Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
76 results about "Hydrodynamic forces" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
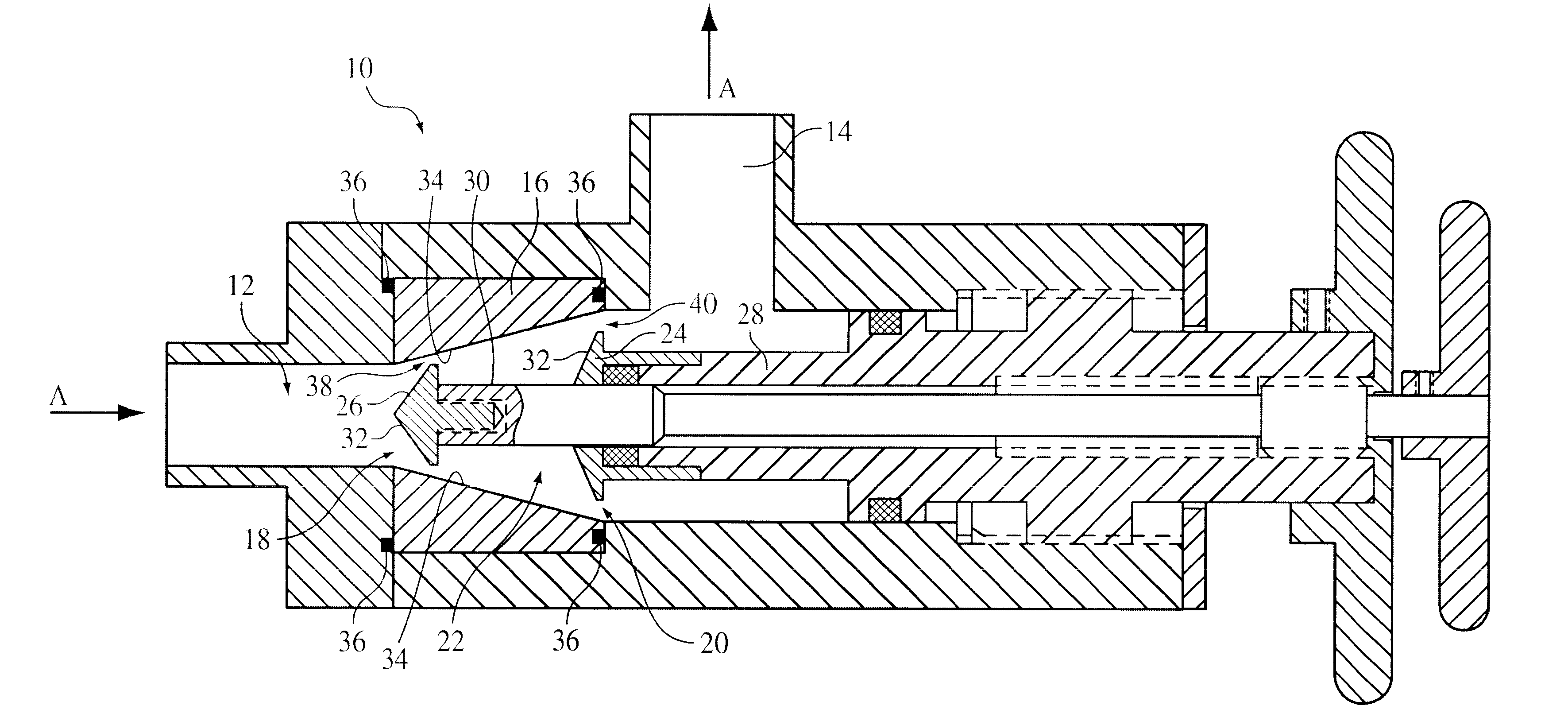
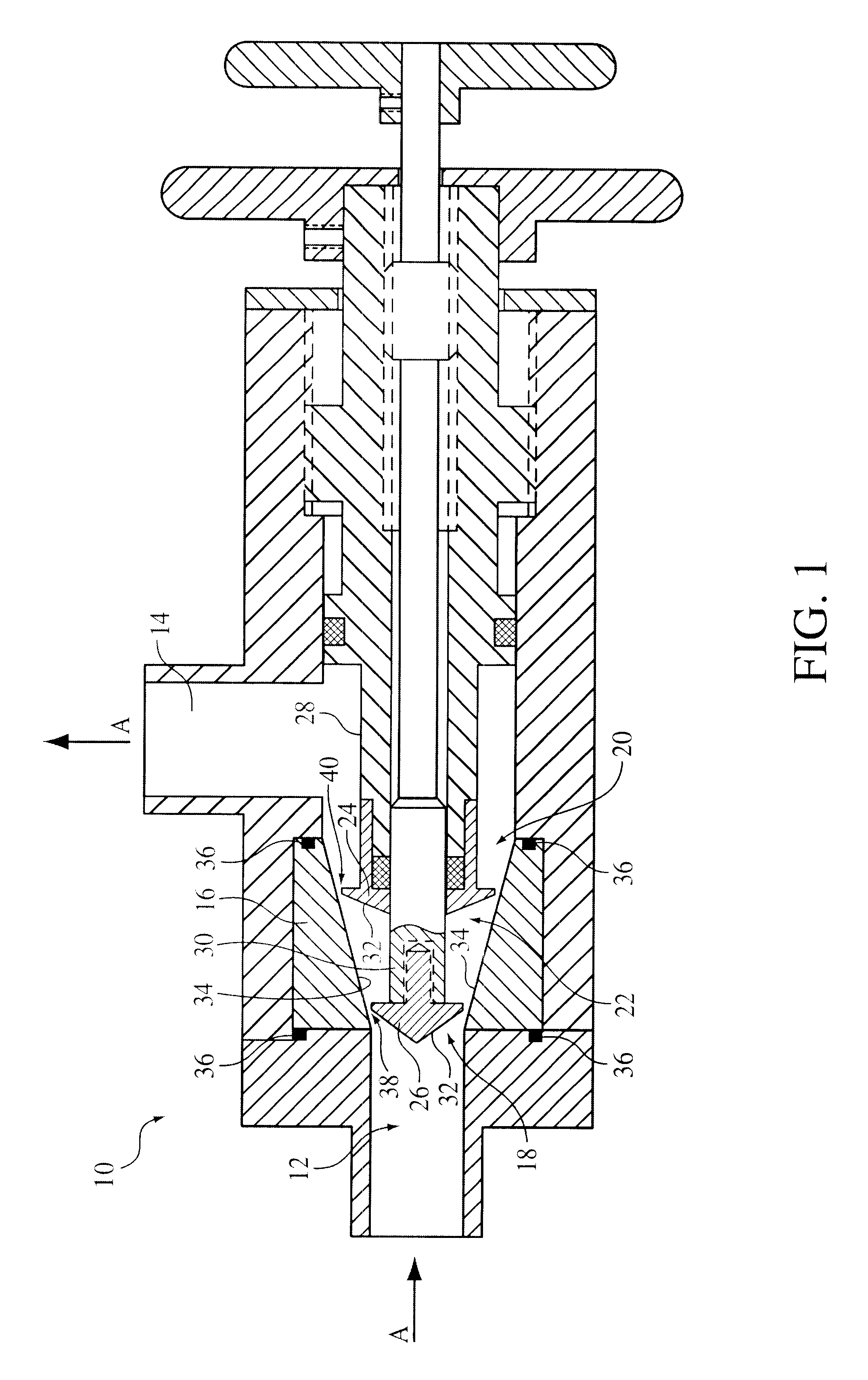
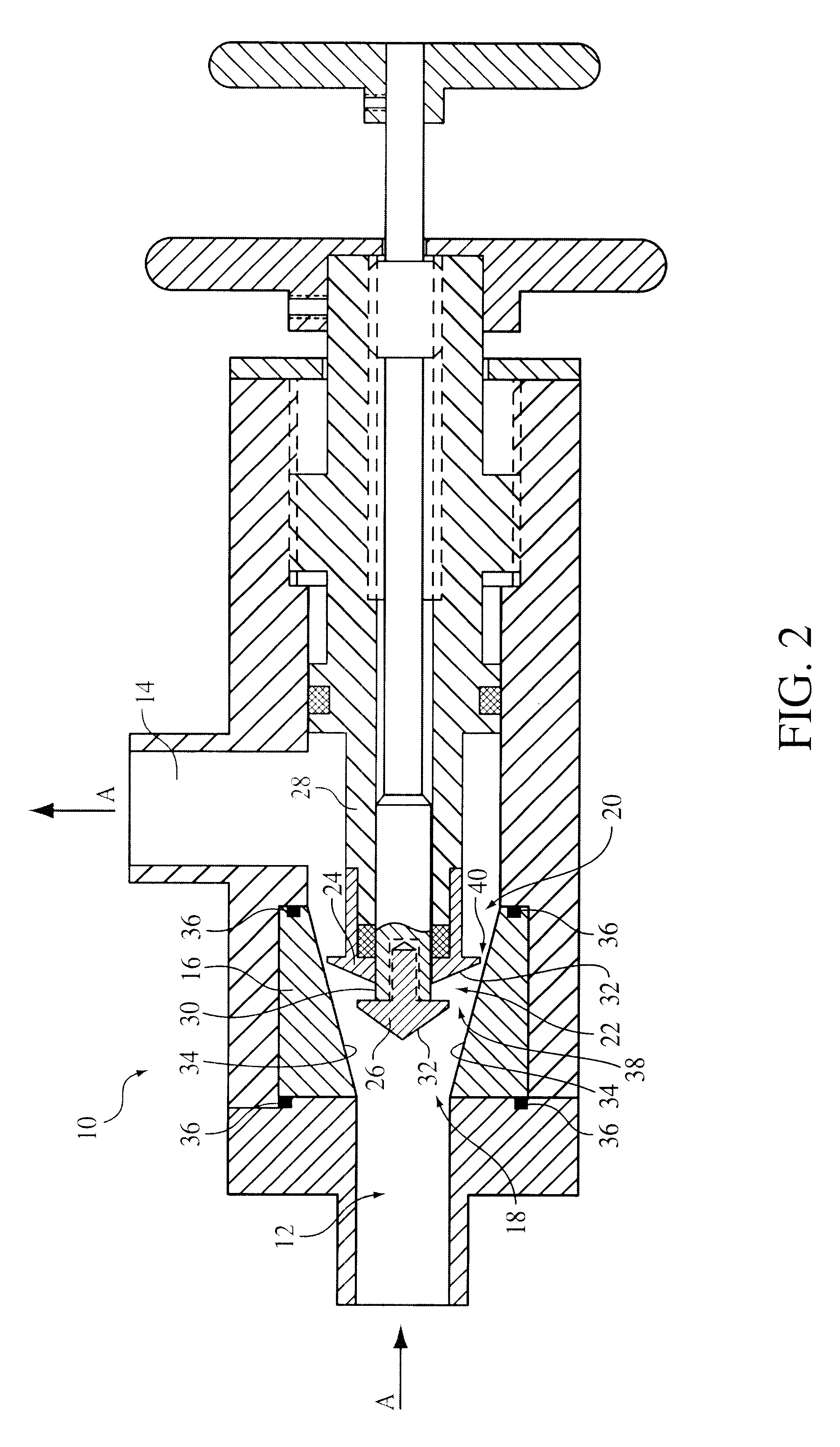
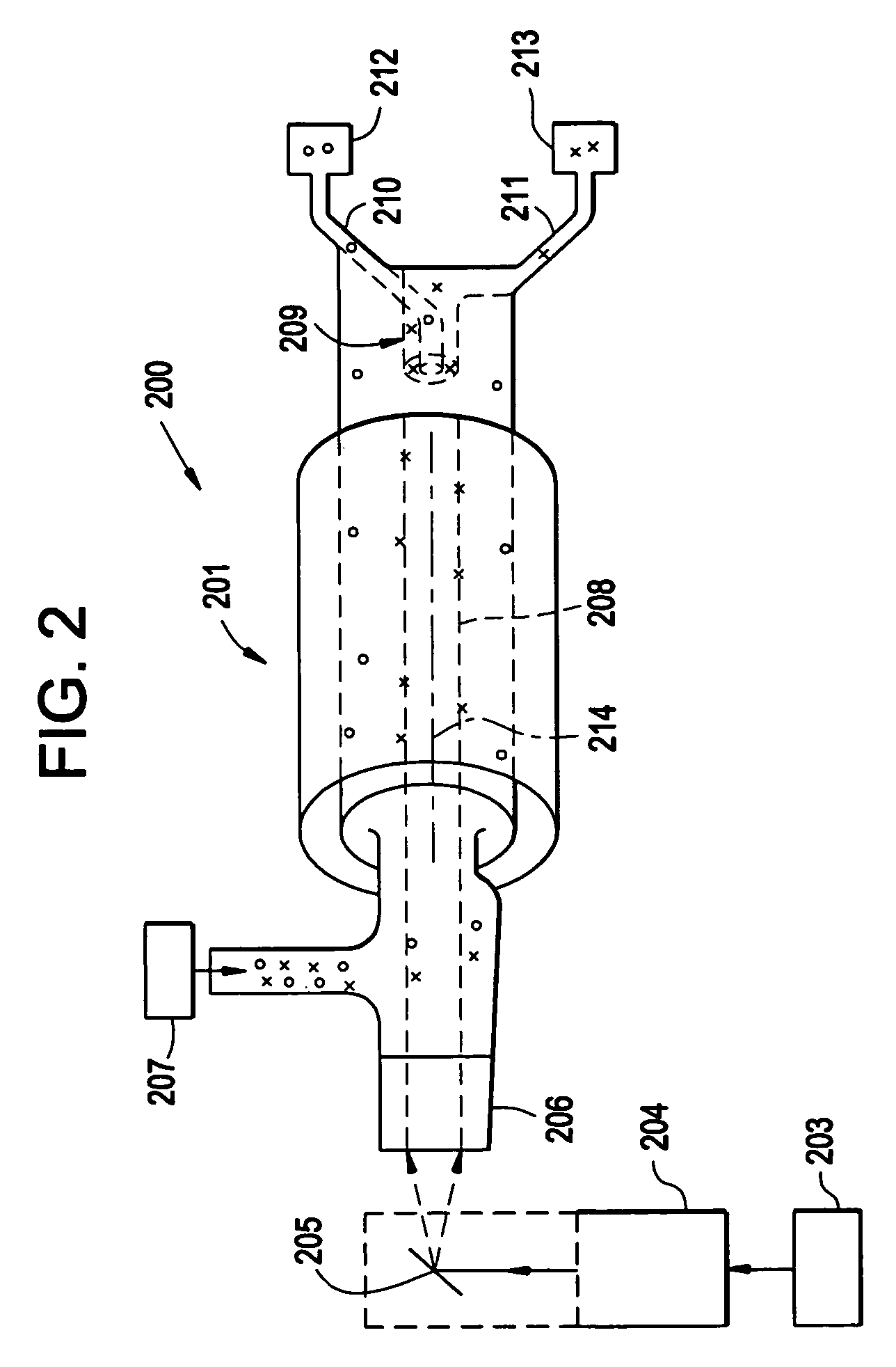
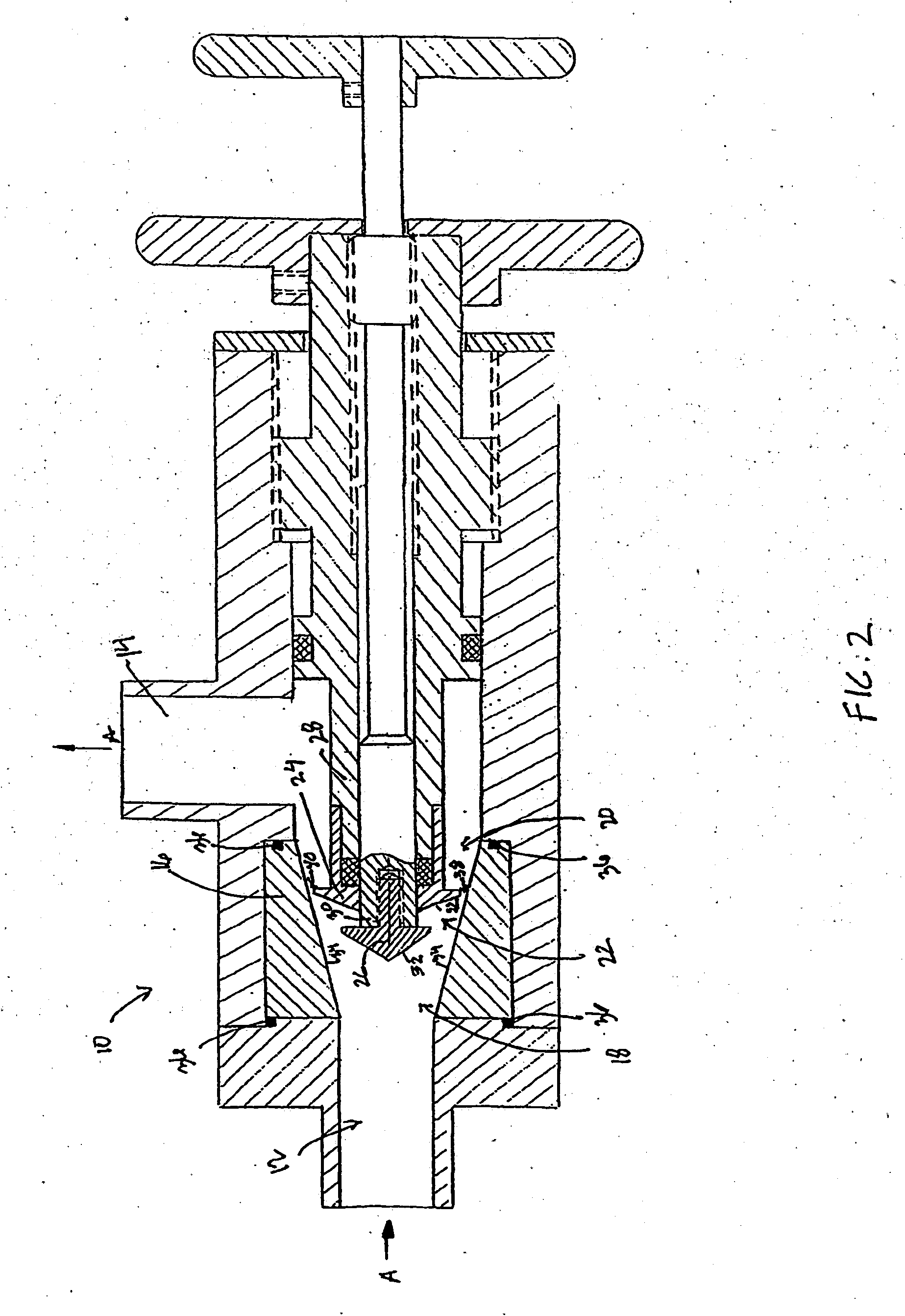
Device and method for creating hydrodynamic cavitation in fluids
This invention provides a device and method for creating hydrodynamic cavitation in fluids which includes a flow-through chamber intermediate an inlet opening and an outlet opening; the flow-through chamber having an upstream opening portion communicating with the inlet opening and a downstream opening portion communicating with the outlet opening; the cross-sectional area of the downstream opening portion being greater than the cross-sectional area of the upstream opening portion; and a cavitation generator located within the flow-through chamber for generating a hydrodynamic cavitation field downstream from the generator. This invention also provides for a device for creating hydrodynamic cavitation in fluids wherein the walls of the flow-through chamber are removable mounted within the device and are interchangeable and replaceable with replacement walls having various shapes and configurations, thereby enabling the flow-through chamber to assume various shapes and configurations to affect cavitation. This invention also provides for a device for a device for creating hydrodynamic cavitation in fluids wherein the baffle elements are removably mounted within the device and are interchangeable and replaceable with replacement baffles having various shapes and configurations thereby enabling variable effects on cavitation.
Owner:ARISDYNE STSTEMS INC
System and method for microfluidic cell culture
ActiveUS20120009671A1Shorten speedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGravitational forceEngineering
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Apparatus for optically-based sorting within liquid core waveguides
InactiveUS20060257089A1Improve reflectivityEasy to classifyCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by optical meansLiquid coreNanoparticle
The present invention is related to an apparatus for the sorting of particles in a fluid medium flowing within a liquid-core waveguide, by combining customized light intensity patterns formed inside the waveguide, and diluting the suspension of particles (i.e., cells, blood, nanoparticles, etc.) flowing within the fluid medium of the waveguide. With this customized light intensity pattern, which controls the optical forces introduced by the light confined within the waveguide, and the control of the hydrodynamic forces introduced by the liquid flow (or multiple channel liquid flows), the sorting of particles can be achieved.
Owner:ARRYX INC
System and method for microfluidic cell culture
InactiveUS20130115606A1Avoid the needHigh densityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGravitational forceEngineering
Microfluidic devices and methods for perfusing a cell with perfusion fluid are provided herein, wherein the gravitational forces acting on the cell to keep the cell at or near a retainer or a retaining position exceed the hydrodynamic forces acting on the cell to move it toward an outlet. Also provided, are methods for assaying cell products within the microfluidic device.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
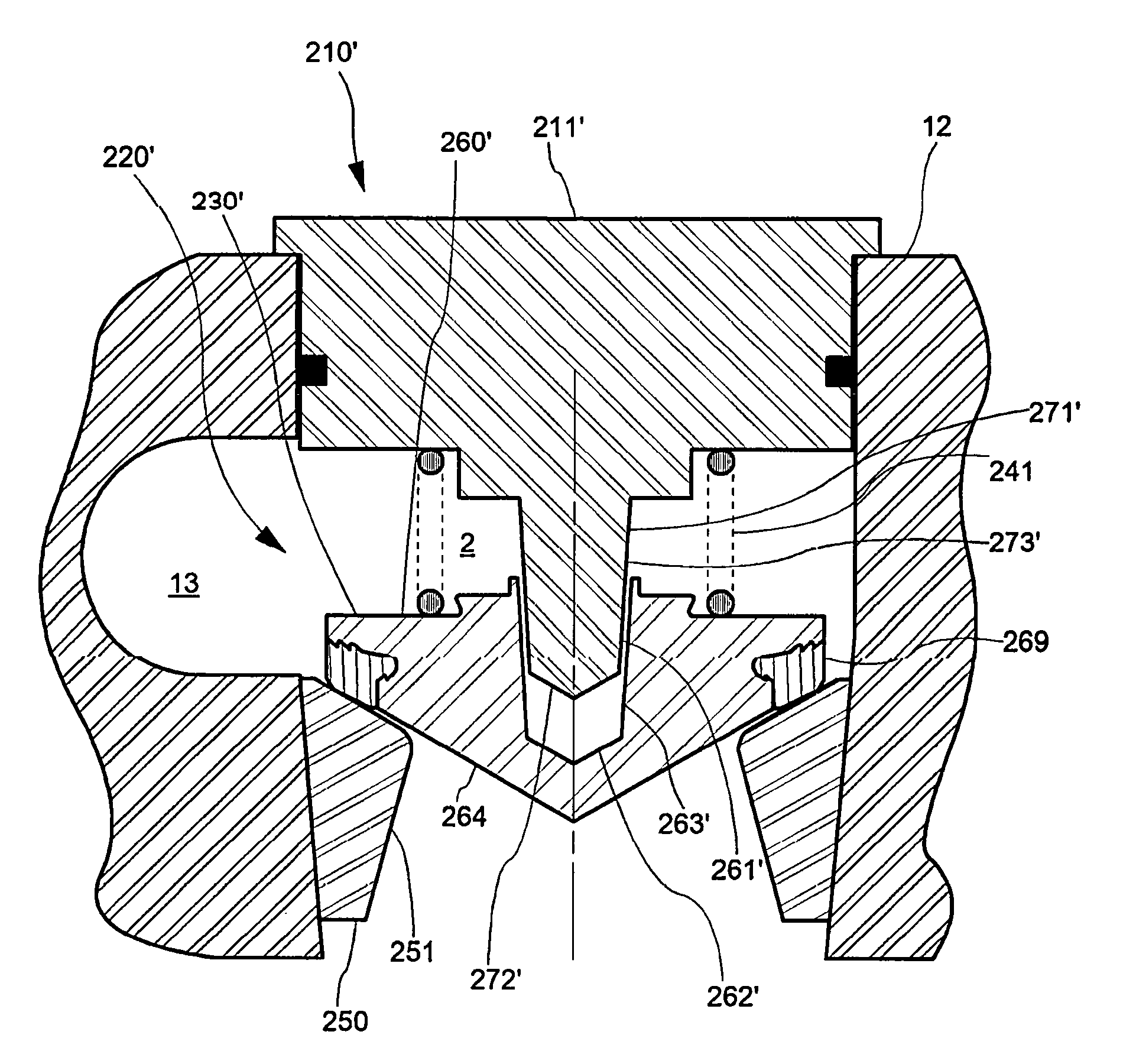
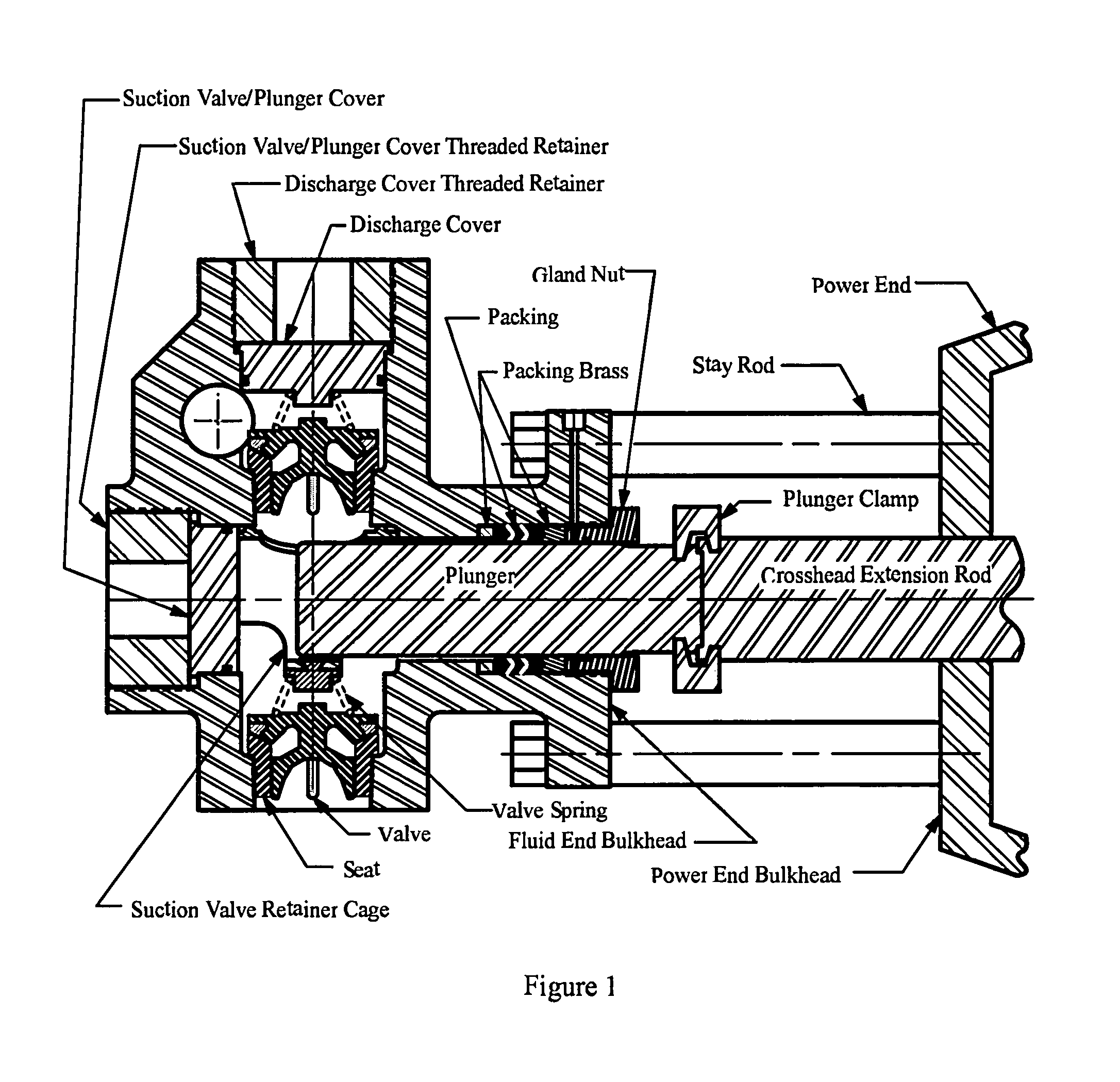
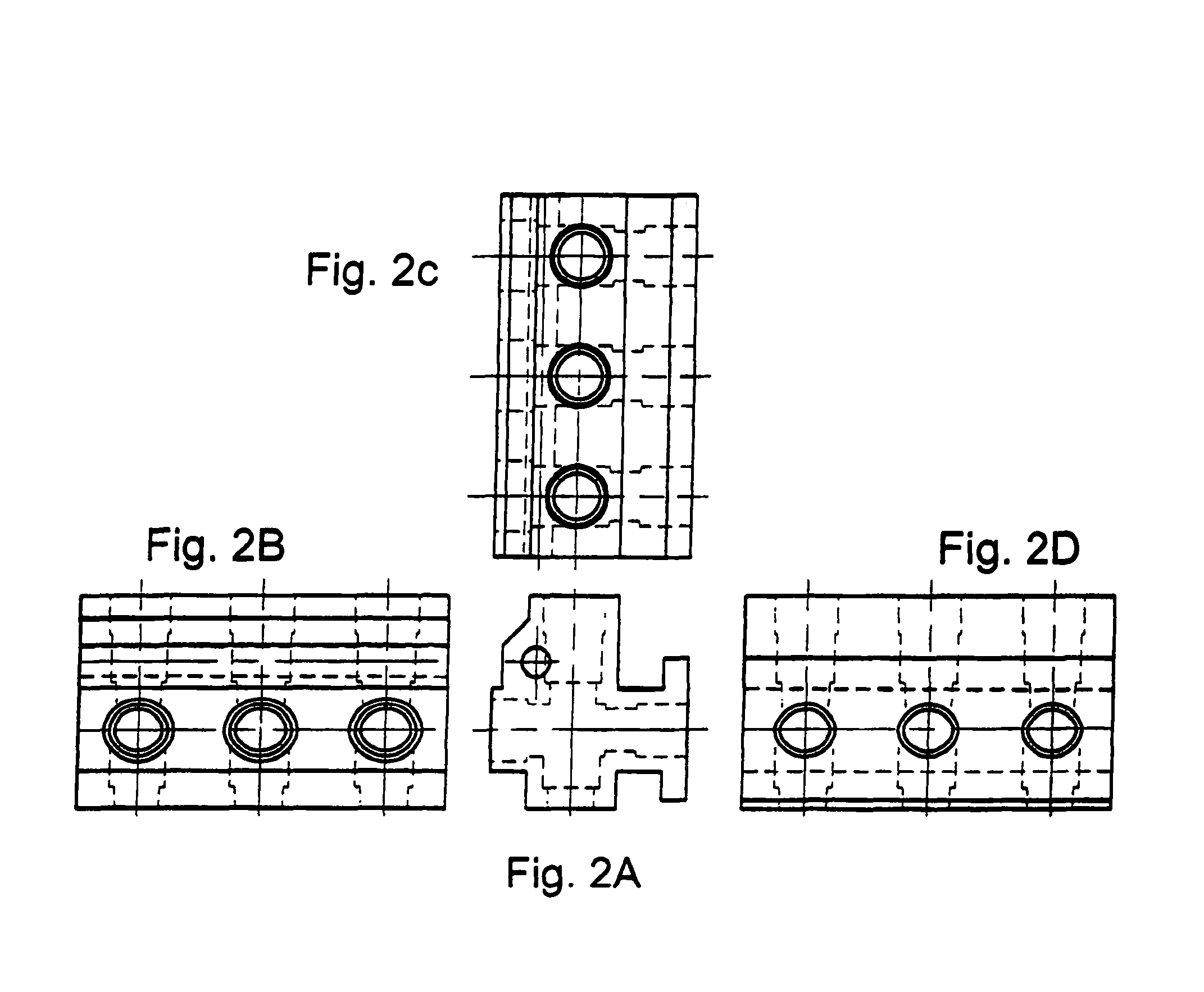
Low turbulence valve
InactiveUS9416887B2High trafficAvoid turbulencePositive displacement pump componentsCheck valvesEngineeringHydrodynamic forces
A positive displacement pump fluid end with multiple fluid chambers and each fluid chamber comprising a valve body, valve seal, seat, spring, and external guide. External top male stem guide is integral to the fluid end discharge cover or the suction valve spring retainer. Female guide is internal and integral with the valve body. When the valve opens hydrodynamic forces and moments align the valve to prevent rotation. An embodiment features tapered male and female guide members to further assist in correct alignment of the valve with the seat. Various additional embodiments assist in venting any trapped fluids between the male and female portions of the guide.
Owner:ALTIS INVESTMENTS LLC
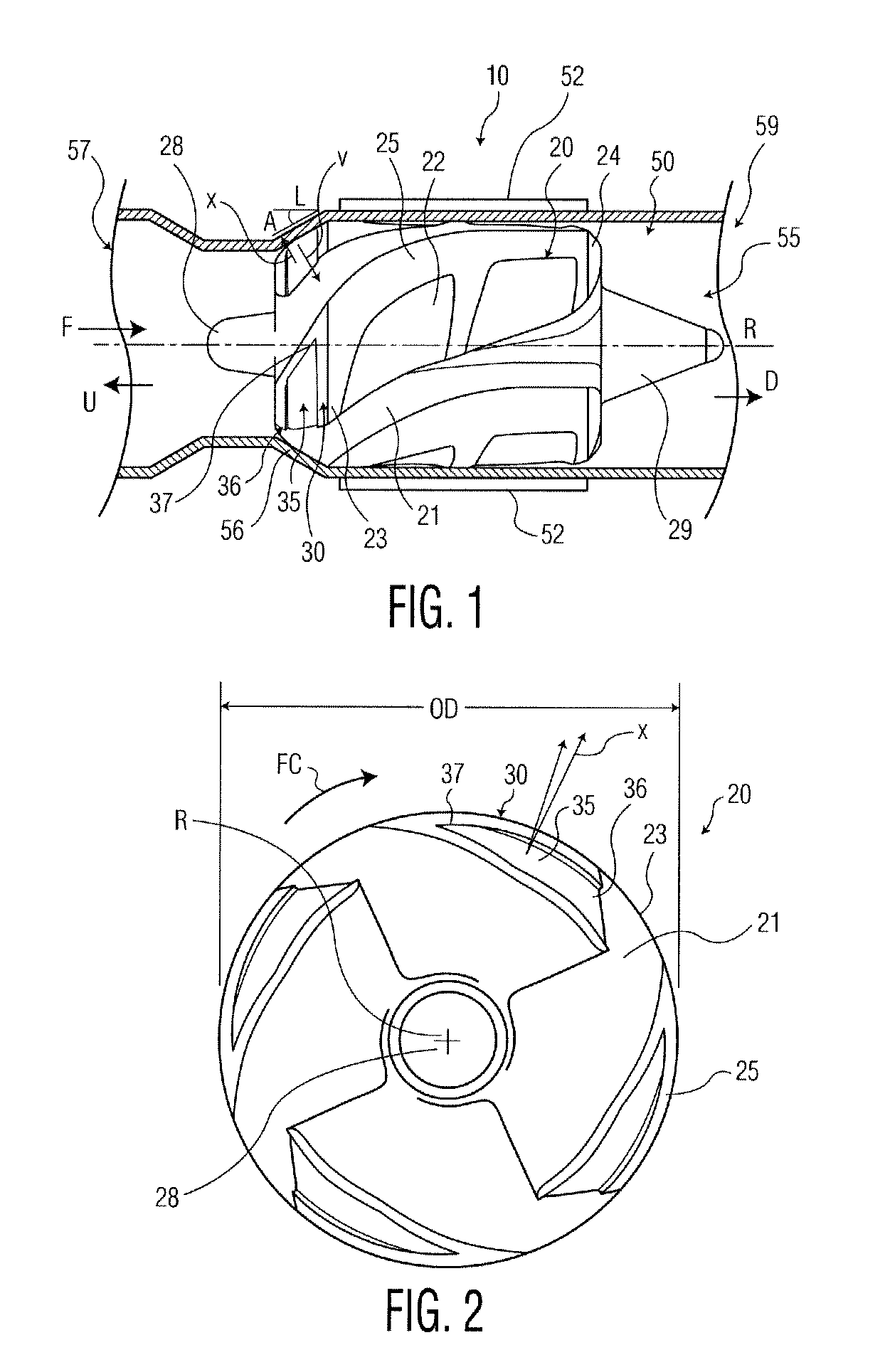
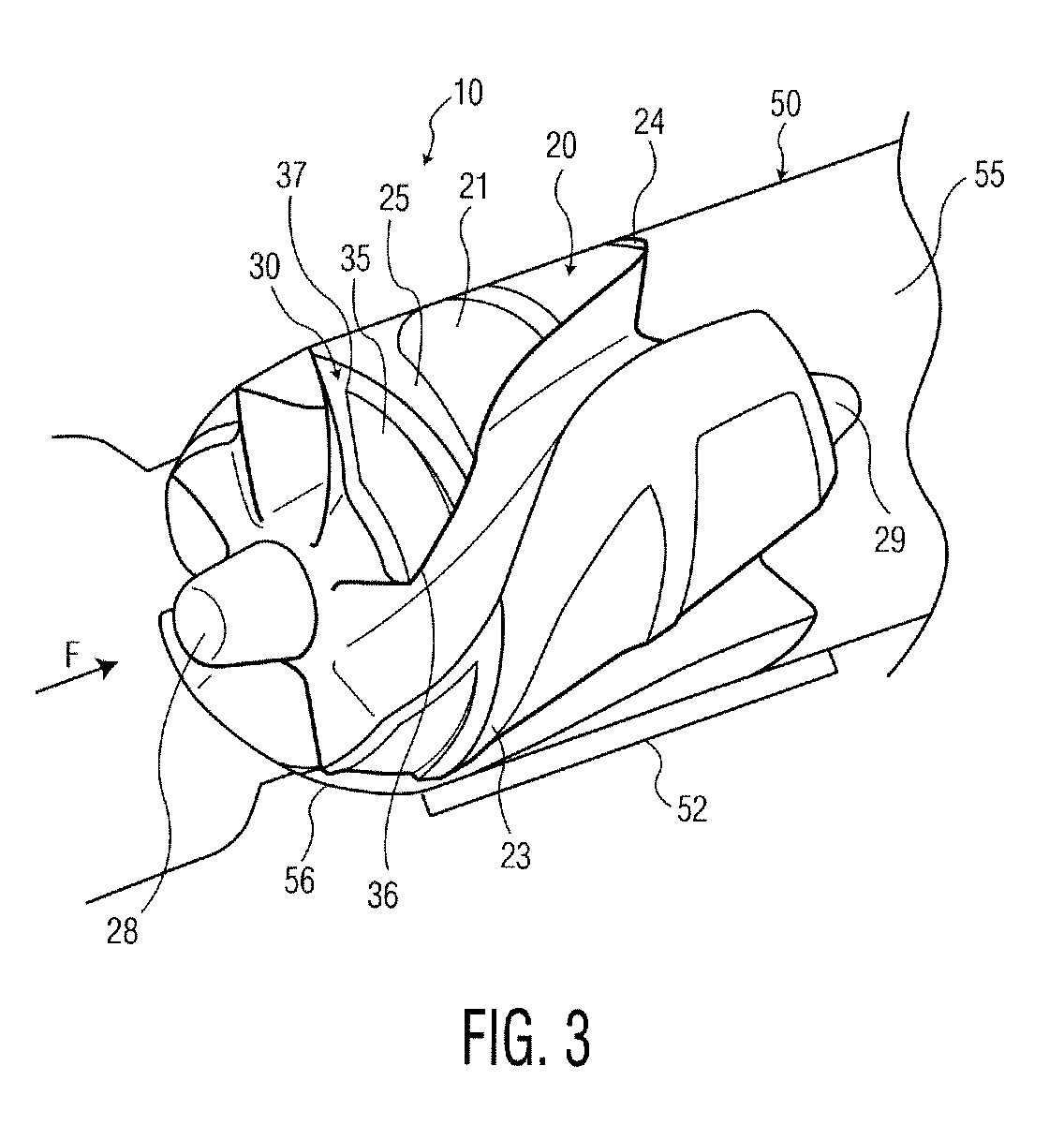
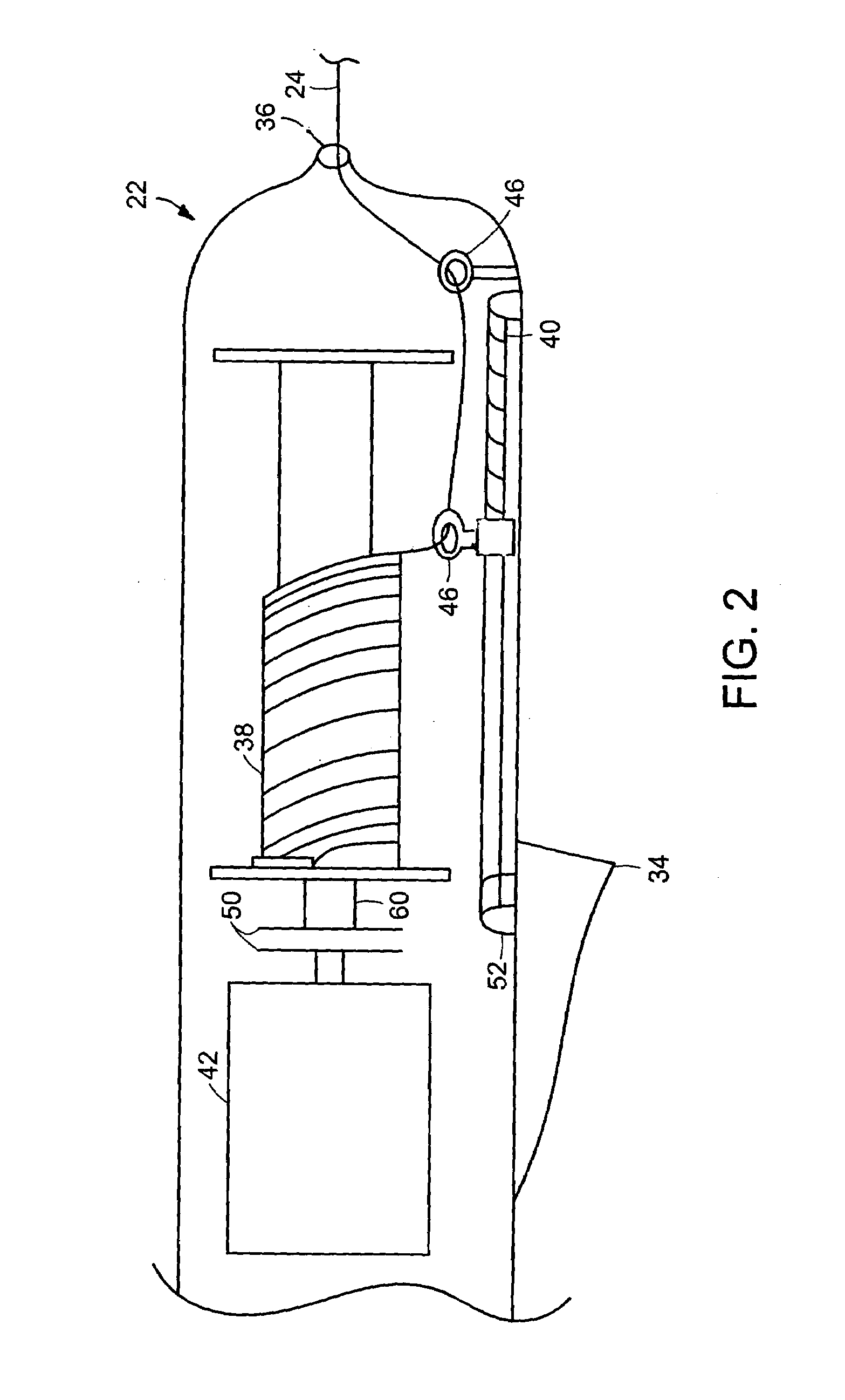
Hydrodynamic chamfer thrust bearing
An axial flow pump for a blood circulating pump for the circulation of blood, the rotor the rotor being constructed and arranged to impel blood in a downstream direction upon rotation of the rotor about its axis in a forward circumferential direction. The rotor is provided with hydrodynamic thrust bearing surfaces, each such thrust bearing surface being constructed and arranged to apply a hydrodynamic force to the rotor with a component of the force in the downstream direction upon rotation of the rotor in the forward circumferential direction.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Rotary pump with levitated impeller having thrust bearing for improved startup
A rotary blood pump comprises an impeller in a pump housing with a pumping chamber between first and second walls. The impeller operates in a levitated position spaced from the first and second walls in response to hydrodynamic forces which are boosted by hydrodynamic bearing features in the walls. At least one of the impeller or the walls includes at least one mechanical thrust bearing extending between the impeller and each of the walls, wherein the mechanical thrust bearing is configured such that when the impeller is not being held in the levitated position by the hydrodynamic forces then the mechanical thrust bearing is engaged to maintain a predetermined separation between the hydrodynamic bearing features and the impeller. The mechanical thrust bearing is configured such that when the impeller is being held in the levitated position by the hydrodynamic forces then the mechanical thrust bearing is unengaged.
Owner:TC1 LLC
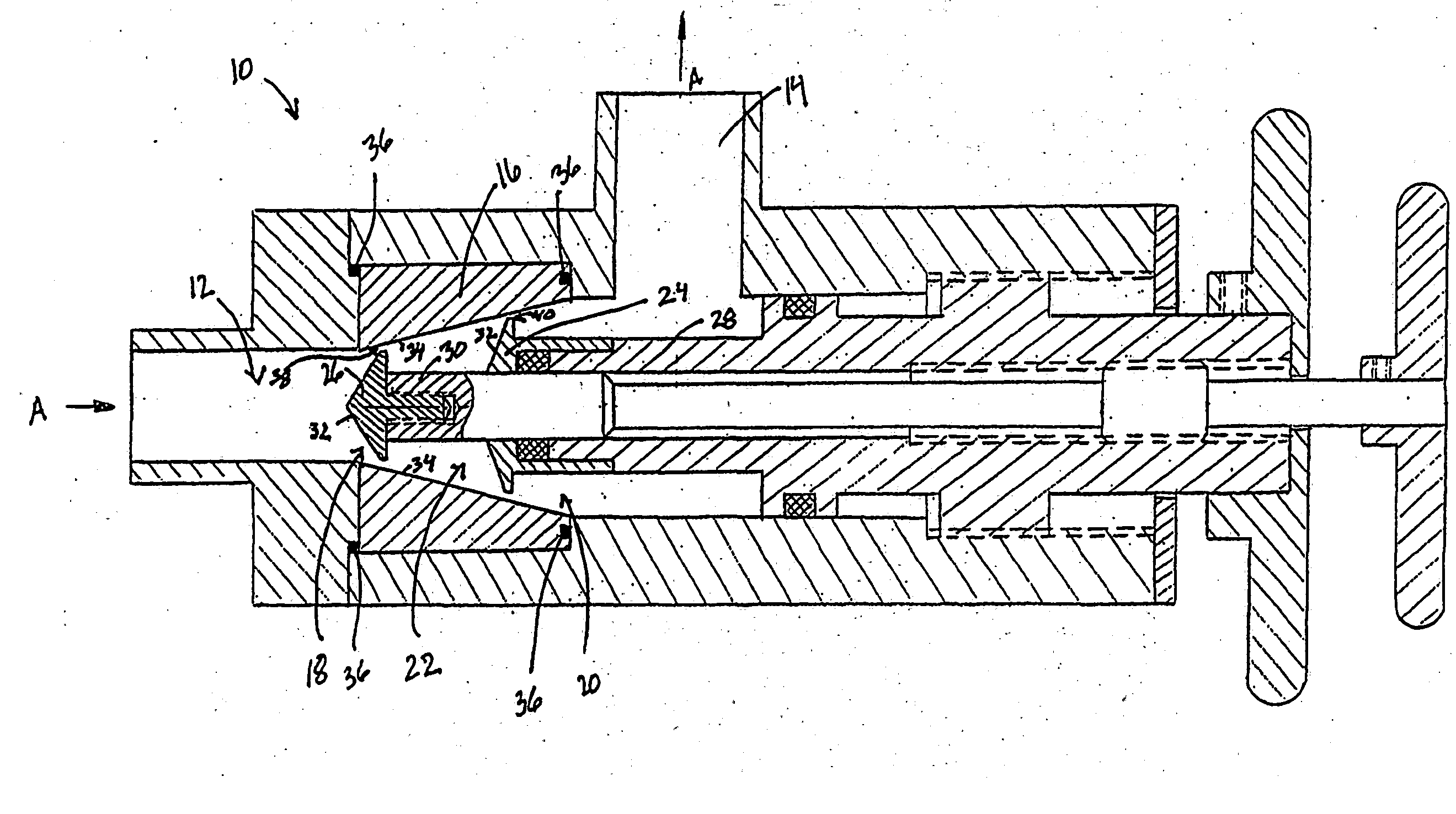
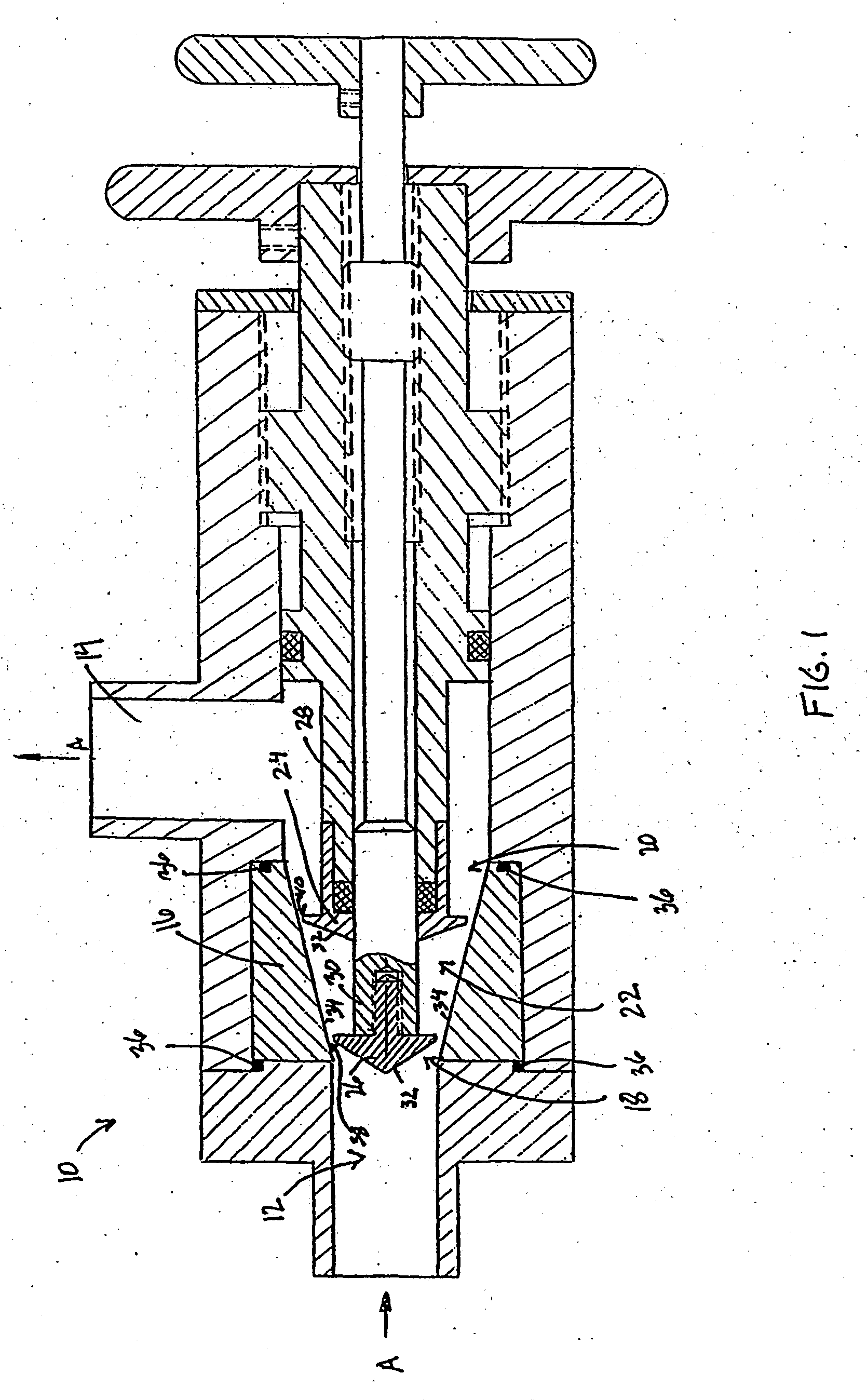
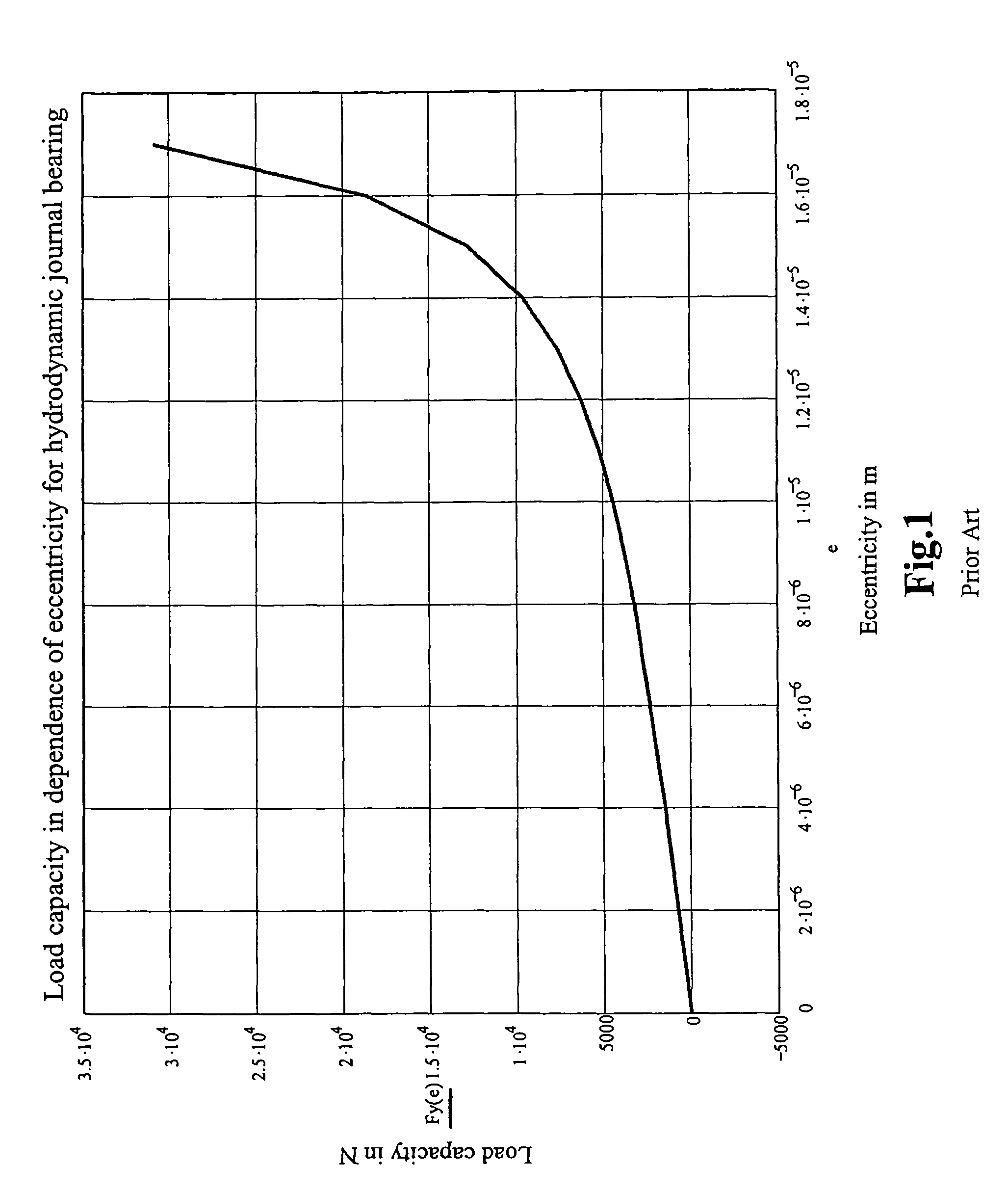
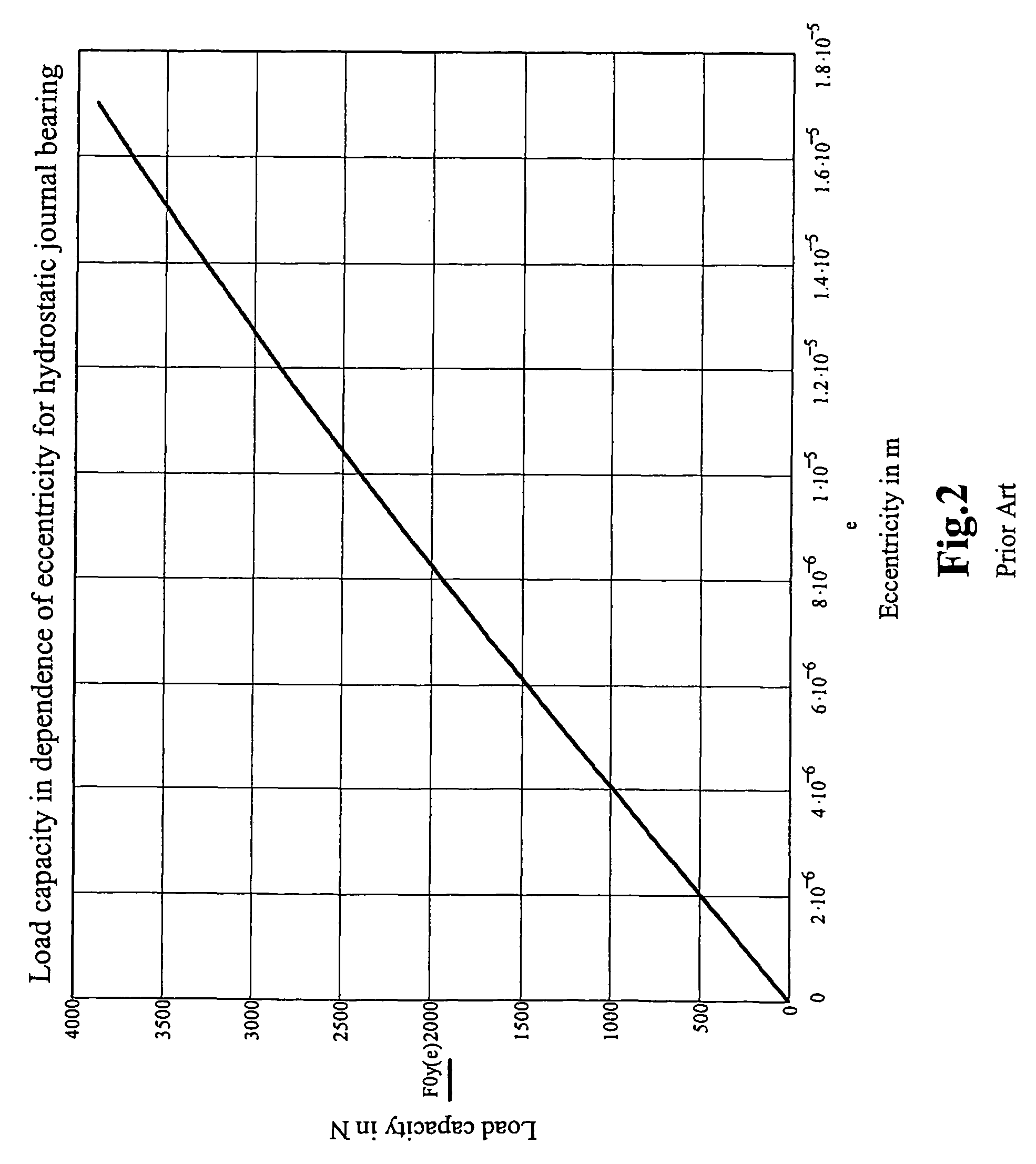
Hybrid hydro (air) static multi-recess journal bearing
InactiveUS20090074337A1Easy to manufactureReduce frictionBearing componentsSliding contact bearingsRotational axisShear friction
Multi-recess hydrostatic journal bearings support a rotating shaft and have inclined surfaces, each inclined surface forming a variable radial gap with the surface of the shaft, the variable gaps converging in the direction of rotation of the shaft to increase hydrodynamic forces, reduce a turbulent component of shear friction, and improve the thermal stability of the journal bearing. The inclined surfaces can be formed in one or more of portions of recess bottoms in recesses, portions of gap lands surrounding recesses, and portions of an inner surface of a bushing.
Owner:ELKA PRECISION
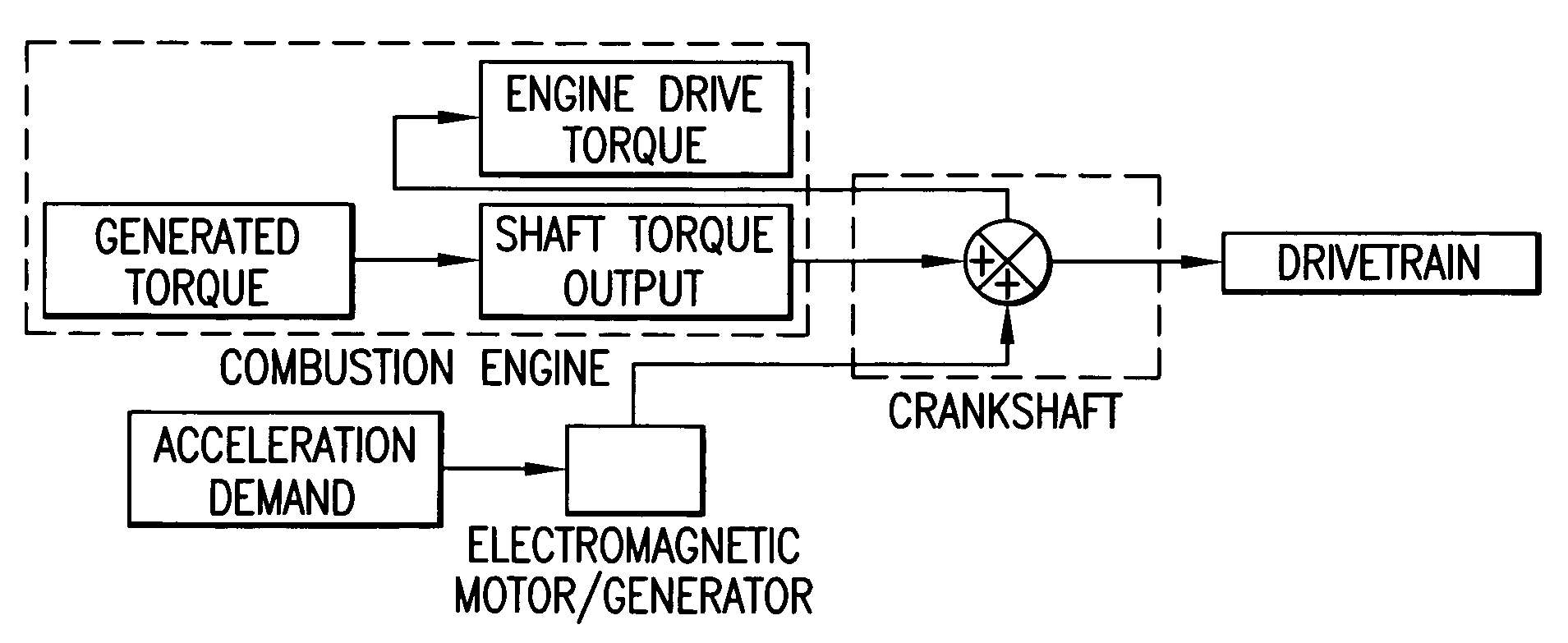
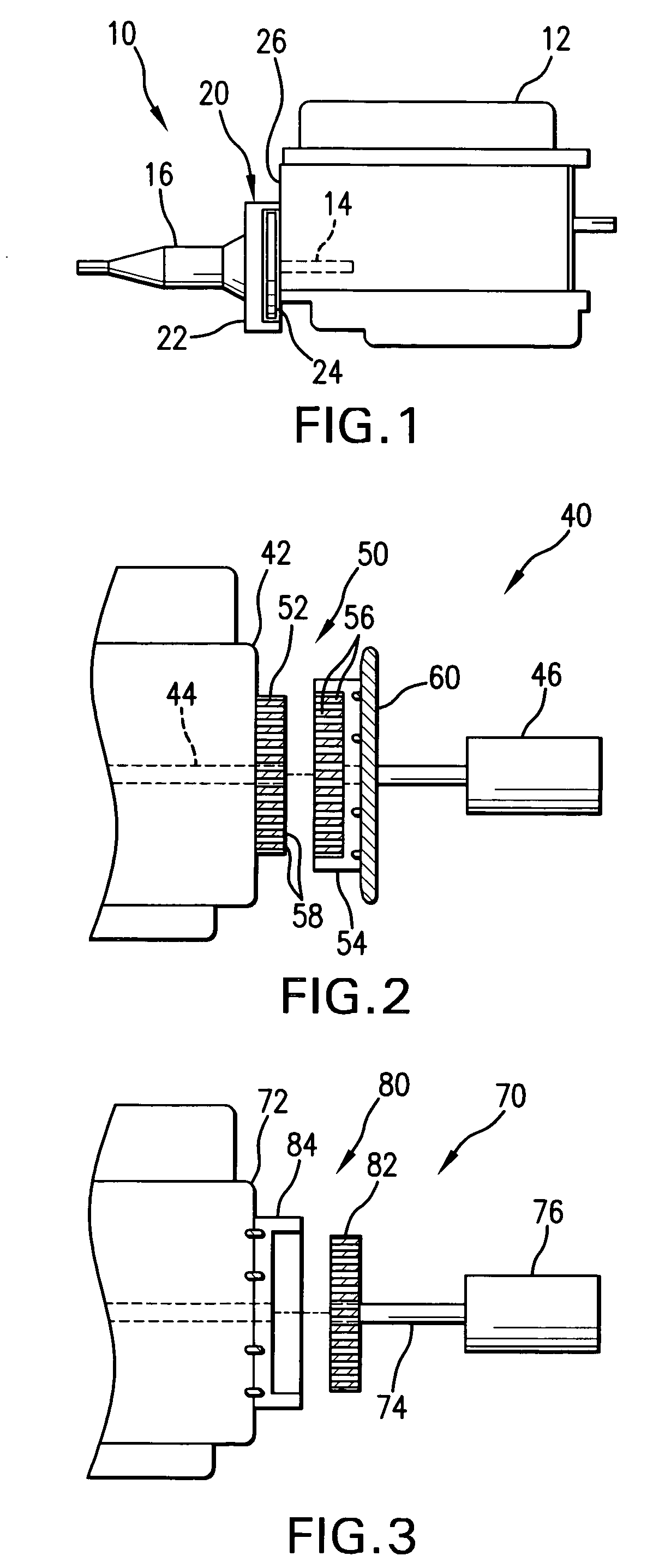
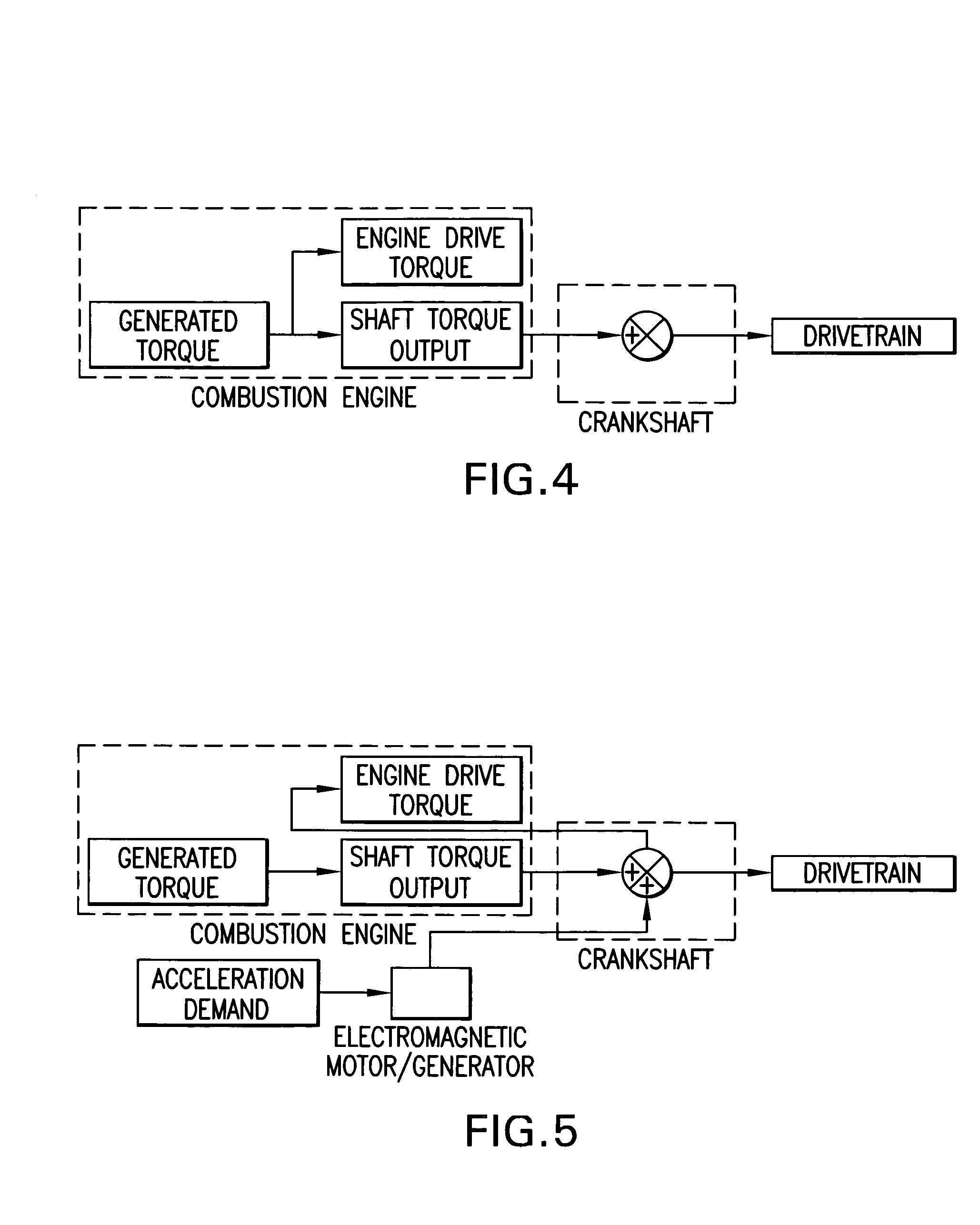
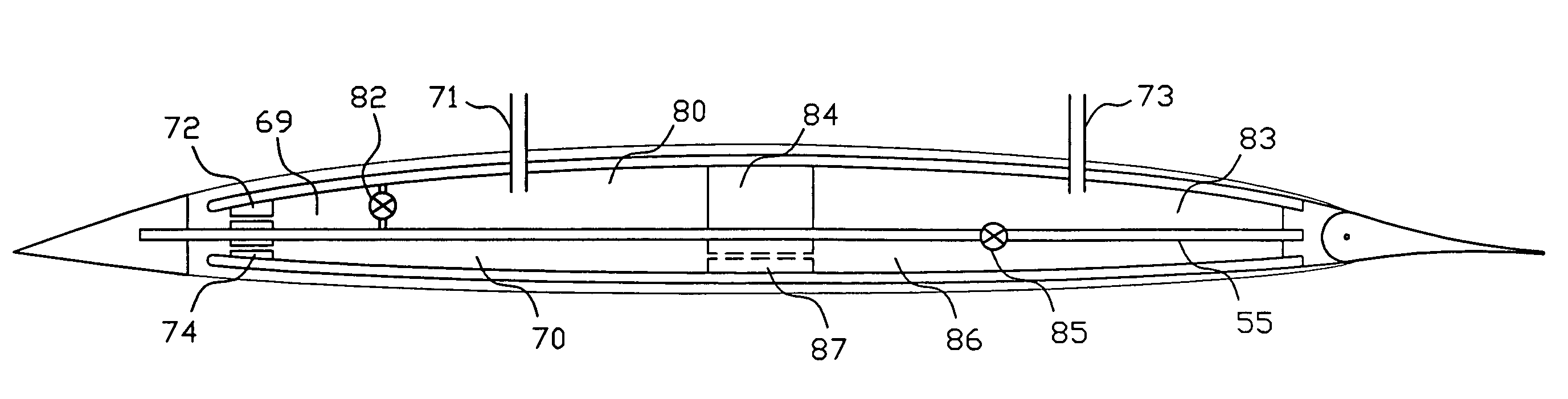
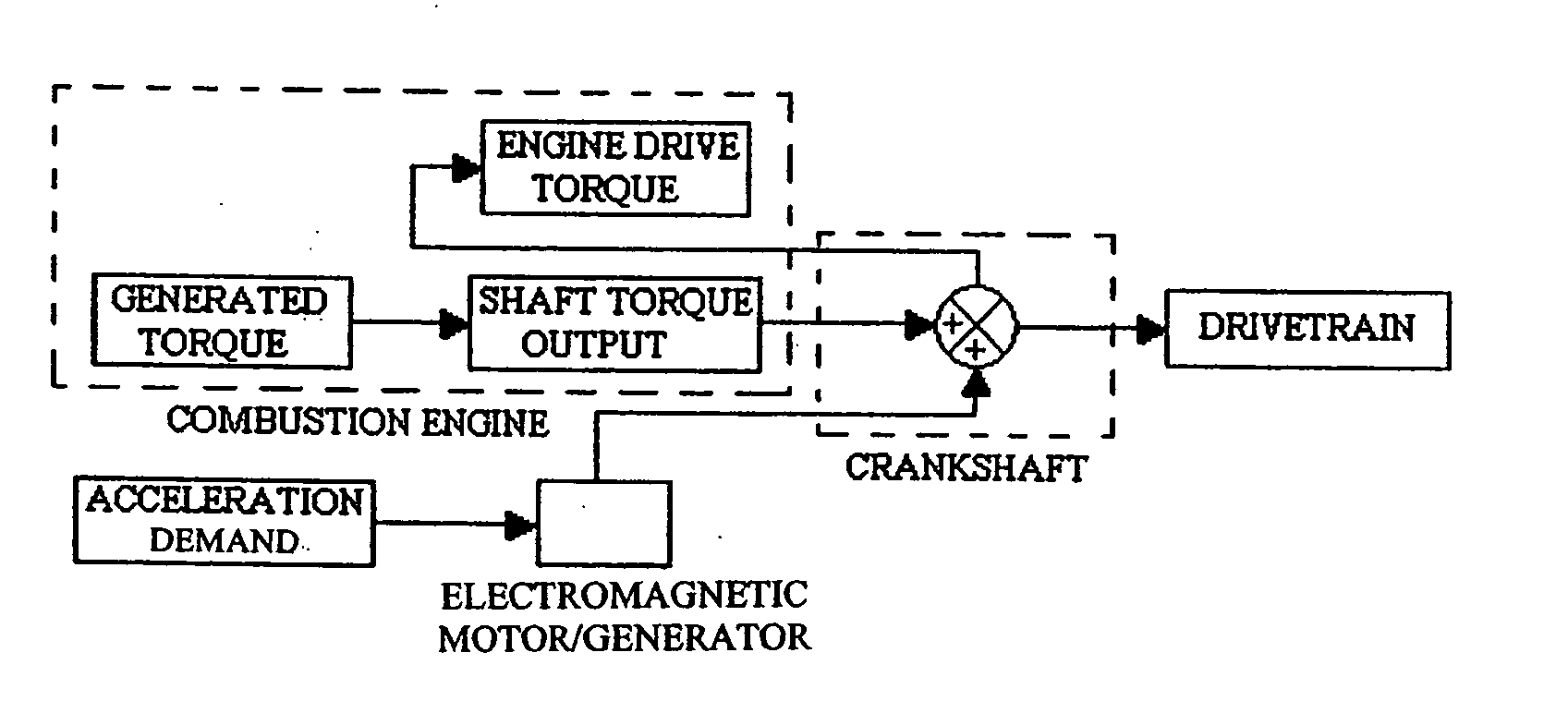
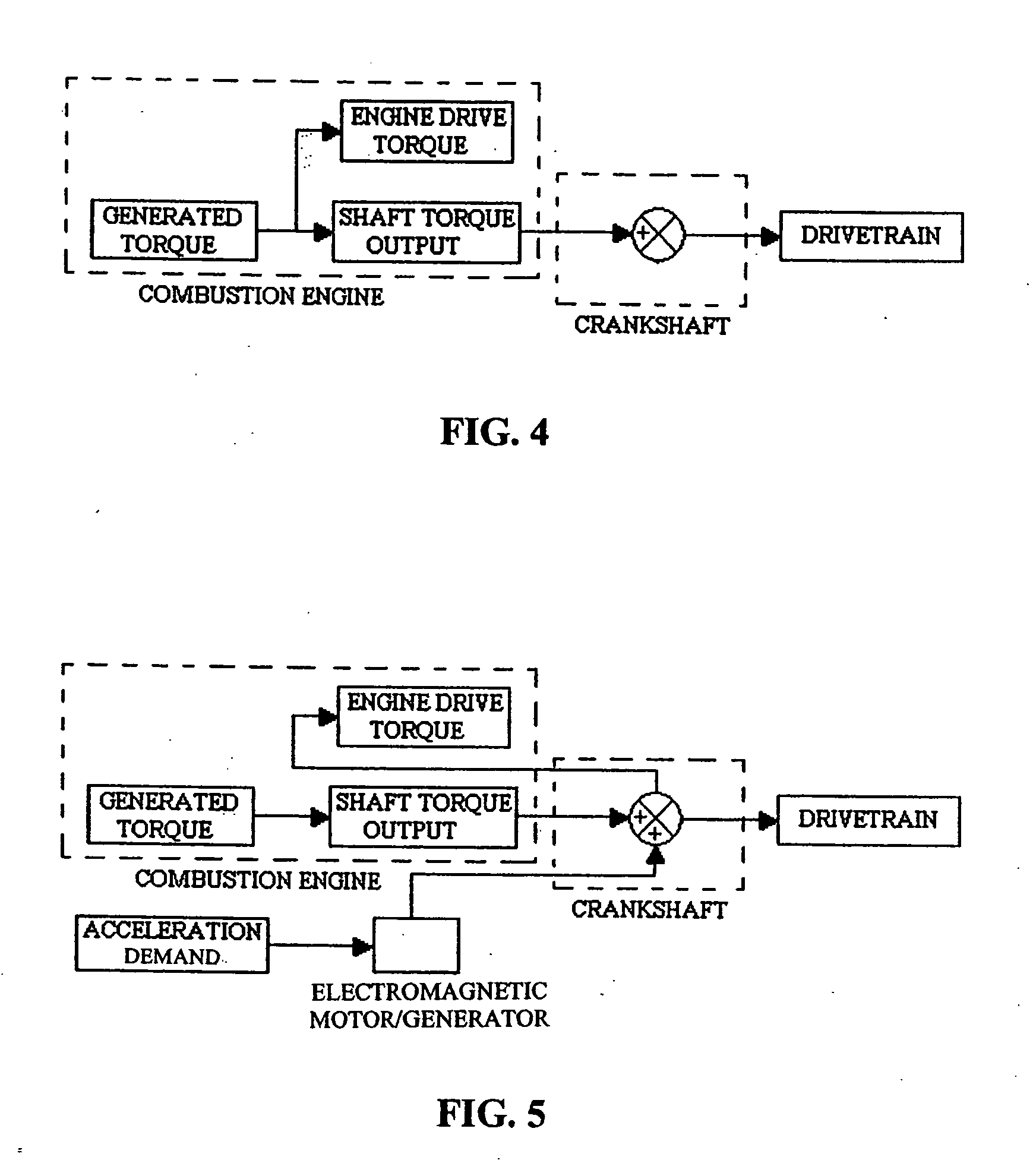
Combustion engine acceleration support using an integrated starter/alternator
ActiveUS7024859B2Increase probabilityImprove efficiencyReciprocating combination enginesCombination enginesAlternatorCombustion
A method of providing acceleration support to a combustion engine using an integrated starter / alternator. The integrated starter / alternator is in rotational combination with the crankshaft and connected to a battery system. The integrated starter / alternator is adapted to function at times as a power source adding torque to rotate the crankshaft to overcome friction and non-linear hydrodynamic forces within the engine. At other times the integrated starter / alternator functions as a power generator for subtracting torque from the crankshaft to provide electrical current to the battery system.
Owner:TURNTIDE TECH INC
Low-drag hydrodynamic surfaces
InactiveUS6901873B1Reduce resistanceEliminate cavitationWatercraft hull designFloating buildingsKeelAtmospheric air
The invention relates to the use of gas cavities to reduce frictional drag on underwater surfaces such as hydrofoils, struts, fins, rudders, keels, propeller blades, ship hulls, underwater bodies, and wetted surfaces in general. Each gas-filled cavity is formed behind a discontinuity in the surface that causes the water boundary layer to separate from the surface. Gas is ejected into a region behind the discontinuity to fill the cavity; the gas can be air. If a cavity is open to the atmosphere, then air can typically fill the cavity naturally without air ejection. Cavities can either be closed or open. A low drag hydrofoil may have a closed cavity on one side, and an open cavity on the other side. For closed cavities, the underlying surface can be shaped to minimize cavity closure drag. Various ways to generate cavities, change hydrodynamic forces, and duct gas internally on hydrofoils and struts with cavities are covered. Different designs of hydrofoil boats, hydrofoil ships and ship hulls that are amenable to drag reduction are presented.
Owner:LANG THOMAS G +1
Plunging towed array antenna
InactiveUS6883452B1Efficient communicationInhibit chafingDefensive equipmentTowing/pushing equipmentEngineeringBuoyancy
A towed antenna system and method of use includes a communication device disposed on a buoyant body attached to a housing by a tether. The housing includes a spool, a reel-wire guide, and a motor. The buoyant body and the reel housing are deployed from and towed at from a submerged platform. Hydrodynamic forces from towing prevent the buoyant body from rising to the surface while maintaining the housing at an equilibrium depth. To establish communication, the tether is released from the spool and the buoyant body rises to the surface. The tether is released until the communication session is over or until the tether is fully deployed. The reel-wire guide prevents the tether from becoming snagged during release. Once the communication session has been completed, the tether is retracted and the buoyant body re-establishes its equilibrium depth.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
System and Method for Distributed Active Fluidic Bleed Control
ActiveUS20160009374A1Mitigate and completely avoid adverseAlter propertiesAircraft stabilisationShaftsEngineeringHydrodynamic forces
A system and method for regulating and actuating bleed over a structure exposed in a fluid motion are disclosed. The bleed inlet and outlet are formed on the surface of the structure establishing fluidic communication across surfaces. The disclosed system and method contemplates active control and regulation of the bleed to modify crossflow properties such as, aerodynamic forces, hydrodynamic forces, vorticity, and moments.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method and device for simulating bottom sludge erosion and transmission feature in rectangular trough
InactiveCN102680204AMaintain propertiesRealize the cutting actionHydrodynamic testingSludgeWater storage tank
The invention discloses a method and a device for simulating bottom sludge erosion and transmission feature in a rectangular trough. The method comprises the following steps of: applying different constant current scouring forces to the surface of columnar bottom sludge with an un-disturbed structure in the vertical direction, so that the columnar bottom sludge is eroded under the actions of different hydrodynamic forces, and simulation of the bottom sludge erosion under the disturbance of different hydrodynamic force strengths is realized; and respectively capturing a suspended load and a bed load in the eroded bottom sludge at the same time, so that simulation of the transmission feature of the eroded bottom sludge is realized. The device comprises a water inlet tank, the flat elongated trough, a water outlet tank, a water storage tank, a columnar sludge sample pipe, a bed load sand capturing device and a suspended load sand capturing device. According to the method and the device, the problems that the external force condition is uncontrollable and the original structure of the bottom sludge is kept are solved by using a constant acting force produced by a constant water level difference on the surface of the bottom sludge; and the bed load and the suspended load produced after the bottom sludge is suspended are effectively collected by adopting different devices respectively, so that an effect of simulating the bottom sludge erosion is achieved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Device and method for creating hydrodynamic cavitation in fluids
This invention provides a device and method for creating hydrodynamic cavitation in fluids which includes a flow-through chamber intermediate an inlet opening and an outlet opening; the flow-through chamber having an upstream opening portion communicating with the inlet opening and a downstream opening portion communicating with the outlet opening; the cross-sectional area of the downstream opening portion being greater than the cross-sectional area of the upstream opening portion; and a cavitation generator located within the flow-through chamber for generating a hydrodynamic cavitation field downstream from the generator. This invention also provides for a device for creating hydrodynamic cavitation in fluids wherein the walls of the flow-through chamber to assume various shapes and configurations to affect cavitation. This invention also provides for a device for a device for creating hydrodynamic cavitation in fluids wherein the baffle elements are removably mounted within the device and are interchangeable and replaceable with replacement baffles having various shapes and configurations thereby enabling variable effects on cavitation.
Owner:ARISDYNE STSTEMS INC
Method of preparing micro-and nanometric particles with labile Products
InactiveUS20090215154A1Increase productionLow dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyBacteriaCrystallographyNanosized particle
The invention relates to a method of obtaining micro- and nanometric polymeric particles in a controlled, reproducible manner. The aforementioned particles have a spherical shape and a very narrow, uniform size distribution. The invention comprises the use of an easy particle-forming method consisting in using hydrodynamic forces to focus a composite microjet formed by two concentric fluids and can be used in the encapsulation of fragile compounds of biological interest, from peptides and proteins to cells and micro-organisms.
Owner:UNIV DE SEVILLA
Telescoping cavitator
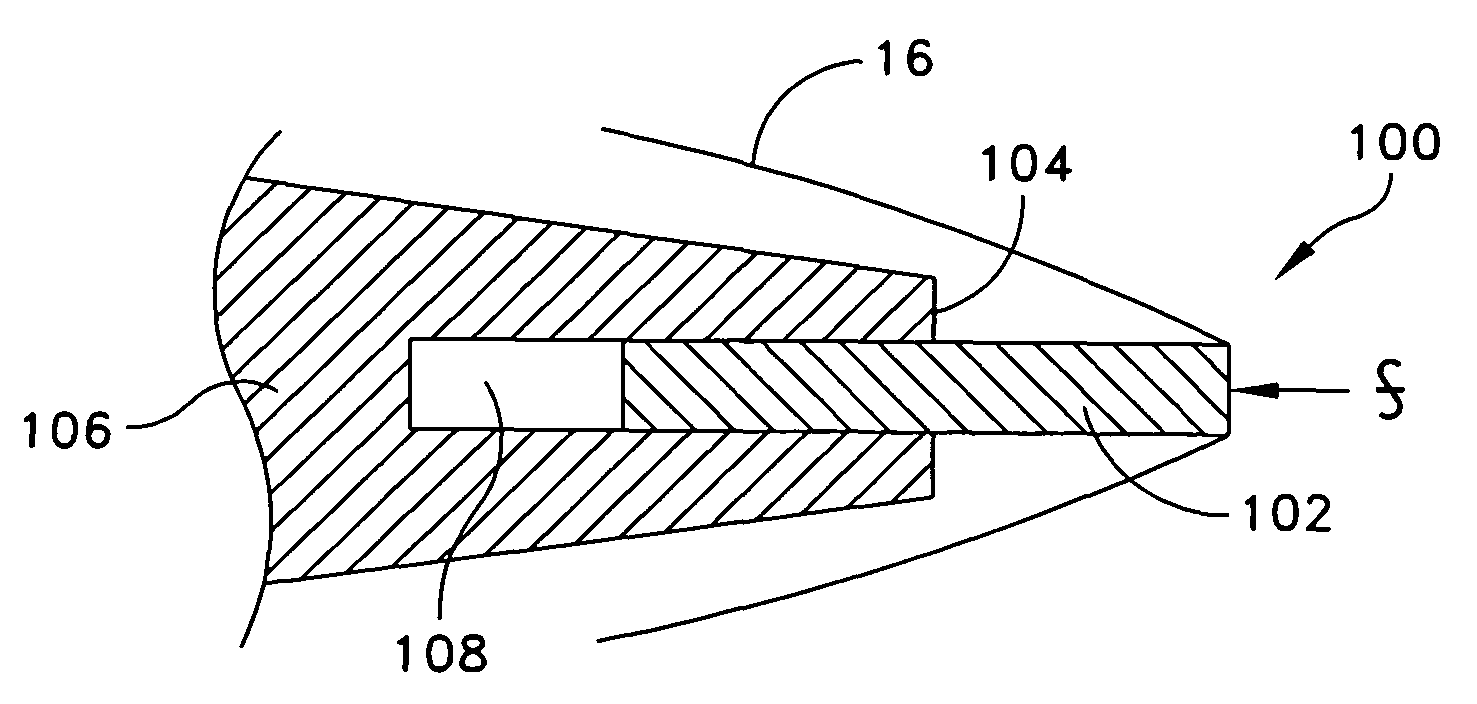
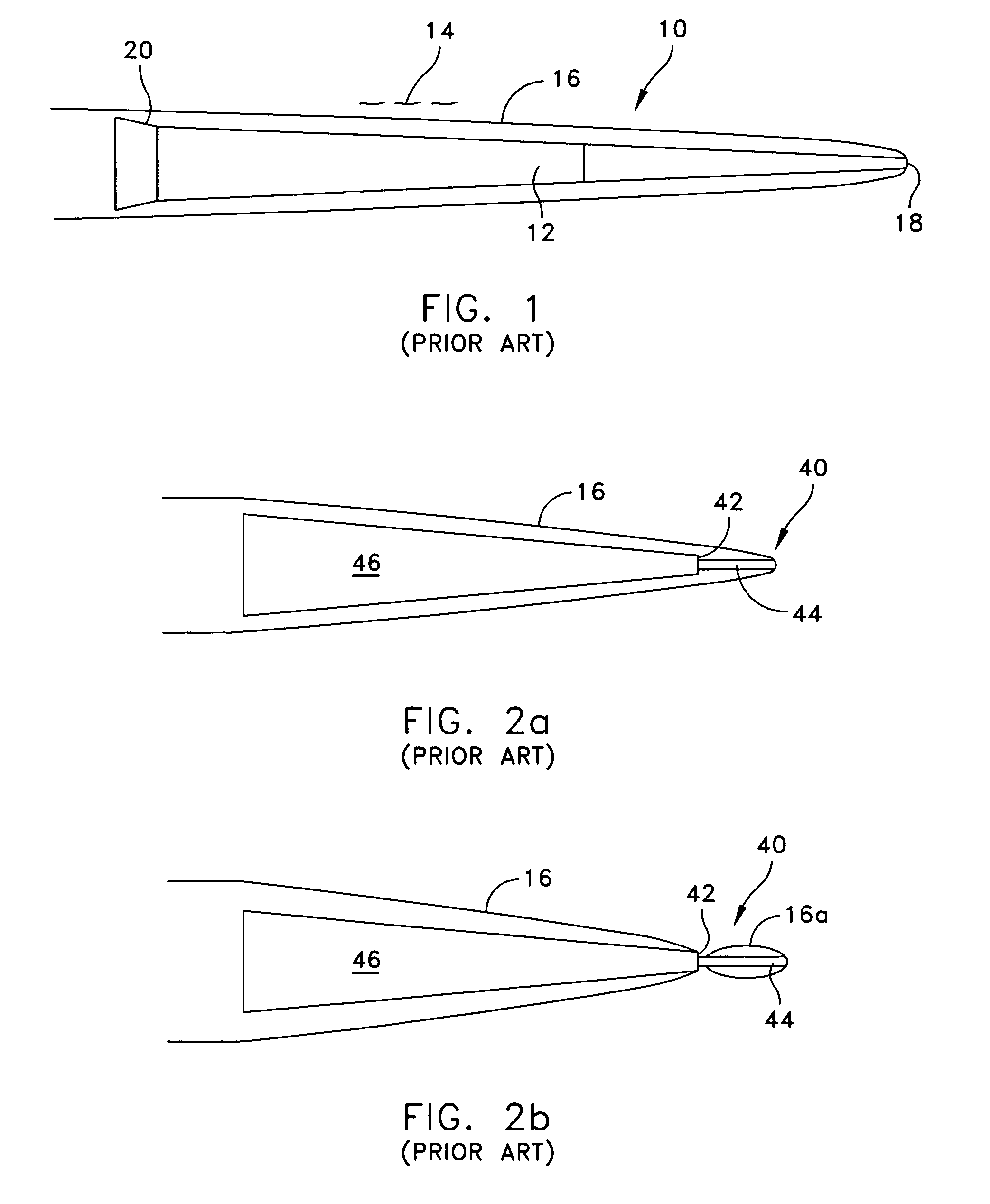
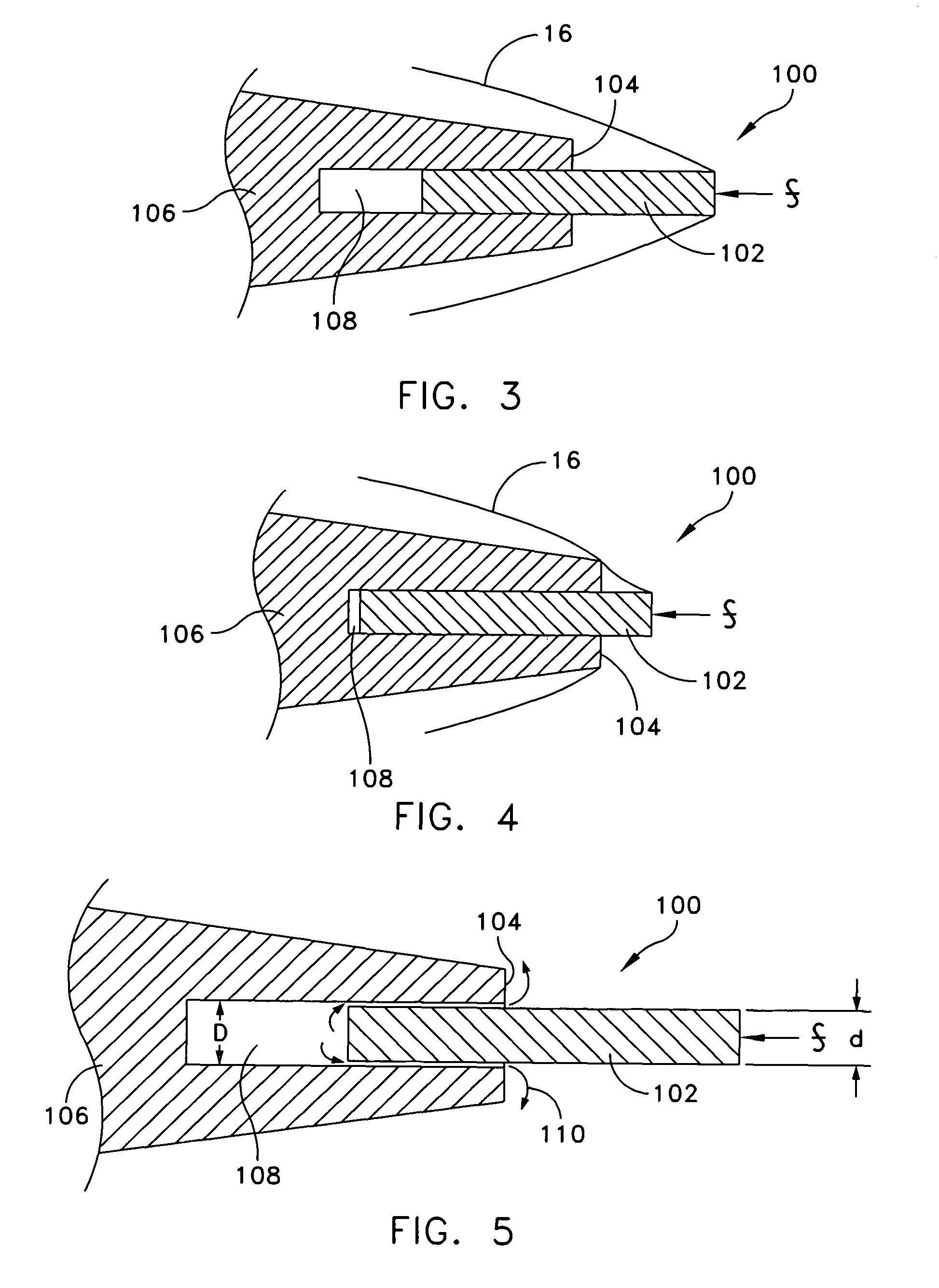
InactiveUS7966936B1Reduce resistanceMaximize rangeAmmunition projectilesMarine torpedoesShape changeEngineering
A high speed underwater projectile configuration that includes a cylindrical telescoping cavitator design capable of providing projectile nose shape change where such change to the projectile nose tip geometry results in supercavitation and a concomitant vaporous cavity in the water that reduces projectile drag resistance while maximizing projectile range and where the projectile nose tip further includes a retractable cavitator piston feature. The projectile nose is designed to house a cylindrical cavitator piston that protrudes forward from the projectile and is held in place until launch. Velocity induced hydrodynamic forces on the forward face of this cavitator piston cause the piston to start moving aft and to gradually cause the piston to retract into the projectile nose, until a larger, secondary cavitator is exposed to the vaporous cavity.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
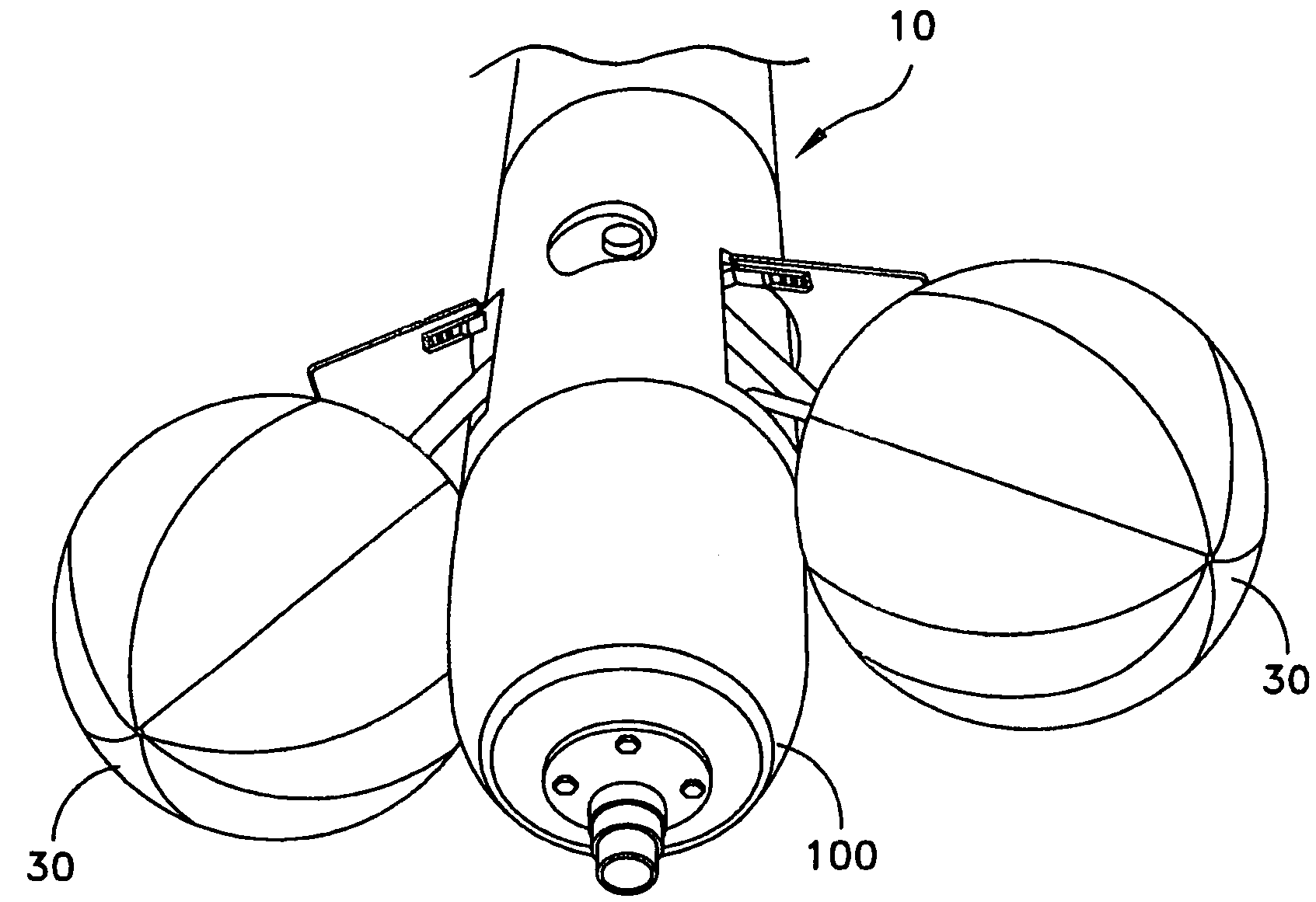
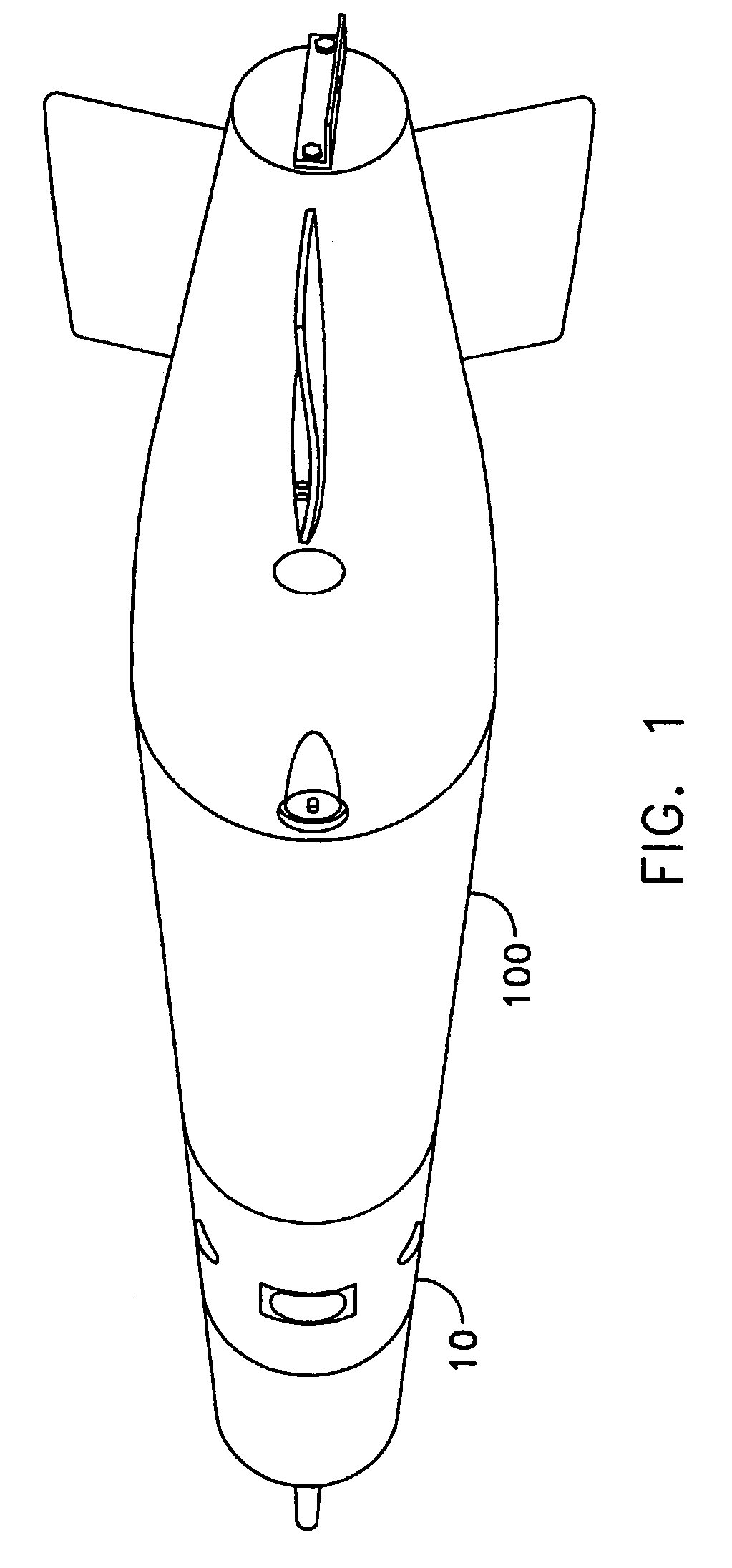
Underwater vehicle deceleration and positive buoyancy assembly
InactiveUS7250568B1Reduce depthShorten the timeMarine torpedoesSelf-propelled projectilesTerminal velocityHydrodynamic forces
An assembly for vehicle deceleration and buoyancy comprises a pair of doors enclosing flotation bags inflatable for buoyant recovery of the torpedo. In operation, the doors are controllably forced open to an initial angle off a longitudinal axis of the assembly to a fully-deployed position by hydrodynamic forces of the movement of the vehicle. From the doors blocking the hydrodynamic forces, the vehicle decelerates. The hydrodynamic braking action of the doors reduces the time required to reach terminal velocity, thus reducing the depth the vehicle sinks and enabling recovery with less gas required for inflation.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
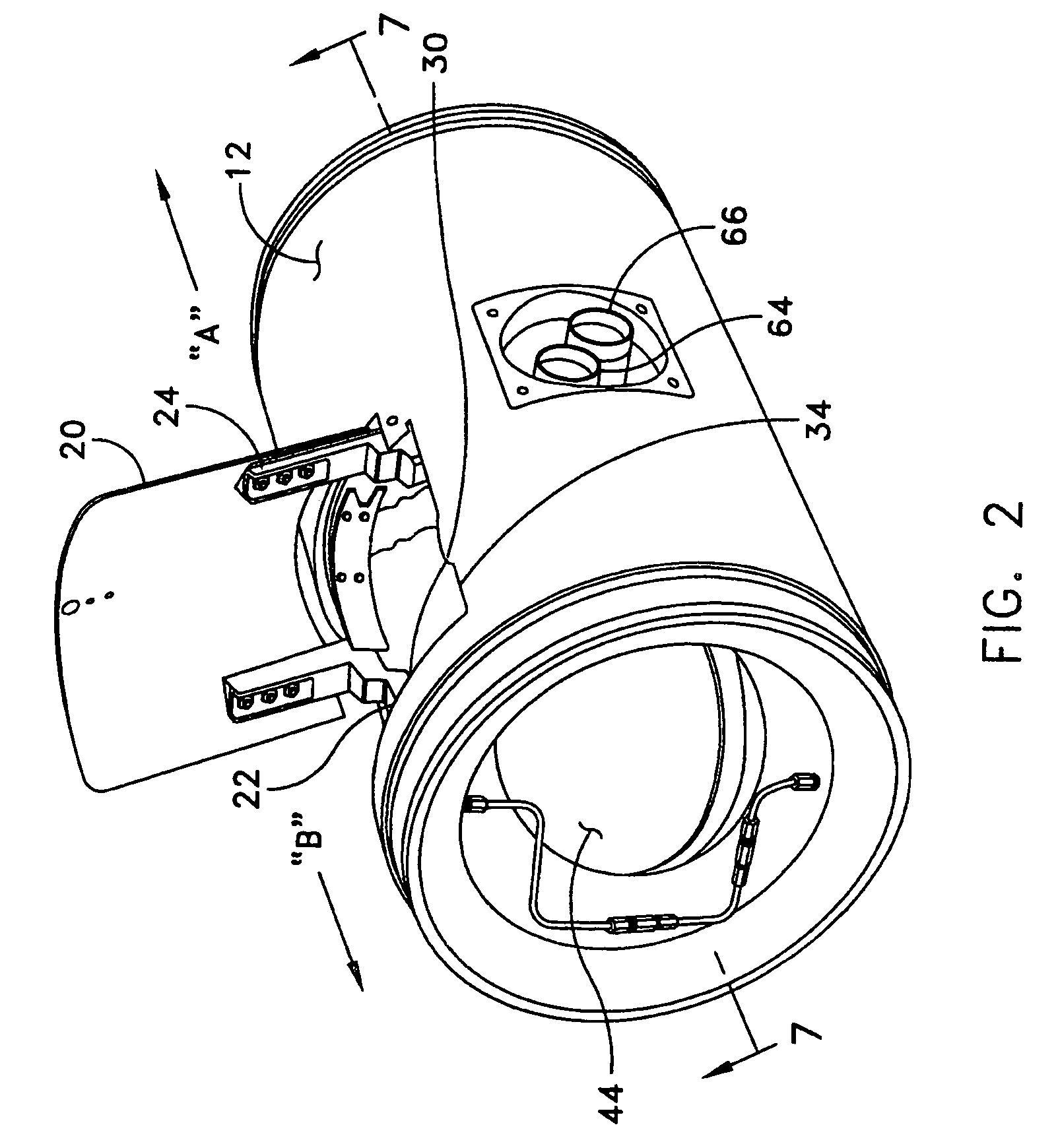
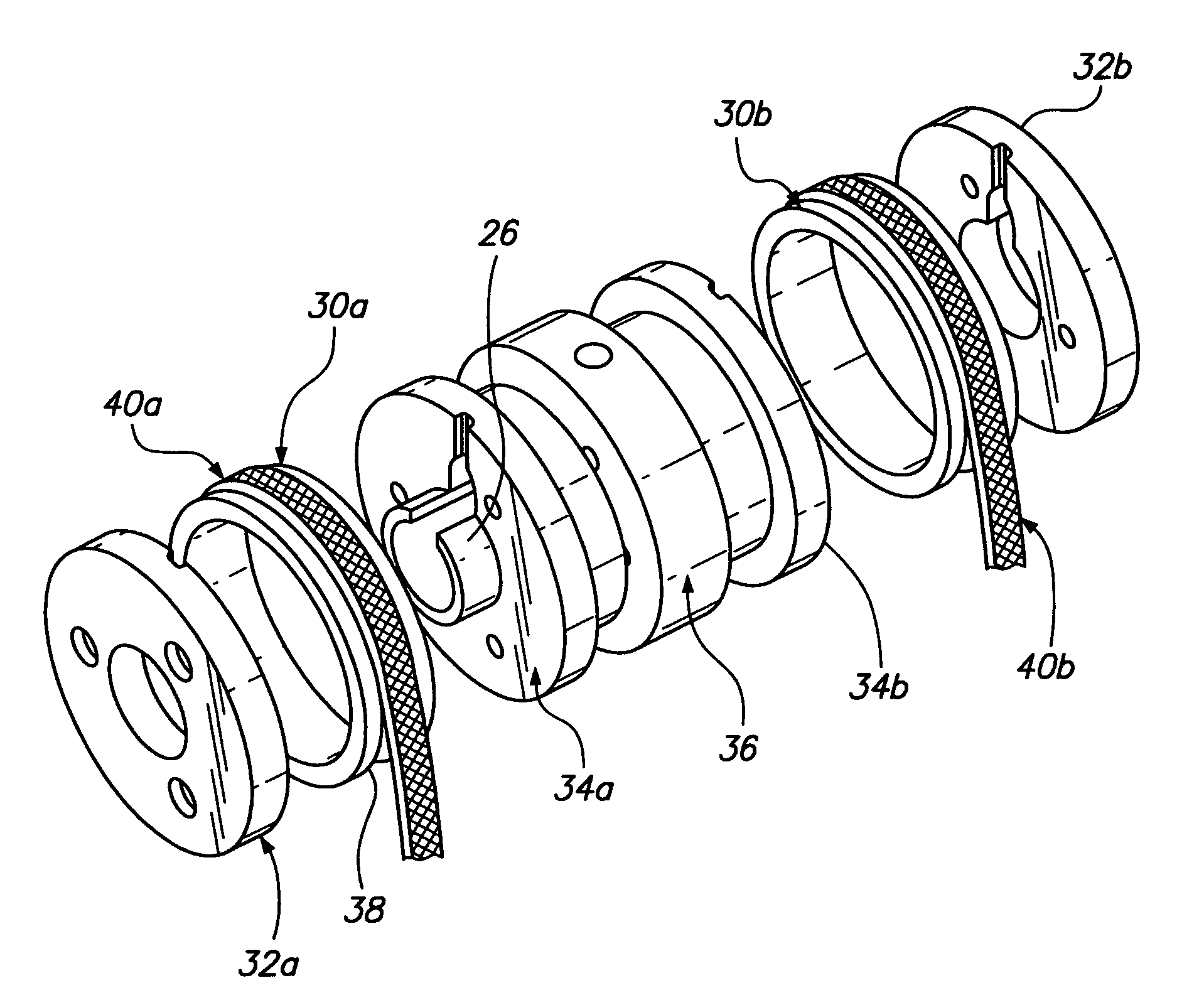
Hydrodynamic slip ring
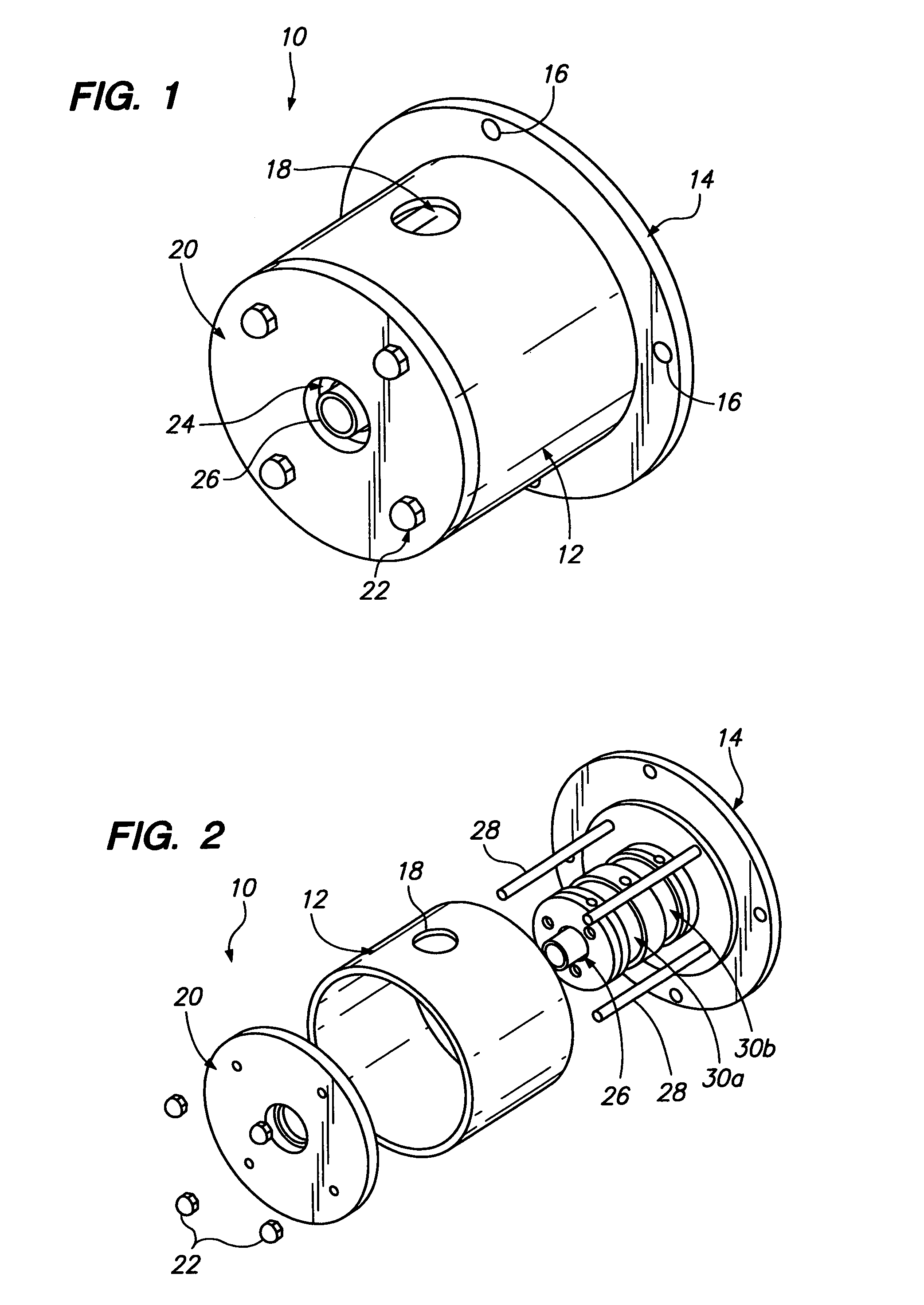
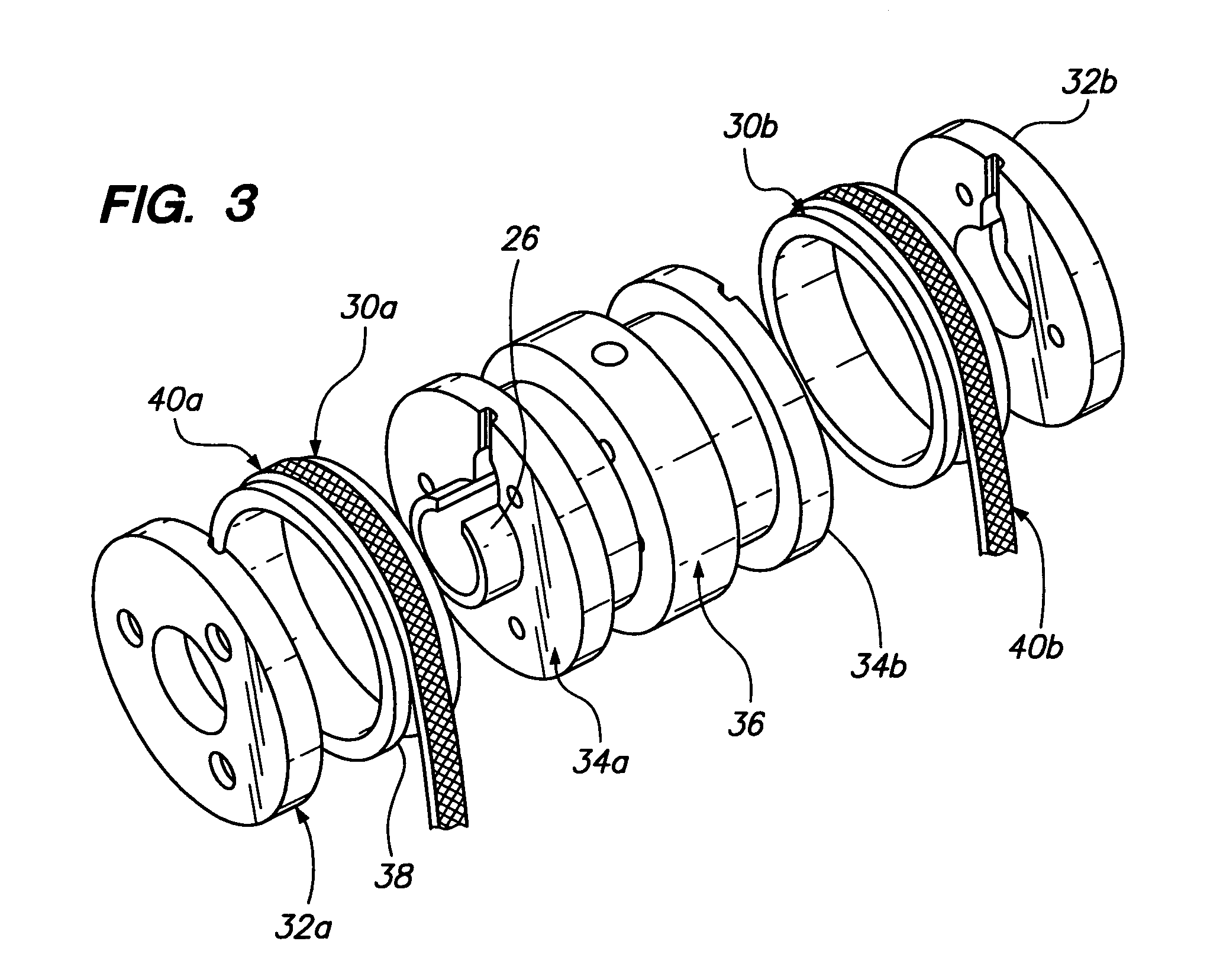
A slip ring assembly for transferring electrical current to an electrical device is disclosed. The slip ring assembly has a housing that is attachable to the electrical device. Disposed within the housing is a rotatable slip ring and a flexible conductor. The flexible conductor is configured to conform to the shape of the slip ring and conduct an electric current. A fluid is contained within the housing. The fluid forms a conductive film between the slip ring and the conductor when the slip ring rotates through hydrodynamic forces. The conductive film is operative to transfer electrical current between the slip ring and the conductor while also preventing wear of the slip ring and conductor.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY POWER SYST
Fluid energy machine
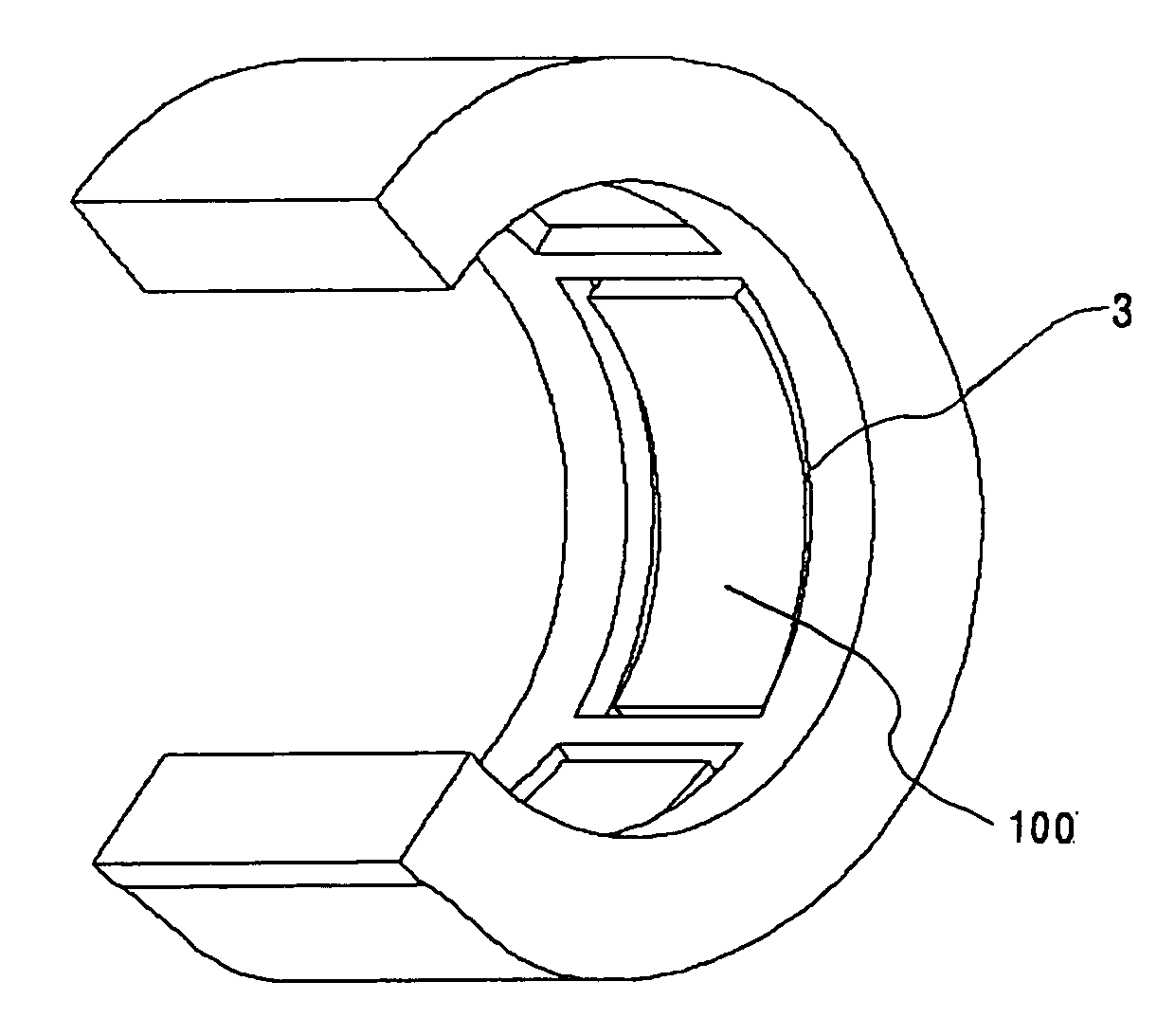
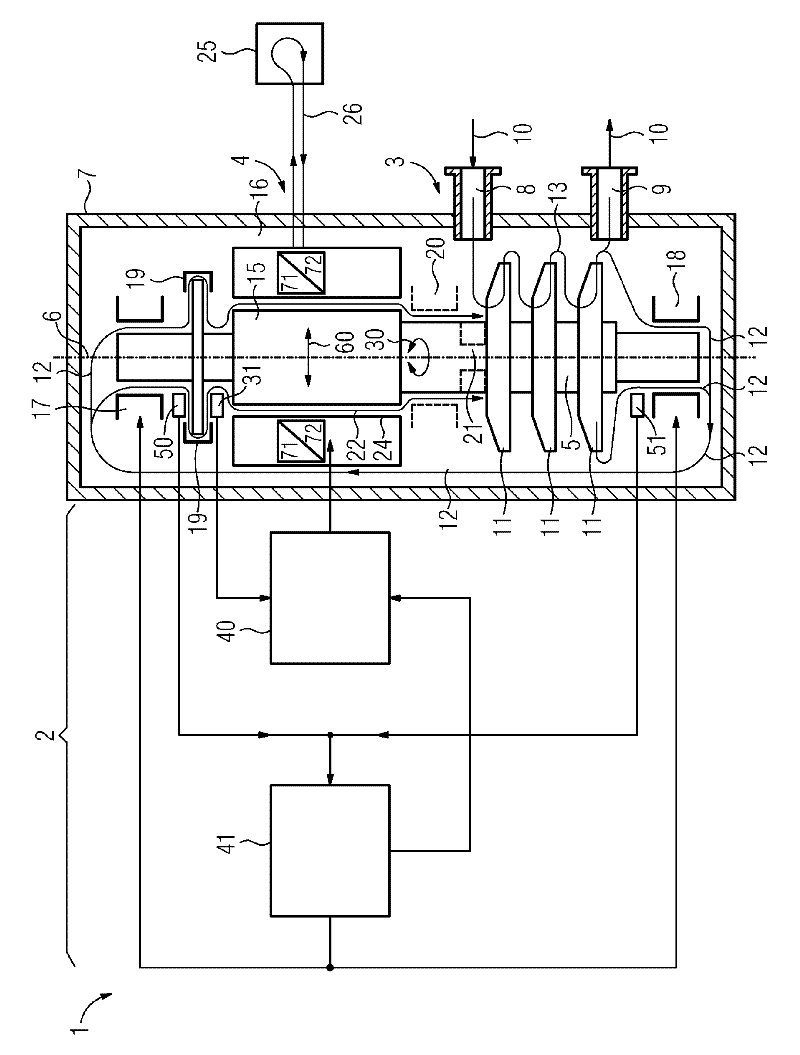
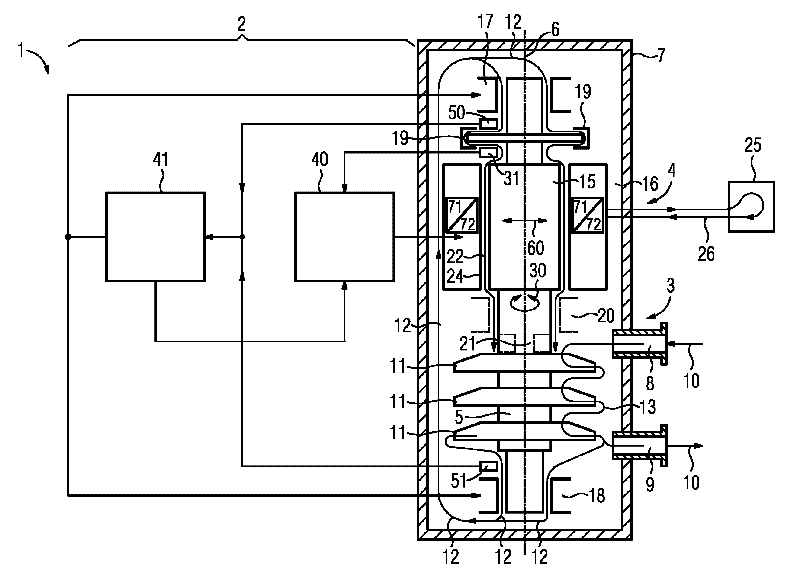
The invention relates to a fluid energy machine (1), in particular compressor (3) or pump, having a housing (7), having a motor (4), having at least one impeller (11), having at least two radial bearings (17, 18) and having at least one shaft (5) which extends along a shaft longitudinal axis (6) and which supports the at least one impeller (11) and a rotor (15) of the motor (4), wherein the shaft (5) is mounted in the radial bearings (17, 18), wherein the motor (4) has a stator (16) which at least partially surrounds the rotor (15) in the region of the motor (4), and wherein a gap (22) which extends in the circumferential direction and along the shaft longitudinal axis (6) is formed between the rotor (15) and the stator (16) and between the rotor (15) and the radial bearings (17, 18), which gap (22) is at least partially filled with a fluid. Conventional fluid energy machines (1) have a restricted operating range as a result of destabilizing aerodynamic or hydrodynamic forces in the gap (22) between the stator (16) and the rotor (15). The invention aims to remedy this in that the motor (4) is also embodied as a bearing and is connected to a controller (2), which activates the motor (4) in such a way that forces (60) acting radially with respect to a shaft longitudinal axis (6) can be exerted in addition to torques (30) for driving the fluid energy machine (1).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Device for studying cracking-degree-variable multi-effect coupled critical collapse test
The invention relates to a device for studying the cracking-degree-variable multi-effect coupled critical collapse test to realize the study on the karst ground collapse test under the conditions different cracking degrees and hydrodynamic forces, determine the critical condition of the collapse of the test model and establish the collapse evaluation benchmark scale. The device comprises a groundwater latent erosion simulation system, a cracking degree control system, a raining simulation system and a real-time monitoring system. The groundwater latent erosion simulation system is a box with an groove shaped like the Chinese character hui and an upper-end opening structure, the inner groove and the outer groove of the groundwater latent erosion simulation system are communicated by small dense holes, and the bottom of the inner groove is provided with a crack; the cracking degree control system covers the lower end opening of the crack and comprises a movable cover plate and an adjusting mechanism; the raining simulation system is fixed above the end opening of the inner groove; and the real-time monitoring system comprises a camera and a monitoring computer, wherein the camera is arranged in the key position of the model, and the monitoring computer is connected with the camera.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY ERYUAN ENG GRP CO LTD
System and method for microfluidic cell culture
ActiveUS10087408B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGravitational forceEngineering
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Polymer mixer powered by hydrodynamic forces
InactiveUS20130112907A1Easy to deployMaximize fire suppressant effectAircraft componentsFlow mixersEnvironmental engineeringHigh velocity
Water is mixed with fire suppressant polymer in a mixer absent a power source. The mixer receives water through a water inlet with water exhibiting high velocity and associated hydrodynamic force. Such velocity is achieved by locating the water inlet connected to a float or other part of an aircraft so that when the aircraft flies over water with the float dipping into the water, water is driven through the opening and into the water inlet of the mixer. A polymer inlet passes into the mixer. A bend is located downstream of the water inlet and the polymer inlet. The bend exhibits sufficient resistance to fluid flow direction therethrough that the polymer is sheared and thoroughly mixed and activated with the water. A colorant inlet is optionally provided within the mixer and the water and polymer mixture is then discharged into a tank for later utilization at a firefighting location.
Owner:DOTEN LEONARD E
Method and apparatus for measuring and determining motion law of spilled oil on water surface in lab
The invention provides a method and apparatus for measuring and determining motion law of spilled oil on water surface in lab and belongs to the technical field of offshore oil engineering. According to the embodiments of the invention, the method herein involves a spilled oil test simulation and measurement system. The method can simulate oceanic hydrodynamic force environment and oil spilling conditions of submarine pipelines, analyzes the images of oil spilling on water surface that are acquired by an image acquiring device and obtains moving patterns of the oil film on water surface under different hydrodynamic forces, so that the method can make accurate estimation of the track of the spilled oil on water surface and spilling range of the spilled oil, provides timely and accurate information for handling oil spilling incident, and provides scientific basis and reference for emergency decision-makers who can adopt timely and accurate anti-oil spilling measurement.
Owner:TIANJIN RES INST FOR WATER TRANSPORT ENG M O T
Combustion engine acceleration support using an integrated starter/alternator
ActiveUS20050166594A1Increase probabilityImprove efficiencyReciprocating combination enginesCombination enginesAlternatorCombustion
A method of providing acceleration support to a combustion engine using an integrated starter / alternator. The integrated starter / alternator is in rotational combination with the crankshaft and connected to a battery system. The integrated starter / alternator is adapted to function at times as a power source adding torque to rotate the crankshaft to overcome friction and non-linear hydrodynamic forces within the engine. At other times the integrated starter / alternator functions as a power generator for subtracting torque from the crankshaft to provide electrical current to the battery system.
Owner:TURNTIDE TECH INC
Polymer mixer powered by hydrodynamic forces
InactiveUS9022133B2Maximize fire suppressant effectIncrease speedAircraft componentsFlow mixersEngineeringEnvironmental engineering
Water is mixed with fire suppressant polymer in a mixer absent a power source. The mixer receives water through a water inlet with water exhibiting high velocity and associated hydrodynamic force. Such velocity is achieved by locating the water inlet connected to a float or other part of an aircraft so that when the aircraft flies over water with the float dipping into the water, water is driven through the opening and into the water inlet of the mixer. A polymer inlet passes into the mixer. A bend is located downstream of the water inlet and the polymer inlet. The bend exhibits sufficient resistance to fluid flow direction therethrough that the polymer is sheared and thoroughly mixed and activated with the water. A colorant inlet is optionally provided within the mixer and the water and polymer mixture is then discharged into a tank for later utilization at a firefighting location.
Owner:DOTEN LEONARD E
Hybrid hydro (air) static multi-recess journal bearing
InactiveUS8646979B2Easy to manufactureReduce frictionBearing componentsSliding contact bearingsRotational axisShear friction
Multi-recess hydrostatic journal bearings support a rotating shaft and have inclined surfaces, each inclined surface forming a variable radial gap with the surface of the shaft, the variable gaps converging in the direction of rotation of the shaft to increase hydrodynamic forces, reduce a turbulent component of shear friction, and improve the thermal stability of the journal bearing. The inclined surfaces can be formed in one or more of portions of recess bottoms in recesses, portions of gap lands surrounding recesses, and portions of an inner surface of a bushing.
Owner:ELKA PRECISION
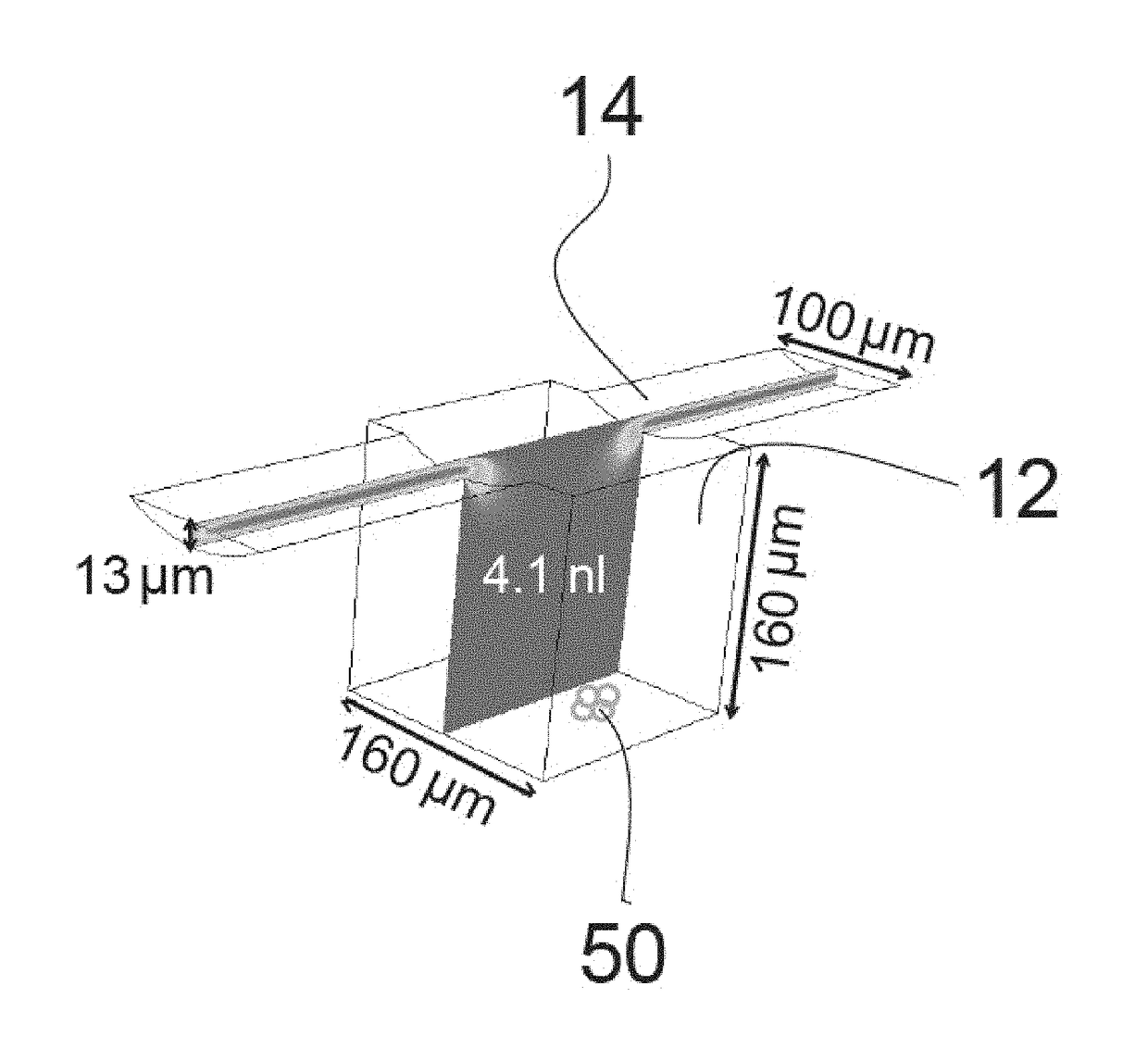
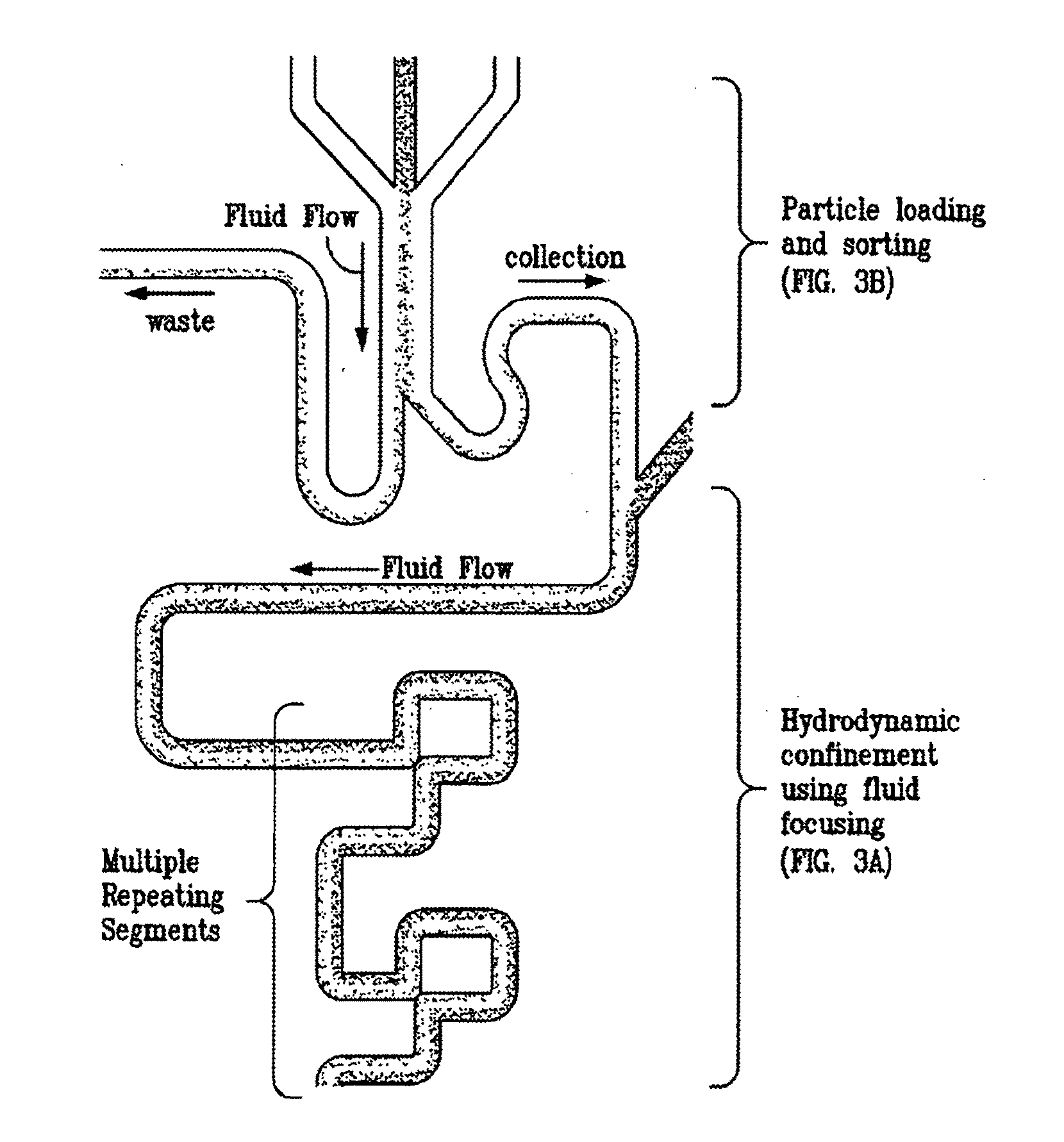
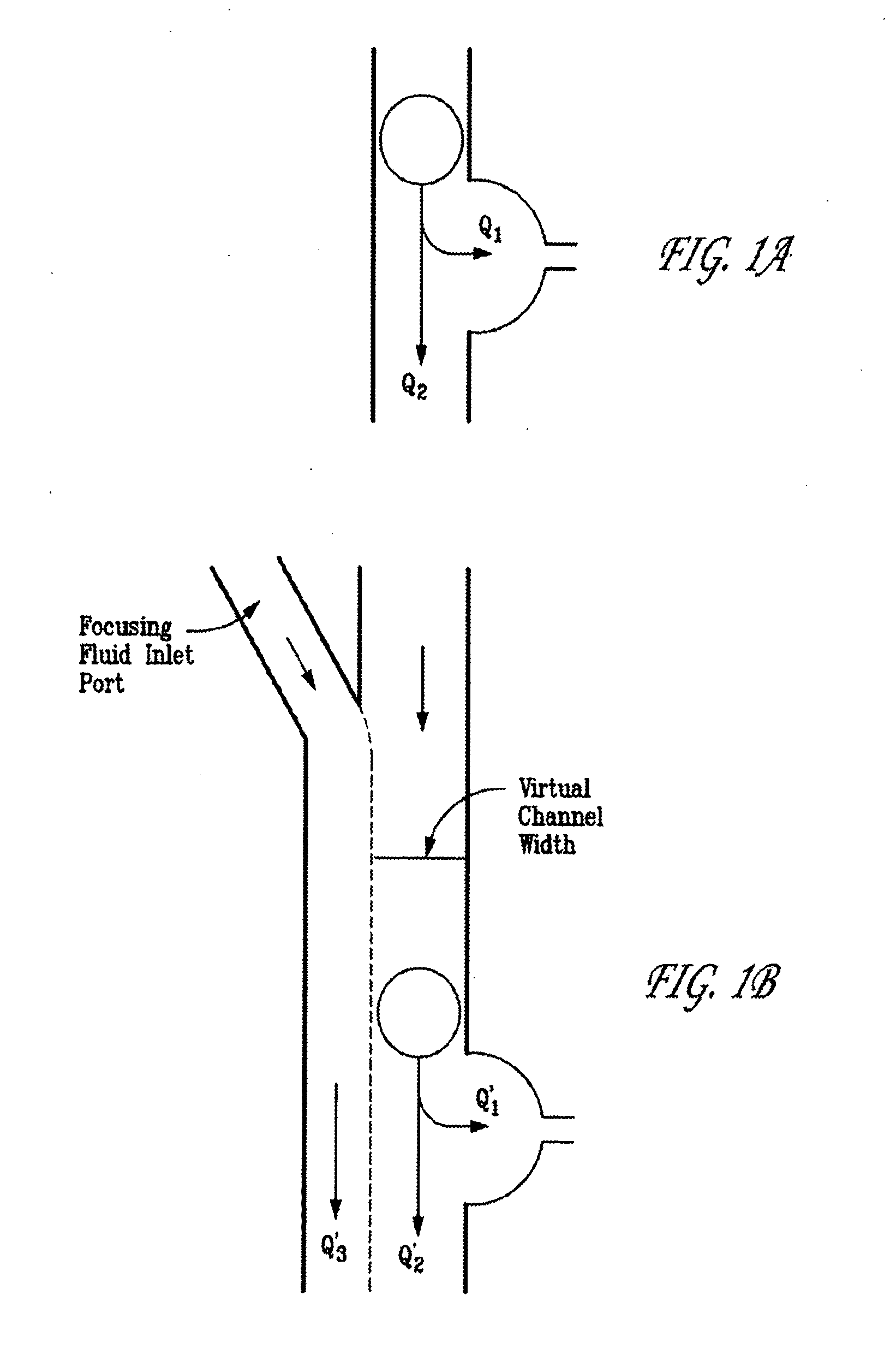
Methods and Devices for Immobilization of Single Particles
Disclosed herein are methods of immobilizing a particle which comprise focusing the flow of a sample fluid containing the particle into a virtual channel which flows towards an unoccupied hydrodynamic trap in a microfluidic channel such that the particle flows into the hydrodynamic trap and becomes immobilized therein. Also disclosed are microfluidic devices which comprise at least one microchannel having at least one hydrodynamic trap, at least one focusing fluid inlet, said focusing fluid inlet is upstream of the hydrodynamic trap such that a focusing fluid introduced therein results in a virtual channel of a sample fluid when present which preferentially flows toward the hydrodynamic trap.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Fluid dynamic bearing with non-linear damping
InactiveUS7193811B2Improve accuracySmall impactMachining electrodesApparatus for flat record carriersLinear correlationEngineering
Thus, if a shock or other disturbance to the system occurs that tilts the bearing assembly, the resulting motion is both a tilting, and a motion which is axial. If a shock axially moves the hub assembly, only an axial motion occurs. Thus the system has a non-linear behavior. Pursuant to this invention, when a tilting disturbance occurs, and some of it is dissipated in a net axial movement at a different frequency, energy is subtracted out of the system with motion that is not linearly related to the disturbance was that created it.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Sediment oxygen demand determination device based on electromagnetic dynamic and using method
InactiveCN103207266ASolve unfavorable problemsEnables Oxygen Consumption Rate DeterminationEarth material testingHand heldElectric machinery
The invention relates to a sediment oxygen demand (SOD) determination device based on electromagnetic dynamic, and a using method. The SOD determination device comprises a testing room, a dynamic room, a magnetic rotor, a magnetic pole, a motor, a dissolved oxygen probe socket, support fixing interfaces and a storage battery, wherein the testing room is in a cylinder structure with the bottom end opened and the runway-shaped cross section; the dissolved oxygen probe socket is formed on one side of the top of the testing room; the support fixing interfaces are arranged at the two ends of the top of the testing room respectively; the dynamic room is a cylindrical barrel and reversely fixed at the top of the testing room; the motor connected with the magnetic pole is arranged in the dynamic room, and is externally connected with the storage battery by a connecting line; the magnetic rotor is placed in the testing room, and is in magnetic connection with the magnetic pole; a hand-held support is connected and fixed to allow the device to be submerged in water and to be filled with overlying water; the dissolved oxygen probe is inserted and sealed; the device is then fixed at the bottom of the water; overlying water circulation of the testing room is adjusted and controlled; and an SOD is determined. The device is simple in structure, easy to dismount, small and exquisite in size, and convenient to carry, and can effectively determine the SOD under the action of different hydrodynamic forces.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
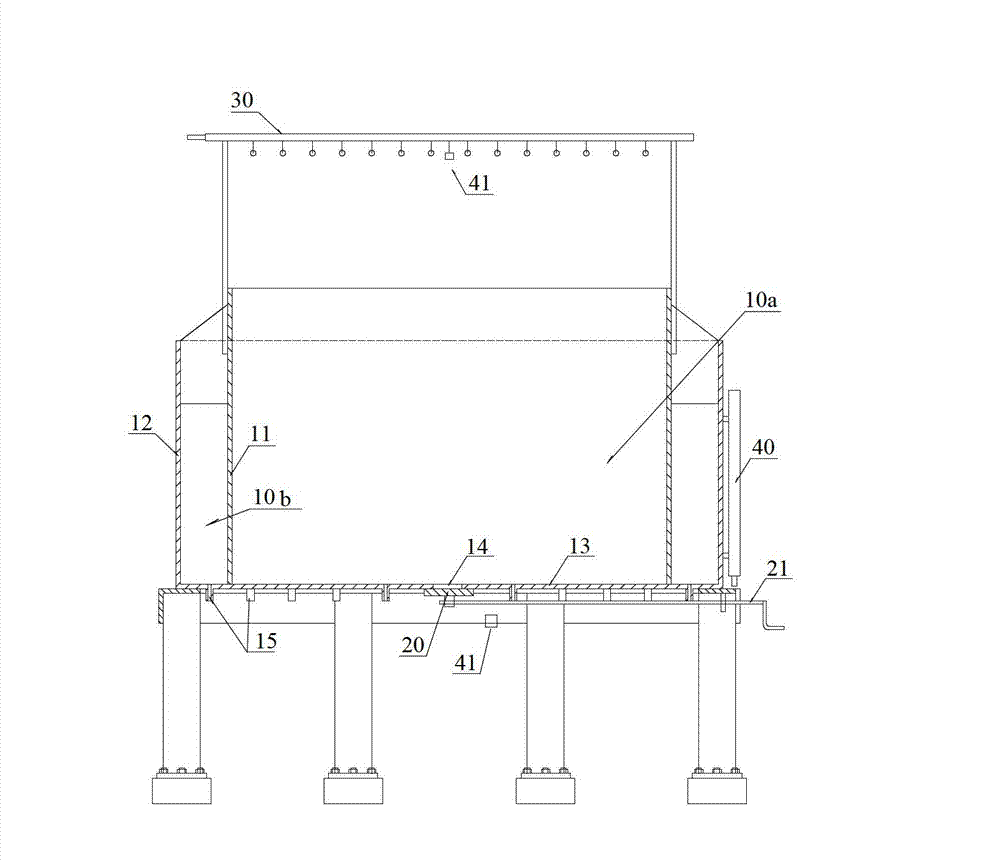
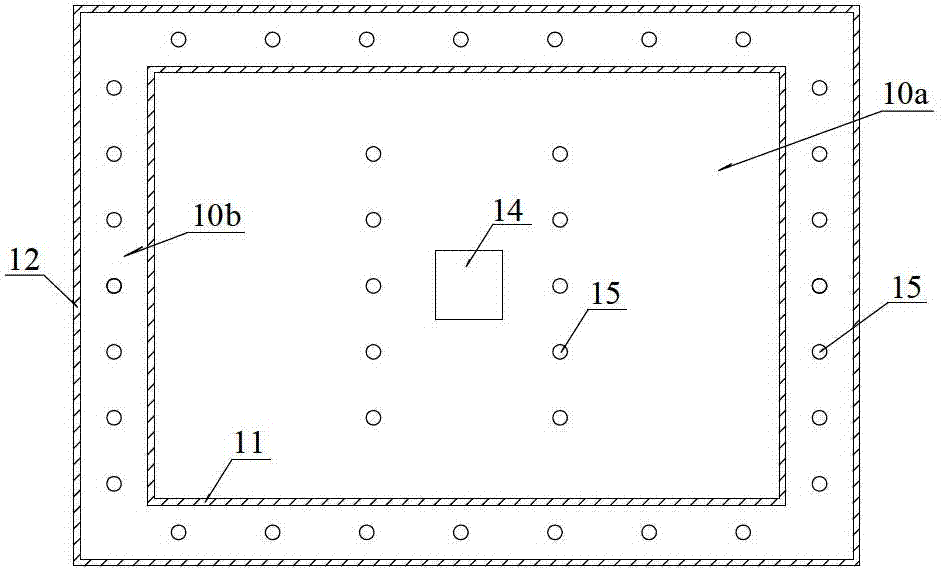
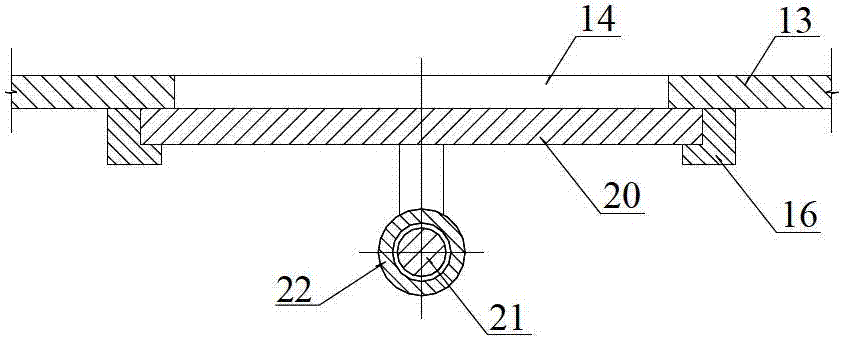
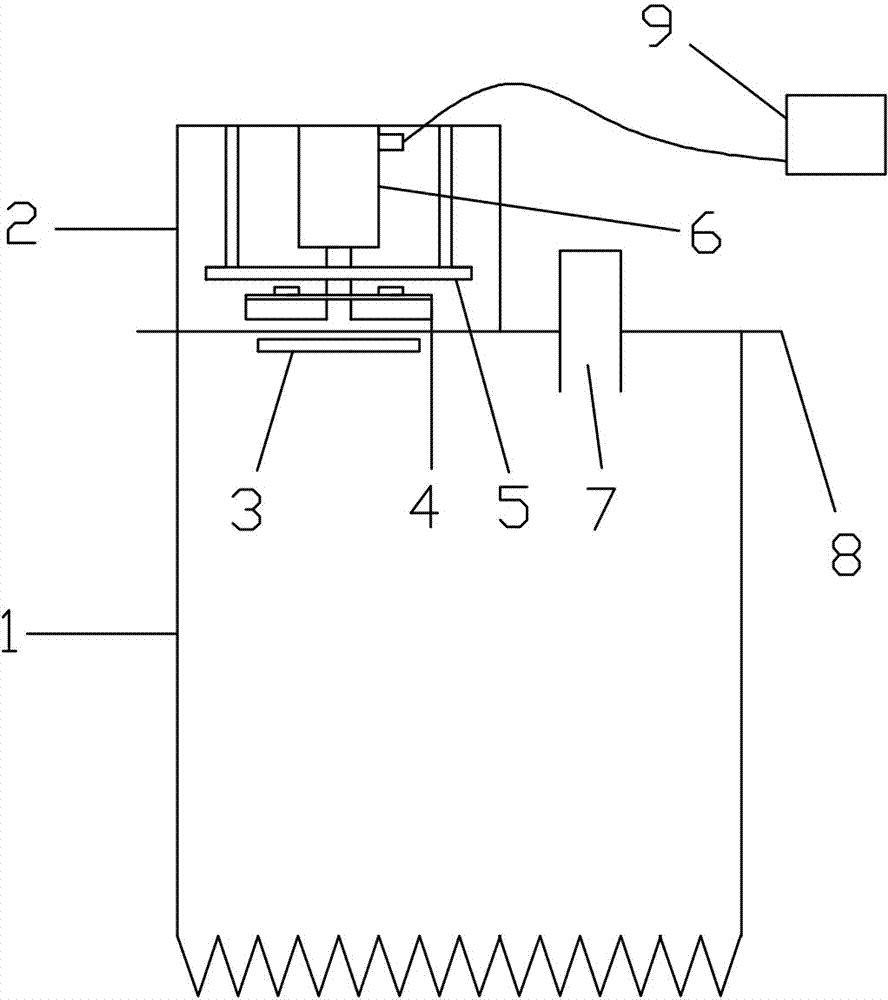
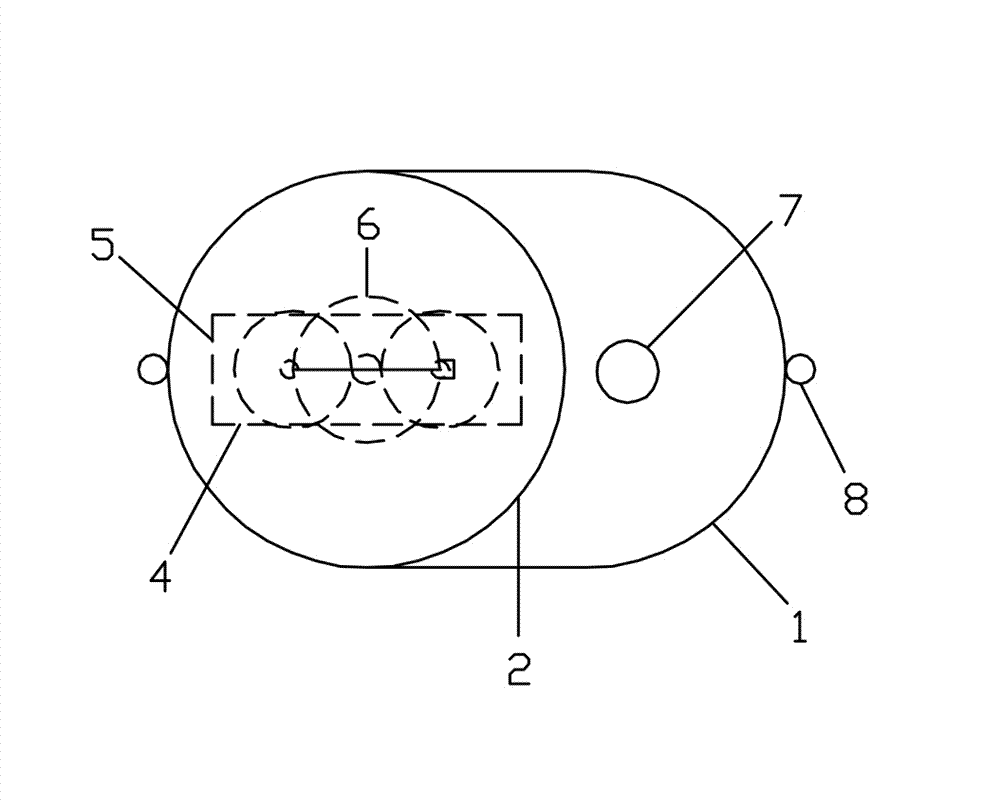
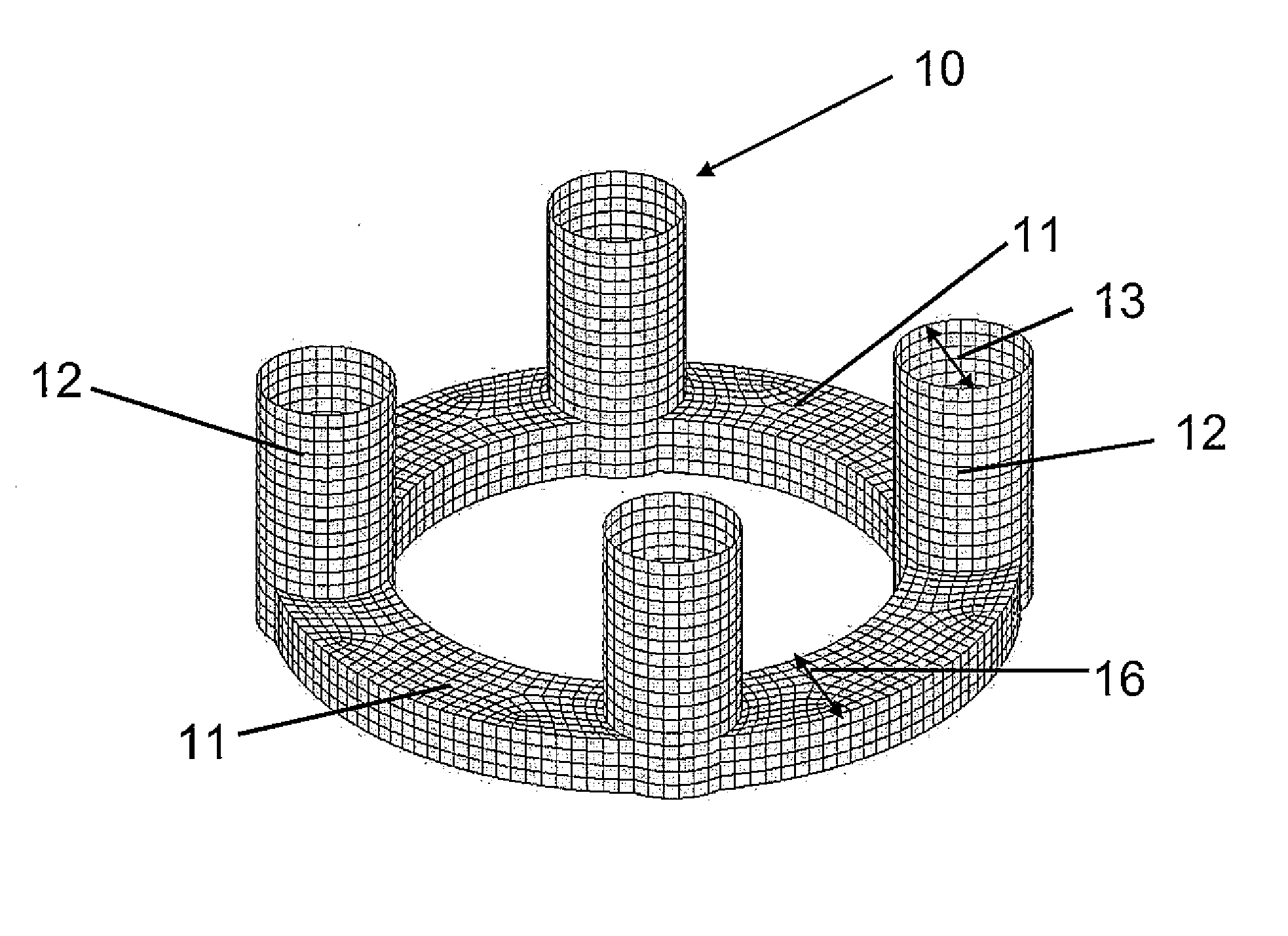
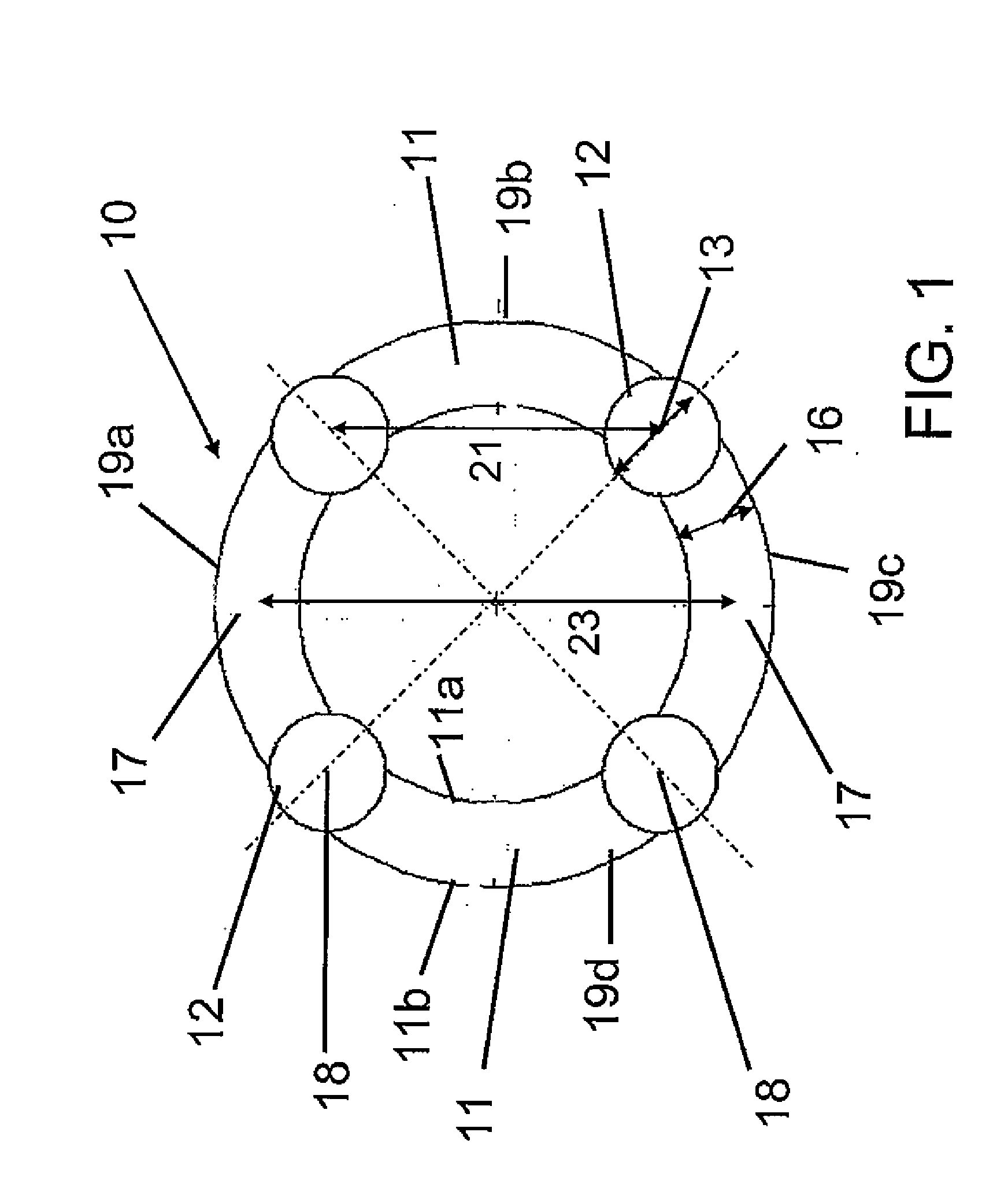
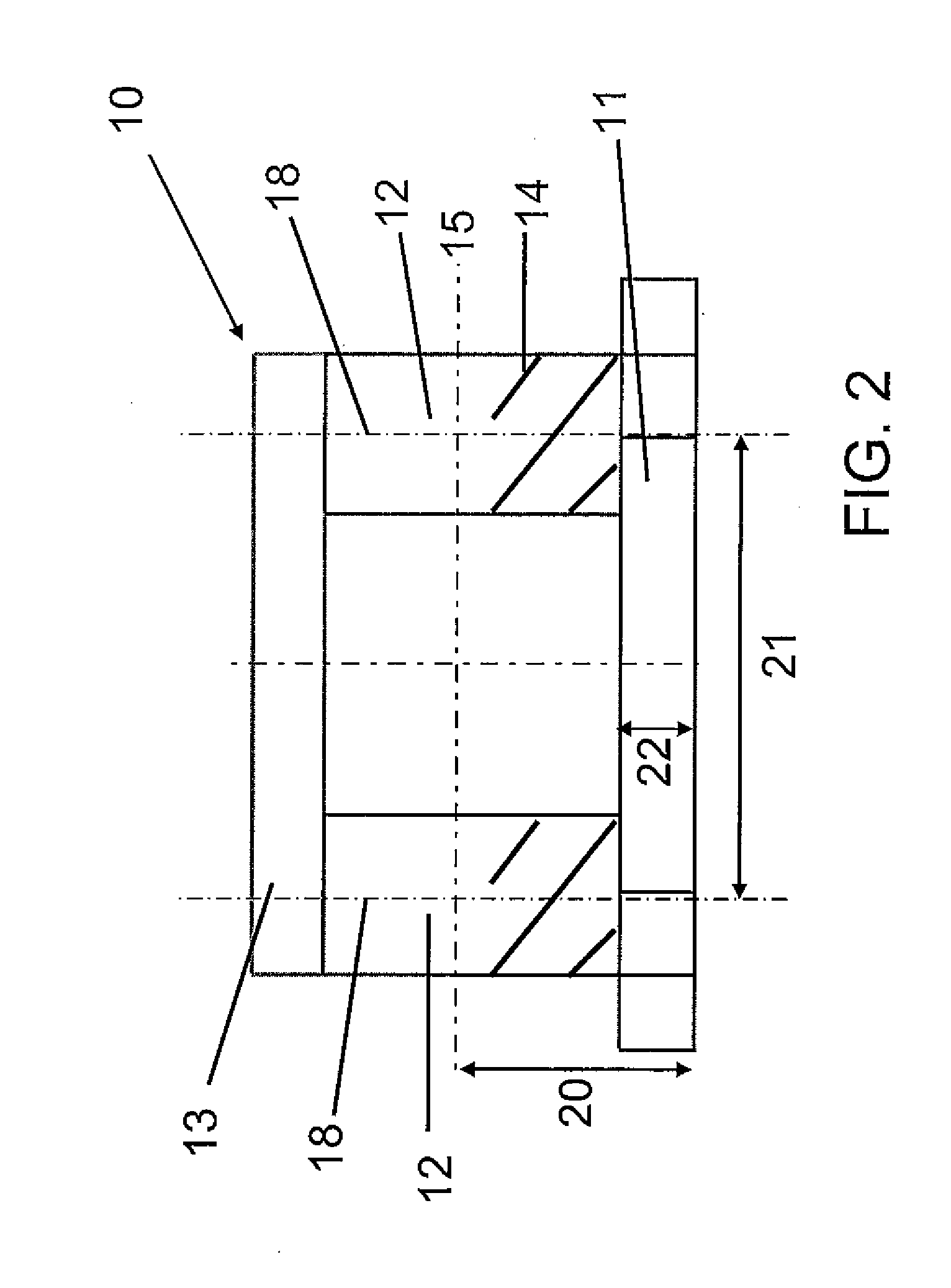
C-semi with minimum hydrodynamic forces
ActiveUS20130319314A1Minimized waveImprove hullFloating buildingsHydrodynamic/hydrostatic featuresCouplingMarine engineering
An offshore floating structure (10) for the drilling and production of oil and gas includes a generally circular toroidal, hollow pontoon (11) of substantially the same radial width throughout a perimeter of the pontoon. The offshore floating structure includes a plurality of columns (12) of substantially a same cross-sectional area, each coupled at a coupling point, on a bottom end thereof to the pontoon at an equidistant point along the perimeter of the pontoon, and adapted to be coupled on a top end to a deck structure. The diameter (23) from a center of the radial width of the pontoon is greater than a distance (21) from a center of one column to a center of an adjacent column.
Owner:AKER SOLUTIONS AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com