Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
163 results about "Endothelial stem cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Endothelial stem cells (ESCs) are one of three types of stem cells found in bone marrow. They are multipotent, which describes the ability to give rise to many cell types, whereas a pluripotent stem cell can give rise to all types. ESCs have the characteristic properties of a stem cell: self-renewal and differentiation. These parent stem cells, ESCs, give rise to progenitor cells, which are intermediate stem cells that lose potency. Progenitor stem cells are committed to differentiating along a particular cell developmental pathway. ESCs will eventually produce endothelial cells (ECs), which create the thin-walled endothelium that lines the inner surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels.
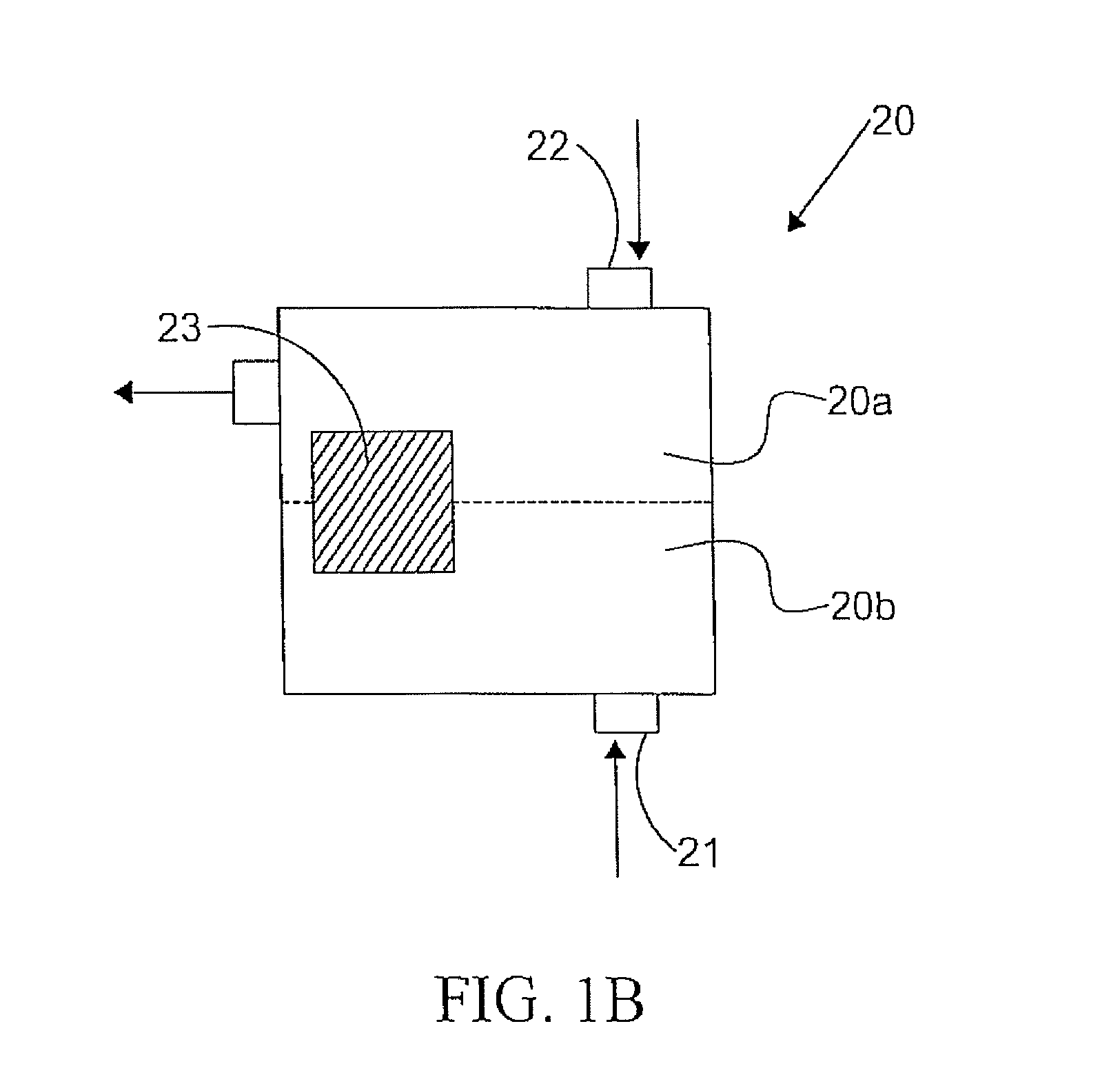
Coatings for implantable medical devices containing attractants for endothelial cells
Provided herein is a coating that includes a chemo-attractant for endothelial cells and methods of making and using the same.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Optimized stent jacket
ActiveUS20100241214A1Reducing platelet aggregationReduce aggregationStentsSurgeryFiberAdditive ingredient
A method of stenting, comprises: implanting a stent assembly in a vessel of a subject, the stent assembly, including: a stent jacket, comprising an expansible mesh structure, formed of fibers of a diameter between about 7 micrometers and about 18 micrometers, the diameter having a property of forming a substantially stable layer of endothelial cells, covering the fibers, thus reducing platelet aggregation, and an expansible stent, operatively associated with the stent jacket. The method further comprises administering to the subject an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) comprising a platelet aggregation reducer for a shortened time period, not exceeding six months, the shortened time period being a consequence of the property. In accordance with some embodiments, the administration of a platelet aggregation.
Owner:INSPIRE M D LTD
Layered bio-adhesive compositions and uses thereof
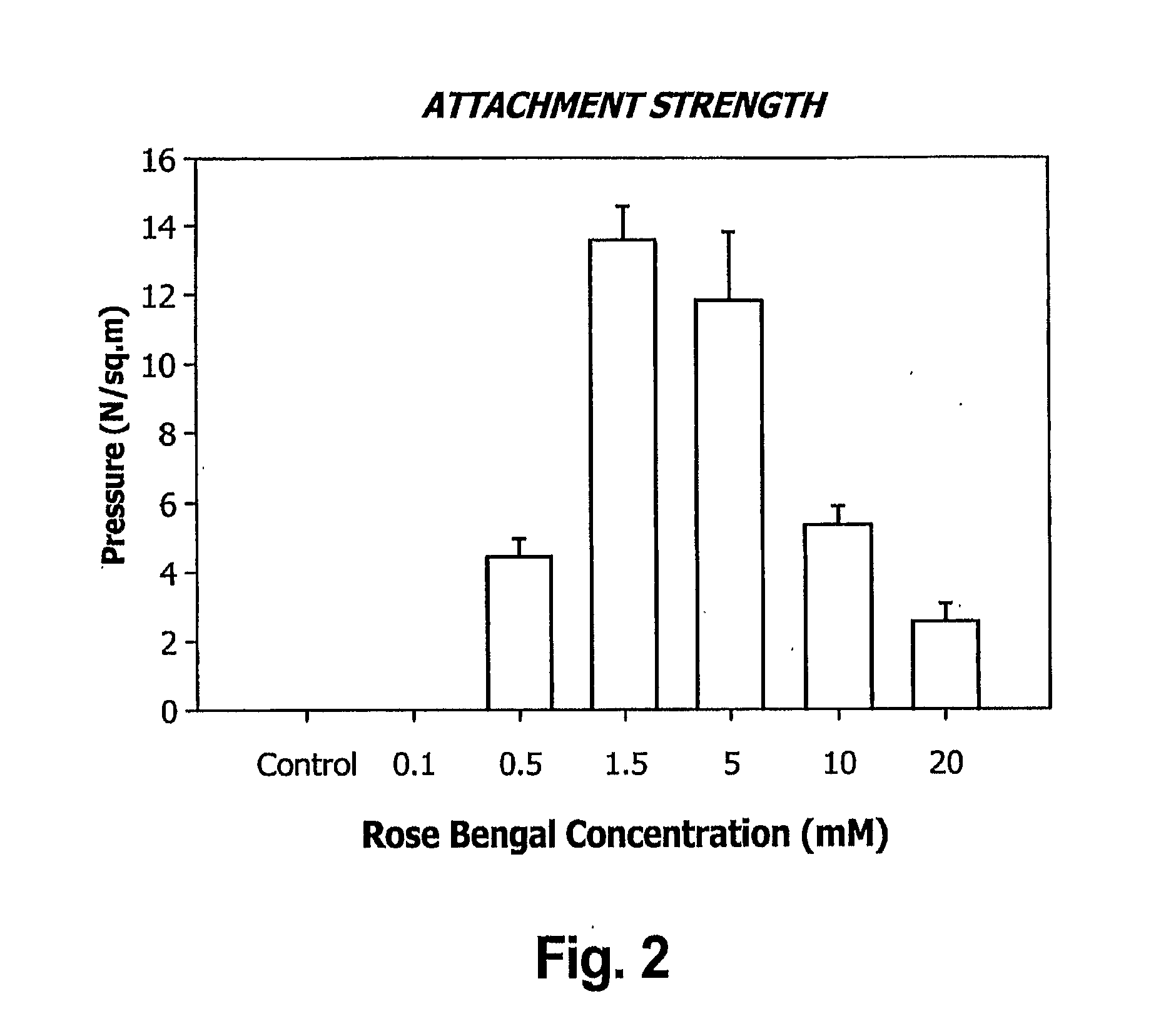
The invention generally provides compositions and methods for promoting and enhancing wound closure and healing. Specifically, the invention provides a biologic composition which comprises a support layer which serves as transport scaffold, for example made of gelatin, which is coated or impregnated with a bio-adhesive molecule such as rose bengal or glyceraldehyde. The composition can also comprise an artificial or biological matrix, optionally processed (i.e. cleaned and coated with extracellular matrix proteins) to enhance cell attachment and survival. The composition can further comprise a monolayer of epithelial, endothelial cells or mesenchymal cells. The invention provides methods for using the compositions for treating wounds due to disease, trauma or surgery. Specific methods for treating ocular wounds are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Covered stent
The invention discloses a covered stent, which comprises a support structure and a tectorial membrane unit, and is characterized in that: the tectorial membrane unit comprises an inner-layer tectorial membrane and an outer-layer tectorial membrane which coats the support structure; the outer-layer membrane coats on the outer side of the inner-layer tectorial membrane; the inner-layer tectorial membrane is a biological membrane with good blood compatibility, and the outer-layer tectorial membrane is a biological membrane which is easy to induce the formation of thrombus; the inner-layer tectorial membrane contacting blood has good blood compatibility, can effectively reduce the formation of the thrombus, and maintains normal blood flowing channels; and the outer-layer tectorial membrane can induce the formation of the thrombus in aneurysm or thrombus of bleeding parts, promotes the aneurysm to be quickly activated and reduced, reduces the mass effect in vivo, simultaneously effectively adheres endothelial cells, promotes differentiation and proliferation of cells, quickens the endothelialization of lesion parts of vessels, and can more effectively treat vascular diseases such as the aneurysm and the like.
Owner:MICROPORT NEUROTECH SHANGHAI
Resorbable Cornea Button
InactiveUS20090222086A1Improve tolerancePromote cell growthBiocideSenses disorderCorneal endothelial cellBiodegradable polymer
The present invention provides a resorbable corneal button comprised of a biodegradable polymer which is capable of supporting the growth and expansion of endothelial cells on it surface for use in transplantation healthy corneal endothelial cells to cornea tissue in need of a transplant and a method of using same.
Owner:CELLULAR BIOENG
Endothelial scaffolds
Provided herein is an endothelial scaffold comprising, consisting of, or consisting essentially of decellularized corneal stroma. In some embodiments, the scaffold has cultured endothelial cells seeded thereon. Methods of treating a patient in need of corneal endothelial transplant are also provided, including implanting the scaffold as described herein onto a cornea of the patient (e.g., by deep keratectomy).
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Purified populations of endothelial progenitor cells
The invention is directed to a purified population of mammalian endothelial stem cells. The invention further provides methods for isolating such populations of cells, methods for using such populations of cells for treating mammals in need of neovascularization and for making vectors for gene therapy, and methods for carrying out gene therapy with such vectors.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +2
Hemangioblast progenitor cells
InactiveUS20040052771A1Reduce bleedingAvoid adjustmentBiocideArtificial cell constructsP-selectinProgenitor
The invention relates to isolated hemangioblast cells. Hematopoietic and endothelial cells are postulated to be derived from a common progenitor, hemangioblast. While hemangioblast has been isolated retrospectively during embryonic stem cell differentiation, it has not been isolated from embryos or from bone marrow. Prospectively stable clonal cell lines have been isolated from mammalian embryos, from embryonic stem cells and from mammalian bone marrow that can differentiate in vitro into tubular structures with both endothelial and hematopoietic markers such as CD34, CD31, Flk-1, TIE2, P-selectin, Sca-1, thy-1, CD45, and smooth muscle actin. Gene expression profiles in the undifferentiated and differentiated cells were consistent with endothelial and hematopoietic differentiation potential. Transplantation studies in isogenic or immunodeficient mice demonstrated that these cells were not tumorigenic. In an appropriate microenvironment, the cells incorporate into the vasculature and participate in hematopoiesis.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
Formative agent of protein complex
InactiveUS20020119946A1Keep for a long timePromote resultsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCartilage cellsCuticle
The present invention proposes formative agent of protein complex, in which a polyphenol is useful component, and the agent is useful as gene complex, cell adhesion inhibitor or immune tolerogen. The polyphenol of forming the agent is selected from catechin group consisting of epigallocatechin-gallate, tannic acids, or proanto-dianisidine, a protein of the protein complex is selected from proteins consisting of animal proteins composed of polypeptide chain of peptide-combined amino acids, vegetative proteins, nucleus proteins, glycogen proteins, lipo-proteins and metal proteins, the gene complex comprises by compositing genes by polyphenol catechins in order to introduce genes to cells of animals or human bodies, a cell composed of the cell adhesion inhibitor is selected from cells consisting of an animal cell including a stem cell, skin cell, mucosa cell, hepatocyte, islet cell, neural cell, cartilage cell, endothelial cell, epidermal cell, osteocyte or muscle cell isolated from human or animal organism, or sperm, ovum or fertilized egg of domestic animals or fishes and a tissue or an organ for transplantation of the immune tolerogen is selected from the tissue or the organ consisting of skin, blood vessel, cornea, kidney, heart, liver, umbilical cord, bowels, nerve, lung, placenta or pancreas.
Owner:BERTELSMANN MUSIC GROUP
Biological artificial blood vessel capable of in vivo capturing endothelial ancestral cell
ActiveCN101066477AAddressing Compliance MismatchesResolve thrombosisImmobilised enzymesPharmaceutical containersAntigenThrombus
The present invention relates to preparation of biological artificial blood vessel capable of in vivo capturing endothelial ancestral cell, and features that the biological artificial blood vessel may be prepared with composite blood vessel material or homogeneous or heterogeneous blood vessel with the antigen eliminated and through surface modification. The biological artificial blood vessel may be used as tissue engineering blood vessel rack, on which smooth muscle cell and / or endothelial cell may be planted. The biological artificial blood vessel of the present invention has excellent mechanical performance and anticoagulant property, and may be in different calibers. It may be in vivo reshaped and in vivo induced to plant endothelial ancestral cell. It can antagonize intravascular thrombogenesis and inhibit the pathological proliferation of smooth muscle cell to avoid angiostenosis and blood vessel blocking.
Owner:广州宏畅生物科技有限公司
Cell delivery matrices
Cell delivery matrices and methods for facilitating local delivery of adipose derived endothelial cells to a target tissue, body cavity, or joint are described. The cell delivery matrix may be a three-dimensional matrix scaffold comprising fibrin derived from the patient's own body. The cell delivery matrix may be biocompatible and semi-permeable. The cell delivery matrix used in the methods of the invention may be comprised of any degradable, bioabsorbable or non-degradable, biocompatible polymer. Regenerative therapies comprising implanting in the subject cell delivery matrices localizing adipose derived endothelial cells are described. The cell delivery matrices maintain the adipose derived endothelial cells at the target for a therapeutically effective amount of time. The adipose derived endothelial cells can be allogenic or syngenic to the subject. The endothelial cells may be delivered alone or in combination with other therapeutic agents.
Owner:TISSUE GENESIS LLC
Embolic material composite and preparation method thereof
An embodiment of the invention discloses an embolic material composite and a preparation method thereof. The embolic material composite comprises polyethylene-vinyl alcohol, a degradable polymer, a contrast agent and dimethylsulfoxide. After the embolic composite is injected into an aneurysm cavity, the polyethylene-vinyl alcohol, the degradable polymer and the contrast agent are precipitated and solidified along with the diffusion of dimethylsulfoxide in blood so that an embolism body is formed, thereby achieving the aim of embolizing the aneurysm. Additionally, the embolism body forms a porous structure because of the gradual degradation of the degradable polymer, so the mass of the embolism body is greatly reduced. Therefore, the embolic material composite can reduce the total mass of the embolism body via the gradual degradation of the degradable polymer, thereby relieving the occupied effect effectively. Furthermore, the finally formed porous structure is in favor of being effectively adhered with endothelial cells, promoting cell differentiation and proliferating and quickening the endothelialization of vessels, and effectively preventing the possible blood recirculation after the embolizing.
Owner:MICROPORT NEUROTECH SHANGHAI
Method for constructing mouse model for conditional knockout of CCR5 gene of endothelial cell
ActiveCN107858373ALow densityIntegrity breachStable introduction of DNAAnimals/human peptidesKnockout animalHIV receptor
The invention discloses a method for constructing a mouse model for conditional knockout of CCR5 gene of endothelial cell. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, obtaining a CCR5loxp / loxp mouse, and mating with a Tie-2-cre / ERT2 mouse, so as to obtain heterozygous mice with specific knockout of CCR5 gene of the endothelial cell; mutually mating the heterozygous mice, so as to obtain homozygous mice with specific knockout of CCR5 gene out of the endothelial cell. The constructing method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the mouse with conditional knockout of endothelial cell gene is constructed via the CRISPR / Cas9 system, the mutation is led into the mouse by a cell specificity method, the missing of the CCR5 target gene occurs at the certain tissue organ of the test animal, the controllability of mechanism study is furthest realized, and the disadvantages that different tissues or cells are not distinguished, and target genes in all tissues or cells of themouse body are all removed in the conventional gene knockout technique is overcome.
Owner:SHANDONG KEYUAN PHARMA
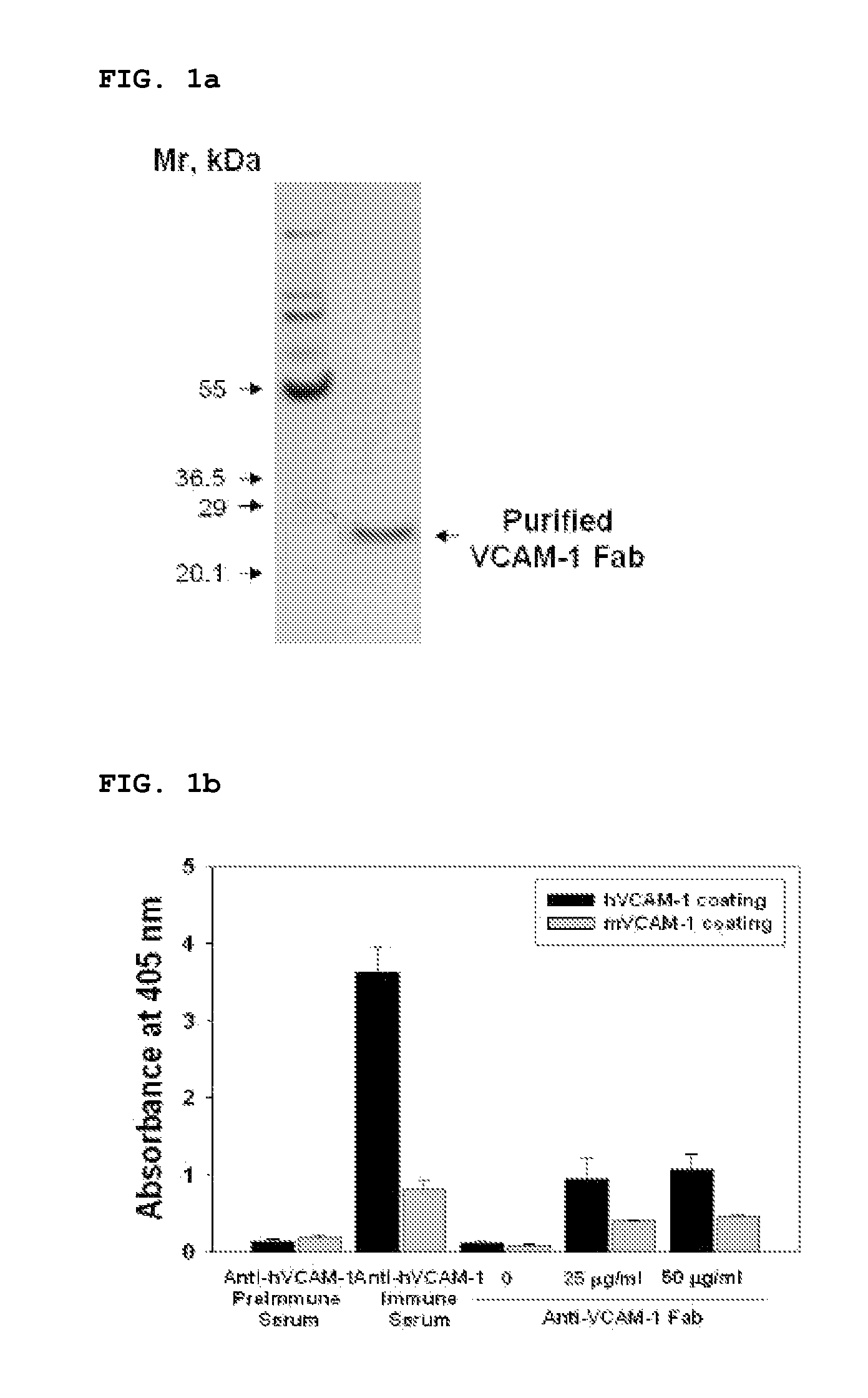
VCAM-1 specific monoclonal antibody
The present invention relates to a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1 or CD106). Specifically, the present invention relates to an antibody that specifically binds to both human and mouse vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), a method for producing the same, a composition for diagnosis or treatment comprising them and a method for diagnosis or treatment using them. The monoclonal antibody of the present invention is the first recombinant monoclonal antibodies that is specific to human and mouse VCAM-1. In addition, the monoclonal antibody of the present invention shows a strong affinity to VCAM-1 expressed in rat skeletal muscle and porcine endothelial cells as well as human and mouse endothelial cells and is found to strongly inhibit the interaction between leukocytes and activated endothelial cells. Accordingly, the monoclonal antibody of the present invention can inhibit a VCAM-1 mediated adhesion of leukocytes to endothelial cells and potently treat VCAM-1 mediated disease, especially inflammatory disease or cancer.
Owner:HANWHA CHEMICAL CORPORATION
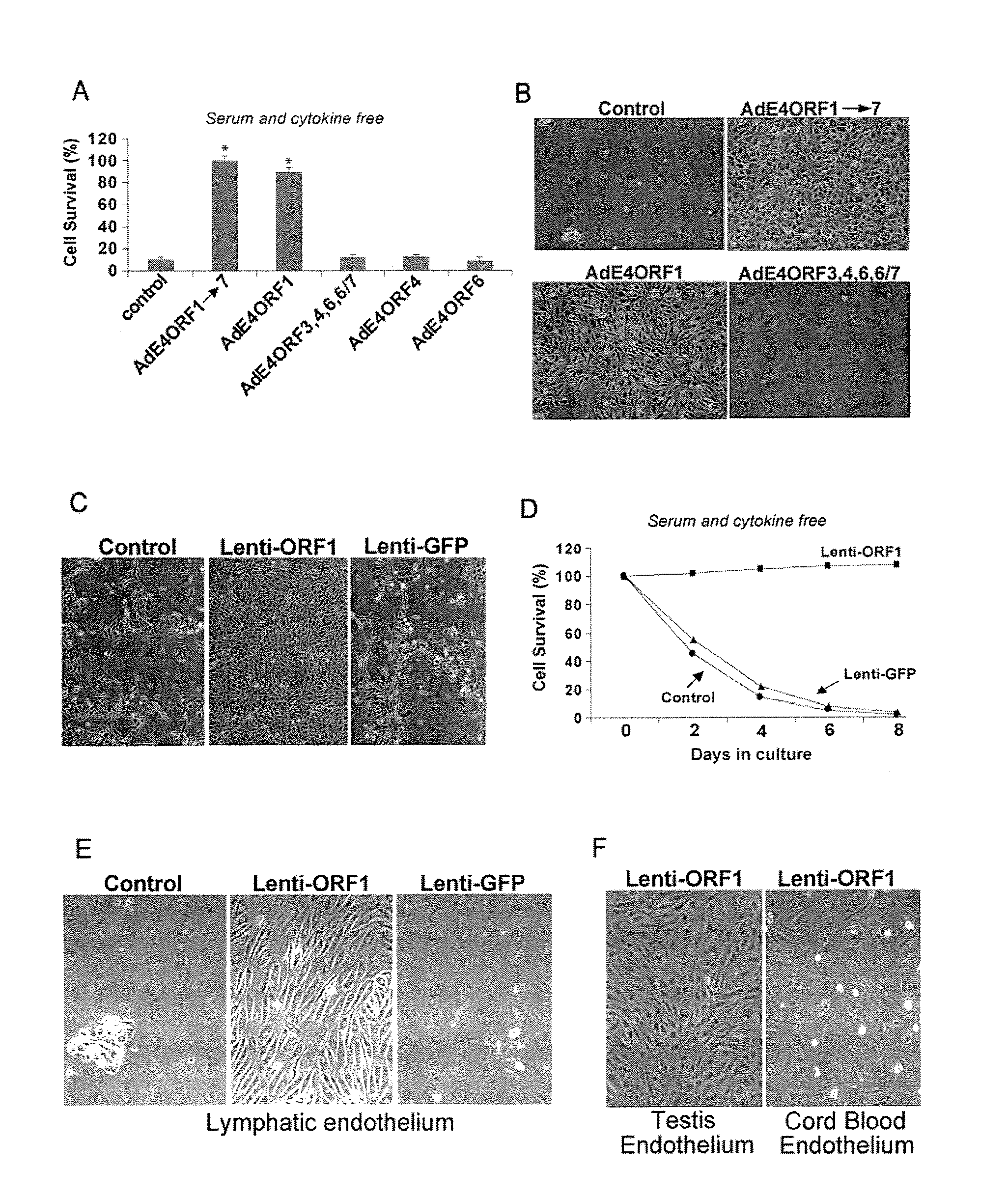
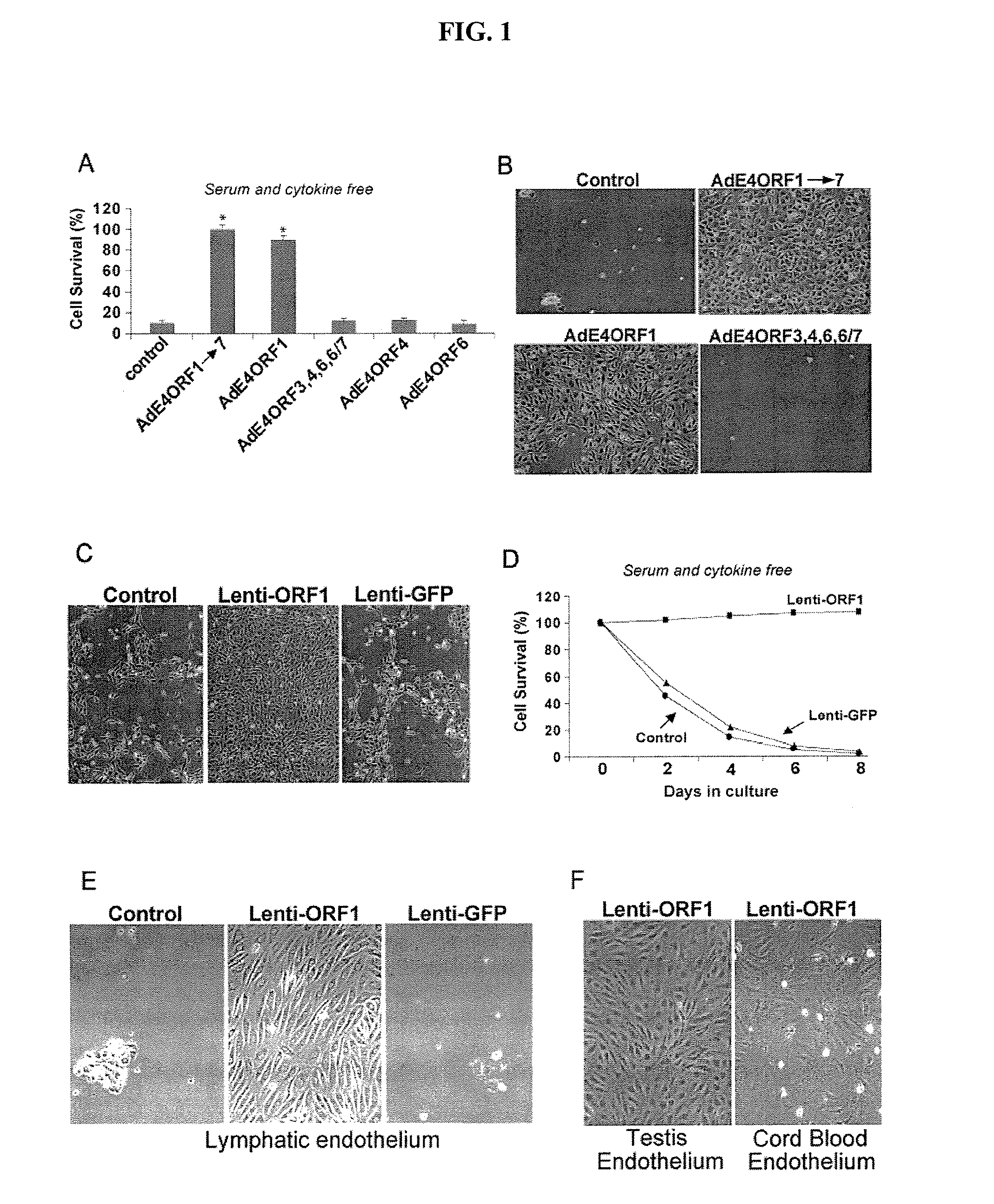
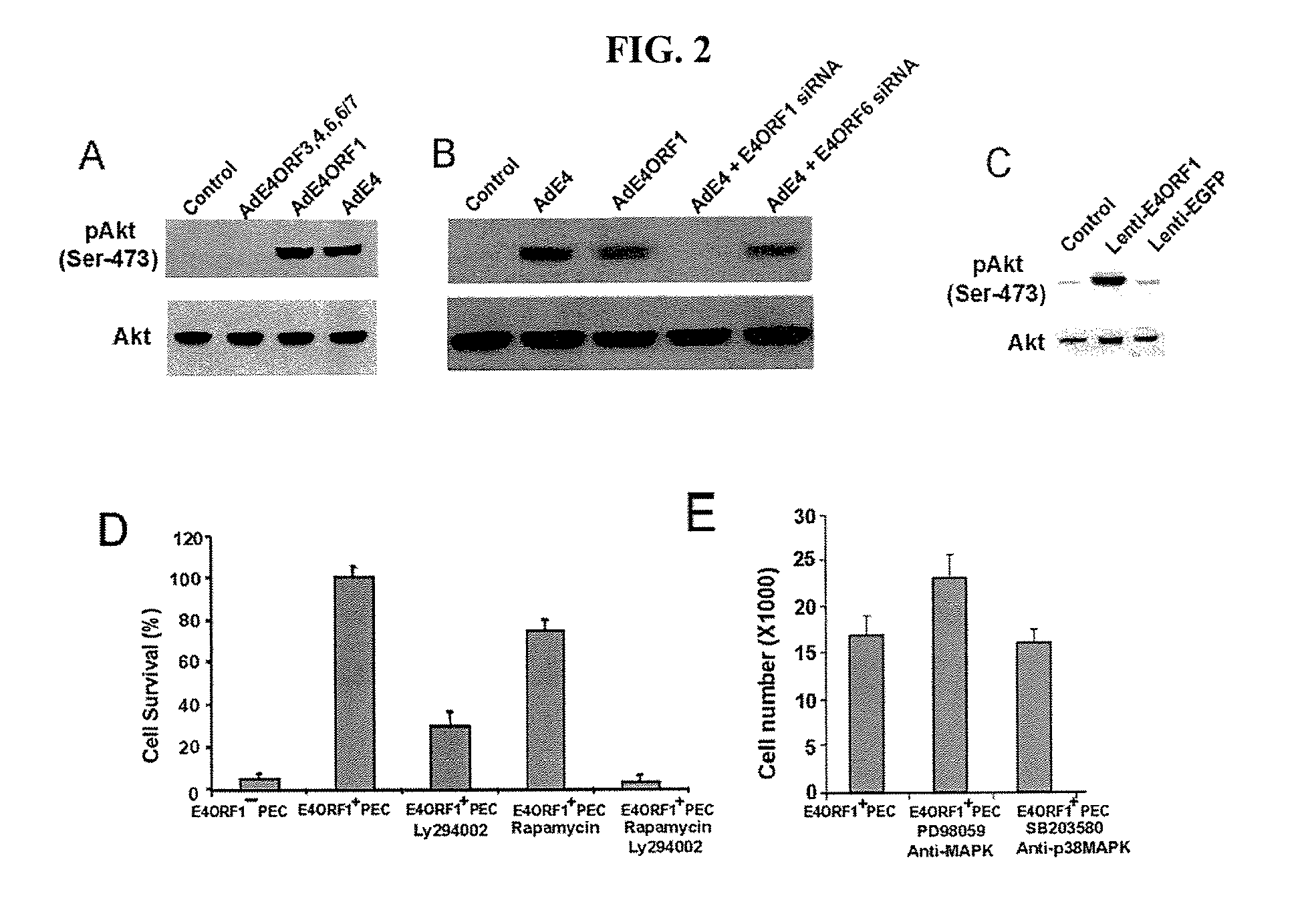
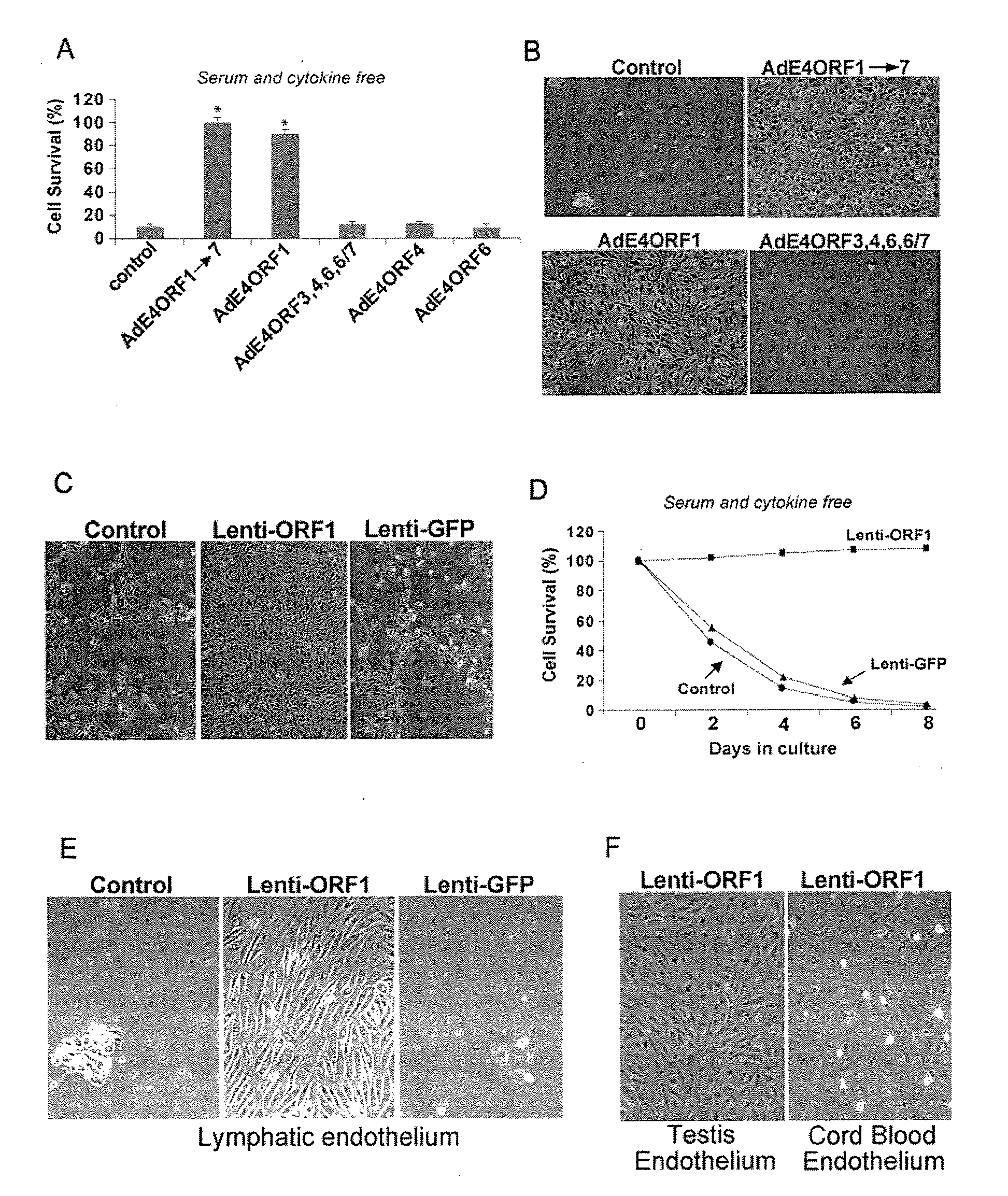
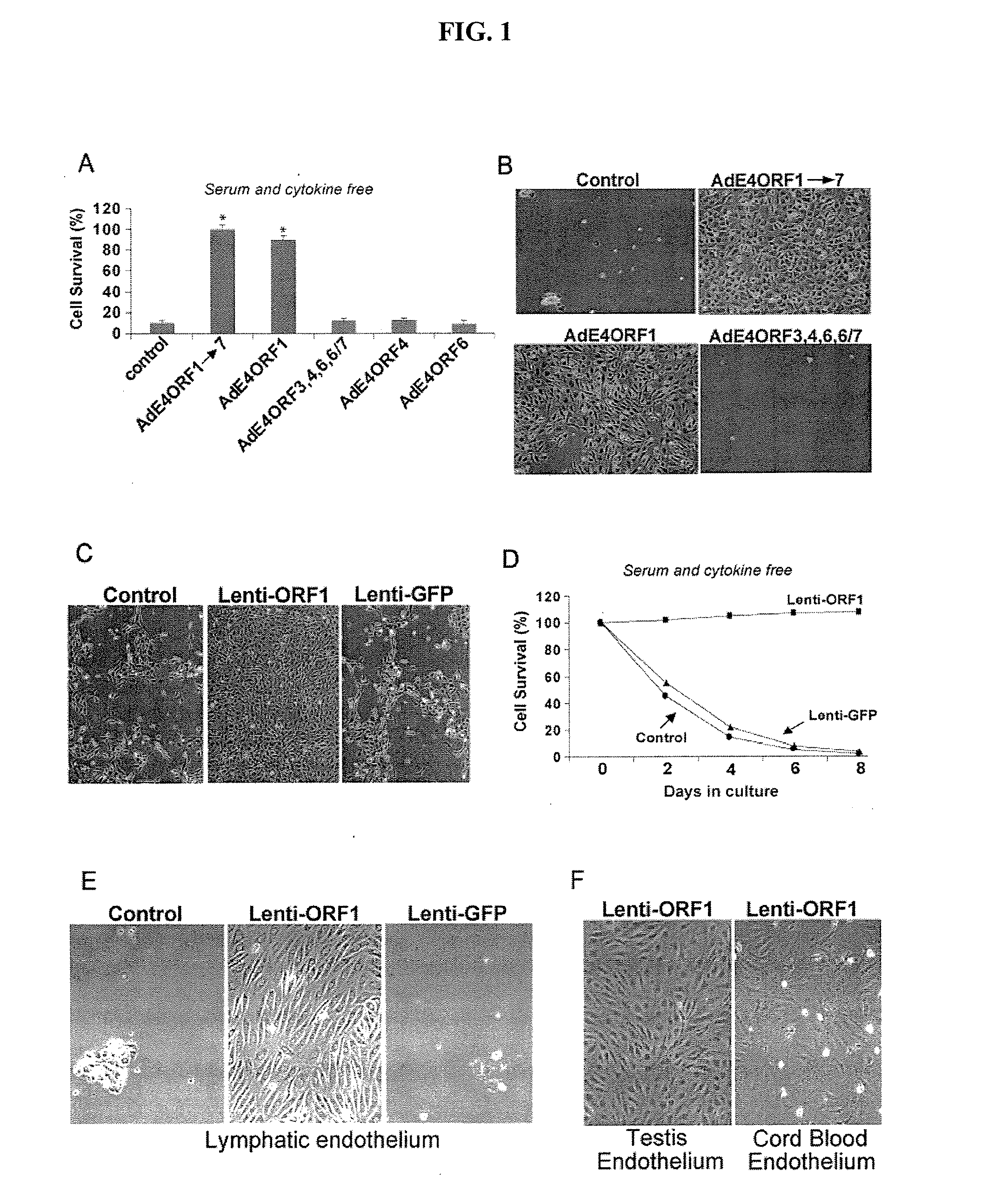
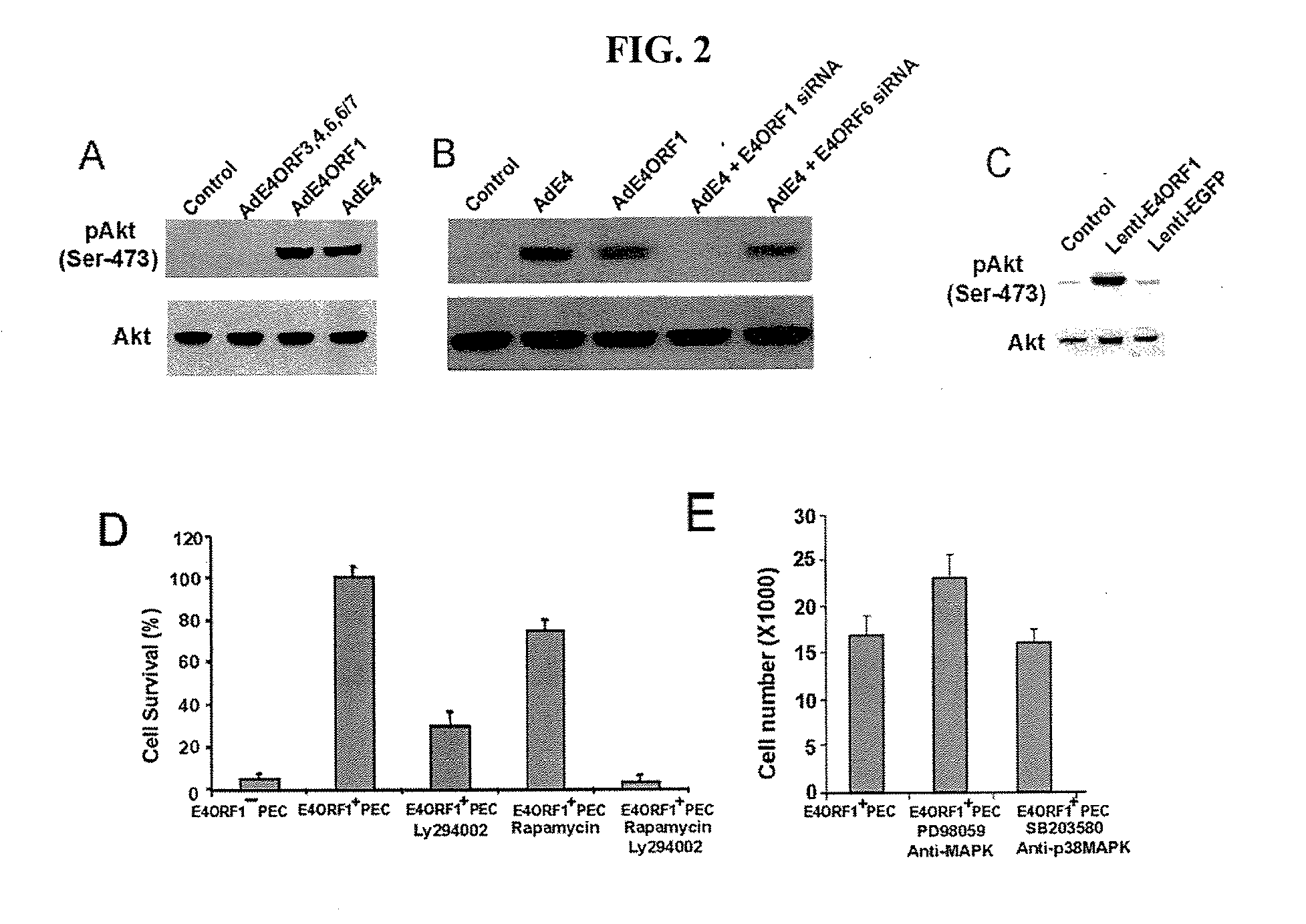
Endothelial cells expressing adenovirus E4ORF1 and methods of use thereof
The present invention relates to adenovirus E4ORF 1 gene and to endothelial cells engineered to express the E40RF 1 gene. The present invention also relates to uses of the E40RF 1 gene, and cells expressing the E40RF1 gene, and to compositions comprising the E4ORF 1 gene, or comprising cells expressing the E4ORF 1 gene.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
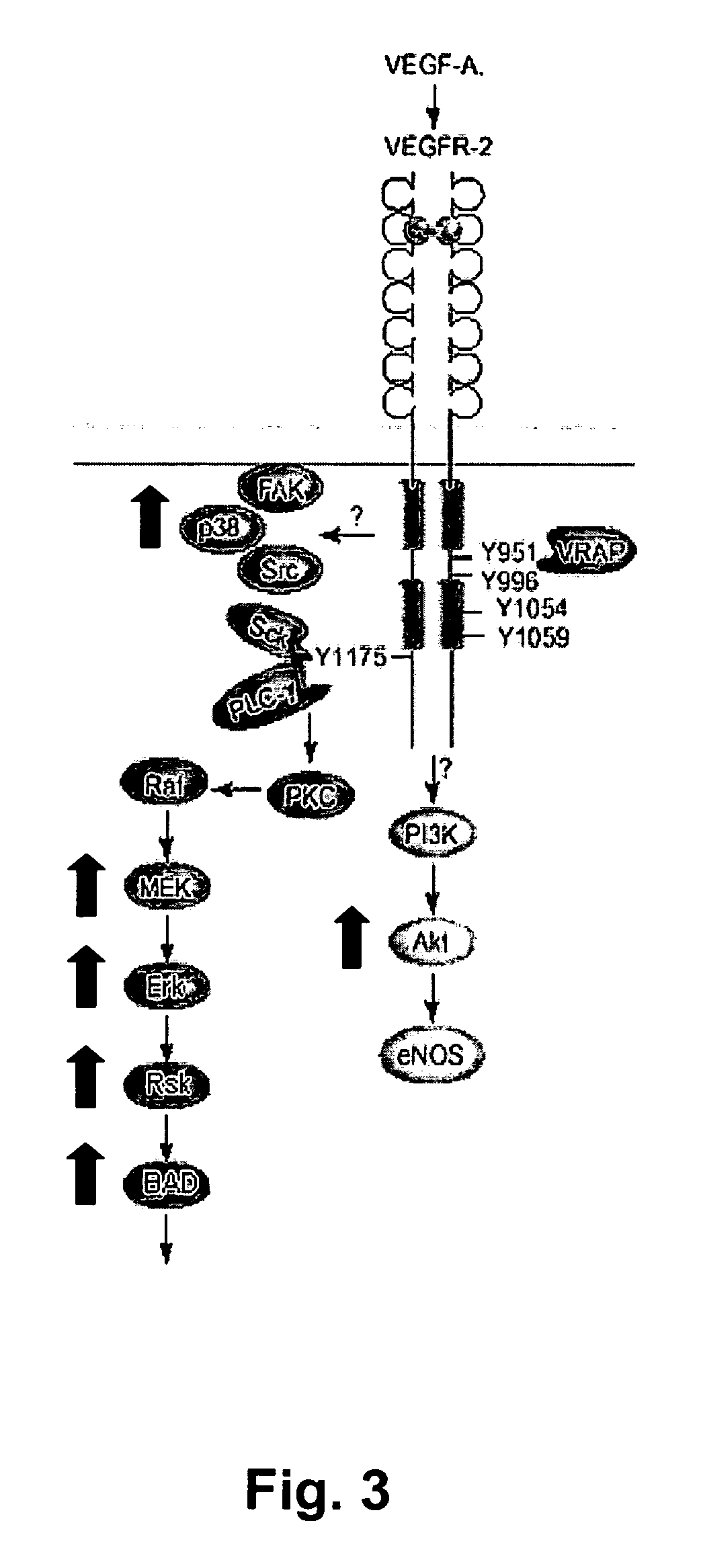
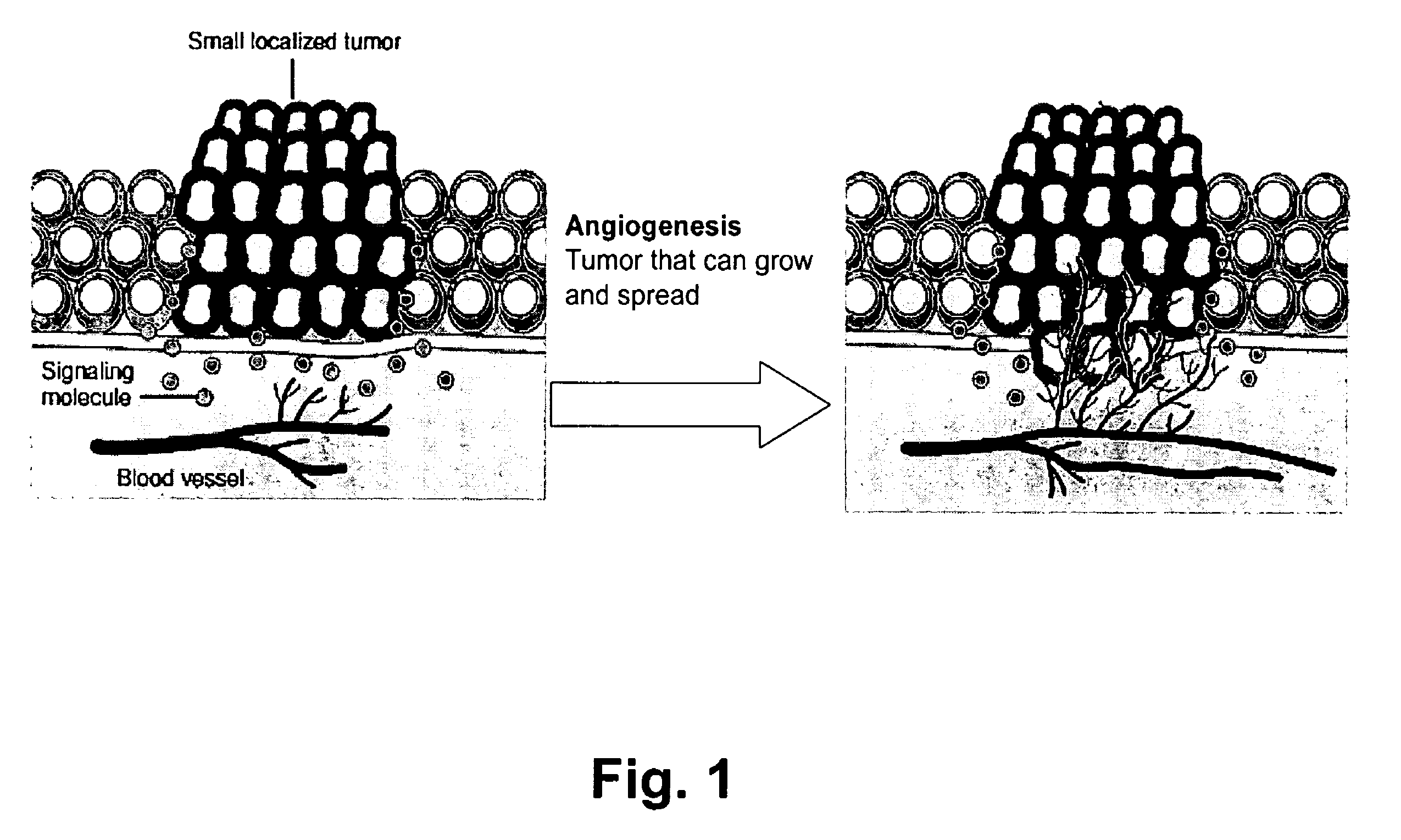
Detection of activation of endothelial cells as surrogate marker for angiogenesis
InactiveUS20060199231A1Sensitively and conveniently measurePeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesCellular componentProtein-protein complex
Methods, compositions and kits are provided for assessing angiogenesis through sensitive, direct detection of activation of endothelial cells at molecular levels. In general, activation of endothelial cells is detected by measuring the levels of cellular components and their protein complexes participating in a specific angiogenesis signaling pathway in endothelial cells. The methods can be used for assessing status of diseases associated with undesirable angiogenesis, such as the likelihood of developing the disease, presence or absence of the disease, prognosis of the disease and the likelihood of response or resistance to a particular anti-angiogenic therapy. The methods can also be used to guide the design of effective therapeutic regimens targeting a specific angiogenic signaling pathway, as well as in conjunction with therapeutic intervention of diseases or conditions associated with undesirable angiogenesis.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Endothelial cell binding coatings for rapid encapsulation of bioerodable stents
Bioerodable devices such as stents containing one or more endothelial cell binding agents are provided.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Replicating viral vectors for gene therapy
InactiveUS20120283318A1MaintenanceAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsGene deliveryHeterologous
The present invention concerns the field of gene therapy and in particular the use of specific adenoviral vector systems for gene therapy, said vector systems offering enhanced efficiency and specificity for gene delivery. More specifically, the present invention provides replicating-competent adenoviral vector systems carrying one or more inserted heterologous gene. The adenoviral vectors system according to the invention are characterized by high binding efficiency and infectivity to cells of neural origin, endothelial cells, carcinoma cells and dendritic cells.
Owner:MEI YA FANG +1
Inducing method for directionally differentiating human embryonic stem cells to corneal endothelial cells
The invention discloses an inducing method for directionally differentiating human embryonic stem cells to corneal endothelial cells. The method comprises the steps of: cultivating the human embryonic stem cells on a mouse embryonic fibroblast feed layer; sorting human embryonic stem cell clone groups in good state; grafting the groups on a human corneal stromal fibroblast layer processed by mitomycin C and cultivating for 7 days, wherein the human embryonic stem cells are differentiated to rosettes; separating and transferring the rosettes from the human corneal stromal fibroblast layer to a culture bottle; cultivating continuously for 7 days by using a neural crest stem cell culture medium; sorting the neural crest stem cells by a flow cytometry; adding the neural crest stem cells into the culture bottle; placing in a 5% CO2 incubator for incubating and cultivating at 37 DEG C by using a human corneal endothelial cell culture medium; changing the liquid every other day; and cultivating for about 10 days to obtain the corneal endothelial cells. The multiplication capacity of the corneal endothelial cells are similar to that of human corneal endothelial cells and the corneal endothelial cells can be transferred to 1-2 generations in vitro maximally. The corneal endothelial cells can be used as seed cells for cornea construction and transplant in tissue engineering.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Stem cell growth factor-like polypeptides
The invention provides novel polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by such polynucleotides and mutants or variants thereof that correspond to a novel human and mouse secreted stem cell growth factor-like polypeptide. These polynucleotides comprise nucleic acid sequences isolated from cDNA libraries prepared from mouse bone marrow and human fetal liver spleen, ovary, adult brain, lung tumor, spinal cord, cervix, ovary, endothelial cells, umbilical cord, placental, lymphocyte, lung fibroblast, fetal brain, and testis. Other aspects of the invention include vectors containing processes for producing novel human secreted stem cell growth factor-like polypeptides, and antibodies specific for such polypeptides.
Owner:KIRIN PHARMA +1
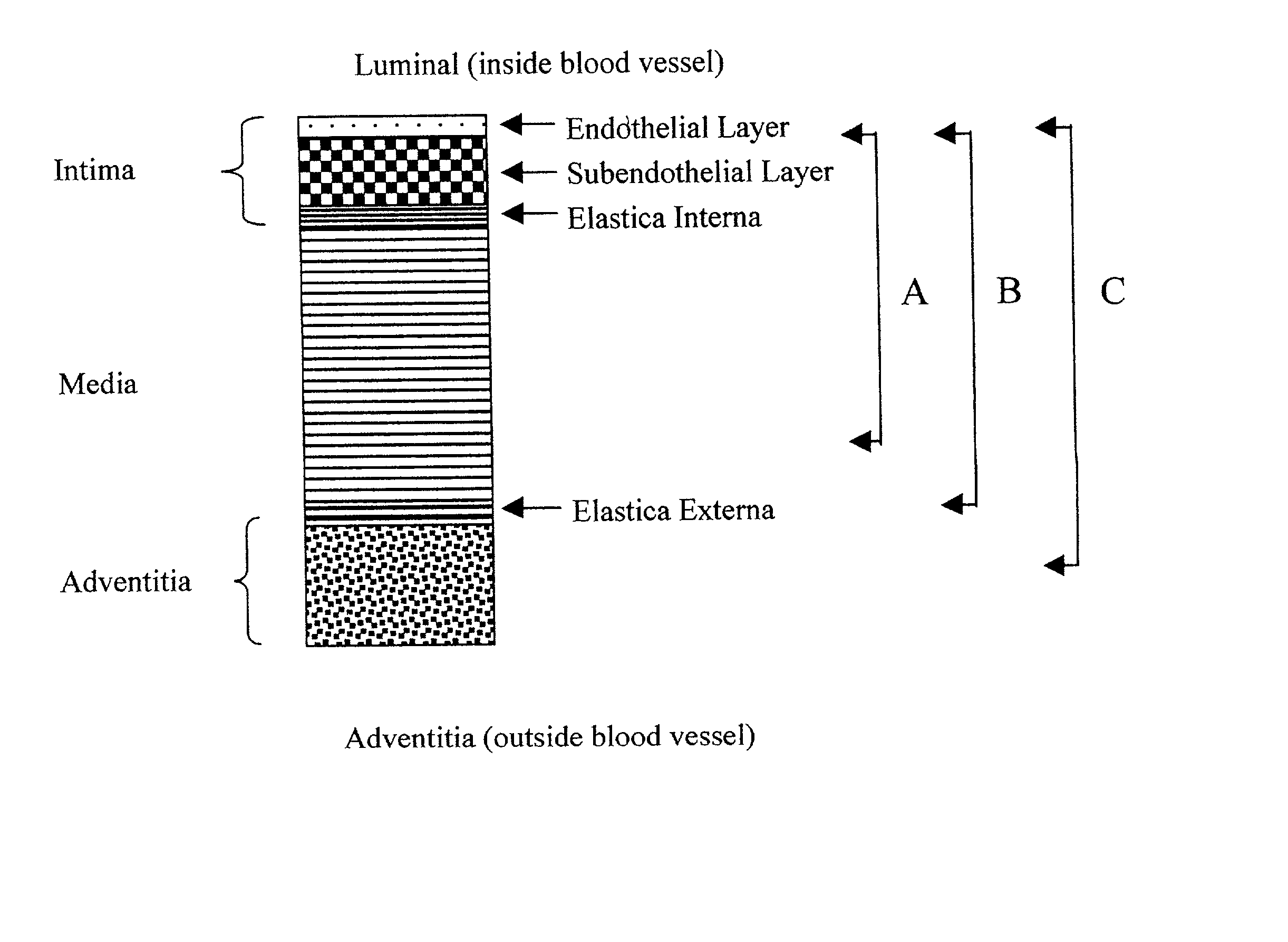
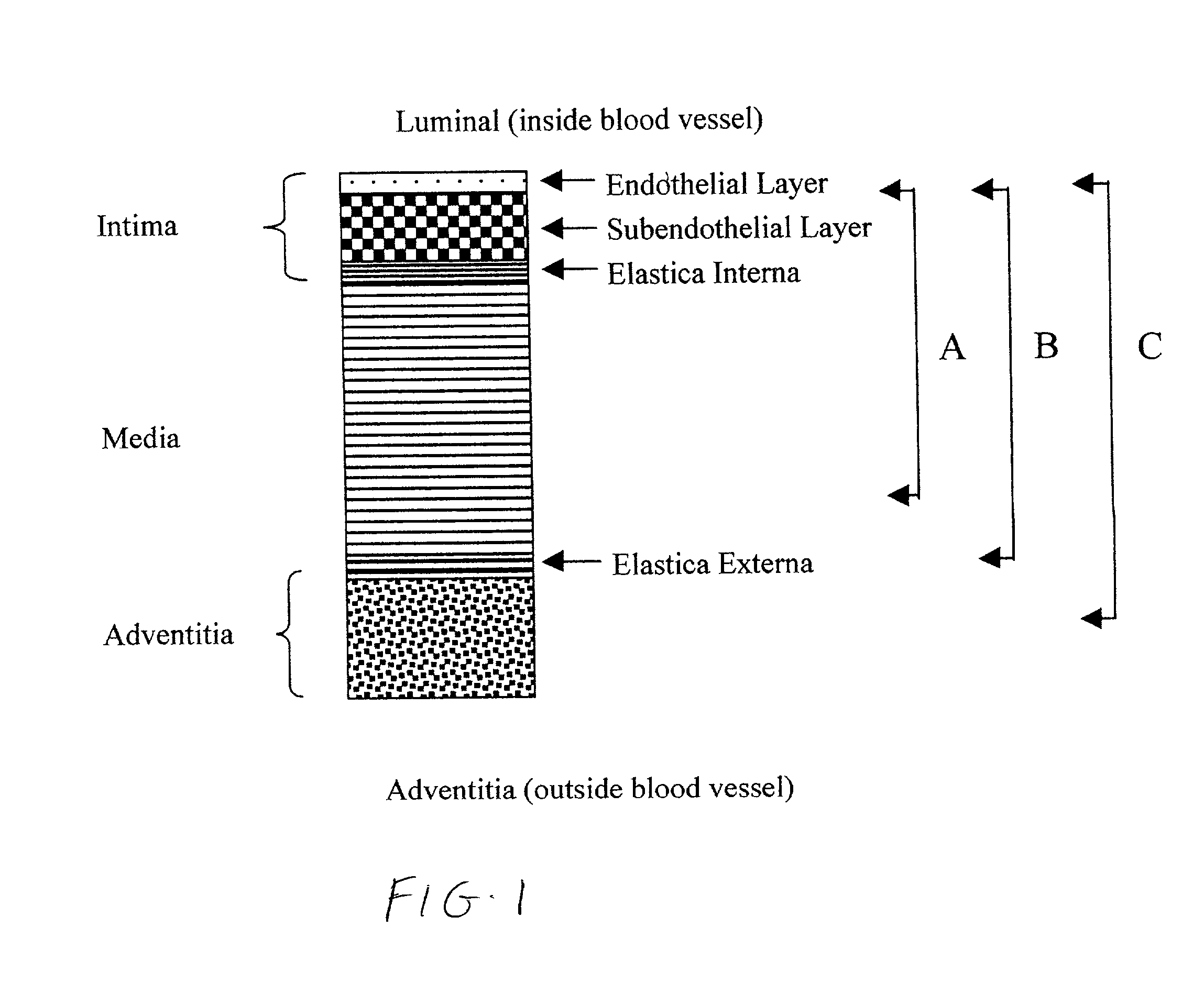
Vascular tissue composition
A tissue composition includes the subendothelial layer, the elastica interna, and at least a portion of the tunica media of a blood vessel harvested from a mammal, with the endothelial cells removed from the blood vessel. The tissue composition can also include a portion of the tunica adventitia of a blood vessel harvested from a mammal. The tissue composition can be formed into a graft, a patch, a connective tissue for surgical repair, an orthopedic graft, and a substrate for cell growth, among other applications. The tissue composition can also be fluidized, or made into powdered form.
Owner:YANG JUN
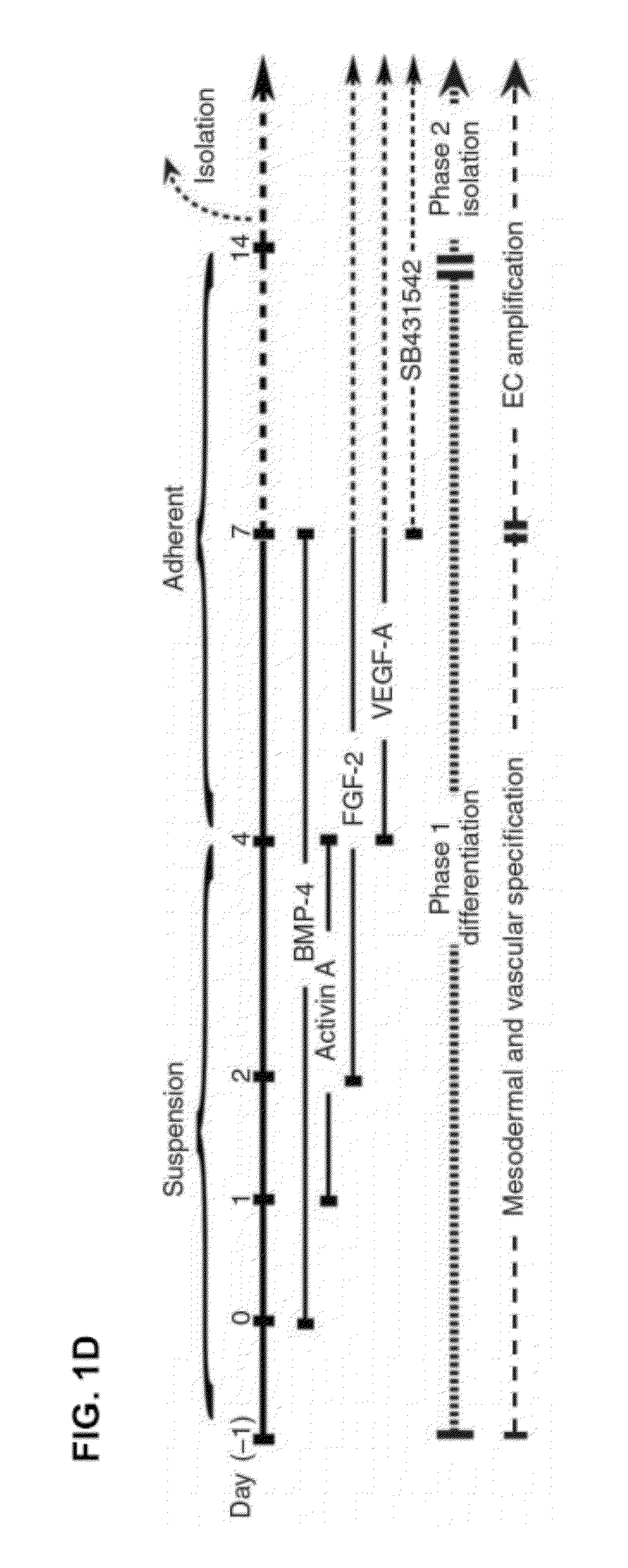
Methods for developing endothelial cells from pluripotent cells and endothelial cells derived
PendingUS20120301443A1Maintain abilityExpanding ECs in cell populationBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsGerm layerStable Populations
Disclosed herein is a method for developing human endothelial cells (ECs) from human embryonic stem cells (ESCs). The method is based on inhibition of TGF signaling following mesoderm induction and during vascular differentiation of hESC-derived cells. Also disclosed herein is a substantially pure and stable population of ECs that maintains a high degree of proliferation and phenotypic homogeneity for extended culture periods. Related pharmaceutical compositions and therapeutic methods are also disclosed. A reporter hESC line useful for tracking the development of ECs is also provided.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Stem cell preparation for repairing skin ulcer
InactiveCN105708860AQuick fixEfficient repairTetracycline active ingredientsTachykinin ingredientsMesenchymal stem cellSkin ulcerations
The invention relates to a stem cell preparation for repairing skin ulcer. The stem cell preparation consists of mesenchymal stem cells and exogenous cell factors. The stem cell preparation is prepared from the mesenchymal stem cells in combination with the exogenous cell factors, so that the directional differentiation of the mesenchymal stem cells towards endothelial cells is promoted; and through the paracrine of the mesenchymal stem cells as well as the exogenous cell factors, the growth of the endothelial cells is stimulated, fibroblast and capillary growth as well as collagen synthesis and granulation in a wound surface are enhanced, and the proliferation of skin keratinocytes and endothelial cells is improved, so that the purpose of rapidly and effectively repairing skin with ulcer injury is achieved.
Owner:SHEN ZHEN ISTEM REGENERATIVE MEDICINE SCI TECH CO LTD
Progenitor endothelial cell capturing with a drug eluting implantable medical device
InactiveUS8088060B2Stimulating positive blood vessel remodelingEnhance and accelerate formationStentsSurgeryProgenitorDrug-Coated Stents
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Vascular tissue composition
A tissue composition includes the subendothelial layer, the elastica interna, and at least a portion of the tunica media of a blood vessel harvested from a mammal, with the endothelial cells removed from the blood vessel. The tissue composition can also include a portion of the tunica adventitia of a blood vessel harvested from a mammal. The tissue composition can be formed into a graft, a patch, a connective tissue for surgical repair, an orthopedic graft, and a substrate for cell growth, among other applications. The tissue composition can also be fluidized, or made into powdered form.
Owner:YANG JUN
Methods and compositions for promoting survival & proliferation of endothelial cells & stimulating angiogenesis
ActiveUS20100093081A1Useful in therapyAvoid the needBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAngiogenesis growth factorGene
The present invention relates to adenovirus E4ORF 1 gene and to endothelial cells engineered to express the E40RF 1 gene. The present invention also relates to uses of the E40RF 1 gene, and cells expressing the E40RF1 gene, and to compositions comprising the E4ORF 1 gene, or comprising cells expressing the E4ORF 1 gene.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Progenitor endothelial cell capturing with a drug eluting implantable medical device
InactiveUS20120172970A1Stimulating positive blood vessel remodelingAvoid dissectionStentsSurgeryProgenitorDrug-Coated Stents
A medical device for implantation into vessels or luminal structures within the body is provided, which stimulates positive blood vessel remodeling. The medical device, such as a stent and a synthetic graft, is provided with a coating with a pharmaceutical composition containing a controlled-release matrix and one or more pharmaceutical substances for direct delivery of drugs to surrounding tissues. The coating on the medical device further comprises one or more barrier layers, and a ligand such as a peptide, an antibody or a small molecule for capturing progenitor endothelial cells in the blood contacting surface of the device for restoring an endothelium at the site of injury. In particular, the drug-coated stents are for use, for example, in balloon angioplasty procedures for preventing or inhibiting restenosis.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Method of conditioning a hybrid synthetic tubular structure to yield a functional human hybrid coronary bypass graft
InactiveUS7968329B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSufficient timeBypass grafts
A method of yielding a functional human hybrid coronary bypass graft is provided. The method includes conditioning a hybrid synthetic tubular structure having stem cells and / or endothelial cells on at least one surface to yield the functional human hybrid coronary bypass graft. Specifically, the method includes placing the hybrid synthetic tubular structure in a system capable of producing three dimensional dynamic conditions for a sufficient time to yield said functional human hybrid coronary bypass graft.
Owner:DANCU MICHAEL
Detection of activation of endothelial cells as surrogate marker for angiogenesis
InactiveUS7939267B2Sensitively and conveniently measurePeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesCellular componentMolecular level
Methods, compositions and kits are provided for assessing angiogenesis through sensitive, direct detection of activation of endothelial cells at molecular levels. In general, activation of endothelial cells is detected by measuring the levels of cellular components and their protein complexes participating in a specific angiogenesis signaling pathway in endothelial cells. The methods can be used for assessing status of diseases associated with undesirable angiogenesis, such as the likelihood of developing the disease, presence or absence of the disease, prognosis of the disease and the likelihood of response or resistance to a particular anti-angiogenic therapy. The methods can also be used to guide the design of effective therapeutic regimens targeting a specific angiogenic signaling pathway, as well as in conjunction with therapeutic intervention of diseases or conditions associated with undesirable angiogenesis.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Method for planting esoderma/endothelial cell on inner surface of artificial blood vessel
InactiveCN1559360AImprove adhesionInhibit hyperproliferationMicroorganismsGenetic material ingredientsBlood vessel featureFluid shear
A method for implanting the endothelial cells on the inner surface of artificial blood vessel features that a biomechanical method is used, that is, an external pulsive fluid shearing force increased step by step acts on the planted endothelial cells to make them be attached well on the inner surface of artificial blood vessel in advance.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com