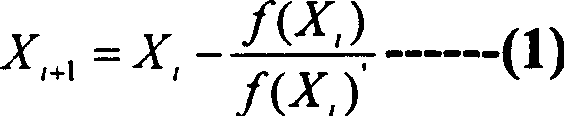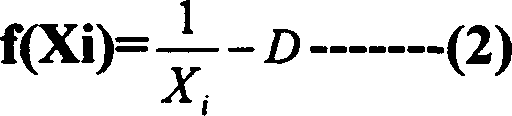Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Fixed point computation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
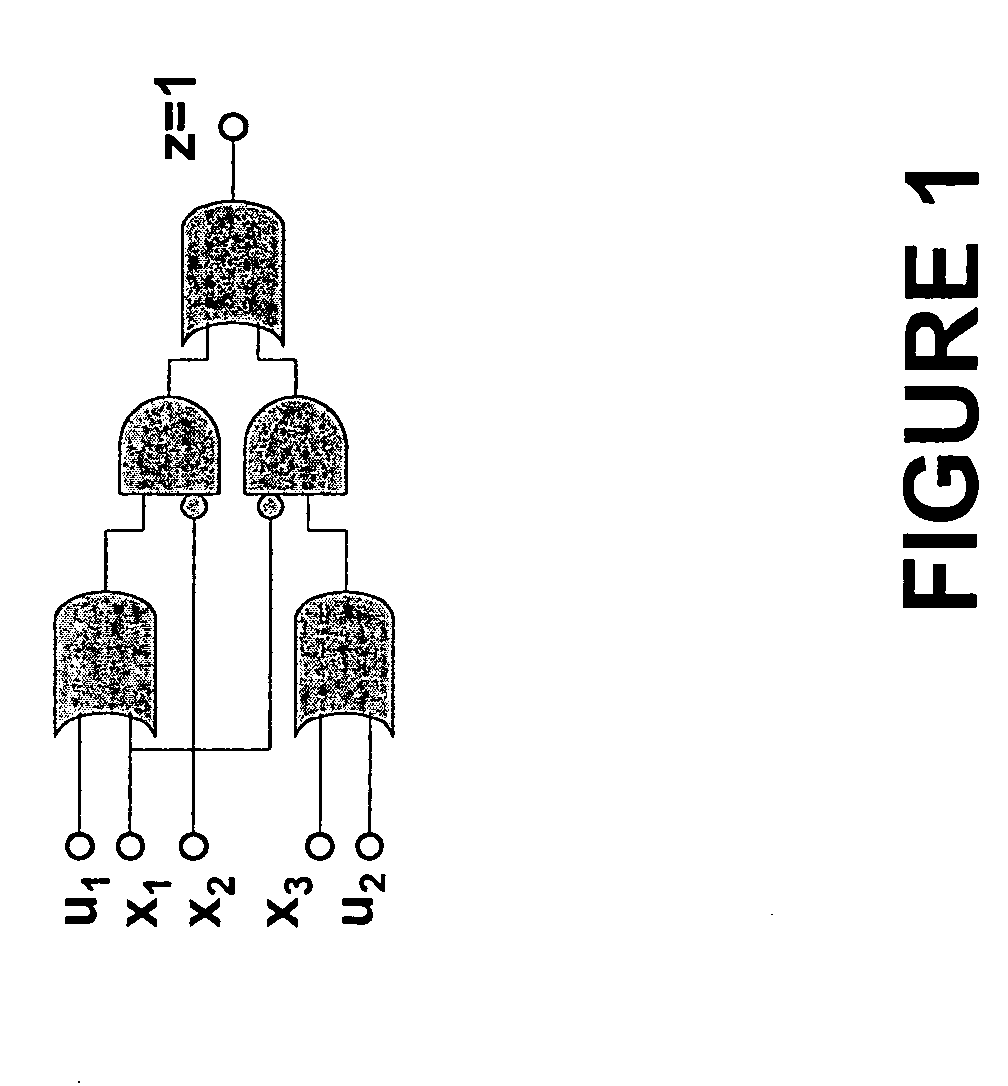
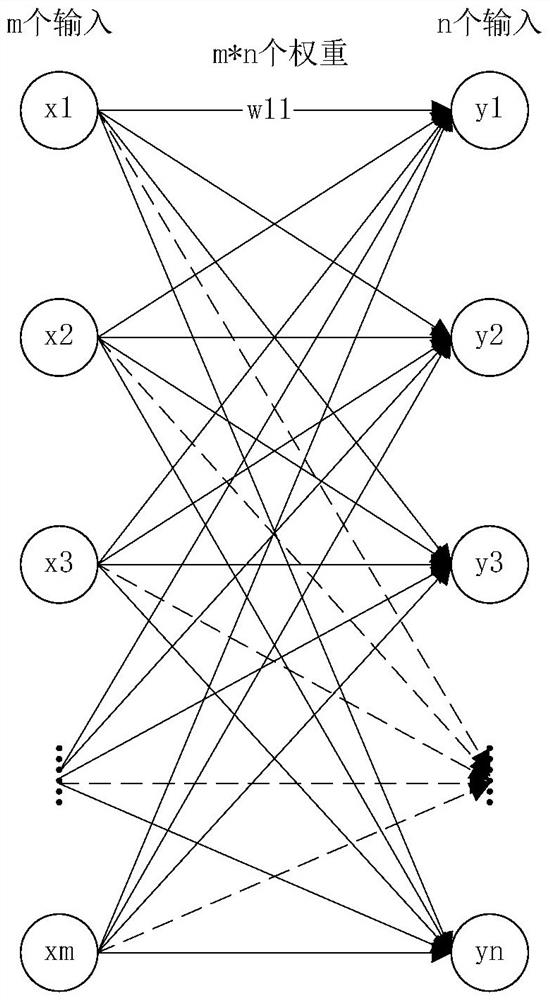
The subset construction is an example of a fixed-point computation, a particular style of computation that arises regularly in computer science. These computations are characterized by the iterated application of a monotone function to some collection of sets drawn from a domain whose structure is known.
FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)-based general matrix fixed-point multiplier and calculation method thereof
ActiveCN104572011AImprove computing efficiencyImprove performanceComputation using non-contact making devicesGeneral matrixControl signal
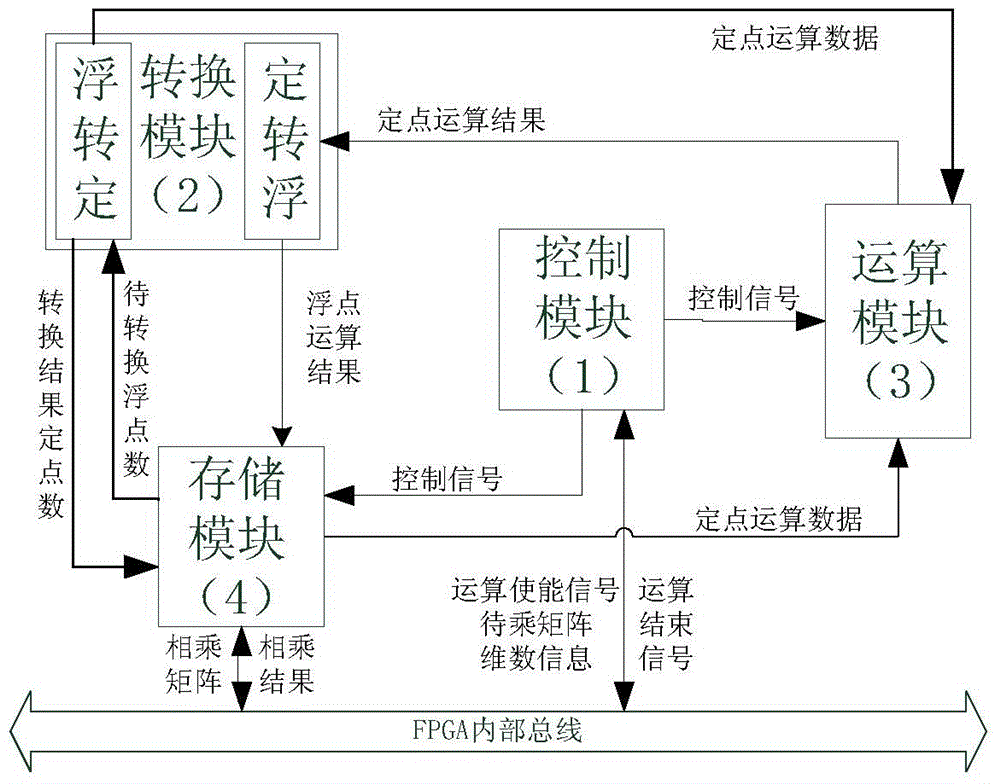
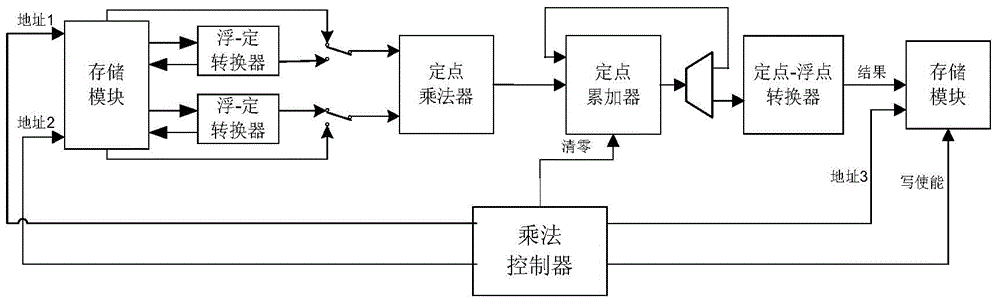
The invention discloses an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)-based general matrix fixed-point multiplier. An internal structure of the multiplier consists of a control module, a conversion module, an operation module and a storage module. The control module is used for generating a control signal according to dimension of a to-be-operated matrix. The conversion module is responsible for performing conversion between a fixed-point number and a floating-point number during operation. The operation module is used for reading operation data from the storage module and the conversion module, performing fixed-point multiplication and fixed-point accumulating operation and storing a result in the storage module. The storage module is used for caching to-be-operated matrix data and result matrix data, providing an interface compatible with a bus signal and allowing access of other components on a bus. The characteristic of high fixed-point calculation efficiency in hardware is fully utilized; by using a unique operation structure, simultaneous conversion and operation of the data are realized to improve the overall operation speed, and a plurality of matrix fixed-point multipliers can be simultaneously used to perform parallel calculation; thus the fixed-point multiplication of an arbitrary dimension matrix can be supported, and meanwhile extremely high calculation efficiency is guaranteed. Compared with matrix multiplication performed by using the floating-point number, the multiplier has the advantage that the calculation efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:上海碧帝数据科技有限公司
Efficient SAT-based unbounded symbolic model checking
ActiveUS20050240885A1Improve performanceReduce stepsComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designFixed point computationQuantifier elimination
An efficient approach for SAT-based quantifier elimination and pre-image computation using unrolled designs that significantly improves the performance of pre-image and fix-point computation in SAT-based unbounded symbolic model checking.
Owner:NEC CORP
Computing method and device based on neural network
InactiveCN106611216ALower requirementSmall amount of calculationNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsAlgorithmFixed point computation
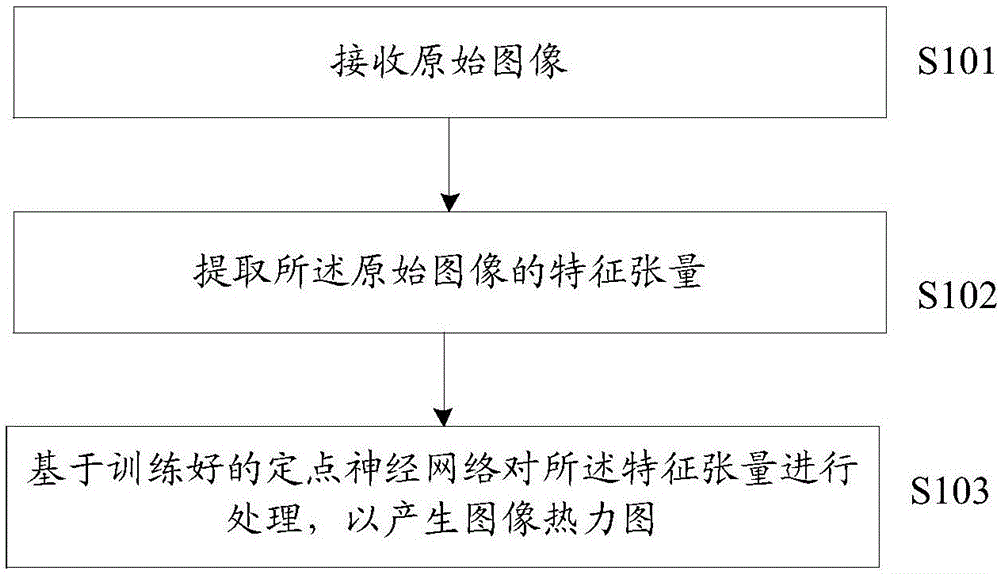
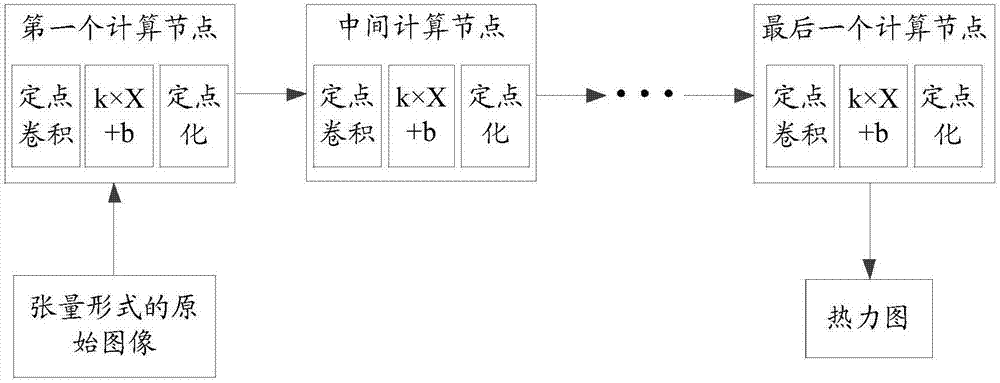
The embodiment of the invention provides a computing method based on a neural network. The method comprises the steps of receiving an original image; extracting a feature tensor of the original image; and processing the feature tensor based on a trained fixed-point neural network to generate an image thermodynamic diagram. The embodiment of the invention provides the computing method in which the neural network is achieved by a fixed-point method, as fixed-point computation is adopted, a computation amount is small, fewer resources are occupied, and thus requirements on hardware is low.
Owner:BEIJING KUANGSHI TECH +1
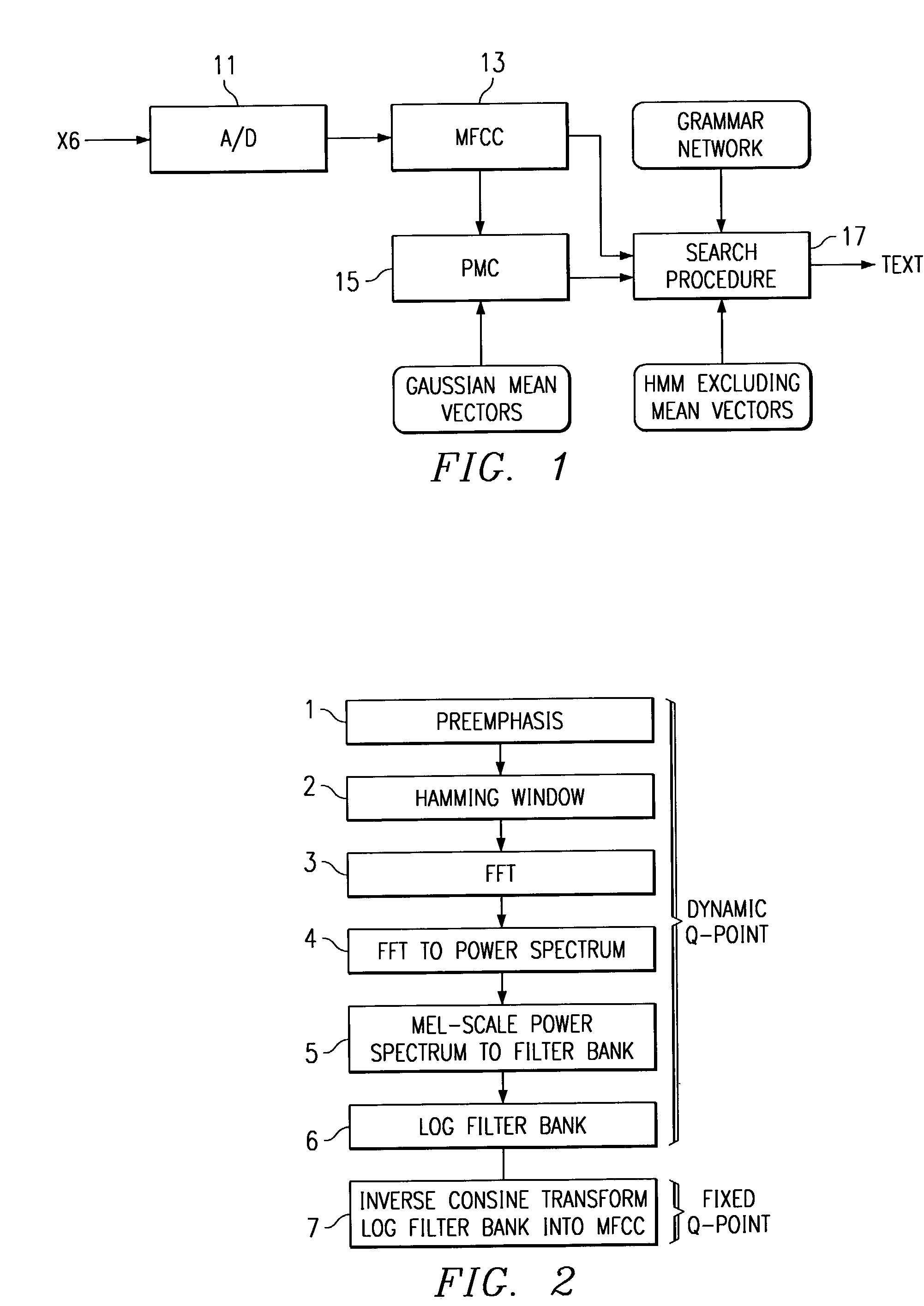
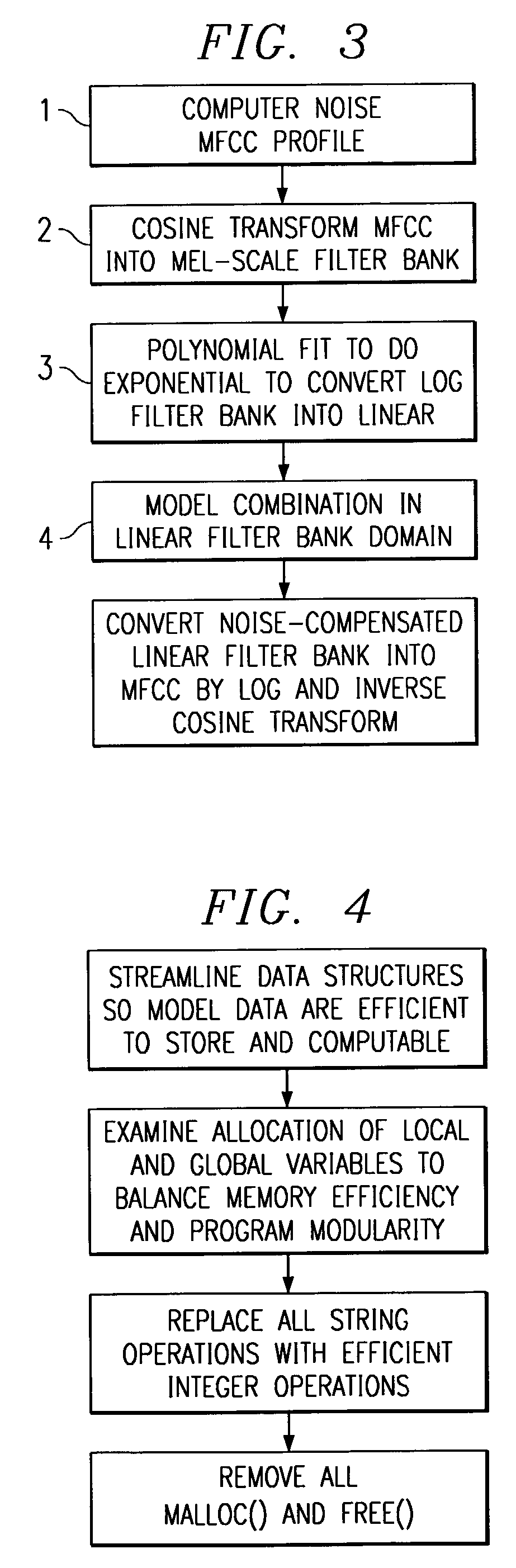
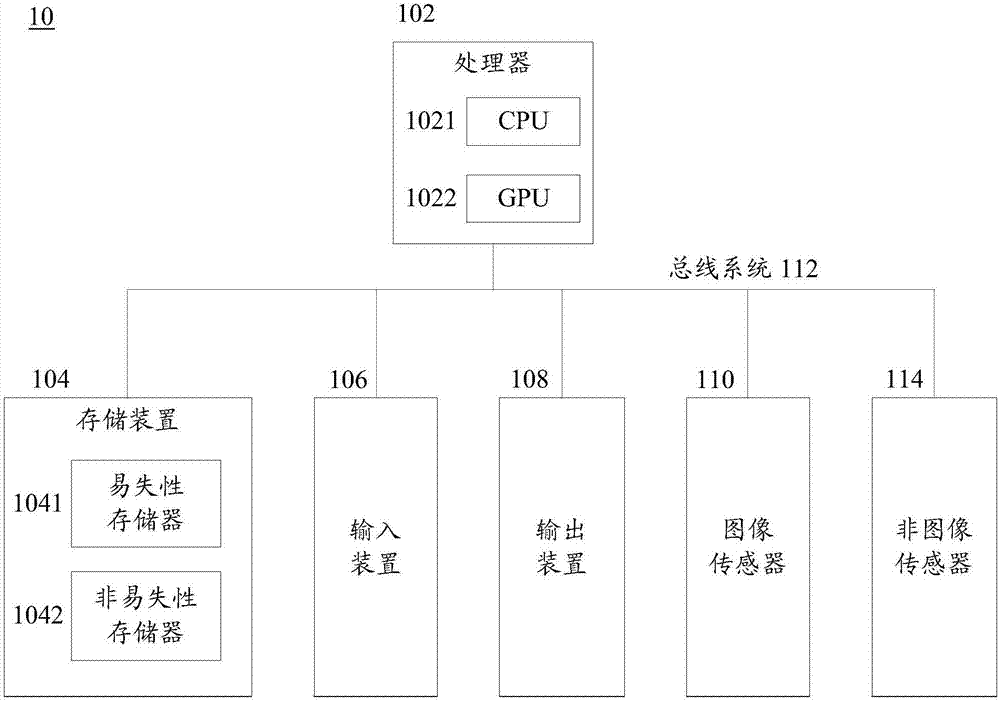
Implementing a high accuracy continuous speech recognizer on a fixed-point processor
A small vocabulary speech recognizer suitable for implementation on a 16-bit fixed-point DSP is described. The input speech xt is sampled at analog-to-digital (A / D) converter 11 and the digital samples are applied to MFCC (Mel-scaled cepstrum coefficients) front end processing 13. For robustness to background noises, PMC (parallel model combination) 15 is integrated. The MFCC and Gaussian mean vectors are applied to PMC 15. The MFCC and PMC provide speech features extracted in noise and this is used to modify the HMMs. The noise adapted HMMs excluding mean vectors are applied to the search procedure to recognize the grammar. A method of computing MFCC comprises the steps of: performing dynamic Q-point computation for the preemphasis, Hamming Window, FFT, complex FFT to power spectrum and Mel scale power spectrum into filter bank steps, a log filter bank step and after the log filter bank step performing fixed Q-point computation. A polynomial fit is used to compute log2 in the log filter bank step. The method of computing PMC comprises the steps of: computing noise MFCC profile, computing cosine transform MFCC into mel-scale filter bank, converting log filter bank into linear filter bank with an exponential wherein to compute exp2 a polynomial fit is used, performing a model combination in the linear filter bank domain; and converting the noise compensated linear filter bank into MFCC by log and inverse cosine transform.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Computing method based on neural network and computing device thereof
ActiveCN106855952ALower requirementSmall amount of calculationBiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionNerve networkAlgorithm
The embodiment of the invention provides a computing method based on a neural network. The computing method comprises the steps that an original image of the tensor form is acquired; fixed point computation is performed on the original image of the tensor form; an image thermal diagram is generated based on the output data of fixed point computation; and the original image is marked based on the image thermal diagram. According to the computing method based on the neural network through the fixed point method, fixed point computation is adopted so that computing burden is low, resource occupation is less and thus the requirement for hardware is low.
Owner:BEIJING KUANGSHI TECH +1
Reachability analysis for program verification
InactiveUS7926039B2High precisionSimplified representationSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsStatic timing analysisProgram proving
An improved method for automatically improving the precision of an extrapolation operator used, for example, in software program verification in connection with the static analysis and model checking of the software programs which rely on fix-point computation. In particular, a new extrapolation-with-care-set operator, together with a method for gradually increasing the precision of this operation by tightening the care set.
Owner:NEC CORP
Reachability analysis for program verification
InactiveUS20080016497A1High precisionSimplified representationSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsProgram provingReachability
An improved method for automatically improving the precision of an extrapolation operator used, for example, in software program verification in connection with the static analysis and model checking of the software programs which rely on fix-point computation. In particular, a new extrapolation-with-care-set operator, together with a method for gradually increasing the precision of this operation by tightening the care set.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for analyzing signals providing instantaneous frequencies and sliding fourier transforms, and device for analyzing signals
The present invention relates to a method for analyzing an initial signal (SI) representative of a wave that propagates in a physical medium, in order to provide parameters characteristic of said initial signal, wherein the method is implemented via a computing platform (PC) requiring only fixed-point calculations with a reduced number of multiplications. The provided parameters may be one or more of the following: instantaneous phase (PI), instantaneous amplitude (AI), instantaneous frequency (FI), and sliding Fourier transform (TFG).
Owner:伊夫列扎
Image feature extraction method, device, apparatus, and readable storage medium
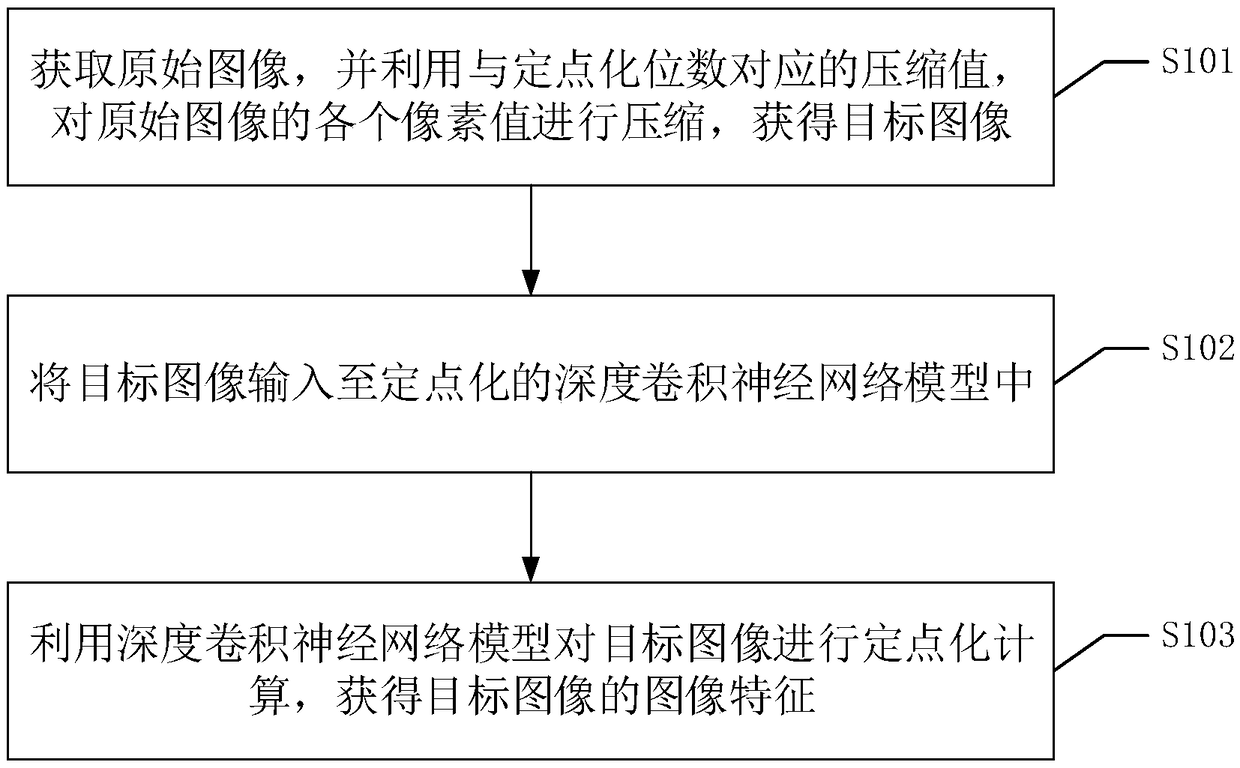
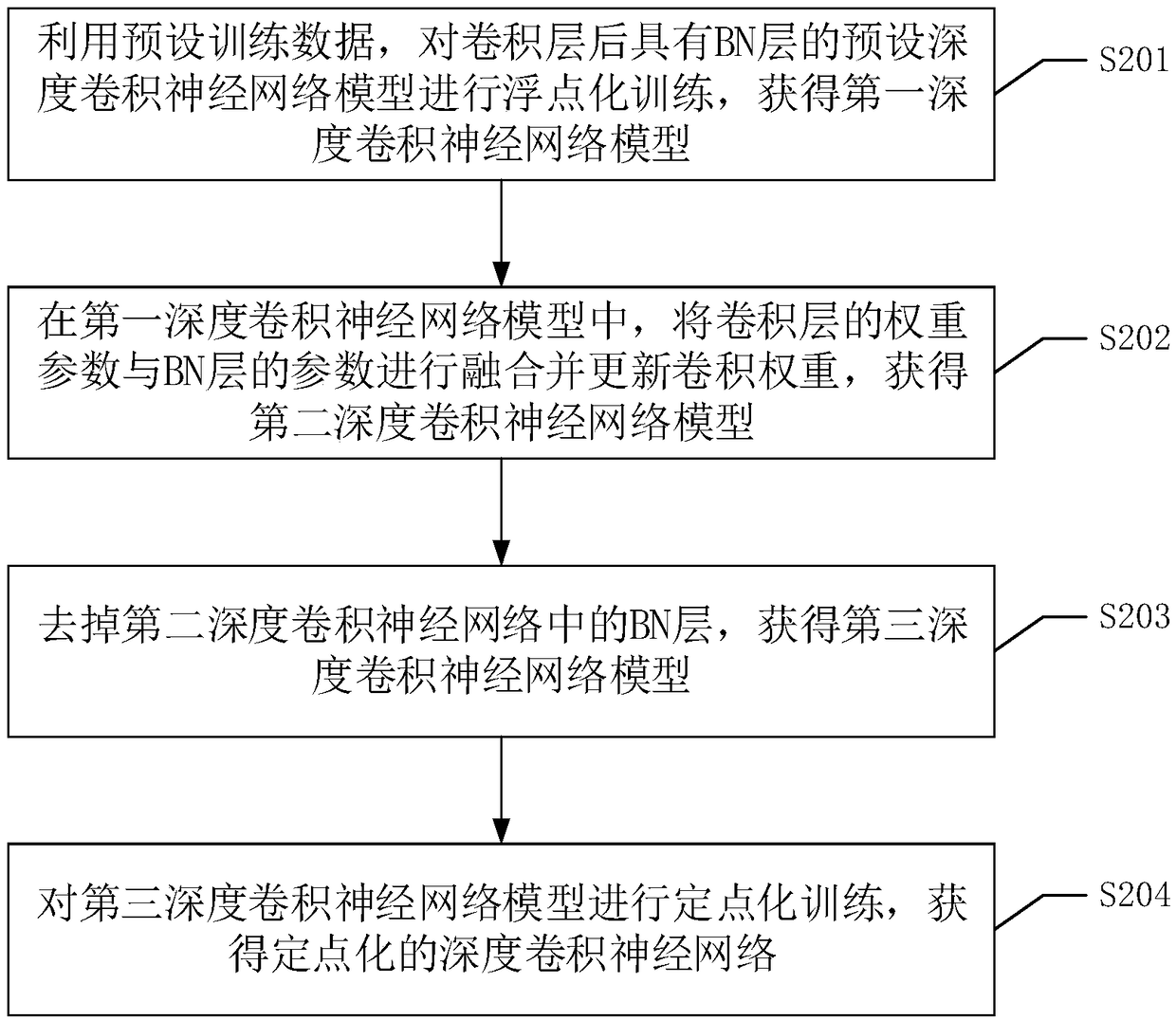
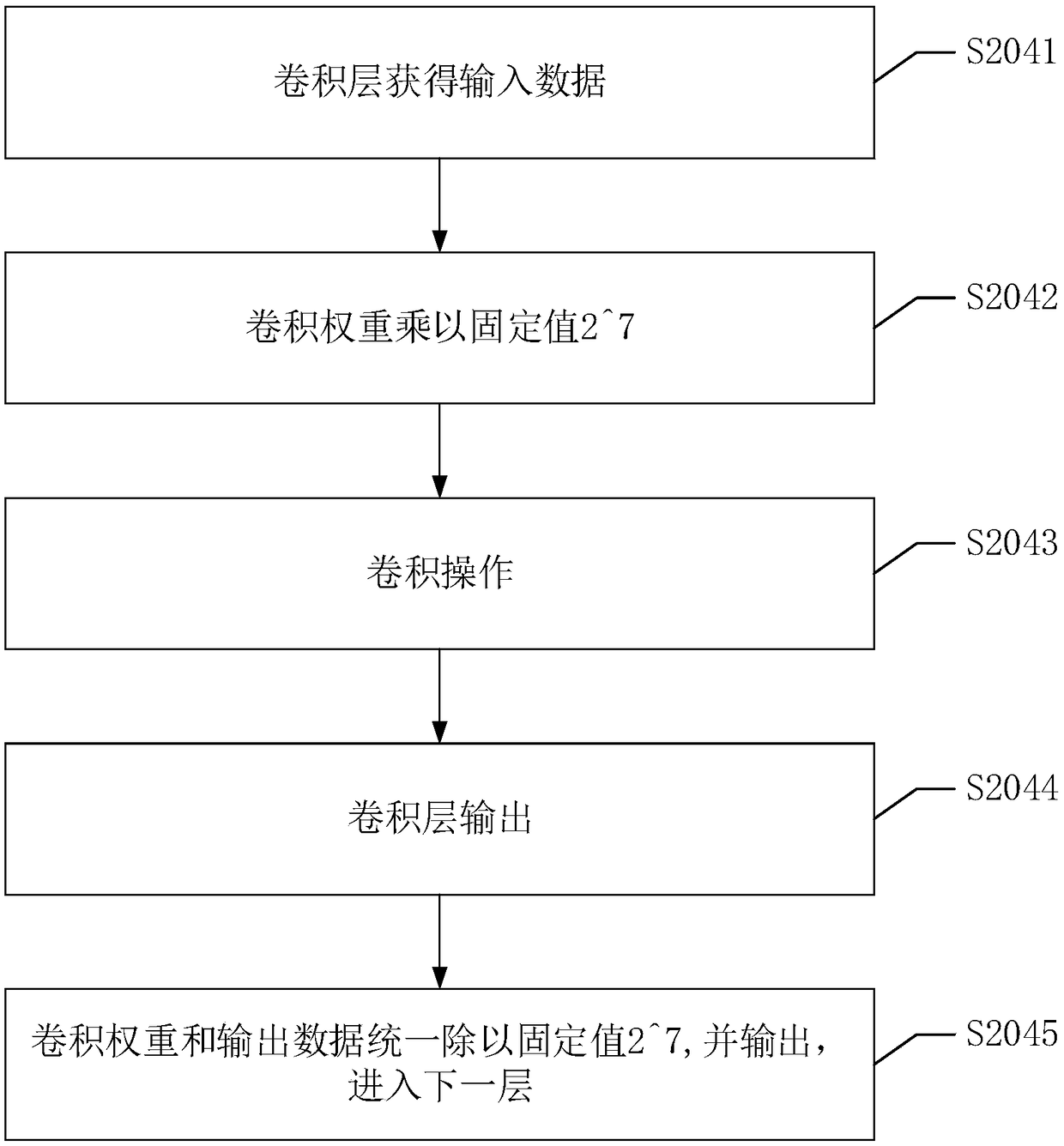
The invention discloses an image feature extraction method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an original image; compressing each pixel value of the original image by using a compression value corresponding to a fixed-point number of bits to obtain a target image; obtaining a target image by using the compression value corresponding to the fixed-point number of bits. The target image is input into a fixed-point depth convolution neural network model. The depth convolution neural network model is used to compute the fixed point of the target image, and the image features of the target image are obtained. Fixed-point computation is faster than floating-point computation in computational speed, and it is easier to be realized in practical application. In feature extraction,fixed-point computing can also reduce the storage overhead, reduce the occupation of computer resources, further improve the computing speed, and then can be used for real-time image feature extraction. The invention also discloses an image feature extraction device, apparatus and a readable storage medium, which have corresponding technical effects.
Owner:SUZHOU KEDA TECH
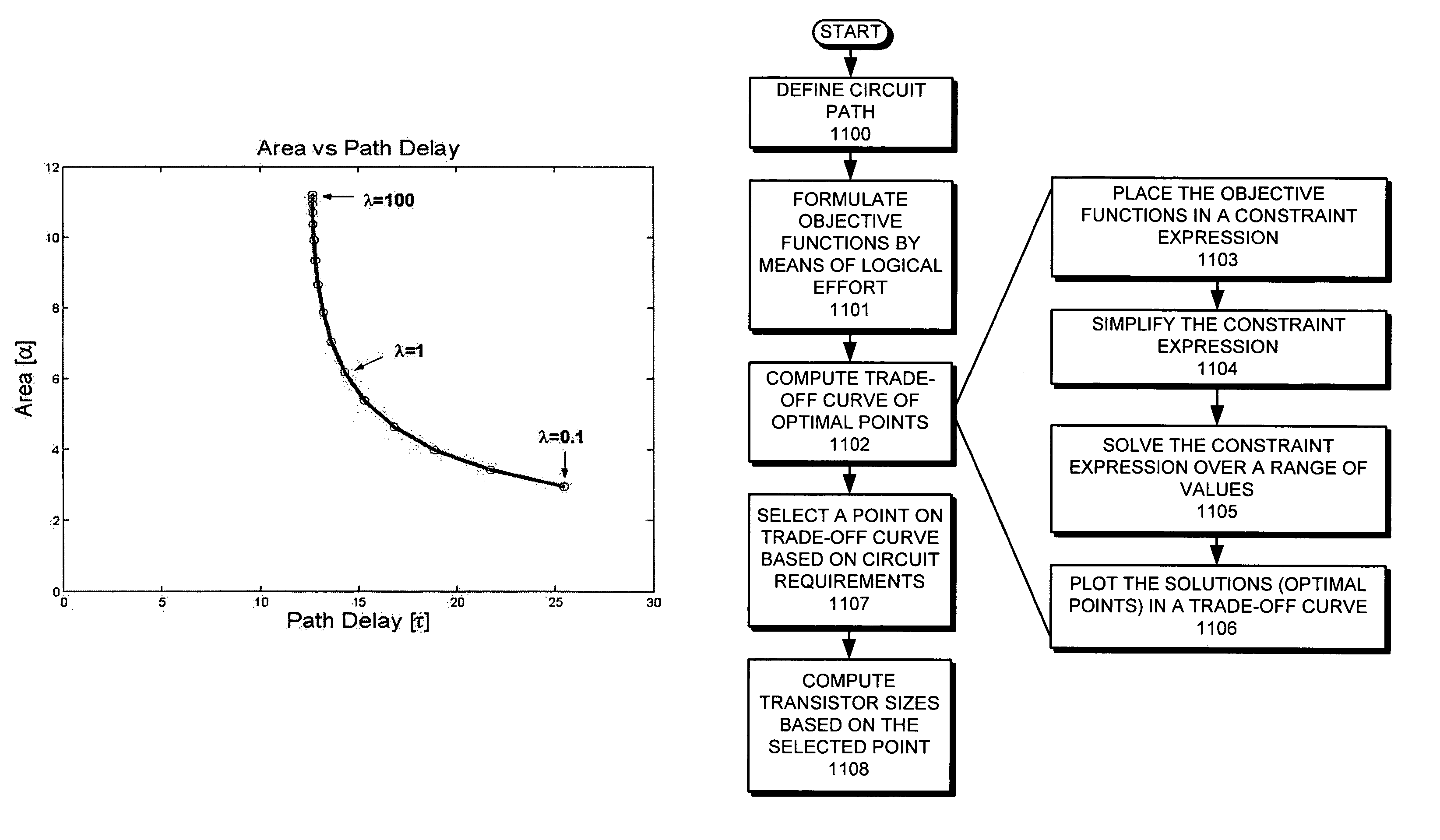
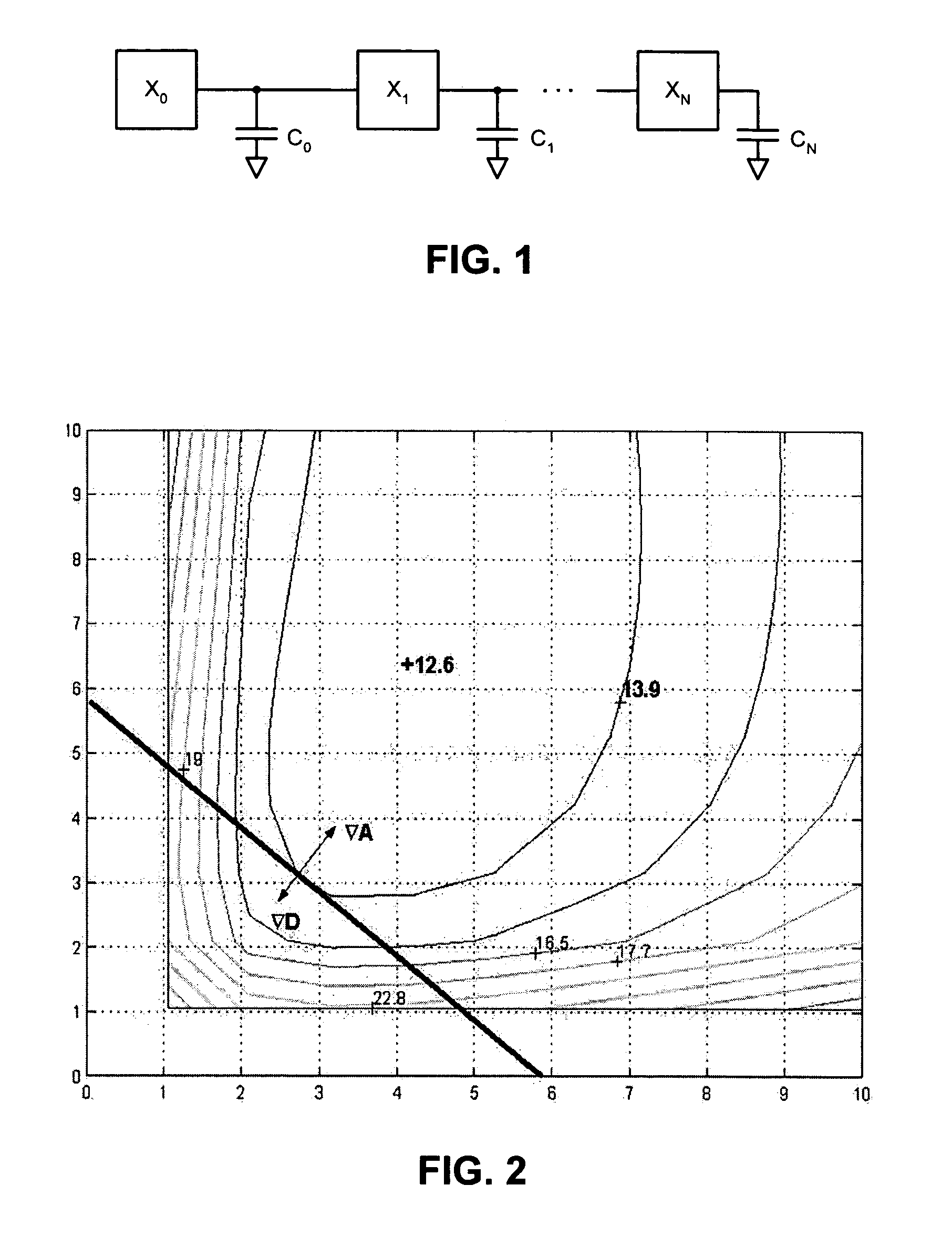
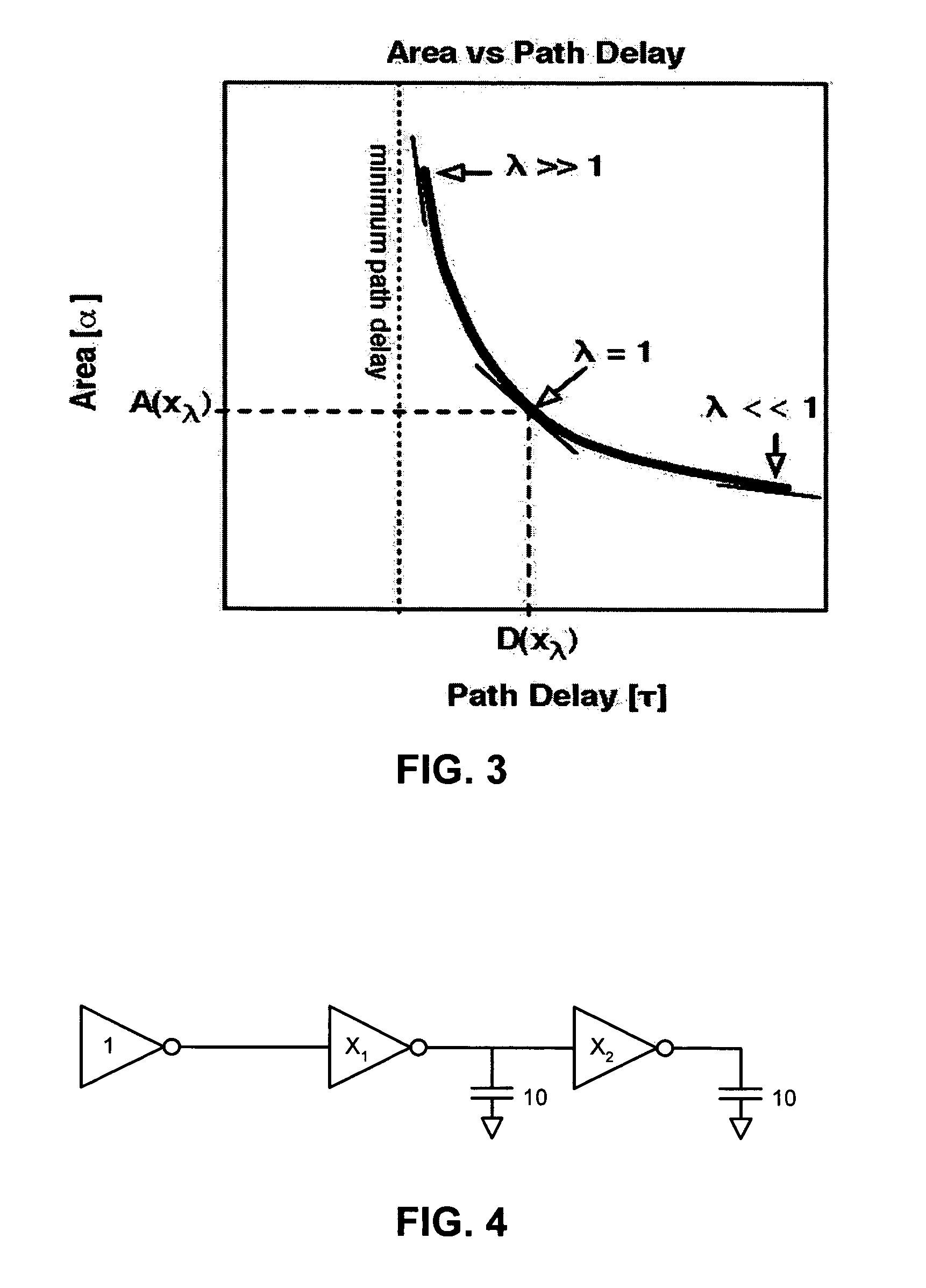
Performing a constrained optimization to determine circuit parameters
ActiveUS7376916B1Computation using non-denominational number representationCAD circuit designAlgorithmTrade offs
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system which performs a constrained optimization of circuit parameters. During operation, the system selects two circuit parameters associated with a circuit path, wherein the optimization is to be performed on the first circuit parameter while a limitation on second circuit parameter functions as a constraint on the optimization of the first circuit parameter. Next, the system generates objective functions which model the first circuit parameter and the second circuit parameter in terms of logical effort. The system then uses the objective functions to generate a constraint expression, wherein the constraint expression mathematically relates the optimization of the first circuit parameter to the constraint on the second circuit parameter. Next, the system computes a trade-off curve using the constraint expression. The system then computes transistor sizes for the circuit path based on a selected point from the trade-off curve.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
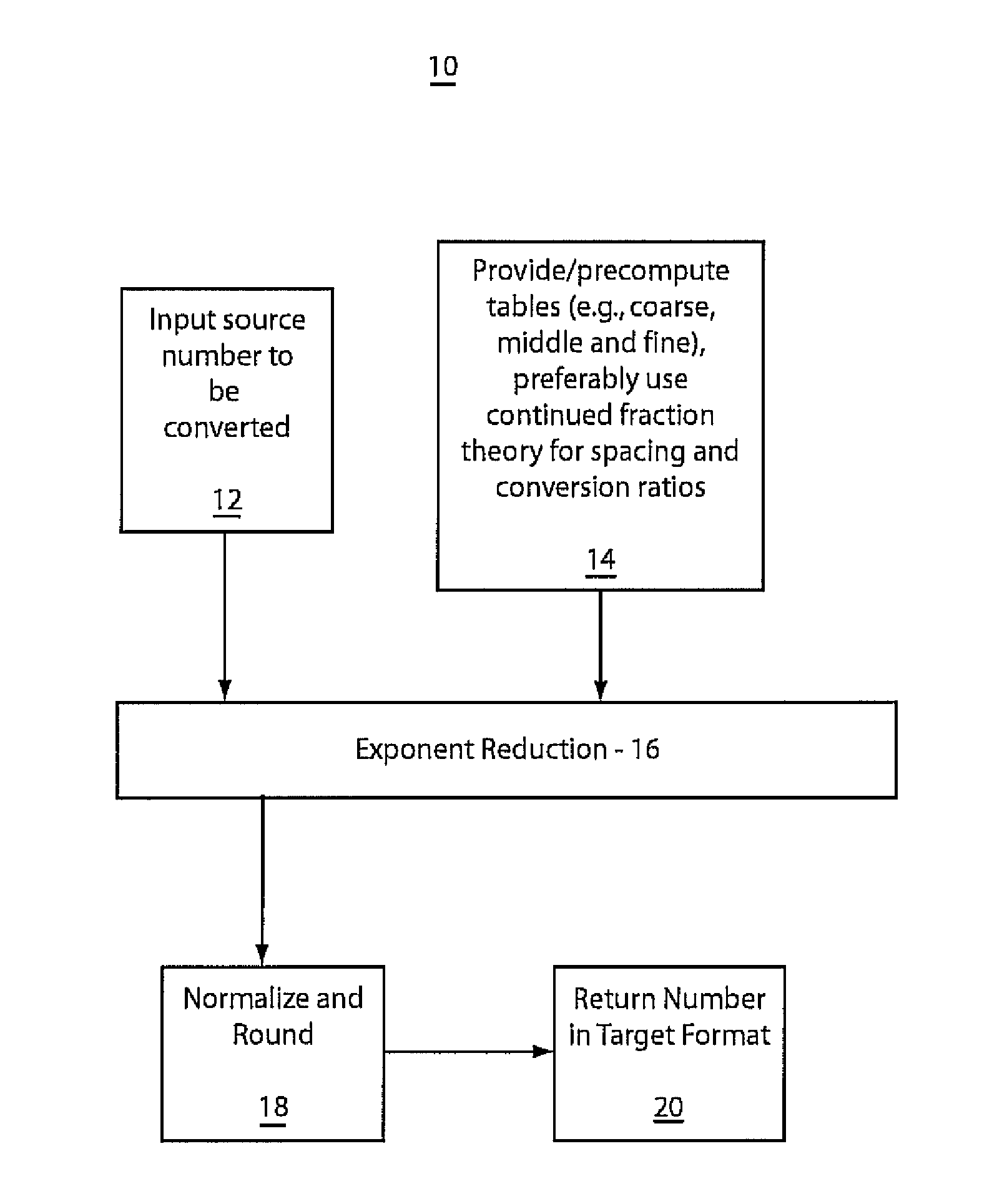
Fast correctly-rounding floating-point conversion
ActiveUS7921144B2Minimize changesTightly bounded computational precisionDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsFloating pointFixed point computation
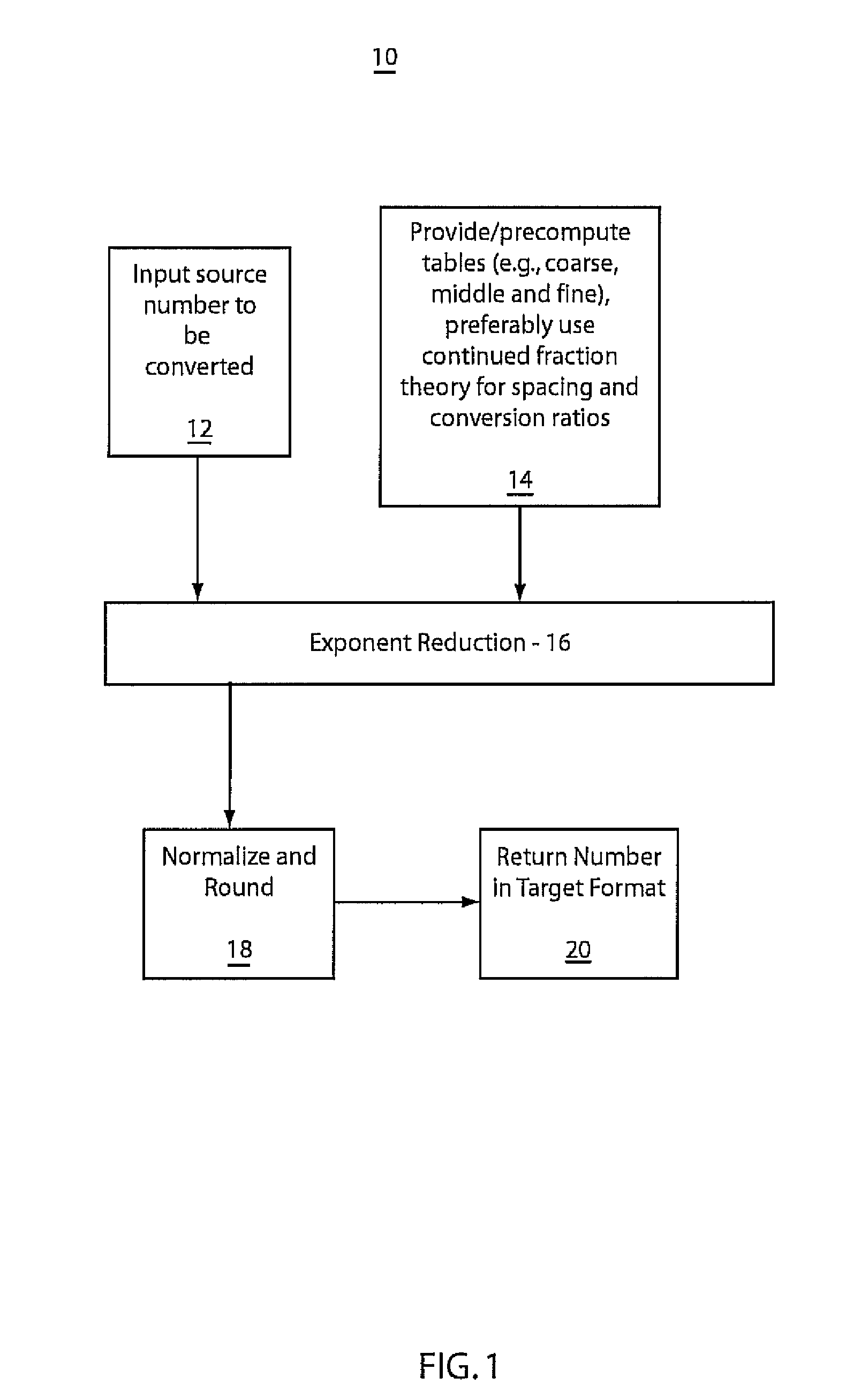
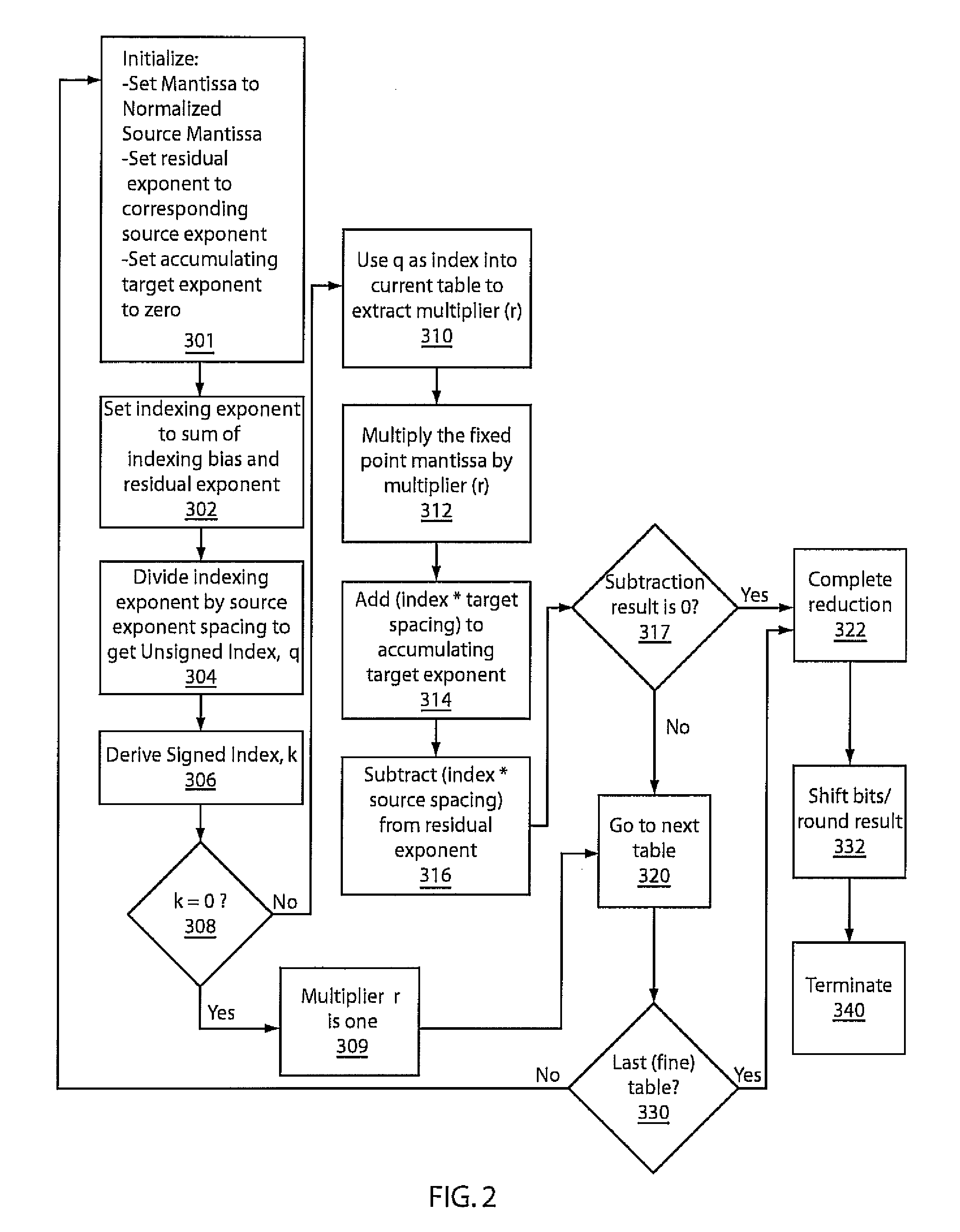
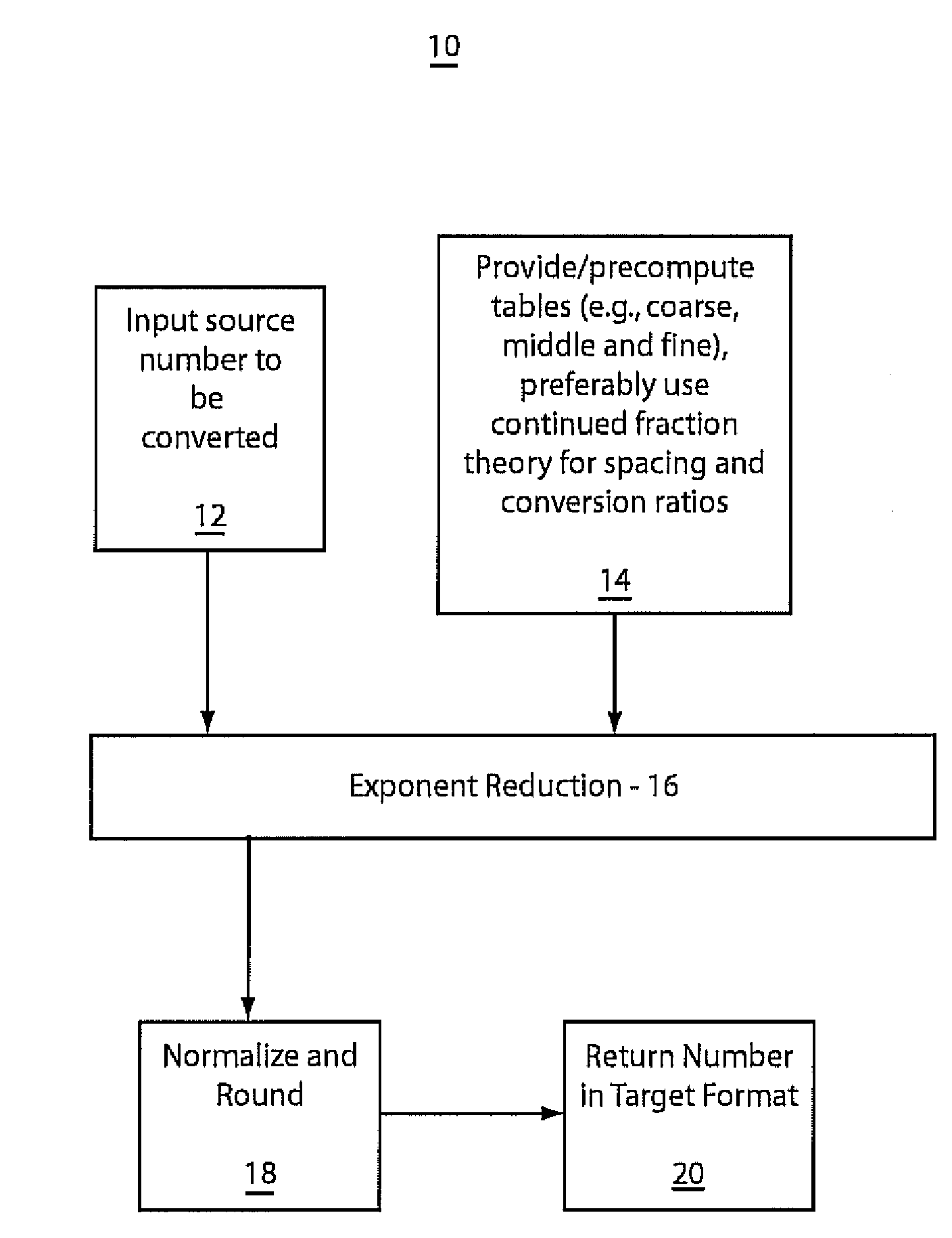
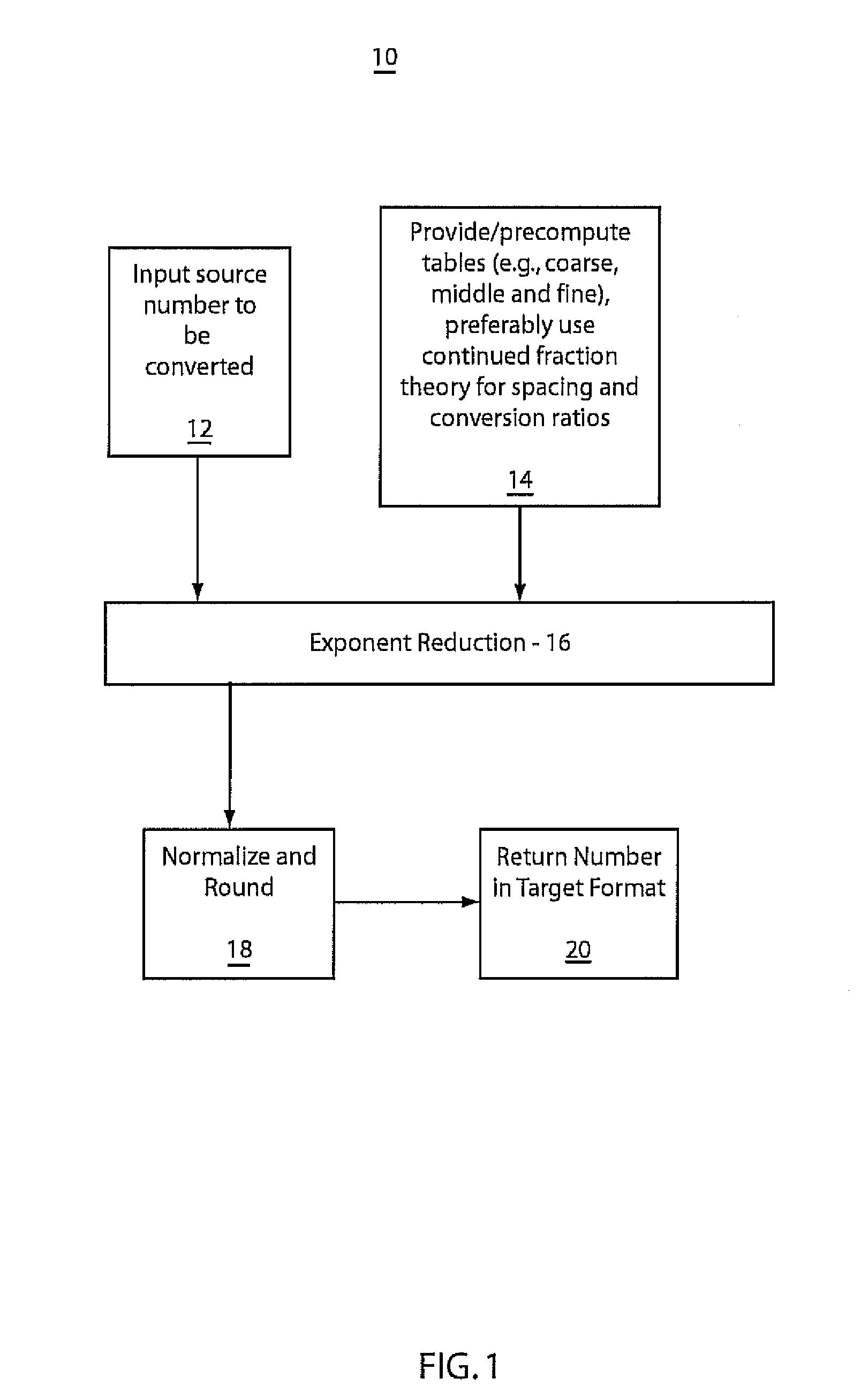
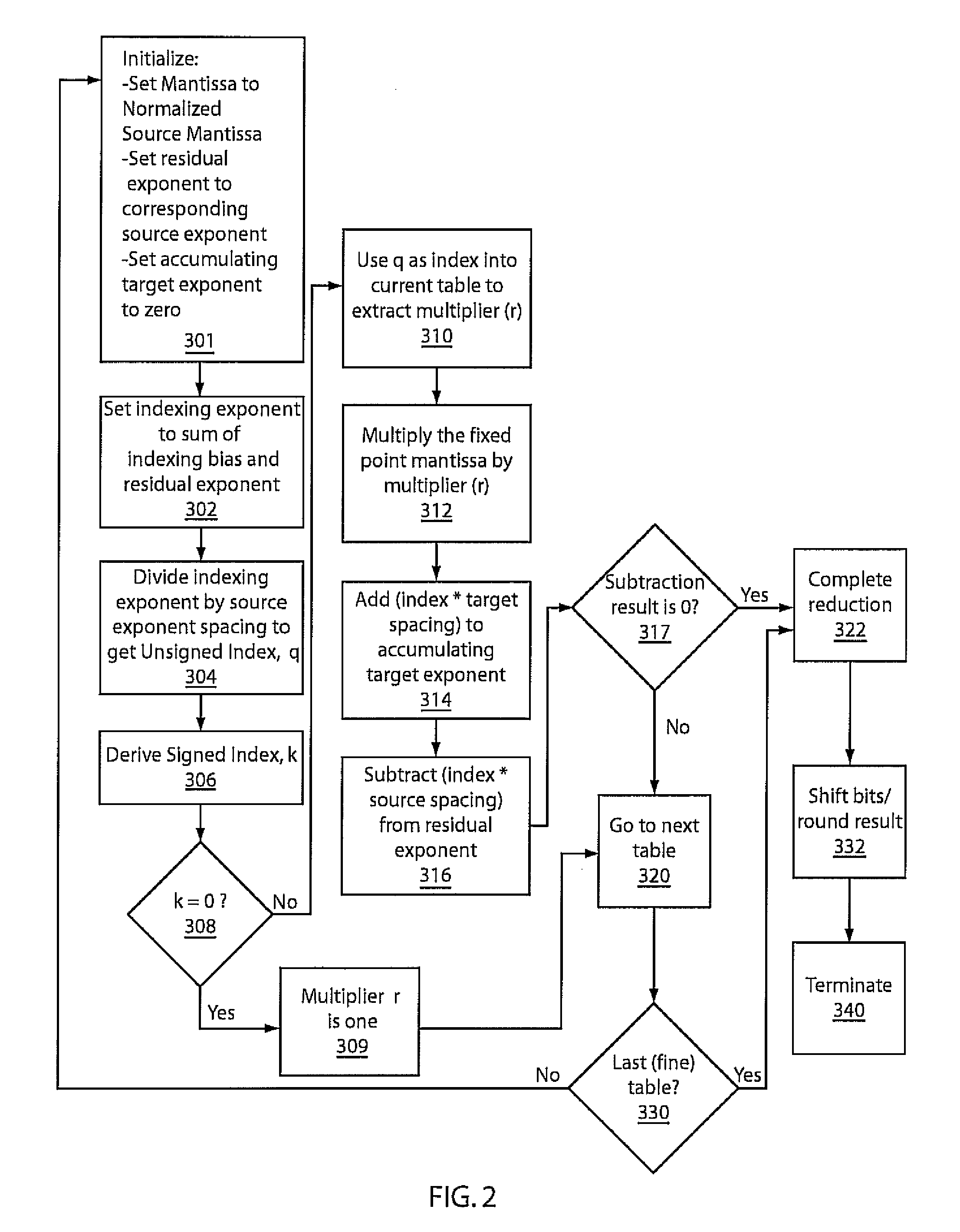
A system and method for converting bases of floating point numbers using fixed-point computation includes tables having different related spacings of exponent indices. The tables are adapted to cross-reference conversion ratios between exponent bases. The tables are characterized by bi-uniform spacings of source and target exponents and including near-unity table entries representing the conversion ratios. A source number is converted into a target number in a different radix by a sequence of reduction operations using a sequence of the tables. The reduction operations include reducing a source number exponent magnitude and accumulating a target exponent and multiplying a source number mantissa by a selected conversion ratio including a near-unity ratio of powers. A final mantissa is normalized and rounded to produce the target number in a new radix.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
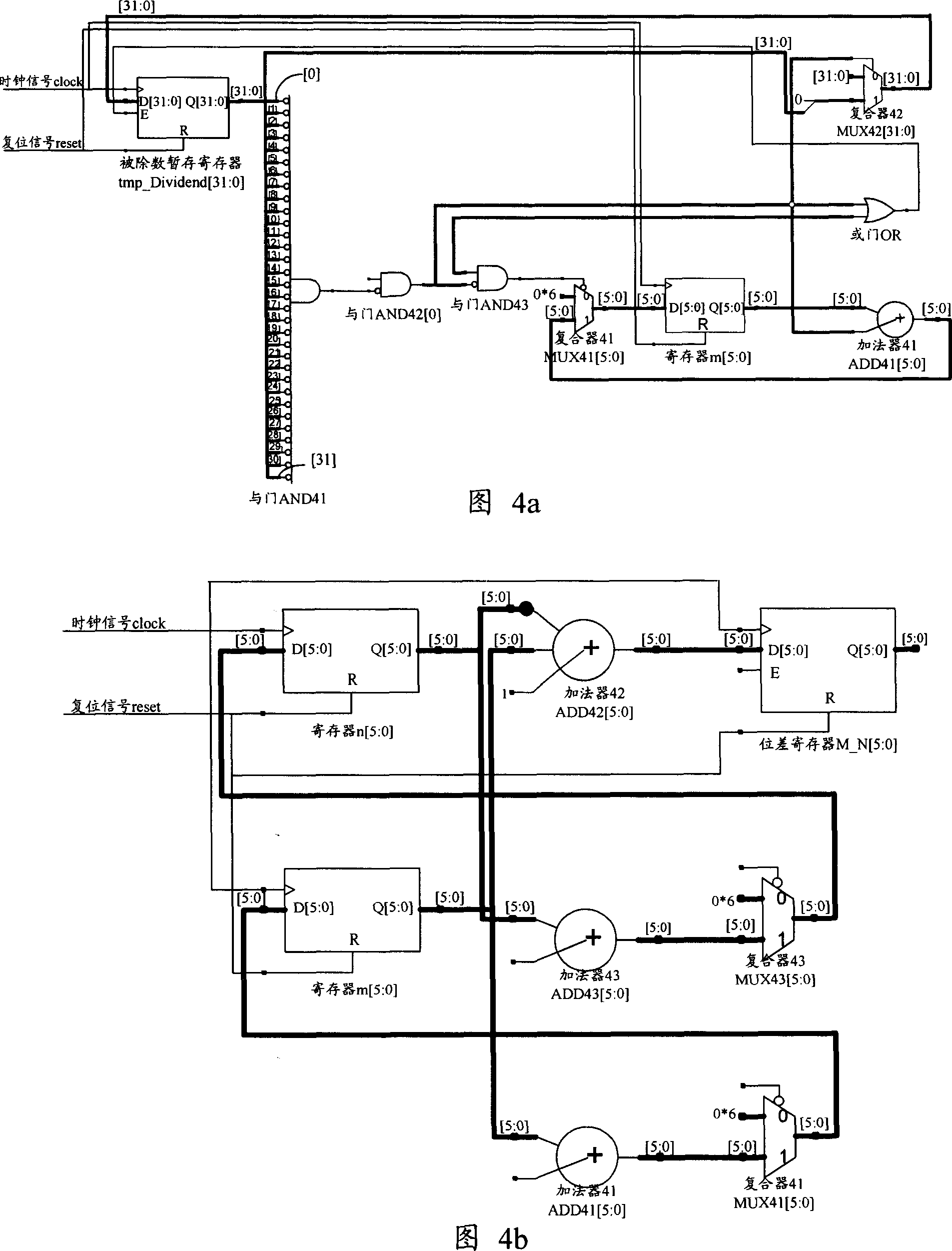
A fixed-point divider and operational method thereof
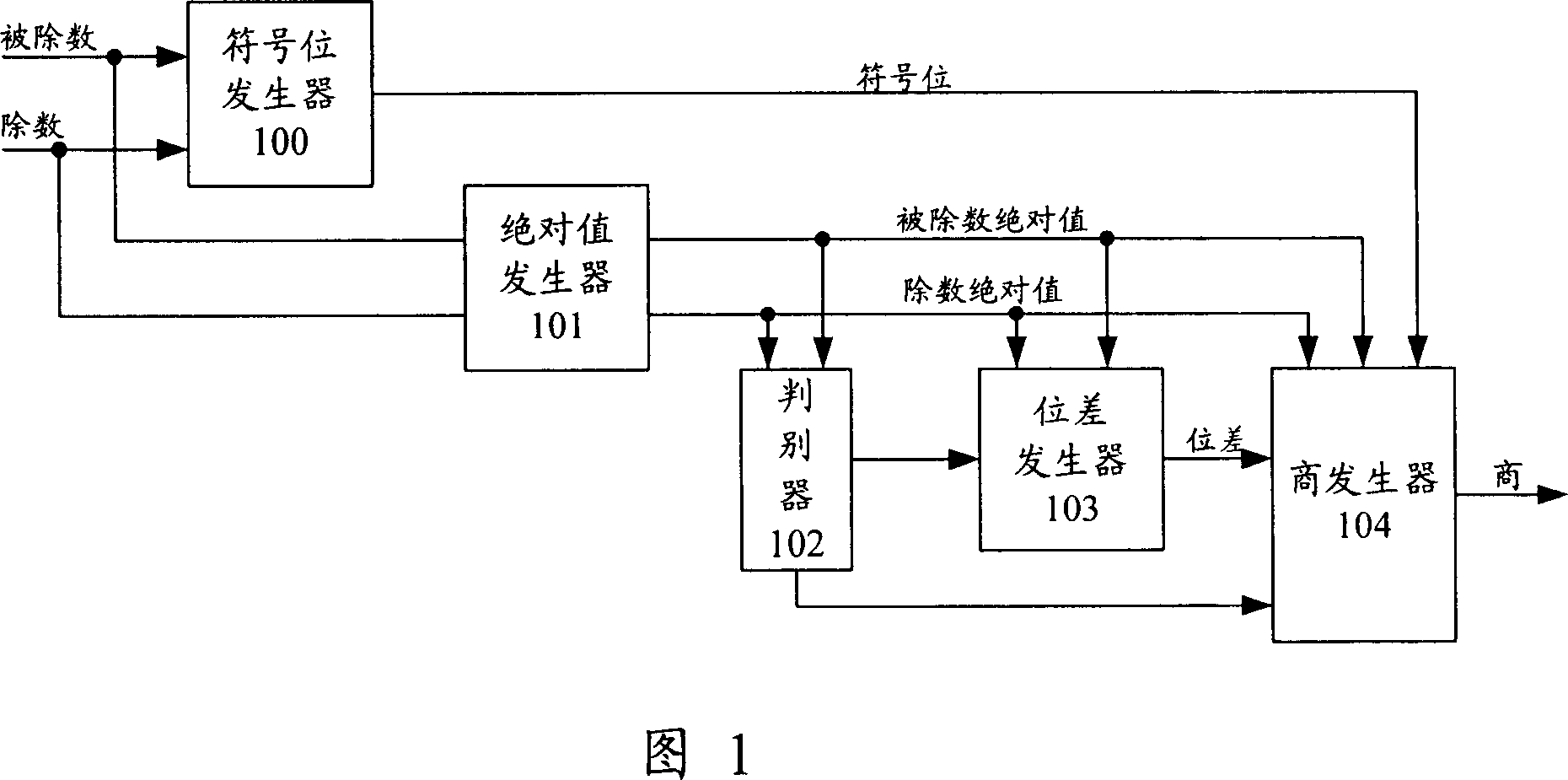
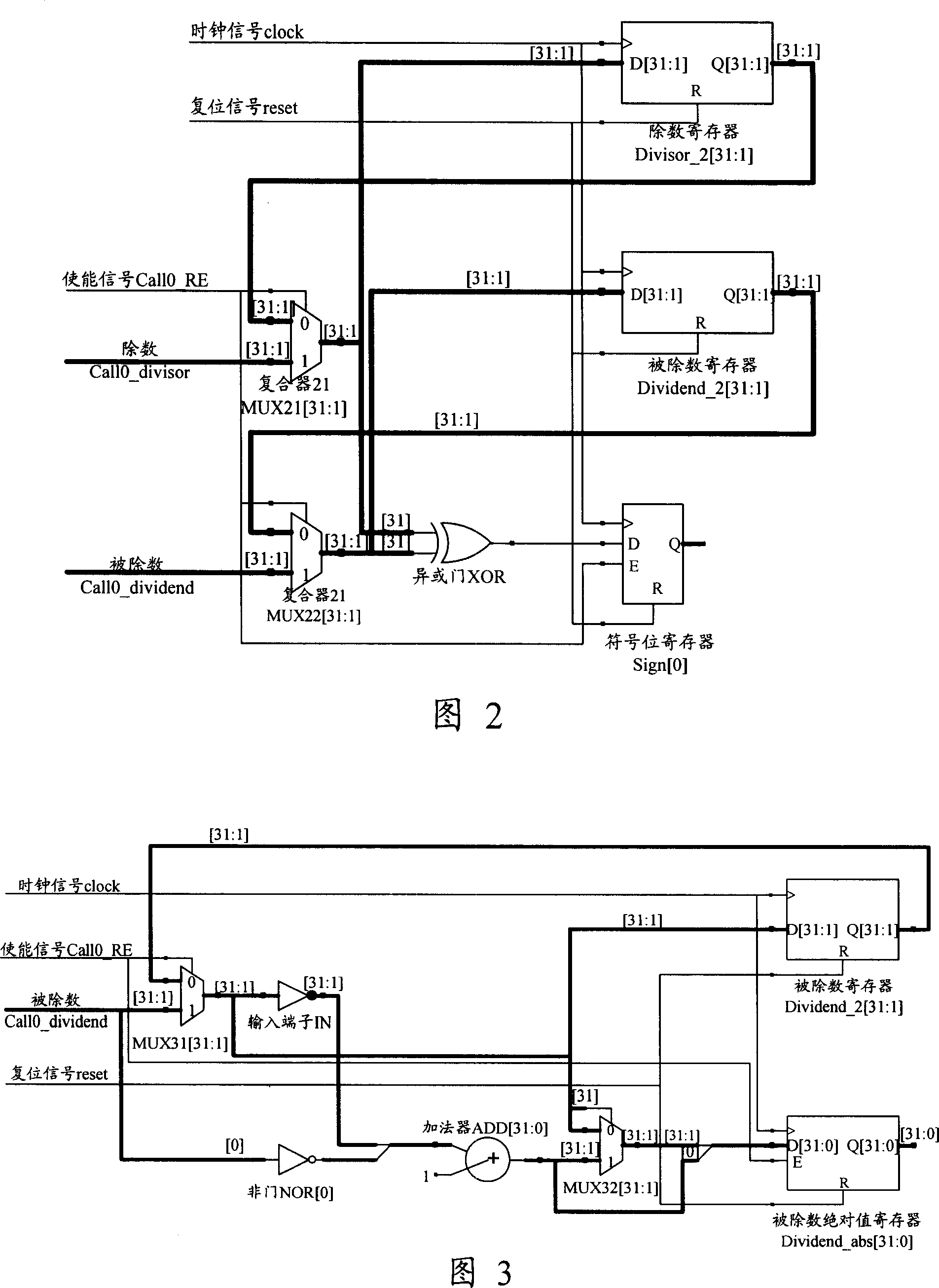
ActiveCN1952875AEasy to implementFewDigital data processing detailsCharacter generatorFixed point computation
This invention discloses a fix point divider, which comprises character generator, absolute generator, judger, difference generator and product generator. This invention also discloses one method of the fix point computation, which comprises the following steps: getting divider and divided absolute value to get product character for memory according to divider and divided; judging whether the divided value is larger or equal to divider absolute; if yes, then computing divided value highest valid bit and that of divider to get the different; getting the divided and divider product according to product bit, absolute value, otherwise output as zero.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
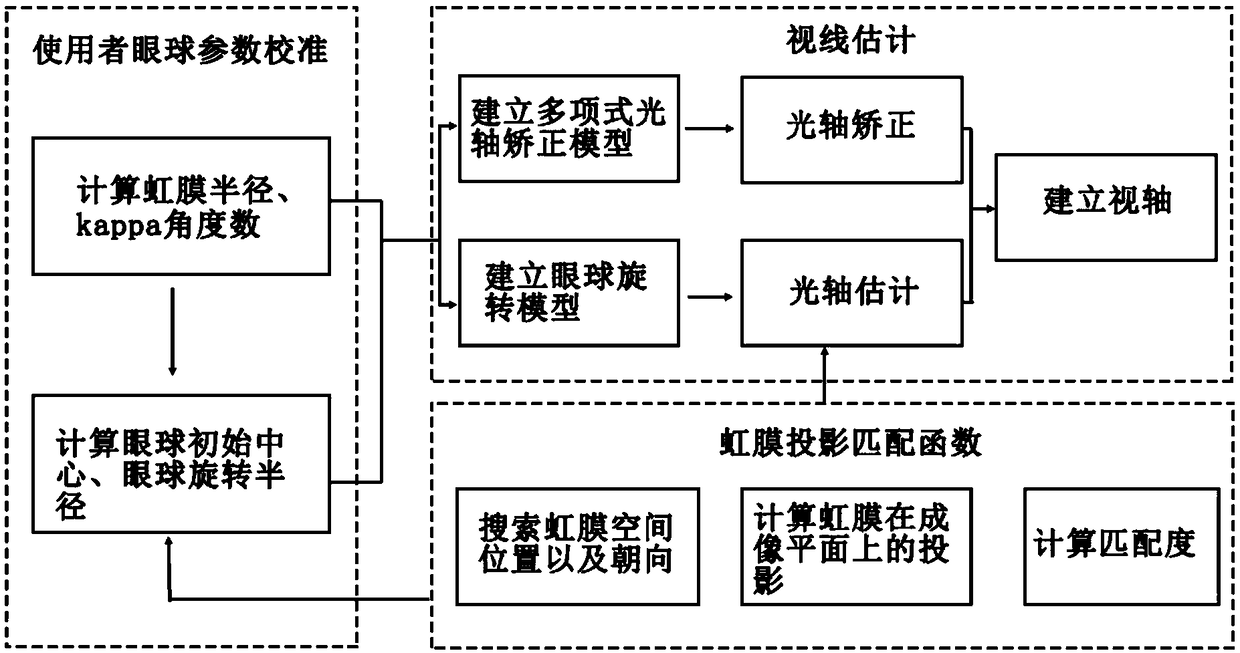
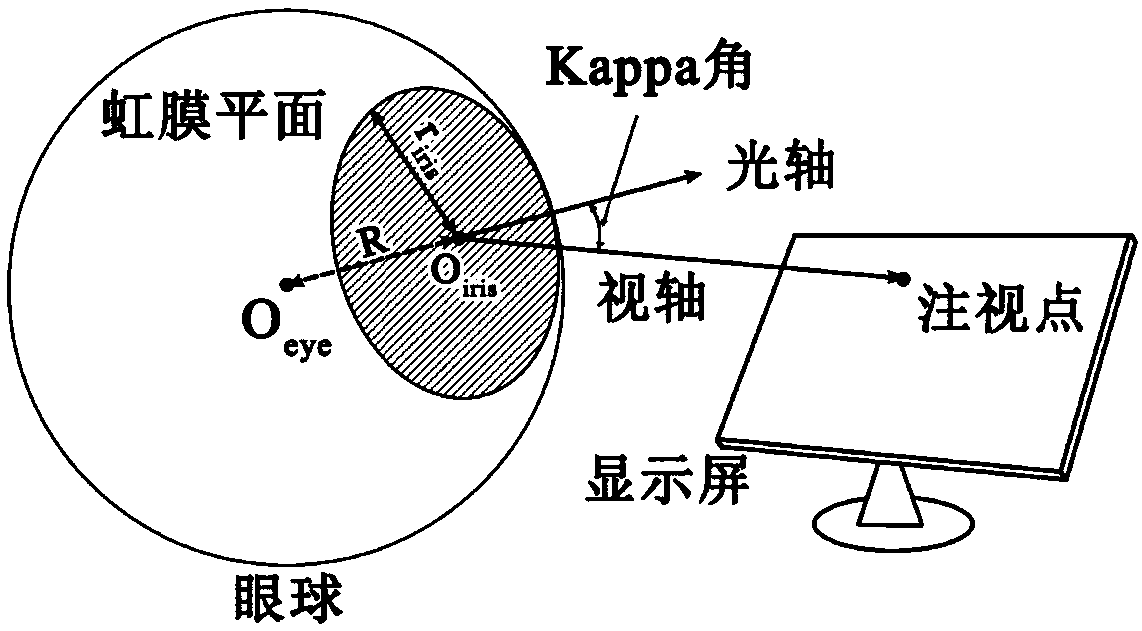
A 3-D line-of-sight estimation method based on iris projection matching function
ActiveCN109308472APrecise positioningHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisHead movementsOptical axis
The invention discloses a three-dimensional line of sight estimation method based on an iris projection matching function. The method firstly calculates human eye parameters and establishes a human eye model by letting a user look at a plurality of standard points on a screen. Then, the spatial position and orientation of the iris are located by the matching function of the eye rotation model andthe iris projection, and the three-dimensional optical axis direction is obtained. Finally, the polynomial correction method is used to correct the optical axis and calculate the direction of the three-dimensional axis of view. This method uses depth camera to estimate 3D line of sight, which provides a fast, accurate and robust solution for 3D line of sight tracking in natural environment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Efficient SAT-based unbounded symbolic model checking
ActiveUS7305637B2Improve performanceReduce stepsComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designFixed point computationQuantifier elimination
Owner:NEC CORP
Use of fixed-point divide in video encode stream control
InactiveCN1855031APulse modulation television signal transmissionComputation using non-contact making devicesENCODEFixed point computation
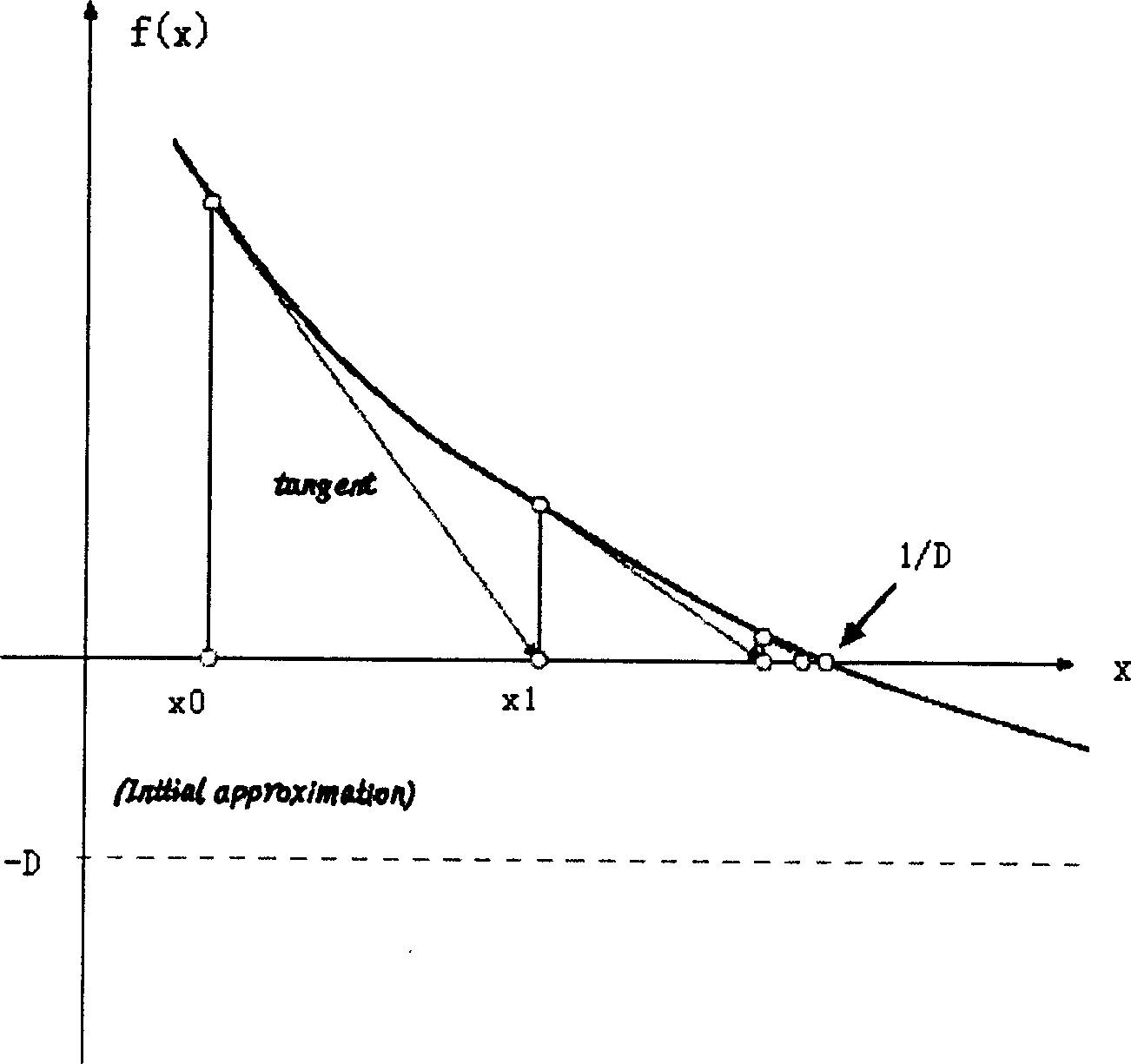
A method for applying division of solving fixed-point number in video code flow rate control uses fixed-point processor to realize fixed-point division by utilizing NEWTON-RAPHSON iteration algorithm of Xi +1=Xi ( 2-DXi ). The method can raise operation speed of division in calculation course maximally under condition that minimum accurate requirement of video compression flow rate control is satisfied.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
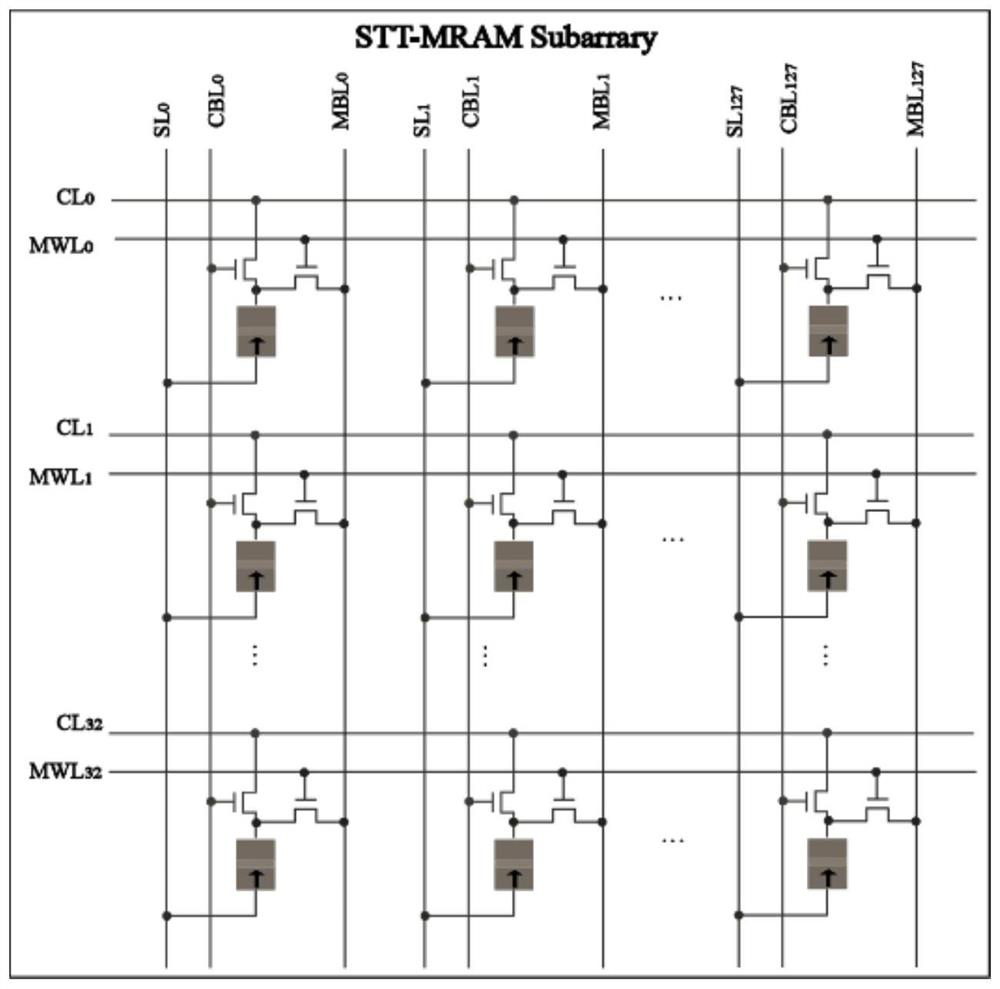
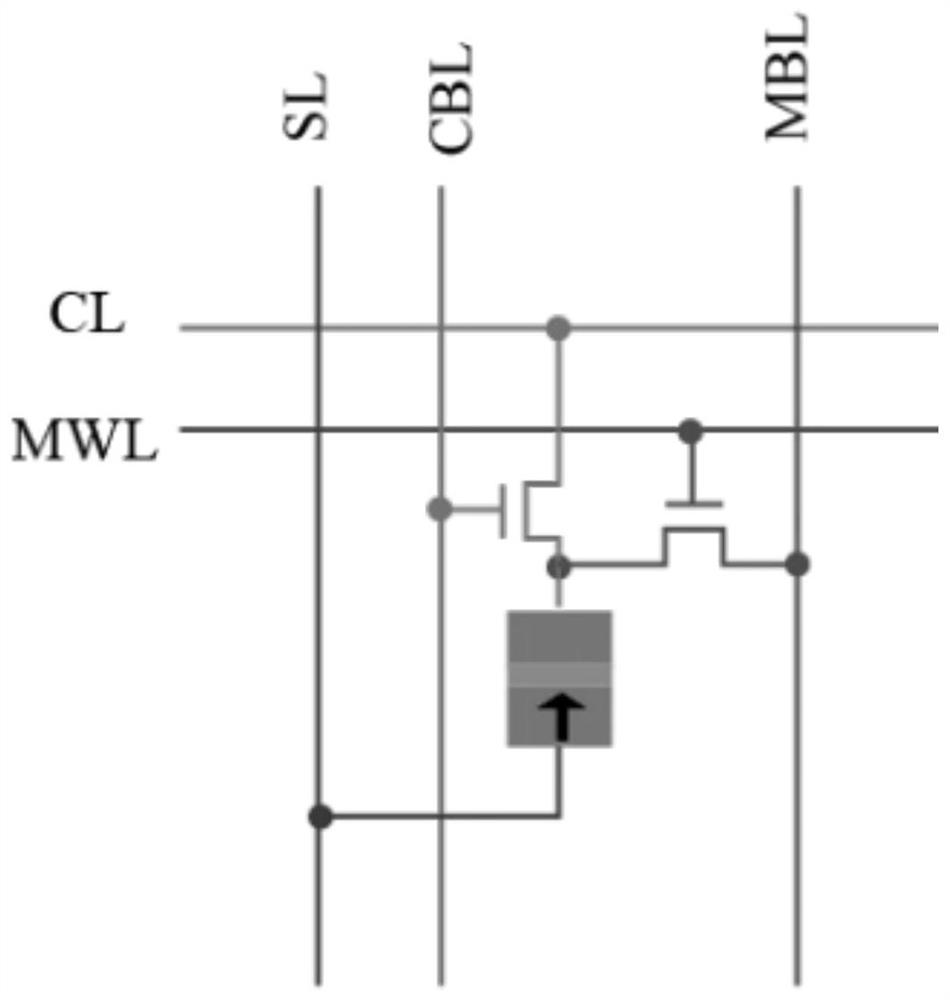
In-memory computing system supporting universal computing based on magnetic random access memory
ActiveCN111798896AImplement storageImprove reconfigurabilityDigital storageBit lineComputer architecture
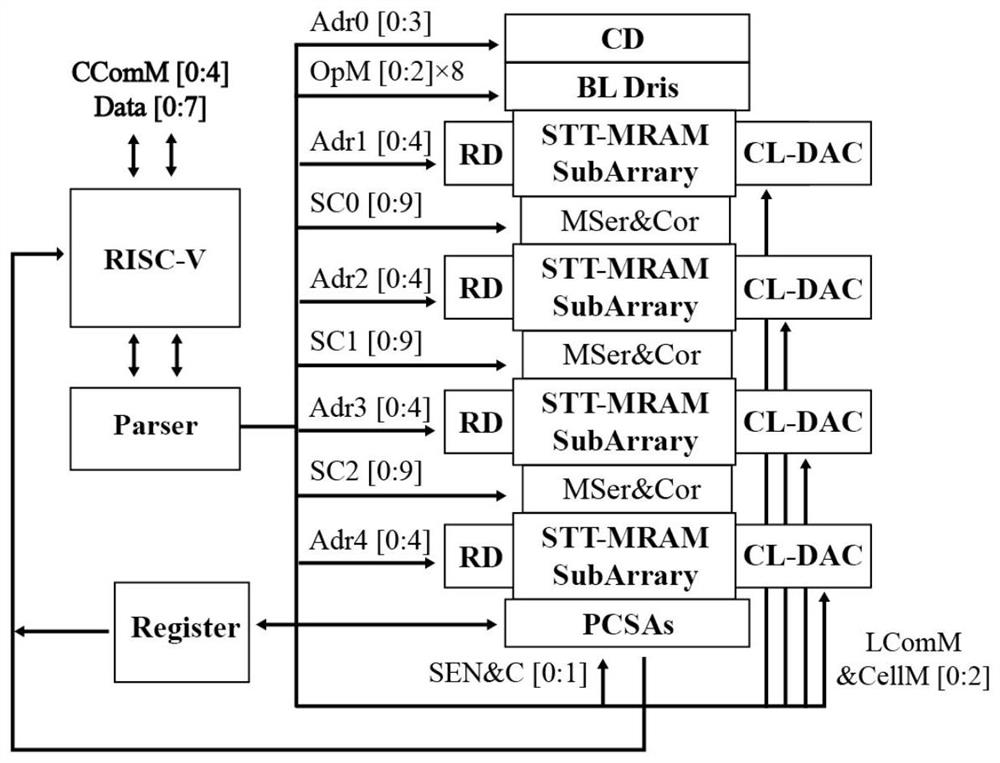
The invention belongs to the field of general in-memory computing, in particular to an in-memory computing system supporting general computing based on a magnetic random access memory. The in-memory computing system comprises a GCIM architecture, and the GCIM architecture comprises a spin transfer torque magnetic random access memory array, a shifter, a connector, a row decoder, a column decoder,a bit line driver, a calculation word line digital-to-analog converter, a pre-charging induction amplifier, a fifth-generation reduced instruction set processor, an instruction parser and a register.According to the invention, storage can be realized in the memory, and calculation operation can be carried out in the memory. Moreover, the method can effectively support general calculation (including logic calculation, fixed-point calculation, floating-point calculation and the like), fully utilizes a plurality of sub-array structures and improved shifters and connectors, improves the reconfigurability and calculation parallelism of the architecture, and improves the calculation efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Acceleration device and method for gene similarity analysis and computer equipment
ActiveCN110990063AImprove the efficiency of similarity analysisImprove analysis resultsConcurrent instruction executionProteomicsFixed point computationProcessing element
The embodiments of the invention provide an acceleration device and method for gene similarity analysis and computer equipment. The acceleration device comprises: a high-speed communication interfacewhich is used for communicating with a host and receiving a to-be-accelerated task distributed by the host; a sequence caching module which is used for caching one or more tasks from a host, wherein each task comprises a plurality of gene sequence data to be subjected to gene similarity analysis; an array processor, which is provided with a processing unit for processing tasks, wherein the processing unit is internally provided with a complete assembly line for processing the tasks based on a data-driven streaming computing mode, and the assembly line is internally provided with a plurality offixed-point computing components required for processing the tasks; a control module, which is configured to be used for distributing the to-be-processed tasks in the sequence caching module to the processing unit; and a task caching module, which is provided with a task caching unit and is used for caching the to-be-processed tasks allocated to the processing unit. With the acceleration device and method in the invention, gene similarity analysis efficiency can be improved, and analysis results can be quickly obtained.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fast correctly-rounding floating-point conversion
ActiveUS20080281890A1Minimize changesTightly bounded computational precisionDigital data processing detailsCode conversionPartition of unityFloating point
A system and method for converting bases of floating point numbers using fixed-point computation includes tables having different related spacings of exponent indices. The tables are adapted to cross-reference conversion ratios between exponent bases. The tables are characterized by bi-uniform spacings of source and target exponents and including near-unity table entries representing the conversion ratios. A source number is converted into a target number in a different radix by a sequence of reduction operations using a sequence of the tables. The reduction operations include reducing a source number exponent magnitude and accumulating a target exponent and multiplying a source number mantissa by a selected conversion ratio including a near-unity ratio of powers. A final mantissa is normalized and rounded to produce the target number in a new radix.
Owner:IBM CORP
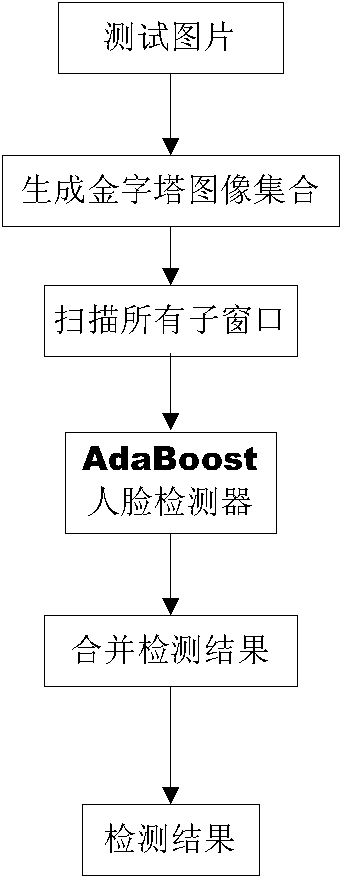
Fixed-point type human face detection method
ActiveCN102779265AEfficient separationHigh speedCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionFace detection
The invention discloses a fixed-point type human face detection method. According to the method, fixed-point number conversion can be realized for parameters of a relevant training floating-point model of a waterfall cascaded classifier in an AdaBoost human face detection algorithm, and fixed-point calculation and conversion can be performed on a relevant floating-point calculation process. The method specifically comprises the steps of: (1) effective separation of relevant parameters of a strong classifier from relevant parameters of a weak classifier from the calibration perspective according to classified calculation characteristics of the strong classifier and the weak classifier in the waterfall cascaded classifier; (2) conversion of the floating-point number of the parameter theta into the fixed-point number, calculation of Harr features and fixed-point calculation of integral image calculation according to the classified calculation characteristics of the weak classifier; (3) conversion of the floating-point number of at and a_th in the strong classifier into the fixed-point number according to the classified calculation characteristics of the strong classifier and parameter definitions; and (4) conversion of floating-point calculation of the AdaBoost human face detection algorithm into fixed-point calculation.
Owner:BEIJING HANBANG GAOKE DIGITAL TECH
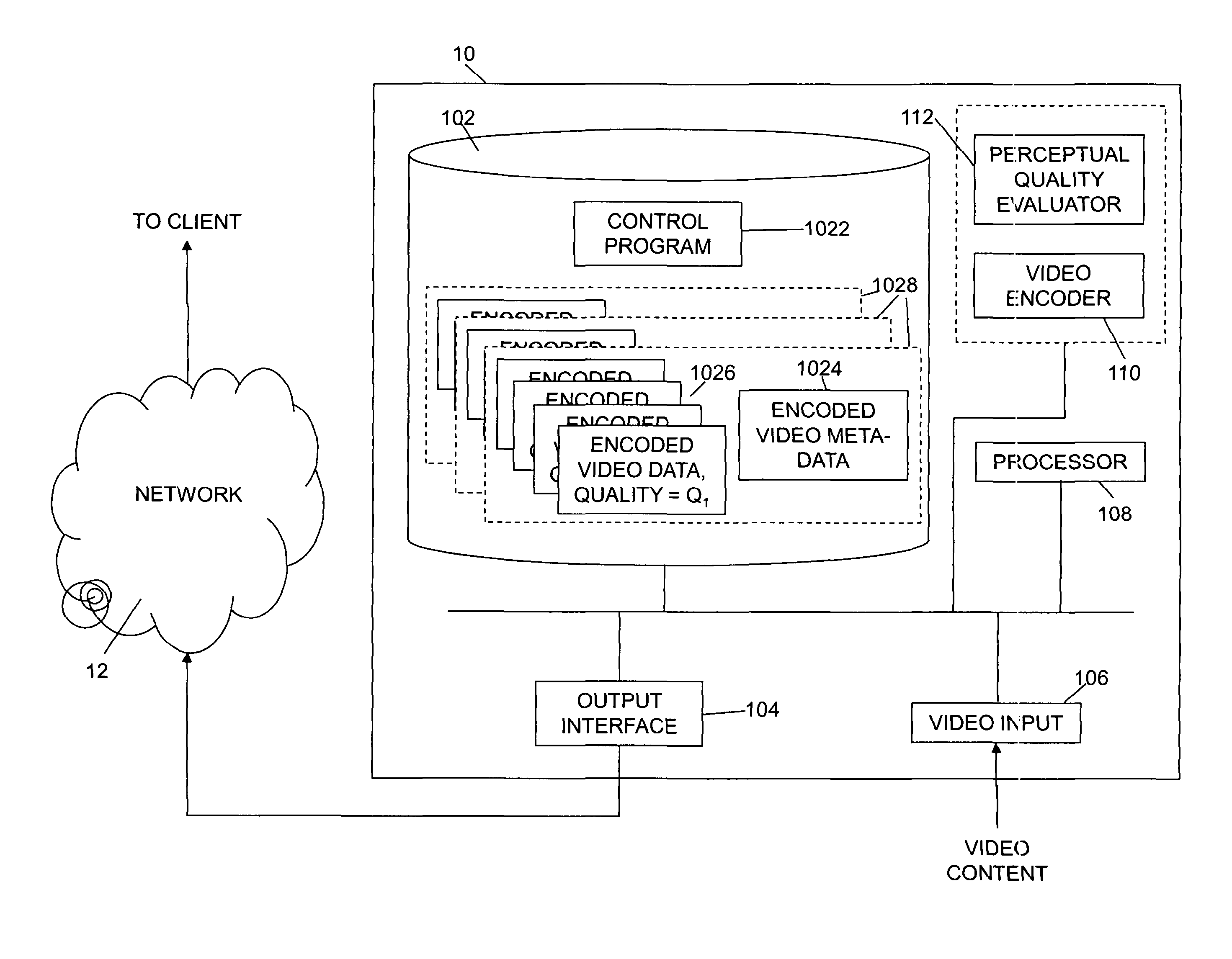
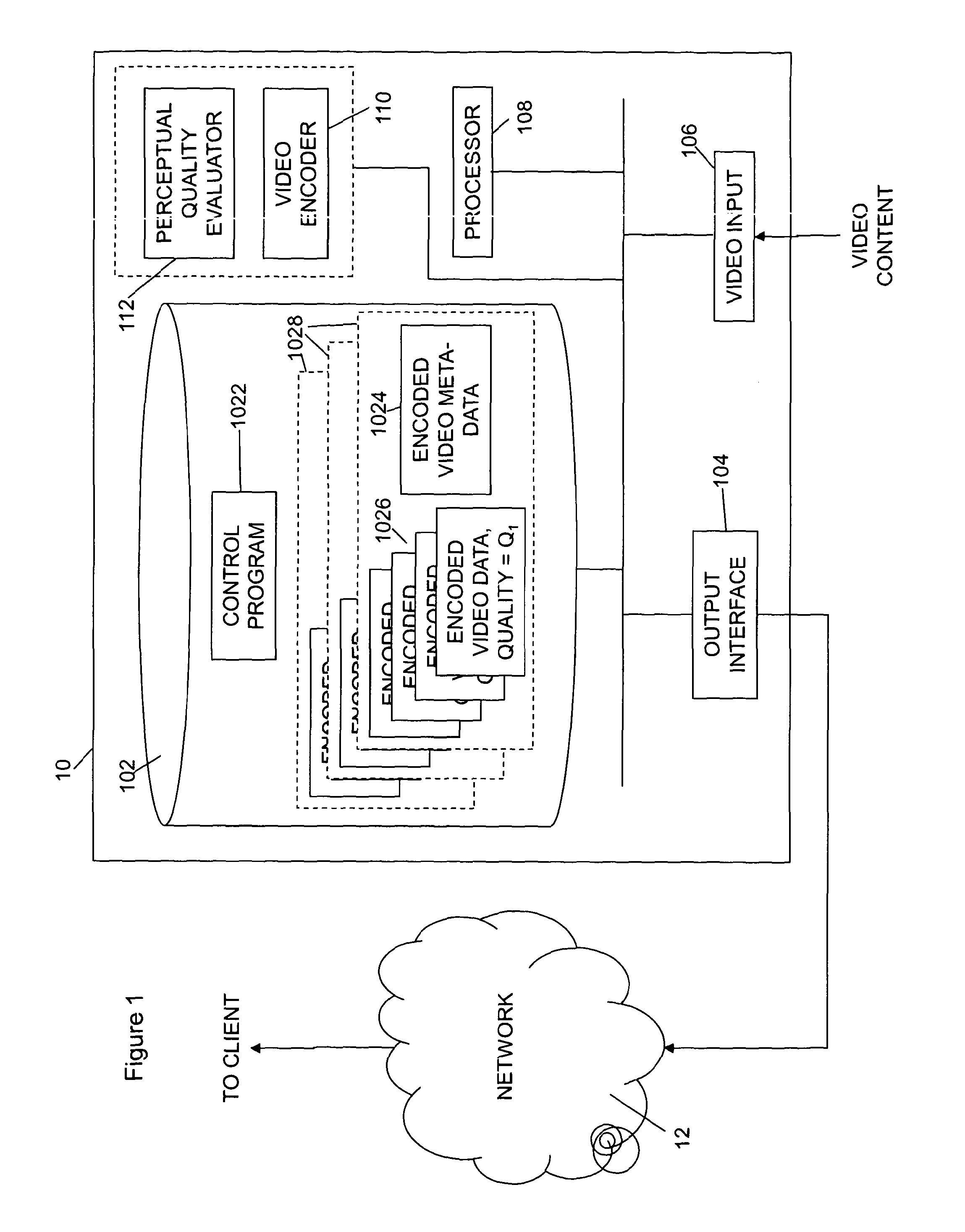
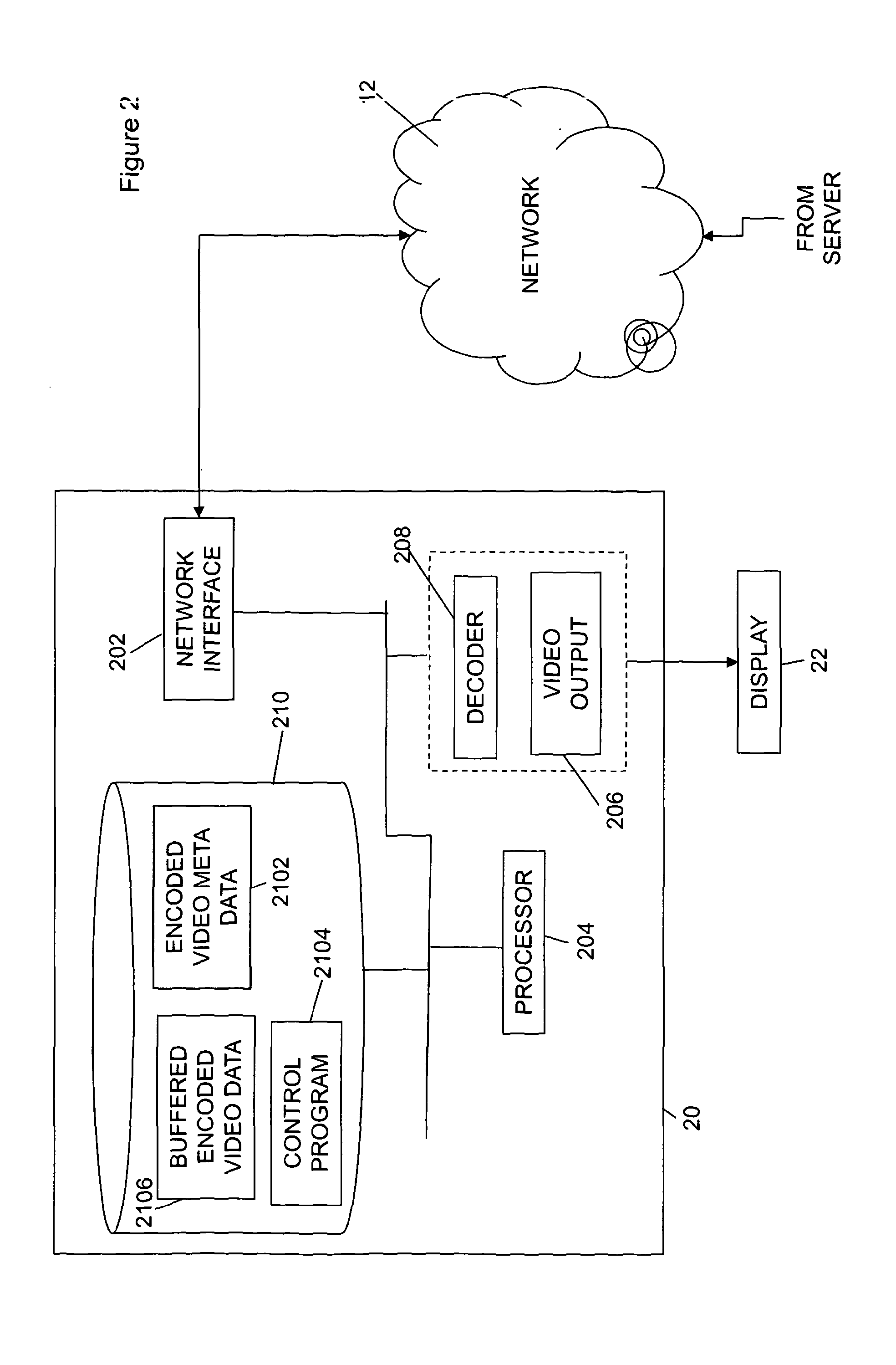
Video streaming over data networks
ActiveUS20130297818A1Multiple digital computer combinationsDigital video signal modificationTime scheduleQuality level
A client device receives streamed encoded content data, such as encoded video data, which has been encoded at a constant perceptual quality. Several different versions of the content are available to be streamed to the device, at different perceptual quality levels. In order to decide which quality level to request from a content server at intervals the device calculates the delivery rates that would be required for each level of quality. The delivery rates are calculated in dependence on so-called critical points, which are points at which a piecewise constant bit rate delivery schedule is just equal to the decoding schedule. There are two classes of critical points, being a first class of critical points, referred to herein as “additional critical points”, which are points on the decoding schedule where, for any particular other point on the decoding schedule before an additional critical point, and assuming that a minimum threshold amount of data is buffered when delivery occurs from the particular point, a constant bit rate delivery schedule that is calculated for the particular point taking into account the buffered minimum amount of data and of such a rate such that buffer underflow does not occur is substantially equal to the decoding schedule. A second class of critical points, referred to herein as “downstairs critical points”, is also defined, which are derived from the decoding schedule as a whole, and which are the points at which a piecewise monotonically decreasing constant bit rate delivery schedule (the so-called “downstairs” schedule), which is calculated such that when delivering the encoded content data from the start buffer underflow does not occur, is substantially equal to the decoding schedule of the encoded content data. When the actual delivery rate received is ahead of the so-called “downstairs” schedule, then the delivery rate required for a particular quality level can be calculated from the second class of critical points. However, when the actual delivery rate received is behind the downstairs schedule, then the delivery rate required is calculated from the first class of critical points.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Method for color space conversion from HSL to RGB
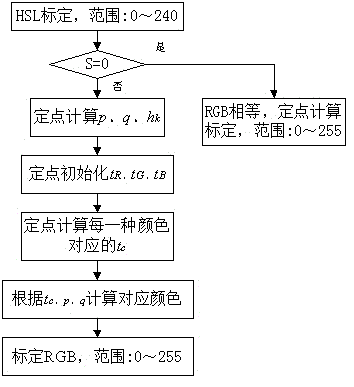
InactiveCN103561252AImprove efficiencyLow costColor signal processing circuitsMicrocomputer system16-bit
The invention discloses a method for color space conversion from HSL to RGB. The method includes the steps that standardization is carried out on the HSL, and the scope ranges from 0 to 240; if S equals to zero, the R, G and B are equal, fixed-point calculation standardization is carried out, and the scope of the RGB ranges from 0 to 255; if the S is not equal to zero, fixed-point calculation is carried out on p, q and hk; fixed-point initialization is carried out on t R, t G and t B; the fixed-point calculation is carried out on tc corresponding to each color; the corresponding colors are calculated according to the tc, the p and the q; standardization is carried out on the RGB, and the scope of the RGB ranges from 0 to 255. The method has the advantages that fixed-pointed processing is adopted, the method can be used in embedded 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit single-chip microcomputer systems and X86 systems, so the application scope is broadened greatly; some applications can be achieved on the single-chip microcomputers, so the system cost is reduced greatly; in addition, the efficiency of the floating point arithmetic mode is also improved.
Owner:无锡硅奥科技有限公司
Non-2-radix DFT optimized signal processing method
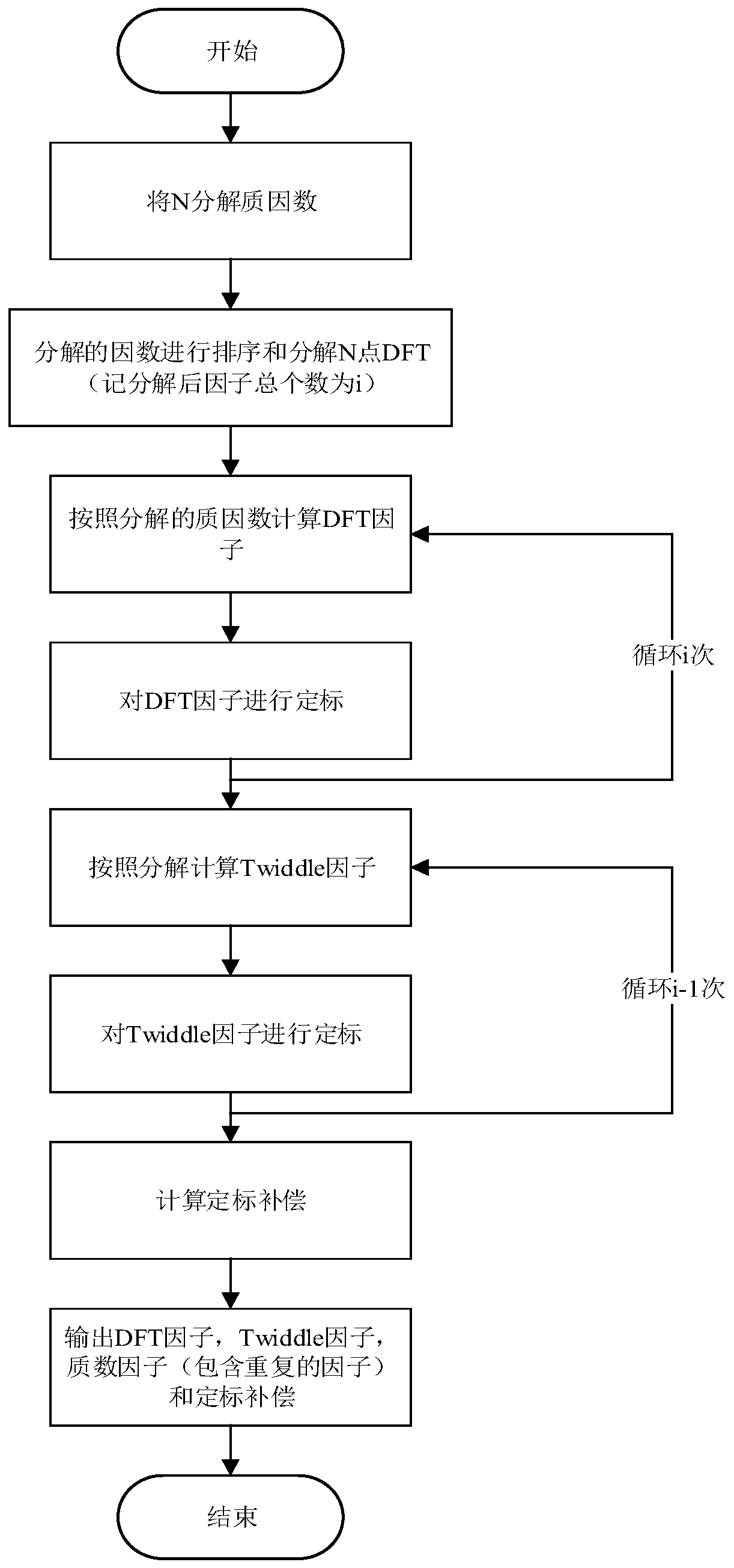
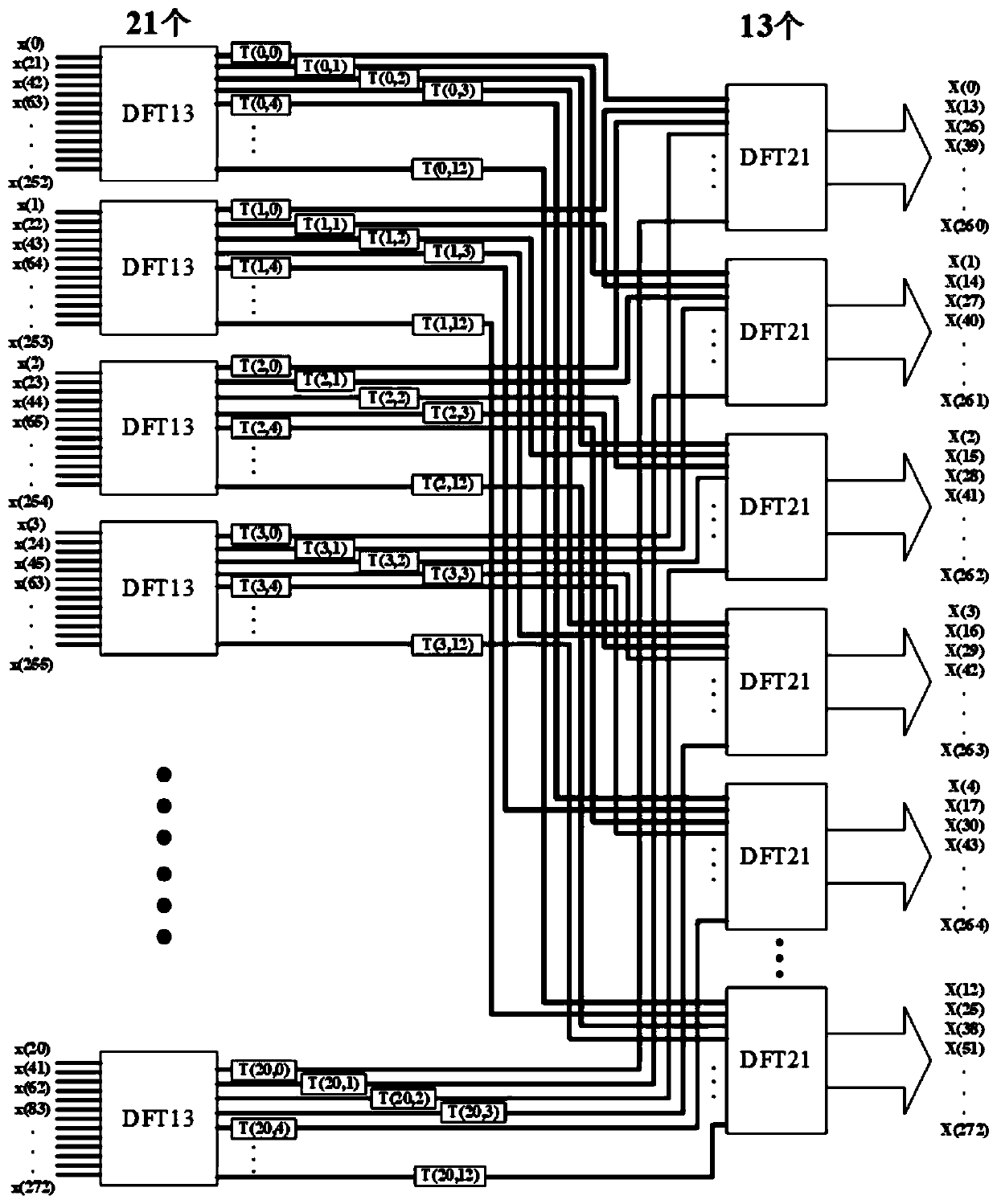
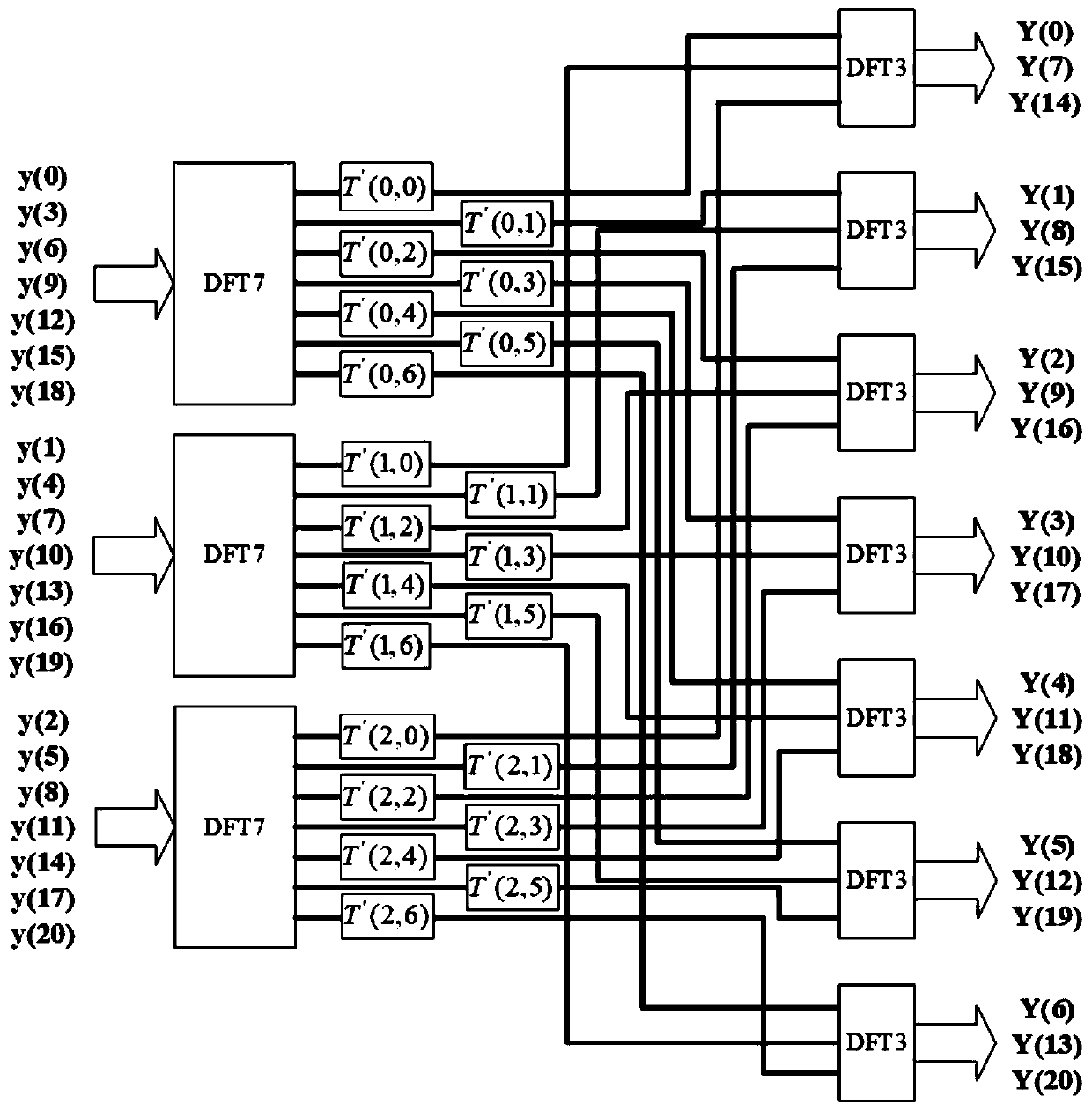
ActiveCN111079075AReduce difficultyGuaranteed accuracyComplex mathematical operationsDigital signal processingAlgorithm
The invention belongs to the field of digital signal processing, and relates to optimization that is carried out on the basis of a Cooley-Tukey algorithm of the non-2-radix DFT; the invention discloses a non-2-radix DFT (Discrete Fourier Transform) optimized signal processing method, which comprises the following steps: optimizing the decomposition of a quality factor of a Cooley-Tukey algorithm,decomposing N-point DFT according to the decomposition of the quality factor, and processing a signal by utilizing the Cooley-Tukey algorithm on said basis. According to the method, the reliability ofsignal processing and the accuracy of fixed-point calculation processing are improved, and the signal processing difficulty of fixed-point non-2-radix N-point DFT is reduced.
Owner:PURPLE MOUNTAIN LAB
Reduction of errors during computation of inverse discrete cosine transform
ActiveCN102016829AReduce visual errorReduce audible errorsPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationFixed point computationFixed-point arithmetic
Techniques are described to reduce rounding errors during computation of discrete cosine transform using fixed-point calculations. According to these techniques, an inverse discrete cosine transform a vector of coefficients is calculated using a series of butterfly structure operations on fixed-point numbers. Next, a midpoint bias value and a supplemental bias value are added to a DC coefficient of the matrix of scaled coefficients. Next, an inverse discrete cosine transform is applied to the resulting matrix of scaled coefficients. Values in the resulting matrix are then right-shifted in order to derive a matrix of pixel component values. As described herein, the addition of the supplemental bias value to the DC coefficient reduces rounding errors attributable to this right-shifting. As a result, a final version of a digital media file decompressed using these techniques may more closely resemble an original version of a digital media file.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
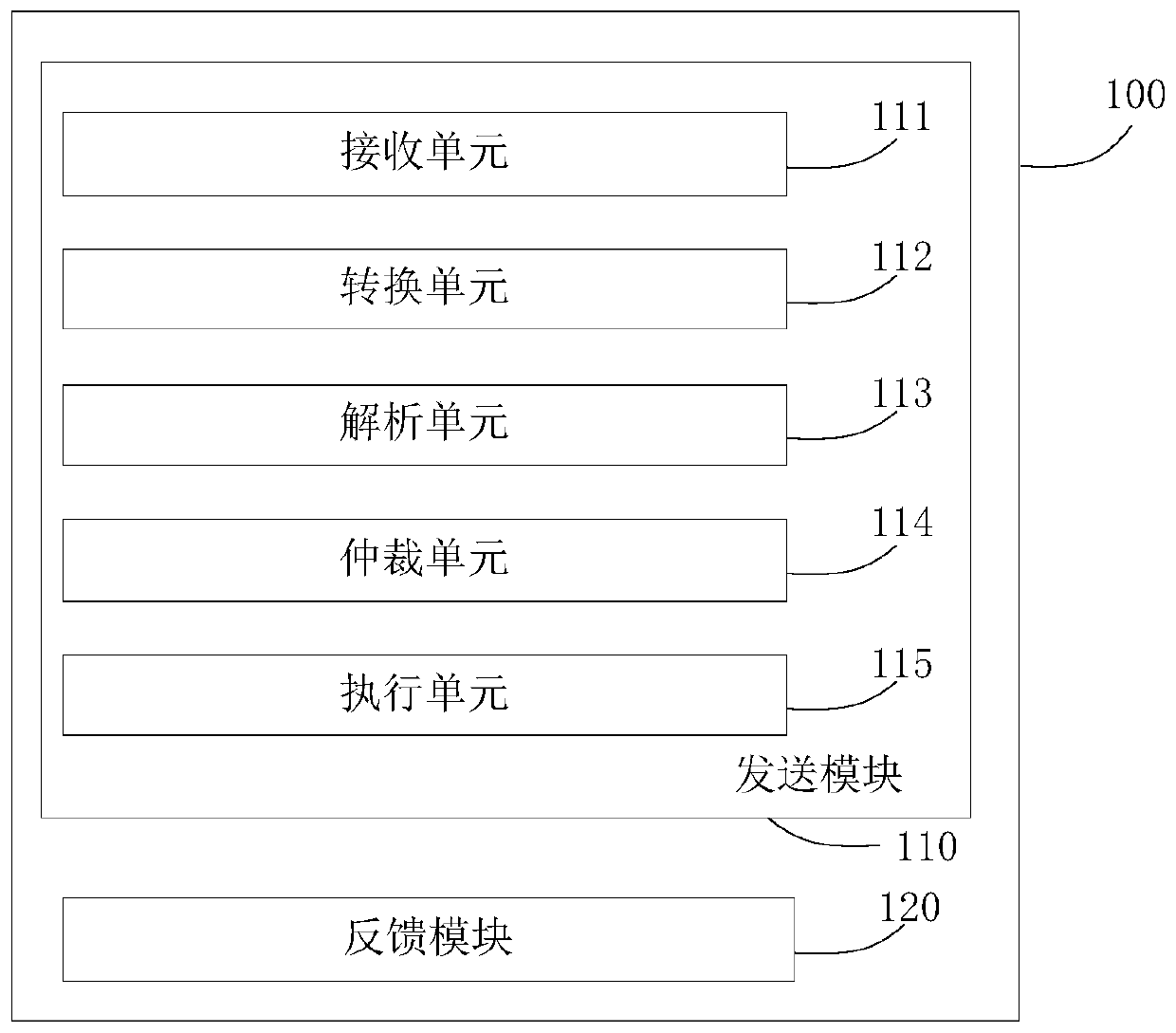
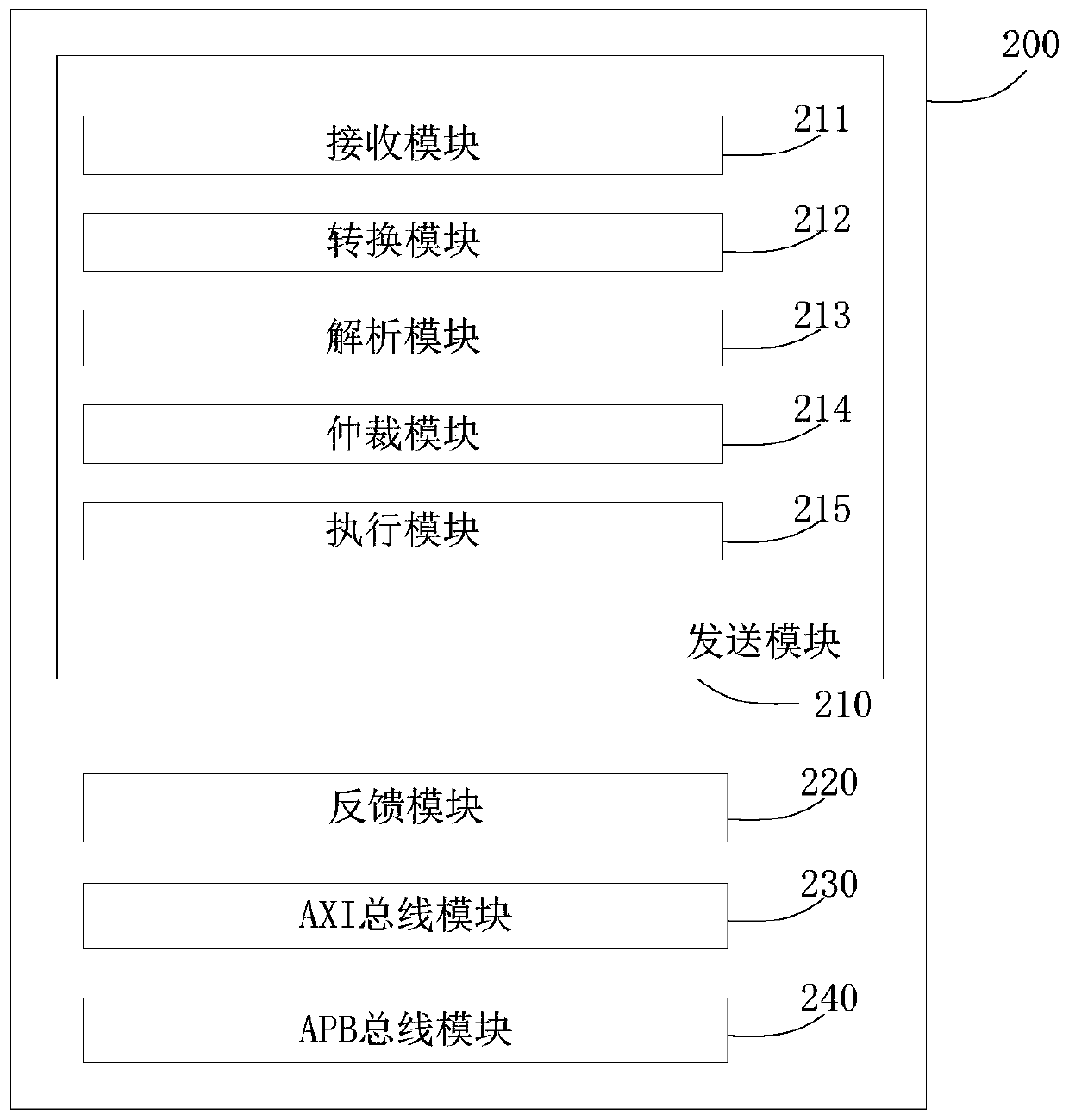
Neural network interaction system and method based on AXI-APB, server and storage medium
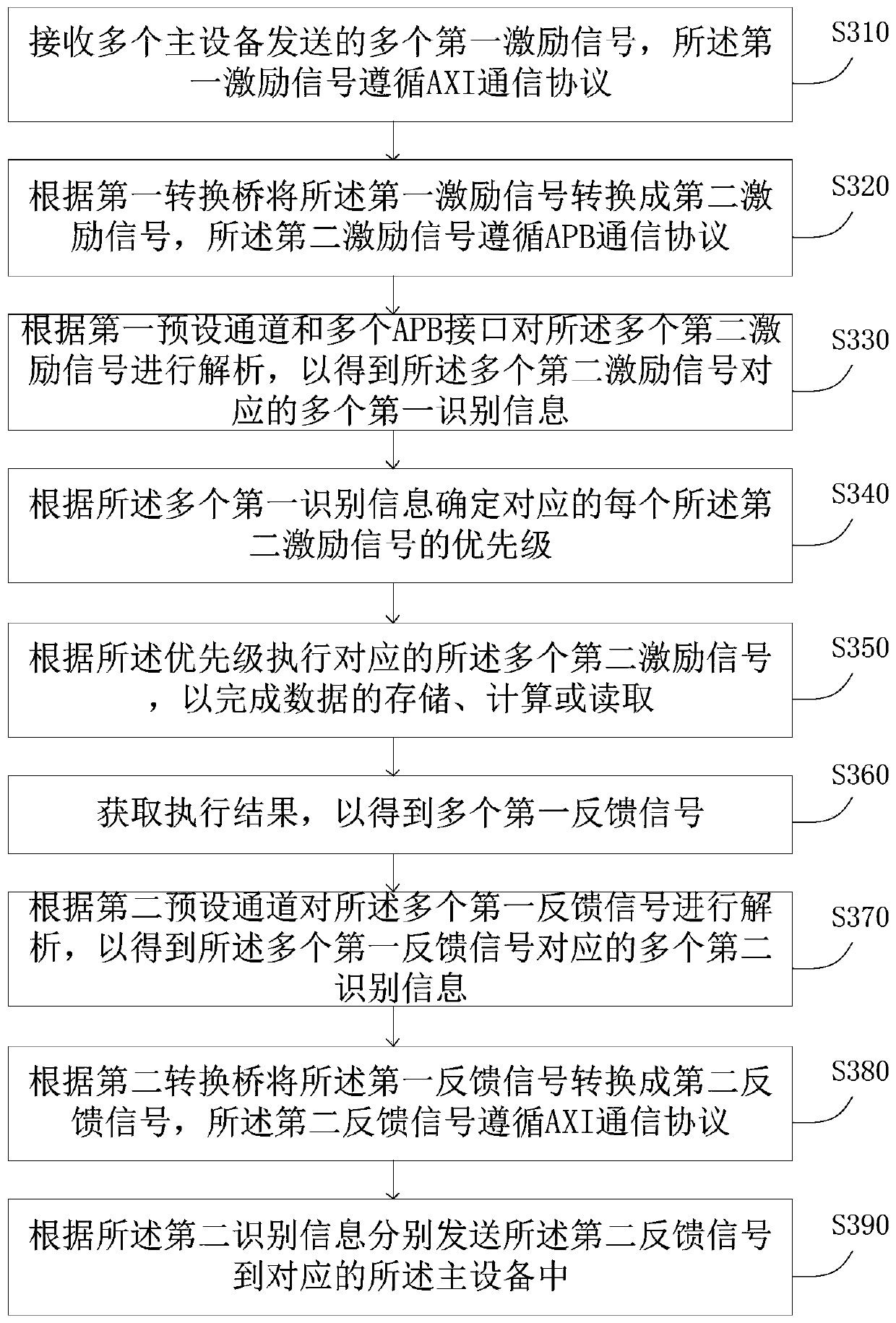
The invention discloses a neural network interaction system and method based on AXI-APB, a server and a storage medium, and the system comprises the following parts: a receiving unit which is used forreceiving a plurality of first excitation signals transmitted by a plurality of pieces of main equipment; a conversion unit that is used for converting the first excitation signal into a second excitation signal according to the first conversion bridge; an analysis unit that is used for analyzing the plurality of second excitation signals according to a first preset channel and the plurality of APB interfaces so as to obtain a plurality of pieces of first identification information corresponding to the plurality of second excitation signals; an arbitration unit that is used for determining the priority of each corresponding second excitation signal according to the plurality of pieces of first identification information; an execution unit that is used for executing a plurality of corresponding second excitation signals according to the priorities; and a feedback module that is used for feeding back the execution result to the corresponding main equipment. According to the invention, through AXI-APB conversion, a plurality of AXI master devices are supported to access one APB slave device through a fixed-point computing rotation training arbitration method, and clock domain crossing and high-frequency requirements are flexibly met according to actual requirements.
Owner:SHENZHEN CORERAIN TECH CO LTD
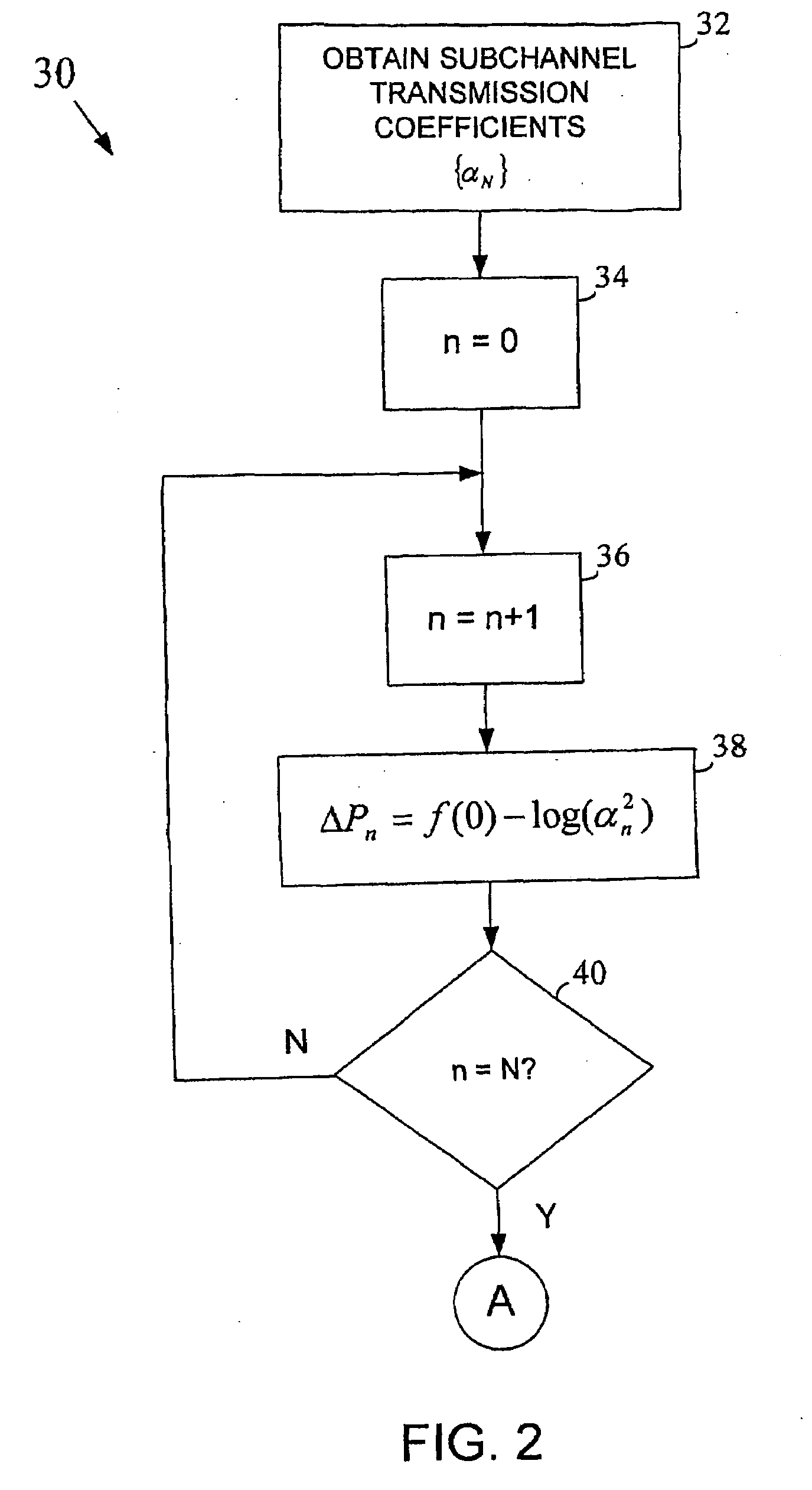
Method and apparatus for performing bit loading in a multicarrier system
InactiveUS20090110086A1Secret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsComputer hardwareCommunications system
Bit loading is performed in a multicarrier communication system in an efficient and computationally simple manner. In at least one embodiment, bit loading techniques are used that allow bit loading to be performed using fixed point computation. A bit loading cost function may be used that is calculated as the difference between two other functions. In one approach, the two other functions may be implemented as lookup tables. Bits may be allocated to subchannels having a lowest cost.
Owner:INTEL CORP
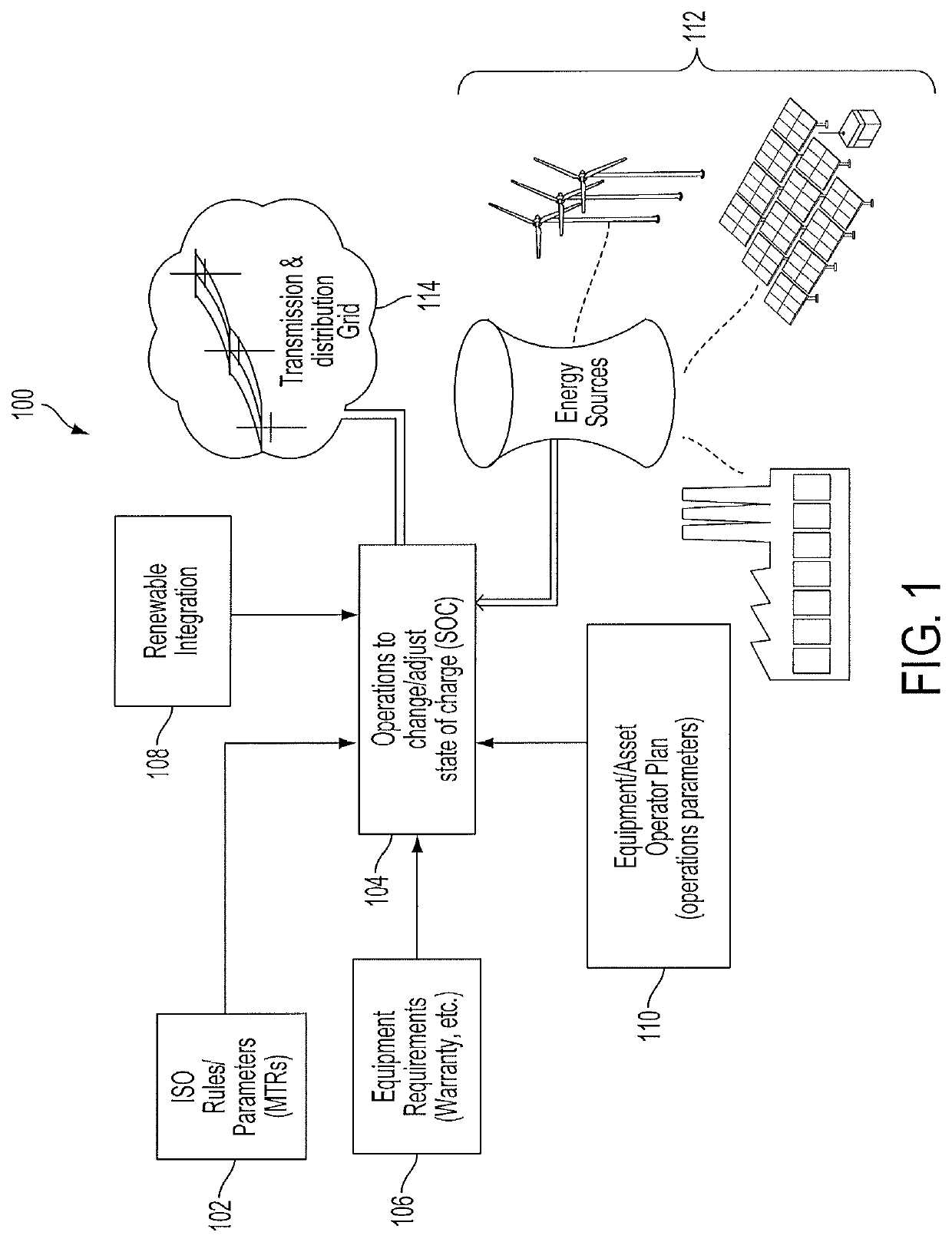
Method and system for performance management of an energy storage device
ActiveUS10886742B2Single network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageFixed point computationAlgorithm Selection
Approaches for managing and maintaining a state of charge of an energy storage device by adjusting (biasing) responses to electrical grid operator commands to perform ancillary services are disclosed. In embodiments, methods and systems regulate a set point regulation in an energy system. In an embodiment, a method determines when the set point needs to be changed, calculates a new set point, and moves the output of the system from an old set point to the new set point at a defined ramp rate. The method then incorporates, as part of a set point algorithm, the capability to restore the energy storage device to a desirable state of charge (SOC). Embodiments implement Dynamic Bias, SOC and Signal Bias Range Maintaining, Operational Limits, and Fixed Signal Bias algorithms and perform Intelligent Algorithm Selection to manage and maintain the SOC of an energy storage device by biasing responses to grid operator commands.
Owner:FLUENCE ENERGY LLC
Safe floating point operation method and system
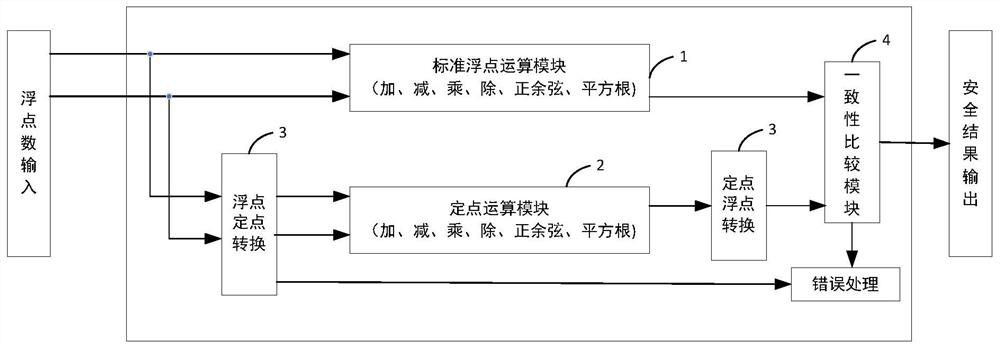
PendingCN113778373AEnsure safetyReduce consumptionDigital data processing detailsCode conversionResource consumptionFixed point computation
The invention relates to a safe floating point calculation method, which adopts two different calculation methods, namely a hard floating point calculation method and a fixed point calculation method, to carry out calculation, and carries out difference comparison on a hard floating point calculation result and a fixed point calculation result so as to ensure the safety of a floating point calculation function. According to the invention, system floating point operation safety is ensured, operation resource consumption is low, and efficiency is high.
Owner:CASCO SIGNAL
Method for automatically restoring a calibrated state of a projection system
ActiveUS11284052B2Simple and error-free alignmentProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
Method for automatically restoring a calibrated state of a projection system, allowing simple and error-free alignment of a projection system in an original error-free state of the system. A calibrated state of a projection system is automatically restored by calculating a position and orientation of at least one camera within the projection system, using fixed points, subsequently m times n markers (9′) are projected onto the projection area, using the markers by cameras to determine a reduced number, compared with the calibration, of second measurement points (QI′) that have one X, Y and Z coordinate each, the reduced number of second measurement points (QI′) is used to perform a calculation of the differences between the second measurement points (QI′) and the associated first measurement points (QI′), a displacement vector is formed, the association between the projector coordinates and 3D coordinates is adapted with the displacement vector.
Owner:DOMEPROJECTION COM GMBH
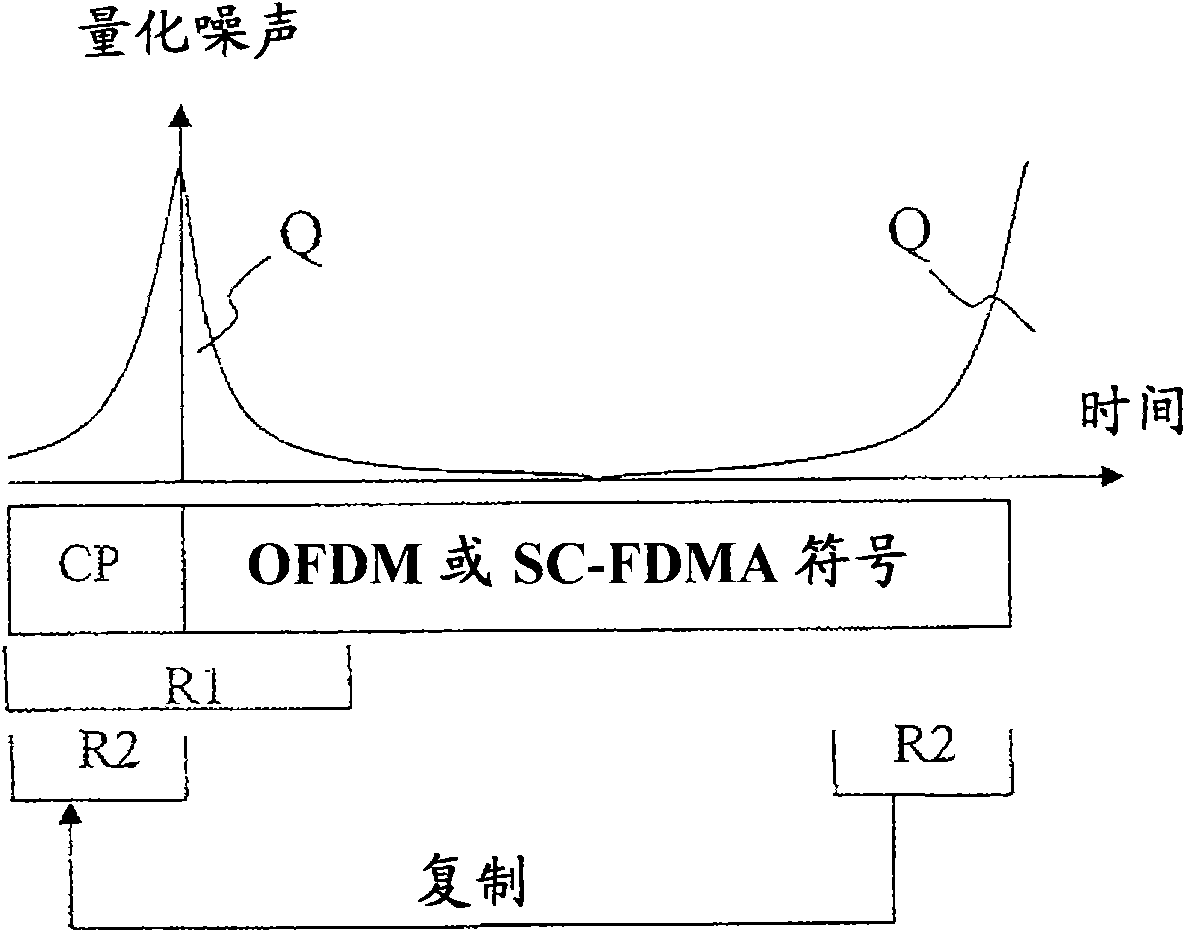
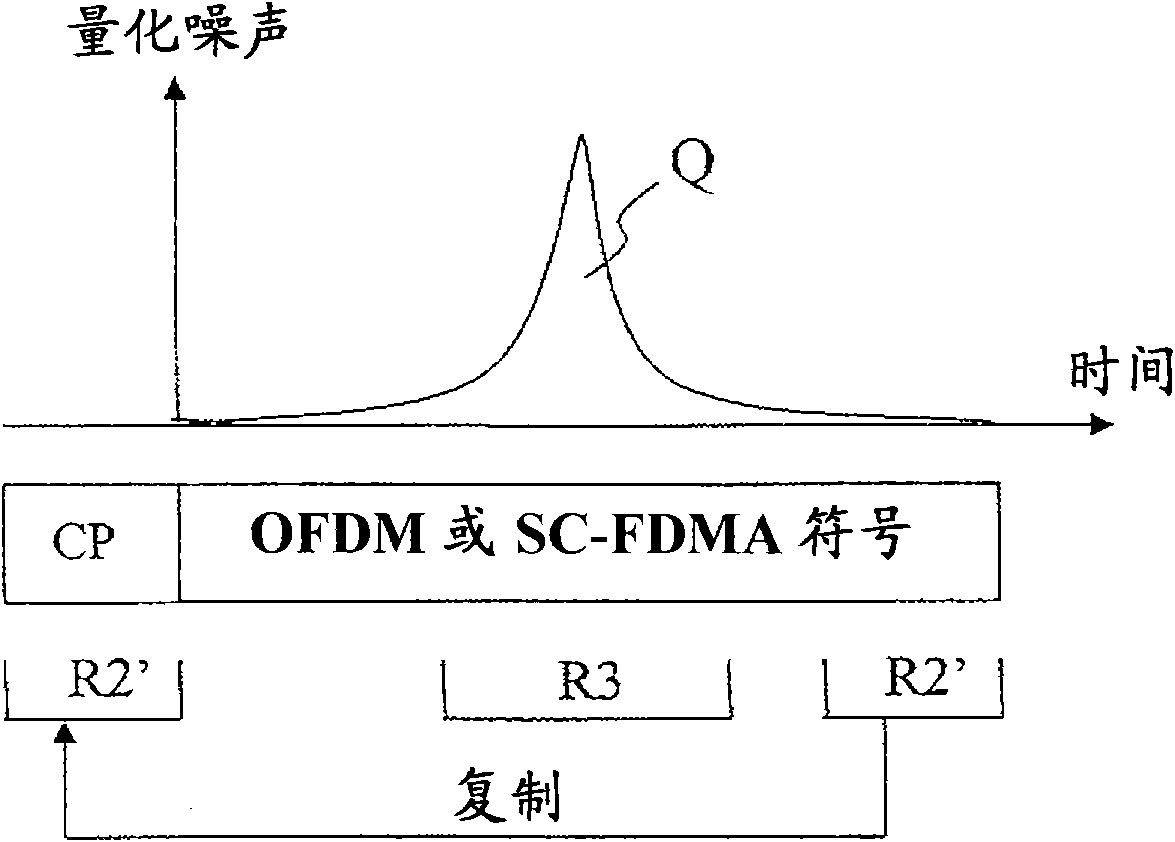
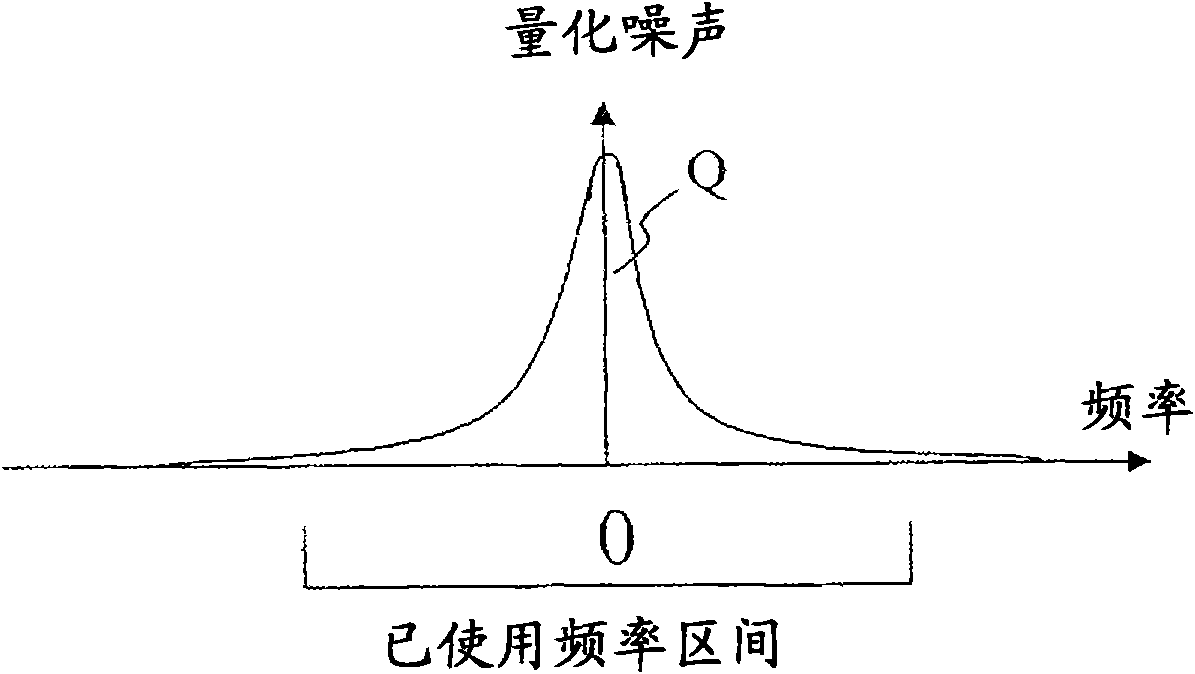
Method for moving quantization noise introduced in fixed-point calculation of fast fourier transforms
ActiveCN102037696AHandling data according to predetermined rulesMulti-frequency code systemsElectronic communicationFourier transform on finite groups
The invention discloses a method in an electronic communication device for processing a digital signal within a wireless communication network in order to transform the digital signal from a first domain representation to a second domain representation in a communication device, comprising the steps of: transforming (86, 98) the signal from the first domain to the second domain resulting in a signal of a first order of values with quantization noise in at least one area of the second domain, and performing (88, 100) a cyclic shift on the transformed signal to move the quantization noise in the second domain, resulting in a first shifted signal.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
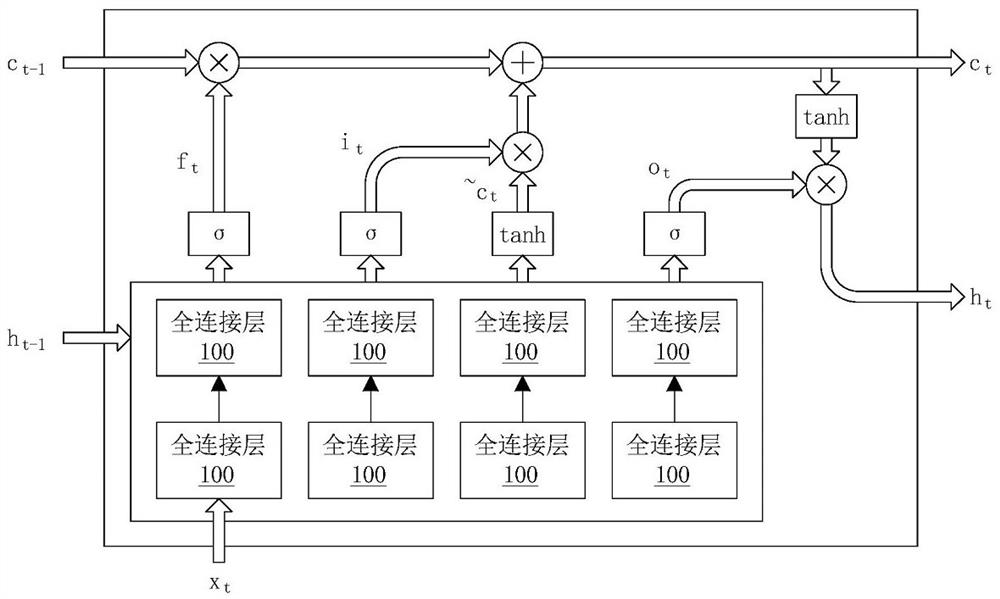
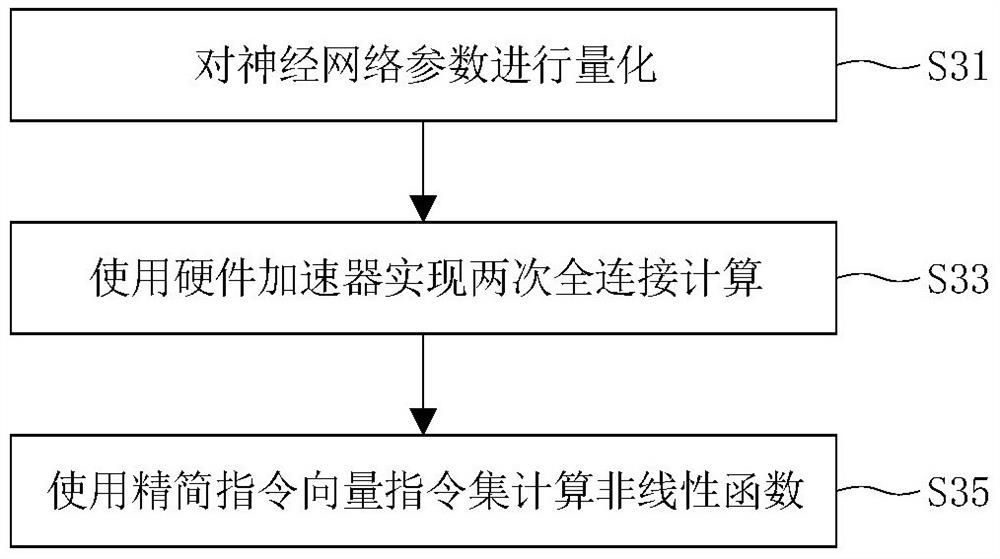
Hardware acceleration method for long short-term memory neural network and computing system
The invention discloses a hardware acceleration method for a long short-term memory neural network and a computing system for executing the method, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, quantizing parameters of the long short-term memory neural network, performing floating-point computation on floating-point data input into the long short-term memory neural network to obtain output floating-point data, and performing quantization according to the output floating-point data; and performing fixed-point calculation in the long short-term memory neural network to output fixed-point data. Then full-connection calculation is executed, specifically, weights in a full-connection layer in any long short-term memory unit in the long short-term memory neural network are rearranged, similar items are combined to execute less-order full-connection layer calculation, and then a specific nonlinear function is calculated by using a simplified instruction vector instruction set; after the steps are repeated, the matrix multiply-accumulate operation of the long-short-term memory neural network can be completed.
Owner:저장진셍일렉트로닉스테크놀러지컴퍼니리미티드
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com