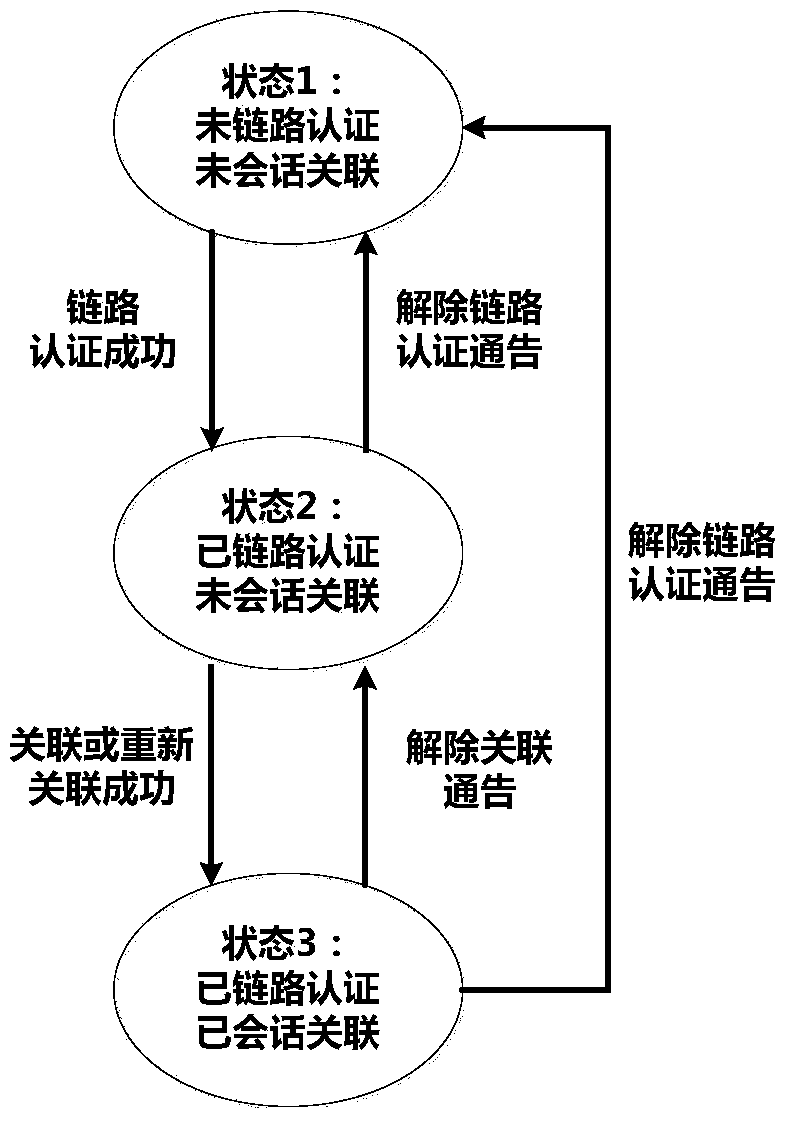
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88 results about "Email authentication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
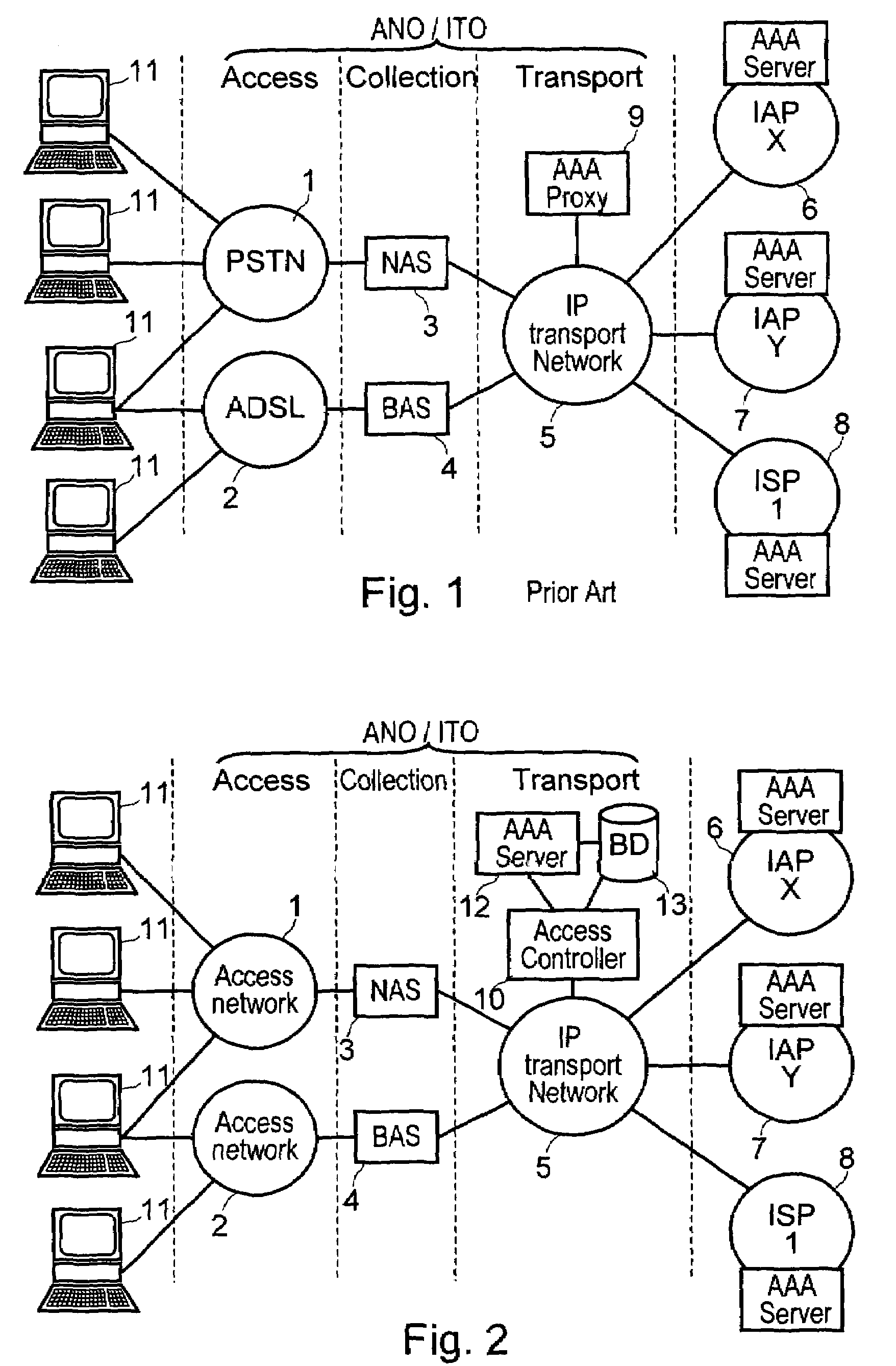
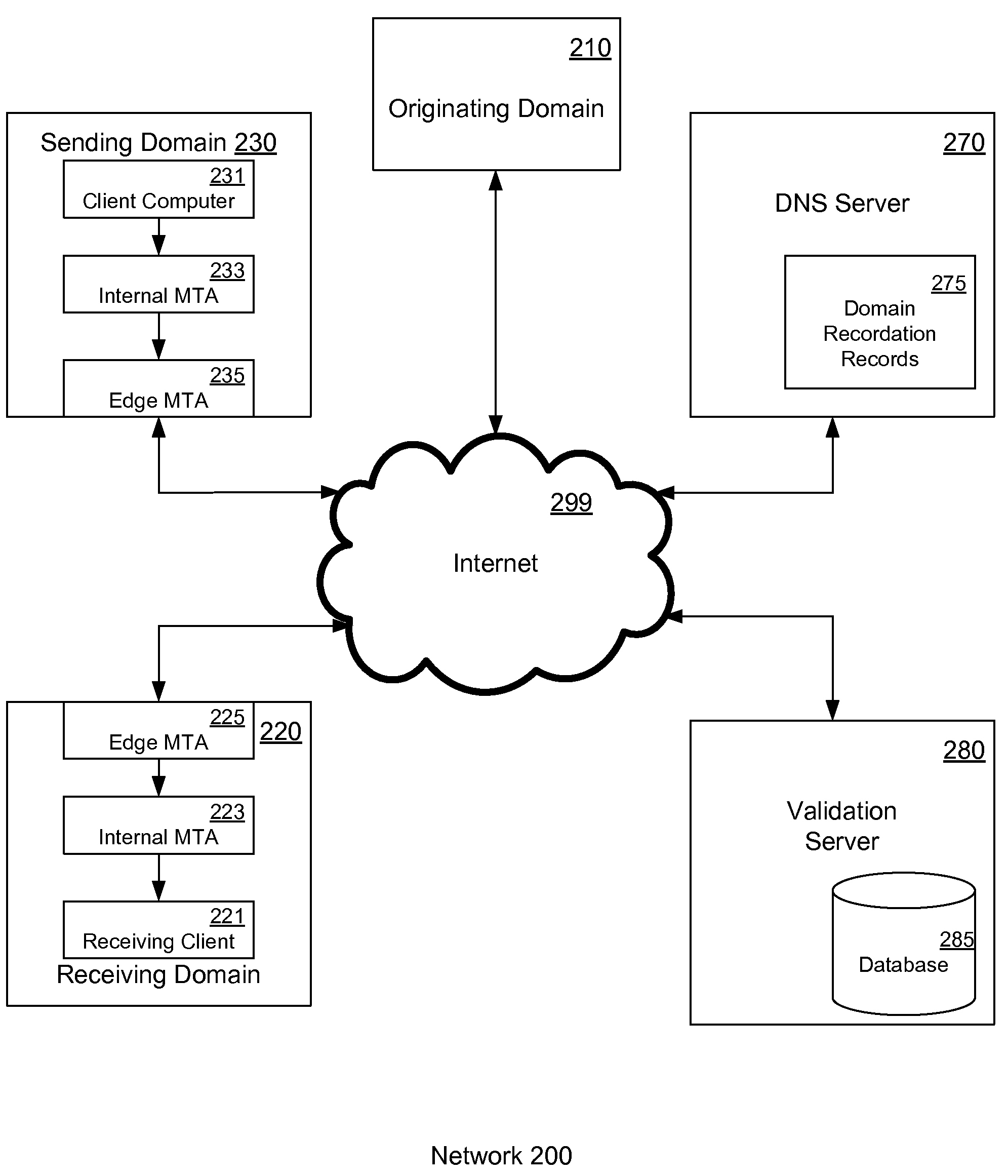
Email authentication, or validation, is a collection of techniques aimed at providing verifiable information about the origin of email messages by validating the domain ownership of any message transfer agents (MTA) who participated in transferring and possibly modifying a message.
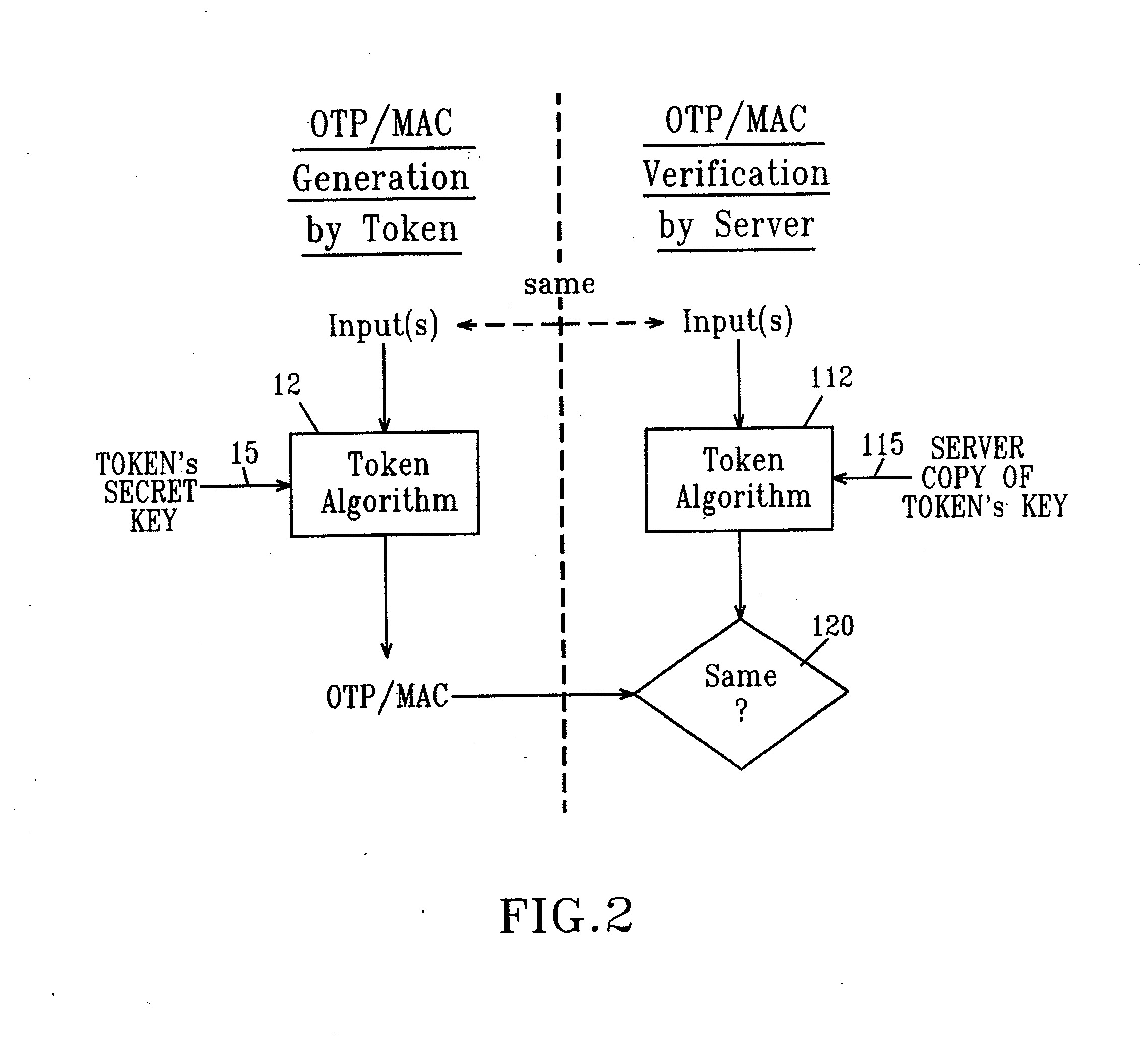
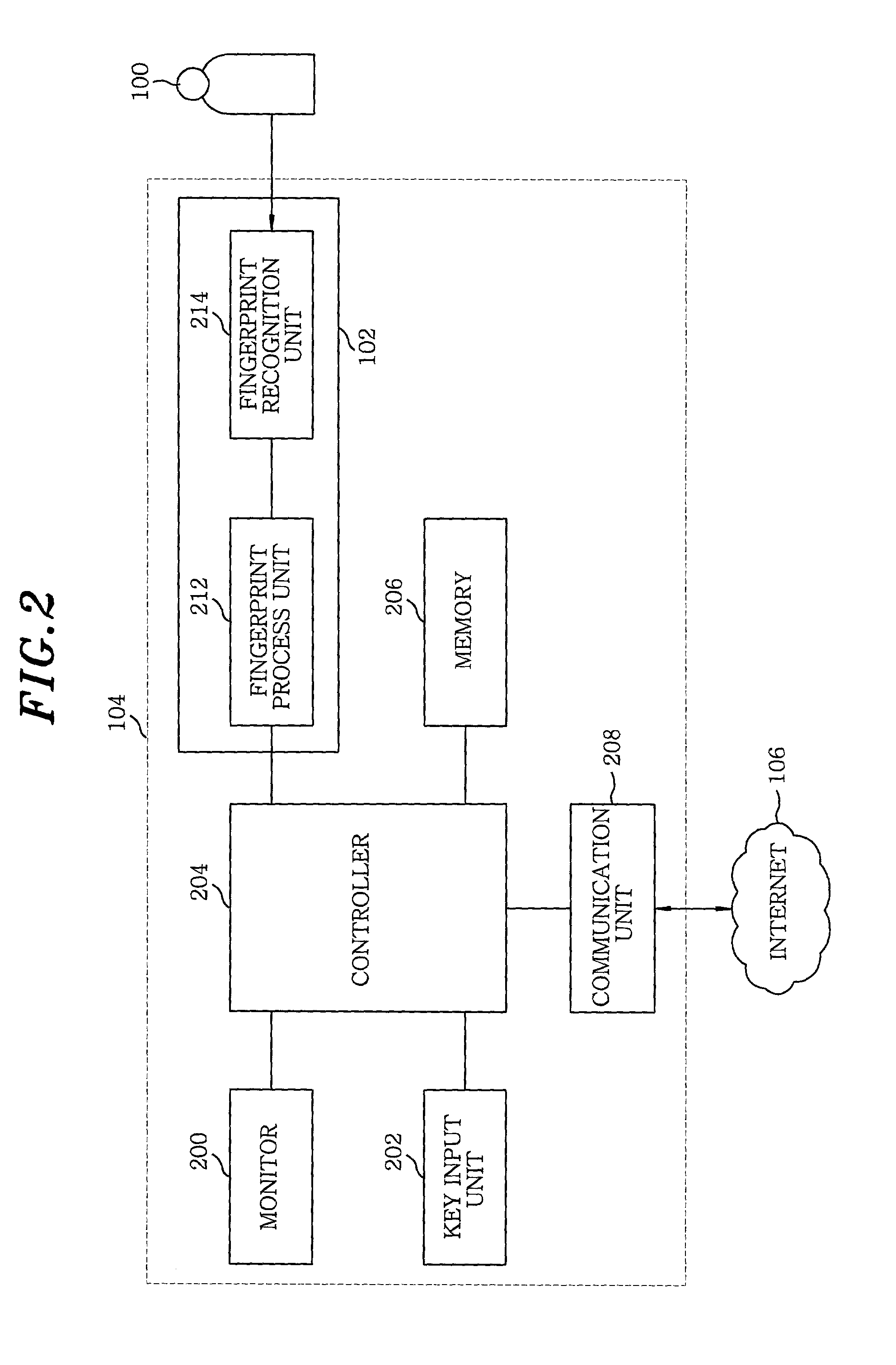
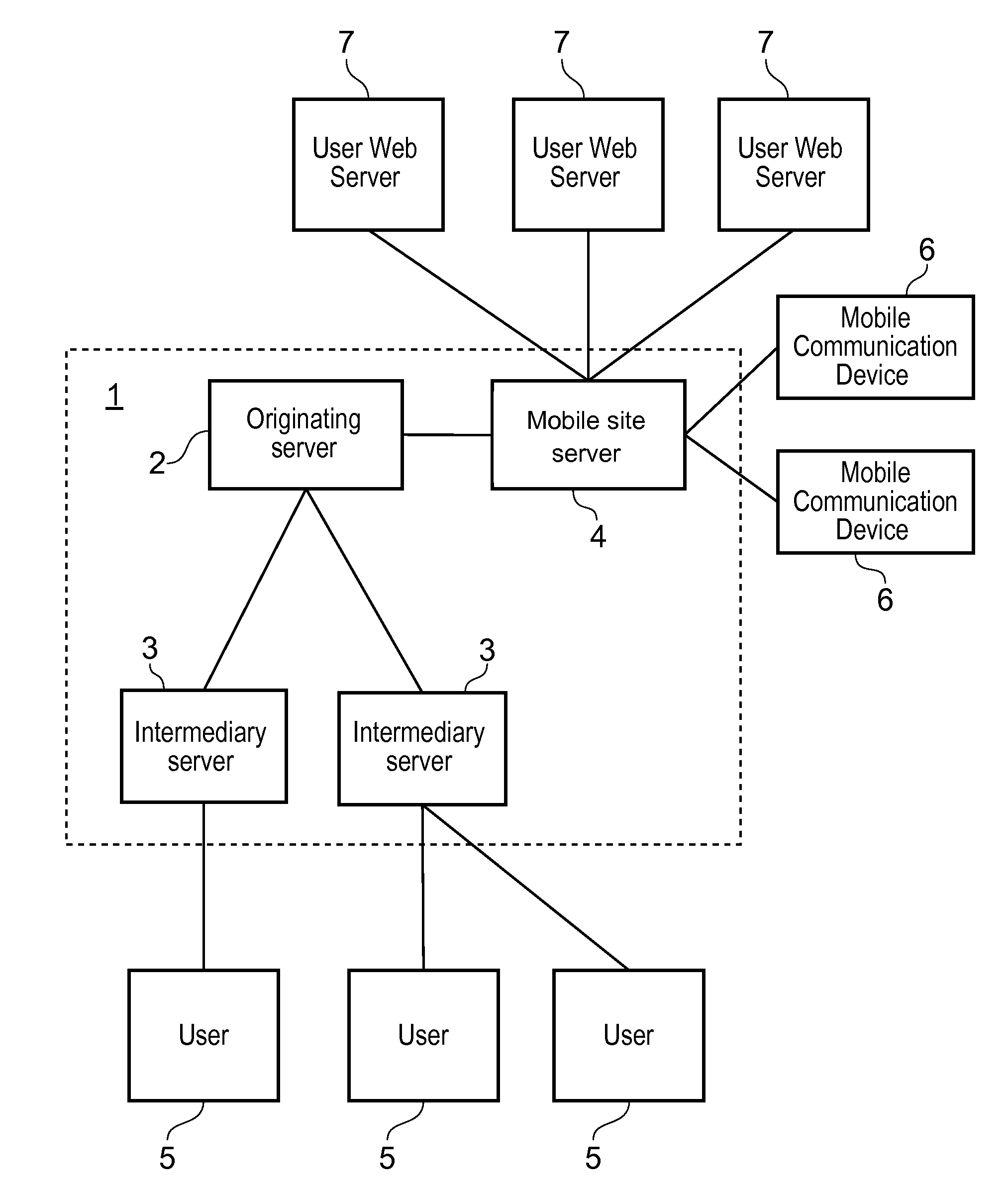
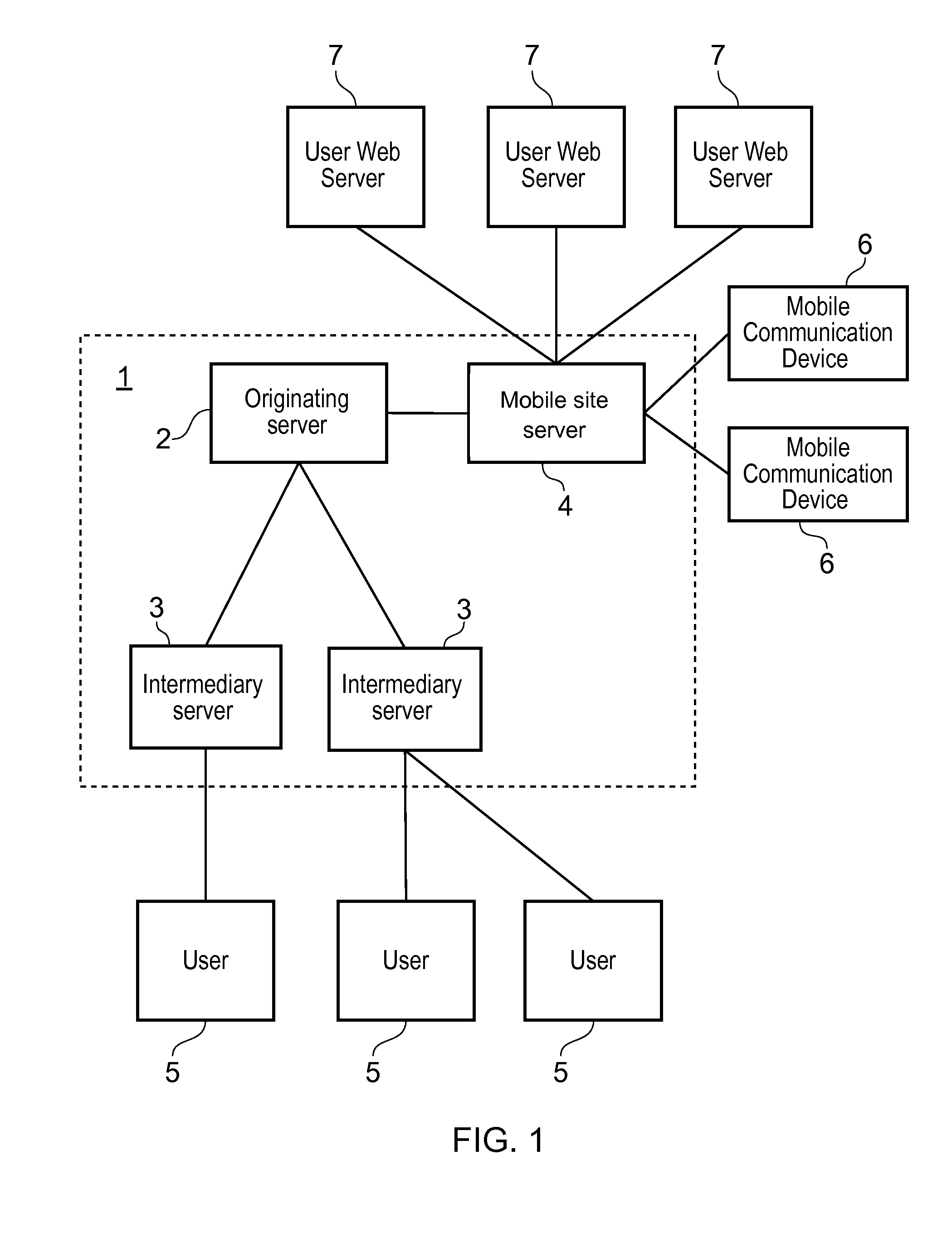
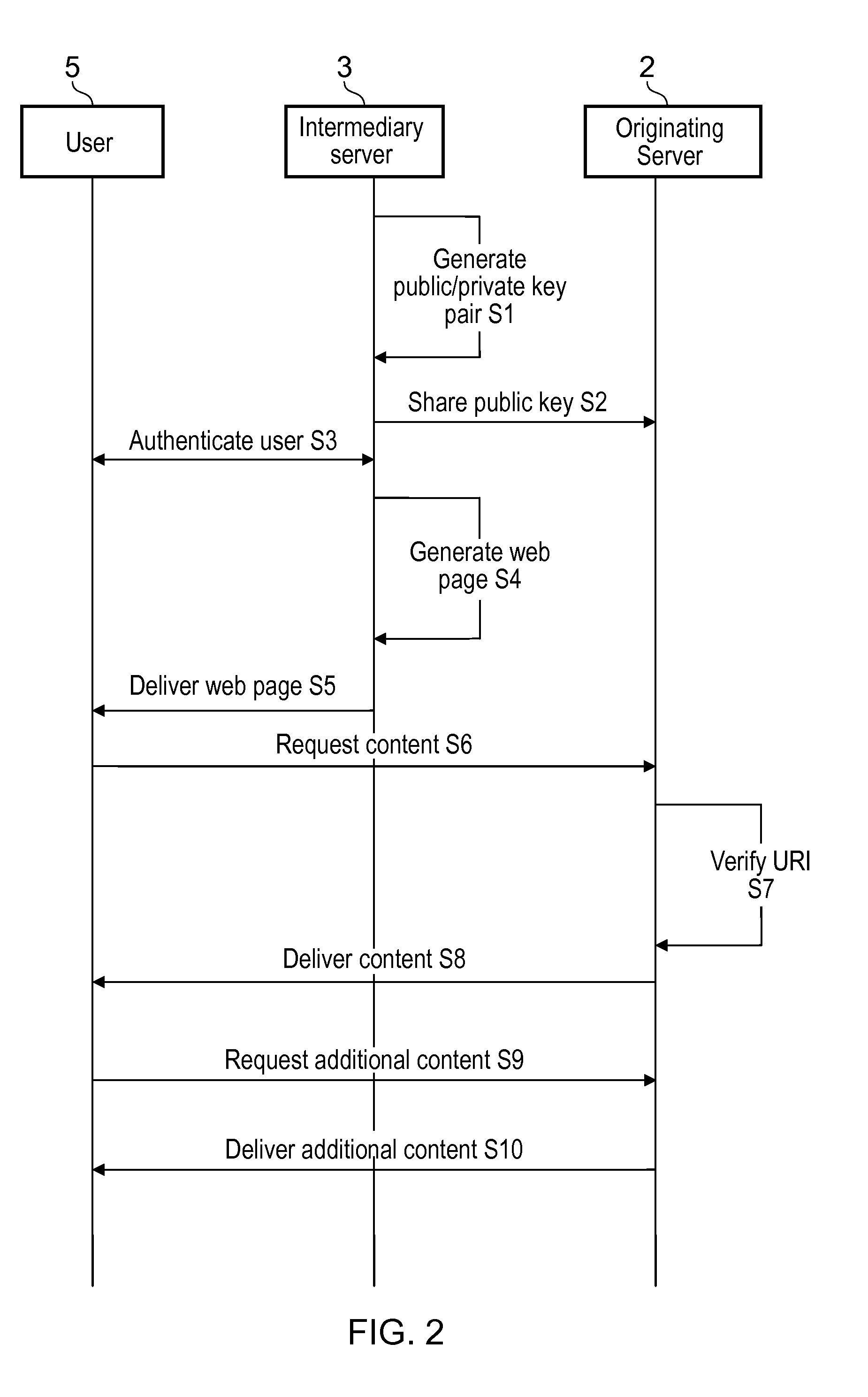
System and method of user authentication for network communication through a policy agent
InactiveUS7039713B1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsData connectionUser authentication
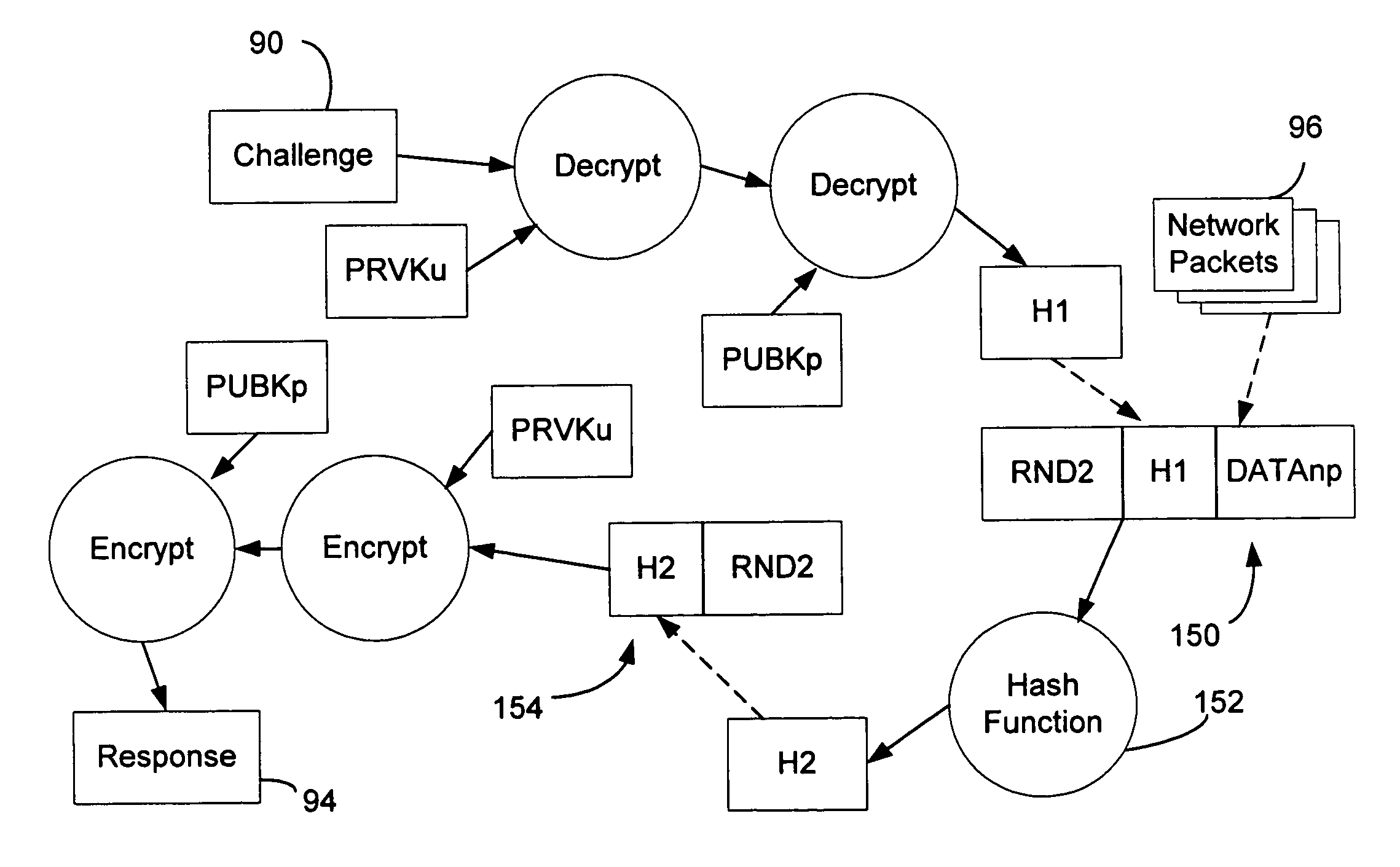
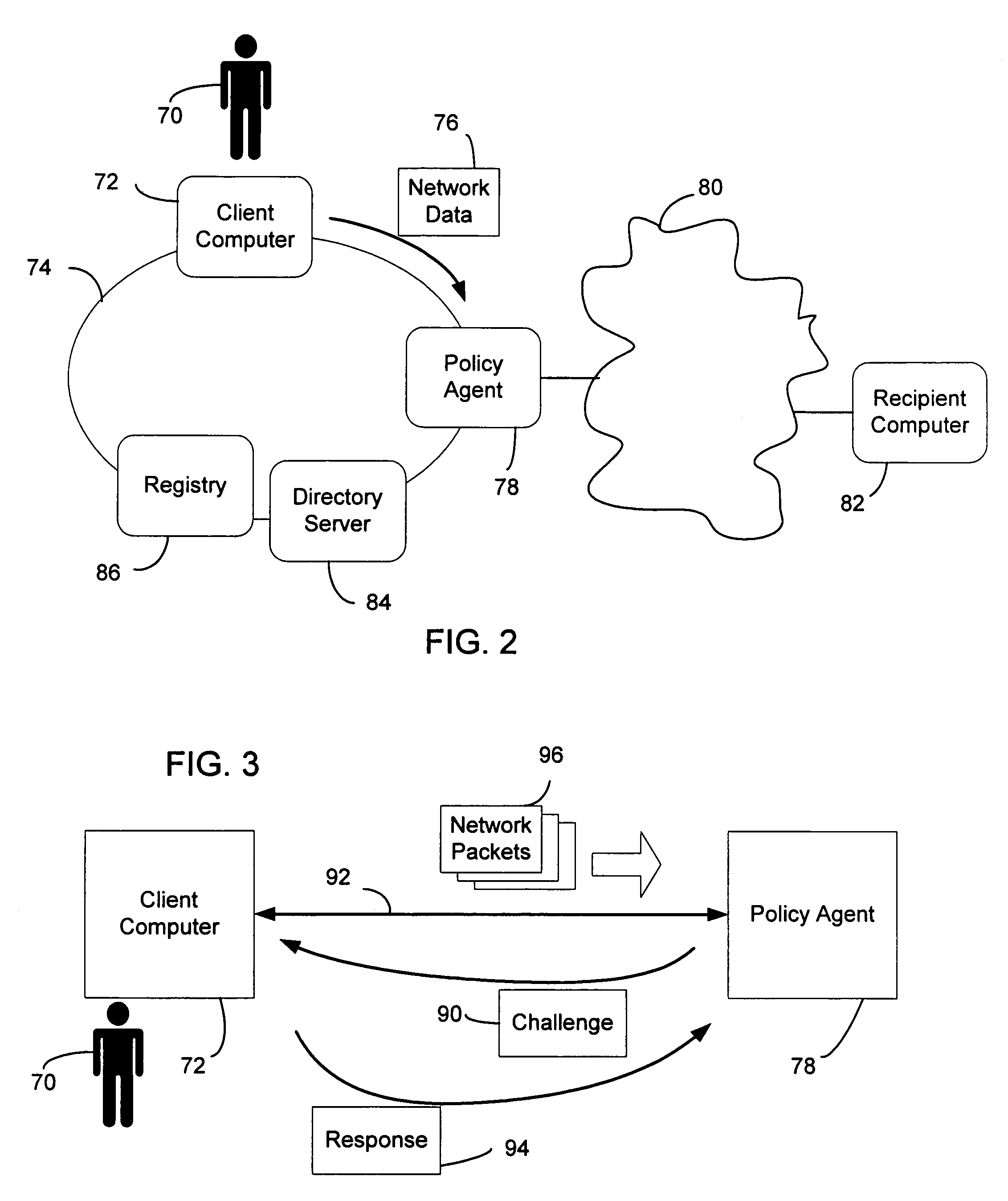
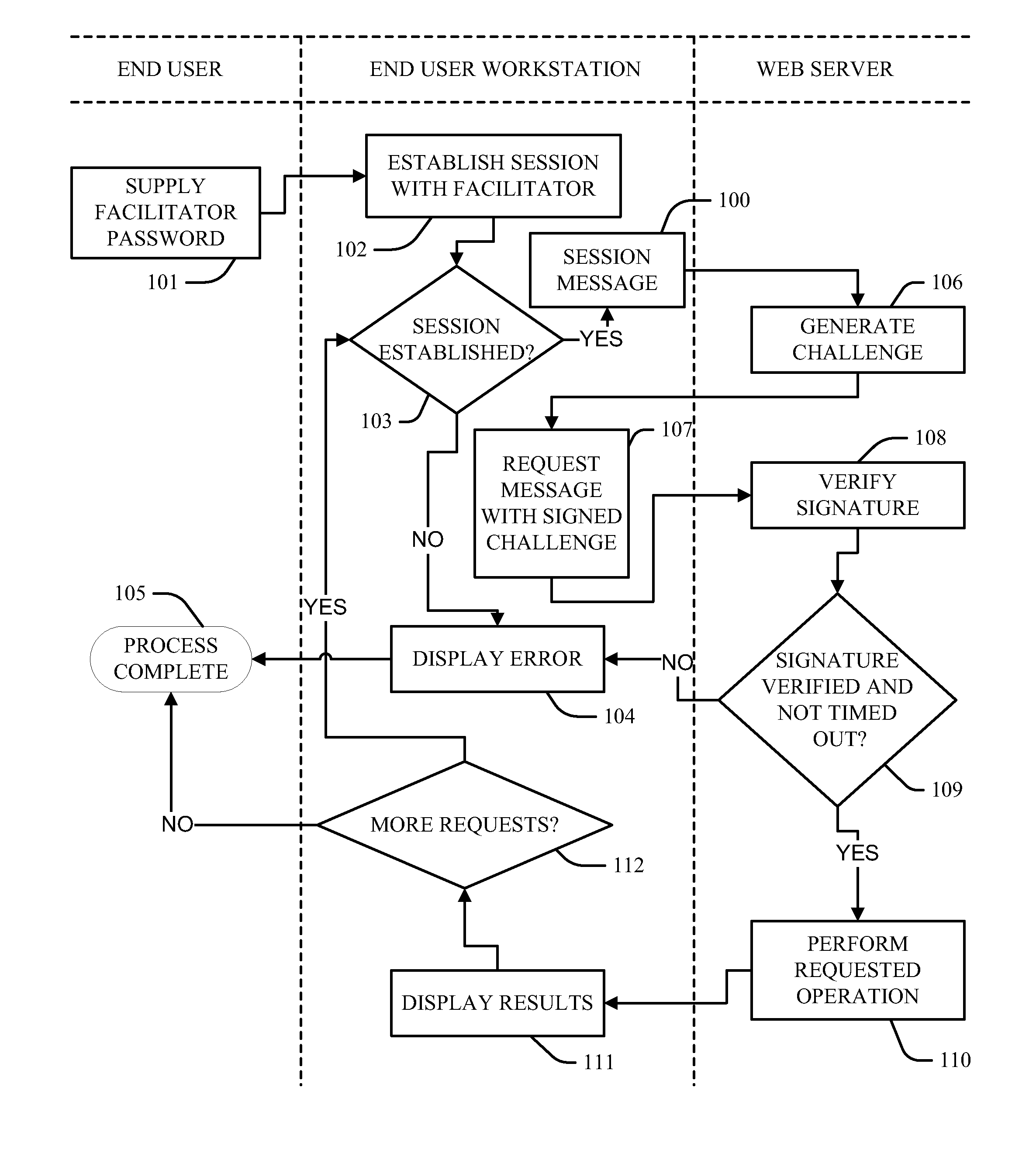
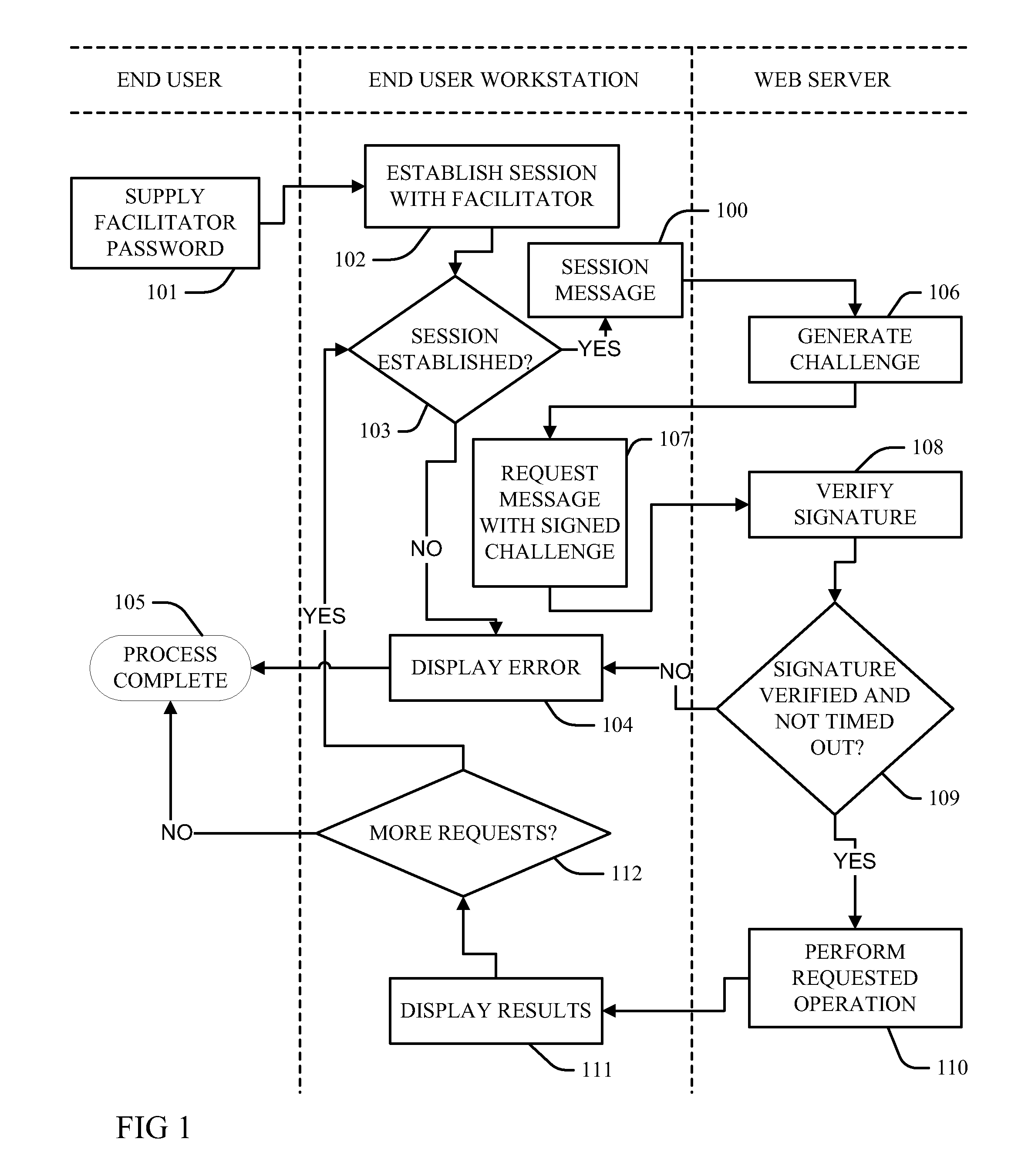
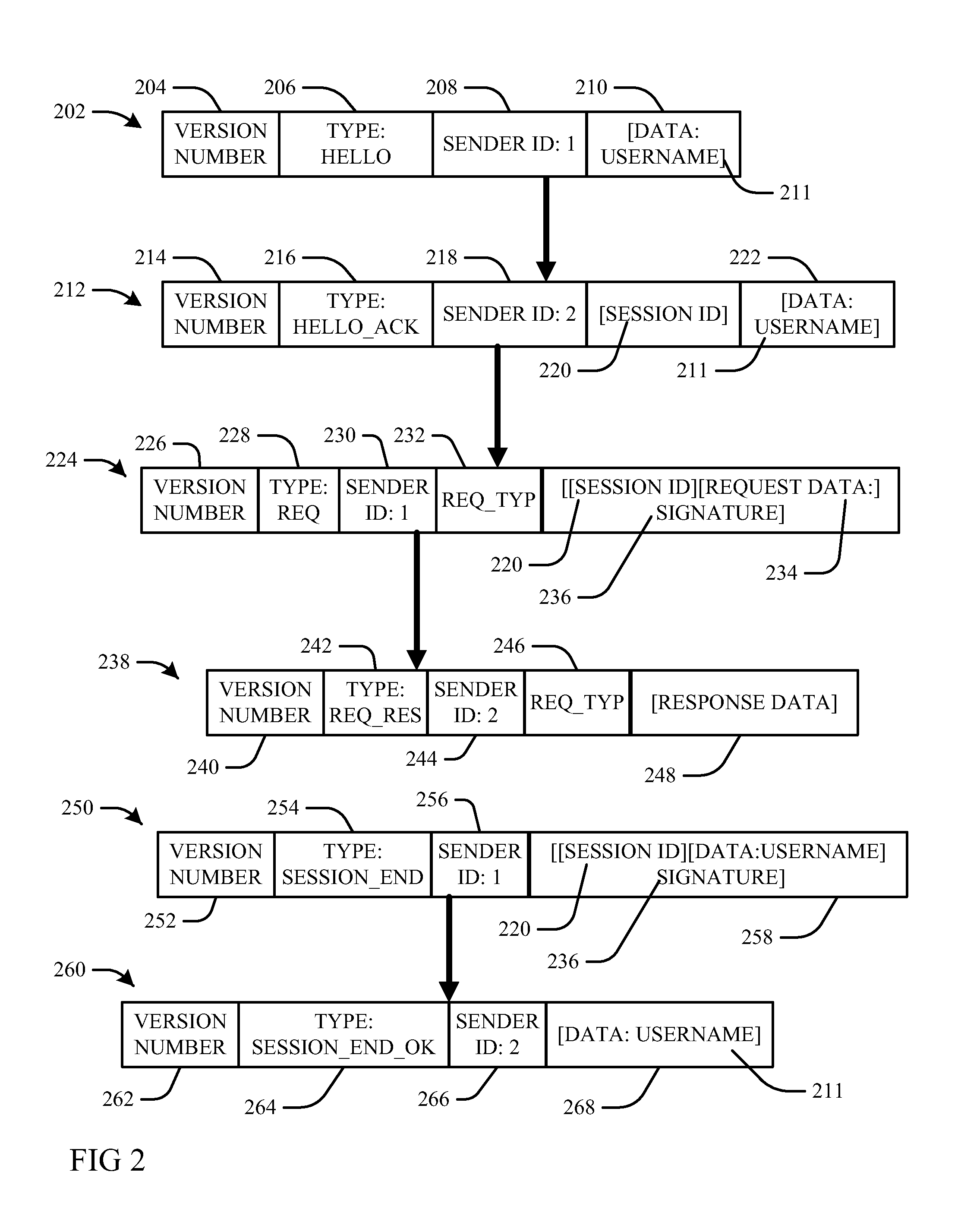
A policy agent of a network performs an out-of-band user authentication process to verify the identity of a user of a client computer and associates the network data received from the client computer with the user. When the client computer initiates a network data connection to or through the policy agent, the policy agent sends an encrypted challenge to the client computer. The challenge is encrypted with a private key of the policy agent. When the client computer receives the challenge, it decrypts the challenge and prepares a message digest value based on the challenge and the network data sent by the user. The message digest value is then encrypted with the private key of the user to form a response, and the response is sent to the policy agent. The policy agent decrypts the response with the public key of the user to obtain the message digest value and calculates a digest value based on the challenge and the received network data. The policy agent then compares the calculated digest value with the decrypted digest value. A match between the two digest values indicates that the user is successfully authenticated and that the received network data are associated with the user. The policy agent may then apply network policies based on the credentials of the authenticated user.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Authentication System and Method
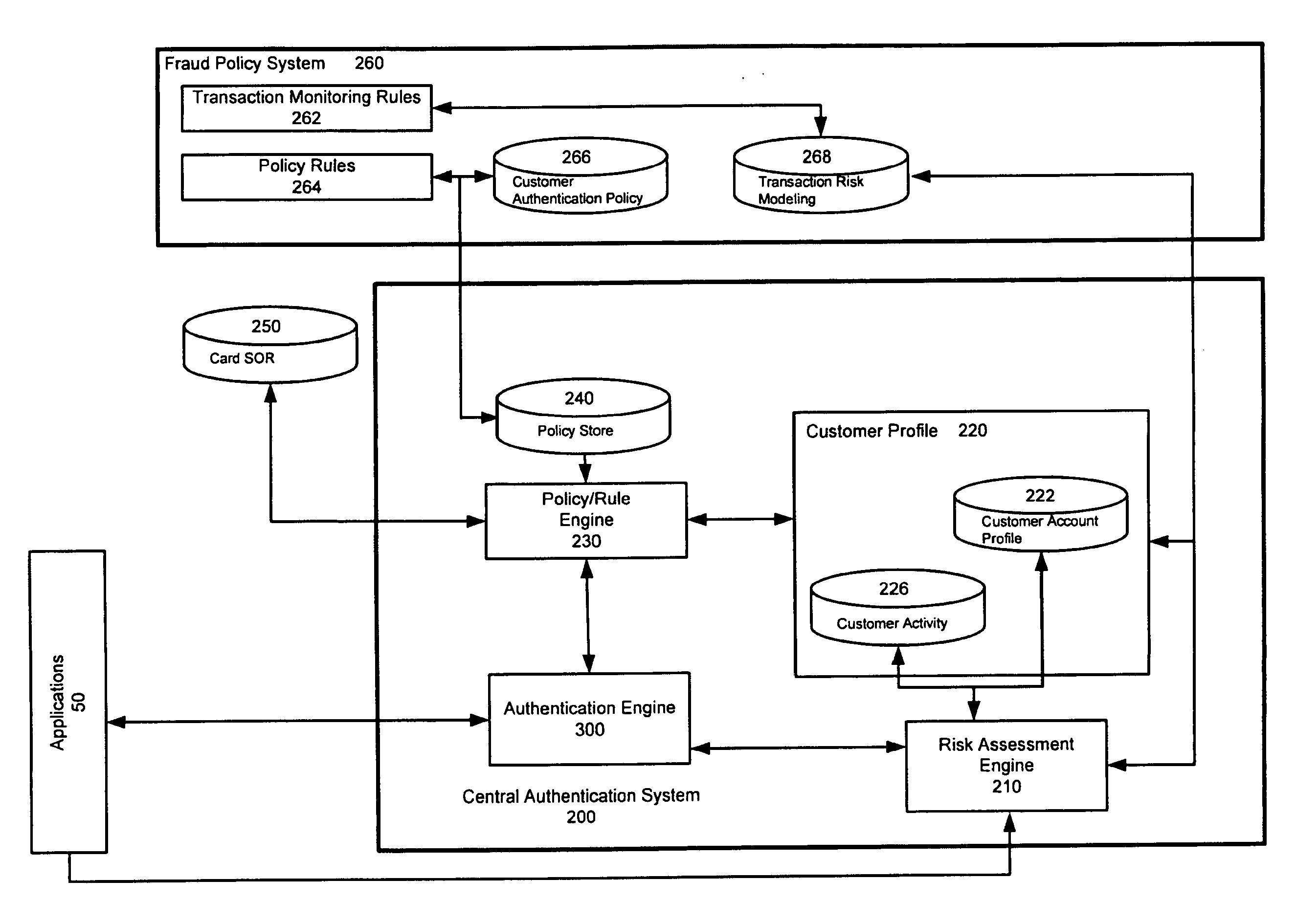
ActiveUS20120297446A1Payment architectureDigital data authenticationInternet privacyCentralized management
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Remote authentication and transaction signatures
InactiveUS20110258452A1Simple ideaUser identity/authority verificationPayment architecturePersonalizationSmart card
The invention provides a method, apparatus, computer readable medium and signal which allows the usage of devices containing PKI private keys such as PKI-enabled smart cards or USB sticks to authenticate users and to sign transactions. The authenticity of the user and / or the message is verified. Furthermore the operation (authentication and / or signing) occurs without the need for an application to have some kind of a direct or indirect digital connection with the device containing the private key. In addition the operation occurs without the need for the PKI-enabled device containing the private key (e.g. a PKI smart card or USB stick) to either support symmetric cryptographic operations or to have been personalized with some secret or confidential data element that can be read by a suitable reader.
Owner:ONESPAN NORTH AMERICA INC
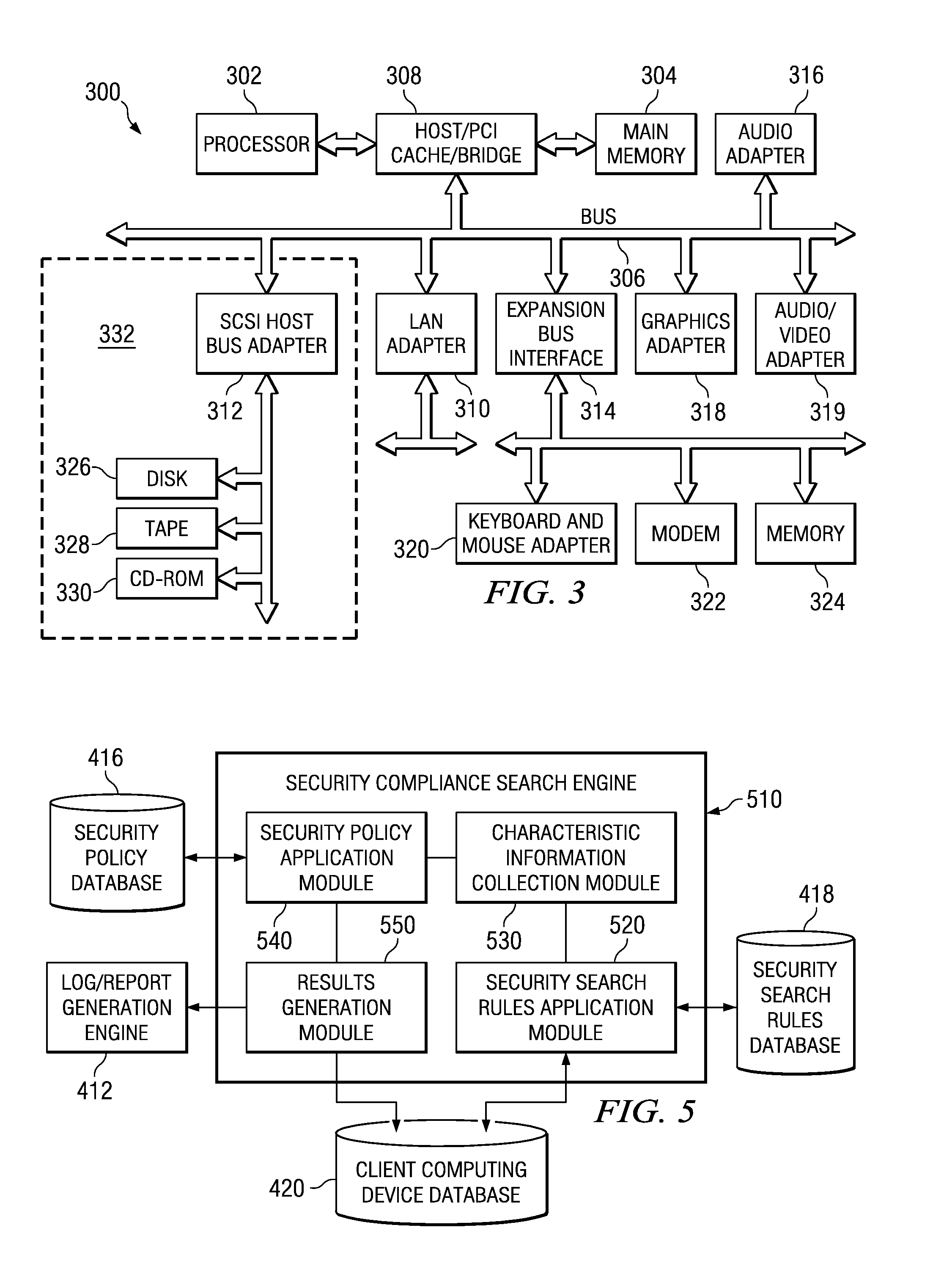
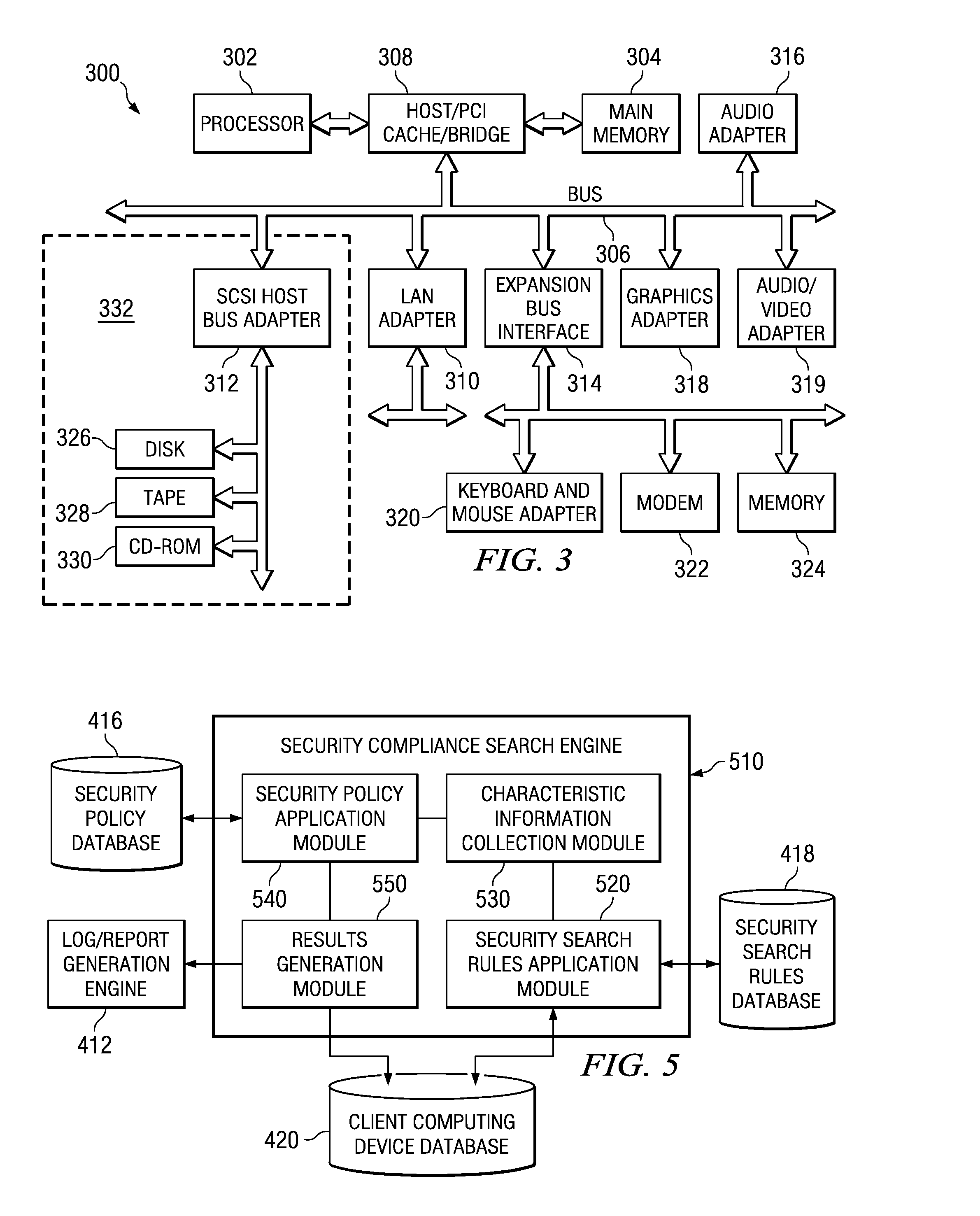
Confidential content reporting system and method with electronic mail verification functionality
InactiveUS20070261099A1Ensure complianceSpecial data processing applicationsSecuring communicationGraphicsGraphical user interface
A confidential content reporting system and method with electronic mail verification functionality are provided. With the system and method, a security compliance search engine is provided for searching items of information to identify items containing confidential content and security violations with regard to this confidential content. Results of the search may be reported to a user via a graphical user interface (GUI) that identifies the item of information, the security violations detected, and suggested corrective actions, such as encryption. A user may interact with the GUI to apply security mechanisms in accordance with the suggested corrective actions. Moreover, the searching and reporting mechanism may be used to search electronic mail messages and their attachments prior to distribution of the electronic mail messages. Automatic modification of the electronic mail message to modify distribution lists and / or content of the electronic mail message may be performed using the mechanisms of the illustrative embodiments.
Owner:IBM CORP
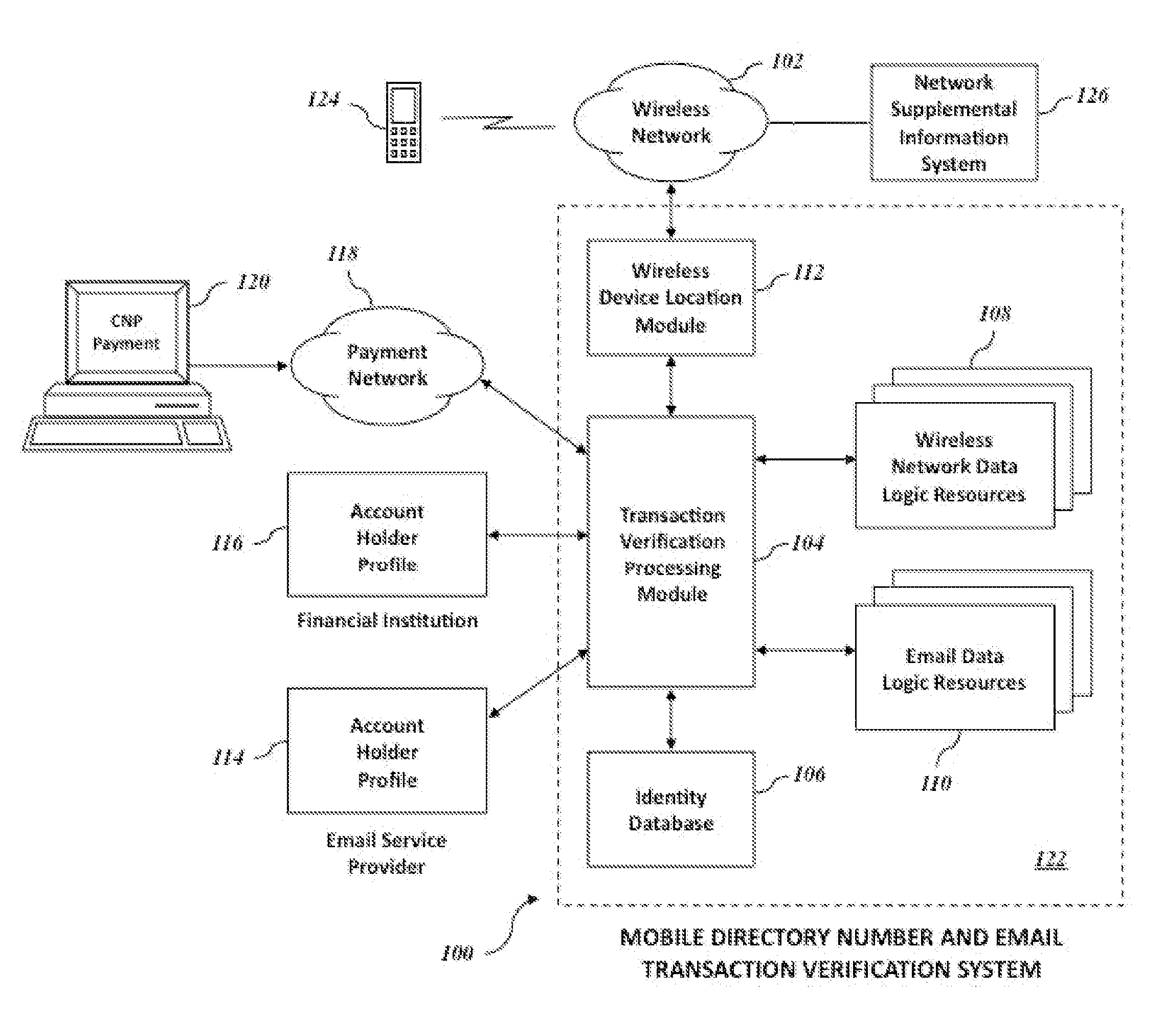
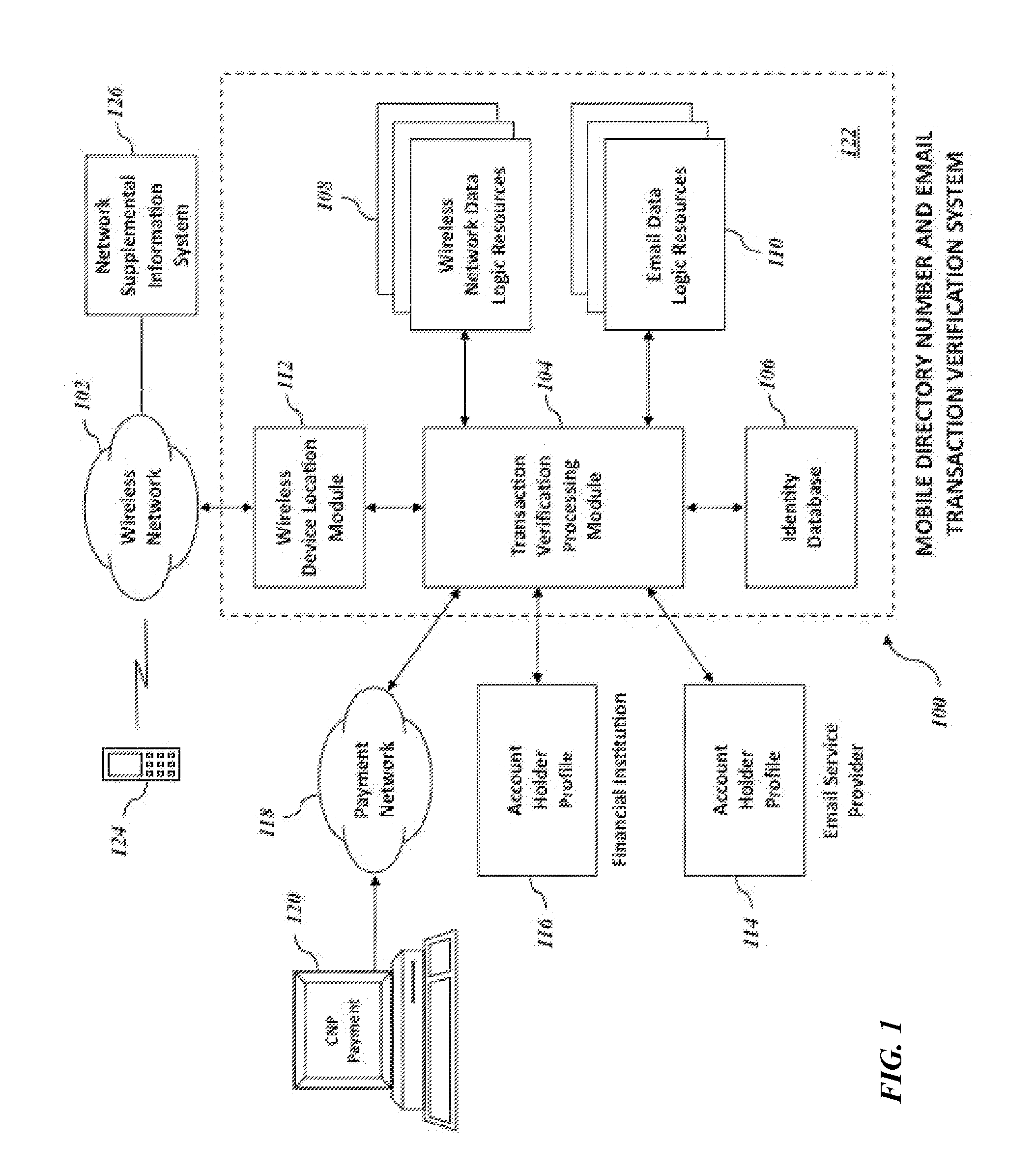
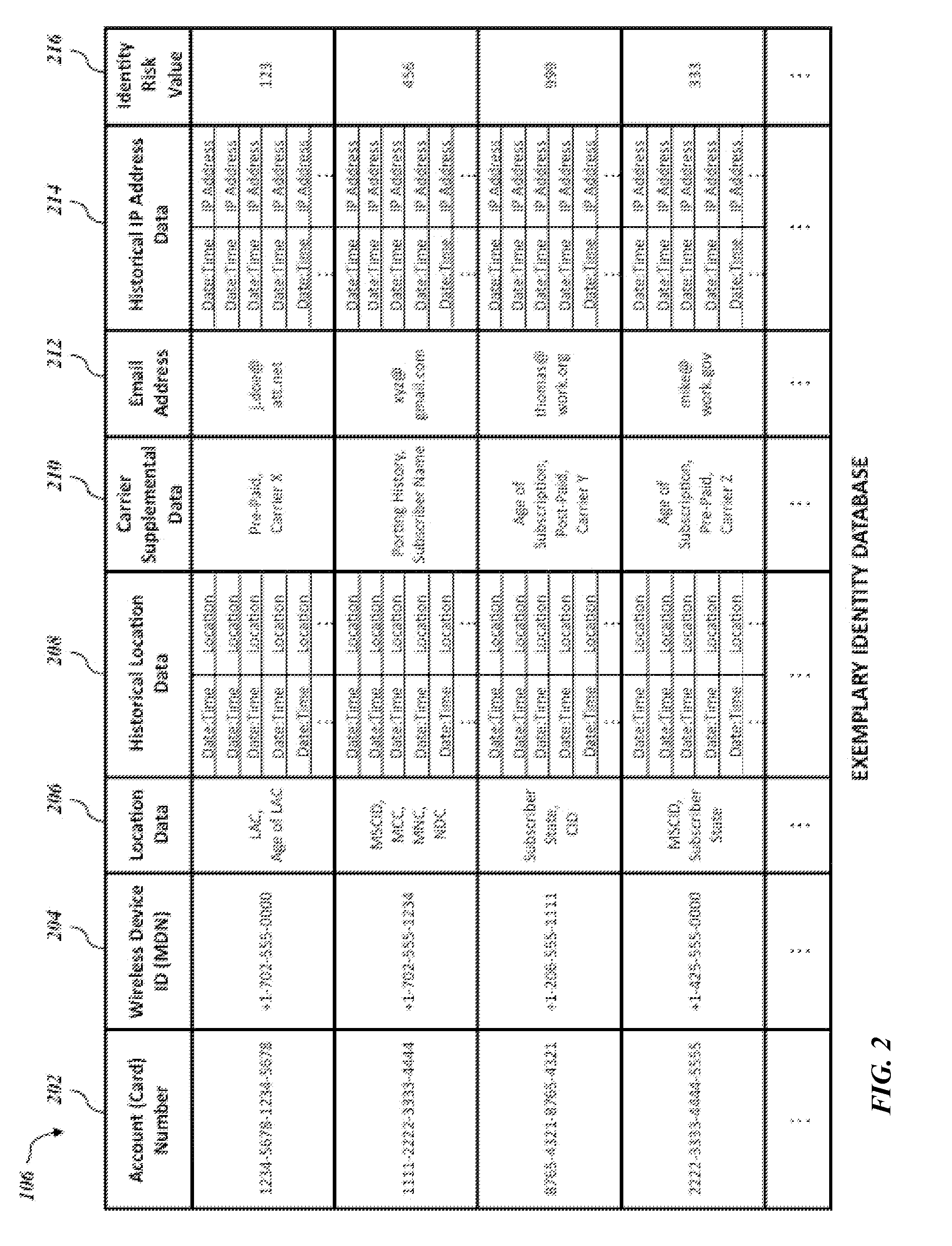
Mobile directory number and email verification of financial transactions
Systems and methods for verifying a financial transaction based on an account number, a mobile directory number associated with the financial transaction, a mobile directory number associated with the account number, an email address associated with the account number, internet protocol address data associated with the financial transaction, and internet protocol address data associated with accesses of the email address.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Confidential Content Reporting System and Method with Electronic Mail Verification Functionality
InactiveUS20080235760A1Knowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A confidential content reporting system and method with electronic mail verification functionality are provided. With the system and method, a security compliance search engine is provided for searching items of information to identify items containing confidential content and security violations with regard to this confidential content. Results of the search may be reported to a user via a graphical user interface (GUI) that identifies the item of information, the security violations detected, and suggested corrective actions, such as encryption. A user may interact with the GUI to apply security mechanisms in accordance with the suggested corrective actions. Moreover, the searching and reporting mechanism may be used to search electronic mail messages and their attachments prior to distribution of the electronic mail messages. Automatic modification of the electronic mail message to modify distribution lists and / or content of the electronic mail message may be performed using the mechanisms of the illustrative embodiments.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
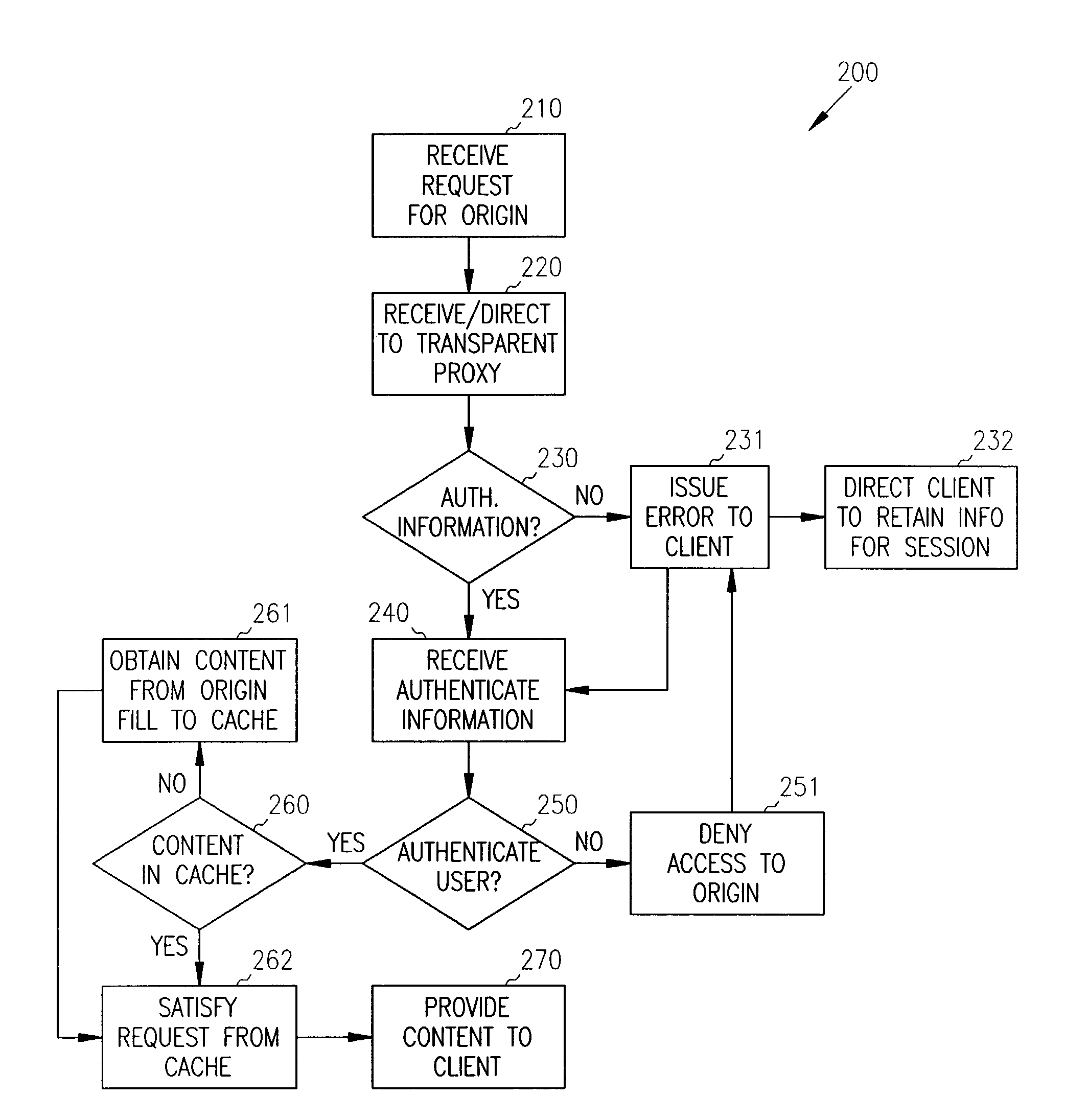
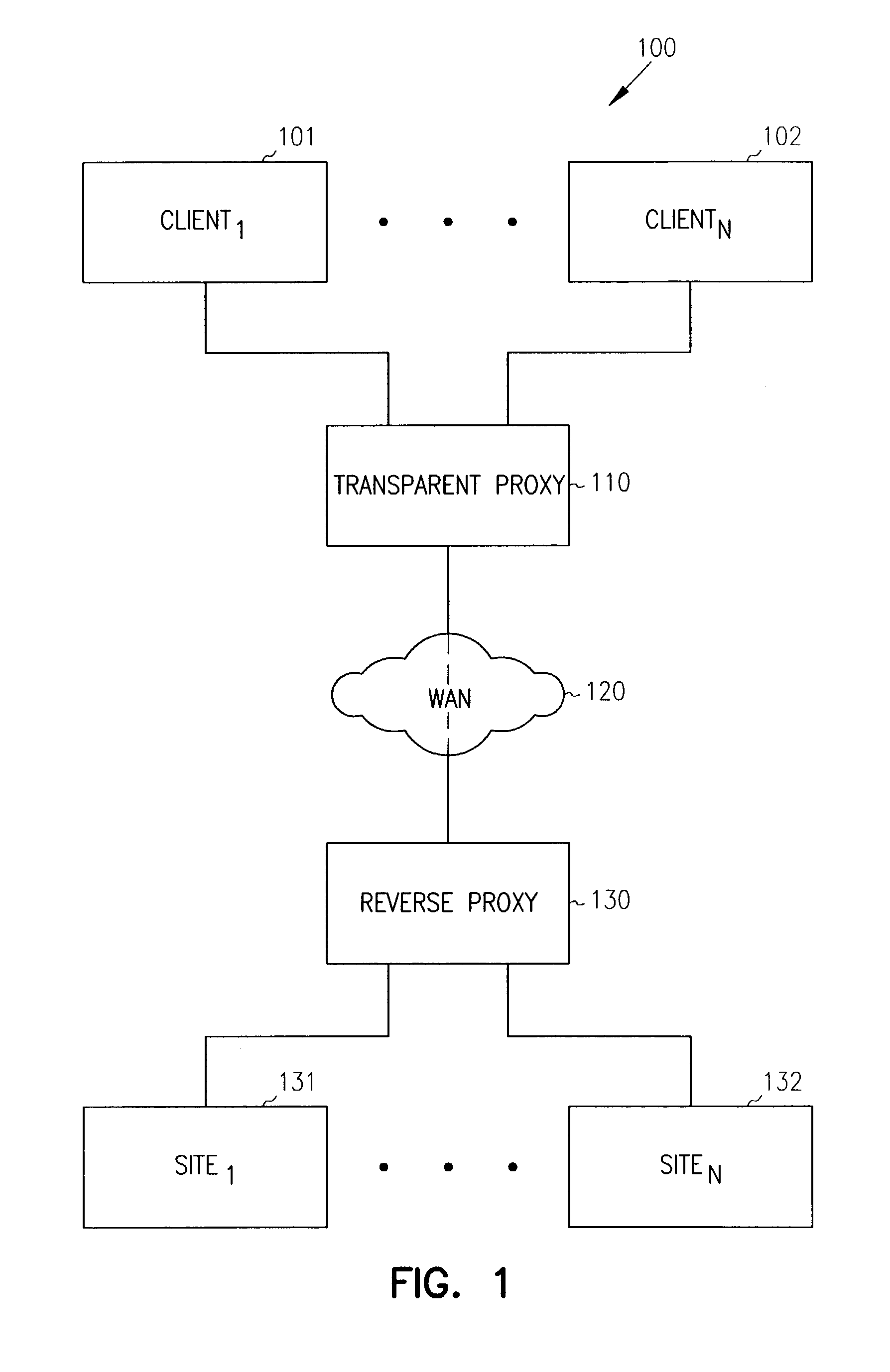
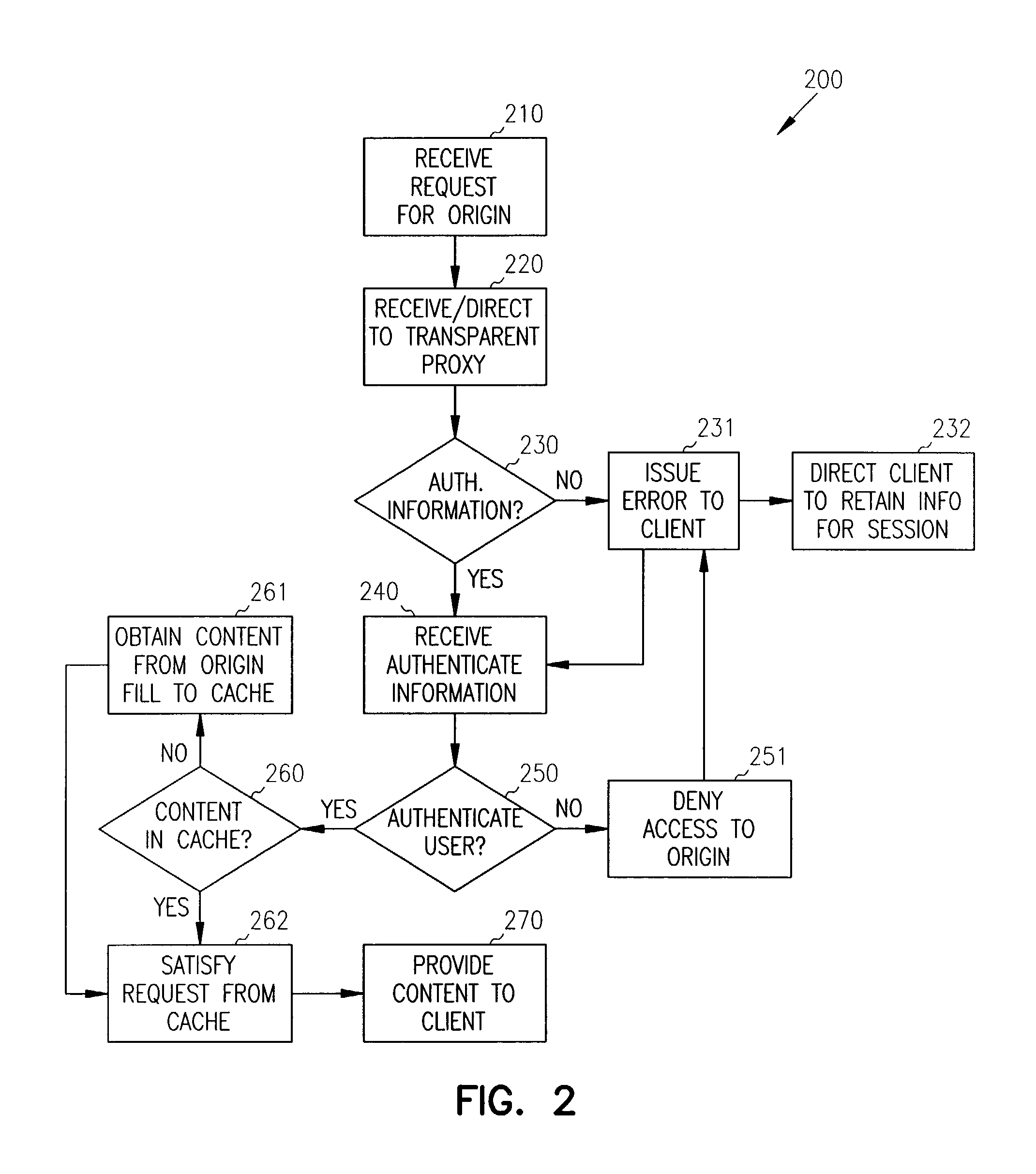
Single sign-on with basic authentication for a transparent proxy
ActiveUS7793342B1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsUser inputInternet privacy
Methods, systems, and data structures are provided for single sign-on with basic authentication on a transparent proxy. A user accesses a client to issue requests for content on an origin server. The transparent proxy requires user authentication before access can be granted to the origin server. The transparent proxy receives the requests and determines if the user is presently authenticated to the origin server. If the user is not authenticated, then the transparent proxy issues a basic authentication error to the client causing the client to prompt the user for authentication information. The transparent proxy directs the client to retain the authentication information and supply it with subsequent requests to the origin server. Further, the transparent proxy independently reconstructs the authentication information for subsequent requests directed to other servers under the handling of the transparent proxy, without requiring additional user action.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
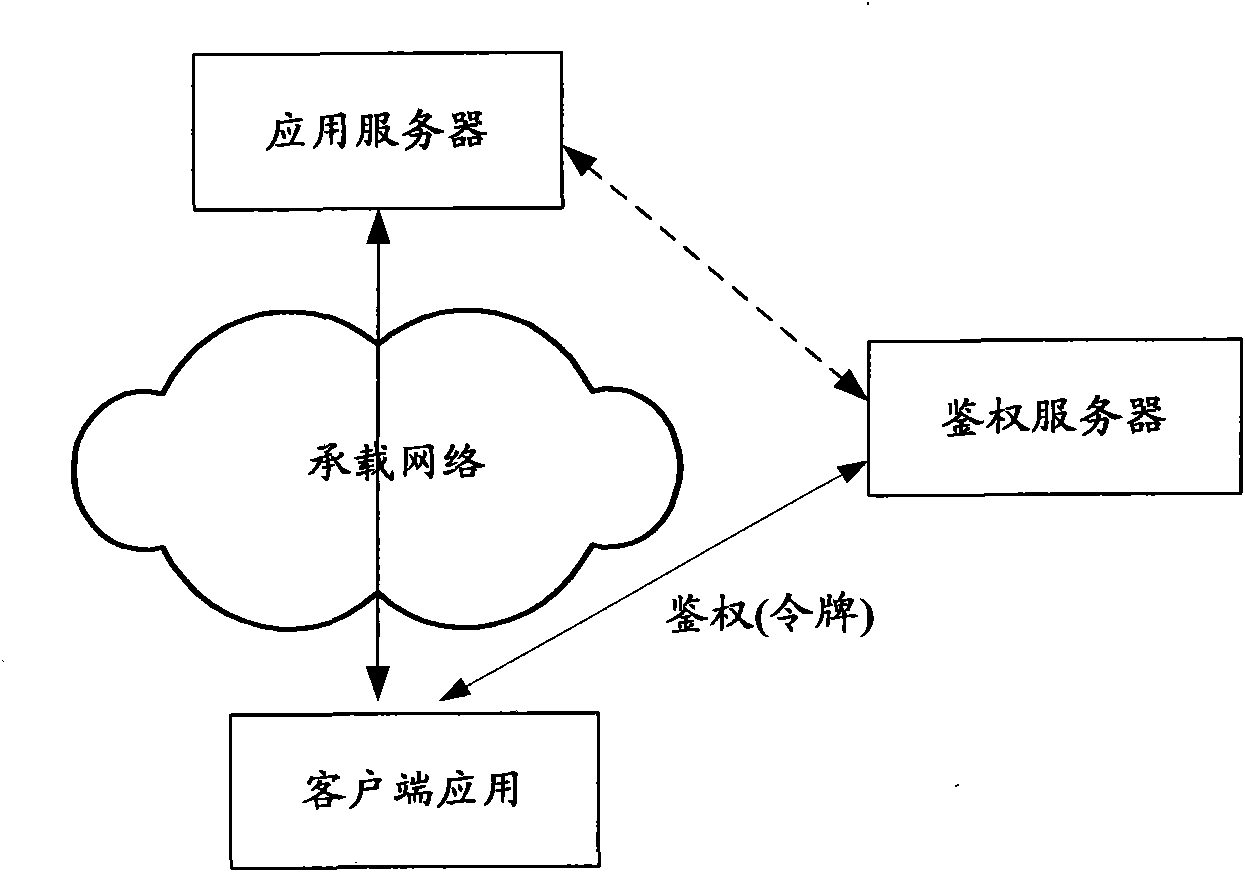
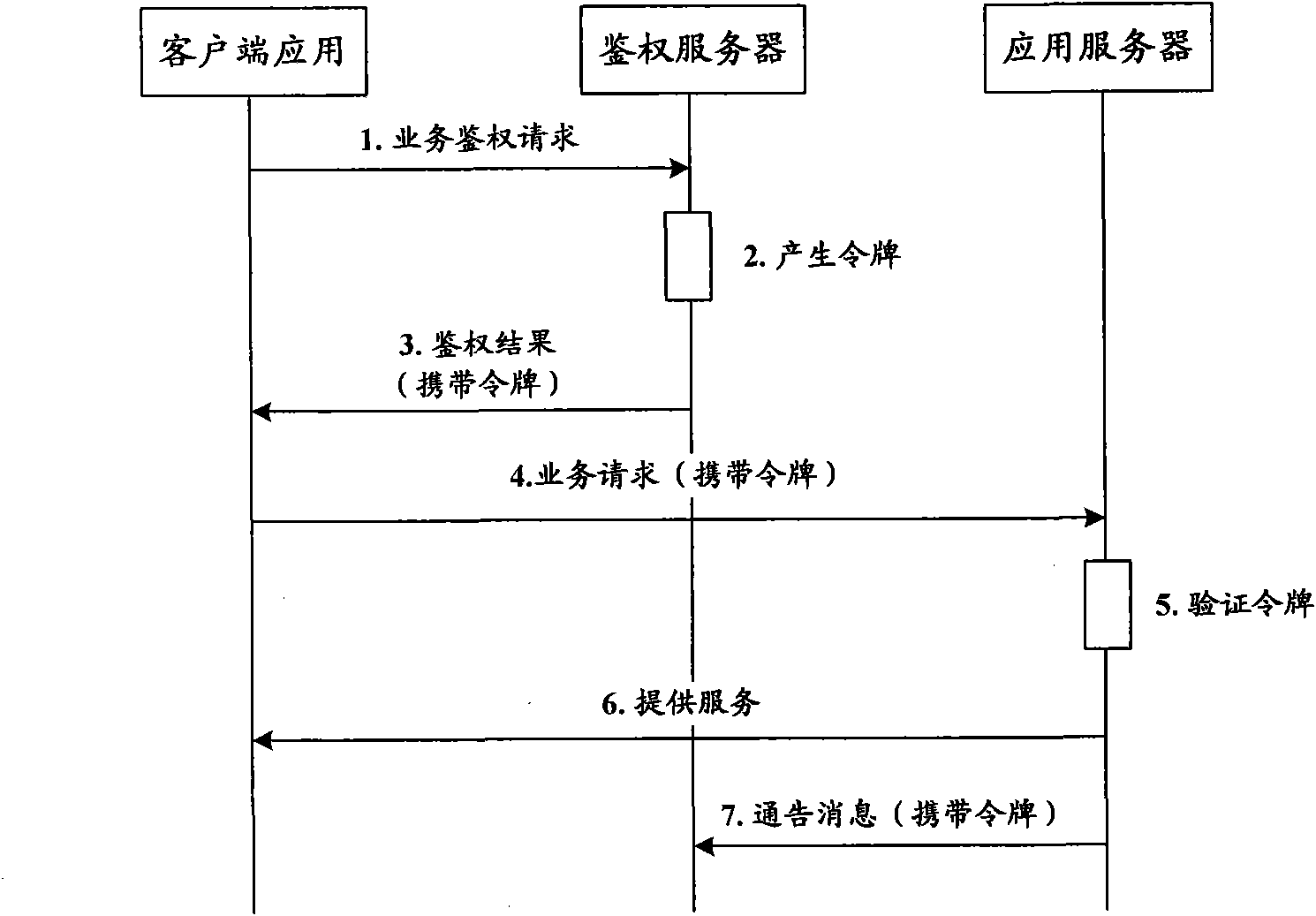
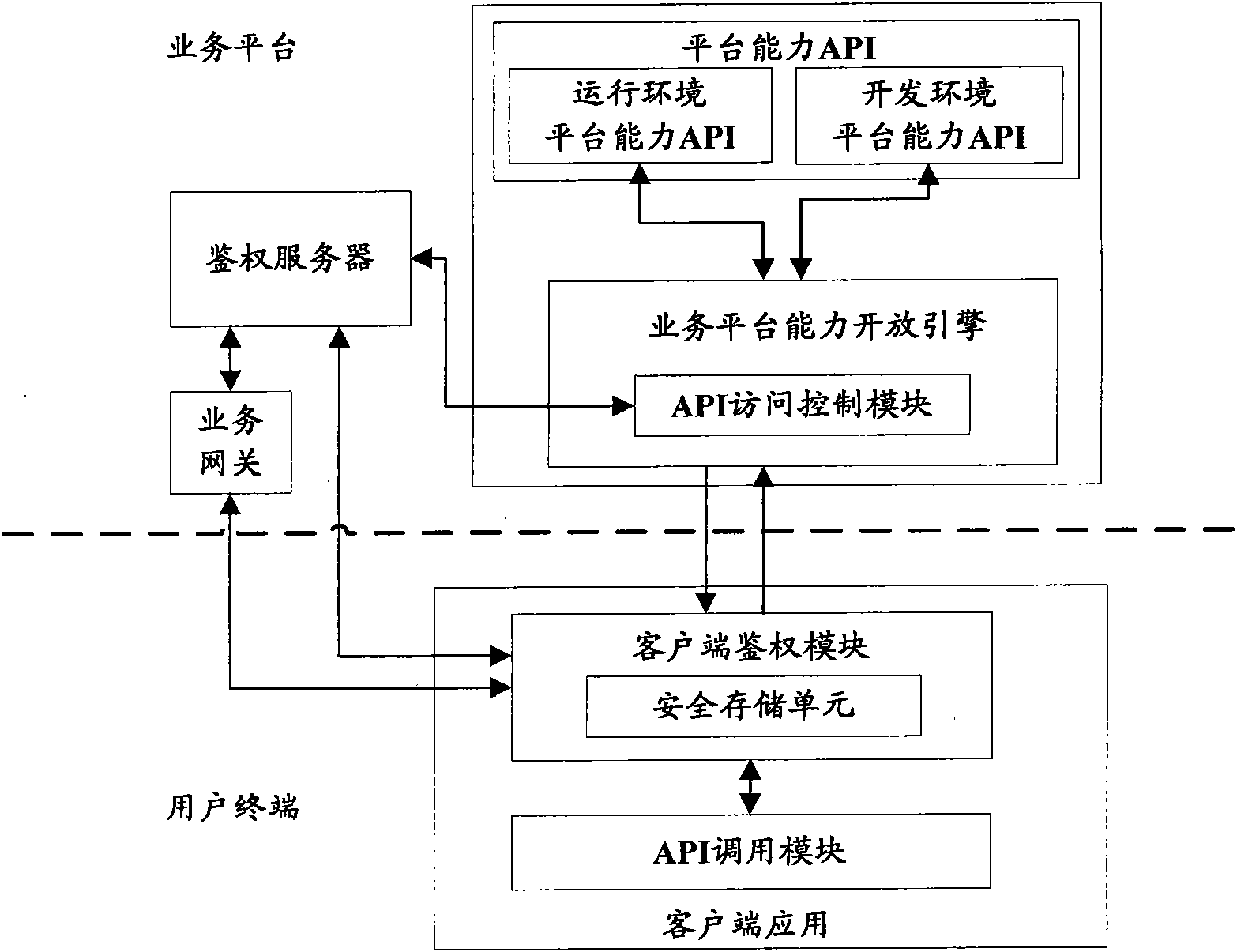
Method, device and system of authentication and service calling
ActiveCN102378170ARealization of legality authentication and authenticationAddressing Security VulnerabilitiesTransmissionSecurity arrangementApplication programming interfaceAuthentication server
The invention discloses a method, device and system of authentication and service calling, used for realizing legality authentication of an authentication server in a service platform to a client side application and promoting the safety reliability of a calling mechanism of a platform capacity API (Application Programming Interface). The authentication server realizes the safe distribution of a clientKey by displacing a test authentication module in the client side application to a client side authentication module preset with an MAC (Media Access Control) fingerprint and the clientKey. When the client side application satisfies a trigger condition, the client side authentication module firstly passes an integrity check based on an MAC fingerprint mechanism and applies for registration to the authentication server based on an MAC1 generated by the shared clientKey and obtains a random authentication factor. When the client side application needs to call the platform capacity API, a dynamic token is generated based on the authentication factor to be carried in a service request. After the dynamic token authentication passes, the platform capacity API is allowed to be called.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM CO LTD
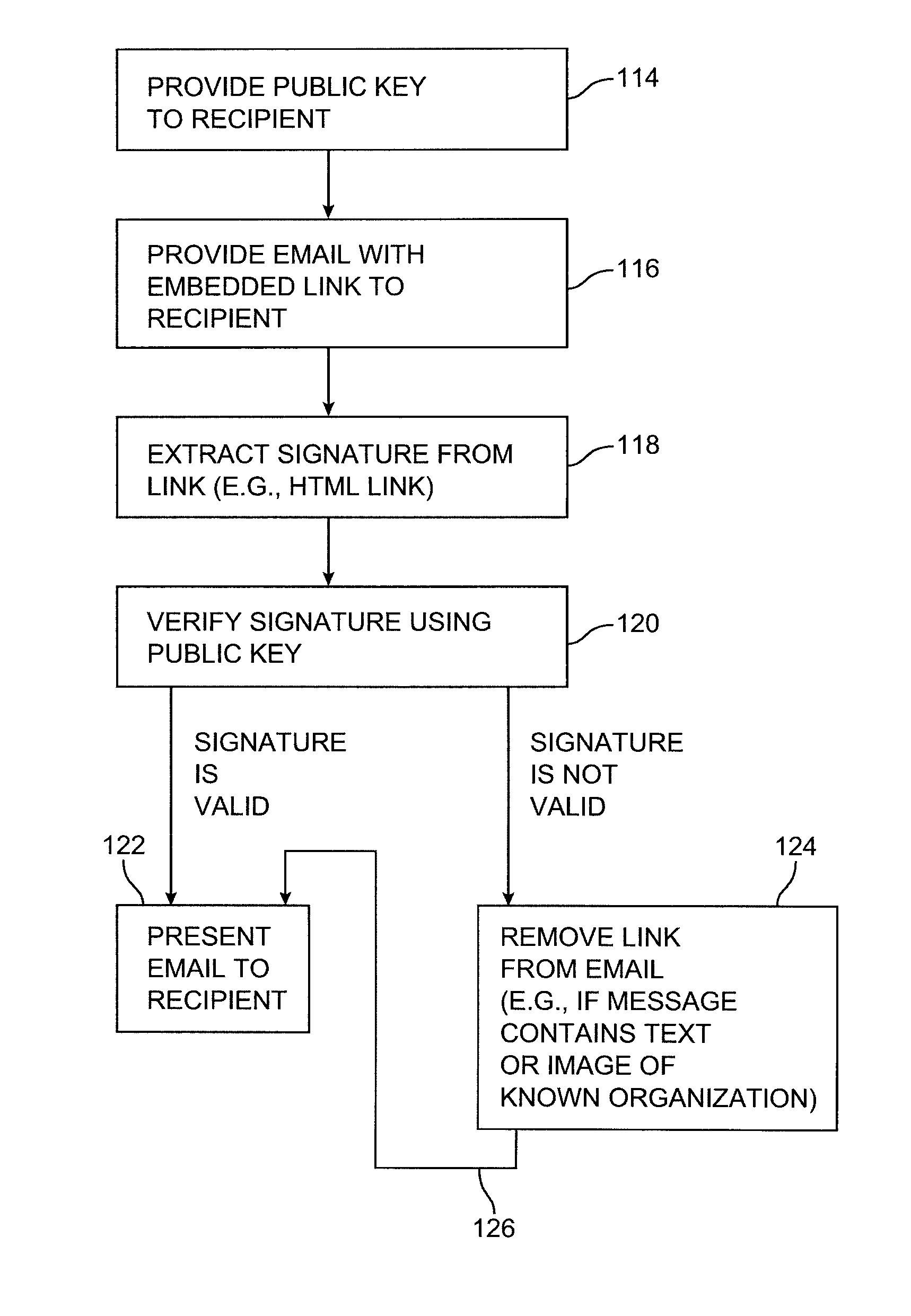
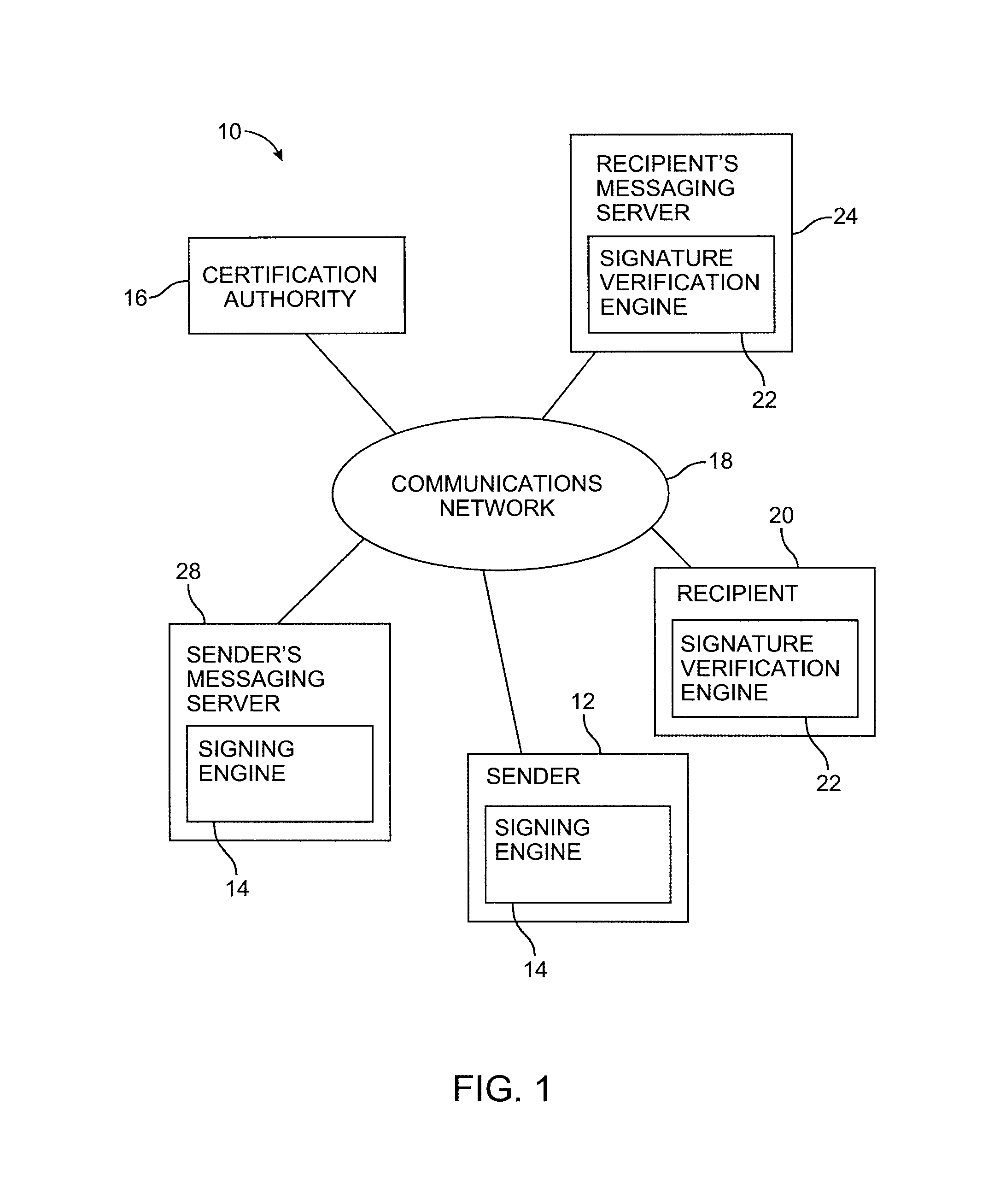
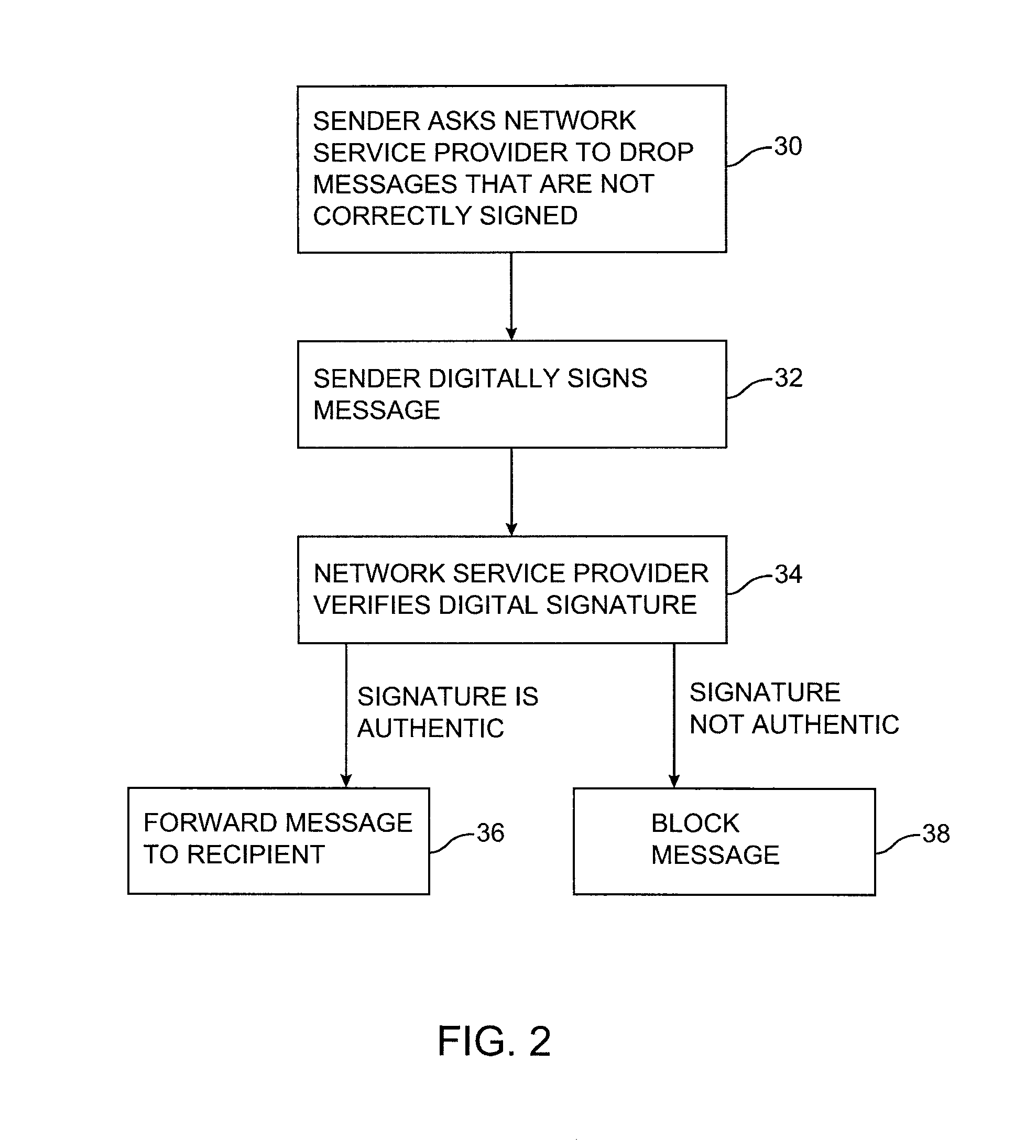
Message authentication using signatures
ActiveUS8429232B1Improve identityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInternet privacyDigital signature
Systems and methods are provided for using digital signatures to help distinguish legitimate email from known or trusted organizations from unsolicited email or forged email. Digital signatures may be used in an email body, mail header, or embedded links. The signatures may be verified by a recipient or internet service provider and may be used in conjunction with spam filtering applications.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
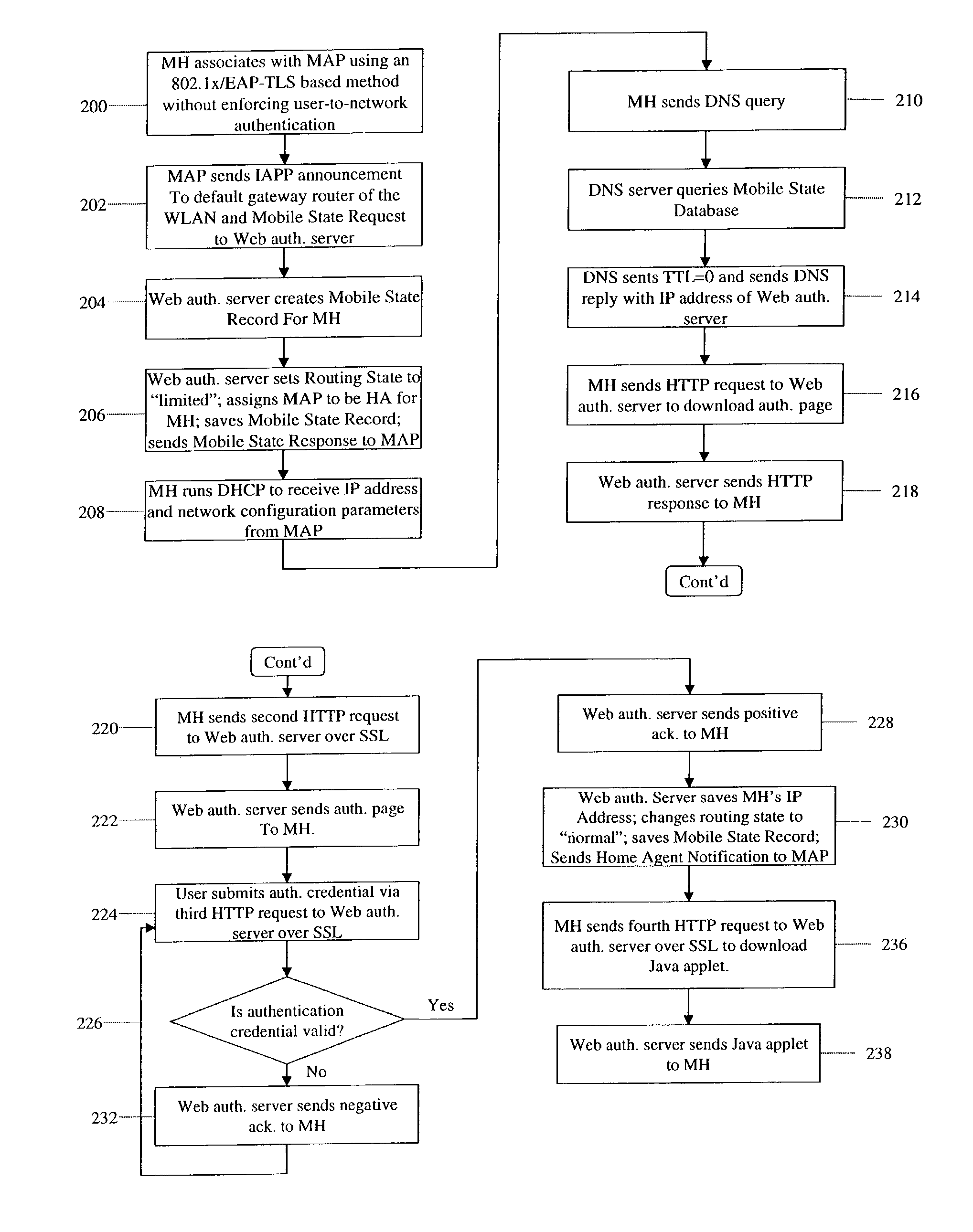
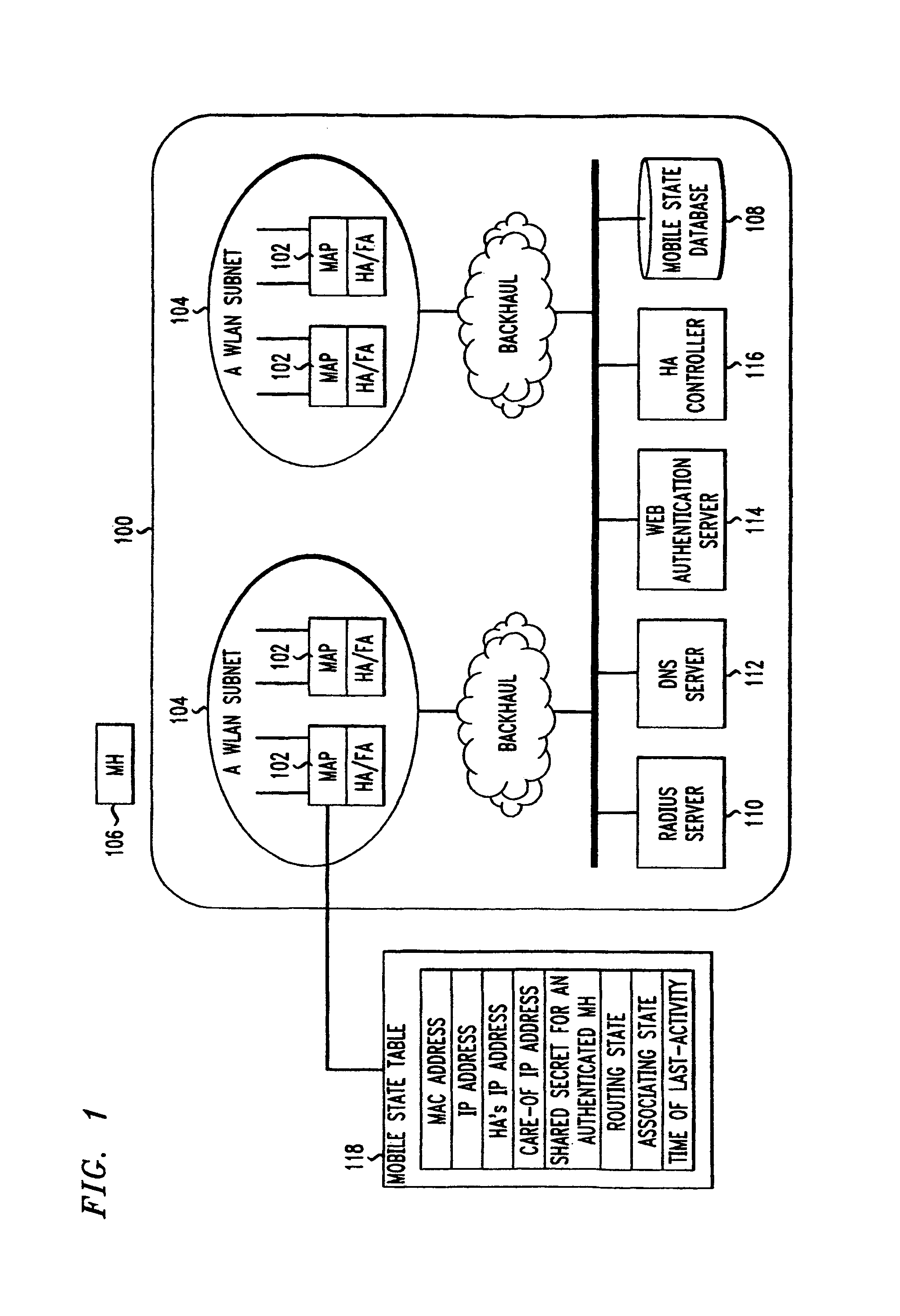
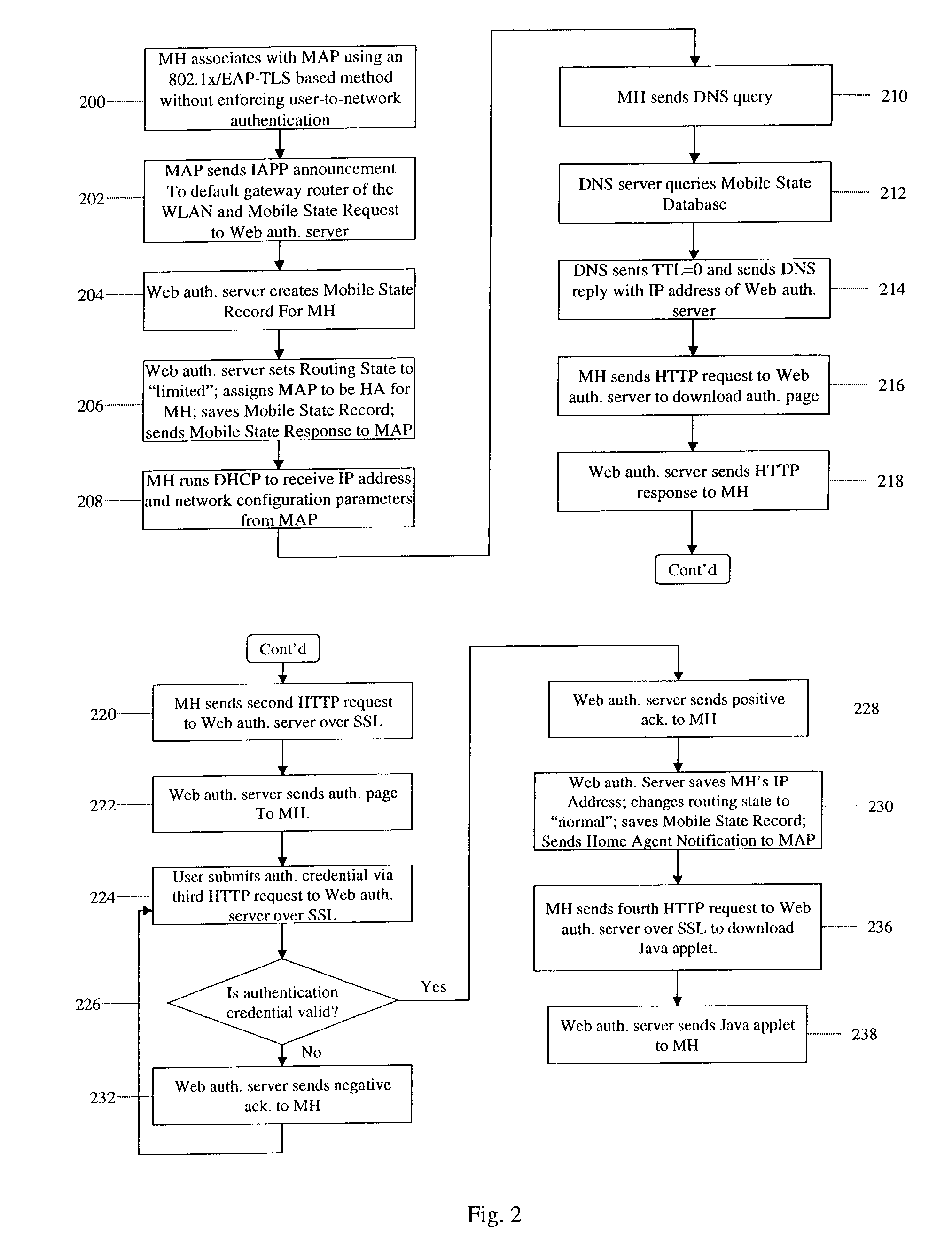
Zero-configuration secure mobility networking technique with web-based authentication interface for large WLAN networks
InactiveUS8817757B2Authentication is convenientAvoid attackNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesIp addressUser authentication
A zero-configuration secure mobility networking technique for WLANs is provided, utilizing split link-layer and a Web-based authentication. The link-layer authentication process facilitates network-to-user authentication and generation of session-specific encryption keys for air traffic using digital certificates to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks without requiring users to have pre-configured accounts. Although any WLAN host can pass the link-layer authentication and obtain link connectivity, the WLAN only allows the host to obtain IP networking configuration parameters and to communicate with a Web-based authentication server prior to initiating the Web-based authentication process that is responsible for user-to-network authentication. The Web-based authentication server employs a Web page for initial authentication and a Java applet for consequent authentications. In the Web page, registered users can manually, or configure their Web browsers to automatically, submit their authentication credentials; new users can open accounts, make one-time payments, or refer the Web-based authentication server to other authentication servers where they have accounts. Once a user is authenticated to the WLAN, the user's mobile host obtains full IP connectivity and receives secure mobility support from the WLAN. The mobile host always owns a fixed IP address as it moves from one access point to another in the WLAN. All wireless traffic between the mobile host and the WLAN is encrypted. Whenever the mobile host moves to a new access point, a Java applet (or an equivalent client-side program delivered over Web) enables automatic authentication of the mobile host to the WLAN. In addition, the ZCMN method supports dynamic load balancing between home agents. Thus, a mobile host can change home agents during active sessions.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
System and method for providing user authentication and identity management
InactiveUS20110138446A1Simple procedureImprove mobilityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordInternet privacy
Owner:BARRETT PAUL D +1
User authentication and authorization method and system for implementing user authentication and authorization method
ActiveCN102111275AEnsure safetyUser identity/authority verificationAuthorization ModeInternet privacy
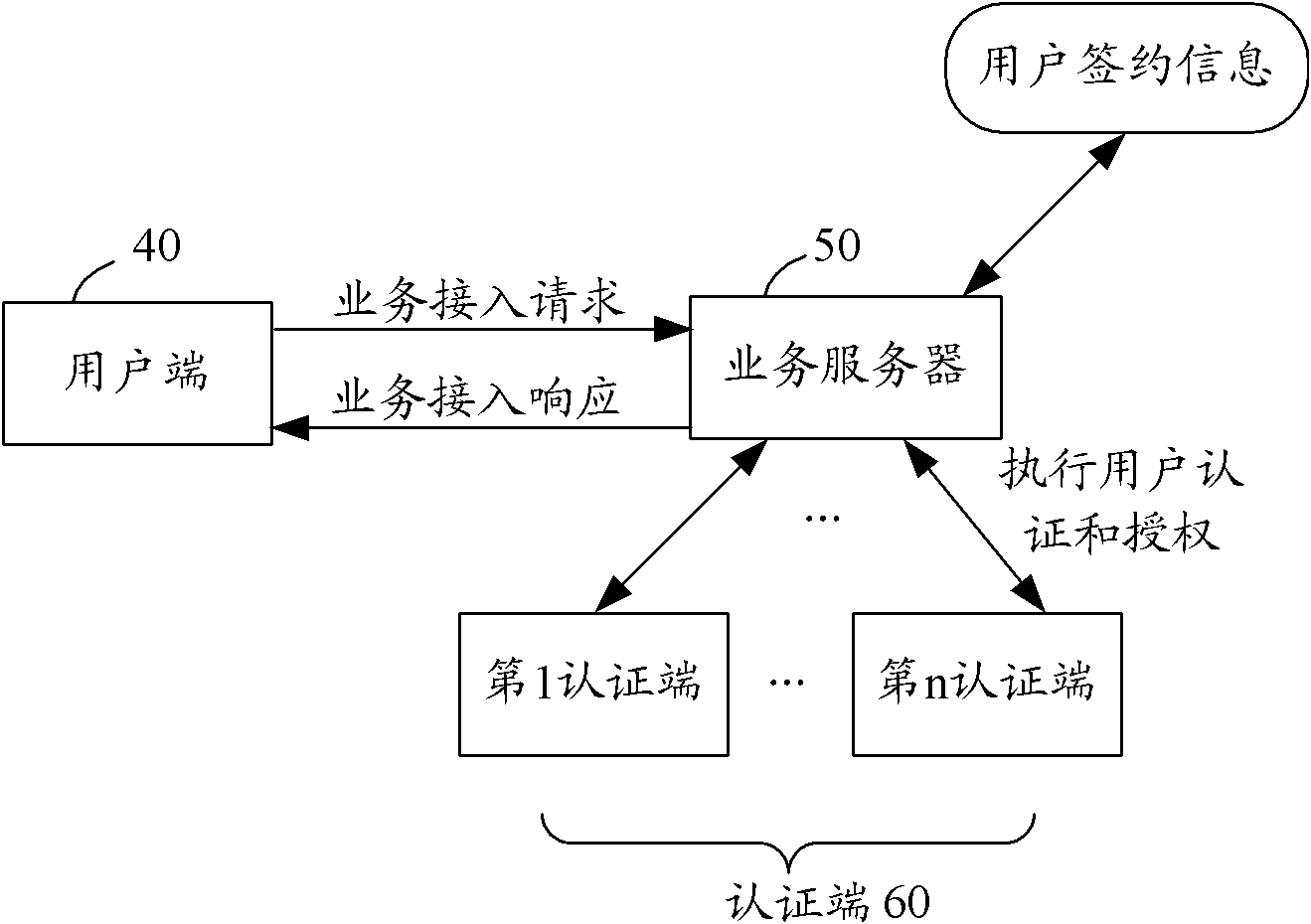
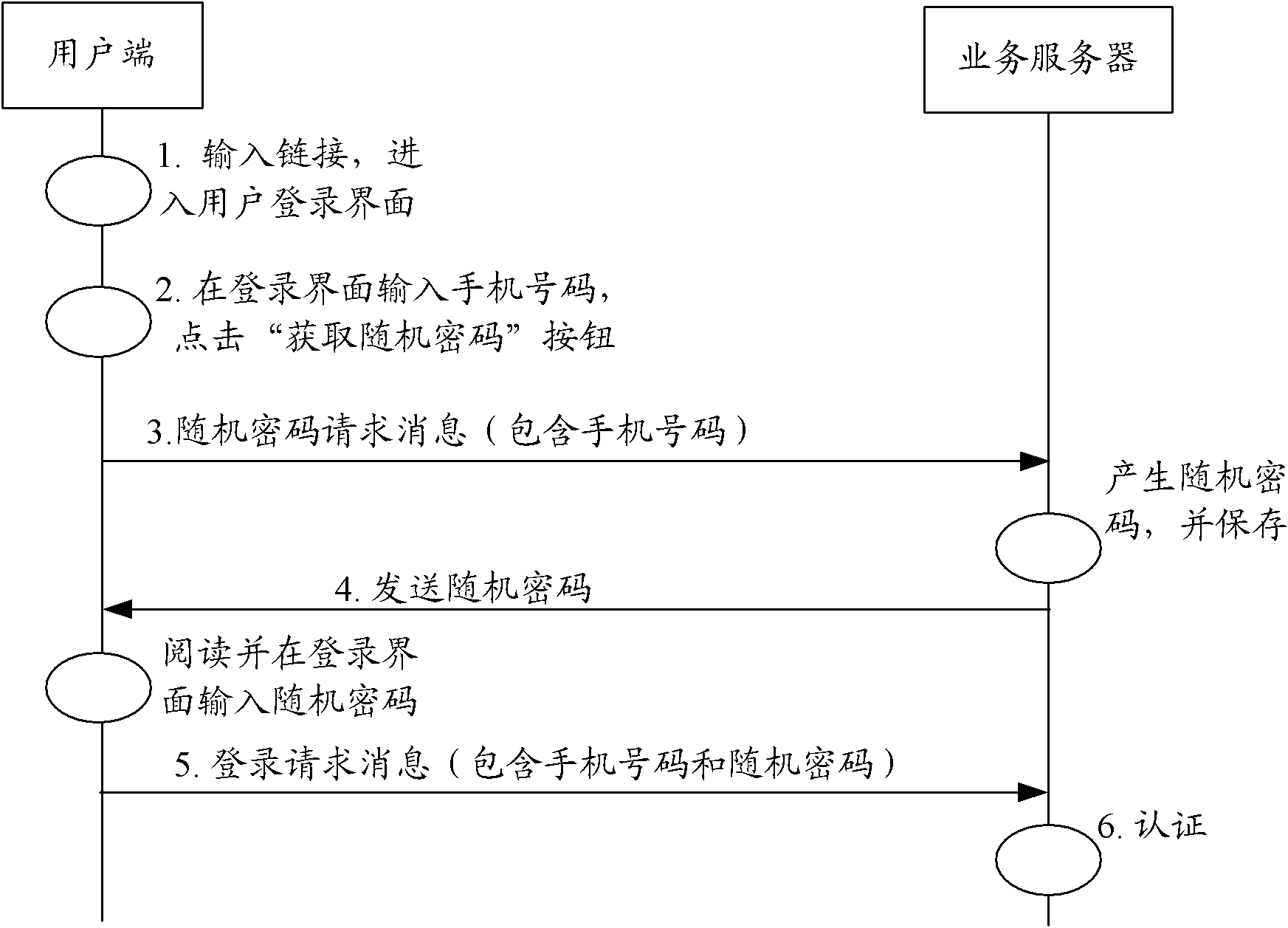
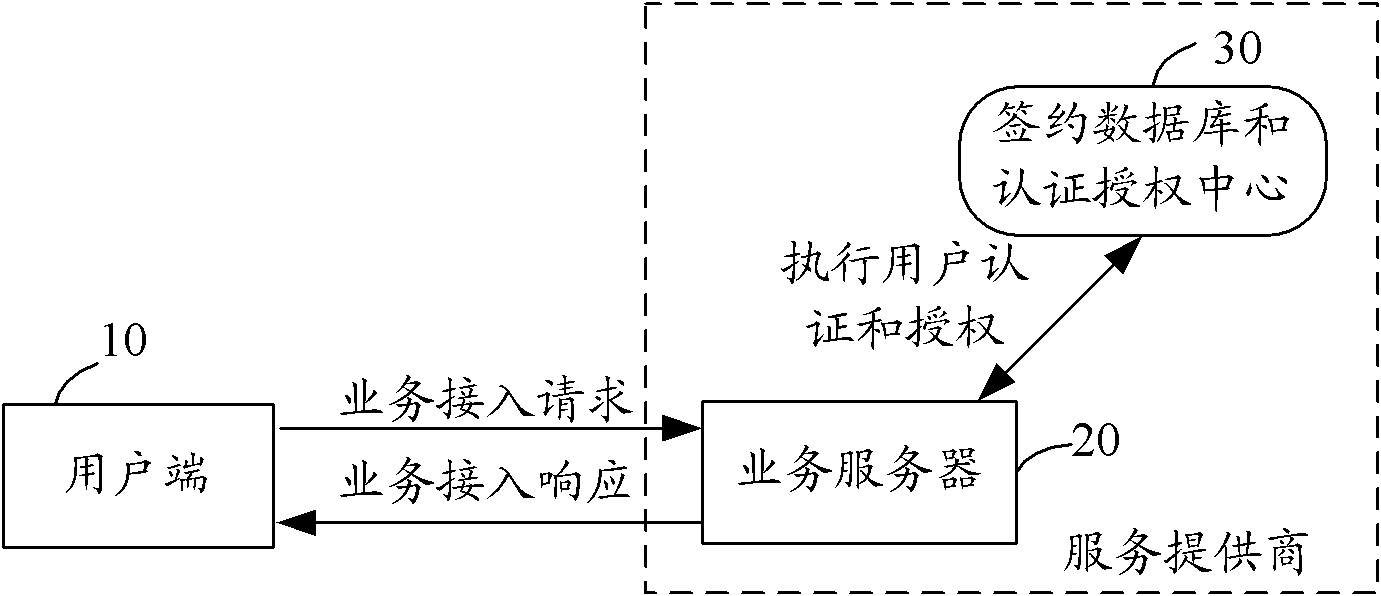
The invention provides a user authentication and authorization method and a system for implementing the user authentication and authorization method. When a user end launches a business access request, a business server checks whether the user is a contracted user in accordance with identity information of the user; if the user is the contracted user based on the user identity information, the communication mode of at least one social relation user is selected from the user contracted information as an authentication end; the business server judges the validity of the user identity in accordance with information provided by the authentication end; and if the user identity is valid, the business server authorizes a user end and carries out corresponding business access responses. The method and the system for implementing the method provided by the invention are used to overcome the defects in a background technology and effectively ensure the security of user information and network services by using a mode that the communication mode of at least one social relation user is selected from the contracted information which is kept at the time of signing a business service by the user as the authentication end, and the business server judges the validity of the user end identity in accordance with the information provided by the authentication end and authorizes the user end.
Owner:王冬梅
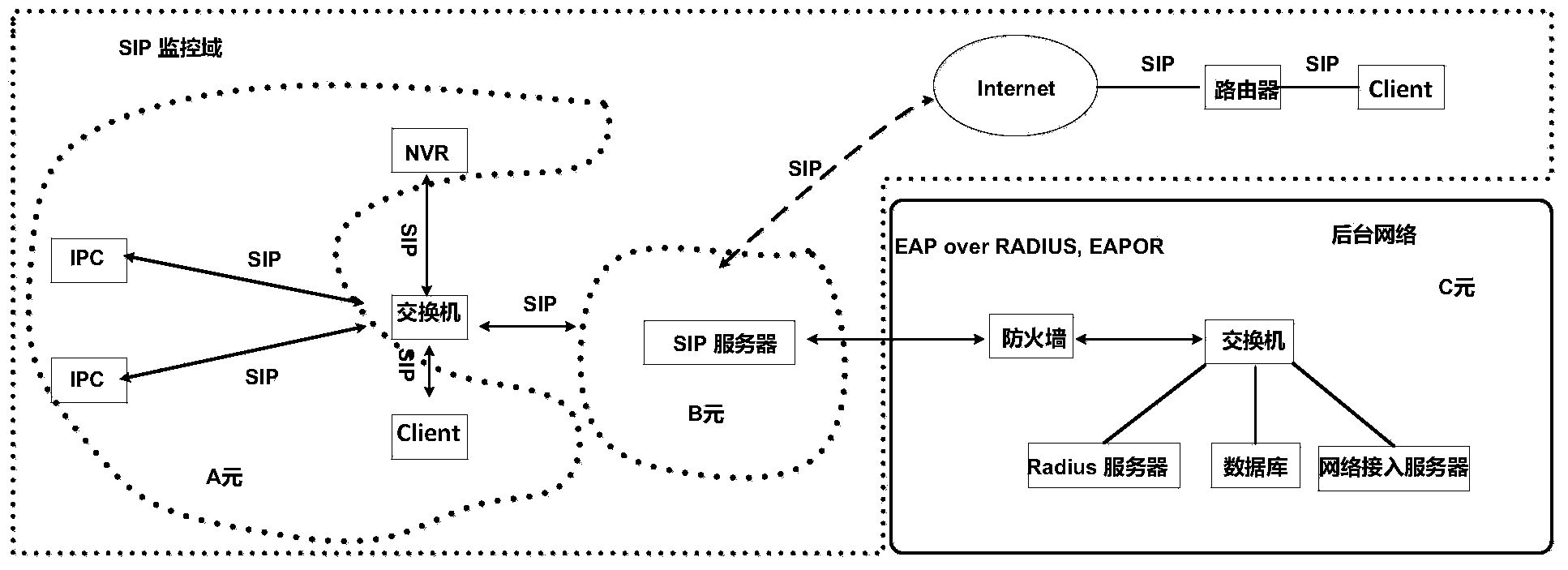
Identity authentication method for accessing SIP security video monitoring system
ActiveCN104168267AUser identity/authority verificationClosed circuit television systemsVideo monitoringComputer terminal
The invention relates to an identity authentication method for accessing an SIP security video monitoring system. The method includes the following steps: SIP terminals carry out identity authentication at an SIP server so as to complete registration; two SIP terminals which need to carry out information interaction carry out unicast key and secure session negotiation with the SIP server respectively; the SIP server sends point-to-point link information to the SIP terminals which need to carry out information interaction and issues related keys; bidirectional identity authentication is carried out between the two SIP terminals through exchange of point-to-point authentication tokens; information interaction is carried out between the SIP terminals which pass the bidirectional identity authentication; and when the SIP terminals leave a current network, cancellation authentication needs to be carried out on the SIP server. The identity authentication method is capable of realizing safe and efficient multi-entity initial authentication between network entities and rapid re-authentication between SIP terminals, and ensuring dual-channel authentication of video signaling flows and media flows and the like so that accessing security is improved significantly and security of data transmission, storage and access is improved.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for restricting automatic out-of-office email response to configured zone
InactiveUS20070192419A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksDomain nameWorld Wide Web
A method for restricting an automatic out-of-office email response to a configured zone includes steps as follows. At least one domain name is specified for receiving the automatic out-of-office email response. An email is received from an email account. It is verified whether the email originates from one of the at least one domain name. When the verification is successful, the automatic out-of-office email response is sent to the email account.
Owner:SIEMENS ENTERPRISE COMM GMBH & CO KG
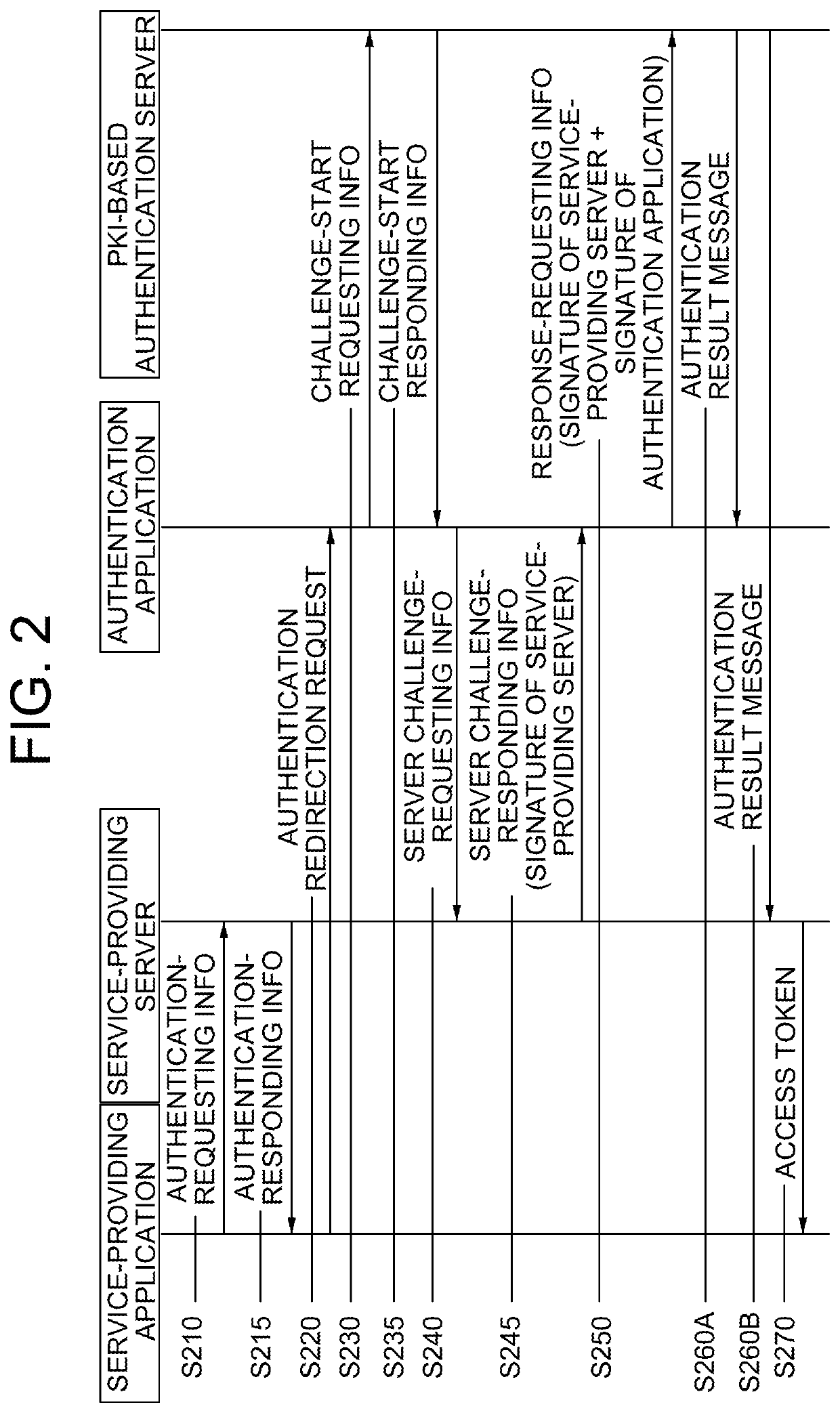
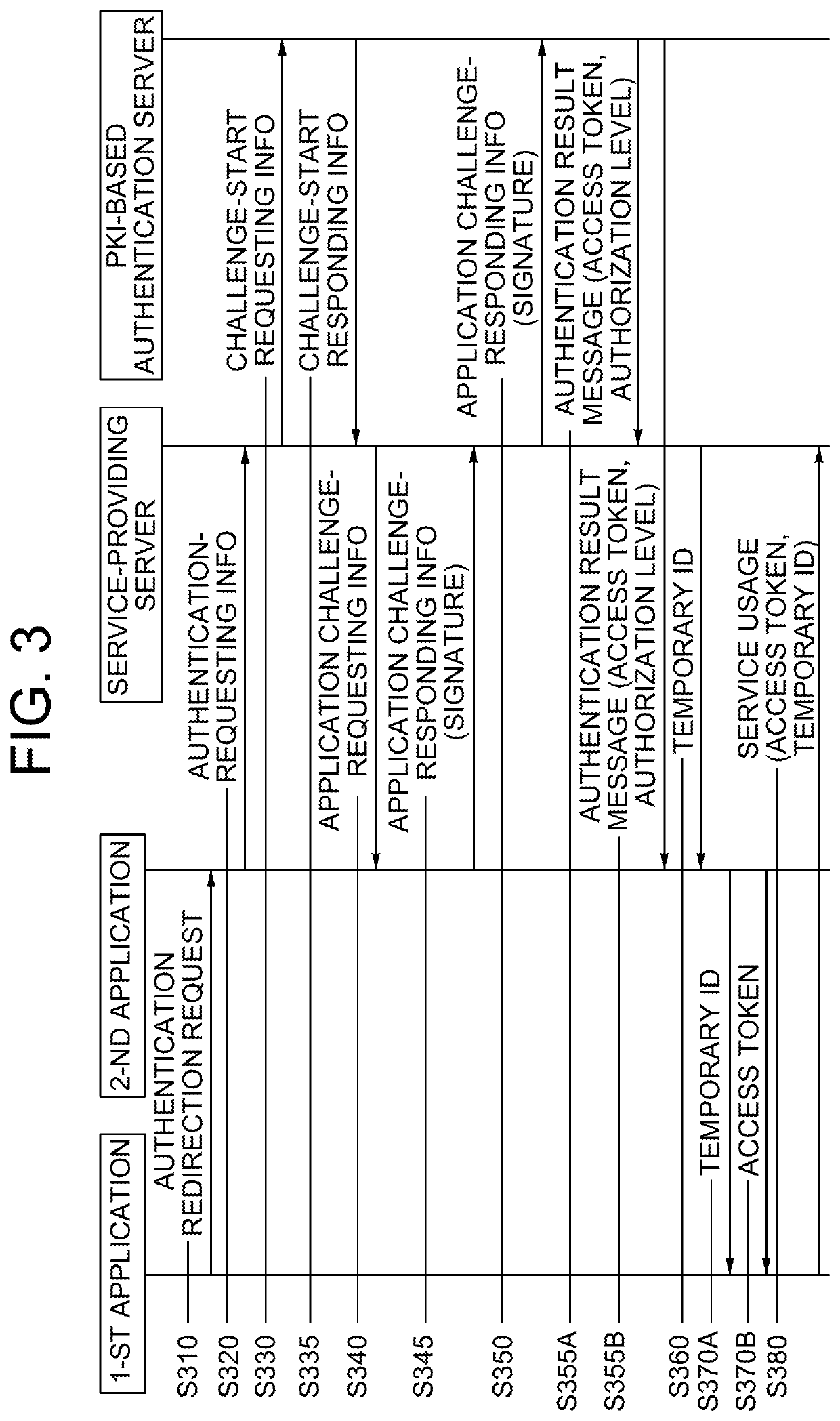
Method for superseding log-in of user through pki-based authentication by using smart contact and blockchain database, and server employing same
ActiveUS20190372786A1Improve securityEffective usabilityEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationAuthentication serverApplication software
Once information requesting superseding of a log-in through an authentication app is obtained from a service provision app on a user terminal, a service provision server transfers authentication request response information to the service provision app and, after an authentication redirection request thereof is transferred to the authentication app and then server challenge request information is obtained, server challenge request response information is transferred to the authentication app, thereby supporting the determination as to whether or not certificates of the server and the app are valid, an authentication result message including information on the validity is obtained from an authentication server, a predetermined access token is transferred to the service provision app, and thereby the log-in is handled by providing support such that a service can be used.
Owner:COINPLUG LNC
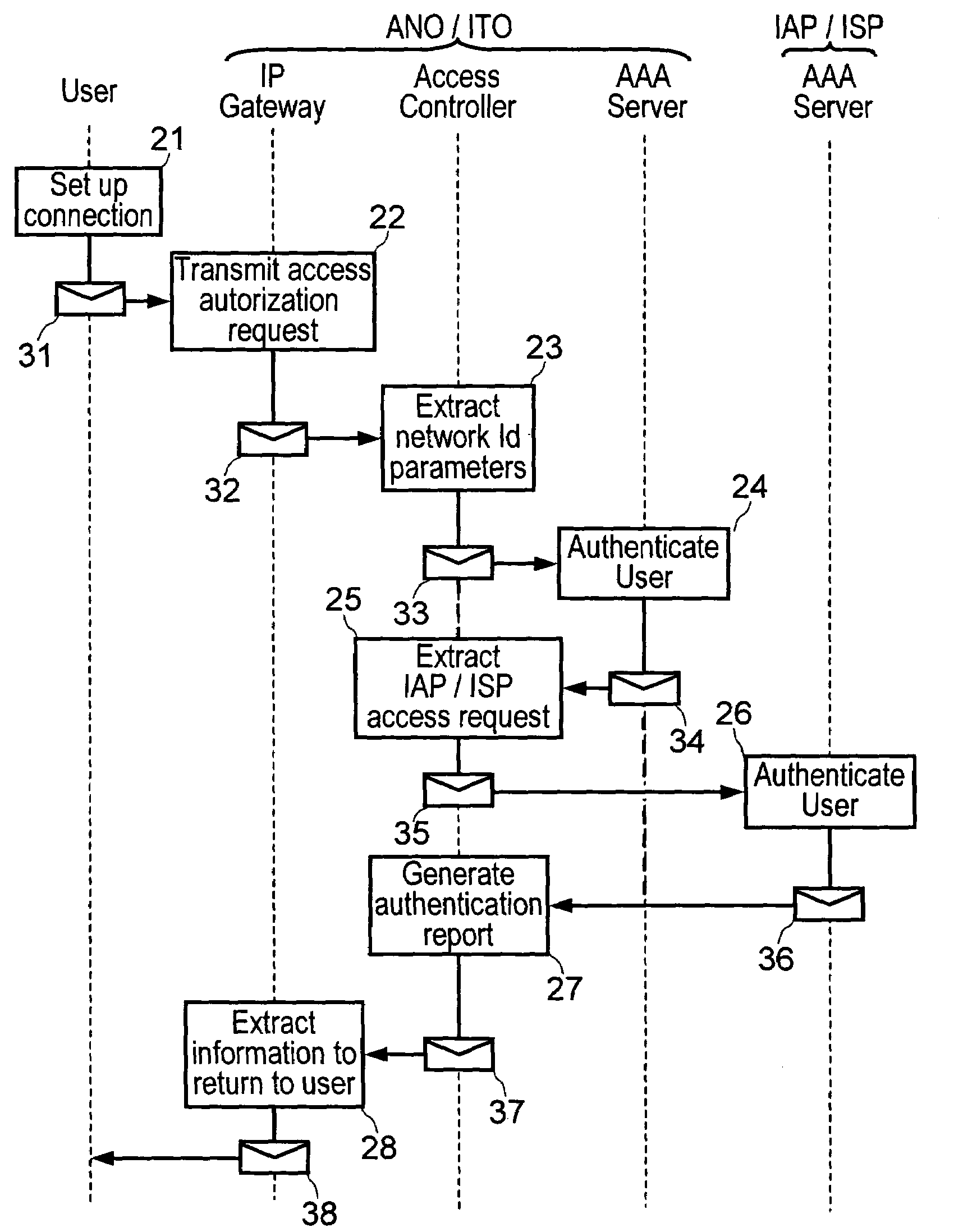
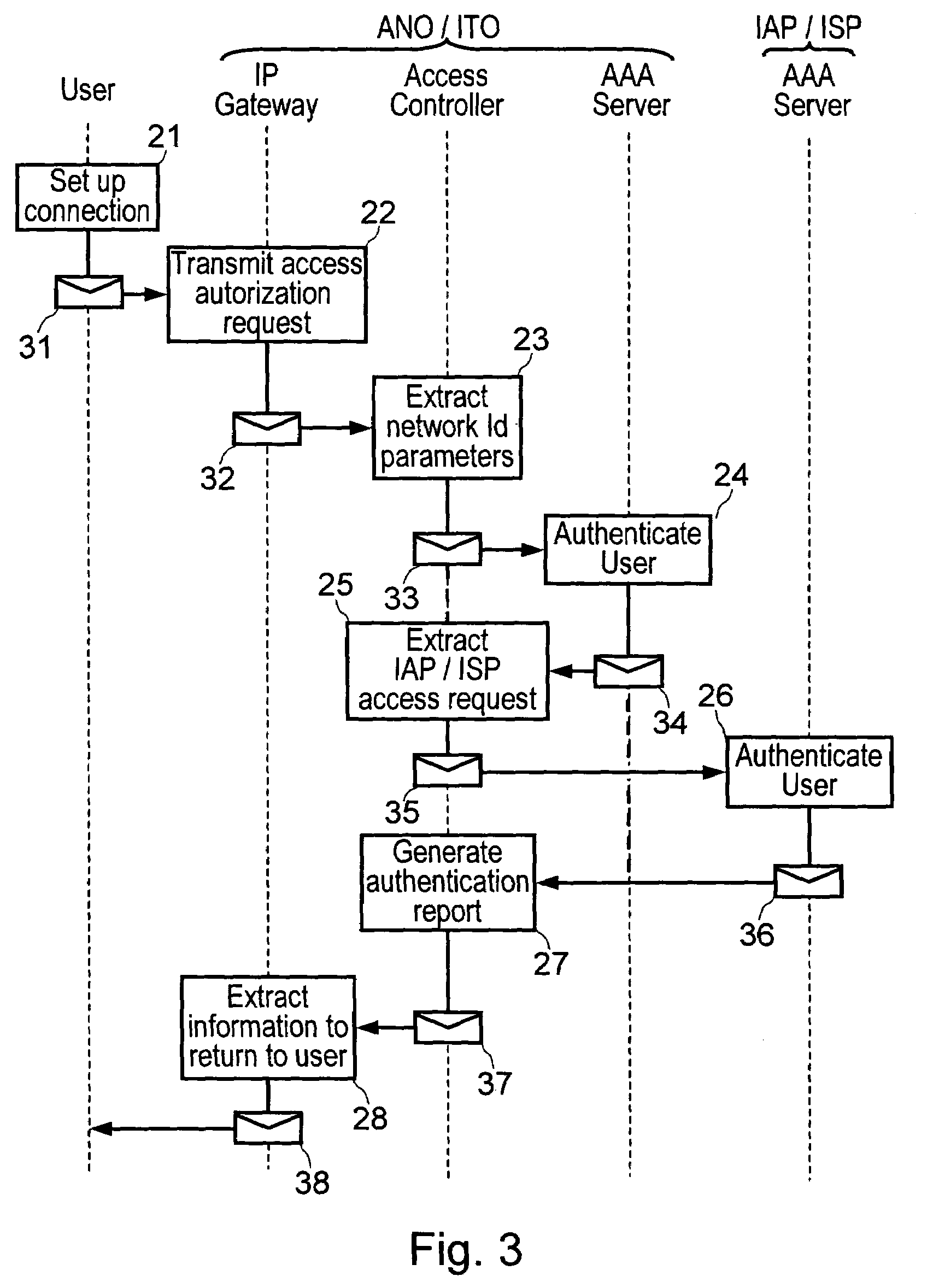
Method and a system for authenticating a user at a network access while the user is making a connection to the Internet
InactiveUS7448075B2Data taking preventionDigital data processing detailsAccess networkUser authentication
The method consists in: a user terminal issuing an access request to an access or IP service provider, the request containing user identification and authentication data with the provider and with an access and IP transport network operator, the access request being transmitted via the access network to an authentication server of the access or IP service provider; previously transmitting the access request to an authentication server of the network operator; the authentication server performing a procedure to authenticate the user on the basis of user identification data with the provider; and transmitting a response message to the user terminal, which response message contains the results of the user authentication by the authentication servers.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
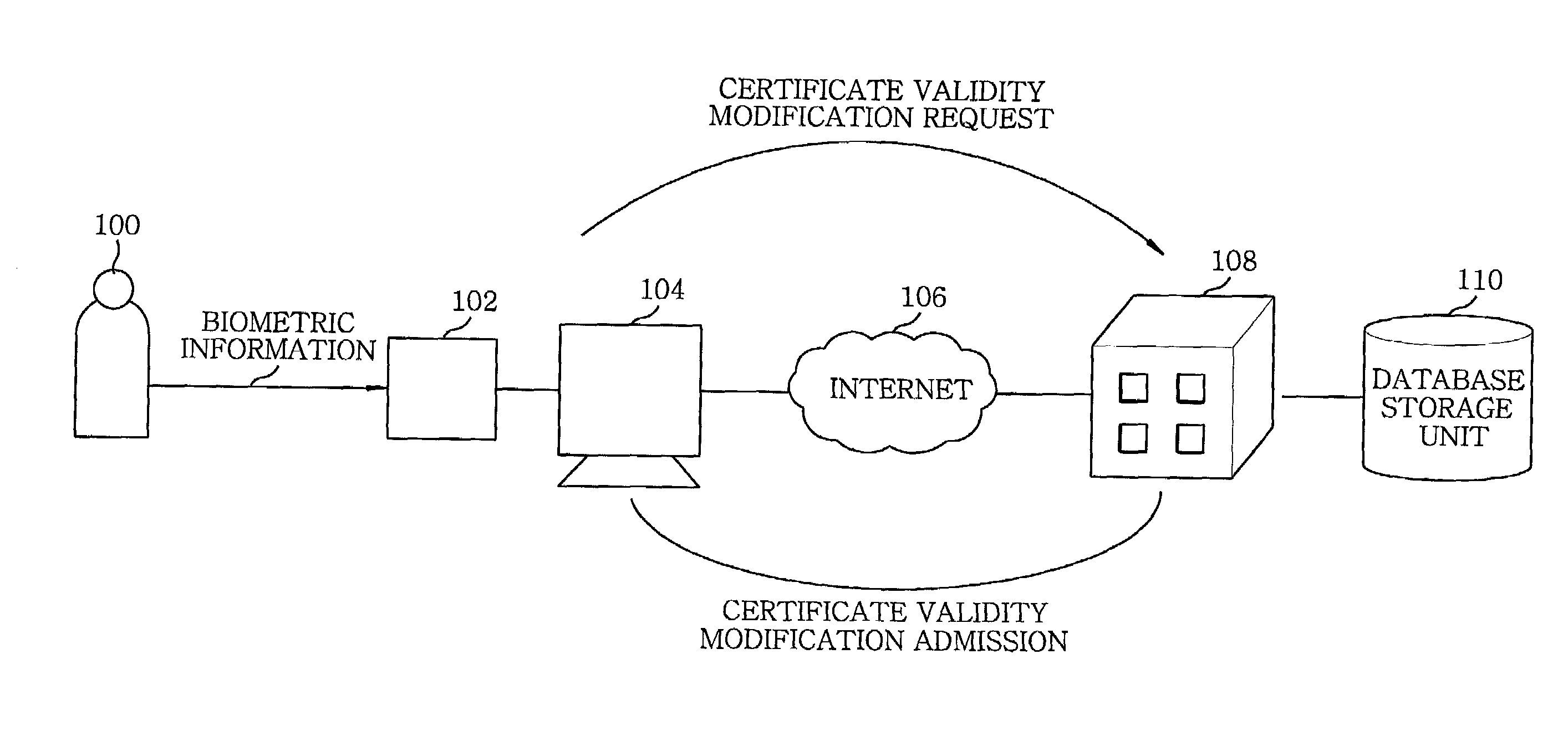
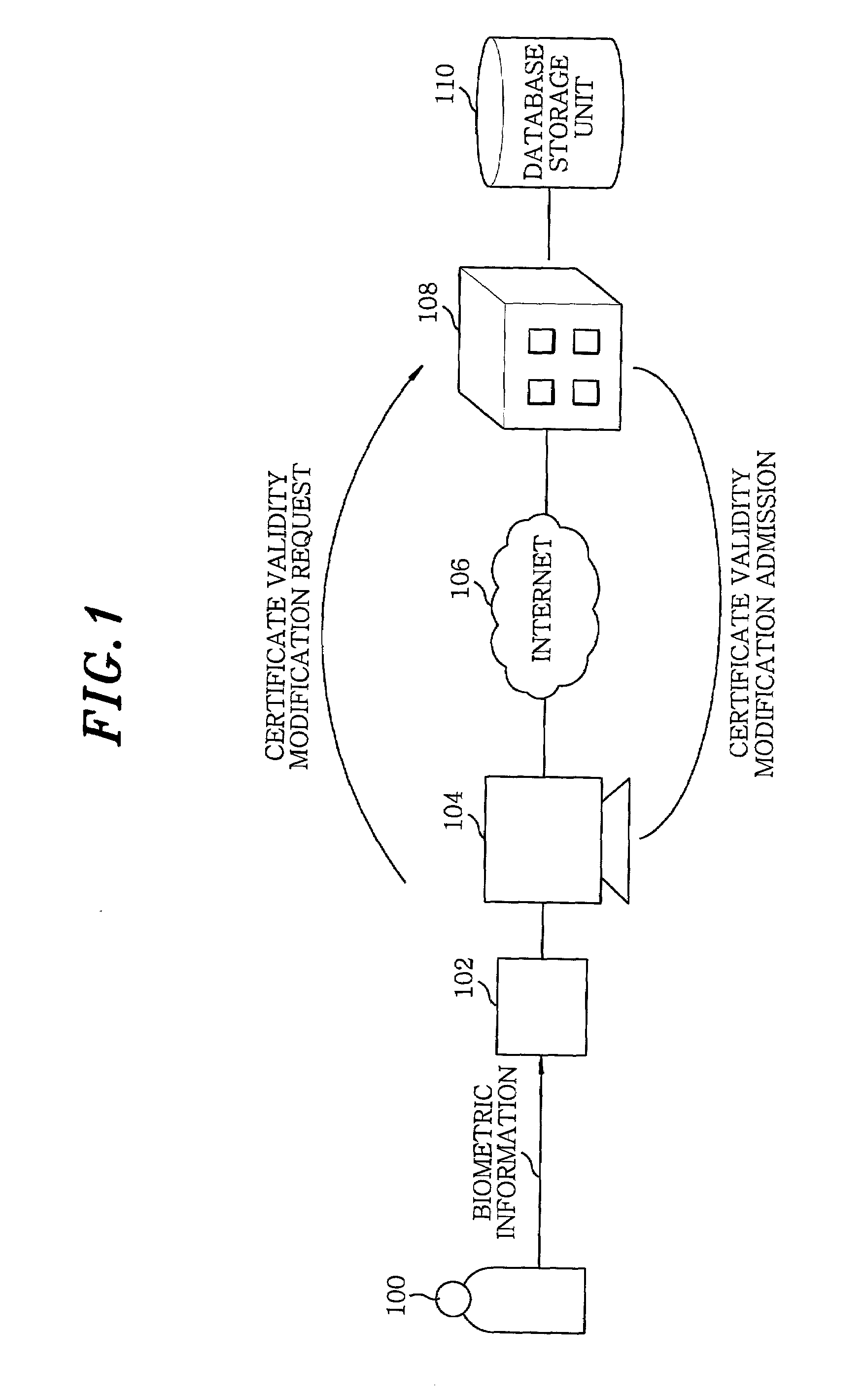
Method for modifying validity of a certificate using biometric information in public key infrastructure-based authentication system
InactiveUS7366904B2Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageRegistration authorityUser authentication
The present invention provides a method for modifying validity of a certificate in a public key infrastructure (PKI)-based authentication system, which is capable of performing online suspension, recovery and revocation of a certificate between a user system and a certificate authority by executing user authentication with guaranteed reliability using user biometric information. Accordingly, there is no need for the user to personally visit a registration authority or certificate authority to modify the certificate validity. The user can easily modify the certificate validity using his / her user system connected online to the certificate authority.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
System and method for login authentication
The invention provides a system and a method for login authentication. The method comprises the steps of: sending login request information by a login end, wherein the login request information comprises a user name; receiving the login request information by an authentication end, after confirming that the login end is a blockchain user, initiating blockchain identity authentication for the loginend; performing second authentication on the login end by the authentication end after the blockchain identity authentication is passed; acquiring user identity information of the login end by the authentication end, and acquiring user identification and a certification organization public key from a blockchain; and verifying the user identity information by using the user identification and thecertification organization public key by the authentication end. The system and the method of the invention have the beneficial effects that: the identification stored in the blockchain can not be tampered, thereby improving security and reducing IT maintenance cost of an enterprise; the second authentication is performed after the identity authentication is passed, thereby greatly improving enterprise level Wi-Fi security; and verification is based on the user identity information, the user does not need to input a Wi-Fi login key, thereby effectively preventing a stealing behavior of a Wi-Fiall-purpose key app.
Owner:上海邑游网络科技有限公司
Method and system for performing authentication on access request
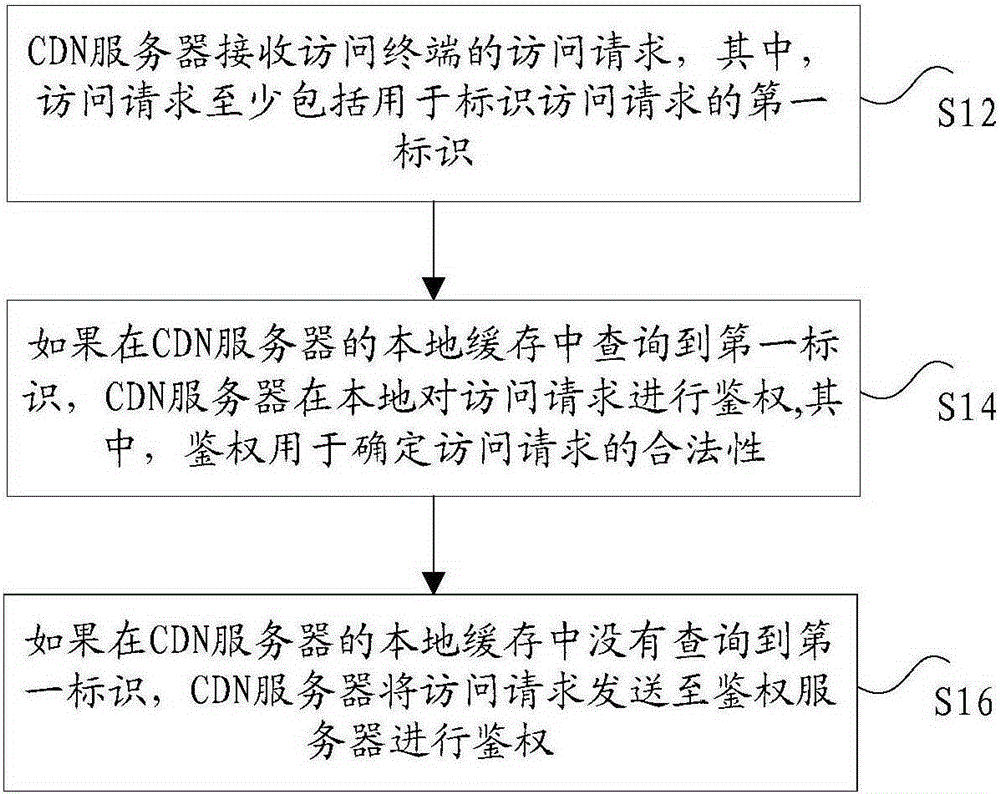
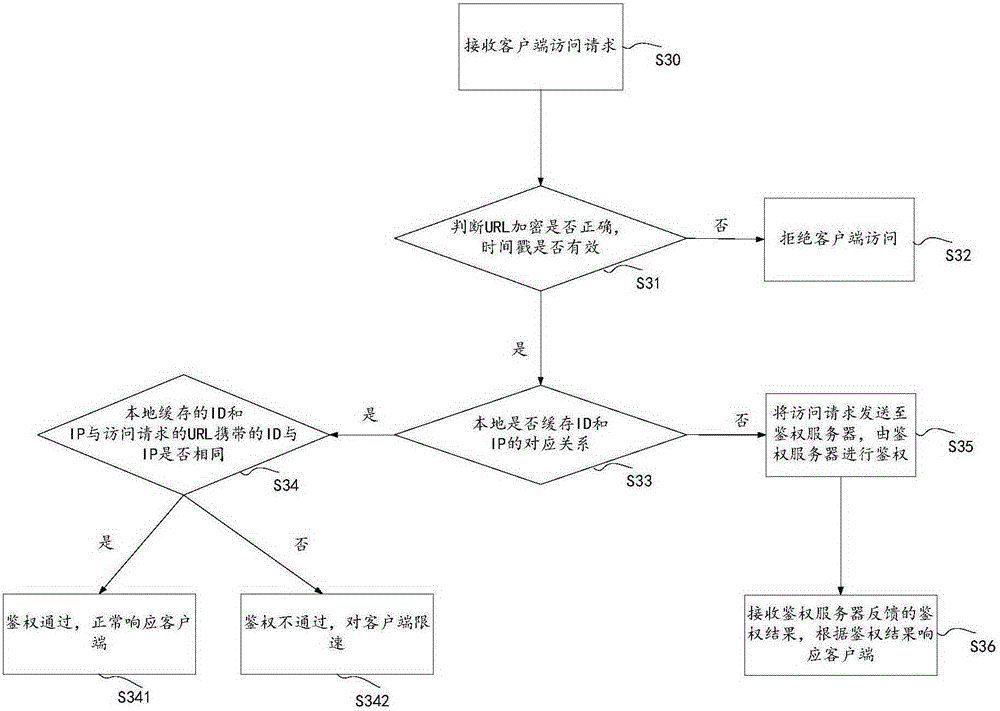
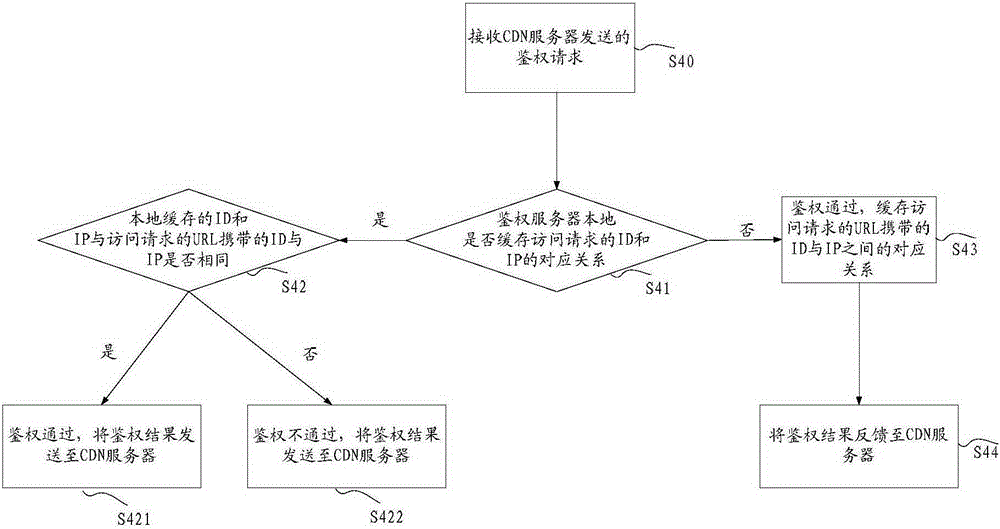
ActiveCN105357190ATroubleshoot technical issues with overloadTransmissionContent distributionAuthentication server
The invention discloses a method and system for performing authentication on an access request. The method comprises the following steps: receiving an access request of an access terminal by a CDN (Content Distribution Network) server, wherein the access request at least comprises a first identification used for identifying the access request; if the first identification is inquired in a local cache of the CDN server, then performing authentication on the access request locally by the CDN server, wherein authentication is used for determining the legality of the access request; and if the first identification is not inquired in the local cache of the CDN server, then transmitting the access request to an authentication server to perform authentication by the CDN server. The method and system for performing authentication on the access request provided by the invention solve the technical problem that an anti-stealing link method of the existing back to the source authentication only depends on the authentication server to recognize a hotlinking request in any case, so that the load of the authentication server is excessive.
Owner:CHINANETCENT TECH
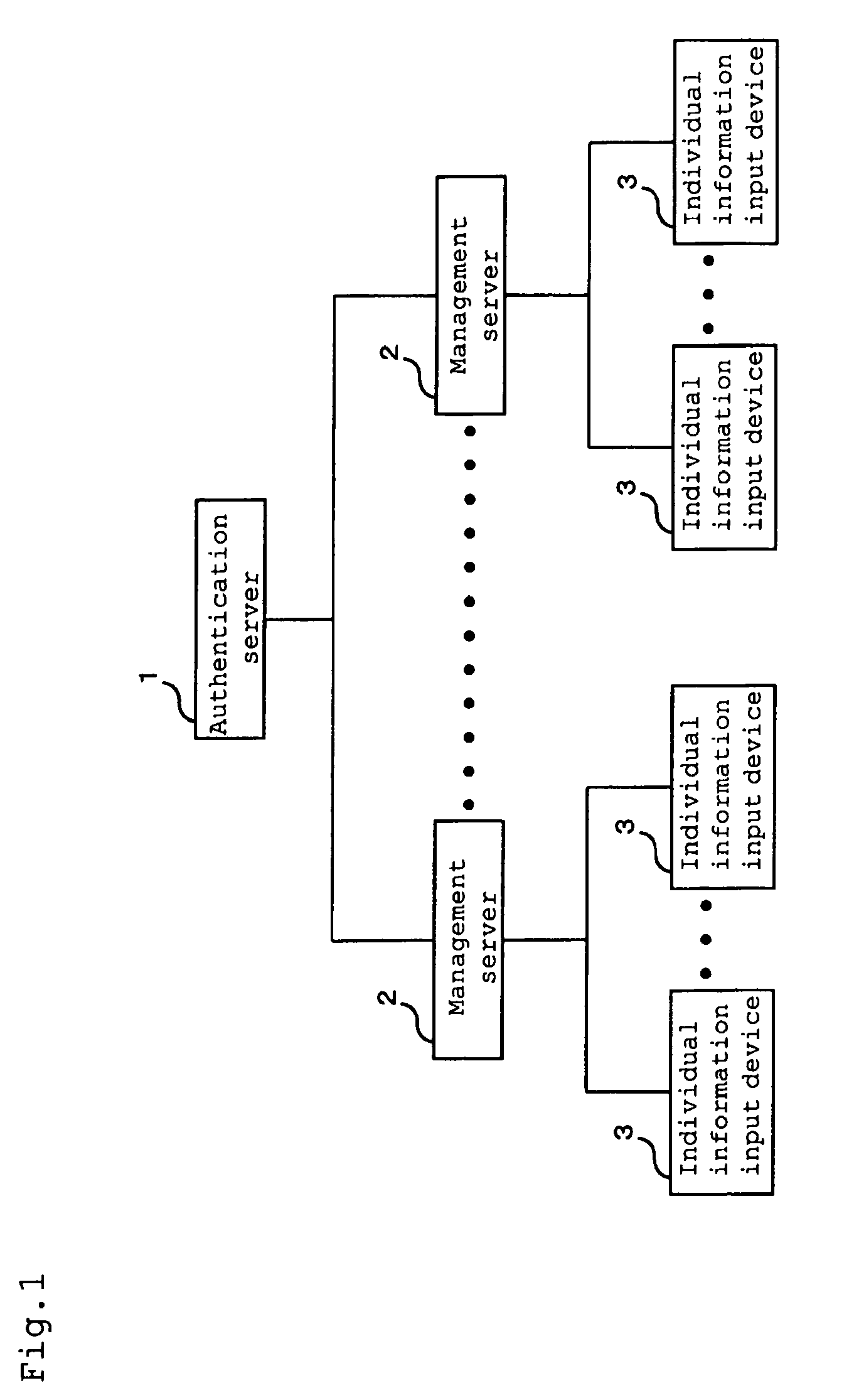
Authentication system
ActiveUS8866586B2Easy to findImprove securityElectric signal transmission systemsTicket-issuing apparatusAuthentication serverElectronic information
[PROBLEMS] To provide an authentication system improving authentication accuracy of existence of a registered person and easily find an unauthorized act to improve the security in a system by performing authentication using coincidence / non-coincidence of biometrics information and temporal / spatial authentication when performing individual authentication via a network by using electronic information which is easily tampered, easily leaks out, and is easily stolen. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] An authentication server (1) includes a database for managing individual information on a registered person to be authenticated. Moreover, the authentication server (1) is connected to a plurality of management servers (2) via a communication network and correlates the individual information transmitted from an individual information input device (3) via the management server (2) with the individual information in the database, thereby authenticating the existence of the registered person.
Owner:IHC CORP
E-mail message authentication and marking extending standards complaint techniques
ActiveUS20090282108A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationMessage authentication codeElectronic mail
A system and method for e-mail authentication. The method includes aggregating a plurality of headers associated with an e-mail message and transmitting the aggregated plurality of headers to a validation service. A validation response is then received from the validation service. The e-mail is authenticated based on the validation response.
Owner:ICONIX INC
Restoring or reissuing of a token based on user authentication
Embodiments described herein relate to an invention for restoring a modified token or reissuing an unfettered token for use in a financial transaction. The systems, methods, and computer program products are configured to: (a) provide to a user a notification indicating a fettered token was generated for a payment vehicle or a token associated with the payment vehicle was modified based at least partially on identifying a potential exposure to loss associated with a financial transaction involving the payment vehicle; (b) receive, from the user, authentication information, wherein the authentication information is useable to authenticate the financial transaction and / or to authenticate the user; and (c) determine whether or not to restore the token associated with the payment vehicle that was modified or to generate an unfettered token and associate the unfettered token with the payment vehicle based at least partially on the authentication information.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
User authentication
InactiveUS20110289316A1Reduce the possibilityAvoid interferenceUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationUser authenticationEmail authentication
Owner:AFILIAS TECH
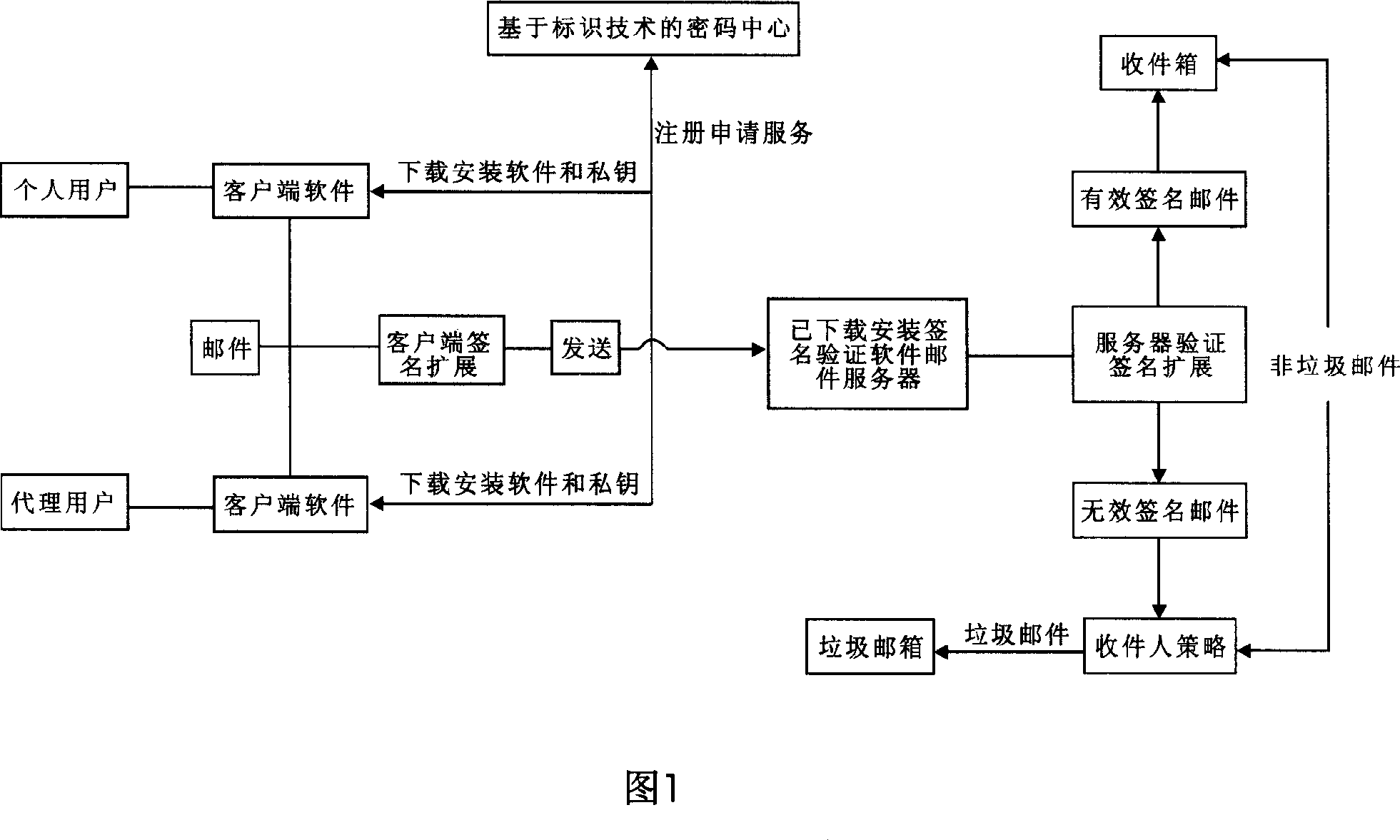
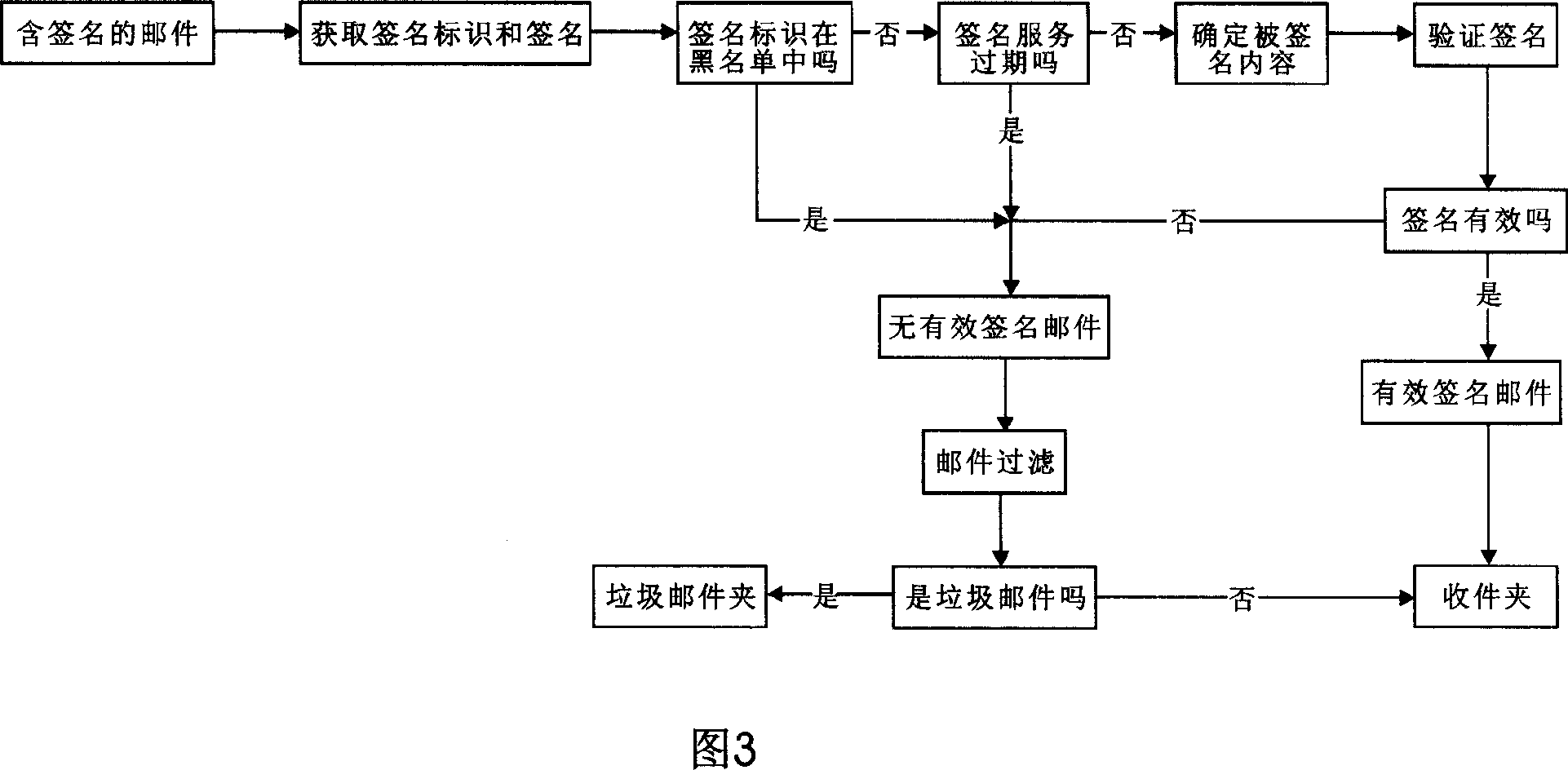
Email authentication and reliable sorted transmission method for identifier-based cryptographic technique
ActiveCN1968091AAccurate classificationPrecise deliveryUser identity/authority verificationData switching networksPasswordEmail authentication
The invention relates to mail identification method and reliability classified transmission method, based on label password technique, wherein it comprises that: user requests register identification and legal mark to the password center; user uses private key and client software to sign and send mail; when user receives mail, judges if it has sign; if there is sign, the mail is effective, but not be filtered. The invention can support lots of users, with simple process and high reliability.
Owner:SHENZHEN OLYM INFORMATION SECURITY TECHOLOGY CO LTD
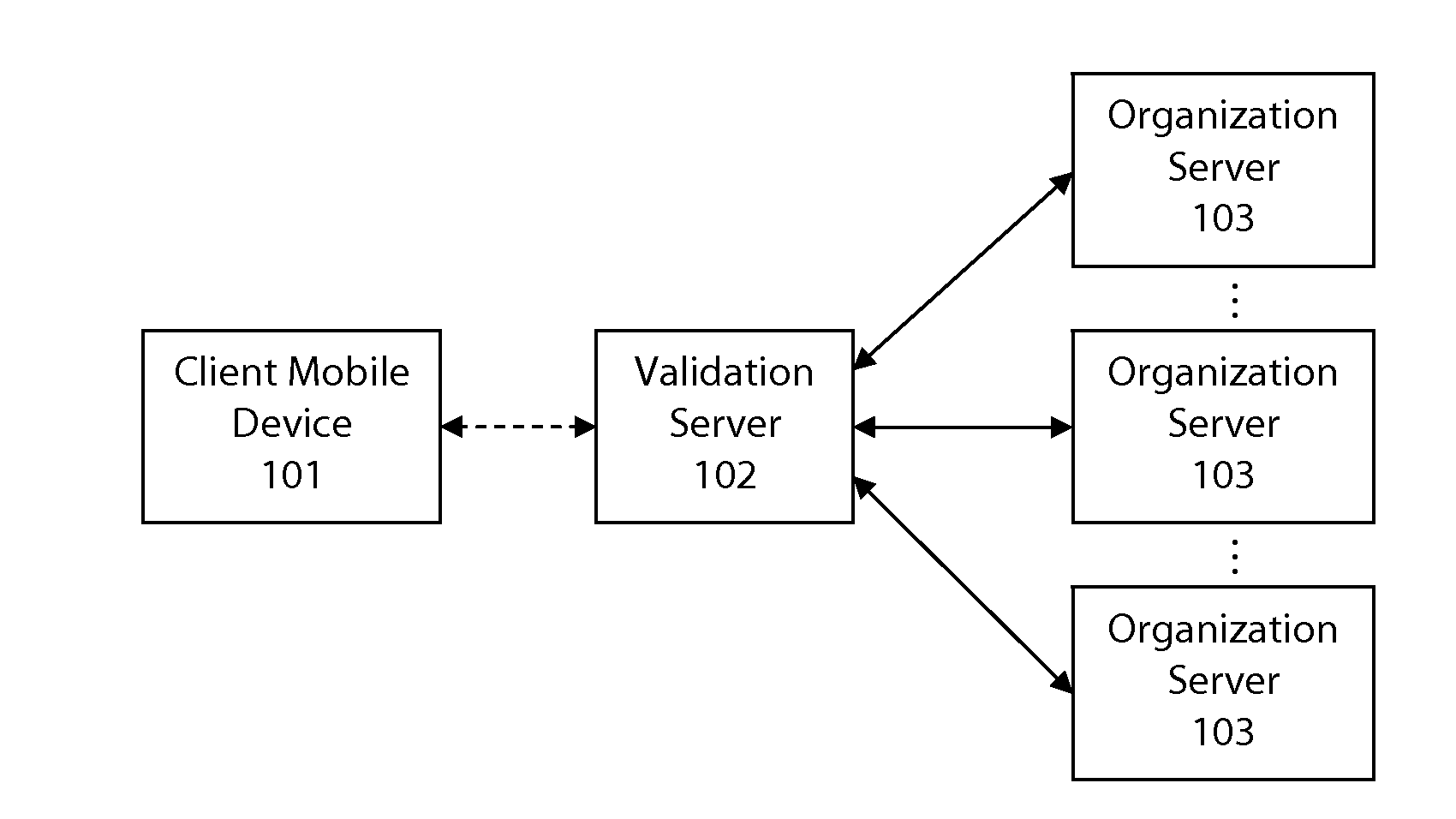
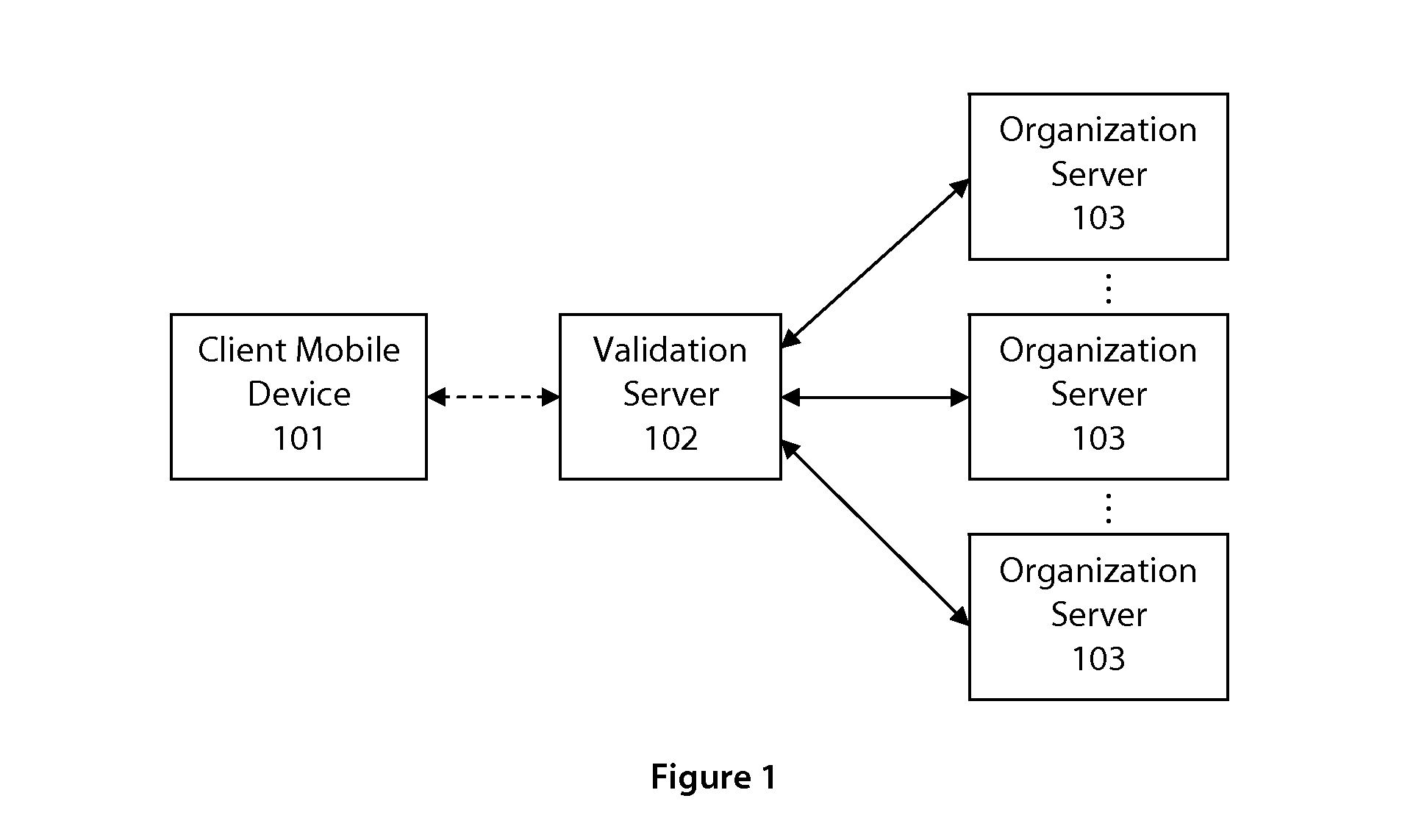
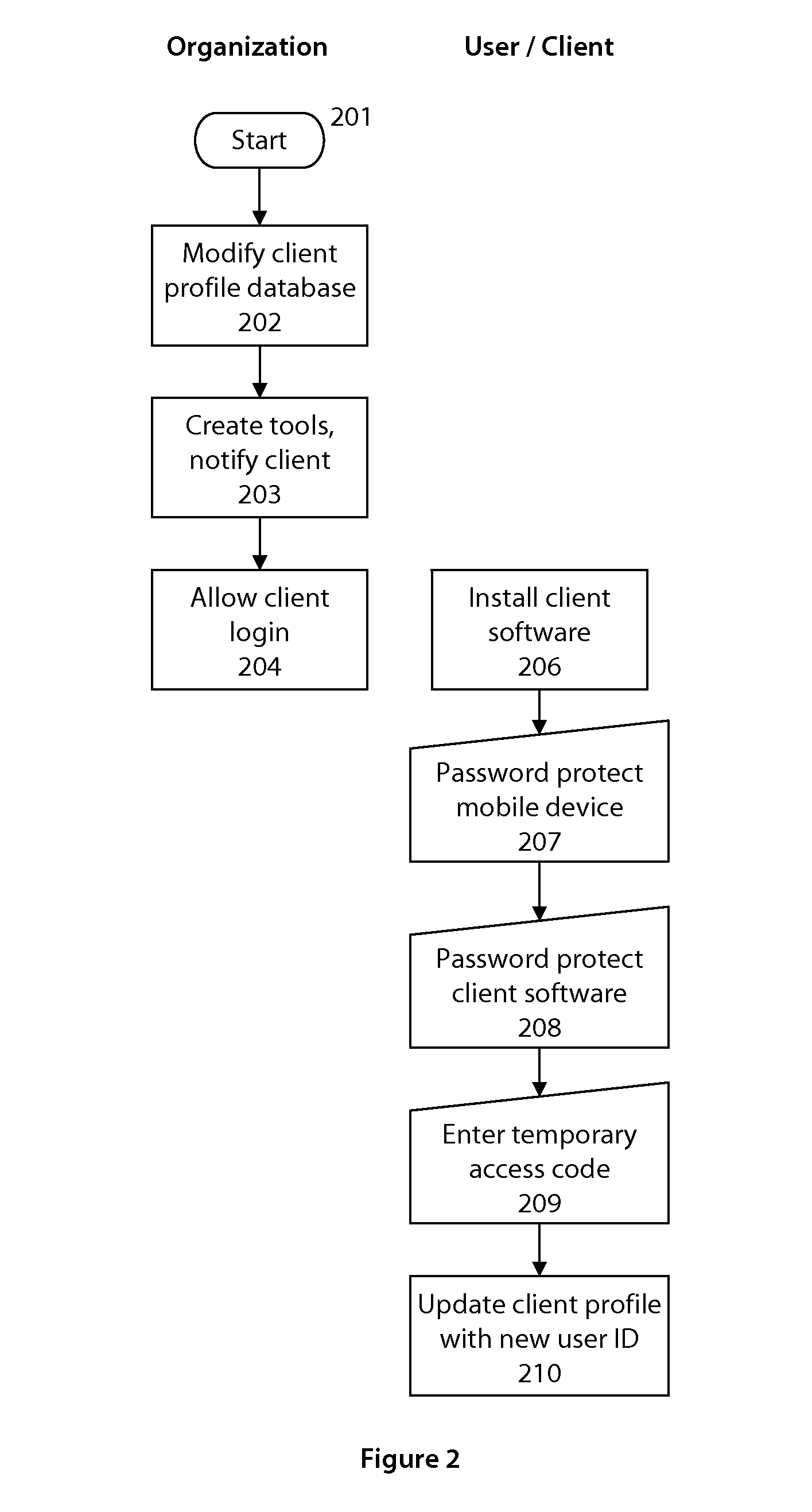
System and method for user authentication
ActiveUS20130081114A1Low costDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsPasswordUser authentication
A system and method for providing authentication of a user is disclosed. The use of a non-confidential and unique user identification number and a temporary access code separates authentication of the user from transmission of any user passwords or user-identifiable data, as well as provides a ubiquitous means to authenticate the user with unrelated organizations, without any information passing between those organizations.
Owner:KINESIS IDENTITY SECURITY SYST
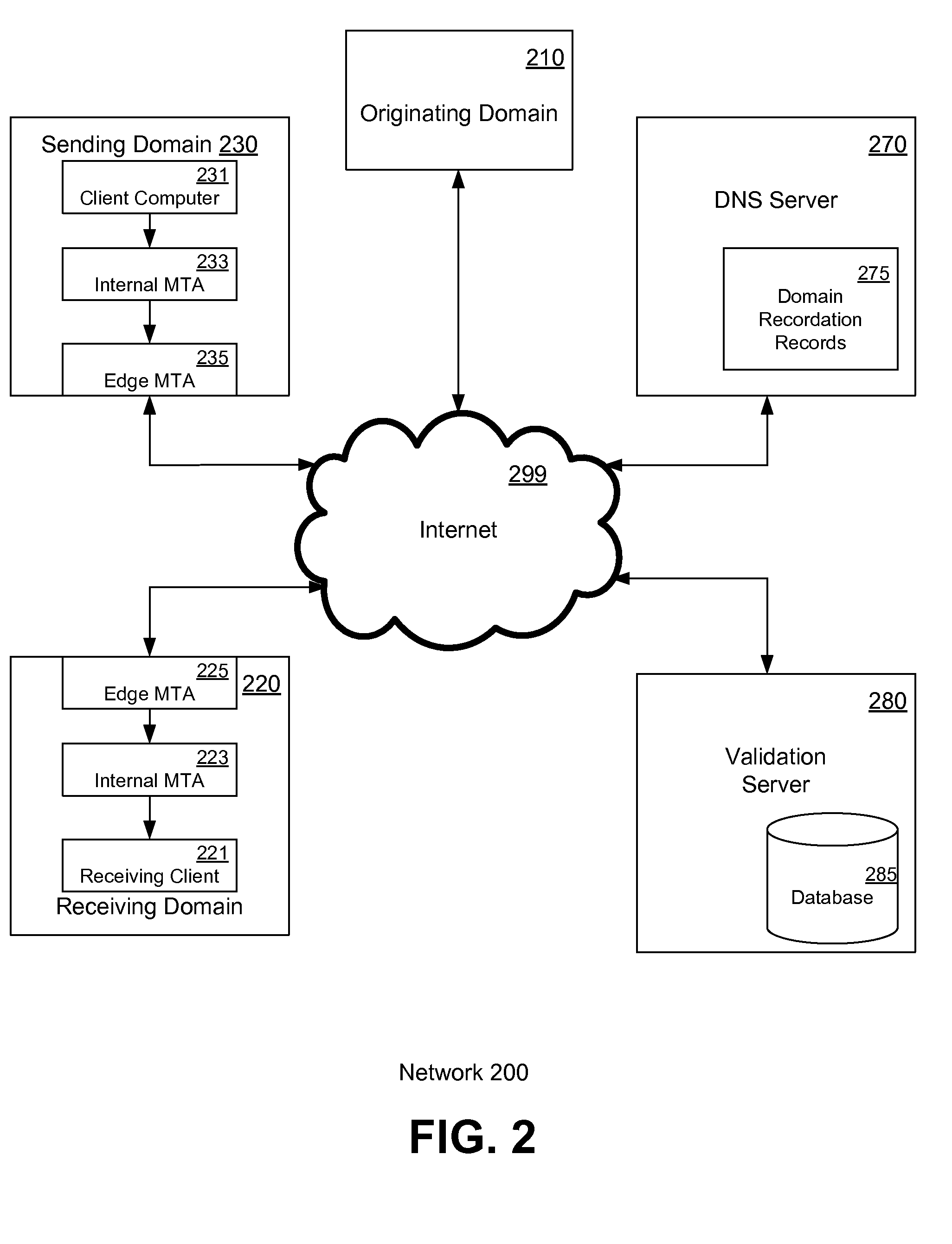
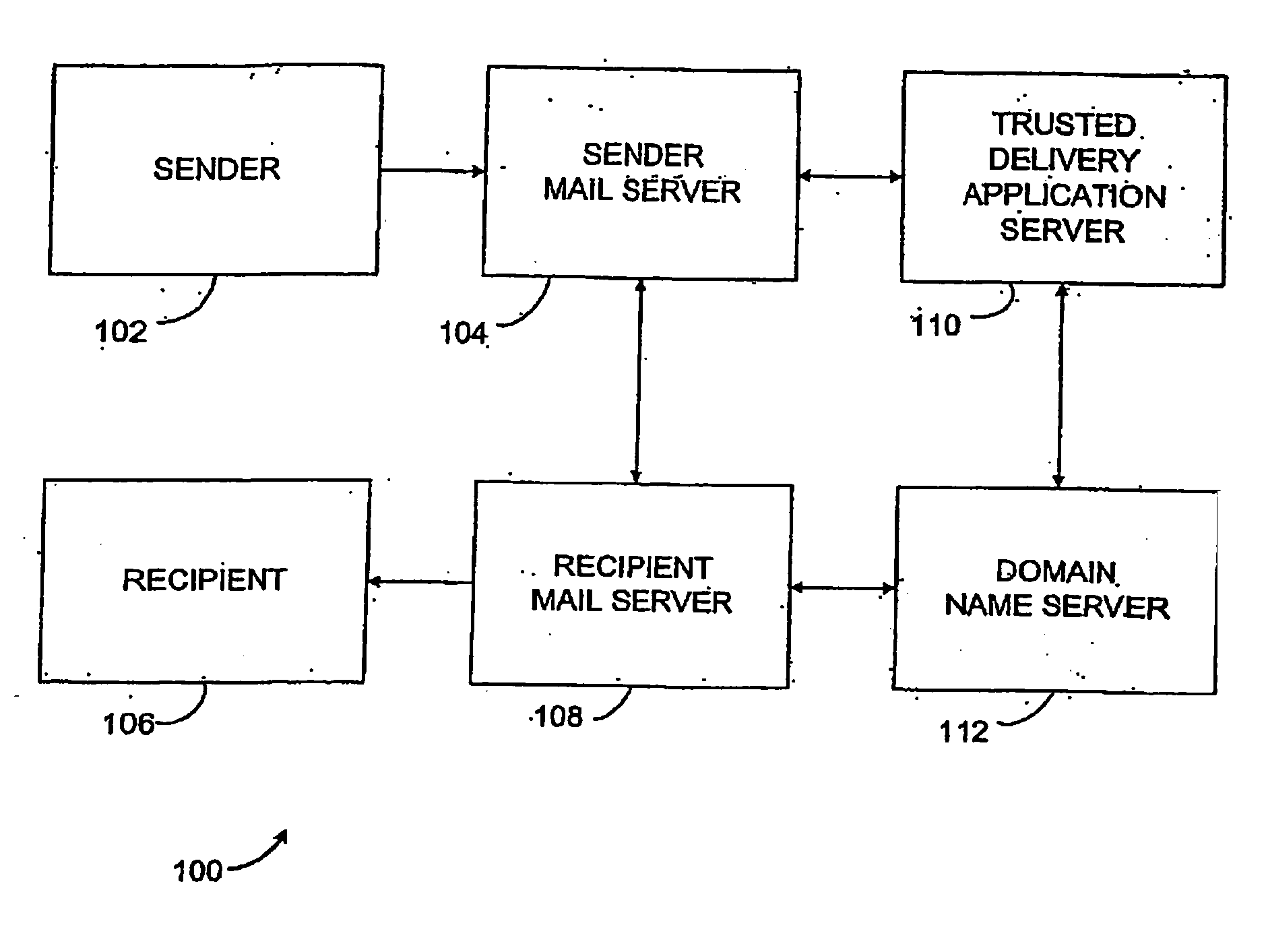
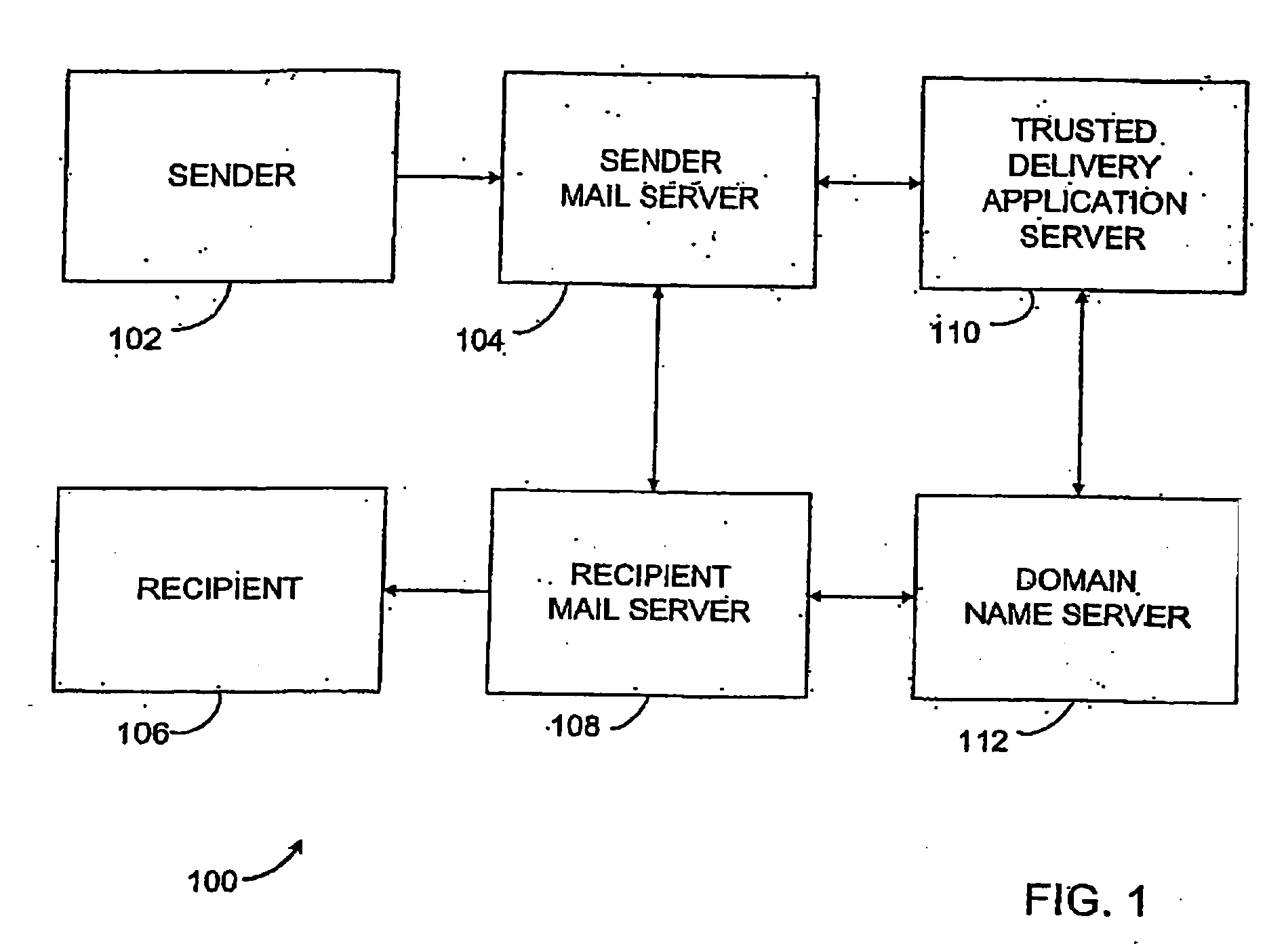
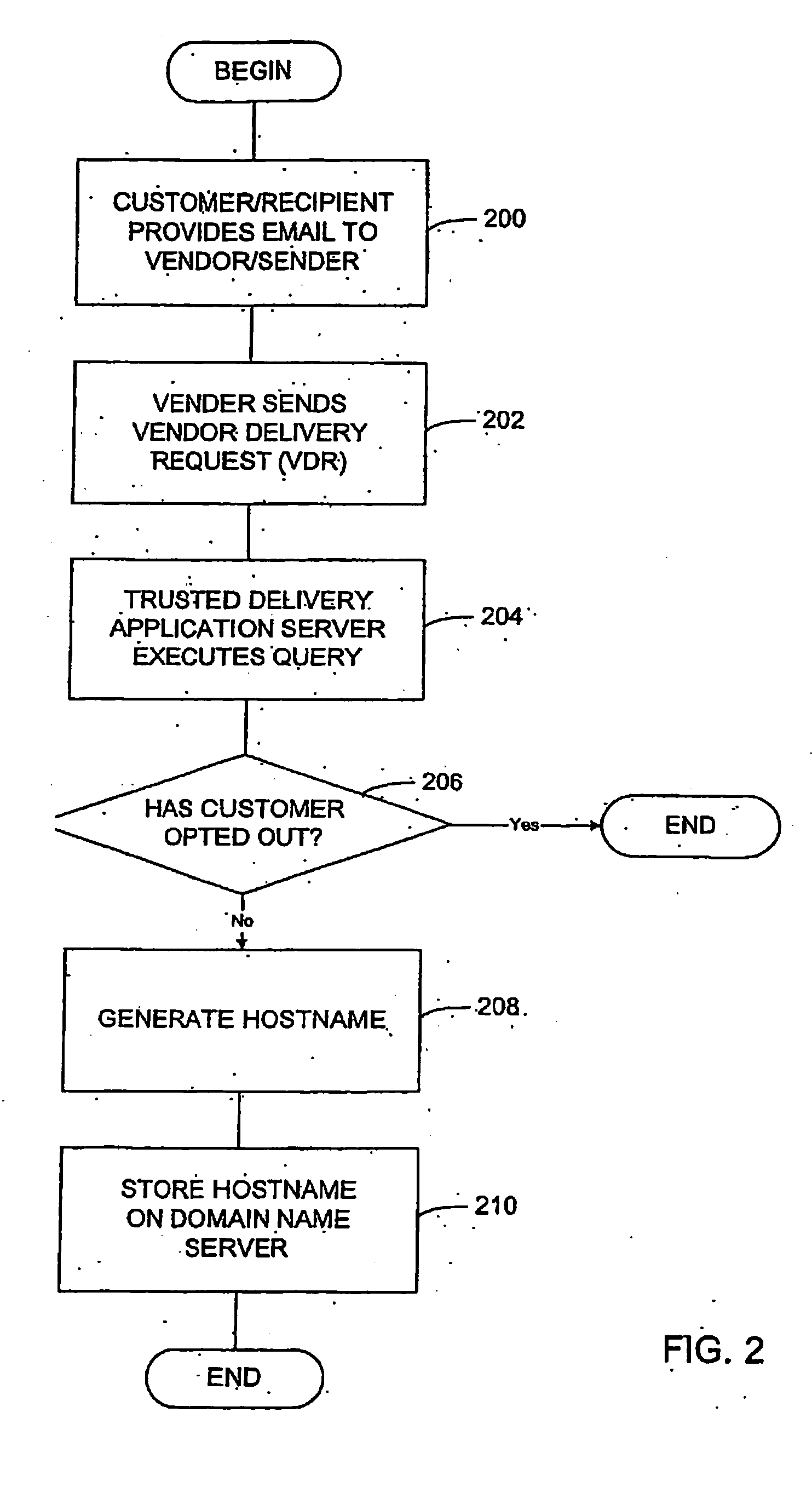
Method and system for delivering electronic messages using a trusted delivery system
InactiveUS20070043813A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksDomain nameName server
A method and system for delivering electronic messages from a sender to a recipient over a communications network. The method includes receiving an email message verification request from a recipient mail server. Authorization of an email message is then verified, and the verification step includes generating a hostname using information in the email message transmission and querying a domain name server using the generated hostname. A verification result is transmitted to the recipient mail server. The verification result is valid when the generated hostname is successfully retrieved from the domain name server. The delivery system may be used to minimize, reduce, or eliminate the blocking or deletion of legitimate emails by spam filter applications.
Owner:TRUSTED DELIVERY
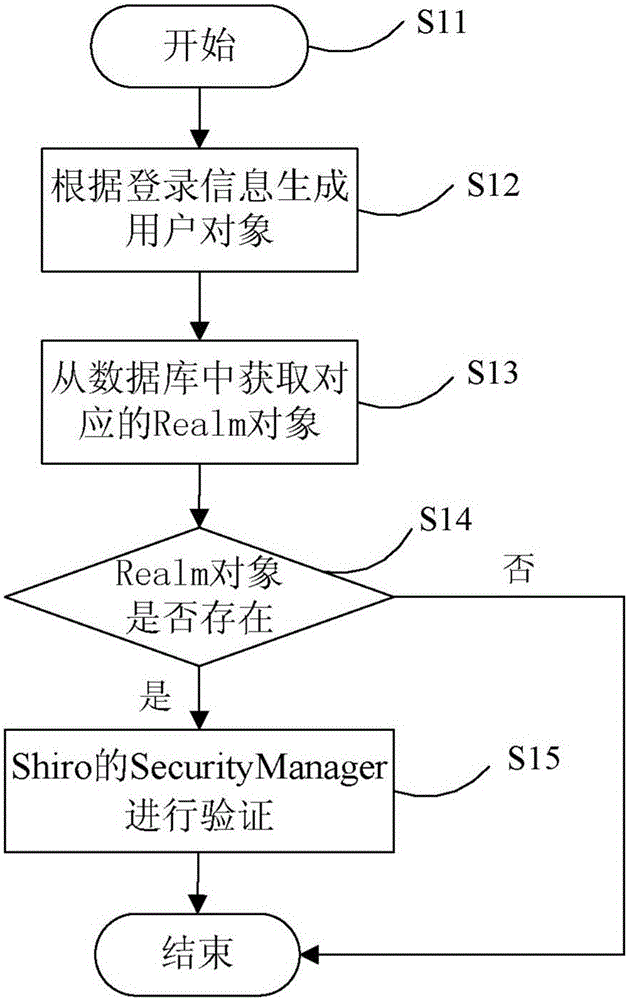
Shiro authentication method based on Redis storage
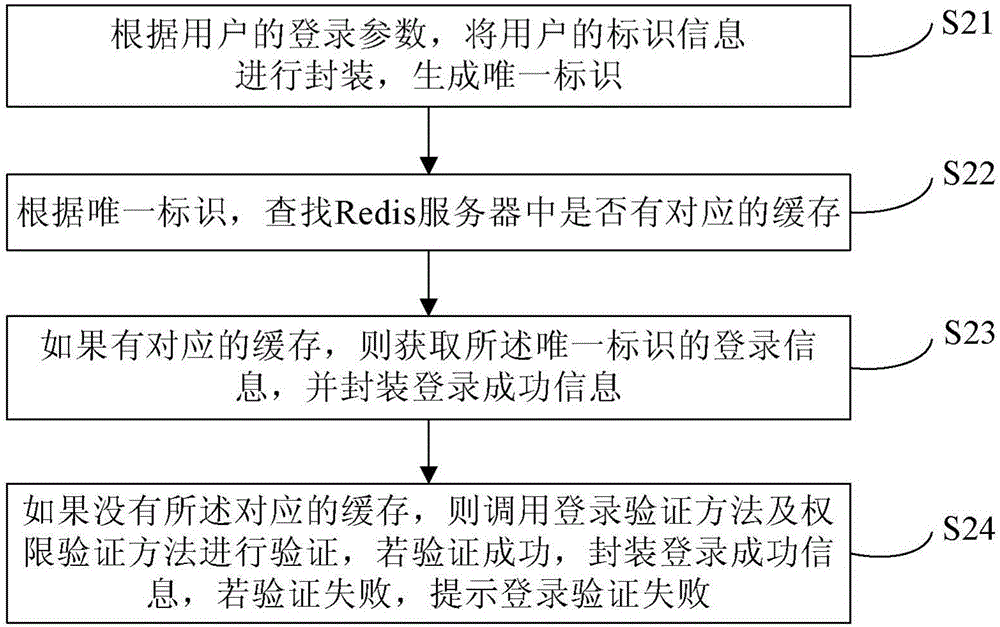
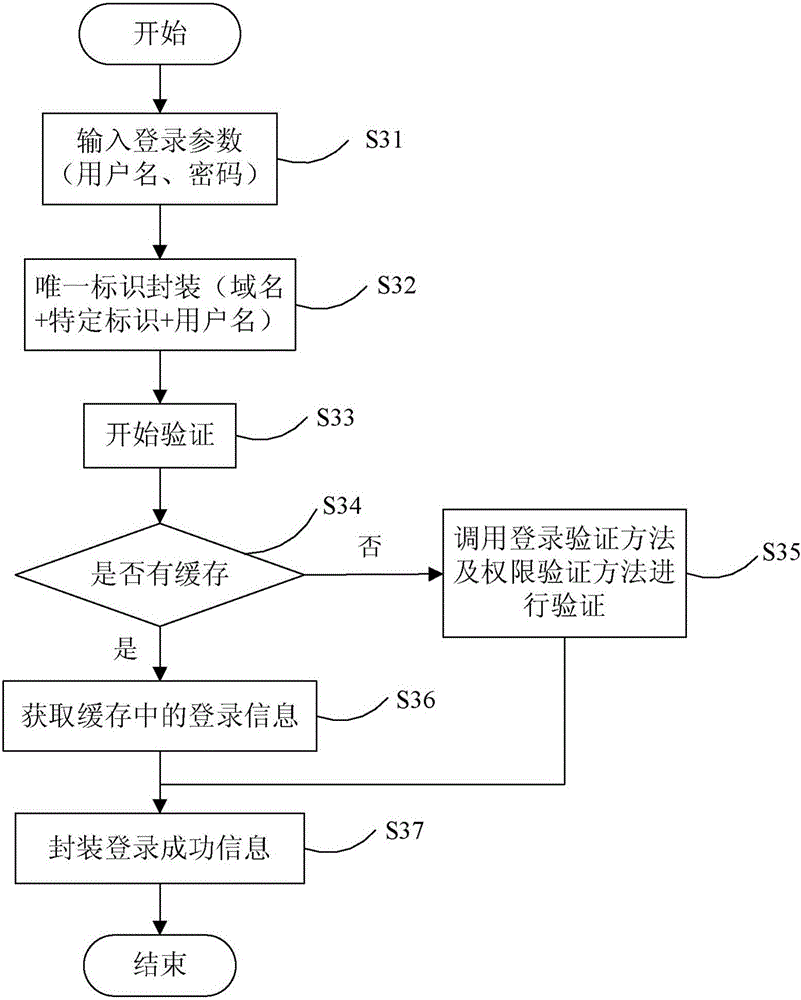
ActiveCN106487744AEasy to operateImprove efficiencyTransmissionHigh level techniquesExpiration TimeValidation methods
The invention provides a Shiro authentication method based on Redis storage. Through placing a session into an Redis for caching, the memory consumption can be reduced to solve the problem of memory overflow; and as an expiration time algorithm is introduced to automatically eliminate a cache, the efficiency and the hit rate of the cache are improved, thereby guaranteeing data to be stored efficiently and reliably. The method comprises the steps of carrying out encapsulation on identification information of a user according to login parameters of the user to generate a unique identifier; according to the unique identifier, finding whether the corresponding cache exists in an Redis server; if the corresponding cache exists, obtaining login information of the unique identifier and encapsulating login successful information; and if the corresponding cache does not exist, calling a login authentication method and an authority authentication method for authentication, if the authentication is passed, encapsulating the login successful information, and if the authentication is failed, prompting the login authentication is failed.
Owner:BEIJING JINGDONG SHANGKE INFORMATION TECH CO LTD +1
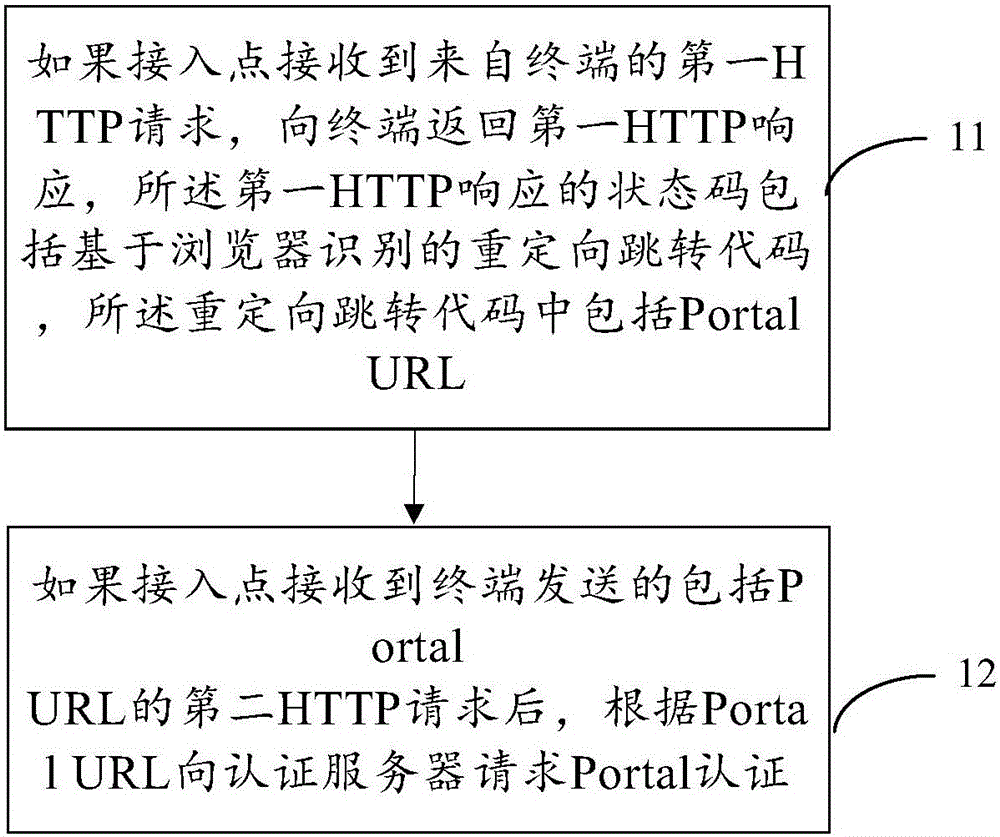
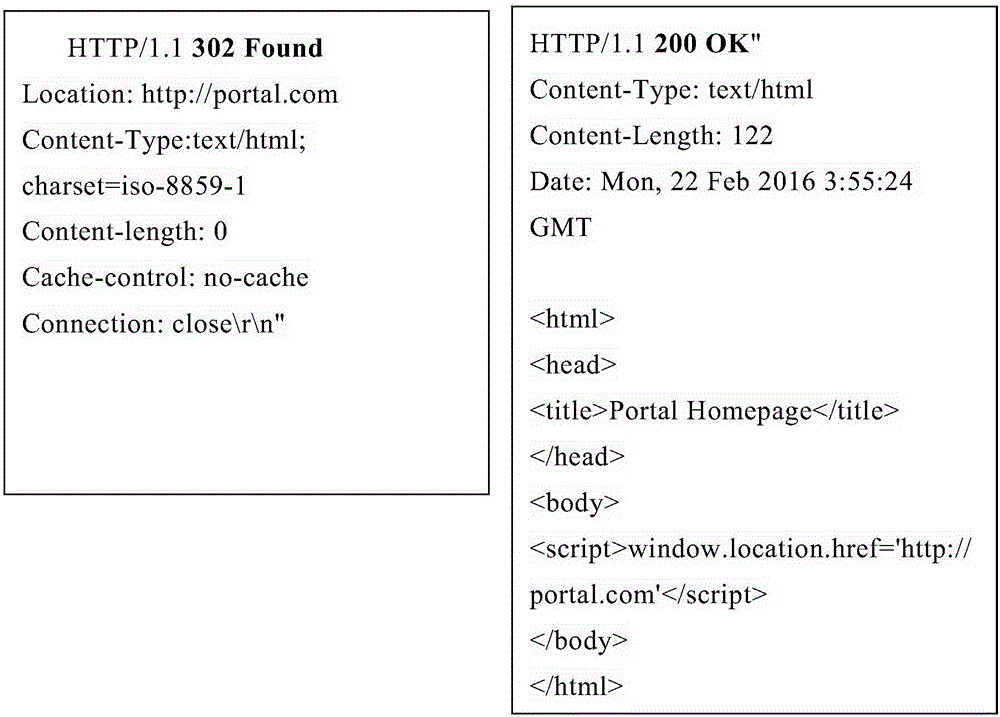
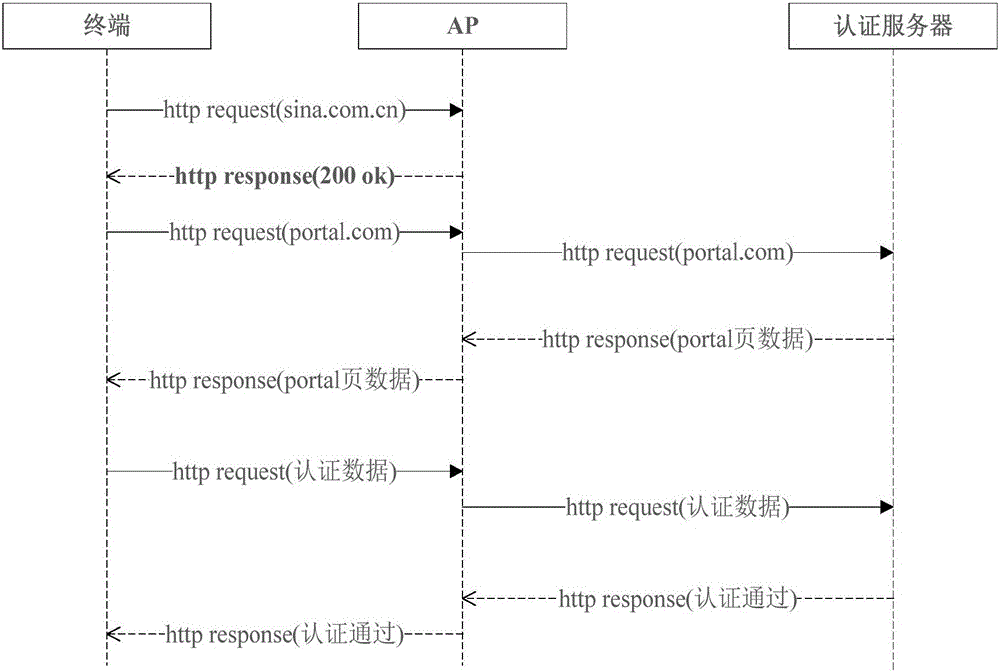
Portal authenticating method and system
This invention provides a portal authenticating method and system. The method comprises the following steps: a terminal sends a first HTTP (Hyper Text Transport Protocol) request to an access point and receives a first HTTP response returned by the access point; a status code of the first HTTP response comprises a redirection jump code based on browser identification; the redirection jump code comprises a uniform resource locator of the portal authentication; the terminal acquires the uniform resource locator of the portal authentication in the first HTTP response, and requests the portal authentication to an authentication server based on the uniform resource locator of the portal authentication. By adopting the method and the system provided in the invention, a plenty of invalid HTTP data packets are reduced to the authentication server, so that the processing pressure of the authentication server is relieved; and thus, a better network service is provided for the access point.
Owner:PHICOMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Remote authentication based on challenge-response using digital certificates
InactiveUS20120117639A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsThird partyDigital signature
Embodiments of the invention provide for authenticating users of web-based applications by presenting a previously acquired signed digital signature. Examples establish secure user sessions between a client and a user in response to a verification of an identification of the user by the client, the client creating a unique username for the user and unlocking access by the user to a client digital signature for use with a request for service from a third party web server. A secure facilitator session is established between the client and a third party web server, wherein messages exchanged with the unique username and a unique session identification indicia of the secure facilitator session signed by the unlocked digital signature result in executed processes requested by the service identifier data if the messages are validated without the client requiring the user to verify user identification for any message until a secure facilitator session ends.
Owner:IBM CORP
Real-name authentication apparatus
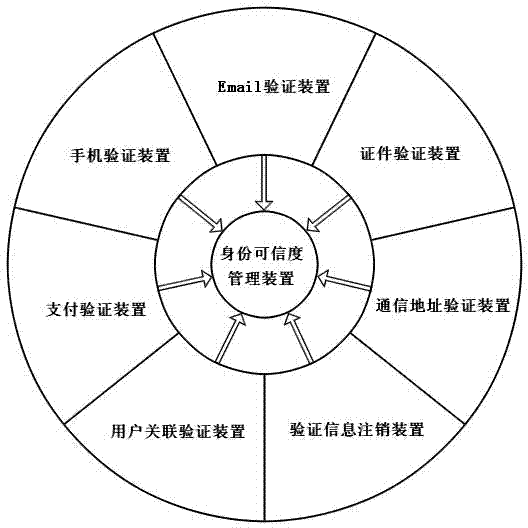
InactiveCN103248483ARapid and reliable expansionDetermine responsibilityUser identity/authority verificationPaymentEmail authentication
The invention discloses a real-name authentication apparatus. The real-name authentication apparatus comprises an identity information authentication apparatus and an identity confidence level management apparatus, wherein the identity confidence level management apparatus is used for determining the identity confidence level of users according to various identity information authentication results of the identity information authentication apparatus; the identity information authentication apparatus comprises but not limits to an Email authentication device, a mobile phone authentication device, a certificate authentication device, a payment authentication device, a communication address authentication device, a user association authentication device and an authentication information logout apparatus. According to the invention, the identity confidence level of the users can be sketched out according to the various authentication results of different information, so that a network virtual community is closer to reality, and a more credible and safe interactive environment is provided for the users in the network virtual community.
Owner:张经纶
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com