Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
103 results about "Fibre coating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
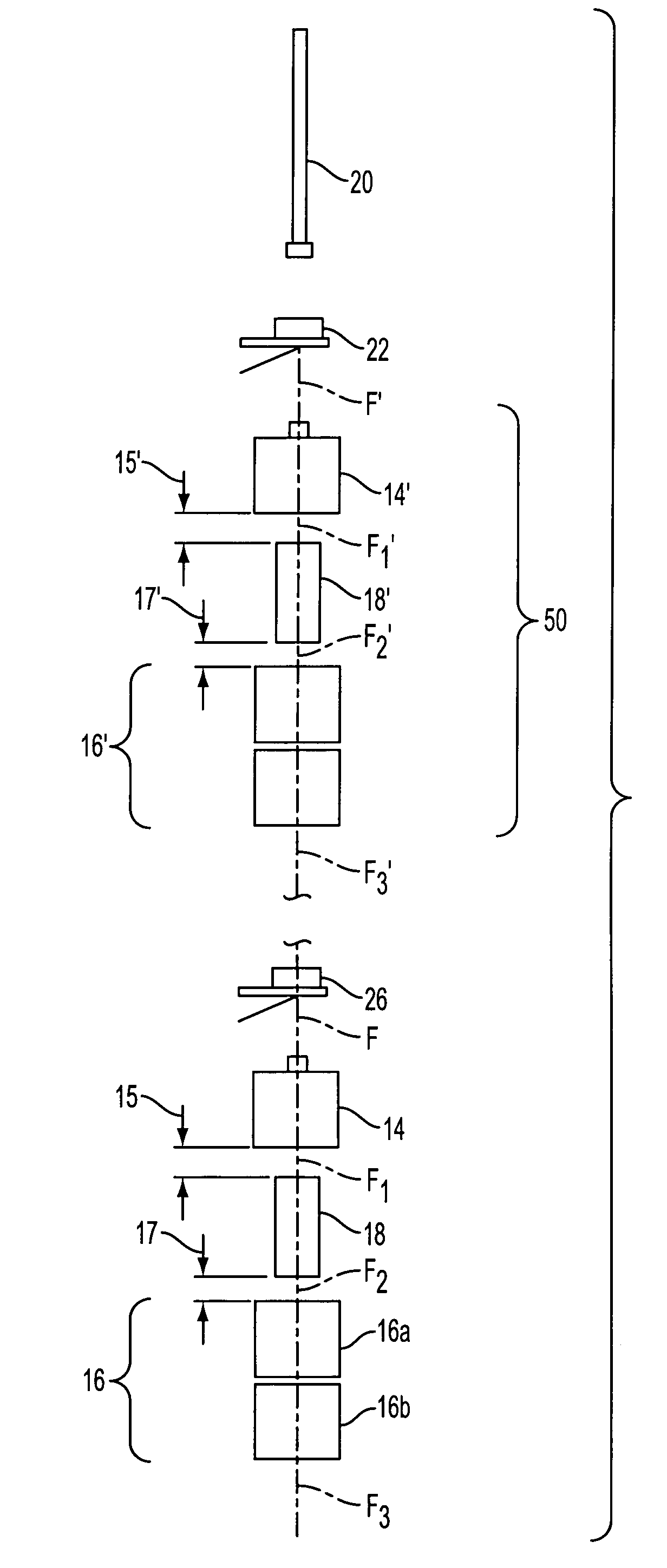
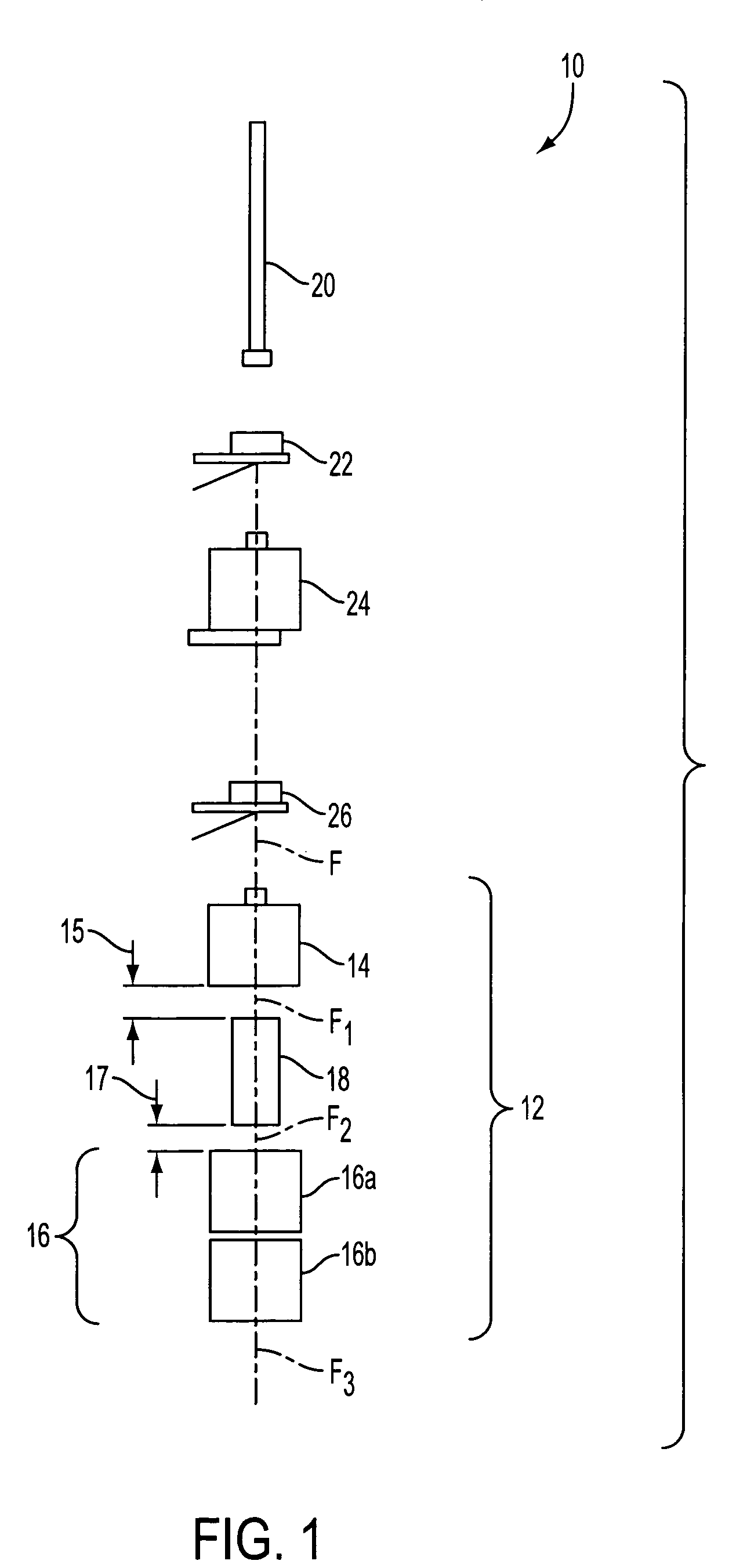
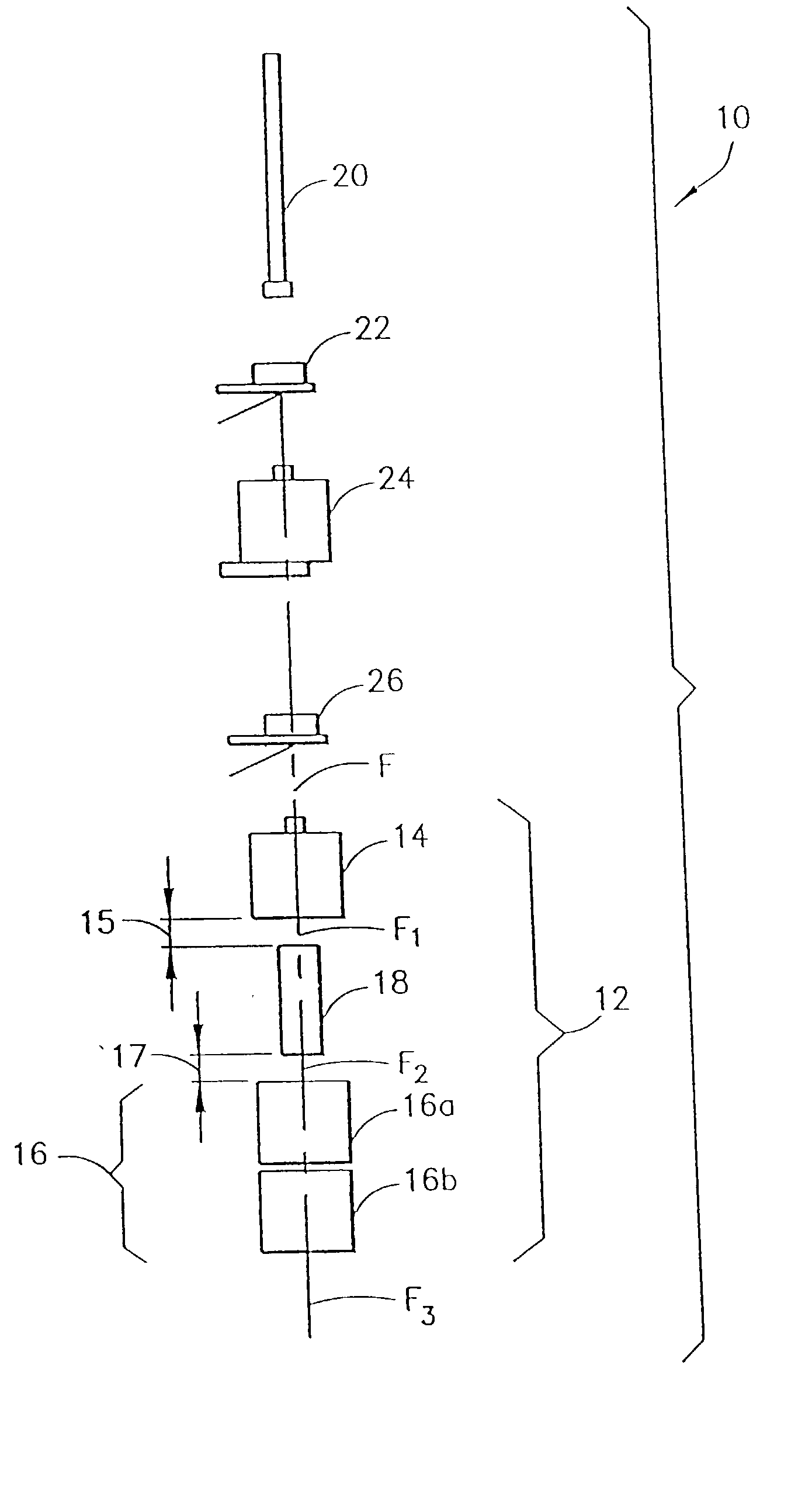
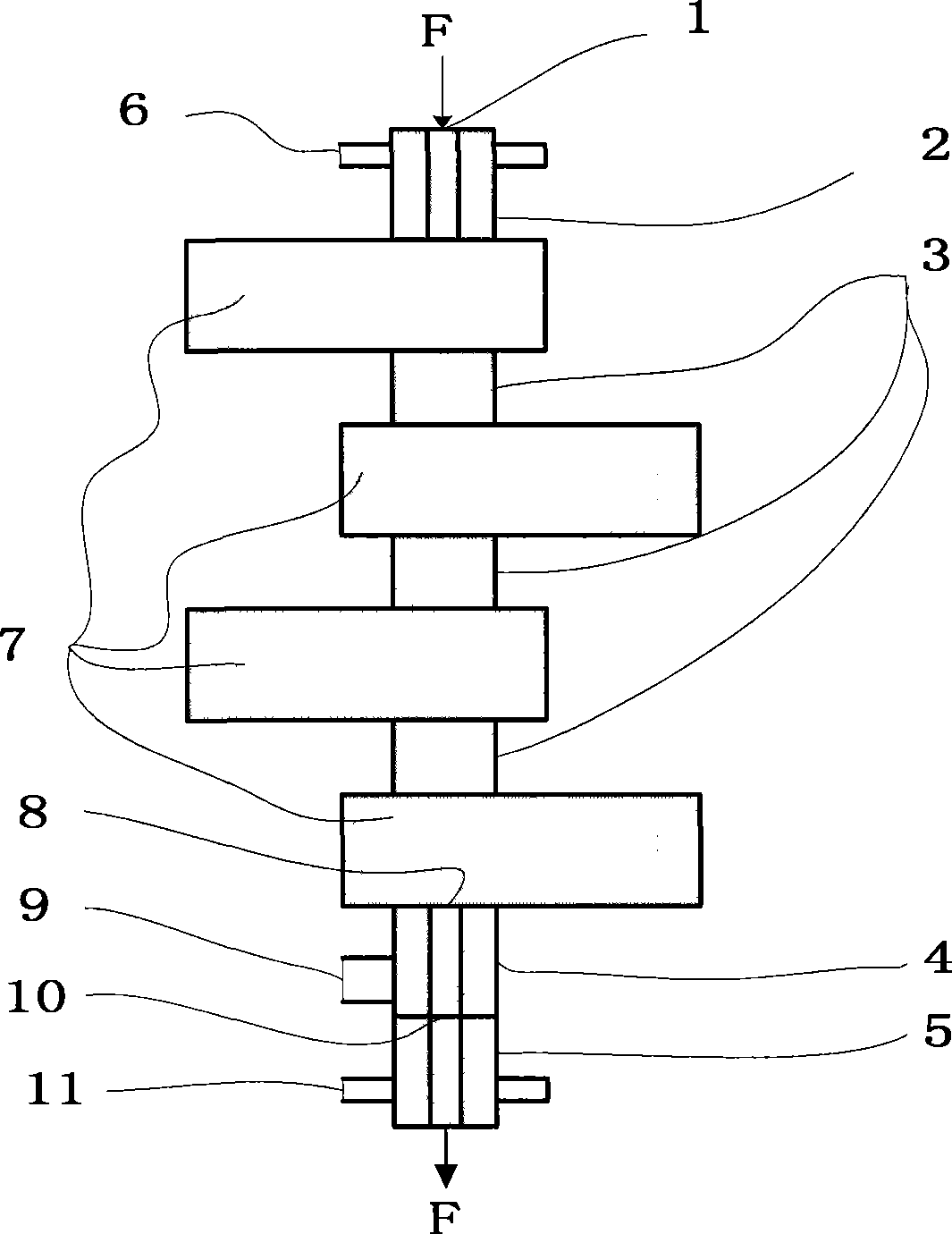
Method and apparatus for curing a fiber having at least two fiber coating curing stages
InactiveUS7322122B2Maintenance savingImprove drawing speedOptical articlesPretreated surfacesTime delaysIrradiation
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for curing a coated fiber, comprising either two fiber coating curing stages separated by a cooling stage, or two fiber coating curing stages separated by a distinct time interval, or both. One of the two fiber coating curing stages responds to the coated fiber, and provides a partially cured fiber coating. The other of the two fiber coating curing stages responds to the partially cured coated fiber for further curing the coating of the fiber. In one embodiment of the invention, a cooling stage is placed between the two curing stages, while in the other the curing stages are placed a set distance apart such that polymerization of the coating initiated by the first curing stage has time to complete prior to the coating being irradiated by the second curing stage. The cooling stage is used to actively remove heat generated during the cure process from the fiber coating, while the time delay is used to allow complete polymerization to occur before subsequent irradiations. These embodiments of the present invention can be used separately or in combination to achieve optimal fiber coating cure.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Single-polarization high power fiber lasers and amplifiers
InactiveUS6954575B2Modelocking stabilityPulse stabilizationLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with polarisationSingle polarizationFibre coating
A novel polarization maintaining optical fiber, which can be used as a high-power polarization maintaining fiber laser or amplifier, is described. Insensitivity of the polarization state to external fiber bending and temperature changes is accomplished by minimizing polarization mode-coupling via reducing stresses inside the fiber core via increasing the fiber diameter. Alternatively, polarization mode-coupling can be minimized by an optimization of the fiber coating to minimize stresses at the interface between the fiber and the coating. As a result insensitivity to polarization mode-coupling is obtained at greatly reduced values of birefringence compared to small-diameter fibers. The fiber is of significant use in any application where polarization stability is important, and will be useful in telecommunications applications in particular for reducing polarization mode dispersion. An implementation in a parabolic pulse-producing fiber laser is also described as one specific high power example.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Polymeric shell adherently supported by a liner and a method of manufacture
ActiveUS20060068140A1Limit stretch abilityPrevent adhesive delaminationDiagnosticsGlovesFiber coatingEngineering
An article comprising at least one cured, liquid-impervious polymeric shell substantially free from defects, at least one liner, and a non-tacky, thermoplastic adhesive layer between the shell and the liner, wherein the adhesive layer is melted and solidified to create a non-tacky bond between the shell and the liner, which can be moisture-absorbing or cut-resistant, whereby the liner supports and limits stretch ability of the shell, thereby preventing adhesive delamination between the adhesive layer and either of the shell and / or the liner; a method for the manufacture of an article comprising a supported, polymeric shell, such as a glove, a gauntlet, an apron, or a boot, comprising providing a cured, liquid-impervious, polymeric shell, providing a knitted / woven liner, incorporating a non-tacky, thermoplastic adhesive layer between the shell and the liner, such as by hot-melt spraying, dry-powder spraying or fiber-coating, creating intimate contact between the shell, the adhesive layer, and the liner, subjecting the shell, the adhesive layer, and the liner to infrared radiation to melt the adhesive layer and create a bond between the shell and the liner, and cooling the shell; as well as other methods.
Owner:ANSELL HEALTHCARE PRODS
Polymer No Donor Predrug Nanofiber Coating for Medical Devices and Therapy
The present invention relates to nanofibers that produce therapeutic amounts of nitric oxide after a delay period, which allows time to install or implant the device into a patient. The nitric oxide release is thus localized to the area of the organism where NO dosing is indicated. The delay time is achieved by cospinning the NO-producing fiber with a fiber that tends to sequester the former's NO-producing functional groups. Fibers of the present invention may be incorporated into medical devices such as stents or other implantable medical devices to prevent the formation of adhesions or scarring in the area of the implant.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Method and apparatus to produce stretchable products
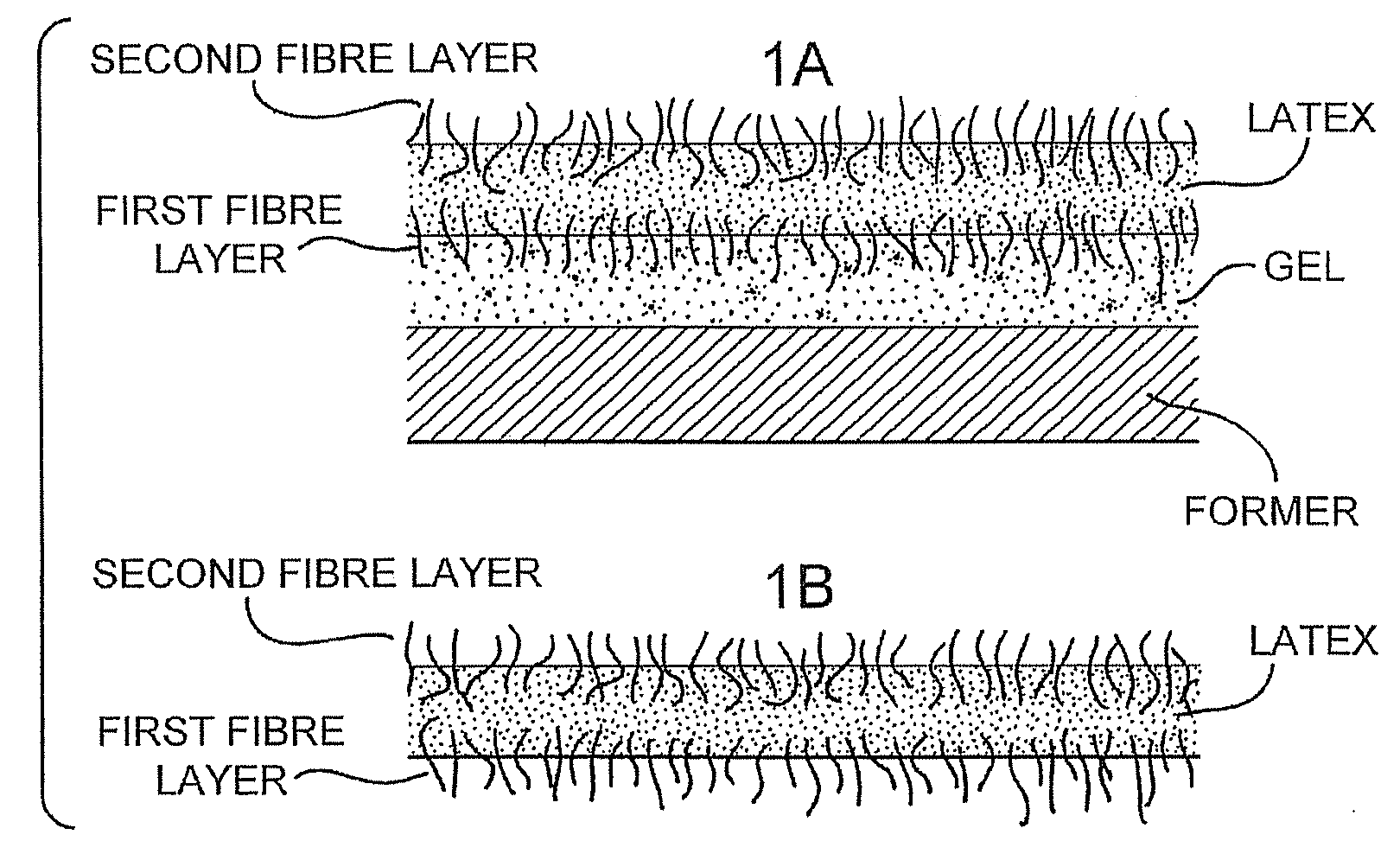
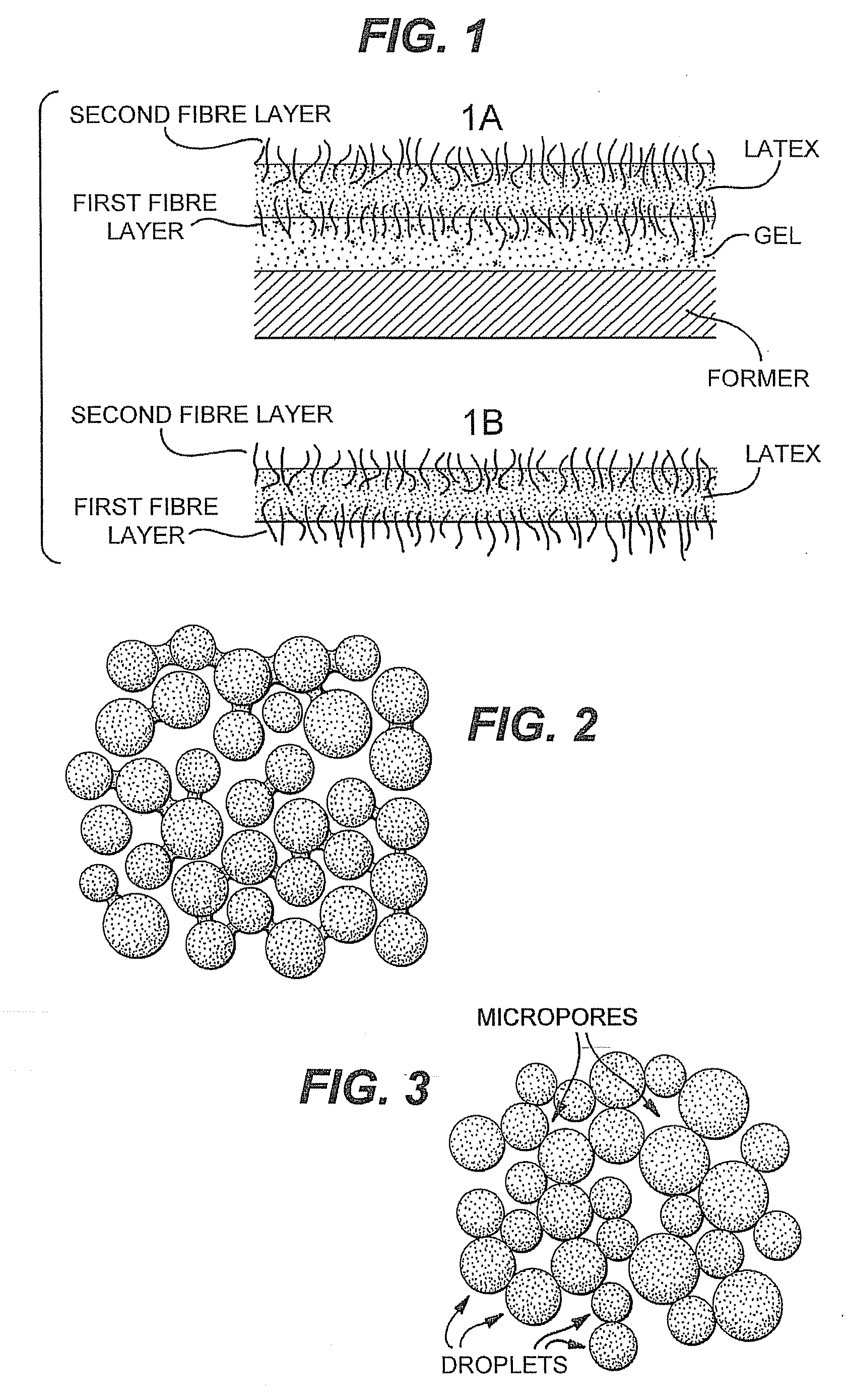
ActiveUS20060113714A1Facilitate temporary adherenceEasy to disassembleButtonsMouldsElastomerFibre coating
The invention provides methods and apparatus for producing flexible, stretchable, and / or elastic products comprised principally of material such as natural elastomers and other synthetic polymers. The method and apparatus for producing stretchable products by spraying product material over a workpiece former, and method and apparatus for creating perforated products by spraying product material over a perforated surface or partly breathable surface, The invention also provides methods and apparatus for making double sided fibre coating of the product and, or to at least coating the product surface on the side facing the wall without the need for removing the product from the wall. The method and apparatus also enable easy removal of the product from the former. Workpiece formers are also provided.
Owner:TAMICARE LTD
Apparatus for forming a microfiber coating
InactiveUS7105058B1Accelerates the removal of moistureReduce moistureLiquid surface applicatorsSpray nozzlesEngineeringAmbient air
An apparatus and method for forming a microfiber coating includes directing a liquid solution toward a deposition surface. The apparatus includes a tube defining a volume through which the liquid solution travels. An electric field is applied between the origin of the liquid solution and the surface. A gas is injected into the tube to create a vortex flow within the tube. This vortex flow protects the deposition surface from entrainment of ambient air from the surrounding atmosphere.
Owner:POLYREMEDY
Capacitive gas sensor and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20100133528A1Excellent gas reaction characteristicSimple processNanotechSolid-state devicesNanofiberOptoelectronics
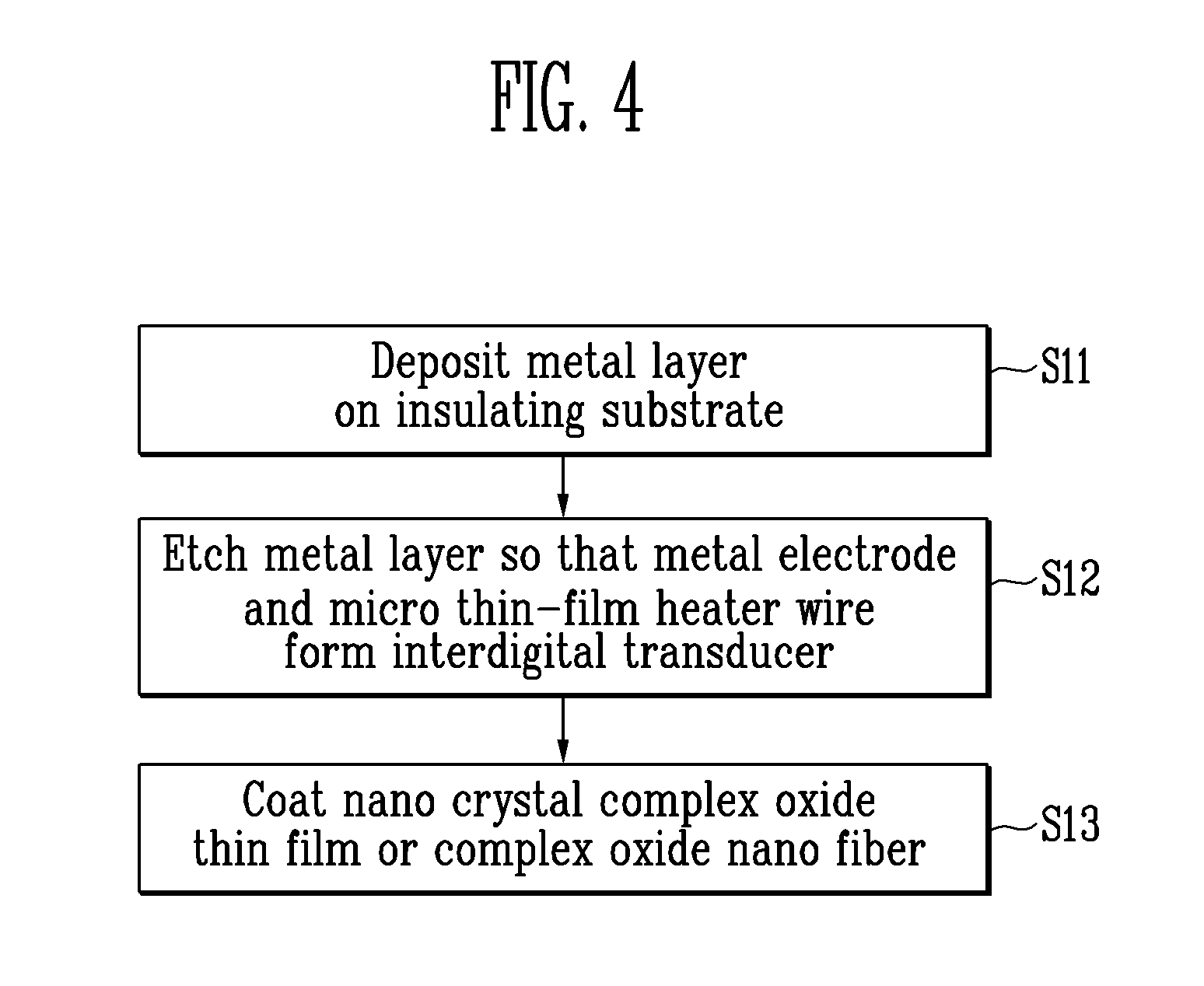
A capacitive gas sensor and a method of fabricating the same are provided. The capacitive gas sensor includes an insulating substrate, a metal electrode and a micro thin-film heater wire integrally formed on the same plane of the insulating substrate, and an oxide detection layer coated on the metal electrode and the micro thin-film heater wire. The fabrication method includes depositing a metal layer on an insulating substrate, etching the metal layer so that a metal electrode and a micro thin-film heater wire form an interdigital transducer on the same plane, and forming a nano crystal complex oxide thin film or a complex oxide nano fiber coating layer on the metal electrode and the micro thin-film heater wire as a detecting layer. The capacitive gas sensor can be easily fabricated and can have excellent characteristics such as high sensitivity, high selectivity, high stability, and low power consumption.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Polymeric shell adherently supported by a liner and a method of manufacture
ActiveUS7803438B2Preventing adhesive delaminationLimit stretch abilityDiagnosticsGlovesHot meltEngineering
An article comprising at least one cured, liquid-impervious polymeric shell substantially free from defects, at least one liner, and a non-tacky, thermoplastic adhesive layer between the shell and the liner, wherein the adhesive layer is melted and solidified to create a non-tacky bond between the shell and the liner, which can be moisture-absorbing or cut-resistant, whereby the liner supports and limits stretch ability of the shell, thereby preventing adhesive delamination between the adhesive layer and either of the shell and / or the liner; a method for the manufacture of an article comprising a supported, polymeric shell, such as a glove, a gauntlet, an apron, or a boot, comprising providing a cured, liquid-impervious, polymeric shell, providing a knitted / woven liner, incorporating a non-tacky, thermoplastic adhesive layer between the shell and the liner, such as by hot-melt spraying, dry-powder spraying or fiber-coating, creating intimate contact between the shell, the adhesive layer, and the liner, subjecting the shell, the adhesive layer, and the liner to infrared radiation to melt the adhesive layer and create a bond between the shell and the liner, and cooling the shell; as well as other methods.
Owner:ANSELL HEALTHCARE PRODS
Culture plate with fiber-coated bottom surface
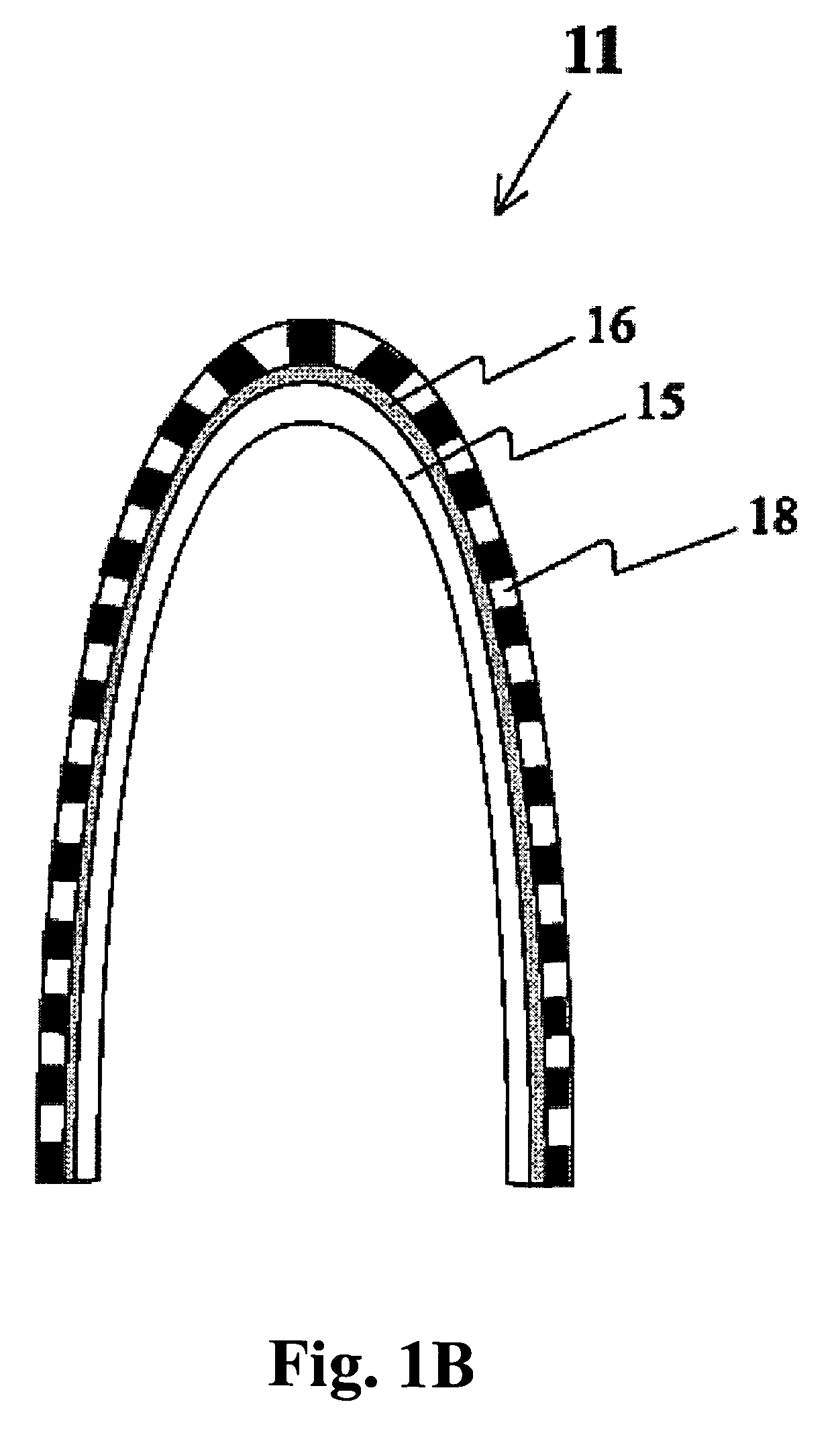
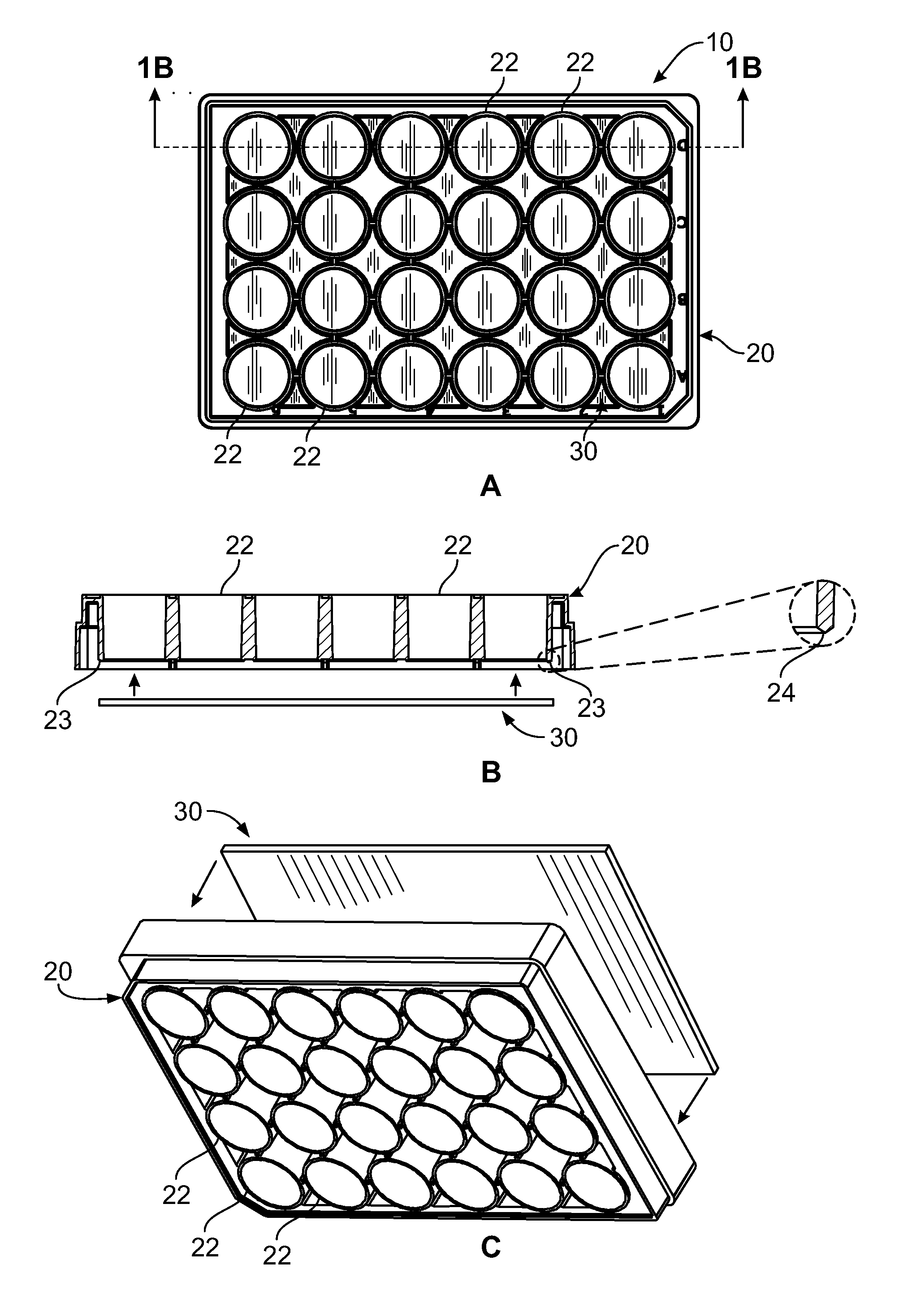
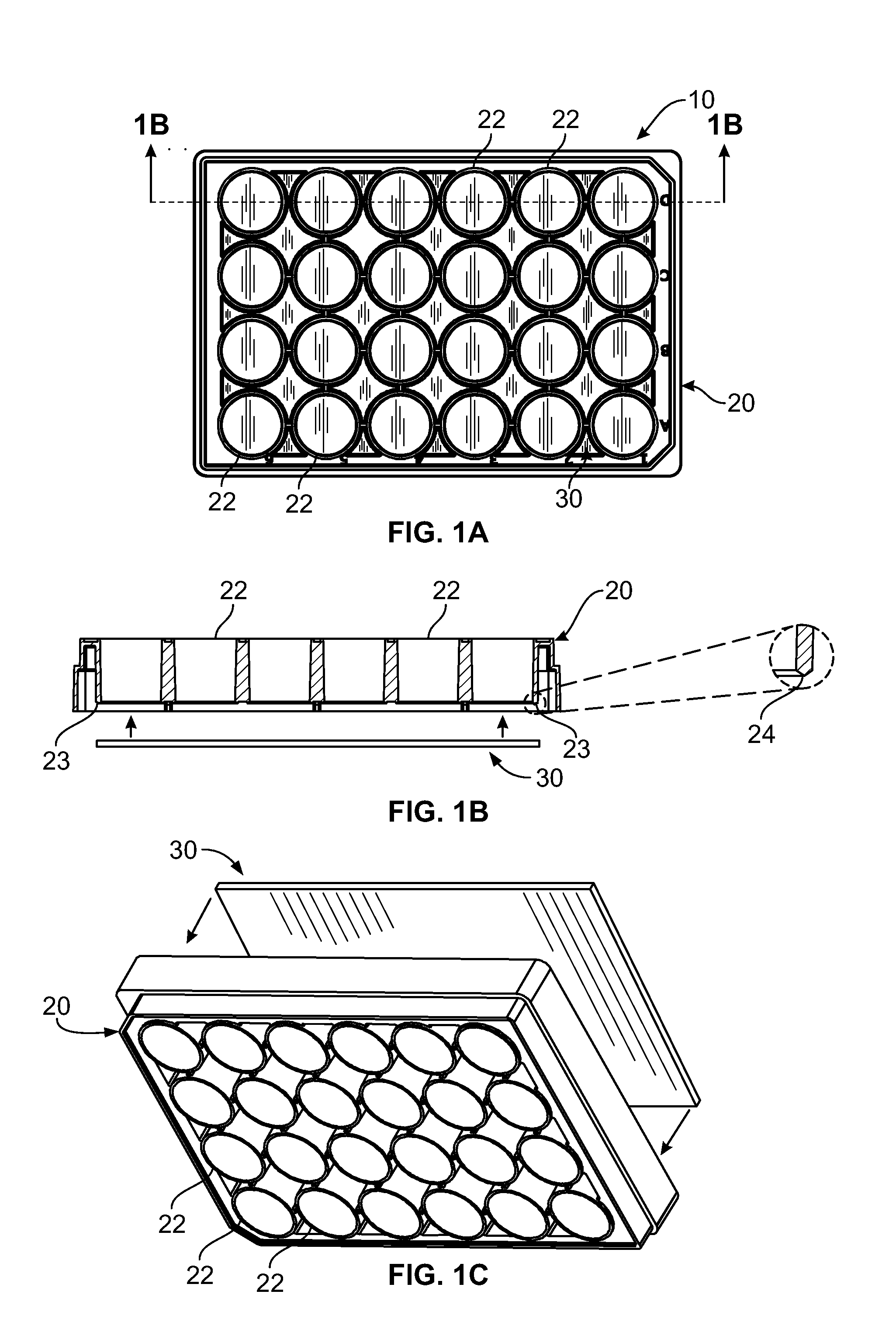
ActiveUS20140057346A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberBiological cell
A cell culture plate that includes an upper portion having at least one discrete chamber with a top edge and a bottom edge; a substantially flat lower portion, wherein at least one layer of polymer fibers has been deposited on the upper surface of the lower portion, and wherein the at least one layer of polymer fibers is conducive to the growth of biological cells thereon; and wherein the bottom edge of the at least one discrete chamber is hermetically sealed to the fiber-coated upper surface of the lower portion to form a well using adhesives, laser welding, or ultrasonic welding.
Owner:NFS IP HLDG LLC
Methods to Produce Stretchable Products
ActiveUS20080292788A1Liquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSolid/suspension decomposition chemical coatingElastomerEngineering
The invention provides methods for producing flexible, stretchable, and / or elastic products comprised principally of material such as natural elastomers and other synthetic polymers. The method for producing stretchable products by spraying product material over a workpiece former, and method for creating perforated products by spraying product material over fibres in an upright position. The invention provides methods for making double sided fibre coating of the product and, or to at least coating the product surface on the side facing the wall without the need for removing the product from the wall.
Owner:TAMICARE LTD
Ceramic forming polymer derived ceramic composite and methods
InactiveUS20040138046A1Resists oxidationLess-expensive to applyLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsCeramic compositeHydrogen
A ceramic composite having a ceramic coating formed from a ceramic forming polymer of adjustable composition. The ceramic forming polymer is capable of producing a weak interface-type fiber coating for the ceramic composite, resists oxidation and is less expensive to apply. The invention also includes methods of using a ceramic forming polymer to provide fiber coatings tailored to the type of matrix, fiber, or other reinforcement used. The material forms micro-porous and nano-porous coatings on the fibers. The porosity in the coatings provides a low strength interface between the fiber and matrix that imparts the toughness needed in the composite. The material can be provided with controlled ratios of carbon, silicon, oxygen and hyrdrogen to optimize bonding to the fibers, bonding of the matrix to the fiber coating, and environmental protection of the fibers.
Owner:STARFIRE SYST
CMC process using a water-based prepreg slurry
A process for forming a ceramic matrix composite component, for example, a turbine component, includes (a) applying a fiber coating to a fiber tow by chemical vapor deposition; (b) pulling the fiber tow through an aqueous slurry composed of high and low temperature binders, silicon carbide powder, carbon black and water to thereby form a prepreg tape; and (c) winding the prepreg tape on a drum.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for curing a fiber having at least two fiber coating curing stages
InactiveUS20030039749A1Good effectFaster rateCladded optical fibreOptical articlesTime delaysIrradiation
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for curing a coated fiber, comprising either two fiber coating curing stages separated by a cooling stage, or two fiber coating curing stages separated by a distinct time interval, or both. One of the two fiber coating curing stages responds to the coated fiber, and provides a partially cured fiber coating. The other of the two fiber coating curing stages responds to the partially cured coated fiber for further curing the coating of the fiber. In one embodiment of the invention, a cooling stage is placed between the two curing stages, while in the other the curing stages are placed a set distance apart such that polymerization of the coating initiated by the first curing stage has time to complete prior to the coating being irradiated by the second curing stage. The cooling stage is used to actively remove heat generated during the cure process from the fiber coating, while the time delay is used to allow complete polymerization to occur before subsequent irradiations. These embodiments of the present invention can be used separately or in combination to achieve optimal fiber coating cure.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
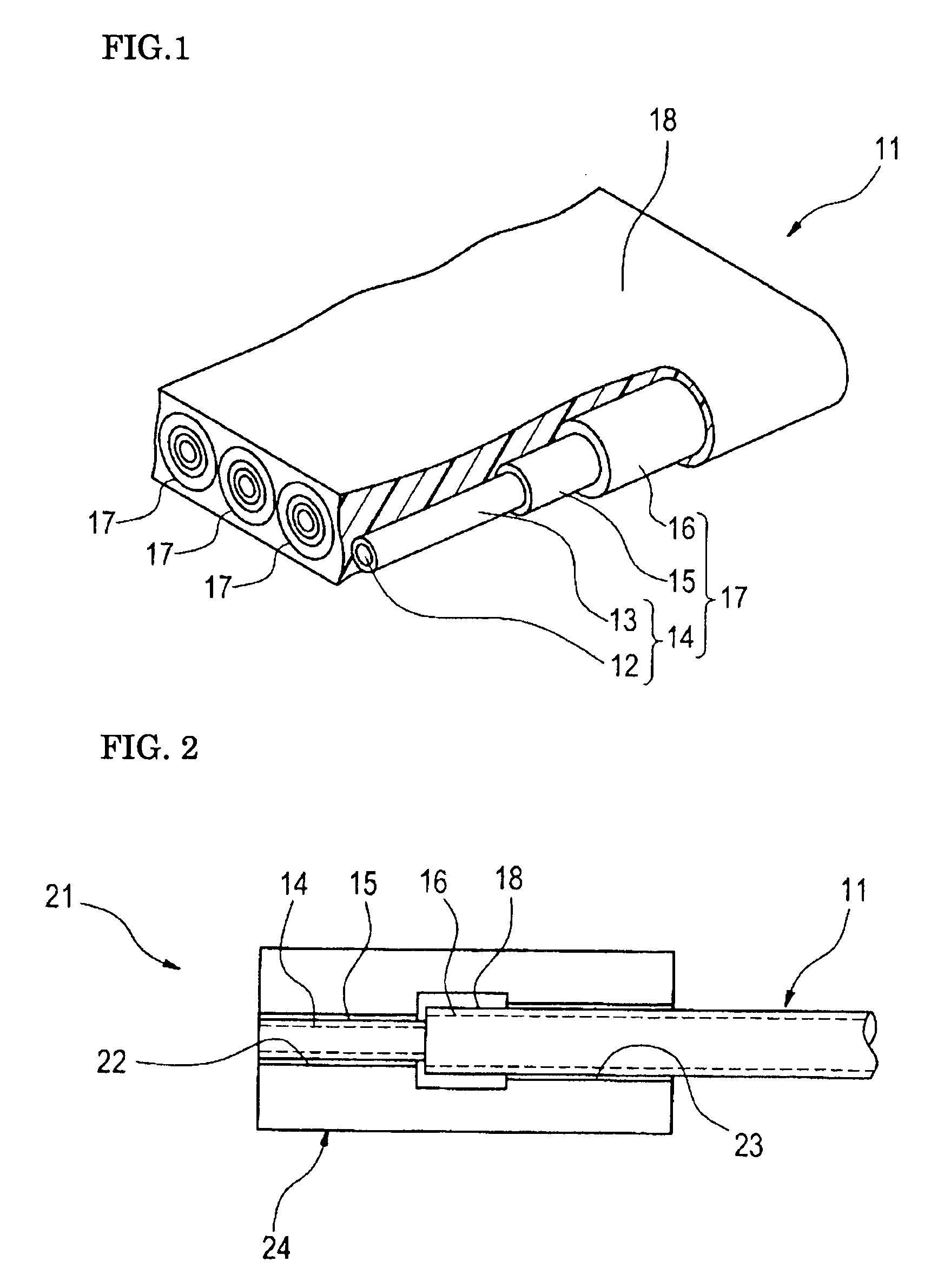
Optical fiber ribbon
ActiveUS20080232750A1Solve problemsGlass optical fibreFibre mechanical structuresUV curingUltraviolet
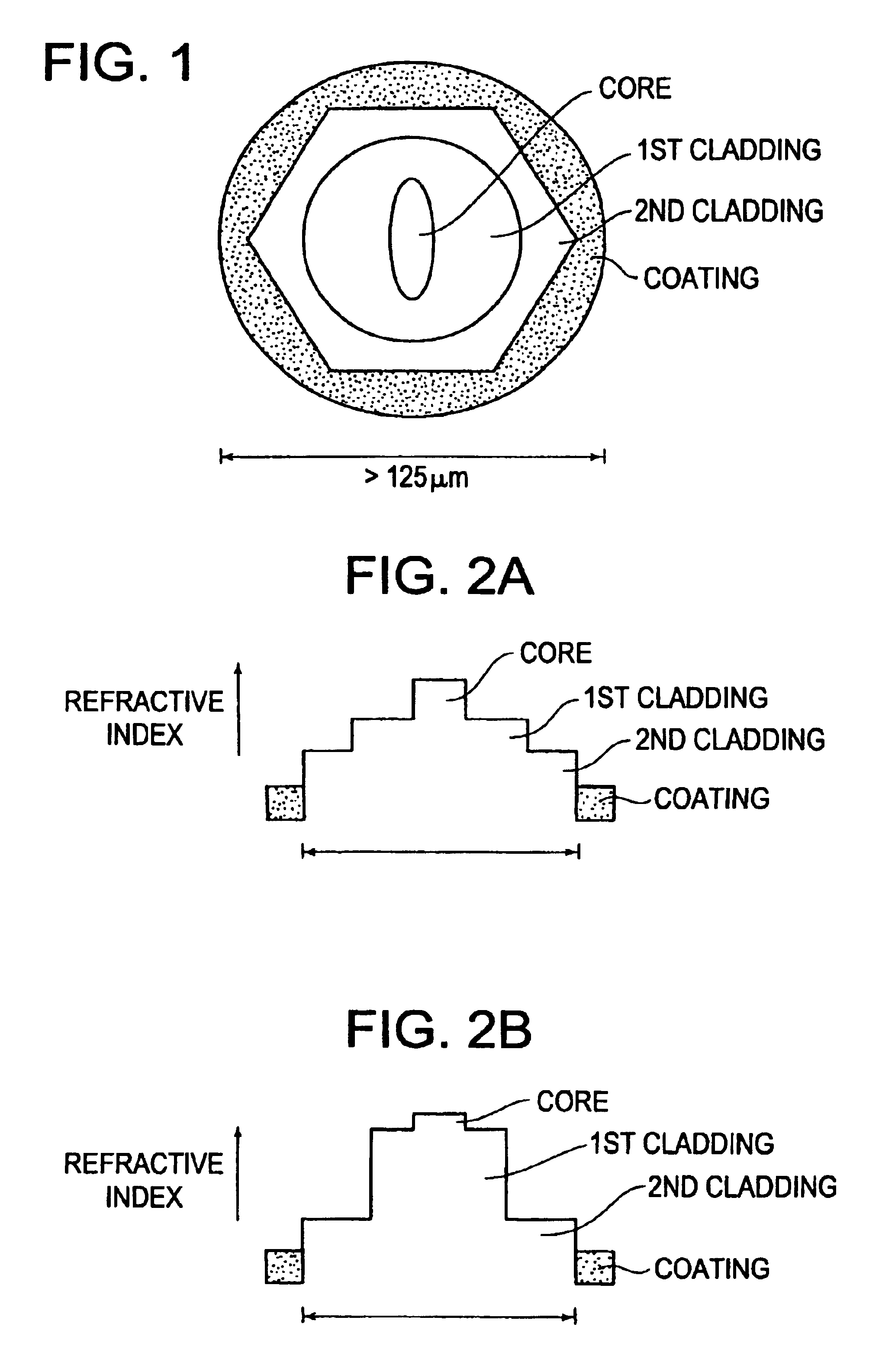
An optical fiber ribbon includes a plurality of optical fibers, each includes a glass optical fiber coated with a fiber coating, that are arranged in parallel, and a ribbon coating that coats the optical fibers arranged in parallel. The optical fiber ribbon has a thickness equal to 300 μm or less. The fiber coating is made of a non-flame-resistant ultraviolet curable resin. The ribbon coating has a thickness equal to 40 μm or more and is made of a flame resistant resin.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method and apparatus to produce stretchable products
ActiveUS7767133B2Easy to disassembleImprove adhesionLaminationLamination apparatusElastomerPolymer science
The invention provides methods and apparatus for producing flexible, stretchable, and / or elastic products comprised principally of material such as natural elastomers and other synthetic polymers. The method and apparatus for producing stretchable products by spraying product material over a workpiece former, and method and apparatus for creating perforated products by spraying product material over a perforated surface or partly breathable surface, The invention also provides methods and apparatus for making double sided fibre coating of the product and, or to at least coating the product surface on the side facing the wall without the need for removing the product from the wall. The method and apparatus also enable easy removal of the product from the former. Workpiece formers are also provided.
Owner:TAMICARE LTD
Fiber ribbon and fiber ribbon attached to connector for wiring in equipment
InactiveUS20100254658A1Easily and satisfactorily be exposedCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresUltravioletYoung's modulus
When a glass fiber and an inner fiber coating layer are to be attached to a connector by removing an outer fiber coating layer while leaving the inner fiber coating layer as it is, a collective coating and the outer fiber coating layer can be removed at a stretch so that the inner fiber coating layer can easily and satisfactorily be exposed. In the ultraviolet curable resin coating layer of a coated optical fiber 17 of an optical fiber ribbon 11 for wiring of equipment, the inner fiber coating layer 15 has a Young's modulus of 600 MPa to 1000 MPa, and the outer fiber coating layer 16 has a Young's modulus of 10 MPa to 300 MPa. The material of the outer fiber coating layer 16 is made by mixing 100 weight parts of base resin, 1-30 weight parts of silicone-based additive, and 0.5 to 40 weight parts of long chain fatty acid ester compound, wherein the base resin is a material made of a urethane metha acrylate oligomer, a mono-functional or multi-functional reactive dilution monomer, and an optical initiator.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
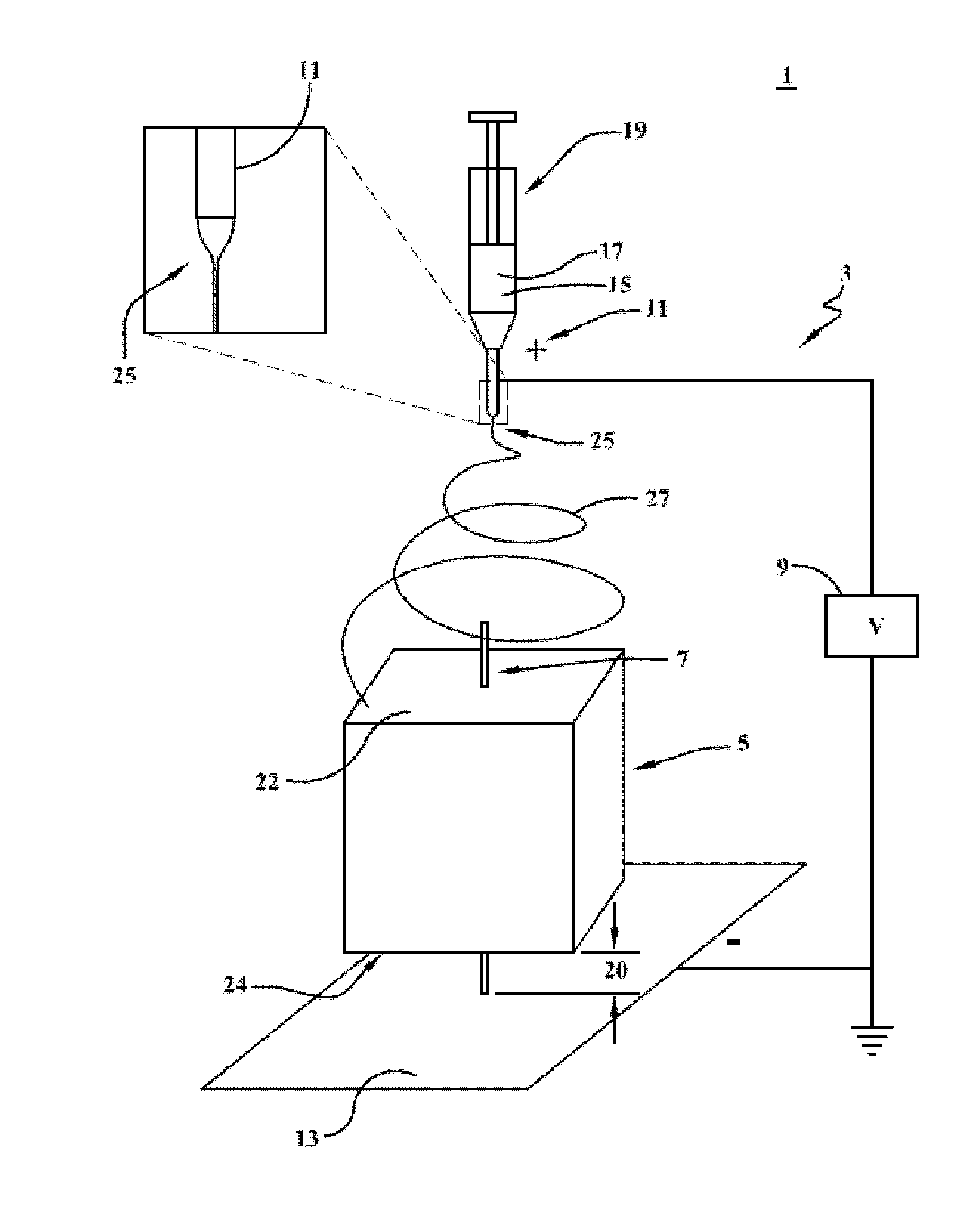
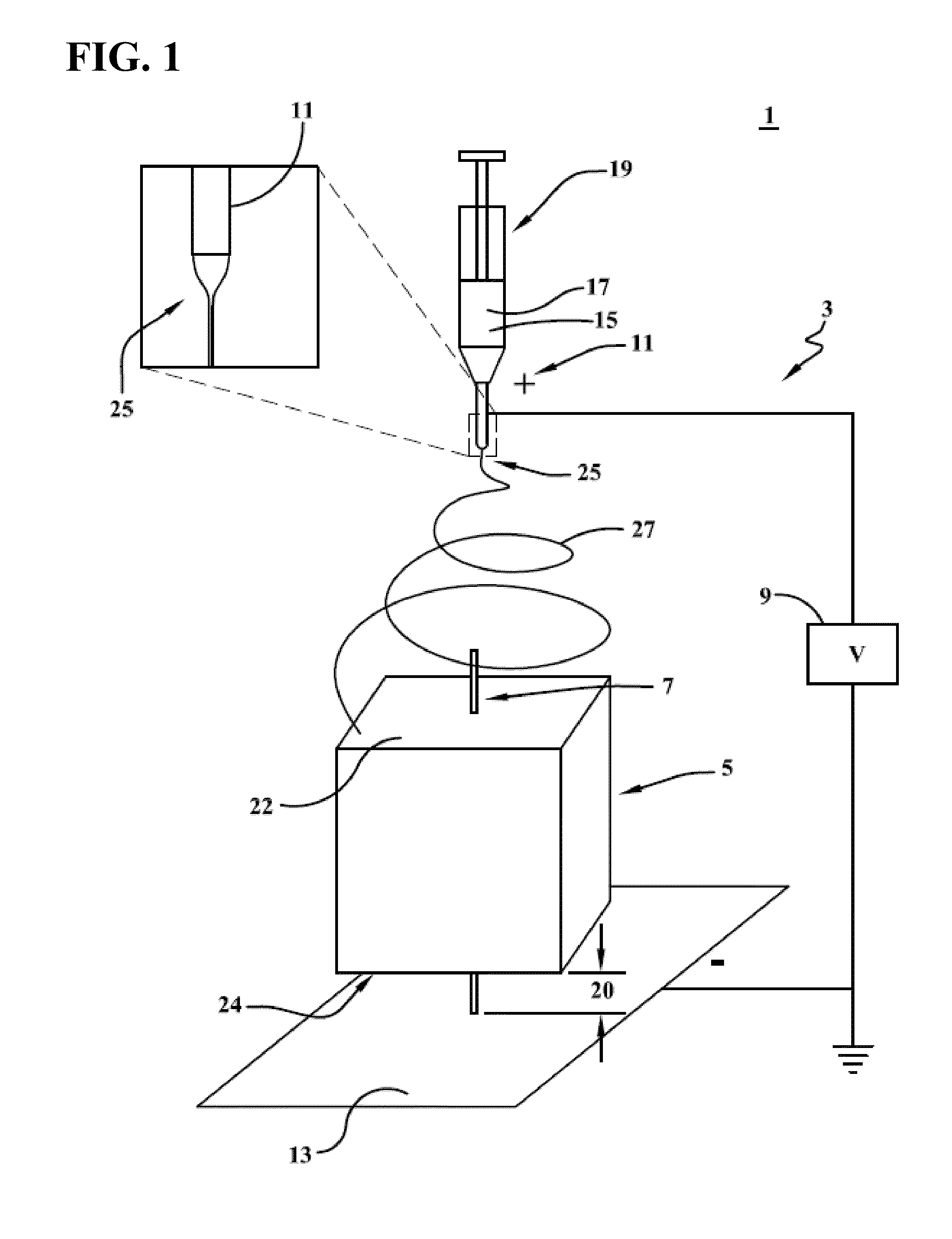
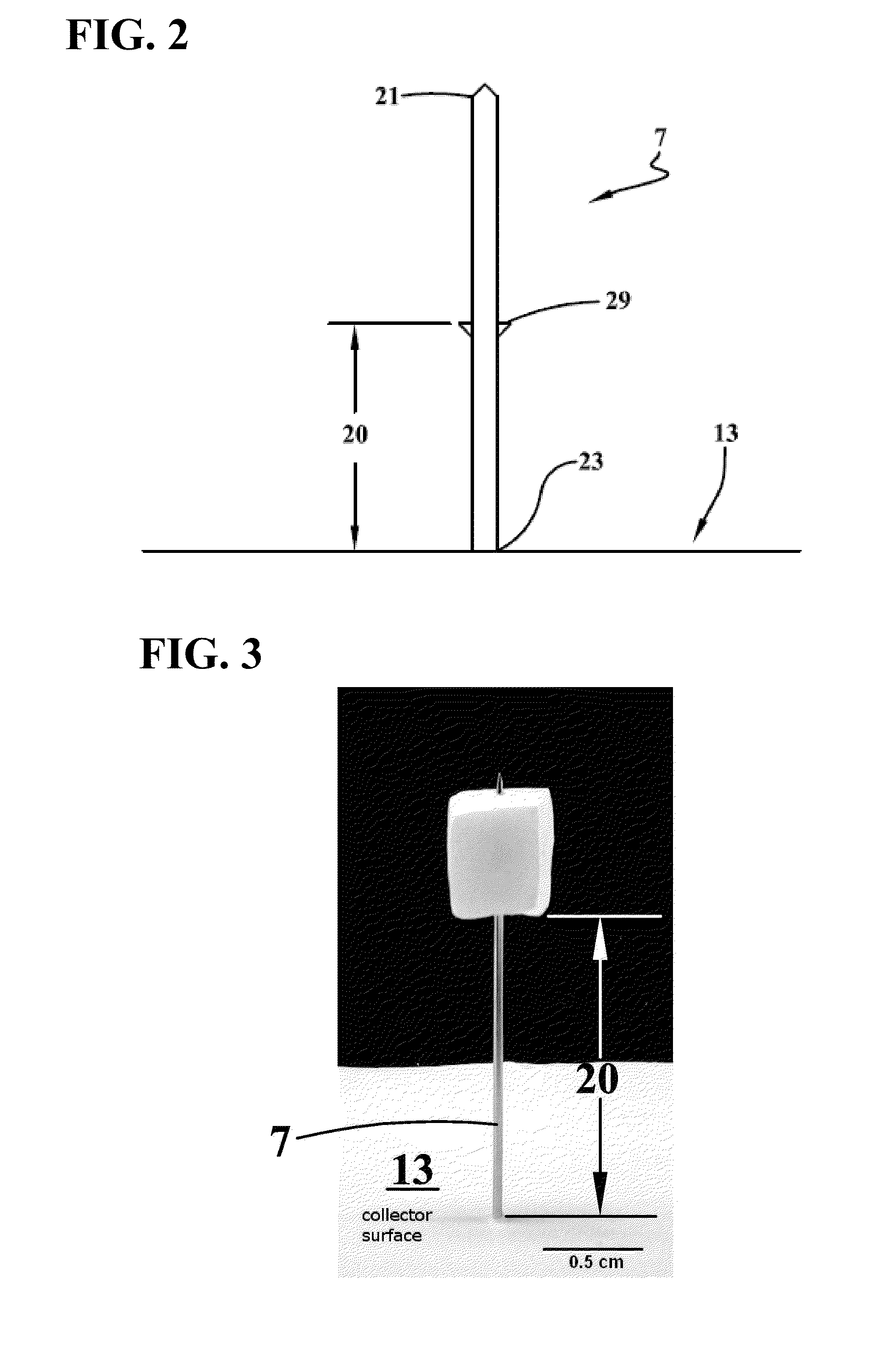
Apparatus and method for electrospinning a nanofiber coating on surfaces of poorly conductive three-dimensional objects
ActiveUS20150273110A1Effective applicationFacilitate depositionFilament/thread formingCoatingsElectrospun nanofibersNanofiber
The present invention is directed to a novel method and apparatus for facilitating and improving efficient application of nanofibers to the surface of poorly conductive three-dimensional objects using electrospinning. The apparatus and associated methods of the present invention provide a much more direct connection between the object and the grounded plate collector while allowing the object to be supported above the collector in a manner which promotes nanofiber deposition over the top, bottom and side surfaces of the object, closely covering all of its surfaces with nanofibers. Moreover, the deposition of electrospun nanofibers according to various embodiments of the present invention expands electrospinning technology to greater numbers of applications in which three-dimensional coatings of a wide nature are advantageous.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Antifouling fibre coatings for marine constructions
ActiveUS20100227111A1Good curative effectImprove efficiencyPretreated surfacesInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureVolumetric Mass DensityMarine equipment
A fibre-coated marine material has antifouling properties, without necessarily containing bioactive agents. At least a part of the marine material is covered by piles of fibres having a thickness of at least 50 μm and a fibre length of at least 3 mm. The thickness-to-length ratio of the fibres is at least 0.010, and the piles of fibres have a density lower than 40 fibres / mm2. The fibre coating can be directly applied onto the marine material, such as ropes and construction parts, or can be present on sheets which can be applied on the marine equipment.
Owner:MATERIALS INNOVATION CENT
Method of coating a ceramic matrix composite fiber
InactiveUS7381445B2Improve coating uniformityCladded optical fibreSpecial surfacesReaction zoneFibre coating
A method of coating a ceramic matrix composite fiber is disclosed. The method includes passing the composite fiber through a reaction zone along a path substantially parallel to a longitudinal axis of the reaction zone. It also includes passing a flow of a fiber coating reactant through the reaction zone. Further, the method includes disrupting a portion of the flow of the fiber coating reactant from a path substantially parallel to a fiber path to create a mixing flow adjacent the composite fiber.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Process for Introducing a Weakening Line Through Material Removal on a Fibrous Coating Material, in Particular Natural Leather
InactiveUS20160067821A1Leather clicking/perforating/clickingPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementMaterial removalEngineering
Method for introducing a line of weakness through removal of material at a fibrous covering material, in particular a natural leather, in which a pulsed laser beam is guided a plurality of times over the back side in a line-shaped manner, wherein only one laser pulse is emitted for each impingement point, and the laser pulse causes an input of energy which leads to a heating of the fibrous covering material at the impingement point to a temperature above an ablation threshold and which maintains the temperature below a limit temperature in regions of the covering material adjoining the impingement point.
Owner:JENOPTIK AUTOMATISIERUNGSTECHN
Process for the preparation of an antimicrobial article
InactiveUS20130052277A1Avoid unnecessary influenceAvoid leachingBiocideMembranesUF - UltrafiltrationSolvent
Disclosed is a process for preparing an antimicrobial article, wherein a silver colloid is formed in situ as a result of the components employed. The process comprises the steps of (i) providing a liquid, which contains a soluble polar polymer in a solvent selected from certain polar organic solvents; (ii) adding a silver salt selected from alpha-functionalized silver carboxylates to said liquid; (iii) allowing the mixture to react with formation of a silver colloid; and (iv) separating the solvent from the mixture and forming of the antimicrobial article. The antimicrobial articles thus obtained may be sheets, films, fibres, coating layers, and especially membranes like a semipermeable membrane for ultrafiltration, water separation or gas separation.
Owner:POLYMERS CRC
Pd/TiO2/cotton fiber composite formaldehyde indoor temperature oxidation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106732816AAvoid the problem of easy sheddingAvoid breakingGas treatmentOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsFiberCoated surface
The invention relates to a Pd / TiO2 / cotton fiber composite formaldehyde indoor temperature oxidation catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is prepared from a cotton fiber carrier, a TiO2 surface coating and a Pd active ingredient dispersed in the surface of the TiO2 coating; the cotton fiber carrier is absorbent cotton fiber; the TiO2 coating is a nano TiO2 coating of which the grain size ranges from 1nm to 10nm; the Pd active ingredient exists in a zero valence form, the grain size of the Pd active ingredient ranges from 1nm to 10nm and the loading capacity of the Pd active ingredient is 0.05-3wt%. The Pd / TiO2 / cotton fiber composite formaldehyde indoor temperature oxidation catalyst has the characteristics of graded middle and large hole structure, light weight and flexibility, Pd and the TiO2 coating as well as carrier cotton fiber are combined firmly, the active ingredient simple substance Pd is well dispersed in the surface of the TiO2 coating and is low in grain size, formaldehyde can be efficiently subjected to catalytic decomposition at indoor temperature, the use amount of noble metal is low, the air resistance is low, and the catalyst can be used in various air purifiers.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Capacitive gas sensor and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7816681B2Excellent gas reaction characteristicSimple processNanotechSolid-state devicesNanofiberOptoelectronics
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optical fibre coating cured auxiliary device of ultraviolet curing oven
ActiveCN101417859AControl oxygen contentQuality improvementGlass making apparatusEngineeringOxygen content
The invention relates to an ultraviolet curing oven optical fiber coating curing assist device which is respectively provided with a gas seal device at an optical fiber entrance and an optical fiber exit of the ultraviolet curing oven. By a unique distributed gas pipe design, two ports of the ultraviolet curing oven form a vertical multiple gas seal structures, thus effectively reducing the air in the curing oven and precisely controlling the oxygen contents in the ultraviolet curing oven; the exit of the curing oven is provided with a smoke extraction device clinging to the curing oven, so as to effectively extracts the smoke and dusts through multiple gas extraction pipes, thereby effectively improving the curing quality of the optical fiber coating.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
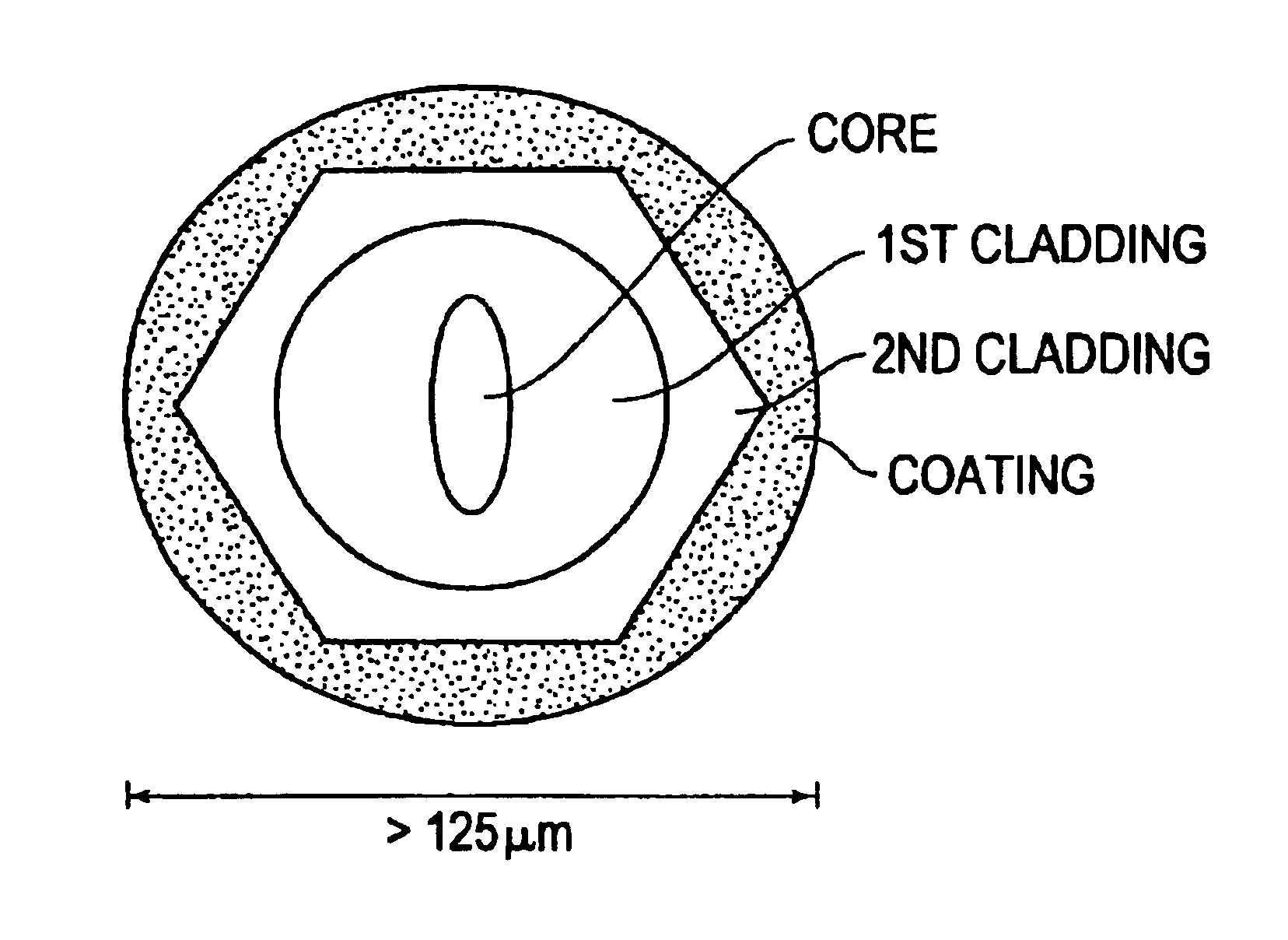
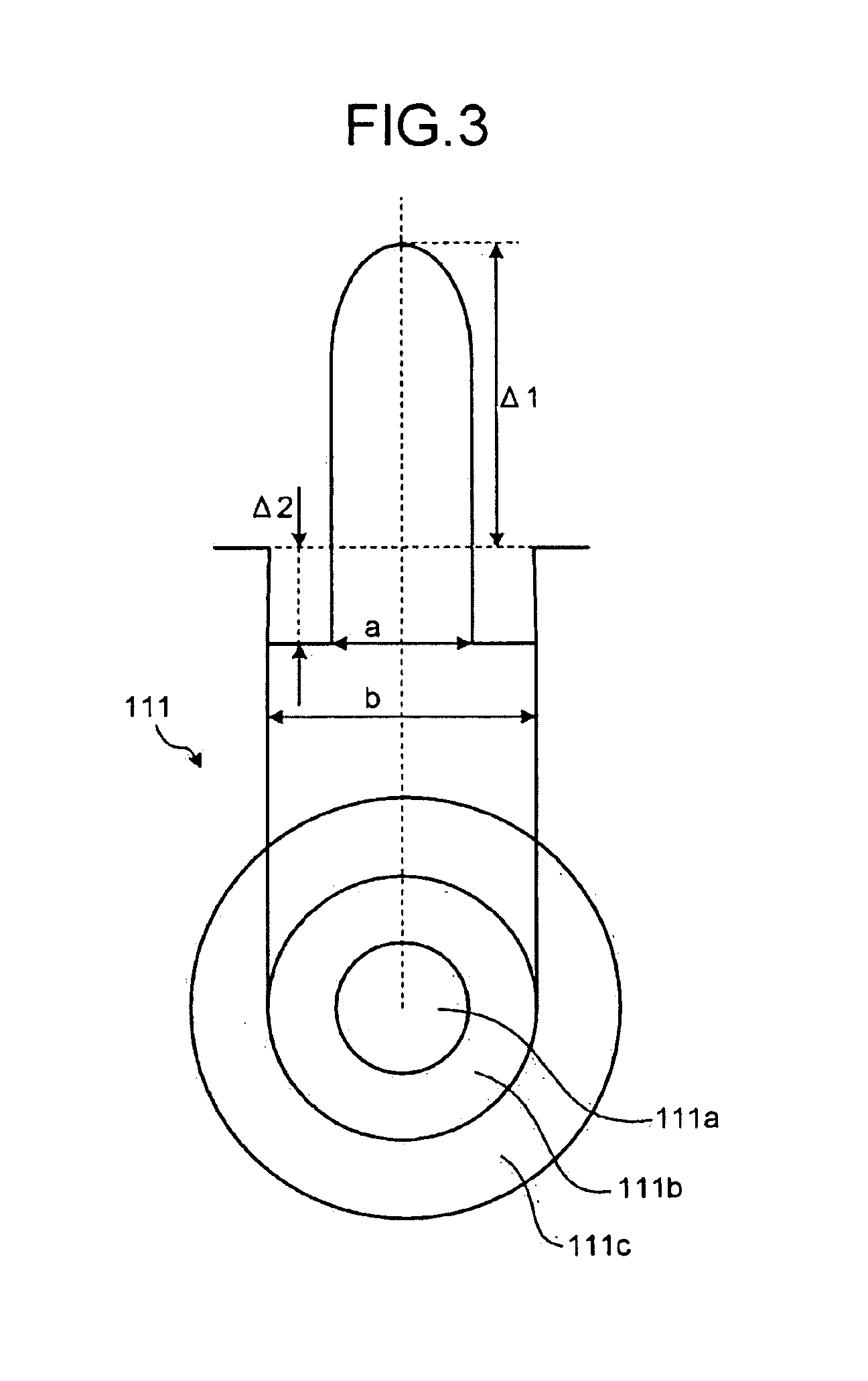
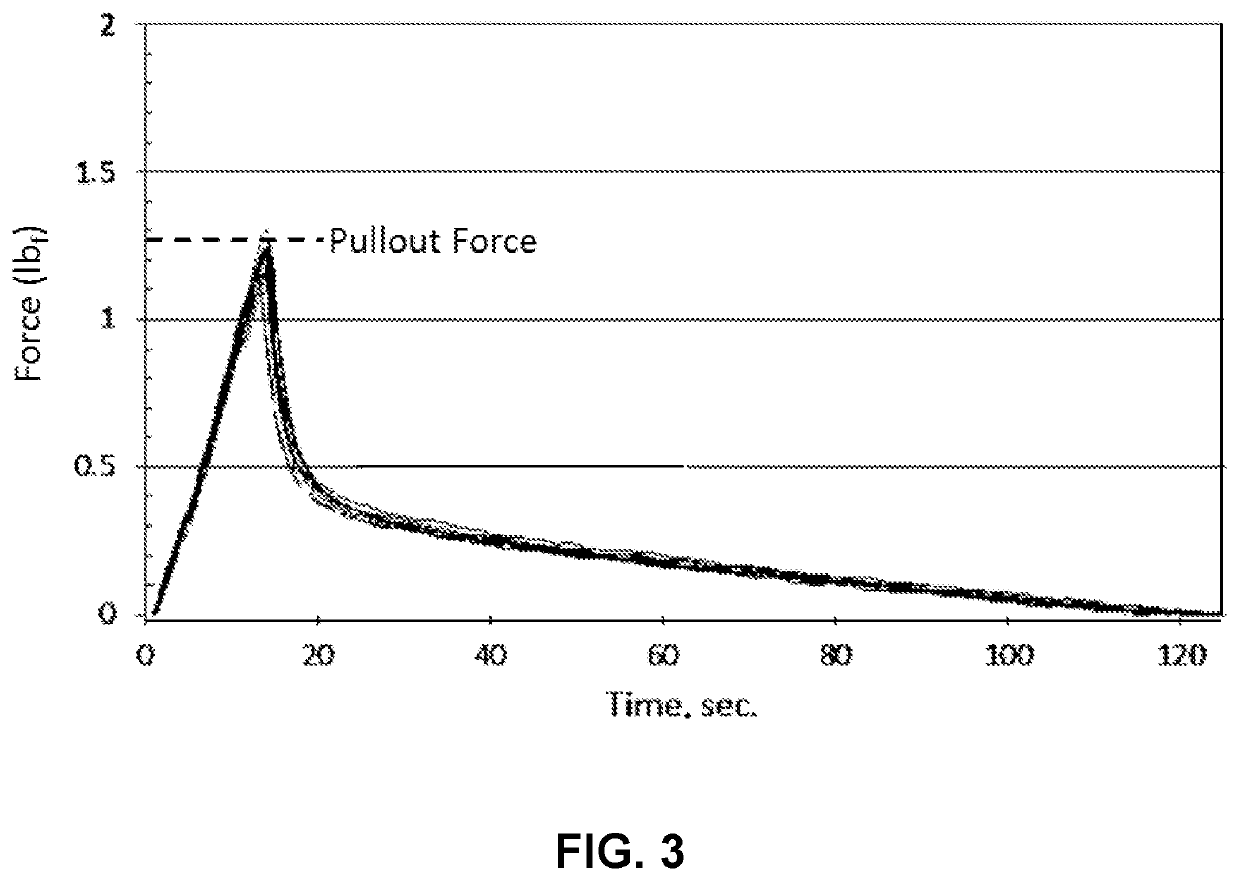
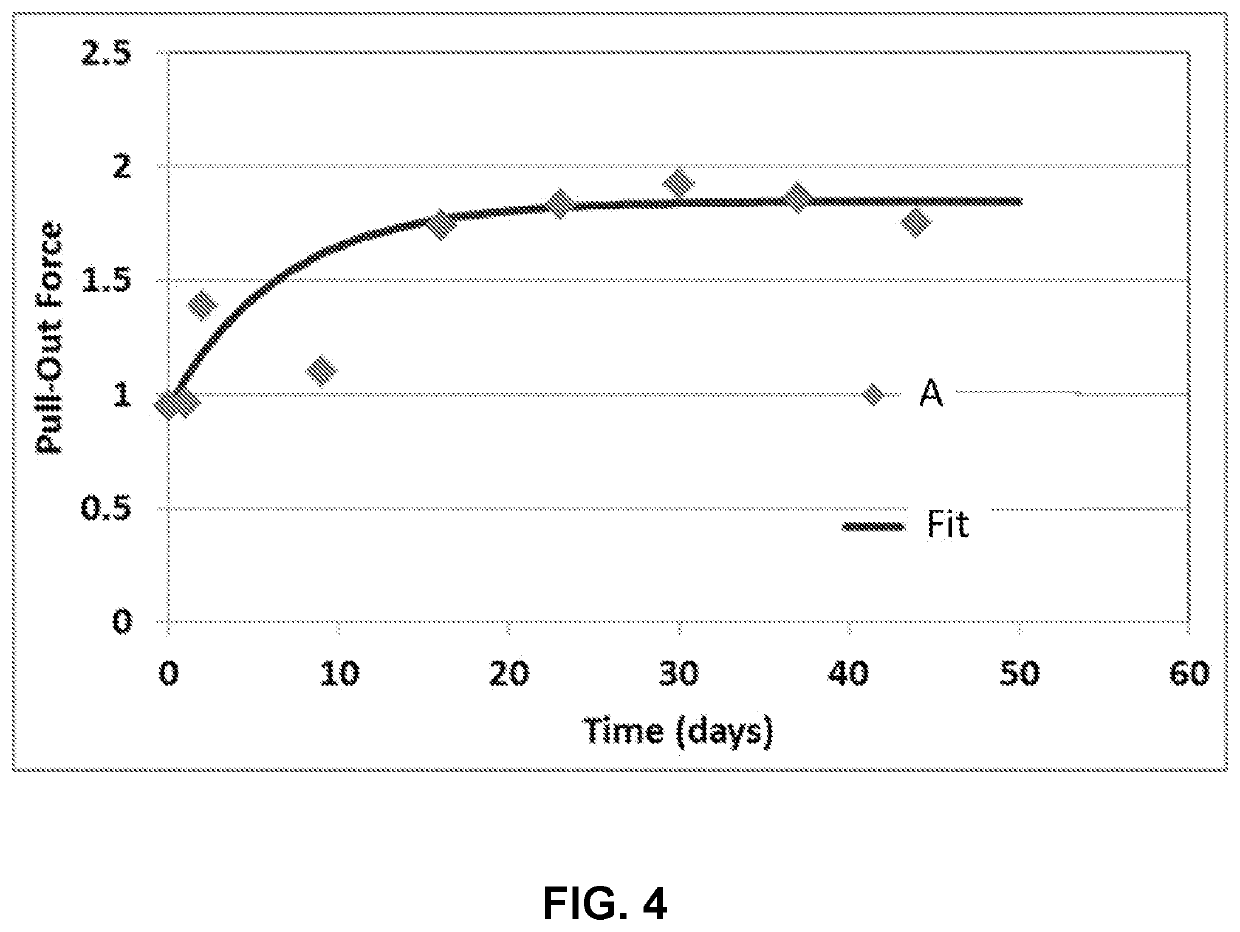
Fiber coatings with low pullout force
ActiveUS20200064546A1Low modulusImprove cohesionGlass optical fibreGlass fibre drawing apparatusGlass fiberYoung's modulus
An optical fiber includes an outer diameter less than 220 μm, a glass fiber that includes a glass core and a glass cladding, a primary coating, and a secondary coating. The glass cladding surrounds and is in direct contact with the glass core. The primary coating surrounds and is in direct contact with the glass fiber. The primary coating can have a Young's modulus less than 0.5 MPa and a thickness less than 30.0 μm. The secondary coating surrounds and is in direct contact with the primary coating. The secondary coating can have a thickness less than 27.5 m. A pullout force of the optical fiber can be less than a predetermined threshold when in an as-drawn state. The pullout force may increase by less than a factor of 2.0 upon aging the primary and secondary coatings on the glass fiber for at least 60 days.
Owner:CORNING INC
Battery electrode substrate, and electrode employing the same
InactiveUS20080085453A1Reduce capacityElectrode carriers/collectorsAlkaline accumulator electrodesSynthetic resinPolymer chemistry
An electrode substrate for a battery has nickel applied as a coat on the surface of a base constituted of crossing of a plurality of fibers including a core formed of synthetic resin and a coating of synthetic resin having a softening temperature lower than the softening temperature of the synthetic resin forming the core. The electrode substrate has the fibers of the base fusion-bonded at a cross point by heat treatment. The ratio of the coating occupying a II-II cross section of the fiber cross point is larger than the ratio of the coating occupying a fiber cross section (III-III cross section) at a site other than at the cross point.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
Optical fiber ribbon
An optical fiber ribbon includes a plurality of optical fibers, each includes a glass optical fiber coated with a fiber coating, that are arranged in parallel, and a ribbon coating that coats the optical fibers arranged in parallel. The optical fiber ribbon has a thickness equal to 300 μm or less. The fiber coating is made of a non-flame-resistant ultraviolet curable resin. The ribbon coating has a thickness equal to 40 μm or more and is made of a flame resistant resin.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
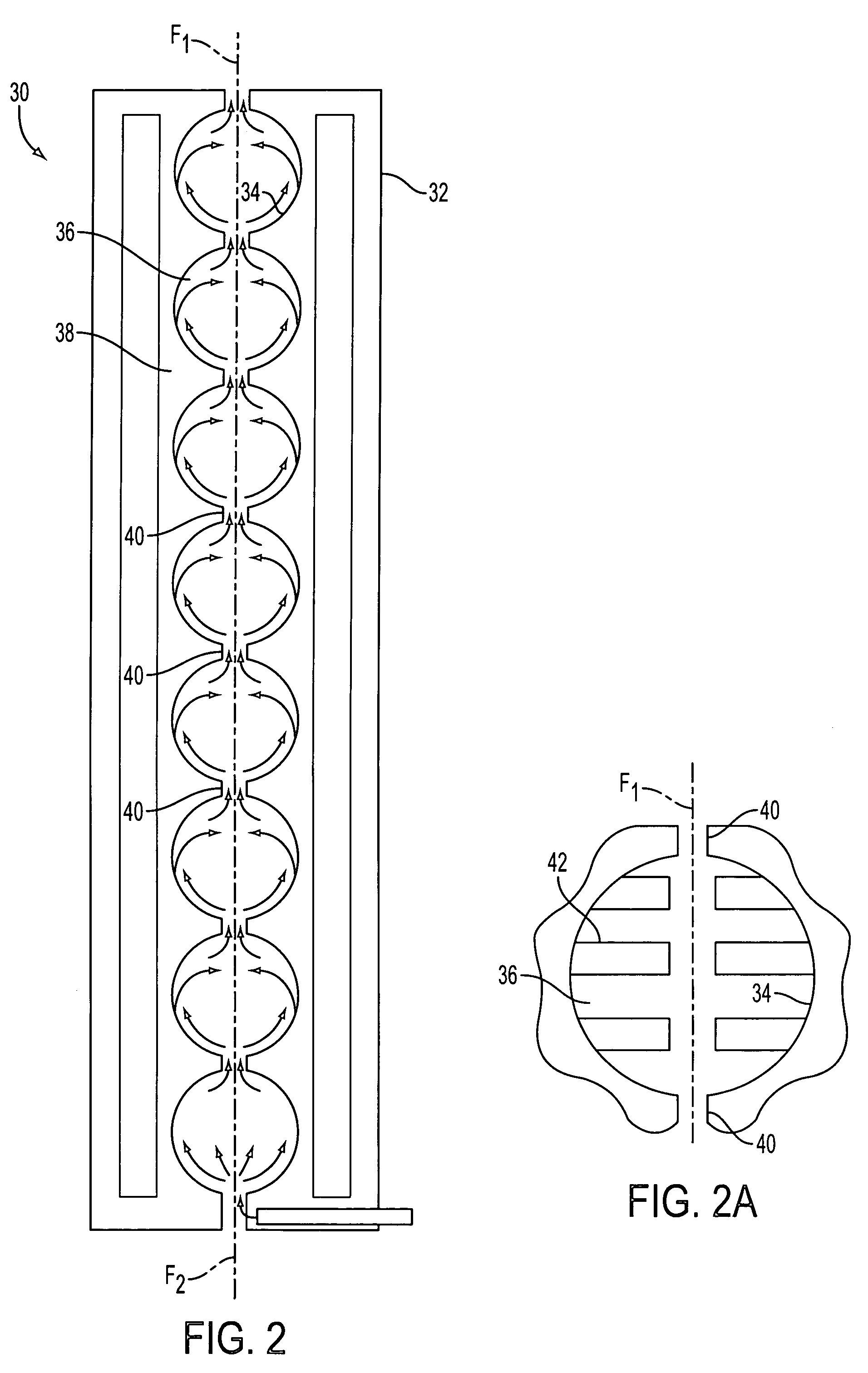
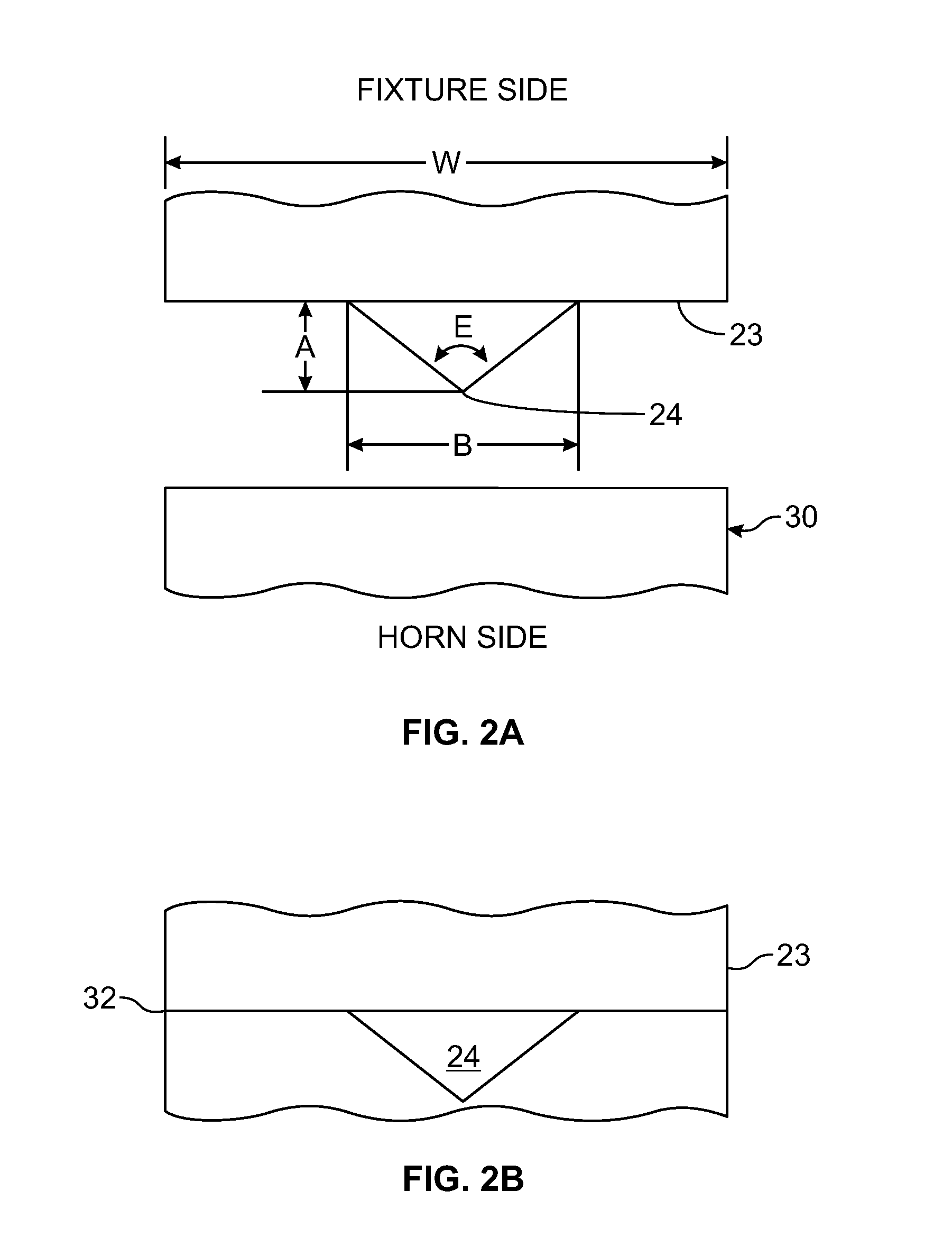
Fibre coating method and apparatus
A fibre unit coating apparatus includes a chamber into which an uncured resin coated fibre unit is passed. Microspheres mixed with air are fed into the chamber via ducts and apertures. As a result rapid and even application of the microspheres can be achieved, and the system allows controllable application of the microspheres by varying the rate of flow of the air / microsphere mixture. Positive pressure chambers are provided to prevent the microspheres from blocking the inlet and outlet points where the fibre unit enters and leaves the chamber.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Composite carrier of metal fiber and inorganic fiber and preparation method
The invention relates to a composite carrier of metal fiber and inorganic fiber and a preparation method. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preserving heat of the metal fiber for 2 hours under the condition of 650-750 DEG C; and transferring into treatment solution containing 1 percent H3PO4 and 0.2 percent SO4 to treat at the temperature of 50 DEG C for 4 hours, washing with water for three times, and drying the moisture; (2) mechanically stirring and mixing each ingredient of an inorganic fiber coating, and then making a layer of wet mixed slurry on a metal fiber screen by using a paper making method; blowing with compressed air of 0.05-0.1 MPa; and rolling into a carrier blank of a concentric circle, a double-core circle or a three-core circle in a wet state; and (3) finally, integrally and simultaneously blowing one end of each the rolled carrier blank at one time by using the compressed air of 0.2-0.4 MPa; raising temperature in a high-temperature furnace along with the furnace at the rate of 80 DEG C / 60 minutes, 120 DEG C / 60 minutes, 200 DEG C / 30 minutes, 300 DEG C / 60 minutes or 500 DEG C / 120 minutes; and then cooling to room temperature along with the furnace. The carrier is sintered into the carrier with the composite structure of spatially and three-dimensionally crossed metal fiber and inorganic fiber after being rolled, is tidy in the macroscopic level and confused in the microscopic level, and is used for SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) and POC (Particle Oxidation Catalyst) post-treatment; a back pressure problem is avoided; the process is simple and convenient; and the cost is equivalent to 1 / 2 that of an imported product under the condition of equivalent performance, so that the cost is saved.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
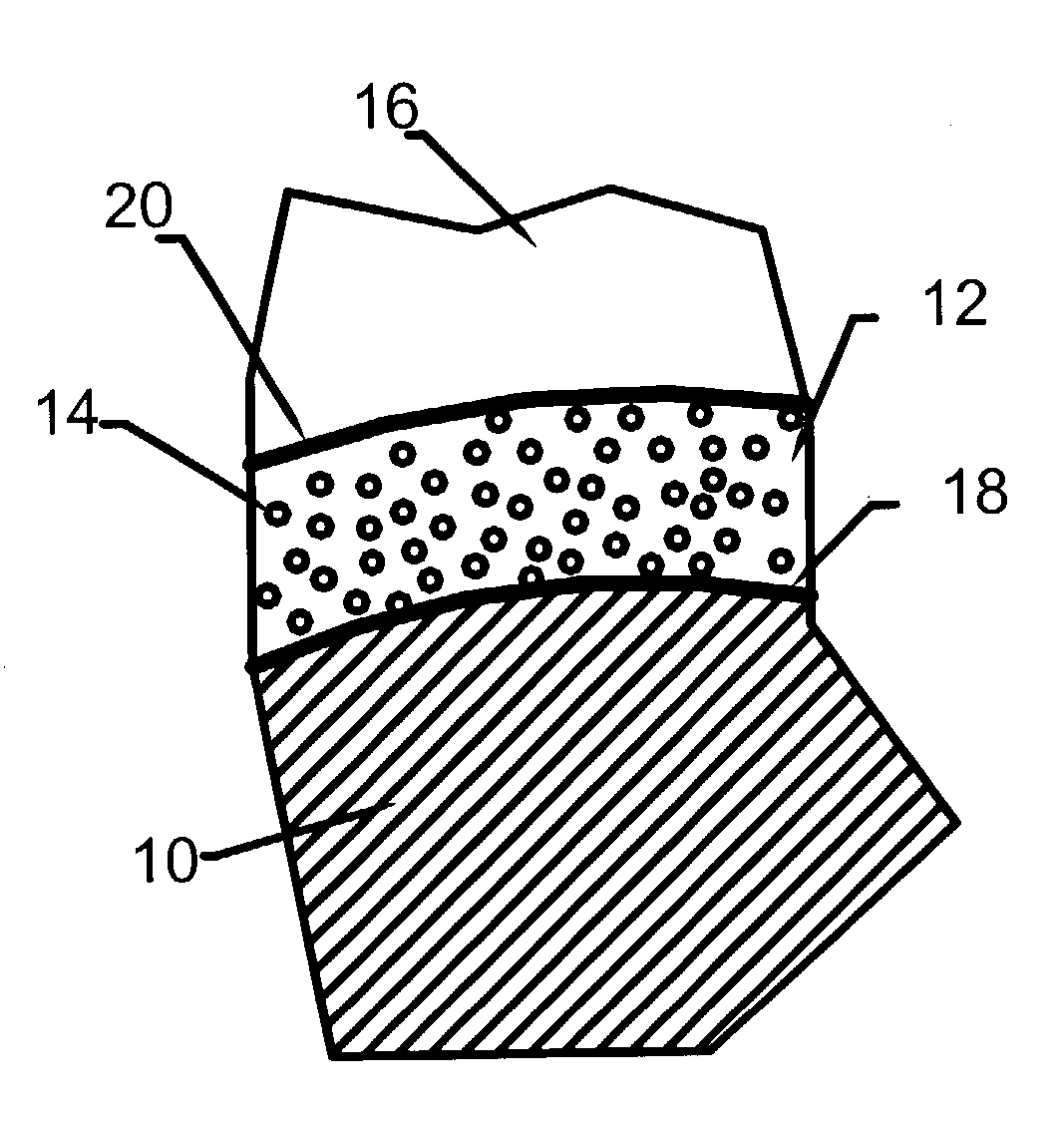
Coated Fibers for Culturing Cells
InactiveUS20110027888A1Simplify the harvesting processLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCultured cellBiology
A coated fiber for cell culture includes a fiber core having an exterior surface and a polymeric coating suitable for culturing cells disposed on at least a portion of the exterior surface of the fiber core. A polypeptide may be conjugated to the polymeric coating. A method for forming the coated fiber includes coating a polymer layer to an exterior surface of a fiber core to produce the coated fiber. The coating may occur as the fiber is being drawn.
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com