Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "International telecommunication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is an agency of the United Nations (UN) whose purpose is to coordinate telecommunication operations and services throughout the world. Originally founded in 1865, as the International Telegraph Union, the ITU is the oldest existing international organization.
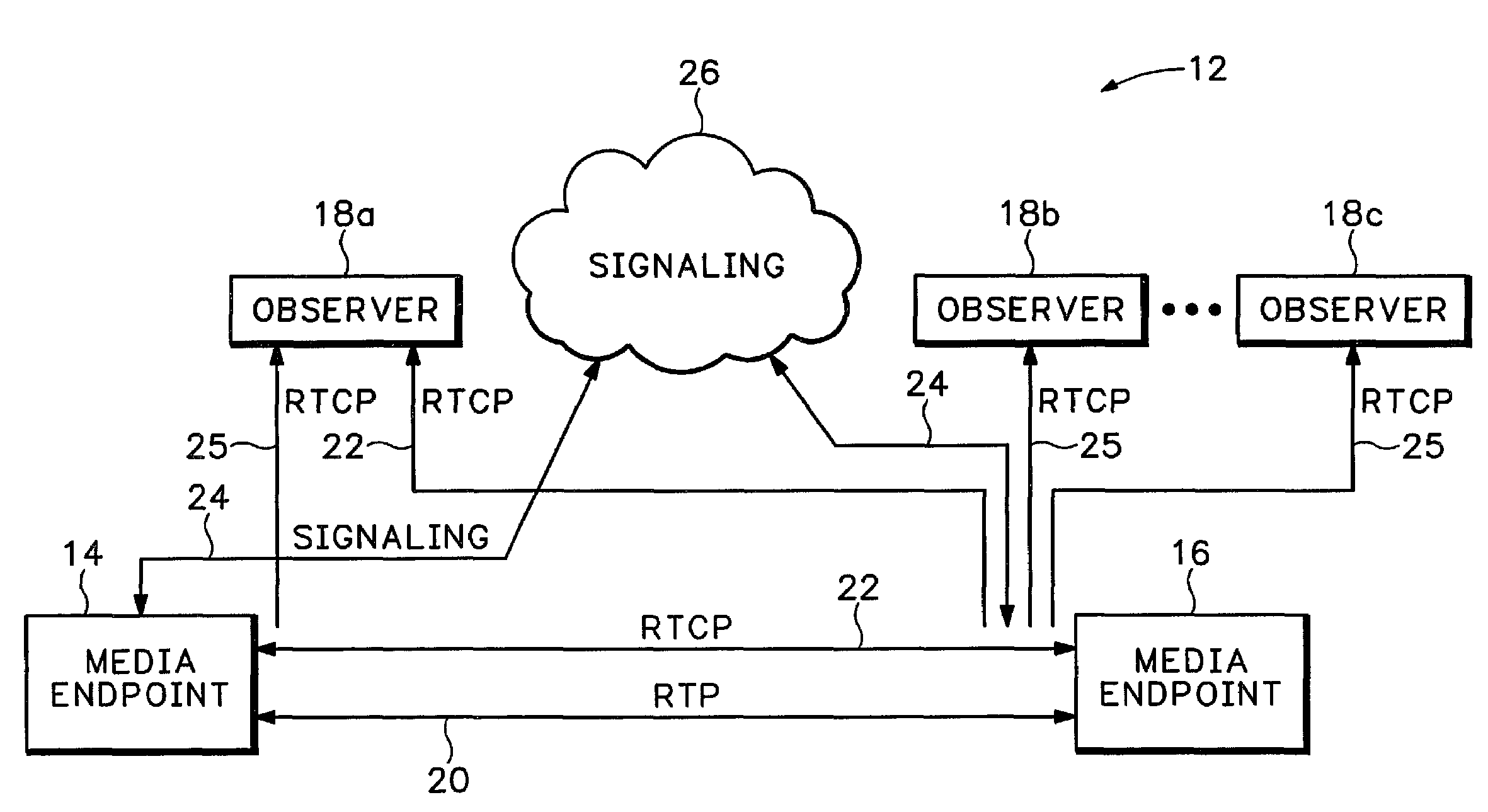
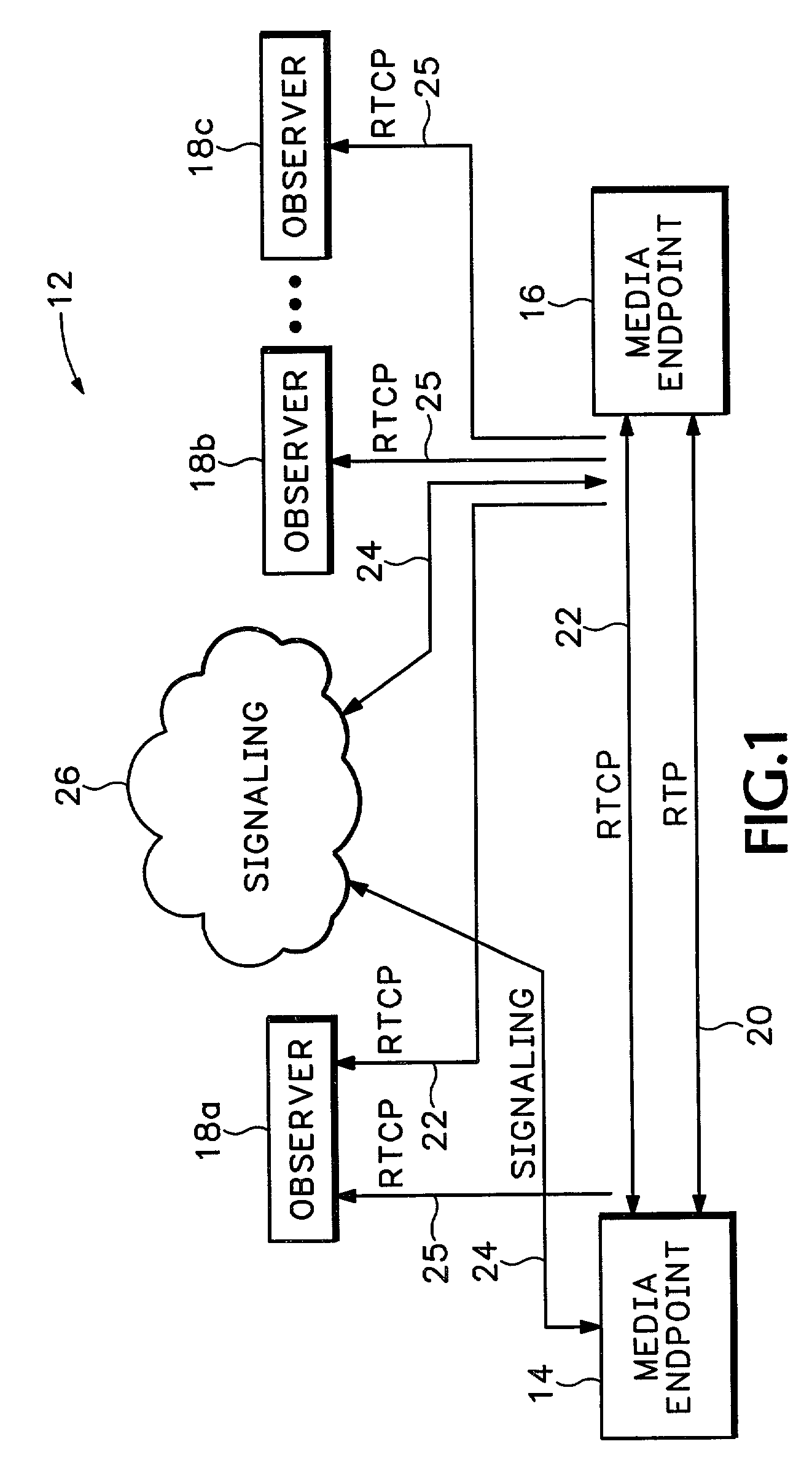
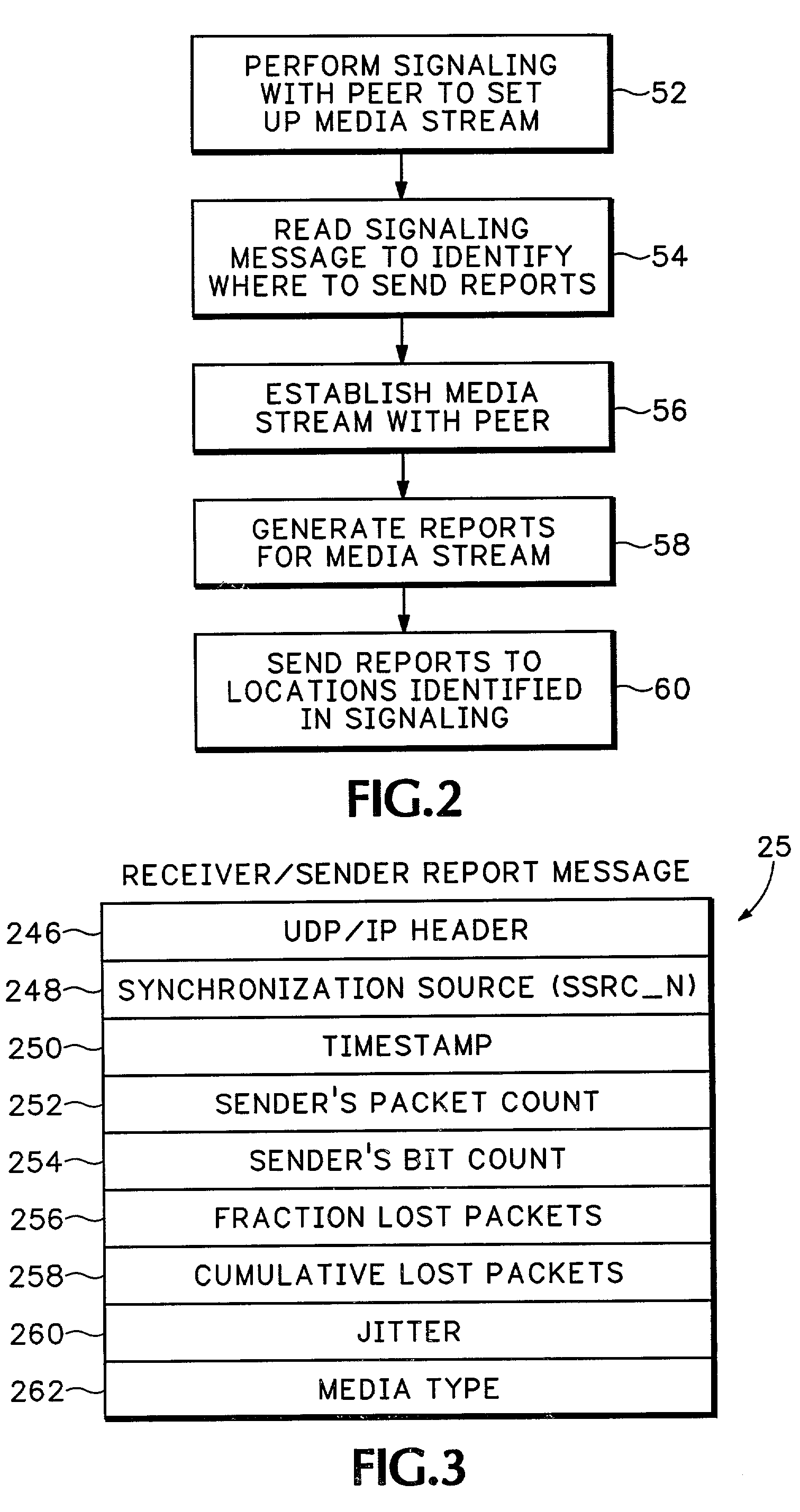
Method and apparatus for media stream monitoring
ActiveUS7310334B1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsSession Initiation ProtocolSignaling protocol
A network processing device is signaled to establish a media path with another network processing device in a packet switched network with Session Initiated Protocol (SIP), International Telecommunication Union (ITU) standard H.323, MGCP, Megaco, or some other signaling protocol. The network processing device receives a request to send information to an observer device that is not directly in the media path. The network processing device then sends information about the media path to the observer device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
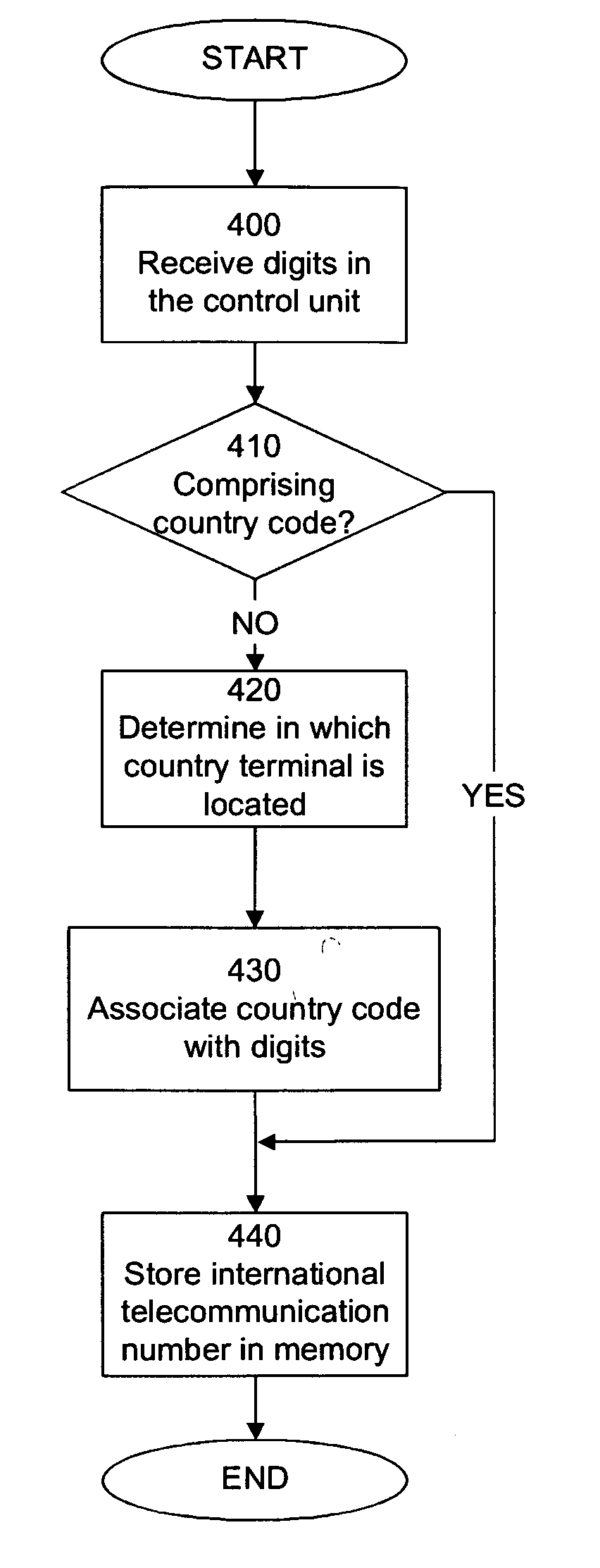
Mobile communication terminal and method therefore
InactiveUS20060094353A1Simple and reliable processThe method is simple and reliableSubstation equipmentRadio relay systemsTelecommunications networkControl unit
A method for providing an international telecommunication number comprising a plurality of digits corresponding to at least a country code, from a mobile telecommunication terminal to a base station, is disclosed. The method comprises receiving a plurality of digits in a control unit in the mobile telecommunication terminal, said digits identifying a subscriber terminal in a telecommunication network, and determining if one or more of the plurality of digits correspond to a country code. If the one or more of the plurality of digits do not correspond to a country code, an international telecommunication number is created by adding a country code to the plurality of digits, whereupon the international telecommunication number is transferred to the base station.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
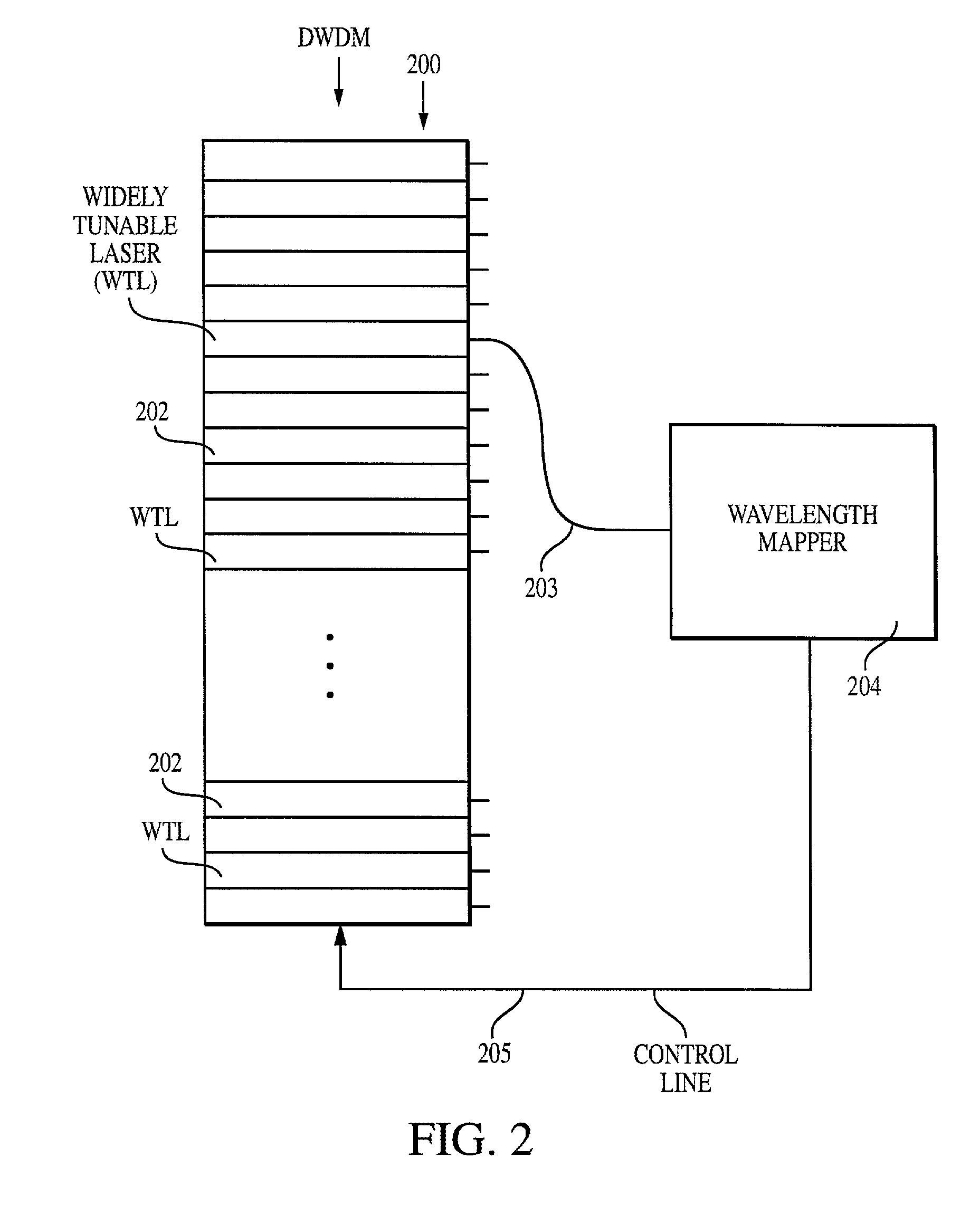
Method and system for locking transmission wavelengths for lasers in a dense wavelength division multiplexer utilizing a tunable etalon
InactiveUS20020041611A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsOptical resonator shape and constructionFiberMultiplexer
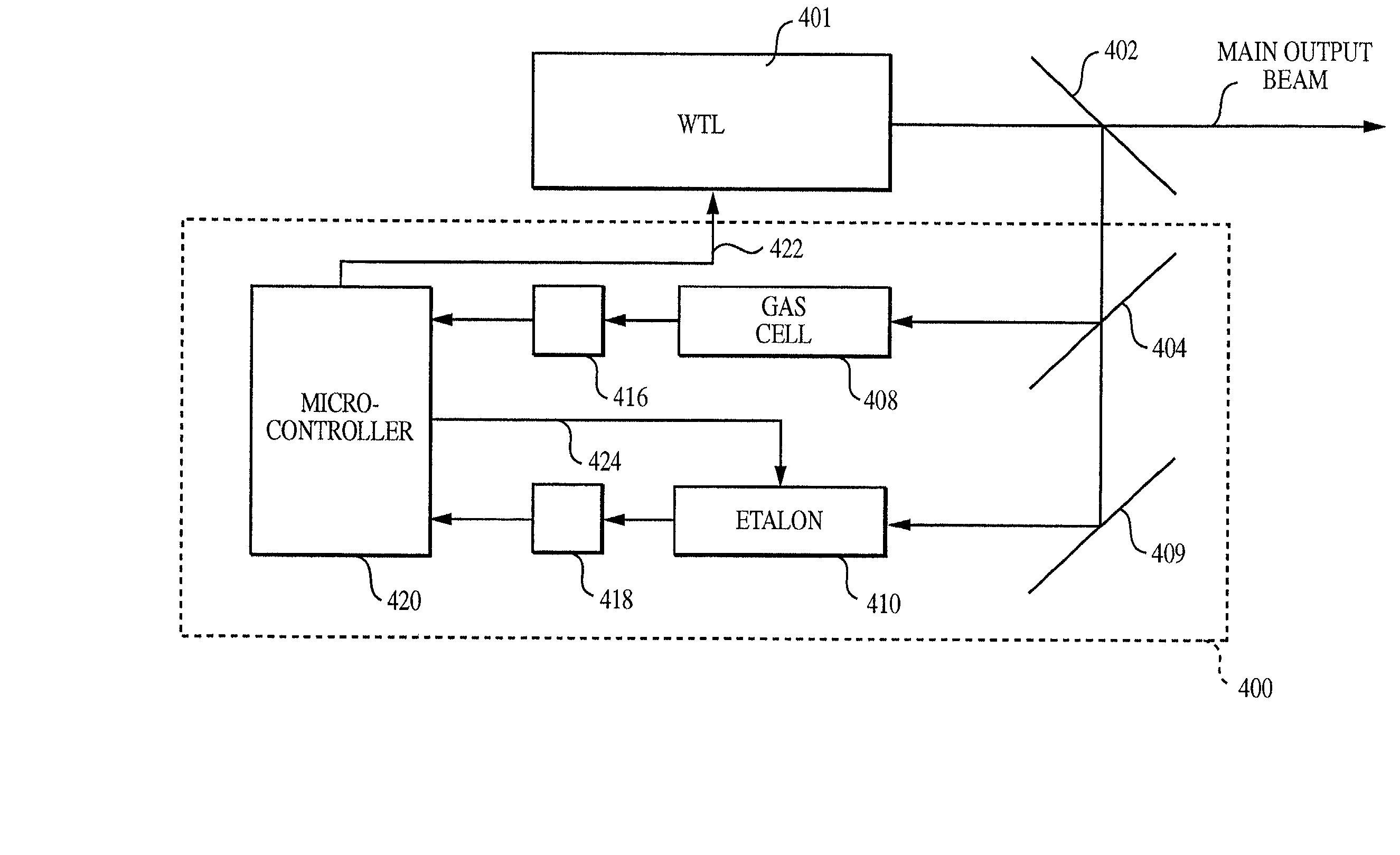
The method and system operate to calibrate a transmission laser of the dense wavelength division multiplexer (DWDM) and to lock the laser to a selected transmission wavelength. In one example, the transmission laser is a widely tunable laser (WTL) to be tuned to one of a set of International Telecommunications Union (ITU) transmission grid lines for transmission through an optic fiber. To lock the WTL to an ITU grid line, a portion of the output beam from the WTL is routed through the etalon to split the beam into a set of transmission lines for detection by an etalon fringe detector. Another portion of the beam is routed directly to a laser wavelength detector. A wavelength-locking controller compares signals from the two detectors and adjusts the temperature of the etalon to align the wavelength of one of the transmission lines of the etalon with the wavelength of the output beam, then controls the WTL in a feedback loop to lock the laser to the etalon line. The wavelength-locking controller thereafter monitors the temperature of the etalon and keeps the temperature constant to prevent any wavelength drift in the etalon. In one example, the optical components are aligned so that laser wavelength detector receives a portion of the laser beam directly from the laser so that phase characteristics of the laser beam are not affected by an intervening beamsplitter thereby permitting improved wavelength locking. In another embodiment, an etalon chirp filter is provided for reducing or eliminating optical frequency chirp, regardless of the particular ITU channel being used for transmission.
Owner:SPECTRASENSORS INC
Broadband MIMO radio frequency transceiving system for next-generation wireless communication network
ActiveCN101944924AAchieving Spectrum Utilization EfficiencyMeet the requirements of digital mobile communication system (4G)Diversity/multi-antenna systemsFrequency spectrumIntermediate frequency
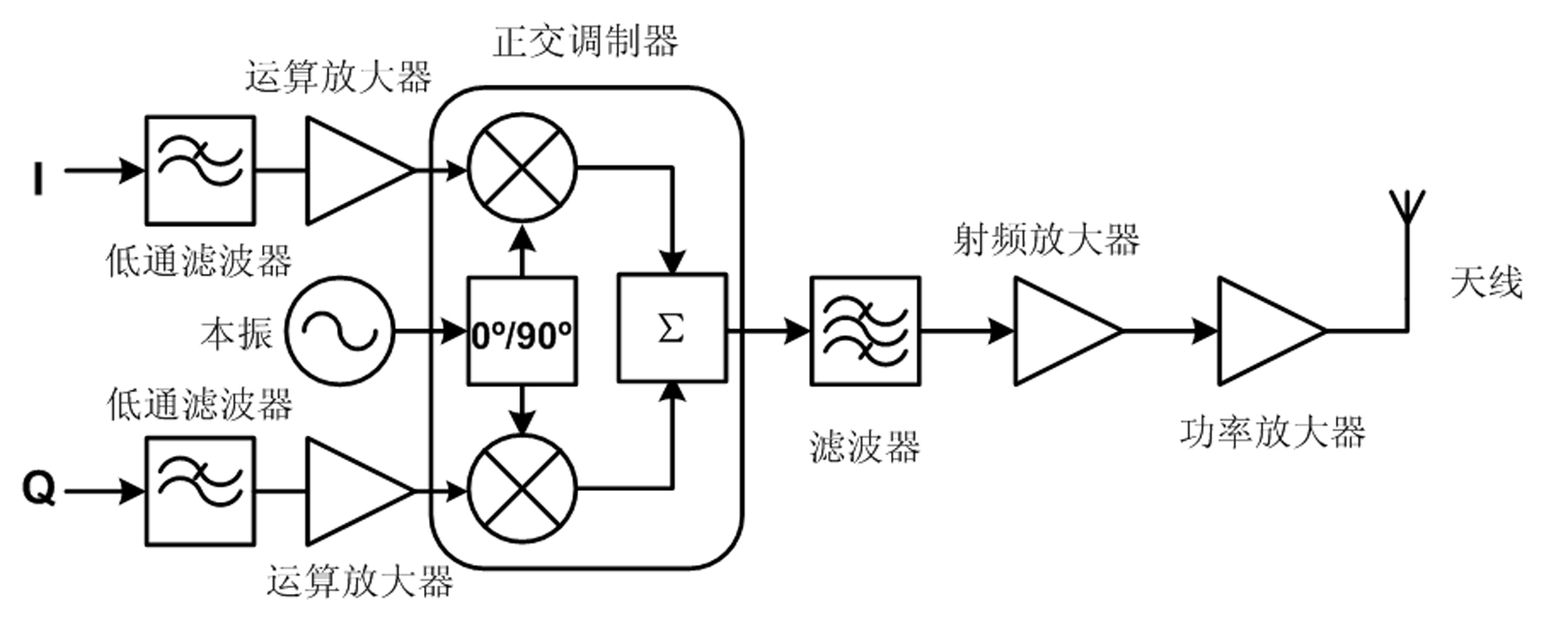
The invention discloses a broadband MIMO radio frequency transceiving system for the next-generation wireless communication network. The system comprises a receiving module, a local oscillation module, a transmitting module, a power supply module and a control module. In the invention, the frequency utilization efficiency of over 10bit / Hz is realized through the adoption of a 100MHZ channel bandwidth and six-transmitting and six-receiving MIMO configuration. Site tests show that the system can support the data transmission rate of over 1Gbit / s and meets the requirements of International Telecommunications Union on the next-generation digital mobile communication system (4G). The system fully combines and takes full advantage of a superheterodyne architecture and a zero intermediate frequency architecture, adopts an asymmetric structure, adopts the zero intermediate frequency architecture in the transmitting module and adopts the superheterodyne architecture in the receiving module. The way reduces the complexity of circuits and the costs of the system while guaranteeing the performances of the system. The local oscillation module of the system adopts an innovative design, so that the cost of the system and the complexity of the circuits are reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
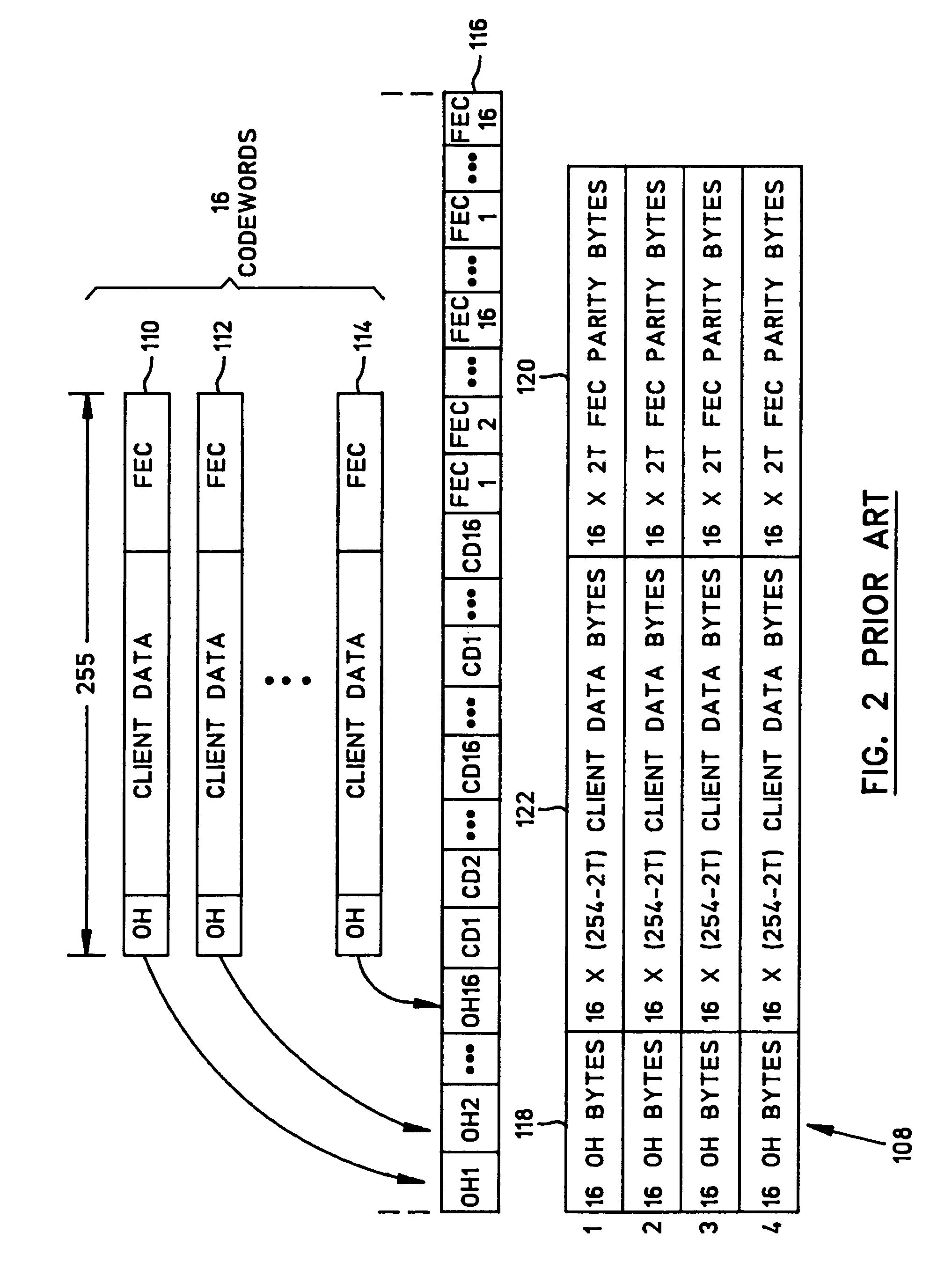
Optical transport network frame structure with in-band data channel and forward error correction
InactiveUS7278081B1Effective distributionLow data rateError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/correctionChannel dataForward error correction
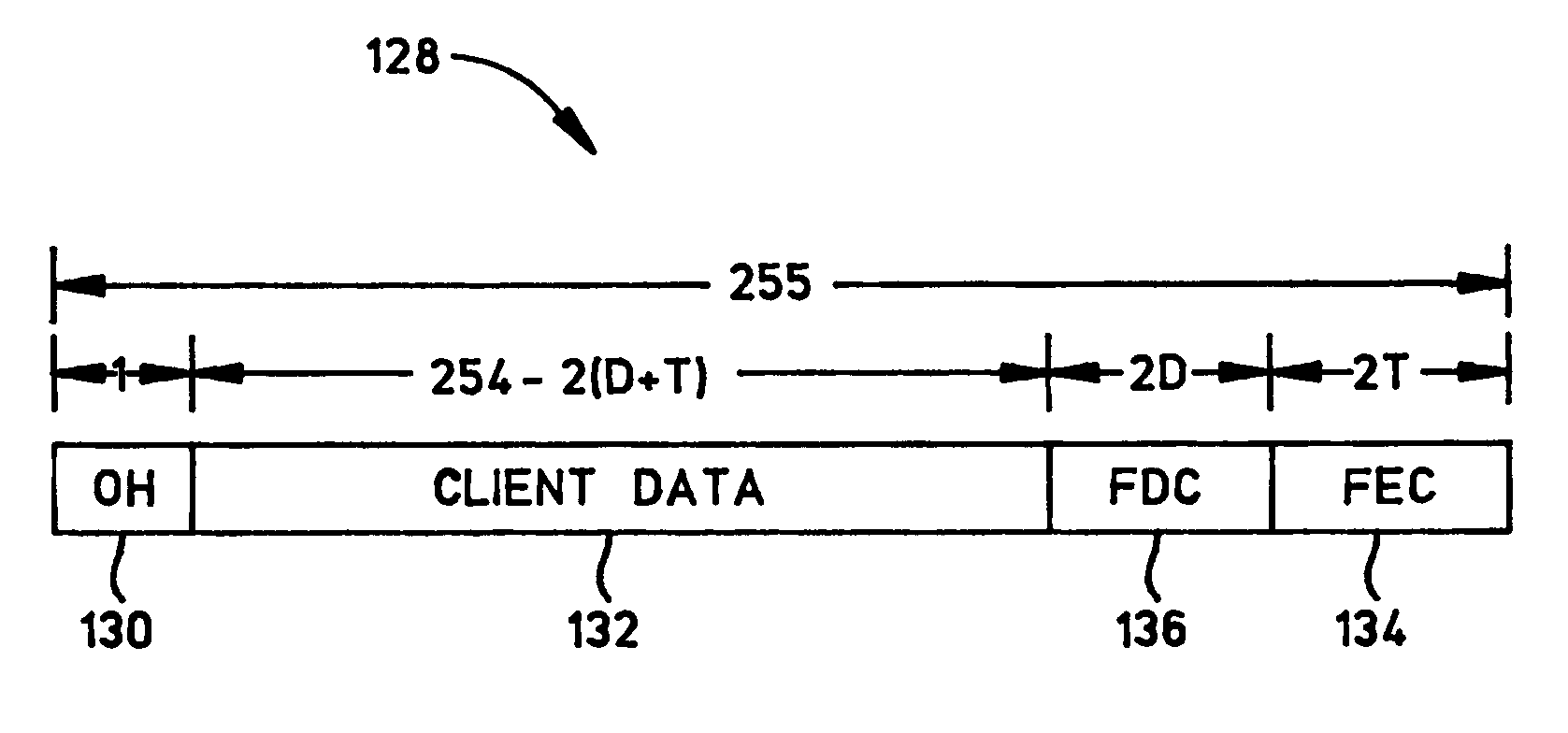
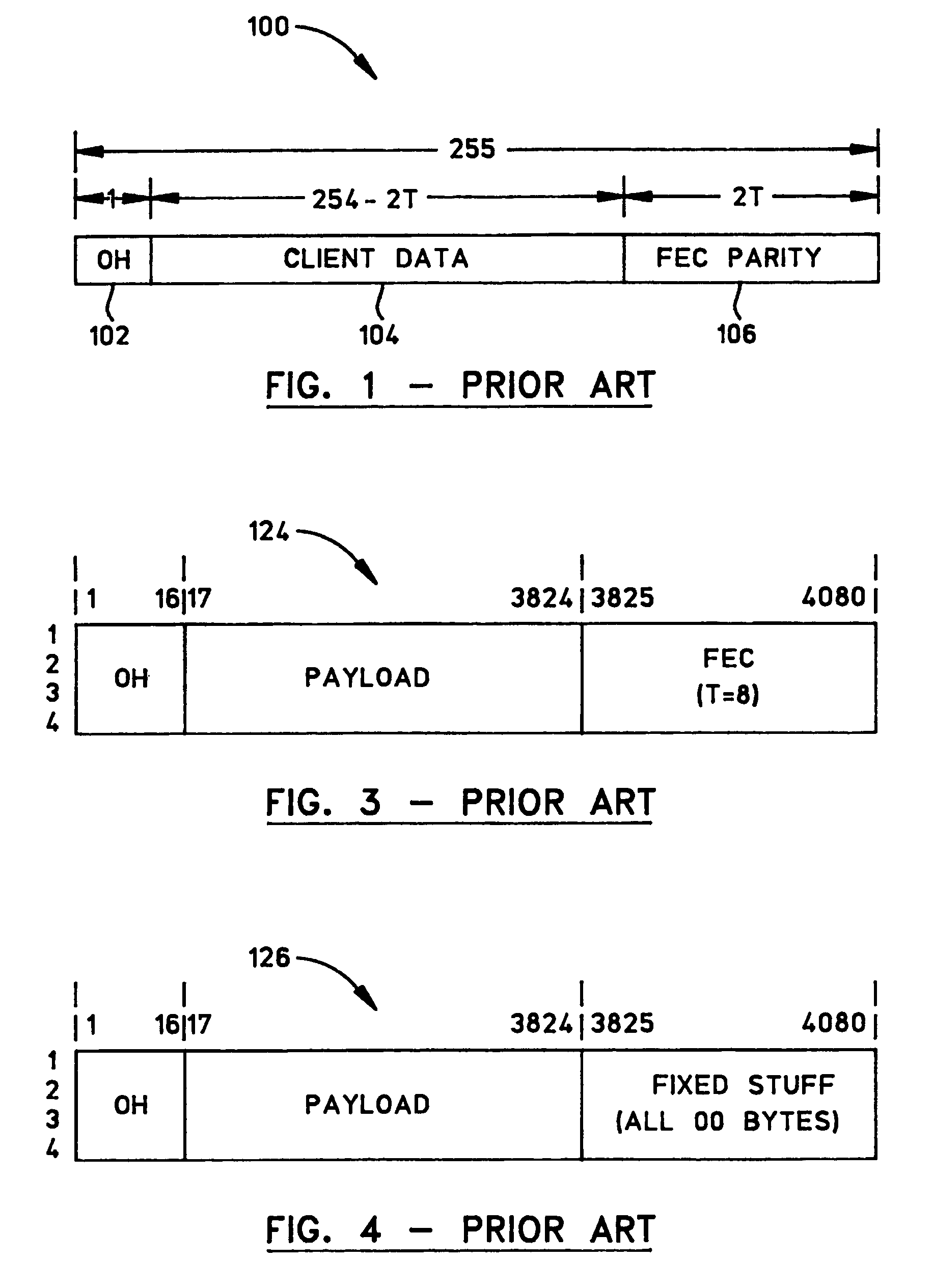
An optical transport network data frame structure is configured to provide an in-band data channel. The in-band channel data is contained in the data frame space that would otherwise be allocated to forward error correction (“FEC”) bytes. Consequently, the provision of the in-band data channel does not affect the number of client data bytes contained in the data frame structure. In accordance with a practical embodiment, the data frame structure is compliant with Intra Domain Interface (IaDI) specifications set forth in International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) Recommendation Guide For Recommendation, G.709 / Y.1331.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
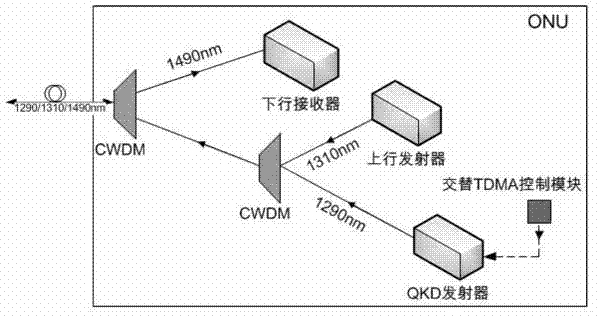
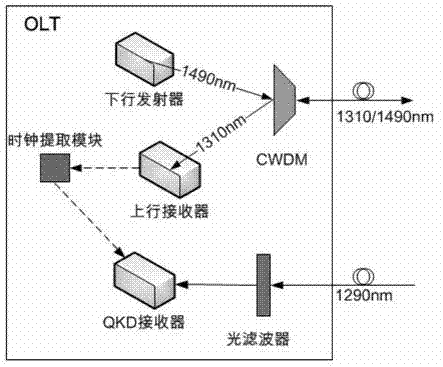
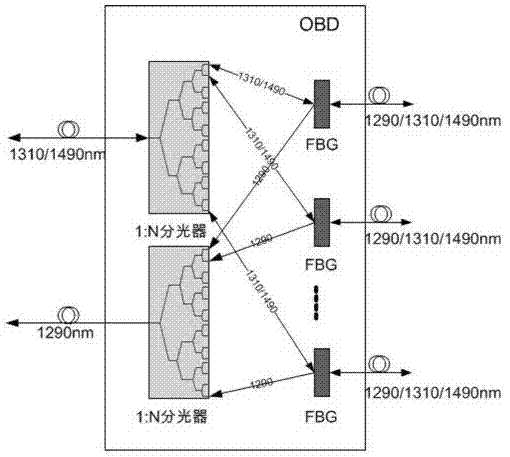
Optical access passive network supportive of quantum communication
ActiveCN103118308AAvoid interferenceAvoid loopholesMultiplex system selection arrangementsKey distribution for secure communicationGratingPassive networks
Disclosed is an optical access passive network supportive of quantum communication. The network is supportive of bidirectional data communication of a GPON (gigabit passive optical network) accordant with the ITU (International Telecommunication Union)-T G.984 standard or an EPON (Ethernet passive optical network) accordant with the IEEE802.3 (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) standard and quantum key distribution (QKD) of uplink direction. An improved optical network unit is adopted in the network to add a QKD emitter and an alternating time-division multiple-address access control module on a basis of an original GPON or EPON, an improved optical line terminal is adopted to add a QKD receiver and a clock extraction module on a basis of the original GPON or EPON, and an improved passive optical splitter is adopted and comprises two 1: N optical splitters and N Bragg gratings (N is the number of the optical network unit). The network integrally greatly avoids inferences, on quantum signals, of high-light signals to enable the QKD to be capable of coexisting with the GPON or EPON. The optical access passive network supportive of quantum communication can thoroughly improve potential security loopholes of common optical access networks and provides a feasible scheme for popularizing the quantum communication technology to a fiber to house (building) FTTx (fiber to the x) access network.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method and system for locking transmission wavelengths for lasers in a dense wavelength division multiplexer
InactiveUS20020163650A1Heat is lostChange in refractive indexSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser output parameters controlFiberFinesse
Owner:SPECTRASENSORS INC
Fabry-perot etalon with independently selectable resonance frequency and free spectral range
InactiveUS6947218B2Substantial linearityGood dispersionUsing optical meansNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumResonance
The invention relates generally to optical interference filters and interferometers. Methods, devices and device components for optical signal generation and processing using optical interference filters and interferometers are presented. The invention provides optical interference filters and interferometers having a selected cumulative reflectance phase dispersion capable of providing substantially independent selectable resonance frequency and free spectral range. An exemplary interference filter of the present invention provides a multi-peak transmission spectrum with substantially independent, selectable control over absolute transmission band frequencies and relative transmission band spacing. The methods and devices provided herein are particularly well suited for frequency matching optical signals to a selected frequency standard, such as the International Telecommunication Union frequency standard.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Fabry-perot etalon with independently selectable resonance frequency and free spectral range
InactiveUS20040042083A1Substantial linearityConstant lengthUsing optical meansNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumResonance
The invention relates generally to optical interference filters and interferometers. Methods, devices and device components for optical signal generation and processing using optical interference filters and interferometers are presented. The invention provides optical interference filters and interferometers having a selected cumulative reflectance phase dispersion capable of providing substantially independent selectable resonance frequency and free spectral range. An exemplary interference filter of the present invention provides a multi-peak transmission spectrum with substantially independent, selectable control over absolute transmission band frequencies and relative transmission band spacing. The methods and devices provided herein are particularly well suited for frequency matching optical signals to a selected frequency standard, such as the International Telecommunication Union frequency standard.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Optical interference filter having parallel phase control elements
The invention relates generally to optical interference filters and interferometers. Methods, devices and device components are presented for separating closely spaced optical channels with minimized cross talk. The invention provides optical interference filters having parallel phase control elements which efficiently transmit light of a selected optical channel or a plurality of selected channels with decreased light loss, particularly decreased insertion loss. An exemplary interference filter of the present invention provides minimized vertical and horizontal recombination error and improved optical path length matching. The invention further provides methods of fabricating optical interference filters with improved piece-to-piece reproducibility. The methods, devices and device components provided herein are particularly well-suited for combining or separating closely spaced optical signals corresponding to transmission channels of a selected frequency standard, such as the International Telecommunication Union frequency standard.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
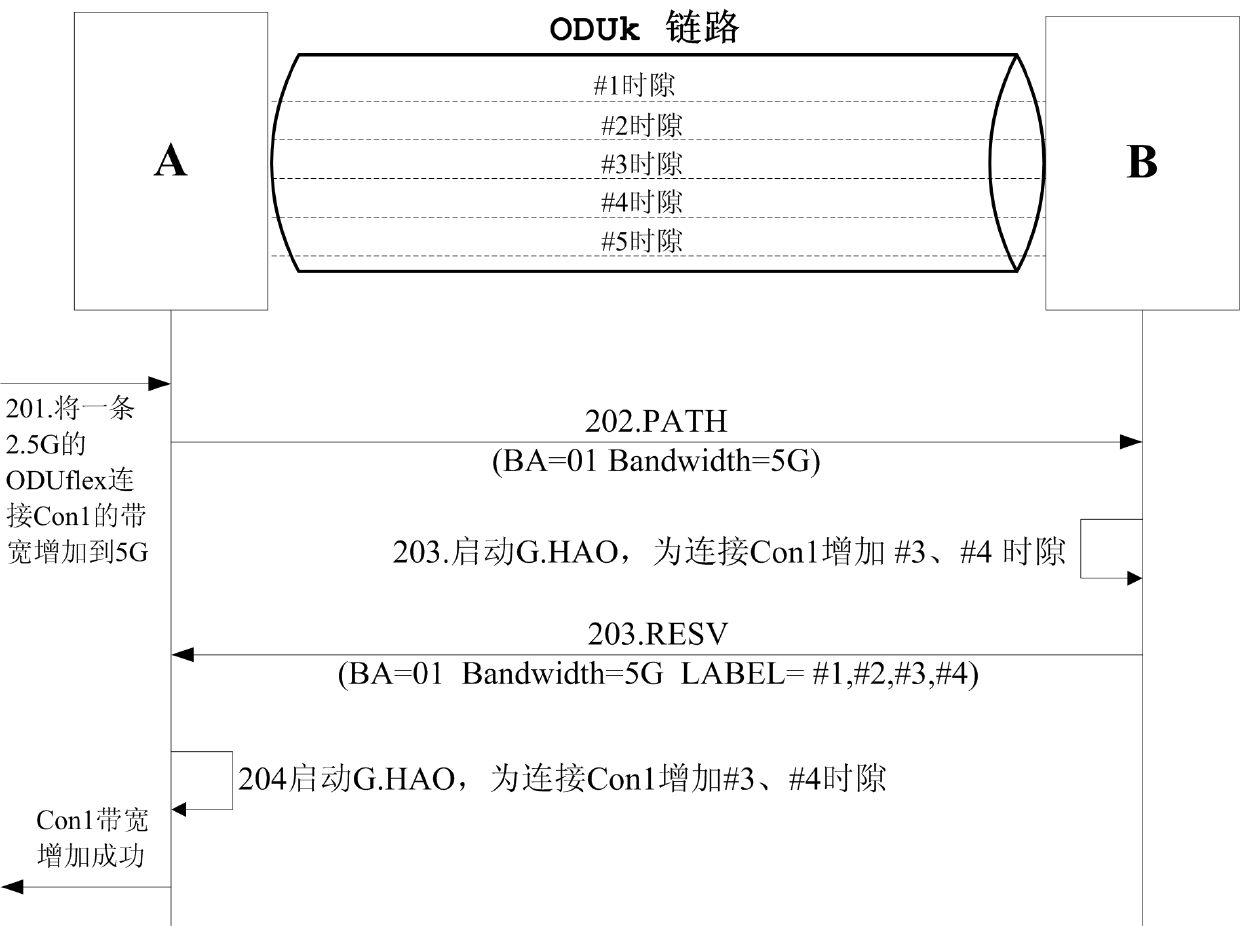
Bandwidth adjustment method and system
InactiveCN102571544ARealize automatic controlData switching networksAutomatic controlSignaling protocol
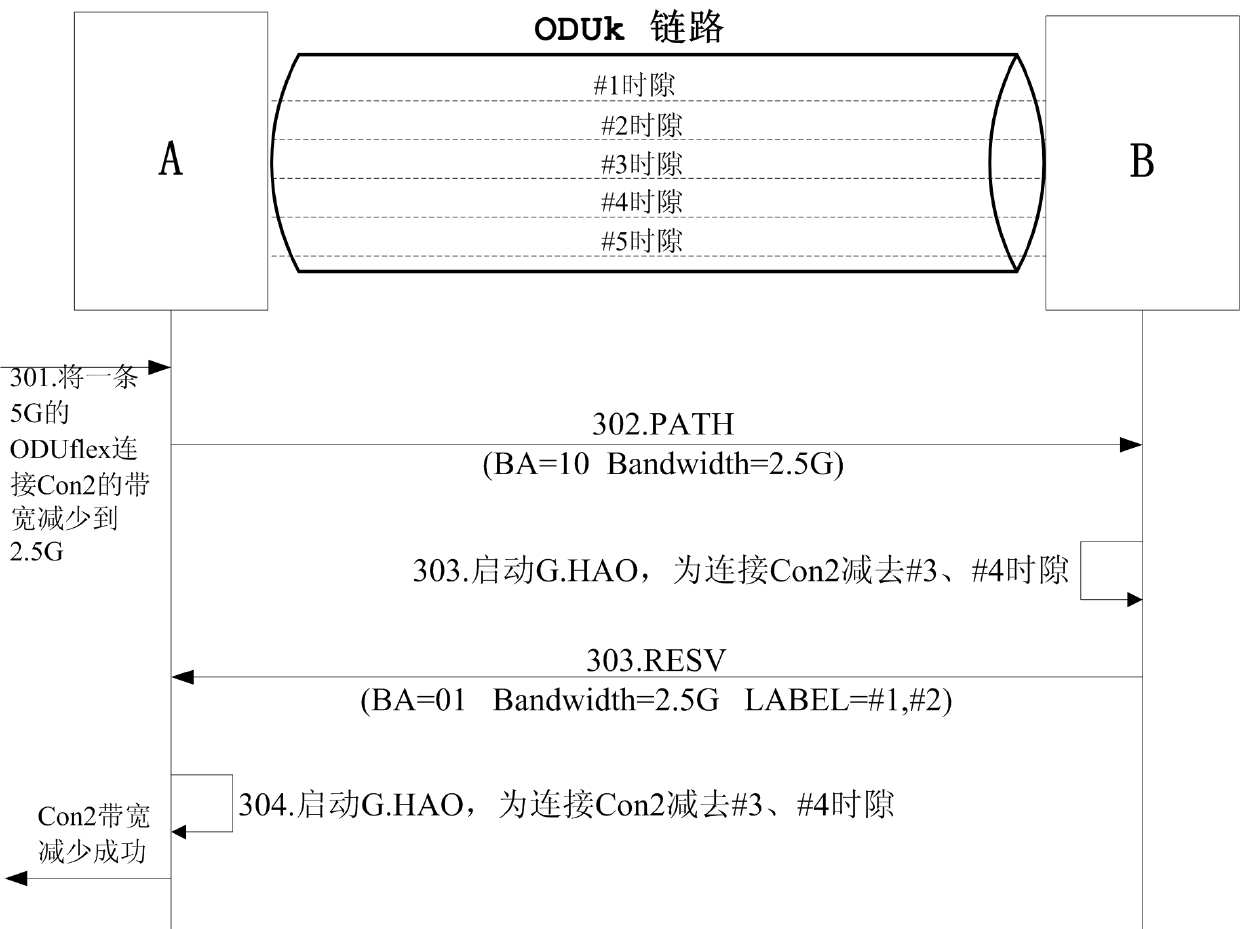
The invention discloses a bandwidth adjustment method and a bandwidth adjustment system, wherein the bandwidth adjustment method comprises the following steps: a control plane of a head node of a service initiates a negotiation for adjusting bandwidths among all nodes on a service connection path through a signaling message; and the control plane of each node on the service connection path notifies a time slot resource to be adjusted to a transmitting plane of the current code, wherein the transmitting plane is used for starting a G.HAO protocol to execute a flexible optical data unit (ODUflex) bandwidth adjustment operation. According to the bandwidth adjustment method and the bandwidth adjustment system, disclosed by the invention, a signaling protocol of the control plane is extended, so that the G.HAO protocol established based on ITU-T (International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector) is supported, and therefore the automatic control of ODUflex bandwidth lossless adjustment is realized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Detection method and detection system for audio frequency transmission characteristics of building intercom system
ActiveCN103607669AAccurate collectionImprove accuracyMultiplex system selection arrangementsNon-electrical signal transmission systemsSound sourcesSound pressure
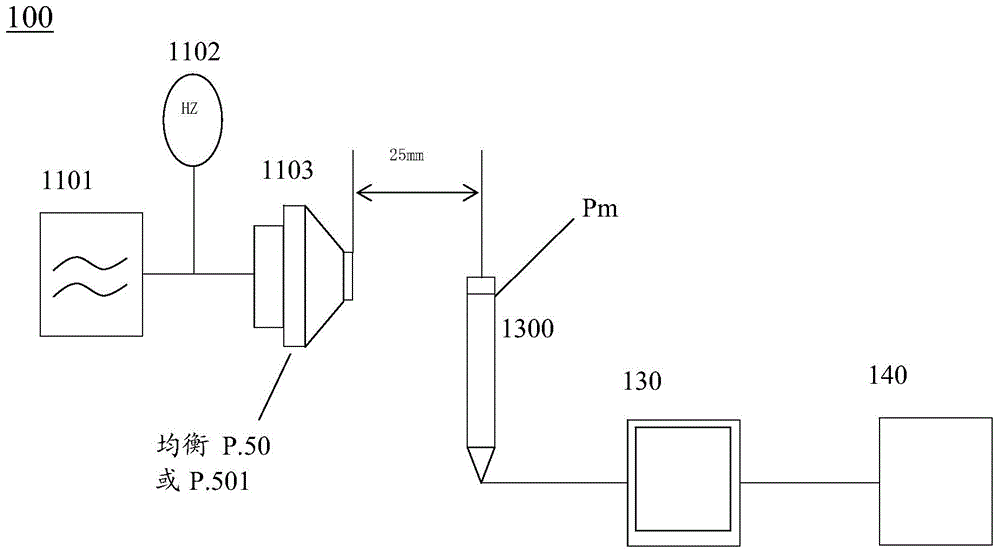
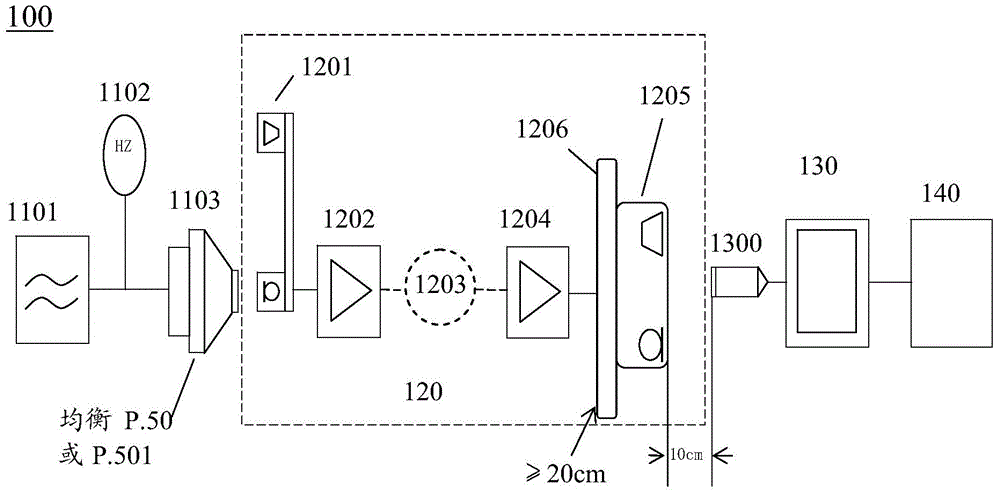
The invention relates to a detection method and a detection system for audio frequency transmission characteristics of a building intercom system. The detection method comprises the steps: a sound source portion generates specific voice signals, the specific voice signals taken as input voice signals are input into a detected access, the specific voice signals are transmitted in the detected access, and are output as detected output voice signals; the specific voice signals comprise a P.50 simulation voice signal or a P.501 human voice signal of the international telecommunication union-telecommunication standardization organization (ITU-T); the sound pressure related to the detected output voice signals are detected based on the detected output voice signals, and audio frequency characteristic parameter values are calculated in dependence on the detected sound pressure related to the detected output voice signals in order to determine audio frequency transmission characteristics of the detected access. By improving the measurement of sound sources, backboards and audio frequency distortion, the detection accuracy and the detection result precision of the audio frequency transmission characteristics of the simulation (bus-mode) building intercom system are improved, and the detection result is relatively close to the actual using effect.
Owner:THE THIRD RES INST OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
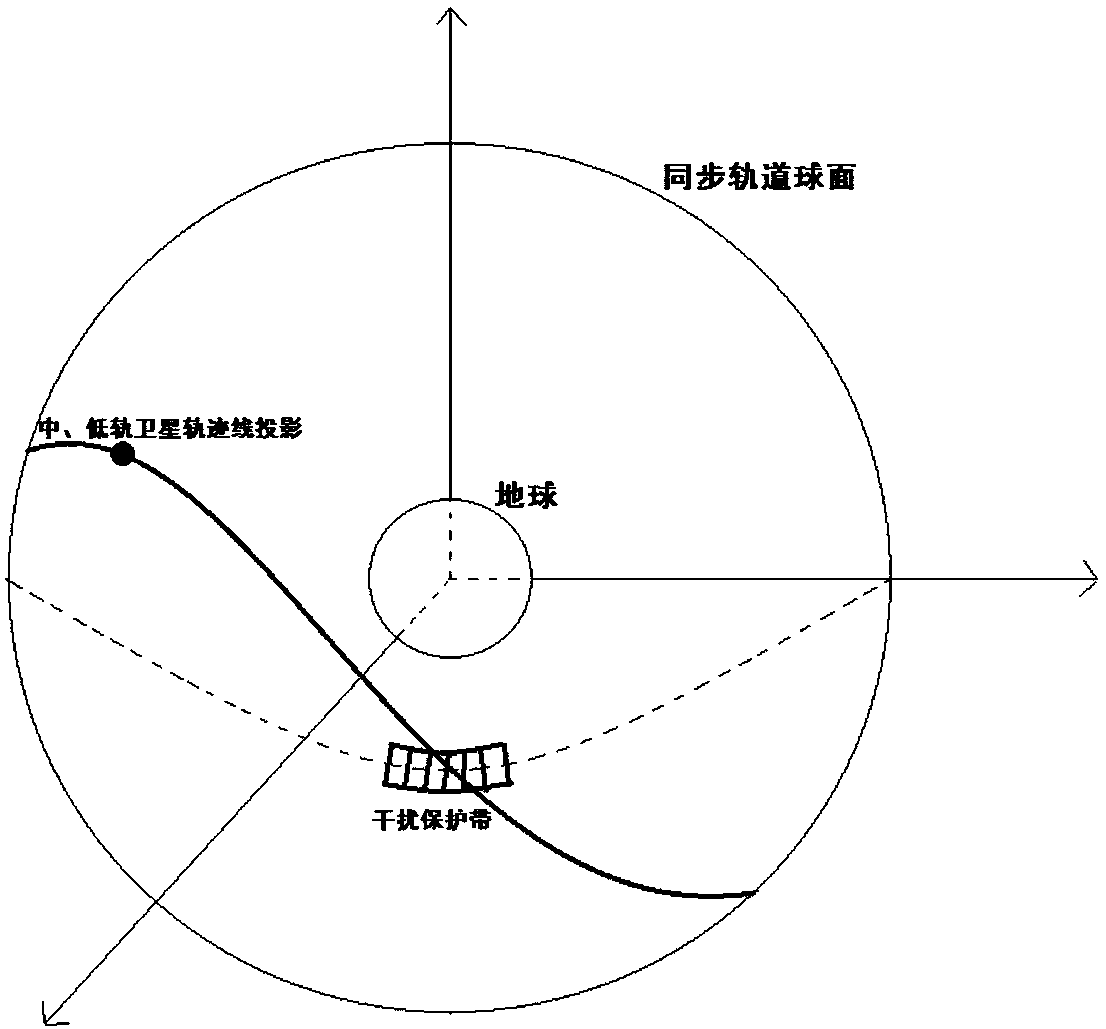
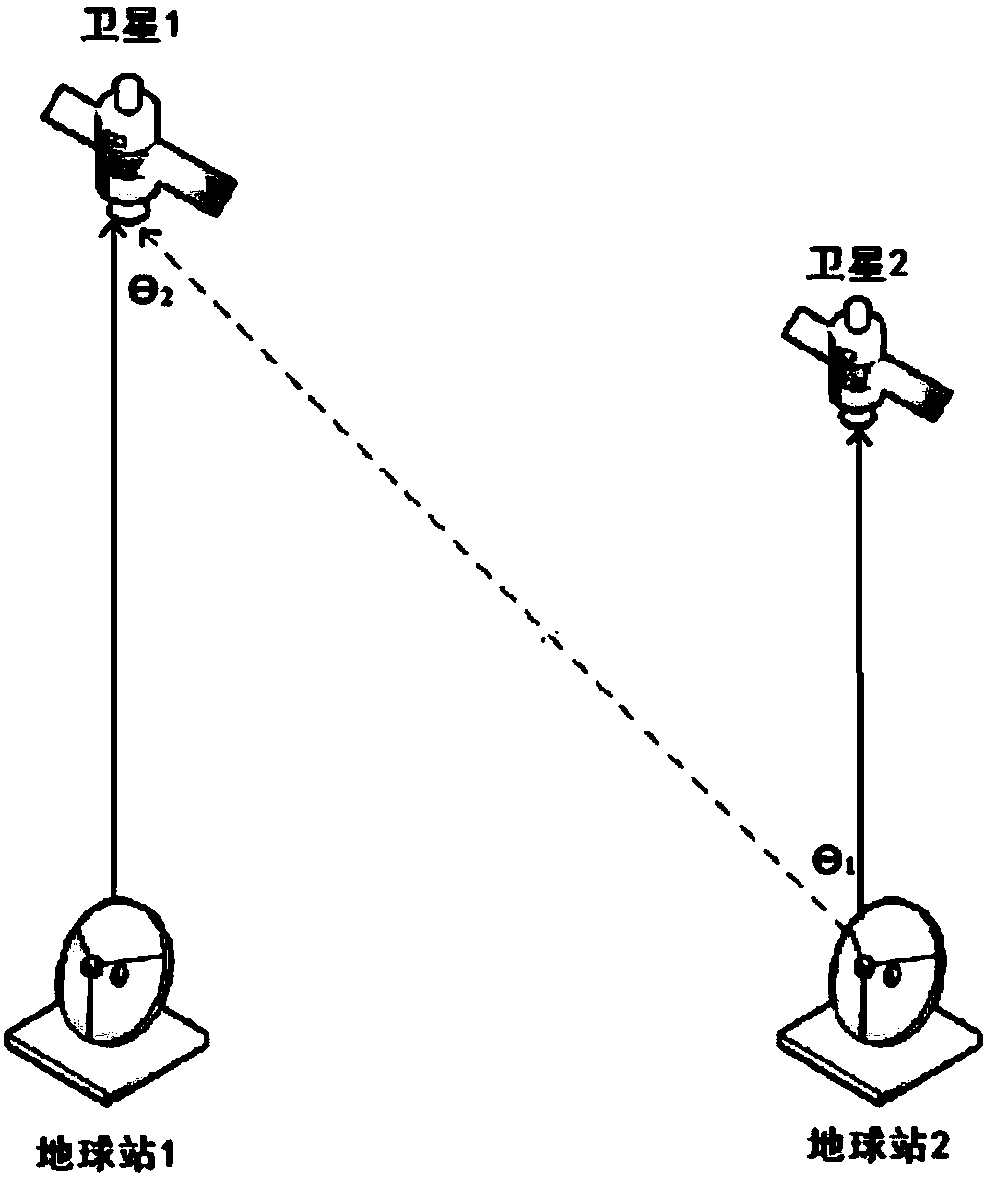
Method for performing interference analysis and avoidance on synchronous orbit satellite communication system
ActiveCN107809298AReduce the amount of online dataReduce the impact of communication qualityNetwork topologiesActive radio relay systemsCommunications systemSynchronous orbit
The invention relates to a method for performing interference analysis and avoidance on a synchronous orbit satellite communication system, characterized by including the following steps: 1) designinga recursive orbit for medium-earth and low-earth orbit satellites in a non-synchronous orbit satellite communication system to ensure that tracks of sub-satellite points of each satellite are periodically overlapped and cross over the equator at a plurality of fixed longitude points; 2) determining a range of the synchronous orbit satellite communication system that needs to perform interferenceanalysis according to relevant protection standards of the International Telecommunication Union; 3) performing interference analysis on the synchronous orbit satellite communication system, and setting corresponding interference protection belt zones for synchronous orbit satellites; and 4) enabling an earth station of the non-synchronous orbit satellite communication system to determine whetherthe medium-earth and low-earth orbit satellites need to take avoidance measures according to predicted system parameters and the running states of each medium-earth and low-earth orbit. The method disclosed by the invention can be widely applied in the field of interference analysis and avoidance of the synchronous orbit satellite communication system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
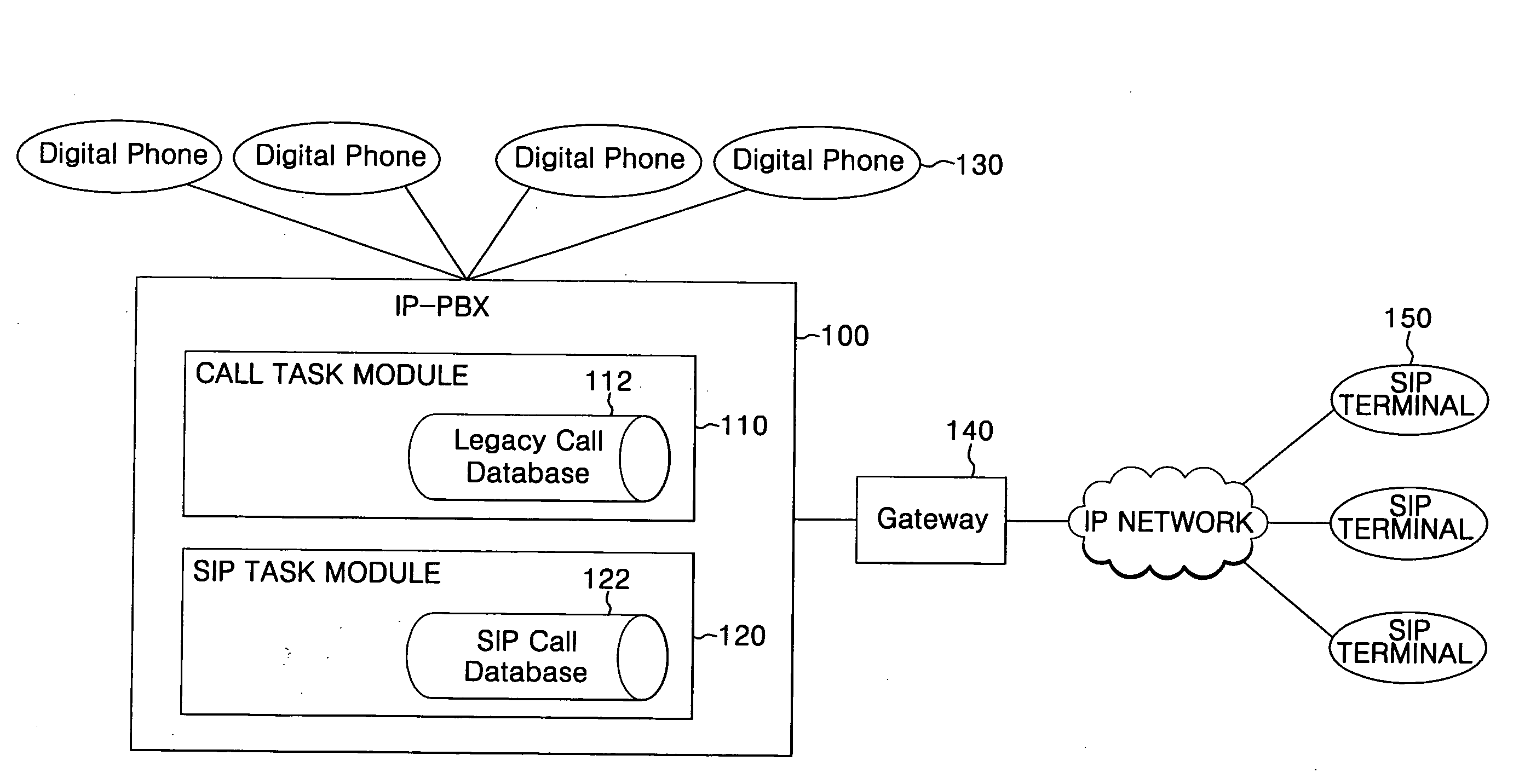
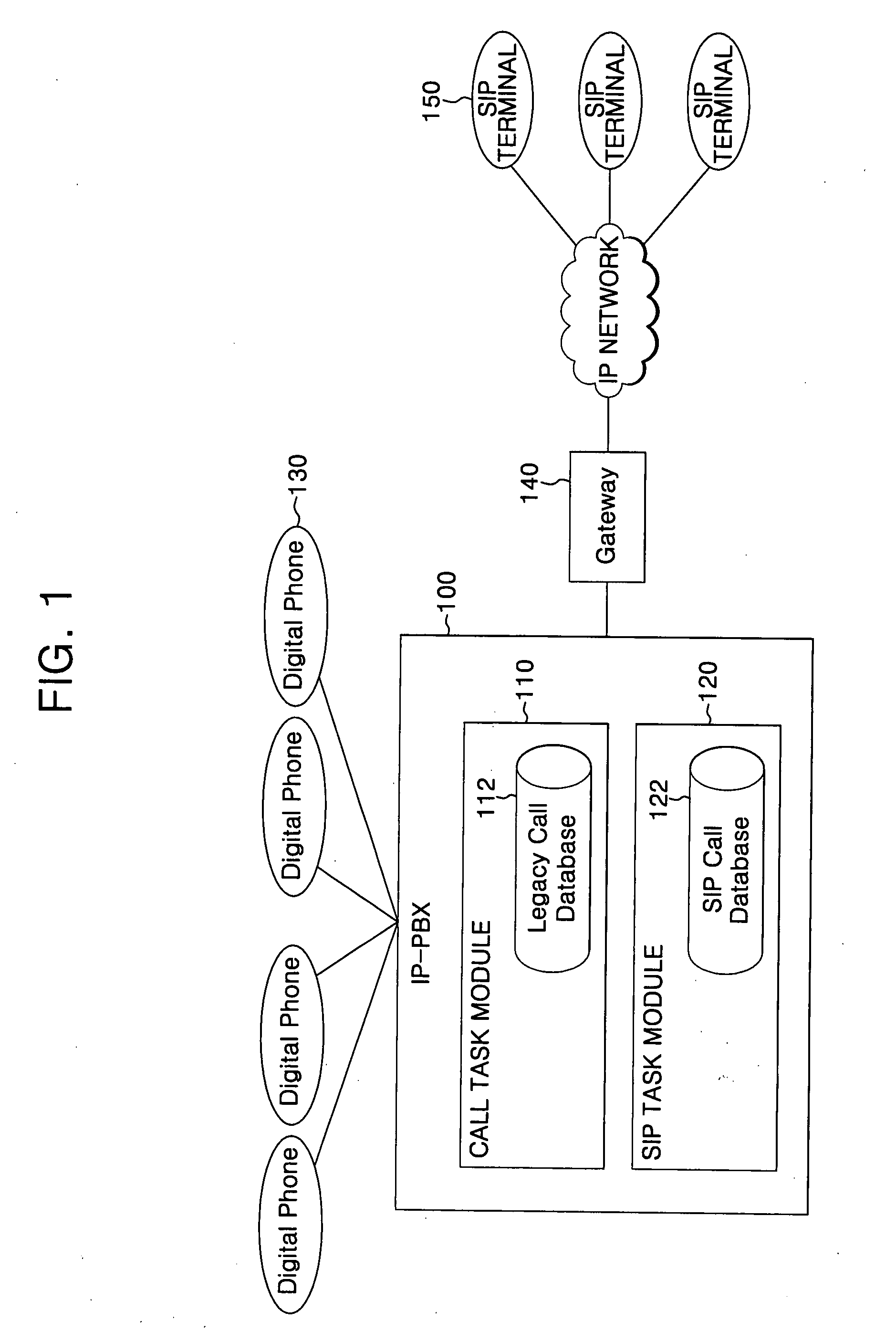
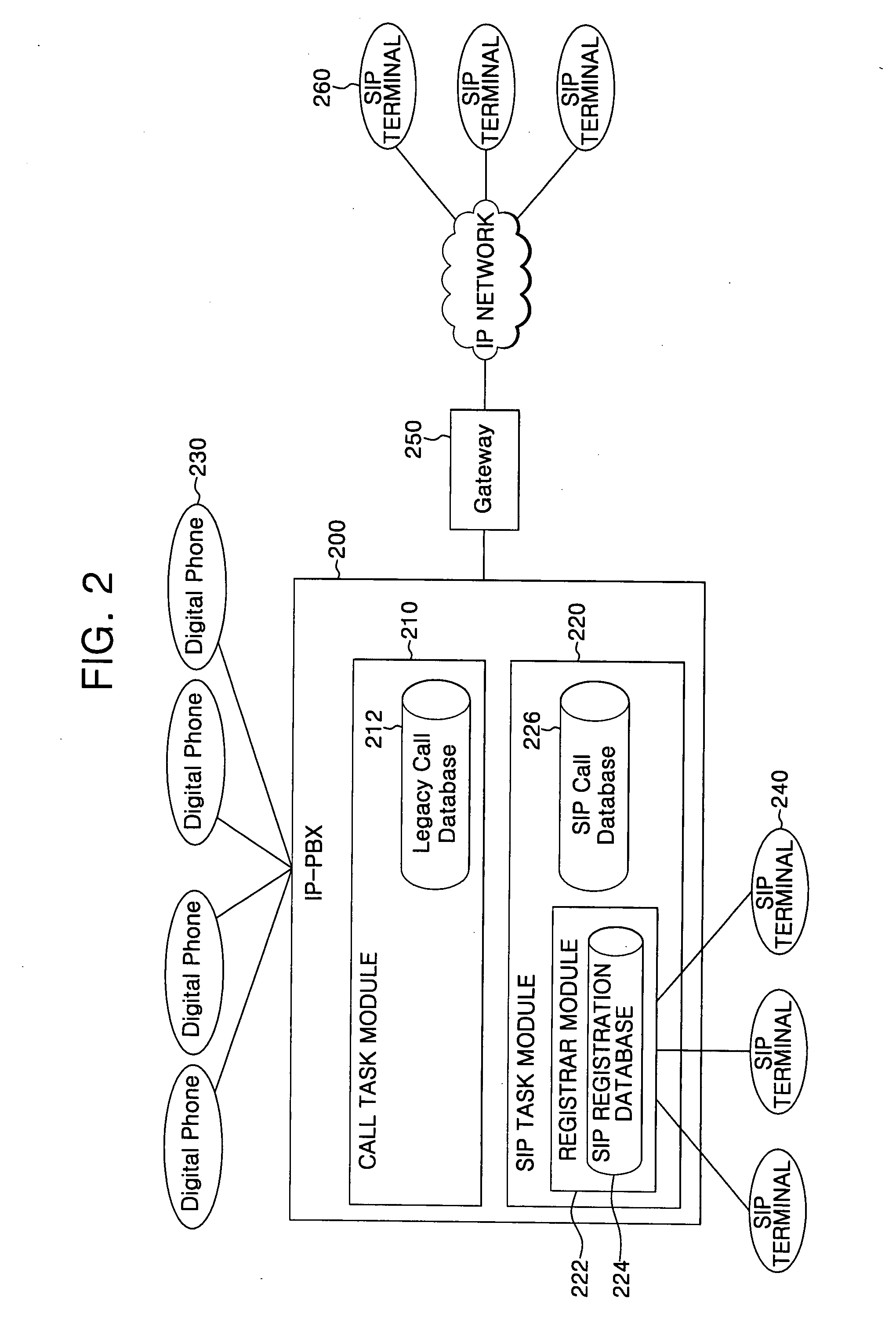
IP-PBX system and method for linking VoIP terminal therewith
InactiveUS20070206585A1Automatic exchangesNetworks interconnectionSession Initiation ProtocolTTEthernet
An Internet protocol (IP)-private branch exchange (PBX) system and a method for linking the system with a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) terminal. The IP-PBX system and method allow the VoIP terminal to be registered at an extension of the IP-PBX system, the VoIP terminal supporting a protocol, e.g., H.323 or session initiation protocol (SIP), standardized by a standardization organization, e.g., the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), or the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
COTM (communication on the move) satellite communication dual polarization quadruple ridged horn array antenna
ActiveCN103390798AGood transceiver gainExcellent transceiver gainWaveguide hornsAntenna arraysRadarSide lobe
The invention relates to a COTM satellite communication dual polarization quadruple ridged horn array antenna which is characterized in that 192 quadruple ridged horns are arranged at equal intervals in a square regular array; an azimuth plane comprises 32 columns, and a pitch plane comprises 6 rows; metal compensation grid plates are arranged at openings of the 192 quadruple ridged horns; each metal compensation grid plate divides each quadruple ridged horn into four small equal radiation units, so that the space of the 768 small radiation units formed on an array plane is smaller than a wave length, and when constant-amplitude same-phase feeding occurs to the planes, grating lobes cannot appear in a visible space, and the technical index requirements of the International Telecommunication for access wide-angle sidelobe envelope can be met. According to the antenna system, all technical indexes are advanced, the work is stable and reliable, the insertion loss is low, noise is little, and the antenna is provided with an ultrathin low profile and particularly suitable for being taken as a COTM satellite communication antenna of a mini-automobile, and can be widely used in fields such as radars, communication, remote sensing, remote measuring and the like.
Owner:NANJING YOUQIAO ELECTRONICS TECH
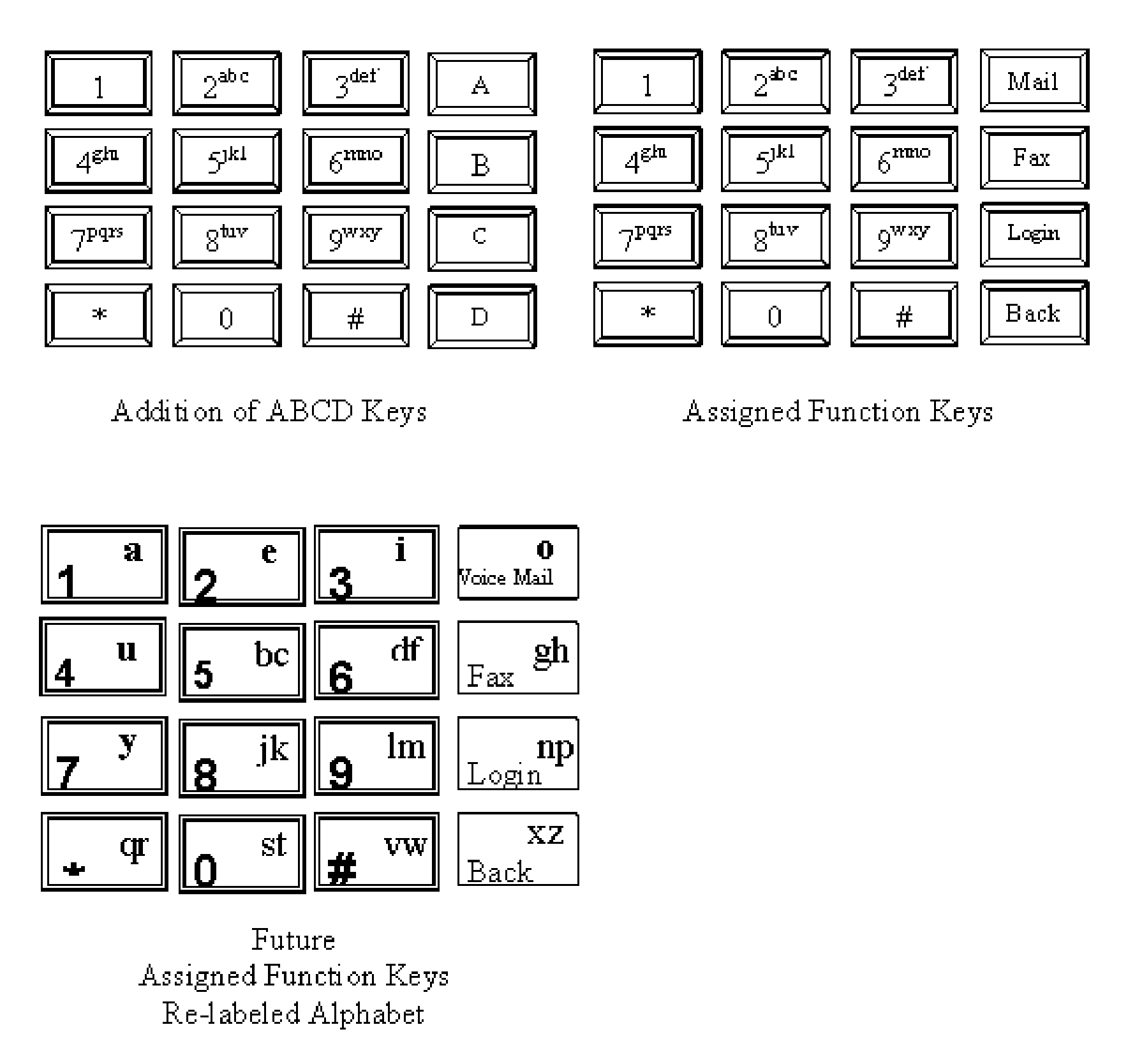
Enhanced user functionality from a telephone device to an IP network
InactiveUS7627110B2Subscriber signalling identity devicesAutomatic exchangesSignal onTelephone network
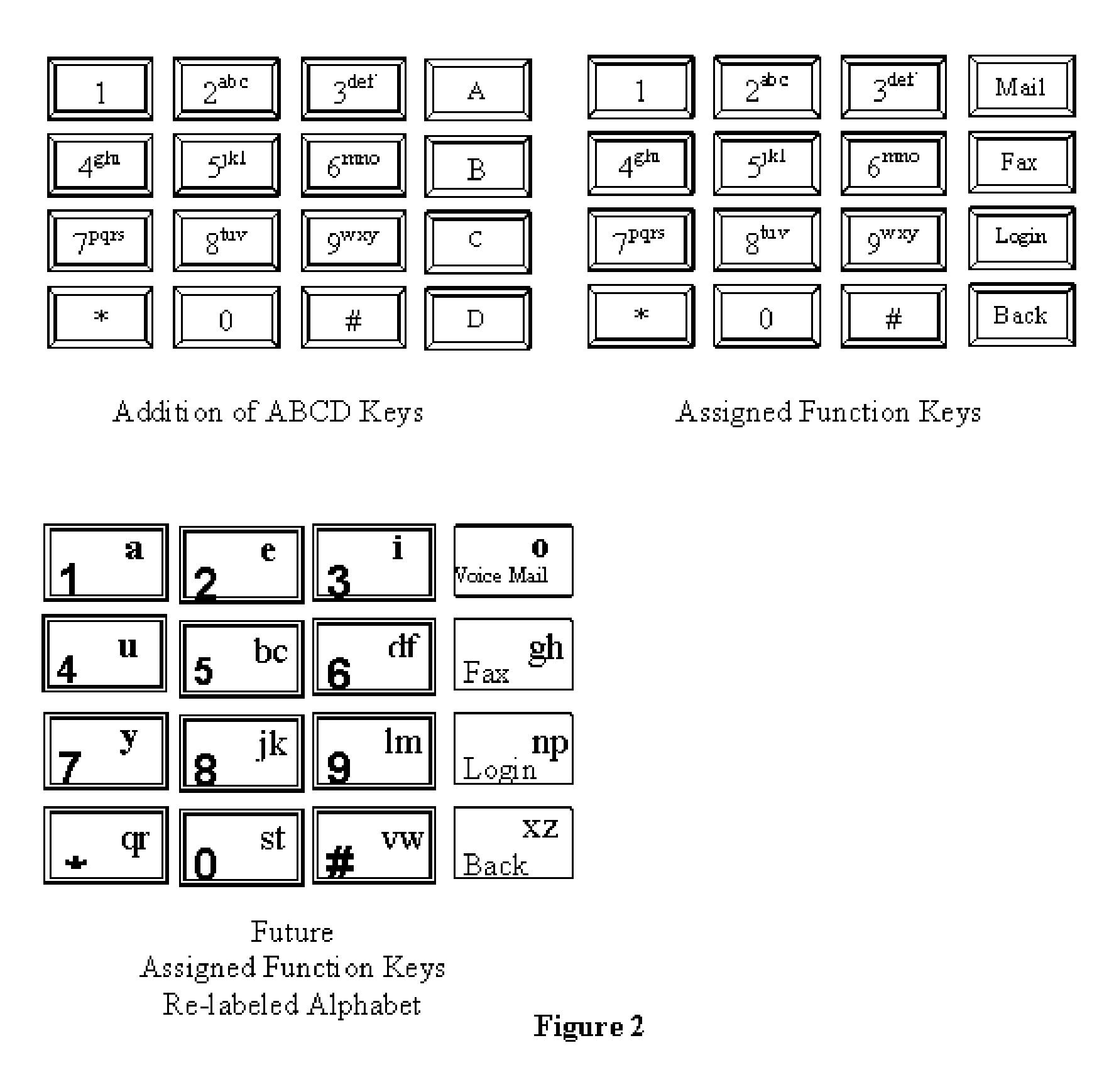
This invention encompasses the utilization of all of the 16 DTMF tone signals on telephone devices and their use for additional adjunct feature controls over IP networks that offer a plethora of new options from telephone devices. Calls on the PSTN only require the 0-9 digits to be used to complete a call following the North American Numbering Plan and International Telecommunications Union (ITU) standards. Conventional telephones electronically have the standard electronics for all 16 DTMF tone signals, but only 12 are utilized on conventional telephones by the typical 4 row and 3 column keypad matrix arrangement. In other words, 25% of the 16 DTMF tones are not being utilized in the public telephone networks. This invention lays the claims surrounding a 100% utilization methodology and possible expansion thereof when communicating to an IP network.
Owner:MOW JOHN BECK
Optical interference filter having parallel phase control elements
The invention relates generally to optical interference filters and interferometers. Methods, devices and device components are presented for separating closely spaced optical channels with minimized cross talk. The invention provides optical interference filters having parallel phase control elements which efficiently transmit light of a selected optical channel or a plurality of selected channels with decreased light loss, particularly decreased insertion loss. An exemplary interference filter of the present invention provides minimized vertical and horizontal recombination error and improved optical path length matching. The invention further provides methods of fabricating optical interference filters with improved piece-to-piece reproducibility. The methods, devices and device components provided herein are particularly well-suited for combining or separating closely spaced optical signals corresponding to transmission channels of a selected frequency standard, such as the International Telecommunication Union frequency standard.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Anti-interference multi-stopband UWB (ultra-wideband) antenna unit aiming at ultra-wideband system
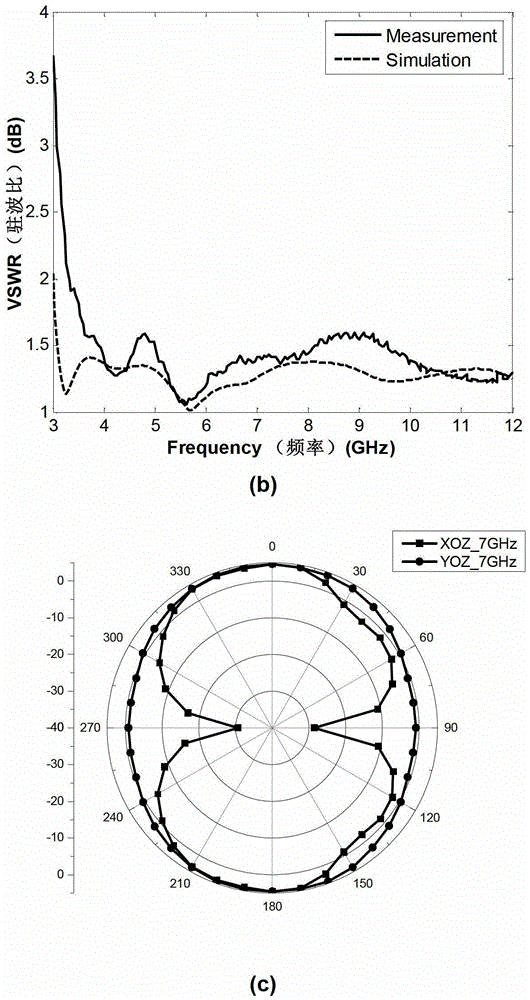
InactiveCN102916246AImprove reliabilityEasy to processRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsUltra-widebandResonance
The invention discloses an anti-interference multi-stopband UWB (ultra-wide-band) antenna unit aiming at an ultra-wideband system. A circular slot is carved in the middle of a square patch of an earth plate, a circular patch serving as a main radiator is arranged in the circular slot, at least one C-shaped parasitic Strip unit is arranged in a slot on the radiator, and at least one C-shaped Slot unit and an inverted-U-shaped unit are arranged on the earth plate. A simple, flexible and highly reliable UWB antenna is provided by means of adding a parasitic resonance unit and a slot resonance unit without increasing the size of the antenna and cost, arbitrary stopband and multi-frequency stopband within a whole UWB frequency range are achieved, and the four-stopband UWB antenna aiming at the downlink waveband and the ITU (international telecommunication union) of the WLAN (wireless local area network) technology and the satellite communication technology of the X waveband has excellent wideband characteristics and omnidirectional radiation characteristics.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
V.8bis suppression method and apparatus for modem relay
The invented method involves one or more gateways sniffing the voice channel during the voice mode. If it is determined that V.8bis signals are being initiated, then the gateway breaks these exchanges by suppressing such signaling, thereby avoiding the above-described detrimental effects. Modem relay communications then are allowed to proceed. Briefly, the method and apparatus involve monitoring a call during a voice mode phase for an initiating signal representative of the defined signaling, the monitoring being performed by a local gateway and, if such an initiating signal is detected during the monitoring, then suppressing such detected signaling in such manner that the signaling does not reach the remote gateway. Preferably, the monitoring is for an initiating signal characterized by a dual tone of defined frequency and duration of approximately 1375 Hz and 2002 Hz for a duration of approximately 400 ms or 285 ms, in agreement with the ITU-T Recommendation V.8bis (standard) adopted by the International Telecommunication Union. Monitoring is continued at least until an answer back from an answering station is received by the gateway. When the suppression succeeds and the remote (non-initiating gateway that may be awaiting such an initiating signal halts any further V.8bis transaction attempts, the local gateway initiates a modem relay session of operation with the remote gateway.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
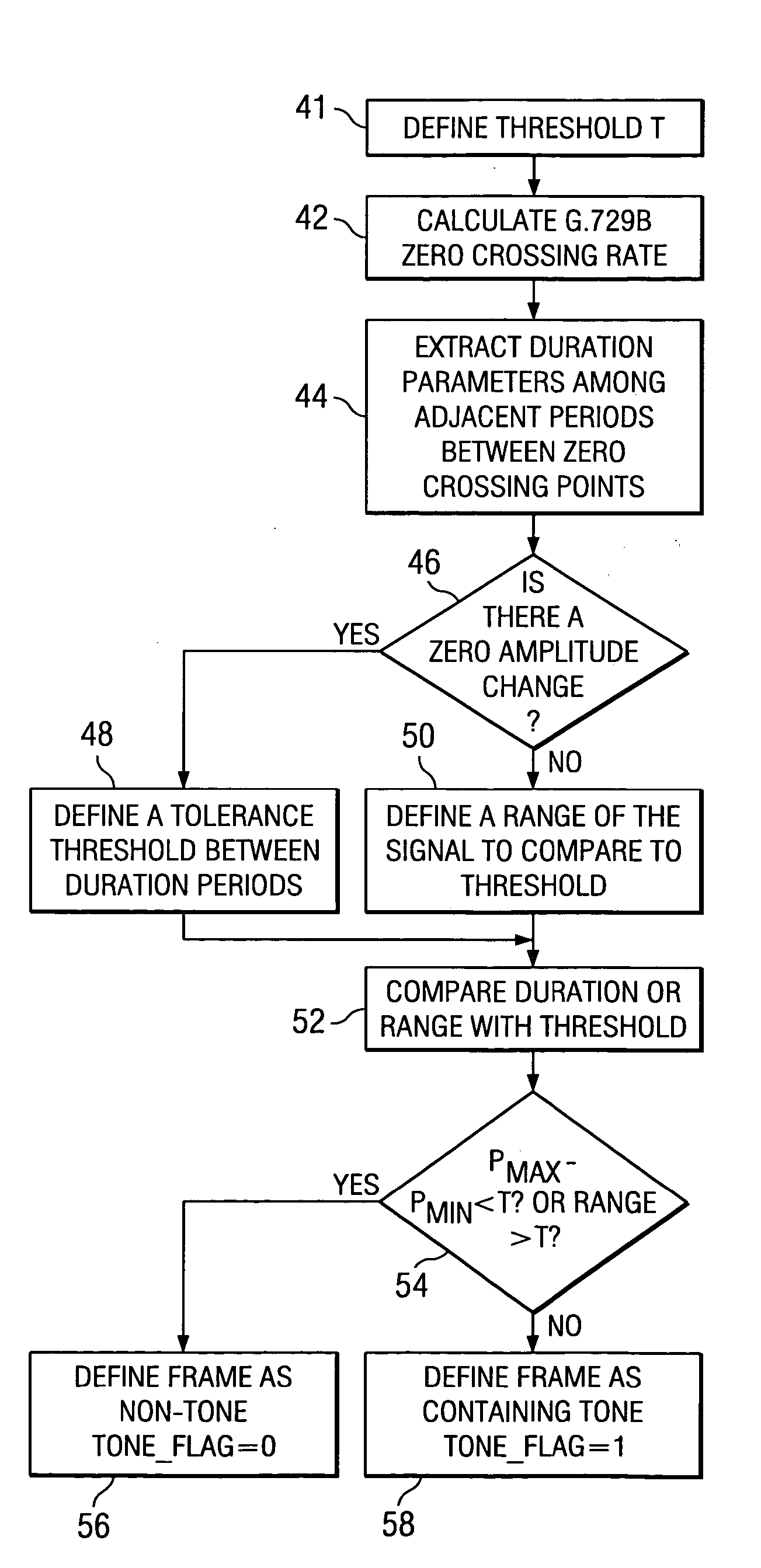
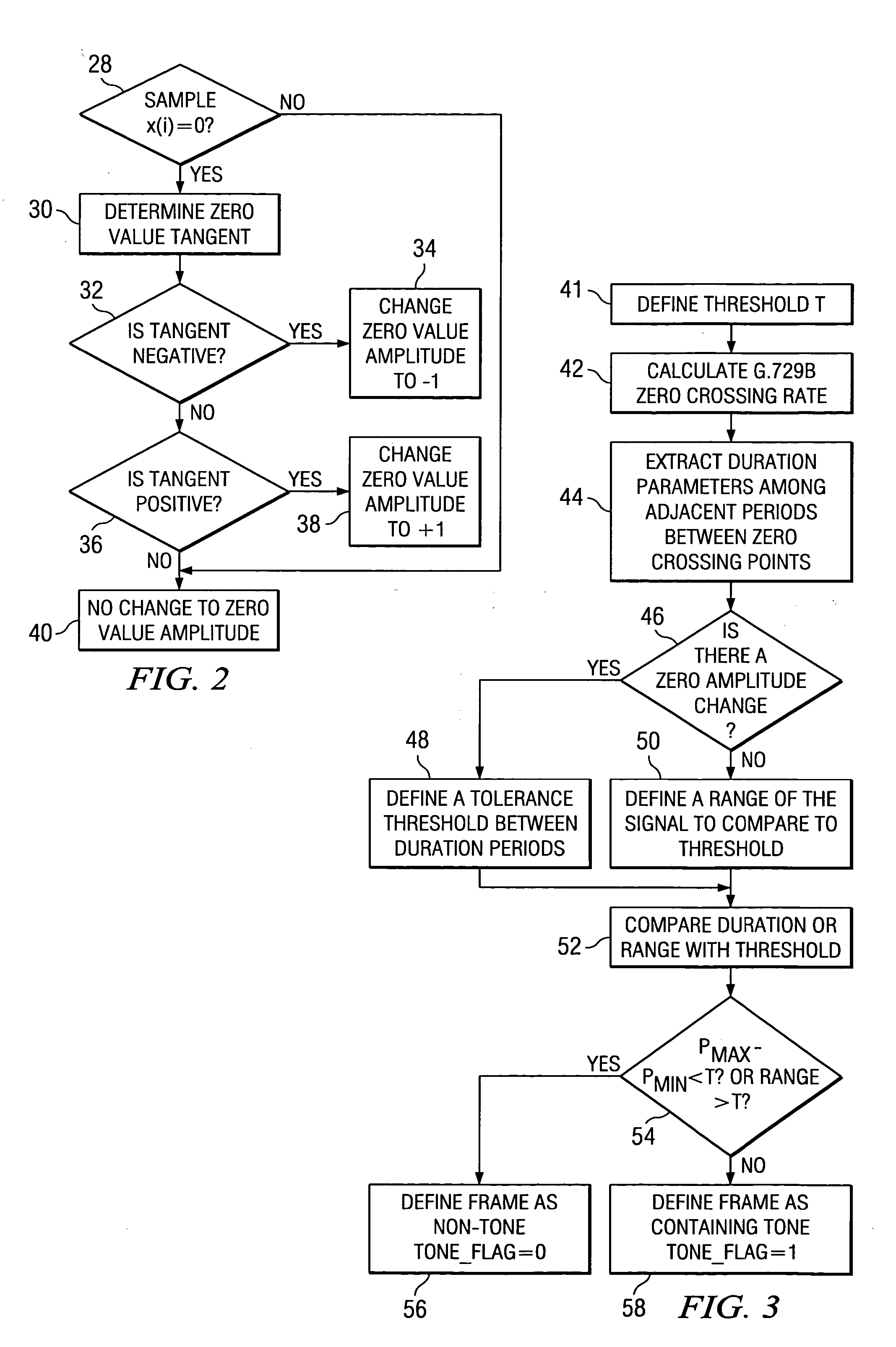
Tone, modulated tone, and saturated tone detection in a voice activity detection device
In a voice activity detection (VAD) device a method for defining tone signals comprises defining a threshold for zero amplitude change, calculating a zero crossing rate of a signal, extracting a set of parameters from a plurality of duration periods of the signal, defining a tolerance threshold between the plurality of duration periods when a zero amplitude change occurs, calculating a maximum difference between the plurality of duration periods, and comparing the maximum difference with the threshold. The method is implemented in the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) recommendation G.729 Annex B VAD.
Owner:TELOGY NETWORKS
C+L band multi-wavelength optical fiber laser with one-way feedback
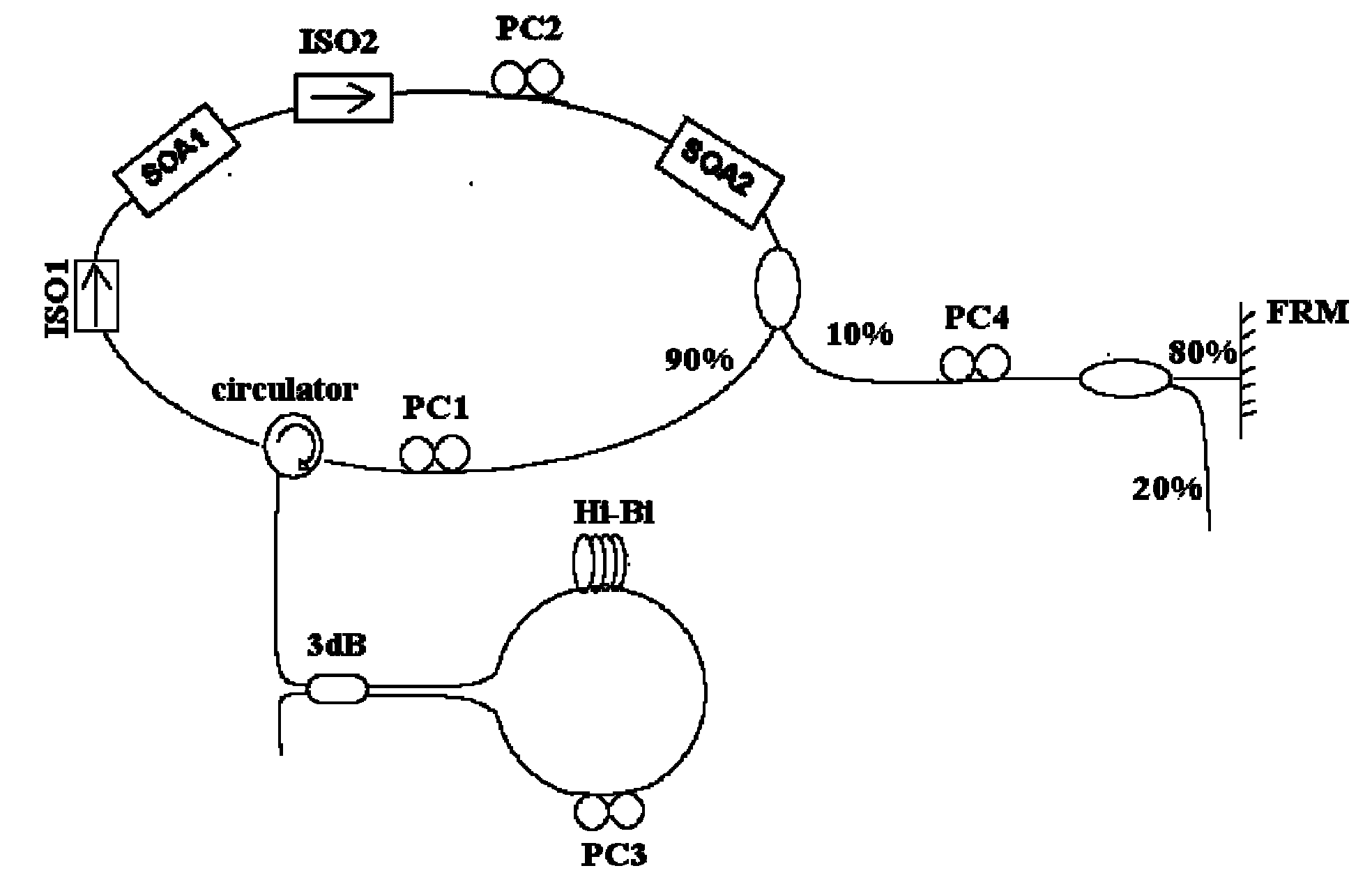
InactiveCN101777727AStable outputSimple structureLaser arrangementsActive medium shape and constructionLine widthPower difference
The invention relates to the field of optical fiber lasers, in particular to a C+L band multi-wavelength optical fiber laser with one-way feedback, which comprises an optical fiber annular chamber, a high birefringence optical fiber annular mirror and an one-way feedback mirror, wherein the optical fiber annular chamber comprises a first semiconductor optical amplifier, a second semiconductor optical amplifier, an optical fiber annular chamber coupler, a first optical isolator, a second optical isolator, a first optical fiber polarization controller, a second optical fiber polarization controller and a circulator; the high birefringence optical fiber annular mirror comprises a 3dB coupler, a high birefringence optical fiber and a third optical fiber polarization controller; and the one-way feedback mirror is formed by sequentially connecting a fourth optical fiber polarization controller, an output coupler and a Faraday feedback mirror. The optical fiber laser of the invention can obtain multi-wavelength stable output in the C+L band at room temperature, the wavelength interval meets the WDM ITU (Wavelength Division Multiplex International Telecommunication Union) standard of 100GHz and can be integrally adjusted continuously in the range of 50GHZ, the line width of the output wavelength of the laser is less than 0.1nm, the output power of each channel is uniform, the power difference between every two wavelengths is less than 6dB, and the signal-to-noise ratio is greater than 25dB.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
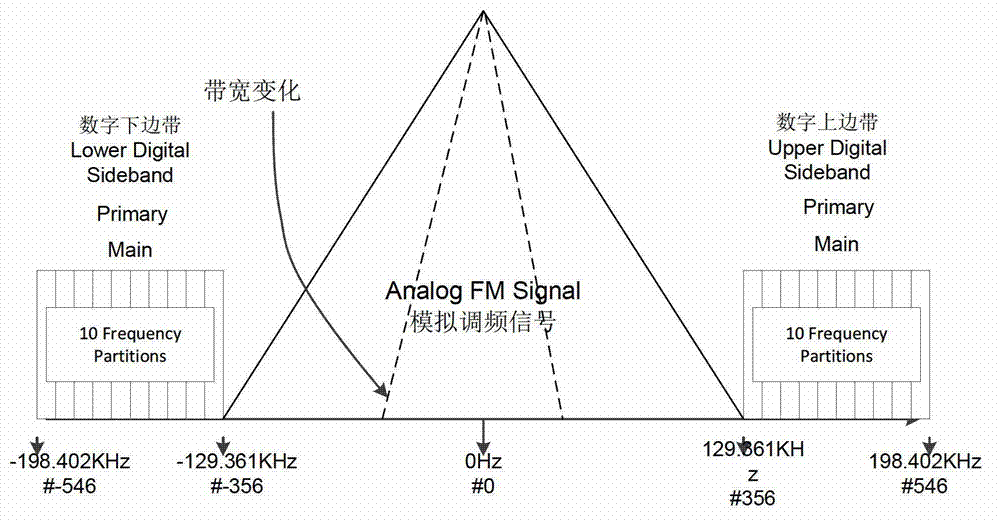
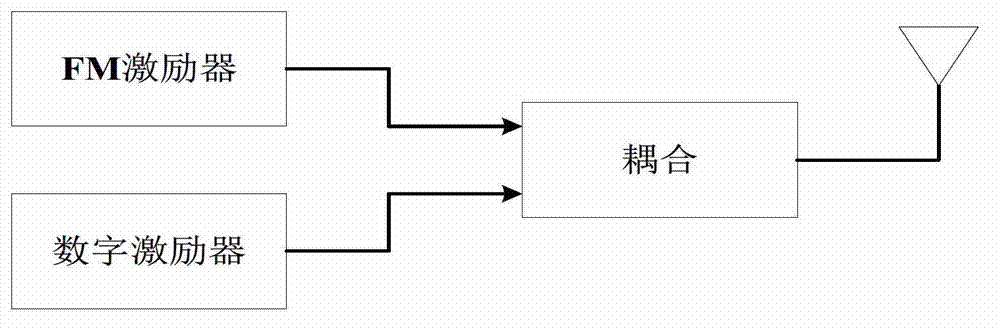
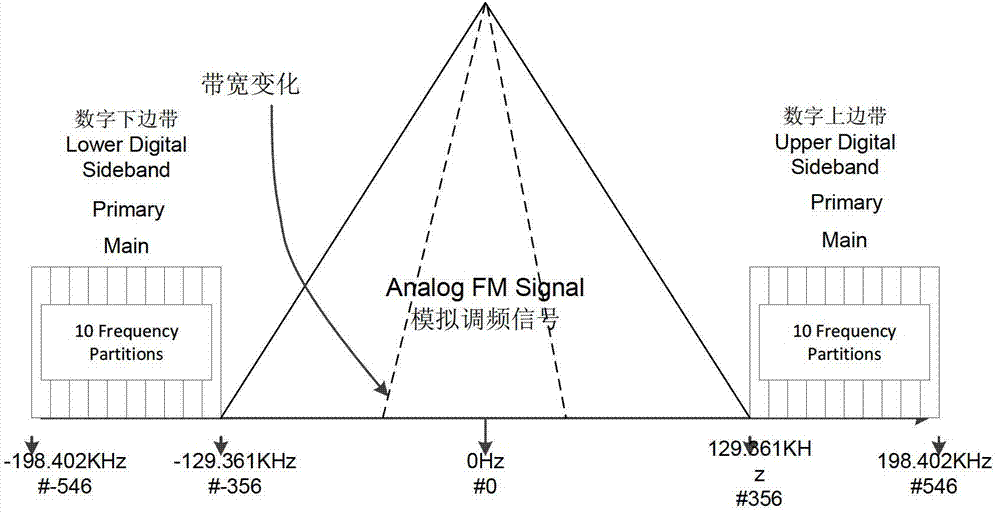
Digital spectrum detection method for in-band on-channel (IBOC) system based on ear perception
The invention discloses a digital spectrum detection method for an in-band on-channel (IBOC) system based on ear perception. By a high-definition (HD)-Radio system, in-band same-frequency transmission of an analog signal and a digital signal is realized; by the in-band same-frequency transmission mode, the digital signal is fixedly arranged at a position deviated from a carrier frequency of 130 to 200 KHZ; by a fixed combination mode, the digital signal is coupled with a frequency modulation (FM) analog signal; and the spectrum bandwidth of the FM analog signal is changed along with a program signal, so that the bandwidth change range is wide. Analog audio quality subjected to signal modulation under spectrum positions of different digital signals according to an international telecommunications union-radiocommunication (ITU-R) base station (BS).1387-1 psychological acoustics model, so that on the premise that the audio signal quality is not influenced, bandwidth which can be saved by signal transmission is counted; and the transmission capacity of the digital signals in the HD-Radio system can be improved.
Owner:苏州威士达信息科技有限公司 +1
Tone, modulated tone, and saturated tone detection in a voice activity detection device
In a voice activity detection (VAD) device a method for defining tone signals comprises defining a threshold for zero amplitude change, calculating a zero crossing rate of a signal, extracting a set of parameters from a plurality of duration periods of the signal, defining a tolerance threshold between the plurality of duration periods when a zero amplitude change occurs, calculating a maximum difference between the plurality of duration periods, and comparing the maximum difference with the threshold. The method is implemented in the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) recommendation G.729 Annex B VAD.
Owner:TELOGY NETWORKS
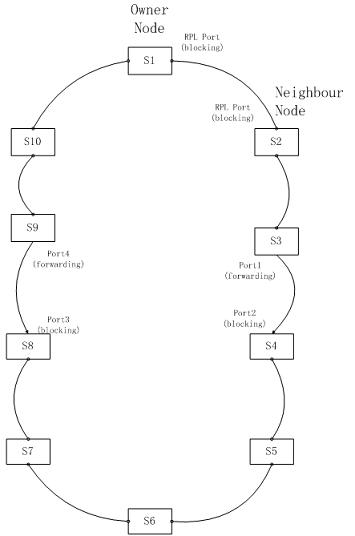
Expansion processing method under international telecommunication union telecommunication standardization sector (ITU-T) G.8032/Y.1344 multi-point fault
ActiveCN102510353AAvoid issues with incorrect transfers between ring nodesImprove reliabilityData switching networksRing networkComputer science
The invention discloses an expansion processing method under international telecommunication union telecommunication standardization sector (ITU-T) G.8032 / Y.1344 multi-point fault. The method comprises the following steps of: defining a protocol expansion frame with a specific target address, and forwarding the protocol expansion frame to a port of a central processing unit (CPU) under the condition that a ring port is blocked; sending a protocol frame through a ring network node, sending an expansion frame and setting a forwarding hop initial value; after the ring network node receives the expansion frame, forwarding the expansion frame which is sent by other nodes through another ring port after forwarding hops in the expansion frame gradually increase or decrease, wherein the forwarding hops of the expansion frame do not exceed a forwarding hop threshold value; and processing the expansion frame according to a flow which is defined by a protocol. The method has the advantages that: on the premise that a protocol state machine is not changed and the convergence speed of a ring network is not influenced, the problem that a loop can be blocked after recovery of breaking points in ITU-T G.8032 / Y.1344 is thoroughly solved; and the method is applicable to the occasions with a high reliability requirement for data communication in a severe industrial environment.
Owner:BEIJING INHAND NETWORKS TECH
An ultra-narrow-band comb filter
InactiveCN102289038AWith polarization splitting functionWith ultra-narrowband multi-channel filtering functionCoupling light guidesBeam splittingCenter frequency
The invention relates to an ultra-narrow band comb type filter, which belongs to a photoelectronic device and solves the problems that the existing comb type filter does not have the polarization beam splitting function, and the single channel has wide band width. The ultra-narrow band comb type filter consists of a photoisolator, a polarization beam splitter, a first multi-channel filter and a second multi-channel filter, wherein an incident light beam enters the polarization beam splitter through the photoisolator and is divided into a path of S light and a path of P light, the S light and the P light respectively enter the first multi-channel filter and the second multi-channel filter to be filtered, the center frequencies of the first multi-channel filter and the second multi-channel filter are staggered and conform to the international telecommunication union regulations, the output channel intervals are respectively 50GHz, 100GHz or 200GHz, and the output of the first multi-channel filter and the output of the second multi-channel filter are the output of the ultra-narrow band comb type filter. The ultra-narrow band comb type filter simultaneously has the polarization beam splitting function of the polarization beam splitter and the ultra-narrow band multi-channel filtering function of the multi-channel filters, adopted optical devices are few, the structure is simple, the output signal line width is narrow, the output channel intervals can select 50GHz, 100GHz or 200GHz, the center frequency conforms to the international telecommunication union regulations, and the ultra-narrow band comb type filter is suitable for being used in dense wave multiplexer systems with different requirements.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
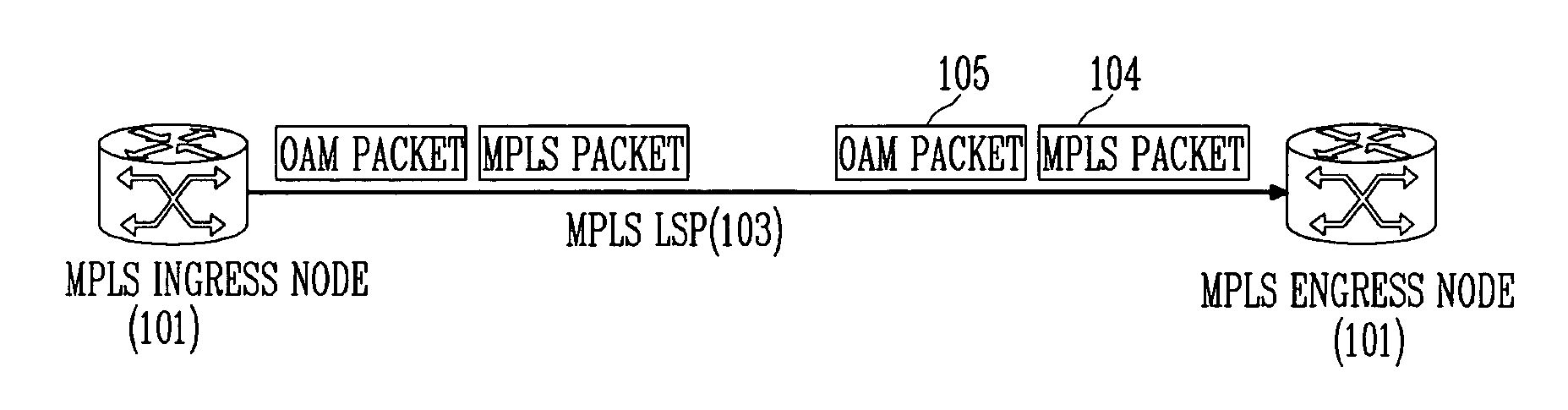
Method for measuring performance of MPLS LSP
InactiveUS20070133540A1Increase the number ofError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsMulti protocolLabel switching
Provided is a method for measuring performance of a multi-protocol label switching label switched path (MPLS LSP), using a fast failure detection (FFD) packet among MPLS operation and management (OAM) packets recommended by International Telecommunication Union-Telecommunication standardization sector (ITU-T) Y.1711 to detect a packet error generated in the MPLS LSP and newly defining bytes not used in the FFD frame to use the bytes for parity check. An ingress node performs the steps of: calculating a parity value of an MPLS packet as byte interleaved parity (BIP)-8 before transmitting the MPLS packet; storing the calculated parity value of the MPLS packet in an MPLS OAM packet of an FFD structure; and transmitting the MPLS OAM packet whenever transmitting the MPLS packet. And an egress node performs the steps of: calculating a parity value of a received MPLS packet; comparing a parity value of an MPLS packet stored in the MPLS OAM packet with the parity value of the received MPLS packet; and when the two parity values are not identical, determining that an error has occurred in the MPLS packet and discarding the MPLS packet.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
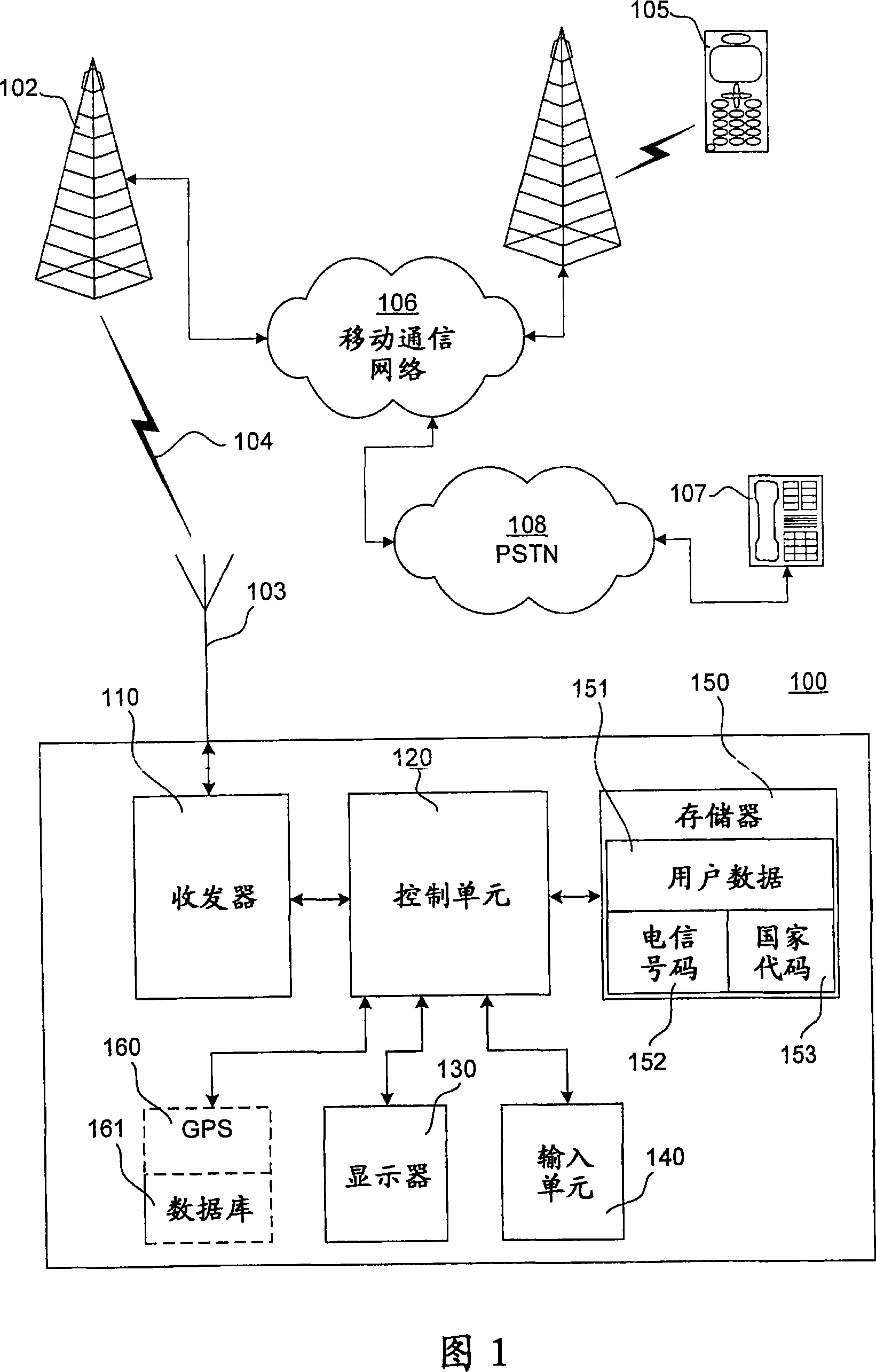
Completion of an international calling number in a mobile communication terminal
InactiveCN101057486AThe method is simple and reliableSubstation equipmentThe Country CodeComputer science
The invention discloses a method used for providing international telecommunication numbers from a mobile communication terminal (105) for a base station (102), wherein, the international telecommunication numbers comprise a plurality of numbers at least corresponding to country codes. The method comprises that: a control unit (200) of the mobile communication terminal (105) receives a plurality of numbers that identify a user terminal in a communication network and confirm whether one or a plurality of number(s) correspond(s) to the country codes, if not, the international telecommunication numbers are created by adding the country codes to a plurality of numbers. Therefore, the international telecommunication numbers are sent to a base station (240) or stored in a telephone (340).
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Enhanced User Functionality from a Telephone Device to an IP Network
InactiveUS20060029211A1Easy to useSubscriber signalling identity devicesAutomatic exchangesSignal onTelephone network
This invention encompasses the utilization of all of the 16 DTMF tone signals on telephone devices and their use for additional adjunct feature controls over IP networks that offer a plethora of new options from telephone devices. Calls on the PSTN only require the 0-9 digits to be used to complete a call following the North American Numbering Plan and International Telecommunications Union (ITU) standards. Conventional telephones electronically have the standard electronics for all 16 DTMF tone signals, but only 12 are utilized on conventional telephones by the typical 4 row and 3 column keypad matrix arrangement. In other words, 25% of the 16 DTMF tones are not being utilized in the public telephone networks. This invention lays the claims surrounding a 100% utilization methodology and possible expansion thereof when communicating to an IP network.
Owner:MOW JOHN BECK
Method for measuring performance of MPLS LSP
InactiveUS7561524B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetMulti protocol
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Dynamic data sending method for in-band on-channel (IBOC) system based on ear perception
The invention discloses a dynamic data sending method for an in-band on-channel (IBOC) system based on ear perception. A digital signal is arranged at different spectrum positions based on an international telecommunications union-radiocommunication (ITU-R) base station (BS).1387-1 psychological acoustics model; and received analog audio quality is analyzed to obtain an ear evaluation level of an audio program under different spectrum positions of the digital signal, so that a relation between each digital signal spectrum position of each frame of signal and a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) evaluation level. When the digital signal is sent, the spectrum position of the digital signal corresponding to a specific level is selected, so that a sub carrier number for transmitting the digital signal is instructed; and the digital signal of the dynamically distributed sub carrier number is coupled with an analog signal. On the premise that each frame of data has uniform ear perception, the available spectrum of the digital signal is increased, and the digital signal transmission capacity under a hybrid mode is improved.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com