening degree of the two bases at the 5' end, and the total length of the probe. The length of the probe sequence is generally 12-15 nt, too long or too short will lead to a decrease in the discrimination between the mutant strand and the wild strand. For EGFR 19del, the length of the probe was designed to be 15 nt due to the low GC content (about 40%) of the sequence near the mutation region. In order to reduce the fluorescence response of the probe to the wild strand as much as possible, the mutation position was initially designed to be 5-6 bases away from the 5' end of the probe....
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2
[0058]In order to use the above probes directly for the detection of EGFR 19del in genomic samples and obtain quantitative and reliable results, we first optimized the PCR conditions for EGFR 19del. For common point mutations, the molecular weight difference between the mutant chain and the wild chain is usually only tens of g / mol. For the EGFR 19del mutation, a deletion of 15 nucleotides was involved, resulting in a molecular weight difference of 4674.1 g / mol between the mutant chain and the wild chain. In order to reduce the DNA quantification error that may be caused by this difference, we designed a longer EGFR 19del amplicon sequence to reduce the relative difference in molecular weight between the mutant and wild-type chains, so that the average molecular weight of the mutant and wild-type chains can be used Calculate the amount concentration of the substance of the amplified sequence. Considering that if the protruding sequence of the 3' end of the...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3
[0065] The above probes are used to detect the abundance of circulating free DNA (cfDNA) EGFR 19del mutation in actual samples, and the operation steps are as follows:
[0066] (1) The cfDNA in the sample was extracted using the QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany), and the extracted DNA was quantified using a NanoDrop 2000 micro-ultraviolet photometer.
[0067] (2) In a 200 μL PCR tube, add 10 μL 10×Q5 Reaction Buffer, 5 μL 19del forward primer (final concentration 500 nM), 5 μL 19del reverse primer (final concentration 500 nM), 1 μL dNTPs (10 mM each dNTP), 1 μL 10 ×LCGreen, 1 μL of 19del standard ssDNA with different abundances of mutant strands (total final concentration of mutant strands and wild strands is 10 pM, change the abundance of mutant strands) or actual samples (final DNA concentration of 0.5 to 1.0 μg / mL), Q5 DNA polymerase (20U / mL), water (up to 50μL). The PCR process (93°C for 8s, 60°C for 20s, 72°C for 20s, 35 c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com