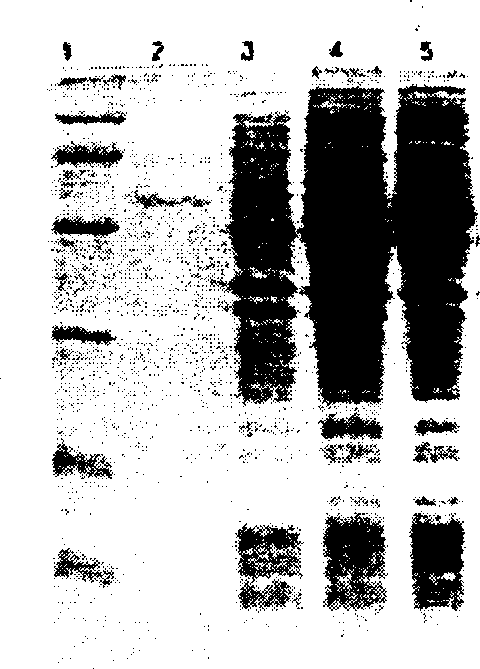Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Escherichia coli DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA is a long molecule. For example, a typical bacterium, like E. coli, has one DNA molecule with about 3,000 genes (A gene is a specific sequence of DNA nucleotides that codes for a protein. We'll talk about this later). If drawn out, this DNA molecule would be about 1 millimeter long.
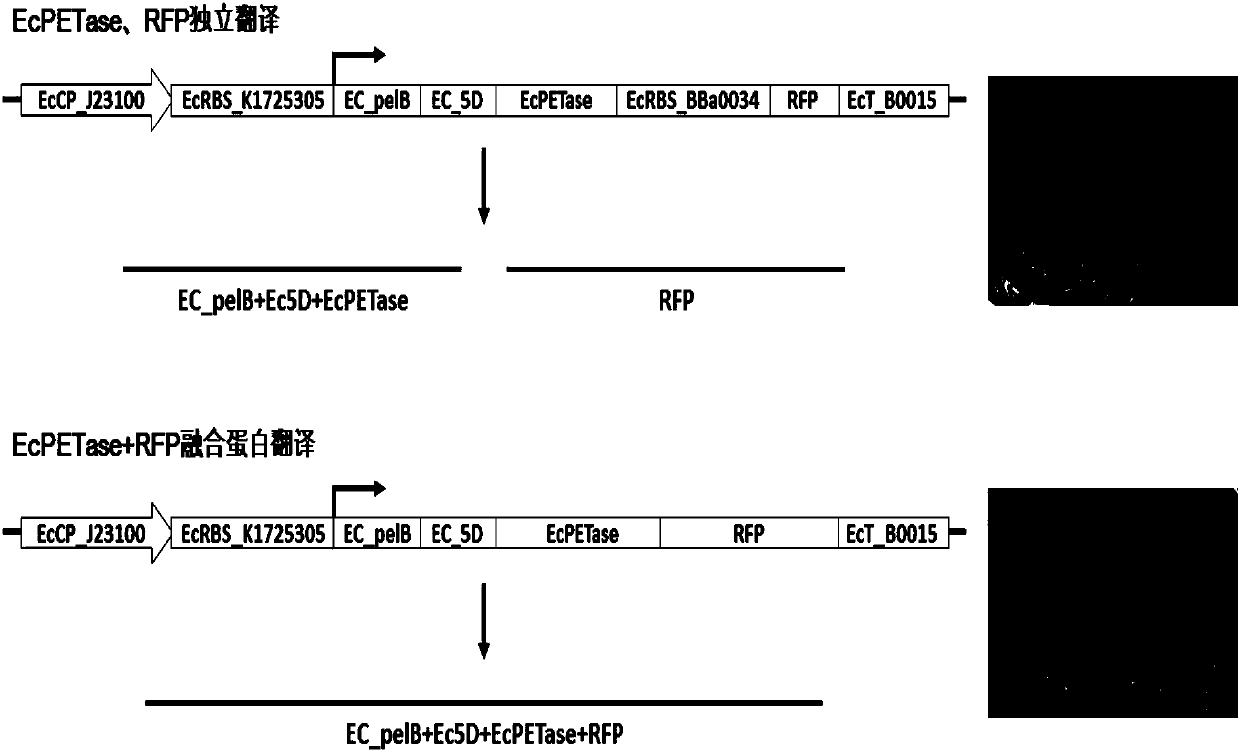
Genetic engineering strain for degrading PET (polyethylene terephthalate) plastics
ActiveCN107794252APossess lipolytic activityPromote efficient degradationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial gene engineering, aims to solve the problem of difficult degradation of the PET (polyethylene terephthalate) plastics, and provides a PET hydrolytic enzyme expression unit, a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) recombined vector built based on the unit and an application of the vector, wherein the vector can effectively secrete colibacillus expressing PET hydrolase (PETase). The DNA recombined vector can effectively achieve secreting type constant expression of the PET hydrolytic enzyme in colibacillus host bacteria, nutrient solution of the vector has remarkable lipase biological activity, PET plastic films can be degraded in continuous culture process, a genetic engineering approach is provided for biodegradation of the PET plastics, andthe vector has a good application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Hot start polymerase reaction using a thermolabile blocker
The invention relates to compositions, methods, and kits for hot start polynucleotide synthesis, including extension of primed polynucleotide templates and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Hot start is provided by a thermally inactivated blocking polymerase protein that binds primed polynucleotide templates and prevents their access to a thermostable nucleic acid polymerase. High temperatures employed in the synthesis reaction cause the blocking polymerase to denature, thereby permitting the action of a thermostable processive polymerase. Compositions of the invention include a specific blocking polymerase protein which is a mutant of the Klenow fragment of E. coli DNA polymerase. The mutant is essentially devoid of polymerase activity, processivity, and 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity. Use of the thermally inactivated blocking polymerase together with a thermostable polymerase reduces non-specific priming and accumulation of unwanted amplification products, increasing the specificity and sensitivity of the synthesis reaction.
Owner:STRATAGENE INC US
Isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent and isothermal nucleic acid amplification method
ActiveCN105543402ASimplify the amplification reaction processLower requirementMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LHelicase
The invention provides an isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent. The isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent is characterized by comprising components as follows: 100-800 mM of a Tris-HCl buffer solution, 10-150 mM of sodium chloride, 10-150 mM of potassium chloride, 10-50 mM of magnesium chloride, 5-15 mM of dithiothreitol, 5%-20% of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 10-20 mM of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), 1-5 mM of dNPTs, 10-50 mM of phosphoenolpyruvate, 500-1,500 ng / mu l of pyruvate kinase, 10-500 ng / mu l of BSA (bovine serum albumin), 25-200 pmol of each primer in a primer group, 50-200 ng / mu l of T4 bacteriophage DNA helicase gp41 protein, 100-500 ng / mu l of streptomyces coelicolor recA protein, 200-1,000 ng / mu l of single-strand binding protein and 50-200 ng / mu l of escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. The invention further provides an isothermal nucleic acid amplification method. According to the isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent and the isothermal nucleic acid amplification method, nucleic acid amplification under the isothermal condition at the lower temperature is realized, and a traditional nucleic acid amplification reaction process is greatly simplified.
Owner:刘国宪
Escherichia coli DNA photolyase and construction method thereof
ActiveCN105062999AHigh activityImprove antioxidant capacityBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliA-DNA
The invention discloses escherichia coli DNA photolyase and a construction method thereof. The enzyme has the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 (in the description). The construction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a DNA photolyase gene from the conventional WT escherichia coli; designing a mutation primer to obtain a mutational gene segment; connecting the mutational gene segment with pET22b plasmid; constructing recombinant expression plasmid pET22b-A377S; converting the recombinant expression plasmid into a competent cell of escherichia coli; constructing genetically engineered bacterium BL21 (DE3) / pET22b-A377S for mutant enzyme expression. According to the invention, better expression is achieved under the conditions of 18 DEG C and 1 mM ITPG; the expressed photolyase is more stable in activity, and the antioxidant effect of the enzyme is remarkably improved.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Method for constructing BAC subclone library
InactiveCN1884575ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiologyDNA
This invention provides a kind of improved construction method of BAC subclone base. The processing steps are: extraction and purification of BAC DNA, the fragememtation and end trimming of BAC DNA; the recollection of target fragment and the attachment of vector; the transformation of attachment. For example, the BAC subclone base built by corn is with more than 1500 clones. The empty clone and coliform DNA pollution rate is lower than 5%. The inserted fragment is 3kb in average. This method is easy, cheap, fast and effective.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Site-directed mutagenesis escherichia coli DNA photolyase and construction method thereof
ActiveCN105087535AHigh activityImprove antioxidant capacityBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliA-DNA
The invention discloses a site-directed mutagenesis escherichia coli DNA photolyase and a construction method thereof. The photolyase has an amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a DNA photolyase gene from the existing WT escherichia coli, designing a mutation primer to obtain a mutated gene fragment, and connecting the mutated gene fragment with a pET22b plasmid to construct a recombinant expression plasmid pET22b-A377N; and converting the recombinant expression plasmid into an escherichia coli competent cell to construct a genetic engineering bacterium BL21(DE3) / pET22b-A377N for mutant enzyme expression. The site-directed mutagenesis escherichia coli DNA photolyase obtains better expression under a 1mM ITPG condition at 18 DEG C. The expressed photolyase is more stable in activity, and the antioxidation effect of the photolyase is significantly improved.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Nucleic acid diluent
The invention relates to a nucleic acid diluent. The nucleic acid diluent comprises 1*TE, F68 and DNA selected from the group consisting of Lambda DNA, pUC19 plasmid DNA, pUC18 plasmid DNA, pBR322 plasmid DNA, denatured protamine DNA, pUC57 plasmid DNA, pTZ19R DNA, Escherichia coli DNA and sssDNA. The nucleic acid diluent provided by the invention can be used for dilution of a standard substance and a sample in quantitative PCR and has the effects of protecting and stabilizing the standard substance and the sample. The invention also relates to a standard substance solution prepared from the nucleic acid diluent and a quantitative PCR method using the standard substance solution.
Owner:SHANGHAI MYGT BIOPHARMACEUTICAL LLC
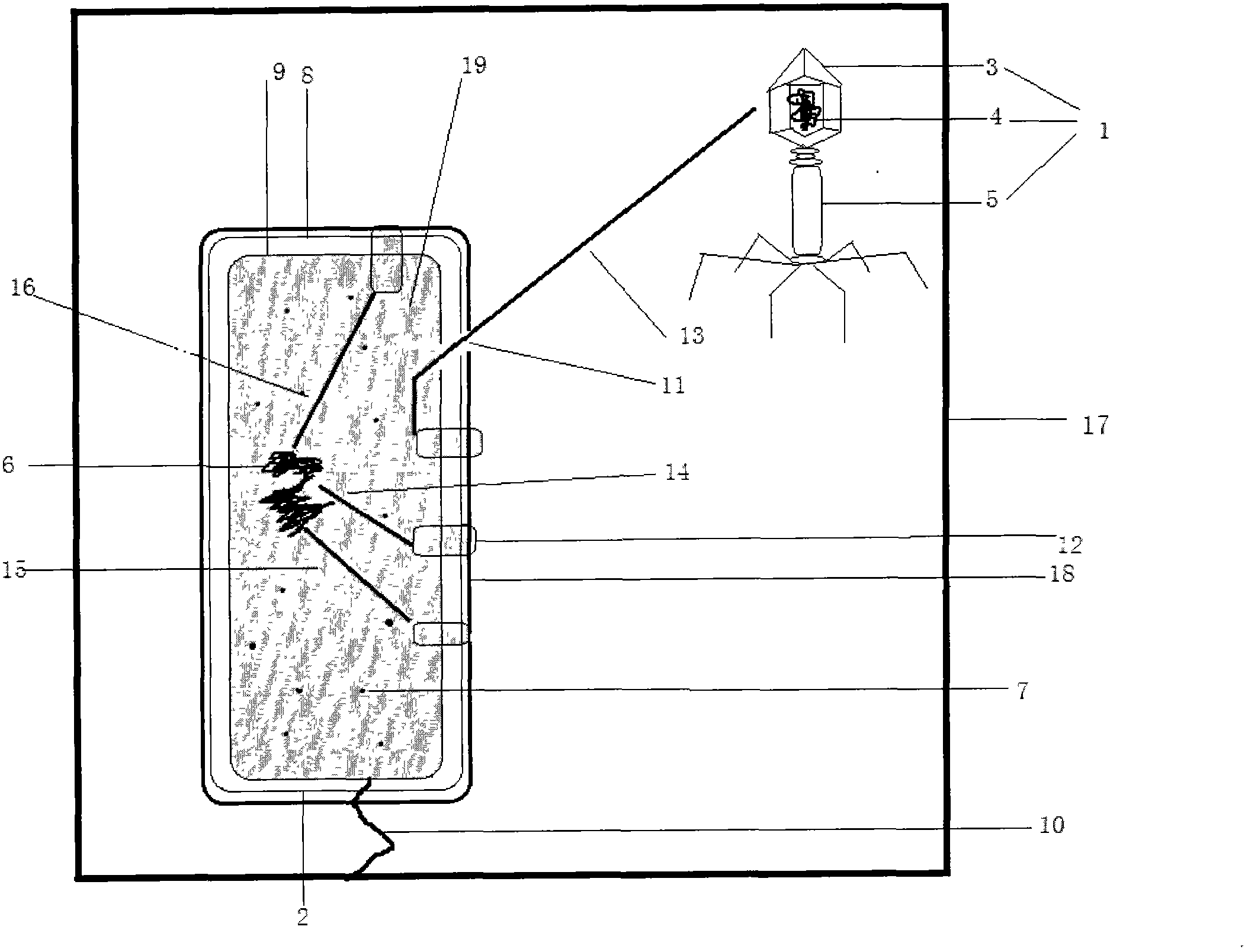
Teaching demonstration model for bacteriophage invading bacteria
InactiveCN103456205AThorough understandingIncrease interest in learningEducational modelsEscherichia coliCell membrane
The invention relates to an emulational teaching model for demonstrating how a bacteriophage invades bacteria, in particular to a teaching demonstration model for a bacteriophage invading bacteria. The teaching demonstration model comprises a T4 bacteriophage model and an escherichia coli thallus model. The T4 bacteriophage model is composed of a protein head module and a hollow protein tail module, and a bacteriophage DNA molecule module is included in the protein head module. The escherichia coli thallus model is composed of simulative flagellums, a capsule, a cell wall module, a cell membrane module, an escherichia coli DNA molecule module, a ribosome module and a cytoplasm module, small holes are formed in the capsule, the cell membrane and the cell wall of the model, and therefore the NDA molecule module of the bacteriophage model can move into the escherichia coli thallus model conveniently. Multiple rails facilitating the moving of all the modules and a baffle hiding the protein shell of the model are arranged on the base plate of the whole model and the cytoplasm module.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
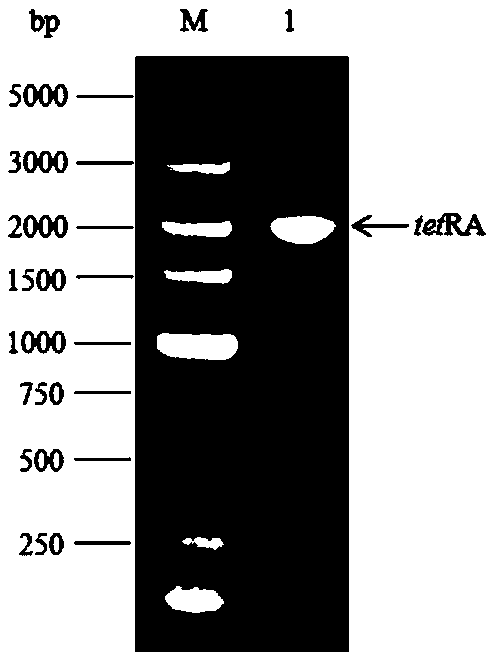
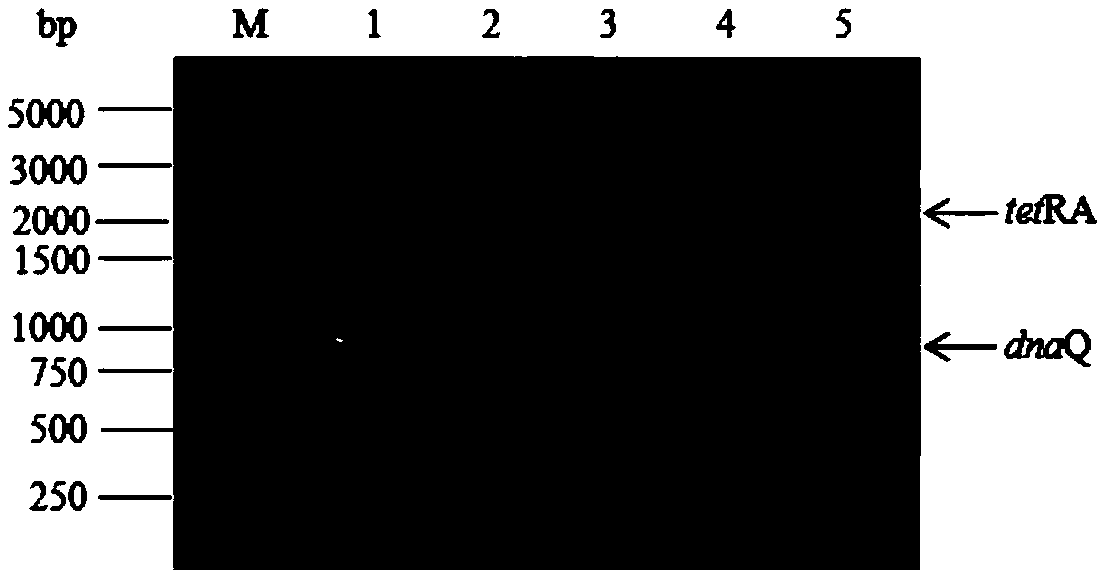
Mutator strain with loss of correcting function of escherichia coli dnaQ gene, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN109554323AImprove breeding efficiencyIncreased frequency of genetic mutationsBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliPolymerase L
The invention discloses a mutator strain with loss of correcting function of escherichia coli dnaQ gene, and a preparation method and applications thereof. The mutator strain is obtained by knocking out, inserting inactivating or mutating gene dnaQ of encoded escherichia coli DNA polymerase III epsilon subunit so as to lose the correcting function during DNA replication. The method knocks out thegene dnaQ of eth encoded escherichia coli DNA polymerase III epsilon subunit by using a lambada-Red recombinase method, and obtains the mutator strain with loss of correcting function during DNA replication. The mutation capacity of the strain is 25000 times as high as that of wild types, and the strain is an efficient means of gene mutagenesis. At the same time, the strain reduces the working time cost for screening mutants with excellent traits, and improves the efficiency of scientific research work and engineering bacteria selection.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF BIOENG
Protein crystal comprising the processivity clamp factor of DNA polymerase and a ligand, and its uses
InactiveUS7635583B2Antibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliProcessivity clamp
A protein crystal having the processivity clamp factor of DNA polymerase that is the β subunit of DNA polymerase III of Escherichia coli and a peptide of about 3 to about 30 amino acids, in particular of about 16 amino acids. The peptide includes all or part of the processivity clamp factor binding sequence of a processivity clamp factor interacting protein, such as prokaryotic Pol I, Pol II, Pol III, Pol IV, Pol V, MutS, ligase I, α subunit of DNA polymerase, UmuD or UmuD′, or eukaryotic pol ε, pol δ, pol η, pol ι, pol κ.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Kit and method for extracting and purifying escherichia coli DNA from complicated sample
ActiveCN107828784ASimple experimentShorten experiment timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationEscherichia coliMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a kit and a method for extracting and purifying escherichia coli DNA from a complicated sample, and belongs to the field of molecular biology. The kit for extracting and purifying the escherichia coli DNA from the complicated sample comprises (1) carboxylated nano magnetic bead Eget103 coupled with gp37 protein, (2) sample diluent, (3) sample lysate, (4) nucleic acid cleaning fluid, (5) DNA eluent, and (6) nucleic acid adsorption magnetic beads. According to the kit and the method, the carboxylated nano magnetic bead Eget103 coupled with gp37 protein are specifically combined with escherichia coli to purify the escherichia coli, and then DNA is extracted from the purified escherichia coli by a magnetic bead method. In the whole process, no isolation and purificationculture of the escherichia coli is needed, and the DNA is directly extracted; therefore, the experimental process is simplified, and the experimental time is greatly shortened.
Owner:山东凯景生物技术有限公司
Multi-PCR detection primers for detecting four sheep pathogenic bacteria and detection method
ActiveCN105087814AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed FeaturesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSalmonella DNADiagnosis laboratory
The invention discloses multi-PCR detection primers for detecting four sheep pathogenic bacteria and a detection method. The primers include Klebsiella pneumoniae upstream and downstream primers, proteus mirabilis upstream and downstream primers, escherichia coli upstream and downstream primers and salmonella upstream and downstream primers. According to the detection method, the primers are adopted to perform multi-PCR amplification reaction with Klebsiella pneumoniae DNA, proteus mirabilis DNA, escherichia coli DNA and salmonella DNA as templates, PCR amplification reaction products are added into loading buffer, the mixture is put into agarose gel containing ethidium bromide, and electrophoresis detection is performed to verify the specificity of the primers. The detection method has the advantages that molecular detection with high sensitivity can be achieved just through conventional instruments, and the detection sensitivity of the method is high; meanwhile, no complex operation system is needed, and detection can be performed under common laboratory conditions; besides, the method is easy and fast to implement, high in sensibility and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting escherichia coli in coastal seawater
InactiveCN106167823AShorten detection timeOvercoming the inability to detect non-culturable E. coliMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPlasmid
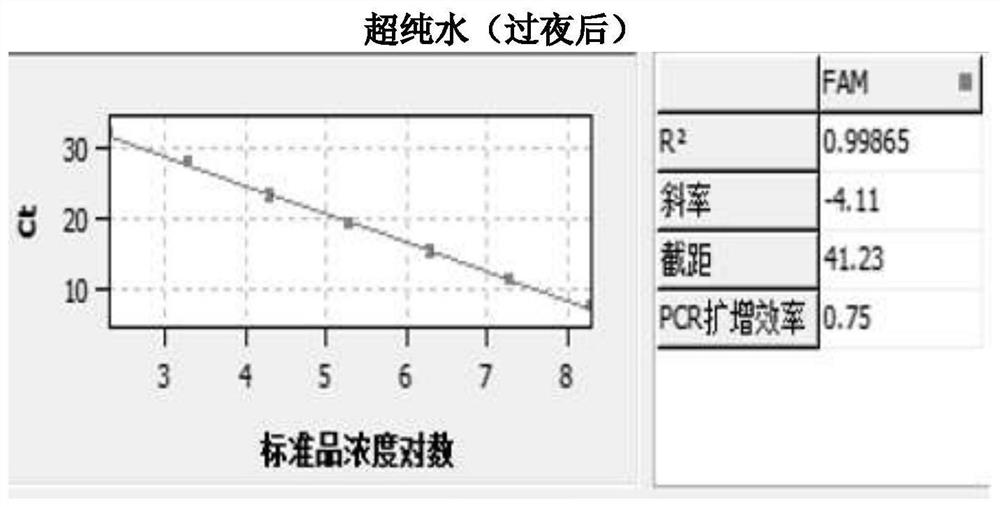
The invention discloses a method for detecting escherichia coli in coastal seawater. The method comprises the steps of extracting escherichia coli DNAs, amplifying target fragments, constructing a standard plasmid template, establishing a Q-PCR quantitative standard curve and measuring the number of escherichia coli in an environmental sample. Compared with current detection based on a selective culture method, the method has the advantages that first detection time is shortened from 10-12 d of the original method to 1 d, and is only 3-4 h on the conditions that the standard curve is finished; the problem that escherichia coli cannot be measured in the original method is solved, and the identification accuracy is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Process for purification preparing DNA optical repairase
InactiveCN1624118AActivity determinationFewer separation stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsPurification methodsUltraviolet
A process for preparing high-purity DNA photorepairase includes such steps as sing gentic engineering method to obtain the DNA photorepairase with His marker of colibacillus, and affinity chromatography by Ni-ion affinity chromatographic column. Its advantages are high purity (90%) short period, and low cost.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method of preparing DNA probe, kit and application thereof
The invention provides a method of preparing a DNA probe, a kit, a method of detecting content of bacillus coli DNA in a biological product, and a method of determining a production process of a biological product. The method of preparing the DNA probe comprises the steps of (1) ultrasonic crushing cell genomic DNA of bacillus coli, wherein in the ultrasonic crushing treatment, the concentration of the cell genomic DNA of bacillus coli is 20 mcg / ml; and (2) incubating the product of ultrasonic crushing and a labeling reagent so as to acquire the DNA probe, wherein the DNA probe carries the label. The DNA probe prepared by the method can detect the volume of residual bacillus coli DNA in biological products (comprising middle sample, semi-finished product and finished product) exclusively,flexibly, quickly and accurately.
Owner:WUHAN OPTICS VALLEY HUMANWELL BIO PHARMA
Nucleotide specific for escherichia coli 0149 O-antigen
The invention provides a nucleotide specific for Escherichia coli 0145 O-antigen, which is the total nucleotide sequence of the gene cluster for controlling the synthesis of O-antigens in Escherichia, e.g. isolated nucleotide represented by SEQ ID No:1, with overall length of 16932 bases, or nucleotide of SEQ ID No:1 including one or more inserted, deleted or substituted bases and sustaining the functions of the isolated nucleotides, it also includes the oligonucleotides of glycosyl transferase genes and oligosaccharide unit treatment genes in the O-antigen gene cluster originated from Escherichia 0145. The invention proves the high specifity of oligonucleotides for Escherichia coli 0145 O-antigen through PCR. A method for detecting and identifying Escherichia 0145 by means of the oligonucleotide according to the invention is also disclosed.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Kit for detecting human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveCN101812543AHigh sensitivityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid amplification techniqueBiotechnology
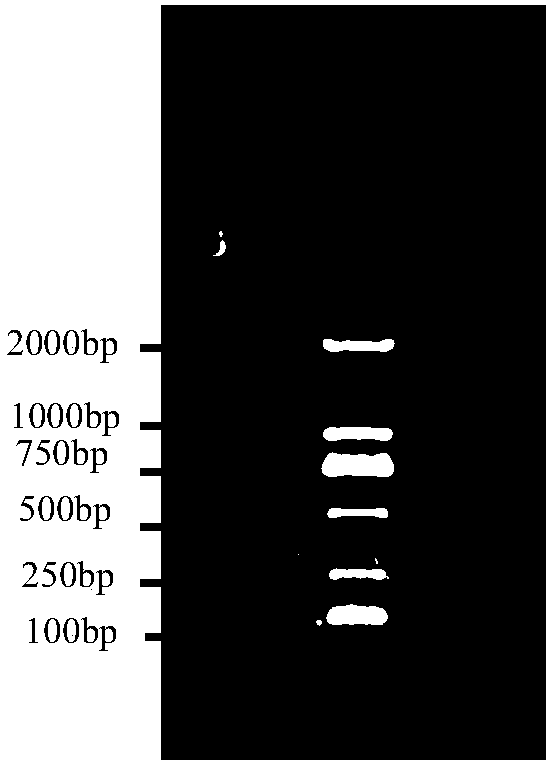
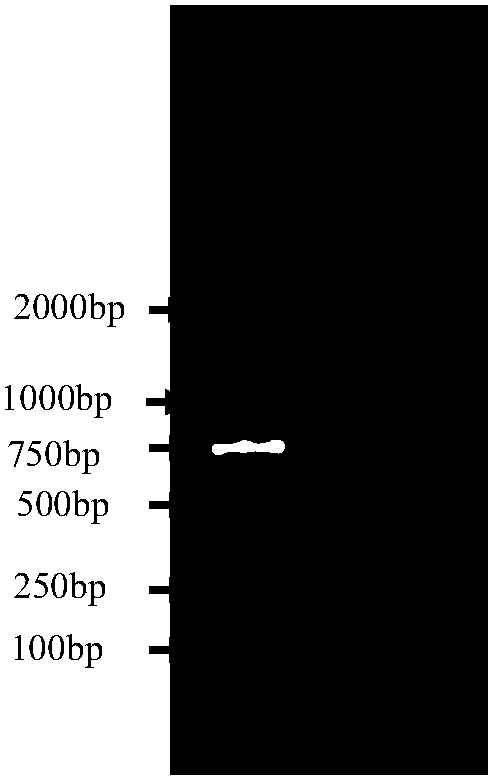
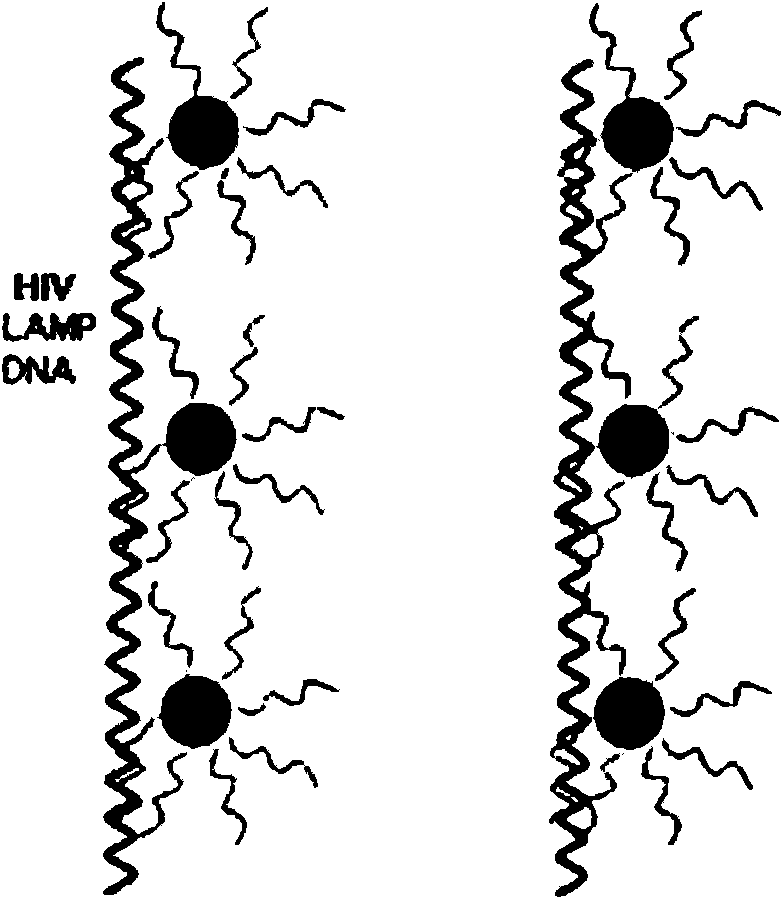
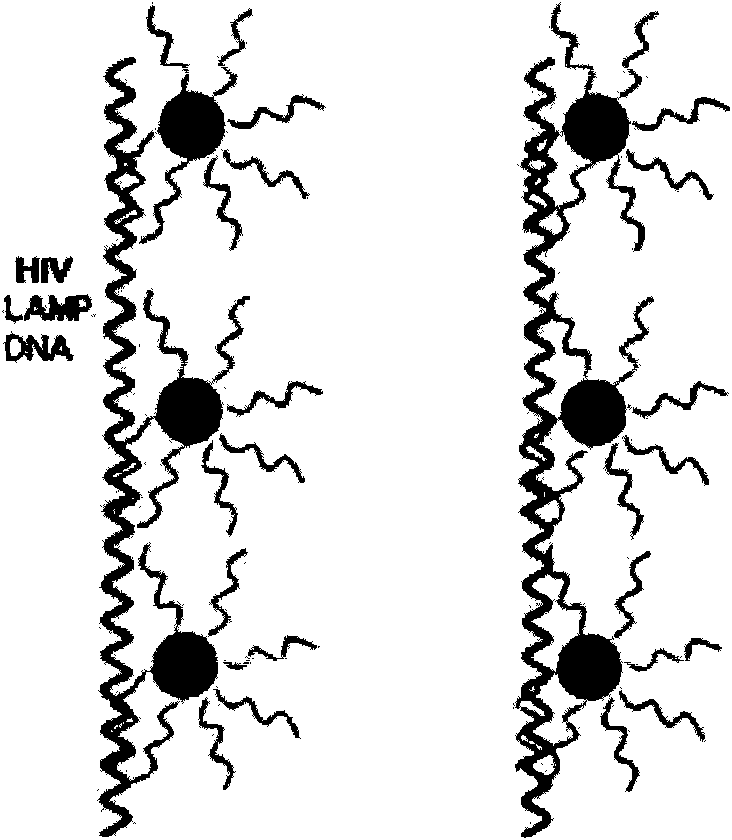
The invention relates to a kit for detecting product DNA by utilizing nano-gold particles after human immunodeficiency virus is amplified through a loop-mediated isothermal nucleic acid amplification technique, which belongs to the technical field of biological detection. The kit combines the loop-mediated isothermal nucleic acid amplification technique with a biological nanotechnology to improve the detection sensitivity of biological molecules, is a method with simple operation, rapidness, accuracy and no need for professional instruments and equipment, and can be widely applied to high-sensitivity HIV detection in the fields of household diagnosis, clinical diagnosis, infectious diseases control, environment monitoring, inspection and quarantine, biotechnology and the like. The kit comprises two parts, namely (1) the nano-gold particles marked with molecular robes capable of identifying specific sequences of HIV and (2) a loop-mediated isothermal nucleic acid amplification system capable of amplifying the escherichia coli DNA in to-be-detected samples or performing a reverse transcription process and then amplifying the RNA of the HIV in the to-be-detected samples.
Owner:天津朝海科技有限公司
Fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting escherichia coli
InactiveCN106978506AEfficient and accurate extractionImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPcr method
The invention discloses a fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting escherichia coli. The fluorescent quantitative PCR method comprises the following steps: S1. designing a specific primer and a fluorescent probe according to target gene sequence; S2. selecting an escherichia coli, and extracting DNA / RNA of the sample; S3. converting the extracted RNA into cDNA; and S4. detecting the extract of the last step by using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer. The fluorescent quantitative PCR method has the following advantages: 1. being capable of accurately and efficiently extracting high-purity escherichia coli DNA, and beneficial to improvement of experimental results; 2. constructing a standard curve equation by utilizing a double-standard curve standard, so as to calculating the number of escherichia coli in the sample; and 3. providing a rapid and high-efficiency detection system which is flexible, simple and convenient to operate, and can be used for qualitative and quantitative detection of escherichia coli.
Owner:WUHAN IGENEBOOK BIOTECH CO LTD
Process for purification preparing DNA optical repairase
InactiveCN1274818CFewer separation stepsEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsPurification methodsUltraviolet
A process for preparing high-purity DNA photorepairase includes such steps as sing gentic engineering method to obtain the DNA photorepairase with His marker of colibacillus, and affinity chromatography by Ni-ion affinity chromatographic column. Its advantages are high purity (90%) short period, and low cost.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Nucleotide peculiar to 0-antigen of 110 type bacillus coli
The invention provides a nucletoide which is specific to O-antigen of Escherichia coli type O110, it is a nucleotide complete sequence of gene cluster for controlling synthesis of O-antigen in escherichia coli type, as the separated nucleotide shown by SEQ ID No:1, its total length has 9800 bases; or the nucleotide of SEQ ID No:1, which has one or several inserted, deleted or substituted bases, and retains the function of the described separated nucleotide at the same time; it also includes the oligonucleotide of the glycosyltransferase gene and oligosaccharide unit treatment gene originated from O-antigen gene cluster of Escherichia coli type O110. Said invention utilizes PCR to verify that the oligonucleotide has high specificity to O-antigen of escherichia coli type O110, and said invention also discloses the method for detecting and identifying Escherichia coli type O110 in human body.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Nucleotide peculiar to 0-antigen of 041 type bacillus coli
The invention provides a nucleotide which is specific to O-antigen of Escherichia coli O41, it is a nucleotide complete sequence of gene cluster for controlling the synthesis of O-antigen in Escherichia coli O41, as the separated nucleotide shown by SEQ ID No:1, its total length has 15377 bases; or the nucleotide of SEQ ID No:1, which has one or several inserted, deleted or substituted bases, and retains the function of the described separated nucleotide at the same time; it also includes the oligonucleotide of the aligosacharide unit treatment gene (including wzx gene or gene whose function is similar to that of WZX and WZY gene or gene whose function is similar to that of wzy) originated from O-antigen gene cluster of Escherichia coli O41. Said invention utilizes PCR to verify that the oligonucleotide has high specificity to O-antigen of Escherichia coli O41, and said invention also discloses the method for detecting and identifying Escherichia coli O41 in human body.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Dna-linked enzyme-coupled assays
ActiveUS20170240952A1Improve throughputIncrease costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCell freeDNA Modification
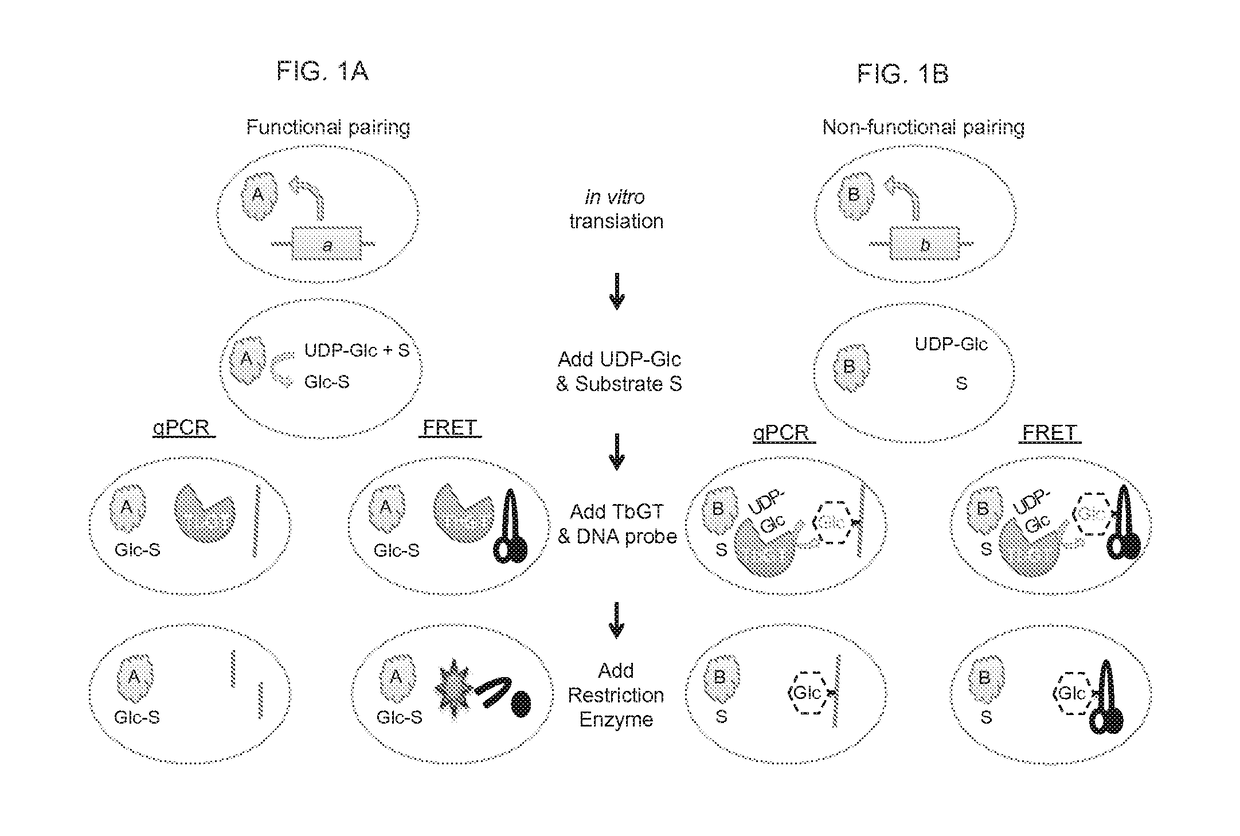
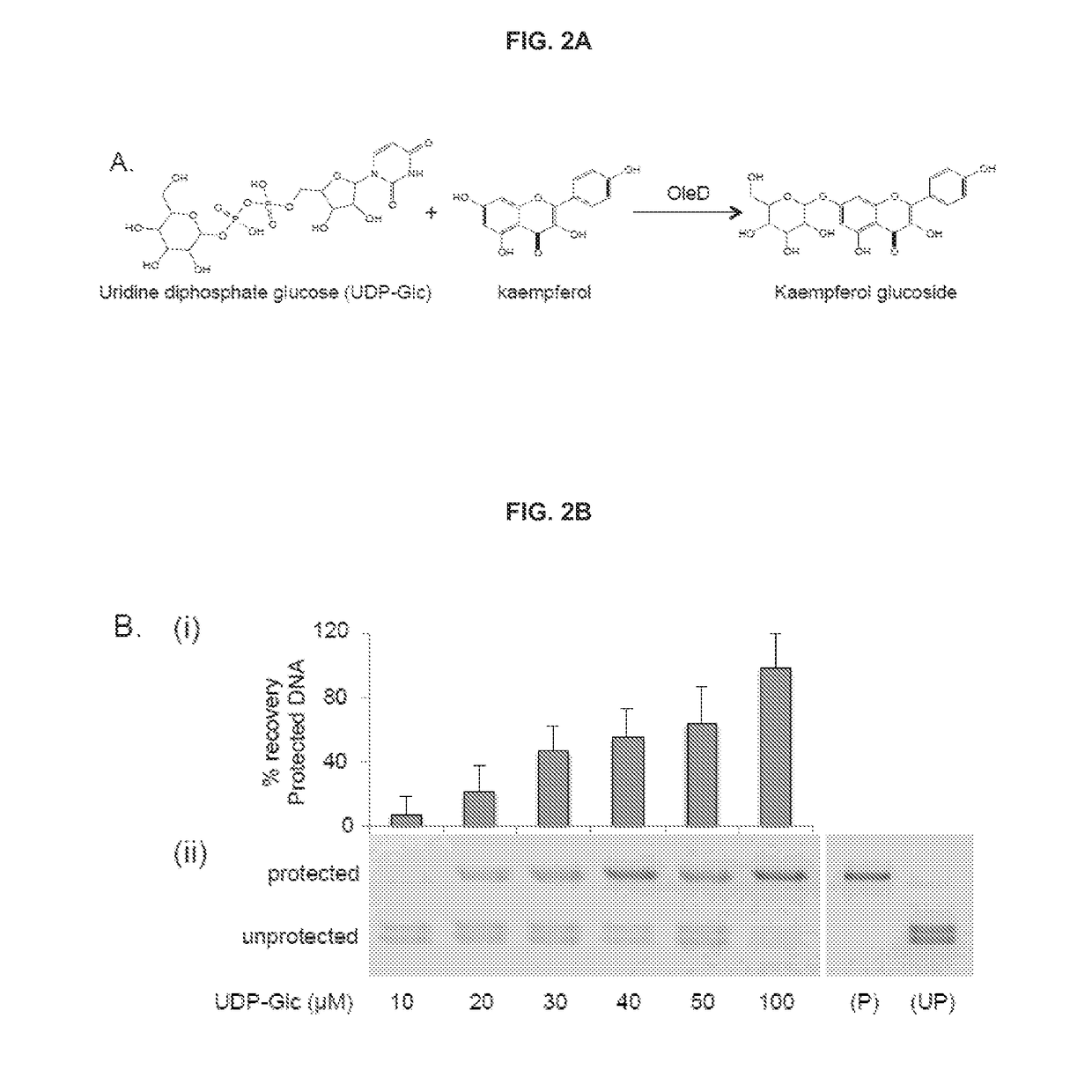
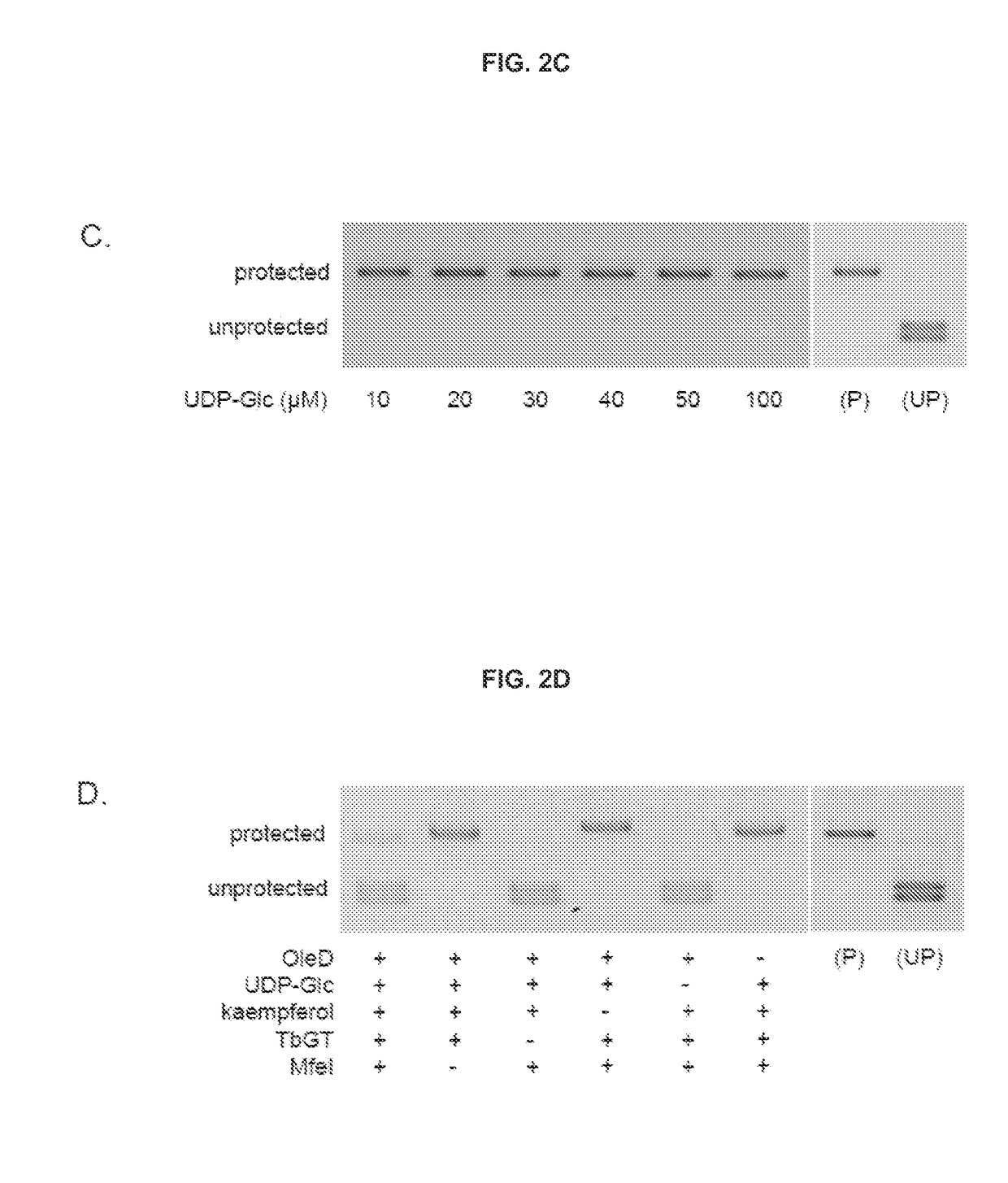
Traditional enzyme characterization methods are low-throughput, and therefore limit engineering efforts in synthetic biology and biotechnology. Here we propose a DNA-linked enzyme-coupled assay (DLEnCA) to monitor enzyme reactions in a high-throughput manner. Throughput is improved by removing the need for protein purification and by limiting the need for liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LCMS) product detection by linking enzymatic function to DNA modification. DLEnCA is generalizable for many enzymatic reactions, and here we adapt it for glucosyltransferases, methyltransferases, and oxidoreductases. The assay utilizes cell free transcription / translation systems to produce enzymes of interest, while UDP-Glucose and T4-β-glucosyltransferase are used to modify DNA, which is detected post-reaction using qPCR or similar means of DNA analysis. For monitoring methyltransferases, consumption of SAM is observed by coupling to EcoRI methyltransferase. For monitoring oxidoreductases, consumption of NADH is observed by coupling to Taq or E. coli DNA ligase. OleD and two glucosyltransferases from Arabidopsis were used to verify the assay's generality toward glucosyltransferases. Two methyltransferases from human and Arabidopsis were used to verify the assay's generality towards methyltransferases. We show DLEnCA's utility by mapping out the substrate specificity for these enzymes and observing the multiple steps of a biosynthetic pathway.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for constructing BAC subclone library
InactiveCN1884575BSimple and fast operationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiologyDNA
This invention provides a kind of improved construction method of BAC subclone base. The processing steps are: extraction and purification of BAC DNA, the fragememtation and end trimming of BAC DNA; the recollection of target fragment and the attachment of vector; the transformation of attachment. For example, the BAC subclone base built by corn is with more than 1500 clones. The empty clone and coliform DNA pollution rate is lower than 5%. The inserted fragment is 3kb in average. This method is easy, cheap, fast and effective.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Nucleotide to 0-antigen specificity of Escherichia coli 0140 type
The invention provides a nucleotide specific to O-antigens of Escherichia coli O140, a full sequence of gene cluster in Escherichia coli O140, controlling O-antigen synthesis, such as the separated nucleotide shown in SEQ IN No.1, with a overall length of 14009 basic groups; or a nucleotide in SEQ IN No.1 having one or many inserted, deleted or substituted basic groups and simultaneously maintaining functions of the separated nucleotide; also including an oligonucleotide coming from glycosyltransferase gene and oligosaccharide unit-processing gene in the O-antigen gene cluster of Escherichia coli O140; by PCR, the invention verifies that oligonucleotide has specificity to all the O-antigens of Escherichia coli O140; the invention also discloses a method of using the oligonucleotide to detect and identify Escherichia coli O140 in the human body and environment.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Nucleotide to 0-antigen specificity of escherichia coli 0154 type
The invention provides a nucleotide specific to O-antigens of Escherichia coli O154, a full sequence of gene cluster in Escherichia coli O154, controlling O-antigen synthesis, such as the separated nucleotide shown in SEQ IN No.1, with a overall length of 13635 basic groups; or a nucleotide in SEQ IN No.1 having one or many inserted, deleted or substituted basic groups and simultaneously maintaining functions of the separated nucleotide; also including an oligonucleotide coming from glycosyltransferase gene and oligosaccharide unit-processing gene in the O-antigen gene cluster of Escherichia coli O154; by PCR, the invention verifies that oligonucleotide has specificity to all the O-antigens of Escherichia coli O154; the invention also discloses a method of using the oligonucleotide to detect and identify Escherichia coli O154 in the human body and environment.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
A kind of multiple PCR detection primer and detection method for detecting four kinds of sheep pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN105087814BGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed FeaturesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSalmonella DNAMultiplex pcrs
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Nucleotide peculiar to 0-antigen of 051 type bacillus coli
The invention provides a nucleotide which is specific to O-antigen of Escherichia coli O51, it is a nucleotide complete sequence of gene cluster for controlling synthesis of O-antigen in Escherichia coli O51, as the separated nucleotide shown by SEQ ID No:1, its total length has 13343 bases; or the nucleotide of SEQ ID No:1, which has one or several inserted, deleted or substituted bases, and retains the function of the described separated nucleotide at the same time; it also includes the oligonucleotide of the oligosaccharide unit treatment gene (including wzx gene or gene whose function is similar to that a wzx and wzy gene or gene whose function is simlar to that of wzy) originated from O-antigen gene cluster of Escherichia coli O51. Said invention utilizes PCR to verify that the oligonucleotide has high specificity to O-antigen of Escherichia coli O51, and said invention also discloses the method for detecting and identifying Escherichia coli O51 in human body.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Primer group for quantitative detection of escherichia coli DNA on surface of urinary catheter
PendingCN112280833AMeet the requirements of visualizationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationUrinary catheterEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a primer group for quantitative detection of escherichia coli DNA on the surface of a urinary catheter. The primer group consists of an outer primer pair F3 / B3, an inner primerpair FIP / BI and a loop primer pair loop F / loop B, the invention also relates to a rapid quantitative detection method adopting the primer group. The invention also relates to a rapid quantitative detection kit containing the primer group. The detection method and the kit disclosed by the invention are simple and convenient to operate, rapid, accurate and easy to popularize, have higher sensitivity, do not need expensive instruments, can be used in on-site pathogen and primary hospital detection, and have important significance for monitoring and controlling Escherichia coli on the surface ofa urinary catheter.
Owner:SHANGHAI CITY JIADING DISTRICT CENT HOSPITAL
A kind of Escherichia coli dna photorepair enzyme and construction method thereof
ActiveCN105062999BImprove antioxidant capacityPhotorepair enzyme activity is stableBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliA-DNA
The invention discloses escherichia coli DNA photolyase and a construction method thereof. The enzyme has the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 (in the description). The construction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a DNA photolyase gene from the conventional WT escherichia coli; designing a mutation primer to obtain a mutational gene segment; connecting the mutational gene segment with pET22b plasmid; constructing recombinant expression plasmid pET22b-A377S; converting the recombinant expression plasmid into a competent cell of escherichia coli; constructing genetically engineered bacterium BL21 (DE3) / pET22b-A377S for mutant enzyme expression. According to the invention, better expression is achieved under the conditions of 18 DEG C and 1 mM ITPG; the expressed photolyase is more stable in activity, and the antioxidant effect of the enzyme is remarkably improved.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Method and kit for determining the content of Escherichia coli dna in biological products
ActiveCN107365832BRealize monitoringImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEnterobacter sp
Owner:WUHAN OPTICS VALLEY HUMANWELL BIO PHARMA +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com