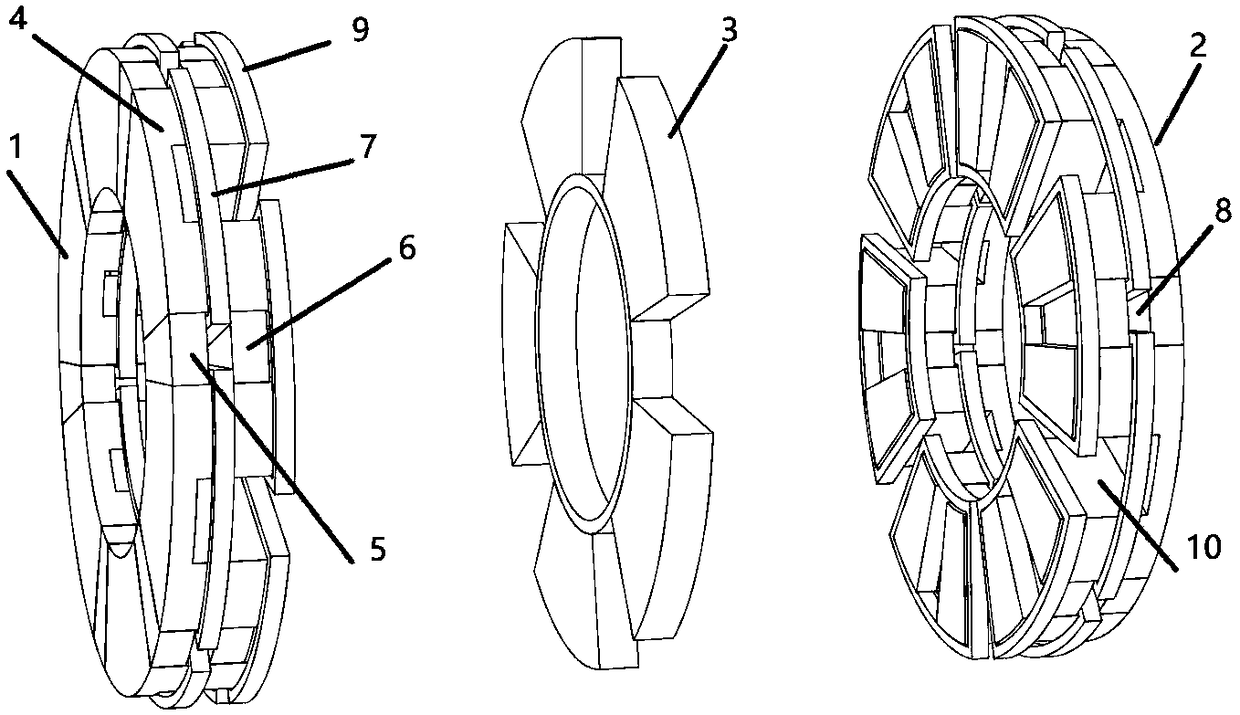
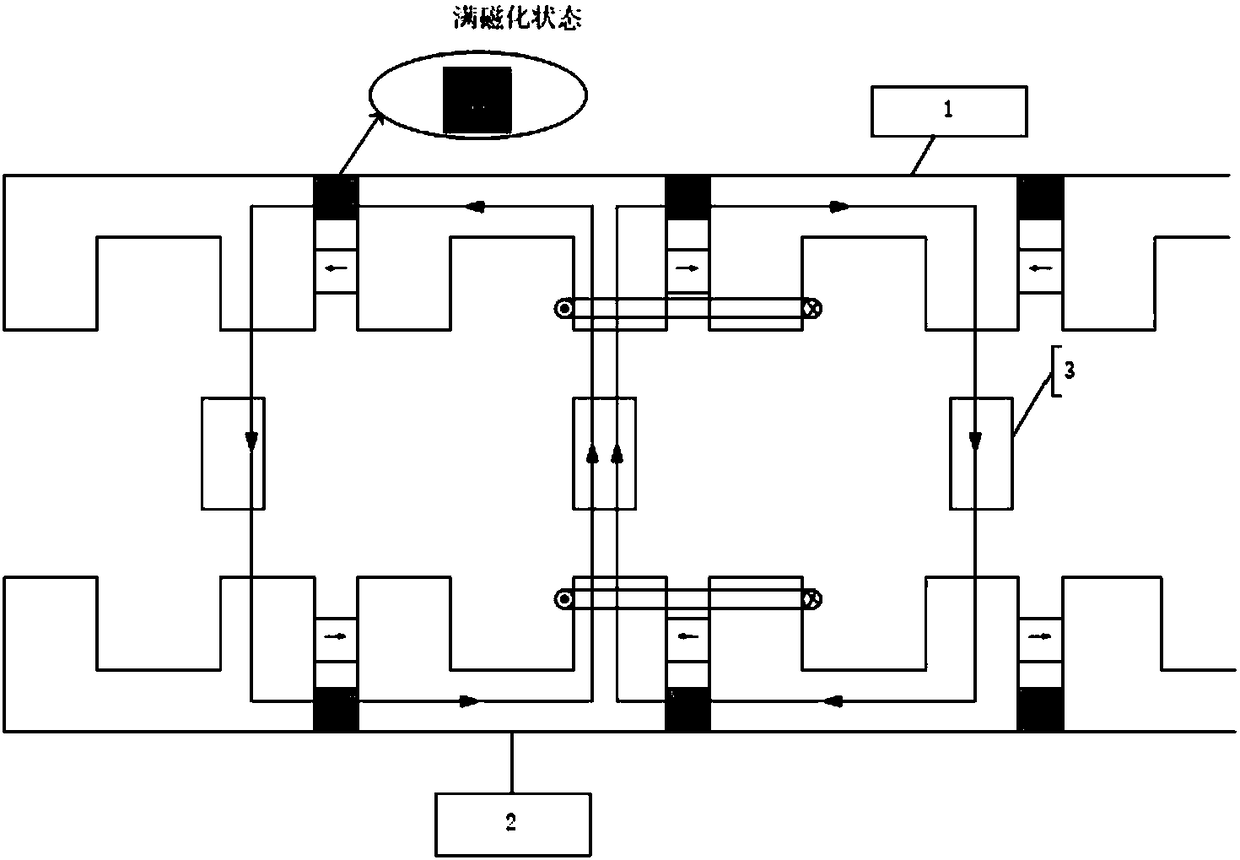
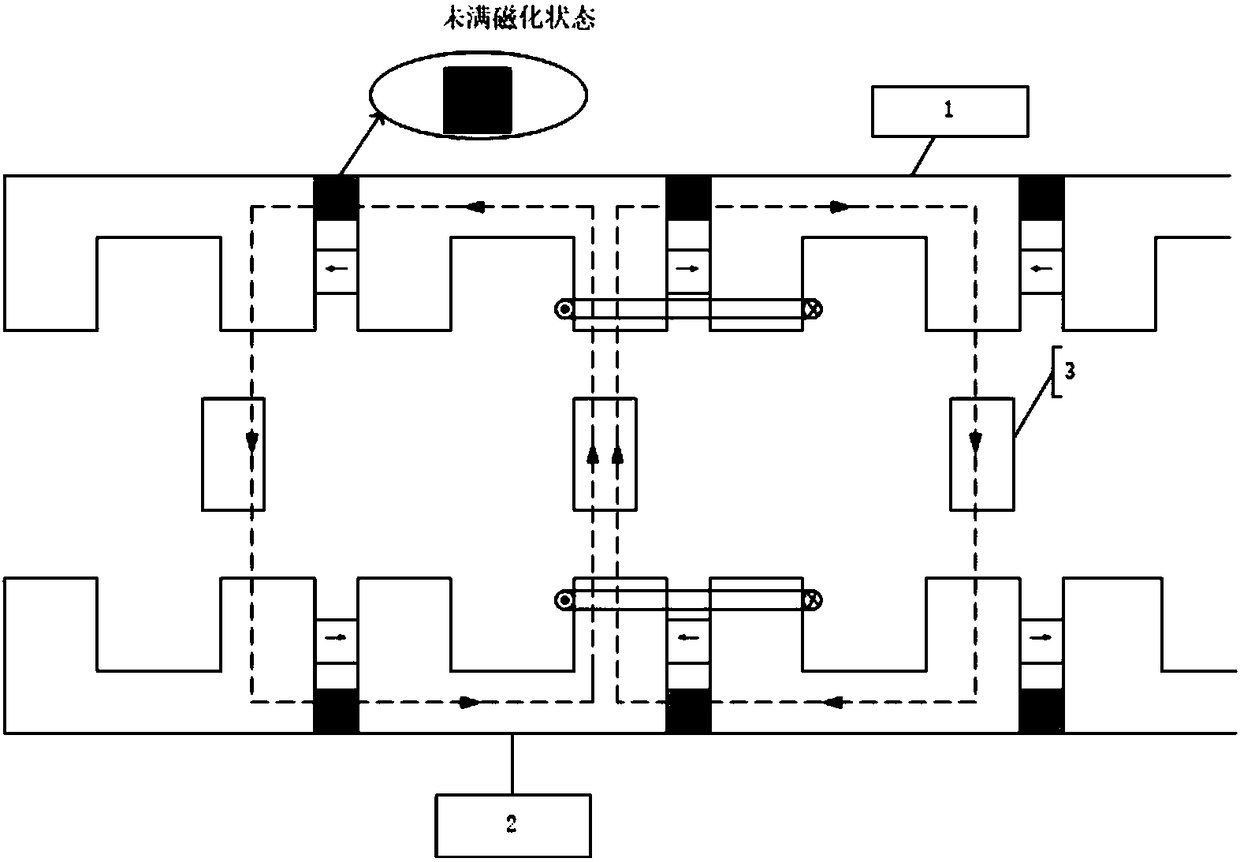
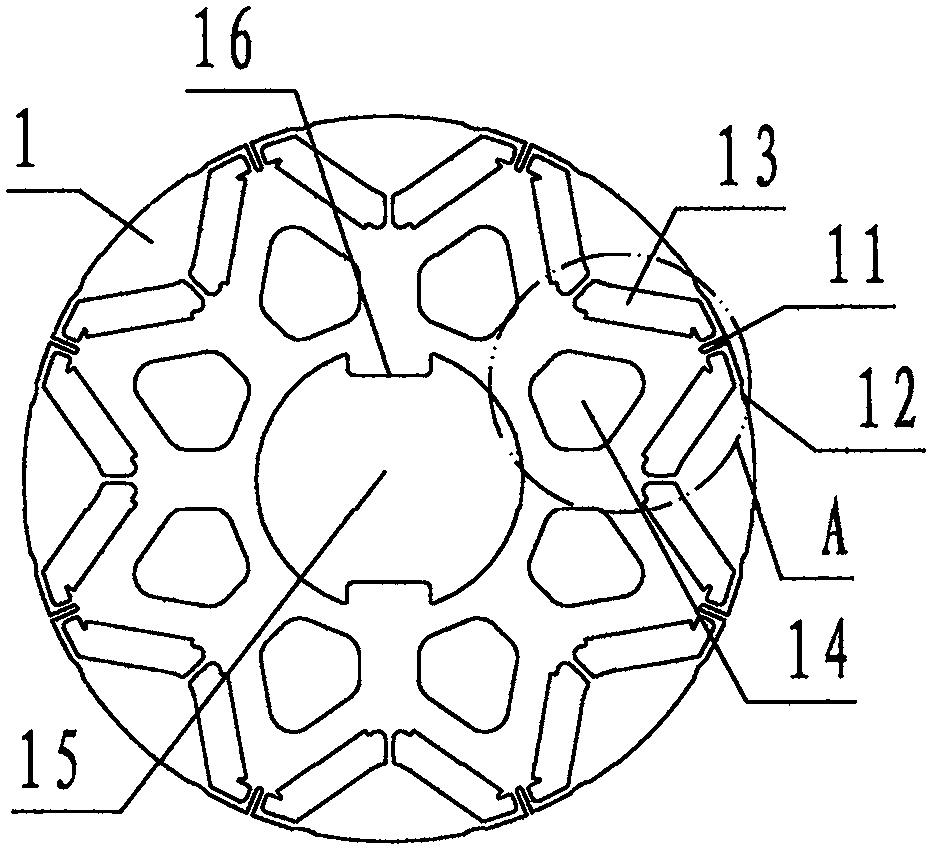
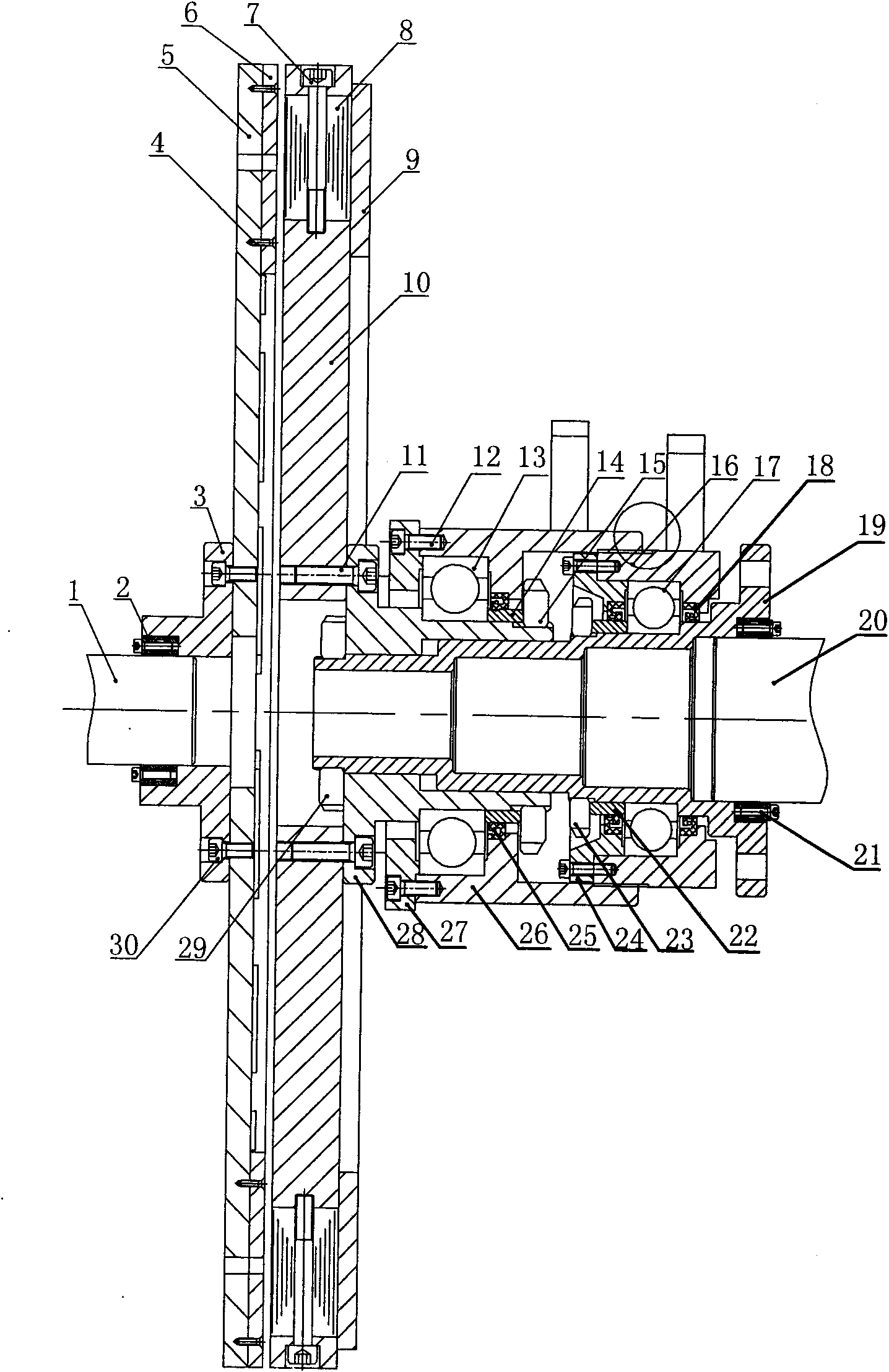
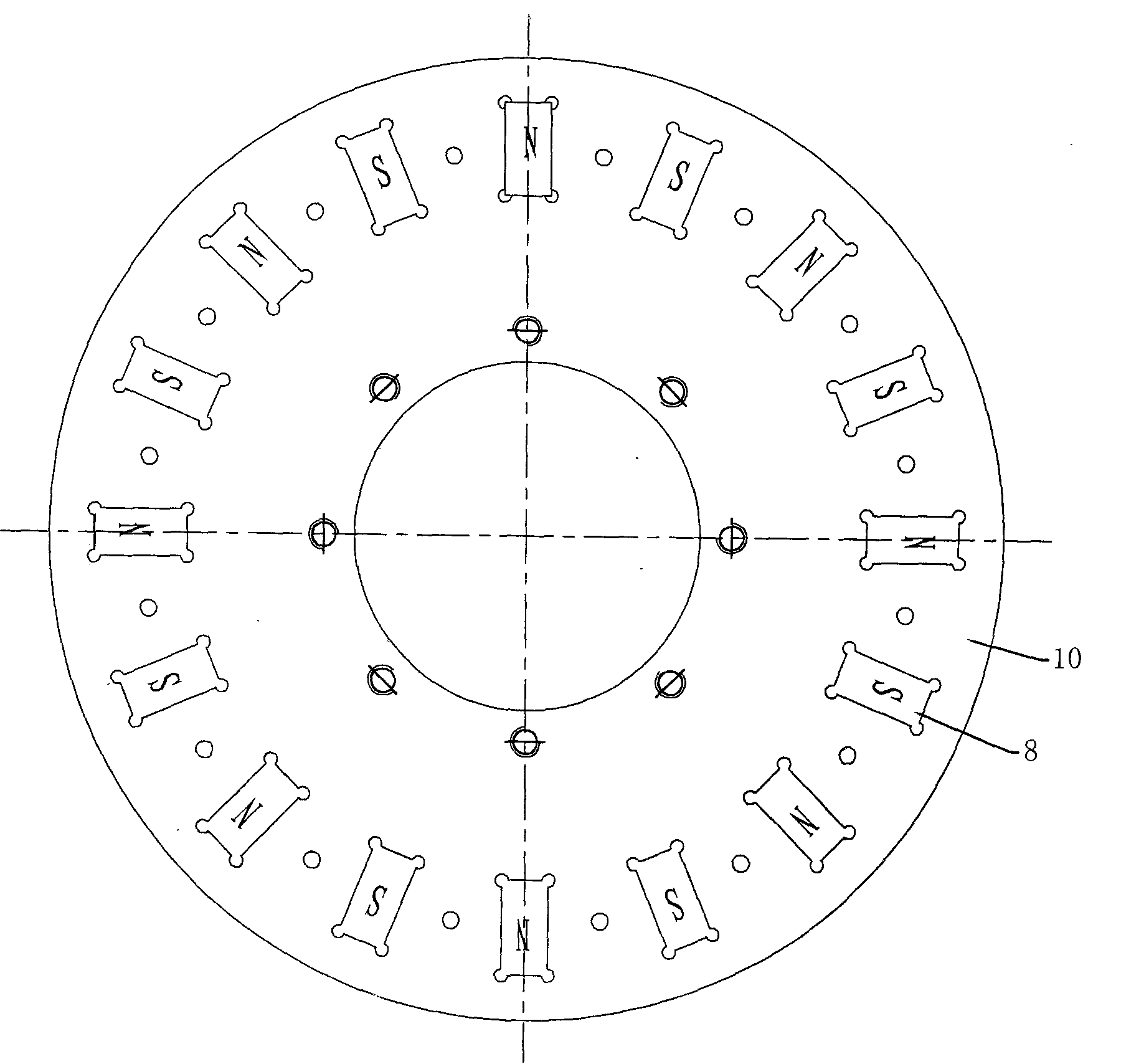
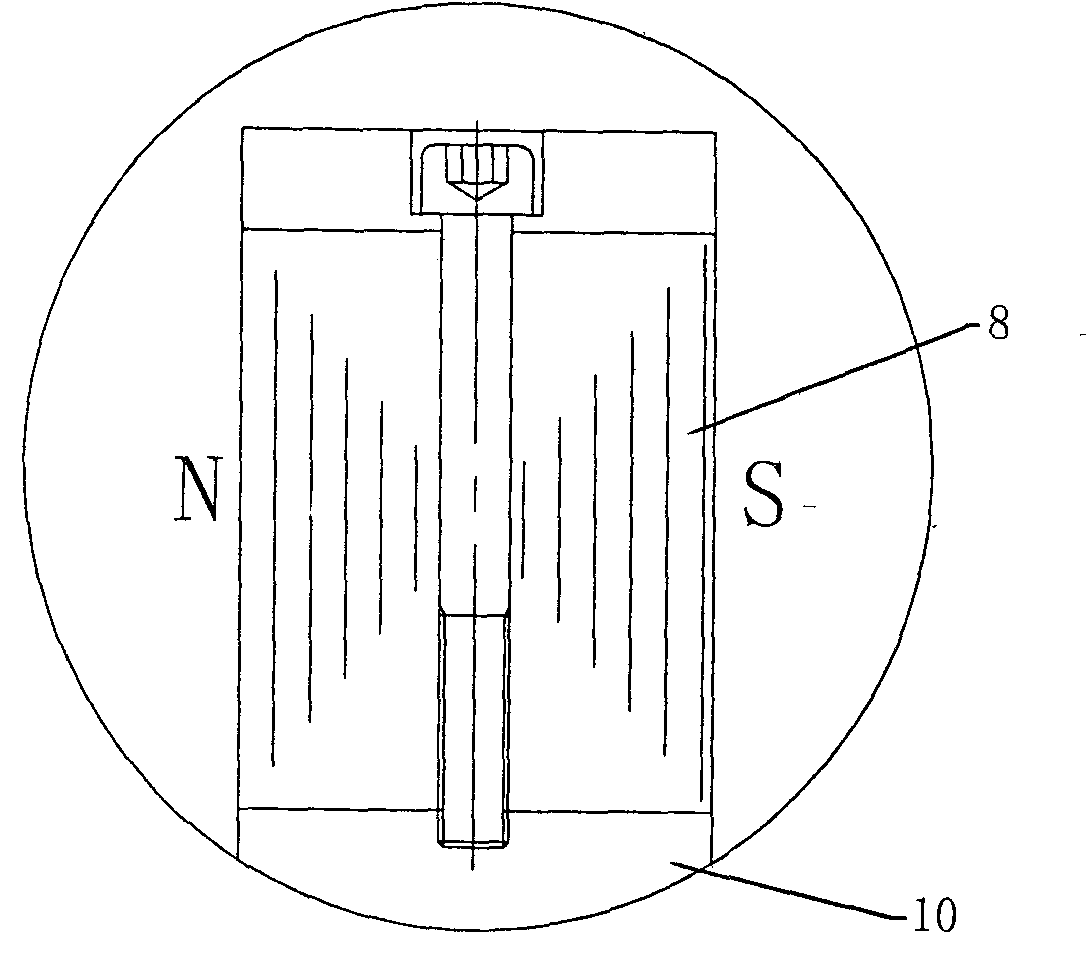
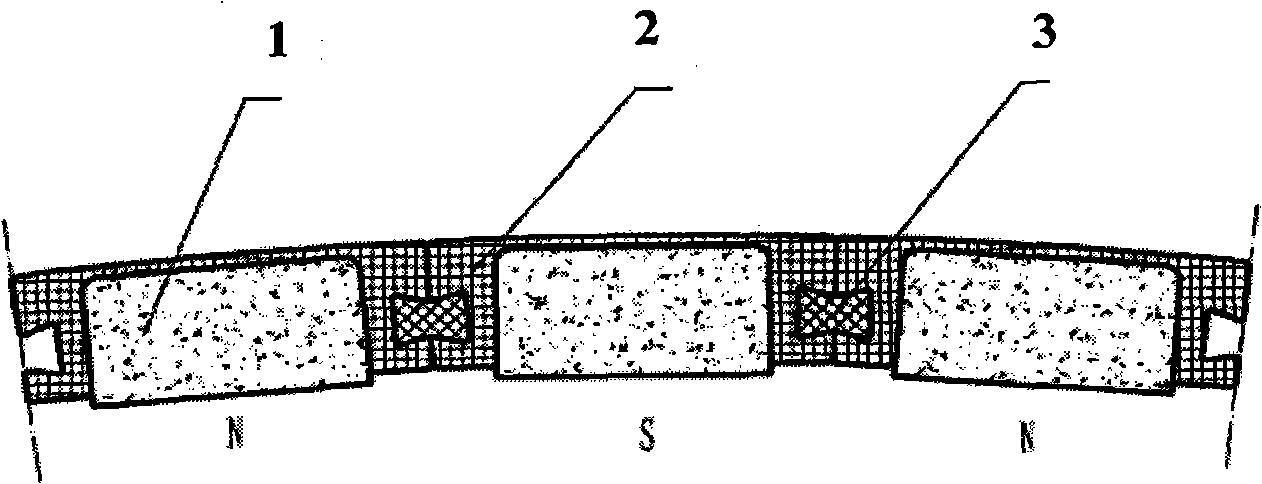
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
148 results about "Electropermanent magnet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
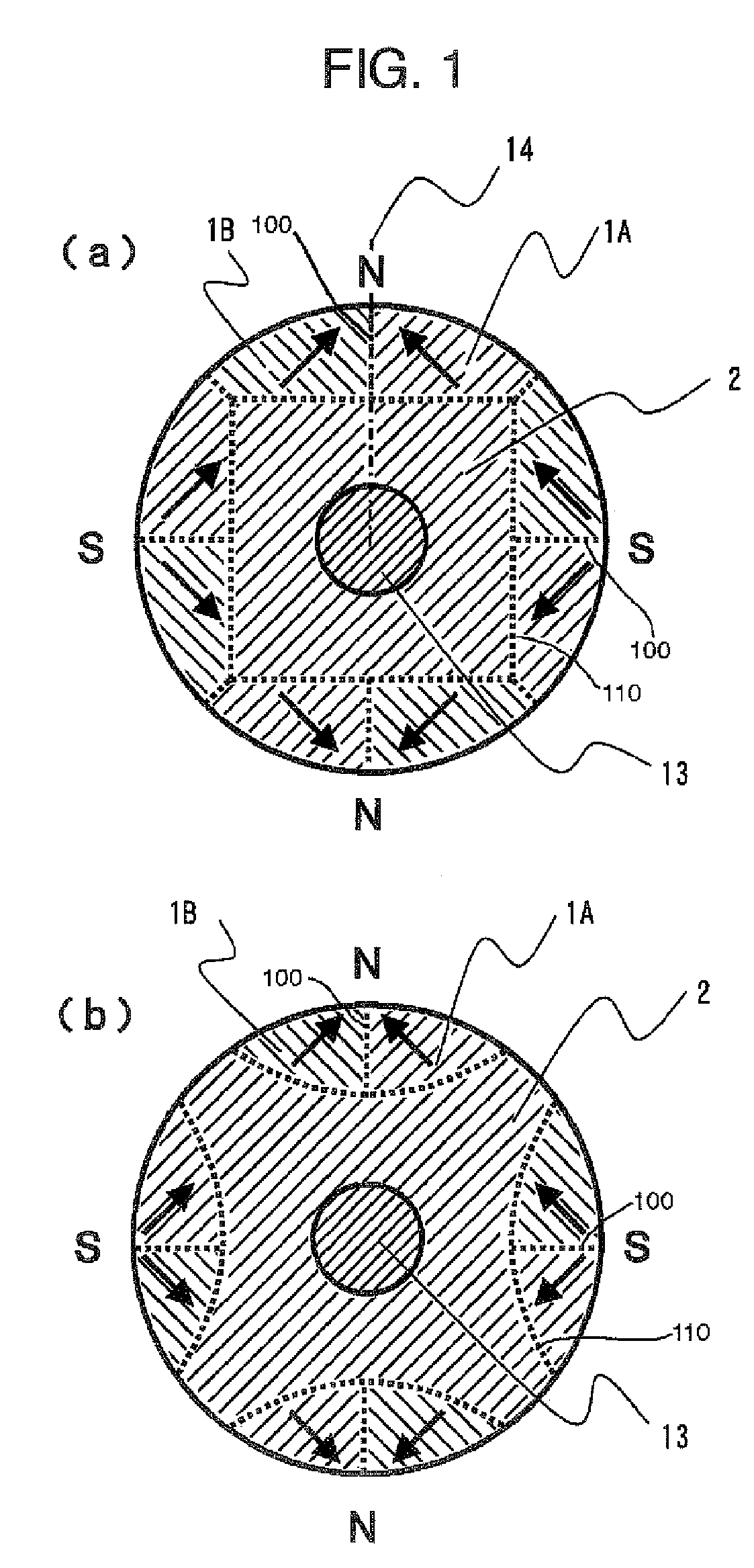
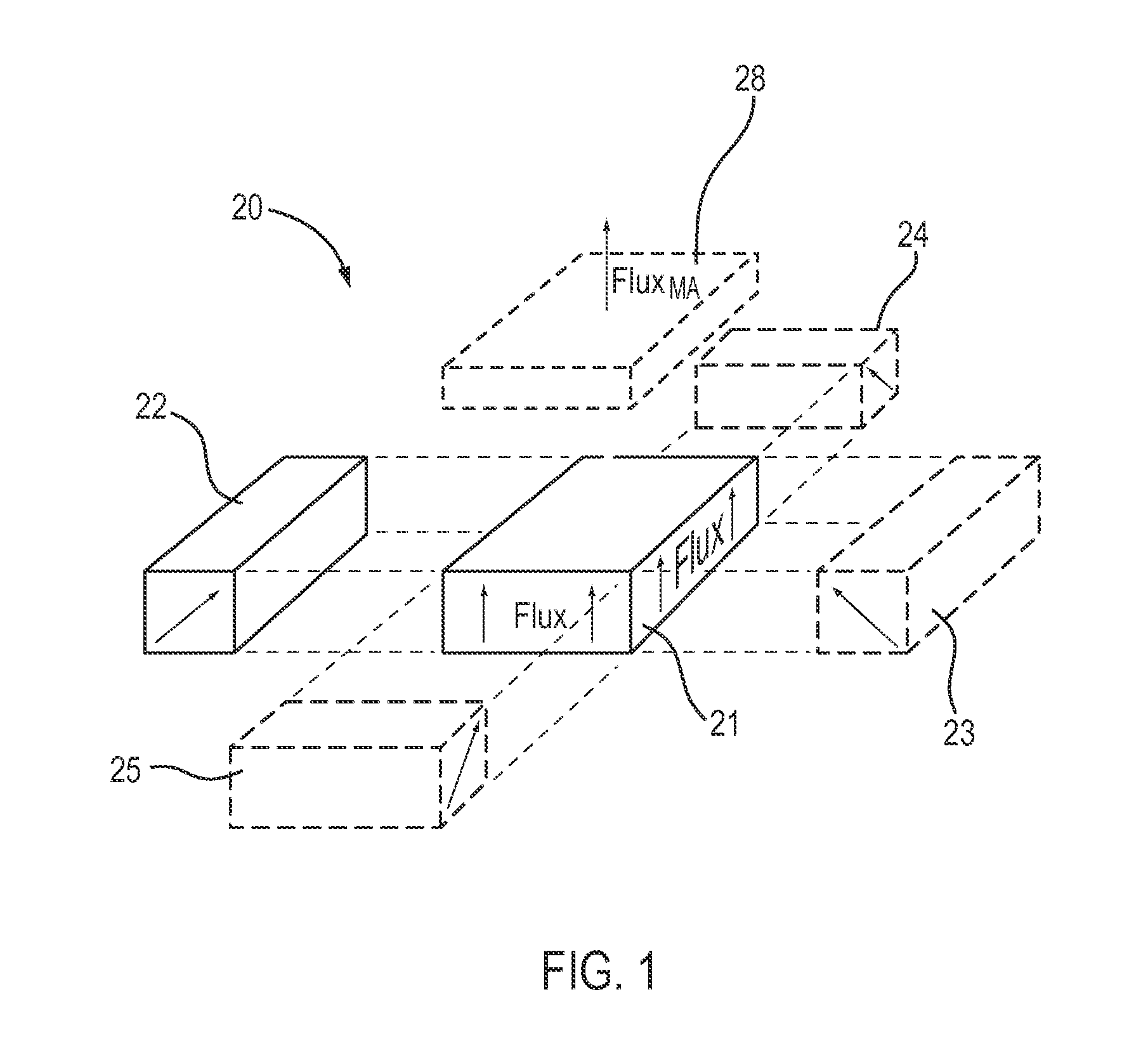
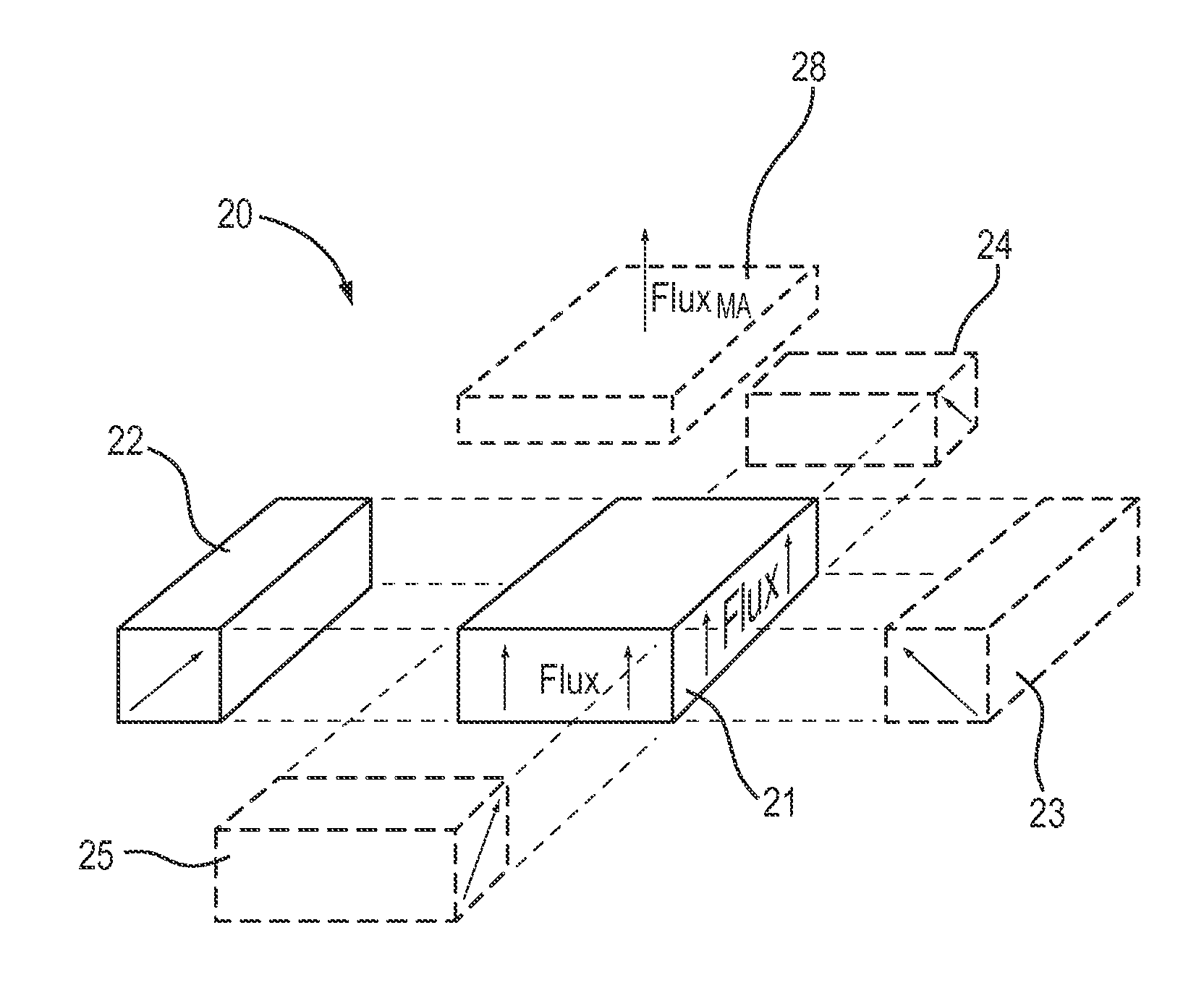
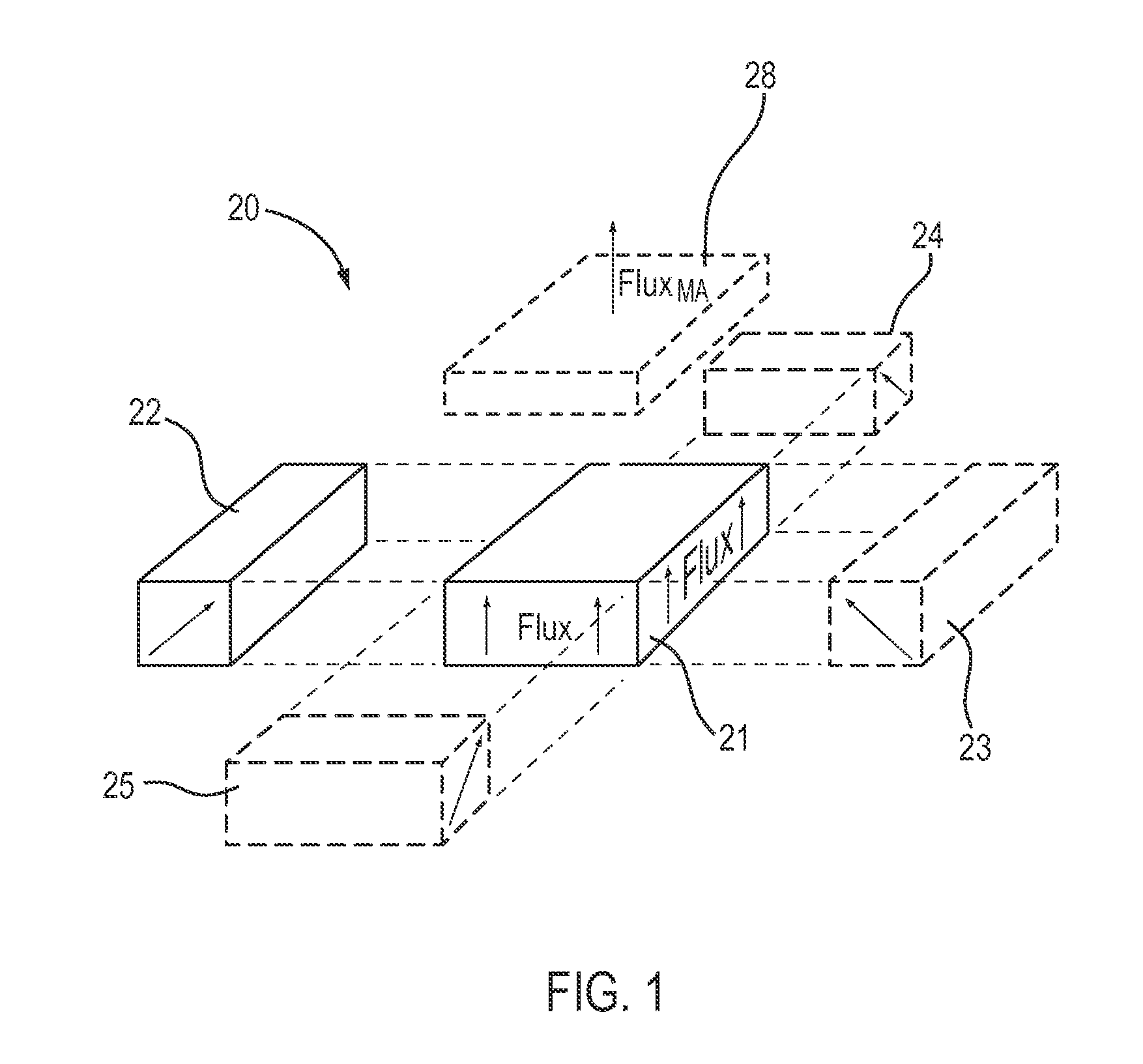
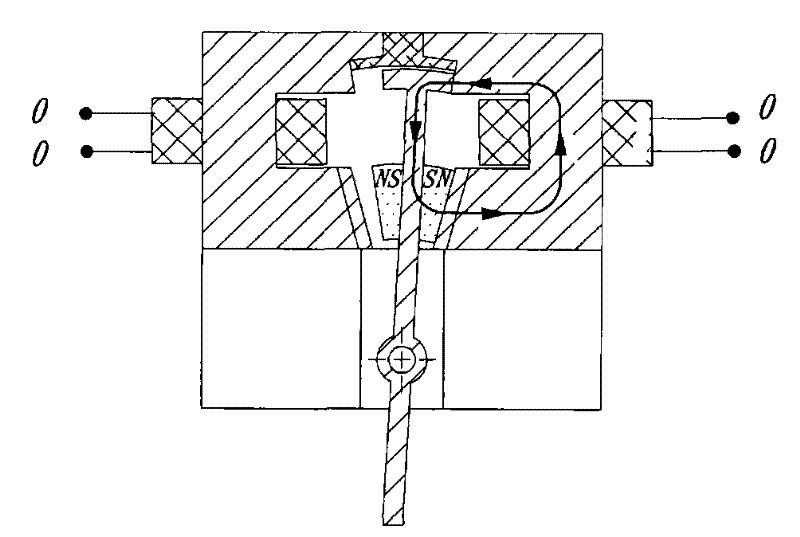
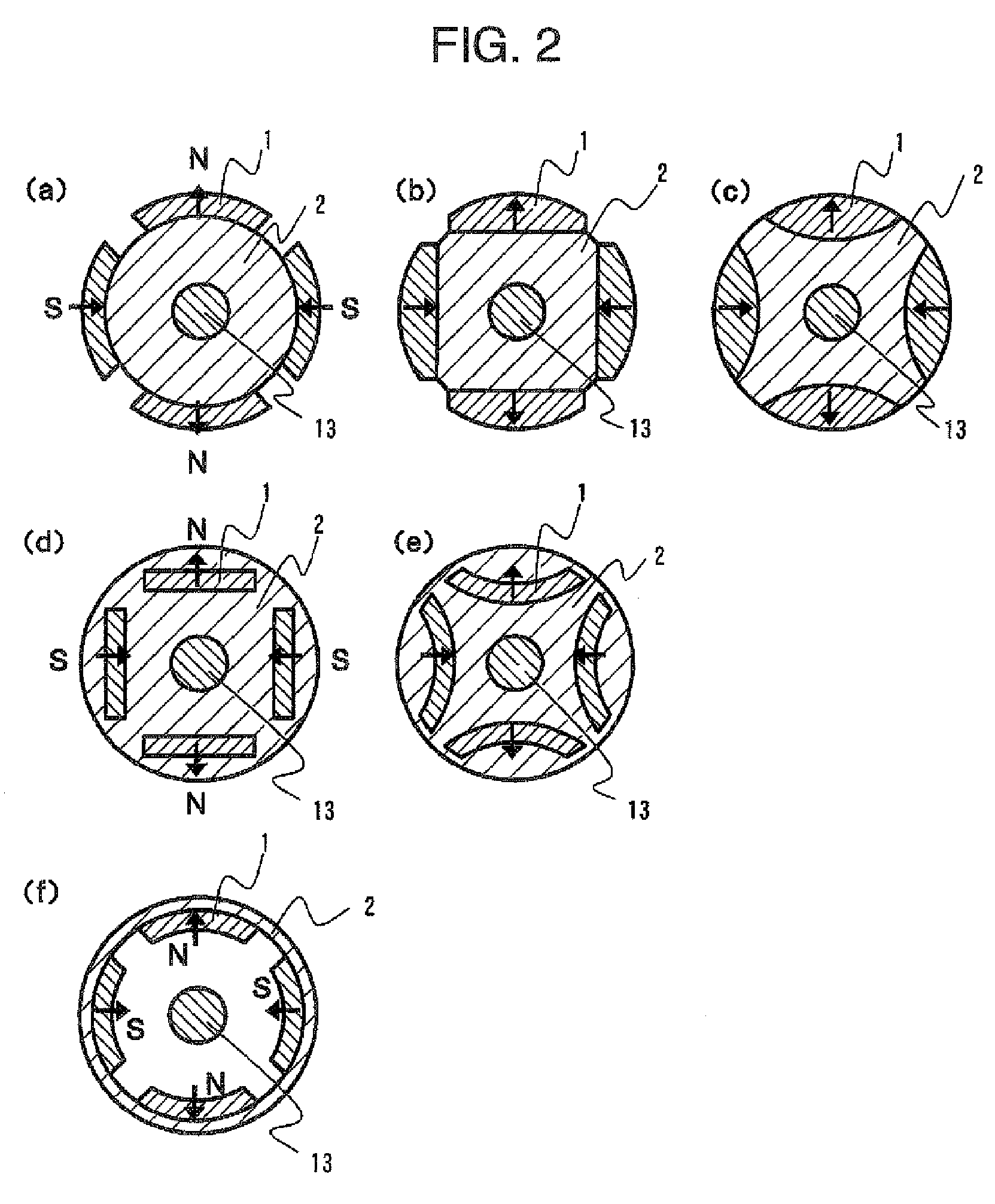
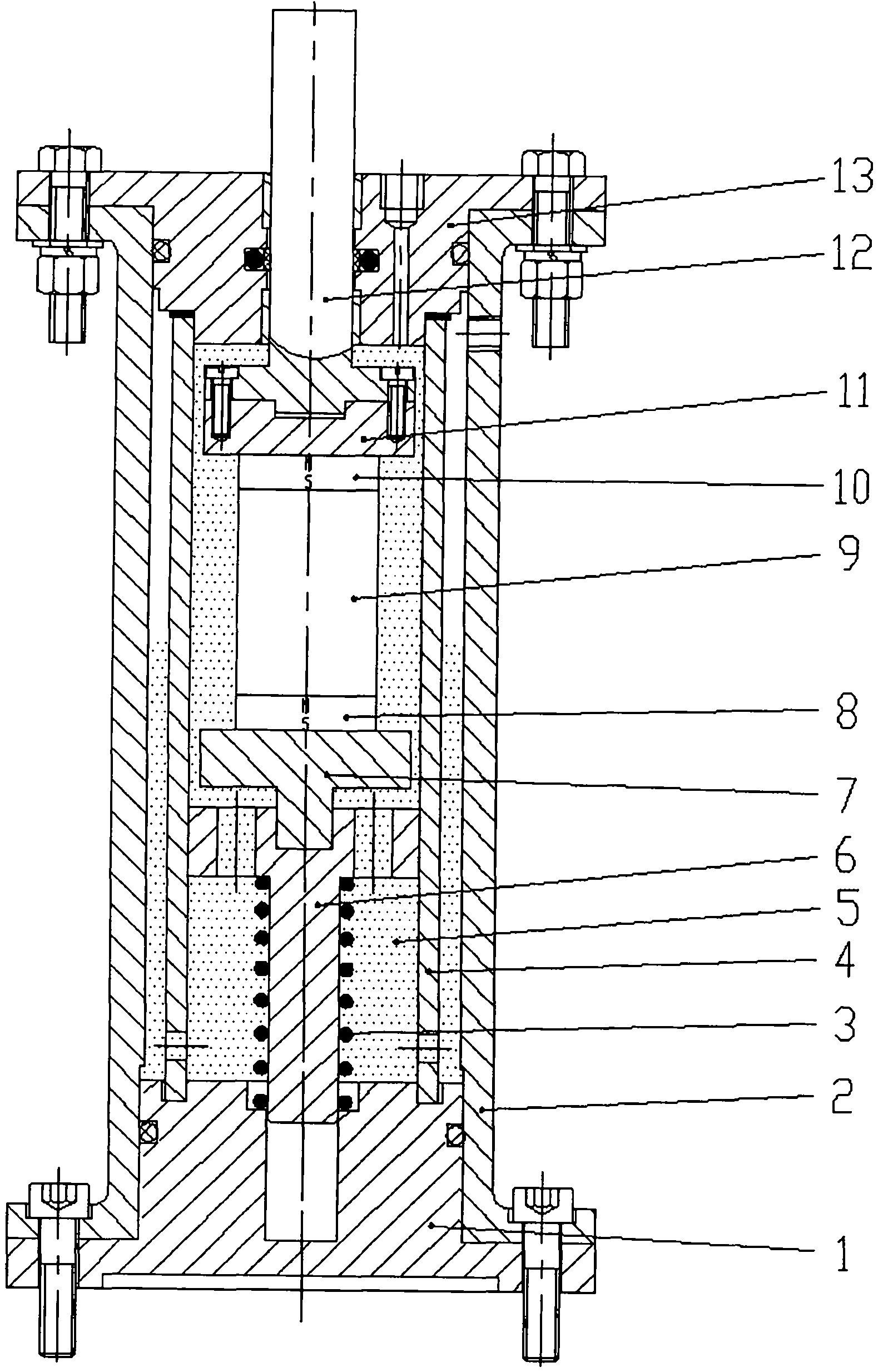
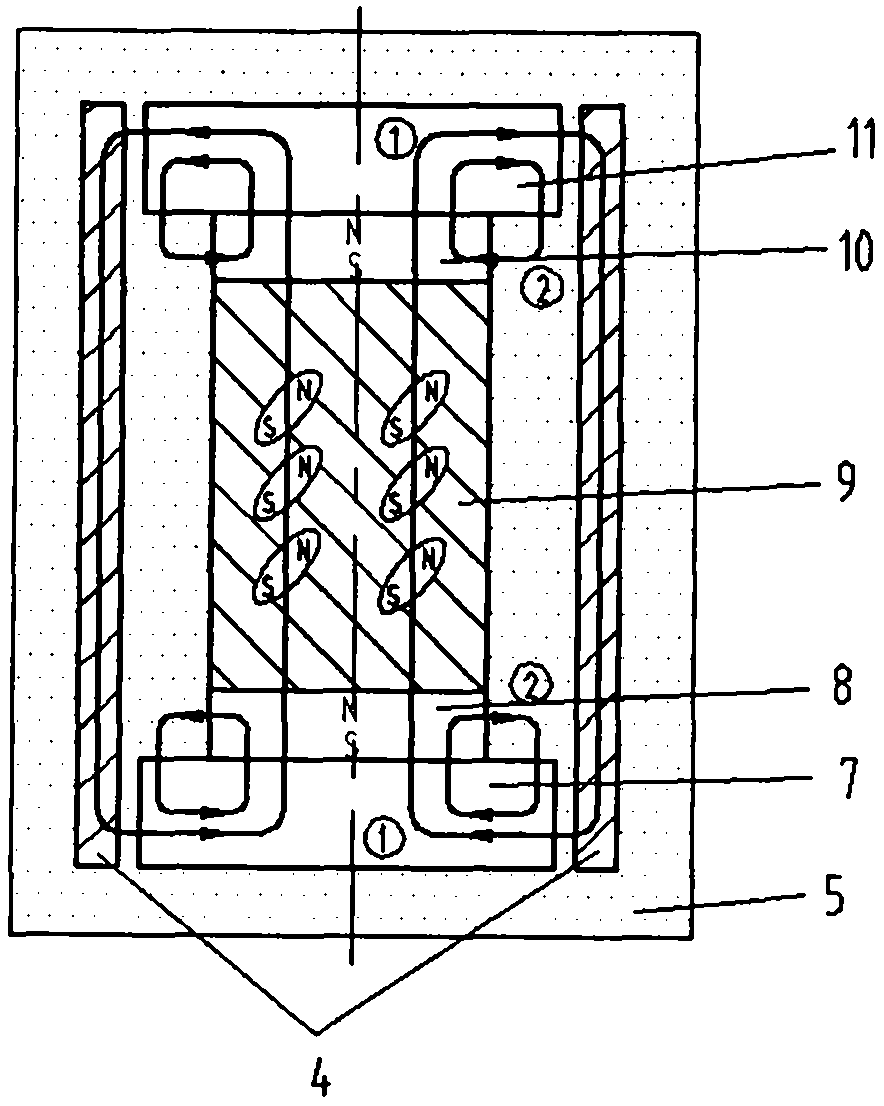
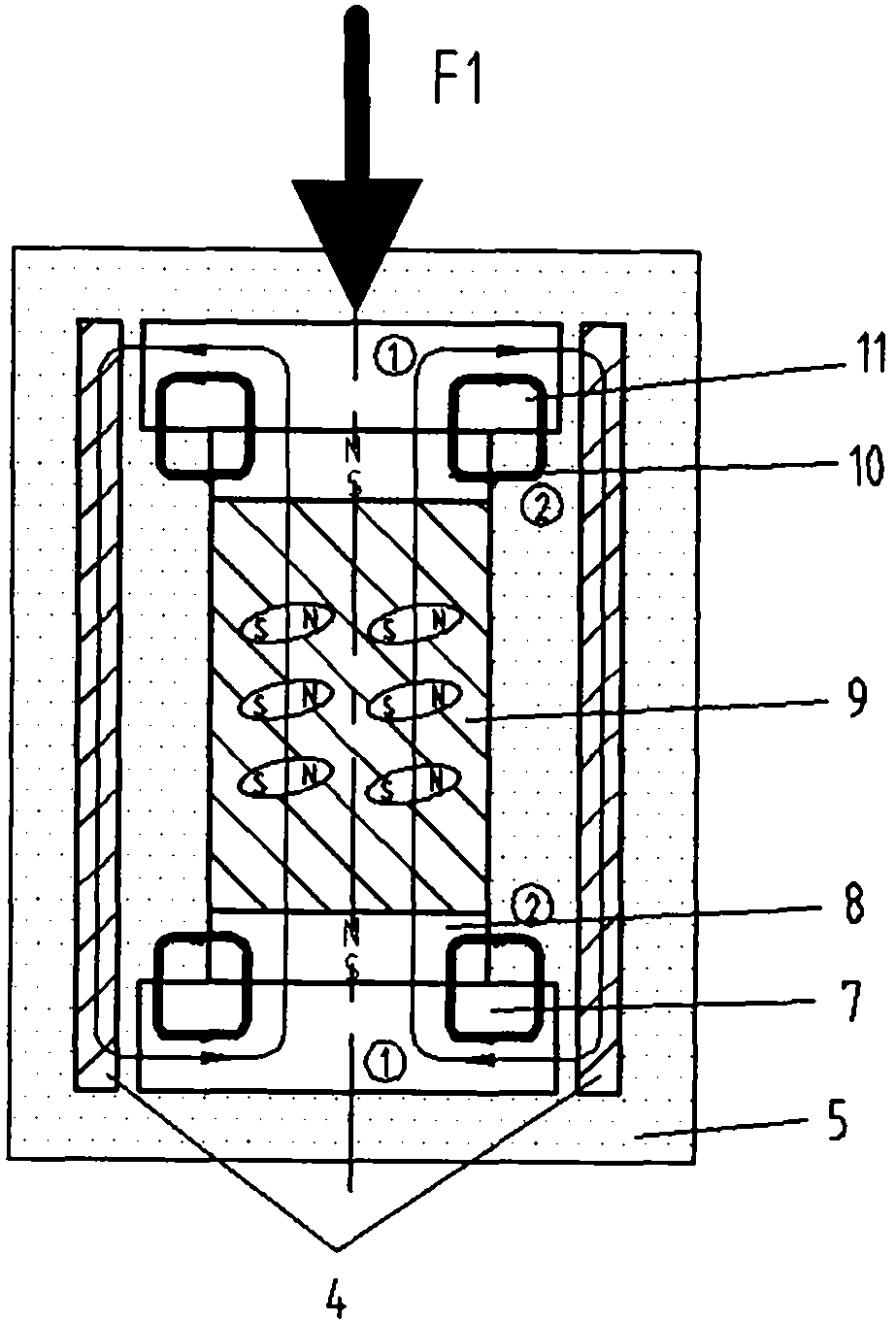
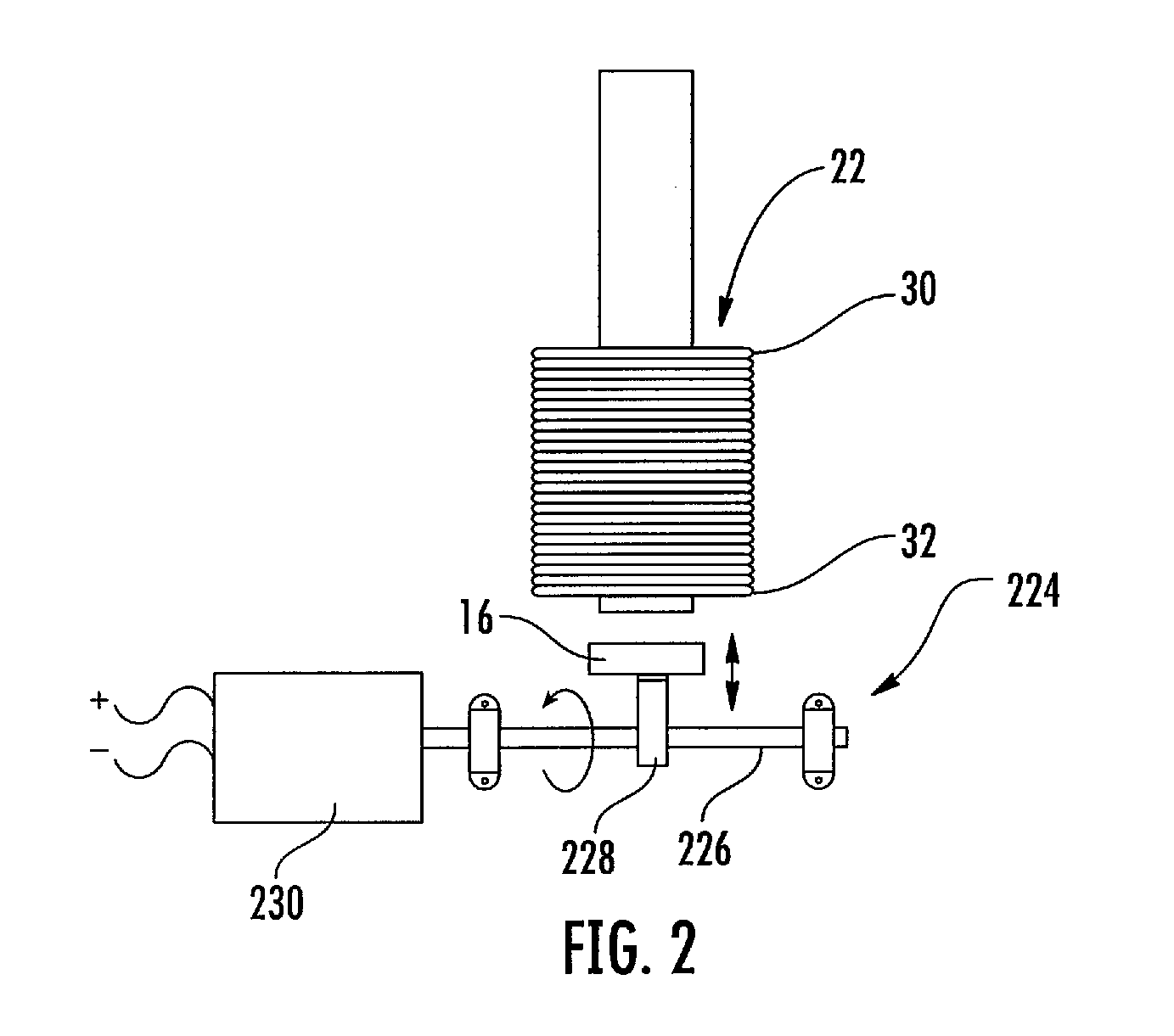
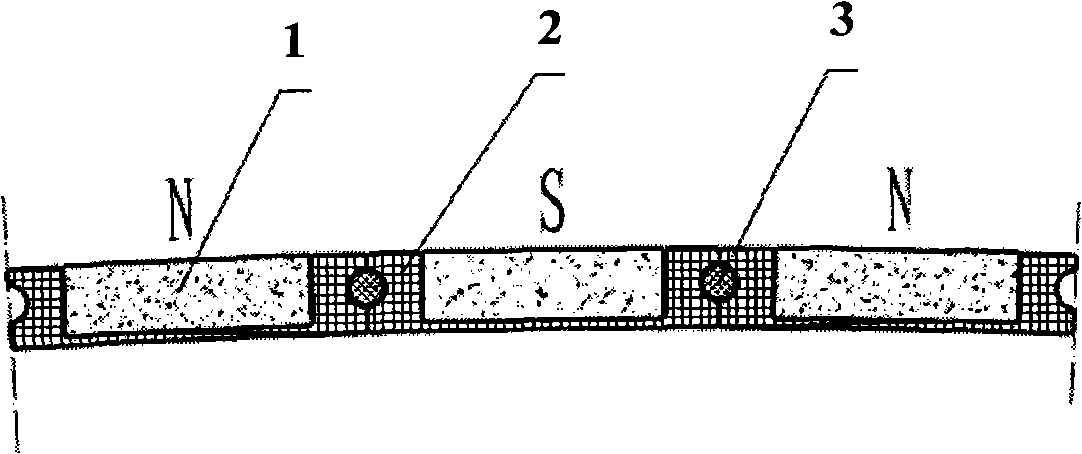
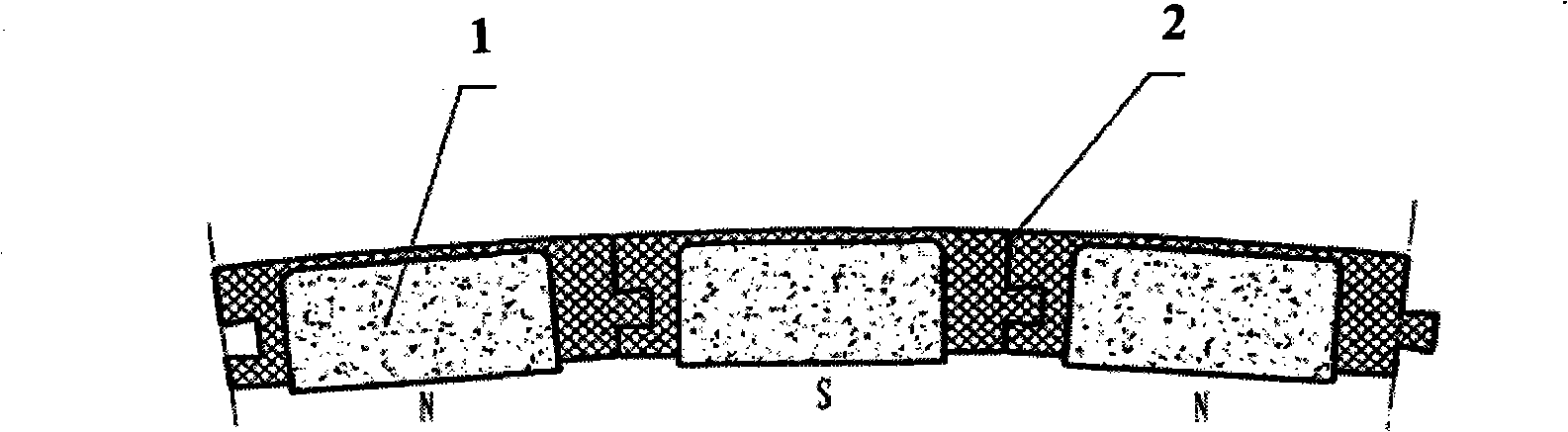
An electropermanent magnet or EPM is a type of permanent magnet in which the external magnetic field can be switched on or off by a pulse of electric current in a wire winding around part of the magnet. The magnet consists of two sections, one of "hard" (high coercivity) magnetic material and one of "soft" (low coercivity) material. The direction of magnetization in the latter piece can be switched by a pulse of current in a wire winding about the former. When the magnetically soft and hard materials have opposing magnetizations, the magnet produces no net external field across its poles, while when their direction of magnetization is aligned the magnet produces an external magnetic field.
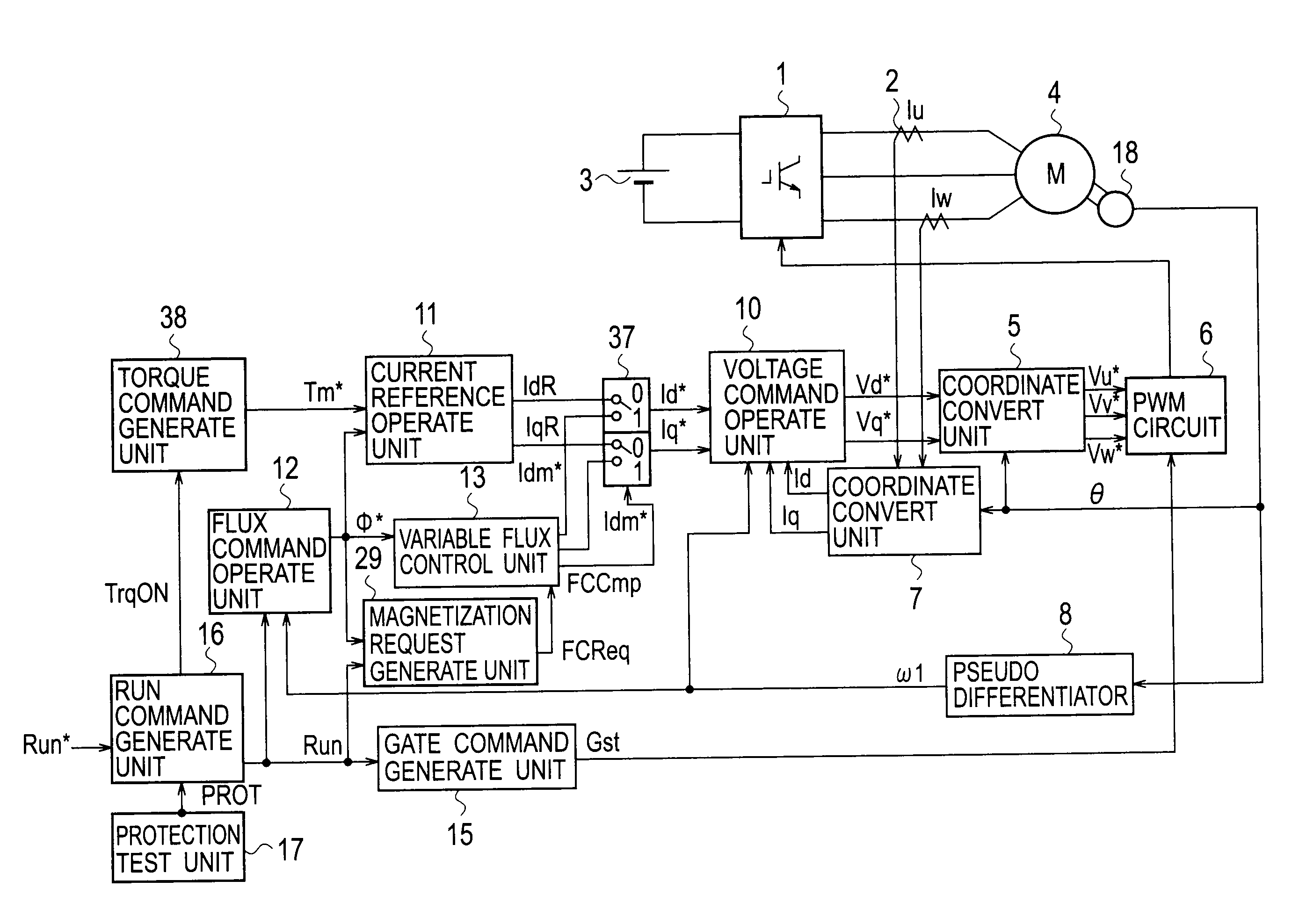
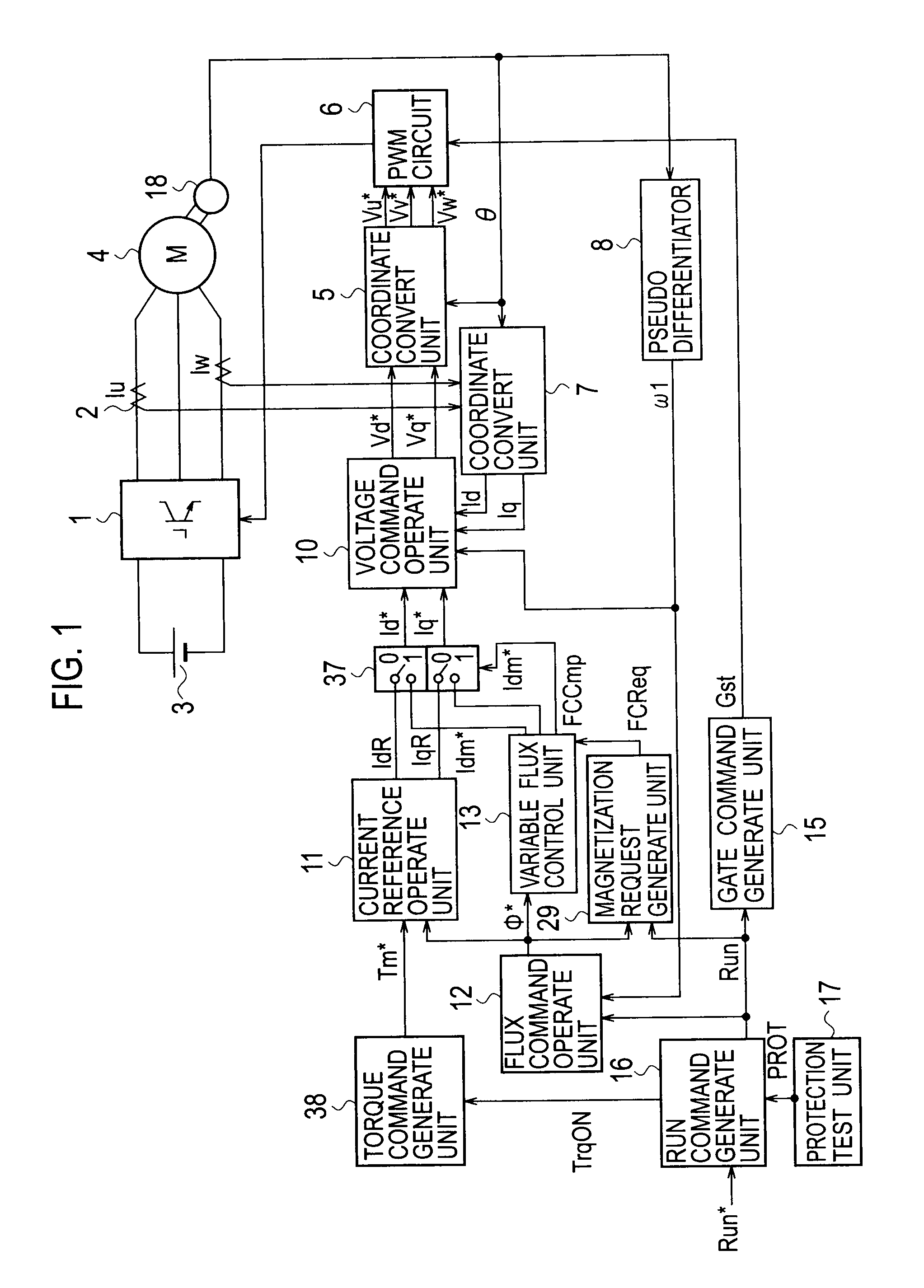
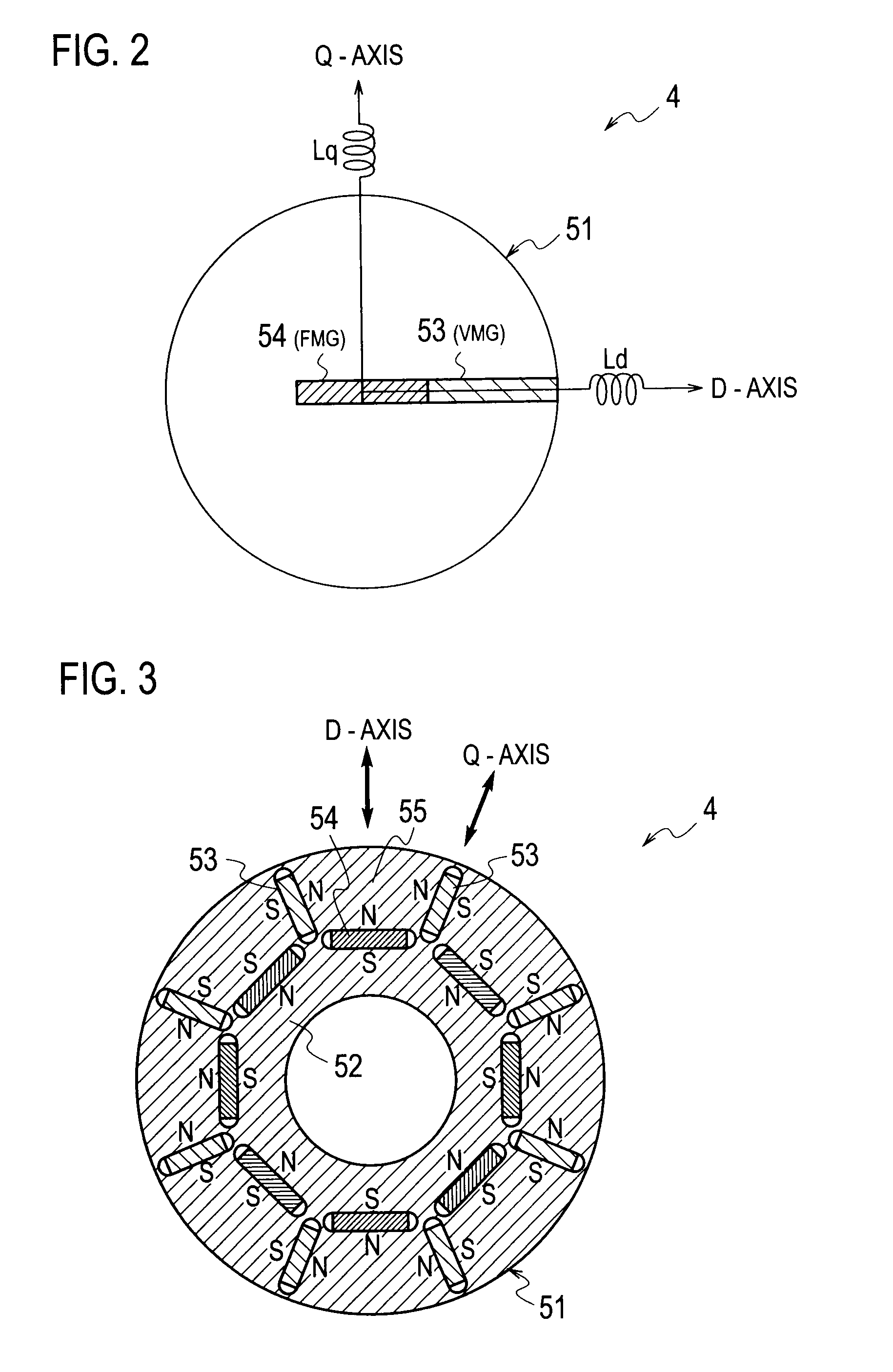
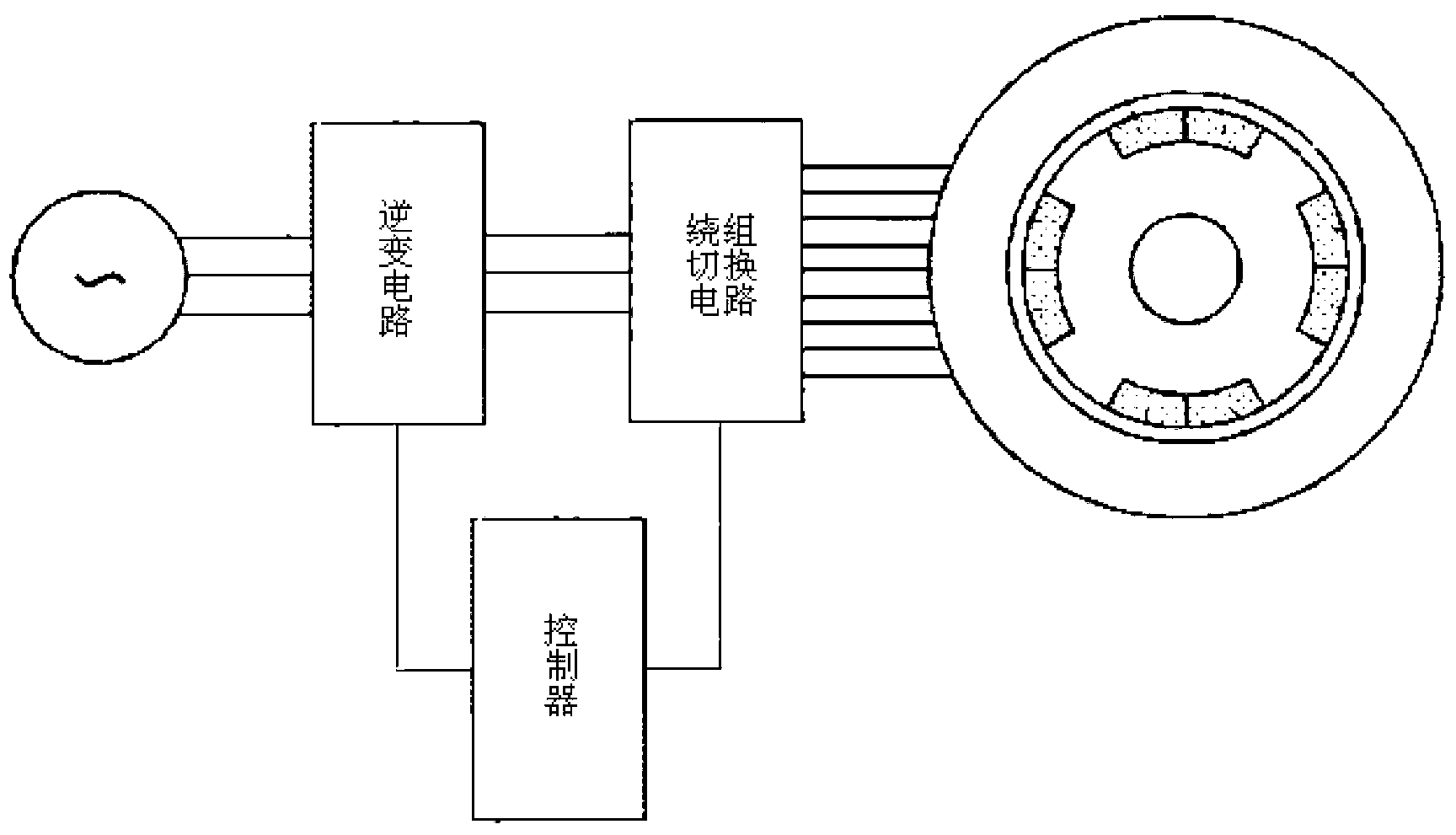
Variable-flux motor drive system
ActiveUS20090261774A1Prevent braking forceImprove securityMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlMotor drivePermanent magnet motor
A variable-flux motor drive system including a permanent-magnet motor including a permanent magnet, an inverter to drive the permanent-magnet motor, and a magnetize device to pass a magnetizing current for controlling flux of the permanent magnet. The permanent magnet is a variable magnet whose flux density is variable depending on a magnetizing current from the inverter. The magnetize device passes a magnetizing current that is over a magnetization saturation zone of magnetic material of the variable magnet. This system improves a flux repeatability of the variable magnet and a torque accuracy.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
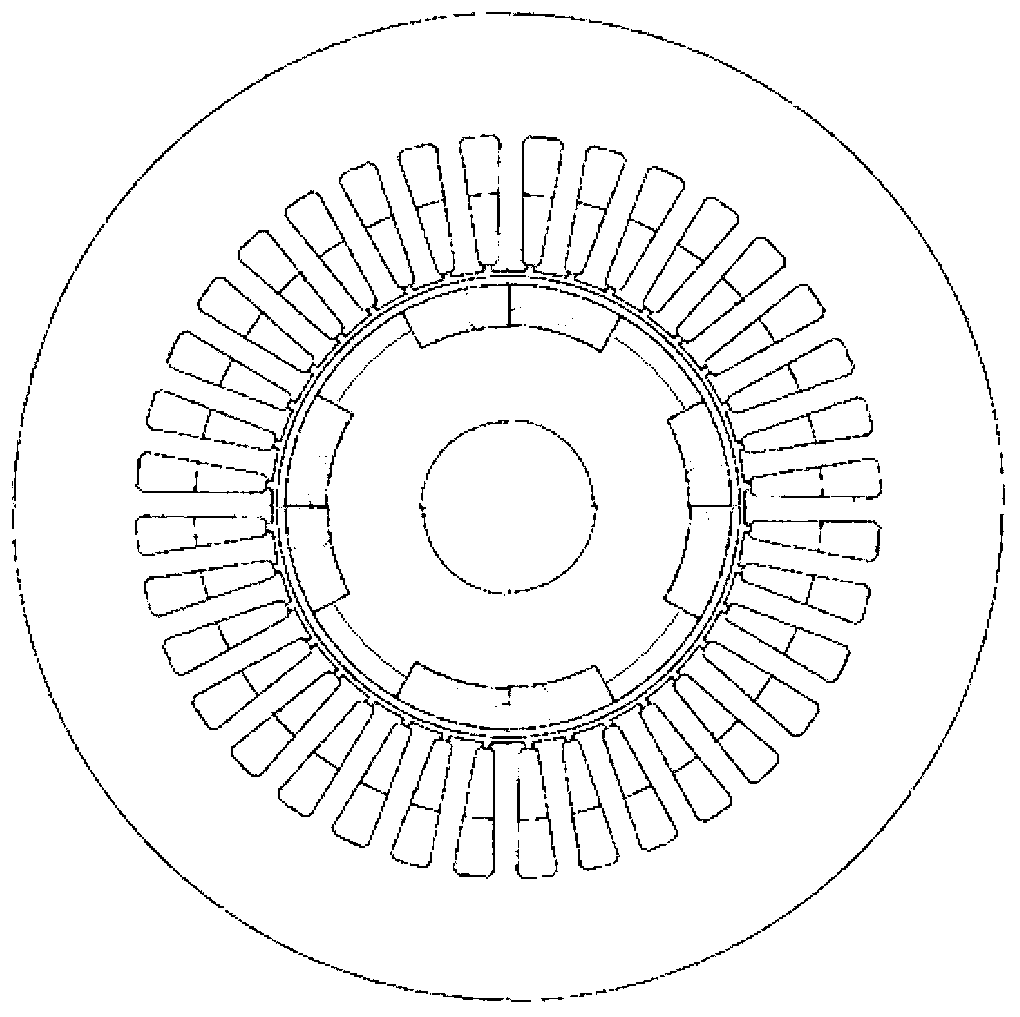
Rotor for Motor and Method for Producing the Same
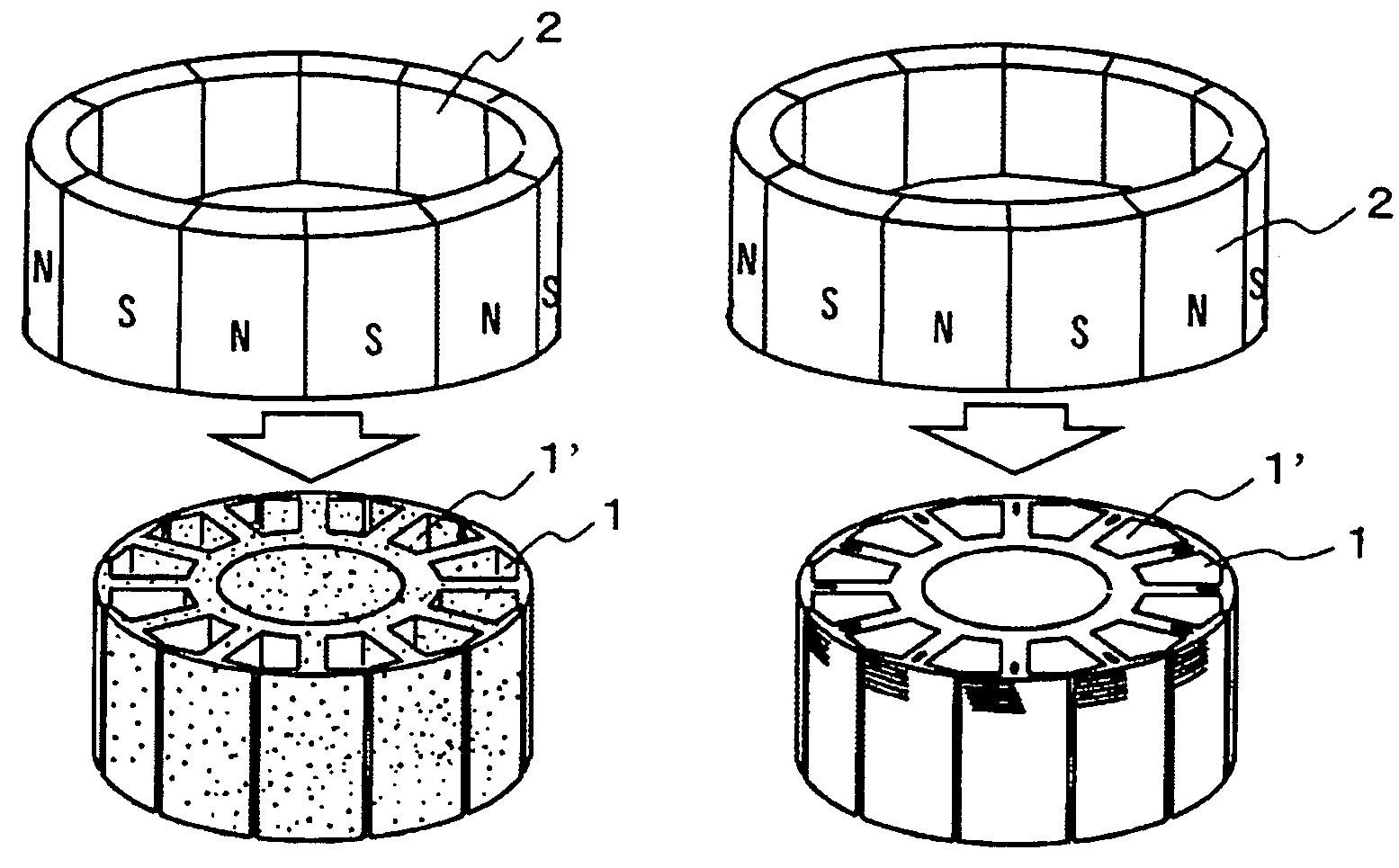
InactiveUS20080218007A1Stable and small in pole pitchSimple structureMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnetsStructural reliabilityMagnetization
A surface magnet type rotor and an inner magnet type rotor having good motor characteristics in which bonding strength is high between a magnet section and a soft magnetic yoke section, and structural reliability is high even in high speed use, and its producing method. The rotor comprises an anisotropic bond magnet section and a soft magnetic section wherein the anisotropic bond magnet section is preformed in magnetic field and then formed to be integrated with the soft magnetic section in nonmagnetic field. Subsequently, it is heat hardened to produce a surface magnet type rotor. Magnet units, each having a magnetic pole composed by bonding a pair of permanent magnets such that the directions of magnetization become symmetric with respect to the bonding surface, are linked such that magnetic poles of different polarities appear alternately on the magnetic action surface thus forming an anisotropic magnet body. Good motor characteristics can be attained by setting an angle to 5-40° between the direction of magnetization of the permanent magnet and a diametral direction passing the bonding surface.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Flux focusing arrangement for permanent magnets, methods of fabricating such arrangements, and machines including such arrangements
ActiveUS8400038B2Improve effective coercivityImprove efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetsConductor CoilDynamo
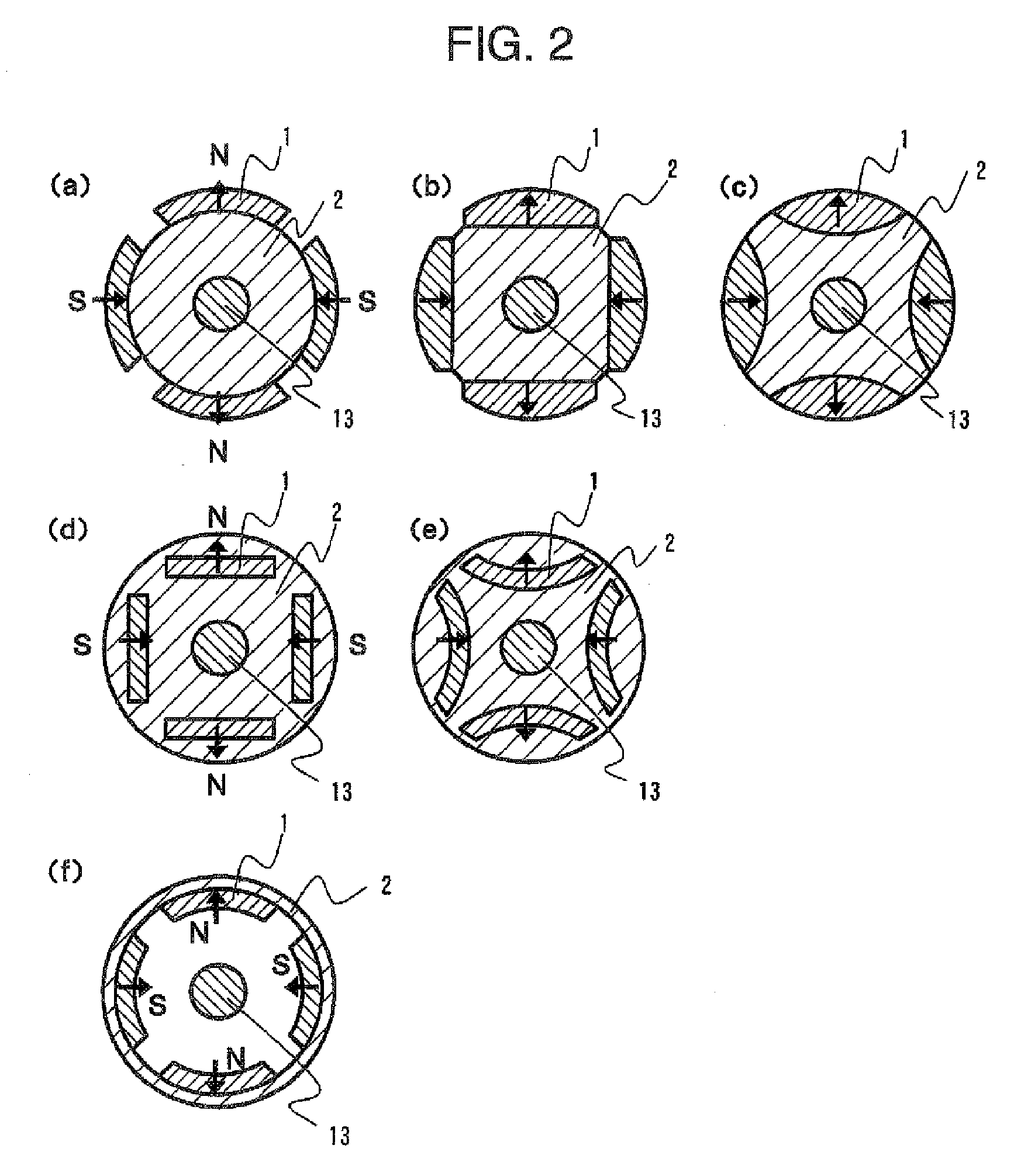
Numerous arrangements for permanent magnets are disclosed that can focus the flux produced by the magnets. Depending on the particular application in which the disclosed designs and techniques are used, efficiency and reliability may be increased by minimizing flux leakage, increasing peak flux density, and shaping the flux fields to improve the effective coercivity of the flux focusing permanent magnet arrangement when loaded, and to achieve customized voltage and current waveforms. The disclosed magnet assemblies may be incorporated into a machine, such as a motor / generator, having windings and may be disposed for movement relative to the windings. The magnet assembly may be mounted on a support formed of one or more ferromagnetic materials, such as a back iron The disclosed flux focusing magnet assemblies may be formed using a variety of manufacturing methods.
Owner:BWP GRP
Flux focusing arrangement for permanent magnets, methods of fabricating such arrangements, and machines including such arrangements
ActiveUS8397369B2Improve effective coercivityImprove efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesConductor CoilDynamo
Numerous arrangements for permanent magnets are disclosed that can focus the flux produced by the magnets. Depending on the particular application in which the disclosed designs and techniques are used, efficiency and reliability may be increased by minimizing flux leakage, increasing peak flux density, and shaping the flux fields to improve the effective coercivity of the flux focusing permanent magnet arrangement when loaded, and to achieve customized voltage and current waveforms. The disclosed magnet assemblies may be incorporated into a machine, such as a motor / generator, having windings and may be disposed for movement relative to the windings. The magnet assembly may be mounted on a support formed of one or more ferromagnetic materials, such as a back iron. The disclosed flux focusing magnet assemblies may be formed using a variety of manufacturing methods.
Owner:BWP GRP
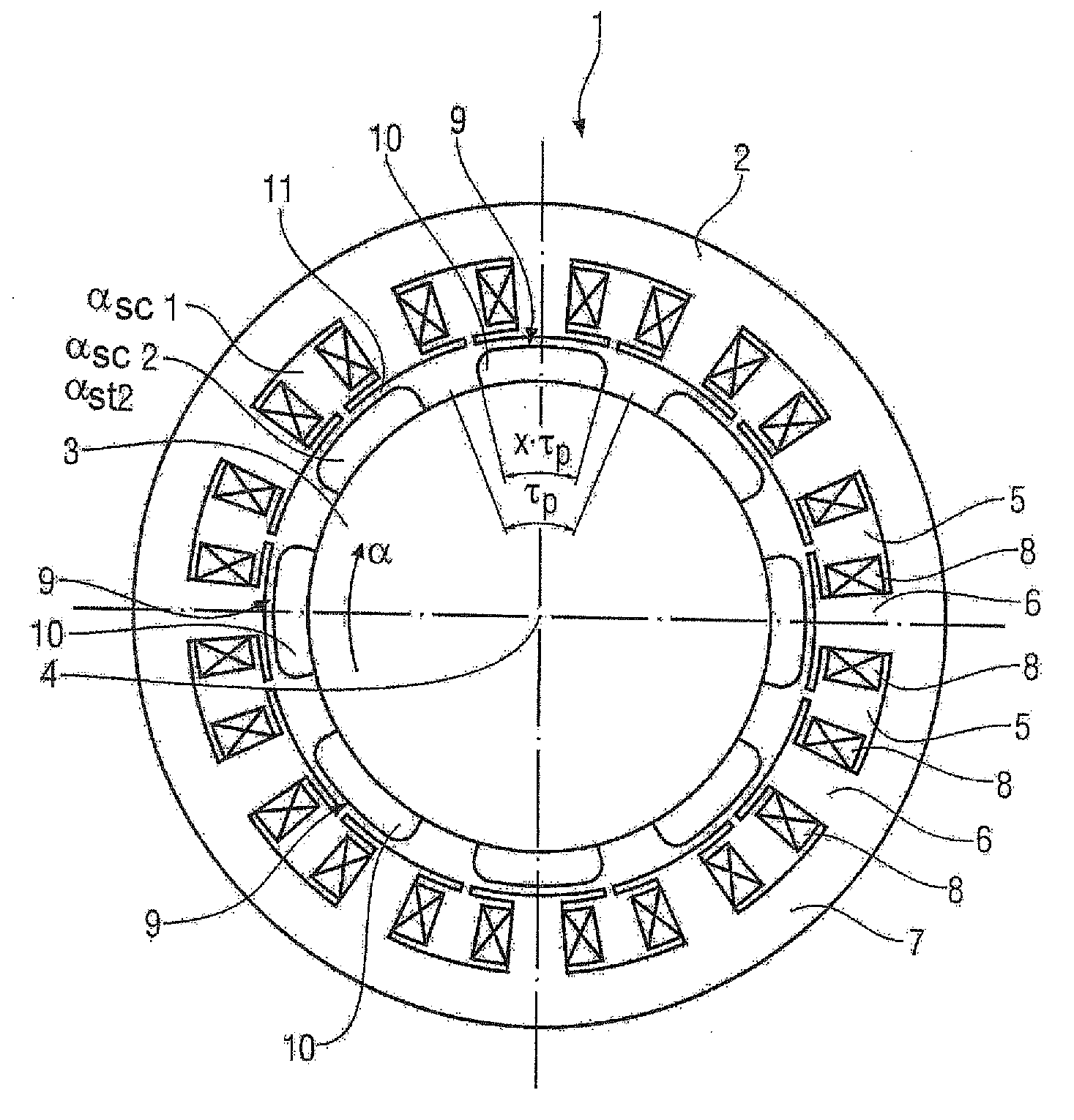
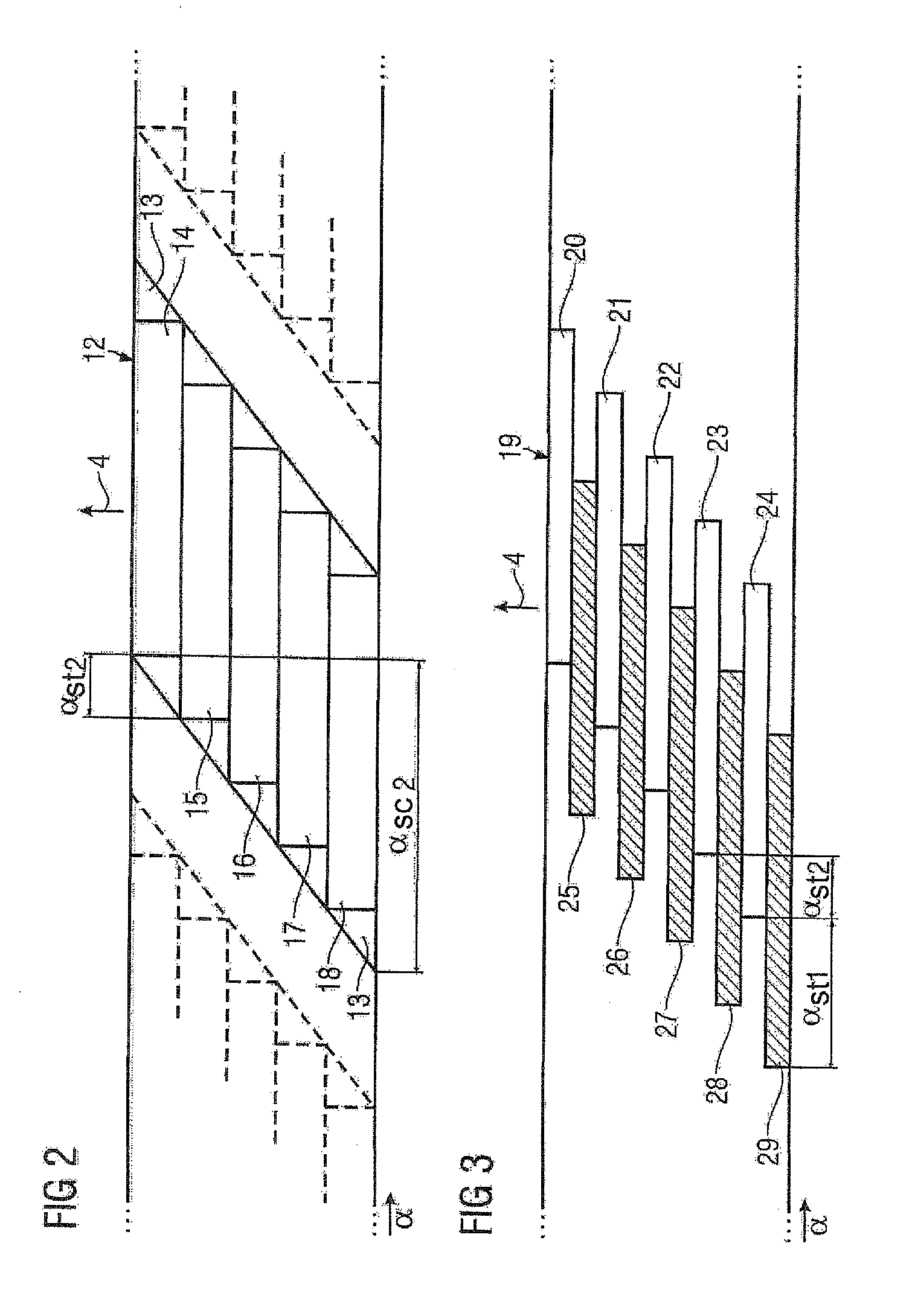
Permanent-magnet synchronous machine with suppression means for improving the torque ripple
InactiveUS20100264770A1Easy to manufactureEasy to solveMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPermanent magnet synchronous machineSkew angle
A permanent-magnet synchronous machine for suppressing harmonics includes a stator and a rotor with permanent magnets. Each permanent magnet represents a magnetic pole and is, when viewed in the circumferential direction of the rotor, shaped as a parallelogram or an arrow. The pole coverage is less than one. The permanent magnets are staggered at a staggering angle, wherein the permanent magnets of one pole are arranged in the axial direction with an increasing offset of a circumferential angle in relation to a first permanent magnet of this pole. Each permanent magnet is skewed at a skew angle defined by a circumferential angle of a projection of a tip portion of the parallelogram or arrow. The optimal skew and staggering angles are calculated from the design parameters for the stator and the number of pole pairs and the number of poles in the axial direction of the rotor.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and device for generating mechanical reciprocating bistable motion by virtue of electromagnetism
InactiveCN102214980AEfficient use ofImprove energy efficiency ratioDynamo-electric machinesLinear motionReciprocating motion
The invention relates to a method and device for generating mechanical reciprocating bistable-state motion by virtue of electromagnetism. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: jointing two identical permanent magnets symmetrically on a motion component; placing the parts, adhered to the permanent magnets, of the motion component between two magnetic pole air gaps of an alternating magnetic field; sucking, shutting and repelling the permanent magnets on the motion component repeatedly by virtue of two magnetic poles by the alternating magnetic field so as to drive the motion component to perform reciprocating motion; and regulating the position and structure between the motion component and the two magnetic poles of the alternating magnetic field, thus the motion component can be enabled to perform reciprocating swing and reciprocating linear motion. The invention also provides the device for generating mechanical reciprocating bistable motion by virtue of electromagnetism; through exciting or rotating the permanent magnets by an alternating power source, the alternating magnetic filed is formed on a soft magnet; and the parts, to which the permanent magnets are attached, of a swinging rod and a pushing rod are placed in the magnetic air gaps of the soft magnet. According to the invention, the characteristics of the permanent magnets that the permanent magnets are stressed in the alternating magnetic field and the permanent magnetic tends to be stable once being sucked with the magnetic poles of the alternating magnetic field are utilized, the structure of the device is simplified, and the state is maintained to be stable without energy consumption.
Owner:戴珊珊
Permanent magnet electrical machines and methods of assembling the same
ActiveUS20140265700A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesPermanent magnet rotorElectric machine
An electric machine comprising a permanent magnet rotor assembly is provided. The electric machine comprises a permanent magnet rotor assembly comprising a plurality of permanent magnets coupled to a rotor disk and a plurality of magnet shims coupled to the plurality of permanent magnets opposite the rotor disk. Each magnet shim of the plurality of magnet shims has a substantially complementary shape as a respective permanent magnet of the plurality of permanent magnets. The electric machine further comprises a stator core comprising a plurality of stator teeth that define a plurality of slots therebetween. At least one of the plurality of magnet shims is configured to direct magnetic flux from at least one of the plurality of permanent magnets to at least one stator tooth of the plurality of stator teeth.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AUSTRALIA PTY LTD
Permanent magnet rotor assembly provided with welded magnet retaining elements
The present disclosure is concerned with a permanent magnet rotor for an electric machine provided with an internal stator and a coaxial external rotor. To overcome the drawbacks associated with the use of an adhesive to mount the permanent magnets to the rotor body, permanent magnet retaining elements are mounted to the inner surface of the rotor, between adjacent magnets.
Owner:TM4 INC
Pole-changing control permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN103219816AReduce lossWide speed rangeMagnetic circuit rotating partsLow speedSynchronous motor
The invention discloses a pole-changing control permanent magnet synchronous motor, relating to a pole-changing control permanent magnet synchronous motor system and belonging to the field of motors. The synchronous motor is characterized in that permanent magnets of a rotor (secondary) are divided into strong-magnetism permanent magnets and weak-magnetism permanent magnets, wherein the weak-magnetism permanent magnets are not magnetized before the operation of the motor, magnet limbs and grooves at / in the surface of the air gap side of the rotor (secondary) are alternatively arrayed along the directions of relative motions of the rotor (secondary) and a stator (primary), the strong-magnetism permanent magnets and the weak-magnetism permanent magnets are alternatively arrayed along the directions of relative motions of the rotor (secondary) and the stator (primary) according to a certain rule; and the strong-magnetism permanent magnets are embedded into the grooves, and the weak-magnetism permanent magnets are fixed on the surfaces of the magnet limbs. According to the pole-changing control permanent magnet synchronous motor, in an application process, the polarity of the magnetic field of the rotor (secondary) can be controlled according to a direct-axis component of the current of the stator (primary), the changing of the number of poles of the main magnetic field of the motor is realized, and furthermore, and the torque (push force) in low speed of the motor and the efficiency in high speed of the motor are improved, so that the speed adjustable range of the motor is broadened.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Permanent-magnet-biased axial magnetic bearing
InactiveCN102562800ASimple structureEasy to controlShaftsEngine componentsMagnetic bearingMagnetic poles
The invention discloses a permanent-magnet-biased axial magnetic bearing in the technical field of magnetic bearings. The permanent-magnet-biased axial magnetic bearing comprises a stator assembly and a rotor assembly; the stator assembly comprises an axial stator, an axial control winding, a septum magnet, a magnetizer and a permanent magnet; the rotor assembly comprises a rotation shaft and a rotor core; the axial control winding is wound on a magnetic pole of the axial stator; the rotor core is sleeved on the rotation shaft; the magnetizer is arranged in the axial stator, and the external end of the magnetizer is connected with the internal end of the axial stator; the septum magnet is arranged in the axial stator, the external end of the septum magnet is connected with the internal end of the axial stator; the permanent magnet is adhered to one side of the magnetizer, and the external end of the permanent magnet is contacted with the inner end face of the septum magnet; and the rotor core is arranged in the axial stator. The permanent-magnet-biased axial magnetic bearing has a simple structure, and is high in critical rotation speed, and low in power consumption; and magnetic flux flows in an axial direction and is decoupled with the radial suspension force completely, so the permanent-magnet-biased axial magnetic bearing is convenient to control.
Owner:NANJING COLLEGE OF CHEM TECH
Permanent magnet coupling mechanism between shafts
InactiveCN103326541ACreative optimizationChange areaDynamo-electric gearsPermanent magnet rotorCoupling
The invention relates to a permanent magnet coupling mechanism between shafts. The permanent magnet coupling mechanism between the shafts is used for transmitting torque between the two rotating shafts. The mechanism comprises a permanent magnet rotor and a conductor rotor, wherein a conical air gap is formed between the permanent rotor and the conductor rotor. A permanent magnet on the permanent magnet rotor comprises main magnets and auxiliary magnets. The multiple main magnets are circumferentially distributed. A magnetizer made of permeability magnetic materials is arranged between every two adjacent main magnets. One auxiliary magnet is arranged on one side, away from the conductor rotor, of each magnetizer. The directions of the magnetic poles of the main magnets are located in the circumferential direction of the permanent magnet rotor. The directions of the magnetic poles of the adjacent main magnets are in the face-to-face direction or the back-to-back direction. The directions of the magnetic poles of the auxiliary magnets are the radial directions of the permanent magnet rotor. The directions of the magnetic poles of the adjacent auxiliary magnets are opposite. The magnetic poles of the positions of the side faces where the two main man magnets and one auxiliary magnet are contacted with the same magnetizer are respectively the same polarity. The permanent magnet coupling mechanism between the shafts is large in transmitting torque, adjustable in transmitting torque, compact in structure, convenient to install, and stable and reliable in transmission and adjustment.
Owner:JIANGSU MAGNET VALLEY TECH
Permanent magnet traction device with wider speed increasing range
InactiveCN101752922ASimple structureReasonable structureMagnetic circuit rotating partsConstant powerMagnetic poles
The invention relates to a permanent magnet traction device with wider speed increasing range, which is used for improving the speed increasing performance of a permanent magnet; the technical proposal is that: a plurality of the permanent magnets are embedded in a rotor, the permanent magnets are cuboid and are arrayed along the circumference which is coaxial with the rotor, every four permanent magnets form one group, the cross sections of the four permanent magnets form a W-shaped permanent magnet, and the synthesized magnetizing direction of the same W-shaped permanent magnet is consistent radially, and the synthesized magnetizing direction of the two adjacent W-shaped permanent magnets is opposite, and the W-shaped permanent magnets form a magnetic pole of the rotor; in the invention, the arraying mode of the embedded permanent magnets and a magnetic circuit structure of the rotor are more rational, thereby expanding the constant power speed adjustable range of a permanent magnet synchronization traction motor and improving the weak magnetism speed expanding performance of the permanent-magnet motor; in addition, the permanent magnet traction device has simple structure and is easy to produce and manufacture, the raw material is saved and the efficiency is high.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Non-contact transmission friction-electromagnetic composite wave energy collector adapted to complex excitation
ActiveCN111682794ABroadbandImprove sealingMachines/enginesPermanent-magnet clutches/brakesUniversal jointMechanical drive
The invention relates to a non-contact transmission friction-electromagnetic composite wave energy collector adapted to complex excitation. The device collector comprises a floating ball, a rocker, alifting rod and a frequency-increasing electromagnetic power generation assembly, the floating ball is rigidly connected with the top of the rocker; the bottom end of the rocker is connected with thelifting rod through a universal joint; an electret rolling ball capable of rolling is arranged in the floating ball; a metal pole I and a metal pole II are arranged on the lower surface in the floating ball; the lifting rod is arranged in a lifting sleeve; a spring is arranged between the lifting rod and the lifting sleeve; a driving permanent magnet combination is arranged on the lifting rod; thelower end of the lifting sleeve is connected with a frequency-increasing electromagnetic power generation assembly, the frequency-increasing electromagnetic power generation assembly is provided witha driven permanent magnet combination, the driving permanent magnet combination is in magnetic coupling connection with the driven permanent magnet combination, the driven permanent magnet combination is in mechanical transmission connection with a power generation permanent magnet, and the power generation permanent magnet is correspondingly provided with a power generation induction coil. The collector can effectively work in a marine all-weather climate environment, adapts to complex wave excitation, and has a frequency increasing function and high reliability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Electric grinding device
ActiveCN105598797AHigh torqueLarge acting fluxPortable grinding machinesManicure/pedicureBiological bodyMagnetic poles
The invention discloses an electric grinding device which comprises a swing motor and a grinding head driven by the swing motor. The swing motor comprises a U-shaped magnet yoke, four permanent magnets and a swing arm. Two supporting legs of the U-shaped magnet yoke are wound by coils. The end faces of the two supporting legs can produce alternating magnetic poles under the control of a control circuit. The four permanent magnets comprise the first permanent magnet, the second permanent magnet, the third permanent magnet and the fourth permanent magnet which are sequentially distributed on the same circle with the supporting point as the circle center. The radial end face of the first permanent magnet and that of the fourth permanent magnet are the same in polarity. The control circuit produces alternating pulses with the adjustable pulse width, and the movement direction of the permanent magnets alternately changes, so that reciprocated swing is formed, the swing arm drives the grinding head to slightly swing at a high speed in a reciprocated mode, and the body surfaces (such as skin and fingernails) of the living bodies (such as the human body and animals) are cleaned.
Owner:胡建坤
Dual-rotor flux-switching motor for vehicle
ActiveCN105356699AIncreased torque output capabilityImprove power densityMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsThree-phaseRotor flux
The present invention discloses a dual-rotor flux-switching motor for a vehicle. A stator is formed by three-phase armature winding, Ns stator core modules and Ns armature slots, Ns=3Nc, and Nc is the coil number of single-phase windings. The Ns stator core modules are uniformly distributed along a circumferential direction. An armature slot is arranged between each two stator core modules, and the three-phase armature winding is placed in the armature slots. A hybrid permanent magnet module is fixedly embedded at the middle of each of the stator core modules along a radial direction. Each of the hybrid permanent magnet modules is formed by a ferrite permanent magnet and two identical NdFeB permanent magnets, and the ferrite permanent magnet and the NdFeB permanent magnets at two sides are closely and seamlessly connected. A significant series magnetic circuit is formed in the magnet flux path of two adjacent permanent magnets. Compared with a traditional magnet flux switching permanent magnet motor in a parallel magnetic circuit, the stator tooth part easy saturation problem is significantly improved, and the utilization rate of the permanent magnet is effectively improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Dual-stator hybrid permanent-magnet memory motor
PendingCN108347145AGuaranteed Power DensitySave materialMagnetic circuit stationary partsMemory motorPower density
The invention discloses a dual-stator hybrid permanent-magnet memory motor. The dual-stator hybrid permanent-magnet memory motor comprises a first stator, a second stator, a rotor, an U-shaped statorcore, an Al-Ni-Co permanent magnet and a NdFeB permanent magnet, wherein the stators and the rotor are of salient pole structures, the first stator and the second stator are opposite in positions, therotor is arranged between the two stators, the U-shaped stator core is uniformly wound to form a round shape, the two permanent magnets are embedded between two stator teeth, the NdFeB permanent magnet is near to the rotor, the permanent magnet on the single stator are alternatively magnetized along a circumferential direction, and the magnetization directions of the permanent magnets at oppositepositions of the two stators are opposite. By the dual-stator hybrid permanent-magnet memory motor, the power density of the motor can be effectively improved, the magnetization states of the permanent magnets are changed by applying a pulse current to a magnetic adjustment coil so as to expand a running range of the motor, and the problem of excessively large torque among tooth grooves of the motor is effectively solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
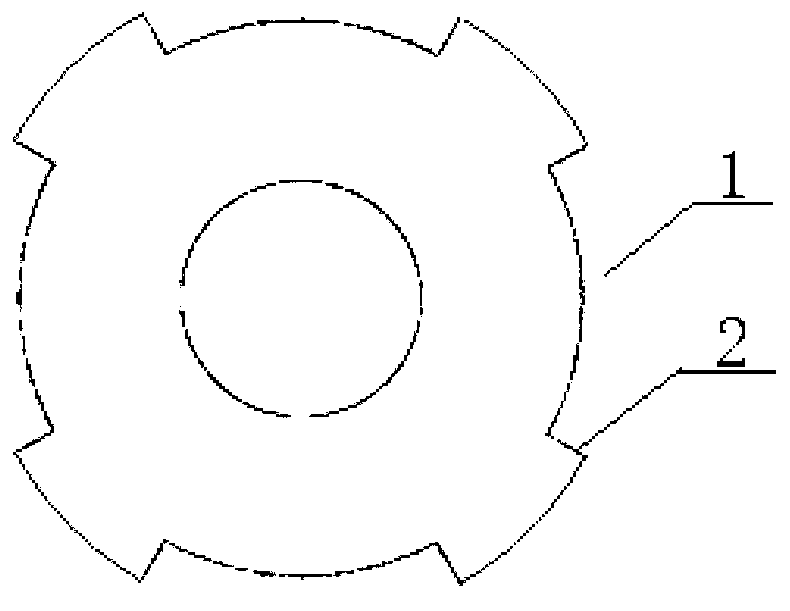
Rotor punching sheet for permanent-magnet motor of electric vehicle
PendingCN108110927AHarmonic reductionReduce torque rippleMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinesPunchingMagnetic reluctance
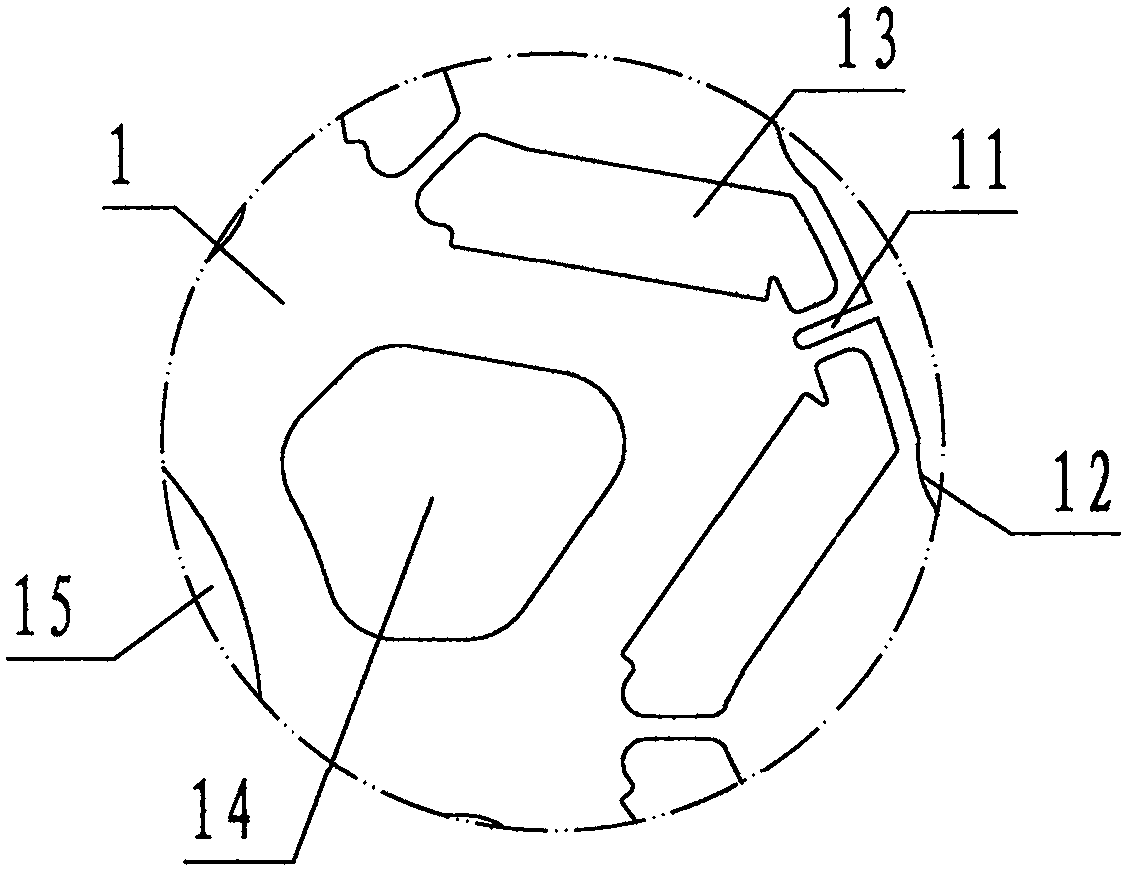
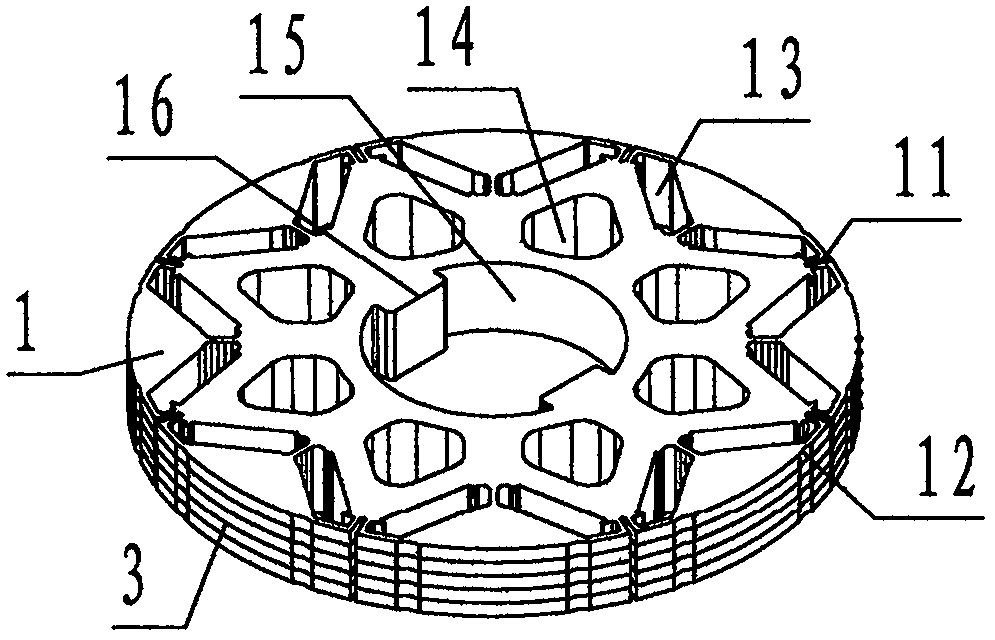
The invention discloses a rotor punching sheet for a permanent-magnet motor of an electric vehicle. The rotor punching sheet comprises a sheet base (1), wherein the sheet base (1) is provided with magnetic isolation grooves (11), magnetic gap notches (12), permanent-magnet holes (13), weight reduction holes (14), a rotation shaft hole (15) and tenon keys (16). During application, a plurality of sheet bases are correspondingly superposed to form a rotor core, the rotation shaft hole is used for fixedly connecting a rotor shaft, the permanent-magnet holes are used for fixedly bearing permanent magnets, and thus, a permanent-magnet motor rotor is formed; during working and on the basis of a principle that air reluctance larger than iron core reluctance, the magnetic isolation grooves are usedfor improving reluctance, magnetic short-circuit is reduced, and the output power of the permanent-magnet motor rotor is improved; the magnetic gap notches are used for balancing distribution densityof a magnetic line, local enrichment of the magnetic line is suppressed, the torque pulse amplitude of the permanent-magnet motor rotor is reduced, and the torque fluctuation is smoothed; and the weight reduction holes are used for reducing weight and material cost, the technical scheme of an air-cooling passage of a cooling rotor is formed, so that the permanent-magnet motor of the electric vehicle achieves the purposes of reducing harmonic, torque pulse and cost and improving efficiency.
Owner:山东双林新能源科技有限公司
Rotor for motor and method for producing the same
InactiveUS8039998B2Stable and small in pole pitch and dispersionHigh in output and efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsInorganic material magnetismStructural reliabilityMagnetic poles
A surface magnet type rotor and an inner magnet type rotor having good motor characteristics in which bonding strength is high between a magnet section and a soft magnetic yoke section, and structural reliability is high even in high speed use, and its producing method. The rotor comprises an anisotropic bond magnet section and a soft magnetic section wherein the anisotropic bond magnet section is preformed in magnetic field and then formed to be integrated with the soft magnetic section in nonmagnetic field. Subsequently, it is heat hardened to produce a surface magnet type rotor. Magnet units, each having a magnetic pole composed by bonding a pair of permanent magnets such that the directions of magnetization become symmetric with respect to the bonding surface, are linked such that magnetic poles of different polarities appear alternately on the magnetic action surface thus forming an anisotropic magnet body. Good motor characteristics can be attained by setting an angle to 5-40° between the direction of magnetization of the permanent magnet and a diametral direction passing the bonding surface.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
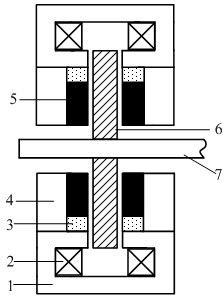
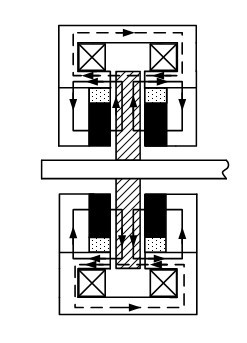
Direct-acting bidirectional proportion electromagnet
ActiveCN104361973ASmall impactFast dynamic responseElectromagnets with armaturesEngineeringMagnetic loop
A direct-acting bidirectional proportion electromagnet comprises a magnetism isolating ring, a first guide sleeve, a second guide sleeve, an armature, a push rod, a control coil and a coil retainer, wherein a groove is formed in the circumferential direction of the coil retainer which is used for winding the control coil to form a current excitation source; cylindrical pole shoes of the first guide sleeve and the second guide sleeve are opposite to a cylinder outside the armature and are an airgap away from each other to form a left pole shoe pair and a right pole shoe pair, of which the airgaps are equal; the magnet poles of the same nature of a first permanent magnet and a second permanent magnet are respectively attracted by the left end and the right end of the armature; the other magnet pole of the first permanent magnet attracts a first magnetic-conductive part, and the other magnet pole of the second permanent magnet attracts a second magnetic-conductive part; the two poles of the first and second permanent magnets, together with the first guide sleeve and the second guide sleeve, form a first permanent magnet field and a second permanent magnet field respectively through the first magnetic-conductive part or the second permanent magnet; the armature push rod is connected with the armature; the first guide sleeve and the second guide sleeve are respectively at two sides of the magnetism isolating ring and are connected with the magnetism isolating ring.
Owner:沛县度创科技发展有限公司
Passive magnetorheological tensile damping adaptive control method and device
ActiveCN101915282ACompact structureOverall small sizeNon-rotating vibration suppressionSoft magnetMechanical energy
The invention discloses passive magnetorheological tensile damping adaptive control method and device. A soft magnet inner cylinder is arranged in an outer cylinder, both ends of a giant magnetostrictive material arranged in the soft magnet inner cylinder are respectively connected with one end of an upper permanent magnet and one end of a lower permanent magnet, the other end of the upper permanent magnet and the other end of the lower permanent magnet are respectively connected with one end of an upper field yoke and one end of a lower field yoke, the other end of the upper field yoke is connected with one end of a piston rod in the soft magnet inner cylinder, the other end of the piston rod extends out of an end cover, a T-shaped guide piston is arranged in a hole at the lower end of the soft magnet inner cylinder, the other end of the lower field yoke is connected with the large end of the T-shaped guide piston, and the small end of the T-shaped guide piston is sleeved with a spring and arranged in a center hole of a bottom cover; an input magnetic loop is formed by adopting the permanent magnets, the field yokes and magnetorheological fluid media; and an output magnetic loop is formed by adopting the giant magnetostrictive material, the permanent magnets, the field yokes, the magnetorheological fluid media and soft magnet materials. The invention omits coils and an external power supply and can realize the conversion from vibration mechanical energy of a controlled structure to magnetic field energy by only using few materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
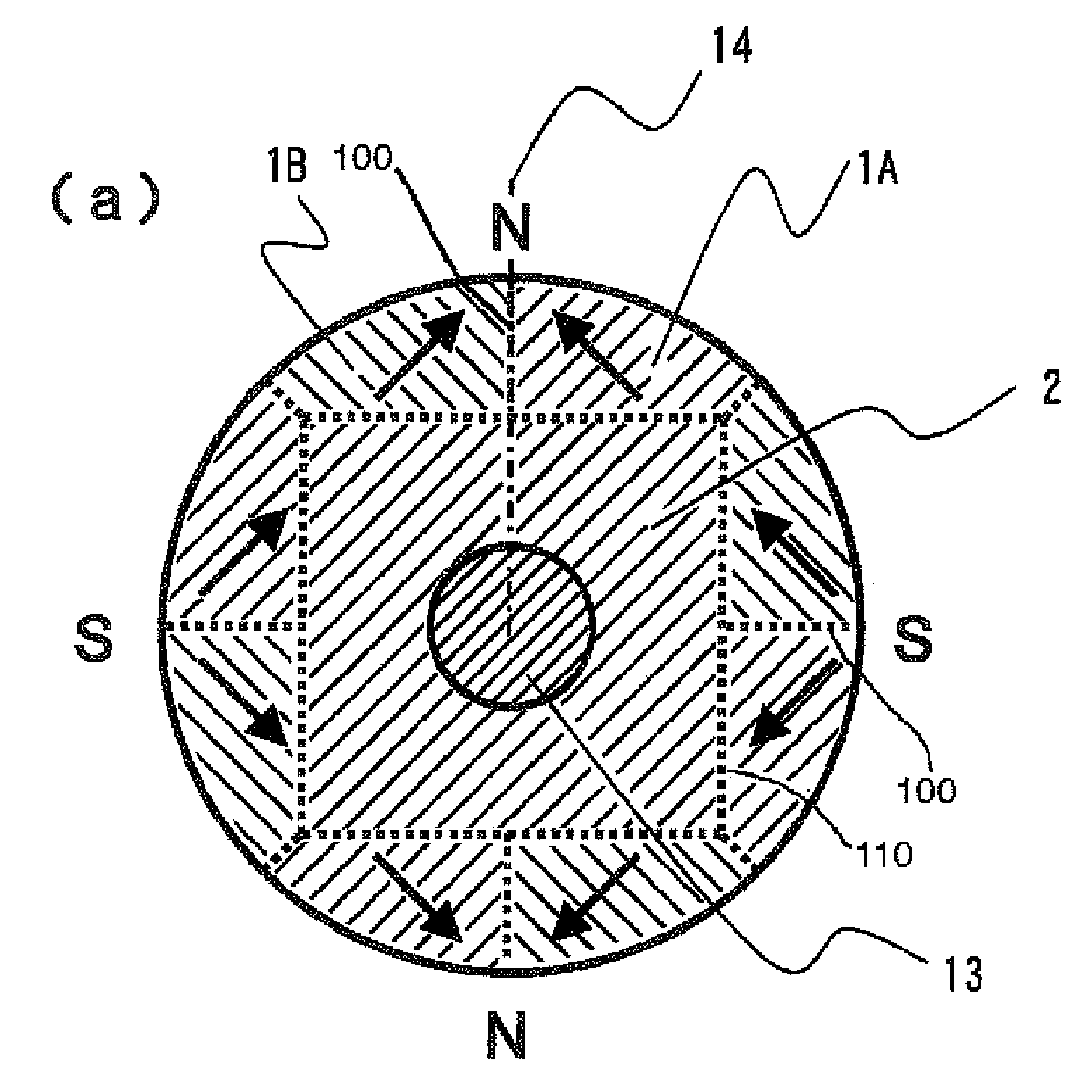
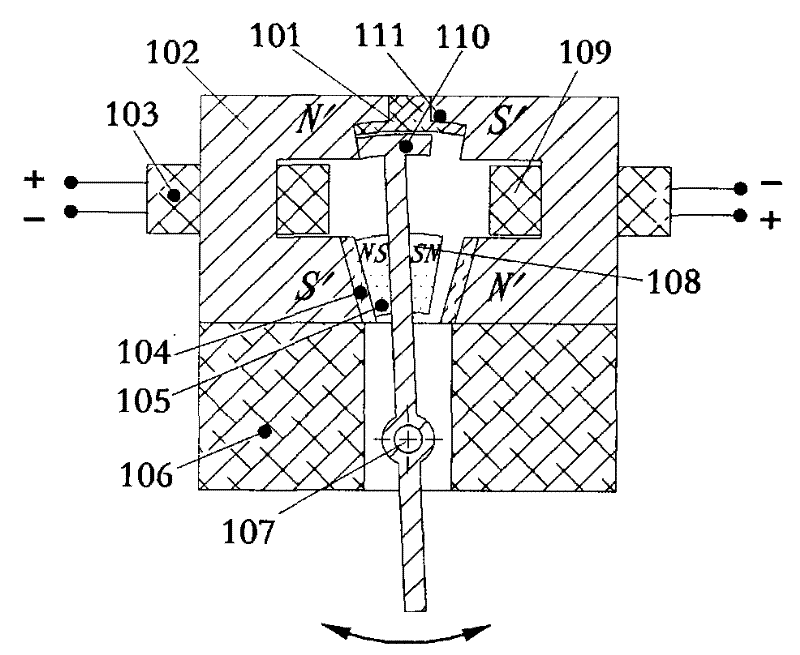
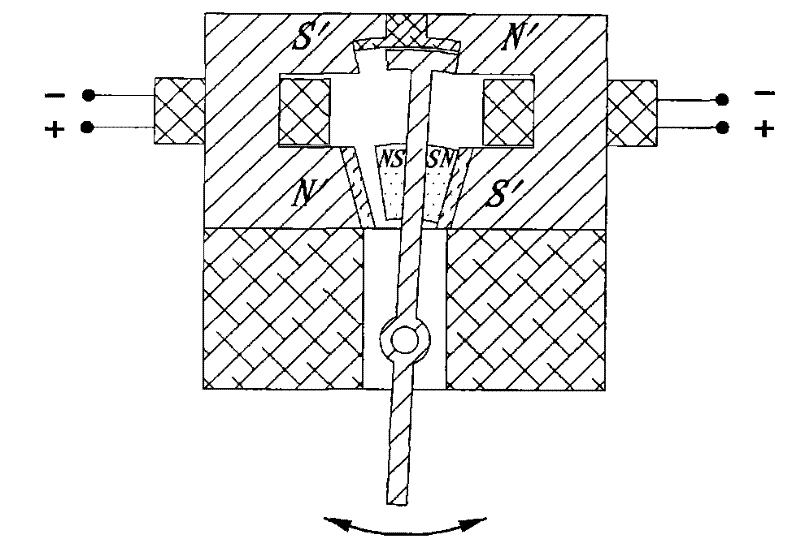
Electro-permanent magnet for power microwave tubes
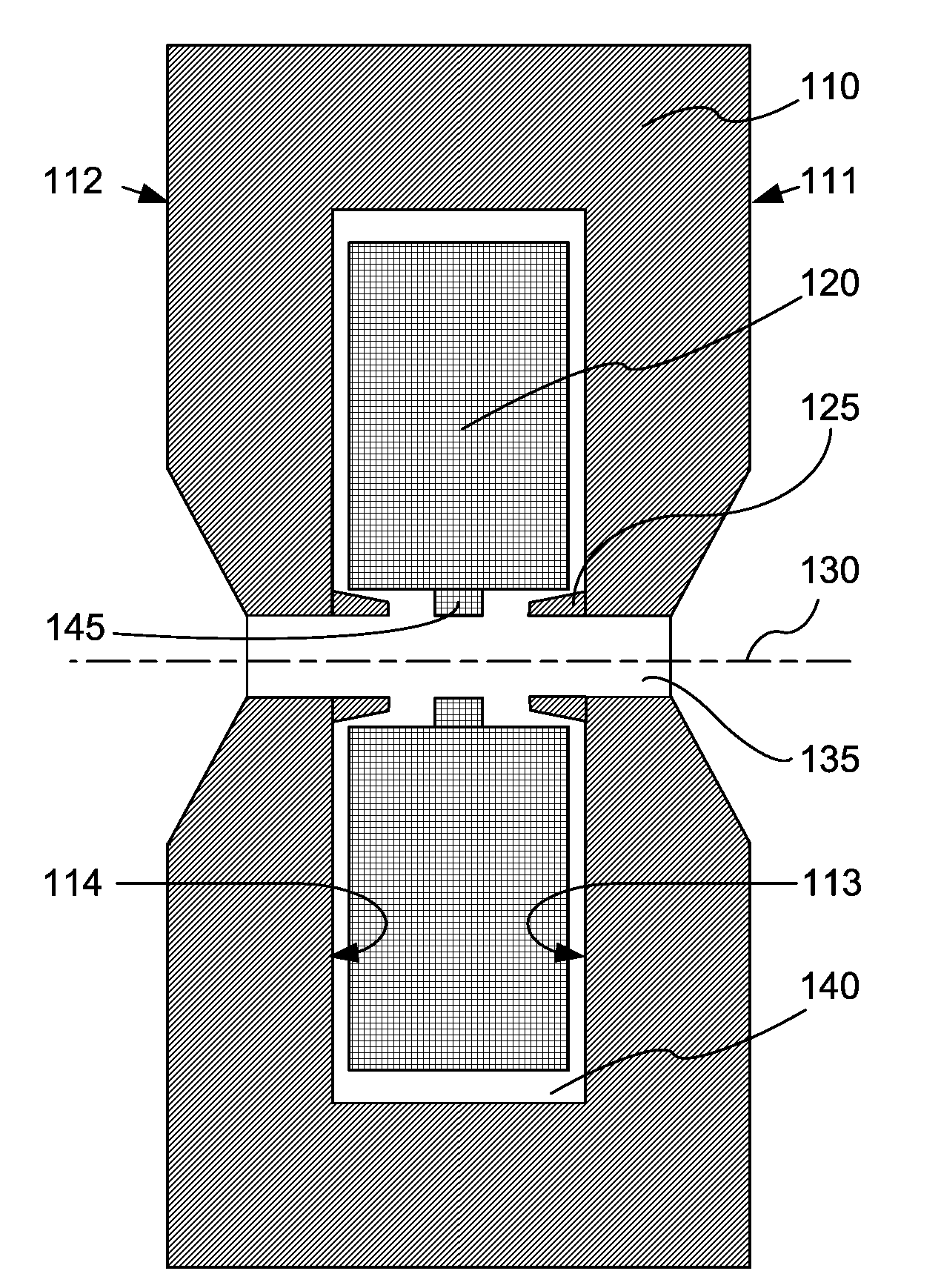
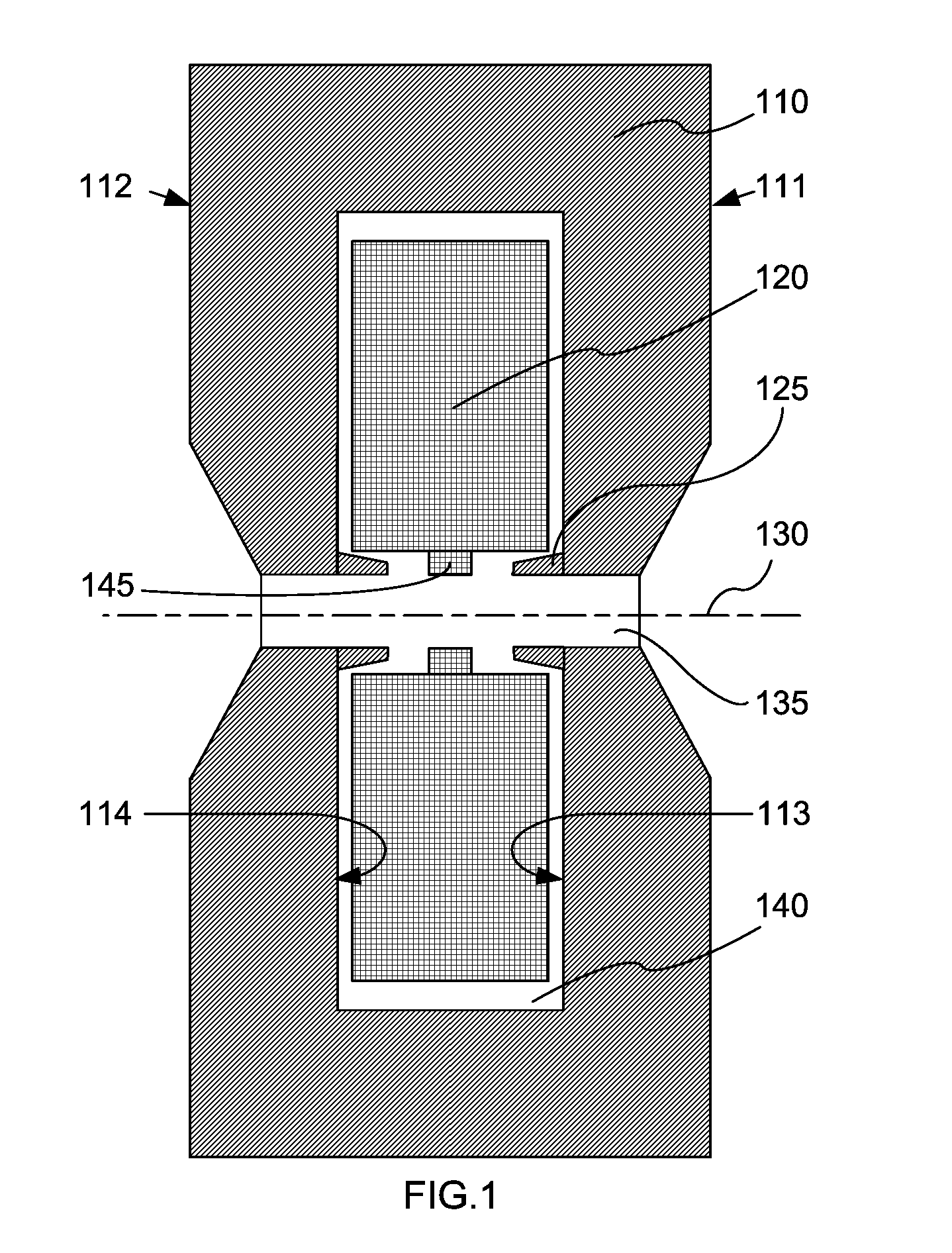
InactiveUS20080018255A1Small sizeHigh magnetic flux densityTransit-tube focussing arrangementsPermanent magnetsResonant cavityMicrowave tube
A magnet configuration for a power microwave tube with a resonant cavity comprises a permanent magnet (110) with an axis-aligned through-bore (135) of sufficient size to contain the resonant cavity. The permanent magnet has an inner chamber (140) that is centered on the axis (130) with opposite magnet poles aligned along the axis. The magnet configuration further comprises an electromagnet coil (120) fitting in the chamber and encircling the axis such that the coil produces a magnetic field that reinforces the magnetic field from the permanent magnet. An optional protrusion (125) spanning the through-bore narrows an air gap between the poles. The method provides a magnetic field in a power microwave generator by combining a permanent magnet with an electromagnet in accordance with the magnet configuration and energizes the electromagnetic coil, which may be by pulsing the coil current.
Owner:BARNETT LARRY R
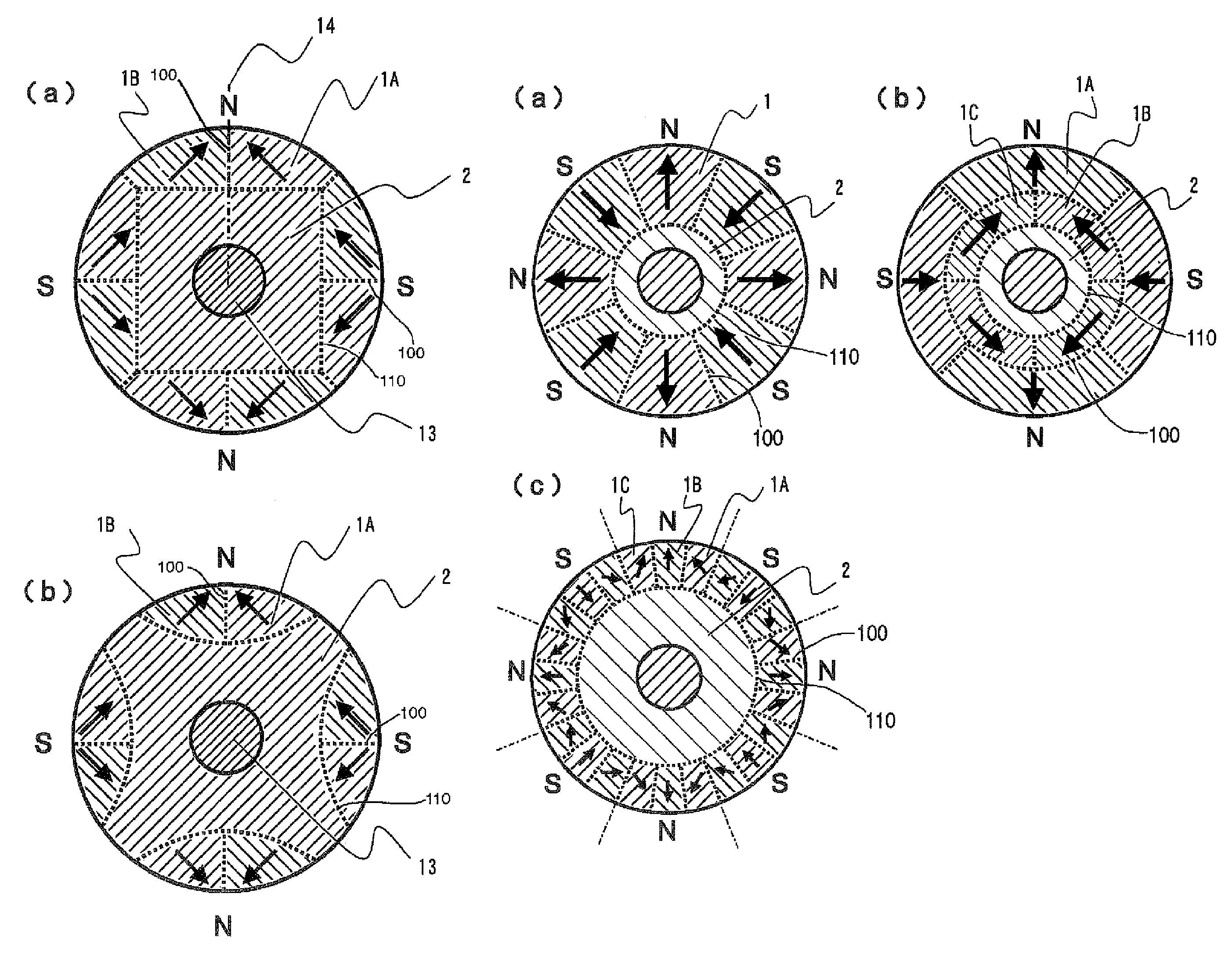
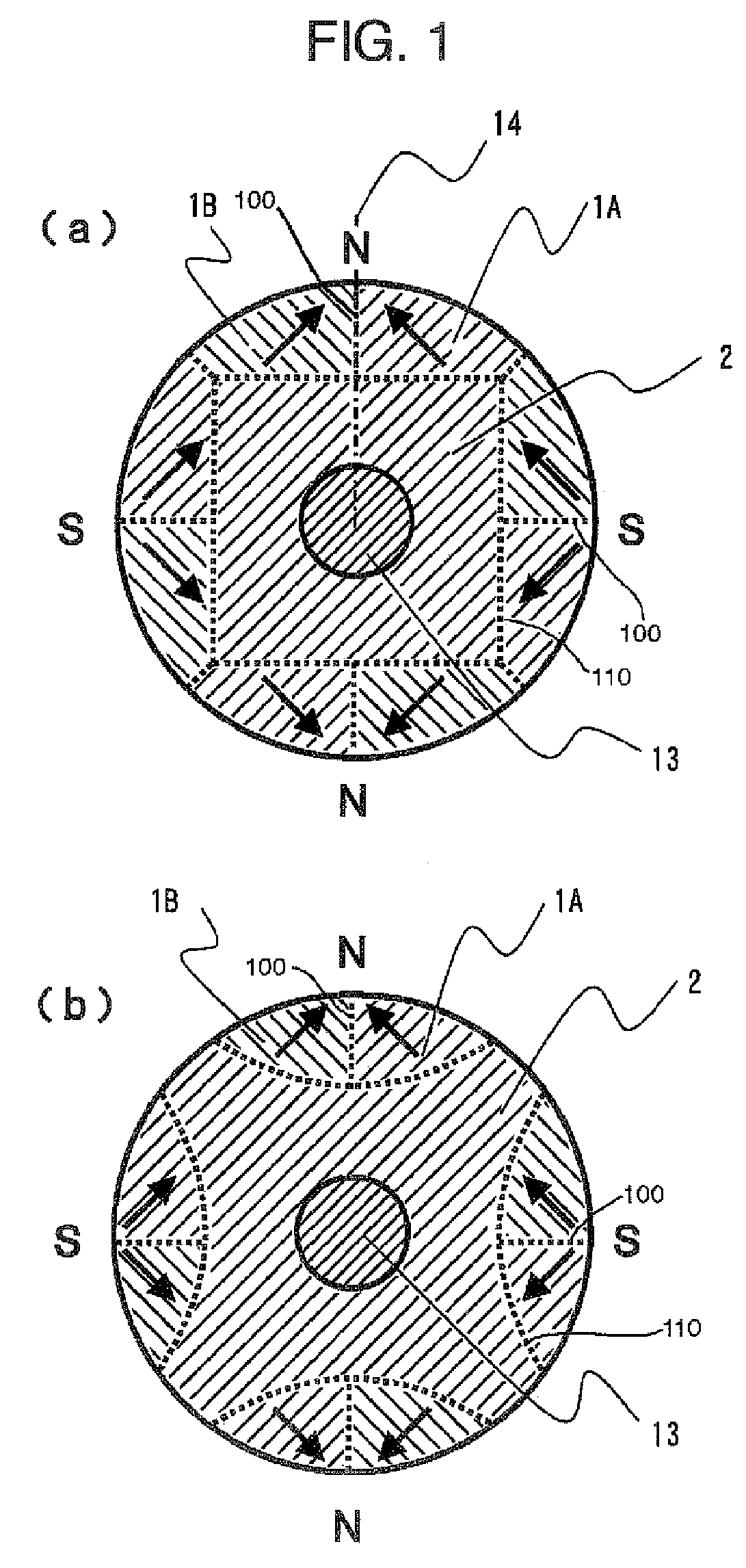
Mixed type excitation permanent magnet, rotor for rotating electric machine using same and generator
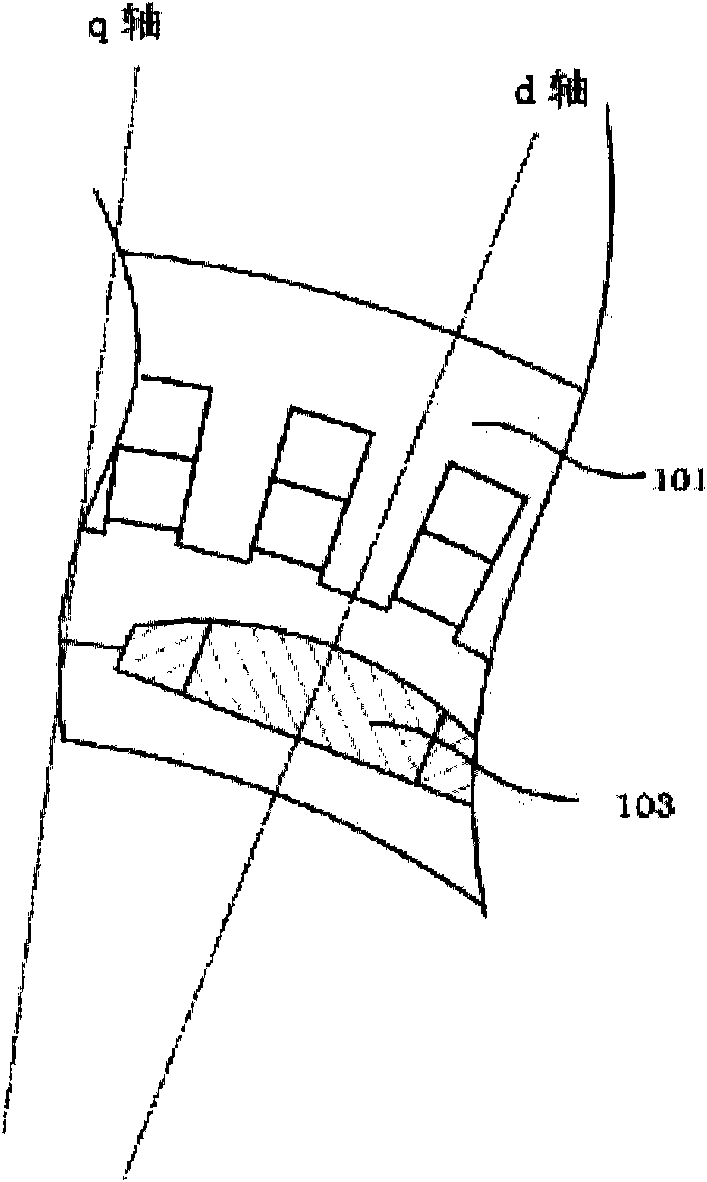
InactiveCN102611216AReduce inputMiniaturizationMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnetsHybrid typeResidual flux
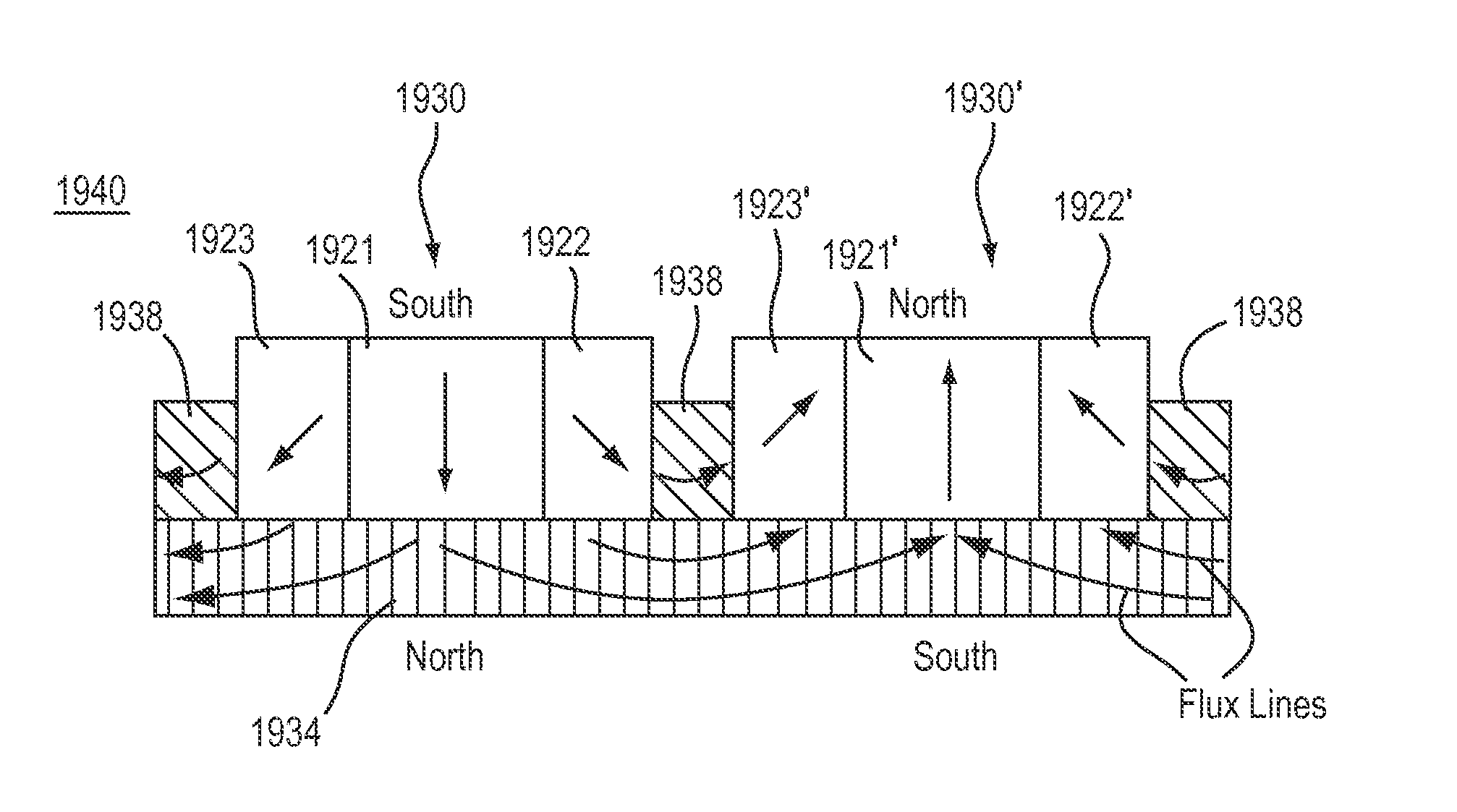
The invention discloses an excitation permanent magnet which is used on a rotor of a rotating electric machine, wherein more than two kinds of permanent magnets with different characteristics are combined, the excitation permanent magnet is divided into more than three parts along the width direction, a high coercive force permanent magnet A is used within a range which takes the central axis (i.e. d axis) of the excitation permanent magnet as a center, as for the part which is deviated outward from the d axis, a permanent magnet B group which has low coercive force and high residual flux density compared with the permanent magnet A is used. The mixed magnet of two magnets which have different using characteristics is taken as the excitation permanent magnet, the input amount of the high-priced and coercive force magnets is reduced, so the cost is reduced, and resources are protected.
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK +1
Three-phase permanent magnet brushless motor
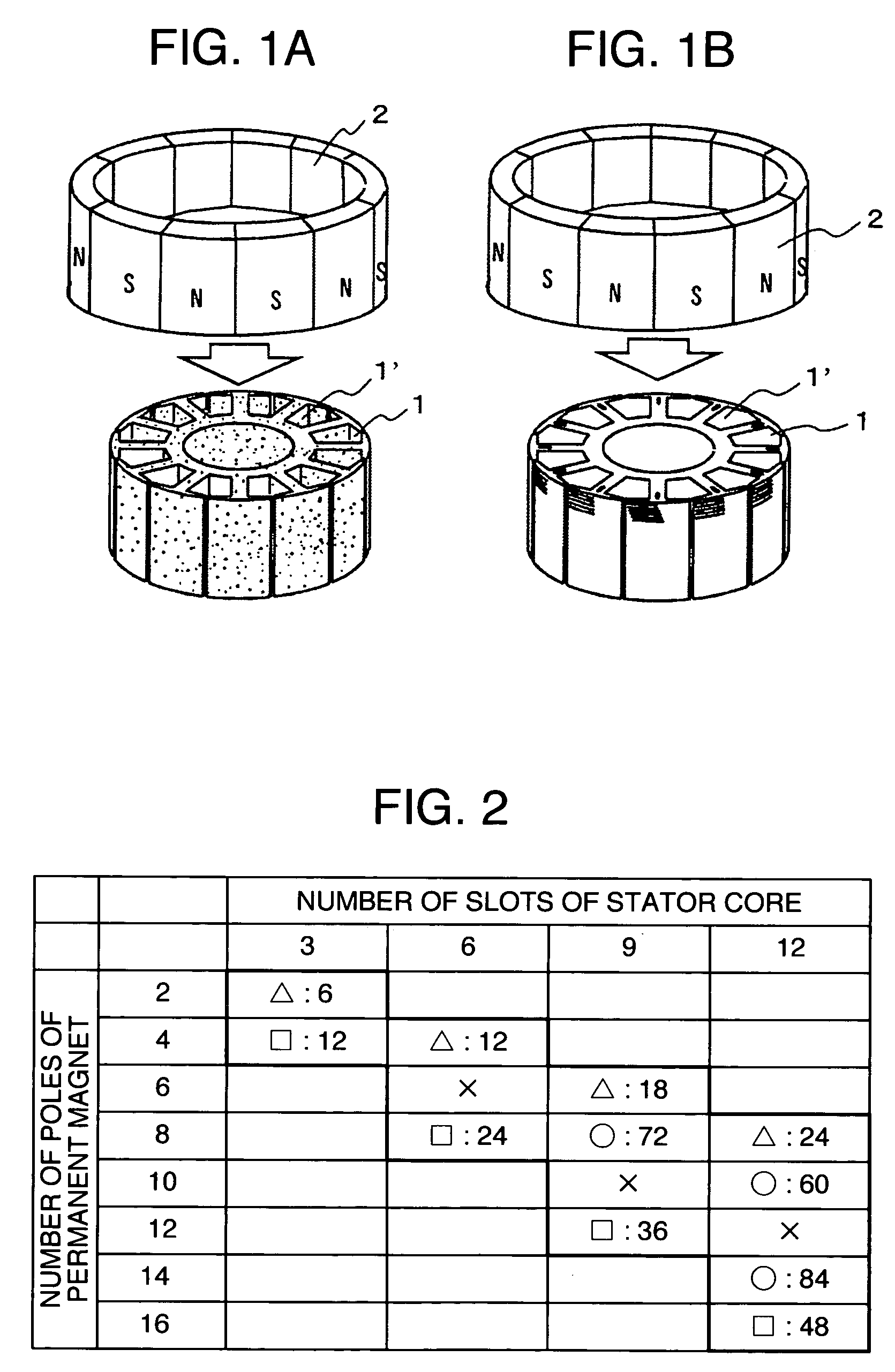
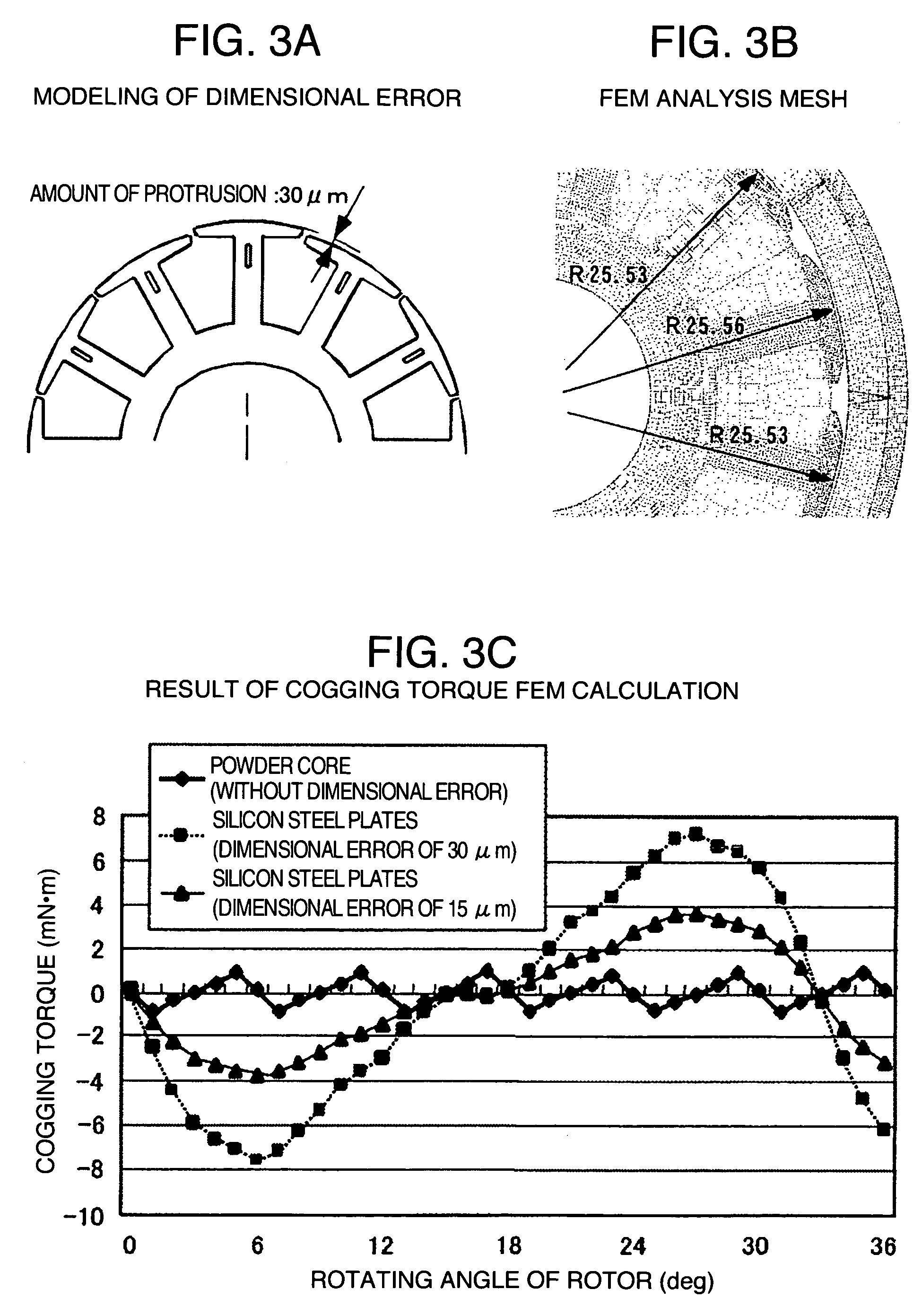
InactiveUS7592734B2Easy to limitEliminates variationMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesBrushless motorsHigh density
A three-phase permanent magnet brushless motor comprises a stator having three-phase windings, and a rotor having a permanent magnet with a plurality of poles for serving as a field magnet. The stator comprises a stator core which includes a powder core that is compacted at a high density in at least teeth thereof. A combination of the number of magnetic poles of the rotor with the number of slots of the stator satisfies a condition that a least common multiple of the number of slots and the number of magnetic poles is 60 or more in a region in which the number of magnetic poles is 16 or less, and the number of slots is 12 or less. The powder core is made by compacting magnetic powders to have a green density of 7.5 g / cm3 or higher.
Owner:JAPAN SERVO CO LTD +2
Device and Control System for Producing Electrical Power
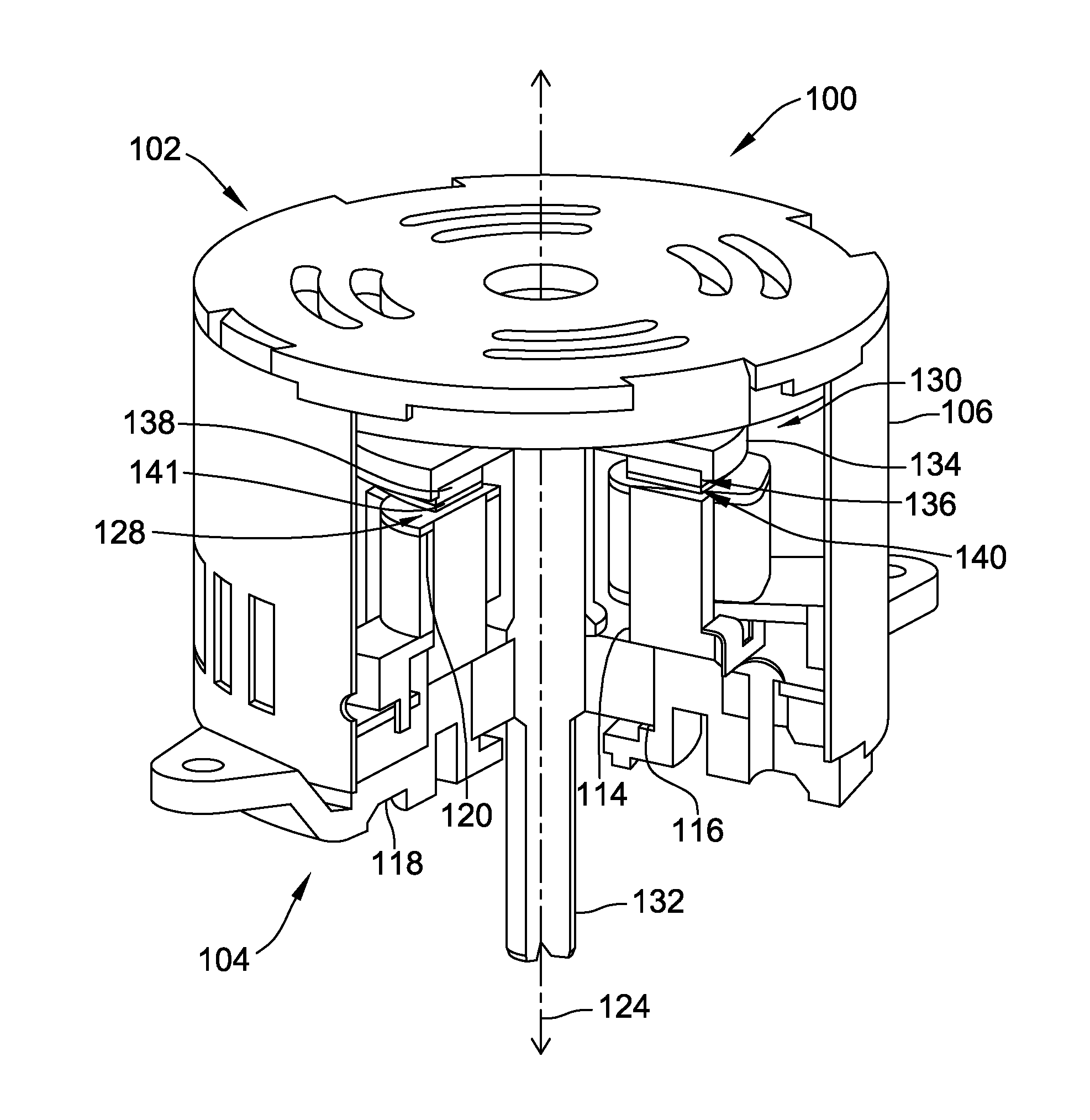
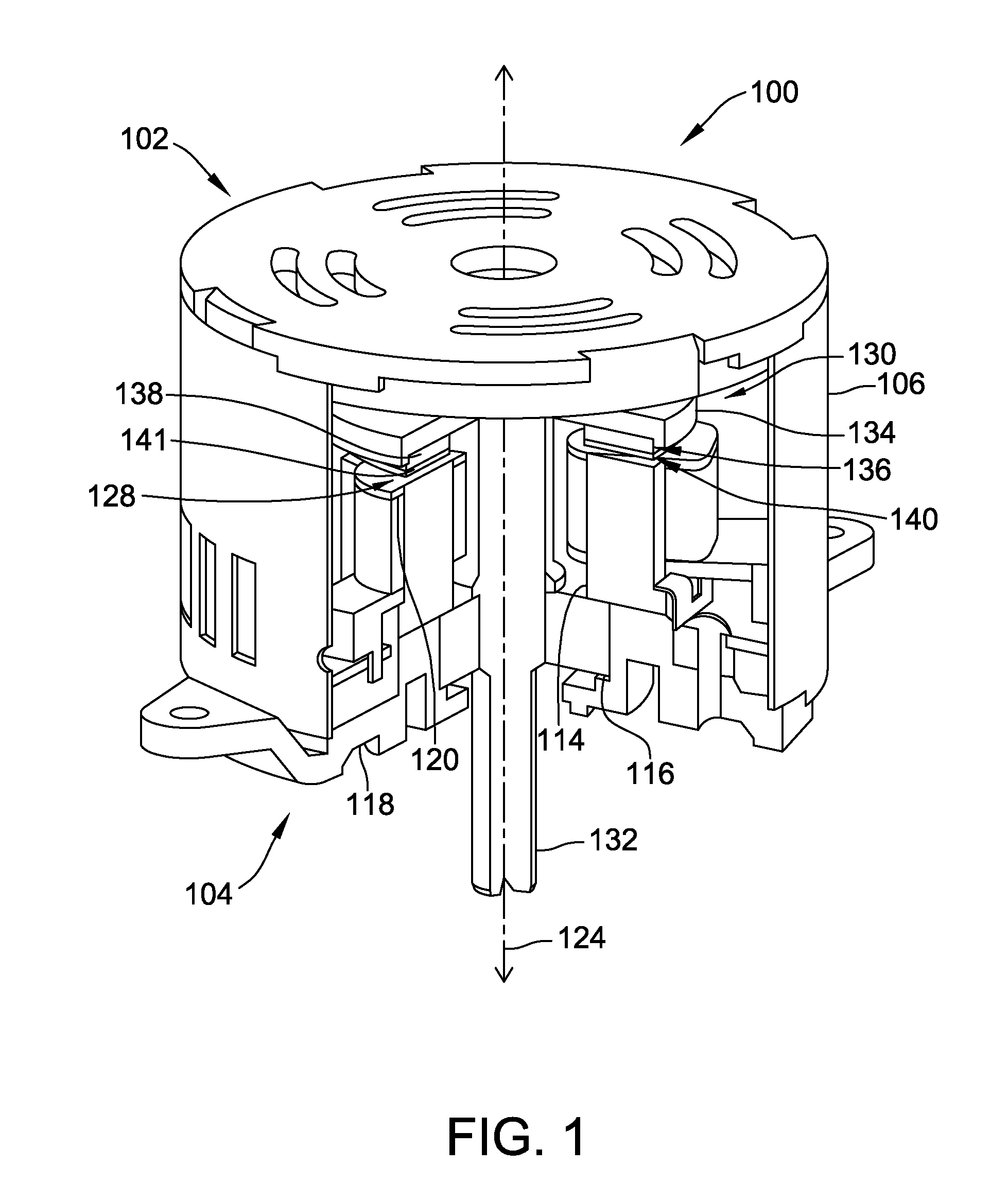
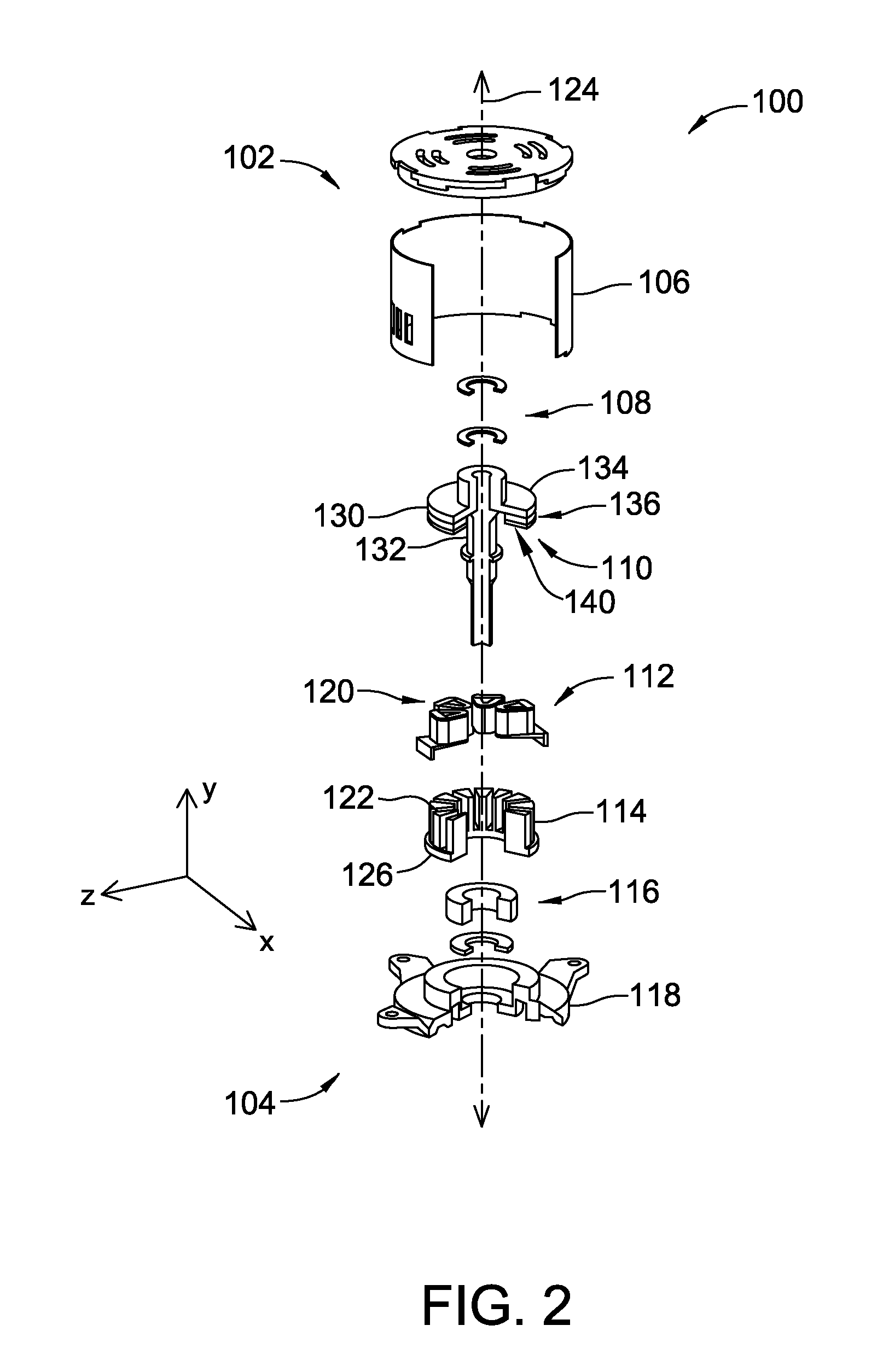
Briefly, the invention involves a system and method for generating electrical power. The system includes an electromagnet positioned with one pole directed toward a like pole of a permanent magnet. The permanent magnet is preferably mounted for oscillating movement toward the pole of the electromagnet. A control system for the electromagnet is provided to supply direct current (DC) power in the form of square wave pulses which coincide with the position of the permanent magnet. Power is collected upon the collapse of the magnetic field within the electromagnetic magnet. In some embodiments the present device is supplied in the form of a reciprocating engine which provides rotary motion in addition to the electrical power generated.
Owner:MAGNETIC MILES LLC
Electrical machine with magnetic brake directly on the rotor
ActiveUS20090127950A1Short structureLow costDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesMechanical energy handlingConductor CoilElectromagnet
An electrical machine includes a stator having circumferentially arranged winding heads, with a winding head space being defined radially beneath the winding heads. Interacting with the stator is a rotor which has a rotatable laminated core. A magnetic brake is received in the winding head space and includes a magnet module having at least one permanent magnet which is axially resiliently fixed and constraint against rotation and which is magnetized in an axial direction, and an electromagnet which is arranged axially adjacent to the permanent magnet and securely fixed thereto. The electromagnet produces a magnetic field with a main direction oriented in an axial direction. Interacting with the at least one permanent magnet and the electromagnet is a ring-shaped armature which is secured directly and rigidly to the rotor so as to establish a fixed rotative engagement between the armature and the rotor.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Permanent-magnet speed governor
InactiveCN101783576AAchieve complete no-load startChange the air gapAsynchronous induction clutches/brakesPush and pullElectrical conductor
The invention relates to a permanent-magnet speed governor, which comprises a first shaft and a second shaft, wherein the first shaft and the second shaft are coaxial, a conductor disc is installed on the first shaft and the second shaft is connected with a permanent-magnet rotating disc. The conductor disc and the permanent-magnet are placed close to each other. The conductor disc is formed by an outer rotating disc made of ferromagnetic material and an inner rotating disc made of conductor material, wherein the outer rotating disc and the inner rotating disc are attached together. The permanent-magnet rotating disc is made of non-ferromagnetic material. A group of permanent magnets are annularly installed on the permanent-magnet rotating disc. The magnetic pole direction of the permanent magnets is in parallel with the axis of the rotating disc, and every two adjacent ends are heteropolar. The invention has the advantages that non-contact power transmission is realized, the vibration is reduced, the motor can be started up fully with no load during startup, the torque transferred between the permanent-magnet rotating disc and the conductor disc can be varied through adjusting a handle installed on an outer sleeve to push a bearing to axially move on the shaft, to push-and-pull the permanent-magnet rotating disc to axially move and to vary the air gap between the permanent-magnet rotating disc and the conductor disc, repeatable, adjustable and controllable output torque and rotating speed can be realized, and the goal of speed regulation and energy saving is obtained.
Owner:王荣松
Permanent magnetism magnetic pole component for high-power permanent magnet motor
ActiveCN101355277AEasy to assembleImprove work performanceMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnetsThermal insulationMagnetic poles
The invention relates to a permanent-magnet magnetic pole component for a high-power permanent-magnet motor, comprising permanent magnets, a magnetic conduction yoke of a rotor, magnet protection positioning covers and magnetic pole locking pins, wherein the permanent magnets, the magnetic conduction yoke of the rotor and the magnet protection positioning covers form a permanent-magnet magnetic pole through adhesion, the arrangement of alternate N and S pole permanent-magnet magnetic poles is formed on the magnetic conduction yoke of the rotor, and two or a plurality of permanent-magnet magnetic poles are mutually connected to form the permanent-magnet magnetic pole component. The permanent-magnet magnetic pole component realizes the corrosion resistance and the thermal insulation of neodymium-iron-boron magnets, and greatly prolongs the service life of the permanent magnets.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONG KE SAN HUAN HI TECH
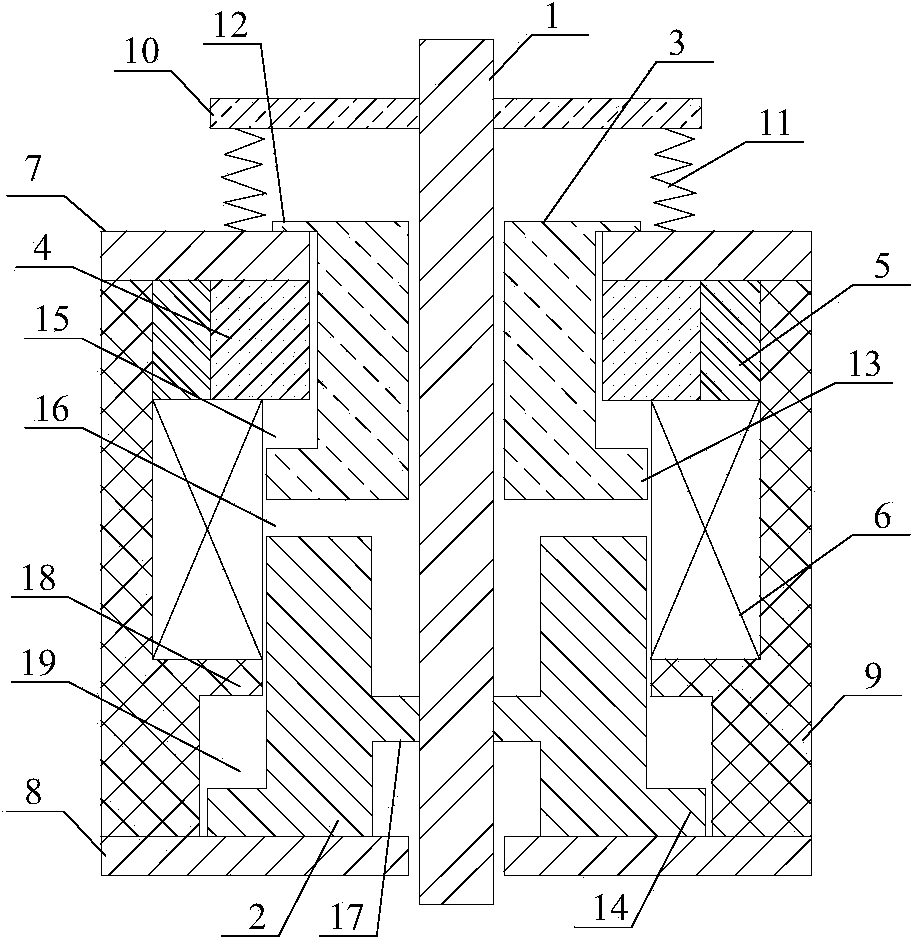
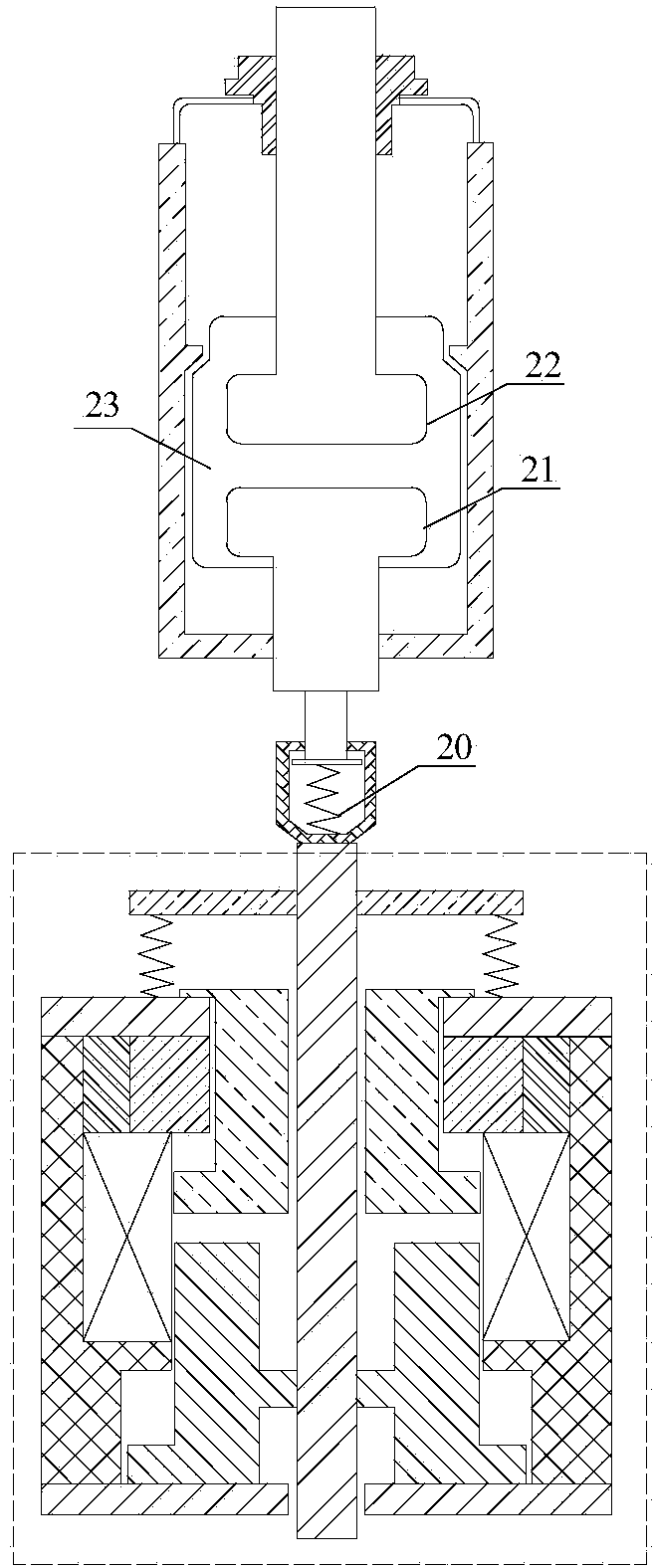
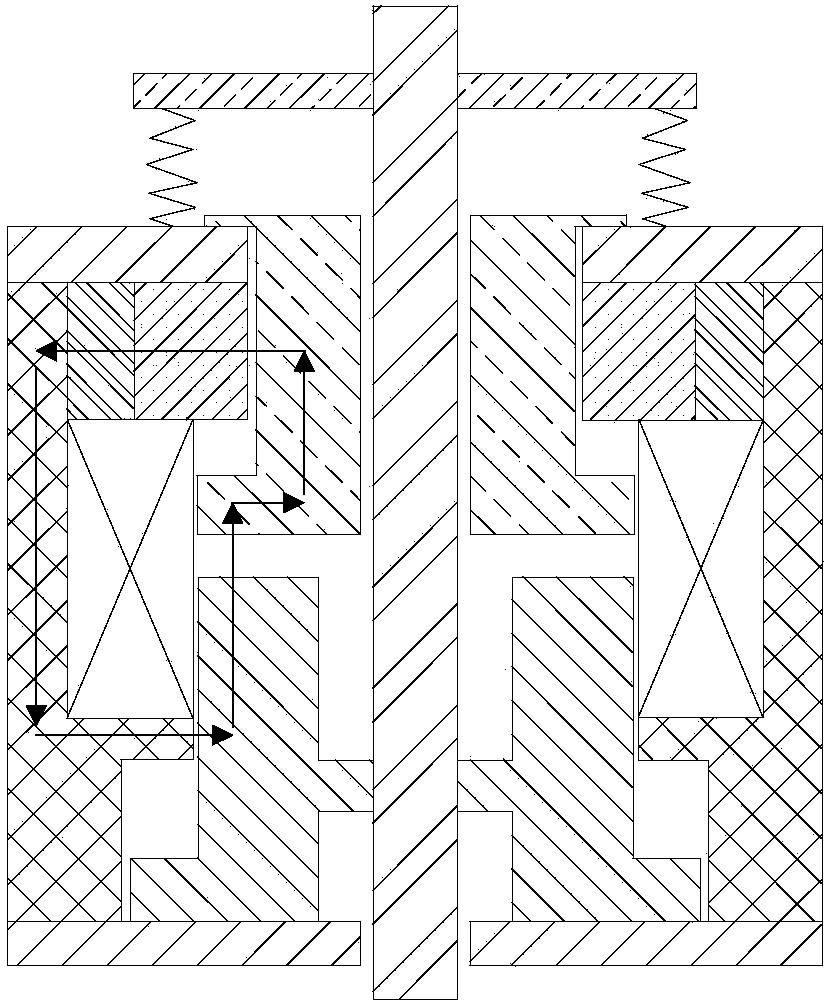
Combining electropermanent magnets and magnetorheological fluid to control an operation of an input device
ActiveUS11048344B1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectromagnets without armaturesMagnetorheological fluidEngineering
Aspects of the invention include a computer peripheral device comprising an input element that operates based on a performance characteristic, an electropermanent magnet (EPM) assembly including a permanent magnet configured to generate a magnetic field and a magnetizing assembly configured to set an intensity of the magnetic field generated by the permanent magnet, and a magnetorheological (MR) material coupled to the input element. The MR material has a viscosity that changes based on the magnetic field and affects the performance characteristic of the input element.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
Double-acting iron core permanent magnet operating mechanism
InactiveCN103474287ASmall closing starting currentJust speed reductionSwitch power arrangementsHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesState of artNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a double-acting iron core permanent magnet operating mechanism which comprises a guide rod (1), a primary iron core (2), a secondary iron core (3), a static iron core (4), a permanent magnet (5), a coil (6), a first cover plate (7), a second cover plate (8), a magnet yoke (9), a beam (10) and two breaking brake springs (11). The primary iron core (2), the secondary iron core (3) and the magnet yoke (9) are cylindrical, the first cover plate (7) is arranged on the top of the magnet yoke (9), and the second cover plate (8) is arranged at the bottom of the magnet yoke (9). Compared with a permanent magnet operation structure in the prior art, the double-acting iron core permanent magnet operating mechanism is little in switch-on current, rigid resultant velocity is obviously reduced, and rigid component velocity is increased obviously. Compared with a permanent magnet operation mechanism with a single movable iron core in the prior art, according to the double-acting iron core permanent magnet operating mechanism, the maximum current in the whole switch-on process is reduced by about 50%.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Rotor arrangement and electromechanical transducer having non-parallel permanent magnets
InactiveUS20130278087A1Reduce widthImprove efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsWind energy generationAxial rotationElectromechanical transducer
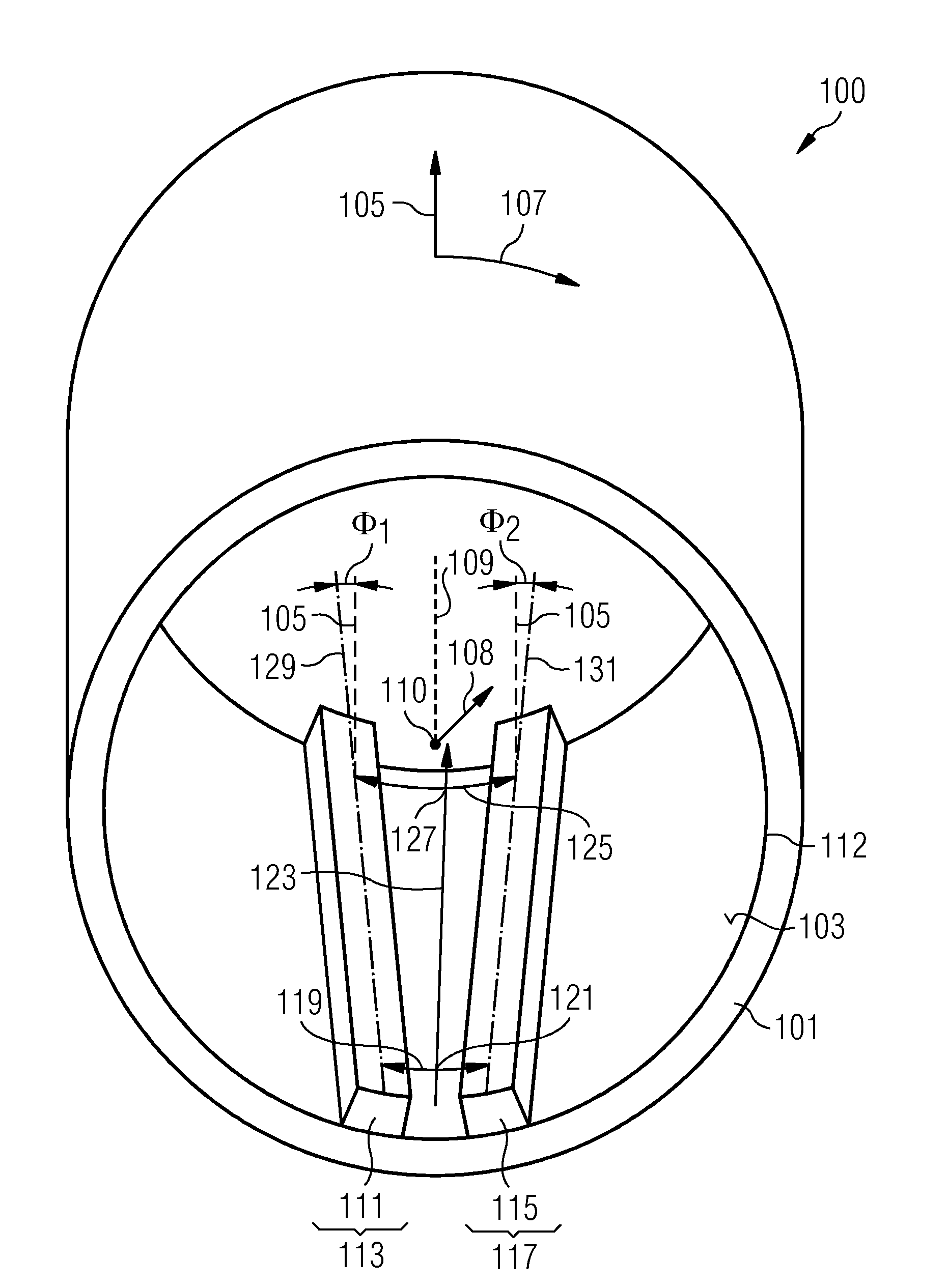
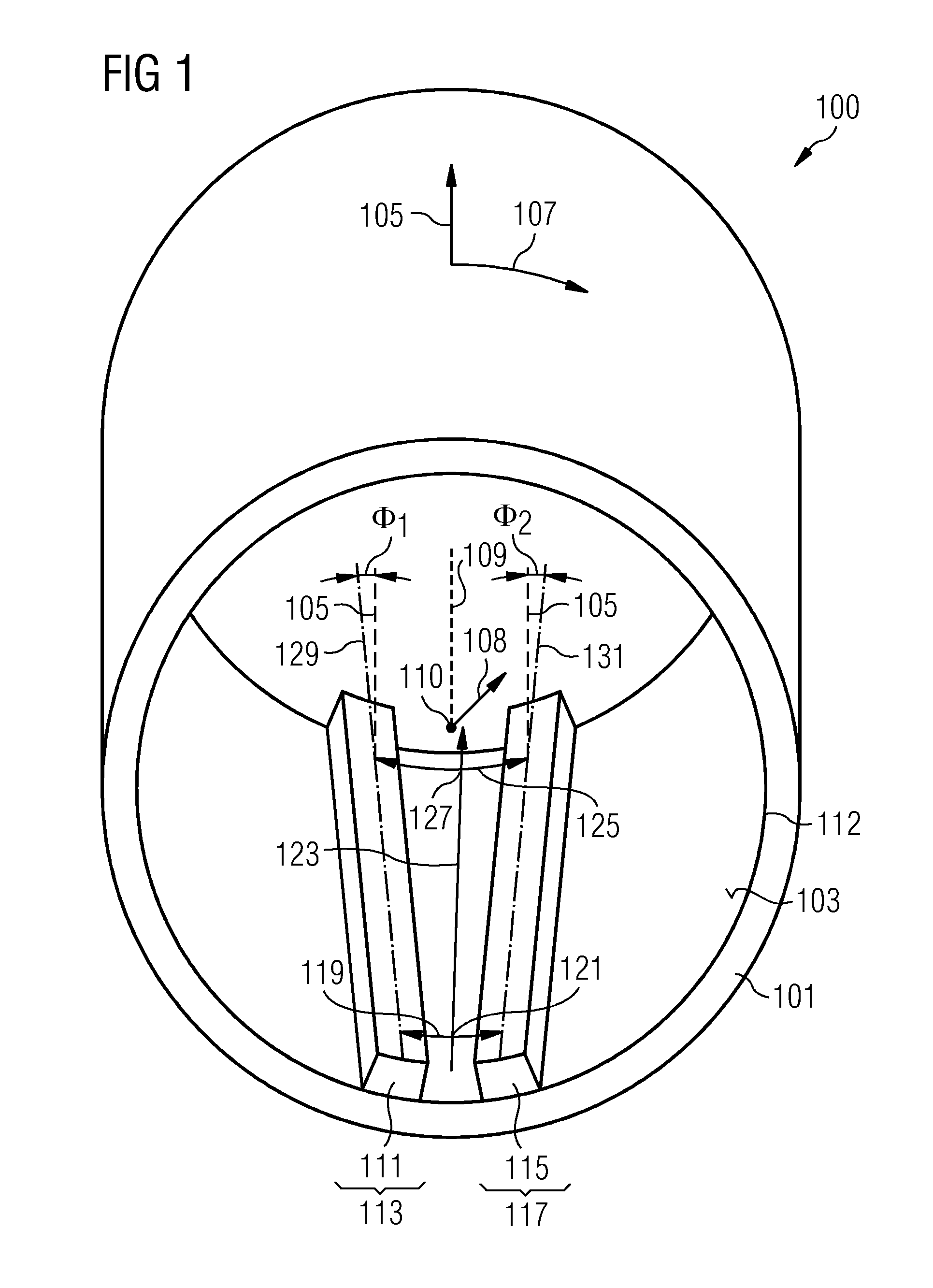
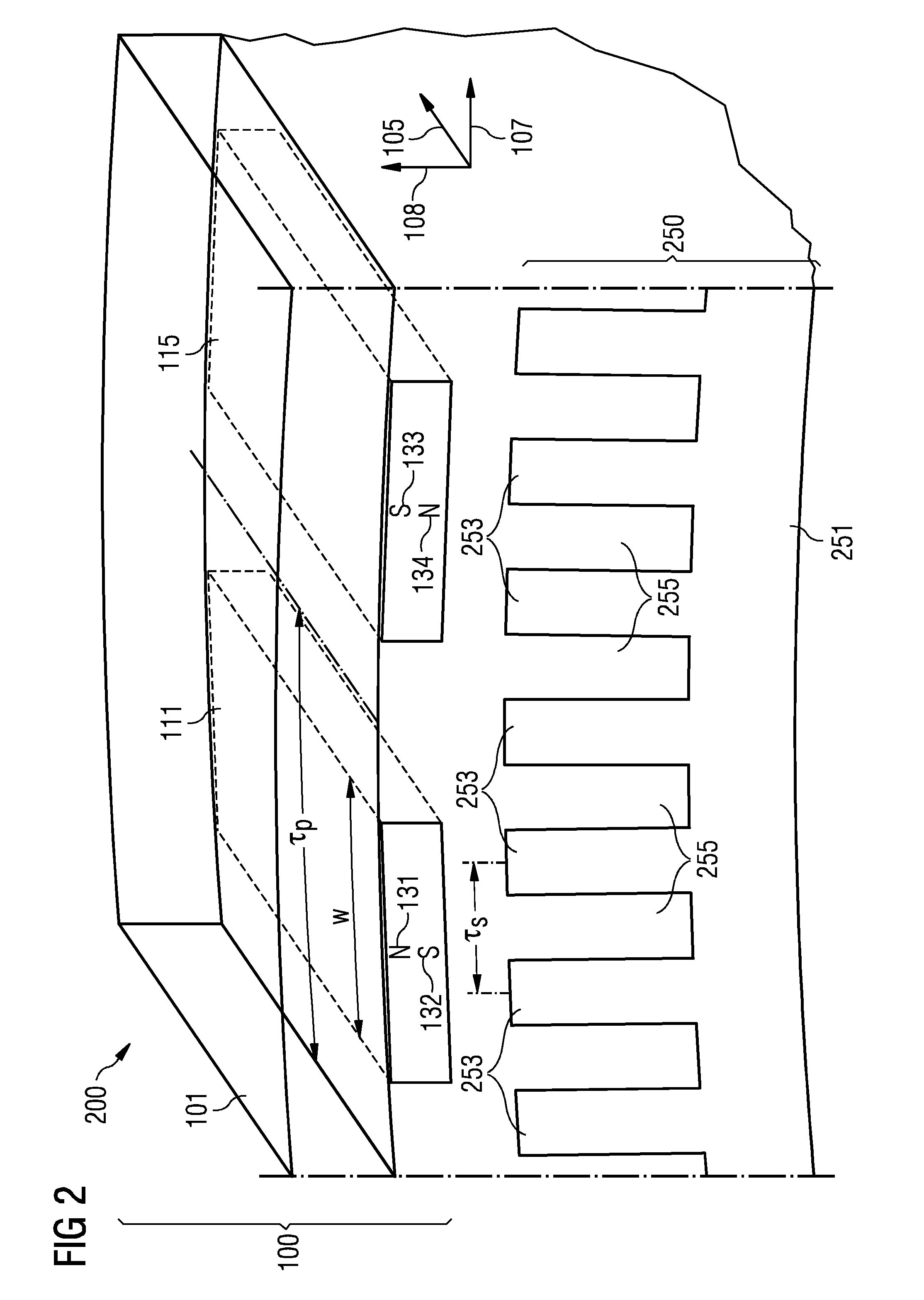
A rotor arrangement includes a support structure providing a mounting surface extending in an axial direction and a circumferential direction. The support structure is adapted to rotate around the axial direction. A first permanent magnet system is arranged at the mounting surface at a first circumferential region. A second permanent magnet system is arranged at the mounting surface at a second circumferential region. A circumferential distance between the first magnet system and the second magnet system at a first axial position differs from the circumferential distance between the first magnet system and the second magnet system at a second axial position.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com