Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
106 results about "Java applet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Java applet was a small application written in the Java programming language, or another programming language that compiles to Java bytecode, and delivered to users in the form of Java bytecode. The user launched the Java applet from a web page, and the applet was then executed within a Java virtual machine (JVM) in a process separate from the web browser itself. A Java applet could appear in a frame of the web page, a new application window, Sun's AppletViewer, or a stand-alone tool for testing applets.
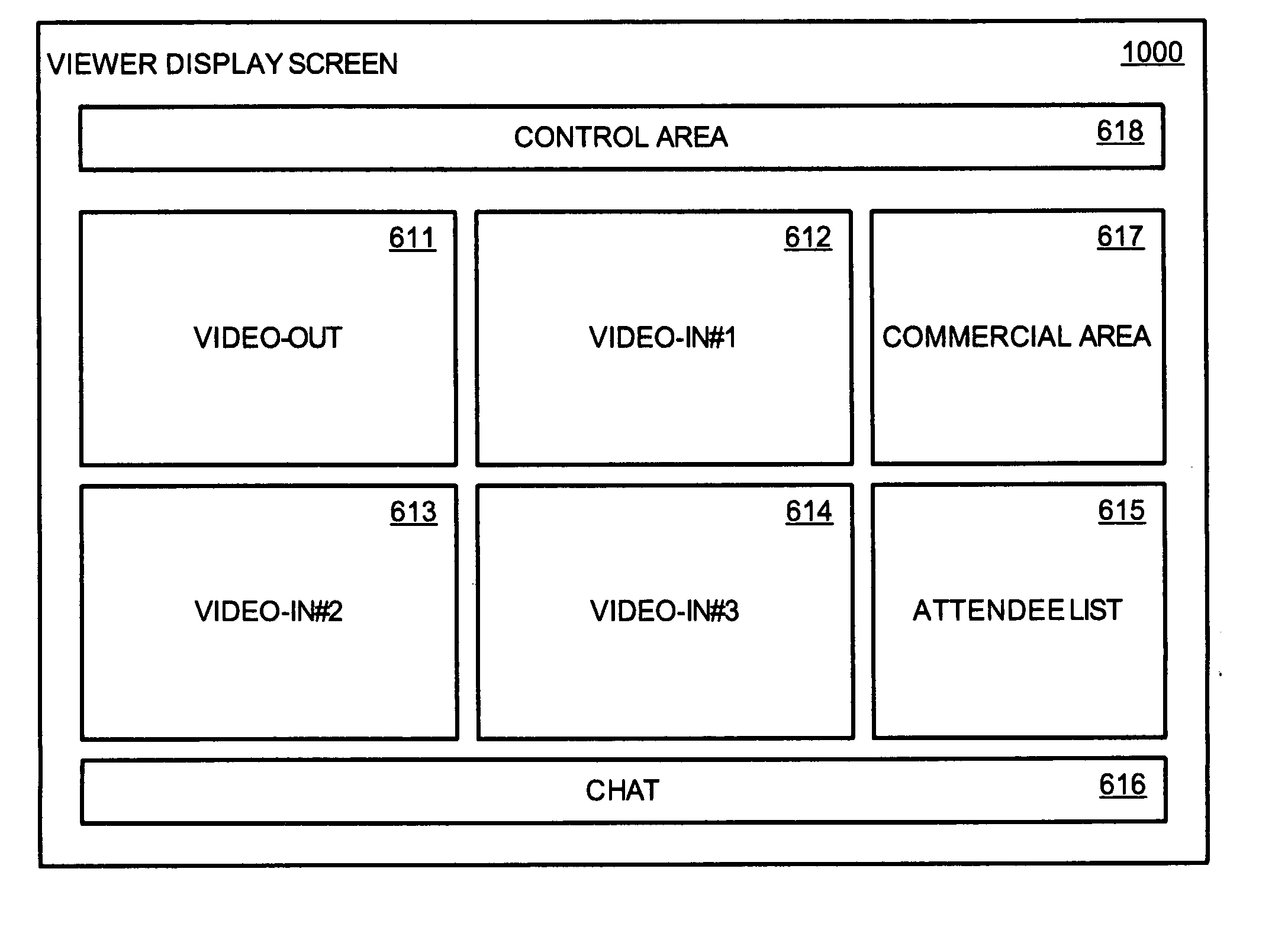
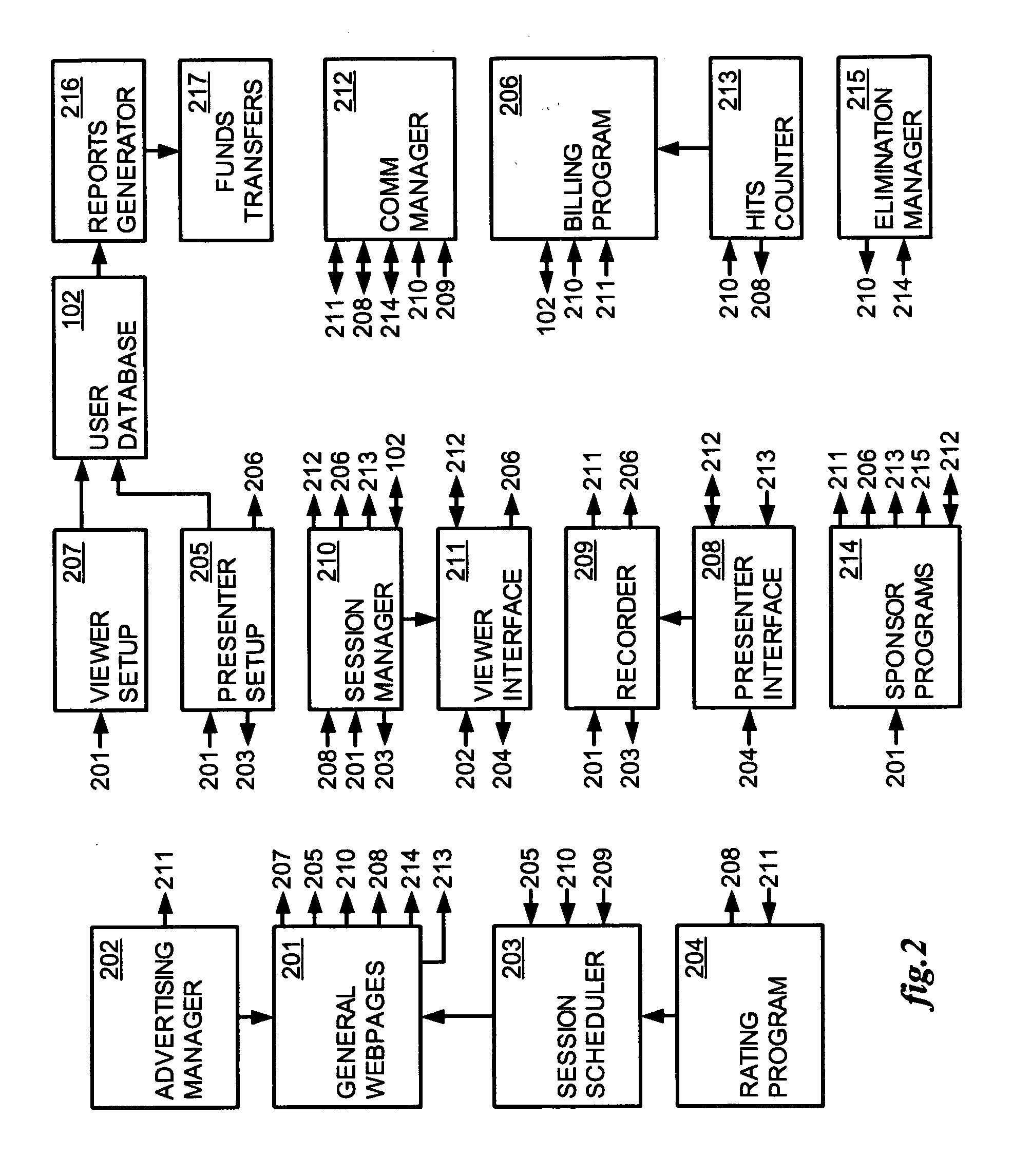
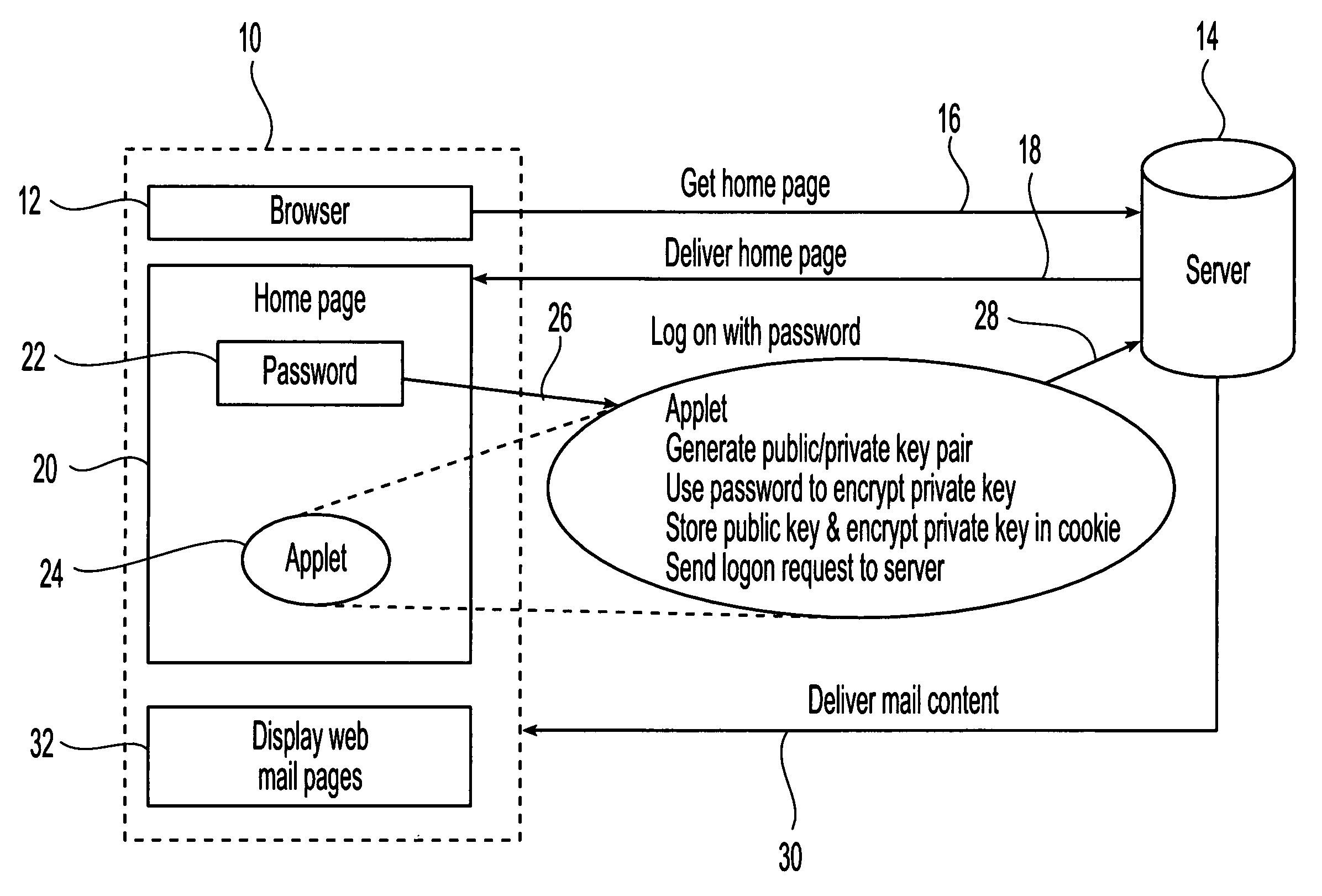
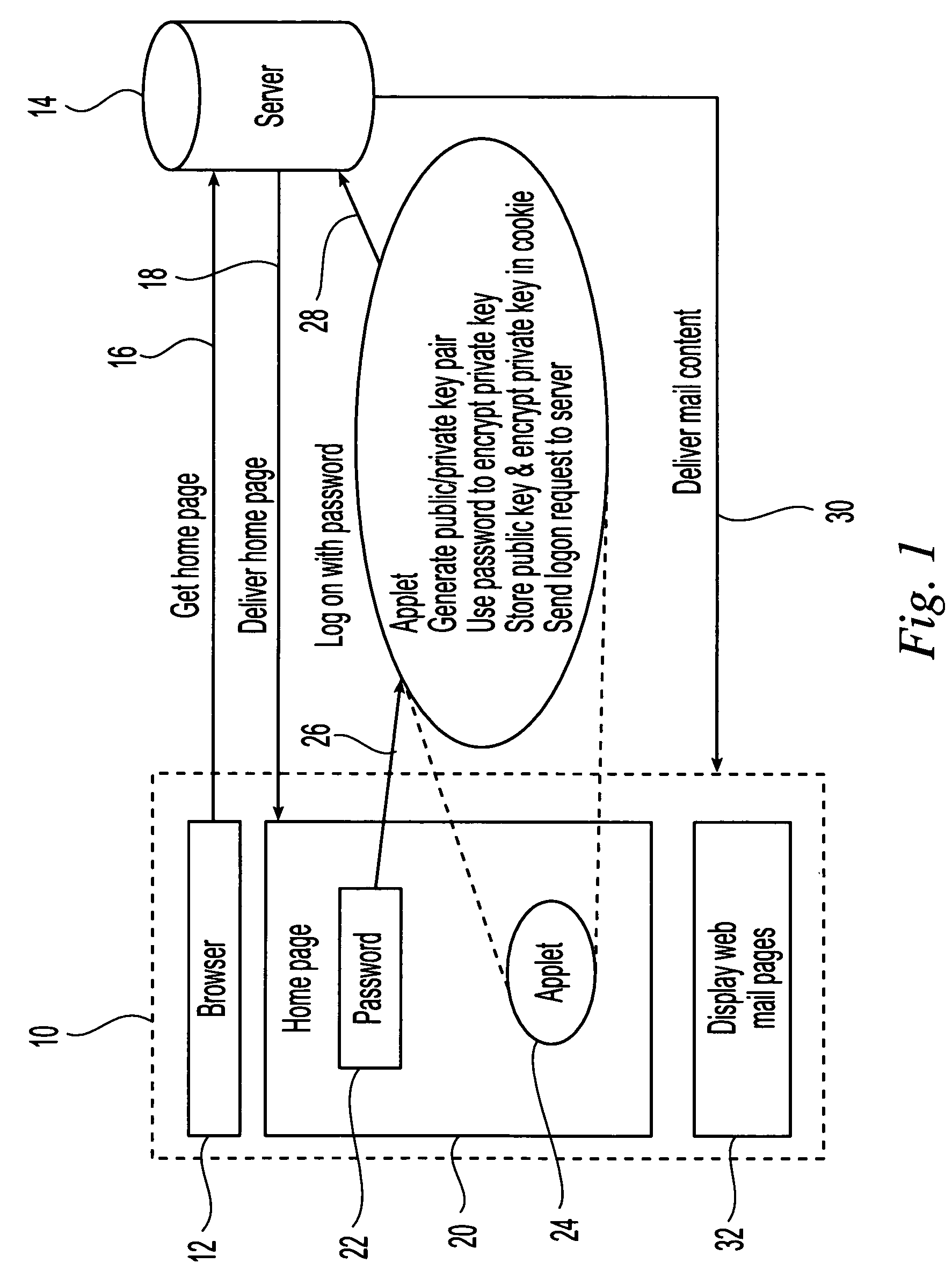
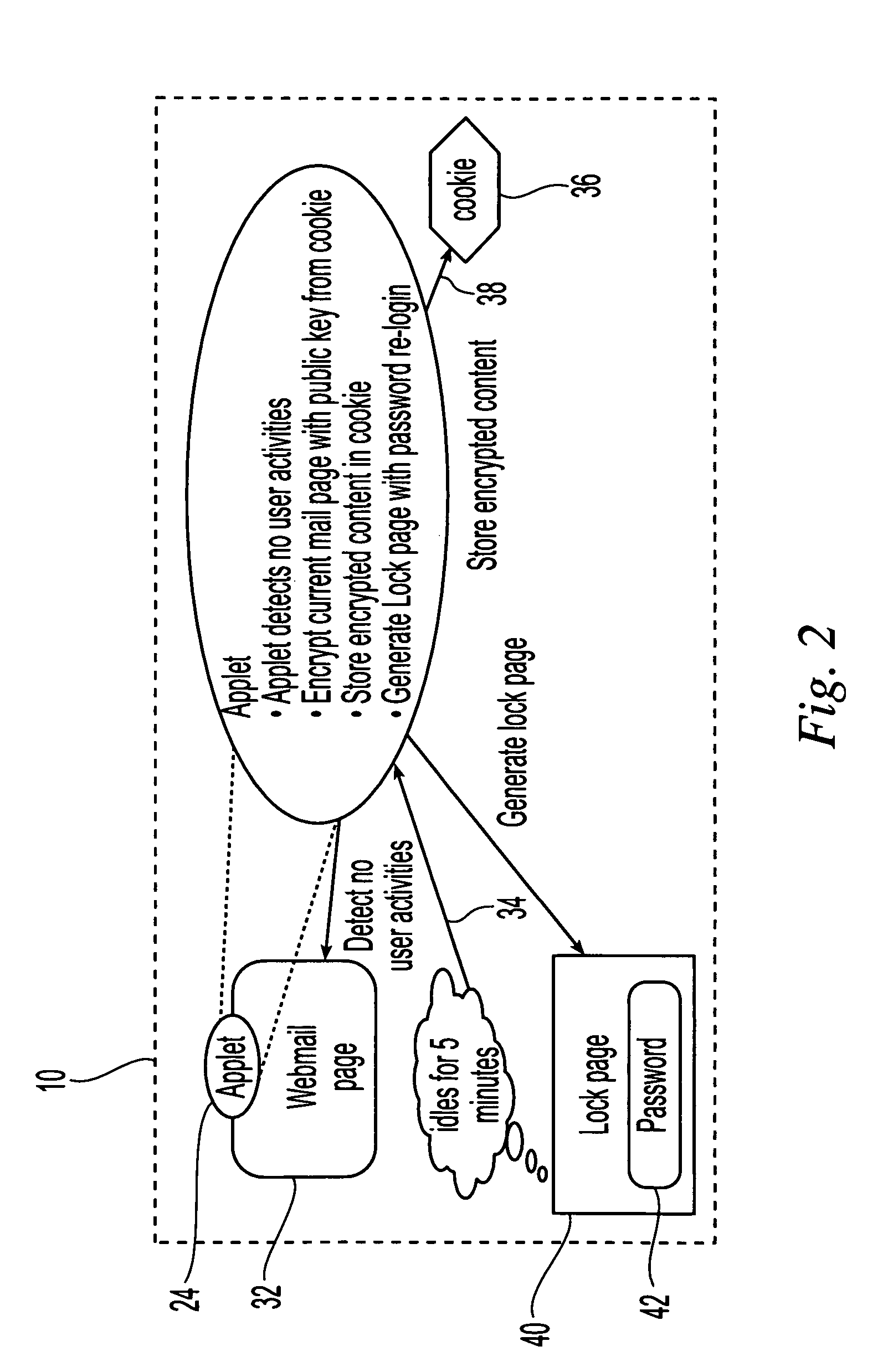
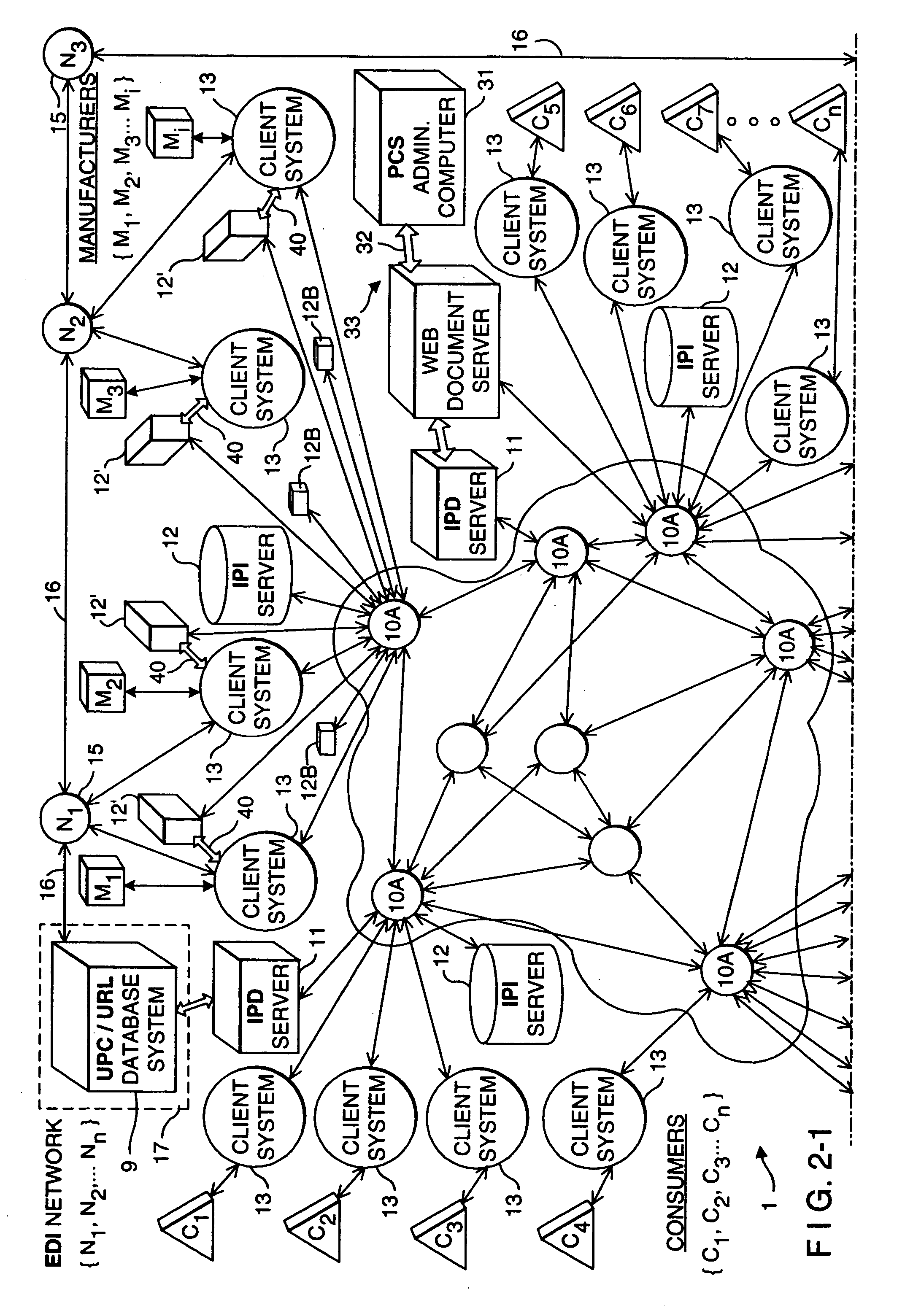
Method and apparatus for broadcasting live personal performances over the internet
InactiveUS20050138560A1Reliable and safe and purchasingEasily interfaceTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsPaymentWeb browser
A method and apparatus for broadcasting live personal performances over the Internet employs a web server to manage scheduling and broadcasting of the performances over the Internet, as well as collections and payments for products and services sold by presenters to viewers in conjunction with their performances. The server receives audio / video data from presenter operated computers through an uploaded presenter program, and relays the received audio / video data to viewer operated computers for viewing in media players invoked by their web browsers responding to an uploaded HTML document or JAVA applet. Viewers select performances to view from a program schedule provided on a webpage hosted by the web server. Both viewers and presenters are registered with the web server to facilitate payments for products and services, and their financial information stored in a secure user database.
Owner:ORIDUS
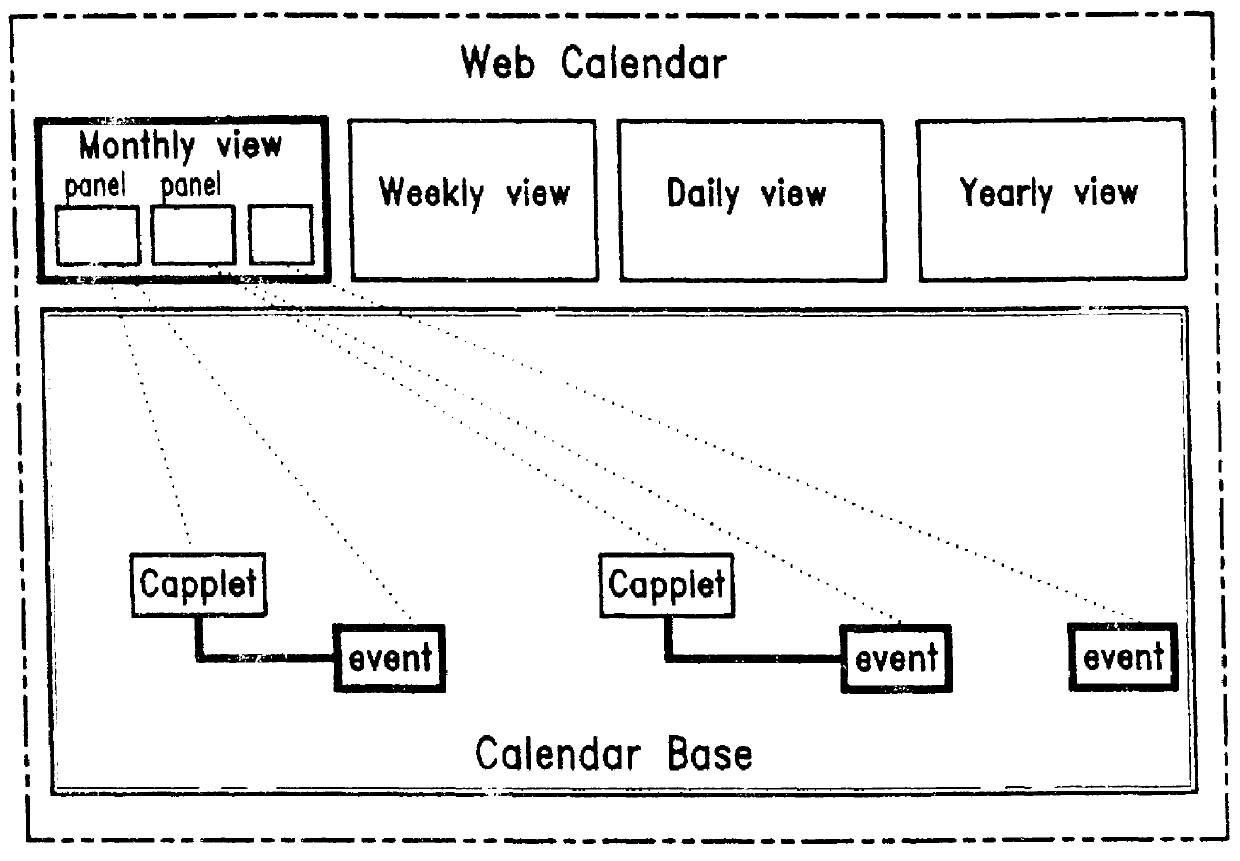
Web calendar architecture and uses thereof
InactiveUS6018343ADigital data processing detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInternet groupwarePersonal organizer
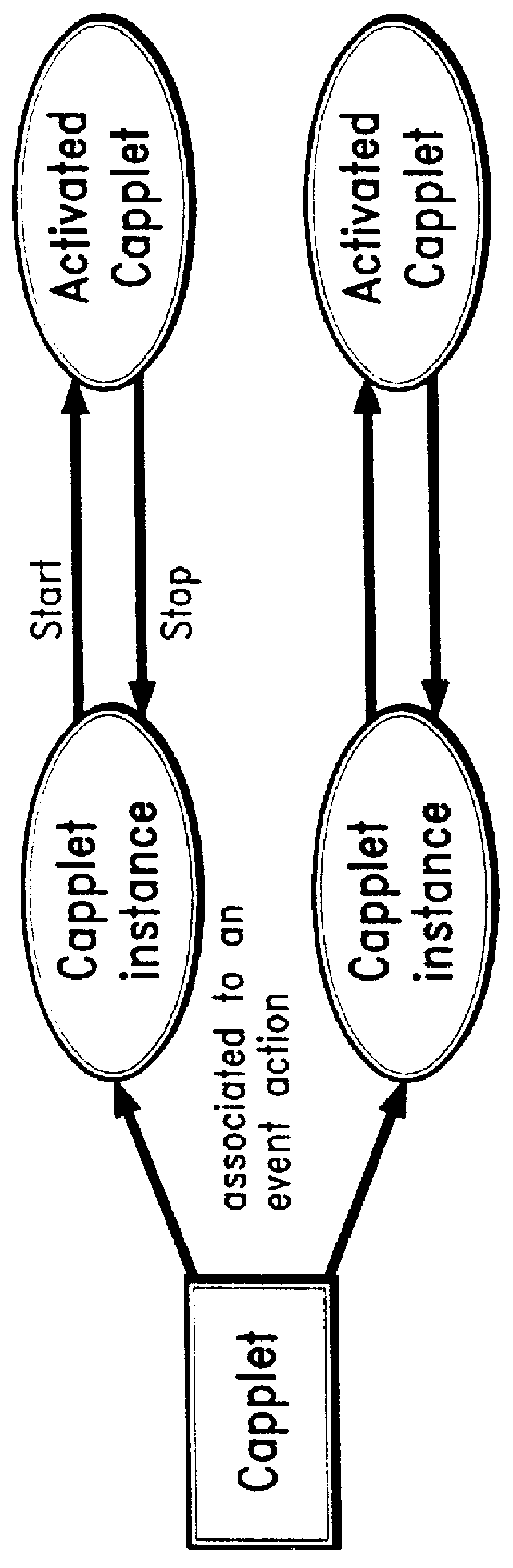
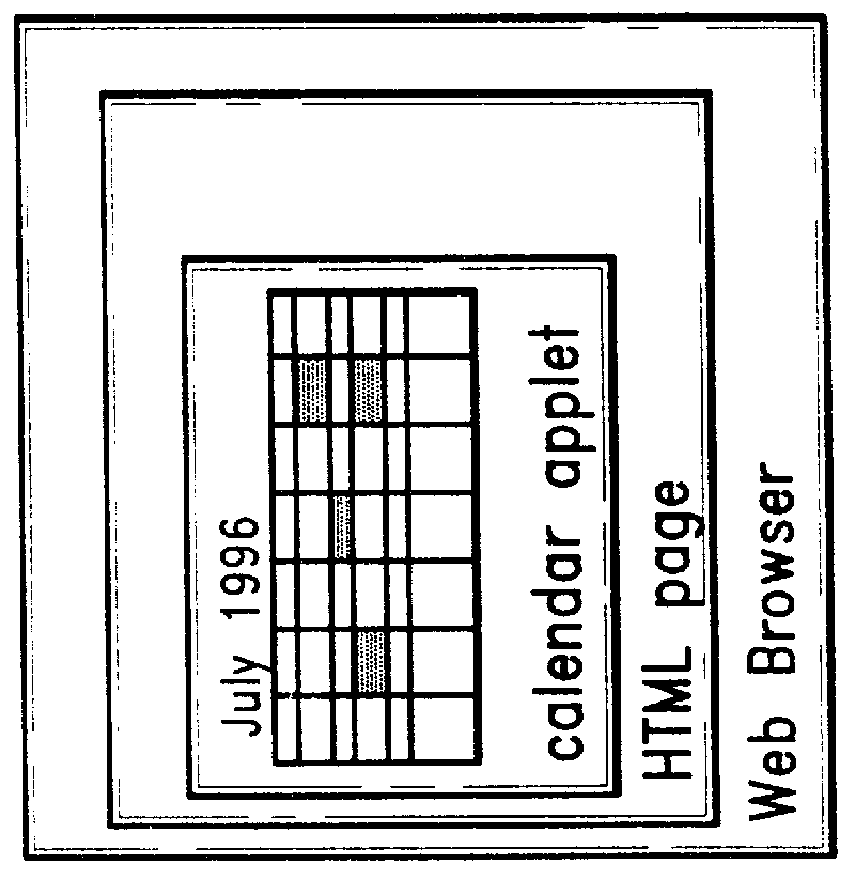
An architecture for facilitating Web-based client-side calendar event scheduling includes a Web Calendar scheduling tool which takes input via either a mouse and / or a keyboard to achieve a) an Internet personal organizer, b) multimedia effects associated with scheduled events, c) an Internet groupware that shares group members' individual schedules, d) an Internet transaction associated with scheduled events, and e) an open platform that supports any Java applet. Users of the Web Calendar can schedule events, associate a special purpose Capplet TM with scheduled events, and store them for future reference or public use. It features concurrent Capplet TM views running under one of four calendar grids: yearly, monthly, weekly, and daily. The architecture also supports multimedia animation in pop-up windows whose dimensions are defined dynamically by an invocation method. It is an open platform on which any user can create a special purpose applet and run it on the Web Calendar.
Owner:VIVINT INC
Method of <script> based remote JavaScript function call of web page
InactiveUS6941562B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsReal-time dataWeb browser
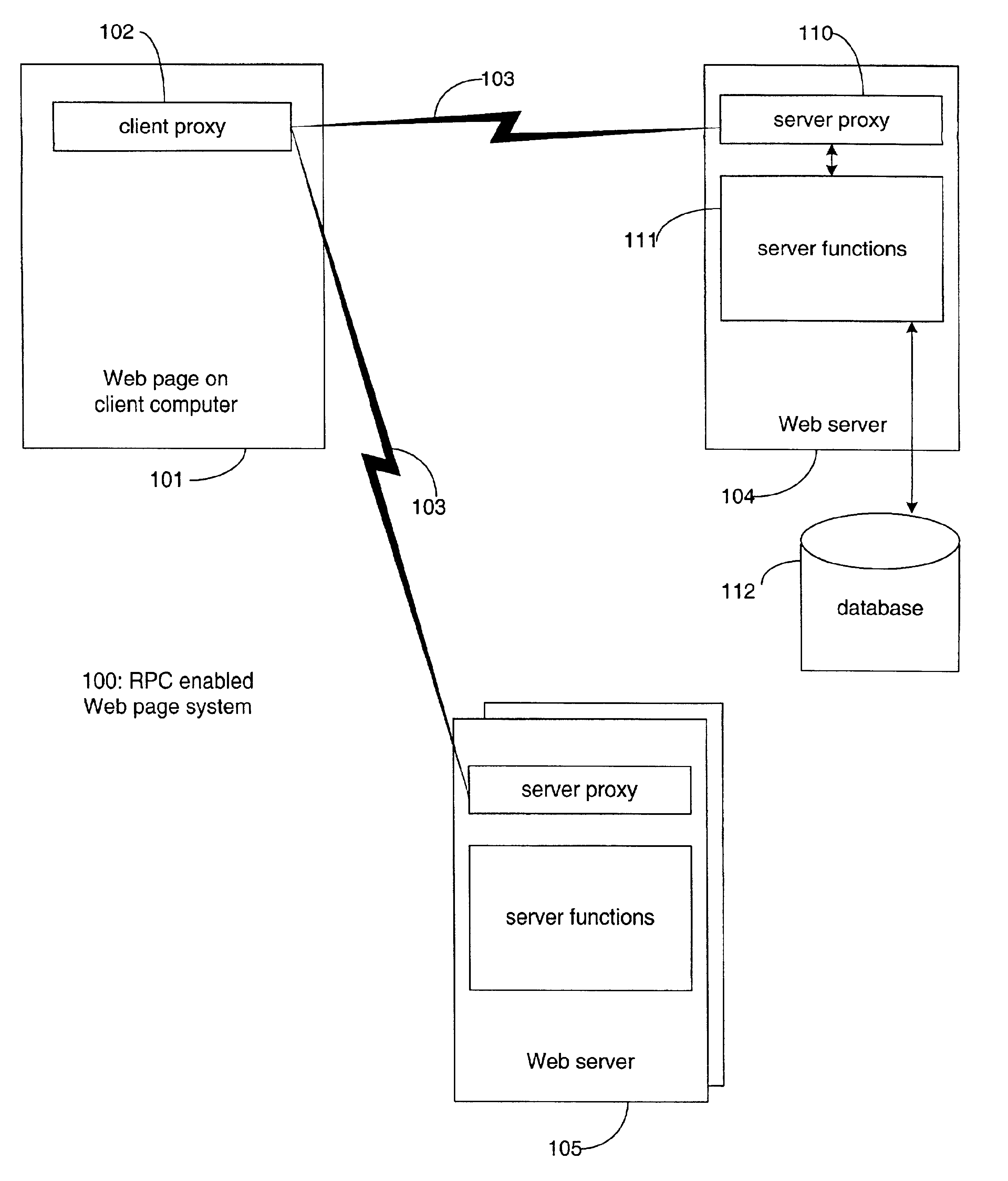
The present invention permits a JavaScript-based Remote Procedure Call (RPC) to be executed from a Web page displayed in a Web browser window, without utilizing browser plug-in, Java Applet, or ActiveX technology. Traditionally, clunky downloads and Web browser plug-ins has been required to enable Web page interactivity, which greatly compromises the performance and reach of the Web page. Based purely on HTML and JavaScript, the present invention utilizes the HTML <script> element to pass data to the server and execute a remote procedure, receiving the resulting output to the same displayed Web page. The present invention can be used to build a lightweight Web page that offers real-time data and interactivity.
Owner:NETGRATUS INC +1
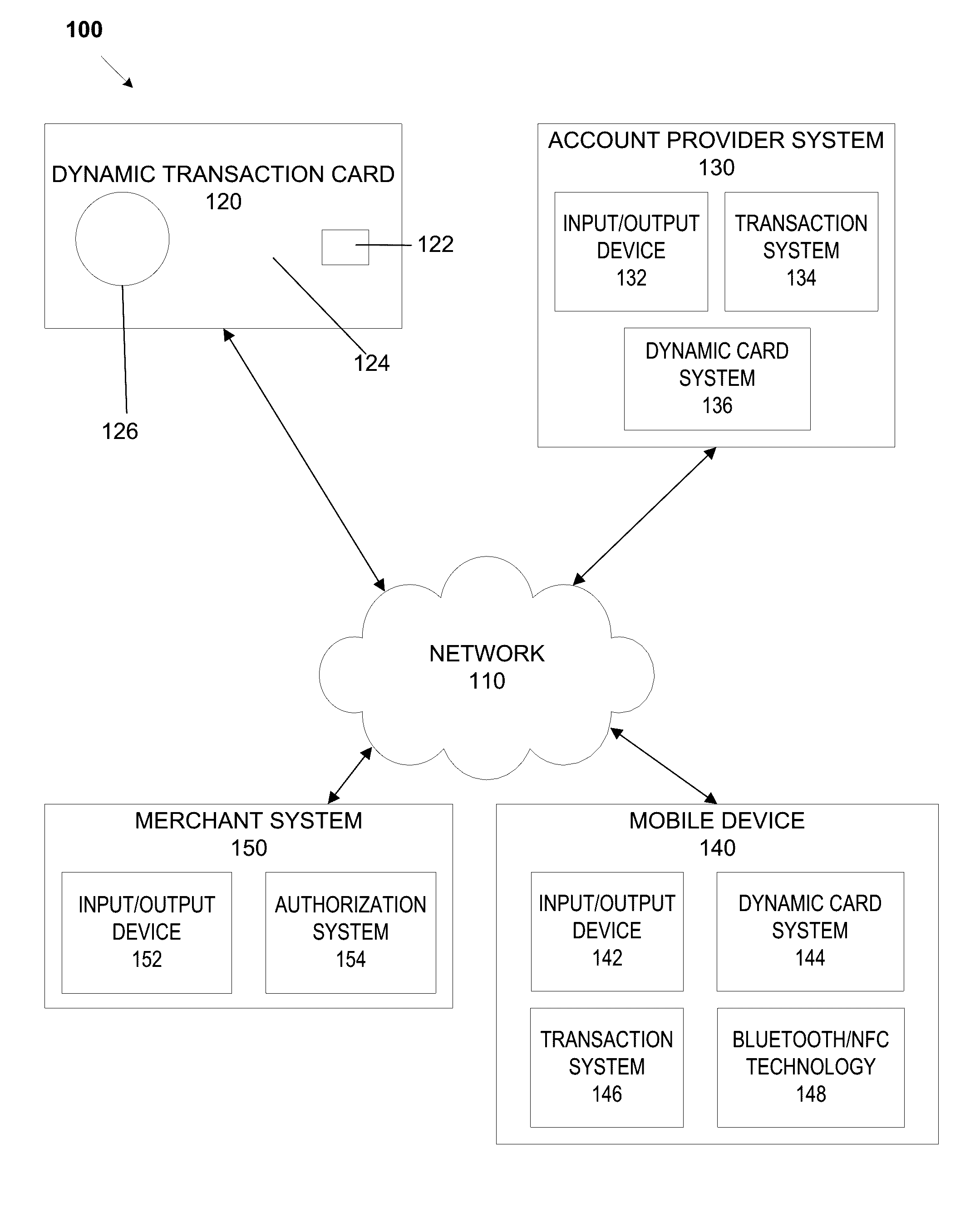
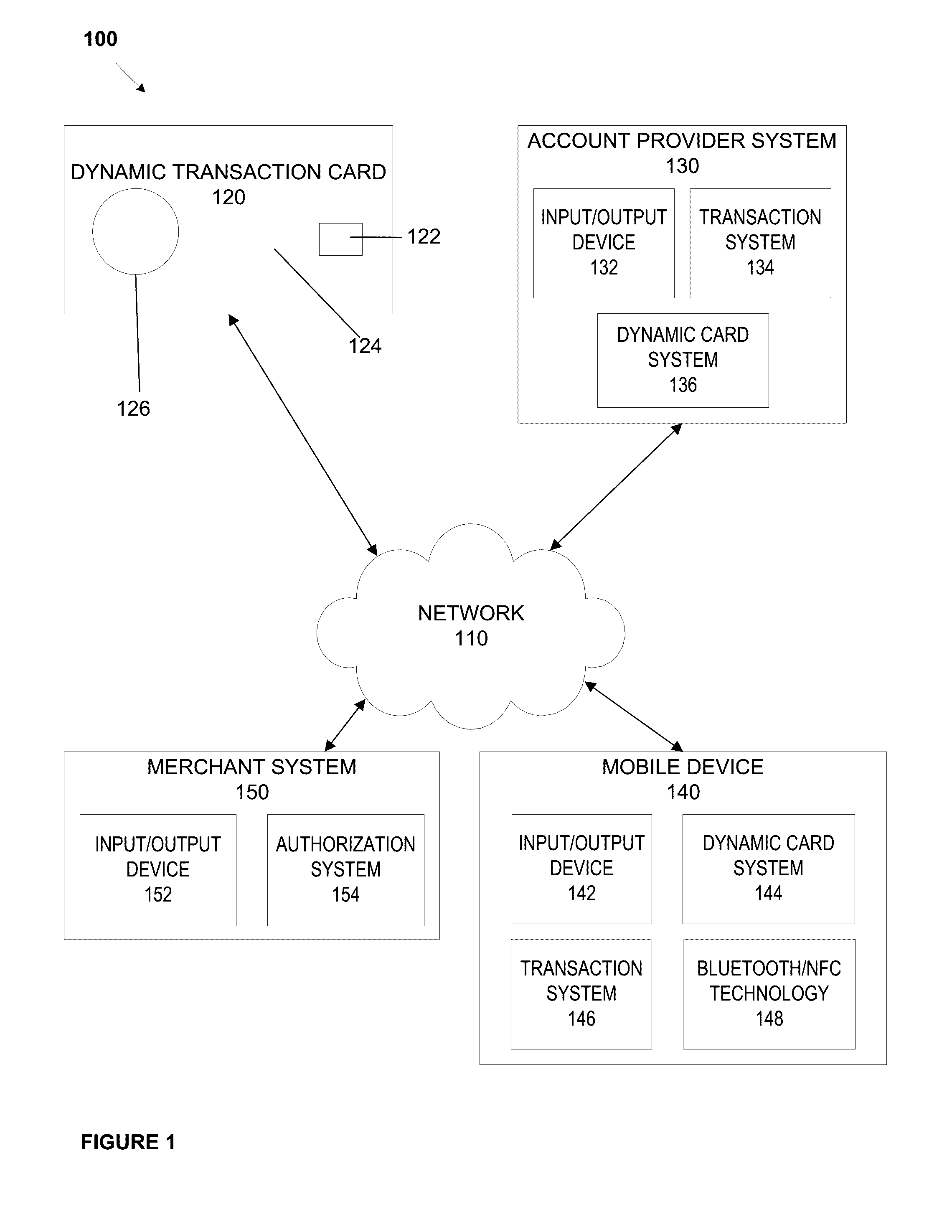
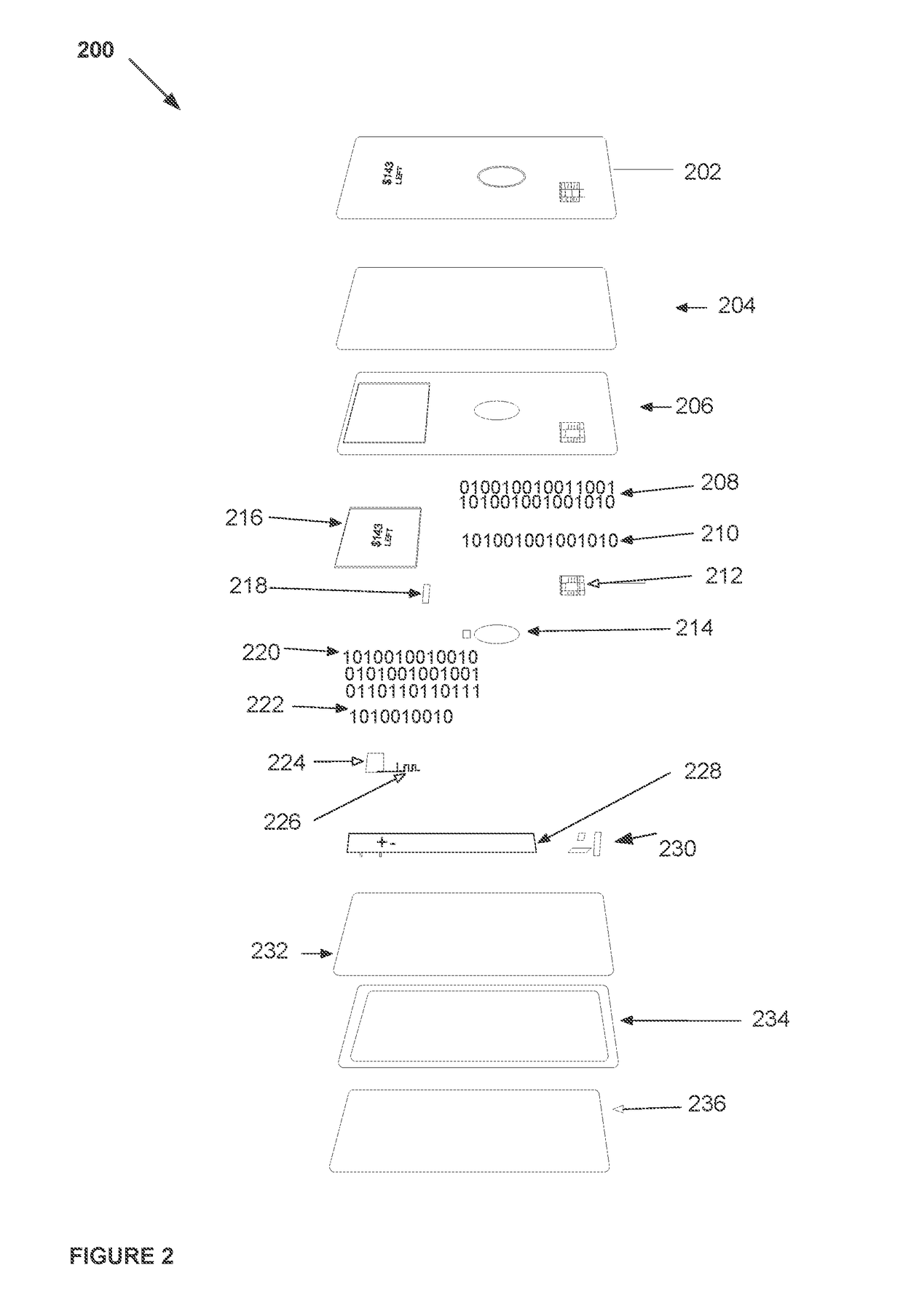
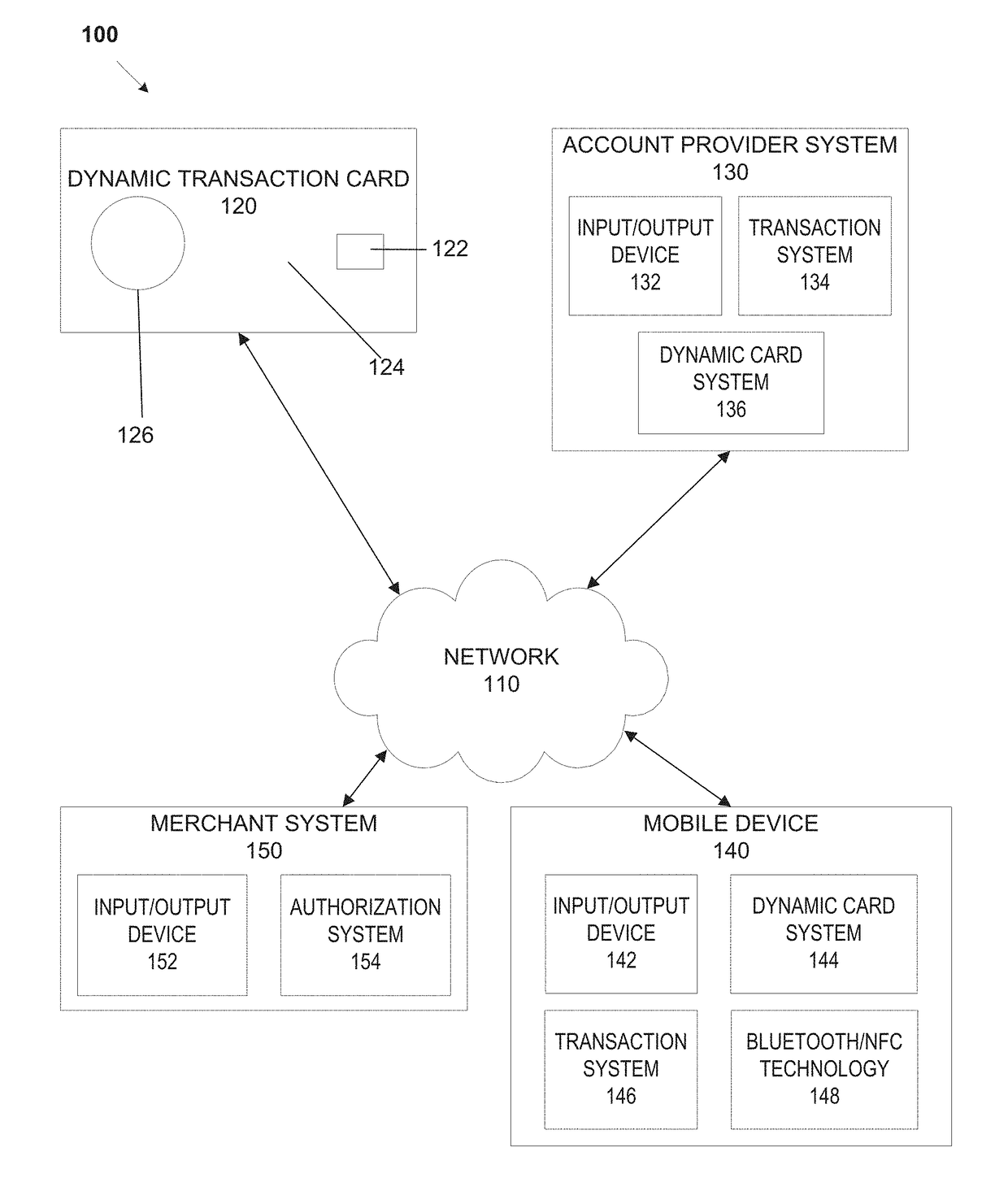
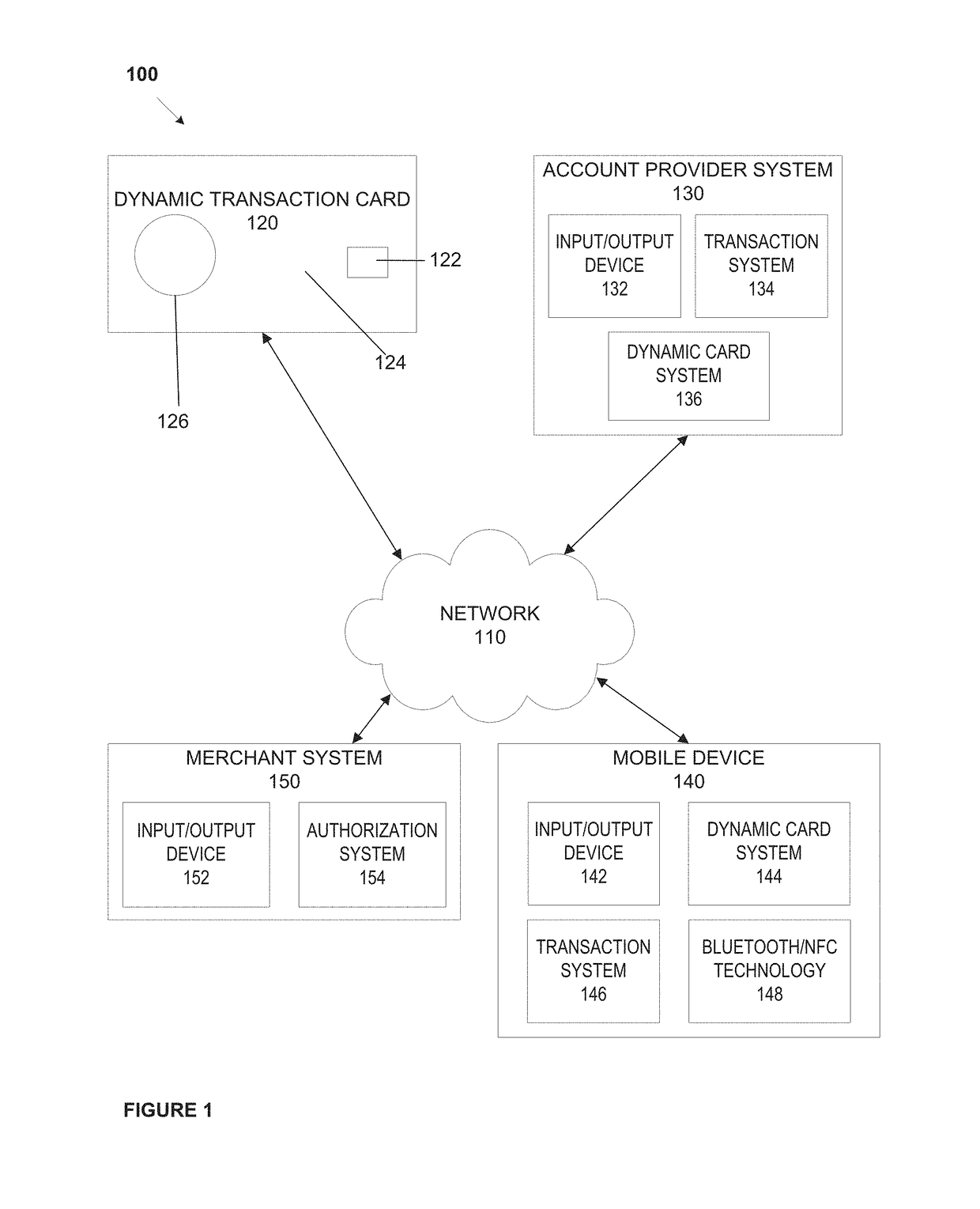
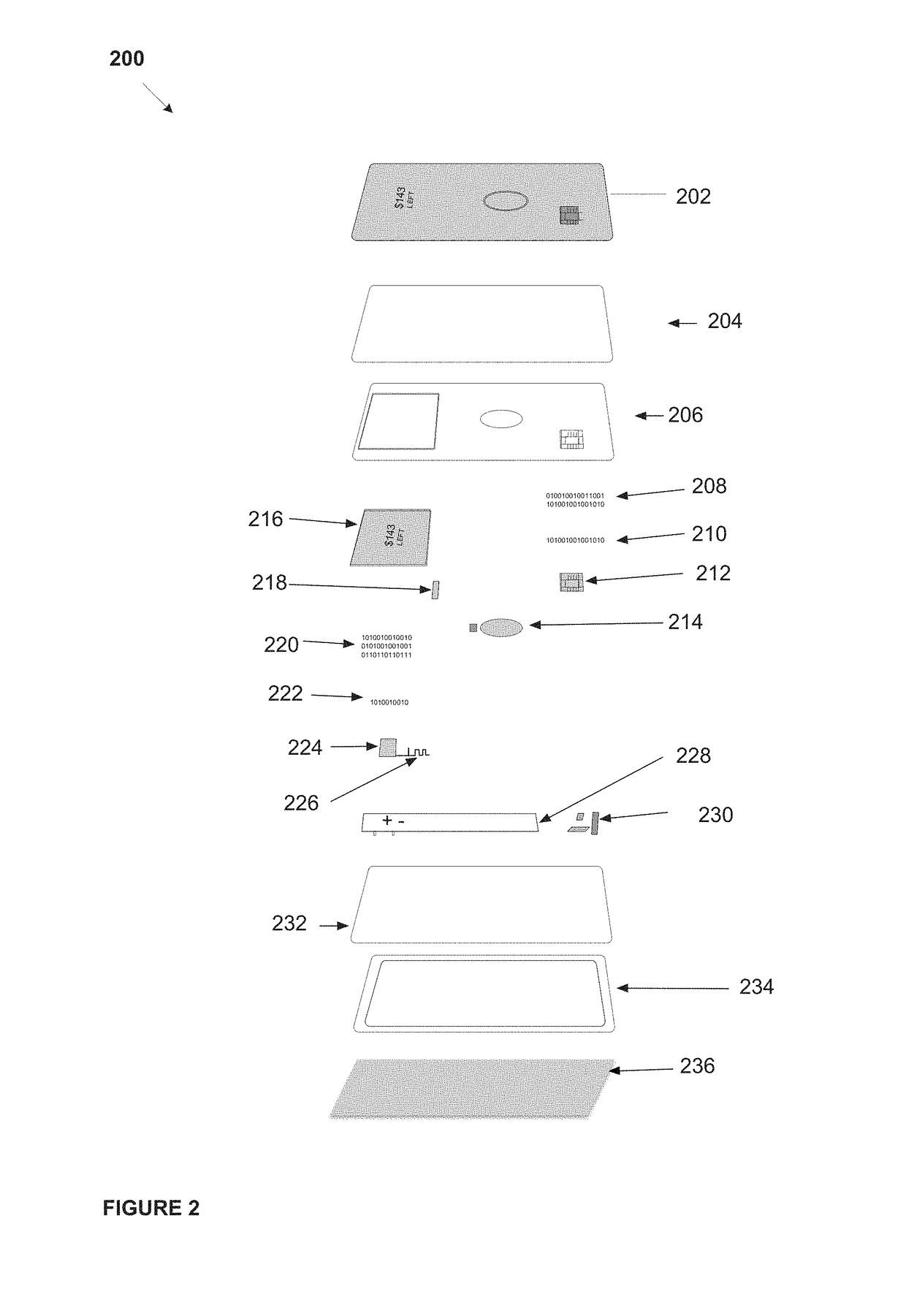
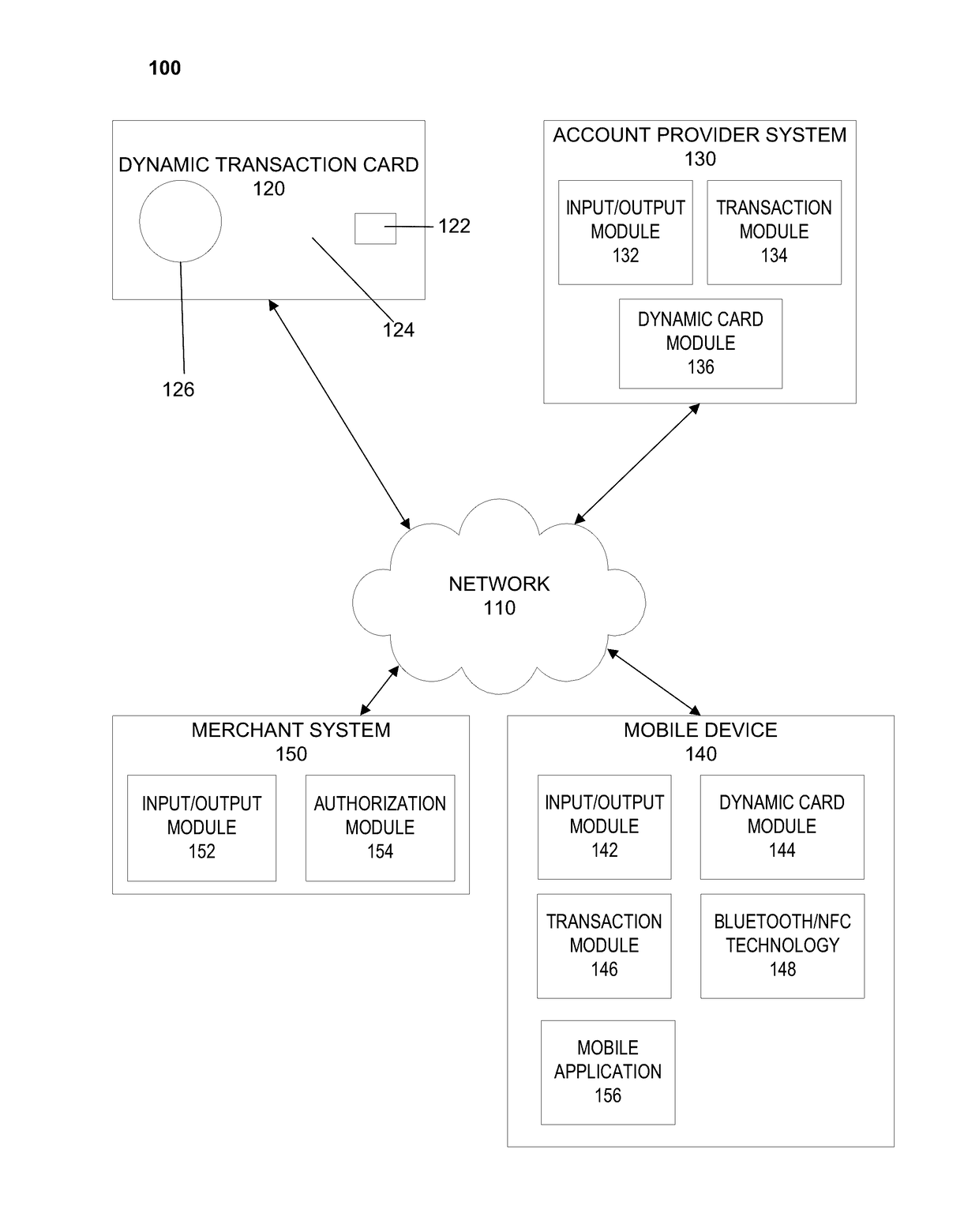
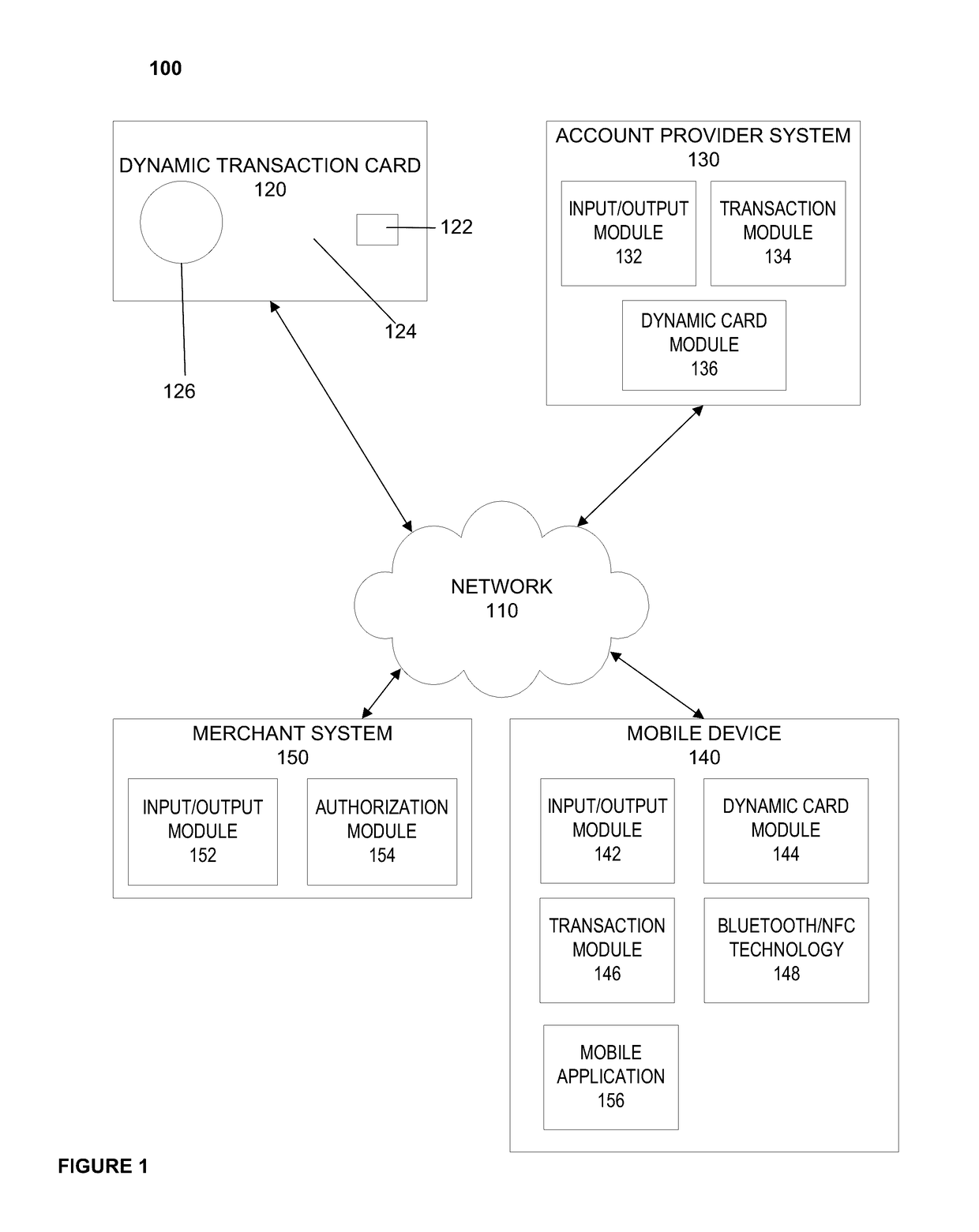
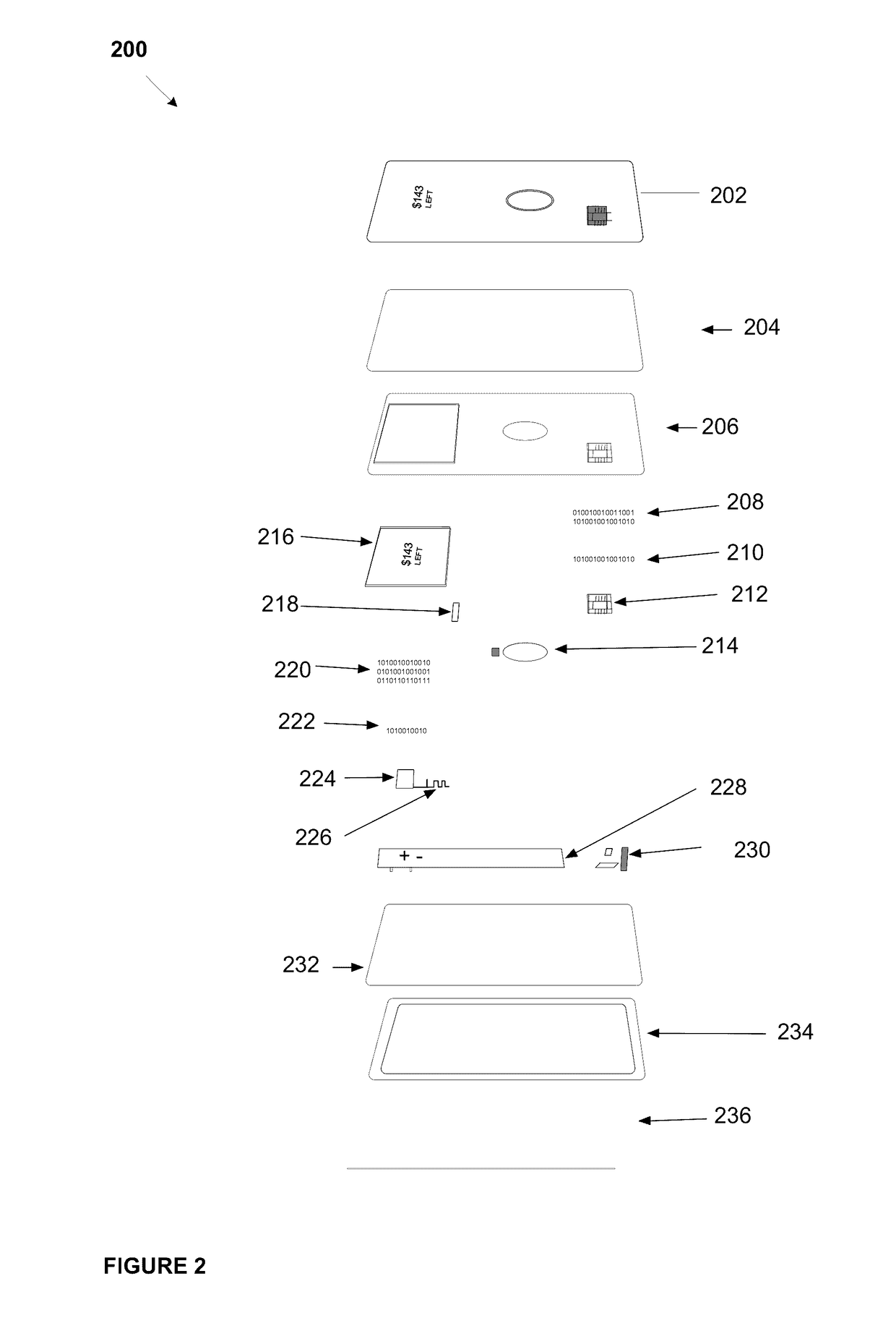
System, method, and apparatus for a dynamic transaction card
ActiveUS20160307189A1Connection securityRecord carriers used with machinesProtocol authorisationMicrocontrollerDot-matrix display
A dynamic transaction card that includes a transaction card having a number of layers, each of which may be interconnected to one another. For example, a dynamic transaction card may include an outer layer, a potting layer, a touch sensor layer, a display layer (including, for example, LEDs, a dot matrix display, and the like), a microcontroller storing firmware, Java applets, Java applet integration, and the like, an EMV chip, an energy storage component, one or more antenna (e.g., Bluetooth antenna, NFC antenna, and the like), a power management component, a flexible printed circuit board (PCB), a chassis, and / or a card backing layer.
Owner:CAPITAL ONE SERVICES
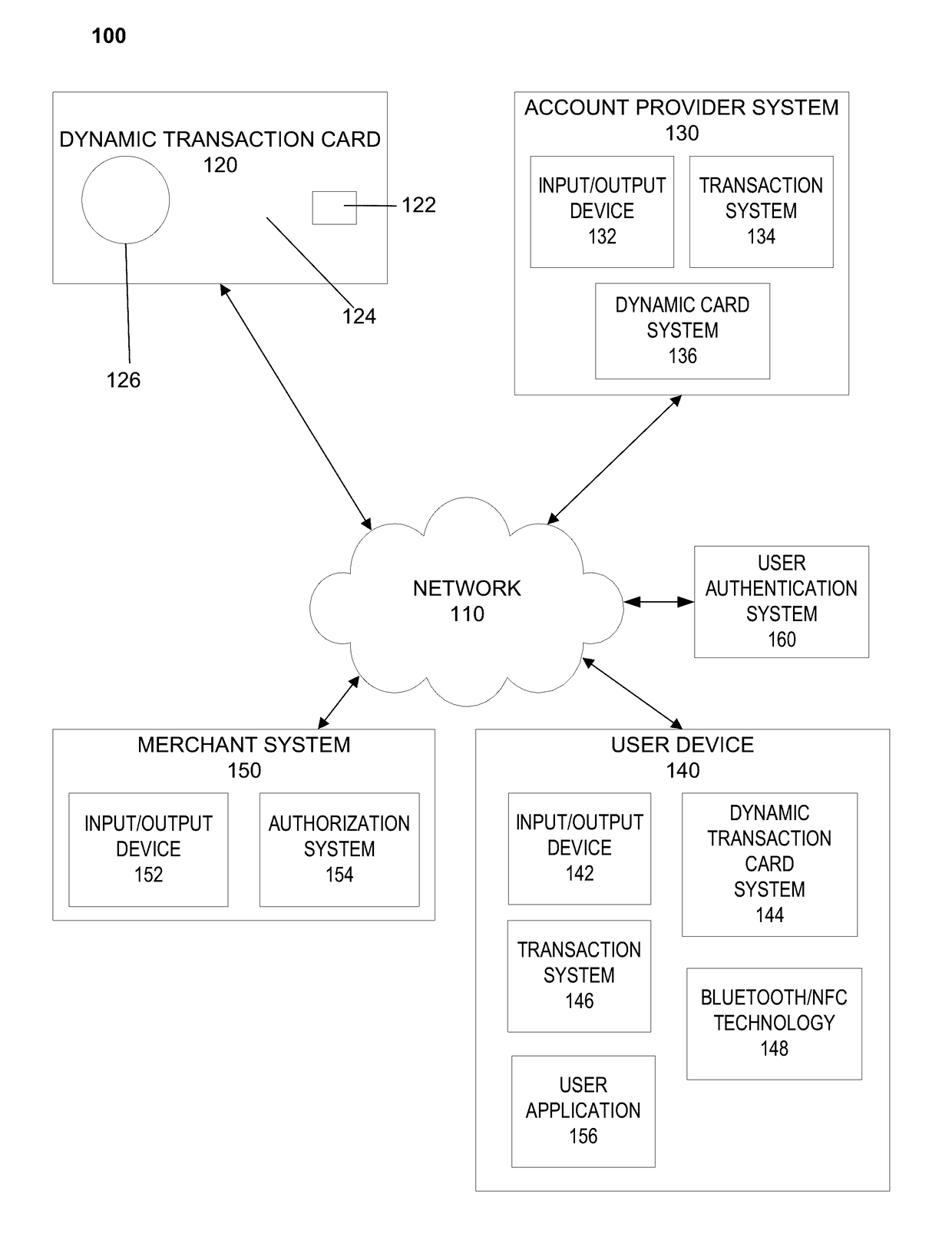
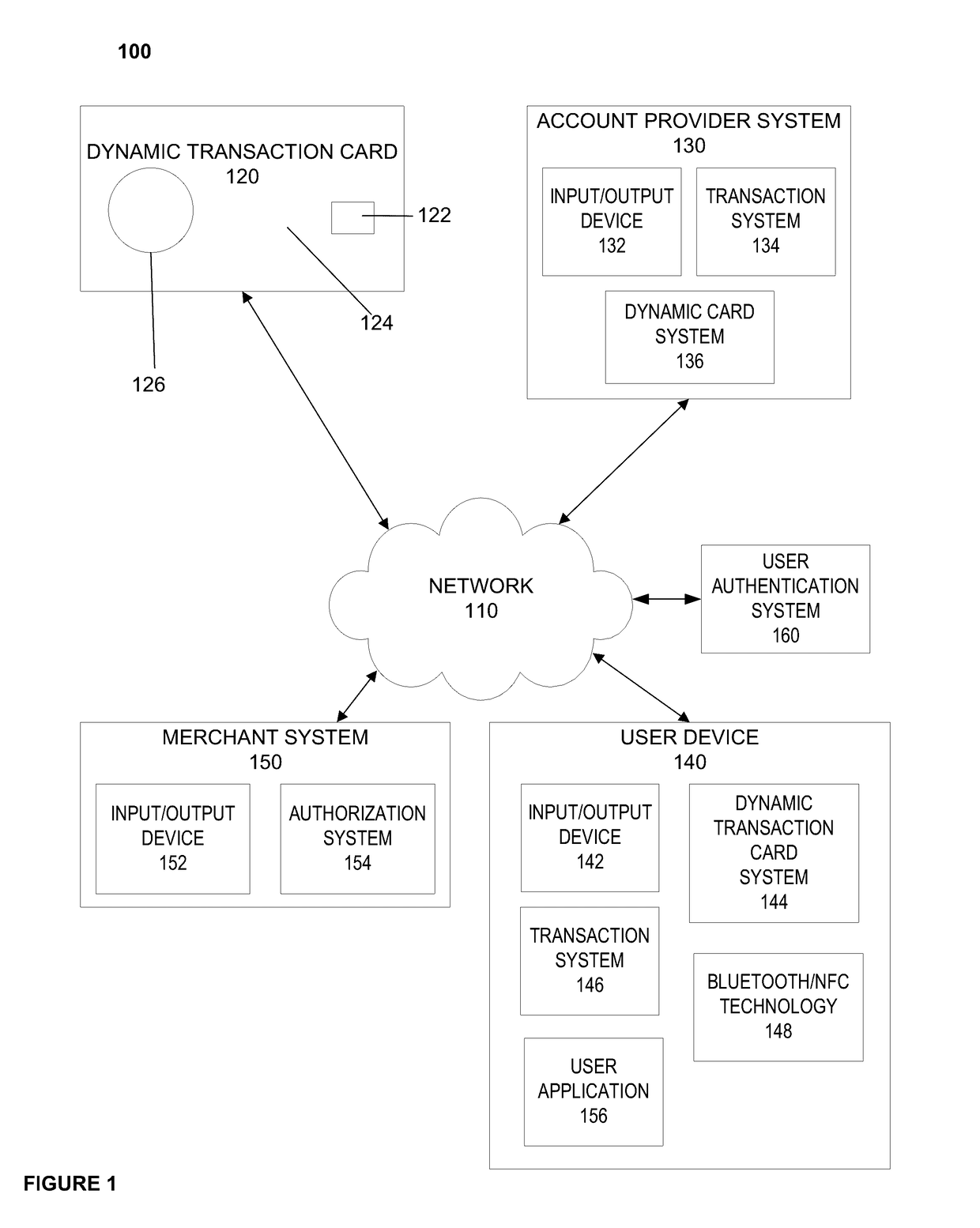
Dynamic transaction card protected by gesture and voice recognition
ActiveUS20170154328A1Connection securityPoint-of-sale network systemsRecord carriers used with machinesMicrocontrollerDot-matrix display
A dynamic transaction card that includes a transaction card having a number of layers, each of which may be interconnected to one another. For example, a dynamic transaction card may include an outer layer, a potting layer, a sensor layer that may be utilized to activate a dynamic transaction card by authenticating the card user as authorized to use the card through user authentication input recognition, which may be gesture and voice recognition processing, a display layer (including, for example, LEDs, a dot matrix display, and the like), a microcontroller storing firmware, Java applets, Java applet integration, and the like, an EMV™ chip, an energy storage component, one or more antenna (e.g., Bluetooth™ antenna, NFC antenna, and the like), a power management component, a flexible printed circuit board (PCB), a chassis, and / or a card backing layer.
Owner:CAPITAL ONE SERVICES
System, method, and apparatus for a dynamic transaction card
ActiveUS9978058B2Add featureConnection securityPayment architectureRecord carriers used with machinesMicrocontrollerDot-matrix display
A dynamic transaction card that includes a number of layers, each of which may be interconnected to one another. For example, a dynamic transaction card may include an outer layer, a potting layer, a sensor layer, a display layer (including, for example, LEDs, a dot matrix display, and the like), a microcontroller / microprocessor storing firmware, Java applets, Java applet integration, and the like, an EMV processor, an energy storage component, one or more antenna (e.g., Bluetooth antenna, NFC antenna, and the like), a power management component, a flexible printed circuit board (PCB), a chassis, and / or a card backing layer. A display layer may include enhanced features such as the use of display components as a barcode generator.
Owner:CAPITAL ONE SERVICES
Dynamic transaction card protected by dropped card detection
ActiveUS20170109730A1Connection securityElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingPayment architectureFree fallingMicrocontroller
A dynamic transaction card that includes a transaction card having a number of layers, each of which may be interconnected to one another. For example, a dynamic transaction card may include an outer layer, a potting layer, a sensor layer that may detect and identify a card free fall and / or subsequent impact, which may trigger a microcontroller to send a mobile notification to a cardholder notifying the user that the card has been dropped, and / or may disable or deactivate the card and / or a user account associated with the card, a display layer (including, for example, LEDs, a dot matrix display, and the like), a microcontroller storing firmware, Java applets, Java applet integration, and the like, an EMV™ chip, an energy storage component, one or more antenna (e.g., Bluetooth™ antenna, NFC antenna, and the like), a power management component, a flexible printed circuit board (PCB), a chassis, and / or a card backing layer.
Owner:CAPITAL ONE SERVICES
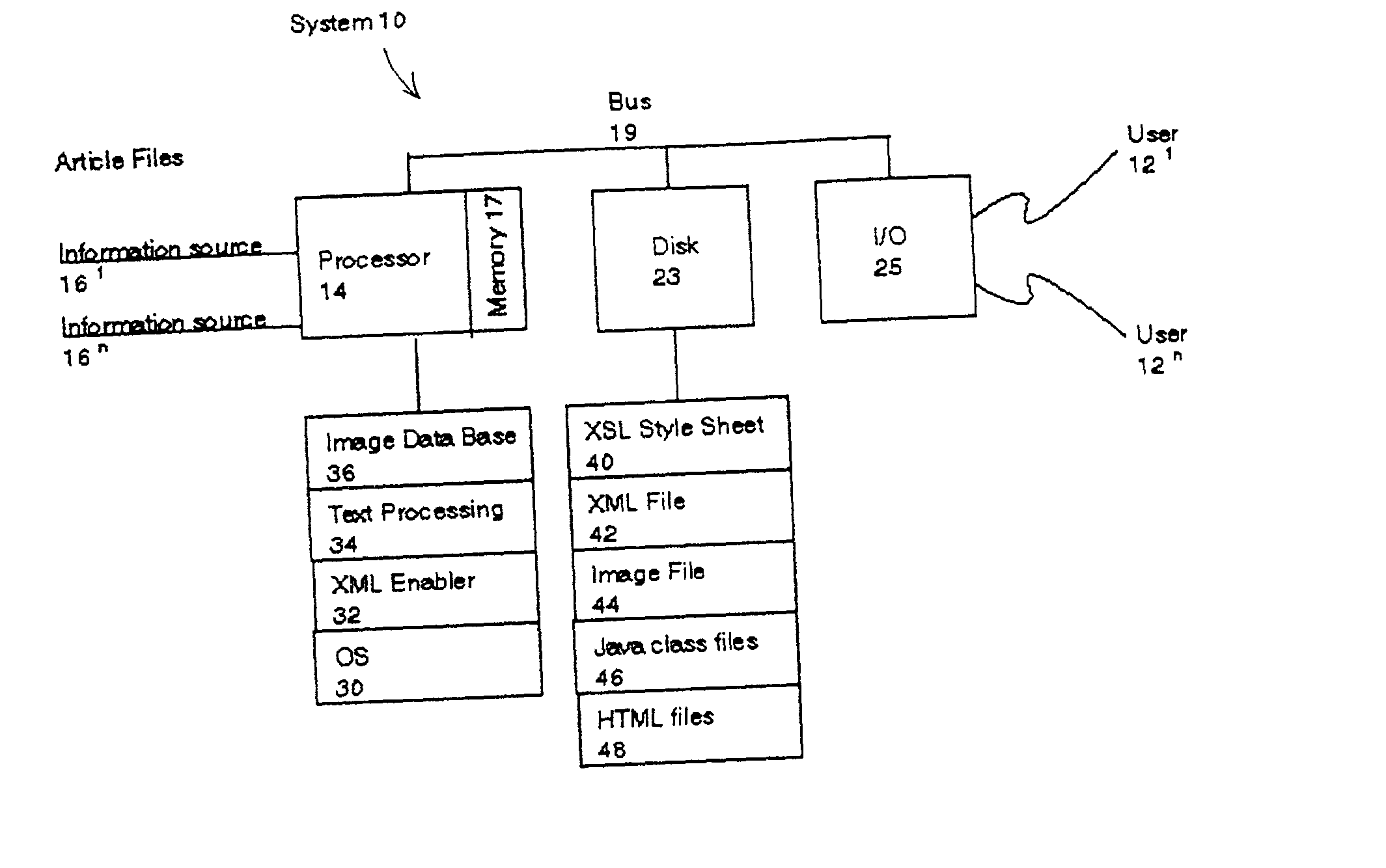
System & method for creating, editing, an on-line publication
InactiveUS20030204814A1Natural language data processingWebsite content managementQuery stringComputation process
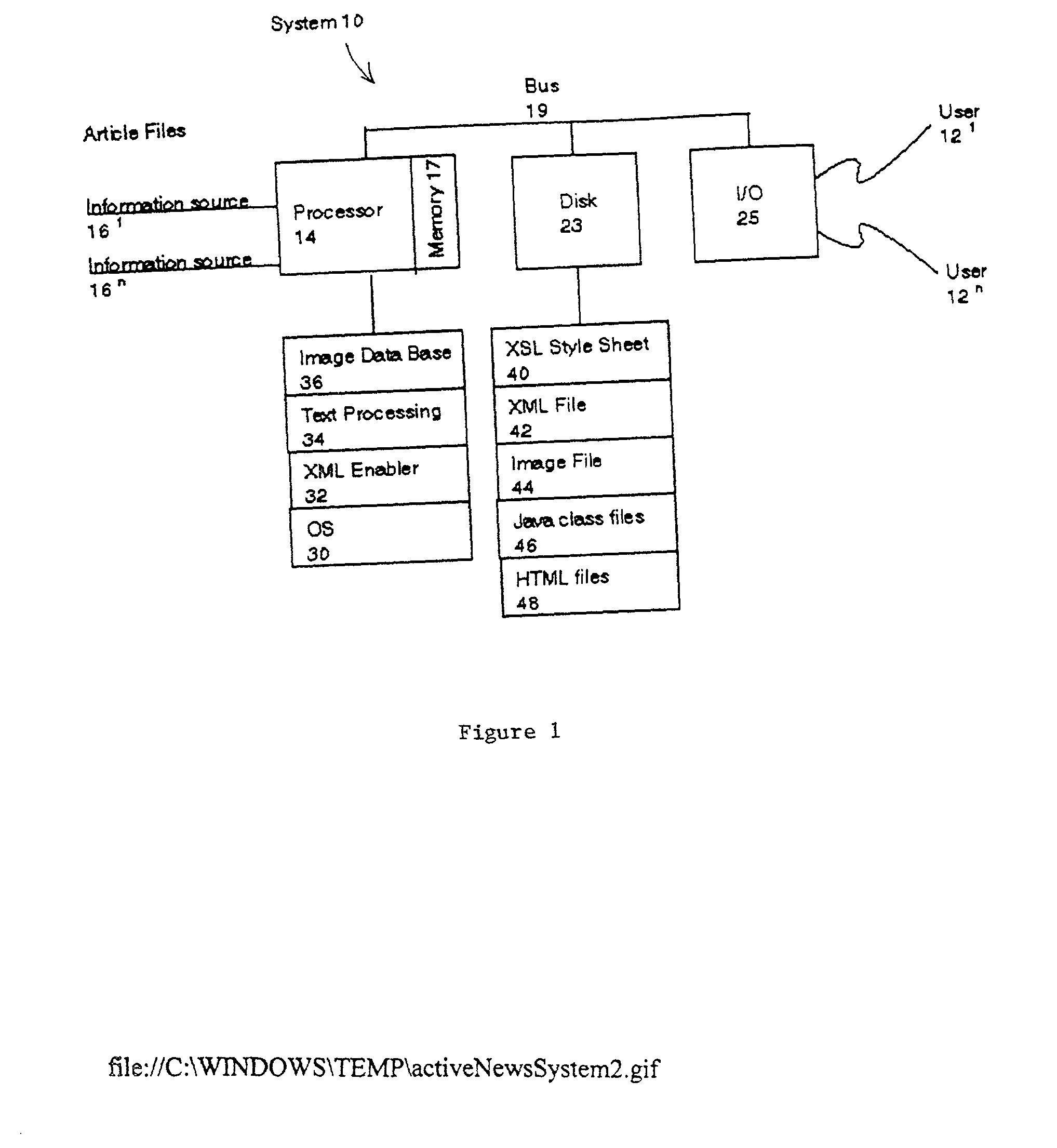
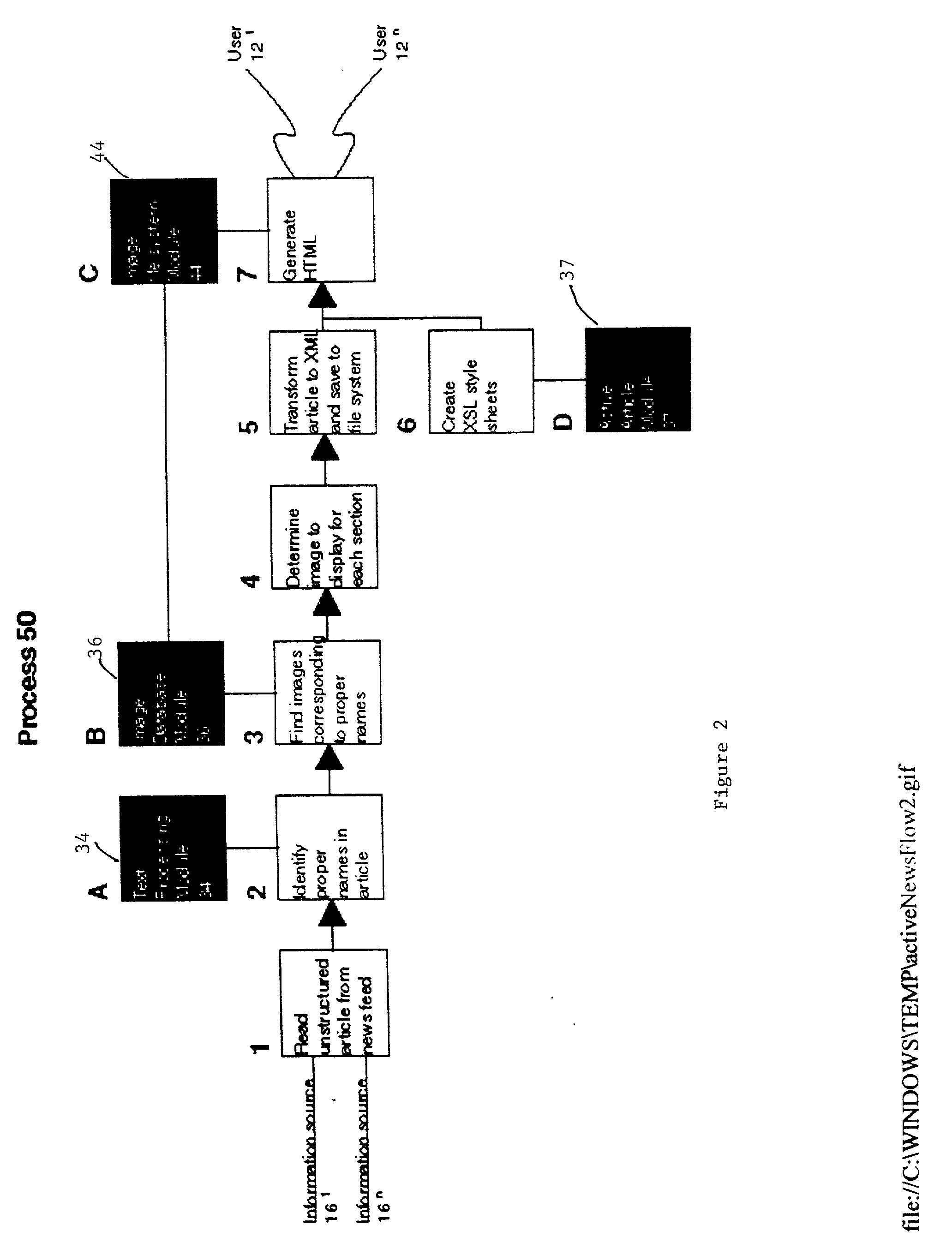
A system and method automatically generate an on-line document from raw text into an engaging, interactive form for a plurality of viewers. Unstructured articles are read from an information feed. A computation process extracts and tags proper names of people, products, organizations, and places and categorizes them. An image database is used to link these proper names with image files. The image database consists of a series of attribute-value pairs for active searching of names. A URL query string is inputted to the database to extract the location of the image in the database file system. An Extensible Markup Language (XML) file is created from the raw text of the article, the list of proper names in the processed data and the image file references. The XML file is stored in a file system. An Extensible Stylesheet Language (XSL) file provides templates containing computational relationships between the text and images. The XML and XSL style sheets are combined to generate a Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) file containing an on-line story of the unstructured articles in a Java Applet which allows the system to provide a variety of interactive behaviors for a final presentation available by a viewer from a browser.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for distributed acquisition of data from computer-based network data sources
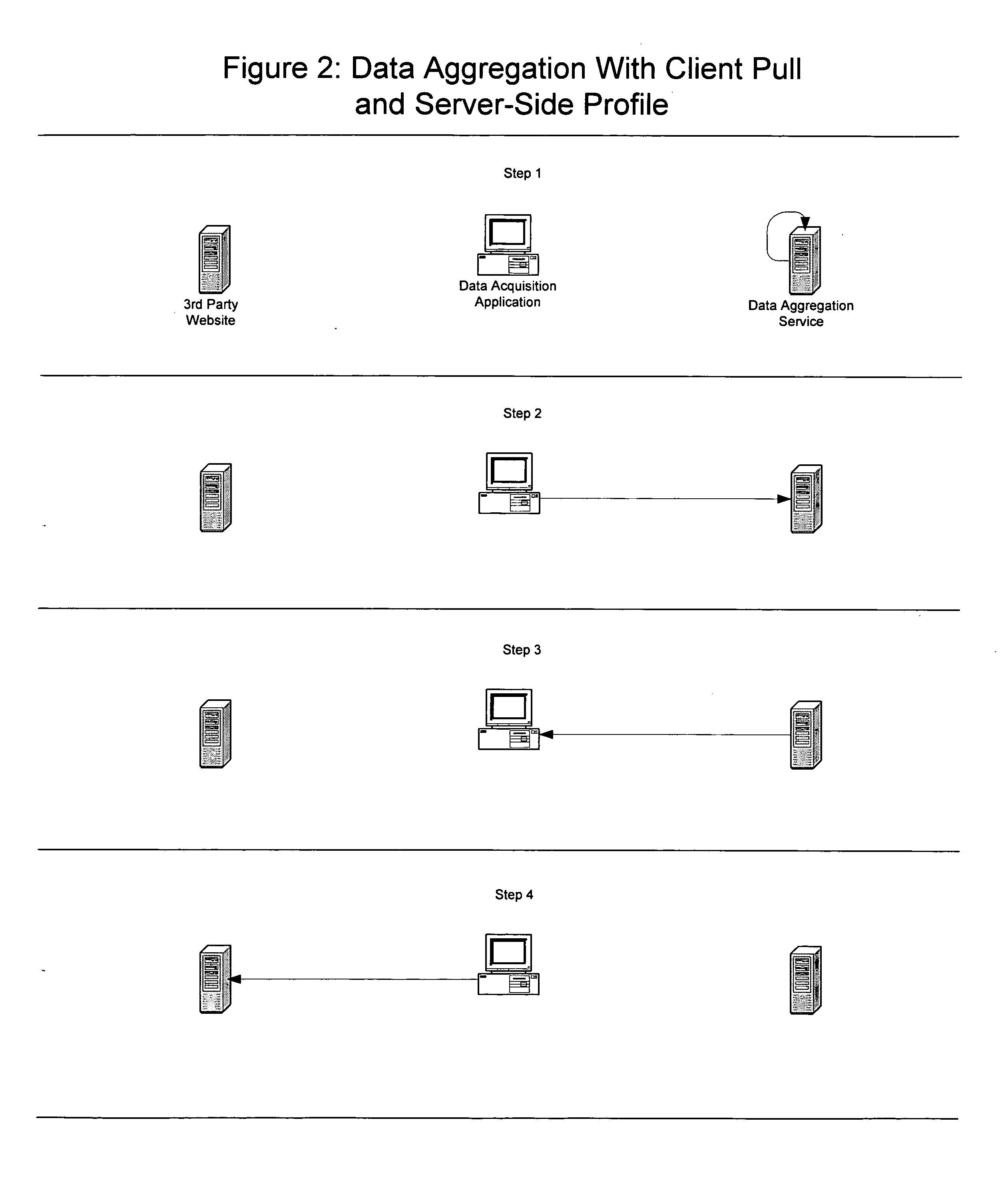
InactiveUS20040117376A1Reduce in quantityReduce effortDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData aggregatorData acquisition
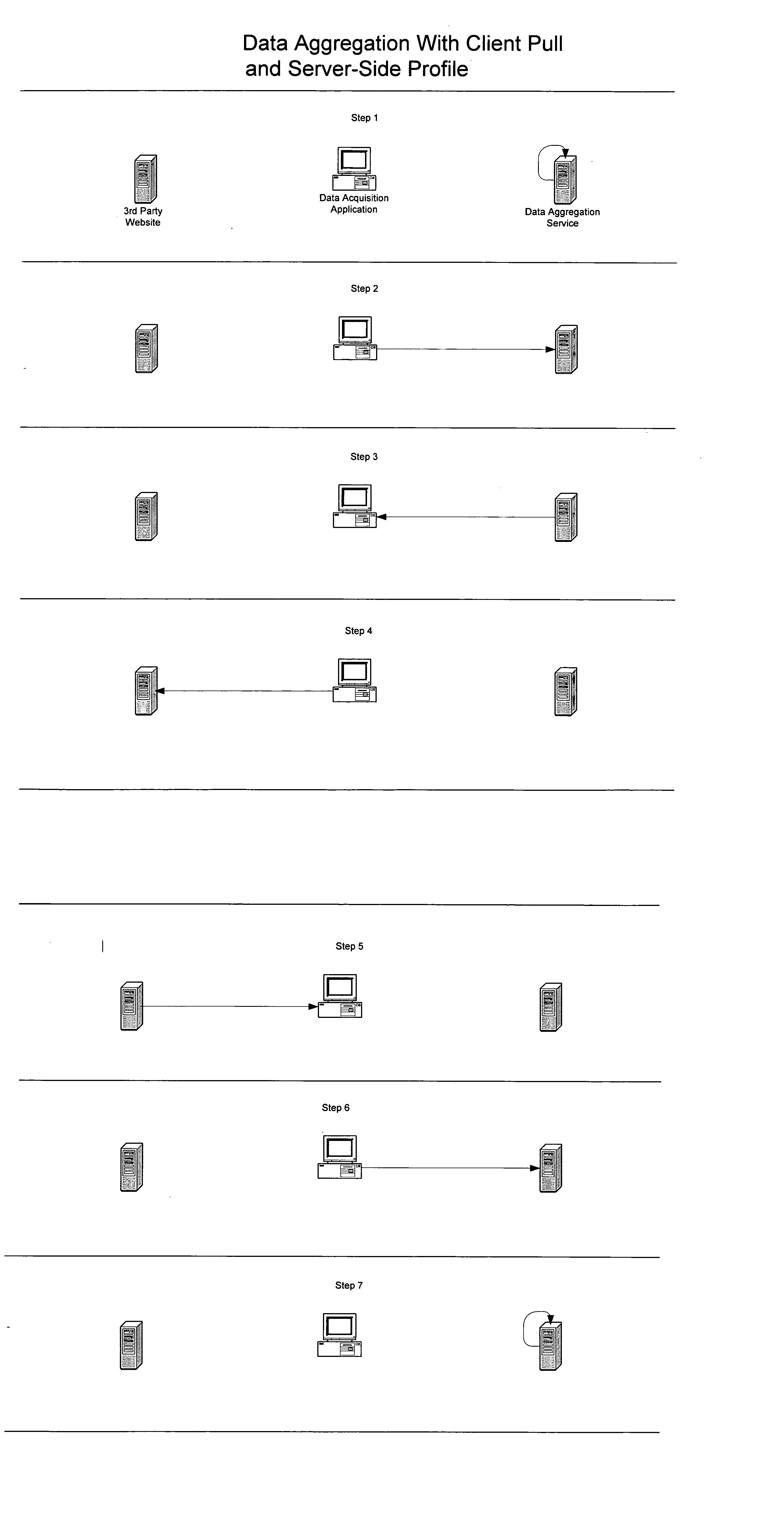
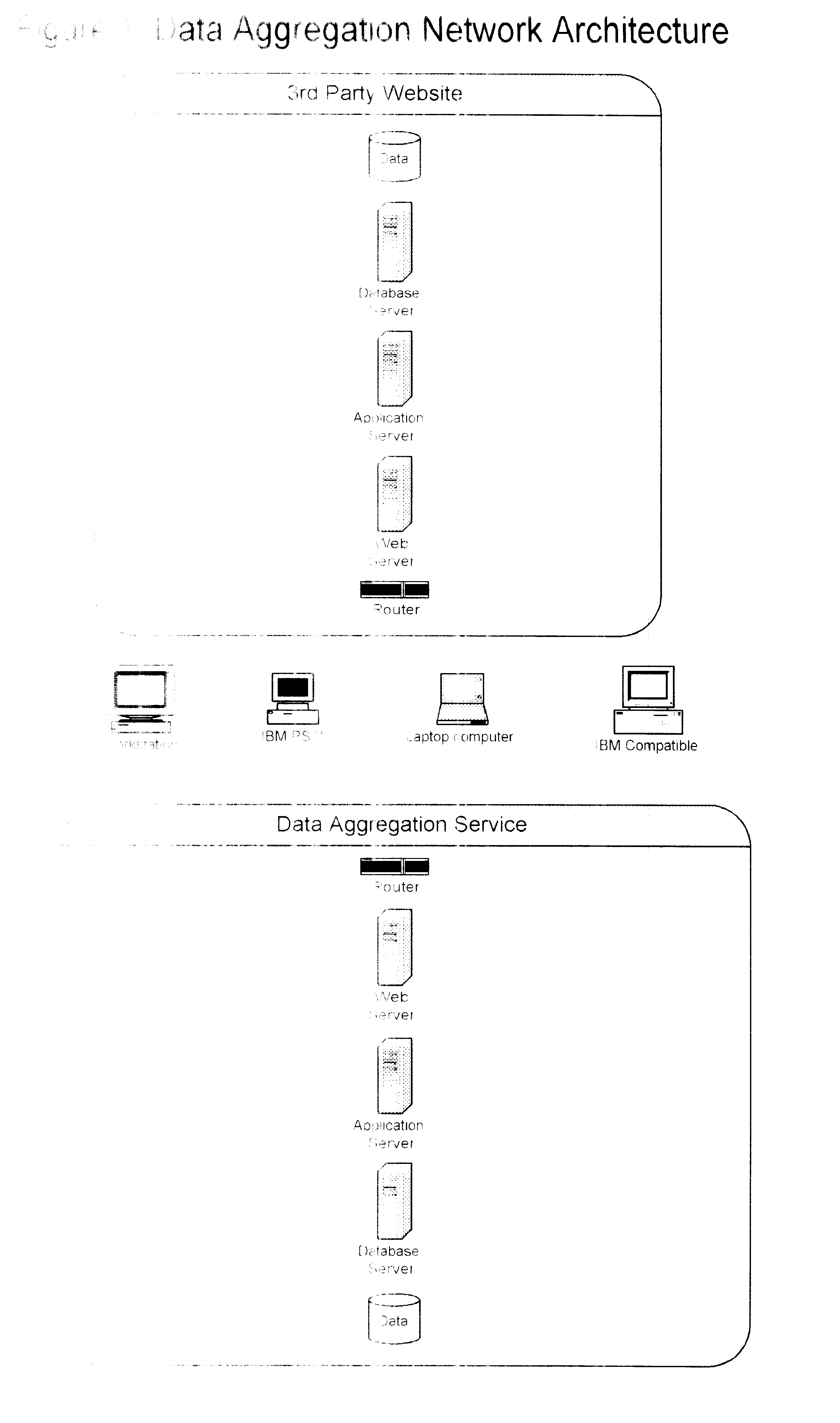
A method for facilitating efficient automated acquisition of data from computer-based network data sources, such as Internet websites, by means of one or more data aggregation servers and a distributed network of one or more client computers (each operated by and / or on behalf of one or more end users), that does not trigger "trespass on chattels" protection, violate copyright protection of database compilations of non-copyright data or allow data sources to easily detect automated data acquisition. In a specific embodiment, each user runs a java applet within their Internet browser that frequently polls a server connected to a database storing the user's preferences. Based on the user's preferences and other data stored in the database, the server generates requests (each to be issued by the client machine to a particular website) and tells the user's applet to issue those requests. Response(s) (or a processed version of those responses) returned to the server may be used by the client machine and / or returned to the server where they may be parsed, stored in the database, made available to the user (and, potentially, other users) and may trigger the server to generate follow-on requests. This method has many potential uses, including, but certainly not limited to, the aggregation of real estate data from numerous websites for homebuyers.
Owner:OPTIMALHOME
System and method for carrying out information-related transactions
InactiveUS6386453B1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionDocument preparationUniform resource locator
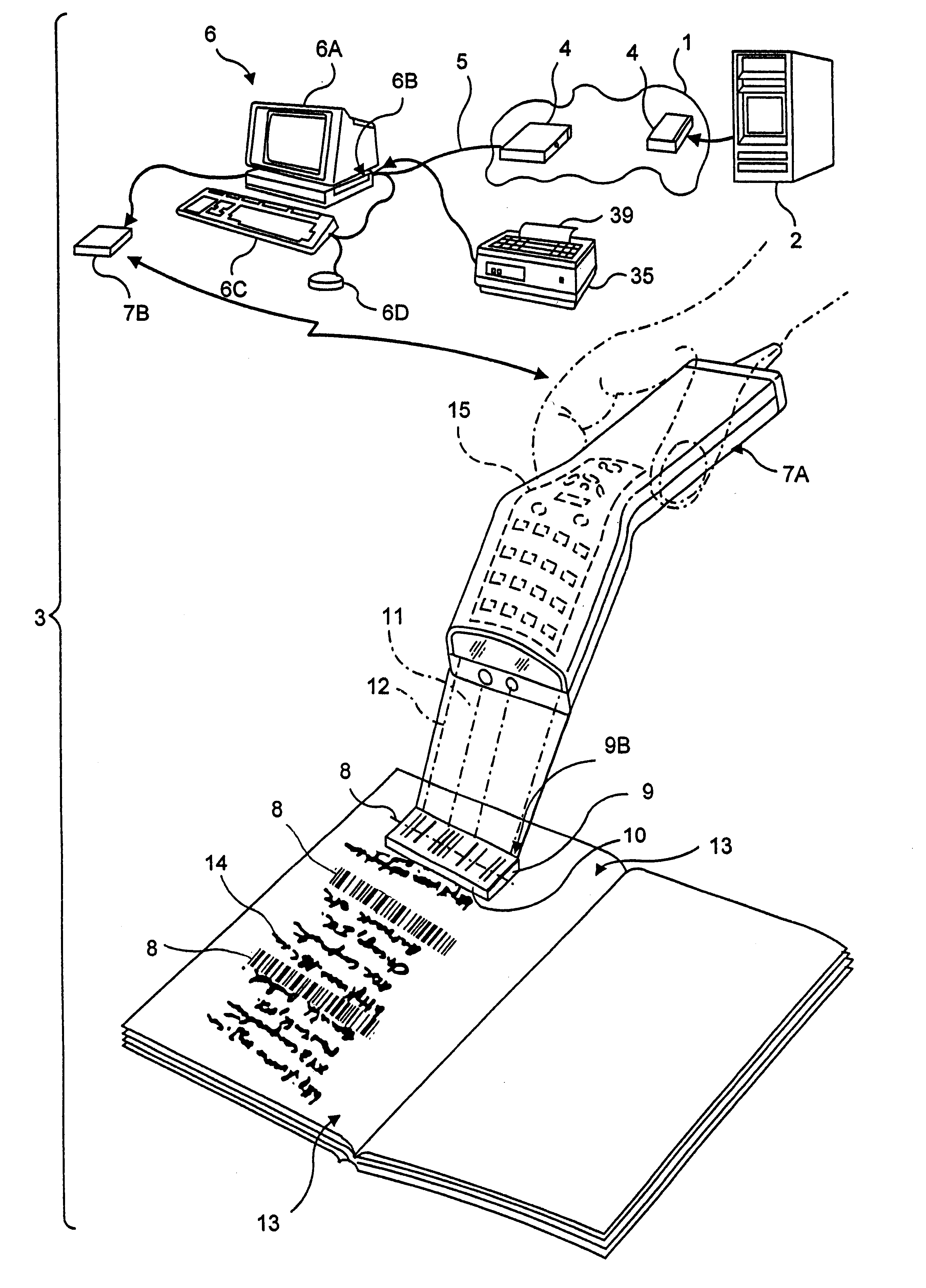
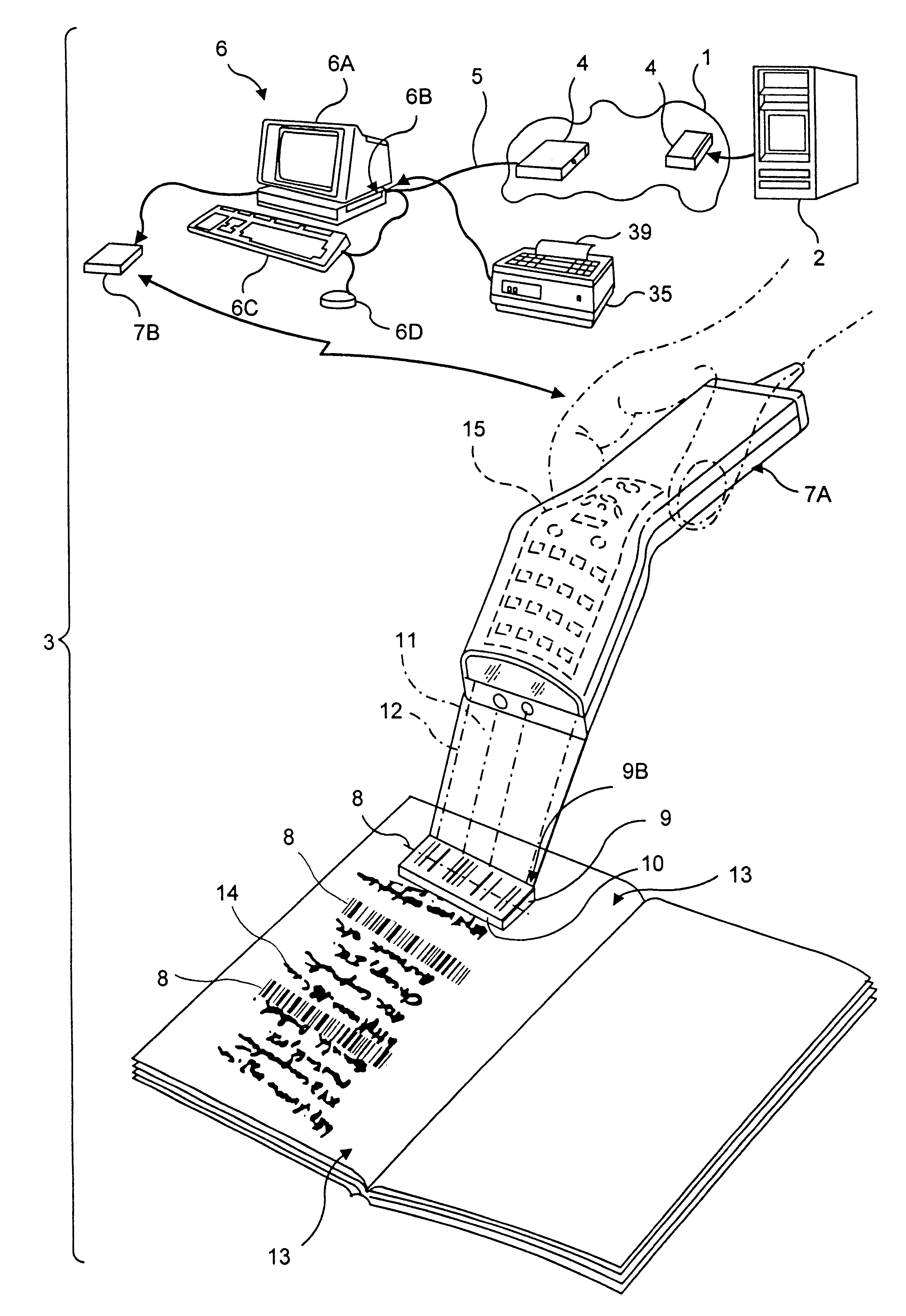
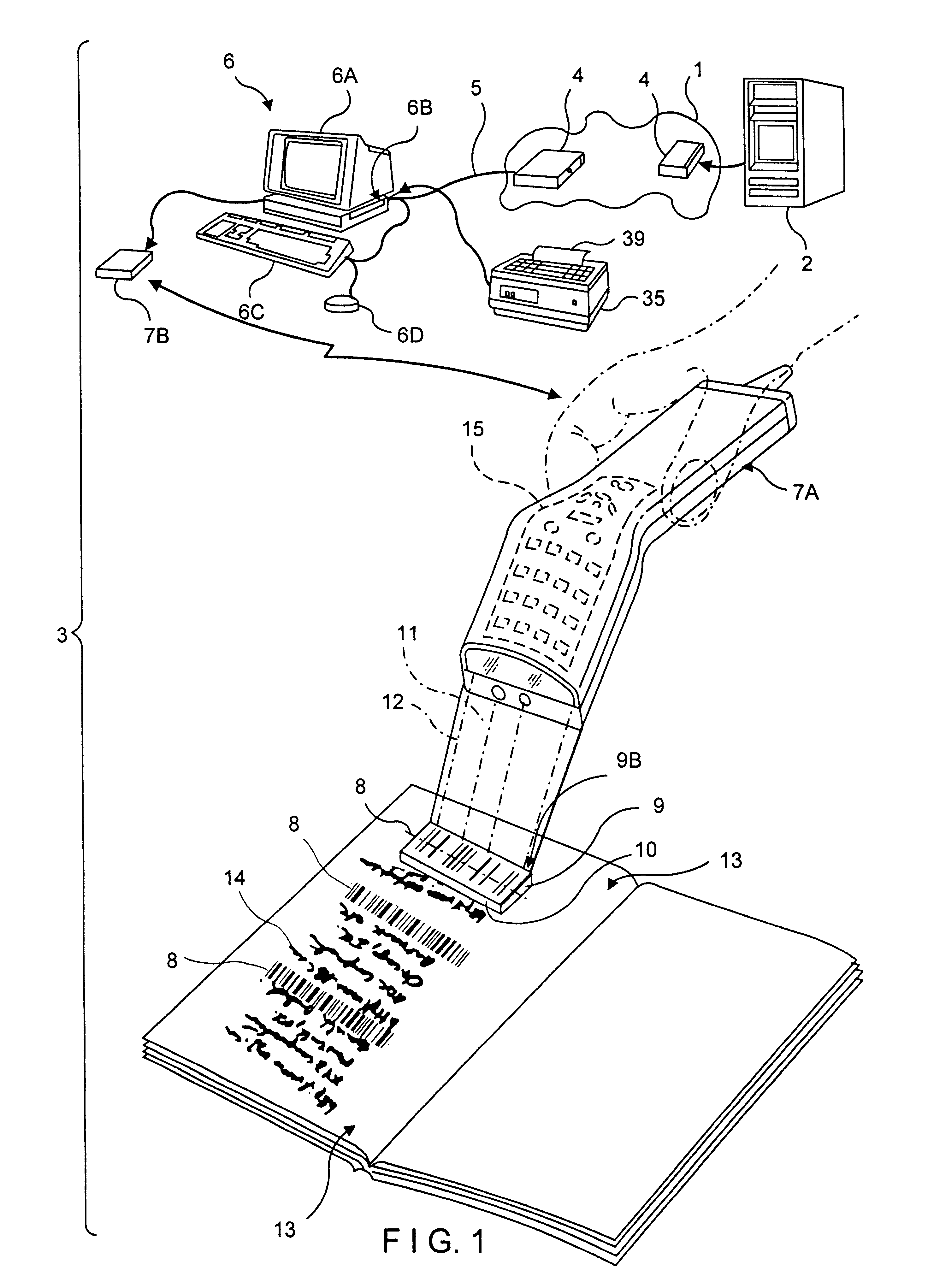
A novel transaction method and system, wherein a transaction Java-Applet is embedded within an HTML-encoded document stored in an HTTP server at predetermined URL. When a code symbol (8) encoded with the URL is read using a code symbol reader (7, 7A) interfaced with a Java-enabled Internet terminal, the corresponding HTML document is automatically accessed and displayed at the terminal, and the transaction Java-Applet initiated for execution so that the customer, consumer or client desiring the transaction can simply and conveniently conduct the information-related transaction over the Internet. The transaction-enabling Internet terminal (3) can be in the form of an Internet kiosk installed in a public location, in the manner as conventional ATMs.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Method of and system for producing transaction-enabling graphical user interfaces at internet-enabled terminals in response to reading bar code symbols pointing to html-encoded documents embedded with java-applets and stored on HTTP information servers
InactiveUS6412699B1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionFinancial transactionUniform resource locator
A code symbol driven system and method are disclosed for producing graphical user interfaces which enable prespecified information-related transactions over the Internet. In the illustrative embodiment, the code symbol reader is integrated with a Java-enabled Internet terminal. The code symbol reader is used to read a code symbol (e.g., magstripe or bar code) encoded with information related to or specifying a predetermined Uniform Resource Locator (URL). The predetermined URL specifies the location of a HTML-encoded document that is stored in an HTTP server and contains one or more transaction-enabling Java-Applets. When the code symbol is read using the code symbol reader, and data representative of the URL is provided to a Java-enabled browser program, the corresponding HTTP document is automatically accessed and displayed at the terminal. The transaction-enabling Java-Applet embedded therein is executed in order to produce a graphical user interface on the display screen of the terminal, thereby enabling the user to carry out data entry and display operations related to the prespecified information-related transaction. The transaction-enabling Internet terminal of the present invention can be in the form of an Internet kiosk installed in a public location, in the manner as conventional ATMs. By virtue of the present invention, the code symbol driven system can be easily deployed for use by the mass population so that they can easily conduct various types of information-related transactions, including electronic-commerce, over the Internet.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Updating objects contained within a webpage
InactiveUS7640512B1Additional drawbackDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)Java applet
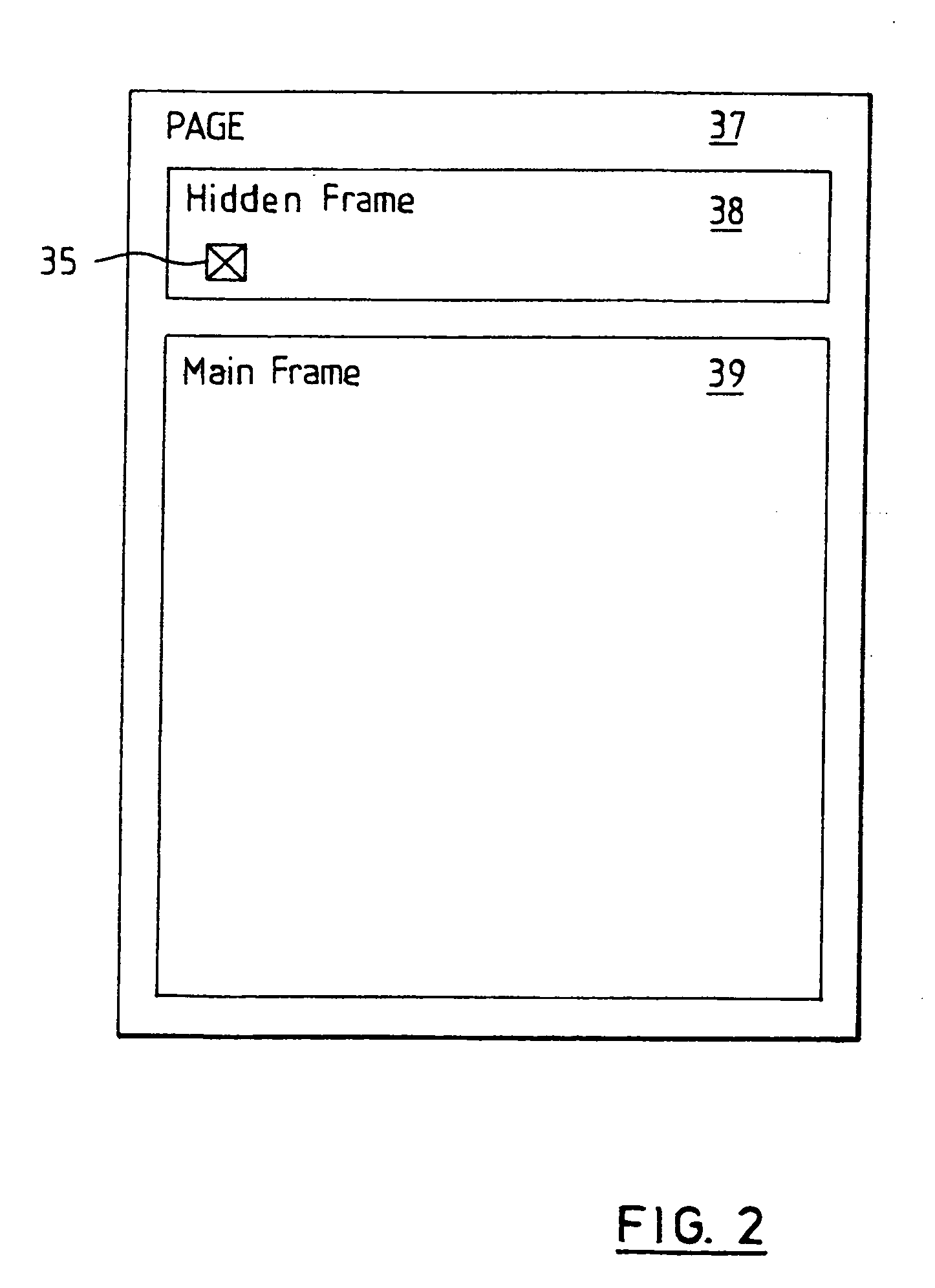
Selectively updating objects of webpage without requiring that the entire web page be refreshed, without Java applets and without requiring user intervention. A webpage is defined to contain a frame and at least one updateable object that is external to the frame. The frame attributes of height and width may each be set to a value of zero, rendering it invisible on the displayed webpage. The frame is configured to periodically request updated data from a server in response to a timer reaching a threshold value. The updated data may comprise a Script or other instruction set for causing the frame to update at least one updateable object. The Script or other instruction set may be executable by the frame without user interaction. The Script may instruct the frame to interact with, for example, an external Script running within the webpage external to the frame. The external Script may interact with and modify the updateable object, which may be an HTML element, without refreshing the web page.
Owner:AUTOMATED LOGIC CORP
Remote access to print job retention
InactiveUS7239409B2Multiple digital computer combinationsElectrographic process apparatusWeb browserJob retention
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for remotely managing and accessing print jobs stored in job retention of a printing device, including displaying, printing, canceling, prioritizing, and otherwise controlling various aspects of the print jobs and / or the print queue. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention makes use of a Java-enabled Web browser on a workstation, a java applet accessible by the Web browser, and an embedded Web server incorporated in a printing device to provide the management and access functions. Rasterized images of the print jobs may also be viewed by using the applet file viewer.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
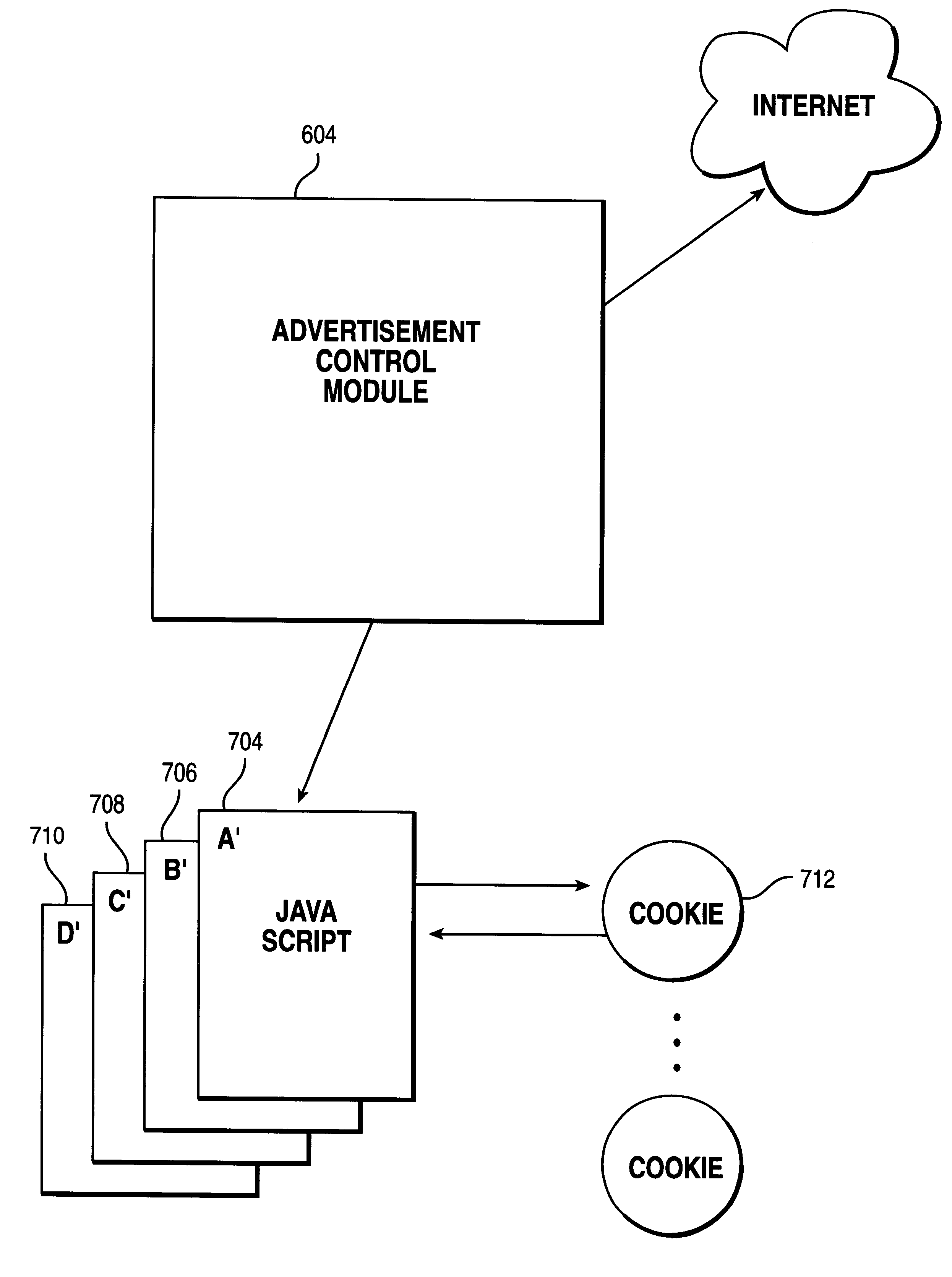
Method and apparatus for detecting actual viewing of electronic advertisements and transmitting the detected information
An apparatus and method for detecting the actual viewing of advertisements contained in Web pages or the like, recording the detected information, and transmitting the recorded information when necessary. The above noted features are accomplished through the use of a Java Applet in combination with JavaScripts (or other Dynamic HTML language) and cookies.
Owner:SAP AG
Approach to provide self-protection function to web content at client side
ActiveUS7475152B2Increase flexibilityProvide securityComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsProtection mechanismApplication software
The present invention utilizes agents embedded in content delivered to clients across a network to provide client-side security for the data delivered to a client. These embedded agents provide application-specific protection for the delivered content in which they are embedded and eliminate the need for using plug-ins for security functions. Different agents, e.g. programs such as Java applets, are configured having a variety of different client or application specific protection mechanisms, and the agents are dynamically configured, e.g. selected, in accordance with the application, the client to be protected or other environment criteria. Once the agent has been appropriately configured, the agent is embedded in the content, and the content is delivered to the client. Once delivered, the embedded agent is uploaded to the client and executed, providing the configured security protection at the client side for the content in which it was embedded.
Owner:IBM CORP
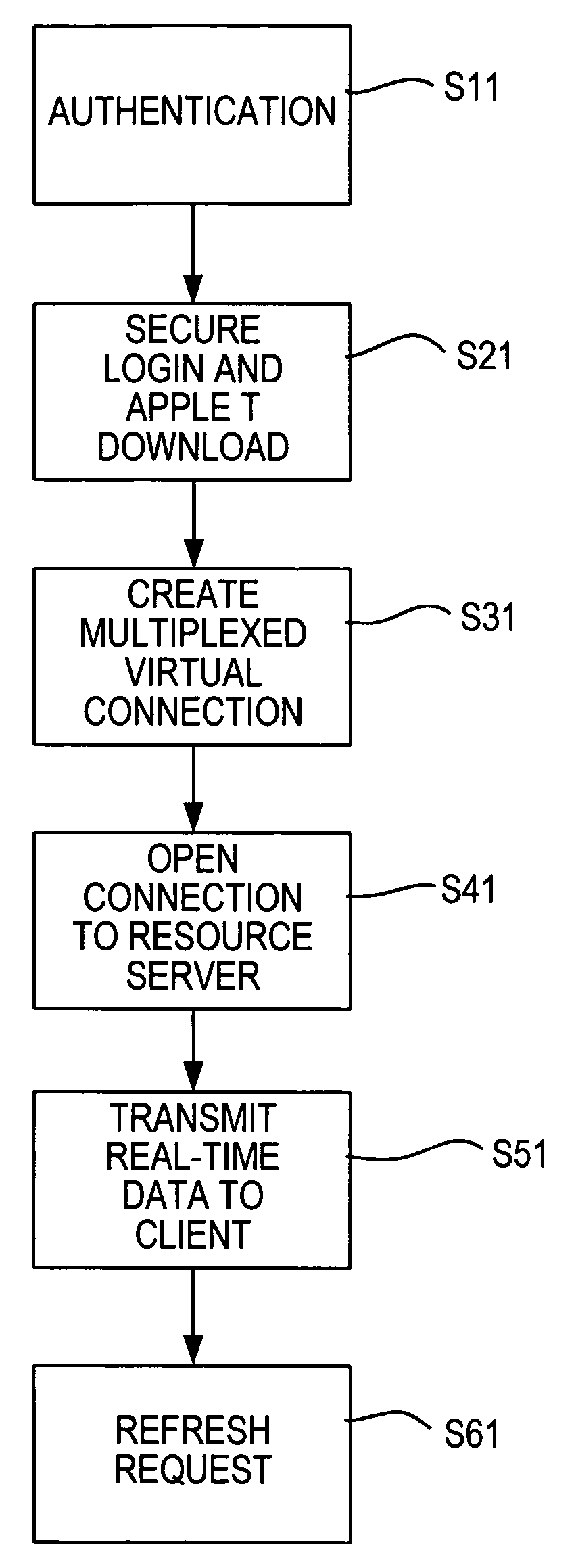
Asynchronous hypertext messaging system and method
InactiveUS20050086295A1FinanceData switching by path configurationCommunications systemReal-time data
An asynchronous hypertext messaging system and method are disclosed. The system and method use existing hypertext transfer protocols and is capable of transmitting real-time asynchronous data between server and client regardless of firewalls or proxy servers implemented at the client or the server. In a communication system comprising a client and server interconnected by an internet, initial authentication is performed initially between the server and the client. A secure log in is performed by the client with the server in conjunction with a possible java applet download. The communication server then initiates a multiplexed virtual connection between the server and the client and transmission of asynchronous real-time data can occur over the virtual connection. The virtual connection is periodically refreshed by a request issued from the java applet.
Owner:REFINITIV US ORG LLC
Method and system for updating/reloading the content of pages browsed over a network
InactiveUS20050108418A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsClient agentReal-time web
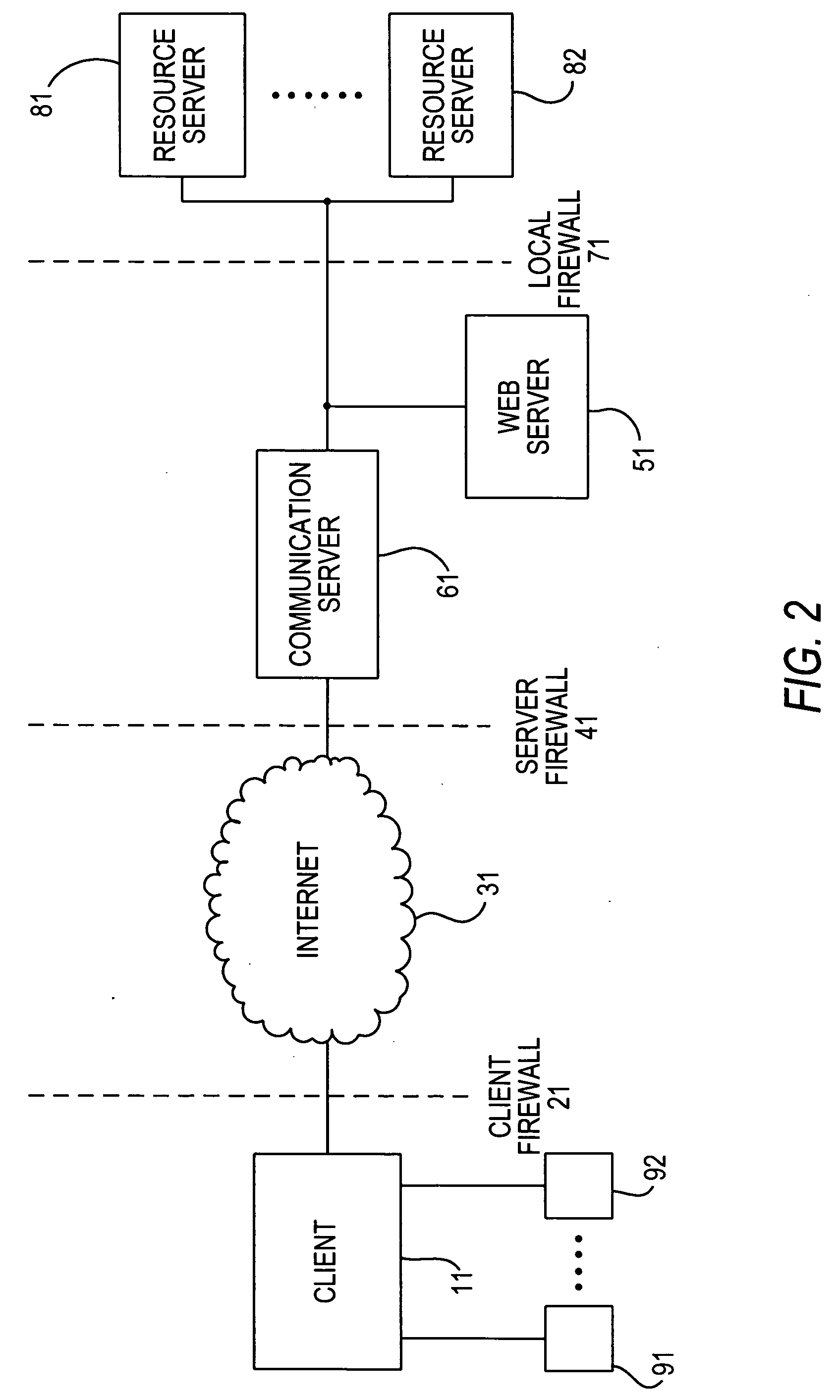
The present invention provides a real-time means of automatically updating the content of a user pre-selected set of web pages without any activity required on the part of the user to initiate each web page updating procedure. This is achieved by incorporating into a browser of a user's computing device software code that is responsive to real-time web page content change notification messages to cause the browser to reload a URL identified in the change notification message. Alternatively, the software code may comprise a Java applet or the like embedded in a downloaded web page that is responsive to change notification messages to cause the browser to reload a web page whose URL is identified in the message or to reload a currently displayed web page. The change notification messages are generated by applications whose web page content has changed and the messages are relayed in real-time to push client agents comprising said software code by a message broker agent. The invention offers many advantages including reducing unnecessary web page reload operations and thus reducing network traffic.
Owner:IBM CORP
System for detecting vulnerabilities in web applications using client-side application interfaces
ActiveUS20060195588A1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionNetwork serviceUser defined
An improved method and apparatus for client-side web application analysis is provided. Client-side web application analysis involves determining and testing, using client-side application interfaces and the like, data input points and analyzing client requests and server responses. In one embodiment, a security vulnerability analyzer is employed to analyze web page content for client-side application files, such as Flash files and Java applets, extract web addresses and data parameters embedded in the client-side application file, and modify the data parameters according to user-defined test criteria. The modified data parameters are transmitted as part of a request to a respective web server used to service the client-side application files. The security vulnerability analyzer analyzes the response from the server to ascertain if there are any security vulnerabilities associated with the interface between the client-side application file and the web server.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method and apparatus for providing security certificate management for Java Applets
InactiveUS6023764ADigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionWeb browserWeb service
The present invention defines a means for establishing a secure connection between a Java Applet and a secure web server for protocols other than Https via the use of a Java Security Service. More specifically, the present invention uses the web browser's installed certificates to setup and establish an encrypted session between the Java Applet and the secure web server. The secure connection is then used to retrieve the certificates required by the Java security service.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for carrying out electronic-commerce transactions using web documents embodying electronic-commerce enabling applets automatically launched and executed in response to reading url-encoded symbols pointing thereto
A novel electronic-commerce enabling method and system are disclosed, wherein an electronic-commerce enabling Java-Applet is embedded within an HTML-encoded document stored in an HTTP server at predetermined URL. When a code symbol (e.g., magstripe or bar code) encoded with the URL is read using a code symbol reader interfaced with a Java-enabled Internet terminal, the corresponding HTTP document is automatically accessed and displayed at the terminal, and the electronic-commerce enabling Java-Applet initiated for execution so that the customer, consumer or client desiring to conduct an electronic-commerce transaction can simply and conveniently conduct electronic-commerce over the Internet. The electronic-commerce enabling Internet terminal can be in the form of an Internet kiosk installed in a public location, in the manner as conventional ATMs. By virtue of the present invention, universal transaction machine (UTMs) can be easily deployed for use by the mass population so that they can easily conduct various types of electronic-commerce over the Internet.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Secure file transfer system
InactiveUS6978378B1Unauthorized memory use protectionAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSecure transmissionUser input
A secure file transfer system which, in its preferred embodiments, uses a Java applet sent to a client computer from a server computer to double encrypt files sent from the client computer to the server computer. Once a file is sent to the server, the system notifies a recipient that a secure document awaits pickup. The system preferably uses a public shared key agreement scheme for one method of encryption and an elliptical encryption scheme for the other. The applet comes to the client computer with a shared secret key for the public key scheme and all parameters required for the elliptical encryption scheme. Upon receiving a request for secure transfer, the server sends the applet with the encryption parameters to the client machine, which must be running a client-side application or a Java-enabled browser. The applet prompts the user for the file to be transferred and encrypts the file with the elliptical encryption method. The applet then sends the encrypted file to the server in blocks, encrypting each block with the public key scheme as it is sent. The system decrypts the blocks and reassembles them into the encrypted file and then notifies the recipient of the file's presence.
Owner:BLUETIE
System and method for accessing internet-based information resources by scanning Java-Applet encoded bar code symbols
InactiveUS6338434B1Simple methodEasy accessCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsInformation resourceBarcode
A novel hand-supportable wireless Internet-enabled terminal is disclosed, wherein a transaction-enabling Java-Applet is embedded within 2-D bar code symbol. An HTML-encoded document and code associated with the transaction-enabling Java-Applet is created and stored in an HTTP server for use in enabling a predetermined information-related transaction. When a bar code symbol encoded with a transaction-enabling Java-Applet is read using the hand-supportable wireless Internet-enabled terminal, the corresponding code on the HTTP Server is automatically accessed and one or more HTML-encoded documents are displayed at the hand-supportable wireless Internet-enabled terminal, and the transaction-enabling Java-Applet initiated for execution so that the customer, consumer or client desiring the transaction can simply and conveniently conduct the information-related transaction over the Internet.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
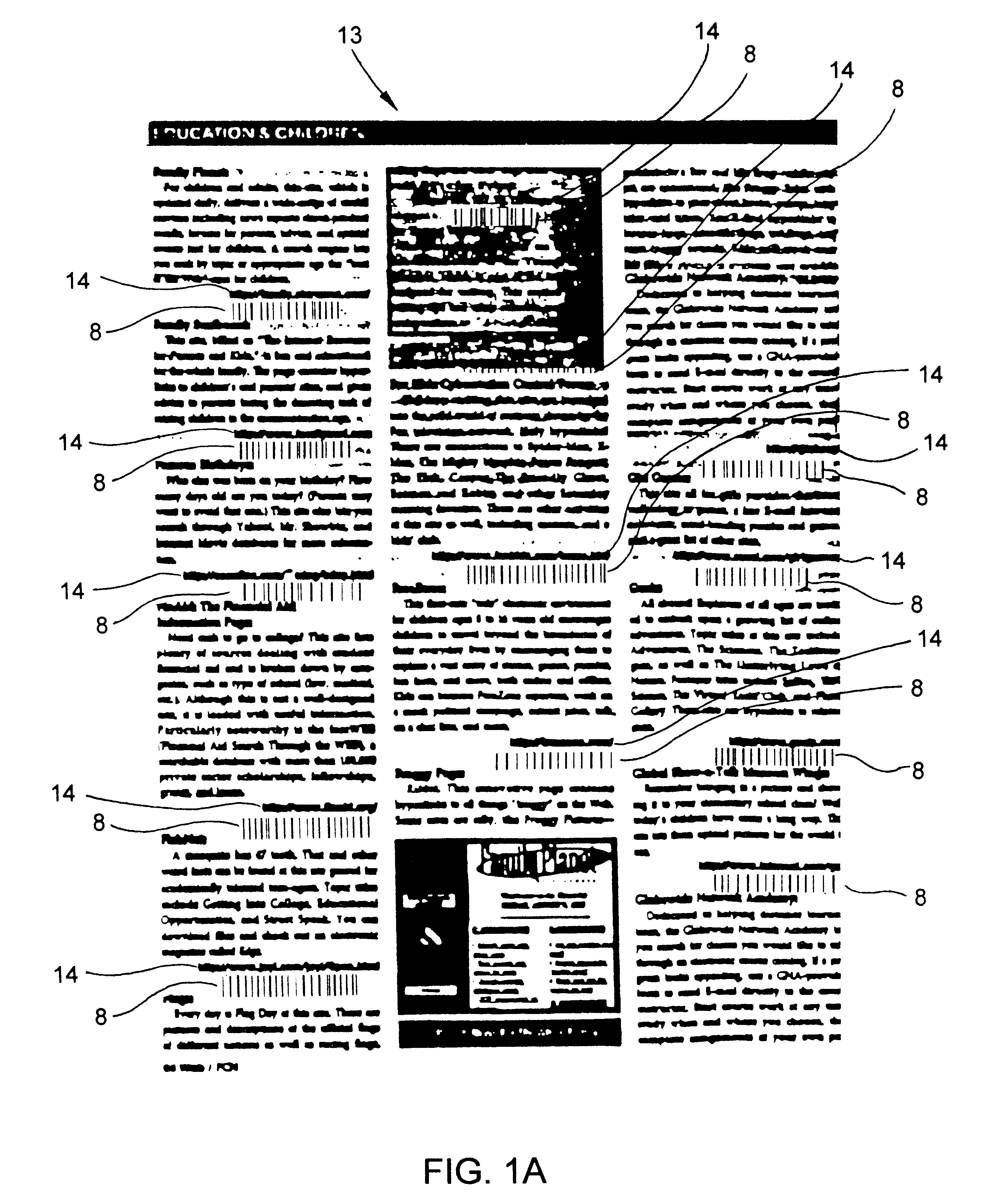
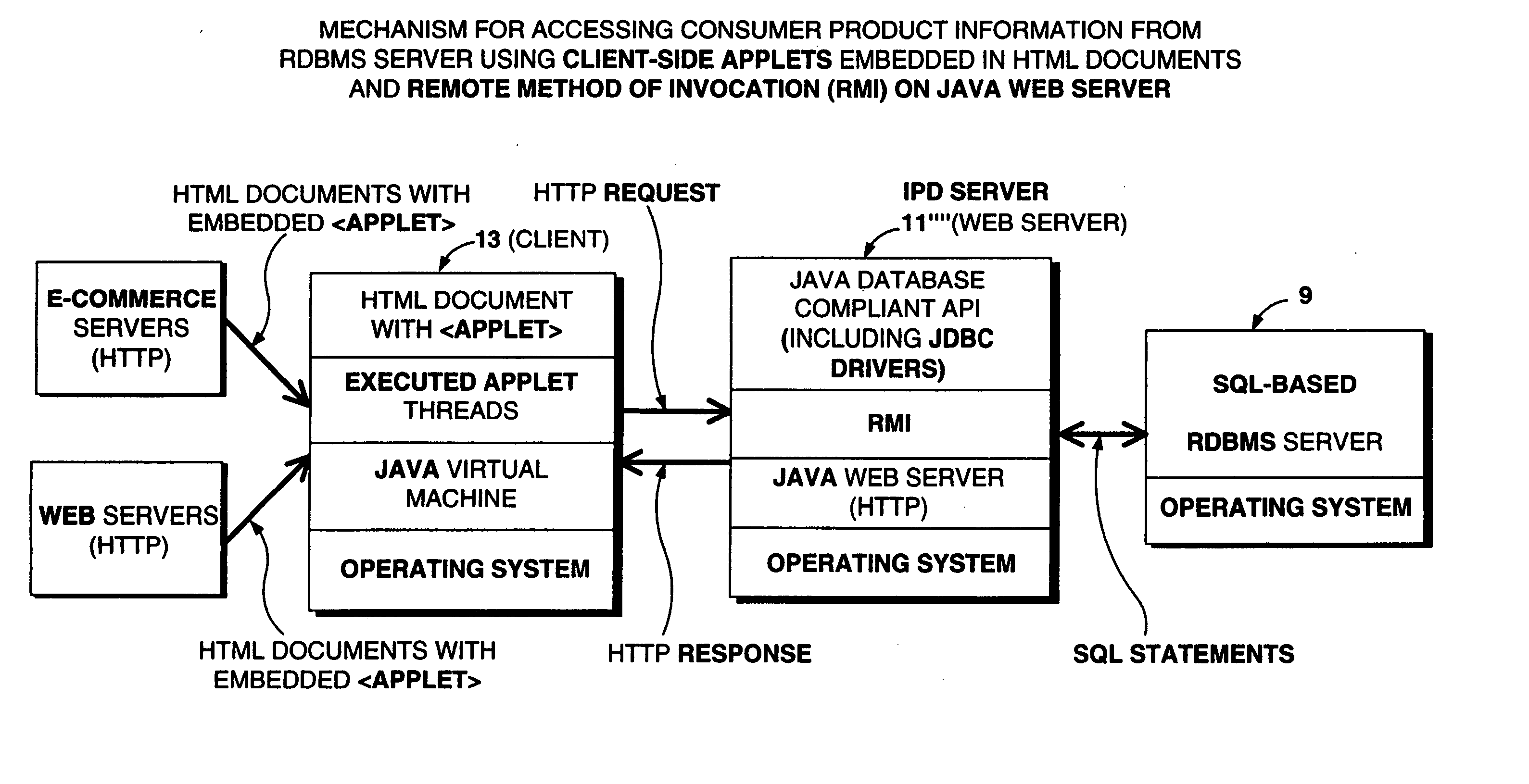
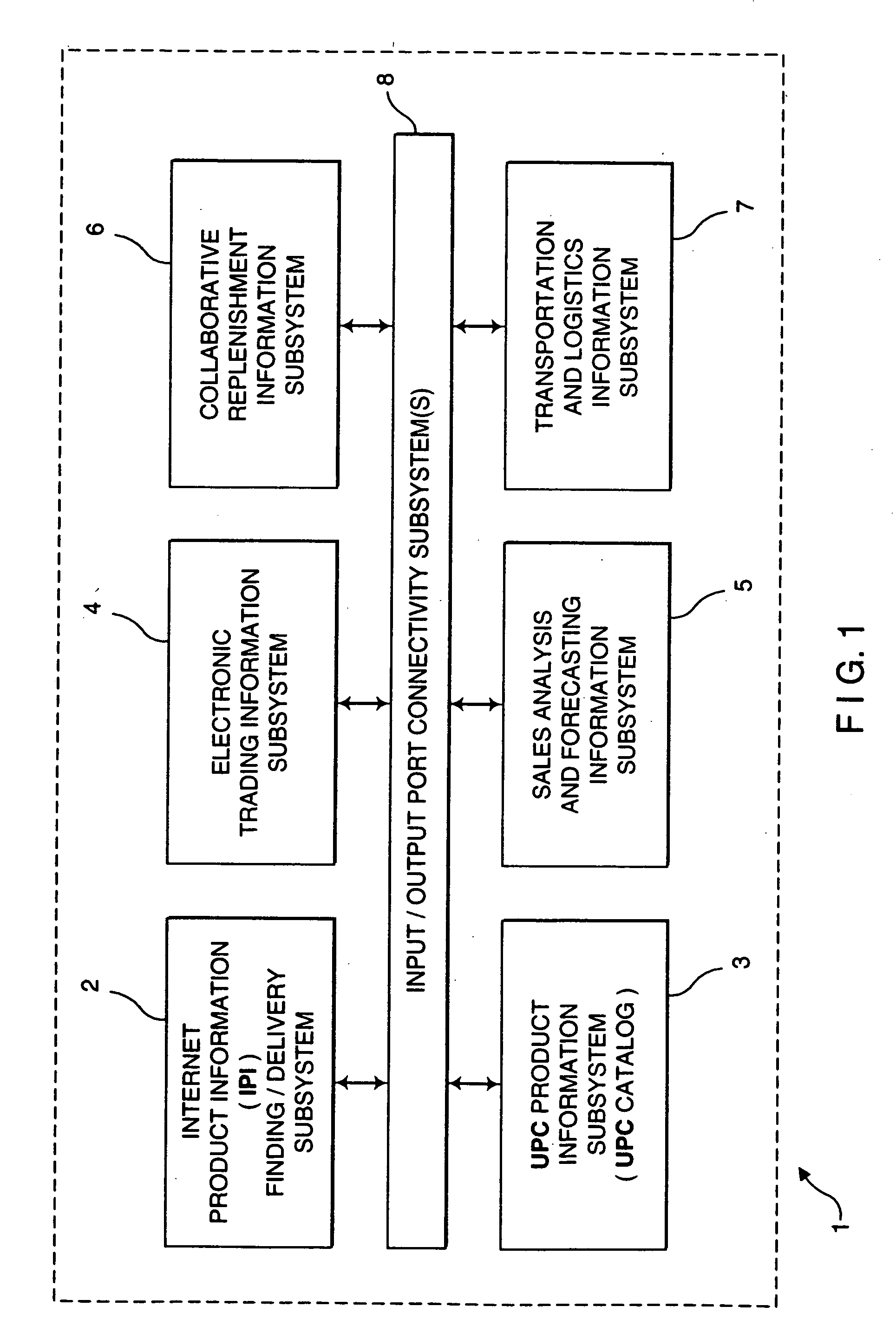
Method of and system for accessing consumer product related information at points of consumer presence on the World Wide Web(WWW) at which UPN-encoded java-applets are embedded within HTML-encoded documents
InactiveUS20060212361A1High acceptanceEasy to disassembleDigital data information retrievalAdvertisementsAlternative technologyPoint of presence
Method of and system for delivering consumer product related information to consumers over the Internet. The system and method involves creating an UPN-encoded Consumer Product Information (CPIR) enabling Applet for each consumer product registered within a manufacturer-managed UPN / URL database management system. Each CPIR-enabling Applet is encapsulated within an executable file and then stored in the UPN / URL database management system. Each CPIR-enabling Applet is searchable and downloadable by, for example, (1) retailers purchasing products from an electronic-commerce enabled product catalog, (2) advertisers desiring to link consumer product information to Web-based product advertisements, or (3) anyone having a legitimate purpose of disseminating such information within the stream of electronic commerce. After downloading and extraction from its encapsulating file, the CPIR-enabling Applet is embedded within an HTML-encoded document associated with, for example, an EC-enabled store, on-line auction site, product advertisement, Internet search engine or directory, and the like. Upon encountering such an Applet-encoded HTML document on the WWW, the consumer need only perform a single mouse-clicking operation to automatically execute the underlying CPIR-enabling Applet (on either the client or server side of the network), causing a UPN-directed search to be performed against the manufacturer-defined UPN / URL Database, and the results thereof displayed in an independent Java GUI, without disturbing the consumer's point of presence on the WWW. Preferably, the CPIR-enabling Applets are realized using Java™ technology, although it is understood that alternative technologies can be used to practice the system and methods of the present invention.
Owner:PERKOWSKI THOMAS J
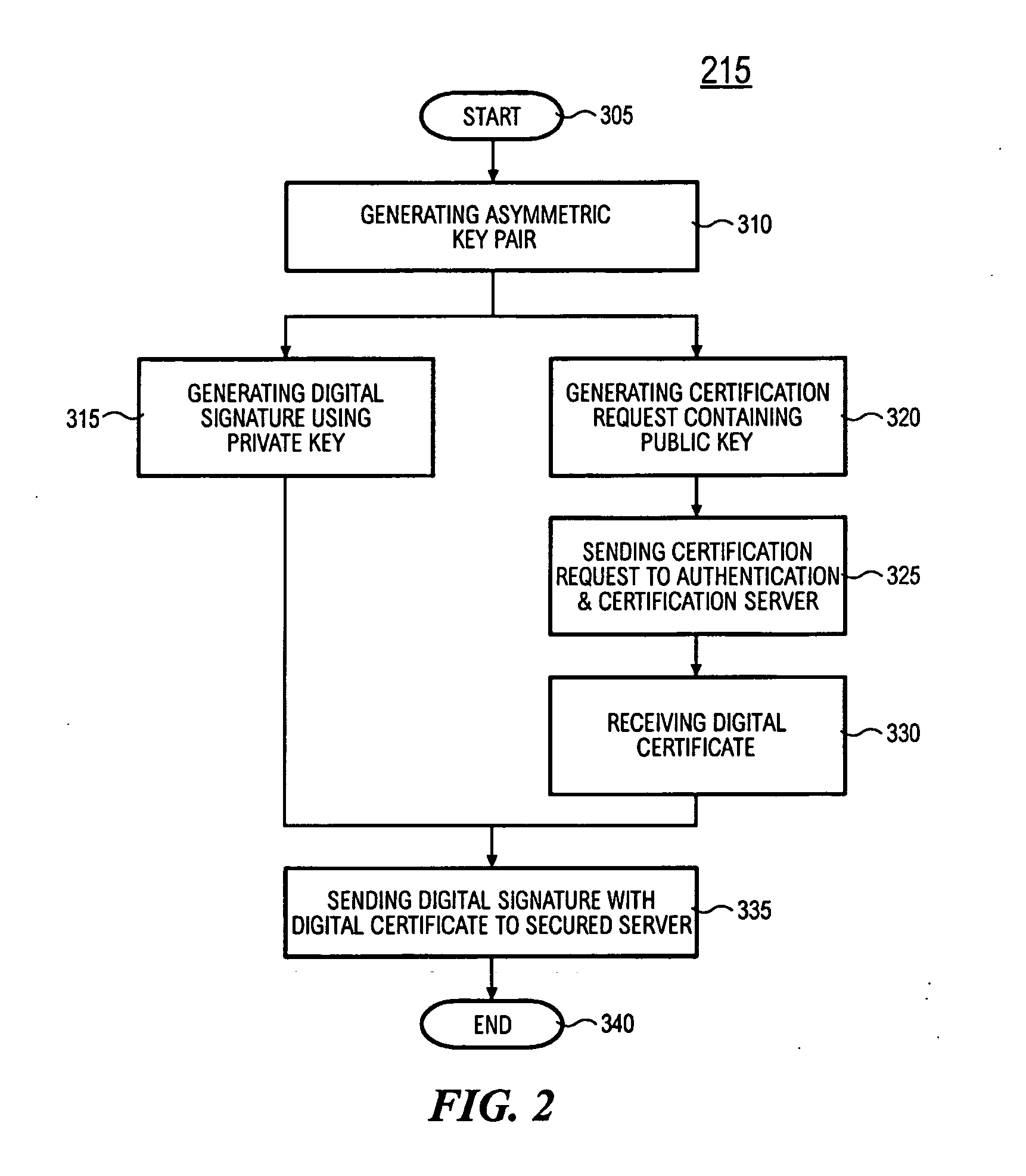
System and method for implementing digital signature using one time private keys
InactiveUS20060020811A1Digital data processing detailsPublic key for secure communicationWeb browserDigital signature
The OTPK module 40 is essential to the present embodiment. It may be considered to be a software module implemented on the signing entity 20. The OTPK module 40 may be dynamically downloaded for use or implemented as a pre-installed client plug-in. The OTPK module 40 may perform its role without significant intervention from a user when operating as the signing entity 20. The OTPK module 40 may be implemented as a PKCS#11 or CAPI DLL or a Java Applet or ActiveX plugin embedded within the Internet Web Browser. It may be automatically executed when performing secure transactions requiring digital signatures. The OTPK module 40 serves to independently and without additional instruction from a user carry out the steps of generating the asymmetric key pairs comprising the public key and the private key. The OTPK module 40 then contacts the authentication and certification server 50 for authenticating the identity of the signing entity 20. At this point, the user of the signing entity 20 may be prompted for a password or the password may have been entered earlier as part of a 2-factor authentication to the authentication and certification server 50. The private key is then automatically used to generate a digital signature for the signing entity 20. At this point onwards, the private key is then irretrievably deleted such that it cannot be re-used or copied for future use.
Owner:DATA SECURITY SYST SOLUTIONS PTE
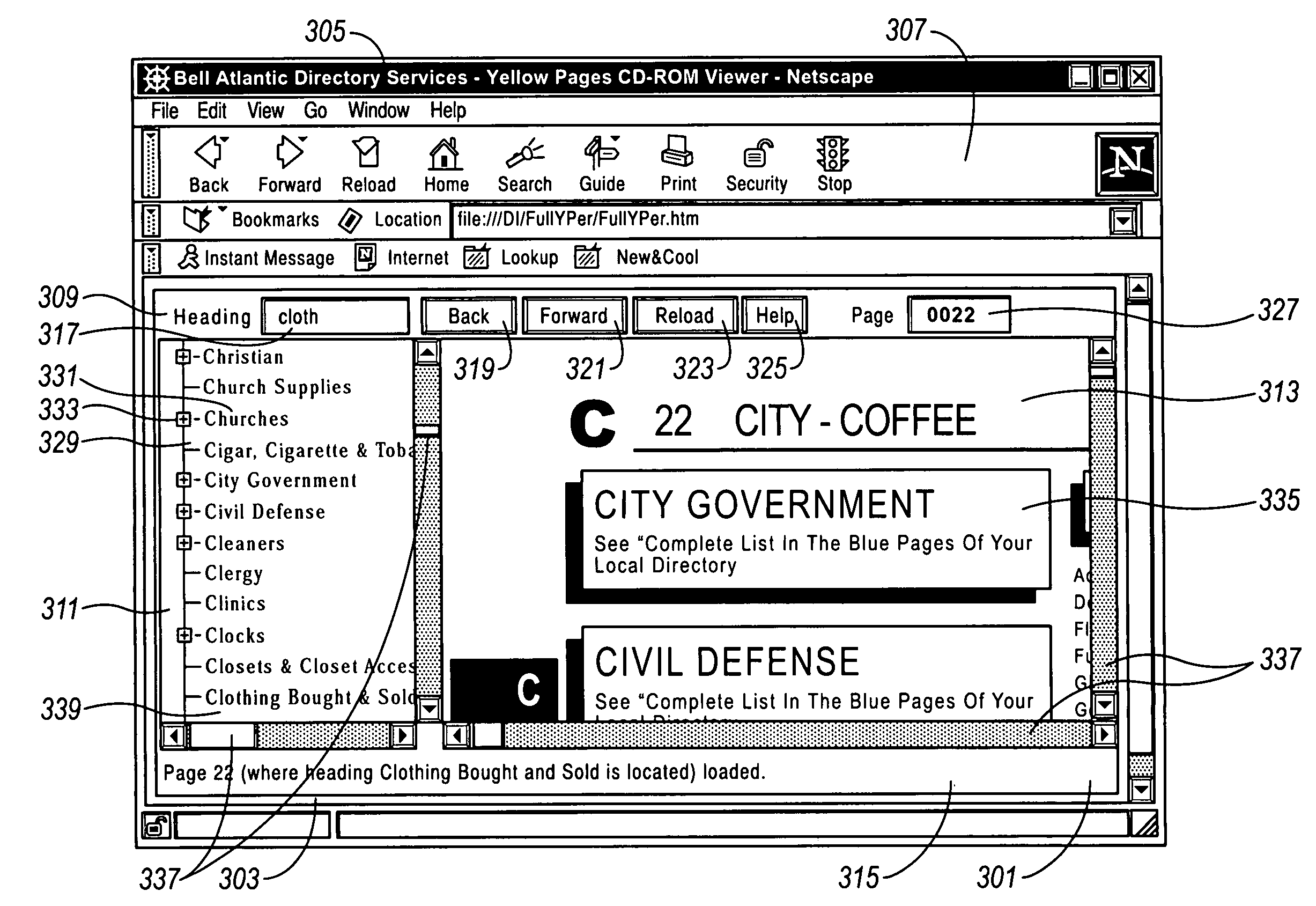
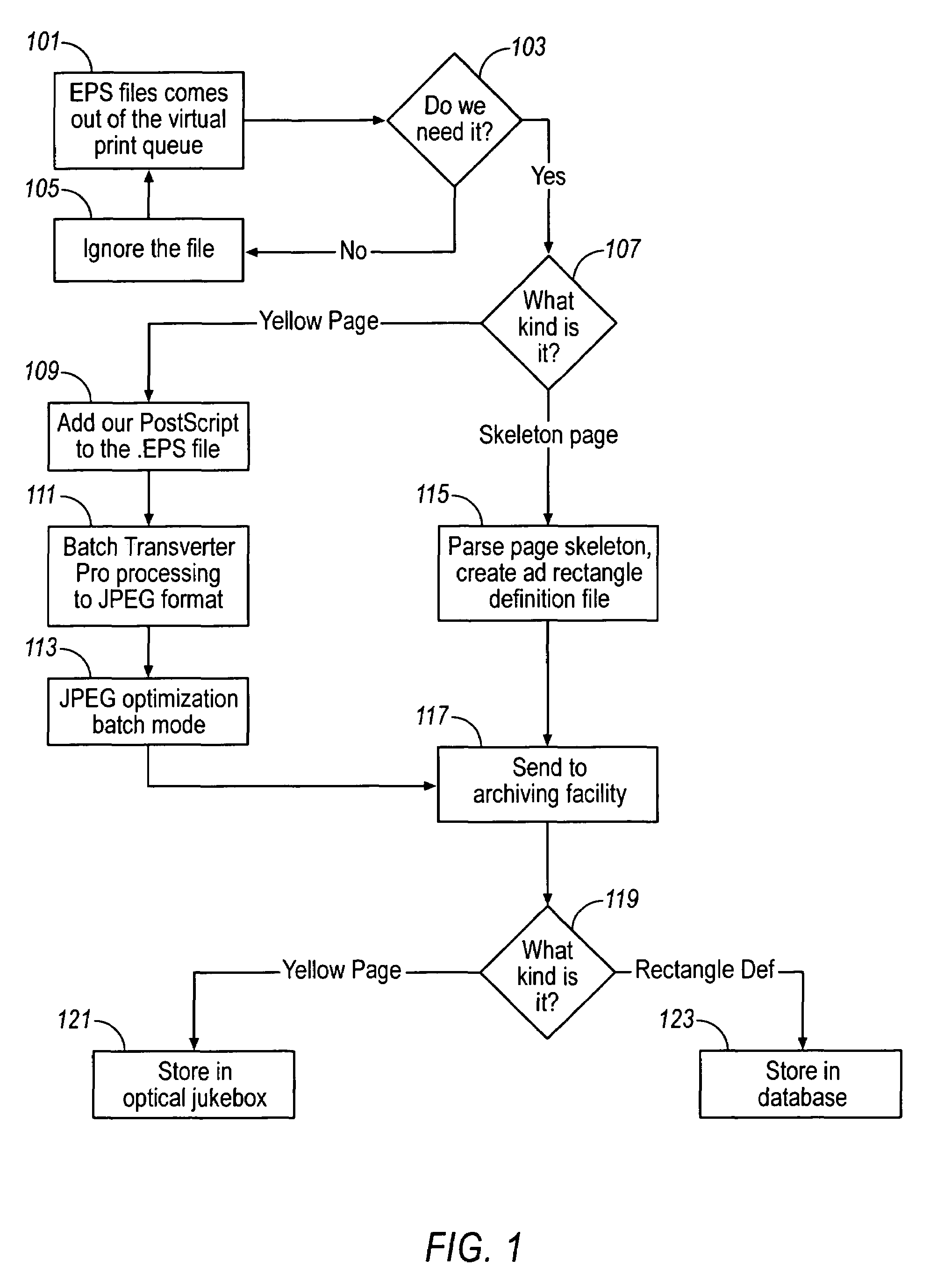
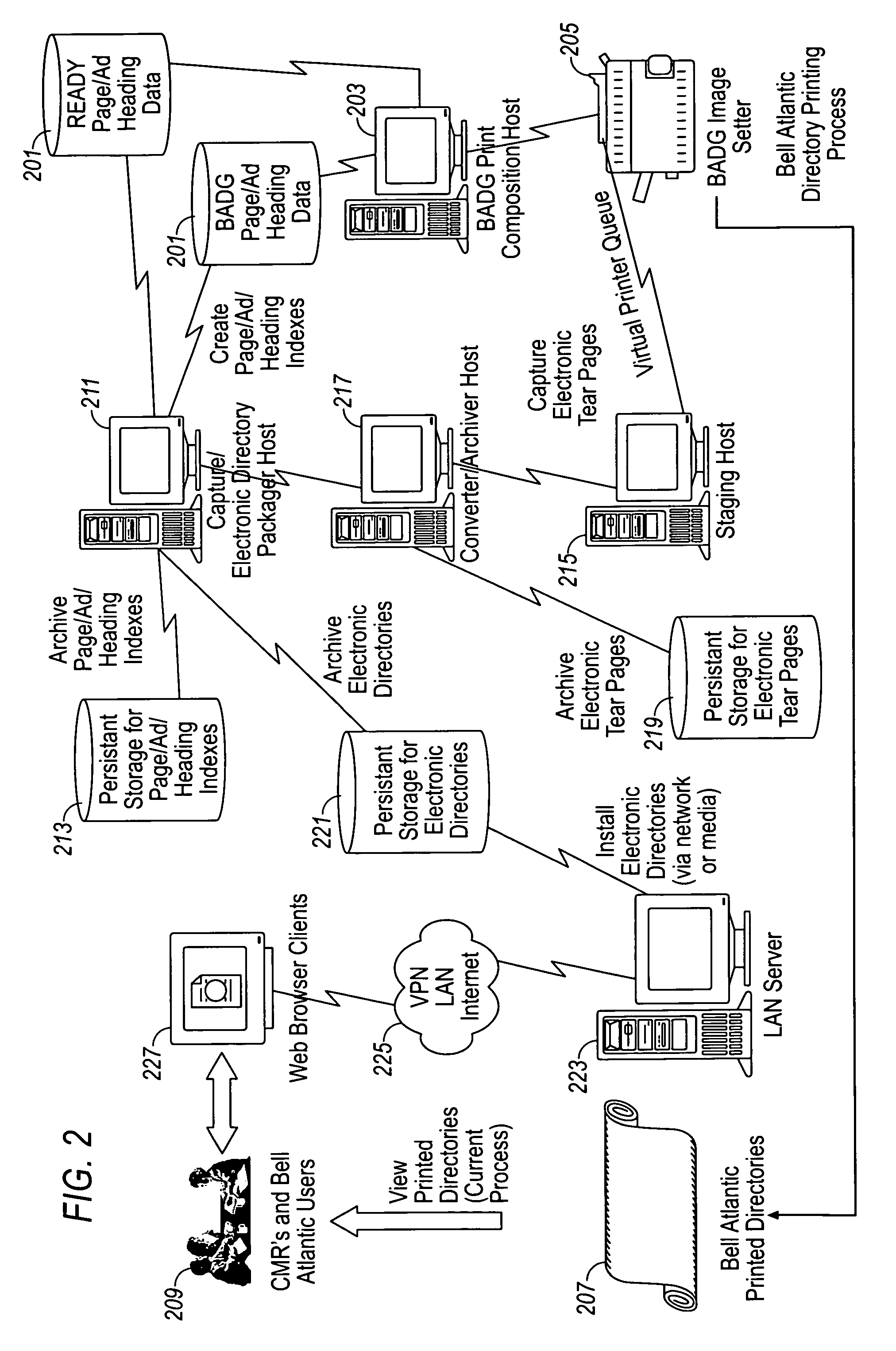
Method, storage medium and system for electronically viewing multi-page document while preserving appearance of printed pages
An electronic Yellow Pages viewer shows the pages of a Yellow Pages directory as they appear in the bound version. The print queue used to print the bound version is intercepted, and each page is rasterized into a JPEG file or otherwise converted into an image file. The page / header / advertisement data are parsed to create an index which associates each Yellow Pages heading with the first page on which that heading appears. The viewer runs as a Java applet inside a World Wide Web browser and allows a user to access a page by typing the name of a heading, selecting the heading from a tree view or typing a page number. A Yellow Pages advertiser receives an electronic bill with an electronic tear sheet showing the page on which the advertisement appears. The bill can also include one or more of the reverse page, the opposite page, or other pages in the same heading. The advertisement can be selectively highlighted.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
System and method for continuous monitoring and measurement of performance of computers on network
InactiveUS7577701B1Valuable informationAccurately reflectMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksThe InternetNetworked system
Performance on a networked system is monitored through five interlocking monitoring techniques. A network monitoring process causes pseudo messages to be sent from various points in the network and monitors the progress of the pseudo messages. A client-server monitoring process monitors server availability and receives logs from various client-server processes and determines the performance of both server and server processes, which can be grouped by end-user location. A mainframe monitoring process monitors the performance of the various hardware and software components on a mainframe. A reporting and administration process compiles reports and makes them remotely available over the Internet. An e-business monitoring process monitors servers accessible to customers over the Internet by use of a Java applet which sends time stamps indicating access. The five processes are tied together through a central data repository, called a data mart.
Owner:MAGNAFOX LLC
System, method, and apparatus for a dynamic transaction card
ActiveUS20160307089A1Connection securityAdd featurePayment architectureRecord carriers used with machinesMicrocontrollerLED display
A dynamic transaction card that includes a number of layers, each of which may be interconnected to one another. For example, a dynamic transaction card may include an outer layer, a potting layer, a sensor layer, a display layer (including, for example, LEDs, a dot matrix display, and the like), a microcontroller / microprocessor storing firmware, Java applets, Java applet integration, and the like, an EMV processor, an energy storage component, one or more antenna (e.g., Bluetooth antenna, NFC antenna, and the like), a power management component, a flexible printed circuit board (PCB), a chassis, and / or a card backing layer. A display layer may include enhanced features such as the use of LED display components as a photosensor.
Owner:CAPITAL ONE SERVICES
Apparatus for and method of providing and measuring data throughput to and from a packet data network
A digital subscriber link data network incorporates a throughput test server (TTS) to provide fault identification, isolation, and verification of DSL service availability and data rates. An asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) terminal unit—remote (ATU-R) is connected to an ADSL terminal unit—central office (ATU-C) over a conventional copper loop or equivalent. Data connectivity via a packet switch provides access to high speed data networks, TTS connectivity and interfaces to service providers (SPS). Upon receiving a test request, a technician routes a customer to the TTS. The customer uses a web browser to access the TTS and download executable testing software, e.g., a JAVA applet. The applet causes test messages to be sent to and received from the TTS and computes upstream and downstream data rates that is displayed to the customer together with whether the measured data rates are consistent with a specified class of service.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Zero-configuration secure mobility networking technique with web-based authentication interface for large WLAN networks
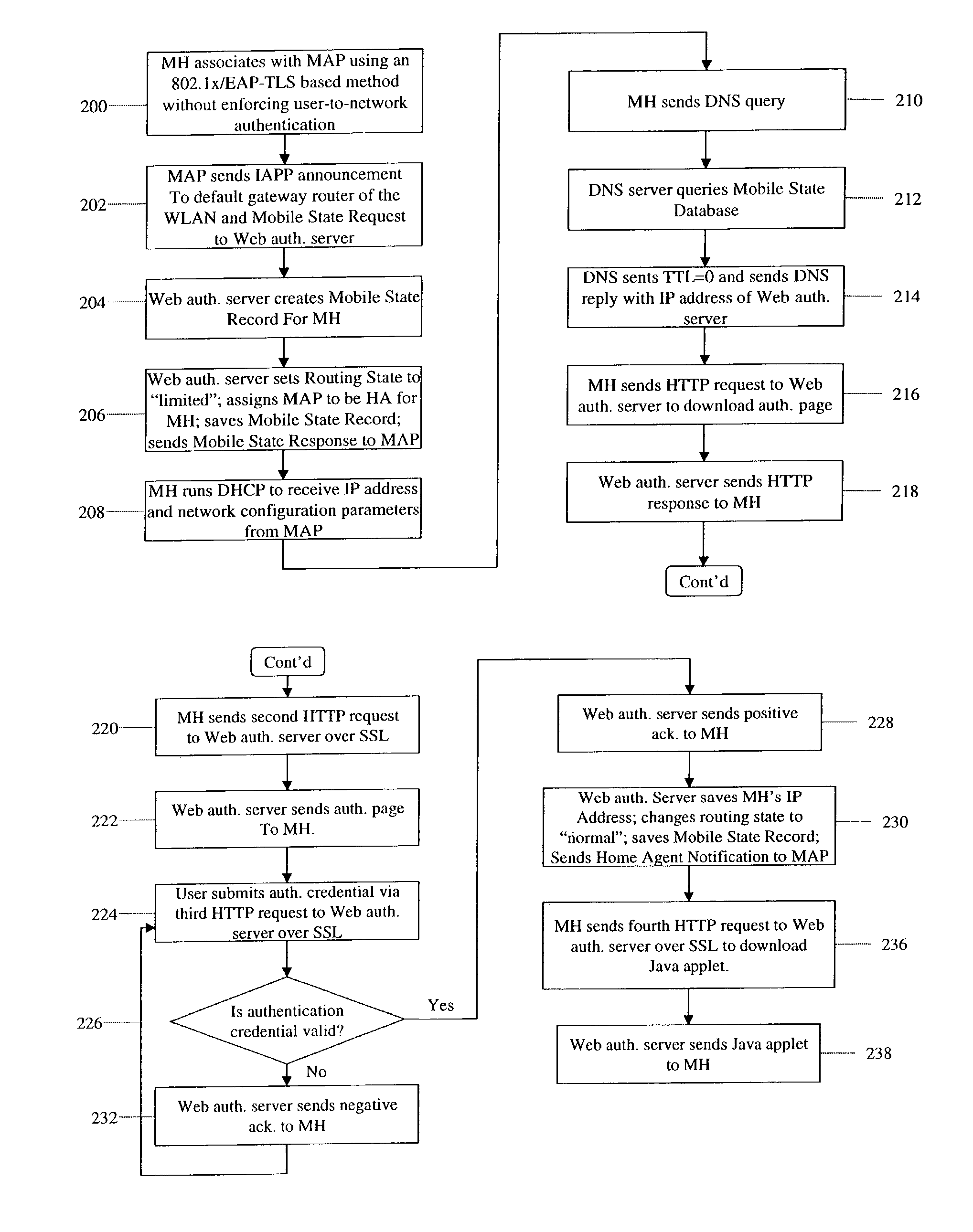
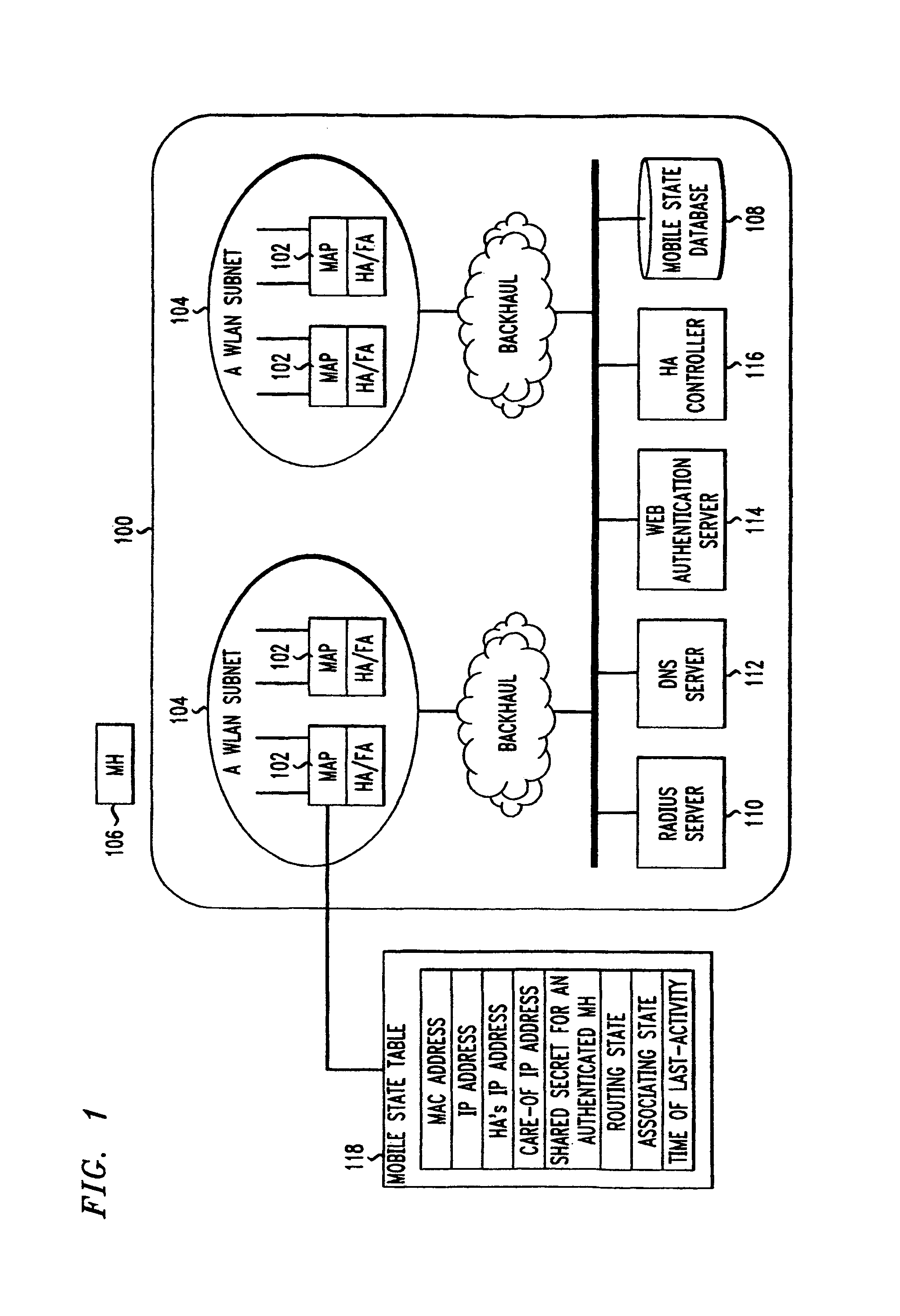
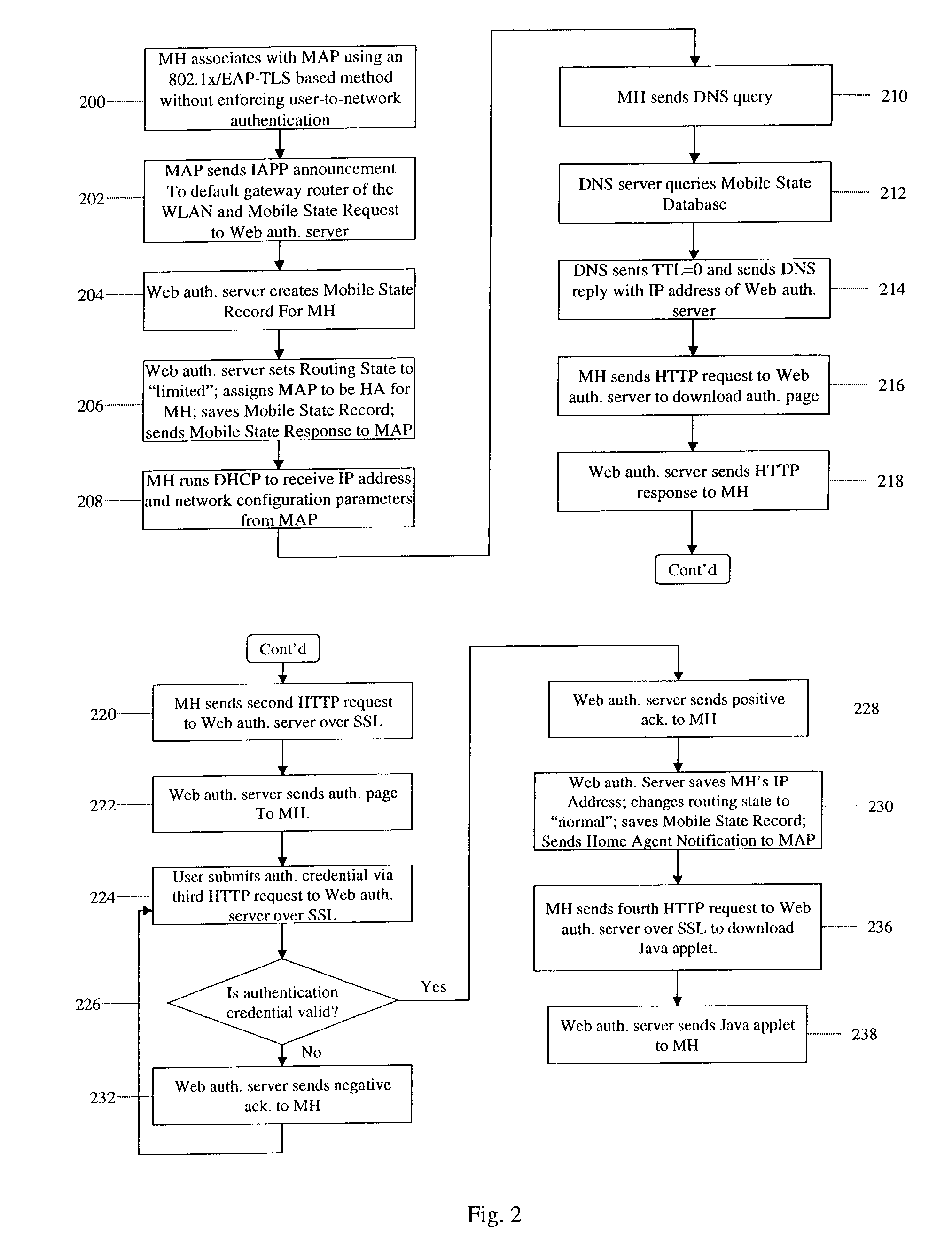
InactiveUS8817757B2Authentication is convenientAvoid attackNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesIp addressUser authentication
A zero-configuration secure mobility networking technique for WLANs is provided, utilizing split link-layer and a Web-based authentication. The link-layer authentication process facilitates network-to-user authentication and generation of session-specific encryption keys for air traffic using digital certificates to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks without requiring users to have pre-configured accounts. Although any WLAN host can pass the link-layer authentication and obtain link connectivity, the WLAN only allows the host to obtain IP networking configuration parameters and to communicate with a Web-based authentication server prior to initiating the Web-based authentication process that is responsible for user-to-network authentication. The Web-based authentication server employs a Web page for initial authentication and a Java applet for consequent authentications. In the Web page, registered users can manually, or configure their Web browsers to automatically, submit their authentication credentials; new users can open accounts, make one-time payments, or refer the Web-based authentication server to other authentication servers where they have accounts. Once a user is authenticated to the WLAN, the user's mobile host obtains full IP connectivity and receives secure mobility support from the WLAN. The mobile host always owns a fixed IP address as it moves from one access point to another in the WLAN. All wireless traffic between the mobile host and the WLAN is encrypted. Whenever the mobile host moves to a new access point, a Java applet (or an equivalent client-side program delivered over Web) enables automatic authentication of the mobile host to the WLAN. In addition, the ZCMN method supports dynamic load balancing between home agents. Thus, a mobile host can change home agents during active sessions.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method achieving XenServer virtual machine remote control on https
InactiveCN103200215ARealize the proxy functionSolve the problem that the XenServer virtual machine console cannot be accessed directlyNetworks interconnectionApplication serverRemote control
The invention discloses a method achieving XenServer virtual machine remote control on https. The method comprises a VNC client capable of operating on a browser and a VNC agent server used for identity verification and RFB data transmission, wherein the VNC client is based on a Java Applet technology, transmits VNC remote control data through the https, deploys on a web and a Java application server and can operate on the browser provided with JVM. Because the https is adopted to transmit the data, the VNC client can solve the problem that a firewall limits outer network access well. The VNC agent server is used for solving the problem of Applet safe limit when the VNC client accesses a VNC service end of an XenServer, and at the same time achieves safe verification to client identity through an XML-RPC interface of the XenServer. The method enables any browser of the client to achieve the remote control and access of an XenServer virtual machine.
Owner:PCI TECH GRP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com