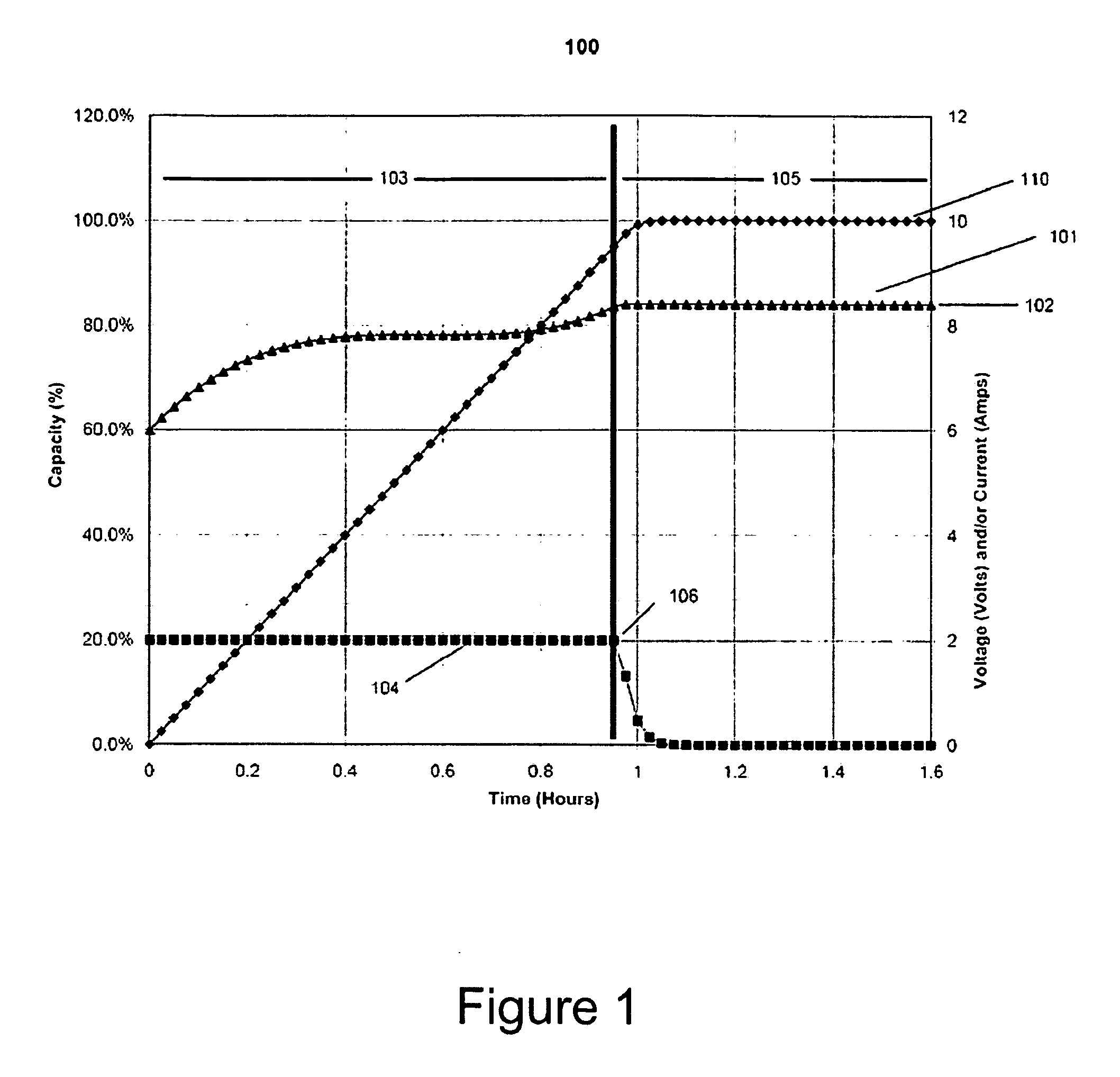
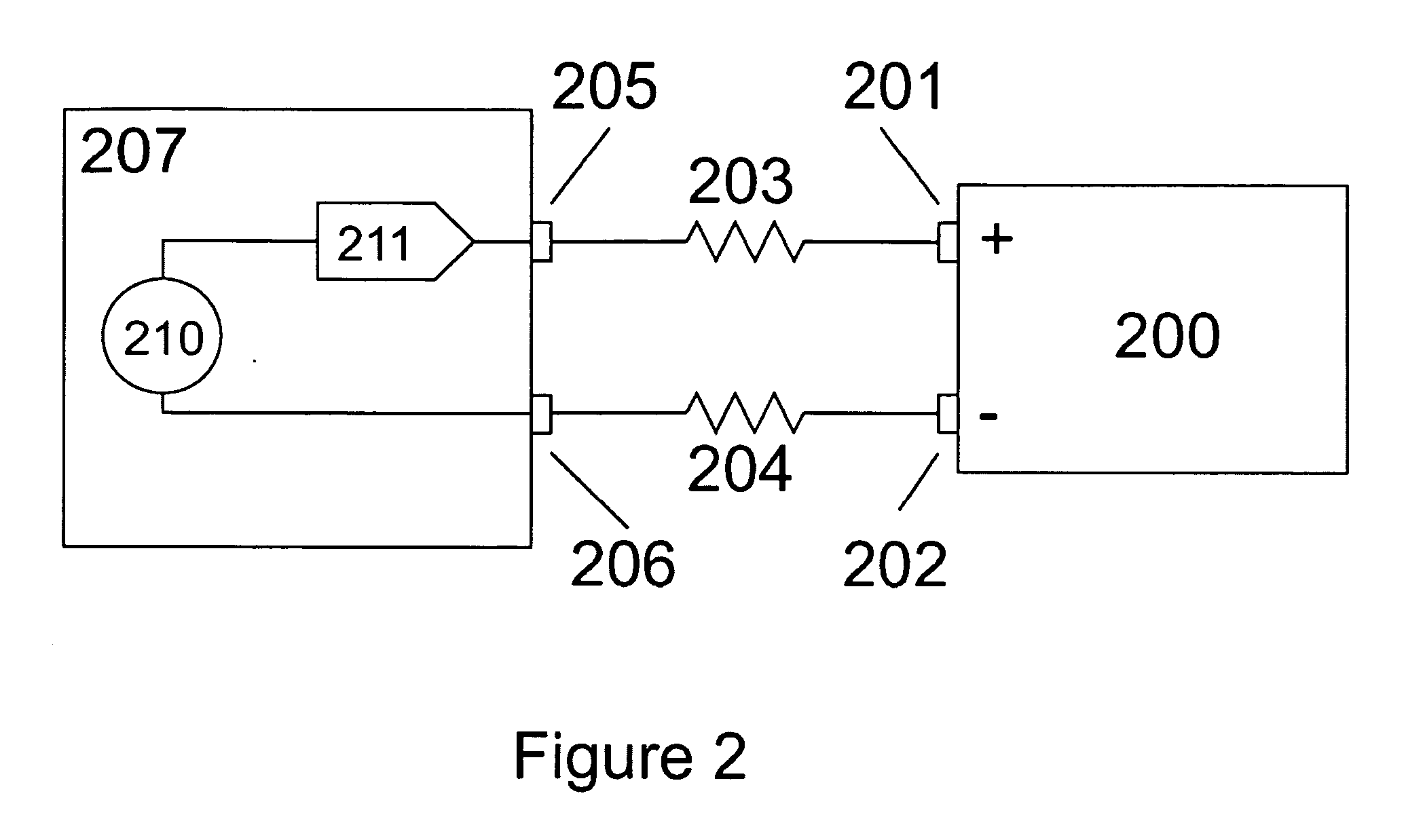
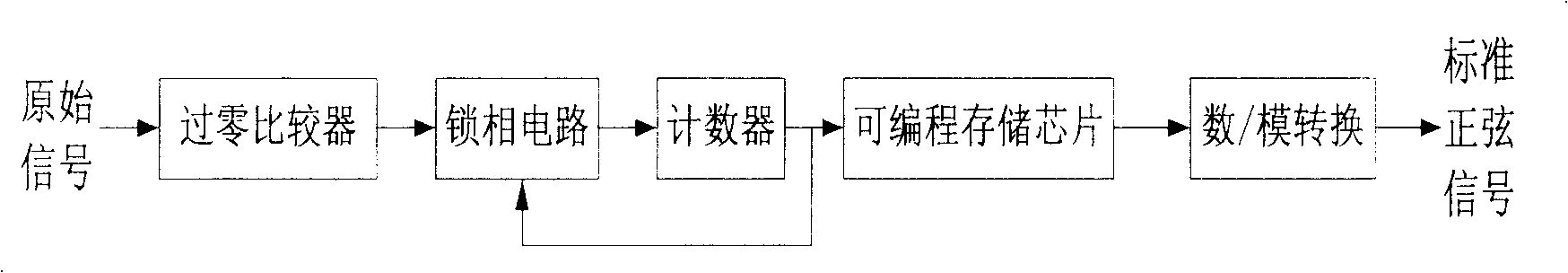
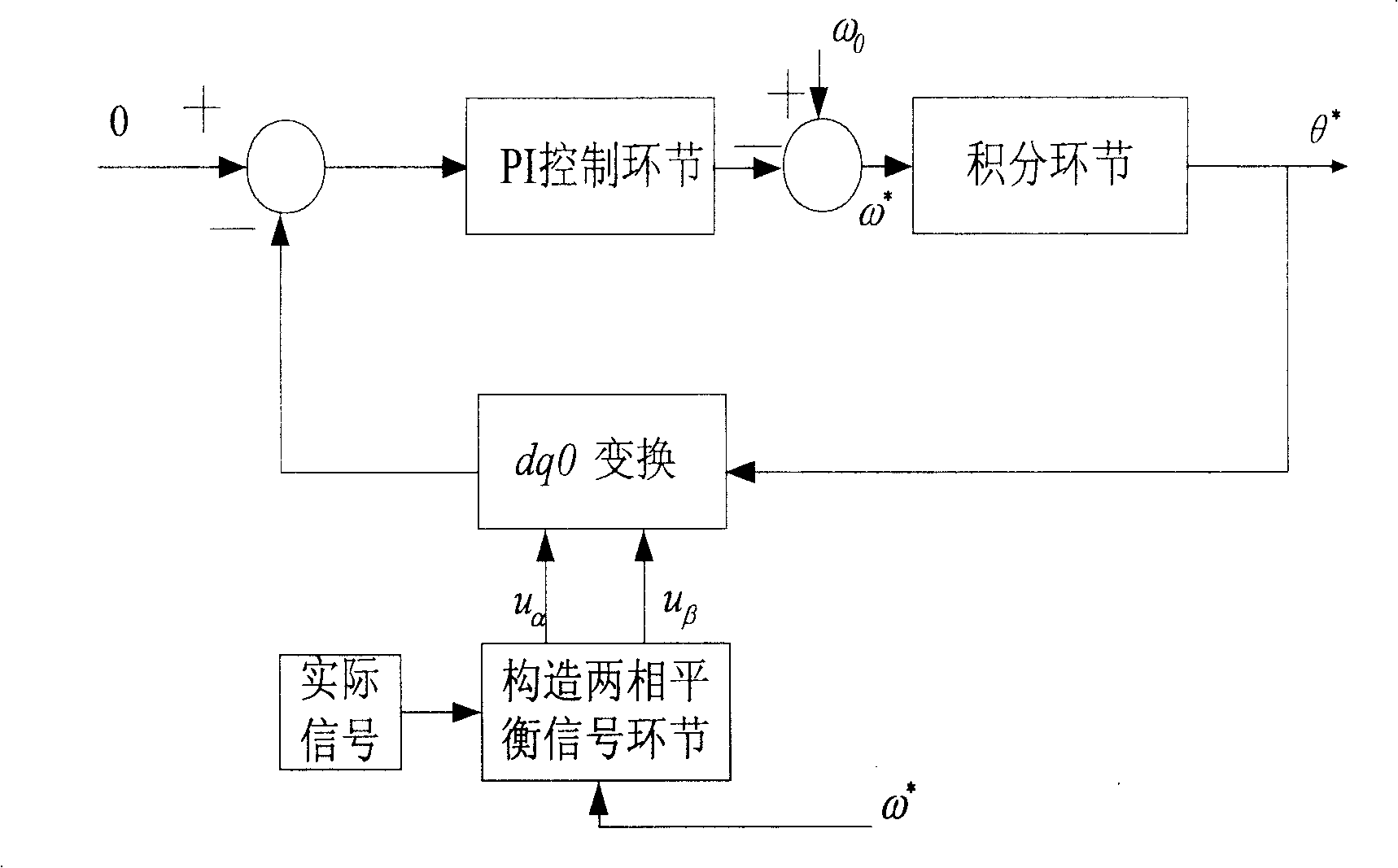
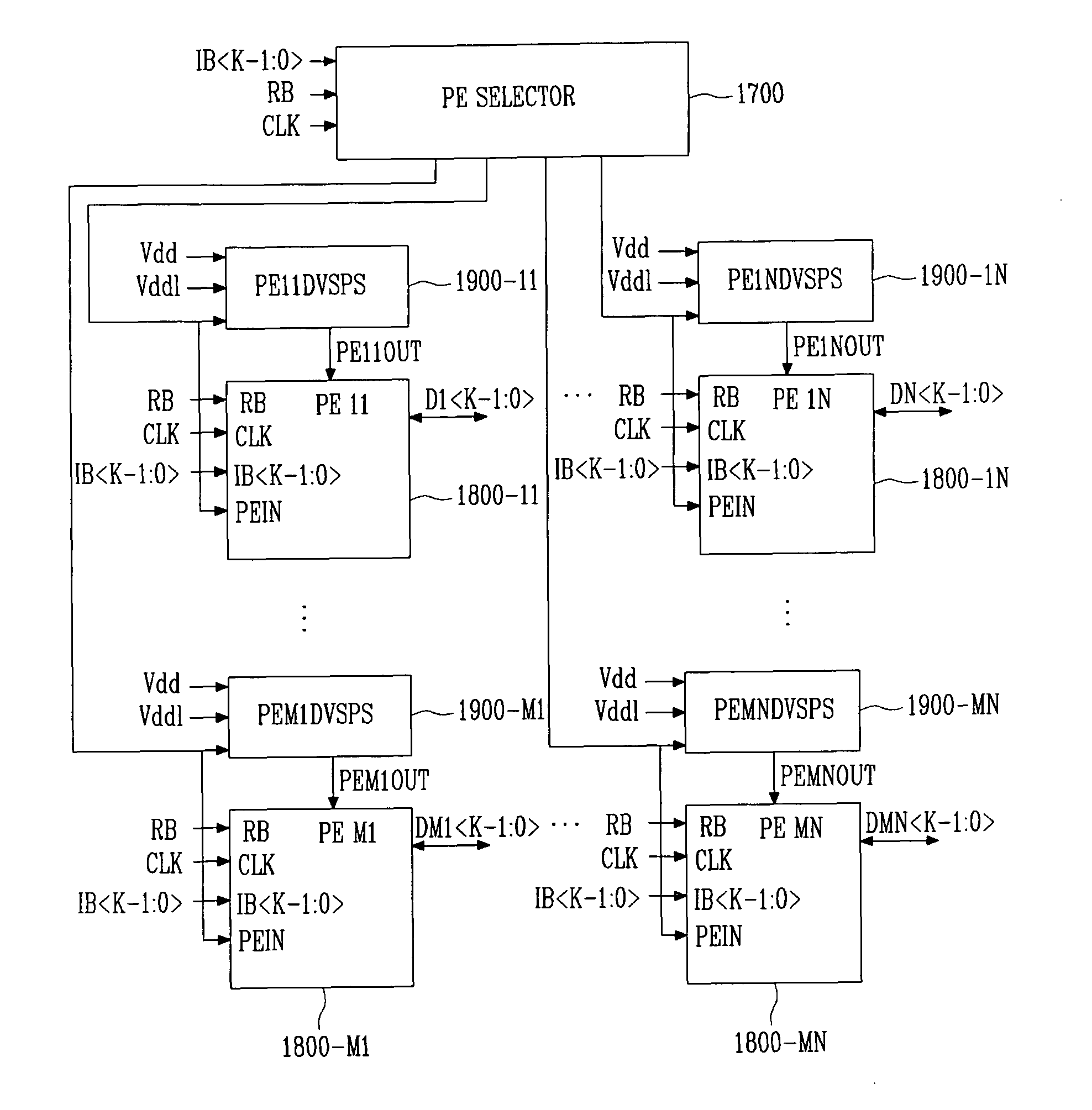Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
103 results about "Dynamic voltage scaling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dynamic voltage scaling is a power management technique in computer architecture, where the voltage used in a component is increased or decreased, depending upon circumstances. Dynamic voltage scaling to increase voltage is known as overvolting; dynamic voltage scaling to decrease voltage is known as undervolting. Undervolting is done in order to conserve power, particularly in laptops and other mobile devices, where energy comes from a battery and thus is limited, or in rare cases, to increase reliability. Overvolting is done in order to increase computer performance.
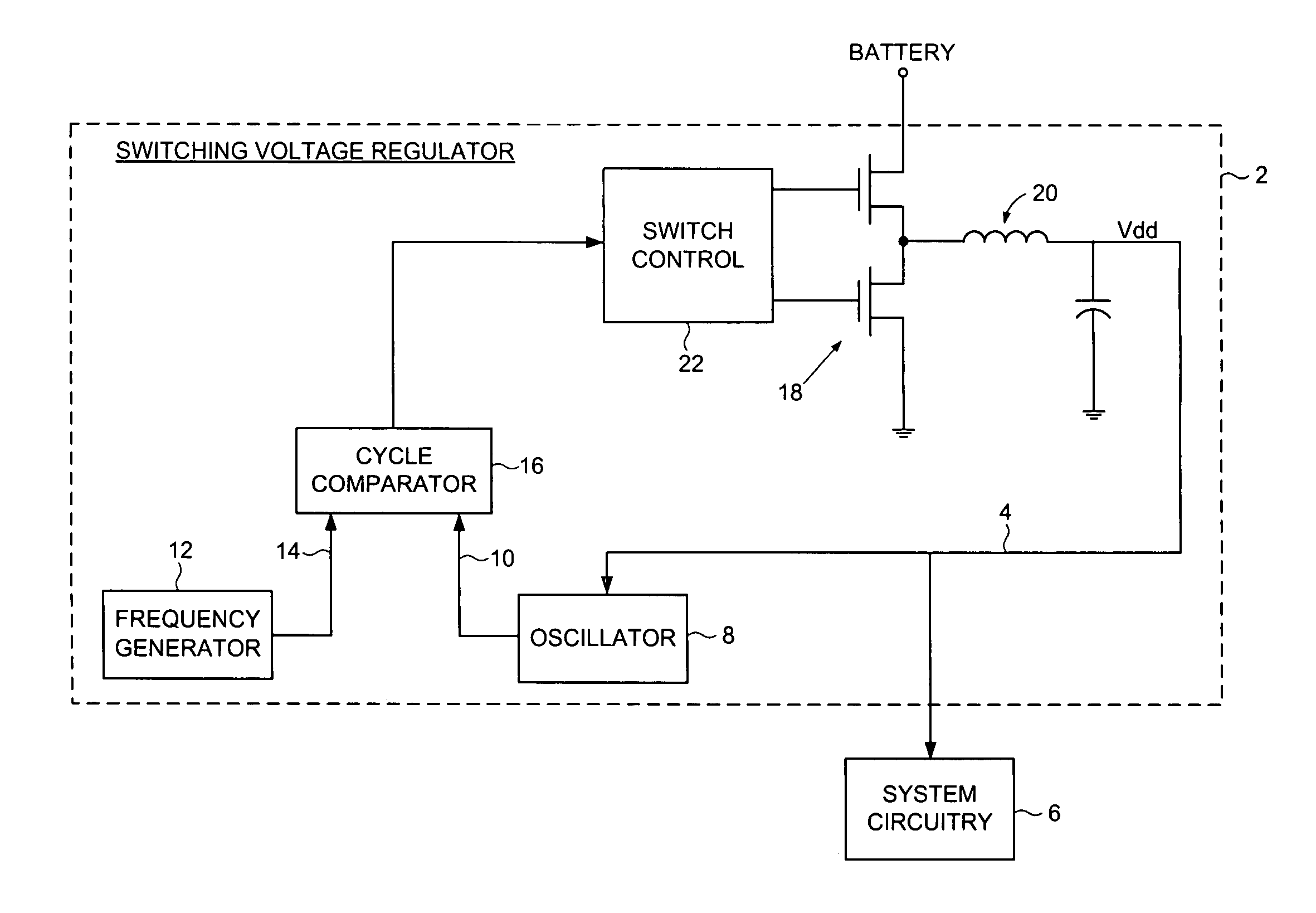
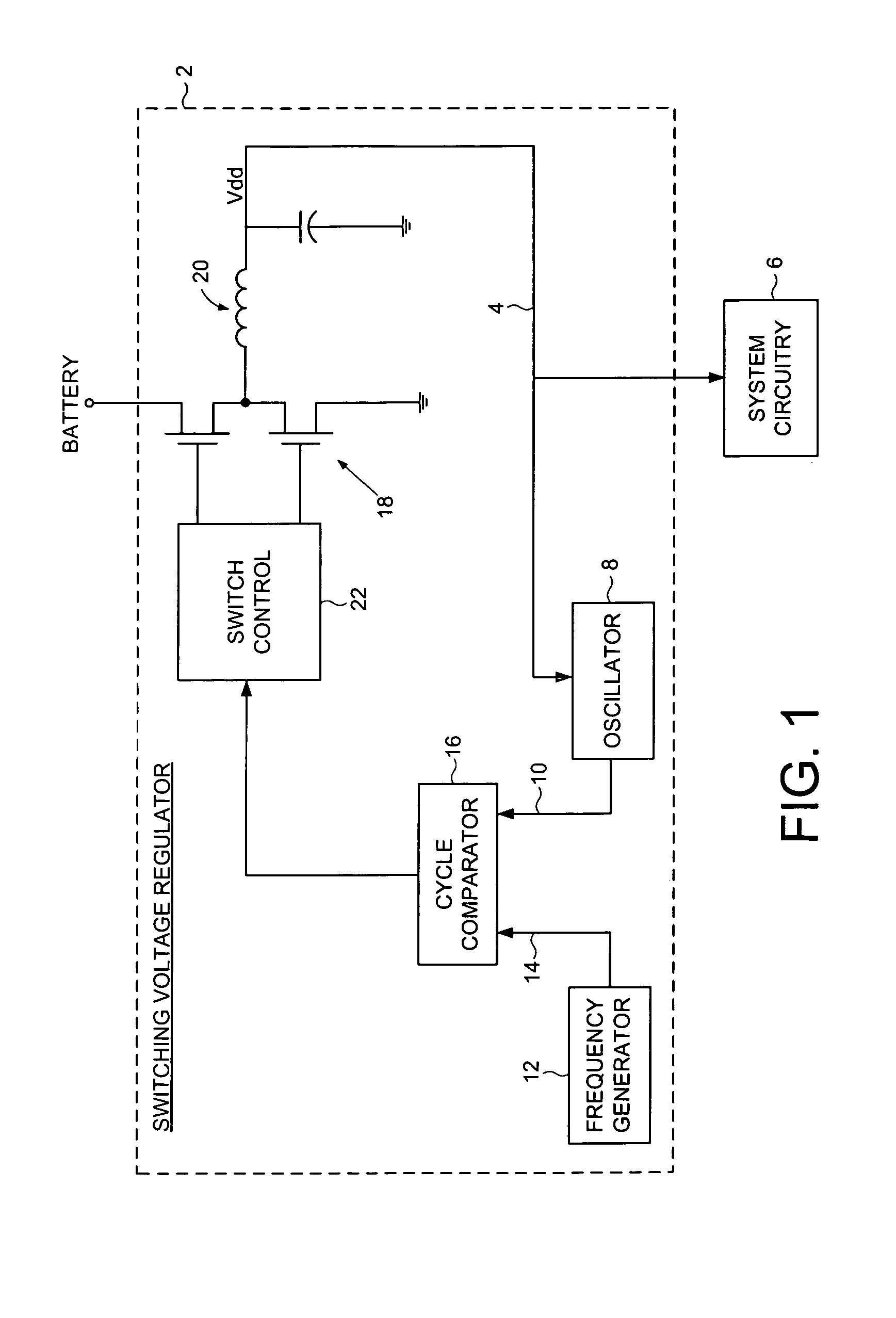
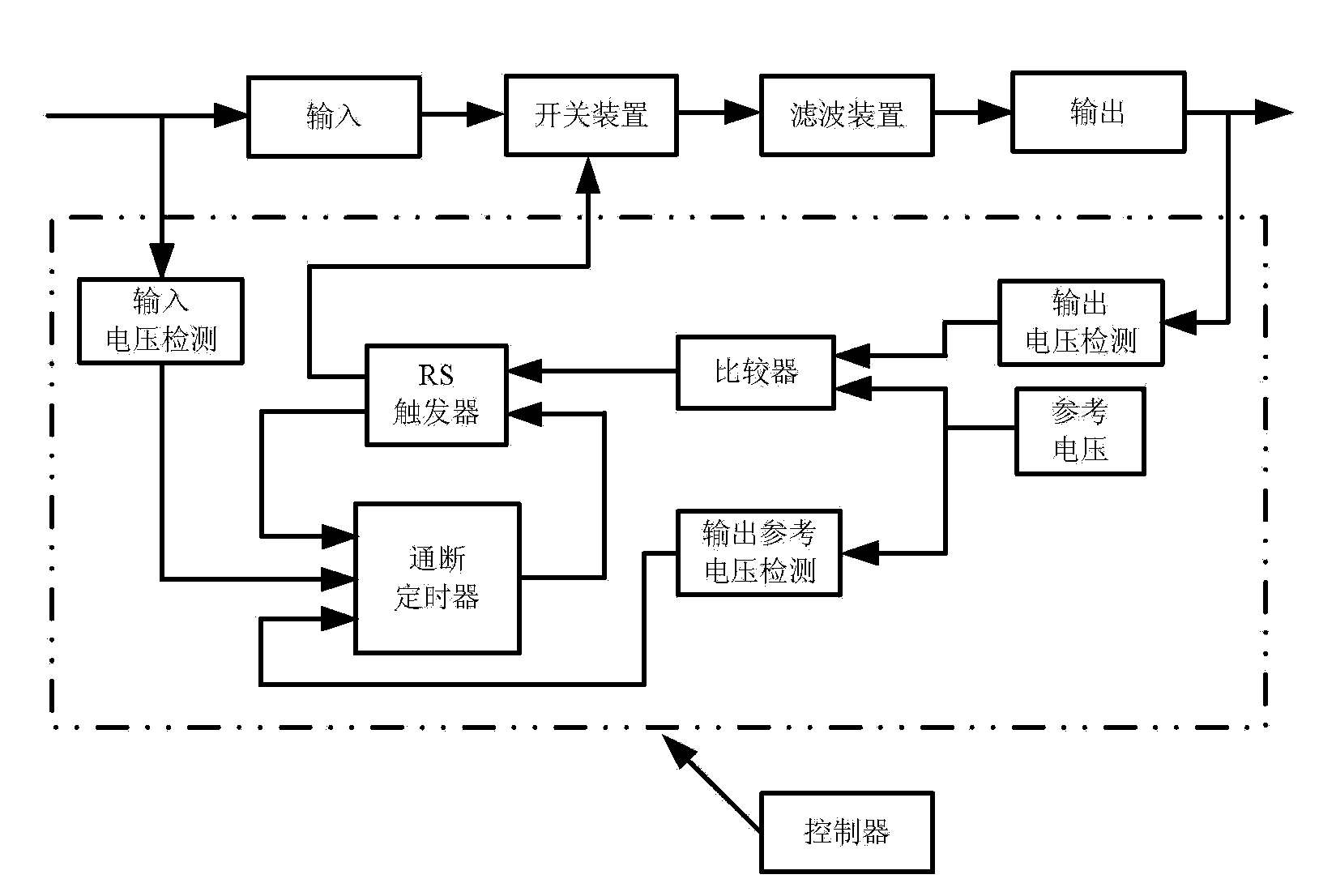
Switching voltage regulator comprising a cycle comparator for dynamic voltage scaling
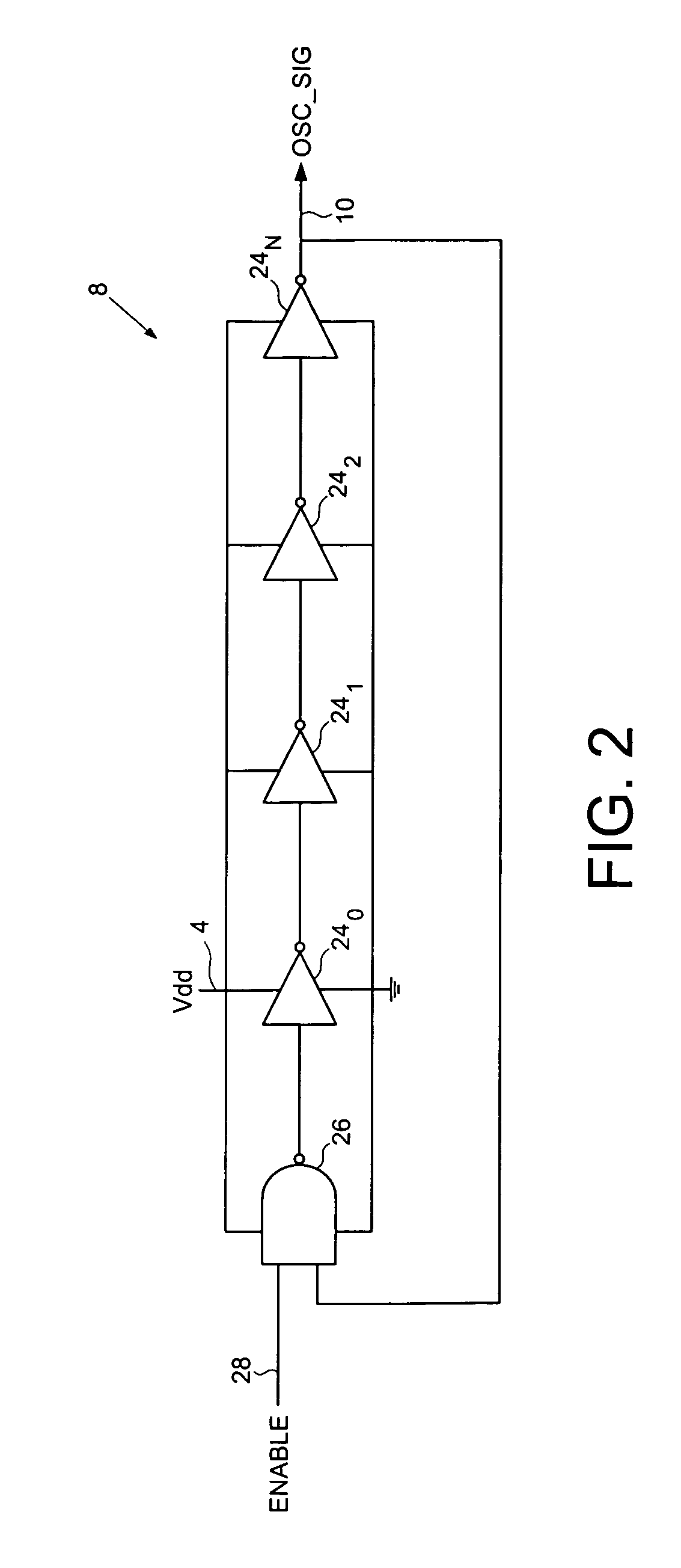
A switching voltage regulator is disclosed for regulating a voltage supplied to system circuitry. The switching voltage regulator comprises an oscillator operable to generate an oscillator signal representing a gate speed of a reference circuit in the system circuitry, and a frequency generator operable to generate a reference signal representing a target gate speed of the reference circuit. A cycle comparator compares at least one cycle of the oscillator signal to at least one cycle of the reference signal, and switching circuitry charges a charging element based at least on part on the comparison.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Chip packages with power management integrated circuits and related techniques
InactiveUS20100165585A1Decrease in transient response timeReduce the difficulty of circuit designDc network circuit arrangementsElectric signal transmission systemsElectrical devicesVoltage regulation
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Dynamic voltage scaling system based on on-chip monitoring and voltage prediction
ActiveUS20130154583A1Overcomes drawback of natureImprove directivityReliability/availability analysisPower supply for data processingVoltage converterConverters
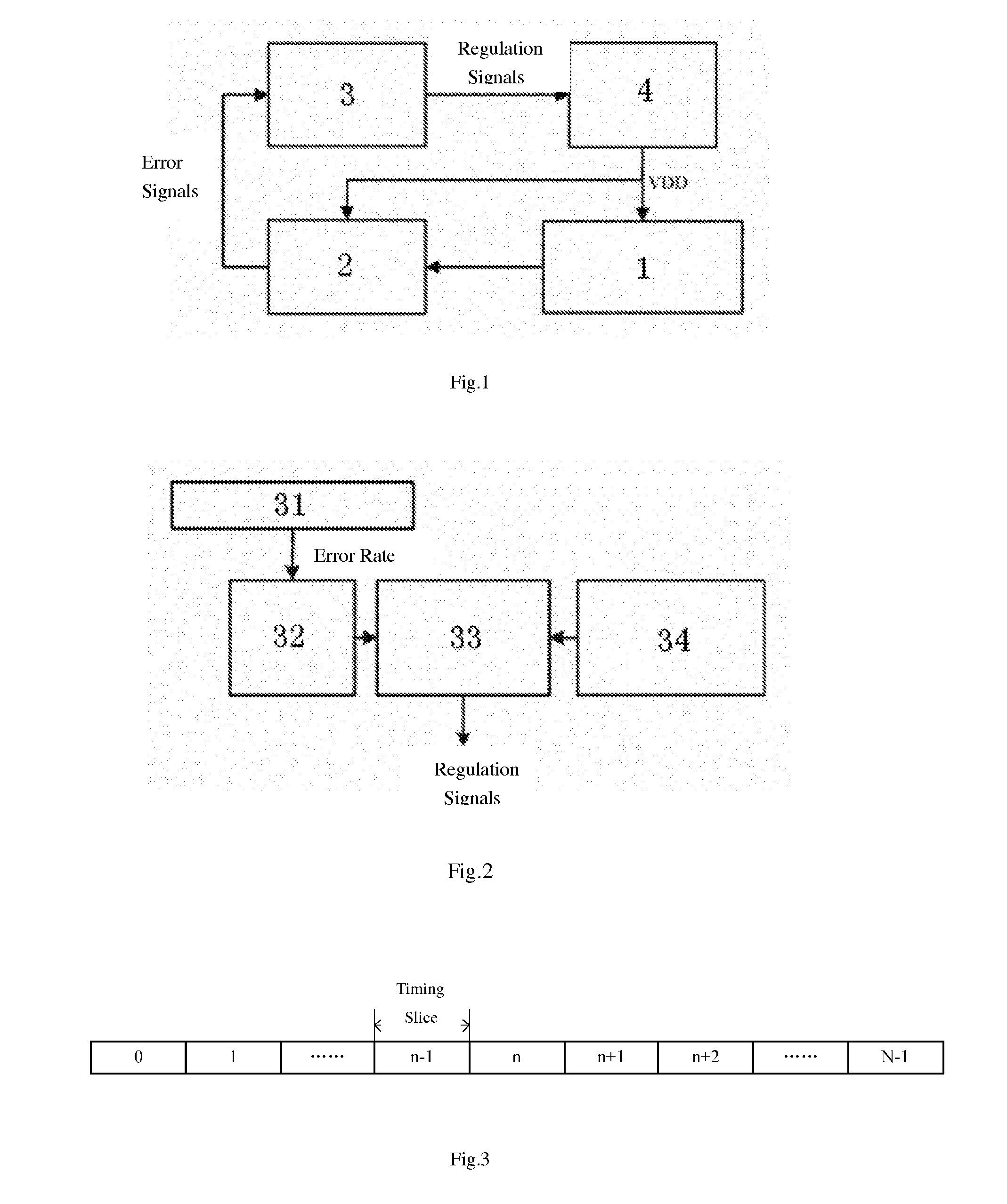
The present invention discloses a dynamic voltage scaling system based on on-chip monitoring and voltage prediction, comprising a main circuit that has integrated on-chip monitoring circuits, a supply voltage scaling module, and voltage converters, wherein, the supply voltage scaling module comprises a sampling and statistics module designed to calculate the error rate of the main circuit in the current time slice, a state recording module designed to record the error rate and the corresponding supply voltage, an error prediction module, and a state transition probability generation module; the error prediction module predicts the error trend of the main circuit in a future time slice according to the state recording module and the state transition probability generation module, and generates regulation signals and sends to the corresponding voltage converters, so as to generate the voltage required for operation of the entire main circuit. The present invention utilizes the Markov theory to predict the “future” timing violation level of the circuit according to the “past” working condition and “current” working condition of the main circuit, and reserves some time for voltage scaling in the voltage converters; as a result, the dynamic voltage scaling has high directivity and purposiveness.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Dynamic voltage regulation system applied for low energy consumption and implementation method
ActiveCN102063144AConvenient and efficient management mechanismAccurate working conditionElectric variable regulationConvertersHemt circuits
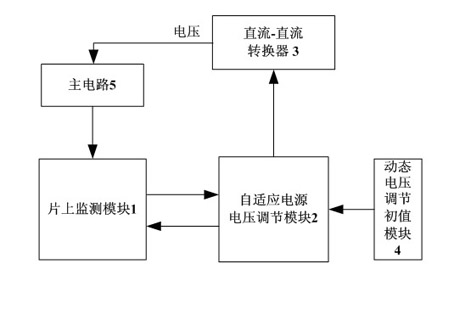
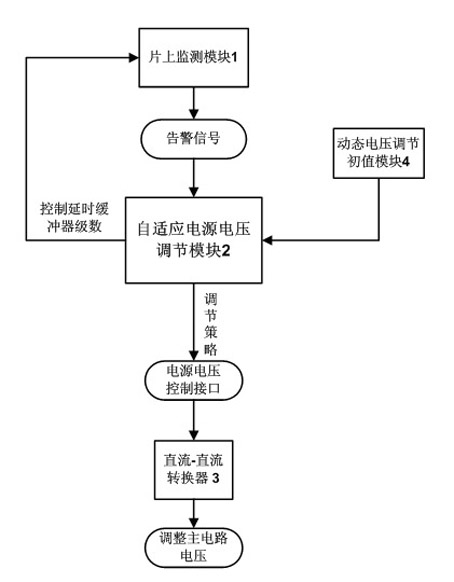
The invention relates to a dynamic voltage regulation system applied for low energy consumption, which is characterized by comprising an on-chip monitoring module (1), a self-adaption power supply voltage regulation module (2), a dc-dc convertor (3), a dynamic voltage regulation initial module (4) and a main circuit (5), wherein the on-chip monitoring module (1) monitors errors; the self-adaption power supply voltage regulation module (2) self-adaptively adjusts voltage according to a real-time system parameter; and the dynamic voltage regulation initial module (4) determines the initial voltage of the system and the level of a buffer. The method and the system lower the working voltage of a chip, reduce voltage margin, expand the range of the working voltage and reduce the power consumption of the chip.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Dynamic voltage scaling
ActiveUS7739531B1Minimize power consumptionPacked tightlyEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringDynamic voltage scaling
An apparatus and method for dynamically controlling the maximum frequency of operation of the IC is provided. The invention optimizes power consumption in a device by measuring a current maximum frequency of operation and adjusting IC operating voltage to provide a desired maximum operating frequency. The invention provides an apparatus and method for controlling multiple voltages in an IC to independently adjust maximum operating frequencies for a plurality of separate portions of the IC. The invention may equally be applied to a group of ICs. The invention further provides a method for calibrating an IC. Thus, the apparatus facilitates the operation of an IC at a minimum voltage for a selected maximum frequency, thereby minimizing power consumption overall a wide range of operating frequencies.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
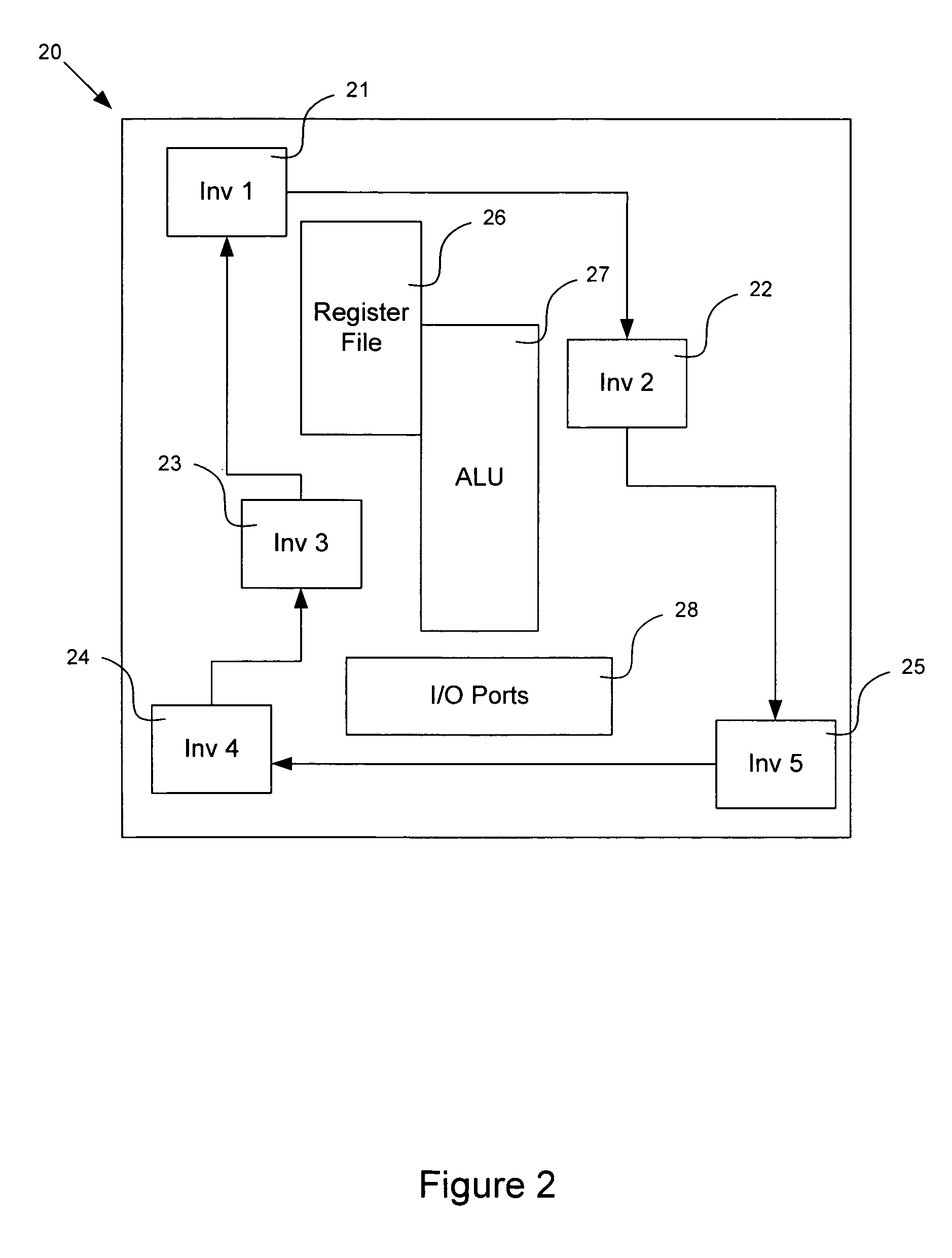
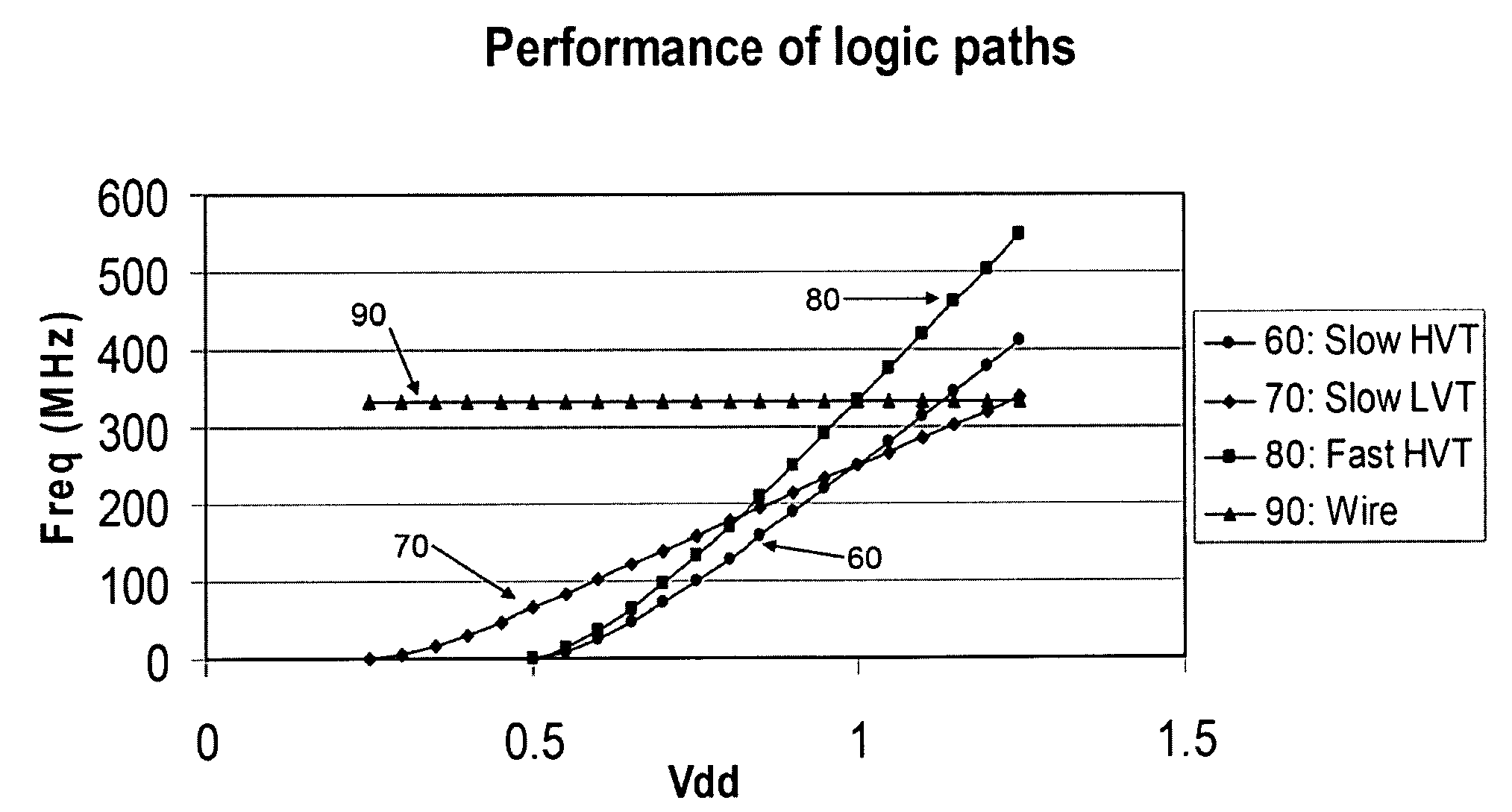
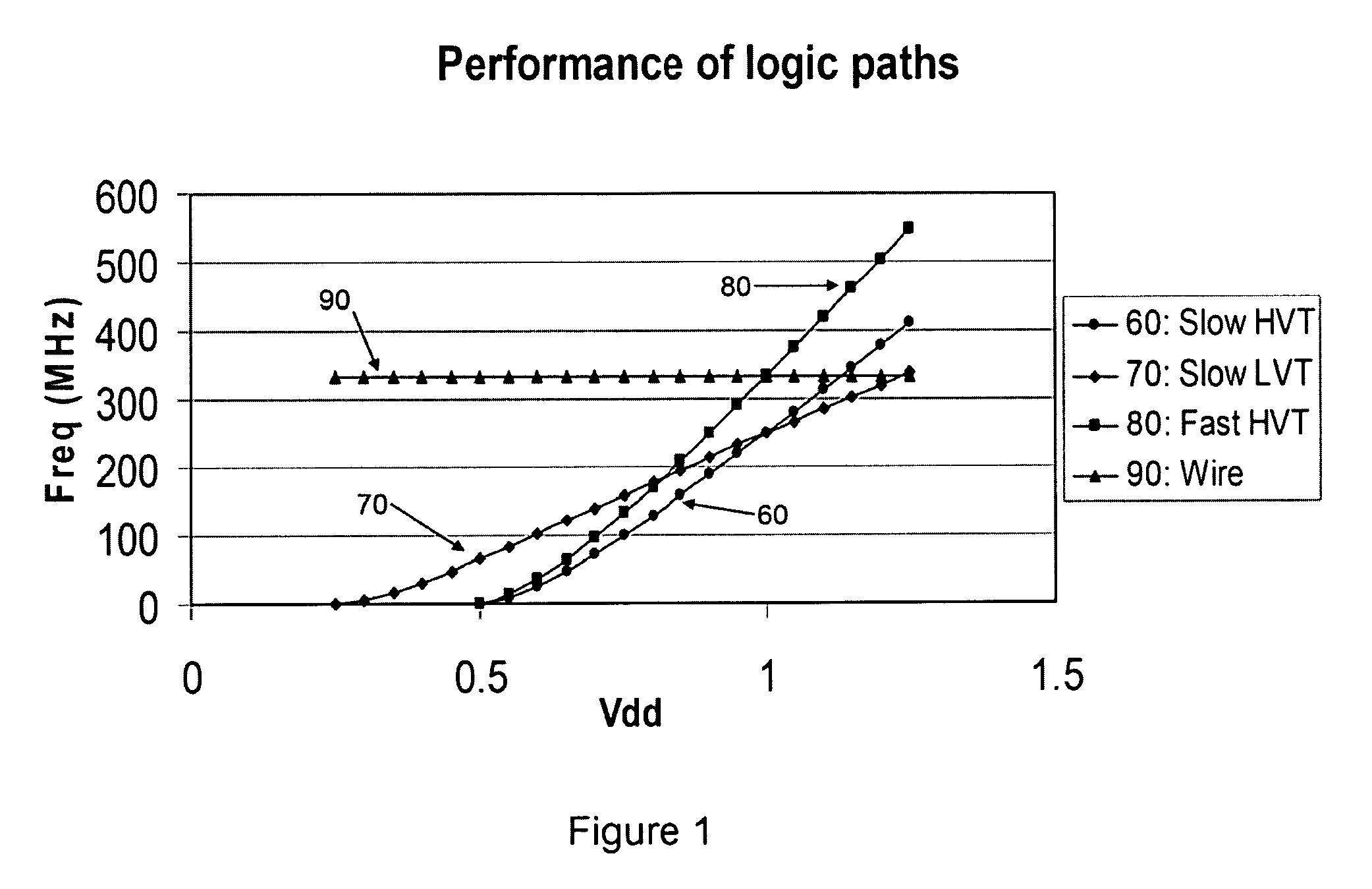
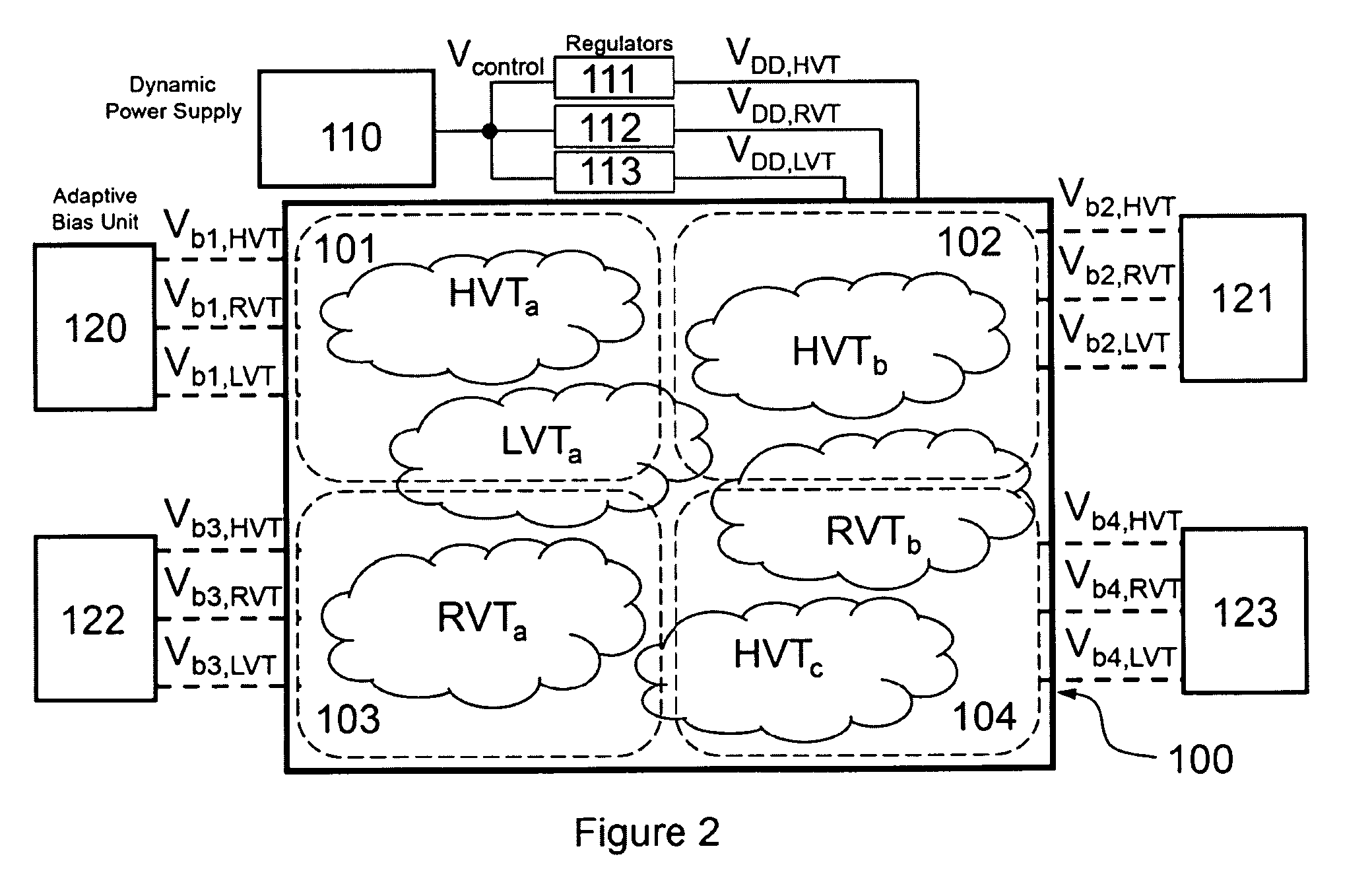
Compensation of process and voltage variability in multi-threshold dynamic voltage scaling circuits
InactiveUS7525373B1Minimize changesReduce variationEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsLow voltageVoltage regulation
This invention relates to adaptively compensating for variations in integrated chip circuitry due to delays caused by multiple thresholds. The multi-threshold adaptive dynamic scaling system disclosed compensates for normal on-chip variations which affect system process and voltage variability, as well as overall performance. This system regulates a voltage control and provides high voltage thresholds, regular voltage thresholds, and low voltage thresholds to compensate for threshold voltage variations.
Owner:BIOLITEC PHARMA MARKETING +1
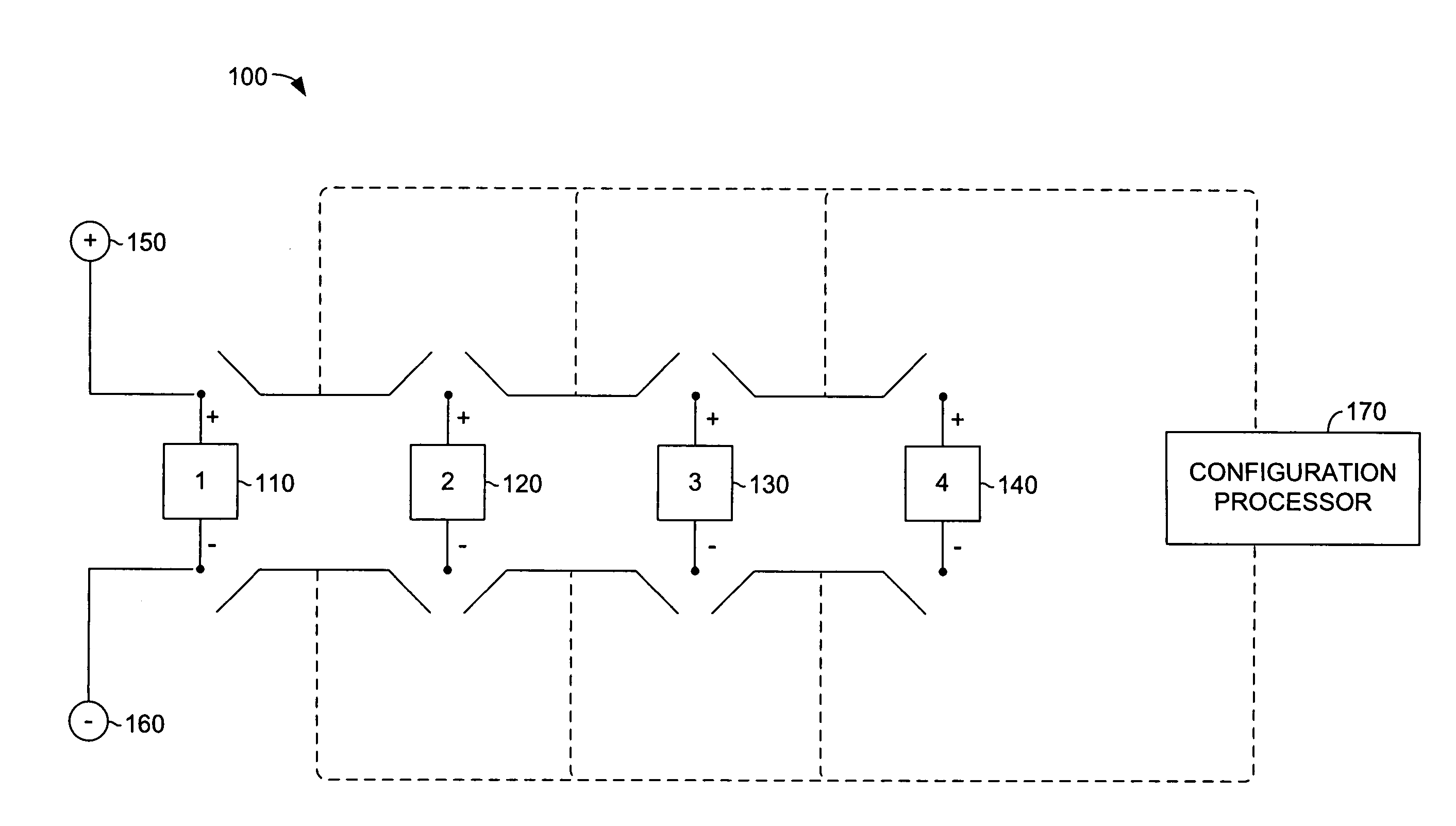
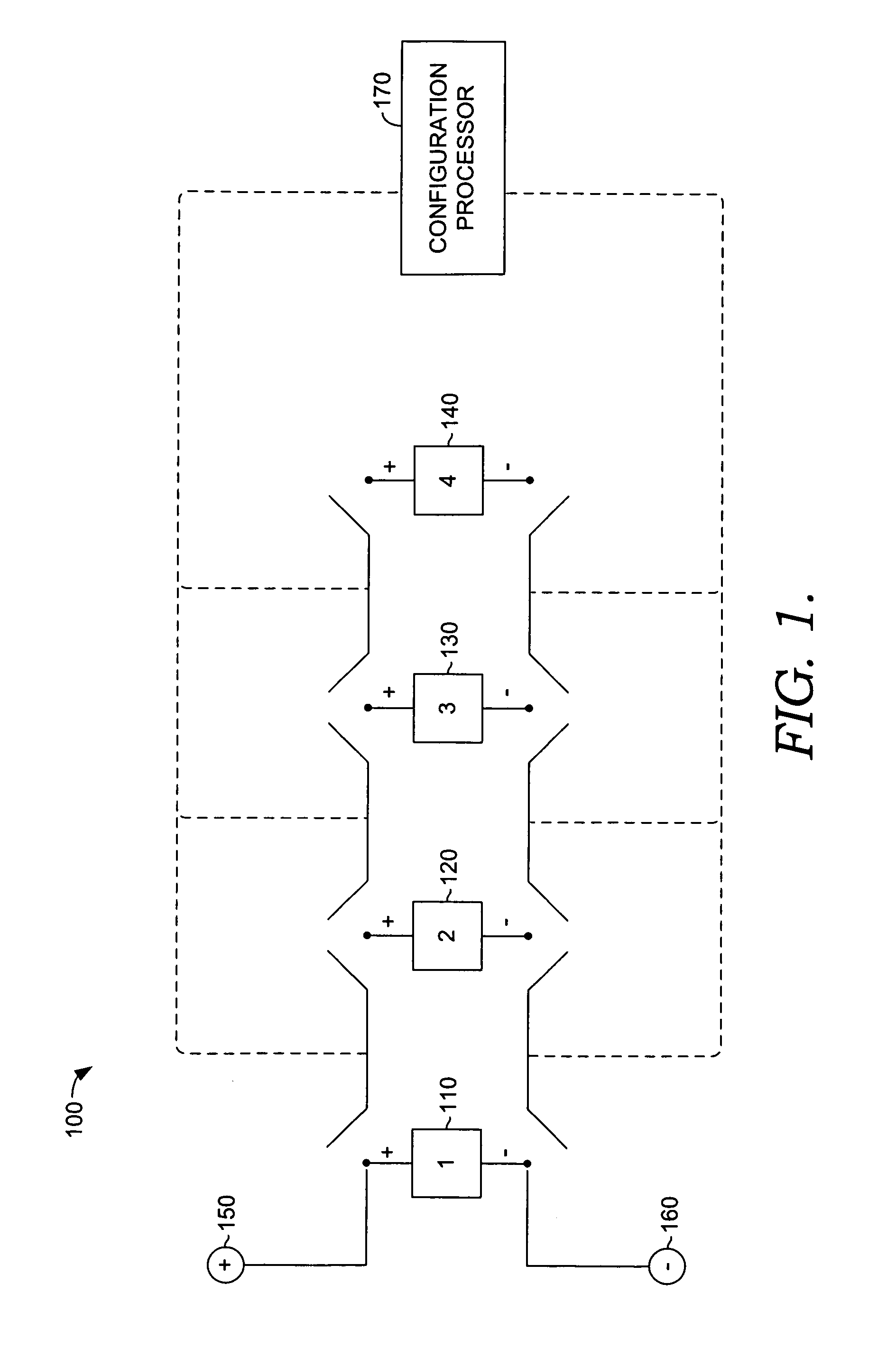
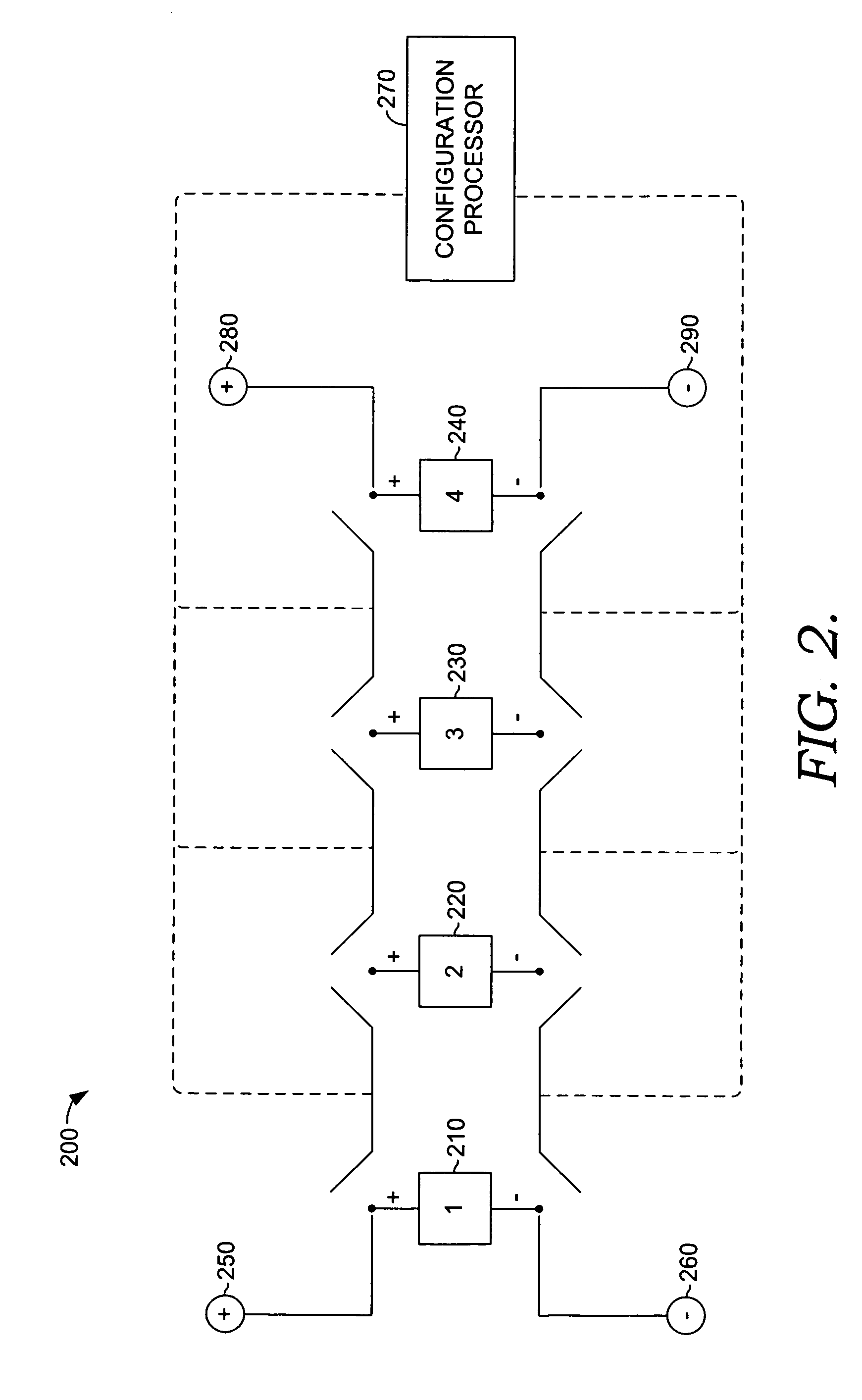
Adaptive reconfigurable battery
InactiveUS20090286149A1Primary cell to battery groupingSecondary cells charging/dischargingConfiguration designEngineering
Embodiments of the present invention relate to methods and apparatus for a dynamic reconfigurable battery system for supporting power-aware computing. The present invention allows each cell of a multi-cell battery to be charged and / or discharged separately depending on an external load that is applied to the system. The present invention, the dynamic reconfigurable multi-cell battery system, may support dynamic voltage scaling (DVS) by providing fine-tuned voltage levels to satisfy the various power requirements imposed by different system components. Another embodiment of the present invention includes taking advantage of power requirement diversity in a power-aware computing platform to fully utilize a battery's capacity. Also, this system is adaptable to isolate fully discharged or failed cells from other functioning cells. The dynamic reconfigurable design of the present invention provides a solution for an emergent power supply for mission-critical tasks.
Owner:NUTECH VENTURES +1
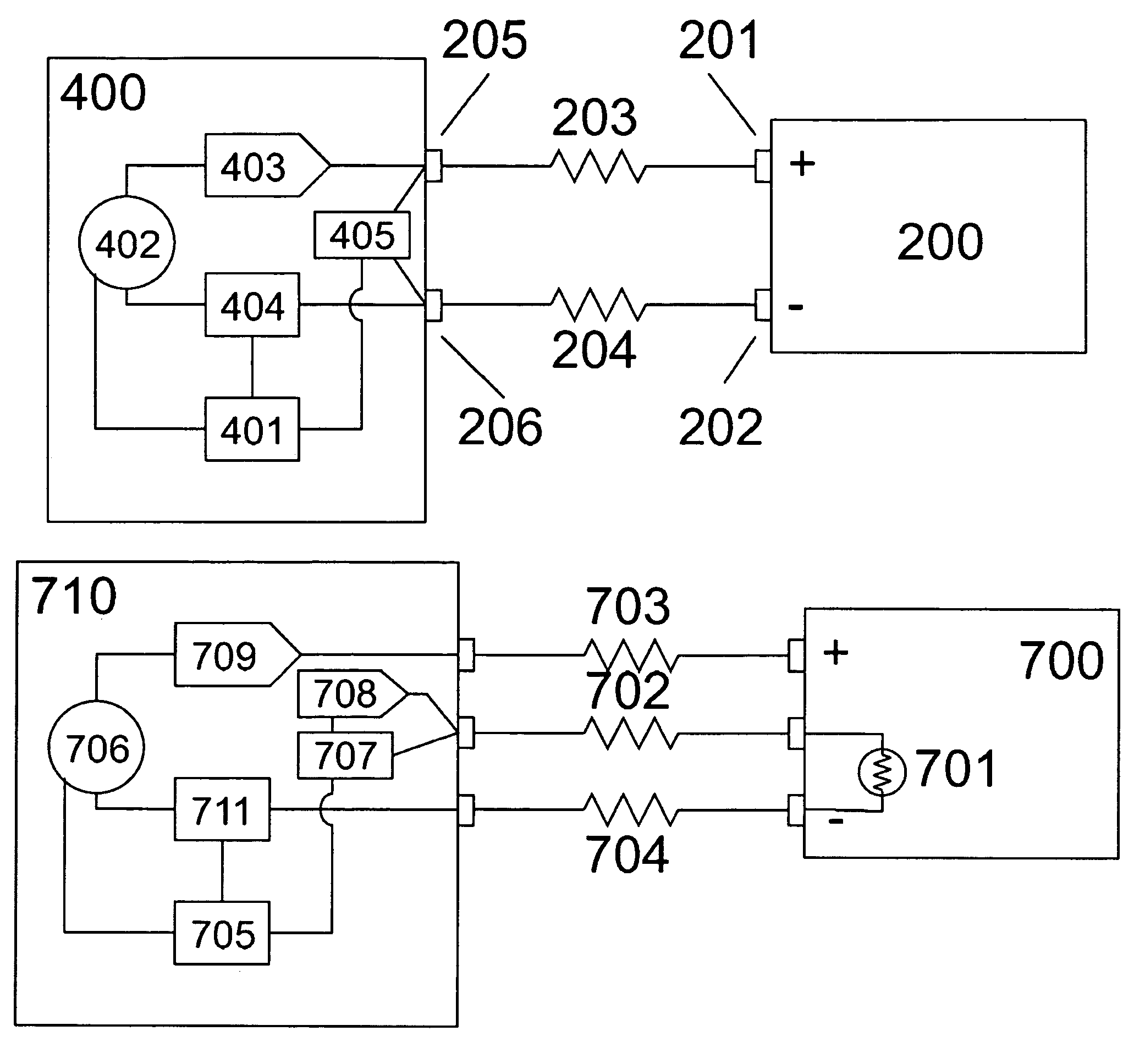
Remote battery charging system with dynamic voltage adjustment and method of use
InactiveUS20090289604A1Easy to useImprove securityBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerVoltage converterElectrical resistance and conductance
In a remote battery charging system comprising a charging circuit there is always a voltage loss due to inherent resistances in the system from such things as connectors and conductors. These resistances create voltages losses in the system such that charging times are increased substantially. The present invention compensates for voltage losses on the system by generating a dynamic adjustment voltage over the charging period. A voltage translator circuit is used to measure charging circuit output voltage and current over a plurality of incremental time periods during the charging period an calculate a signal proportional to changes in output voltage and current over the incremental time period. The signal is then applied to the charging circuit to offset any voltage losses.
Owner:GALVION POWER SYST INC
Method of realizing single-phase phase-locked loop by software
InactiveCN101291150AFast trackingAccurate trackingPulse automatic controlLow-pass filterElectric power system
The present invention relates to a method for realizing single-phase phase-locked loop by adopting software, comprising the following steps of: constituting an input signal in an alpha-beta coordinate system with a standard signal as a reference (1); carrying out PI adjustment through the output of dq0 conversion q axle component based on the instantaneous reactive power theory, carrying out frequency correction through the output of the PI adjustment step, using an output signal of the frequency correction step as a reference, and carrying out phase correction through using the integration step (2); designing a low pass filter and ensuring the speed and the accuracy of the tracking of the phase-locked loop (3); speeding up the calculation by adopting 16 bit fixed point TMS320C2812DSP programming (4). The method adopts closed-loop control, which is high in stability and quick in tracking speed, with the transient response time less than 0.04s and wide frequency range of the locked phase between about 45 and 55Hz, is not interfered by the harmonic waves and the twinkling fluctuation of the system voltage or current, can accurately and quickly track the fundamental wave frequency and the phase information of the voltage and current in an electric power system, and provides system synchronous frequency signals for active filters and dynamic voltage adjustors, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI POWER TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTION CO LTD
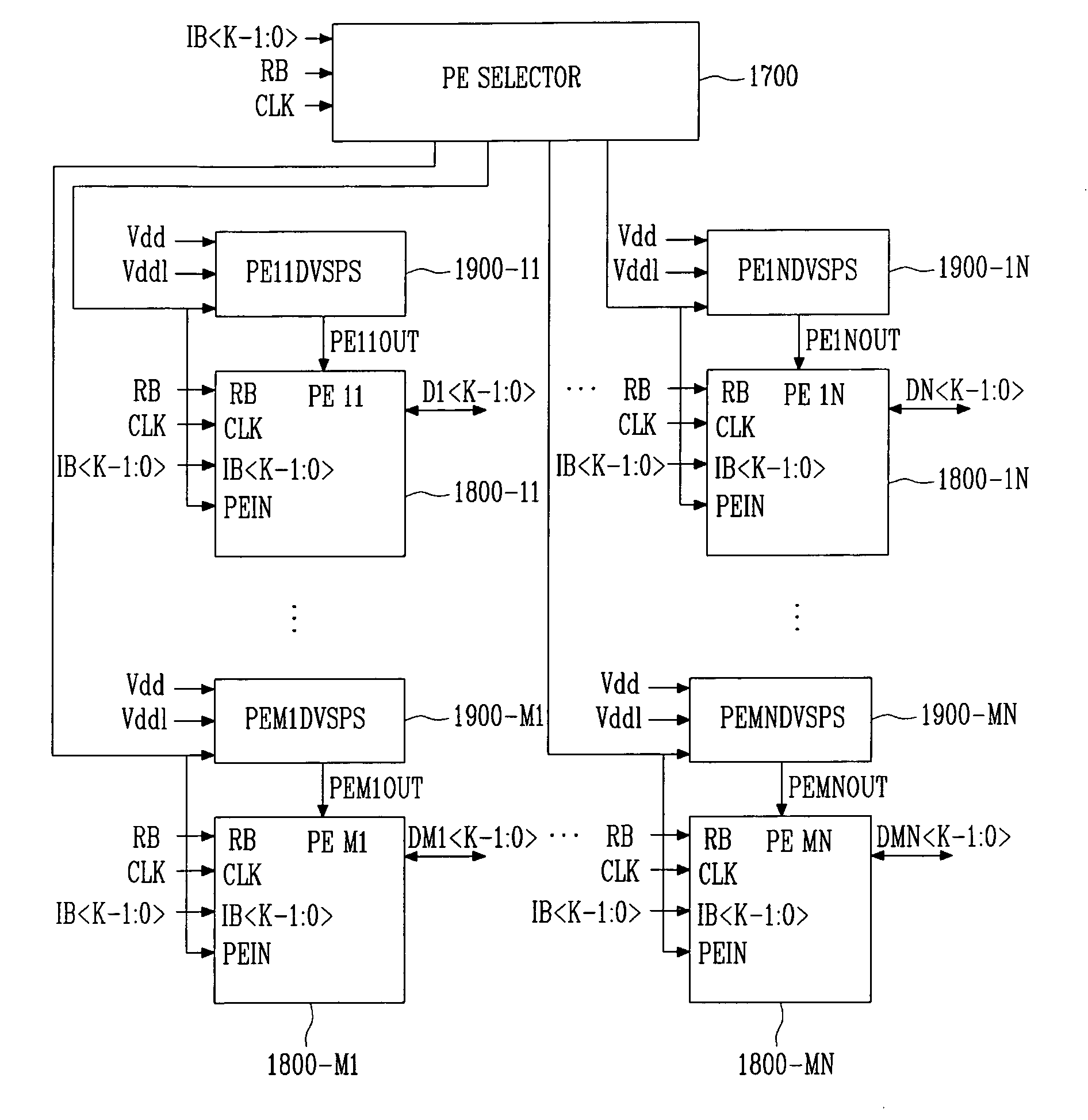
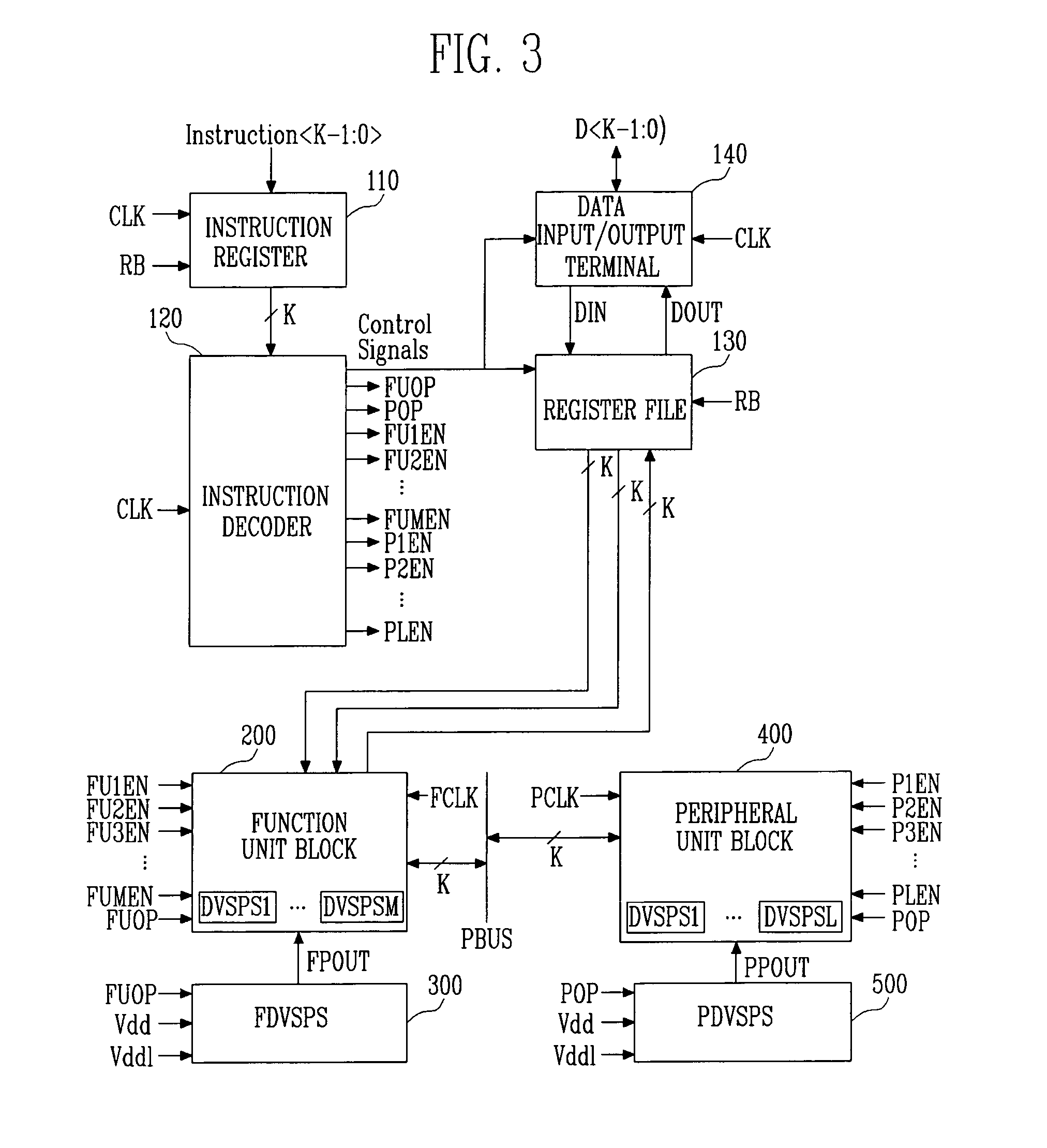
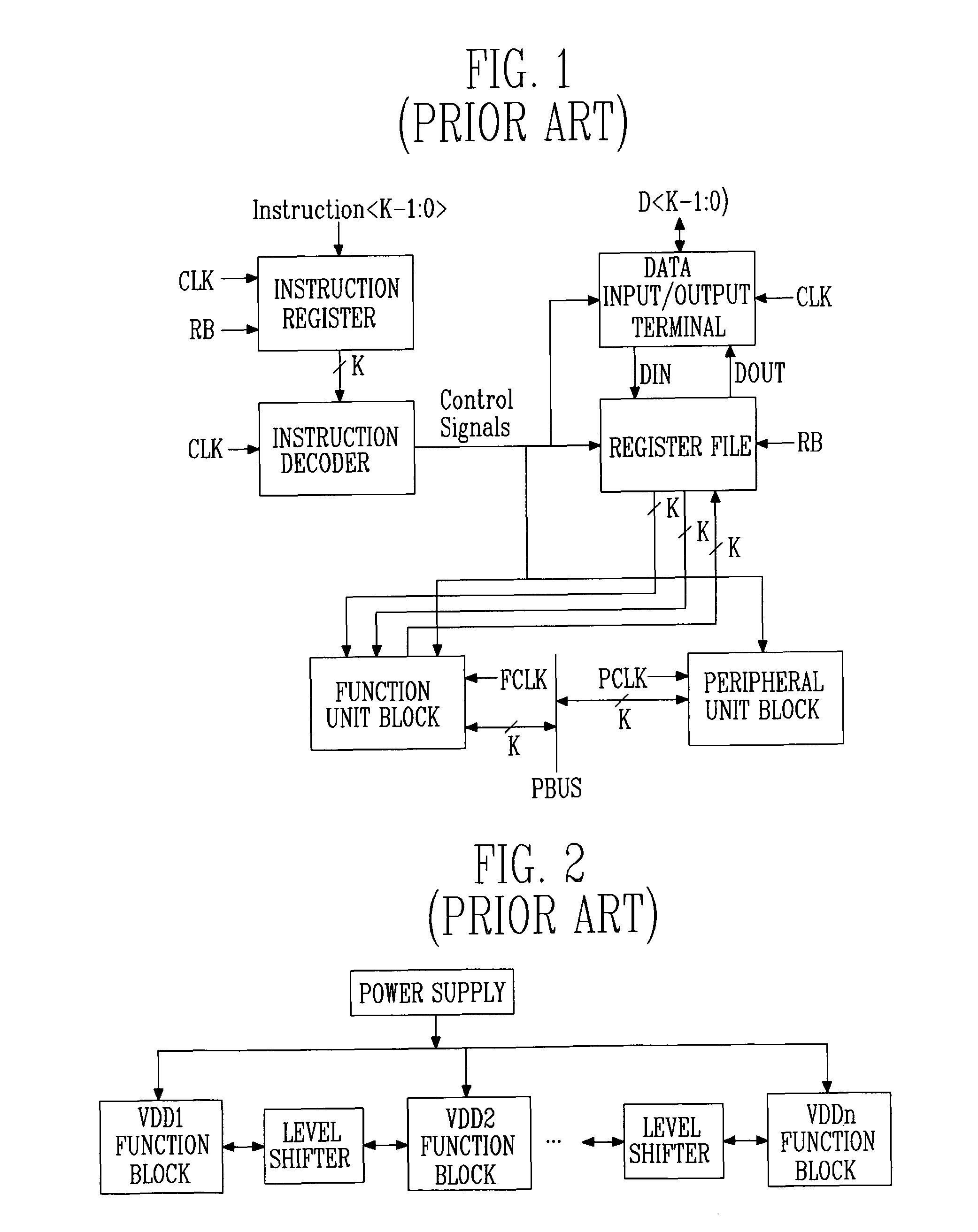
Highly energy-efficient processor employing dynamic voltage scaling
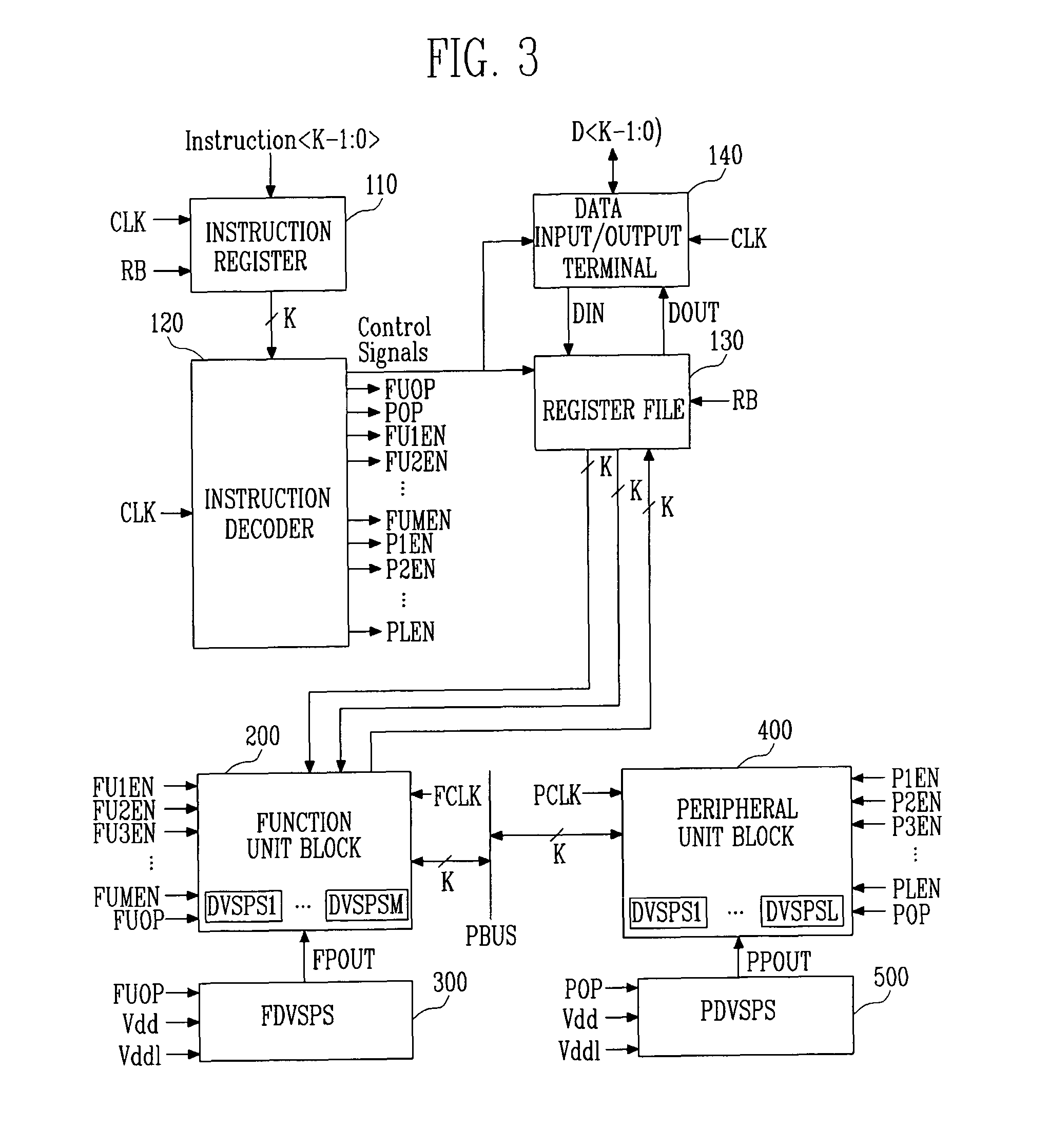
ActiveUS20070150763A1Maximize energy efficiencySimple structureEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingHigh energyParallel computing
Provided is a highly energy-efficient processor architecture. The architecture employs 2-stage dynamic voltage scaling (DVS) and a sleep mode for high energy efficiency, dynamically controls the power supply voltage and activation of an embedded processor with instructions, and thus can prevent performance deterioration while reducing power consumption.A highly energy-efficient processor employing the processor architecture includes: a function unit block for performing an operation according to instructions input from the outside; at least one peripheral unit block for performing data communication with an external device; an instruction decoder for interpreting the input instructions and determining operation modes of the function unit block and peripheral unit block required for executing the interpreted instructions; a function unit block driver for applying a different power supply voltage according to the operation mode of the function unit block to the function unit block; and a peripheral unit block driver for applying a different power supply voltage according to the operation mode of the peripheral unit block to the peripheral unit block.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
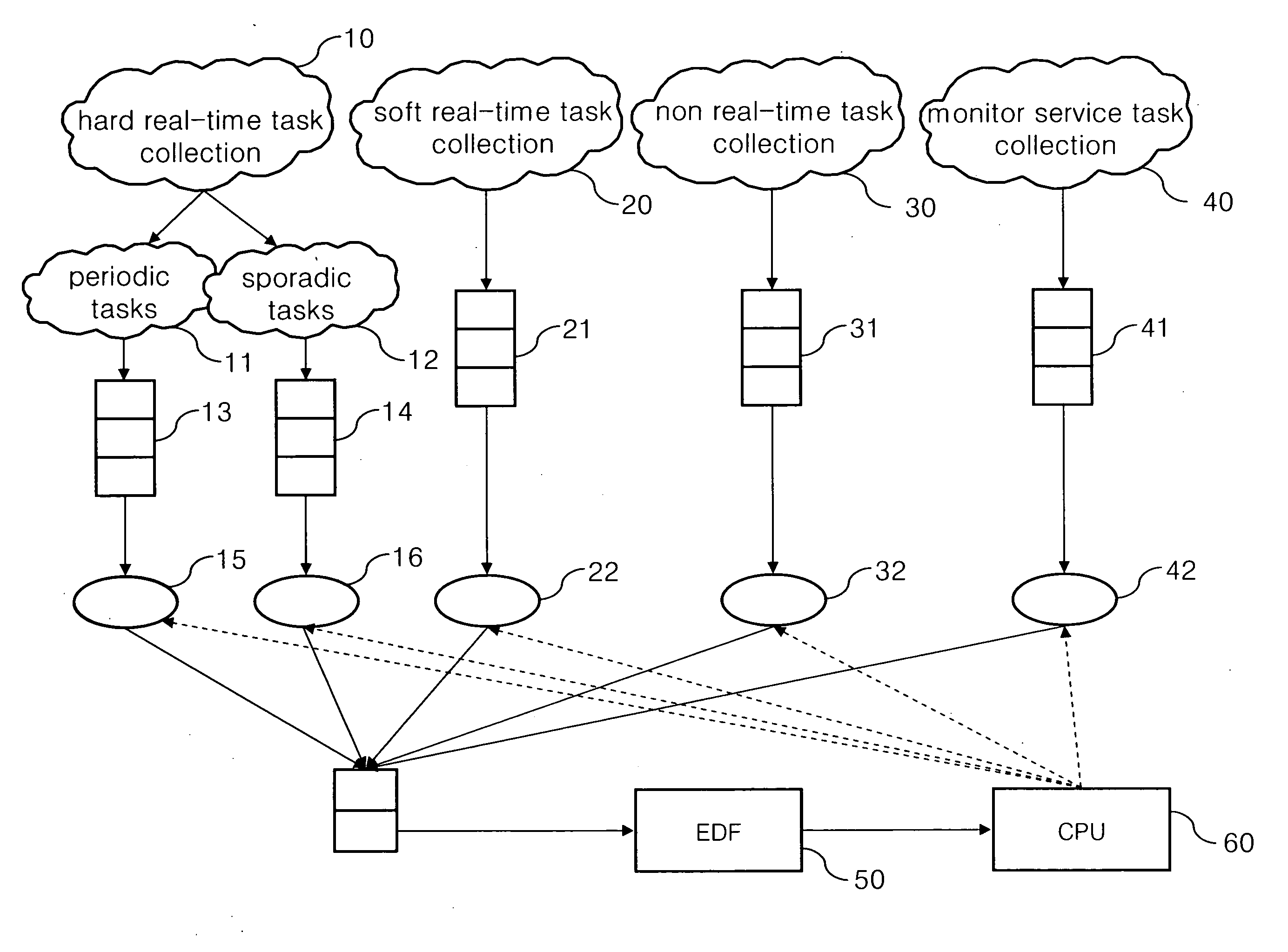
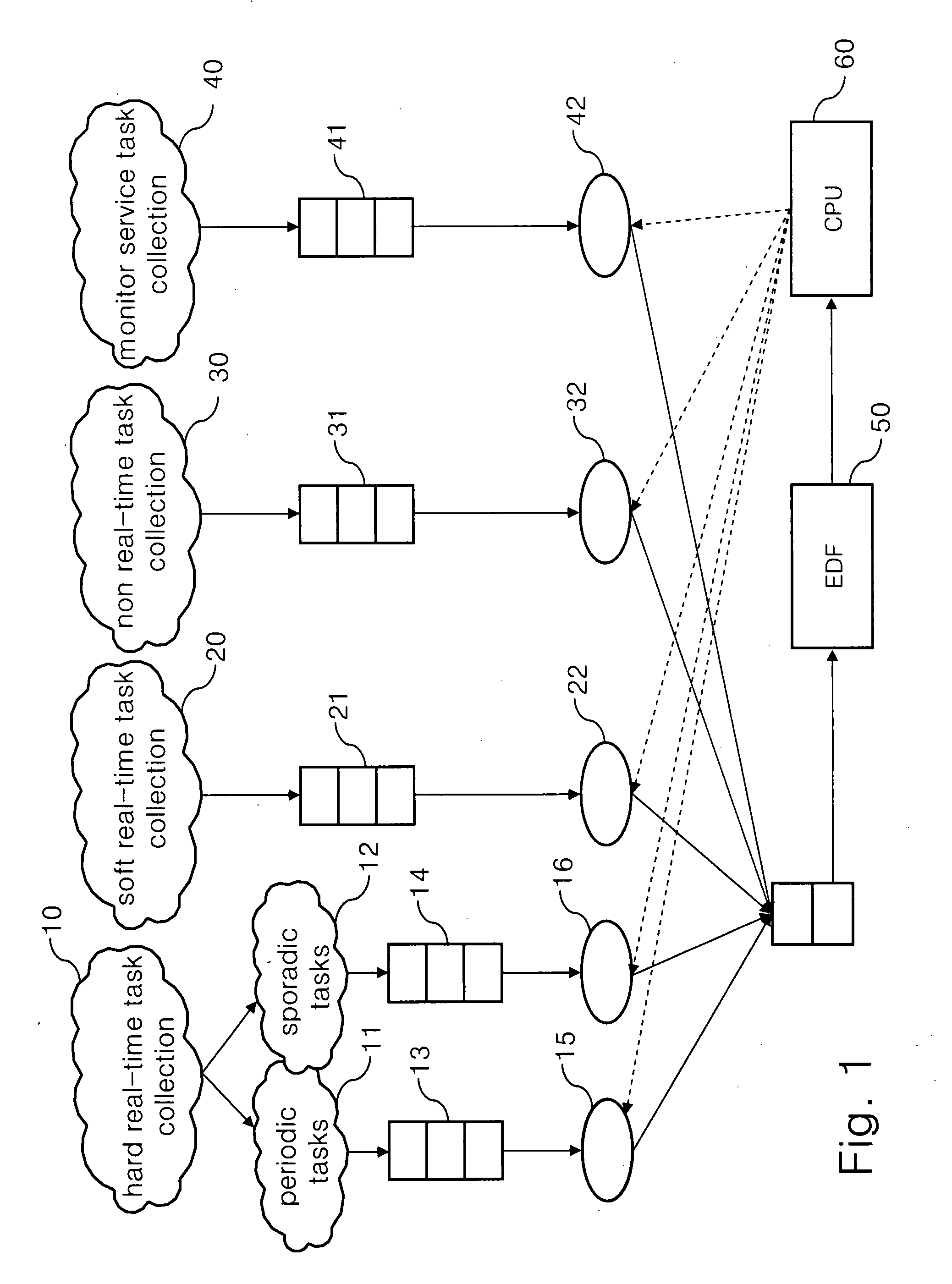
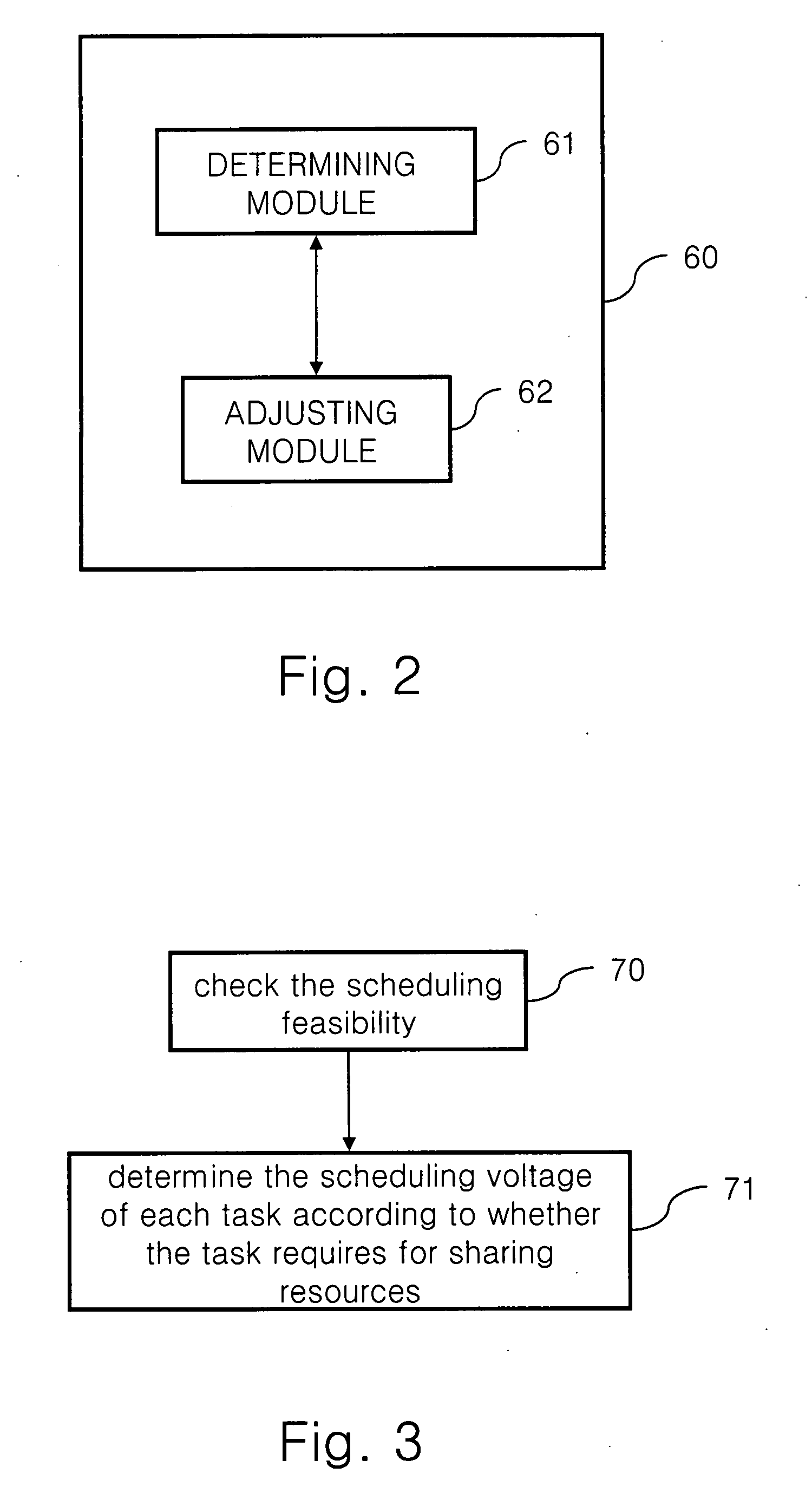
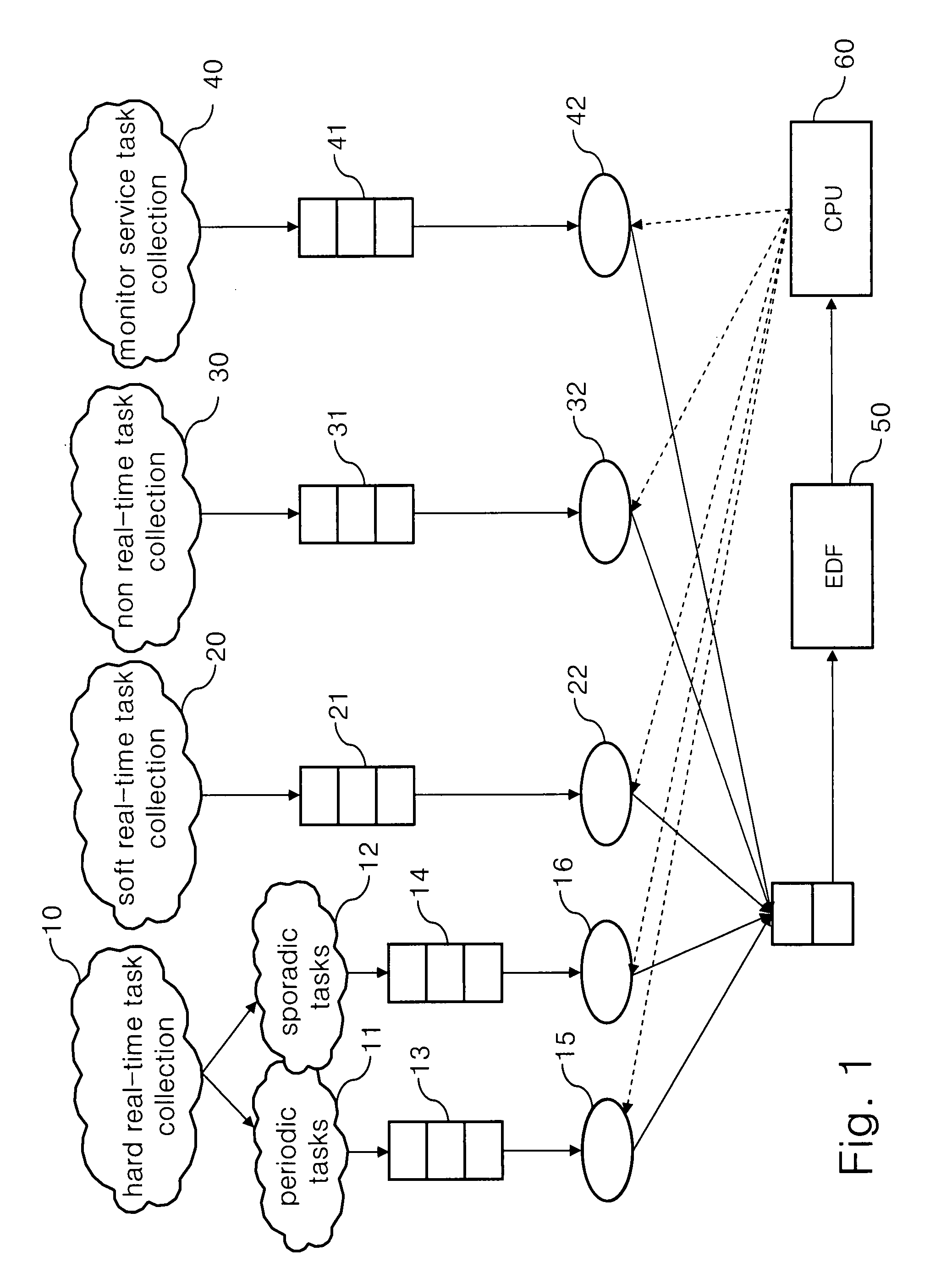
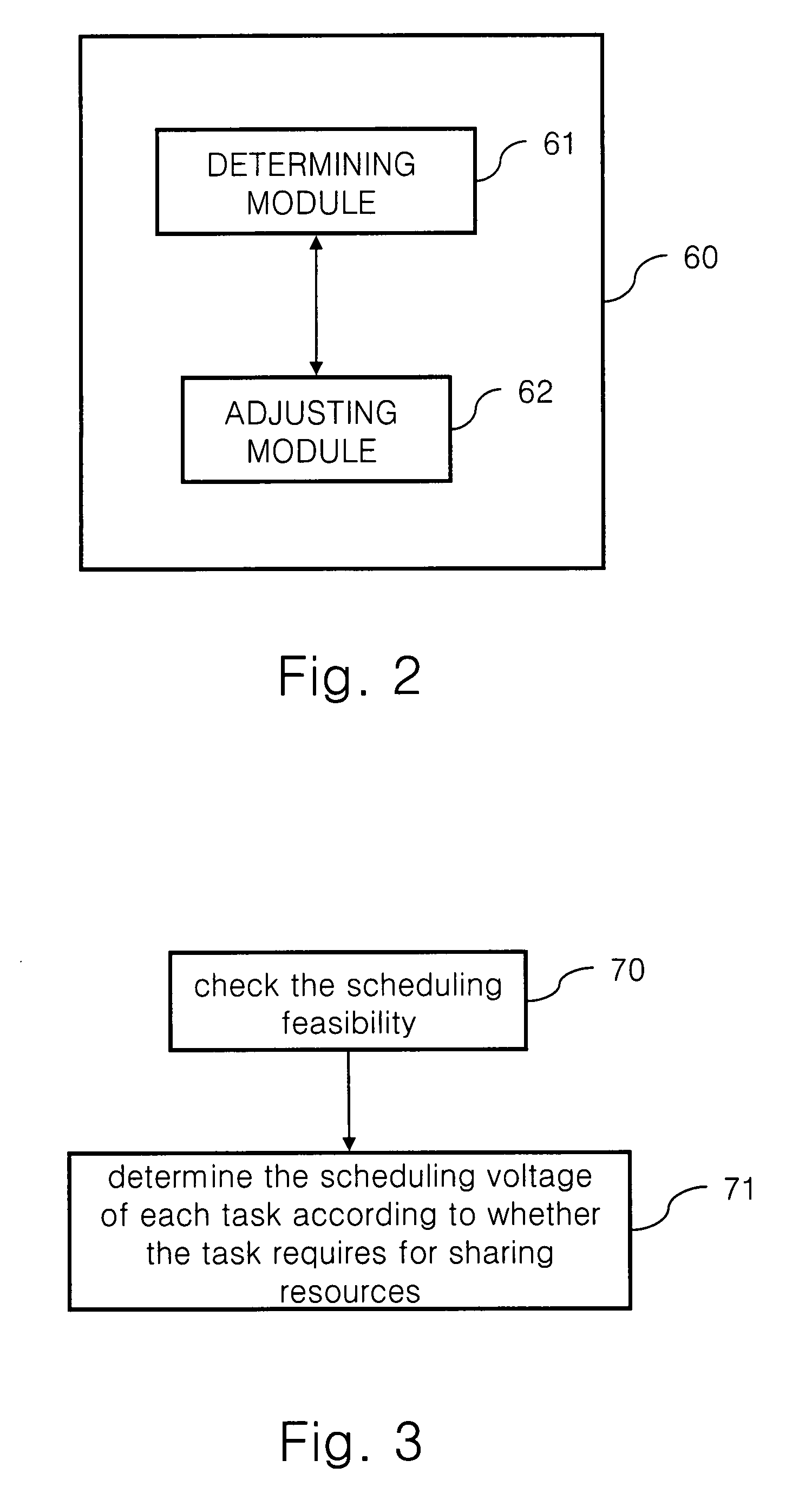
Dynamic voltage scaling scheduling mechanism for sporadic, hard real-time tasks with resource sharing
InactiveUS20080148273A1Improve energy efficiencyFlexibility of schedulingEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementWork cycleDynamic voltage scaling
A dynamic voltage scaling scheduling method executes one of the steps. When one task in the delayed task set requires for being executed, a working voltage required for executing the task is increased, and the task is removed from the delayed task set; when one task in the delayed task set requires for sharing resources, the working voltage required by the task is set as the current working voltage or a larger one in the minimum upper bounds of all the works requiring for sharing resources; and when one task does not belong to the delayed task set, but the waiting time has exceeded the period of the work, the working voltage for executing the task is reduced, and the task is added in the delayed task set.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
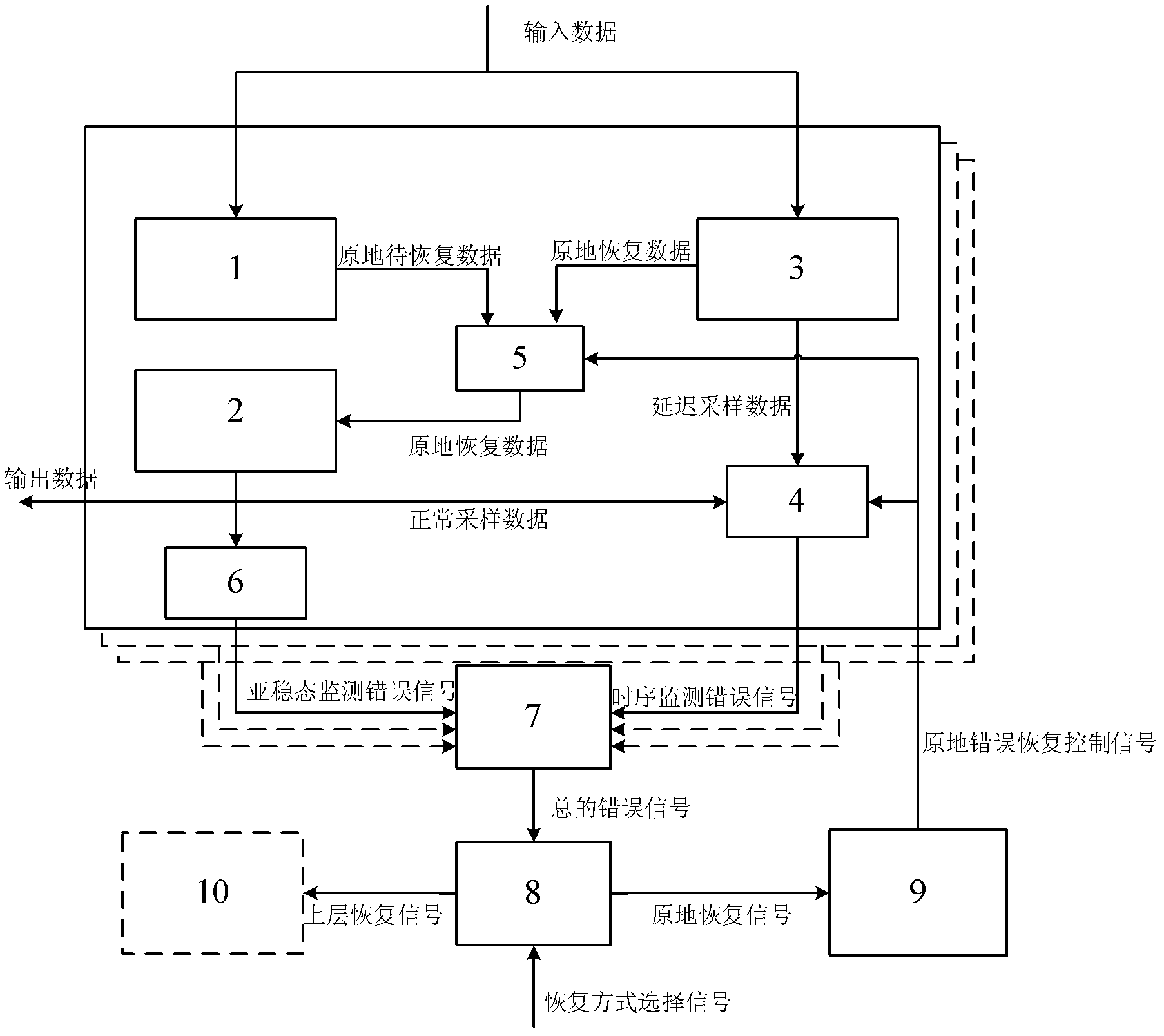
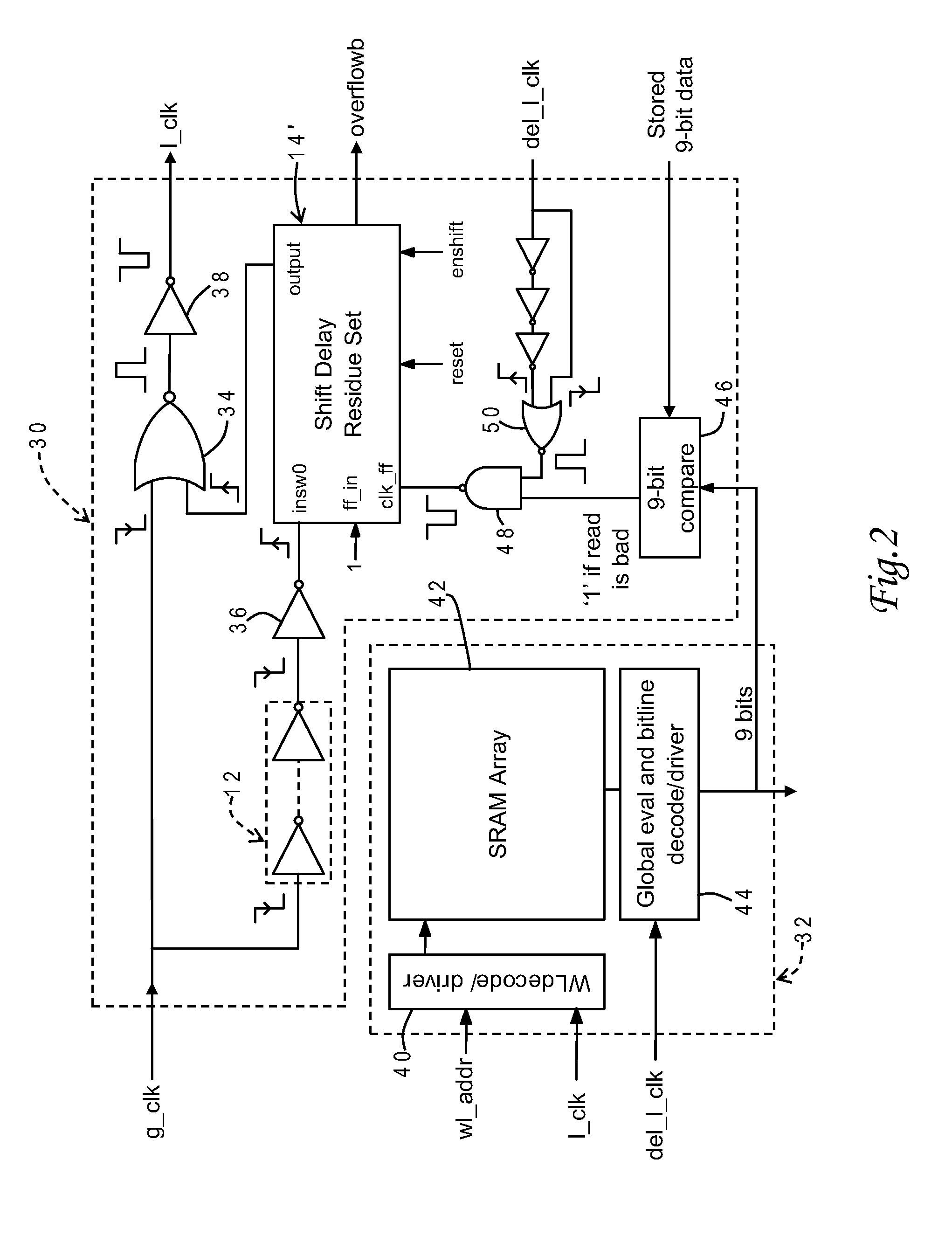
Dynamic voltage scaling system-oriented on-chip monitoring circuit
ActiveCN102520754AImplement in-place error recoverySimple structureElectric variable regulationProcessor registerControl signal
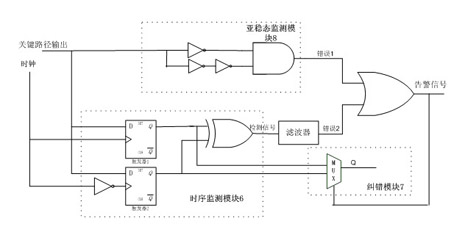
The invention discloses a dynamic voltage scaling system-oriented on-chip monitoring circuit, which is characterized by comprising a master register circuit (1), a slave register circuit (2), a shadow register circuit (3), an error signal generation circuit (4), an in-situ error correction selector (5), a metastable state monitoring circuit (6), an error signal integration circuit (7), a restoration mode selection circuit (8) and an in-situ error restoration control signal generation circuit (9). By the dynamic voltage scaling system-oriented on-chip monitoring circuit, the influence of factors such as a process, voltage, temperature noise and the like on a main circuit can be effectively resolved into the variation of delay characteristics of a key unit and a special path to reflect the actual conditions of each part in a chip, and a dynamic voltage scaling effect is greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
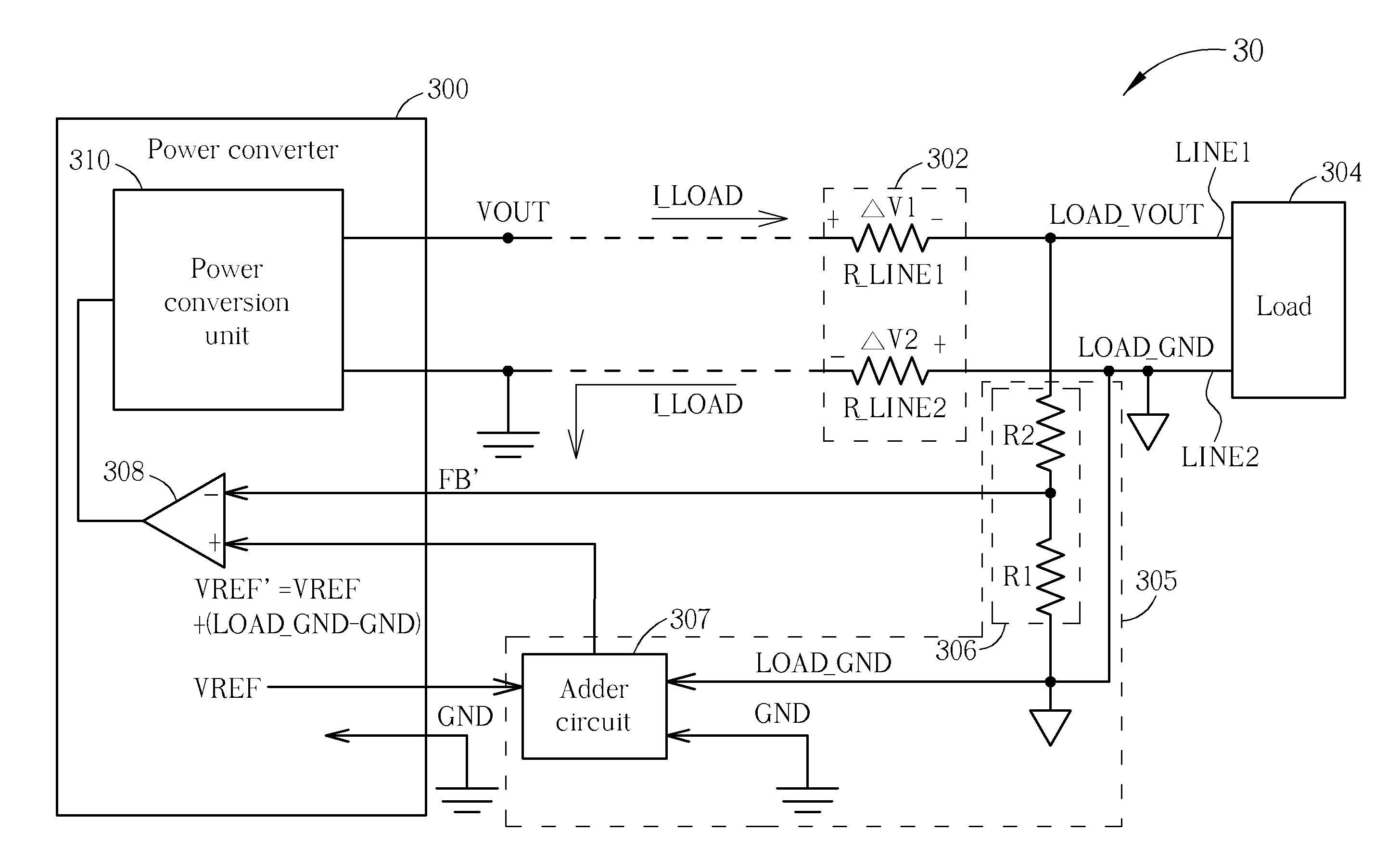
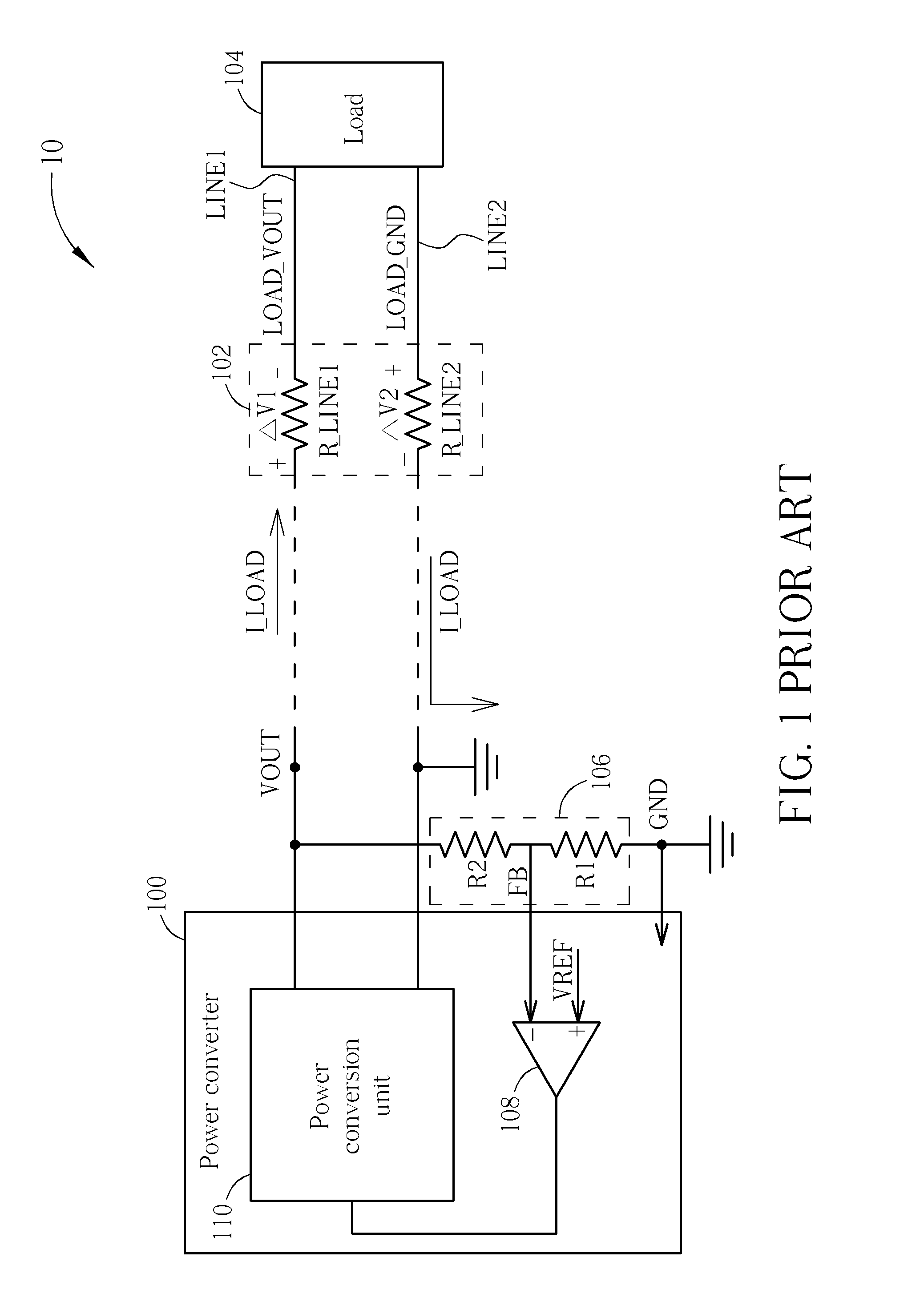
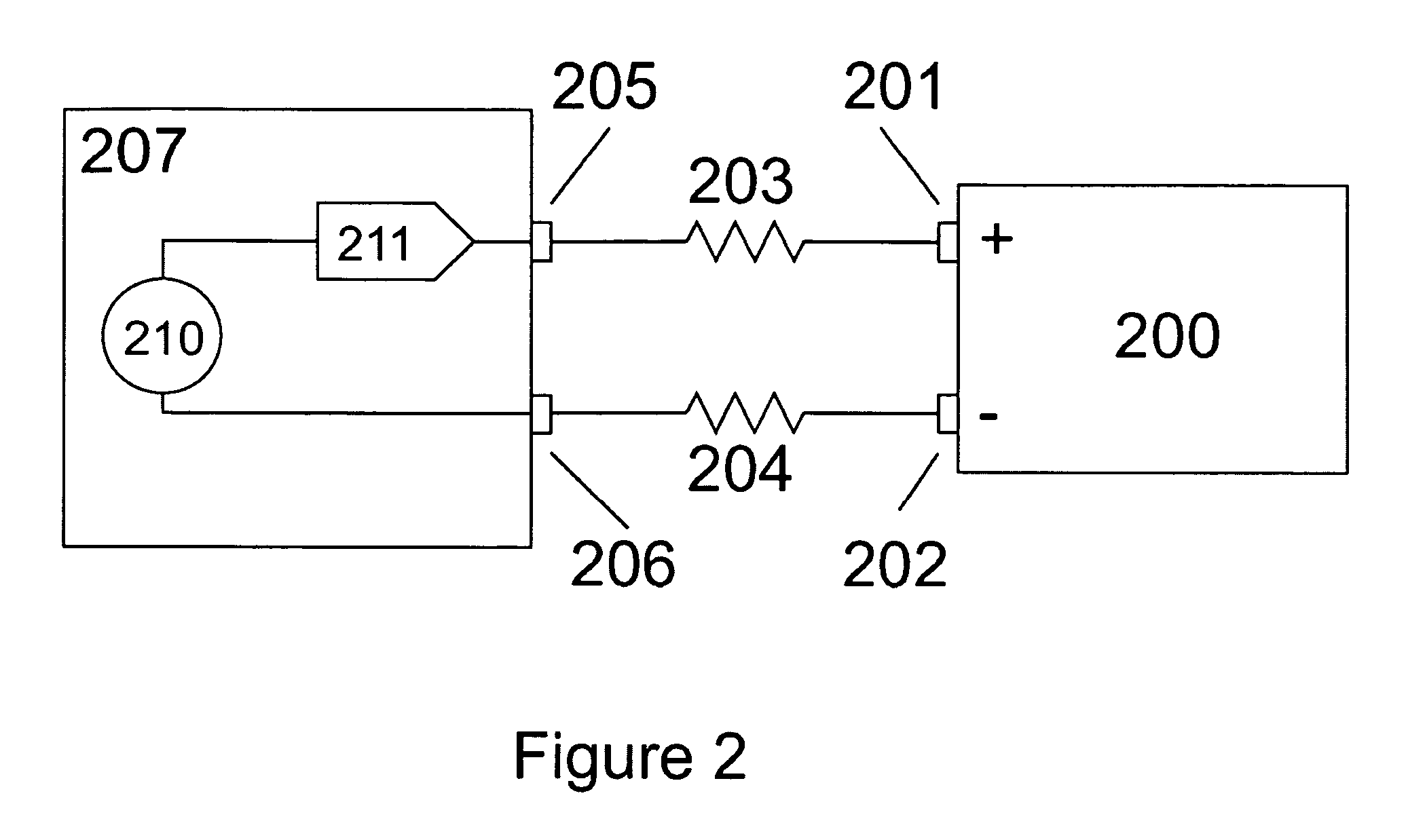
Dynamic Voltage Adjustment Device and Power Transmission System Using the Same
ActiveUS20130162226A1Dc-dc conversionAc network voltage adjustmentElectric power transmissionDrivetrain
The present invention discloses a dynamic voltage adjustment device for dynamically adjusting an output voltage of a power transmission system which generates the output voltage according to a feedback signal and a reference signal and transmits the output voltage to a remote load via a transmission line to generate a load current. The dynamic voltage adjustment device comprises a first signal terminal, for receiving a first signal corresponding to a forward transmission voltage drop of the transmission line; a second signal terminal, for receiving a second signal corresponding to a reverse transmission voltage drop of the transmission line; a third signal terminal for receiving a reference voltage; a feedback circuit, for generating a feedback signal according to the first signal; and a adder circuit, for generating the reference signal according to the second signal and the reference voltage.
Owner:ANPEC ELECTRONICS CORPORATION
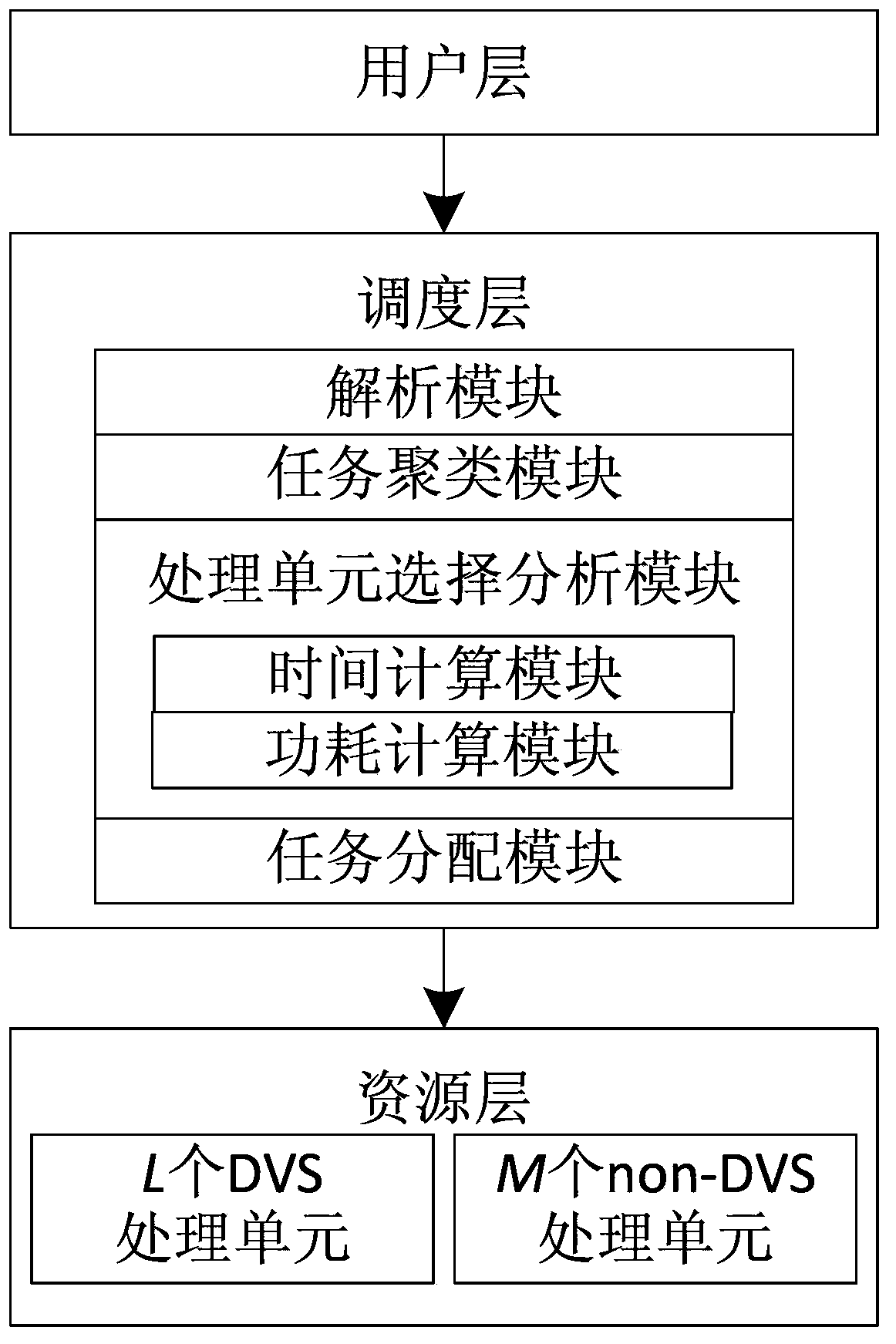
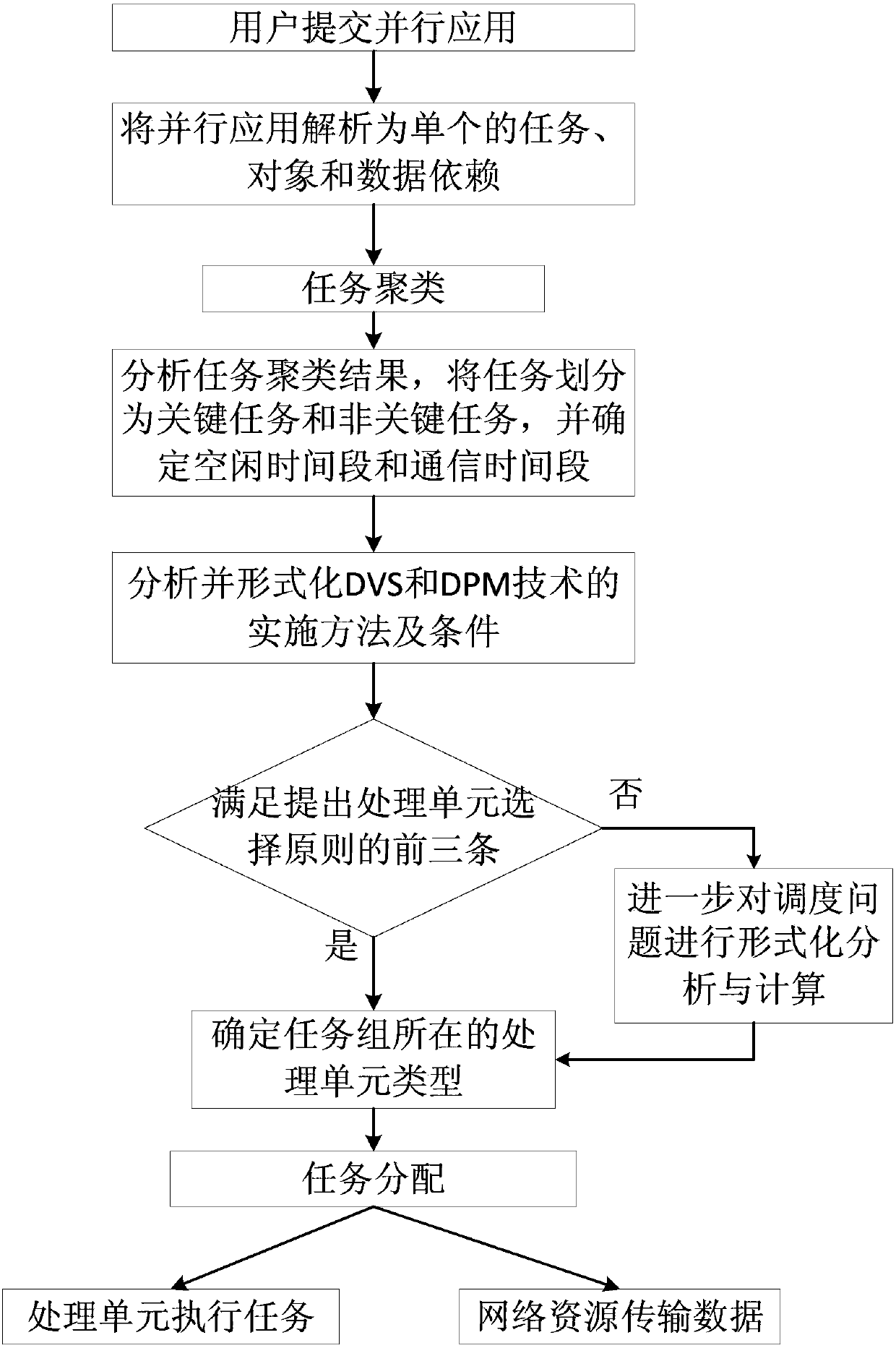
Power consumption sensing scheduling system and power consumption sensing scheduling method for parallel application for hybrid computation environments
ActiveCN103399626ATaking into account DVS/non-DVS hybridApplication execution time is minimizedEnergy efficient ICTResource allocationDynamic voltage scalingData transmission
The invention discloses a power consumption sensing scheduling system and a power consumption sensing scheduling method for parallel application for hybrid computation environments. The power consumption sensing scheduling system comprises a user layer, a scheduling layer and a resource layer. The user layer transmits user requests to the scheduling layer, the scheduling layer transmits execution tasks and data required by the execution tasks to the resource layer and comprises an analysis module, a task clustering module, a processing unit selection analysis module and a task distribution module, analysis results of the analysis module are transmitted to the task clustering module, clustering results of the task clustering module are transmitted to the processing unit selection analysis module, the processing unit selection analysis module comprises a time computation module and a power consumption computation module, selection analysis results of the processing unit selection analysis module are transmitted to the task distribution module, and the resource layer comprises a plurality of DVS (dynamic voltage scaling) processing units and a plurality of non-DVS processing units. The power consumption sensing scheduling system and the power consumption sensing scheduling method have the advantages that DVS and non-DVS hybrid characteristics of the system are taken into consideration on the premise that application execution time minimization is a scheduling task, and execution power consumption of the application is reduced to the greatest extent.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
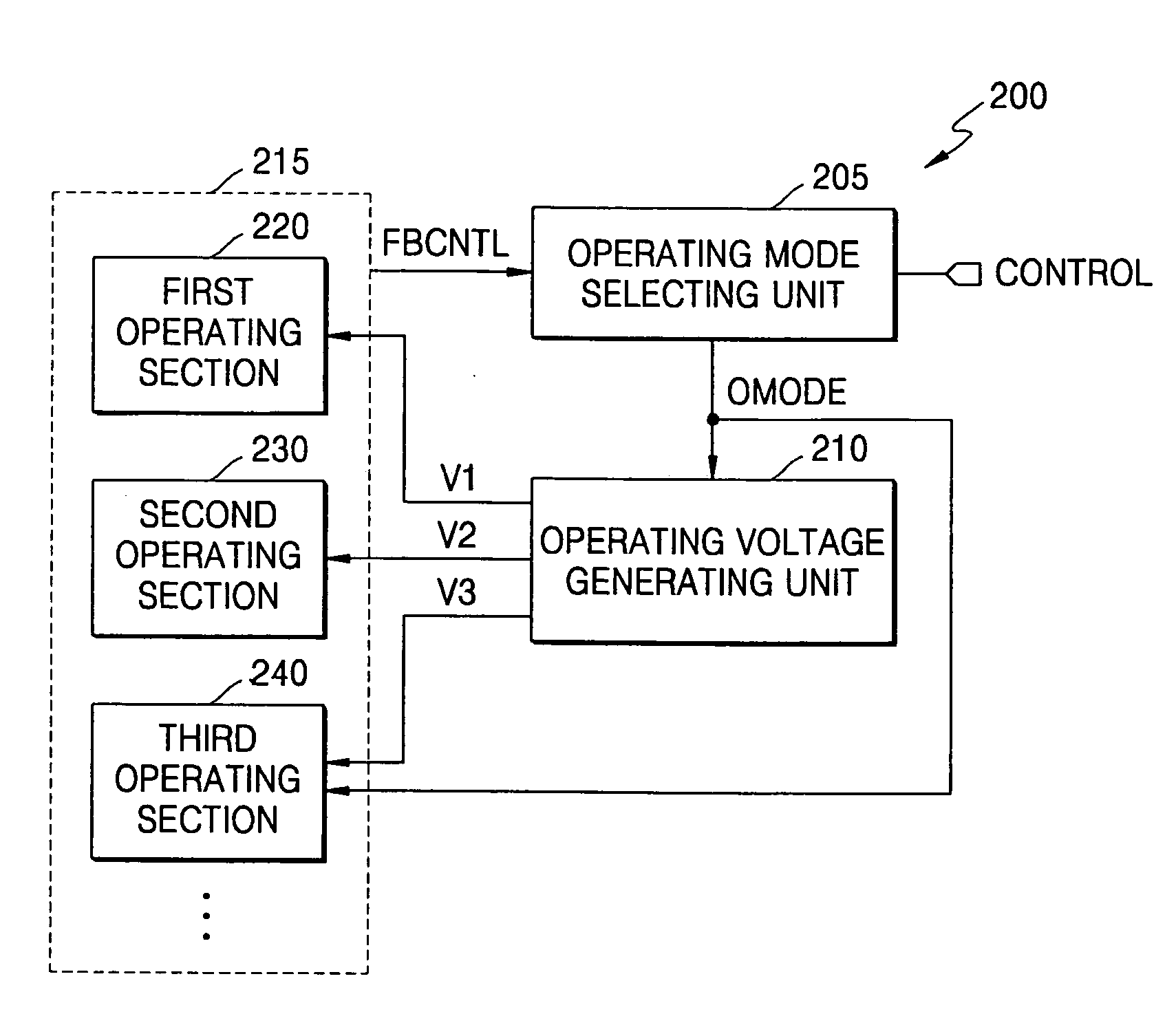
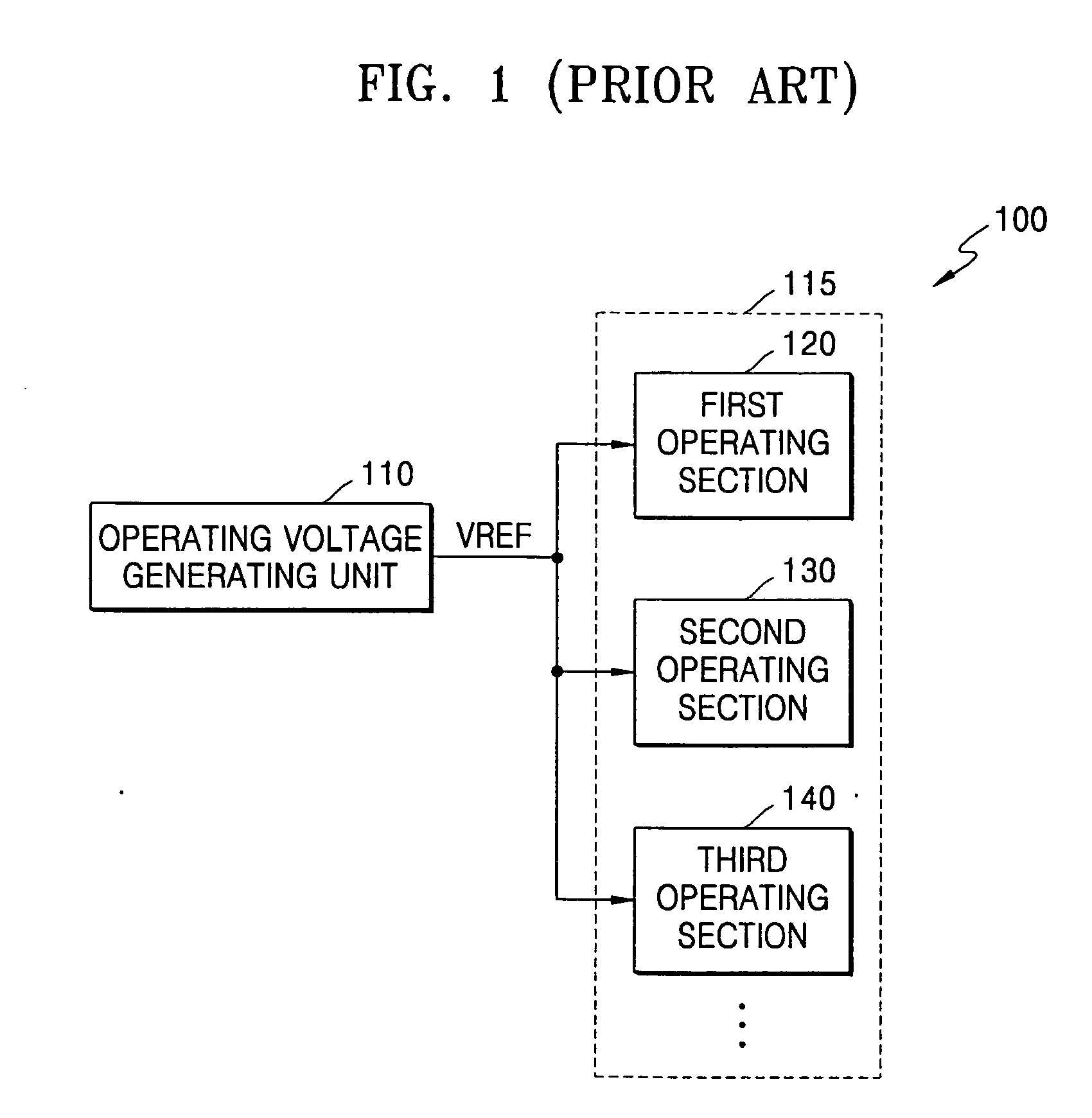
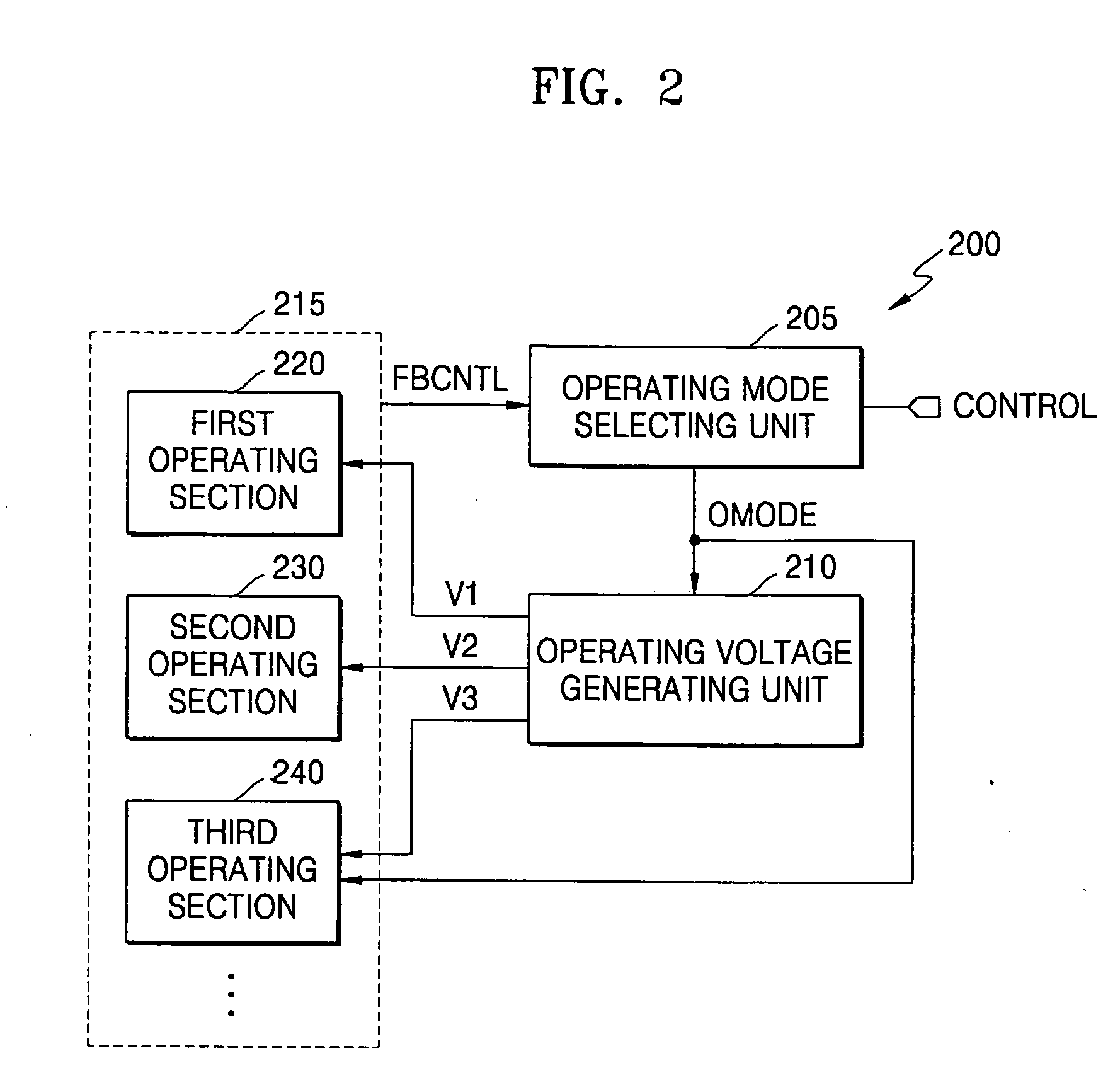
Integrated circuit devices that support dynamic voltage scaling of power supply voltages
ActiveUS20050188233A1Easy to operatePower memory access operationEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementVoltage generatorLow voltage
An integrated circuit device is provided with a power supply voltage generator therein. This voltage generator is configured to respond to an operating mode control signal by generating first and second power supply voltages at equivalent voltage levels when the operating mode control signal designates a normal mode of operation within the integrated circuit device. The power supply voltage generator is also configured to reduce the first and second power supply voltages to unequal lower voltage levels when the operating mode control signal designates a power saving mode of operation within the integrated circuit device. The power supply voltage generator may also generate a third power supply voltage at a constant level during both the normal and power saving modes of operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Remote battery charging system with dynamic voltage adjustment and method of use
InactiveUS8138723B2Batteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerVoltage converterElectrical resistance and conductance
In a remote battery charging system comprising a charging circuit there is always a voltage loss due to inherent resistances in the system from such things as connectors and conductors. These resistances create voltages losses in the system such that charging time are increased substantially. The present invention compensates for voltage losses on the system by generating a dynamic adjustment voltage over the charging period. A voltage translator circuit is used to measure charging circuit output voltage and current over a plurality of incremental time periods during the charging period an calculate a signal proportional to changes in output voltage and current over the incremental time period. The signal is then applied to the charging circuit to offset any voltage losses.
Owner:GALVION POWER SYST INC
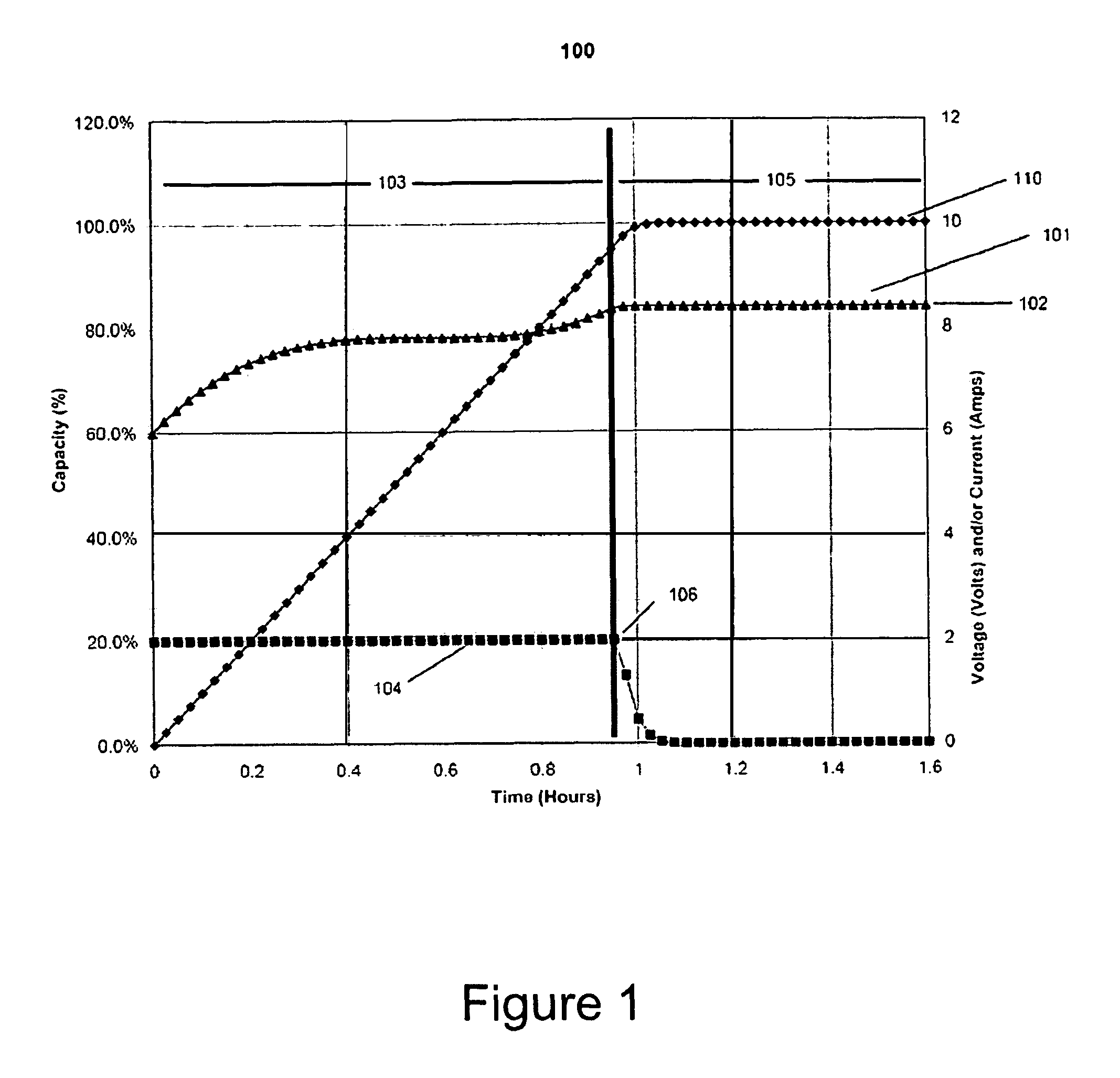
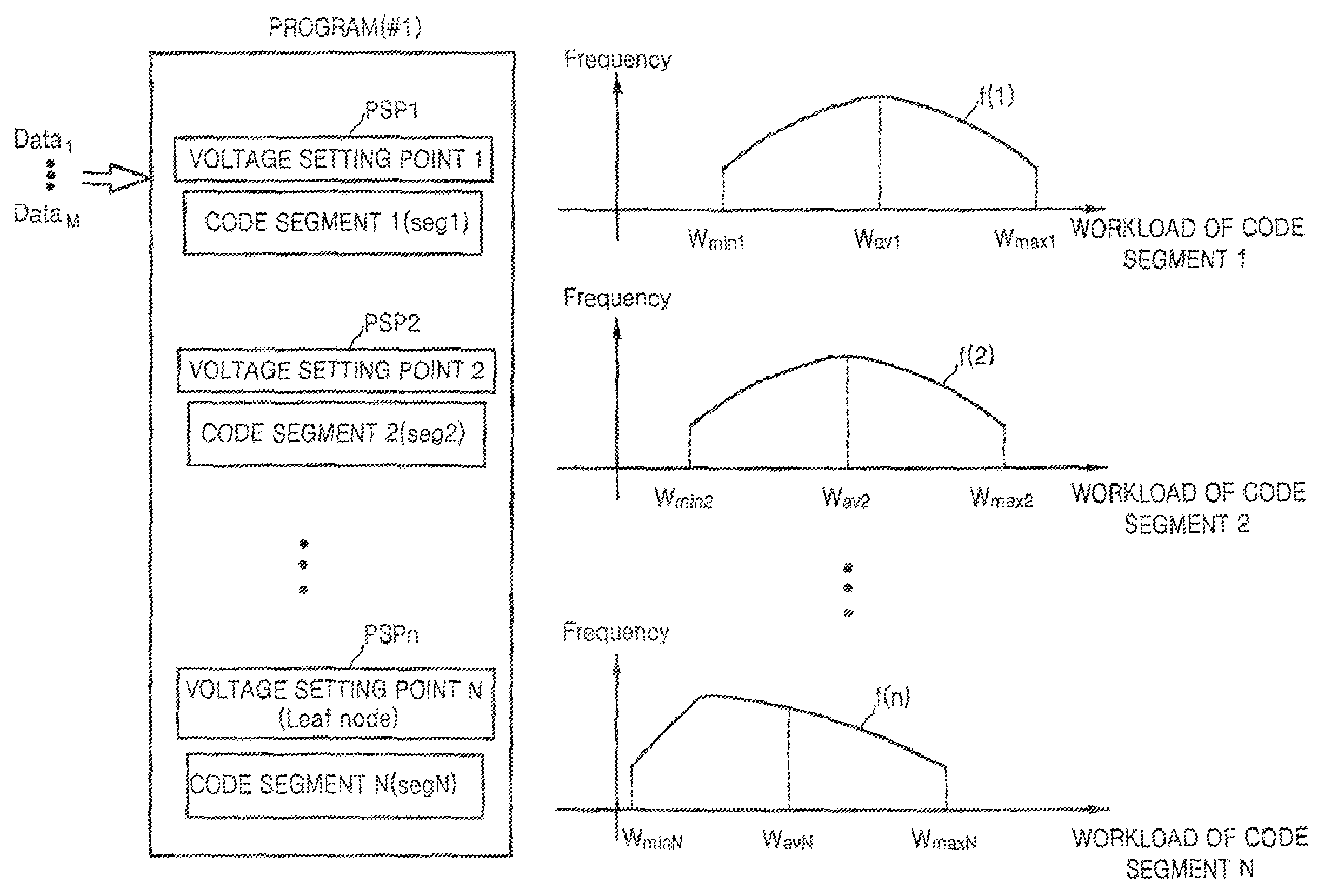
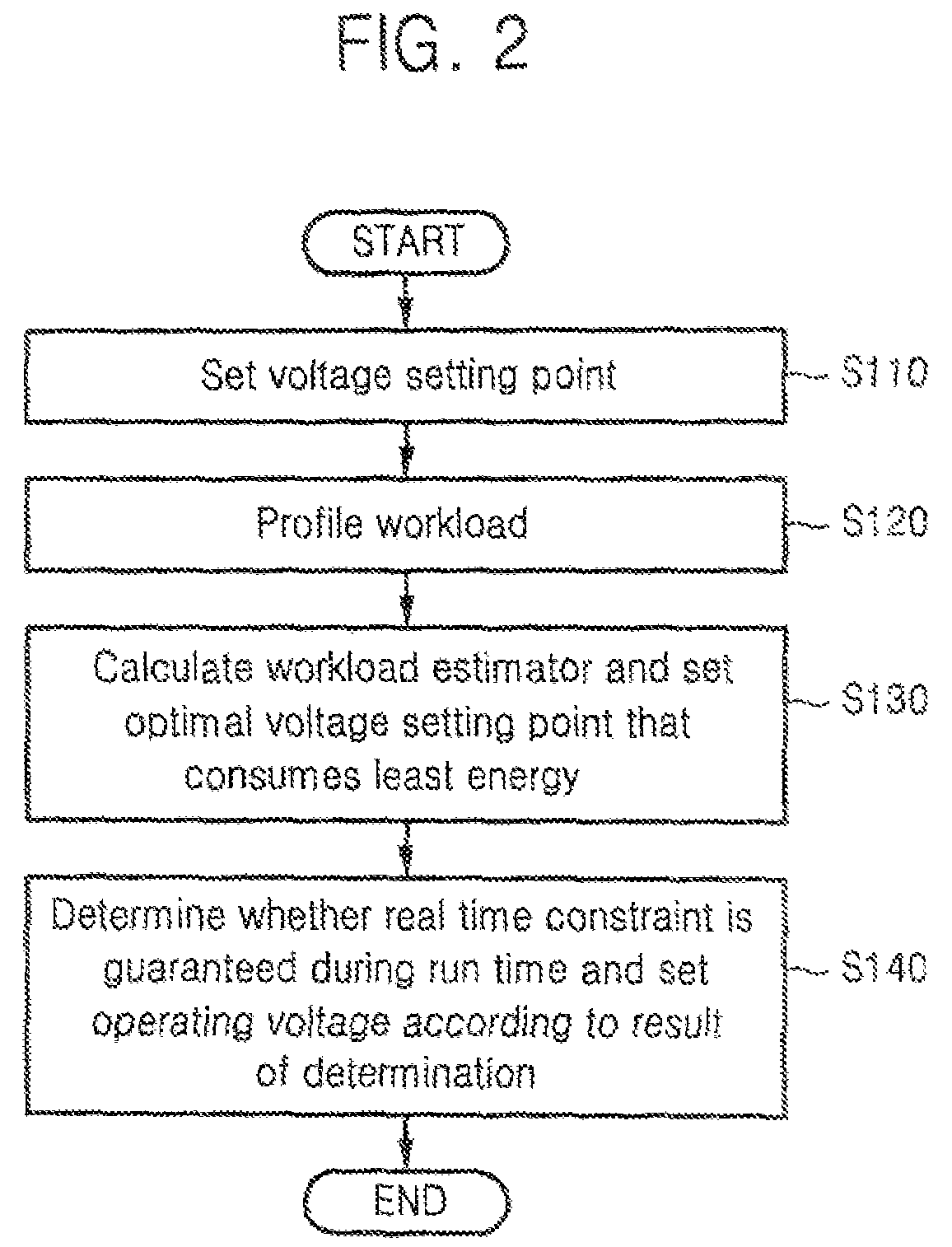
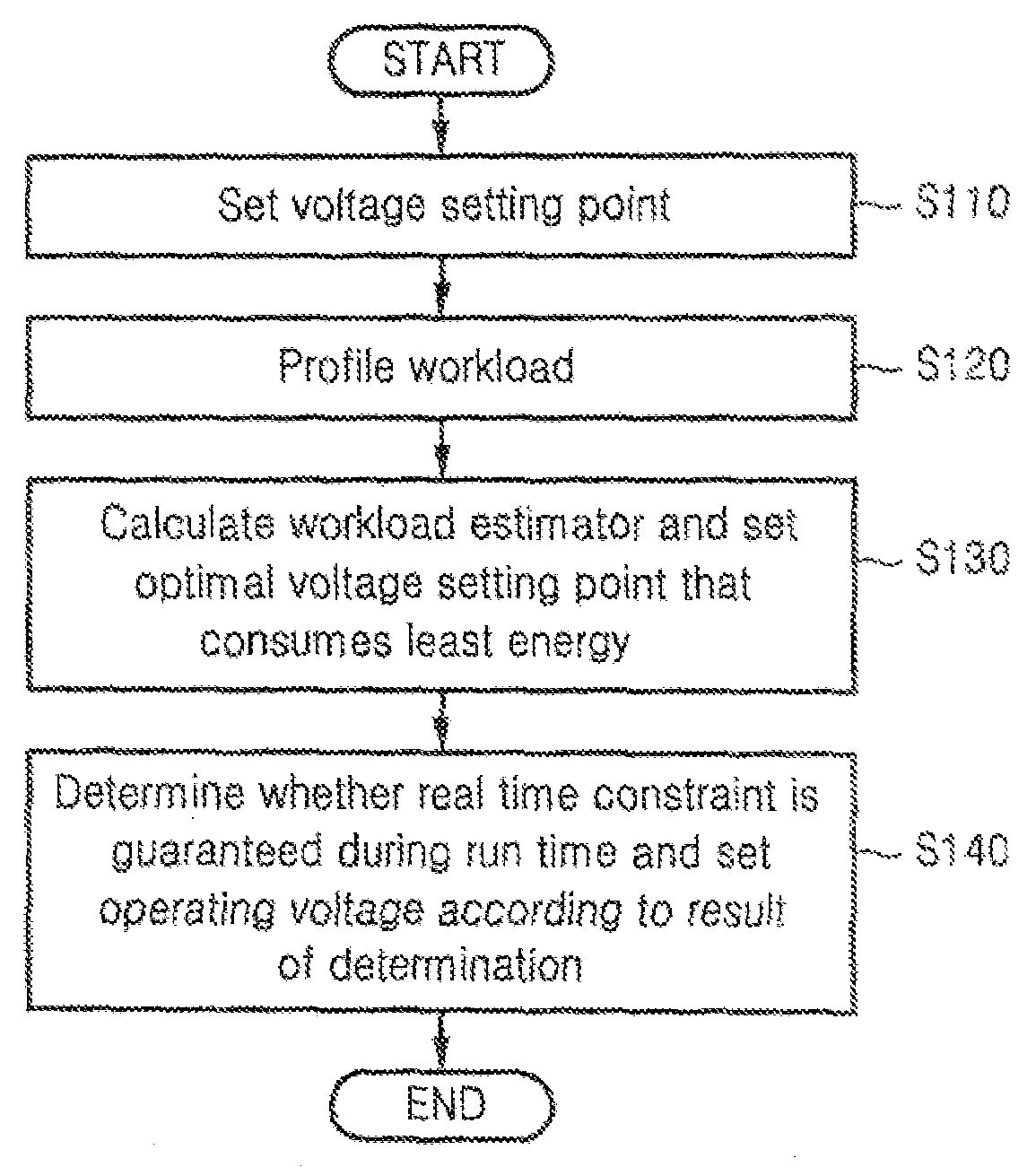
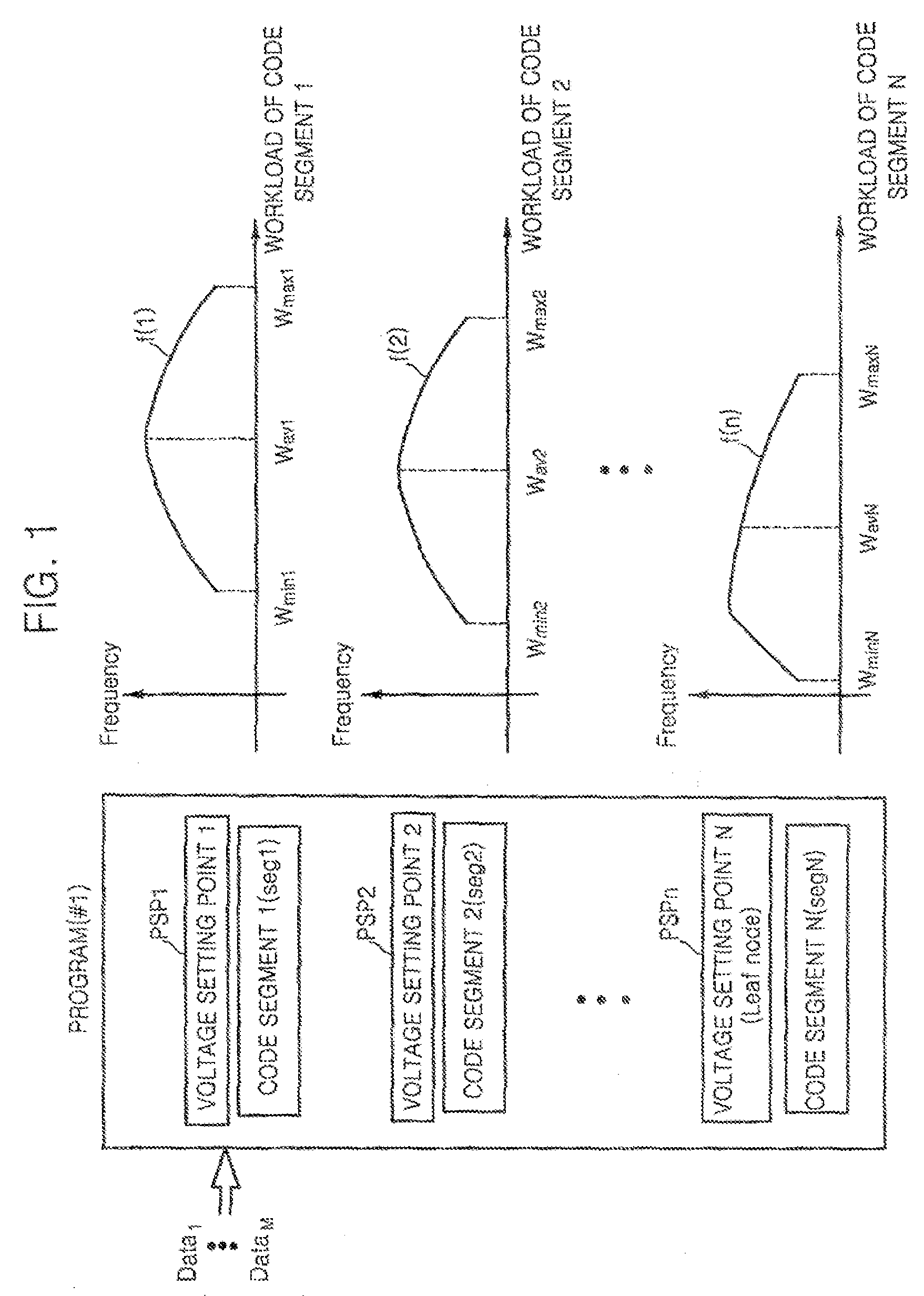
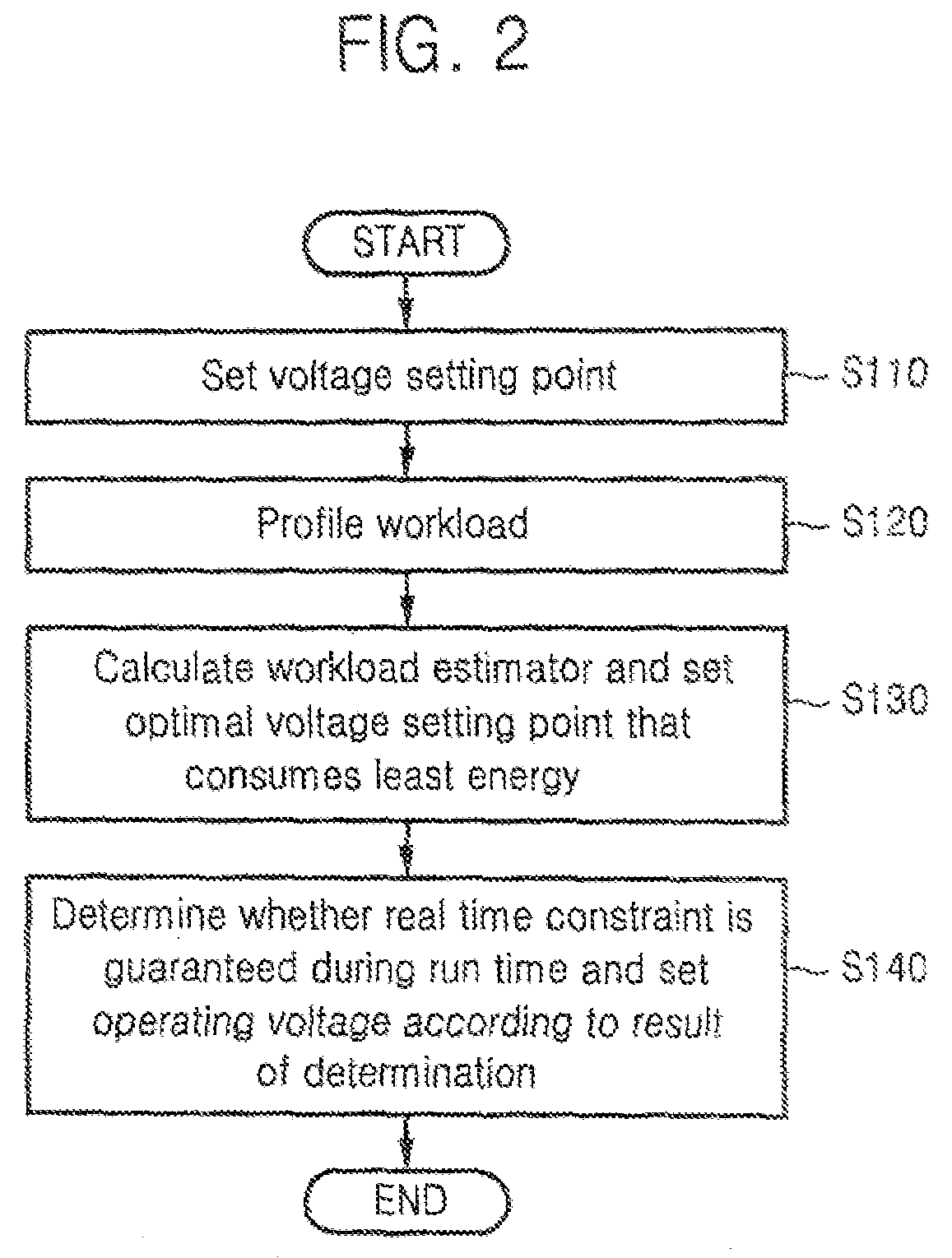
Dynamic voltage scaling method of CPU using workload estimator and computer readable medium storing the method
A method for scaling a dynamic voltage of a CPU is achieved by setting a voltage setting point for each of a plurality of code segments of a program, and profiling workload by measuring a workload variation of each of the code segments based on data that changes whenever measured, selecting a plurality of combinations, each having a plurality of voltage setting points, and calculating workload estimators corresponding to the voltage setting points of each of the selected combinations based on the workload variation measured in the workload profiling operation, selecting an optimal combination that consumes a least energy of the CPU based on the workload estimators, and determining whether a real time constraint is satisfied when an operating voltage is set based on the workload estimator corresponding to each of the voltage setting points of the optimal combination during runtime, and setting the operating voltage based on a result of the determination.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
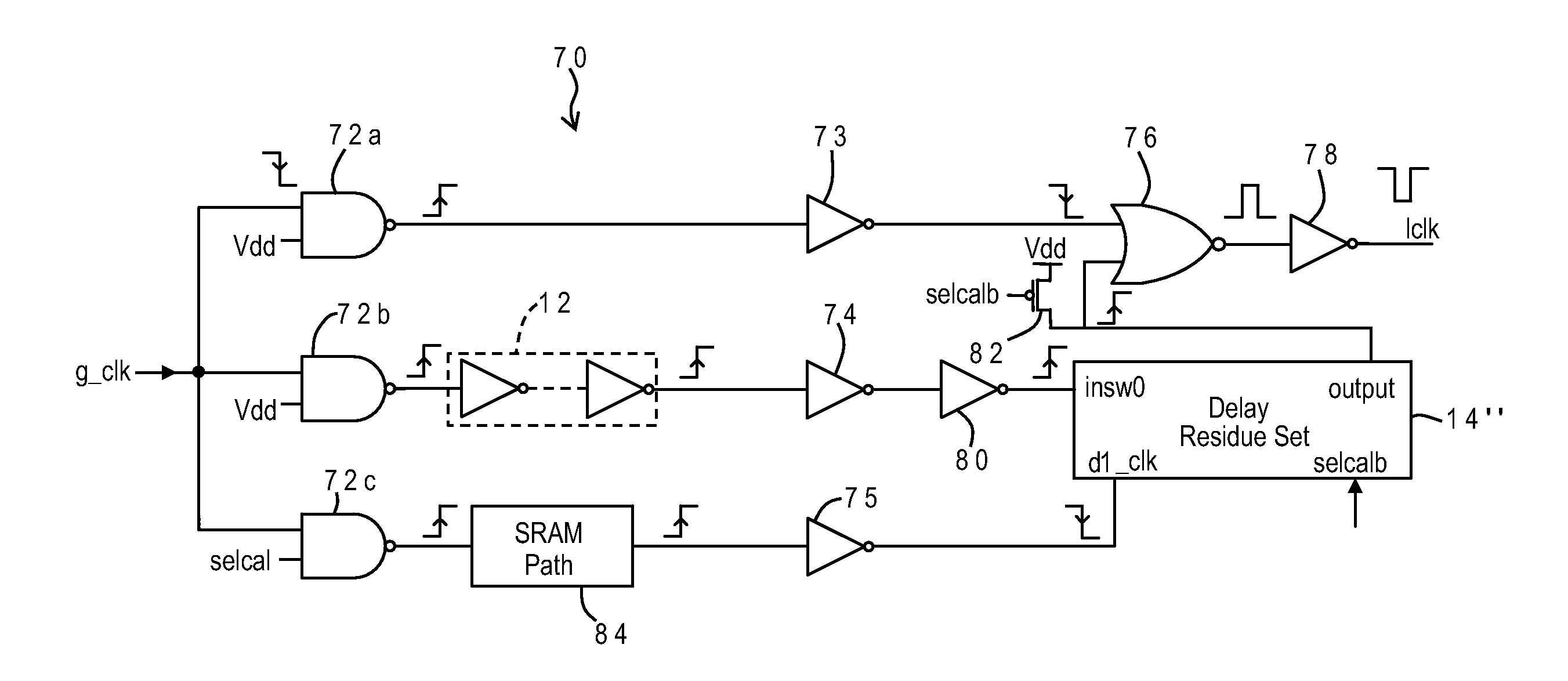
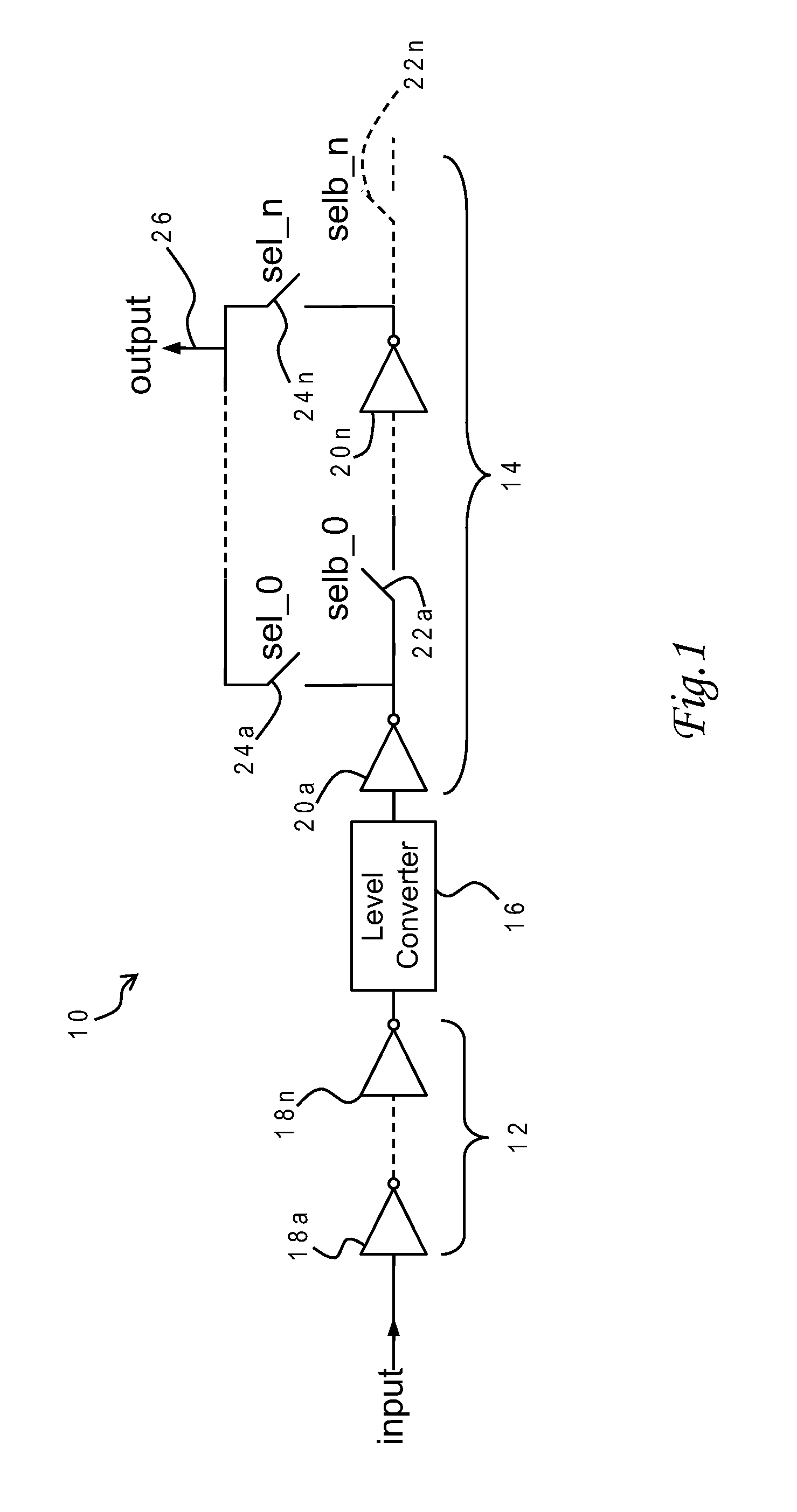
Optimizing Sram Performance over Extended Voltage or Process Range Using Self-Timed Calibration of Local Clock Generator
InactiveUS20100085823A1Easy to optimizeImprove performancePulse automatic controlDigital storageStatic random-access memoryLow voltage
A delay circuit has a fixed delay path at a lower voltage level, a level converter, and an adjustable delay path at a higher voltage level. The fixed delay path includes an inverter chain, and the adjustable delay path includes serially-connected delay elements selectively connected to the circuit output. In an application for a local clock buffer of a static, random-access memory (SRAM), the lower voltage level is that of the local clock buffer, and the higher voltage level is that of the SRAM. These voltages may vary in response to dynamic voltage scaling, requiring re-calibration of the adjustable delay path. The adjustable delay path may be calibrated by progressively increasing the read access time of the SRAM array until a contemporaneous read operation returns the correct output, or by using a replica SRAM path to simulate variations in delay with changes in voltage supply.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Chip packages with power management integrated circuits and related techniques
InactiveUS20140021522A1Shorten the timeReduce the difficulty of circuit designTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical devicesVoltage regulation
Chip packages having power management integrated circuits are described. Power management integrated circuits can be combined with on-chip passive devices, and can provide voltage regulation, voltage conversion, dynamic voltage scaling, and battery management or charging. The on-chip passive devices can include inductors, capacitors, or resistors. Power management using a built-in voltage regulator or converter can provide for immediate adjustment of the voltage range to that which is needed. This improvement allows for easier control of electrical devices of different working voltages and decreases response time of electrical devices. Related fabrication techniques are described.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Highly energy-efficient processor employing dynamic voltage scaling
ActiveUS7805620B2Simple structureMaximize energy efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingHigh energyParallel computing
Provided is a highly energy-efficient processor architecture. The architecture employs 2-stage dynamic voltage scaling (DVS) and a sleep mode for high energy efficiency, dynamically controls the power supply voltage and activation of an embedded processor with instructions, and thus can prevent performance deterioration while reducing power consumption.A highly energy-efficient processor employing the processor architecture includes: a function unit block for performing an operation according to instructions input from the outside; at least one peripheral unit block for performing data communication with an external device; an instruction decoder for interpreting the input instructions and determining operation modes of the function unit block and peripheral unit block required for executing the interpreted instructions; a function unit block driver for applying a different power supply voltage according to the operation mode of the function unit block to the function unit block; and a peripheral unit block driver for applying a different power supply voltage according to the operation mode of the peripheral unit block to the peripheral unit block.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
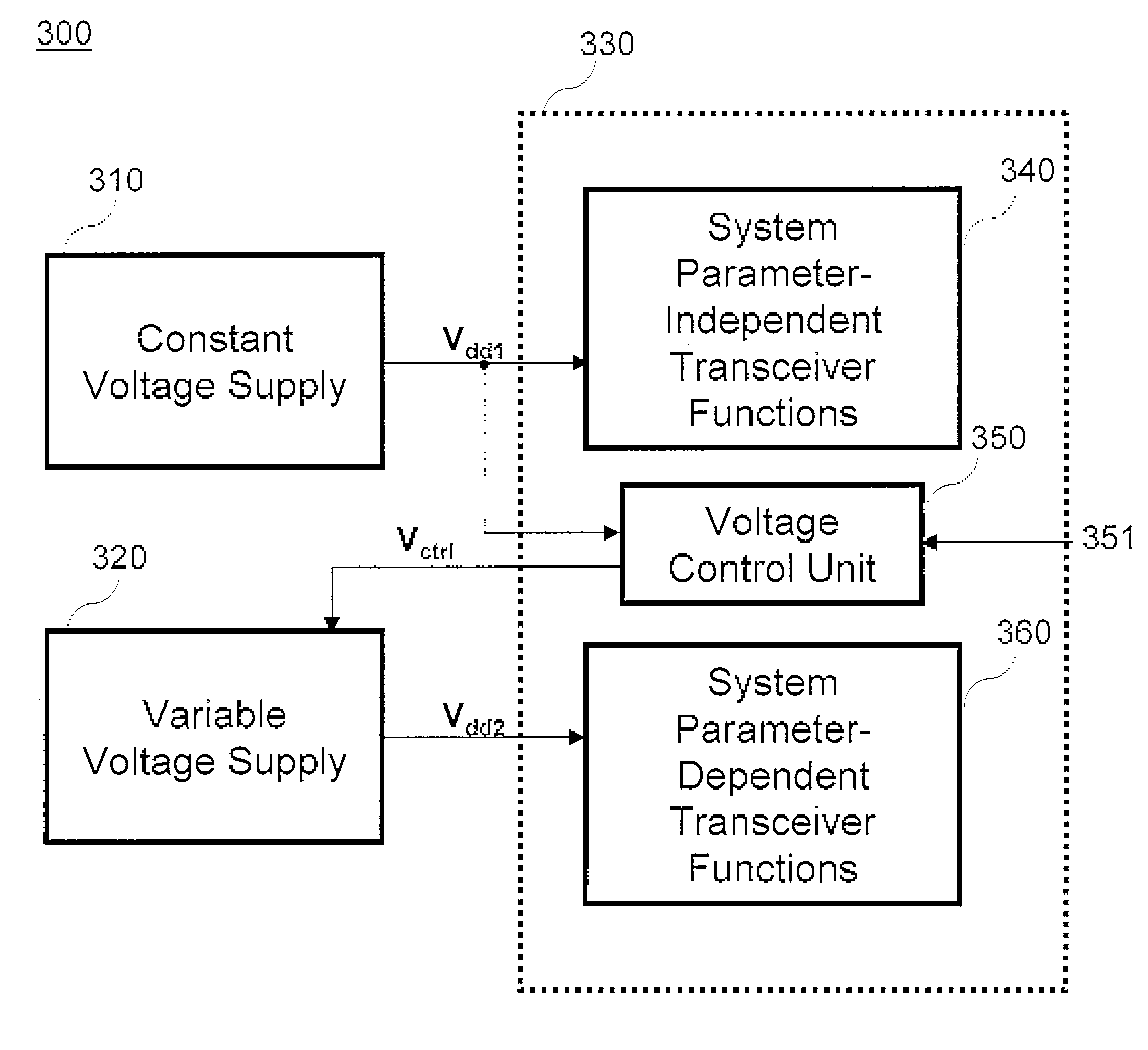
Dynamic Voltage Scaling for Packet-Based Data Communication Systems
ActiveUS20080297133A1Magnetic measurementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemIndependent function
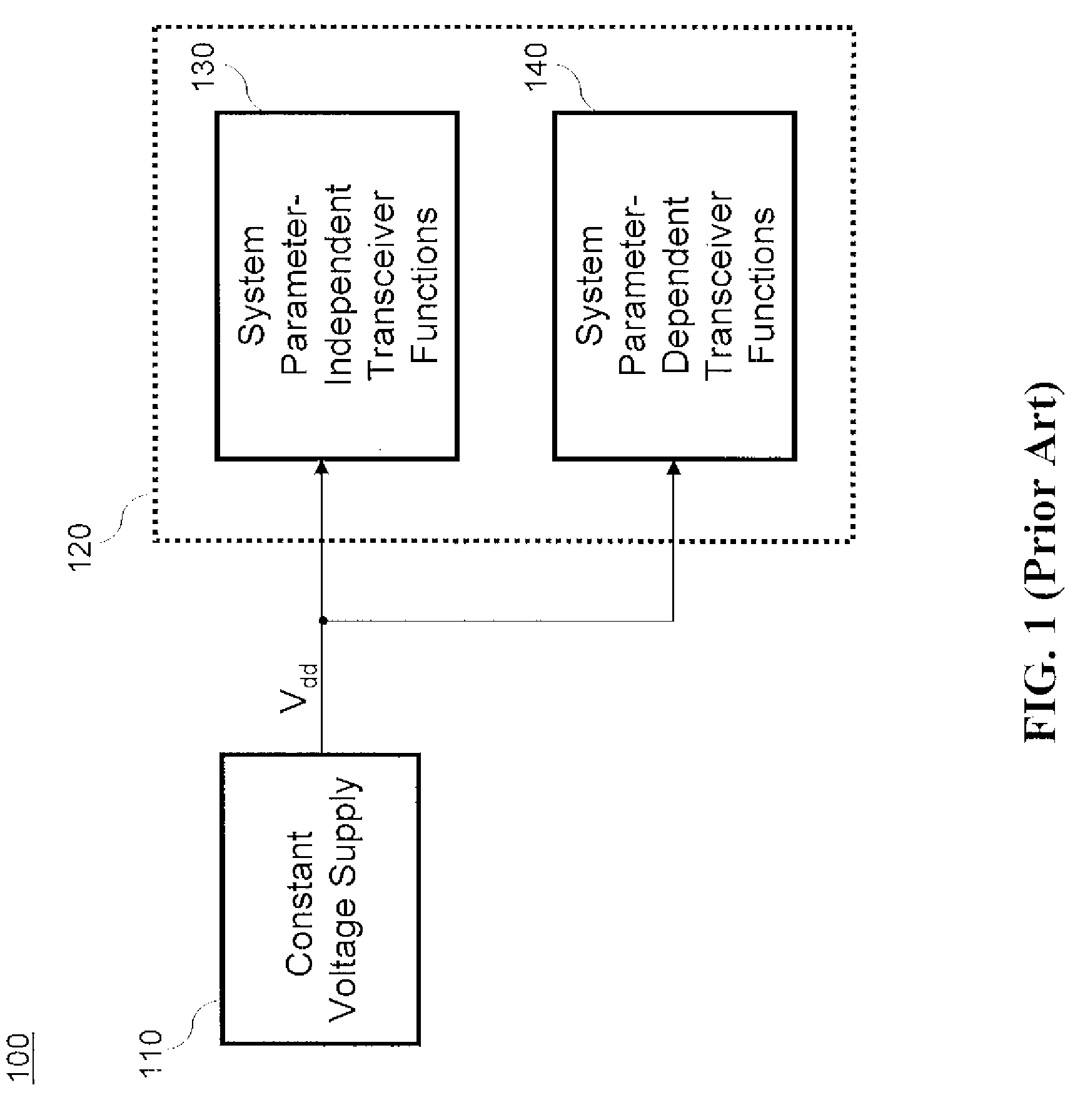
A dynamic voltage scaling system for a packet-based data communication transceiver includes a constant voltage supply, a variable voltage supply, and a voltage control unit. The constant voltage supply is configured to supply a constant voltage to at least one parameter-independent function of the transceiver, and the variable voltage supply is configured to supply a variable voltage in accordance with a control signal to at least one parameter-dependent function of the transceiver. Parameter-independent transceiver functions perform operations independent of a predetermined parameter and parameter-dependent transceiver functions perform operations dependent on the predetermined parameter The voltage control unit is configured to generate the control signal based on information provided by at least one parameter-independent transceiver function about the predetermined parameter.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
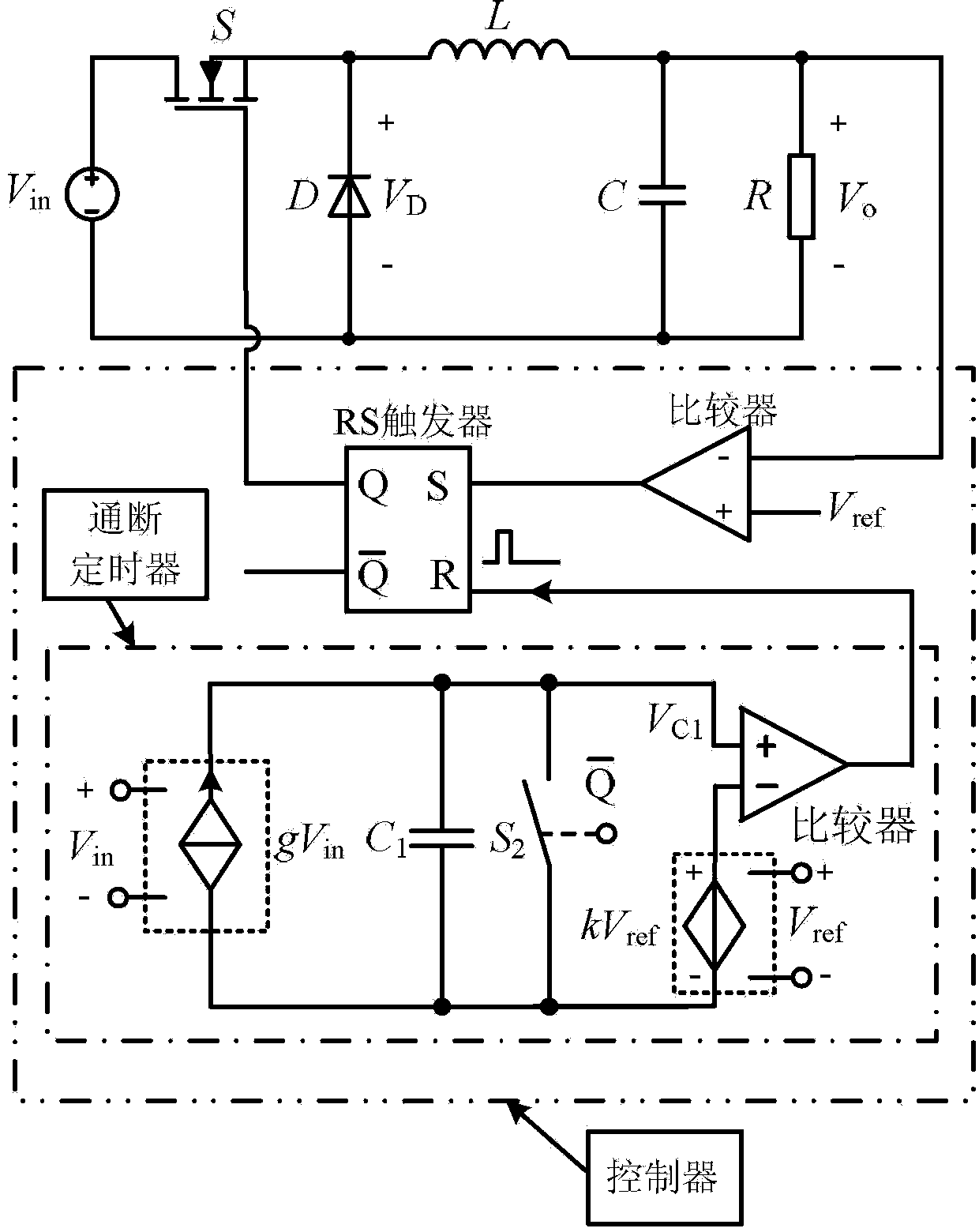
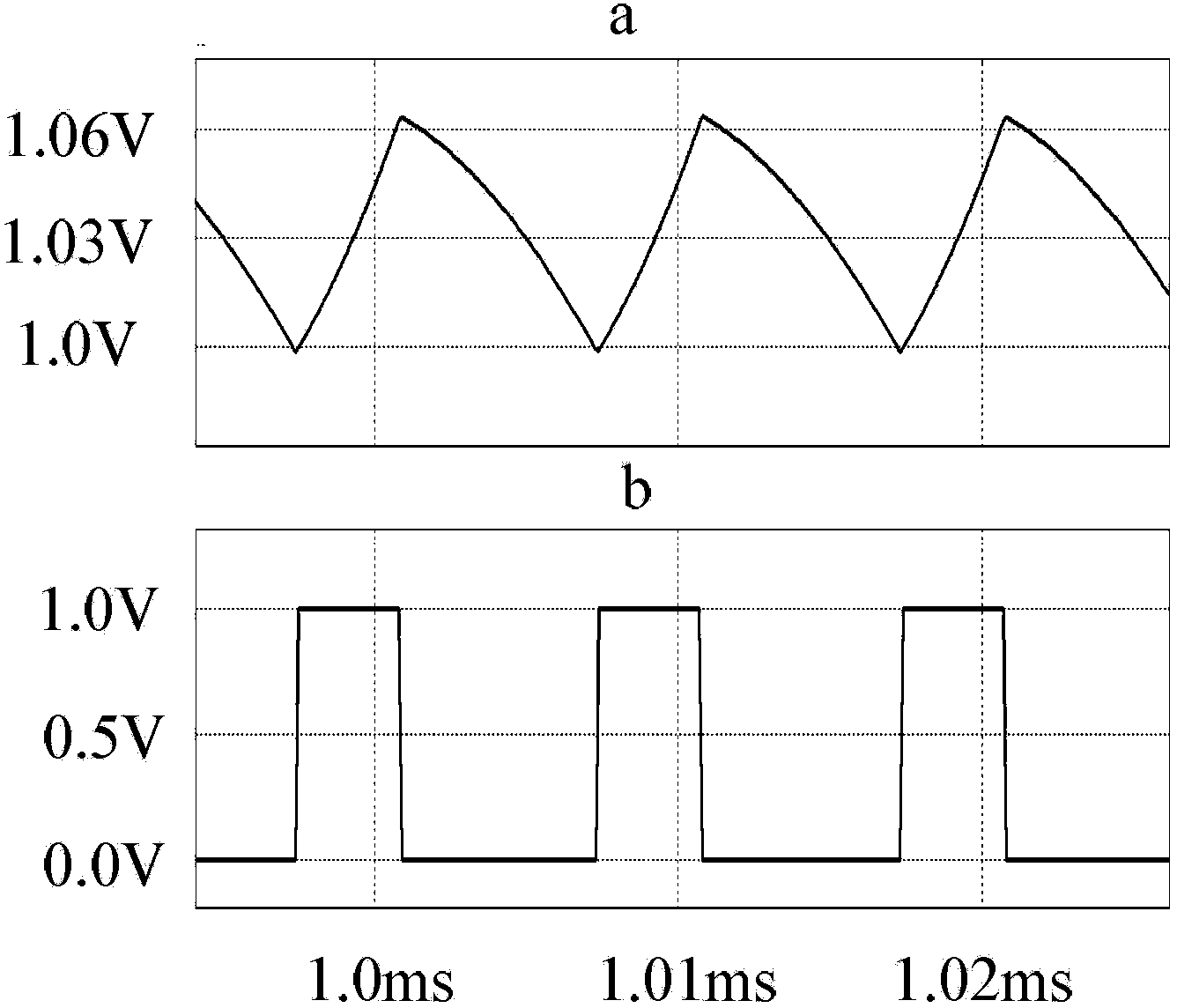
Fixed-frequency constant on-off time control method of dynamic voltage regulating switch converter
InactiveCN103414342ASimple designFast transient responseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationControl signalVoltage reference
The invention discloses a fixed-frequency constant on-off time control method of a dynamic voltage regulating switch converter and a device thereof. According to an output voltage and an output voltage reference, a comparison signal is generated, and is combined with a timing signal generated by an on-off timer so as to control an RS trigger; the RS trigger produces a control signal to control a switch converter; the arranged on-off timer is controlled by an input voltage and the output reference voltage, so that on-off time of the on-off timer automatically changes with the input voltage and the output reference voltage; and a switch frequency maintains constant. According to the invention, the advantages of fast transient response speed and good stability, and the advantage that the switch frequency does not change with the input voltage, the output reference voltage, and the load current are realized.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
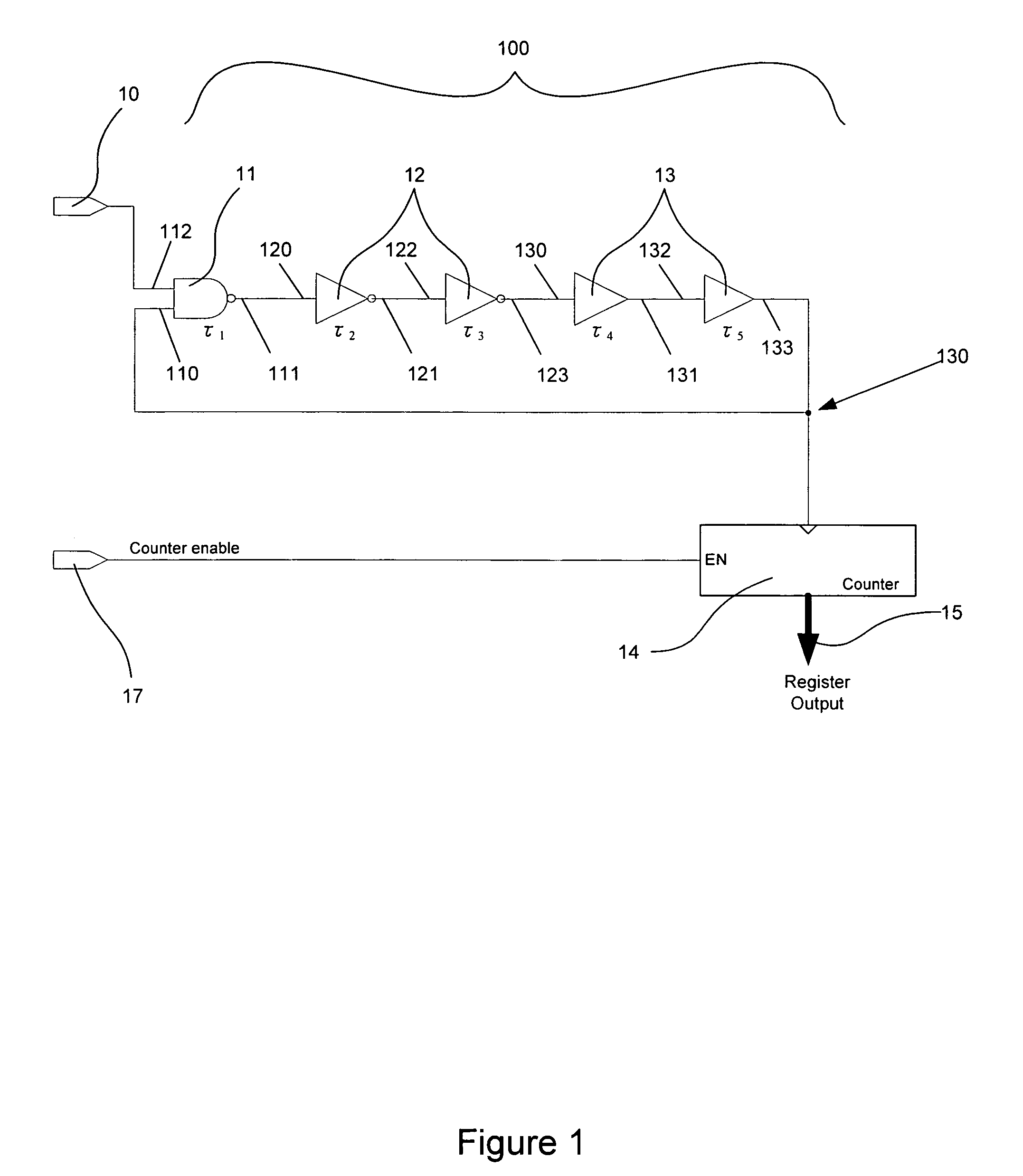
Dynamic voltage scaling for self-timed or racing paths
ActiveUS7622979B2Improve performanceDesign moreDigital storageElectric pulse generatorEngineeringDynamic voltage scaling
A timing-constrained circuit (e.g., a self-timed circuit) of optimal performance is achieved by allowing the delay of the circuit to be changed dynamically as a function of operating conditions (e.g., operating voltages or temperatures). The delay of timing signals in the timing-constrained circuit for a given operating condition may be selected to have the minimum margin for that operating condition among the available delays to maximize performance over the entire dynamic range of operating conditions.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Sensor dormancy mechanism integrating dynamic voltage scaling and dynamic energy management
InactiveCN101932086AReduce power consumptionExtend your lifePower managementEnergy efficient ICTLow voltageOperation mode
The invention discloses a sensor dormancy mechanism integrating dynamic voltage scaling and dynamic energy management, belonging to the technical field of wireless sensor network application. The mechanism expands the dynamic energy management strategy of a sensor node and adds a low-voltage operation mode integrating the dynamic voltage scaling to the dormancy mode. When time interval of event occurrence can not satisfy the optimized time threshold for entering into the dormancy mode, the purpose of lowering power dissipation is achieved by lowering processor operating voltage. The invention can effectively lower power dissipation of the wireless sensor network based on the multi-hops route mode and prolong the service life of the sensor network.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Dynamic voltage scaling scheduling mechanism for sporadic, hard real-time tasks with resource sharing
InactiveUS8112644B2Improve energy efficiencySave energyEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementWork cycleDynamic voltage scaling
A dynamic voltage scaling scheduling method executes one of the steps. When one task in the delayed task set requires for being executed, a working voltage required for executing the task is increased, and the task is removed from the delayed task set; when one task in the delayed task set requires for sharing resources, the working voltage required by the task is set as the current working voltage or a larger one in the minimum upper bounds of all the works requiring for sharing resources; and when one task does not belong to the delayed task set, but the waiting time has exceeded the period of the work, the working voltage for executing the task is reduced, and the task is added in the delayed task set.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
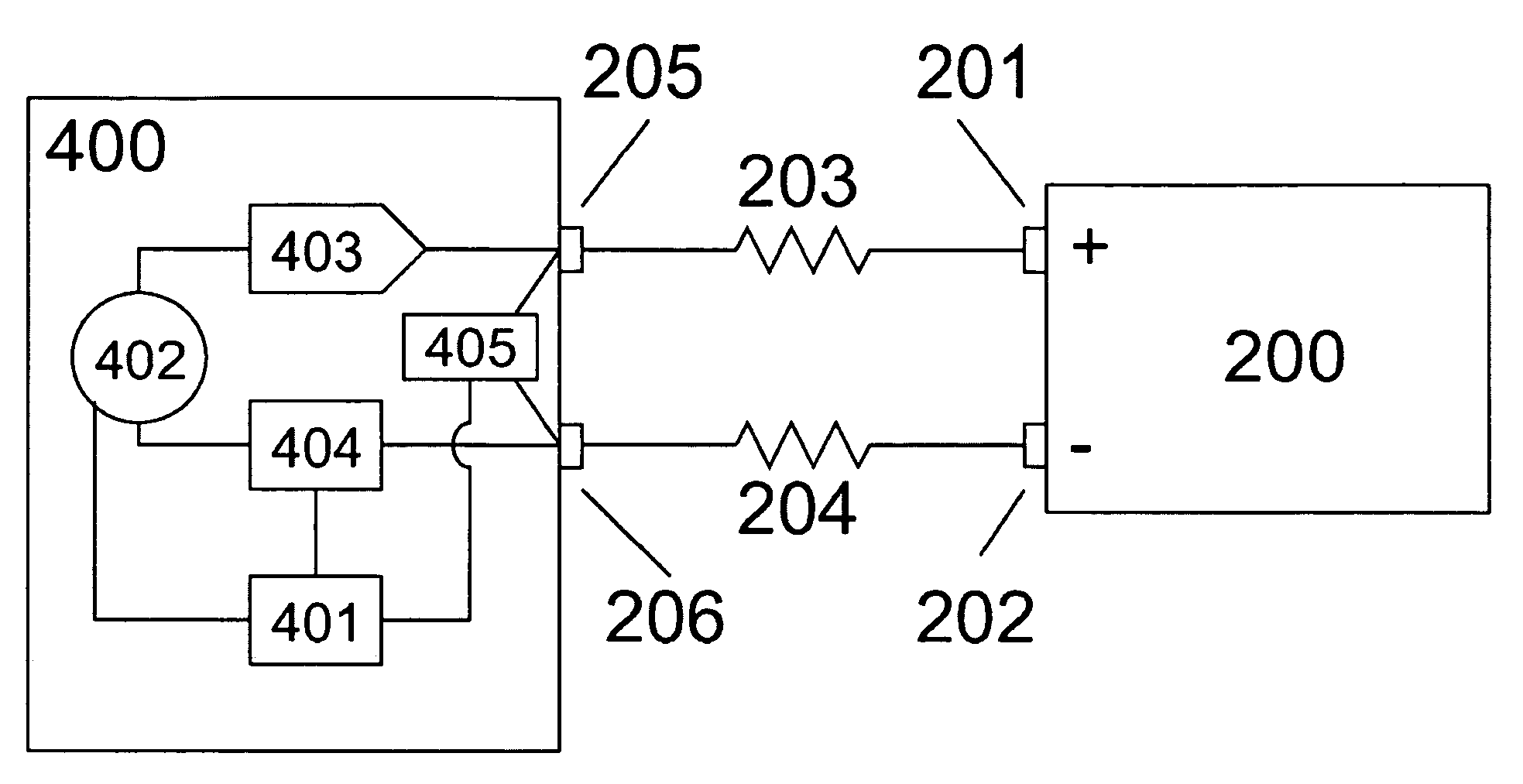
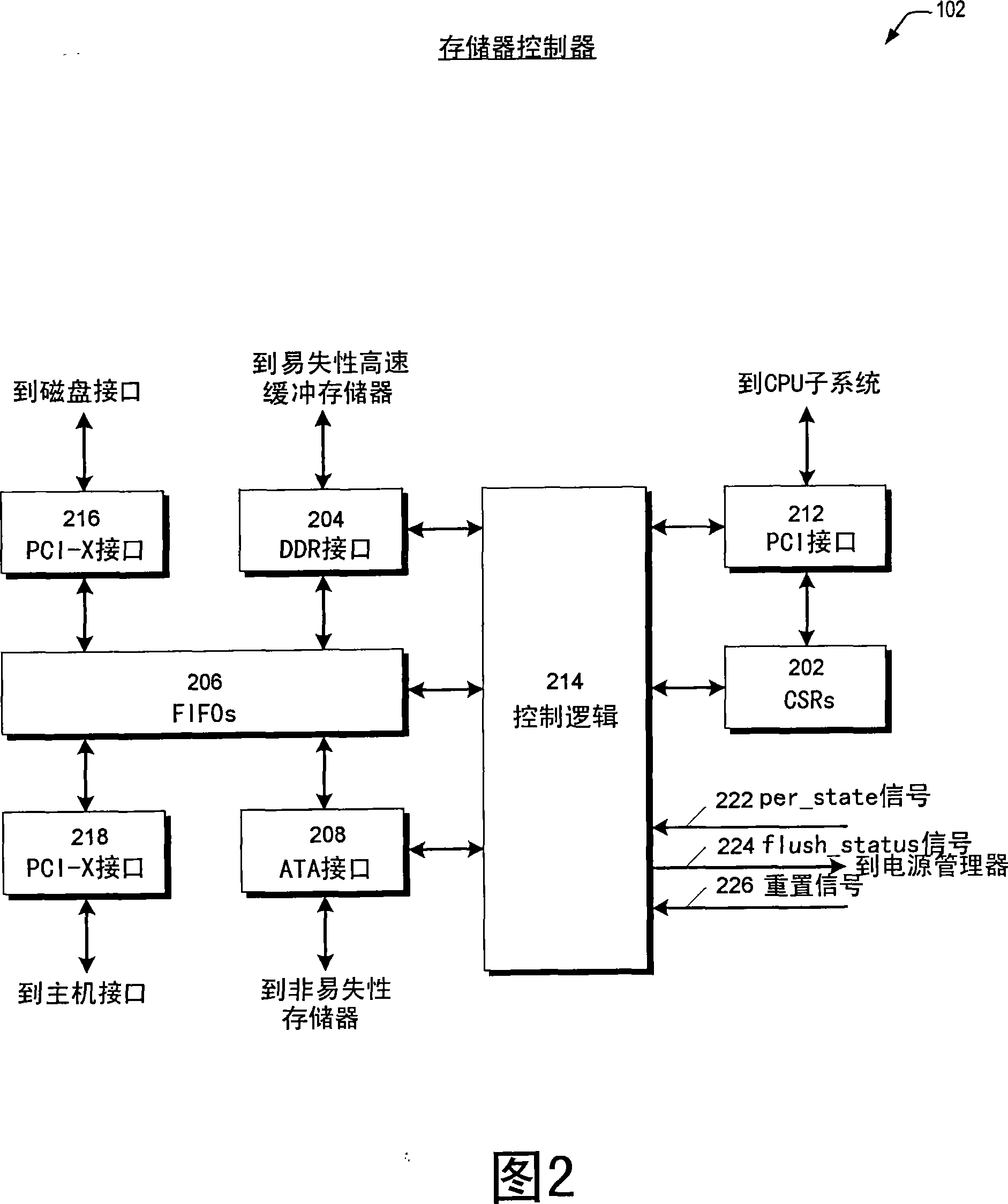
Storage controller having dynamic voltage for regulating super capacitance
A storage controller having a capacitor bank for storing electrical energy to supply electrical energy when a main power source is interrupted, a temperature sensor capable of sensing the temperature of the capacitor bank, and a CPU, the storage controller detecting the capacitor when operating at a first voltage value Whether the temperature of the bank has exceeded a preset threshold, and determine whether the expected life of the capacitor bank is less than the guaranteed life. If the expected lifetime is less than the guaranteed lifetime, the CPU reduces the operating voltage of the capacitor bank to a second value in order to increase the capacitor bank lifetime. In one embodiment, the CPU reduces voltage if the cumulative normalized run time of the capacitor bank is greater than the cumulative calendar run time. In another embodiment, if the capacitance drop percentage of the capacitor bank is greater than the calendar capacitance drop percentage, the CPU reduces the voltage.
Owner:DOT HILL SYST
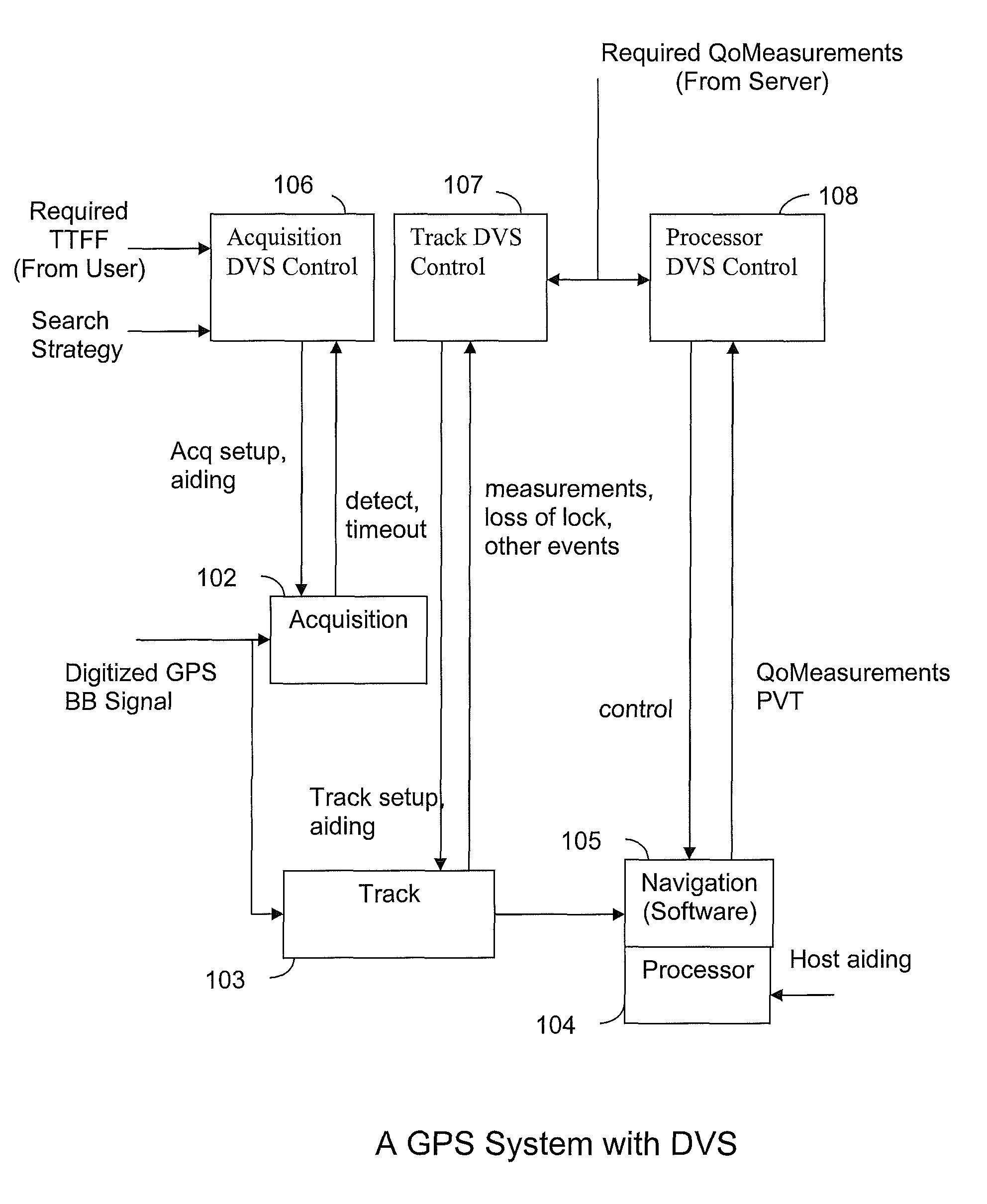
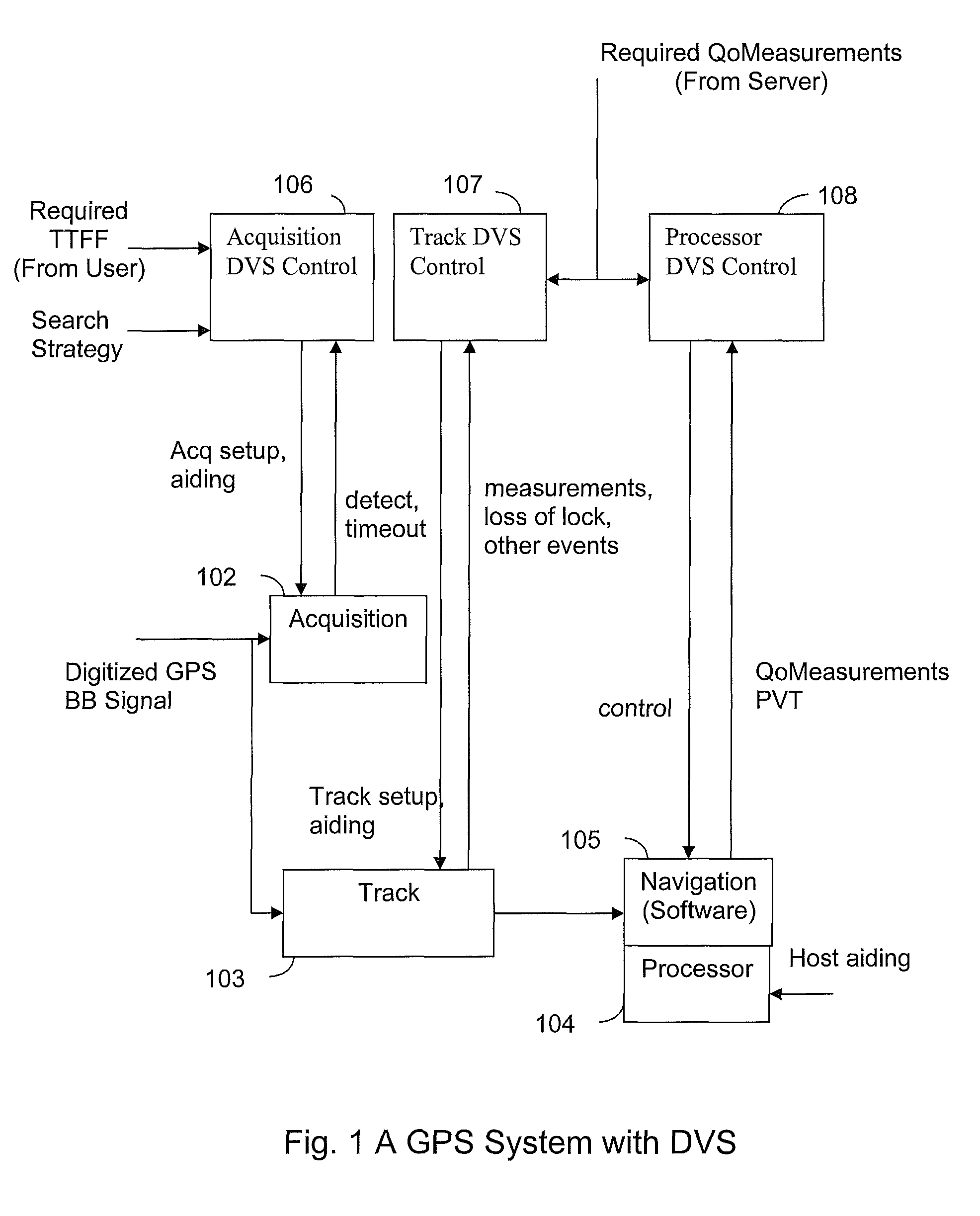
System and method for dynamic voltage scaling in a GPS receiver
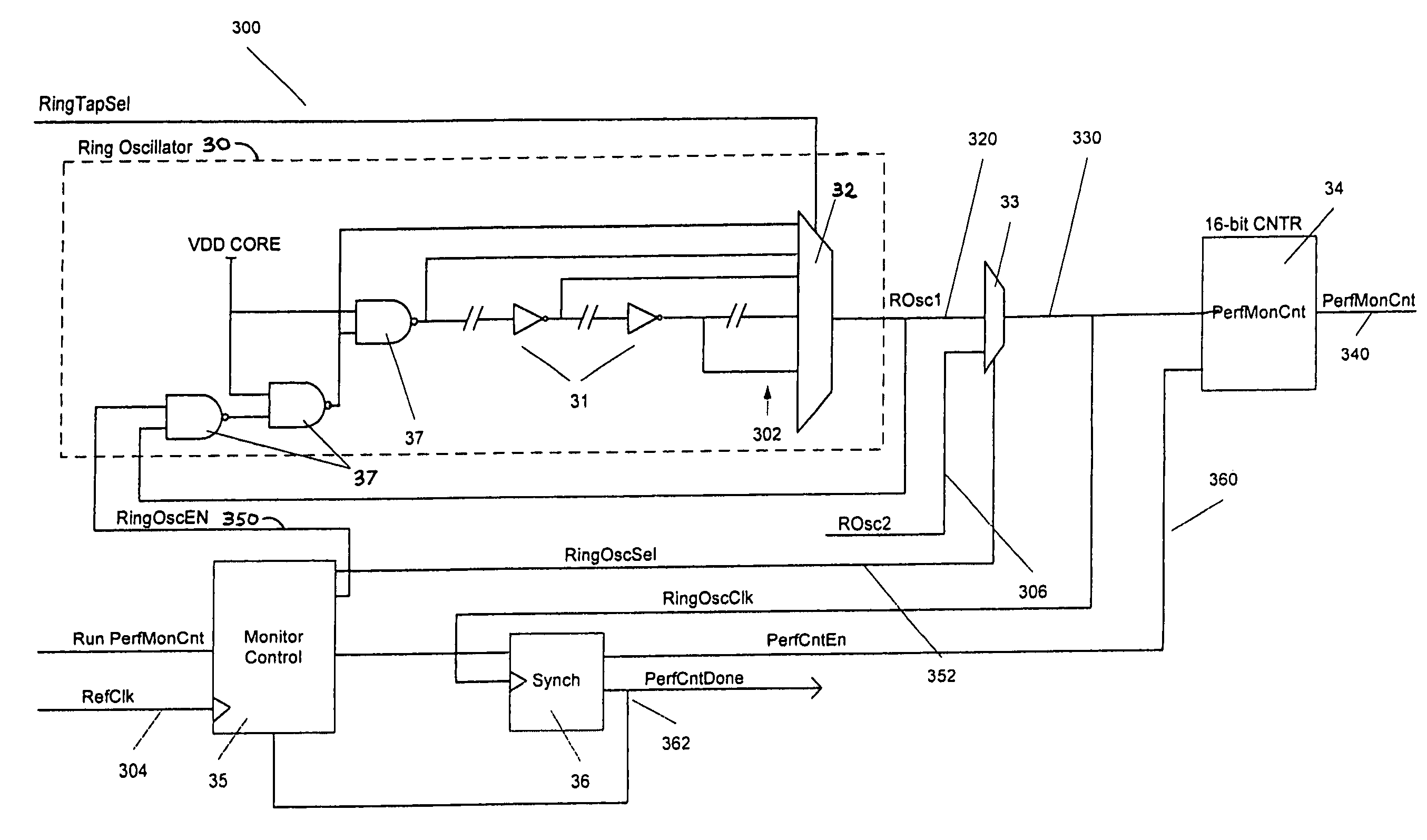
InactiveUS8009090B2Minimize power consumptionReduce power consumptionDigital data processing detailsSatellite radio beaconingClock rateGps receiver
Systems and methods are disclosed herein to dynamically vary supply voltages and clock frequencies, also known as dynamic voltage scaling (DVS), in GPS receivers to minimize receiver power consumption while meeting performance requirements. For the baseband circuitry performing satellite acquisition and tracking, supply voltages and clock frequencies to the baseband circuitry are dynamically adjusted as a function of signal processing requirements and operating conditions for reducing baseband power consumption. Similarly, the supply voltage and clock frequency to the processor running navigation software and event processing are dynamically adjusted as a function of navigation performance requirements and event occurrences to reduce processor power consumption.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
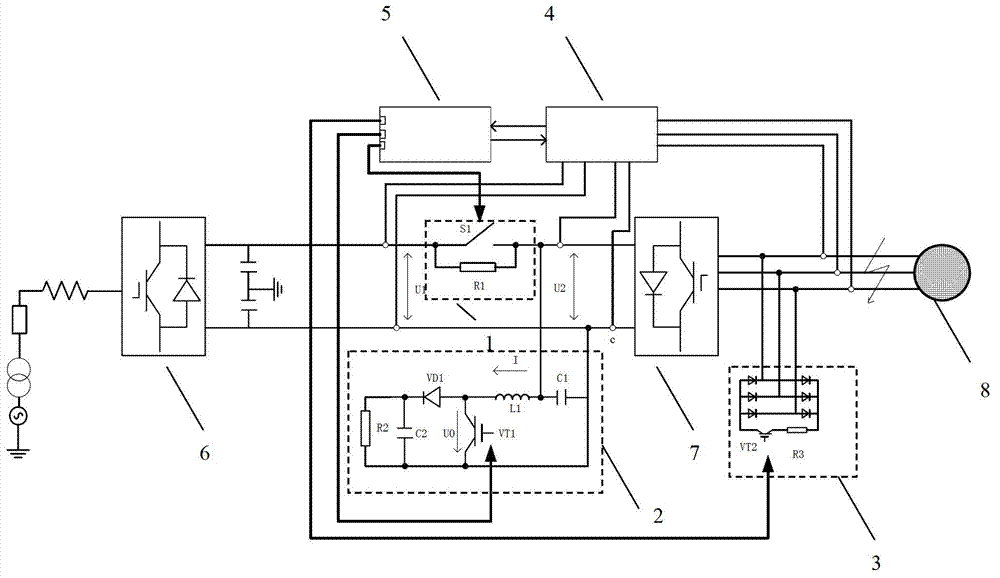
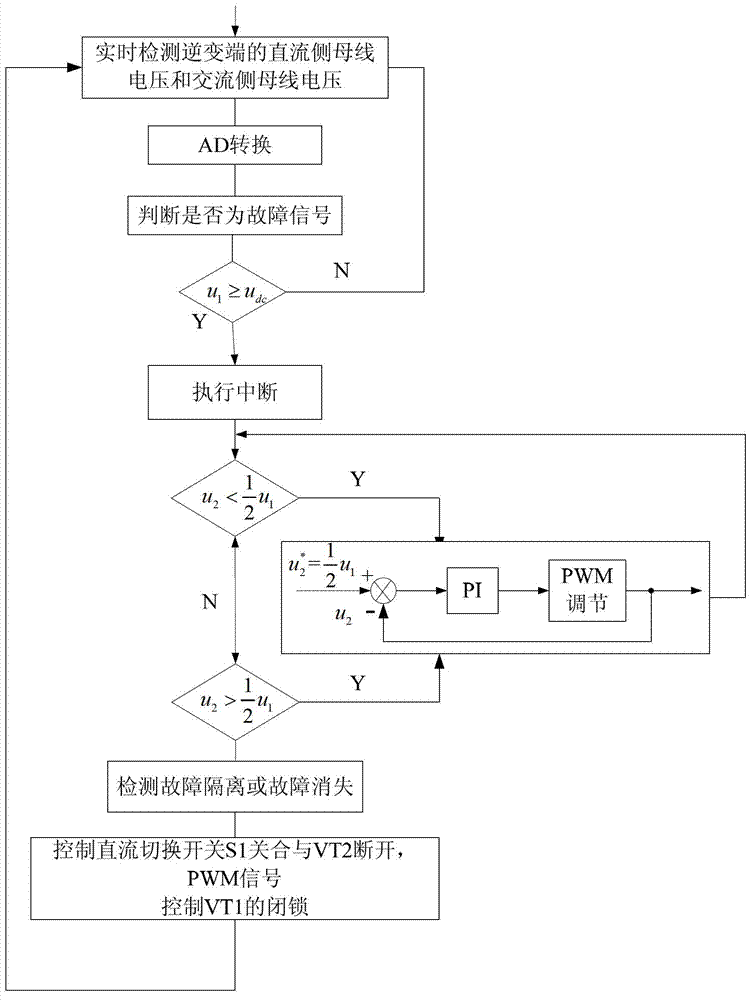
Device and method for controlling fault ride-through of power grid of flexible direct-current transmission system
InactiveCN102820646AImproved AC fault ride-through capabilitySuppress overvoltageDc network circuit arrangementsElectric power transfer ac networkOvervoltageBusbar
A device for controlling fault ride-through of a power grid of a flexible direct-current transmission system comprises a control unit, a detection unit, a switchable braking resistor unit, a power voltage regulation unit and a full-bridge braking unit, wherein the switchable braking resistor unit is used for primary power release of output of a rectification end, the power voltage regulation unit is used for secondary power release of output of the switchable braking resistor unit, and the full-bridge braking unit is used for tertiary power release of output of an inversion end. By a method for controlling fault ride-through of the power grid of the flexible direct-current transmission system, direct-current side busbar voltage and alternating-current side busbar voltage are detected in the real time, and when a fault signal is detected, a direct-current change-over switch is switched off, and a second fully-controlled switch is switched on to dynamically enable a first fully-controlled switch to be on for dynamic voltage regulation, so that maximum residual power transmission is achieved. The method is capable of effectively inhibiting overvoltage of a direct-current busbar, avoiding latching of devices of the direct-current transmission system and guaranteeing maximum residual power transmission, and the devices of the direct-current transmission system can be normally operated during fault.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Dynamic voltage scaling method of CPU using workload estimator and computer readable medium storing the method
A method for scaling a dynamic voltage of a CPU is achieved by setting a voltage setting point for each of a plurality of code segments of a program, and profiling workload by measuring a workload variation of each of the code segments based on data that changes whenever measured, selecting a plurality of combinations, each having a plurality of voltage setting points, and calculating workload estimators corresponding to the voltage setting points of each of the selected combinations based on the workload variation measured in the workload profiling operation, selecting an optimal combination that consumes a least energy of the CPU based on the workload estimators, and determining whether a real time constraint is satisfied when an operating voltage is set based on the workload estimator corresponding to each of the voltage setting points of the optimal combination during runtime, and setting the operating voltage based on a result of the determination.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
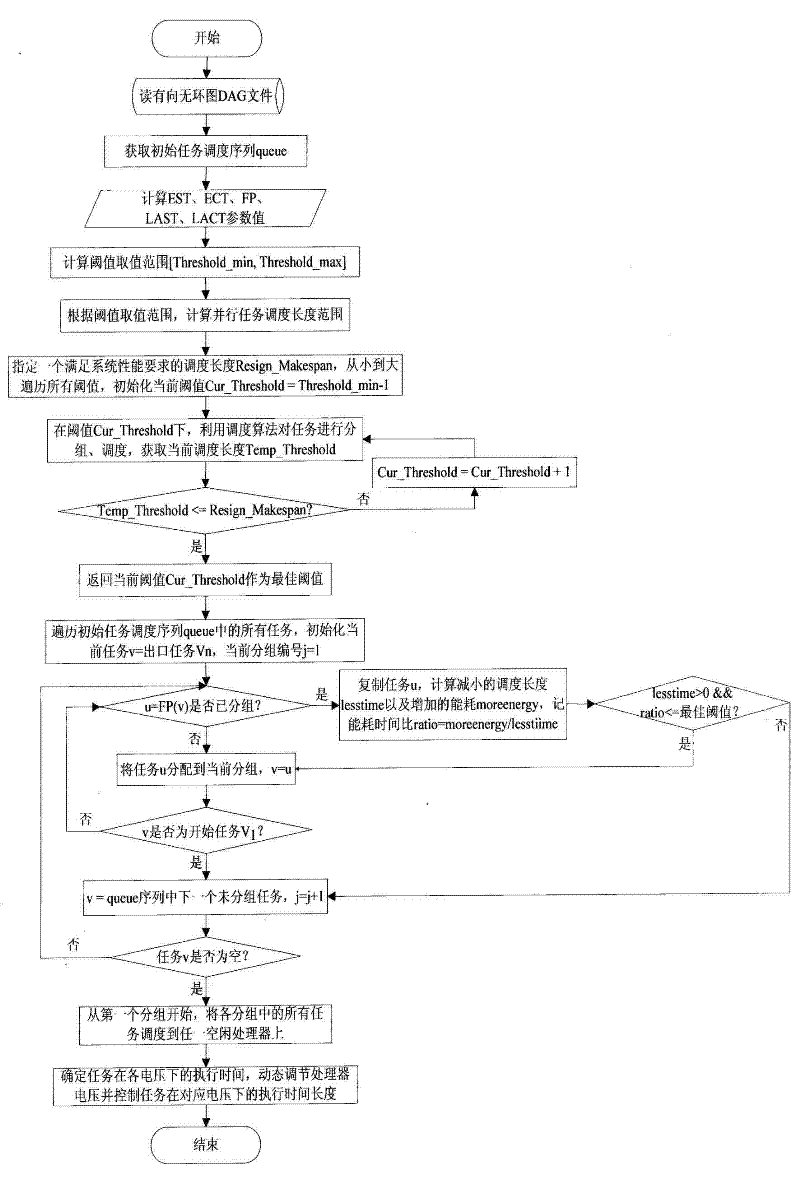
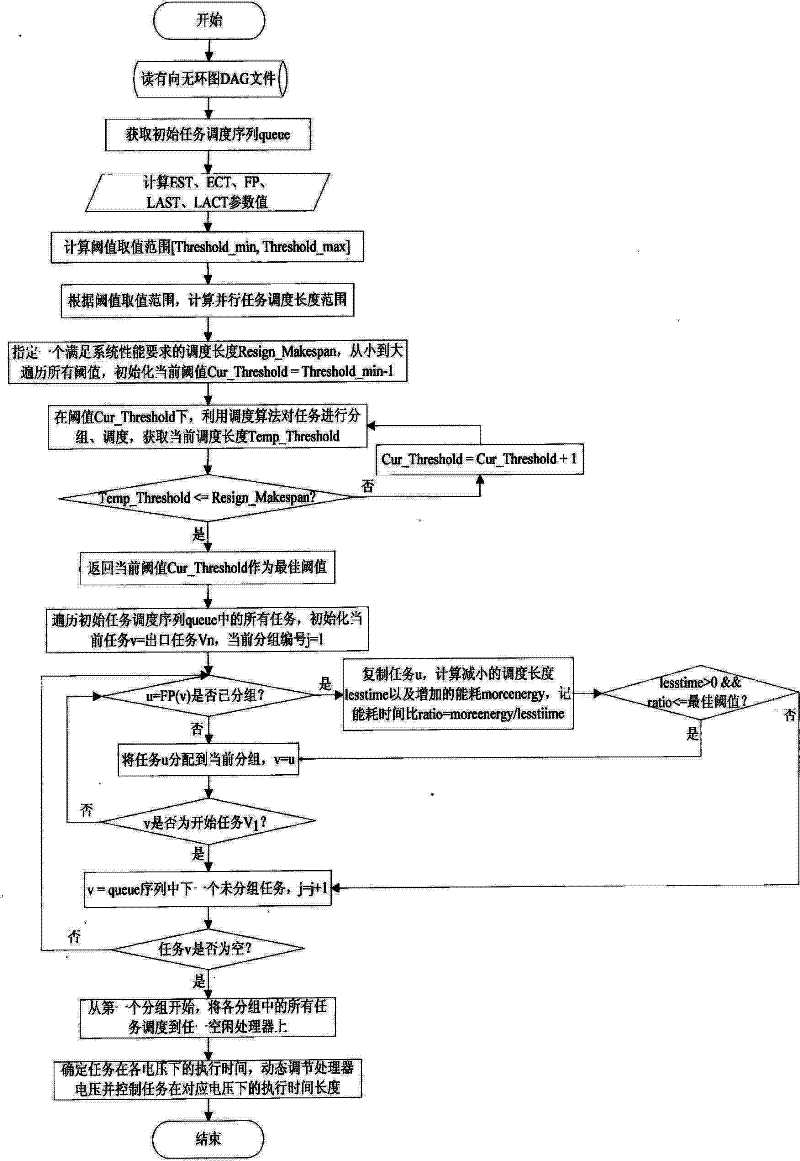
Self-adaptive energy-saving dispatching method in isomorphic cluster system based on dynamic voltage regulation technology
InactiveCN102650957AHigh energy consumptionReduce energy consumptionResource allocationPower supply for data processingIdle timeCluster systems
The invention discloses a self-adaptive energy-saving dispatching method in an isomorphic cluster system based on a dynamic voltage regulation technology. The self-adaptive energy-saving dispatching method comprises the following specific steps of: reading a parallel task directed acyclic graph (DAG) file; acquiring an initial task dispatching sequence; acquiring an optimal threshold; dynamically acquiring an optimal threshold according to the parallel task, the system environment and the user performance demand; grouping the tasks: controlling the replication of the tasks by using the optimal threshold, i.e., selectively replicating an optimal precursor of the tasks to balance the performances and energy consumption of the system to acquire an approximate optimal grouping; mapping the tasks: dispatching various groups to a processor which is not occupied; and regulating the voltage of the processor: dynamically adjusting the voltage of the processor by using the idle time of the tasks so as to reduce energy consumption of the processor. According to the self-adaptive energy-saving dispatching method disclosed by the invention, the requirements on the performances and energy consumption of the system are comprehensively considered and the optimal threshold of the system can adapt to the parallel task and the system environment; and the task replication is controlled by using the optimal threshold to acquire the approximate optimal grouping, so that a final dispatching result ensures that the energy consumption is reduced as much as possible on the premise of meeting the requirements of the system.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com