Genetic engineering strain for degrading PET (polyethylene terephthalate) plastics
A hydrolase and amino acid technology, applied in plastic recycling, bacteria, hydrolase and other directions, can solve the problems of slow growth of strains, low metabolic efficiency, difficult industrial application, etc., and achieve the effect of simple and efficient degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1. Design, construction and preparation of recombinant DNA vectors of Escherichia coli secreted type often expressing PET hydrolase (PETase)
[0041] Through artificial synthesis, Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd. was entrusted to synthesize the PET hydrolase secreted normally expressed unit in pUC57-EcPETase:
[0042] EcCP_J23100+EcRBS_K1725305+EC_pelB+Ec_5D+Ec_PETase+EcT_B0015(Seq ID No. 1). This unit is composed of 6 sub-functional units. The specific design and specific structure of each sub-unit are described as follows:
[0043] 1), EcCP_J23100: Escherichia coli constitutive expression constant promoter, the nucleotide sequence is shown in the 1st to 35th position of Seq ID No.1;
[0044] 2), EcRBS_K1725305: Escherichia coli protein translation RBS sequence, the nucleotide sequence is shown in the 36th to 62nd position of Seq ID No.1;
[0045] 3), EC_pelB: Escherichia coli protein secretion and expression signal peptide, carry out codon optimizat...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2. Evaluation of expression activity of pUC57-EcPETase recombinant DNA vector
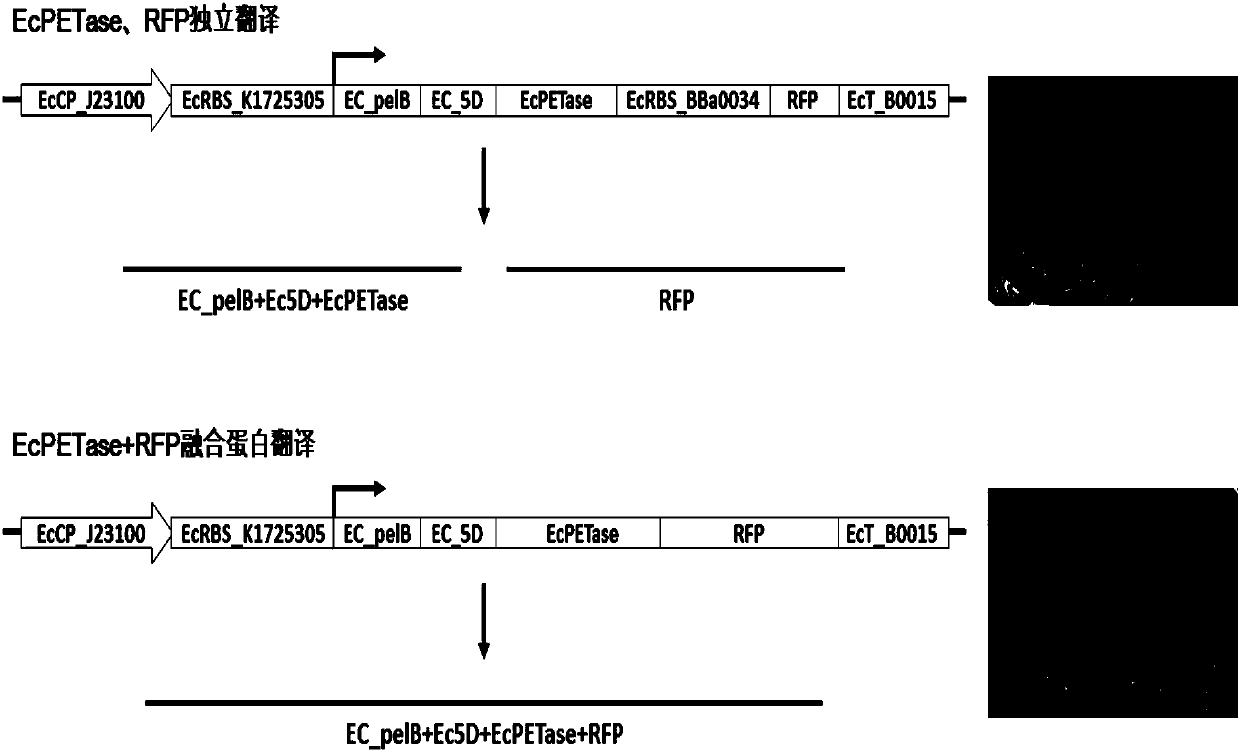
[0051] Based on the constructed pUC57-EcPETase and the reported red fluorescent protein (RFP) reporter vector (pSB1C3-BBa_J04450), the RFP reporter gene was further introduced into the downstream of the PETase expression box of the pUC57-EcPETase recombinant DNA plasmid by a synthetic method, and the same Two EcPETase+RFP co-expression vectors initiated by the promoter (EcCP_J23100): 1) EcPETase and RFP have independent RBS sequences, and are transcribed at the same time, and the translation products are 2 independent proteins (EcPETase, RFP); 2) EcPETase and RFP expression The frame was fused using only 1 RBS sequence, and the translation product was 1 fusion protein (EcPETase-RFP fusion protein). The two EcPETase+RFP co-expression vectors were transformed into the expression strain E.coliBL21. After screening and identification, red recombinant colonies were seen on the LB plate at...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3, pUC57-EcPETase genetic engineering Escherichia coli strain lipase activity and PET plastic degradation experiment
[0054] With reference to the pUC57-EcPETase genetically engineered Escherichia coli strain culture and sample preparation scheme in Example 2, a concentrated sample of the overnight culture product of the pUC57-EcPETase genetically engineered Escherichia coli strain was obtained, using pNPB as a substrate, reference literature: "oshida S , Hiraga K, Takehana T, Taniguchi I, Yamaji H, Maeda Y, Toyohara K, Miyamoto K, Kimura Y, Oda K. 2016. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate). Science, 351(6278):1196- 1199. "The experimental method disclosed in, testing the EcPETase in the culture solution of pUC57-EcPETase genetically engineered Escherichia coli strain. The experimental results showed that the pUC57-EcPETase genetically engineered Escherichia coli strain had significant lipase biological activity, and its pNPB h...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com