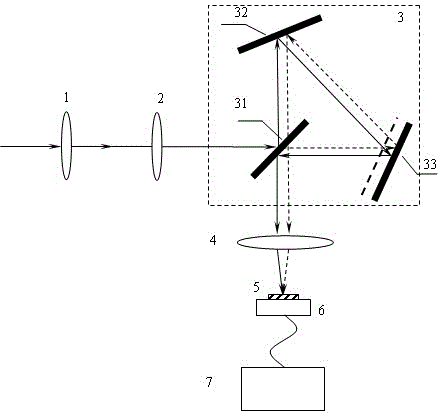Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
221 results about "Interferometric imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
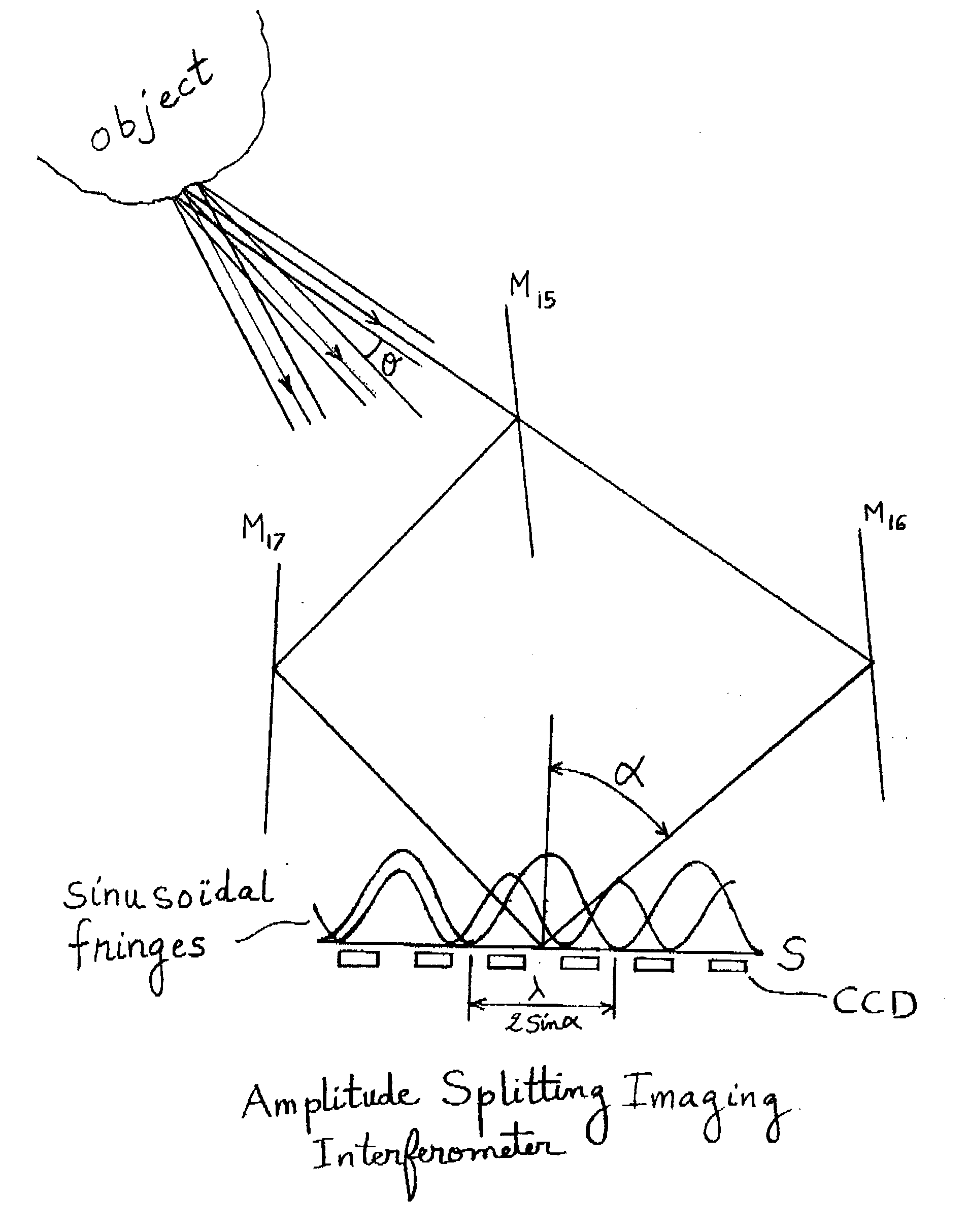
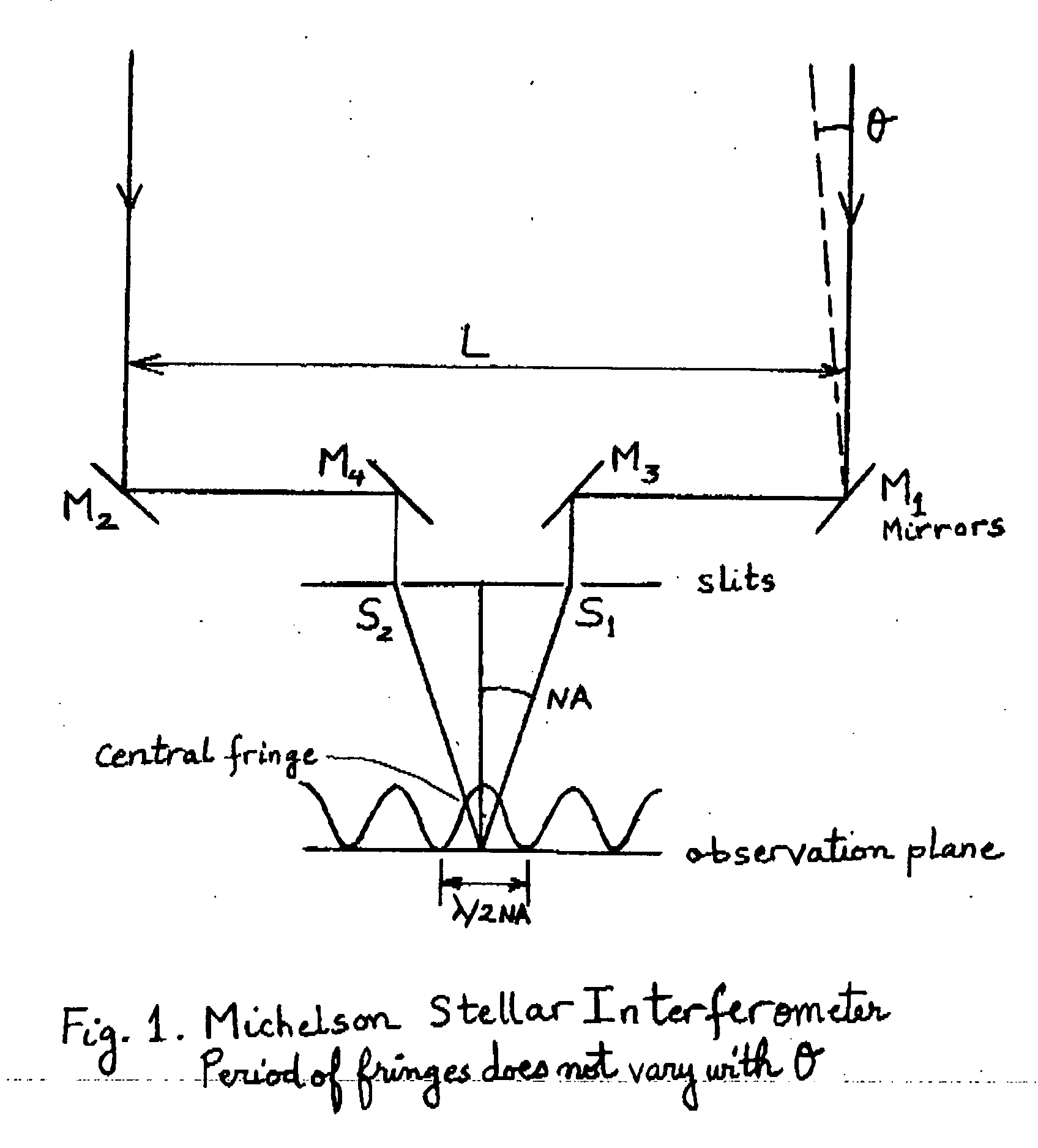
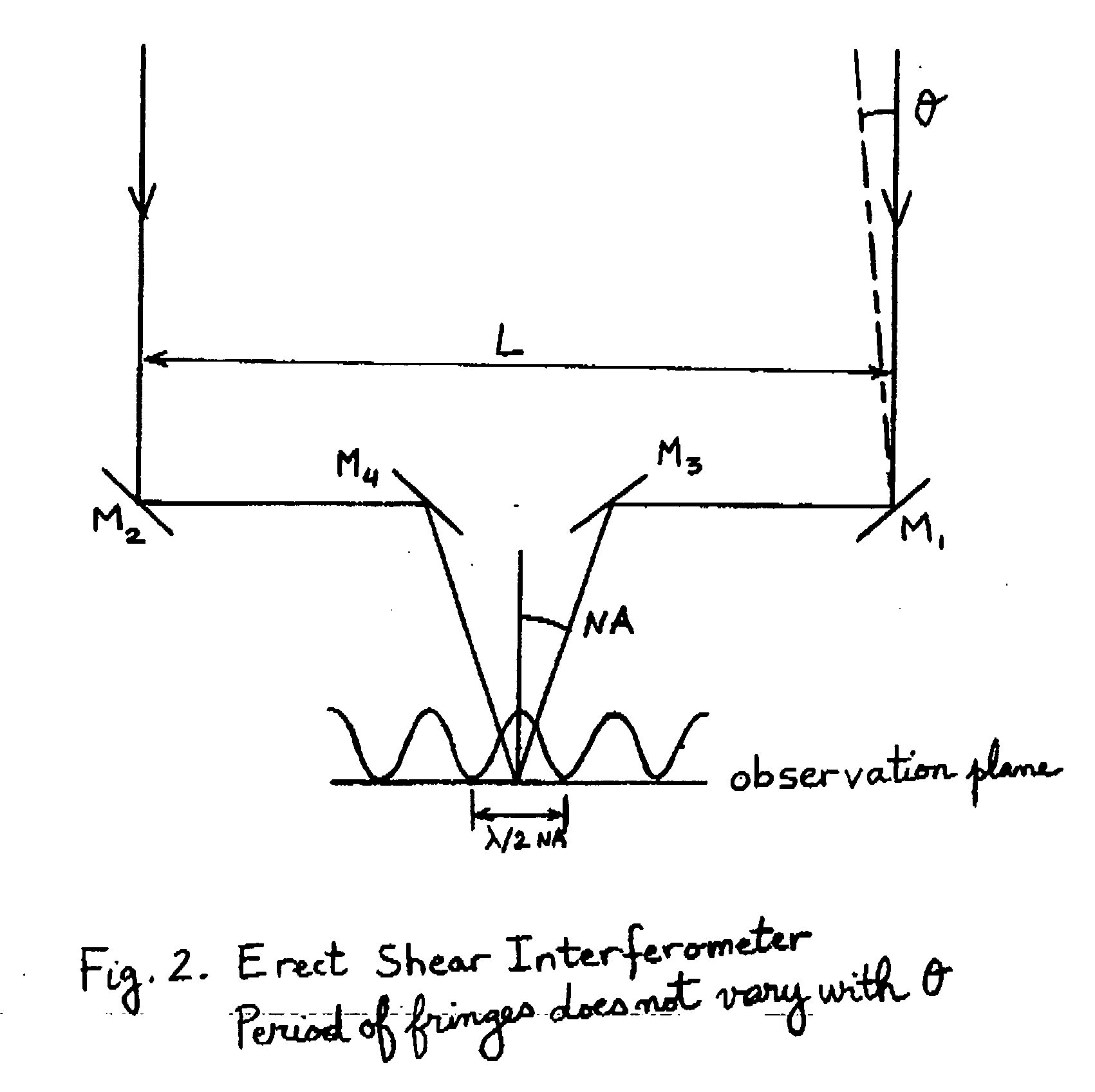
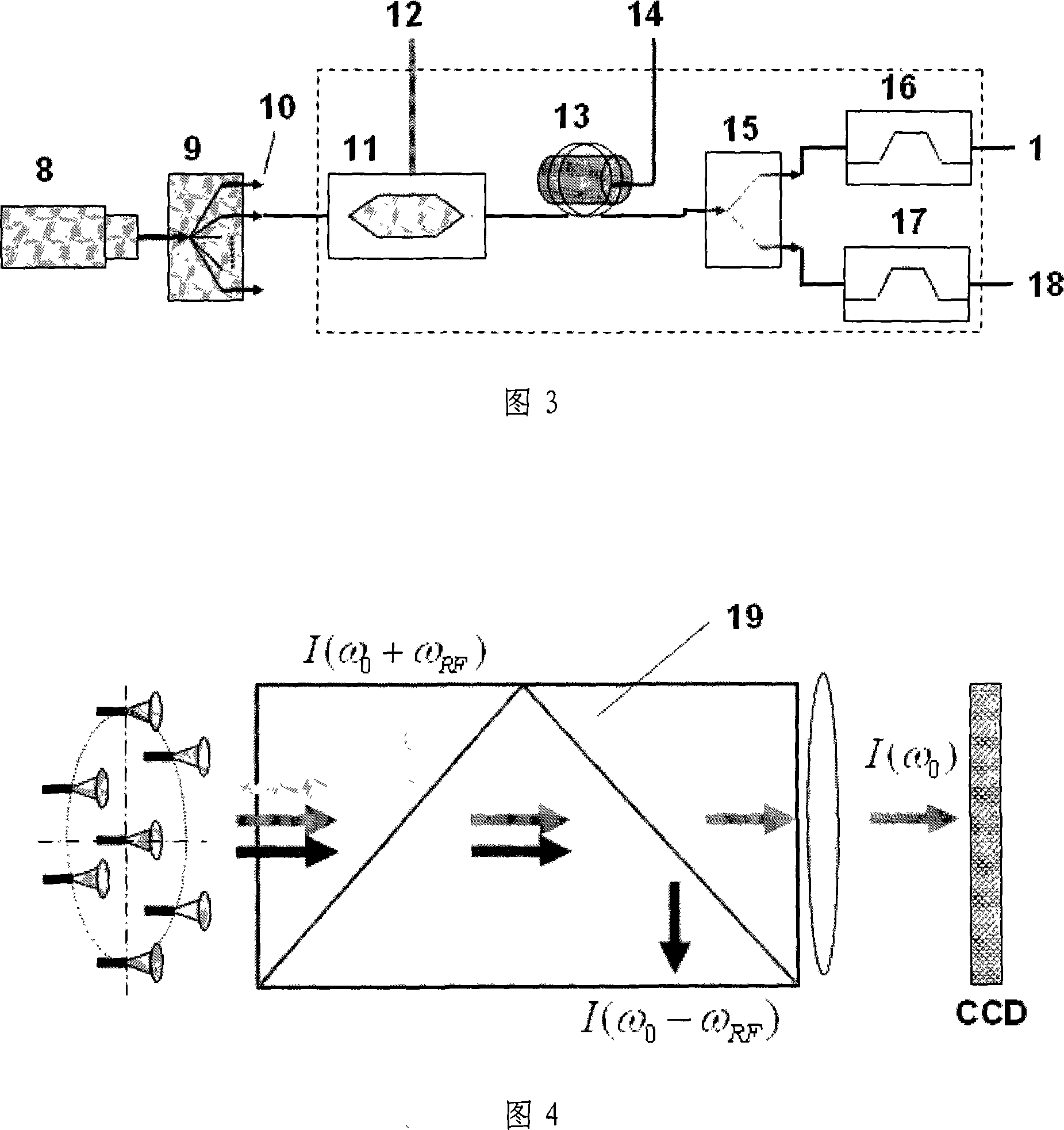
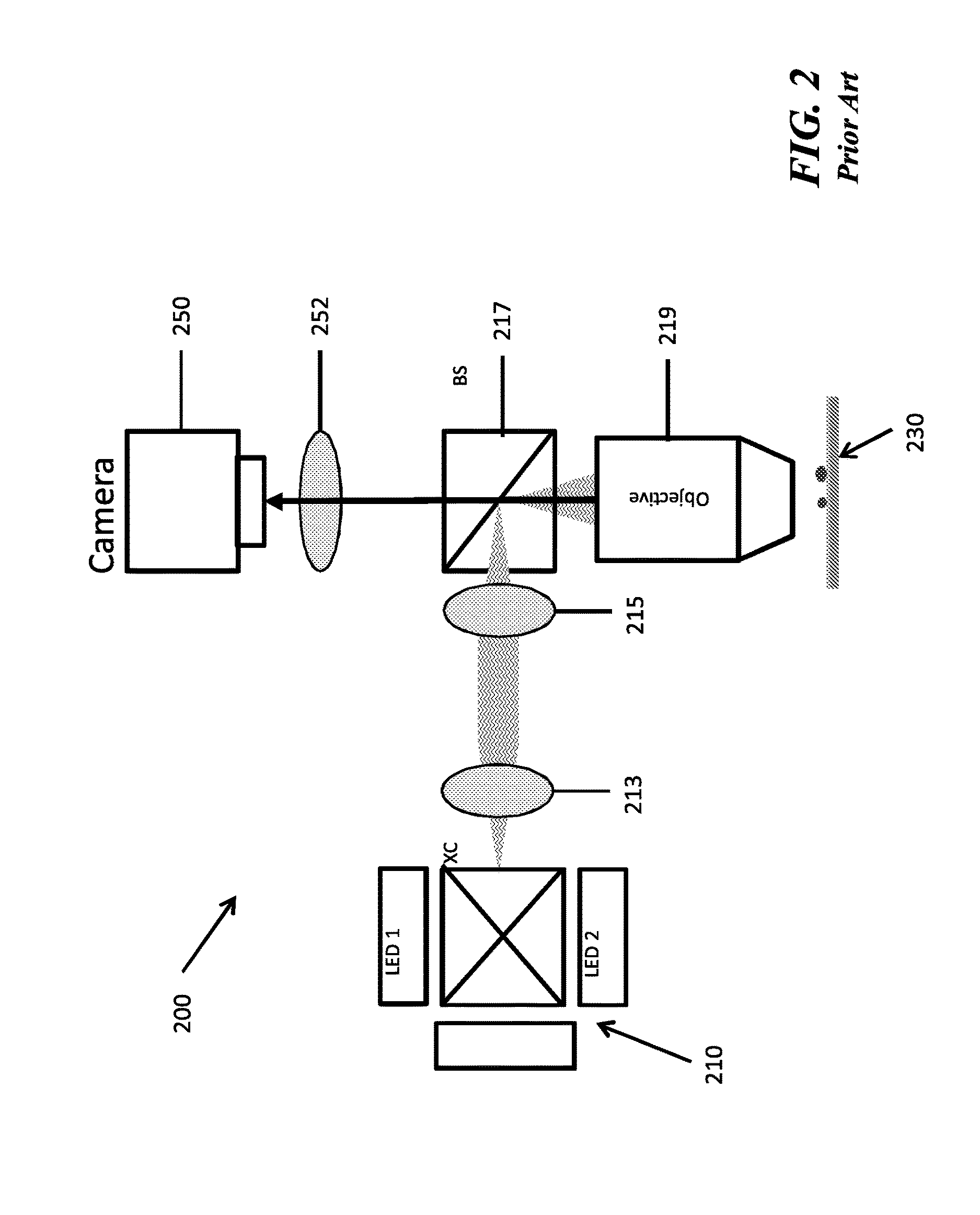
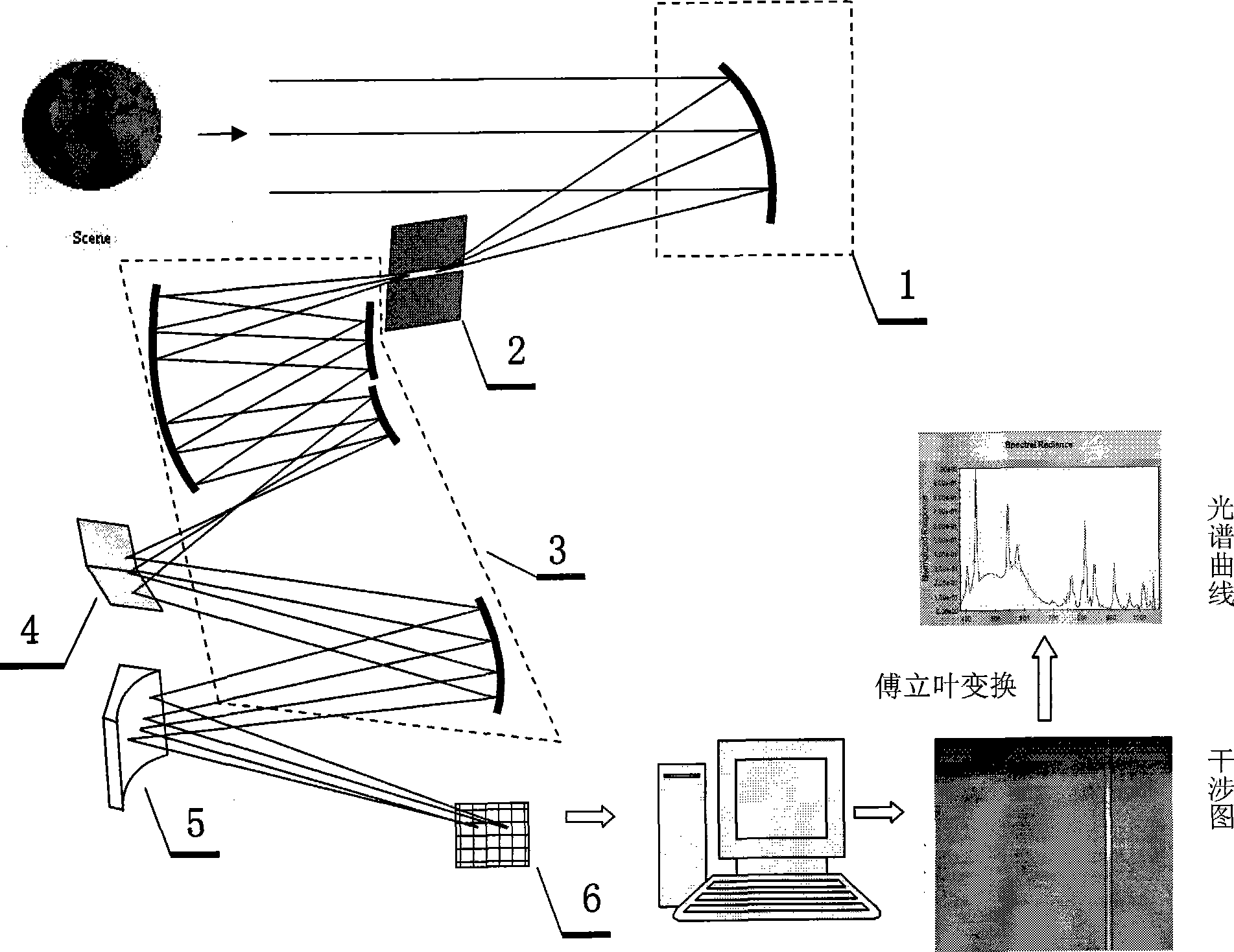
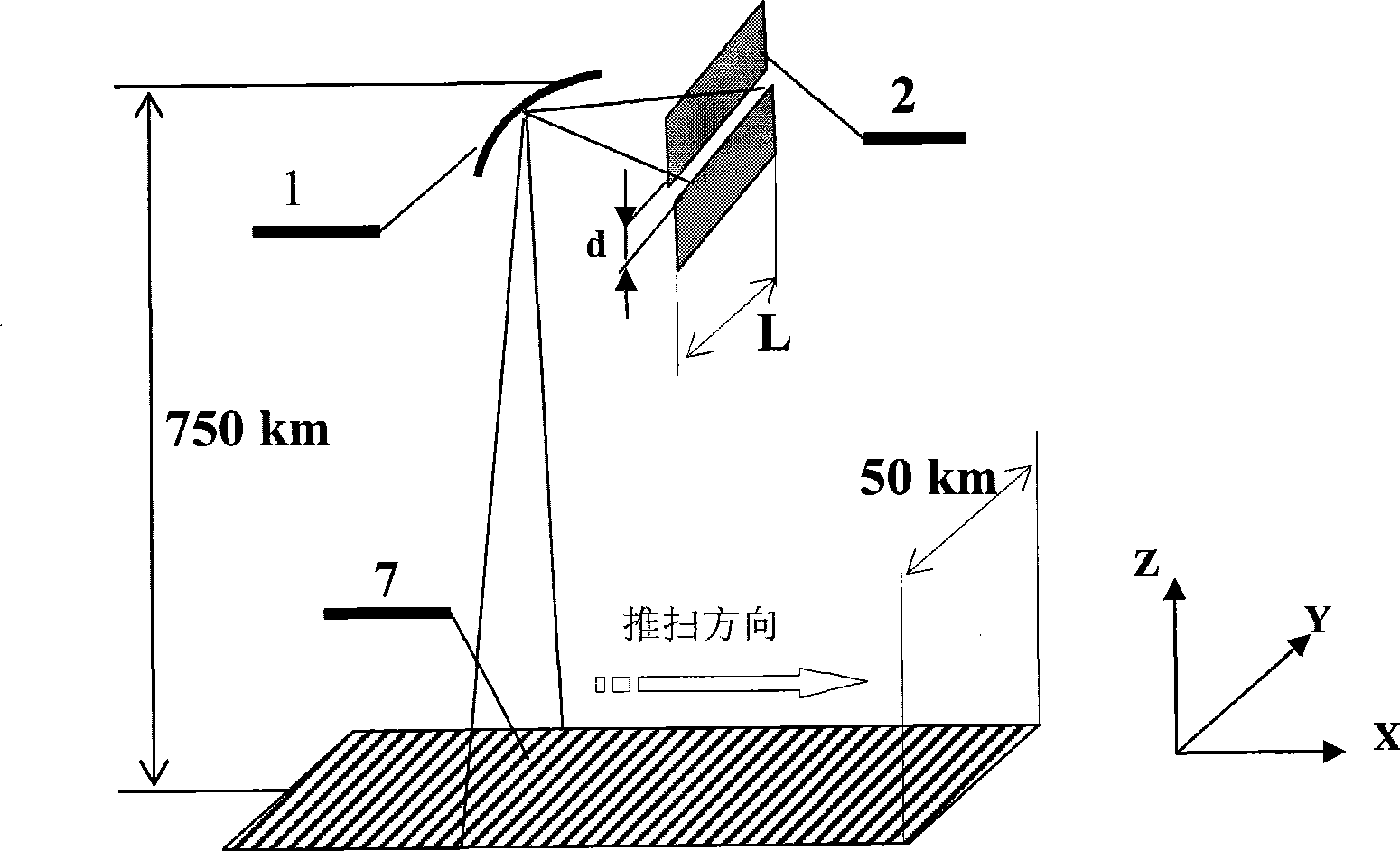
An Imaging Michelson interferometer is simply a Michelson interferometer where the telescope focal plane is imaged onto a detector array. An interferogram is recorded for every pixel in the field of view, and hence a spectrum can be obtained for every object.
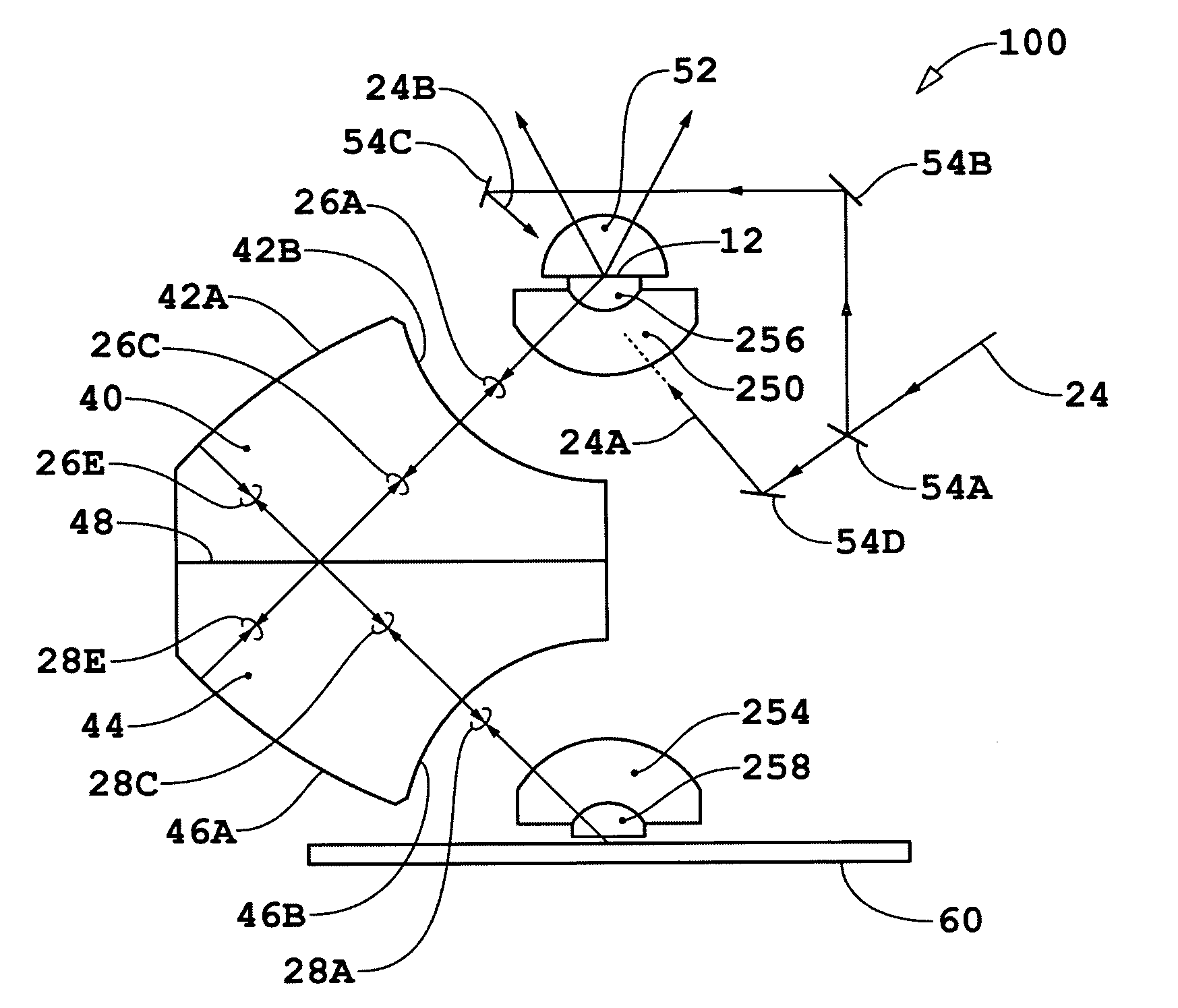
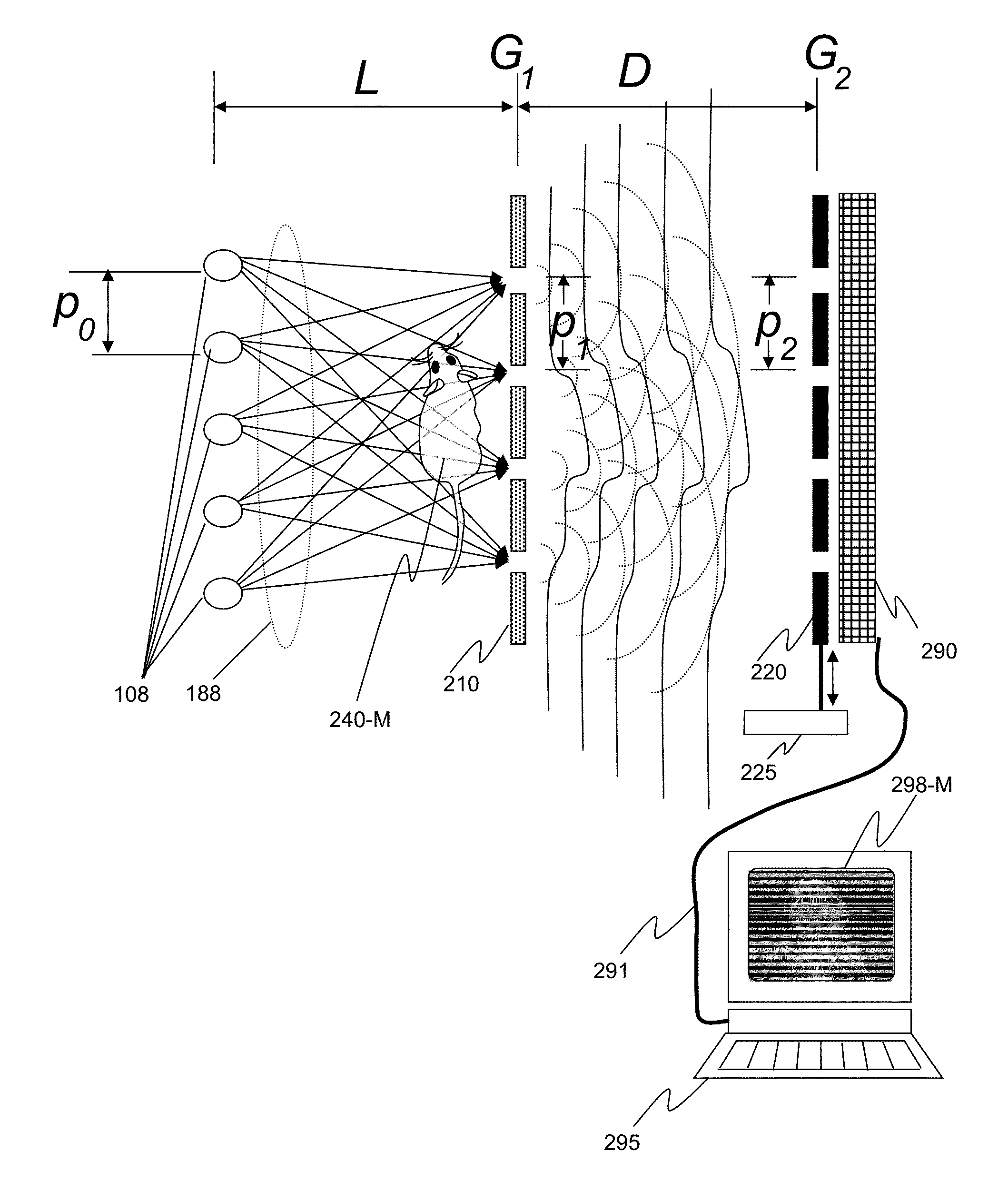
X-ray interferometric imaging system
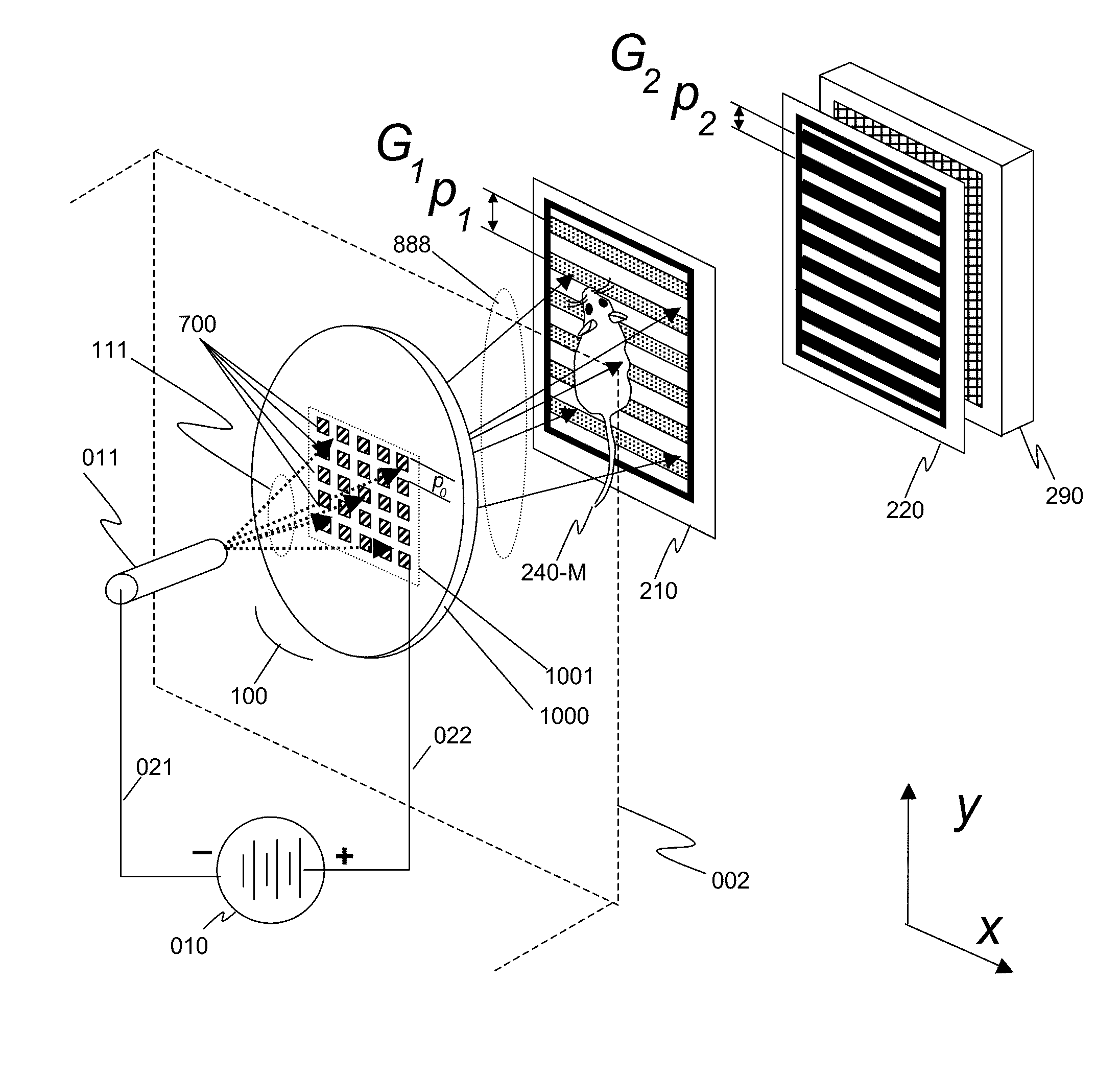
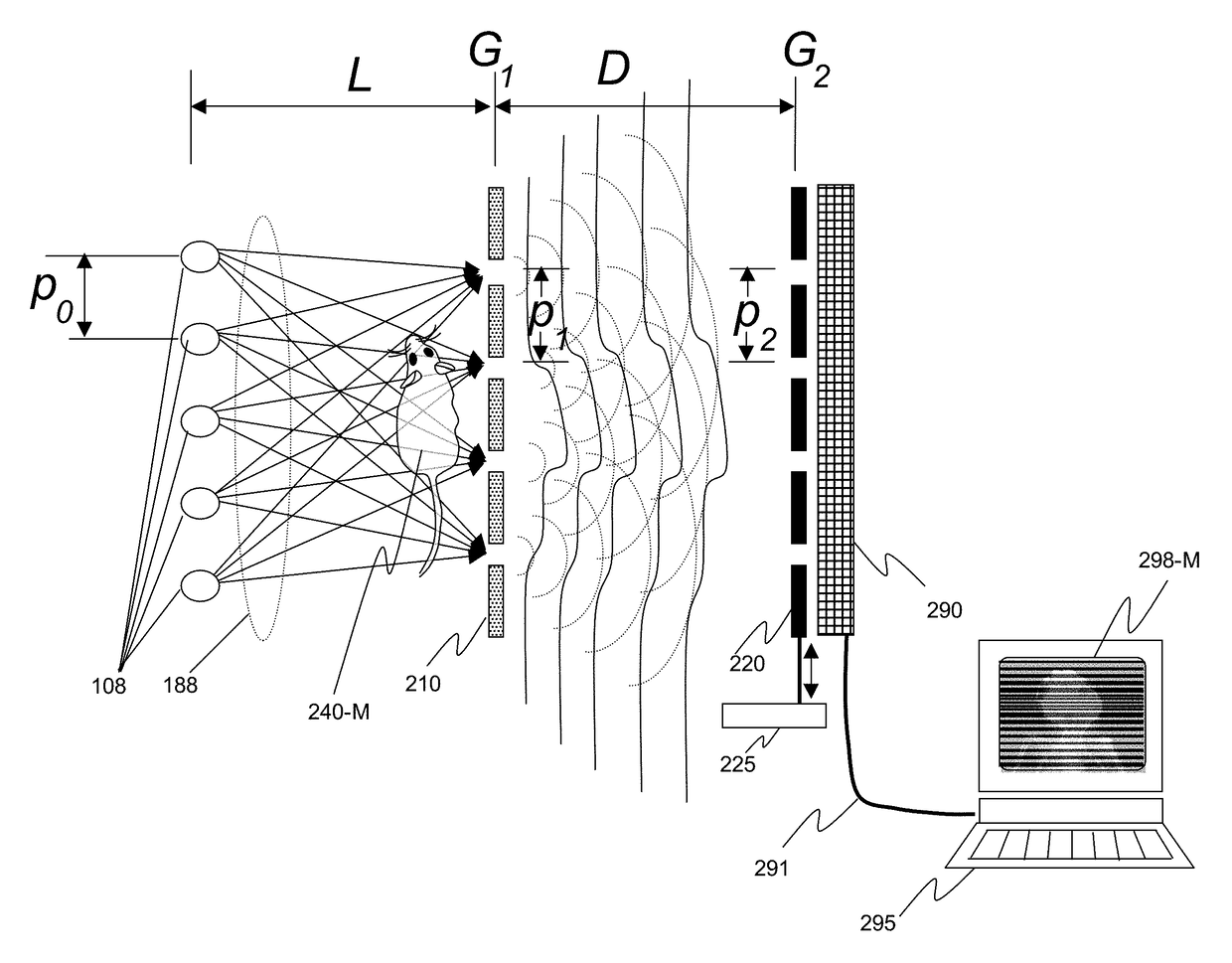
InactiveUS20150117599A1Increase brightnessLarge x-ray powerImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayGrating
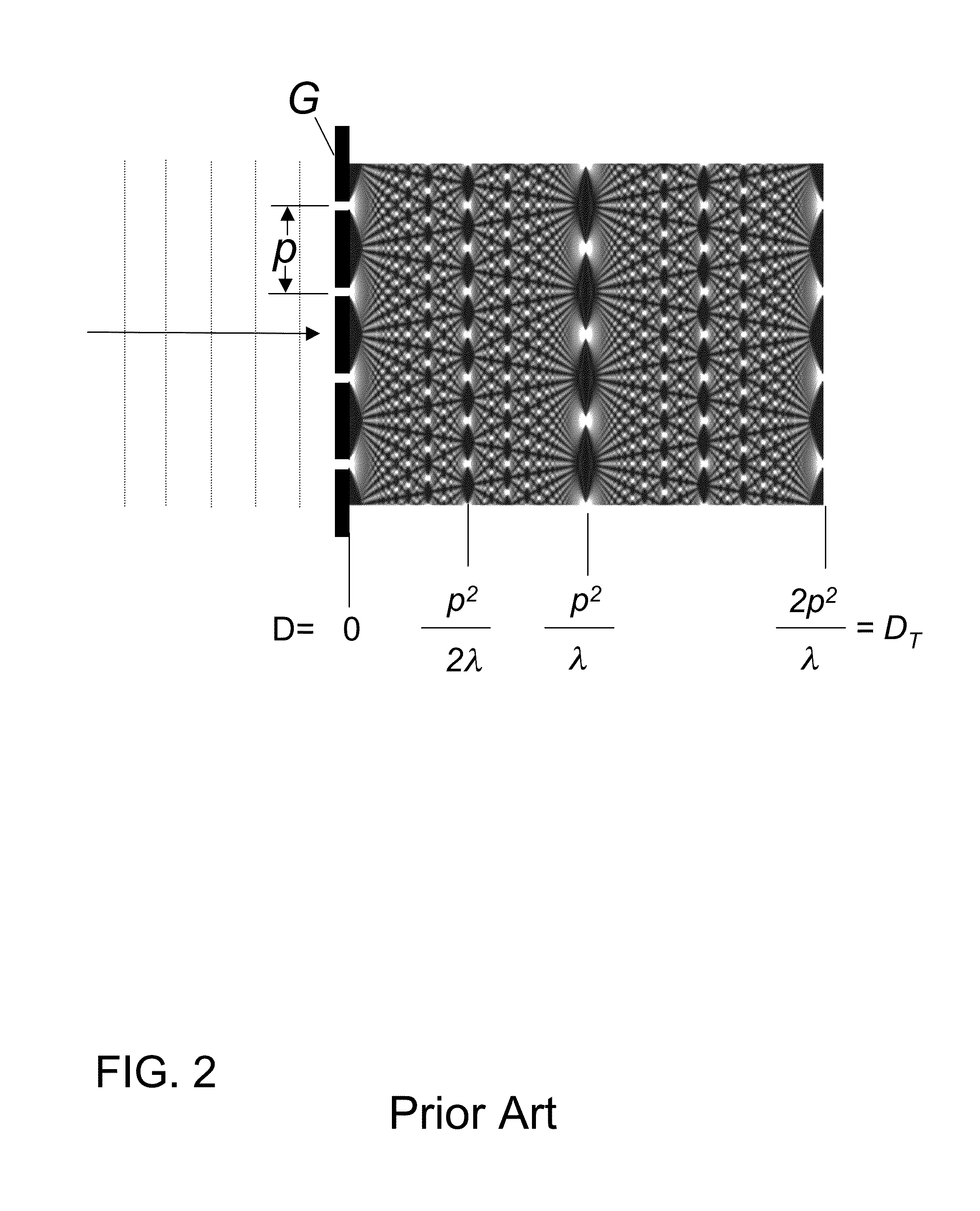
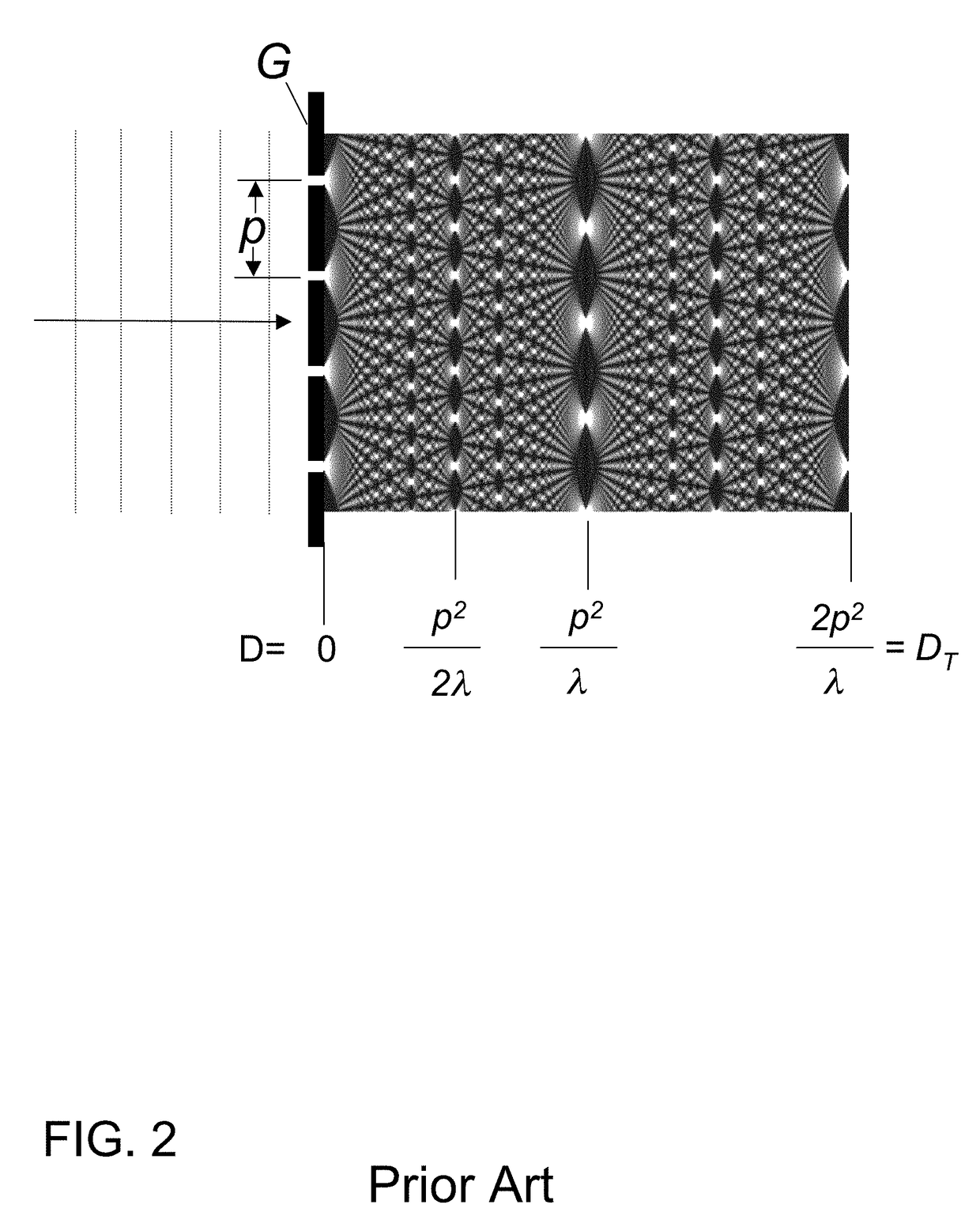
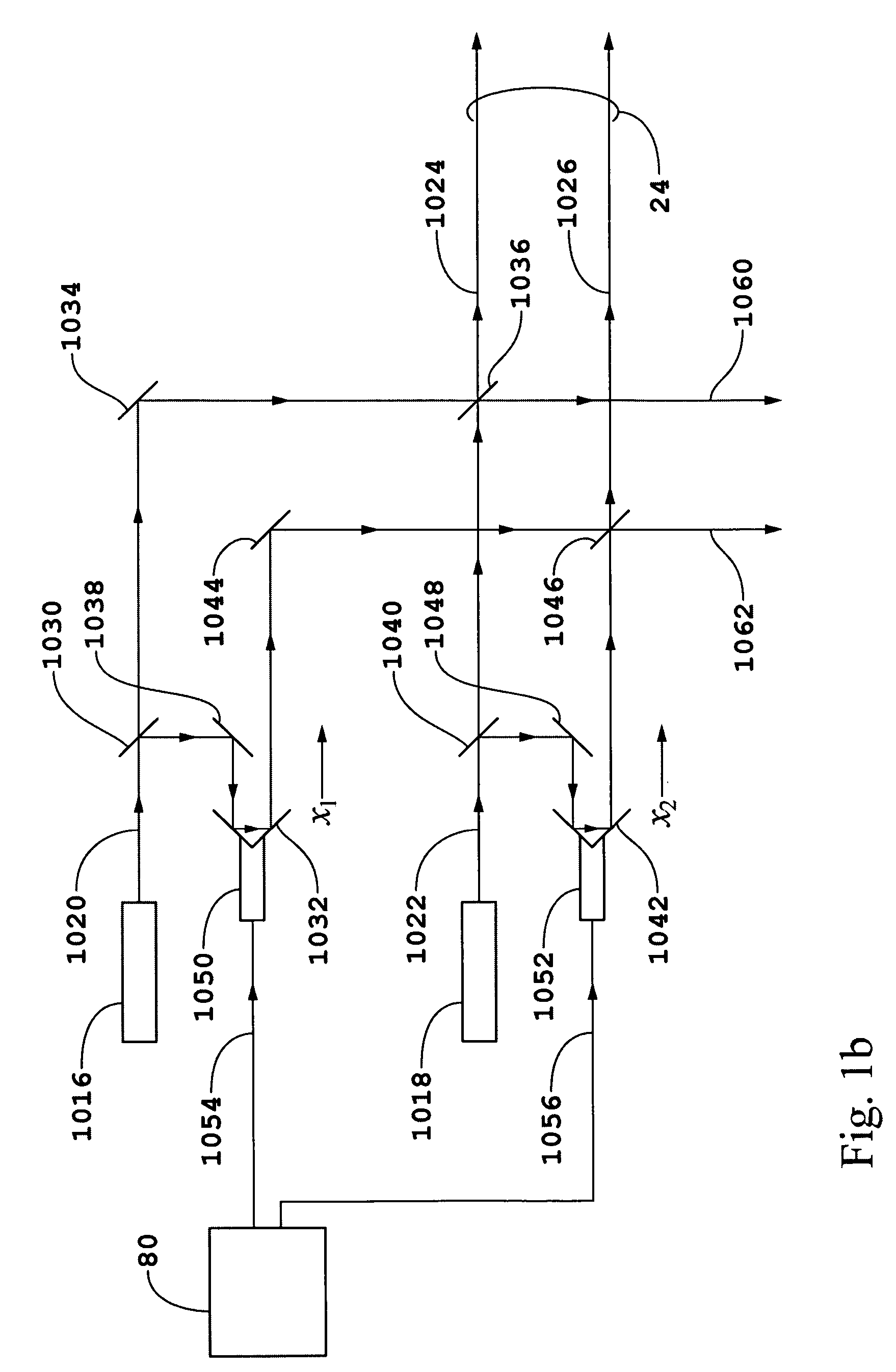
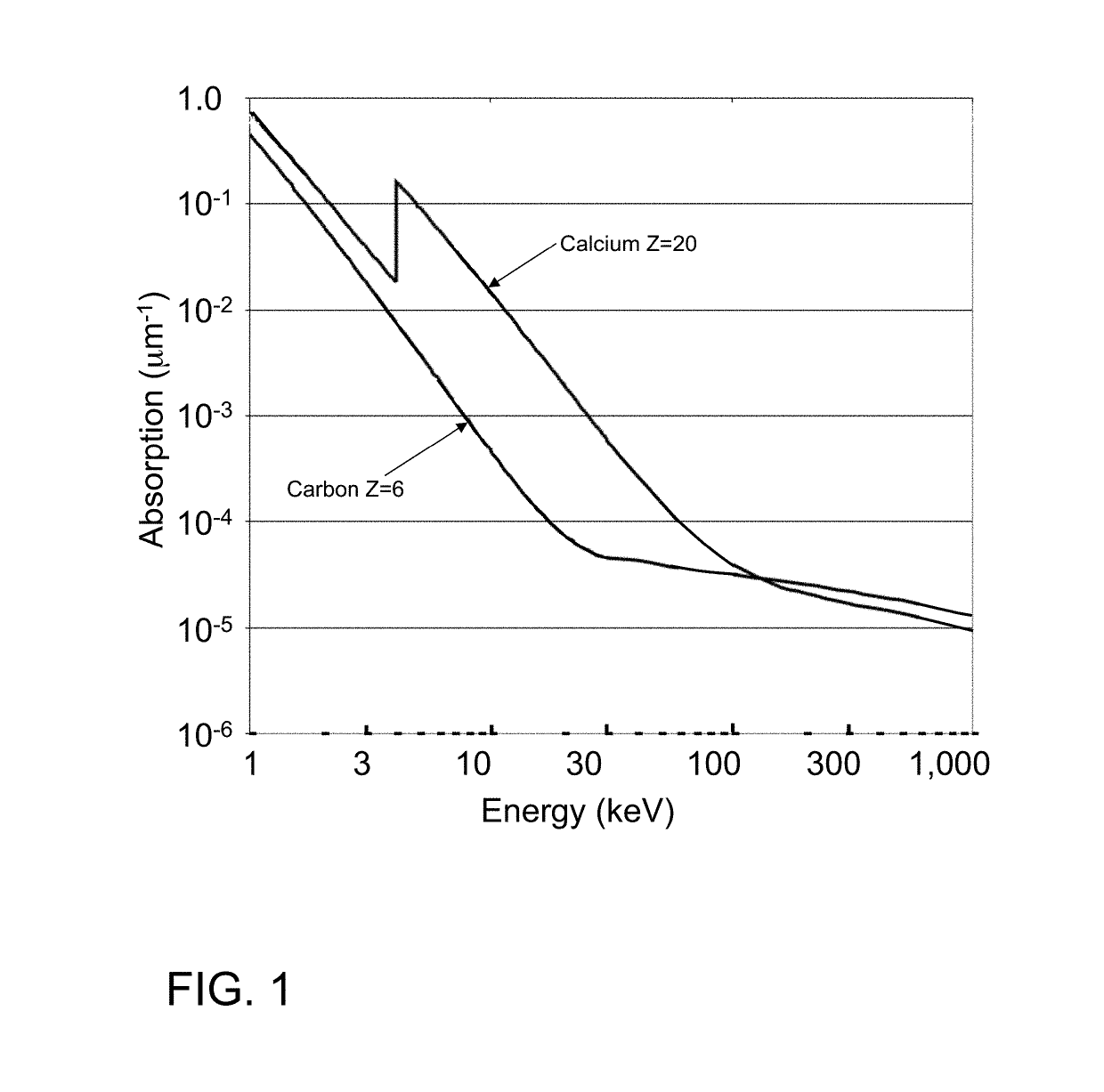
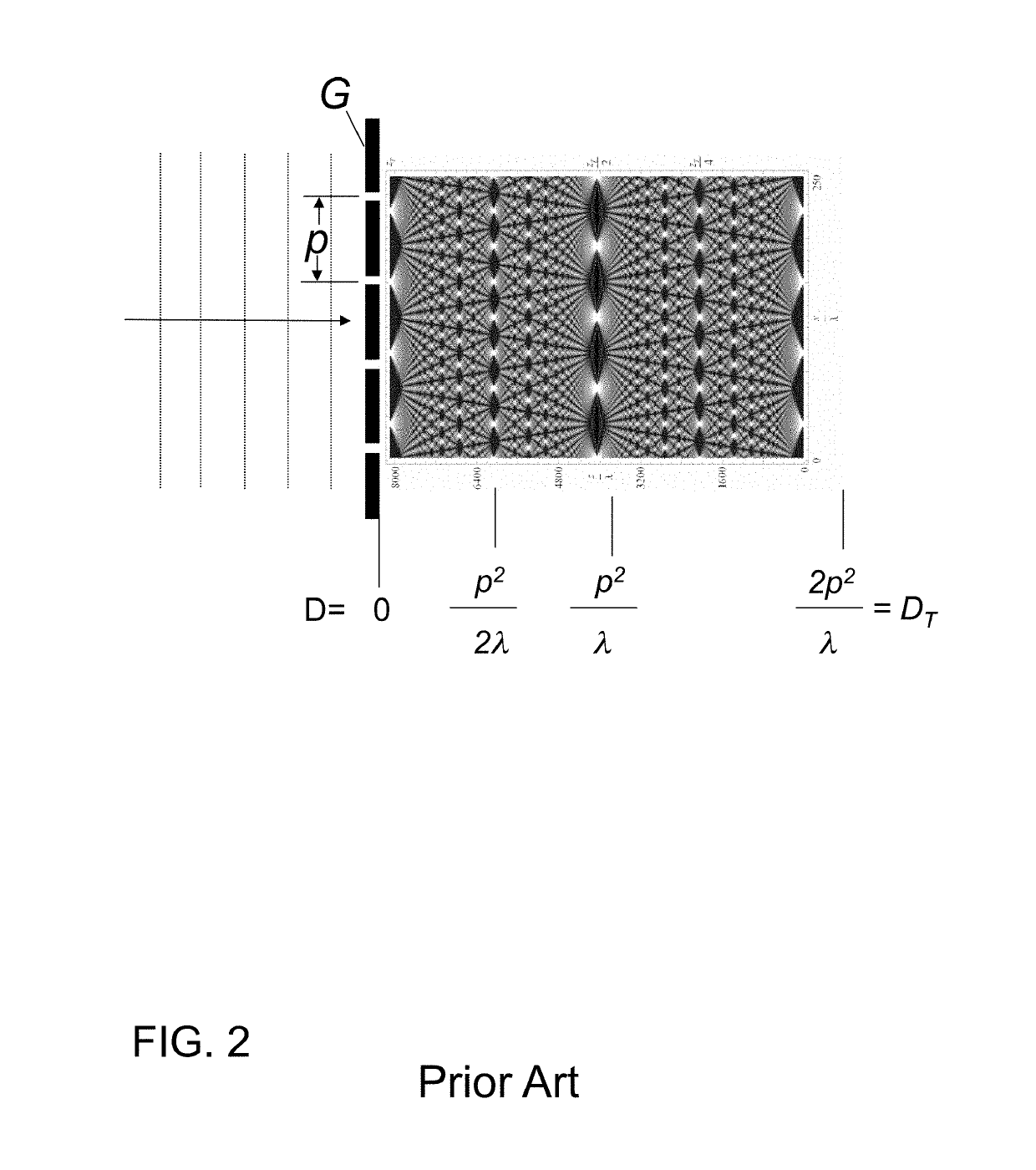
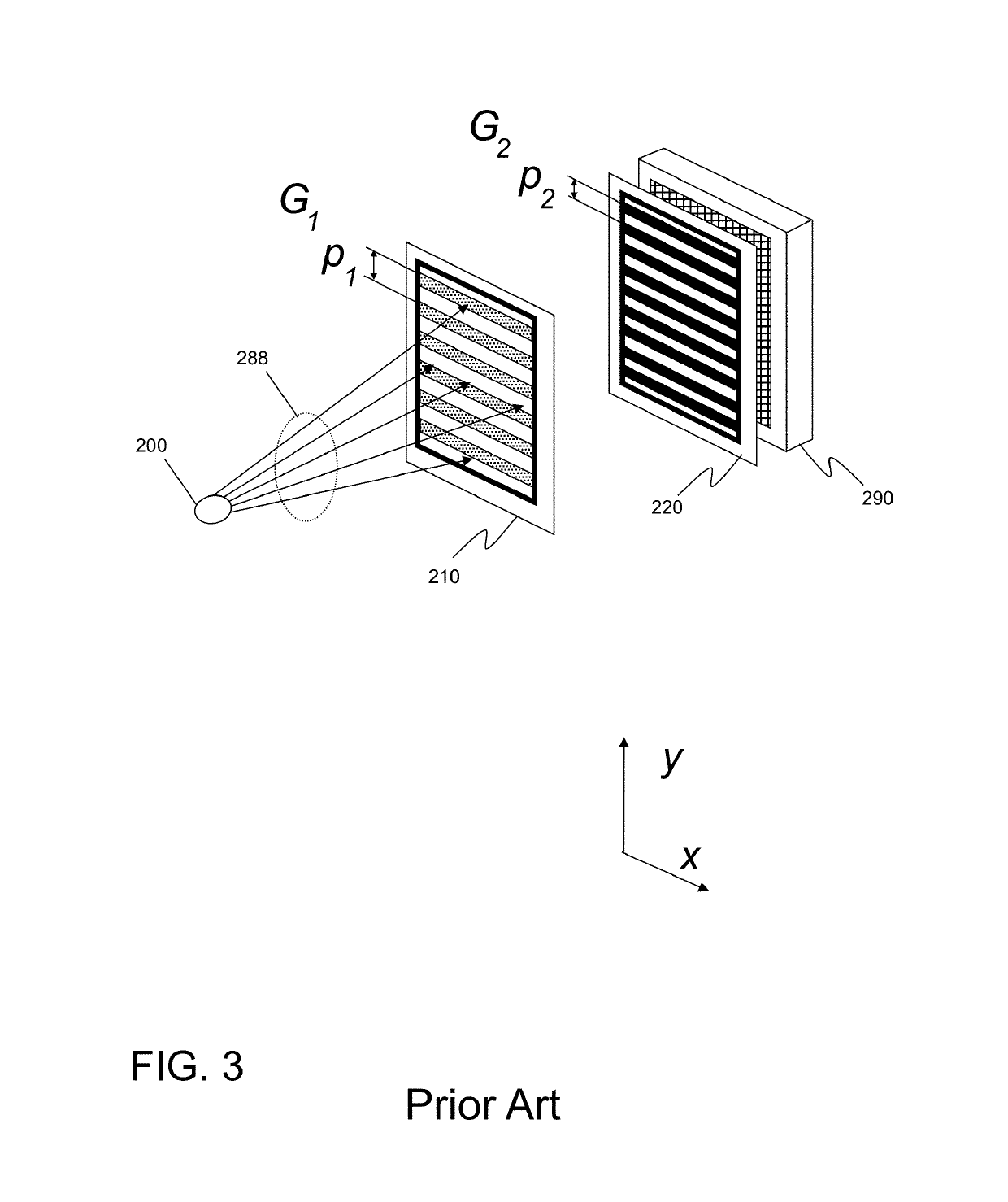
We disclose an x-ray interferometric imaging system in which the x-ray source comprises a target having a plurality of structured coherent sub-sources of x-rays embedded in a thermally conducting substrate. The system additionally comprises a beam-splitting grating G1 that establishes a Talbot interference pattern, which may be a π phase-shifting grating, and an x-ray detector to convert two-dimensional x-ray intensities into electronic signals. The system may also comprise a second analyzer grating G2 that may be placed in front of the detector to form additional interference fringes, and a means to translate the second grating G2 relative to the detector.In some embodiments, the structures are microstructures with lateral dimensions measured on the order of microns, and with a thickness on the order of one half of the electron penetration depth within the substrate. In some embodiments, the structures are formed within a regular array.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
X-ray interferometric imaging system
ActiveUS9719947B2Lightweight productionIncrease brightnessImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayGrating
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Interferometric defect detection and classification
InactiveCN102089616APhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansRelative phaseControl system
Systems and methods for using common-path interferometric imaging for defect detection and classification are described. An illumination source generates and directs coherent light toward the sample. An optical imaging system collects light reflected or transmitted from the sample including a scattered component and a specular component that is predominantly undiffracted by the sample. A variablephase controlling system is used to adjust the relative phase of the scattered component and the specular component so as to change the way they interfere at the image plane. The resultant signal is compared to a reference signal for the same location on the sample and a difference above threshold is considered to be a defect. The process is repeated multiple times each with a different relative phase shift and each defect location and the difference signals are stored in memory. This data is used to calculate an amplitude and phase for each defect.
Owner:焕・J・郑
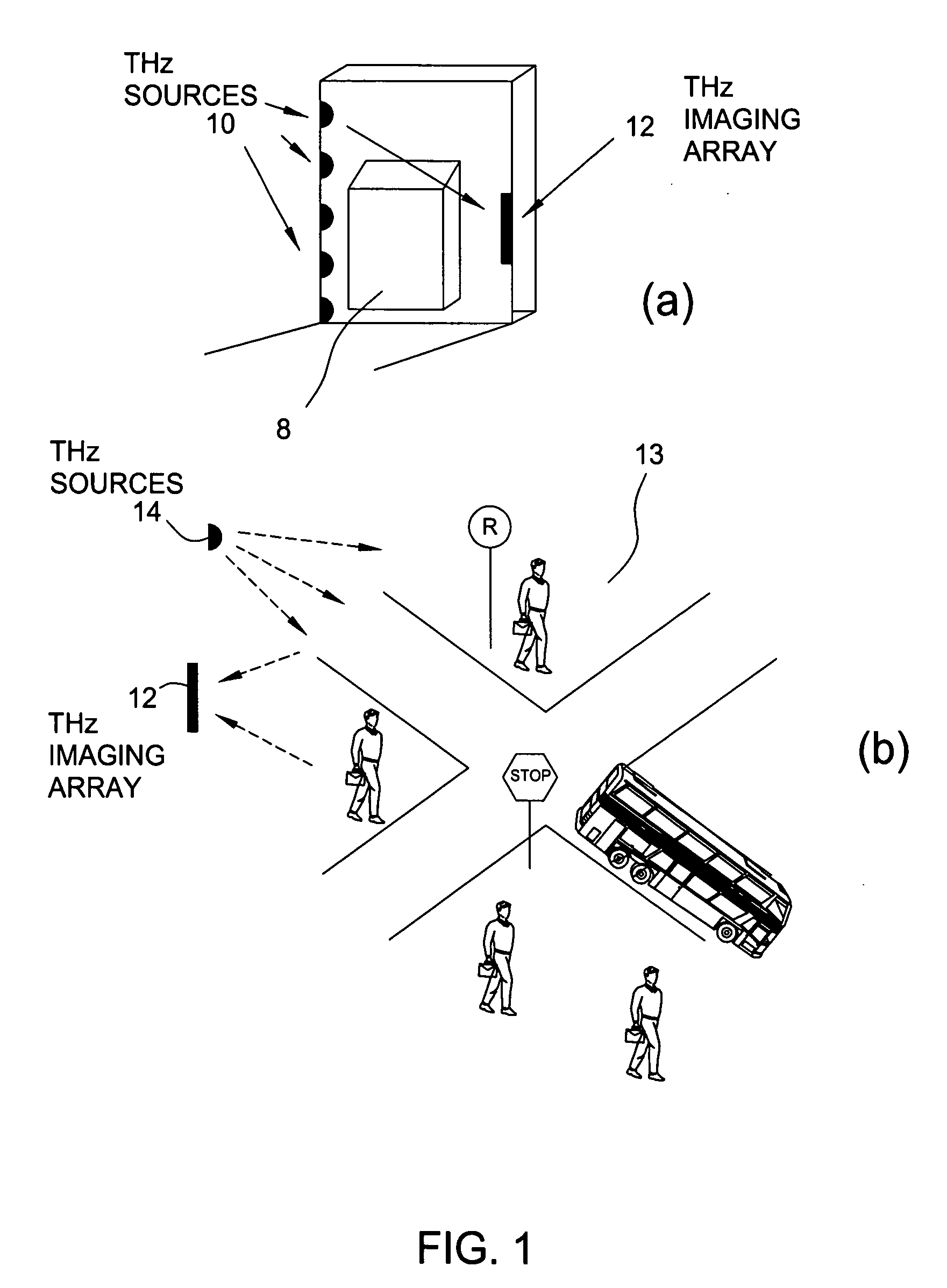
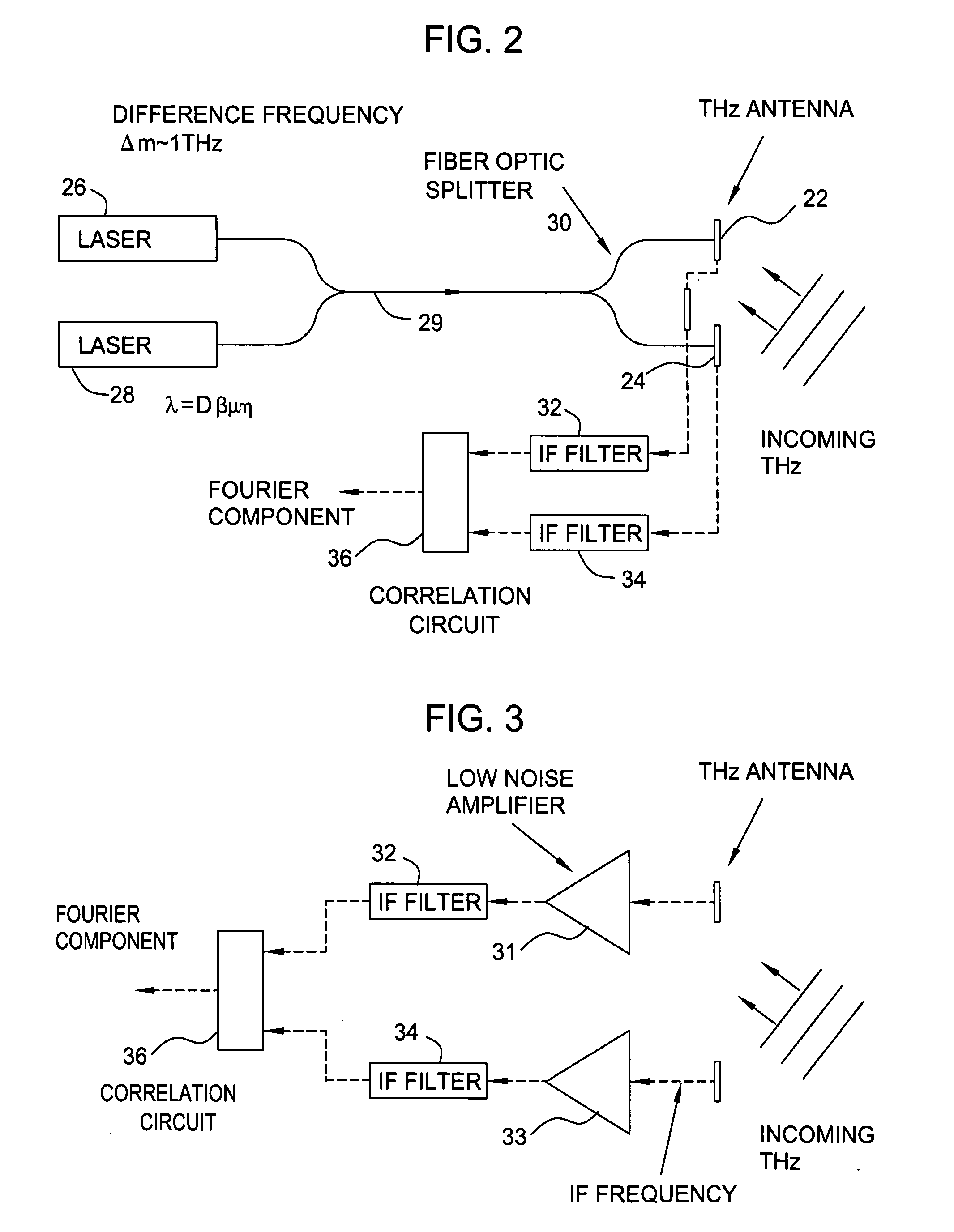
Terahertz imaging for near field objects
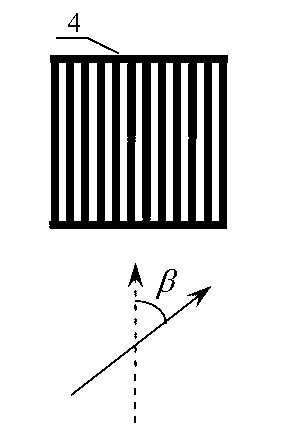
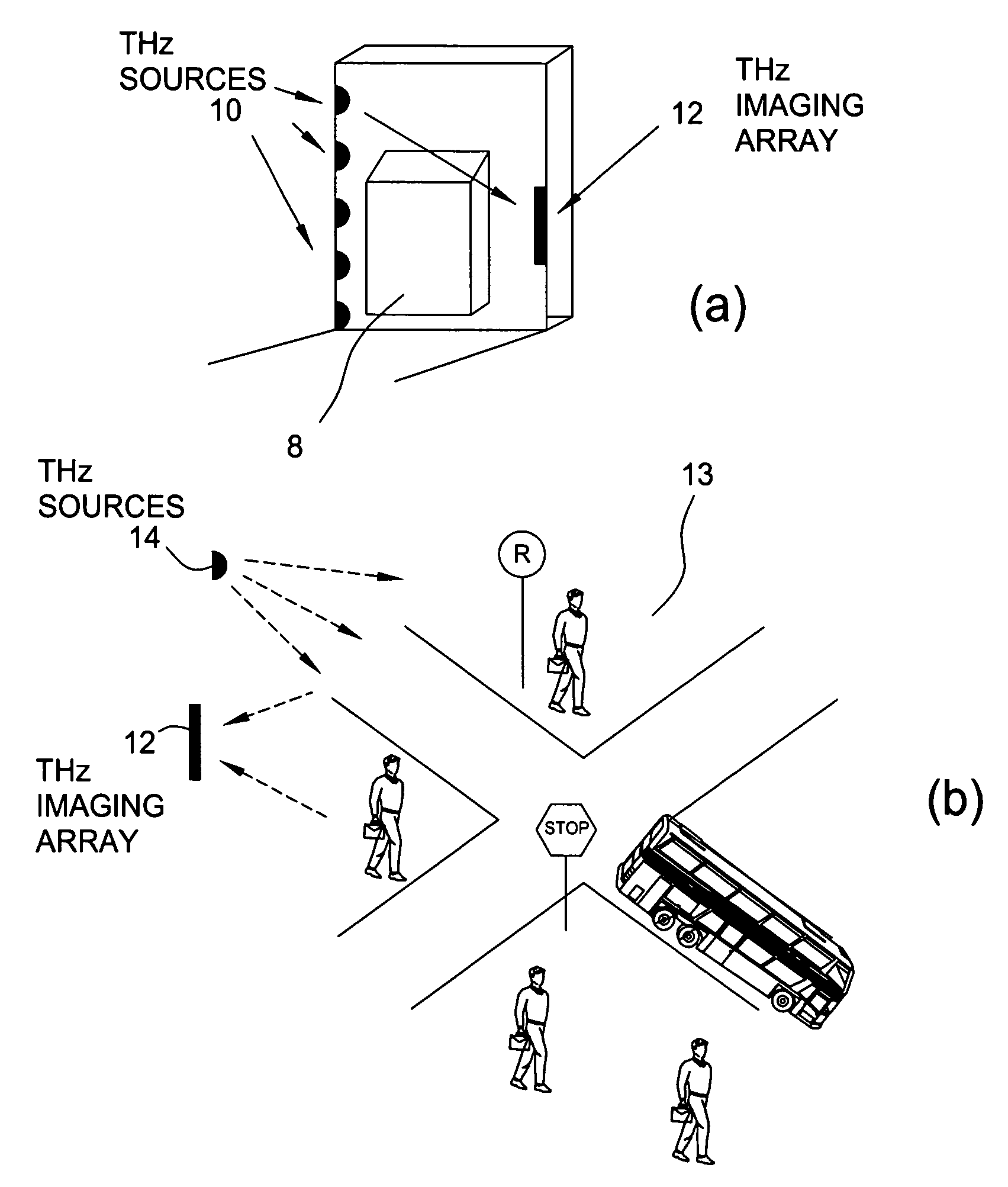
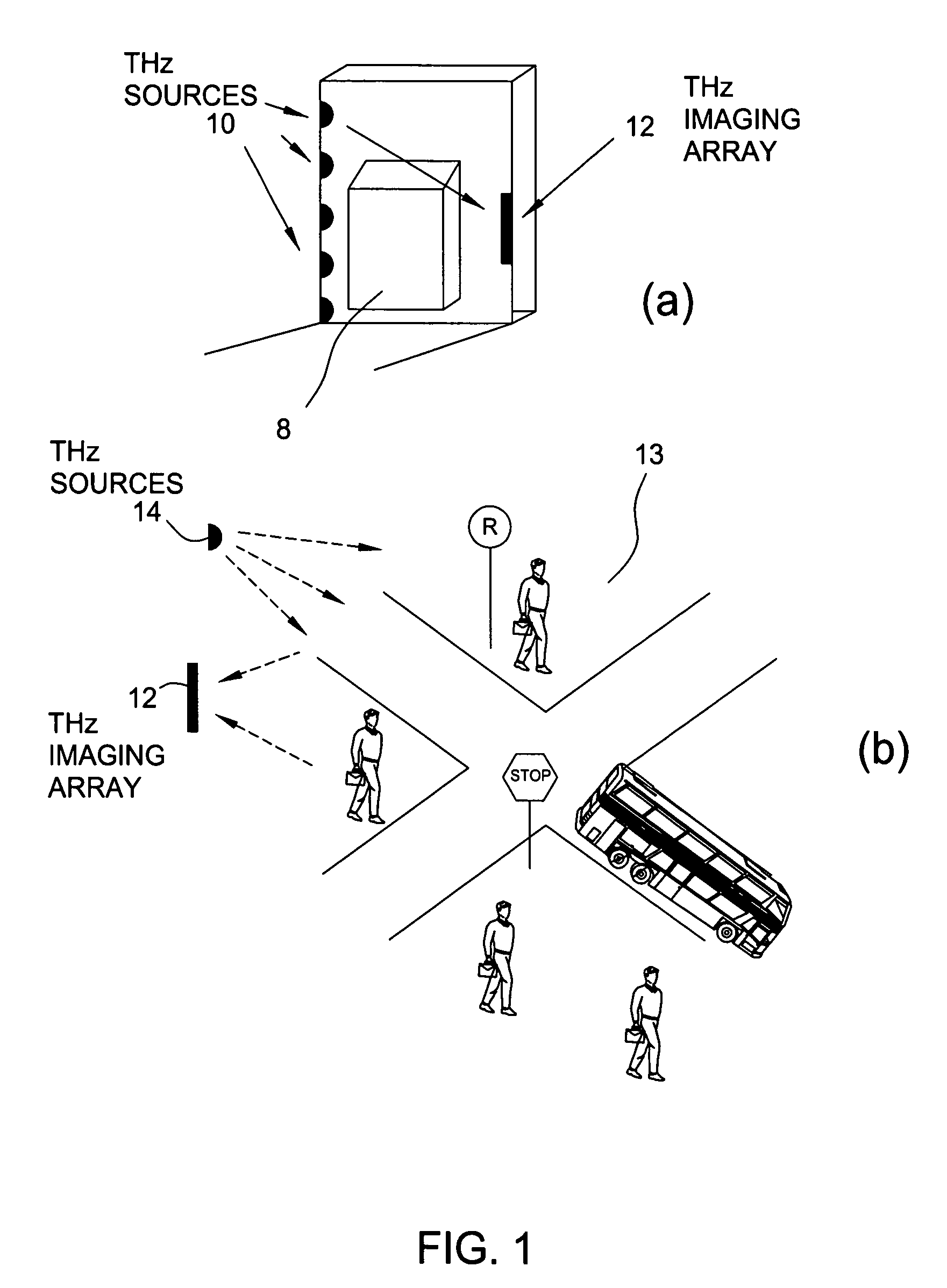
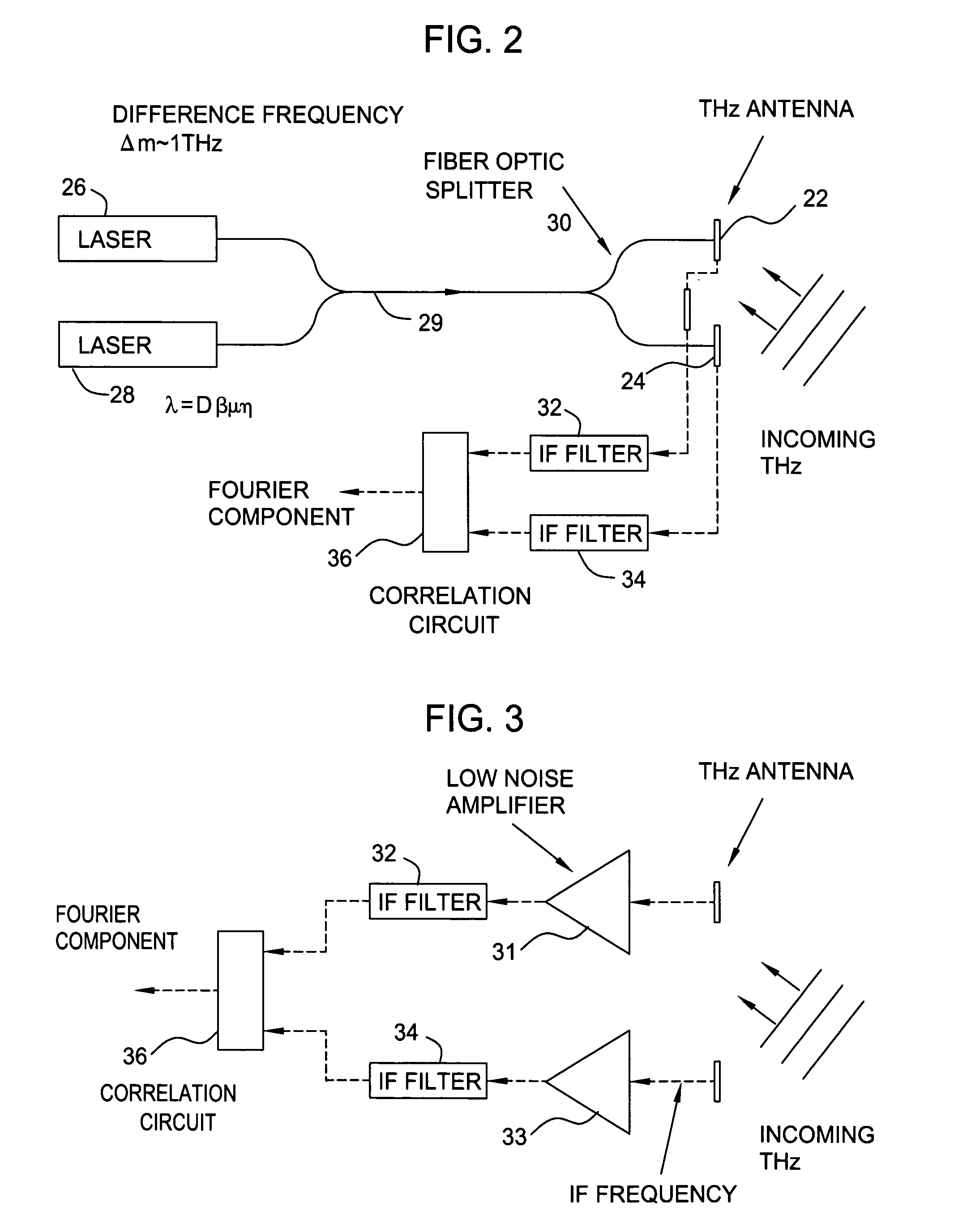
ActiveUS20060054824A1Distortion problemEffective regulationRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyInterferometric imagingDetector array
Near field imaging using a THz imaging system is realized by utilizing an interferometric imaging detector array that includes detector elements disposed on a surface curved, physically or artificially, to match substantially the curvature of the wave front for received THz signals. Generally, the near field is an environment wherein the distance to an object of interest is on the order of 10-100 times larger than the physical size of the THz imaging array. Typical distances from the object or target to the imaging array is anticipated to be in the 0.5 m-50 m range. Curvature of the detector array corrects a distortion problem in prior THz imaging systems that utilized planar interferometric imaging arrays based on a planar wave front assumption for received THz signals.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Spectrum polarization detection device and method for synchronous polarization modulation interference imaging
InactiveCN103063303AHigh spectral resolutionImprove accuracyInterferometric spectrometryPolarisation spectroscopyLight intensityPhysics
The invention discloses a spectrum polarization detection device and a method for synchronous polarization modulation interference imaging. The spectrum polarization detection device comprises a preposed polarization imaging system, an image plane interference imaging spectrometer and a signal processing system which are arranged on the same optical axis in sequence. Incident light forms four groups of light beams with different polarization state information through a polarization element and the light beams are separated on a space of a back focal plane of a microlens array. The separated light beams shoot into a lateral cutting beam splitter after passing through a collimator objective lens and are divided into two crosswise, and optical path difference information is brought in. Two branches of emergent light passes through a postpositional imaging objective lens, a target image with interference information and polarization state information is obtained on a target face of a detector, and the target image is transformed into an electrical signal and enters a signal processing system. Fourier transform is carried out, and light intensity information, spectral information and complete Stokes polarization information of a two-dimensional space of each target point are obtained. The spectrum polarization detection device for synchronous polarization modulation interference imaging has the advantages of being high spectral resolution, high in signal to noise ratio and simultaneous in complete Stokes polarization information and can be used for spectrum detection of a narrow band or a wide band.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Apparatus and methods for overlay, alignment mark, and critical dimension metrologies based on optical interferometry
InactiveUS20050275848A1Degrading measurement sensitivityThe result is accurateInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansMetrologyInterferometric imaging
Methods and apparatus based on optical homodyne displacement interferometry, optical coherent-domain reflectometry (OCDR), and optical interferometric imaging are disclosed for overlay, alignment mark, and critical dimension (CD) metrologies that are applicable to microlithography applications and integrated circuit (IC) and mask fabrication and to the detection and location of defects in / on unpatterned and patterned wafers and masks. The metrologies may also be used in advanced process control (APC), in determination of wafer induced shifts (WIS), and in the determination of optical proximity corrections (OPC).
Owner:ZETETIC INST
X-ray interferometric imaging system
ActiveUS20160066870A1Lightweight productionIncrease brightnessImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayGrating
An x-ray interferometric imaging system in which the x-ray source comprises a target having a plurality of structured coherent sub-sources of x-rays embedded in a thermally conducting substrate. The structures may be microstructures with lateral dimensions measured on the order of microns, and in some embodiments, the structures are arranged in a regular array.The system additionally comprises a beam-splitting grating G1 that establishes a Talbot interference pattern, which may be a π or π / 2 phase-shifting grating, an x-ray detector to convert two-dimensional x-ray intensities into electronic signals, and in some embodiments, also comprises an additional analyzer grating G2 that may be placed in front of the detector to form additional interference fringes. Systems may also include a means to translate and / or rotate the relative positions of the x-ray source and the object under investigation relative to the beam splitting grating and / or the analyzer grating for tomography applications.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Static birefringent polarizing inteference imaging spectrometer
InactiveCN101046409AIncrease the working bandImprove transmittanceInterferometric spectrometryOptical elementsBeam splitterPrism
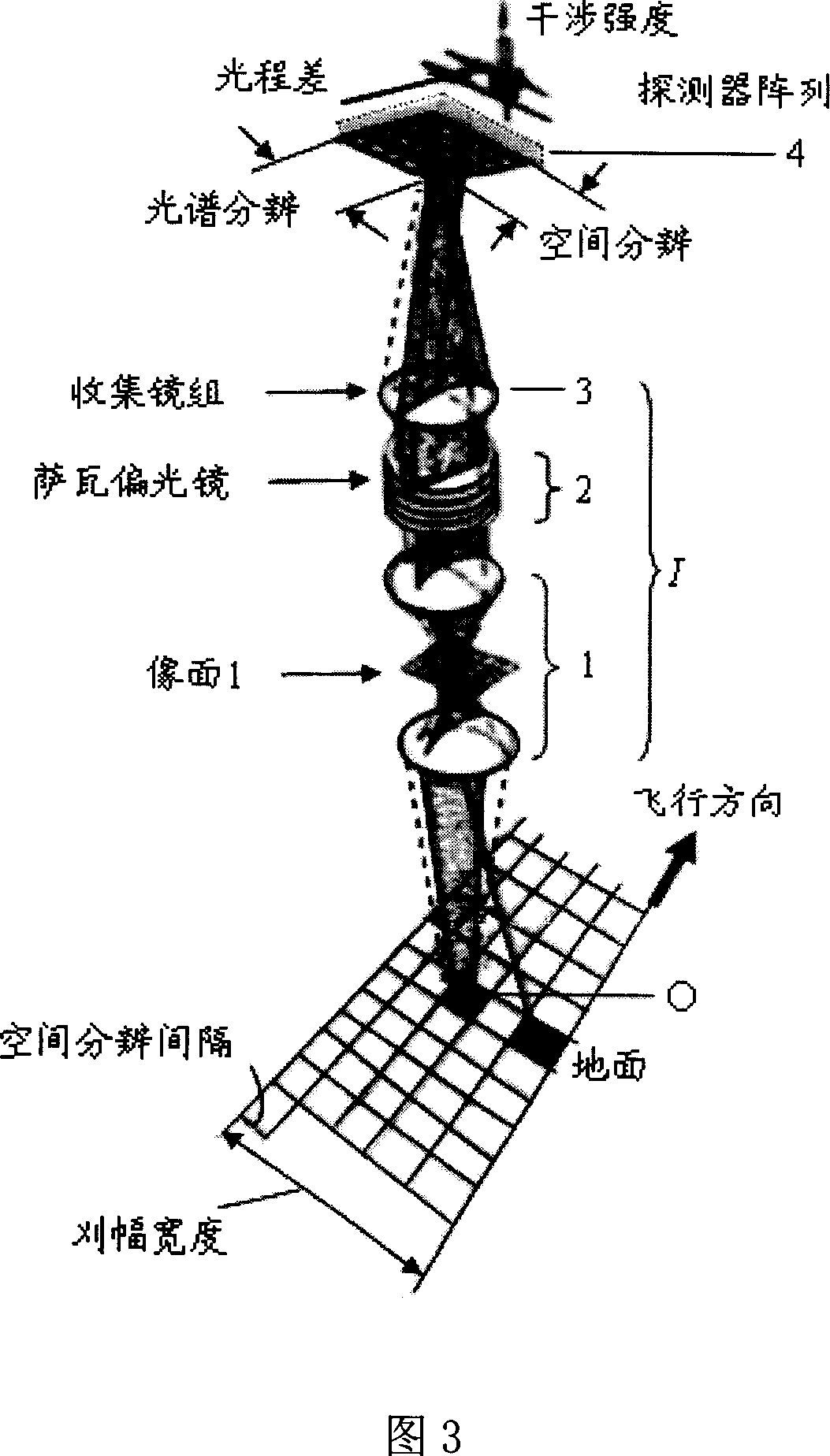
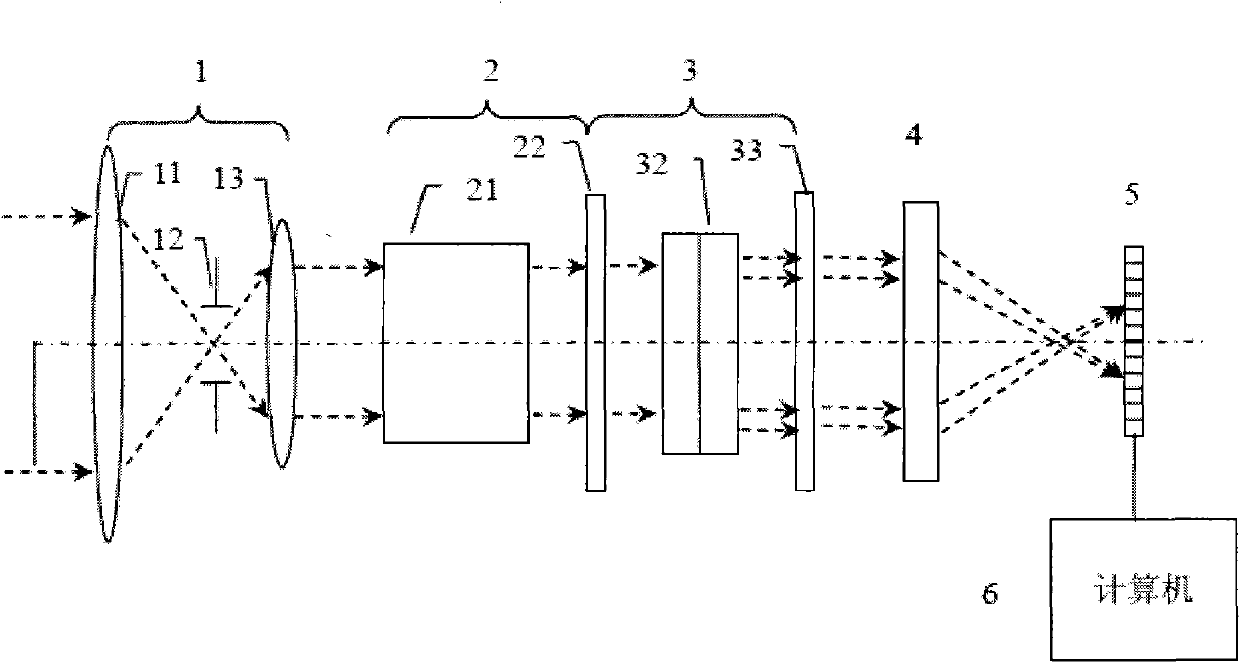
The static birefringent polarizing interference imaging spectrometer consists of a pre-telescope system, a polarizing interferometer, an imaging lens set and an area array detector arranged coaxially and successively in the incident light direction, as well as a computerized signal treating system connected to the output of the area array detector. The polarizing interferometer consists of a polarizer, a Savart polariscope and an analyzer. The present invention adopts Savart polariscope as the transverse shearing beam splitter, and the advantages of infinitely far target, linear light path, simple structure, high stability, high S / N ratio, high resolution, etc.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Apparatus and methods for overlay, alignment mark, and critical dimension metrologies based on optical interferometry
InactiveUS7298496B2The result is accurateImprove accuracyInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansMetrologyInterferometric imaging
Methods and apparatus based on optical homodyne displacement interferometry, optical coherent-domain reflectometry (OCDR), and optical interferometric imaging are disclosed for overlay, alignment mark, and critical dimension (CD) metrologies that are applicable to microlithography applications and integrated circuit (IC) and mask fabrication and to the detection and location of defects in / on unpatterned and patterned wafers and masks. The metrologies may also be used in advanced process control (APC), in determination of wafer induced shifts (WIS), and in the determination of optical proximity corrections (OPC).
Owner:ZETETIC INST
X-ray interferometric imaging system
ActiveUS10349908B2Lightweight productionIncrease brightnessImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayGrating
An x-ray interferometric imaging system includes an x-ray source with a target having a plurality of discrete structures arranged in a periodic pattern. The system further includes a beam-splitting x-ray grating, a stage configured to hold an object to be imaged, and an x-ray detector having a two-dimensional array of x-ray detecting elements. The object is positioned between the beam-splitting x-ray grating and the x-ray detector, the x-ray detector is positioned to detect the x-rays diffracted by the beam-splitting x-ray grating and perturbed by the object to be imaged.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Interferometric imaging with reduced aperture
InactiveUS20060154156A1High resolutionInterferometersUsing optical meansImage resolutionInterferometric imaging
Owner:FARAH JOHN
Integral aperture phase measurement and compensation method and system
The invention provides a method and a system for measuring and compensating comprehensive apache photon imaging phases, which comprises using interfering results of electrooptical modulation rear carrier waves to abstract error information of phases, thereby a purpose of measuring and compensating in real time for phase errors of an interfering imaging system can be realized, and the invention belongs to the technical field of interfering-type imaging remote sensing and high spatial resolution military detections. In the invention, the comprehensive apache photon imaging is that after field radiating signals are received and lowered frequency by an antenna array, the field radiating signals are transformed as optical wave signals through an electro-optic modulator and are transmitted to fiber ends to form fiber array imaging. Certain errors can be produced in the process of accepting and transmitting the field signals, while the phase errors have great influence to imaging qualities, thereby the invention provides that a fiber filter is used to separate out fiber medium carrier waves; the phase errors of a path can be abstracted by a plurality of the interfering results, and finally phase delays and compensator are used to correct the phase errors for fibers.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A dual-channel differential polarization interference imaging spectrometer
ActiveCN102297722AEasy accessImprove detection abilityInterferometric spectrometryOptical elementsWollaston prismInterferometric imaging
The invention relates to a double-channel differential polarizing interference imaging spectrometer, which comprises a collimating lens, a Wollaston prism, a Savart polarizer, a linear polarizer, an imaging lens, a plane array detector, a connecting lead and a computer processing system, wherein after light emitted by a target passes through the double-channel differential polarizing interference imaging spectrometer, interference images of a parallel component and a vertical component of the target can be acquired by using the plane array detector; the interference images are input to the computer processing system through the connecting lead, and Fourier transformation and image fusion processing are respectively performed on the two interference images, so that spectral images of the parallel component and the vertical component of the target can be inversed; the difference of the two spectral images is a differential polarizing spectral image of the target; and the ratio of the difference of the two spectral images to the sum of the two spectral images is a linear polarizing spectral image of the target. The spectrometer has the advantages of simple and compact structure, high sampling precision, good stability, no rotary component, and capability of acquiring the differential polarizing spectral image and the linear polarizing spectral image of the target.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Scanner device for interference type image-forming microwave radiometer
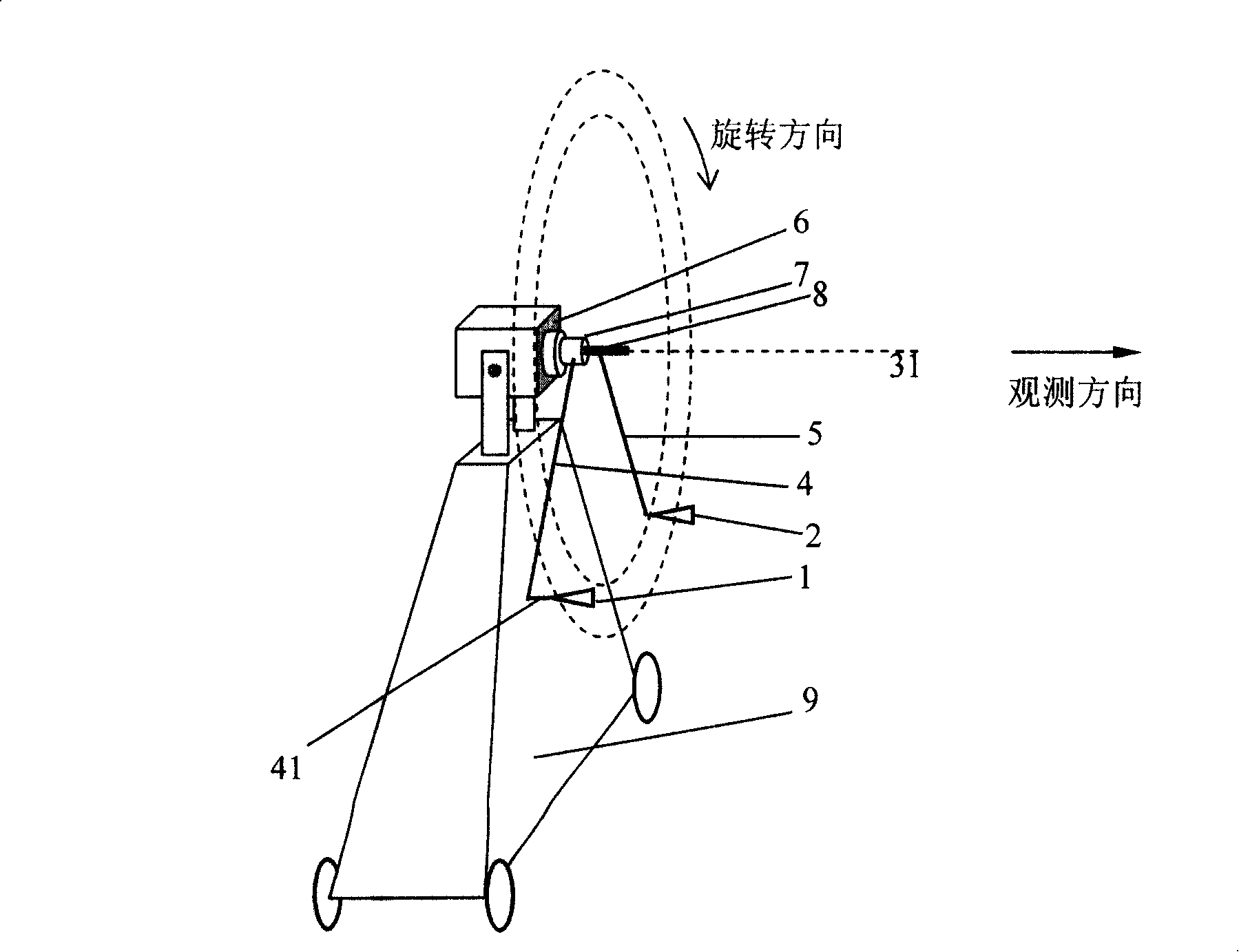
InactiveCN101241154AReduce complexityLow costElectromagentic field characteristicsInterferometric imagingMicrowave radiometer
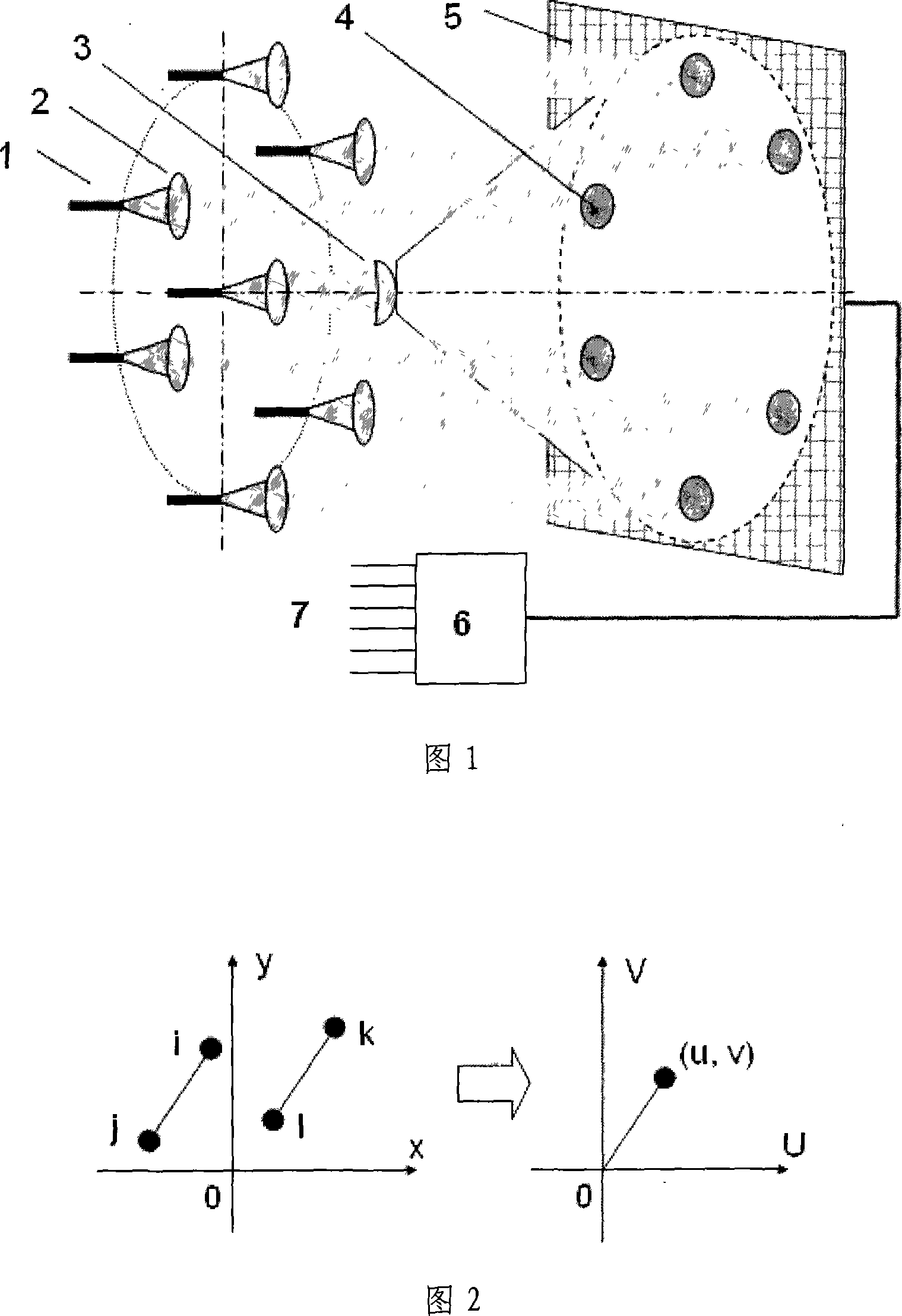
The present invention discloses a scanning device for interferometric imaging microwave radiometer, which comprises of scanning equipment for interferometric imaging microwave radiometer, rotating device, and at least two antenna units connected through connected device and rotating device respectively to rotate antenna units in one plane coaxially, the distances from phase centre to rotate axel of said at least two antenna units are respectively called the first distance and the second distance which is shorten than the first distance. The present invention reduces the complexity of observation system and cost, improving the precision and stability of system.
Owner:CENT FOR SPACE SCI & APPLIED RES
Interferometer spectrometer flat field method
InactiveCN101144737AEliminate errorsResolve inconsistenciesRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectrographRadiation field
The invention relates to a flat field method for an imaging interferometer. The optical axis of the flat field imaging interferometer is collimated to the center of the opening of the flat field light source, the interferometry image data output by the flat field imaging interferometer is acquired by an image acquisition card, and sent to the computer to processing, the flat field correction matrix is calculated, the flat field uncertainty is analyzed, and the flat field correction matrix is acquired. The invention solves the technical problem that the allsidedness and the effect of the correction are correspondingly poor in the technical background. The invention is mainly utilized on the flat field of an entire spatial modulation imaging interferometer to eliminate the system error, and the inconsistence of the response between pixels can be corrected at one-time. The invention is also suitable for the flat field of the imaging interferometer embarked on a plane or a satellite during the flying processing by utilizing the ground standard radiation field.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
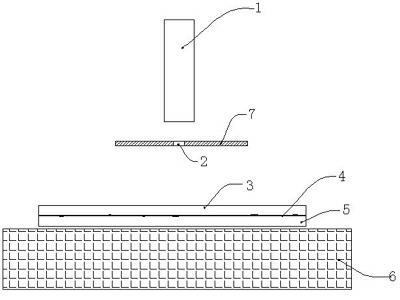
Device and method for analyzing and counting blood cells by lensless holographic diffraction imaging
InactiveCN102660457AExpand field of viewReasonable designBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideMiniaturization
The invention discloses a device and method for analyzing and counting blood cells by lensless holographic diffraction imaging, relating to blood cell detection and counting technology. The invention has a lensless simple structure and wide view, can realize miniaturization, and can monitor thousands of cells with different concentrations in real time. The device comprises a glass slide for placing a sample and a cover slip arranged on the glass slide, and is characterized in that a CCD or CMOS chip is arranged below the glass slide, a light source is arranged above the glass slide, an aperture is arranged between the light source and the glass slide and is arranged on the light extraction route of the light source. The method comprises the following steps: putting a blood cell sample between the glass slide and the cover slip and with well pressing, adjusting the light source above the glass slide, and adjusting the position of the sensitive chip below the glass slide to let the light emitted from the light source pass through the aperture and be vertically incident on the cover slip, and letting the CCD or CMOS ship arranged below the glass slide record the interference images after the light passes through the blood cell sample.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
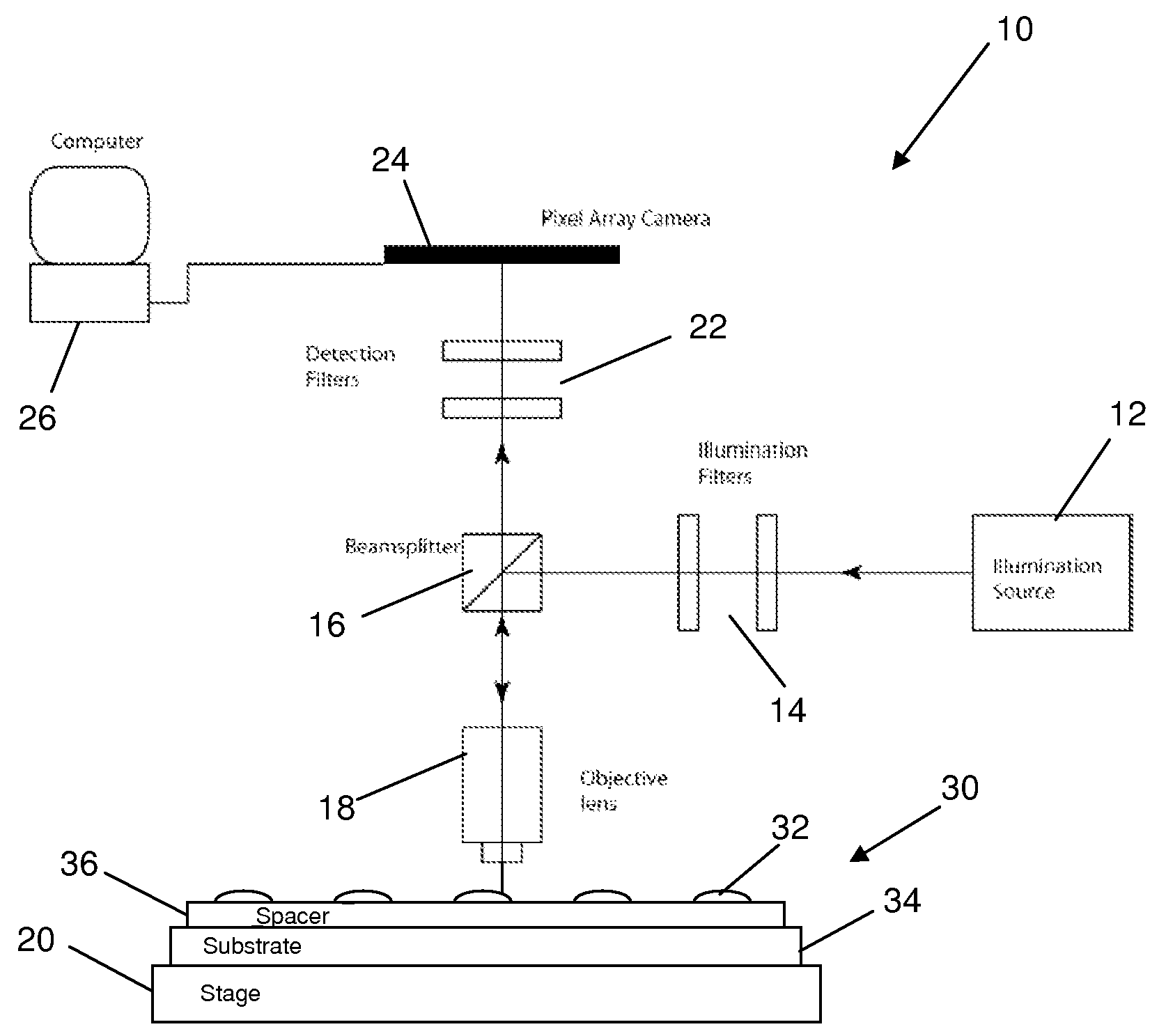
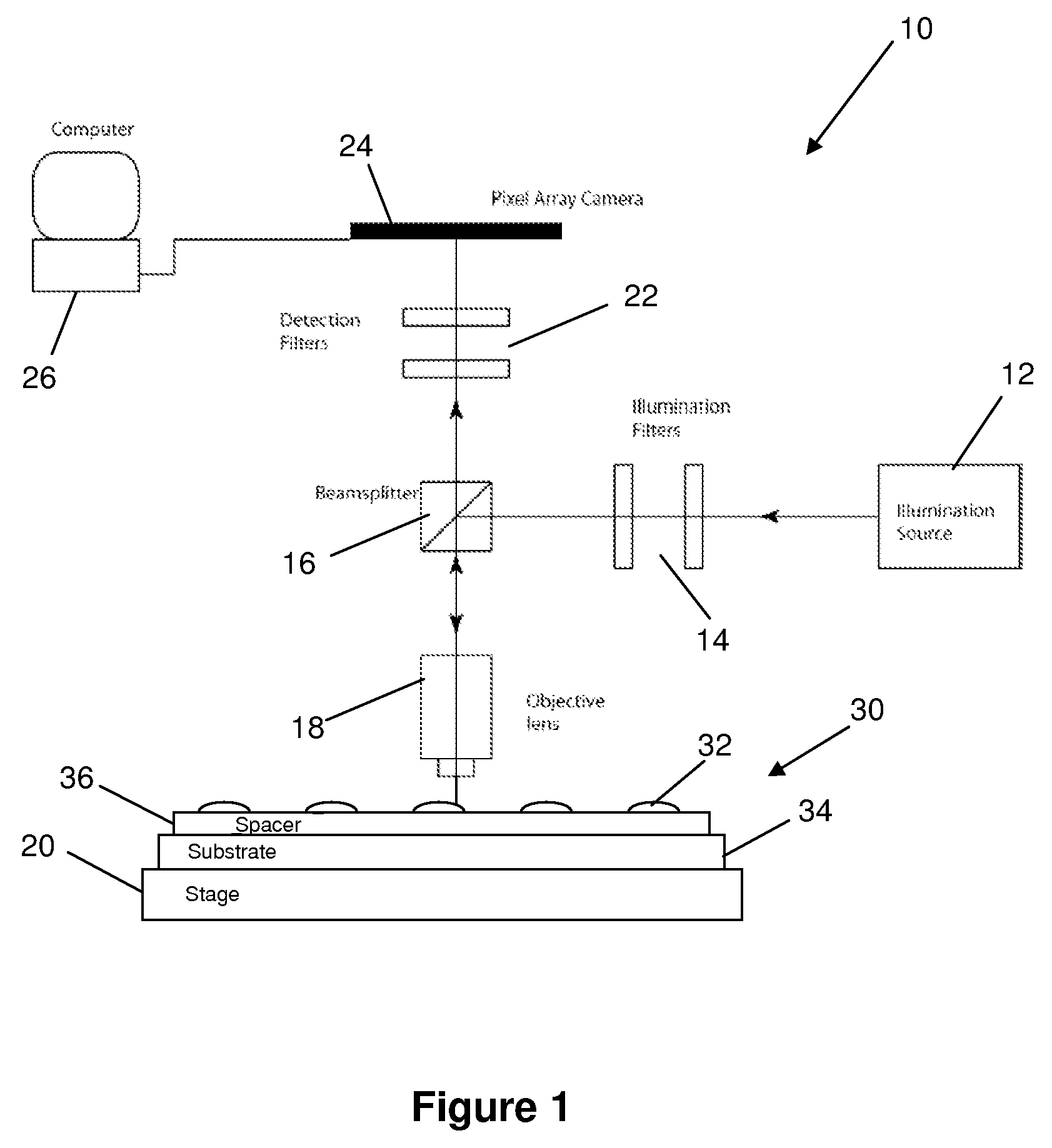
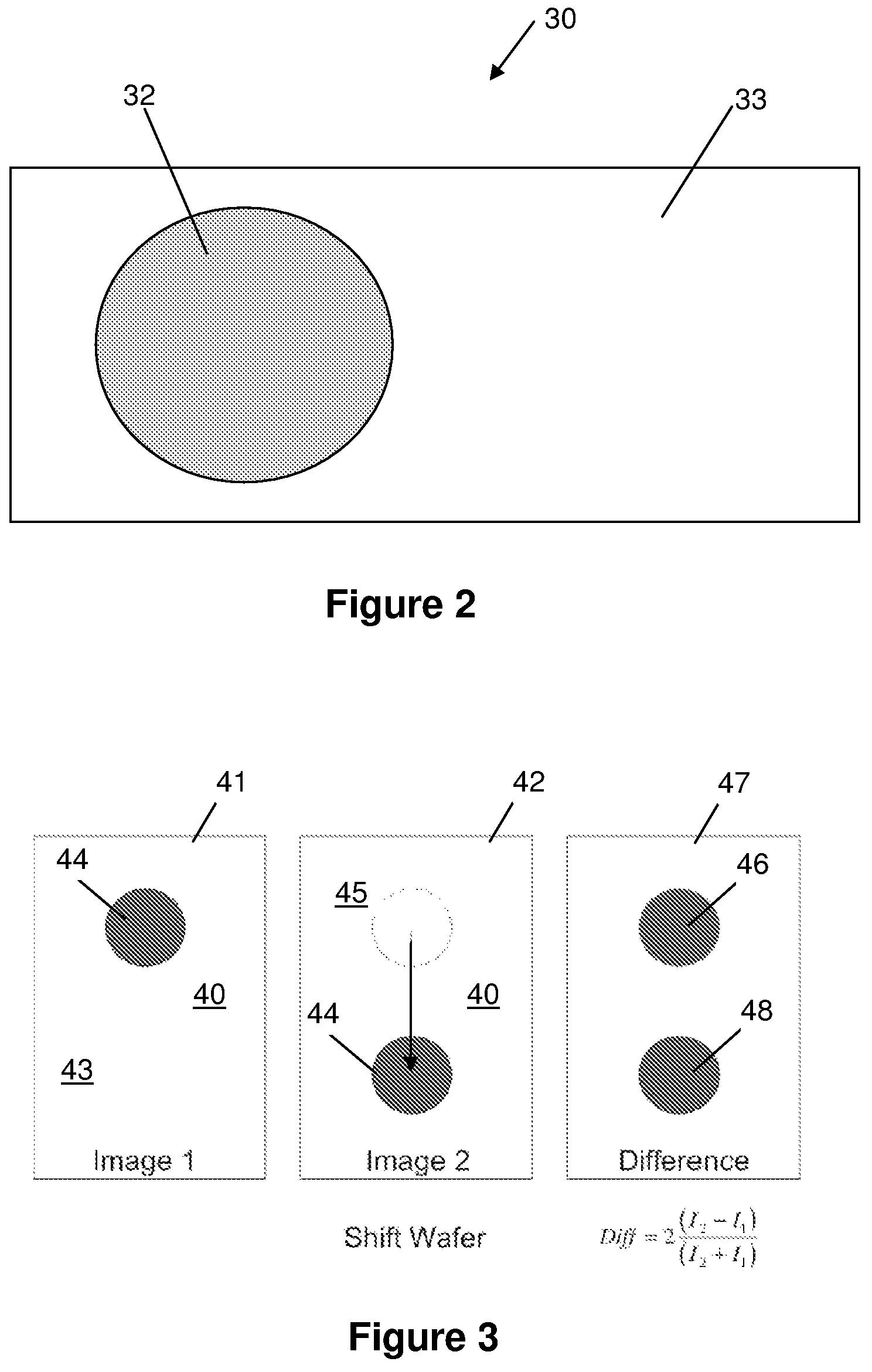
Molecular interferometric imaging process and apparatus
ActiveUS7522282B2Increase speedHigh sensitivitySamplingPhase-affecting property measurementsAnalyteReference image
A molecular interferometric imaging system for detecting an analyte in a sample, that includes an illumination source providing a beam of radiation; a pixel array for detecting radiation in an image plane; a biolayer designed to react to the analyte when it comes in contact with the sample; a substrate designed to convert phase modulation into intensity modulation which can be detected and imaged directly by the pixel array, the biolayer being on the substrate; a reference surface; an image switching means for switching between a first position for collecting a sample image of the biolayer, and a second position for collecting a reference image of the reference surface; and a processing means for producing a composite image using the sample image and the reference image for illumination normalization.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
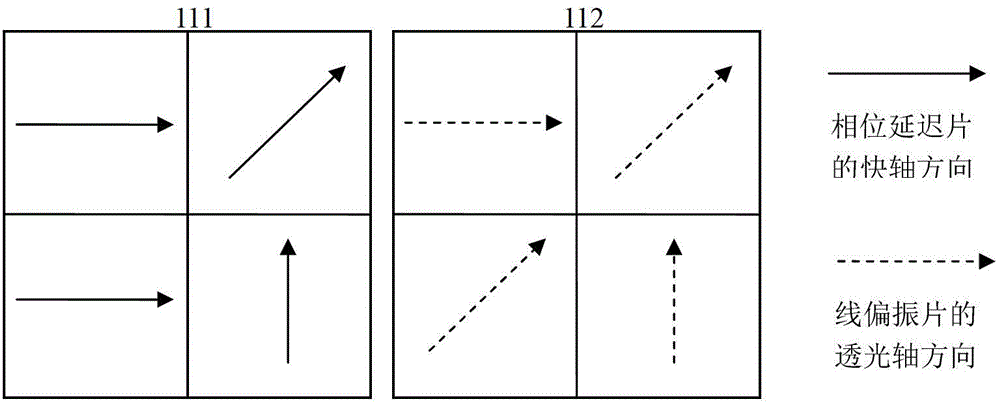
Micro-polarization modulation array for achieving full-polarization imaging
ActiveCN103063300AAchieve synchronous fetchSimple structureRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryGratingPolarizer
The invention discloses a micro-polarization modulation array for achieving full-polarization imaging. The micro-polarization modulation array for achieving the full-polarization imaging is composed of a micro-phase delayer array and a polarizing film, wherein the micro-phase delayer array is composed of a first crystal grating and a second crystal grating which are adhered, the directions of trunkings of the first crystal grating and the second crystal grating are mutually perpendicular, the second crystal grating is adhered with the polarizing film, and a through optical axis of the polarizing film and a fast axis of the first crystal grating are parallel. The micro-polarization modulation array for achieving the full-polarization imaging is used for an interference imaging spectrometer to lead in polarization information, easy and convenient to use, a polarization is not required, a theoretic aliasing phenomenon does not exist in interfering information which corresponds to polarization states, and spectral resolution and accuracy of restoring spectrums of an interference kind imaging spectrum polarization technique are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Terahertz imaging for near field objects
ActiveUS7105820B2Distortion problemEffective regulationRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyWavefrontInterferometric imaging
Near field imaging using a THz imaging system is realized by utilizing an interferometric imaging detector array that includes detector elements disposed on a surface curved, physically or artificially, to match substantially the curvature of the wave front for received THz signals. Generally, the near field is an environment wherein the distance to an object of interest is on the order of 10–100 times larger than the physical size of the THz imaging array. Typical distances from the object or target to the imaging array is anticipated to be in the 0.5 m–50 m range. Curvature of the detector array corrects a distortion problem in prior THz imaging systems that utilized planar interferometric imaging arrays based on a planar wave front assumption for received THz signals.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
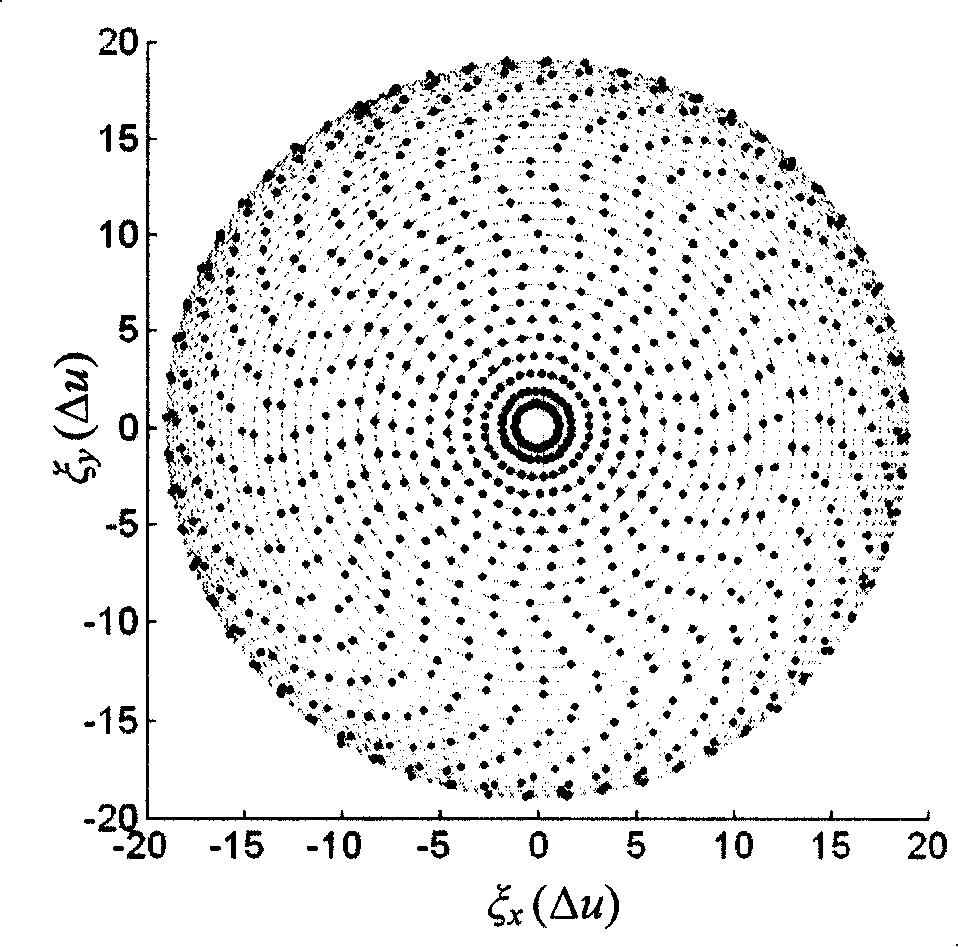
Microseism interference imaging method
ActiveCN104765064AImprove positioning efficiencyAvoid influenceSeismic signal receiversSeismic signal processingMutual correlationInterferometric imaging
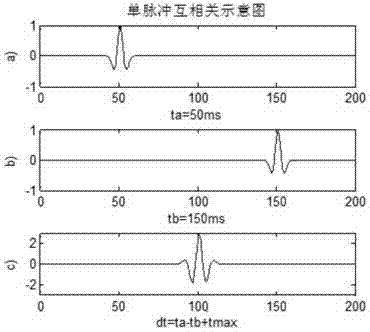
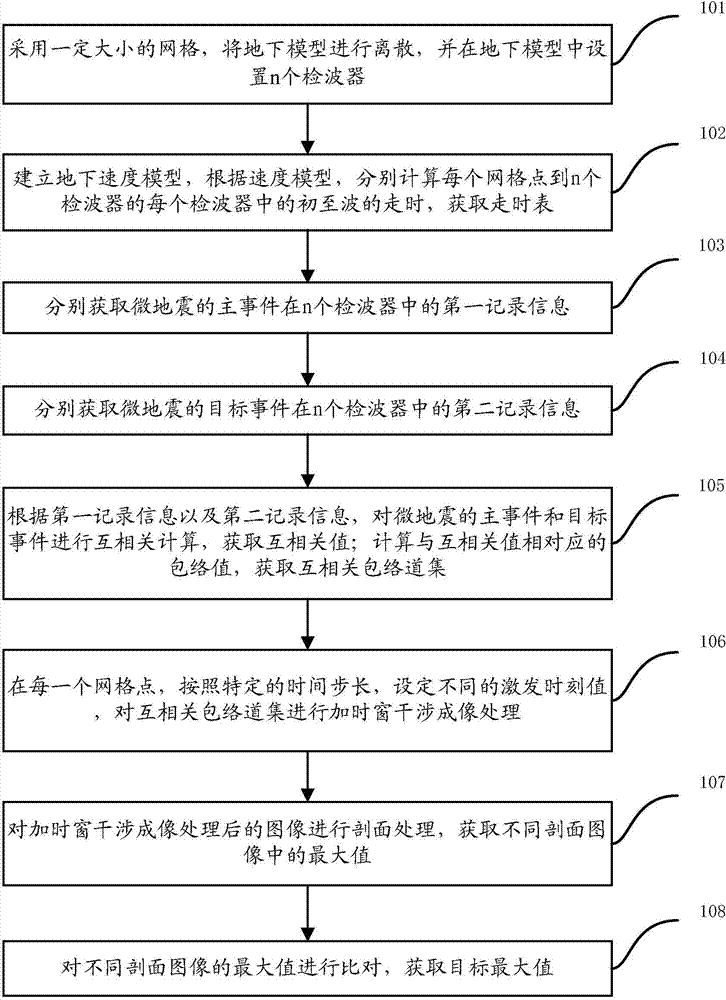
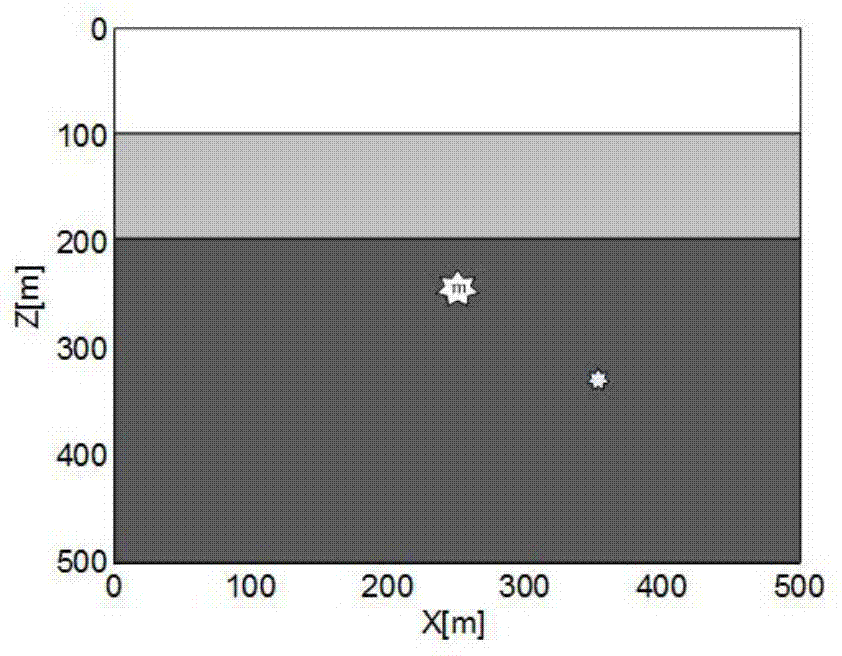
The invention relates to a microseism interference imaging method. The method includes the steps of dispersing an underground model through meshes of a certain size, arranging n detectors in the underground model, establishing an underground speed model, calculating the travel time between each mesh point and the preliminary wave of each detector according to the speed model, obtaining first record information of a main event of a microseism in the n detectors and second record information of a target event in the n detectors, conducting mutual correlation calculation on the main event and the target event of the microseism according to the first record information and the second record information, obtaining an envelope and a mutual correlation envelope gather, setting different trigger moment values at each mesh point according to the specific time step, conducting time-window-added interference imaging on the mutual correlation gather, conducting section processing on a processed image, obtaining the maximum values in different section images, comparing the maximum values of different section images, and obtaining the target maximum value.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molecular interferometric imaging process and apparatus
ActiveUS20080129981A1Increase speedHigh sensitivitySamplingPhase-affecting property measurementsAnalyteReference image
A molecular interferometric imaging system for detecting an analyte in a sample, that includes an illumination source providing a beam of radiation; a pixel array for detecting radiation in an image plane; a biolayer designed to react to the analyte when it comes in contact with the sample; a substrate designed to convert phase modulation into intensity modulation which can be detected and imaged directly by the pixel array, the biolayer being on the substrate; a reference surface; an image switching means for switching between a first position for collecting a sample image of the biolayer, and a second position for collecting a reference image of the reference surface; and a processing means for producing a composite image using the sample image and the reference image for illumination normalization.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
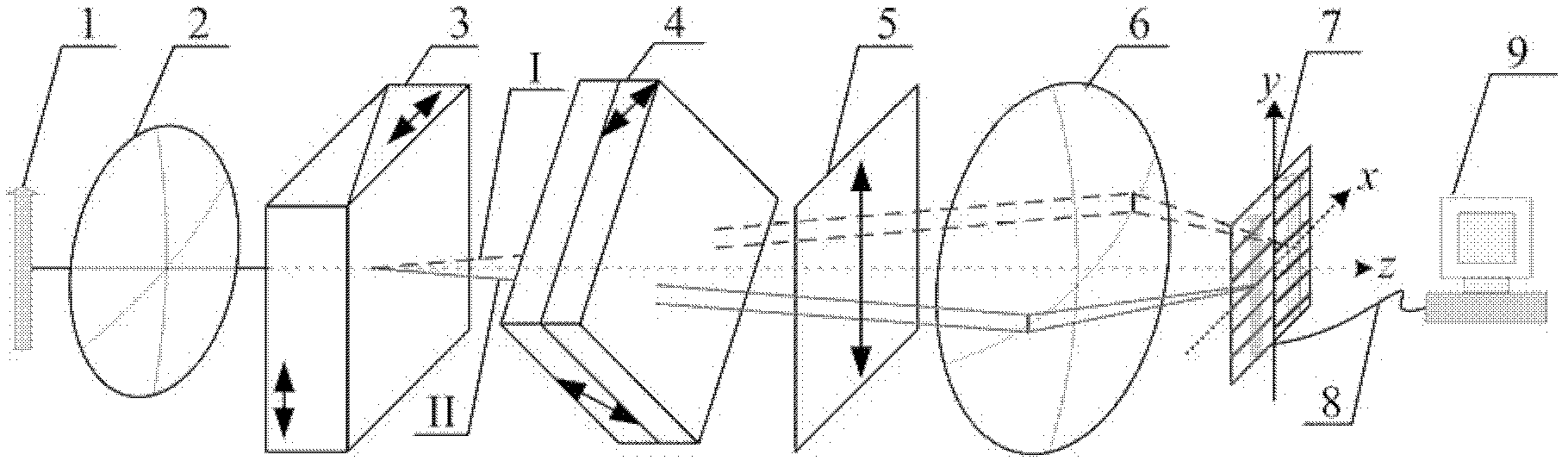
Interference imaging spectroscopy device and method for improving spectral resolution
ActiveCN103076092AEquipped with image plane interference imaging spectroscopy technologySimple methodInterferometric spectrometryBeam splitterSpectral bands
The invention discloses an interference imaging spectroscopy device and an interference imaging spectroscopy method for improving spectral resolution. The device comprises a front optical system, a dispersion flat plate Sagnac lateral shear beam splitting system, an imaging system and a signal processing system which are arranged along an optical path in sequence, wherein incident light of each point of a target enters the front optical system to eliminate stray light and form a collimated light beam; the light beam then enters the dispersion flat plate Sagnac lateral shear beam splitting system; the light is laterally sheared by the lateral shear beam splitting system; because of the flat plate dispersion effect, the shear distance changes along with light wavelength, and further optical path difference information which changes along with wave number is introduced; two beams of light formed by shearing subsequently enter the imaging system; interference information under different optical path differences of each point of the target is acquired by turning the lateral shear beam splitter or the entire system; and discrete fourier transform is performed on the acquired interference information of the target point to obtain high-resolution spectral information and two-dimensional image information of each spectral band are obtained. The device and the method have the advantages of high spectral resolution, high luminous flux, high target resolution and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Polarization enhanced interferometric imaging
ActiveUS20170016821A1High sensitivityIncrease costPolarisation-affecting propertiesInterferometersNanoparticleInterferometric imaging
An imaging system uses polarized light to illuminate the target and then uses a polarization filter to remove the light that is reflected from the target without modification. The target can include one or more anisotropic objects that scatter the light and alter the polarization state of the reflected light and causing it to be selectively transmitted to the imaging device which can record the transmitted light through the filter. The illuminating light can be circularly polarized and the filter can remove the circularly polarized light. The target can include asymmetric nanoparticles, such as nanorods that alter the amplitude or phase of the scattered light enabling pass through the filter to be detected by the imaging device.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Device for detecting full polarization of passive and static coaxial interference imaging spectrum
ActiveCN101793558ARealize the spectroscopic functionHigh spectral resolutionInterferometric spectrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesInterferometric imagingSavart
The invention relates to a device for detecting full polarization of a passive and static coaxial interference imaging spectrum. The device comprises a pre-optical telescopic system, a static all-optical modulation module, a Savart plate-based static interference imaging spectrometer, an imaging lens set and a detector which are coaxially arranged, wherein the rear side of the detector is connected with a signal acquiring and processing system; light emitted by a target source is aligned by the pre-optical telescopic system, then is modulated by the static all-optical modulation module 2 and is changed into two beams of polarized light after passing through the Savart plate-based static interference imaging spectrometer; and the two beams of light are converged on the detector 5, are imaged, generate interference and finally are sent into the signal acquiring and processing system 6 after passing through the imaging set. The device is characterized by simple and compact structure, no moving parts, large luminous flux, and capability of acquiring target two-dimensional space images, one-dimensional spectrum information and complete polarization information once.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and system of adjusting a field of view of an interferometric imaging device
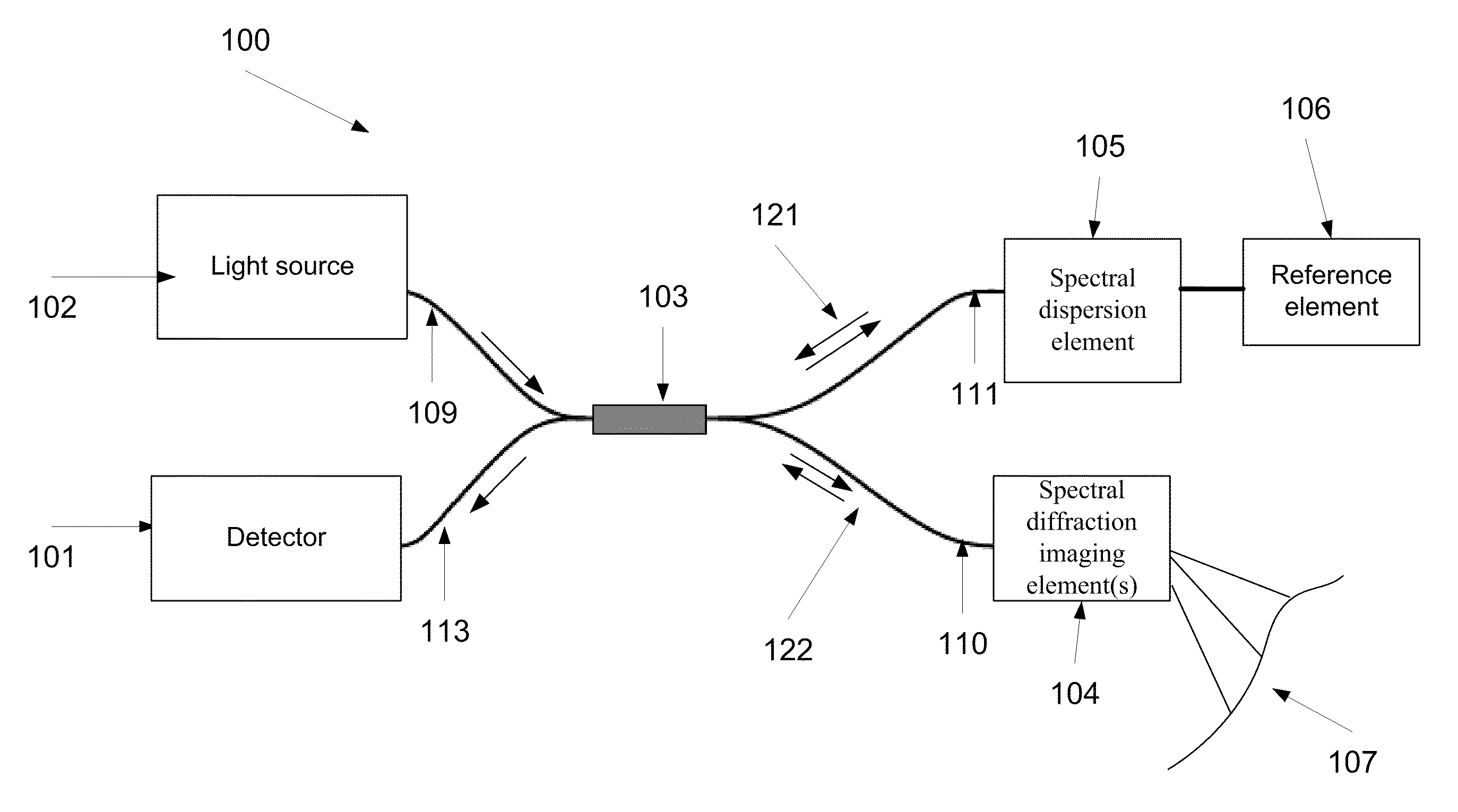
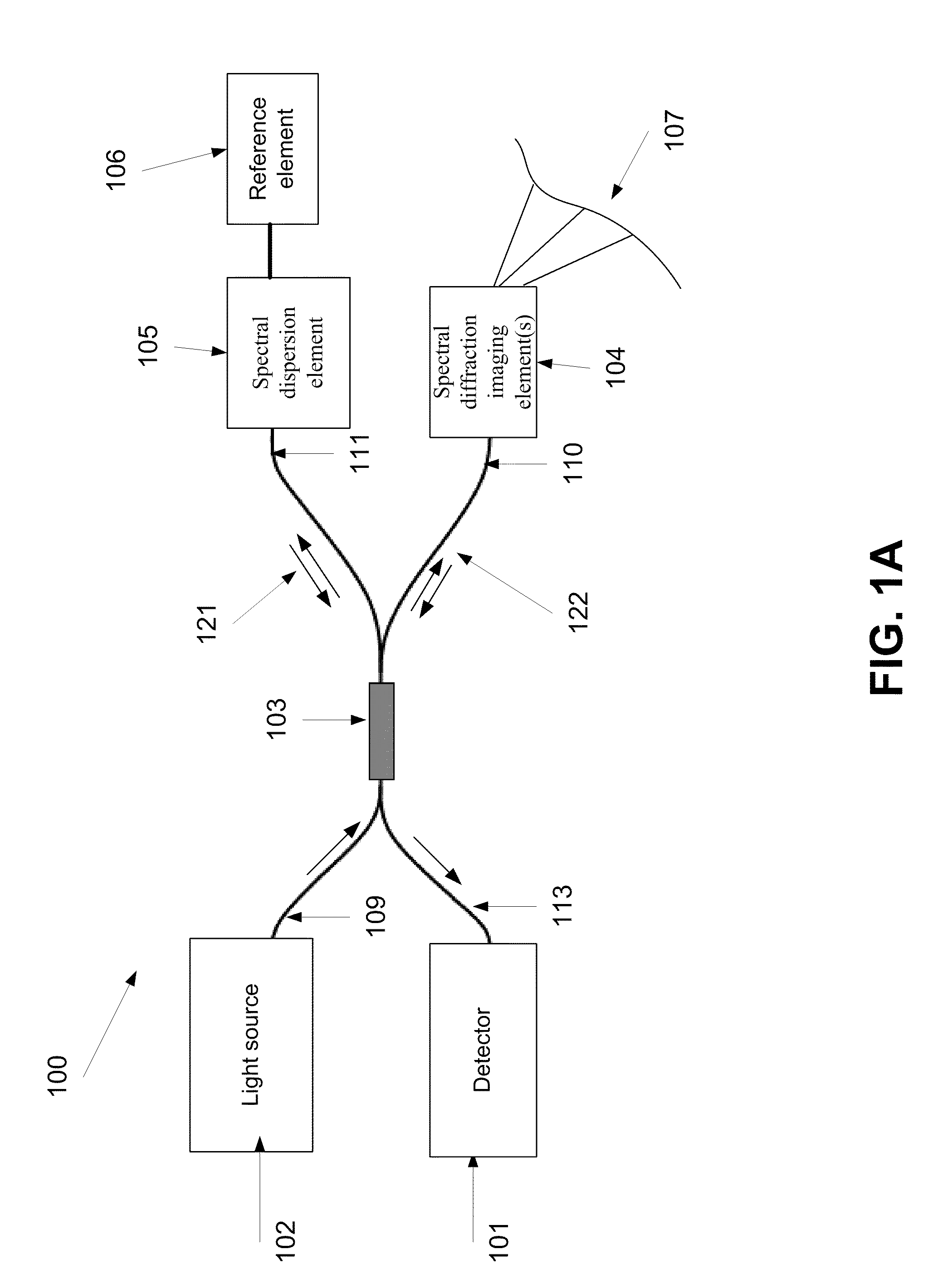
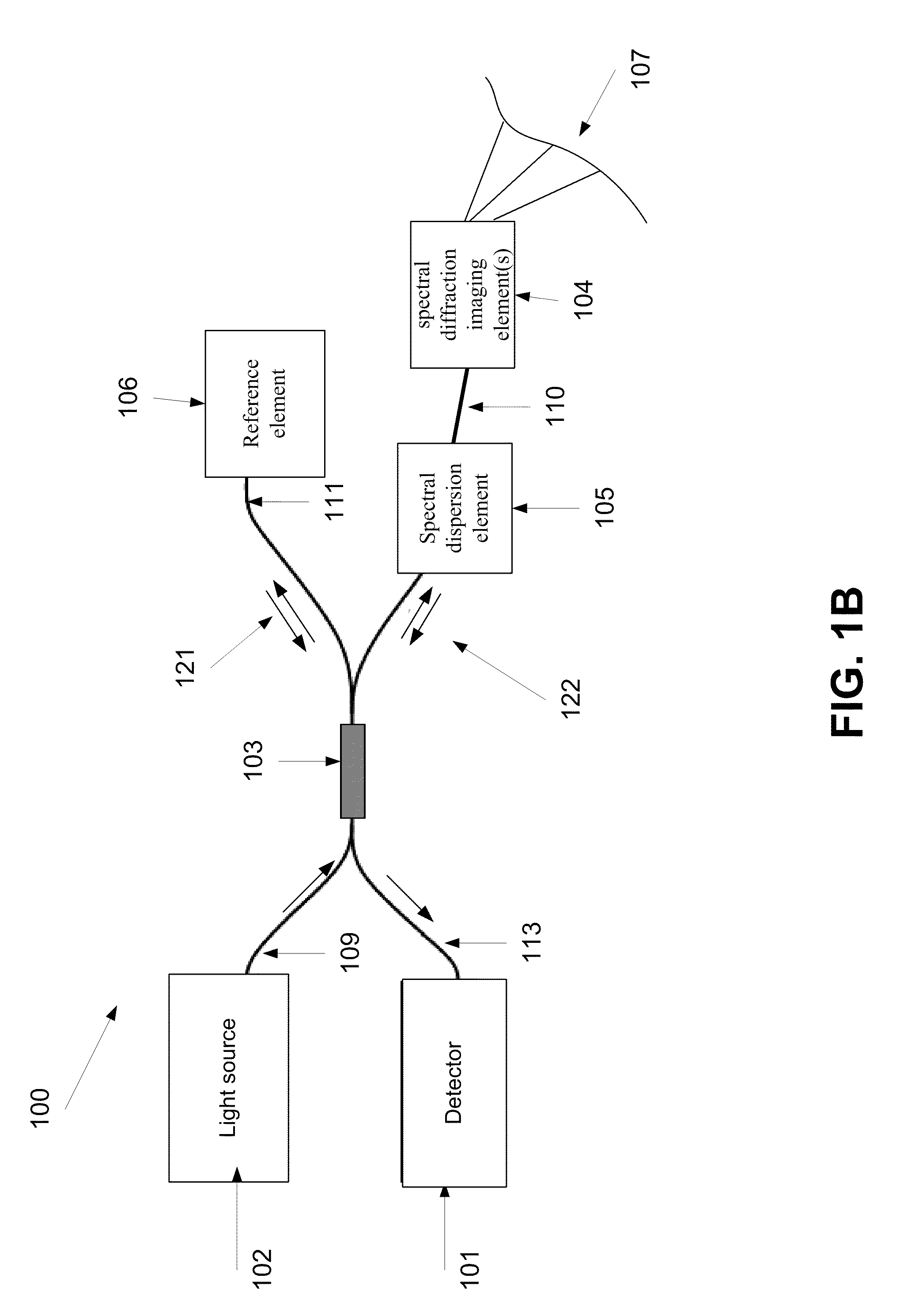
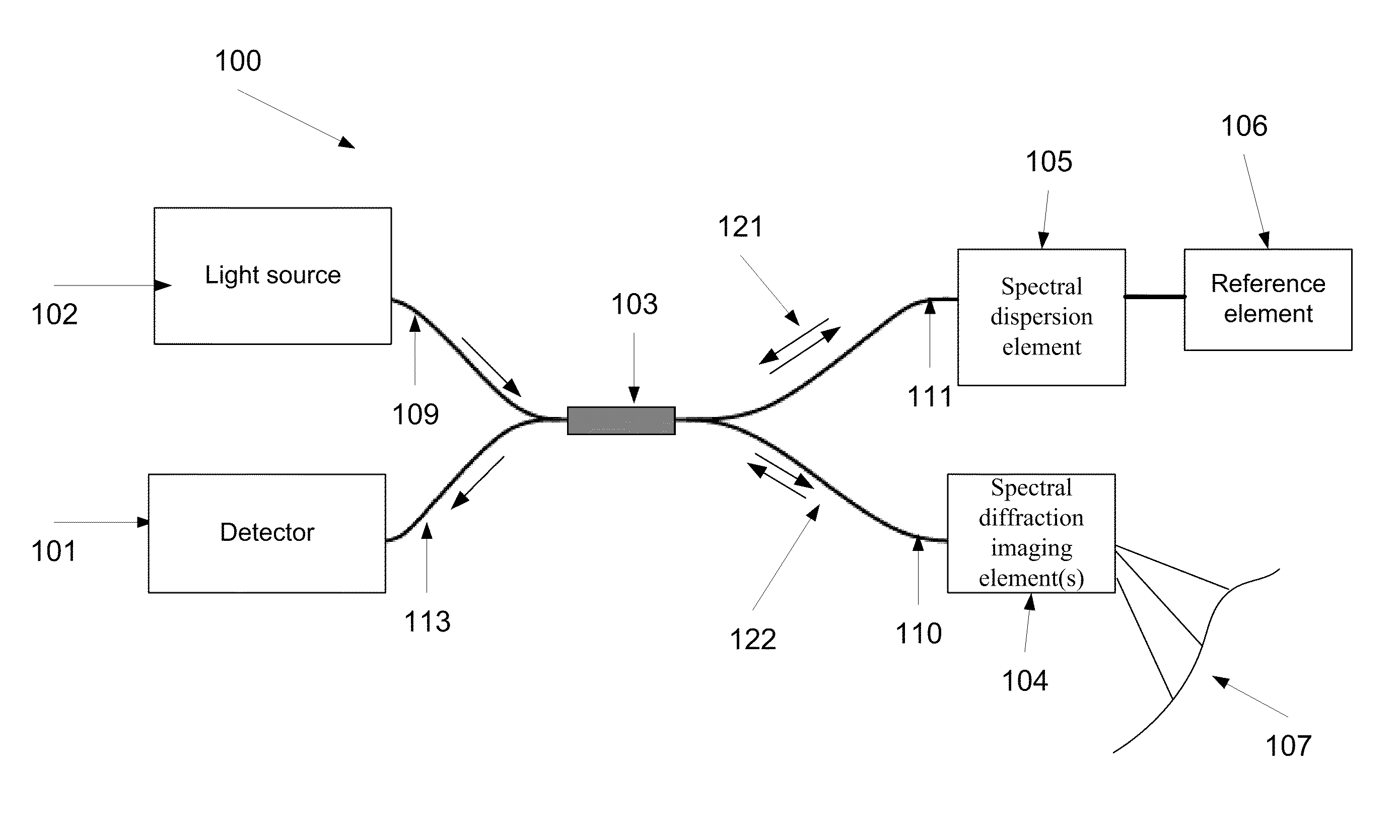
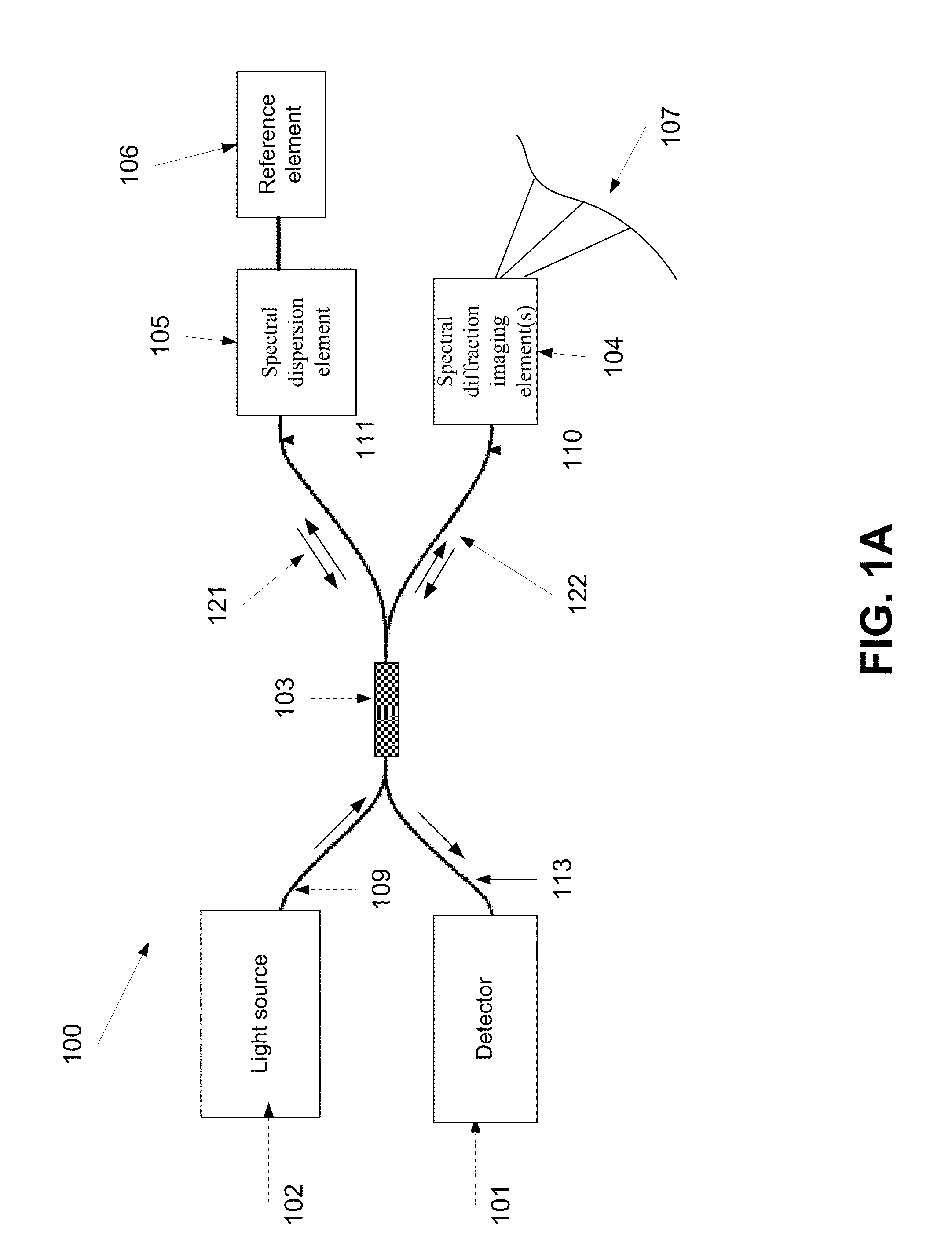
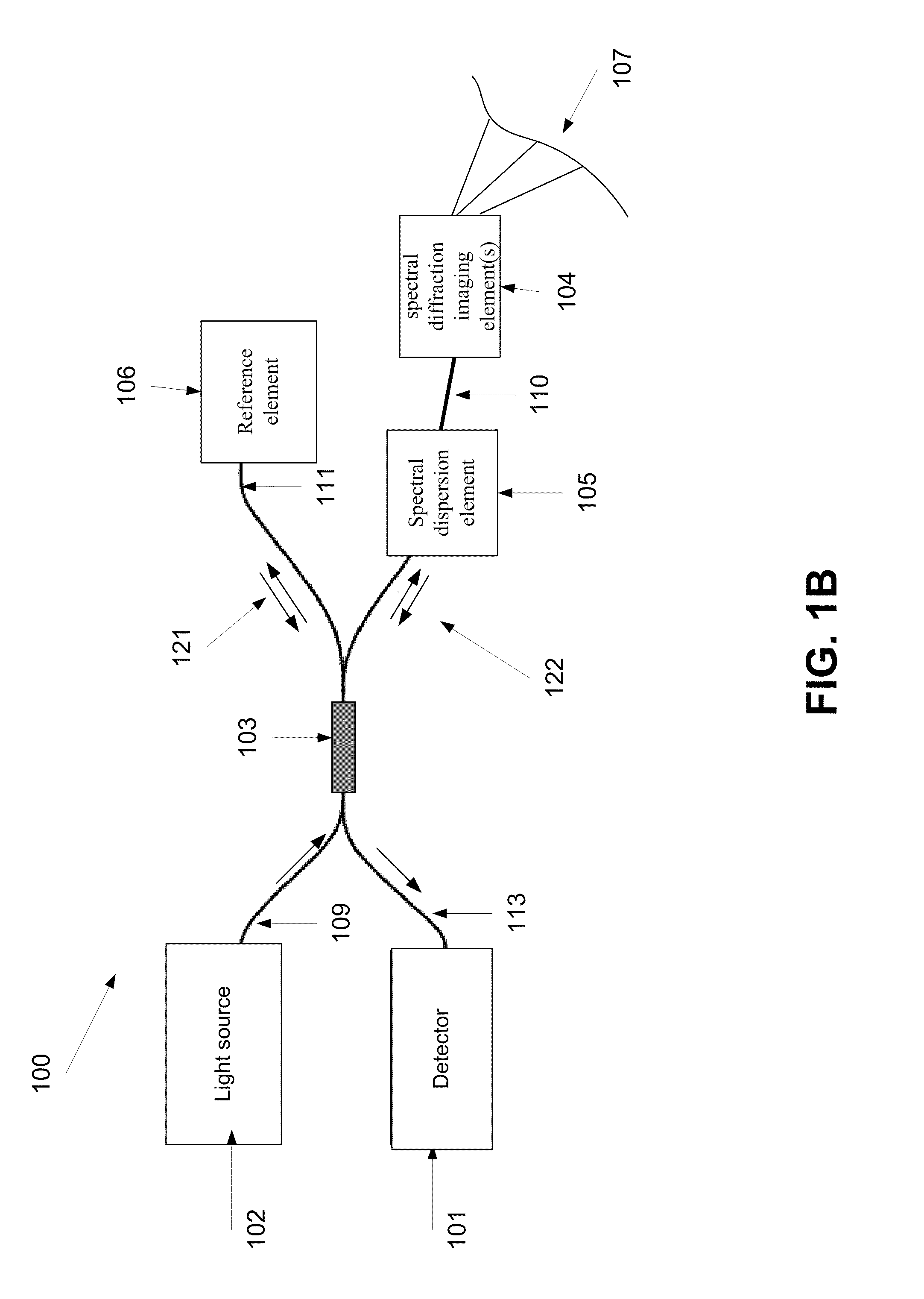
ActiveUS8804133B2Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryInterferometric imagingMethod of images
A method of imaging at least a part of an object. The method comprises splitting electro-magnetic radiation to first and second portions, propagating the first and second portions, spectrally dispersing the first portion toward the part and the second portion toward a reference element, combining between reflections of the spectrally dispersed first and second portions to produce an interference signal, capturing an image of the part from the interference, and adjusting at least one of a tilt of said image plane and a curvature of the image by changing a deviation between the phase of at least one spectral component of the first portion and the phase of at least one spectral component of the second portion.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Micro-polarization array based interference imaging full-polarization spectrum detection device and method
The invention discloses a micro-polarization array based interference imaging full-polarization spectrum detection device and method. The device comprises a front imaging objective, a collimator objective, a Sagnac lateral shearing beam splitter, an imaging objective, a micro-polarization modulation array, a detector and a signal processing system which are arranged sequentially in the direction of an optical path. The method comprises the following steps: step one, incident light is imaged by the front imaging objective, and then a light beam is collimated by the collimator objective; step two, the collimated light beam is laterally sheared by the Sagnac lateral shearing beam splitter; step three, the sheared light beam reaches the micro-polarization modulation array through the imaging objective, one object point corresponds to four polarization pixels, and four groups of interference images in a scene are acquired from a target surface of the detector through push scanning; and step four, the signal processing system acquires the two-dimensional light intensity information, spectral information and full-polarization parameters of all spectrum bands of the scene after spectrum reconstruction and polarization information reconstitution. The method has the advantages of high spectral resolution, high target resolution and synchronous acquisition of full-polarization information.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
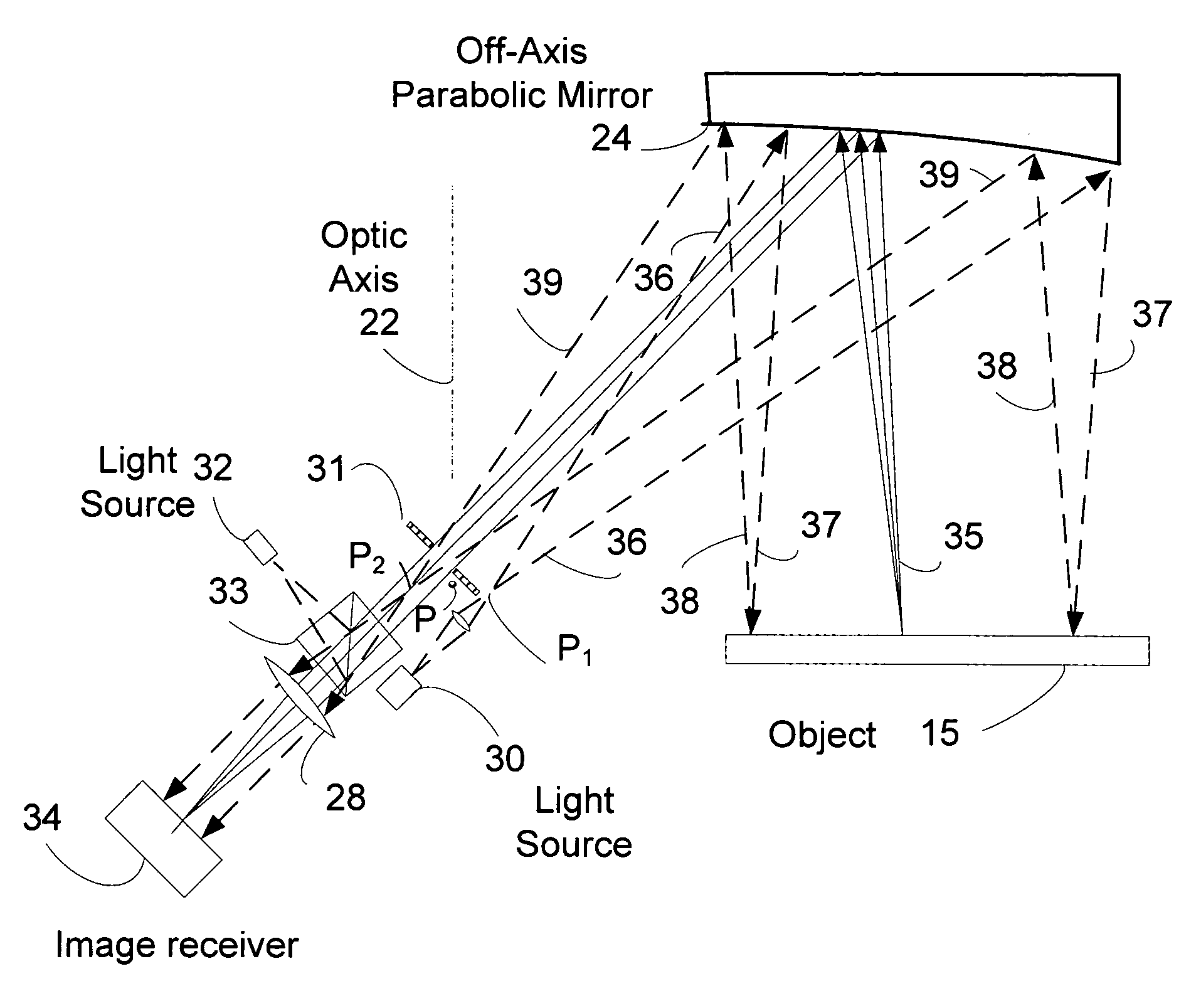
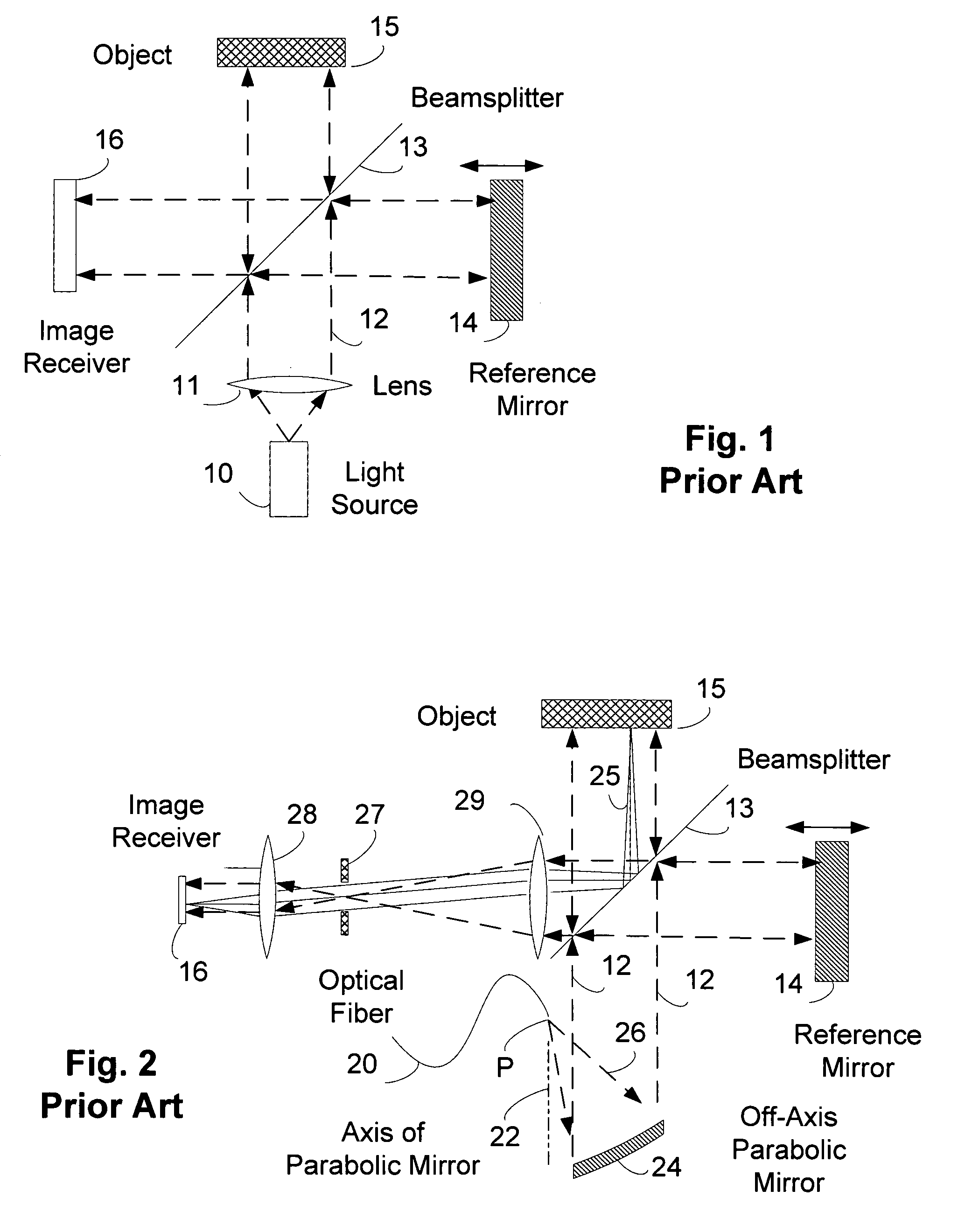
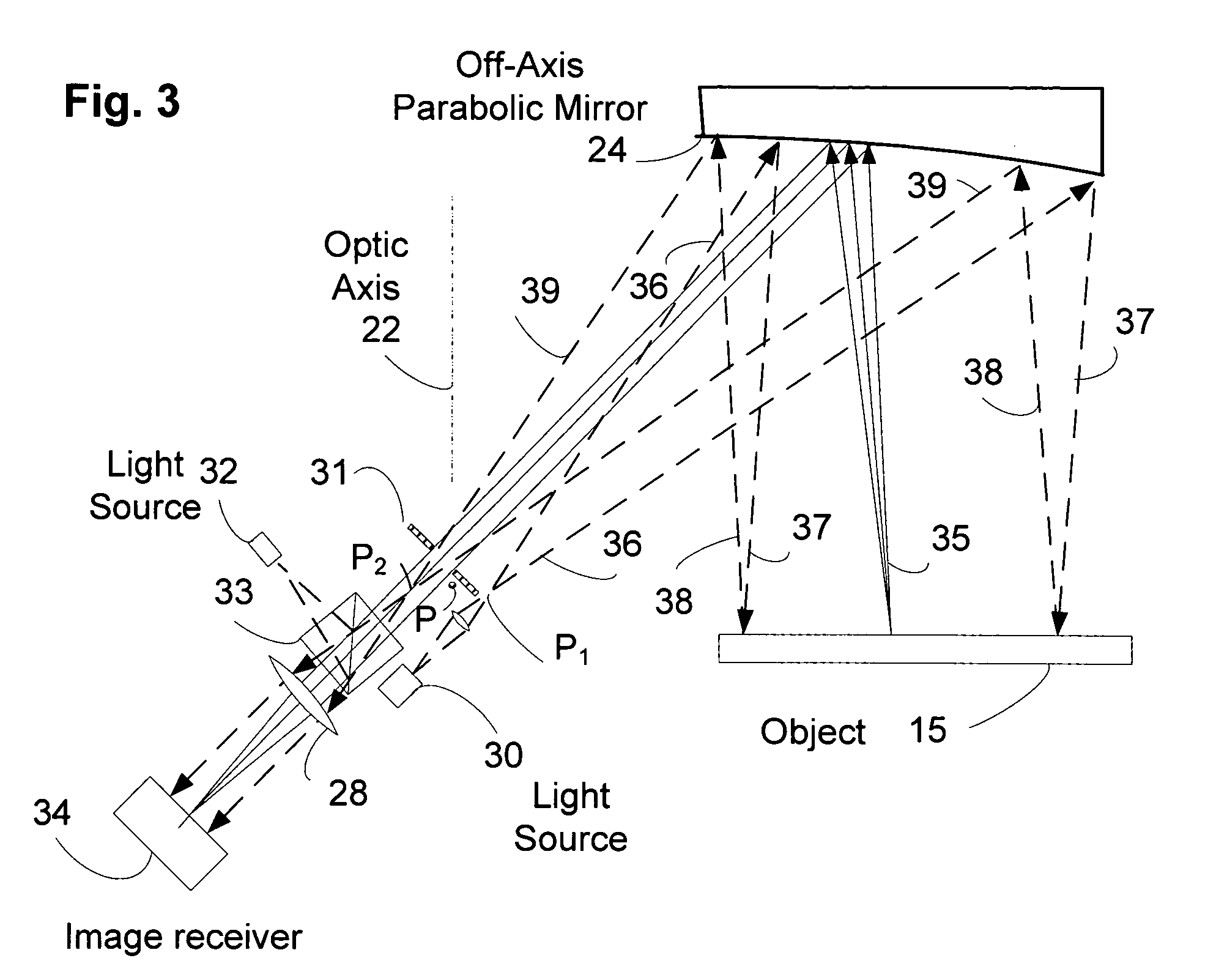
Off-axis paraboloid interferometric mirror with off focus illumination
InactiveUS20070133010A1Lighter and less-expensive optical elementUsing optical meansLight beamInterferometric imaging
An off axis paraboloid mirror is used to provide object illumination in an interferometric imaging system. The light from an object illumination light source diverges from a point apart from the focus point of the paraboloid, proceeds to the parabolic mirror surface, and is reflected as a nearly parallel beam to illuminate the object.
Owner:COHERIX
Compact Fresnel two-sided mirror full reflection large visual field interference imaging optical spectrometer light path structure
InactiveCN101368849AMeet the foldTo achieve the purpose of structure miniaturizationRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsEarth observationAviation
An optical path structure for a compact Fresnel double mirror total-reflection large-field interference imaging spectrometer belongs to the technical field of earth-observation imaging spectrometers. The invention is composed of a reflective pre-posed telescope, an incident slit, a compact collimation structure, a Fresnel double mirror, an off-axis cylindrical reflector and a focal plane detector. The reflective pre-posed telescope enables the target to be imaged on a one-dimensional slit; the image of the slit is projected onto the compact collimation structure; the Fresnel double mirror structure is added in the collimation optical path, so that the light beam is collimated and cut into two beams of coherent parallel light with a certain intersecting angle at the same time; and the two light beams are focalized through the off-axis cylindrical reflector and finally projected to the surface of the focal plane detector so as to form one-dimensional interference fringe distribution and another one-dimensional gray image distribution. The invention is characterized by total reflection, compact collimation and interference structure, wide field of view, high luminous flux and small size of optical structure; and the structure can be applied to the aviation and spaceflight remote sensing earth observation field.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and system for calibrating interference of space-based interferometric imaging radar altimeter
ActiveCN108007476AAchieving a complete estimateEstimates are accurateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarInterferometric imaging
The invention relates to a method and system for calibrating interference of a space-based interferometric imaging radar altimeter. The method comprises the following steps: determining the radar viewing angle of each pixel point of a reference target according to the altitude information of the reference target as well as rail and slant distance parameters acquired by the space-based interferometric imaging radar altimeter; performing polynomial fitting on the spatial variation relation between the unrapping phase and the radar viewing angle; determining the sensitivity of the unwrapping phase and the slant distance on the radar viewing angle separately; determining the length and the inclination angle of a base line; and determining interferometric phase offset. The system comprises a radar viewing angle calculation module, a fitting coefficient calculation module, a sensitivity calculation module, an interferometric base line determining module and an interferometric phase offset determining module. Estimation of the interferometric base line and the interferometric phase offset can be separated by fitting and estimating the sensitivity of the unwrapping phase on the radar viewing angle, so that the three parameters such as the length of the base line, the inclination angle of the base line and the interferometric phase offset, can be completely estimated.
Owner:TECH & ENG CENT FOR SPACE UTILIZATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system of adjusting a field of view of an interferometric imaging device
A method of imaging at least a part of an object. The method comprises splitting electro-magnetic radiation to first and second portions, propagating the first and second portions, spectrally dispersing the first portion toward the part and the second portion toward a reference element, combining between reflections of the spectrally dispersed first and second portions to produce an interference signal, capturing an image of the part from the interference, and adjusting at least one of a tilt of said image plane and a curvature of the image by changing a deviation between the phase of at least one spectral component of the first portion and the phase of at least one spectral component of the second portion.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com